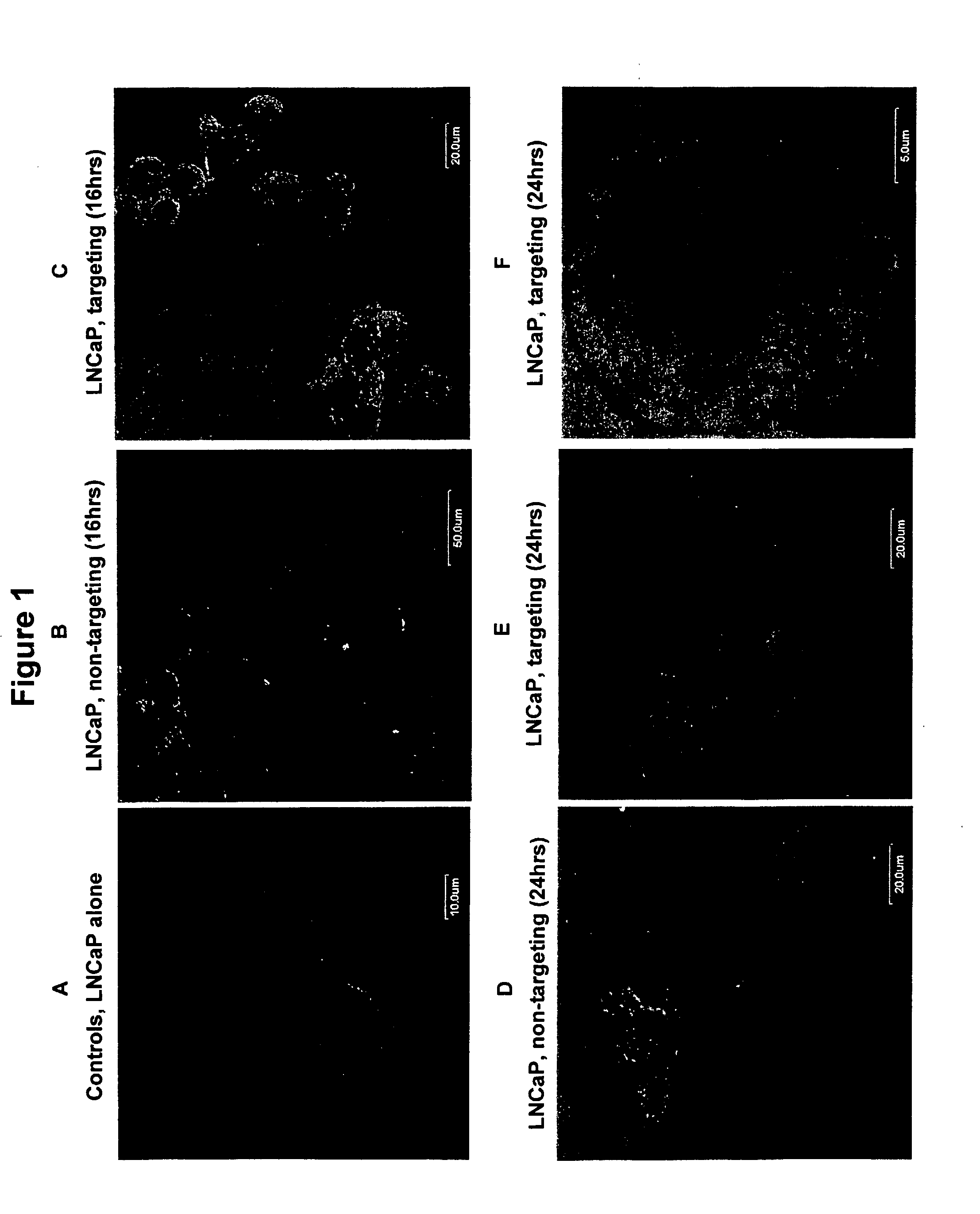
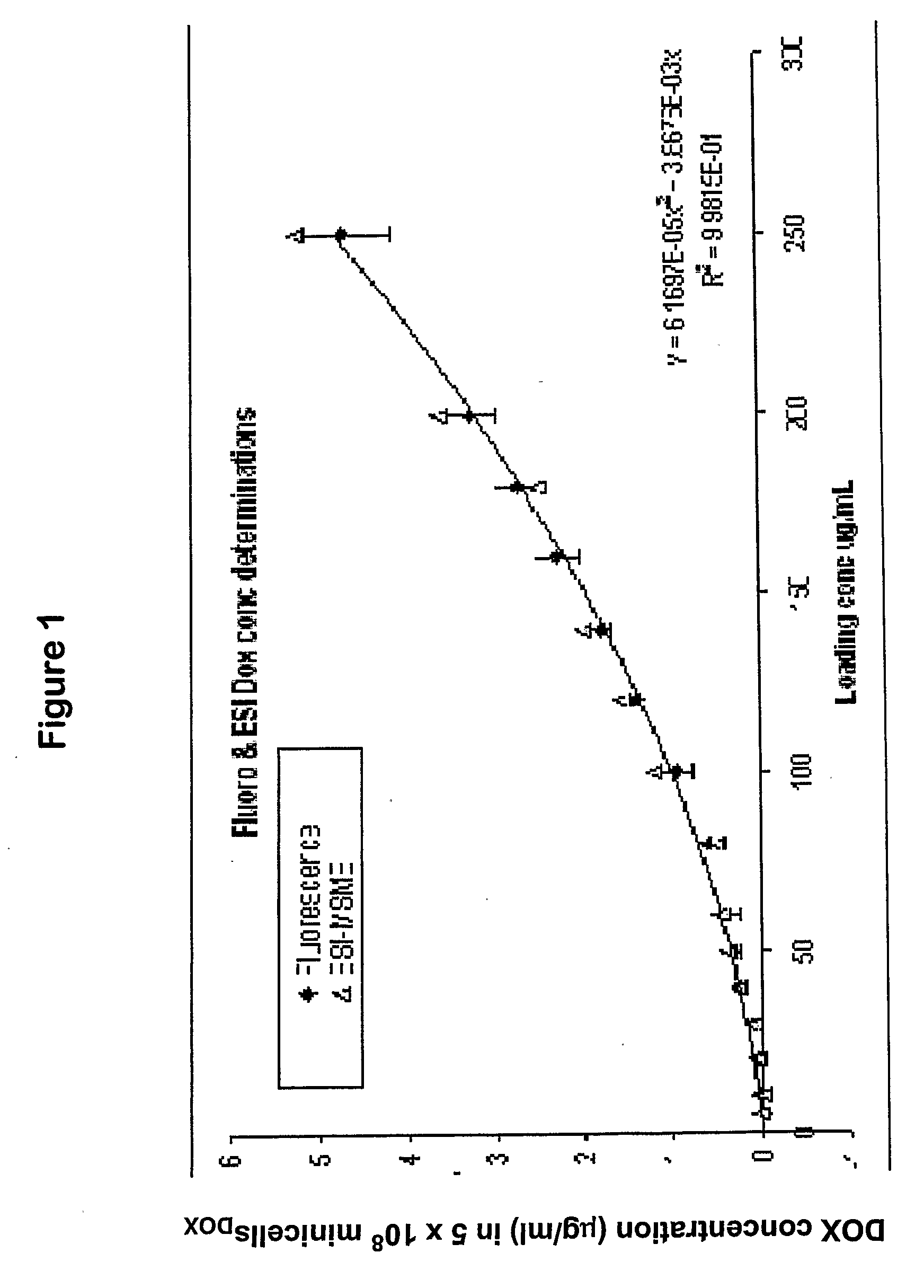
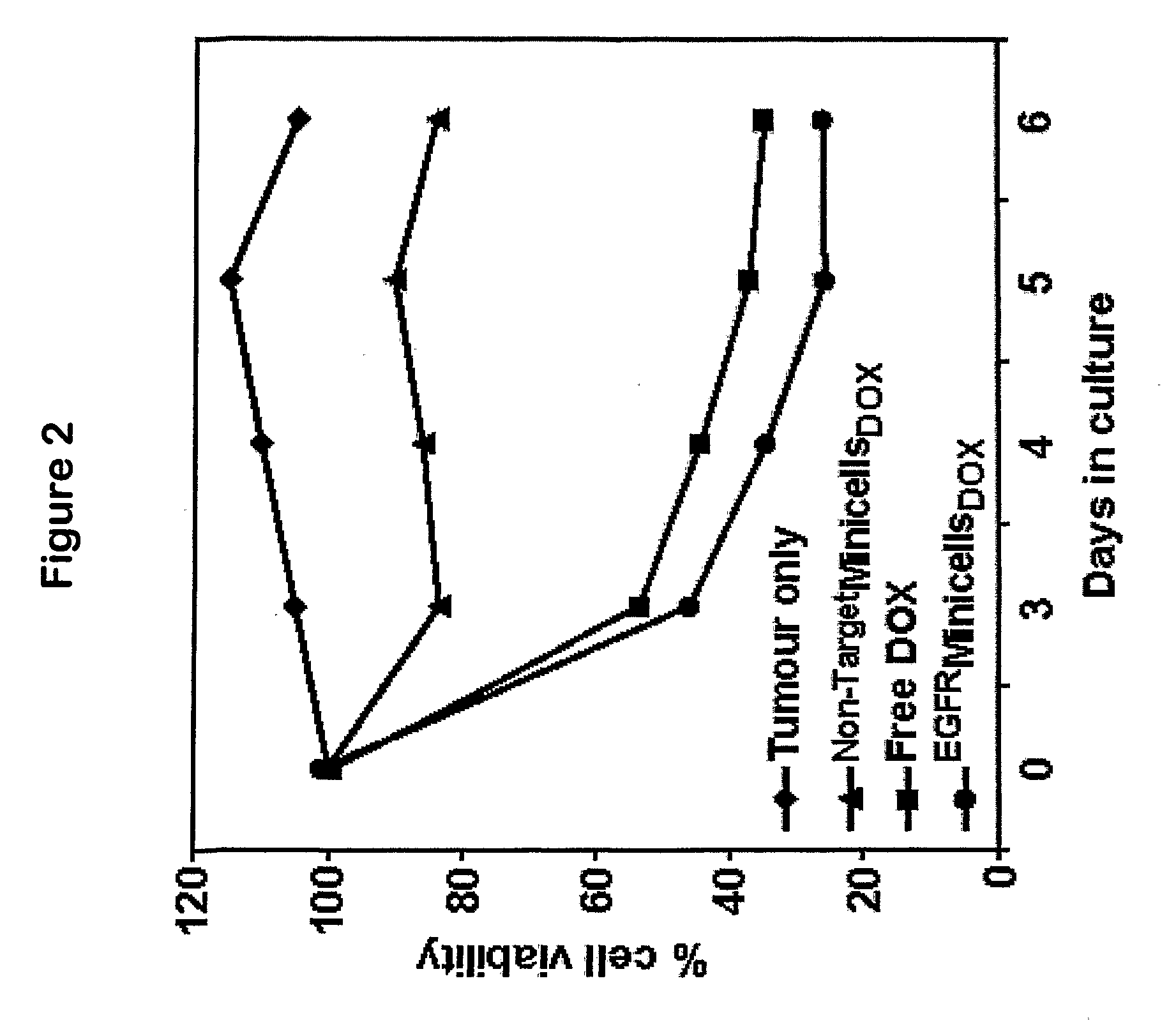
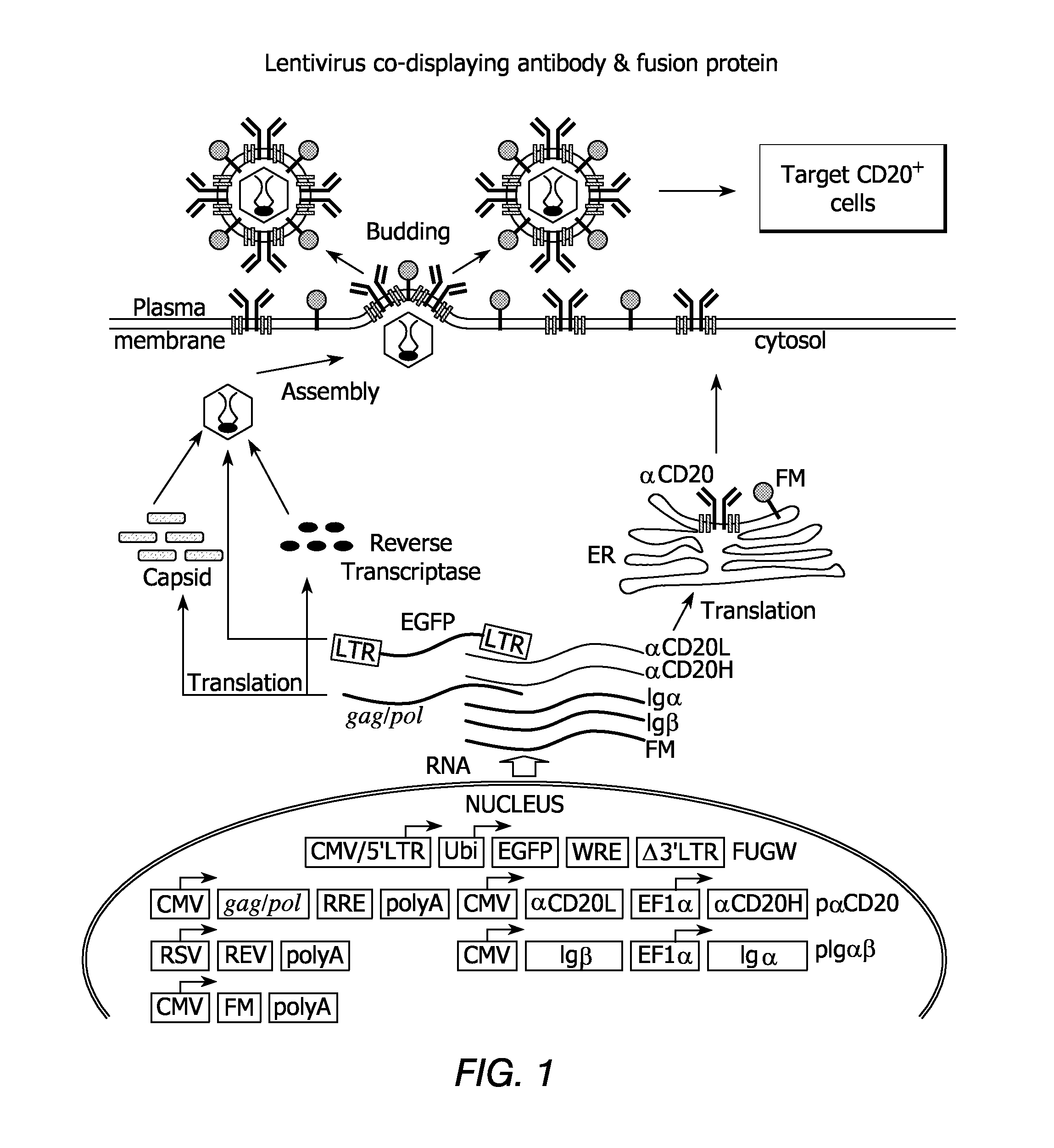
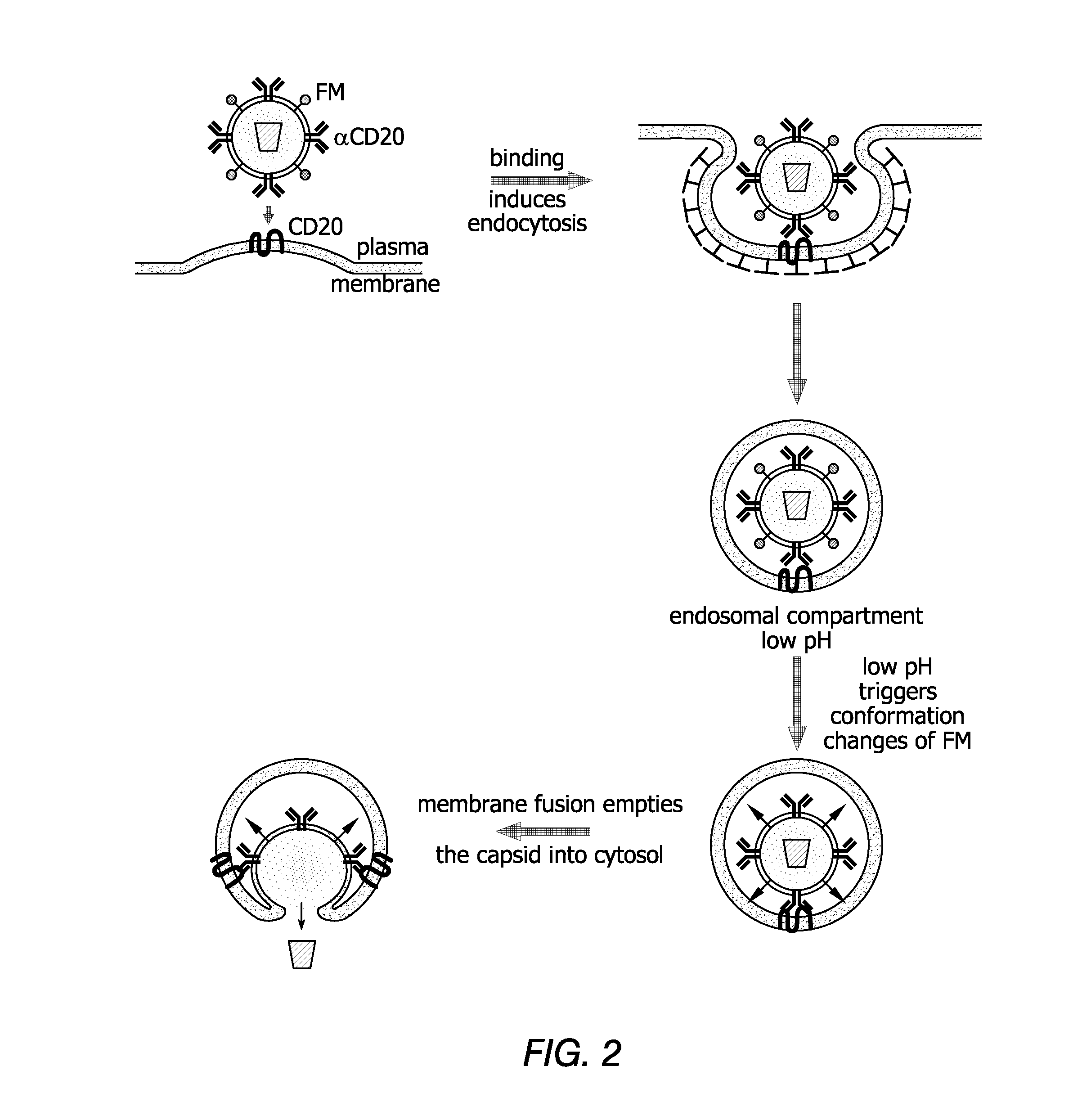
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
506 results about "Endocytosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Endocytosis includes pinocytosis (cell drinking) and phagocytosis (cell eating). It is a form of active transport.
