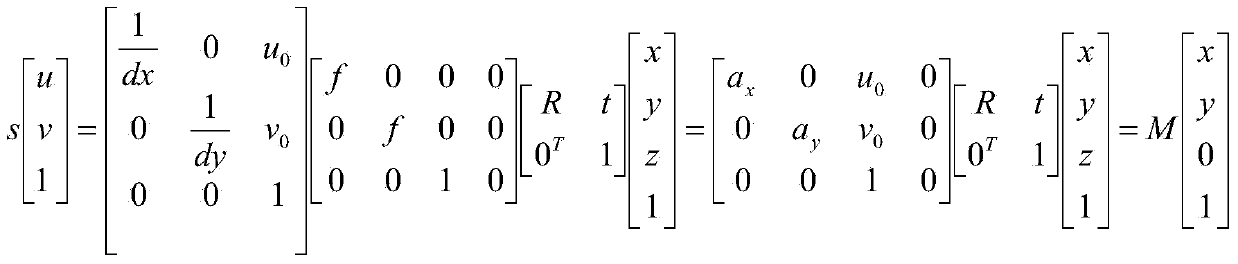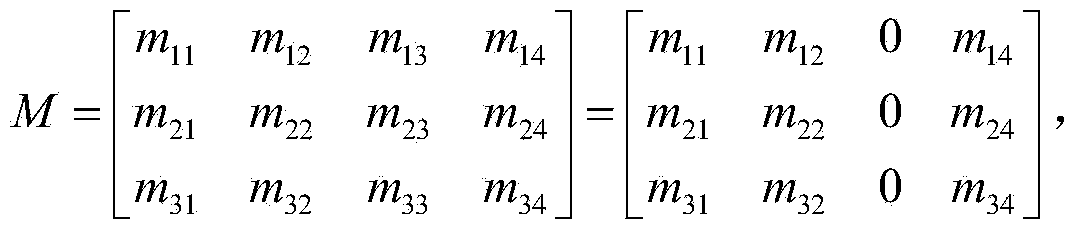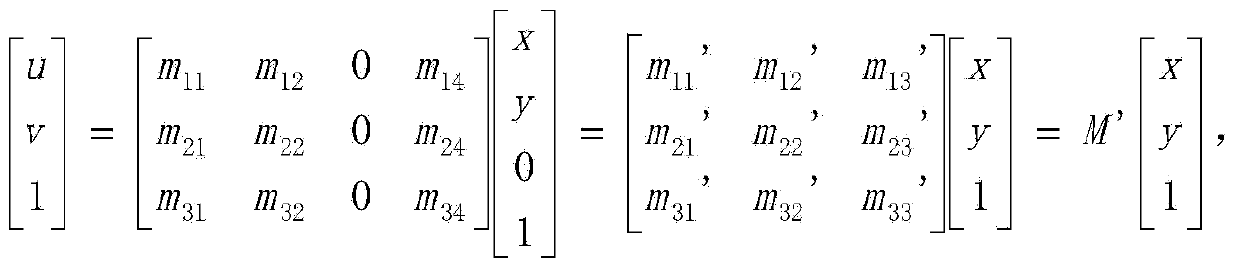Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
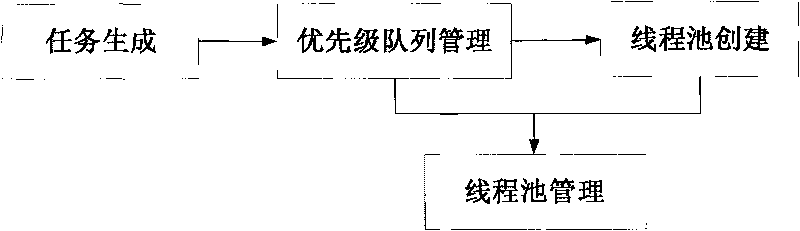
1243 results about "Thread pool" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
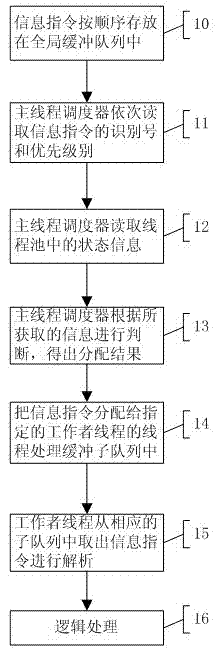
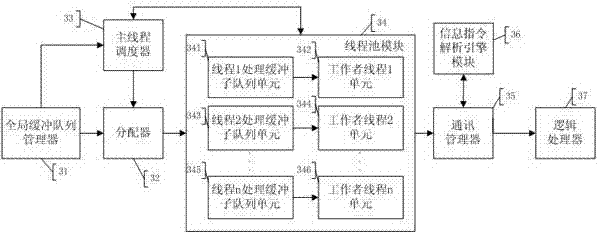
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
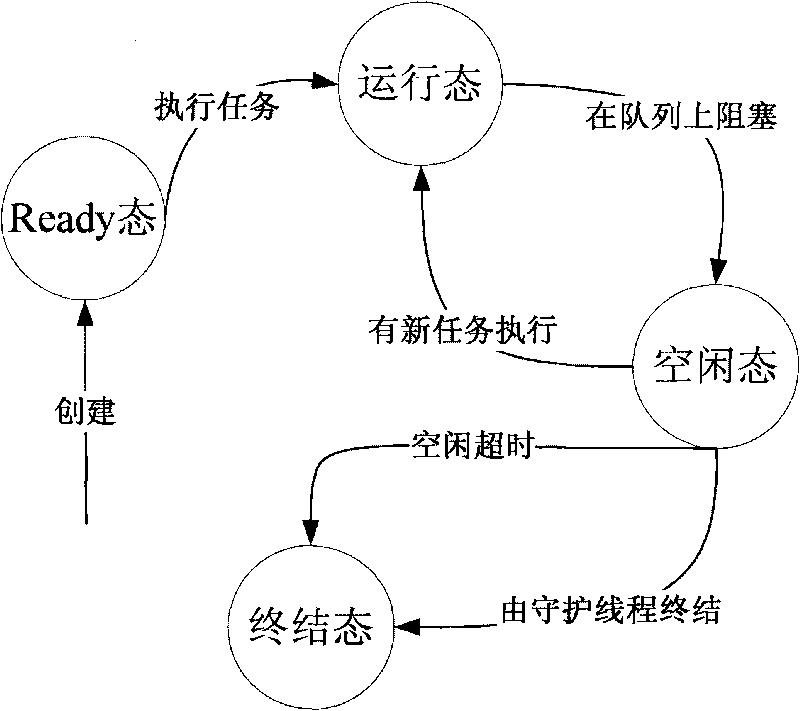
In computer programming, a thread pool is a software design pattern for achieving concurrency of execution in a computer program. Often also called a replicated workers or worker-crew model, a thread pool maintains multiple threads waiting for tasks to be allocated for concurrent execution by the supervising program. By maintaining a pool of threads, the model increases performance and avoids latency in execution due to frequent creation and destruction of threads for short-lived tasks. The number of available threads is tuned to the computing resources available to the program, such as a parallel task queue after completion of execution.
Generic application server and method of operation therefor
InactiveUS7051330B1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsApplication serverState switching
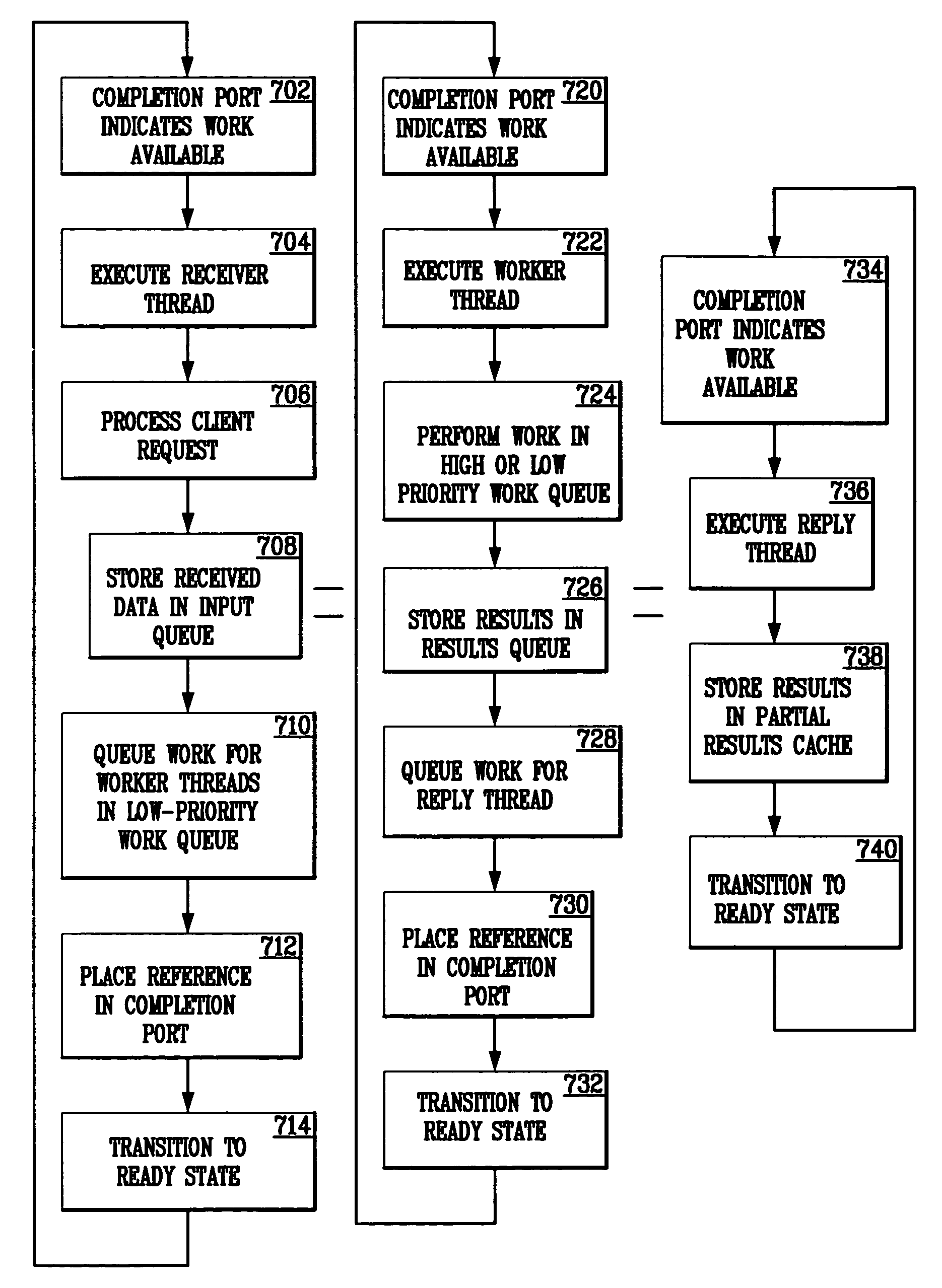
A generic application server is capable of simultaneously receiving requests, processing requested work, and returning results using multiple, conceptual thread pools. In addition, functions are programmable as state machines. While executing such a function, when a worker thread encounters a potentially blocking condition, the thread issues an asynchronous request for data, a state transition is performed, and the thread is released to do other work. After the blocking condition is relieved, another worker thread is scheduled to advance to the next function state and continue the function. Multiple priority work queues are used to facilitate completion of functions already in progress. In addition, lower-priority complex logic threads can be invoked to process computationally intense logic that may be necessitated by a request. Throttling functions are also implemented, which control the quantity of work accepted into the server and server response time.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
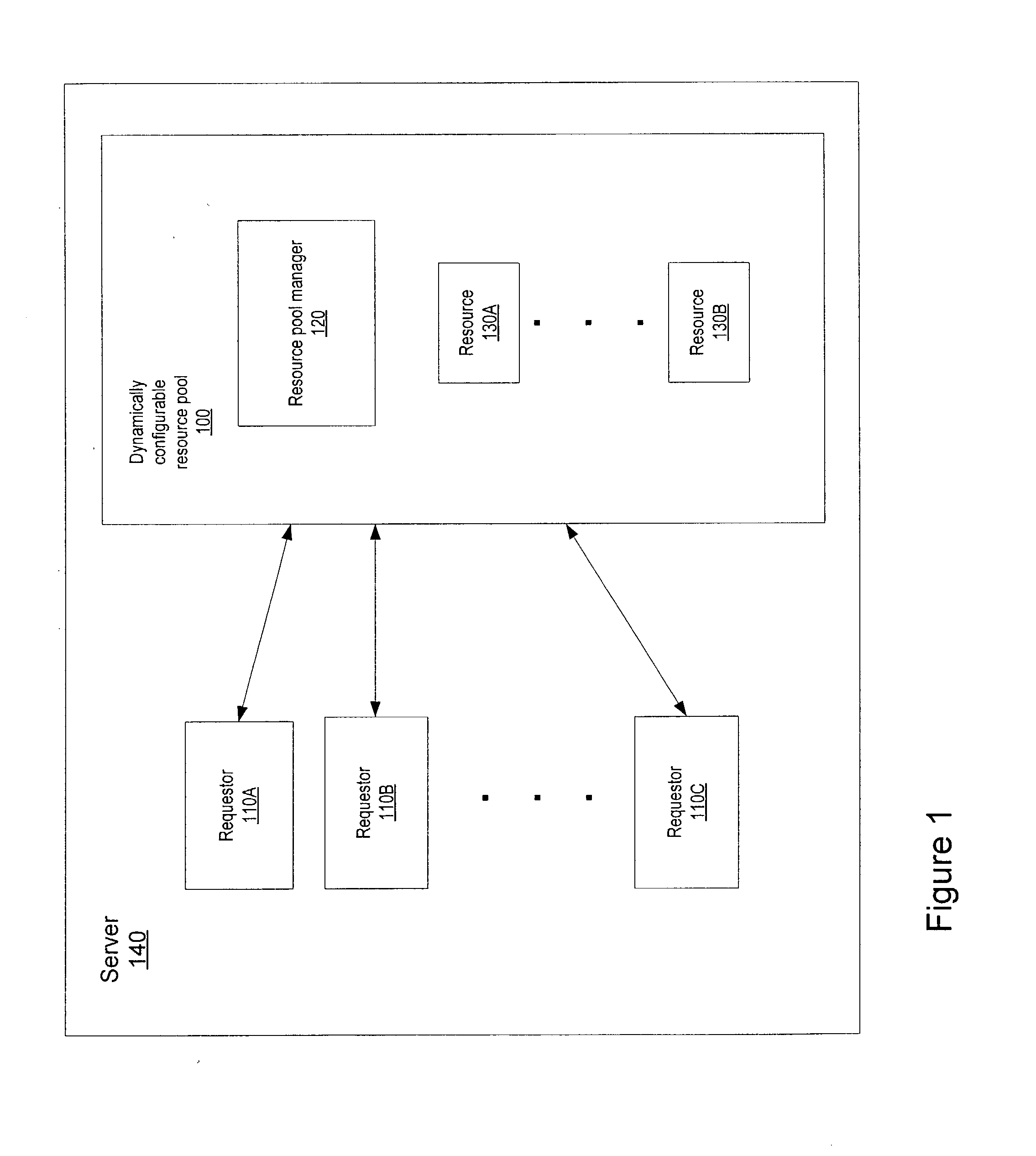
Dynamically configurable resource pool
ActiveUS20040088413A1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsResource poolWeb service
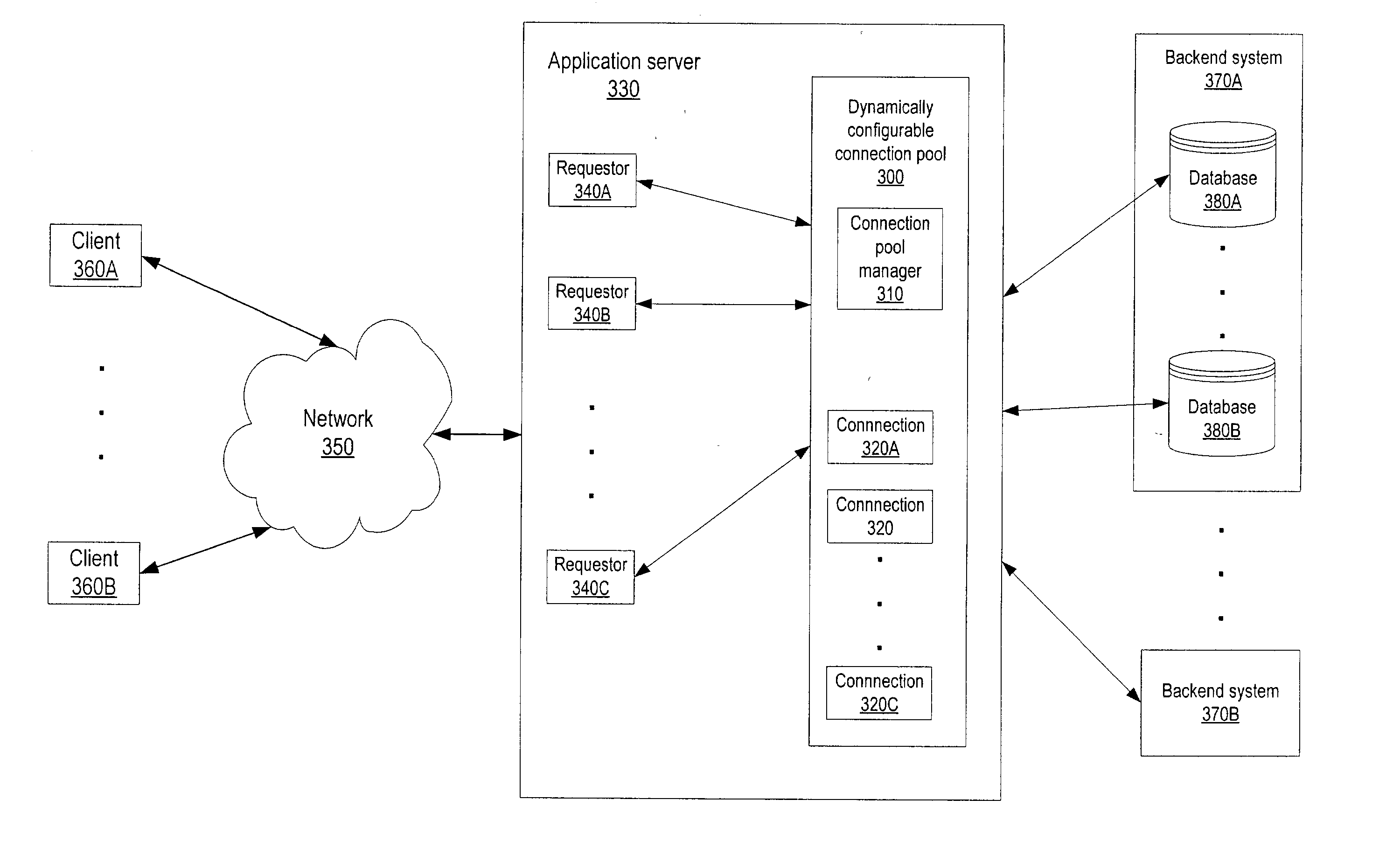
A dynamically configurable resource pool may provide a pool of computing resource for use in a computing system or application, such as a connection pool or a thread pool for server systems such as application and web server systems. In one embodiment, a server may include a resource pool configured to provide a plurality of computing resources. Other components in the server may be configured to request use of one of the computing resources from the connection pool. The resource pool may include a resource pool manager configured to service requests for the computing resources. The resource pool manager may manage configuration of the resource pool. The resource pool manager may also be configured to receive a configuration change request to change the configuration of the resource pool while the resource pool is available for use.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
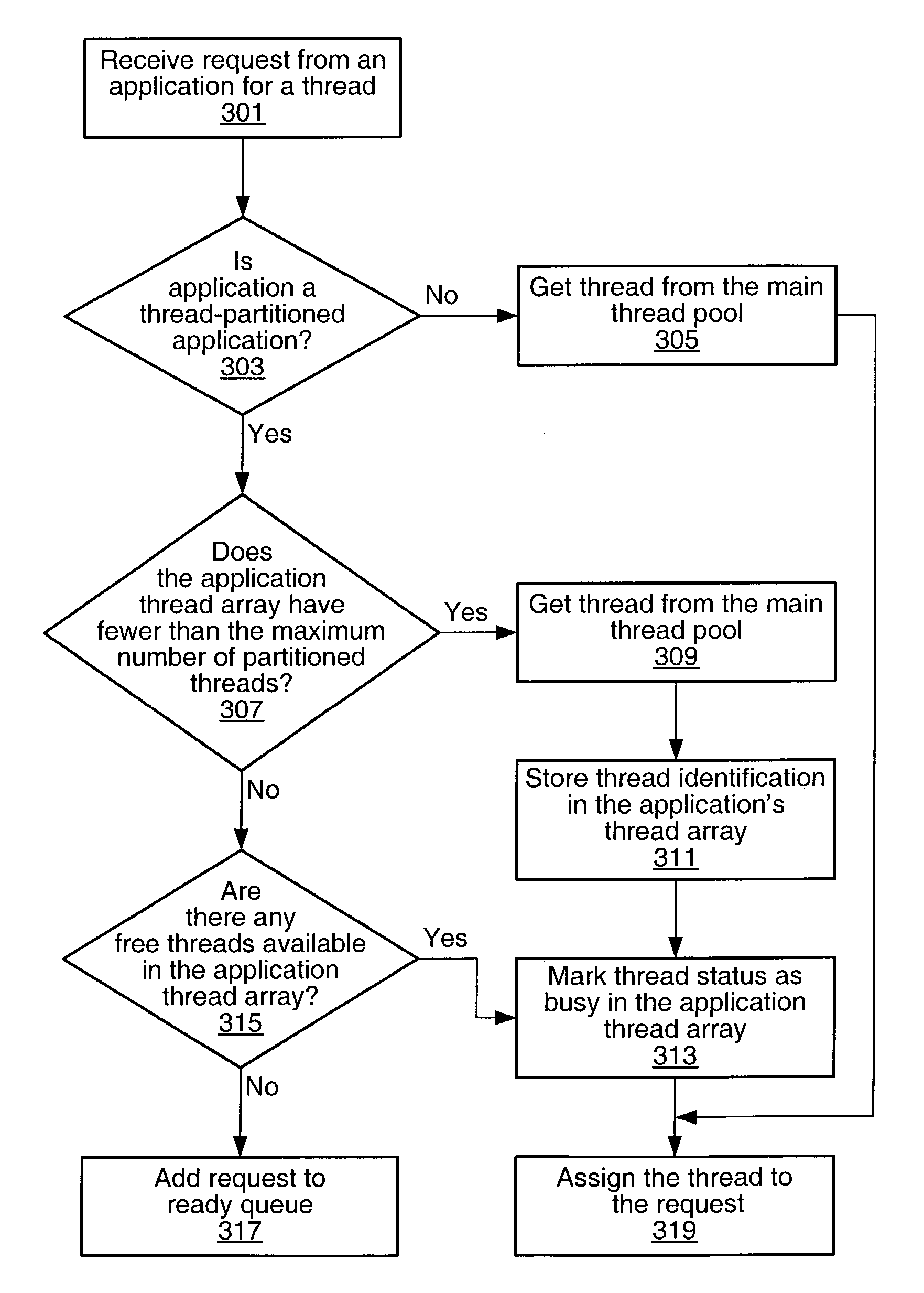
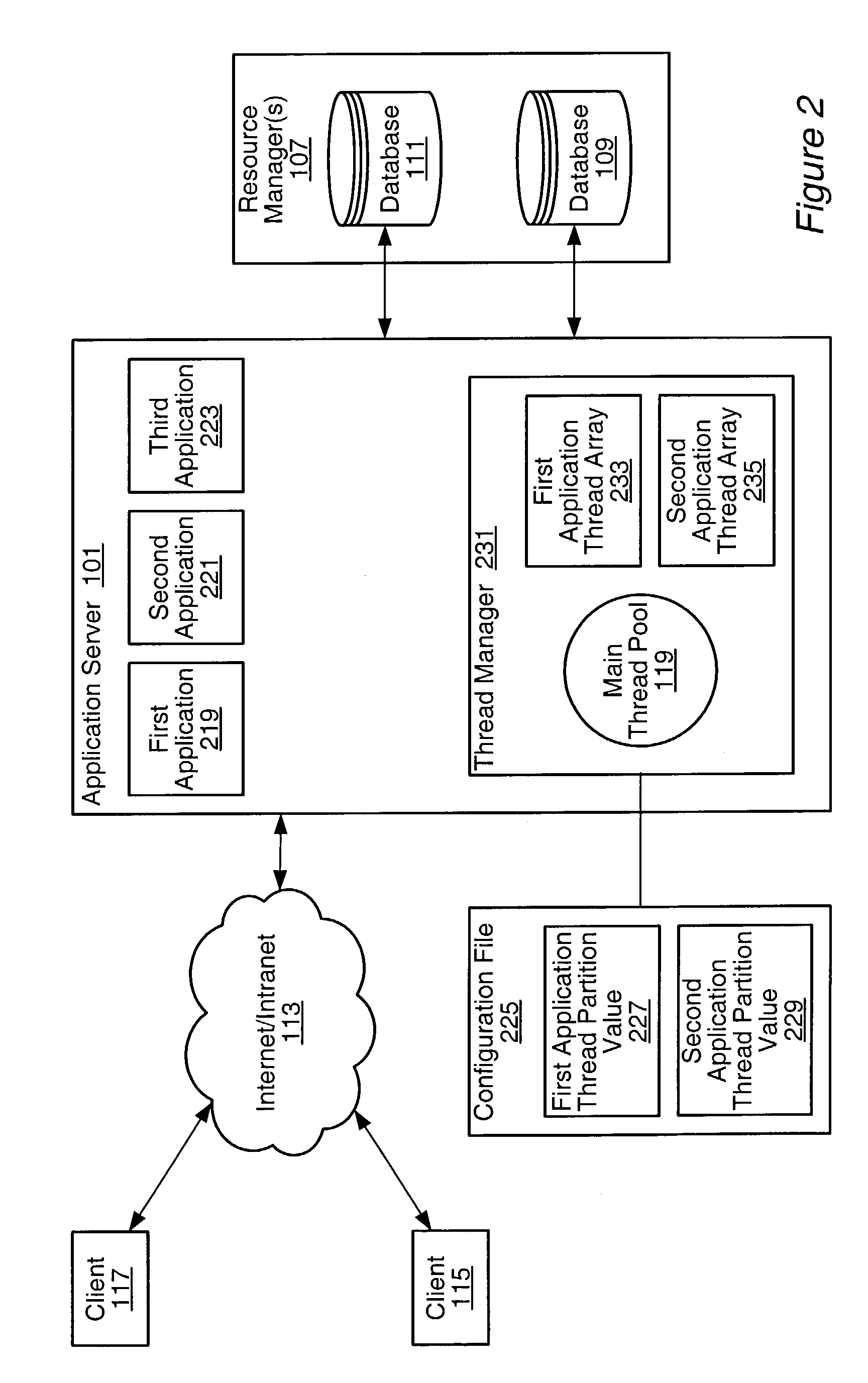
Thread level application partitioning
A system and method for managing threads and thread requests in an application server. If the application is a thread-partitioned application with a request, the thread manager may determine if an application thread array for the application has less than the maximum number of threads partitioned for the application. If it does, the thread manager may retrieve a thread from the main thread pool, and assign it to the request. If it does not, the thread manager may determine if there are any free threads in an application thread array, and if there are, one of the free threads in the application thread array may be assigned to the request. If there are no free threads available in the application thread array, the request may be added to a ready queue.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Virus scanning prioritization using pre-processor checking
