Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
761 results about "Phason" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phason is a quasiparticle existing in quasicrystals due to their specific, quasiperiodic lattice structure. Similar to phonon, phason is associated with atomic motion. However, whereas phonons are related to translation of atoms, phasons are associated with atomic rearrangements. As a result of these rearrangements, waves, describing the position of atoms in crystal, change phase, thus the term "phason". In the superspace picture, aperiodic crystals are obtained from the section of a periodic crystal of higher dimension (up to 6D) at a specific angle, phonon modes are then defined as excitation of the "in plane" real (also called parallel or external) space whereas phasons are excitations of the perpendicular (also called internal) space.
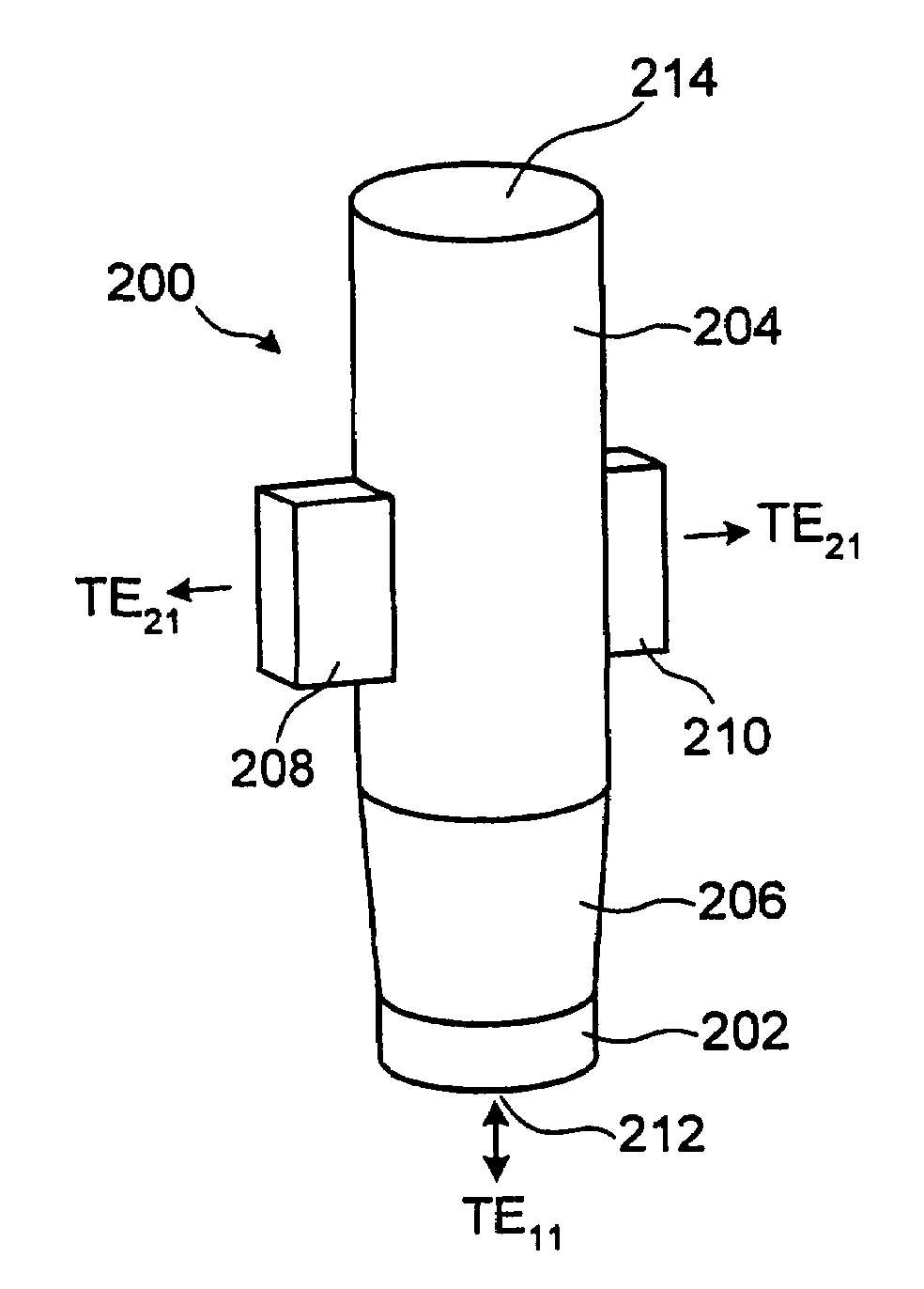
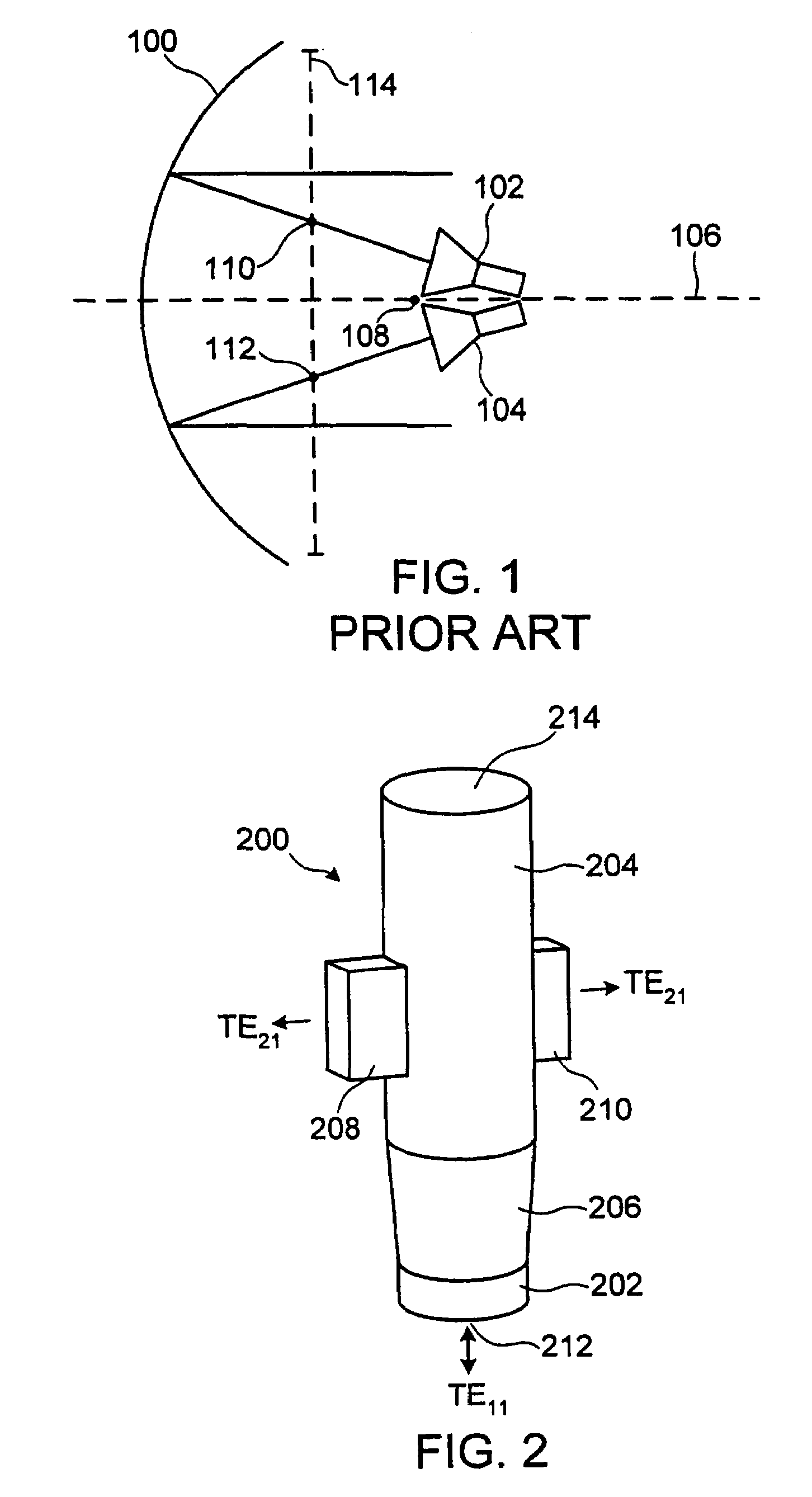
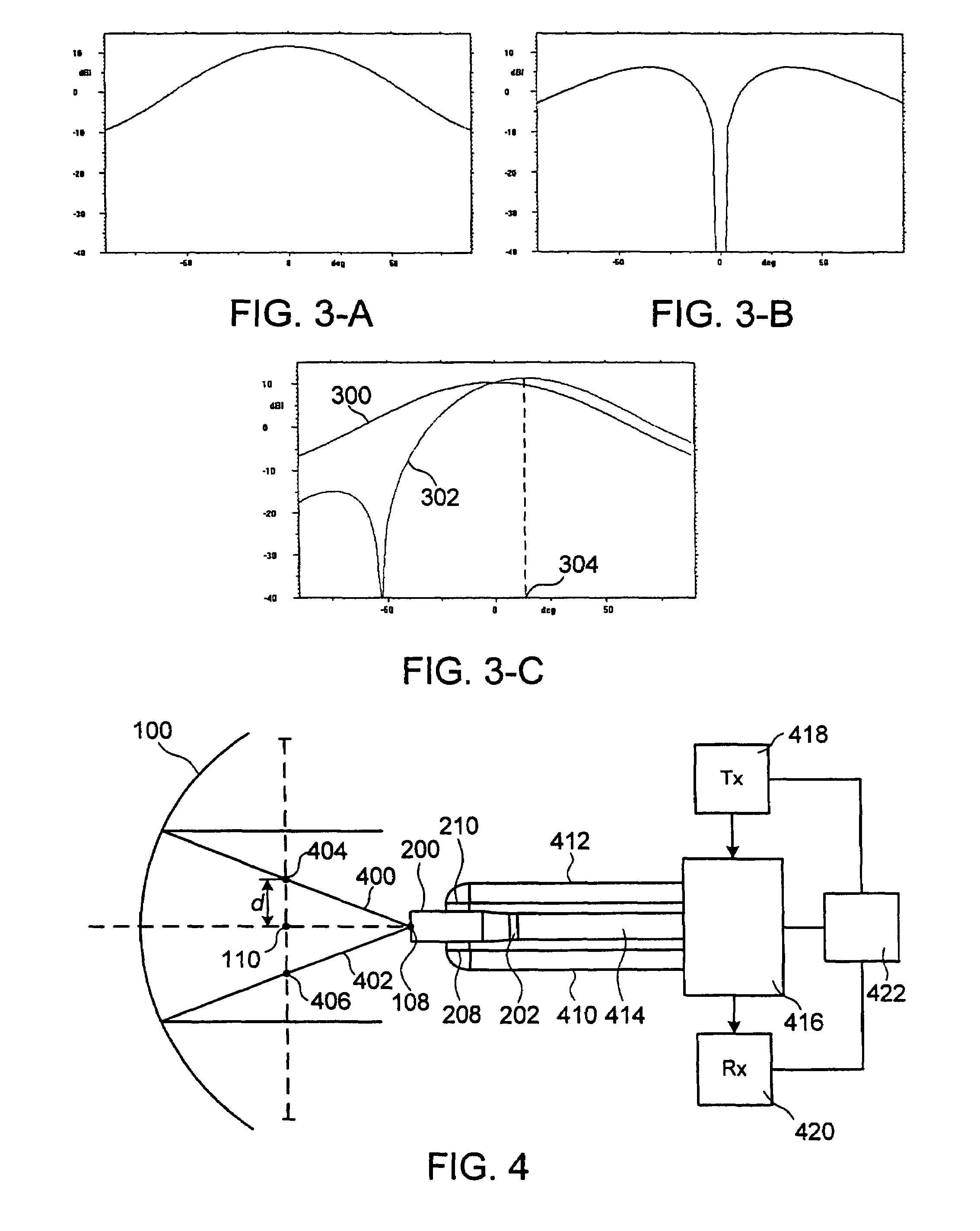
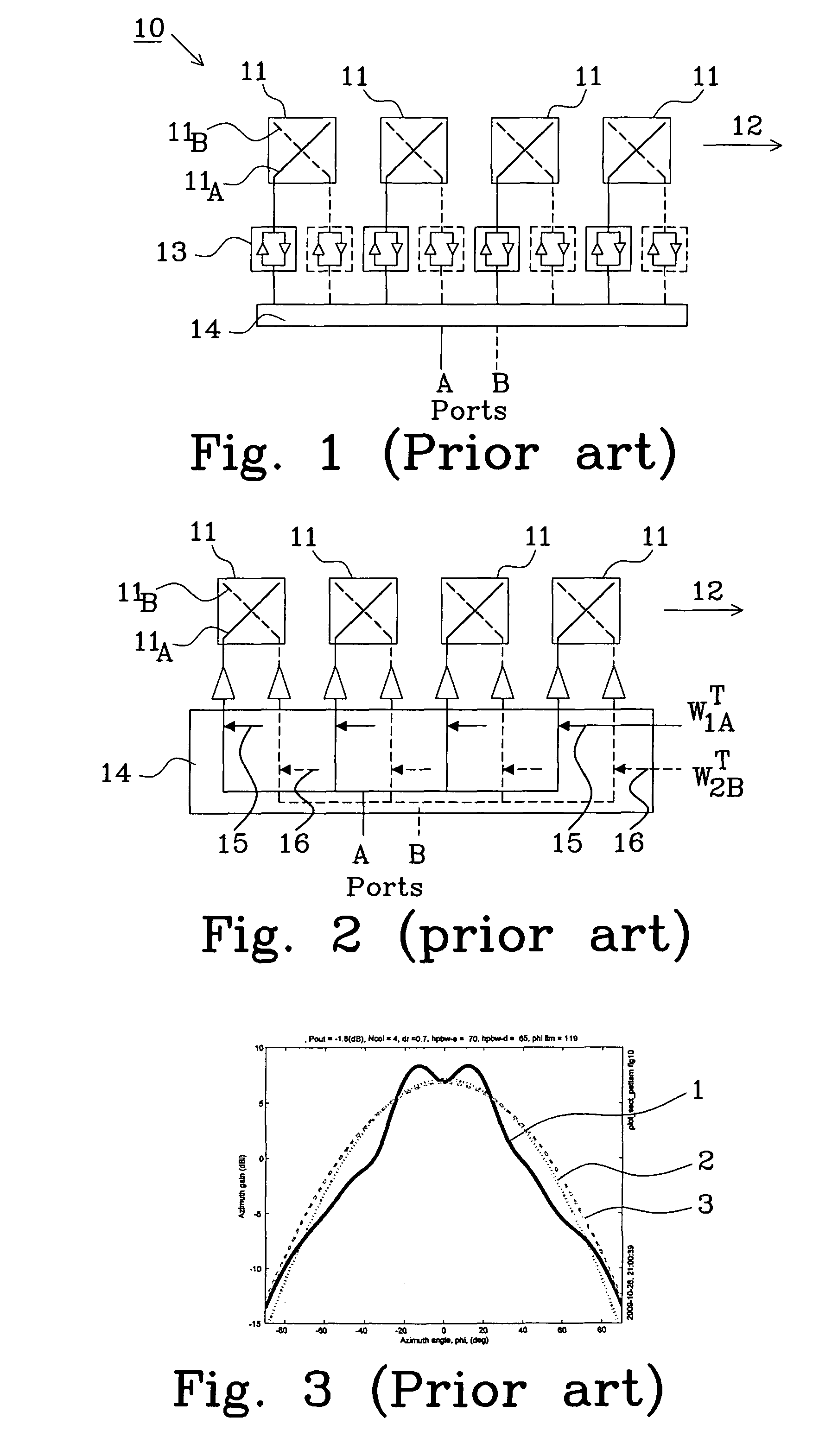
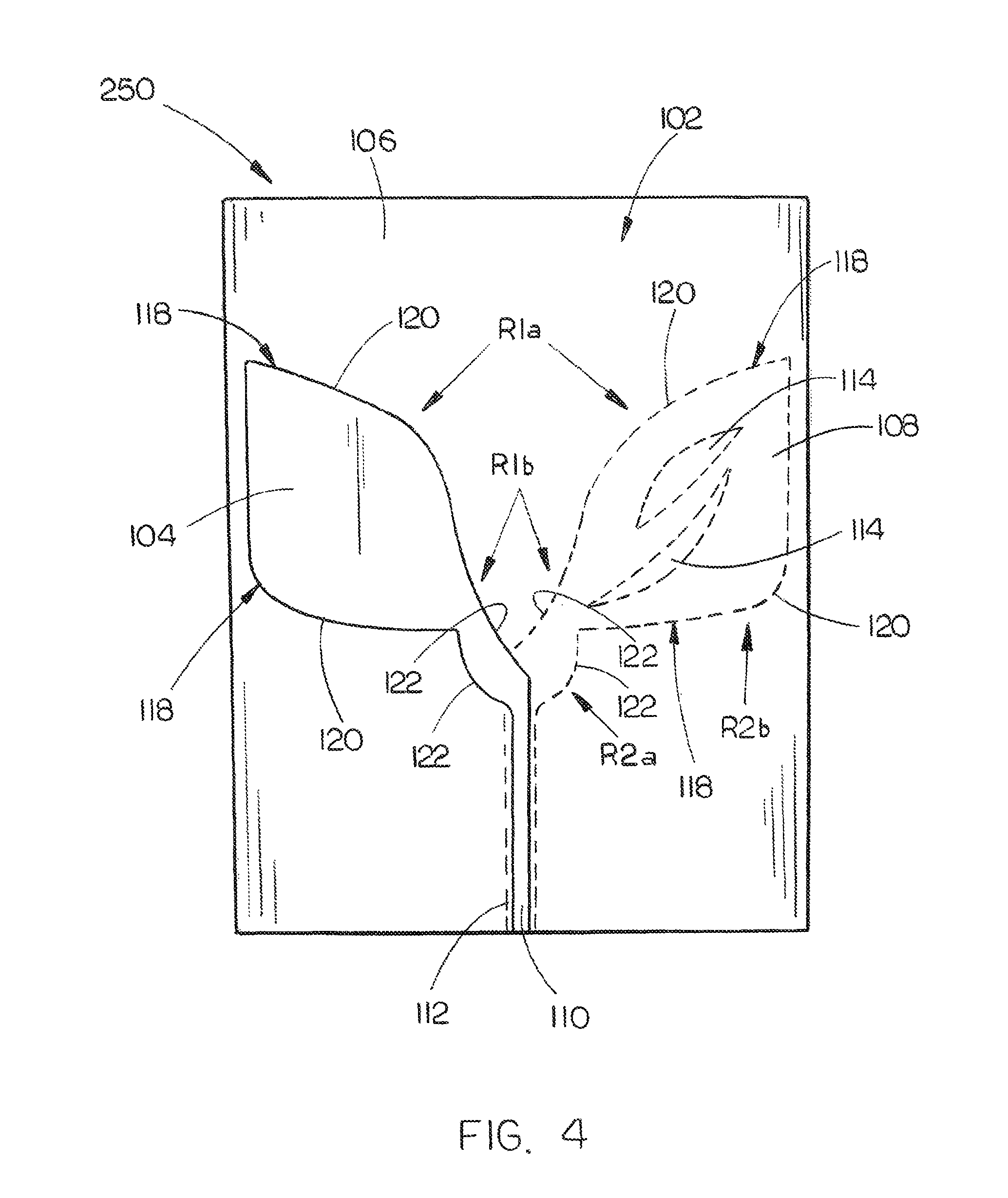
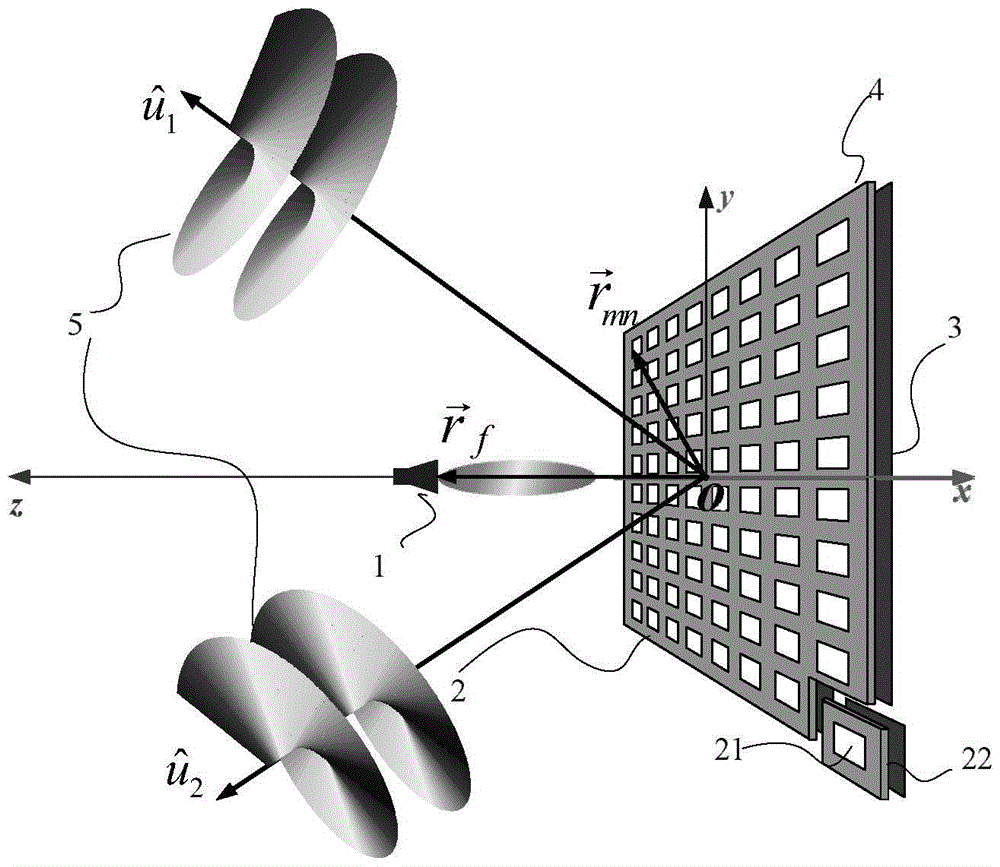
Multiple phase center feedhorn for reflector antenna
A feedhorn driving method and apparatus allows the establishment of multiple phase centers using only a single multimode feedhorn. At least two higher-order modes are extracted from the feedhorn and weighted in amplitude and phase. The phase center separation is established in accordance with an assigned weights. The feedhorn has application in i.a. moving target indication systems.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
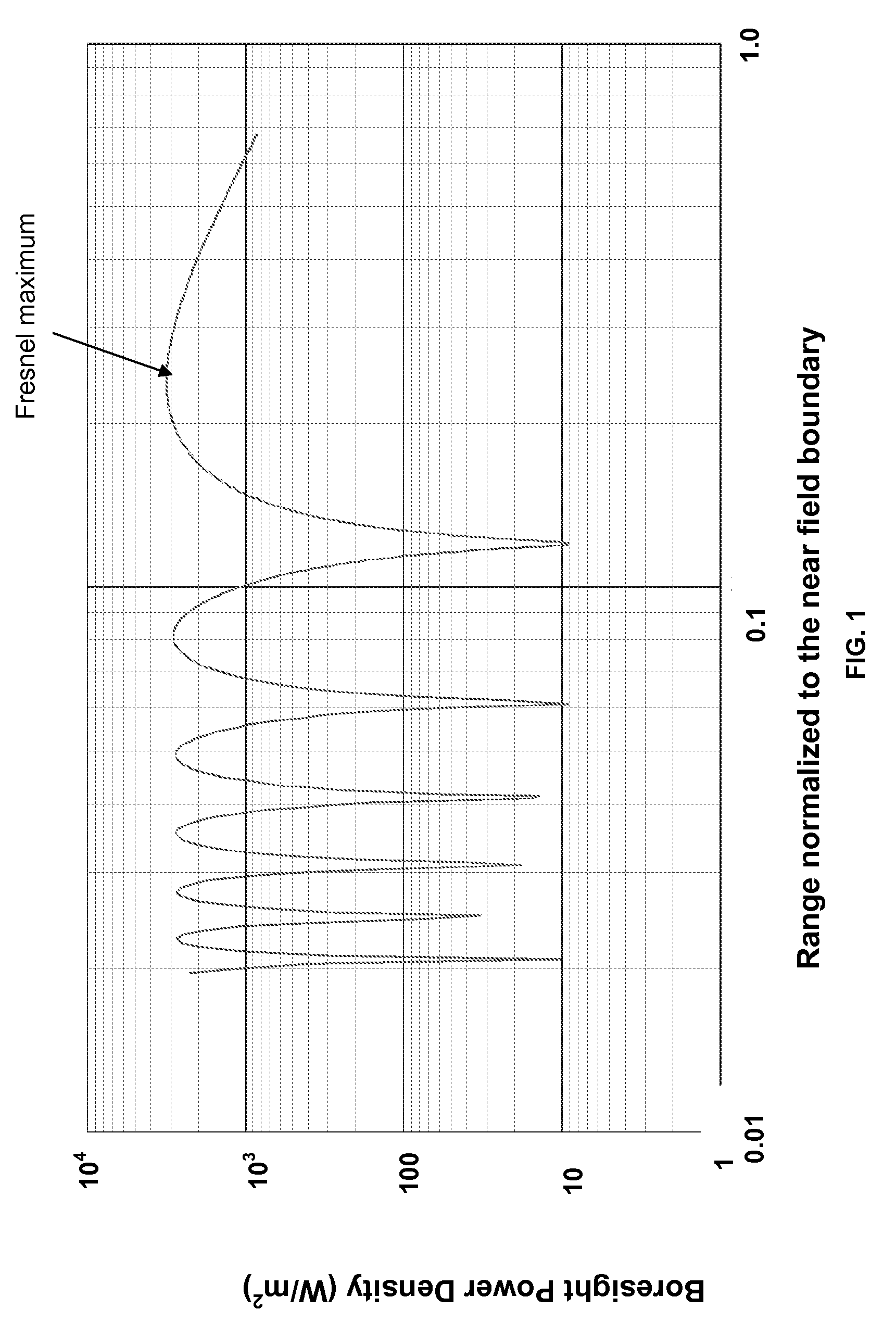
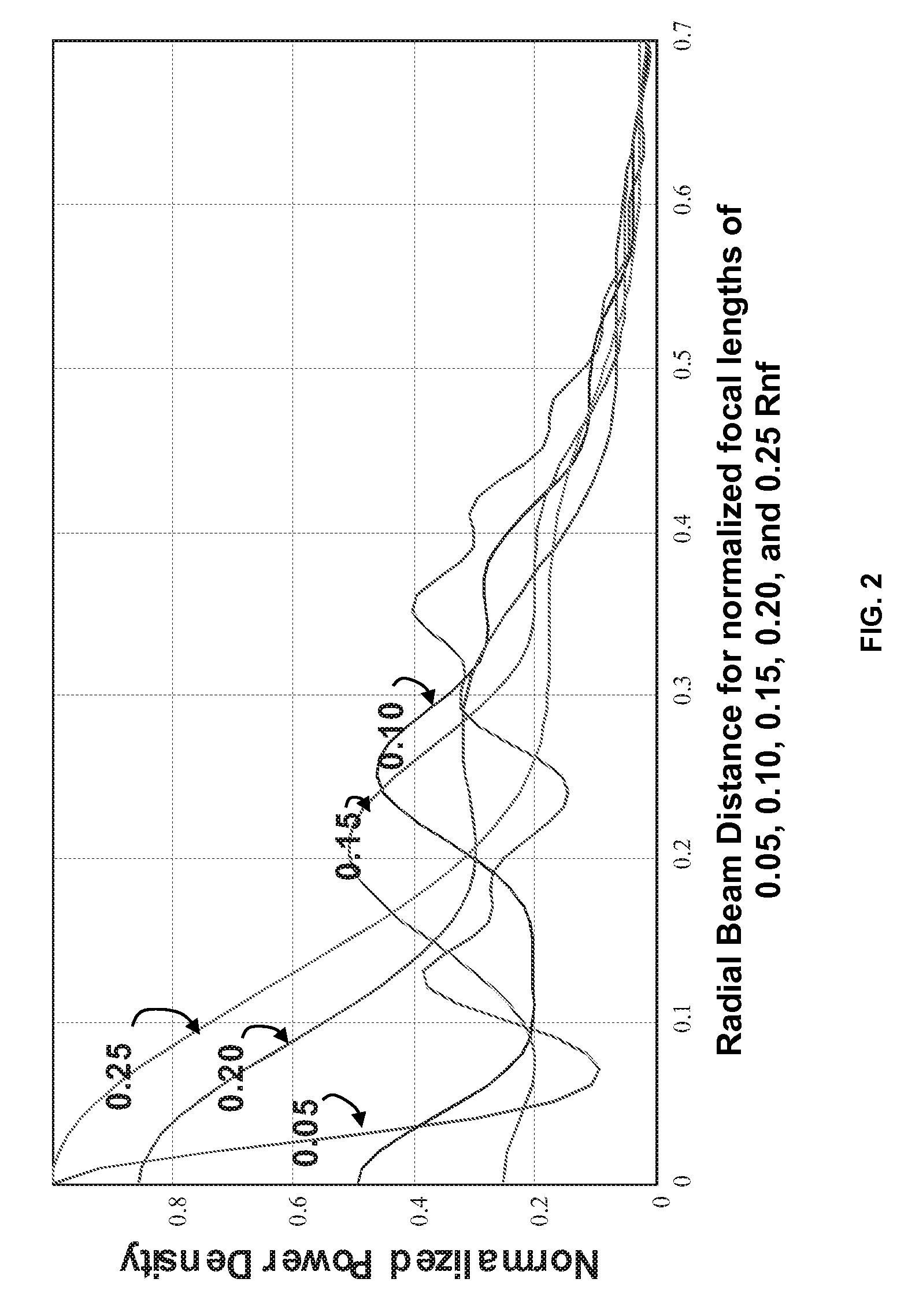
Optimization of near field antenna characteristics by aperture modulation
The approximate radius of curvature of the spherical phase front at the aperture of a transmitting microwave antenna is controlled by an inner section of the aperture attached to the outer section of the aperture by a small number of programmable transducers, thereby controlling the near field shape and power distribution of the transmitted beam.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
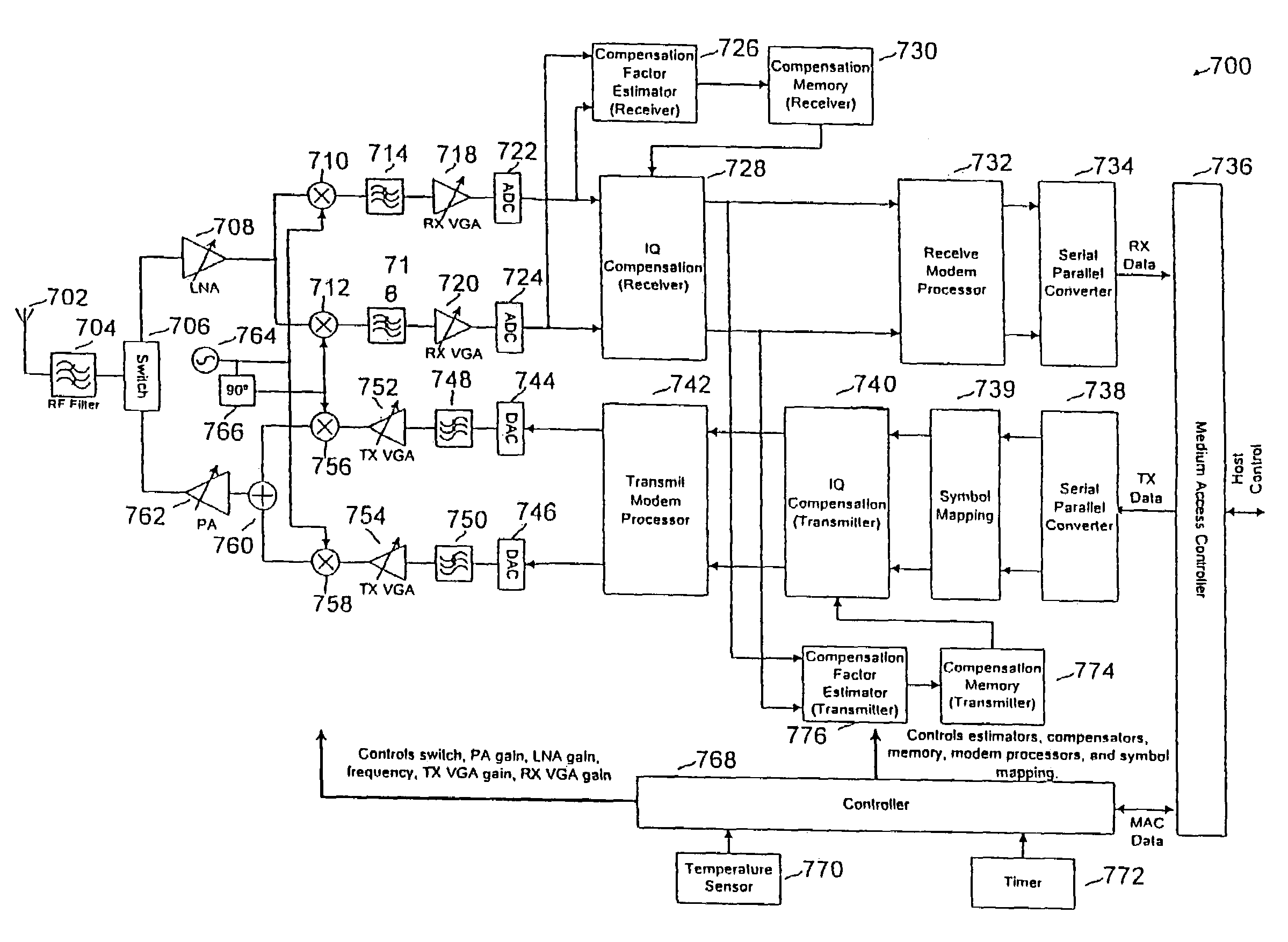
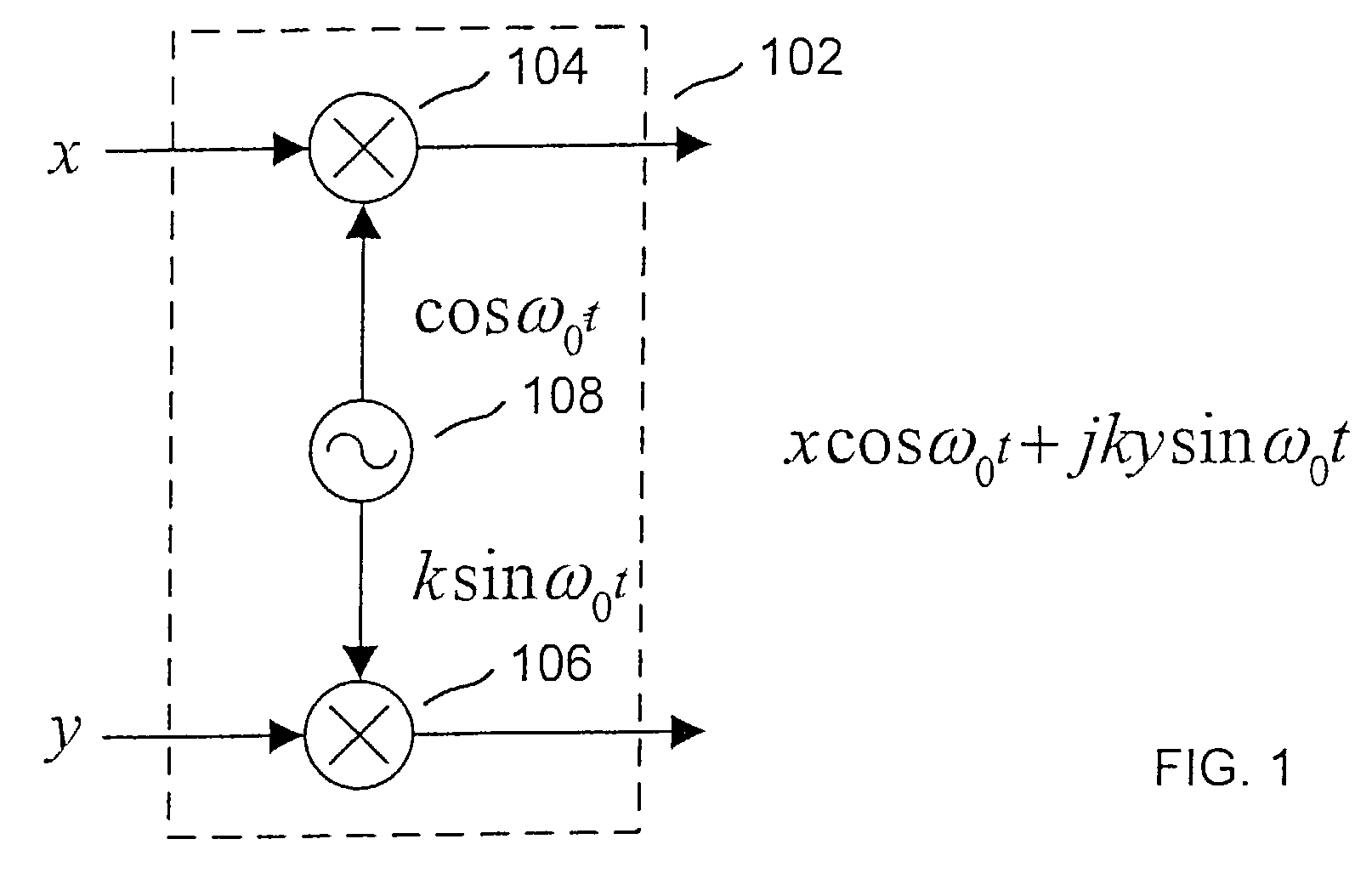
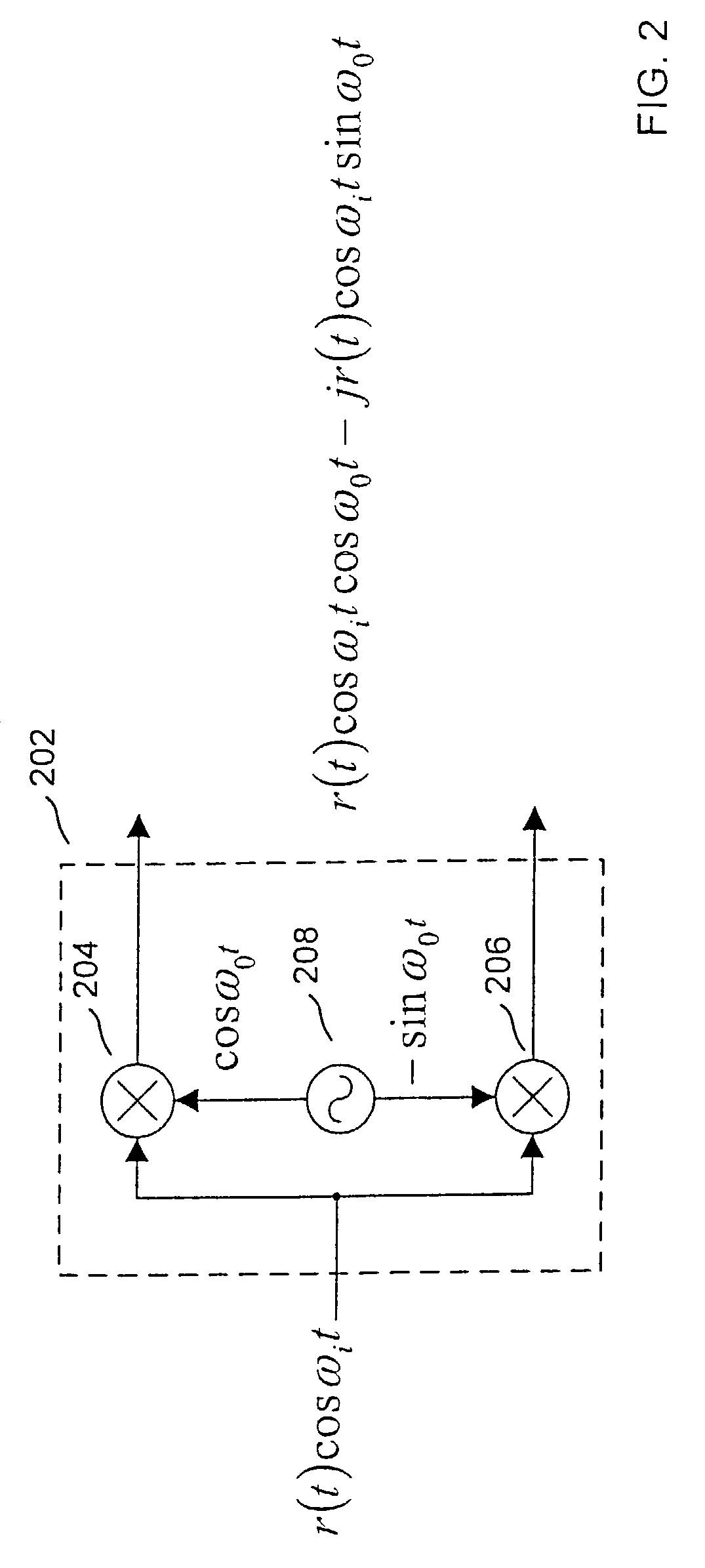
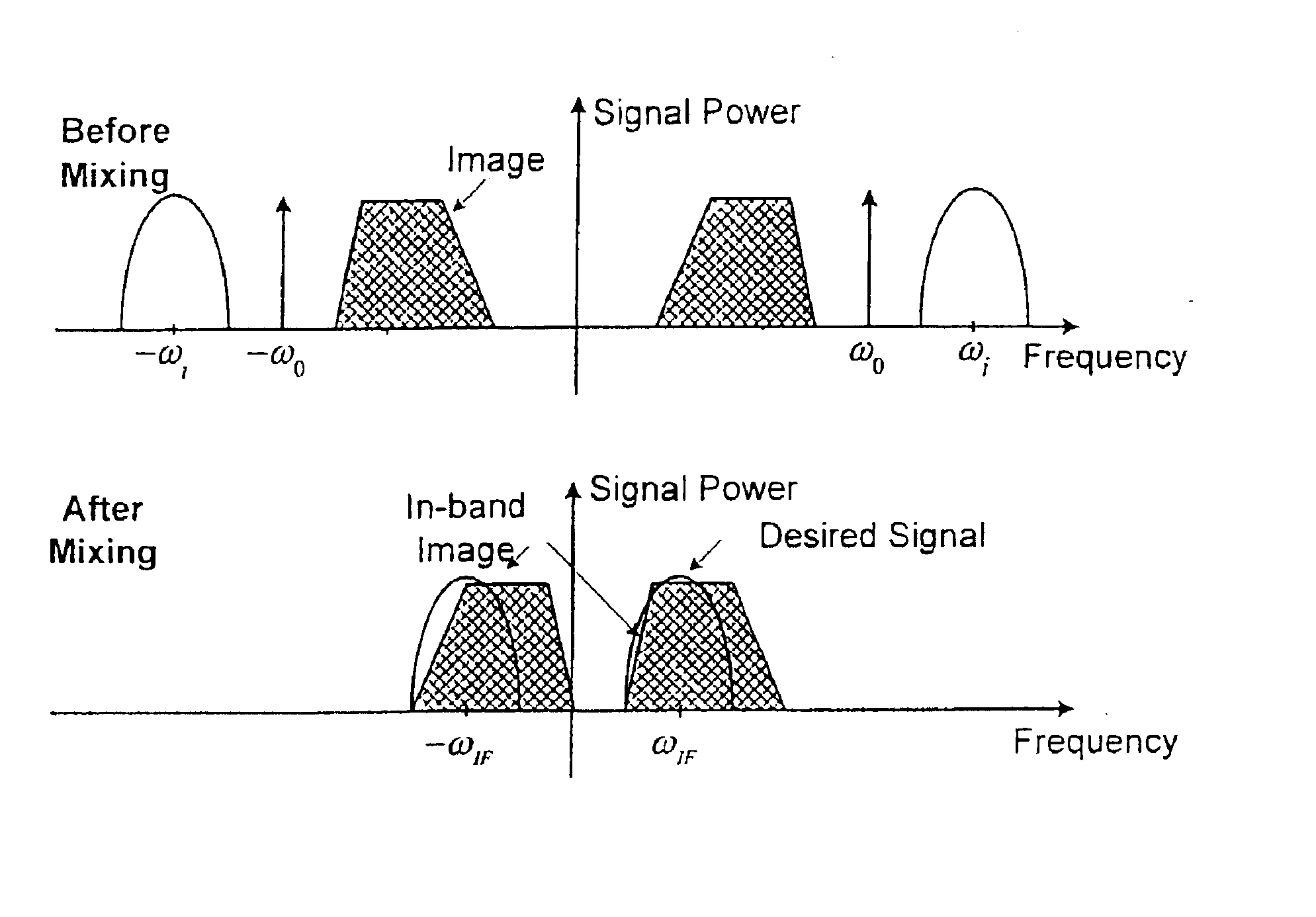
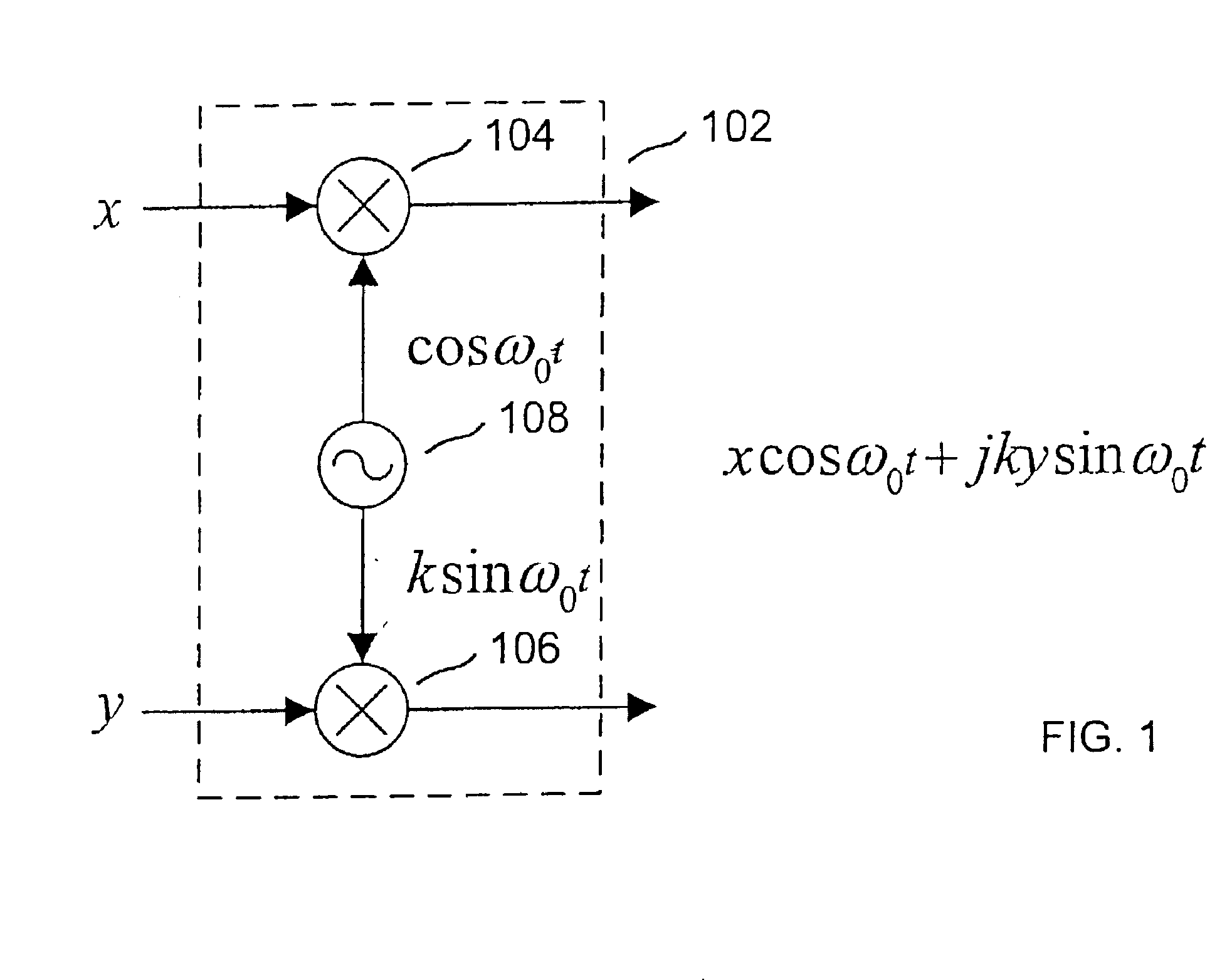
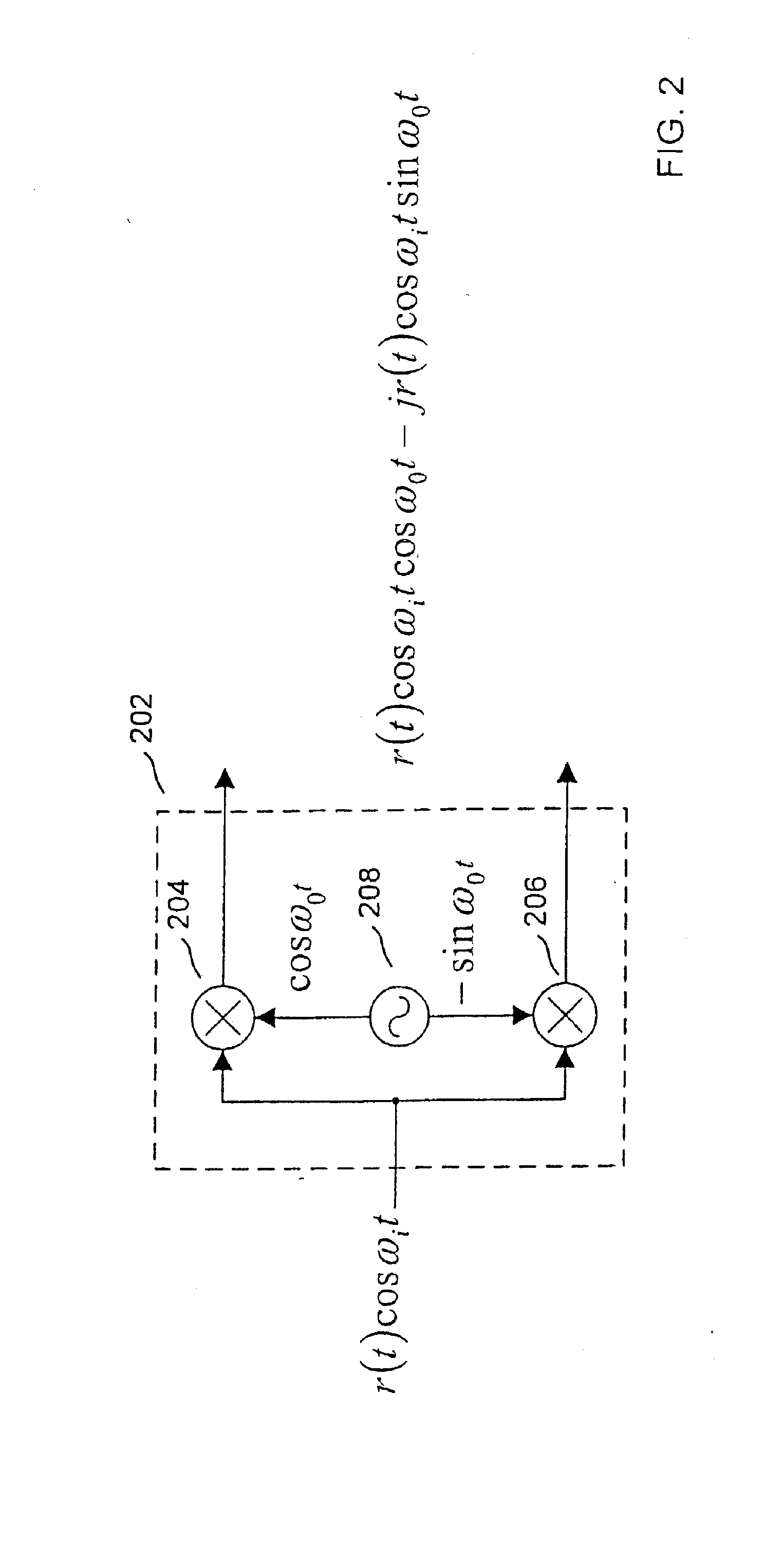
Compensation of I-Q imbalance in digital transceivers
