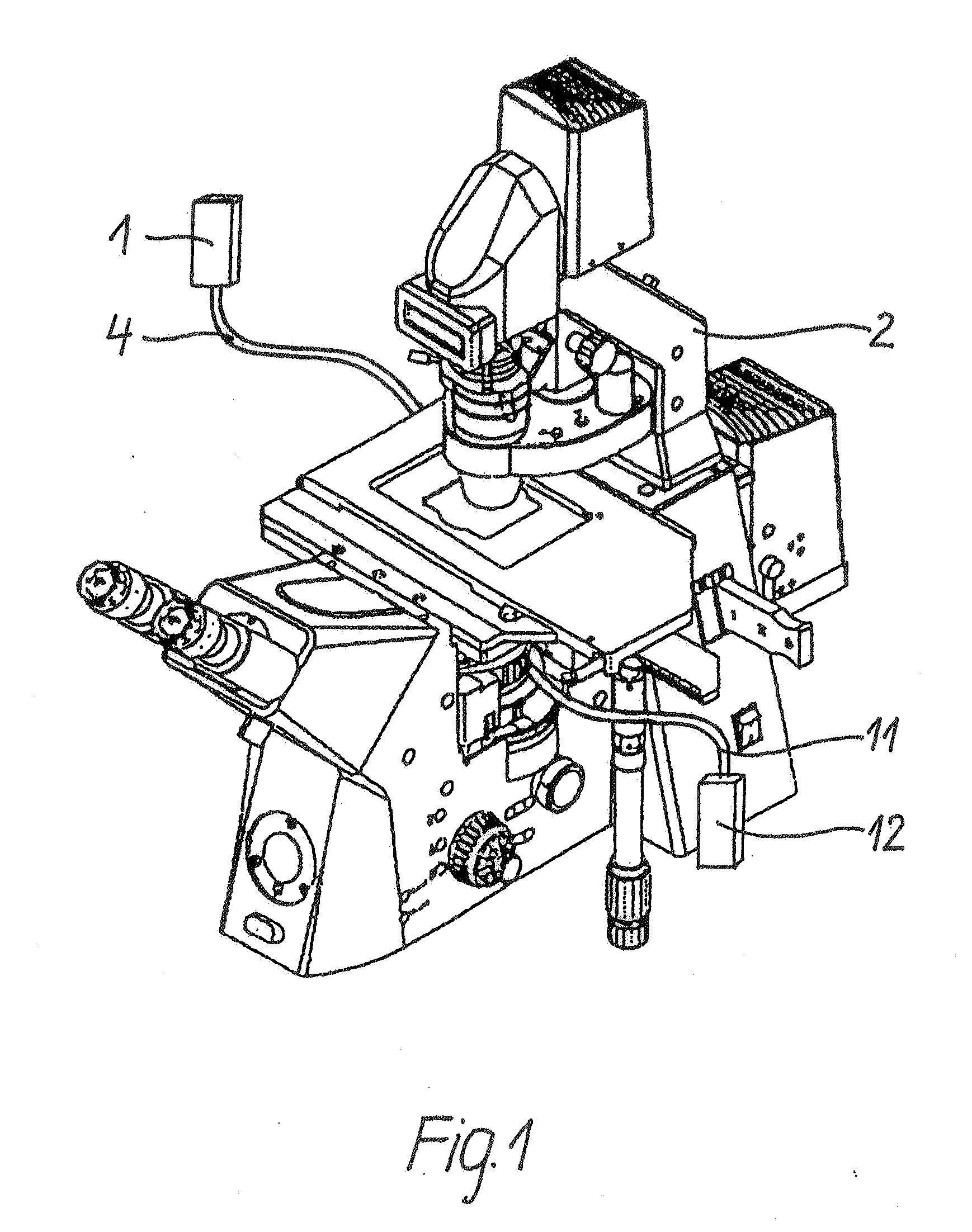
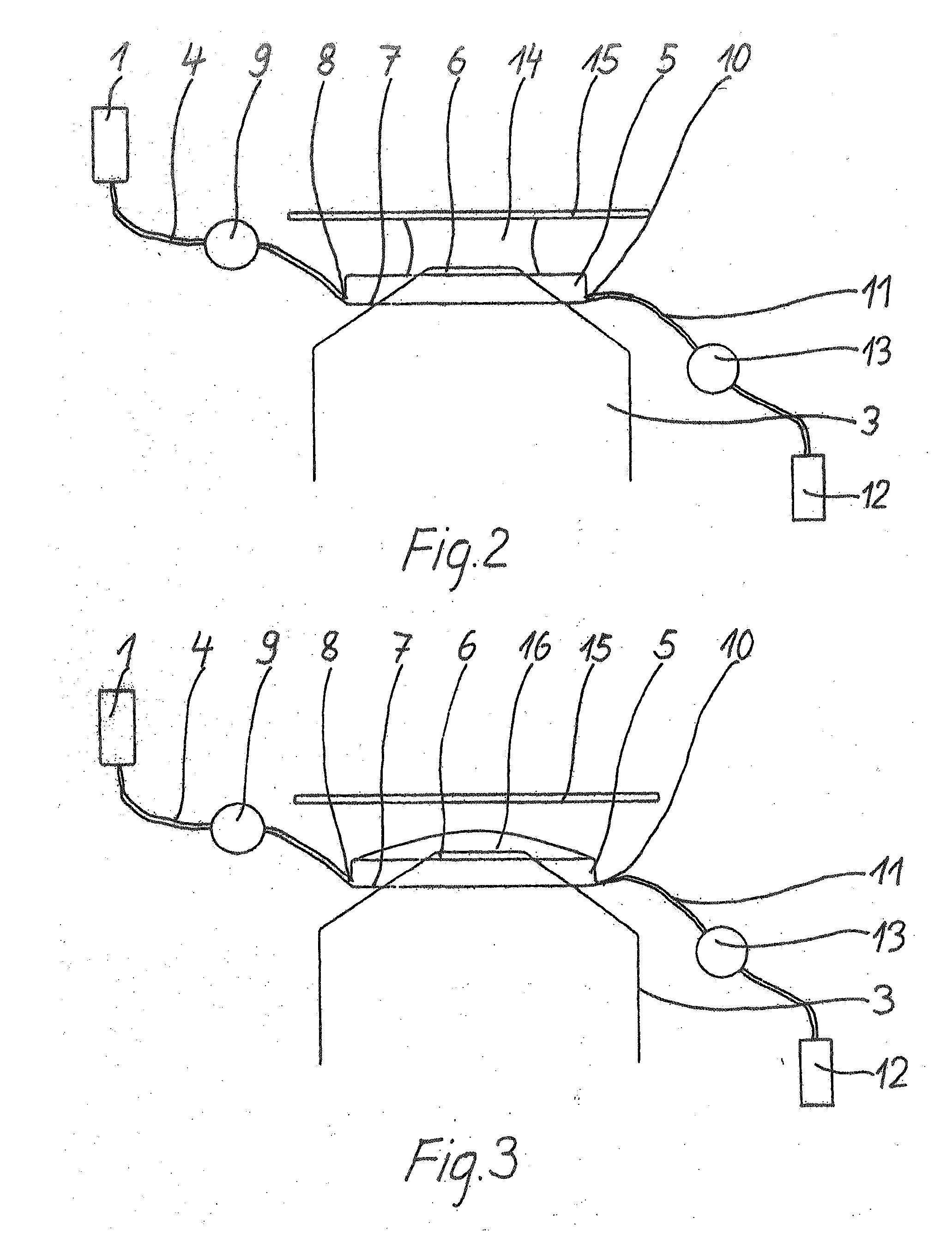
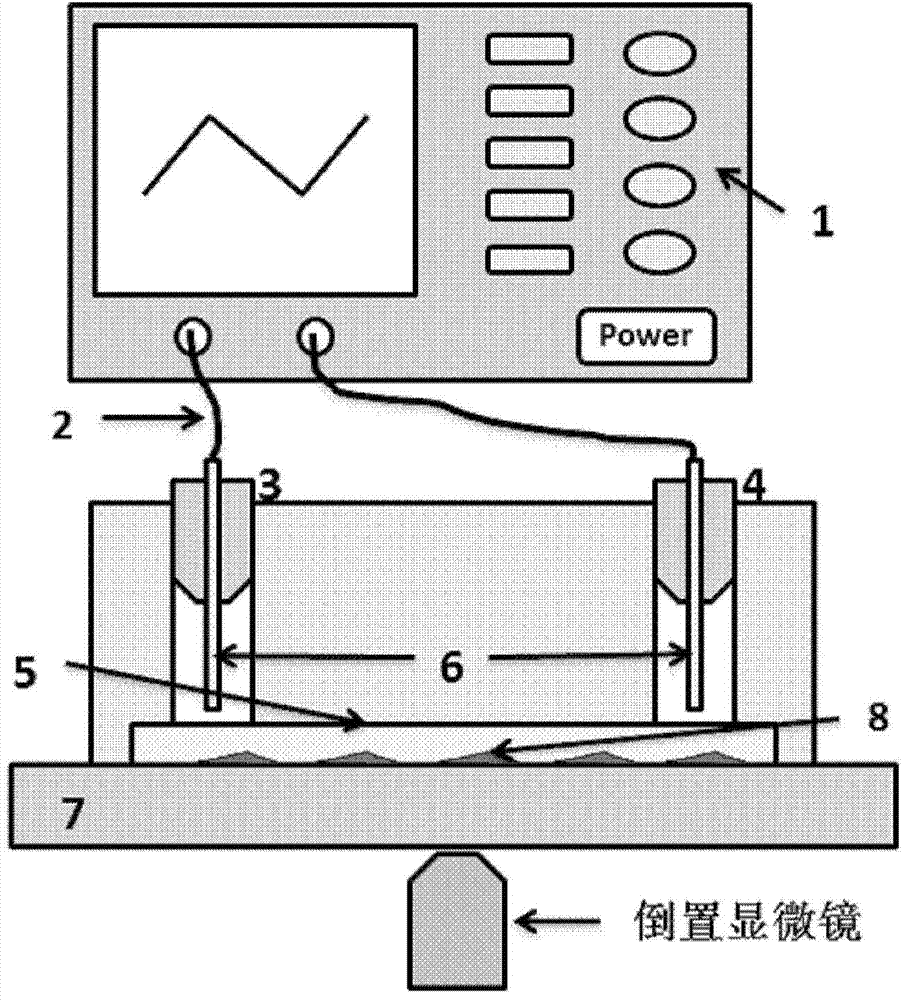
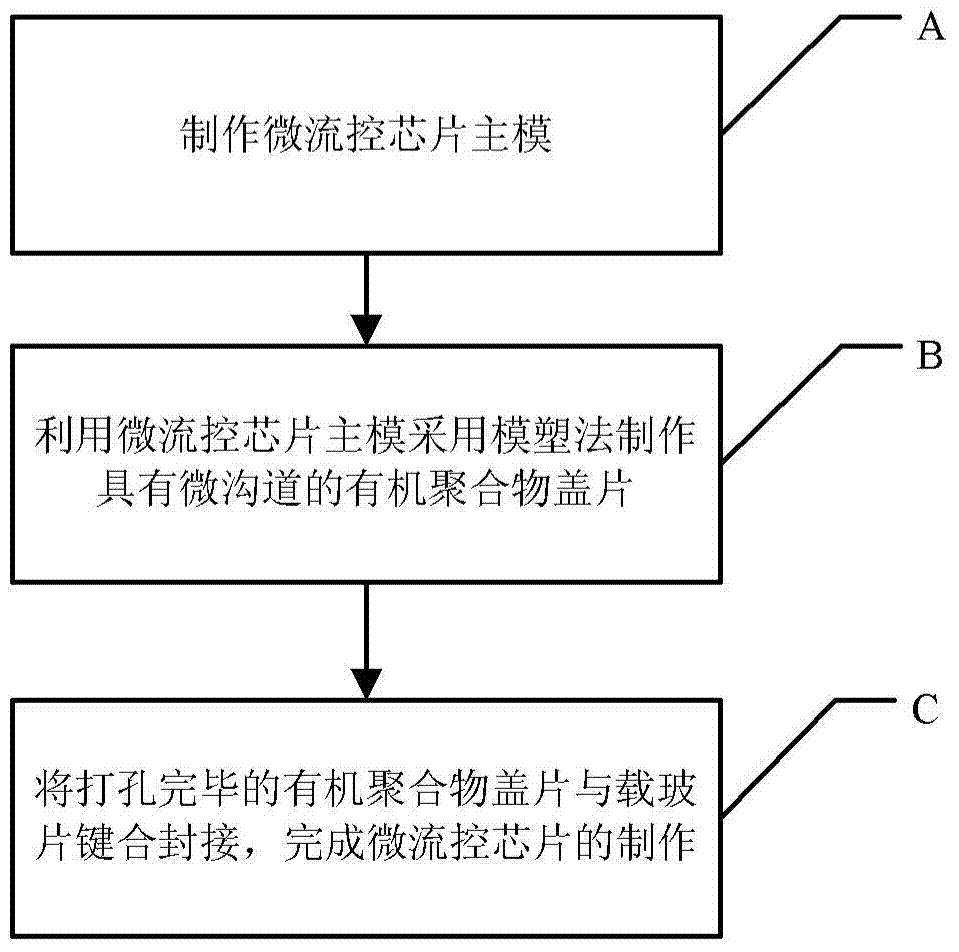
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
211 results about "Inverted microscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An inverted microscope is a microscope with its light source and condenser on the top, above the stage pointing down, while the objectives and turret are below the stage pointing up. It was invented in 1850 by J. Lawrence Smith, a faculty member of Tulane University (then named the Medical College of Louisiana).
Laser capture microdissection optical system
InactiveUS6215550B1Low costCost effectivePreparing sample for investigationMicroscopesLaser capture microdissectionLaser beams
Systems and methods for laser capture microdissection are disclosed. An inverted microscope includes an illumination / laser beam delivery system that is adapted to both illuminate a sample and provide energy for laser capture microdissection of the sample. The systems and methods provide the advantages of increased speed and much lower rates of contamination.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Laser capture microdissection pressure plate and transfer arm
InactiveUS6184973B1Low costCost effectivePreparing sample for investigationMicroscopesOptical axisOptoelectronics
Systems and methods for laser capture microdissection are disclosed. A laser capture microdissection method includes: providing a sample that is to undergo laser capture microdissection; positioning the sample within an optical axis of a laser capture microdissection instrument; providing a transfer film carrier removably positioned in a transfer film carrier handling subsystem, the transfer film carrier having a substrate surface and a laser capture microdissection transfer film coupled to the substrate surface; and then placing the laser capture microdissection transfer film in juxtaposition with the sample by moving the transfer film carrier handling subsystem, the laser capture microdissection transfer film being placed in juxtaposition with a pressure sufficient to allow laser capture microdissection transfer of a portion of the sample to the laser capture microdissection transfer film, without forcing nonspecific transfer of a remainder of the sample to the laser capture microdisection film; and then transferring a portion of the sample to the laser capture microdissection transfer film, without forcing nonspecific transfer of a remainder of the sample to the laser capture microdissection transfer film. Transferring includes moving the laser capture microdissection transfer film and the portion of the sample away from the remainder of the sample with the transfer film carrier handling subsystem. The transfer film carrier handling subsystem can be mounted on an inverted microscope. The systems and methods provide the advantages of increased speed and much lower rates of contamination
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
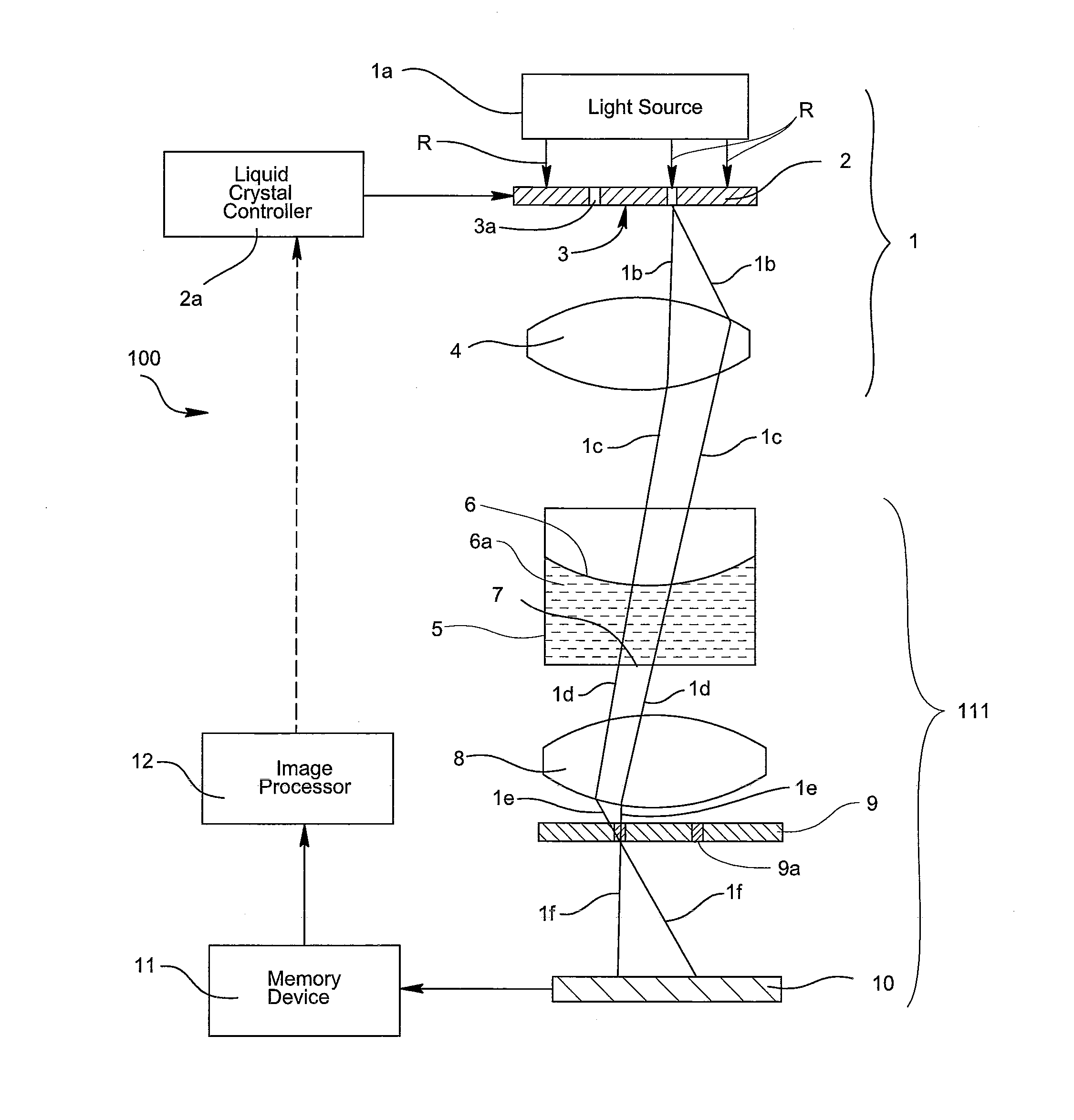
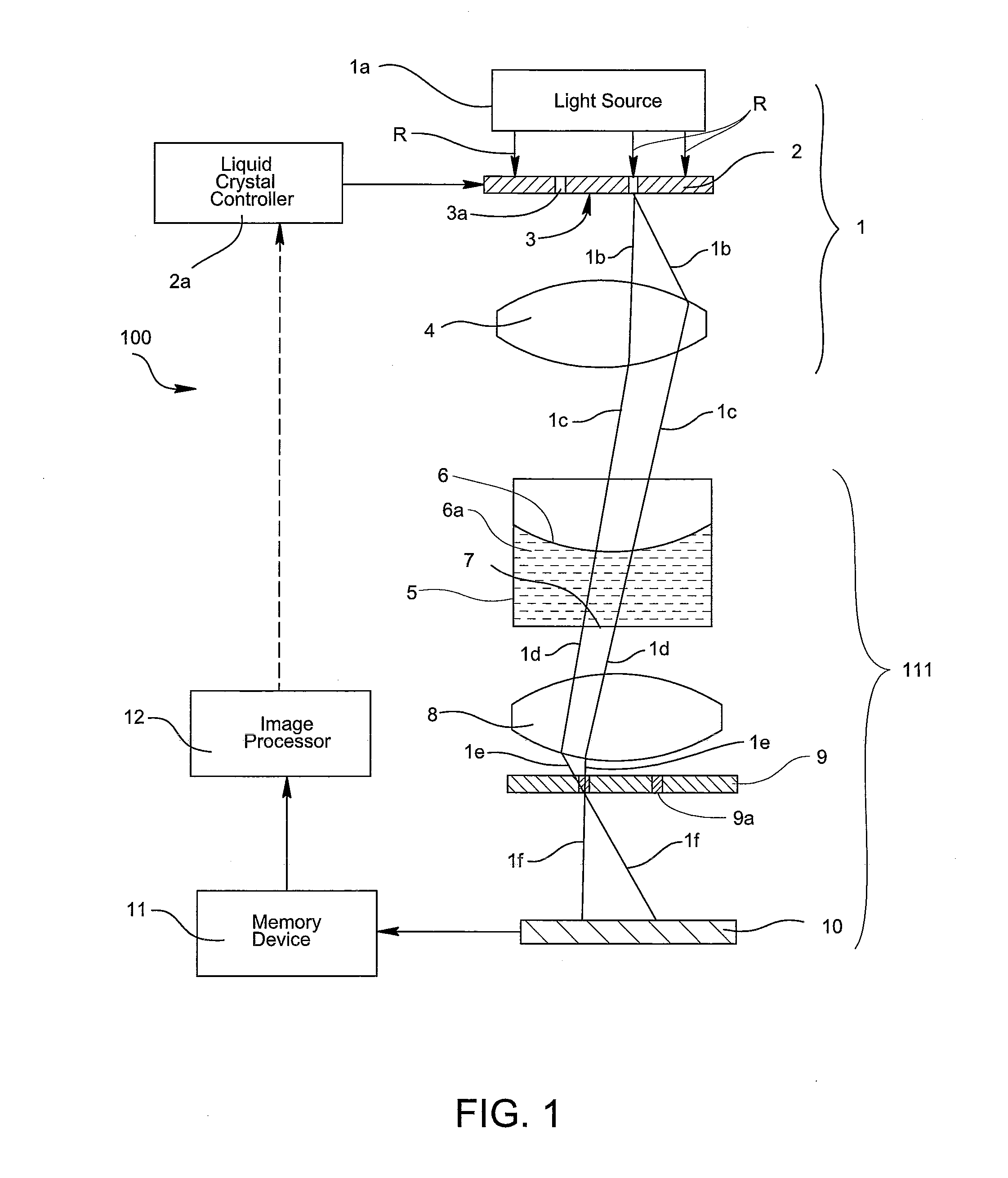
Adaptive phase contrast microscope
InactiveUS20120257040A1Region can be greatEnhance the imageColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsMicro platePhase image
An optical microscope is provided with an adjustable optical phase ring. The adjustable ring provides a way to compensate for distortion in the visible phase ring before the light reaches the sample. In an inverted microscope, when observing transparent cells under a liquid, the visible light phase ring is distorted. By the use of a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) in place of a fixed ring, the projected ring is adjusted to realign the light and produce phase. In a typical micro plate, the meniscus formed produces a lens effect that is realigned by providing changes in the position and pattern, to allow phase imaging over a wider portion of the well. The realignment of the ring can be manual or automated and can be dynamically adjusted based upon an observed image of the sample.
Owner:KAIROS INSTR
Method and System For Collecting Cells Following Laser Microdissection
ActiveUS20080199929A1Efficient advancementMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementLight beamLaser beams
A method of collecting target regions from a target object is described. The method in one embodiment comprises mounting a negatively-charged membrane on a first side of a substrate, mounting a target object on the membrane, positioning a collection material adjacent to the target object, and passing a laser beam from a second side of the substrate, through the substrate, the membrane, and the target object, to dissect target regions from the prepared tissue section, whereby the dissected target regions adhere to the collection material. In another embodiment, the present invention is a system for collecting target regions from a target object. In one embodiment, the system comprises a substrate having a first side and a second side, a negatively-charged membrane adhered to the first side of the substrate, and a collection material mountable adjacent to the membrane. In another embodiment, the system further comprises an inverted microscope, a stage for holding the substrate over the microscope, a generator operable to generate a laser beam to pass through the substrate from the second side and to dissect target regions from a target object mounted on the membrane, whereby the dissected target regions adhere to the collection material. In the preferred embodiments, the target objects are tissues and the target regions are cells.
