Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "Microdissection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microdissection refers to a variety of techniques where a microscope is used to assist in dissection.
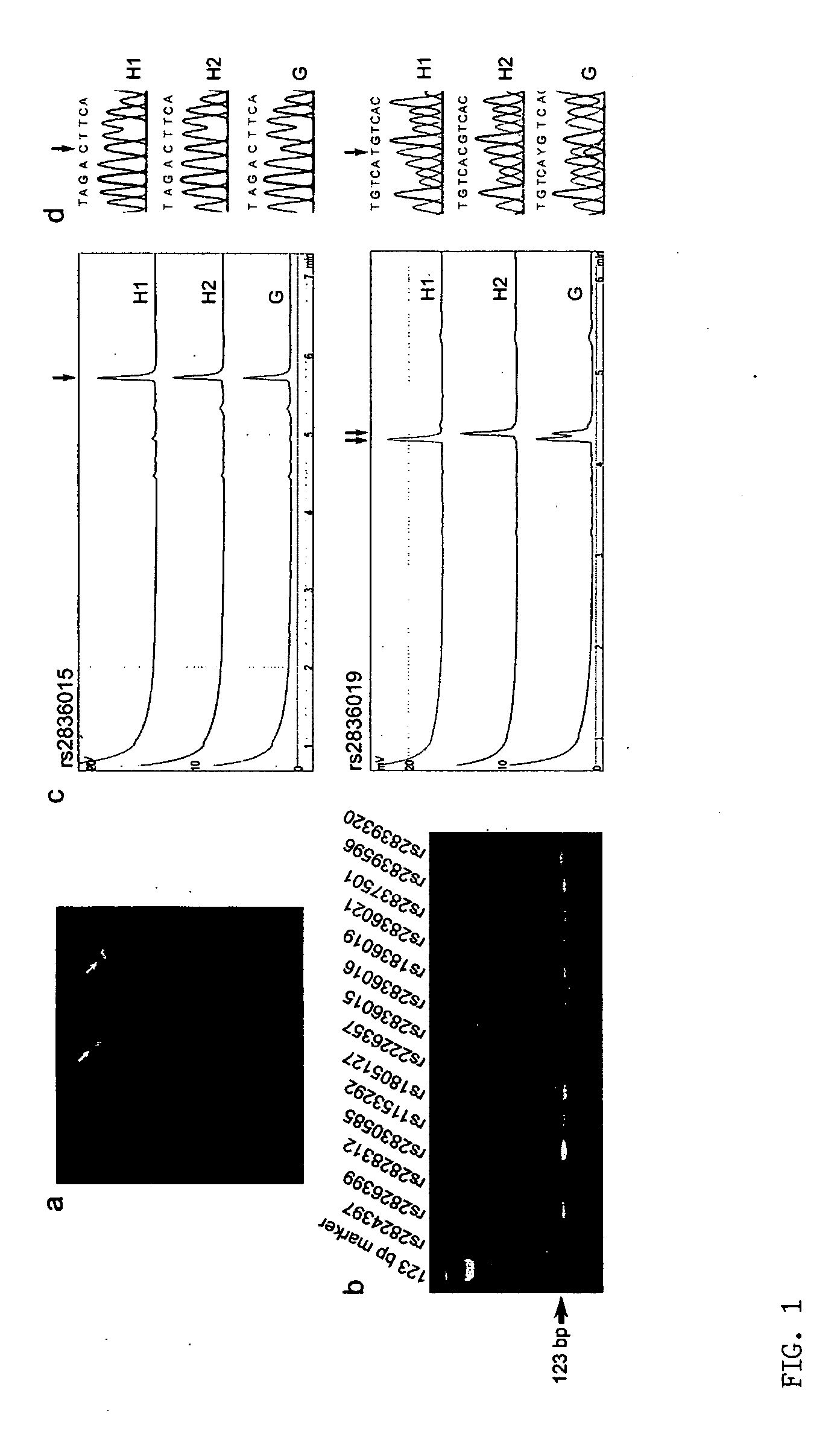
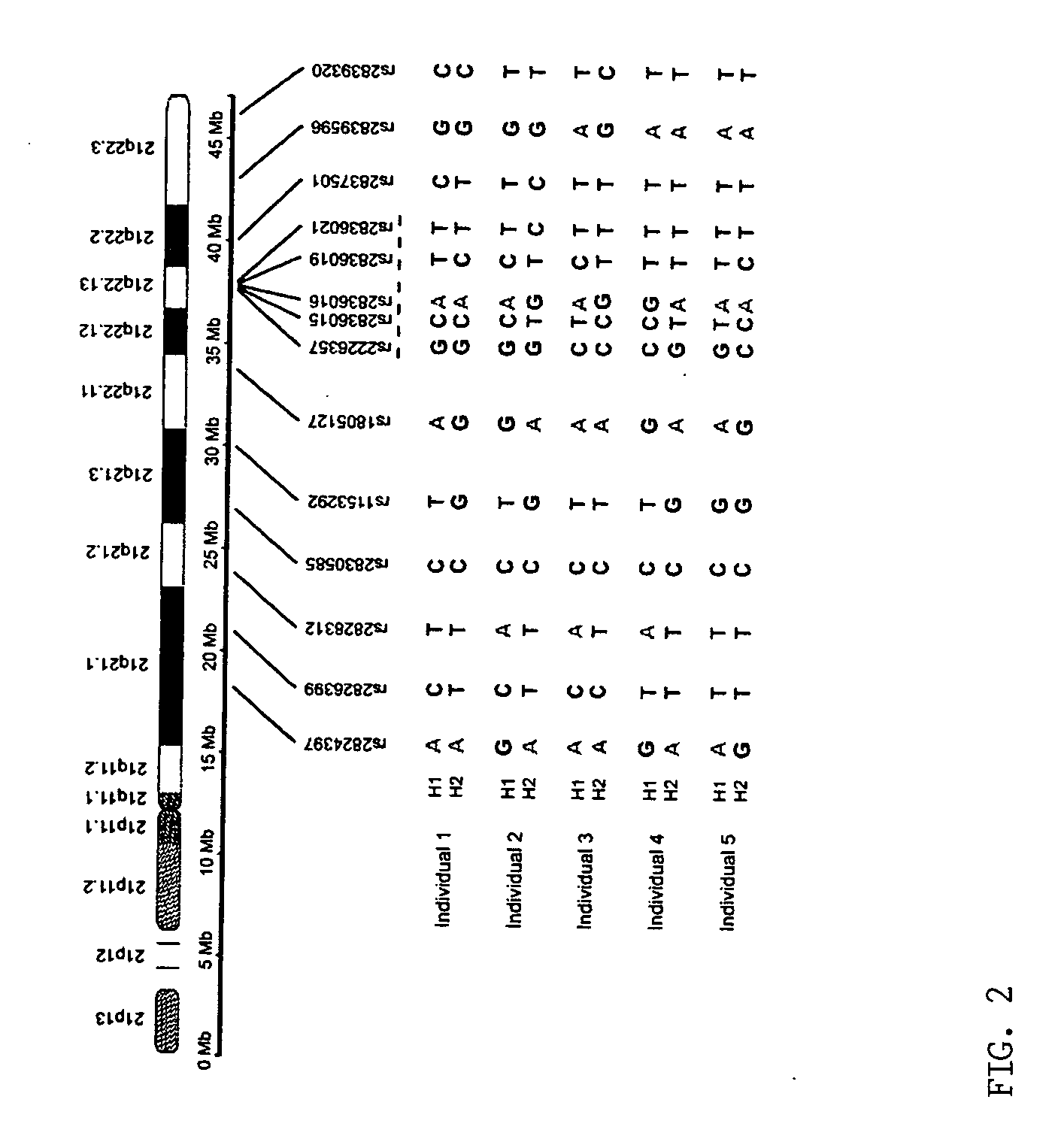
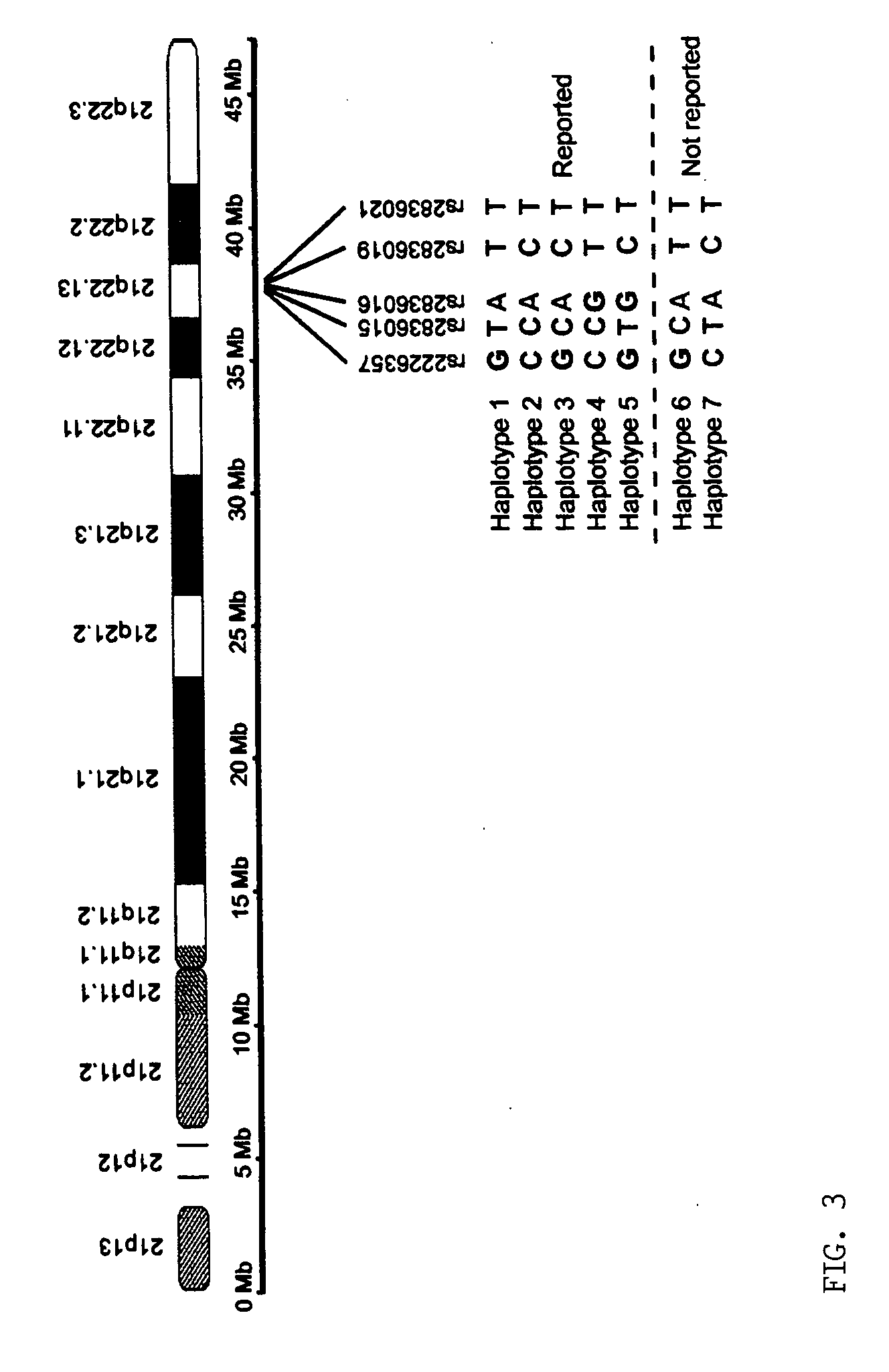
Microdissection-based methods for determining genomic features of single chromosomes
InactiveUS20060211001A1Quick fixPromote associationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAChromosome regions
The present provides a microdissection-based method for identifying a genomic feature present within a visible chromosome region. The method includes steps of: (a) micro-dissecting a single copy of a chromosome to obtain a visible chromosome region; (b) amplifying the visible chromosome region to obtain amplified single chromosome DNA; and (c) subjecting the amplified single chromosome DNA to micro-array analysis whereby such analysis identifies at least one genomic feature present within the visible chromosome region. The method is applicable to determining genomic features including, but not limited to, genomic DNA size, gene content, DNA breakpoint, or DNA polymorphism (e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
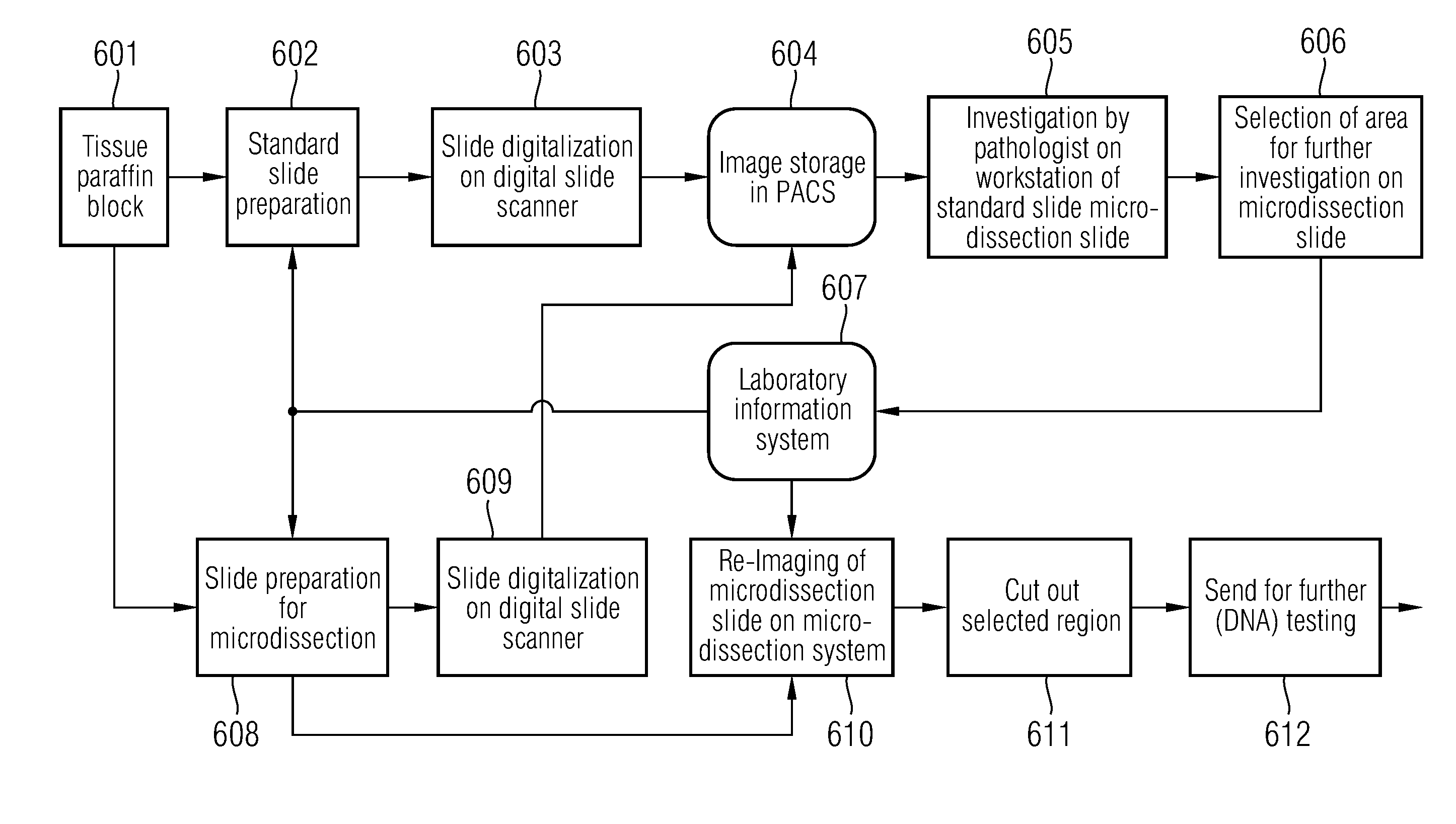
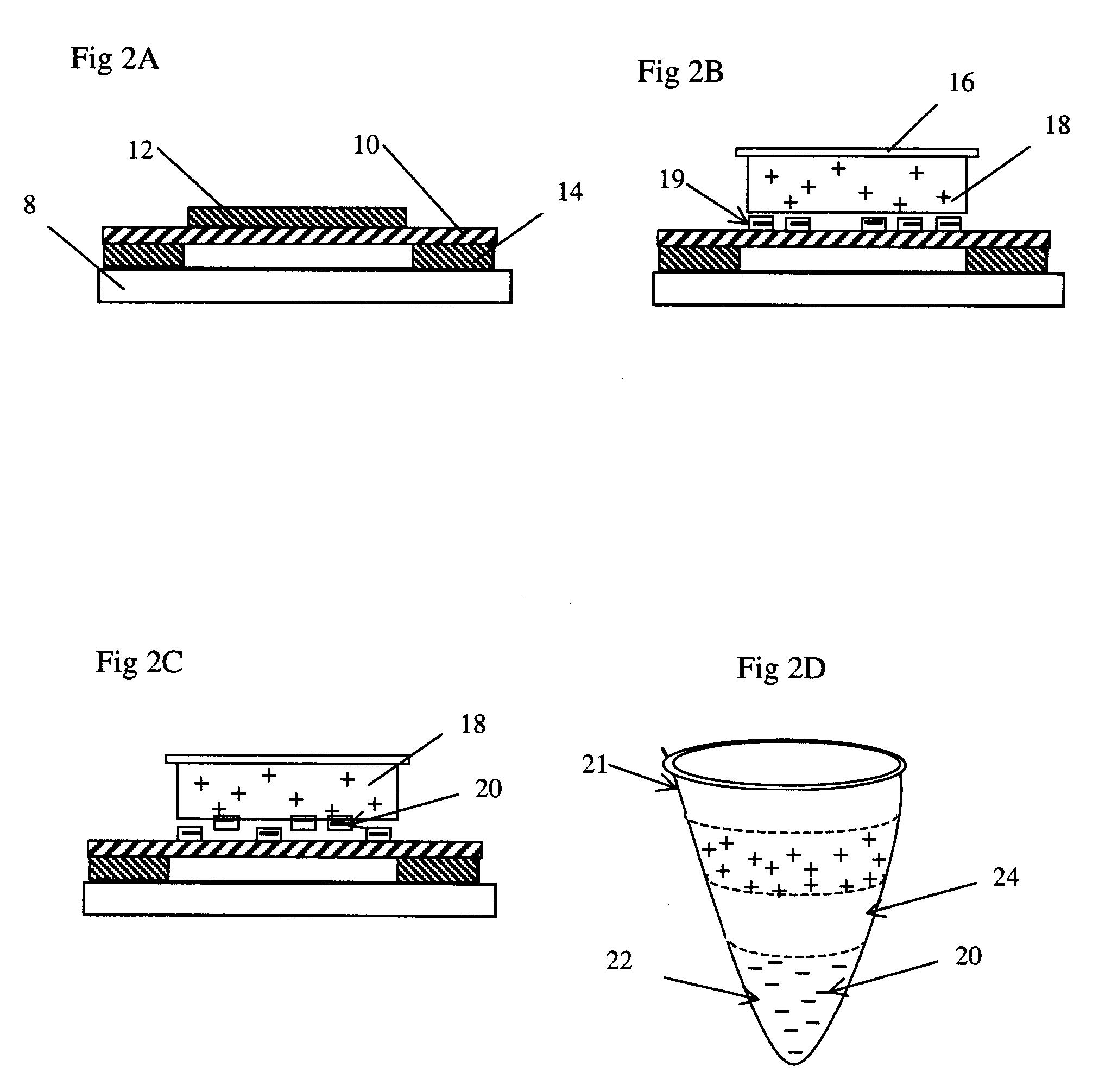
Microdissection method and information processing system
ActiveUS20120045790A1Easy to controlImage enhancementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsInformation processingBiological materials
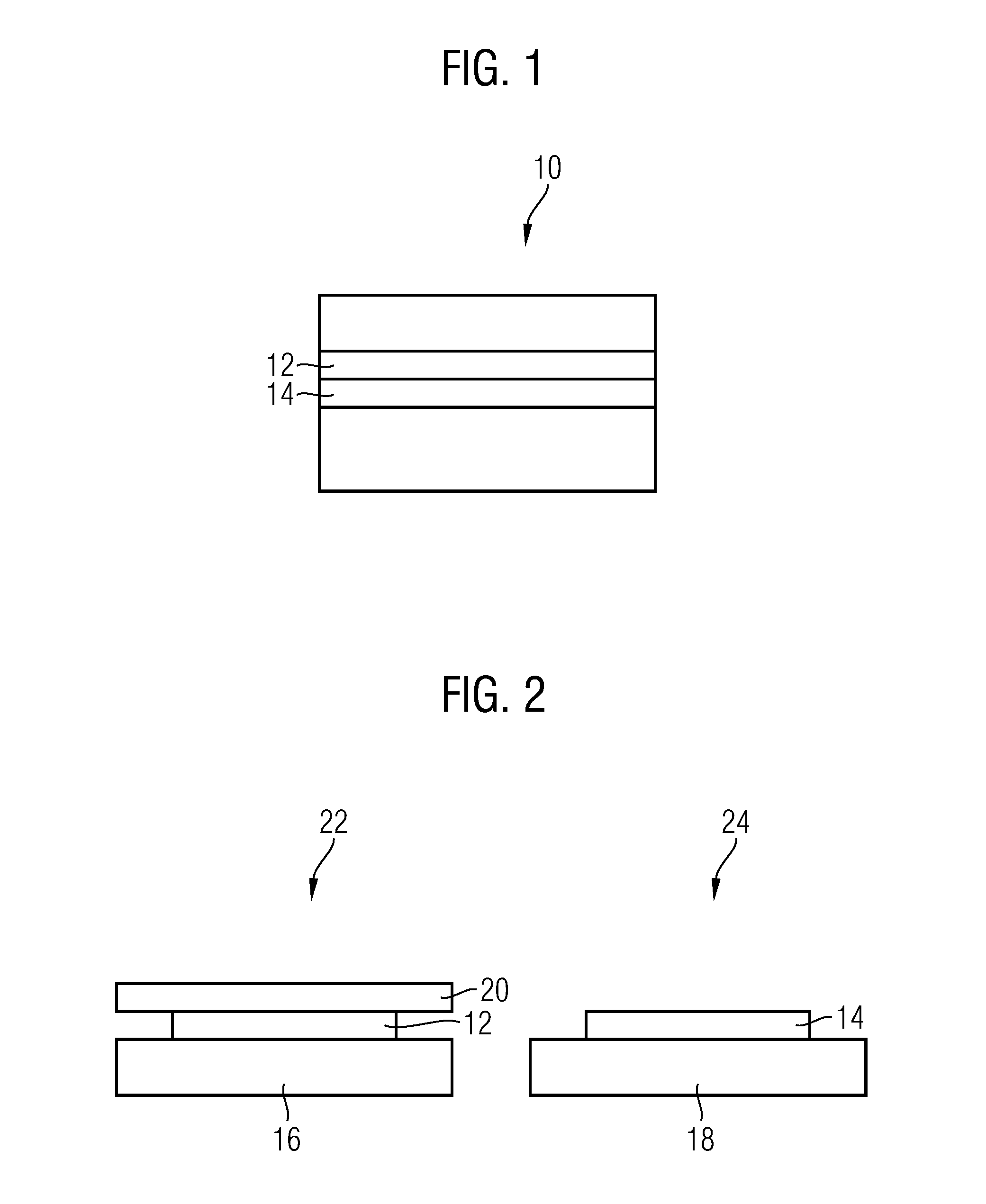
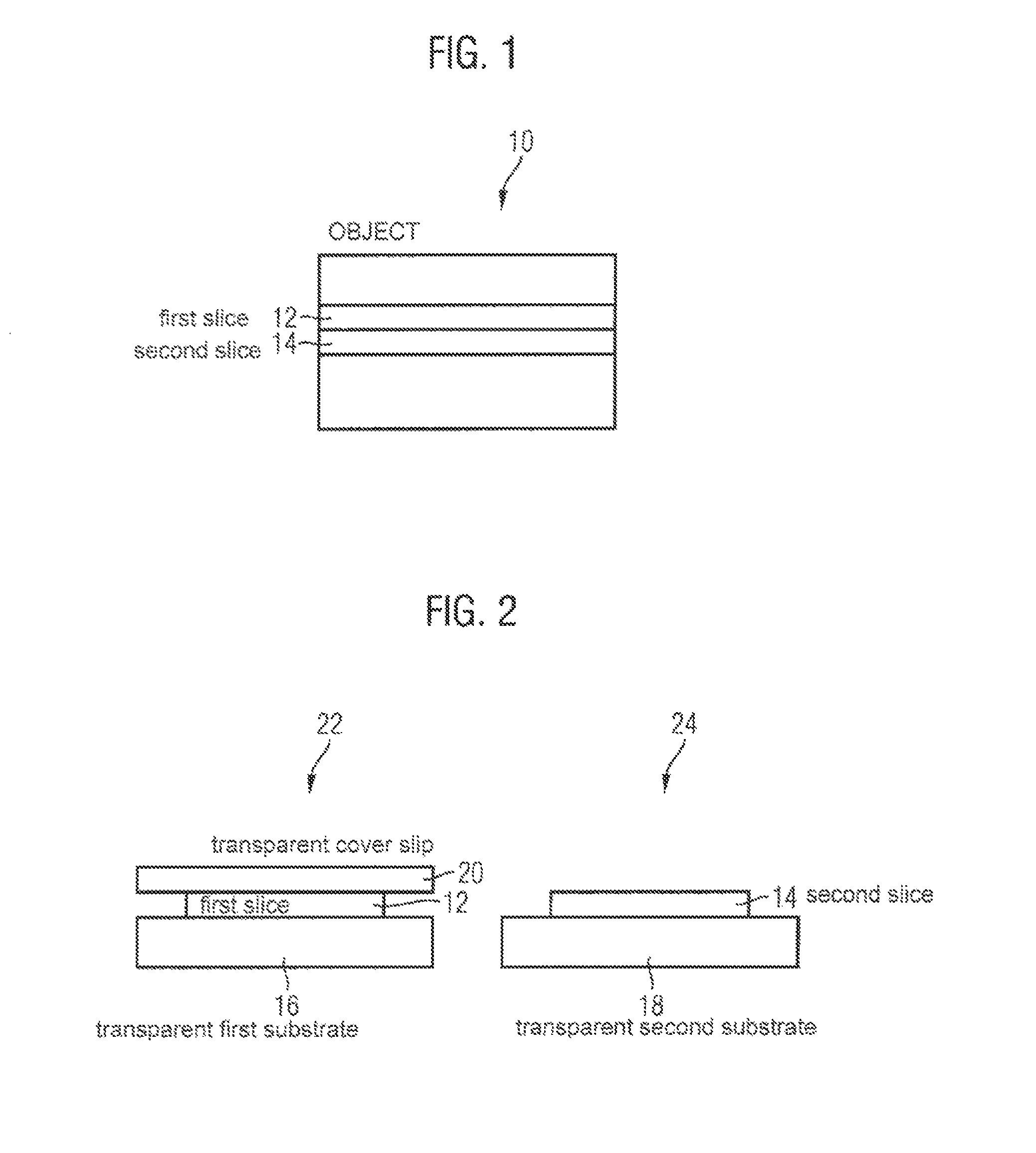
In a first aspect, a method for use in biology, histology, and pathology, comprises: providing a digital first image (44) of a first slice (12) of an object (10) comprising biological material; generating a digital second image (46) of a second slice (14) of the object; determining a region of interest (50) in the second image on the basis of a region of interest (48) in the first image; determining a region of interest in the second slice on the basis of the region of interest (50) in the second image; and extracting material from the region of interest in the second slice. In another aspect, an information processing system, for use in biology, histology and pathology, comprises: a predefined set of process identifiers (64); a set of data records (68, 70, 72) associated with an object (10) comprising biological material, wherein each of the data records comprises: a slice identifier identifying a slice (12; 14) of the object, and a process identifier selected from the set of process identifiers, the process identifier indicating a process to which the slice is intended to be subjected; a user interface (52, 56, 58, 60) for enabling a user to select a data record (68) from the set of data records.