A transceiver includes a switching unit configurable for isolating an input of a receiver from an output of a transmitter during a local calibration mode. A known signal present at the output at a first power level during the calibration mode will also be present at the input at a second power level lower than the first power level and will be converted by the quadrature demodulator. A compensation factor is estimated for compensating the receiver section for imbalances in the in-phase and quadrature phase signals resulting from conversion of the known signal. Remote calibration is implemented using a method for remotely compensating for I-Q imbalance wherein a data packet having a known signal is transmitted to a receiver for conversion by a quadrature demodulator and compensation factors are estimated for compensating for imbalances in the in-phase and quadrature phase signals resulting from conversion of the known signal.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Compensation of i-q imbalance in digital transceivers
A transceiver includes a switching unit configurable for isolating an input of a receiver from an output of a transmitter during a local calibration mode. A known signal present at the output at a first power level during the calibration mode will also be present at the input at a second power level lower than the first power level and will be converted by the quadrature demodulator. A compensation factor is estimated for compensating the receiver section for imbalances in the in-phase and quadrature phase signals resulting from conversion of the known signal. Remote calibration is implemented using a method for remotely compensating for I-Q imbalance wherein a data packet having a known signal is transmitted to a receiver for conversion by a quadrature demodulator and compensation factors are estimated for compensating for imbalances in the in-phase and quadrature phase signals resulting from conversion of the known signal.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
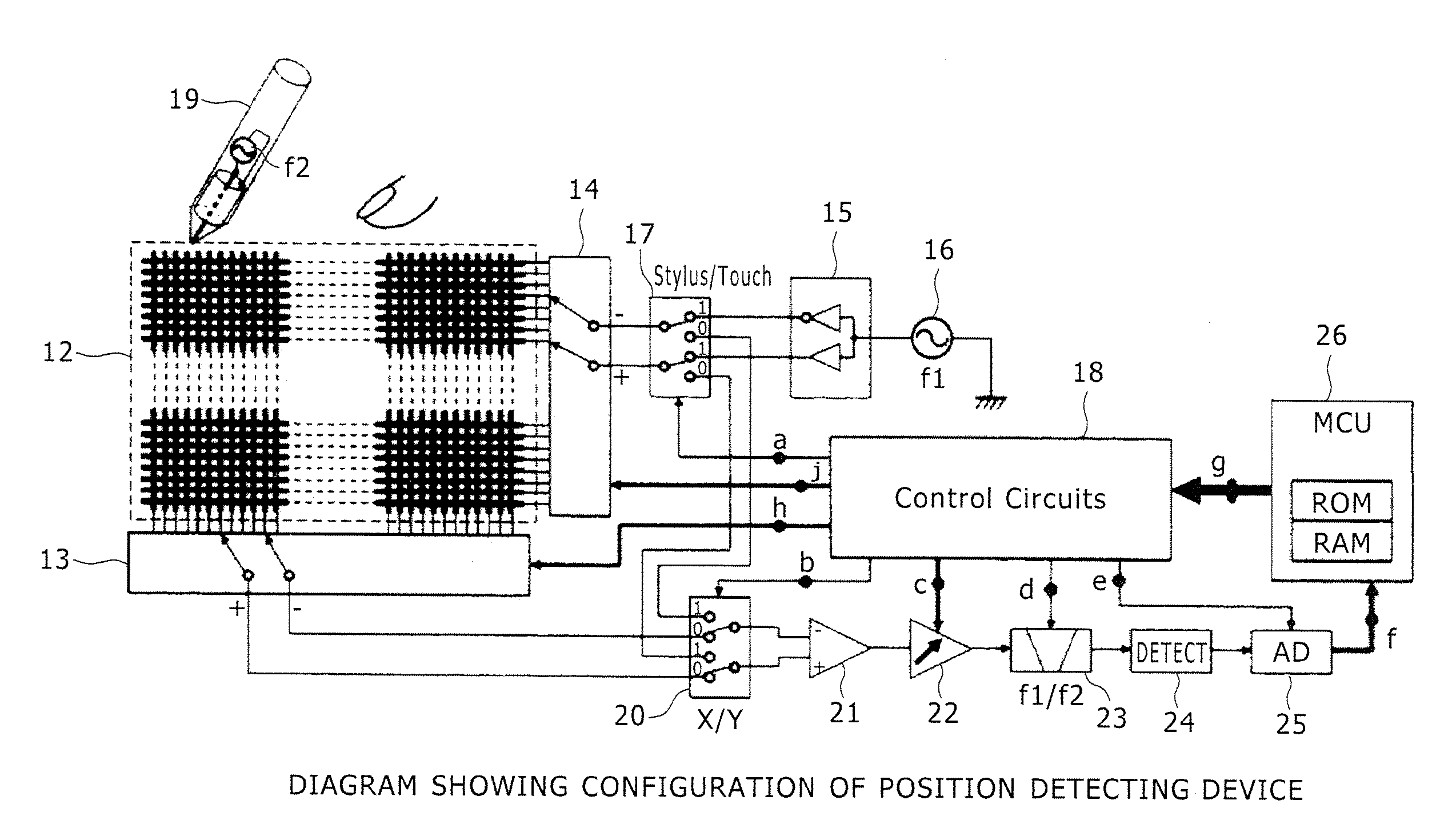
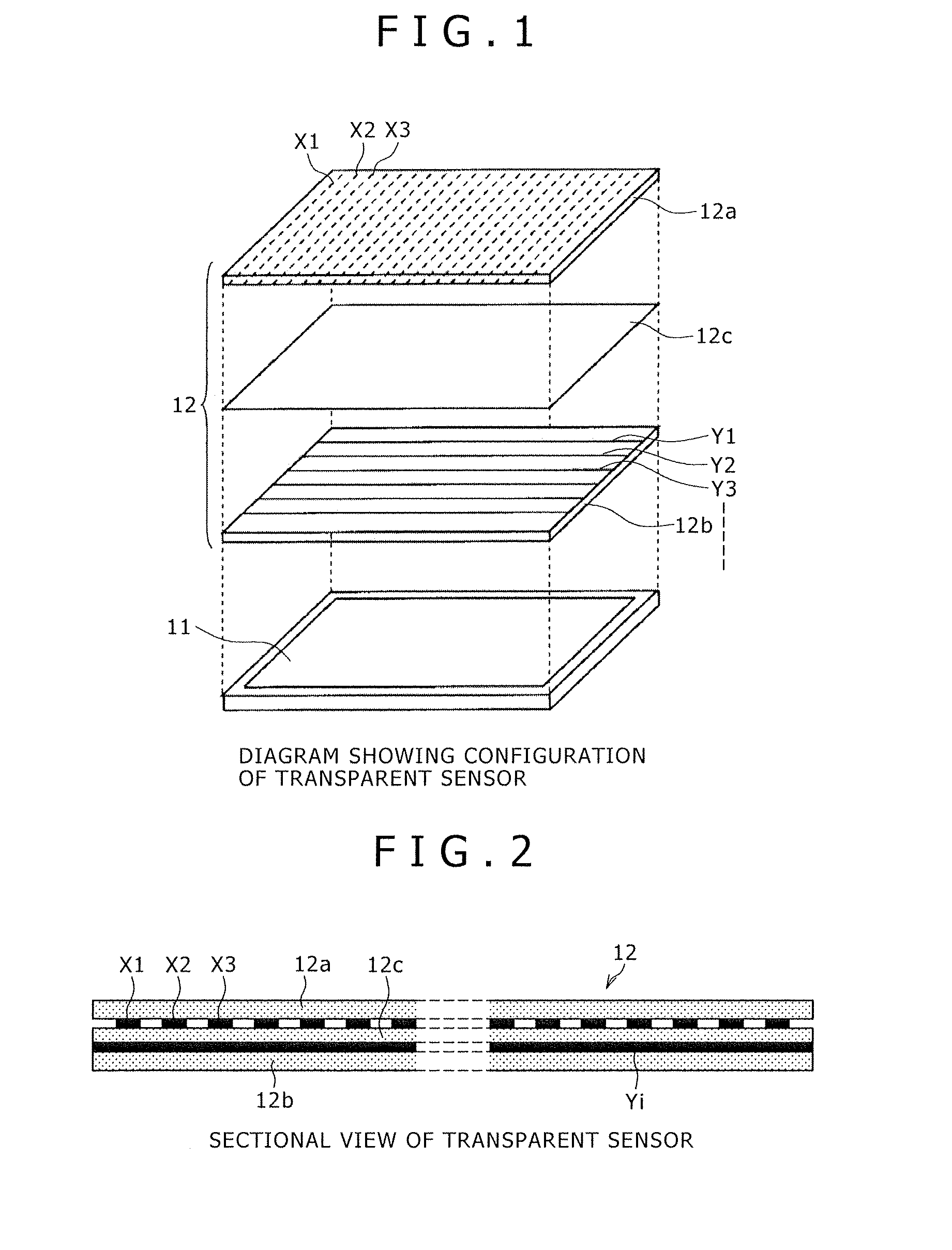
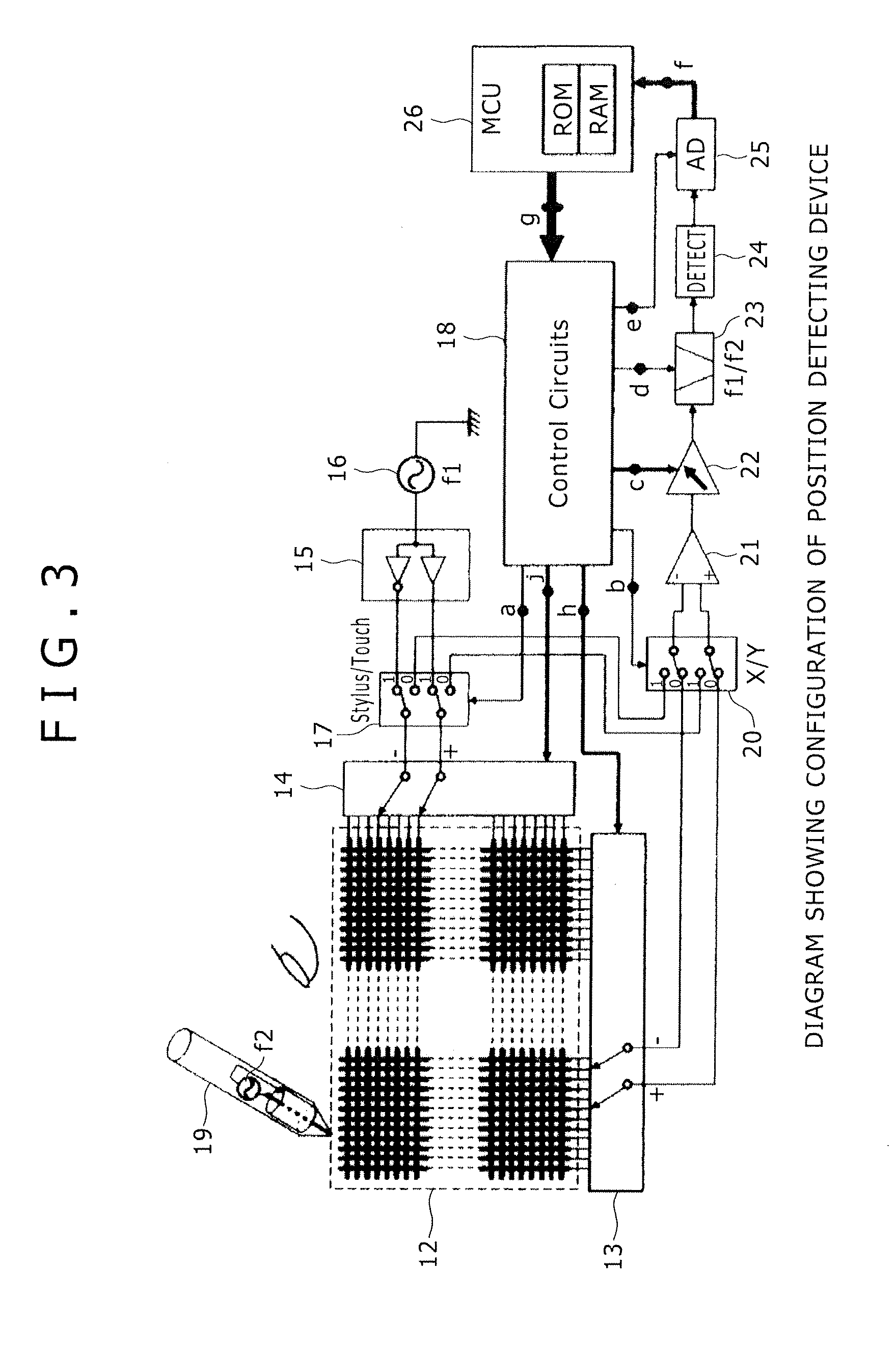
Position detecting device
InactiveUS20140078101A1Accurate detectionAccurately inputInput/output processes for data processingDisplay devicePhason
A position detecting device detects both a finger and a stylus radiating an electric field. The device includes: a substantially transparent sensor disposed on a display device and formed by X-electrodes and Y-electrodes; an X-selecting circuit for selecting two sets of X-electrodes as a positive terminal and a negative terminal; a Y-selecting circuit for selecting two sets of Y-electrodes as a positive terminal and a negative terminal; a driving signal generating circuit for generating signals shifted in phase from each other by 180° as a positive signal and a negative signal; a differential amplifier for amplifying a difference between signals occurring in the positive terminal and the negative terminal selected by one, or respectively each, of the X-selecting circuit and the Y-selecting circuit; and a balanced switching circuit for switching connection of the positive terminal and the negative terminal to the driving signal generating circuit or to the differential amplifier.
