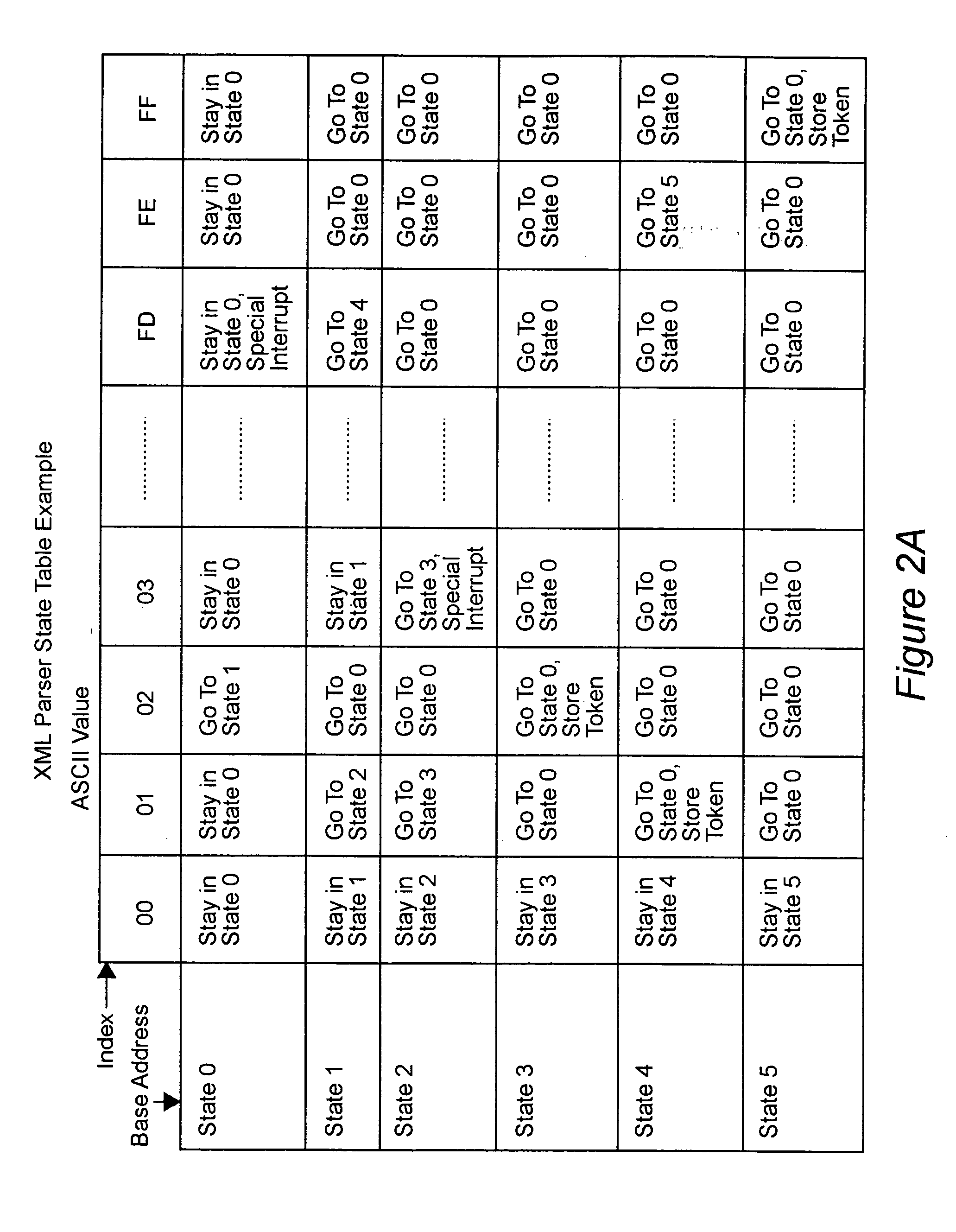
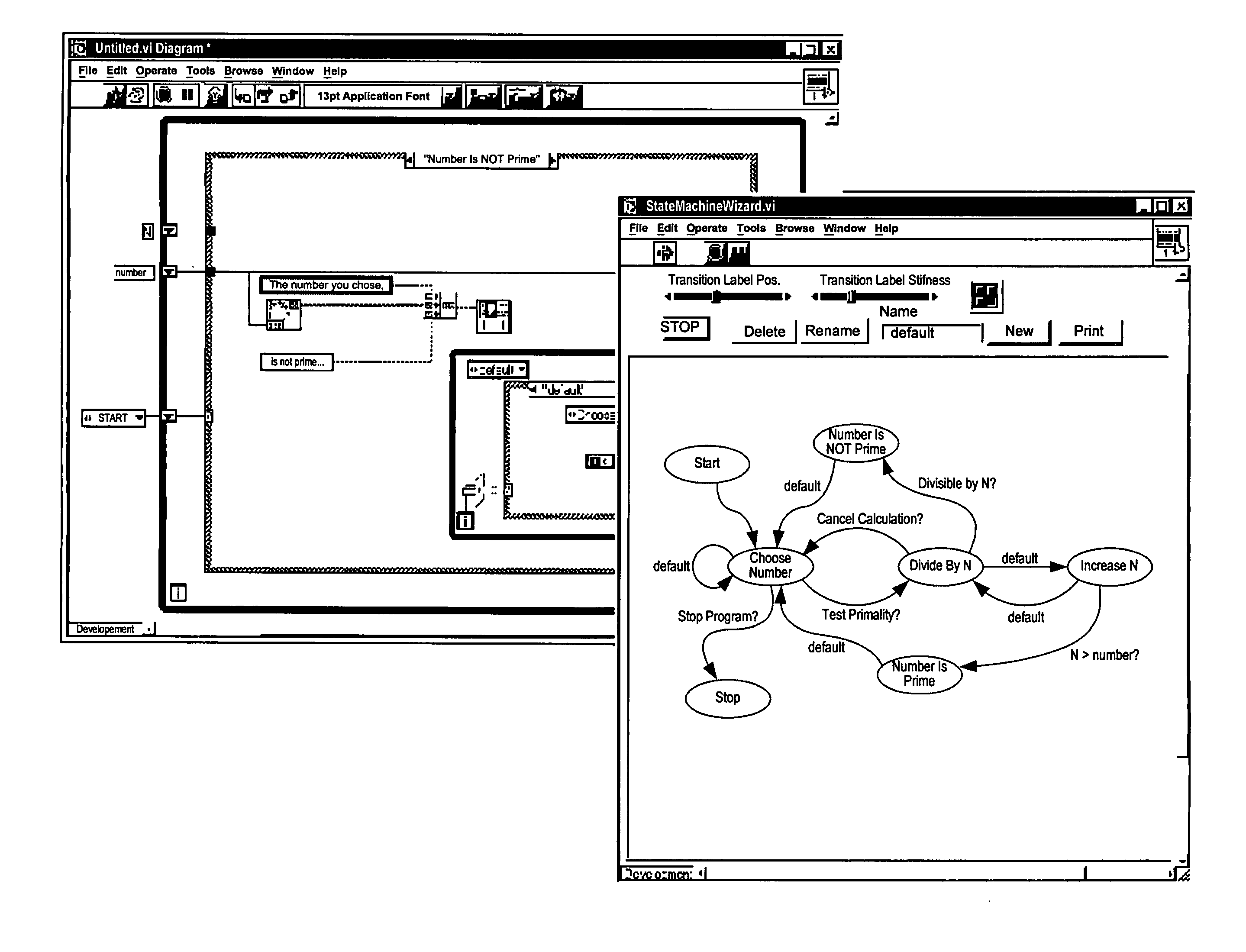
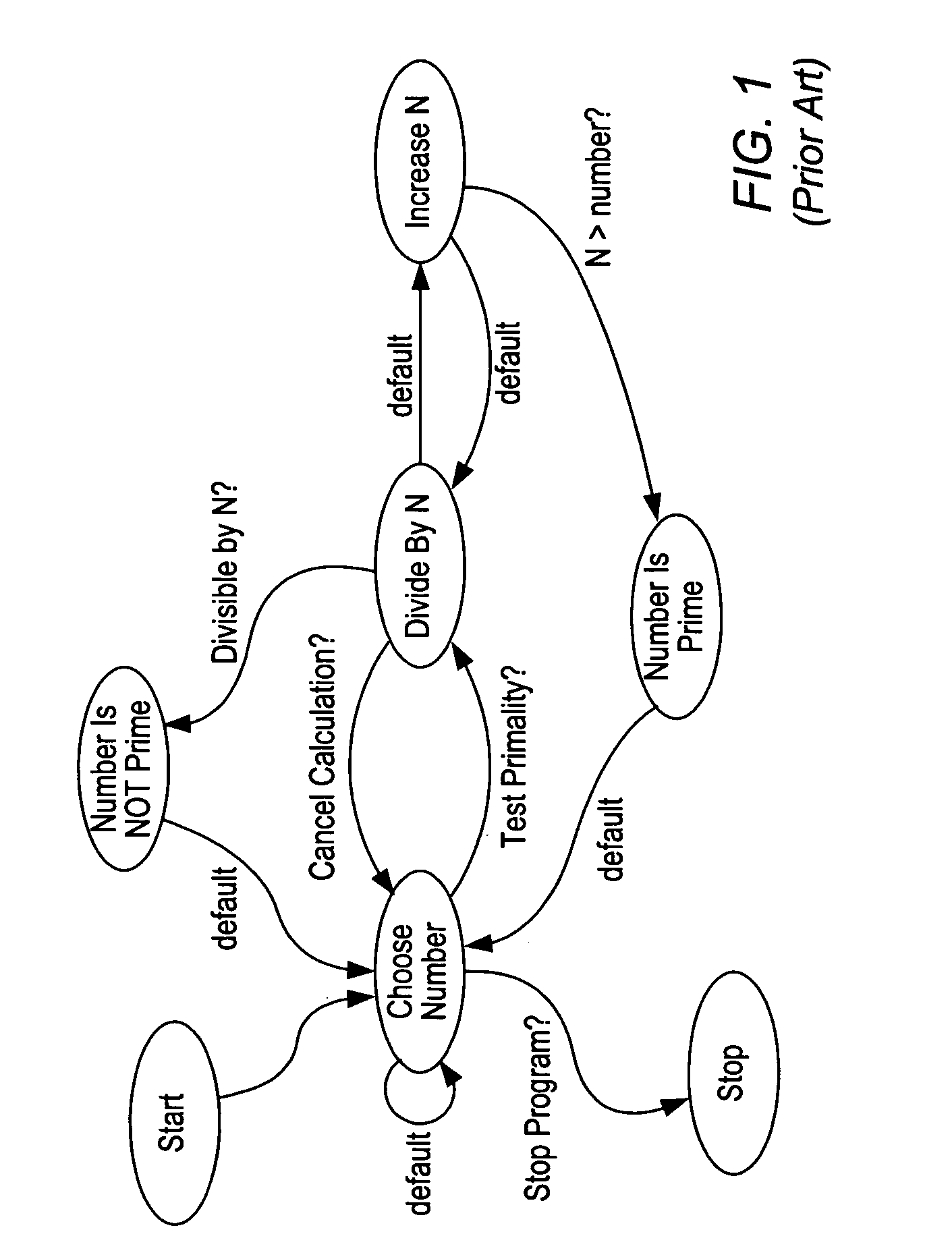
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3253 results about "State switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
State switching (a.k.a. phenotypic switching) is a fundamental physiological process in which a cell/organism undergoes spontaneous, and potentially reversible, transitions between different phenotypes. Thus, the ability to switch states/phenotypes (phenotypic plasticity) is a key feature of development and normal function of cells within most multicellular organisms that enables the cell to respond to various intrinsic and extrinsic cues and stimuli in a concerted fashion enabling them to ‘make’ appropriate cellular decisions. Although state switching is essential for normal functioning, the repertoire of phenotypes in a normal cell is albeit limited.
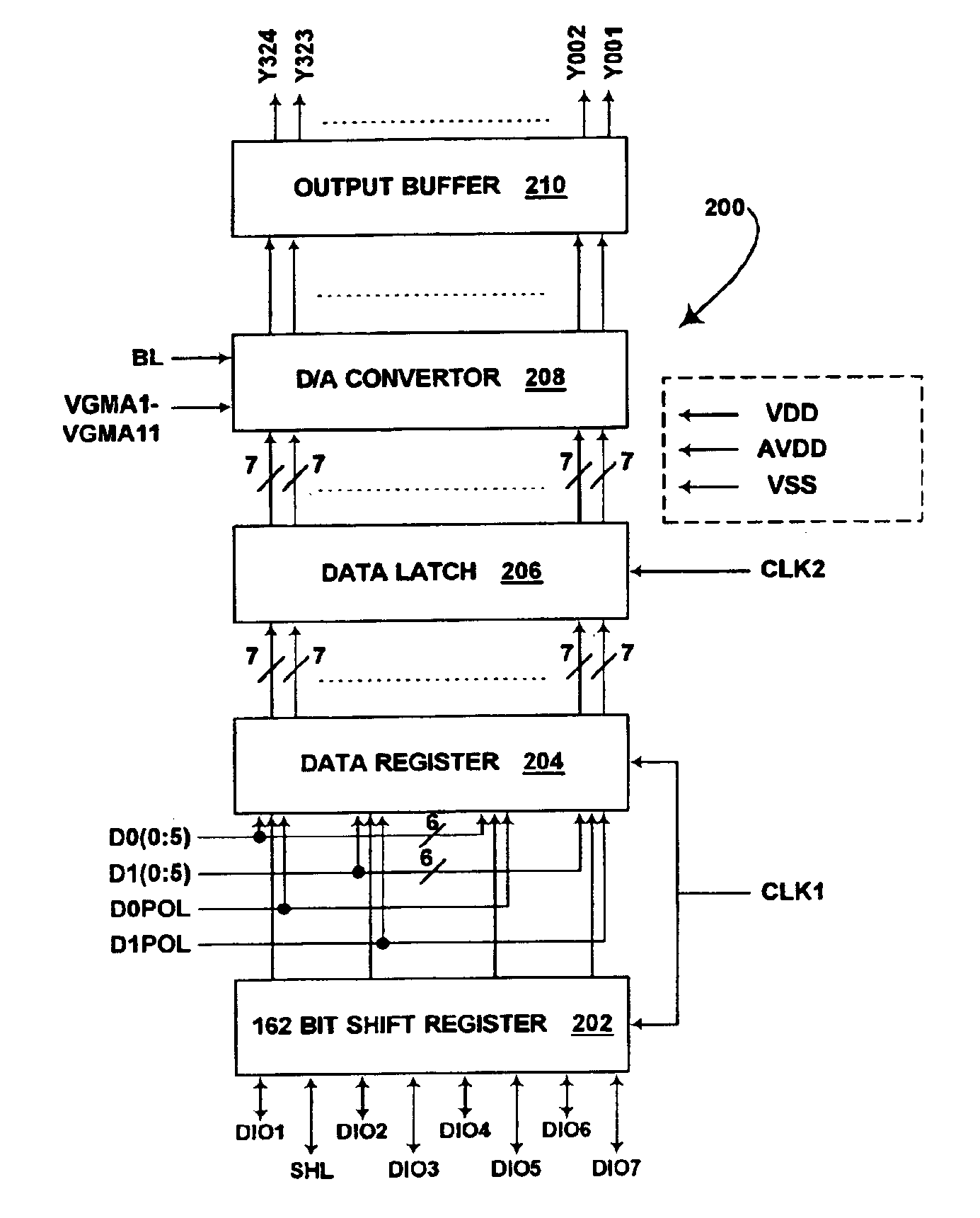
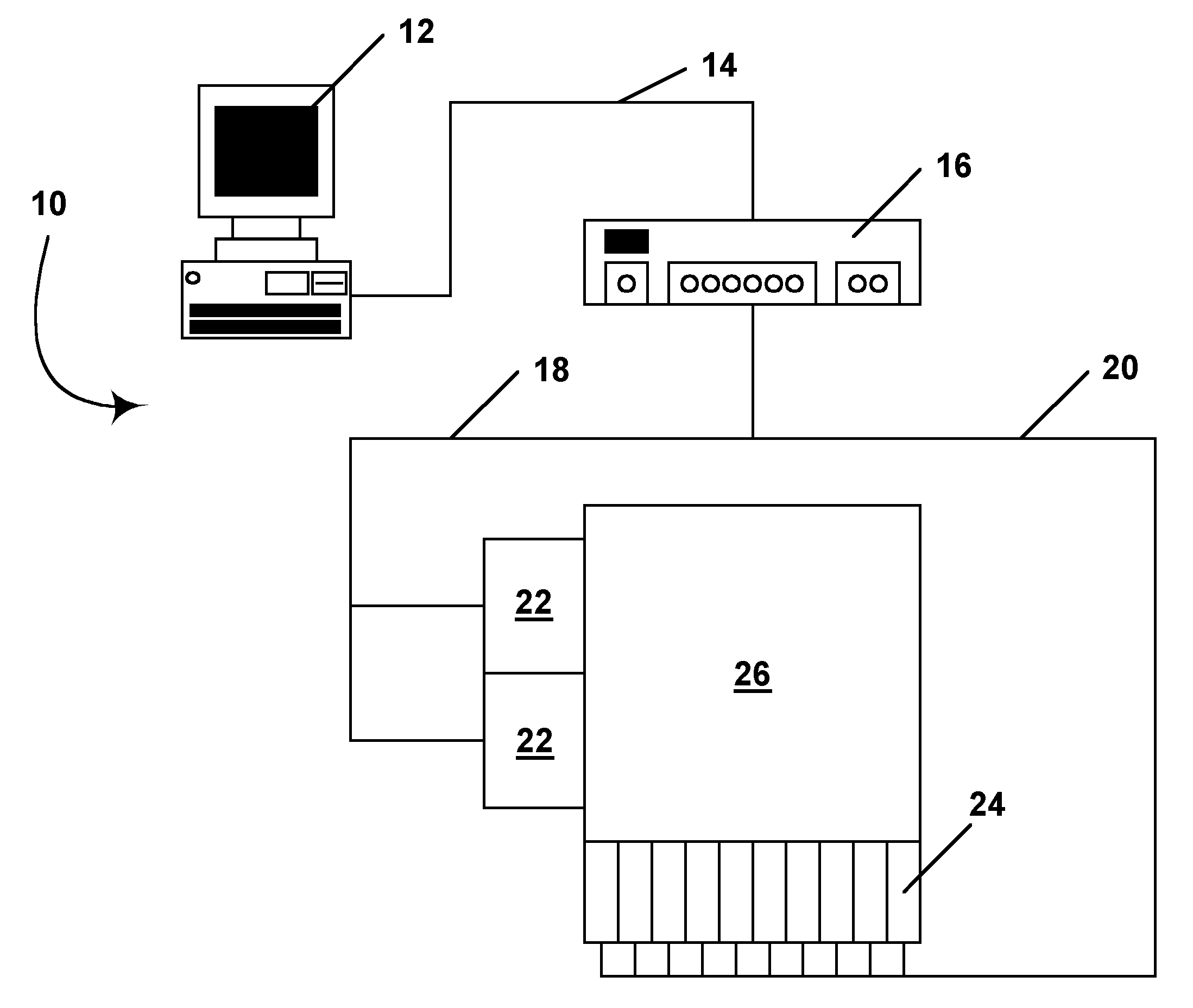
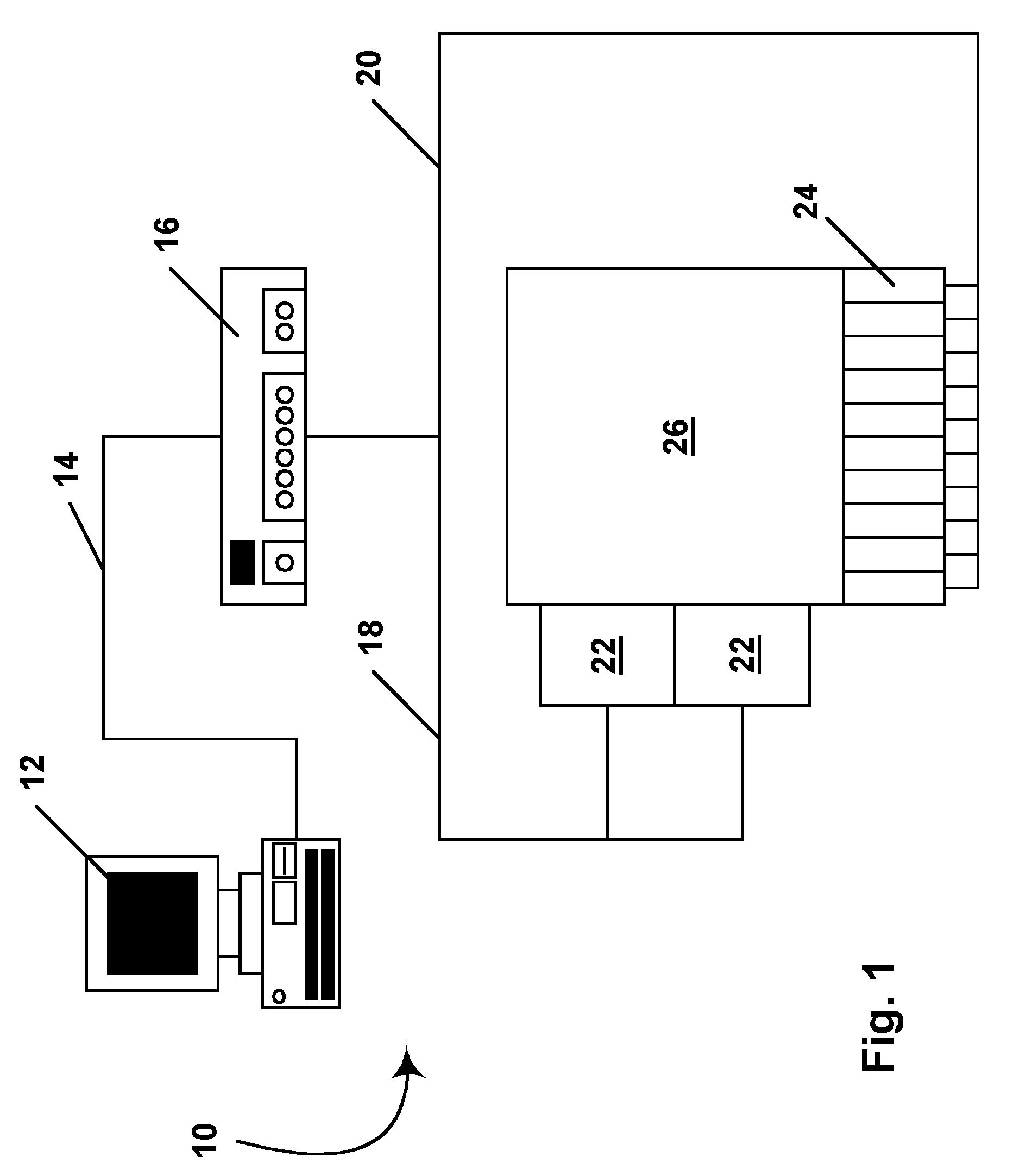
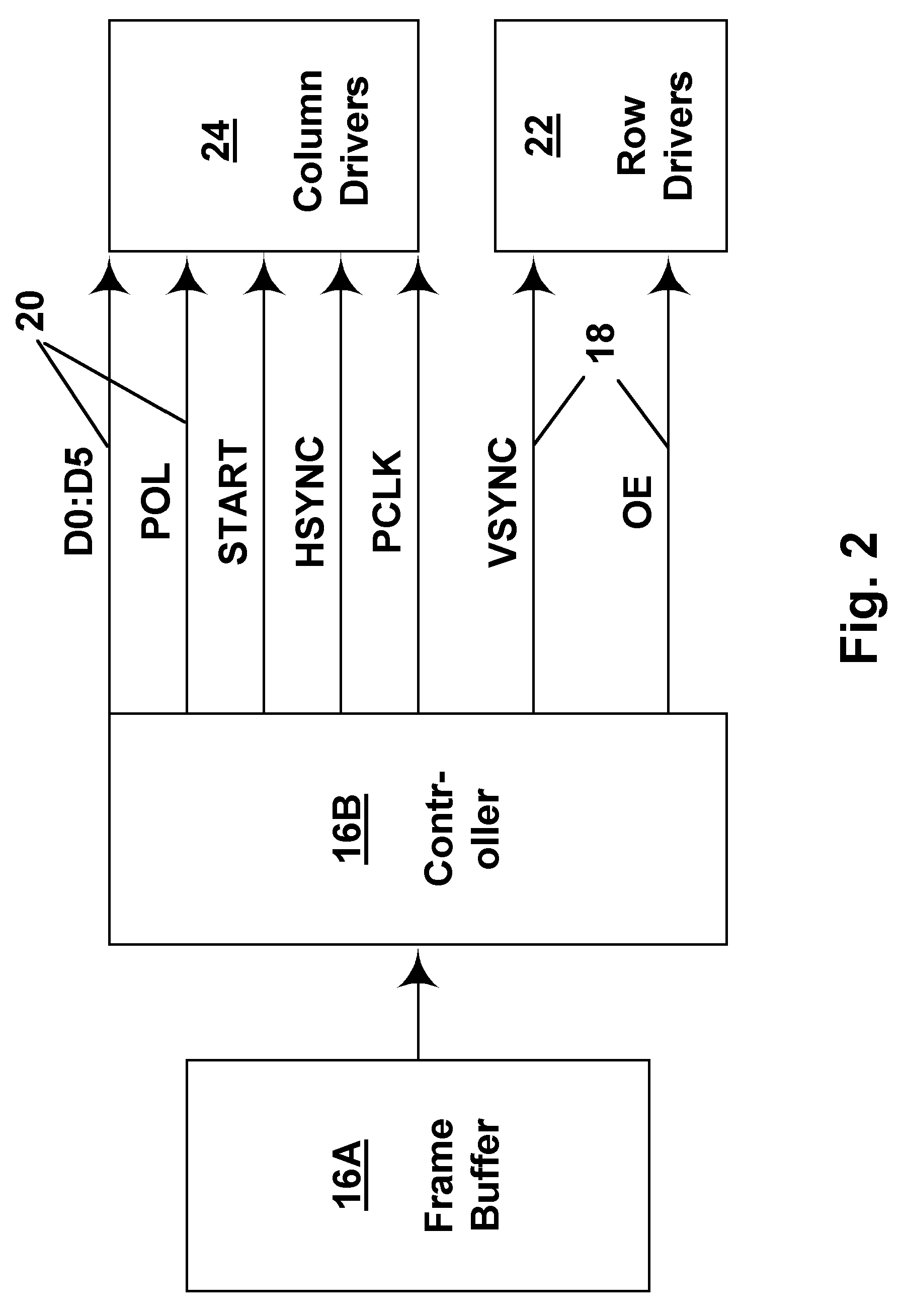
Methods for driving bistable electro-optic displays, and apparatus for use therein
InactiveUS7012600B2Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGray levelDisplay device
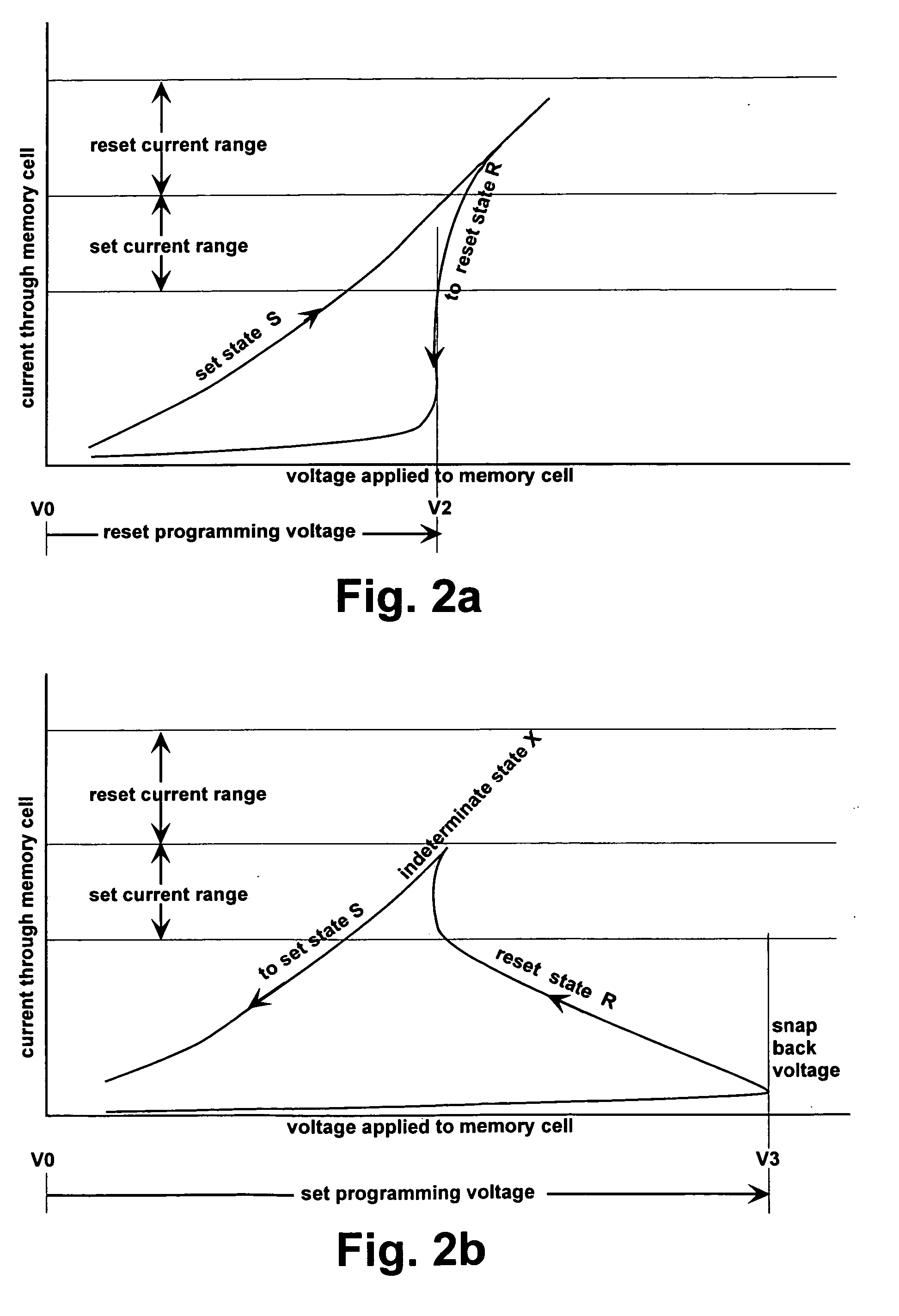
A bistable electro-optic display has a plurality of pixels, each of which is capable of displaying at least three gray levels. The display is driven by a method comprising: storing a look-up table containing data representing the impulses necessary to convert an initial gray level to a final gray level; storing data representing at least an initial state of each pixel of the display; receiving an input signal representing a desired final state of at least one pixel of the display; and generating an output signal representing the impulse necessary to convert the initial state of said one pixel to the desired final state thereof, as determined from said look-up table. The invention also provides a method for reducing the remnant voltage of an electro-optic display.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