ActiveUS7188367B1Promote quick completionMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionParallel computingProgram Thread
A virus scanner is provided in which a pool of pre-processor threads and a queue are interposed between the event filter and the pool of scanner threads. The pre-processor threads perform operations that can be completed quickly to determine whether an object of a scan request needs to be scanned. The pre-processor threads gather characteristics about the scan requests and place them in the queue in a priority order based on those characteristics. The scanner threads select a scan request from the queue based on the priority order. Alternatively, the scan request is selected based on the scan request's characteristics as compared to the characteristics of the scan requests whose objects are currently being scanned by other scanner threads in the pool.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Multitask process monitoring method and system in distributed system environment
ActiveCN102360310AEfficient parallel processingGood for load balancingResource allocationFiltrationMonitoring system
The invention discloses a multitask process monitoring method in the distributed system environment. The method comprises the following steps that: five states of the task execution process of each task execution terminal in the distributed system environment are monitored; an XML (eXtensible markup language) format description file is transported to a task collecting and processing server, the task execution conditions after filtration are written in a database and simultaneously task change information is sent to notify a task scheduling center; the task scheduling center directly submits the information to a task scheduling module after receiving the task change information and the task scheduling module adds the received information to information waiting queues; a scheduling control unit searches for a thread index table for threads of execution of the task and gives the threads of execution to the threads to be executed; and a thread control module monitors a plurality of threads in a work thread pool in real time in the system operation process. The invention also discloses a multitask process monitoring system. The system comprises a plurality of distributed task execution terminals, the task collecting and processing server and the task scheduling center.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Generic application server and method of operation therefor
A generic application server is capable of simultaneously receiving requests, processing requested work, and returning results using multiple, conceptual thread pools. In addition, functions are programmable as state machines. While executing such a function, when a worker thread encounters a potentially blocking condition, the thread issues an asynchronous request for data, a state transition is performed, and the thread is released to do other work. After the blocking condition is relieved, another worker thread is scheduled to advance to the next function state and continue the function. Multiple priority work queues are used to facilitate completion of functions already in progress. In addition, lower-priority complex logic threads can be invoked to process computationally intense logic that may be necessitated by a request. Throttling functions are also implemented, which control the quantity of work accepted into the server and server response time.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Synchronous task scheduler for corba gateway
InactiveUS6839748B1Protect resourcesImprove performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksManaged objectApplication software
