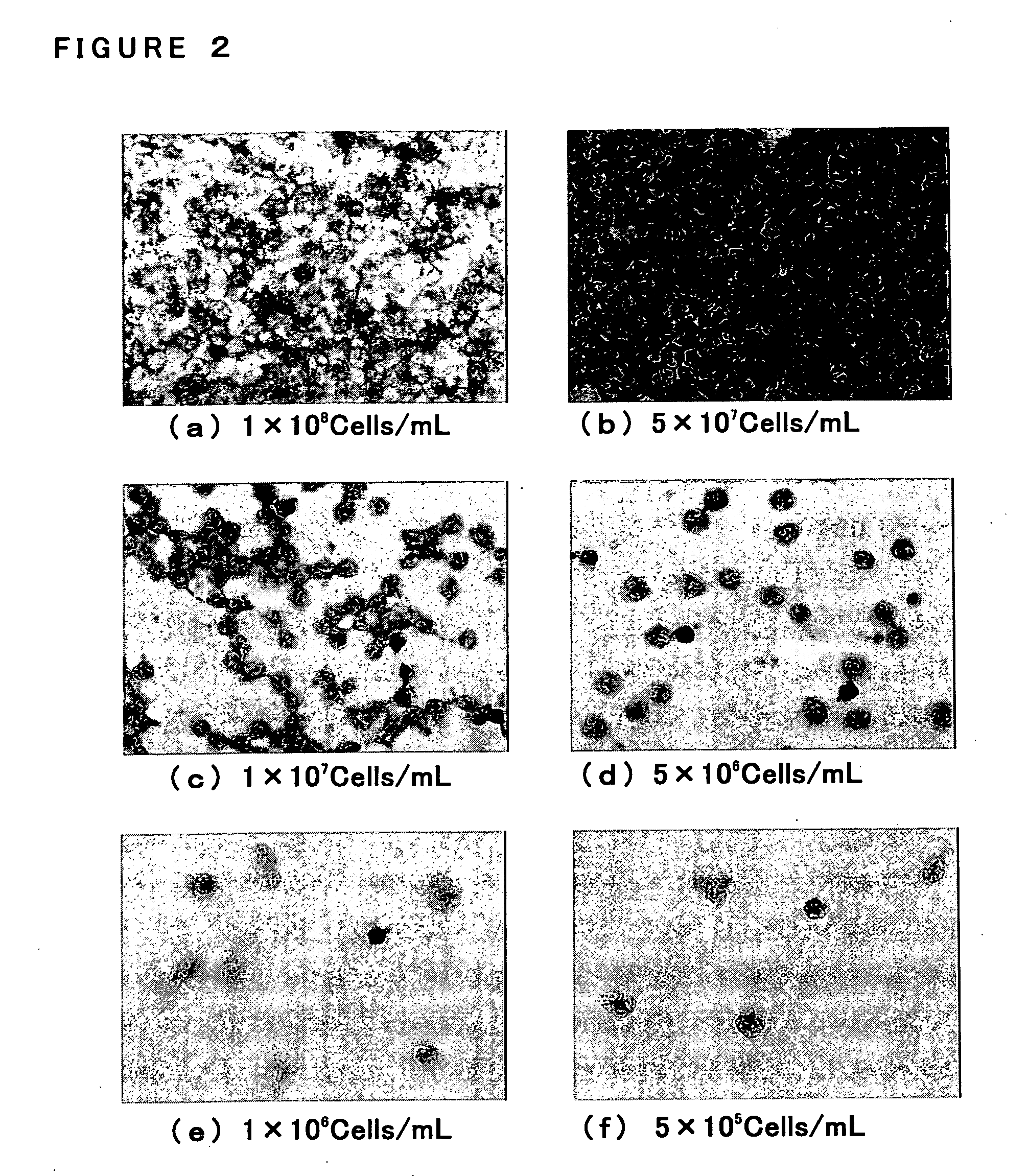
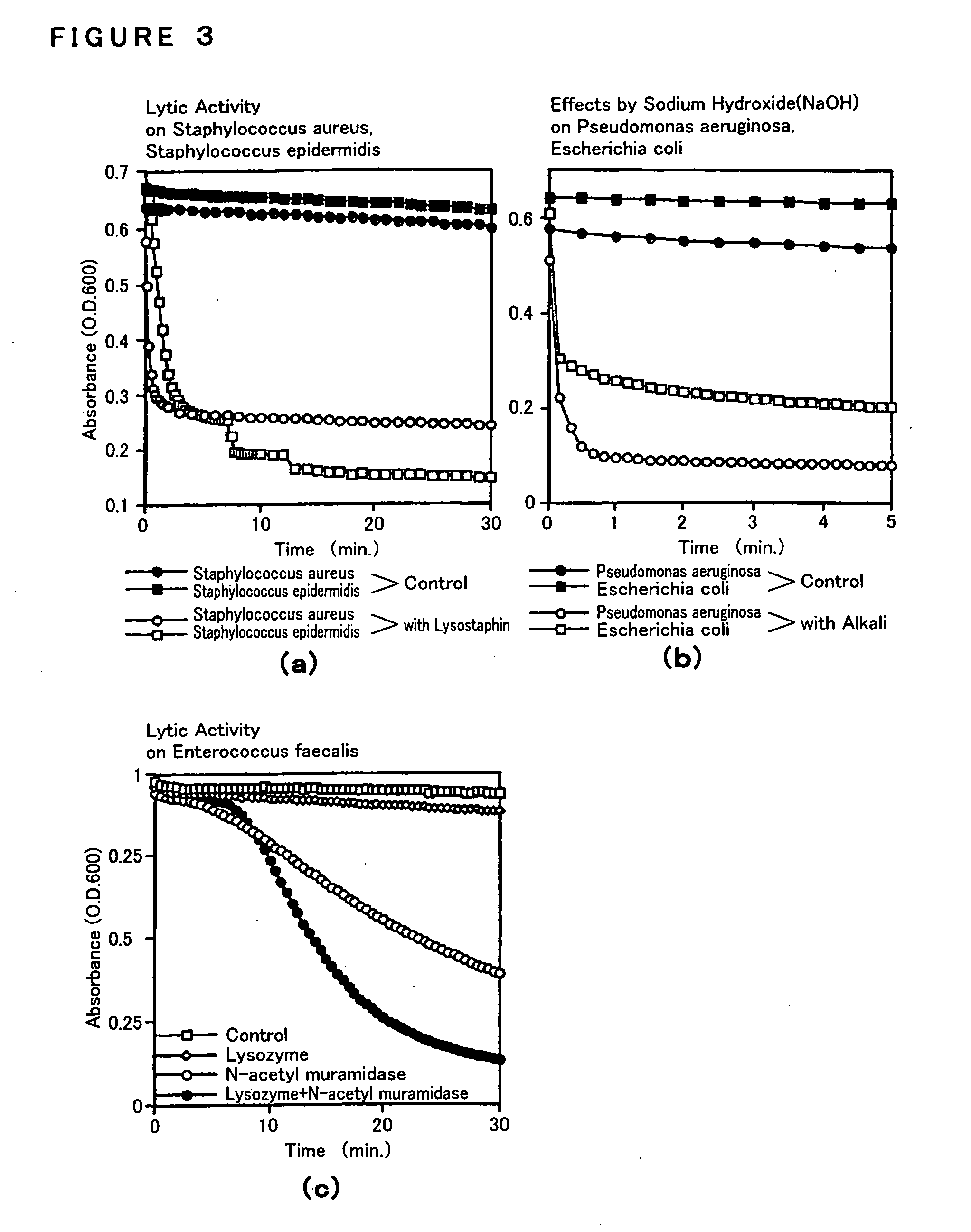
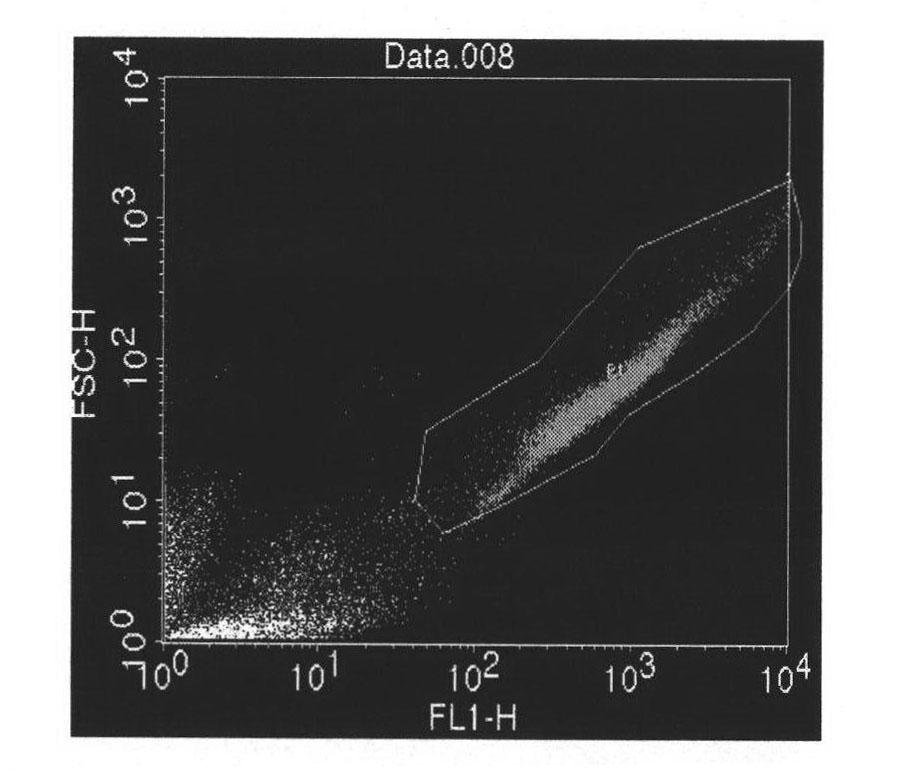
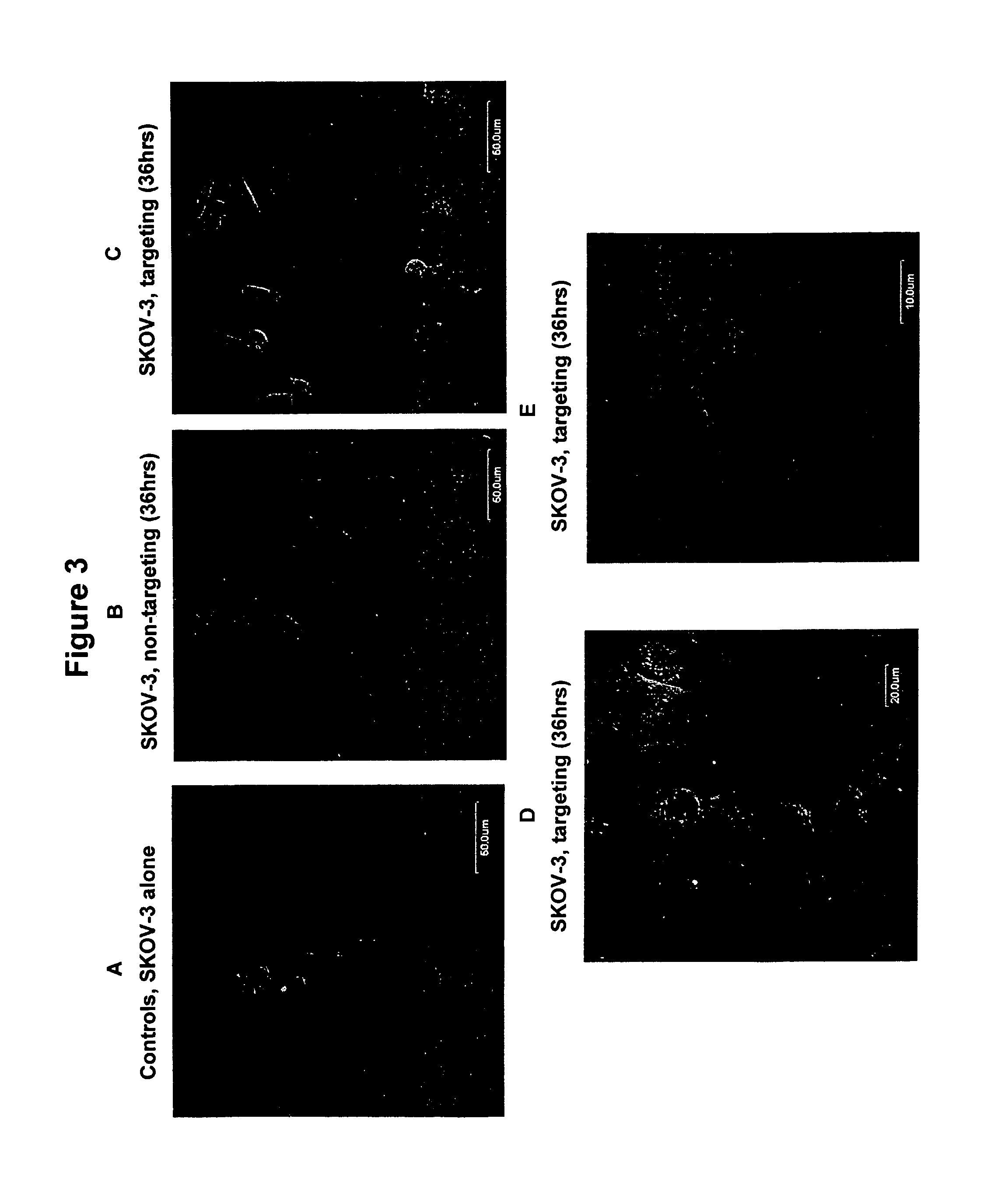
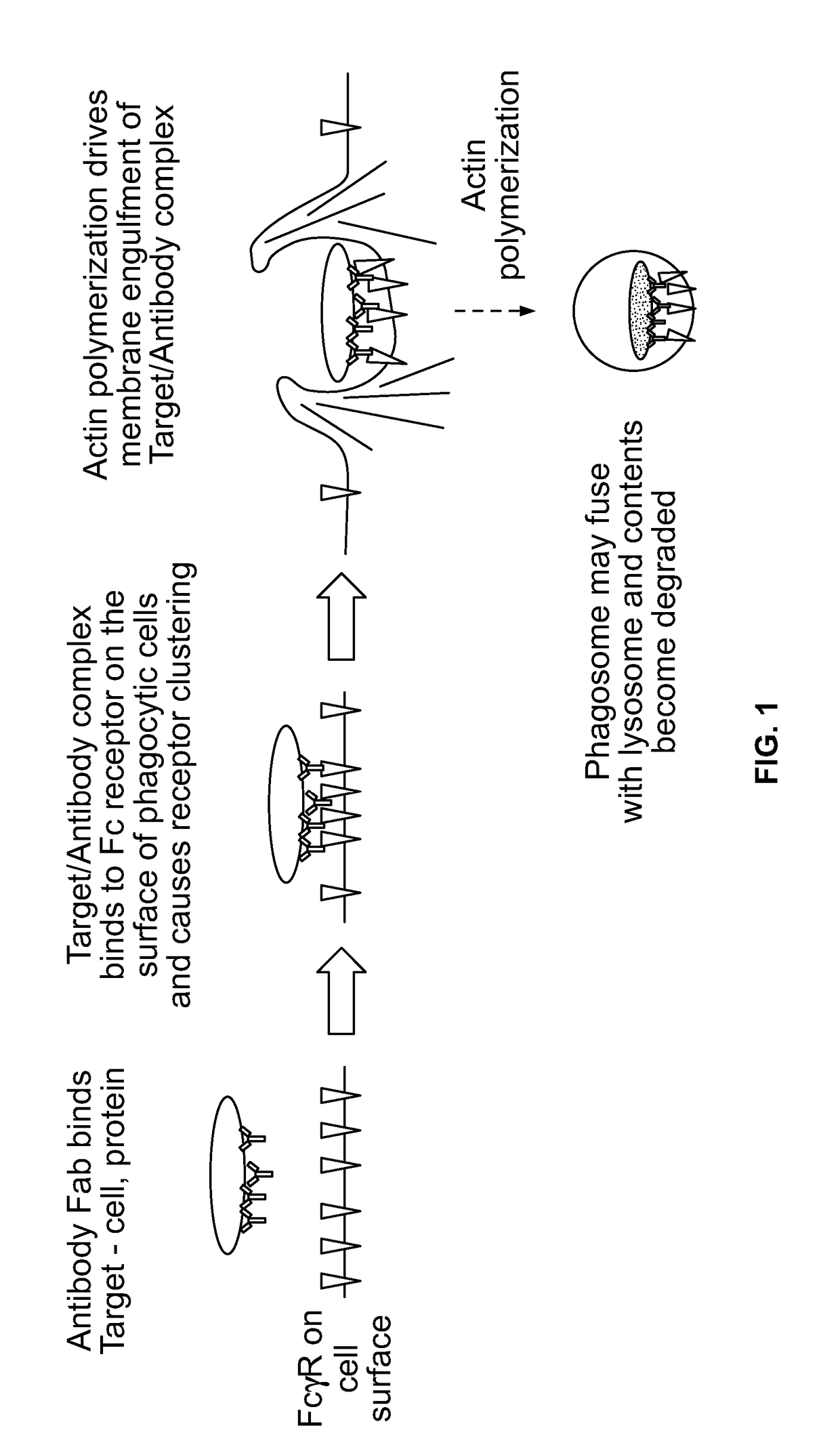
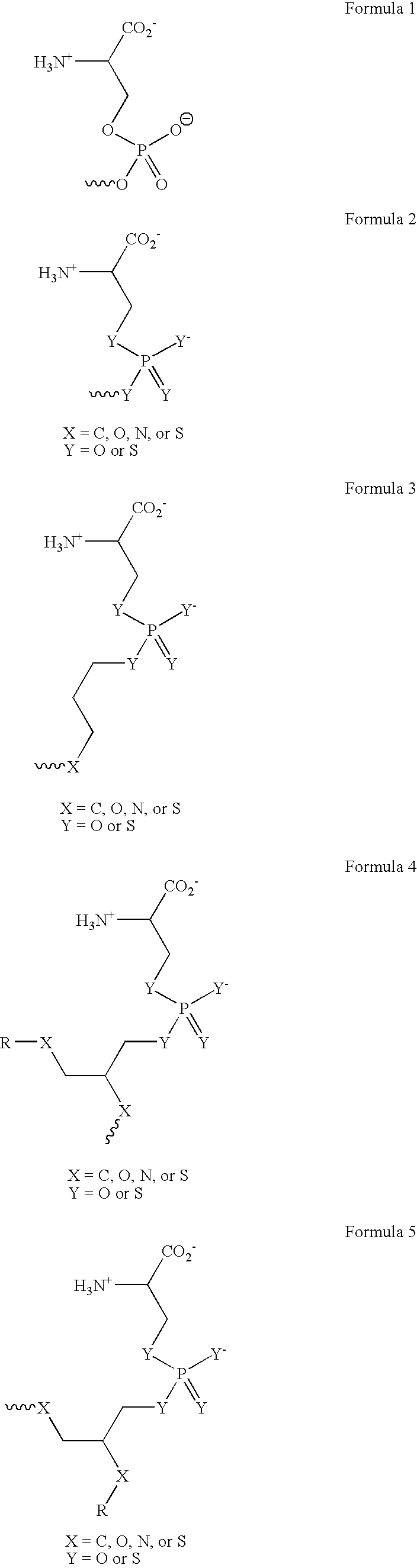