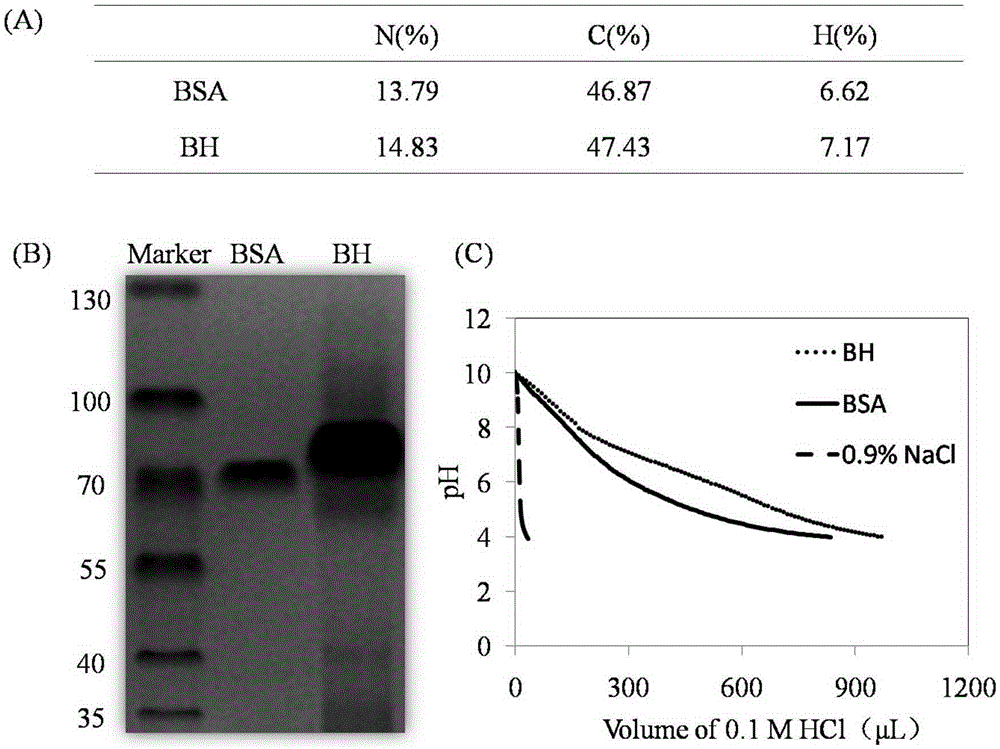
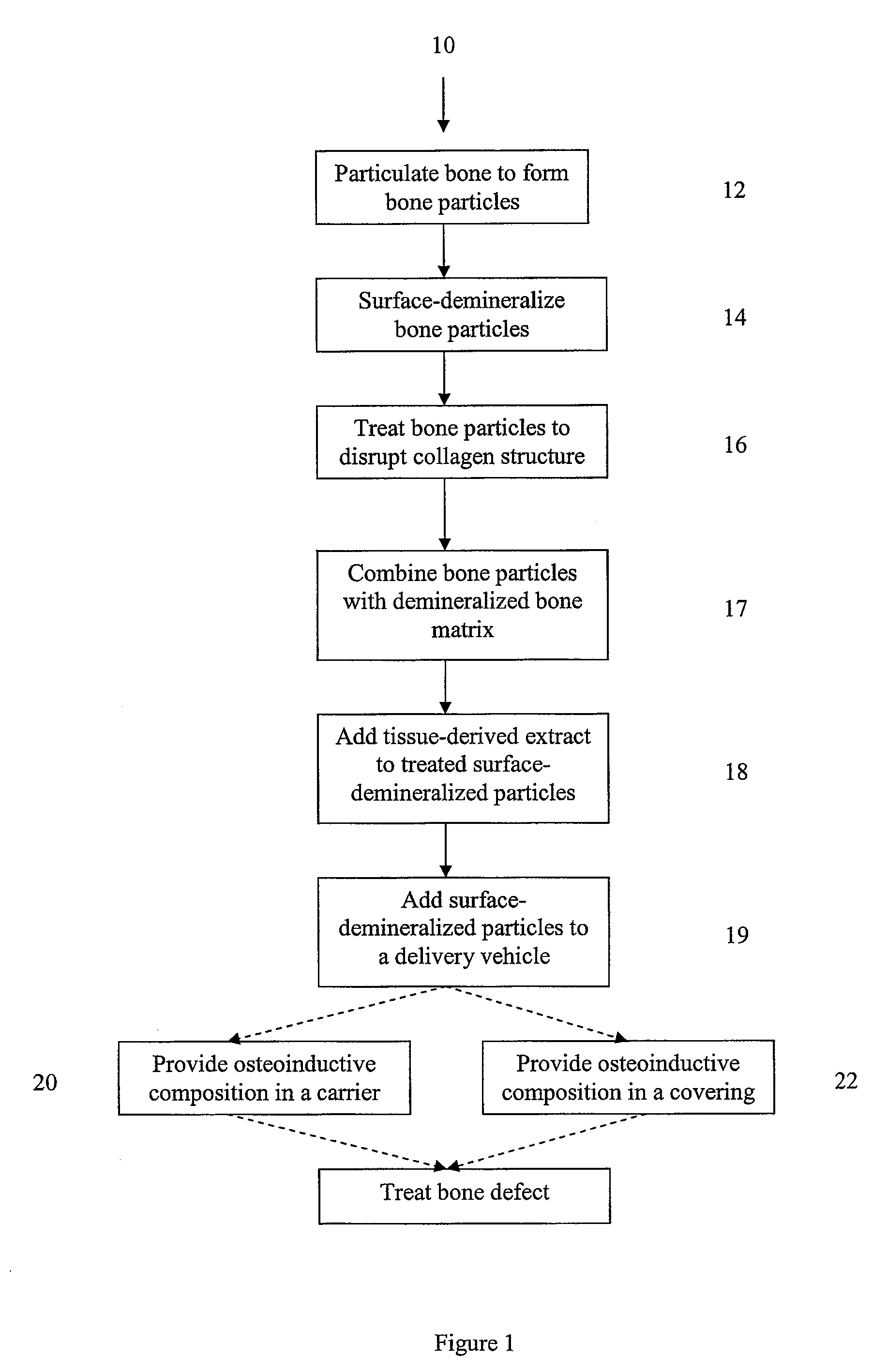
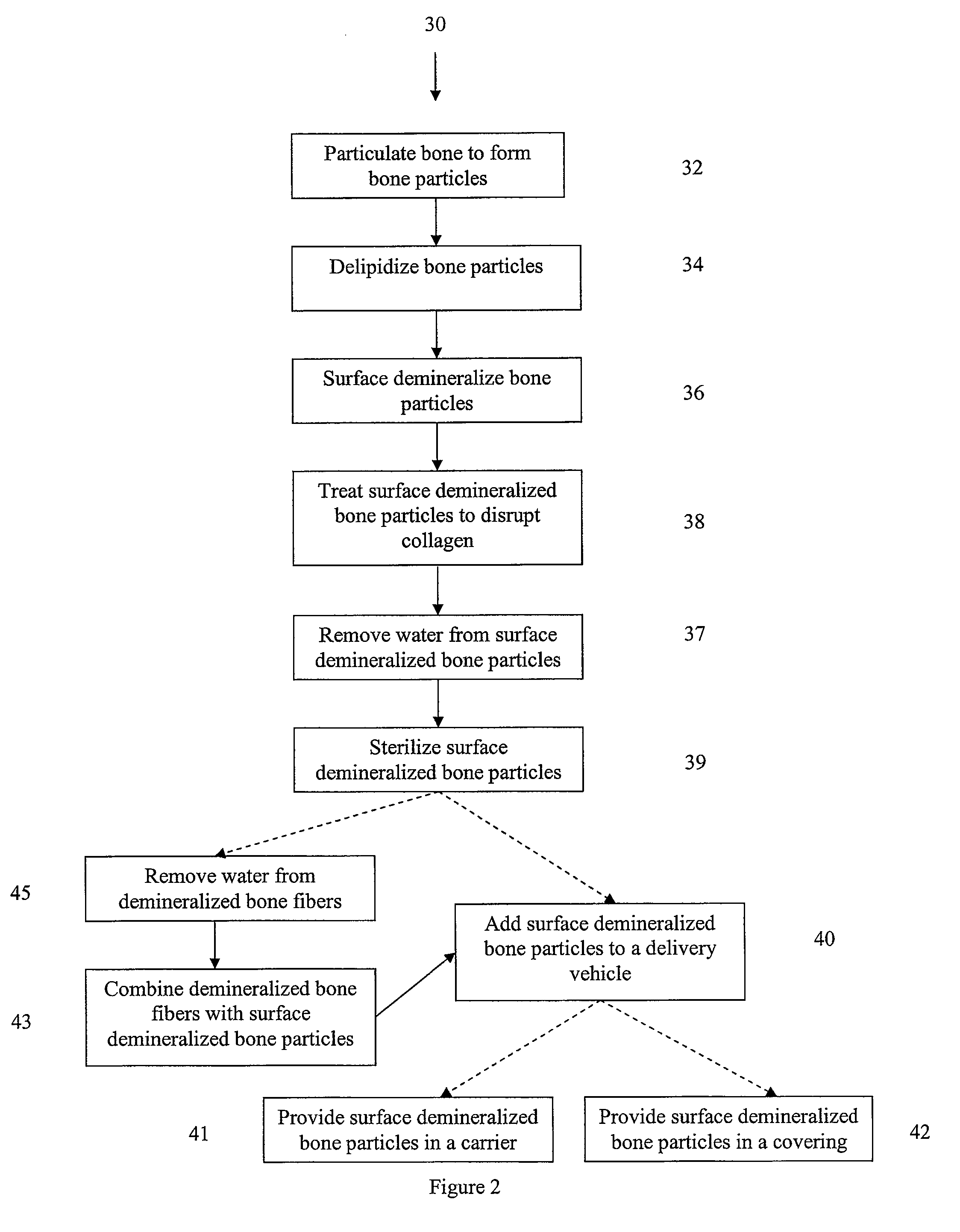
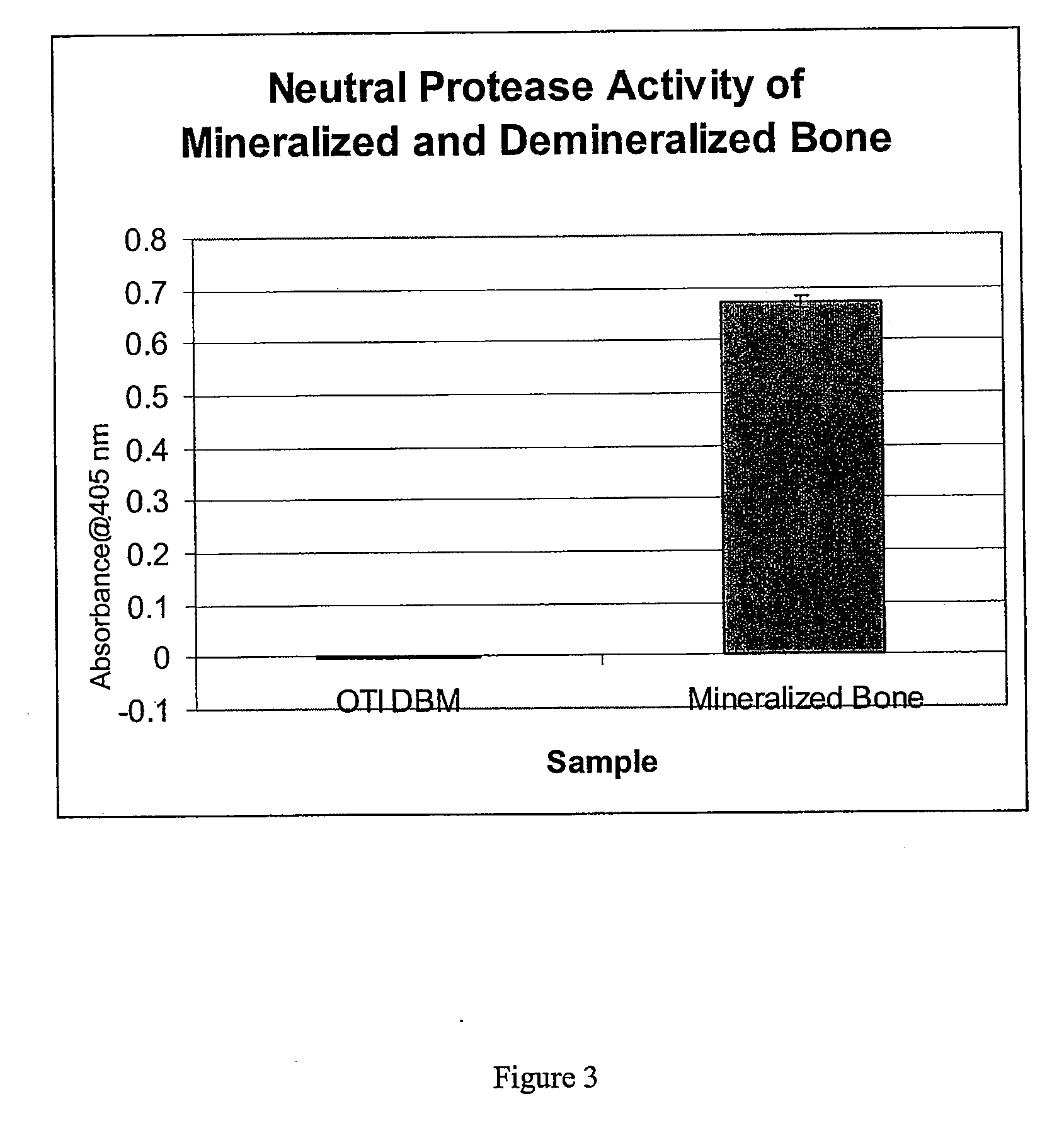
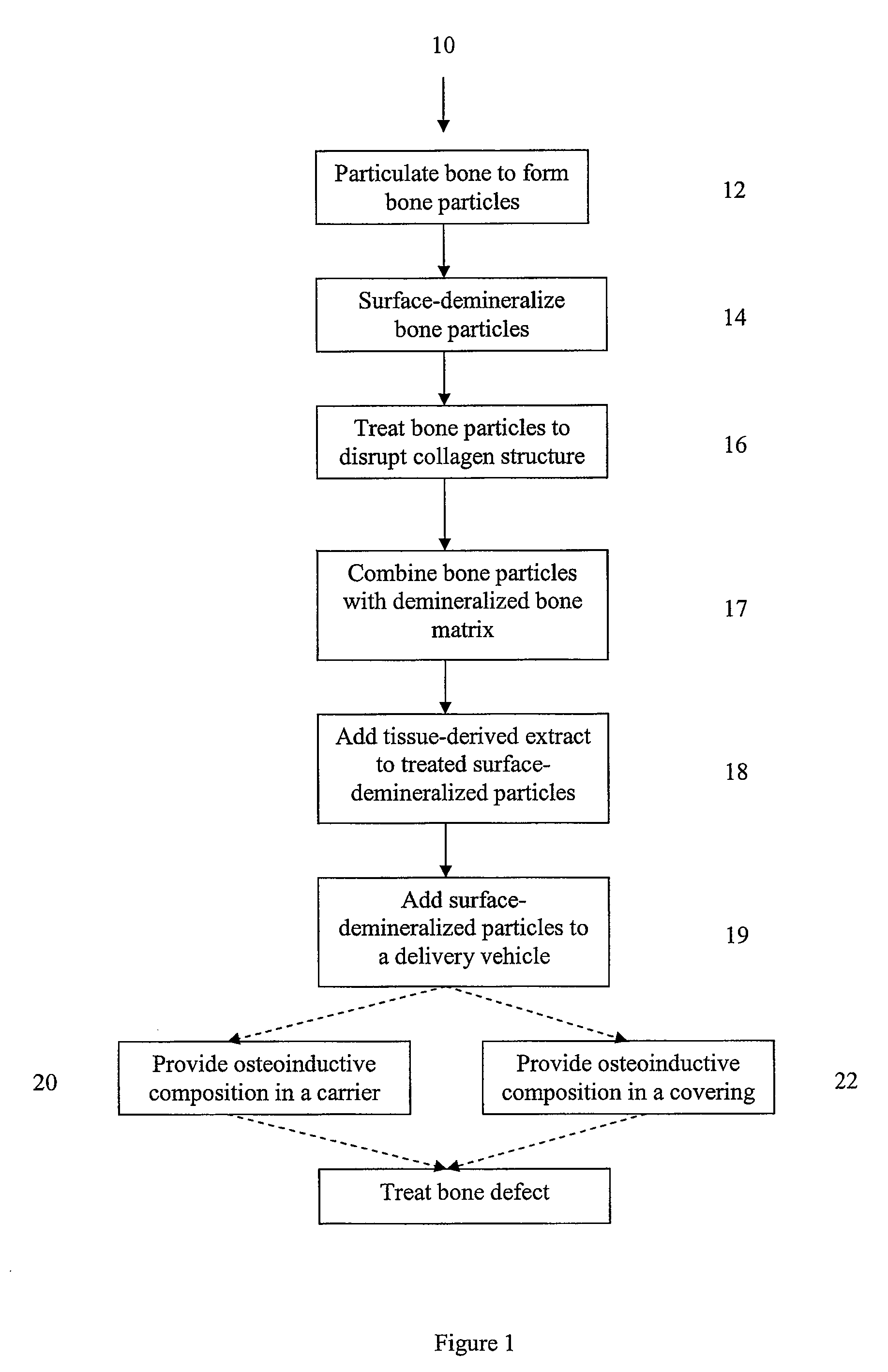
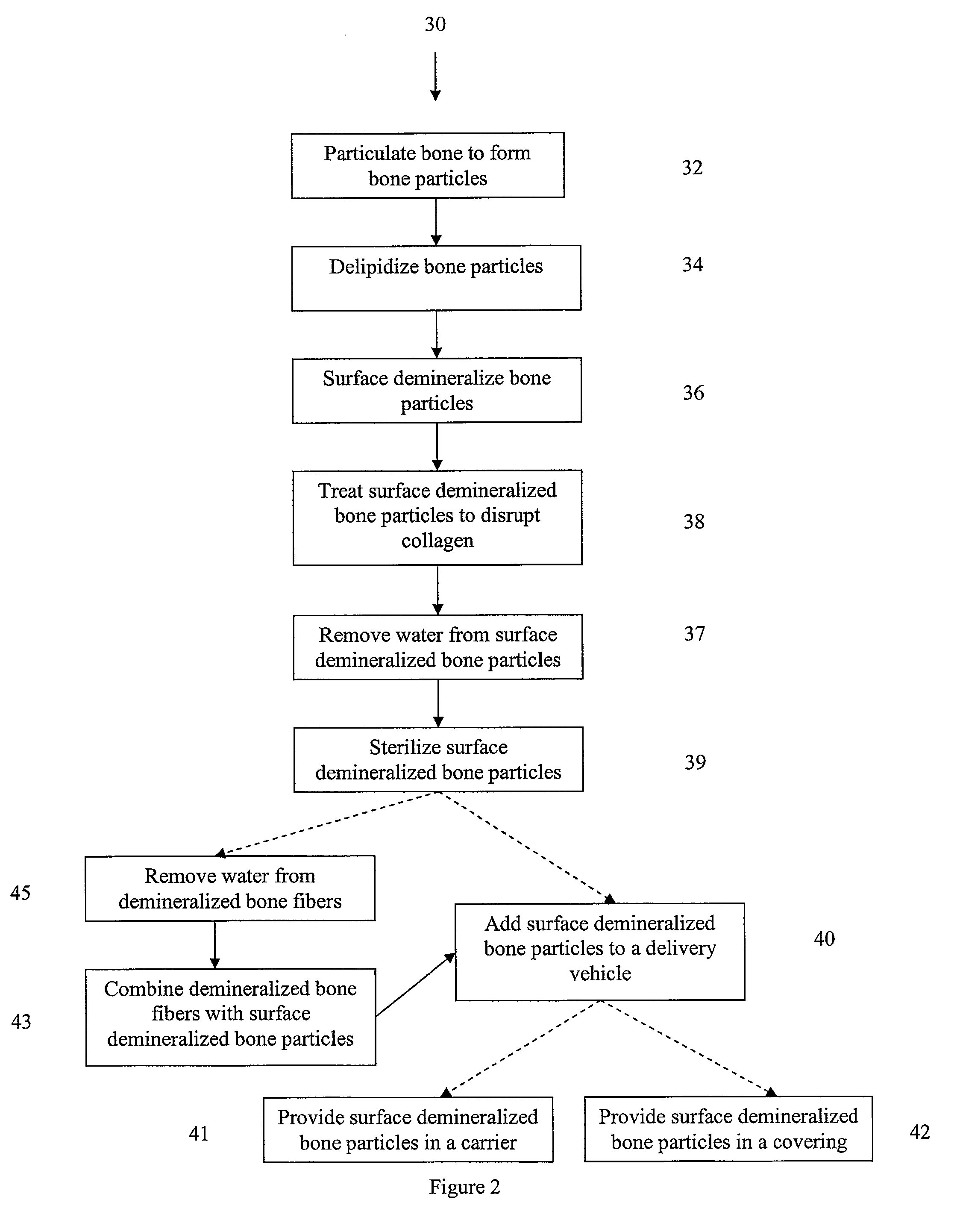
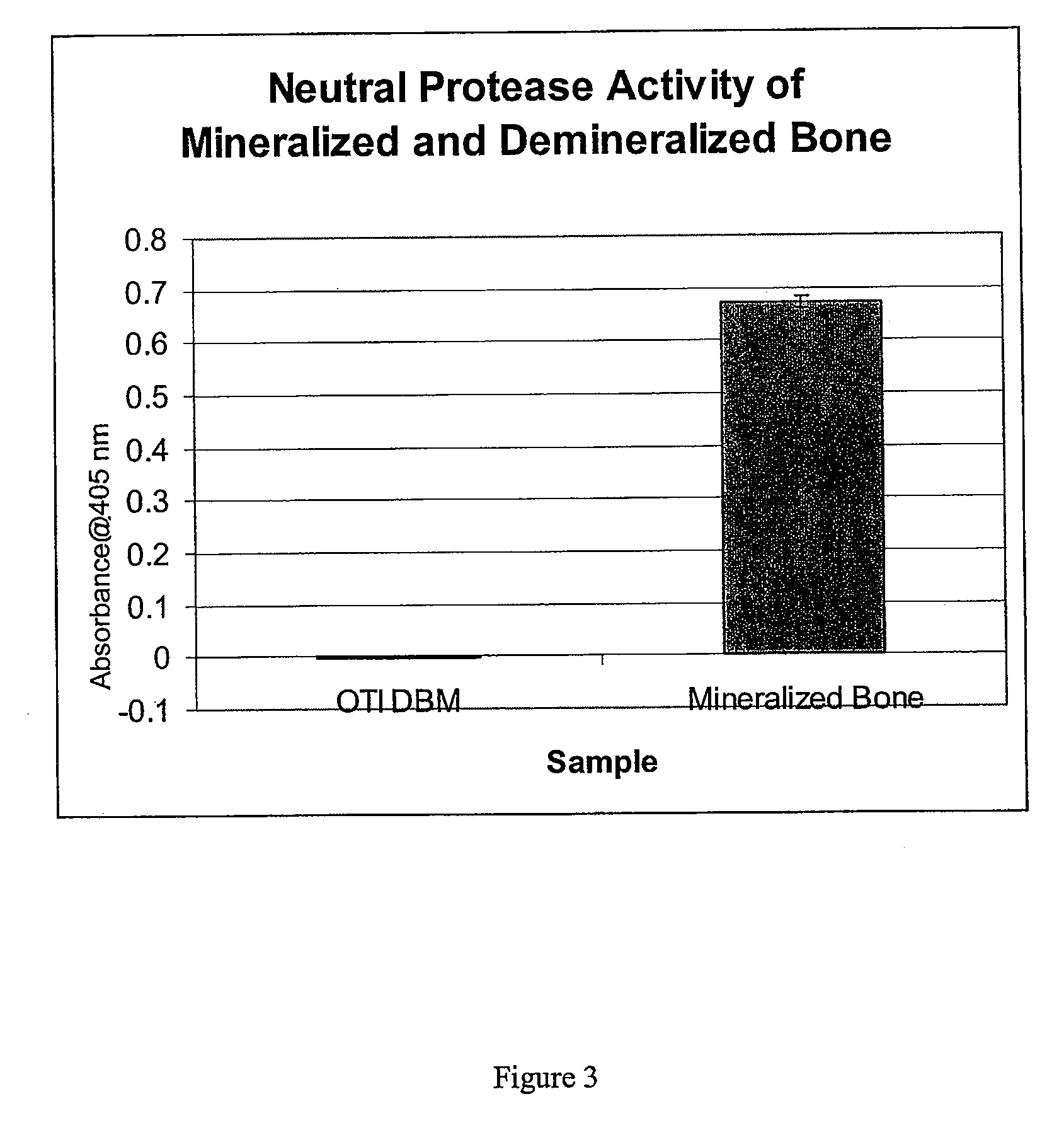
Bone matrix compositions and methods
Osteoinductive compositions and implants having increased biological activities, and methods for their production, are provided. The biological activities that may be increased include, but are not limited to, bone forming; bone healing; osteoinductive activity, osteogenic activity, chondrogenic activity, wound healing activity, neurogenic activity, contraction-inducing activity, mitosisinducing activity, differentiation-inducing activity, chemotactic activity, angiogenic or vasculogenic activity, and exocytosis or endocytosis-inducing activity. In one embodiment, a method for producing an osteoinductive composition comprises providing partially demineralized bone, treating the partially demineralized bone to disrupt the collagen structure of the bone, and optionally providing a tissue-derived extract and adding the tissue-derived extract to the partially demineralized bone. In another embodiment, an implantable osteoinductive and osteoconductive composition comprises partially demineralized bone, wherein the collagen structure of the bone has been disrupted, and, optionally, a tissue-derived extract.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
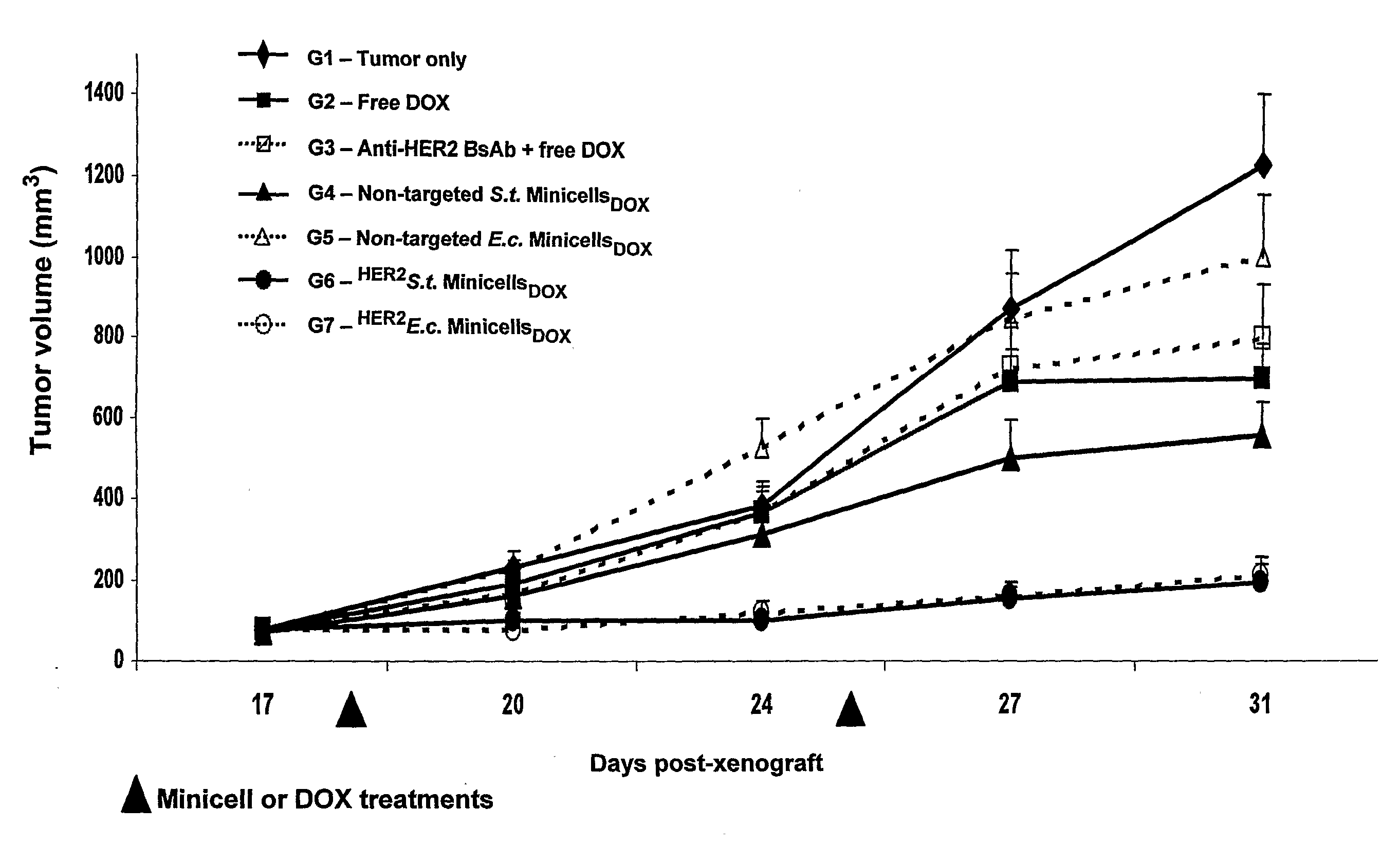
Compositions and Methods for Targeted in Vitro and in Vivo Drug Delivery to Mammalian Cells Via Bacterially Derived Intact Minicells
ActiveUS20080051469A1Low toxicityEliminate side effectsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDrug targettingIn vivo
A composition comprising intact minicells that contain a drug molecule is useful for targeted drug delivery. One targeted drug delivery method employs bispecific ligands, comprising a first arm that carries specificity for a bacterially derived minicell surface structure and a second arm that carries specificity for a mammalian cell surface receptor, to target drug-loaded minicells to specific mammalian cells and to cause endocytosis of the minicells by the mammalian cells. Another drug delivery method exploits the natural ability of phagocytic mammalian cells to engulf minicells without the use of bispecific ligands.