A system and method for a synchronous task scheduler. The synchronous task scheduler may be used with a CORBA Gateway between CORBA-based client manager applications and an enterprise manager. The CORBA Gateway may include components such as an Event Gateway which manages events from managed objects, and a Request Gateway which manages requests and responses of managed objects. The Event Gateway and the Request Gateway may be designed as multi-threaded systems. A thread pool may be used to increase efficiency and performance of the CORBA Gateway. To ensure ordered delivery of events or replies to the CORBA gateway clients in a multi-threaded environment using a thread pool, a synchronous task scheduler may be used. There may be a synchronous task scheduler associated with each client manager to preserve the chronology of messages sent to each. The synchronous task scheduler may maintain an internal message list, and deliver one message at a time from that internal list. The synchronous task scheduler may hold a reference to a thread pool and use that thread pool to deliver messages. When a message is scheduled, the synchronous task scheduler may check if any message is already being delivered. If no prior message is currently being delivered, an available thread may be assigned from the thread pool for delivery of the message and the scheduler may initiate delivery of the message. If a prior message is being delivered, it may enqueue the message in the message list. Then, when the prior message delivery is completed, the scheduler may dequeue the message, assign another thread from the thread pool, and initiate delivery of the message. This may continue until the message list is empty.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Two-Tiered Dynamic Load Balancing Using Sets of Distributed Thread Pools
By employing a two-tier load balancing scheme, embodiments of the present invention may reduce the overhead of shared resource management, while increasing the potential aggregate throughput of a thread pool. As a result, the techniques presented herein may lead to increased performance in many computing environments, such as graphics intensive gaming.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic thread pool tuning techniques
InactiveUS20040139434A1Improve performanceSimple technologyProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationParallel computingEngineering
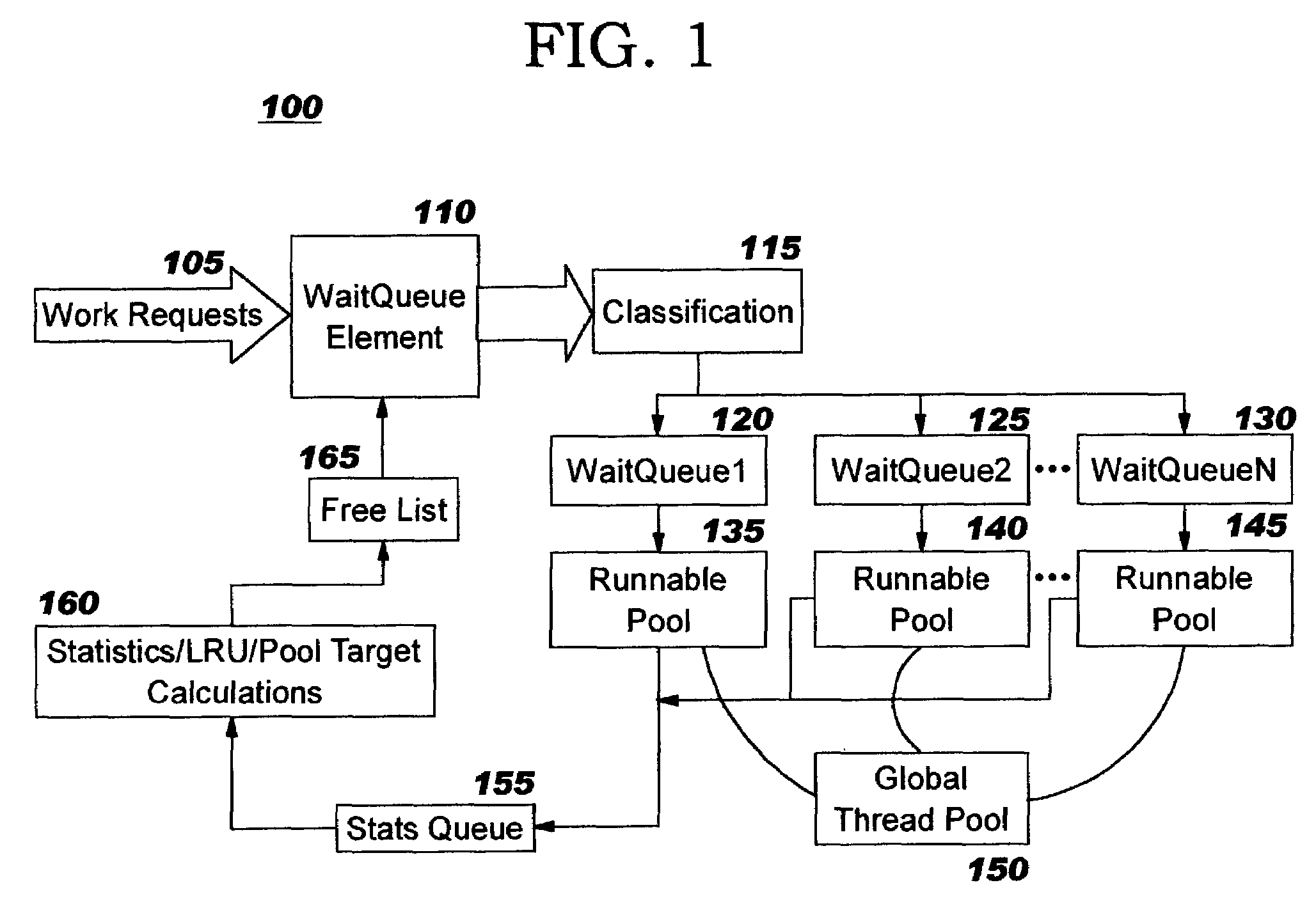
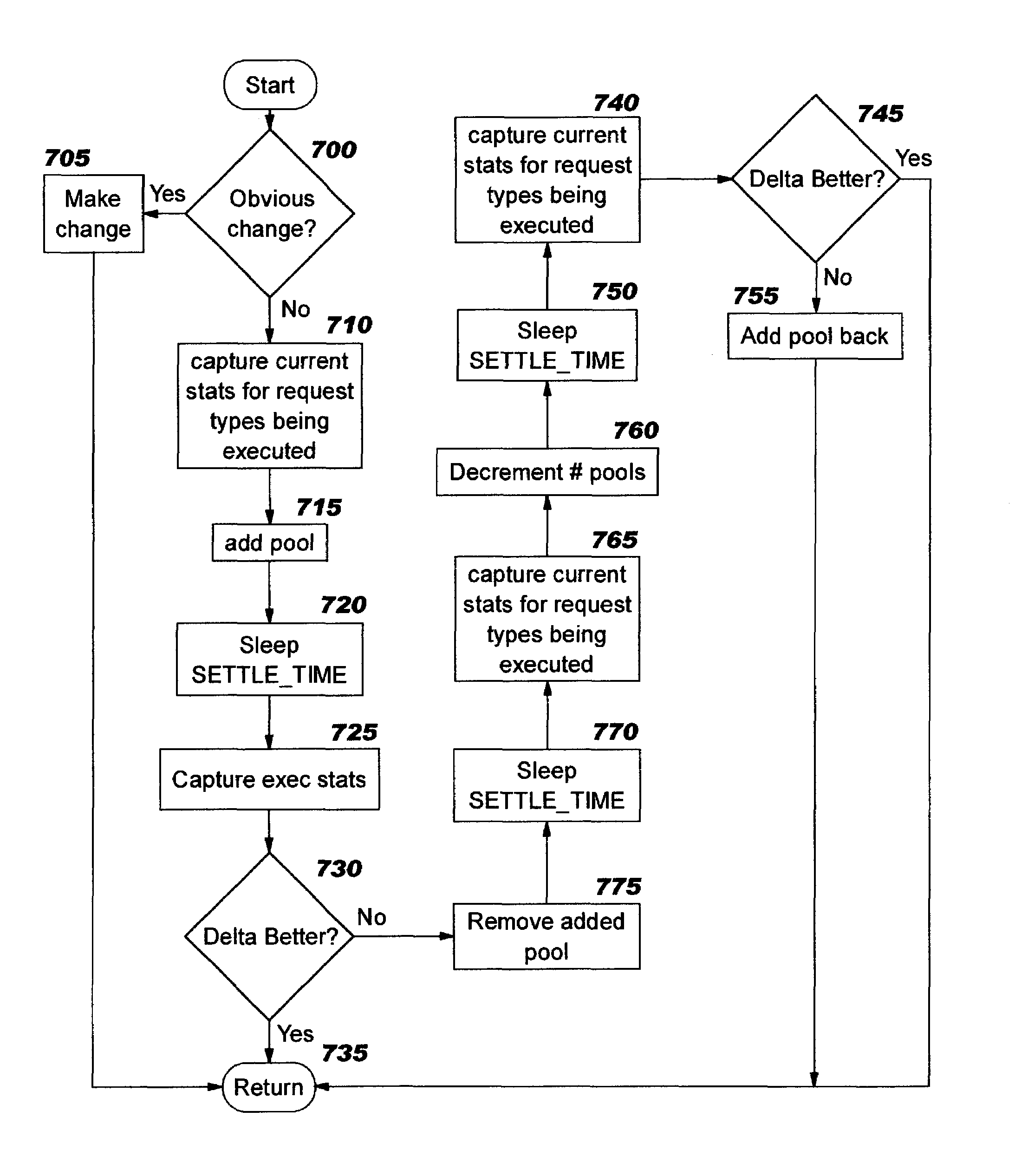
Thread pools in a multithreaded server are programmatically adjusted, based on observed statistics from the server's inbound workload. In a multithreaded server environment, response time to end users is improved while increasing the efficiency of software execution and resource usage. Execution time and wait / queued time are tracked, for various types of requests being serviced by a server. Multiple logical pools of threads are used to service these requests, and inbound requests are directed to a selected one of these pools such that requests of similar execution-time requirements are serviced by the threads in that pool. The number and size of thread pools may be adjusted programmatically, and the distribution calculation (i.e., determining which inbound requests should be assigned to which pools) is a programmatic determination. In preferred embodiments, only one of these variables is adjusted at a time, and the results are monitored to determine whether the effect was positive or negative. The disclosed techniques also apply to tracking and classifying requests by method name (and, optionally, parameters).
Owner:IBM CORP
High-performance Syslog processing and storage method
The invention is high performance Syslog log processing and storing method, and the steps are: (1) receiving log: log sever software receives the syslog data message by separated thread running method via bound UDP port (514), and the data message is generated into data class of syslog, and the data class of syslog is written in log buffer; (2) log buffer: the log buffer takes charge of storing the received syslog log data temporarily; (3) log normalization processing: detects the head of log buffer by separated thread, if the log buffer has new data, and the data will be extracted from buffer queue, and log will execute normalization processing according to field description information of log normalization configuring file, and call the log storing module to store the log as uniform format; (4) log storage: using the storing thread pool to write said normalization log on log storage file, every thread takes charge of writing log data in one file, and several threads can write the logs in different directories and discs, and improve the storing efficiency. The technical schedule adopts asynchronies log processing and intercurrent log storage technique, and two taches can inherit each other and coordinates the problems of log amount and log inercurrent amount, and use time to change time, and improve the log processing ability greatly.