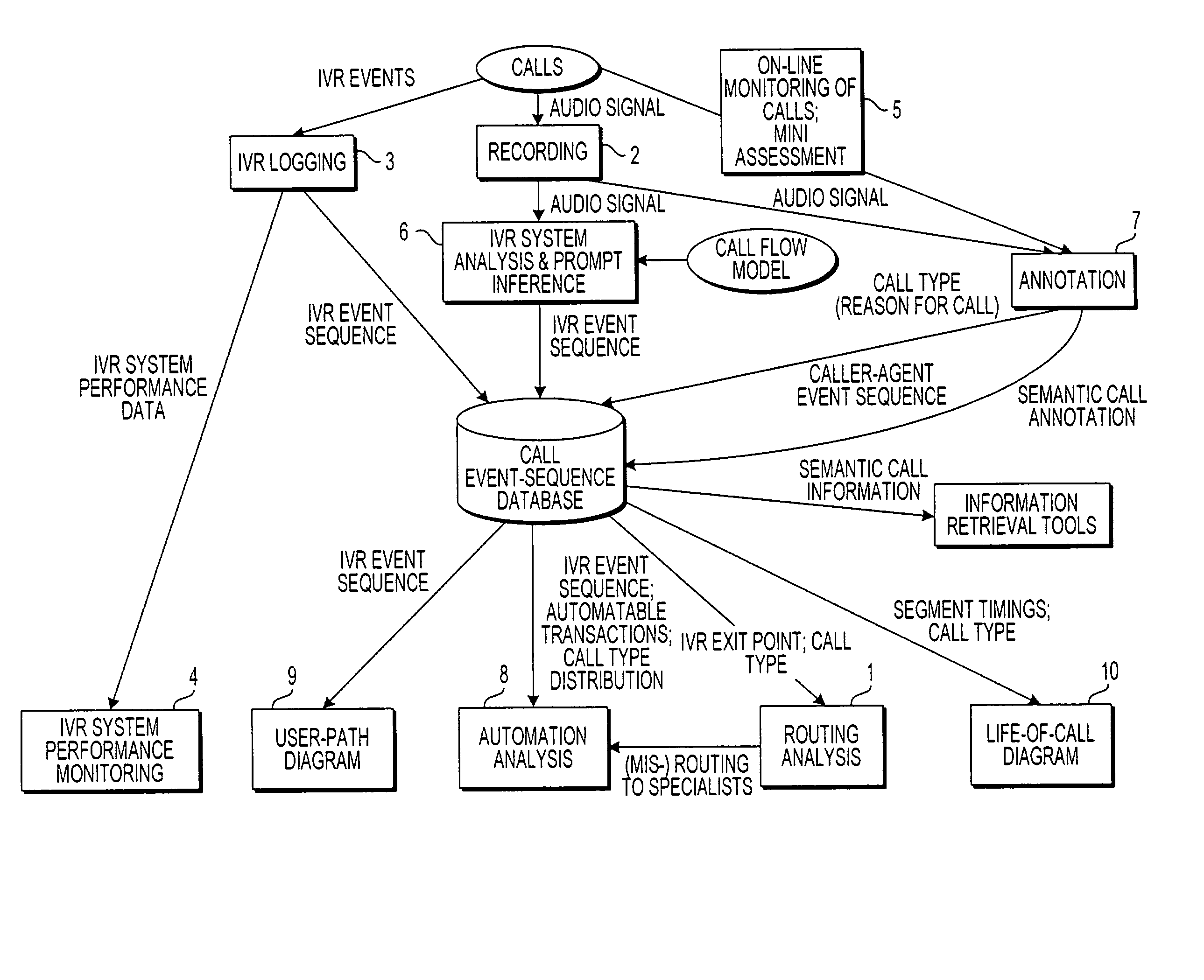
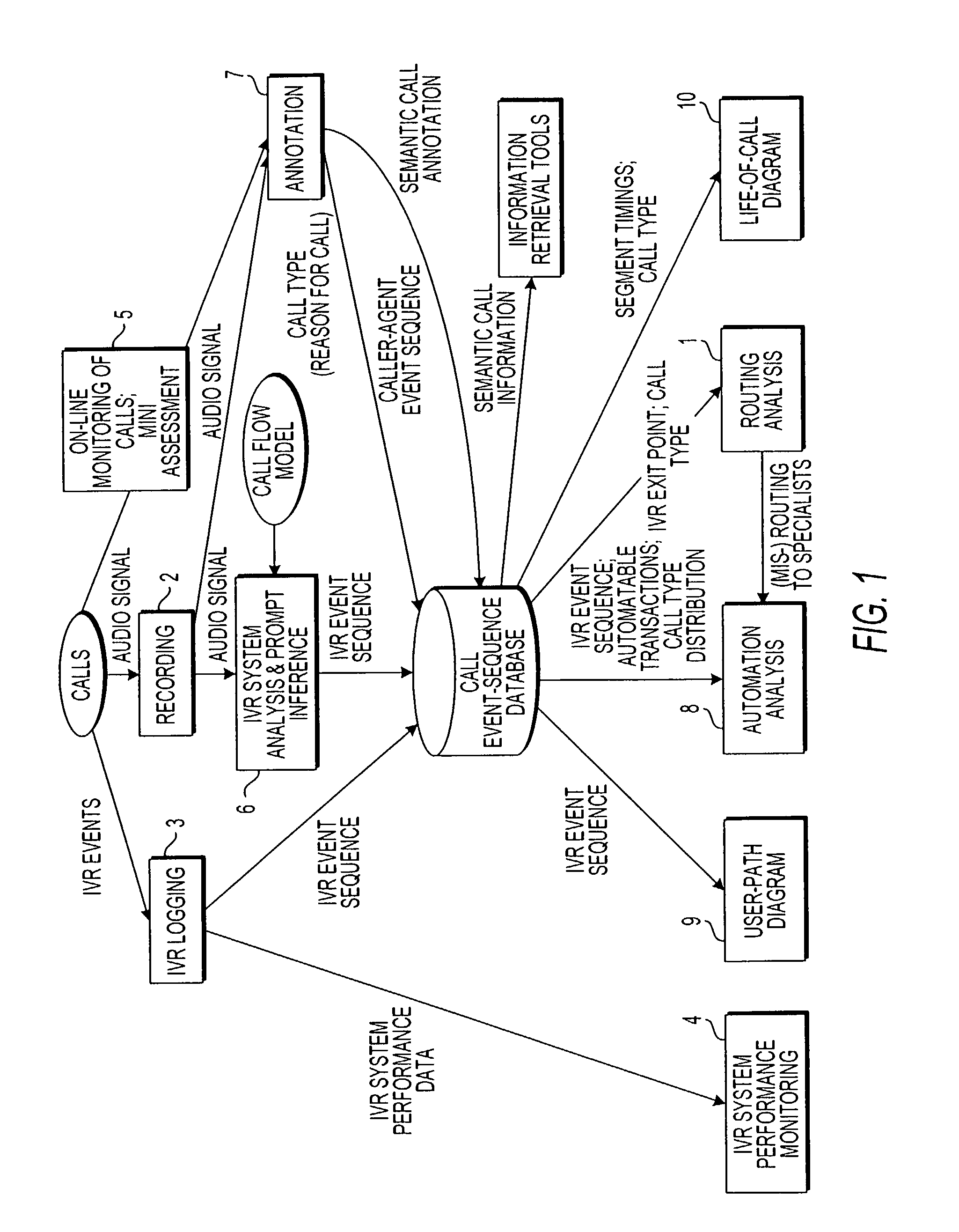
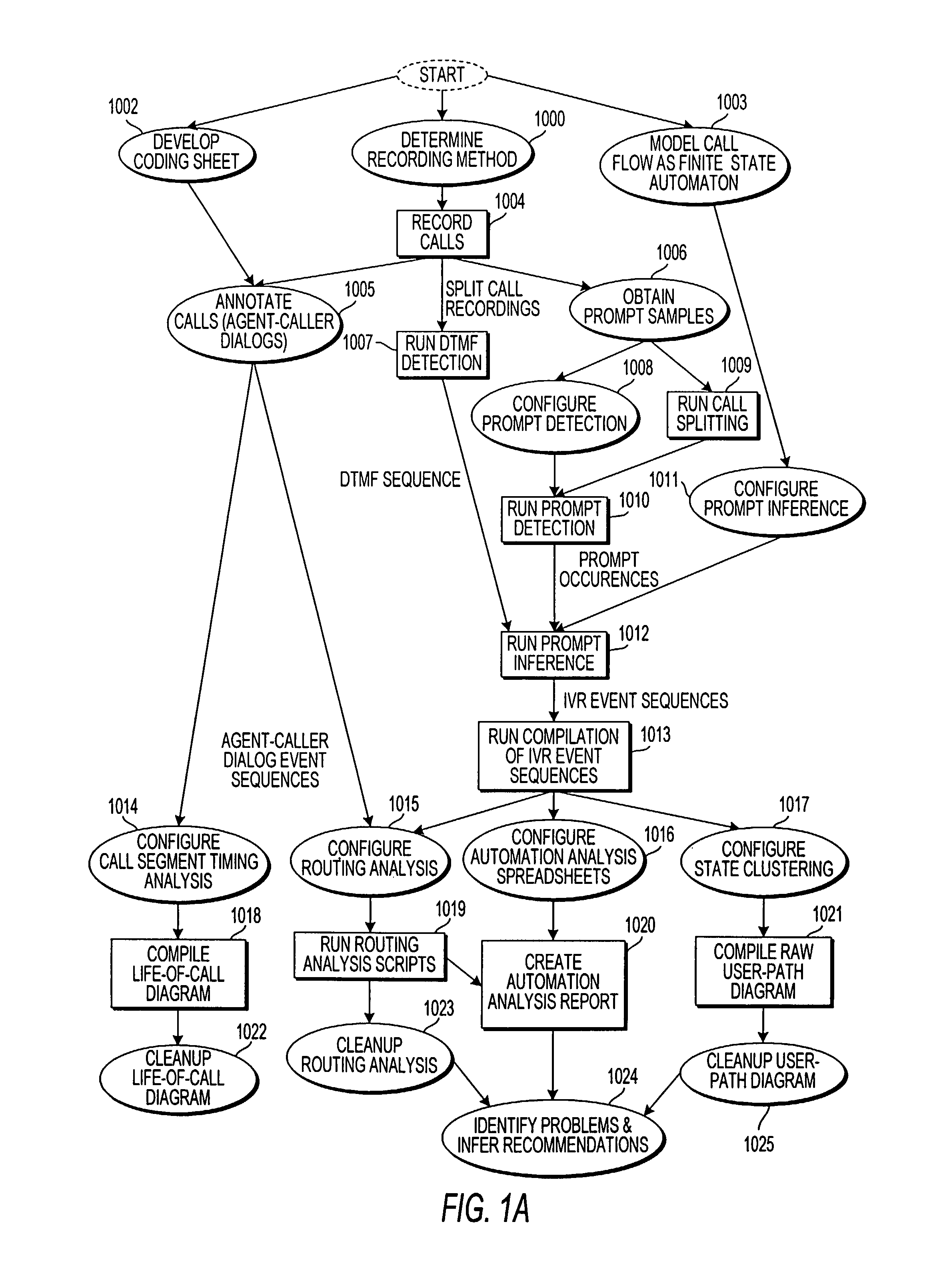
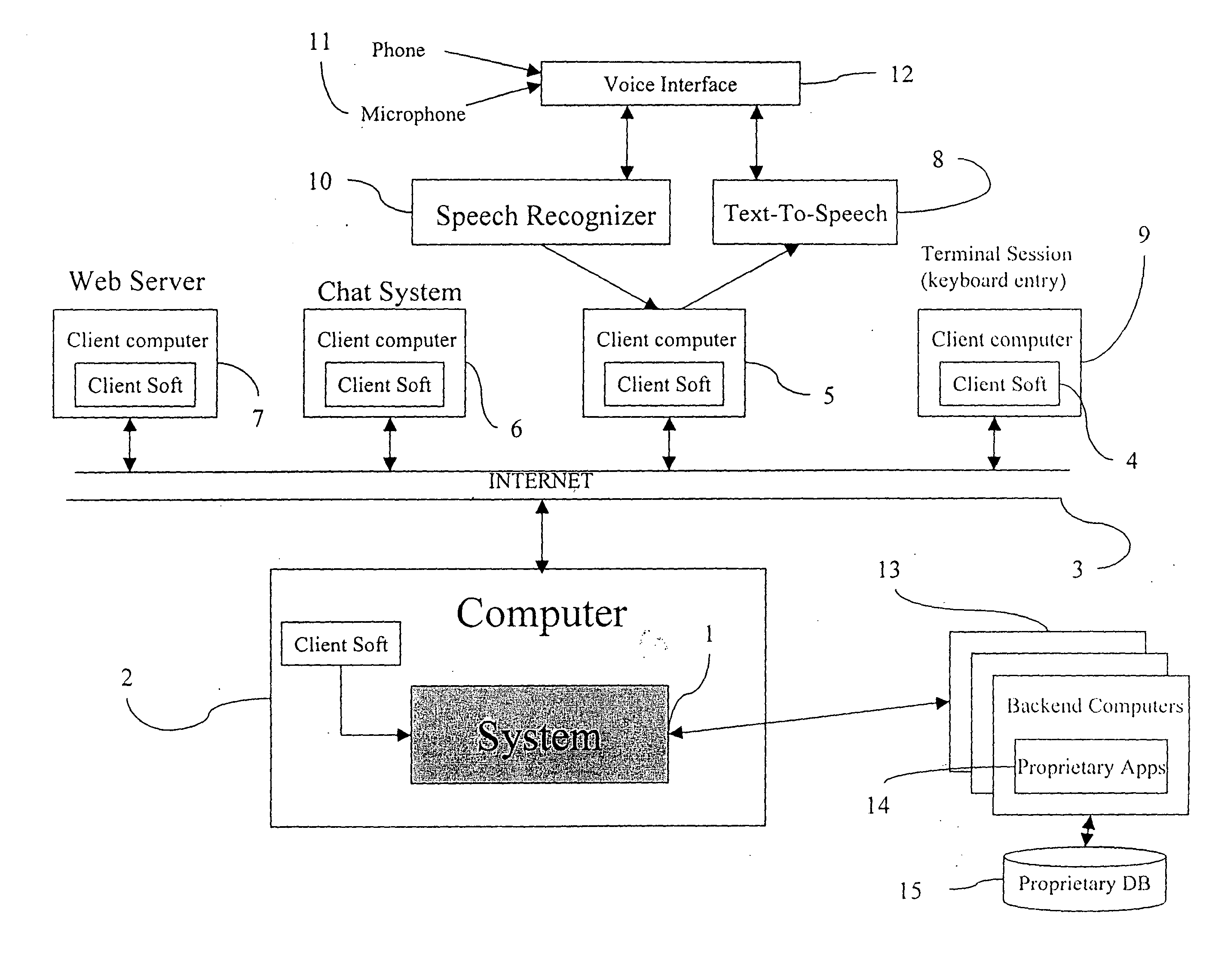
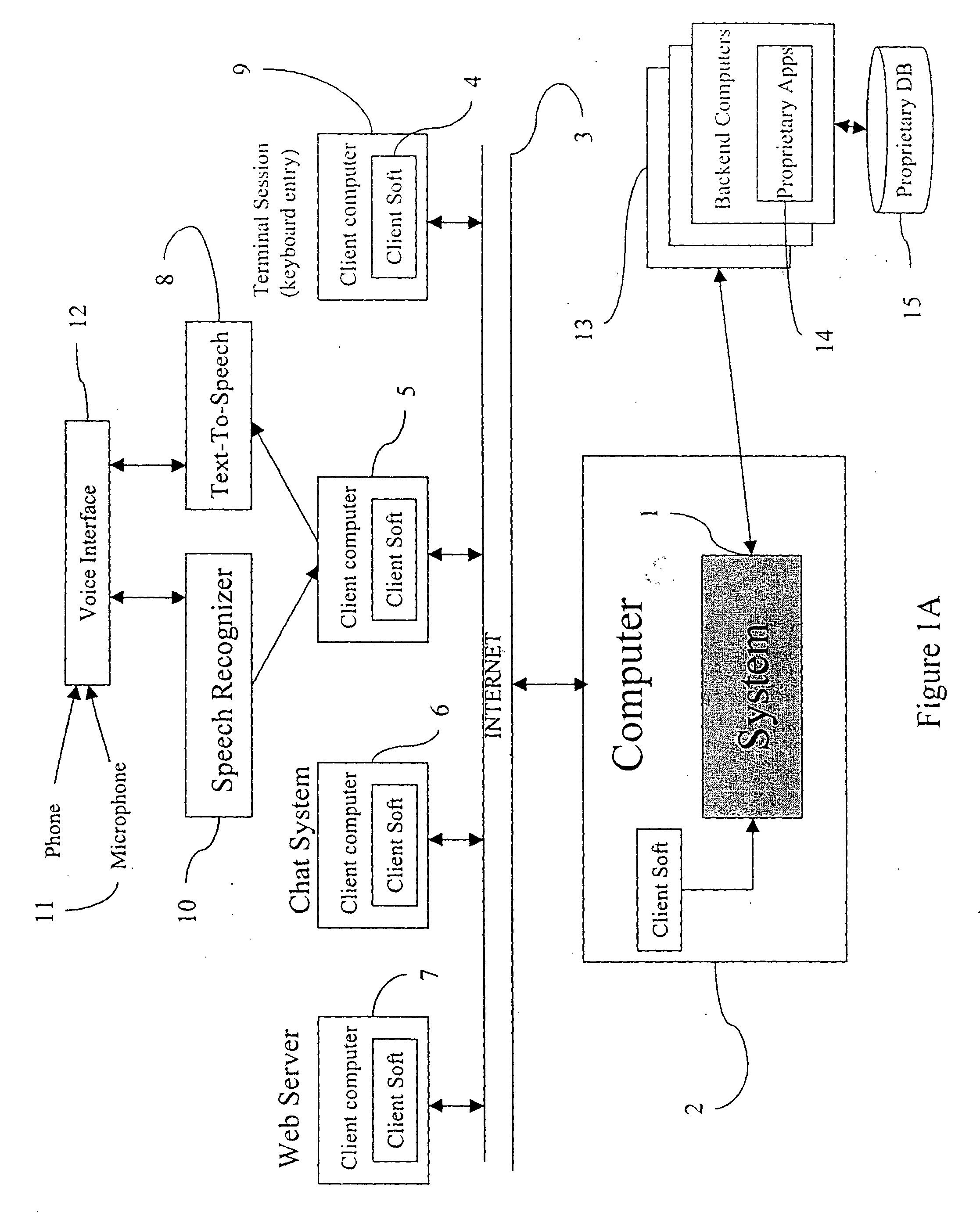
Apparatus and method for visually representing behavior of a user of an automated response system
InactiveUS7039166B1Overcome deficienciesSpeech analysisManual exchangesUser inputFinite-state machine
A system for visually representing user behavior within an interactive voice response (IVR) system of a call processing center generates a complete sequence of events within the IVR system for plural calls to the call processing center, the plurality of calls being recorded from end to end. A call flow of the IVR system is modeled as a non-deterministic finite-state machine, such that a start state of the finite-state machine represents a first prompt of the IVR system, other states of the finite-state machine represent subsequent prompts at which a branching occurs in the call flow of the IVR system, exit conditions are represented as end states, and transitions of the finite-state machine represent transitions between call flow states triggered by data inputted by a user or by internal processing of the IVR system. The complete sequences of events for the plural calls are provided to the finite-state machine to produce a two-way matrix of several counters. The data from the two-way matrix is represented as a state-transition diagram.
Owner:CX360 INC +1
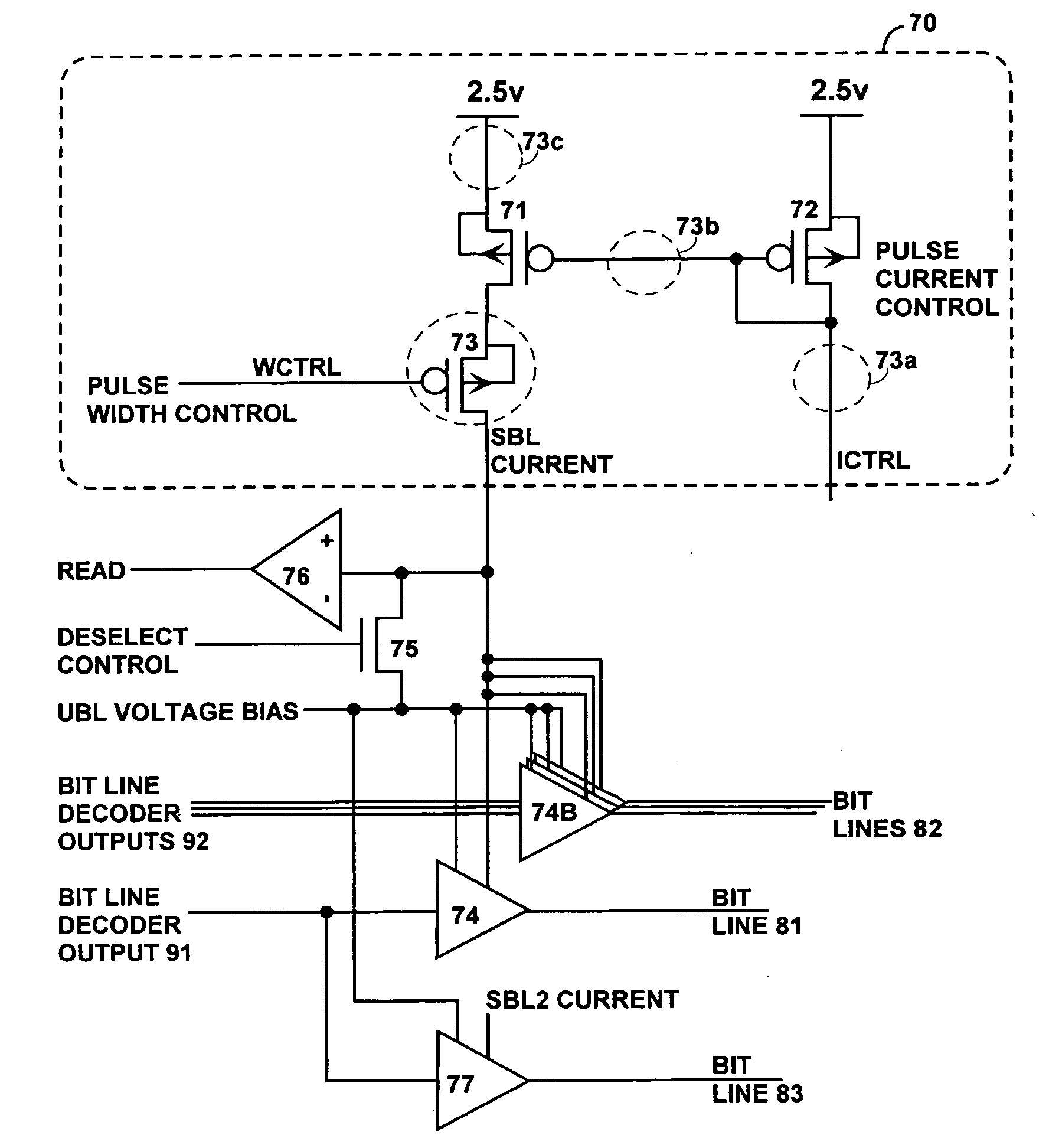
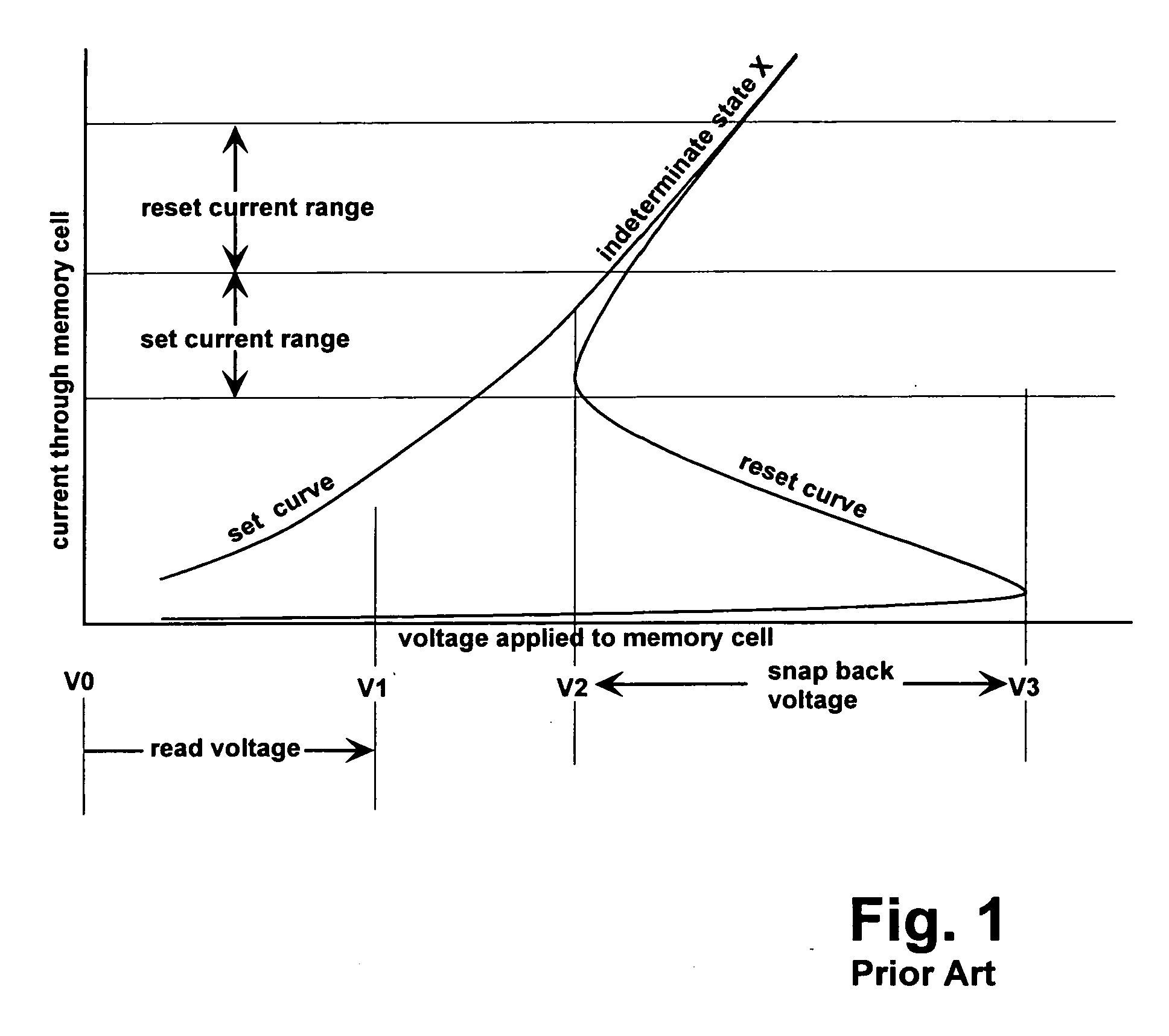
Structure and method for biasing phase change memory array for reliable writing
ActiveUS20060157679A1Minimize leakage currentReduce the possibilitySolid-state devicesDigital storageBit linePhase-change memory