Owner:ENGENEIC MOLECULAR DELIVERY PTY LTD
Method of targeted gene delivery using viral vectors
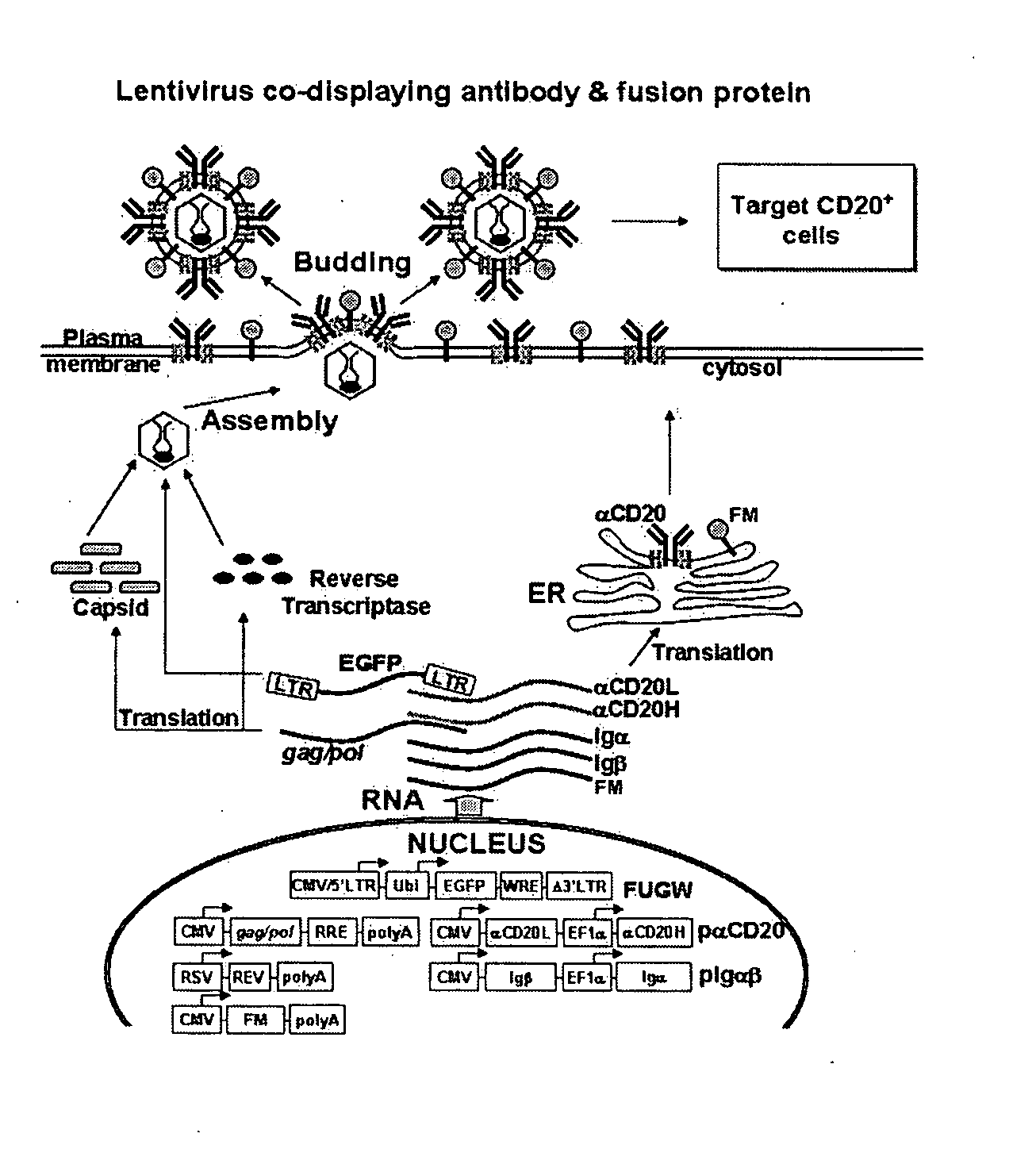
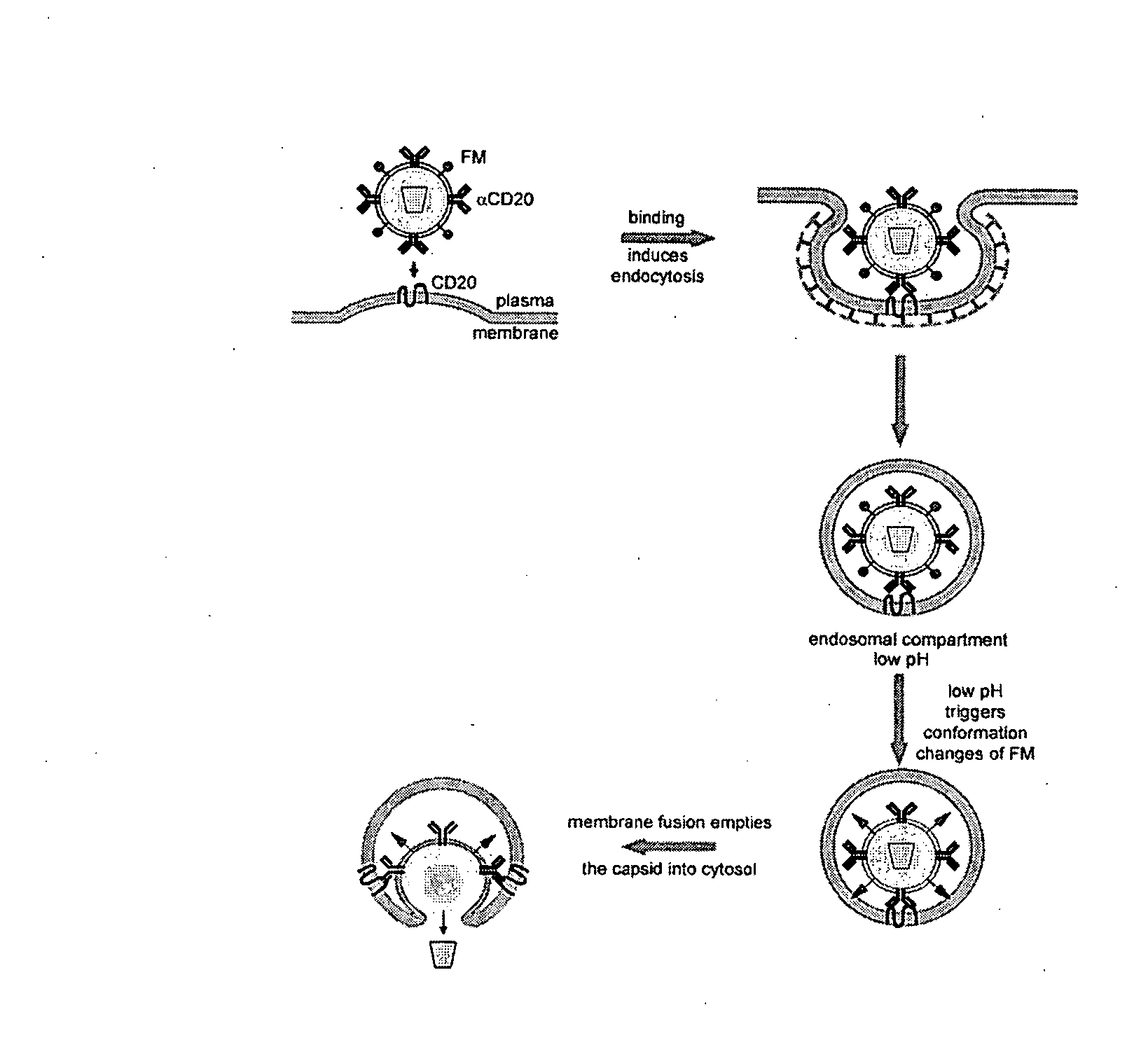
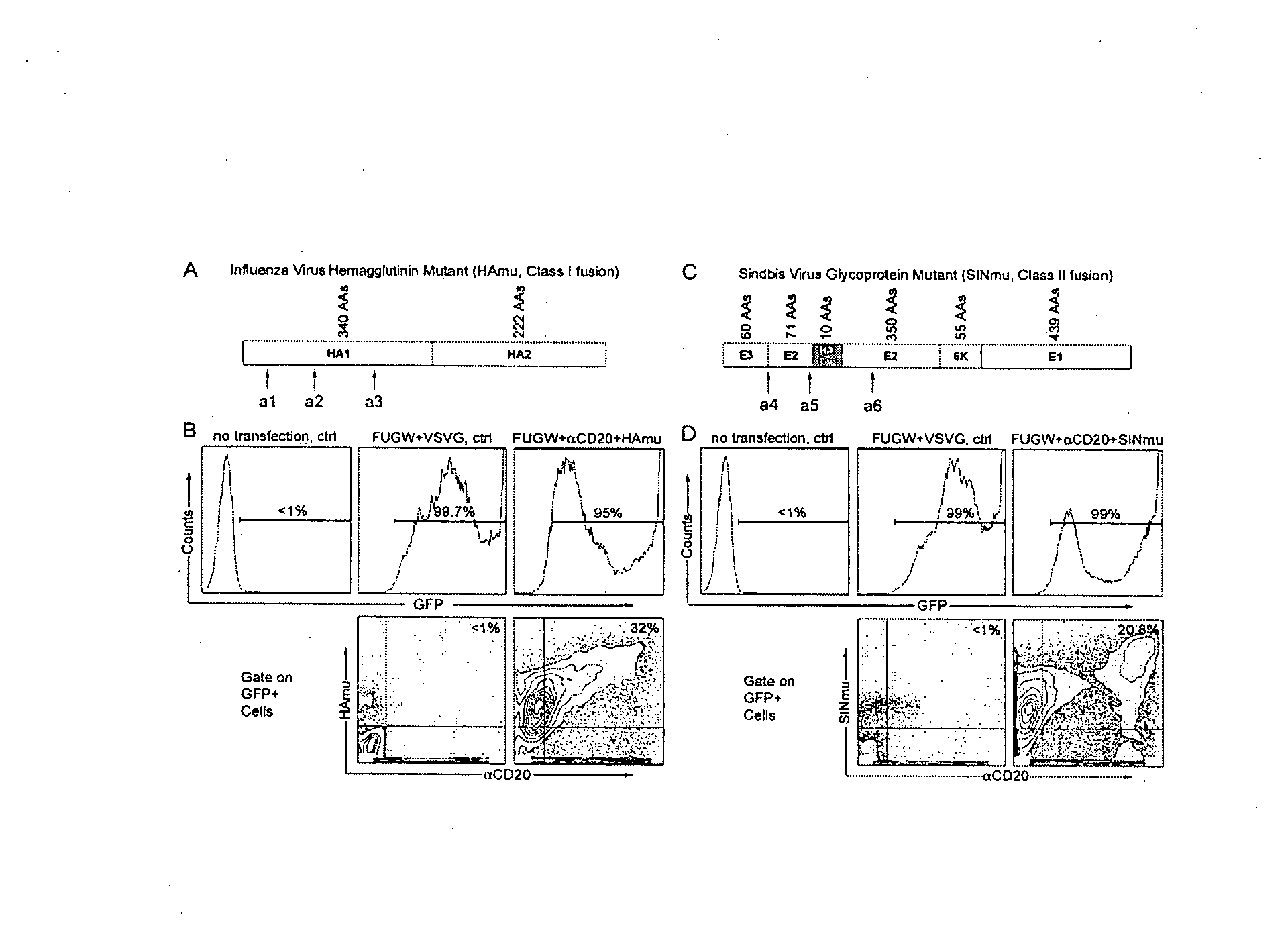
Methods and compositions are provided for delivering a polynucleotide encoding a gene of interest to a target cell using a virus. The virus envelope comprises a cell-specific binding determinant that recognizes and binds to a component on the target cell surface, leading to endocytosis of the virus. A separate fusogenic molecule is also present on the envelope and facilitates delivery of the polynucleotide across the membrane and into the cytosol of the target cell. The methods and related compositions can be used for treating patients having suffering from a wide range of conditions, including infection, such as HIV; cancers, such as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and breast cancer; and hematological disorders, such as severe combined immunodeficiency.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Remote detection of substance delivery to cells
InactiveUS20050112065A1Highly preventive effectIncreasing effect on proton relaxivityDiagnostics using lightDispersion deliveryLipid formationElectrochemical gradient
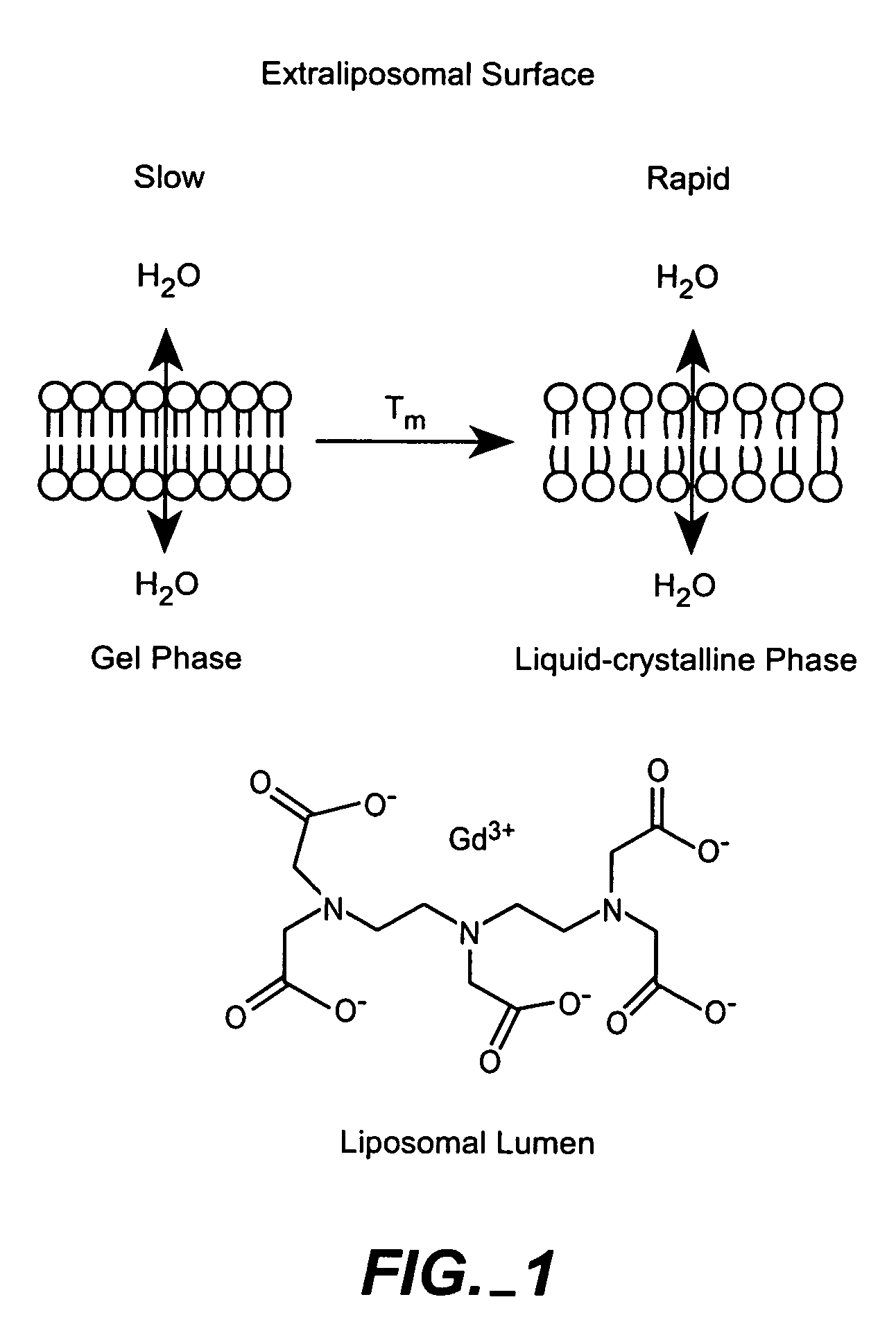
The present invention provides for the development of endocytosis-sensitive probes, and a remote method for measuring cellular endocytosis. These probes are based on the reduced water permeability of a nanoparticle or liposomal delivery system, and inherent degradability or disruption of barrier integrity upon endocytosis. The invention also provides for liposomes having combined therapeutic and diagnostic utilities by co-encapsulating ionically coupled diagnostic and therapeutic agents, in one embodiment, by a method using anionic chelators to prepare electrochemical gradients for loading of amphipathic therapeutic bases into liposomes already encapsulating an imaging agent. The invention provides for imaging of therapeutic liposomes by inserting a lipopolymer anchored, remotely sensing reporter molecules into liposomal lipid layer. The invention allows for an integrated delivery system capable of imaging molecular fingerprints in diseased tissues, treatment, and treatment monitoring.
Owner:SUTTER WEST BAY HOSPITALS
Targeted Gene Delivery to Non-Phagocytic Mammalian Cells Via Bacterially Derived Intact Minicells
ActiveUS20070237744A1High expressionFunction increaseOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaGene deliveryPhagocytic Cell
A method of targeting bacterially-derived, intact minicells to specific, non-phagocytic mammalian cells employs bispecific ligands to deliver nucleic acids efficiently to the mammalian cells. Bispecific ligands, comprising (i) a first arm that carries specificity for a bacterially-derived minicell surface structure and (ii) a second arm that carries specificity for a non-phagocytic mammalian cell surface receptor are useful for targeting minicells to specific, non-phagocytic mammalian cells and causing endocytosis of minicells by non-phagocytic cells.
Owner:ENGENEIC MOLECULAR DELIVERY PTY LTD
Fusion proteins
InactiveUS20110091437A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBinding siteCytotoxicity
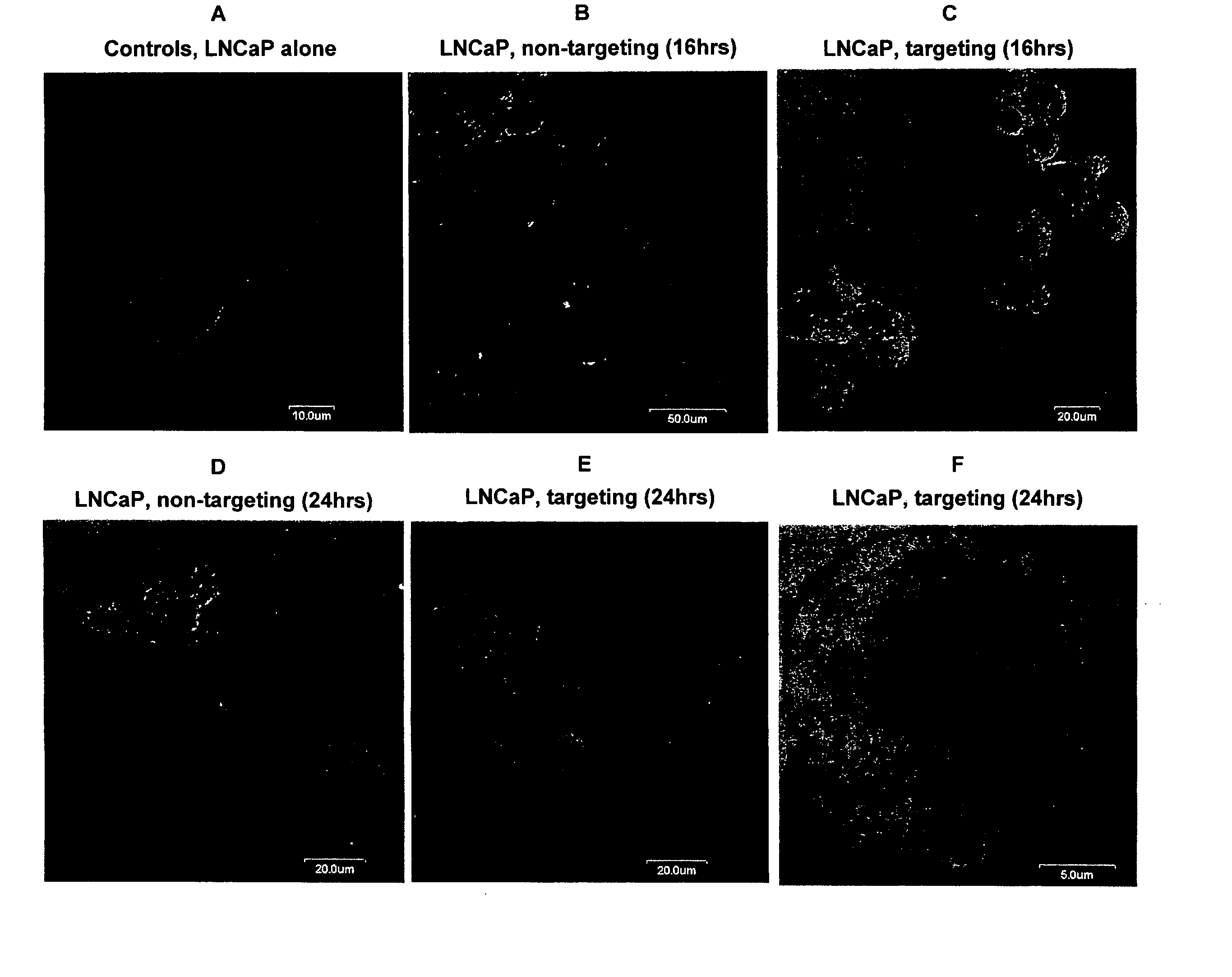
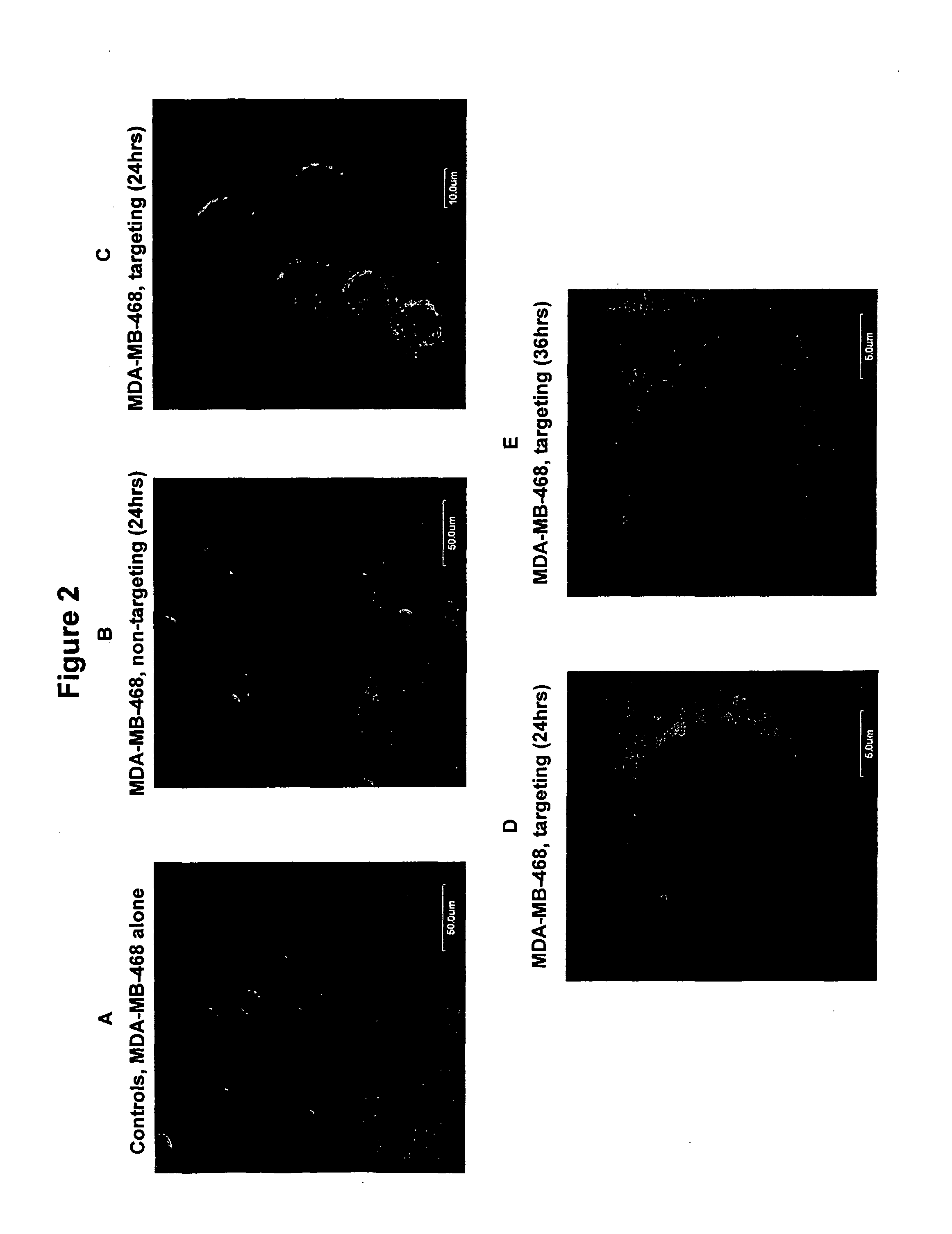
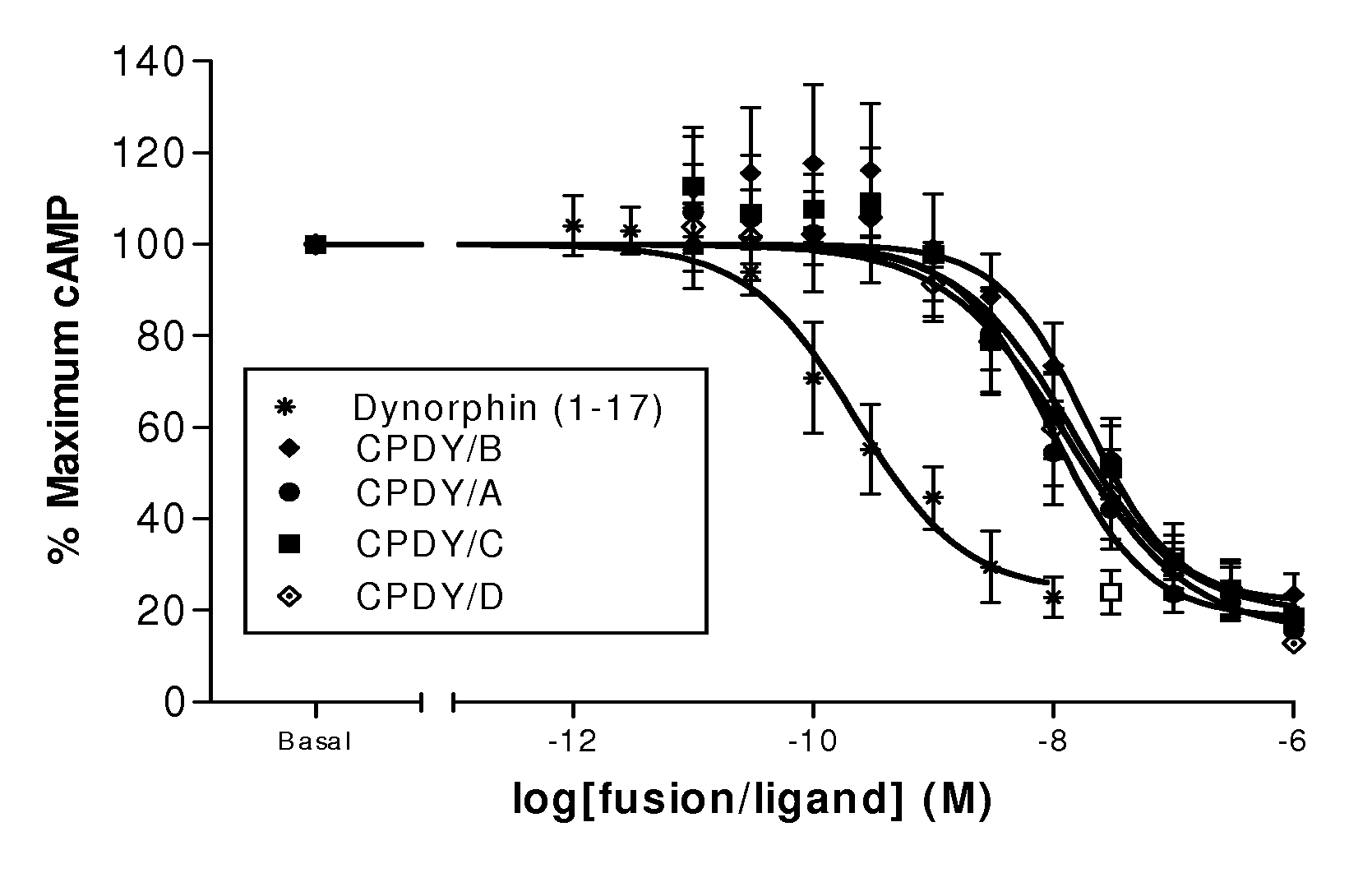
A single chain, polypeptide fusion protein, comprising: a non-cytotoxic protease, or a fragment thereof, which protease or protease fragment is capable of cleaving a protein of the exocytic fusion apparatus of a nociceptive sensory afferent; a dynorphin Targeting Moiety that is capable of binding to a Binding Site on the nociceptive sensory afferent, which Binding Site is capable of undergoing endocytosis to be incorporated into an endosome within the nociceptive sensory afferent; a protease cleavage site at which site the fusion protein is cleavable by a protease, wherein the protease cleavage site is located between the non-cytotoxic protease or fragment thereof and the dynorphin Targeting Moiety; and a translocation domain that is capable of translocating the protease or protease fragment from within an endosome, across the endosomal membrane and into the cytosol of the nociceptive sensory afferent. Nucleic acid sequences encoding the polypeptide fusion proteins, methods of preparing same and uses thereof are also described.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY +1
Method of targeted gene delivery using viral vectors
Methods and compositions are provided for delivering a polynucleotide encoding a gene of interest to a target cell using a virus. The virus envelope comprises a cell-specific binding determinant that recognizes and binds to a component on the target cell surface, leading to endocytosis of the virus. A separate fusogenic molecule is also present on the envelope and facilitates delivery of the polynucleotide across the membrane and into the cytosol of the target cell. The methods and related compositions can be used for treating patients having suffering from a wide range of conditions, including infection, such as HIV; cancers, such as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and breast cancer; and hematological disorders, such as severe combined immunodeficiency.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
