Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Phase front" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
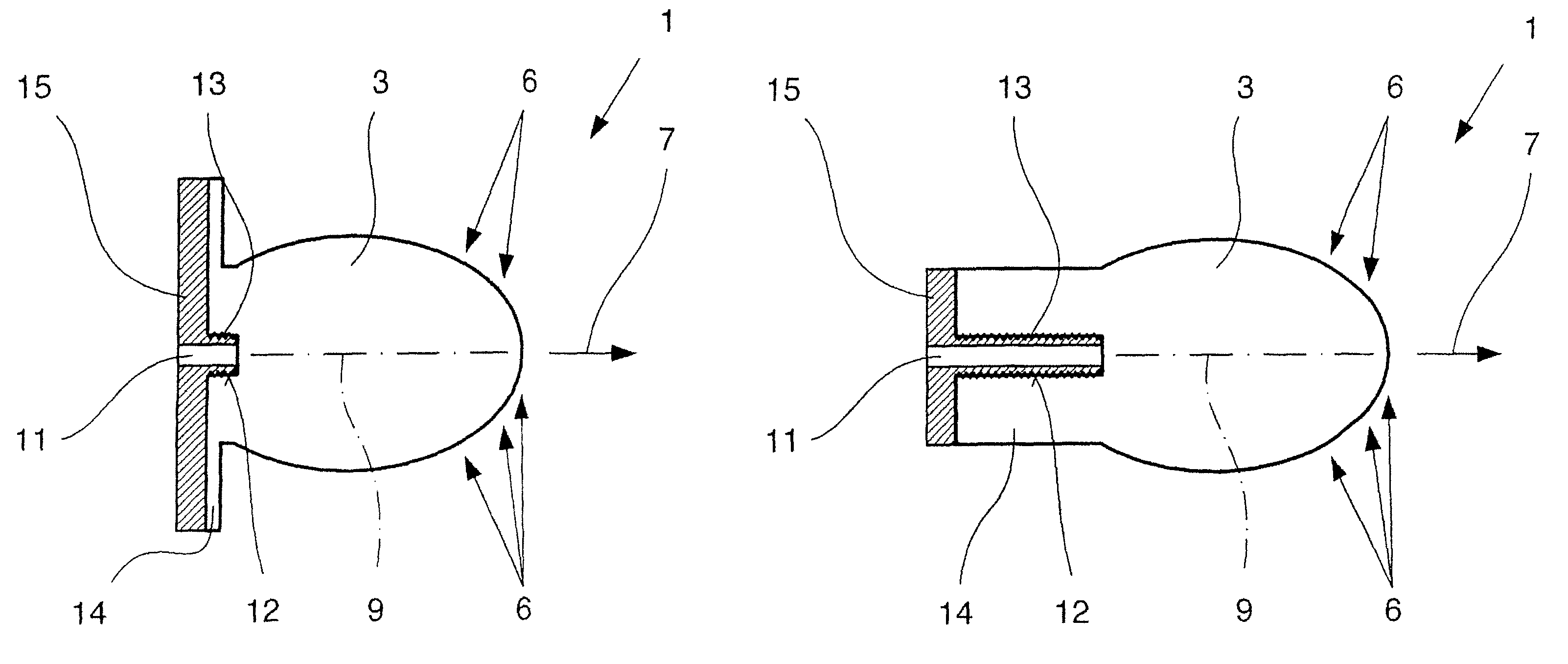
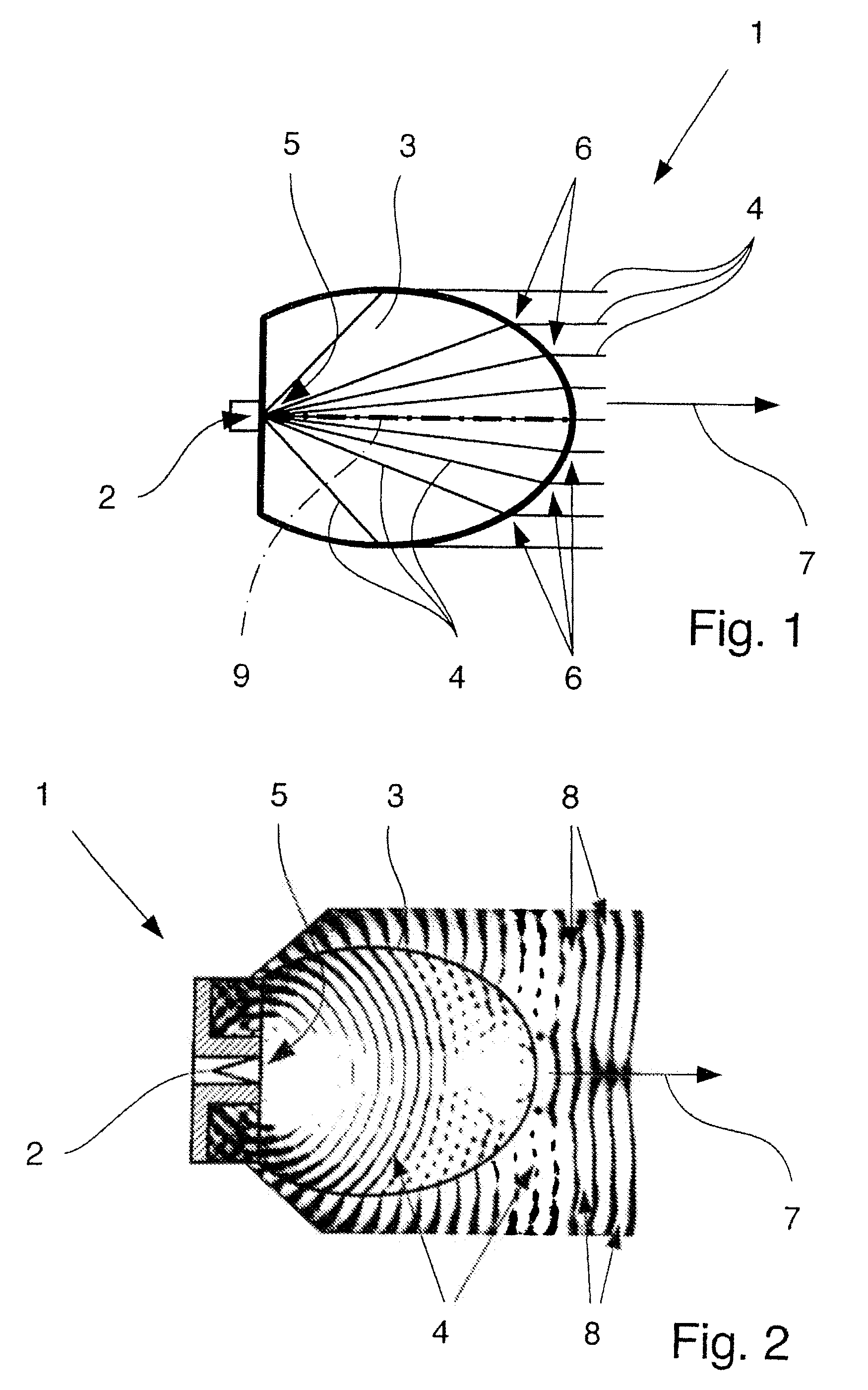
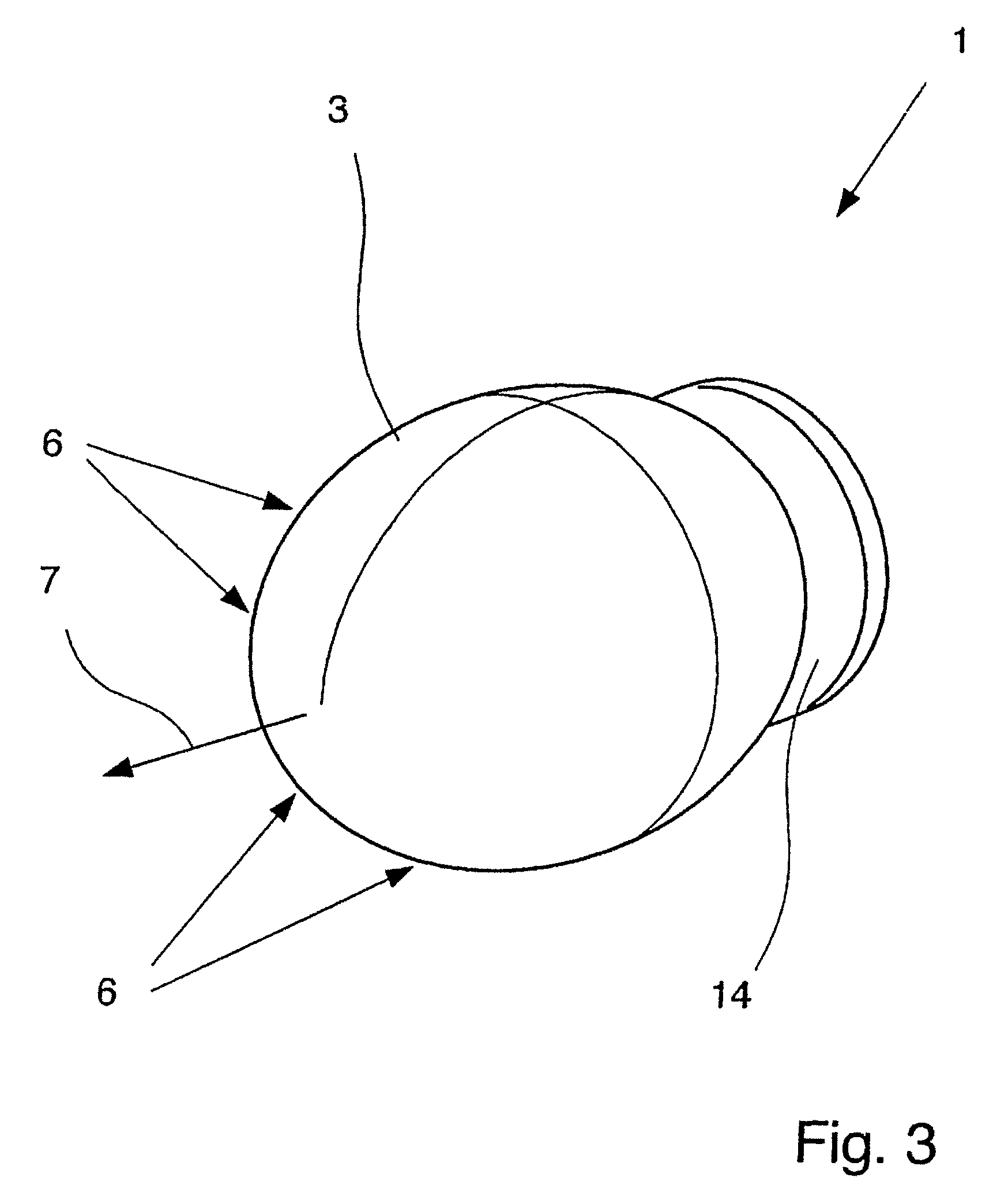
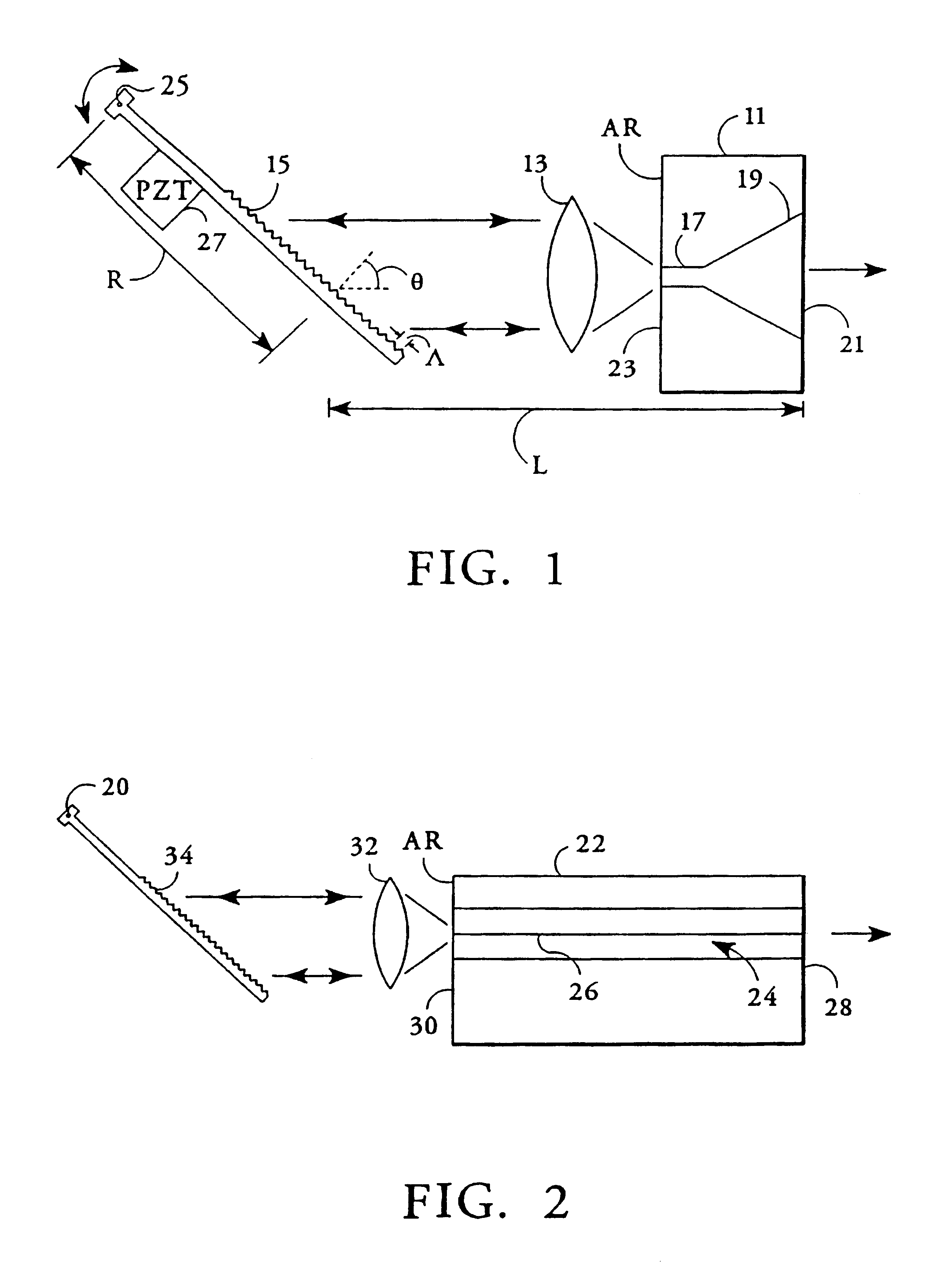
Dielectric antenna with an electromagnetic feed element and with an ellipsoidal lens made of a dielectric material
ActiveUS8917215B2Avoid disadvantagesEasy to packWaveguide mouthsDielectric antennasElectromagnetic radiation
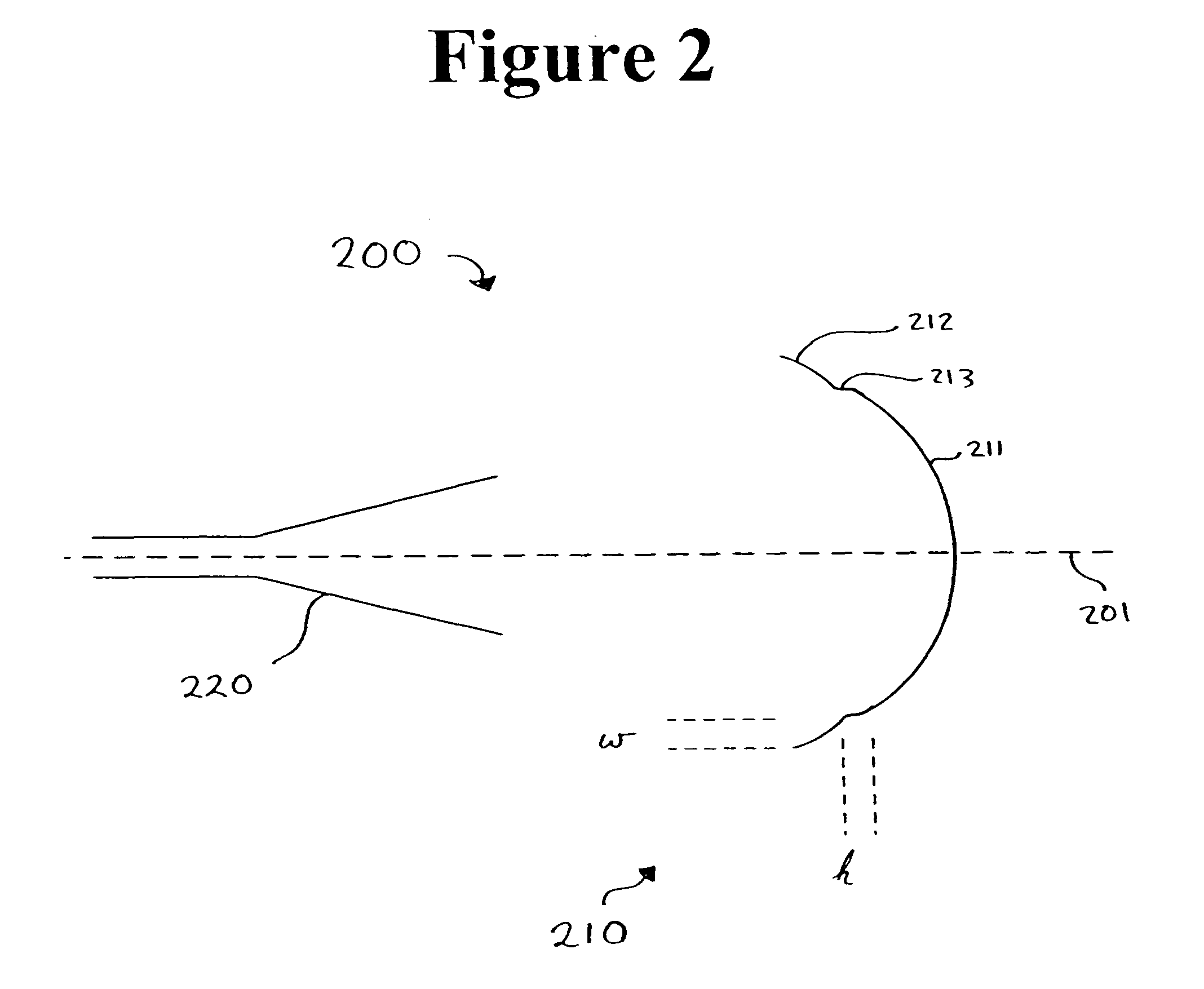
A dielectric antenna with an electromagnetic feed element (2) and with a lens (3) made of a dielectric material, the feed element (2) emitting electromagnetic radiation (4) and the lens (3) being supplied with electromagnetic radiation (4) in the feed region (5), the lens (3) relaying the electromagnetic radiation (4) and radiating it with the transmission region (6). To configure these dielectric antennas such that the disadvantages of the dielectric antennas known from the prior art are at least partially avoided, first of all, the lens (3) is shaped essentially ellipsoidally at least in the transmission region (6) and the lens (3) is arranged relative to the feed element (2) such that the electromagnetic radiation (4) emitted by the lens (3) in the direction of maximum radiation (7) of the antenna has an essentially planar phase front.