A memory array having memory cells comprising a diode and a phase change material is reliably programmed by maintaining all unselected memory cells in a reverse biased state. Thus leakage is low and assurance is high that no unselected memory cells are disturbed. In order to avoid disturbing unselected memory cells during sequential writing, previously selected word and bit lines are brought to their unselected voltages before new bit lines and word lines are selected. A modified current mirror structure controls state switching of the phase change material.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Methods for driving electrophoretic displays using dielectrophoretic forces
InactiveUS20080136774A1Significant energy savingStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectrical conductorIntermediate frequency
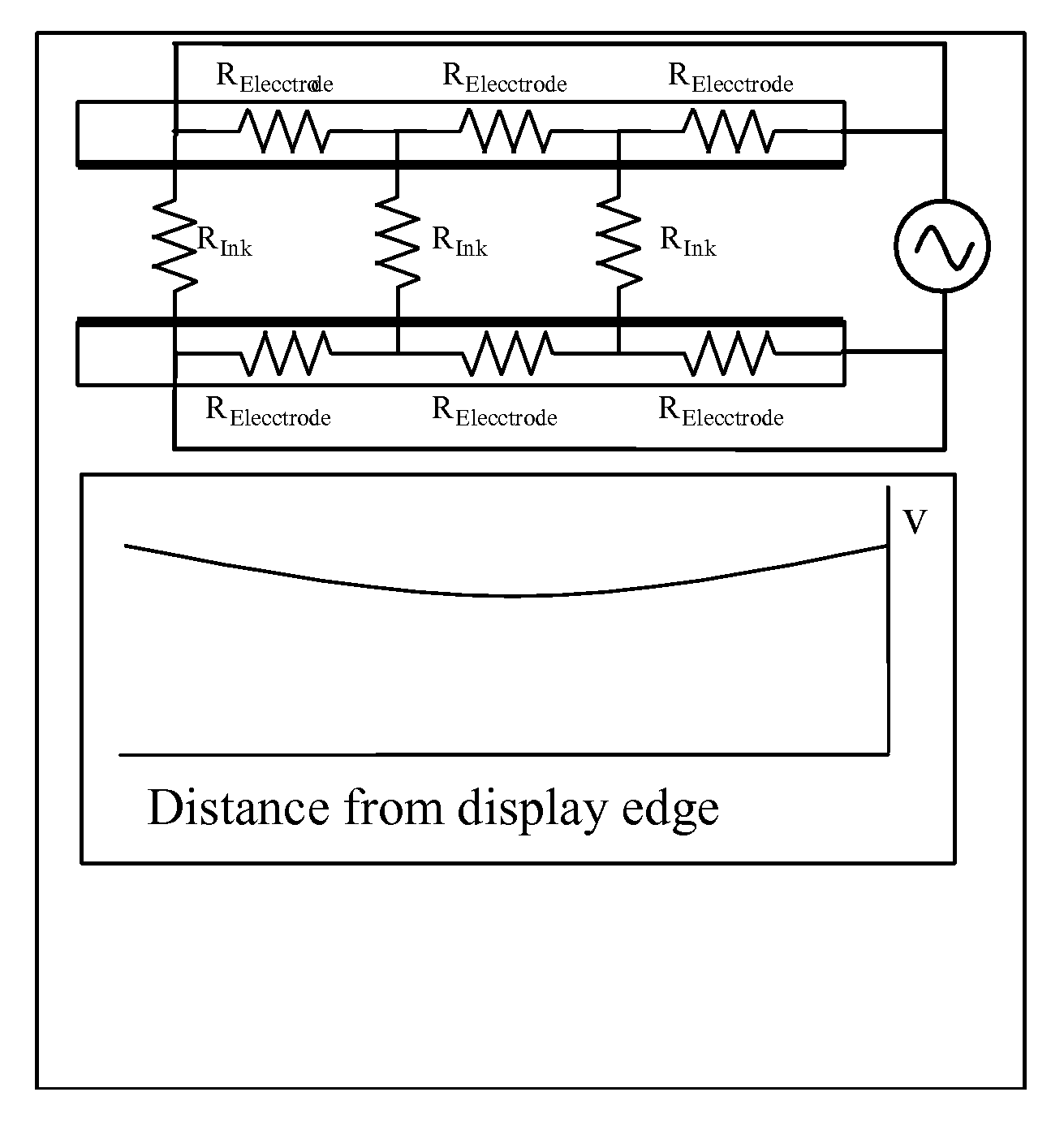
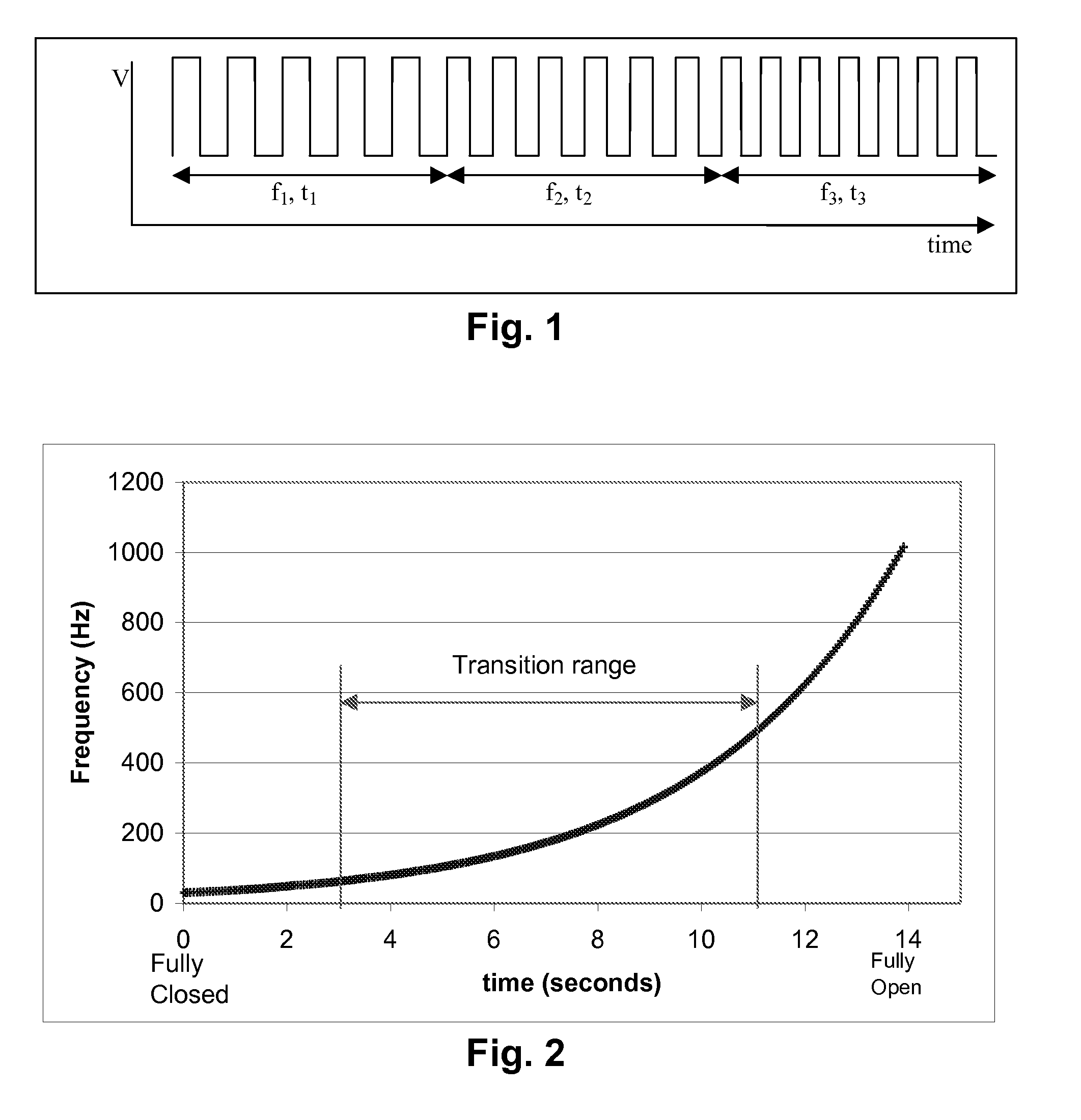
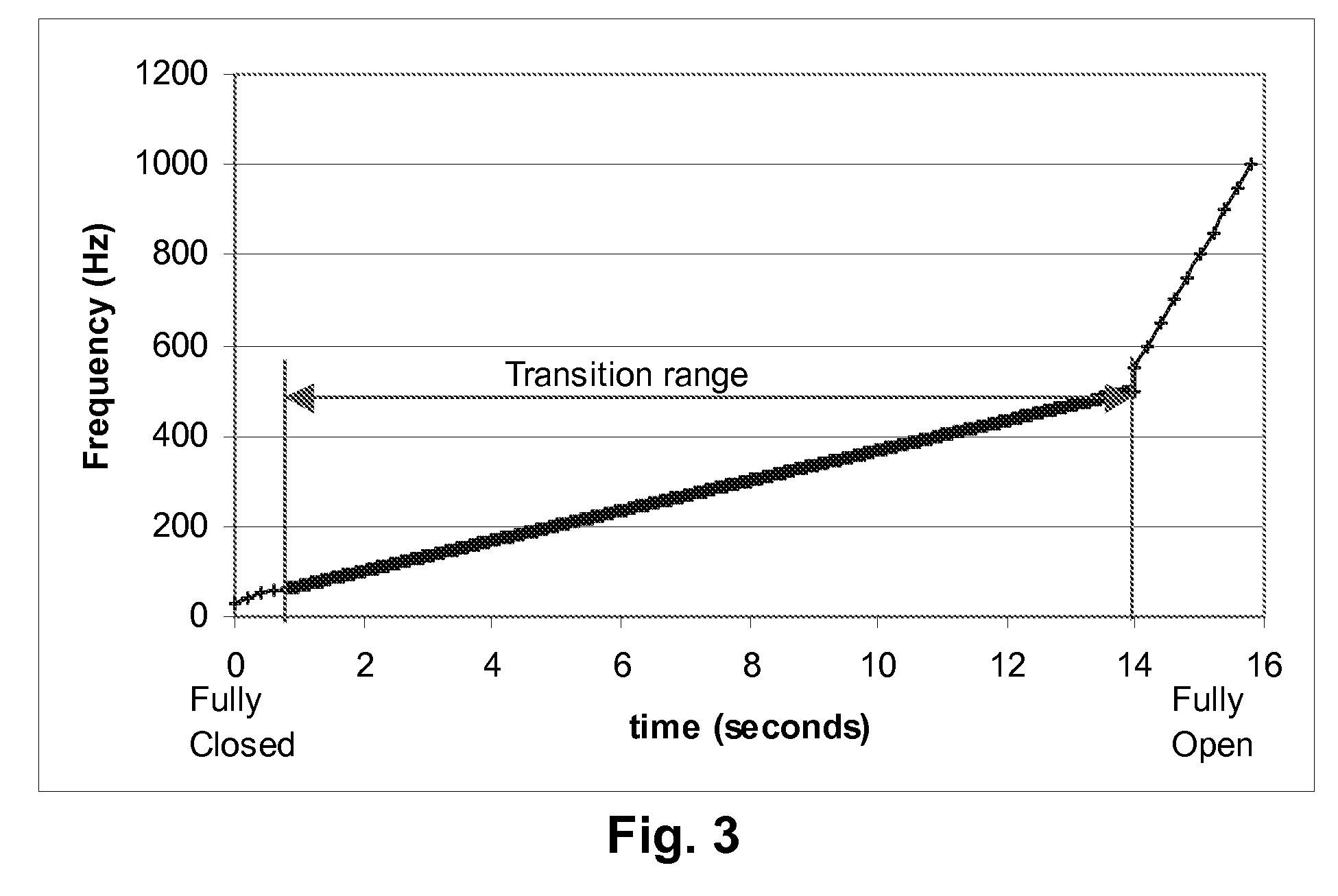
A dielectrophoretic display is shifted from a low frequency closed state to a high frequency open state via at least one, and preferably several, intermediate frequency states; the use of such multiple frequency steps reduces flicker during the transition. A second type of dielectrophoretic display has a light-transmissive electrode through which the dielectrophoretic medium can be viewed and a conductor connected to the light-transmissive electrode at several points to reduce voltage variations within the light-transmissive electrode.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
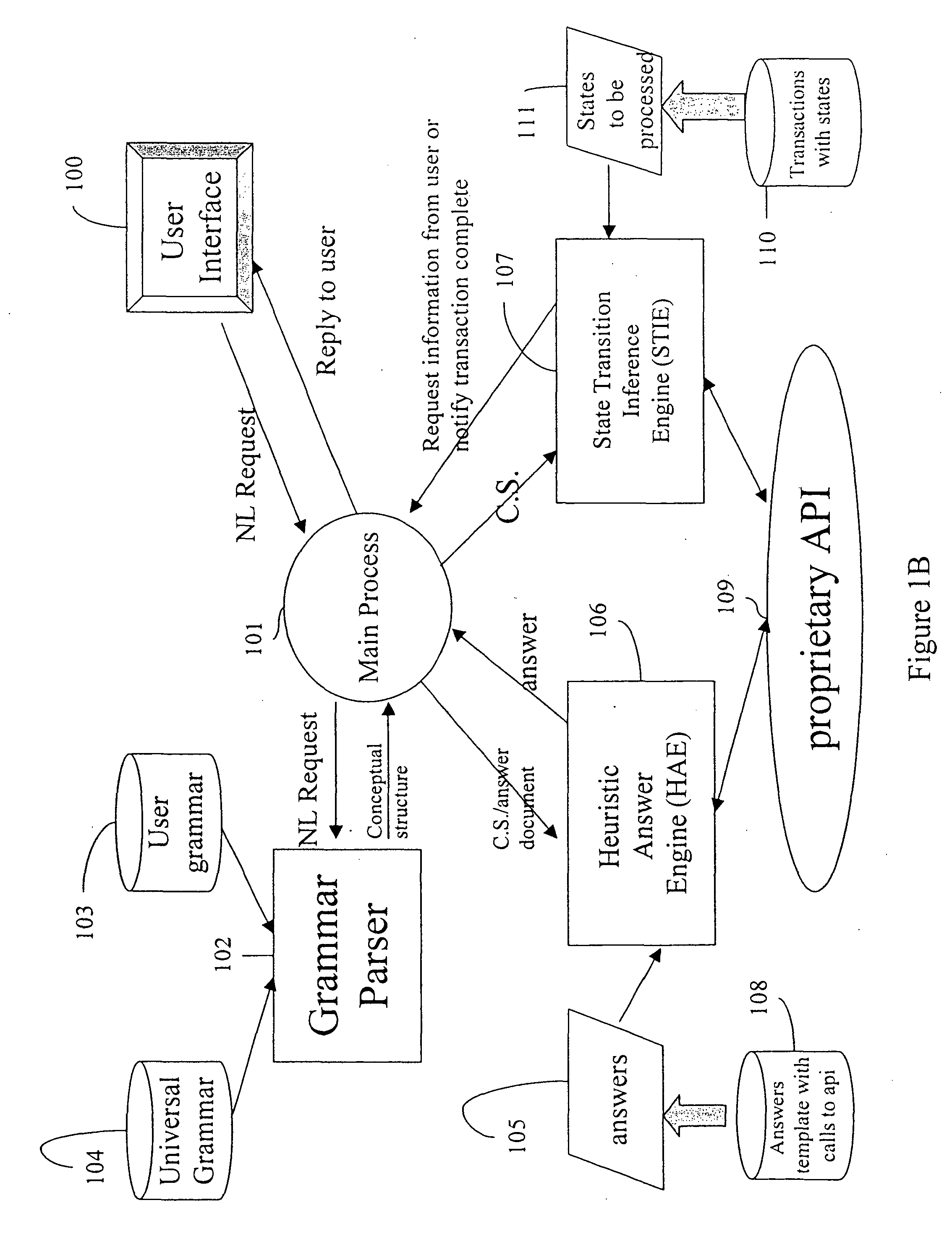
Apparatus and methods for developing conversational applications
InactiveUS20040083092A1Improve speech recognition performanceQuick fixSemantic analysisSpeech recognitionState switchingApplication software
Owner:GYRUS LOGIC INC
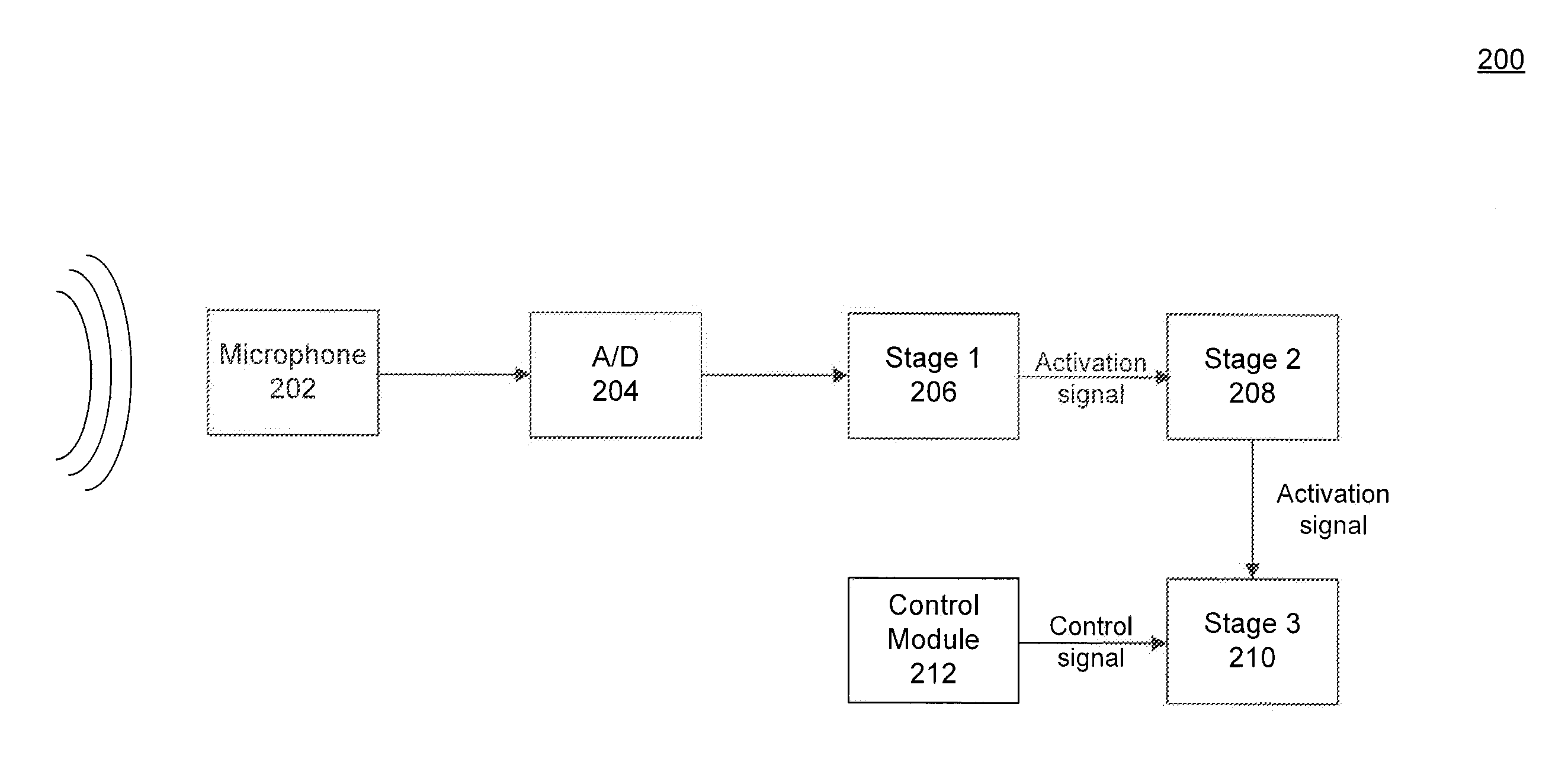
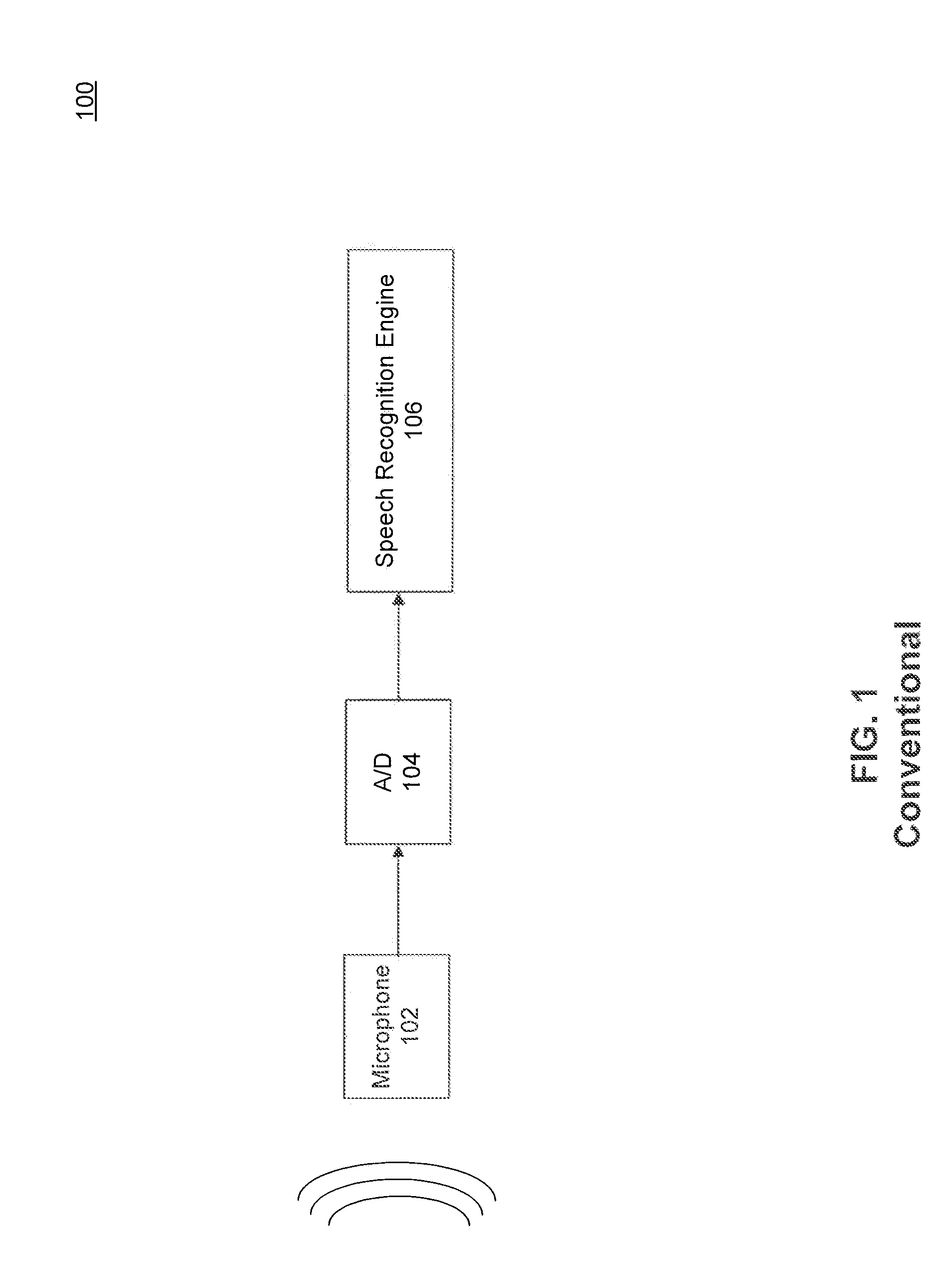
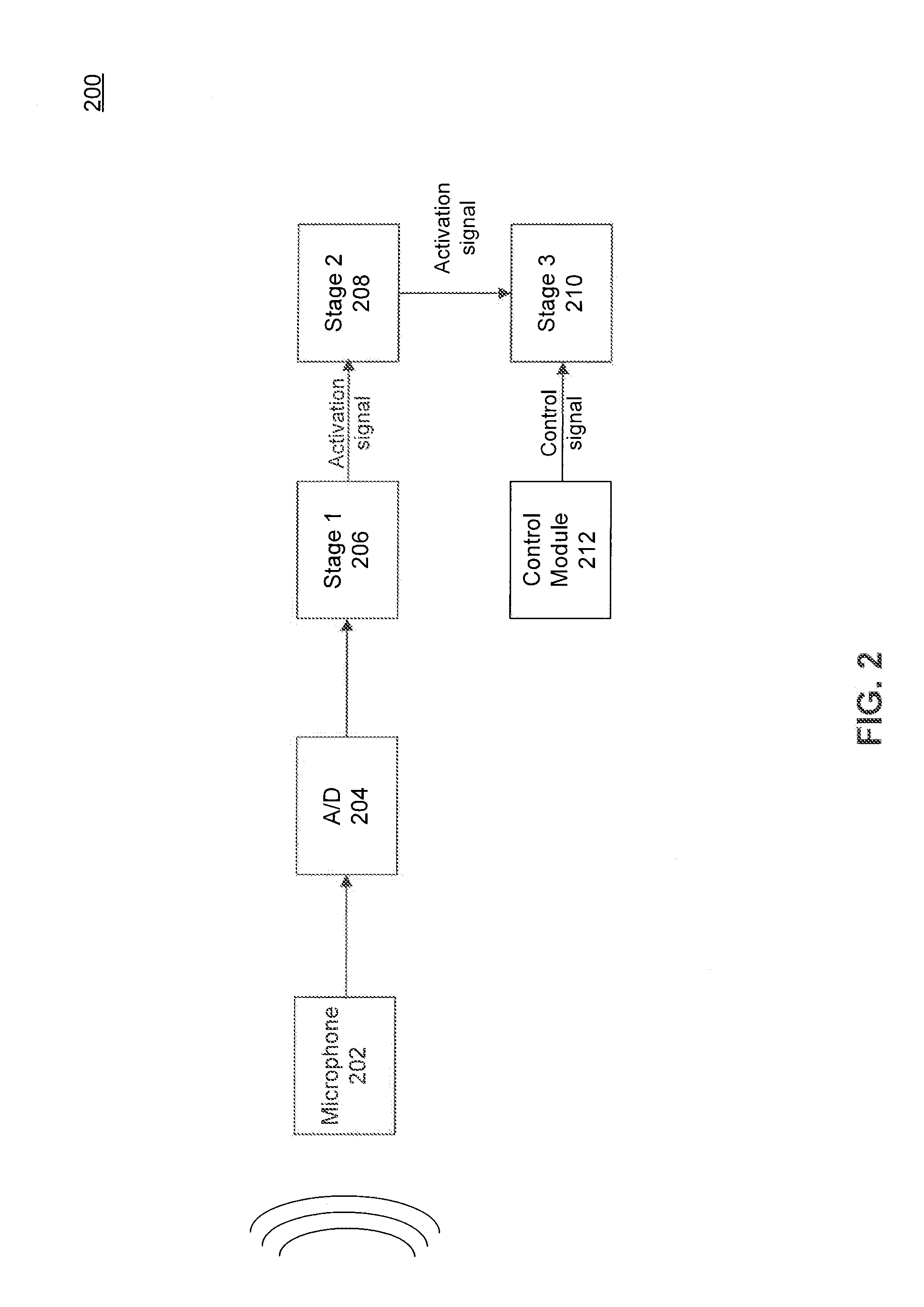
Power-Efficient Voice Activation