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
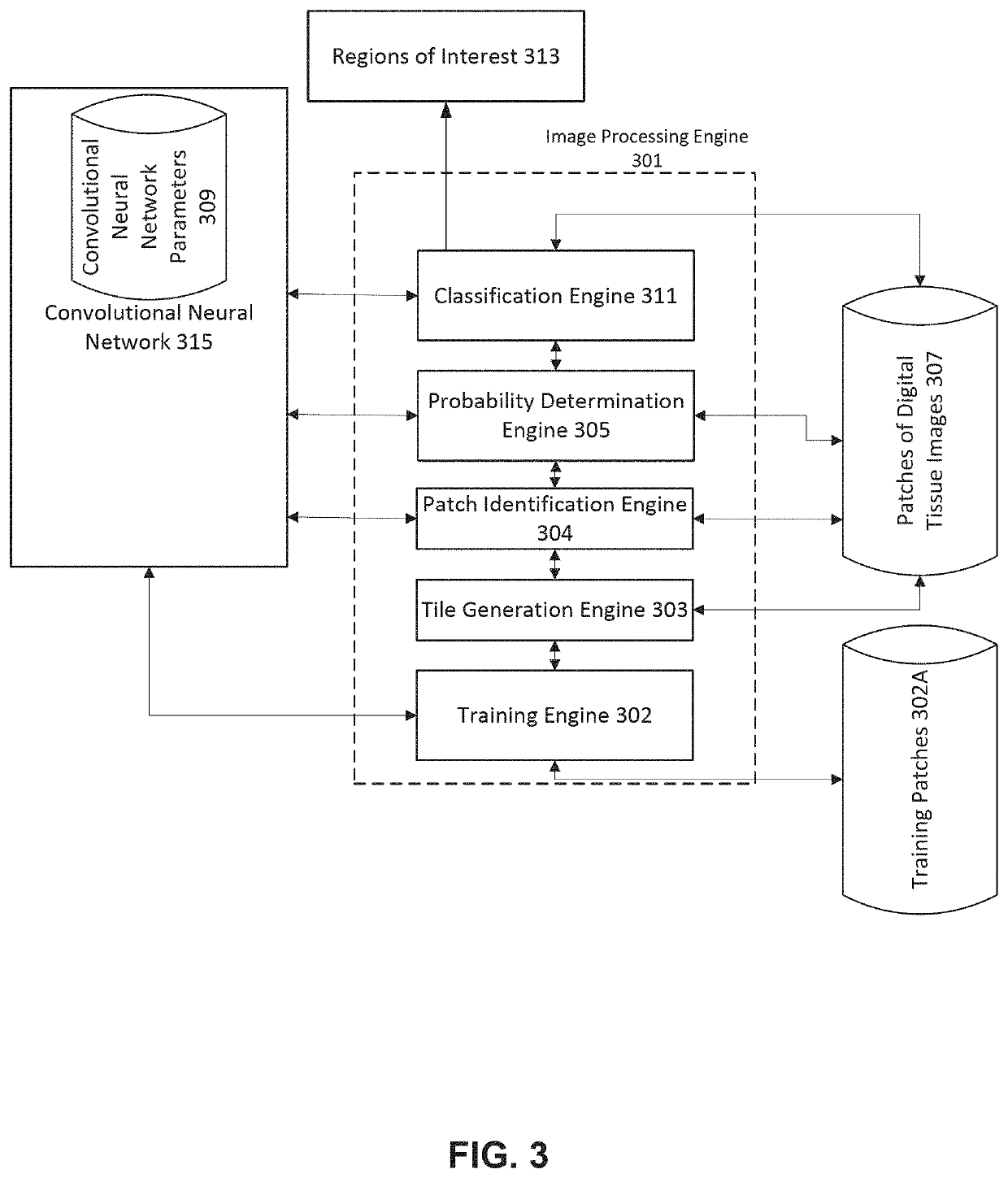
Digital histopathology and microdissection
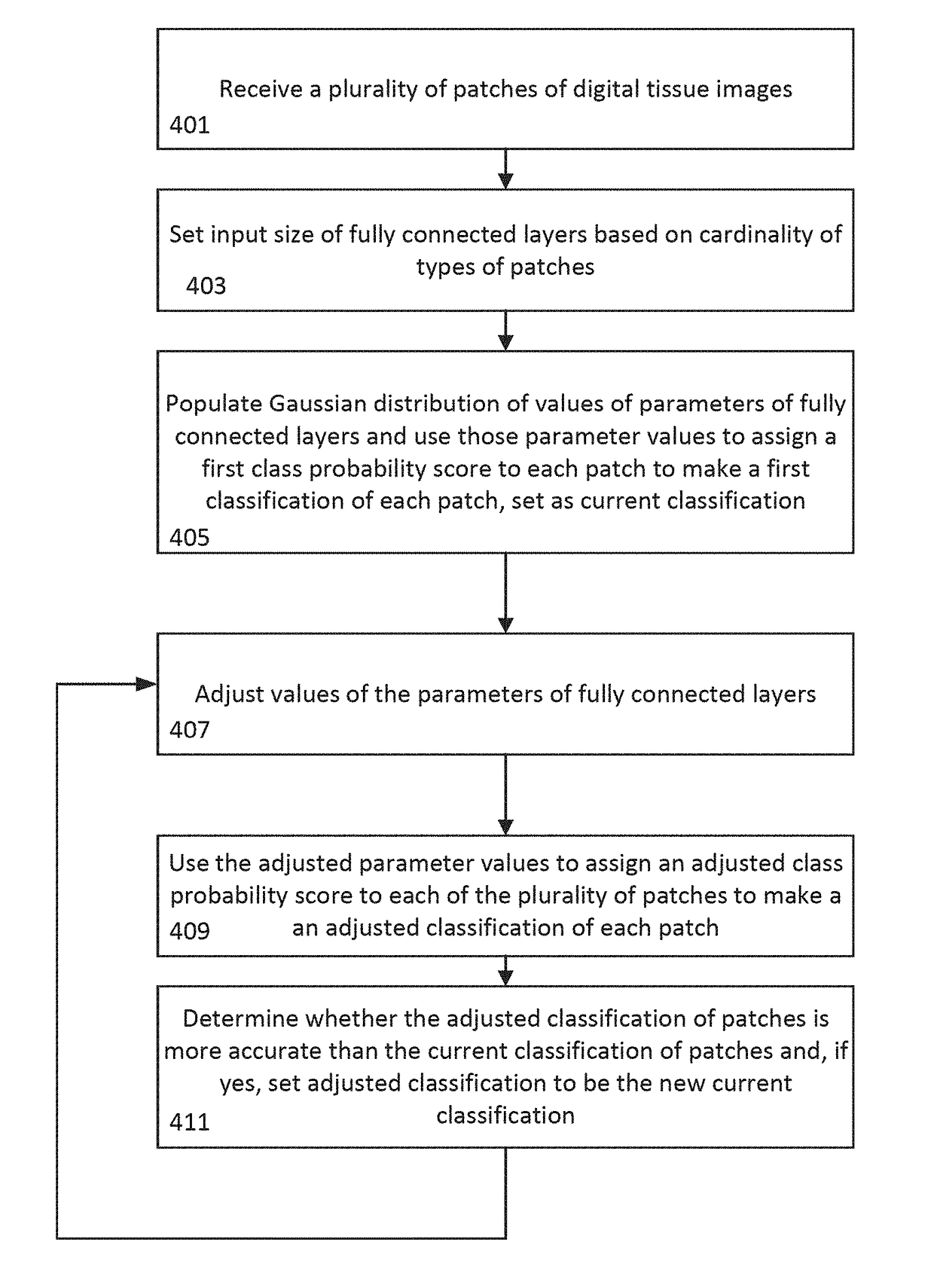
A computer implemented method of generating at least one shape of a region of interest in a digital image is provided. The method includes obtaining, by an image processing engine, access to a digital tissue image of a biological sample; tiling, by the image processing engine, the digital tissue image into a collection of image patches; identifying, by the image processing engine, a set of target tissue patches from the collection of image patches as a function of pixel content within the collection of image patches; assigning, by the image processing engine, each target tissue patch of the set of target tissue patches an initial class probability score indicating a probability that the target tissue patch falls within a class of interest, the initial class probability score generated by a trained classifier executed on each target tissue patch; generating, by the image processing engine, a first set of tissue region seed patches by identifying target tissue patches having initial class probability scores that satisfy a first seed region criteria, the first set of tissue region seed patches comprising a subset of the set of target tissue patches; generating, by the image processing engine, a second set of tissue region seed patches by identifying target tissue patches having initial class probability scores that satisfy a second seed region criteria, the second set of tissue region seed patches comprising a subset of the set of target tissue patches; calculating, by the image processing engine, a region of interest score for each patch in the second set of tissue region seed patches as a function of initial class probability scores of neighboring patches of the second set of tissue region seed patches and a distance to patches within the first set of issue region seed patches; and generating, by the image processing engine, one or more region of interest shapes by grouping neighboring patches based on their region of interest scores.