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
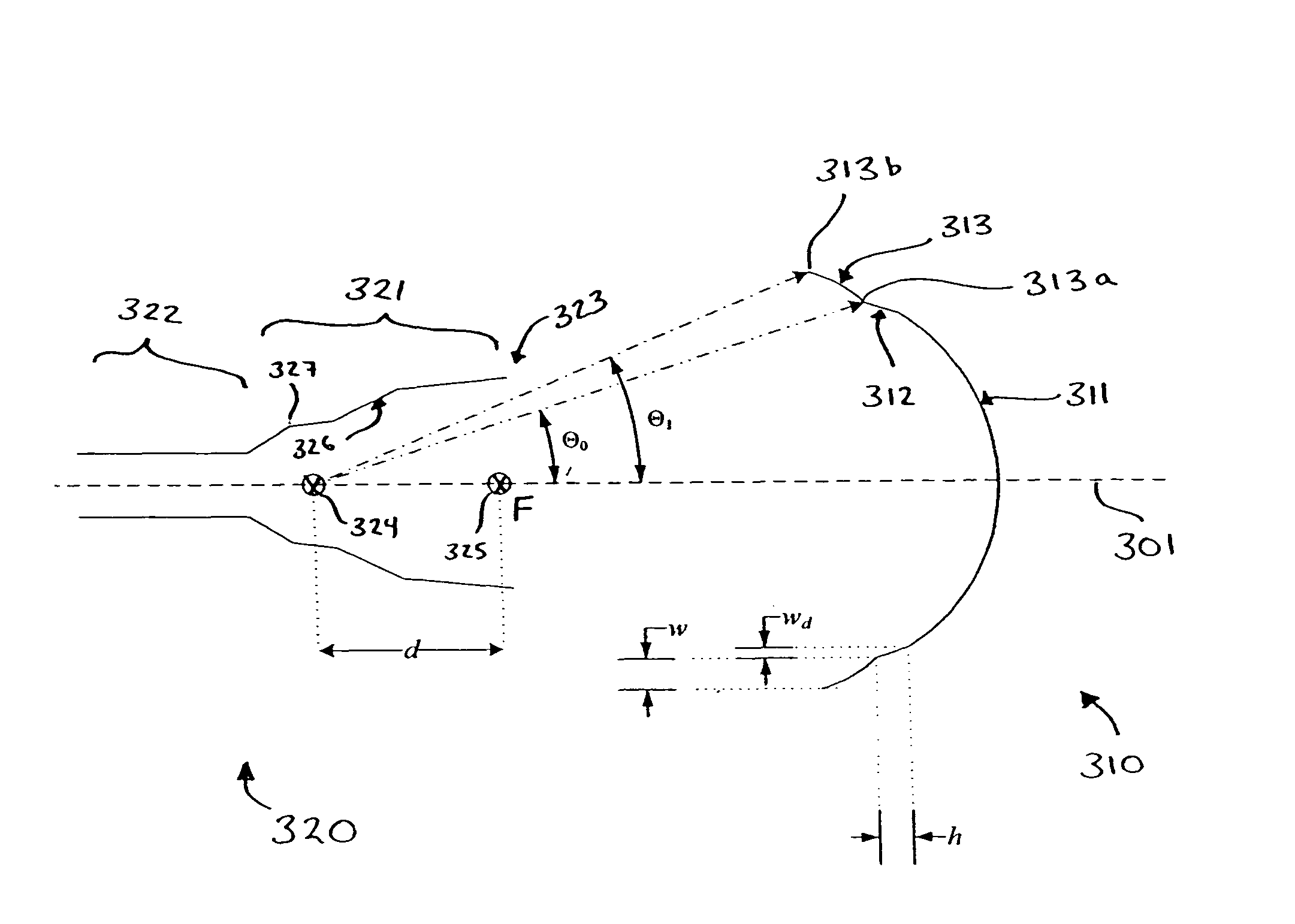
Stepped-reflector antenna for satellite communication payloads
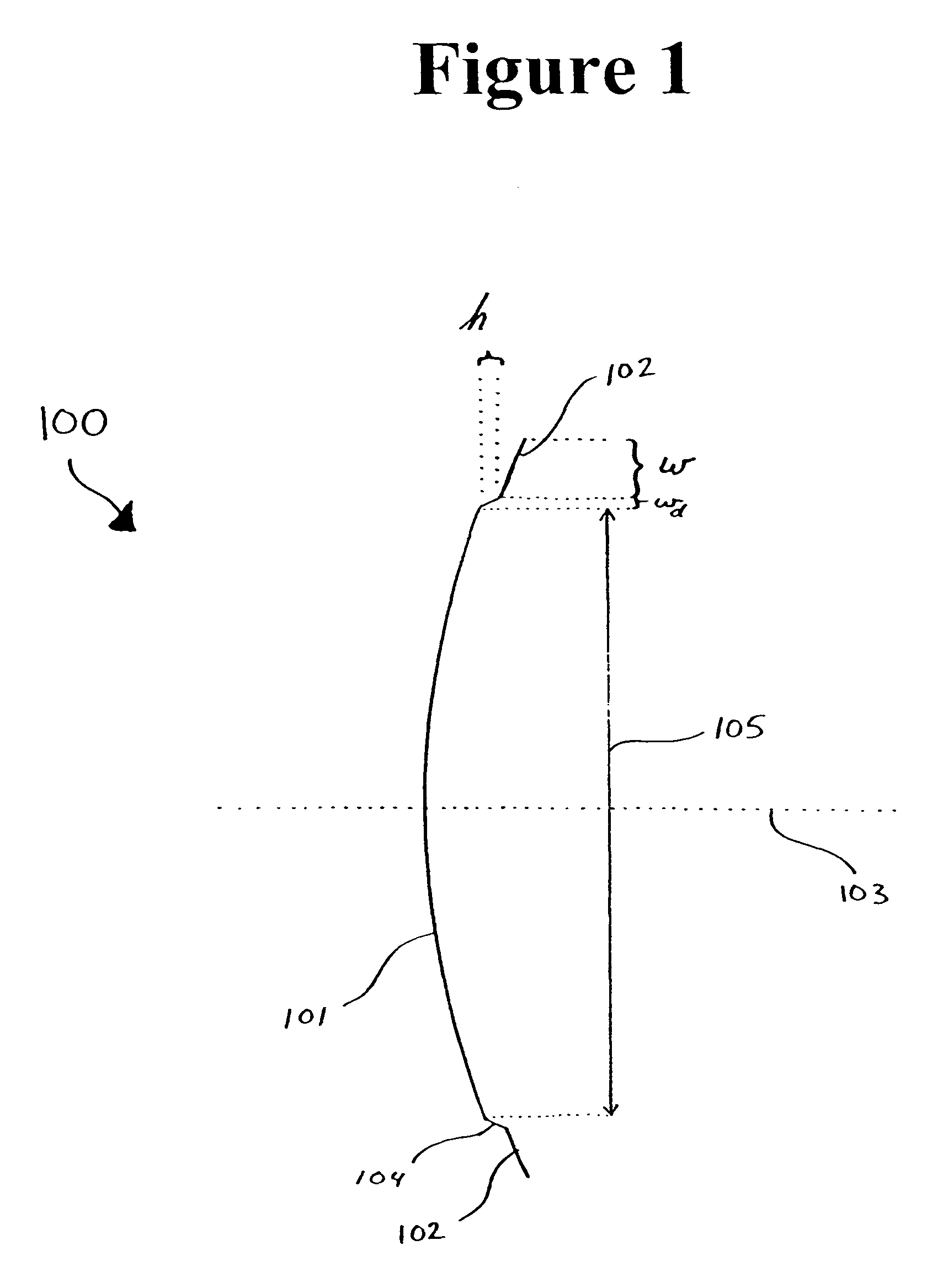
ActiveUS7737903B1Reduce peak-to-edge gain variationImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsPhase shiftedEngineering
A stepped reflector for being illuminated by at least one multiple-band feed is provided. The reflector includes a central region and a first annular region with an annular width of w. The first annular region is axially stepped a height h above the central region, where h is approximately equal tom×[Φ±(ϕ(Θ=0)-ϕ(Θ=Θ0))]×π180×λ2π×12,where m is a positive odd integer, Φ is a desired amount of phase shift of an outer region of a phase front for reflecting off of the reflector, φ is a feed phase contribution for an angle Θ, and Θ0 is an angle formed between an axis of the at least one feed and a line connecting a phase center of the at least one feed and an inner edge of the at least one annular region.The central region and the annular region of the reflector may be parabolically curved or may alternately be shaped. The reflector may be fed by one or more multiple-band horn antennas.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Optimization of near field antenna characteristics by aperture modulation
The approximate radius of curvature of the spherical phase front at the aperture of a transmitting microwave antenna is controlled by an inner section of the aperture attached to the outer section of the aperture by a small number of programmable transducers, thereby controlling the near field shape and power distribution of the transmitted beam.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Method for determining the image quality of an optical imaging system
InactiveUS20060072104A1Avoid loweringImprove image qualityPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansSpatially resolvedImaging processing
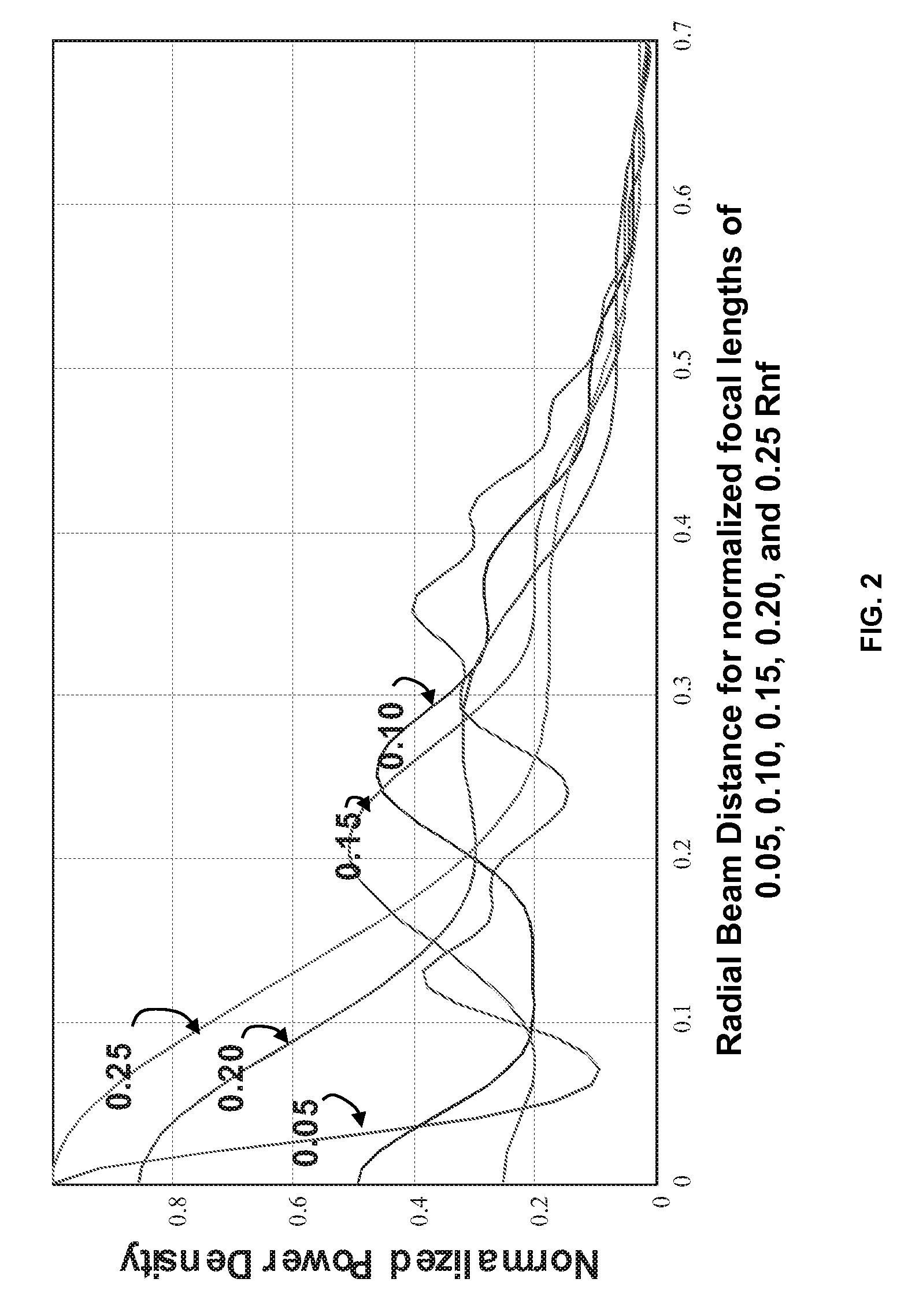
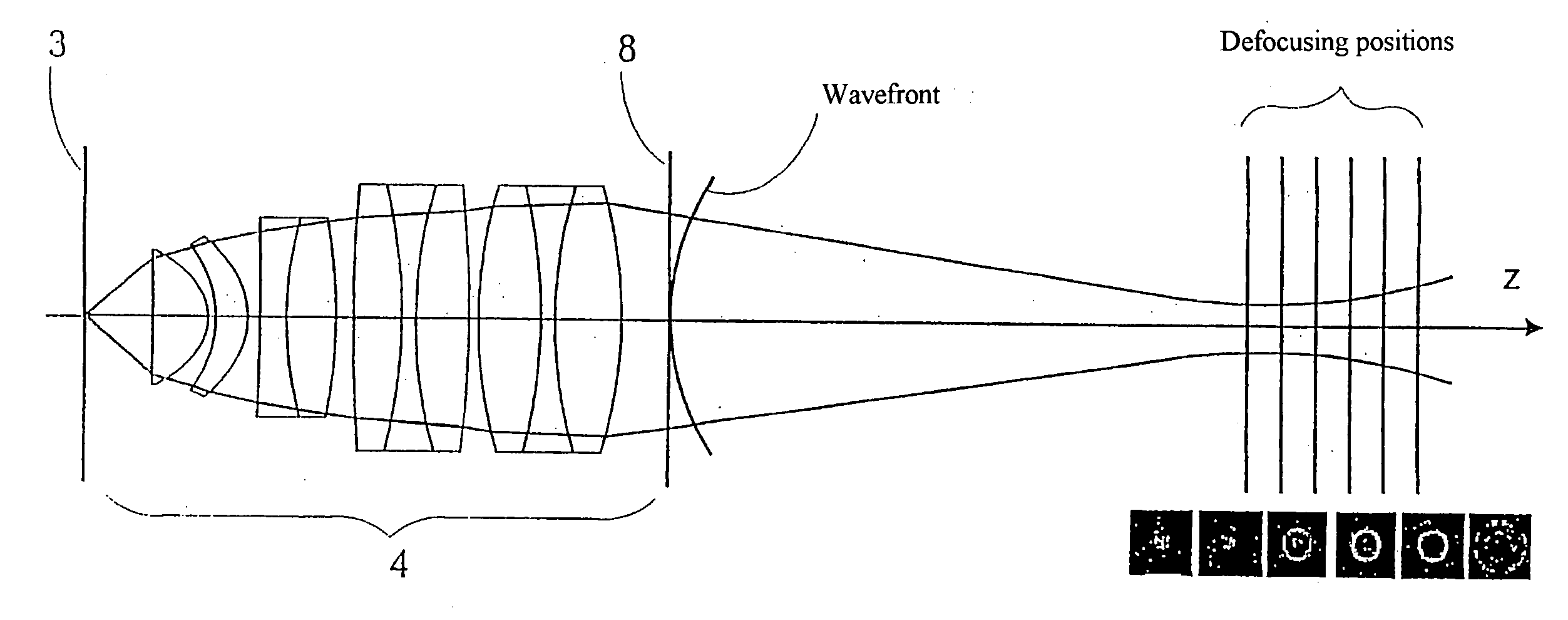
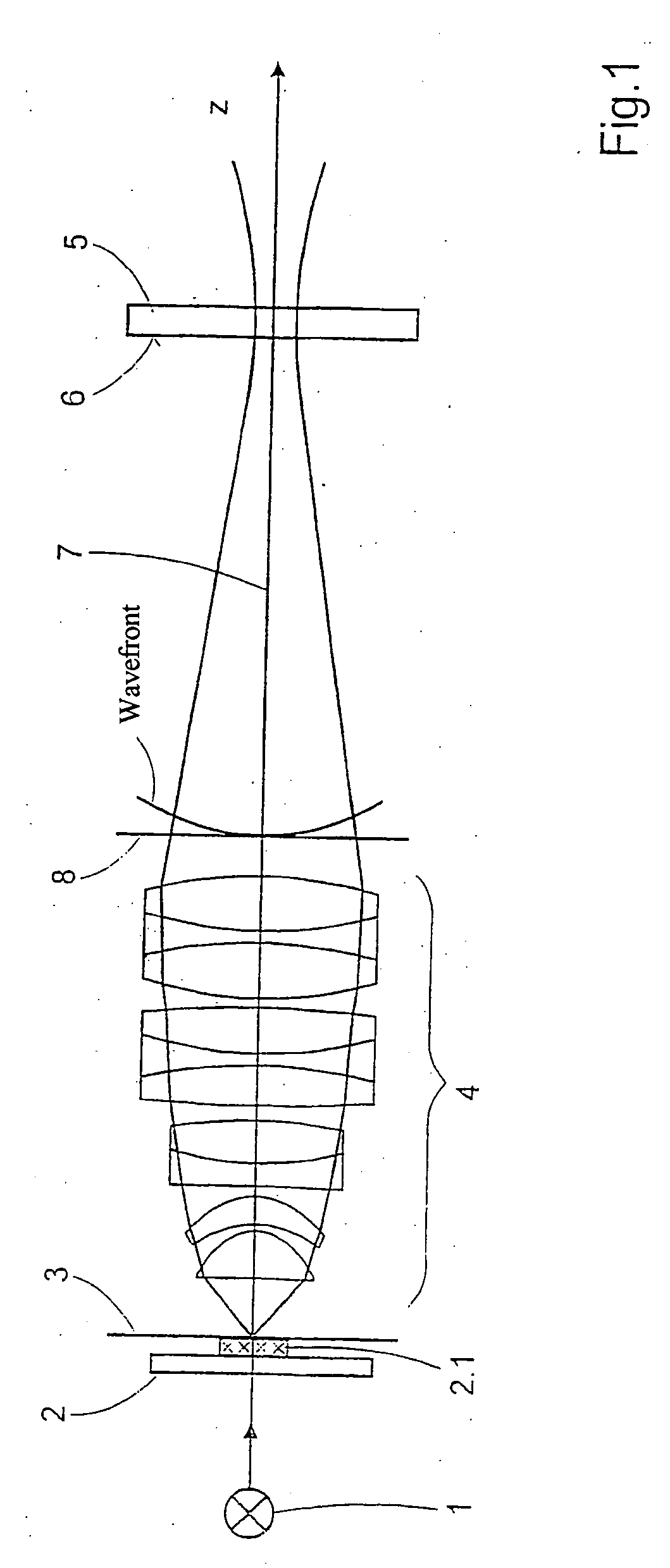
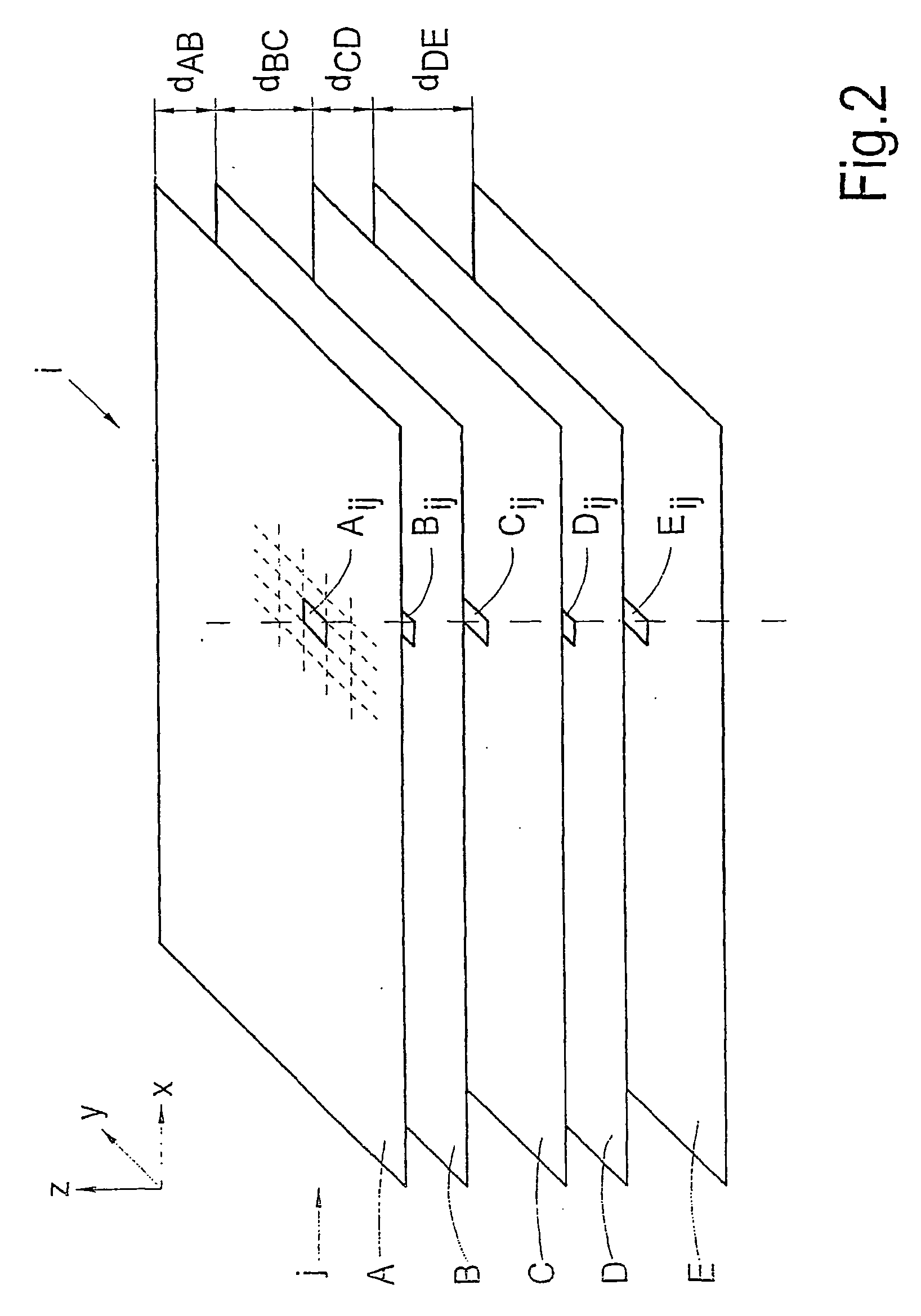
The invention is directed to a method for determining the image quality of an optical imaging system and to the use of the method according to the invention for determining the influence of samples on the amplitude distribution and phase front distribution of the illumination light, of which the amplitude distribution is known in particular. The invention comprises the following steps: adjusting the subassemblies relative to one another in such a way that it is possible to project images of a sample on the detection device; recording a plurality of images of the sample from different reference planes near the focus plane; improving the image quality by image processing, particularly to reduce noise, to compensate for local variations in sensitivity of the detection device, and to center the intensity centroids respectively on a predetermined location in the images; computational linking of the spatially resolved image information, of adjustment values and system variables relating to the optical imaging system, and of information concerning the sample with the aim of determining characteristic numbers that are characteristic of the wavefront deformation caused by the imaging system; and outputting the characteristic numbers and associating them with the imaging system for describing the image quality.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