Owner:QI-ANXIN LEGENDSEC INFORMATION TECH (BEIJING) INC
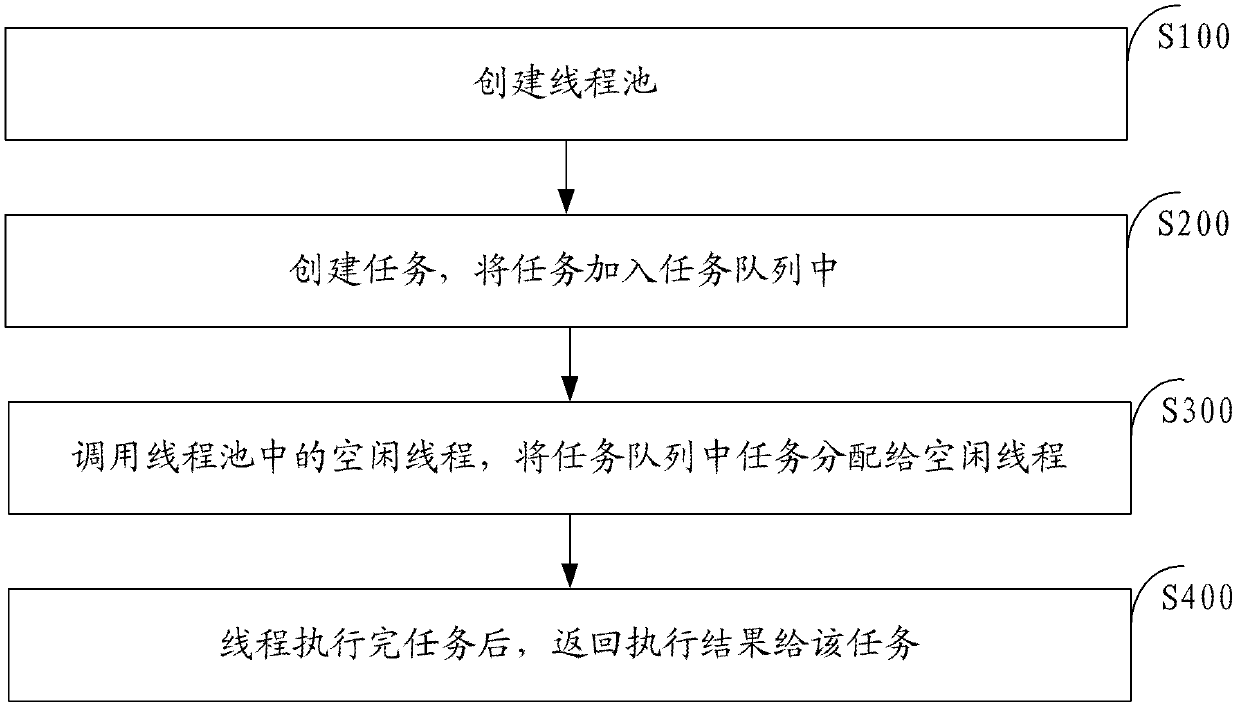
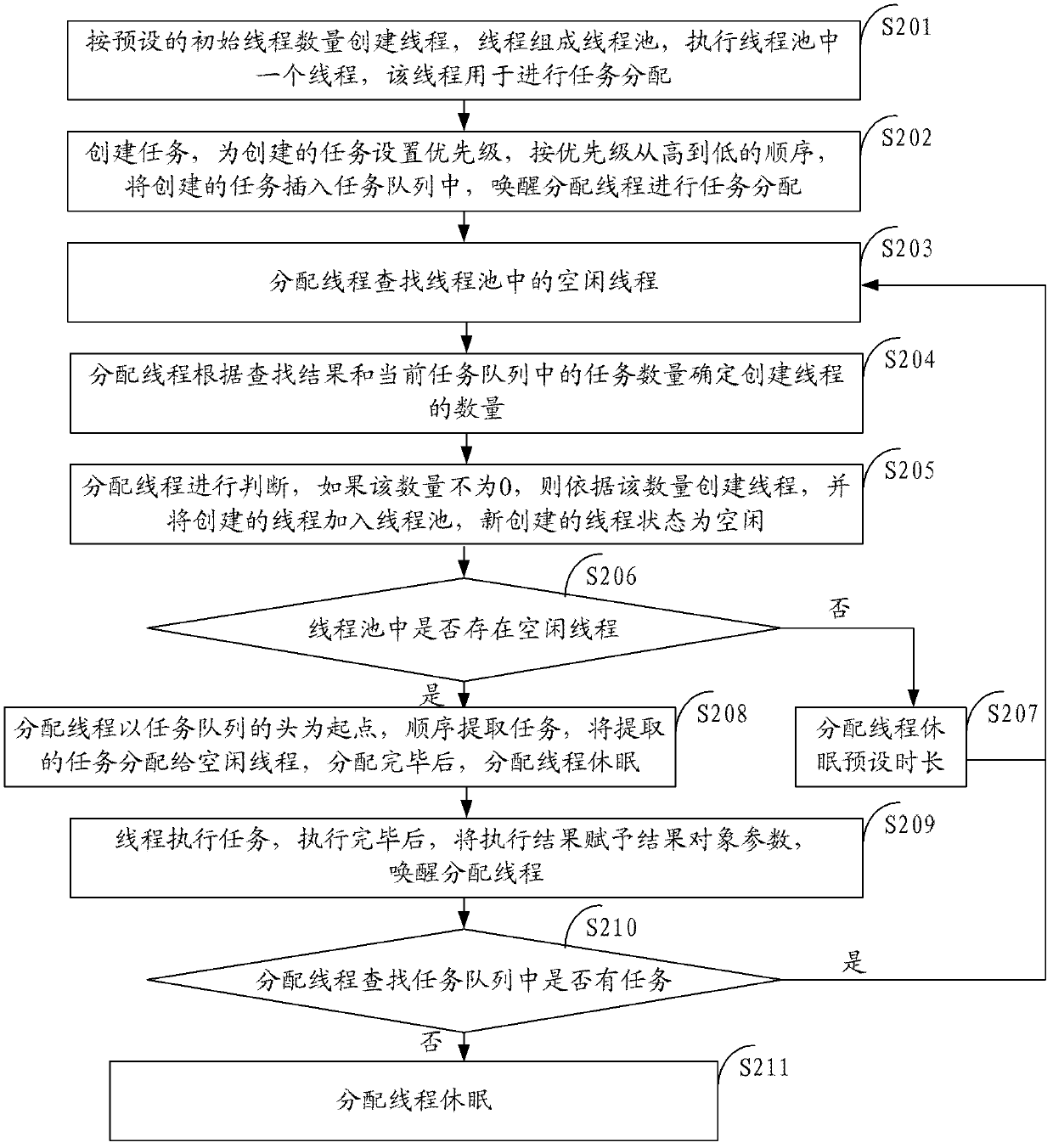
Method and system for distributing thread execution task
InactiveCN102591721AScheduling intelligenceFlexible useResource allocationThread poolOperating system
The invention discloses a method and a system for distributing thread execution task. The method comprises the following steps of: a step 1 of creating a thread pool; a step 2 of creating the task and adding the task into a task queue; a step 3 of calling idle threads in the thread pool and distributing the task in the task queue to the idle threads; and a step 4 of returning an execution result to the task after the threads execute the task. The invention can solve the problems of no feedback of the execution result, insufficient convenience and rapidness of application.
Owner:BEIJING FEINNO COMM TECH
Method for scheduling satellite data product production tasks in parallel based on multithread
ActiveCN101739293ASolve scheduling problemsIncrease the number of tasksResource allocationSatellite dataIdle time
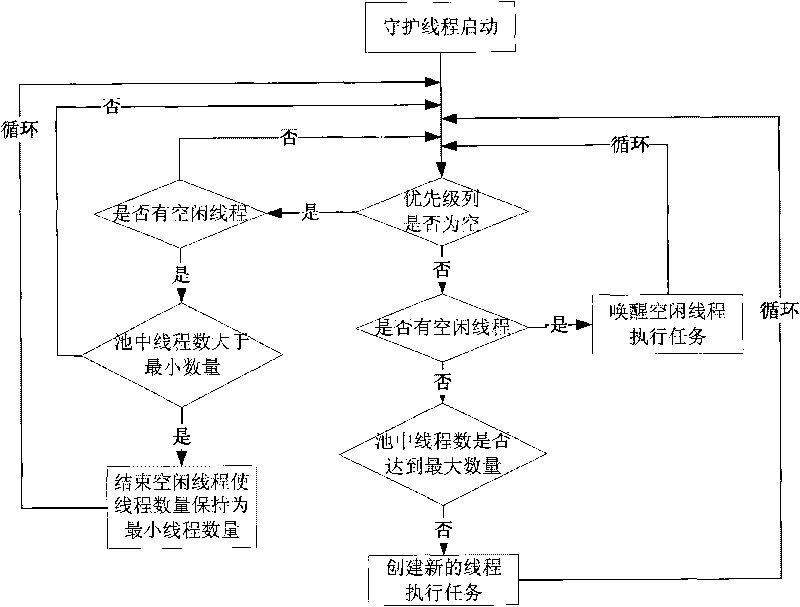
The invention discloses a method for scheduling satellite data product production tasks in parallel based on multithread. The method comprises the following steps: setting priorities for tasks to be scheduled for executing and realizing a uniformed interface; adding the tasks into a priority queue according to an order of the priorities from high to low; setting the maximum number and the minimal number of the tasks of a thread pool, and the longest idle time of a thread; and starting a daemon thread in the thread pool and a plurality of task threads to execute the tasks, wherein the daemon thread regulates the number of the task threads dynamically according to the situation of task amount. The method can utilize system resource rationally, aims at the data product production of a satellite ground application system, and solves the difficult points of complicated product production processes, long task executing time, large task amount, high real time and parallelism degree for scheduling the tasks and the like.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Thread pool management method and system
ActiveCN101599027AReduced execution timeAvoid backlogProgram initiation/switchingError detection/correctionFault toleranceApplication server
The invention discloses a thread pool management method and a thread pool management system. The method comprises the following steps: monitoring the running time of each thread to execute a current task by regularly traversing each thread in a thread pool; and when determining that threads with overtime running exist according to the monitored running time, establishing novel threads, and using the newly established threads to execute tasks which are to be executed by the threads with the overtime running, wherein threads in the thread pool correspond to task queues one by one, and execute tasks in the corresponding task queues; and the tasks to be executed by the threads with the overtime running are task queues corresponding to the threads with the overtime running. The method and the system can improve the task processing efficiency of an application server adopting the thread pool management technology, and provide a fault tolerance mechanism and a thread regeneration mechanism for the thread pool.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Third-party data service system based on Internet-of-Things data collecting
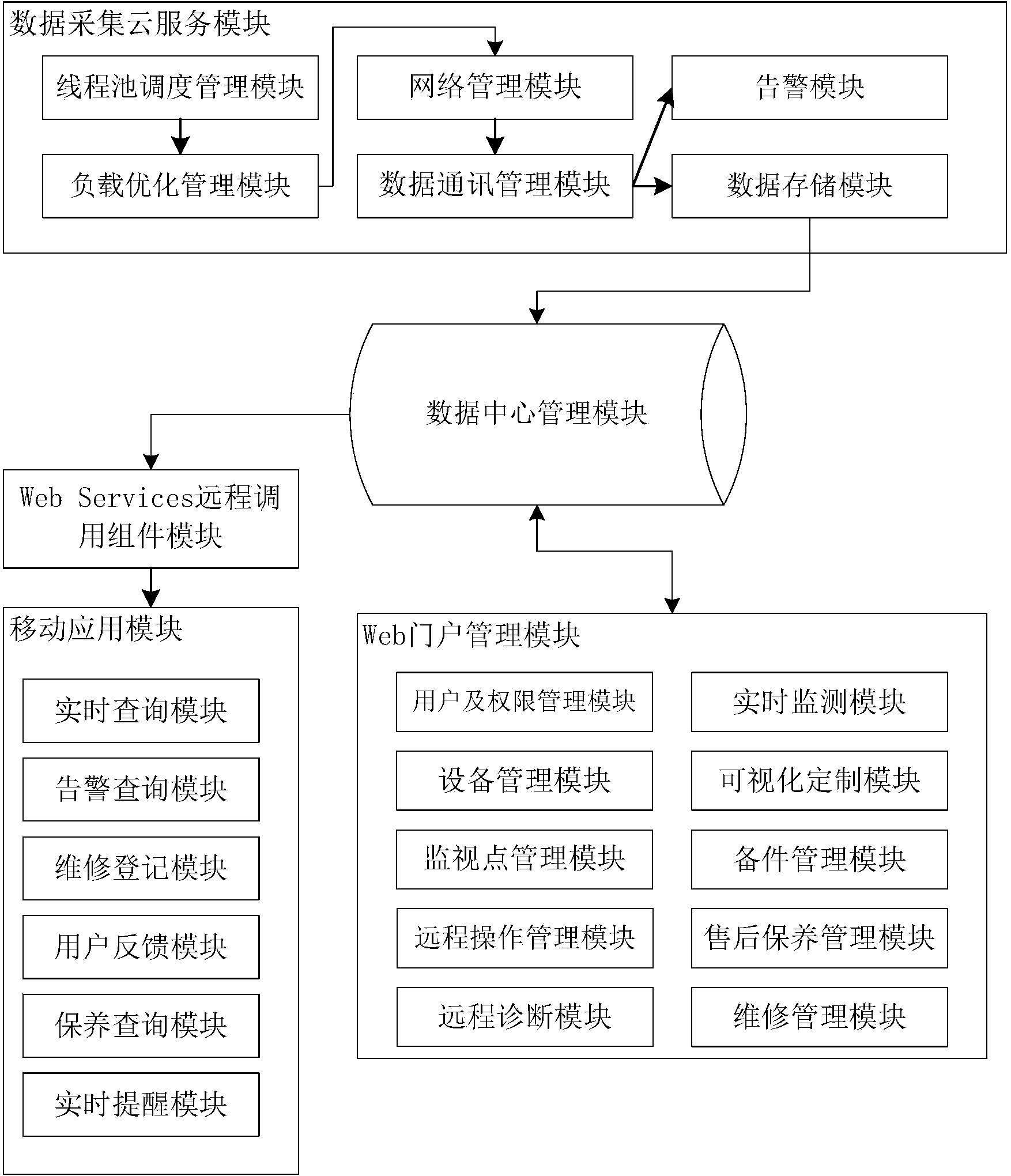
ActiveCN104283967ARealize remote mobile monitoringFlexible configurationTransmissionData centerLoad optimization
The invention discloses a third-party data service system based on Internet-of-Things data collecting. The third-party data service system comprises a data collecting cloud service module, a Web portal management module, a Web Service remote calling assembly module, a mobile application module and a data center management module. The data collecting cloud service module comprises a thread pool dispatching management module, a load optimization management module, a network management module, a data communication management module, a data storage module and an alarm module. The Web portal management module comprises a user and authority management module, an equipment management module, a monitoring point management module, a real-time monitoring module, a visual customization module, a spare part management module, an after-sale maintenance management module, a repair management module, a remote operation management module and a remote diagnosis module. The mobile application module comprises a real-time inquiry module, an alarm inquiry module, a repair registration module, a user feedback module, a maintenance inquiry module and a real-time warning module.
Owner:武汉华喻燃能工程技术有限公司 +1
Lock management thread pools for distributed data systems
ActiveUS20040019892A1Digital data information retrievalProgram synchronisationLocking mechanismData system
A distributed data system may include a plurality of nodes one or more of which may include at least one multi-threaded process operable to access portions of distributed data. A lock mechanism may grant locks to the multi-threaded processes for portions of the distributed data. Only a process holding a lock may access a portion corresponding to the lock. Threads of other processes may not access the portion. A process may include a lock management thread pool dedicated to managing locks for portions of the distributed data for access by other threads of the process. Each lock management thread of the lock management thread pool may request a lock for a portion of distributed data on behalf of the process. The process may hold one or more locks for portions of distributed data corresponding to one or more lock management threads of the lock management thread pool.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Programmatic response-time based workload distribution techniques
InactiveUS7207043B2Improve performanceSimple technologyProgram initiation/switchingElectric devicesQueue timeWorkload
Workload is programmatically distributed across a set of execution resources. In a multithreaded server environment, response time to end users is improved while increasing the efficiency of software execution and resource usage. Execution time and wait / queued time are tracked, for various types of requests being serviced by a server. Multiple logical pools of threads are used to service these requests, and inbound requests are directed to a selected one of these pools such that requests of similar execution-time requirements are serviced by the threads in that pool. The number and size of thread pools may be adjusted programmatically, and the distribution calculation (i.e., determining which inbound requests should be assigned to which pools) is a programmatic determination. In preferred embodiments, only one of these variables is adjusted at a time, and the results are monitored to determine whether the effect was positive or negative. The disclosed techniques also apply to tracking and classifying requests by method name (and, optionally, parameters).
