Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Temporal succession" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Temporal succession. Cosmic time differentiates the supratemporal totality into a diversity of aspects. These aspects are experienced in a cosmic order of earlier and later. The earlier aspects “found” the later aspects.
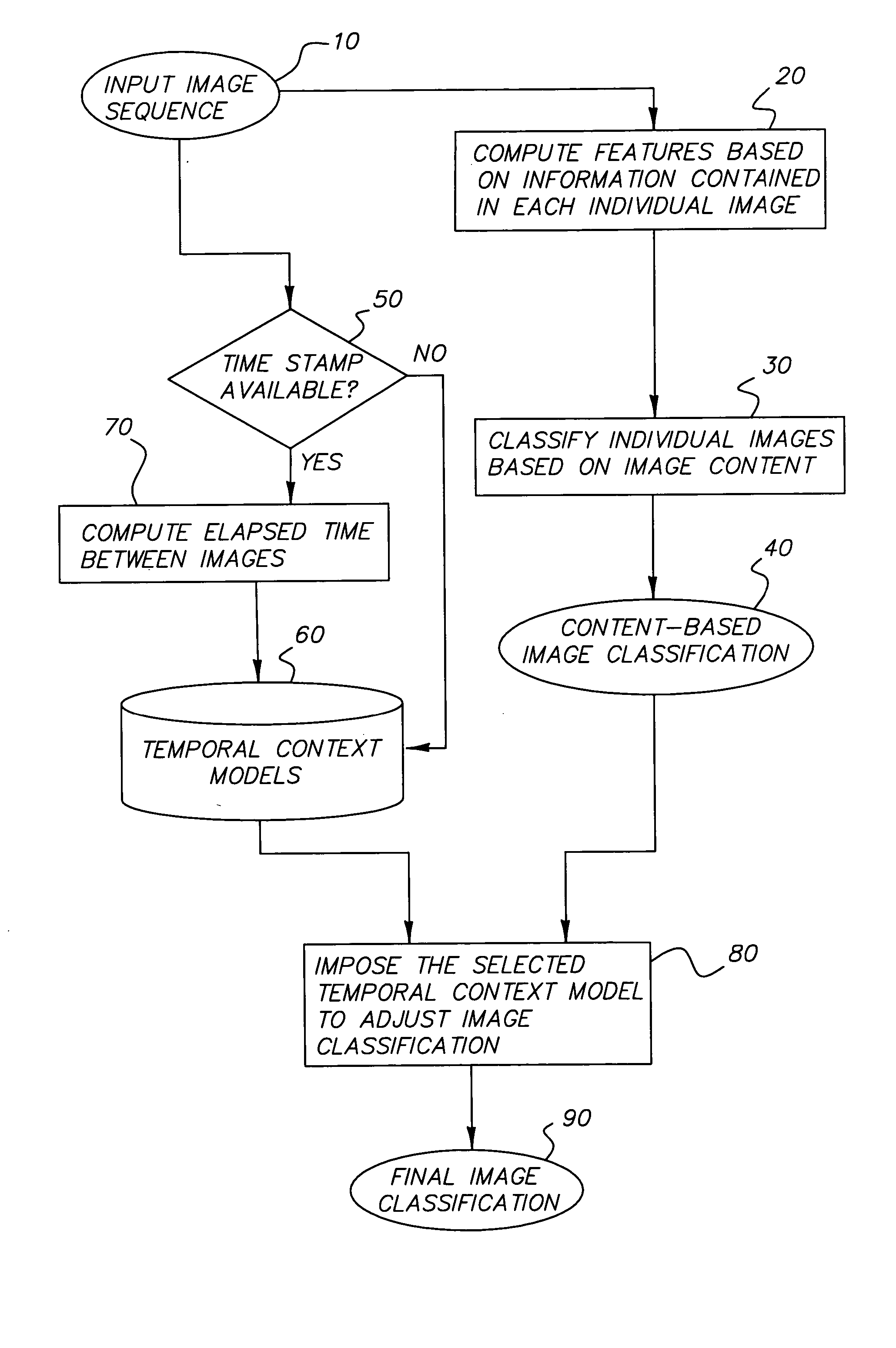
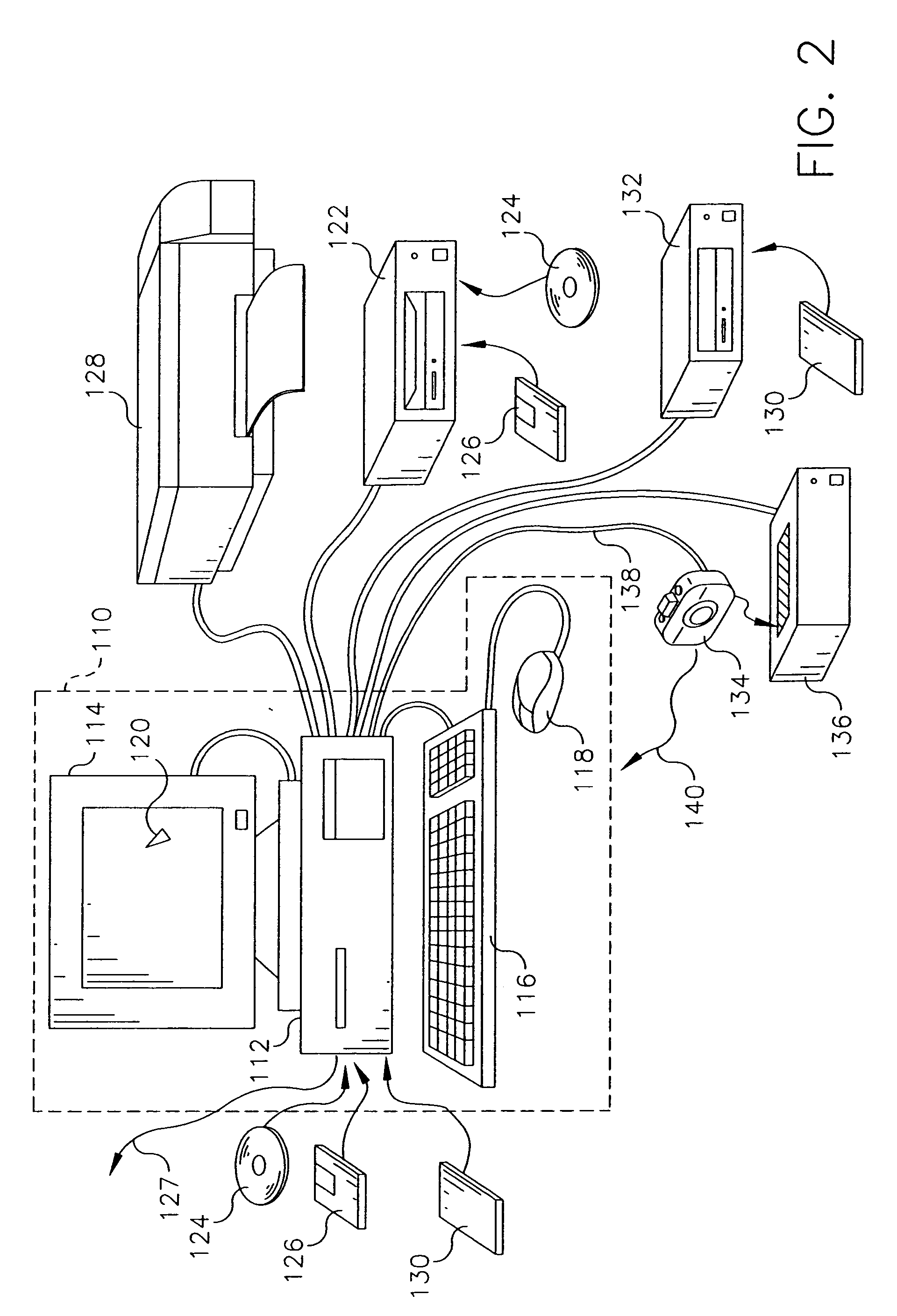
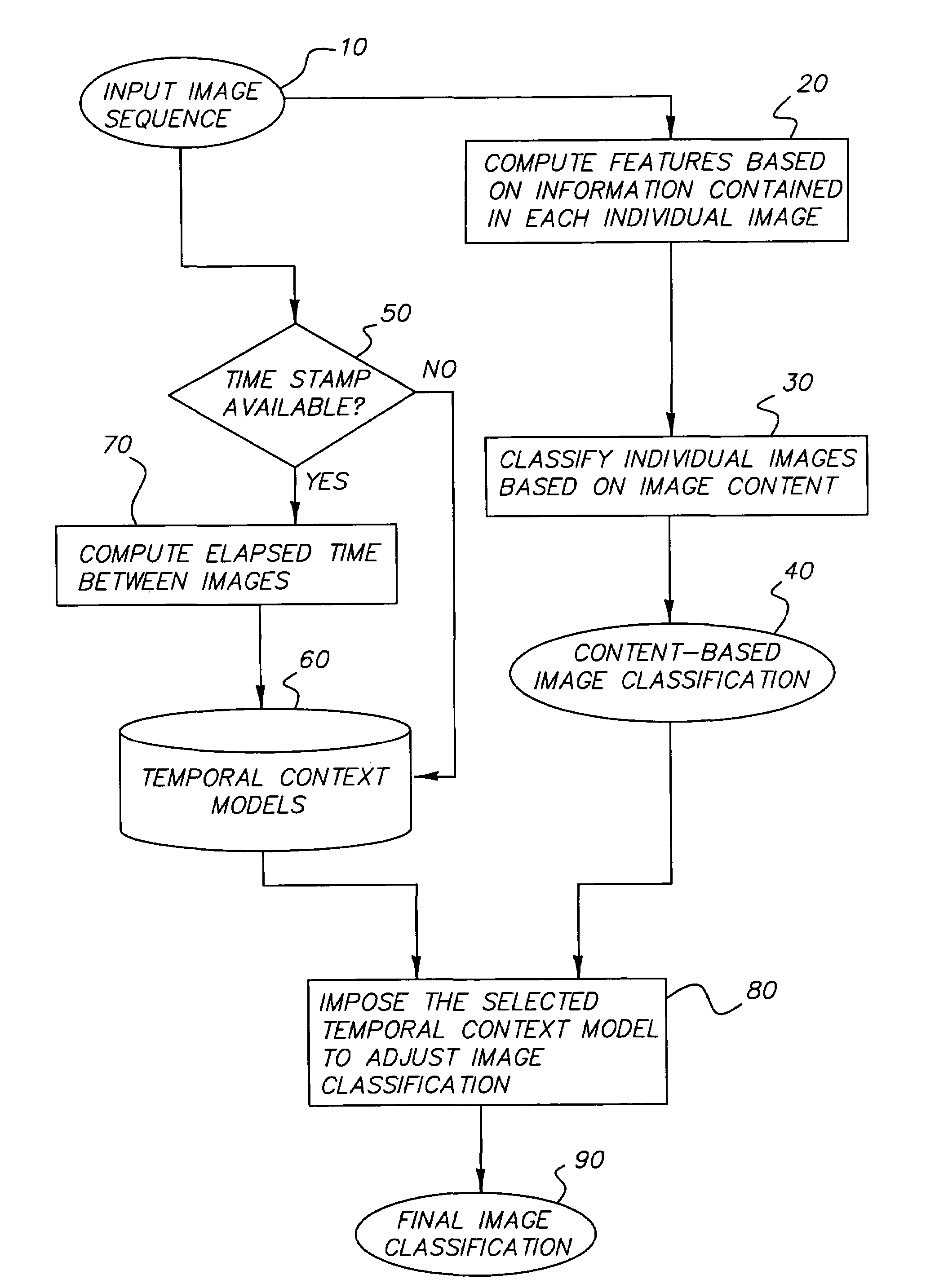
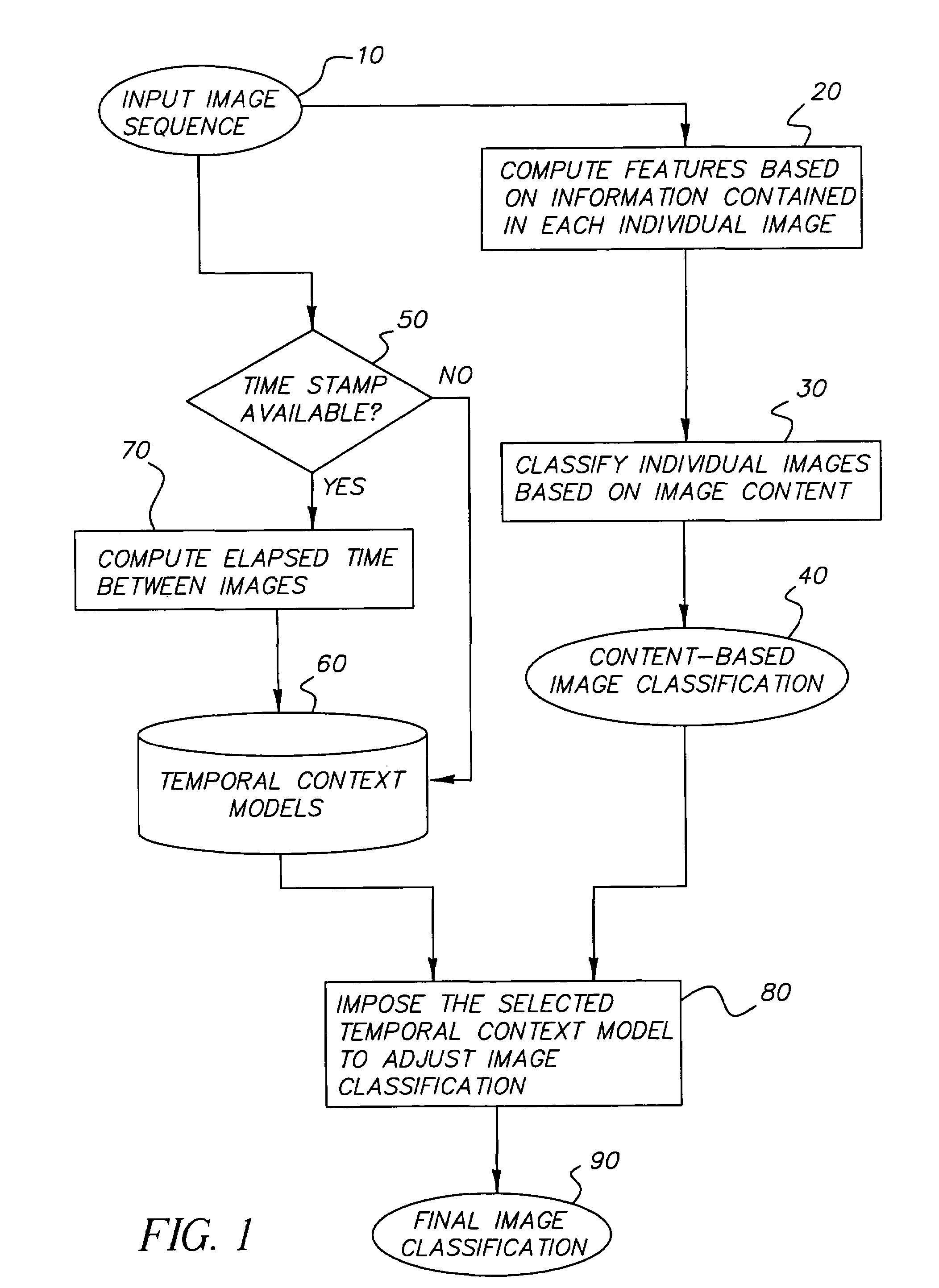
Method of using temporal context for image classification
ActiveUS20050105775A1Improving Image Classification AccuracyCorrect mistakesDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionTemporal context
A method improving scene classification of a sequence of digital images comprising the steps of: (a) providing a sequence of images captured in temporal succession; (b) classifying each of the images individually based on information contained in the image alone to generate a first image classification; and (c) imposing a pre-determined temporal context model on the sequence of images to generate a final image classification for each image in the sequence.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
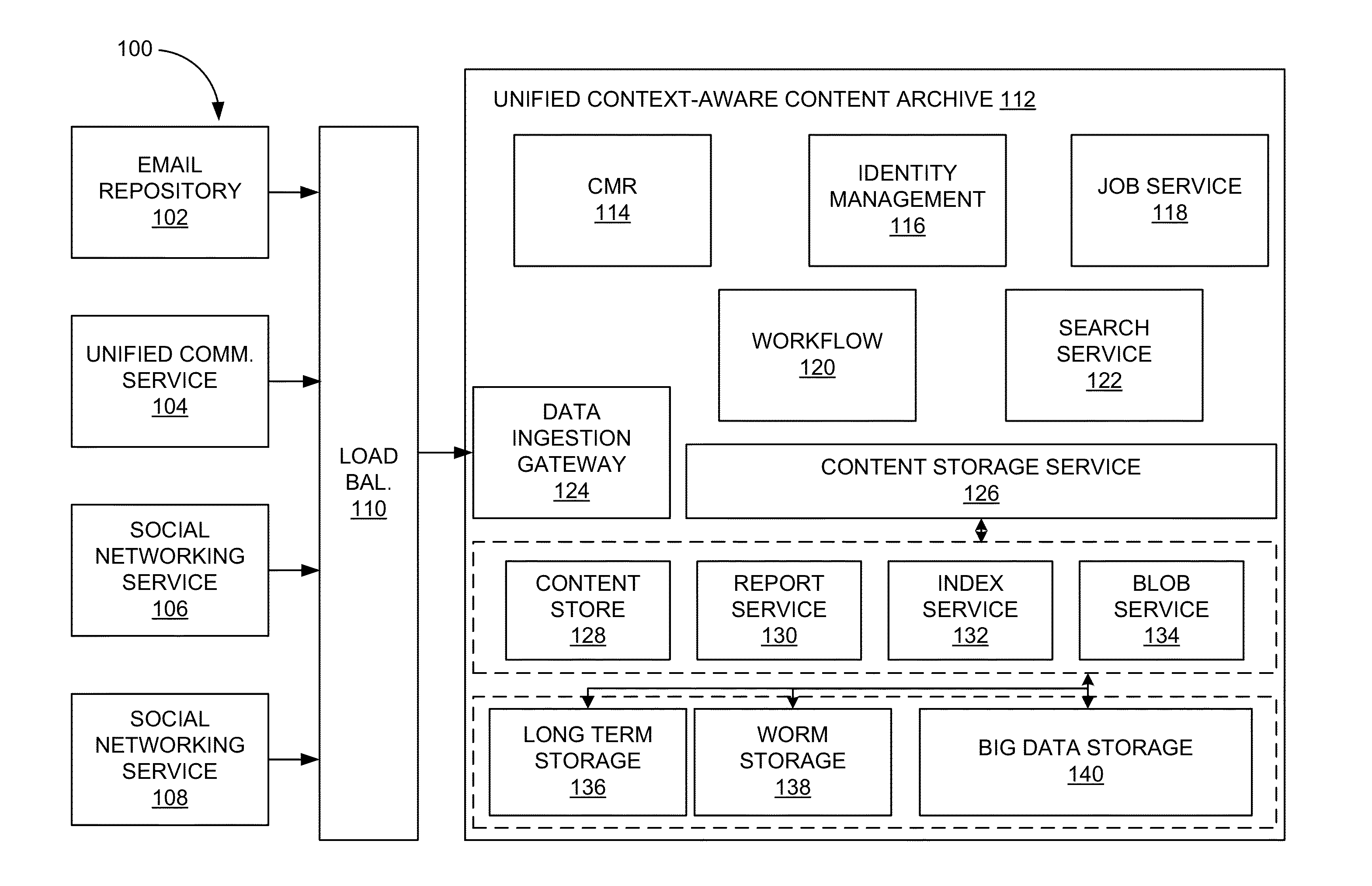
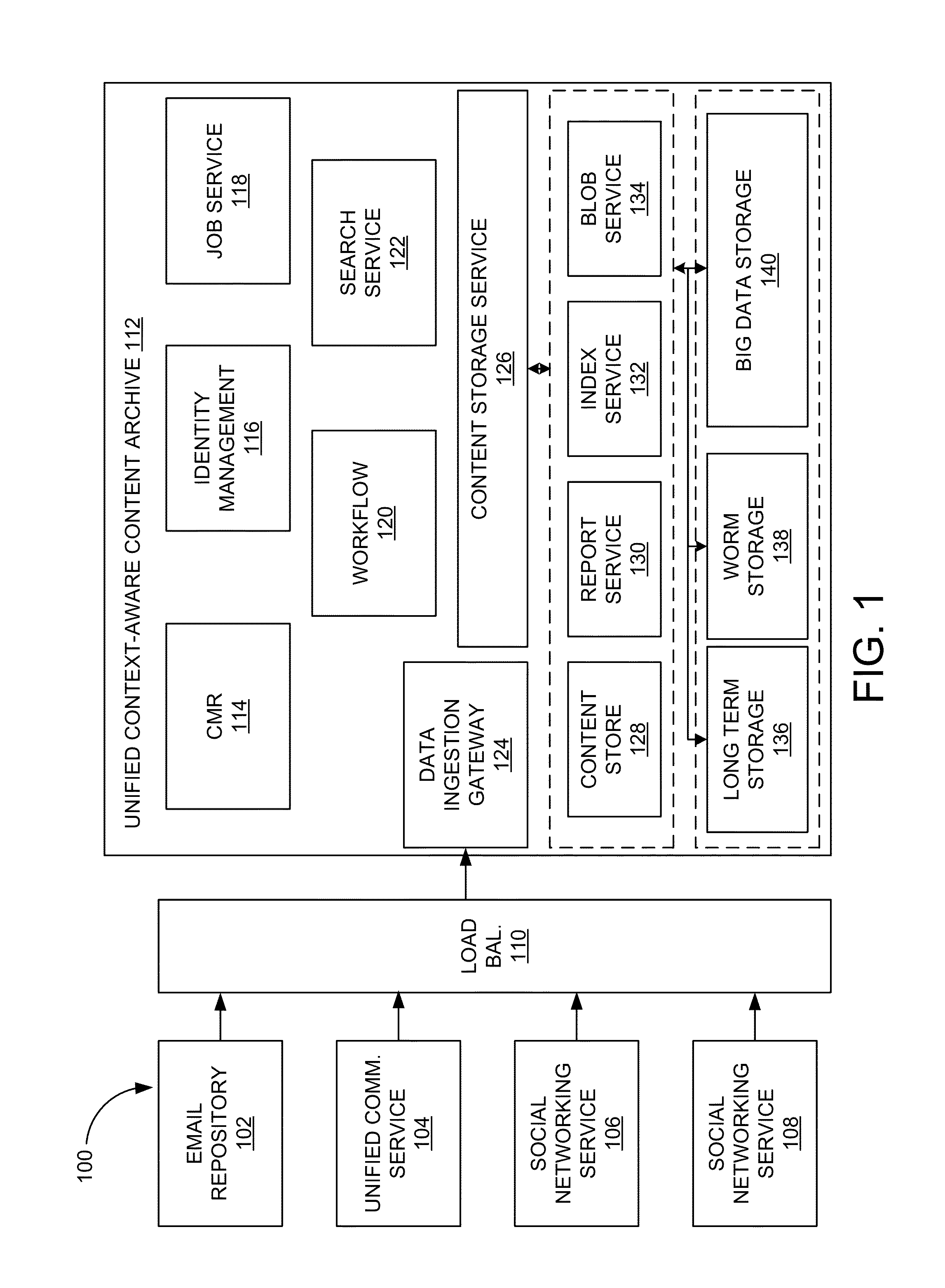
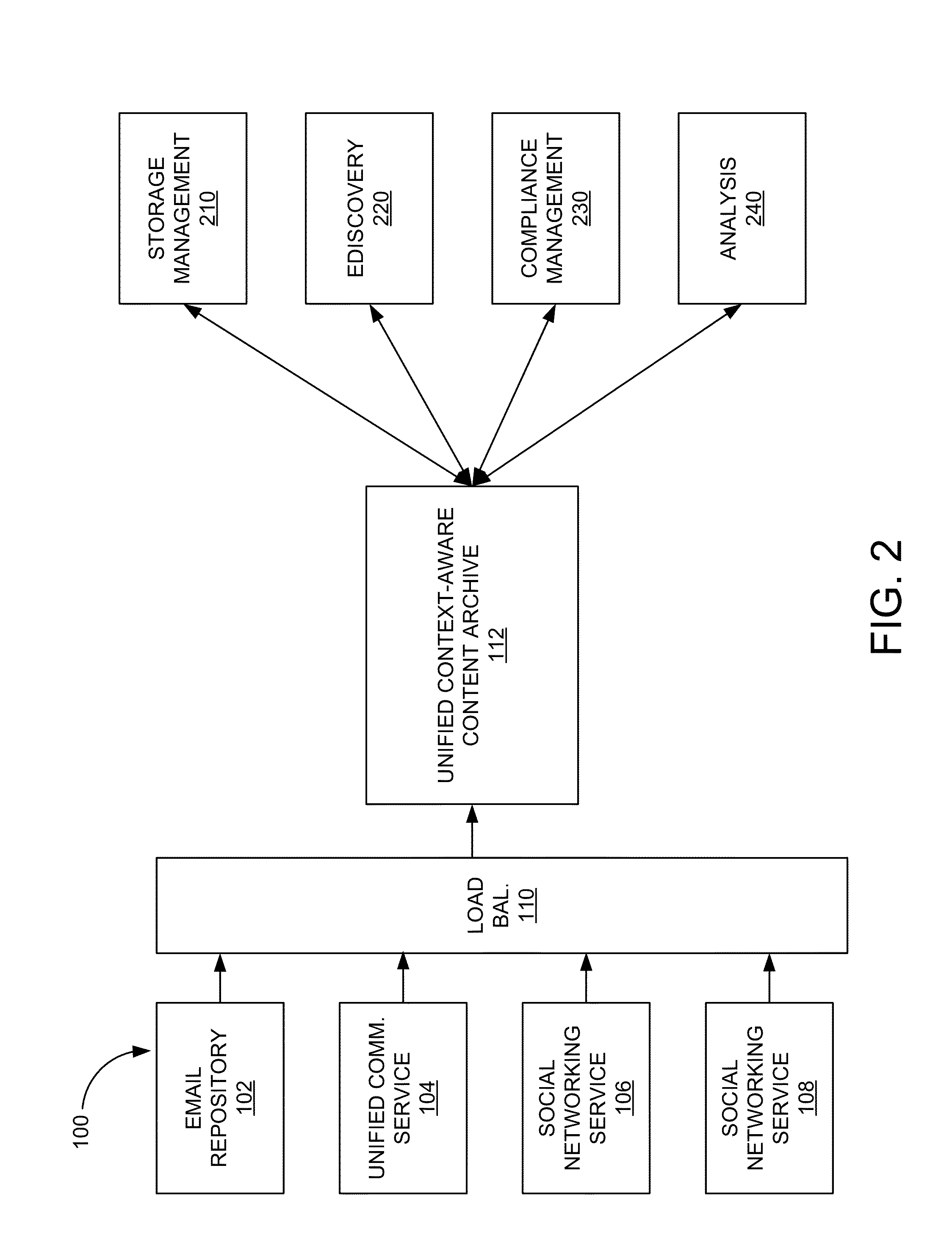
Unified context-aware content archive system
ActiveUS20150039565A1Digital data processing detailsRelational databasesBusiness managementTemporal succession
A unified context-aware content archive system allows enterprises to manage, enforce, monitor, moderate, and review business records associated with a variety of communication modalities. The system may store an information infoset derived or inferred from one or more documents representing communications according to the variety of communication modalities as interaction transcripts. An interaction transcript represents interactions between participants through the documents rather than the documents themselves allowing for derivation or inference of communication events, chronologies, and mappings to be stored in a common data structure. In one aspect, events correlation is provided between participants of communications that can be established by general time series analysis for the purposes of extracting meaningful statistics and interaction contexts and other characteristics of data. In another aspect, chronological mappings are provided of conversations between an established start and end time frame.