Owner:WACOM CO LTD
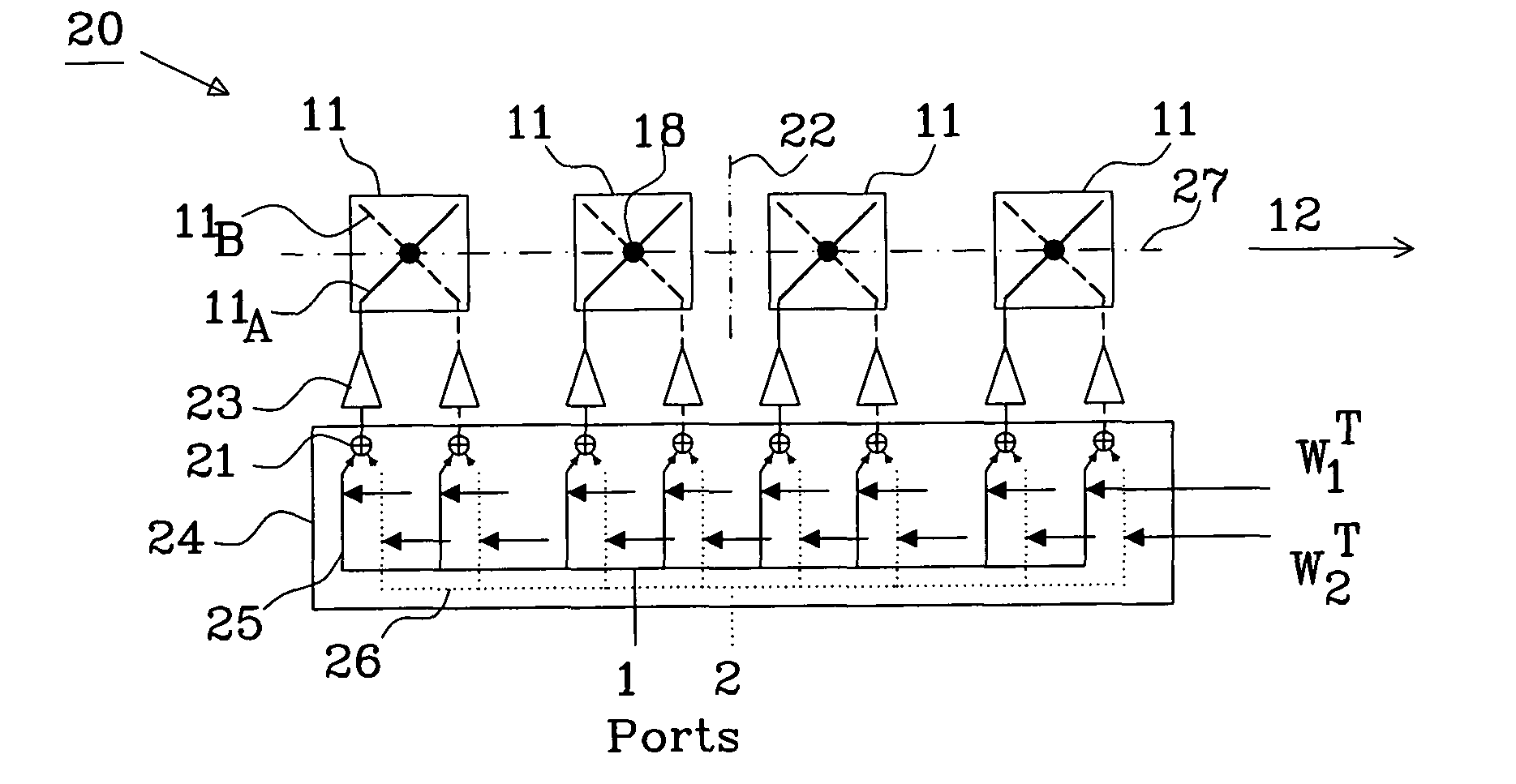
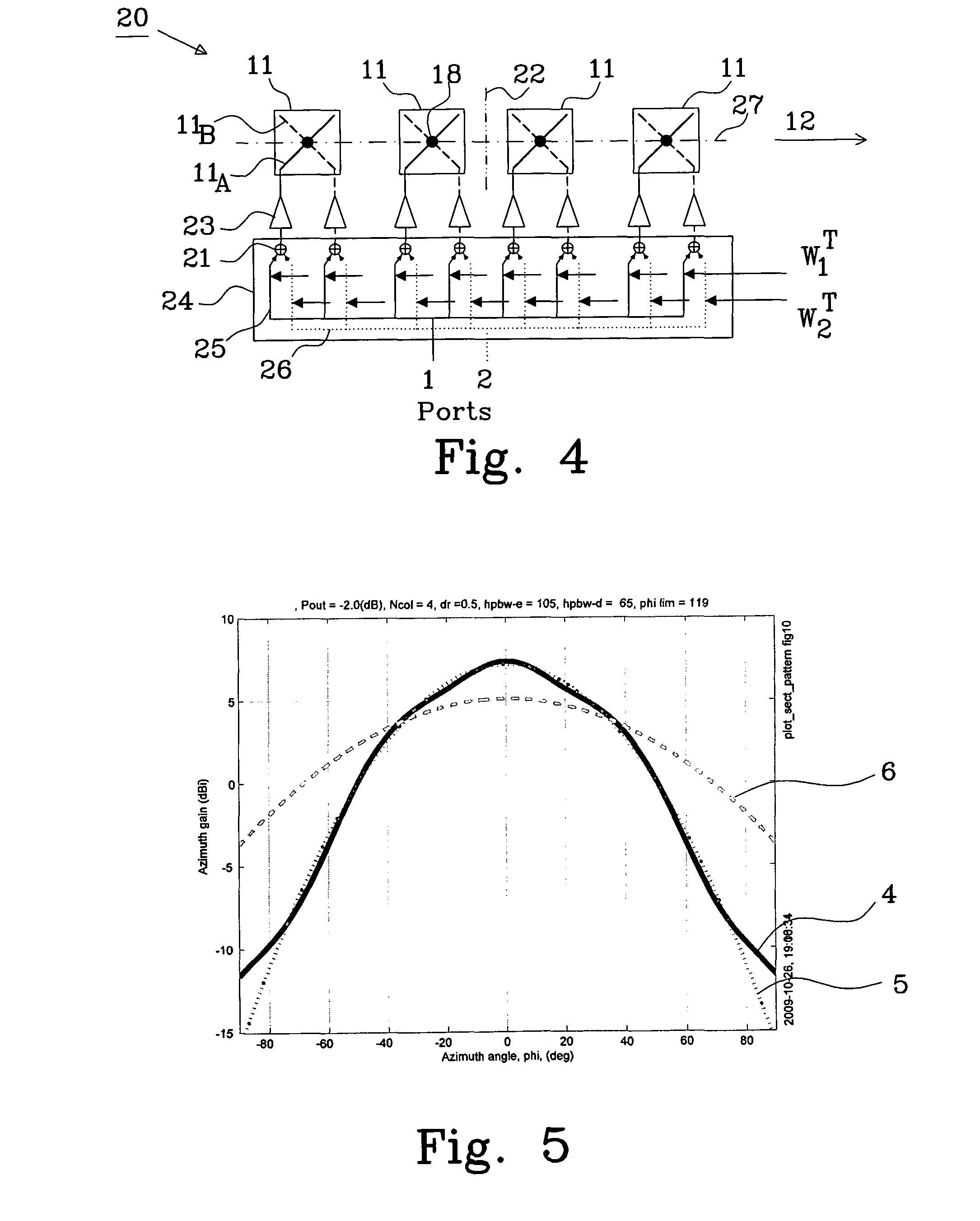
Method of designing weight vectors for a dual beam antenna with orthogonal polarizations
ActiveUS20120212372A1Improved antenna radiation propertyImprove matchPolarisation/directional diversityIndividually energised antenna arraysDual beamLight beam
The present invention relates to a method of generating two beams, having orthogonal polarizations, covering a selected area using an antenna (20) comprising multiple dual-polarized array elements (11). Each dual-polarized array element having a first phase centre (18) associated with a first polarization and a second phase centre (18) associated with a second polarization. The method comprises: designing a first weight matrix having a first non-zero weight vector for the first polarization and a second non-zero weight vector for the second polarization, calculating a second weight matrix based on the weight vectors of the first weight matrix, and applying the first and second weight matrix to the dual-polarized array elements to generate a second beam covering the selected area.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
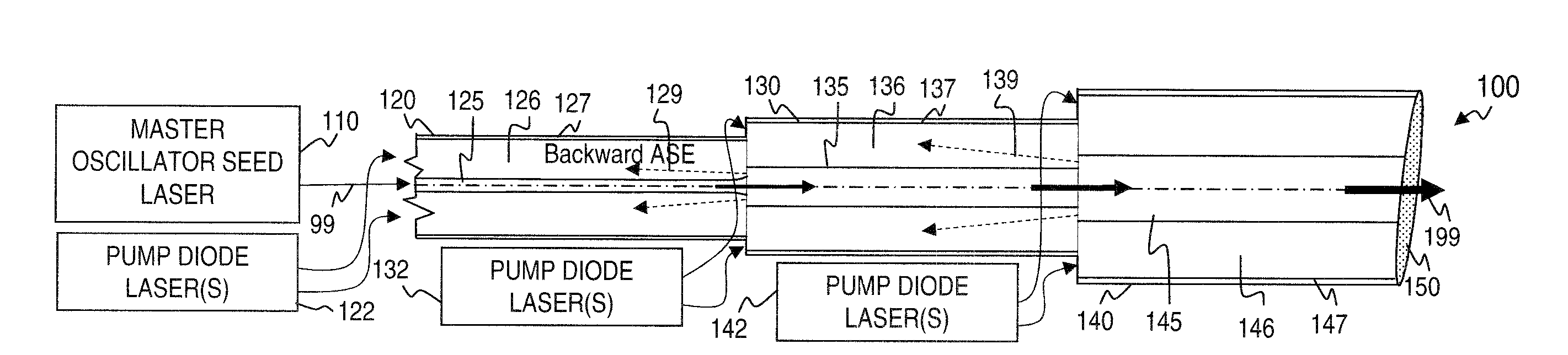
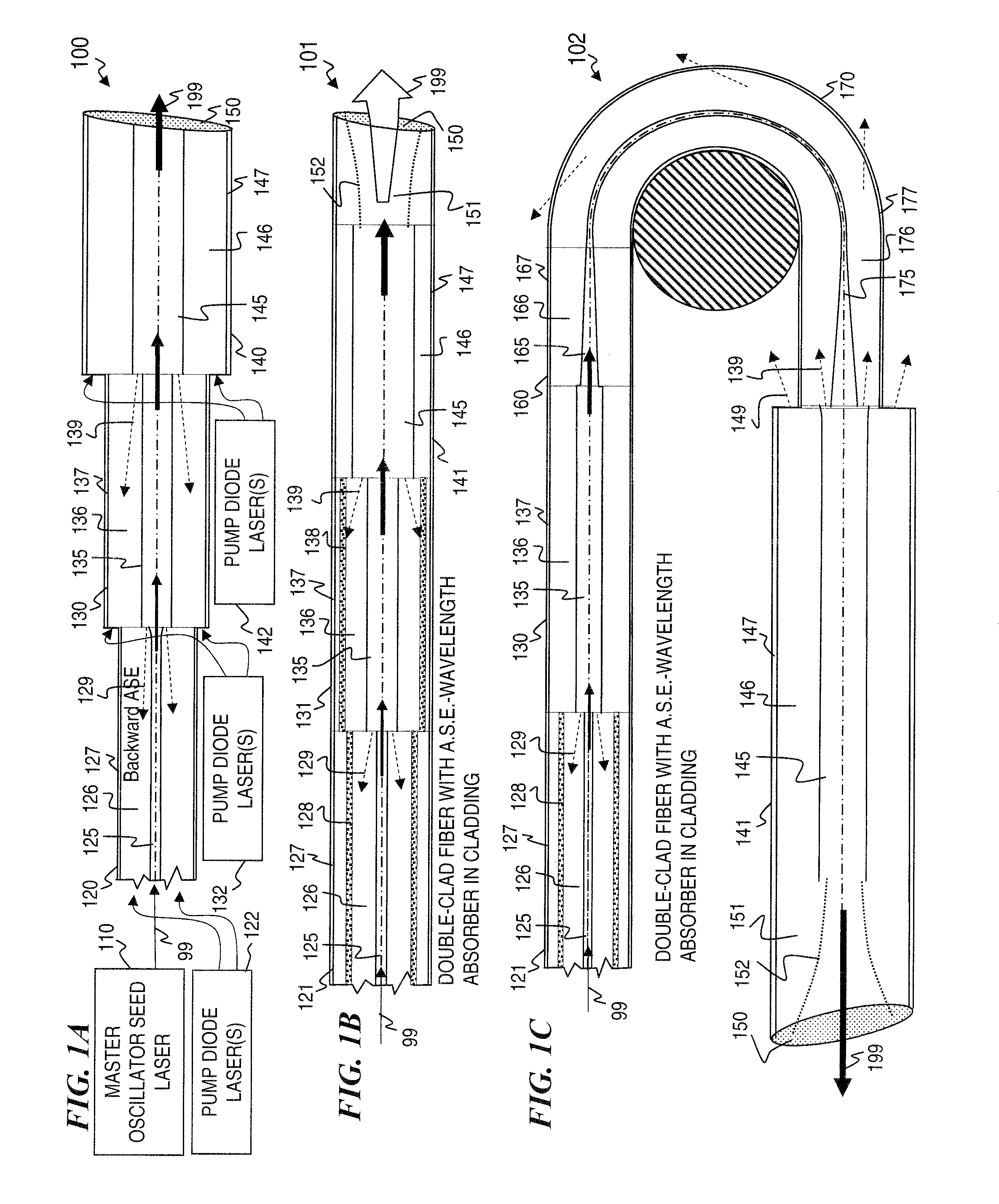
Method and apparatus for optical gain fiber having segments of differing core sizes
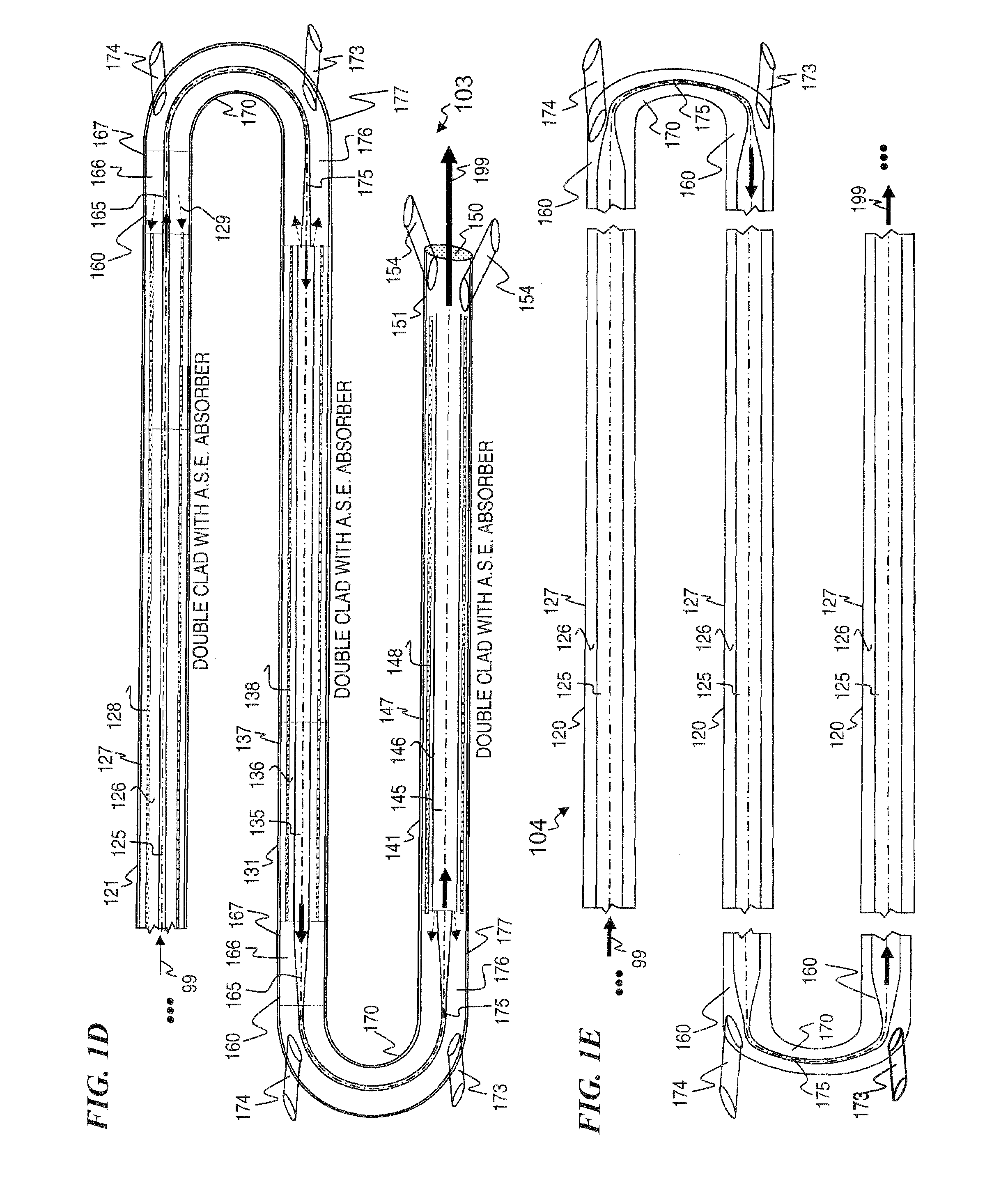
ActiveUS7768700B1Enhanced energy extractionReduce the amount requiredLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionFiberBandpass filtering
Apparatus and method for amplifying laser signals using segments of fibers of differing core diameters and / or differing cladding diameters to suppress amplified spontaneous emission and non-linear effects such as four-wave mixing (FWM), self-phase modulation, and stimulated Brillouin and / or Raman scattering (SBS / SRS). In some embodiments, different core sizes have different sideband spacings (spacing between the desired signal and wavelength-shifted lobes). Changing core sizes and providing phase mismatches prevent buildup of non-linear effects. Some embodiments further include a bandpass filter to remove signal other than the desired signal wavelength and / or a time gate to remove signal at times other than during the desired signal pulse. Some embodiments include photonic-crystal structures to define the core for the signal and / or the inner cladding for the pump. Some embodiments include an inner glass cladding to confine the signal in the core and an outer glass cladding to confine pump light in the inner cladding.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
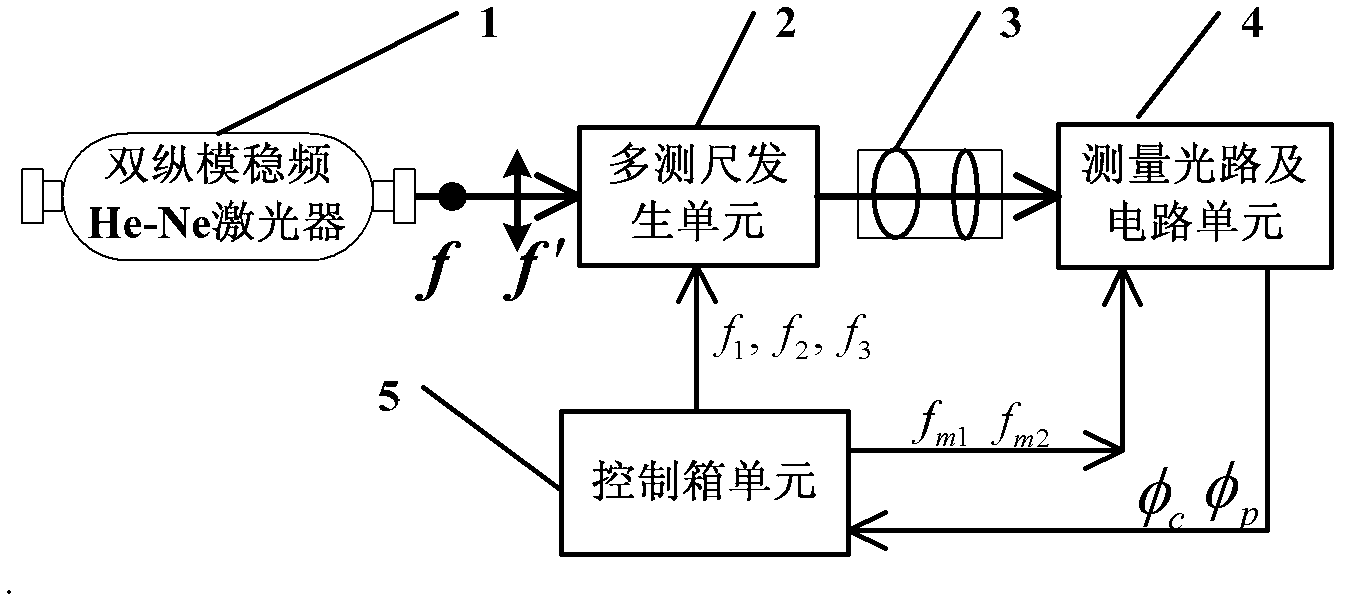
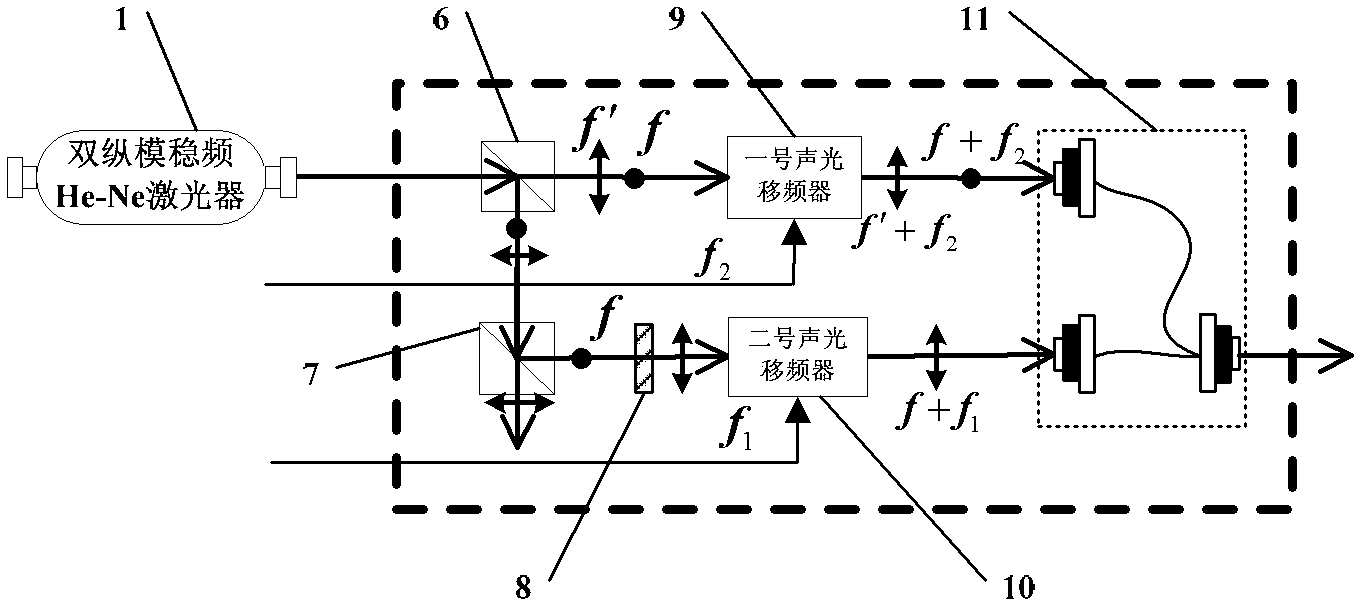
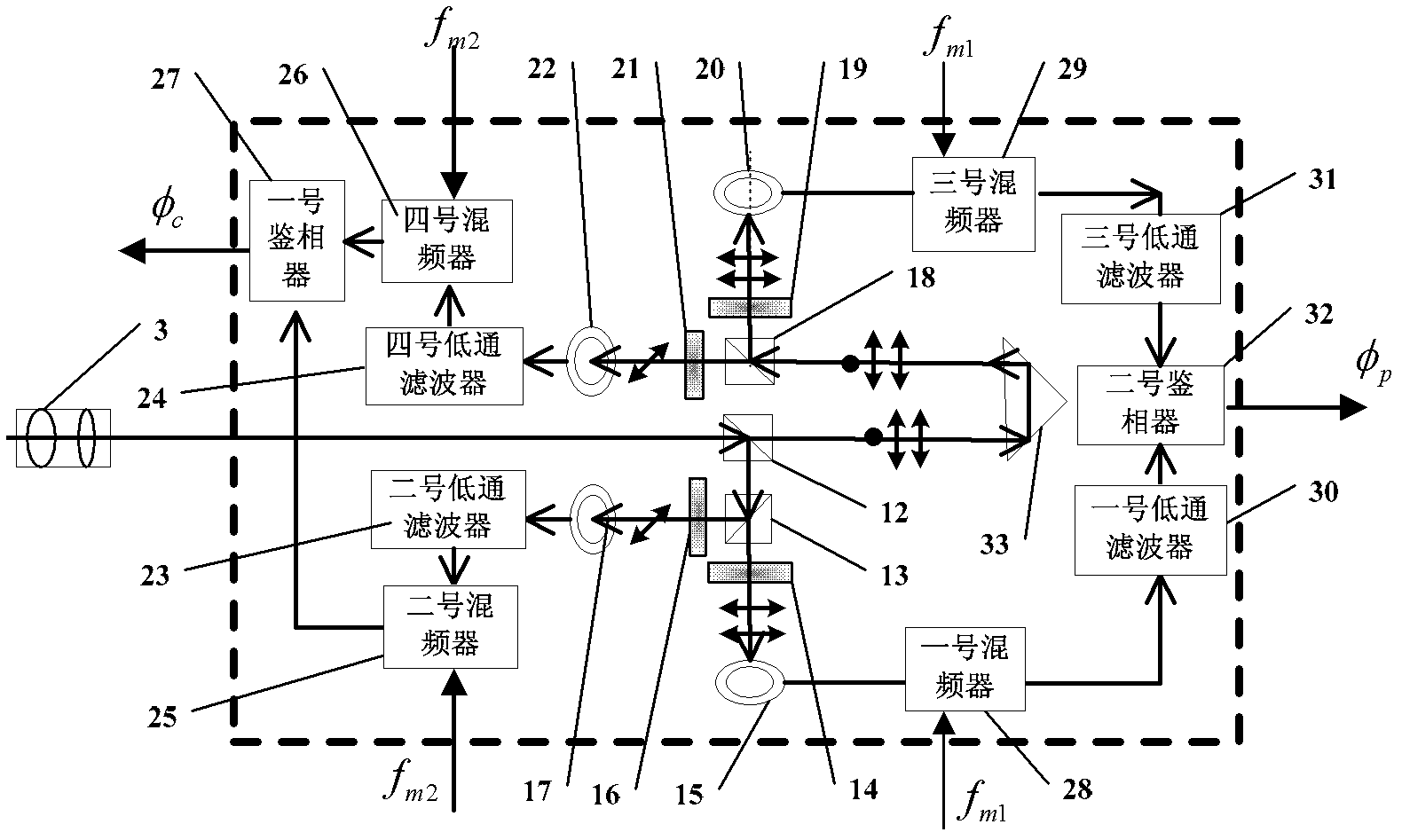
Multi-frequency synchronization phase laser ranging device and method based on dual-acousto-optic shift frequency
The invention discloses a multi-frequency synchronization phase laser ranging device and a method based on dual-acousto-optic shift frequency, relates to the technical field of laser ranging, and mainly relates to a phase laser ranging technology, solving the problem that a device and a method which can achieve both of the synchronism and stability of multiple measuring tapes are in lack in the existing phase laser ranging technology. The multi-frequency synchronization phase laser ranging device based on dual-acousto-optic shift frequency comprises a dual-longitudinal-mode stable frequency He-Ne laser, a multi-measuring-tape generating unit, a bundle expanding and collimating lens set, a light path and circuit measuring unit and a control box unit. The multi-frequency synchronization phase laser ranging method based on dual-acousto-optic comprises the following concrete steps: step one, switching on the dual-longitudinal-mode stable frequency He-Ne laser; step two, taking one beam oflaser as a reference laser beam, and taking the other beam of laser as a measurement laser; step three, taking (f'+f2)-(f+f1) as the accurate measurement tape frequency, and taking a low-frequency electric signal f1-f2 as the rough measurement tape frequency; and step four, moving a measuring cone prism to the target end. The device and the method are used for phase laser ranging.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveUS20060161060A1Faster and accurate perfusion mapImprove time resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac phaseRadio frequency