A voice activation system is provided. The voice activation system includes a first stage configured to output a first activation signal if at least one energy characteristic of a received audio signal satisfies at least one threshold and a second stage configured to transition from a first state to a second state in response to the first activation signal and, when in the second state, to output a second activation signal if at least a portion of a profile of the audio signal substantially matches at least one predetermined profile.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
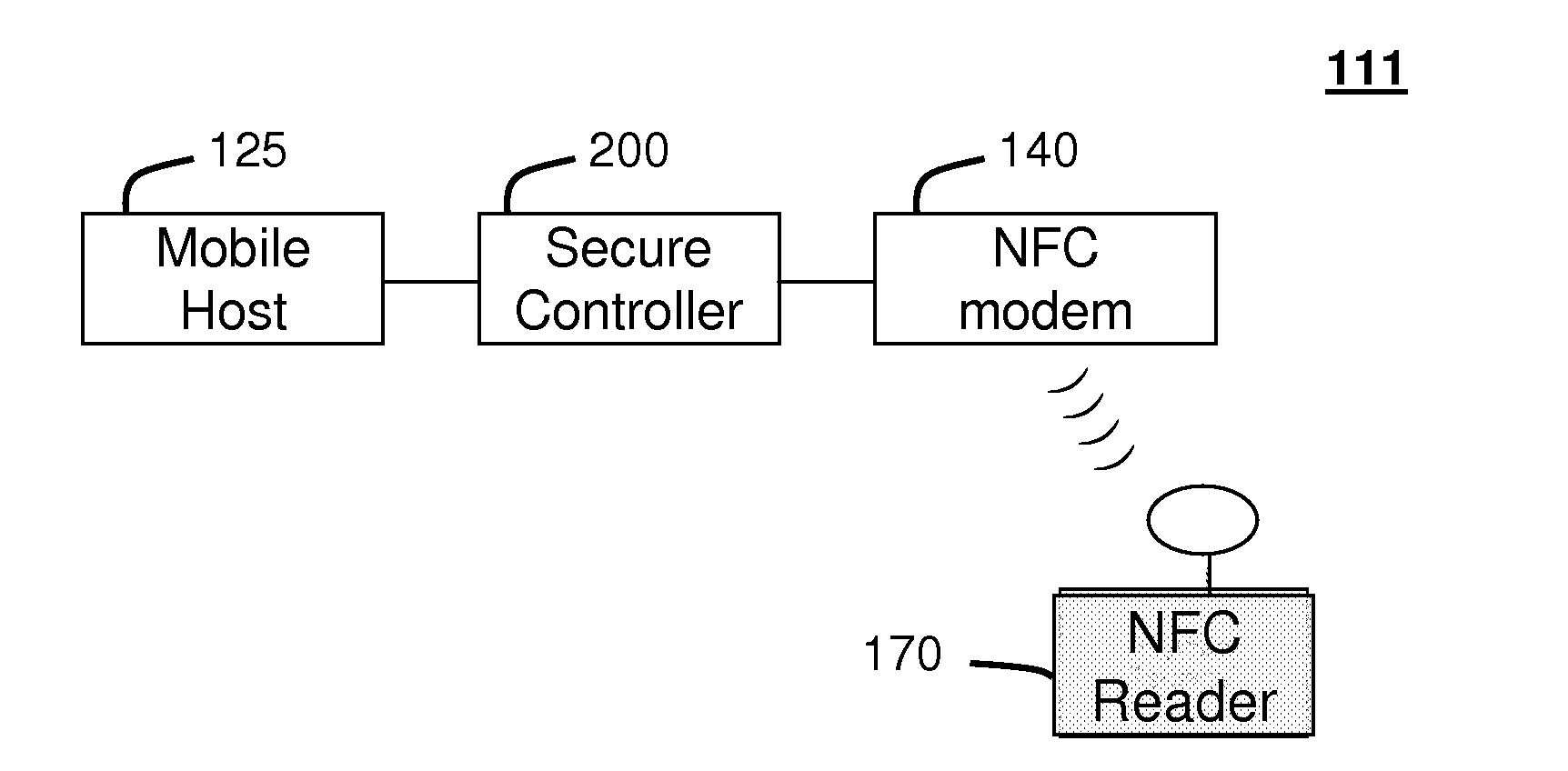
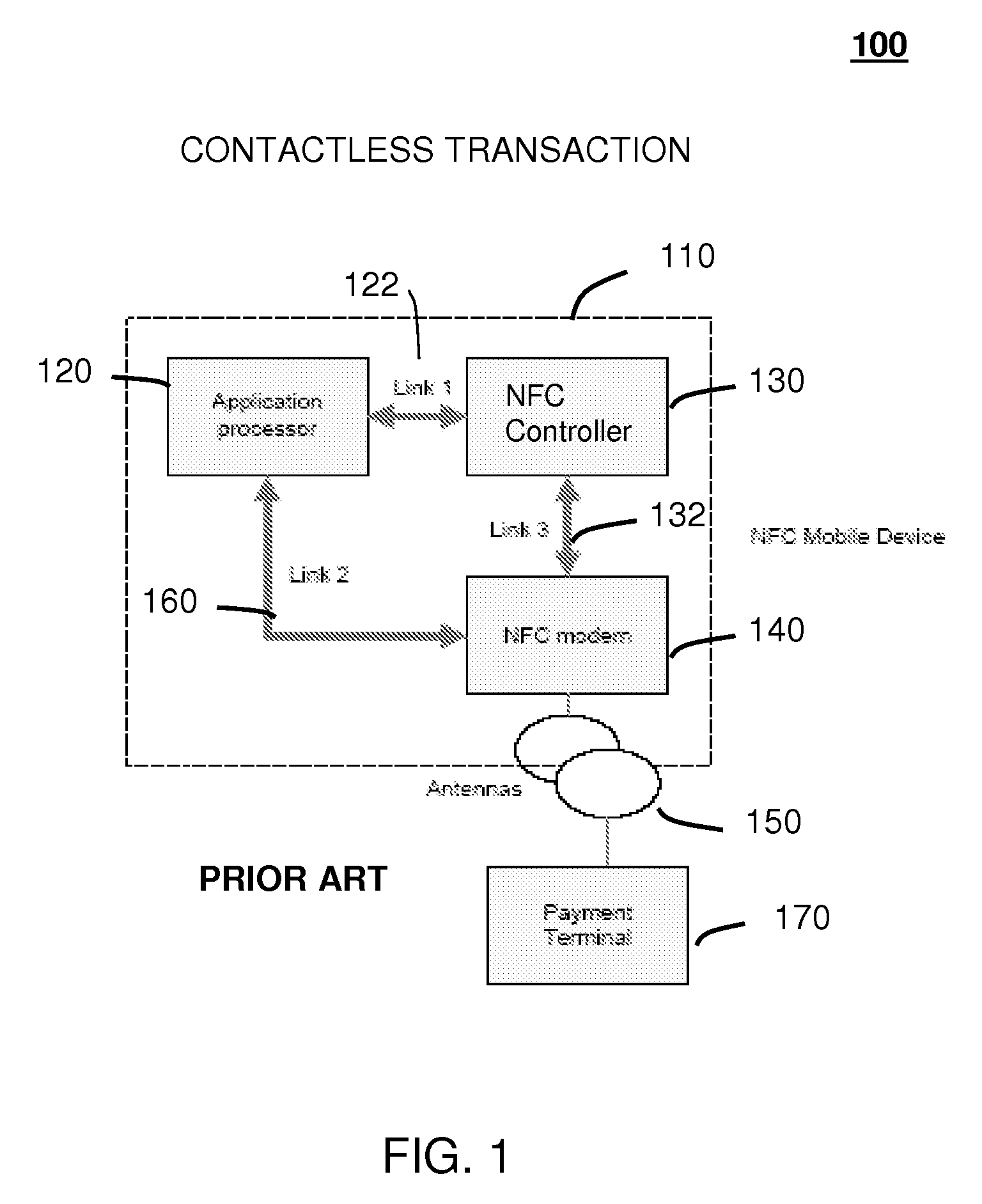
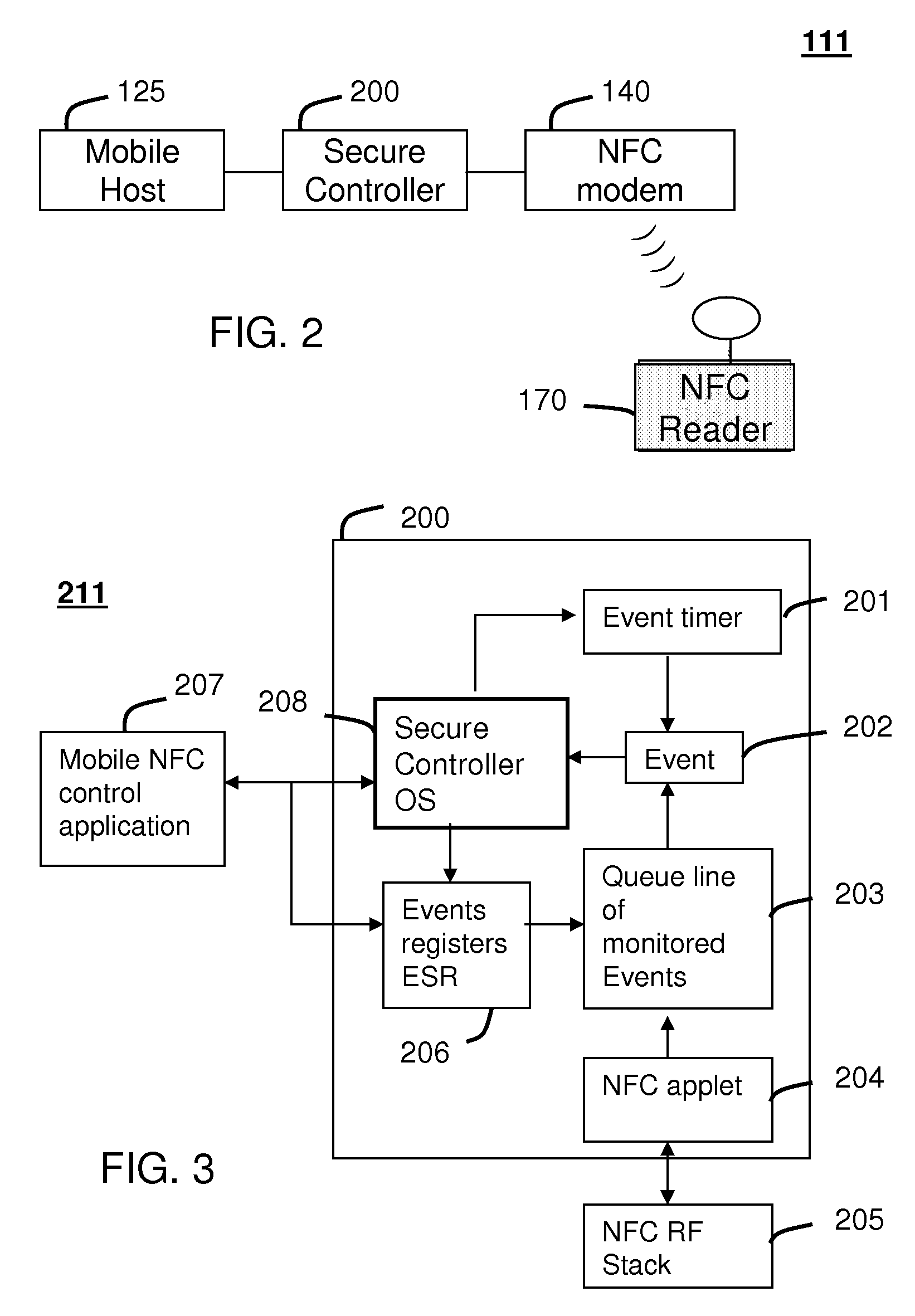
Method and system for monitoring secure applet events during contactless rfid/nfc communication
InactiveUS20080162312A1Reliable monitoringFinanceNetwork topologiesModem deviceApplication programming interface
A system (211) and method (400) for reliable monitoring of secure applet events is provided. The system can include a Near Field Communication (NFC) modem (140) for communicating transaction events, a secure controller (200) for monitoring state transitions caused by the transaction events, and a mobile host (125) for receiving event notifications of the state transitions via an Applications Programming Interface. An NFC reader can send a Transaction Acknowledgement TACK (403) to the NFC modem to confirm a receipt of data associated with an applet event. An INFO message (405) can be included with the TACK for informing a user of secure contactless transaction status through a user interface (190) of the mobile host.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
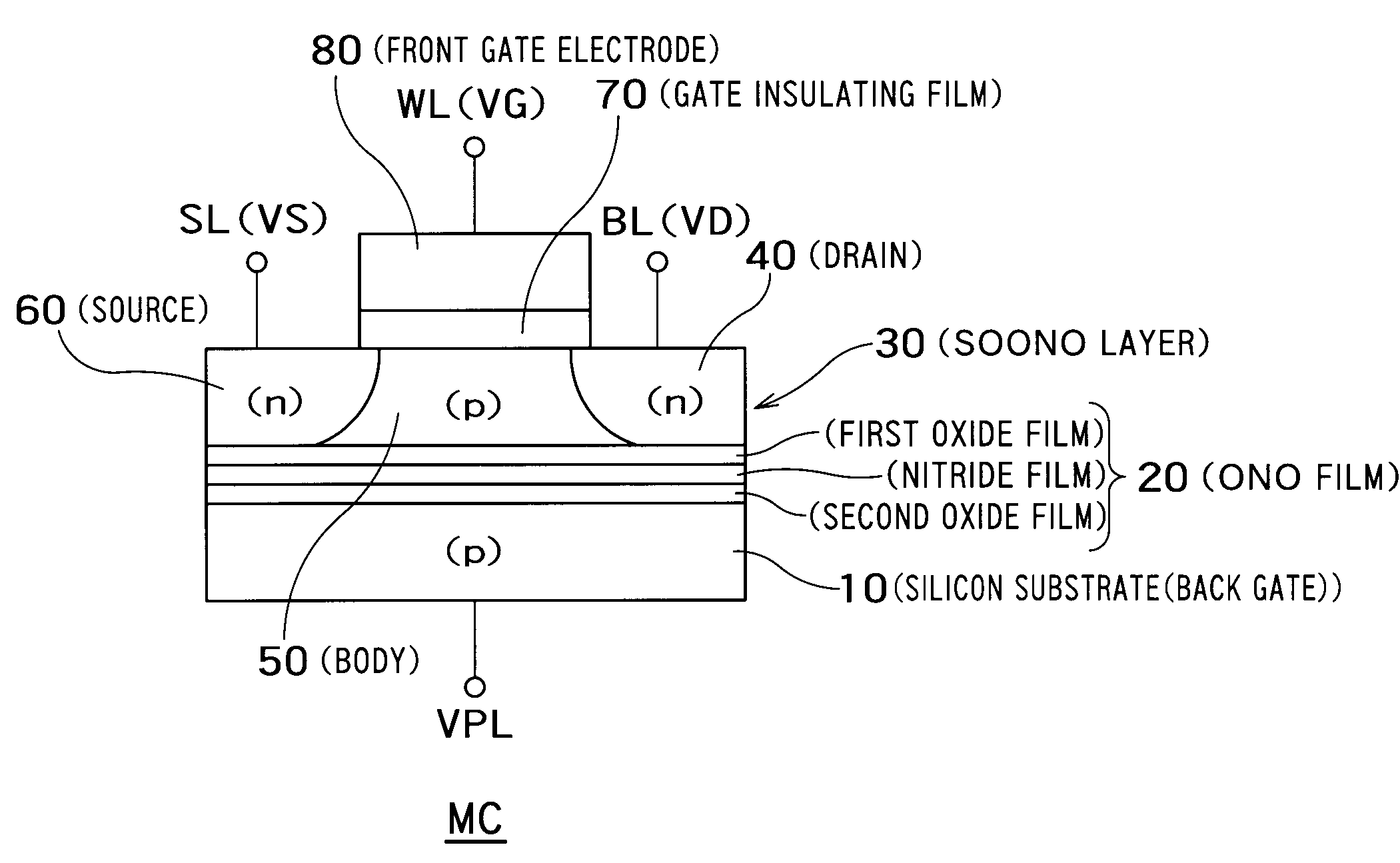
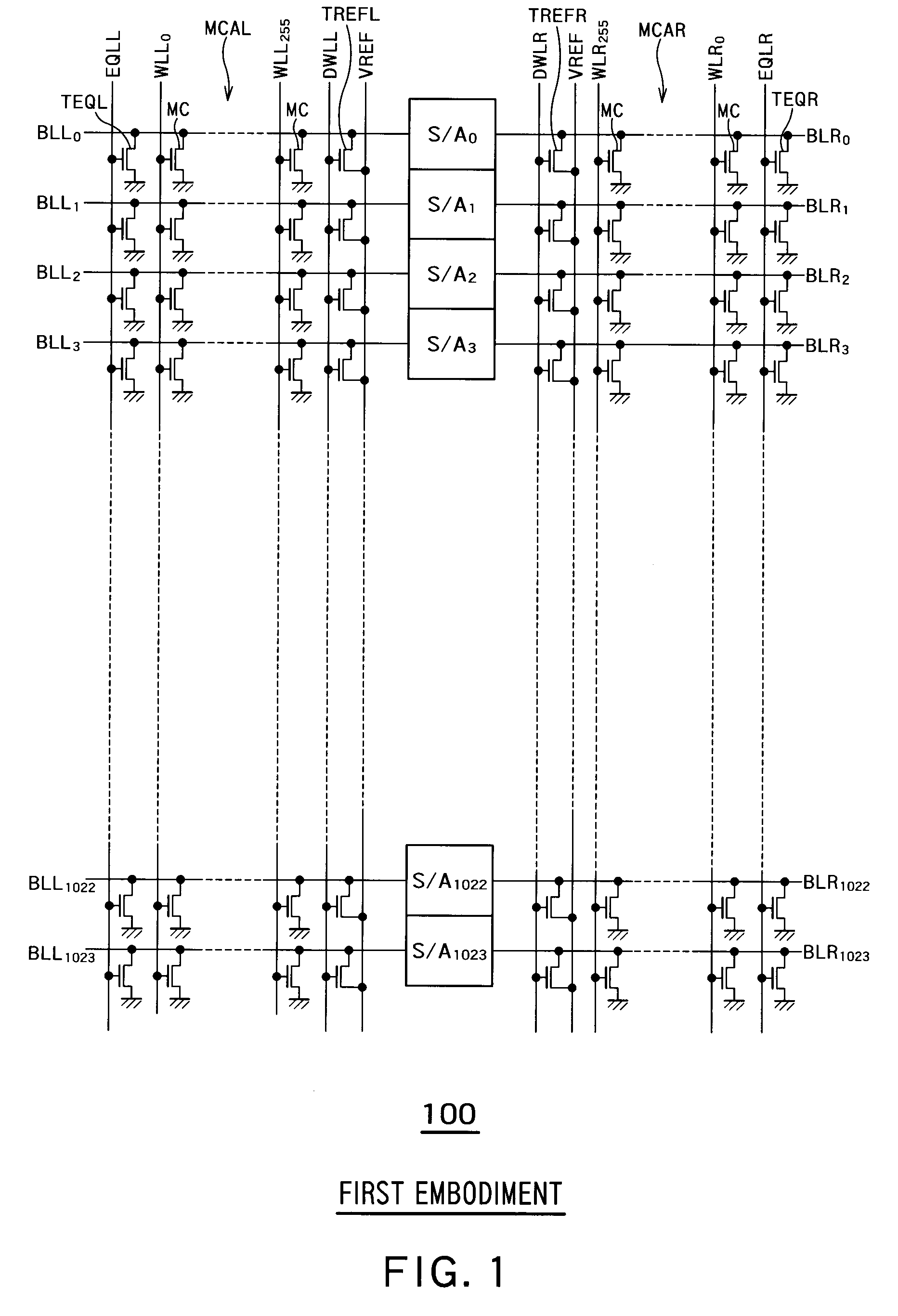
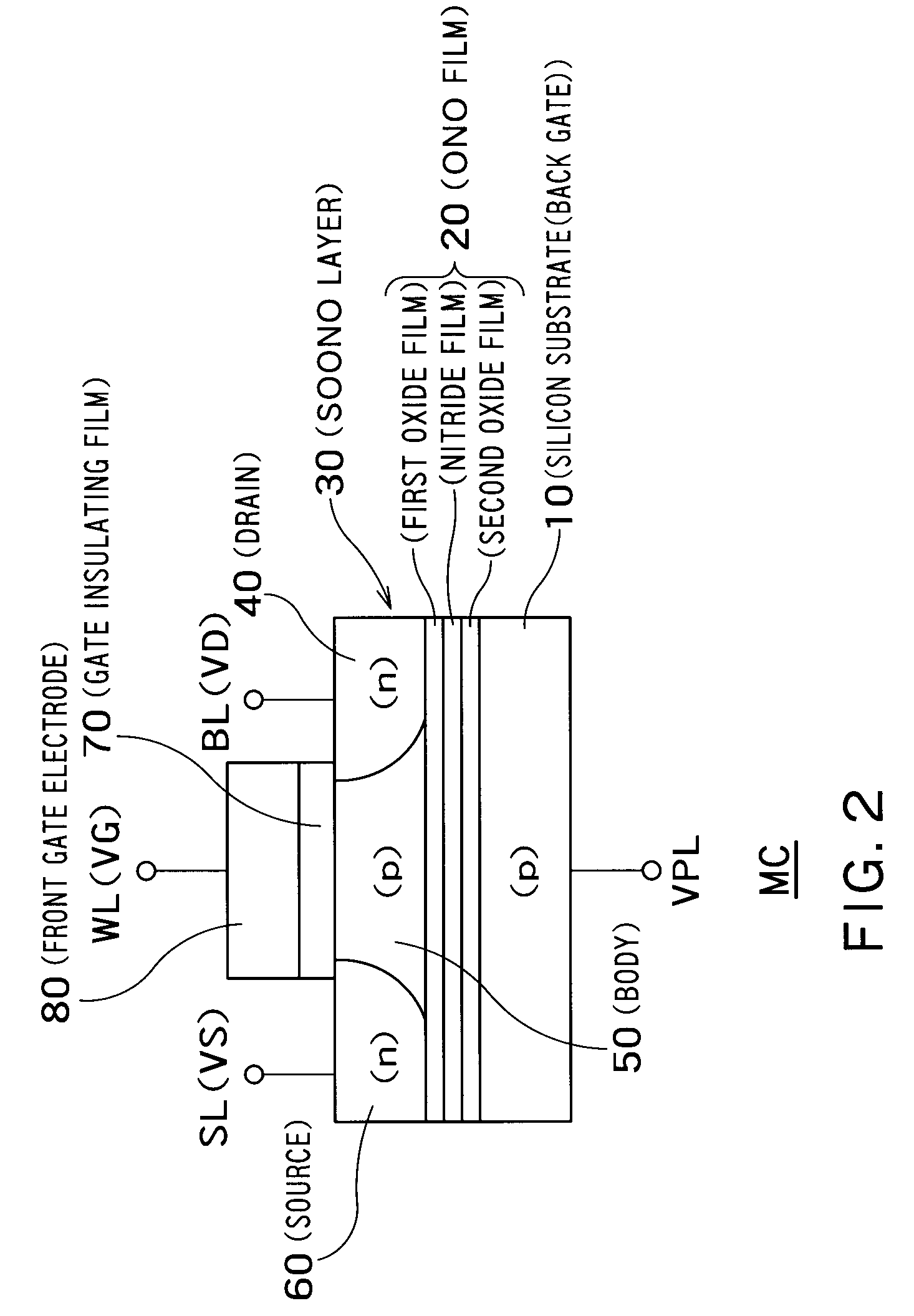
Semiconductor memory device
This disclosure concerns a memory comprising a charge trapping film; a gate insulating film; a back gate on the charge trapping film; a front gate on the gate insulating film; and a body region provided between a drain and a source, wherein the memory includes a first storage state for storing data depending on the number of majority carriers in the body region and a second storage state for storing data depending on the amount of charges in the charge