Owner:NANTOMICS LLC
Method and System For Collecting Cells Following Laser Microdissection
ActiveUS20080199929A1Efficient advancementMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementLight beamLaser beams
A method of collecting target regions from a target object is described. The method in one embodiment comprises mounting a negatively-charged membrane on a first side of a substrate, mounting a target object on the membrane, positioning a collection material adjacent to the target object, and passing a laser beam from a second side of the substrate, through the substrate, the membrane, and the target object, to dissect target regions from the prepared tissue section, whereby the dissected target regions adhere to the collection material. In another embodiment, the present invention is a system for collecting target regions from a target object. In one embodiment, the system comprises a substrate having a first side and a second side, a negatively-charged membrane adhered to the first side of the substrate, and a collection material mountable adjacent to the membrane. In another embodiment, the system further comprises an inverted microscope, a stage for holding the substrate over the microscope, a generator operable to generate a laser beam to pass through the substrate from the second side and to dissect target regions from a target object mounted on the membrane, whereby the dissected target regions adhere to the collection material. In the preferred embodiments, the target objects are tissues and the target regions are cells.
Owner:MOTIC CHINA GRP CO LTD
Deep sub-micron device sample for in-situ transmission electron microscope and preparation method of sample
ActiveCN103743608AFacilitate experimental researchImprove experimental efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationConventional transmission electron microscopeNano-device
The invention discloses a method for preparing a deep sub-micron device sample for an in-situ transmission electron microscope. Ion beams are focused into ion beams with a small size for performing microdissection or grinding by utilizing an electromagnetic lens by adopting a focused ion beam system, accurate positioning sample preparation can be performed, and a deep sub-micron device is obtained. The method comprises the following steps: cutting and thinning the sample by adopting the focused ion beams so as to obtain a thinned sample, inclining a sample stage at 52+ / -(0.5-1.5) degrees relative to the finally thinned sample through conventional focused ion beams, and innovatively inclining the sample stage at 52+ / -7 degrees. The invention also provides a deep sub-micron device sample for the in-situ transmission electron microscope. The sample comprises multiple discrete nano devices which are regular in shape and have the width of less than 20nm and the thickness of less than 100nm. The sample is suitable for research on the in-situ transmission electron microscope and has the high significance in research on the performance of the deep sub-micron device.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Apparatus and method for micromanipulation of microscale objects using laser light delivered through a single optical fiber and axicon lens