Owner:ACTIANCE
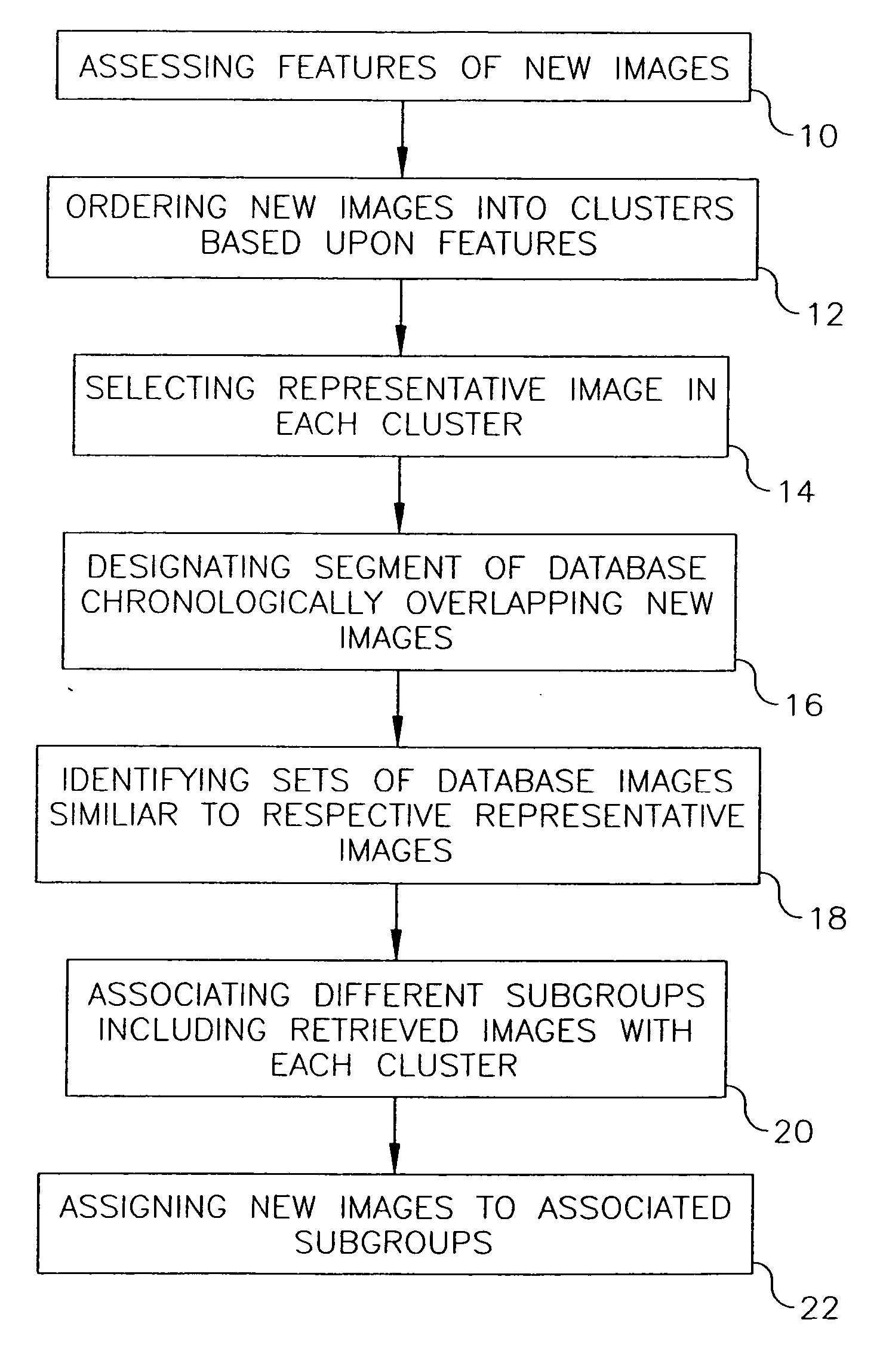
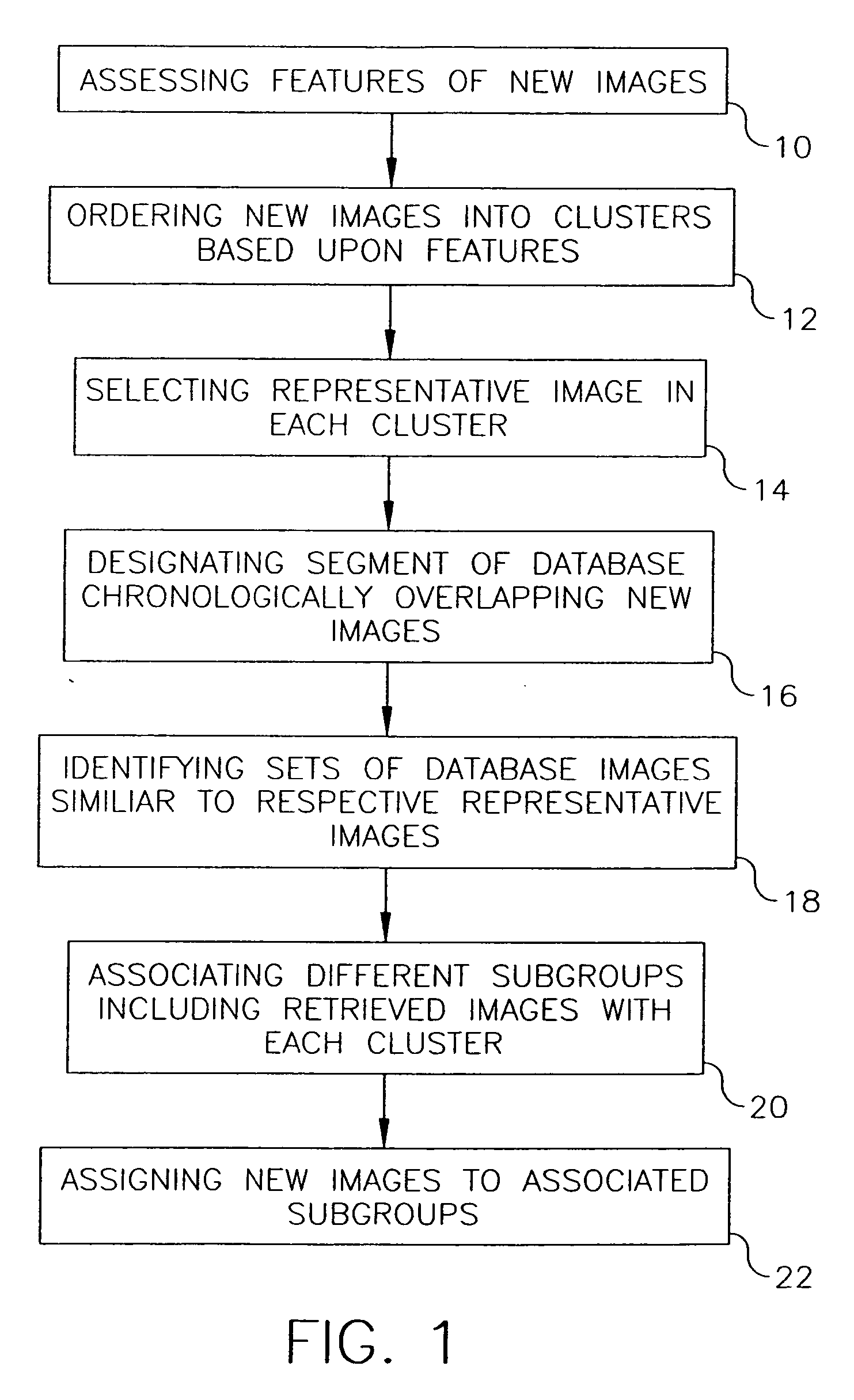
Additive clustering of images lacking individualized date-time information
InactiveUS20060200475A1Digital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionTemporal informationPersonalization
A database has chronologically ordered images classified into event groups based upon a time difference threshold, and into subgroups based upon a similarity measure. In a method and system for combining new images into such a database, new image are ordered into clusters based upon assessed image features. A representative image is selected in each cluster. A database segment chronologically overlapping the new images is designated and a set of database images similar to each representative image are identified in the segment. Different subgroups including one or more retrieved images are associated with each of cluster to provide matched subgroups. The new images are assigned to matched subgroups associated with respective clusters.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Apparatus, system, and method for organizing information by time and place
ActiveUS20090164439A1Easy to browseOvercome problemsDigital data processing detailsGeographical information databasesGeolocationChronological time
An apparatus and method for capturing and organizing information spatio-temporally utilizes a standardized time reference and geographical locations to associate a time and a place to each event that is captured. These events are placed in a coordinate system according to the associated times and places. The apparatus and method may use a meridial clock. A series of related events forms an event path that progresses chronologically. Plural event paths are illustrated in a coordinate system based image of a user interface. Events from different event paths are synchronized so that events that occur in a particular moment are placed in the same time plane. As time progresses, the events emit from the plane into a region representing the past, and a relationship of events with their times and places is illustrated. A map in the plane of the image may facilitate visualization of places and times with events.
Owner:TEMPORAL
Method of using temporal context for image classification
ActiveUS7680340B2Improving Image Classification AccuracyCorrect mistakesDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionContextual image classificationTemporal context
A method for improving scene classification of a sequence of digital images is disclosed herein. Such a method may include providing a sequence of images captured in temporal succession; (b) classifying each of the images individually based on information contained in the image alone to generate a first image classification; and (c) imposing a pre-determined temporal context model on the sequence of images to generate a final image classification for each image in the sequence.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Mobile geolocation
Estimating a location of a first mobile communication unit (220) in a cellular wireless communications system (200) comprises comparing a first signature from the first mobile communication unit with known signatures. The first signature may comprise control information, a set of observable cells and received power level information for the first mobile communication unit (220). A location estimate is provided from the known location of a known signature in a database (410), if that known signature matches the first signature. The comparison may be a correlation to determine the degree of matching. Context information may link two or more known signatures in the database (410), the known signatures having been obtained in temporal succession from one mobile device (258) in use in the system. The context information may be used in the comparison.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS UK
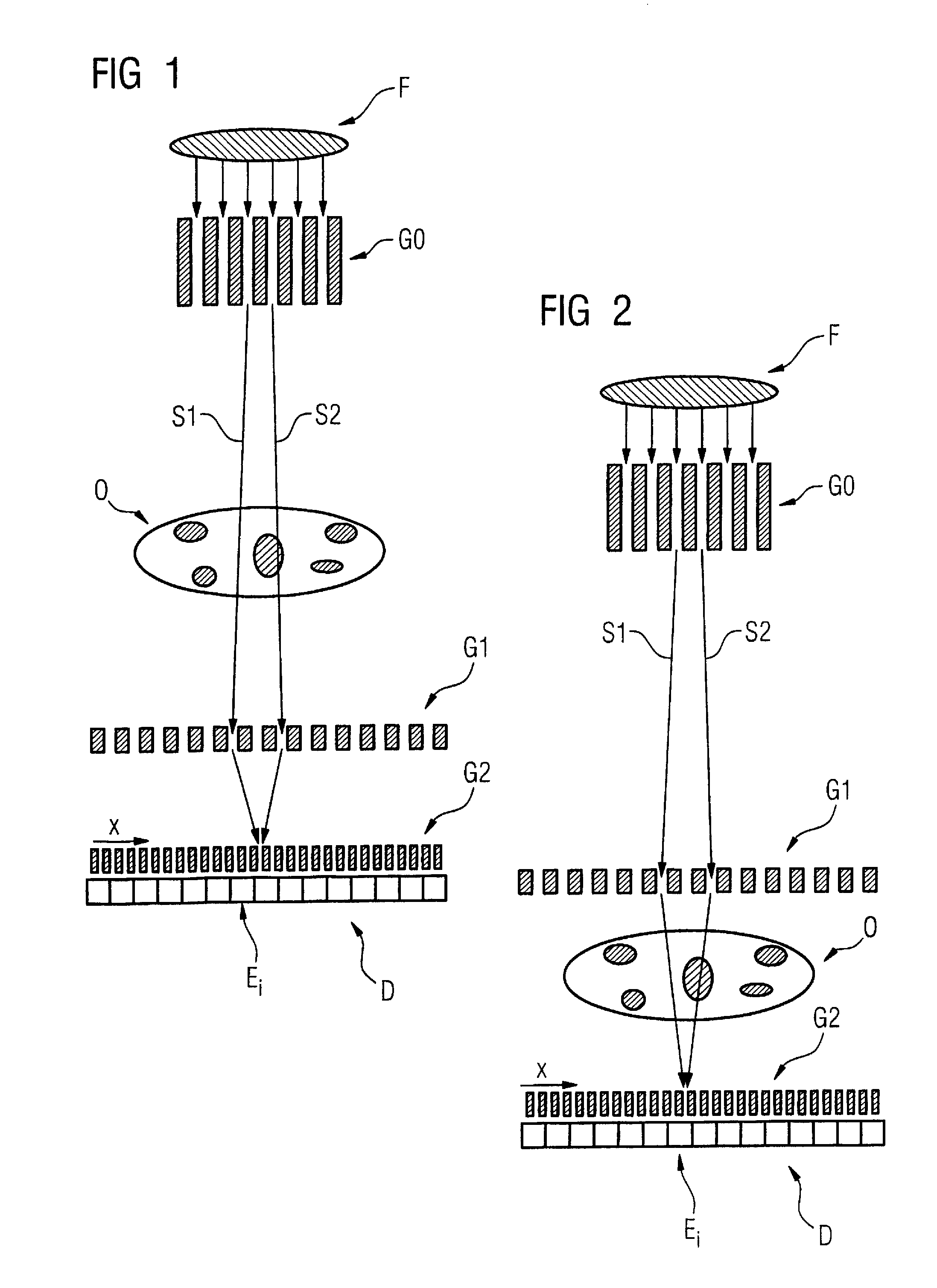
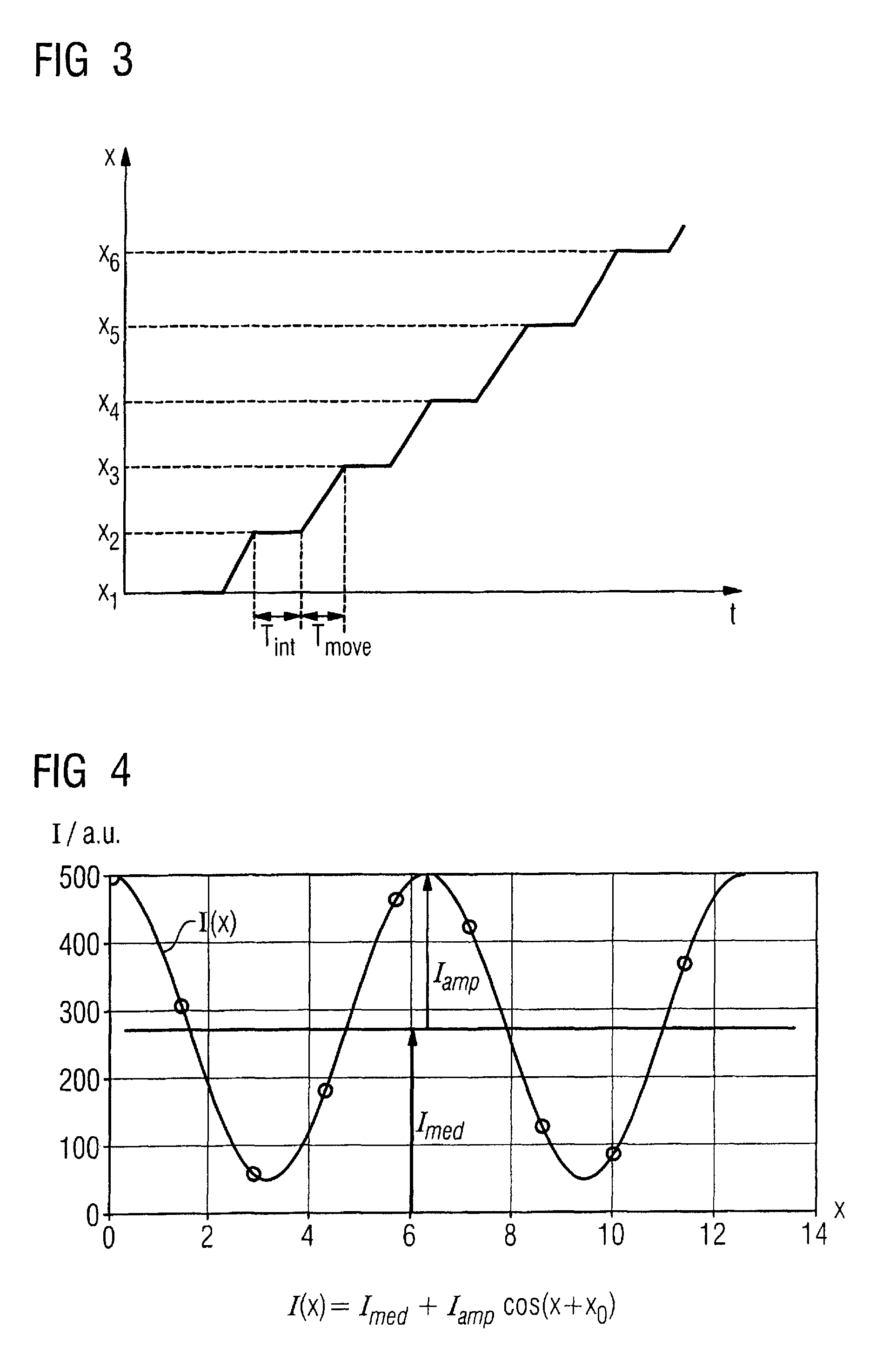
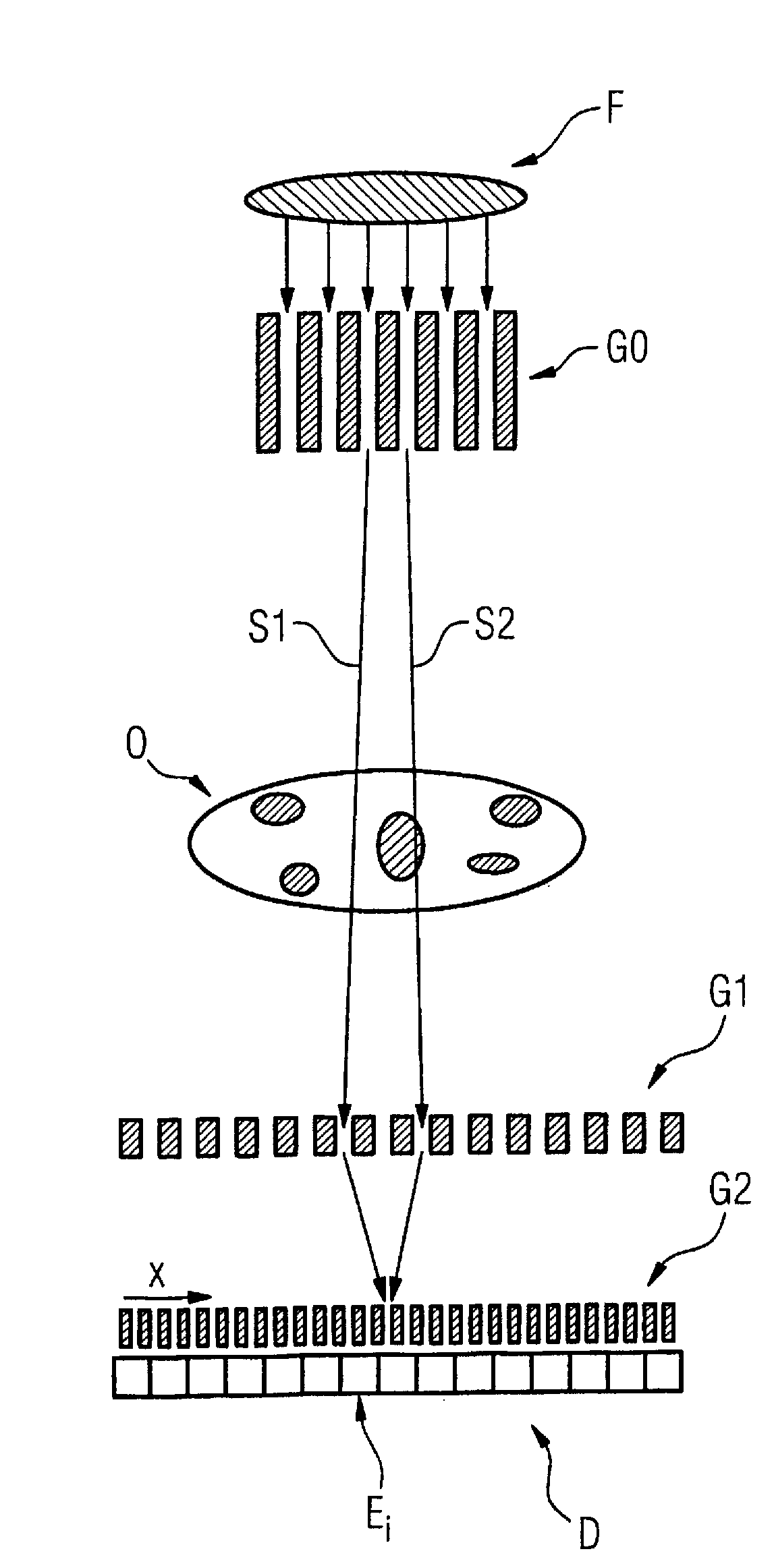
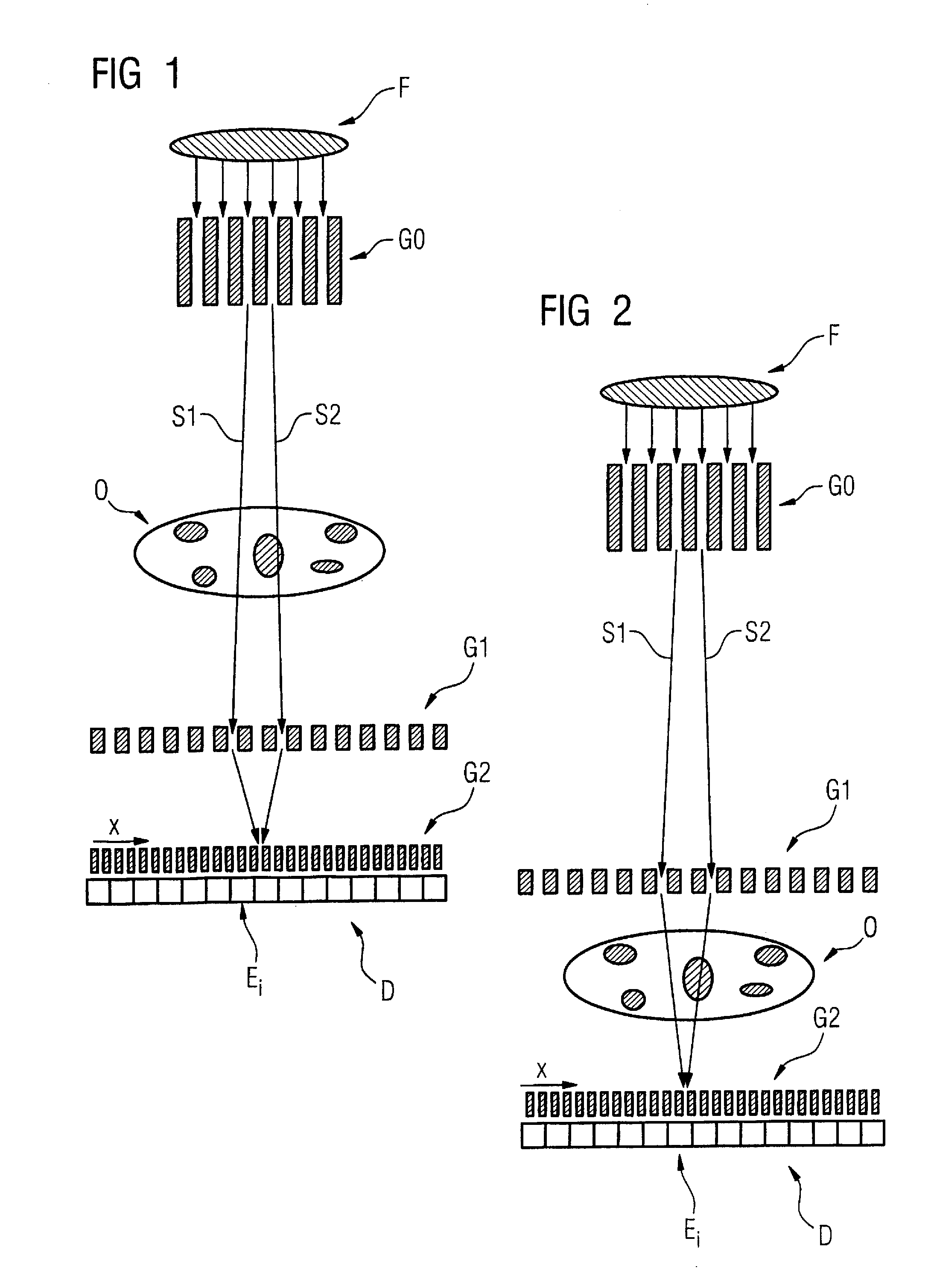
Method to determine phase and/or amplitude between interfering, adjacent x-ray beams in a detector pixel in a talbot interferometer
ActiveUS8005185B2Imaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingPhase gratingX-Ray Phase-Contrast Imaging
In a method to determine phase and / or amplitude between interfering, adjacent x-ray beams in a detector pixel in a Talbot interferometer for projective and tomographical x-ray phase contrast imaging and / or x-ray dark field imaging, after an irradiation of the examination subject with at least two coherent or quasi-coherent x-rays, an interference of the at least two coherent or quasi-coherent x-rays with the aid of an irradiated phase grating is generated, and the variation of multiple intensity measurements in temporal succession after an analysis grating is determined in relation to known displacements of one of the gratings or of an x-ray source fashioned like a grating, positioned upstream in the beam path, relative to one of the gratings. The integrating intensity measurements ensue during a relative movement—thus not during the standstill—of one of the upstream gratings or of the x-ray source fashioned like a grating or of the examination subject, with known speed behavior over a final time interval of a final distance.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method to determine phase and/or amplitude between interfering, adjacent x-ray beams in a detector pixel in a talbot interferometer
ActiveUS20100074395A1Simplify mannerImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayPhase grating