trapping film, and the memory is shifted from the first storage state to the second storage state by converting the number of majority carriers in the body region into the amount of charges in the charge trapping film or from the second storage state to the first storage state by converting the amount of charges in the charge trapping film into the number of majority carriers in the body region.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Methods for driving electro-optic displays, and apparatus for use therein
InactiveUS20050219184A1Reduce residual voltageCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsGray levelDisplay device
A bistable electro-optic display has a plurality of pixels, each of which is capable of displaying at least three gray levels. The display is driven by a method comprising: storing a look-up table containing data representing the impulses necessary to convert an initial gray level to a final gray level; storing data representing at least an initial state of each pixel of the display; receiving an input signal representing a desired final state of at least one pixel of the display; and generating an output signal representing the impulse necessary to convert the initial state of said one pixel to the desired final state thereof, as determined from said look-up table. The invention also provides a method for reducing the remnant voltage of an electro-optic display.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
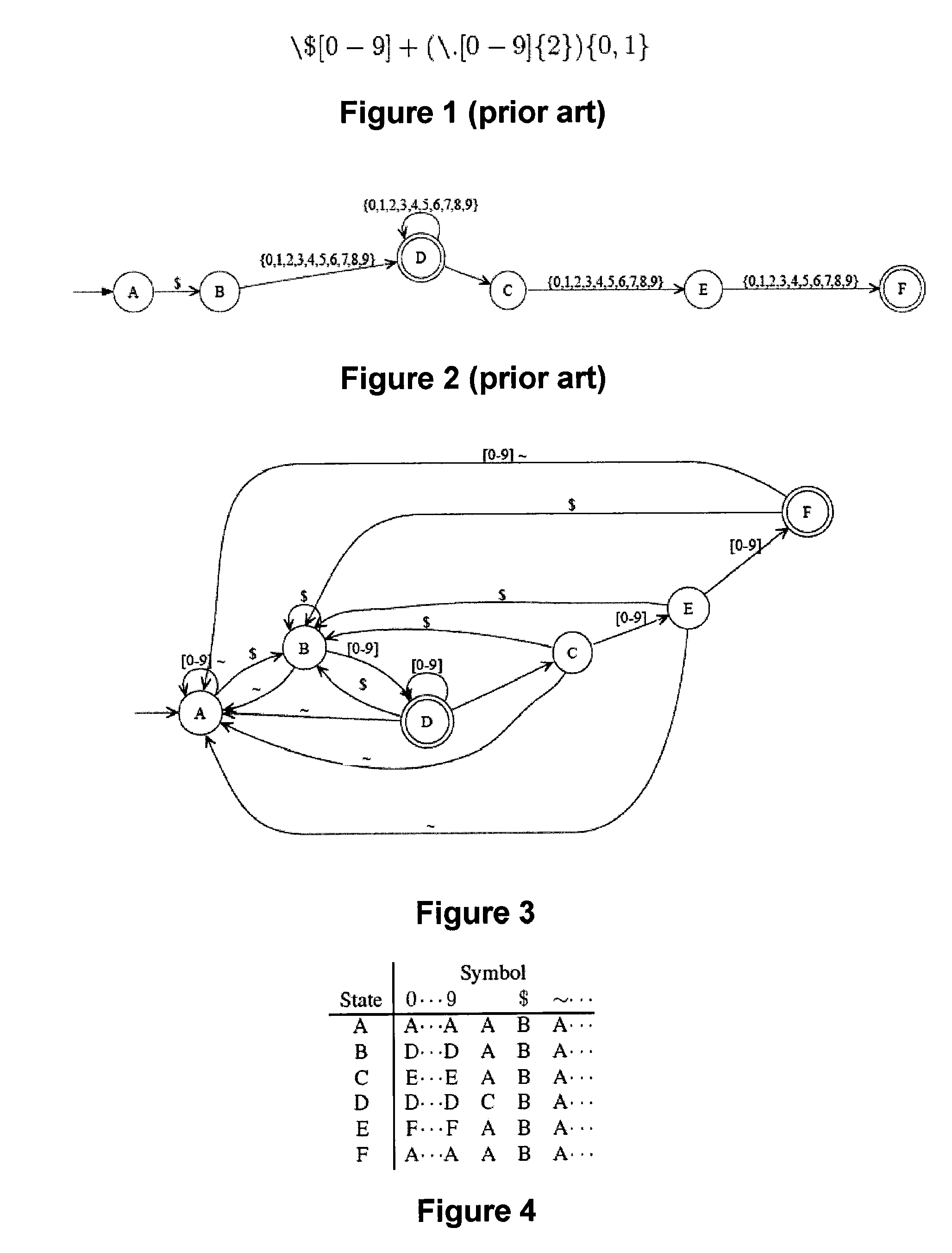
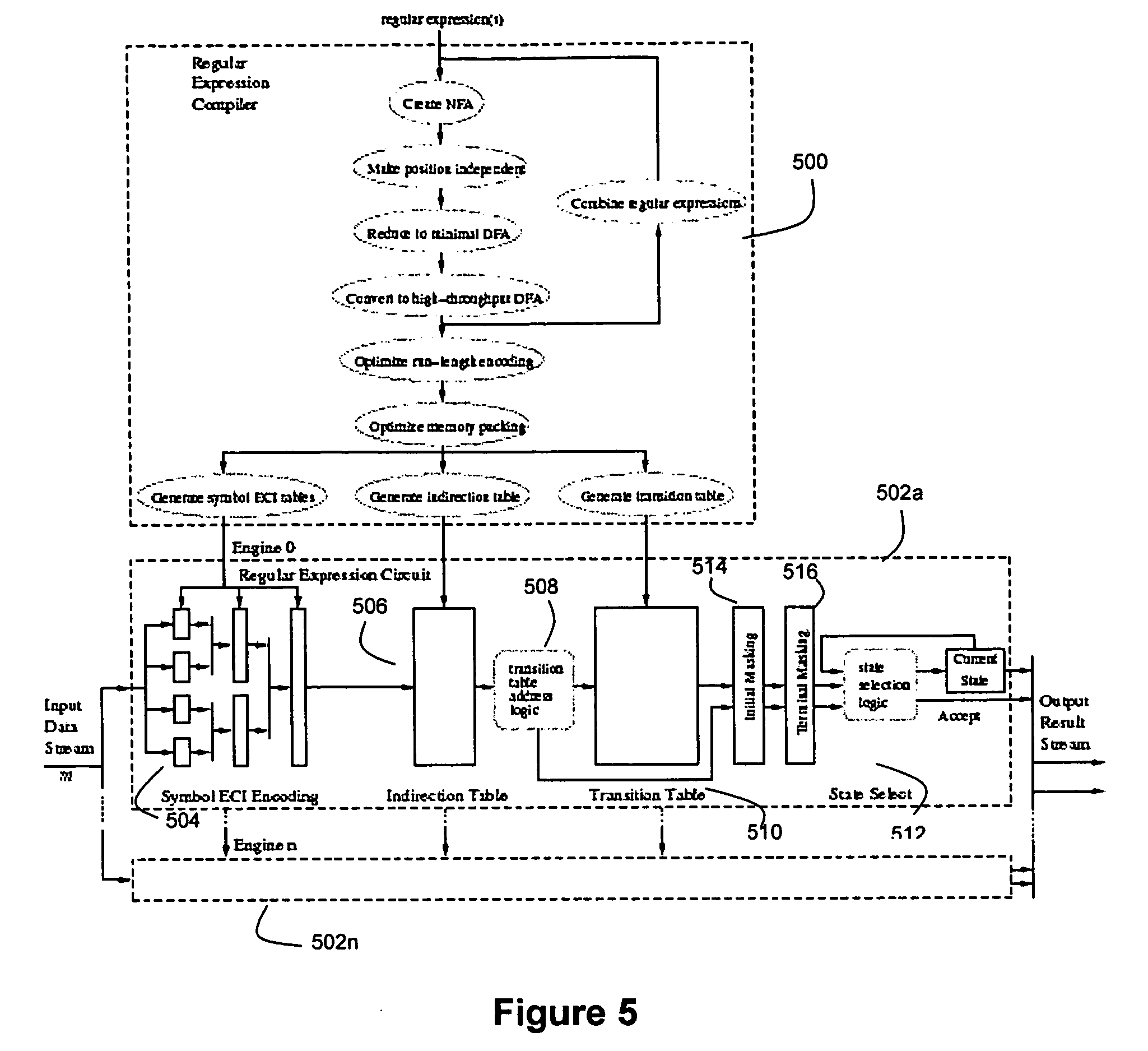
Method and device for high performance regular expression pattern matching
ActiveUS7702629B2Minimize the numberData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalState dependentPattern matching