ActiveUS20100120113A1Improve throughputReduce throughputLaser detailsElectrotherapyLight beamLaser light
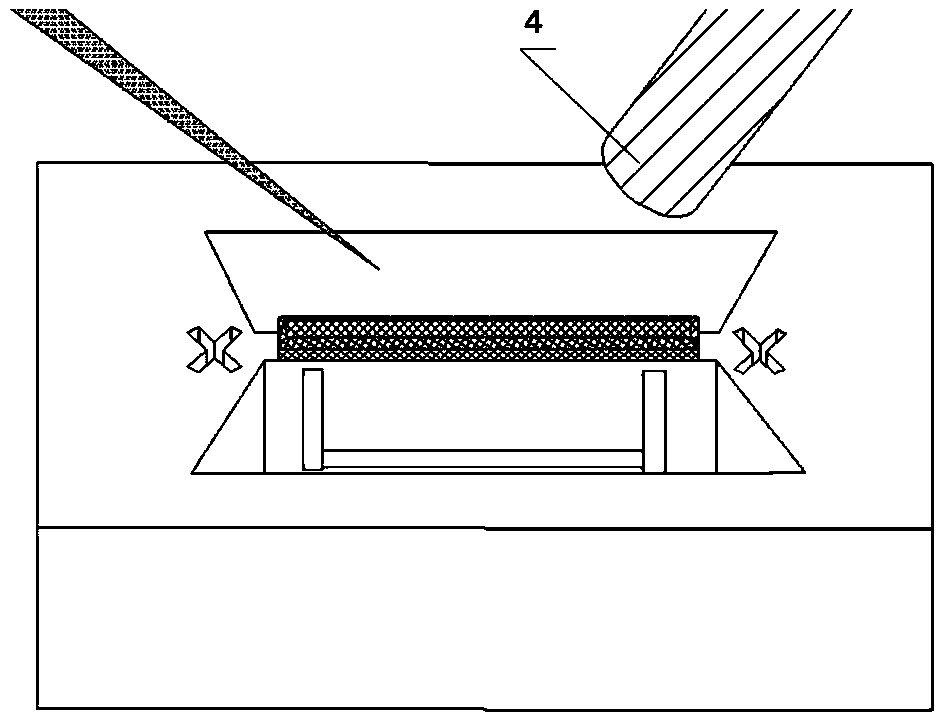
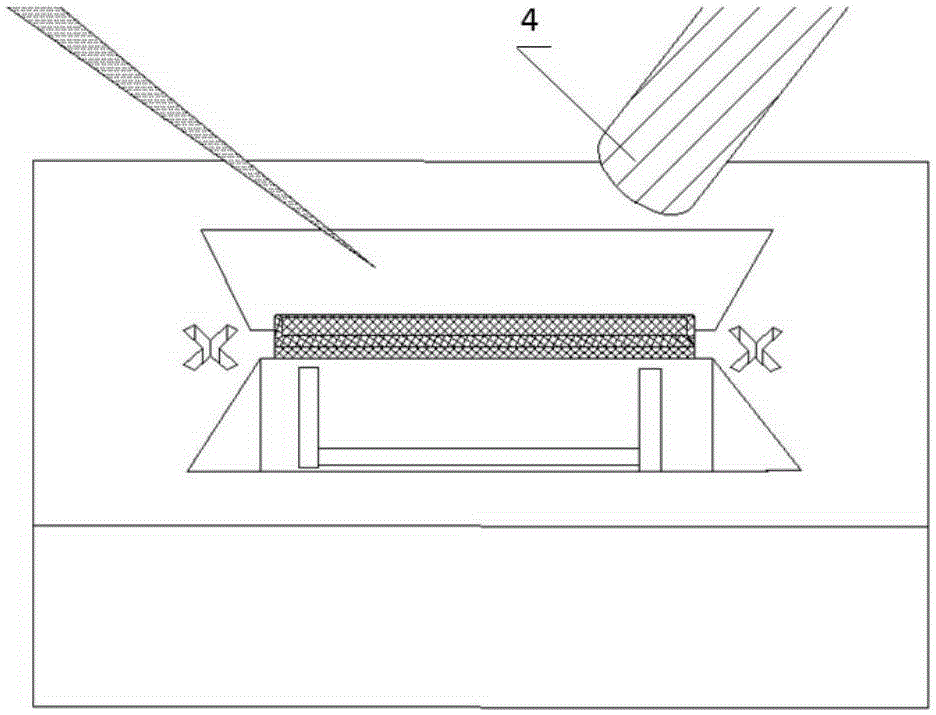
A single optical fiber having a distal end is optically coupled to the laser and distilling terminated with an axicon lens optically coupled to the single optical fiber to form a microscopic distal tip to provide a spatially shaped elongated laser focused spot for microprocessing and / or microdissection of a microscale object. A pulsed or continuous laser beam or superposition of pulsed and continuous laser beams is generated, controllably spatially shaped, selectively oriented, selectively moved via movement of a single optical fiber terminated with the axicon lens, and the oriented, spatially shaped laser beam applied via the single optical fiber terminated with the axicon lens to a living or nonliving microscopic object for manipulation, micro-dissection, alteration / ablation, and excitation of the living or nonliving microscopic object.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biological laser printing for tissue microdissection via indirect photon-biomaterial interactions
ActiveUS20040247777A1Electric discharge heatingVacuum evaporation coatingOptoelectronicsBiological materials
A method of laser forward transfer is disclosed. Photo energy is directed through a photon-transparent support and absorbed by an interlayer coated thereon. The energized interlayer causes the transfer of specific regions of a heterogeneous tissue sample coated thereon across a gap and onto a receiving substrate or into a receiving vessel.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
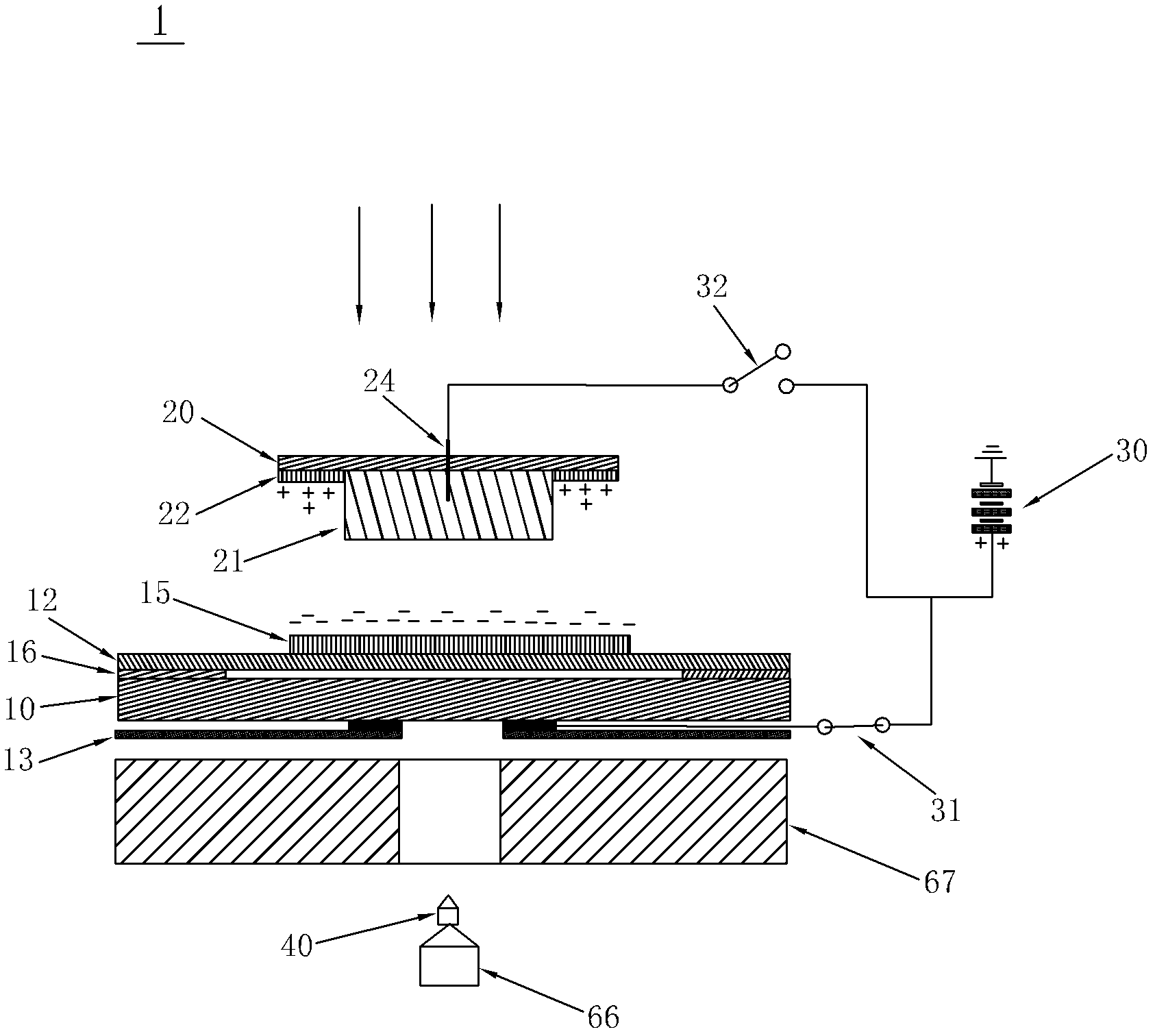
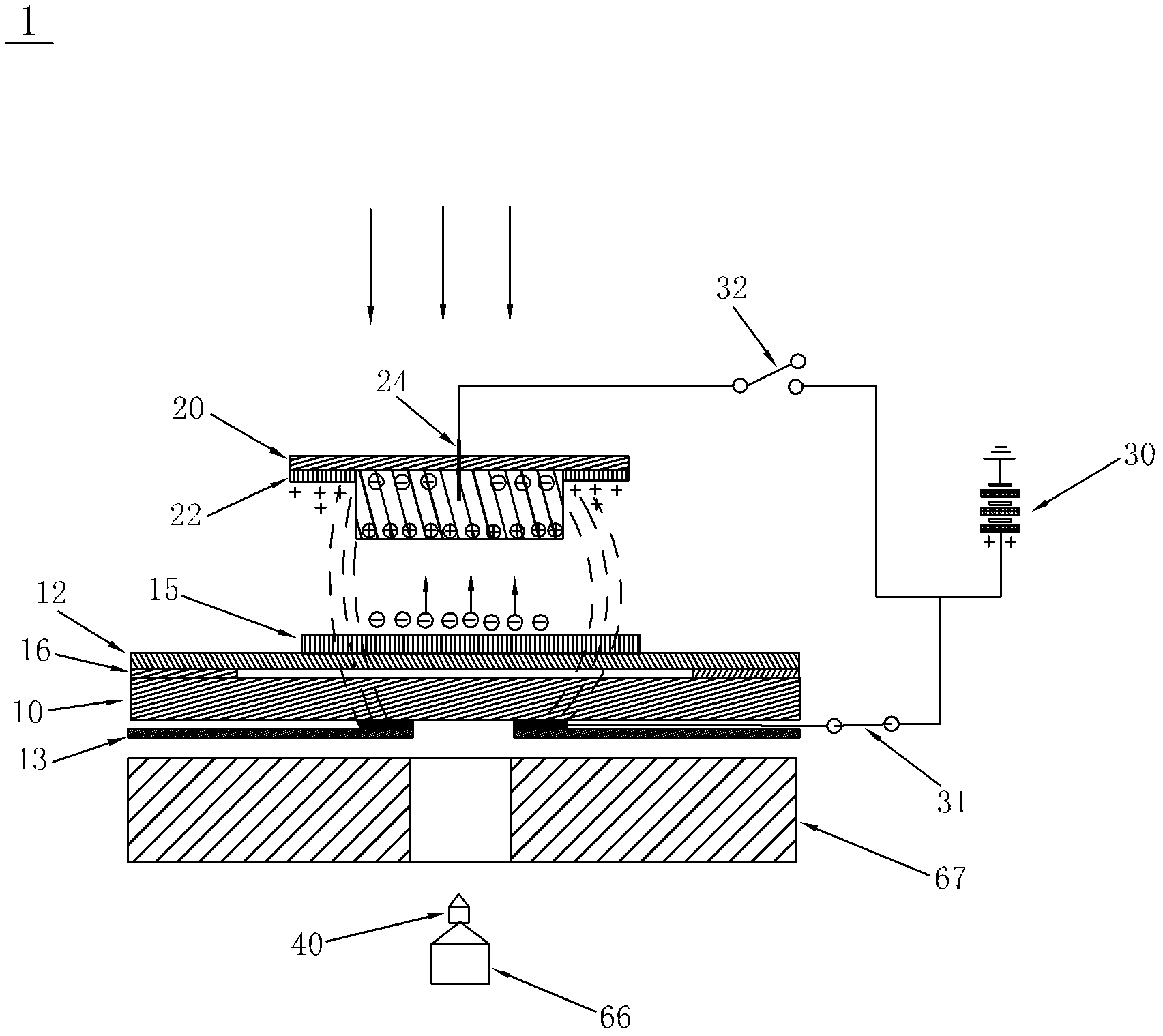
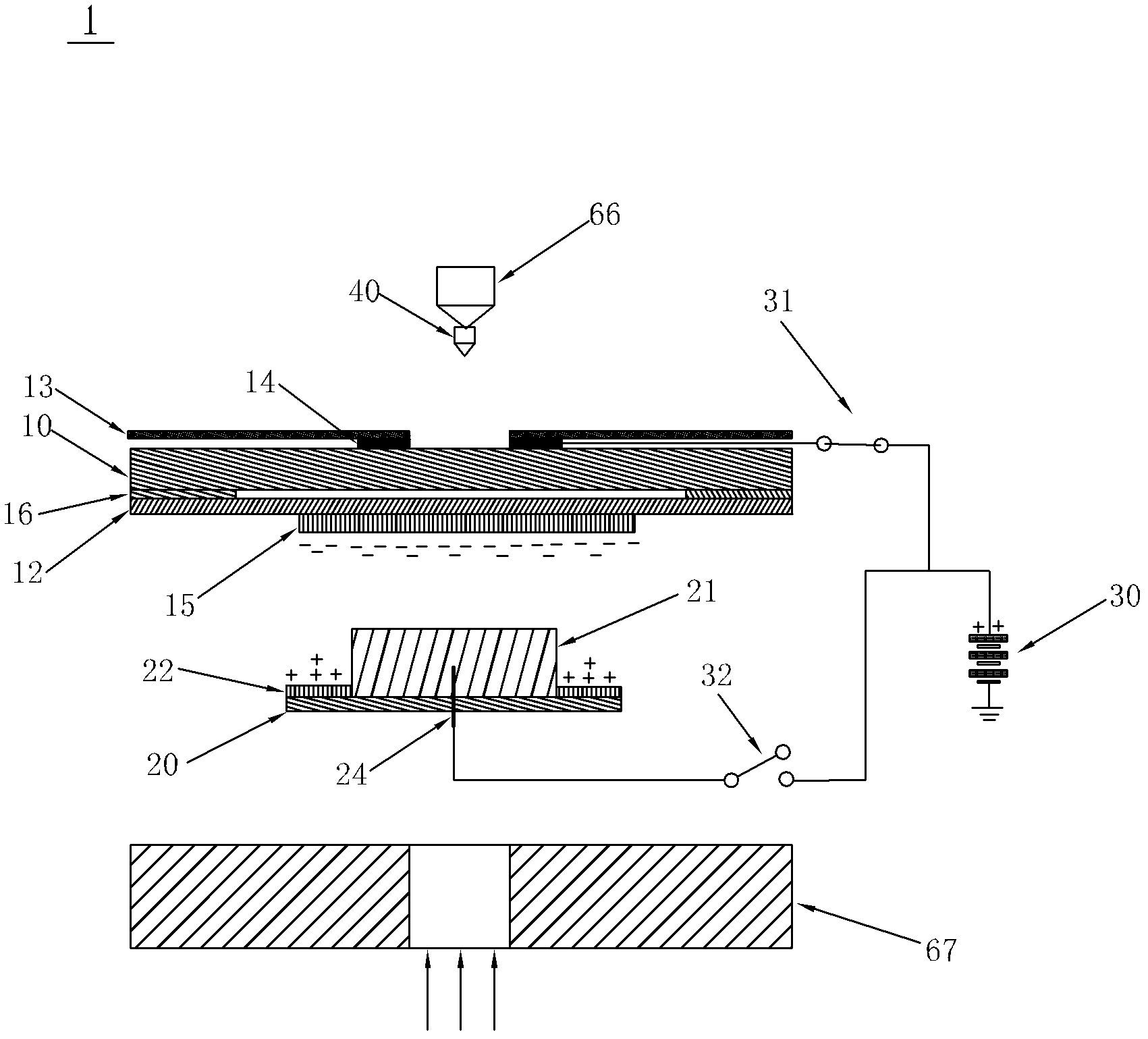
Collection device for collecting cells after laser microdissection, method and system thereof
ActiveCN102628758AWill not harmImprove collection efficiencyWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCell adhesionStatic Charges
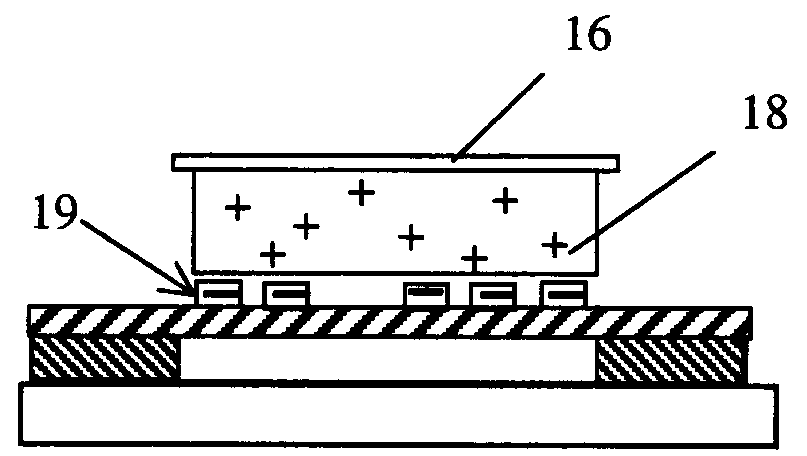
The invention discloses a collection device for collecting cells after laser microdisssection, a method and a system thereof. The device provided by the invention comprises a sample carrier, two sides of which are respectively provided with a transparent film layer and an insulating layer, wherein the transparent film layer fits with the sample carrier and is equipped with cell tissue samples, and a first electrode is disposed between the insulating layer and the sample carrier; a sample collector which is filled with a cell adhesion material for the adhesion of cell tissues and is also provided with a light-sensitive material for photoelectric reaction after laser irradiation; and a power supply device, the positive electrode of which forms break-make stations with the first electrode through a first switch. By the above scheme, the disadvantage that the cell tissue samples during the collection process are polluted and that requirements on materials of the sample carrier and the sample collector are high, carried static charges are inconvenient to preserve and the collection efficiency is poor in the prior art is avoided. According to the cell collection device and the method thereof, functions are stable, and cell tissue samples will not be damaged.