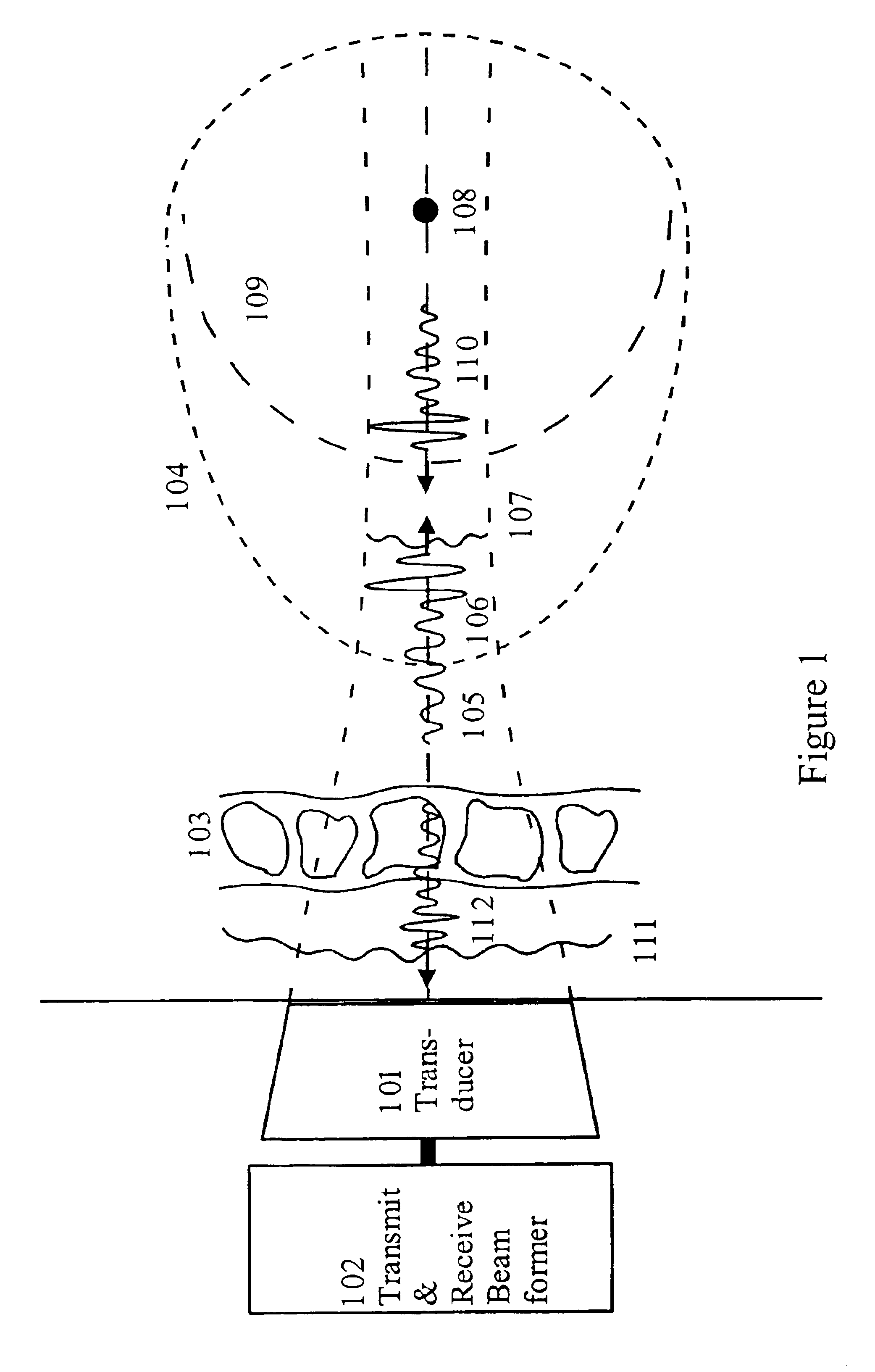
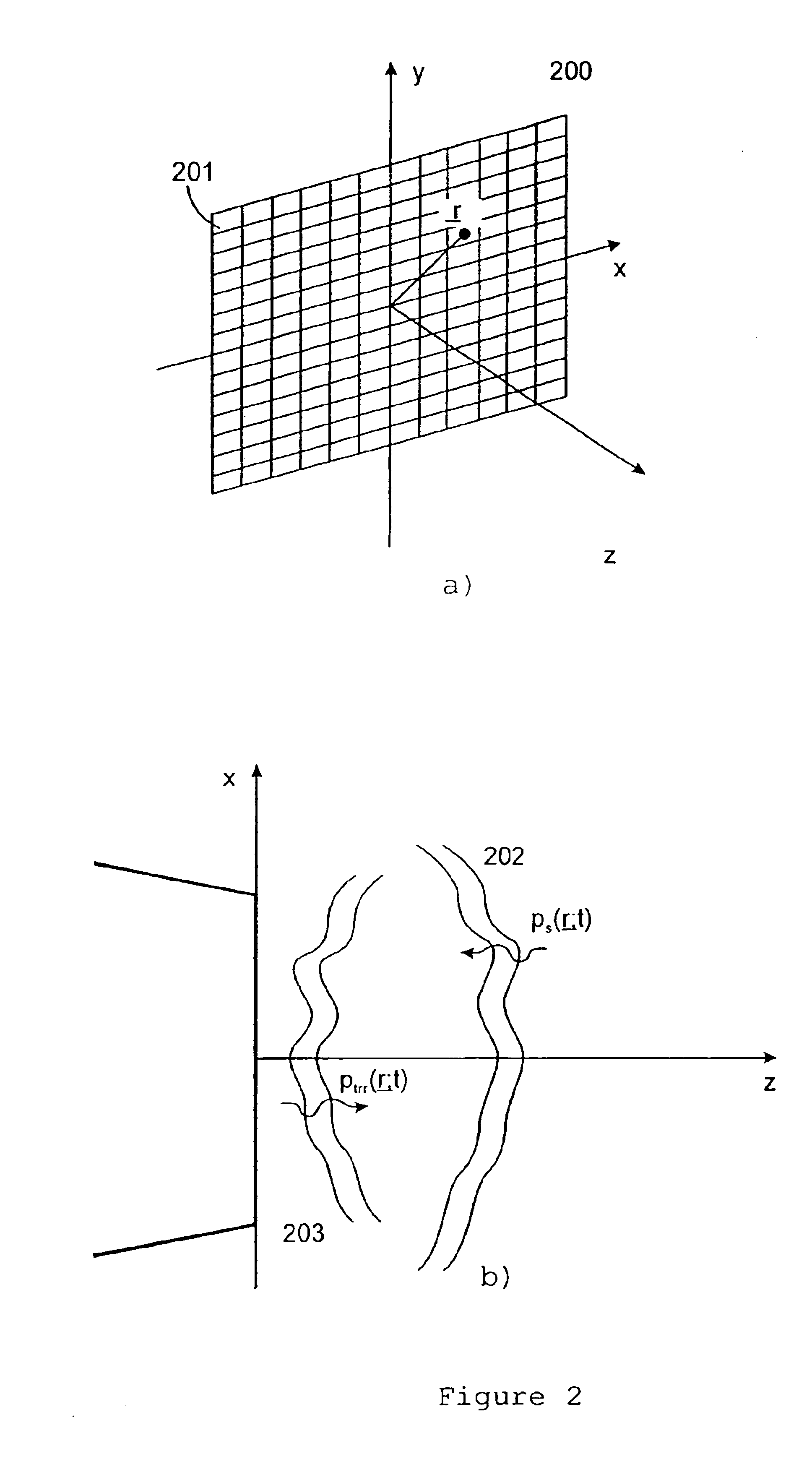
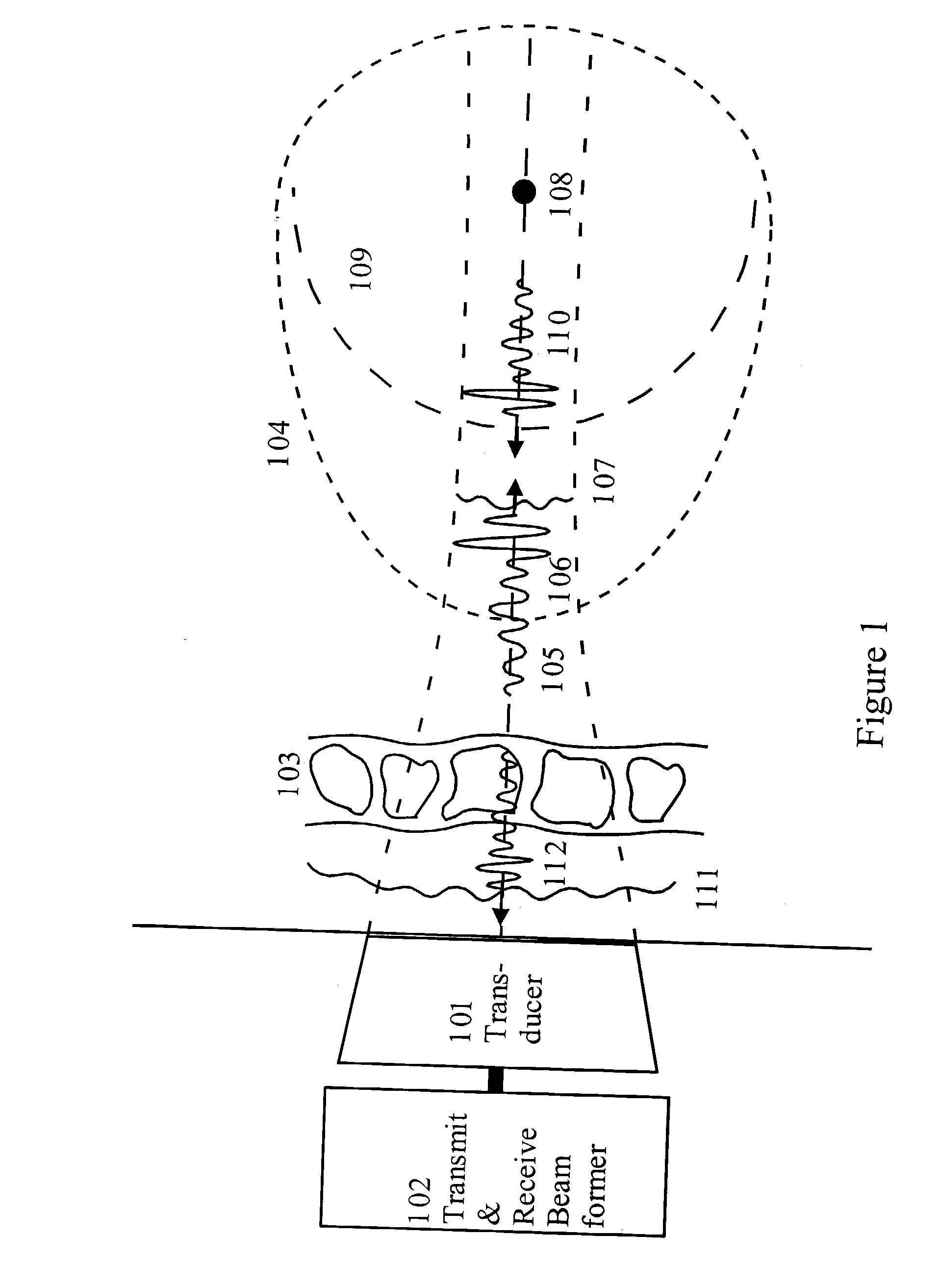
Corrections for pulse reverberations and phasefront aberrations in ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS6905465B2Good estimateReduce impactUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingSonification
A method of correcting for pulse reverberations in ultrasound imaging using two-dimensional transducer arrays, and uses such reduction in element signals and beam signal before estimation of corrections for phase front aberrations of the ultrasound wave. The pulse reverberation is estimated by two transmit events, where the second event is determined by measurement and processing on measurement on echoes of the first event. In a second embodiment of the invention, the reverberation is estimated by a single transmit event, using two receive beams and processing on these. In a third embodiment of the invention the reverberation from very strong scatterers is reduced by adjustment of the active transmit aperture.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJ O SLASHED RN A J +1
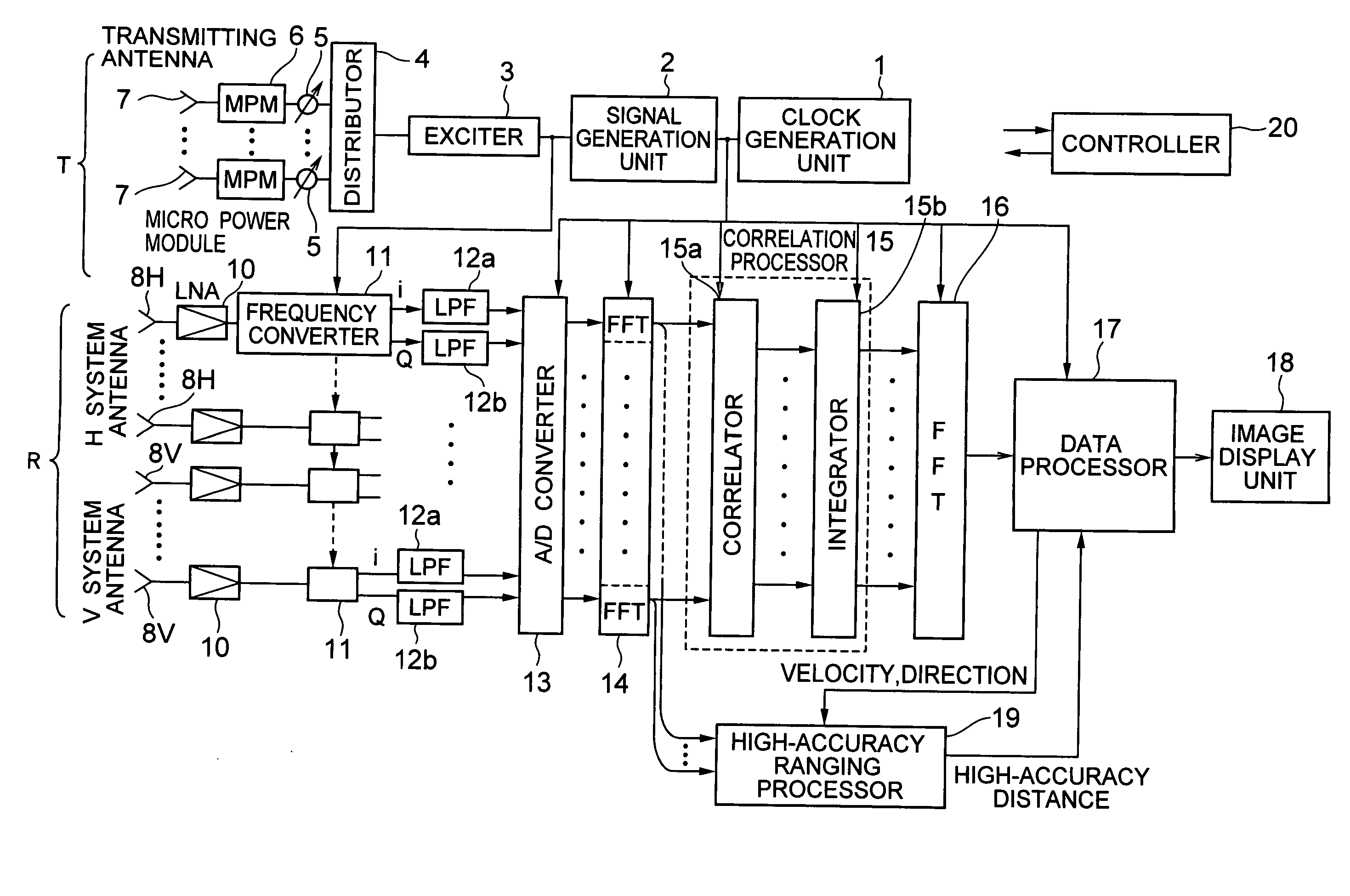
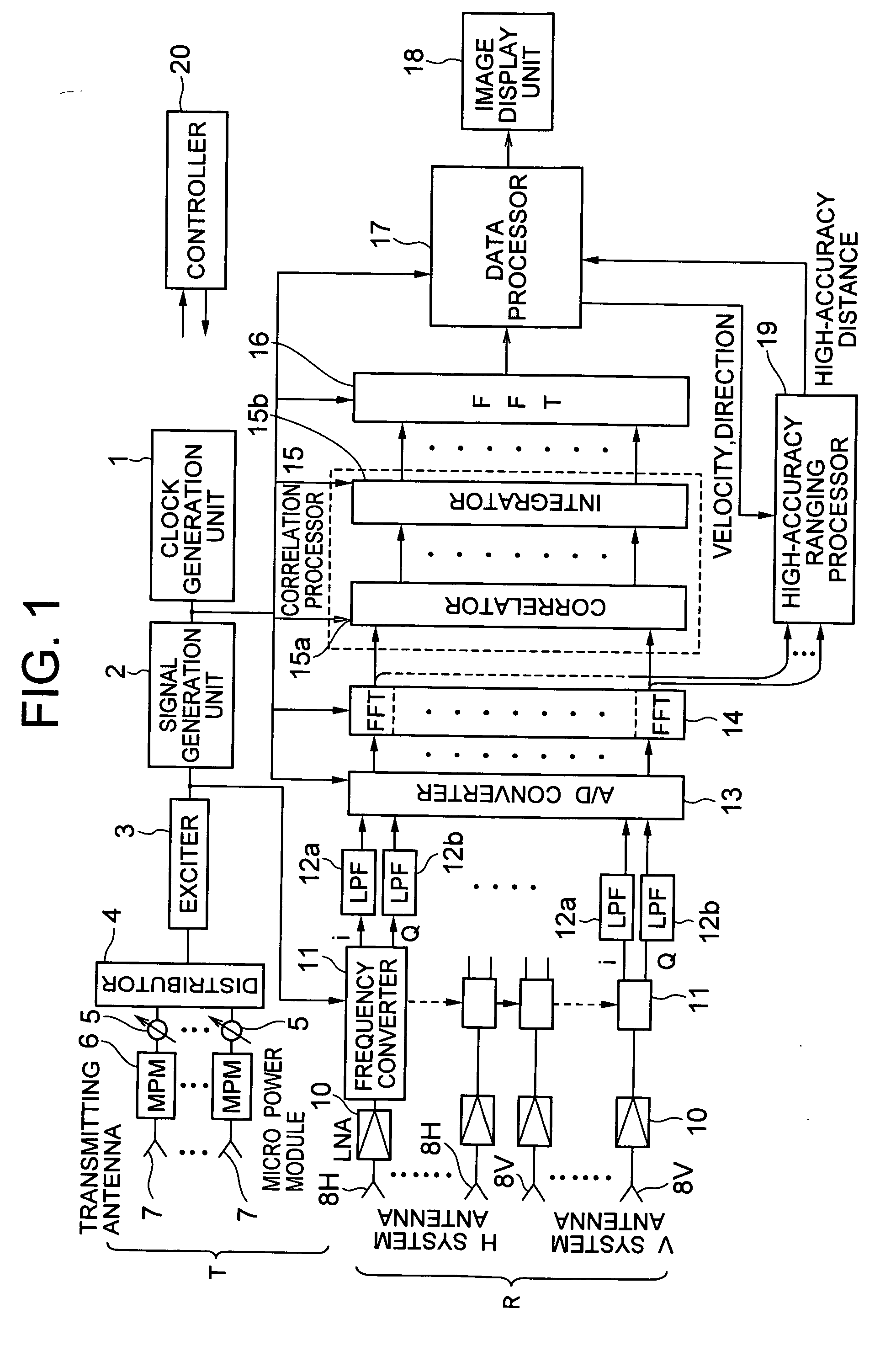
Interferometer-type radar
InactiveUS20060220946A1Easily realizedImprove reliabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarPhase difference
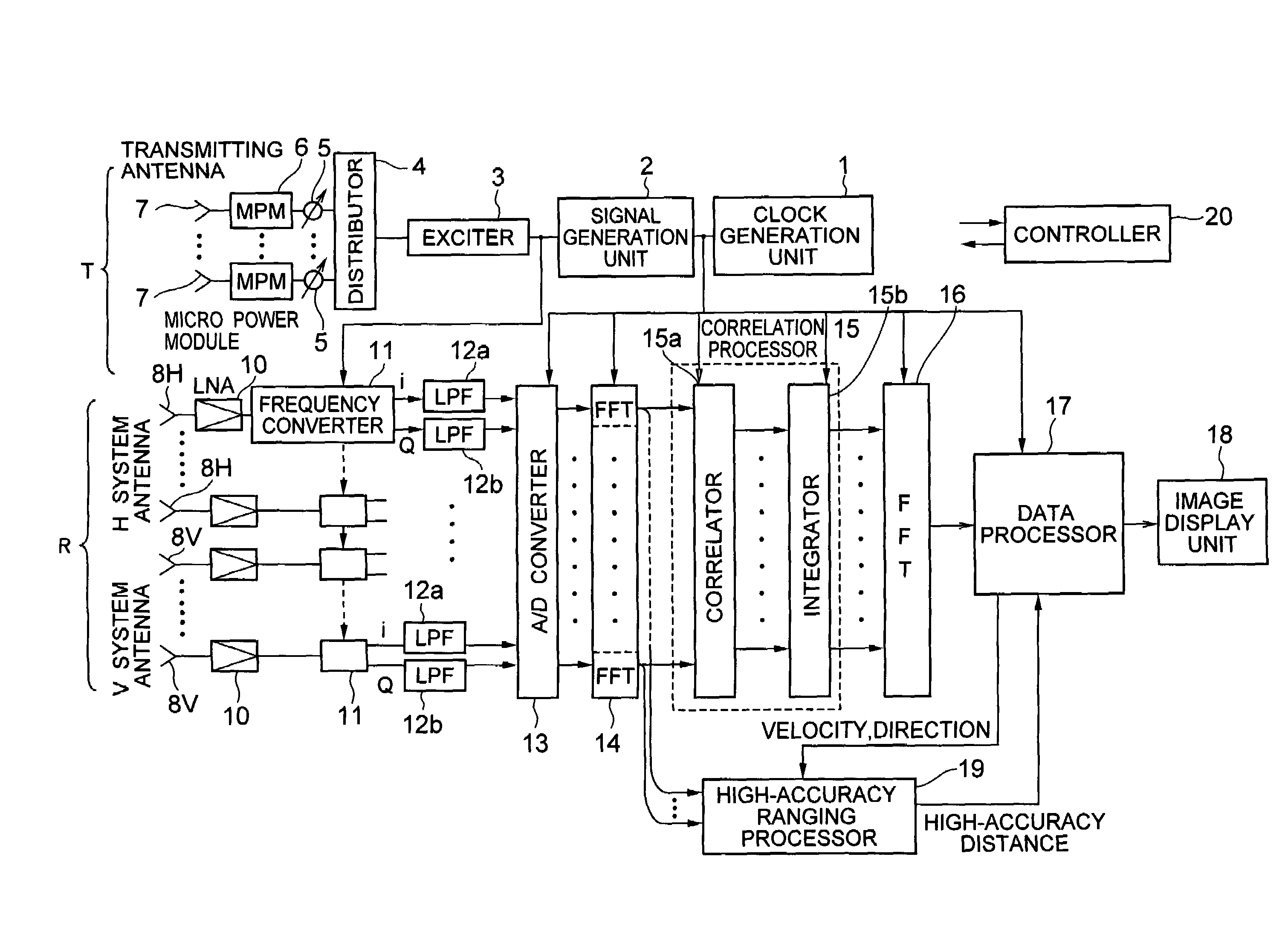
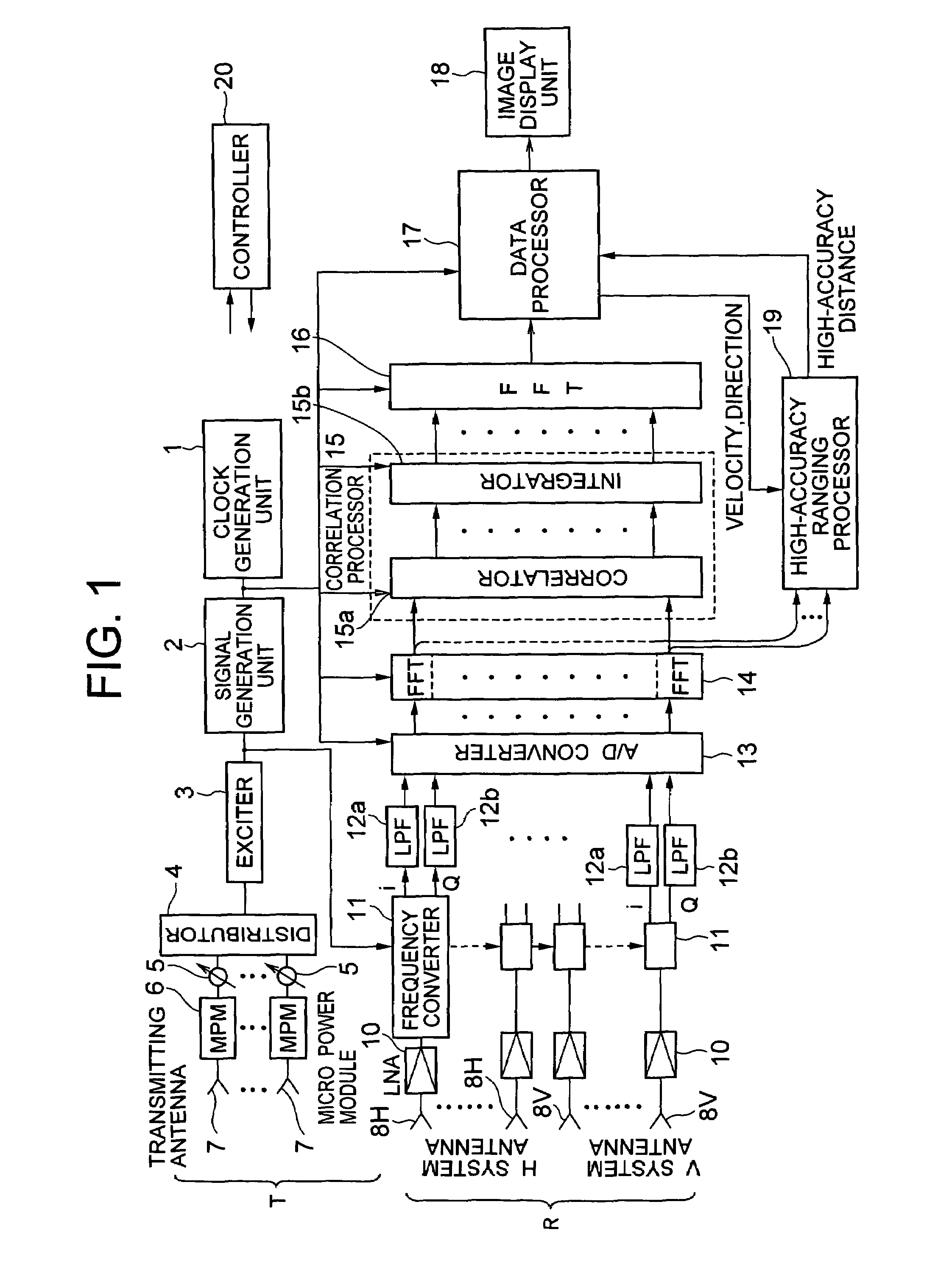
A transmitter for transmitting signals to targets and a receiver for receiving signals reflected from targets are included. The transmitter outputs CW signals for detecting direction and velocity of the target. The receiver performs: a function of receiving signals reflected from targets with a plurality of receiving antennas at the same time as transmitting from the transmitter, and performing spectral analysis with respect to receiving signals to thereby classify them by velocity component; a function of correlating signals of the receiving antenna systems; a function of integrating the signals correlation-processed; and a function of obtaining phase fronts of signals made incident on an antenna face from the phase differences of signals between receiving antennas, and performing two-dimensional FFT to the outputs to thereby measure the direction and velocity of the target.
Owner:NEC CORP
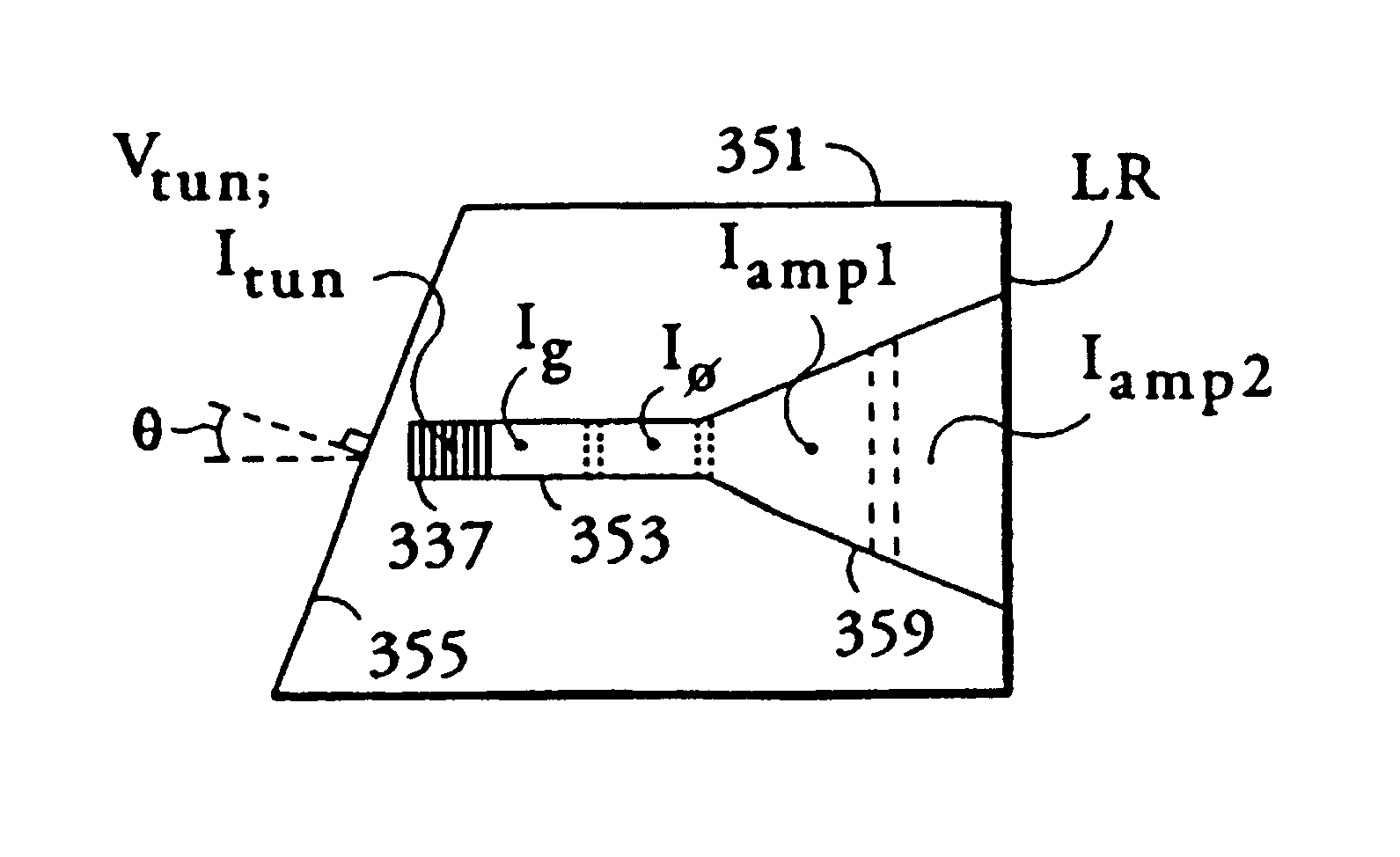
Chip-scale two-dimensional optical phased array with simplified controls
ActiveUS20170255077A1Small sizeMinimal weightWave based measurement systemsCoupling light guidesPhase shiftedLight beam
A device includes an optical splitter comprising a plurality of splitter outputs. The splitter outputs are out of phase and include a non-uniform phase front. The device includes a one-dimensional phase compensation array communicating with the optical splitter. The phase compensation array receives the non-uniform phase front and outputs a uniform phase front. The phase compensation array includes a plurality of array outputs. The device includes a tunable linear gradient phase shifter communicating with said phase compensation array to impart a linearly-varying phase shift across said plurality of array outputs, thereby steering a beam along a first angle in a first plane. The device includes a waveguide grating out-coupler communicating with said linear gradient phase shifter, and a uniform phase shifter communicating with the waveguide grating out-coupler. The uniform phase shifter steers the flat phase front along a second angle in a second plane perpendicular to said first plane.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Solid-state laser oscillator with gain media in active mirror configuration
