Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
71results about How to "Minimize Leakage Current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
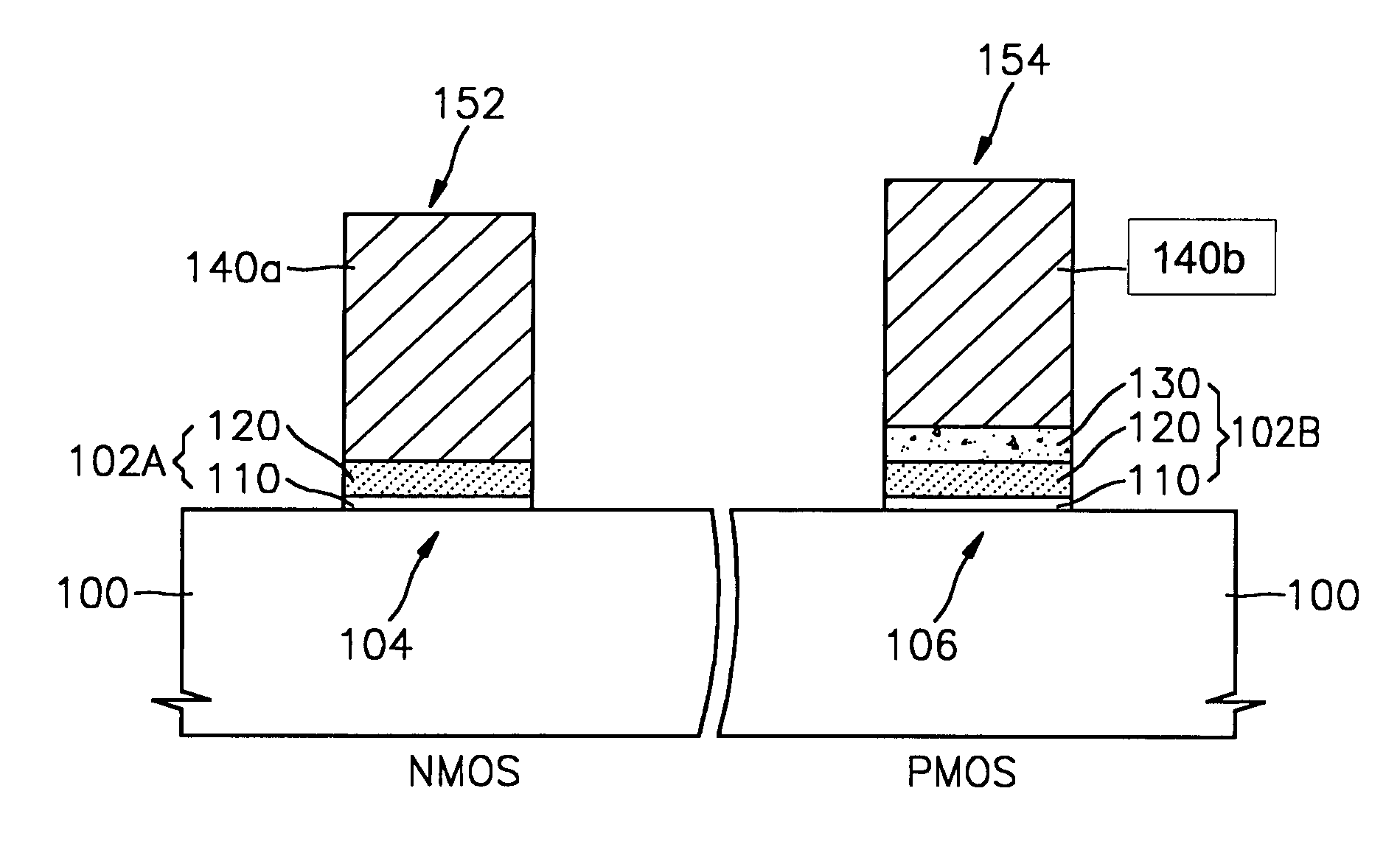
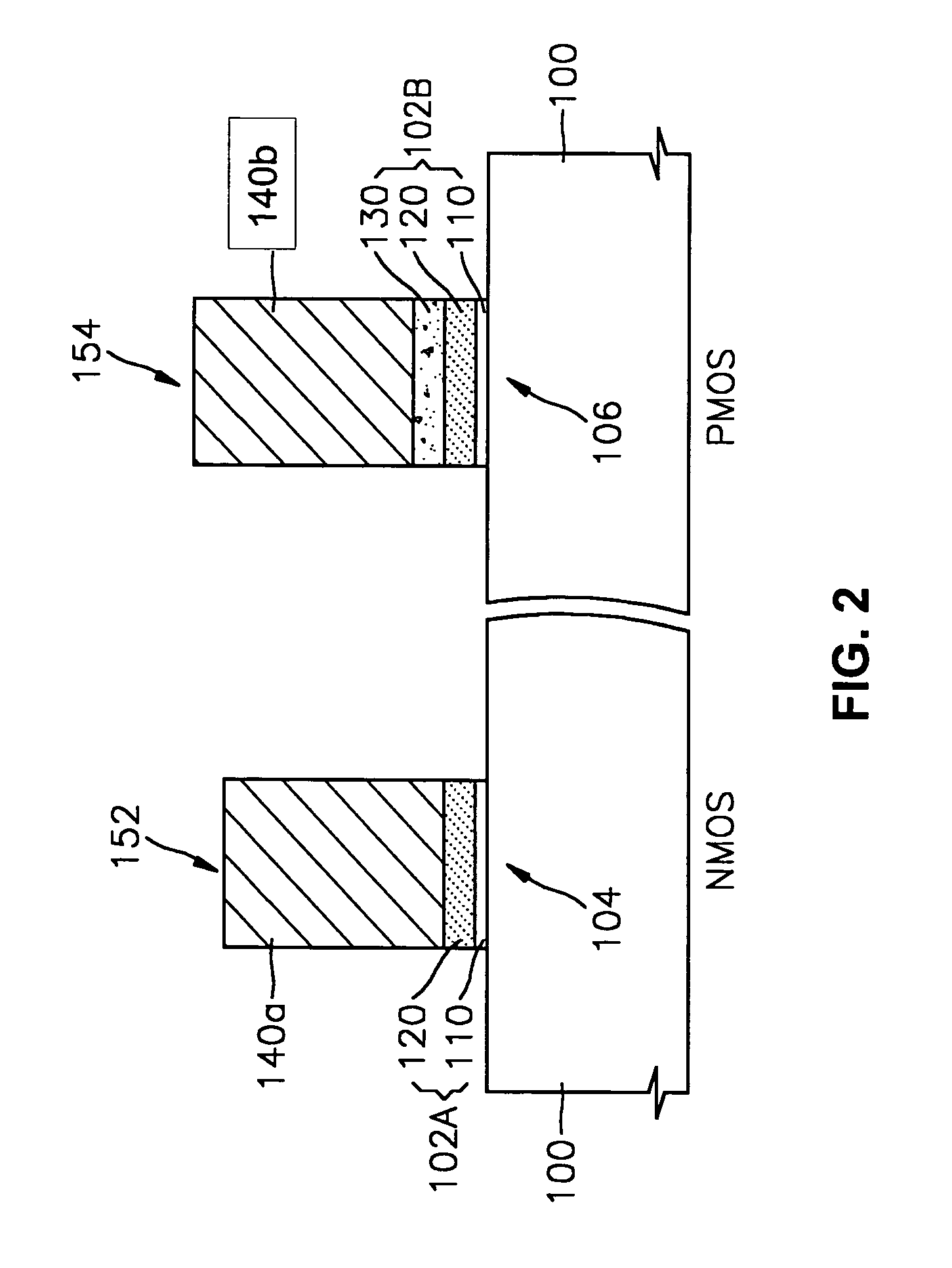
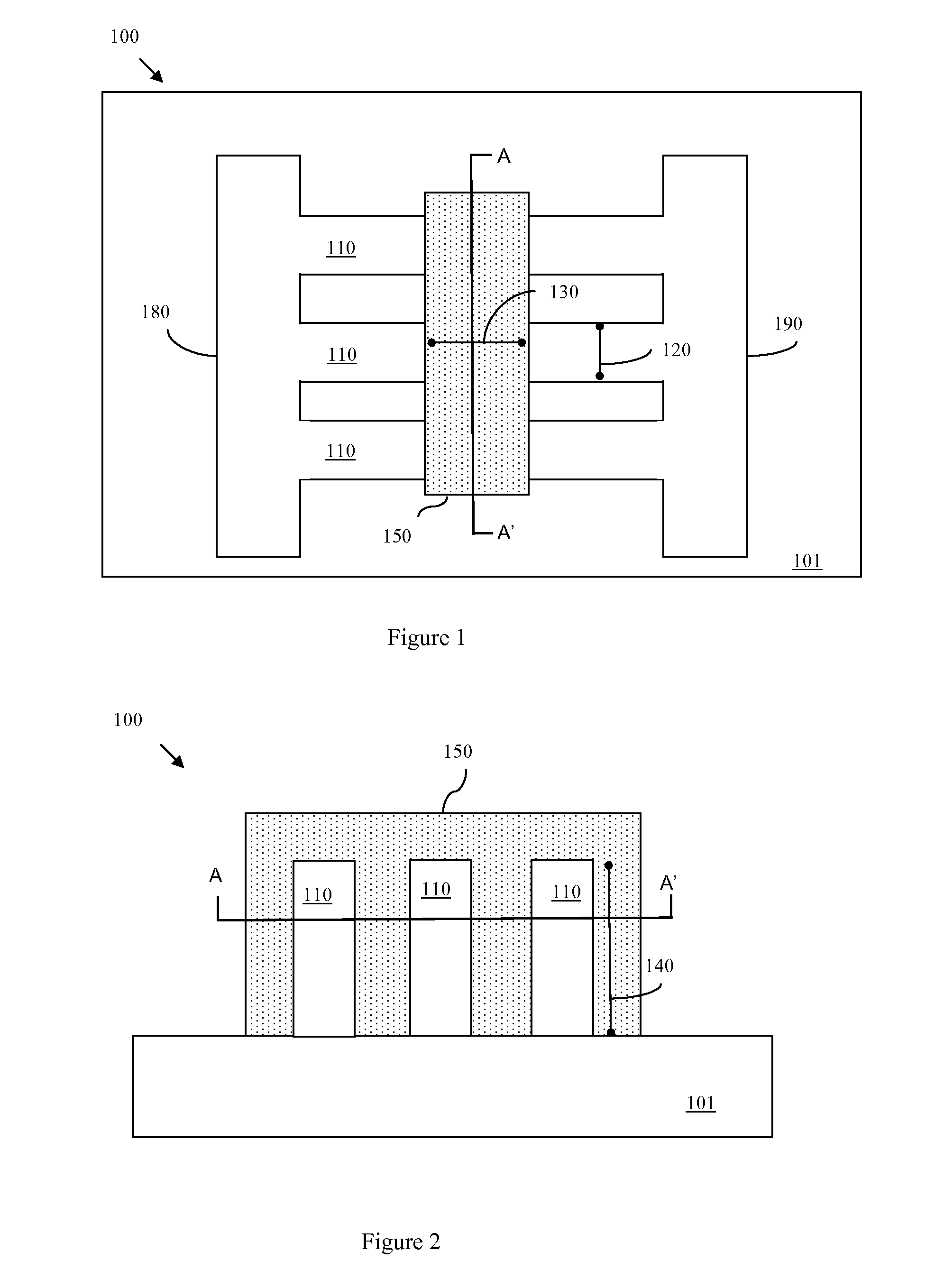
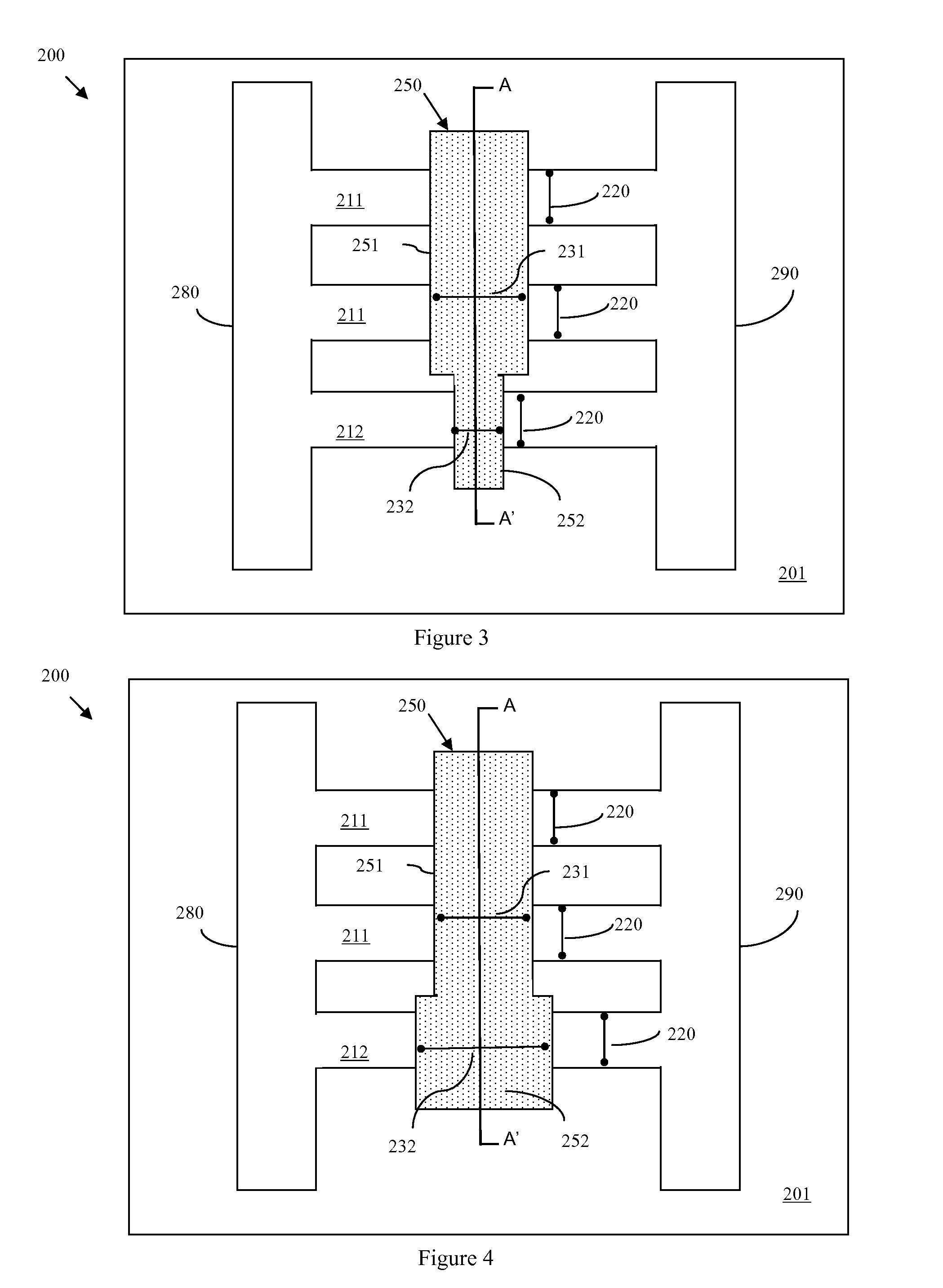
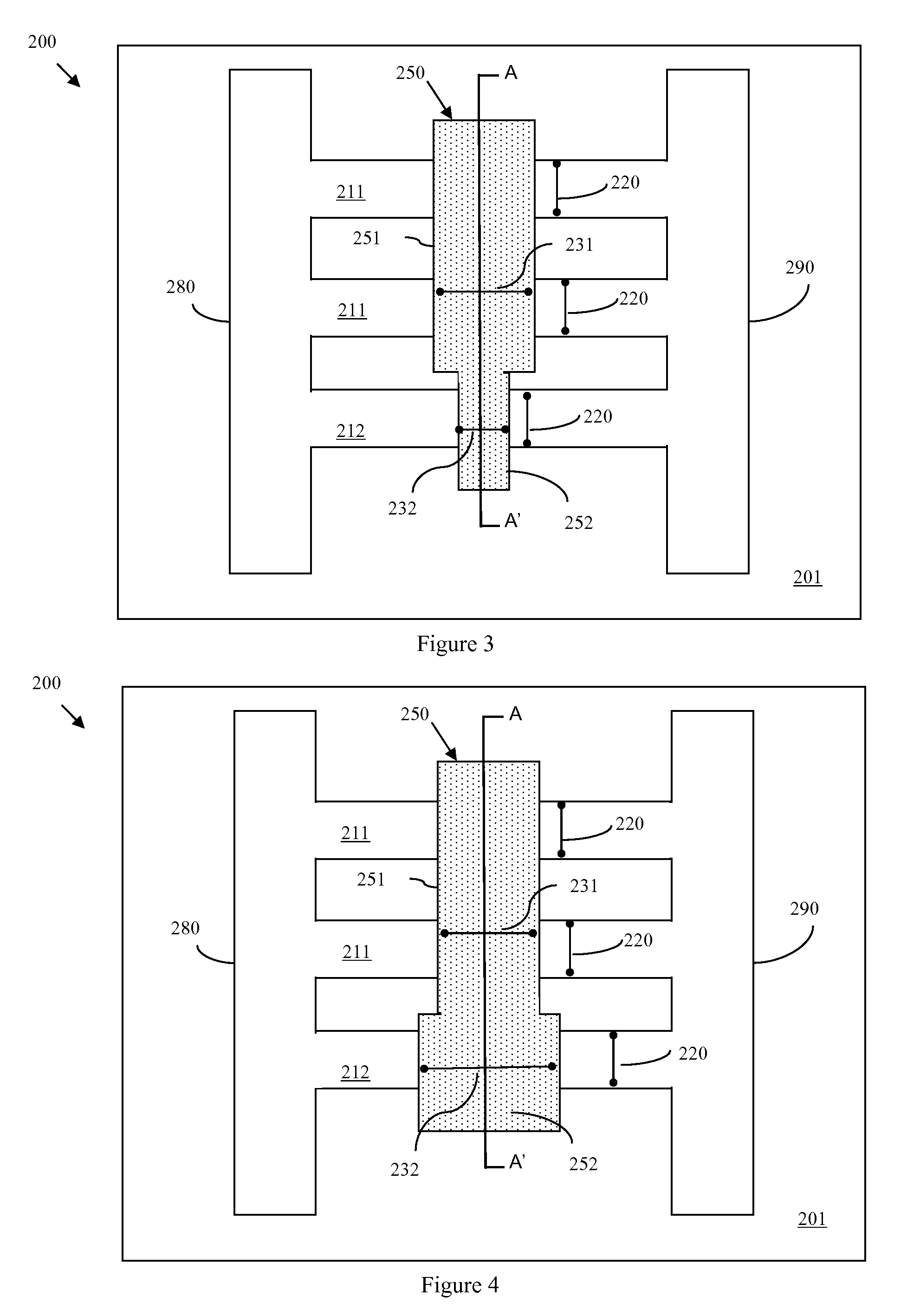
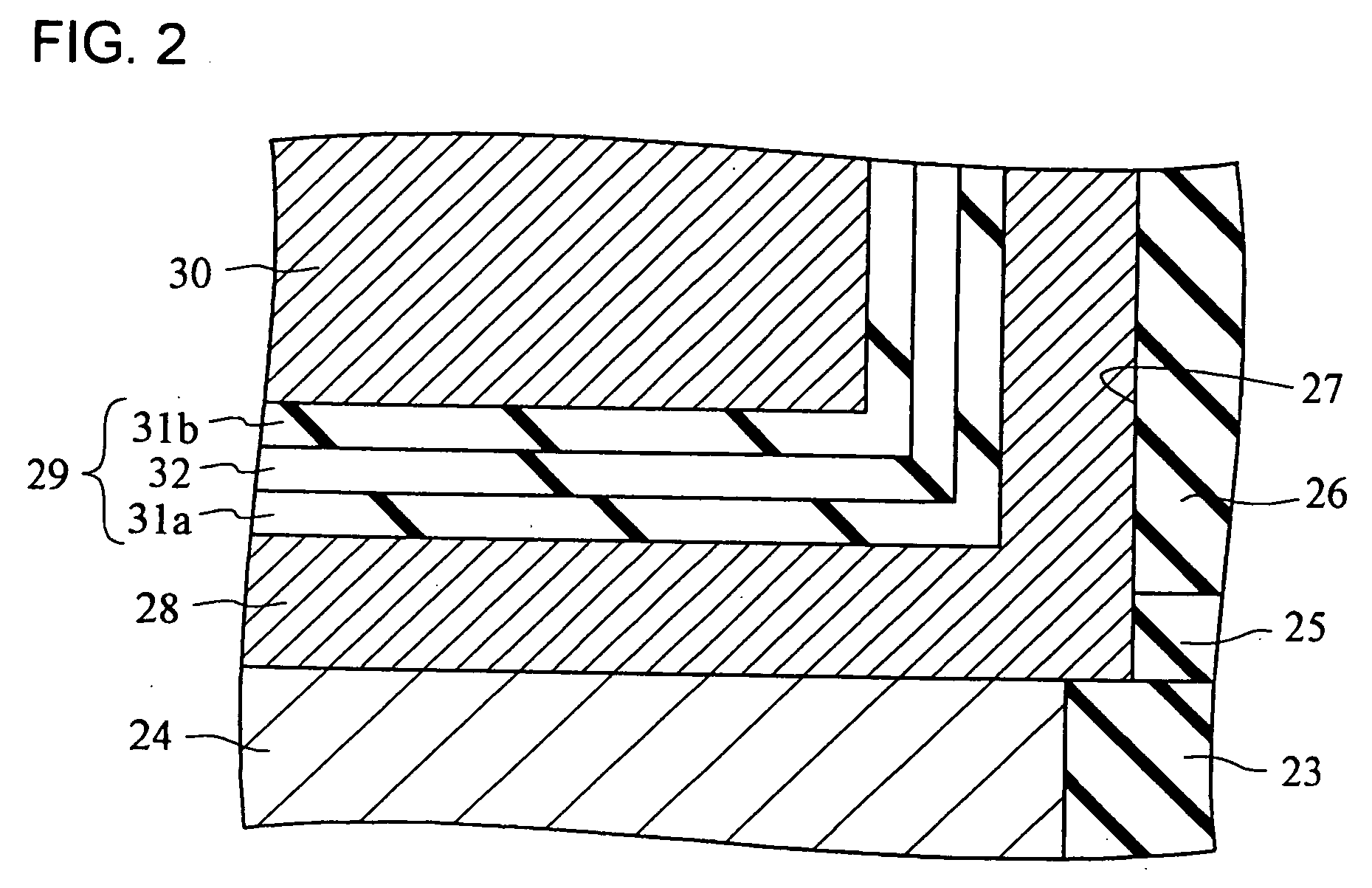
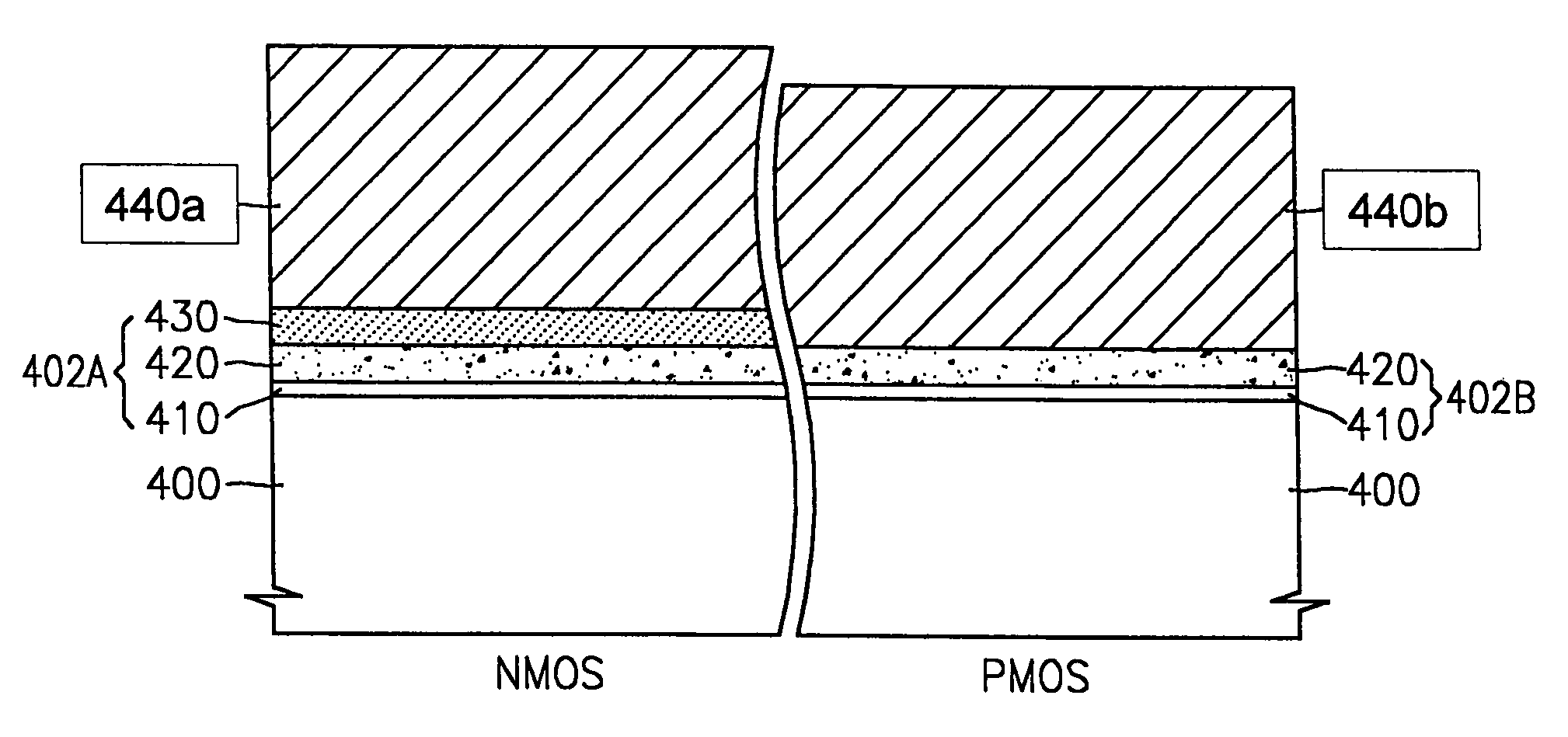
Semiconductor devices having different gate dielectrics and methods for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050098839A1High speedMinimize leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes first and second transistor devices. The first device includes a first substrate region, a first gate electrode, and a first gate dielectric. The first gate dielectric is located between the first substrate region and the first gate electrode. The second device includes a second substrate region, a second gate electrode, and a second gate dielectric. The second gate dielectric is located between the second substrate region and the second gate electrode. The first gate dielectric includes a first high-k layer having a dielectric constant of 8 or more. Likewise, the second gate dielectric includes a second high-k layer having a dielectric constant of 8 or more. The second high-k layer has a different material composition than the first high-k layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
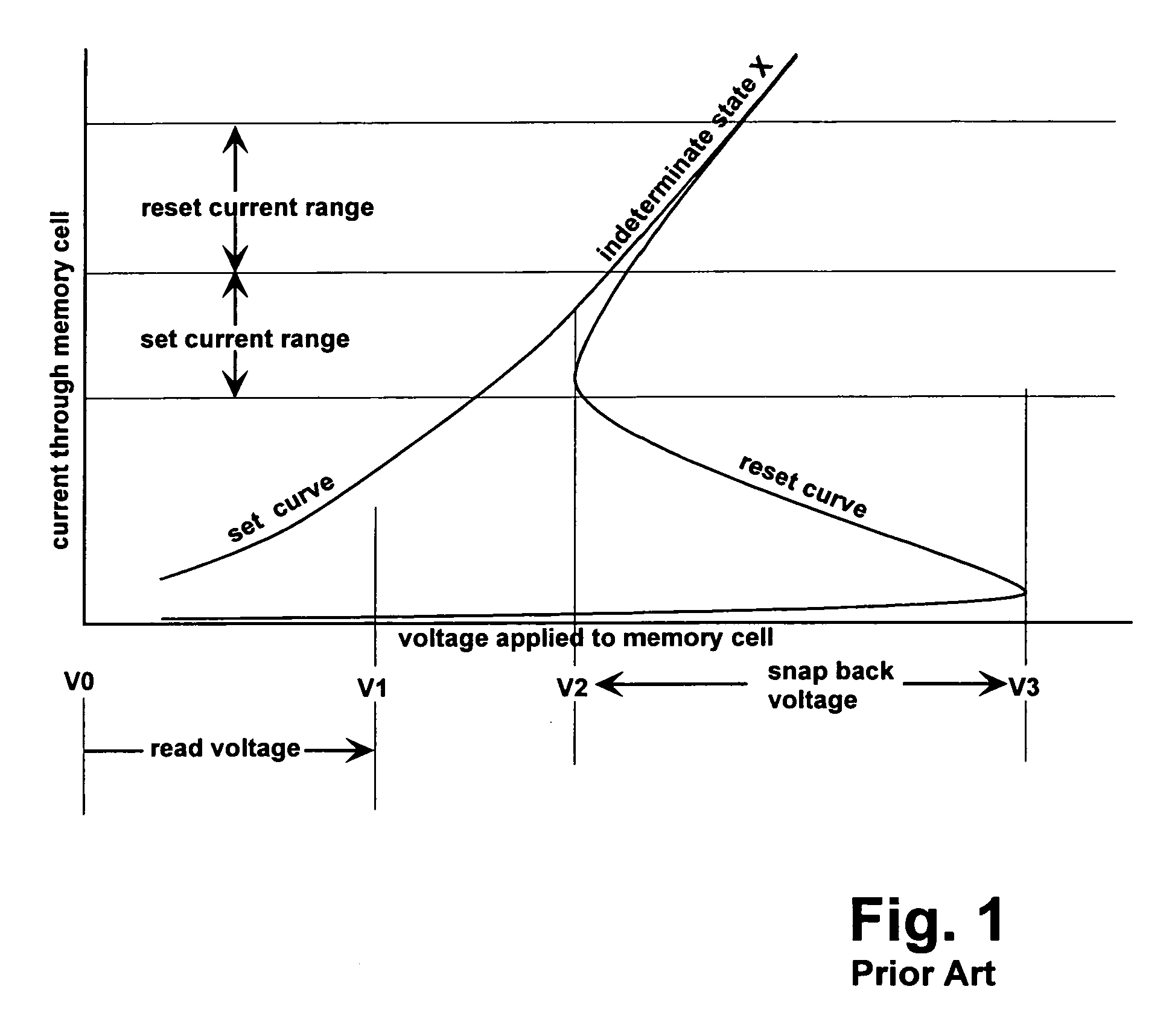
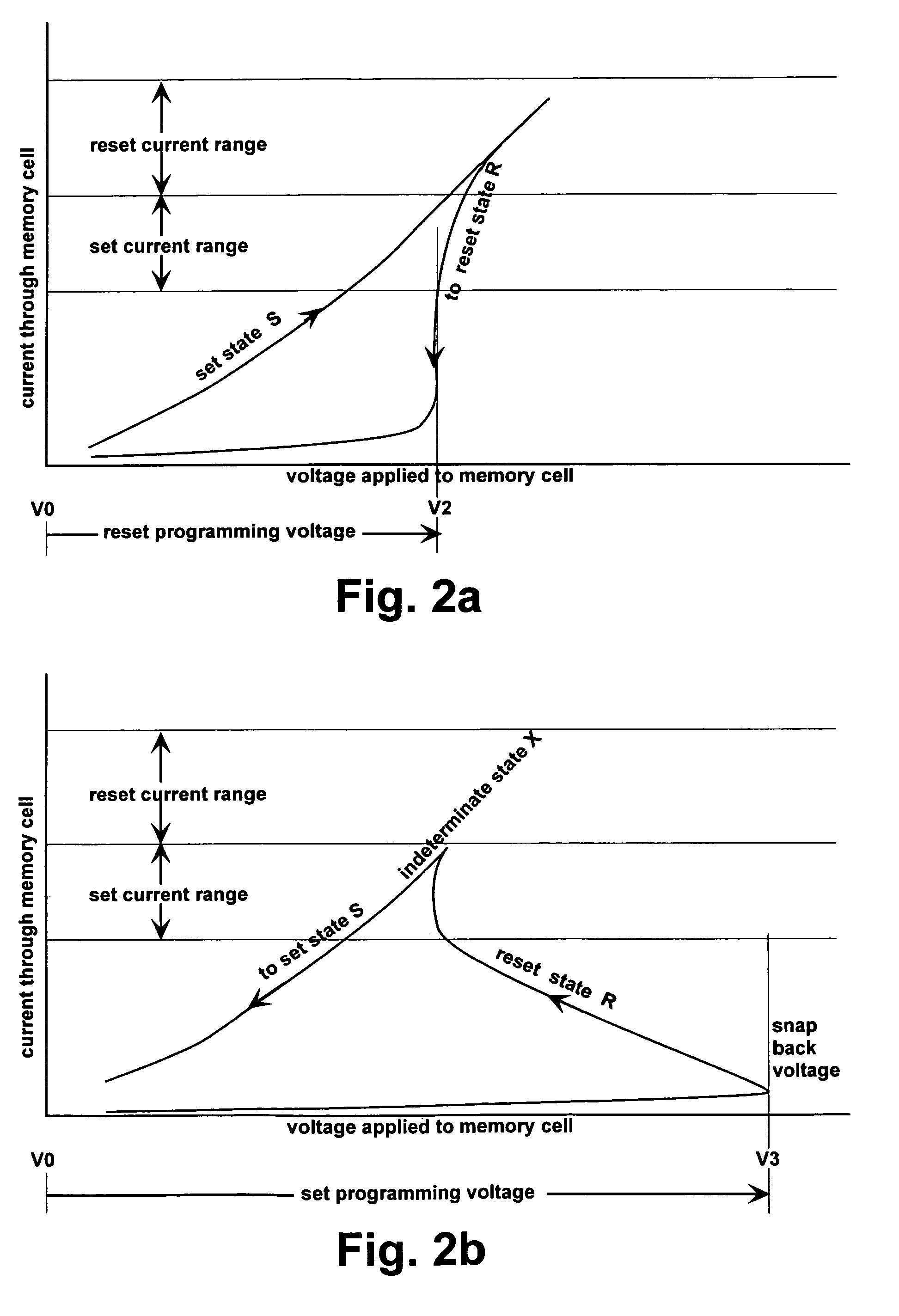
Structure and method for biasing phase change memory array for reliable writing
ActiveUS7307268B2Reduce the possibilityMinimize leakage currentSolid-state devicesDigital storageBit linePhase-change memory