Owner:MOTIC CHINA GRP CO LTD
Single cell microoperation apparatus for microscopic injection
InactiveCN101481653ASimple structureBare microBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicro-operationThree degrees of freedom
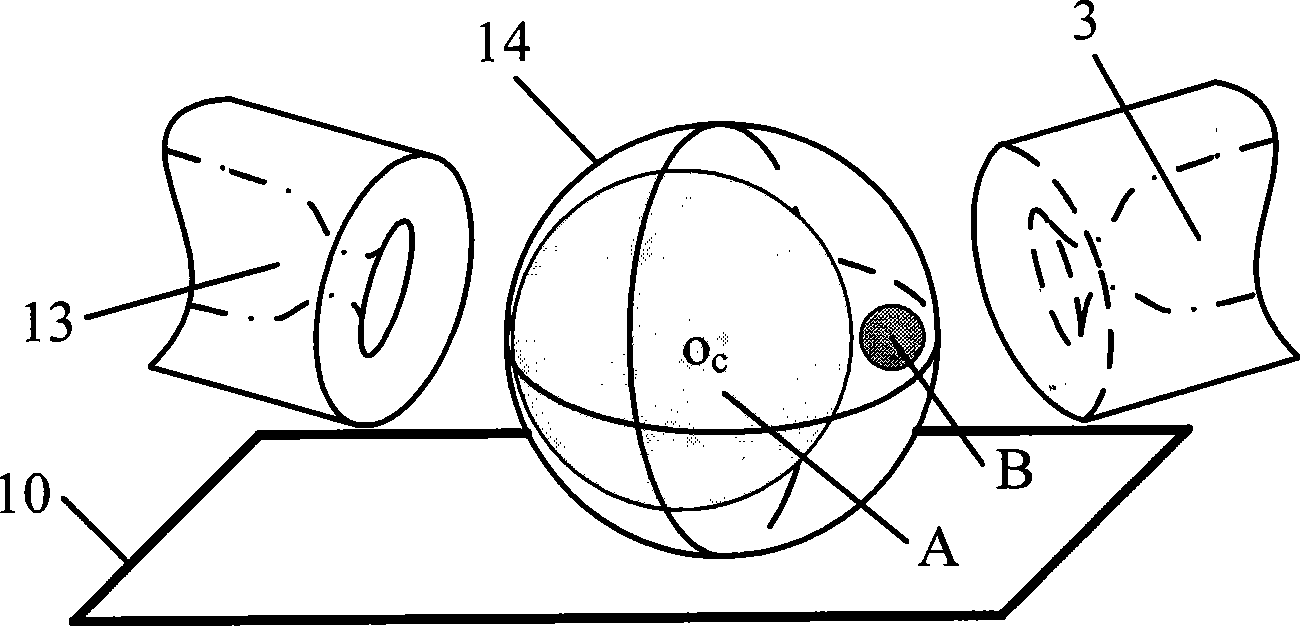
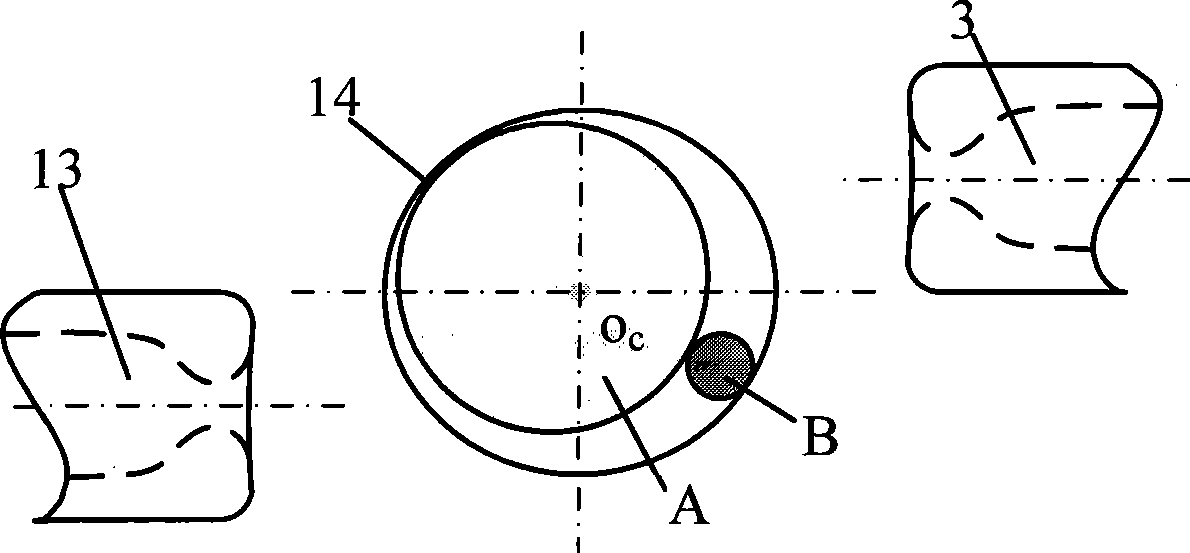
The invention discloses a unicellular micro-operation device used for microinjection. An air supply and a pressure control valve of the device and a left and a right end effectors form a sealed air course through a passage in a holder; the left and the right end effectors are respectively connected with a left and a right three dimensional micromotion stages through the holders; the left and the right three dimensional micromotion stages are symmetrically arranged on the left side and the right side of an inverted microscope worktable; the left and the right end effectors form a unicellular micro-operation flow field with controllable flow rate distribution on the inverted microscope worktable; and a computer collects signals of an image detecting and processing unit to respectively control the pressure control valve and the left and the right three dimensional micromotion stages. The micro-operation device effectively controls the operation environmental flow field of cells, and forms a stable unicellular micro-operation flow field with controllable flow rate distribution to drive the cells to move. Through the invention, the cellular angle in the three dimensional orthogonalized plane can be randomly adjusted, so that the three degrees of freedom (DOF) attitude of the cells can be accurately controlled; and the three dimensional spatial location of the cells is adjusted to realize the accurate positioning of the location and attitude of the cells.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
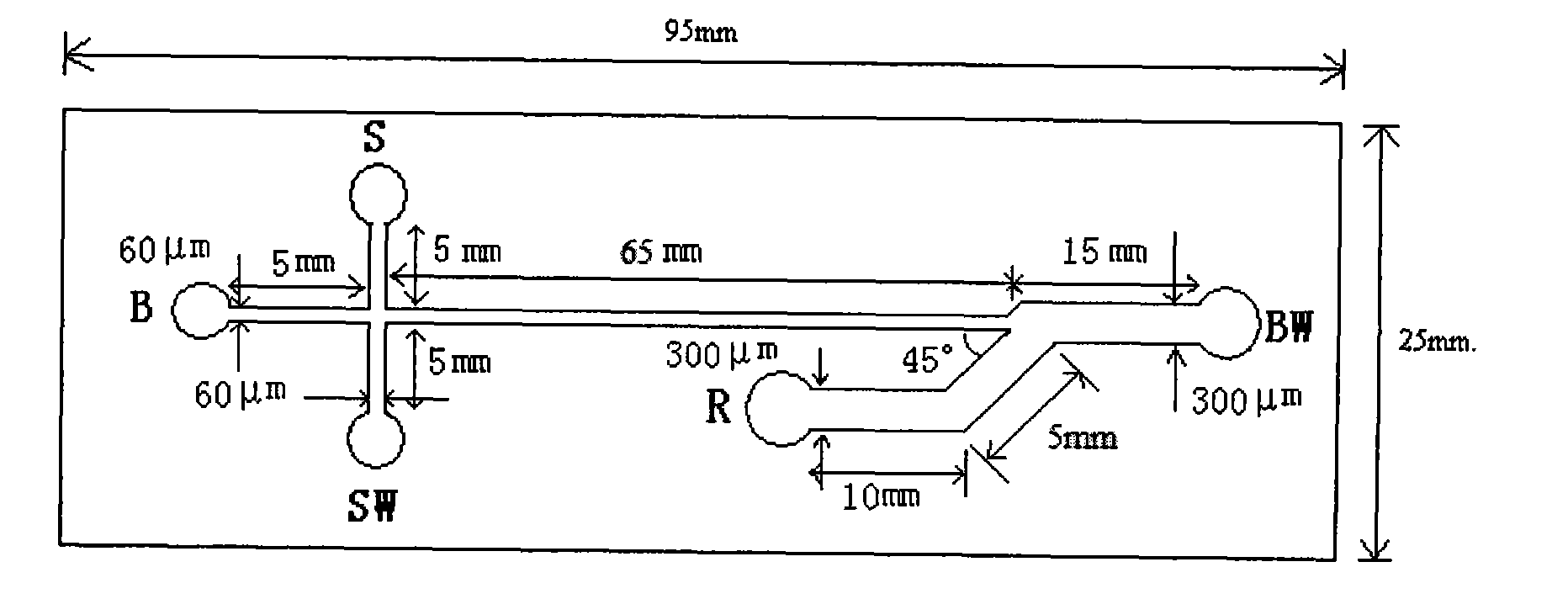
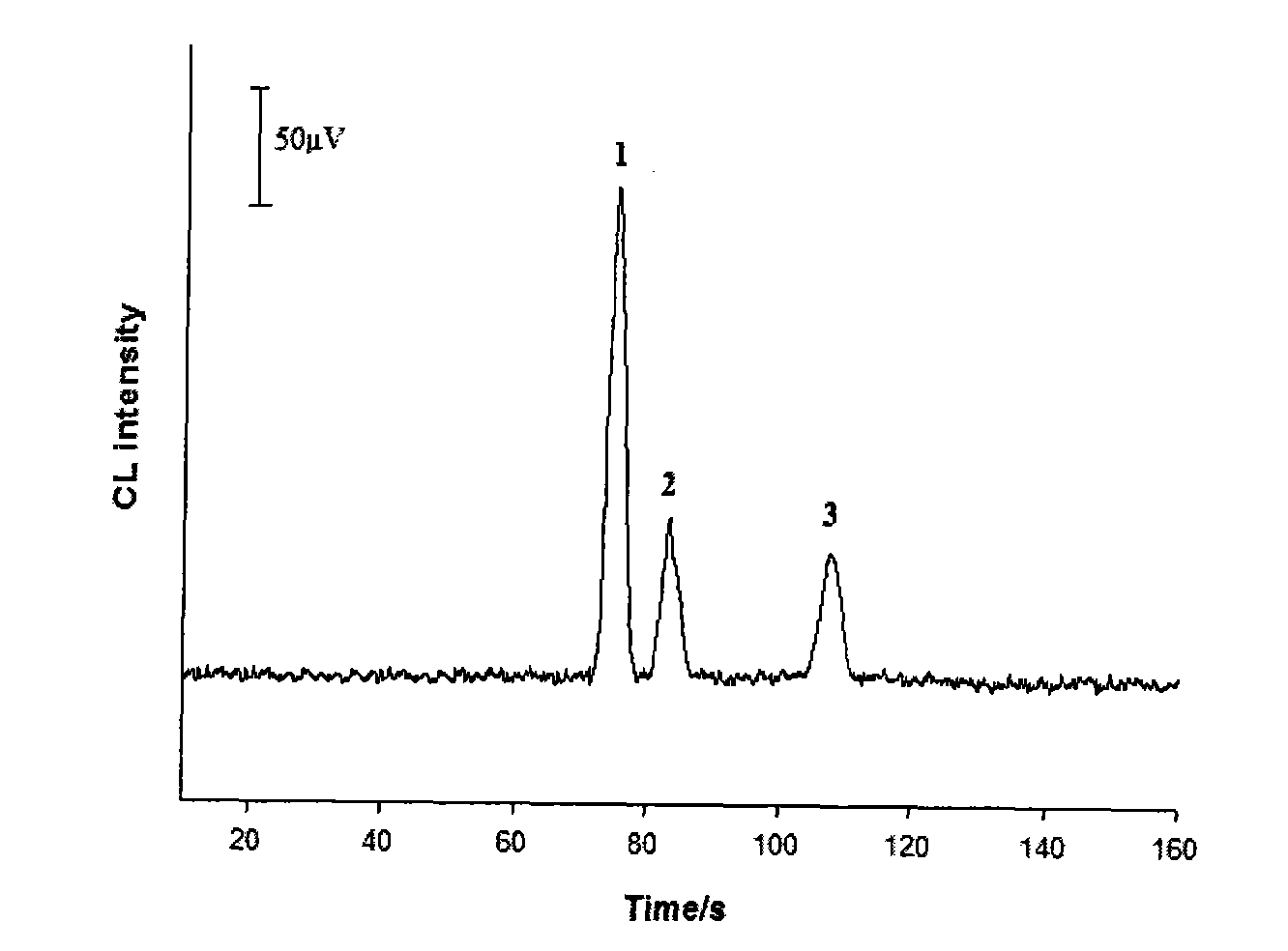
Method for measuring materials inside human single blood erythrocyte by mocro-fluidic chip chemiluminescence
InactiveCN101672788AFast analysisHigh sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceCysteine thiolateData acquisition
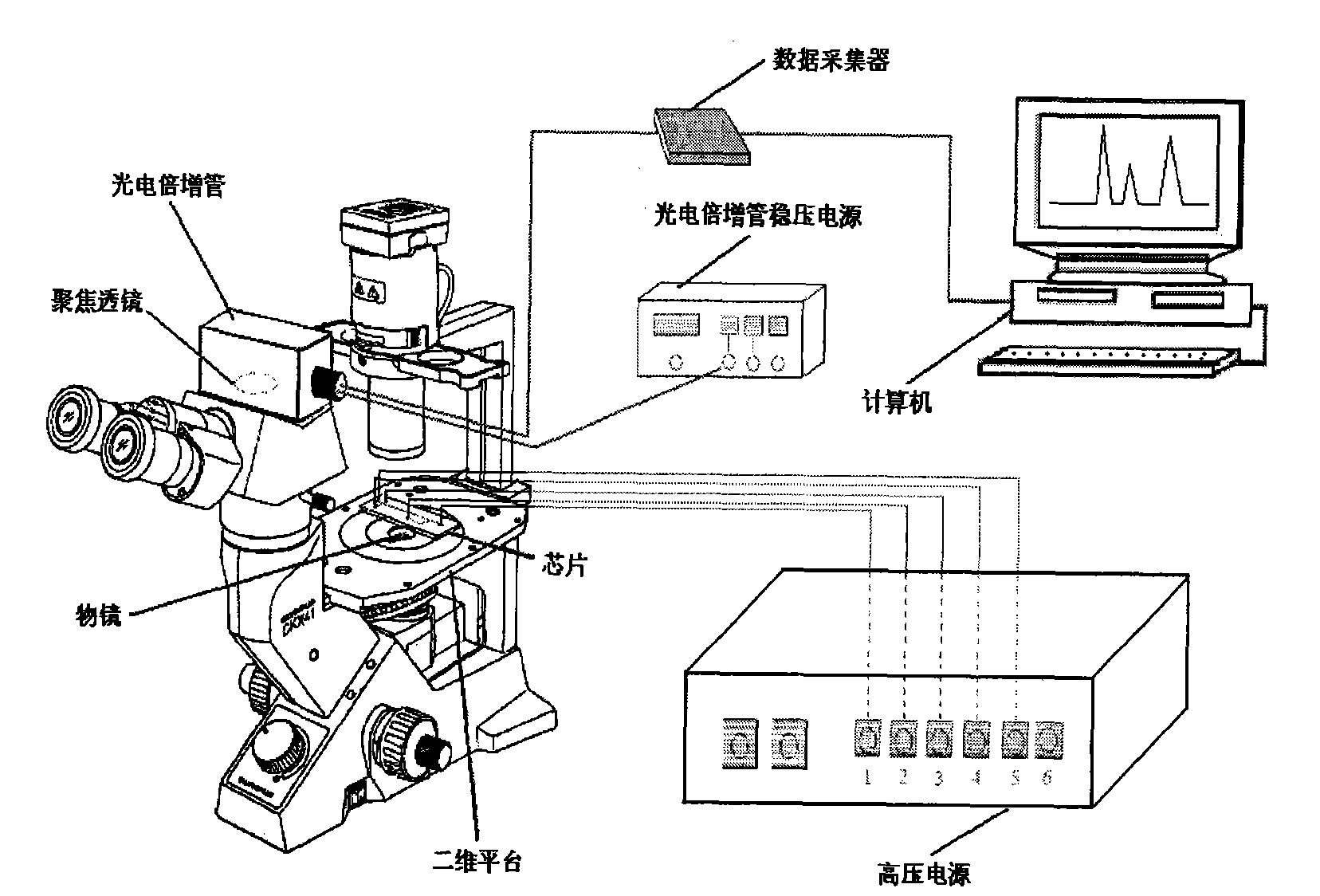
The invention provides a method for measuring materials inside human single blood erythrocyte by mocro-fluidic chip chemiluminescence, which can analyze the contents of cysteine, glutathione and hemoglobin in a single blood erythrocyte. An electrophoresis chemiluminescence detection system of a mocro-fluidic chip is adopted; five power supply output ends of a high voltage power supply are respectively connected with a buffer solution pool B, a sample pool S, a waste liquie pool SW, a chemiluminescence reagent pool R and a buffer waste liquie pool BW of the mocro-fluidic chip; the mocro-fluidicchip is arranged on an objective lens of a chemiluminescence detector; the chemiluminescence detector is an inverted microscope combined with a photomultiplier; the photomultiplier is electrically connected with a data collector; and the data collector is electrically connected with a computer. The method can carry out early diagnosis on occurrence of lesions by measuring the increased degree ofthe concentration of the glutathione and the cysteine in the single blood erythrocyte, has high analysis speed, high sensitivity and high resolution, is suitable for early diagnosis to health examination and the lesions of a human body, and can be used as an effective means of preventive medicine.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Identification of blood elements using inverted microscopy
ActiveUS20080138852A1Reduce testing costsImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationBiological particle analysisMedicineCycle time
A method of identifying the elements of a blood sample including placing an aliquot of blood on a transparent substrate such as a coverslip. The blood is allowed to stand and the cells to settle to form a layer or matrix. Inverted microscopy is used to identify the elements in the sample. Various forms of illumination may be used alone or in multiple combinations. The method improves the accuracy due to homogenous distribution of formed elements in the wet drop or aliquot, simplifies the method, lowers the cost of the test and results in a shortened analytical cycle time.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS HEMATOLOGY INC