Owner:IBM CORP
Programmatic response-time based workload distribution techniques
InactiveUS20040139433A1Improve performanceSimple technologyProgram initiation/switchingElectric devicesQueue timeWorkload
Workload is programmatically distributed across a set of execution resources. In a multithreaded server environment, response time to end users is improved while increasing the efficiency of software execution and resource usage. Execution time and wait / queued time are tracked, for various types of requests being serviced by a server. Multiple logical pools of threads are used to service these requests, and inbound requests are directed to a selected one of these pools such that requests of similar execution-time requirements are serviced by the threads in that pool. The number and size of thread pools may be adjusted programmatically, and the distribution calculation (i.e., determining which inbound requests should be assigned to which pools) is a programmatic determination. In preferred embodiments, only one of these variables is adjusted at a time, and the results are monitored to determine whether the effect was positive or negative. The disclosed techniques also apply to tracking and classifying requests by method name (and, optionally, parameters).
Owner:IBM CORP
Autonomic workload classification using predictive assertion for wait queue and thread pool selection
ActiveUS20050183084A1Improve performanceSimple technologyDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsThread poolApplication server
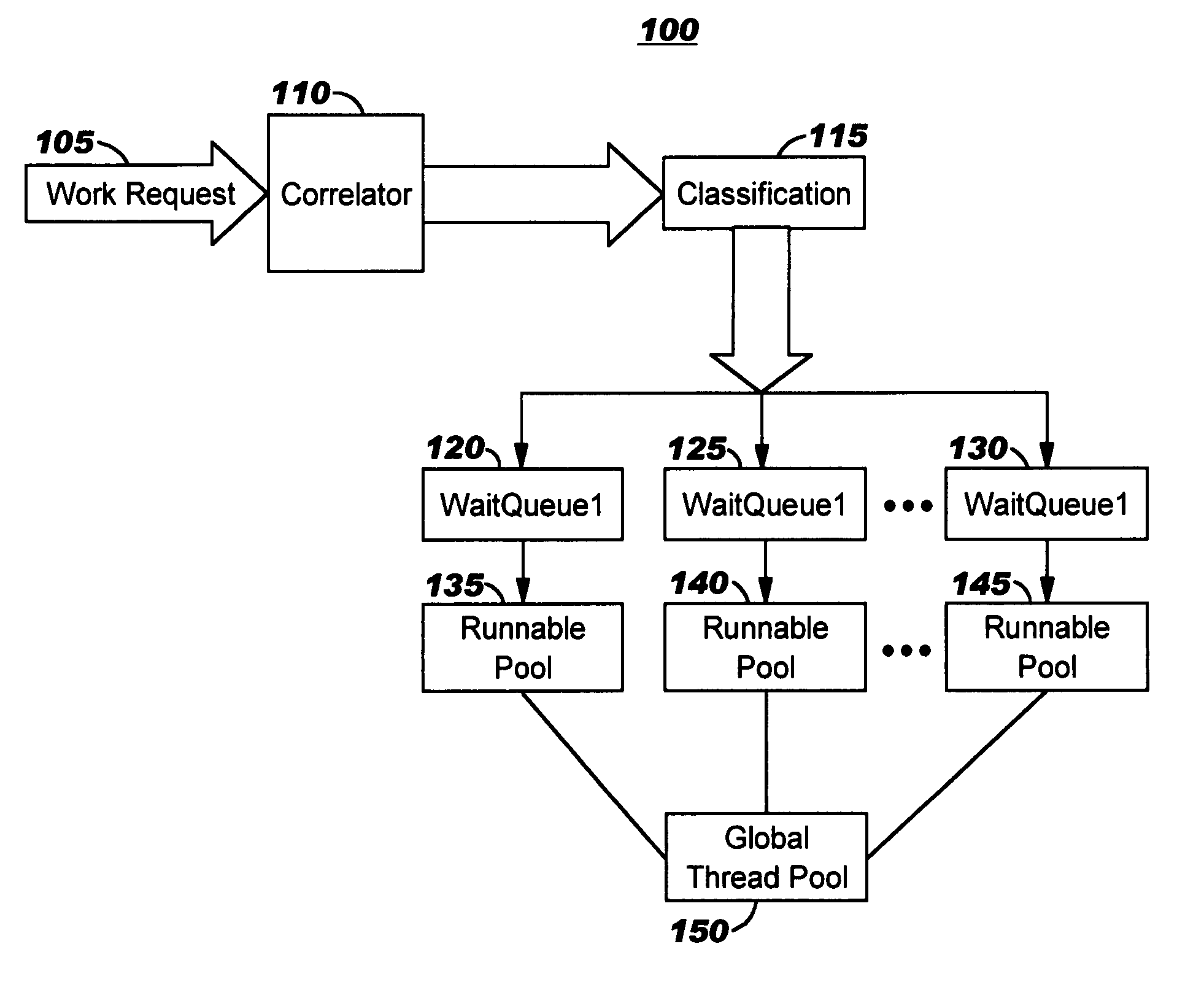
Incoming work units (e.g., requests) in a computing workload are analyzed and classified according to predicted execution. Preferred embodiments track which instrumented wait points are encountered by the executing work units, and this information is analyzed to dynamically and autonomically create one or more recognizers to programmatically recognize similar, subsequently-received work units. When a work unit is recognized, its execution behavior is then predicted. Execution resources are then allocated to the work units in view of these predictions. The recognizers may be autonomically evaluated or tuned, thereby adjusting to changing workload characteristics. The disclosed techniques may be used advantageously in application servers, message-processing software, and so forth.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Monitoring thread usage to dynamically control a thread pool
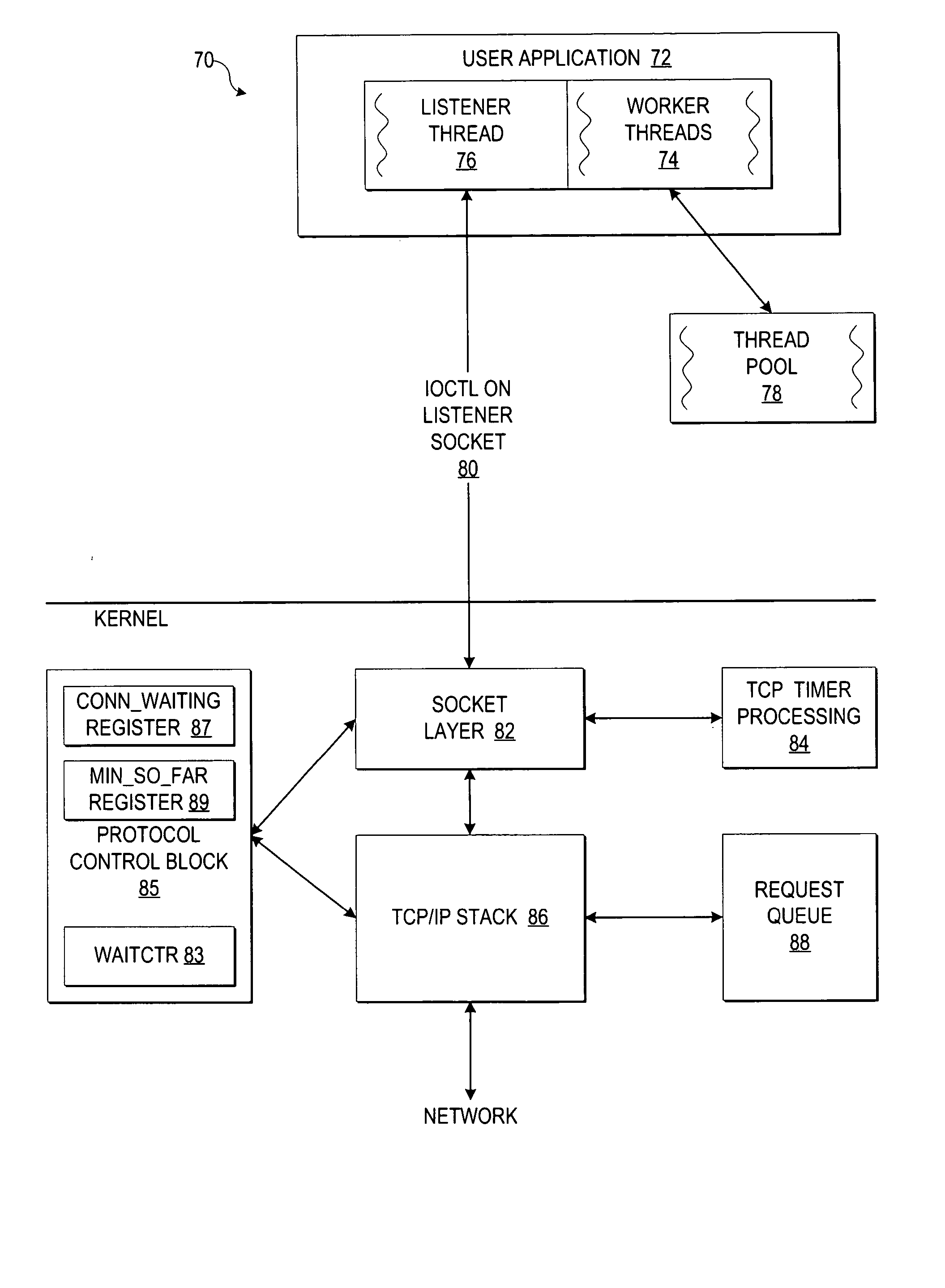
InactiveUS20050086359A1Efficient loadingResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideThread pool
A method, system, and program for monitoring thread usage to dynamically control a thread pool are provided. An application running on the server system invokes a listener thread on a listener socket for receiving client requests at the server system and passing the client requests to one of multiple threads waiting in a thread pool. Additionally, the application sends an ioctl call in blocking mode on the listener thread. A TCP layer within the server system detects the listener thread in blocking mode and monitors a thread count of at least one of a number of incoming requests waiting to be processed and a number of said plurality of threads remaining idle in the thread pool over a sample period. Once the TCP layer detects a thread usage event, the ioctl call is returned indicating the thread usage event with the thread count, such that a number of threads in the thread pool may be dynamically adjusted to handle the thread count.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multithreading framework supporting dynamic load balancing and multithread processing method using the same
InactiveUS20090150898A1Improve performanceMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsDynamic load balancingApplication software
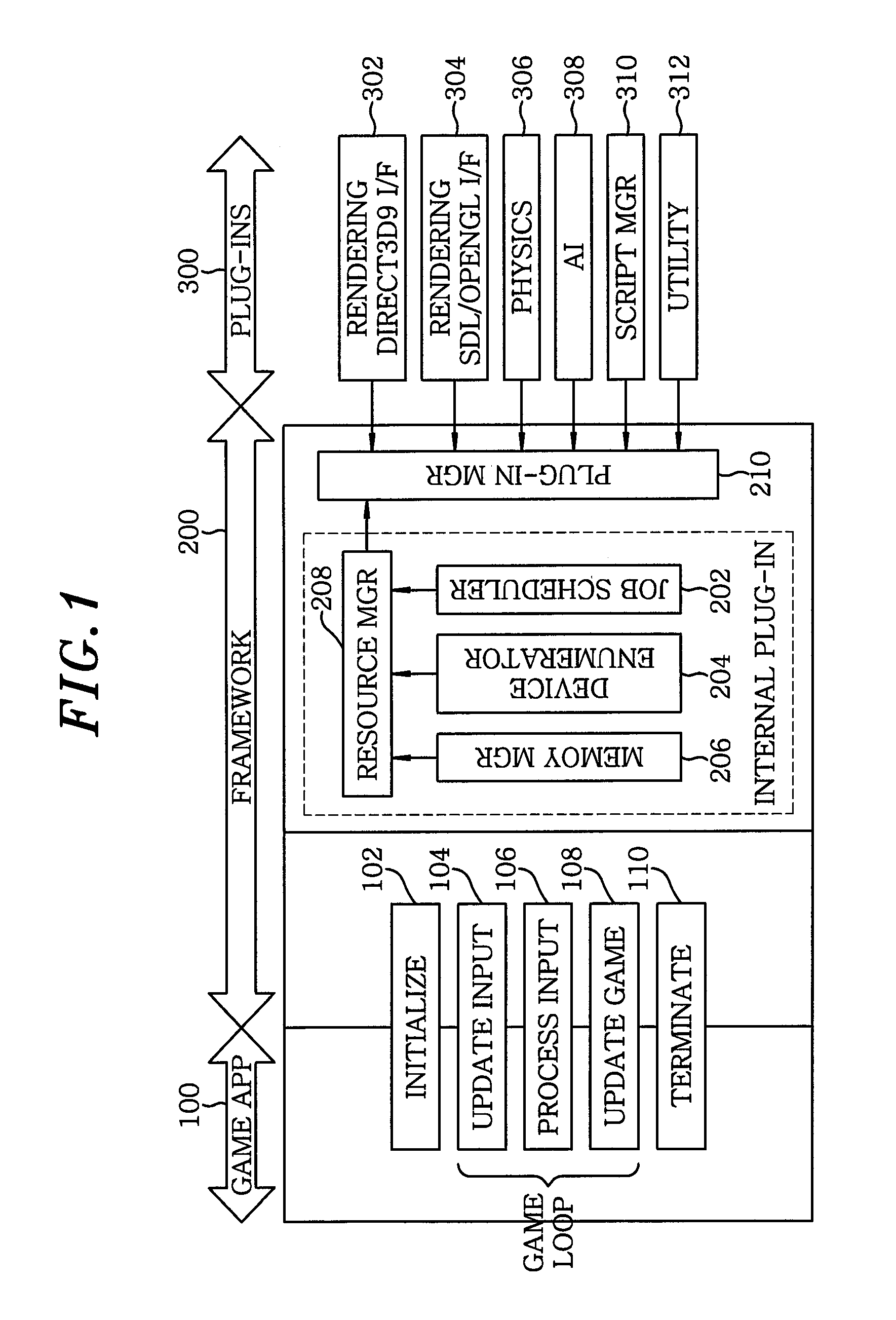