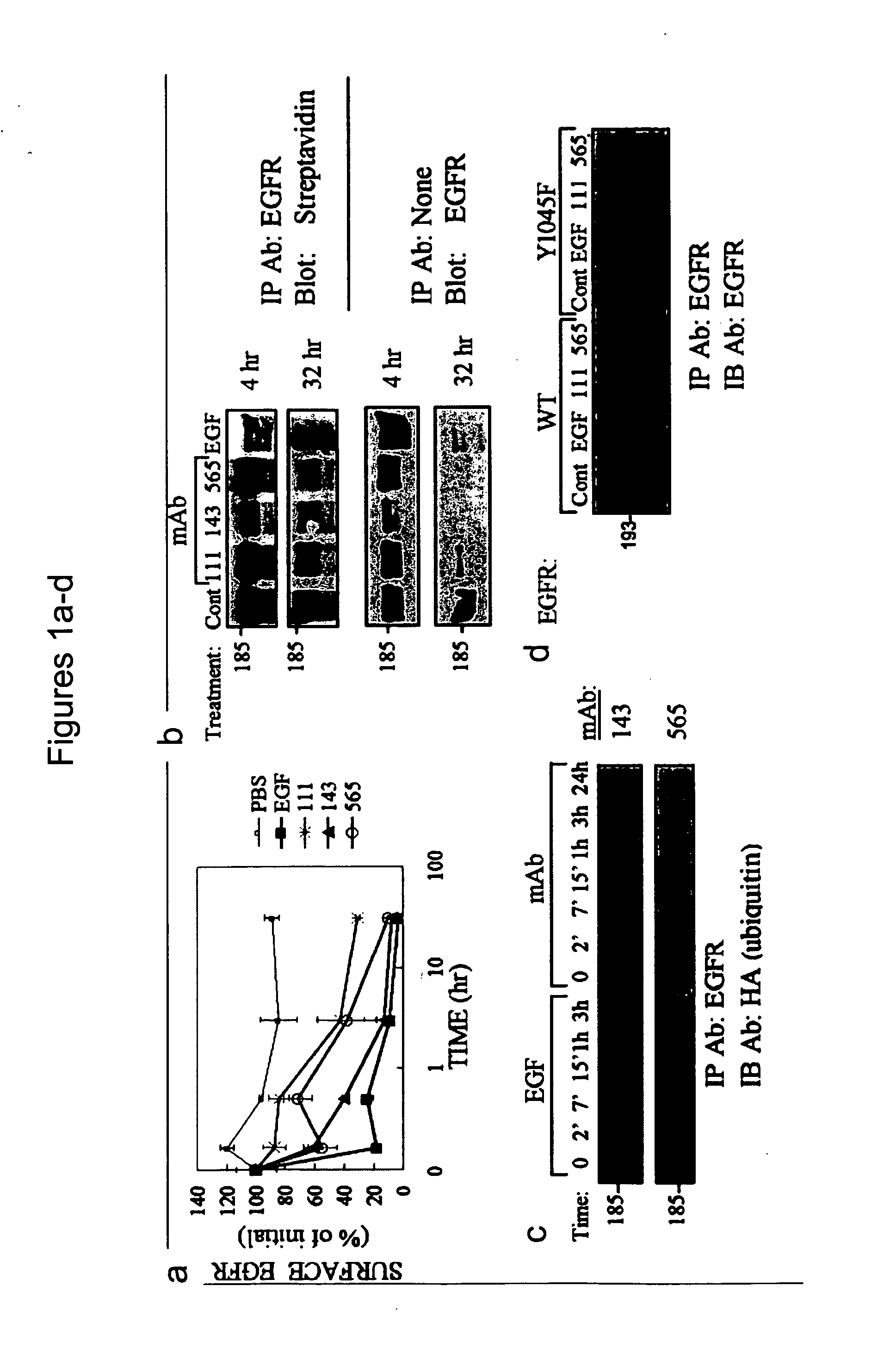
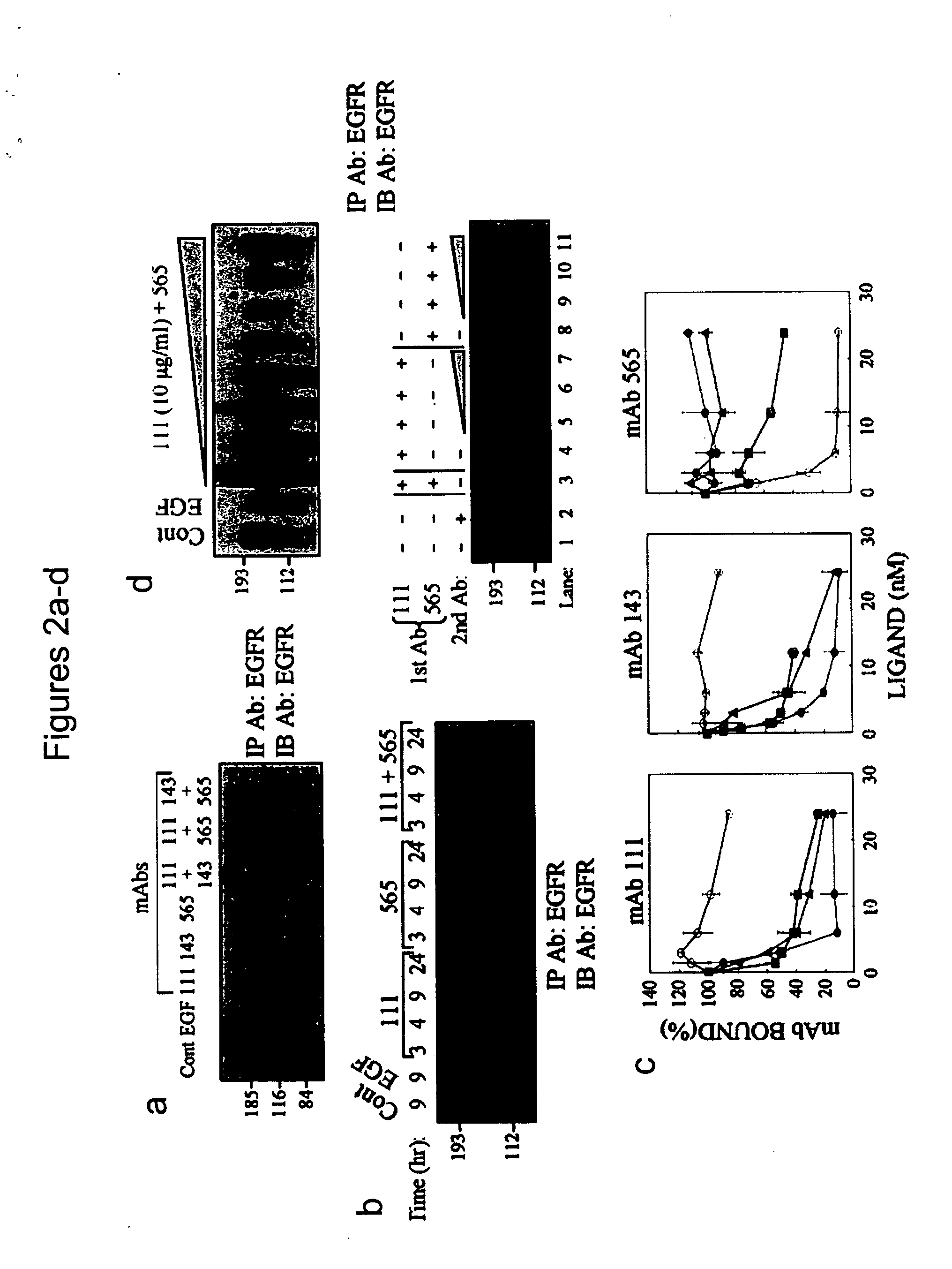
Methods of identifying combinations of antibodies with an improved anti-tumor activity and compositions and methods using the antibodies
ActiveUS20070178102A1Improve anti-tumor activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthAntitumor activity
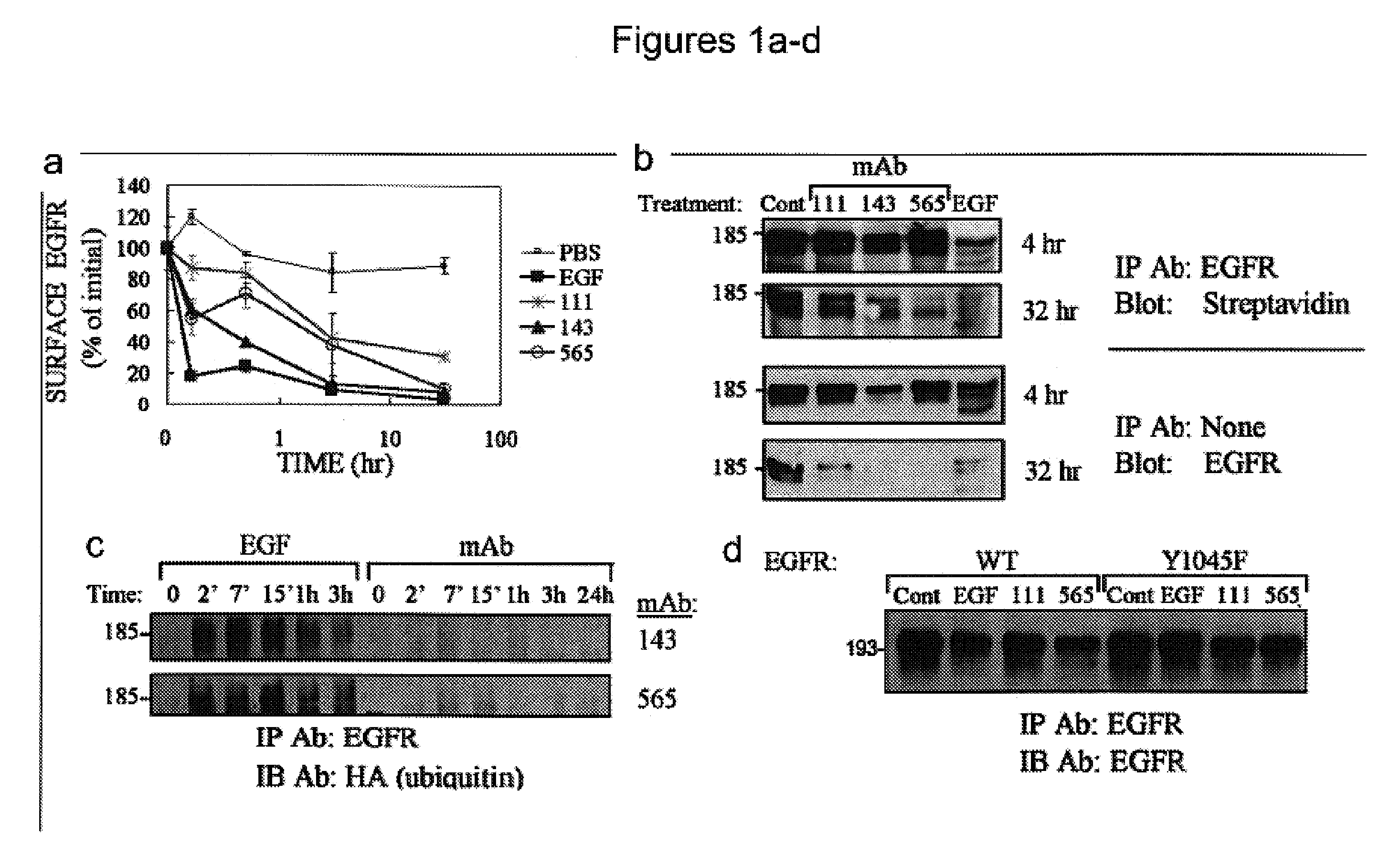
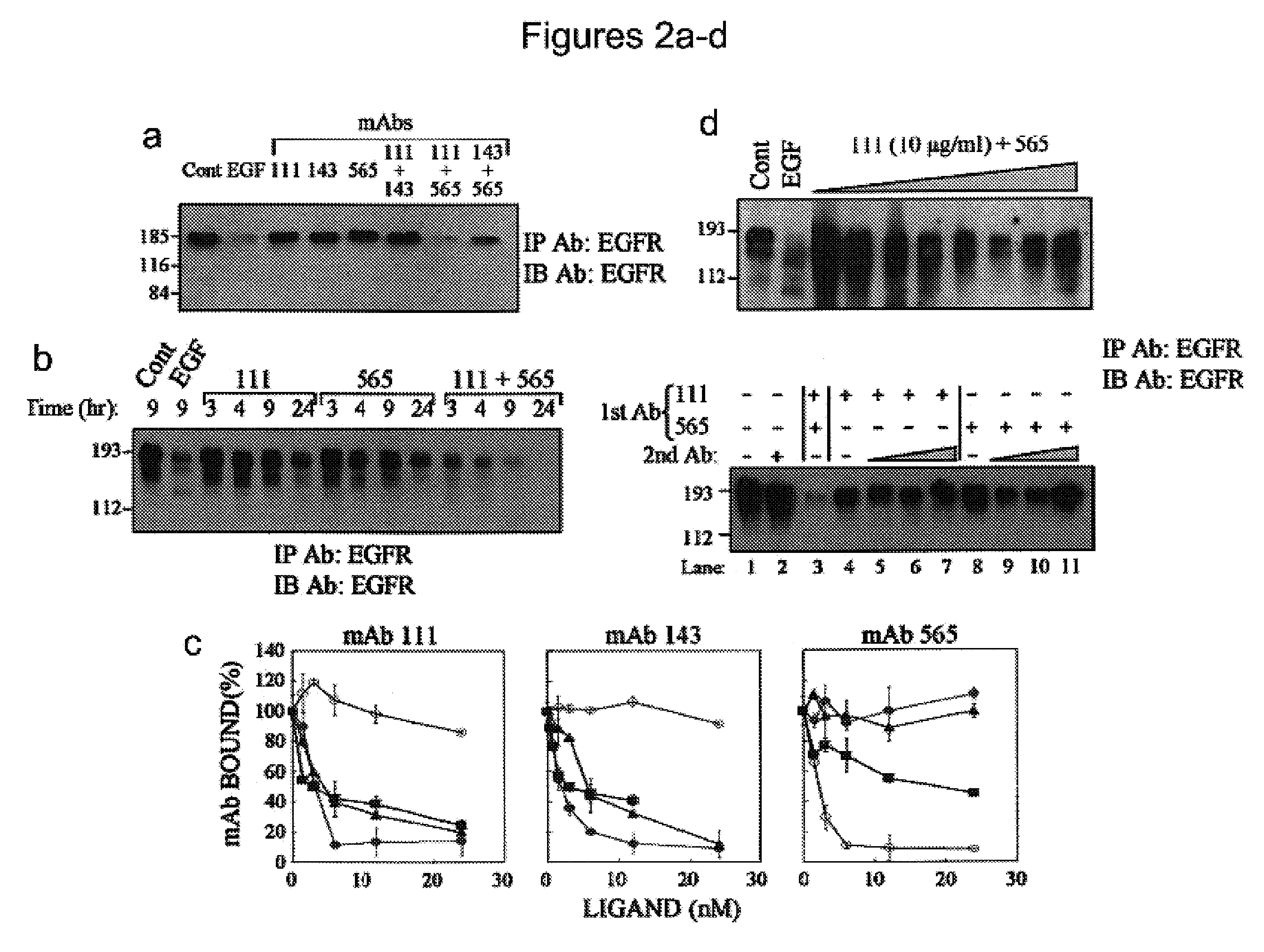
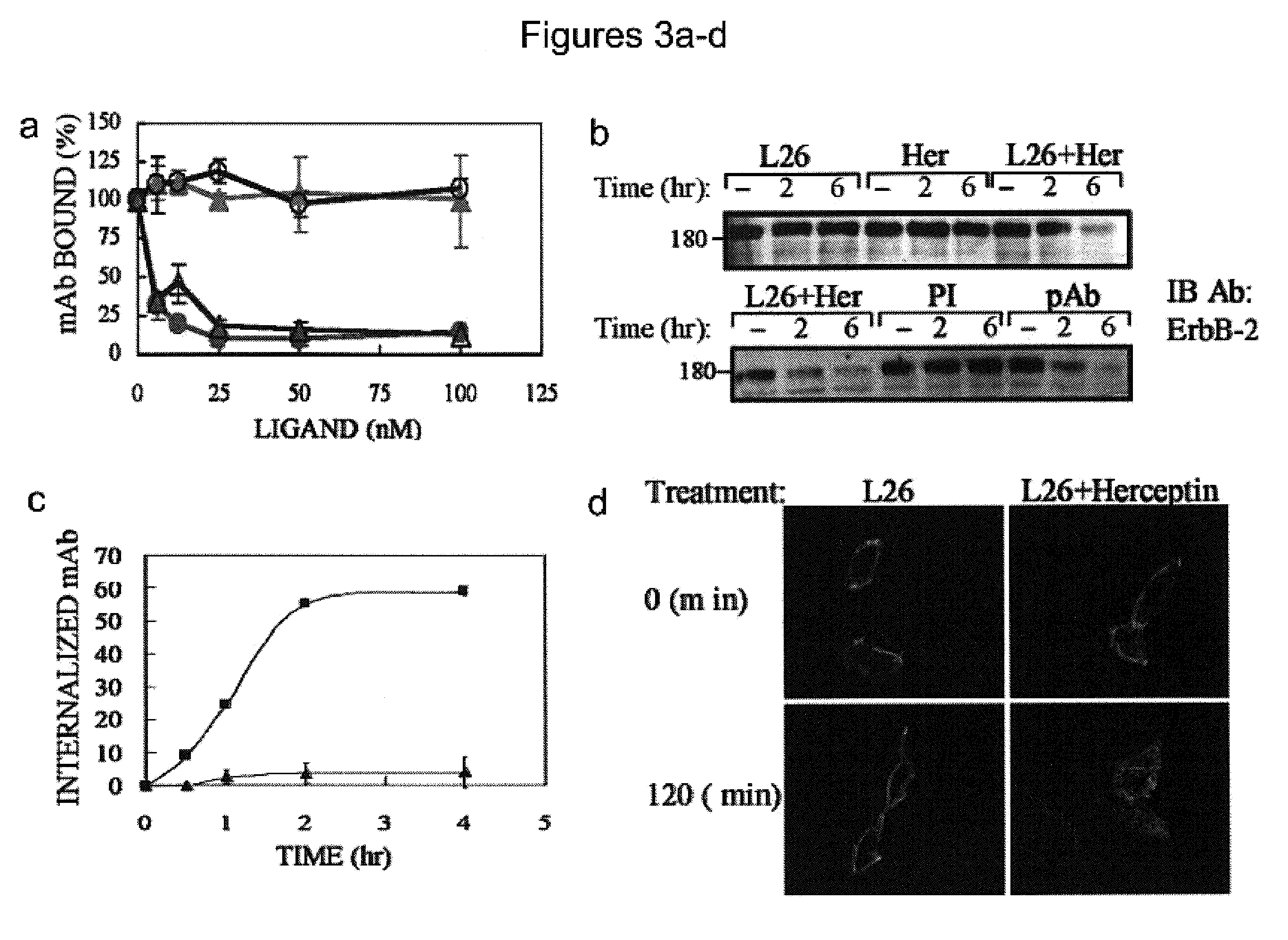
A method of identifying a combination of antibodies with a combined improved anti tumor activity is provided. The method comprising identifying at least two anti RTK antibodies capable of inducing synergistic endocytosis of the RTK in a cell expressing the RTK, thereby identifying the combination of antibodies with the combined improved anti-tumor activity.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Bone matrix compositions and methods
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
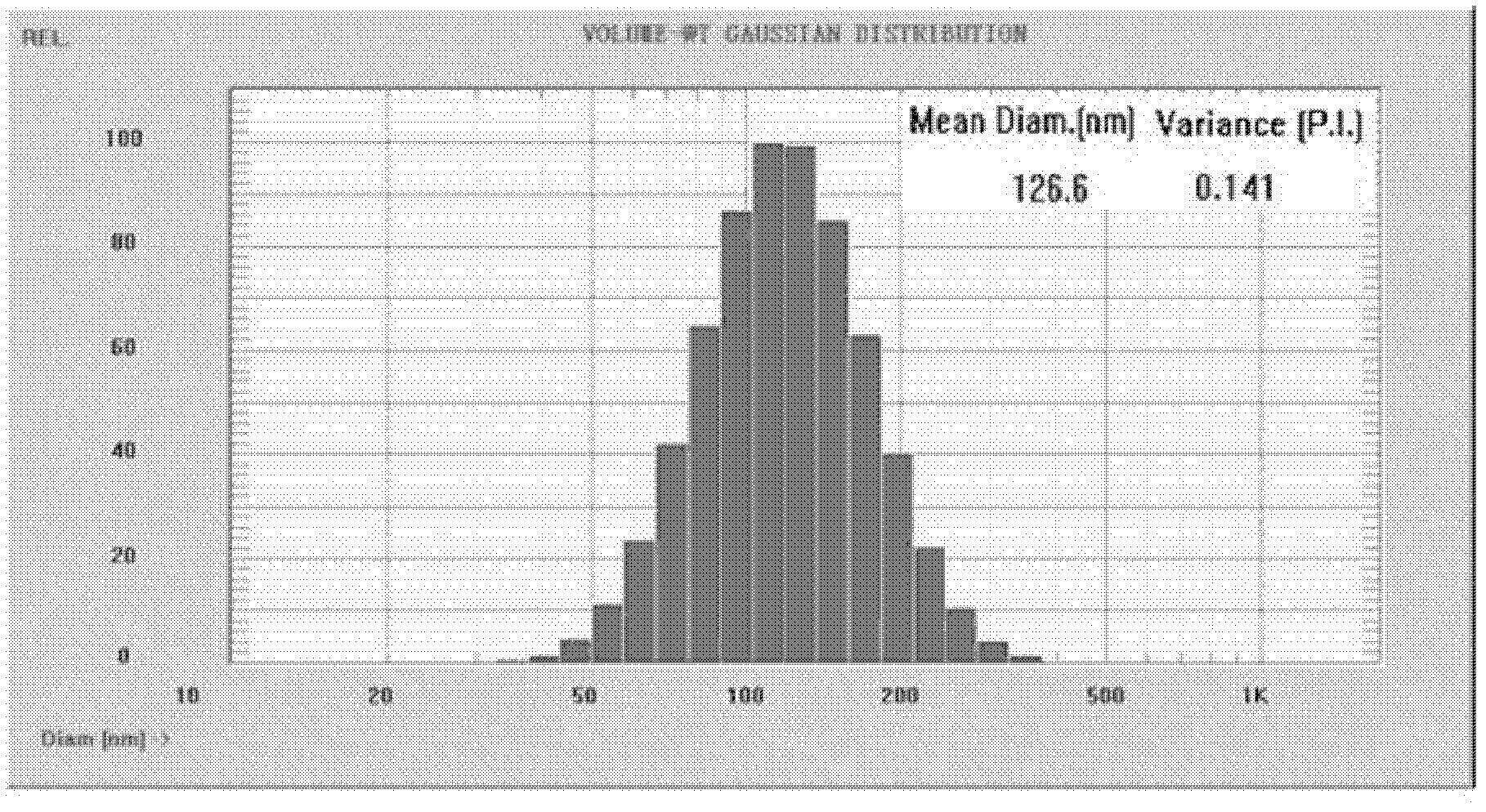
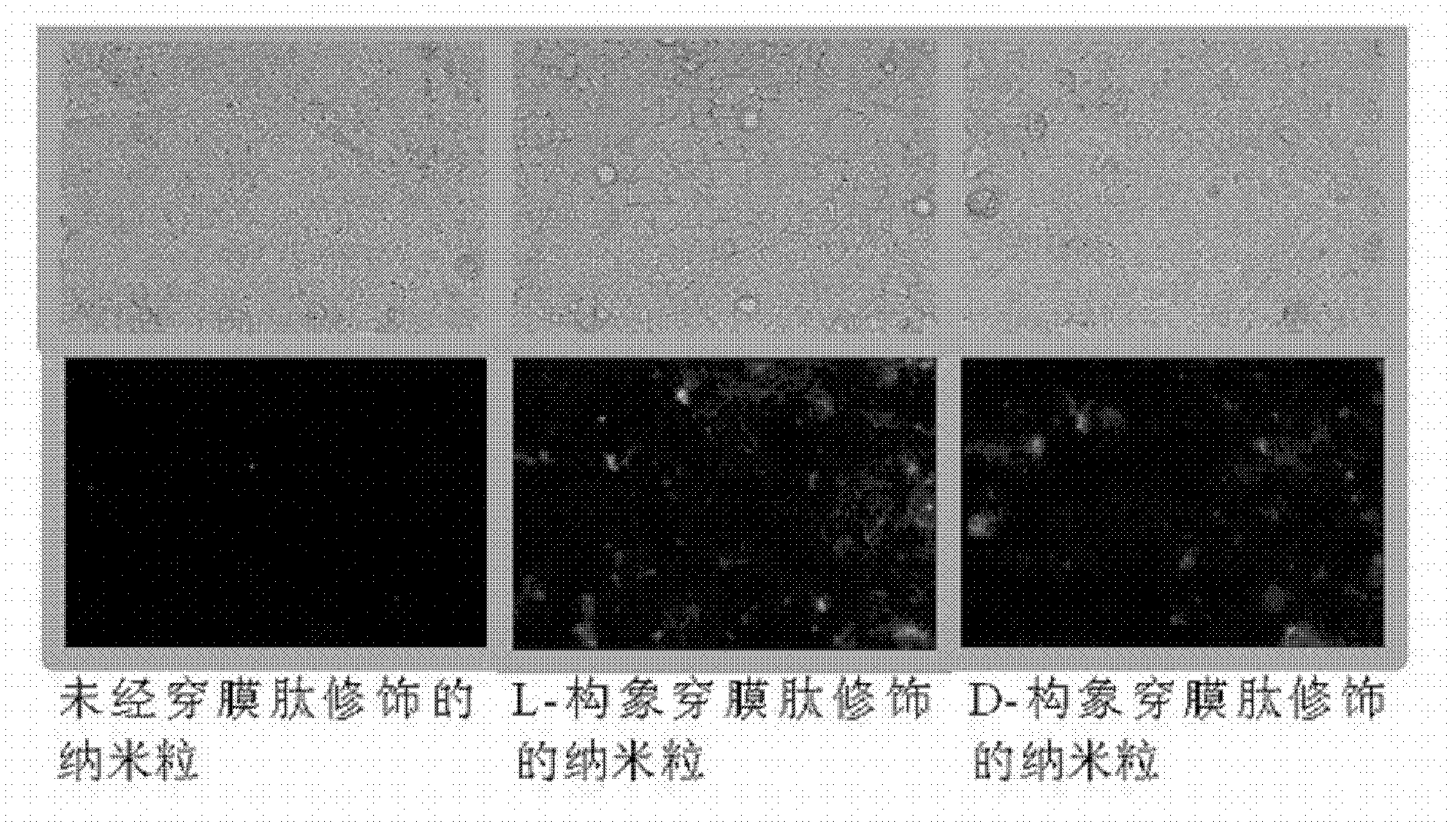
Cell-penetrating peptide modified nanoparticle and its preparation method
InactiveCN102988295AIncreased cellular uptakeImprove biostability in vivoPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSide effectWhole body
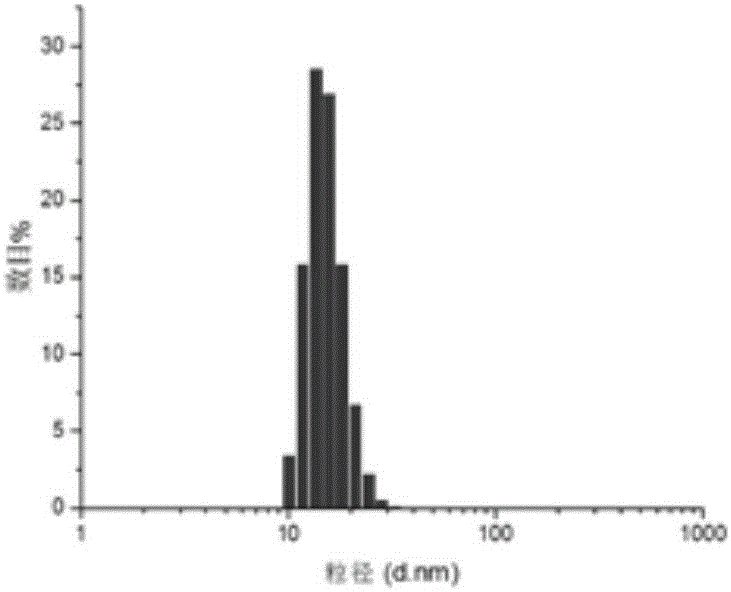
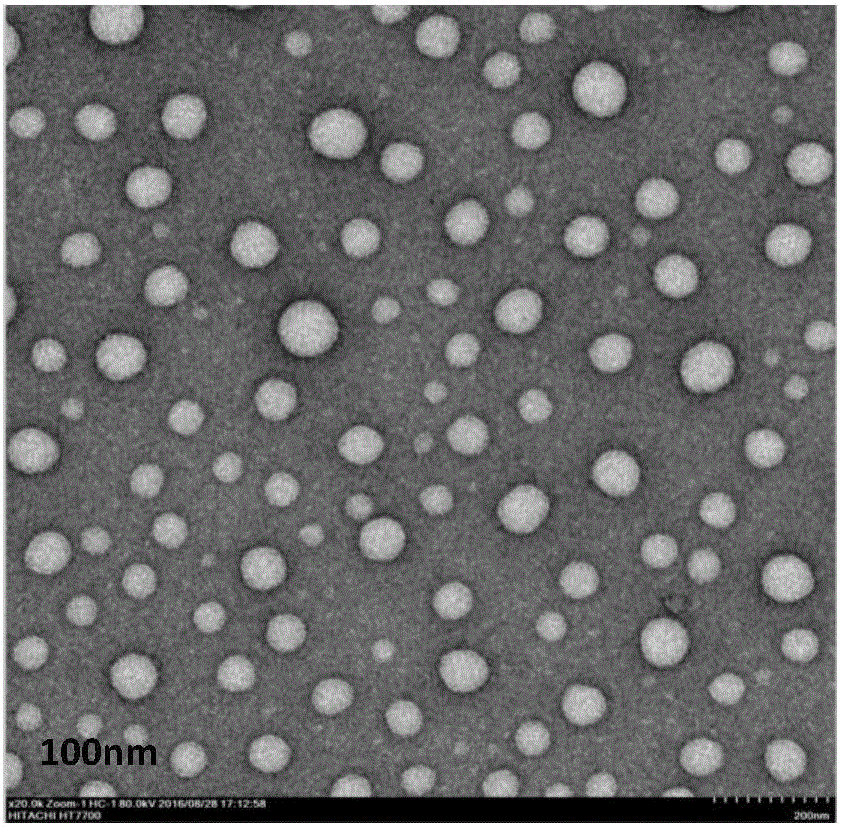
The invention belongs to the medicinal preparation field, relates to a cell-penetrating peptide modified nanoparticle, and concretely relates to a nanoparticle delivery system for oral polypeptide and protein medicines, and its preparation method. The medicine delivery system is composed of the nanoparticle, cell-penetrating peptides modified on the surface of the nanoparticle, and the polypeptide protein medicines sealed by the nanoparticle, wherein the average particle size range of the medicine delivery system is 10-500nm. The cell-penetrating peptide modified nanoparticle and glucosaminoglycan having electronegative cell surfaces undergo electric property attraction and then undergo endocytosis, so the cell-penetrating peptide modified nanoparticle and the glucosaminoglycan are integrally taken into cells; and the cell-penetrating peptide modified nanoparticle has an alimentary canal mucous membrane penetrating capability after the cell-penetrating peptide modified nanoparticle is orally taken, and can deliver the polypeptide protein medicines carried by the cell-penetrating peptide modified nanoparticle to the whole body for blood circulation, so the oral biological utilization degree of the medicines are improved. The cell-penetrating peptide modified nanoparticle has the advantages of improvement of the stability of polypeptide and protein medicines in the alimentary canal, reduction of the application amount of cell-penetrating peptides, and reduction of possible toxic side effects caused by the cell-penetrating peptides.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Specific target polypeptide self-assembled nano-carrier, drug-carrying nanoparticle and preparation method
ActiveCN106822036AGrowth inhibitionInhibit synthesisOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsNanocarriersBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and in particular relates to a specific target polypeptide self-assembled nanoparticle. The nanoparticle is prepared from a hydrophobic anti-tumor drug with a therapeutic dosage and an amphipathic polypeptide which covers the periphery of the hydrophobic anti-tumor drug through a self-assembling manner, wherein the amphipathic polypeptide is a target peptide which can be used for specifically targeting a epidermal growth factor receptor of a tumor cell; a terminal N of the target peptide is coupled with a hydrophobic functional molecule. After the nanoparticle targets the tumor cell, the target peptide is exposed; the nanoparticle targets the tumor cell and enters the tumor cell through receptor-mediated endocytosis, and the drug is released to inhibit DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) synthesis and repairing; the nanoparticle has dual killing effects on the tumor cells and the growth of the tumor cell is inhibited. The amphipathic polypeptide does not generate a covalent bond in a self-assembling process and no reverse reaction is caused; the specific target polypeptide self-assembled nanoparticle is used for treating tumors and has the advantages of no toxin and good biocompatibility.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
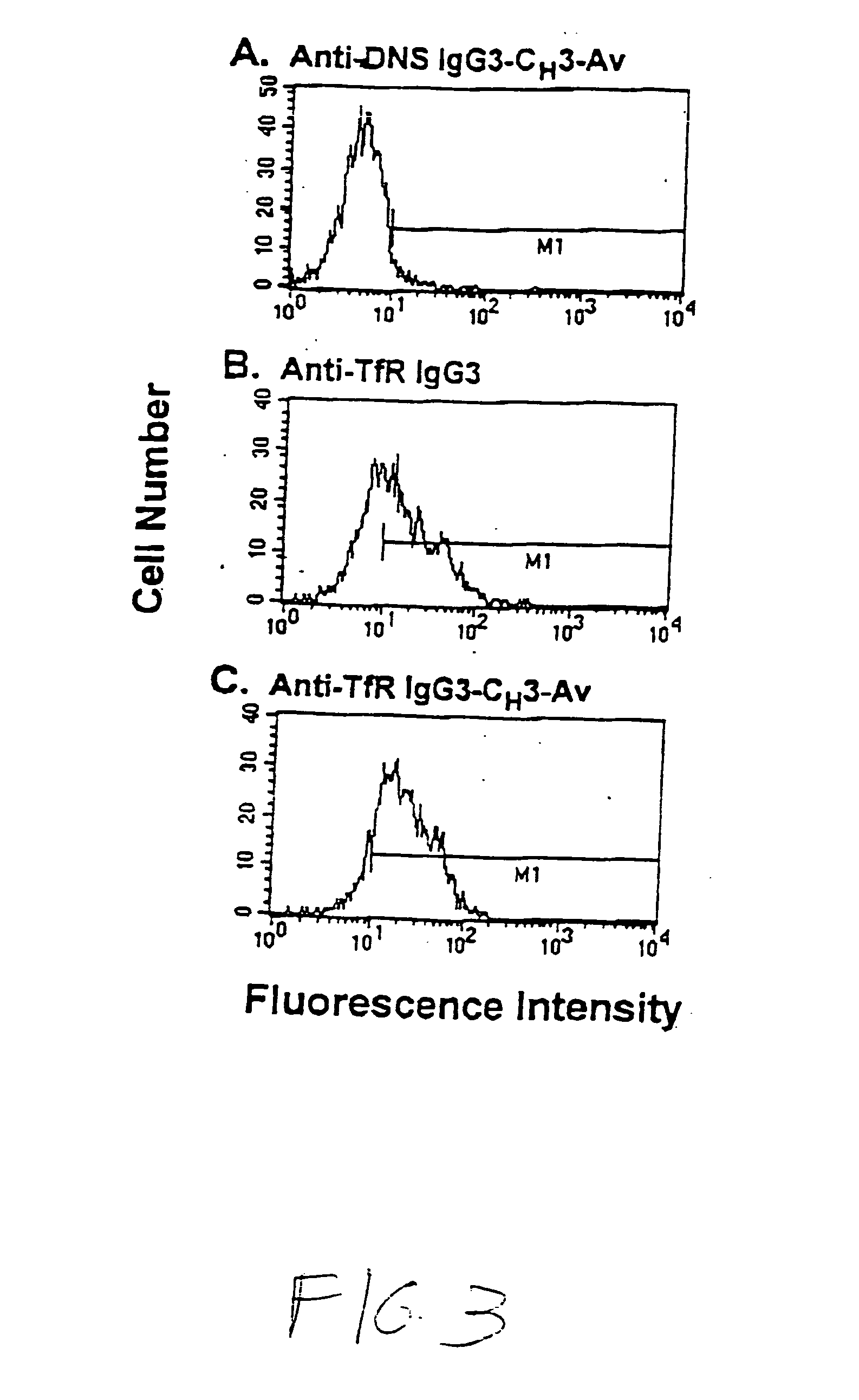
Anti-growth factor receptor avidin fusion proteins as universal vectors for drug delivery