In a method to determine phase and / or amplitude between interfering, adjacent x-ray beams in a detector pixel in a Talbot interferometer for projective and tomographical x-ray phase contrast imaging and / or x-ray dark field imaging, after an irradiation of the examination subject with at least two coherent or quasi-coherent x-rays, an interference of the at least two coherent or quasi-coherent x-rays with the aid of an irradiated phase grating is generated, and the variation of multiple intensity measurements in temporal succession after an analysis grating is determined in relation to known displacements of one of the gratings or of an x-ray source fashioned like a grating, positioned upstream in the beam path, relative to one of the gratings. The integrating intensity measurements ensue during a relative movement—thus not during the standstill—of one of the upstream gratings or of the x-ray source fashioned like a grating or of the examination subject, with known speed behavior over a final time interval of a final distance.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for monitoring surfaces
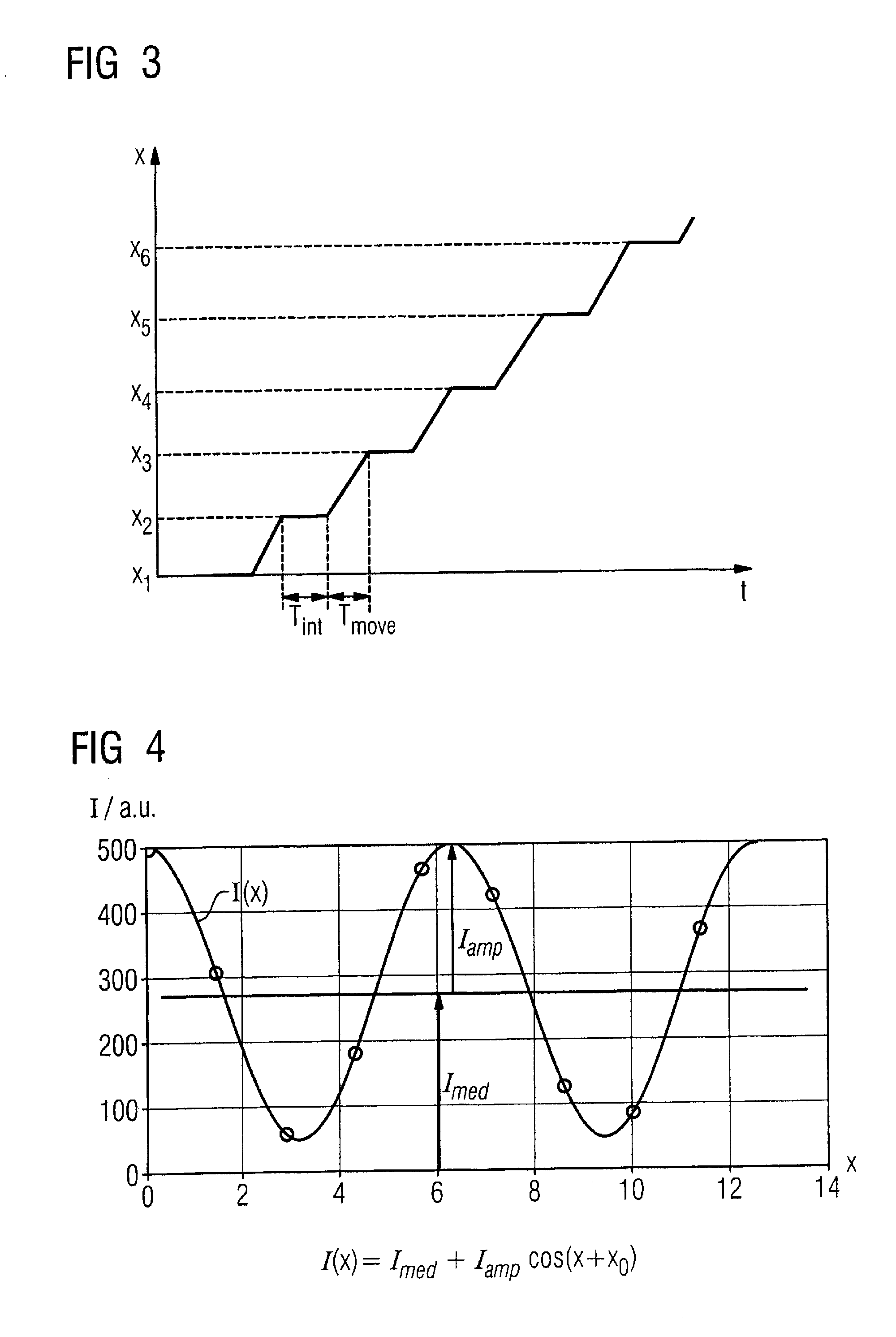
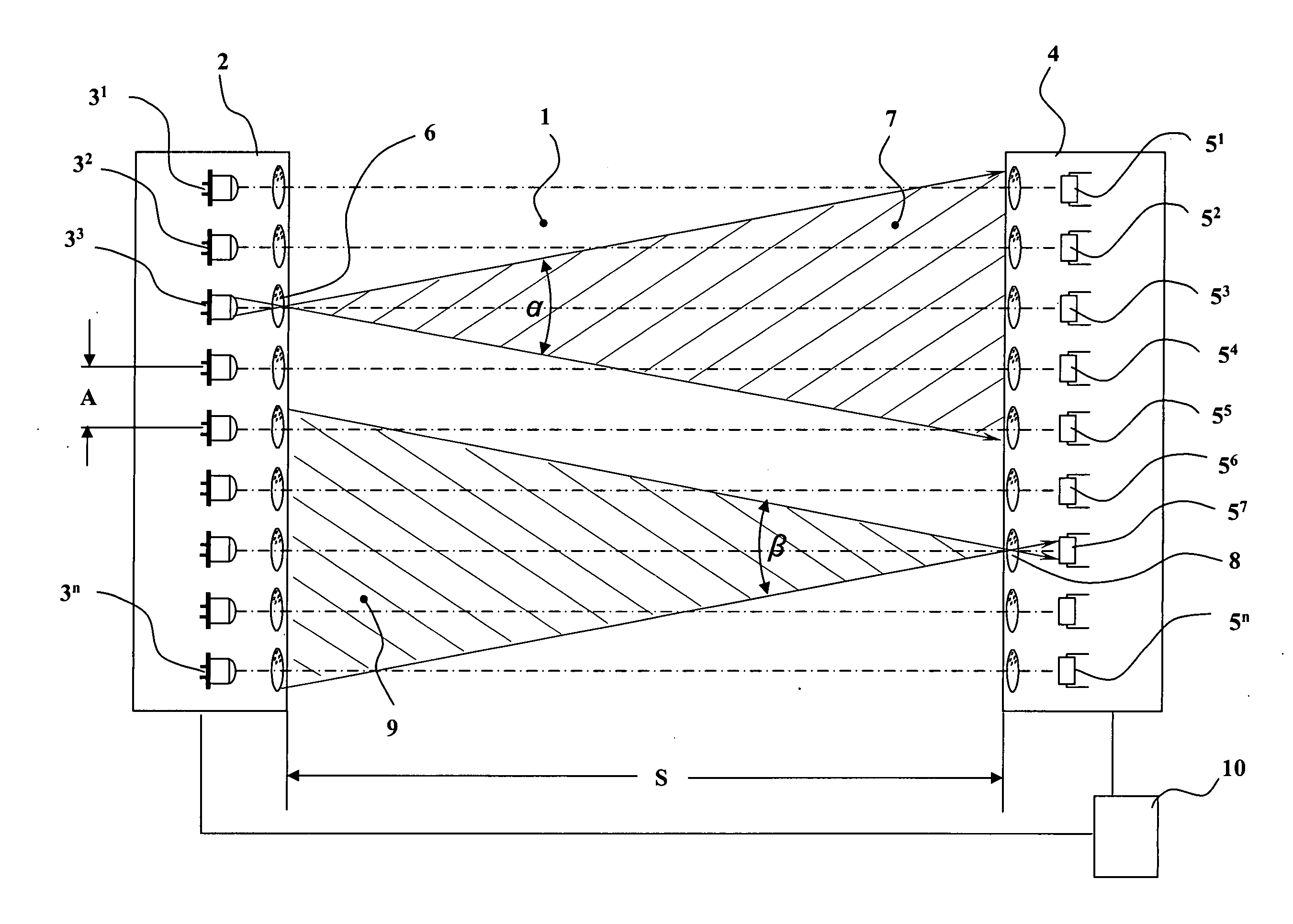
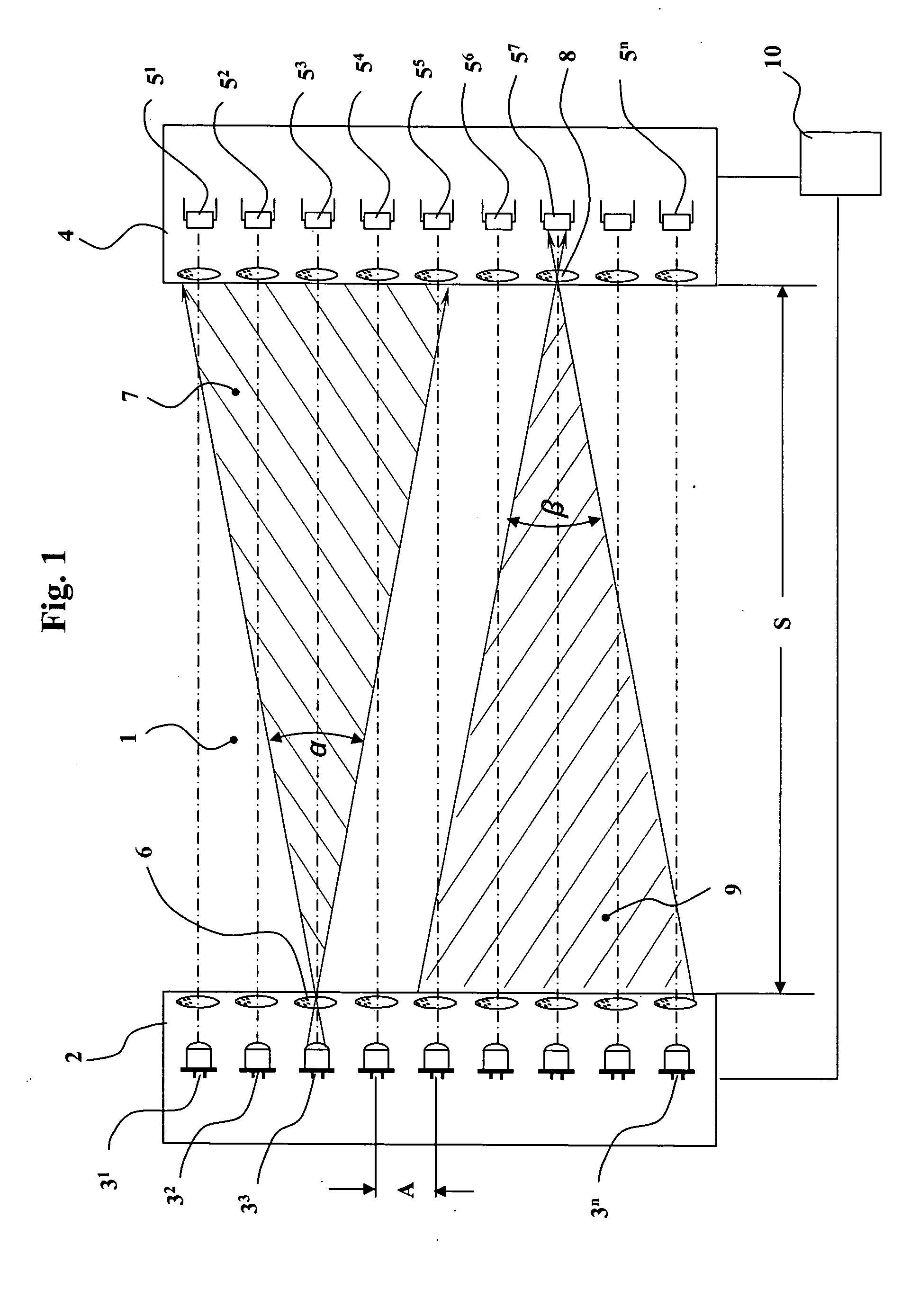
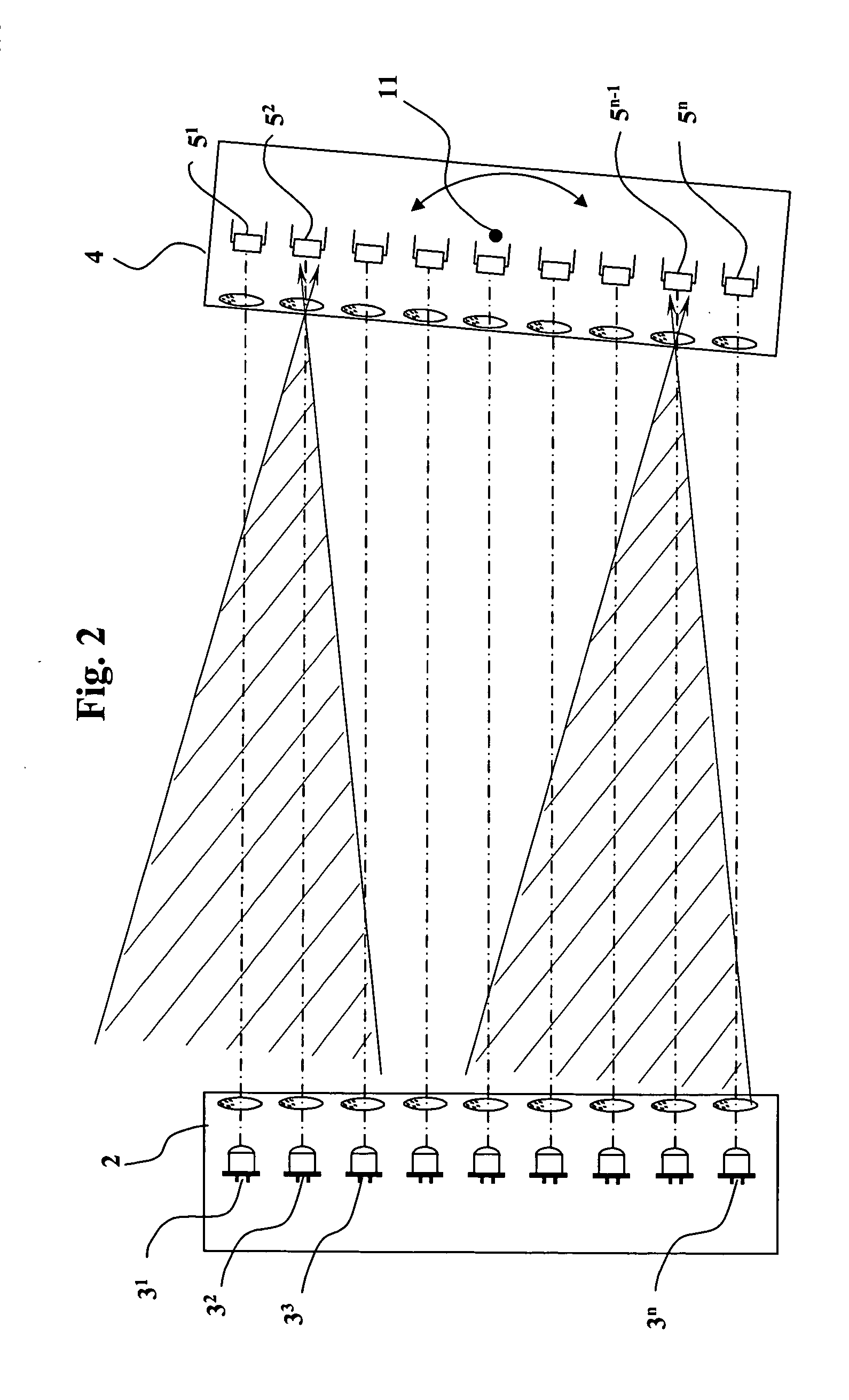
InactiveUS20050133702A1Extended time intervalImprove accuracyOptical detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansTemporal successionOperation mode
A method and apparatus for the monitoring of areas with several light emitters arranged alongside each other, which emit light along a light emitter cone, and several light receivers arranged alongside each other, which receive light from a light receiver cone. The emitters and receivers form several interacting pairs which can be activated individually, in temporal succession (sequentially) and / or cyclically by a control unit during a monitoring mode of operation. The distance of the light emitters from the corresponding light receivers is determined during a distance determining mode of operation from the number of light emitters visible to a light receiver and / or from the number of light receivers seeing a light emitter.
Owner:SICK AG
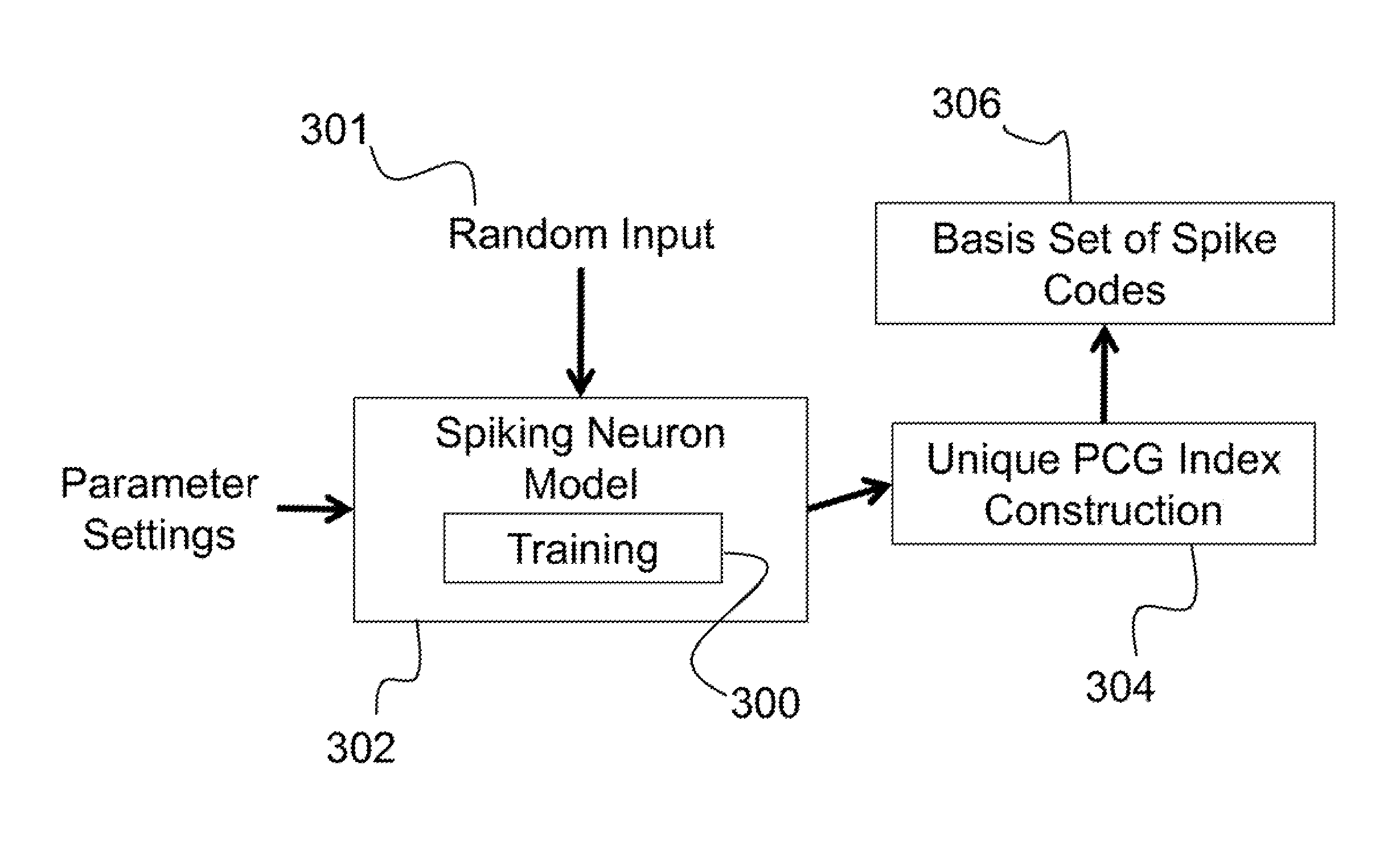
System for representing, storing, and reconstructing an input signal
Described is a system for representing, storing, and reconstructing an input signal. The system constructs an index of unique polychronous groups (PCGs) from a spiking neuron network. Thereafter, a basis set of spike codes is generated from the unique PCGs. An input signal can then be received, with the input signal being spike encoded using the basis set of spike codes from the unique PCGs. The input signal can then be reconstructed by looking up in a reconstruction table, for each unique PCG in the basis set in temporal order according to firing times, anchor neurons. Using a neuron assignment table, an output location can be looked up for each anchor neuron to place a value based on the firing times of each unique PCG. Finally, the output locations of the anchor neurons can be compiled to reconstruct the input signal.
Owner:HRL LAB
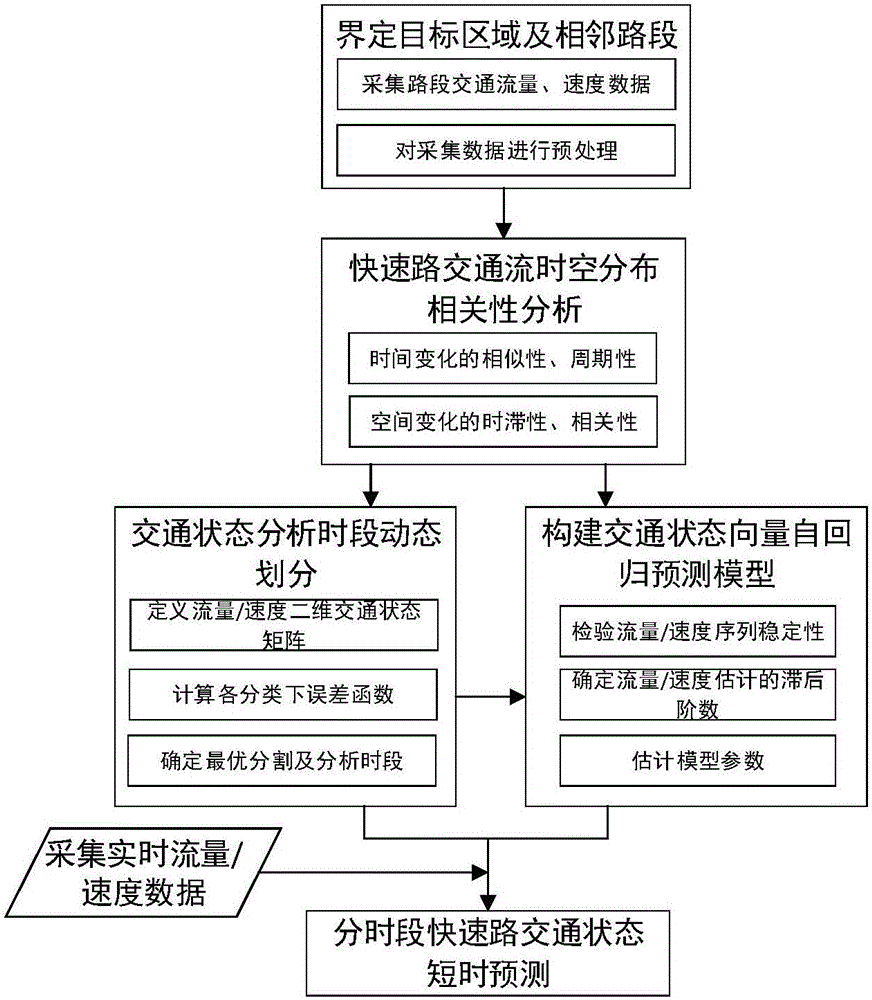
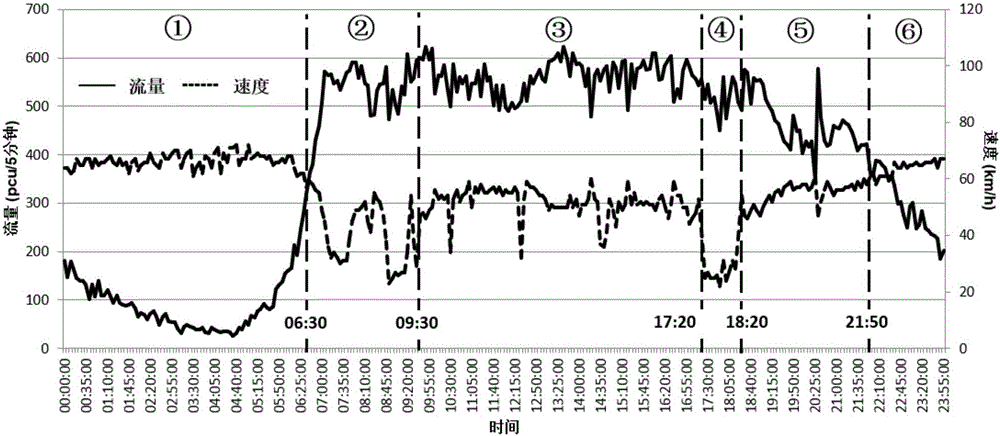
Express way traffic state prediction method taking spatial-temporal correlation into account at different times
ActiveCN105702029AOvercome single predictor variableOvercoming less consideration of the spatio-temporal correlation of traffic flowDetection of traffic movementTraffic characteristicState prediction
The present invention discloses an express way traffic state prediction method taking spatial-temporal correlation into account at different times. The method comprises: firstly, performing analysis period dynamic division of flow, speed and time sequences through adoption of a sequential cluster, and dividing the whole day into analysis periods with different traffic characteristics without disturbing traffic parameter time sequences; and selecting multivariable vector autoregression models aiming at different periods, comprehensively considering the spatial-temporal correlation of the upstream and downstream traffic flows, and predicting the flow or the speed of target places. The dynamic period division of the express way traffic state prediction method taking spatial-temporal correlation into account at different times provides a cheap, easy and substantially improved efficiency basic method for express way traffic state short-time prediction; and compared with a traditional method without considering the upstream and downstream traffic flow influence, the express way traffic state prediction method taking spatial-temporal correlation into account at different times considers the vector autoregression model of the spatial-temporal correlation after the periods are divided, so that the prediction results are obviously improved in precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
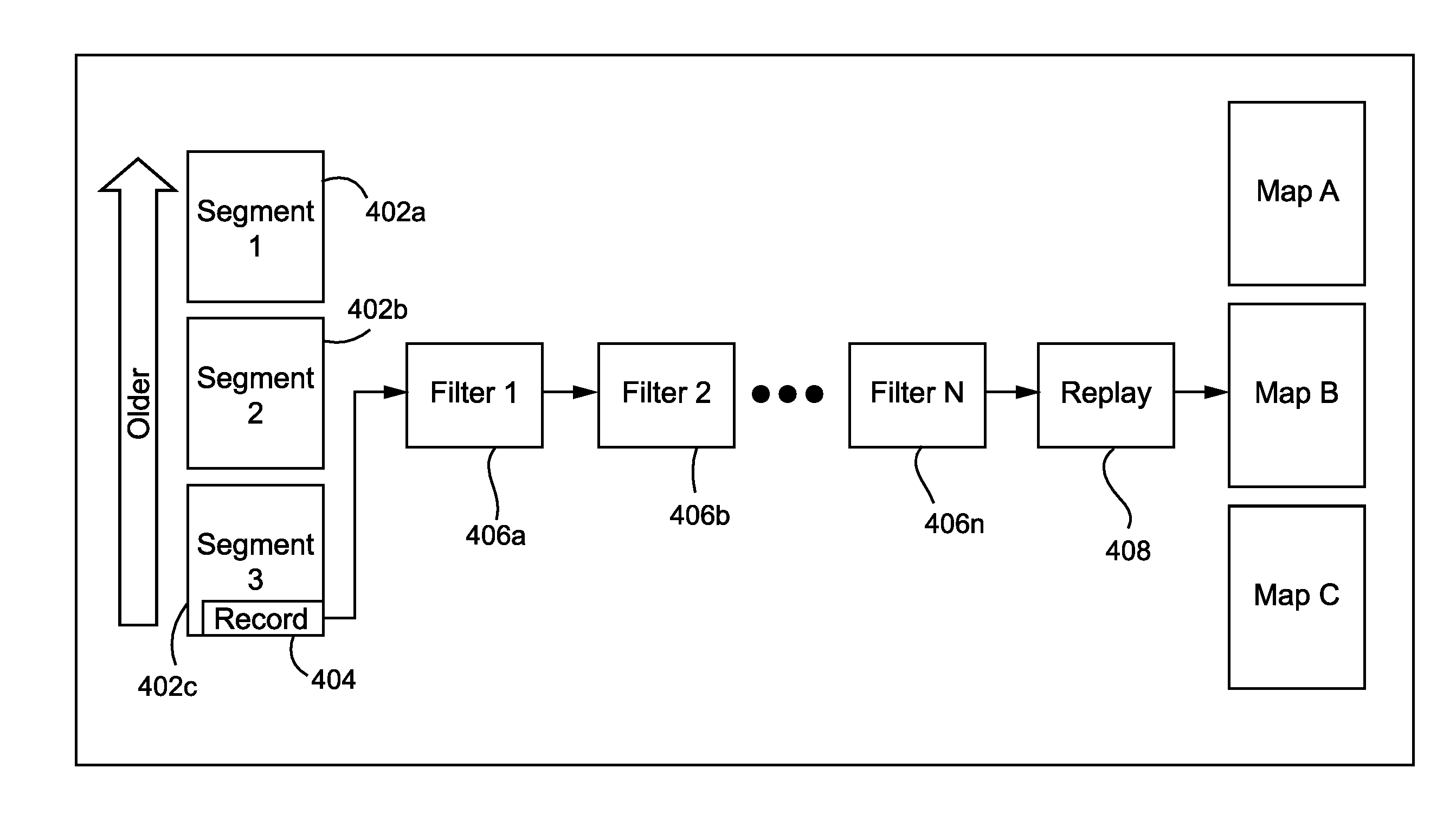
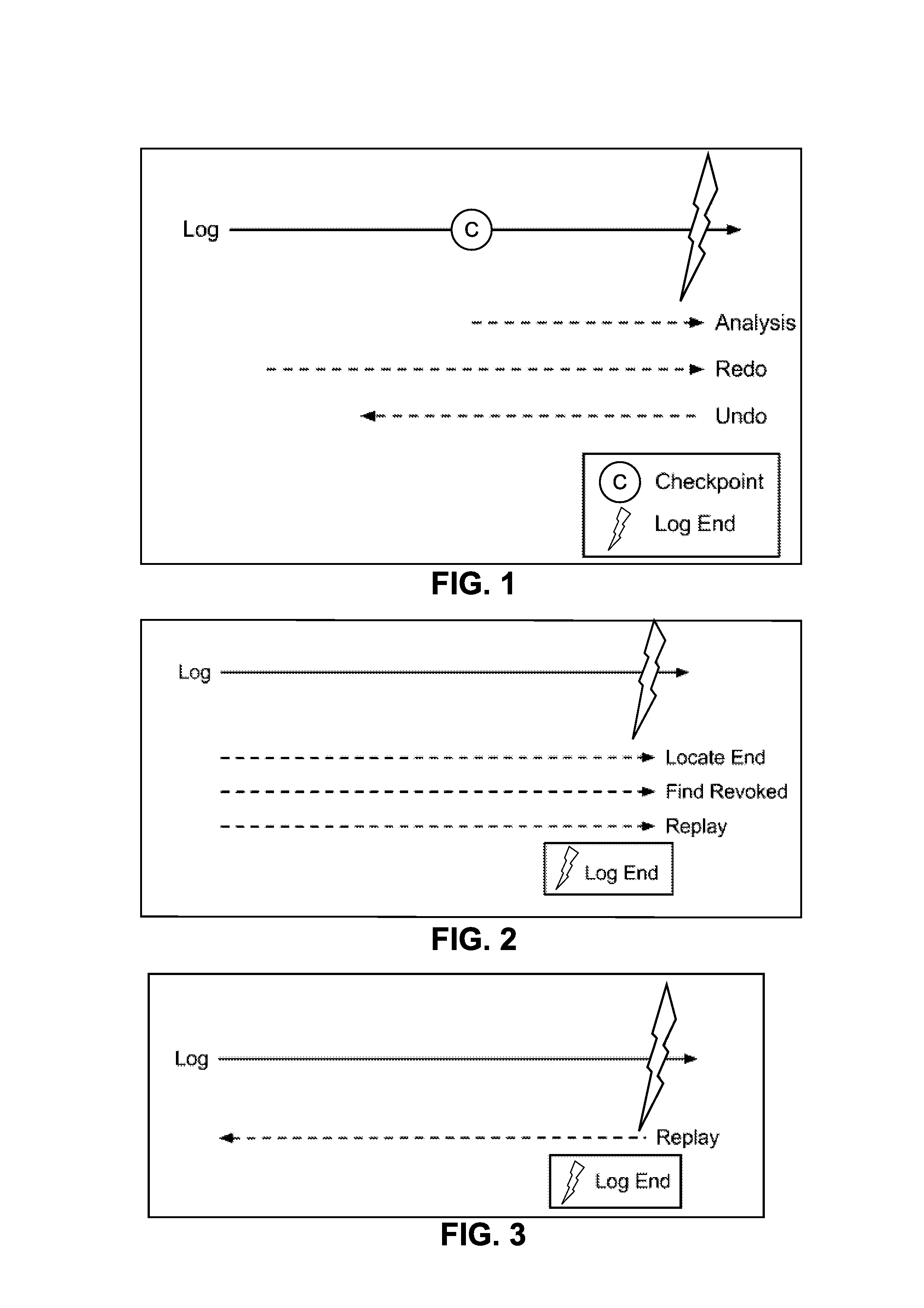
Systems and/or methods for rapid recovery from write-ahead logs
ActiveUS8683262B1Reduce restrictionsEffect recovery timeOther databases retrievalRedundant operation error correctionData setTime efficient
Certain example embodiments provide a single pass, reverse chronological approach to write-ahead log recovery, enabling space- and time-efficient the recovery of stored data from large write-ahead logs to a transient storage medium. The techniques described herein can in certain instances enable fast and efficient recovery, even in scenarios where at the time of a failure requiring such a recovery the live log is potentially multiple terabytes or larger in size. Certain example embodiments make use of a filtering mechanism (e.g., involving potentially stateful delete, skip, and / or transaction filters), a key / value property (allowing a live set of data, once identified, to be applied in any arbitrary order), etc. A simplified environment with a small closed set of mutative operations allows for the performing of recovery backwards by scanning the log from the most recent written record backwards in time (and, in other words, finishing with the oldest record).