Identification of blood elements using inverted microscopy
ActiveUS9176121B2Reduce testing costsImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationBiological particle analysisMedicineCycle time
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS HEMATOLOGY INC
Method of assaying cellular adhesion with a coated biochip
InactiveUS7122301B2Observed effectEfficient separationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementCell adhesionIn vivo
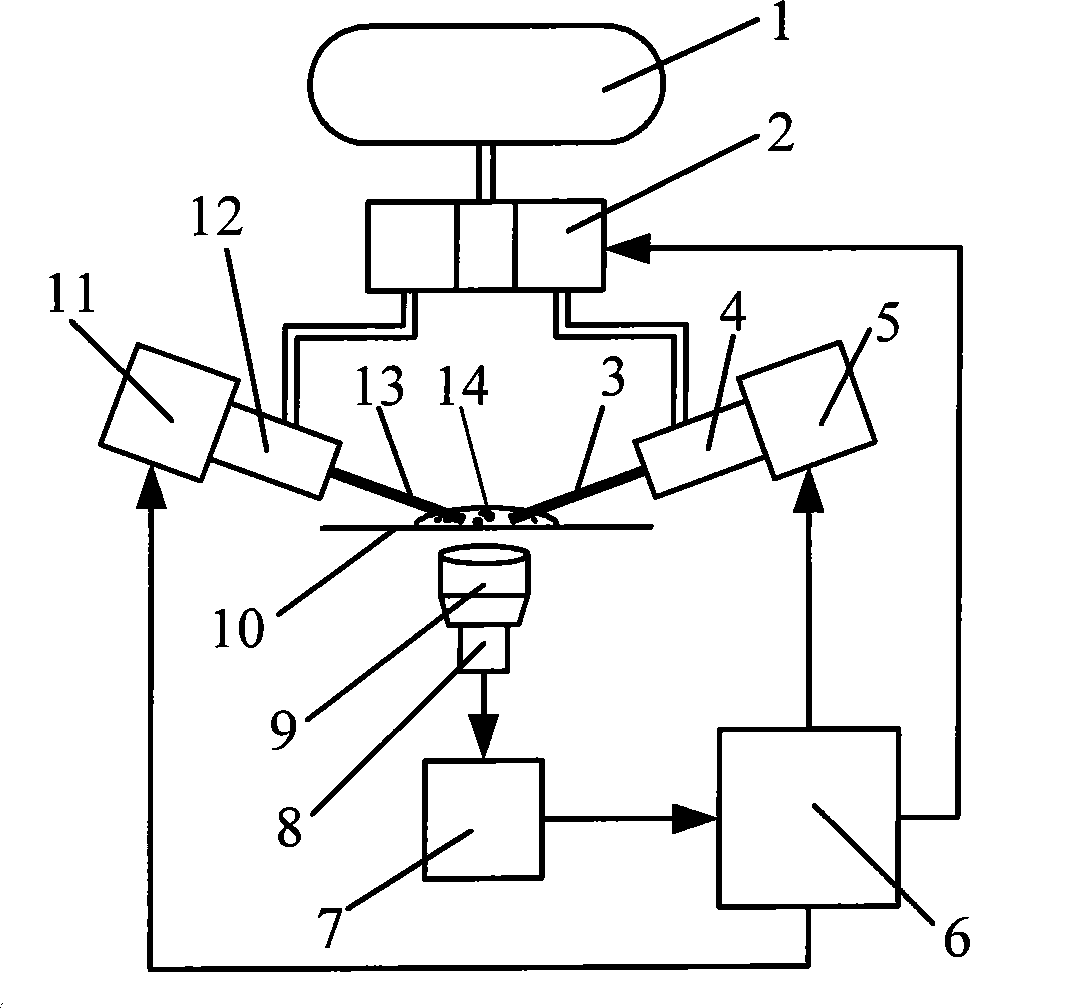
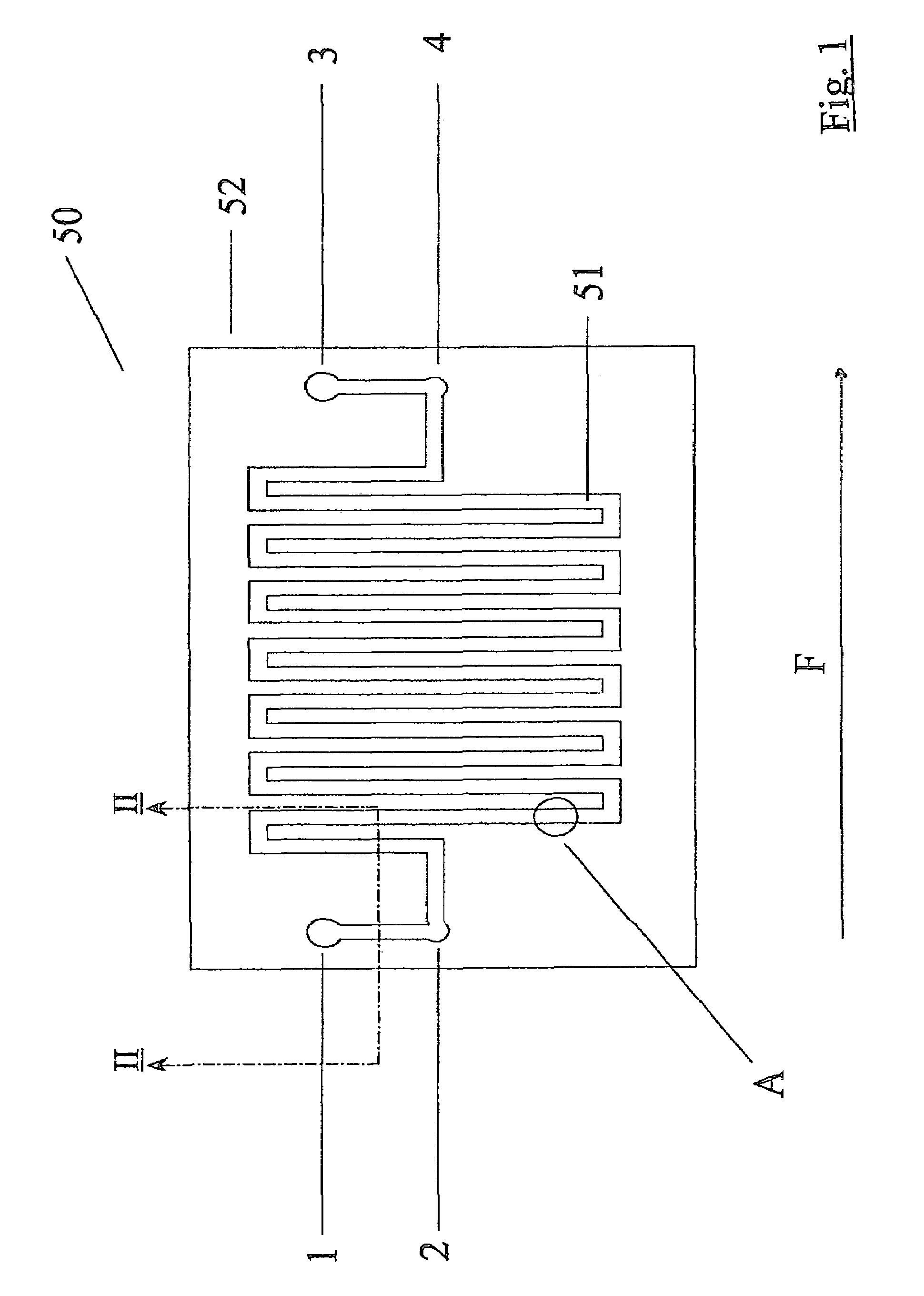
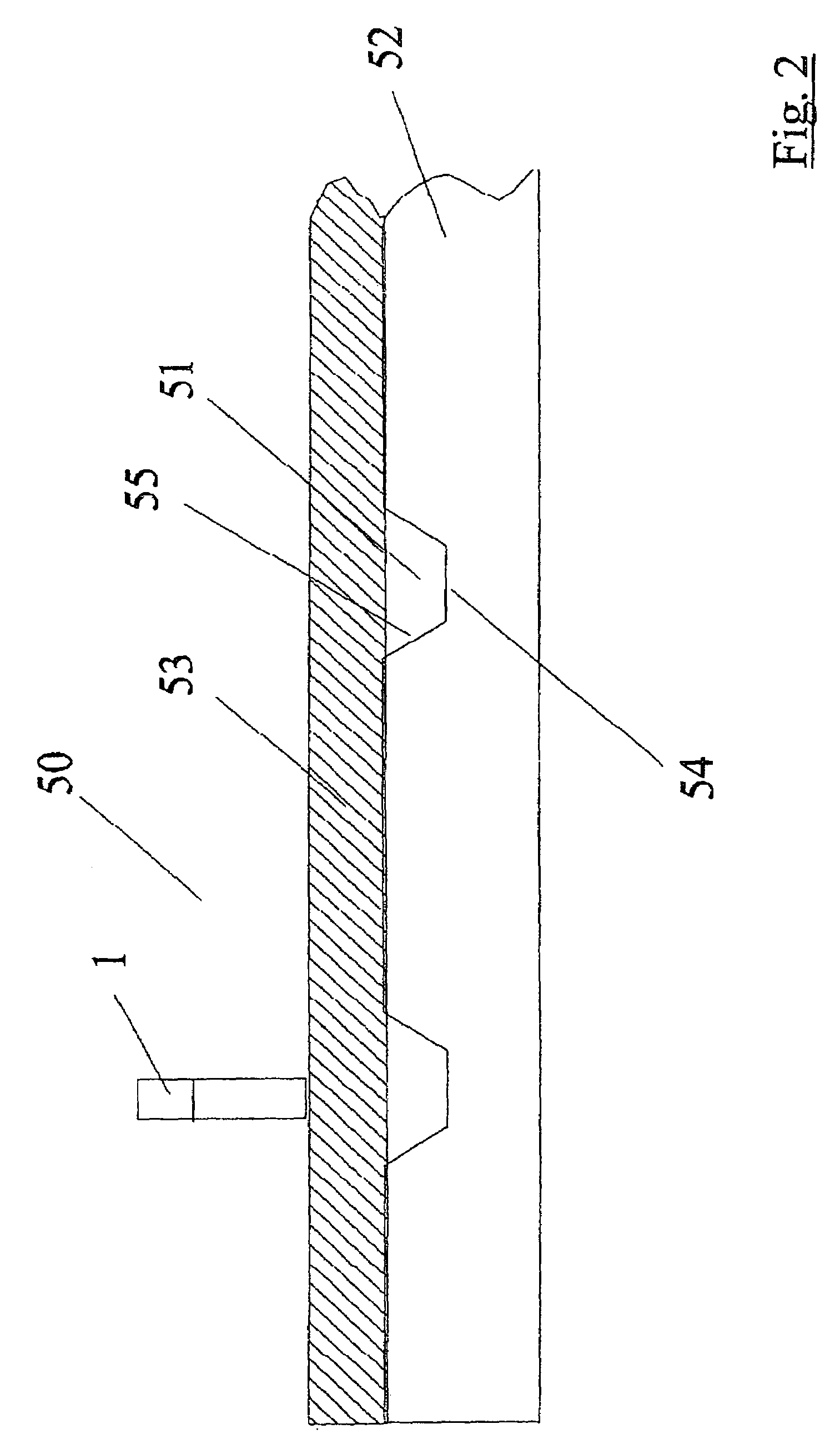
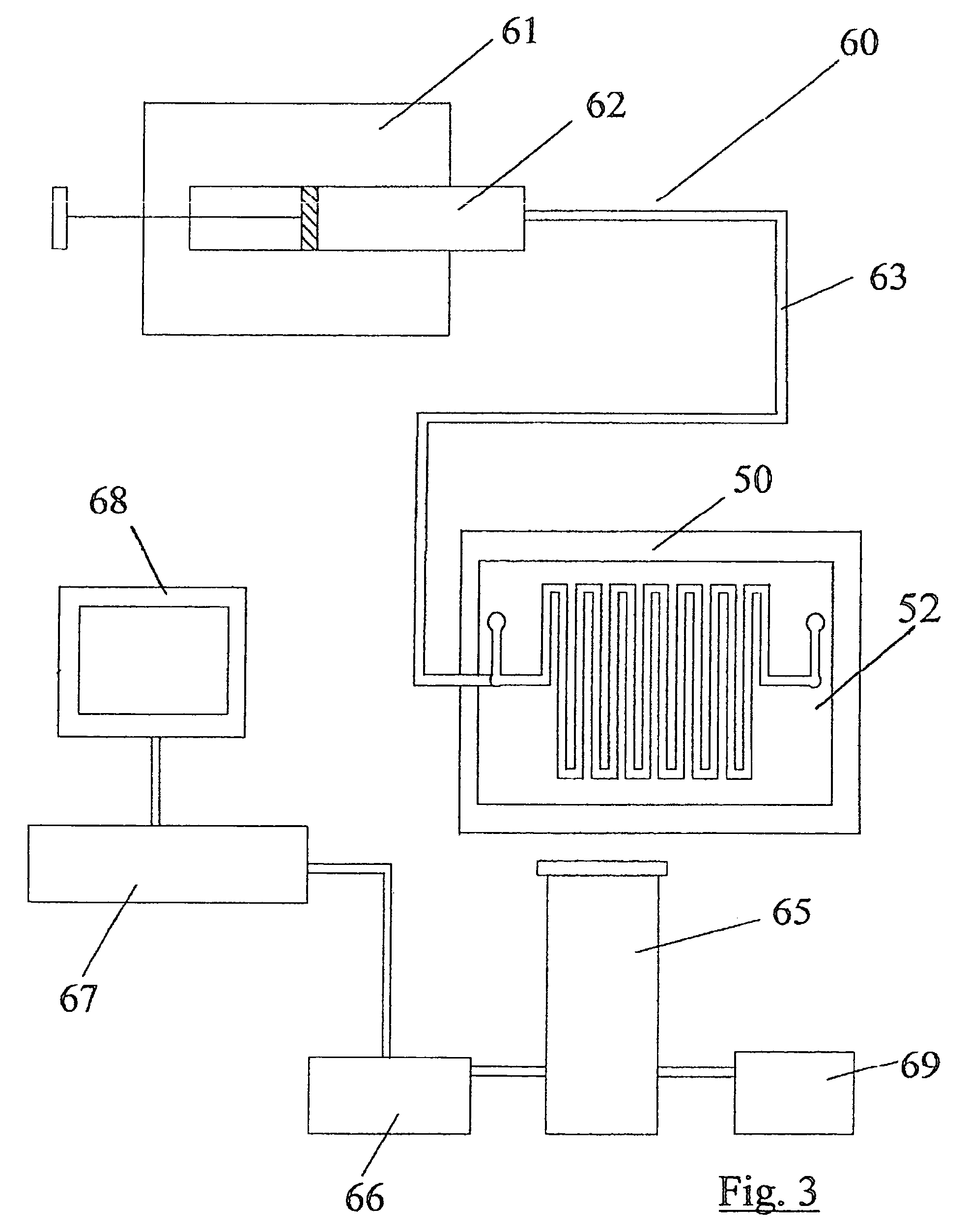
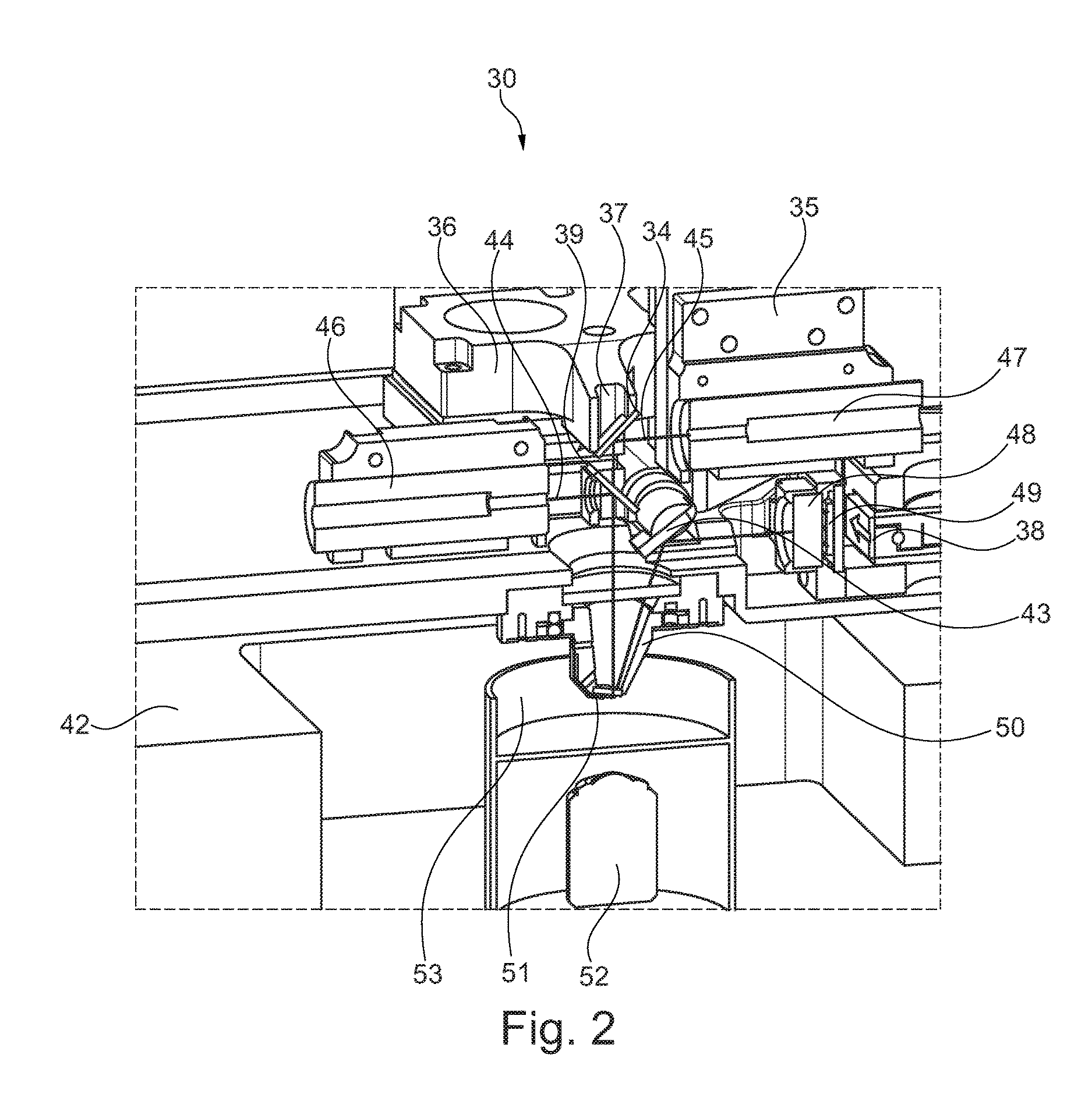
Biological assays using various constructions of biochips are disclosed to mirror in vivo situations. The biochip 50 comprises a microchannel 51 having a liquid outlet port 1, bubble release port 2 and a liquid outlet port 3 with an associated bubble release port 4. A multiplicity of tests can be performed often by coating the bore of the microchannel 50 which various adhesion mediating proteins or the use of chemoattractants. The assay assembly 60 comprises a syringe pump feeding the biochip 50. An inverted microscope 65, digital camera 66 and recorder 67 are provided. A sample liquid containing cells in suspension is injected slowly through the biochip and the effect of the assay recorded over a long period.
Owner:TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN
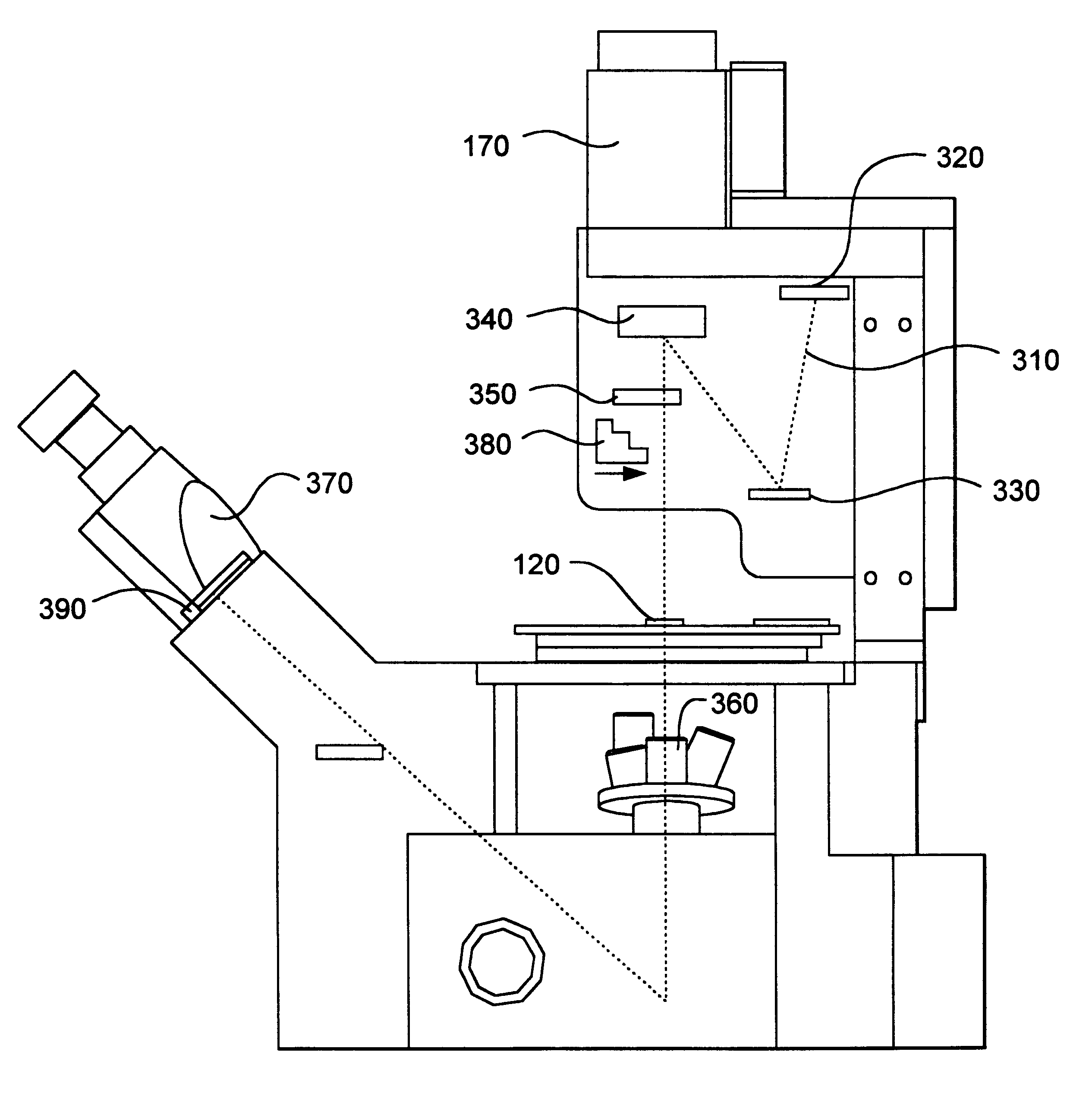
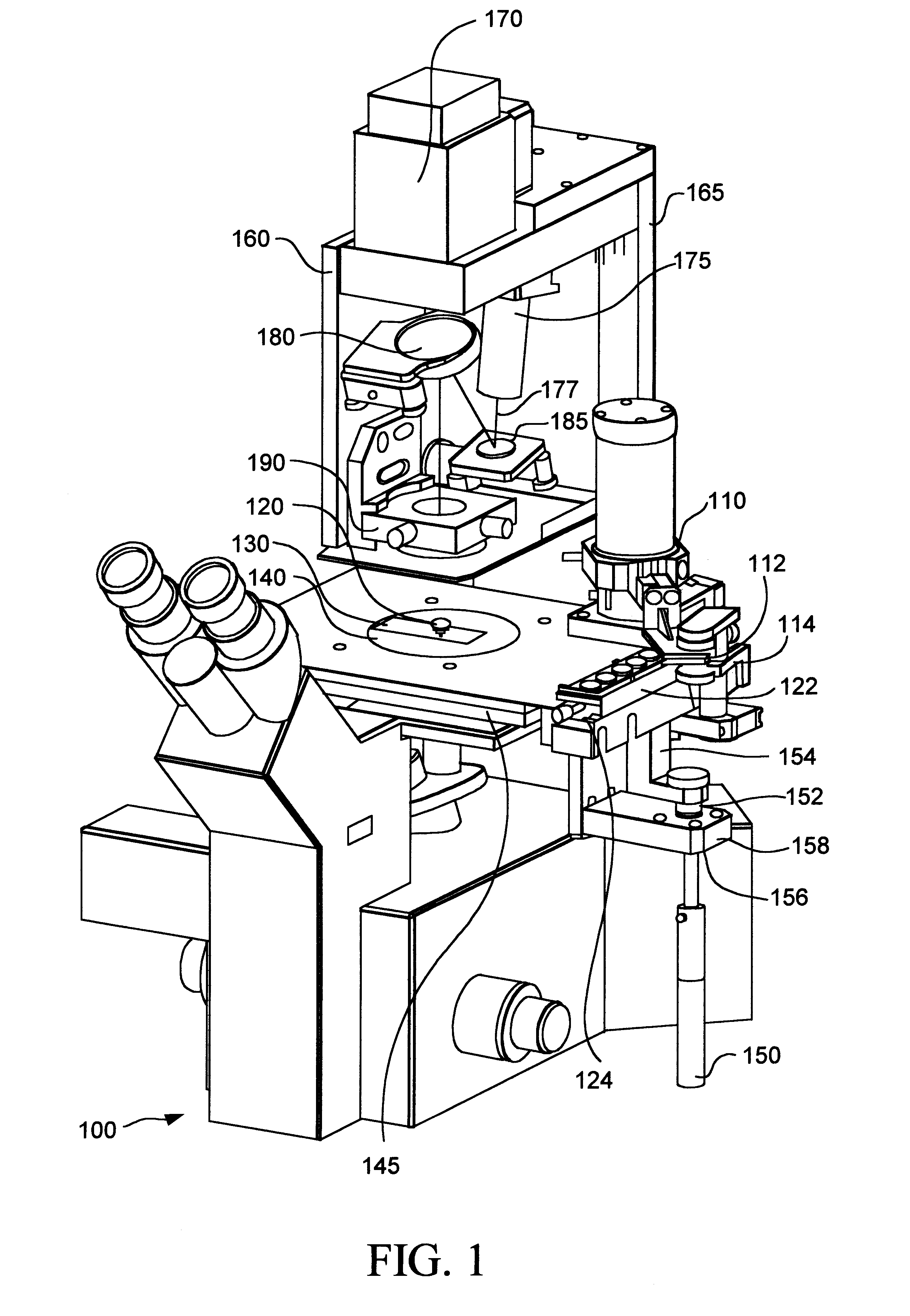
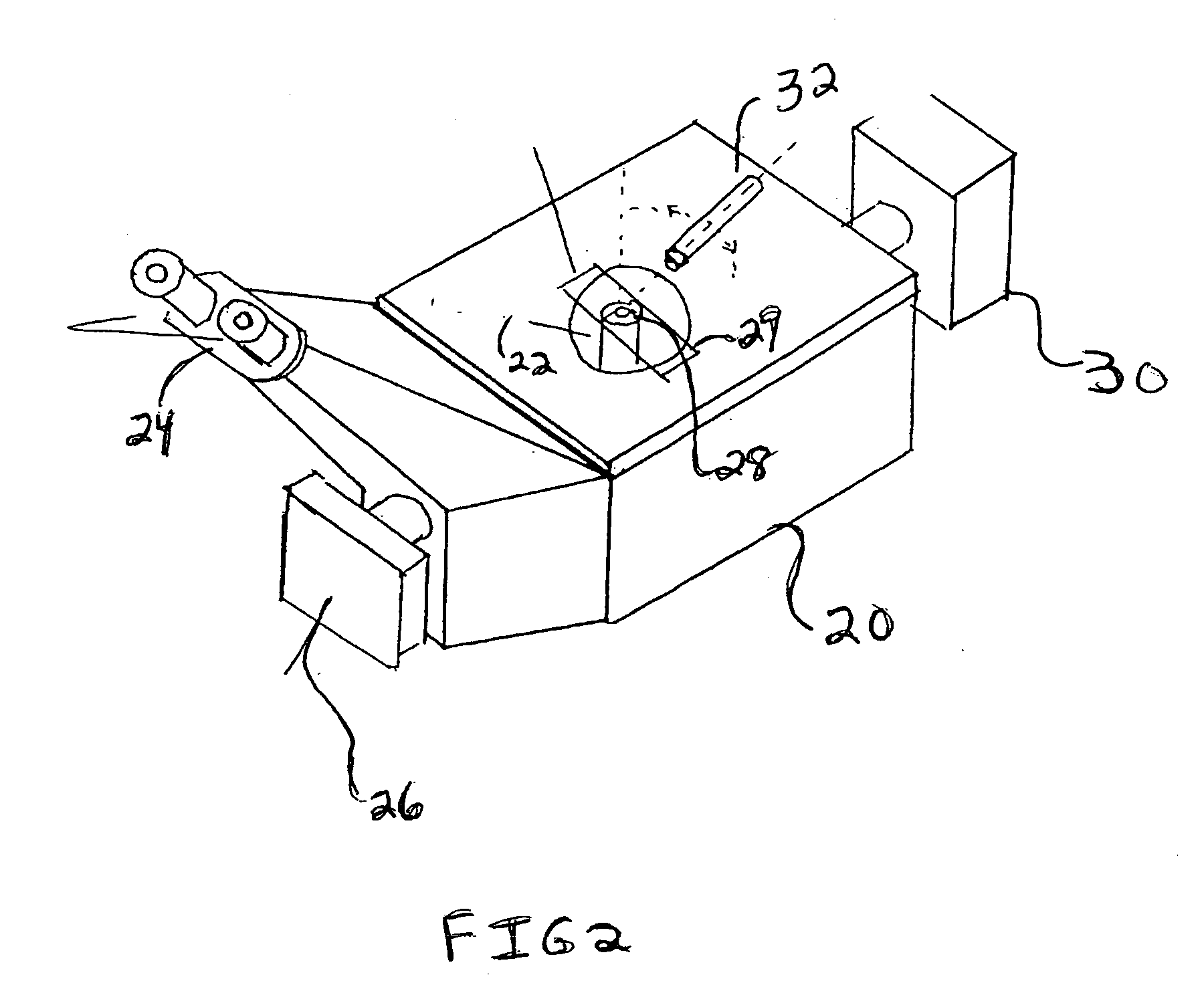
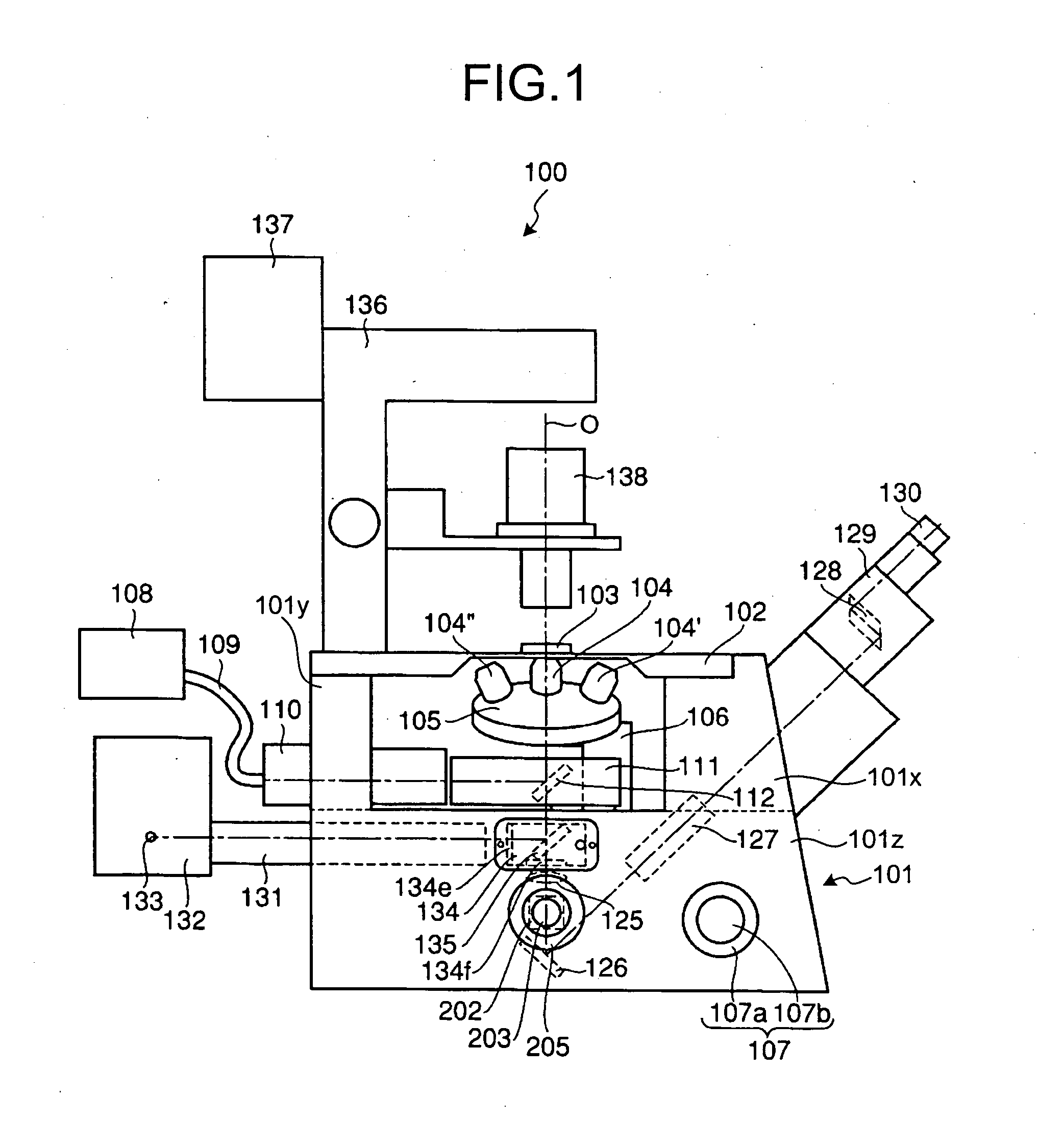
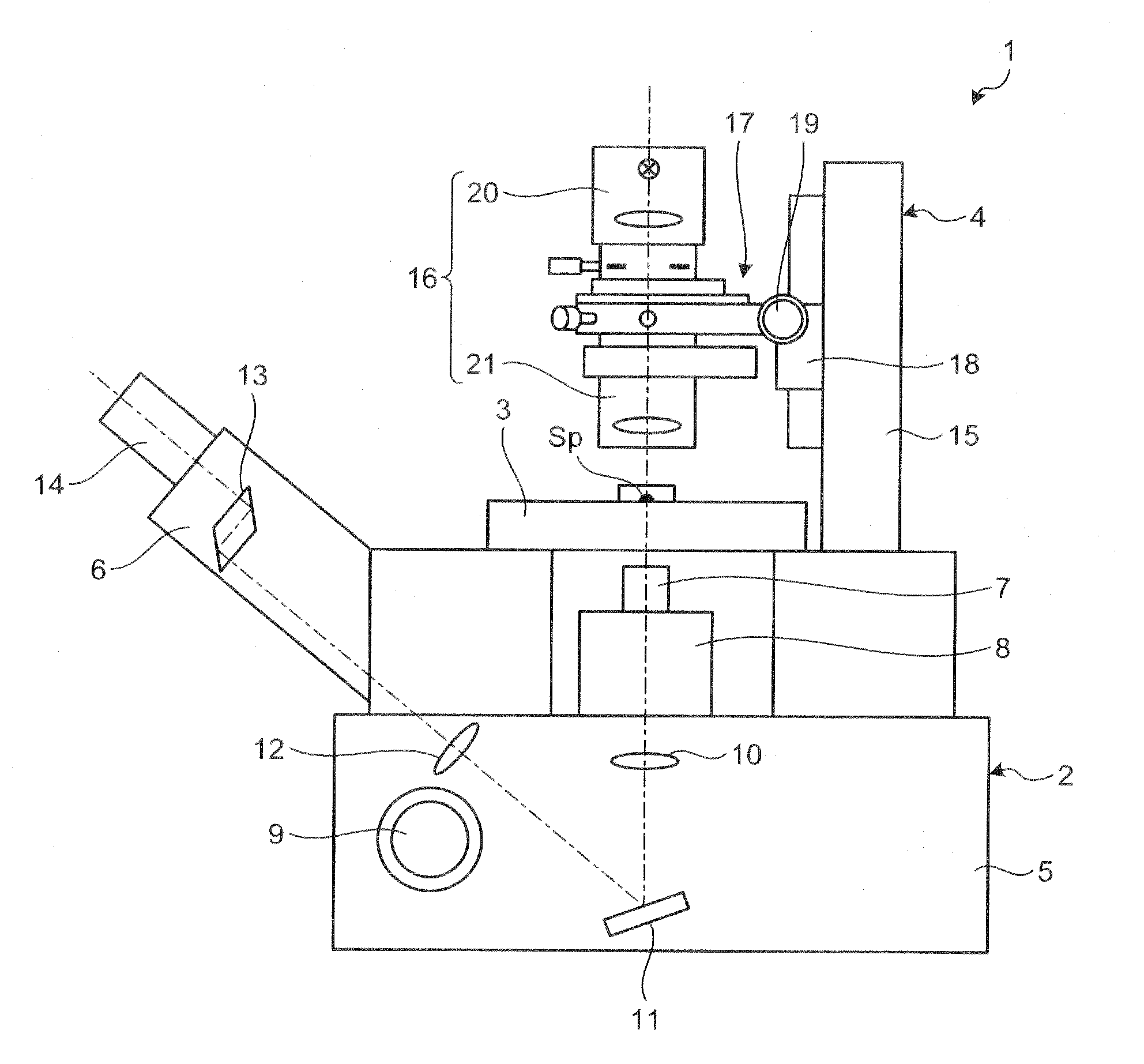
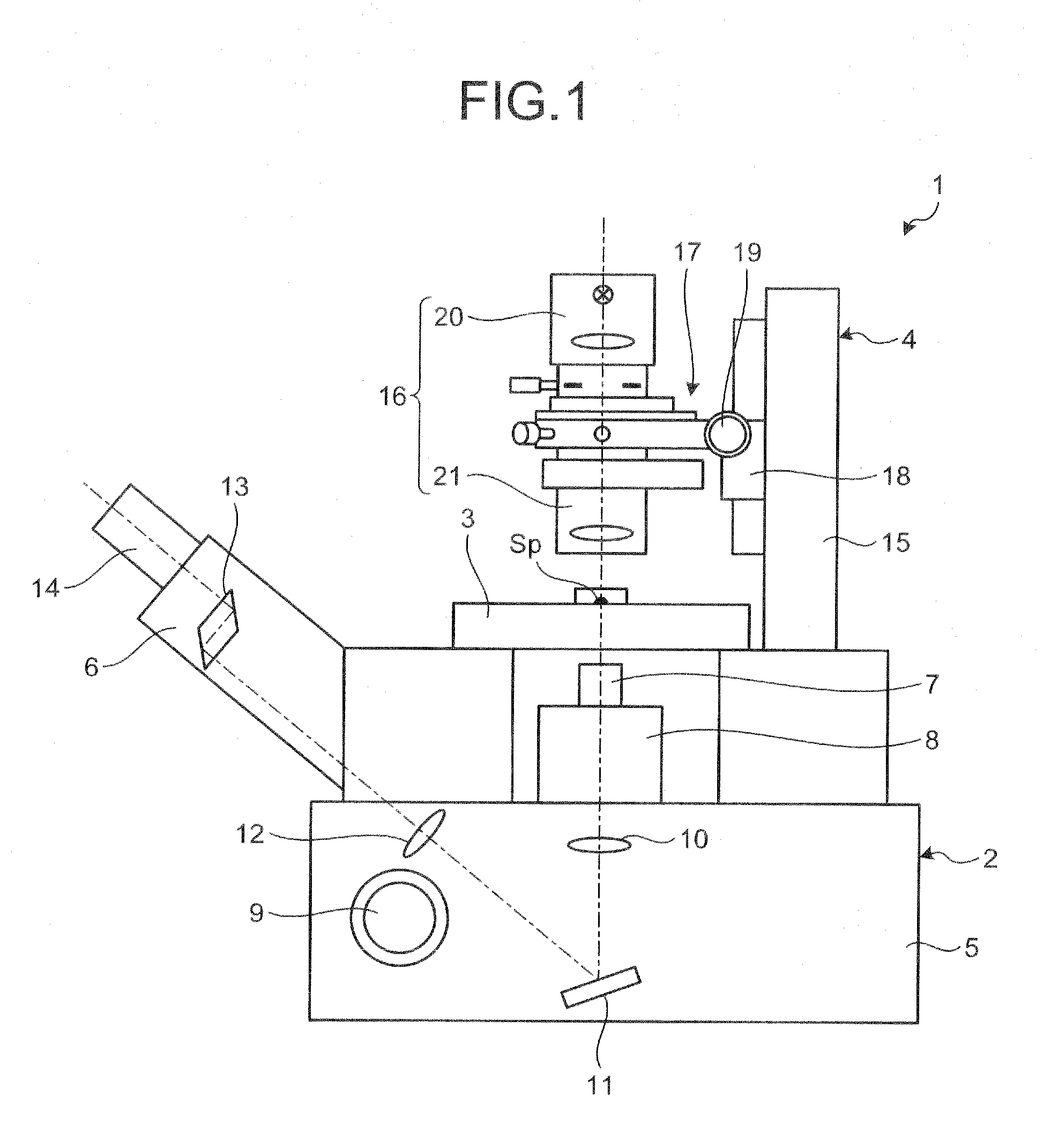
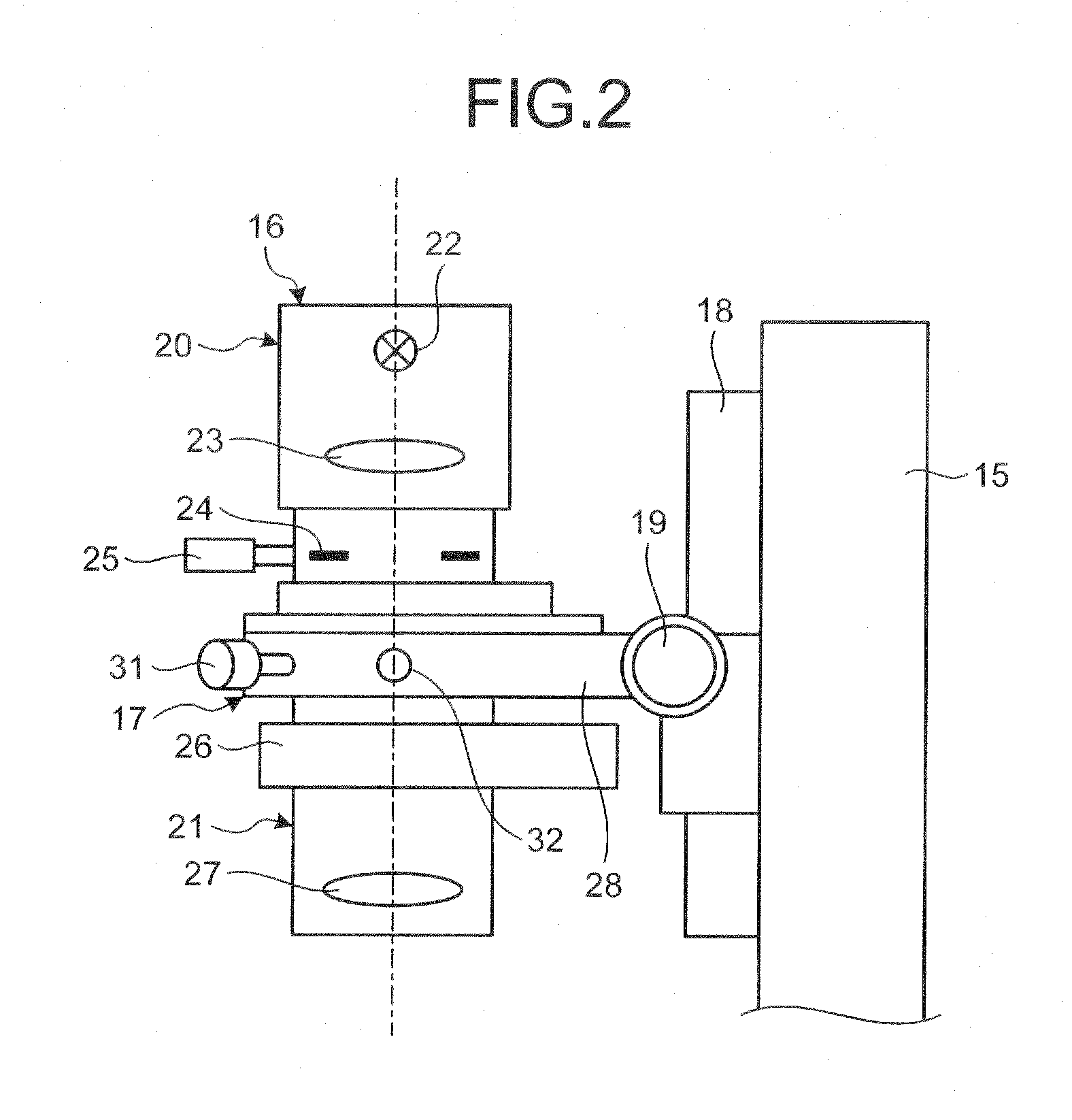
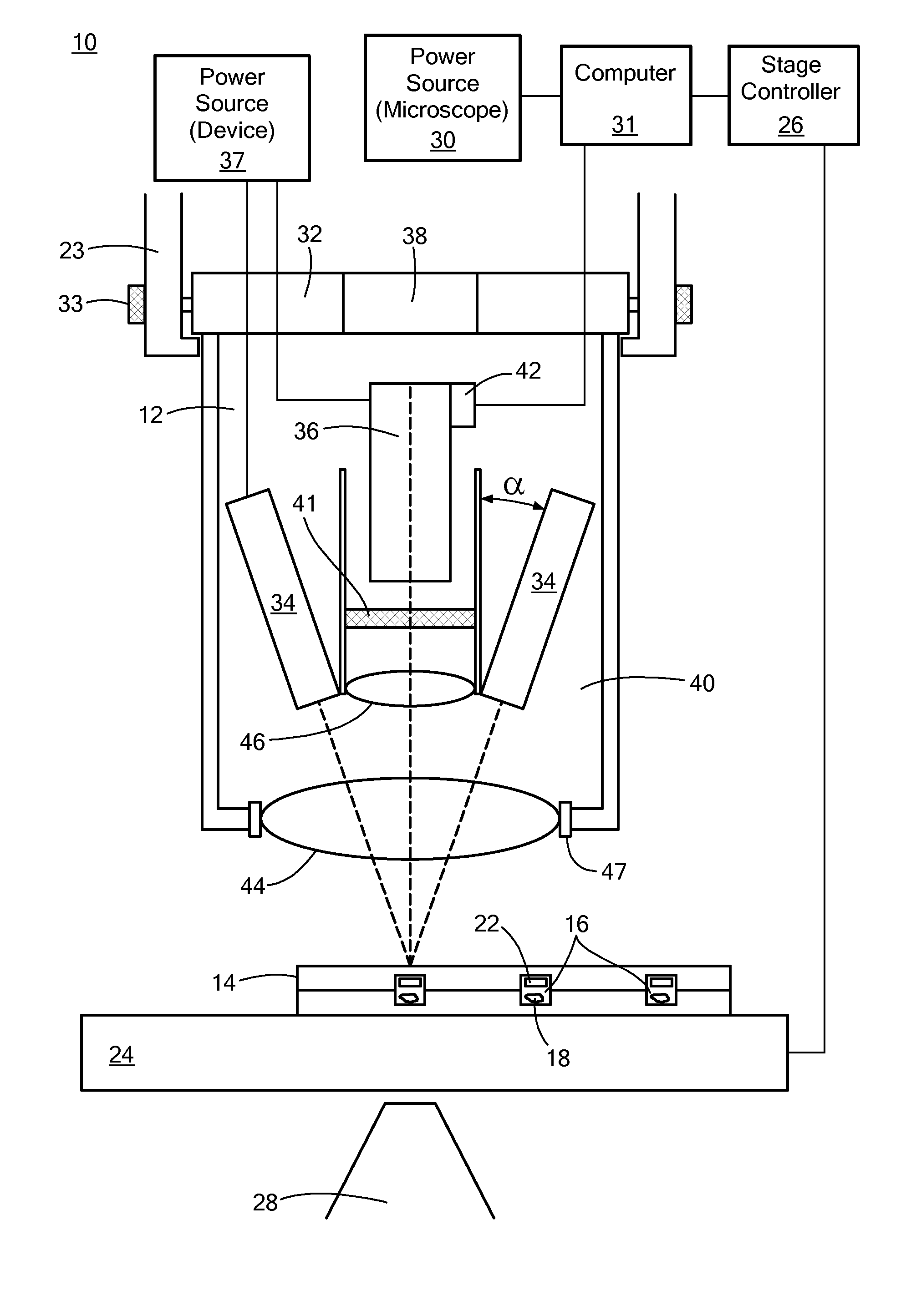
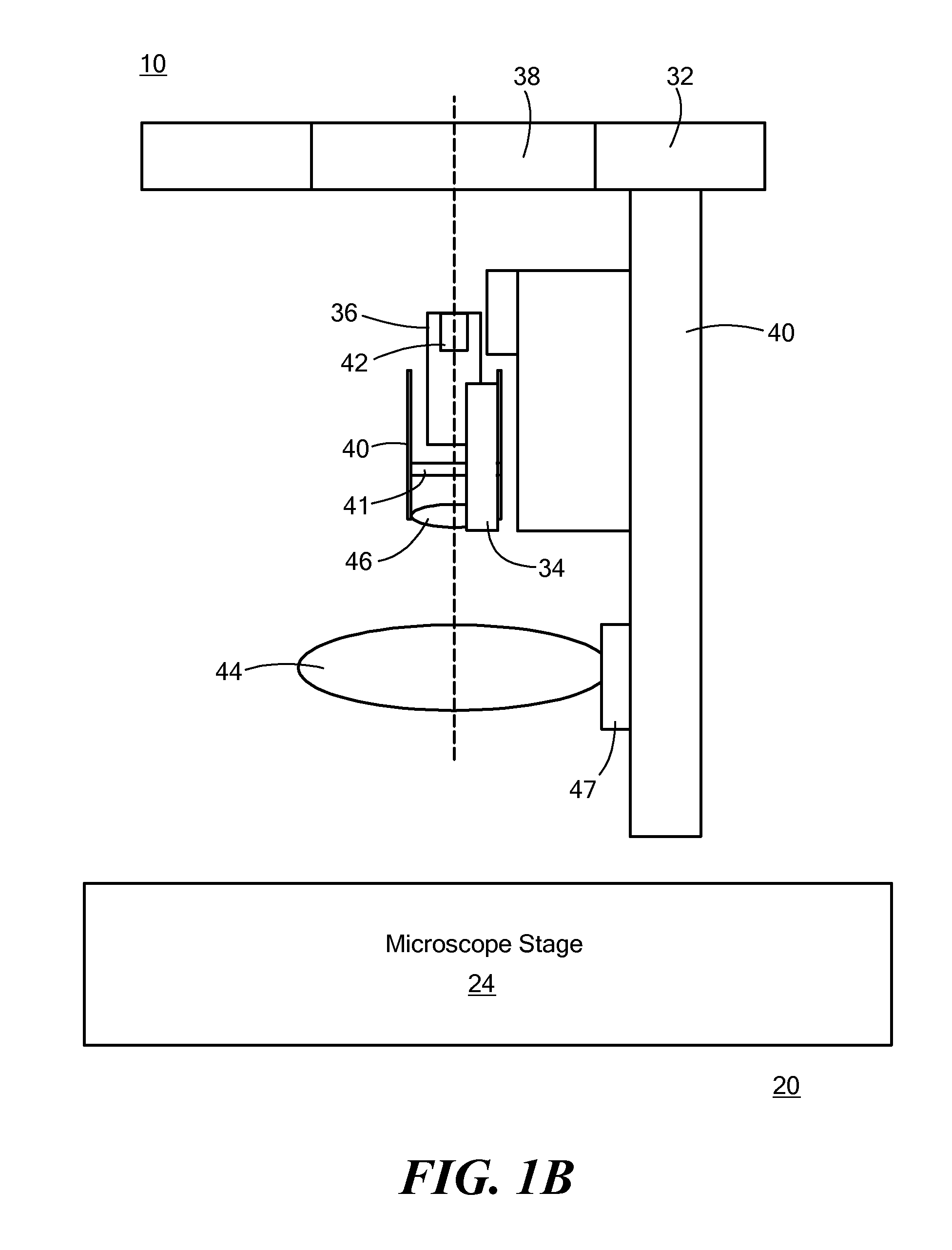
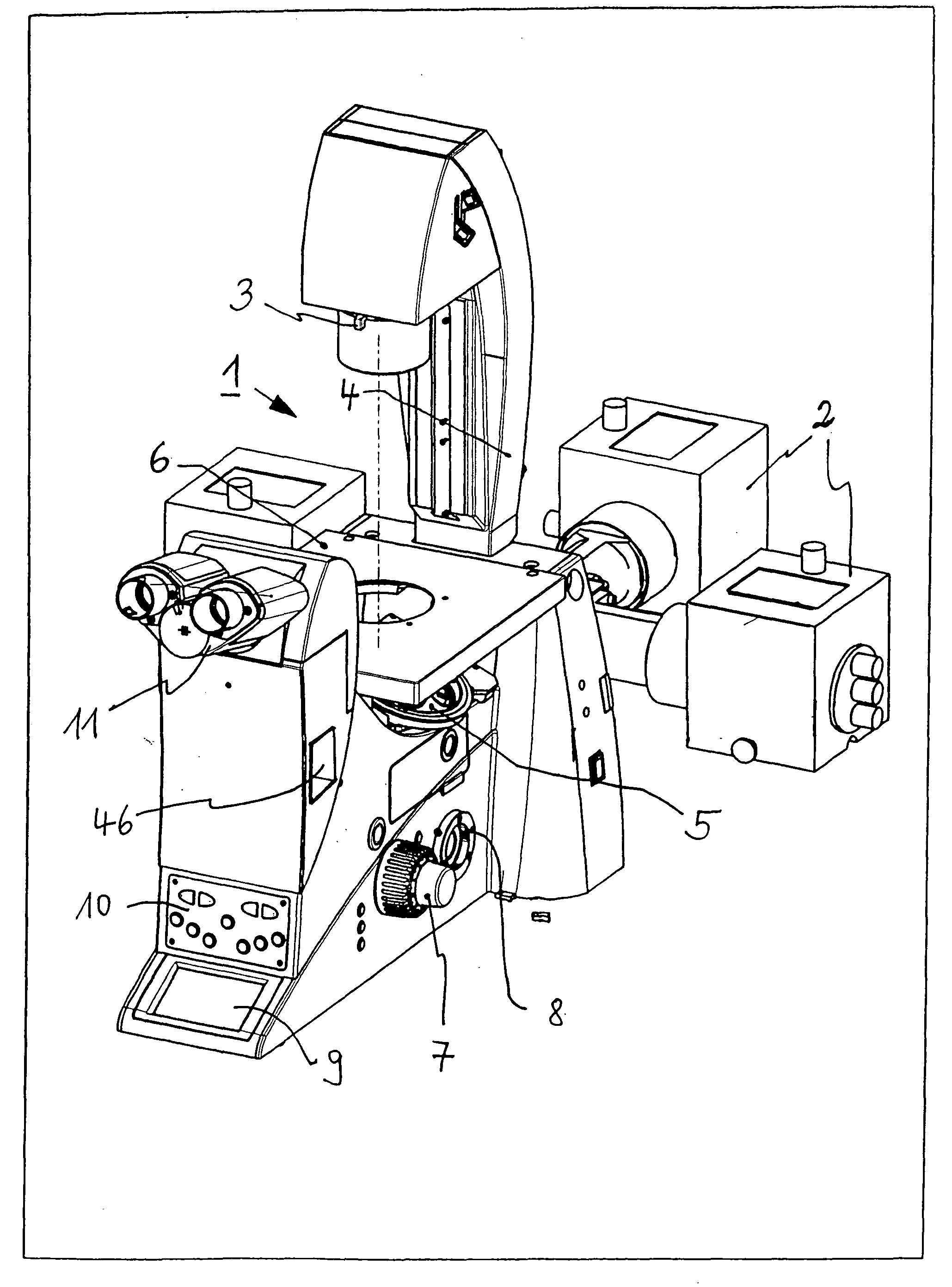
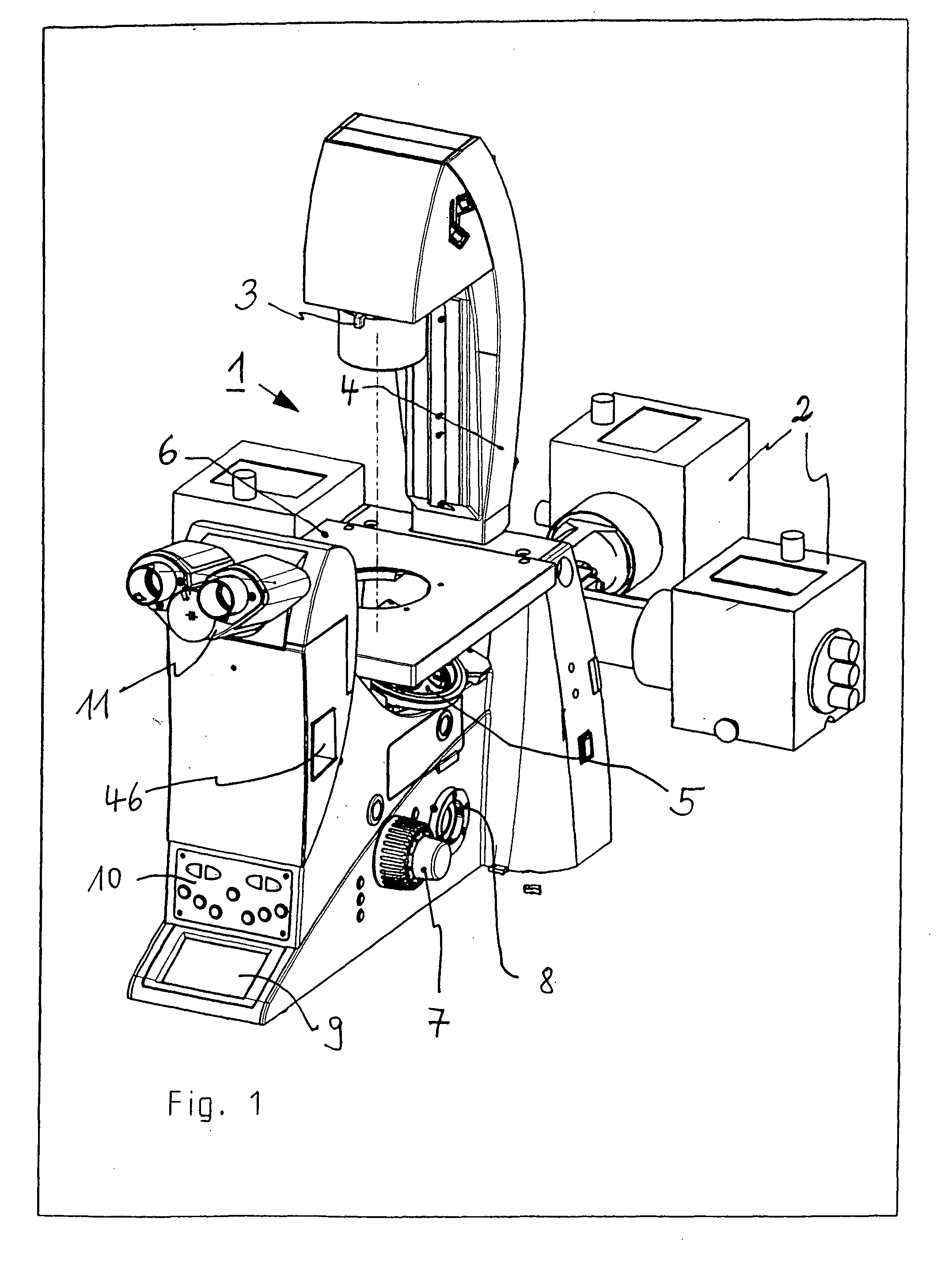
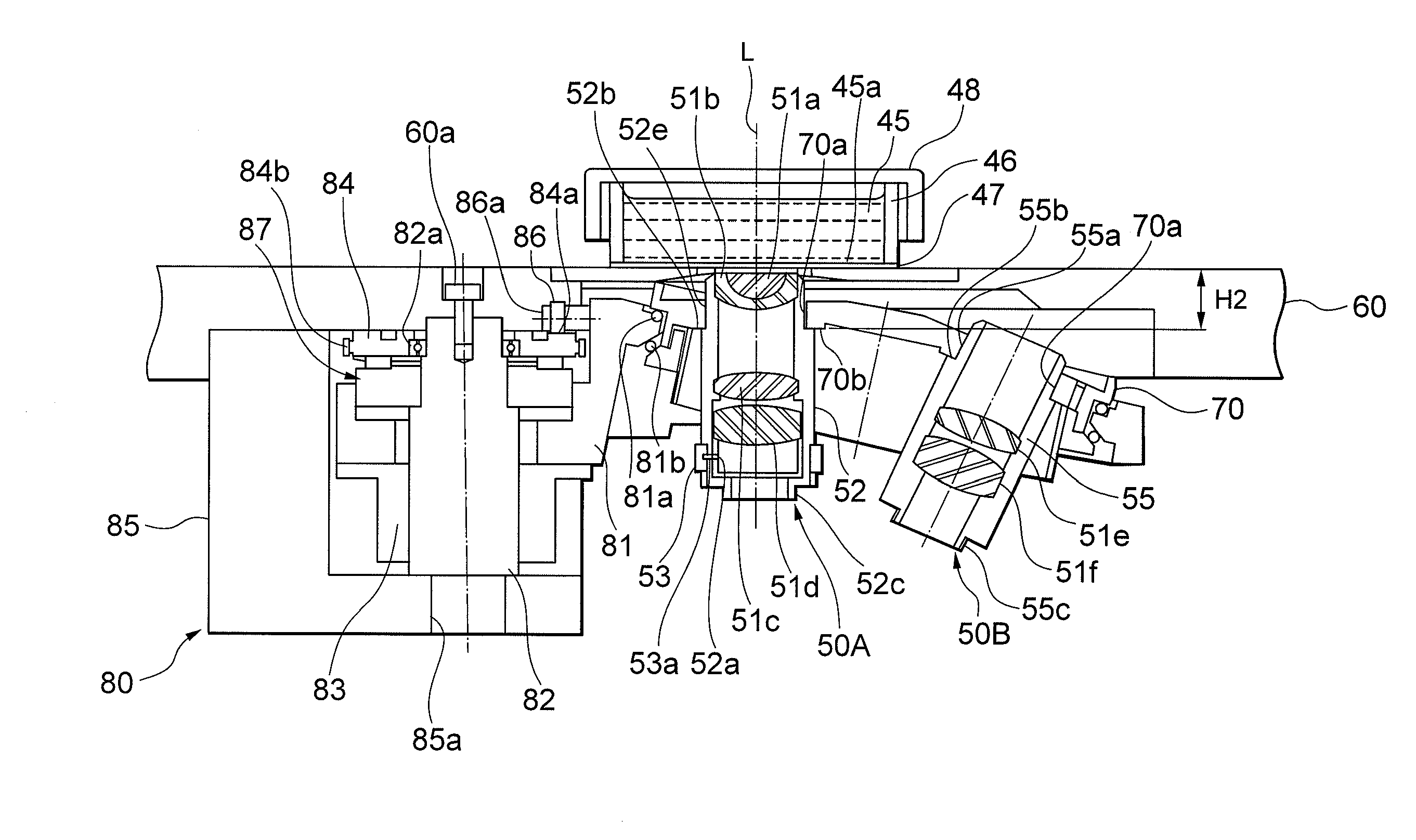
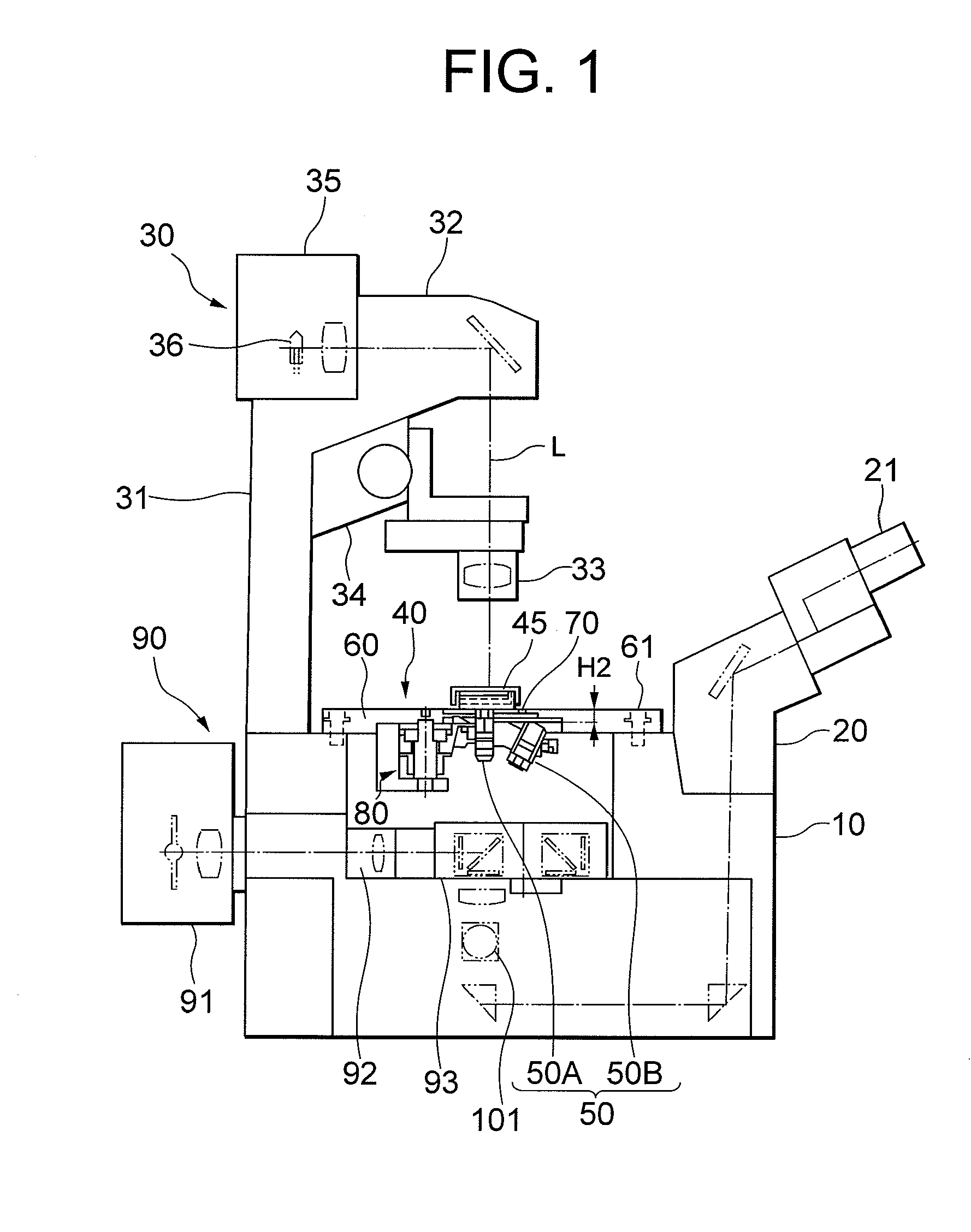
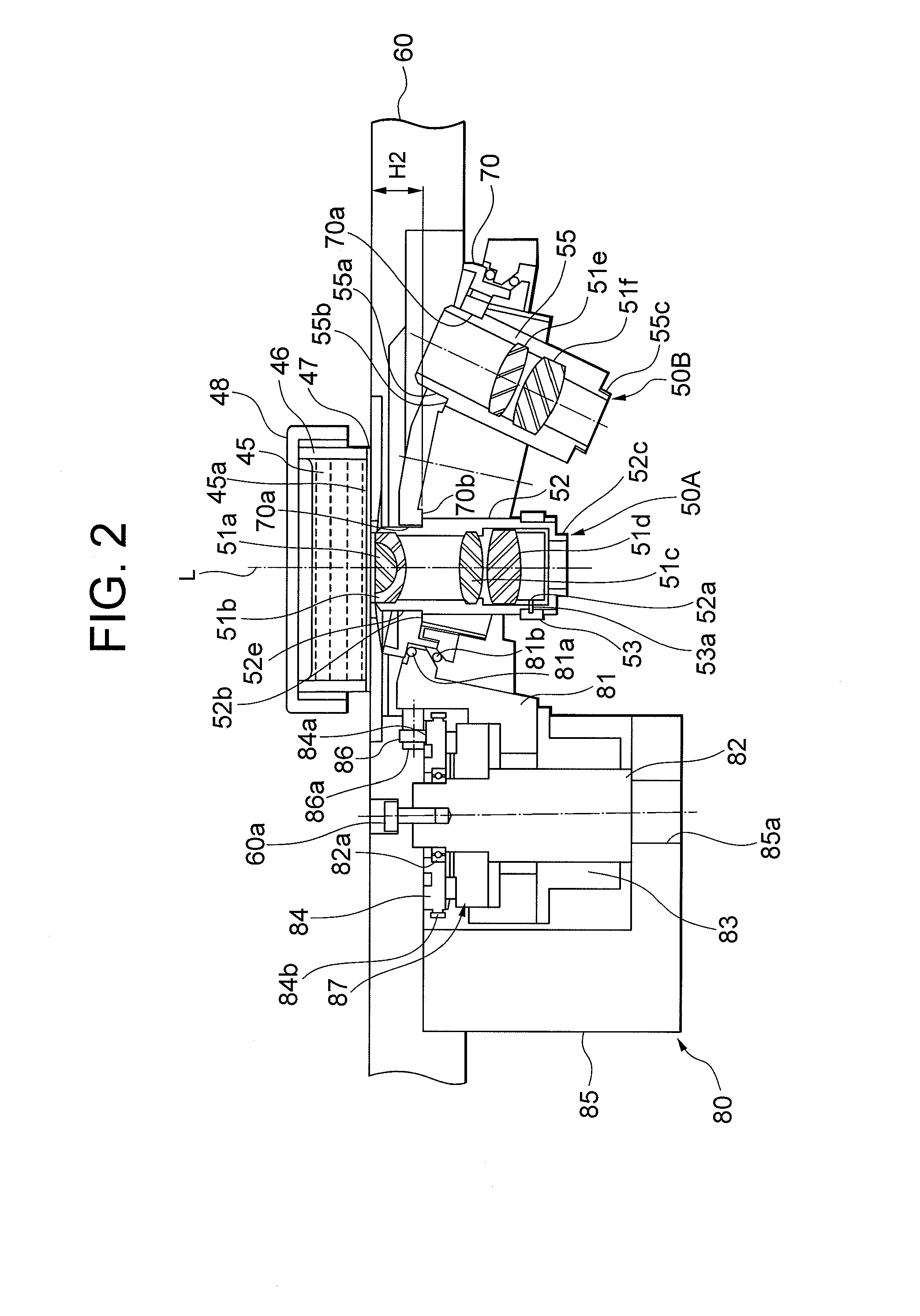
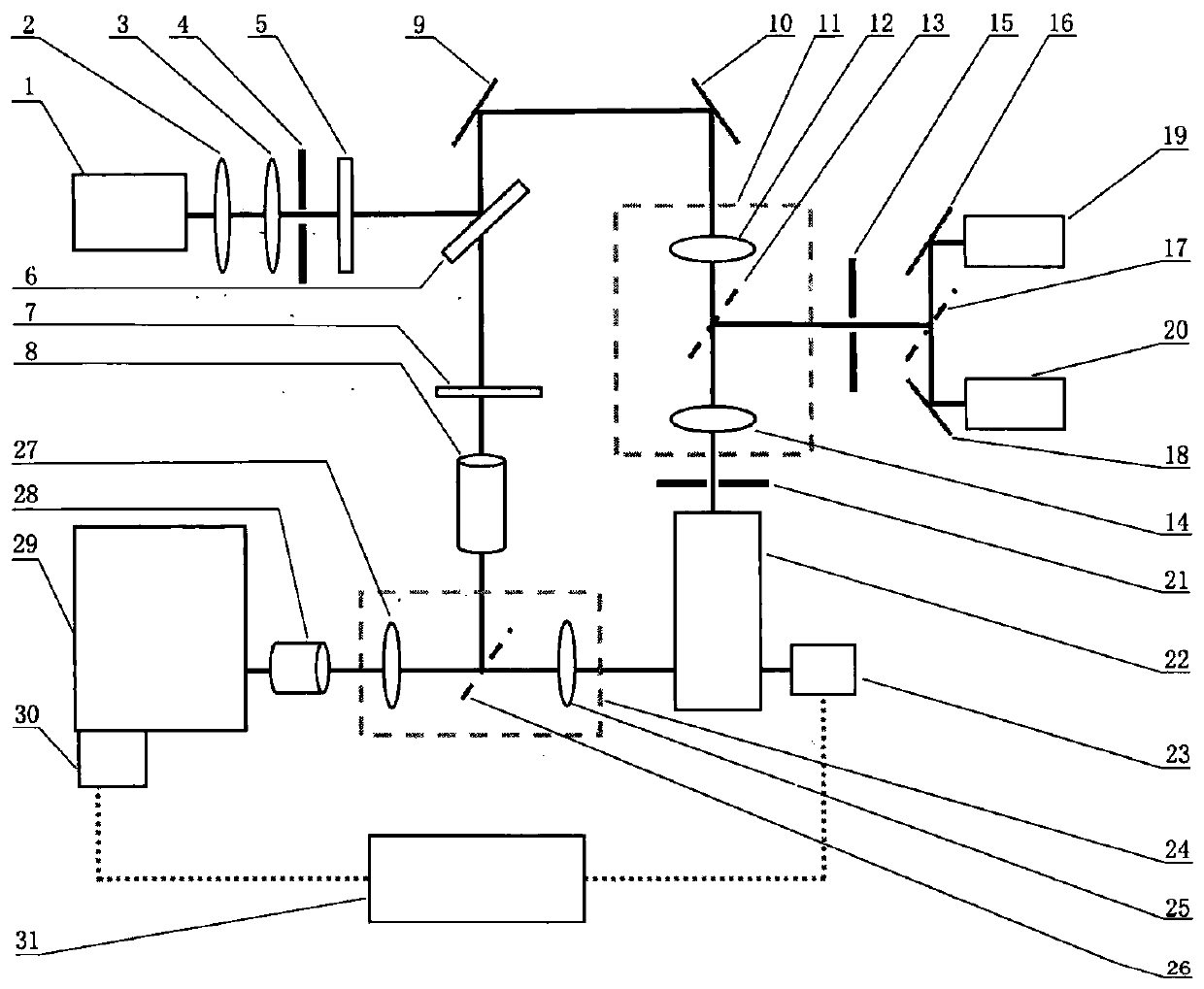
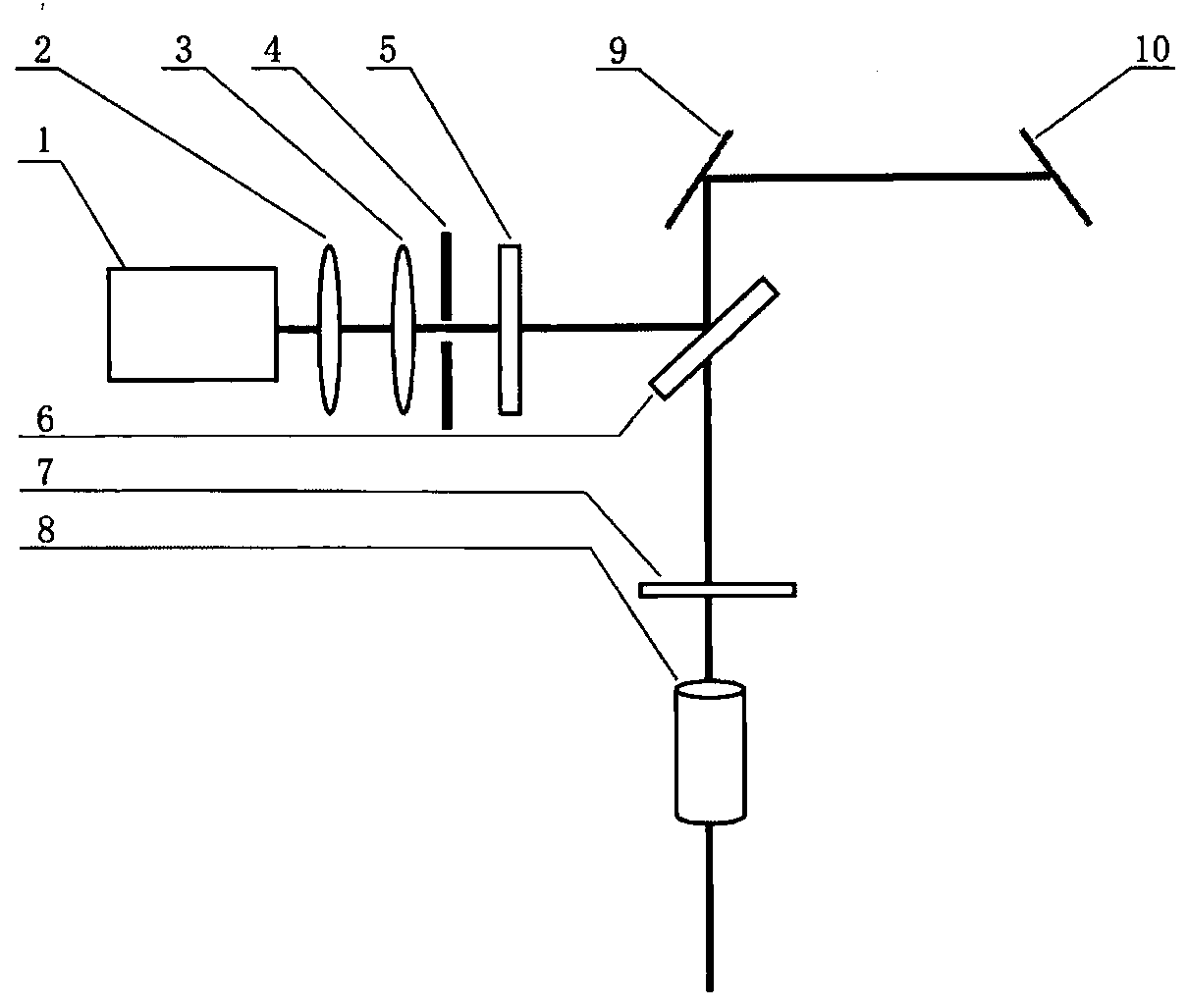
Inverted microscope
An inverted microscope includes a stage on which a sample is disposed, a support which supports the stage, a base which holds the support from below the support, an objective lens which is arranged under the sample and the stage, an imaging lens which is arranged inside the base and which forms an optical image of the sample in cooperation with the objective lens, and an optical path combining / splitting unit which is arranged on a main optical path between the objective lens and the imaging lens and which detachably holds the optical path combining / splitting element that combines / splits the main optical path inside the base.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
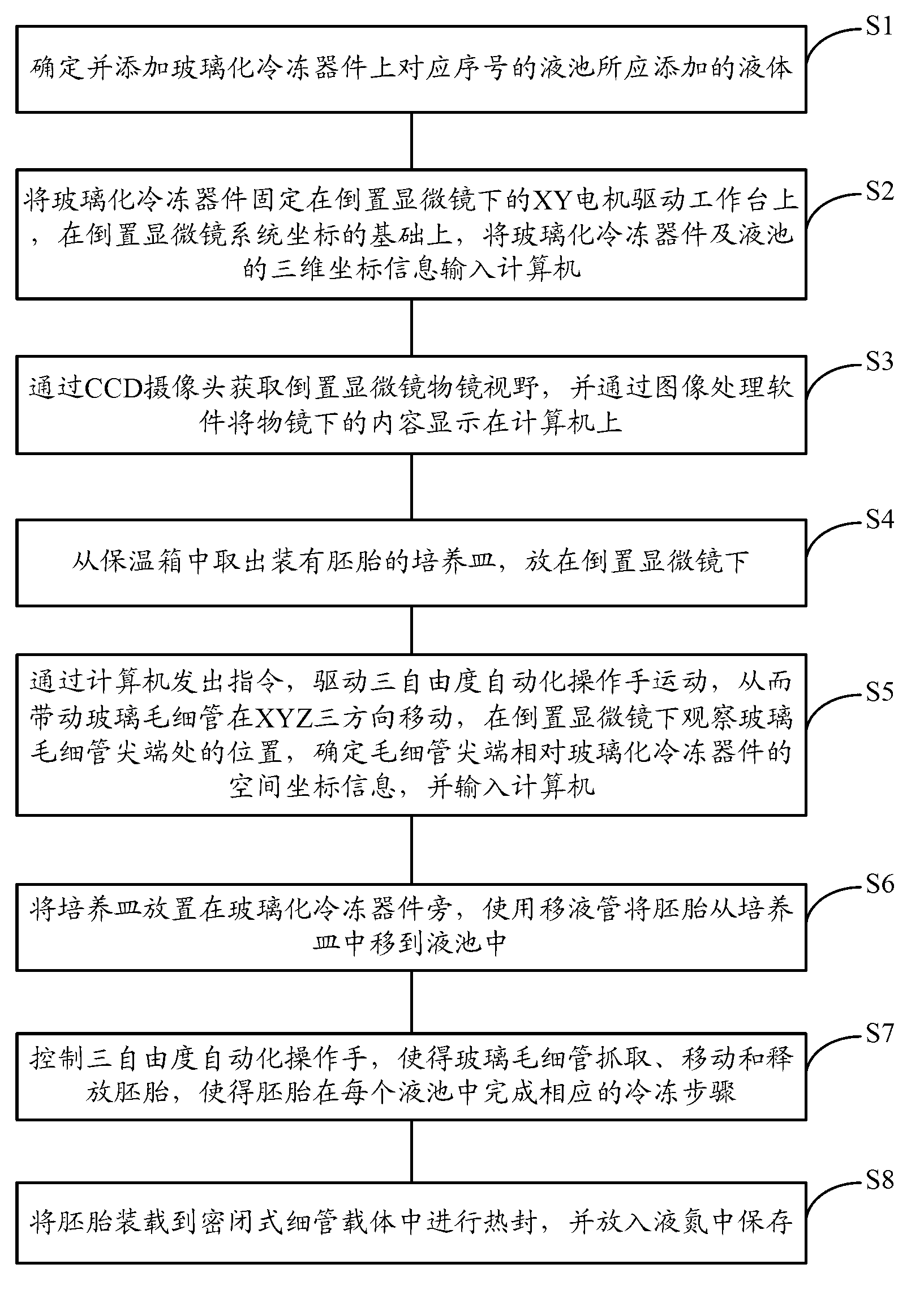
Vitrification automatic operation system and operation method
InactiveCN102835389AReduce complexityImprove work efficiencyDead animal preservationThree degrees of freedomEngineering
The invention discloses a vitrification automatic operation system and operation method; the system comprises a computer, an XY motor driving workbench, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, a vitrification device, an inverted microscope, a three degree-of-freedom automatic operator as well as a capillary tube clamper and a glass capillary tube, wherein the CCD camera is positioned below the XY motor driving workbench; the vitrification device is positioned on the XY motor driving workbench; the inverted microscope is positioned on the vitrification device; the three degree-of-freedom automatic operator is positioned beside the vitrification device; the capillary tube clamper and the glass capillary tube are arranged on the three degree-of-freedom automatic operator; and the vitrification automatic operation system further comprises a hydraulic pump, an operator driver and a stepping motor driver, wherein the hydraulic pump is connected with the computer and used for controlling the capillary tube clamper and the glass capillary tube; the operator driver is connected with the computer and used for driving the three degree-of-freedom automatic operator; and the stepping motor driver is connected with the computer and used for driving the XY motor driving workbench. According to the utility model, as manual operation is replaced with the vitrification automatic operation system and operation method, the process is centralized, the complicatedness in operation is reduced and the working efficiency can be greatly increased.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Multi-sample stage allowing for automatic movement of inverted microscopes