Owner:MOTIC CHINA GRP CO LTD
Laser isolation of viable cells
Methods for laser microdissection isolation of viable cells are provided. Cells of a desired type may be isolated from a diverse population, optionally with detection and exclusion of undesired cells. Desired cells may be isolated from a population that arose from differentiation of pluripotent cells, preferably embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells, and undifferentiated stem cells may be detected and excluded from selection including the isolation of RPE cells sleeted based on morphology (e.g., characteristic mottled appearance) from a population of ES cells. The cells isolated by these methods, including RPE cells, may be essentially free of undifferentiated cells and thus suitable for use in cell-based therapies.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
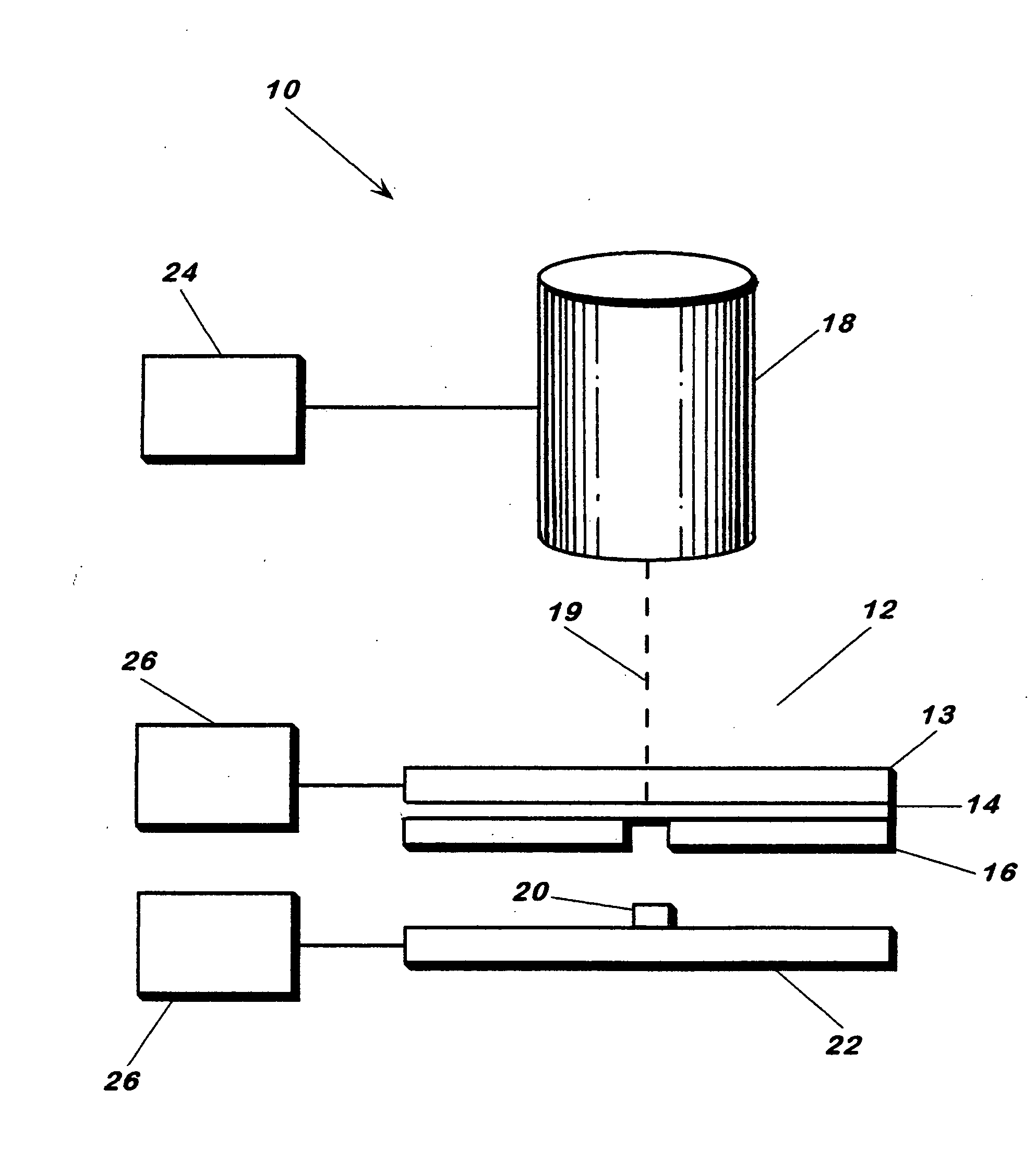
Laser microdissection unit
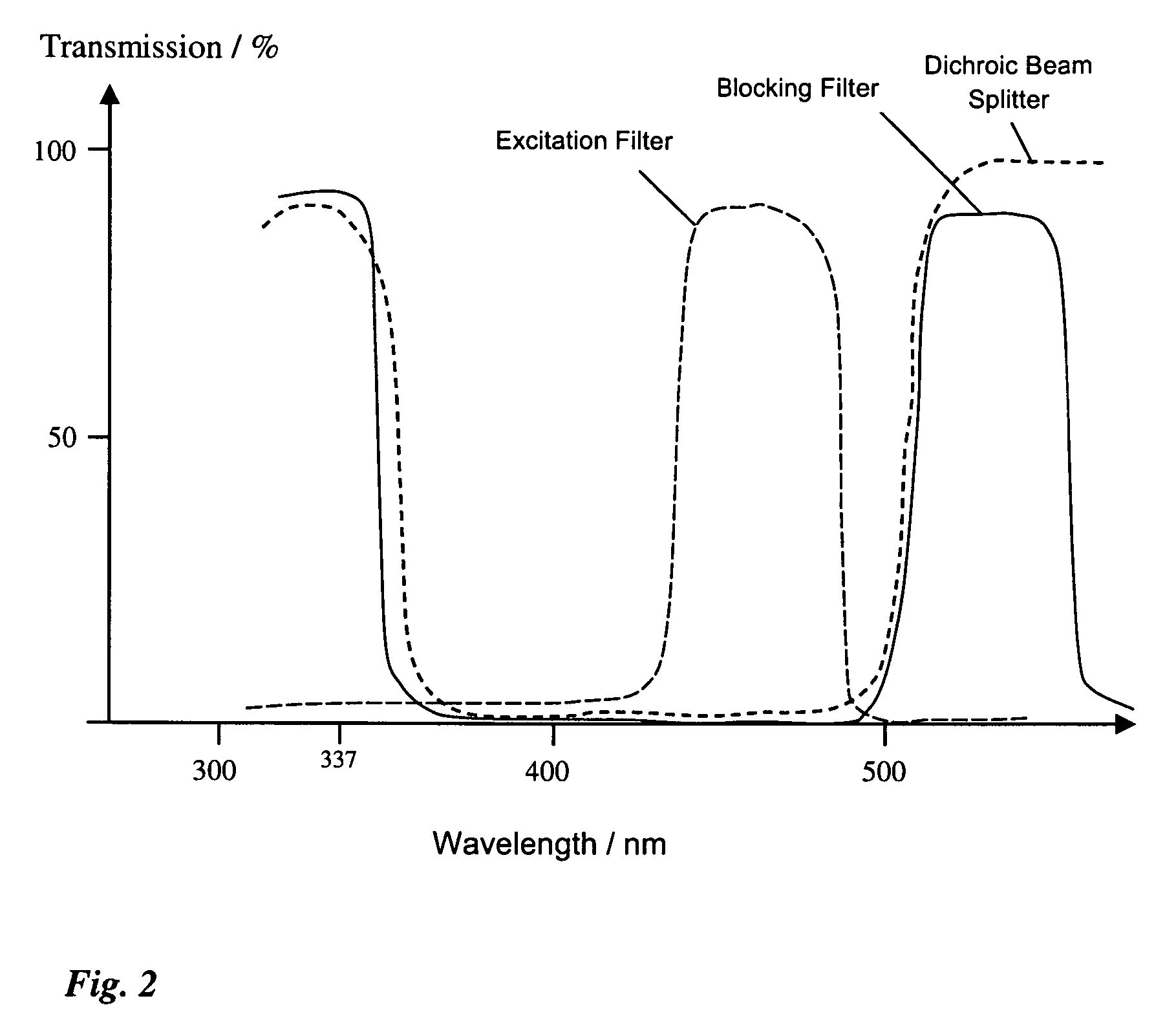
A laser microdissection unit for cutting a microscopic sample using a laser beam of a laser includes a microscope and a fluorescence device. The microscope includes an illumination beam path directed onto the sample, and an imaging beam path configured to image the sample. The fluorescence device includes an excitation filter, a dichroic beam splitter, and a blocking filter. The dichroic beam splitter and the blocking filter are spectrally transparent to the laser beam, and the laser beam is directable through the dichroic beam splitter and the blocking filter onto the sample.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Method for washing and recycling membranate glass slide for microdissection
ActiveCN101576653AFull protection adhesionIncrease stickinessAnionic surface-active compoundsDetergent solventsAlcoholDistilled water
Owner:THE FIRST HOSPITAL OF CHINA MEDICIAL UNIV
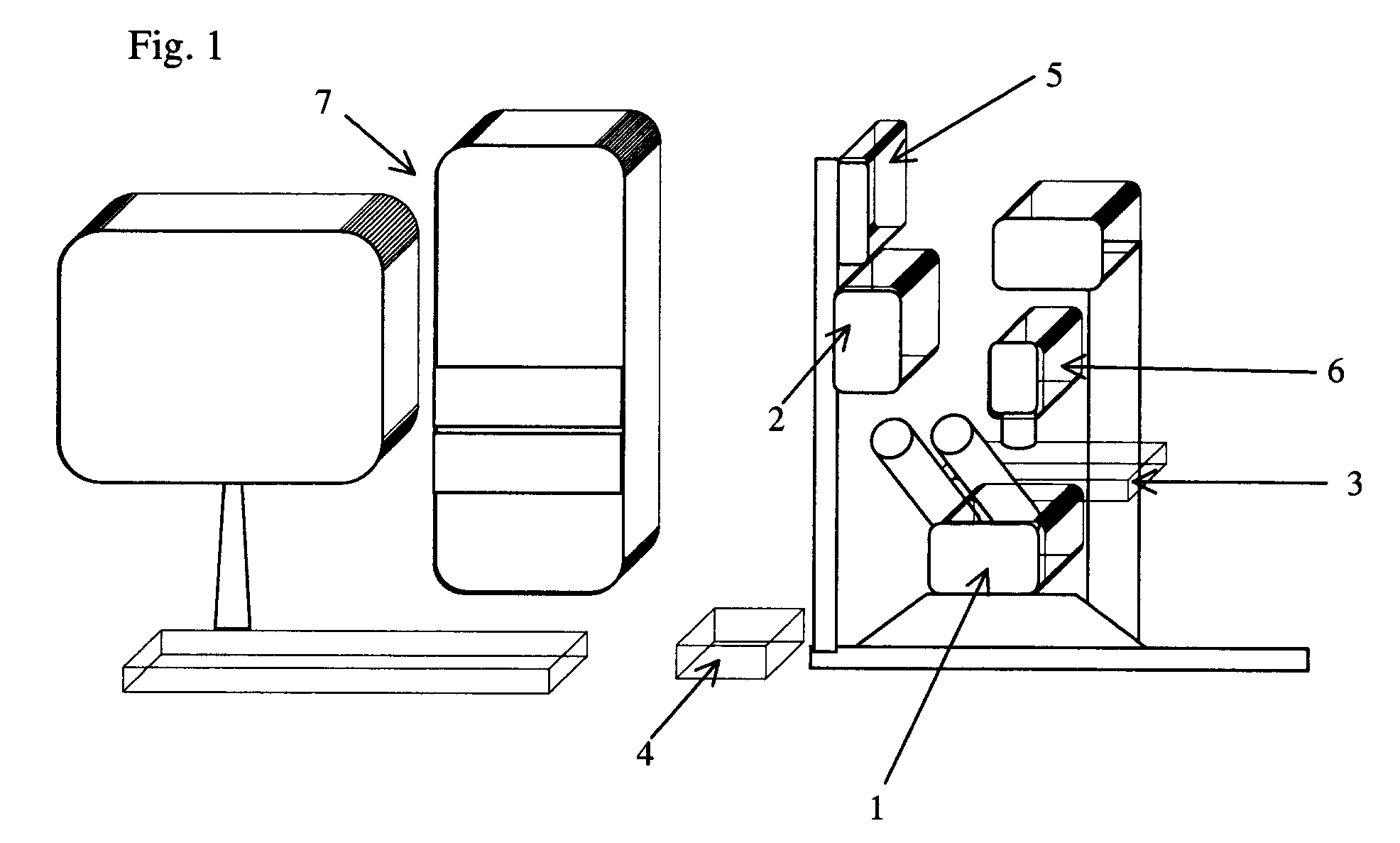
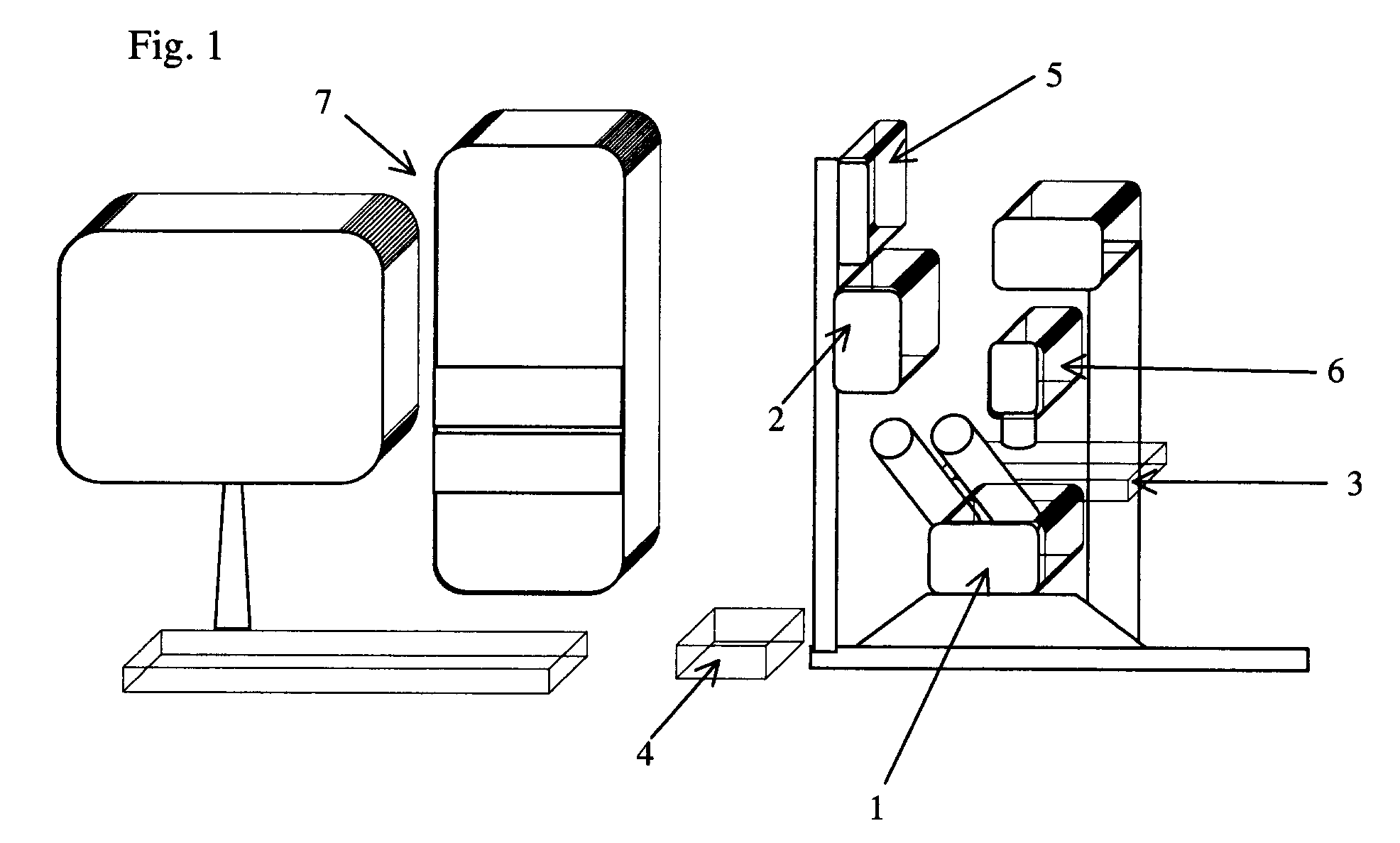
Microdissection device based on piezoelectric ultrasonic vibration
InactiveCN1875893ARealize the cutting operationMeet the vibration state requirementsWithdrawing sample devicesSurgeryCut needleEngineering
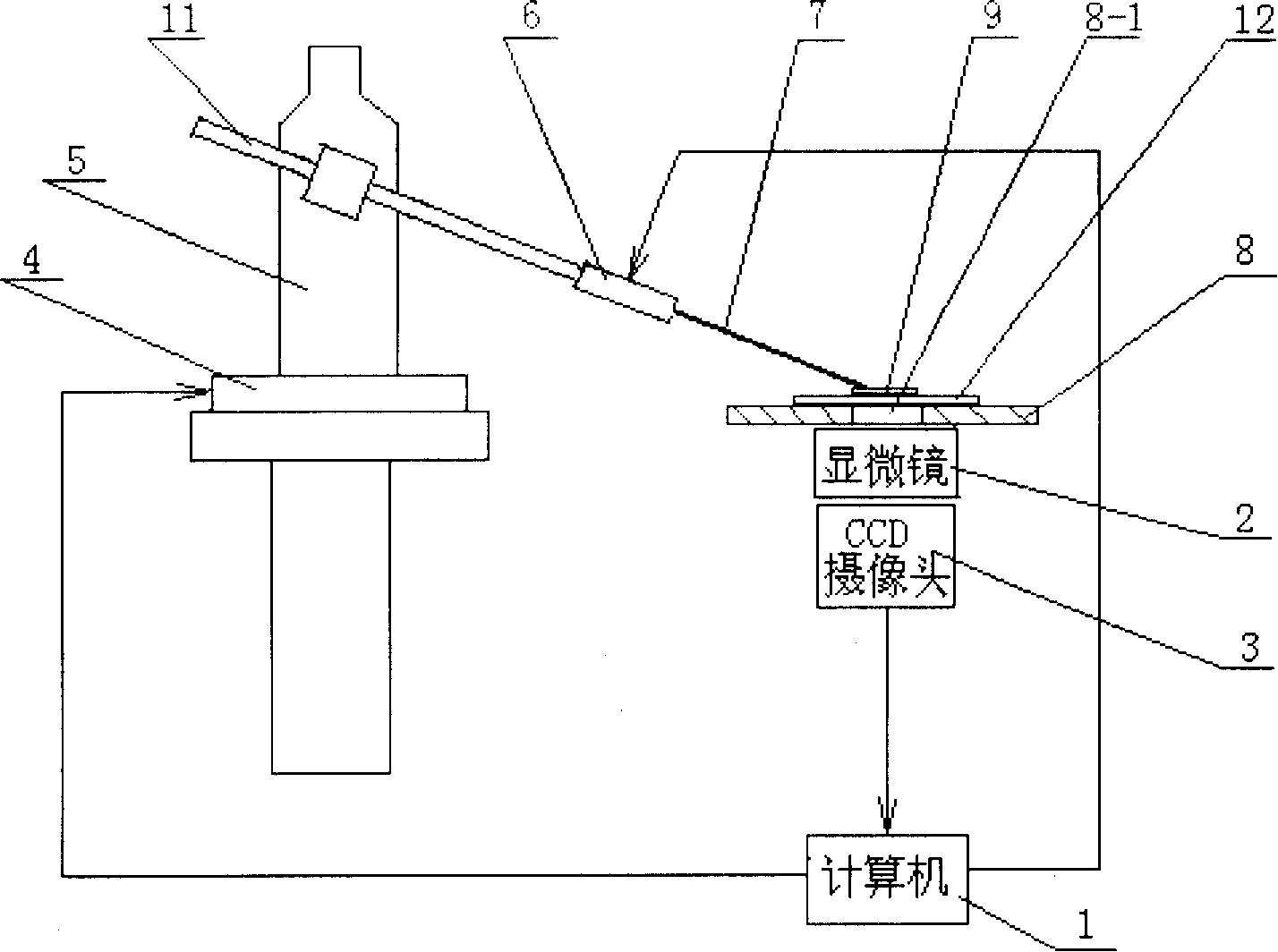
The invention relates the microscopic cutting device. The invention overcomes the defects of strong working strength, fatigability and big personal error. The device comprises computer 1, microscope 2, CCD cam 3, free mechanical micro motion desk 4, clamp 5, ultrasonic vibration emitter 6, cutting needle 7, biological section stage 8 and cutter bar. 2 is installed under 8, 3 is connected with 2 to collect the object magnified by 2, the signal output terminal of 3 is connected with signal input terminal of 1, 4 is installed at the side of 8, the signal output terminal of 1 is connected with controlling terminal of 4, 5 is fixed on the 4, 11 is fixed on the 5, one end of 11 is connected with one end of 6, the other end of 6 is connected with the butt of 7, the tip of 7 extends to the upper surface of 8, and the other signal output terminal of 1 is connected with the input terminal of 6.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
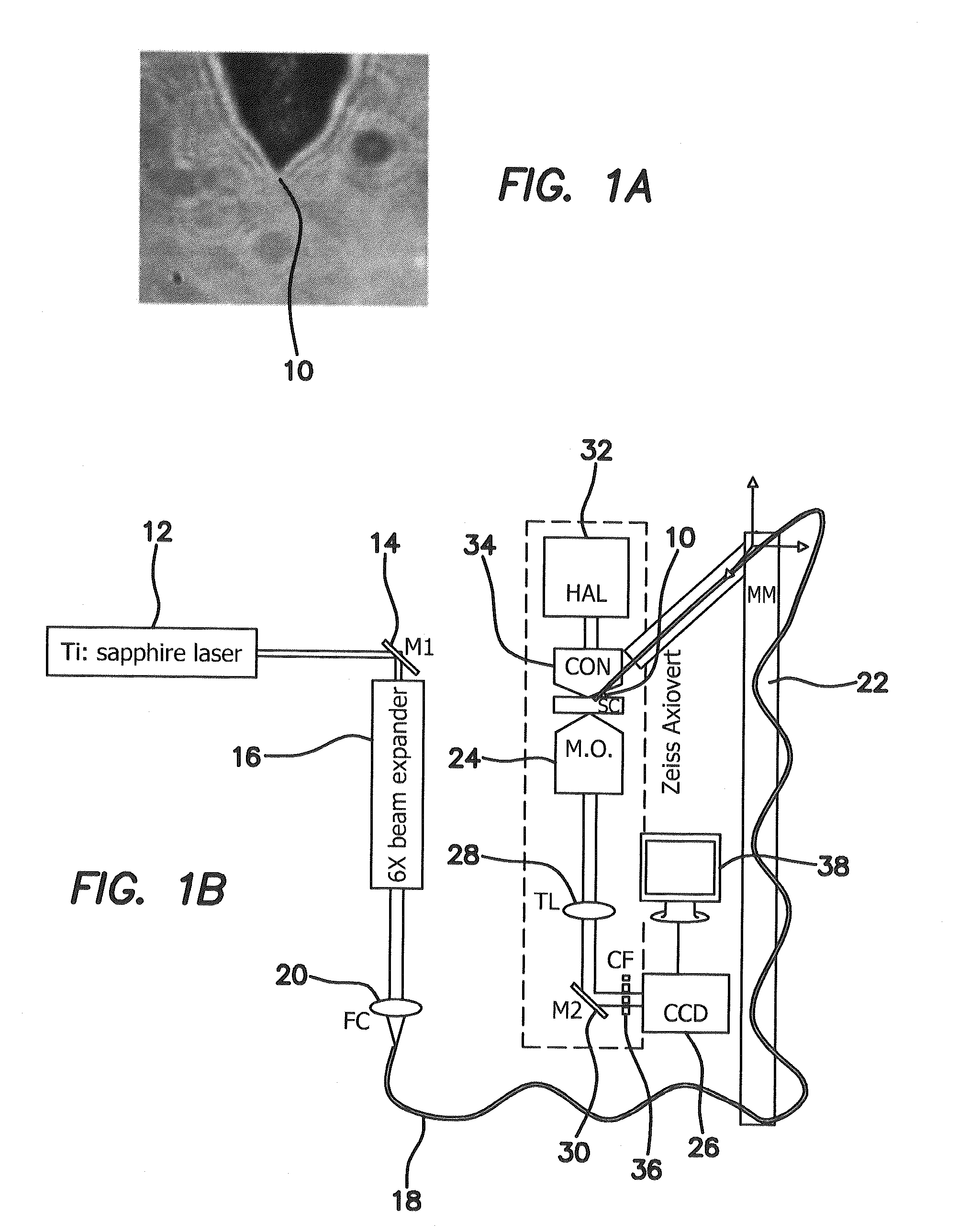
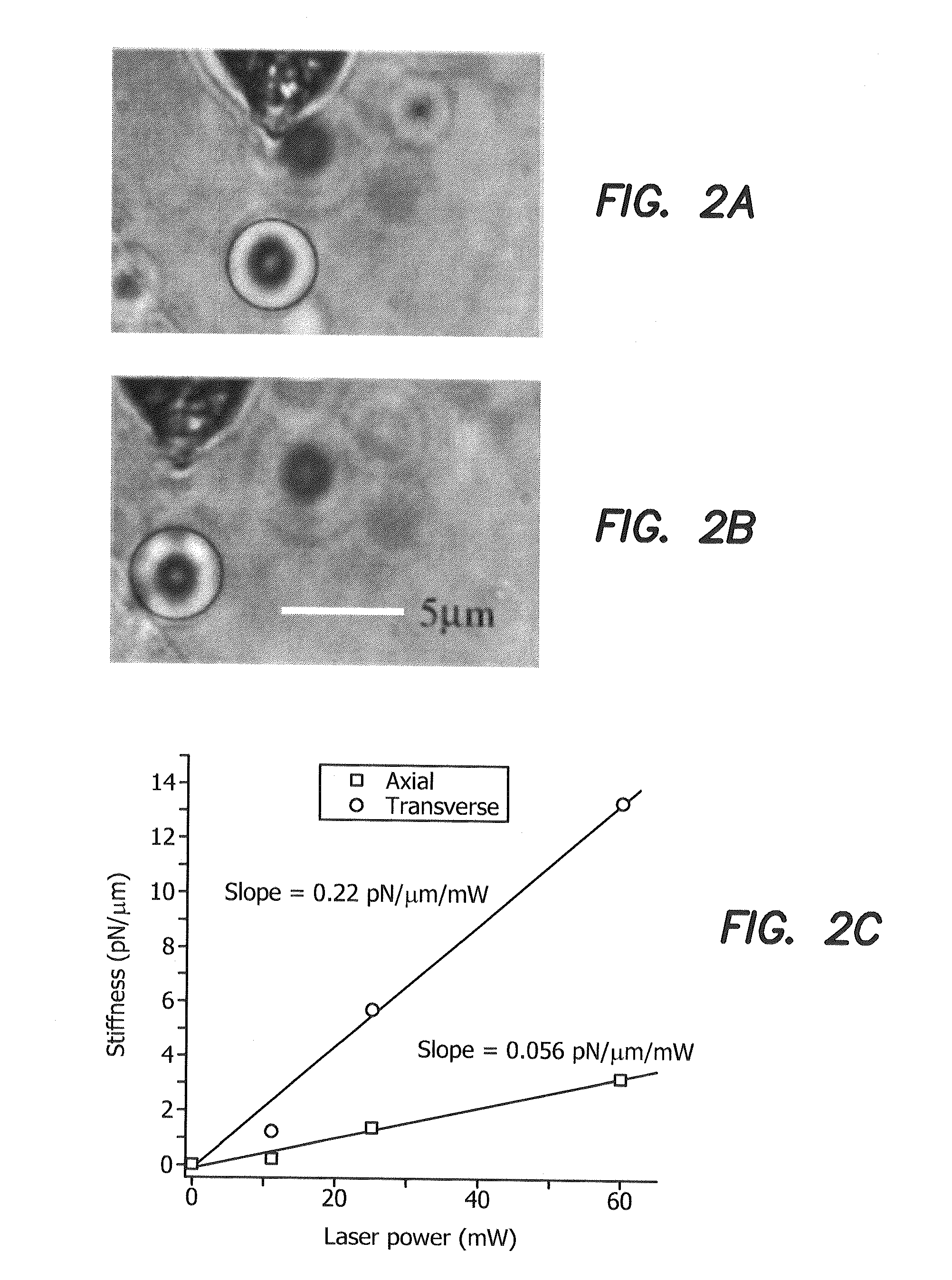