A memory array having memory cells comprising a diode and a phase change material is reliably programmed by maintaining all unselected memory cells in a reverse biased state. Thus leakage is low and assurance is high that no unselected memory cells are disturbed. In order to avoid disturbing unselected memory cells during sequential writing, previously selected word and bit lines are brought to their unselected voltages before new bit lines and word lines are selected. A modified current mirror structure controls state switching of the phase change material.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
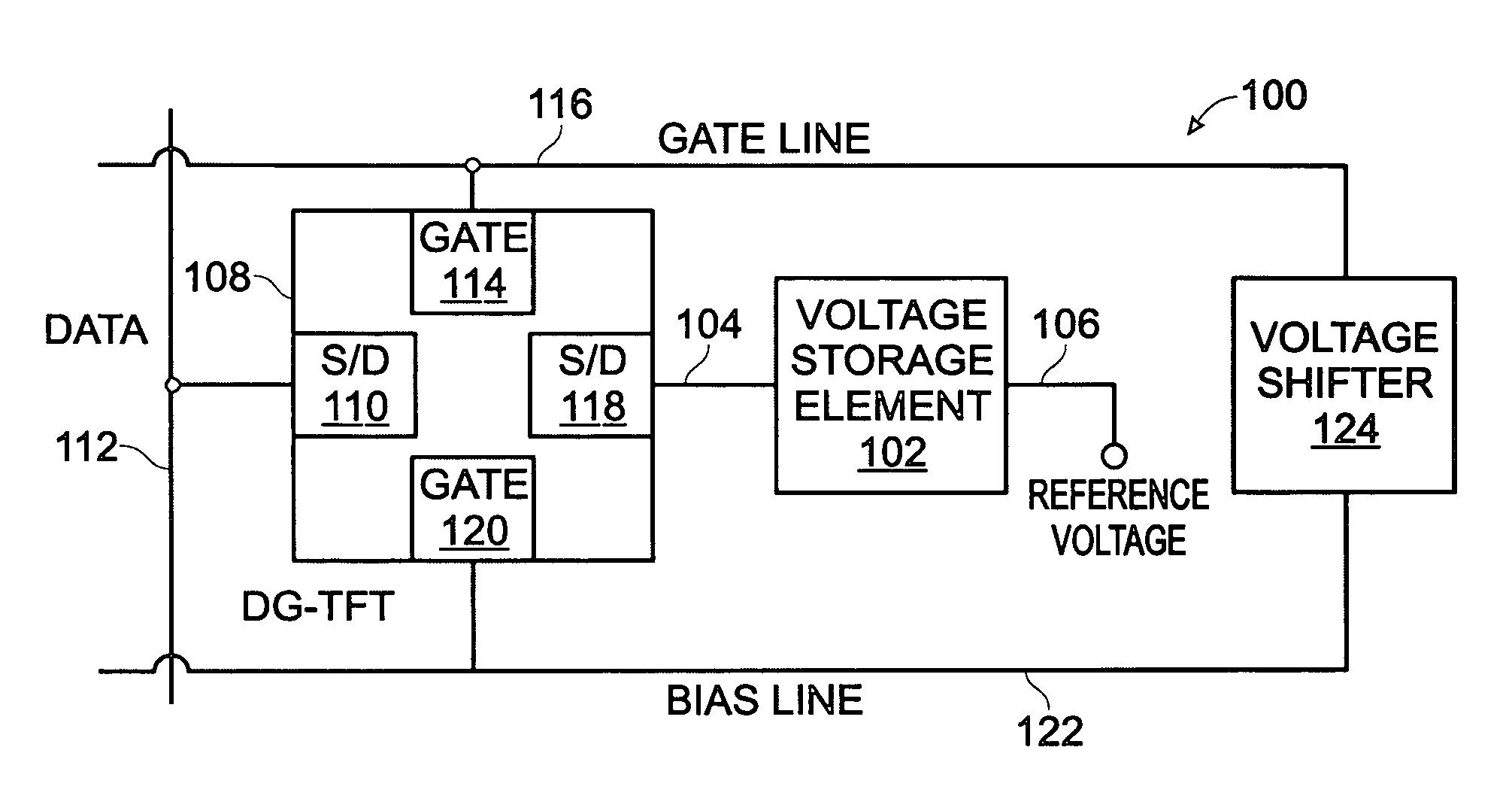
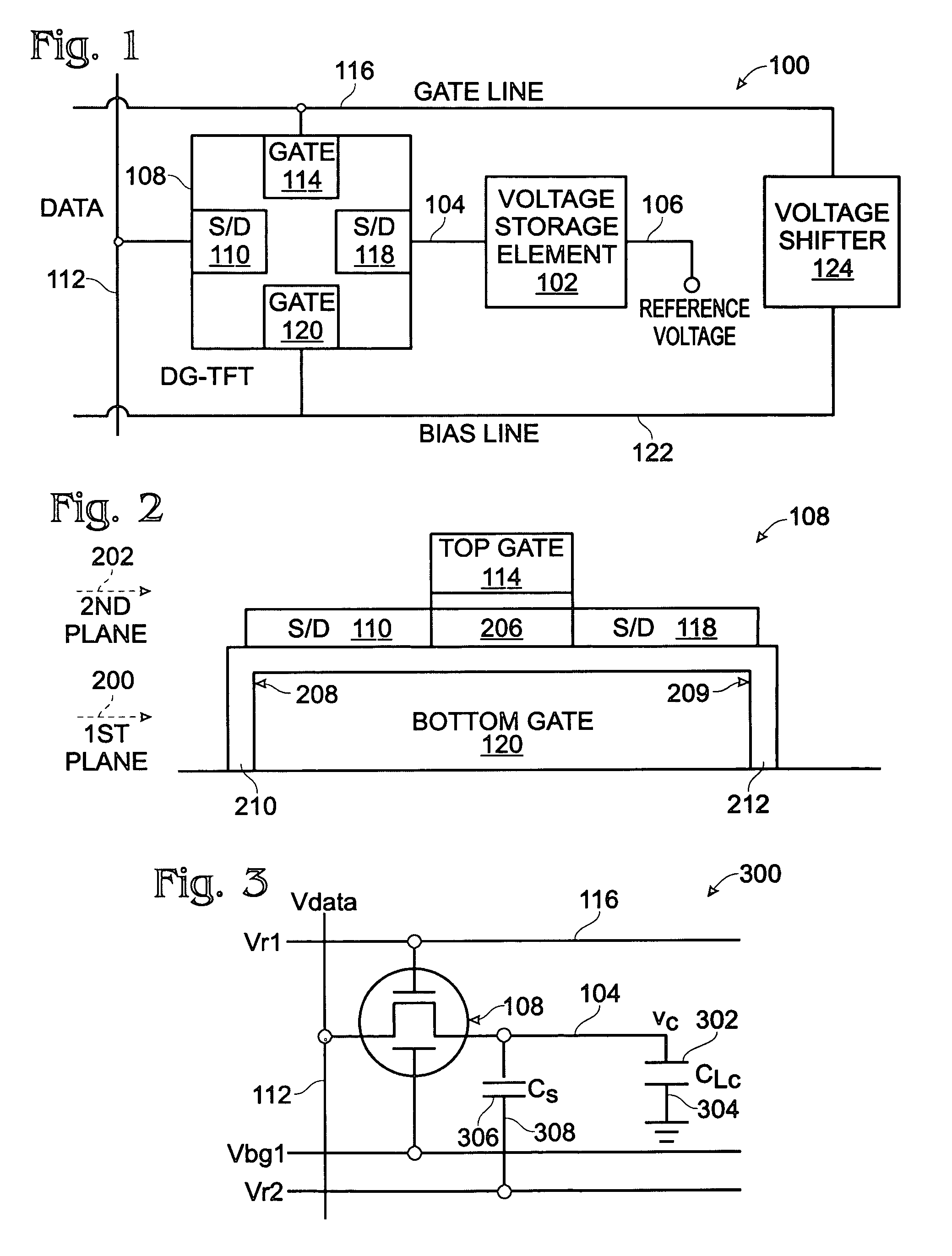
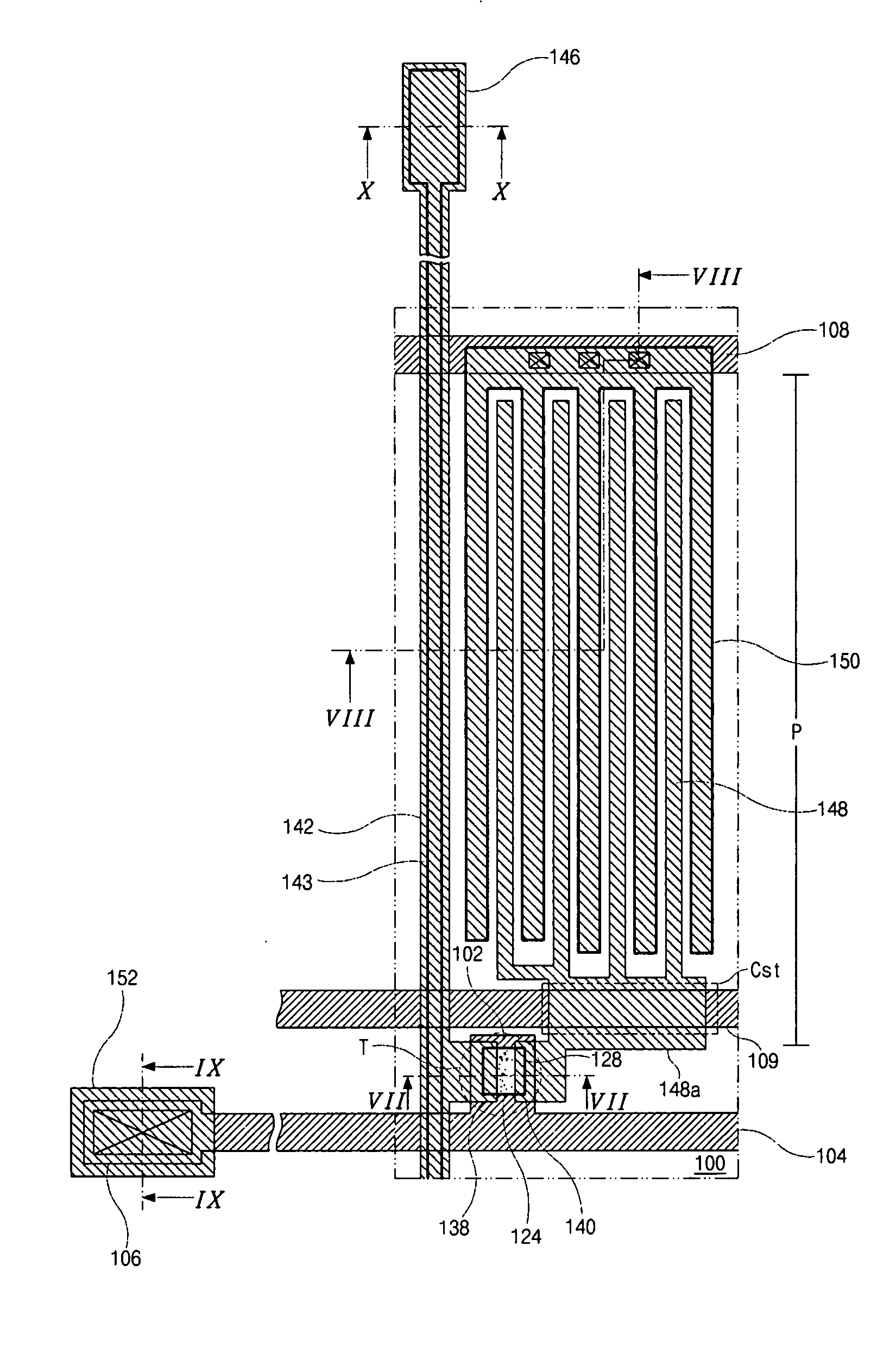
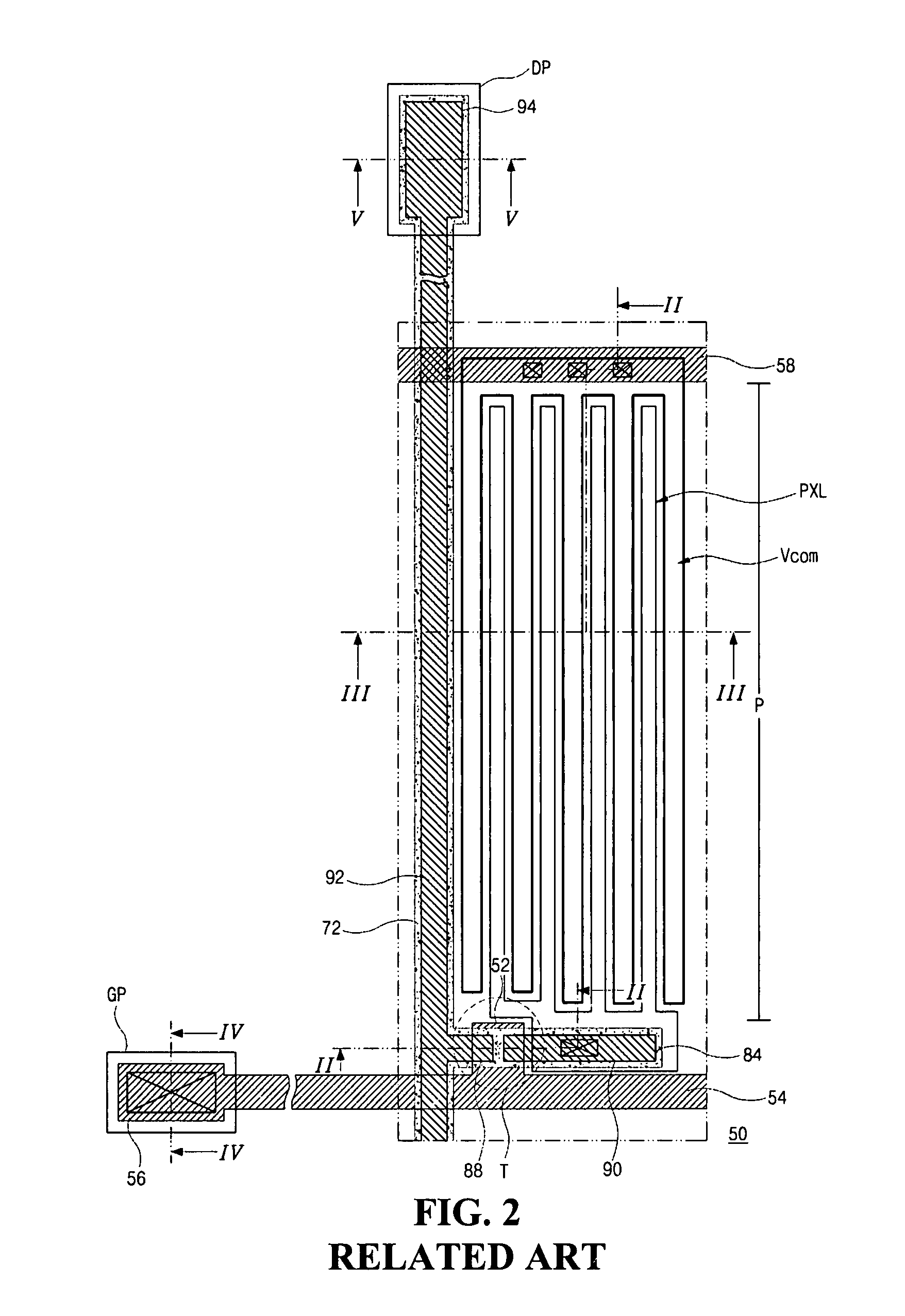
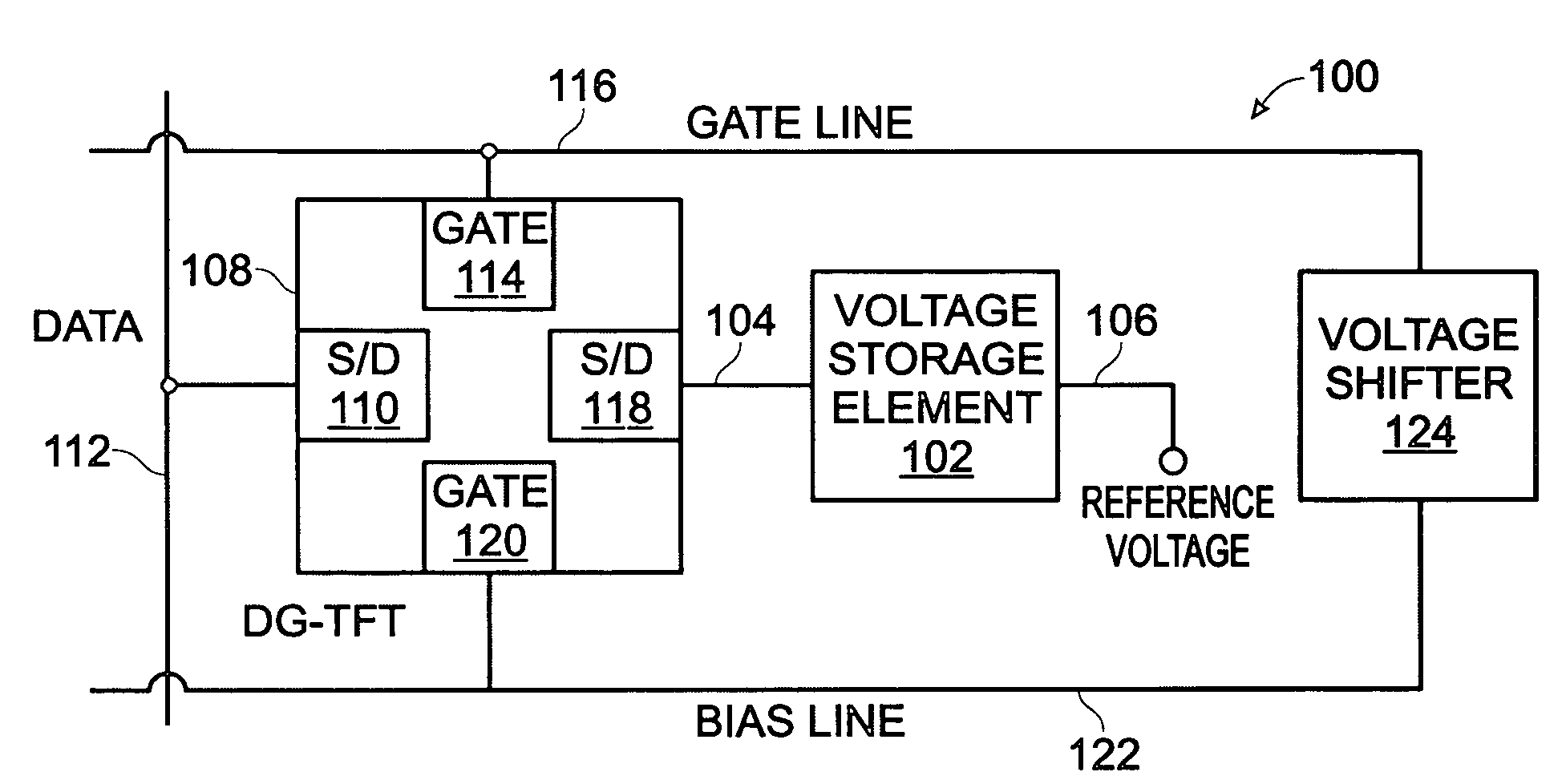
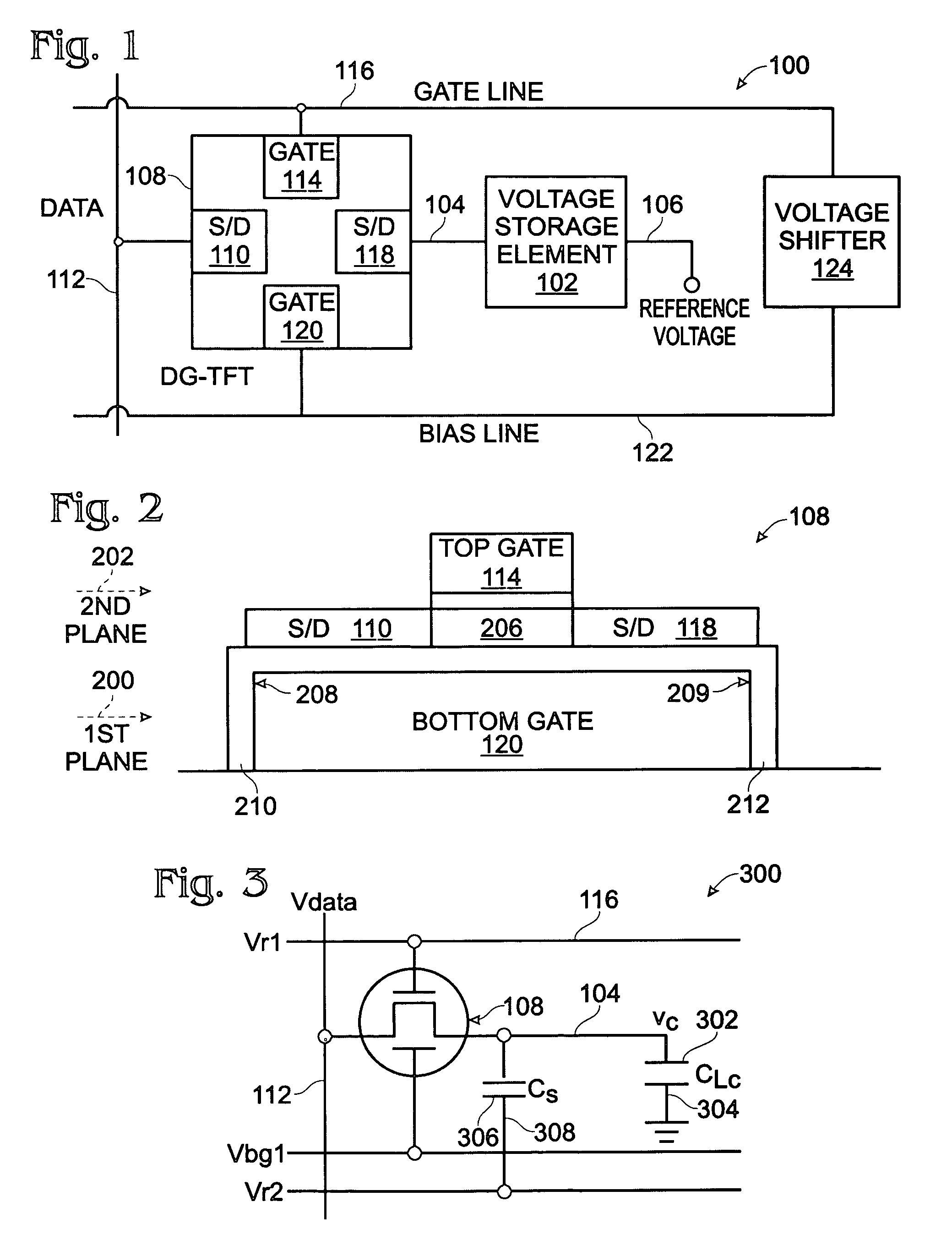
Dual-gate transistor display
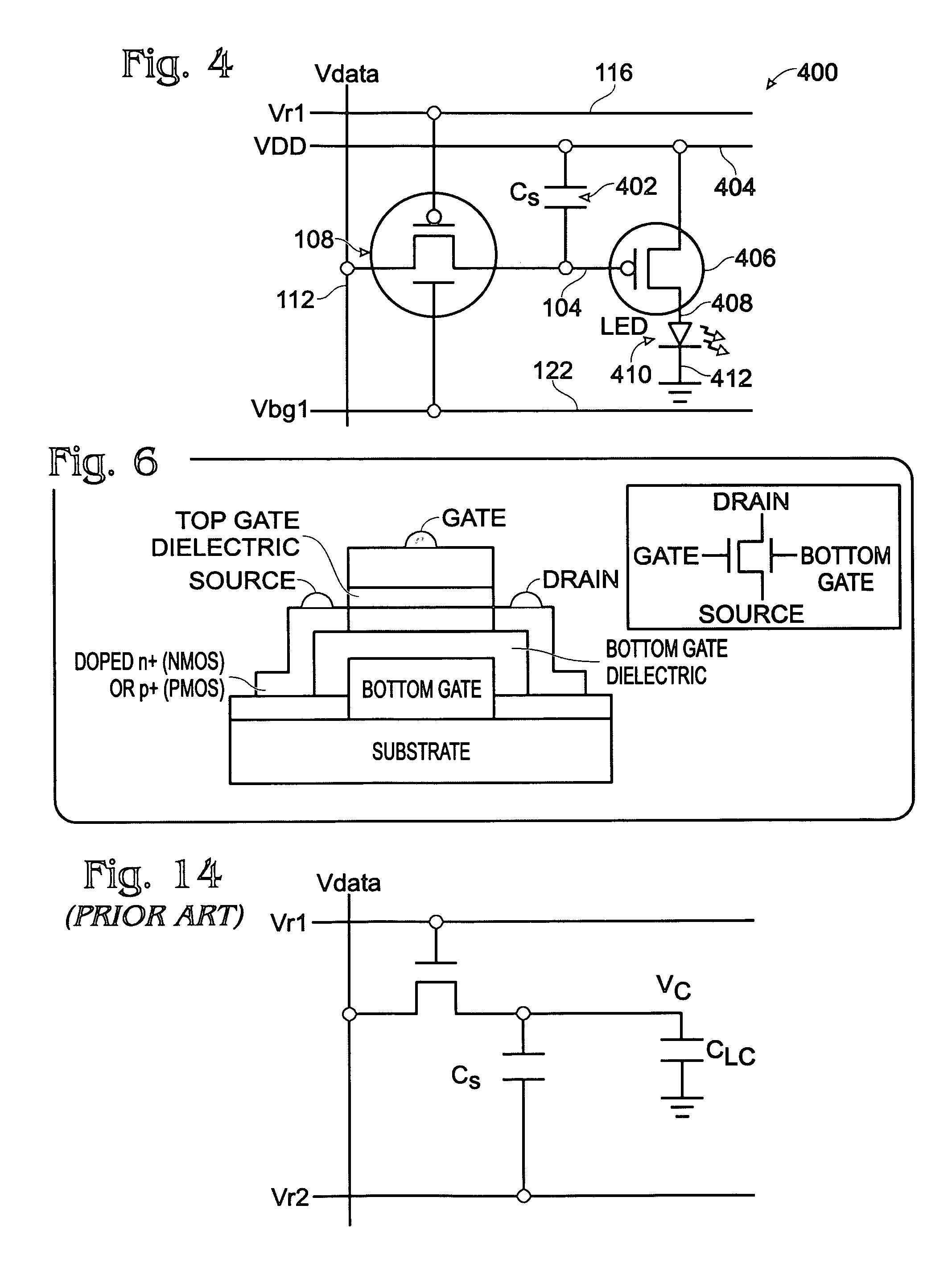
ActiveUS20060066512A1Minimize leakage currentImprove featuresStatic indicating devicesSemiconductor devicesHemt circuitsDisplay device
A dual-gate thin-film transistor (DG-TFT) voltage storage circuit is provided. The circuit includes a voltage storage element, a DG-TFT having a first source / drain (S / D) connected to a data line, a top gate connected to a first gate line, a second S / D region connected to the voltage storage element, and a bottom gate connected to a bias line. In one aspect, the circuit further includes a voltage shifter having an input connected to the first gate line and an output to supply a bias voltage on the bias line. Examples of a voltage storage element include a capacitor, a liquid crystal (LC) pixel, and a light emitting diode (LED) pixel.