InactiveCN103235407ASimplified ReplacementSimplify the focusing processMicroscopesAutosamplerCoupling
The invention relates to a multi-sample stage allowing for automatic movement of inverted microscopes. The multi-sample stage comprises a sample stage base and an objective lens. Screw supports are arranged on the sample stage base. A screw is arranged on the two screw supports through a coupling. The coupling is connected with a drive motor. A slide is arranged on the sample stage base. A sample cell moving rack is arranged on the slide. The top of the sample cell moving rack is screwed to the screw through a connector. A sample cell fixed rack is arranged on the sample stage base and is provided with a sample cell. The upper surface of the sample cell is made of a quartz glass slide, and the lower surface of the sample cell is made of a cover glass. The periphery of each of the quartz glass slide and the cover glass is sealed with epoxy resin. Space between the quartz slide glass and the cover glass is divided into a plurality of independent sample channels. The quartz glass slide is provided with through holes corresponding to the independent sample channels. The through holes are connected with an automatic sample feeder through sample guide tubes. The multi-sample stage is applicable to various inverted microscopes, is small in size, handy, flexible, and simple and fast to operate, and is an effective tool for the biological single-molecular study.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single spore isolation method of phytophthora capsici zoospores
InactiveCN105886451AAvoid easy separationEasy to operateFungiMicroorganism based processesSterile waterAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to a single spore isolation method of phytophthora capsici zoospores. The single spore isolation method comprises the steps that phytophthora capsici is inoculated to a V8 culture medium, sealing is performed with a sealing membrane, culture at the constant temperature of 25 DEG C is performed for 5 days, then the sealing membrane is removed, irradiation is performed for 24 hours, sterile water of 4 DEG C is added to perform induction and constant-temperature release respectively for 25 minutes so as to obtain a zoospore suspension, the suspension is diluted to reach the standard that 1-2 spores exist in each (10*) view, 1 mL of the suspension is taken and added to a V8 culture medium flat plate containing antibiotics in an evenly coated mode, constant-temperature standing is performed for 6 hours, a single germinated zoospore is found through an inverted microscope and is cut by using a scalpel to form a 0.5 cm square mark, it is confirmed that single spores are transferred to a flat antibiotic plate, and purified spores are single spore plants. The single spore isolation method is simple and convenient to operate, high in accuracy and good in rapid separating effect, adopts simple devices and can separate single spores of a large number of phytophthora capsici zoospores within a short time.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
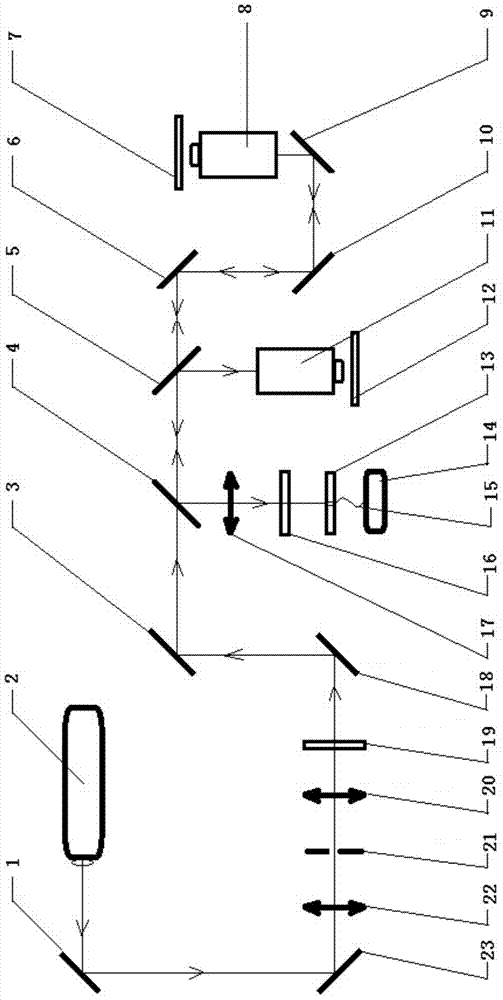
Confocal laser optical tweezers Raman spectroscopy test device capable of being used in upright and inverted manners