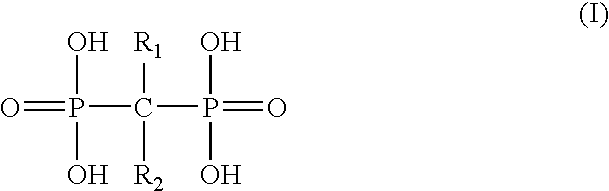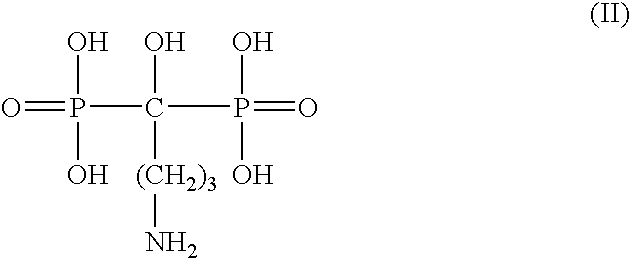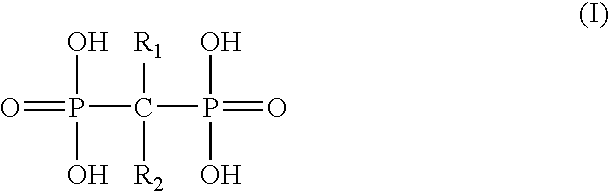Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
139 results about "Phagocytic Cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A type of immune cell that can surround and kill microorganisms, ingest foreign material, and remove dead cells. It can also boost immune responses. Monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils are phagocytes. A phagocyte is a type of white blood cell.