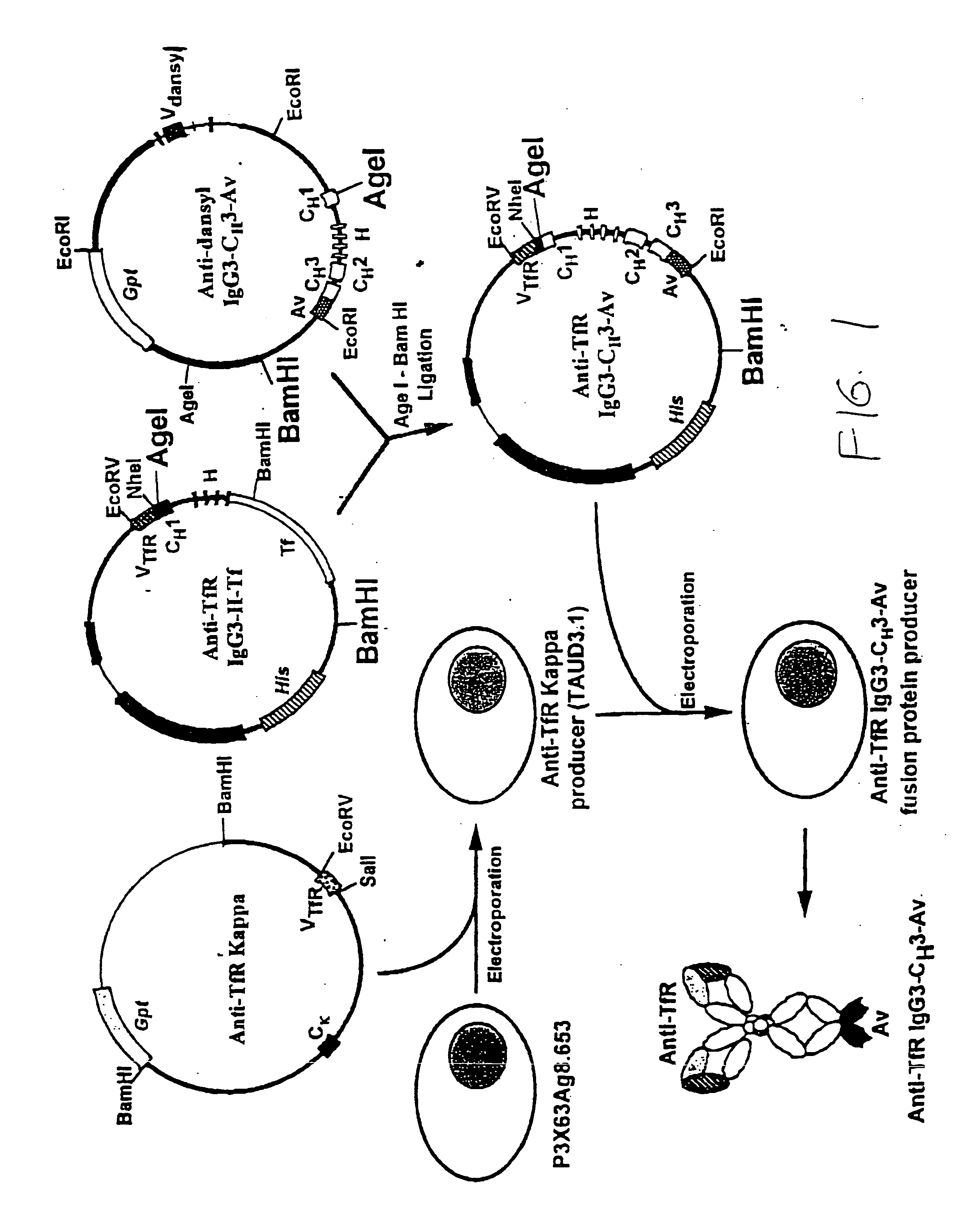
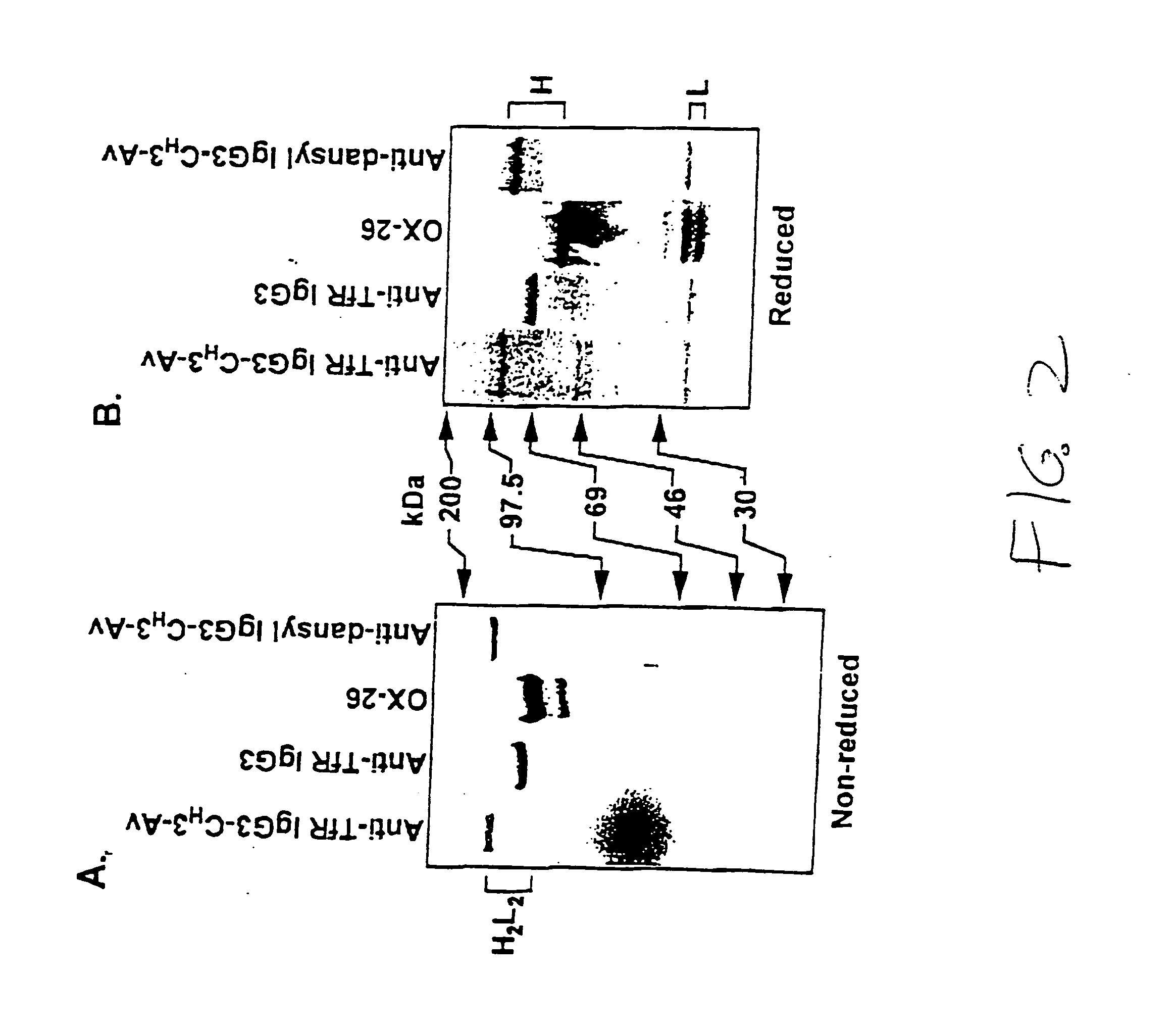
A fusion protein for delivery of a wide variety of agents to a cell via antibody-receptor-mediated endocytosis comprises a first segment and a second segment: the first segment comprising a variable region of an antibody that recognizes an antigen on the surface of a cell that after binding to the variable region of the antibody undergoes antibody-receptor-mediated endocytosis, and, optionally, further comprises at least one domain of a constant region of an antibody; and the second segment comprising a protein domain selected from the group consisting of avidin, an avidin mutein, a chemically modified avidin derivative, streptavidin, a streptavidin mutein, and a chemically modified streptavidin derivative. Typically, the antigen is a protein. Typically, the protein antigen on the surface of the cell is a receptor such as a transferrin receptor-or an insulin receptor. The invention also includes an antibody construct incorporating the fusion protein that is either a heavy chain or a light chain together with a complementary light chain or heavy chain to form an intact antibody molecule. The invention further includes targeting methods and screening methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Targeted delivery of drugs, therapeutic nucleic acids and functional nucleic acids to mammalian cells via intact killed bacterial cells
Owner:ENGENEIC MOLECULAR DELIVERY PTY LTD
Methods of identifying combinations of antibodies with an improved anti-tumor activity and compositions and methods using the antibodies
ActiveUS7498142B2Improve anti-tumor activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody ingredientsAntitumor activityCancer research
A method of identifying a combination of antibodies with a combined improved anti tumor activity is provided. The method comprising identifying at least two anti RTK antibodies capable of inducing synergistic endocytosis of the RTK in a cell expressing the RTK, thereby identifying the combination of antibodies with the combined improved anti-tumor activity.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Anti-tumor nano prodrug system based on dendrimer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101879313AHigh molecular weightImprove hydrophilicityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDendrimerCyclic peptide
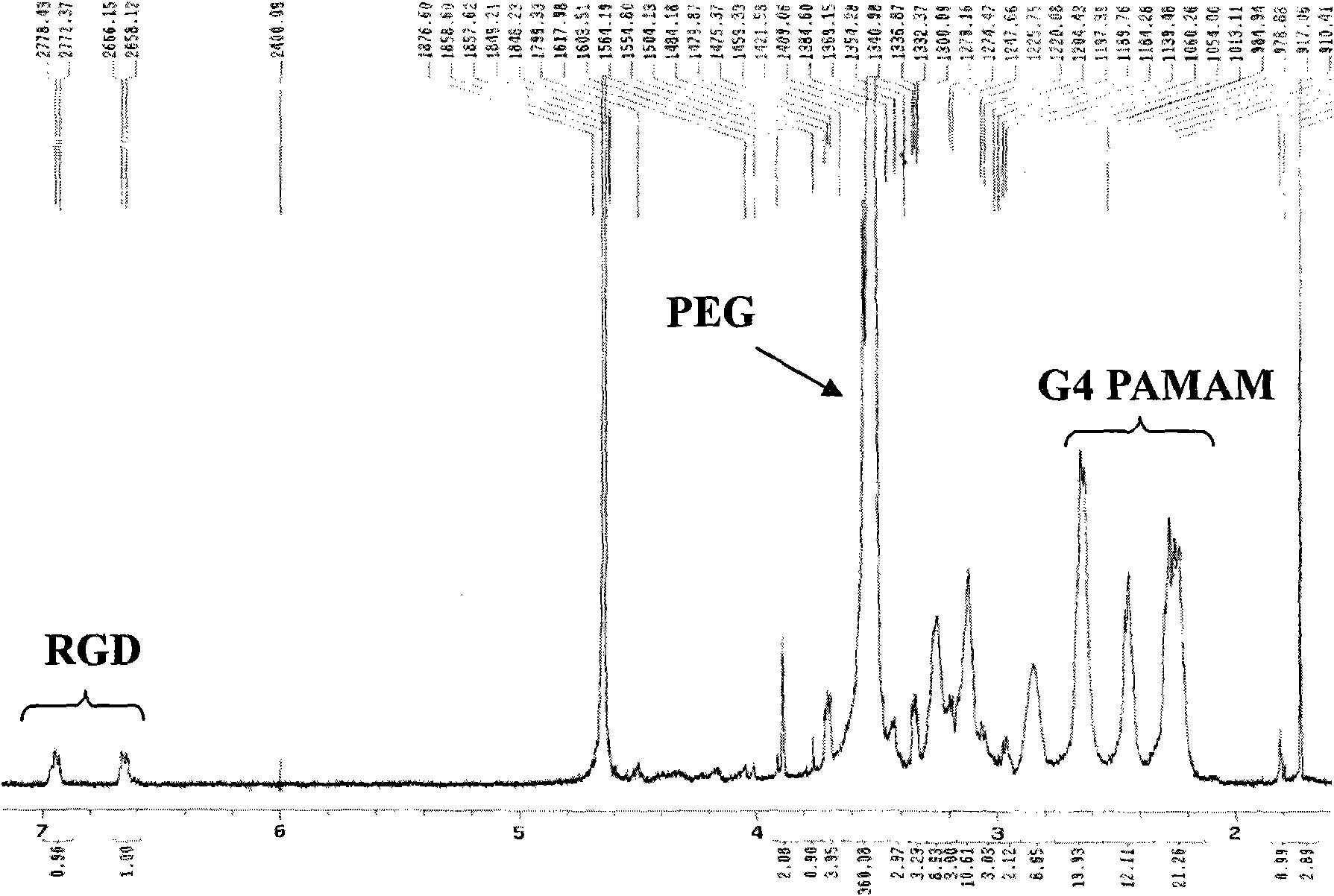
The invention relates to a multi-function nano prodrug system based on a dendrimer, which belongs to the technical field of biomedicines and nano medical science. The nano system comprises four function parts: an outermost layer RGD (arginyl-glycocoll-aspartate) cyclic peptide as an active targeting head group (1), a polyethylene glycol (PEG) hydrophilic chain segment (2) connected with the targeting head group and the dendrimer, an anti-tumour drug (3) connected with the dendrimer by an acid sensitive chemical bond and a dendrimer kernel (4). The general formula of the nano system is RGD-PEG-Dendrimer-DOX (doxorubicine), wherein the macromolecule attribute of a dendrimer vector makes a vector system passively target to tumor tissues through an EPR (Enhanced Permeability and retention) effect; the RGD cyclic peptide makes the vector system actively target to the tumor tissues through the interaction of a ligand and a receptor and promotes the endocytosis of the tumor tissues; the acid sensitive chemical bond ensures that a drug-carrying system is stable in systemic circulation and releases active drugs after arriving tumor positions and entering an acid organelle to perform the function of cytotoxicity.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Novel polypeptide modified tumor targeted liposome of targeted integrin receptor
InactiveCN103417480AIncrease intakeAntitumor effectMacromolecular non-active ingredientsHybrid peptidesTumor targetCholesterol
The invention provides a novel polypeptide modified tumor targeted liposome of a targeted integrin receptor. The novel polypeptide is mainly formed by covalent linkage of ring-shaped RGD and cell penetrating peptides, and not only has the selective targeting capability of an integrin receptor, but also can achieve mediated endocytosis; the liposome mainly comprises phospholipid, cholesterol, lipid-polyethyleneglycol and lipid-polyethyleneglycol-novel polypeptide ligand chimeric substance, and is a very potential tumor targeted treatment carrier.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
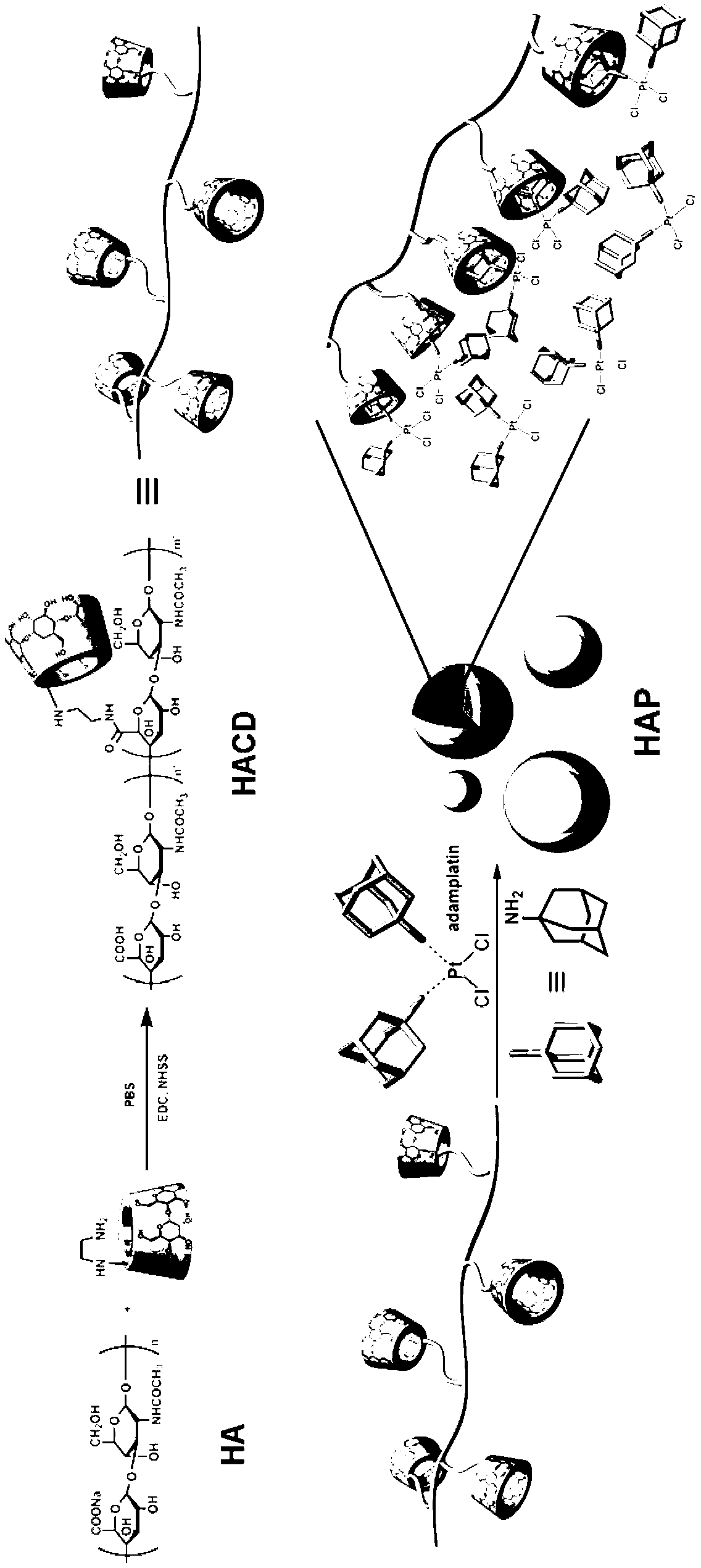
Supramolecule assembly of targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin and preparation of supramolecule assembly
InactiveCN102698286AAchieve selective killingSmall toxicityHeavy metal active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectCancer cell