The invention relates to a confocal laser optical tweezers Roman spectroscopy test device capable of being used in upright and inverted manners. The confocal laser optical tweezers Roman spectroscopy test device is composed of a semiconductor Roman laser, a spatial filter, a short-pass dichroic beam-splitting optical path system, a spectrometer, an upright microscope and an inverted microscope. The laser is connected with the spatial filter in an optical path manner. The spatial filter is connected with the short-pass dichroic beam-splitting optical path system in an optical path manner. The short-pass dichroic beam-splitting optical path system is connected with the upright microscope in an optical path manner. The short-pass dichroic beam-splitting optical path system is connected with a Roman detector in an optical fiber manner. The short-pass dichroic beam-splitting optical path system is connected with the upright microscope through a reflector in the optical path manner. The short-pass dichroic beam-splitting optical path system is connected with the inverted microscope through other reflectors in an optical path manner. By the test device, activity of cells can be guaranteed, and biochemical analysis of the cells can be performed. Upright and inverted laser optical tweezers Roman spectroscopy systems which can be switched mutually, flexibly and conveniently through a rotary table with a 45-degree reflector can be used in a combined manner or independently.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
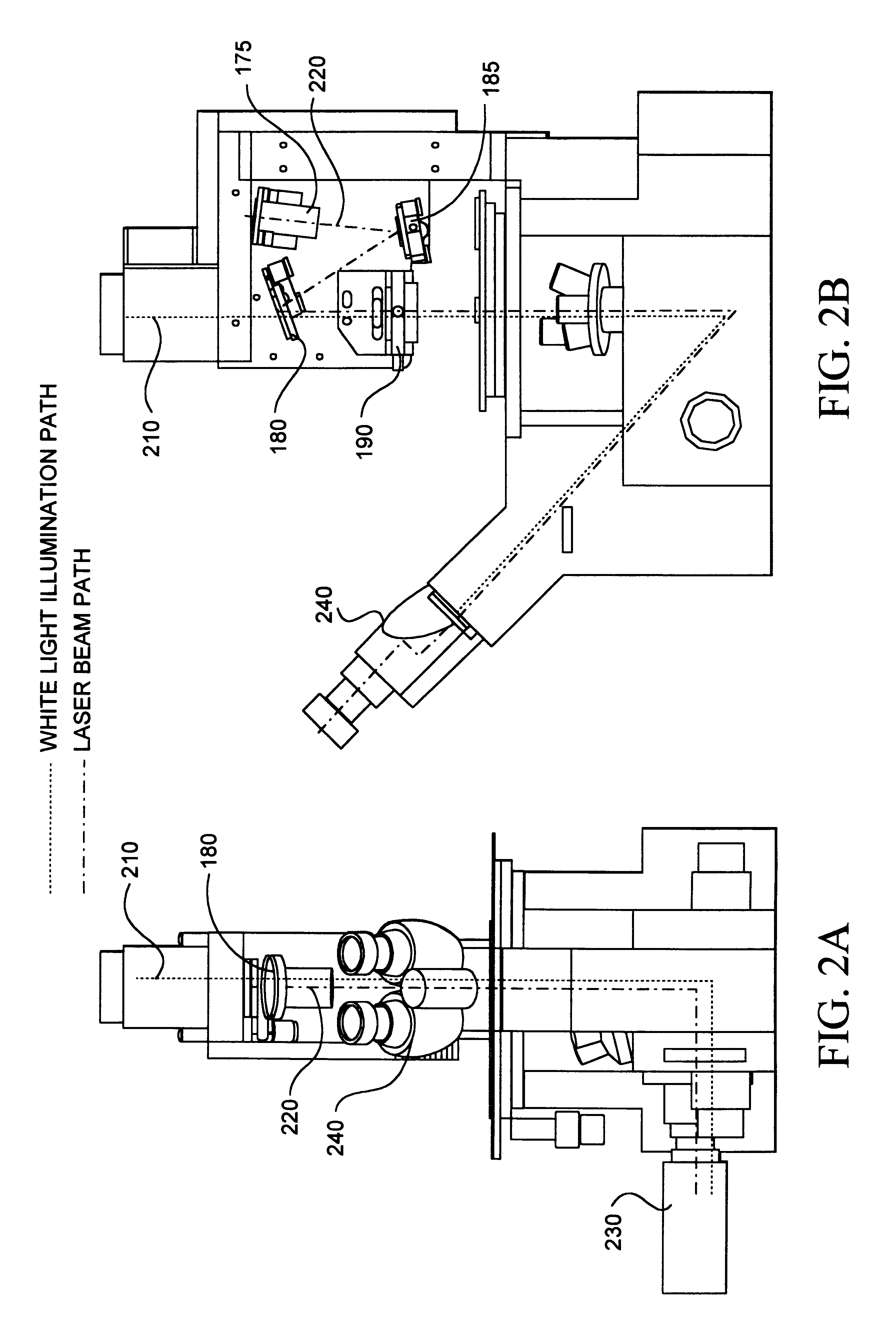
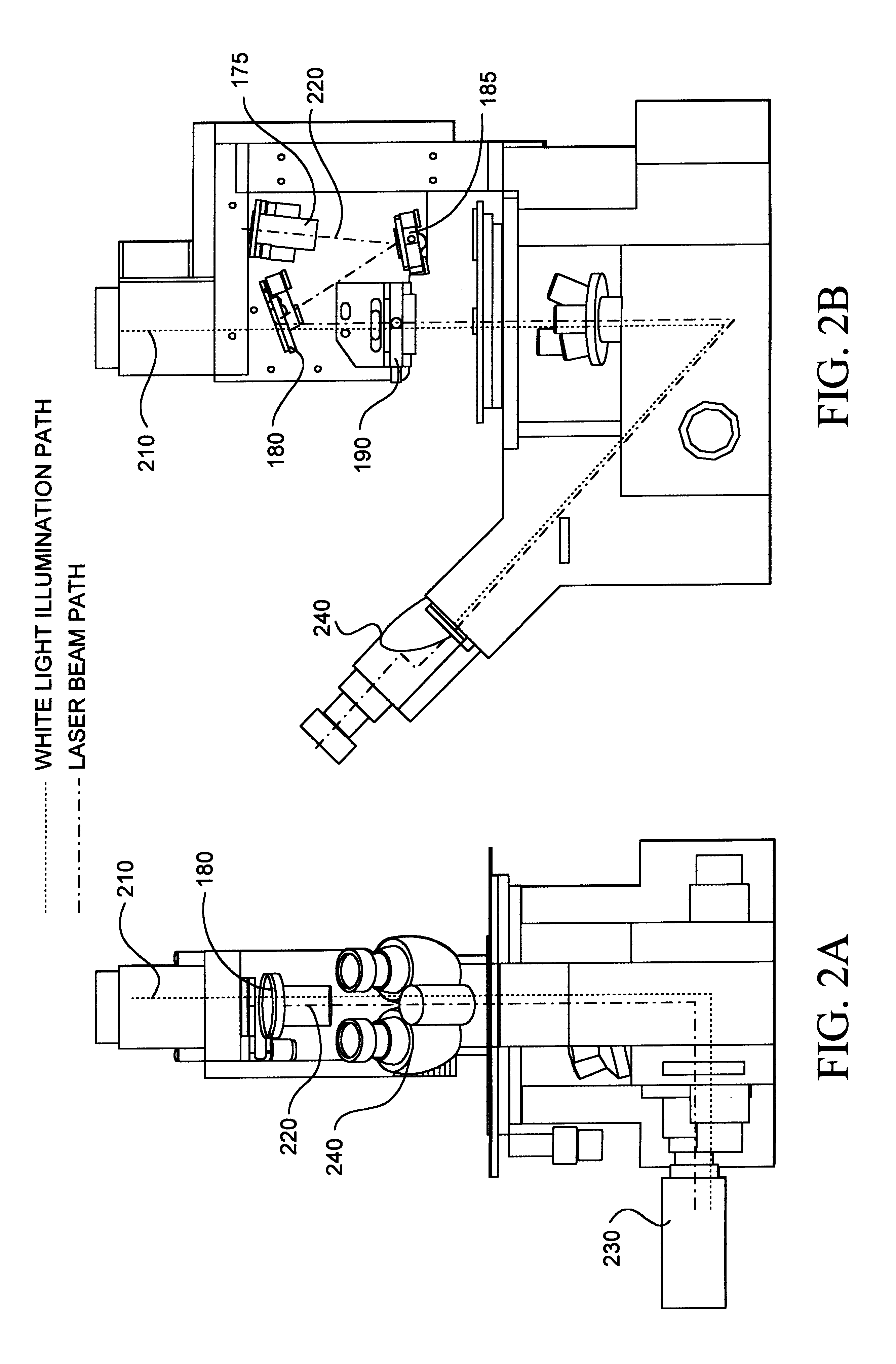
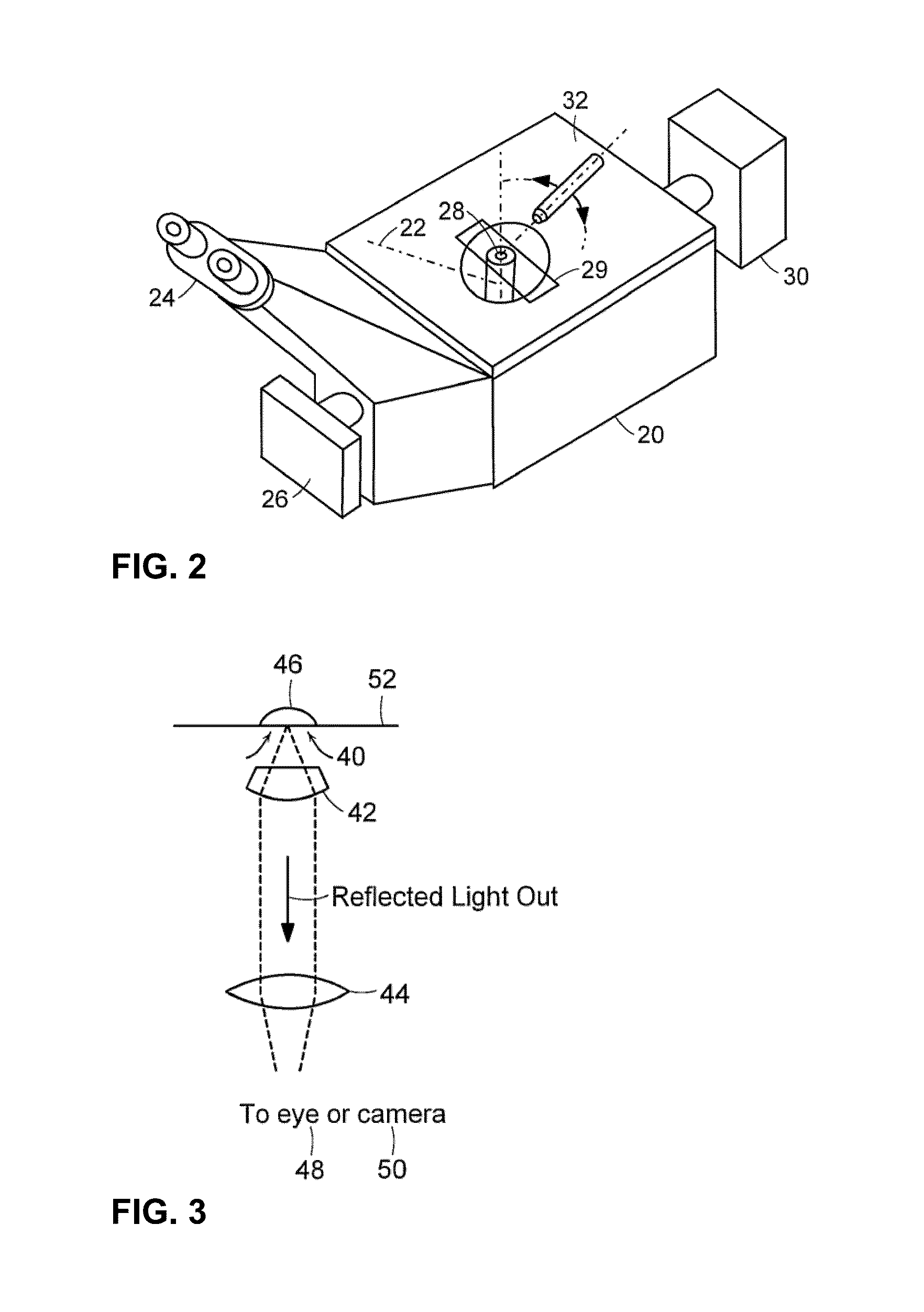
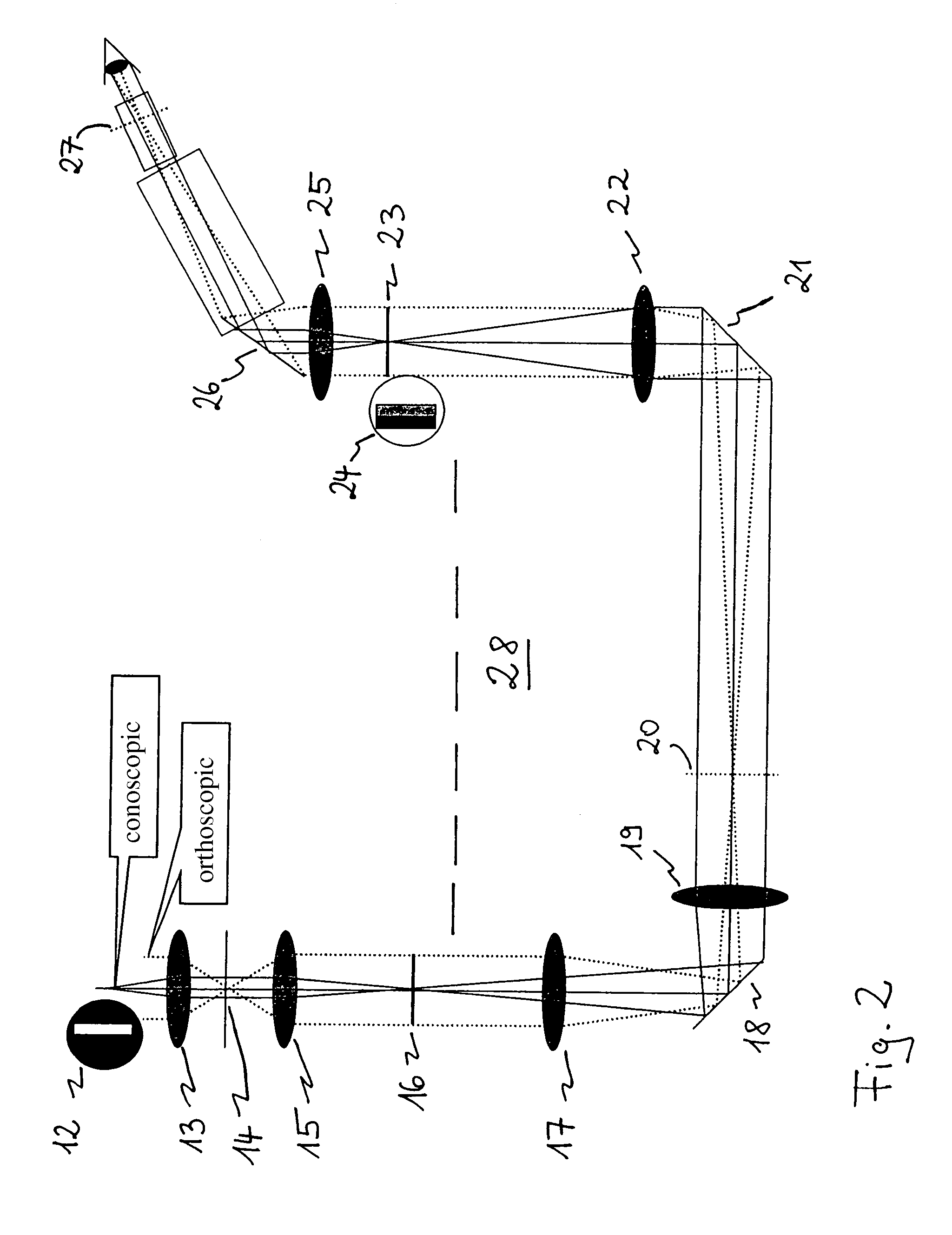
Illuminating unit and inverted microscope
An illuminating unit that is a part of a microscope for forming an image of a specimen being an observation object, that is located above a stage on which the specimen is placed, and that applies transmitting illumination light to the specimen includes a light source unit including a light source that generates the transmitting illumination light, and a condenser unit that includes a condenser lens for collecting and applying the transmitting illumination light emitted by the light source unit onto the specimen, and that is detachably connected to the light source unit.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method and device for the immersion and cleaning of the front lens of microscope objectives
InactiveUS20070047093A1Good solvent performanceDeterioration of optical characteristicMicroscopesFully automaticInverted microscope
A method and a device are provided for the immersion and for the cleaning of the front lens of microscope objectives in fully automatic microscope systems, in particular inverted microscopes, for the examination of biological and / or chemical samples by which, besides an automatic immersion process, an automatic cleaning of the front lens of the microscope objective is achieved at the same time at the conclusion of the immersion process. In a method in which water is preferably used as immersion liquid, the immersion liquid is provided at the same time as a cleaning liquid for the automatic cleaning of a front lens of a microscope objective at the conclusion of the immersion process. The device according to the invention for implementing the method comprises a receiving vessel which can be placed on the front lens of the microscope objective. Openings are provided in the receiving vessel and are connected to a tube system for supplying fresh immersion and cleaning liquid from a reservoir vessel and for discharging the soiled liquid into a receiving vessel.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MIKROLMAGING
Device and system for mechanical measurement of biomaterial
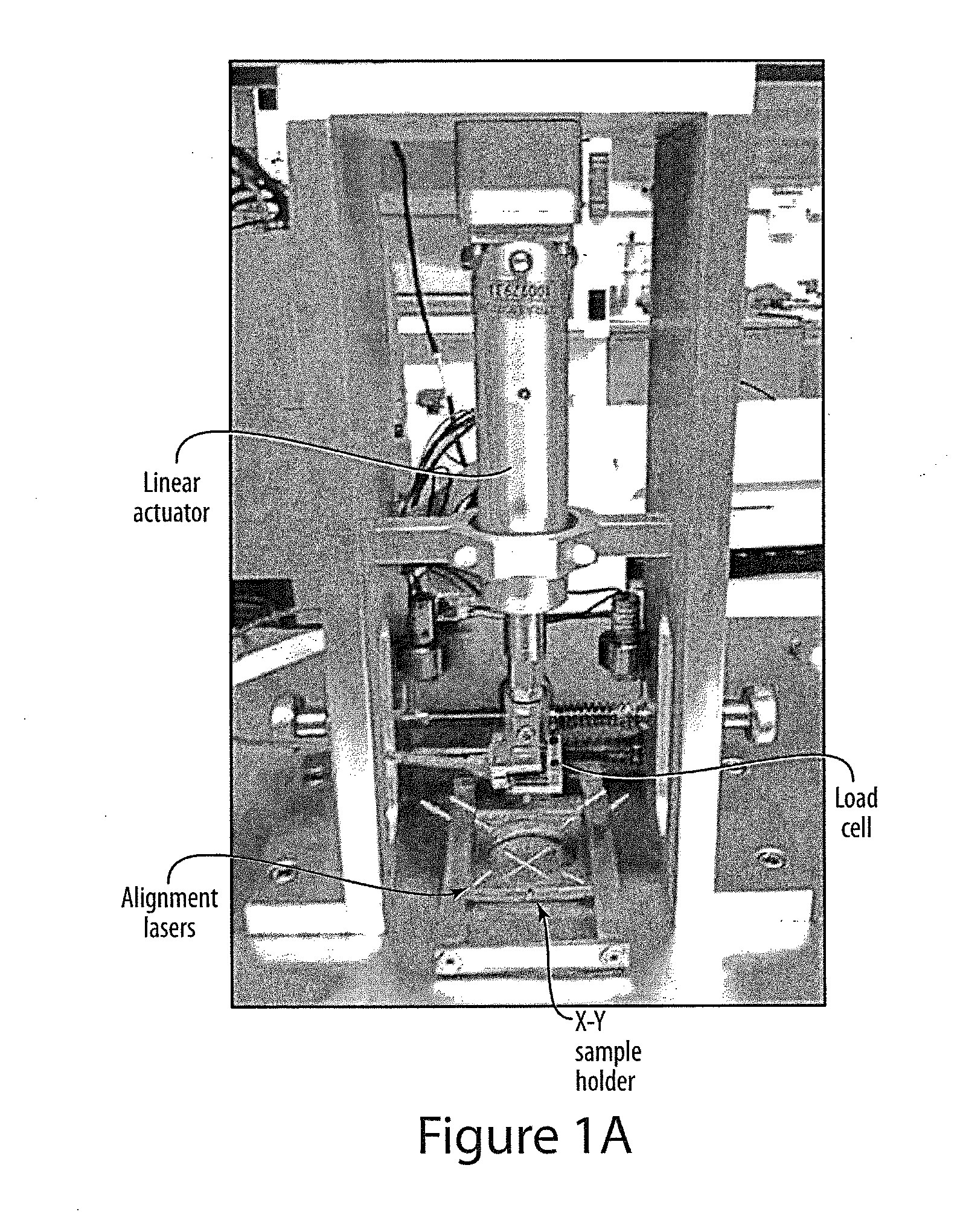
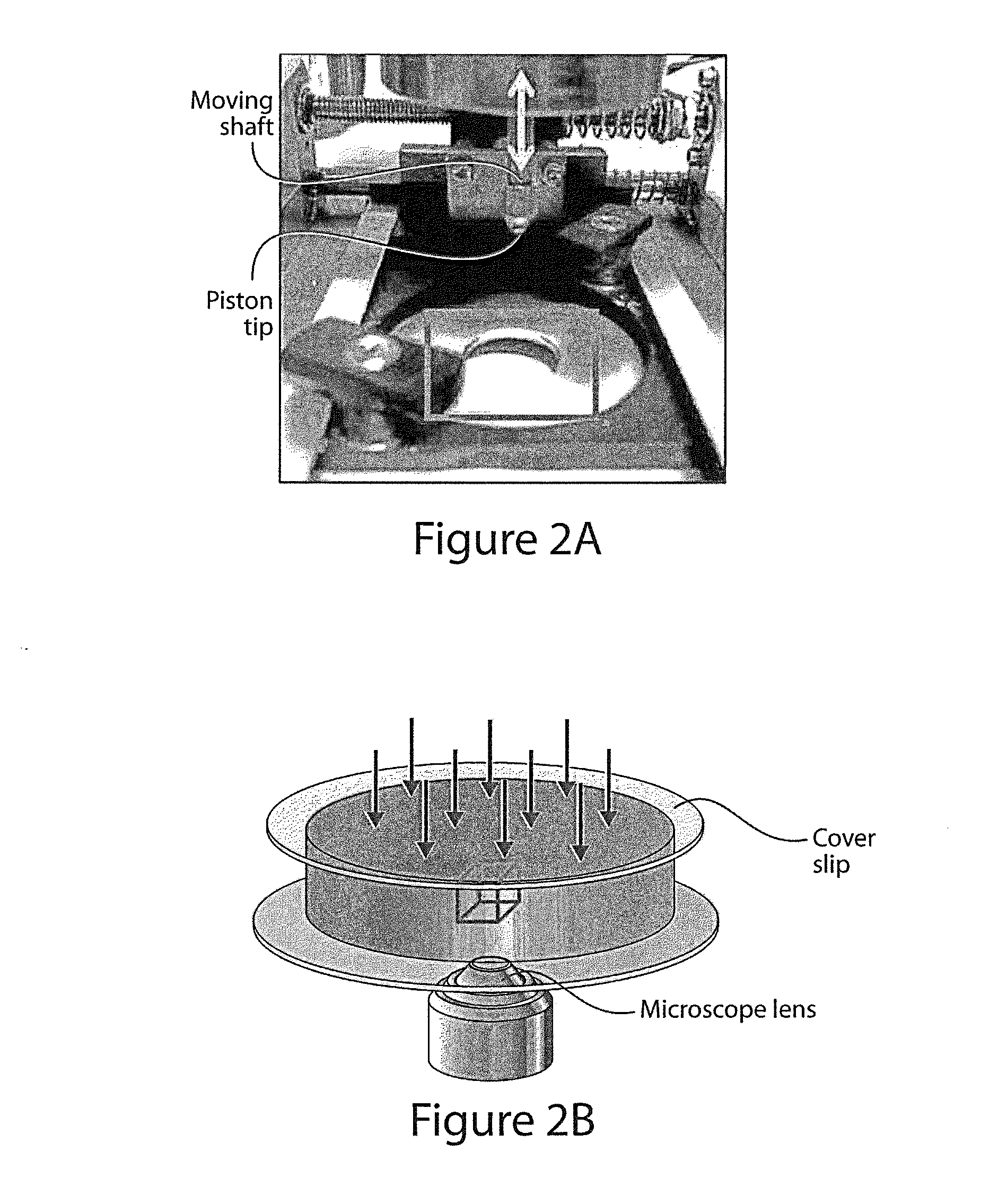
InactiveUS20140295538A1Improve accuracyHigh precision measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGrowth phaseData set
A test device applies a defined mechanical load to a soft biomaterial such as a cell culture and a microscope forms a volume image data set showing the strain field or displacement field occurring in the medium. The data set is processed to determine fundamental mechanical properties of the cell, its interaction with the surrounding medium, or its responses loading or deformation of its surrounding medium. The device may also be used to calibrate or determine fundamental mechanical properties of the medium. The device includes a linear actuator that bears against the specimen, and adapted for a volume imaging device such as a scanning laser confocal microscope that forms a volume image data set of the specimen. The specimen may be supported in a Petri dish and is preferably imaged from below by an inverted