InactiveUS6888872B2Large fundamental mode sizeExcellent transverse mode controlOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionOptical coatingOptical field
An apparatus and method for achieving a near diffraction-limited, high-average power output from a solid-state laser oscillator are provided. The solid-state laser uses multiple disk-shaped laser gain media having a large optical aperture placed in an unstable resonator. The laser gain media is provided with optical coatings for operation in the active mirror configuration and is attached to a rigid, cooled substrate, which allows it to maintain a prescribed shape even when experiencing significant thermal load. The resonator is configured so as to preferentially support low order optical modes with transverse dimensions sufficiently large to efficiently fill the gain media apertures. Resonator configurations capable of producing standing wave or traveling wave optical fields are disclosed. The resonator may include means for intracavity correction of an optical phase front by adaptive optics. Also disclosed is an arrangement of resonator gain elements in axisymmetric arrays suitable for integration into a compact and lightweight laser system.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
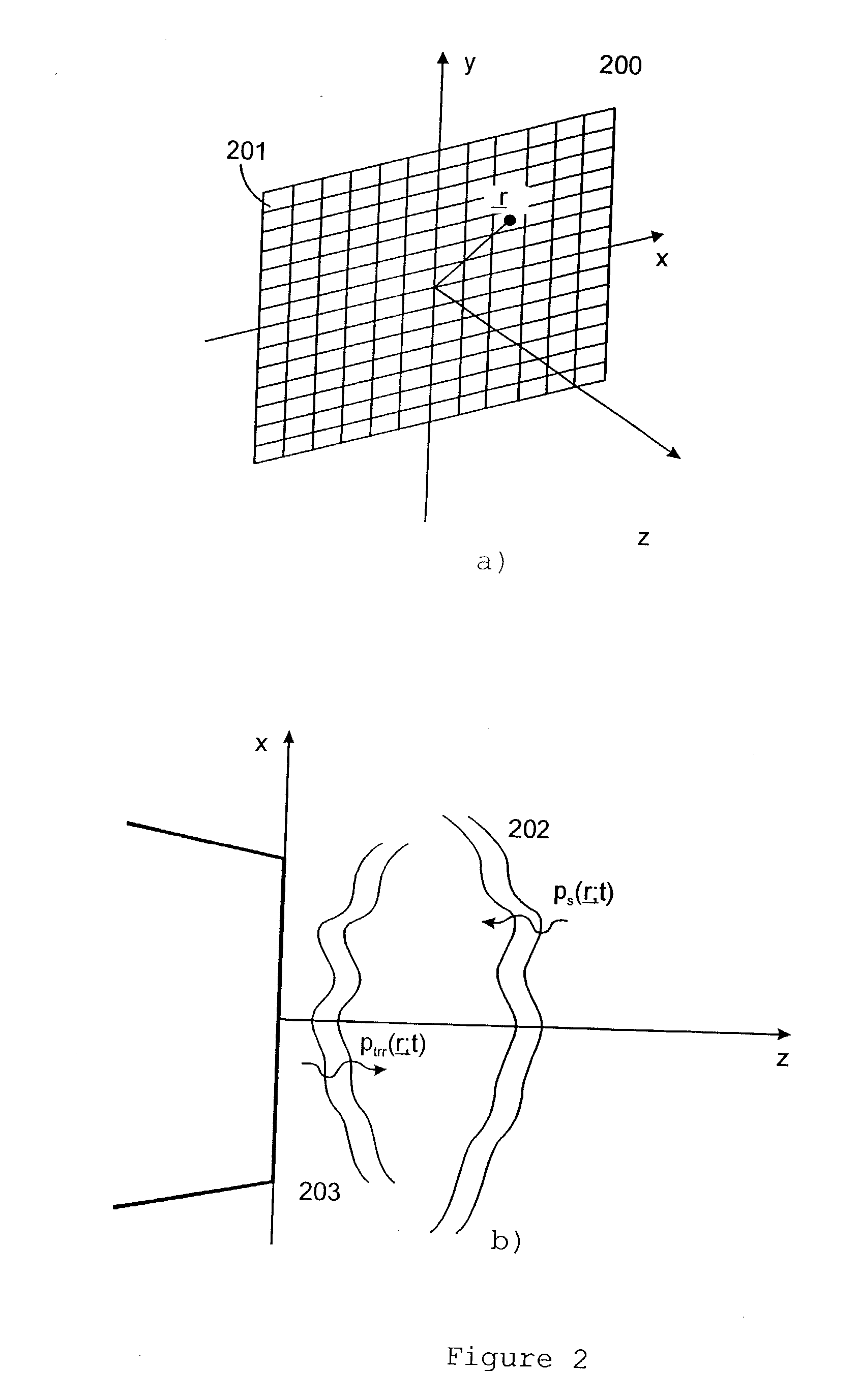
Coherent Image Formation for Dynamic Transmit Beamformation
ActiveUS20090306512A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsUltrasonographyData set
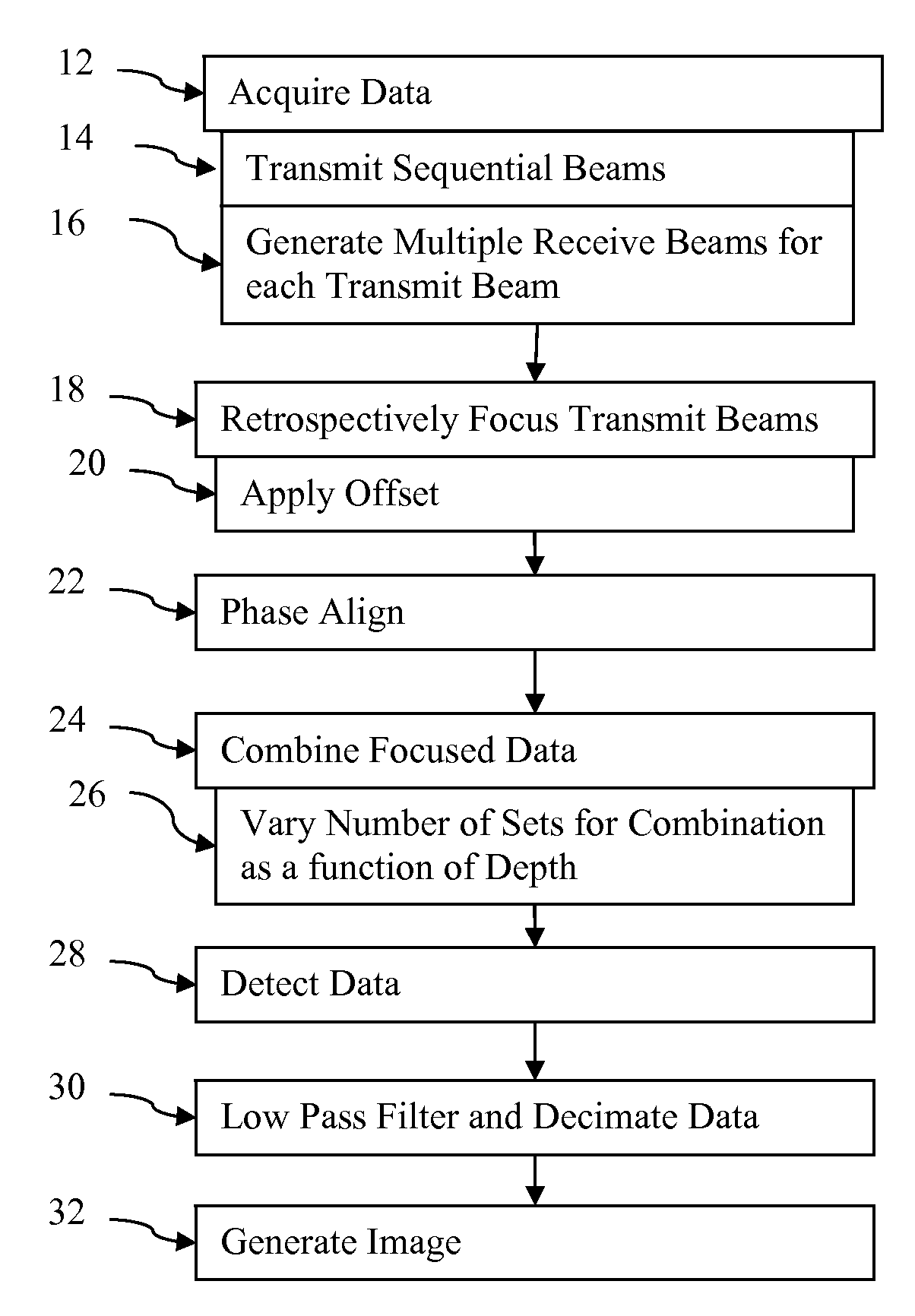
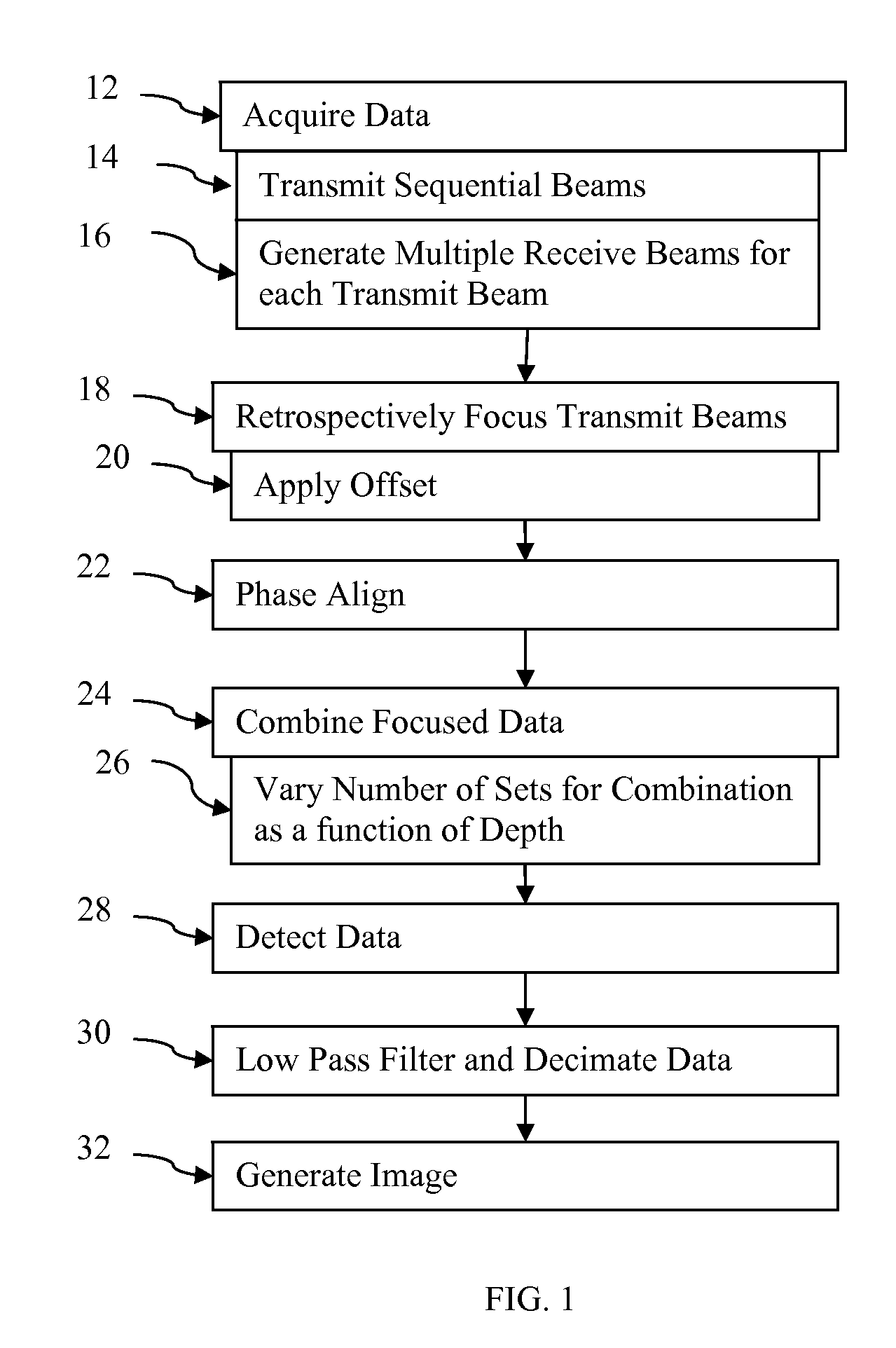
Retrospective dynamic transmit beamformation is provided in medical ultrasound imaging. Using parallel receive beamformation, sets of data representing locations in at least a common field of view are obtained, each set in response to a transmit with a spatially distinct phase front. The common field of view receive data are time aligned and amplitude weighted for retrospective transmit focusing and retrospective transmit apodization, respectively. A time offset, such as of a cycle or more in some cases, is applied to the receive data for retrospective transmit focusing. The offset is selected to emulate shifting the transmit delay profile to be tangentially intersecting with the dynamic receive delay profile for each location which is the desired transmit delay profile. A weight is applied to the receive data for retrospective transmit apodization. The weight is selected based on the desired transmit apodization profile. The offset and weighted data representing a same location from different transmit events is coherently combined. The number of sets of data offset, weighted and combined may vary as a function of depth for dynamic transmit beamformation.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
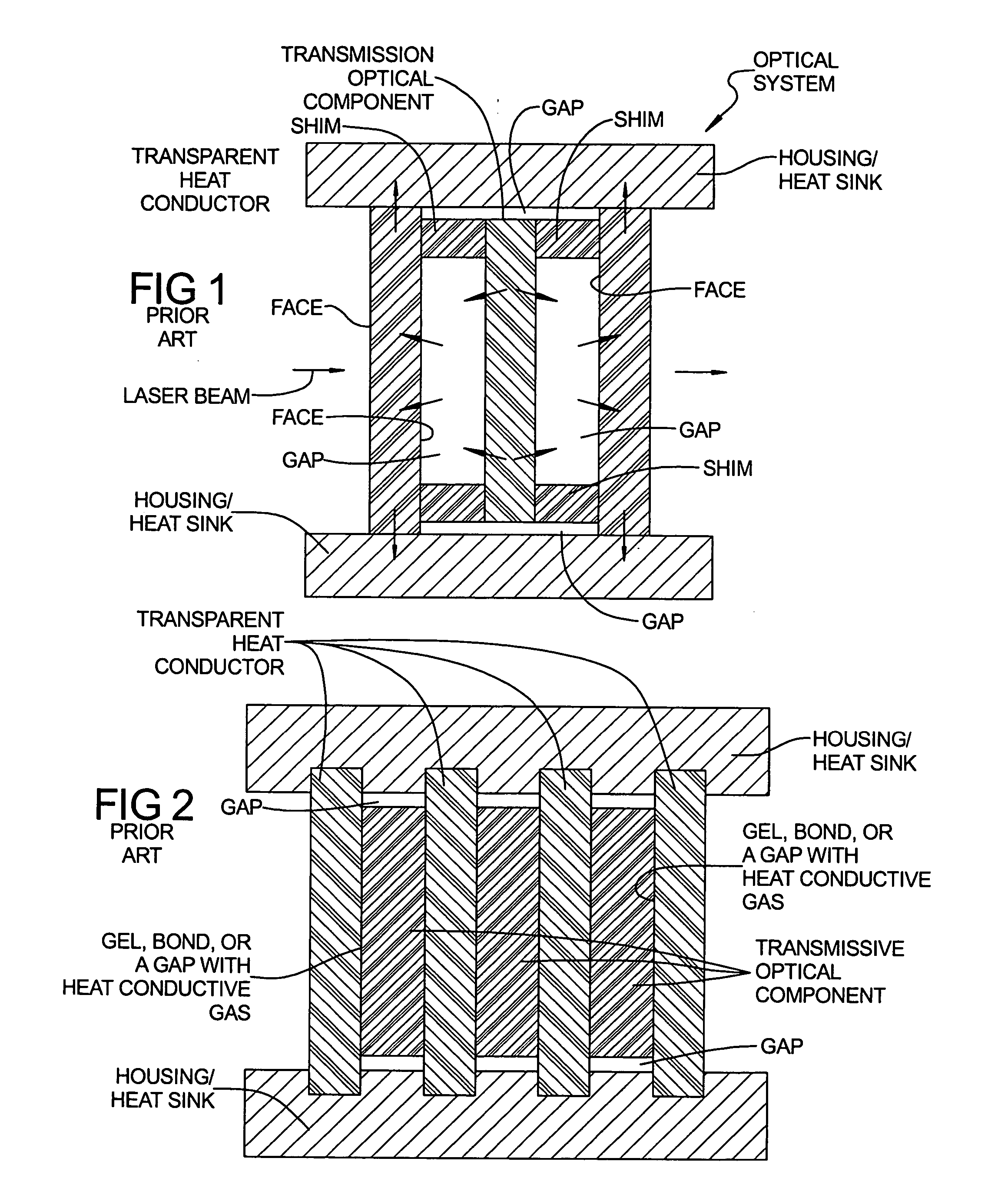
Apparatus and method for face cooling of optical components of a laser system