Disclosed herein is an improved architecture for regular expression pattern matching. Improvements to pattern matching deterministic finite automatons (DFAs) that are described by the inventors include a pipelining strategy that pushes state-dependent feedback to a final pipeline stage to thereby enhance parallelism and throughput, augmented state transitions that track whether a transition is indicative of a pattern match occurring thereby reducing the number of necessary states for the DFA, augmented state transition that track whether a transition is indicative of a restart to the matching process, compression of the DFA's transition table, alphabet encoding for input symbols to equivalence class identifiers, the use of an indirection table to allow for optimized transition table memory, and enhanced scalability to facilitate the ability of the improved DFA to process multiple input symbols per cycle.
Owner:IP RESERVOIR
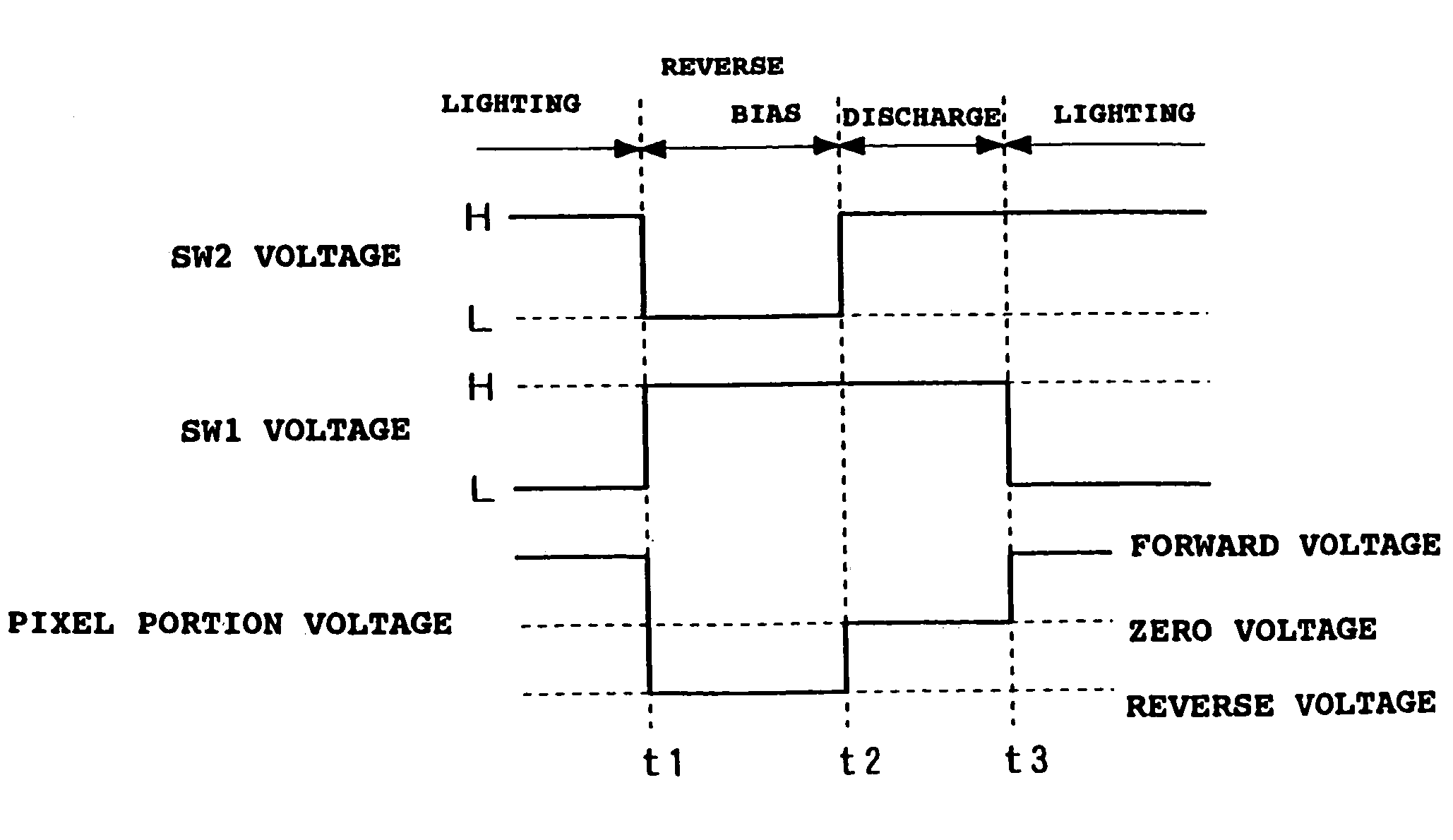
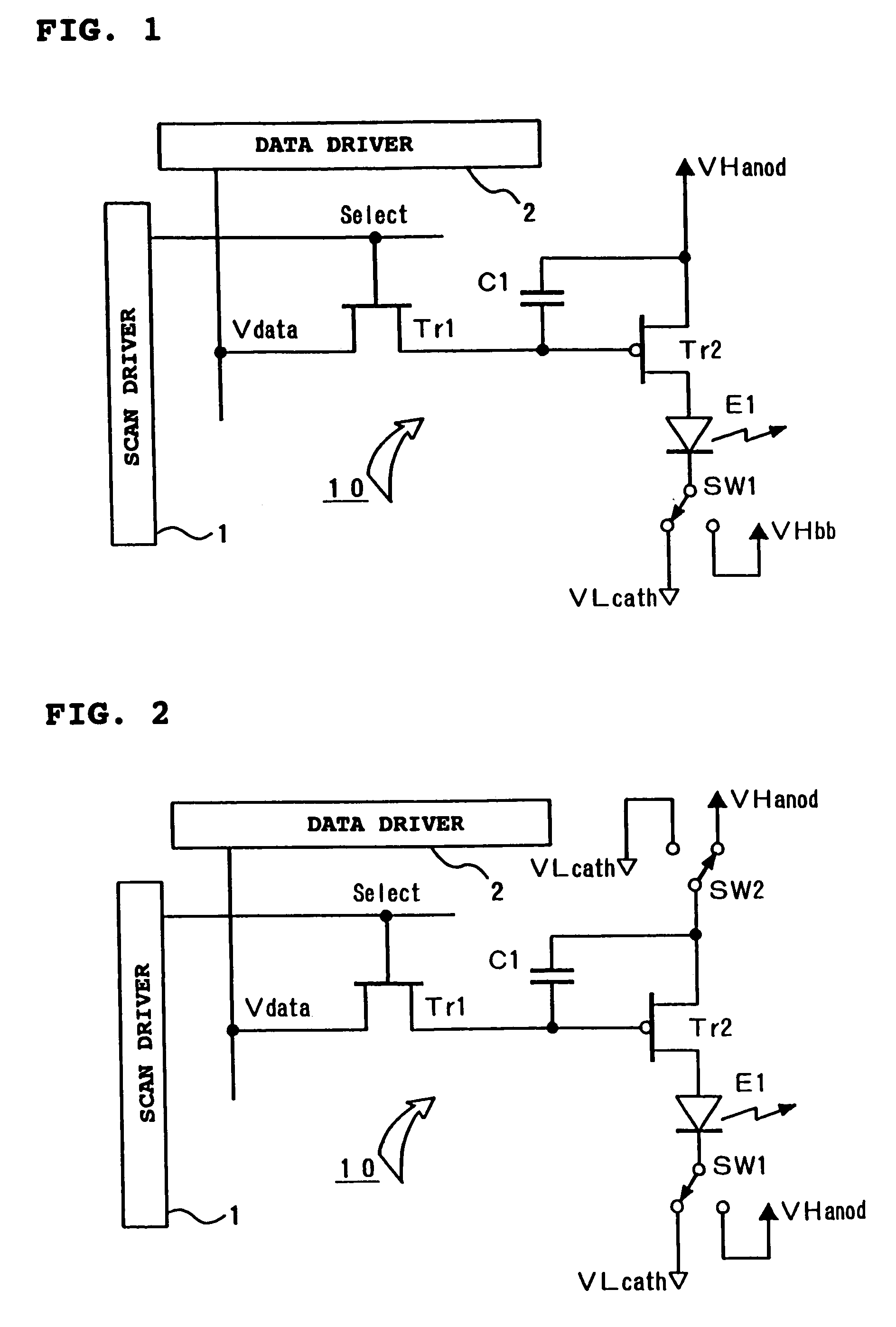
Drive methods and drive devices for active type light emitting display panel
InactiveUS7193589B2Static indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesEffect lightParasitic capacitance
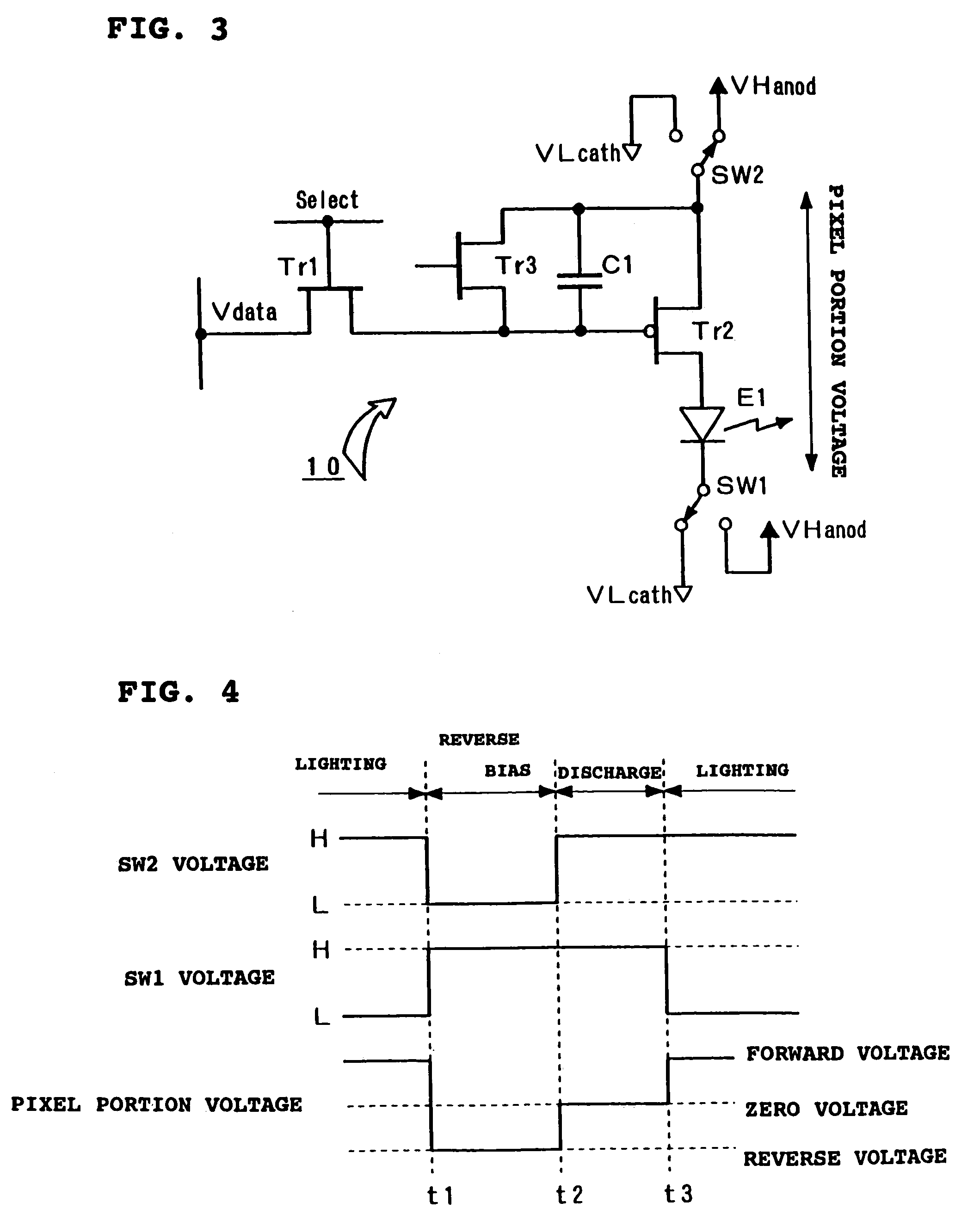
In a drive device for an active type light emitting display panel which can apply a reverse bias voltage to an EL element, in order to be able to compensate deterioration in light-emitting efficiency of the EL element accompanied by applying of the reverse bias voltage and the like, one pixel 10 is composed of a controlling TFT (Tr1), the driving TFT (Tr2), a capacitor C1, and the EL element E1. Switching switches SW1, SW2 mutually enables a supplying state of a forward current to the EL element E1 and an applying state of the reverse bias voltage to be selected. In one control form according to the present invention, when the applying state of the reverse bias voltage shifts to the supplying state of the forward current, by switching one switch first, the anode and cathode of the EL element E1 are made to the same electrical potential to allow electrical charges to be discharged. Thus, charge of the forward current for a parasitic capacitance of the EL element E1 can be performed rapidly, and rising of the lighting operation of the EL element can be advanced.