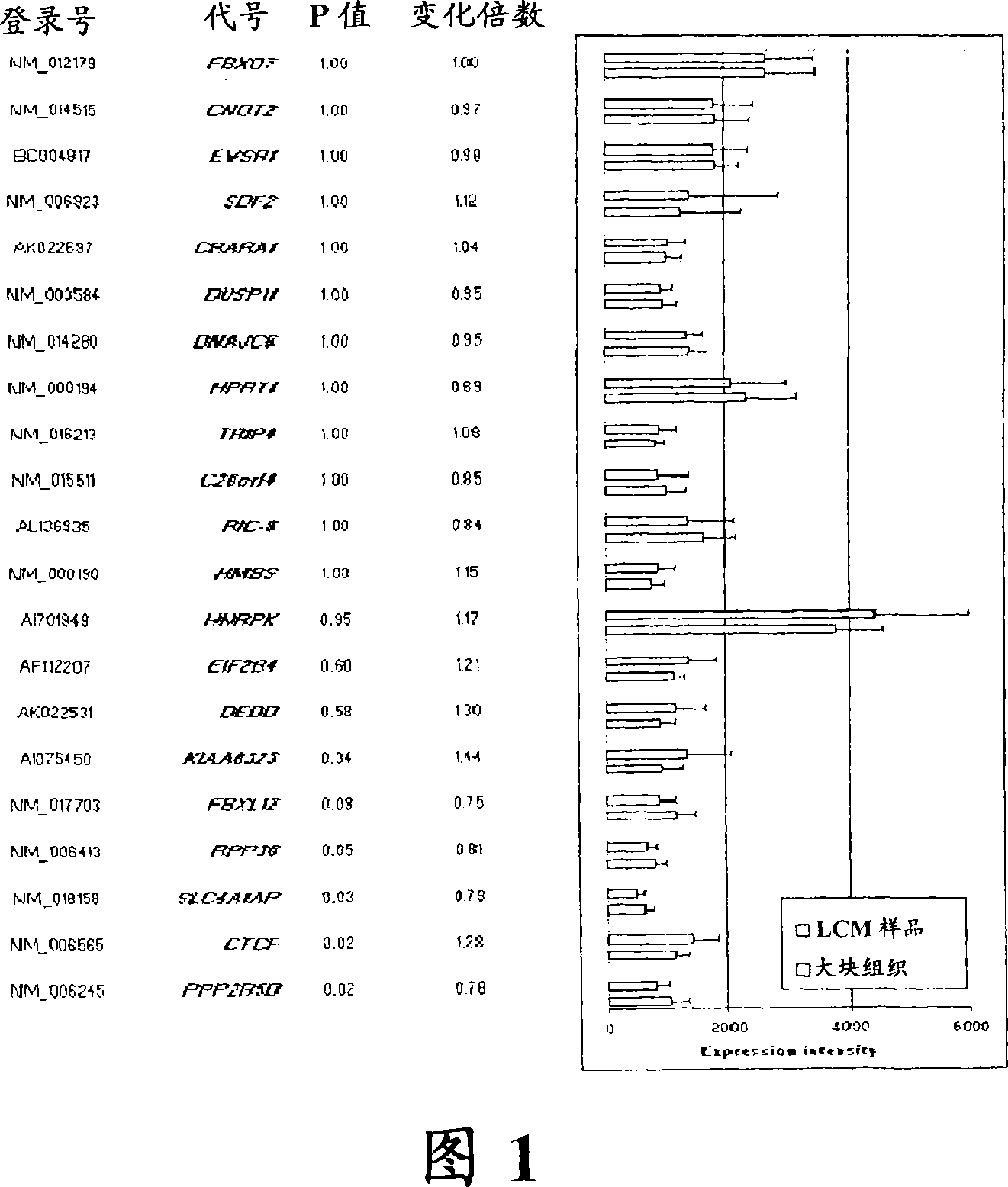
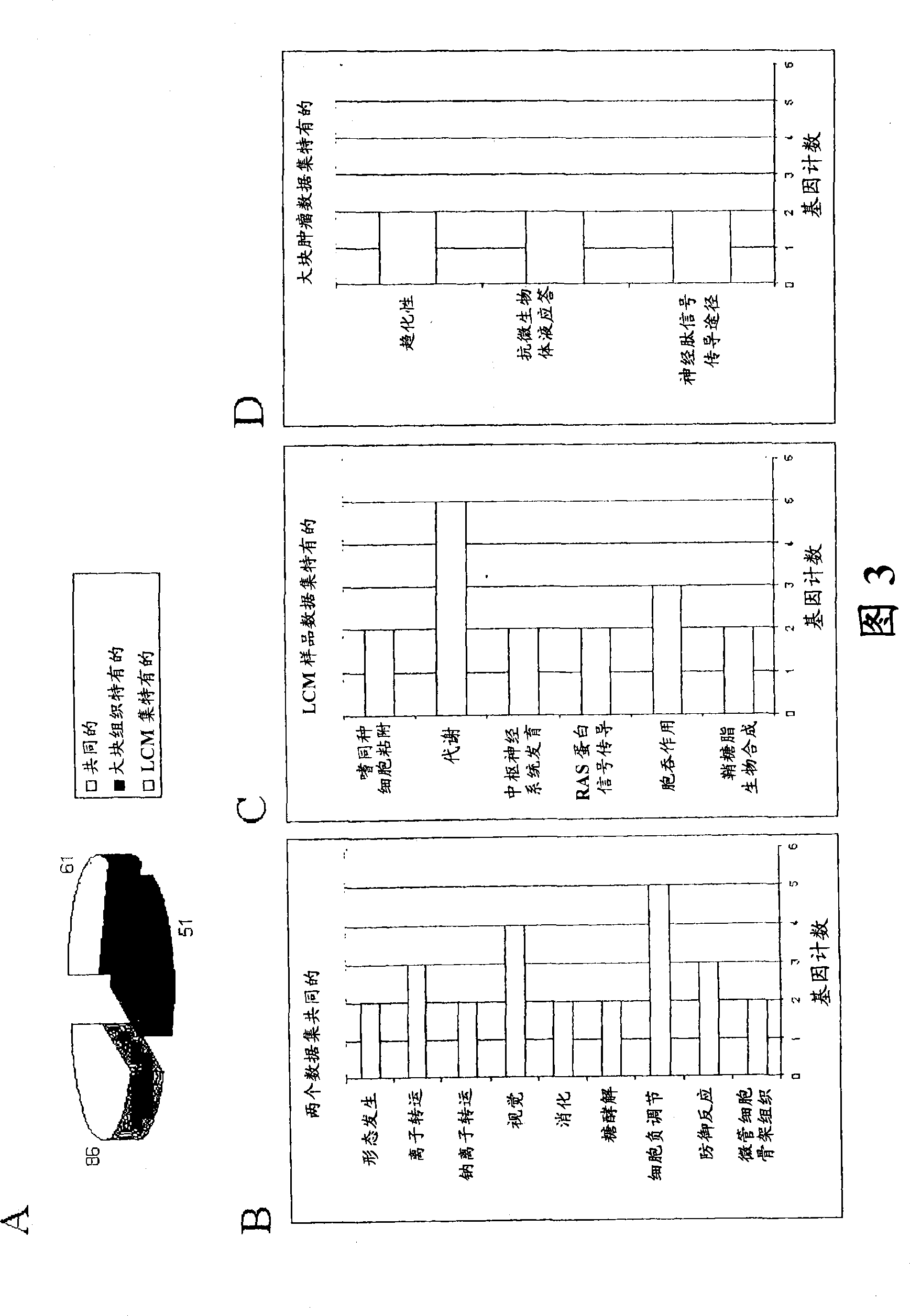
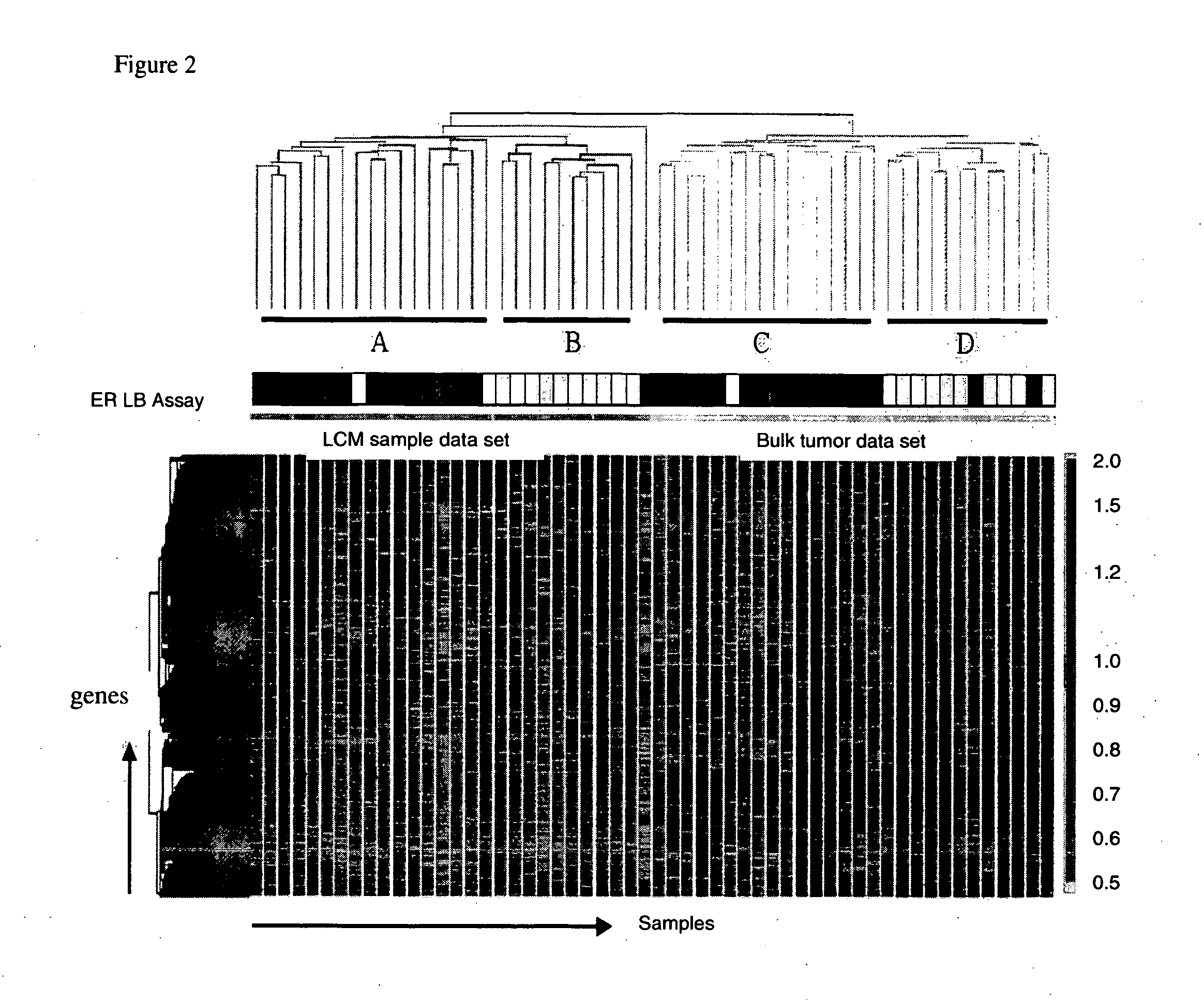
Laser microdissection and microarray analysis of breast tumors reveal estrogen receptor related genes and pathways
InactiveCN101965190APeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPathway analysisLaser micro dissection
About 70% to 80% of breast cancers express estrogen receptor-a (ERa), and estrogens play important roles in the development and growth of hormone-dependent tumors. Together with lymph node metastasis, tumor size and histological grade, ER status is considered one of the prognostic factors in breast cancer, and an indicator for hormonal treatment. 147 genes and 112 genes with significant P- value and having significant differential expression between ER+ and ER- tumors were identified from the LCM data set and bulk tissue data set, respectively. 61 genes were found to be common in both data sets, while 85 genes were unique to the LCM data set and 51 genes were present only in the bulk tumor data set. Pathway analysis with the 85 genes using Gene Ontology suggested that genes involved in endocytosis, ceramide generation, Ras / ERK / Ark cascade, and JAT- STAT pathway may play roles related to ER. The gene profiling with LCM-captured tumpr cells provides a unique approach to characterize and study epithelial tumor cells and to gain an insight into signaling pathways associated with ER.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
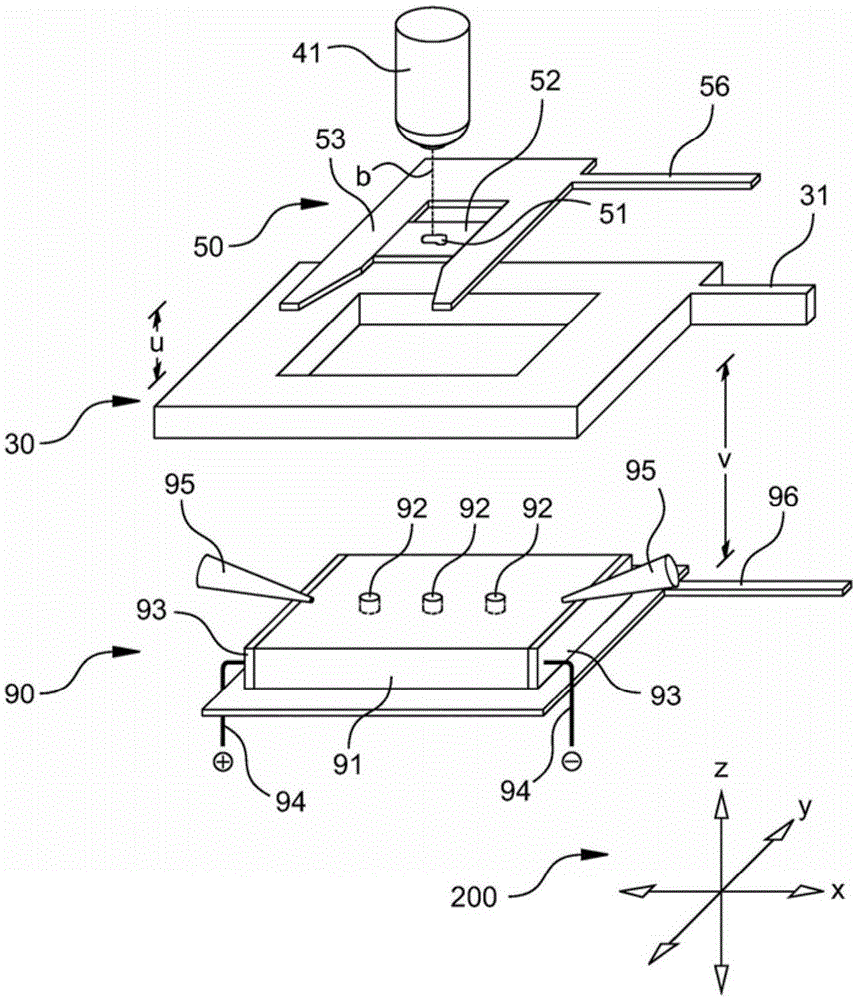
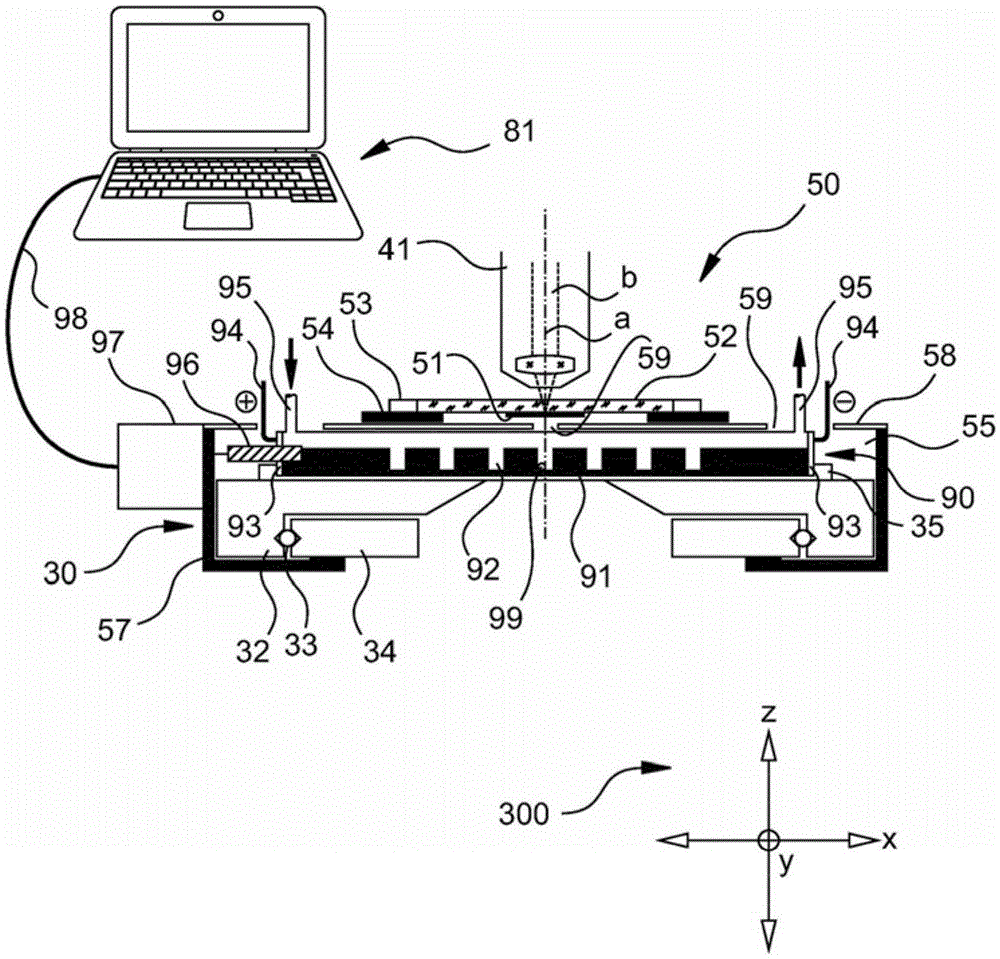
Laser microdissection system and examination method for samples containing nucleic acid
ActiveCN105358971AAdjustable intersectionPredict damagePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresisExamination method
The invention relates to a laser microdissection system (100), comprising a microscope (10). The microscope comprises a reflected-light device (76), a microscope objective (41), and a laser unit (70). A beam path (b) of a laser beam of the laser unit (70) extends through the reflected-light device (76) and through the microscope objective (41) and intersects with an object plane (15) of the microscope objective (41) at an adjustable point of intersection. An electrophoresis unit (90) having an electrophoresis gel (91) is attached, or can be attached by means of coupling elements (35), below the object plane (15), wherein the electrophoresis gel (91) has at least one gel pocket (92) and the laser microdissection system (100) comprises positioning means (96) for positioning the electrophoresis gel (91) in parallel with the object plane (15) and in relation to a defined reference position, such that dissectates (99) of a sample (51) that can be arranged in the object plane (15), which dissectates are obtained by means of the laser beam of the laser unit (70), can be captured in the at least one gel pocket (92). The invention further relates to a corresponding electrophoresis unit (90) and an examination method.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Method and system for collecting cells following laser microdissection
ActiveUS8664002B2Efficient advancementMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementLight beamEngineering
Owner:MOTIC CHINA GRP CO LTD