InactiveUS20060088067A1Increase powerRule out the possibilityActive medium shape and constructionLaser cooling arrangementsDifferential pressureLight beam
A cooling system for use in with a transmissive optical element of a high average power laser (HAP). The system includes at least one optically transmissive element (TOC) that is held by a differential pressure in thermal contact with a heat sink assembly. In one embodiment, the heat sink assembly includes an optically transparent heat conductor (THC) attached to at least one face of the TOC. A vacuum formed between adjacent faces of the TOC and THC urges the facing planar surfaces into thermal contact with one another. Waste heat generated in the TOC is conducted to the THC. The temperature gradient inside the TOC is maintained substantially parallel to the direction of a laser beam being directed through the THC so that a given phase front of the beam exposes TOC material to the same temperature. As a result, the TOC does not perturb the phase front of the laser beam.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
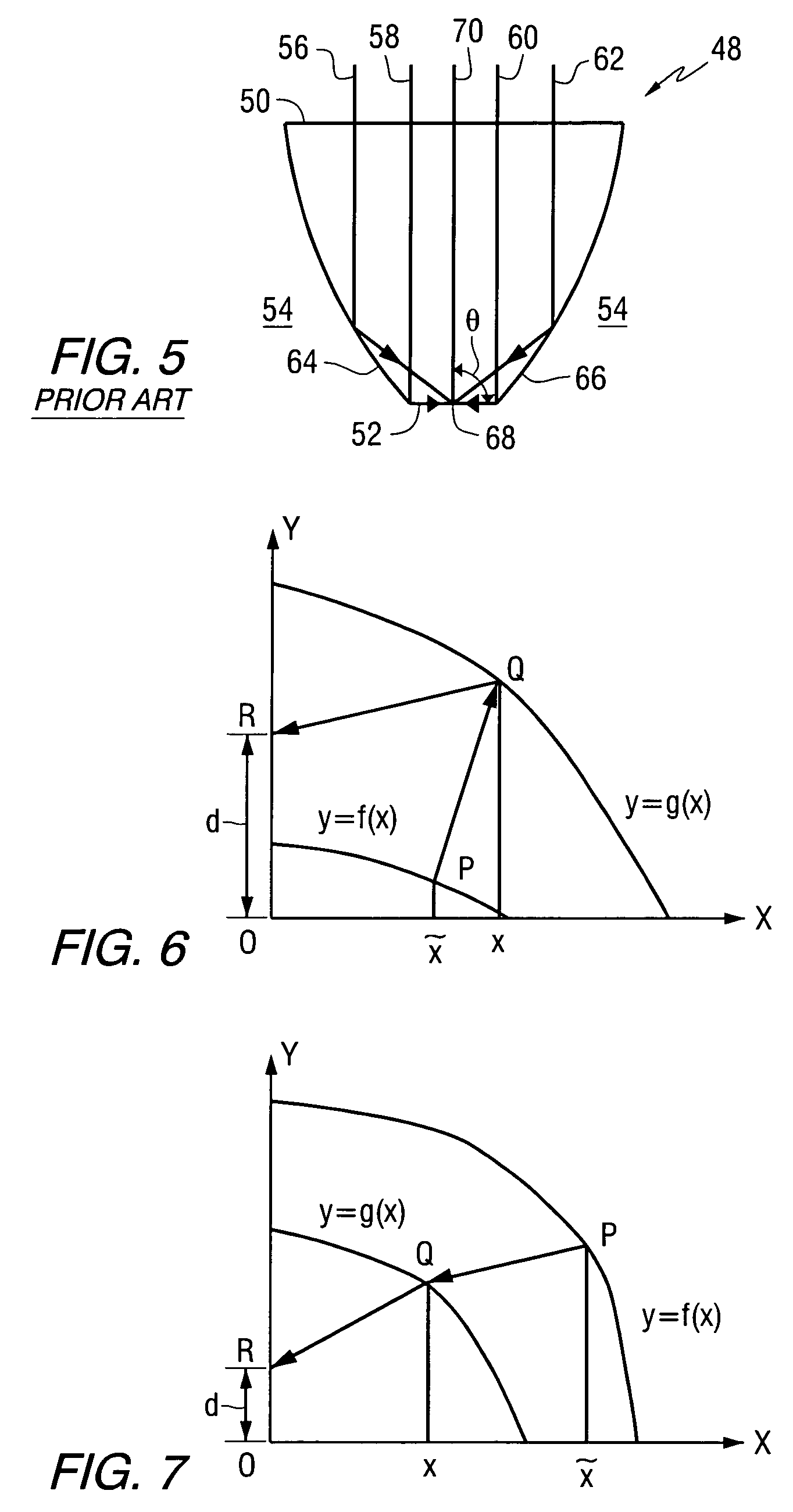
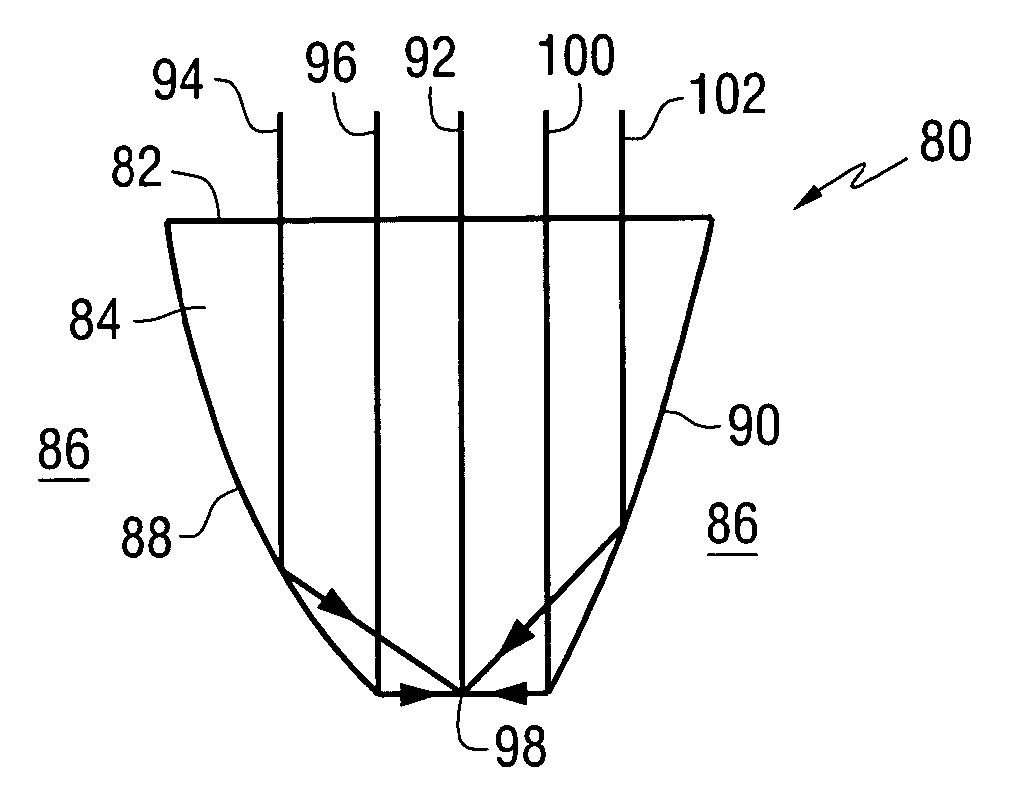
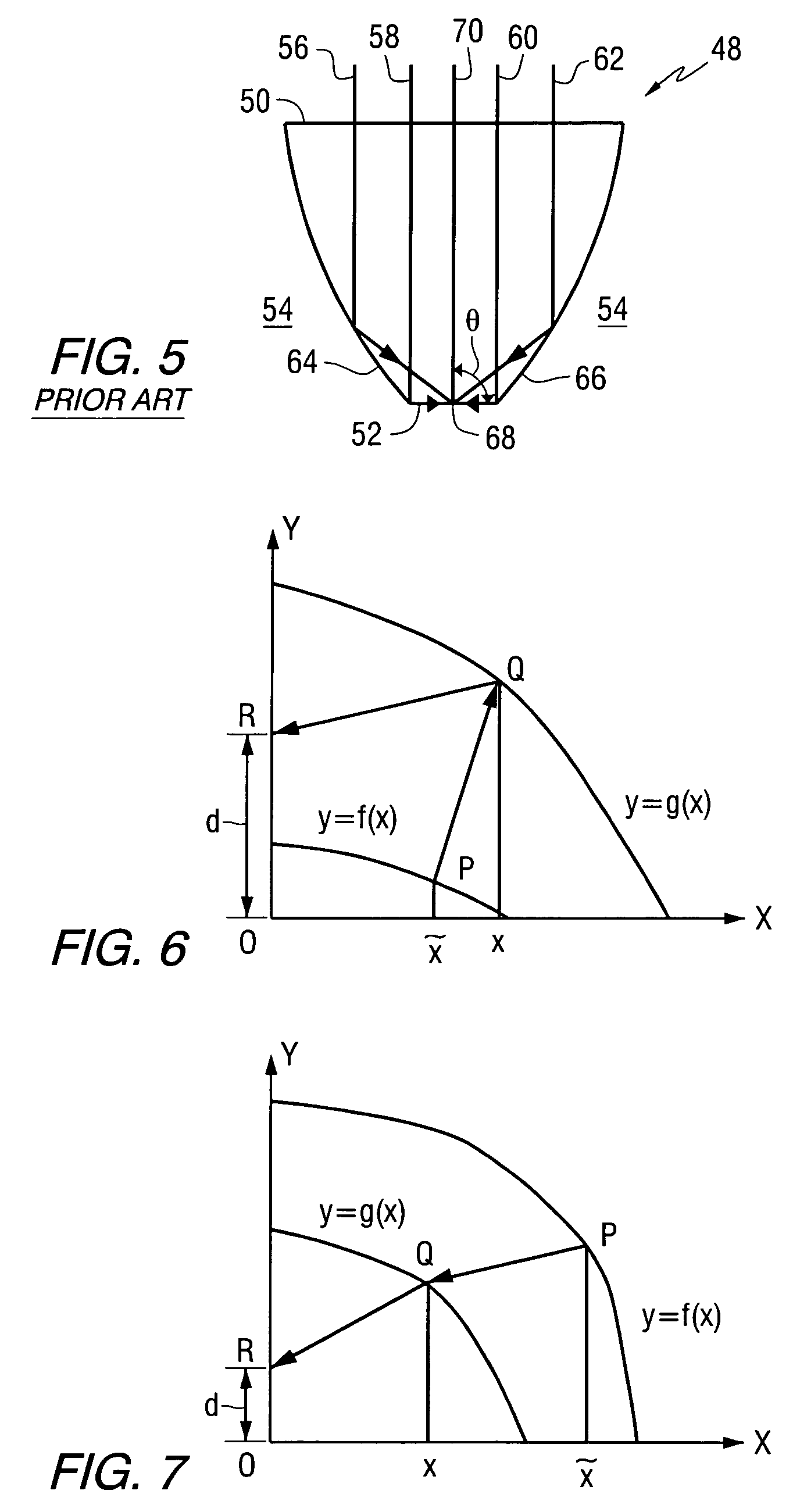
Phase offset integrated solid immersion mirror and lens for a general phase front
An apparatus comprises a condenser for directing electromagnetic radiation to a focal point, the condenser comprising a first interface on a first side of a longitudinal axis for directing a first plurality of rays of the electromagnetic radiation to a focal point and a second interface on a second side of the longitudinal axis for directing a second plurality of rays of the electromagnetic radiation to the focal point, wherein the first and second interfaces are shaped such that at the focal point, the second plurality of rays are about 180° out of phase with respect to the first plurality of rays.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
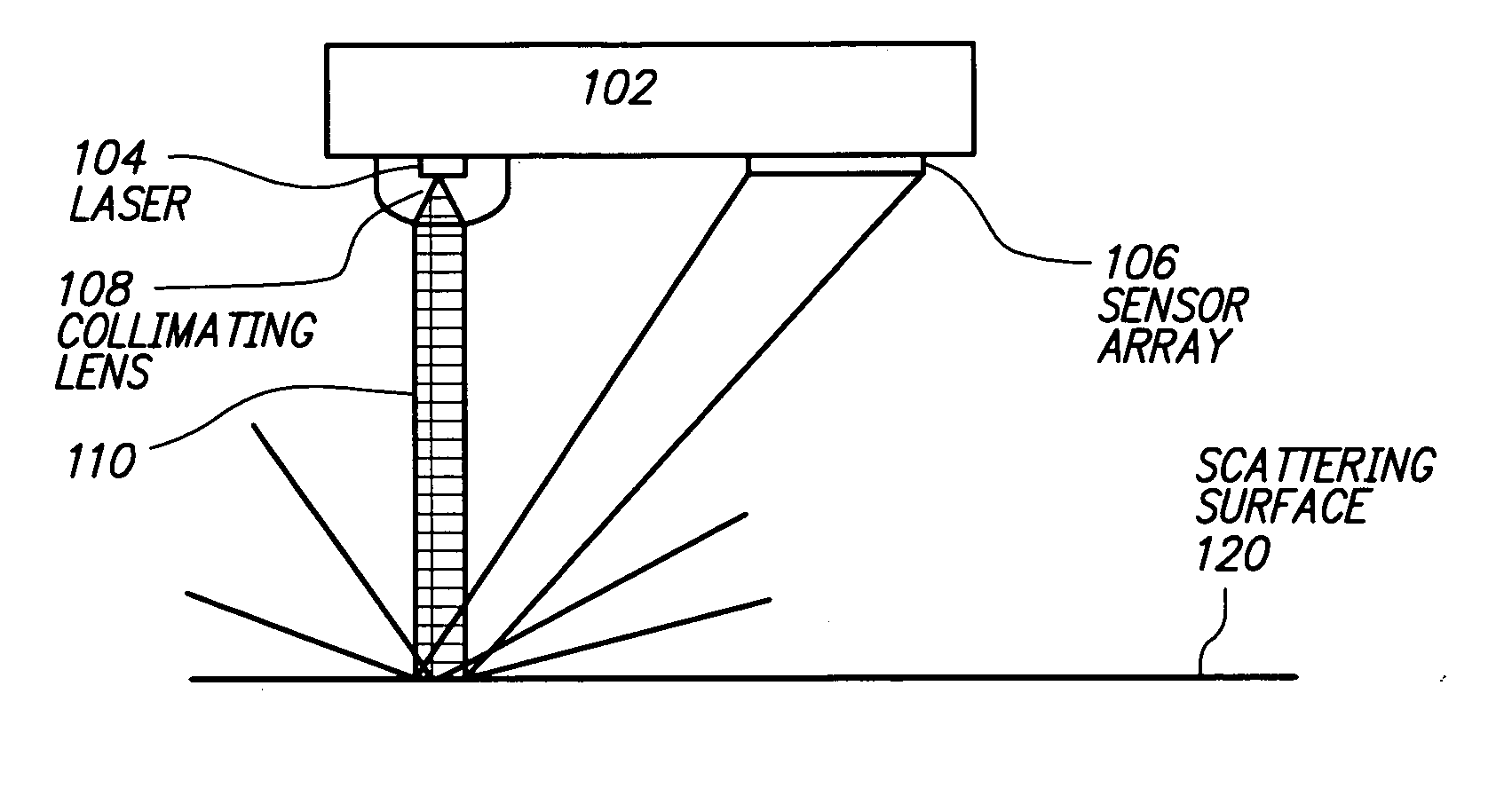
Speckle navigation system
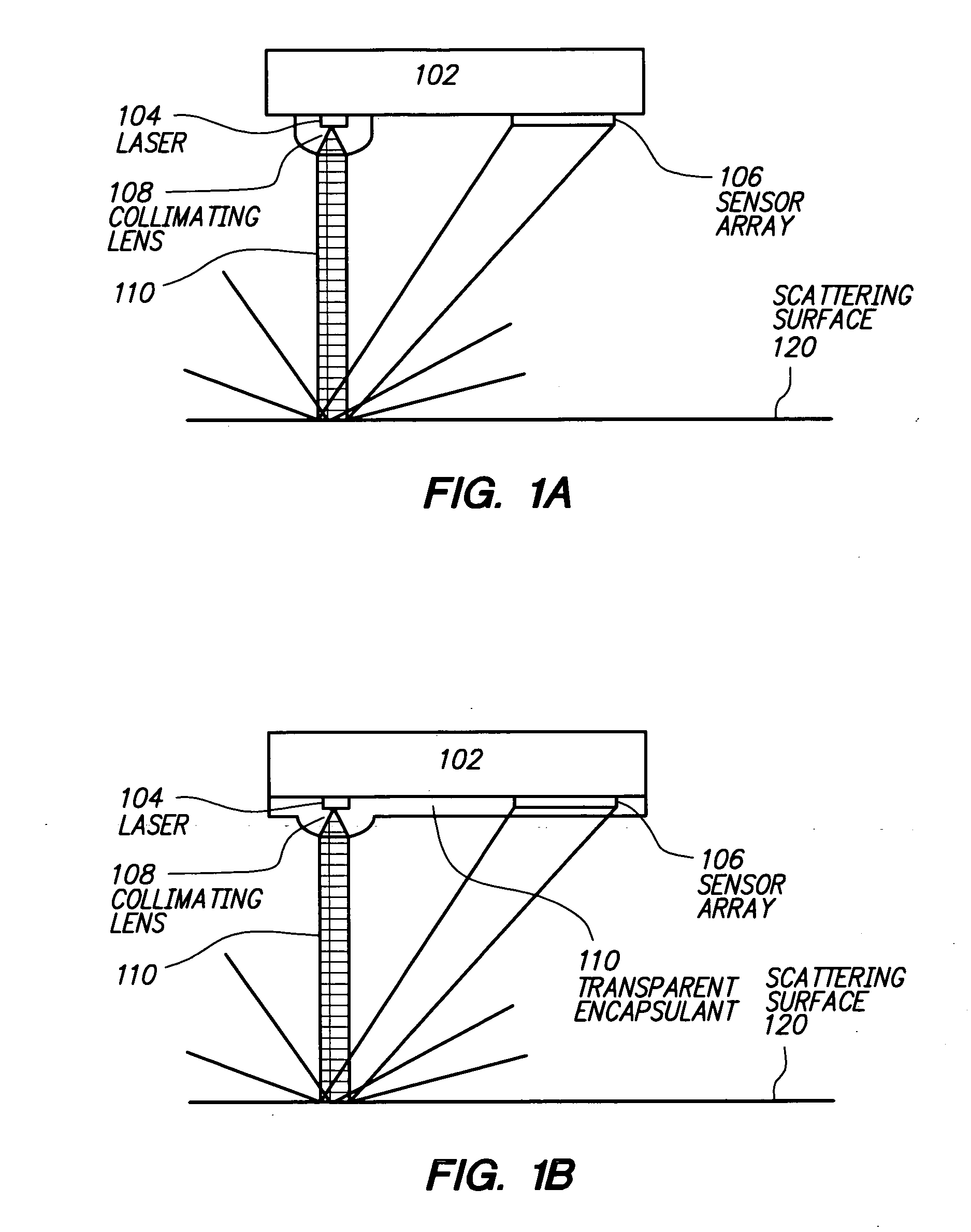
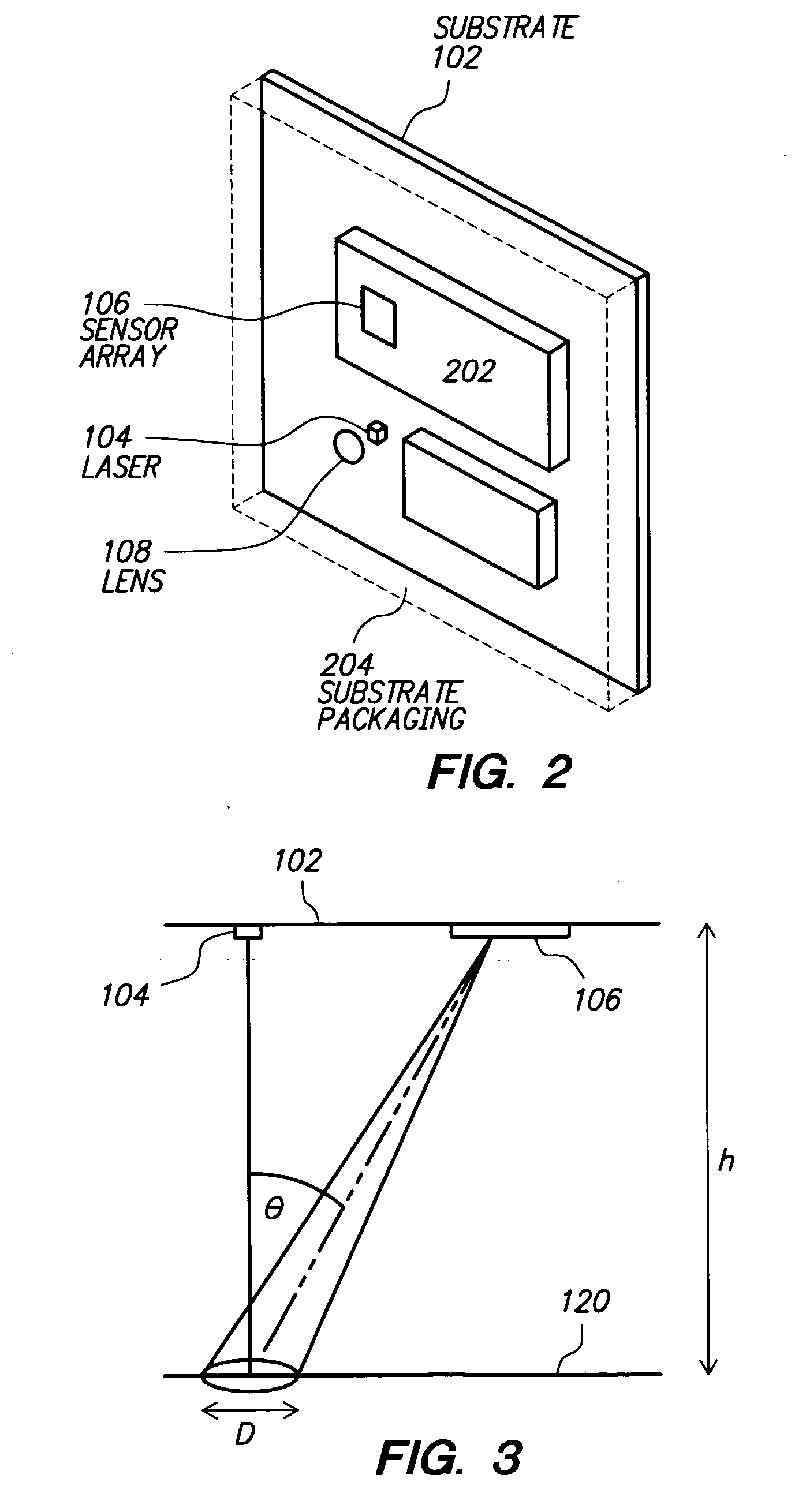
ActiveUS20070139381A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsSensor arrayDevice form
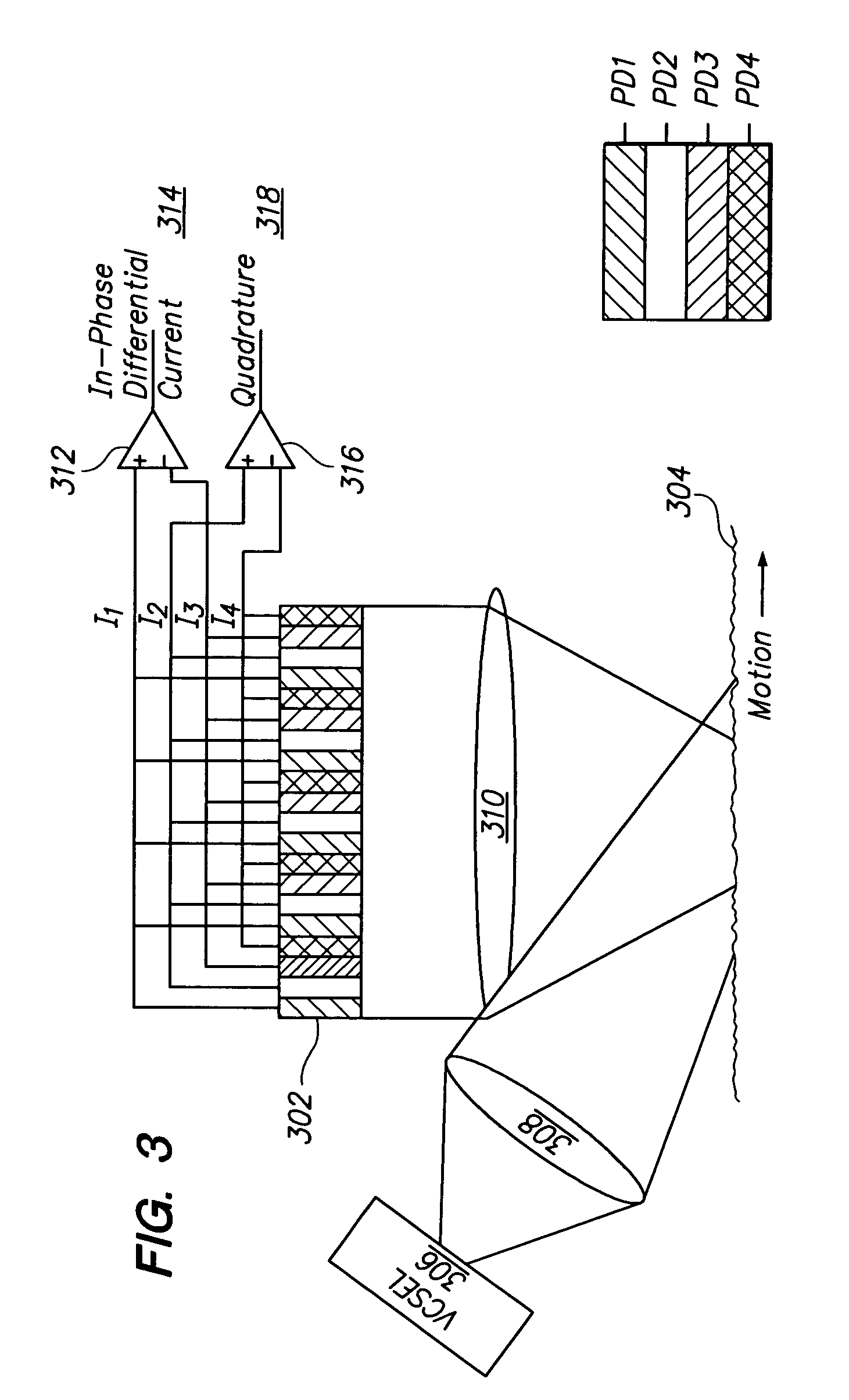
One embodiment relates to a laser positioning device for sensing relative movement between a data input device and a surface by determining displacement of image features in a succession of images of the surface. The device forms a single integrated package, which includes a planar substrate and a transparent encapsulant that also embodies a collimating lens. Both a coherent light source and a sensor array and associated circuitry are configured on the planar substrate. Another embodiment relates to a method of sensing relative movement between a data input device and a surface. Coherent light is emitted from a laser and collimated so as to form a collimated illumination beam with a predetermined diameter, D, and a substantially uniform phase front. A speckle pattern is generated by impingement of the collimated illumination beam on the surface and detected by a sensor array. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Corrections for pulse reverberations and phasefront aberrations in ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS20030199763A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingSonification
A method of correcting for pulse reverberations in ultrasound imaging using two-dimensional transducer arrays, and uses such reduction in element signals and beam signal before estimation of corrections for phase front aberrations of the ultrasound wave. The pulse reverberation is estimated by two transmit events, where the second event is determined by measurement and processing on measurement on echoes of the first event. In a second embodiment of the invention, the reverberation is estimated by a single transmit event, using two receive beams and processing on these. In a third embodiment of the invention the reverberation from very strong scatterers is reduced by adjustment of the active transmit aperture.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJ O SLASHED RN A J +1
Semiconductor gain medium with multimode and single mode regions
InactiveUSRE37051E1High power amplificationIncrease powerOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionOptical cavityAudio power amplifier
A semiconductor gain medium has an optical cavity comprising a multimode region permitting propagation of light with a diverging phase front and a single mode region. An optical cavity is formed by optical feedback within the medium. Preferably, the feedback comprises a combination of a cleaved facet and a grating. The gain medium may be an amplifier or, in addition to the amplifier, may include a resonator cavity, or operate as an unstable resonator.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
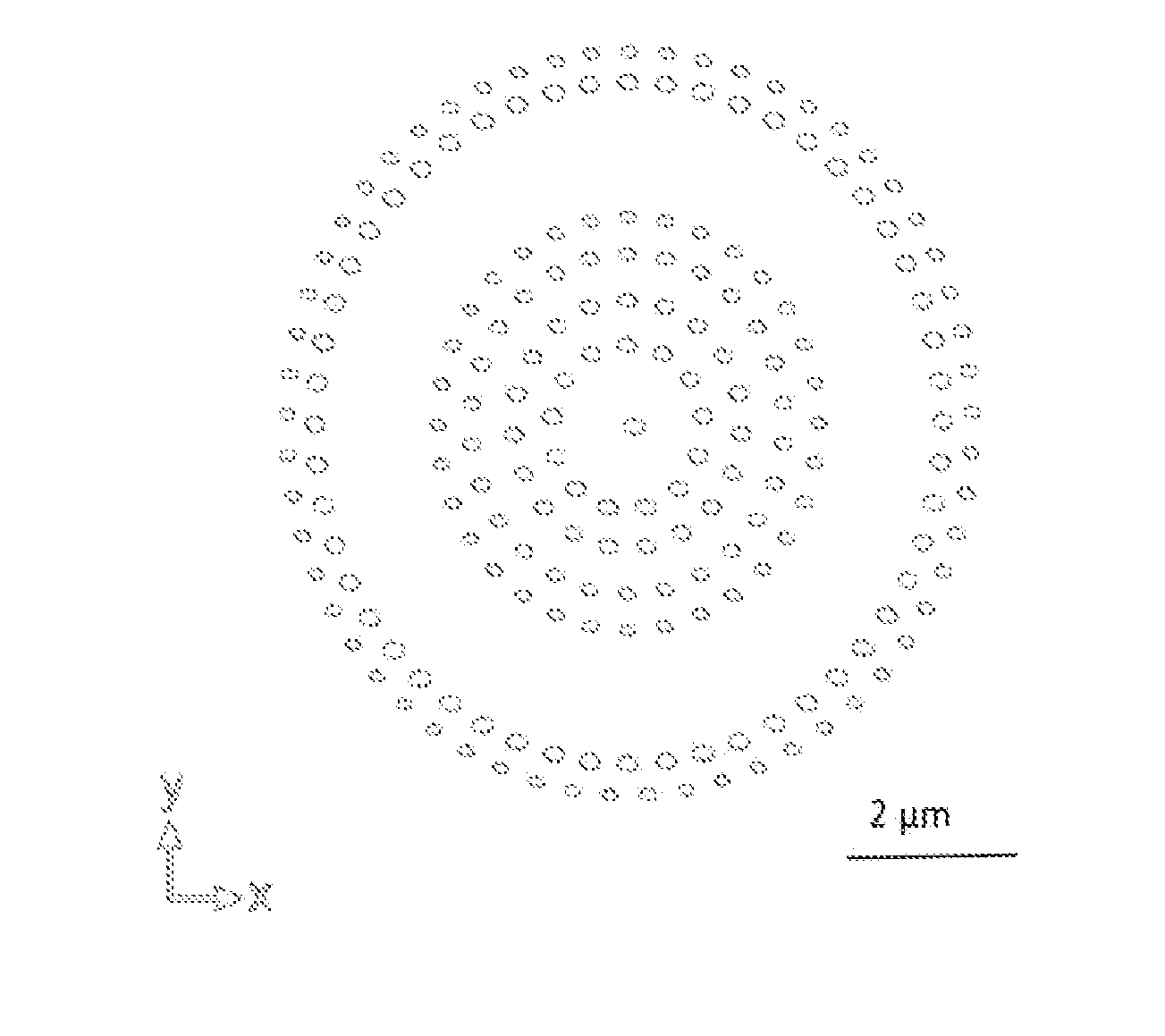
Holey optical device
A planar optical device, comprised of sets of nanometer-scale holes milled into a thin metal or ceramic film of subwavelength thickness serves to form arbitrary waveform of light. The holes form a pattern, preferrably rings, of various sizes in order to achieve a given phase front of light due to photonic effect. When designed as a lens, the device focuses incident light into a tight focal spot. In symmetric design, the focusing property of the device does not depend on the incident polarization angle. The lens can be manufactured based on high-throughput fabrication methods and easily integrated with a chip or placed at the end of an optical fiber.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Interferometer-type radar
InactiveUS7394422B2Easily realizedImprove reliabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarPhase difference
A transmitter for transmitting signals to targets and a receiver for receiving signals reflected from targets are included. The transmitter outputs CW signals for detecting direction and velocity of the target. The receiver performs: a function of receiving signals reflected from targets with a plurality of receiving antennas at the same time as transmitting from the transmitter, and performing spectral analysis with respect to receiving signals to thereby classify them by velocity component; a function of correlating signals of the receiving antenna systems; a function of integrating the signals correlation-processed; and a function of obtaining phase fronts of signals made incident on an antenna face from the phase differences of signals between receiving antennas, and performing two-dimensional FFT to the outputs to thereby measure the direction and velocity of the target.