The invention discloses a supramolecule assembly of targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin. The supramolecule assembly is a binary supramolecule assembly which is synthesized on the basis of cyclodextrin-decorated hyaluronic acid and adamplatin. A preparation method of the supramolecule assembly is characterized in that the cyclodextrin-decorated hyaluronic acid and the adamplatin are respectively synthesized, and through the strong non-covalent interaction of cyclodextrin and adamantine and the amphiphilic action of molecules, a supermolecule nano particle which takes the hydrophilic hyaluronic acid as a shell and the adamplatin as a core is formed. The supramolecule assembly disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the supramolecule assembly of the targeting-delivery anticancer adamplatin has a simple synthetic route, is low in preparation cost and high in productivity, and is suitable for amplification synthesis and practical production application; and through endocytosis in which a malignant cell surface hyaluronic acid receptor serves as a medium, the supramolecule assembly (HAP) is brought in cancer cells in a target manner, so that the protection of normal cells and the targeting selective killing of cancer cells are realized, the anti-cancer activity is obviously improved, and toxic and side effects are obviously reduced.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
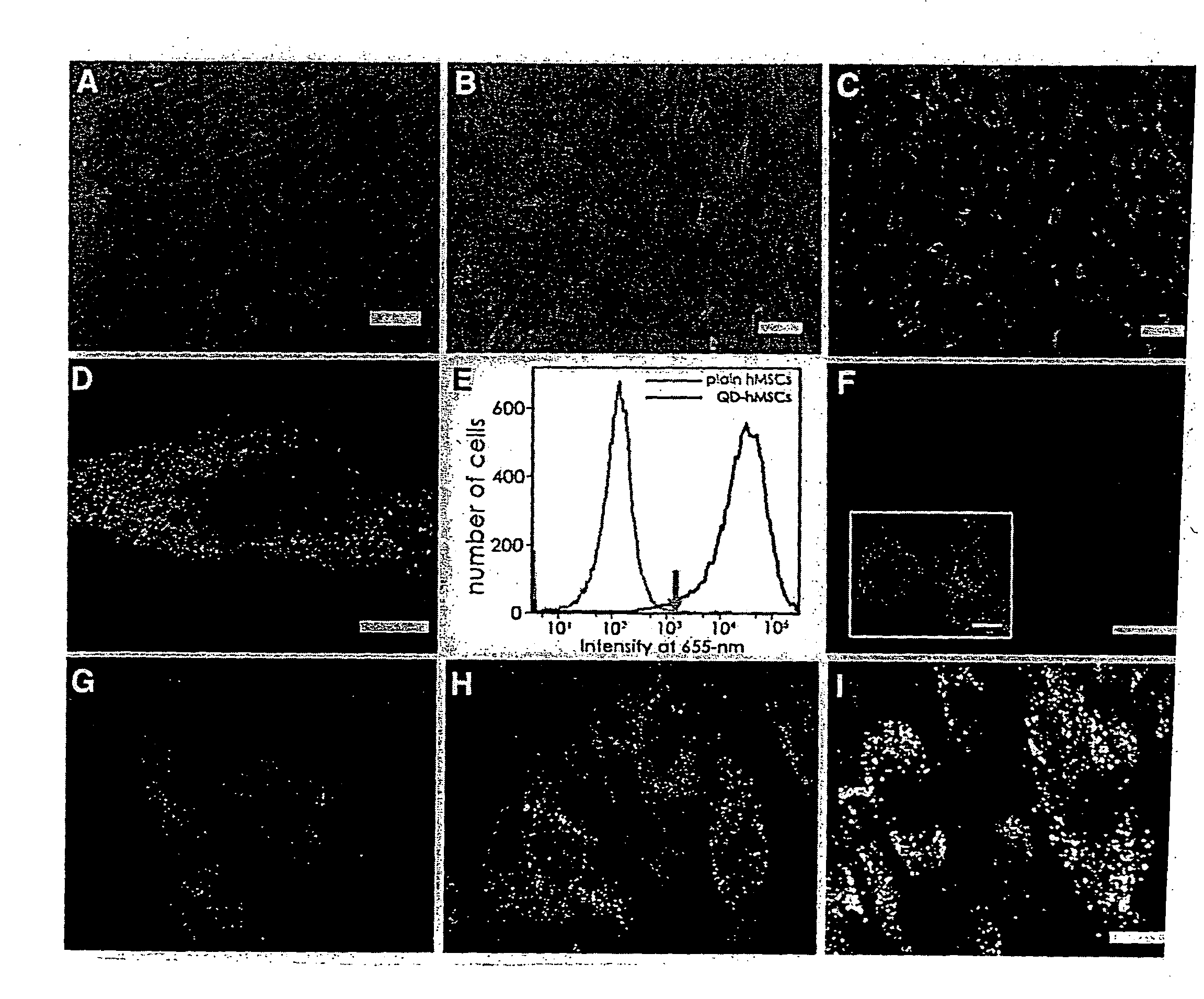
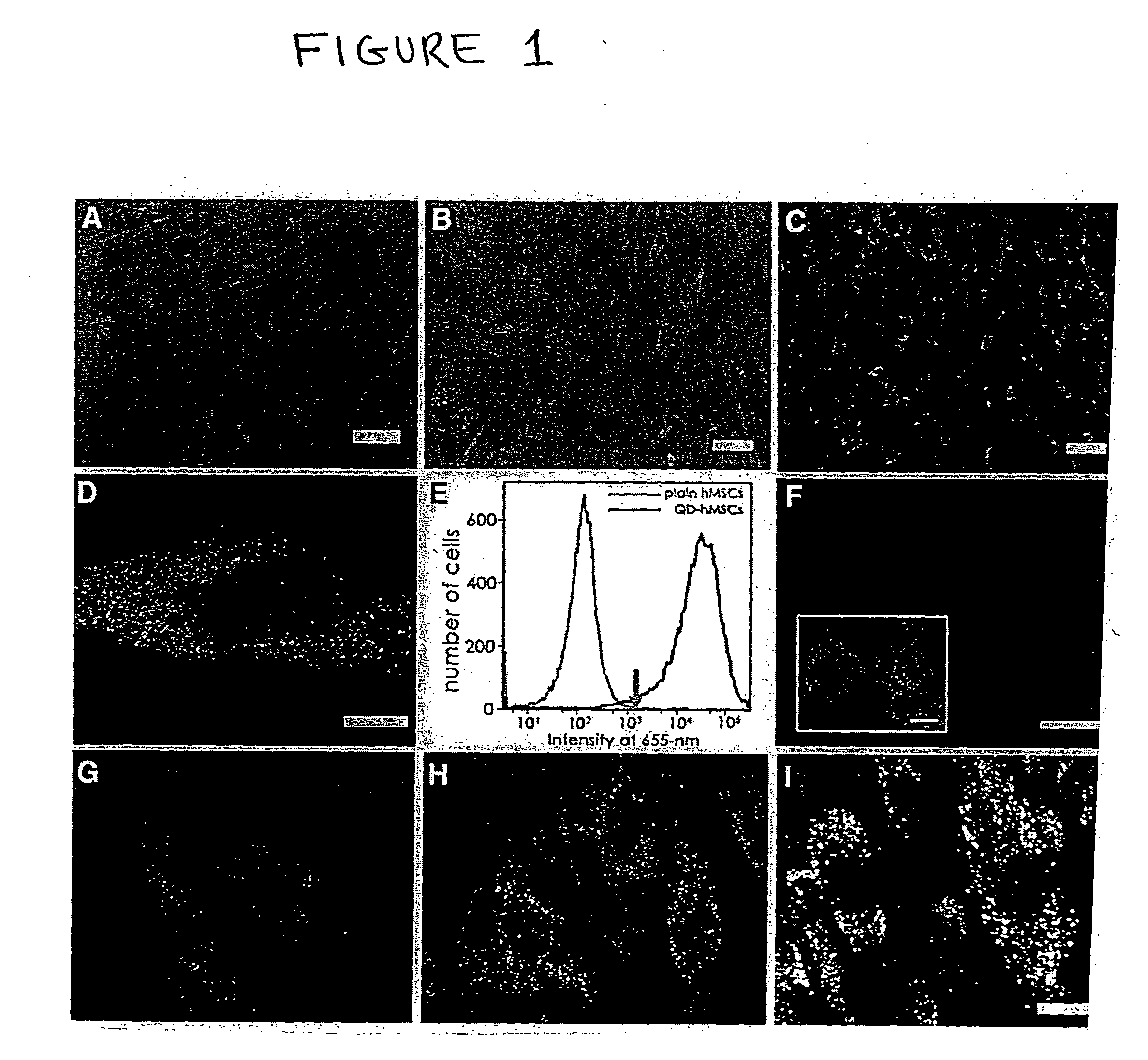
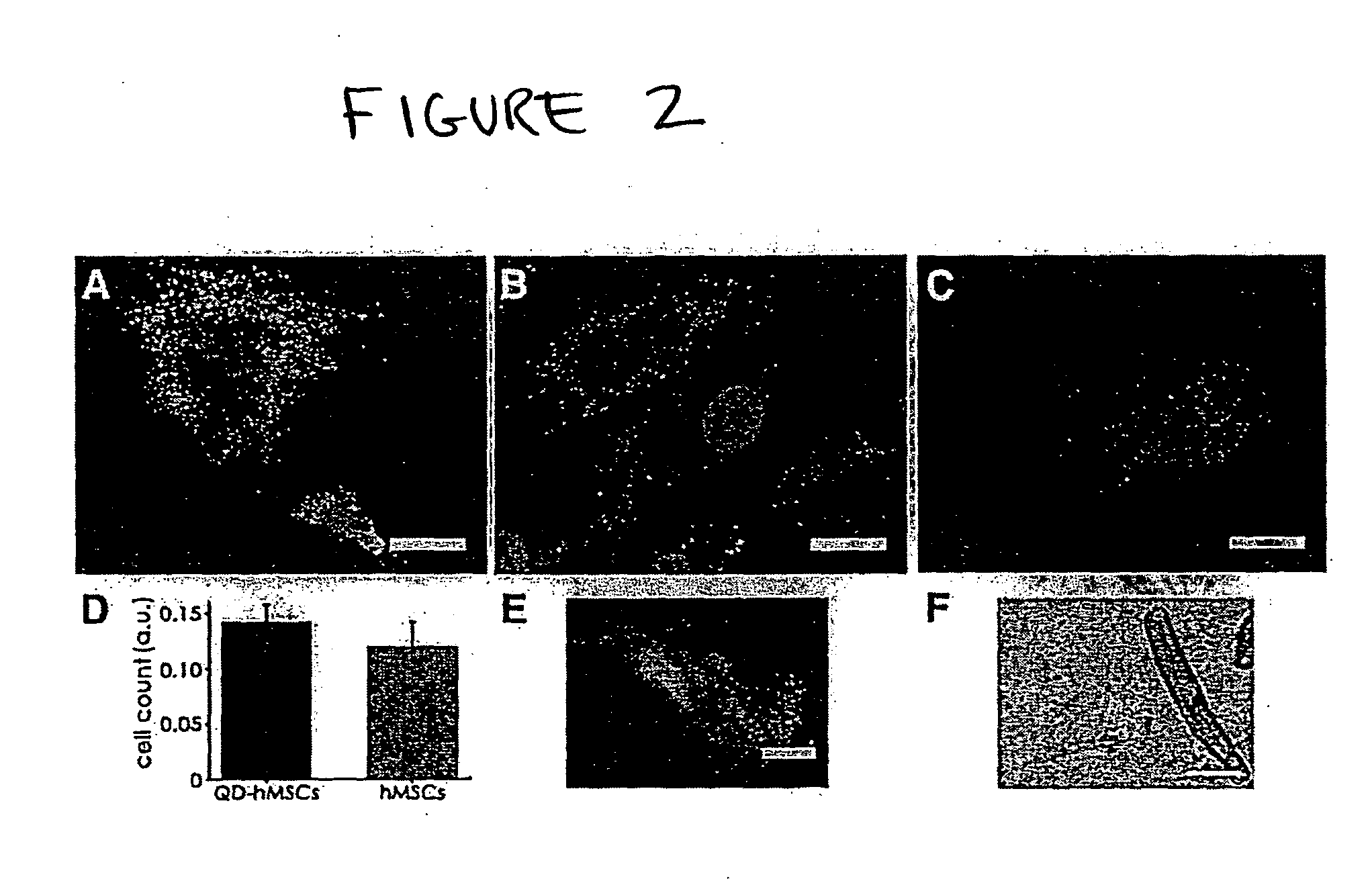
Quantum dot labeled stem cells for use in cardiac repair
InactiveUS20100158805A1Easy to useLack of cellular toxicityBiocidePowder deliveryCytosolFluorescence
The present invention provides methods and compositions relating to the labeling of target cells with quantum dots (QDs). Specifically, a delivery system is disclosed based on the use of negatively charged QDs for delivery of a tracking fluorescent signal into the cytosol of target cells via a passive endocytosis-mediated delivery process. In a specific embodiment of the invention the target cell is a stem cell, preferably a mesenchymal stem cell (MSC). Such labeled MSCs provide a means for tracking the distribution and fate of MSCs that have been administered to a subject to promote cardiac repair. The invention is based on the discovery that MSCs can be tracked in vitro for up to at least 6 weeks. Additionally, QDs delivered in vivo can be tracked for up to at least 8 weeks, thereby permitting for the first time, the complete 3-D reconstruction of the locations of all MSCs following administration into a host.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Exosome-encapsulated nano drug-loading system for tumor treatment and preparation thereof
ActiveCN108543074AIngestion behaviorExcellent killing effectOrganic active ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsExocytosisTumor targeting
The invention discloses an exosome-encapsulated nano drug-loading system for tumor treatment, and preparation thereof. The system is obtained by utilizing cell endocytosis of a drug-loading nanometermaterial and then exocytosis. The drug-loading nanometer material is loaded with an antitumor medicine including at least one of a chemotherapeutic, a medicine used for immunotherapy and a medicine used for modifying a tumor microenvironment. The composition, structure and the like of the key outer component biofilm encapsulating the nano drug-loading system are improved, and compared with the prior art, the exosome-encapsulated nano drug-loading system provides a novel route for biofilm-based biological processed nanoparticles. By utilization of the exosome-encapsulated nano drug-loading system, the composition and the structure of the exosome can be maintained greatly, and the obtained exosome-encapsulated nano drug-loading system has good stability and tumor targeting performance duringblood circulation. .
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for treating tumors using low strength electric fields
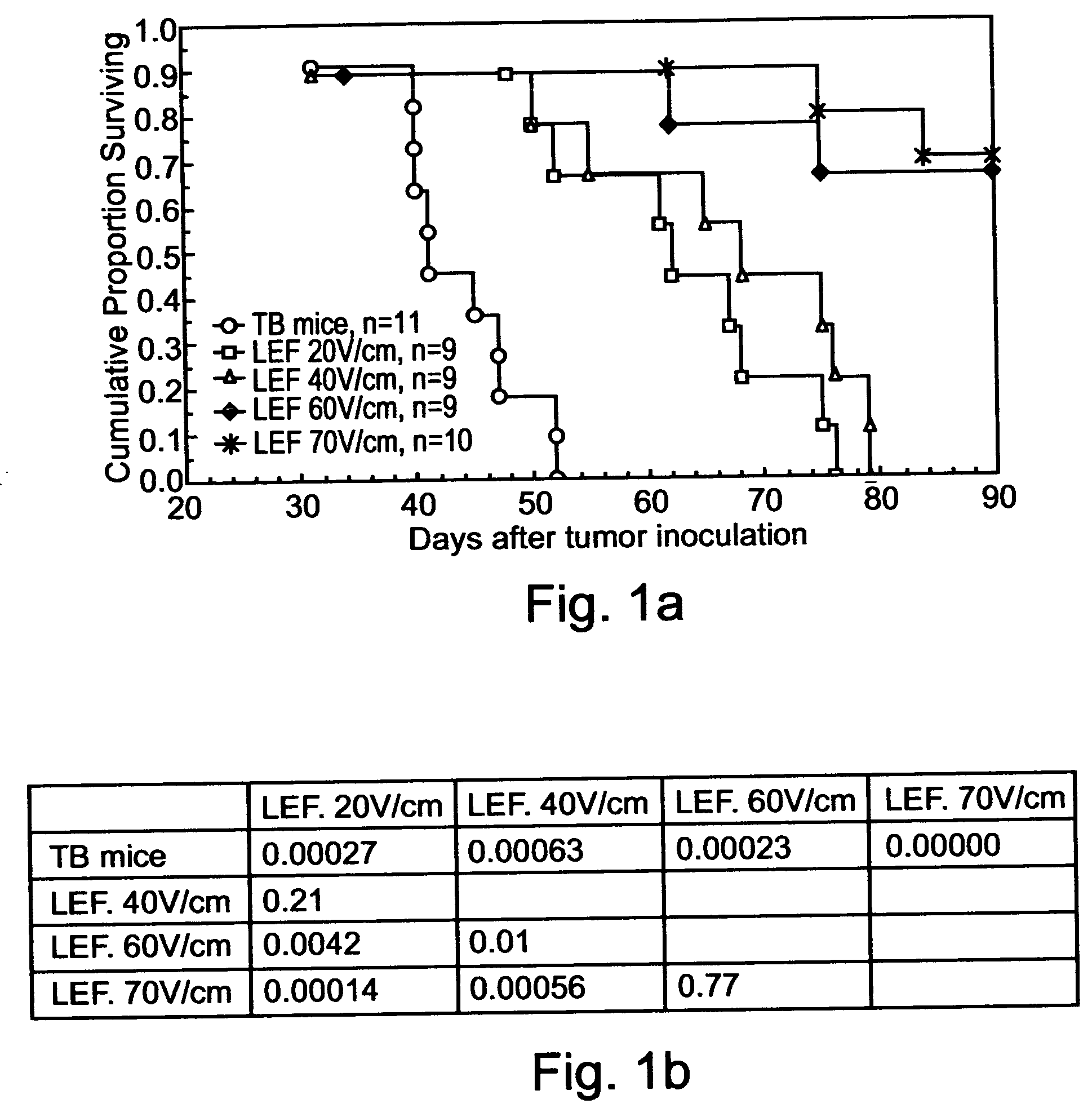
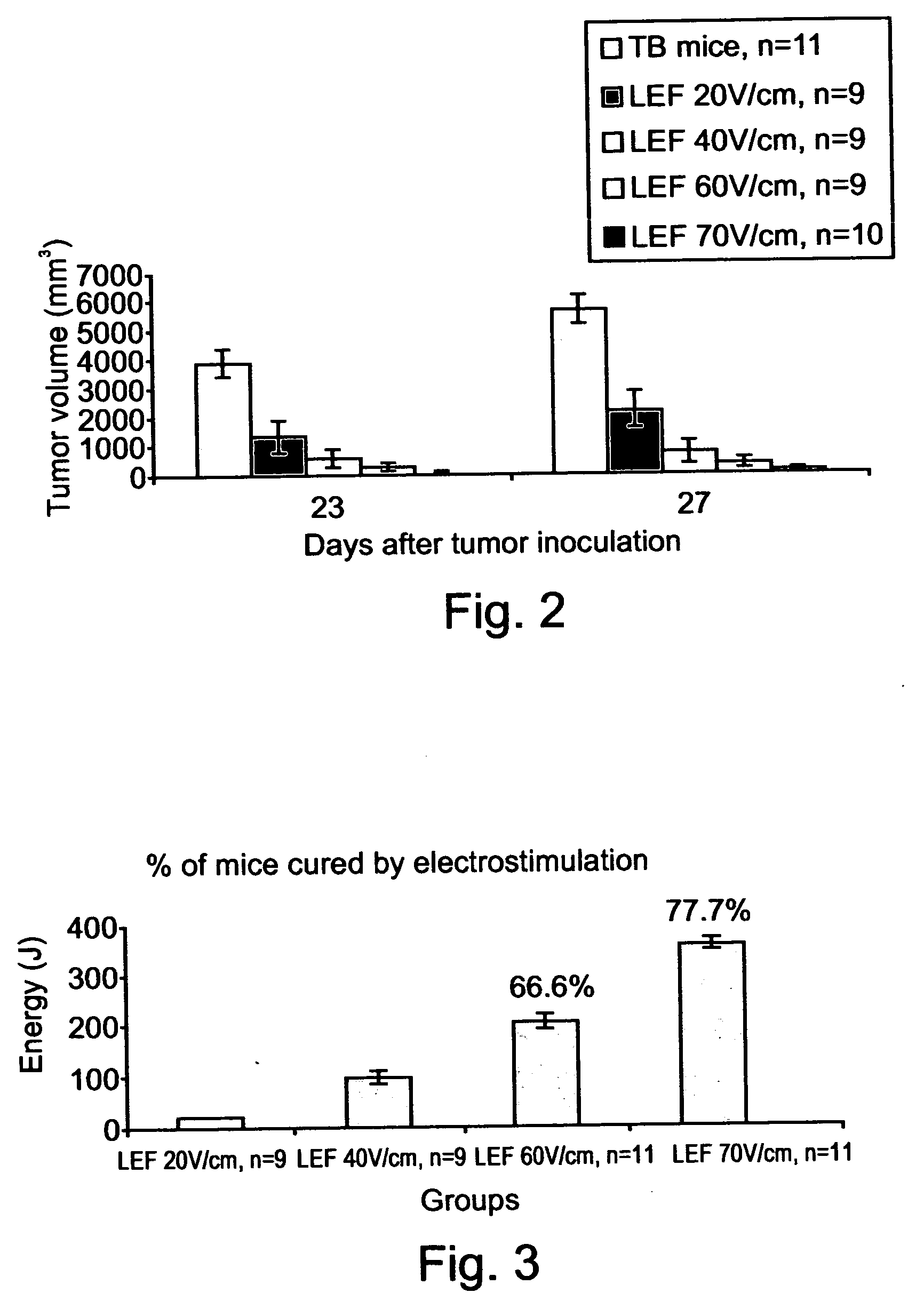
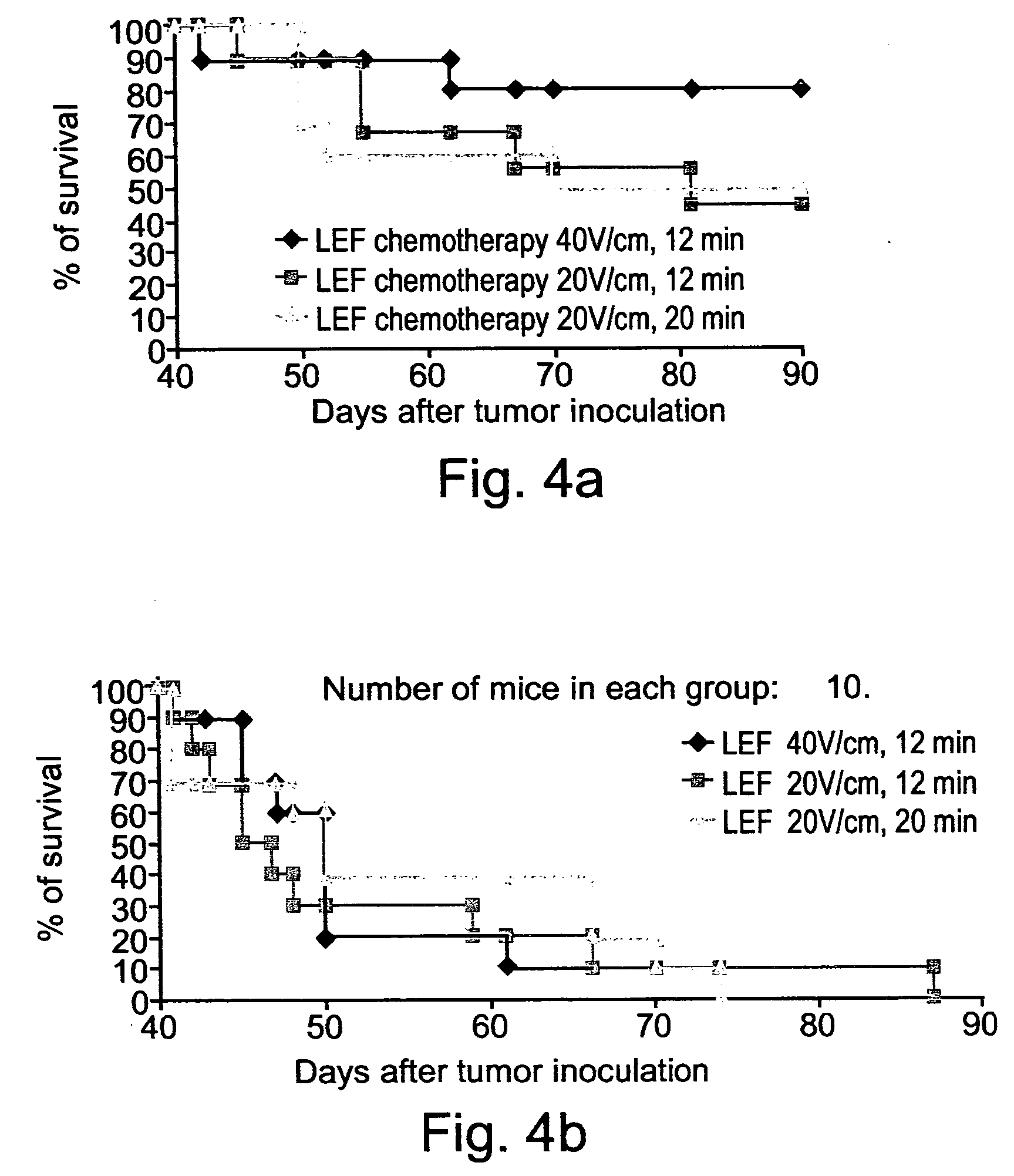
InactiveUS20040158288A1Effective treatment of cancerEffective immune responseHeavy metal active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsElectric field pulseOncology
A method of treating tumor tissue of an individual is provided. The method is effected by applying to cells of the tumor tissue electrical field pulses having a strength, a repetition frequency and a pulse width selected capable of inducing endocytosis mediated cell death thereby treating the tumor tissue.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Biodegradable cationic polymer
A biodegradable cationic polymer is disclosed. The biodegradable cationic polymer of the invention has amino groups in the backbone and side chains, self-assembles cationic complexes with nucleic acids, and delivers nucleic acids into a cell by endocytosis. The biodegradable cationic polymer of the invention also has very low cytotoxicity. Methods of making and using the biodegradable cationic polymer are further disclosed.