Compositions and methods for enhancing phagocytosis or phagocyte activity
ActiveUS20050113297A1Enhances and incites phagocytosisBetter targets for phagocytosisSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWhite blood cellCell type specific
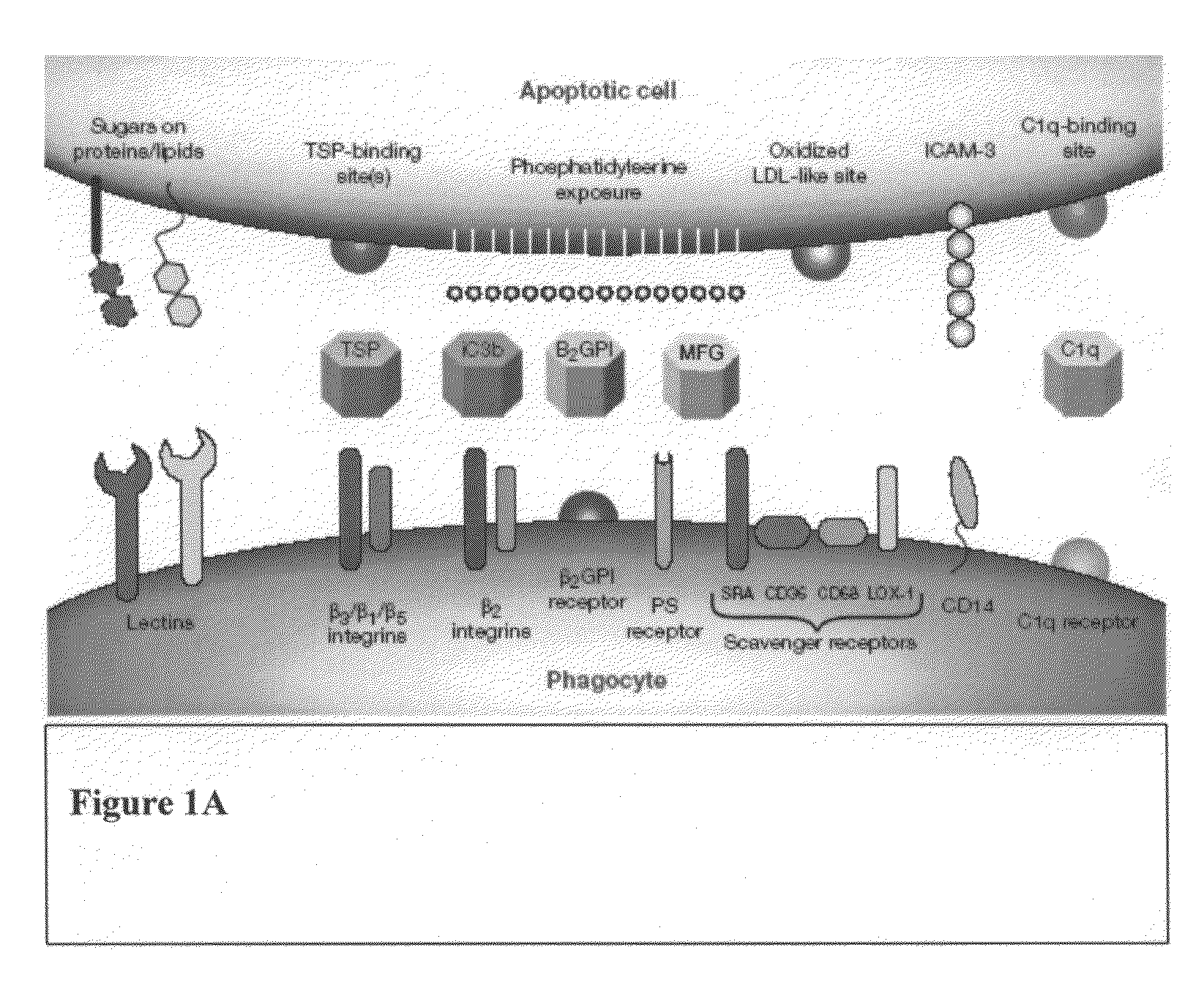
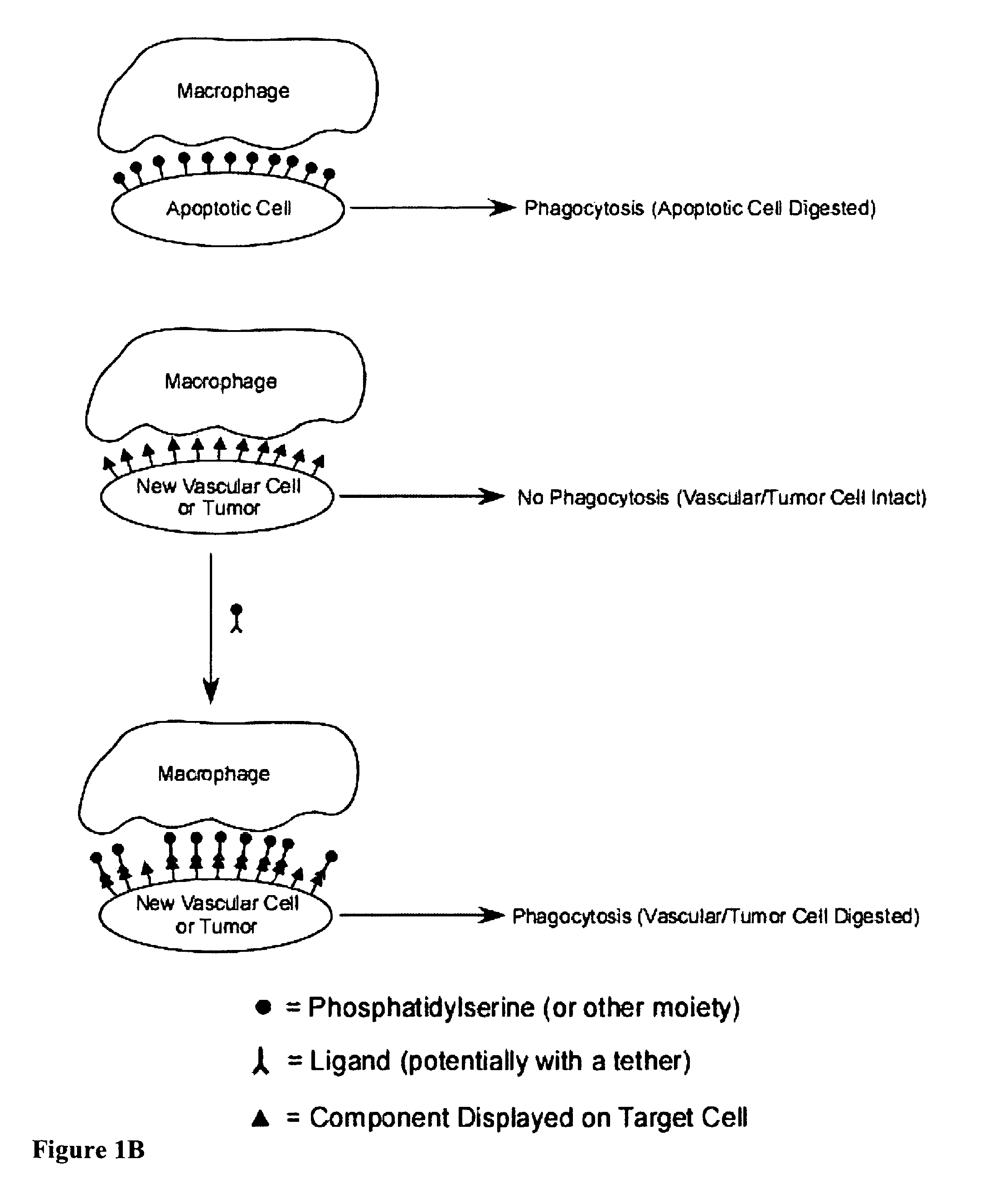
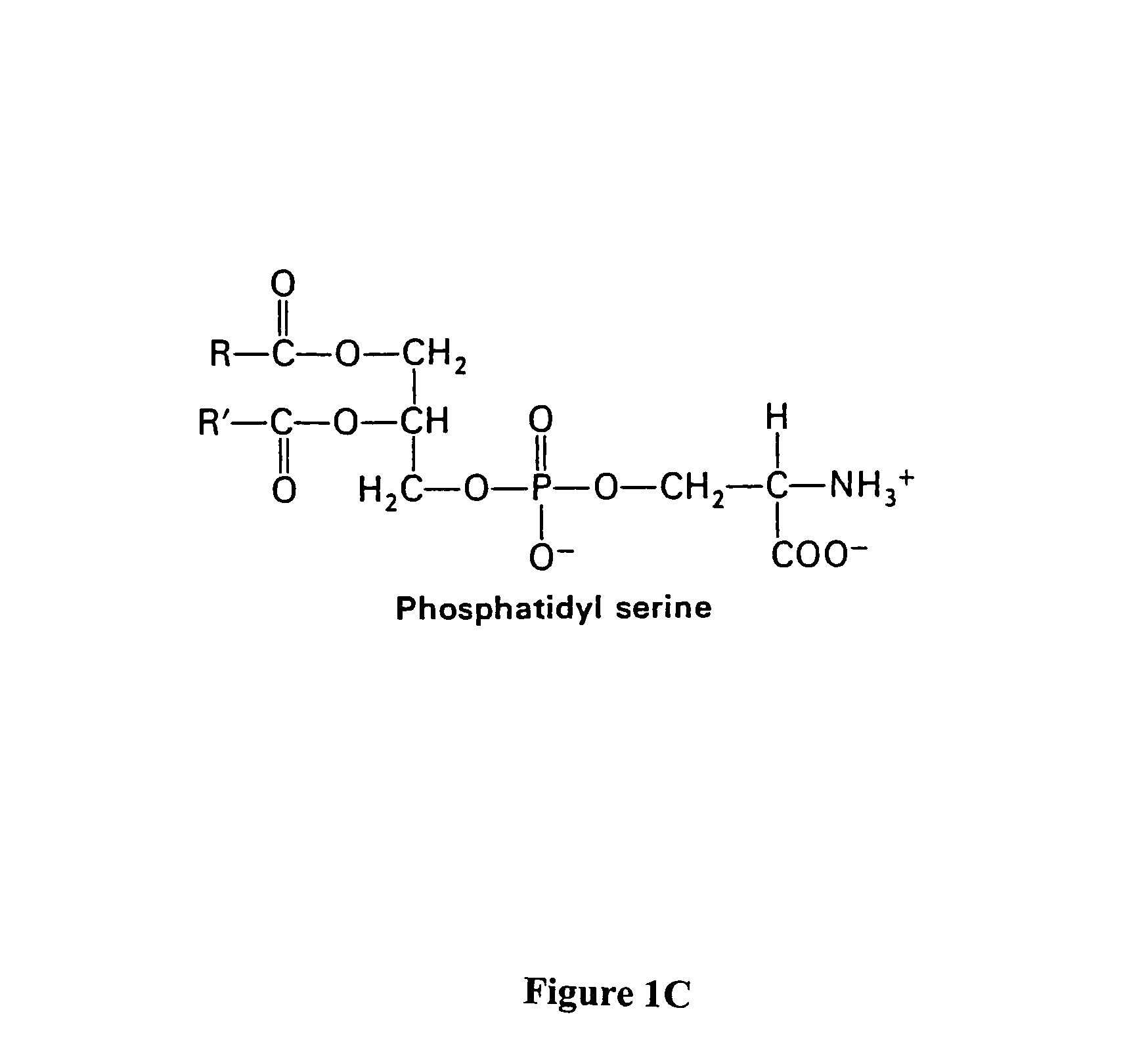
The present invention provides a system for enhancing clearance or destruction of undesirable cells or noncellular molecular entities by tagging such cells or noncellular molecular entities with a marker that targets the cells or noncellular molecular entities for phagocytosis (phagocytic marker). The target cells can be, for example, endothelial cells, tumor cells, leukocytes, or virus-infected cells. In certain embodiments of the invention the tagging is accomplished by administering a composition comprising an antibody or ligand linked to the phagcytotic marker, wherein the antibody or ligand binds to a cell type specific