Owner:NEC CORP
Nonlinear frequency mixer using quasi-phase-matching gratings having beam-modifying patterns
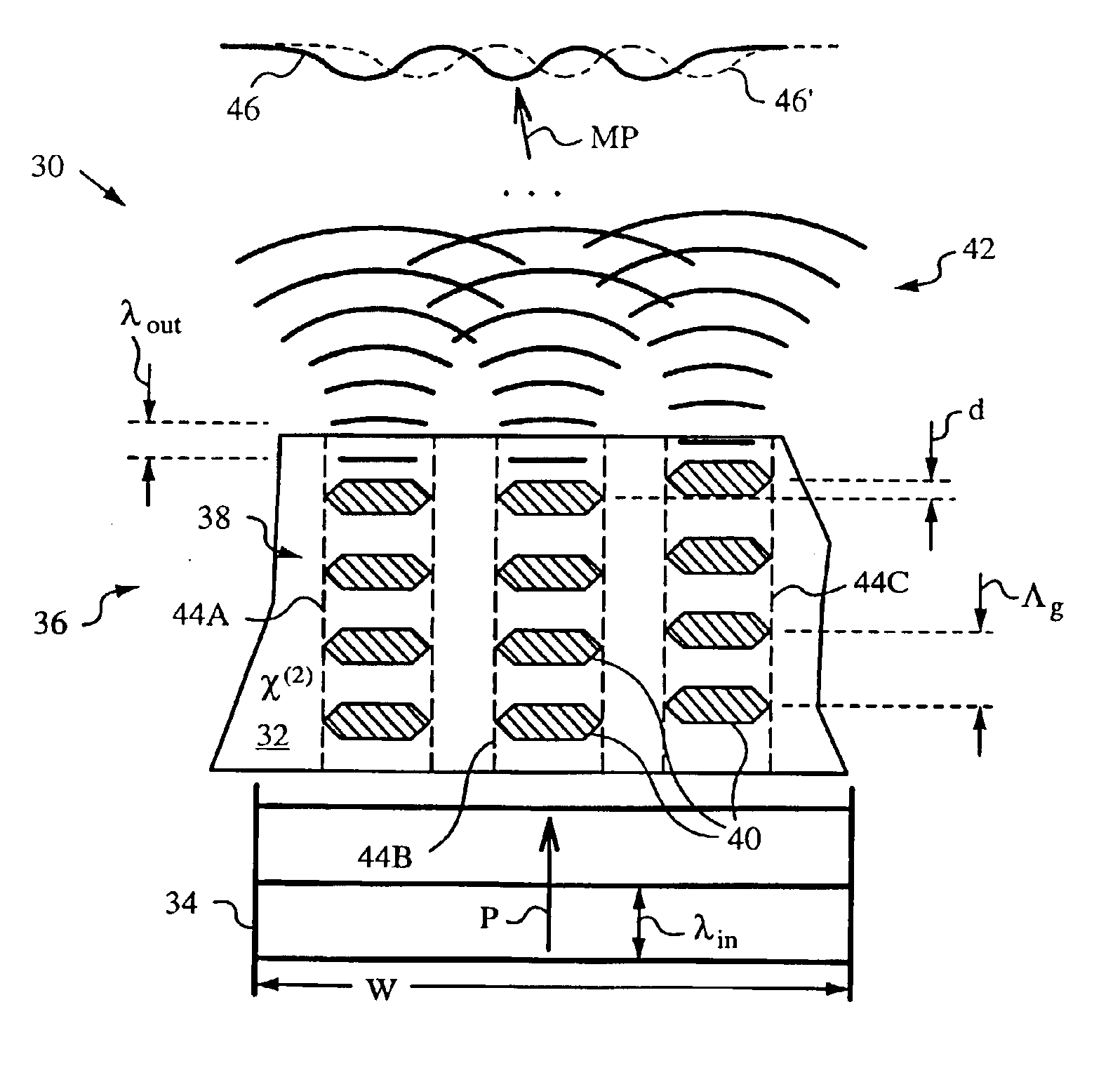
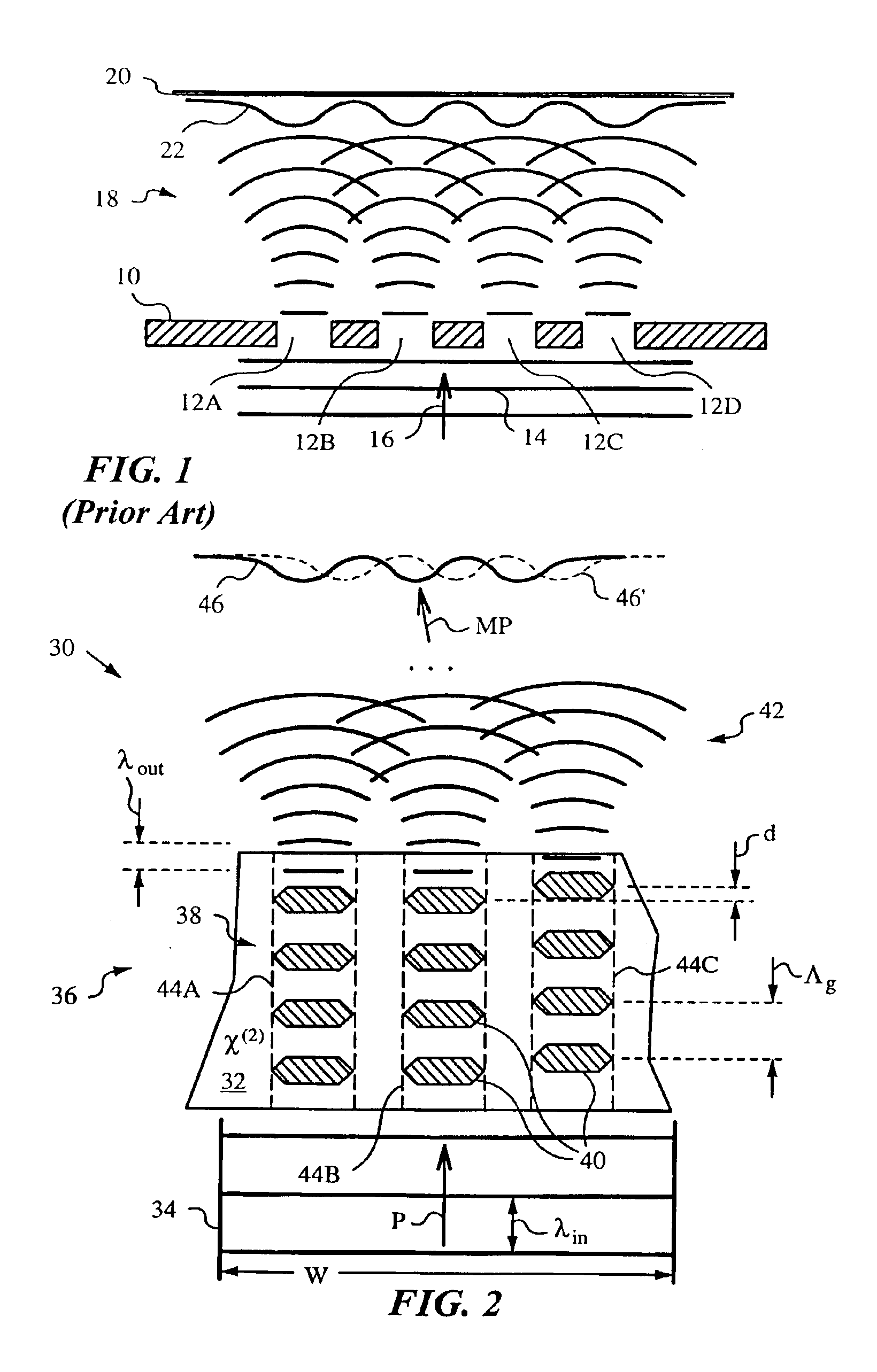
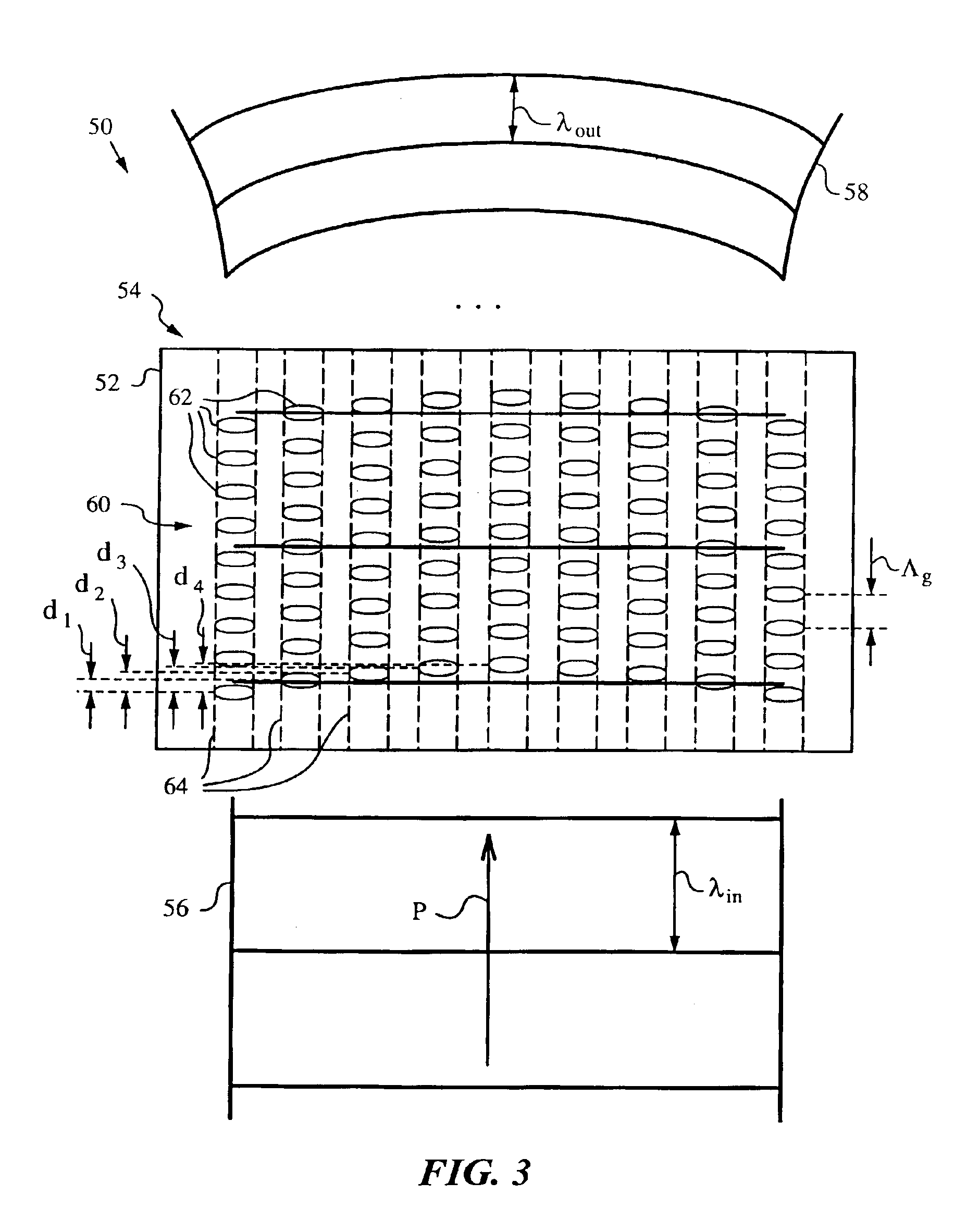
A method and a nonlinear frequency mixer employing the method to generate at least one output light from at least one input light with the aid of a quasi-phase-matching (QPM) grating for quasi-phase-matching the input and output light involved in a nonlinear frequency mixing operation such as three-wave mixing, four-wave mixing or other nonlinear operation mediated by a susceptibility of the nonlinear optical material. The QPM grating has a beam-modifying pattern with features for wave front shaping. More specifically, the features shape the wave fronts of the output light by diffraction or phase front shaping to thereby modify its propagation. This modification of propagation can be used to steer, focus, defocusing, split and / or collimate the output light. The features themselves can have various geometric shapes and sizes, even on the order of the wavelength of the output light, and they can include domains exhibiting a nonlinear optical susceptibility χ, such as the second-order susceptibility χ(2), domain edges, and / or spacings between such domains.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Beam steering apparatus for a traveling wave antenna and associated method
InactiveUS6833819B2Easy constructionIndividually energised antenna arraysLeaky-waveguide antennasLight beamTraveling-wave antenna
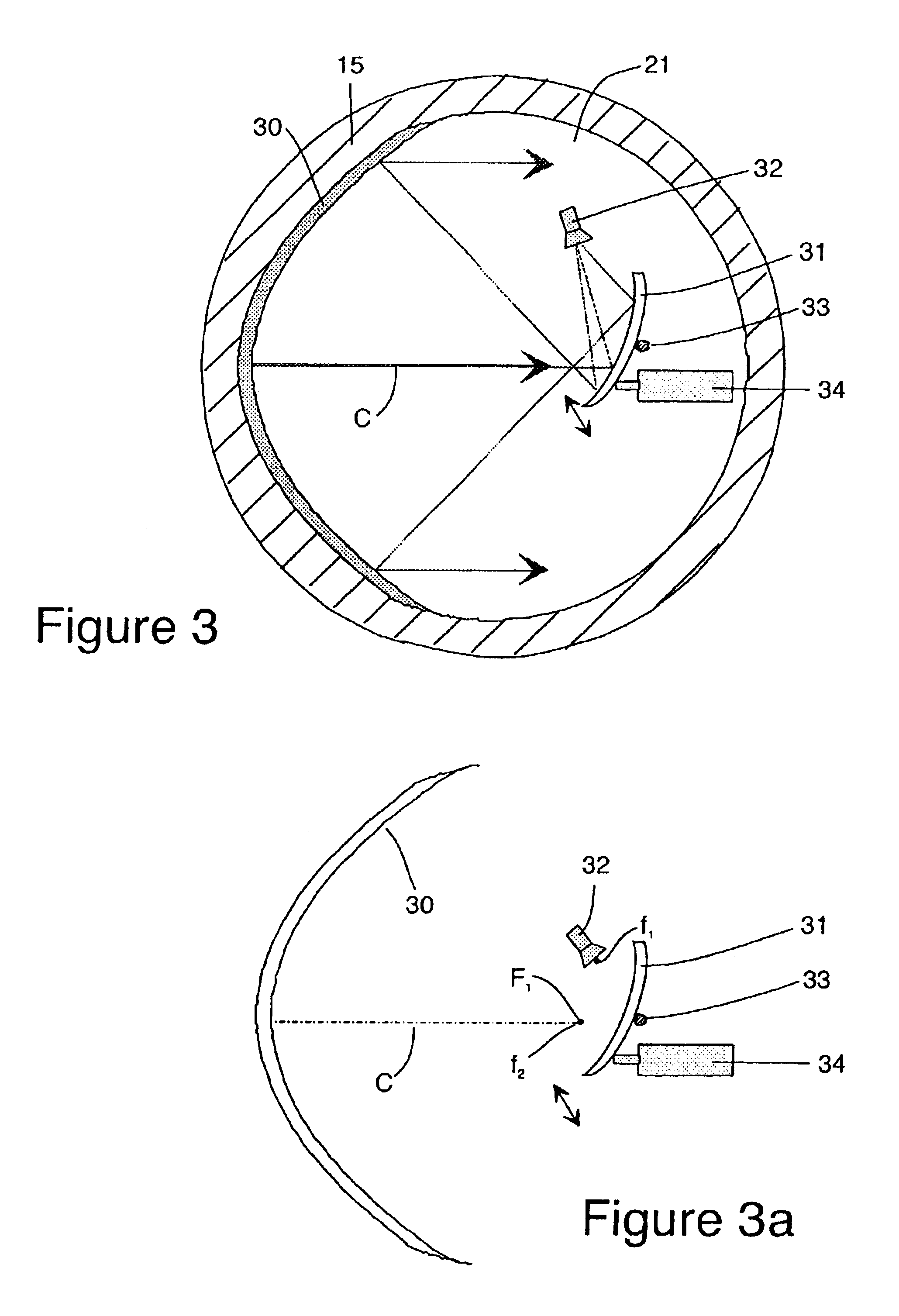
Steering of an electromagnetic beam of energy in the upper plate of a plate waveguide of a traveling wave antenna concurrently with the formation of a flat phase front and collimation of the electromagnetic beam is achieved by providing a second waveguide beneath the lower plate of the first waveguide and providing a 180% bend parabolic main reflector to reflect the energy beam to the upper plate of the upper waveguide. A feed horn is located in the lower waveguide and illuminates a pivotal subreflector which reflects the energy to the parabolic main reflector. By rotating the subreflector about its pivot point, the beam which is radiated to the upper waveguide is angularly shifted or steered.