microscope. Preferably the actuator device attaches to or forms the specimen stage of microscope. Digital correlation of volumes in the data set allow computation of modulus, stress distribution and other mechanical characteristics of cell-matrix interactions, as well as mechanical properties of the cell and the matrix in response to changing loads, evolving chemical or ionic environment and growth phases. The test device may be operated to measure local mechanical parameters, to evaluate or design tissue-engineered implants, and to explore the mechanical properties of tissues, cells and cellular processes a micrometer scale with high accuracy.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Microscope accessory and microplate apparatus for measuring phosphorescence and cellular oxygen consumption
InactiveUS20120153188A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrowell PlateEngineering
A device and system that allows an inverted microscope with a movable x-y stage to also function as a time-resolved plate reader. The device, which is sized to fit into the condenser holder of an inverted microscope, not only provides plate-reading function at very low cost compared to that of purchasing a plate reader, but it also allows the correlation of plate reader measurements with images of a specimen. The device and system is also able to measure other parameters associated with cell metabolism, such as pH changes.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
High-throughput screening system and method of fast growing microalgae strains
InactiveCN106148159AImprove accuracySolve the technical bottleneck of difficult to obtain single-cell level analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to a high-throughput screening system and method of fast growing microalgae strains. The system comprises a liquid drop monodisperse single cell wrapping unit and a reinjecting screening unit. The method comprises steps as follows: microalgae cells are washed and dispersed in gel to proper concentration and injected into a micro-fluidic chip to form monodisperse single cell liquid drops, and microspheres wrapped in an oil phase are subjected to deoiling, filtration and redispersion and cultured in a constant-temperature incubator; whether living cells exist and the growing speed of the cells are judged according to imaging by the aid of an inverted microscope, gel amplification pictures are collected through random interval sampling, gel microspheres where the cells grow are counted, the growth condition of microalgae in the single cell level is further monitored, and the microalgae strains with remarkable growth rate difference are separated on the basis. According to the constructed high-throughput screening system and method of the fast growing microalgae strains, the system is simple, the cost is low, and the system and the method can be used for screening of phenotypic correlation of growth of a mutant library of alga.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY +1
Osteoblast electrical stimulation system based on microfluidic technology and operation method thereof
ActiveCN103789206ARealize analysisEvaluate the impactCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCamera lensOsteoblast
The invention provides an operation method of an osteoblast electrical stimulation system based on a microfluidic technology. The osteoblast electrical stimulation system comprises a microfluidic chip, an inverted microscope, two elastic sealing plugs and an electrical stimulation signal source, wherein the microfluidic chip is prepared from a transparent material and is provided with a micro-channel which is used for bearing a cell culture medium and providing space environments for the culture of osteoblast, and an inlet and an outlet are respectively formed in the two ends of the micro-channel; a camera lens of the inverted microscope is aligned at the middle part of the micro-channel from the bottom of the microfluidic chip; the two elastic sealing plugs are used for respectively plugging the inlet and the outlet of the micro-channel; the electrical stimulation signal source is used for providing electrical stimulation signals, and the two electrodes of the electrical stimulation signal source respectively penetrate through the two elastic sealing plugs and then extend below the liquid level of the cell culture medium in the micro-channel. The osteoblast electrical stimulation system provided by the invention can be used for realizing the analysis of single osteoblast and assessing the influencing effect of different potential differences on the single osteoblast.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