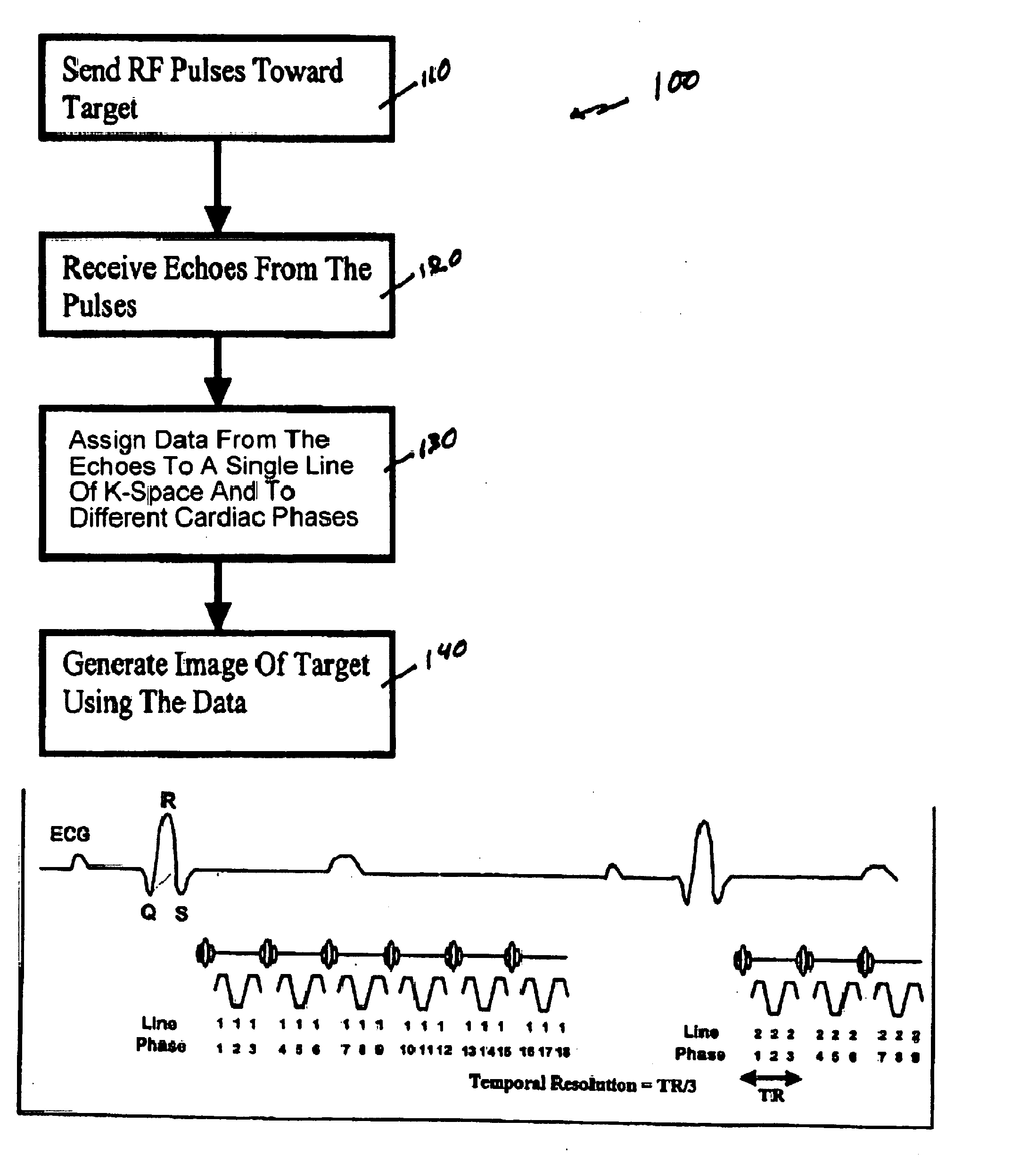
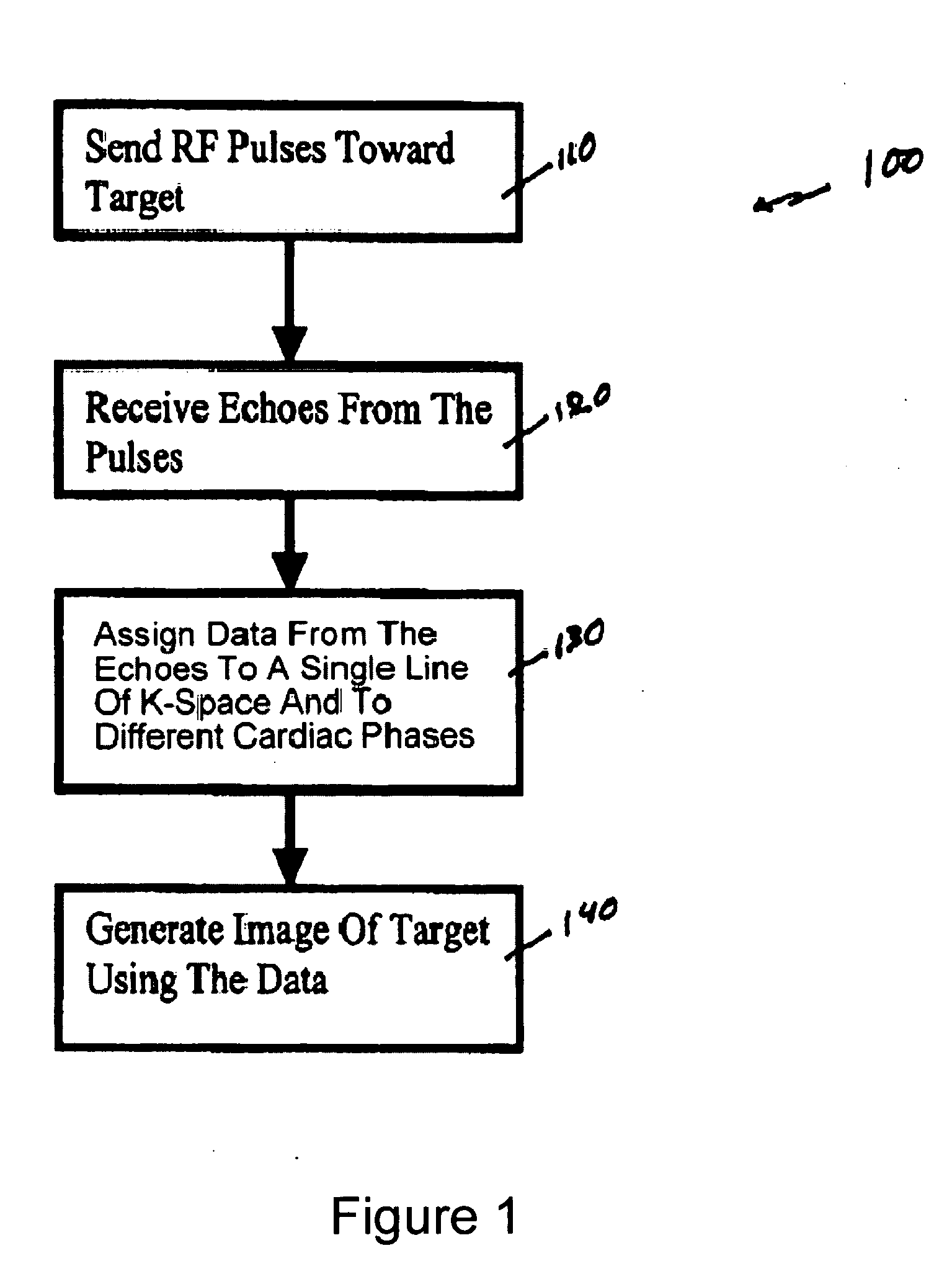
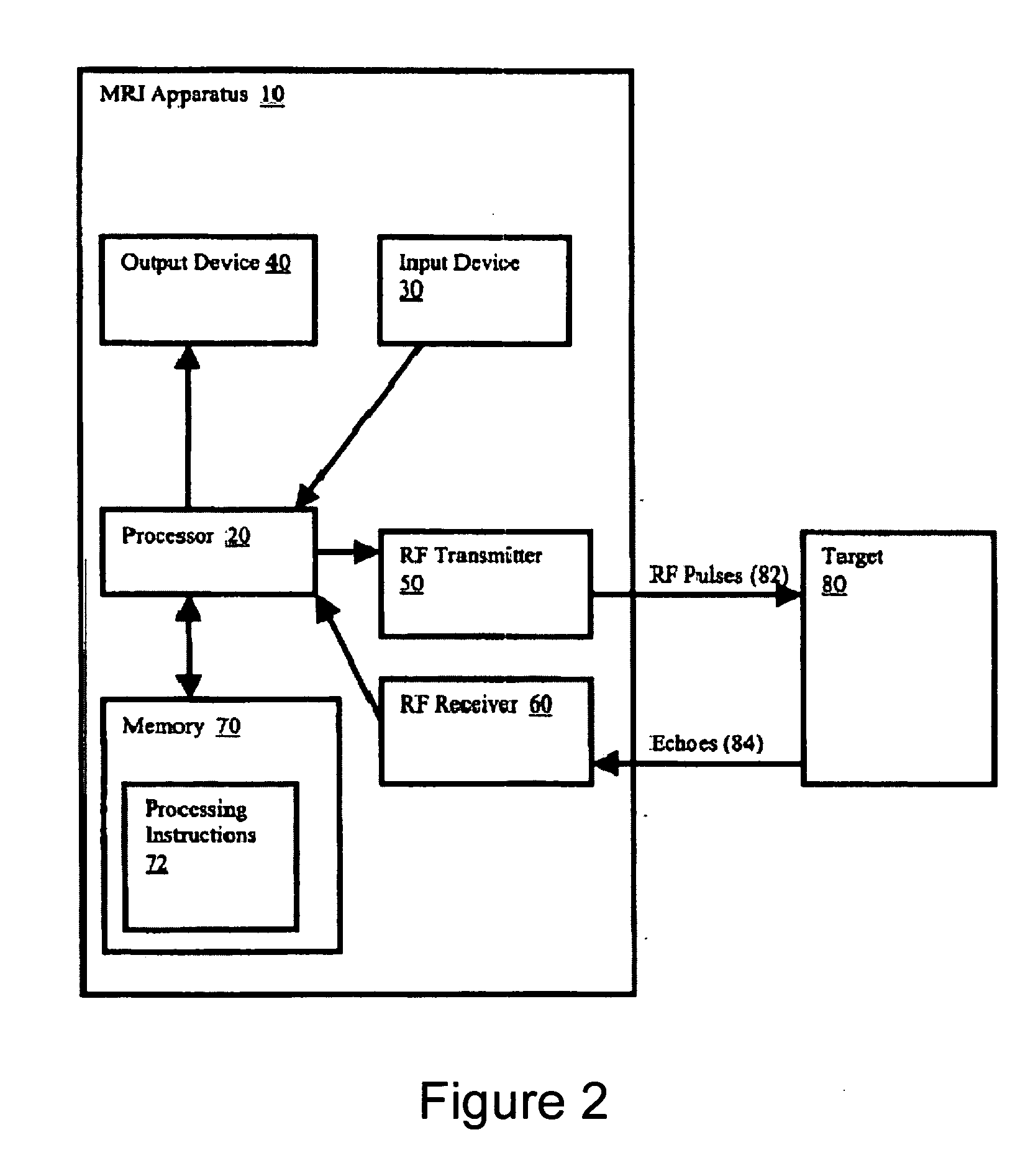
Method, systems and arrangements are provided for creating a high-resolution magnetic resonance image (“MRI”) or obtaining other information of a target, such as a cardiac region of a patient. Radio-frequency (“RF”) pulses can be transmitted toward the target by, e.g., an RF transmitter of an MRI apparatus. In response, multiple echoes corresponding to the plurality of pulses may be received from the target. Data from each of the echoes can be assigned to a single line of k-space, and stored in memory of the apparatus. An image of the target, acceleration data and / or velocity data associated with a target can be generated as a function of the data. In one exemplary embodiment, the data from different echoes may be assigned to the same k-space line, and to different cardiac phases. In one further embodiment, parallel processing may be used to improve the resolution of the image acquired during a single breath-hold duration. In yet another embodiment, utilizing a segmented implementation, multiples lines of k-space are acquired for a given cardiac phase (or time stamp) per trigger signal. The present invention may be utilized for the heart or for any other anatomical organ or region of interest for the evaluation and study of flow dynamics with very high temporal resolution.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
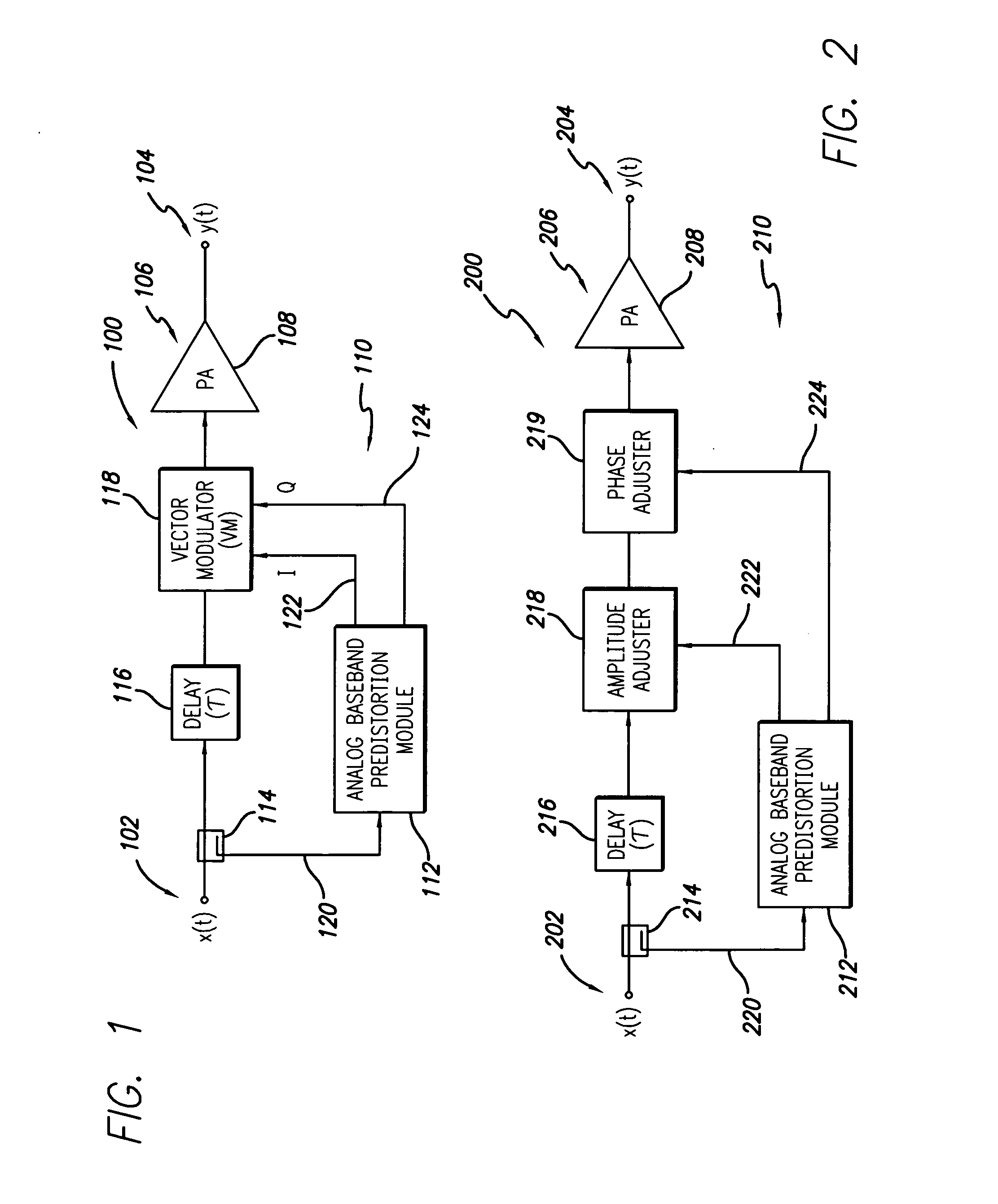
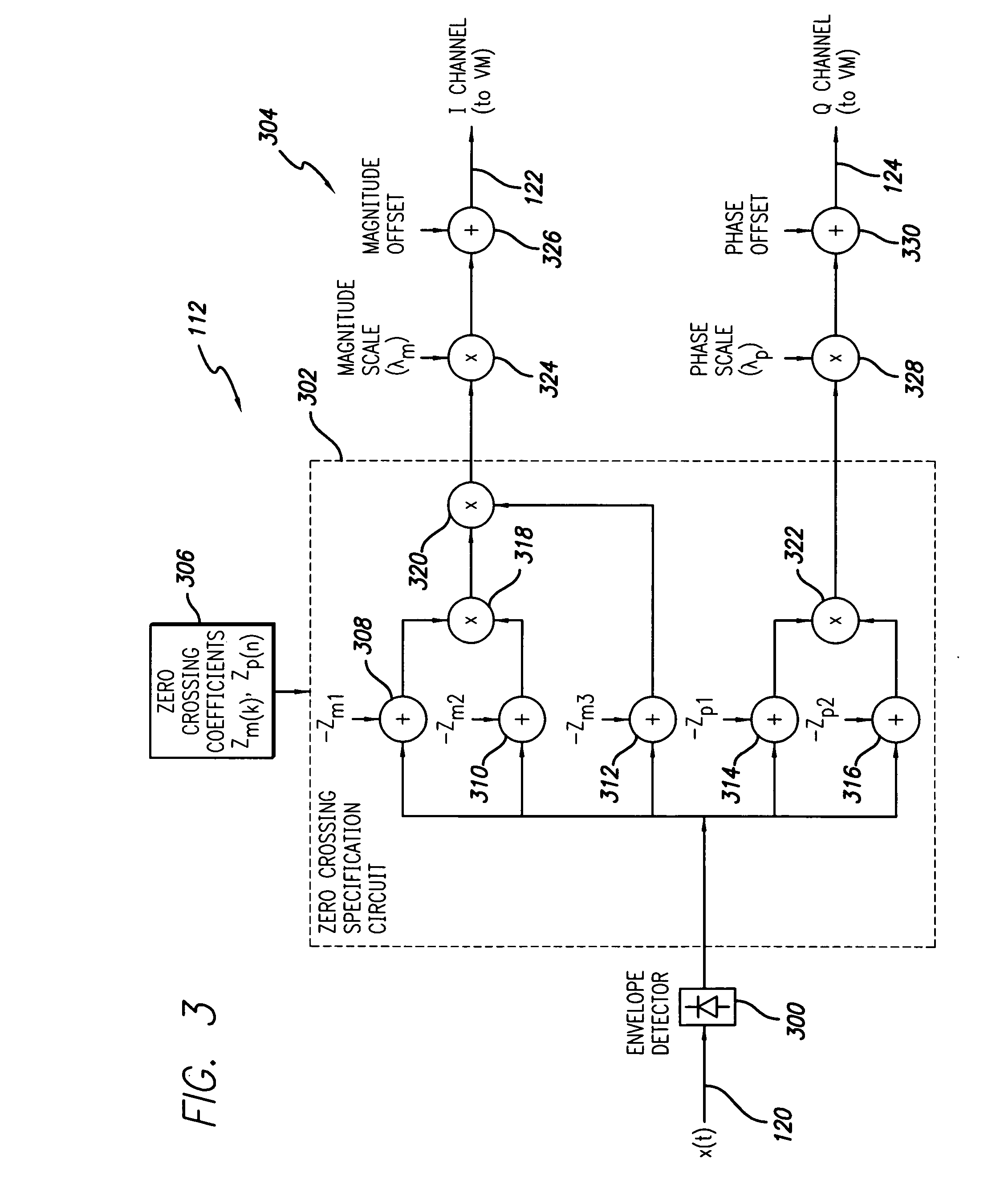
RF power amplifier system employing an analog predistortion module using zero crossings
ActiveUS20060217083A1Correct nonlinearityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationPhase correctionAudio power amplifier
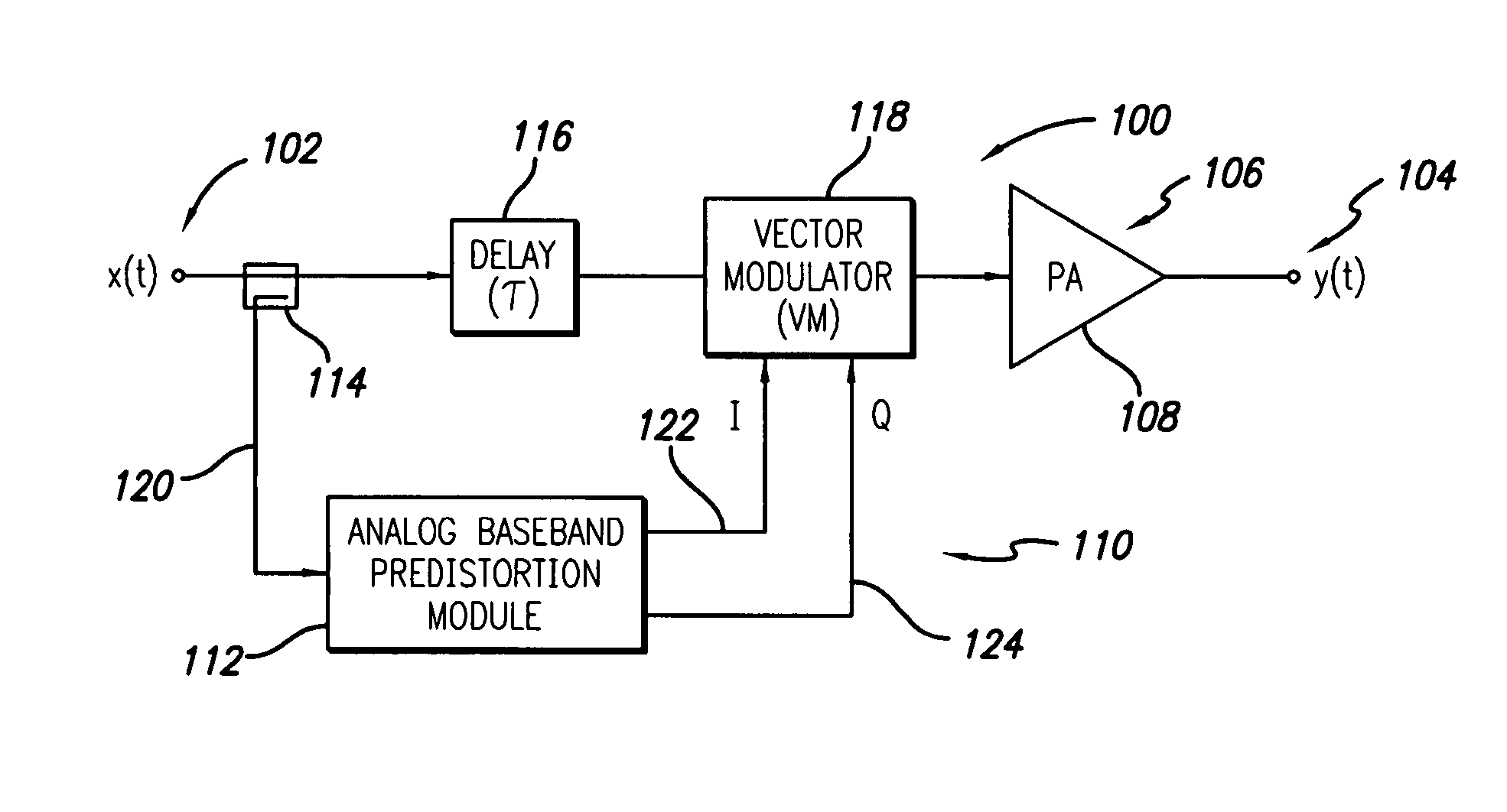
An RF amplifier system employing an analog predistortion module is disclosed. The disclosed analog predistortion module is based on zero crossings of the gain error curves (AM-AM and AM-PM curves minus DC). The hardware structure uses the product of first-order functions avoiding the need for large differential swings in the coefficients to shape the lower part of the gain curves. The higher-order nonlinear functions are preferably derived from a single envelope detector. An equal number of multipliers are preferably used in each path when the order of the magnitude and phase corrections are equal or differ by one, thus reducing delay mismatches between the magnitude and phase correction signals.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Adaptive phase contrast microscope
InactiveUS20120257040A1Region can be greatEnhance the imageColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsMicro platePhase image
An optical microscope is provided with an adjustable optical phase ring. The adjustable ring provides a way to compensate for distortion in the visible phase ring before the light reaches the sample. In an inverted microscope, when observing transparent cells under a liquid, the visible light phase ring is distorted. By the use of a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) in place of a fixed ring, the projected ring is adjusted to realign the light and produce phase. In a typical micro plate, the meniscus formed produces a lens effect that is realigned by providing changes in the position and pattern, to allow phase imaging over a wider portion of the well. The realignment of the ring can be manual or automated and can be dynamically adjusted based upon an observed image of the sample.