Chromosome specimen preparation liquid for laser microdissection and application thereof
InactiveCN102251024AGood dispersionEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementAcetic acidSpecimen preparation
The invention relates to a chromosome specimen preparation liquid for laser microdissection and application thereof. The specimen preparation liquid comprises methanol, glacial acetic acid and chloroform of which the volume ratio is (5-10):(1-3):(1-3), preferably 8:1:1. The chromosome specimen preparation liquid provided by the invention is used for preparing a chromosome specimen for laser microdissection. In the chromosome specimen for laser microdissection, which is prepared by the chromosome specimen preparation liquid, the chromosomes are well dispersed, thereby facilitating the subsequent microdissection operation. Meanwhile, the preparation method provided by the invention is simple and practical, is easy to operate, and is convenient for common technical personnel to use.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Multi-PCR detection method for minim DNA
InactiveCN101245389APrevent competitive inhibitionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyInitial sample
The invention relates to a multi-PCR detection method of trace DNA, which can avoid the competition inhibition problem due to the excessive primers of the multi-PCR technology by changing the concentration and the adding mode of the primers, so the multi-PCR detection method can be used for the very limited DNA of an initial sample, in particular to a plurality of very valuable clinical samples, such as, fertilized eggs and the obtained cells by laser capture and microdissection, etc. The whole detection proposal of the invention has simple operation process, high specificity, very high sensitivity and PCR efficiency, easy automation and wide application prospect in practical application.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Method and device for three dimensional microdissection
ActiveUS9200989B2Optimal utilisationDissect material volumesWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationSpatial directionLaser beams
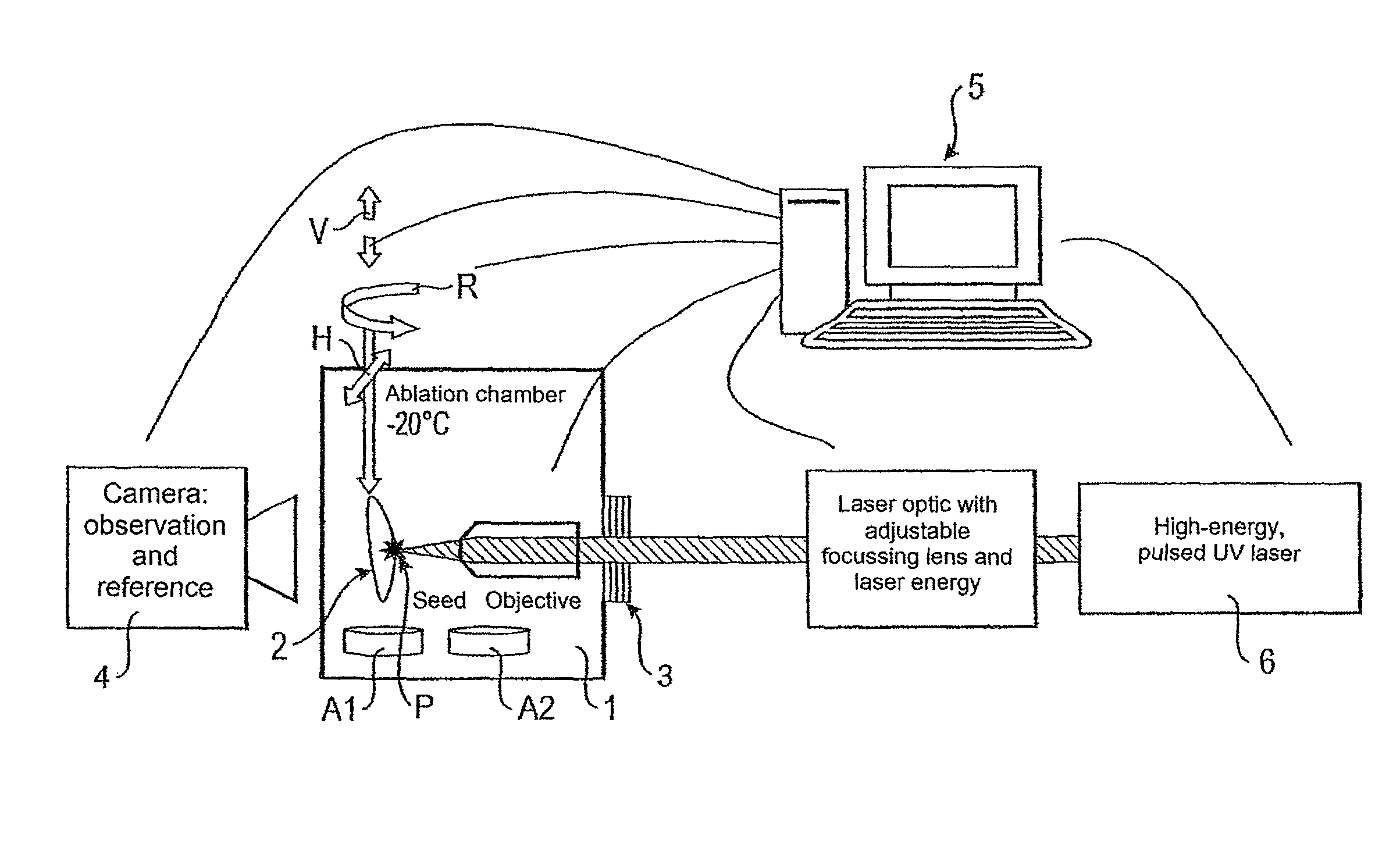
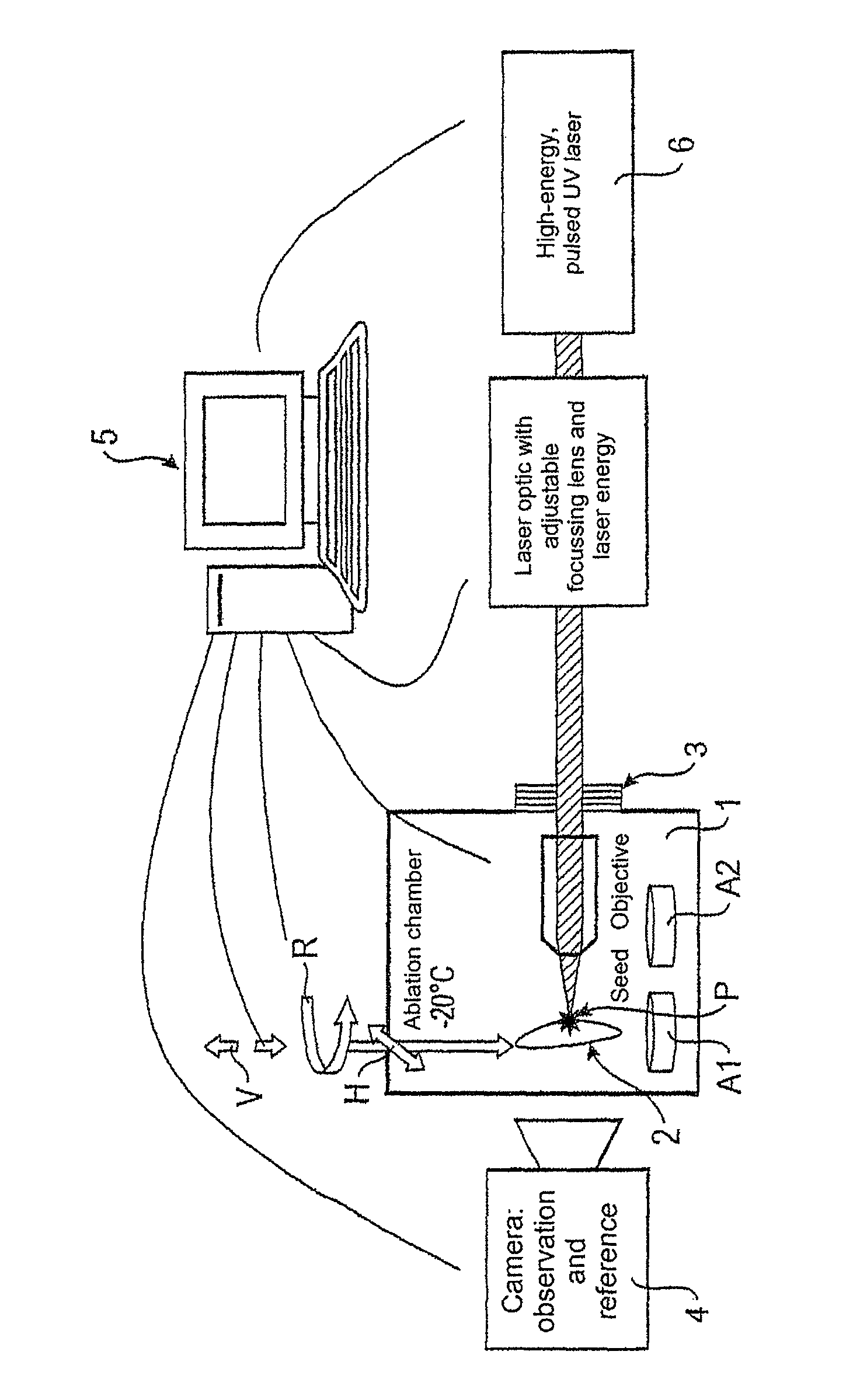
A method for three-dimensional microdissection for separating defined structures in the sub-millimeter range by cold laser ablation or multi-photon absorption, whereby exposure of the structures to be separated is performed using directional information in all spatial directions. Also, a 3D microdissection system for separating defined, three-dimensional structures from a sample, having: a control unit (5); an ablation chamber (1) with a sample holder, on which the sample to be processed is mounted and which is movable along a linear axis V and rotatable about a rotary axis R. The sample holder has positioning devices connected to the control unit. The positioning devices move the sample holder along another linear axis H and rotate it about rotary axis R, and a laser device (6) is introduced into the ablation chamber at least partially through a laser window (3) in the ablation chamber. The ablation chamber is connected to the control unit and has an adjustable optic, such that the laser beam is focused near the sample.