marker present on or in the cell surface of a target cell. In preferred embodiments of the invention, the phagocytic marker comprises phosphatidylserine or a group derived from phosphatidylserine, thrombospondin-1, annexin I, or a derivative of any of these.
Owner:APELLIS PHARMA
Targeted Gene Delivery to Non-Phagocytic Mammalian Cells Via Bacterially Derived Intact Minicells
ActiveUS20070237744A1High expressionFunction increaseOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaGene deliveryPhagocytic Cell
A method of targeting bacterially-derived, intact minicells to specific, non-phagocytic mammalian cells employs bispecific ligands to deliver nucleic acids efficiently to the mammalian cells. Bispecific ligands, comprising (i) a first arm that carries specificity for a bacterially-derived minicell surface structure and (ii) a second arm that carries specificity for a non-phagocytic mammalian cell surface receptor are useful for targeting minicells to specific, non-phagocytic mammalian cells and causing endocytosis of minicells by non-phagocytic cells.
Owner:ENGENEIC MOLECULAR DELIVERY PTY LTD
Method of treating acute coronary syndromes
InactiveUS20040266734A1Inhibitory activityInhibition amountBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsPhagocytic CellManagement of acute coronary syndrome
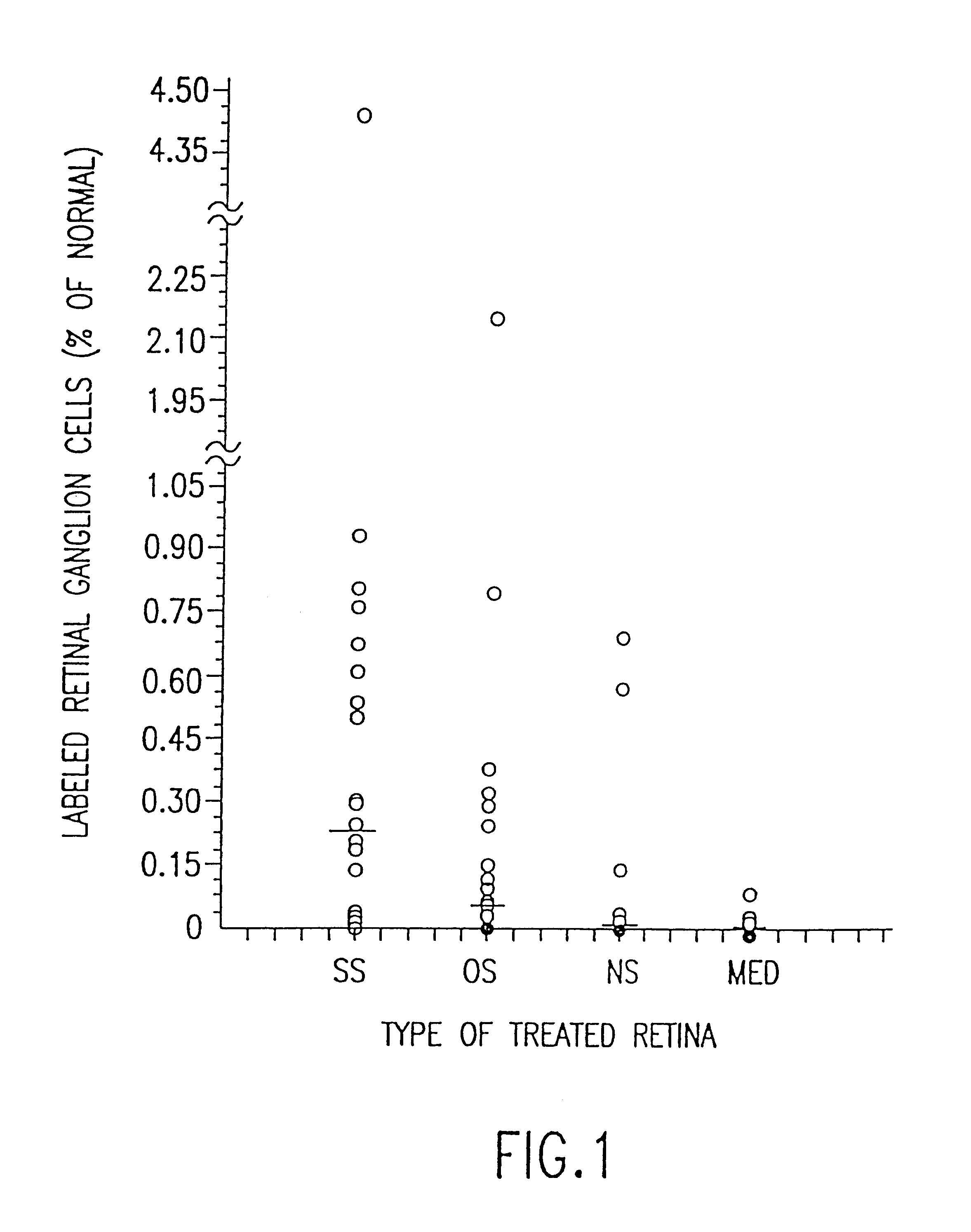
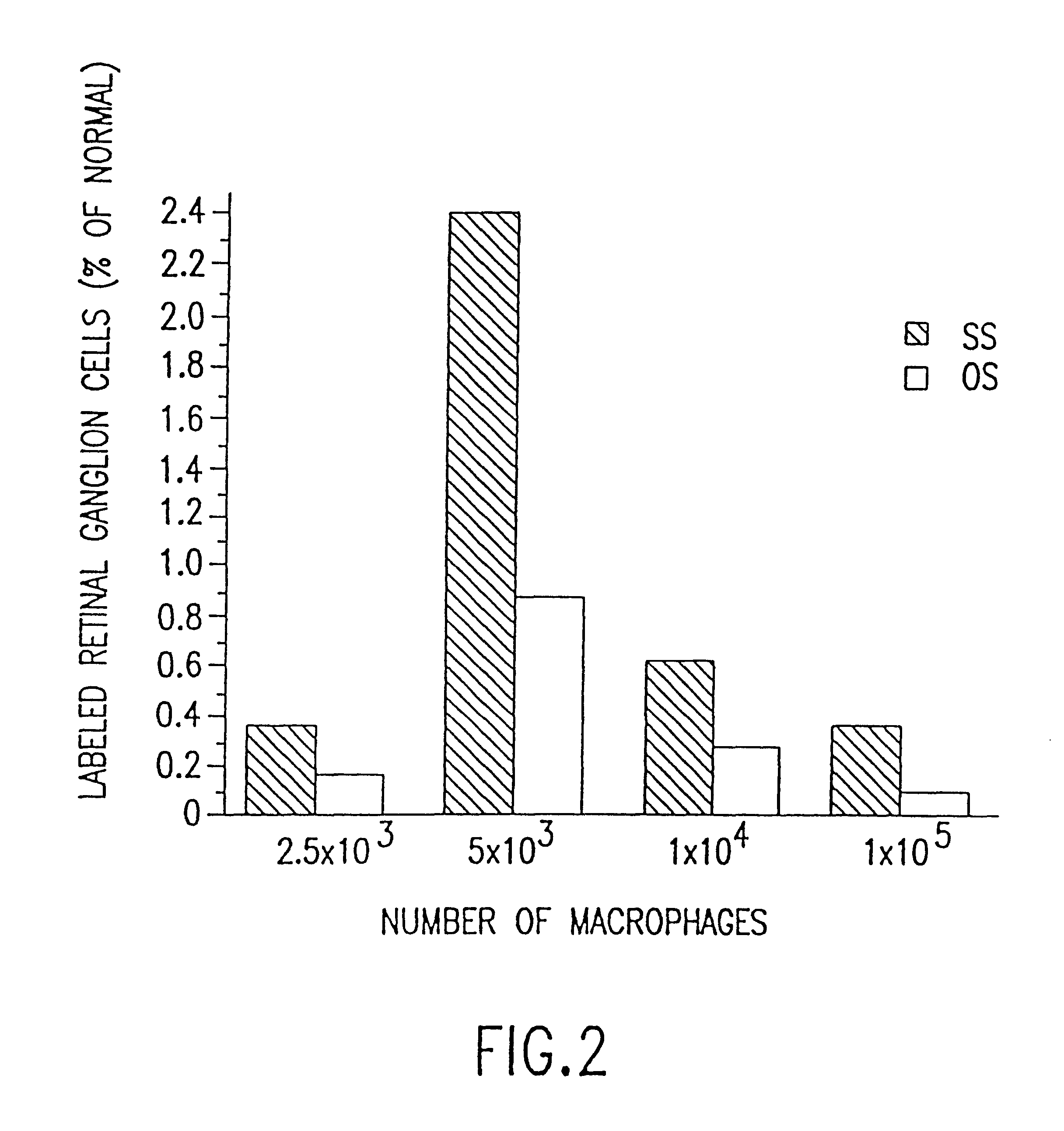
The present invention relates to methods and compositions designed for the treatment or management of acute coronary syndromes, particularly, unstable angina and acute myocardial infarction. The methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of a formulation containing one or more therapeutic agents which specifically decreases or inhibits the activity of phagocytic cells and / or eliminates or diminishes the amount of phagocytic cells including, but not limited to, macrophages and monocytes. The formulations are specifically targeted to phagocytic cells. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions of formulations containing one or more therapeutic agents of the invention for administration to subjects currently suffering from or having recently suffered an acute coronary syndrome such as unstable angina and acute myocardial infarction.
Owner:ZULI HLDG LTD
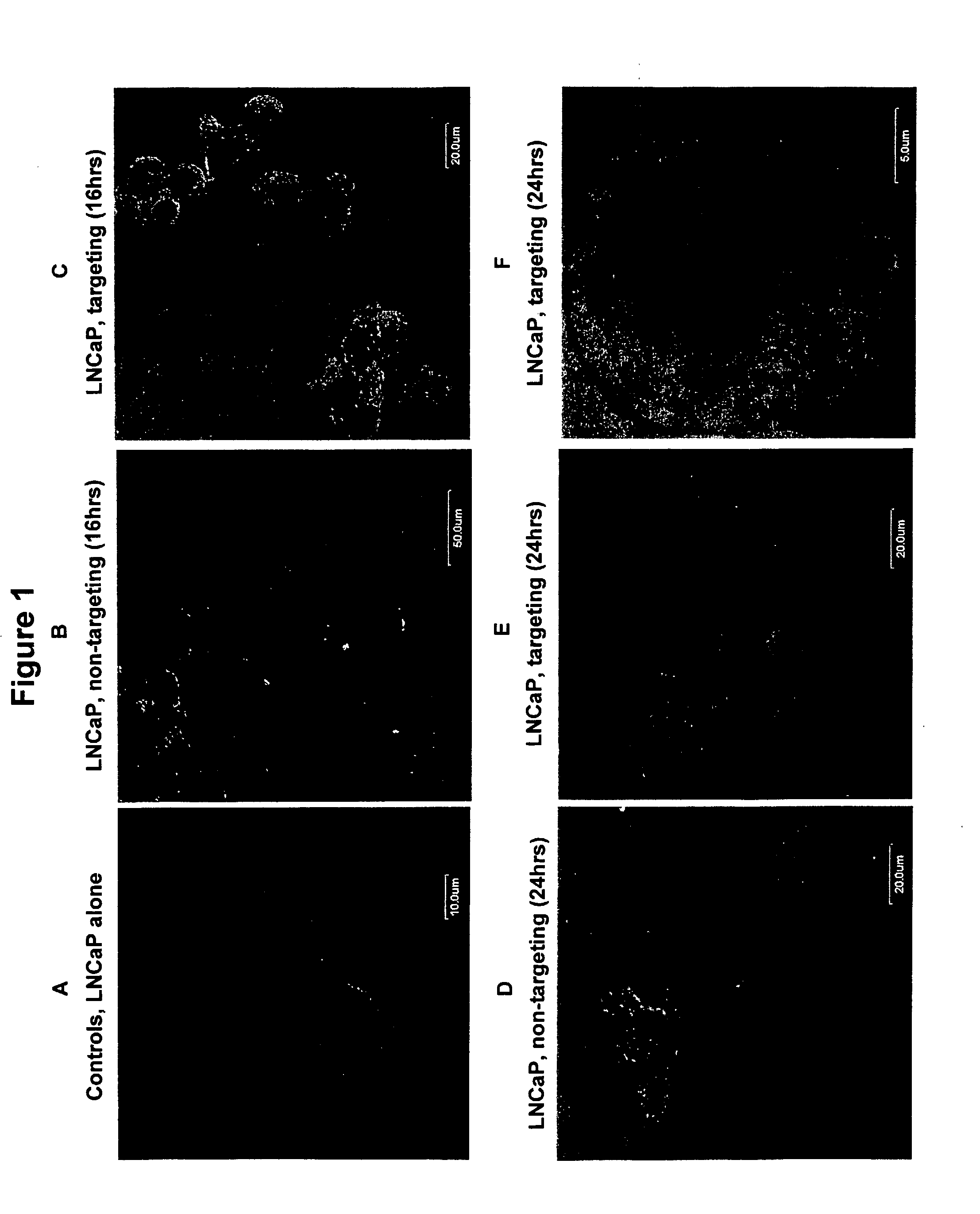
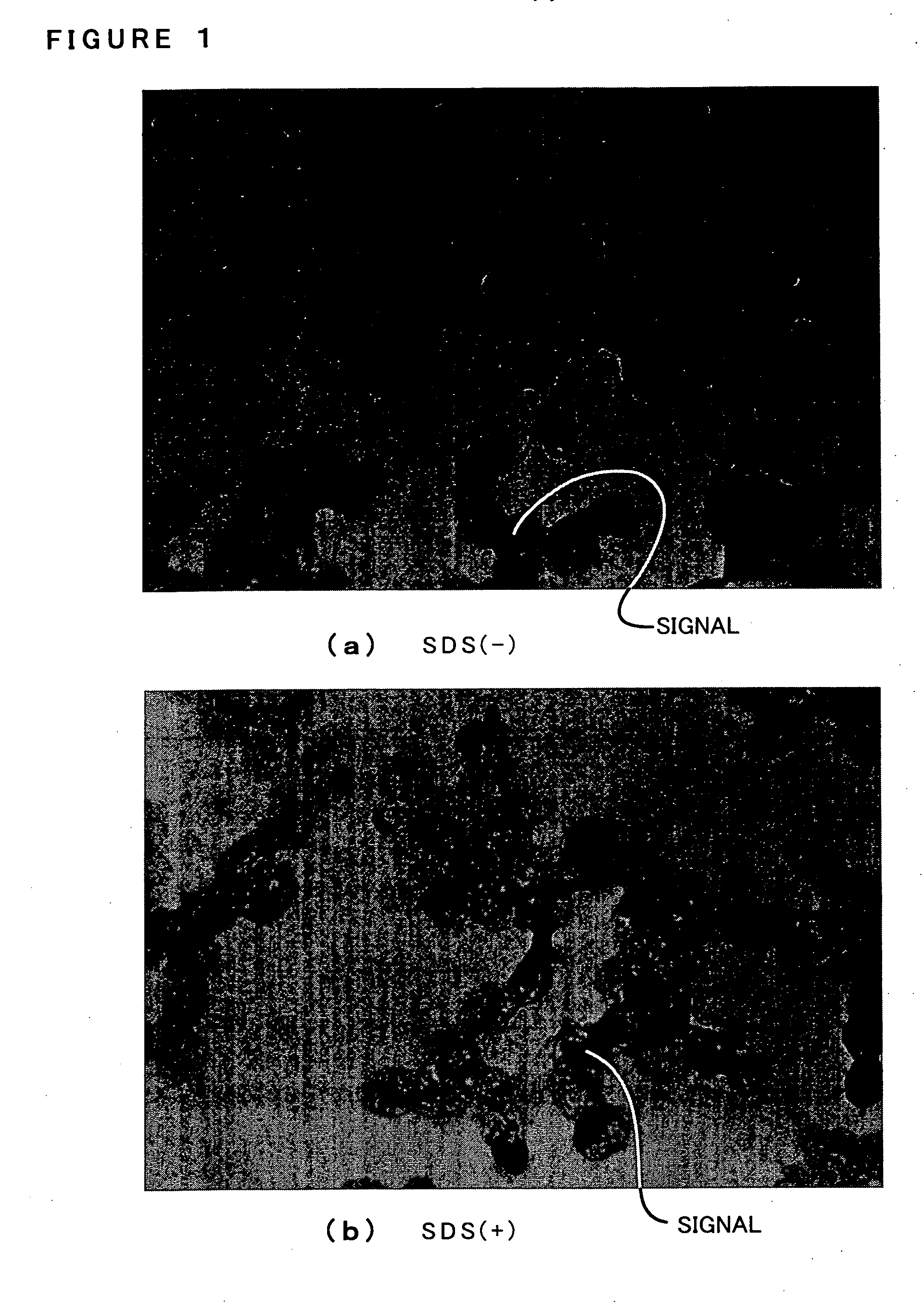
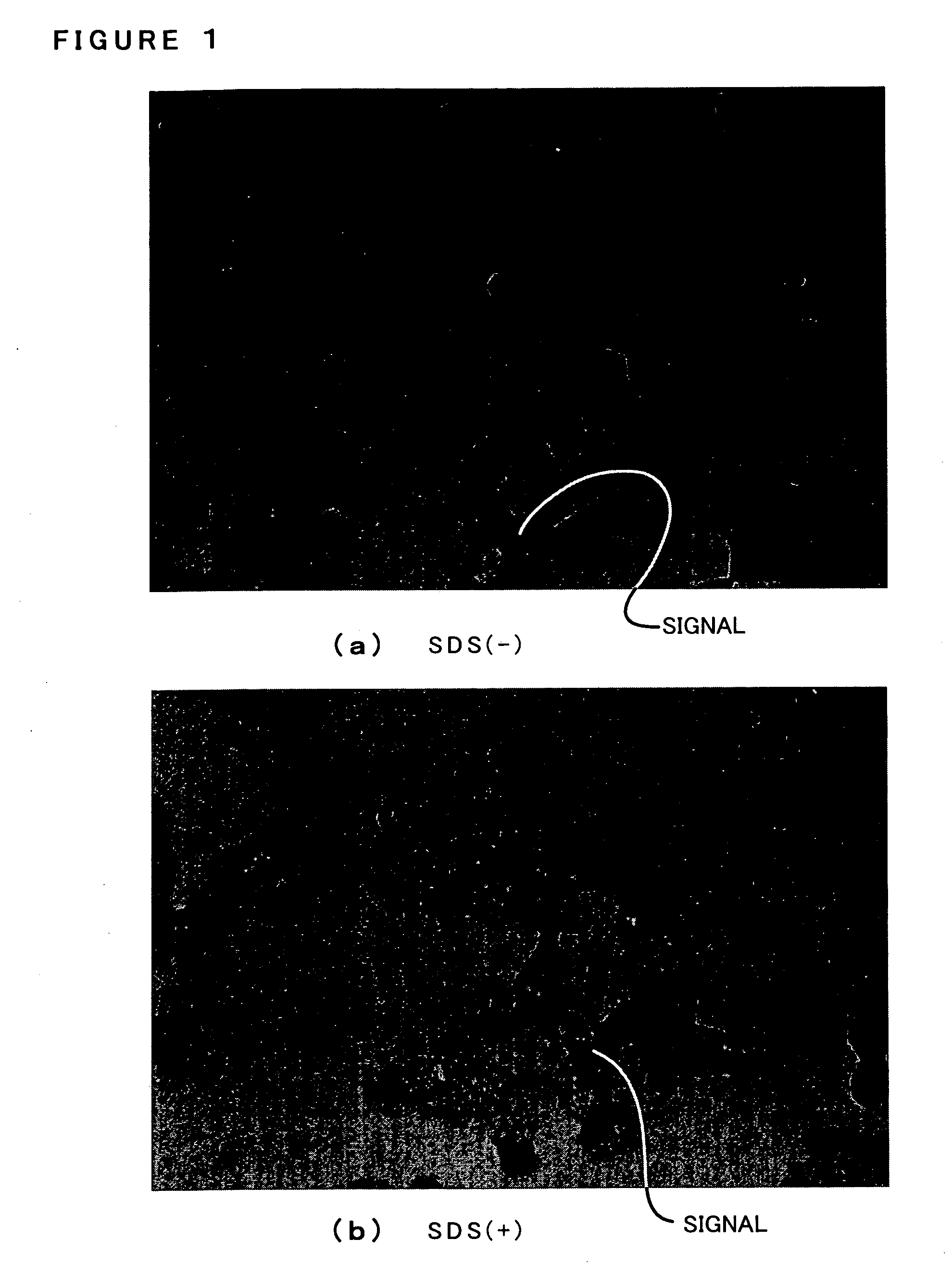
Phagocytic cell delivery of RNAI
ActiveUS8815818B2Strong specificityReduced off-target silencingAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderParticulatesPhagocytic Cell
The present invention provides a particulate delivery system for delivering an RNAi construct to phagocytic cells such as macrophages, comprising various configurations of a complex comprising a phagocytic cell-targeting moiety and an RNAi construct. The invention further provides methods of making the delivery system, and their uses, such as treating phagocytic cell-associated disease conditions.