Owner:KAIROS INSTR
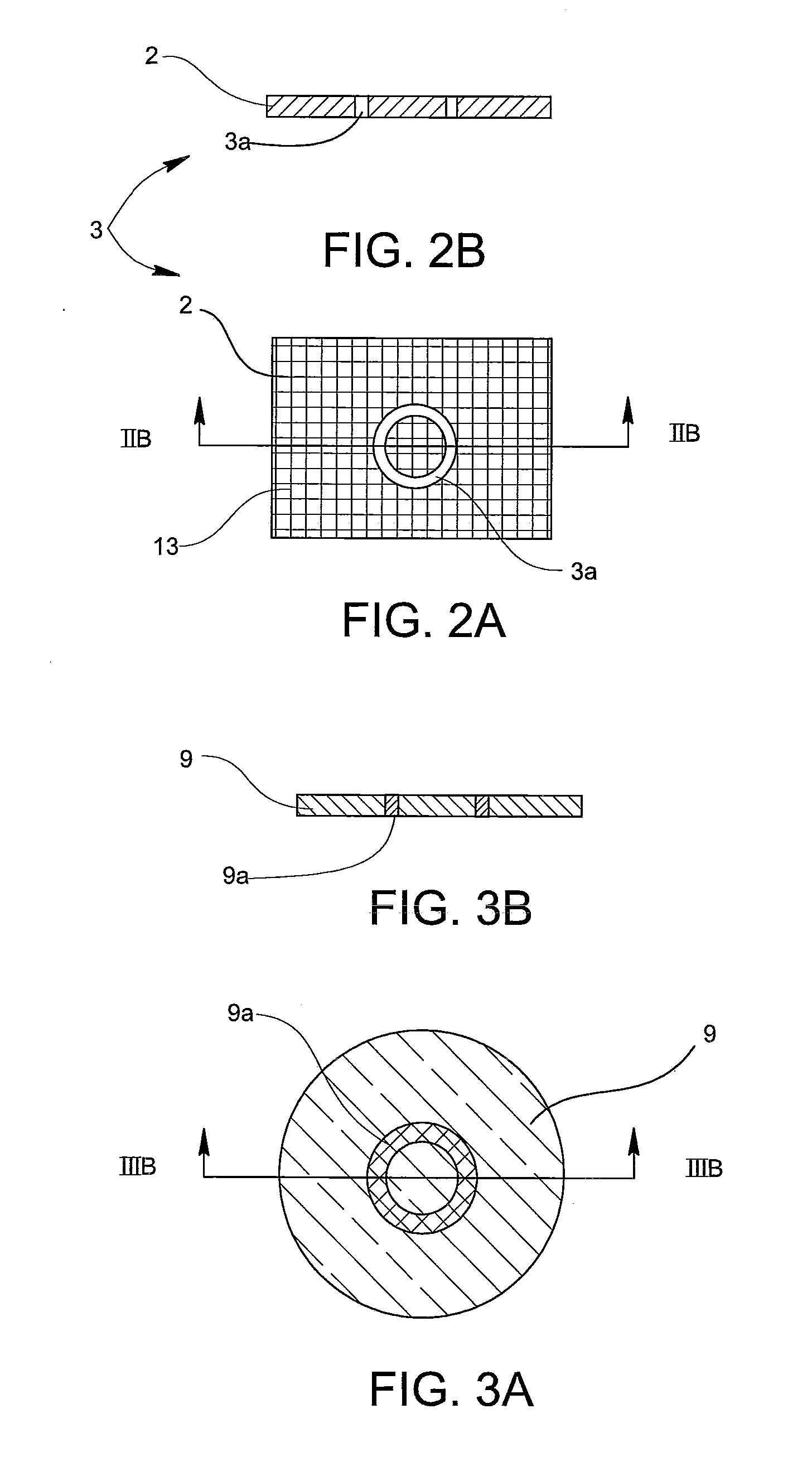
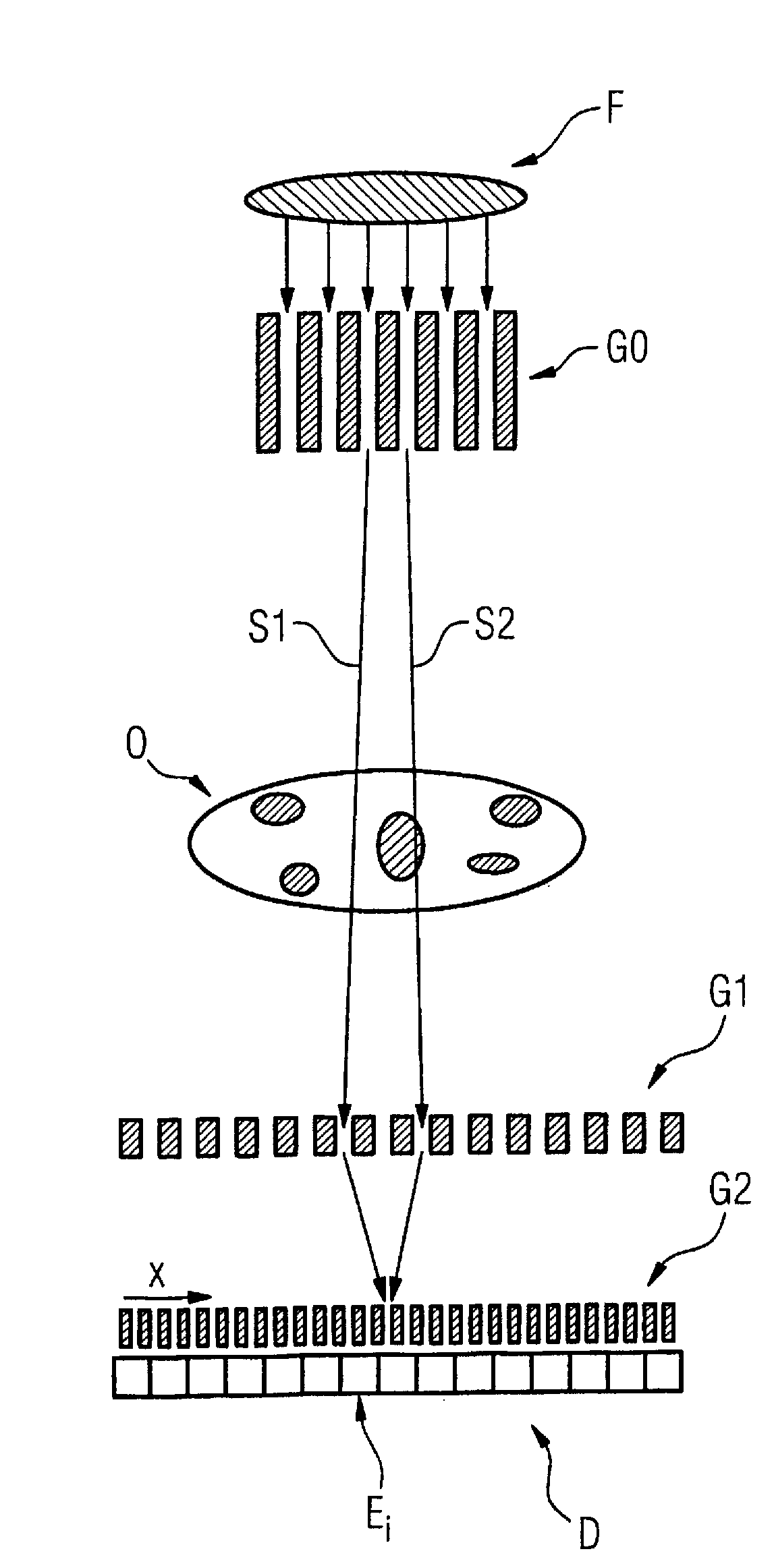
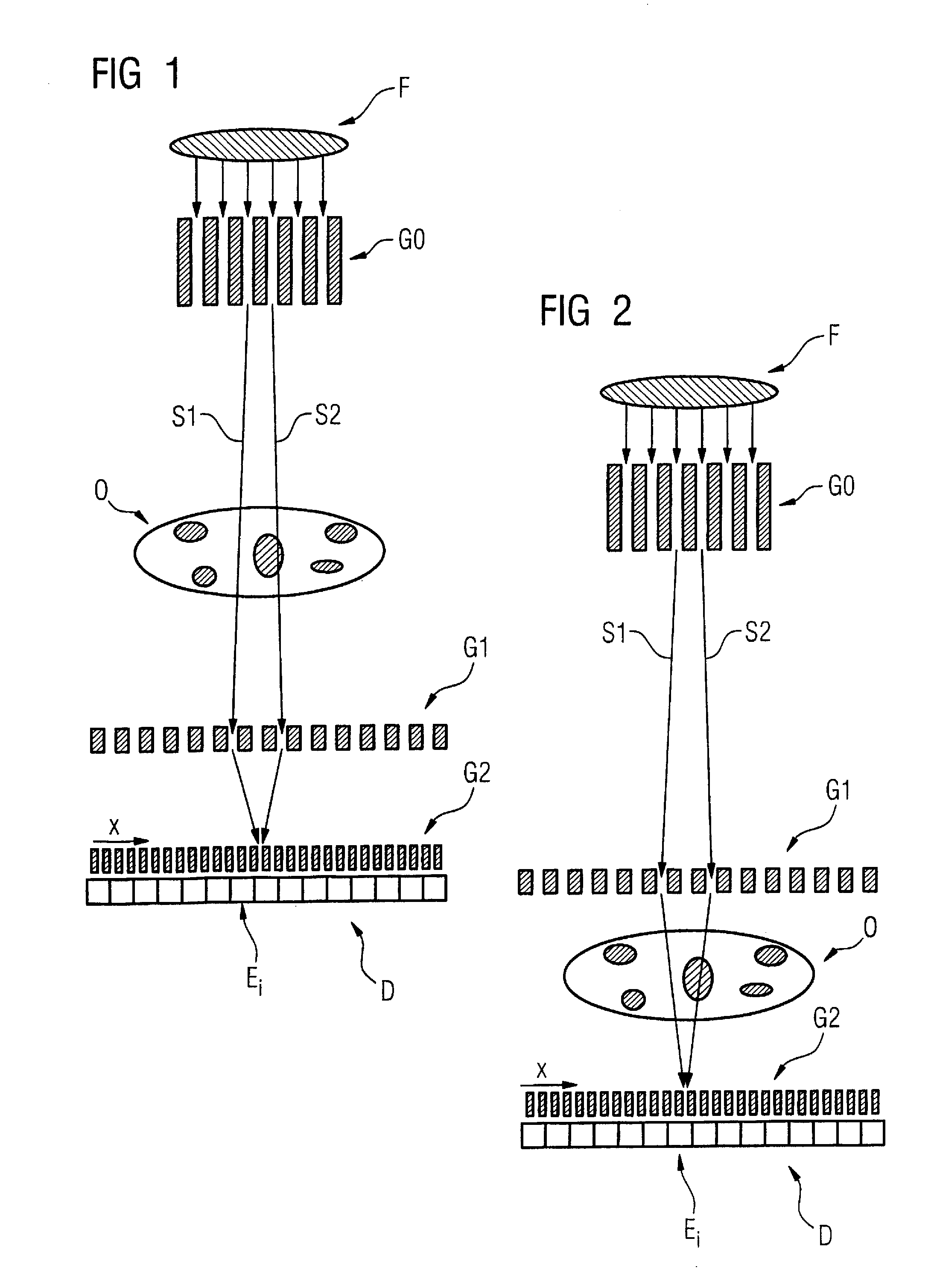
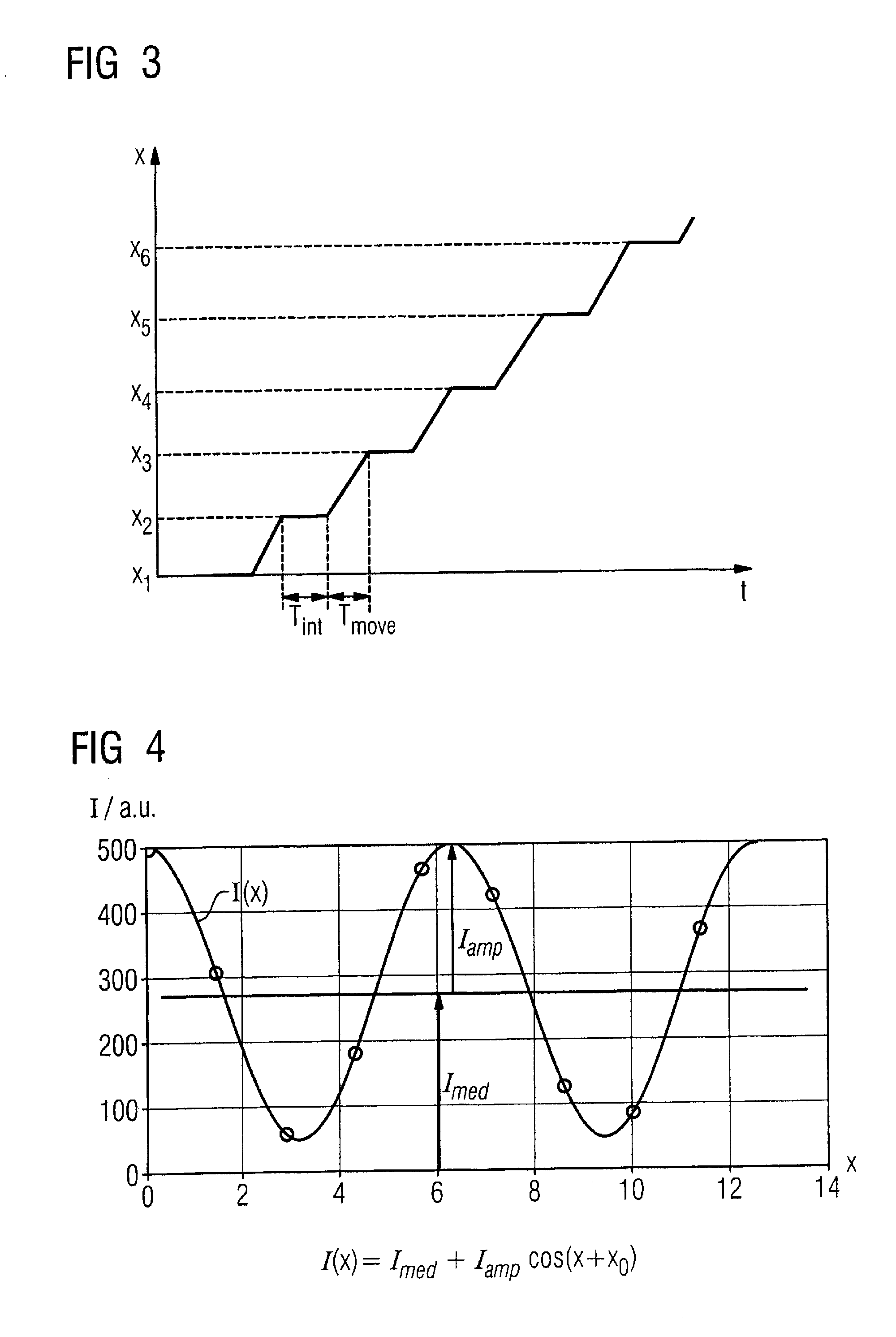
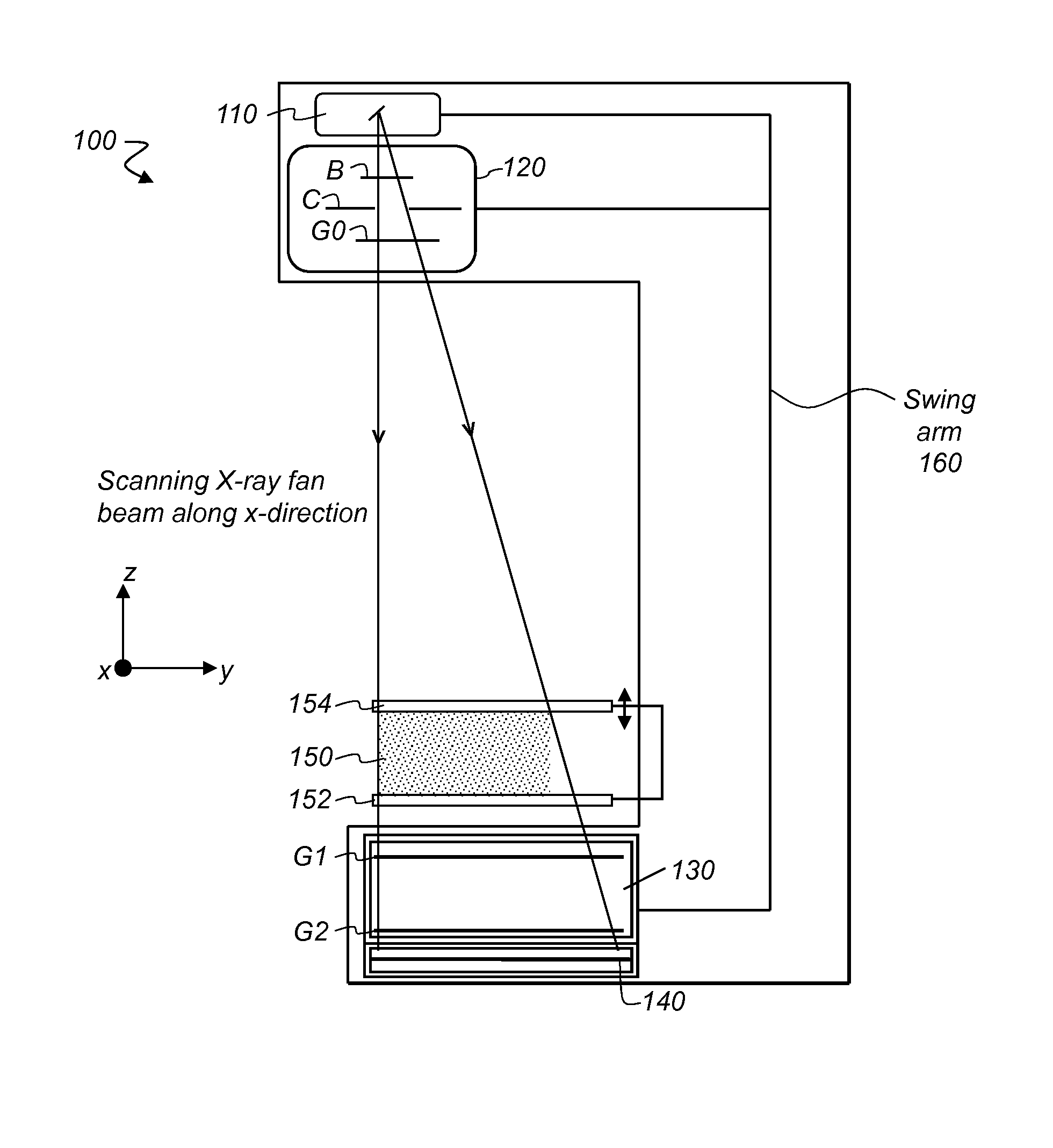
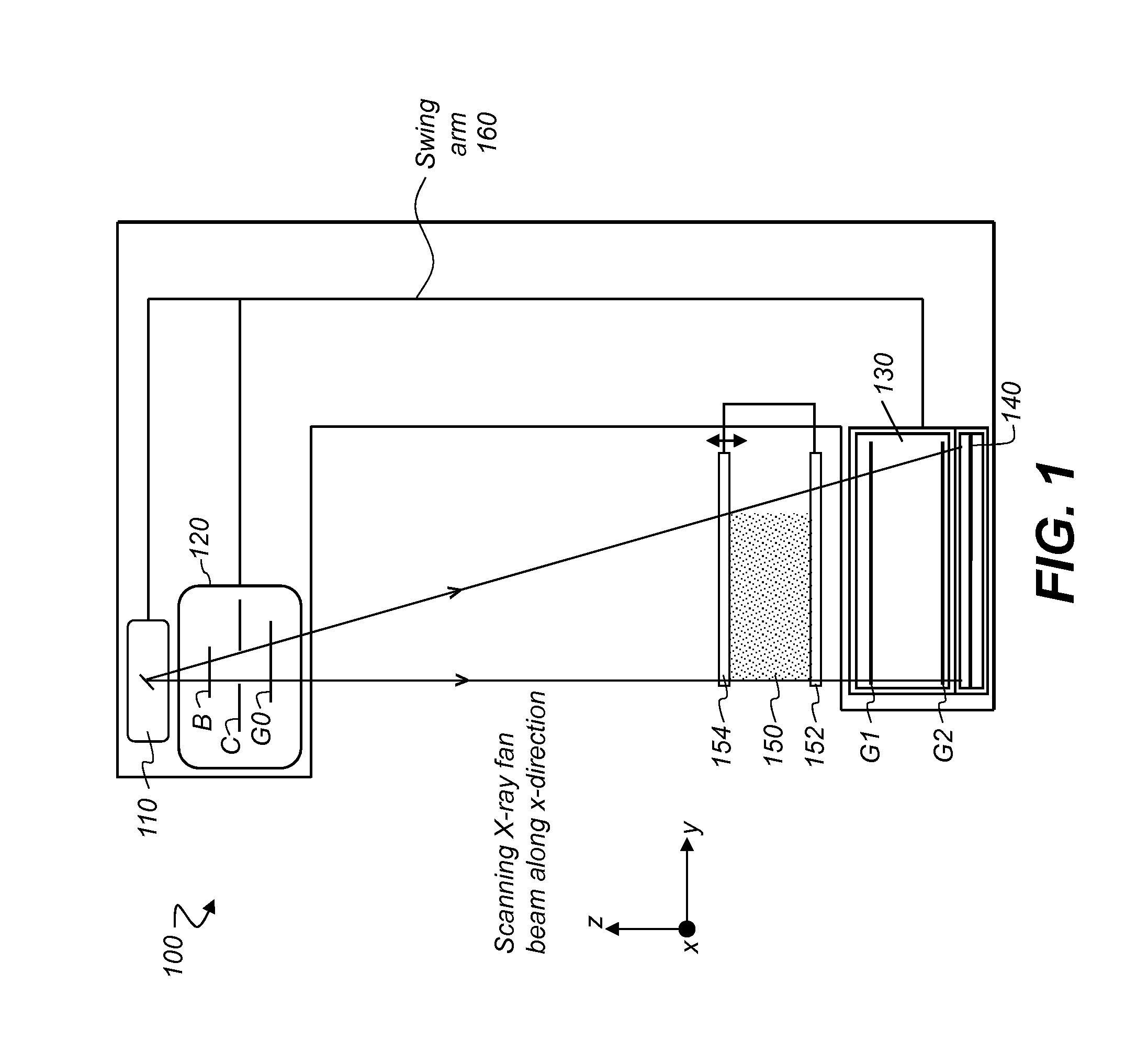
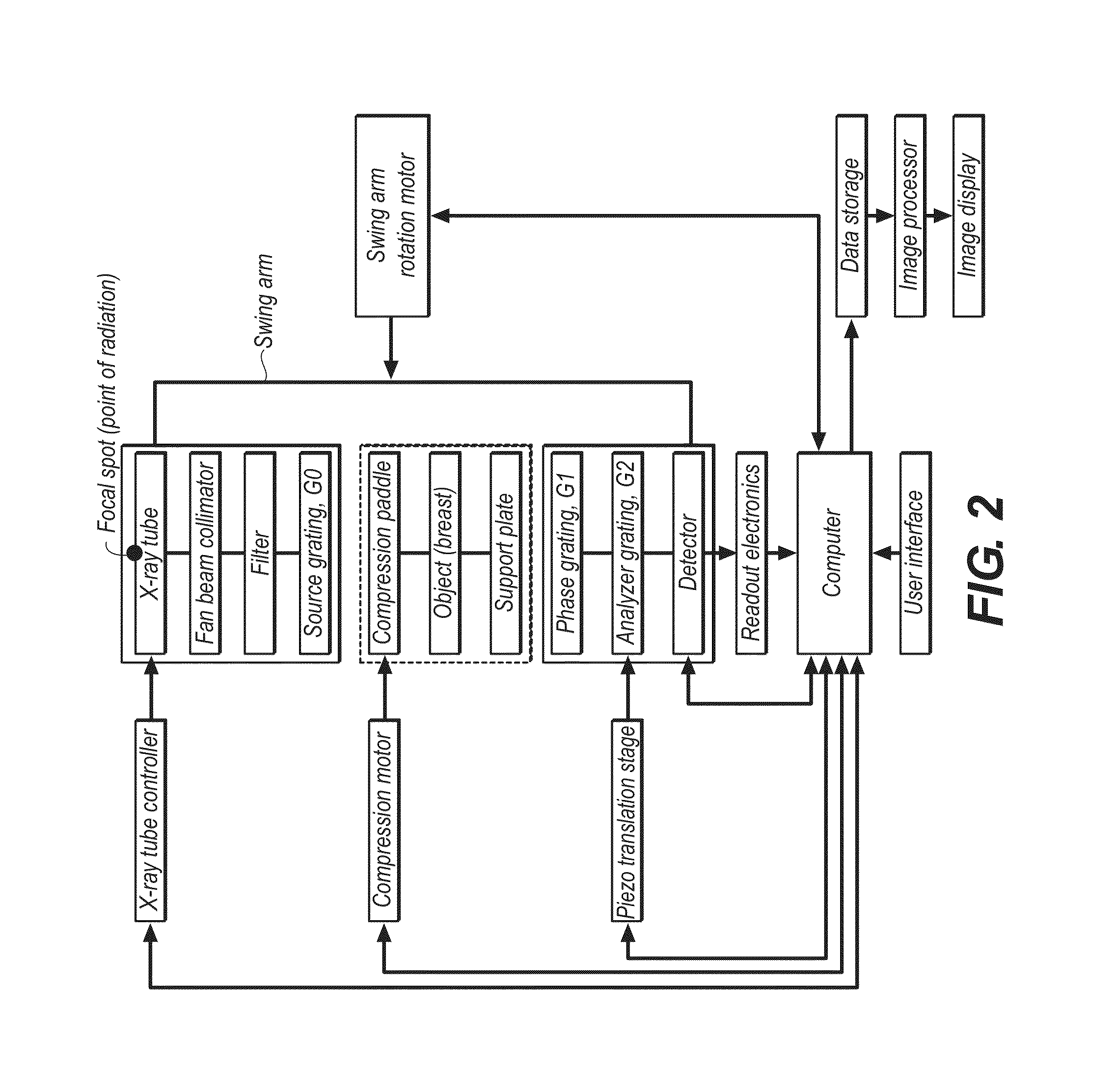
Method to determine phase and/or amplitude between interfering, adjacent x-ray beams in a detector pixel in a talbot interferometer
ActiveUS20100074395A1Simplify mannerImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayPhase grating
In a method to determine phase and / or amplitude between interfering, adjacent x-ray beams in a detector pixel in a Talbot interferometer for projective and tomographical x-ray phase contrast imaging and / or x-ray dark field imaging, after an irradiation of the examination subject with at least two coherent or quasi-coherent x-rays, an interference of the at least two coherent or quasi-coherent x-rays with the aid of an irradiated phase grating is generated, and the variation of multiple intensity measurements in temporal succession after an analysis grating is determined in relation to known displacements of one of the gratings or of an x-ray source fashioned like a grating, positioned upstream in the beam path, relative to one of the gratings. The integrating intensity measurements ensue during a relative movement—thus not during the standstill—of one of the upstream gratings or of the x-ray source fashioned like a grating or of the examination subject, with known speed behavior over a final time interval of a final distance.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
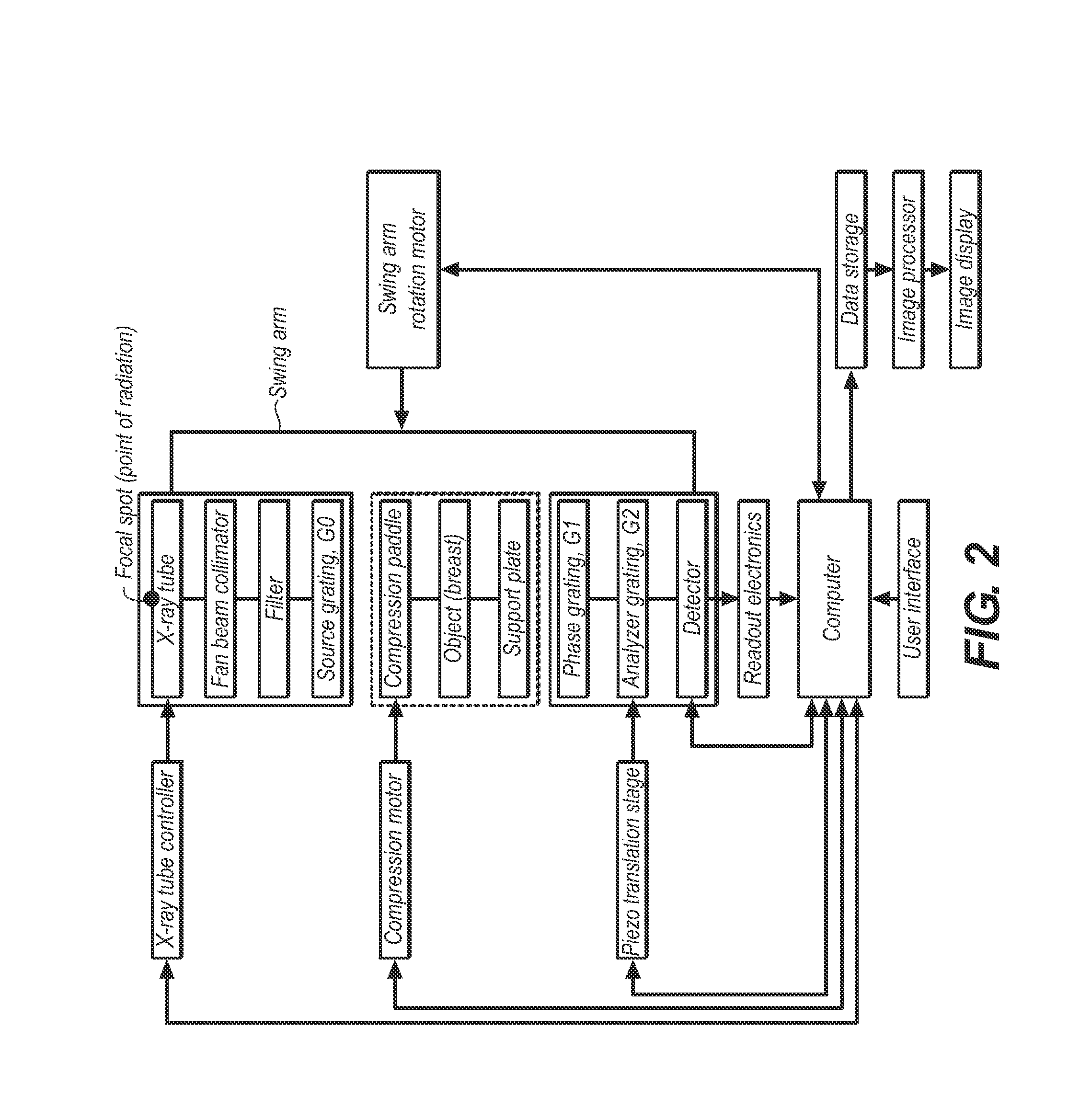
Spectral grating-based differential phase contrast system for medical radiographic imaging
ActiveUS20140185746A1Imaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionBeam energyBeam shaping
Embodiments of methods and apparatus are disclosed for obtaining a phase-contrast digital radiographic imaging system and methods for same that can include an x-ray source for radiographic imaging; a beam shaping assembly including a collimator and a source grating, an x-ray grating interferometer including a phase grating, and an analyzer grating; and an x-ray detector, where a single arrangement of the beam shaping assembly, the x-ray grating interferometer and a position of the detector is configured to provide spectral information (e.g. at least two images obtained at different relative beam energies).
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
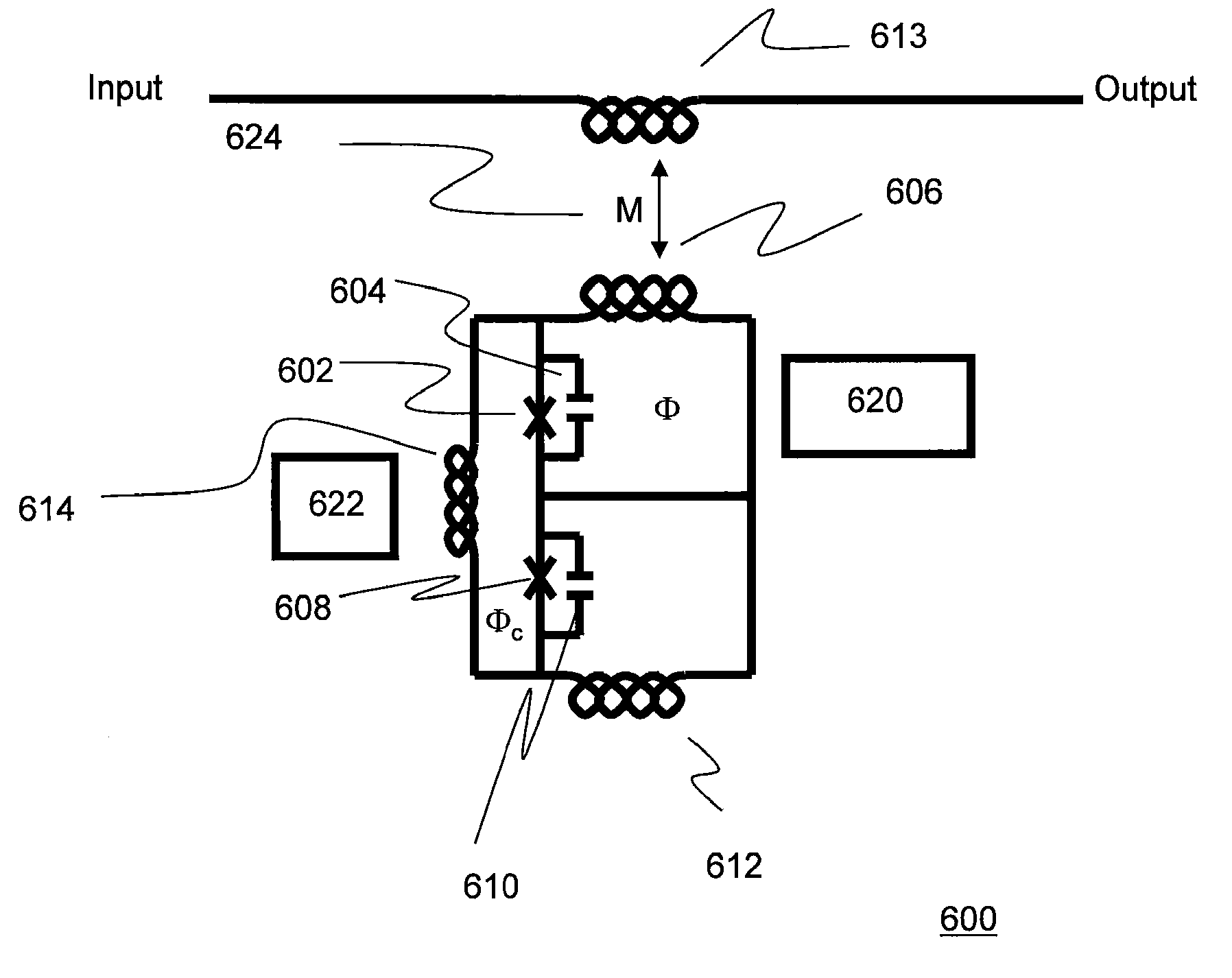
Microwave readout for flux-biased qubits
A method for determining whether a quantum system comprising a superconducting qubit is occupying a first basis state or a second basis state once a measurement is performed is provided. The method, comprising: applying a signal having a frequency through a transmission line coupled to the superconducting qubit characterized by two distinct, separate, and stable states of differing resonance frequencies each corresponding to the occupation of the first or second basis state prior to measurement; and measuring at least one of an output power or phase at an output port of the transmission line, wherein the measured output power or phase is indicative of whether the superconducting qubit is occupying the first basis state or the second basis state.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Spectral grating-based differential phase contrast system for medical radiographic imaging
Embodiments of methods and apparatus are disclosed for obtaining a phase-contrast digital radiographic imaging system and methods for same that can include an x-ray source for radiographic imaging; a beam shaping assembly including a collimator and a source grating, an x-ray grating interferometer including a phase grating, and an analyzer grating; and an x-ray detector, where a single arrangement of the beam shaping assembly, the x-ray grating interferometer and a position of the detector is configured to provide spectral information (e.g. at least two images obtained at different relative beam energies).