Owner:HRL LAB
Phase offset integrated solid immersion mirror and lens for a general phase front
An apparatus comprises a condenser for directing electromagnetic radiation to a focal point, the condenser comprising a first interface on a first side of a longitudinal axis for directing a first plurality of rays of the electromagnetic radiation to a focal point and a second interface on a second side of the longitudinal axis for directing a second plurality of rays of the electromagnetic radiation to the focal point, wherein the first and second interfaces are shaped such that at the focal point, the second plurality of rays are about 180° out of phase with respect to the first plurality of rays.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
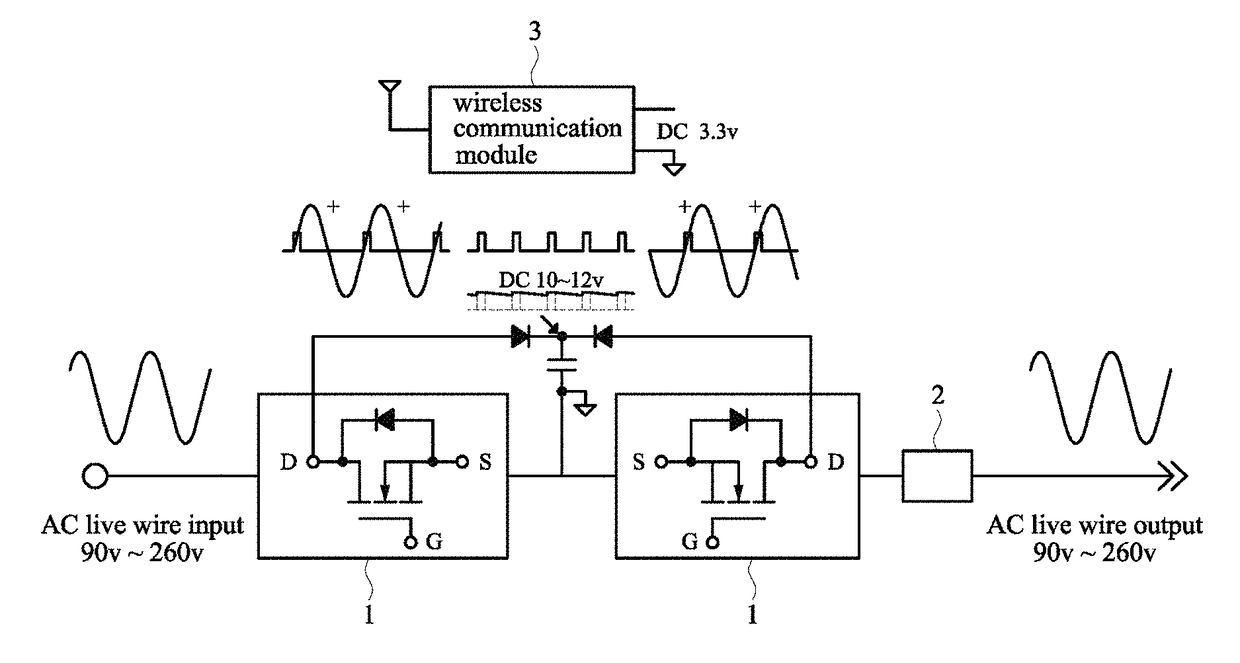
Single fire-wire phase-front dynamic AC power fetching module
ActiveUS9837928B1Reduce EMI noiseIncrease powerAc-dc conversion without reversalAc-ac conversionBasic power supplyFull bridge
A single fire-wire phase-front dynamic AC power fetching module, comprising: two series-connected type synchronous power fetching circuits connected in parallel, and an electronic switch connected thereto, one series-connected type synchronous power fetching circuit is used to perform positive phase AC power fetching, while the other series-connected type synchronous power fetching circuit is used to perform negative phase AC power fetching. The electronic switch is formed by a relay or a silicon control crystal (TRIAC) controlled by an MCU microprocessor. As such, through adopting bi-directional dynamic full-bridge type power fetching, for a single fire wire, it is able to perform power fetching twice in a cycle. The duration of power fetching can be regulated automatically depending on the load, to compensate for the power, and supply it to an outside circuit as the basic power supply.
Owner:LOONG YEE INDAL CORP
Chip scale optical systems
An optical phased array including a wafer, optical waveguides, a root optical waveguide, the root optical waveguide being optically connected at one end to one optical waveguide, another end of the root optical waveguide constituting an optical port, optical couplers disposed in an array and located on the wafer, the optical waveguides optically connecting the optical couplers to the optical port via respective optical paths, one optical path per optical coupler, configurable optical delay lines; each configurable optical delay line being disposed in one respective optical path from the respective optical paths; the configurable optical delay lines being configured such that the optical couplers emit a non-planar phase front near field radiation pattern from light received from a light source coupled to the optical port.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Method for improving mechanical dephosphorization of iron scale of low-carbon cold heading steel wire rod
ActiveCN102699055AGuaranteed shiftMeet the requirements of the transformationWork treatment devicesMetal rolling arrangementsTemperature controlWire rod
A method for improving the mechanical dephosphorization of iron scale of a low-carbon cold heading steel wire rod belongs to the technical field of steel rolling. Processing steps and control technical parameters are as follows: finish rolling inlet temperature is controlled to be 920 DEG C-950 DEG C, and the finish rolling temperature rising range is controlled to be 80 DEG C-100 DEG C; the spinning temperature is controlled to be 880 DEG C-920 DEG C; the opening times and a heat holding cover of an air cooling line and the opening degree of a fan are regulated, the cooling rate of the phase front section of a spun steel wire rod is controlled to be 2-3 DEG C / s; the temperature of the spun steel wire rod is controlled to be 760 DEG C-740 DEG C when the spun steel wire rod enters the heat holding cover, and the heat holding cover is uncovered at the temperature being 620 DEG C-600 DEG C; and the temperature of the spun steel wire rod is controlled to be 580 DEG C-600 DEG C when the spun steel wire rod is discharged from the heat holding cover, the fan is additionally arranged when the spun steel wire rod is discharged from the heat holding cover, the cooling rate of the spun steel wire rod passing through a temperature zone being 5000 DEG C-400 DEG C rapidly is controlled to be 3-5 DEG C / s, and the passing time is controlled to be 15-25s. The method has the advantages that the phase structure conversion phenomenon in an FeO layer in the iron scale on surface of a hot rolling steel wire rod is reduced obviously, the mechanical dephosphorization is improved obviously, and the wire breaking rate and the loss of a die in the user pulling process are reduced.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
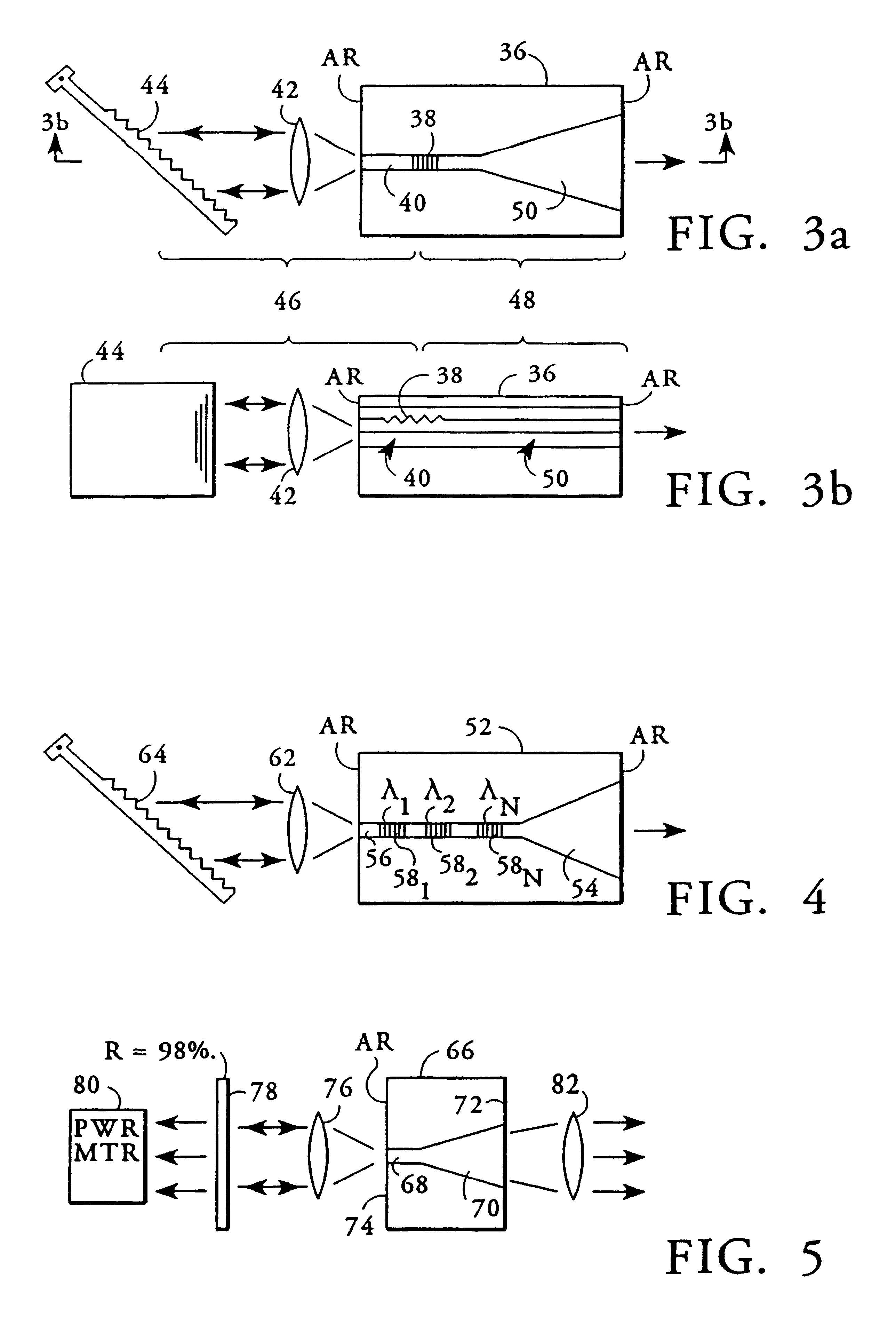
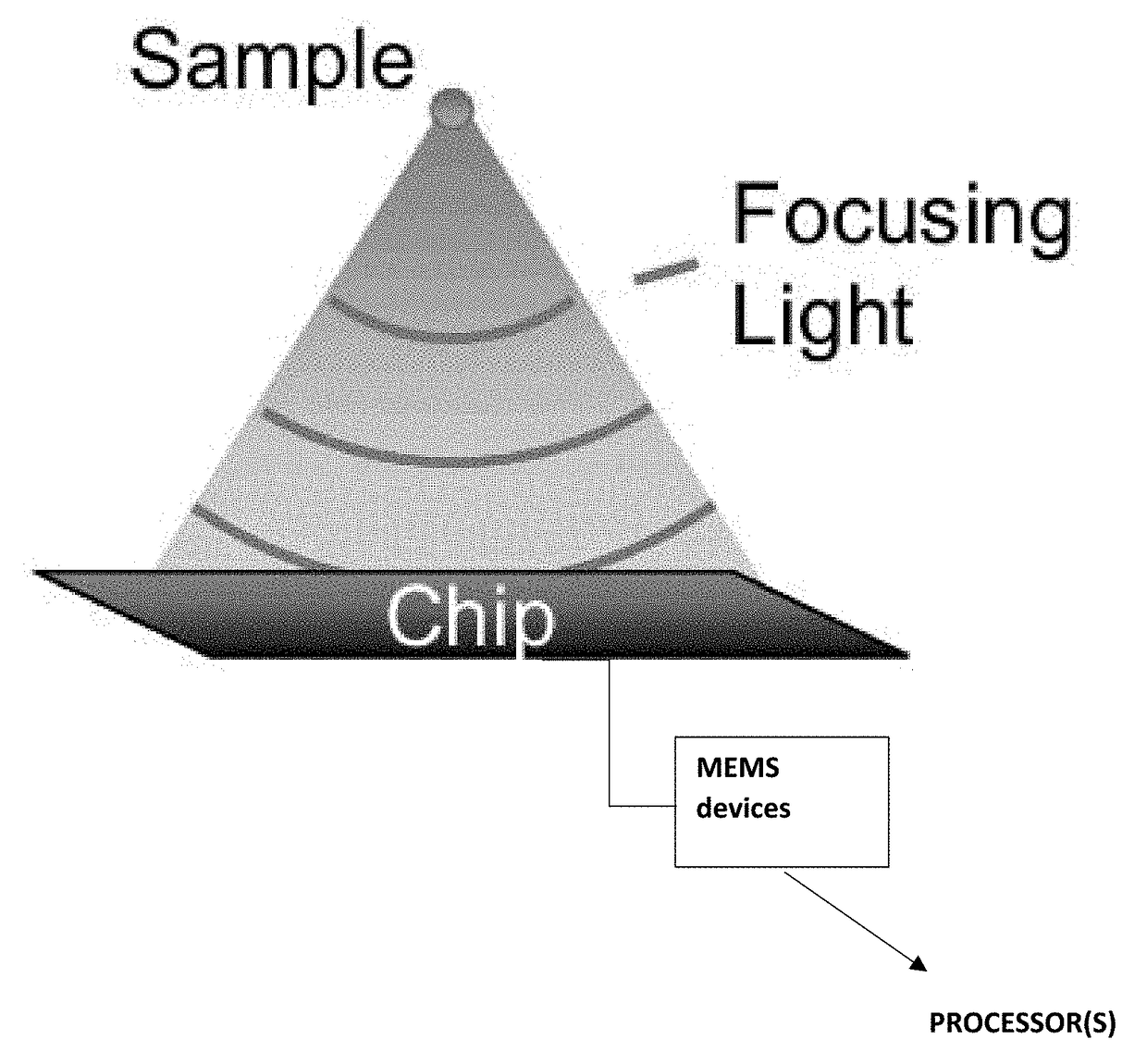
Measuring modal content of multi-moded fibers
ActiveUS20090262337A1Provide informationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical apparatus testingSpatially resolvedFiber
The output modal content of optical fibers that contain more than one spatial mode may be analyzed and quantified by measuring interference between co-propagating modes in the optical fiber. By spatially resolving the interference, an image of the spatial beat pattern between two modes may be constructed, thereby providing information about the modes supported by the optical fiber. Measurements of the phase front exiting the optical fiber under test are advantageously performed in the far field.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Holey optical device
A planar optical device, comprised of sets of nanometer-scale holes milled into a thin metal or ceramic film of subwavelength thickness serves to form arbitrary waveform of light. The holes form a pattern, preferrably rings, of various sizes in order to achieve a given phase front of light due to photonic effect. When designed as a lens, the device focuses incident light into a tight focal spot. In symmetric design, the focusing property of the device does not depend on the incident polarization angle. The lens can be manufactured based on high-throughput fabrication methods and easily integrated with a chip or placed at the end of an optical fiber.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Apparatus and method for phase fronts based on superluminal polarization current
ActiveUS20100039324A1Reduce vulnerabilityIndividually energised antenna arraysDirectional antennaElectron
An apparatus and method for a radiation source involving phase fronts emanating from an accelerated, oscillating polarization current whose distribution pattern moves superluminally (that is, faster than light in vacuo). Theoretical predictions and experimental measurements using an existing prototype superluminal source show that the phase fronts from such a source can be made to be very complex. Consequently, it will be very difficult for an aircraft imaged by such a radiation to detect where this radiation has come from. Moreover, the complexity of the phase fronts makes it almost impossible for electronics on an aircraft to synthesize a rogue reflection. A simple directional antenna and timing system should, on the other hand, be sufficient for the radar operators to locate the aircraft, given knowledge of their own source's speed and modulation pattern.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC +1
Coherent image formation for dynamic transmit beamformation
ActiveUS8241216B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsUltrasonographySonification
Retrospective dynamic transmit beamformation is provided in medical ultrasound imaging. Using parallel receive beamformation, sets of data representing locations in at least a common field of view are obtained, each set in response to a transmit with a spatially distinct phase front. The common field of view receive data are time aligned and amplitude weighted for retrospective transmit focusing and retrospective transmit apodization, respectively. A time offset, such as of a cycle or more in some cases, is applied to the receive data for retrospective transmit focusing. The offset is selected to emulate shifting the transmit delay profile to be tangentially intersecting with the dynamic receive delay profile for each location which is the desired transmit delay profile. A weight is applied to the receive data for retrospective transmit apodization. The weight is selected based on the desired transmit apodization profile. The offset and weighted data representing a same location from different transmit events is coherently combined. The number of sets of data offset, weighted and combined may vary as a function of depth for dynamic transmit beamformation.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Optical positioning device having shaped illumination
ActiveUS7285766B2Input/output for user-computer interactionSolid-state devicesField of viewPhase front
One embodiment relates to an optical displacement sensor for sensing relative movement between a data input device and a surface by determining displacement of optical features in a succession of frames. The sensor includes an illuminator and a detector. The illuminator has a light source and illumination optics to illuminate a portion of the surface with a planar phase-front. The detector has a plurality of photosensitive elements and imaging optics. The illuminator and the detector are configured such that the illuminated portion of the surface is less than fifty percent larger than a field of view of the photosensitive elements of the detector. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Multiple cell liquid crystal optical device with coupled electric field control
ActiveCN103492935AStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectrical resistance and conductanceOptical property
A liquid crystal optical device is provided. The optical device includes a liquid crystal cell controlling optical properties of light passing therethrough and has a liquid crystal layer, a planar electrode located to one side of said liquid crystal layer, an electric field control structure located to the opposite side of the liquid crystal layer, and a wavefront adjustment structure configured to provide optical phase front adjustment. In some embodiments the wavefront adjustment structure is a conductive floating electrode. In other embodiments the wavefront adjustment structure is a weakly conductive structure having spatially variable sheet resistance. In other embodiments, the wavefront adjustment structure a weakly conductive structure having spatially variable sheet resistance having a frequency dependent characteristic.
Owner:LENSVECTOR
Non-equal phase front correction method of material complex permittivity quasi-optical cavity method wideband test
InactiveCN107144736ASolving Difficult Broadband Accurate TestsImproving the test accuracy of complex permittivityDielectric property measurementsElectromagnetic fieldFrequency shift
The present invention provides a non-equal phase front correction method of a material complex permittivity quasi-optical cavity method wideband test. The sample wideband complex permittivity accuracy test can be realized. Gaussian beam electromagnetic field phase distribution in a quasi-optical cavity is analyzed, and an actual phase distribution function at the upper surface of a sample is obtained according to the upper surface of a sample to be tested, namely the matching relation of the air and a waist radius at a medium area interface. The perturbation theory is employed to solve the stored energy at the gap of the surface plane and the wavefront spherical surface so as to obtain frequency shift caused by phase mismatching of the sample surface and the wavefront. The non-equal phase surface at the upper surface of the sample is corrected through combination of a preset format; the influence of non-equal phase surface errors caused by thickness of the sample in the quasi-optical cavity method wideband test is corrected, the wideband test of the material complex permittivity through adoption of the quasi-optical cavity method can be effectively performed, and the precision of the multimode wideband test of the quasi-optical cavity method can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Optical positioning device having shaped illumination
ActiveUS20050258347A1Input/output for user-computer interactionSolid-state devicesField of viewPhase front
One embodiment relates to an optical displacement sensor for sensing relative movement between a data input device and a surface by determining displacement of optical features in a succession of frames. The sensor includes an illuminator and a detector. The illuminator has a light source and illumination optics to illuminate a portion of the surface with a planar phase-front. The detector has a plurality of photosensitive elements and imaging optics. The illuminator and the detector are configured such that the illuminated portion of the surface is less than fifty percent larger than a field of view of the photosensitive elements of the detector. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com