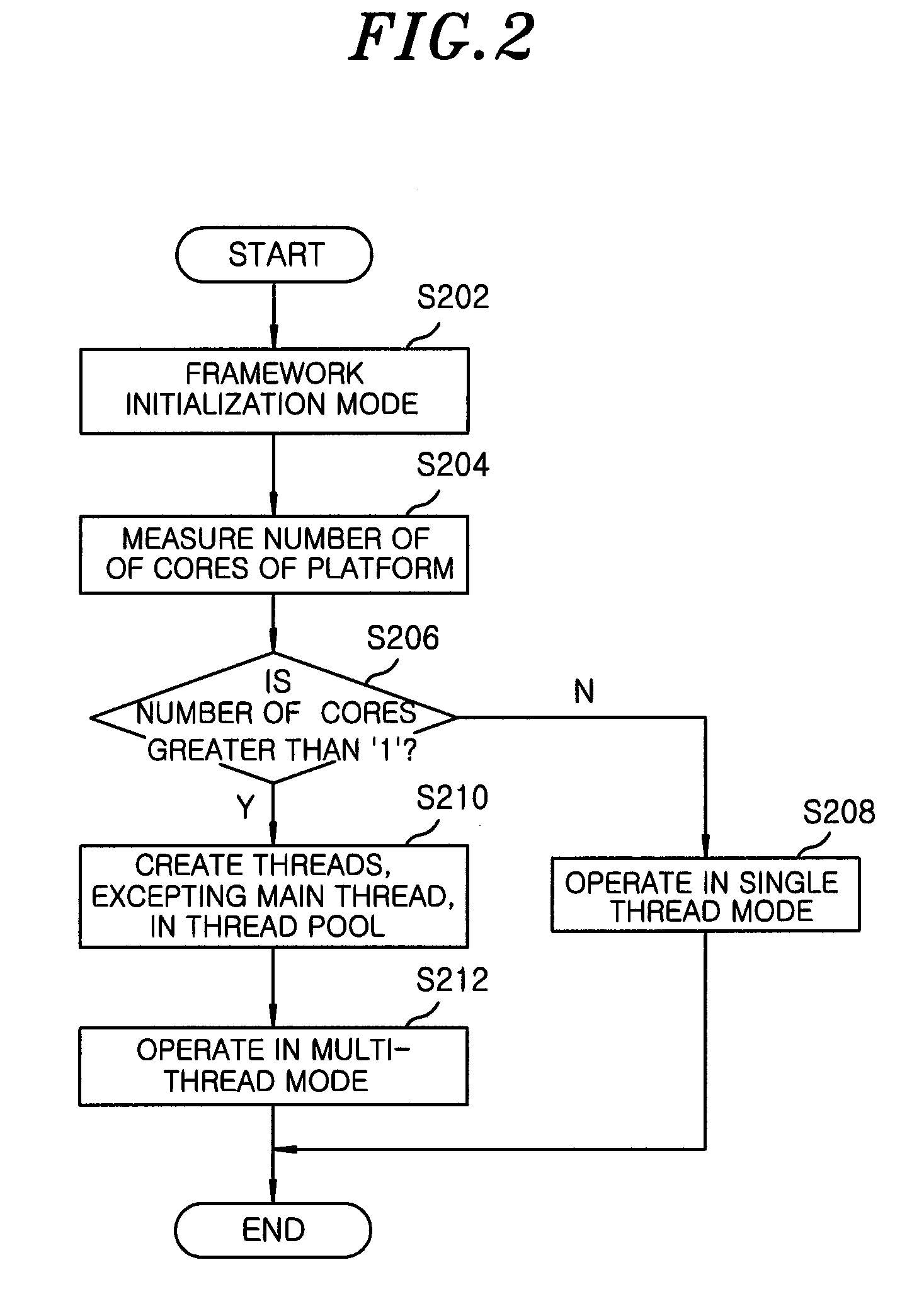
A multithreading framework supporting dynamic load balancing, the multithreading framework being used to perform multi-thread programming, the multithreading framework includes a job scheduler for performing parallel processing by redefining a processing order of one or more unit jobs, transmitted from a predetermined application, based on unit job information included in the respective unit jobs, and transmitting the unit jobs to a thread pool based on the redefined processing order, a device enumerator for detecting a device in which the predetermined application is executed and defining resources used inside the application, a resource manager for managing the resources related to the predetermined application executed using the job scheduler or the device enumerator, and a plug-in manager for managing a plurality of modules which performs various types of functions related to the predetermined application in a plug-in manner, and providing such plug-in modules to the job scheduler.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Processing techniques for servers handling client/server traffic and communications
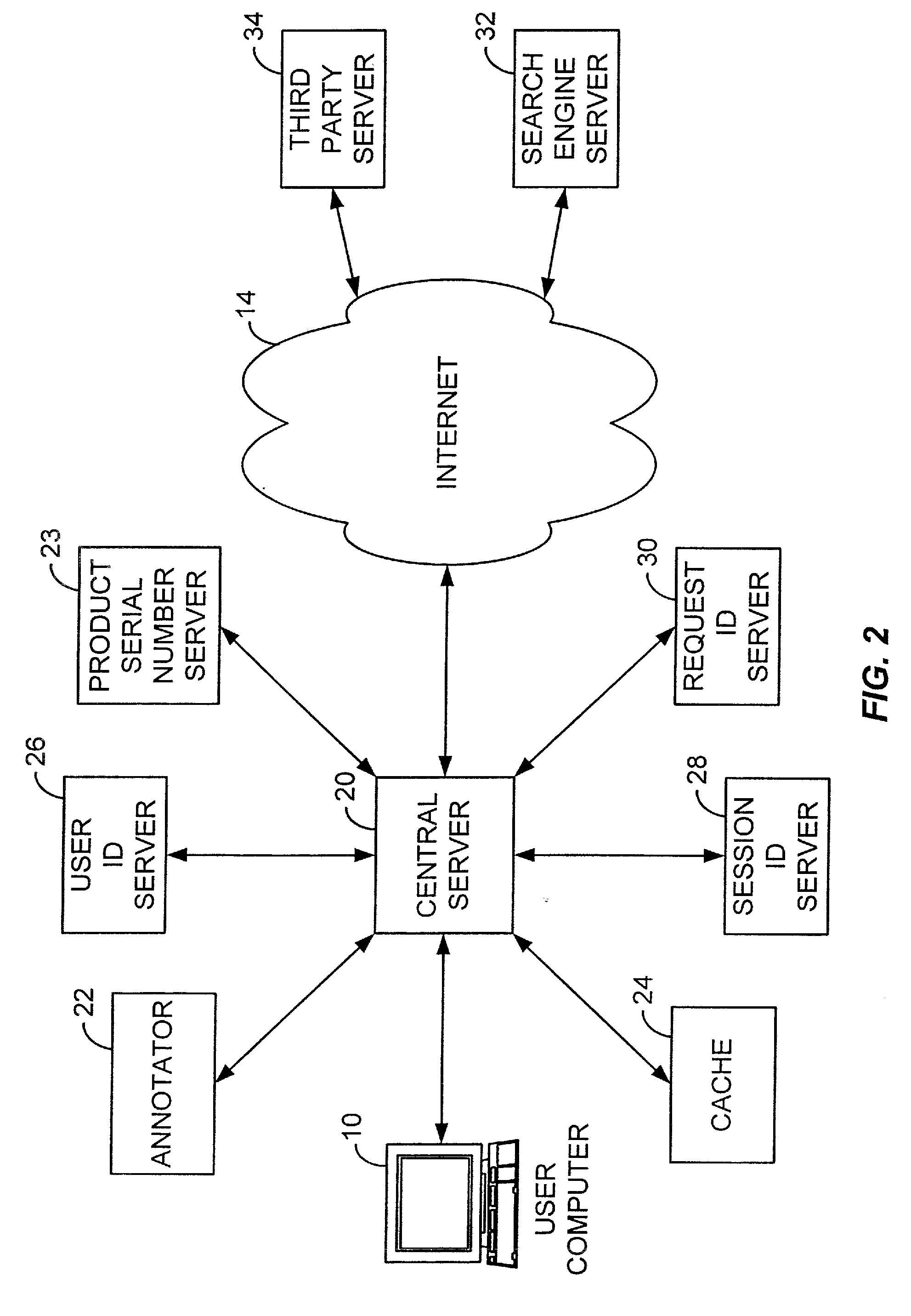
InactiveUS7437725B1Improve performanceMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsRelevant informationOperational system
The present invention relates to a system for handling client / server traffic and communications pertaining to the delivery of hypertext information to a client. The system includes a central server which processes a request for a web page from a client. The central server is in communication with a number of processing / storage entities, such as an annotation means, a cache, and a number of servers which provide identification information. The system operates by receiving a request for a web page from a client. The cache is then examined to determine whether information for the requested web page is available. If such information is available, it is forwarded promptly to the client for display. Otherwise, the central server retrieves the relevant information for the requested web page from the pertinent server. The relevant information is then processed by the annotation means to generate additional relevant computer information that can be incorporated to create an annotated version of the requested web page which includes additional displayable hypertext information. The central server then relays the additional relevant computer information to the client so as to allow the annotated version of the requested web page to be displayed. In addition, the central server can update the cache with information from the annotated version. The central server can also interact with different servers to collect and maintain statistical usage information. In handling its communications with various processing / storage entities, the operating system running behind the central server utilizes a pool of persistent threads and an independent task queue to improve the efficiency of the central server. The pool of threads are continually maintained and monitored by the operating system. Whenever a thread is available, the operating system identifies the next executable task in the task queue and assigns the available thread to such task so as to allow it to be executed. Upon conclusion of the task execution, the assigned thread is released back into the thread pool. An additional I / O queue for specifically handling input / output tasks can also be used to further improve the efficiency of the central server.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Remote process transfering method and system in distribution type control system
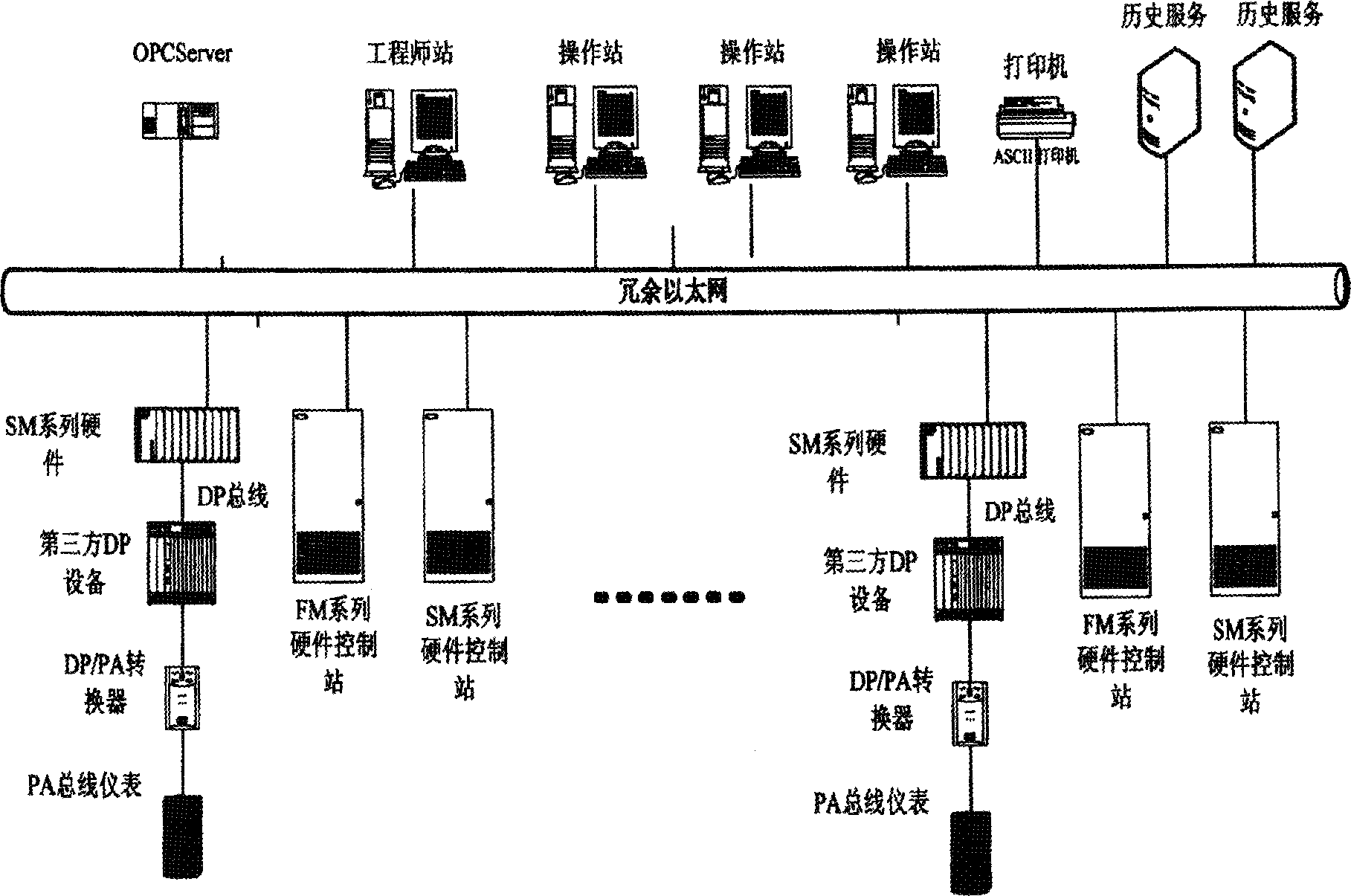
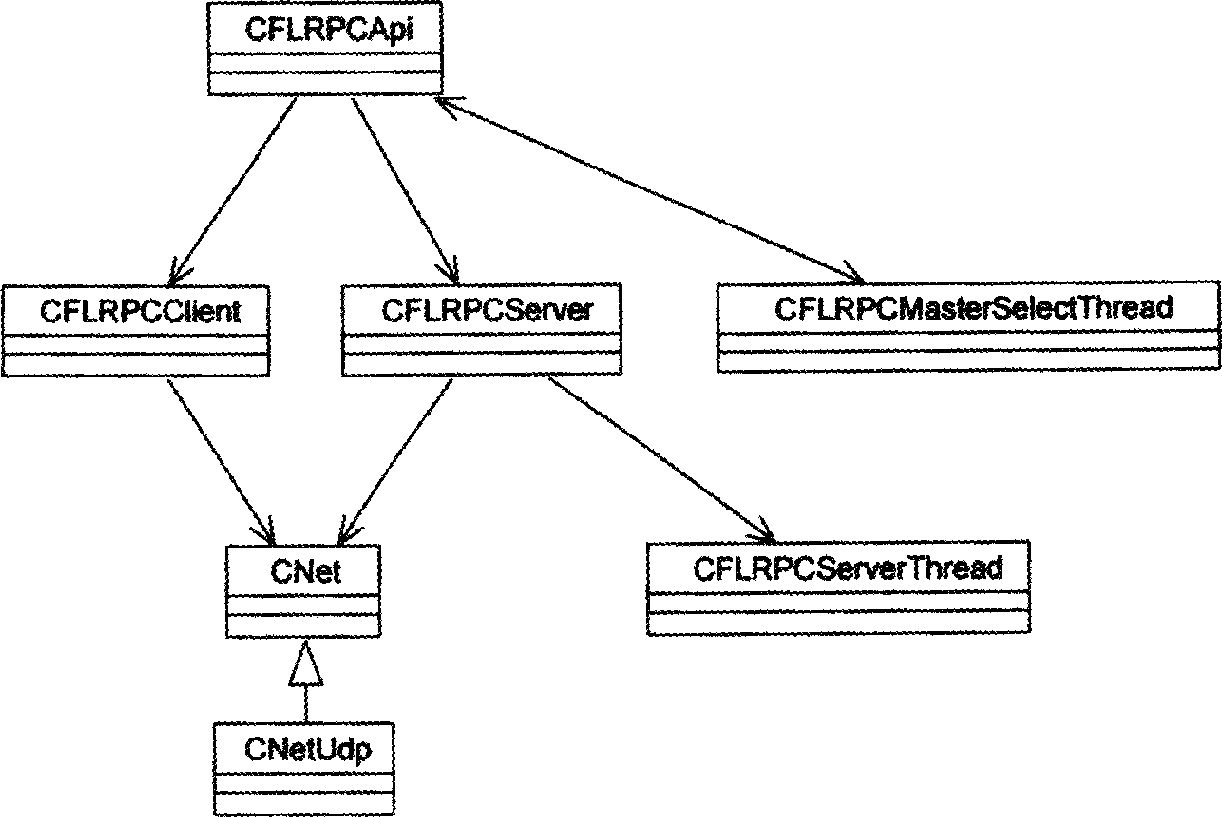
ActiveCN1852209AMasking complexityRealize dual network redundancy switching functionData switching by path configurationDistribution controlControl system