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
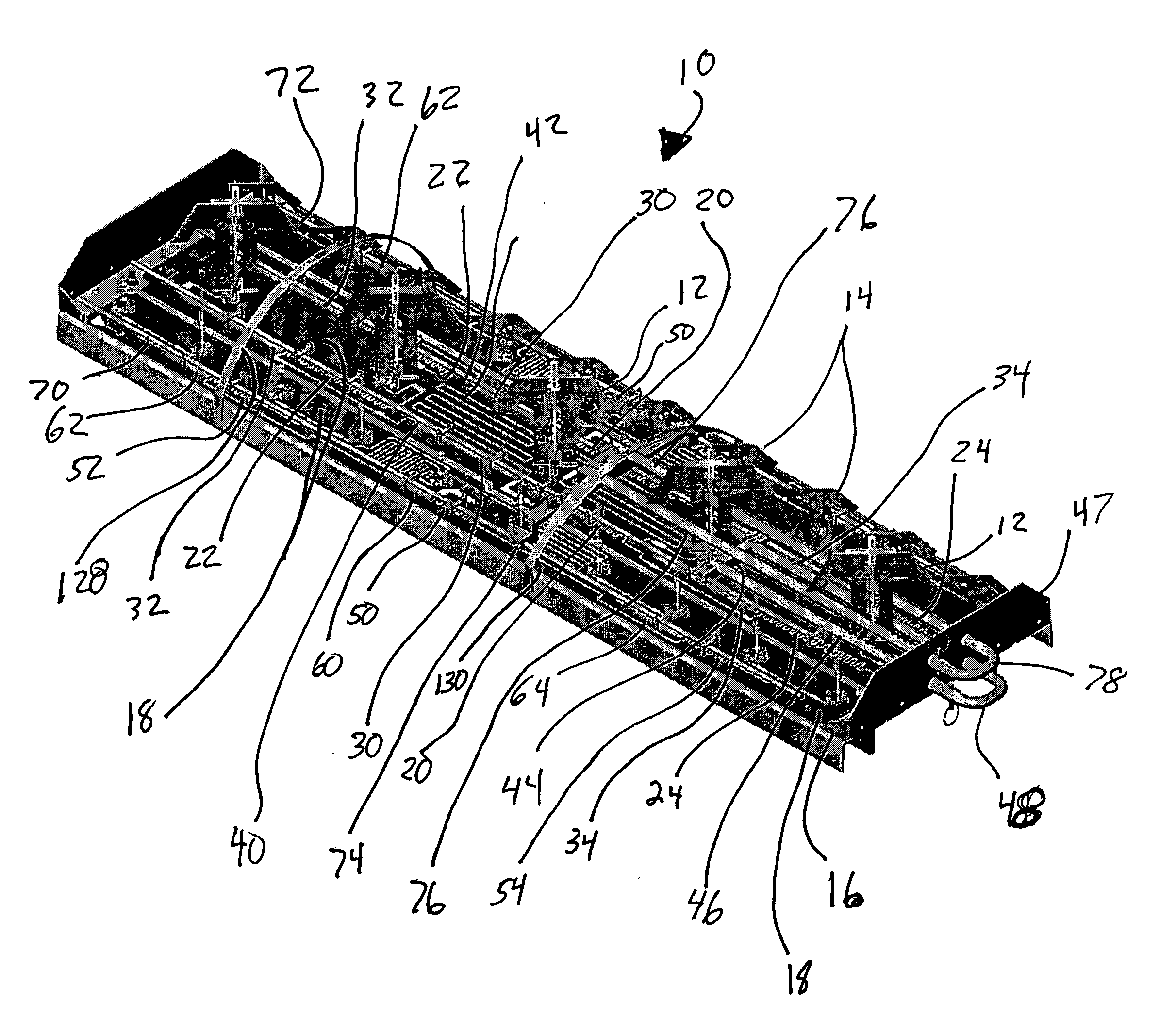
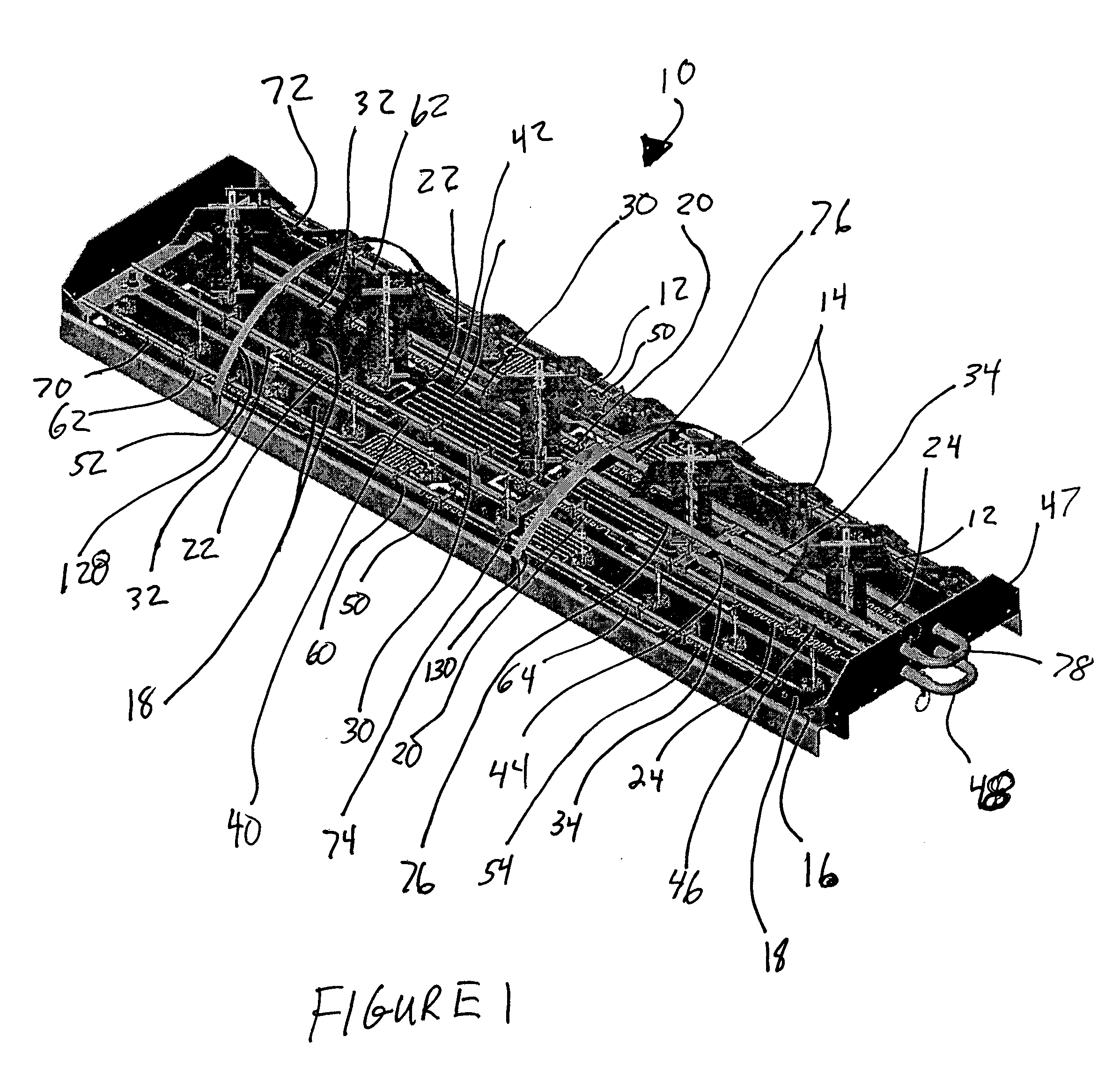
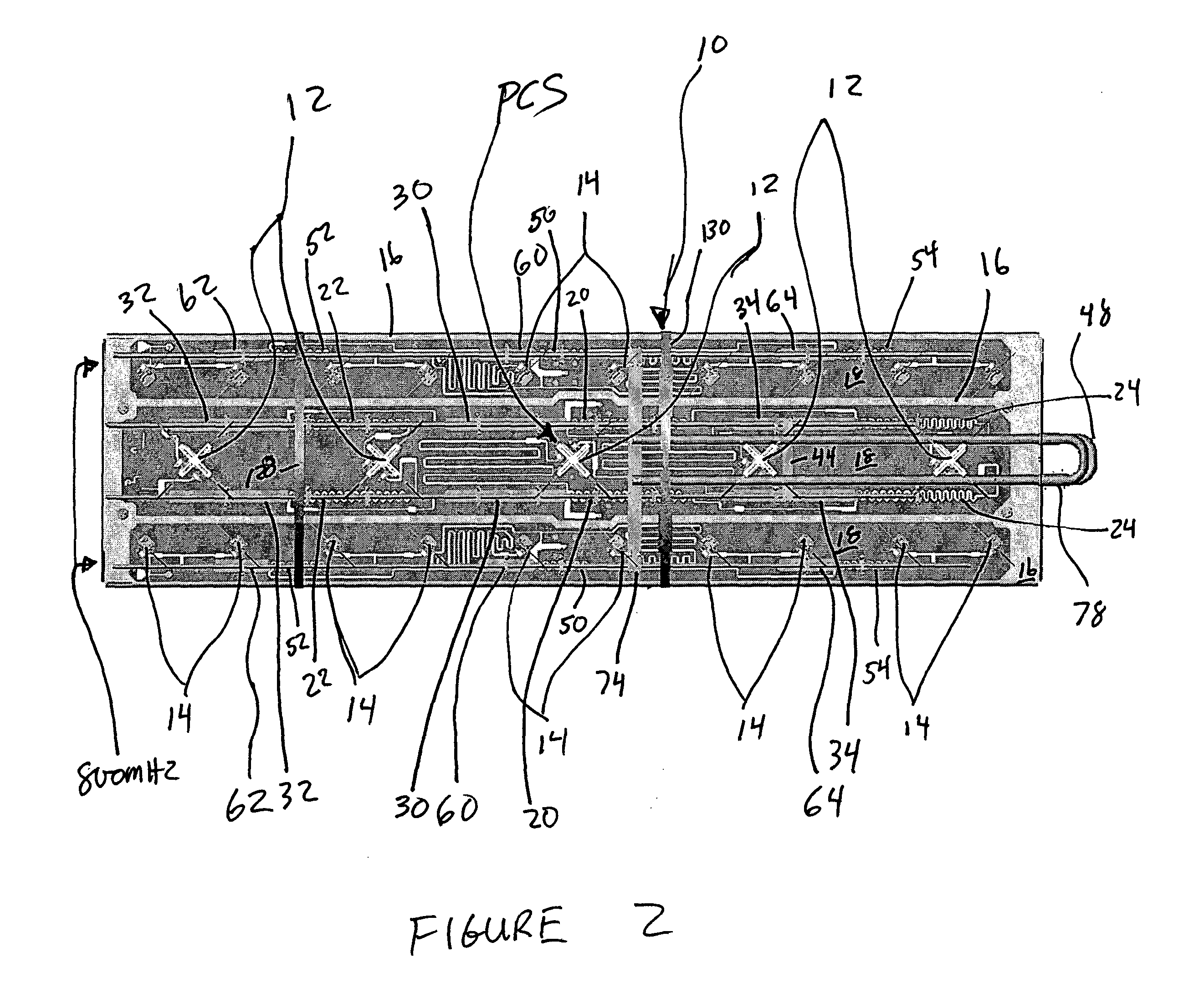
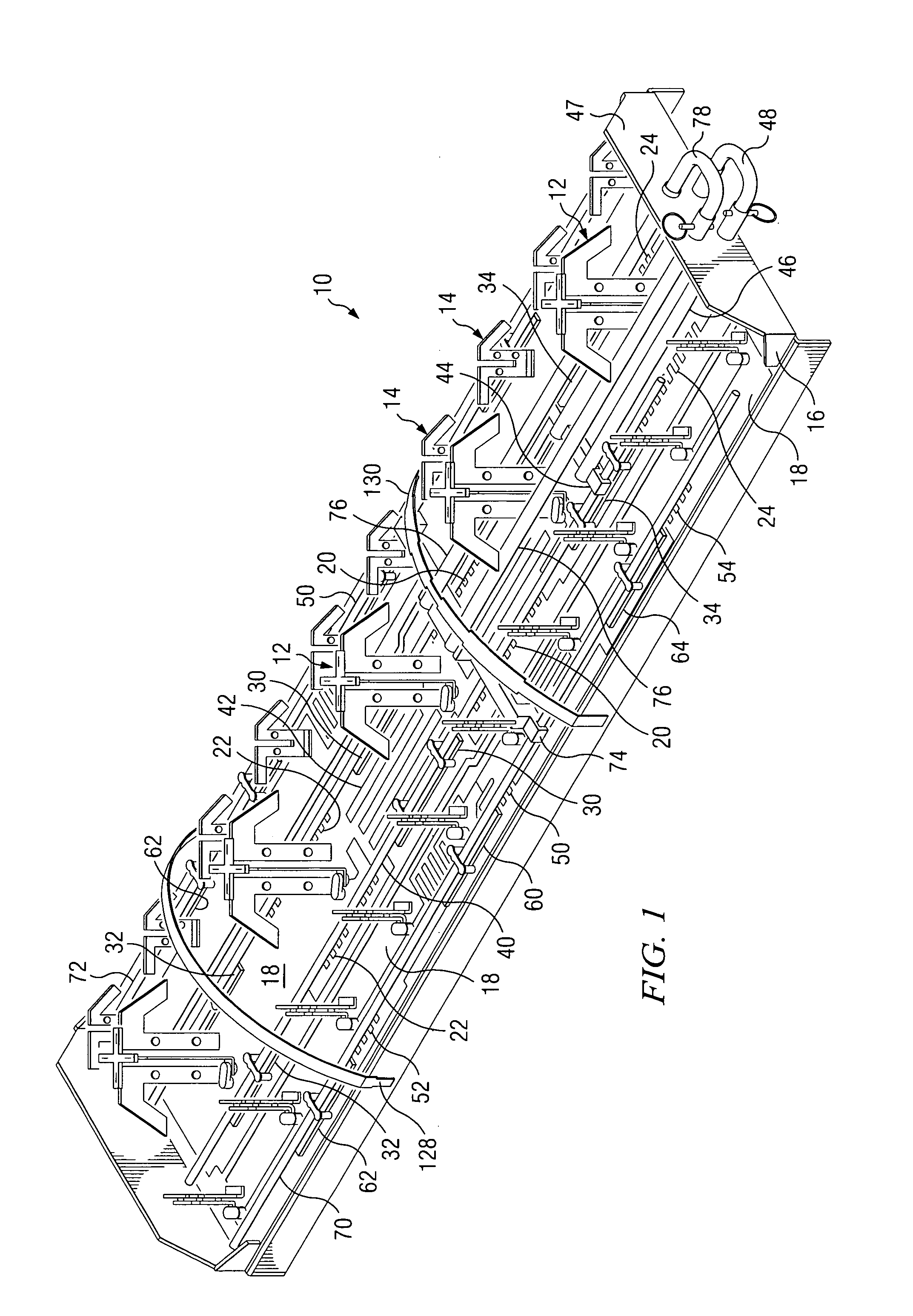
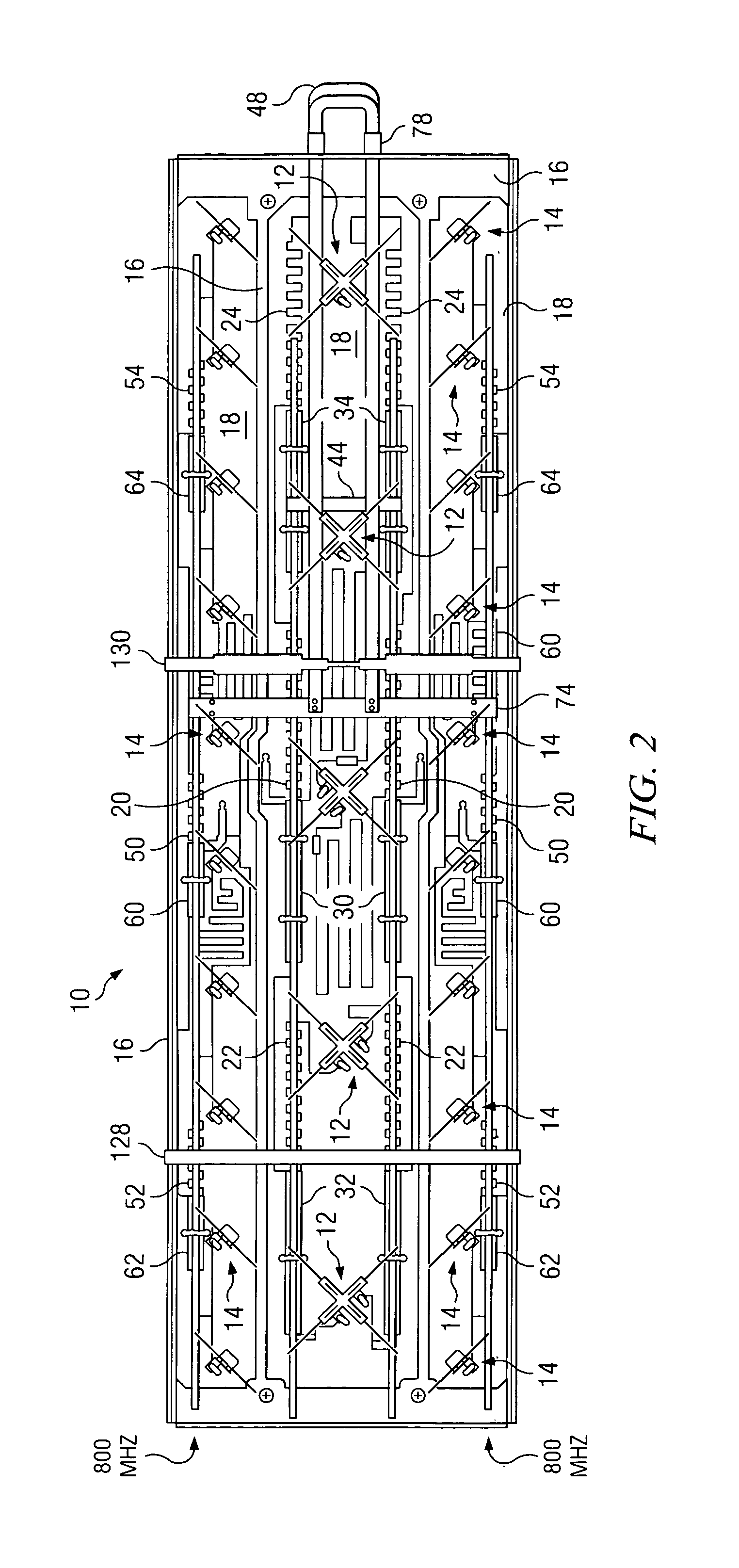
Dual band, dual pol, 90 degree azimuth BW, variable downtilt antenna
InactiveUS20050057417A1Uniform phase shift and downtiltUniform adjustmentAntenna supports/mountingsPolarised antenna unit combinationsDielectricCapacitance
A dual band, dual pol, variable downtilt, 90 degree azimuth beamwidth antenna (10). The antenna includes dipole elements (12, 14) forming both a PCS band and a cellular band antenna. The PCS band antenna has two sections disposed each side of the cellular band antenna, the elements of each being positioned 90° with respect to the other. A microstrip feed network formed upon a common PC board (18) feeds the respective dipole elements, and has serpentine portions with a corresponding dielectric member slideable thereover to establish the phase of the associated dipole antennas and achieve a linear downtilt of the respective antenna array. A slide rod adjustment assembly (100) provides unitary movement of the dielectric members between two different slide rods. These dielectric members are secured with adhesive to the respective slide rods to achieve good dielectric control and no use of hardware. The radiating dipole elements are capacitively coupled to each microstrip, and are also capacitively associated reflector element. One arm of the reflector element is offset at least 45 degrees with respect to the other arm to improve cross polarization.
Owner:ALLEN TELECOM LLC
Dual band, dual pole, 90 degree azimuth BW, variable downtilt antenna
InactiveUS7173572B2Uniform phase shift and downtiltUniform adjustmentAntenna supports/mountingsIndividually energised antenna arraysCapacitanceDielectric
Owner:ALLEN TELECOM LLC
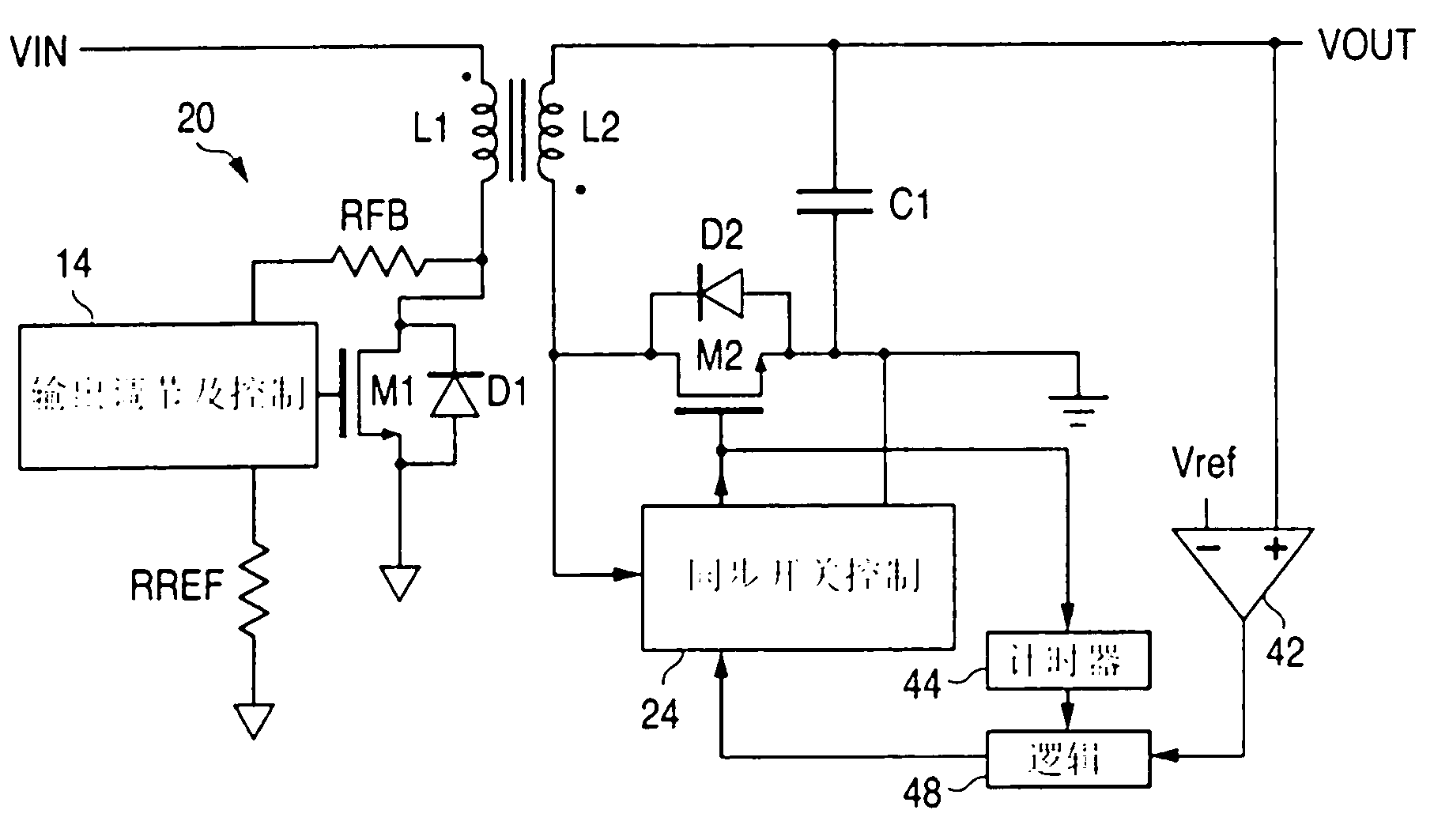
Flyback converter with primary side voltage sensing and overvoltage protection during low load operation
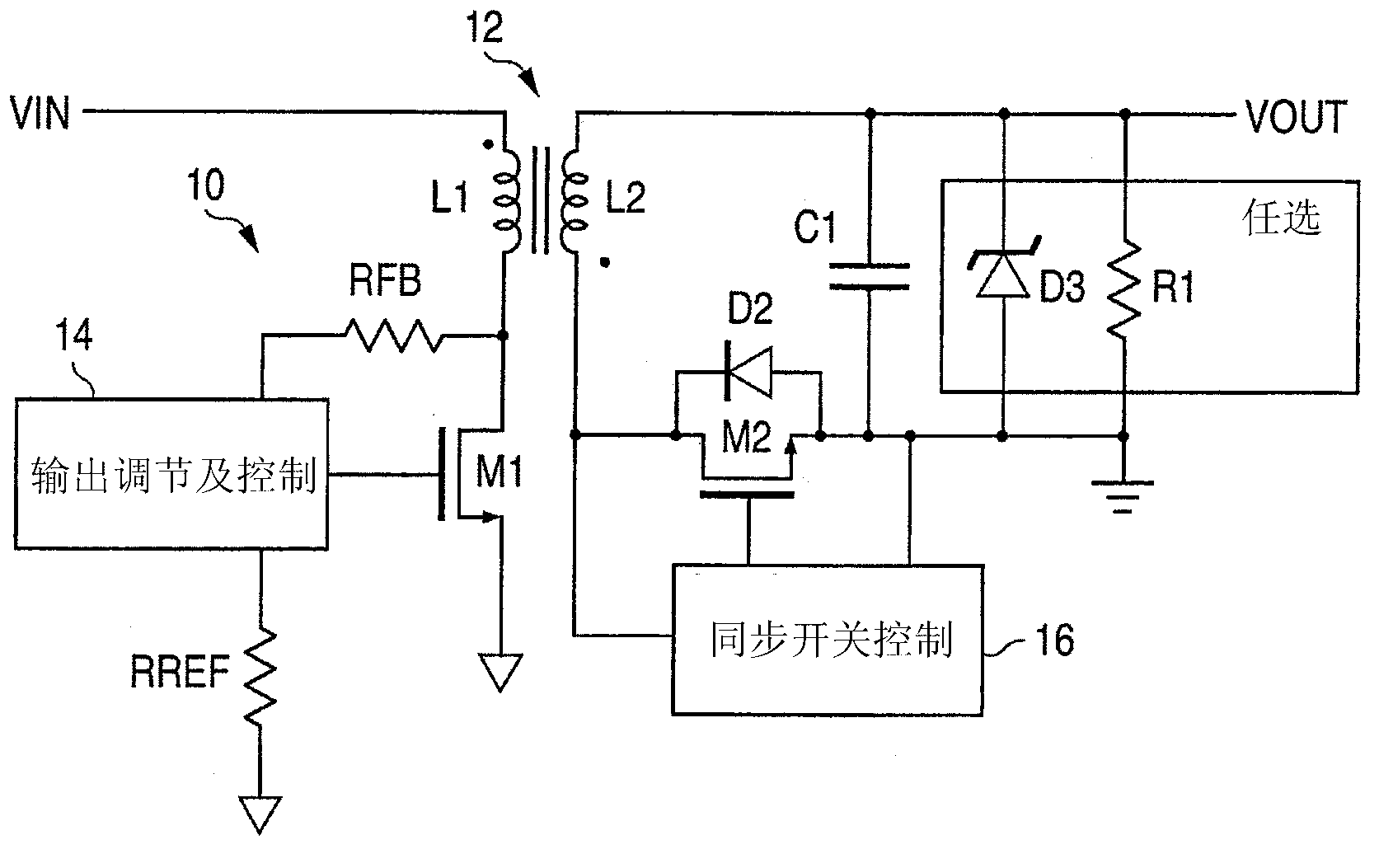
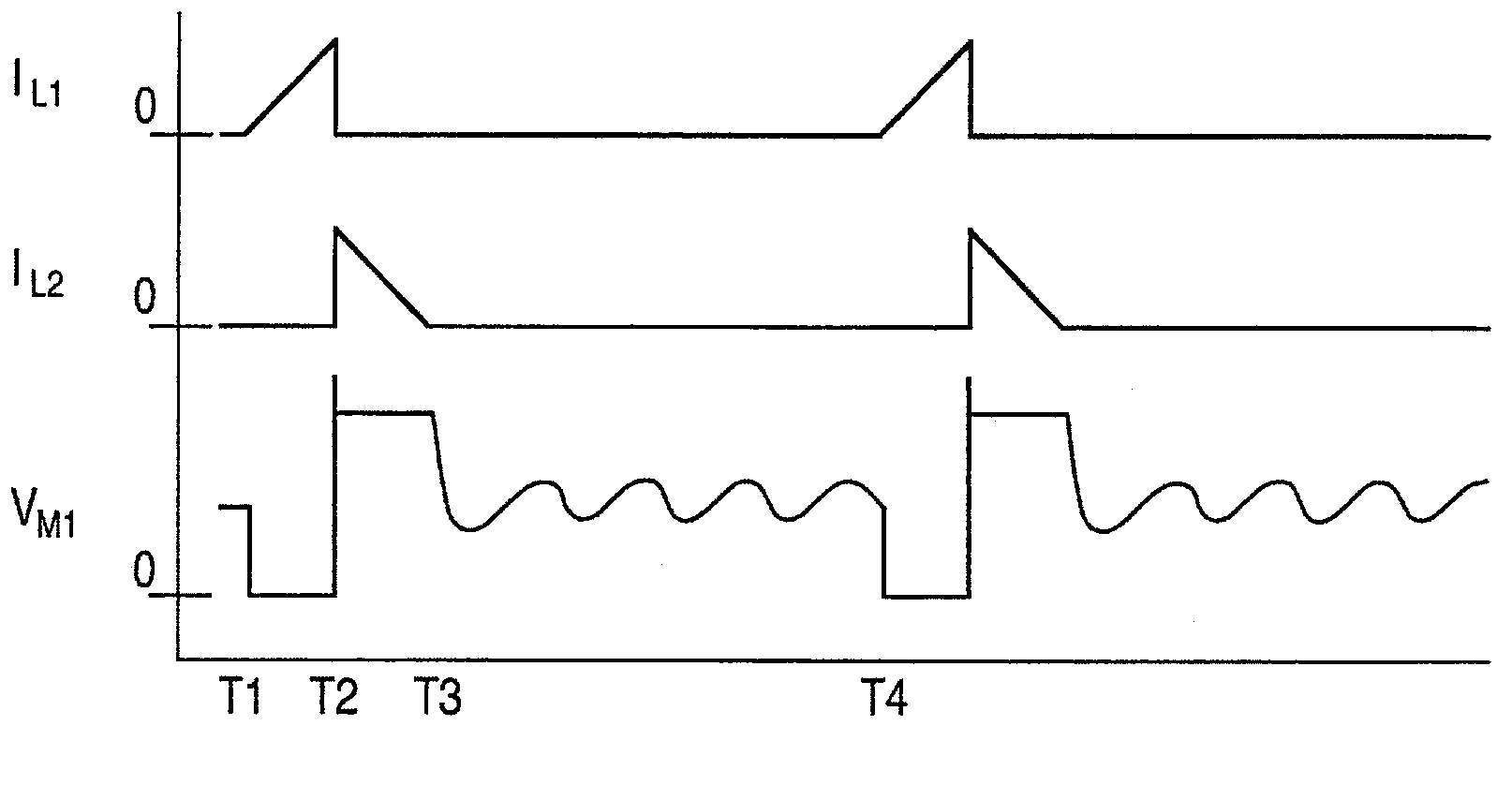
A flyback converter (20) uses primary side sensing to sense the output voltage for regulating feedback. The flyback converter comprises a transformer with a primary winding (L1) and a secondary winding (L2), a first transistor (M1) coupled to the primary winding for conducting a current through the primary winding when the first transistor is on a second transistor (M2) for conducting a current through the secondary winding when the second transistor is on a regulator (14) coupled to the first transistor for controlling a duty cycle of the first transistor to regulate an output voltage of the converter, the regulator being configured to control the first transistor to have a minimum duty cycle, an output capacitor (C1) coupled to an output terminal of the converter, a synchronous rectifier controller (24) coupled to the second transistor for controlling the second transistor to be on or off, a comparator (42) having one input coupled to receive a voltage corresponding to the output voltage of the converter and having another input connected to a reference voltage representing a threshold voltage exceeding a regulated voltage of the converter, wherein triggering of the comparator signifies an over-voltage condition, an output of the comparator being coupled so as to control the synchronous rectifier controller to turn the second transistor on for an interval to conduct a reverse current through the secondary winding, upon an over-voltage condition being detected, to reduce the output voltage of the converter to mitigate the over-voltage condition, and a diode (D1) coupled to the primary winding to conduct a current through the primary winding after the interval without turning on the first transistor, such that power is transferred from a secondary side of the transformer to the power source while mitigating the over-voltage condition.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Low profile quasi-optic phased array antenna
ActiveUS20080278394A1Amplitude weightingNon-resonant long antennasIndividually energised antenna arraysLight beamBeam steering
A phased array antenna device is described. The phased array antenna device includes at least one one-dimensional phased array of radiating elements arranged along an array direction, a lens, and a phase control element. The lens is arranged such that divergent beams from the radiating elements are collimated by the lens in a direction orthogonal to the array direction to produce a beam. The phase control element is configured to apply a linear phase gradient to the radiating elements thereby providing one-dimensional electronic beam steering for the antenna device. The antenna device may additionally include one or two mechanical positioners to mechanically move the at least one one-dimensional phased array in directions orthogonal to the array direction, where the phased array enables scanning along the array direction.