Owner:SHARP KK
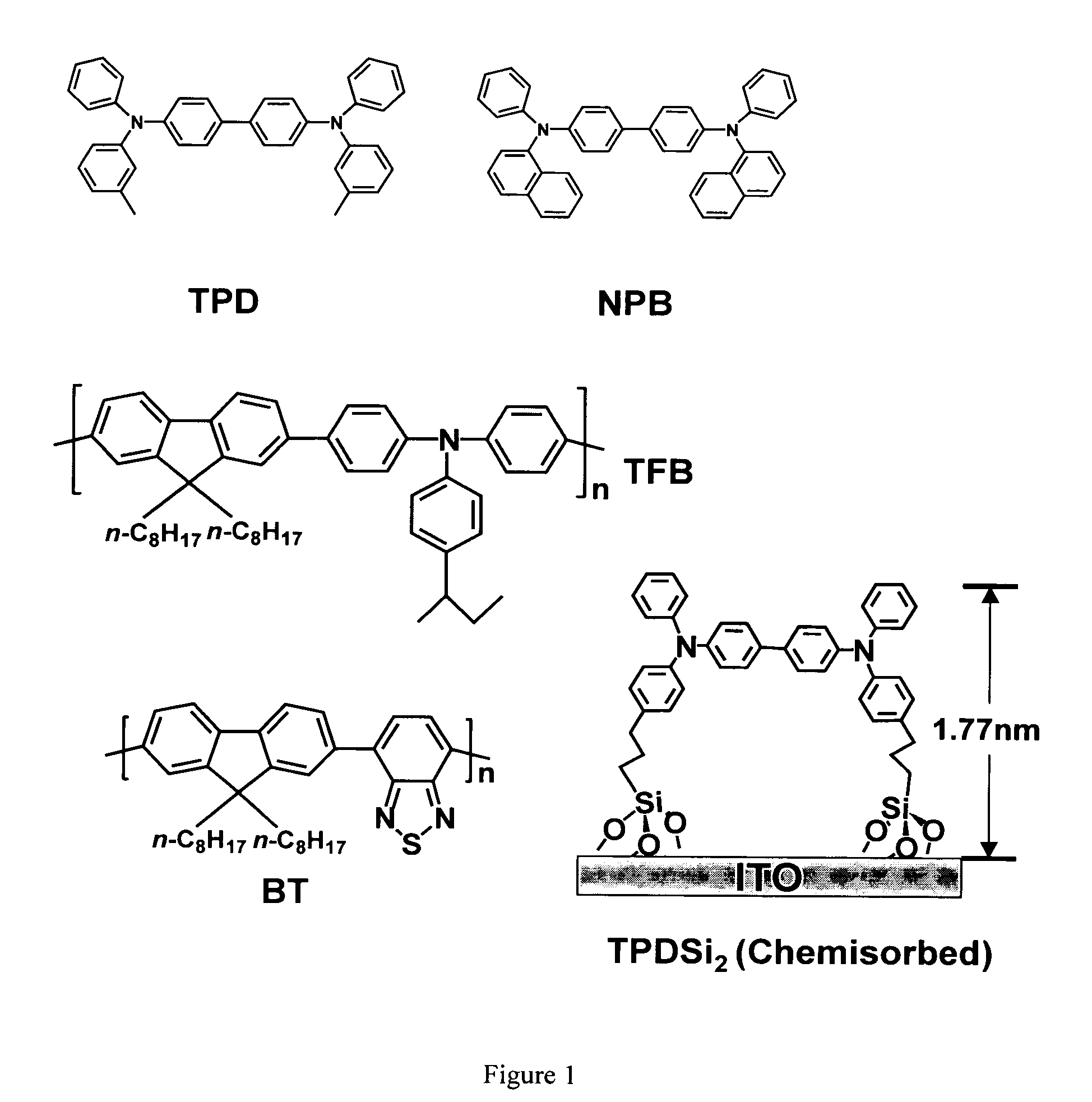
Hole transport layer compositions and related diode devices
ActiveUS20050147846A1Improve performanceExcellent hole injectionDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhotochemistryCyclic amines
Hole transport layer compositions comprising a silylated aryl amine and a polymeric component, to enhance performance of an associated electroluminescent device.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
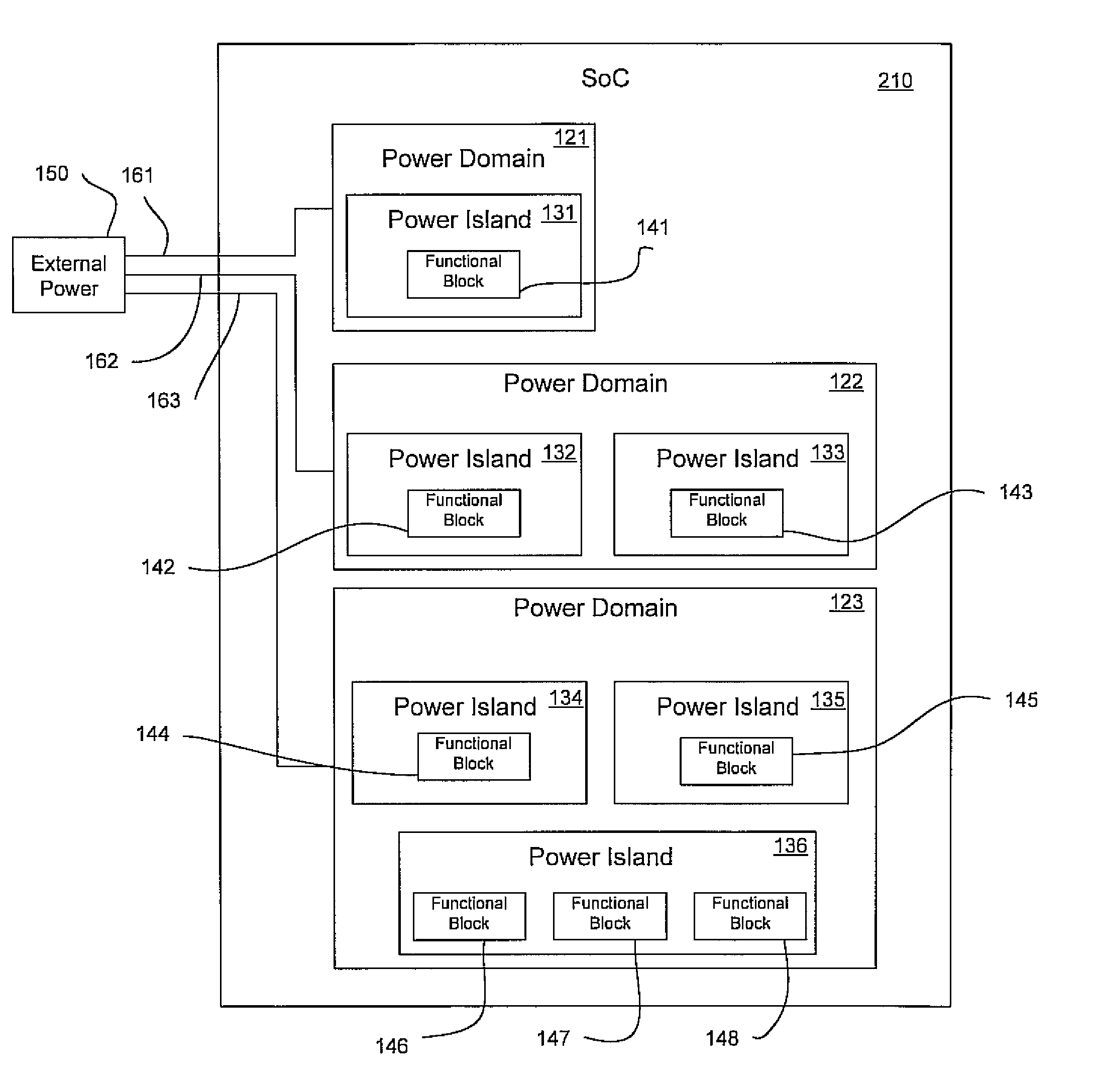
Integrated circuit device having power domains and partitions based on use case power optimization
ActiveUS20090201082A1Minimize leakage currentSolve the large leakage currentEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsEngineeringPower domains
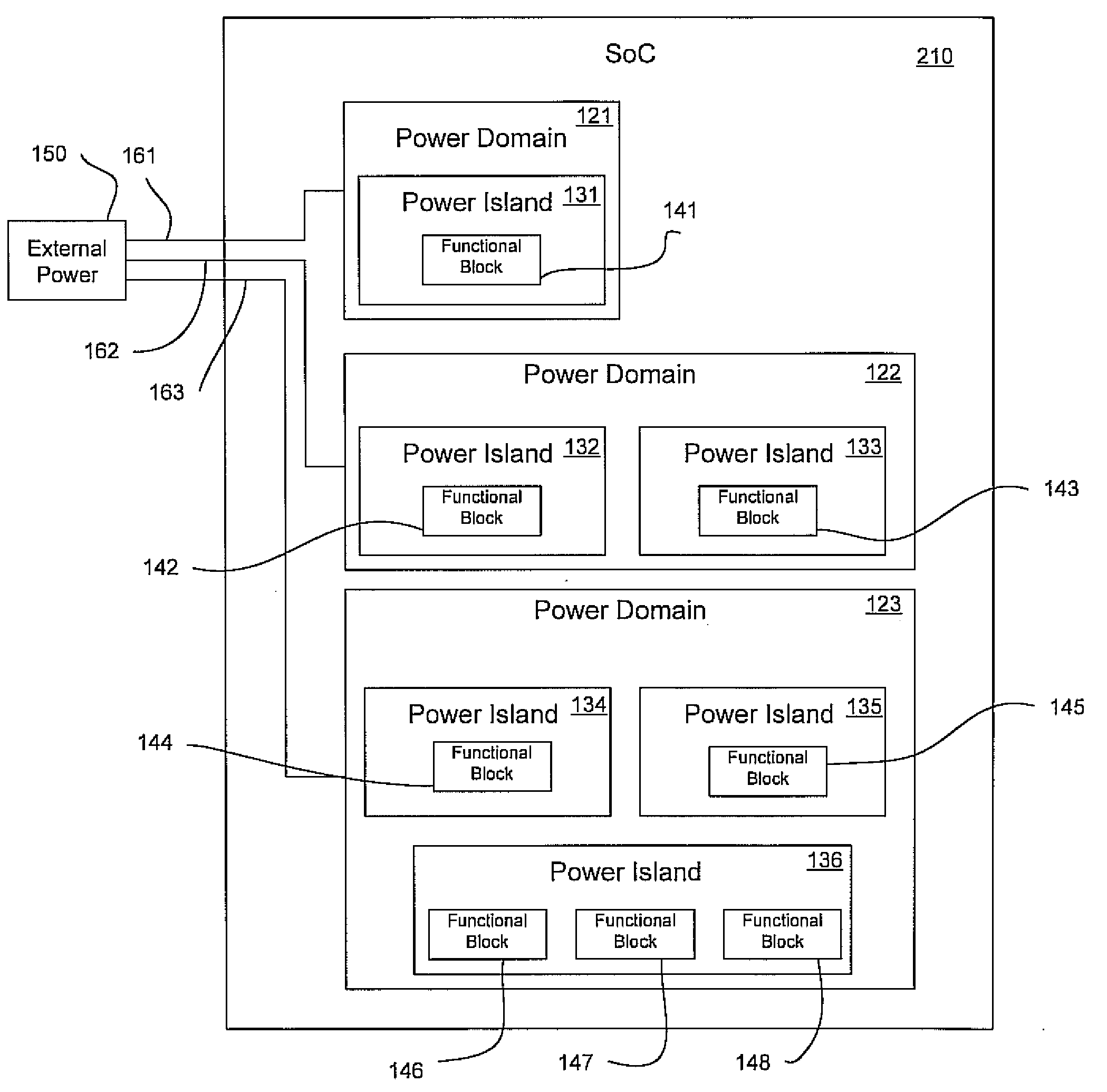
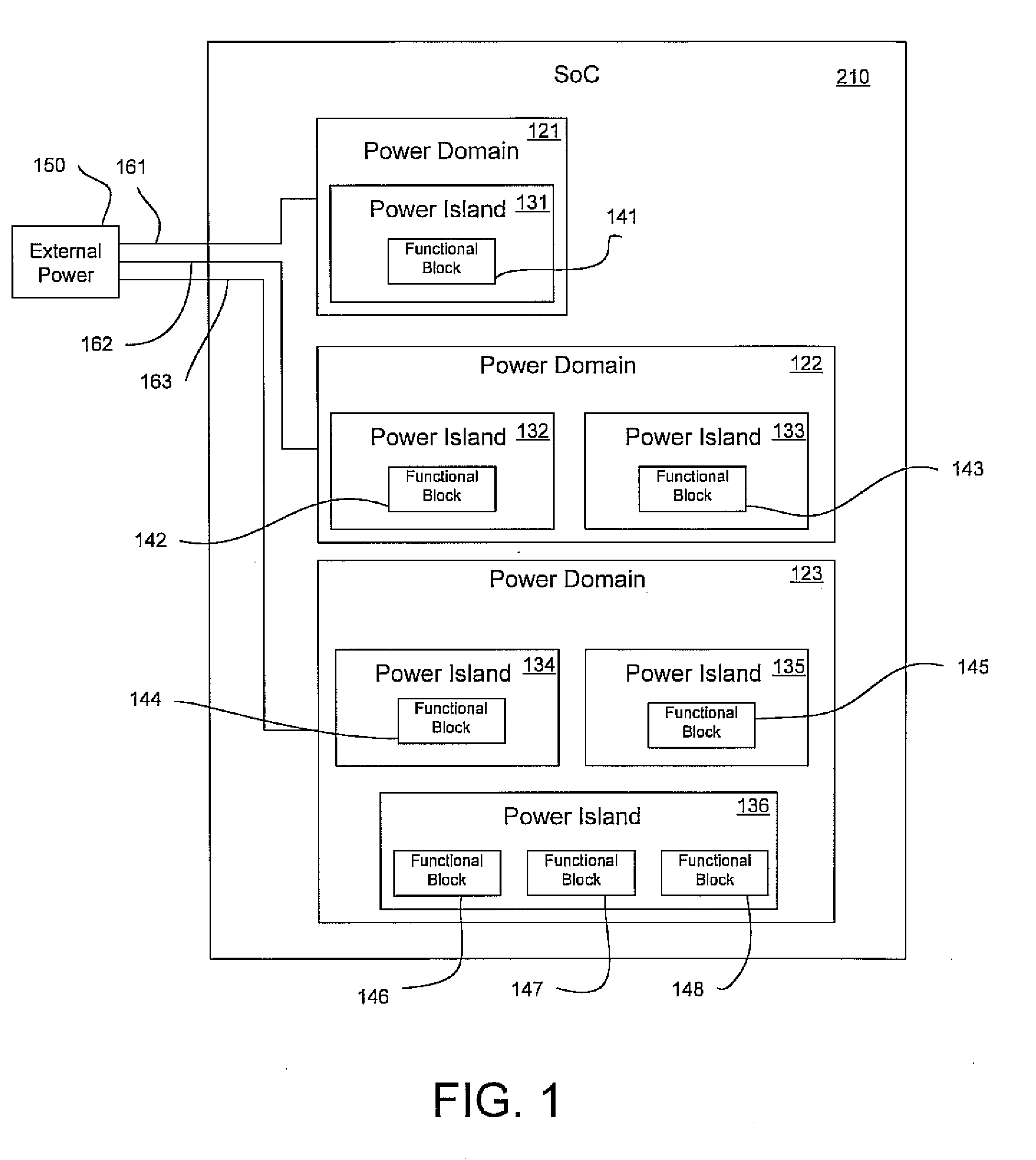
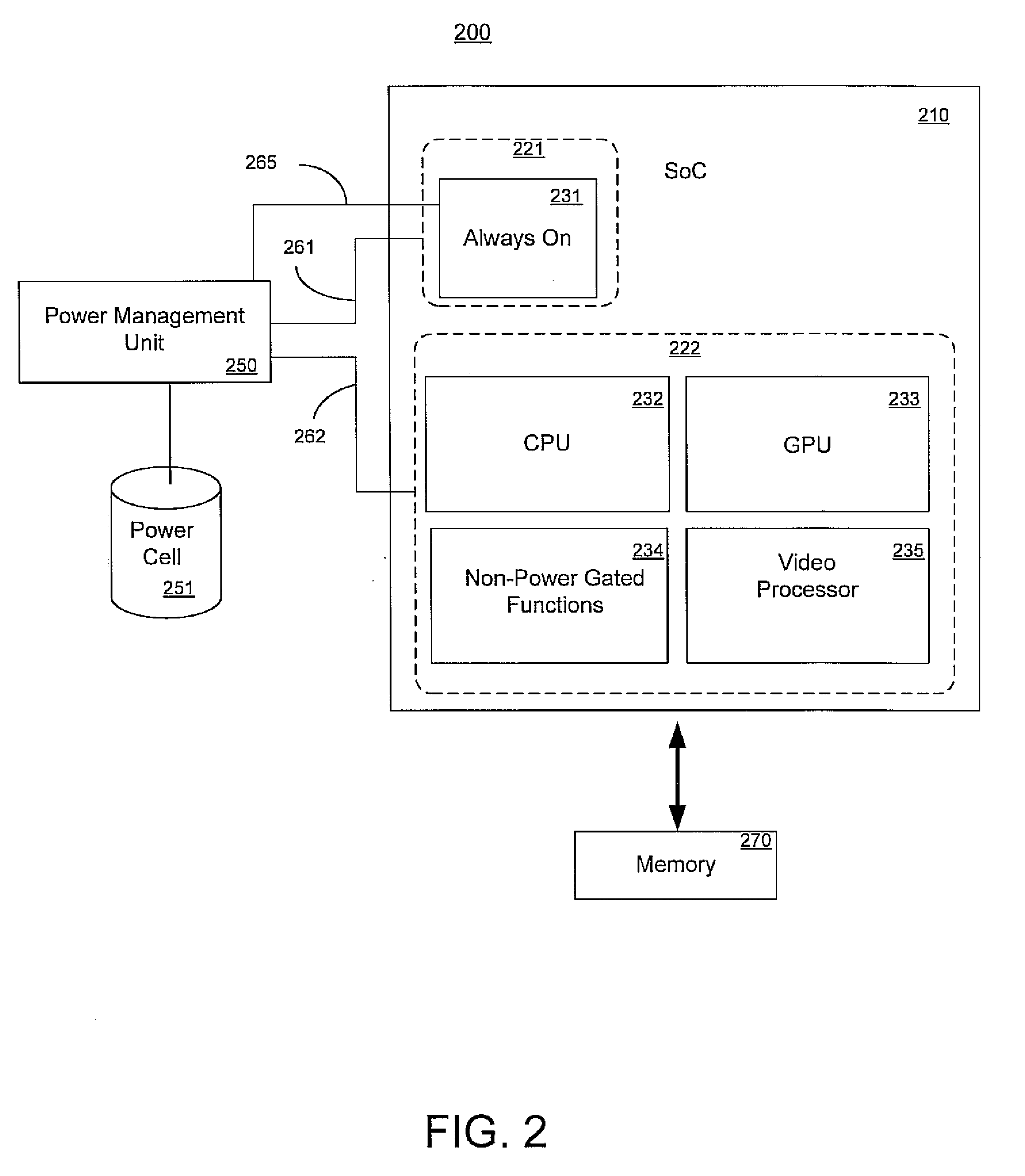
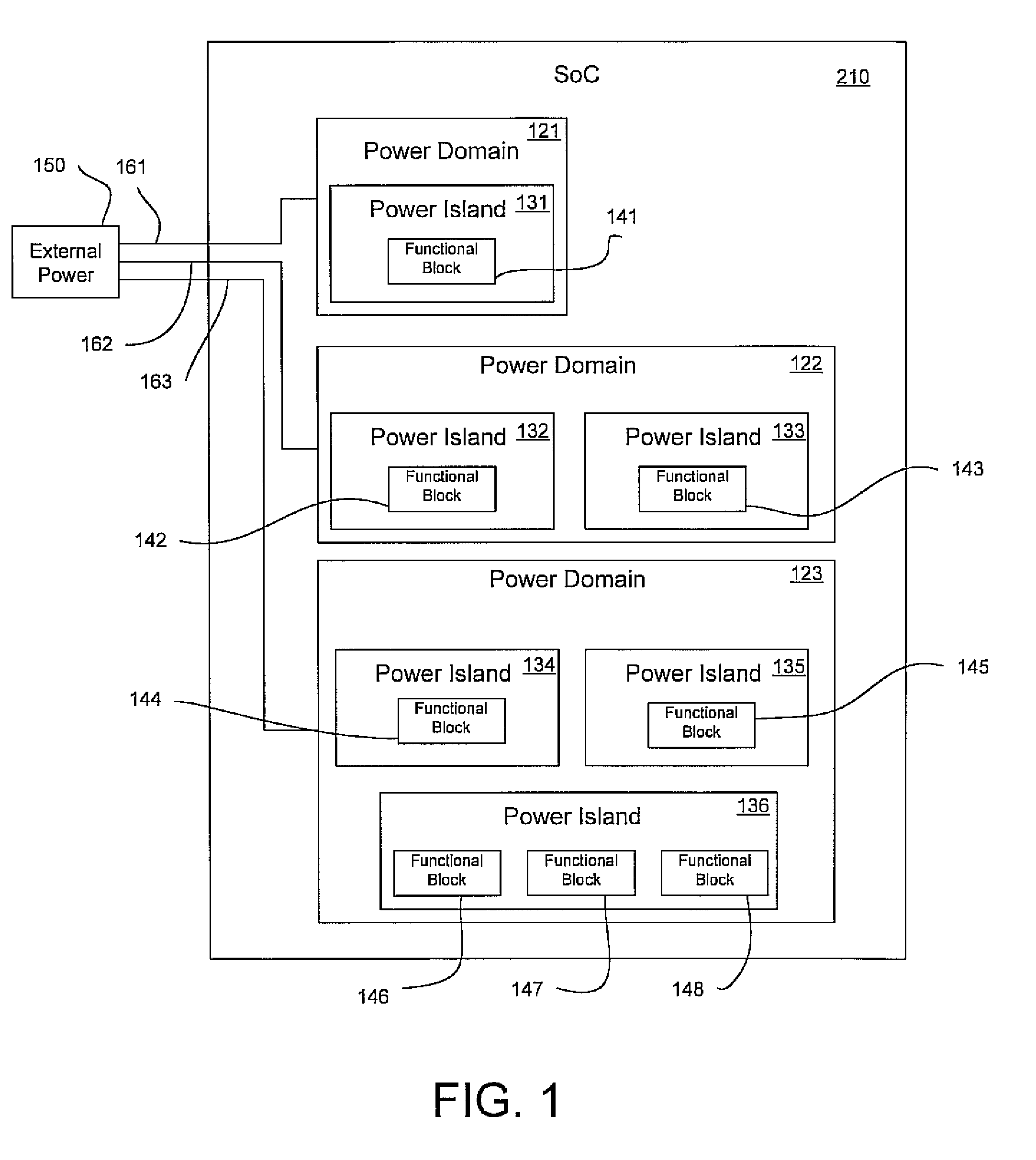
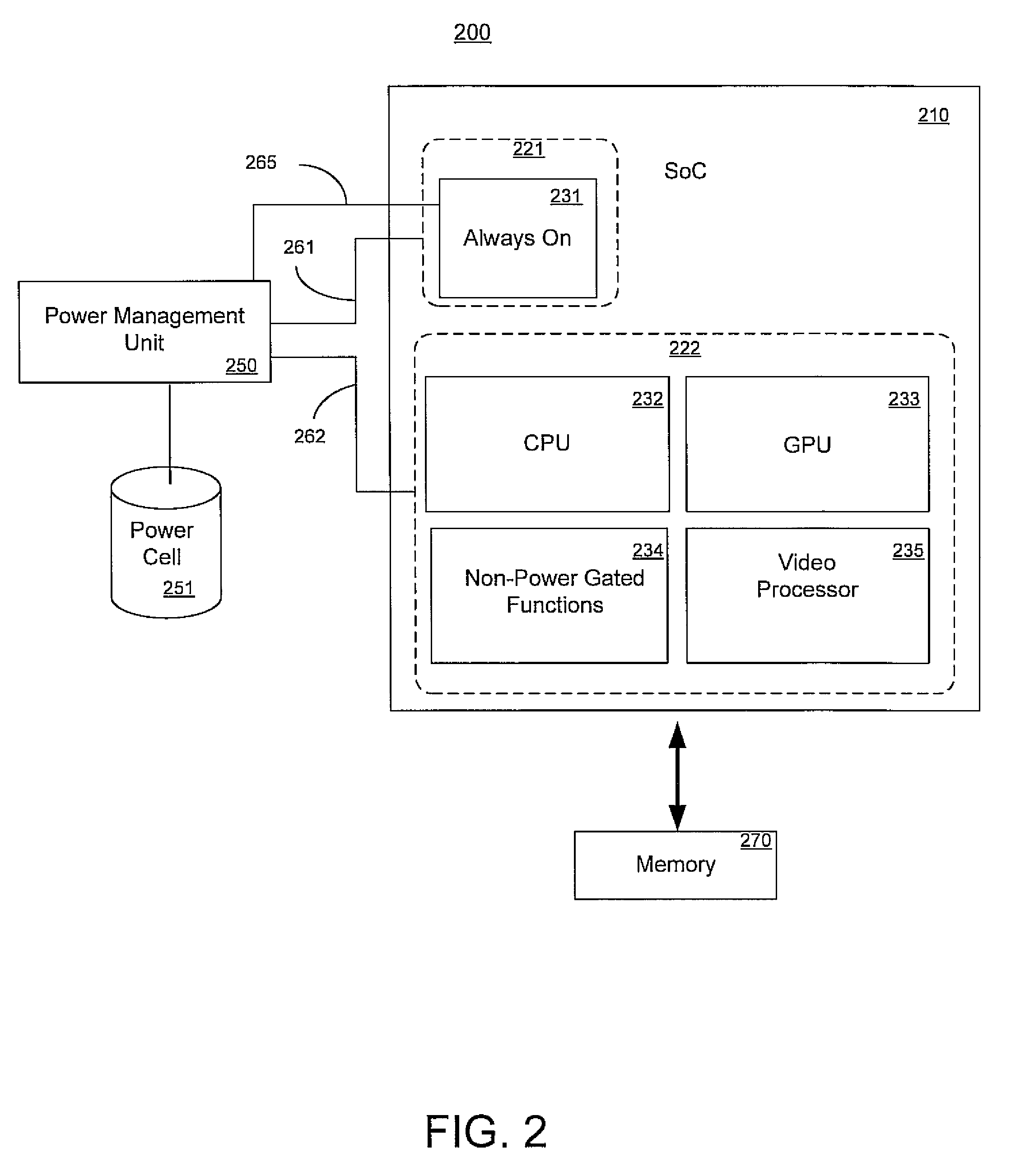
A programmable SoC (system on a chip) having optimized power domains and power islands. The SoC is an integrated circuit device including a plurality of power domains, each of the power domains having a respective voltage rail to supply power to the power domain. A plurality of power islands are included within the integrated circuit device, wherein each power domain includes at least one power island. A plurality of functional blocks are included within the integrated circuit device, wherein each power island includes at least one functional block. Each functional block is configured to provide a specific device functionality. The integrated circuit device adjusts power consumption in relation to a requested device functionality by individually turning on or turning off power to a selected one or more power domains, and for each turned on power domain, individually power gating one or more power islands.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
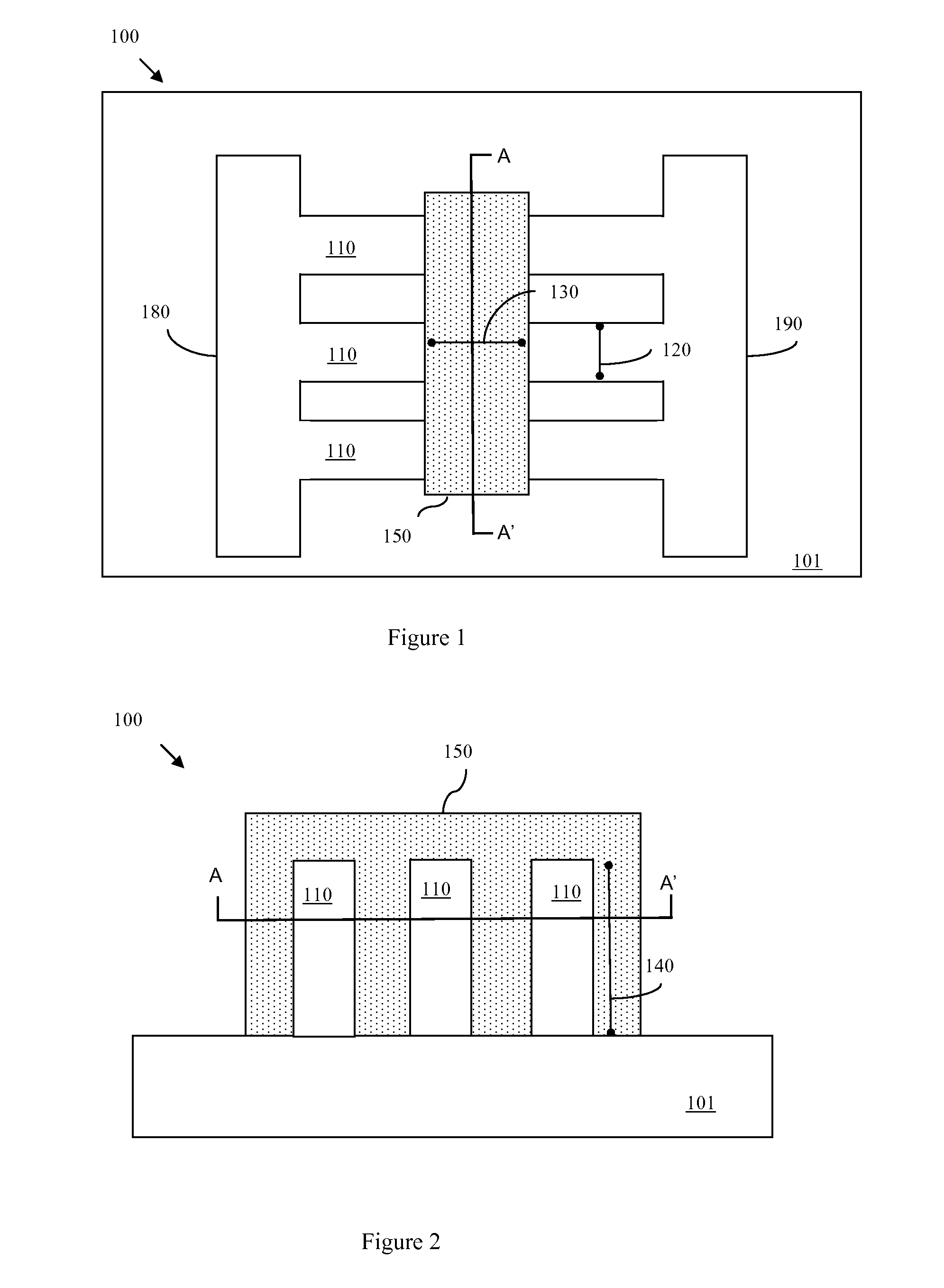
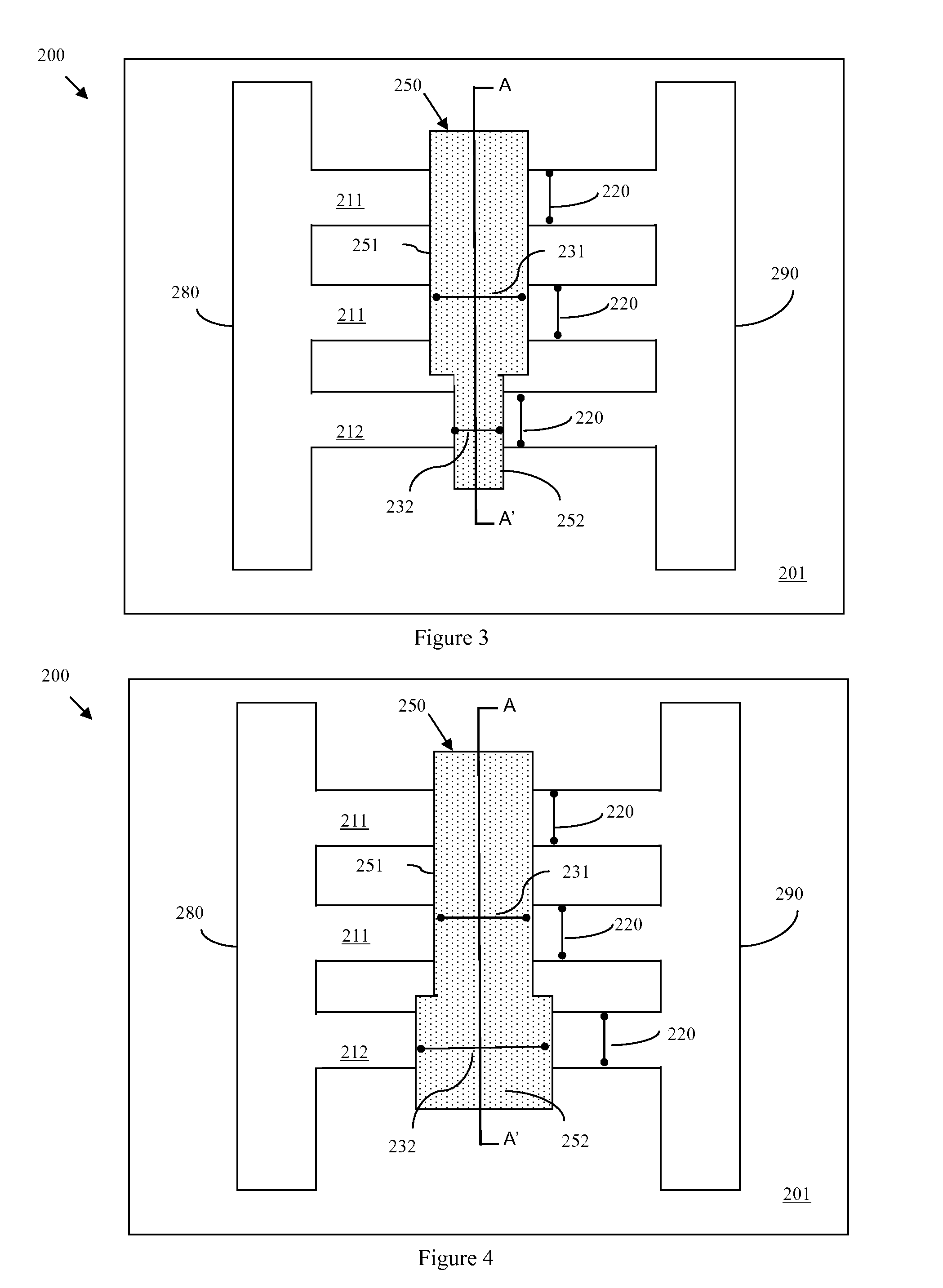
Method of forming a multi-fin multi-gate field effect transistor with tailored drive current
ActiveUS20090209074A1Tailored drive currentIncrease width of deviceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentChannel width