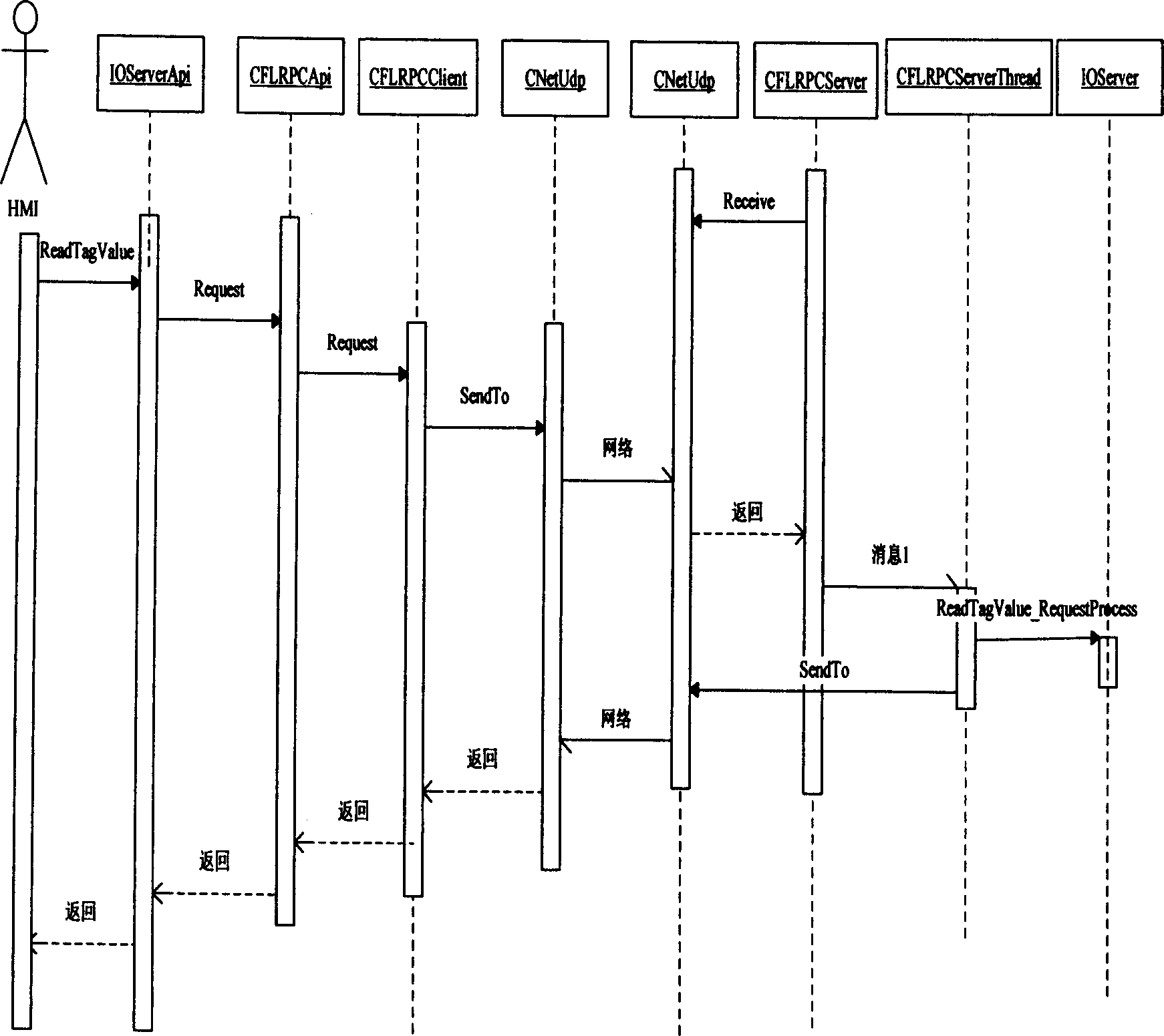
Following modules are included at two ends of remote procedure call (RPC): external interface module for providing external uniform interface; client end module and server end module accessible by the external interface module; network interface module accessible by modules at client end and server end; and module of service process thread pool accessible by the server module. After receiving message of RPC, the external interface module obtains all configuration parameters of server task, creates an instance of client end module, and initiates call; client end module accomplishes packaging data and slicing segment, the network interface module sends the packaged data and sliced segment to server module at opposite end as well as carries out switching processes; after recombining segment of RPC messages, server module starts process threaded, and returns result back to caller along original route. Features are: easy of use, masking complexity, and redundant dual networks switching.
Owner:北京和利时控制技术有限公司
Dynamic thread pool tuning techniques
InactiveUS7237242B2Improve performanceSimple technologyProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationQueue timeWorkload
Thread pools in a multithreaded server are programmatically adjusted, based on observed statistics from the server's inbound workload. In a multithreaded server environment, response time to end users is improved while increasing the efficiency of software execution and resource usage. Execution time and wait / queued time are tracked, for various types of requests being serviced by a server. Multiple logical pools of threads are used to service these requests, and inbound requests are directed to a selected one of these pools such that requests of similar execution-time requirements are serviced by the threads in that pool. The number and size of thread pools may be adjusted programmatically, and the distribution calculation (i.e., determining which inbound requests should be assigned to which pools) is a programmatic determination. In preferred embodiments, only one of these variables is adjusted at a time, and the results are monitored to determine whether the effect was positive or negative. The disclosed techniques also apply to tracking and classifying requests by method name (and, optionally, parameters).
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Data backup method of distributed file system
ActiveCN103761162AReduce data transferReduced execution timeRedundant operation error correctionSpecial data processing applicationsClustered dataDistributed source
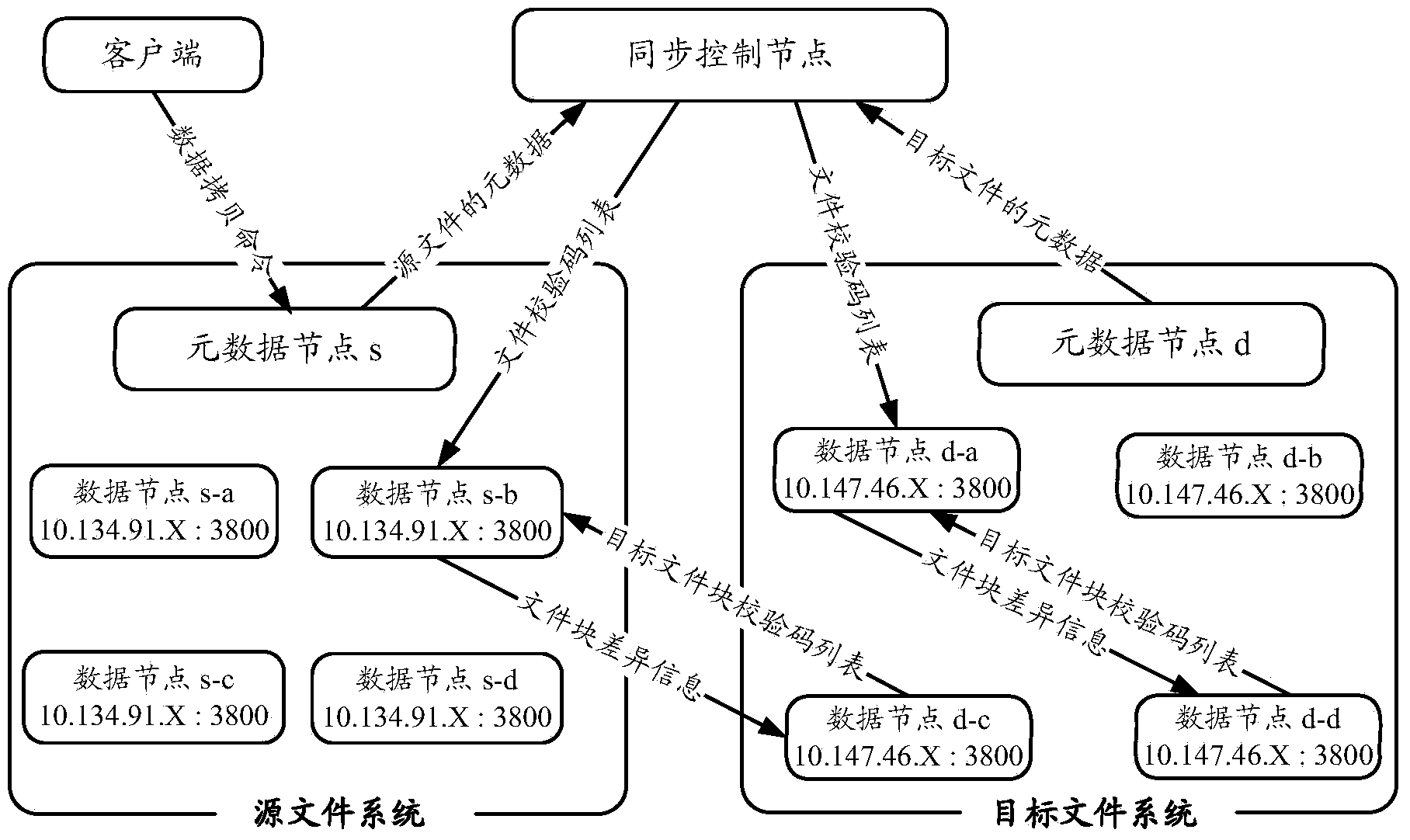
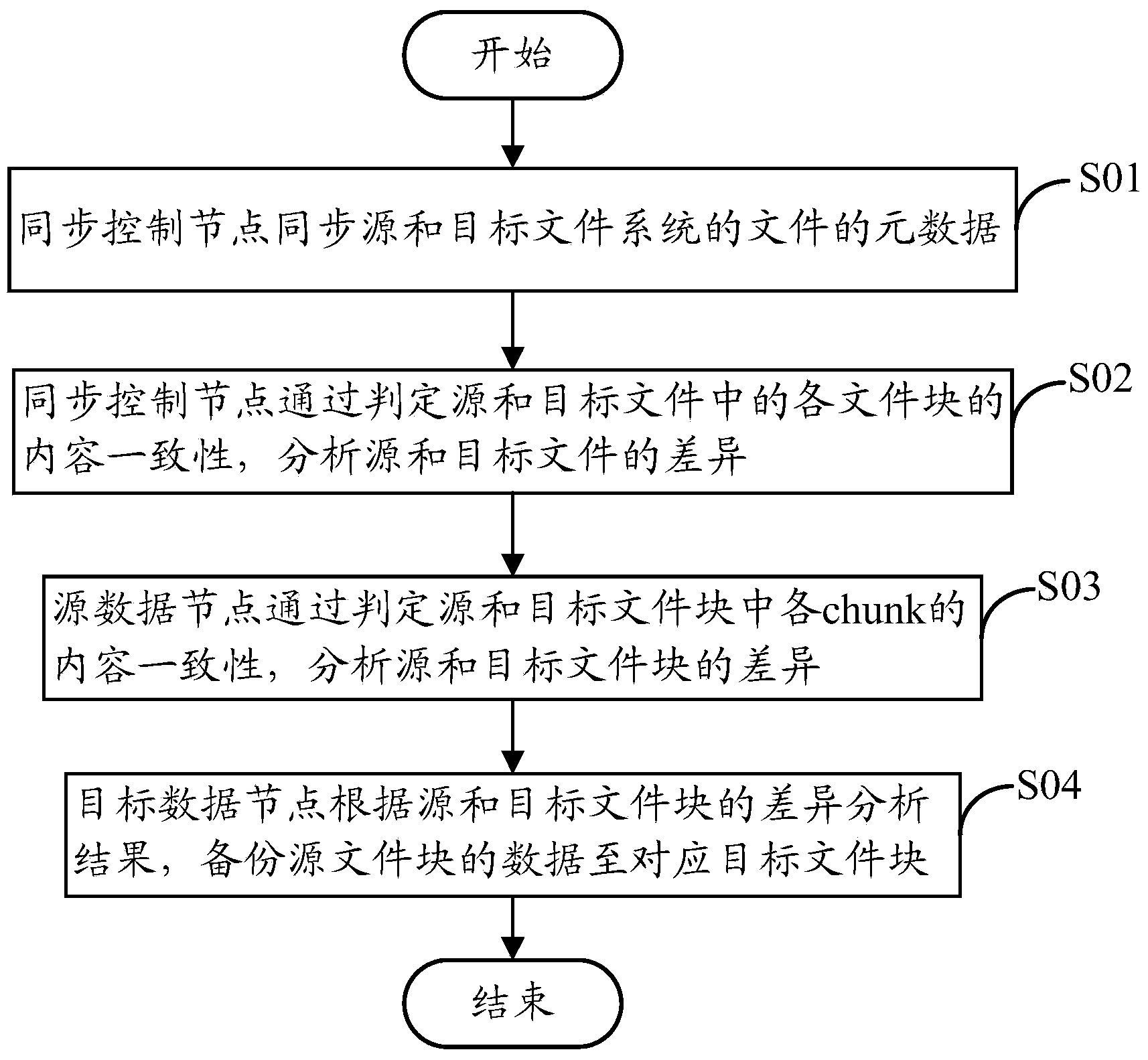
The invention provides a data backup method of a distributed file system. The method includes: setting up a thread pool by a synchronous control node, distributing source files to each thread according to a copy list, and parallelly conducting metadata synchronization of each source file and the corresponding target file; judging content consistency of each file block in the source files and the target files by each thread of the synchronous control node to analyze difference between each distributed source file and the corresponding target file; judging content consistency of each chunk in the source files and the target files by a source data node to analyze difference between the source file blocks and the target file blocks; duplicating data of the source file blocks to the corresponding target file blocks by a target data node according to the difference analyzing results of the source file blocks and the target file blocks. Data transmission among trans-cluster data nodes can be reduced by effectively using existing data of the target files of a target file system, and data backup execution time is shortened since file backup is completed by taking a file block as a unit.