Owner:CHIA NAN UNIV PHARMACY & SCI
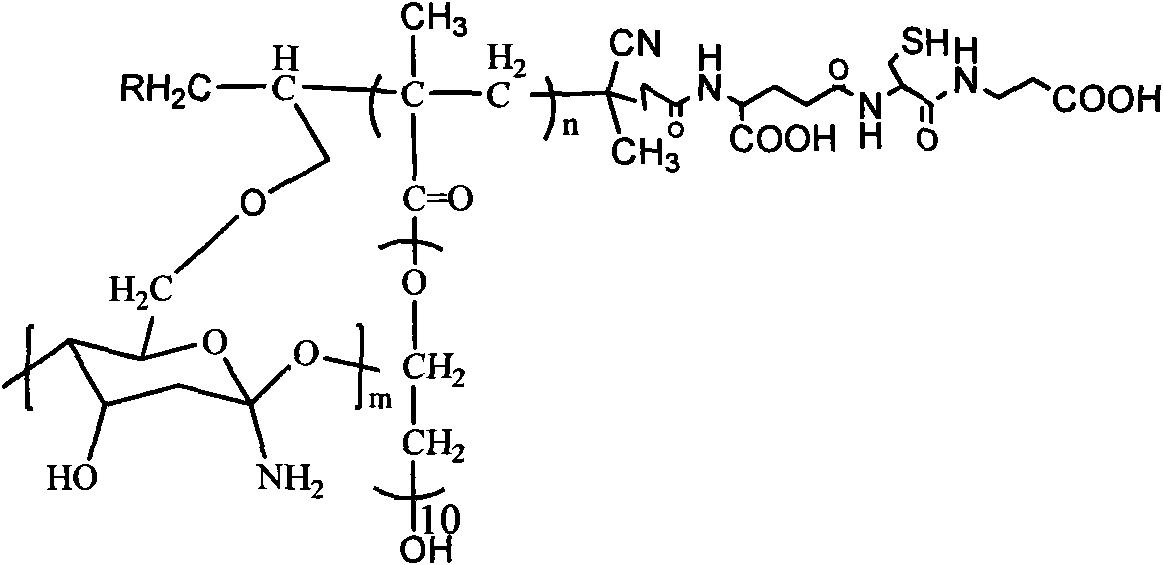
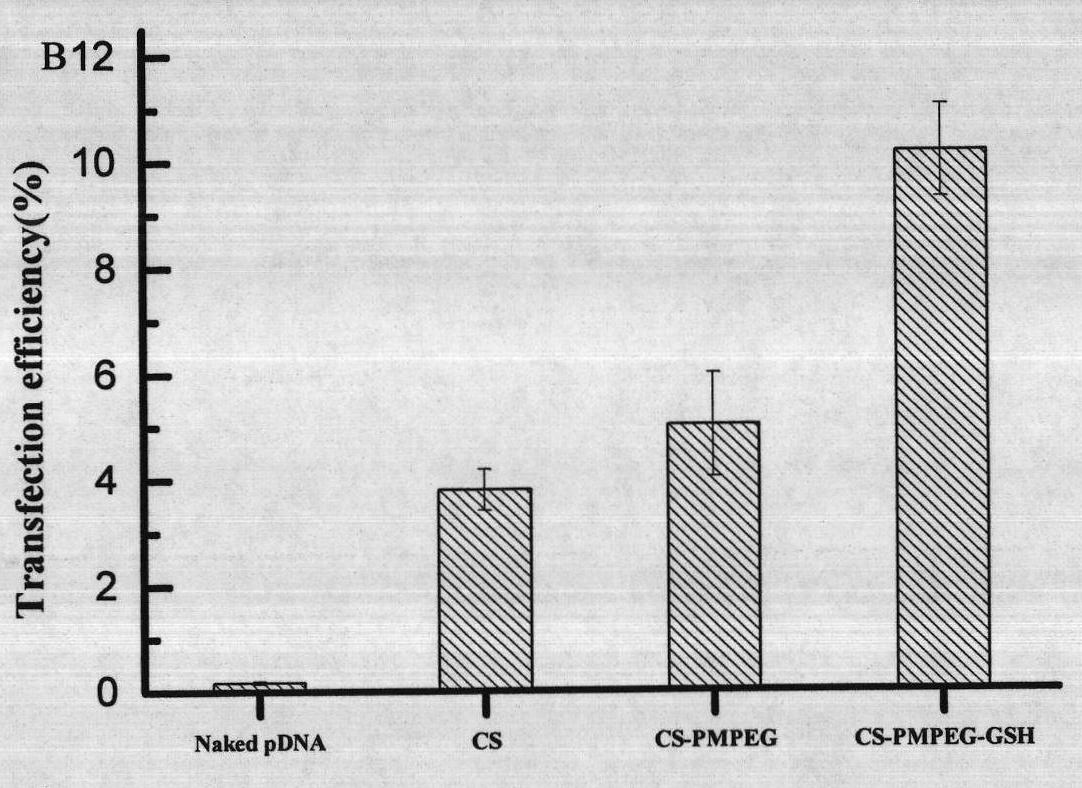
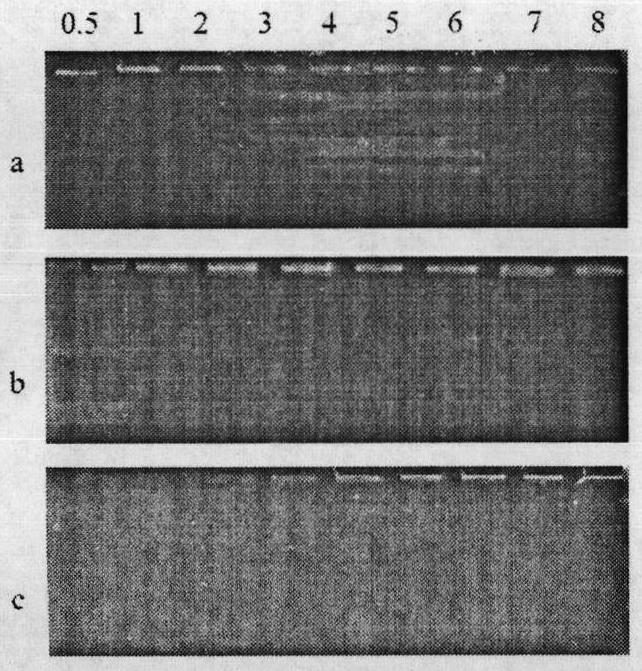
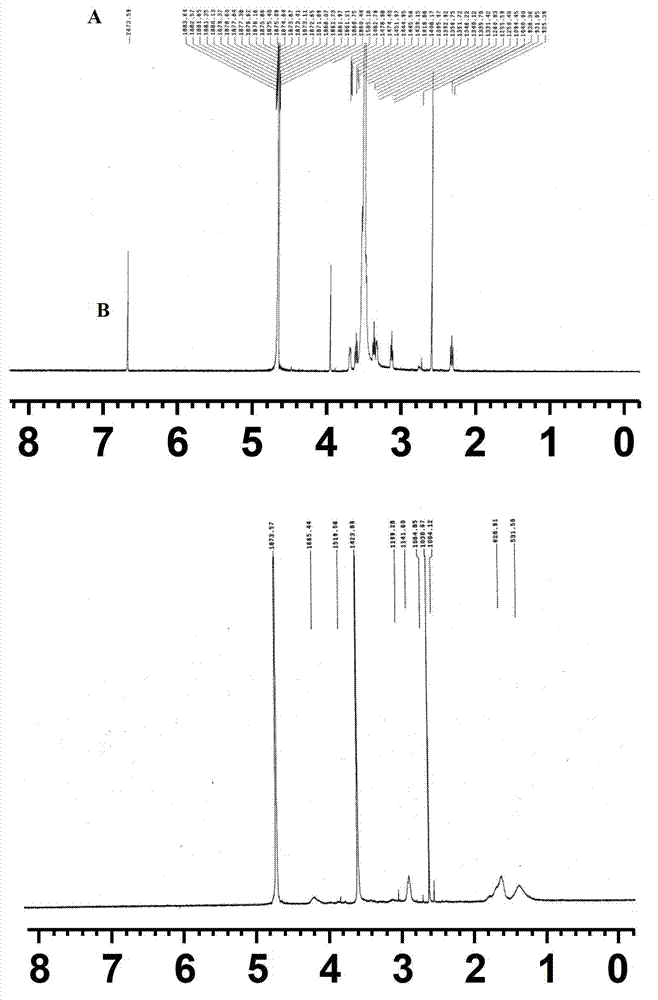
Glutathione-modified chitosan copolymer serving as non-viral gene carrier material and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN102140171AGood biocompatibilityReduce immune rejectionVector-based foreign material introductionActivation methodPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a glutathione-modified chitosan copolymer serving as a non-viral gene carrier material and preparation and application thereof, which belong to the fields of gene therapy and novel materials. A preparation method of the copolymer comprises the following steps of: (1) synthesizing an allyl-modified chitosan derivative; (2) synthesizing brush-like PEG (Polyethylene Glycol) polymer chains with different molecular weights through RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer); (3) grafting the brush-like PEG onto a chitosan framework by adopting a free radical coupling method; and (4) linking glutathione to the chain end of the brush-like PEG by adopting an EDC (1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethyllaminopropyl) Carbodiimide hydrochloride) / NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide) activation method to obtain a glutathione-modified chitosan copolymer carrier material. The glutathione-modified chitosan copolymer obtained by adopting the technology serves as the non-viral gene carrier material. By adopting the copolymer, the endocytosis function of a composite nanoparticle formed from the copolymer and DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) can be remarkably enhanced, the releasing mechanism of DNA from a composite particle after cell entrance is improved, and the non-viral gene carrier material with a high transfection efficiency is further obtained.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Slightly acidic environment targeted polypeptide modified tumor targeted nano drug delivery system, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103705465AIncrease intakeSmall toxicityPowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsDendrimerTumor target
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a slightly acidic environment targeted polypeptide modified tumor targeted nano drug delivery system, and a preparation method thereof. The slightly acidic environment targeted polypeptide modified tumor targeted nano drug delivery system is prepared via self-assembly of a slightly acidic environment targeted polypeptide modified dendrimer encapsulated gene, wherein the surface of the dendrimer is rich of amino groups. According to the preparation method, a polypeptide of transmembrane helix protein C derived from bacteria visual purple is used for modifying a high molecular carrier, enrichment and adhesion onto cells is realized via a pH sensitive cell membrane insertion method, and entering into cells is realized via electrostatic adsorption guided endocytosis, so that untaking of tumor cells on drugs is improved, and toxic and side effects are reduced. According to the tumor targeted nano drug delivery system, cell membrane is taken as the target point, and the polypeptide is taken as the target head group in tumor slightly acidic environment, targeting and curing efficiency are high, the preparation method is simple and convenient, and tumor cell drugs, which are derived from human or animal, and is used for targeted therapy, can be prepared.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Functional albumin and preparation method of nano preparation of functional albumin
ActiveCN105288647AThe synthesis method is simpleChange isoelectric point to basicPowder deliveryOvalbuminExocytosisDrug release
The invention discloses functional albumin and a preparation method of a nano preparation of the functional albumin. The nano preparation of the functional albumin consists of the functional albumin, metal ions and a drug; the metal ions can simultaneously form coordination bonds with the functional albumin and the drug, and can form nanoparticles through induced self-assembly. The nano preparation, through an endocytosis mediated by an albumin receptor (SPARC) on the surface of tumor cells, can deliver the drug into the drug-resistant tumor cells, so as to effectively avoid the exocytosis effect of a p-gp pump on the drug, and then as the coordination bonds break in an acid tumor cell environment through a pH responsibility, the drug releases in cytoplast, enters cell nucleus and inlays in DNA so as to inhibit the synthesis of nucleic acid; and therefore, the growth of the tumor cells is inhibited. Through in vitro characterization, the nano preparation can achieve the relatively good pH responsibility; and through activity evaluation on a cellular level, the system is capable of effectively delivering the drug into the cells, so as to achieve relatively good pH responsive release.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
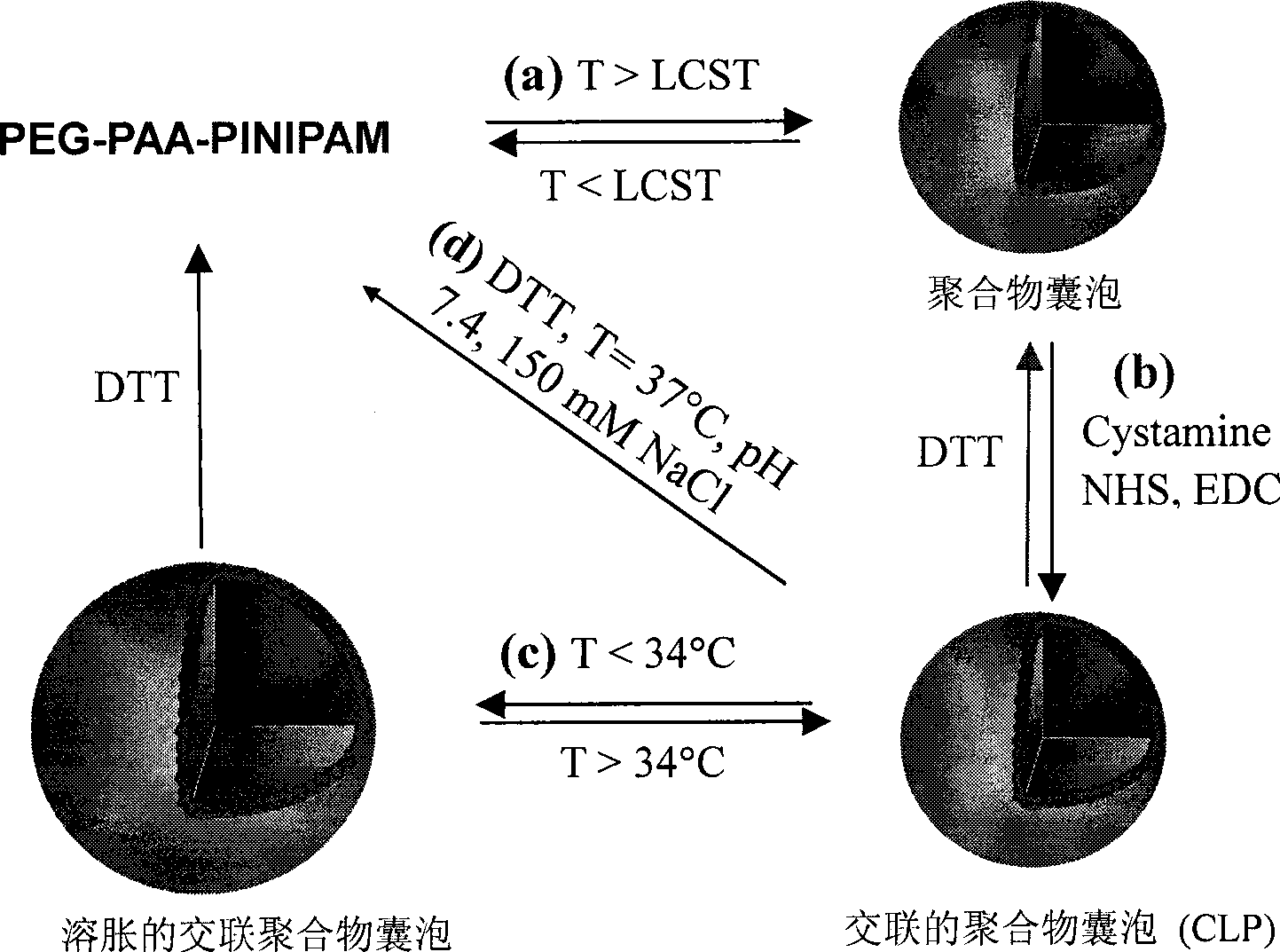
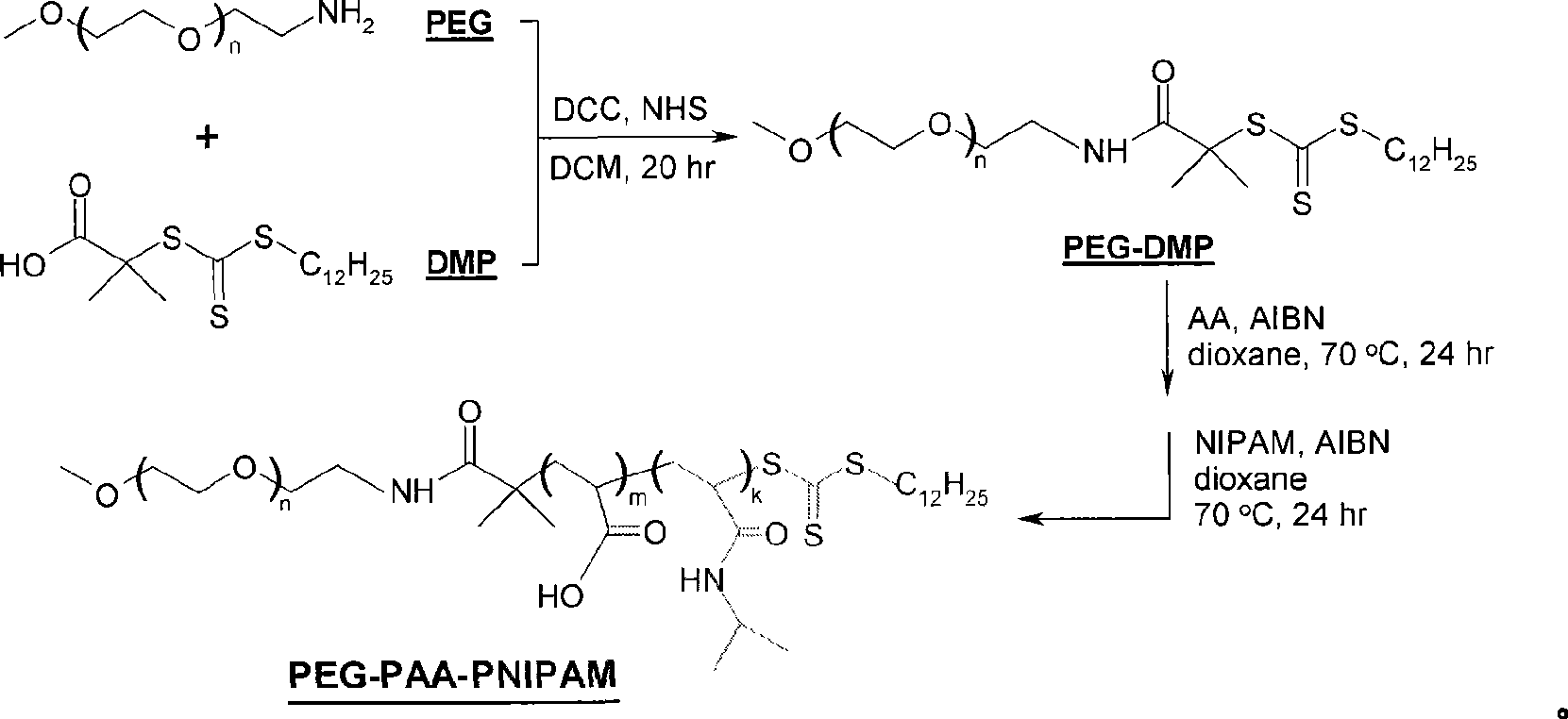
Interface-cross-linked temperature-sensitive polymer vesicle and use thereof
InactiveCN101519495AConvenient and Efficient PackingOvercome efficiencyPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCross-linkIn vivo
The invention discloses an interface-cross-linked temperature-sensitive polymer vesicle and a method for preparing the same. The interface-cross-linked temperature-sensitive polymer vesicle is formed by a block copolymer which at least comprises a hydrophilic block, a cross-lined interstrand block and a temperature sensitive block, wherein the hydrophilic block forms the membrane shell of the polymer vesicle, the temperature sensitive block forms the membrane nuclear of the polymer vesicle, and the cross-lined interstrand block forms the interface of the polymer vesicle to cross-link the interface of the polymer vesicle to stabilize the structure of the vesicle, and thus the interface-cross-linked temperature-sensitive polymer vesicle is formed; as the vesicle is formed in an aqueous solution system and the interface of vesicle is cross-linked, the small molecule drug, macromolecular drug and probe molecule entrapment efficiency of the polymer vesicle, the circulation stability in vivo blood and the efficiency of endocytosis by tumor cells are improved; and as a result, the bioavailability of drugs is improved and the polymer vesicle can be expelled out of the body conveniently.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
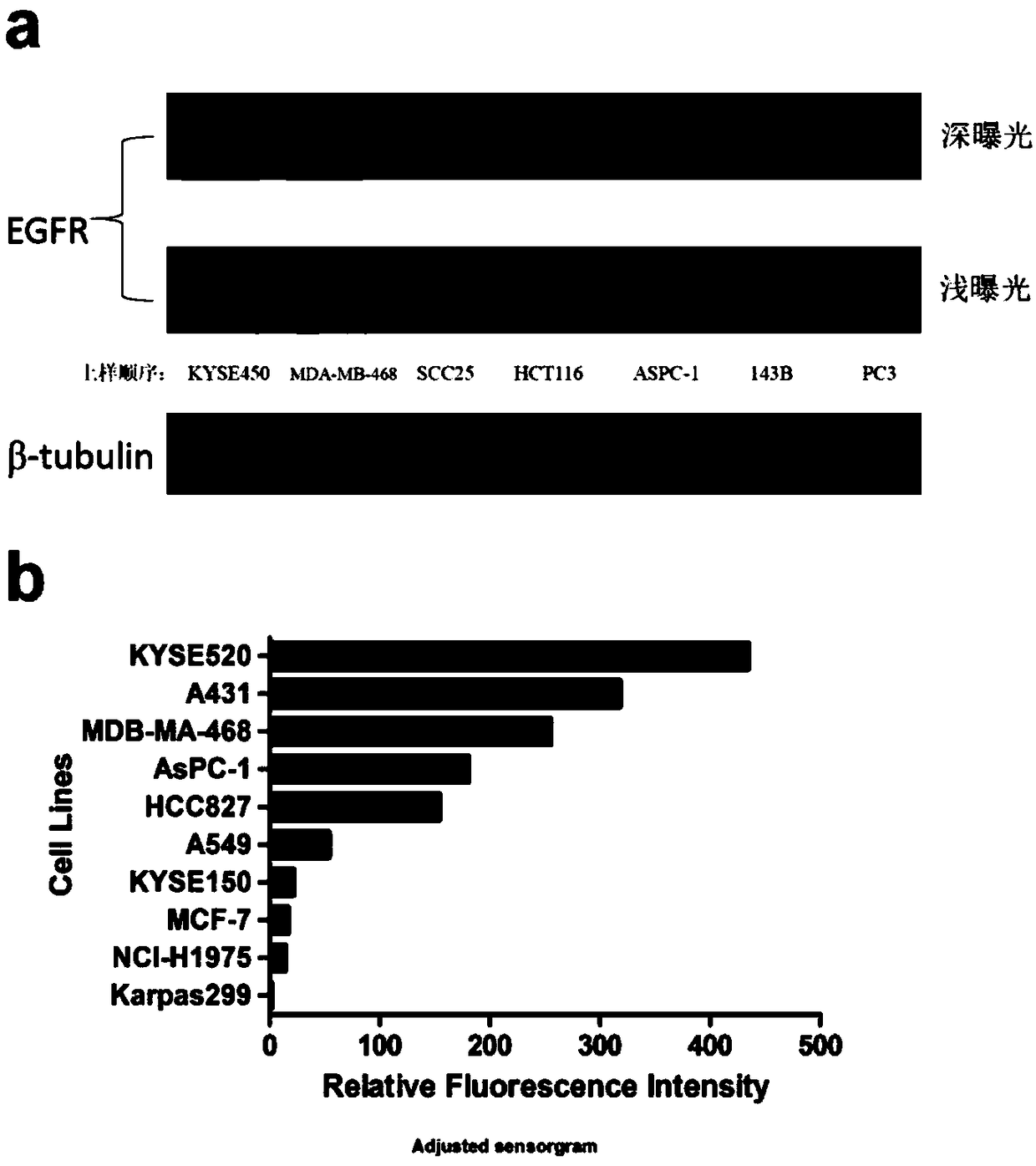