Owner:SOFTWARE AG USA
Computer Vision Systems and Methods for Unsupervised Representation Learning by Sorting Sequences
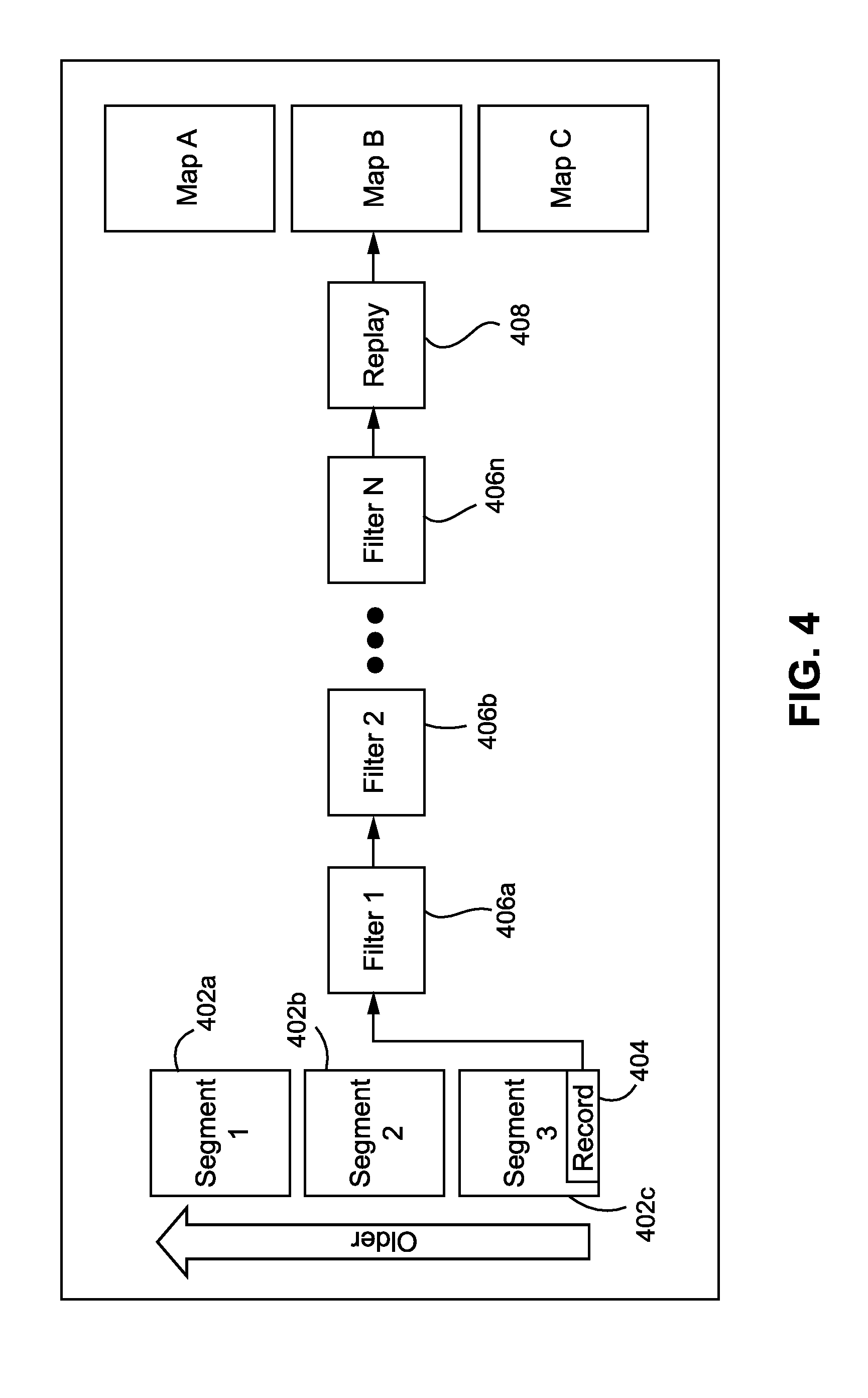
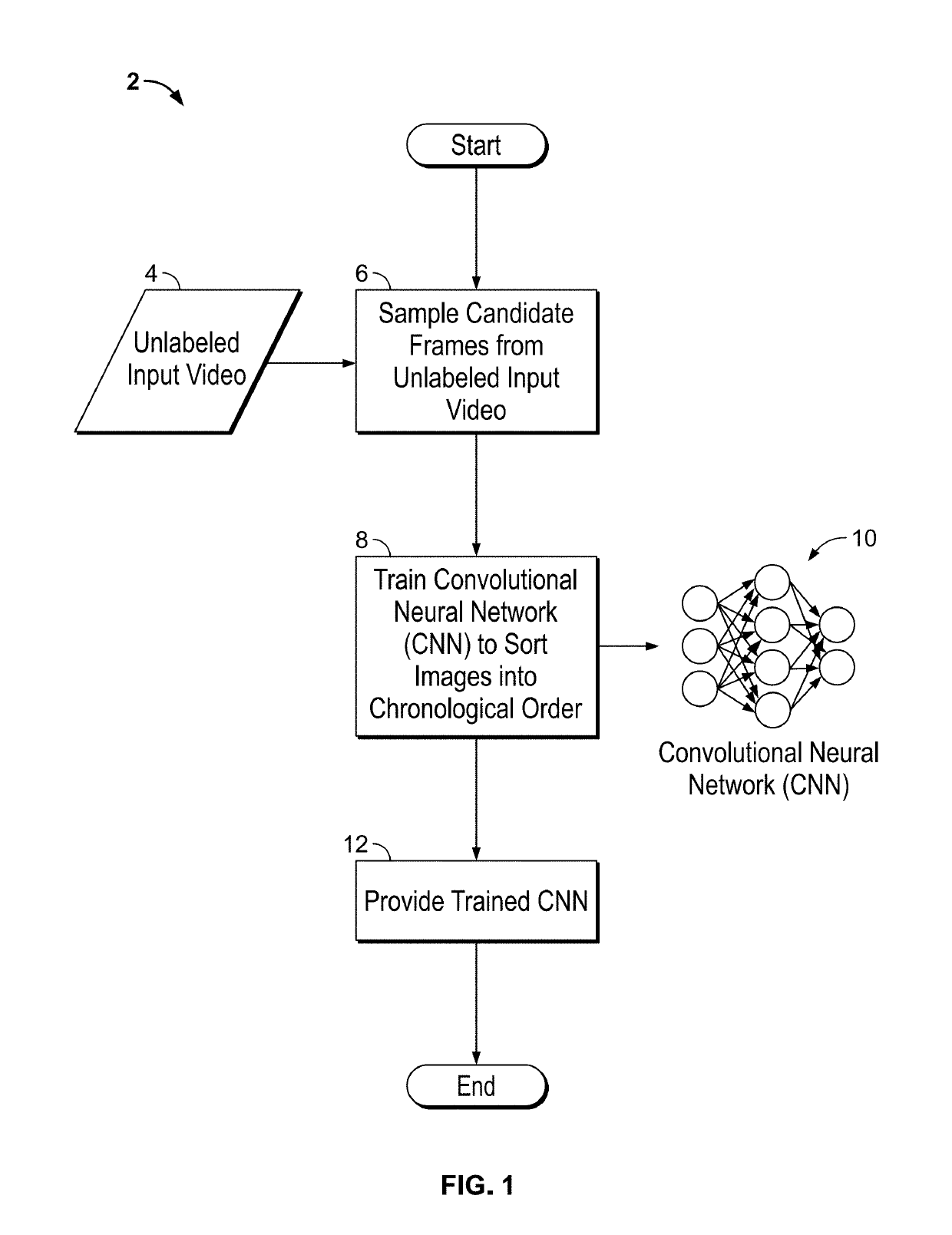
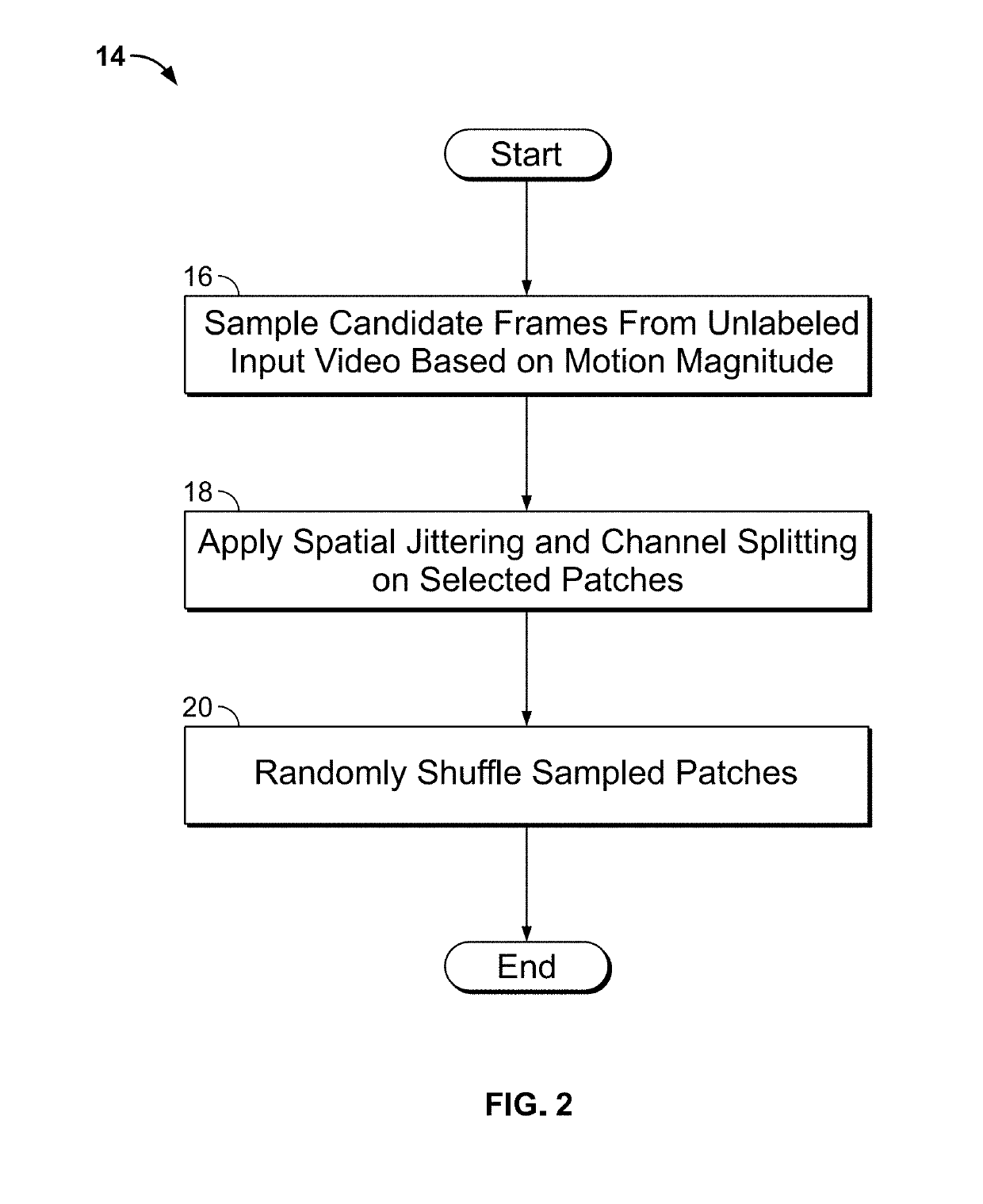
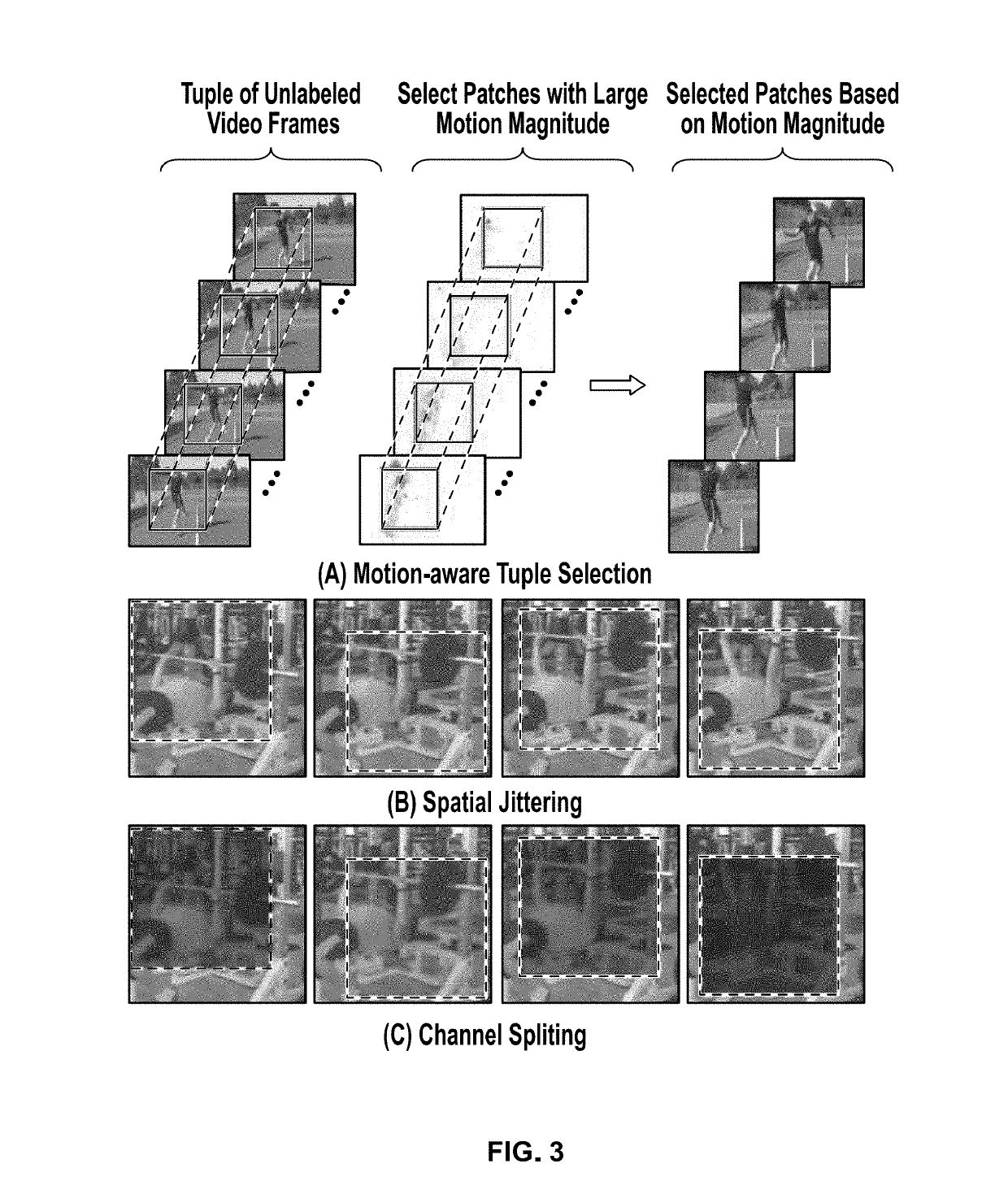
InactiveUS20190228313A1Facilitate machine learningImage analysisData sortingTemporal successionDigital image
Systems and methods for unsupervised representation learning by sorting sequences are provided. An unsupervised representation learning approach is provided which uses videos without semantic labels. The temporal coherence as a supervisory signal can be leveraged by formulating representation learning as a sequence sorting task. A plurality of temporally shuffled frames (i.e., in non-chronological order) can be used as inputs and a convolutional neural network can be trained to sort the shuffled sequences and to facilitate machine learning of features by the convolutional neural network. Features are extracted from all frame pairs and aggregated to predict the correct sequence order. As sorting shuffled image sequence requires an understanding of the statistical temporal structure of images, training with such a proxy task can allow a computer to learn rich and generalizable visual representations from digital images.
Owner:INSURANCE SERVICES OFFICE INC
Method for transmitting a multicarrier signal designed for limiting interference, signal, emitting device, receiving method and device and corresponding computer programs
ActiveUS20090213949A1Reduce distractionsAccurate estimateSpatial transmit diversityTransmission path divisionCarrier signalEngineering
A method is provided for transmitting a multi-carrier signal formed of a temporal succession of symbols comprised of a set of data elements. The method includes: calculating an interference affecting a set of at least two data elements which are to be protected and are spaced out two by two from no more than one time carrier and no more than one frequency carrier, the interference taking into account the value of the data elements to be protected and values of the data elements of a contour ring consisting of carriers immediately adjacent to data elements to be protected, and; determining at least one value to be attributed to at least one data element of the contour ring for reducing, upon reception, the calculated interference.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
Light source employing laser-produced plasma
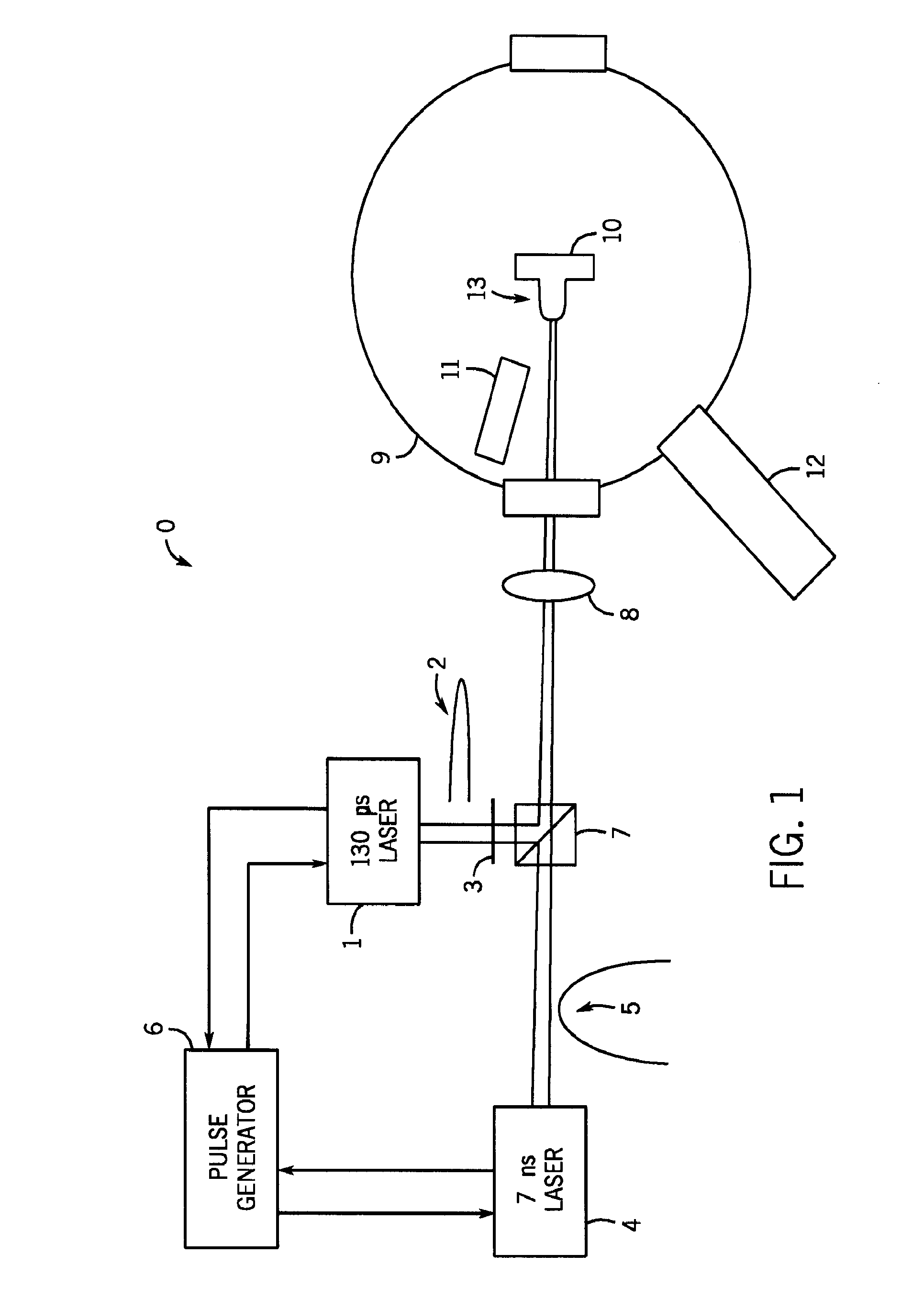
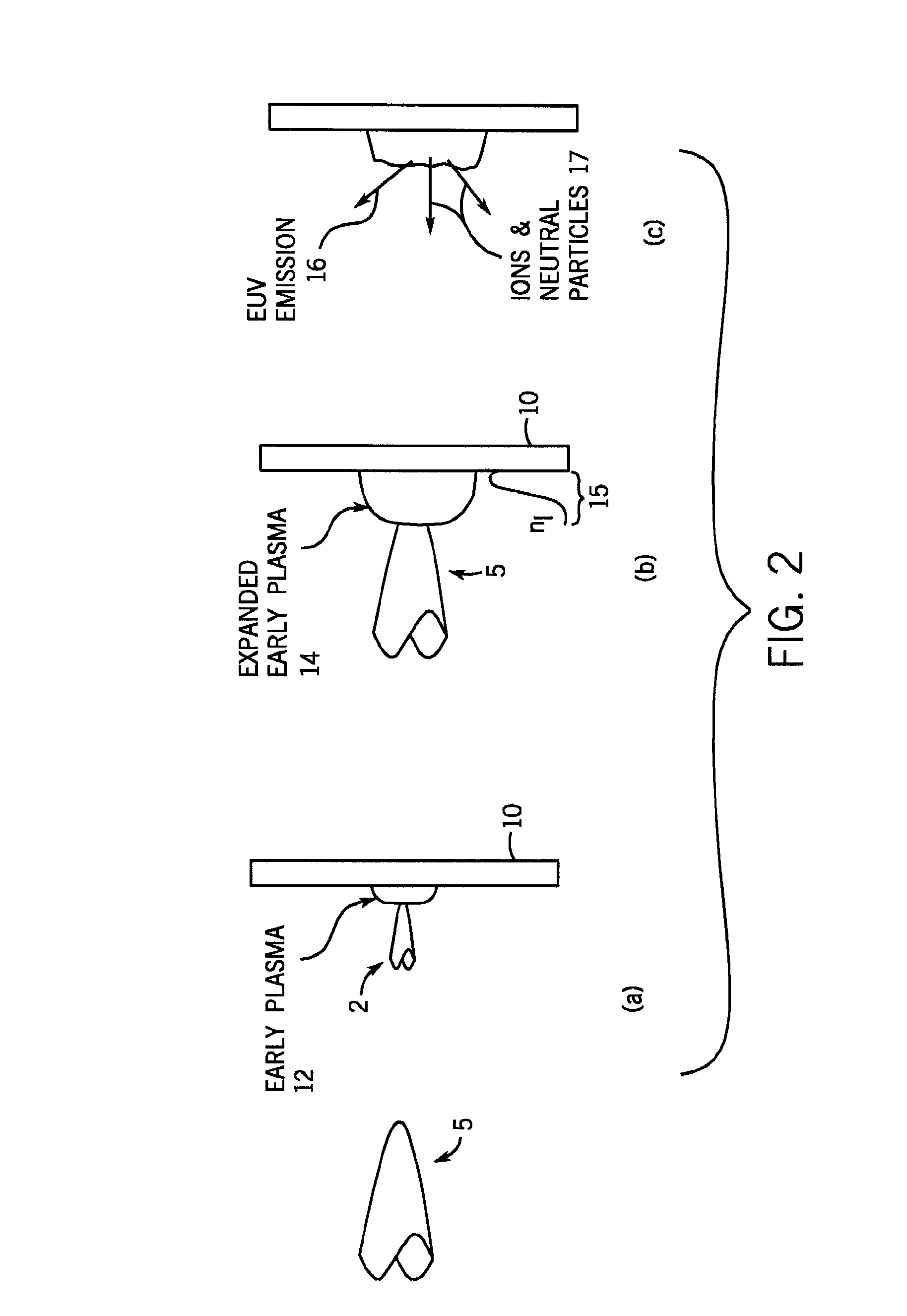
InactiveUS20100051831A1Reduce generationRadiation pyrometryElectric arc lampsTime segmentTemporal succession
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