Owner:SMITHS INTERCONNECT INC
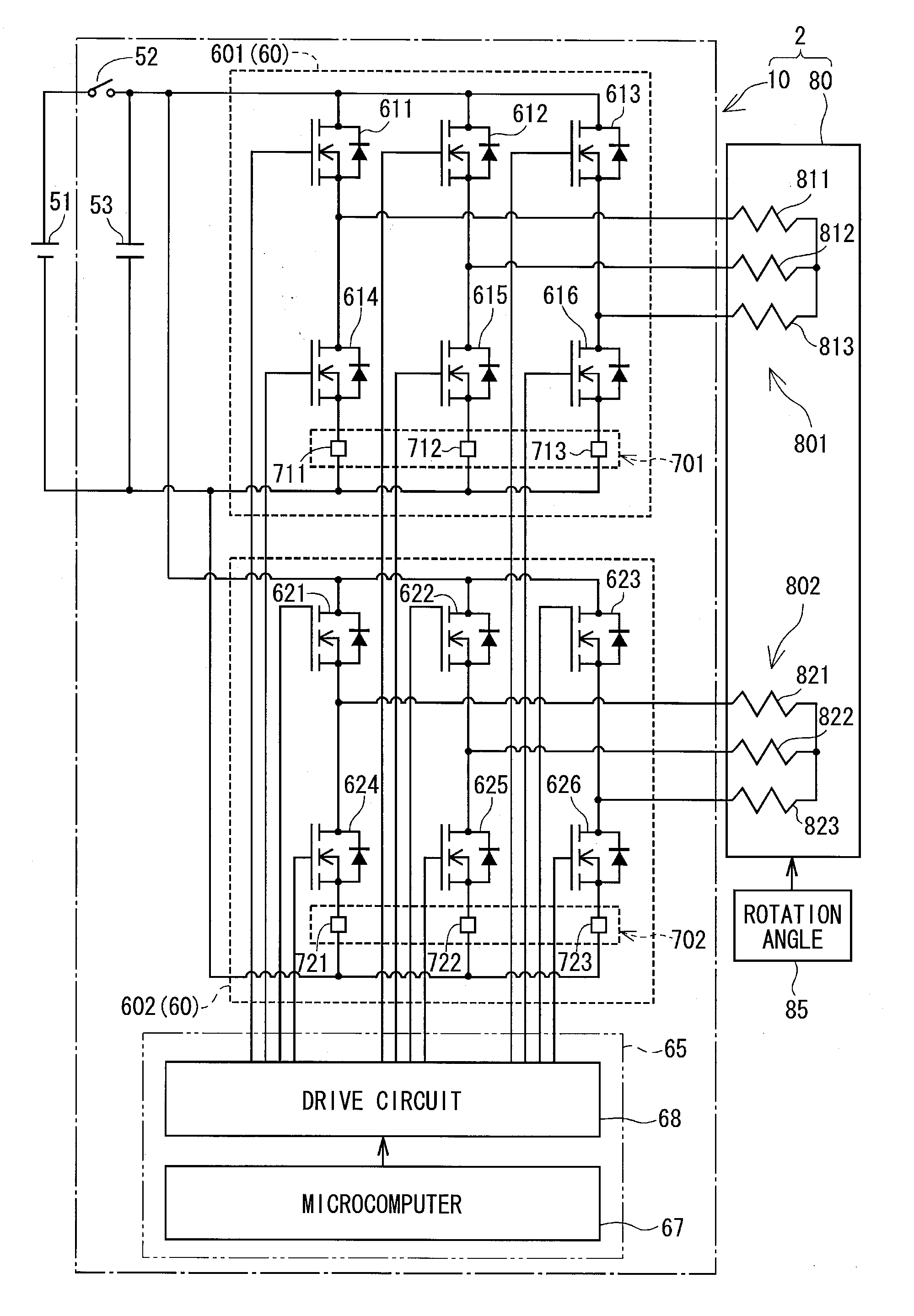
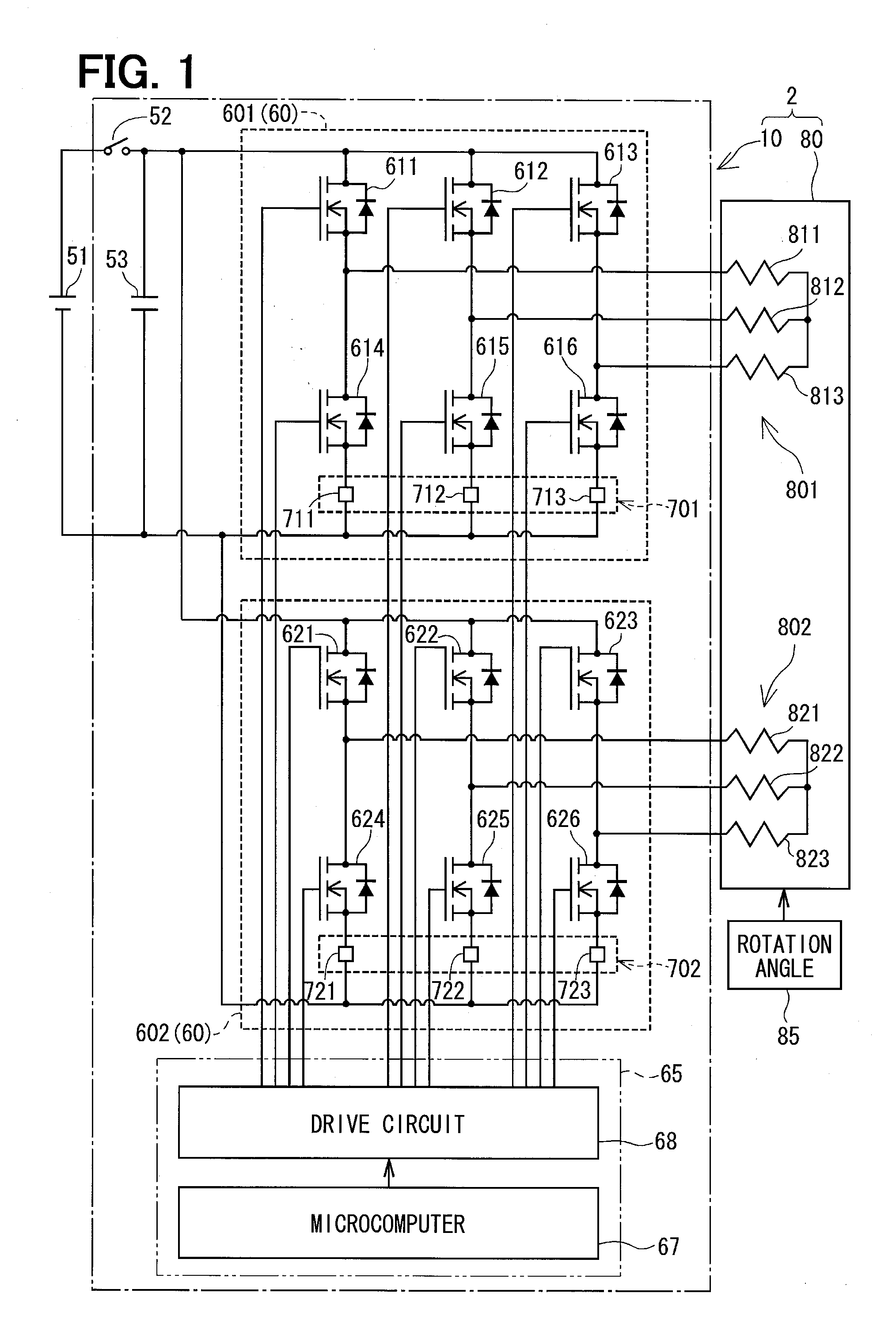
Three-phase rotary machine control apparatus
ActiveUS20130033210A1Suppress torque rippleSuppress overheatSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsPhase currentsThree-phase
A first inverter and a second inverter supply two coil sets forming a three-phase motor with AC voltages, which are the same in amplitude but shifted by 30° in phase. Current detectors detect phase currents supplied from the inverters to the coil sets. Temperature estimation sections estimate temperatures of the inverters or the coil sets based on an integration value of the phase current detection values. A current command value limitation section limits upper limits of current command values of both coil sets based on the estimated temperatures Tm1 and Tm2. Thus, the inverters and the coils sets are protected from overheating without increasing torque ripple.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Liquid crystal waveguide having two or more control voltages for controlling polarized light
A waveguide and method for controllably altering an optical phase delay (OPD) of light traveling along a propagation direction through the waveguide. Many embodiments are disclosed, and in one example, a waveguide may include a core for guiding the light through the waveguide; at least one cladding adjacent the core, wherein the at least one cladding has liquid crystal molecules disposed therein; at least one electrode for receiving a first voltage for controllably altering the optical phase delay of the TE polarized light traveling through the waveguide; and at least one electrode for receiving a second voltage for controllably altering the optical phase delay of the TM polarized light traveling through the waveguide.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Phase center coincident, dual-polarization BAVA radiating elements for UWB ESA apertures
The present disclosure is directed to a dual polarized antenna array including a first BAVA (a horizontal polarization input), a second BAVA (a vertical polarization input), and a cradle assembly. The substrates of the first and second BAVAs each include a notched portion. The cradle assembly includes a base plate having four channel modules connected thereto. Edge portions of the substrates of the first and second BAVAs are received by the cradle assembly via channels of the channel modules and apertures of the base plate. The substrates of the BAVAs are interleaved via their notched portions so that the substrate of the second BAVA is an orthogonal orientation relative to the substrate of the first BAVA.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
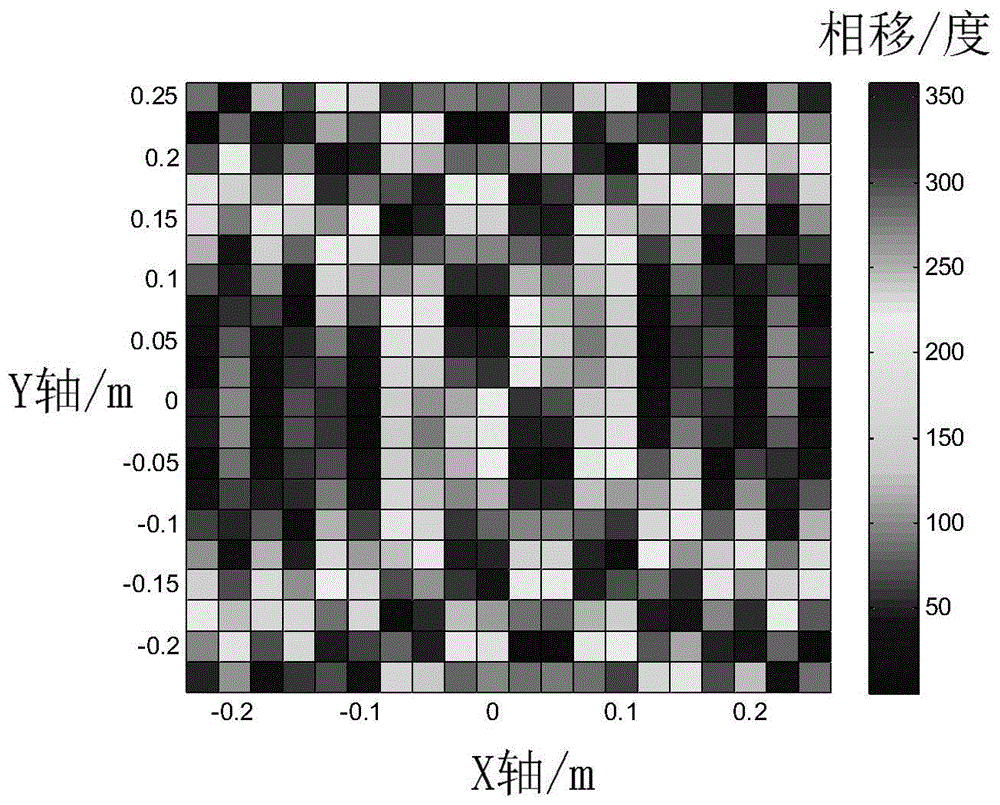
System and method for correcting on-orbit amplitude phase of phased-array antenna
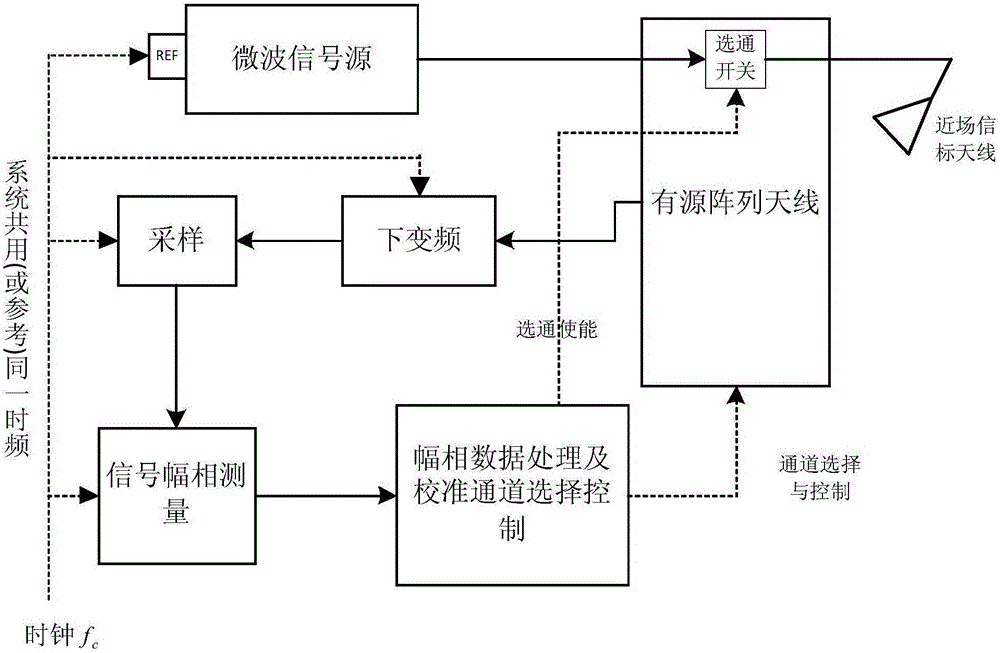
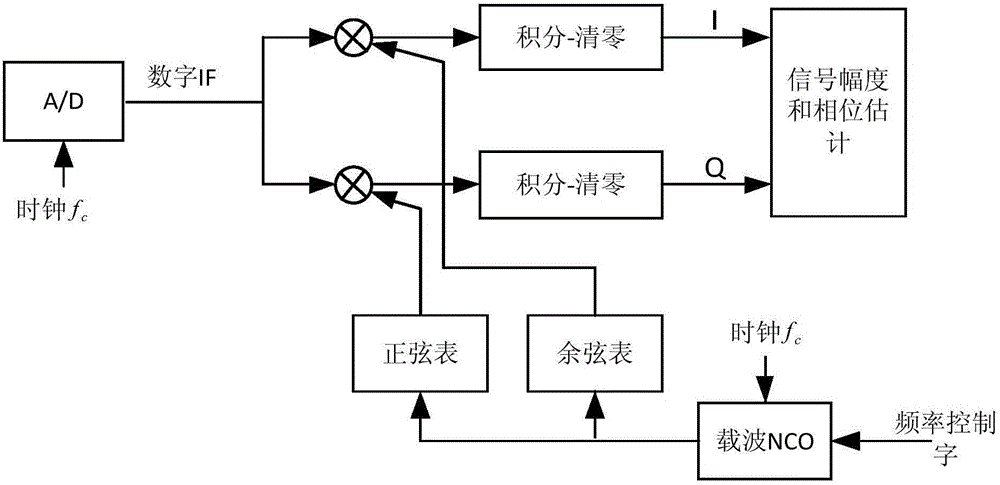
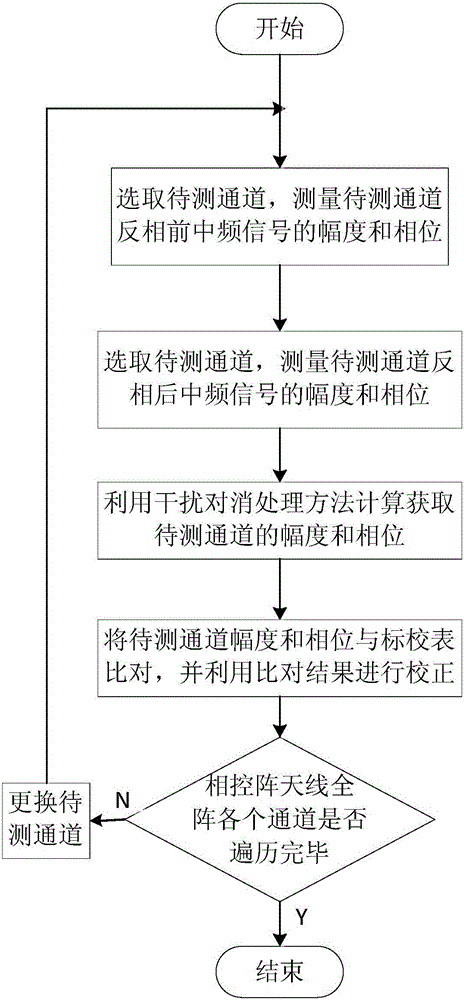
ActiveCN105162536AAchieve gatingSave hardware resourcesPropogation channels monitoringSystem hardwarePhase array antenna
The invention relates to a system and method for correcting an on-orbit amplitude phase of a phased-array antenna. A signal output by a microwave signal source and used for correcting is transmitted through a beacon antenna in a phased-array near field and received by a certain channel to be detected of the phased-array antenna; the output signal is subjected to down-conversion and AD acquisition; amplitude and phase measurement of the signal can be completed through a signal processing module; finally, the measured amplitude and phase of the signal are subjected to data processing; obtaining of the amplitude and the phase of the channel to be detected is completed; and amplitude phase correction is completed. According to the invention, on the basis of the beacon in the phased-array near field, with the help of an interference cancellation principle, the amplitude phase measurement influence to the channel to be detected by leaking (multipath) signals can be eliminated; the accuracy of a measurement result is increased; the implementation principle is simple; system software resources are saved; in the aspect of implementing amplitude phase measurement, a single-channel amplitude phase measurement scheme is selected and used; an auxiliary reference channel is not adopted; and thus, system hardware resources and the cost are saved.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Wireless power supply apparatus
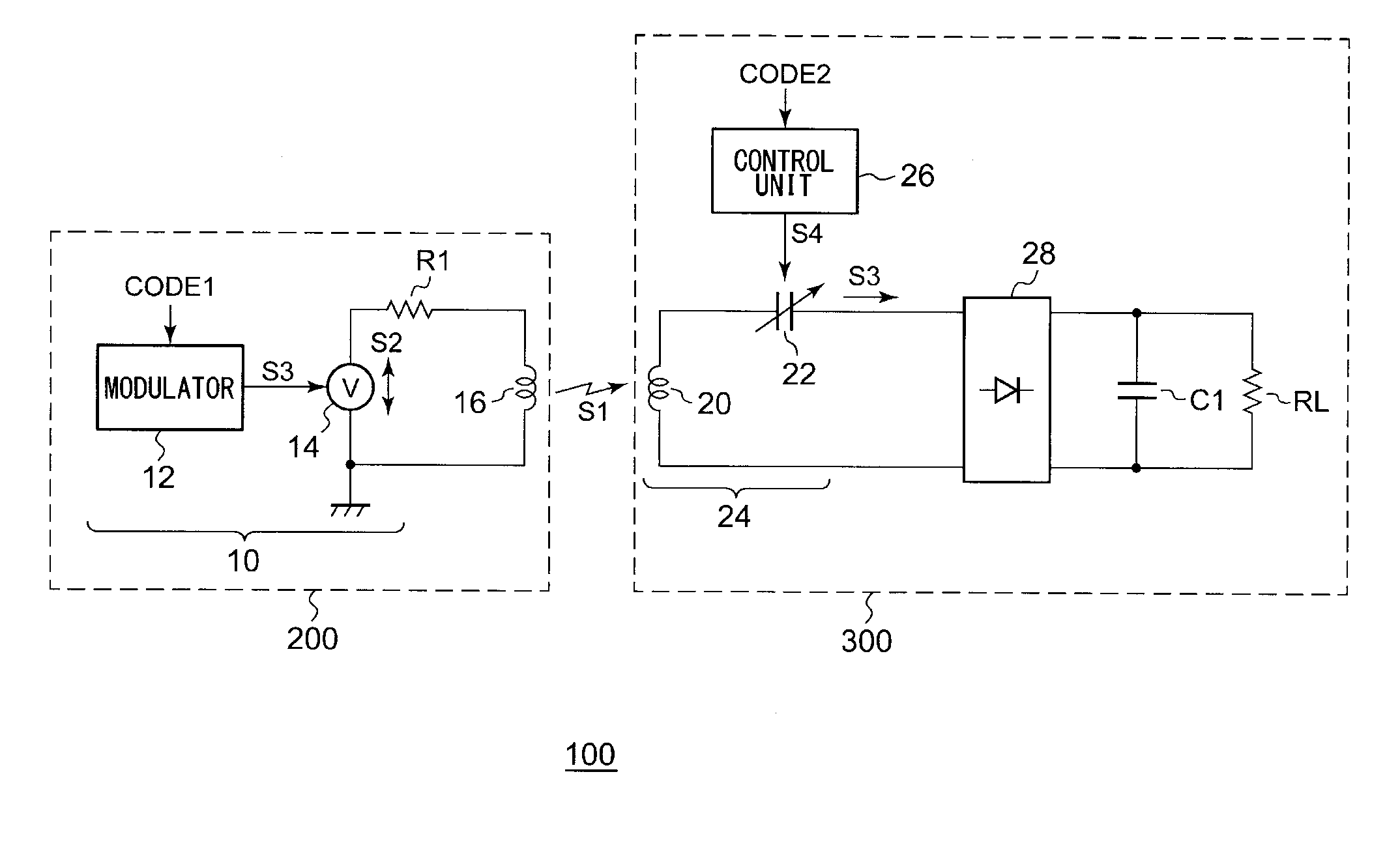
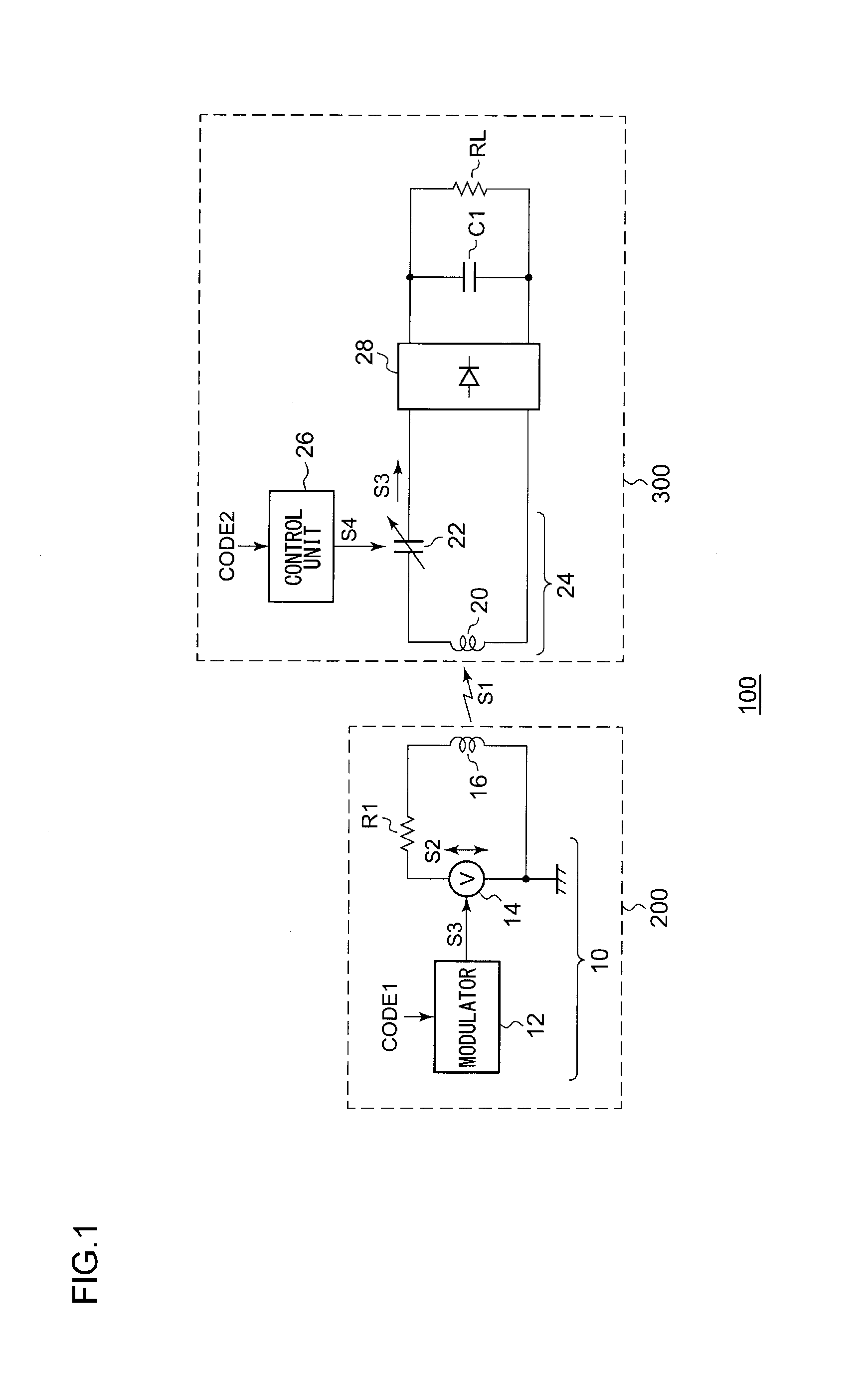
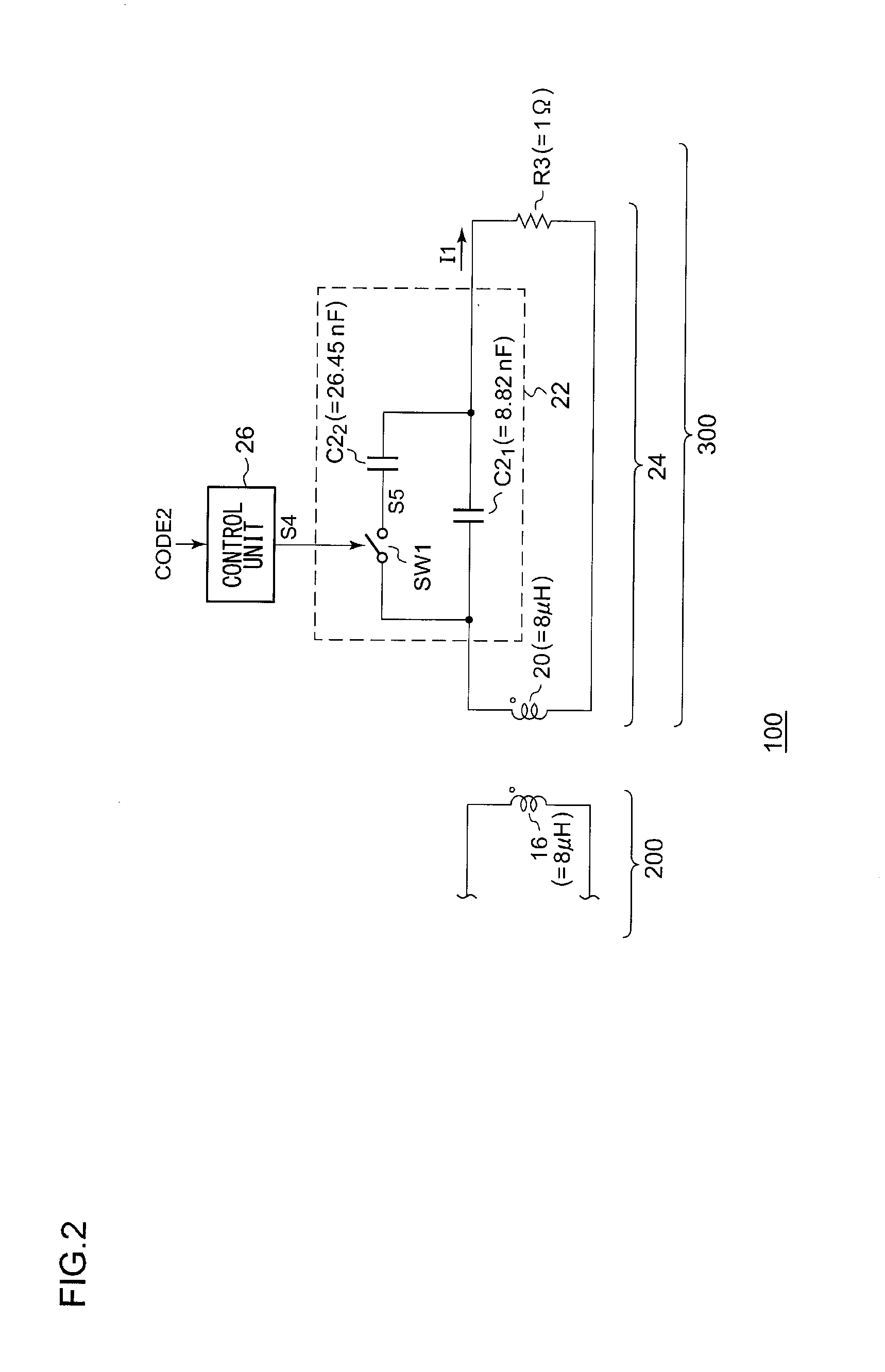
ActiveUS20110235800A1Near-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemEngineeringElectromagnetic field
A wireless power supply apparatus generates an electric signal frequency-modulated or otherwise phase-modulated according to a transmission-side code that is determined beforehand with a wireless power reception apparatus. The electric signal thus generated is transmitted via a transmission coil so as to generate an electric power signal including any one of an electric field, a magnetic field, and an electromagnetic field. The wireless power reception apparatus receives the electric power signal using a reception coil. A control unit changes the impedance of a resonance circuit that comprises the reception coil and a resonance capacitor, according to a reception-side code that is to correspond to the transmission-side code.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Method for generating multiple orbital angular momentum beams
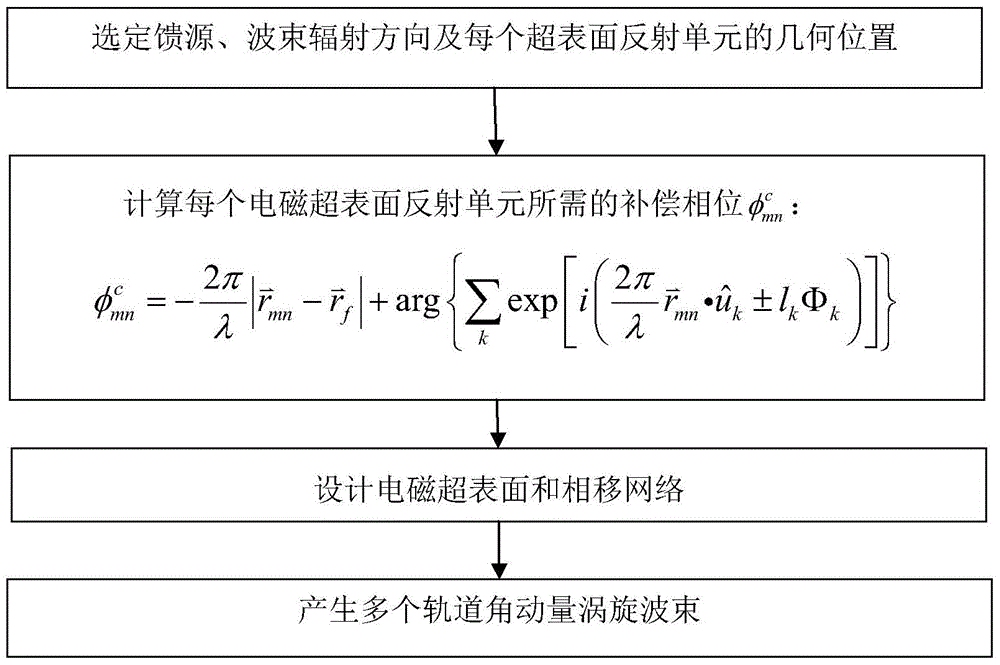
ActiveCN105680162AReduce lossImprove radiation efficiencyRadiating elements structural formsWavefrontMomentum