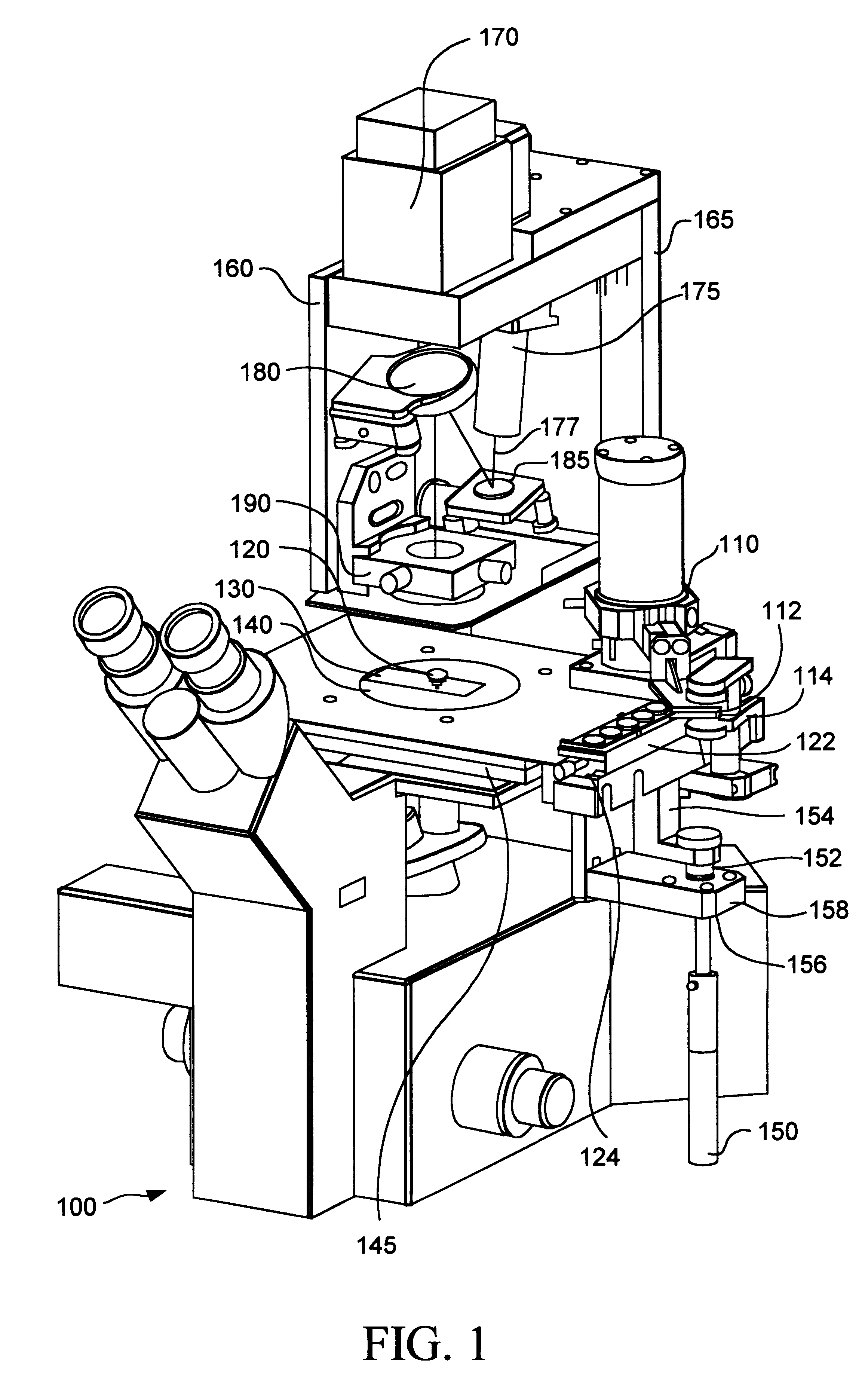
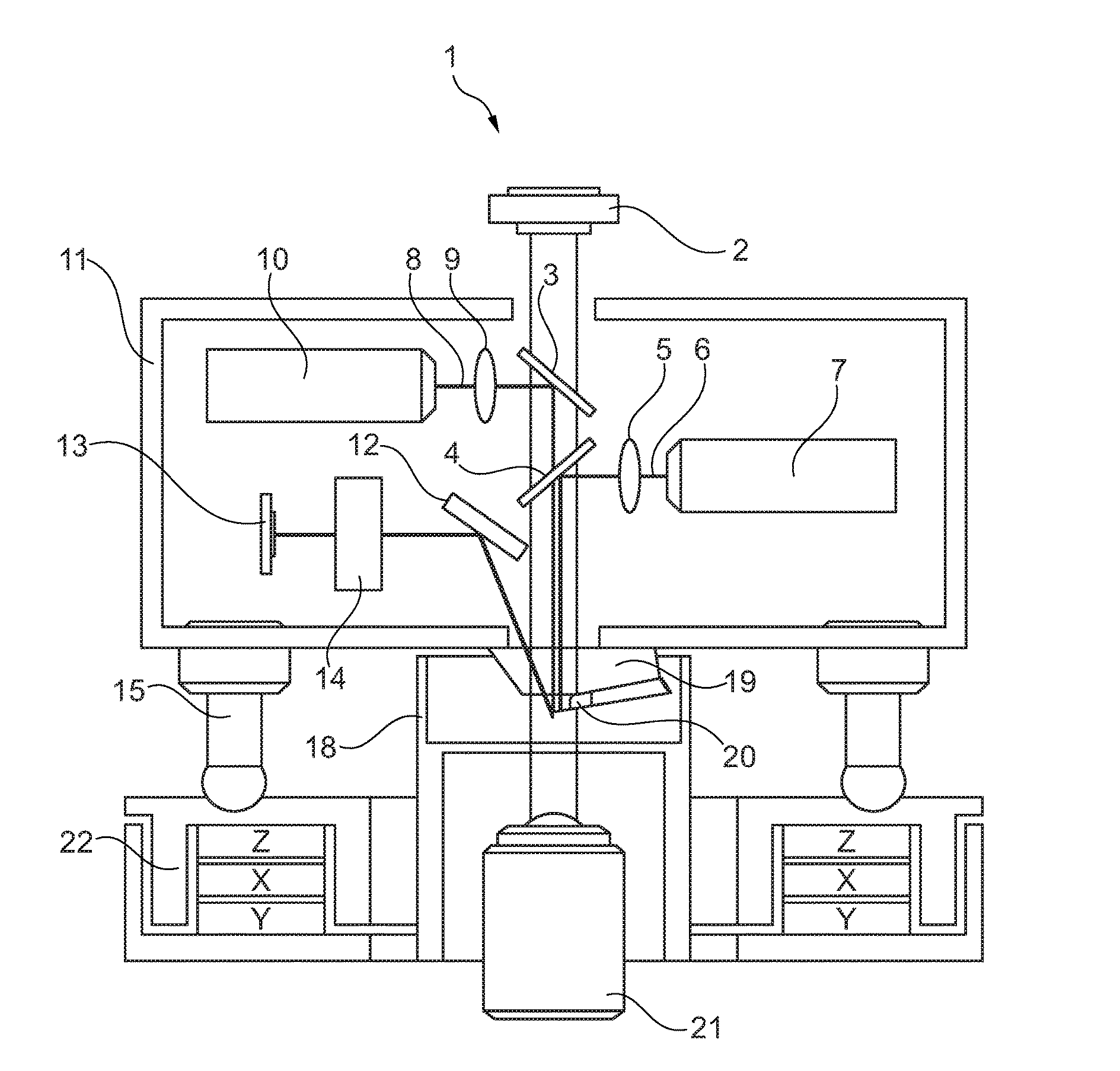
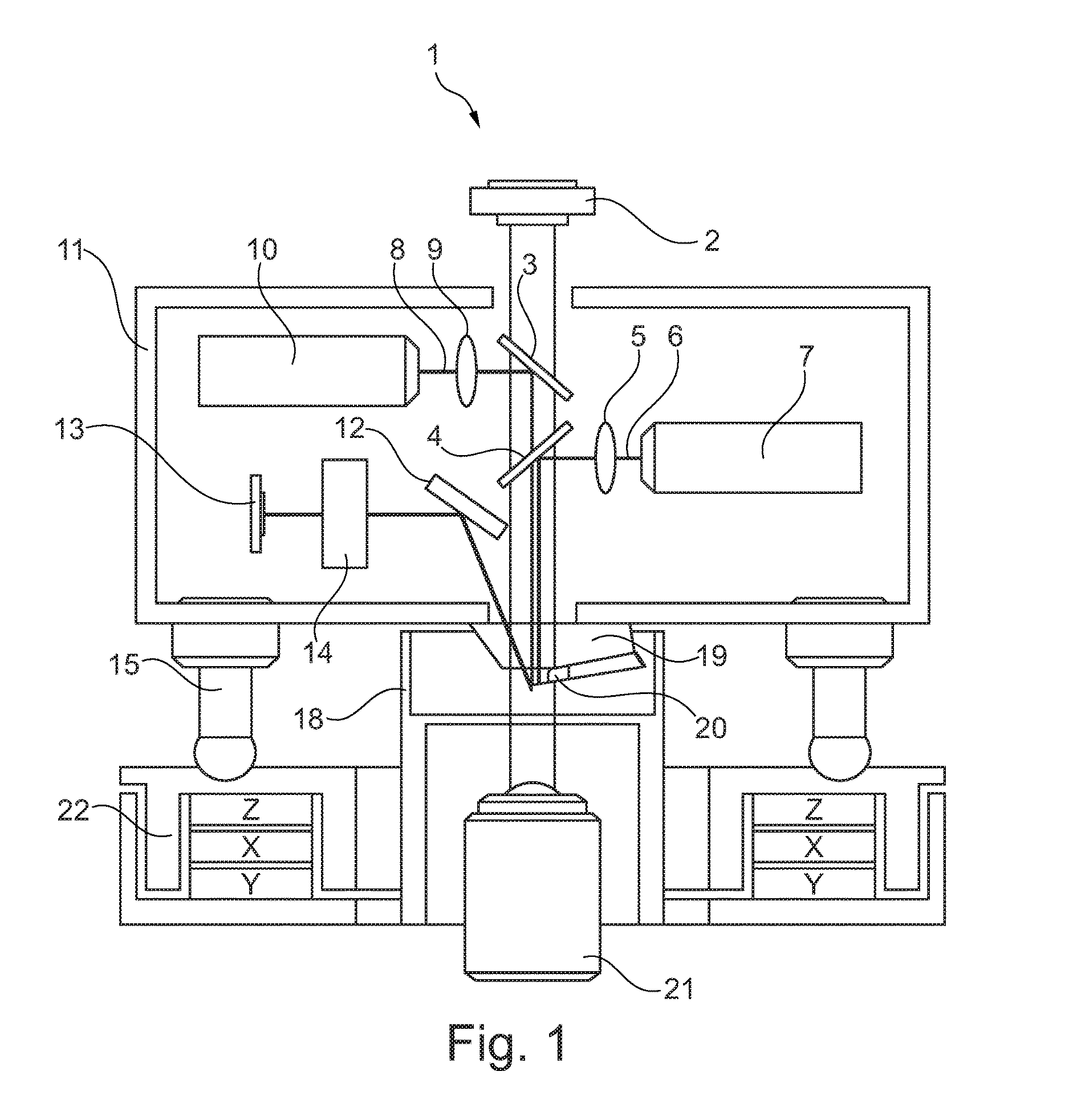
Inverted microscope
An inverted microscope for the high-contrast imaging of objects includes multiple objectives configured to be disposable in an imaging beam path. Each objective has a respective objective pupil associated therewith. A lens system is also provided for generating respective intermediate images of the respective objective pupils. A modulator disposing device, which includes a plurality of modulators, is configured to dispose the modulators at predetermined respective locations on an optical axis corresponding to the locations of the respective intermediate images of the respective objective pupils so as to contrast an object image.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Novel holographic optical tweezers system based on Talbot effect
InactiveCN102162908AReduce calculationLow powerRadiation/particle handlingMicroscopesImaging analysisOptical axis
The invention relates to laser holographic optical tweezers, and provides a novel holographic optical tweezers system based on the Talbot effect with a simple structure and high operability. The novel holographic optical tweezers system comprises a laser, a first lens, a second lens, a reflector, a holographic element, an inverted microscope, a CCD image sensor and a computer, wherein the two lens are sequentially arranged between the laser beam output end of the laser and the reflector in tandem; the laser and the two lenses have the same optical axis; the focuses of the two lenses are in coincidence with each other when the two lenses are placed in the initial positions; the focus position of the laser beam can be controlled by micro-adjusting the distance between the two lenses so as to make the focus point of the laser beam located on the holographic element; a particle is placed on the object stage of the inverted microscope; the particle can be arranged in a Talbot self-imaging position of the holographic element by adjusting the distance between the object stage of the inverted microscope and the holographic element; and the information output end of the CCD image sensor isconnected with the computer for image analysis and processing.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
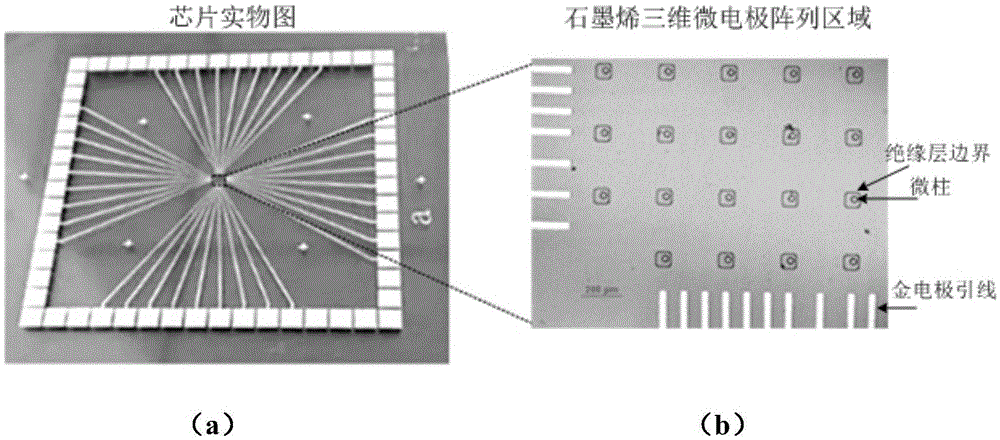
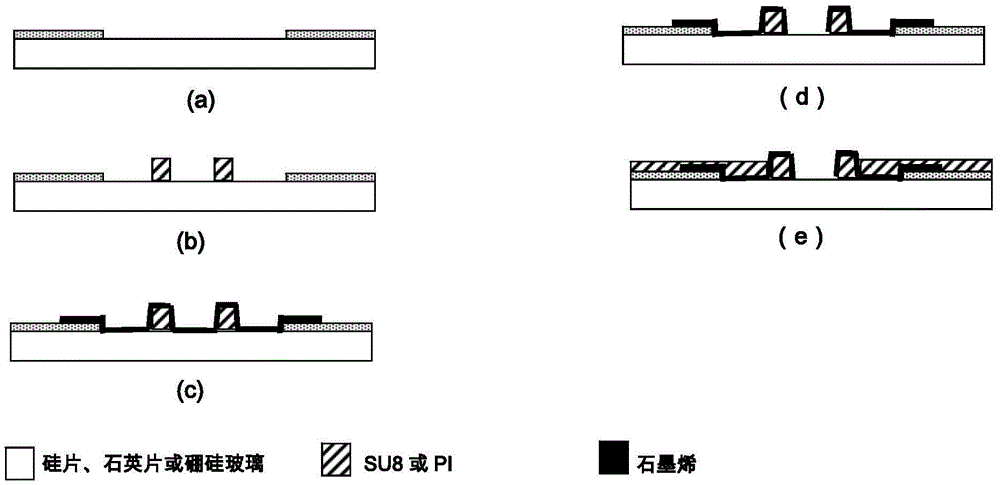
Graphene three-dimensional microelectrode array chip, and method and application thereof
ActiveCN105460882AImproved ability to detect weak electrical signalsGood light transmissionSemi-permeable membranesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsMicro columnMicroelectrode
The invention relates to a graphene three-dimensional microelectrode array chip, and a method and application thereof. The graphene three-dimensional microelectrode array chip is characterized in that a micro-column array is produced by utilizing negative photoresist, and a microelectrode array is produced by covering a single-layer graphene film on the microelectrode array; and the microelectrode array chip comprises two parts, namely a transparent graphene three-dimensional microelectrode array area and a peripheral gold electrode lead pin. A microelectrode site is a three-dimensional bulge. The three-dimensional microelectrode dome shaped (or hill shaped) microelectrode structure is beneficial for the rigid microelectrode site and the soft cell or tissue to form tight electric coupling, and the graphene has excellent electrical property, so that the electrophysiological detection sensitivity of the microelectrode array can be improved. In addition, the graphene three-dimensional microelectrode array on a transparent substrate is convenient for observation through an inverted microscope and application of various cell microscopic imaging methods, and can be combined with a micro-fluidic chip.