Owner:TOHOKU PIONEER CORP
Generic application server and method of operation therefor
InactiveUS7051330B1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsApplication serverState switching
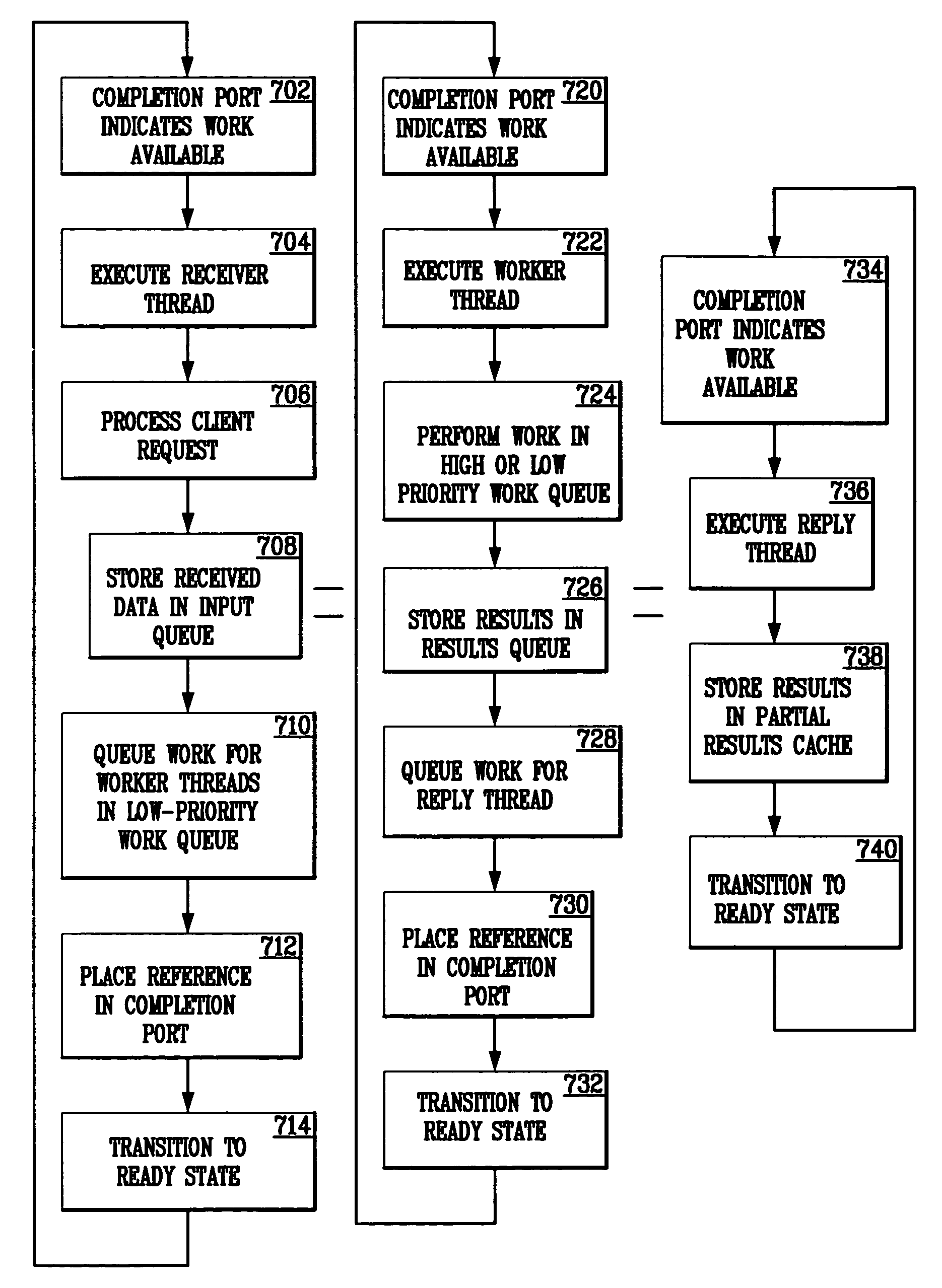
A generic application server is capable of simultaneously receiving requests, processing requested work, and returning results using multiple, conceptual thread pools. In addition, functions are programmable as state machines. While executing such a function, when a worker thread encounters a potentially blocking condition, the thread issues an asynchronous request for data, a state transition is performed, and the thread is released to do other work. After the blocking condition is relieved, another worker thread is scheduled to advance to the next function state and continue the function. Multiple priority work queues are used to facilitate completion of functions already in progress. In addition, lower-priority complex logic threads can be invoked to process computationally intense logic that may be necessitated by a request. Throttling functions are also implemented, which control the quantity of work accepted into the server and server response time.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
State conversion method, state keeping method and device, and user equipment
The invention discloses a state conversion method, and a state keeping method and device, and belongs to the technical field of communications. The method comprises the following steps: when user equipment is under an unactivated state and satisfies a first predetermined condition, converting the user equipment into an idle state from the unactivated state; when the user equipment is under the unactivated state and satisfies a second predetermined condition, keeping the user equipment under the unactivated state; and when the user equipment is under the unactivated state and satisfies a third predetermined condition, converting the user equipment into a connected state from the unactivated state, wherein the unactivated state is an intermediate state between the connected state and the idle state. The state conversion method, and the state keeping method and the device provided by the invention solve the problem that when the UE (User Equipment) receives and sends small data packet services in 4G (the 4th Generation mobile communication technology), the UE needs to switch between an RRC (Radio Resource Control) connected state and an RRC idle state back and forth to lead to signaling resources waste, thereby achieving the effects that the UE can receive and send the small data packet services under the unactivated state, and the signaling resources are saved.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
Mobile communication terminal and method
InactiveUS20090146962A1Easy to useMitigate such drawbackPower managementDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareDisplay device
A device including a display, a memory and a tap detector arranged to generate a detection signal upon detection of a tap command. The device is arranged to assume either an idle state, in which the display is inactive, or a second state, in which the display is active and displaying information stored in the memory. The device is arranged to transit from the idle state to the second state when a tap is detected i.e. upon generation of the detection signal.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
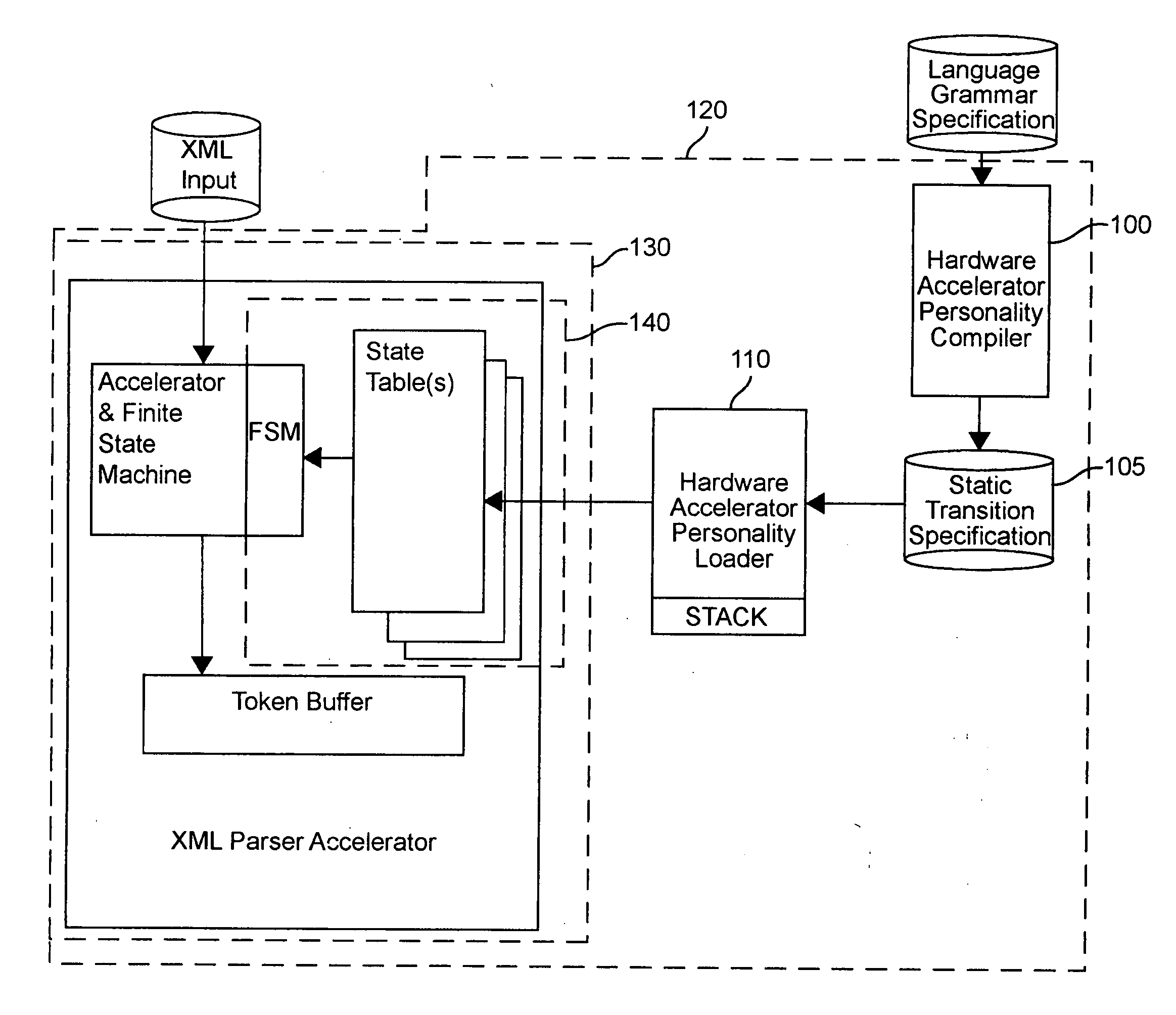
Hardware accelerator personality compiler
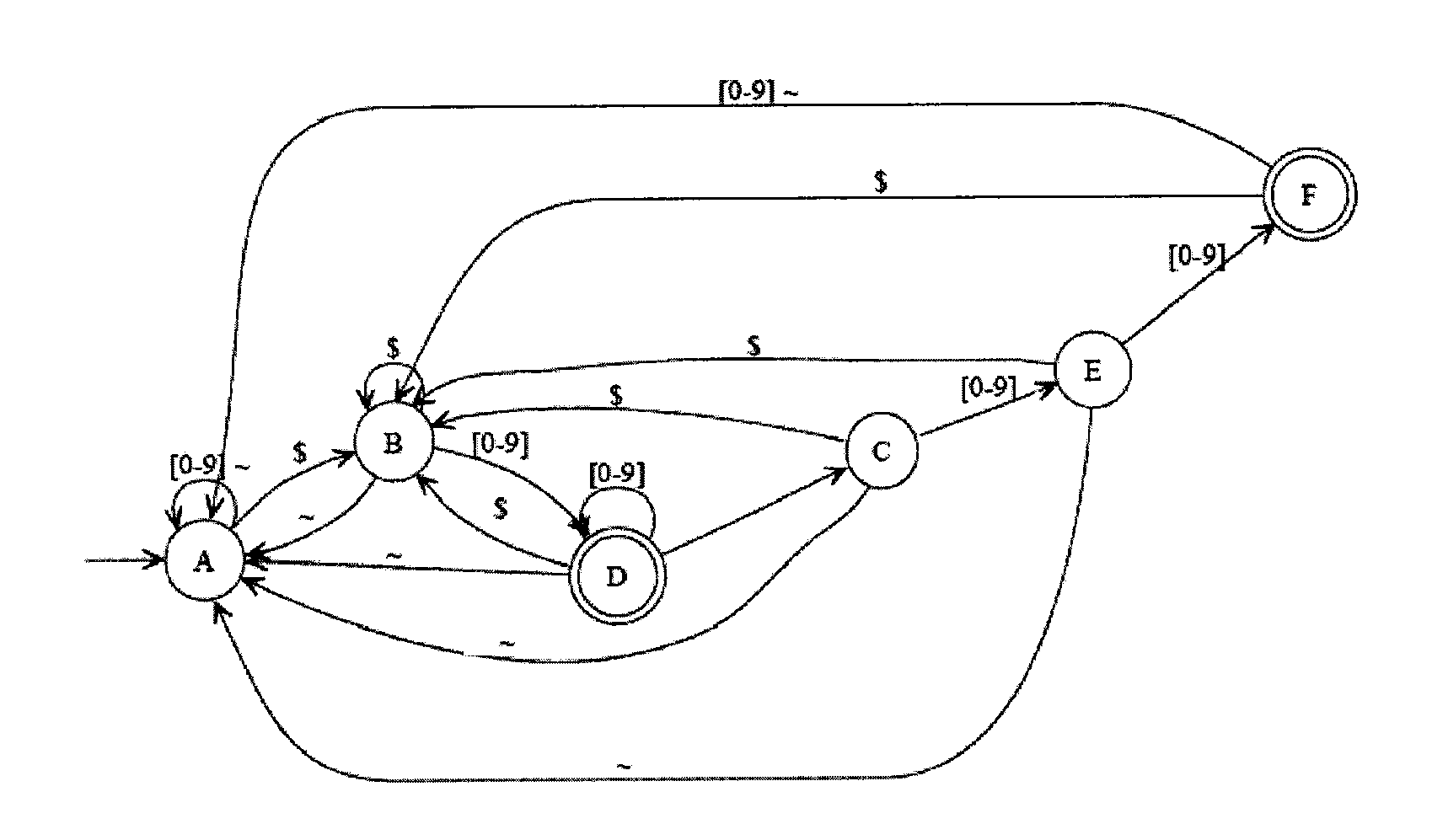
InactiveUS20040172234A1Software engineeringSpecial data processing applicationsState switchingAutomaton
Error-free state tables are automatically generated from a specification of a group of desired performable functions, such as are provided in a programming language in a formal notation such as Backus-Naur form or a derivative thereof by discriminating tokens corresponding to respective performable functions, identifications, arguments, syntax, grammar rules, special symbols and the like. The tokens may be recursive (e.g. infinite), in which case they are transformed into a finite automata which may be deterministic or non-deterministic. Non-deterministic finite automata are transformed into deterministic finite automata and then into state transitions which are used to build a state table which can then be stored or, preferably, loaded into a finite state machine of a hardware parser accelerator to define its personality.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
System and method for automatically generating a graphical program in response to a state diagram
InactiveUS7200838B2Easy to update dynamicallyEasy to fillVisual/graphical programmingRequirement analysisGraphicsState diagram
System and method for programmatically generating a graphical program in response to state diagram information. The state diagram information specifies a plurality of states and state transitions. A graphical program generation program (GPG program), receives the state diagram information and automatically, i.e., programmatically, generates a graphical program (or graphical program portion) based on the state diagram information. The GPG program automatically includes graphical source code in a block diagram of the graphical program, which serves as a framework of the states specified by the state diagram information and the state transitions, with various “placeholders” or “containers” enabling the user to easily fill in the graphical program with source code specifying execution instructions for each state and Boolean conditions for each state transition. The specific graphical source code automatically generated depends on programming features supported by a particular graphical programming development environment with which the graphical program is associated.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Architecture for multiple interacting robot intelligences
InactiveUS7328196B2Programme-controlled manipulatorAutonomous decision making processLTM - Long-term memoryShort-term memory
An architecture for robot intelligence enables a robot to learn new behaviors and create new behavior sequences autonomously and interact with a dynamically changing environment. Sensory information is mapped onto a Sensory Ego-Sphere (SES) that rapidly identifies important changes in the environment and functions much like short term memory. Behaviors are stored in a DBAM that creates an active map from the robot's current state to a goal state and functions much like long term memory. A dream state converts recent activities stored in the SES and creates or modifies behaviors in the DBAM.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Method and apparatus for controlling the visual presentation of data
InactiveUS7102643B2Quick changeCathode-ray tube indicatorsAnimationVisual presentationState dependent
According to one aspect of the invention, disclosed herein is a method of controlling a visual presentation of data to a viewer, the presentation comprising a plurality of display configuration states through which data content is presented to a viewer, the presentation being responsive to transition input to transition from a current display configuration state to a next display configuration state, the method comprising: (1) providing a plurality of transition effects; (2) for each pair of potentially successive display configuration states, associating a transition effect therewith; (3) receiving transition input indicative to transition from a current display configuration state to a next display configuration state, the transition defining a pair of successive display configuration states; and (4) during the transition from the current display configuration state to the next display configuration state, presenting to the viewer the transition effect associated with the defined pair of successive display configuration states. According to another aspect of the invention, disclosed herein is a method of controlling a visual presentation of data to a viewer, the presentation comprising a plurality of display configuration states through which data content is presented to the viewer, the method comprising: (1) providing a plurality of style guides, each style guide having a plurality of display configuration states corresponding thereto; (2) for each style guide, associating each of its corresponding display configuration states with a plurality of counterpart display configuration states in the other style guides; (3) for a presentation having a previously-defined style guide, selecting a different style guide therefor; and (4) replacing the presentation's display configuration states with their counterparts in the different style guide.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Creating a virtual machine image with a software deployment system
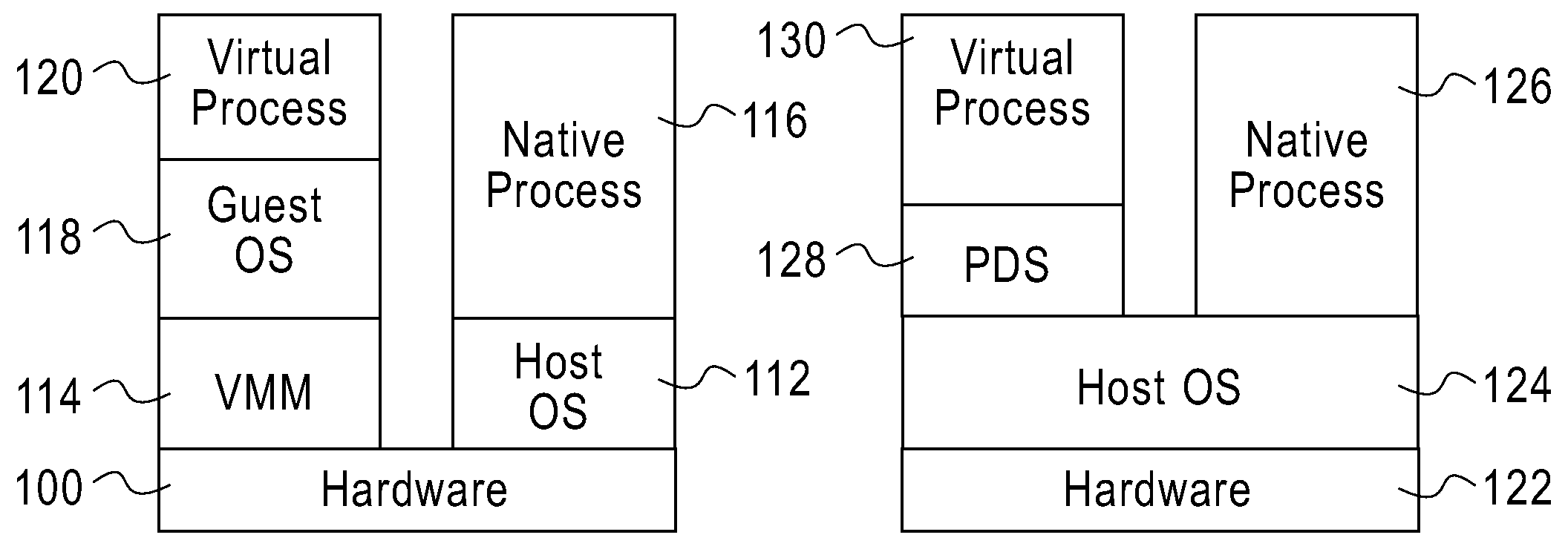
InactiveUS20080307414A1Deficiency correctedSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsState switchingSoftware deployment
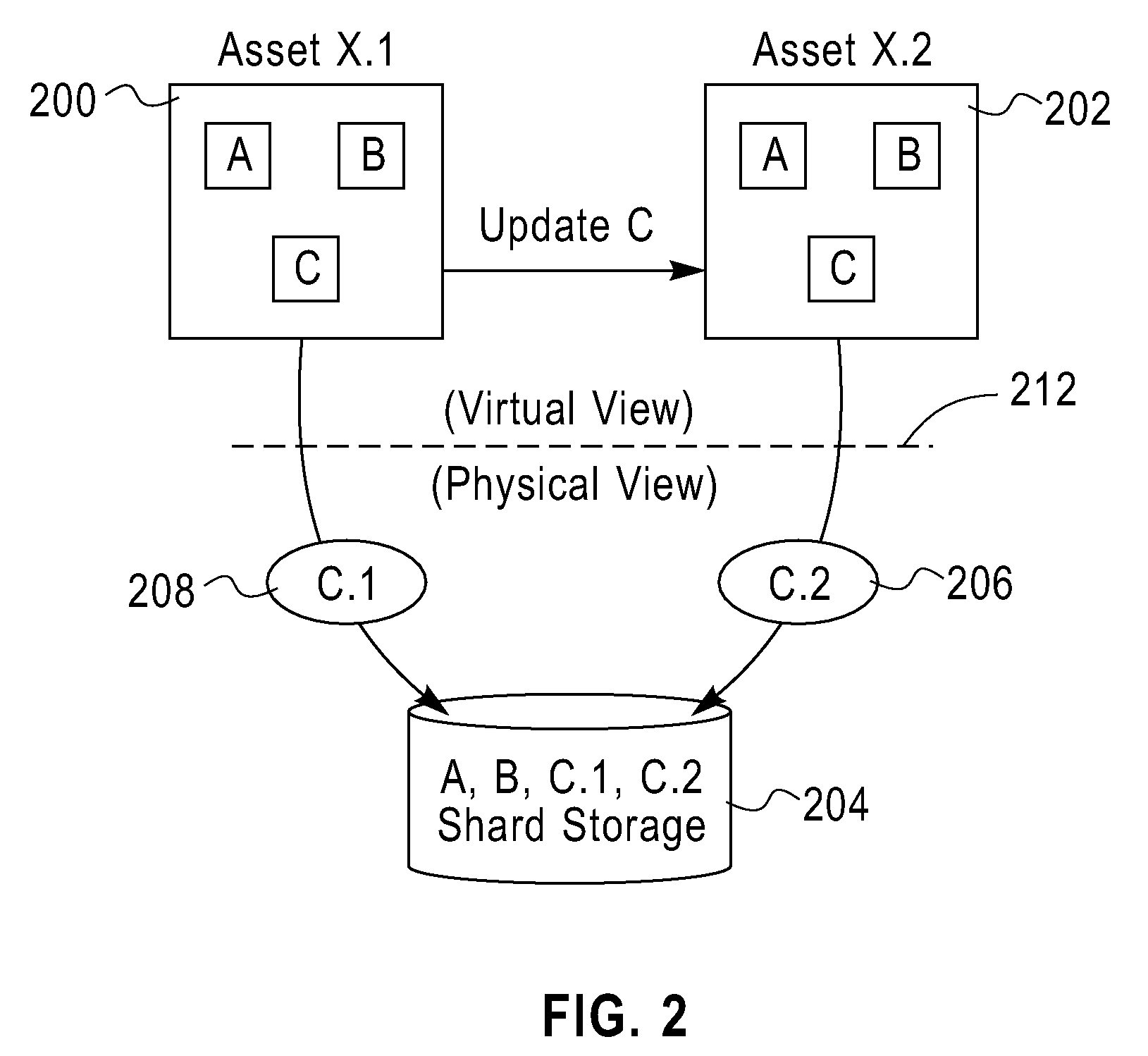
A novel method is disclosed for capturing an installed state of a conventional application and converting the captured state into a virtual application. The novel method starts with a bare machine in a known state, preferably soon after the OS was installed. Installation scripts are used to install one or more software applications along with required components and dependencies. Other artifacts can be added and configured such as files, trees, directories, entries, data, values, among others. These also may include updates to various system databases, such as the Windows registry in which certain metadata is stored. The installed applications are tested and verified to work as desired. Undesired artifacts can be deleted manually or removed by the OS. The state of the virtual machine with the installed applications is captured. The installed applications can be tested on the frozen virtual machine. If the user determines that the installed applications are working properly, a virtual machine image is prepared and then written out. The resulting output is a new populated virtual application container that encapsulates the applications installed and configured by the user. If the user determines that one or more installed applications do not work properly during testing, then the frozen virtual machine can be unfrozen and any deficiencies corrected. The virtual machine image is stored as a launch document and a set of shards. The virtual machine image represents the state of the virtual machine along with the installed applications at the time the preparation virtual machine was frozen.