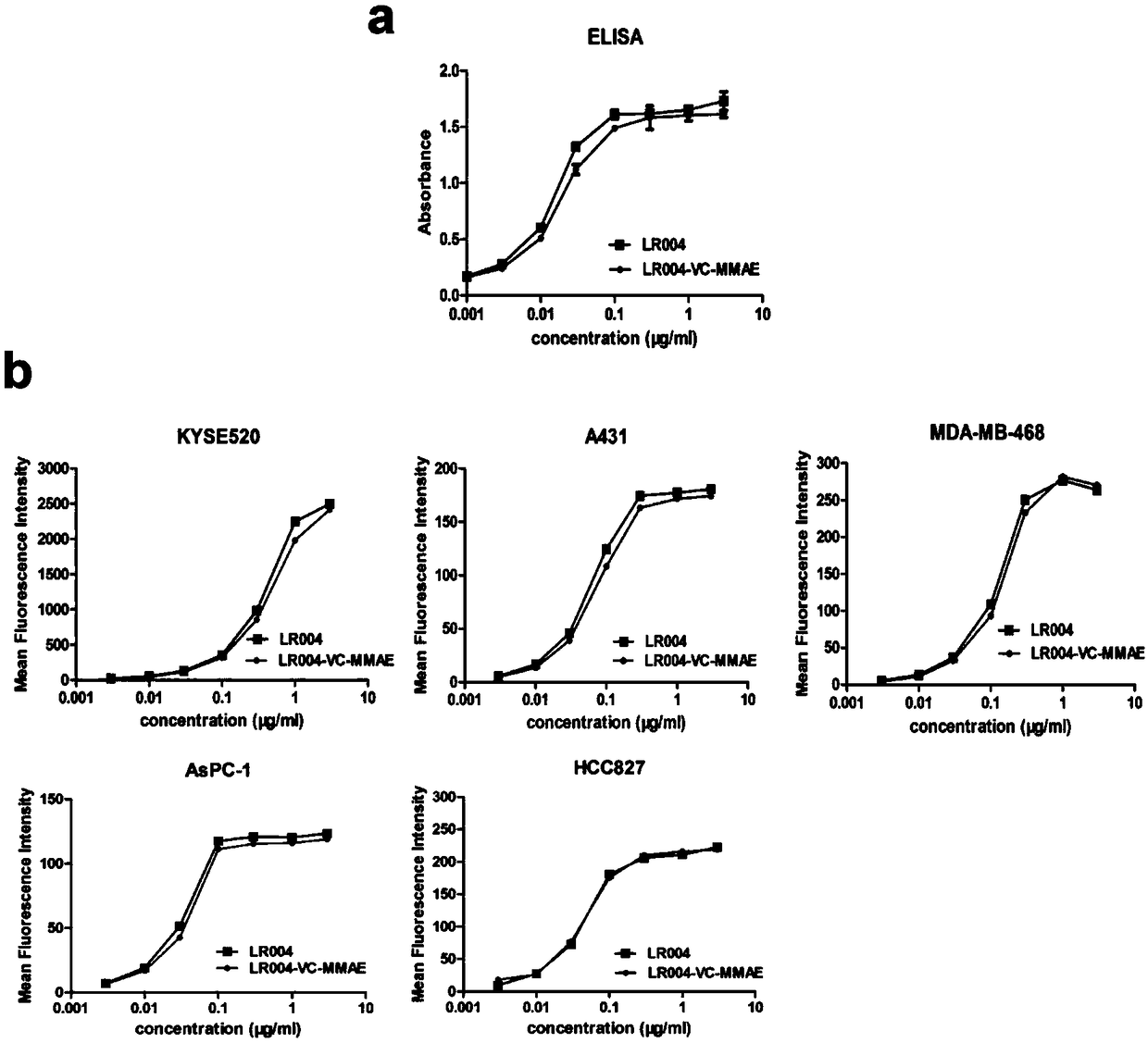
An antibody-coupled drug targeting on EGFR, a preparation method thereof, and uses thereof
ActiveCN109200291ADid not affect stabilityStable and controllable qualityTetrapeptide ingredientsAntibody ingredientsHalf-lifeAntibody conjugate
The invention discloses an antibody coupling drug targeting on EGFR, a preparation method thereof and uses thereof. The antibody-conjugated drug targeting EGFR is named LR004-VC-MMAE consisting of anantibody, a cytotoxic drug and a linker, wherein the antibody drug conjugate has a structure represented by the formula I, wherein mAb is an LR004 monoclonal antibody, n=2-8. The novel antibody-conjugated drug LR004-VC-MMAE can not only target EGFR antigen, but also has strong cytotoxicity to tumor cells. Compared with LR004 itself, it did not affect the affinity, endocytosis and targeting of theantibody, and better retained its biological function. Compared to LR004, the antitumor effect of LR004-VC-MMAE antibody-conjugated drug is significantly improved, and the tumor disappeared. Comparedto LR004, LR004-VC-MMAE antibody-conjugated total antibody showed longer half-life, slower clearance rate, lower concentration of free MMAE in plasma, shorter half-life and faster clearance rate, which is conducive to reduce toxicity.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Acid sensitive polymer prodrug, nanoparticles of prodrug and application of nanoparticles
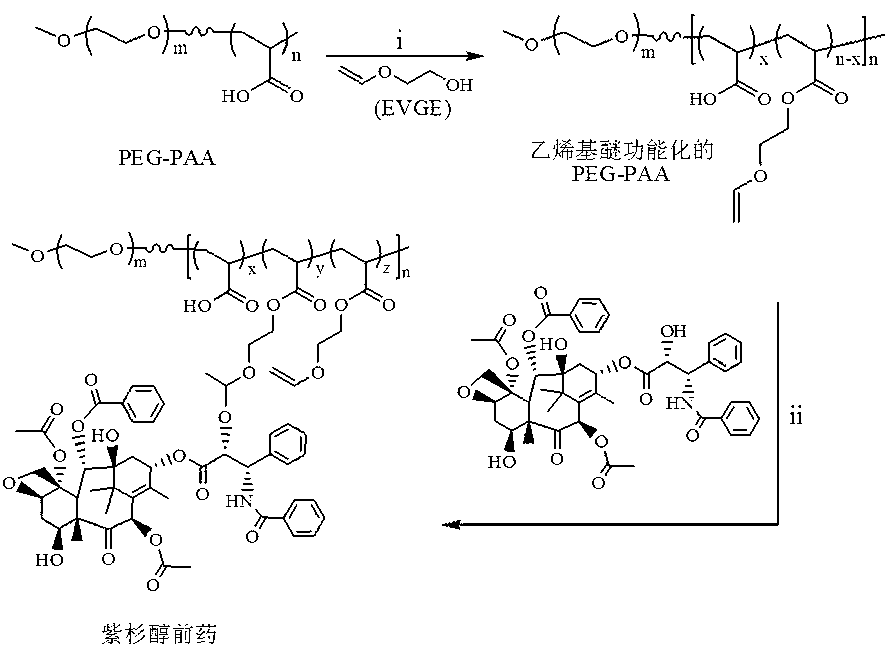
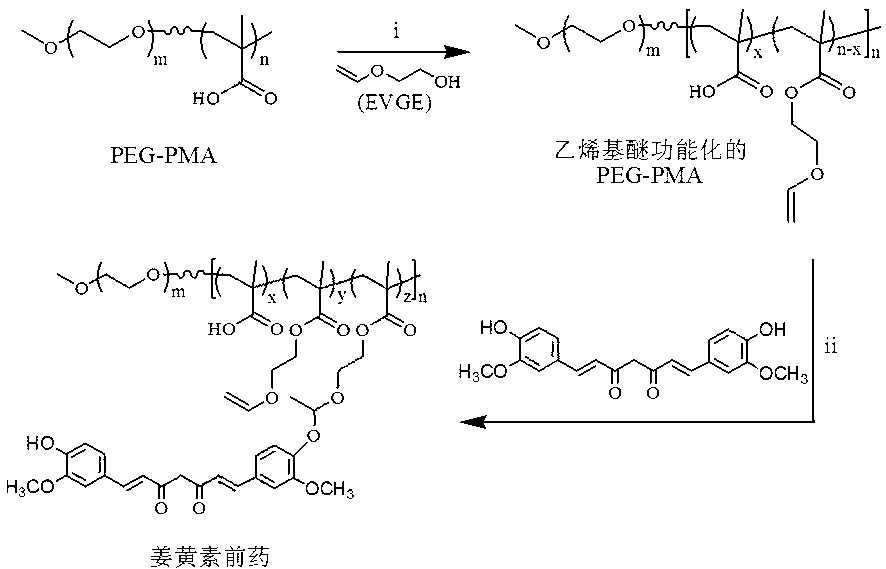
ActiveCN103285400APowerful killingBeneficial for combination therapyPowder deliveryKetone active ingredientsVinyl etherCancer cell
The invention discloses an acid sensitive polymer prodrug, nanoparticles of the prodrug and application of the nanoparticles. In the acid sensitive polymer prodrug, a polymer precursor is a vinyl ether-functionalized water-soluble A-B type two-block polymer; drug molecules are linked with the A-B type two-block polymer through an acetal bond; the acid sensitive polymer prodrug is self-assembled in water solution to form predrug micellar nanoparticles in which a polyethylene glycol hydrophilic chain segment serves as an outer surface and an anti-cancer drug bound to a polymer main chain through the acetal bond serves as a hydrophobic core. The pH sensitive prodrug and the nanoparticles of he prodrug are simple in preparation method, and good in tumor inhibitory effect; the nanoparticles also can efficiently encapsulate another hydrophobic anticancer drug; the kill capability to the cancer cell is enhanced; and the efficiency of endocytosis of the cell to the nanoparticles can be enhanced by coupling specific target molecules onto the surfaces of the nanoparticles. Thus, the inhibitory effect on the tumor cell is enhanced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Antibody-rnase-conjugate
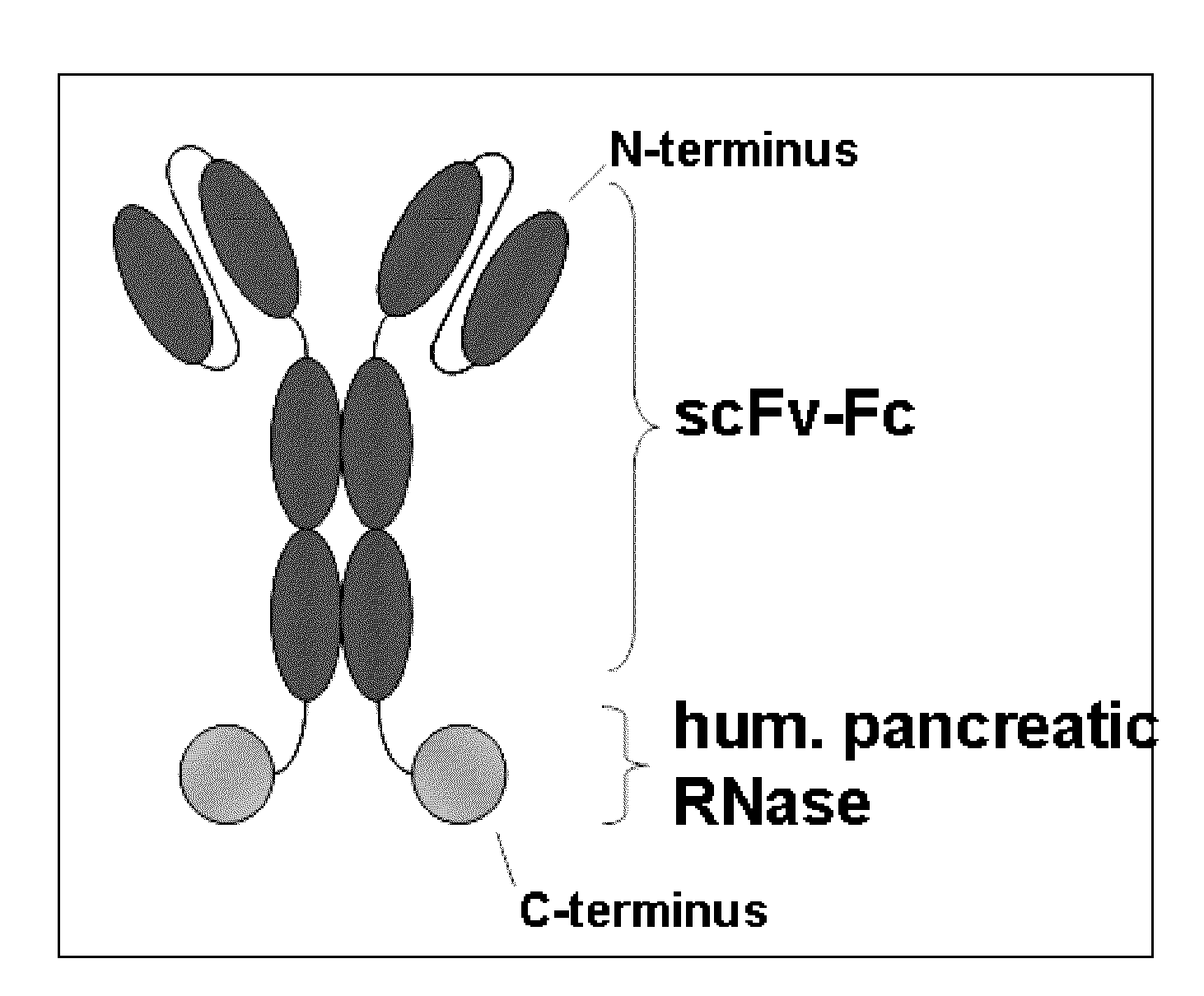
InactiveUS20100015661A1Strong specificityHigh cytotoxic activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesCytotoxicityConjugated protein
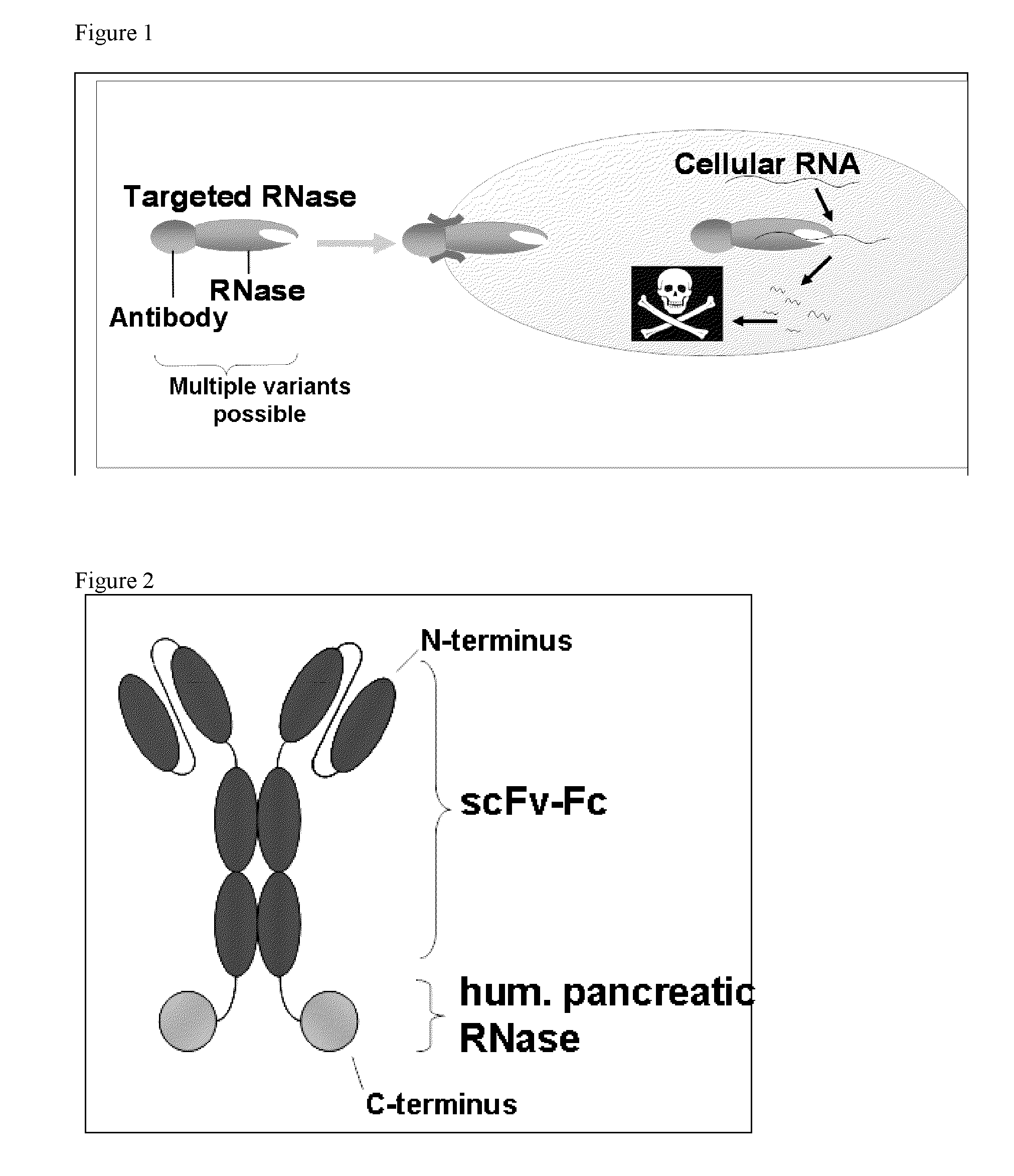
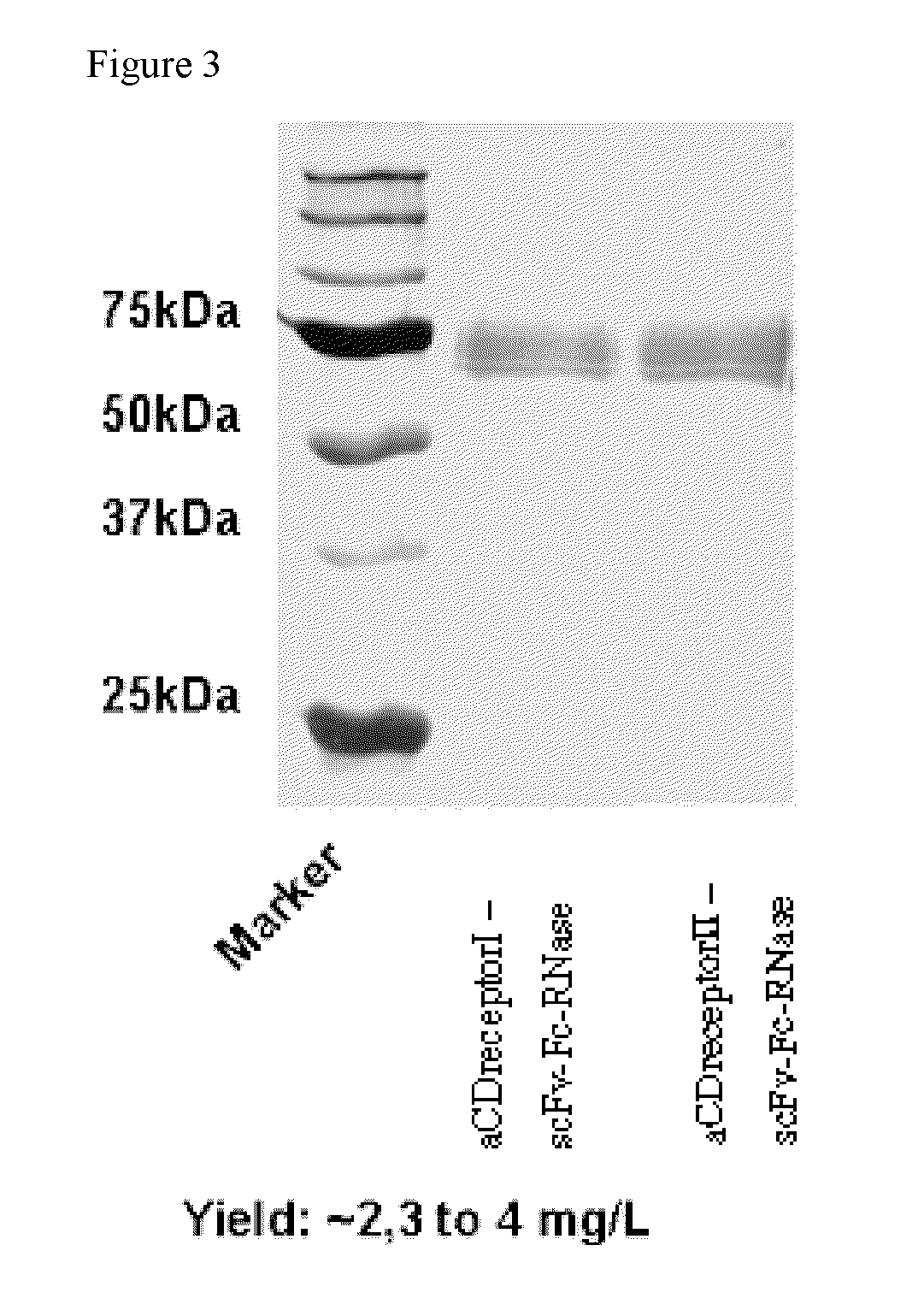
The present invention provides a novel antibody-RNase conjugate which is a single chain protein, providing both the specificity of its antibody portion and the RNase activity of its RNase portion, resulting in an antigen specific effectiveness against cells when applied in vivo or in vitro, wherein the RNase portion is effectively cytotoxic in at least a fraction of cells presenting the antigen, e.g. after internalization by endocytosis. In detail, the present invention provides scAb-RNase conjugate having the principal structure of scFvFc-RNase. This structure could also be shown to allow the effective production of antigen-specific and cytotoxic conjugate protein in cell culture, the conjugate having a high activity with respect to antigen specificity and cyto toxicity.
Owner:MAB FACTORY
C3N4 nanocomposite, preparation method and application of C3N4 nanocomposite
InactiveCN105535972AEffective and rapid conversionIt has the effect of photodynamic therapy on tumorPhotodynamic therapyInorganic non-active ingredientsCancer cellSinglet oxygen
The invention provides a C3N4 nanocomposite, a preparation method and application. The C3N4 nanocomposite takes a C3N4 two dimensional nanosheet loading a transition metal element as a carrier, and a photosensitizer is loaded on the carrier. Compared with the prior art, the C3N4 two dimensional nanosheet loading the transition metal element is taken as the carrier, the photosensitizer is loaded on the carrier, the C3N4 nanocomposite can enter a cancer cell by effective endocytosis of the cell, the transition metal element can perform catalytic decomposition on hydrogen peroxide in the cancer cell to generate oxygen, under the irradiation of laser, the photosensitizer can effectively and quickly convert oxygen molecules into singlet oxygen, and thus generates toxicity to the cancer cell and kills the cancer cell, and accordingly an effect of treating tumor by photodynamics is achieved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Organic near-infrared two-photon fluorescent dye
InactiveCN103122154AAchieve markupGood water solubilityMethine/polymethine dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementSolubilityLysosome
The invention belongs to the field of chemistry and relates to an organic near-infrared two-photon fluorescent dye with a structure in a formula I in the specification. The organic near-infrared two-photon fluorescent dye has the beneficial effects that after being excited, the organic near-infrared two-photon fluorescent dye simultaneously shows stronger luminous efficiency of single-photon near-infrared fluorescence and two-photon fluorescence; the efficiency of two-photon fluorescence is obviously improved compared with that of other carbocyanine dyes; living cell fluorescence microscope experiments show that probes prepared from the fluorescent dye can enter tumor cell lysosome through endocytosis and can be imaged and simultaneously monitored by single-photon fluorescence and two-photon fluorescence microscopes; the dye can achieve synchronous single-photon near-infrared fluorescence and two-photon fluorescence imaging in the in-vivo and in-vitro states; and the fluorescent dye has the characteristics o good water solubility and stable chemical properties, can be used or bio-macromolecular markers and in the field of medical image diagnosis and especially has strong application value in optical image guided tumor excision.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com