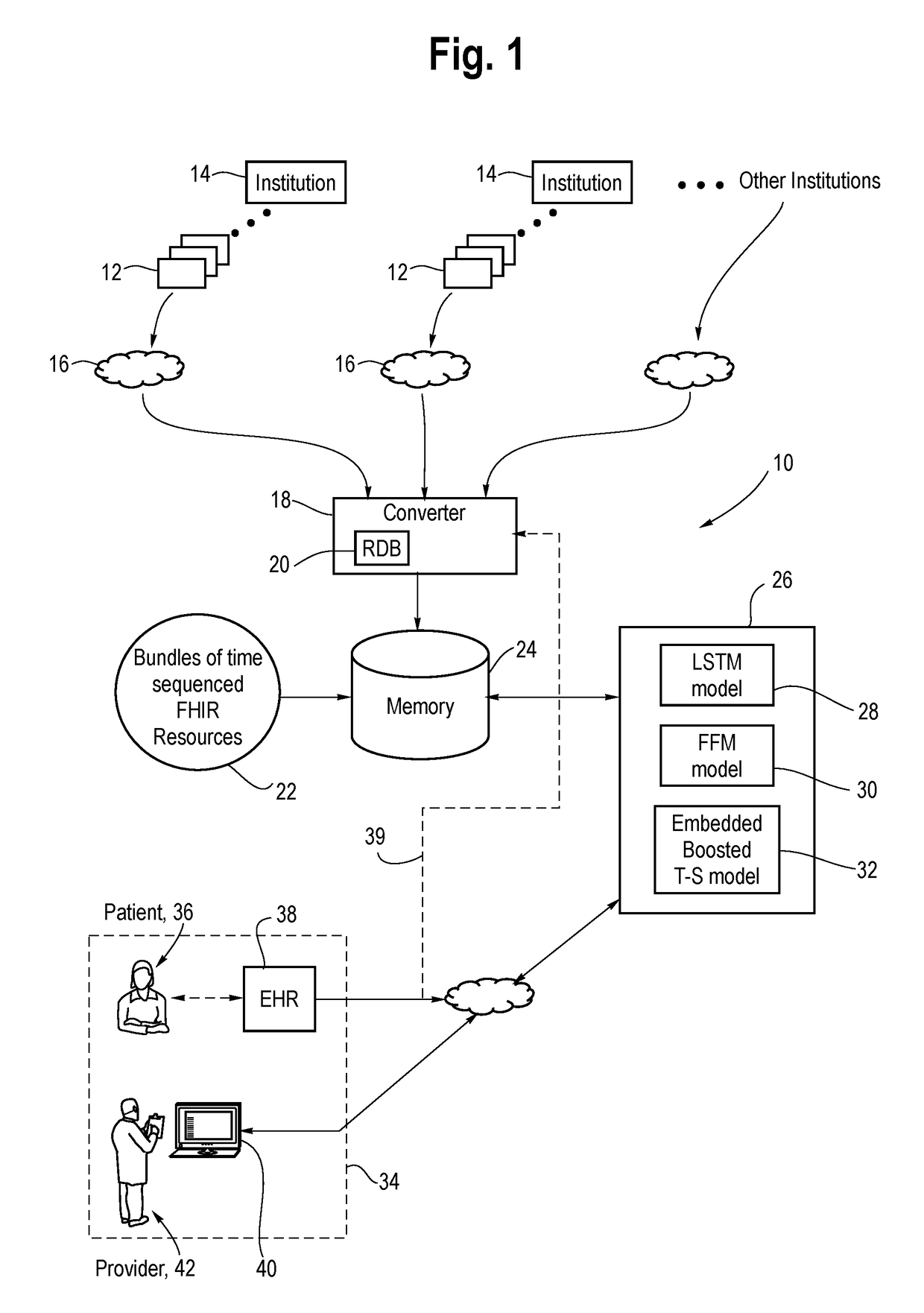
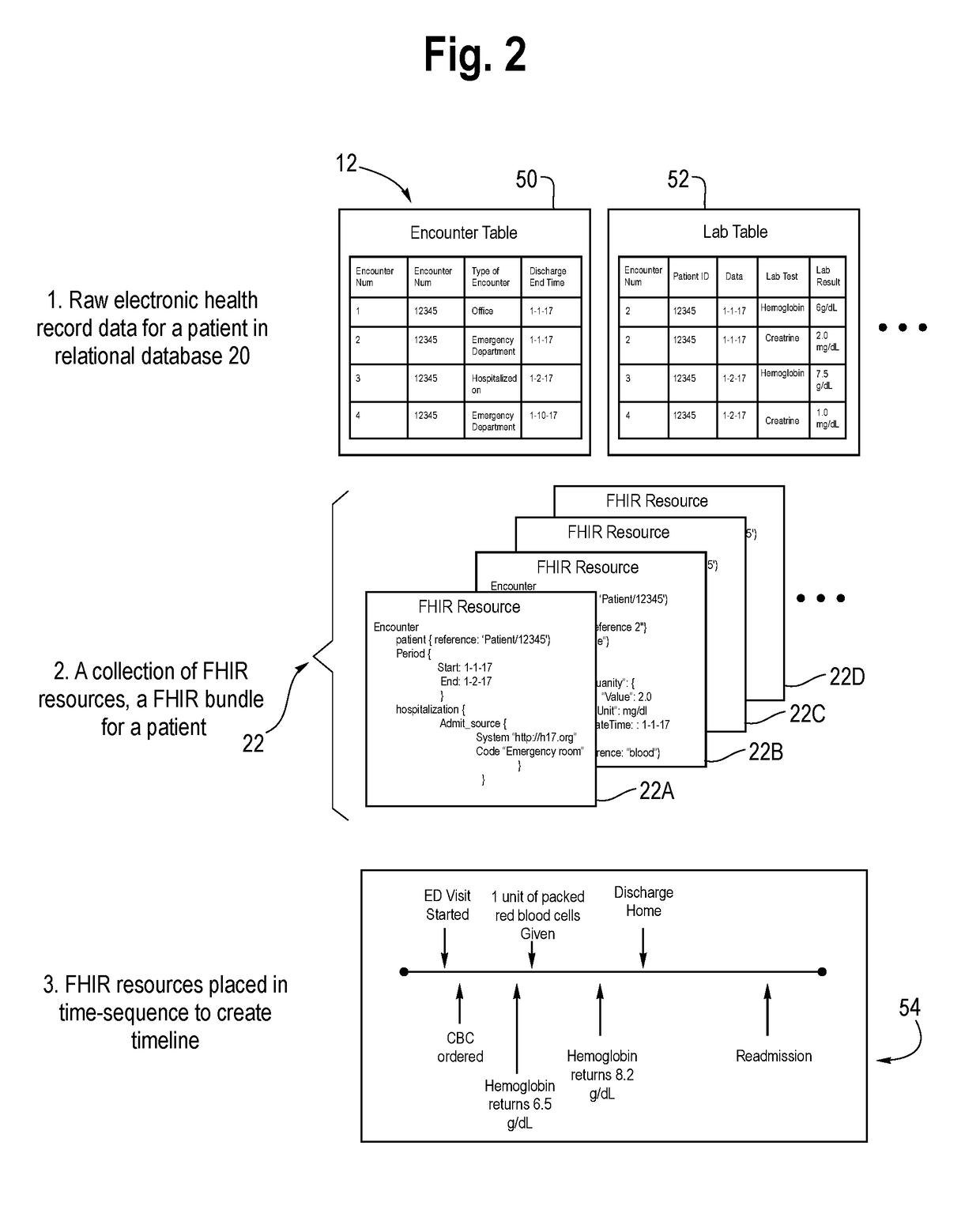
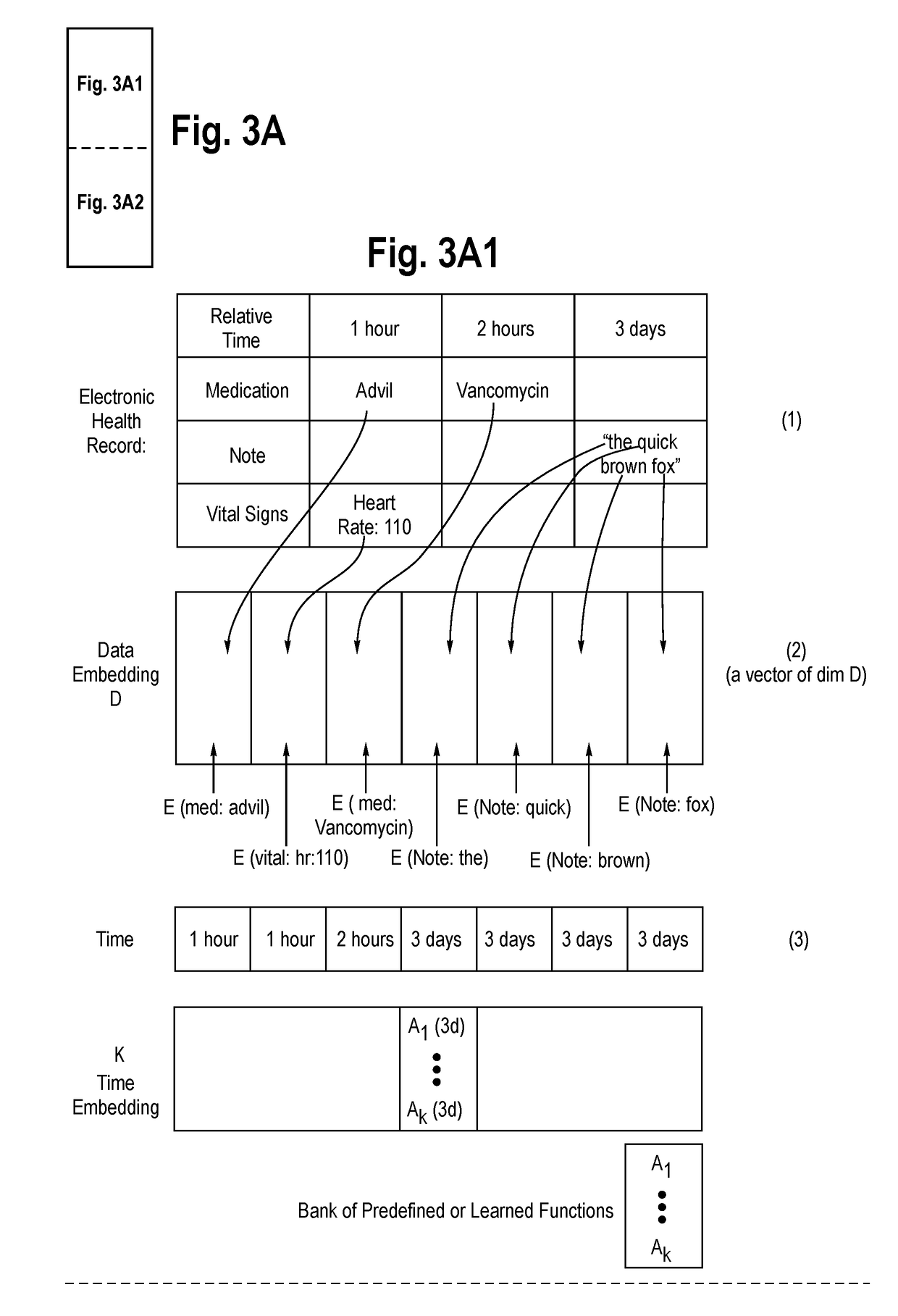
System and Method for Predicting and Summarizing Medical Events from Electronic Health Records
ActiveUS20190034590A1Medical data miningHealth-index calculationTemporal successionChronological time
A system for predicting and summarizing medical events from electronic health records includes a computer memory storing aggregated electronic health records from a multitude of patients of diverse age, health conditions, and demographics including medications, laboratory values, diagnoses, vital signs, and medical notes. The aggregated electronic health records are converted into a single standardized data structure format and ordered arrangement per patient, e.g., into a chronological order. A computer (or computer system) executes one or more deep learning models trained on the aggregated health records to predict one or more future clinical events and summarize pertinent past medical events related to the predicted events on an input electronic health record of a patient having the standardized data structure format and ordered into a chronological order. An electronic device configured with a healthcare provider-facing interface displays the predicted one or more future clinical events and the pertinent past medical events of the patient.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
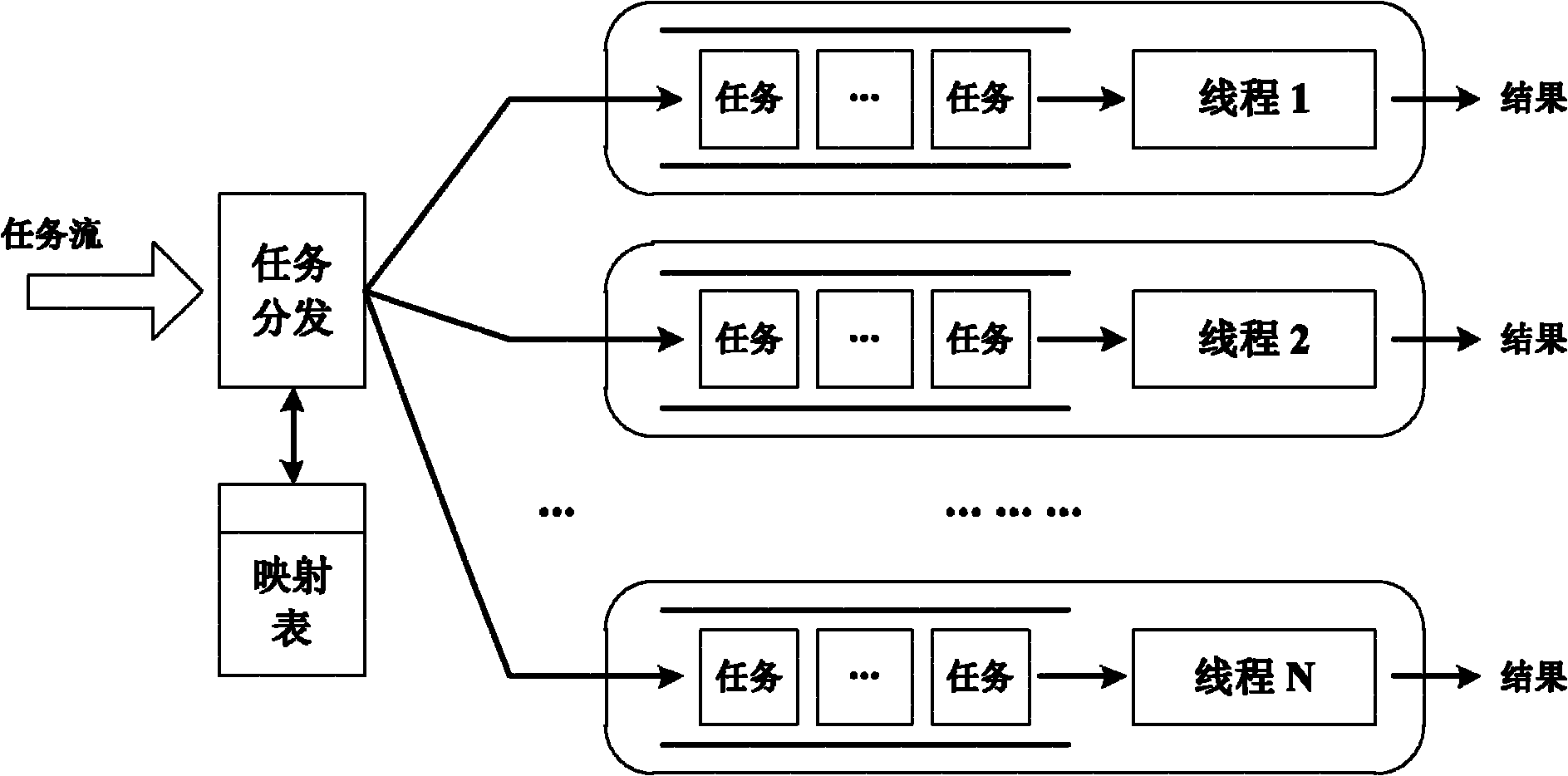
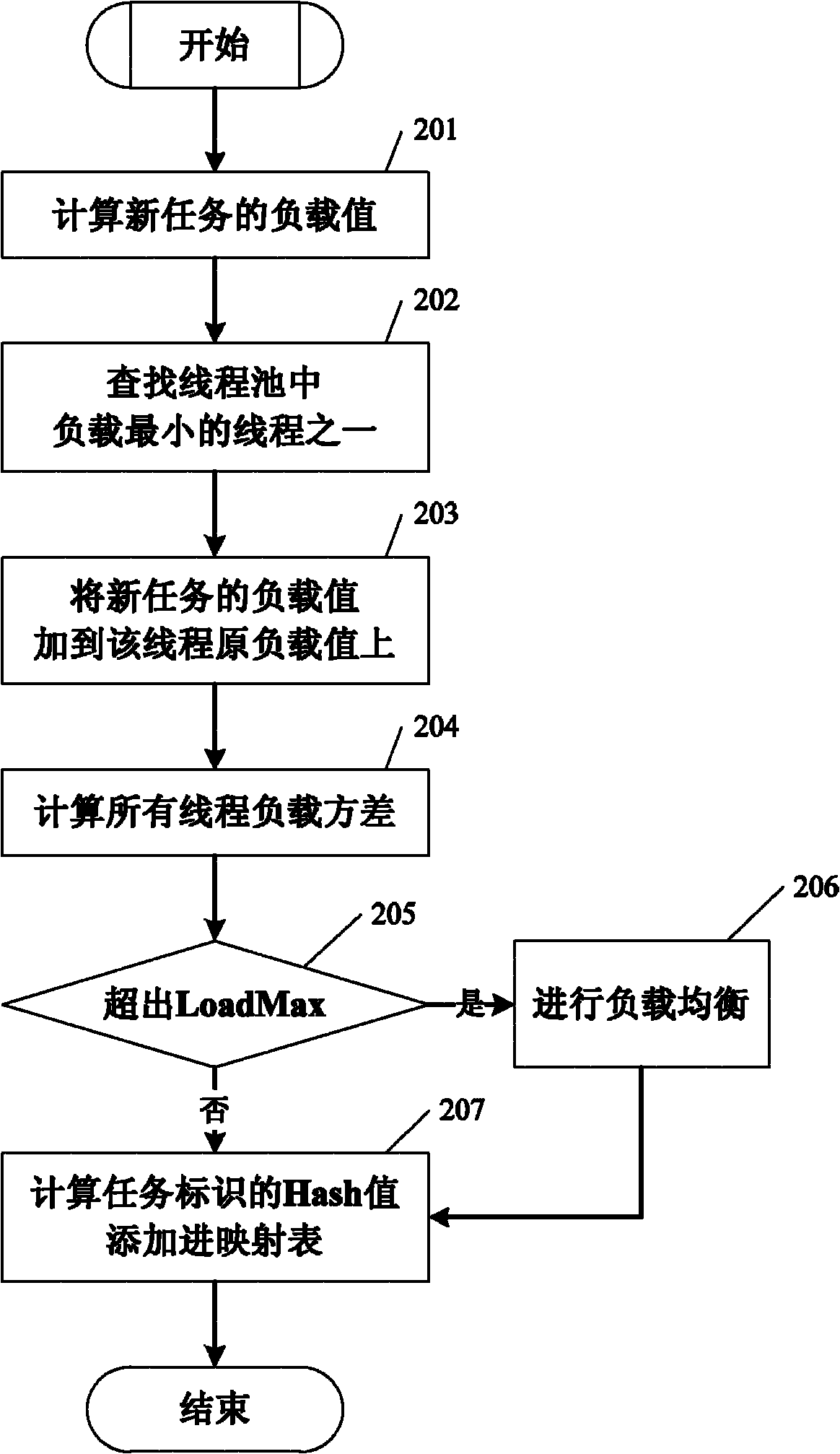
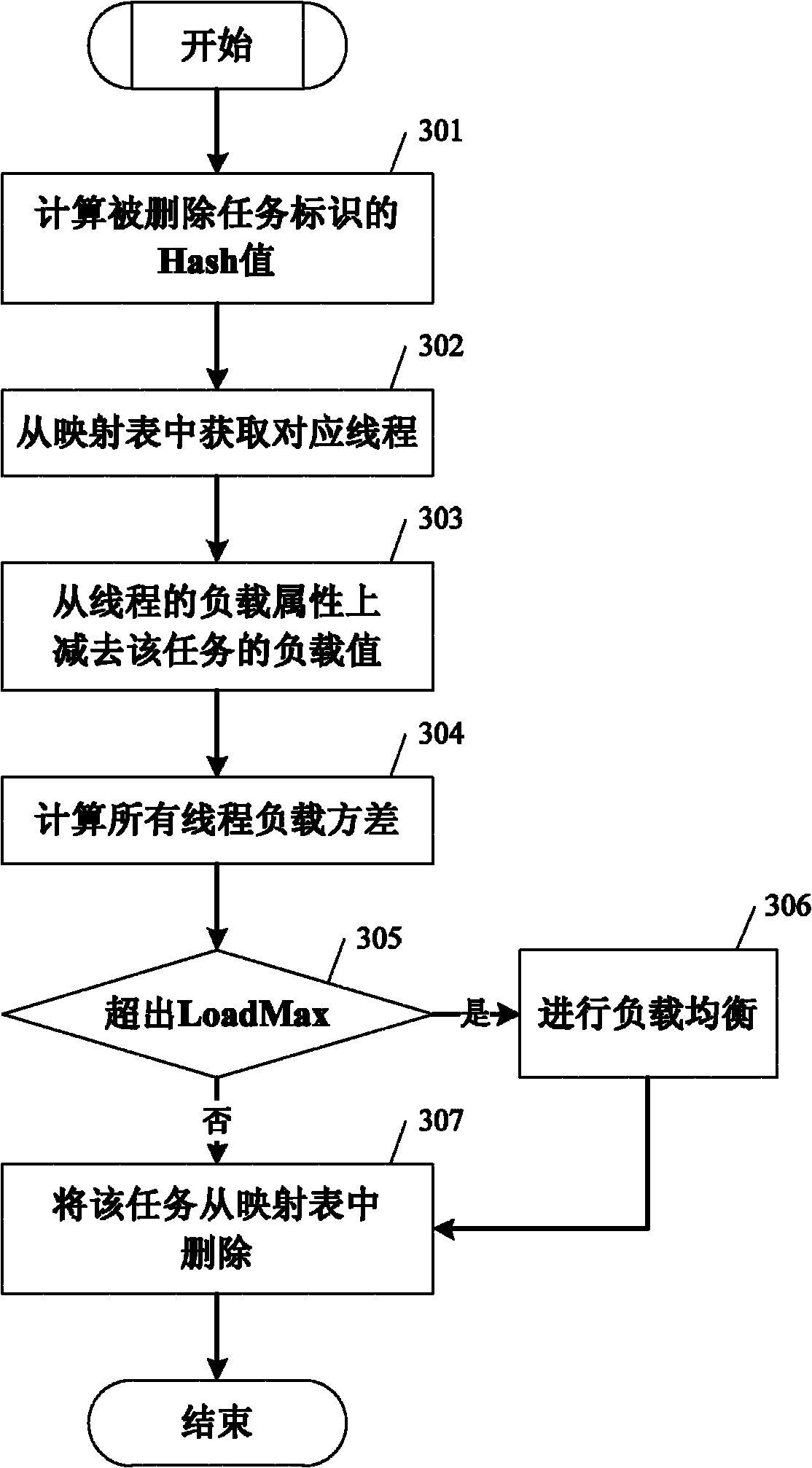
Method for designing thread pool capable of ensuring temporal succession
InactiveCN102122252AConsistent loadImprove concurrencyResource allocationTemporal successionThread pool
The invention relates to a method for designing a thread pool capable of ensuring temporal succession. The method comprises the following steps of: maintaining a task for the thread pool and marking the task into to a Hash mapping table of a thread ID, for managing the task distribution; adding an attribute parameter to thread parameters: a load (LThread) used for identifying the total quantity of the distributed tasks of each thread; and instead of sharing the same task queue by all the threads, configuring a corresponding task queue for each thread in the thread pool, wherein each thread can search for a new task from the corresponding task queue, and a single monitoring thread is arranged. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that: 1) by utilizing the new added function of the mapping table, the temporal successions for inputting and outputting data of each task can be guaranteed to be completely consistent, and 2) the loads on all threads can be guaranteed to be always consistent by the monitoring thread started at regular time, thereby achieving the best concurrent property.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