Owner:IBM CORP
Network Connection Hand-off Using State Transformations
ActiveUS20120239725A1Improve scalabilityImprove resource usageMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionServer agentNetwork connection
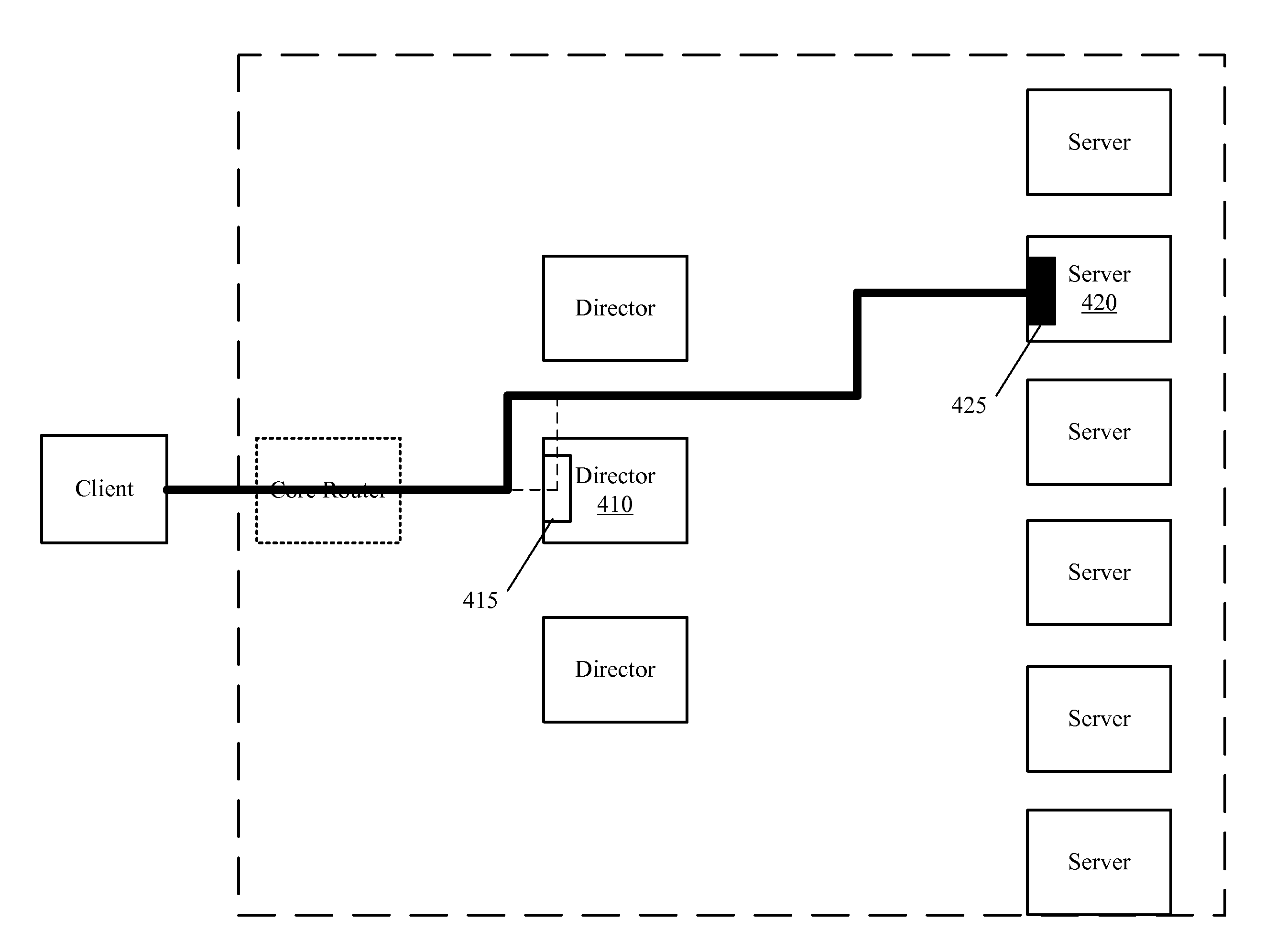
Some embodiments provide a director agent, a server agent, and a specialized hand-off protocol for improving scalability and resource usage within a server farm. A first network connection is established between a client and the director agent in order to receive a content request from the client from which to select a server from a set of servers that is responsible for hosting the requested content. A second network connection is established between the server agent that is associated with the selected server and a protocol stack of the selected server. The first network connection is handed-off to the server agent using the specialized hand-off protocol. The server agent performs network connection state parameter transformations between the two connections to create a network connection through which content can be passed from the selected server to the client without passing through the director.
Owner:EDGIO INC
Power management method and related power management system
ActiveUS20110231682A1Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingComputerized systemState switching
A power management method is disclosed. The power management method comprises the step of a computer system checking existence of a manufacturing identifier (ID) of a human interface device (HID) when the computer system is operated in a first mode; the computer system continuously detecting whether the HID exist when the manufacturing ID exists; the computer system starting a timer when the computer system detects that the HID does not exist; the computer system entering a second mode when the timer expires; the HID determining whether the computer system is operated in the second mode, when plugged into the computer system; the HID performing state transition on the computer system when determining that the computer system is in the second mode; and the computer system entering the first mode when detecting the state transition.
Owner:I O INTERCONNECT LTD
Puncturing system
ActiveUS20080262387A1Accurate processingEasy to controlCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringPuncture WoundEngineering
The invention relates to a puncturing system for generating a puncture wound for obtaining a sample of a body fluid, comprising a press-on part to be pressed onto a body part in which a puncture wound is to be generated, a triggering means, by the actuation of which a user can trigger a puncturing motion of a puncturing element after the press-on part is pressed on, and a testing facility for determining at least one test parameter on which a sample-obtaining probability depends. A securing facility is also provided that, in a locked state, locks the triggering means such that no puncturing motion can be triggered, and, in a triggering state, releases the triggering means such that a puncturing motion can be triggered by actuation thereof, whereby the securing facility is transitioned from the locked state to the triggering state by the testing facility when the test parameter determined by the testing facility meets defined minimum requirements. A signaling facility is also provided for signaling a transition of the securing facility to the triggering state and / or for signaling that the securing facility is in the triggering state. The invention also relates to a method for preparing a puncturing system for generating a puncture wound.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Radio frequency identification-based power management system and method for wireless communication devices
InactiveUS20060022802A1Add deviceEnhanced network security featureSubscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesCommunications systemState switching
A wireless communication system implements various RFID-based methods for wireless communication devices and wireless network infrastructures. The communication system includes an RFID tag and a wireless communication device. The RFID tag is configured to receive an RFID interrogation signal and, upon receipt thereof, to supply one or more transition signals. The wireless communication device is configured to operate in a plurality of operational states, is coupled to receive the transition signals, and is configured, upon receipt thereof, to transition from at least a first operational state to a second operational state.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
Apparatus and method for controlling operational states of medium access control layer in a broadband wireless access communication system
InactiveUS20050047429A1Minimize power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemBroadband
Disclosed is a method for controlling an operational state of a medium access control layer in a broadband wireless access communication system. The method includes the steps of performing an uplink access of a contention-based scheme to an access point using resources required to perform the uplink access according to the contention-based scheme when data to be transmitted in an access state is detected, and being allocated resources required to perform an uplink access of a contention-free scheme from the access point in a case of failing in the uplink access of the contention-based scheme; and performing a state transition from the access state into the traffic state in a case of having been allocated the resource required for the contention-free scheme, and performing the uplink access of the contention-free scheme to the access point using the allocated resource in the traffic state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Structure and method for biasing phase change memory array for reliable writing
ActiveUS7307268B2Reduce the possibilityMinimize leakage currentSolid-state devicesDigital storageBit linePhase-change memory
A memory array having memory cells comprising a diode and a phase change material is reliably programmed by maintaining all unselected memory cells in a reverse biased state. Thus leakage is low and assurance is high that no unselected memory cells are disturbed. In order to avoid disturbing unselected memory cells during sequential writing, previously selected word and bit lines are brought to their unselected voltages before new bit lines and word lines are selected. A modified current mirror structure controls state switching of the phase change material.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
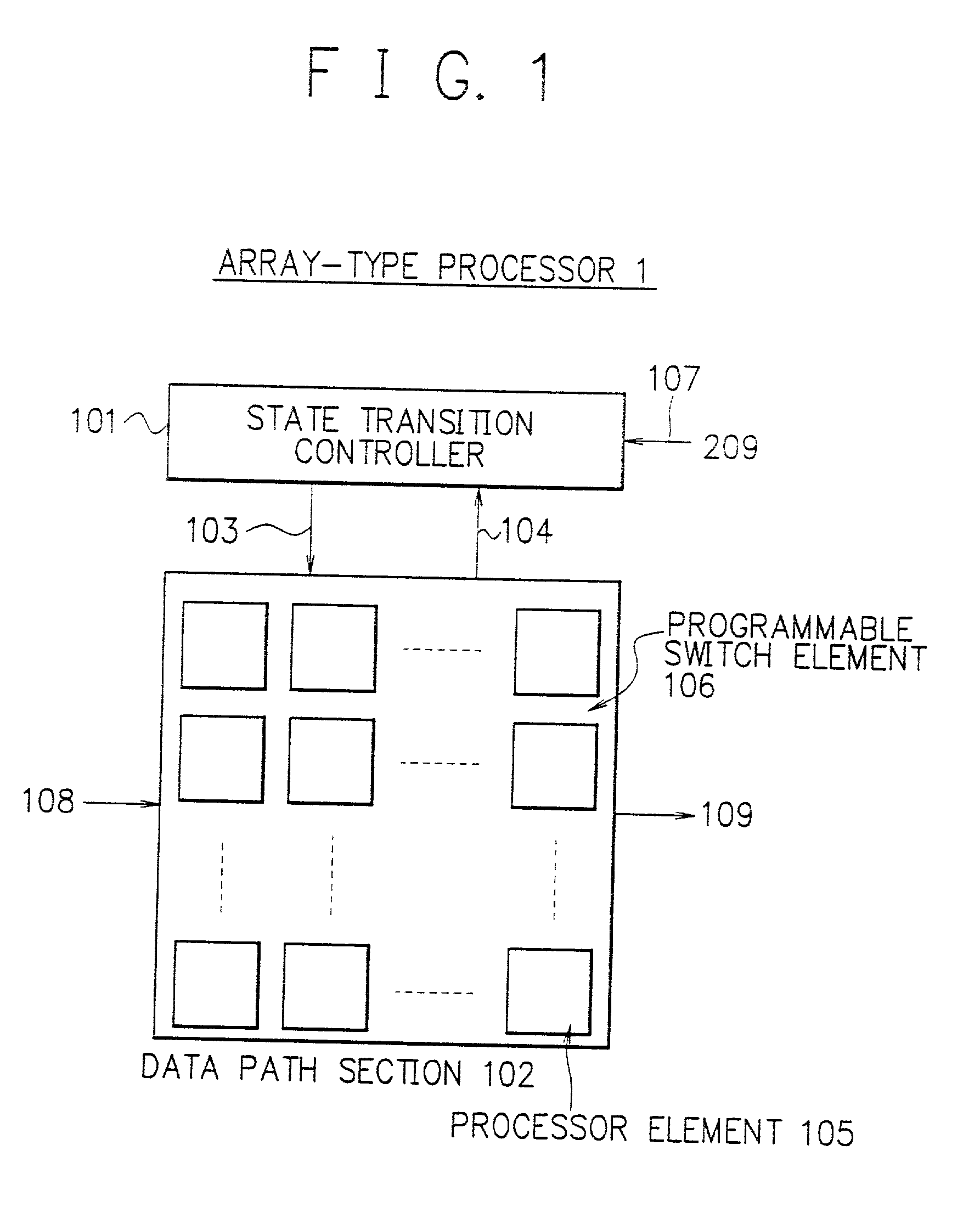
Array-type processor
InactiveUS20010018733A1Efficient implementationEfficient executionSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsSpecific program execution arrangementsDatapathState switching
To execute all processing in an array section of an array-type processor, each processor must execute processing of different types, i.e., processing of an operating unit and processing of a random logic circuit, which limits its size and processing performance. A data path section including processors arranged in an array are connected via programmable switches to primarily execute processing of operation and a state transition controller configured to easily implement a state transition function to control state transitions are independently disposed. These sections are configured in customized structure for respective processing purposes to efficiently implement and achieve the processing of operation and the control operation.
Owner:NEC CORP
High spatial resolution imaging
ActiveUS20060038993A1Improve spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationComing outOptical property
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Method for analyzing state transition in web page
InactiveUS20070150556A1Automatically and efficiently record and reproduceAccessibility and efficiencyMultiple digital computer combinationsWebsite content managementState switchingWeb page
A method that enables a tester to efficiently perform confirmation behavior of a Web page that utilizes DHTML or difference in behavior of the Web page among various browsers, or assignment of information relating to accessibility of the Web page or verification of the information. A method is provided that analyzes change in a Web page by determining states that can dynamically occur in response to an external event in a Web page that utilizes DHTML by analyzing at least one of DOM, style information for when rendered on a browser, input data from a user, and the value of a global variable in JAVA®SCRIPT, storing data that can identify each of the states, identifying state transition between the stored states, and reproducing the stored states.
Owner:IBM CORP
User interaction system and method
ActiveCN103246351AImprove experienceReduce learning costsInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingInteraction systemsInteraction interface
An embodiment of the invention discloses a user interaction system and method. The user interaction system comprises a three-dimensional interaction interface display module, a gesture recognition module, and an information arithmetic processing module, wherein the three-dimensional interaction display module is used for providing a user with a three-dimensional interaction interface; the gesture recognition module is used for capturing gesture trajectory and gesture shapes produced when the user is browsing the three-dimensional interaction interface as well as sending the gesture trajectory information and the gesture shape information to the information arithmetic processing module; when the distance between the gesture trajectory and preset spatial points is determined to meet a preset distance threshold value, and the gesture shapes are determined to meet a preset state switching condition, the information arithmetic processing module is used for determining a corresponding interaction operation command as well as sending a three-dimensional interaction result interface with the interaction operation command executed to the three-dimensional interaction interface display module; and then the three-dimensional interaction interface display module further provides the user with the three-dimensional interaction result interface.
Owner:刘广松 +1
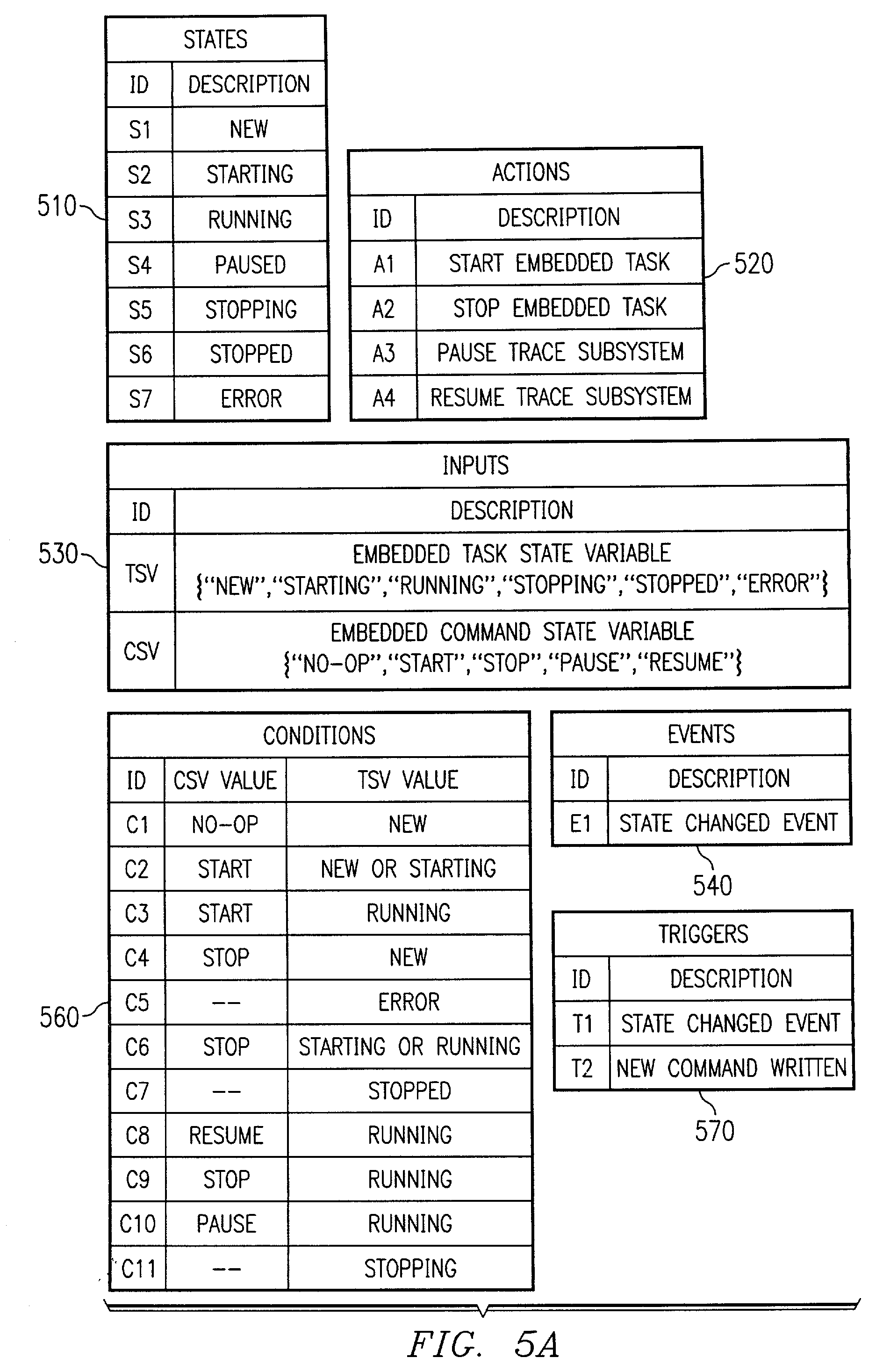
Method, apparatus, and program for a state machine framework
InactiveUS6993706B2Visual/graphical programmingProgram loading/initiatingGraphicsArray data structure
A programming framework is provided for designing and implementing software state machines. A state machine initializer may be created that defines the states, conditions, actions, triggers, and state transitions for the software state machines. A set of user interfaces, such as graphical user interfaces, may also be provided for creating initializers. An abstract state machine object may then be created that creates an instance of a particular state machine initializer. The state machine initializer acts as a helper to the state machine object, which uses the initializer to create an array of state transition objects. Once the state machine objects creates the array of state transition objects, the state machine is ready to run. A set of programming interfaces may also be provided to define the programming framework.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com