Owner:上海前瞻创新研究院有限公司
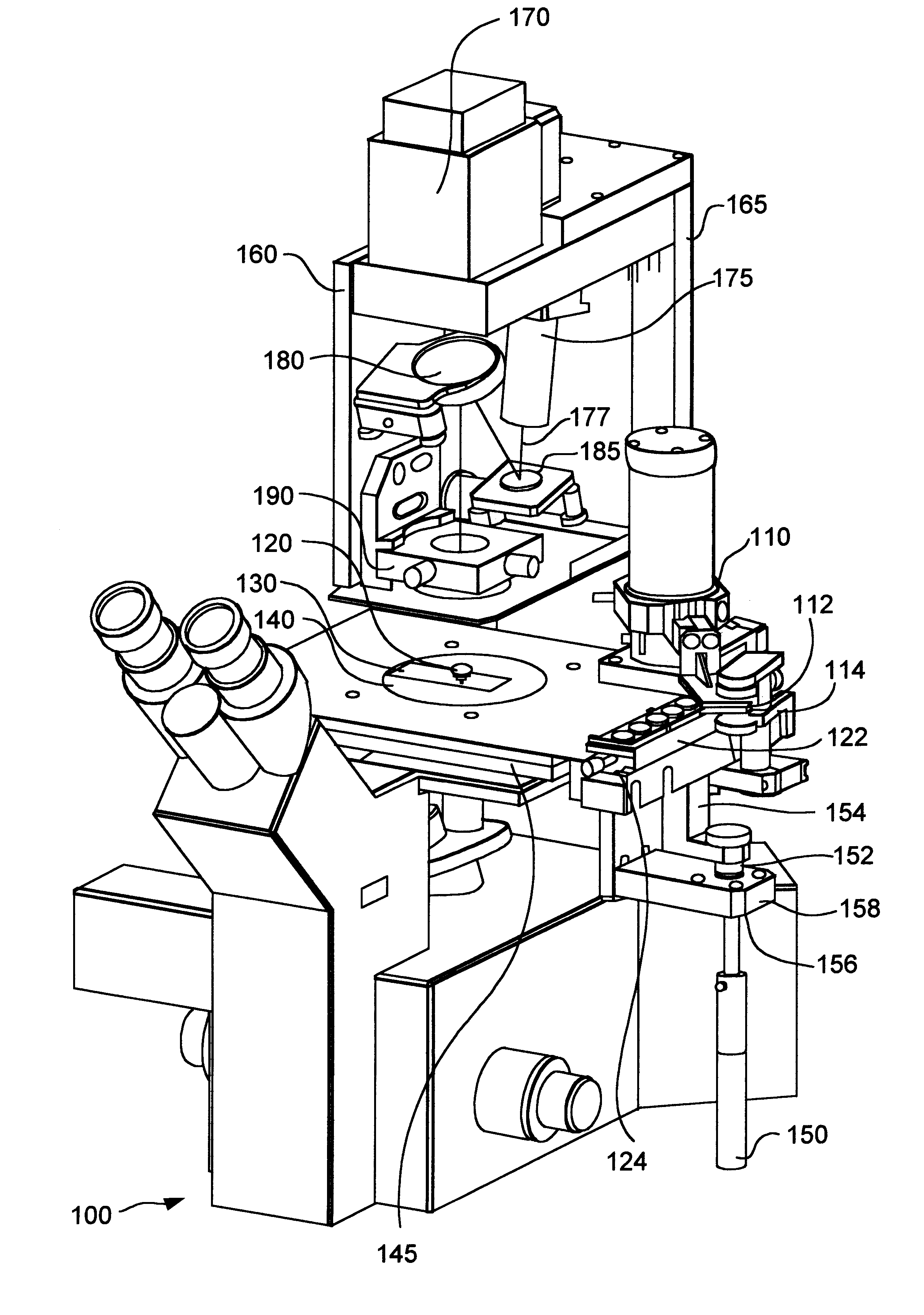
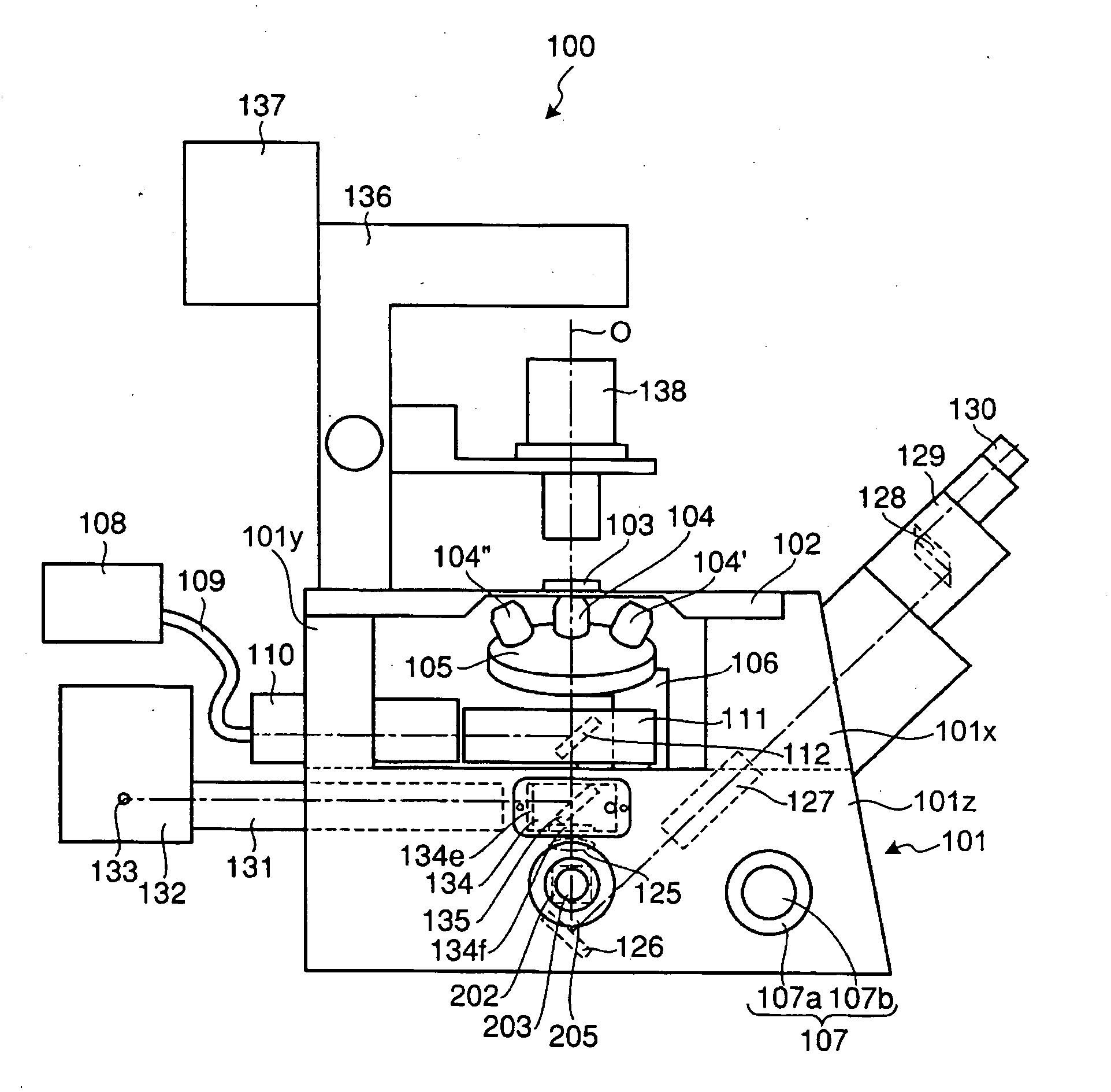
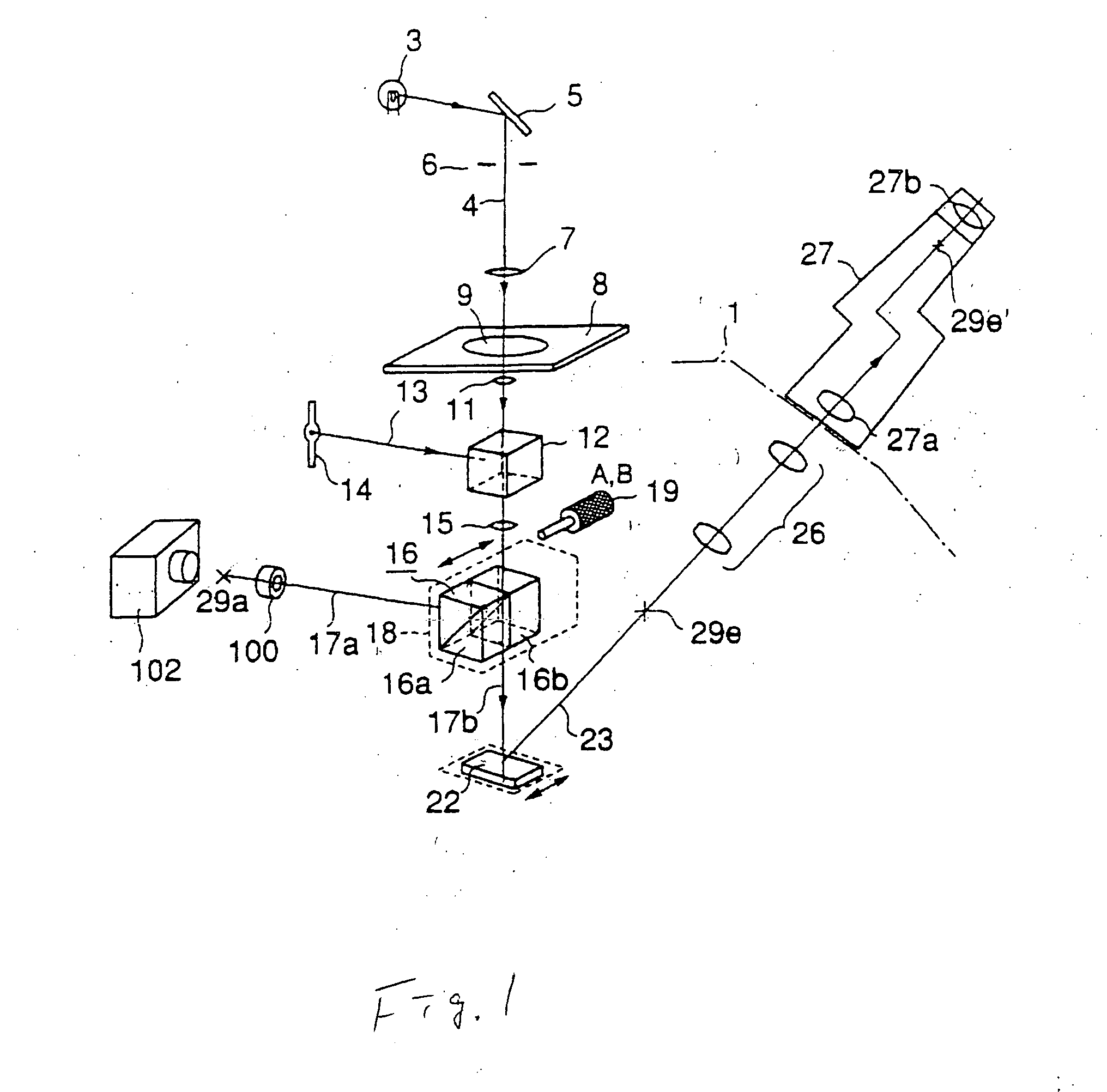
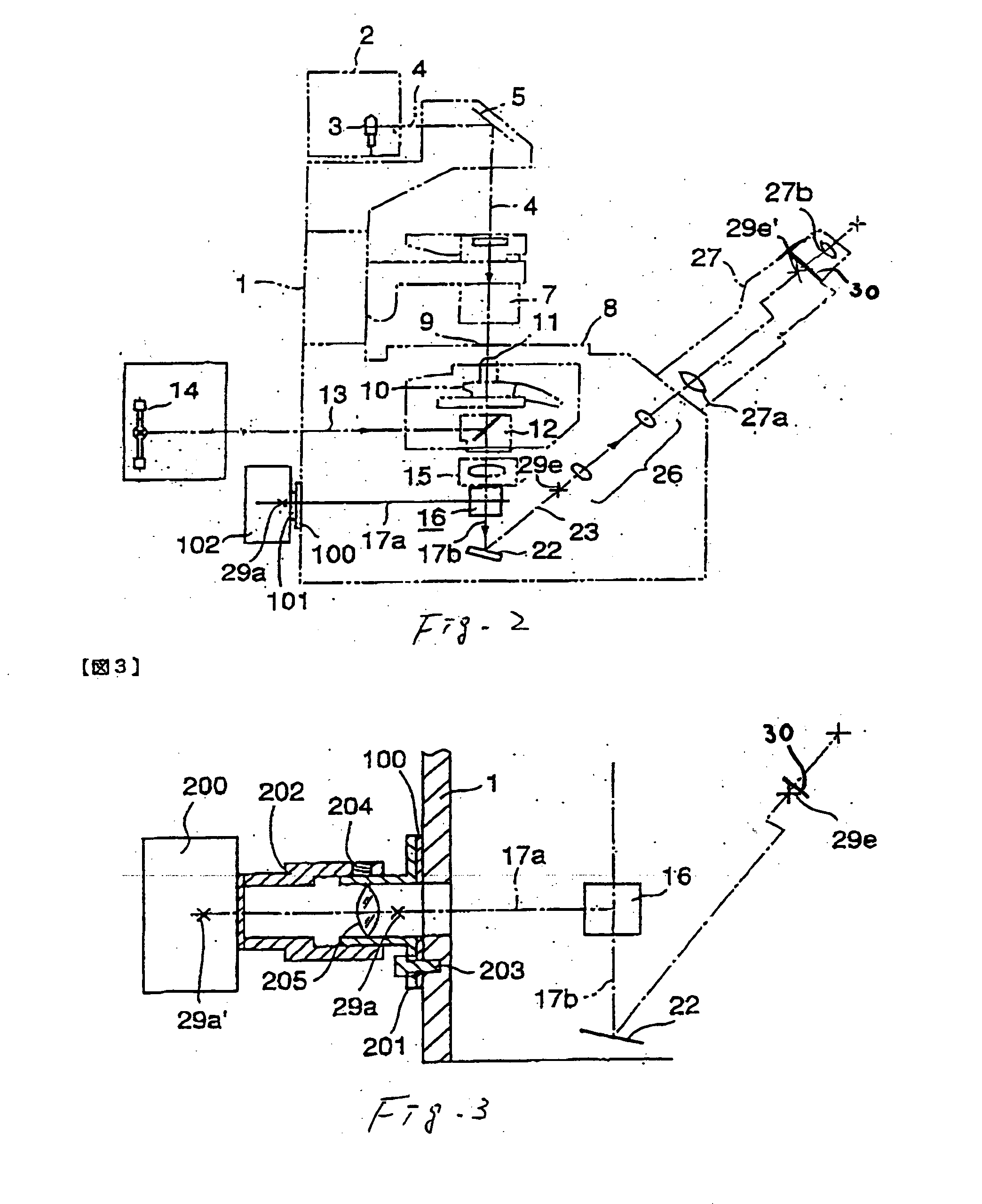
An inverted microscope
A microscope includes an objective lens, an image-forming lens, a reflecting mirror for directing transmitted light passing through the image-forming lens to a front side of the microscope, and a first optical element for directing light from the image-forming lens to an imaging optical path running to a backside of the microscope. The first optical element is disposed between the image-forming lens and the reflecting mirror, with a port disposed in the imaging optical path, and an imaging device coupled to the port. The imaging device includes an image plane, the image plane substantially corresponding to the focal plane.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
Cell cultivation device applied to microscopic observation
InactiveCN105331536AImplement updateLess distracting factorsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscopic observationInterference factor
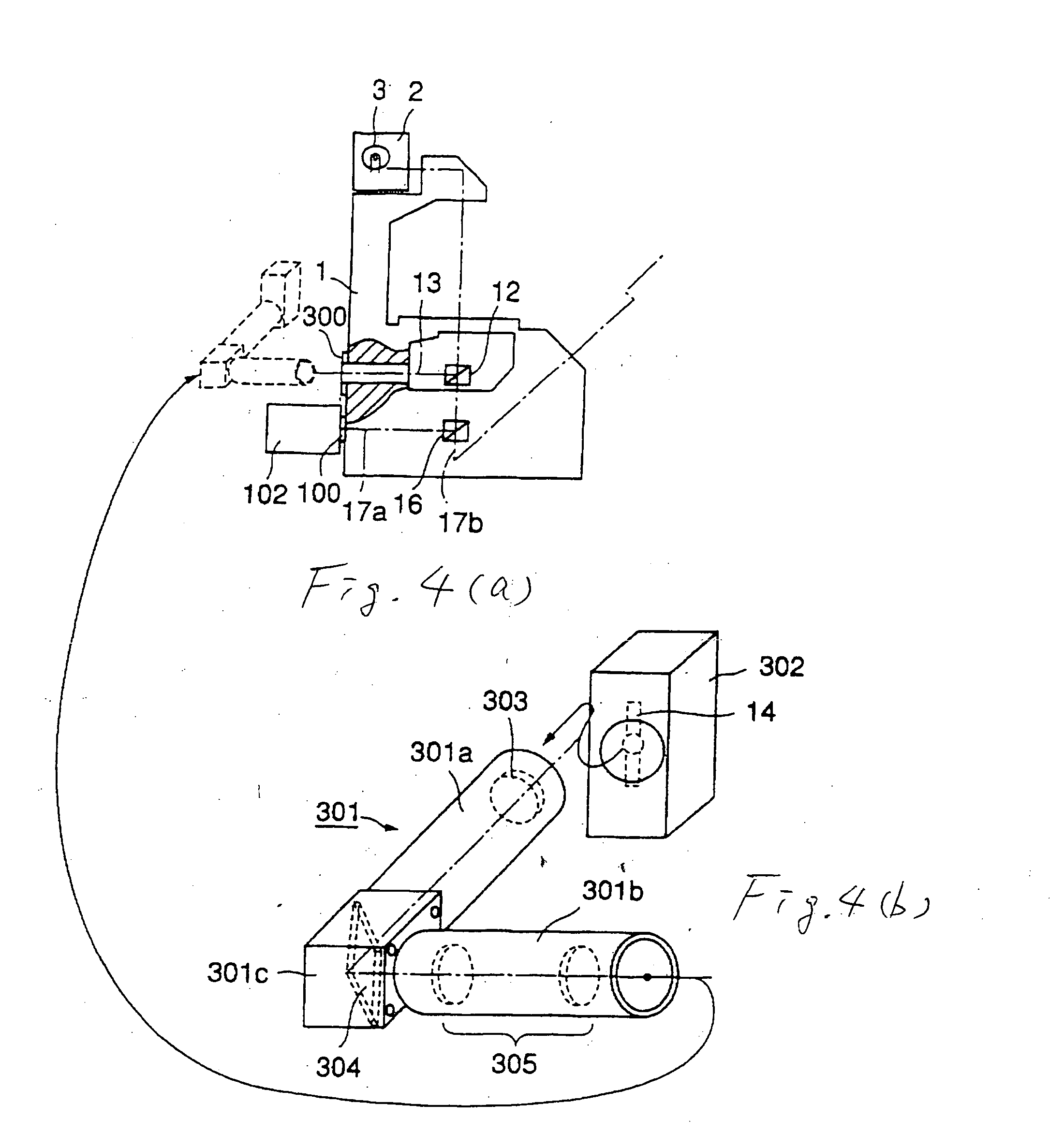
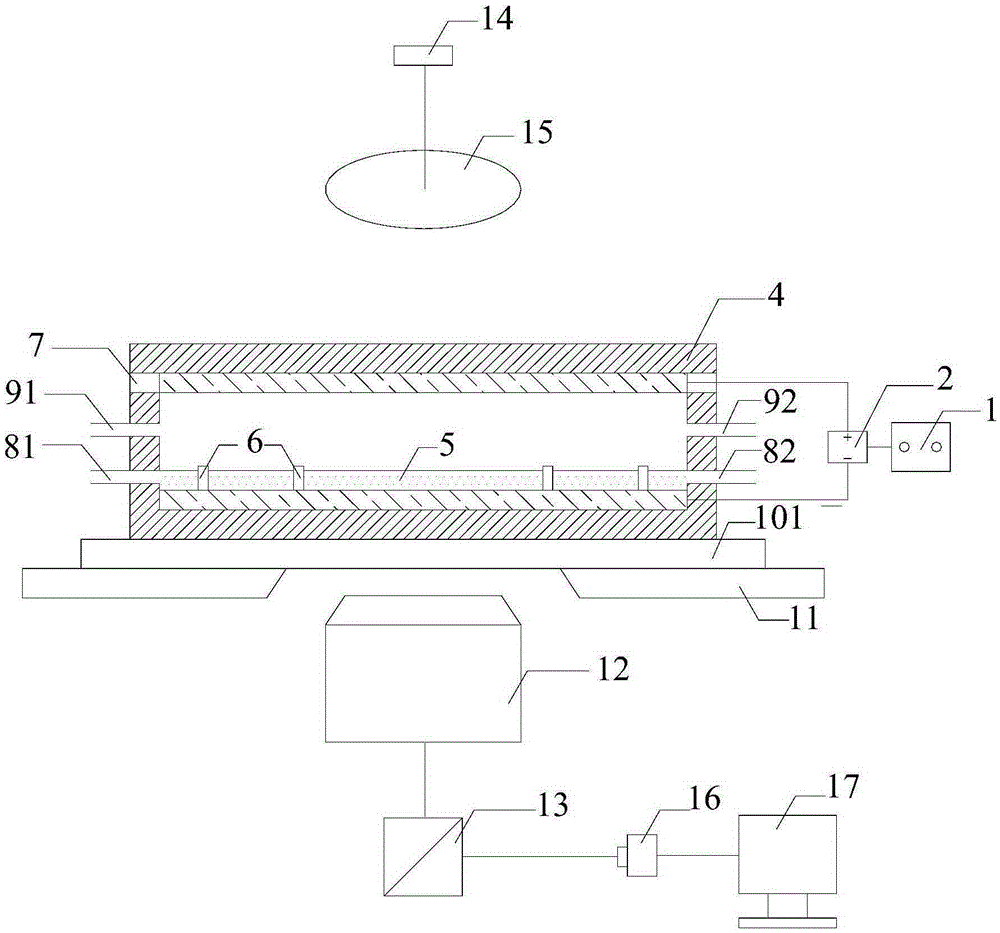
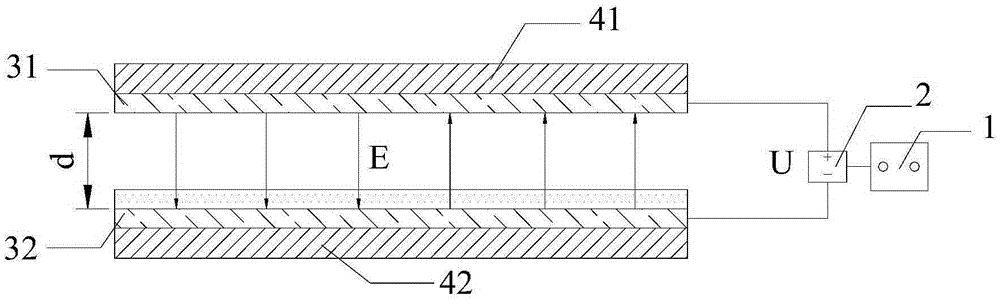
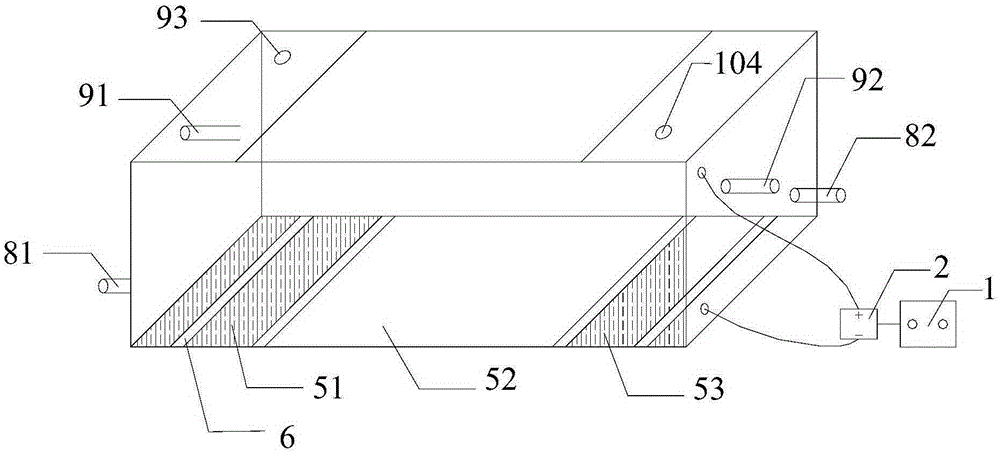
The invention discloses a cell cultivation device applied to microscopic observation. The cell cultivation device comprises a cultivation tank, wherein a cover body is arranged at the top of the cultivation tank, the cover body and a base plate of the cultivation tank are made of transparent materials, a first conducting layer and a second conducting layer are respectively arranged on the inner side faces of the cover body and the base plate and are connected with electrodes of a power source, and a space between the first conducting layer and the second conducting layer after being powered on forms an electric field; a culture solution inlet and outlet are formed in the tank body of the cultivation tank. According to the cell cultivation device applied to the microscopic observation, the two conducting layers are arranged in parallel to generate a static electric field; an inverted microscope is utilized to in-situ observe a cell biological process exposed in a strong static field in real time, so that the interference factor is reduced largely, and objective evaluation of the biological effect of the static field on a cell level is facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Method for screening effective sites of flavonoid substances in golden camellia acting on nasopharyngeal carcinoma
InactiveCN104480183AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProteomics methodsFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for screening effective sites of flavonoid substances in golden camellia acting on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The method comprises the following steps: extracting flavonoid substances in golden camellia for acting on nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell strains such as CNE-1, CNE-2, C666-1 and the like cultured in vitro and taken as models, discovering that flavonoid-like substances in a golden camellia extract can be used for inhibiting nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by applying a laser confocal inverted microscope, a fluorescence labelling mRNA differential display technology, a proteomics method, matrix-assisted time of flight mass spectroscopy and other technologies, also performing location detection on the expression of genes such as bcl-2, notch1 and the like in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and revealing the effective sites of the flavonoid substances in golden camellia in inhibition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma activity from the change of protein levels. According to the method disclosed by the invention, deep research can also be performed by virtue of differentially-expressed proteins, action mechanisms of the proteins can be clarified, and meanwhile, the proteins can be possibly taken as action target molecules of medicines for clinically treating nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Owner:SCHOOL OF MEDICINE JIAYING UNIV
Objective lens, nosepiece and inverted microscope equipped therewith
ActiveUS20100091363A1Reduce focus shiftReduce focusMicroscopesMountingsImaging lensInverted microscope
An objective lens to be fitted into a fitting hole of a nosepiece of a microscope includes an imaging lens that is composed of a plurality of lens groups, and a lens barrel that holds the imaging lens. The lens barrel is formed with a fitting portion that is fitted to the fitting hole of the nosepiece and provided at an outer circumference of a tip portion side away by a given distance from the tip portion where a first lens group in the imaging lens is held, and a mount surface that comes into contact with a contact surface of the fitting hole of the nosepiece upon fitting at the fitting portion. The nosepiece is equipped with the objective lens. The inverted microscope is equipped with the nosepiece fitting the objective lens.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Optical super-resolution imaging system based on inverted microscope and micro-sphere lens and dynamic imaging method using same
InactiveCN107402443AExpand nanoscale imagingExpand operabilityMicroscopesCantilevered beamAtom force microscopy
The invention discloses an optical super-resolution imaging system based on an inverted microscope and a micro-sphere lens which can realize optical super-resolution imaging under an inverted microscope. The optical super-resolution imaging system includes an optical mirror, a micro-sphere lens, an atomic force microscope scanning probe, a sample stage, an optical inverted microscope, and a displacement stage. The atomic force microscope scanning probe is pasted through a substrate thereof onto the optical mirror. The micro-sphere lens is fixed to a cantilever beam and a tip of the atomic force microscope scanning probe, and is positioned below the optical mirror. The optical mirror is fixed to the displacement stage above the optical mirror. The sample stage is positioned below the micro-sphere lens. The optical inverted microscope is positioned below the sample stage, and the objective lens of the optical inverted microscope is positioned right below the micro-sphere lens. The invention further provides a dynamic imaging method using the system. The system of the invention is especially suitable for observing the internal structure of living cells and other occasions.
Owner:苏州显纳精密仪器有限公司
Multimode coupling in-situ microscopic spectral imaging system
InactiveCN110441235AAvoid measurement biasAchieve independent acquisitionMaterial analysis by optical meansObservational errorPath switching
The invention discloses a multimode coupling in-situ microscopic spectral imaging system. The system is composed of an inverted microscope, an exciting light source module, a light path switching module, a spectral imaging and spectrum test module, and refers to a plurality of spectrum and imaging measurement functions in the same micron-order area of a sample, comprising measuring microcell Ramanspectrum and microcell fluorescence spectrum, fluorescence microimaging, microcell transmittance spectrum, transmittance microimaging, microcell reflection spectrum and reflection microimaging. The system has the characteristics that multimode and multidimensional in-situ detection and analysis can be performed on the same microcell of the sample with no need to moving the sample to various kindsof detection equipment; the acquired sample microcell information can be represented in situ, namely that various kinds of information such as the Raman spectrum, fluorescence spectrum and imaging, transmittance spectrum and imaging, reflection spectrum and imaging of the same microcell of the sample can be acquired in real time. Measurement errors caused by transferring of the sample are eliminated, and the reliability of the test result is greatly improved.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Atomic force microscope measuring device
InactiveUS20170023611A1Maximizes excitation efficiencyImprove efficiencyRaman scatteringScanning probe techniquesAtomic force microscopyMeasurement device
Atomic force microscope measuring device comprising a micro-cantilever and an intensity modulated laser exciting the cantilever, wherein the measuring device comprises an optical microscope, in particular a fluorescence microscope, a confocal microscope, a fluorescence energy transfer (FRET) microscope, a DIC and / or phase contrast microscope, all of those in particular construed as an inverted microscope.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com