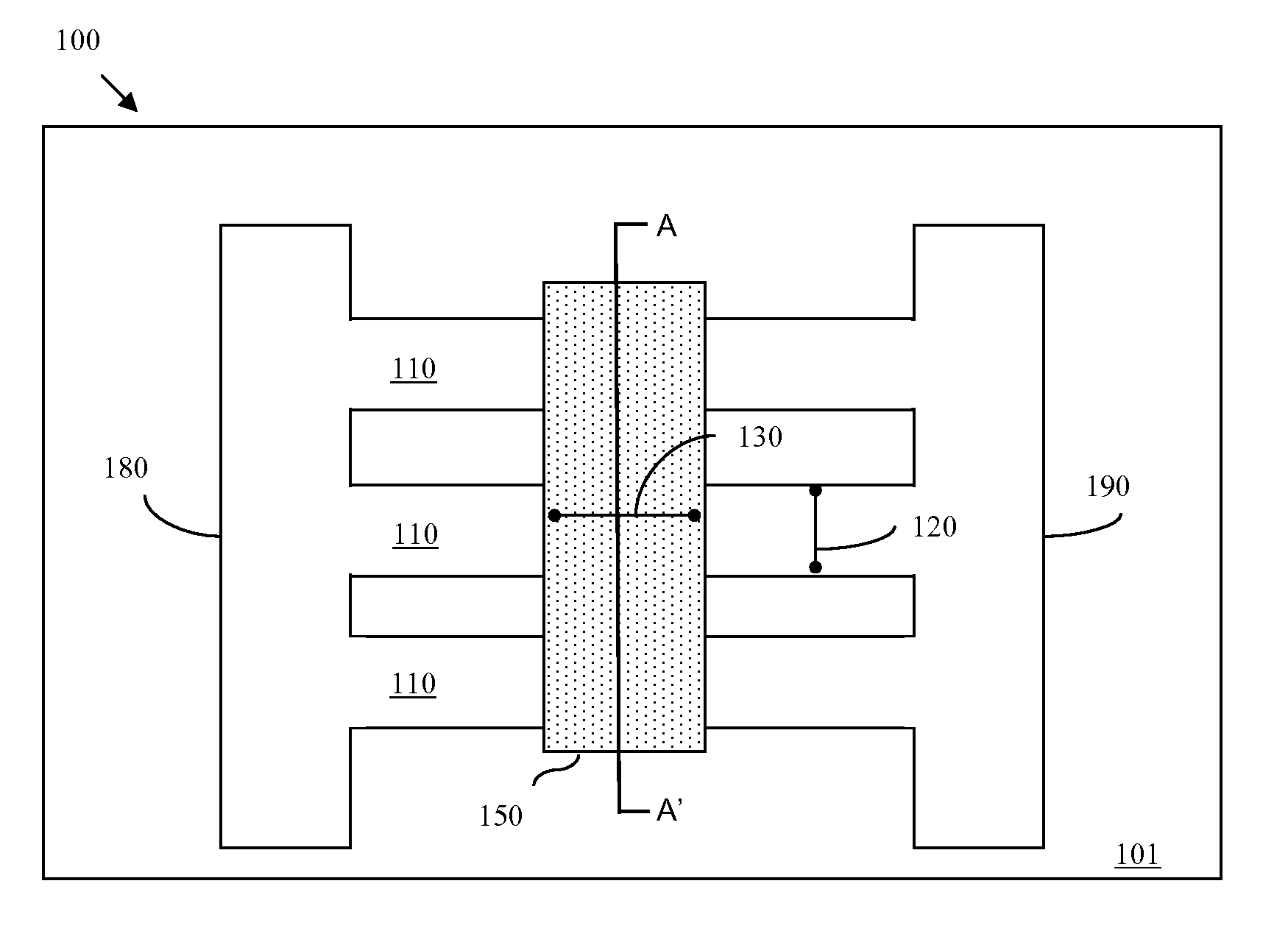
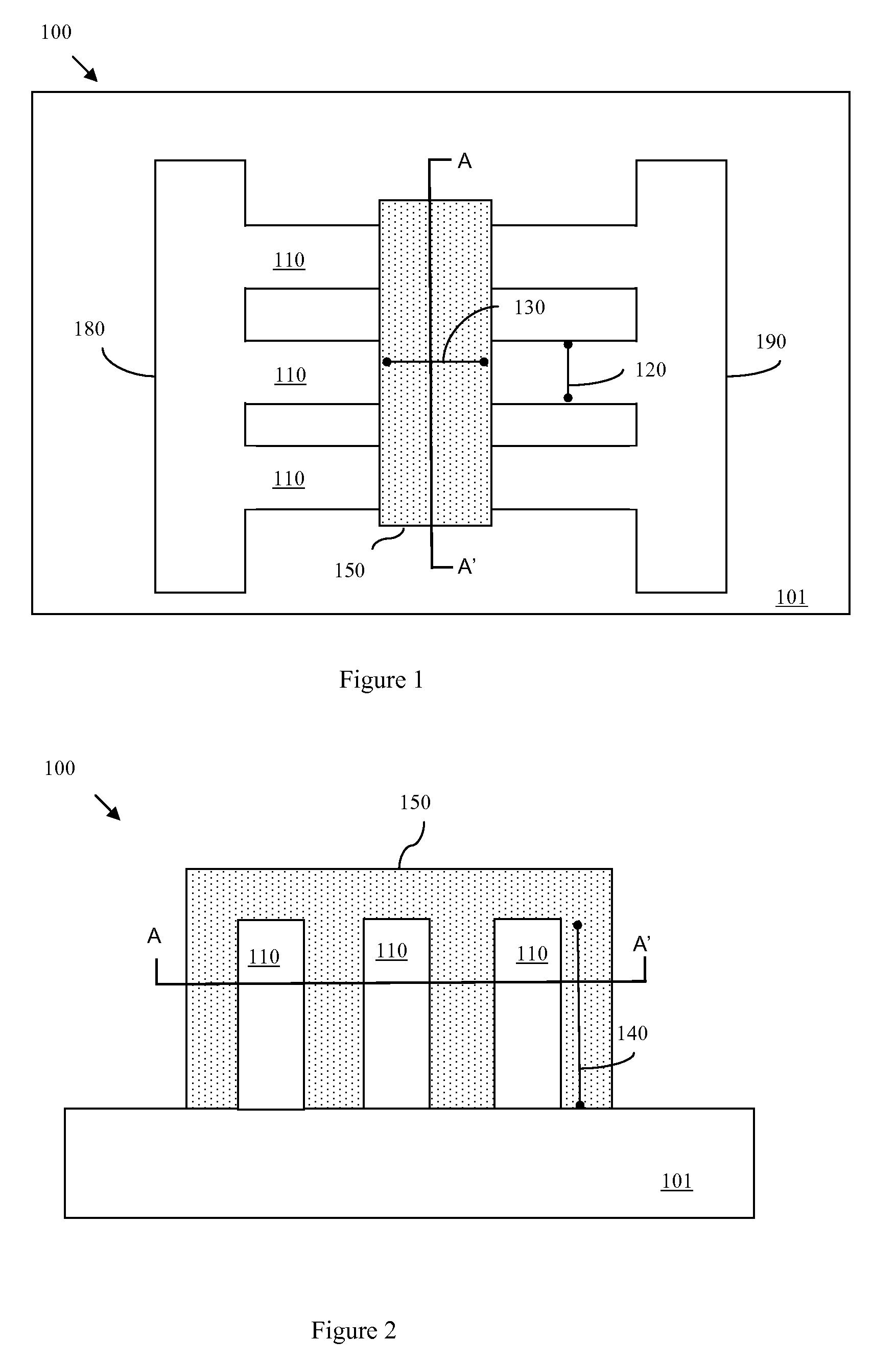
Disclosed are embodiments of an improved multi-gated field effect transistor (MUGFET) structure and method of forming the MUGFET structure so that it exhibits a more tailored drive current. Specifically, the MUGFET incorporates multiple semiconductor fins in order to increase effective channel width of the device and, thereby, to increase the drive current of the device. Additionally, the MUGFET incorporates a gate structure having different sections with different physical dimensions relative to the semiconductor fins in order to more finely tune device drive current (i.e., to achieve a specific drive current). Optionally, the MUGFET also incorporates semiconductor fins with differing widths in order to minimize leakage current caused by increases in drive current.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
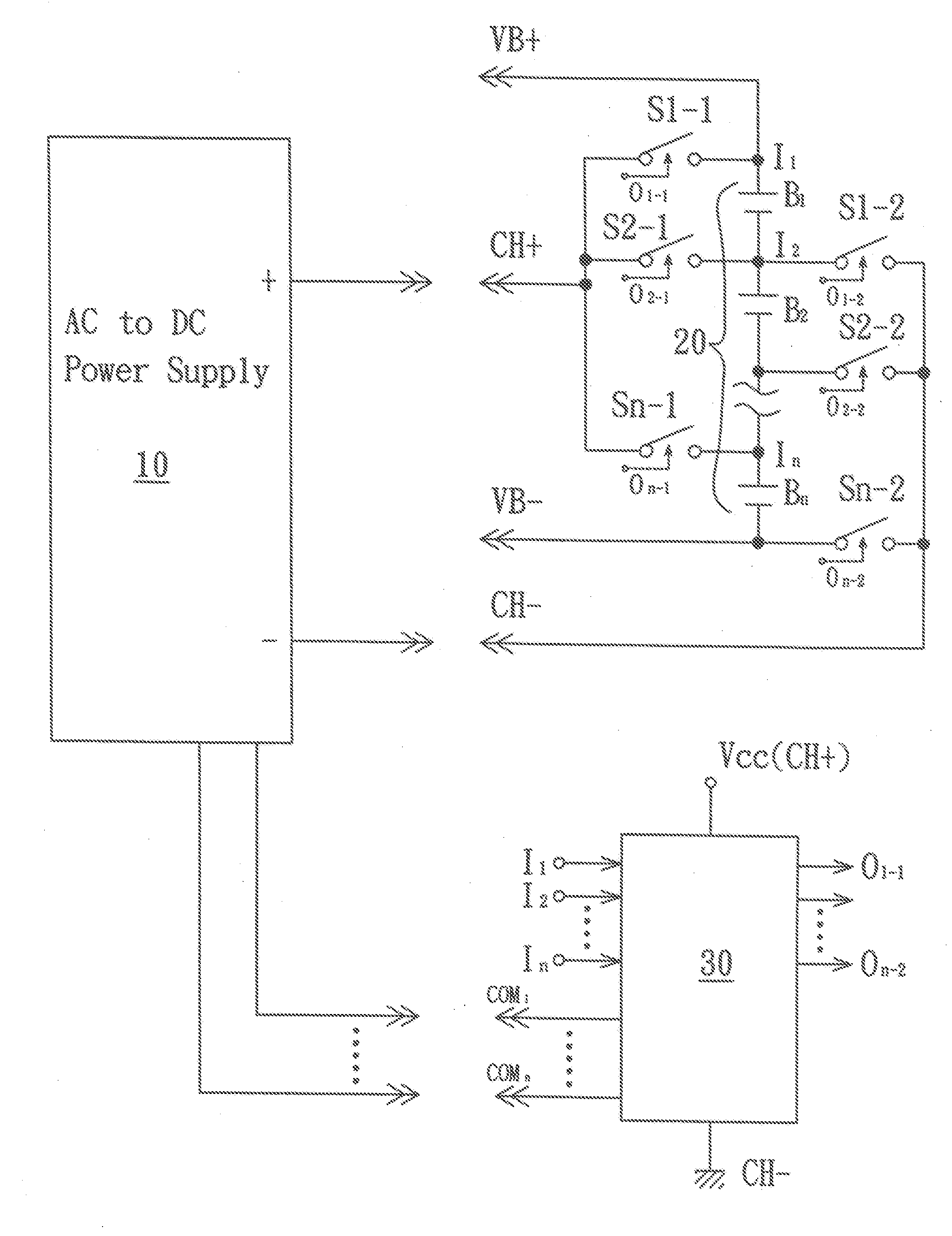
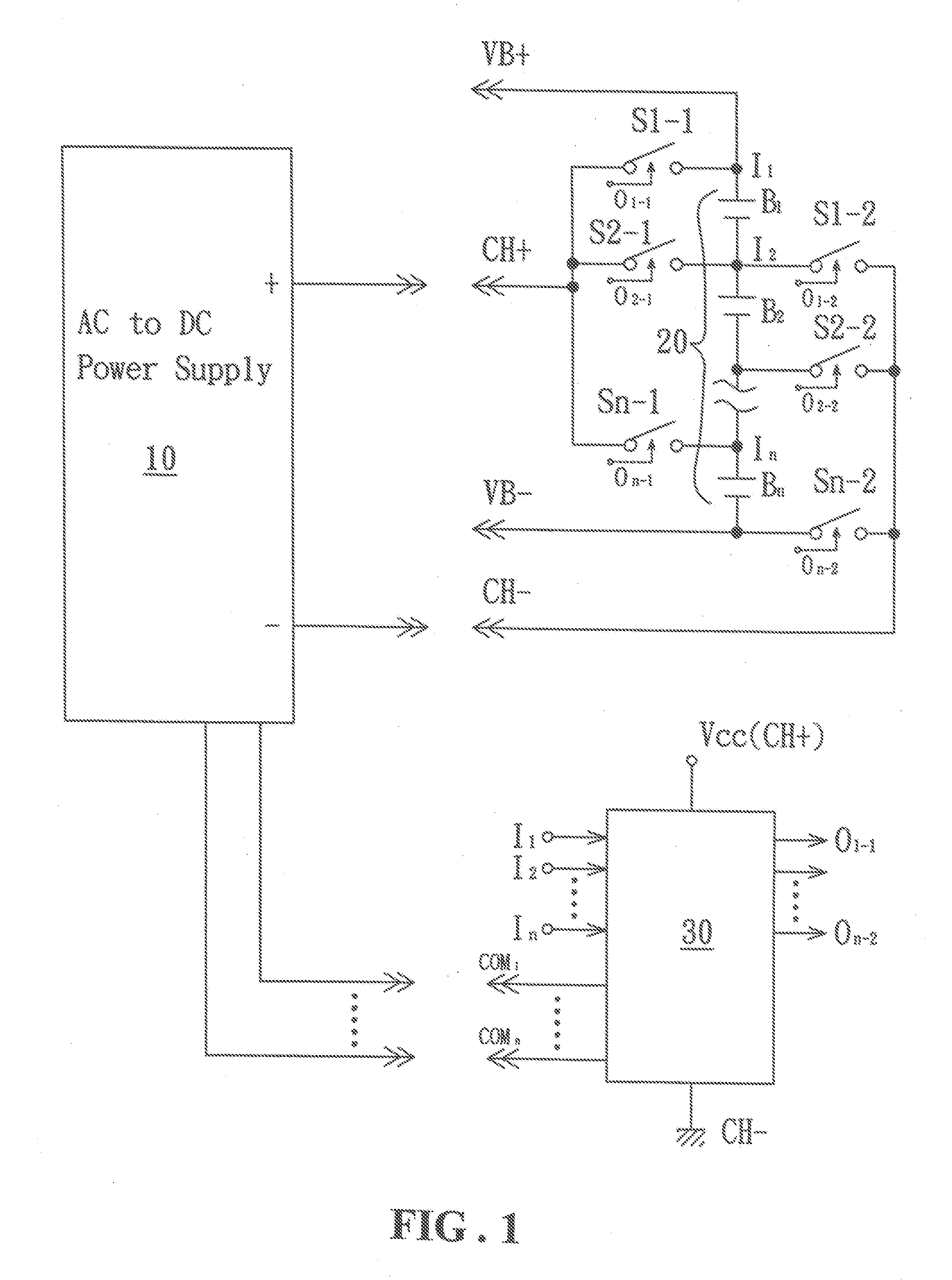
Balanced charging/discharging circuit for lithium battery set
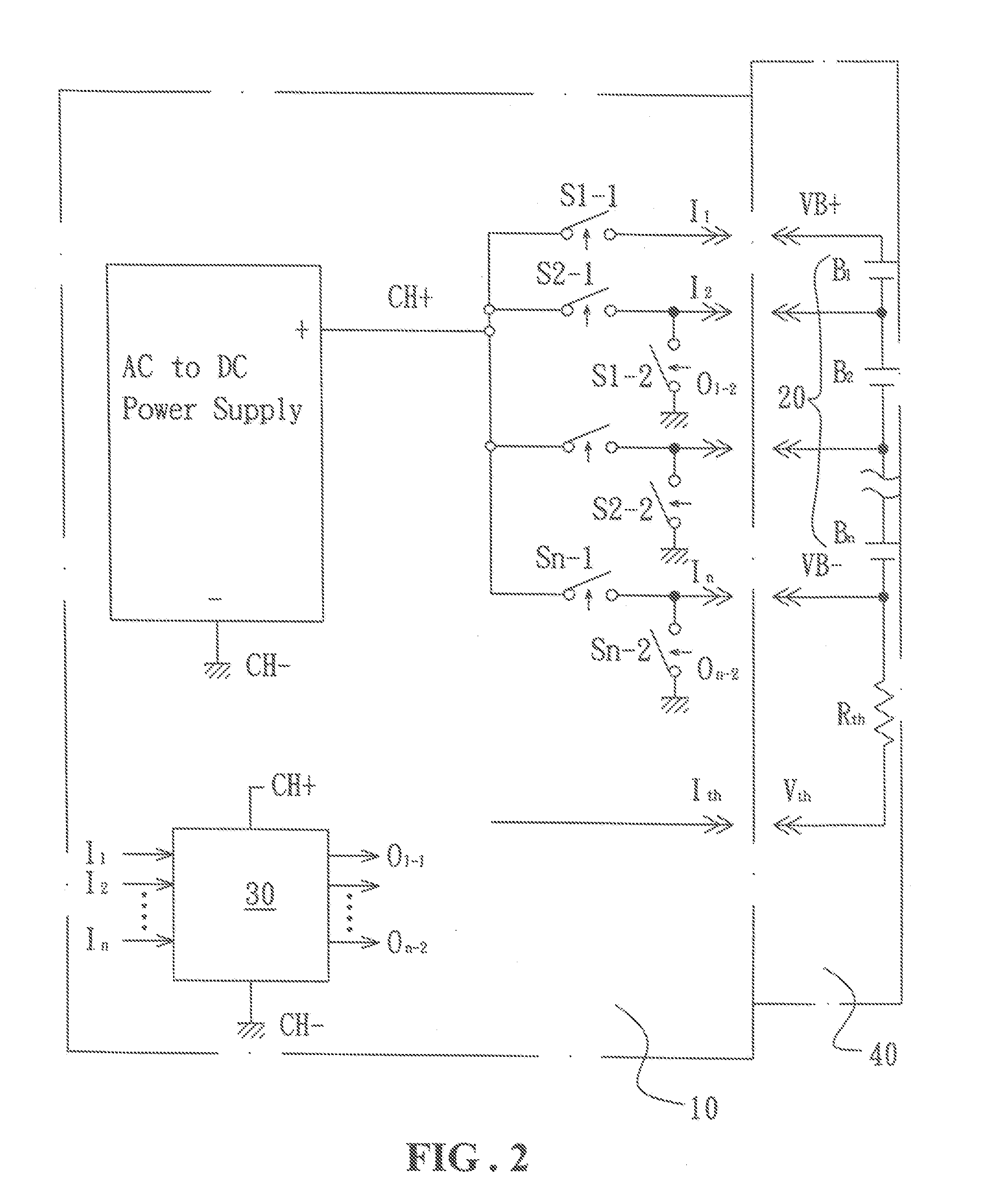
InactiveUS20090091295A1Reduce riskMinimize leakage currentParallel/serial switchingSafety/protection battery circuitsBattery chargeControl signal
A balanced charging / discharging circuit for a lithium battery set, including a plurality of serially connected lithium batteries each having a positive electrode controlled by a corresponding control signal to selectively establish connection with a positive electrode of a battery charging circuit, and a negative electrode controlled by a corresponding control signal to selectively establish connection with a negative electrode of the battery charging circuit. Voltage of the positive and negative electrodes of each of the serially connected lithium batteries is transmitted to a corresponding terminal of a control circuit respectively so that the control circuit generates a corresponding transfer signal to the battery charging circuit and supplies the control signal to establish connection of a corresponding series of lithium batteries for charging. Battery sets arranged in series or in parallel can be charged with the maximum current and the service life is extended and charging time is shortened.