Owner:MMI MOLECULAR MACHINES & INDS
Method for obtaining vascular cambium of woody plant and application thereof
ActiveCN110926851AImprove homogeneityComplete structureWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyVascular cambium
The invention provides a method for obtaining a vascular cambium of a woody plant and application thereof. According to the method, the vascular cambium in a woody plant tissue paraffin section containing the vascular cambium is obtained through a laser microdissection method. According to the method, the pure cambium tissue of the woody plant neolamarckia cadamba is successfully separated throughorganic combination of paraffin section and laser microdissection technologies. According to the method, the paraffin section process is optimized, LMD parameters are debugged, a laser microdissection technical system of the vascular tissue cells of the seedlings of the neolamarckia cadamba is established, and a high-quality vascular cambium is obtained. The application of the method disclosed bythe invention in similar tissues of woody plants is not reported, the tissue and organ cells obtained by the method are relatively high in homogeneity and complete in cell structure, and a foundationis laid for further researching molecular biology and genomics research of cambium.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Dripping piece preparation method of plant chromosome
InactiveCN106350593AIncrease the number ofEasy to observeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisDispersityCell wall
The invention provides a dripping piece preparation method of plant chromosome. The dripping piece preparation method includes steps of placing a plant organ in nitrous oxide gas for pretreatment, and then fixing the plant organ after pretreatment by stationary liquid, and performing enzymolysis on a cell wall of the plant organ by enzyme, and breaking the plant organ after enzymolysis, and preparing the cell suspension liquid; dripping the cell suspension liquid on a glass slide or a cover glass; forming a plant chromosome specimen. The reagent applied to the method is low in toxicity; the crack obtained through treatment is dispersed in a circular or ellipse form by comparing with regular piece making method, the distribution is uniform, and chromosome intersection is few, and dispersing degree is good; a complete chromosome can be obtained; the preparation method can prepare the chromosome slice with stable quality, clear chromosome and good dispersity; the prepared chromosome slice can be applied to cytological identification, manufacturing of permanent slice, hybridization in-situ, microdissection, and microscope separation, and so on.
Owner:YANGTZE NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Microdissection method and information processing system
ActiveUS8995733B2Facilitates controlling workflowBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage enhancementInformation processingBiological materials
A method for use in biology, histology, and pathology includes providing a digital first image of a first slice of an object having biological material; generating a digital second image of a second slice of the object; determining a region of interest in the second image based on a region of interest in the first image; determining a region of interest in the second slice based on the region of interest in the second image; and extracting material from the region of interest in the second slice.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Deep submicron device samples and preparation methods for in-situ transmission electron microscopy
ActiveCN103743608BFacilitate experimental researchImprove experimental efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationNano-deviceIn situ transmission electron microscopy
The invention discloses a method for preparing a deep sub-micron device sample for an in-situ transmission electron microscope. Ion beams are focused into ion beams with a small size for performing microdissection or grinding by utilizing an electromagnetic lens by adopting a focused ion beam system, accurate positioning sample preparation can be performed, and a deep sub-micron device is obtained. The method comprises the following steps: cutting and thinning the sample by adopting the focused ion beams so as to obtain a thinned sample, inclining a sample stage at 52+ / -(0.5-1.5) degrees relative to the finally thinned sample through conventional focused ion beams, and innovatively inclining the sample stage at 52+ / -7 degrees. The invention also provides a deep sub-micron device sample for the in-situ transmission electron microscope. The sample comprises multiple discrete nano devices which are regular in shape and have the width of less than 20nm and the thickness of less than 100nm. The sample is suitable for research on the in-situ transmission electron microscope and has the high significance in research on the performance of the deep sub-micron device.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
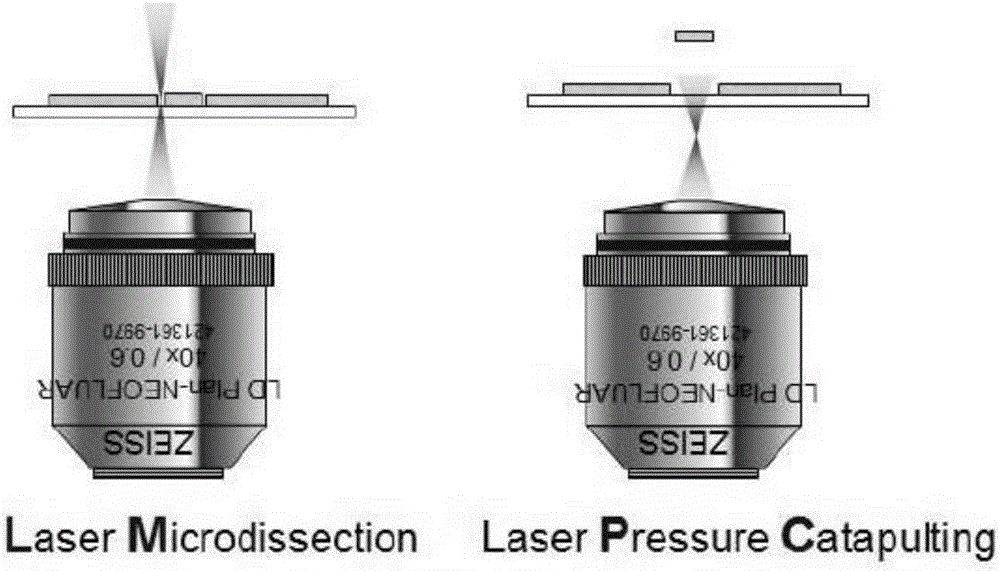
Method for laser microdissection, and laser microdissection system
ActiveCN107110749APreparing sample for investigationAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsRadiologyNuclear medicine
A method for laser microdissection includes detecting at least a portion of an object to be dissected in an image-producing manner in a laser microdissection system and generating a first digital object image. A first processing specification is defined based on the first digital object image. In a first processing step, the object is processed using a laser beam of the laser microdissection system in accordance with the first processing specification. At least a portion of the object is detected in an image-producing manner and a second digital object image is generated. A second processing specification is defined during execution of the first processing step based on the second digital object image. In a second processing step, the object is processed using the laser beam of the laser microdissection system in accordance with the second processing specification.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Apparatus and method for micromanipulation of microscale objects using laser light delivered through a single optical fiber and axicon lens
ActiveUS8571365B2Reduce throughputImprove throughputElectrotherapyLaser detailsLight beamLaser light
A single optical fiber having a distal end is optically coupled to the laser and distilling terminated with an axicon lens optically coupled to the single optical fiber to form a microscopic distal tip to provide a spatially shaped elongated laser focused spot for microprocessing and / or microdissection of a microscale object. A pulsed or continuous laser beam or superposition of pulsed and continuous laser beams is generated, controllably spatially shaped, selectively oriented, selectively moved via movement of a single optical fiber terminated with the axicon lens, and the oriented, spatially shaped laser beam applied via the single optical fiber terminated with the axicon lens to a living or nonliving microscopic object for manipulation, micro-dissection, alteration / ablation, and excitation of the living or nonliving microscopic object.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Laser microdissection unit
A laser microdissection unit for cutting a microscopic sample using a laser beam of a laser includes a microscope and a fluorescence device. The microscope includes an illumination beam path directed onto the sample, and an imaging beam path configured to image the sample. The fluorescence device includes an excitation filter, a dichroic beam splitter, and a blocking filter. The dichroic beam splitter and the blocking filter are spectrally transparent to the laser beam, and the laser beam is directable through the dichroic beam splitter and the blocking filter onto the sample.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
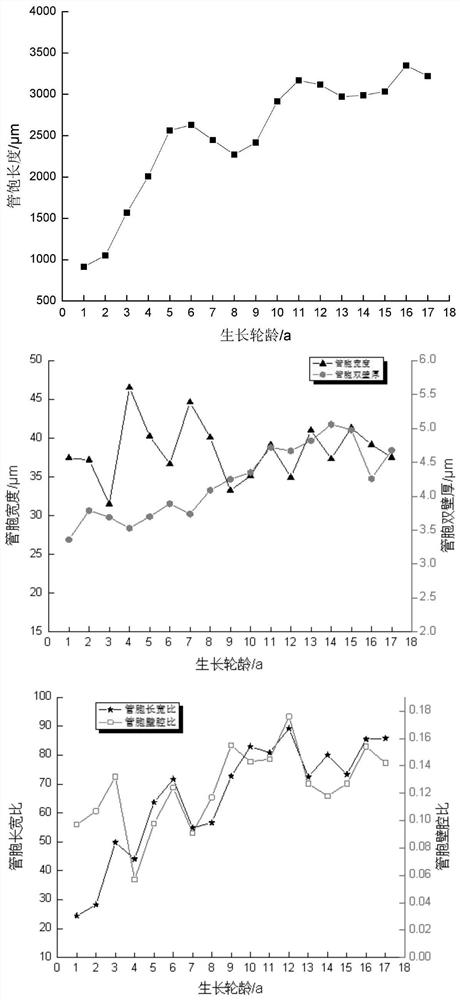
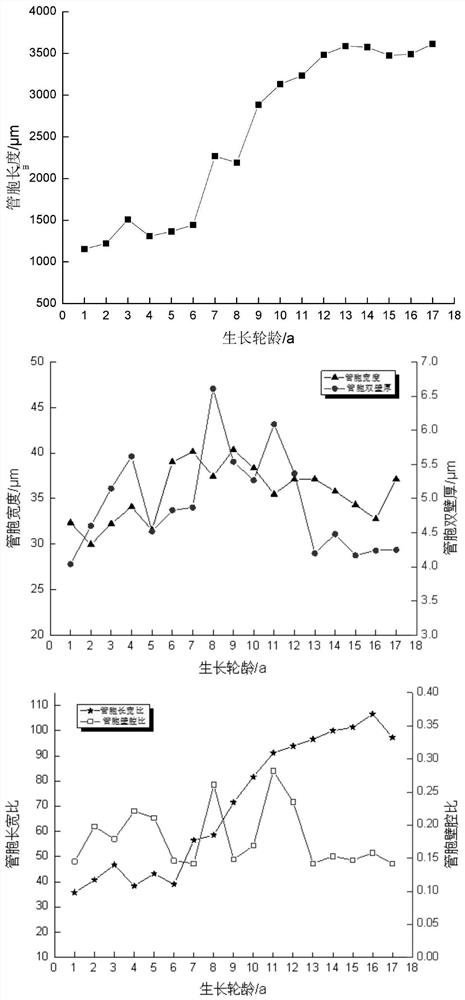
Method for evaluating physical and mechanical properties of wood based on micromorphological characteristics of wood
ActiveCN111624114AIncrease profitMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationStepwise regressionComputer science
The invention provides a method for evaluating physical and mechanical properties of wood based on microscopic morphological characteristics of wood, which is characterized by comprising the followingsteps: 1, sampling: selecting wood at the bottom end of a to-be-analyzed wood section; 2, testing: testing the micromorphological characteristics of the selected wood; 3, evaluation: establishing a regression model for the bending strength, the bending elasticity modulus and the tensile strength of the wood according to the tested data, and evaluating the parameters according to the regression model. The invention provides a method for evaluating the physical and mechanical properties of wood based on the micromorphological characteristics of wood wherein stepwise regression analysis is carried out by taking the bending strength, the bending elasticity modulus and the microsection tensile strength of China fir as dependent variables and microdissection indexes as independent variables, and a regression equation is established; therefore, the method can predict the bending strength, the bending elasticity modulus and the tensile strength of the cunninghamia lanceolata, provides a theoretical basis for reasonable processing and utilization of wood, directional cultivation of forest trees and the like, and has important significance for improving the utilization rate of the wood.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Digital histopathology and microdissection
Owner:NANTOMICS LLC
Laser microdissection and microarray analysis of breast tumors reveal estrogen receptor related genes and pathways
InactiveUS20080305959A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathway analysisEstrogen receptor
About 70% to 80% of breast cancers express estrogen receptor-α (ERα), and estrogens play important roles in the development and growth of hormone-dependent tumors. Together with lymph node metastasis, tumor size and histological grade, ER status is considered one of the prognostic factors in breast cancer, and an indicator for hormonal treatment. 147 genes and 112 genes with significant P-value and having significant differential expression between ER+ and ER− tumors were identified from the LCM data set and bulk tissue data set, respectively. 61 genes were found to be common in both data sets, while 85 genes were unique to the LCM data set and 51 genes were present only in the bulk tumor data set. Pathway analysis with the 85 genes using Gene Ontology suggested that genes involved in endocytosis, ceramide generation, Ras / ERK / Ark cascade, and JAT-STAT pathway may play roles related to ER. The gene profiling with LCM-captured tumor cells provides a unique approach to characterize and study epithelial tumor cells and to gain an insight into signaling pathways associated with ER.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Microdissection technology of tobacco chromosomes
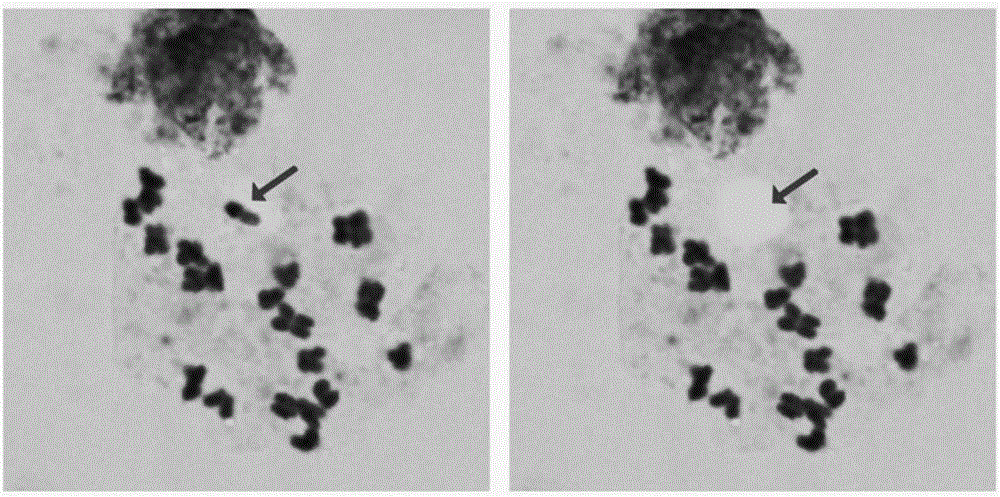
The invention discloses a microdissection technology of tobacco chromosomes. The microdissection technology is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) preparing a chromosome specimen: after immersing ripe and full seeds of tobaccos, putting the seeds into a culture dish and germinating; after roots grow to 0.5cm to 1cm, scissoring fresh root tips from 9:00 to 11:00 in the morning; putting the roots into a saturated alpha-bromnaphthalene solution and pre-treating at room temperature; washing and fixing by Carnoy I stationary liquid for one night; washing and putting the roots into distilled water and carrying out low percolation; treating with cellulose-pectinase mixed enzyme liquid and washing; putting the roots into the distilled water and carrying out the low percolation; putting root tip meristems on a slide and dropwise adding the stationary liquid; crushing materials and coating, and removing large tissue residues; then adding the stationary liquid; dyeing and washing to remove a dyeing solution; marking a good metaphase of microscope inspection for later use; (2) carrying out microdissection on the chromosomes: putting the specimen slide onto an objective table of a laser microdissection system and setting a cutting path; mounting a centrifugal tube with a viscous tube cover on an automatic recycling device of the laser microdissection system; treating the viscous centrifugal tube for later use after the chromosomes are cut and recycled.
Owner:GUIZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Identification method of nucleated cells and application thereof
InactiveCN101948901AGood typing resultImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationTypingCell separation
The invention provides an identification method of nucleated cells and an application thereof, the identification method of the nucleated cells can be applied in a single-cell separation detection platform with the combination of the micromanipulator capture method and LV-PCR and the single-cell separation detection platform with the combination of the laser microdissection method and the LV-PCR,and the method comprises the following steps: placing a sample containing the nucleated cells in a centrifugal tube containing buffer solution, oscillating the centrifugal tube to lead the cells on the sample to fall off, and obtaining cell suspension of the cells of the sample; and adding gentian violet or haematoxylin into the cell suspension for dyeing, wherein the final concentration of the gentian violet is 0.1-0.5 mu g / mu l, the dyeing time is 2-7 minutes, the final concentration of the haematoxylin is 1-7 mu g / mu l, and the dyeing time is 3-7 minutes. The use of the cell identificationmethod in the two single-cell separation detection platforms can realize effective identification of the cells of the sample, lead the follow-up LV-PCR amplification inhibition to be weak and obtain good DNA typing result.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com