Owner:清能艾科(深圳)能源技术有限公司
Thread pool processing method and system capable of fusing synchronous and asynchronous features
ActiveCN103197968AReduce waiting timeMultiple Prioritization OpportunitiesProgram initiation/switchingThe InternetThread pool
The invention provides a thread pool processing method and a thread pool processing system capable of fusing synchronous and asynchronous features. A large number of task requests on the internet are subjected to asynchronous processing by the thread pool, so that mutual influence is avoided and the waiting time is short. Synchronous processing is realized for single user operation, the output requirement according to the service sequence is met, and optimization mechanism capable of performing priority processing is provided for the task request with high importance.
Owner:FOCUS TECH +1
Task request processing method and device and enterprise information system
ActiveCN106095585AImprove securityImprove stabilityResource allocationEnterprise integrationDistributed computing
The invention provides a task request processing method and device and an enterprise information system. The method comprises the steps that any background server receives a task request message sent by an enterprise service bus; a task is generated according to the received task request message, and the task is added to a task table in a database; the any background server in an idle state captures the unexecuted task from the task table and executes the captured task in a thread pool. The task request processing process is broken up into two processes capable of being executed independently by two different servers. For the same task request, execution is conducted according to a normal execution sequence; task execution is conducted when corresponding background servers are in an idle state, tasks are executed by means of the thread pool, in this way, it is well guaranteed that tasks can be executed, the safety and stability of the background servers are improved, and customer experience is improved.
Owner:CHINA CONSTRUCTION BANK
Non-contact real-time online vibration measurement method based on images
InactiveCN104048744AEasy to handleReal-time online outputImage analysisSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementThread poolTest object
The invention discloses a non-contact real-time online vibration measurement method based on images, and belongs to the field of vibration measurement and analysis. The method includes the steps that a vibration process of a target object is recorded through a high-speed camera, all frames of images contained in a vibration video of the target object are extracted through vibration measurement software arranged in a computer and are stored in a memory pool opened up by the vibration measurement software arranged in the computer, a thread pool is created in the vibration measurement software arranged in the computer, corresponding image frames are extracted from the memory pool by different threads in the thread pool in order, coordinates of the images and an actual object are established so that the size conversion matrix M between the images and the actual object can be solved, and therefore actual coordinates and displacement imaged through the camera are mapped in the vibration process and a measuring result and a data curve are output. A non-contact measurement mode is adopted in the method, vibration characteristics of test objects cannot be changed, measurement accuracy is high, and vibration characteristic measurement can be conducted on vibration objects under poisonous and harmful, high-temperature and dangerous environments.
Owner:安徽天俣科技有限公司
Processing techniques for servers handling client/server traffic and communications
InactiveUS20090031311A1Improve performanceMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsRelevant informationOperational system
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Synchronizing file system directories
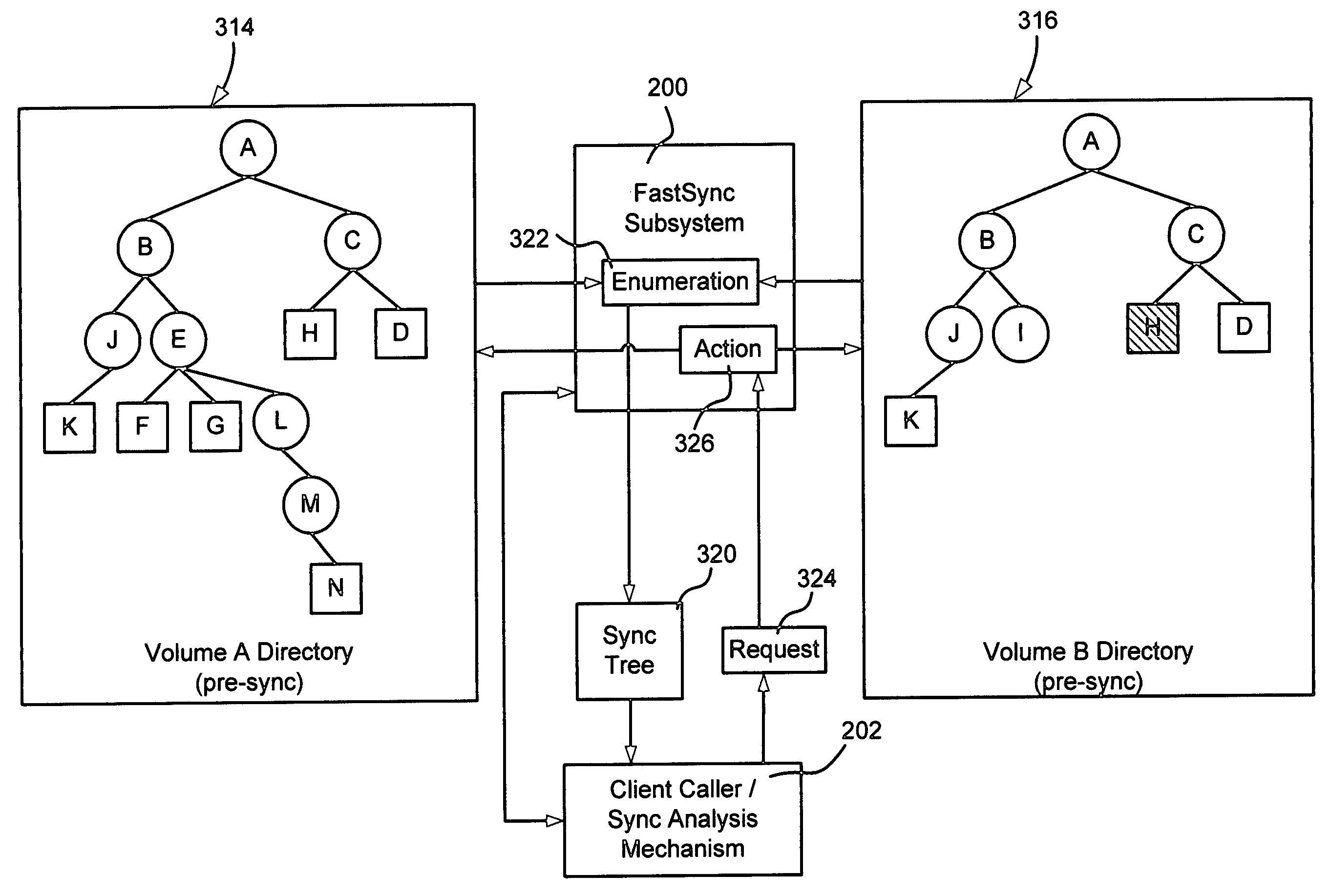
InactiveUS7634514B2Good synchronizationFast and reliable synchronizationDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsAs DirectedNetwork packet
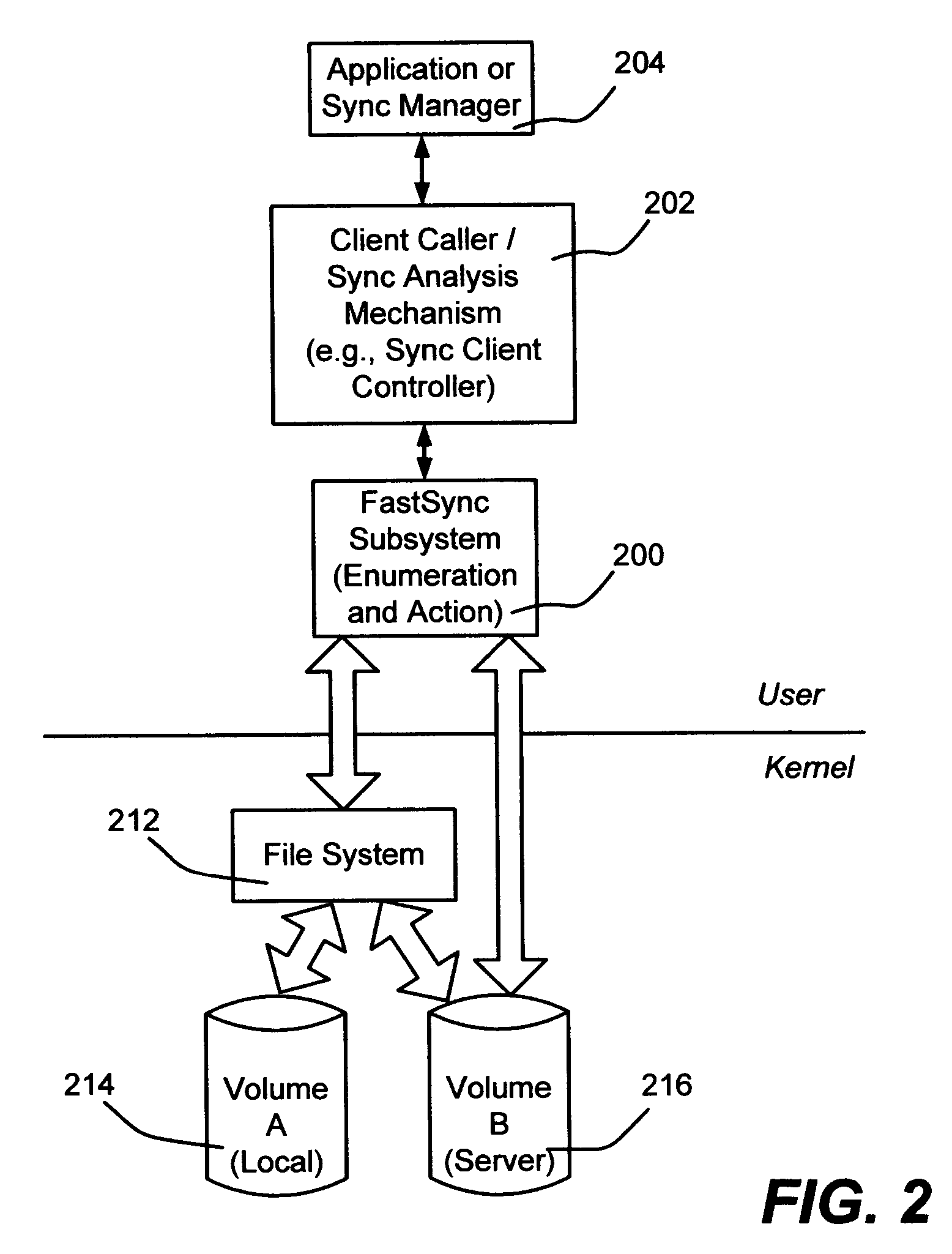
Described is a system and method that facilitates fast and reliable synchronization of computer / file system directories. A synchronization (FastSync) subsystem operates in a discovery / enumeration phase to provide a calling client with a set of the differences between directories, and then operates in an action phase to perform operations as directed by the client to synchronize the different directories. The discovery / enumeration and action phases use parallel operation and I / O (input / output) pipelining. Multiple threads are used during enumeration to enumerate each directory's children, and enqueues each sub-directory to be handled by a new thread. During the action phase, when an operation is requested, the FastSync subsystem packages up the operation, item pointer, and context information into an internal context block and queues that packet as a work item for a process thread pool to handle.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Distributed data acquisition system and method based on cloud computing
ActiveCN103037019AShorten Acquisition LatencyReduce congestionTransmissionVirtualizationData acquisition
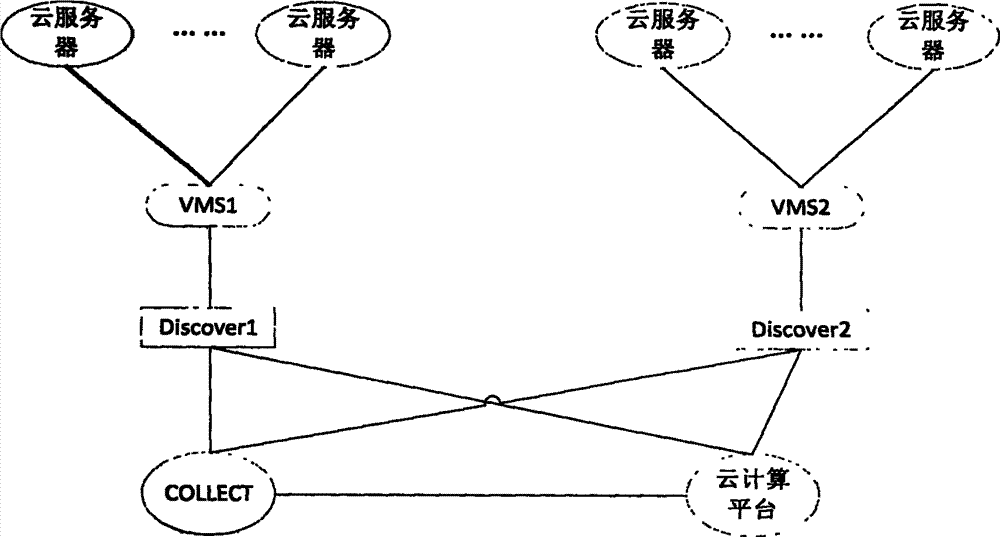
The invention relates to a distributed data acquisition system and method based on cloud computing. The system comprises a cloud server, at least one VMS (Virtualization Management Software), at least one Discover node, a Collect node and a cloud computing platform, wherein the cloud server is composed of at least one server, the VMS is used for managing the cloud server, and the Discover node is used for information acquisition. An acquisition program, a scheduler program and a control program are separately and independently arranged, an acquisition strategy, a data acquisition time stamp and an acquisition cycle can be self-defined, a thread pool mechanism is adopted, and multiple-VMS, multiple-object different data can be acquired at the same time. An acquisition task is executed through a thread preemption mode in a thread pool, the data acquisition delay is shortened, the acquisition task block is reduced, and the data acquisition efficiency is increased.
Owner:BEIJING TEAMSUN TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com