Owner:WAN WEI LIANG
DRAM with nanofin transistors
ActiveUS20070228433A1Minimize drain leakage currentImprove DRAM retention timeTransistorNanoinformaticsBit lineSubject matter
One aspect of the present subject matter relates to a memory. A memory embodiment includes a nanofin transistor having a first source / drain region, a second source / drain region above the first source / drain region, and a vertically-oriented channel region between the first and second source / drain regions. The nanofin transistor also has a surrounding gate insulator around the nanofin structure and a surrounding gate surrounding the channel region and separated from the nanofin channel by the surrounding gate insulator. The memory includes a data-bit line connected to the first source / drain region, at least one word line connected to the surrounding gate of the nanofin transistor, and a stacked capacitor above the nanofin transistor and connected between the second source / drain region and a reference potential. Other aspects are provided herein.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Multi-fin multi-gate field effect transistor with tailored drive current
ActiveUS20090206374A1Tailored drive currentIncrease width of deviceTransistorSolid-state devicesDriving currentField-effect transistor
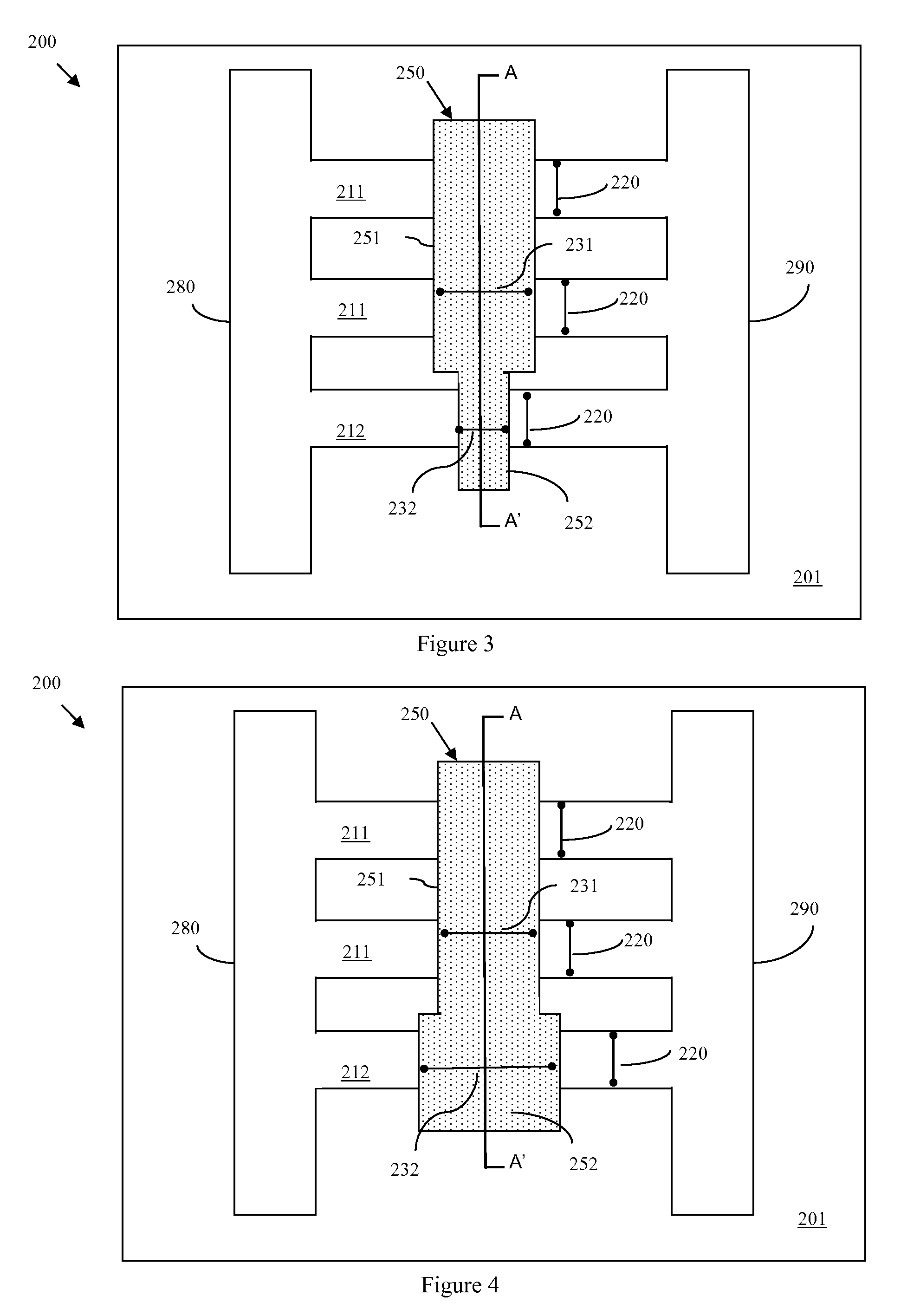
Disclosed are embodiments of an improved multi-gated field effect transistor (MUGFET) structure and method of forming the MUGFET structure so that it exhibits a more tailored drive current. Specifically, the MUGFET incorporates multiple semiconductor fins in order to increase effective channel width of the device and, thereby, to increase the drive current of the device. Additionally, the MUGFET incorporates a gate structure having different sections with different physical dimensions relative to the semiconductor fins in order to more finely tune device drive current (i.e., to achieve a specific drive current). Optionally, the MUGFET also incorporates semiconductor fins with differing widths in order to minimize leakage current caused by increases in drive current.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method of forming a multi-fin multi-gate field effect transistor with tailored drive current
ActiveUS8022478B2Increase widthEasy to tuneSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentEngineering
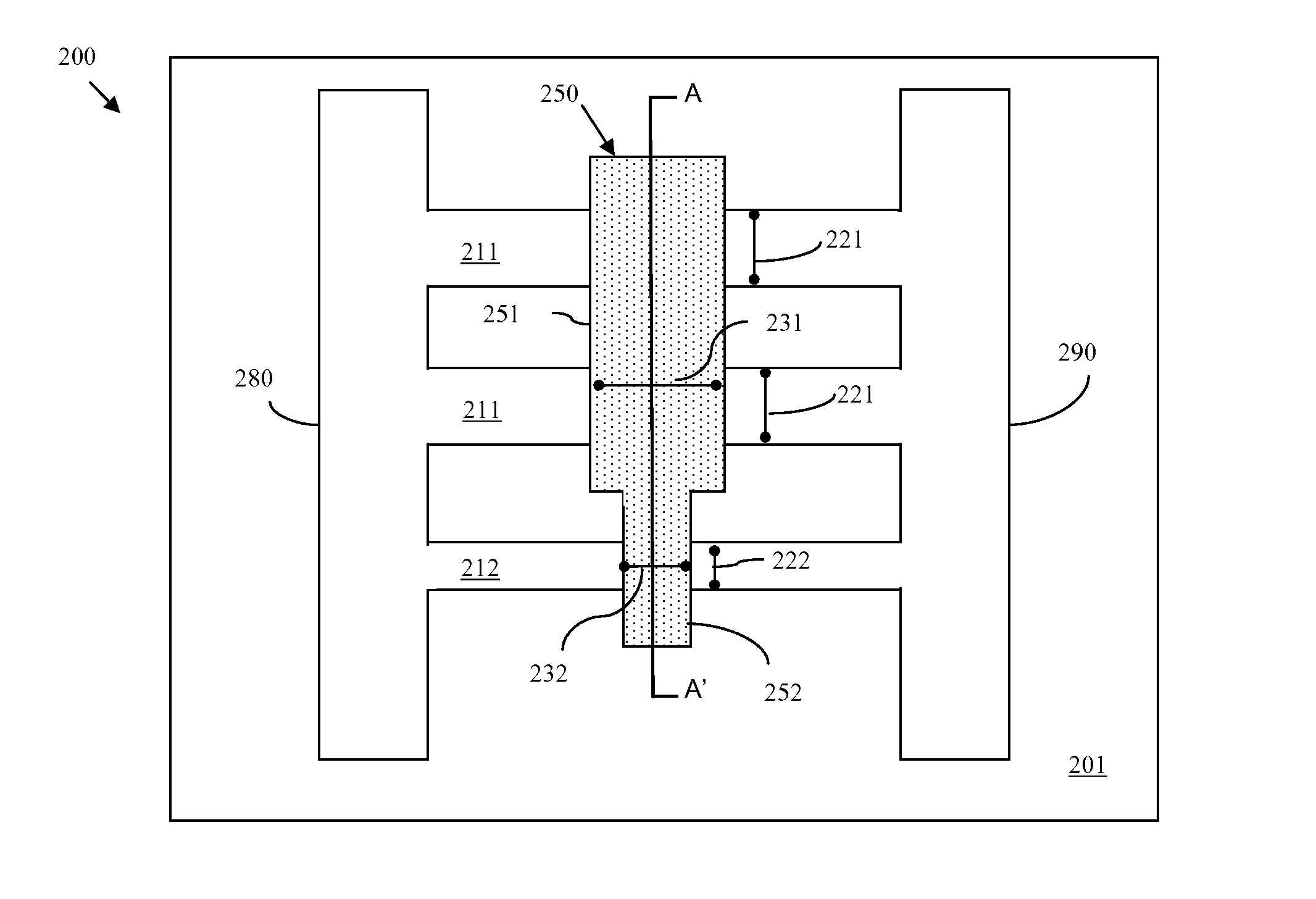
Disclosed are embodiments of an improved multi-gated field effect transistor (MUGFET) structure and method of forming the MUGFET structure so that it exhibits a more tailored drive current. Specifically, the MUGFET incorporates multiple semiconductor fins in order to increase effective channel width of the device and, thereby, to increase the drive current of the device. Additionally, the MUGFET incorporates a gate structure having different sections with different physical dimensions relative to the semiconductor fins in order to more finely tune device drive current (i.e., to achieve a specific drive current). Optionally, the MUGFET also incorporates semiconductor fins with differing widths in order to minimize leakage current caused by increases in drive current.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
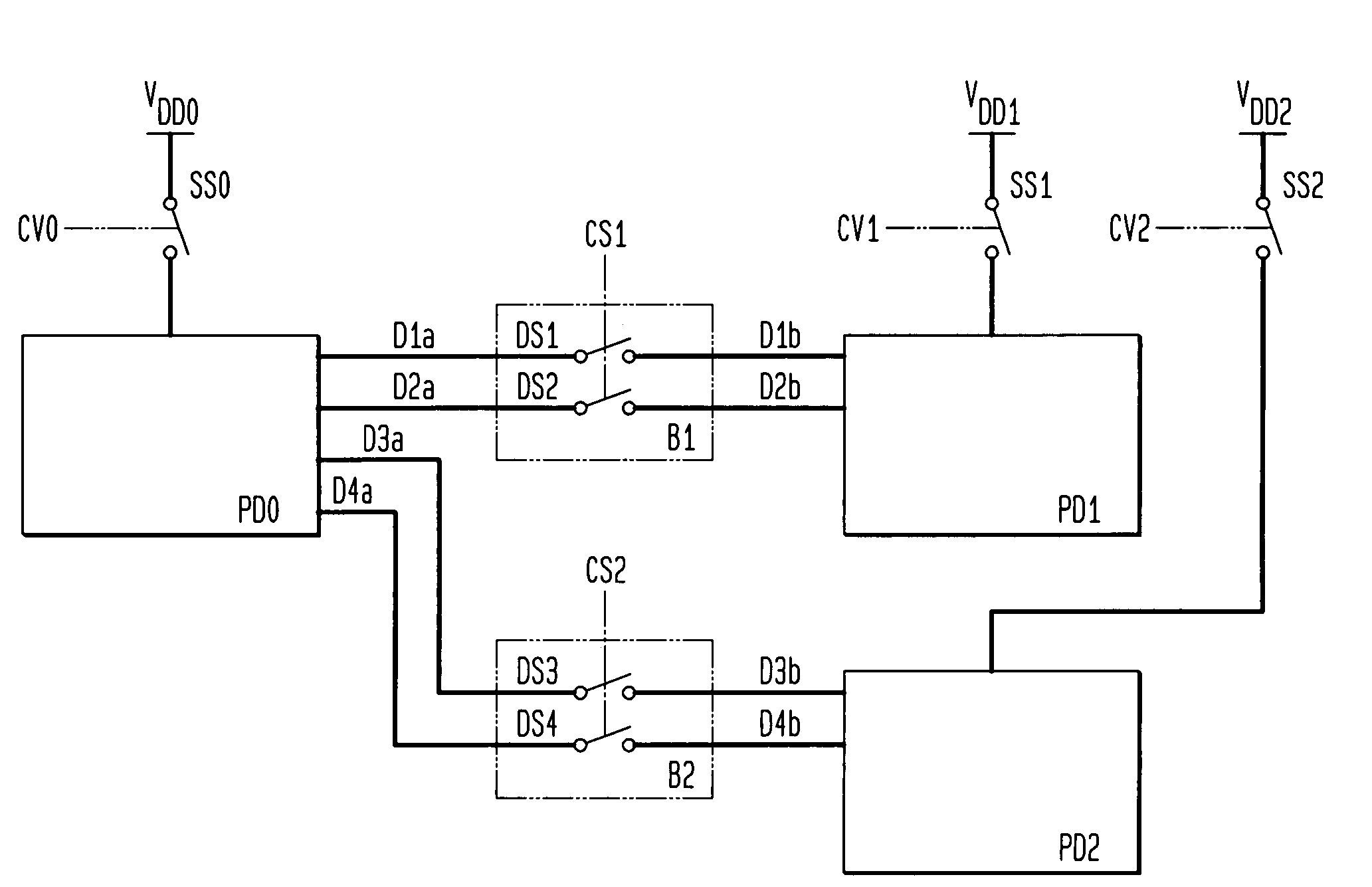
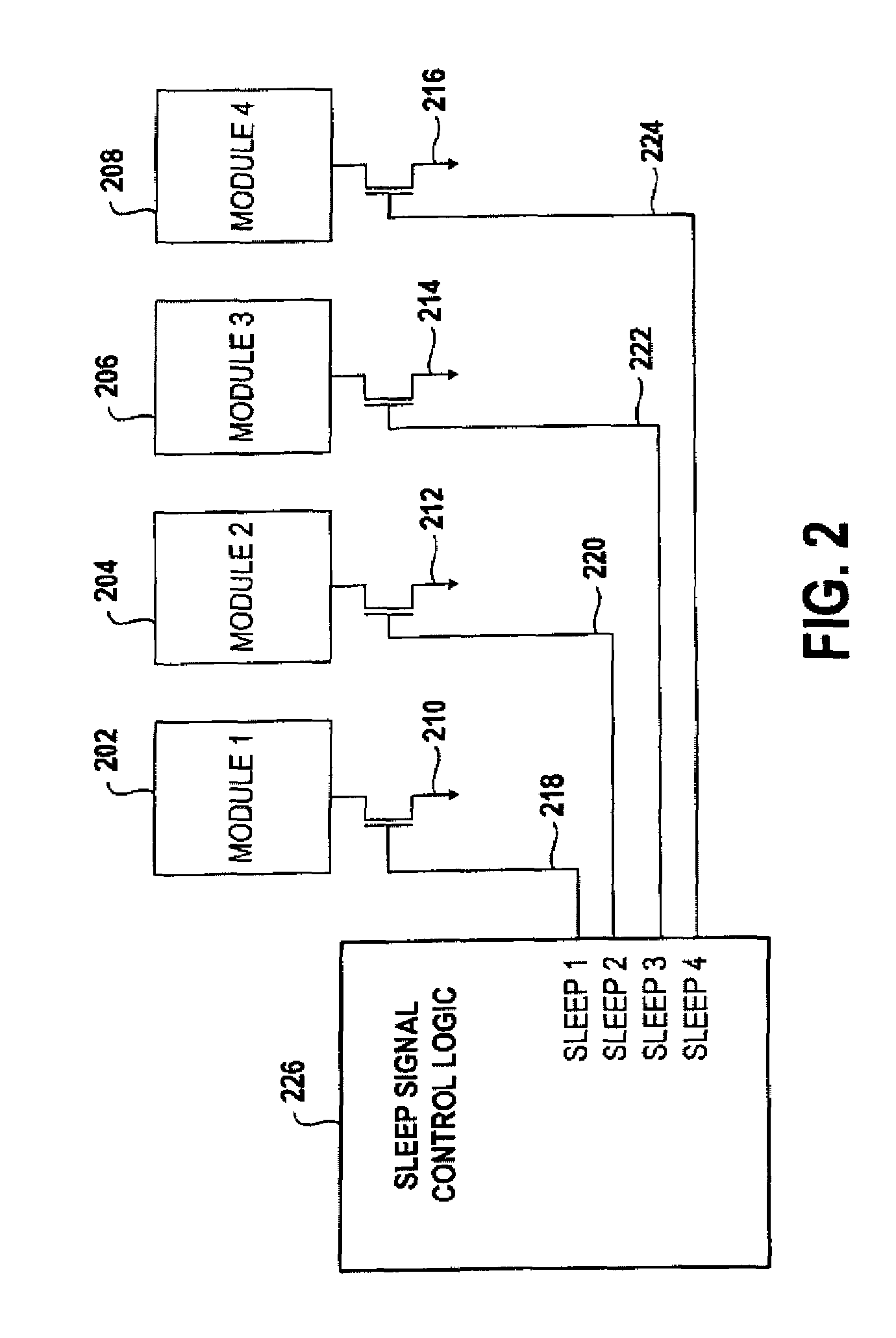
Integrated circuit with multiple power domains
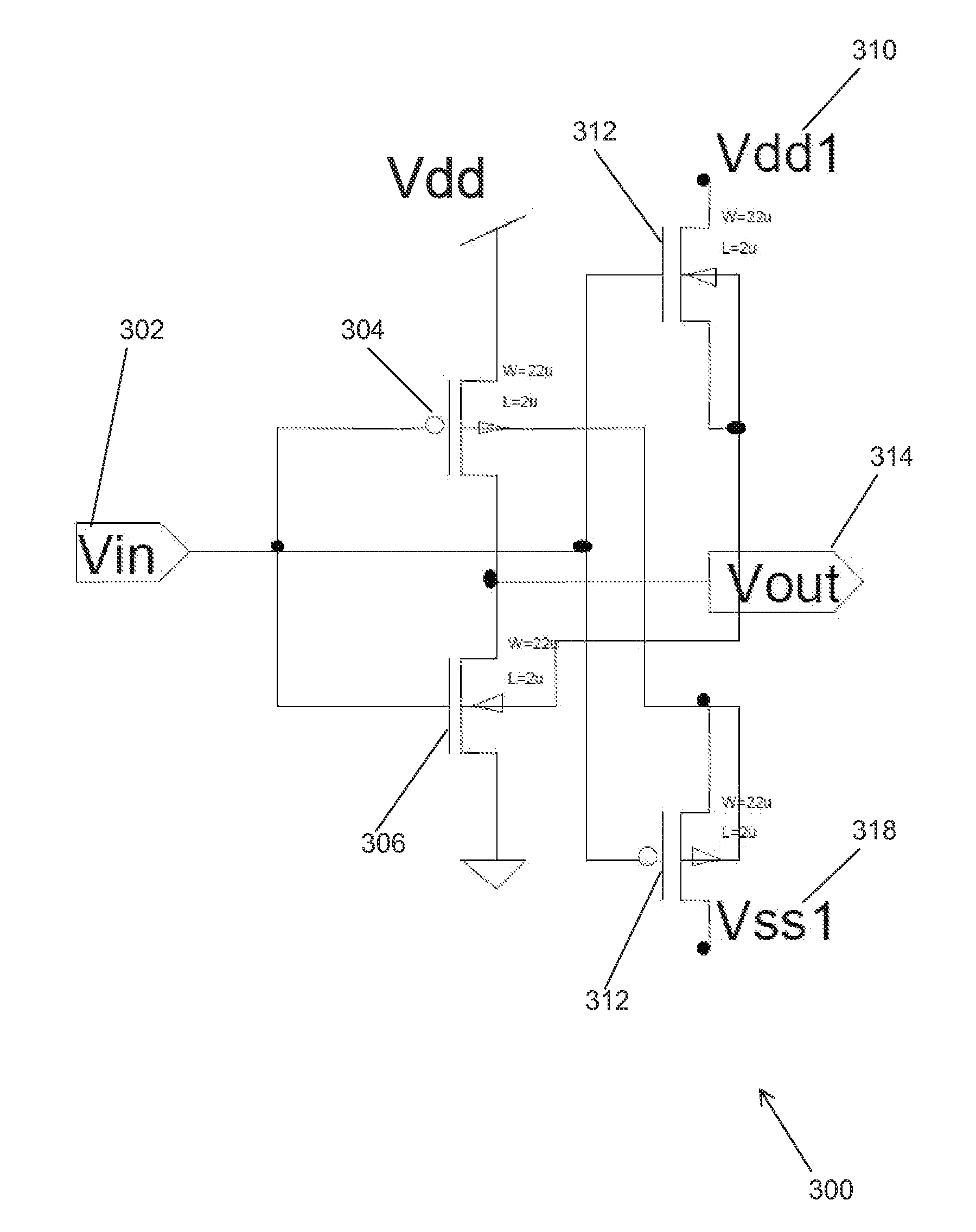
ActiveUS7279927B2Minimize leakage currentSave powerReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLoad circuitData signal
An integrated circuit having two or more power domains that include load circuits in different portions of the integrated circuit is disclosed. In order to conserve power, the circuits in one of the power domains are shut down by disconnecting the power source serving that domain. The load circuits in each power domain are buffered from the load circuits in other power domains by buffer cells. The buffer cells reduce leakage currents in the power domain that is shut down, by restricting data signals from the “live” power domain from reaching the shut-down power domain, and further by providing predetermined voltage signals to the load circuits in the shut-down power domain that are selected to minimize leakage currents in the inactive load circuits. The invention further provides a corresponding method for reducing power consumption in an integrated circuit having at least two power domains separated by a buffer cell.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
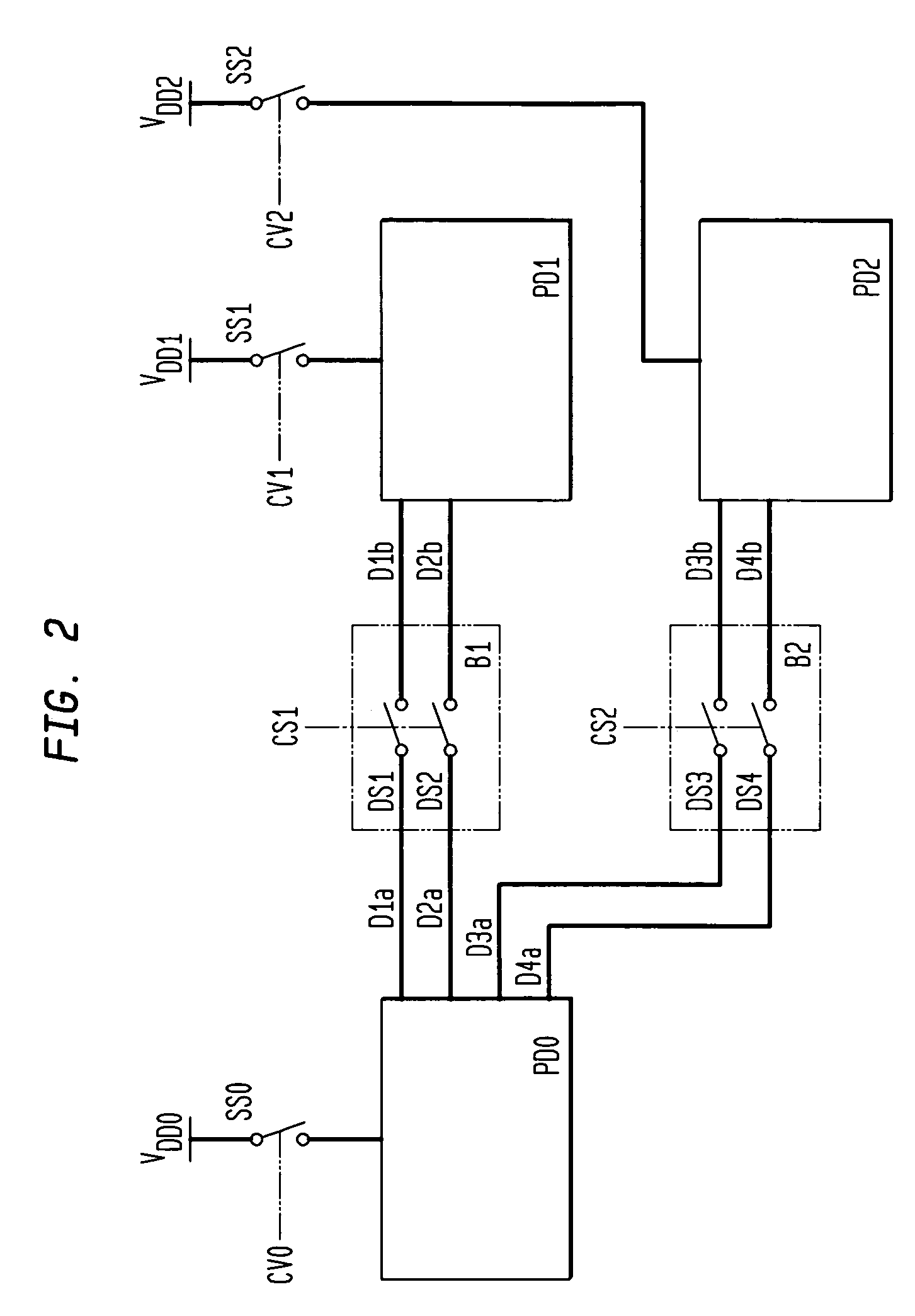
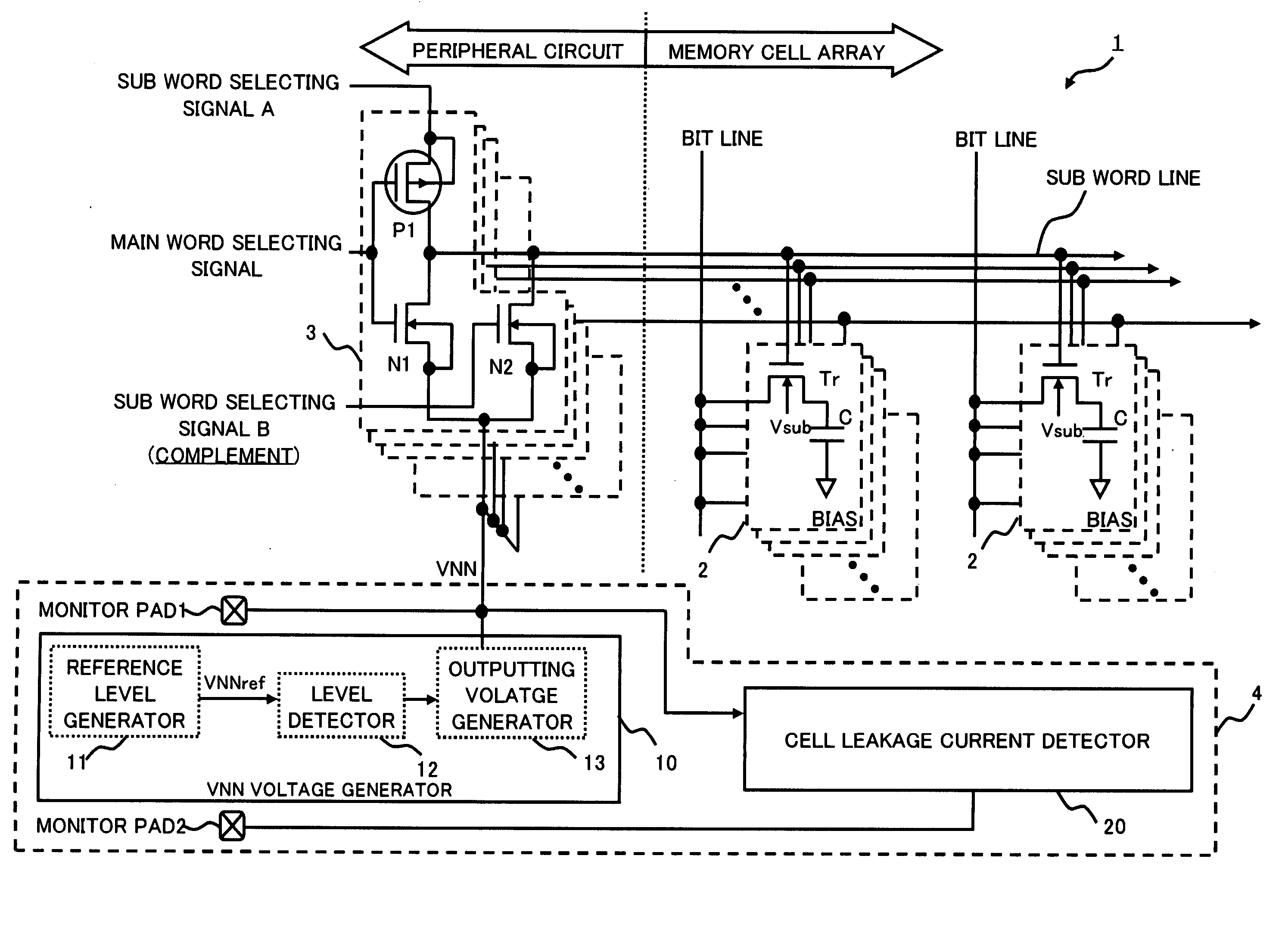
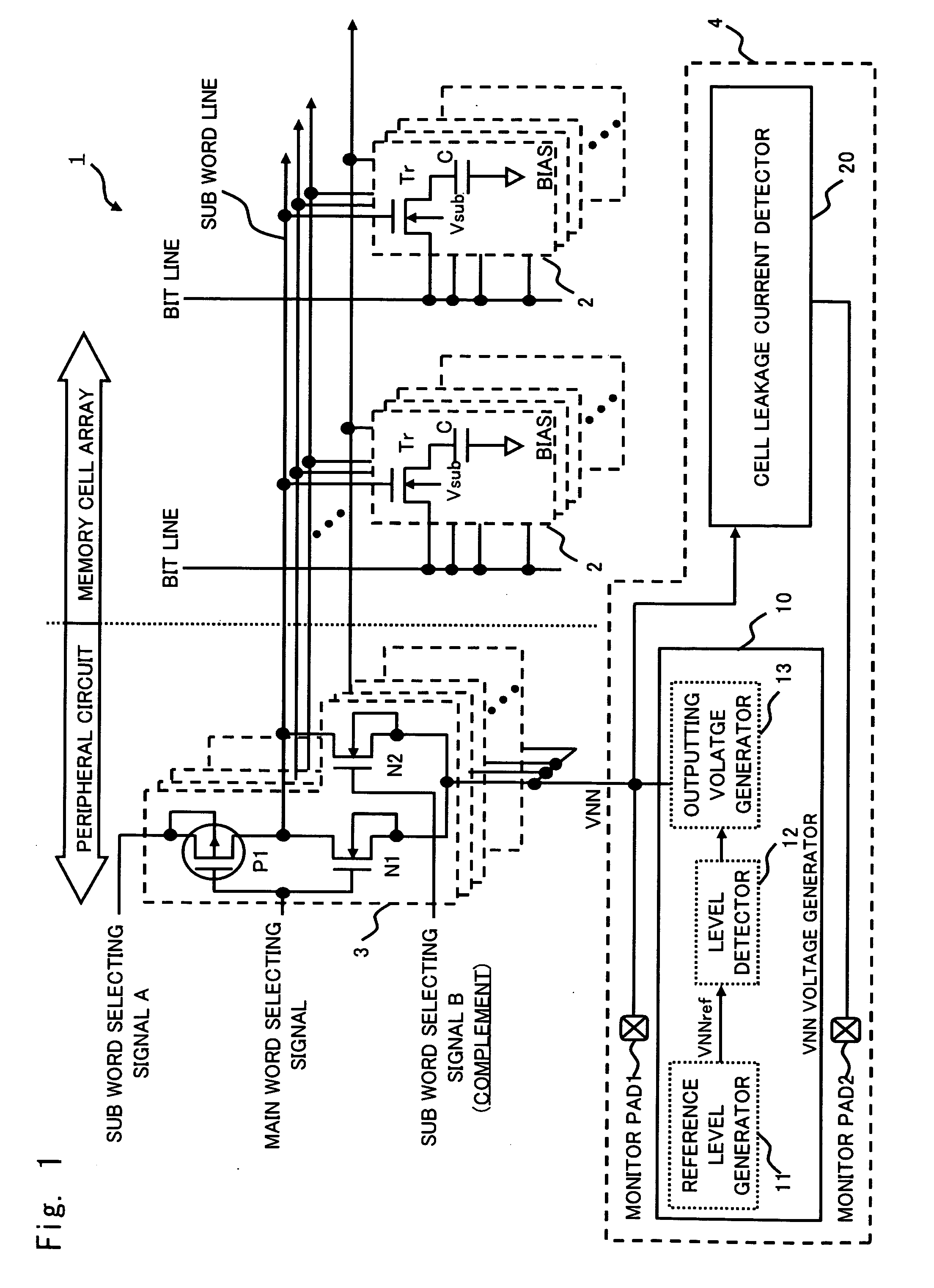
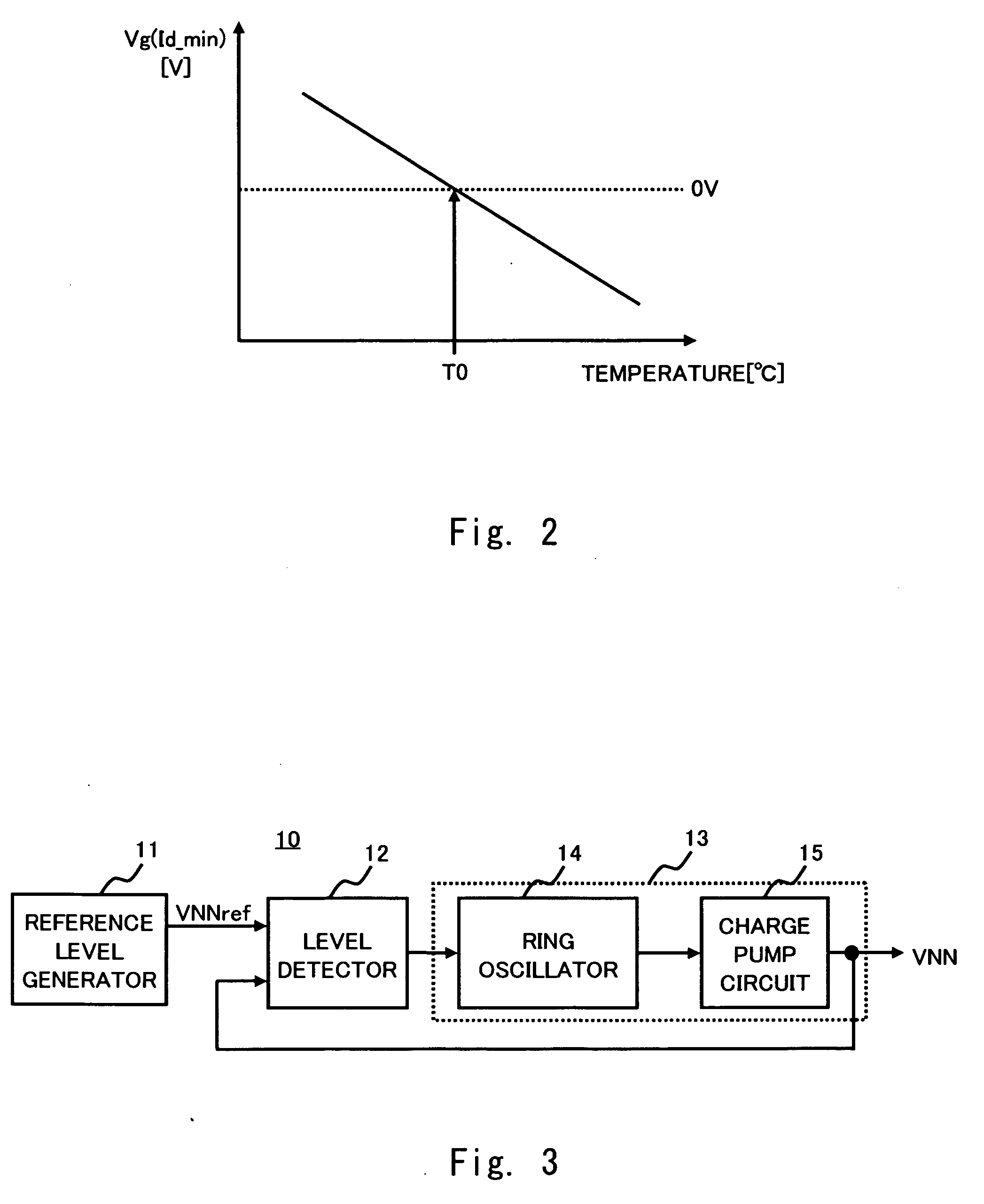
InactiveUS20070109700A1MinimizeMinimise currentDigital storageElectric pulse generator detailsEngineeringDrain current
The semiconductor integrated circuit device includes a voltage control circuit that generates a control voltage for deactivating a field effect transistor by a gate voltage. The voltage control circuit controls a voltage so as to substantially minimize the leakage current which flows when the field effect transistor is inactive with respect to a device temperature.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Array substrate for liquid crystal display device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080122767A1Avoid noiseMinimize leakage currentStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesLiquid-crystal displayOhmic contact