The invention discloses a method for generating multiple orbital angular momentum beams, and mainly aims at solving the problems that multiple orbital angular momentum vortex beams which radiate towards different directions and are the same or different in mode number cannot be simultaneously generated under a single working frequency in the prior art. According to the implementation scheme, the method comprises the following steps: selecting a feed source, a wave beam radiation direction and a geometric position of each reflecting unit; calculating a compensation phase matrix required by each super-surface reflecting unit according to the geometric position, the working frequency and the required orbital angular momentum mode; selecting electromagnetic super-surface units with different sizes to design a phase-shift network; putting the feed source at the central axial position of the electromagnetic super-surface and making an incident wave sent out from the feed source radiate the electromagnetic super-surface to obtain a compensation phase provided by the phase-shift network; and generating multiple orbital angular momentum vortex beams with vortex wavefronts in the set direction. The method can effectively improve the capacity and the coverage area of an orbital angular momentum wireless communication system and is used for modulating and multiplexing different signals in the wireless communication system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Metamaterials and Acoustic Lenses in Haptic Systems
The properties of metamaterials are derived both from the inherent properties of their constituent materials and from the geometrical arrangement of those materials. Metamaterials may be stacked or otherwise manipulated to transform substantially monochromatic signal into a second signal having a desired amplitude and phase. Metamaterials may be used with acoustic devices to create haptic feedback with desired properties or to transform the shape of certain devices. Metamaterials may be used in rotating devices with openings that transform a monochromatic signal into a non-monochromatic signal.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
Inhibition method and device for distance direction blur of multichannel synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
ActiveCN103869313ADistance blur suppressionImprove imaging effectRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTarget signalRadar
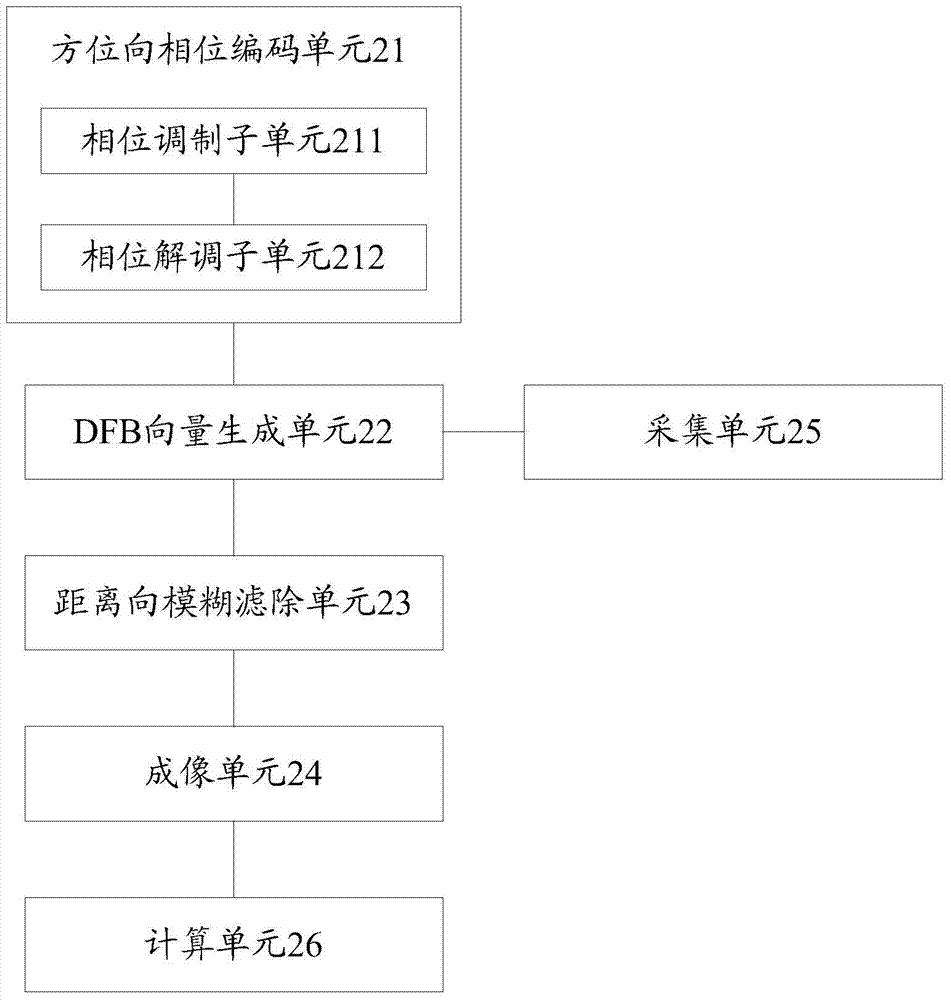
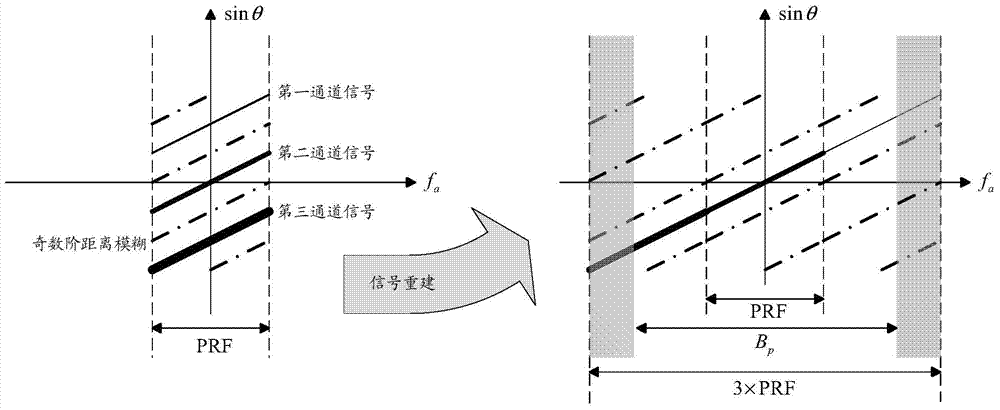
The invention discloses an inhibition method and device for the distance direction blur of a multichannel synthetic aperture radar (SAR). The inhibition method for the distance direction blur of the SAR comprises the steps of performing phase modulation on an emission signal and performing phase demodulation on an echo signal by using azimuth phase coding, so a distance blurred signal and the target signal are separated from each other in the azimuth Doppler domain; generating an azimuth DFB (distributed feed back) vector by using a multichannel collecting signal, and forming zero trap at the position where the distance direction blurred signal is positioned by using the DFB vector so as to filter out the distance direction blur in the target signal; imaging the target signal of which the distance direction blur is filtered out, thus obtaining the target SAR image with the inhibited distance direction blur.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
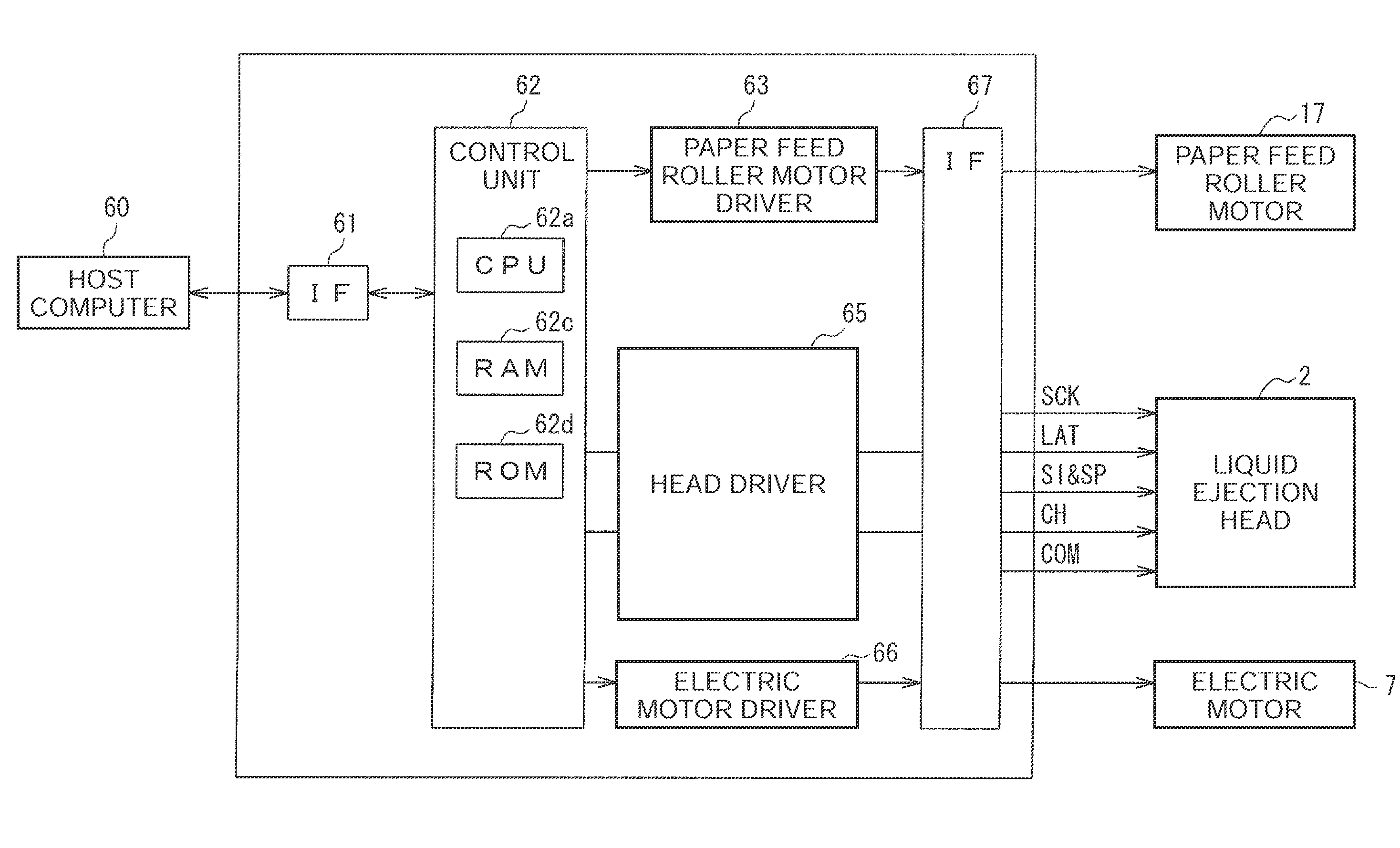
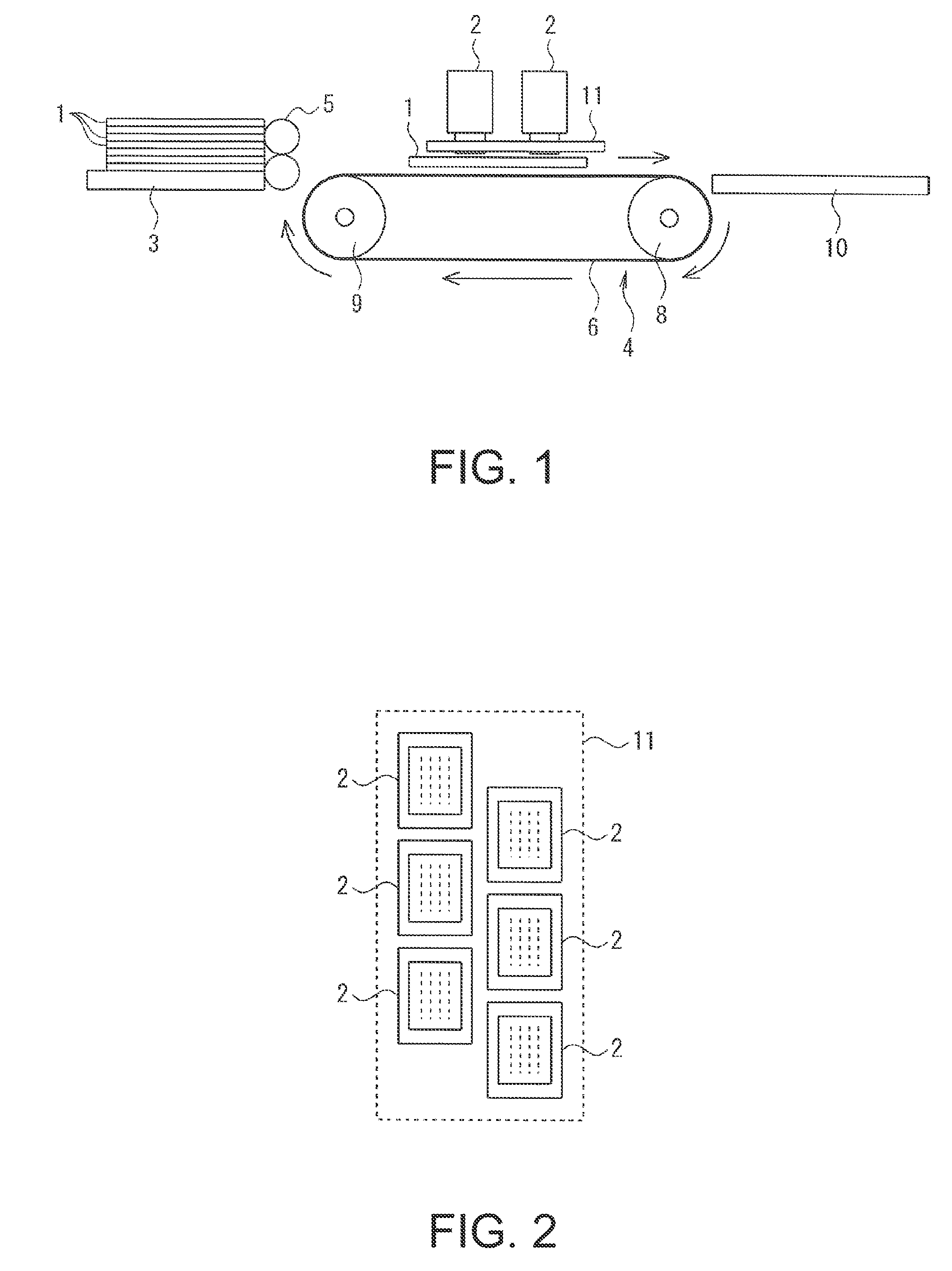
Liquid ejection device and liquid ejection printer
ActiveUS20110109674A1Reduce power lossEliminate needFluid jet surgical cuttersOther printing apparatusNegative feedbackDifferential signaling
A liquid ejection device includes: a drive waveform generator generating a drive waveform signal; a modulator performing pulse modulation on a signal from the drive waveform generator to provide a modulated signal; a digital power amplifier performing power amplification on the modulated signal to provide an amplified digital signal; a Lowpass Filter smoothing the amplified digital signal to provide a drive signal of an actuator; a compensator advancing the phase of the drive signal to provide a negative feedback signal; and a subtractor providing a differential signal between the drive waveform signal and the negative feedback signal as an input signal to the modulator.
Owner:COLUMBIA PEAK VENTURES LLC
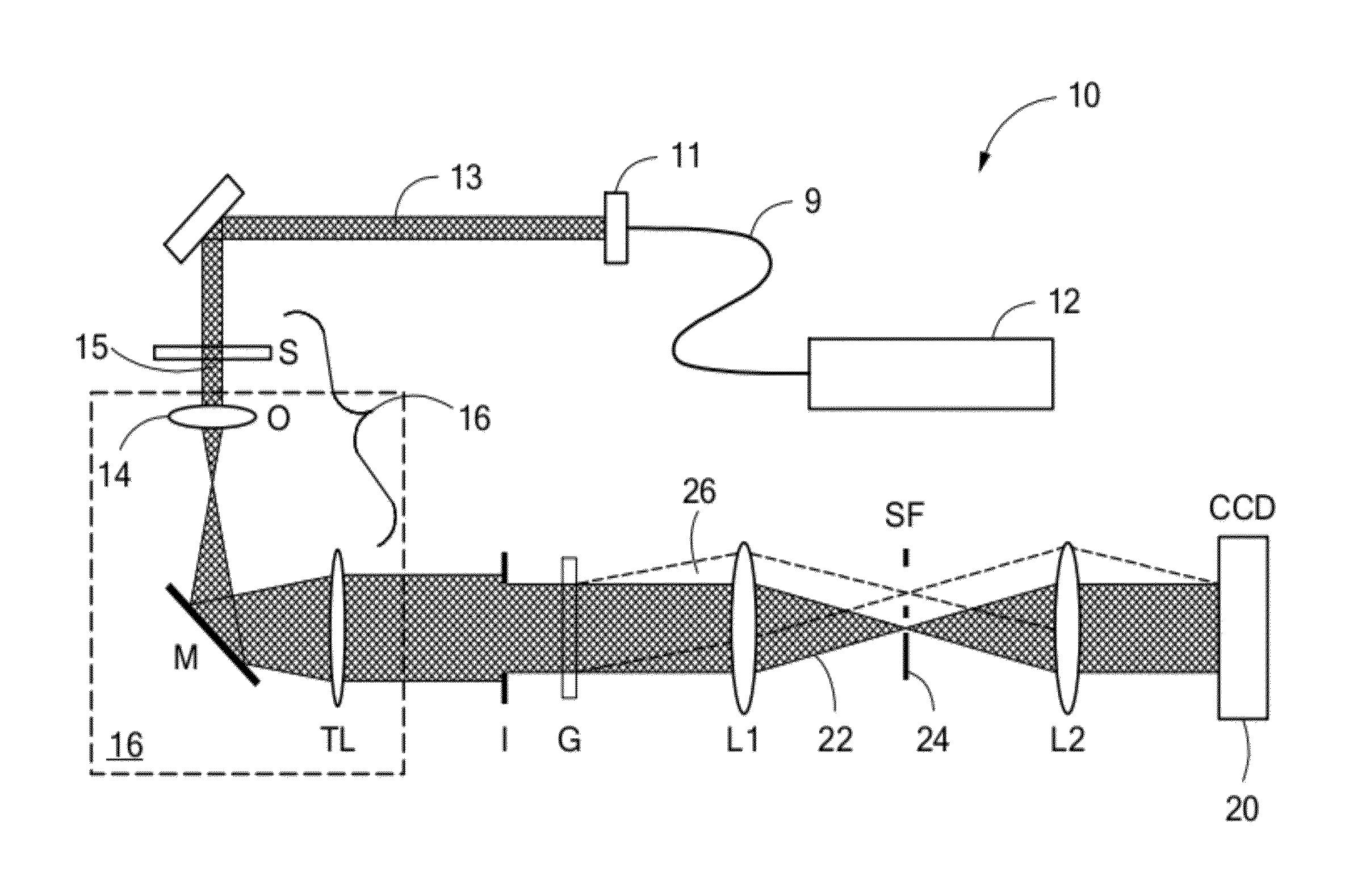
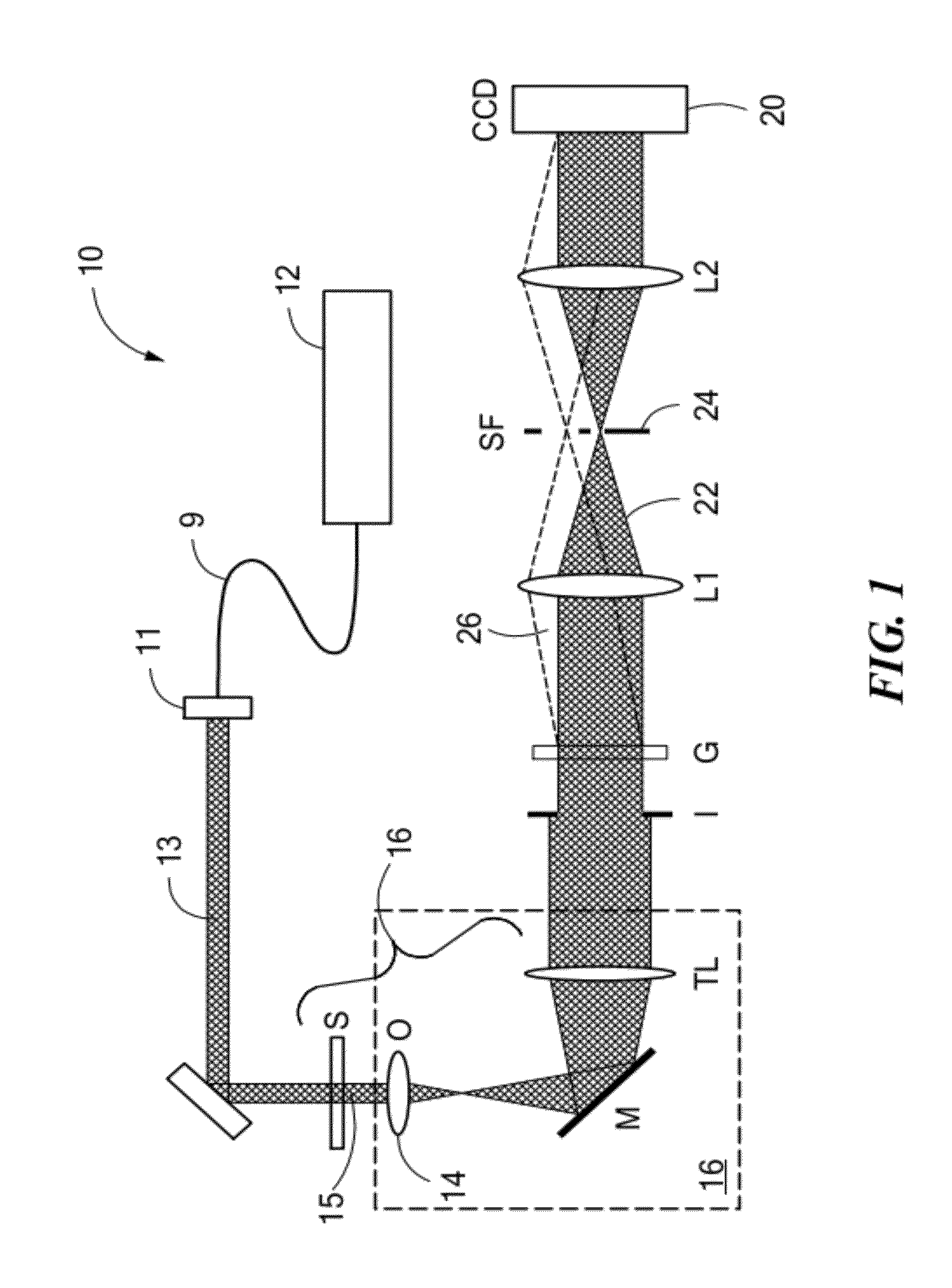
Spatial Light Interference Microscopy and Fourier Transform Light Scattering for Cell and Tissue Characterization
ActiveUS20120105858A1Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFourier opticsFourier transform on finite groups
Methods and apparatus for rendering quantitative phase maps across and through transparent samples. A broadband source is employed in conjunction with an objective, Fourier optics, and a programmable two-dimensional phase modulator to obtain amplitude and phase information in an image plane. Methods, referred to as Fourier transform light scattering (FTLS), measure the angular scattering spectrum of the sample. FTLS combines optical microscopy and light scattering for studying inhomogeneous and dynamic media. FTLS relies on quantifying the optical phase and amplitude associated with a coherent image field and propagating it numerically to the scattering plane. Full angular information, limited only by the microscope objective, is obtained from extremely weak scatterers, such as a single micron-sized particle. A flow cytometer may employ FTLS sorting.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Multi pre-focused annular array for high resolution ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS20020139193A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh resolution ultrasoundSonification
An annular ultrasound bulk wave transducer array for electronic depth steering of symmetric focus from a near focus Fn to a far focus Ff includes elements that are divided into k groups with different fixed prefocusing. The central group participates in beam forming from Fn to Ff, the next outer group in beam forming from Fn1>Fn to Ff, and the kth outer group in beam forming from Fnk>Fn,k-1 to Ff. The fixed focus for the kth group is selected at Fk between Fnk and Ff. In this manner, beam formation close to Fn is performed only by the central group. By steering the focus outward from Fn, the focal diameter increases and, at a depth where the focal diameter exceeds a limit, the next outer group of elements is included in beam formation. This increase in aperture area reduces the focal diameter with subsequent increases in diameter as the focus is further steered toward Ff. In the same manner, the kth group of elements is included in beam formation for steered foci deeper than Fnk, presenting a growing aperture that enables maintenance of tae diameter below limits with a low total number of elements and avoids impractically small widths of the annular elements. The elements may also be subdivided in the angular direction, allowing for phase aberration correction.
Owner:PREXION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com