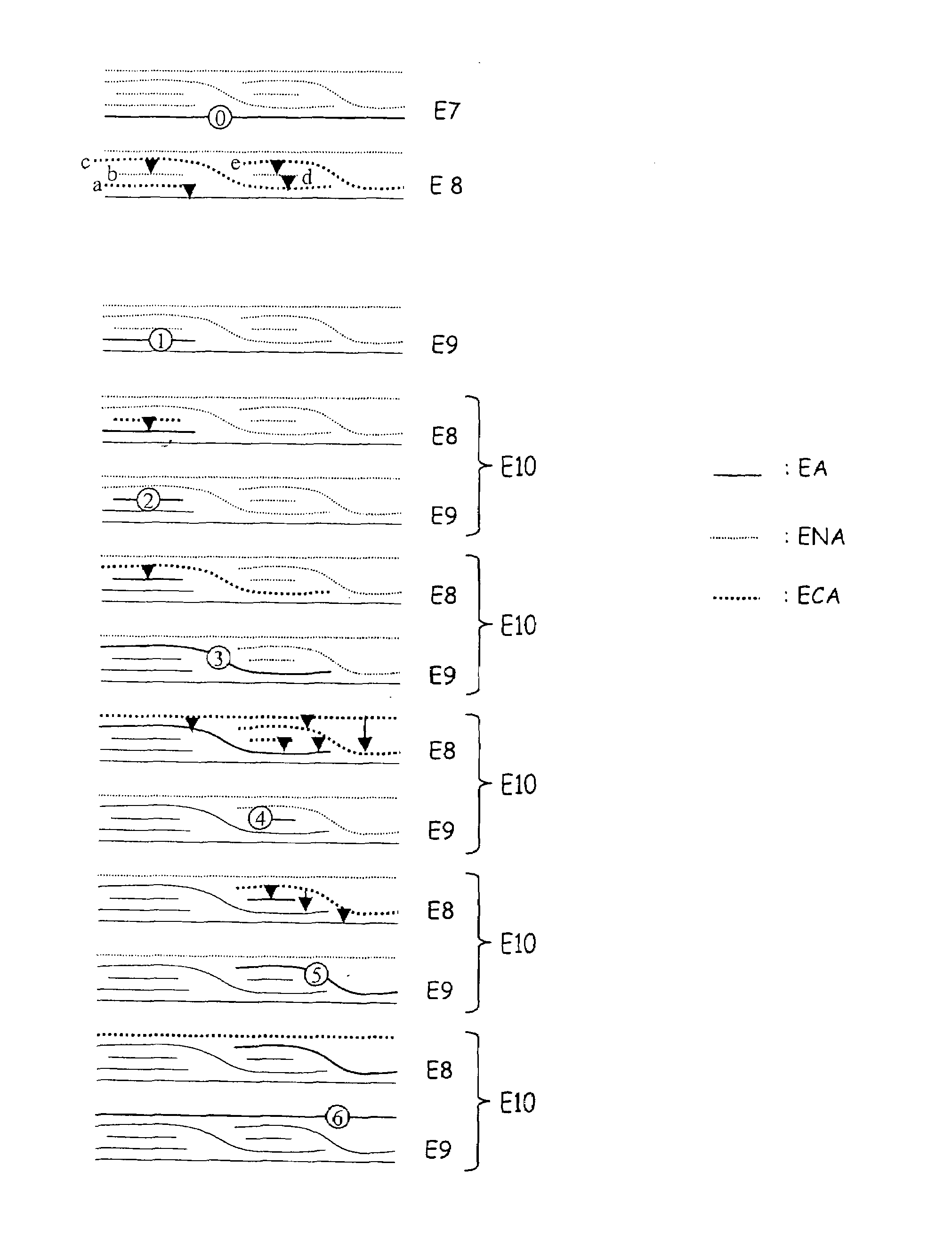
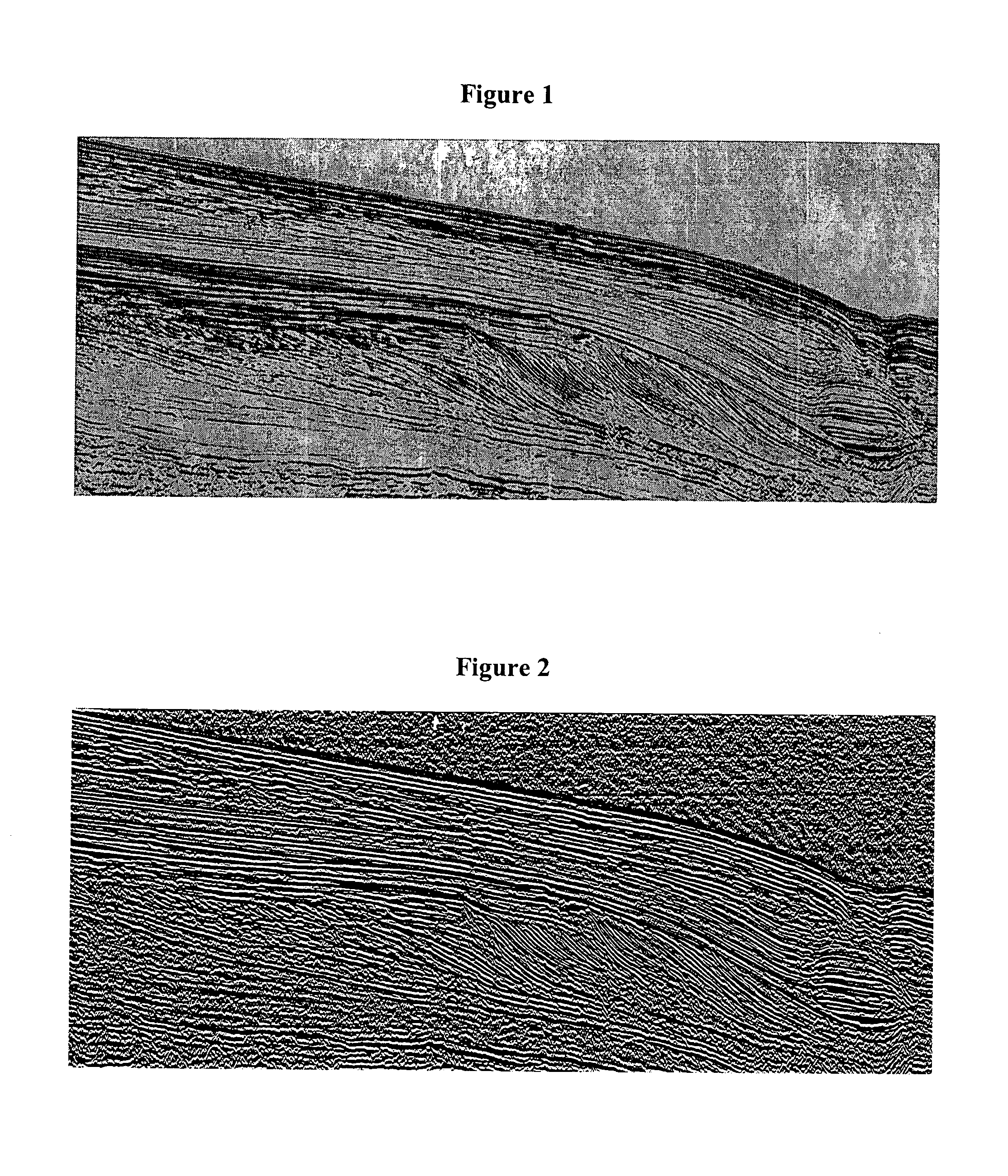
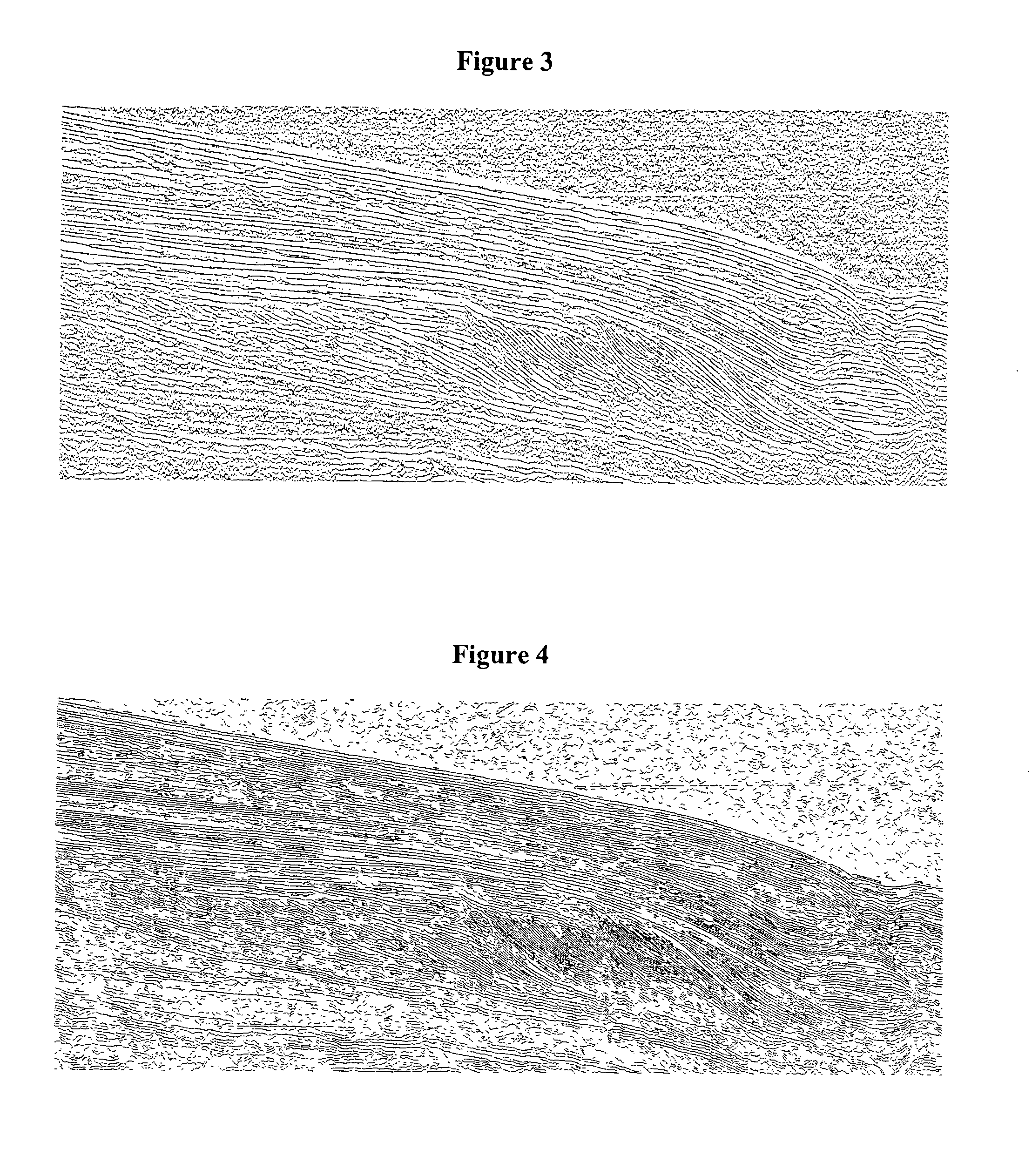
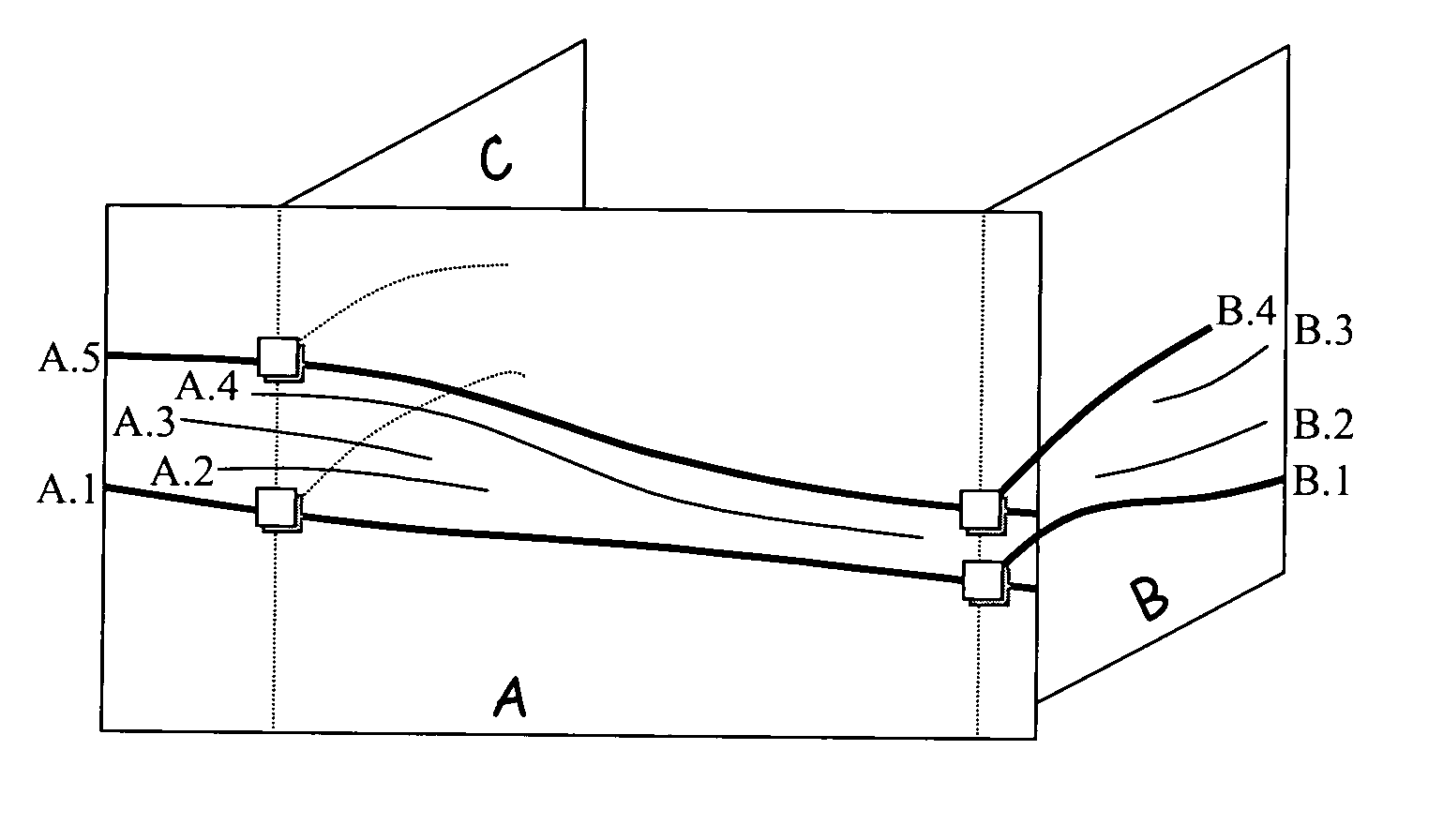
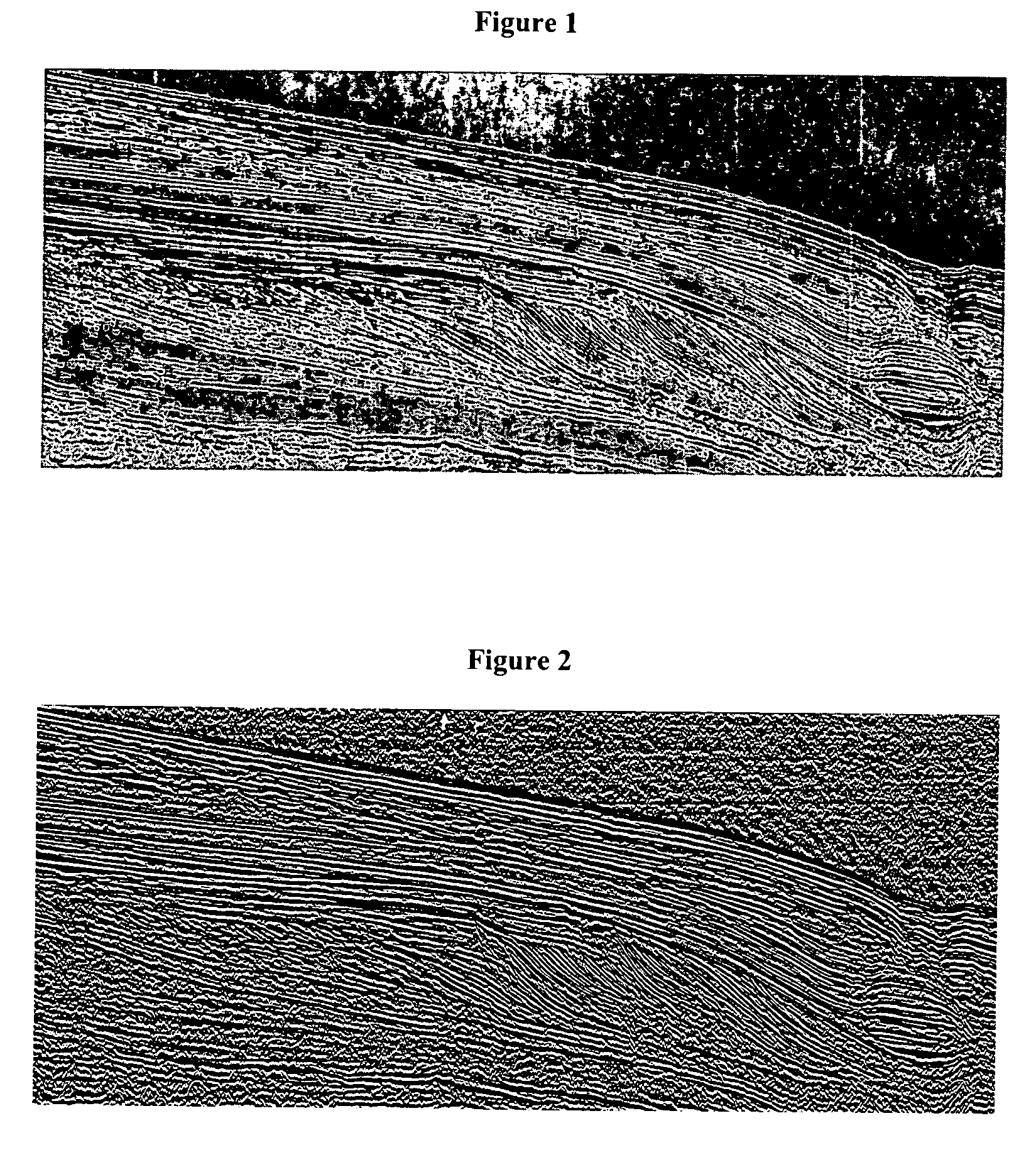
Method of sedimentologic interpretation by estimation of various chronological scenarios of sedimentary layers deposition
ActiveUS7257488B2SeismologySpecial data processing applicationsRelevant informationChronological time
A method having application for the development of oil reservoirs for automatically extracting from a seismic image pertinent information for sedimentologic interpretation by using estimations of realistic chronological scenarios of sedimentary layers deposition. The method includes iterative estimation of a first and of a second chronological scenario of the deposition of sedimentary layers, assuming that each reflector settles at the earliest and at the latest possible moment during the sedimentary depositional process. A chronological level number is assigned to a group of initial reflectors. Then a chronological level number is incremented by one and decremented by one which numbers are assigned to the reflectors including pixels located above and respectively below the initial reflectors and above and respectively below no other reflector. An interpretation of these two chronological scenarios is eventually carried out so as to reconstruct the depositional conditions of the sedimentary layers.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
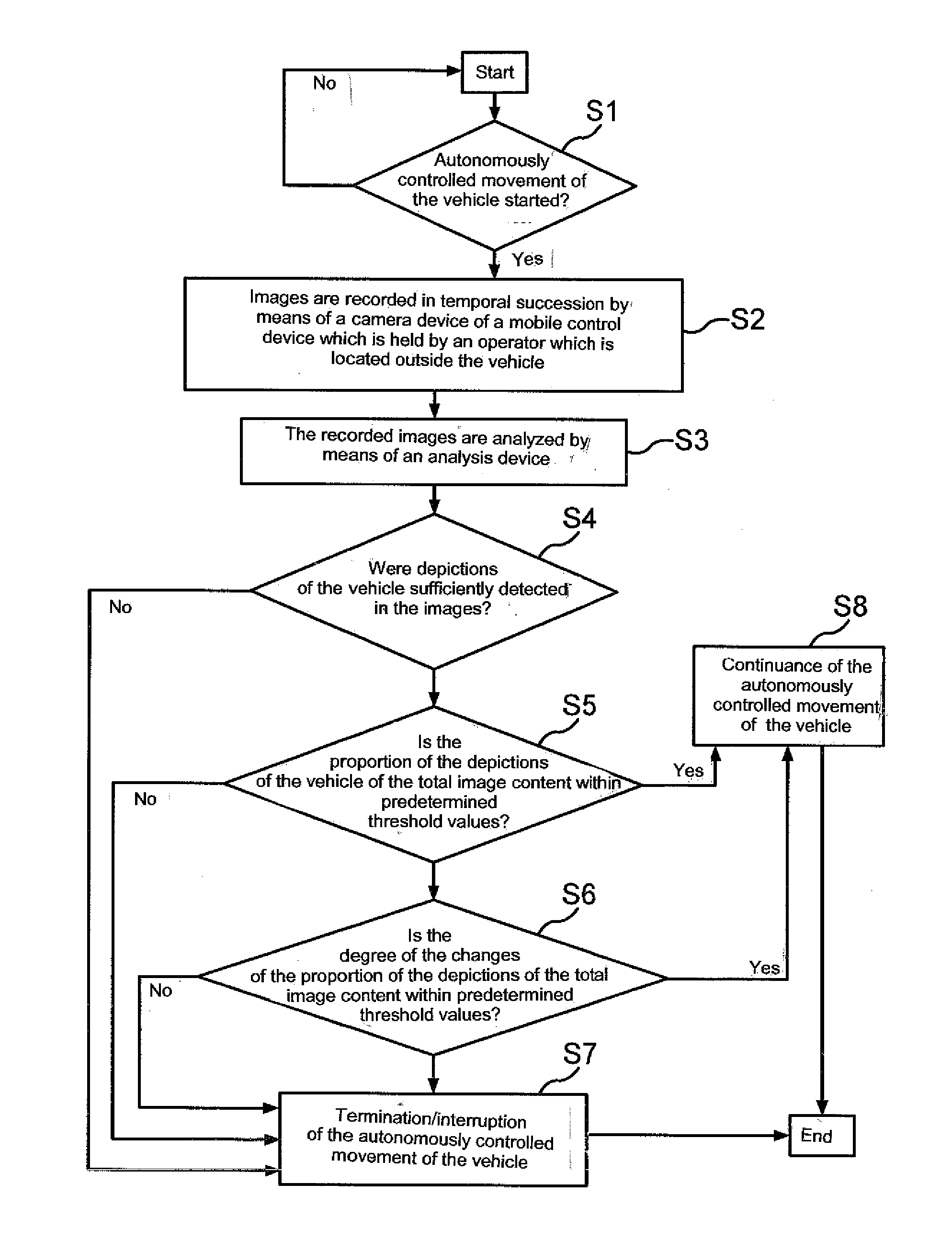
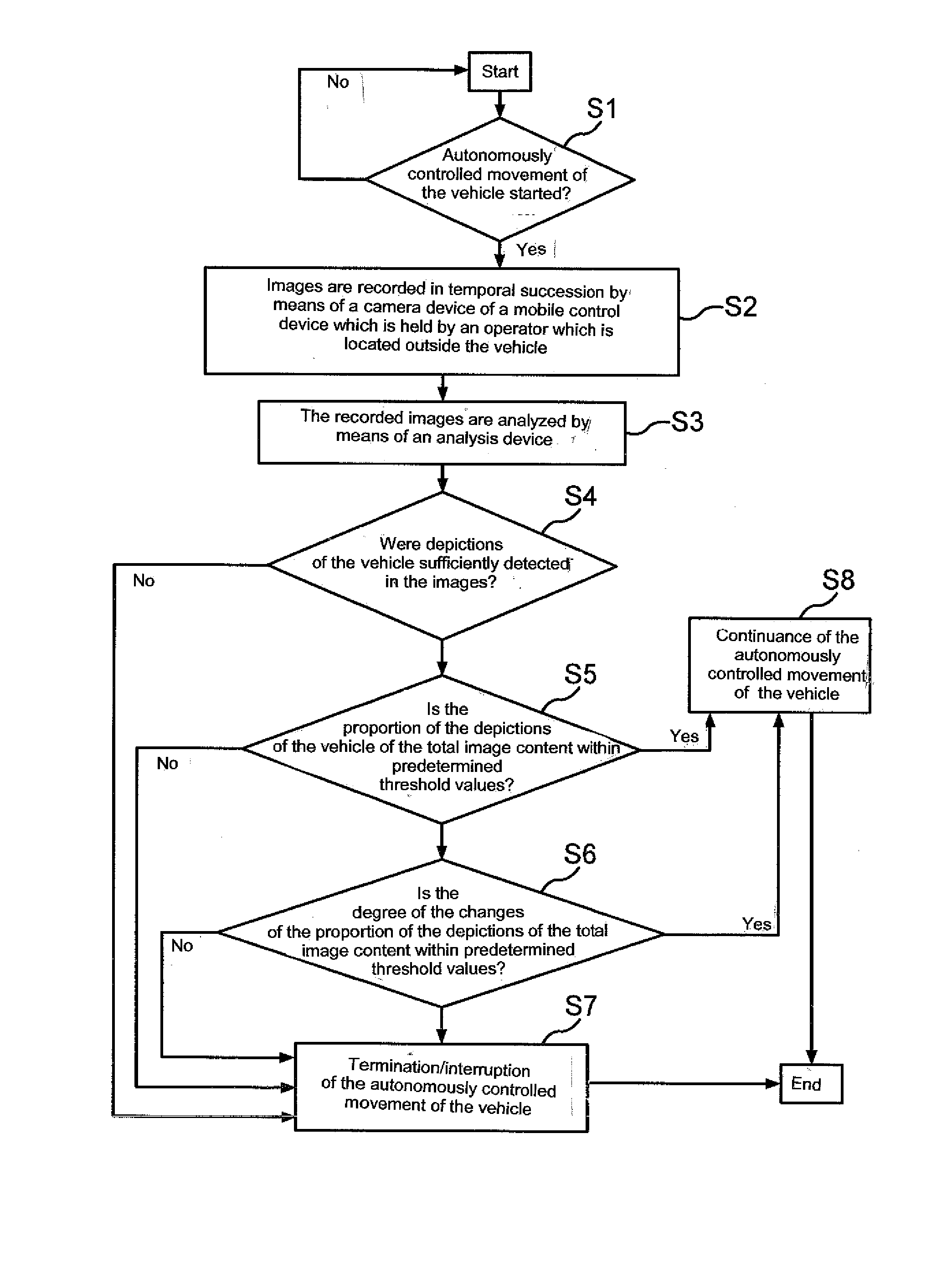
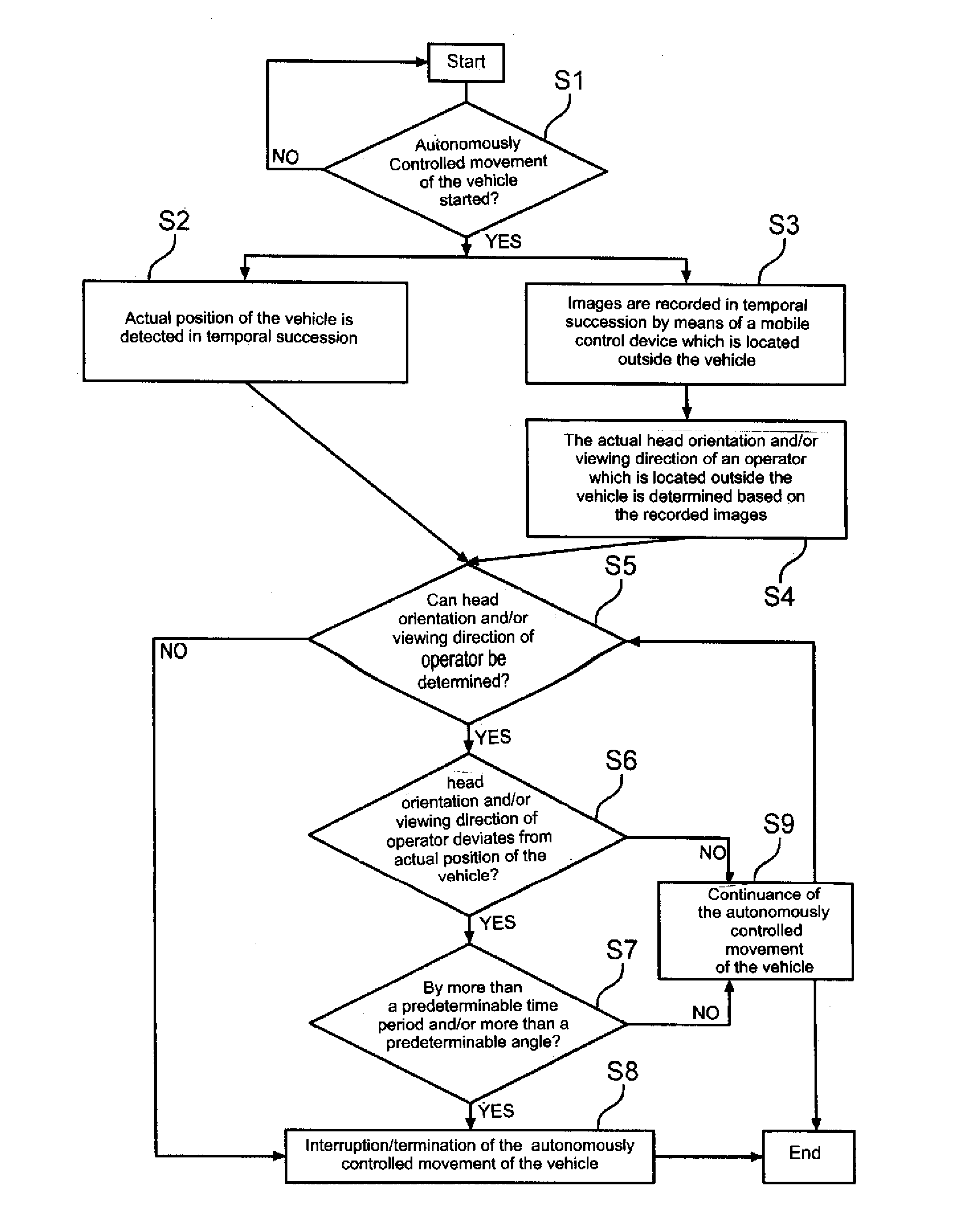
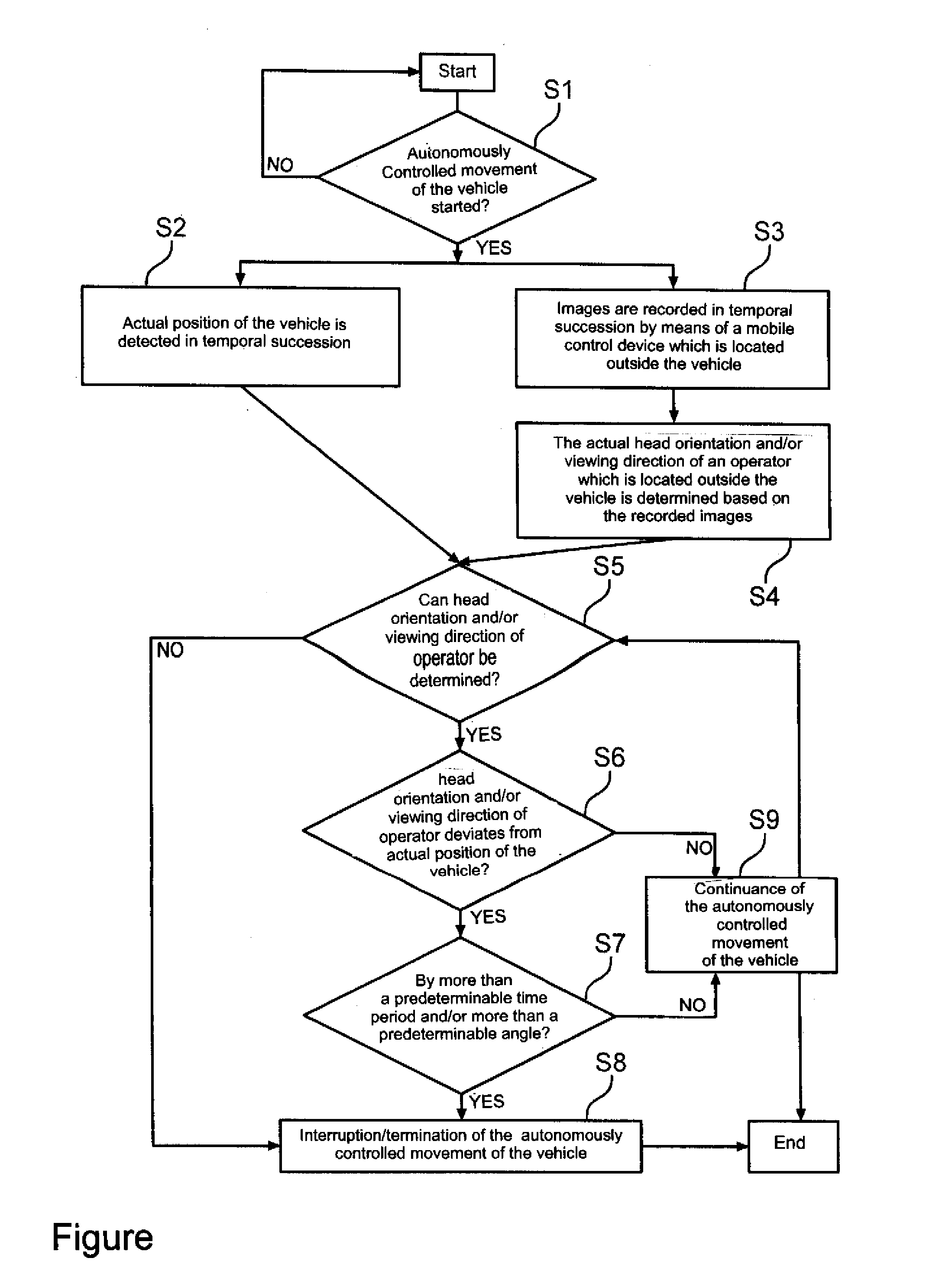
Method and system for operating a vehicle by monitoring the movement of the vehicle by means of a camera device of a mobile control device
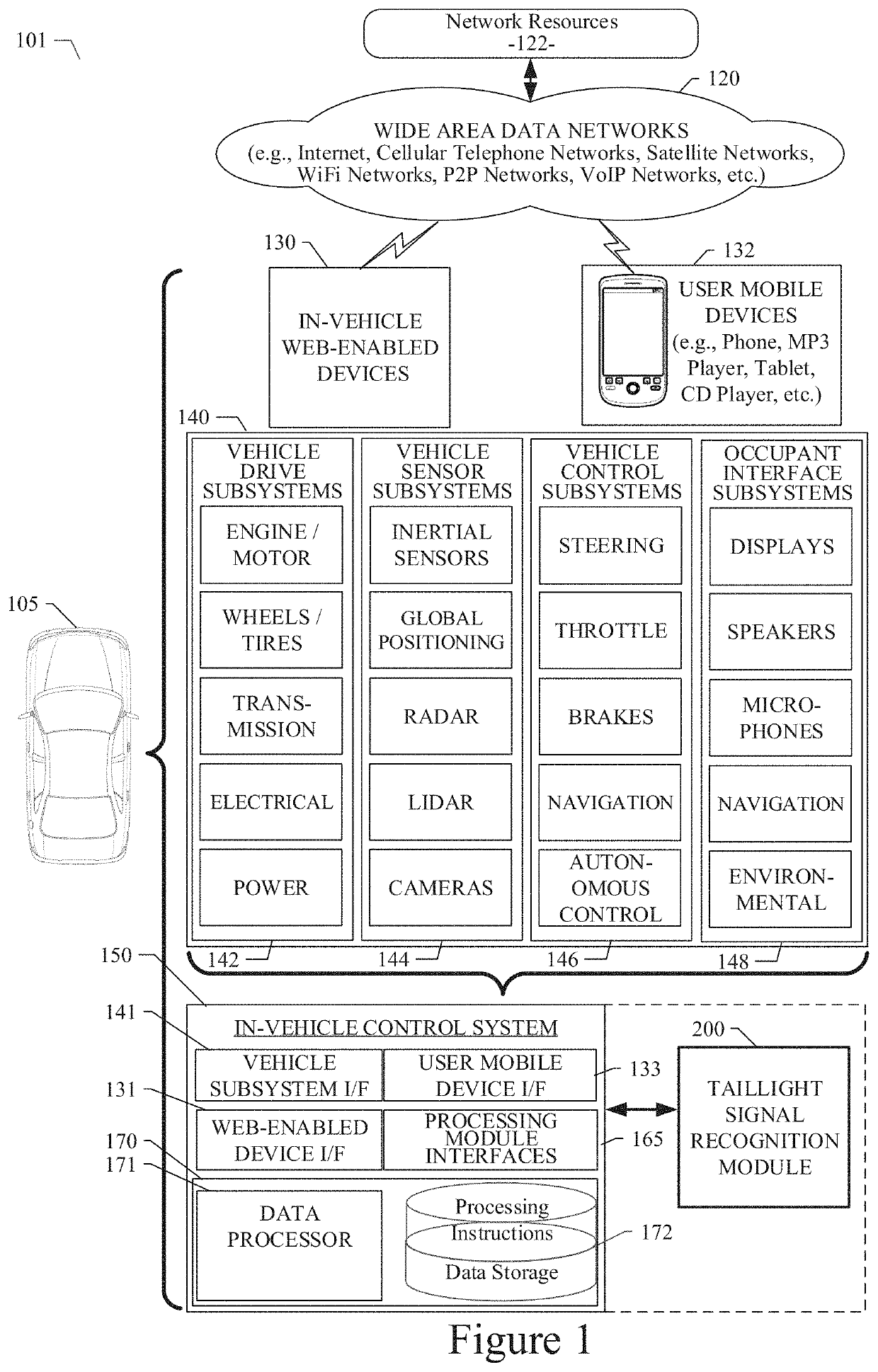
In a method for operating a vehicle which performs an autonomously controlled movement, images of the vehicle are recorded in temporal succession with a mobile control which is held by an operator located outside the vehicle, a position of the vehicle in the images, a change of the position of the vehicle in the images, a proportion of the depiction of the vehicle of the total image content and / or a change of the proportion is analyzed by an analysis device, and in case the vehicle was not or only incompletely detected in the images, the proportion of the depiction of the vehicle of the total image content, the change and or degree of change of the proportion is above or below a predeterminable threshold value, the autonomously controlled movement of the vehicle ins interrupted or terminated.