An array substrate for a liquid crystal display device includes a substrate, a gate line on the substrate, a thin film transistor including a gate electrode of the gate line, a gate insulating layer over the gate electrode, an active layer on the gate insulating layer and ohmic contact layers on the active layer, and source and drain electrodes over the ohmic contact layers, a pixel electrode electrically connected to the drain electrode, a data line electrically connected to the source electrode and crossing the gate line, a common electrode spaced apart from the pixel electrode, and a passivation layer directly between the pixel electrode and the common electrode and directly between the source and drain electrodes.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
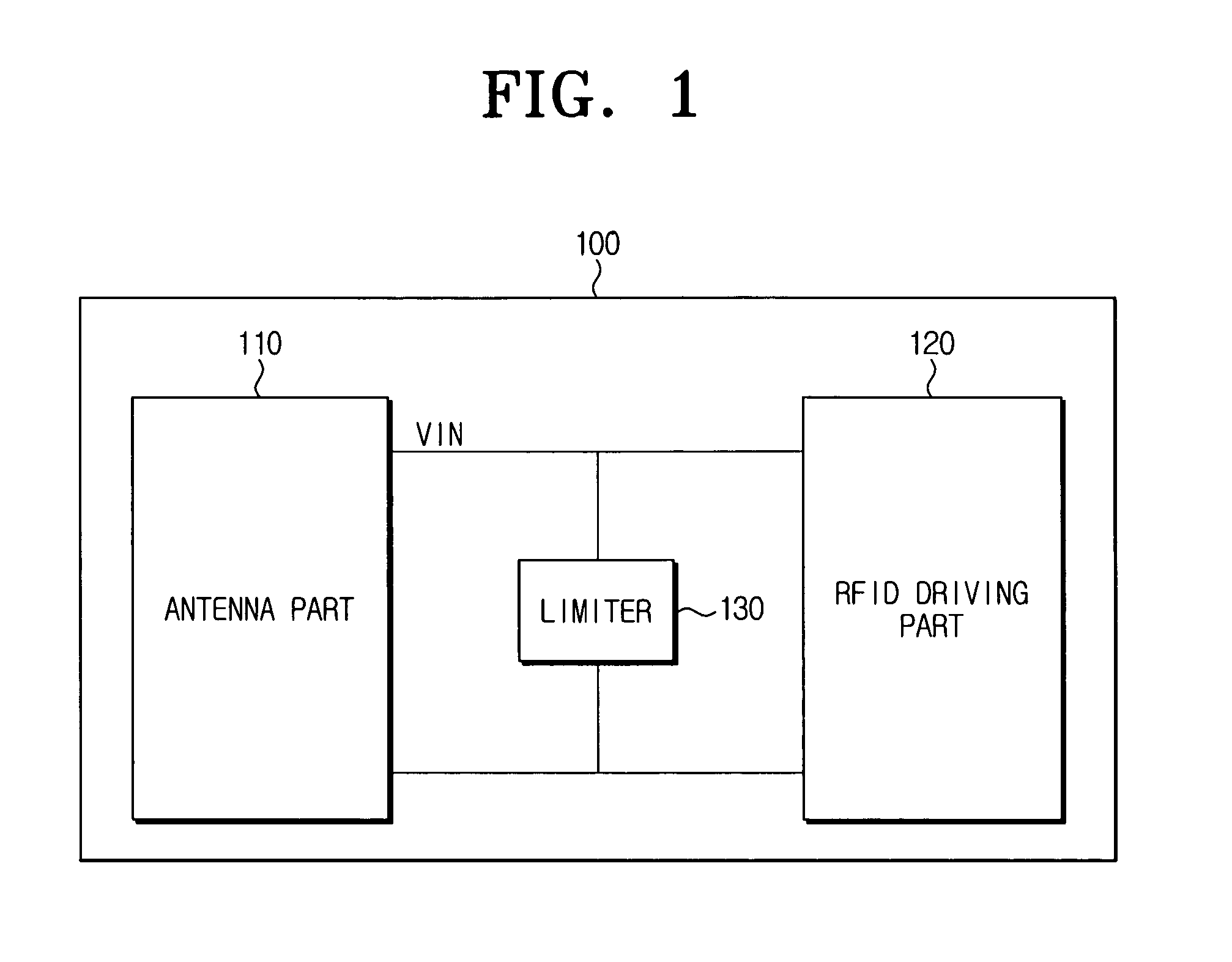
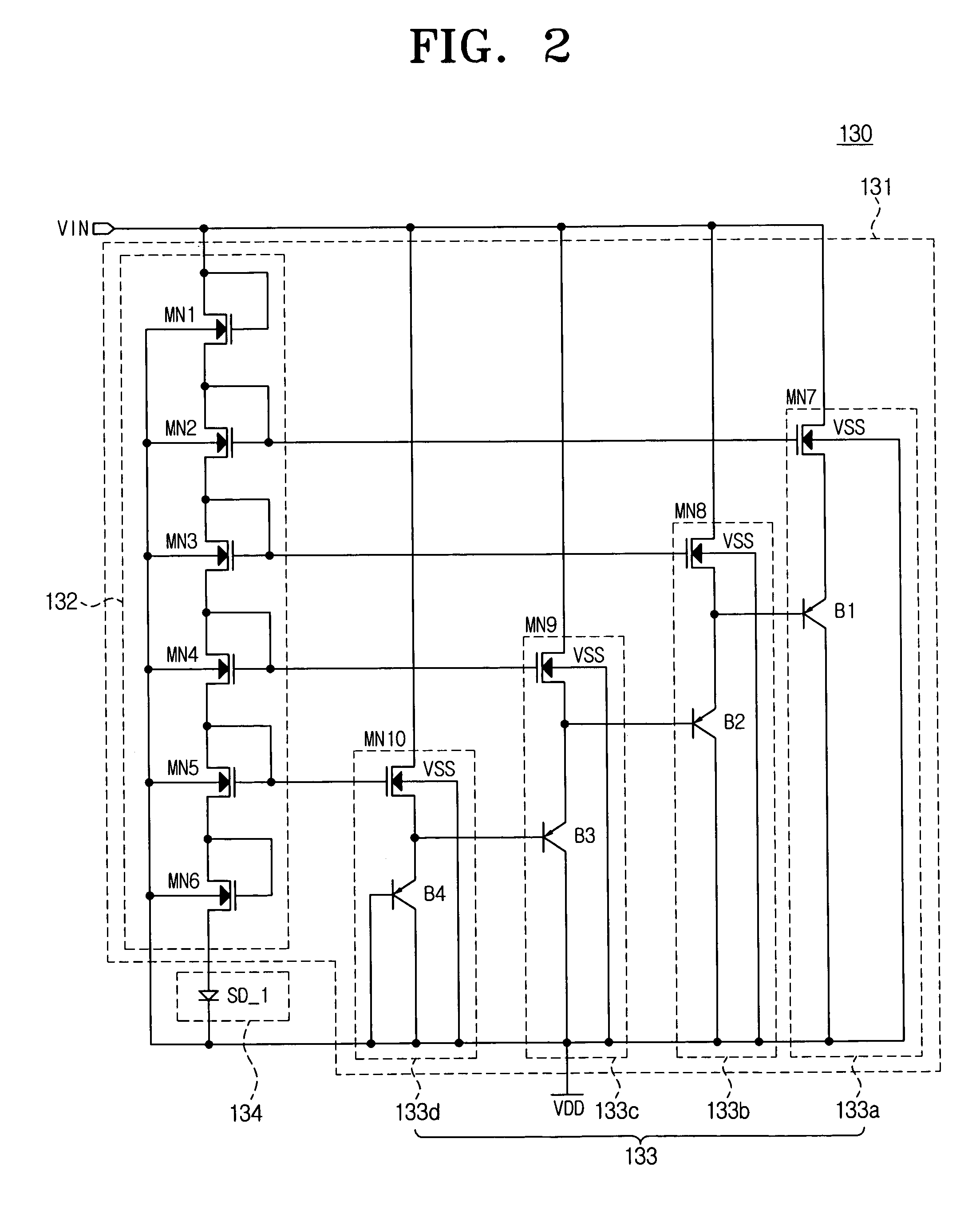
Limiter for controlling overvoltage and RFID tag having the same
ActiveUS7482930B2Maximize leakage currentMinimize leakage currentAc-dc conversion without reversalSubscribers indirect connectionOvervoltageEngineering
A limiter for controlling an overvoltage and an RFID tag having the same are provided. The limiter includes a first limiter part and a second limiter part serially connected to the first limiter part. The second limiter part has at least one limit diode whose threshold voltage is lower than that of elements in the first limiter part. Accordingly, if an overvoltage is input, the limiter can maximize the input current drop so that the limiter can maximize the leakage voltage. As a result, the RFID tag can prevent the RFID driving part from being damaged due to the overvoltage. In addition, the RFID tag can normally operate regardless of the intensity of the driving voltage input from the RFID reader, so that the yields of products can improve.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-fin multi-gate field effect transistor with tailored drive current
Disclosed are embodiments of an improved multi-gated field effect transistor (MUGFET) structure and method of forming the MUGFET structure so that it exhibits a more tailored drive current. Specifically, the MUGFET incorporates multiple semiconductor fins in order to increase effective channel width of the device and, thereby, to increase the drive current of the device. Additionally, the MUGFET incorporates a gate structure having different sections with different physical dimensions relative to the semiconductor fins in order to more finely tune device drive current (i.e., to achieve a specific drive current). Optionally, the MUGFET also incorporates semiconductor fins with differing widths in order to minimize leakage current caused by increases in drive current.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
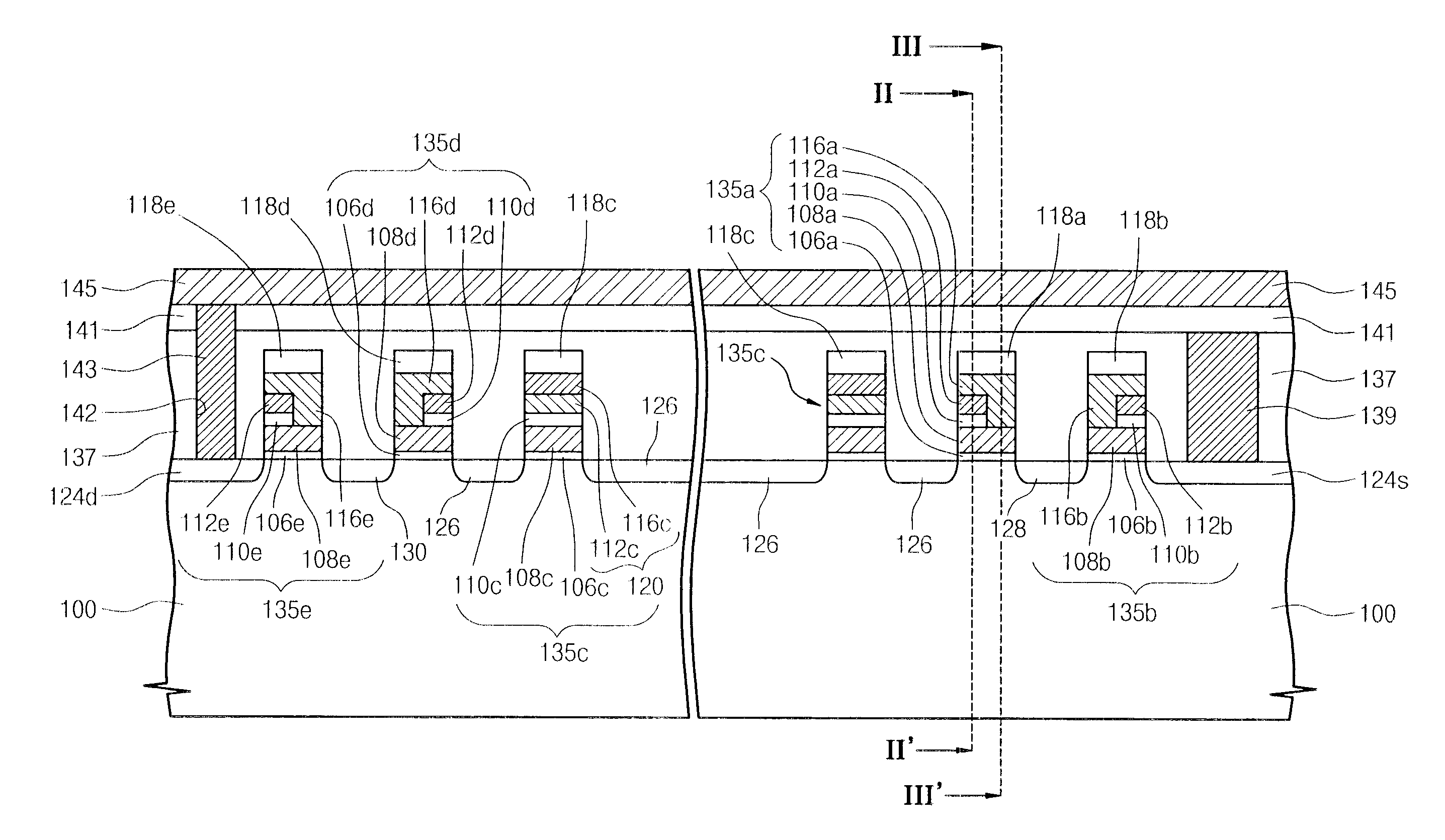
NAND flash memory device and methods of its formation and operation
InactiveUS20060239083A1MinimizeMinimize leakage currentSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical currentTransistor
A NAND flash memory device, and methods of forming and operating the same are provided. The NAND flash memory device includes first and second selection gate lines sequentially disposed at one side of a plurality of cell gate lines. A first selection transistor including the first selection gate line serves as a buffer for decreasing a highly boosted channel voltage of a non-selected cell to minimize the leakage current of the NAND flash memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dual-gate transistor display
ActiveUS7532187B2Minimize leakage currentImprove featuresStatic indicating devicesSemiconductor devicesBottom gateDisplay device
A dual-gate thin-film transistor (DG-TFT) voltage storage circuit is provided. The circuit includes a voltage storage element, a DG-TFT having a first source / drain (S / D) connected to a data line, a top gate connected to a first gate line, a second S / D region connected to the voltage storage element, and a bottom gate connected to a bias line. In one aspect, the circuit further includes a voltage shifter having an input connected to the first gate line and an output to supply a bias voltage on the bias line. Examples of a voltage storage element include a capacitor, a liquid crystal (LC) pixel, and a light emitting diode (LED) pixel.
Owner:SHARP KK
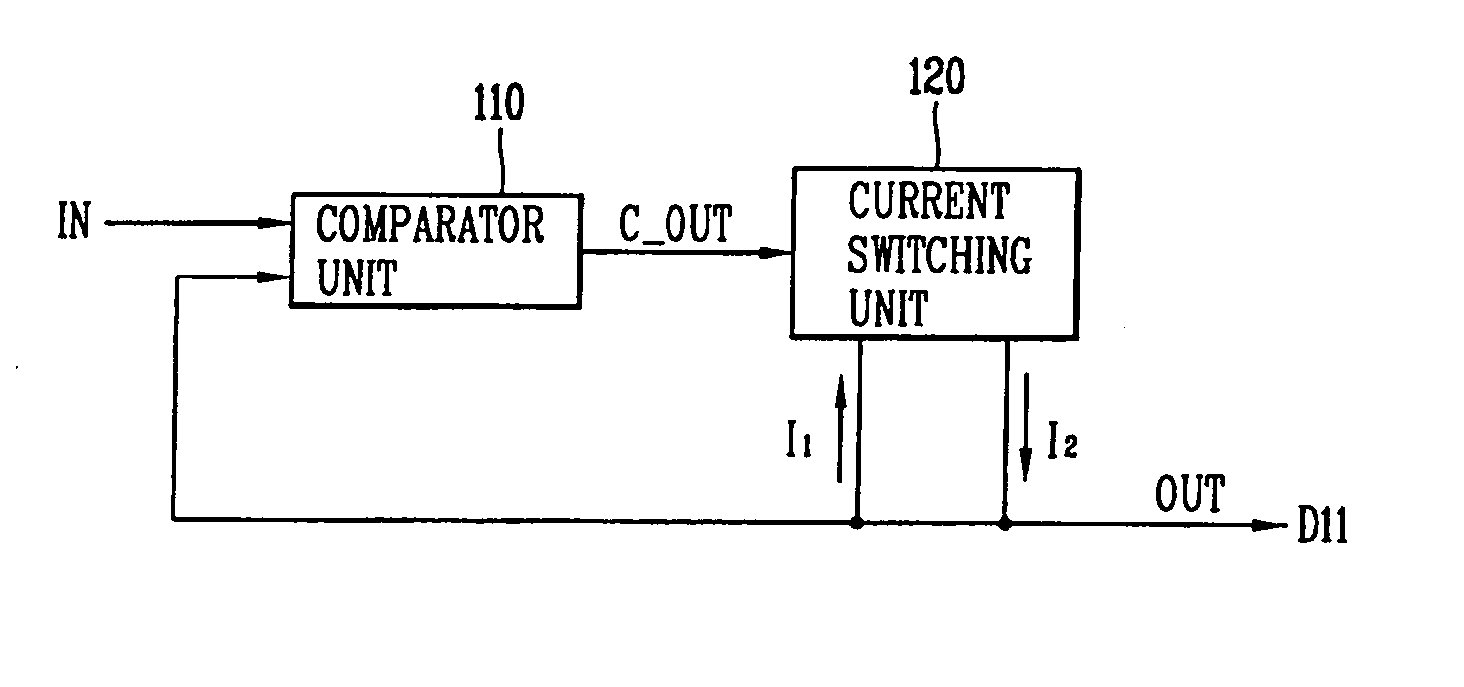
Analog buffer and method for driving the same
InactiveUS20050156863A1Reduce power consumptionImprove the display effectStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsControl signalEngineering
An analog buffer includes a comparator unit for comparing an input signal to be charged on a signal line of a display panel with an output signal charged on the signal line of the display panel to output a control signal; and a current switching unit for discharging an output current from the signal line of the display panel or charging an input current on the signal line of the display panel in accordance with the control signal output by the comparator unit the comparator unit smallest and to thus minimize leakage current.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
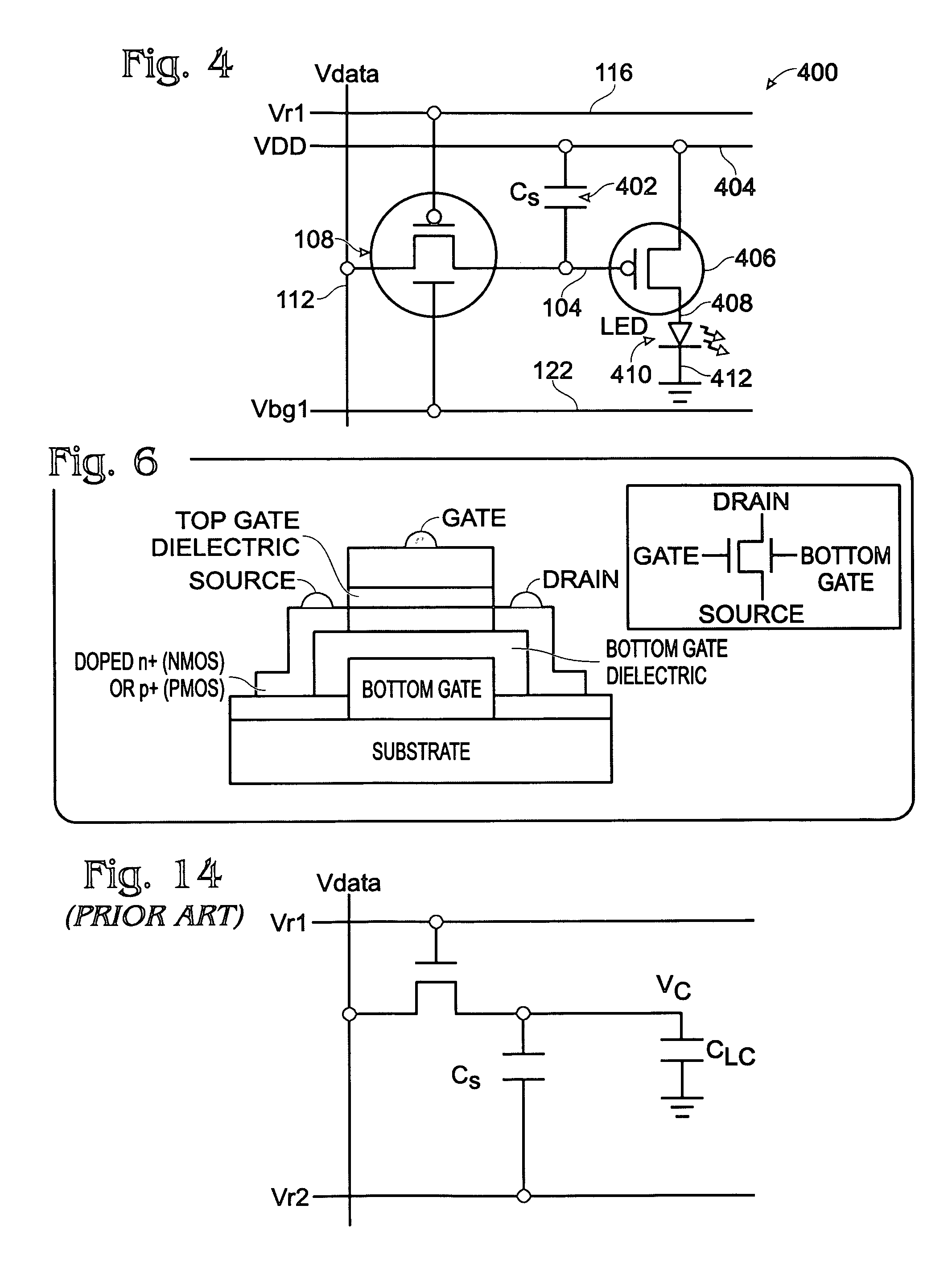
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080224263A1Minimize leakage currentSufficient capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorMetal
A semiconductor device including a capacitor which includes a first electrode, a second electrode, and a dielectric layer disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode, the dielectric layer including: a first paraelectric film formed of a material containing a first metal element and at least one kind of second metal element; a second paraelectric film disposed between the first electrode and the first paraelectric film; and a third paraelectric film disposed between the second electrode and the first paraelectric film, wherein the second paraelectric film is formed of a material containing the first metal element but substantially not containing the second metal element, and the third paraelectric film is formed of a material containing the first metal element but substantially not containing the second metal element.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
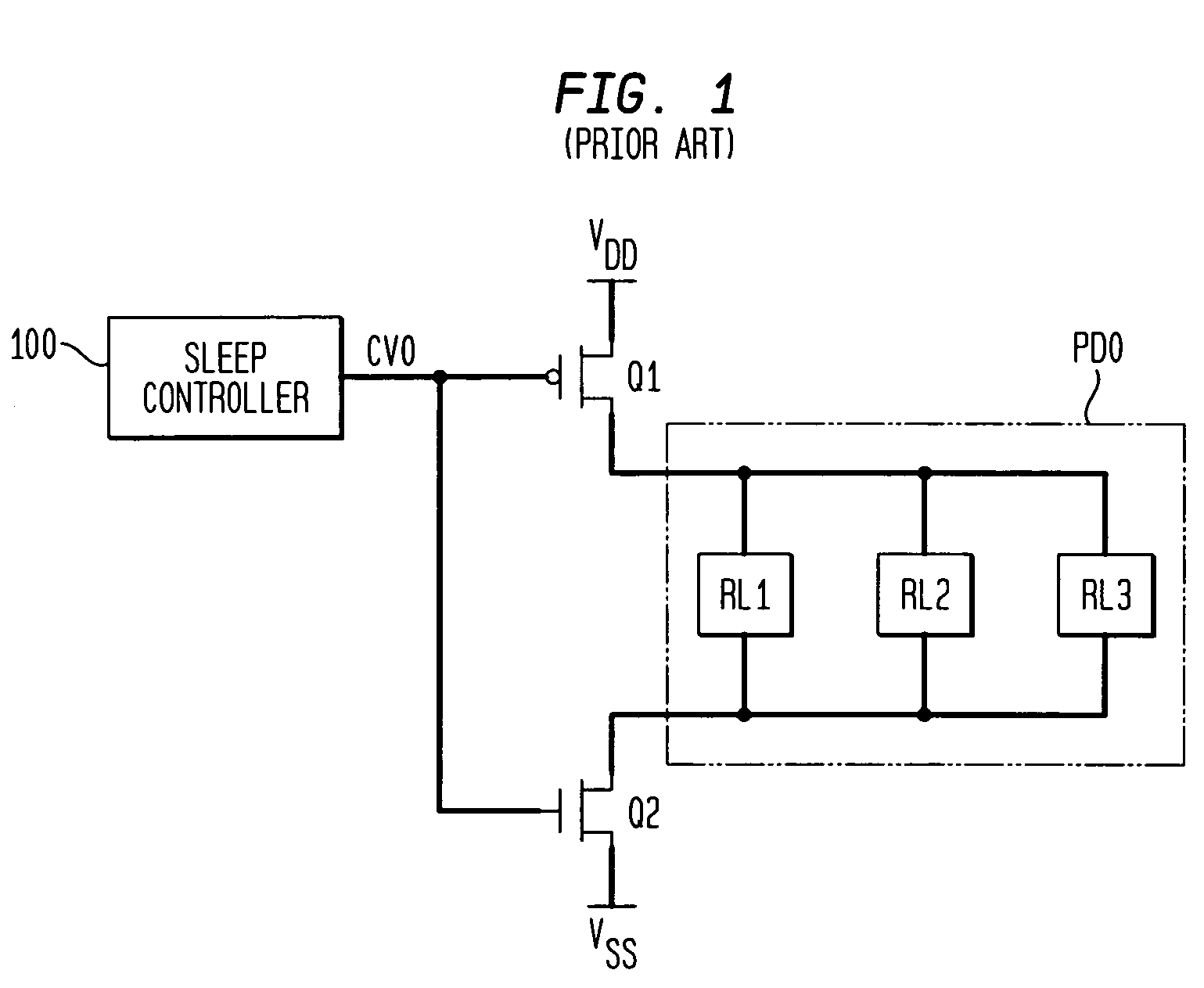
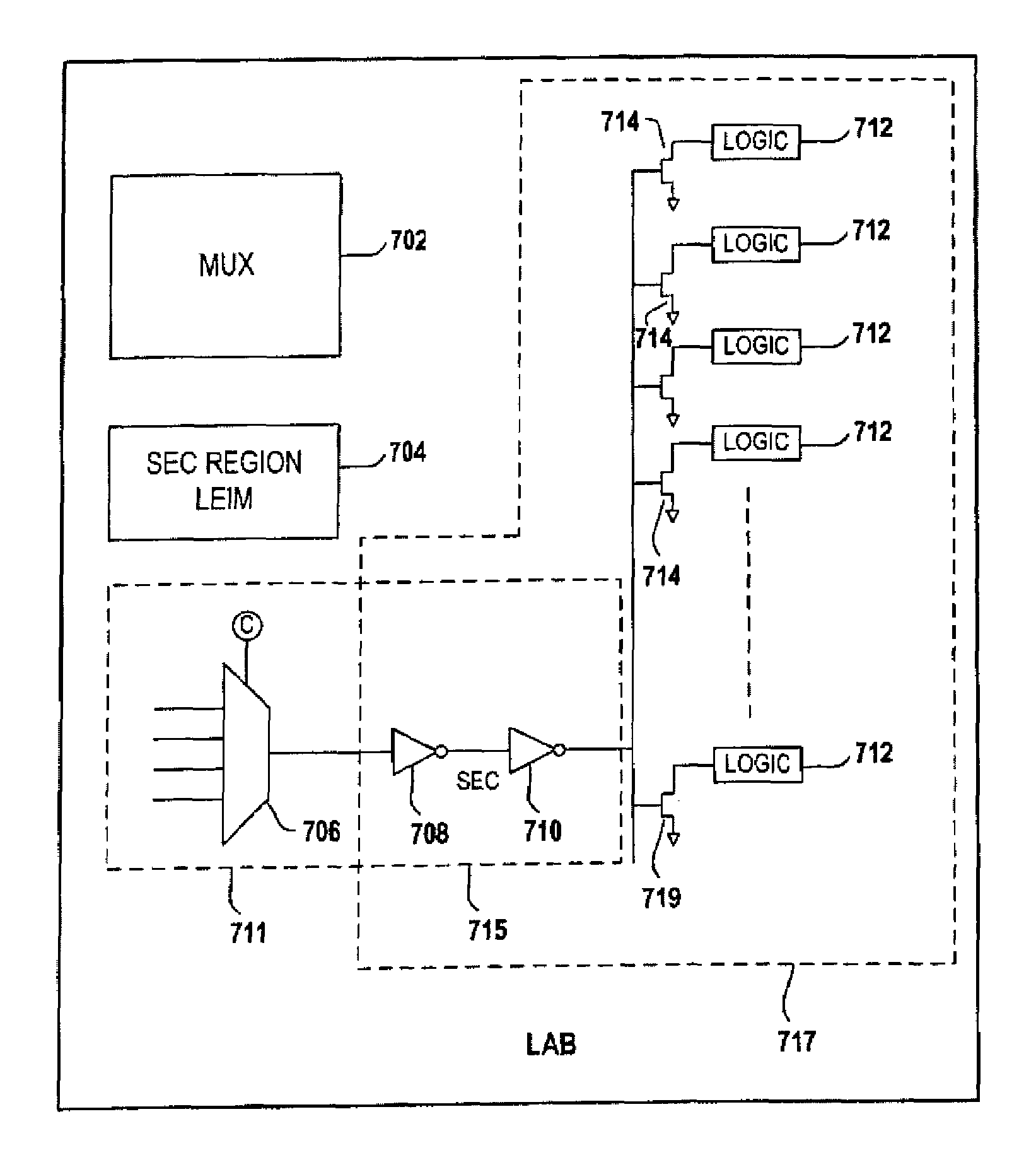
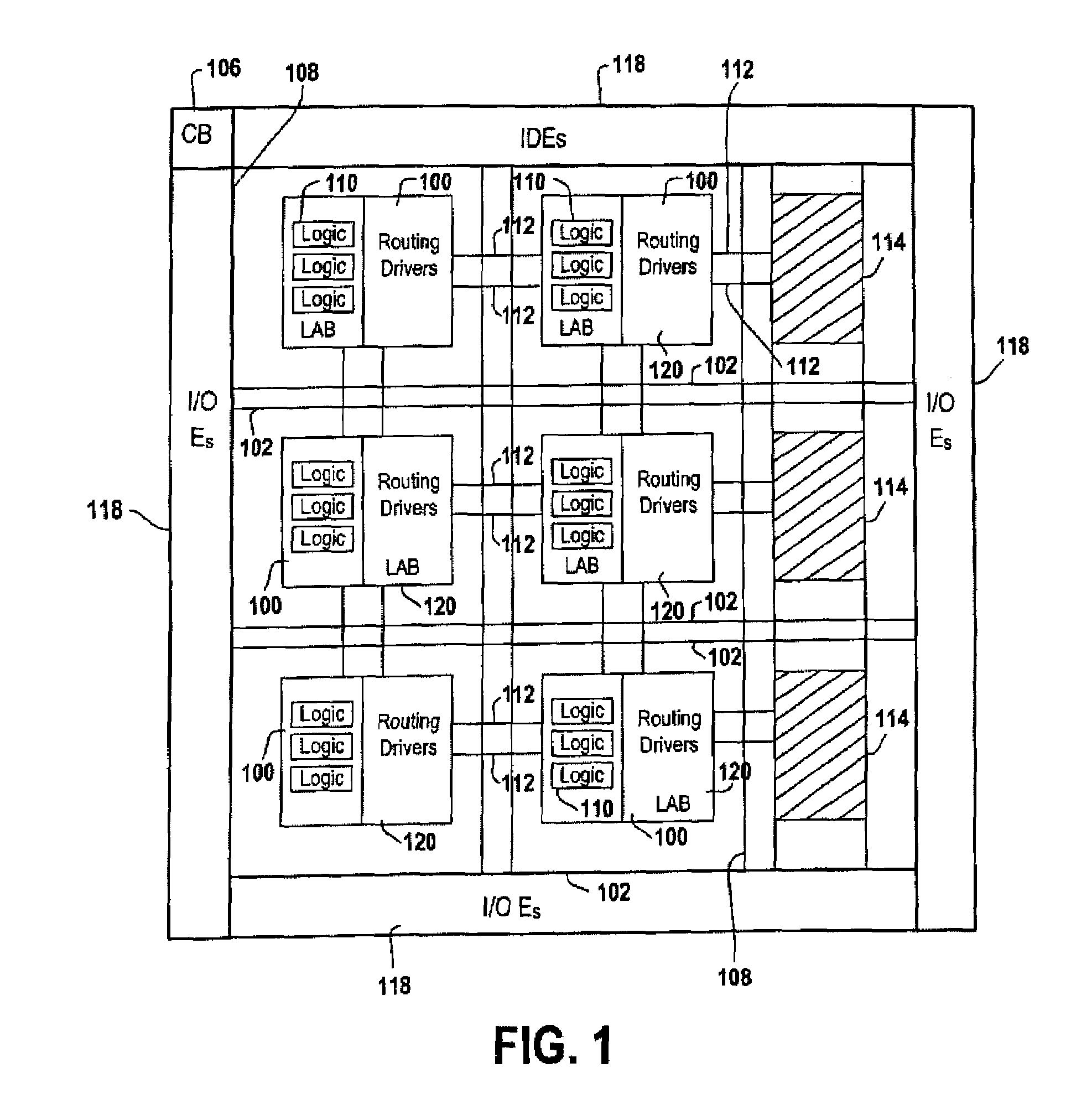
Method of reducing leakage current using sleep transistors in programmable logic device
ActiveUS7518399B1Reduce leakage currentMinimize leakage currentPower reduction by control/clock signalSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceErasable programmable logic device
A programmable logic device (PLD) having minimal leakage current for inactive logic blocks is provided. The PLD includes an array of logic blocks. Among the array of logic blocks, one of the array of logic blocks monitors the level of activity of each of the remaining logic blocks. The level of activity may be monitored by observing the input and output pin of the logic blocks. The PLD further includes a plurality of driven wires defining a routing pattern between the array of logic blocks. When one of the array of logic blocks detect inactivity in any one of the remaining logic blocks for a certain duration, the one of the array logic blocks transmits a signal invoking a sleep mode for the inactive logic blocks. A sleep transistor with a threshold voltage level that is capable minimizing the leakage current is associated with each of the remaining block. The gate of the sleep transistor receives the signal transmitted by one of the array logic blocks and the signal switches off the sleep transistor.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
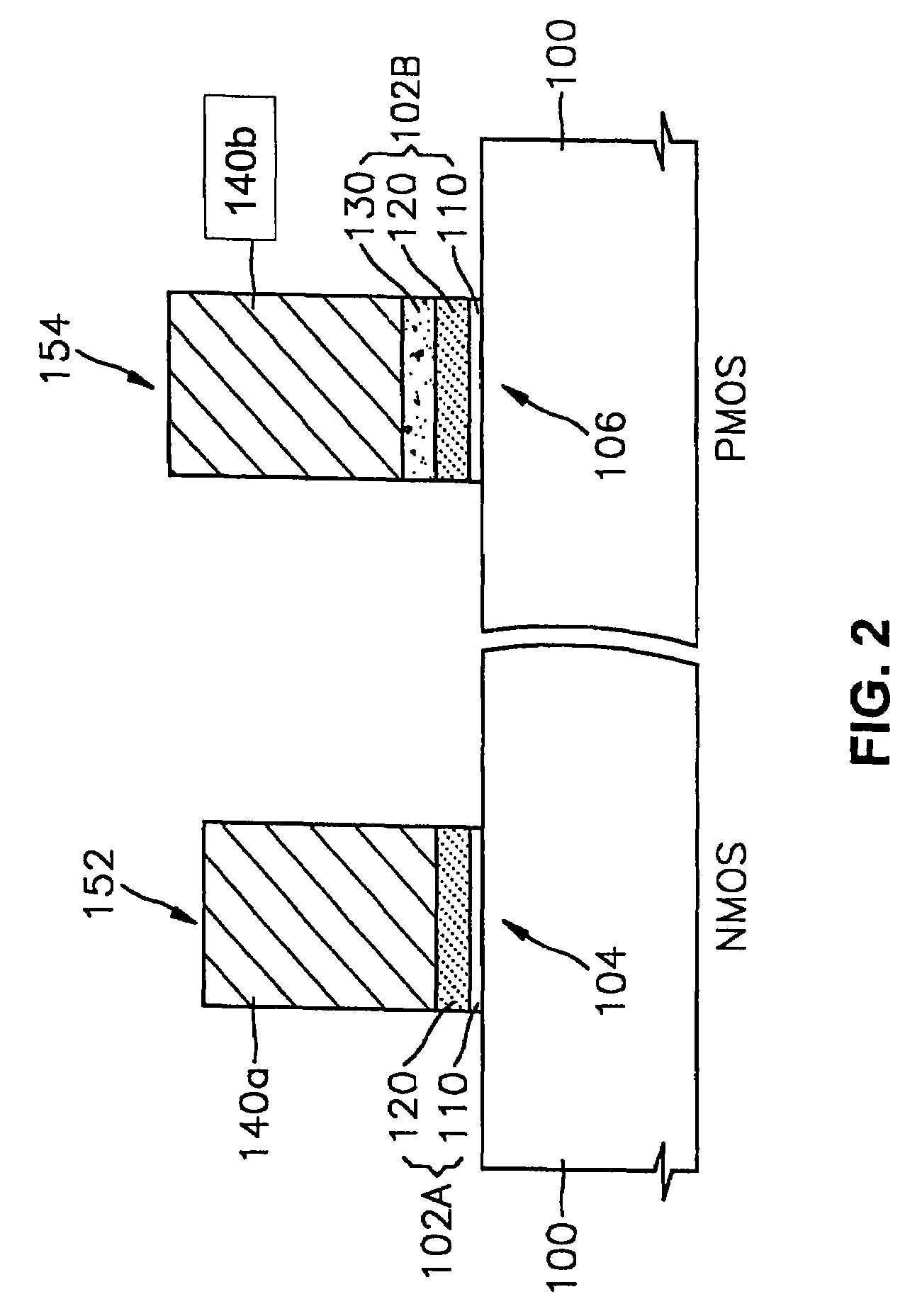
Semiconductor devices having different gate dielectrics and methods for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7586159B2Reduce negative impactIncrease speedTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricDevice material
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
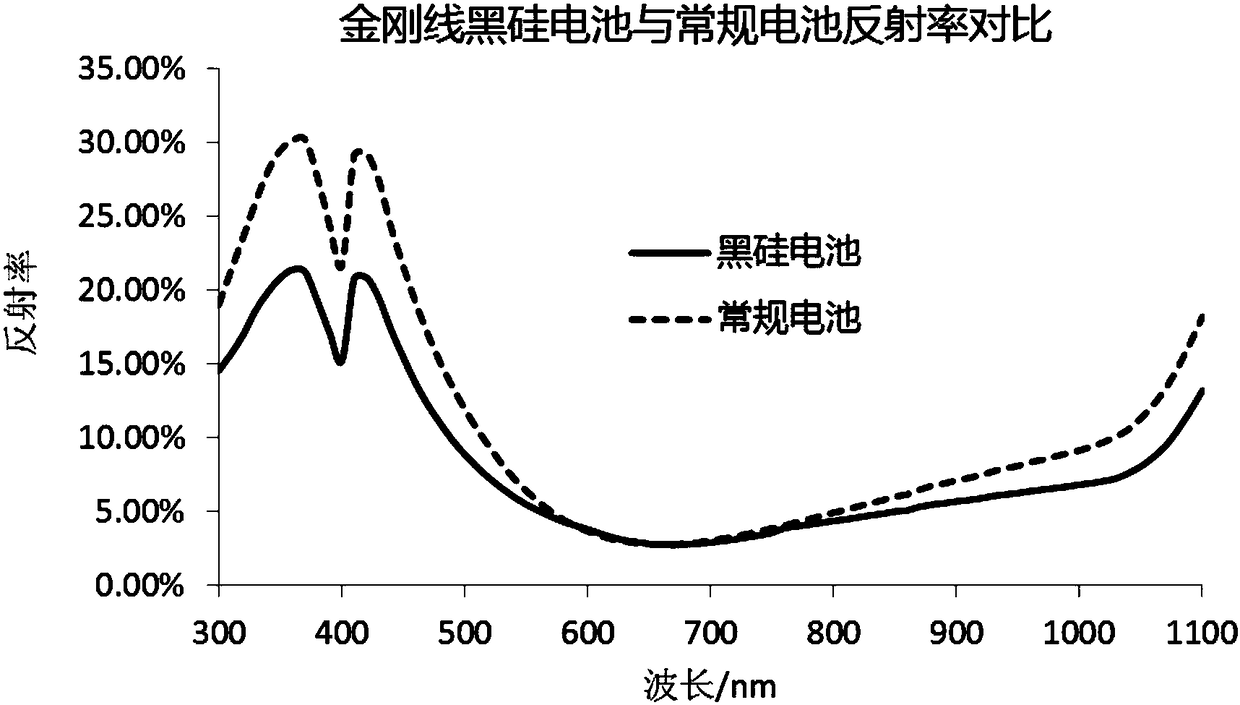
Preparation method for black-silicon poly-silicon PERC cell structure with selective emitter
InactiveCN108365022ASolve the problem of high surface reflectivityImprove conversion efficiencyAfter-treatment detailsFinal product manufactureScreen printingSilver electrode
The invention relates to a preparation method for a black-silicon poly-silicon PERC cell structure with a selective emitter. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1) forming a nanometer texturing surface on a front surface of a silicon wafer, wherein a back surface is a polishing surface; (2) performing front-surface diffusion of the silicon wafer to form anN-type layer, and removing front-surface phosphorosilicate glass and a back-surface pn junction; (3) depositing a silicon nitride anti-reflection film layer on the front surface of the silicon wafer,and depositing a passivation dielectric layer on the back surface; (4) dotting or routing the back surface of the silicon wafer, and printing a silver electrode and aluminum paste; (5) performing low-temperature sintering to form a local aluminum back field; (6) spraying a mixed solution of phosphoric acid and alcohol on the front surface of the silicon wafer, and forming a main grid line regionand a secondary grid line region after heavy doping by laser; and (7) immersing the front surface of the silicon wafer in an electroplating solution, electroplating the front surface of the silicon wafer under an illumination condition, and annealing after electroplating. By the preparation method, the defects that a high-quality fine grid line is difficult to form by silk-screen printing and thegrid line and a selective emitter cannot be enabled to be accurately aligned are overcome, and shielding and leakage current caused by an electrode are minimum.
Owner:WUXI SUNTECH POWER CO LTD
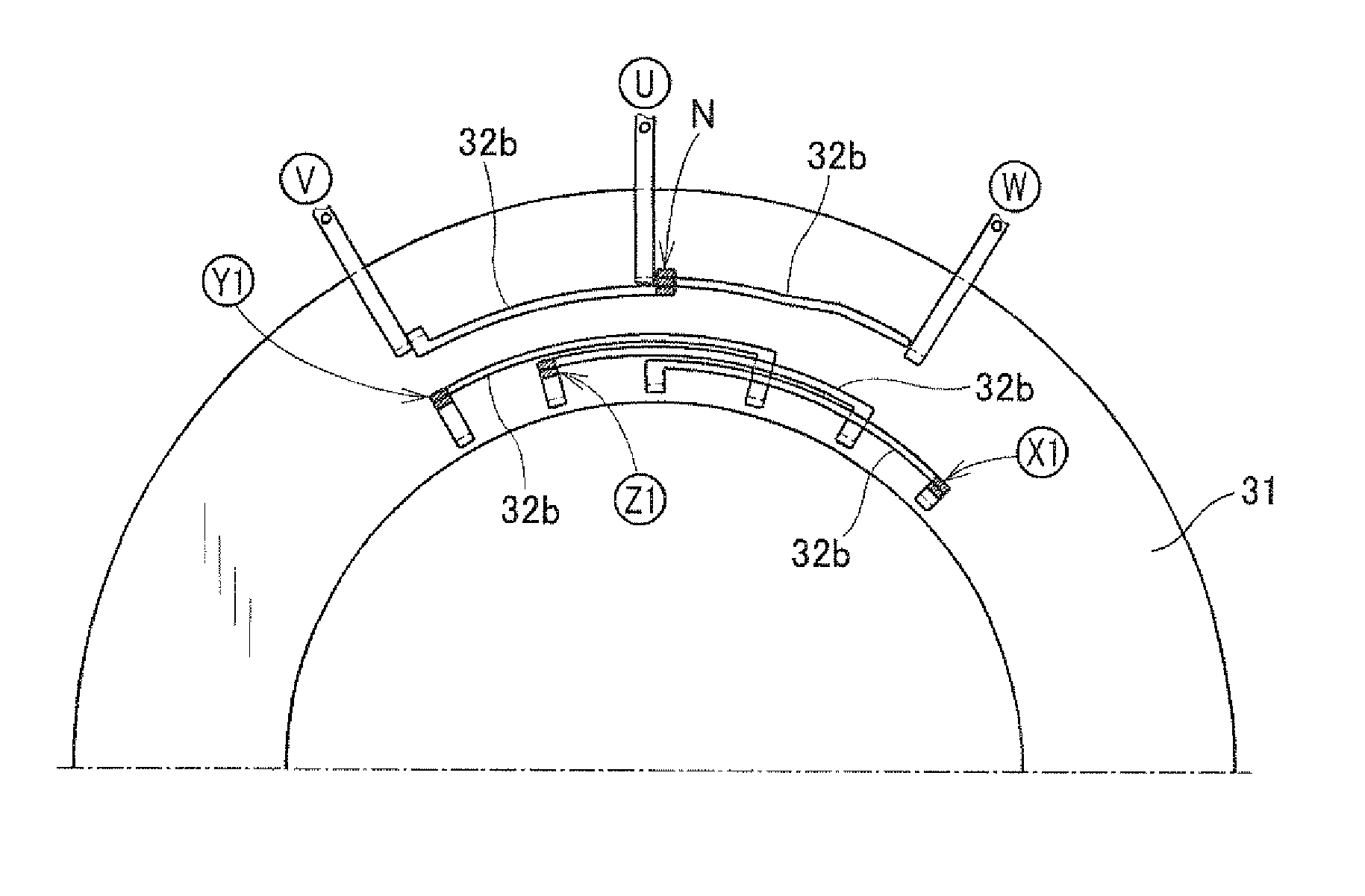
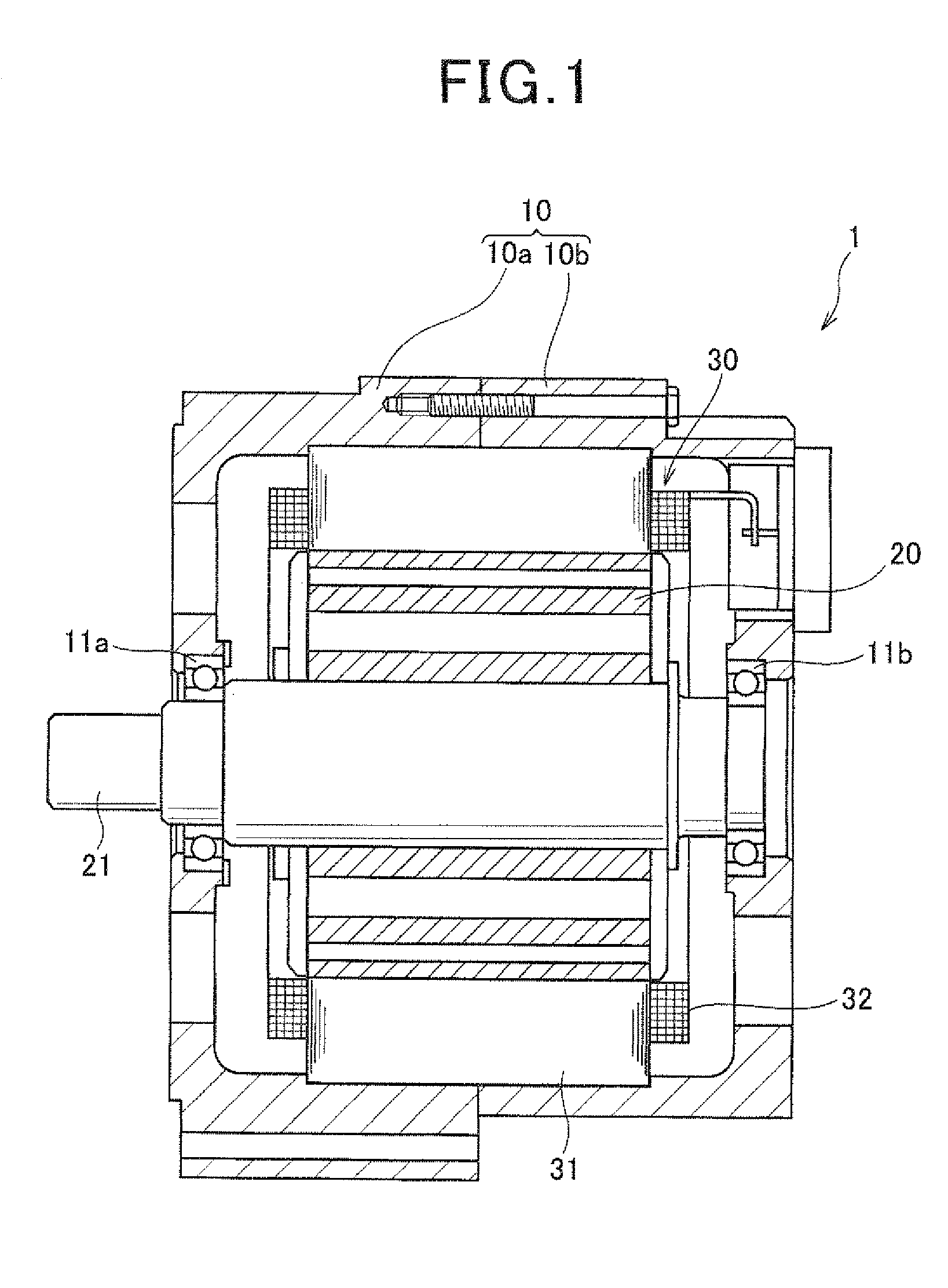
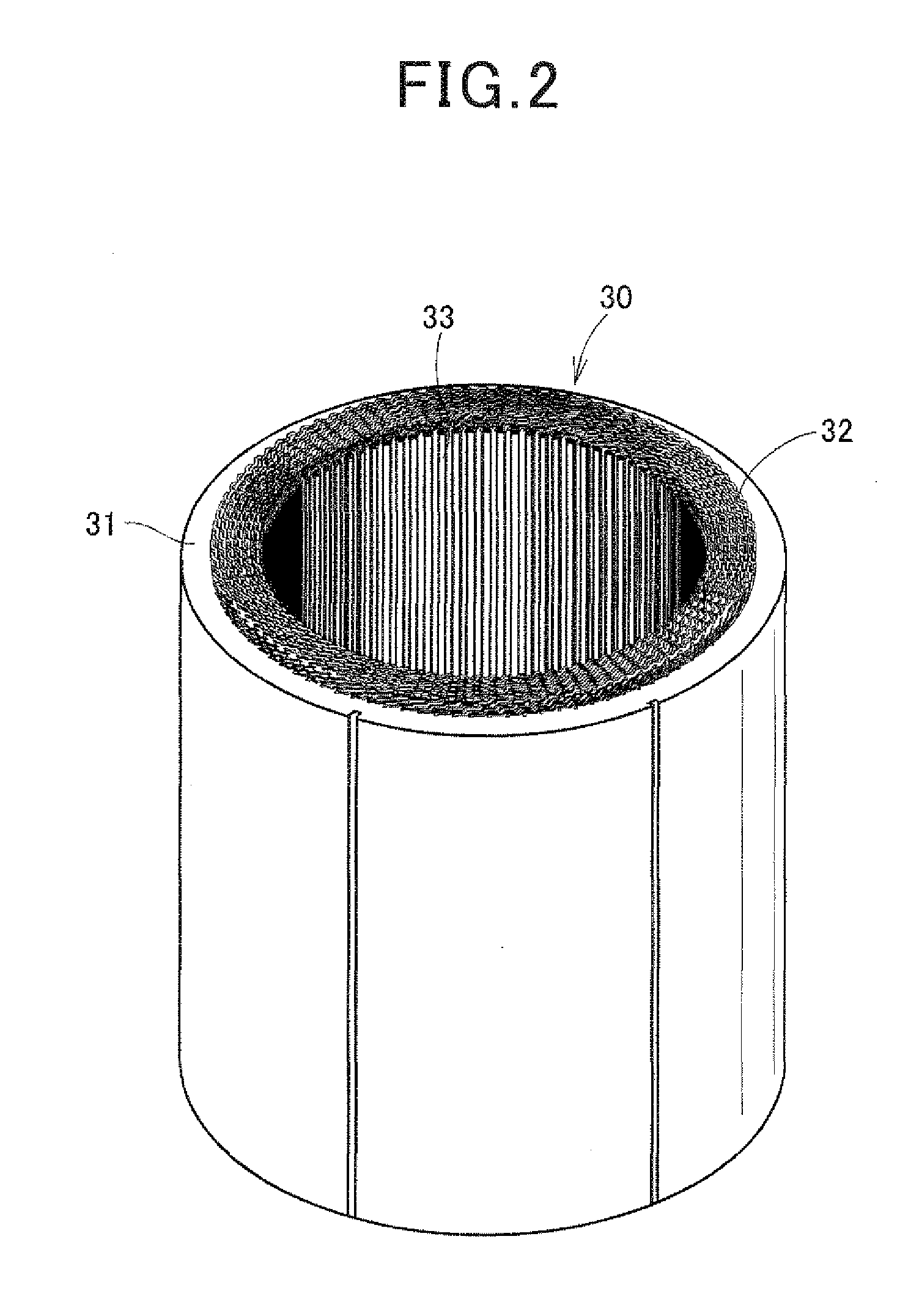
Stator designed to minimize leakage current and electric rotating machine using same
ActiveUS20110163625A1Minimize undesirable movementSimple structureSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuitElectric machineEngineering
A stator which may be employed in an electric rotating machine. The stator includes a stator winding which includes in-slot portions disposed in slots of a stator core. The in-slot portions are arrayed in each of the slots in a form of multiple layers aligned in a radial direction of the stator core. The stator winding is made up of a first winding and a second winding which are connected together through a joint. The first winding is defined by a portion of the stator winding between the joint and an end of the stator winding which is to be connected to an external. The second winding includes the in-slot portion placed within at least one of the slots as an outermost layer that is one of the layers placed most outwardly in the radial direction of the stator core. This results in a great decrease in leakage current.
Owner:DENSO CORP
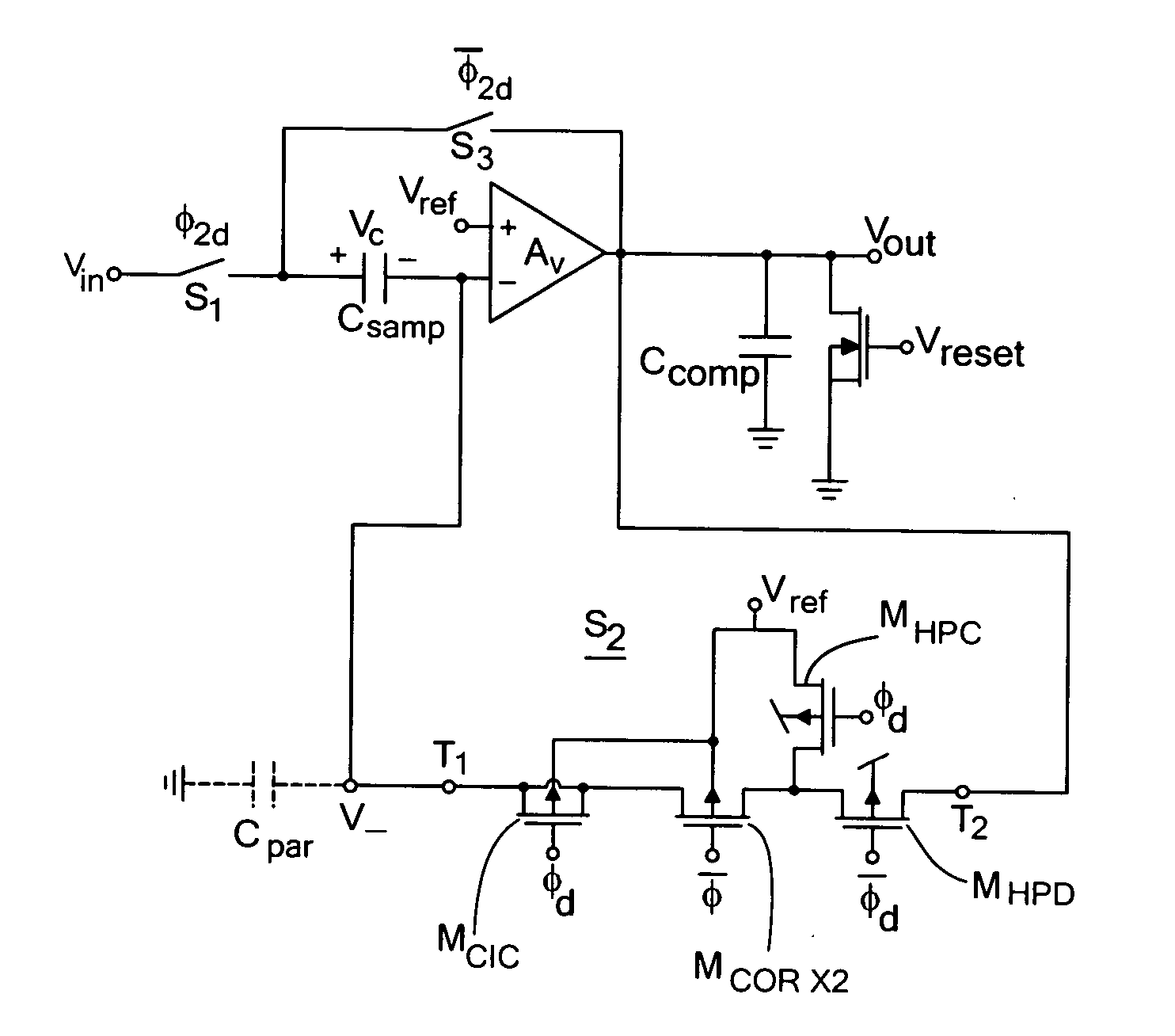
Analog storage cell with low leakage
ActiveUS20060087362A1Minimize accumulation mode conductionMinimize leakage currentElectric analogue storesElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierDevice form
An analog storage cell circuit includes a switch that minimizes subthreshold conduction and diode leakage, as well as an accumulation-mode coupling mechanism to minimize overall switch leakage to minimize accumulation-mode leakage. In one embodiment, an analog storage circuit includes a sample and hold circuit including an amplifier having first and second inputs and a switch coupled to the first input of the amplifier. The switch includes a first switching device forming a core of the switch, a second switching device coupled to the first switching device to disconnect the first switching device from a first terminal during the hold phase, and a third switching device coupled to the first switching device to connect the first switching device to a second terminal during the hold phase to minimize accumulation mode conduction in the first switching device.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Circuit and method for generating word line off voltage
InactiveUS7898897B2Minimize leakage currentImprove the level ofDigital storageVoltage generatorHemt circuits
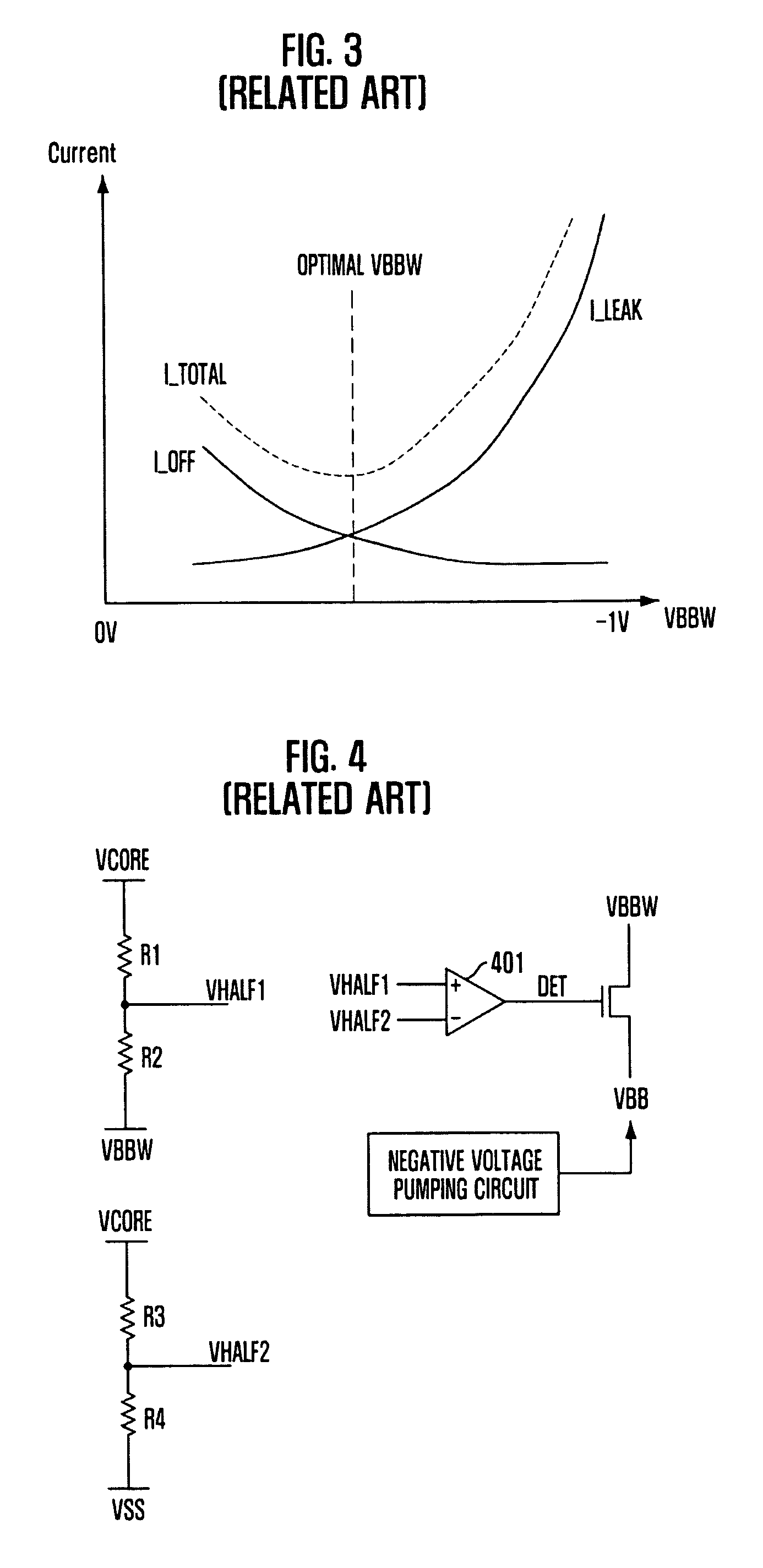
A circuit and method for generating a word line off voltage which can minimize a leakage current by actively adjusting a level of the word line off voltage. The circuit includes a current information provider for providing information about an amount of current flowing through a cell transistor, and a voltage generator for generating a word line off voltage with a varying level depending on the information.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Methods and apparatus for ultra-low leakage analog storage
ActiveUS7436221B2Minimize leakage currentMinimizes conductionElectric analogue storesElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierDevice form
An analog storage cell circuit includes a switch that minimizes subthreshold conduction and diode leakage, as well as an accumulation-mode coupling mechanism to minimize overall switch leakage to minimize accumulation-mode leakage. In one embodiment, an analog storage circuit includes a sample and hold circuit including an amplifier having first and second inputs and a switch coupled to the first input of the amplifier. The switch includes a first switching device forming a core of the switch, a second switching device coupled to the first switching device to disconnect the first switching device from a first terminal during the hold phase, and a third switching device coupled to the first switching device to connect the first switching device to a second terminal during the hold phase to minimize accumulation mode conduction in the first switching device.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Hole transport layer compositions and related diode devices
ActiveUS7449509B2Excellent hole injectionImprove performanceConductive materialSolid-state devicesArylSilylation
Hole transport layer compositions comprising a silylated aryl amine and a polymeric component, to enhance performance of an associated electroluminescent device.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Integrated circuit device having power domains and partitions based on use case power optimization
ActiveUS9411390B2Reduce power consumptionReduce standby power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingEngineeringPower domains
A programmable SoC (system on a chip) having optimized power domains and power islands. The SoC is an integrated circuit device including a plurality of power domains, each of the power domains having a respective voltage rail to supply power to the power domain. A plurality of power islands are included within the integrated circuit device, wherein each power domain includes at least one power island. A plurality of functional blocks are included within the integrated circuit device, wherein each power island includes at least one functional block. Each functional block is configured to provide a specific device functionality. The integrated circuit device adjusts power consumption in relation to a requested device functionality by individually turning on or turning off power to a selected one or more power domains, and for each turned on power domain, individually power gating one or more power islands.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
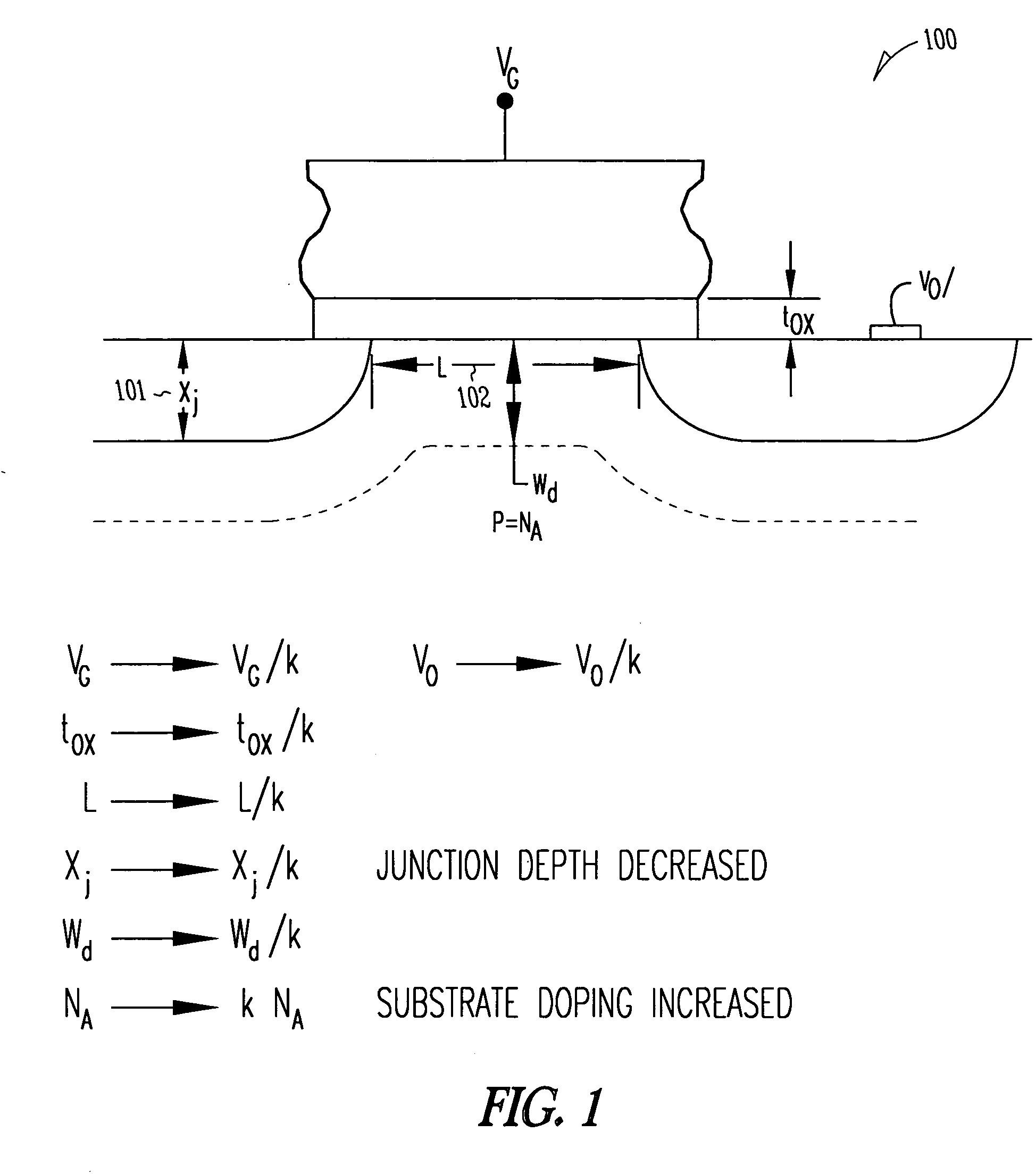
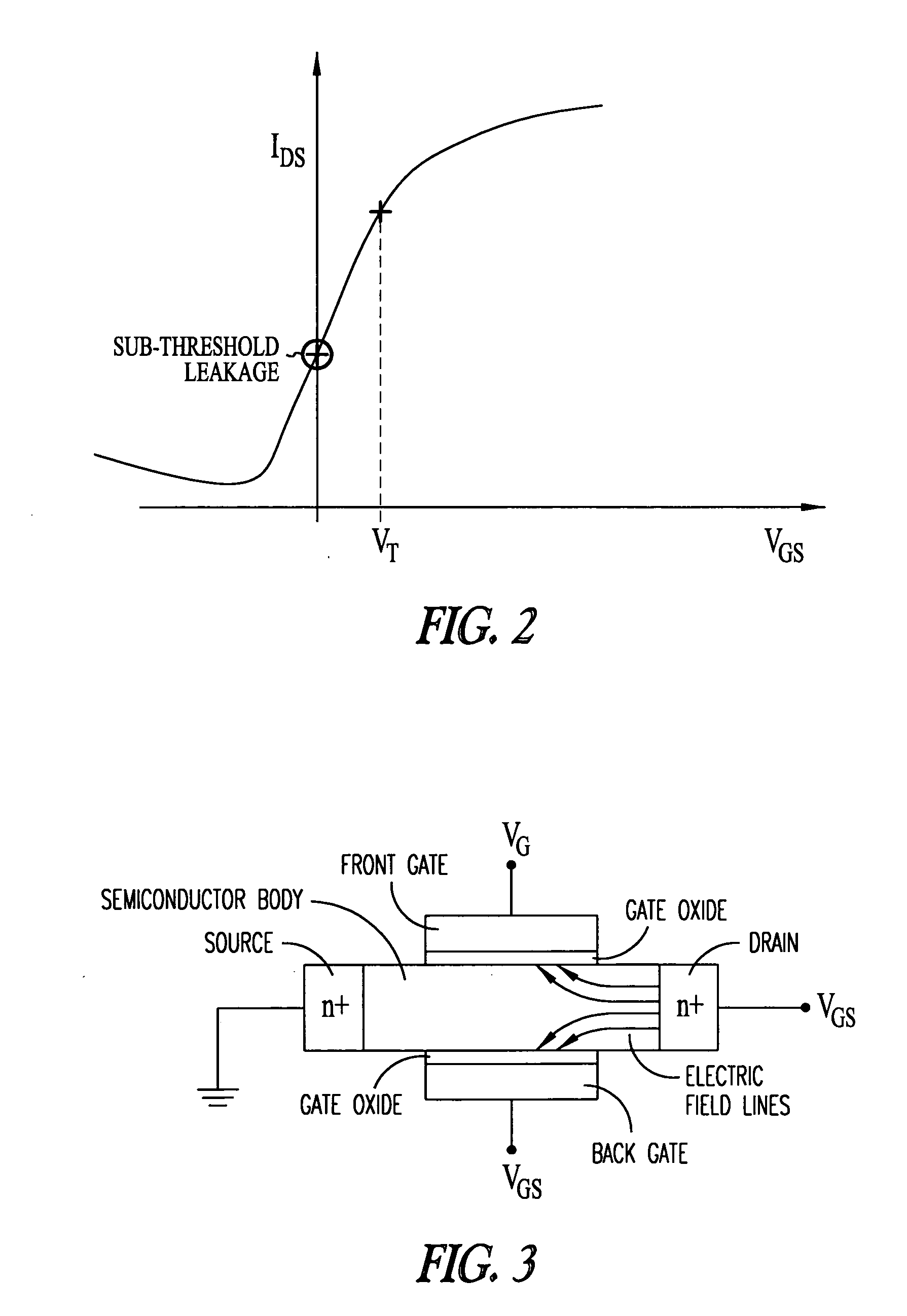
Systems and methods for dynamic mosfet body biasing for low power, fast response VLSI applications
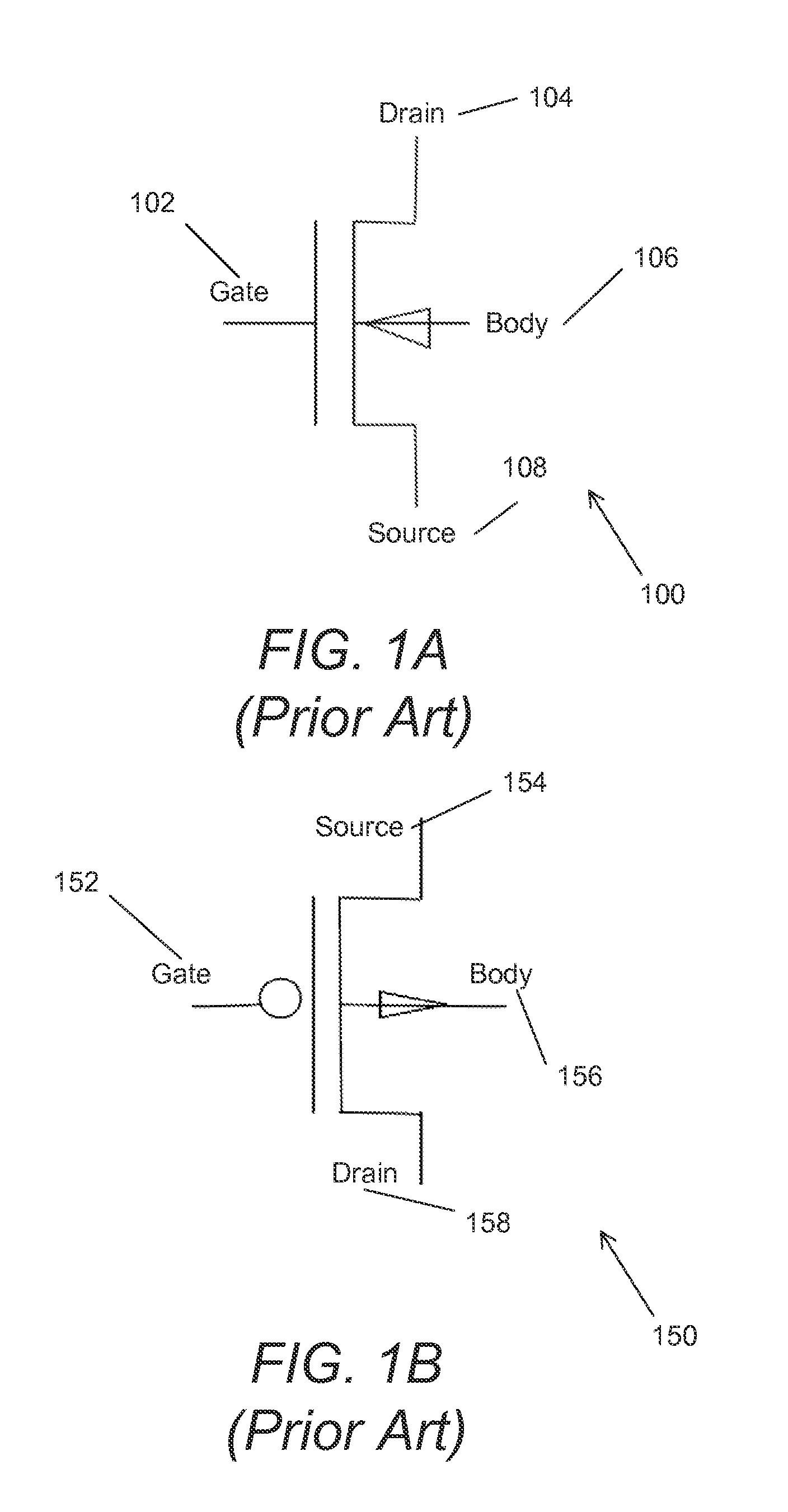
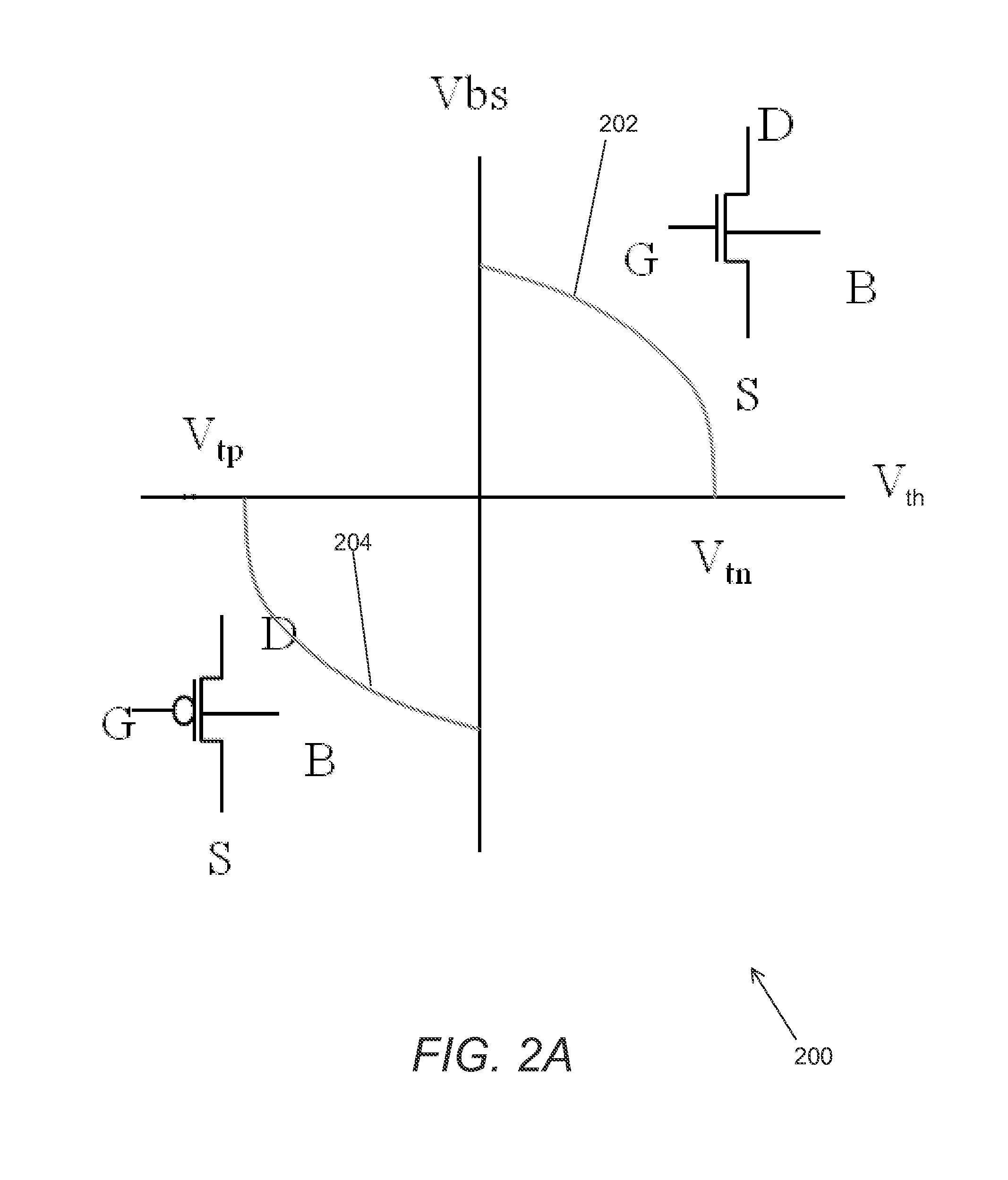
InactiveUS20120206188A1Minimize leakage currentShort response timeElectronic switchingMOSFETComputer terminal
Systems and methods in accordance with embodiments of the invention are disclosed that include MOSFET transistor operation by adjusting Vbs, or the voltage applied to the body terminal of the MOSFET transistor, to control the threshold voltage (Vth) in order to minimize leakage current and increase response time. One embodiment includes a n-channel metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (NMOS), including: a gate terminal; a source terminal; a drain terminal; a body terminal; and control circuitry, where the control circuitry is configured to bias the body terminal at a first voltage when voltage applied to the gate terminal turns the transistor OFF and a second voltage when voltage applied to the gate terminal turns the transistor ON; and where the first voltage is of a lower value than the second voltage.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for fabricating CMOS image sensor
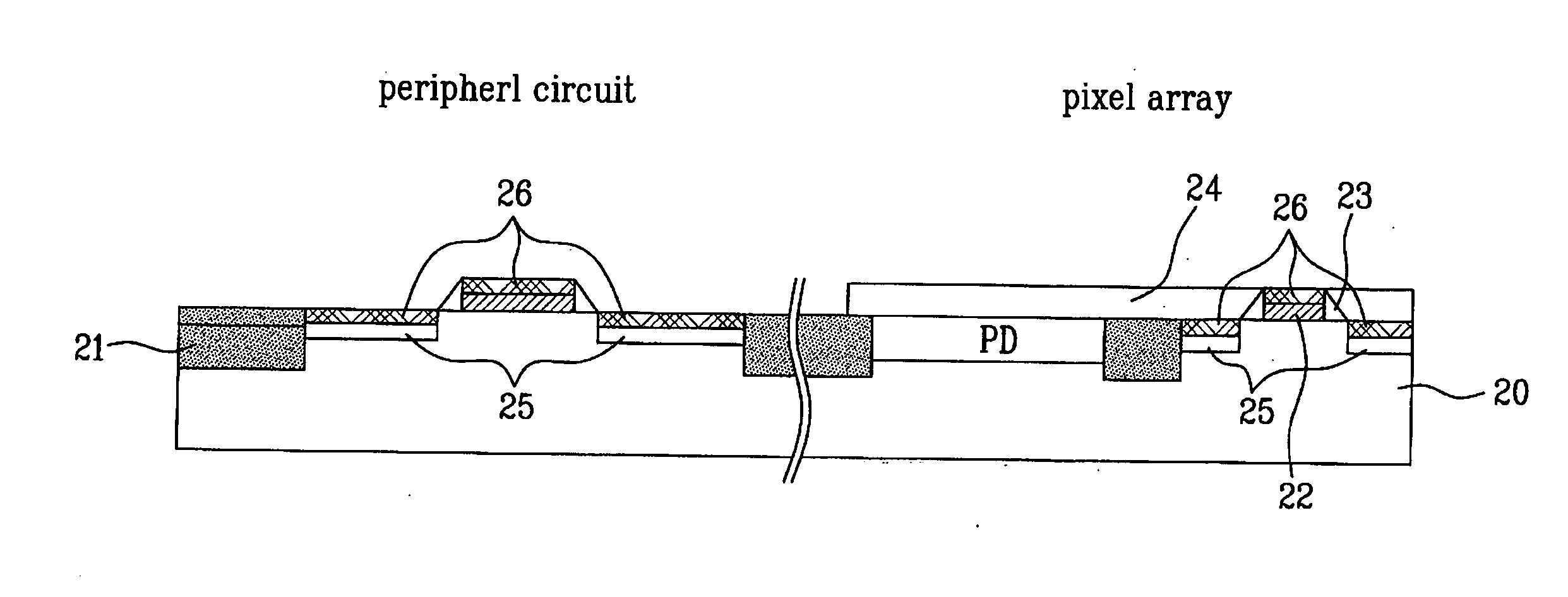
InactiveUS20060001062A1Minimize leakage currentIncrease productionTransistorTelevision system detailsCMOSPixel array
A method for fabricating a CMOS image sensor is disclosed, to minimize the leakage current and to improve the yield, which includes the steps of preparing a semiconductor substrate including a peripheral circuit and a pixel array, wherein the pixel array is comprised of a photodiode and a readout circuit; defining an active area and a field area in the semiconductor substrate; forming a field oxide layer in the field area of the semiconductor substrate; forming gate electrodes in the peripheral circuit and the readout circuit of the pixel array; forming a photodiode in a photodiode portion of the pixel array; forming source and drain junctions at both sides of the gate electrode in the semiconductor substrate of the active area; forming a salicide prevention layer in the semiconductor substrate of the pixel array; and forming salicide layers in the surface of the gate electrode and the source and drain junctions in the peripheral circuit by using the salicide prevention layer as a mask.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com