Owner:AUDI AG
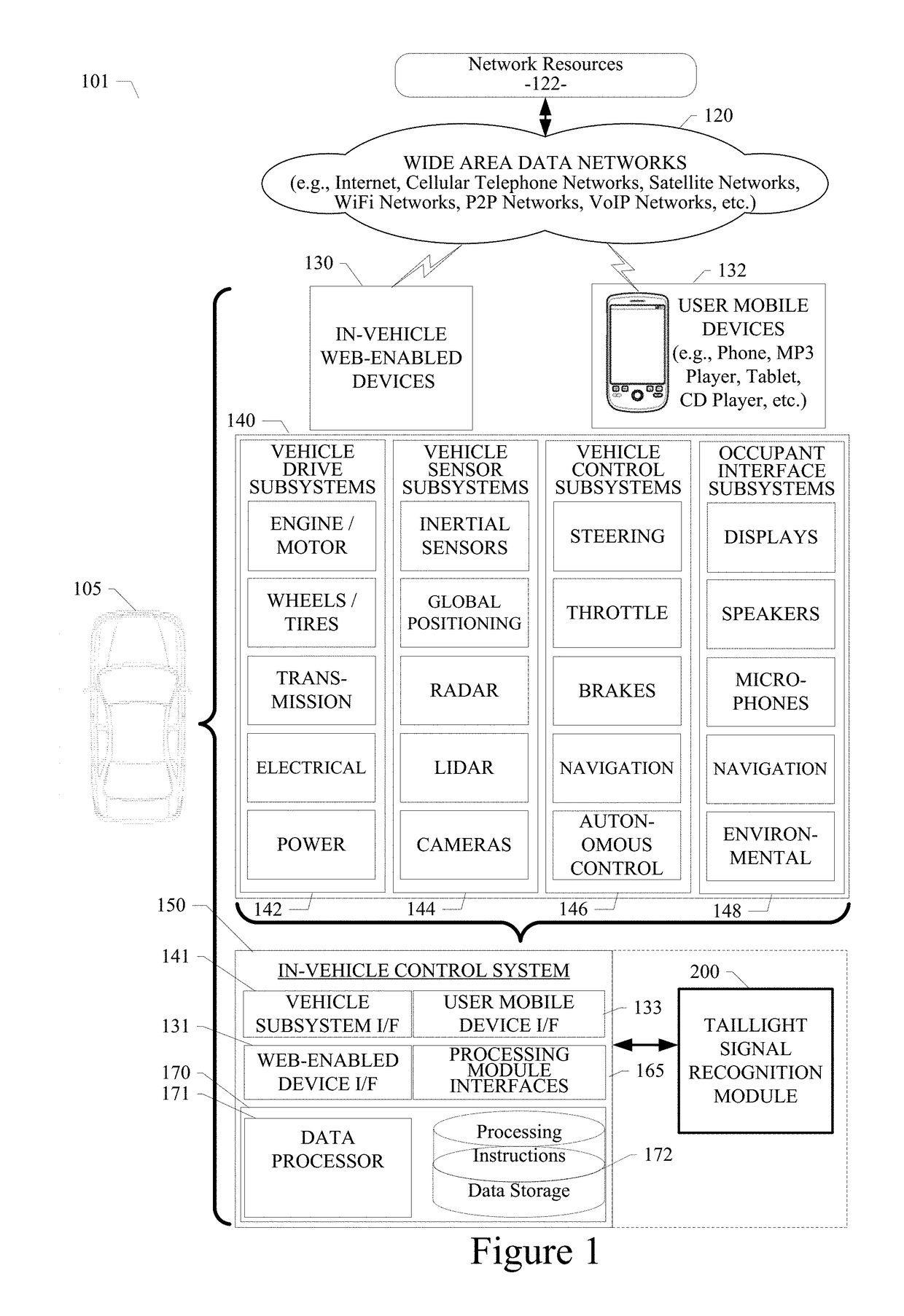
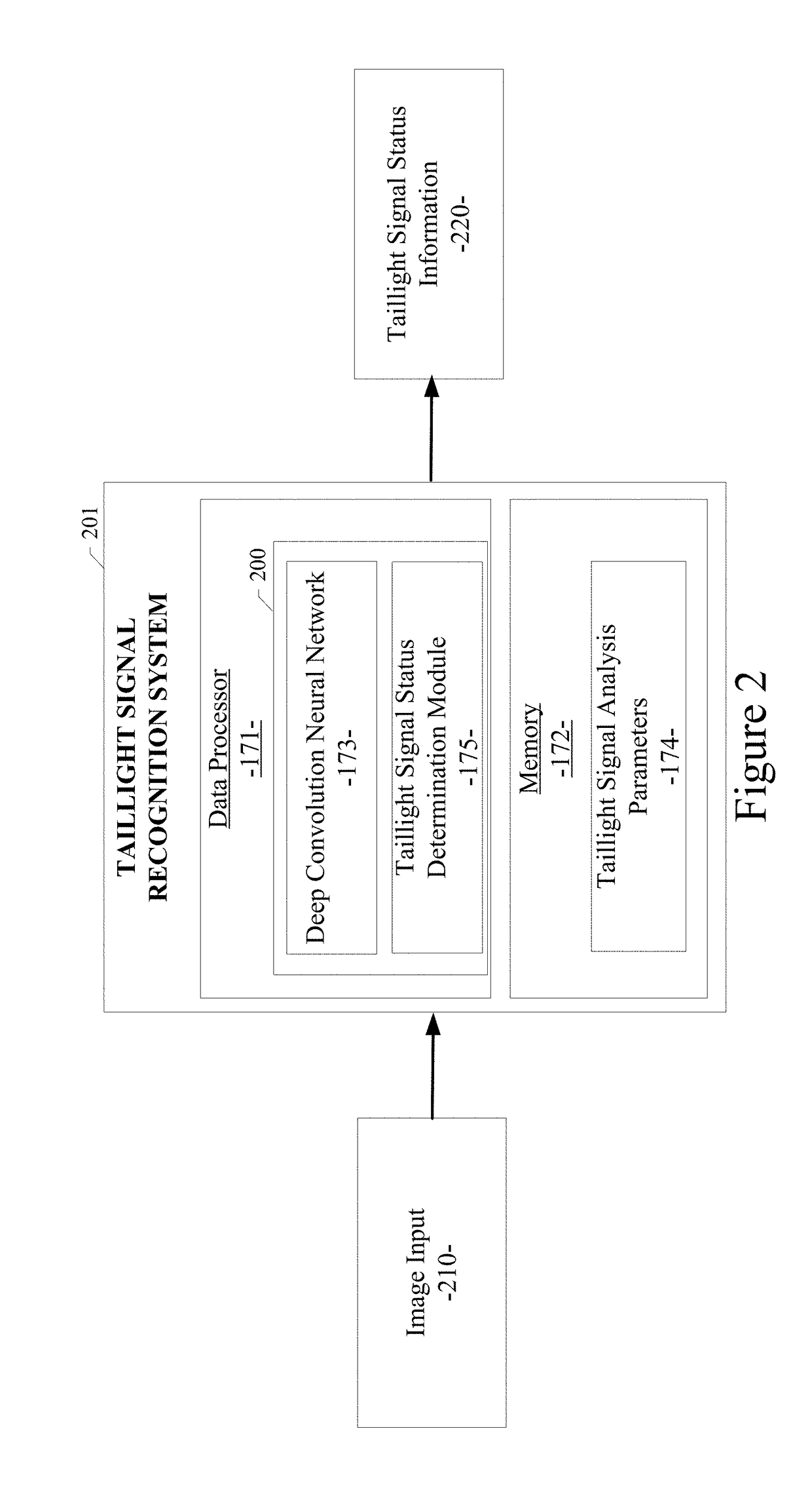
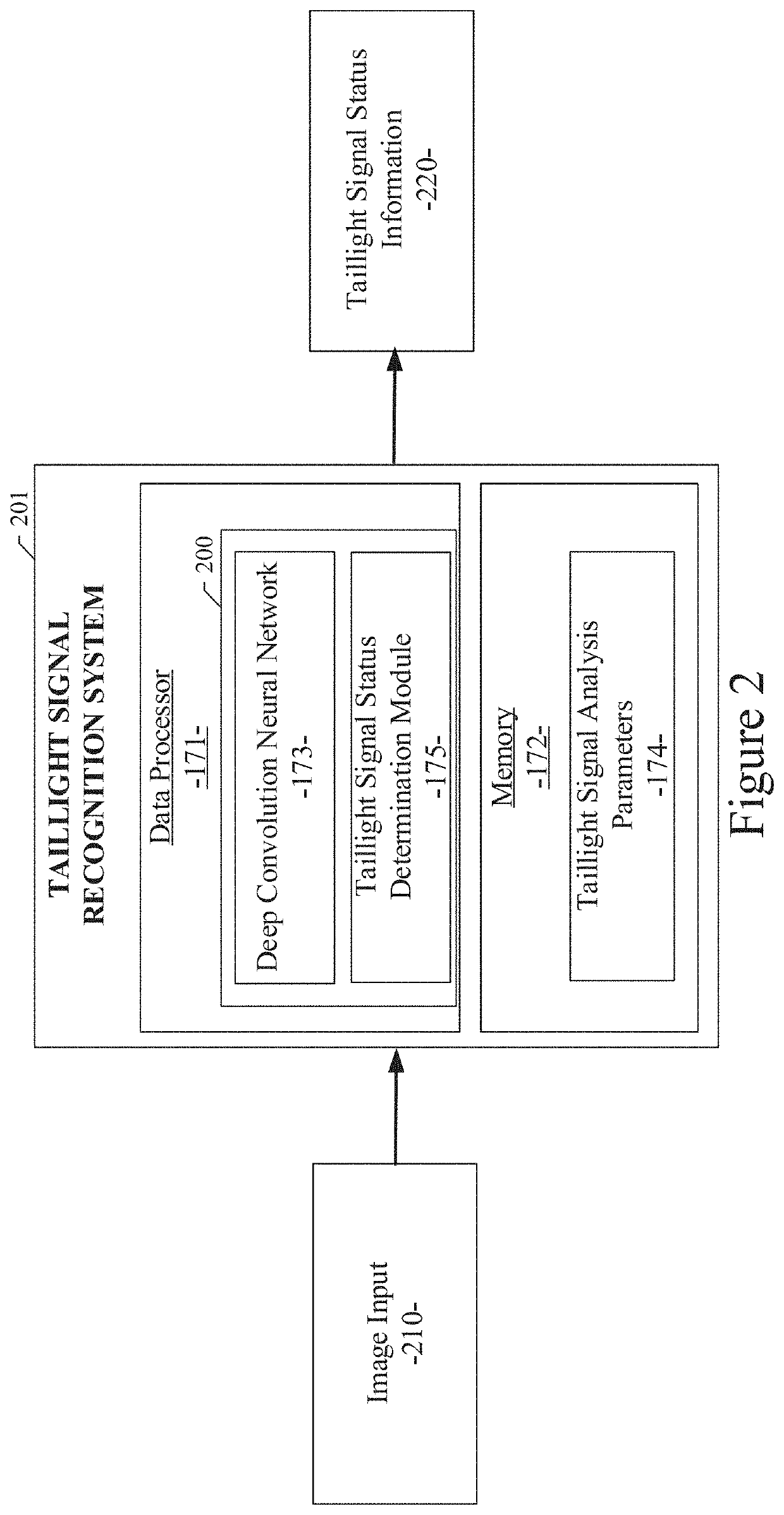
System and method for detecting taillight signals of a vehicle
ActiveUS20190087672A1Automatic detectionAgricultural vehiclesAutonomous decision making processGround truthData set
A system method for detecting taillight signals of a vehicle using a convolutional neural network is disclosed. A particular embodiment includes: receiving a plurality of images from one or more image-generating devices; generating a frame for each of the plurality of images; generating a ground truth, wherein the ground truth includes a labeled image with one of the following taillight status conditions for a right or left taillight signal of the vehicle: (1) an invisible right or left taillight signal, (2) a visible but not illuminated right or left taillight signal, and (3) a visible and illuminated right or left taillight signal; creating a first dataset including the labeled images corresponding to the plurality of images, the labeled images including one or more of the taillight status conditions of the right or left taillight signal; and creating a second dataset including at least one pair of portions of the plurality of images, wherein the at least one pair of portions of the plurality of the images are in temporal succession.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
Smoke detection by way of two spectrally different scattered light measurements
A device and a method for detecting smoke based on the principle of optical scattered light measurements are described. The device (100) described comprises a light emitting device (110), configured to issue a temporal succession of light pulses, wherein a first light pulse comprises a first spectral distribution and a second light pulse comprises a second spectral distribution different from the first spectral distribution. The device (100) further comprises a light receiver (120), configured to receive a first scattered light from the first light pulse and a second scattered light from the second light pulse, and configured to prepare a first output signal that is indicative for the first scattered light, and a second output signals that is indicative for the second scattered light. Also, the device (100) described comprises an evaluation unit that is configured to compare the first output signal with the second output signal. Preferably, the light emitting device (110) and the light receiver (120) are arranged directly adjacent to one another.
Owner:SIEMENS SWITZERLAND
Network server arrangement for processing non-parametric, multi-dimensional, spatial and temporal human behavior or technical observations measured pervasively, and related method for the same
ActiveCN103154928ASave storage capacitySave number of actionsMathematical modelsNatural language analysisHuman behaviorData stream
This invention generally discusses wireless devices, servers and communications networks. In particular the invention pertains to performing observations in one or more mobile terminals and processing and distributing the related data in a server side system through layered data processing activities, and conversion of non- parametric data into parameterized form through the utilization of statistical filtering and semantic data structures. It is further explained how such multi-layer, parametrized data can be utilized for predictive purposes, and how feedback loops can be built with the physical world to improve future predictions. The invention is applicable in various applications, for example in systems where precise digital profiles of users need to be built on a continuous basis, and such profiles need to be dynamically linked to one or several actions triggered by emerging characteristics in the data. The multi-layer approaches makes it possible to structure output statistics into continuous and standardized, periodic datasets, even though input data is highly unorganized, non-chronological, and sporadic. Similarly, the invention describes how the multi-layer data storage structure and chosen statistical operations make it possible to build virtually an infinite number of further aggregations and averages based on the output data streams.
Owner:ARBITRON MOBILE
Method of sedimentologic interpretation by estimation of various chronological scenarios of sedimentary layers deposition
ActiveUS20060247858A1Great tortuosityShorten the lengthSeismologySpecial data processing applicationsRelevant informationTemporal succession
A method having application for the development of oil reservoirs for automatically extracting from a seismic image pertinent information for sedimentologic interpretation in order to reconstruct the depositional conditions under which sedimentary layers have formed, by means of estimations of realistic chronological scenarios of sedimentary layers deposition. The method comprises iterative estimation of a first and of a second chronological scenario of the deposition of sedimentary layers, assuming that each reflector settles at the earliest, respectively at the latest possible moment during the sedimentary depositional process. A chronological level number is assigned to a group of initial reflectors. Then a chronological level number incremented by one, respectively decremented by one, is assigned to the reflectors made up from pixels located above, respectively below the initial reflectors and above, respectively below no other reflector. An interpretation of these two chronological scenarios is eventually carried out so as to reconstruct the depositional conditions of the sedimentary layers.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
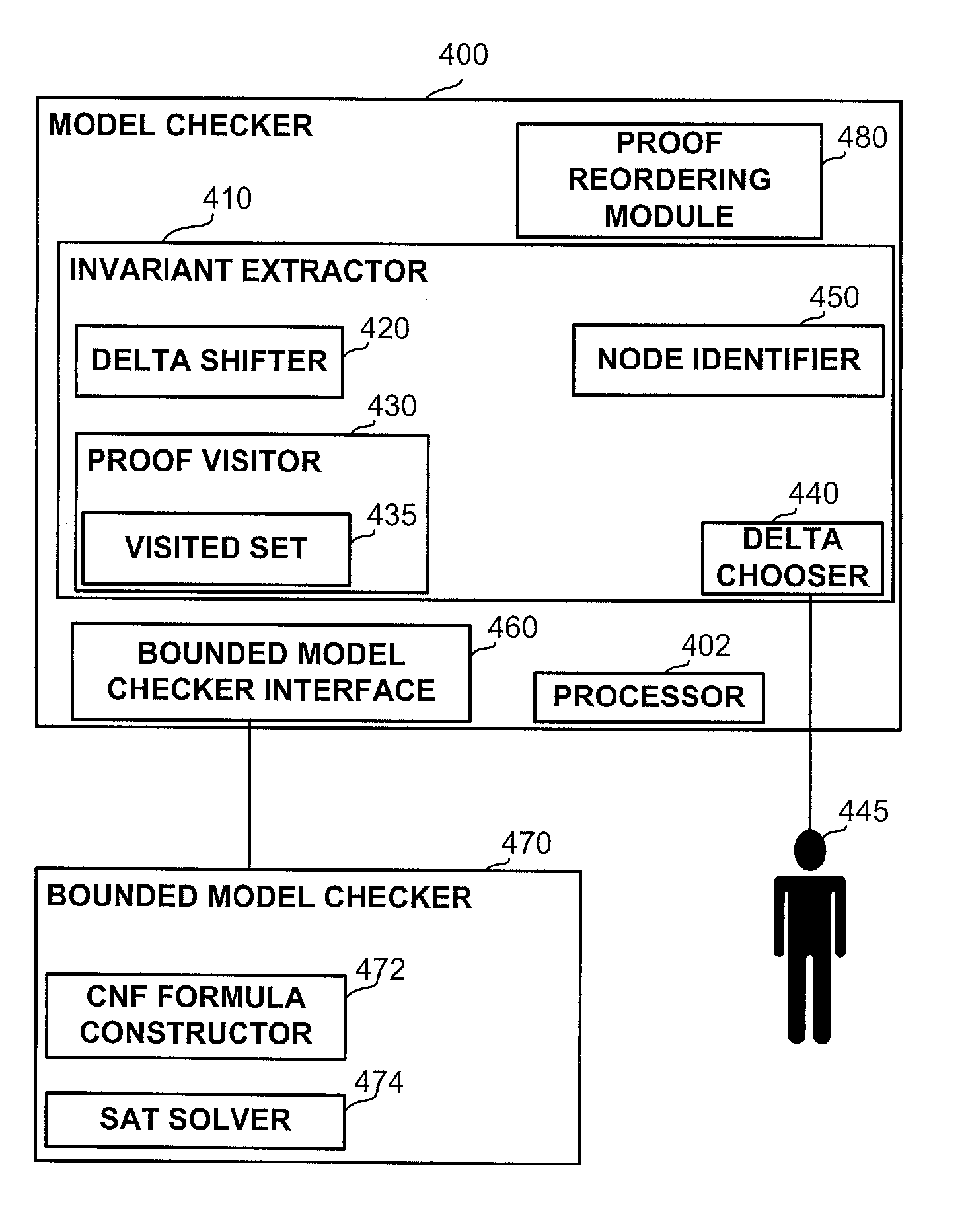
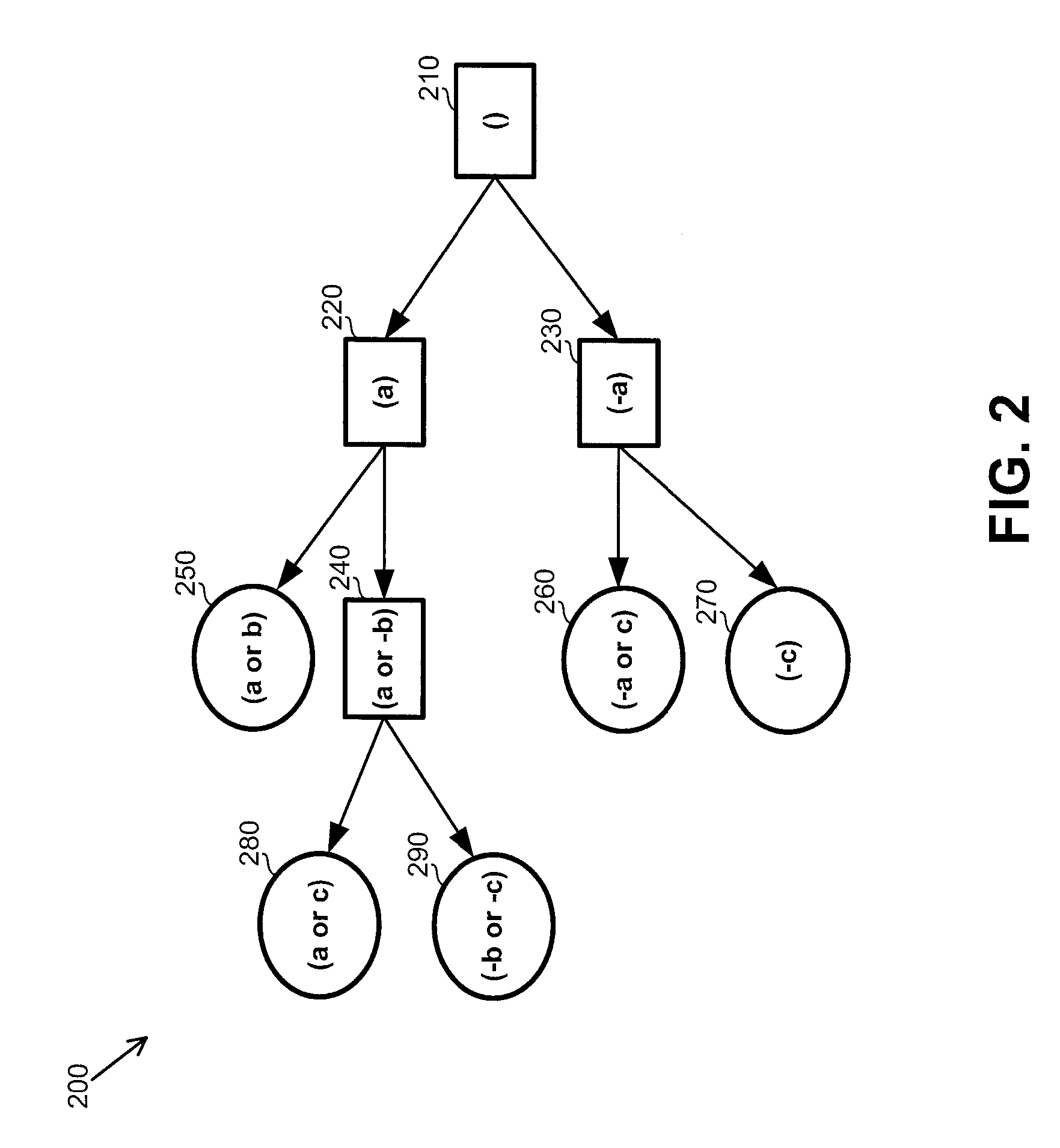
Utilizing an unsat proof for model checking
InactiveUS20110010139A1Computation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designTemporal successionSatisfiability
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
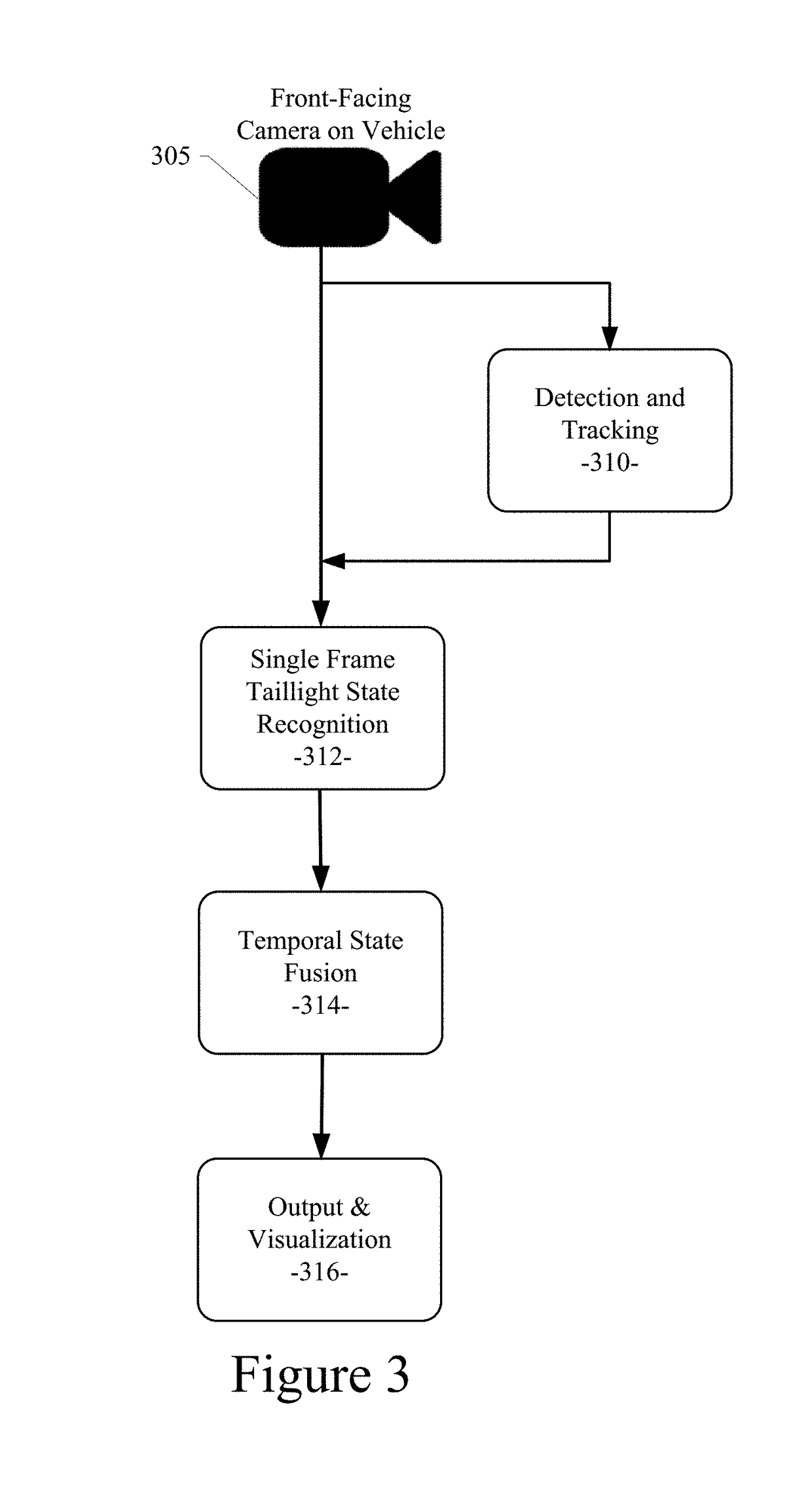
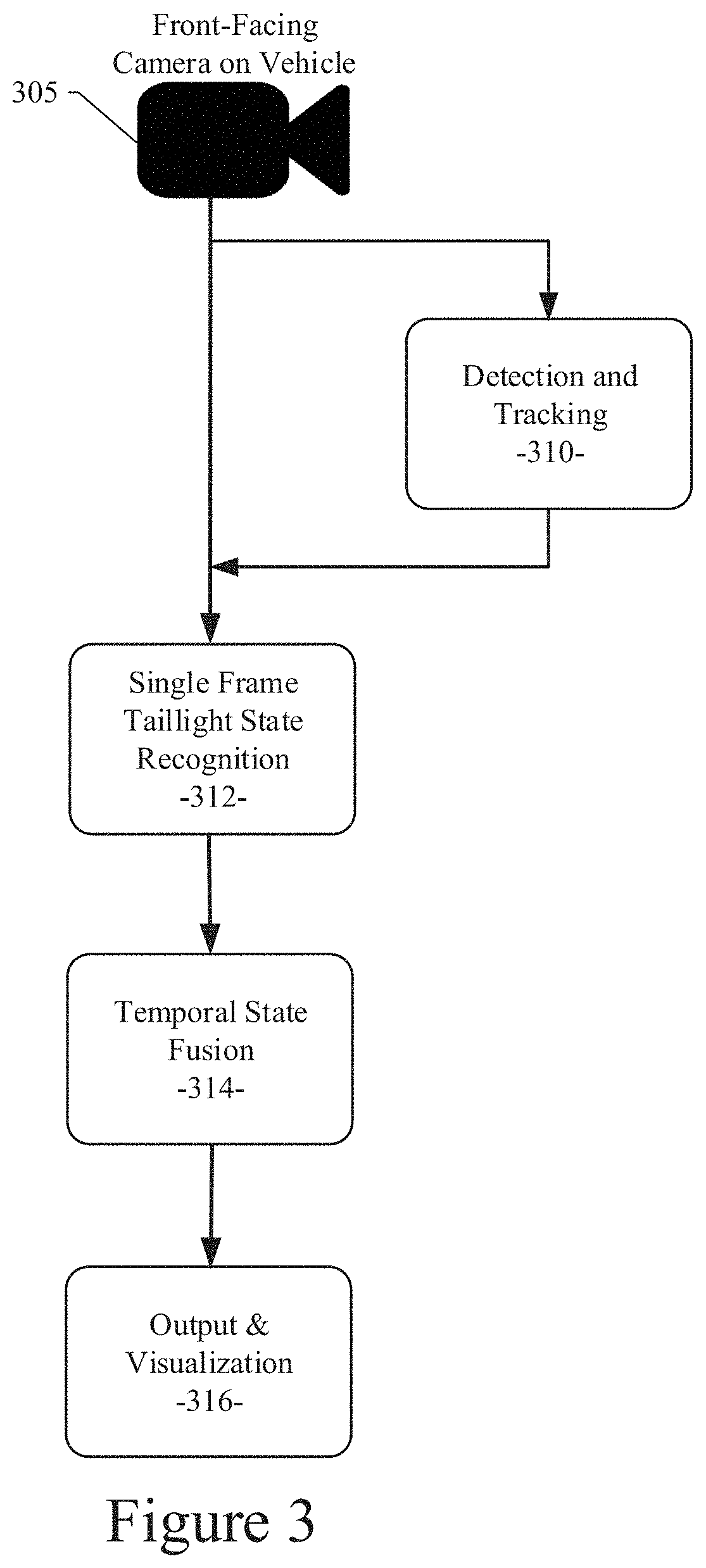
System and method for vehicle taillight state recognition
ActiveUS20190370574A1Automatic detectionAccurate trajectory level taillight state recognitionAutonomous decision making processCharacter and pattern recognitionMultiple frameTemporal succession
A system and method for taillight signal recognition using a convolutional neural network is disclosed. An example embodiment includes: receiving a plurality of image frames from one or more image-generating devices of an autonomous vehicle; using a single-frame taillight illumination status annotation dataset and a single-frame taillight mask dataset to recognize a taillight illumination status of a proximate vehicle identified in an image frame of the plurality of image frames, the single-frame taillight illumination status annotation dataset including one or more taillight illumination status conditions of a right or left vehicle taillight signal, the single-frame taillight mask dataset including annotations to isolate a taillight region of a vehicle; and using a multi-frame taillight illumination status dataset to recognize a taillight illumination status of the proximate vehicle in multiple image frames of the plurality of image frames, the multiple image frames being in temporal succession.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
Method and system for operating a vehicle by monitoring the head orientation and/or viewing direction of an operator by means of a camera device of a mobile control device
ActiveUS20140058587A1Accurately determineDigital data processing detailsSteering partsReal-time computingTemporal succession
A method for autonomously controlling a movement of a vehicle includes detecting a respective actual position of the vehicle in temporal succession; recording in temporal succession with a first camera device of a mobile control device images of an operator located outside the vehicle, the mobile control device being held by the operator; determining with an analysis device an actual head orientation and / or a viewing direction of the operator based on the recorded images; and interrupting or terminating the autonomously controlled movement of the vehicle in response to at least one of two instances, a first instance in which the actual head orientation and / or viewing direction of the operator cannot be detected, a second instance in which the head orientation and / or viewing direction of the operator deviates for longer than a predeterminable time period and / or by a predeterminable angle from the actual position of the vehicle
Owner:AUDI AG
Mr imaging system with freely accessible examination volume
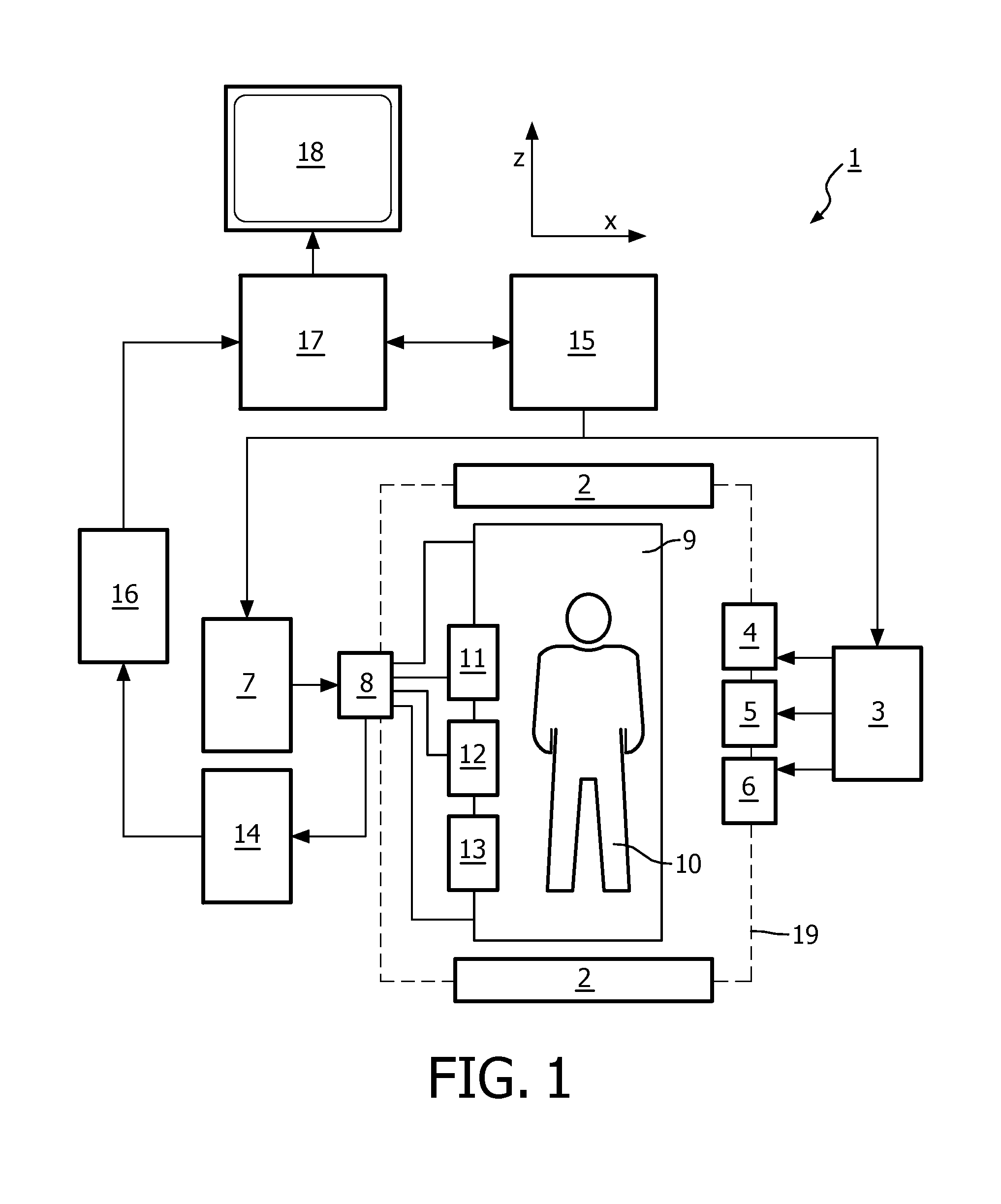
InactiveUS20120169340A1High imagingIncrease the magnetic field strengthMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTravel modeTemporal succession
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging system (1) comprising: a main magnet for generating a uniform, steady magnetic field within an examination volume (21), an RF waveguide (19) for guiding travelling RF waves along an axis of the examination volume (21) in at least one travelling mode of the RF waveguide (19), at least one RF antenna (9) for transmitting RF pulses to and / or receiving MR signals from a body (10) of a patient positioned in the examination volume (21), wherein the RF antenna (9) is configured to couple to the at least one travelling mode of the RF waveguide (19), and wherein the RF antenna (9) is located on the imaging system such that the examination volume (21) is freely accessible, a control unit (15) for controlling the temporal succession of RF pulses, and a reconstruction unit (17) for reconstructing an MR image from the received MR signals. Further, the invention relates to an RF antenna (9) for an MR imaging system (1), wherein the RF antenna (9) is formed by an electrically conductive plate (22) comprising at least one recess (23).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Methods for transmitting and receiving a multicarrier signal, carrying out a channel estimation, and corresponding devices and computer program products
ActiveUS20090316569A1Reduce ISIEliminate distractionsModulated-carrier systemsFrequency-division multiplexTransmission channelTemporal succession
A method is provided for receiving a received signal corresponding to a multicarrier signal transmitted by at least one transmitter via a transmission channel. The multicarrier signal is formed by a temporal succession of symbols consisting of a set of data elements including informative data elements with real values, and pilots for at least some of the symbols. Due to groups of at least two pilots being respectively located in an adjacent region in the time / frequency space, the reception method includes a step of extracting at least two complex values corresponding the pilots of the group of the adjacent region, once they have passed through the transmission channel, and a step of estimating the transmission channel in the adjacent region on the basis of the complex values. The modulation used is the type of OFDM OQAM.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
Method and system for solving satisfiability problems
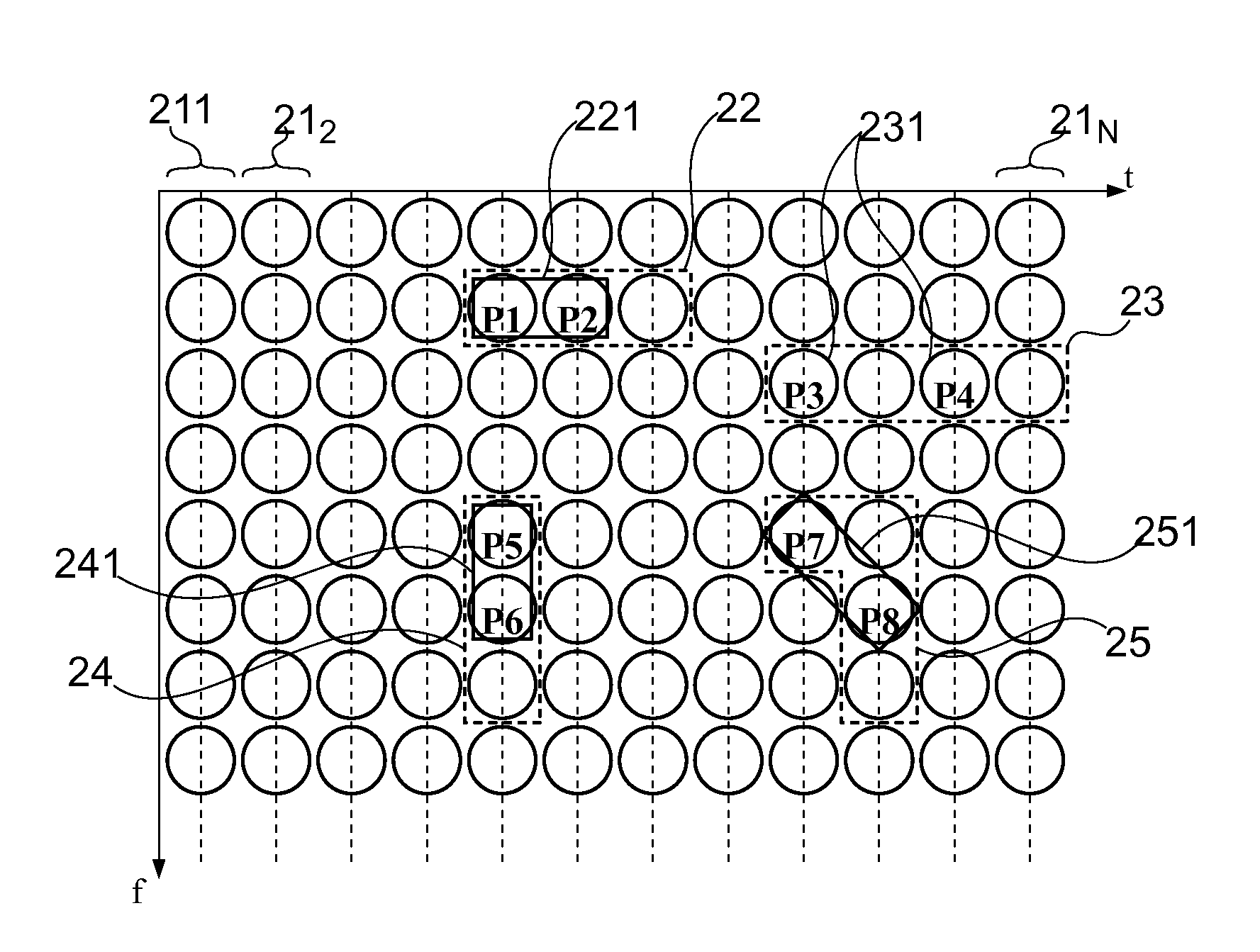
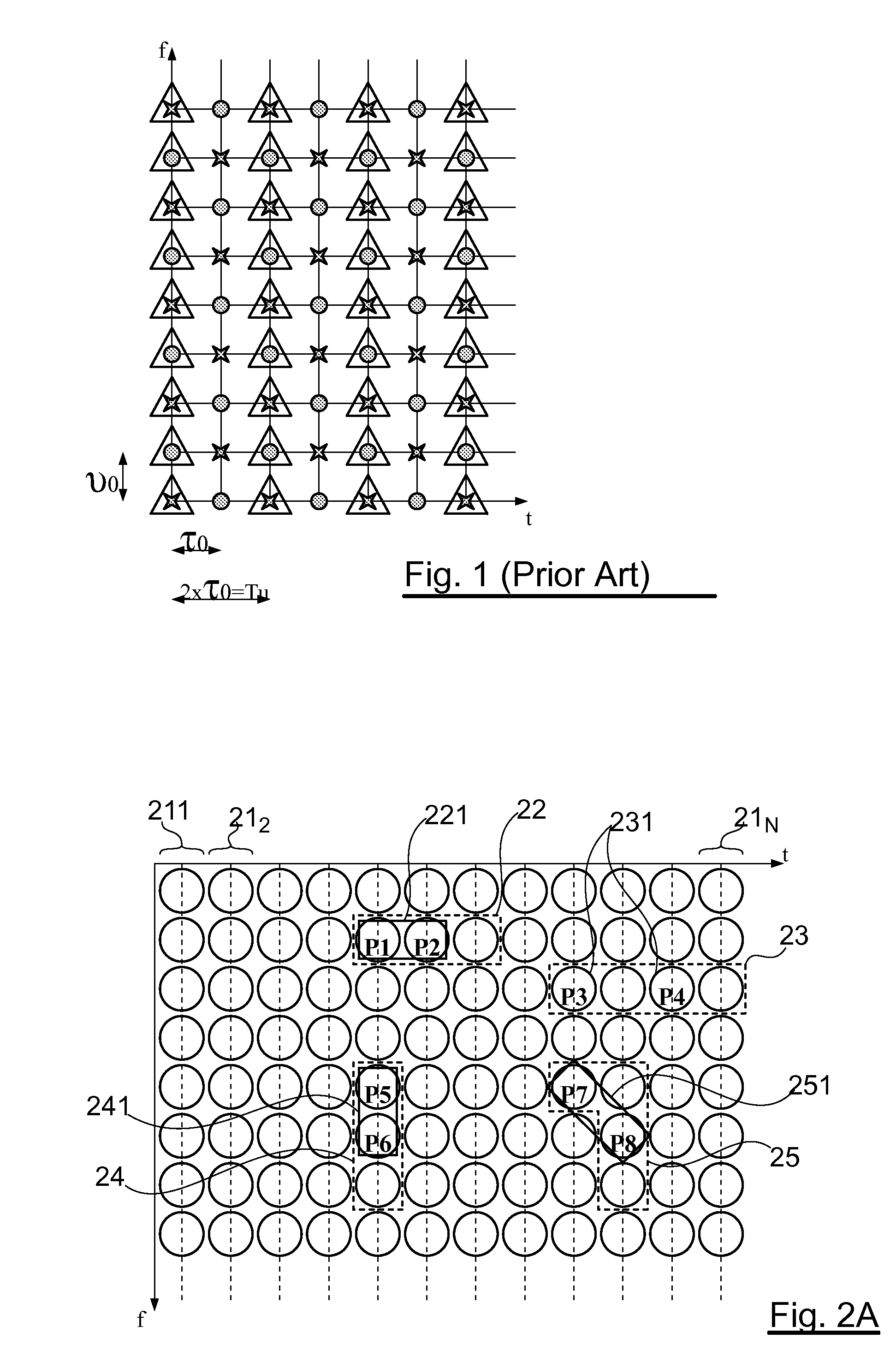
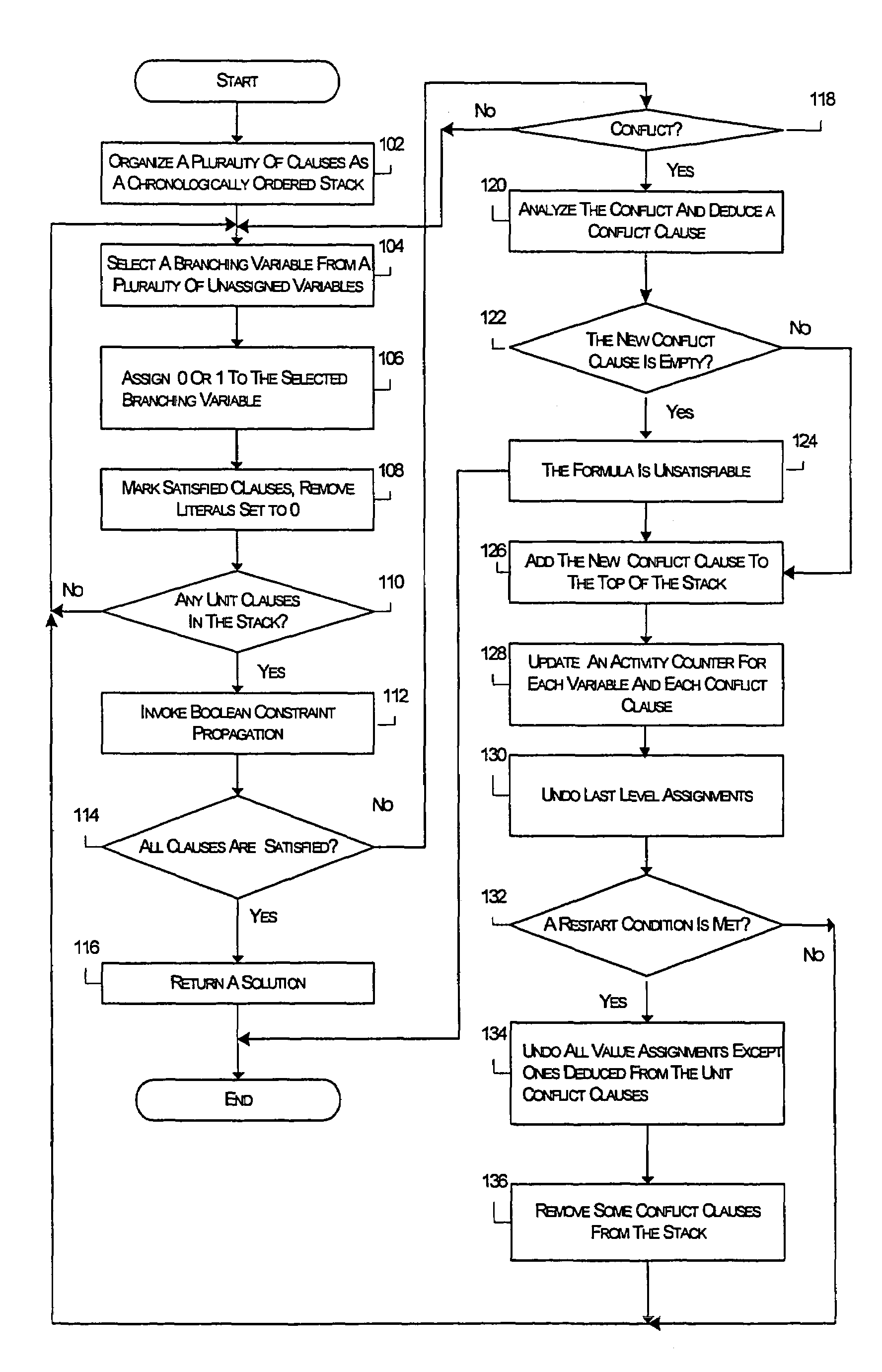
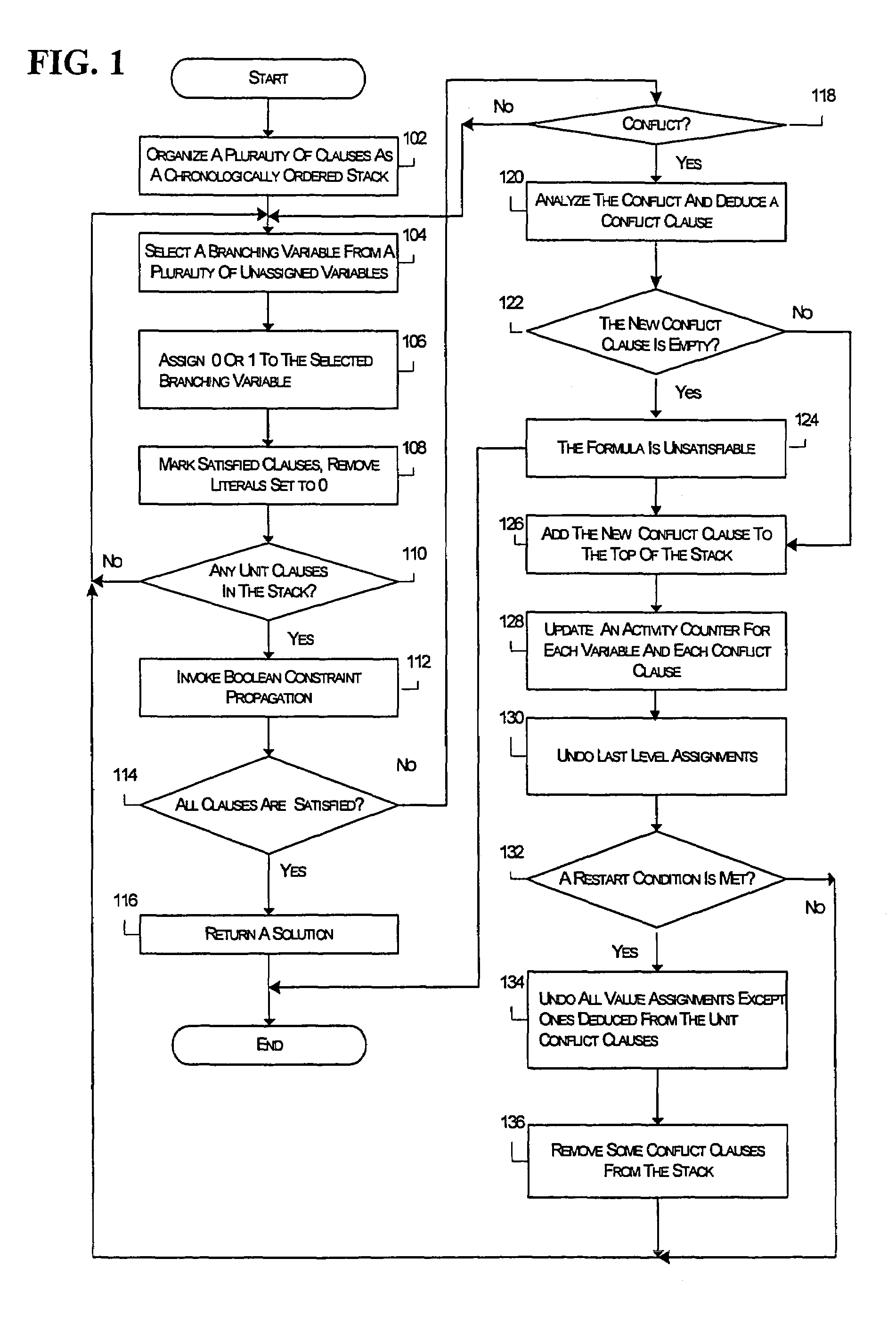
InactiveUS7356519B1Digital computer detailsDigital dataMaximum satisfiability problemTemporal succession
A method and system for solving satisfiability problems is disclosed. In one embodiment, clauses in a satisfiability problem are organized as a chronologically ordered stack. In another embodiment, the activity of each variable in the satisfiability problem is monitored. An activity counter is maintained for each variable and is incremented each time the variable appears in a clause used in generating a conflict clause. In an embodiment, a branching variable is selected from among the variables in the top clause of the stack when the top clause is a conflict clause. In a further embodiment, one or more conflict clauses in the stack are removed when the search tree is abandoned. In a still further embodiment, the value assigned to a branching variable is selected for purposes of having a uniform distribution of positive and negative literals.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Methods for transmitting and receiving a multicarrier spread-spectrum signal, corresponding signal, computer program products and transmission and reception devices
ActiveUS20100238978A1Large bit rateReduce accessMultiplex code generationRadio transmissionCarrier signalTemporal succession
A method and apparatus are provided for transmitting a multicarrier spread-spectrum signal formed by a temporal succession of multicarrier symbols, using OQAM modulation and a plurality of inter-orthogonal spreading codes. The method includes spreading at least one complex-value data symbol, representative of a source data signal to be transmitted, over a set of sub-carriers of at least one multicarrier symbol, each of the sub-carriers modulating a complex value.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com