Owner:PHIO PHARMA CORP
Engineering shape of polymeric micro- and nanoparticles
InactiveUS20080112886A1Produced in advanceMicromachined deliveryGranular deliveryPhagocytic CellSpherical granule
Compositions containing polymeric micro- and nanoparticles with non-spherical shapes and methods for making and using such particles are described herein. The particles have a size range from an average diameter of about Compositions containing polymeric micro- and nanoparticles with non-spherical shapes and methods for making and using such particles are described herein. The particles have one or more dimensions ranging from about 5 nm to about 100 μm, preferably about 100 nm to 10 μm. The particles can have any of a wide variety of non-spherical shapes. The particles are generally formed by manipulation of spherical particles embedded in a polymeric film. A wide variety of resulting shapes can be made. The resulting shape is a function of whether the films are manipulated in a first and / or second dimension, and the processes used to liquefy the microparticles. Variations of the method of manufacture may be used to generate particles having the desired shapes in large, reproducible quantities. The resulting non-spherical shaped particles can be used to alter uptake by phagocytic cells and thereby clearance by the reticuloendothelial system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Phagocytic cell delivery of rnai
ActiveUS20120016005A1Improve stabilityStrong specificityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseasePhagocytic Cell
The present invention provides a particulate delivery system for delivering an RNAi construct to phagocytic cells such as macrophages, comprising various configurations of a complex comprising a phagocytic cell-targeting moiety and an RNAi construct. The invention further provides methods of making the delivery system, and their uses, such as treating phagocytic cell-associated disease conditions.
Owner:PHIO PHARMA CORP
Mononuclear phagocytes and their use to promote axonal regeneration
InactiveUS6267955B1Increase capacityEnhance phagocytic activityBiocideNervous disorderPhagocyteDisease
Methods and compositions are disclosed for the use of allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes to promote axonal regeneration in the central nervous system of a mammal. In one embodiment, allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes are cultured together with stimulatory tissue, such as skin, dermis or at least one nerve segment, and are subsequently administered into the central nervous system of a mammal at or near a site of injury or disease. In an alternative embodiment, autologous monocytes, preferably stimulated autologous monocytes, are administered into the central nervous system of a mammal at or near a site of injury or disease. CNS administration of mononuclear phagocytes may optionally be combined with administration of an adjuvant factor (e.g. aFGF) to the CNS, anti-inflammatory therapy of the mammal, or both. Methods for screening stimulatory tissue and cells and methods and compositions for cryopreserved allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes are also disclosed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Method of inhibiting overactivity of phagocytes or lymphocytes in an individual
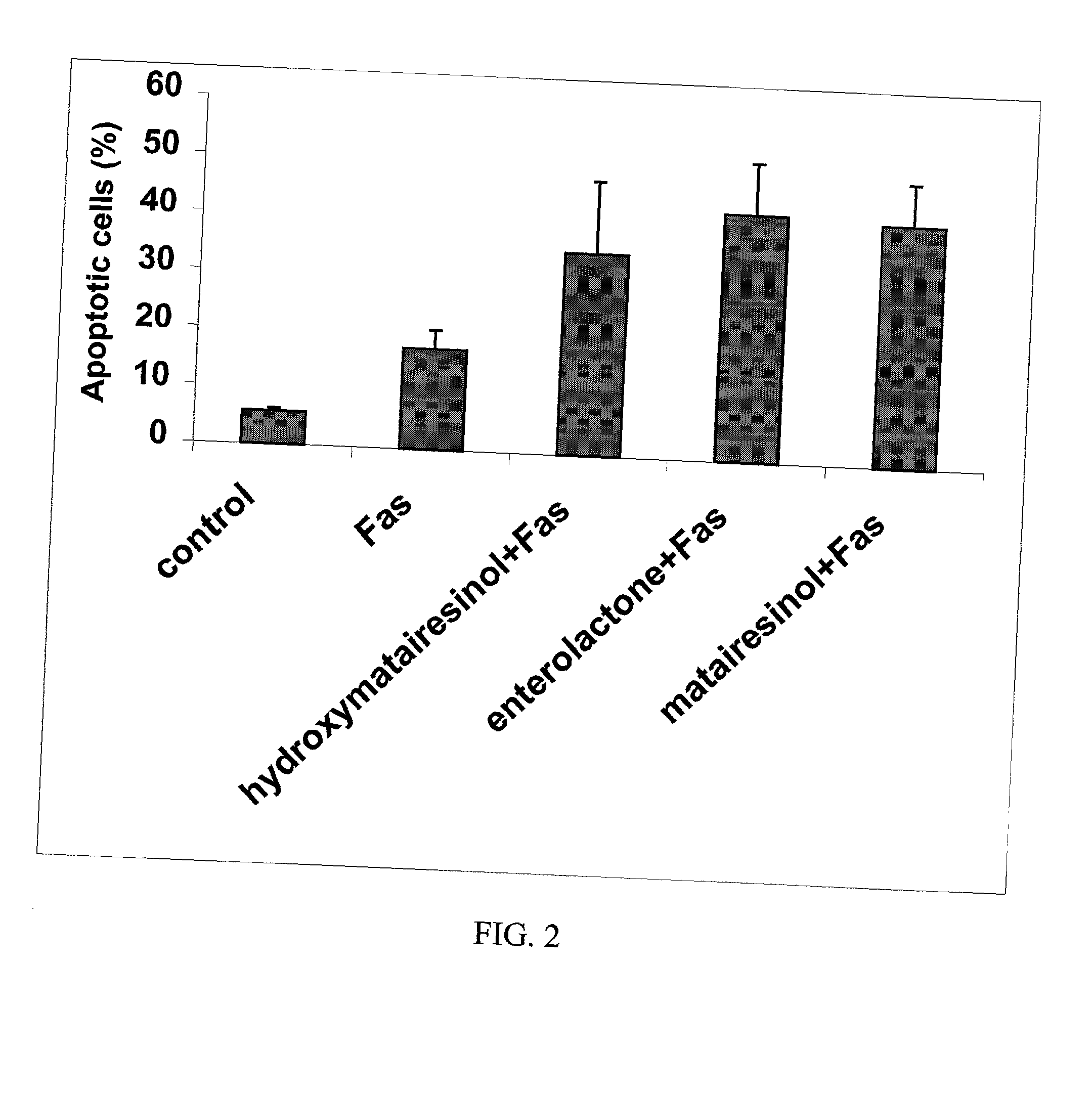
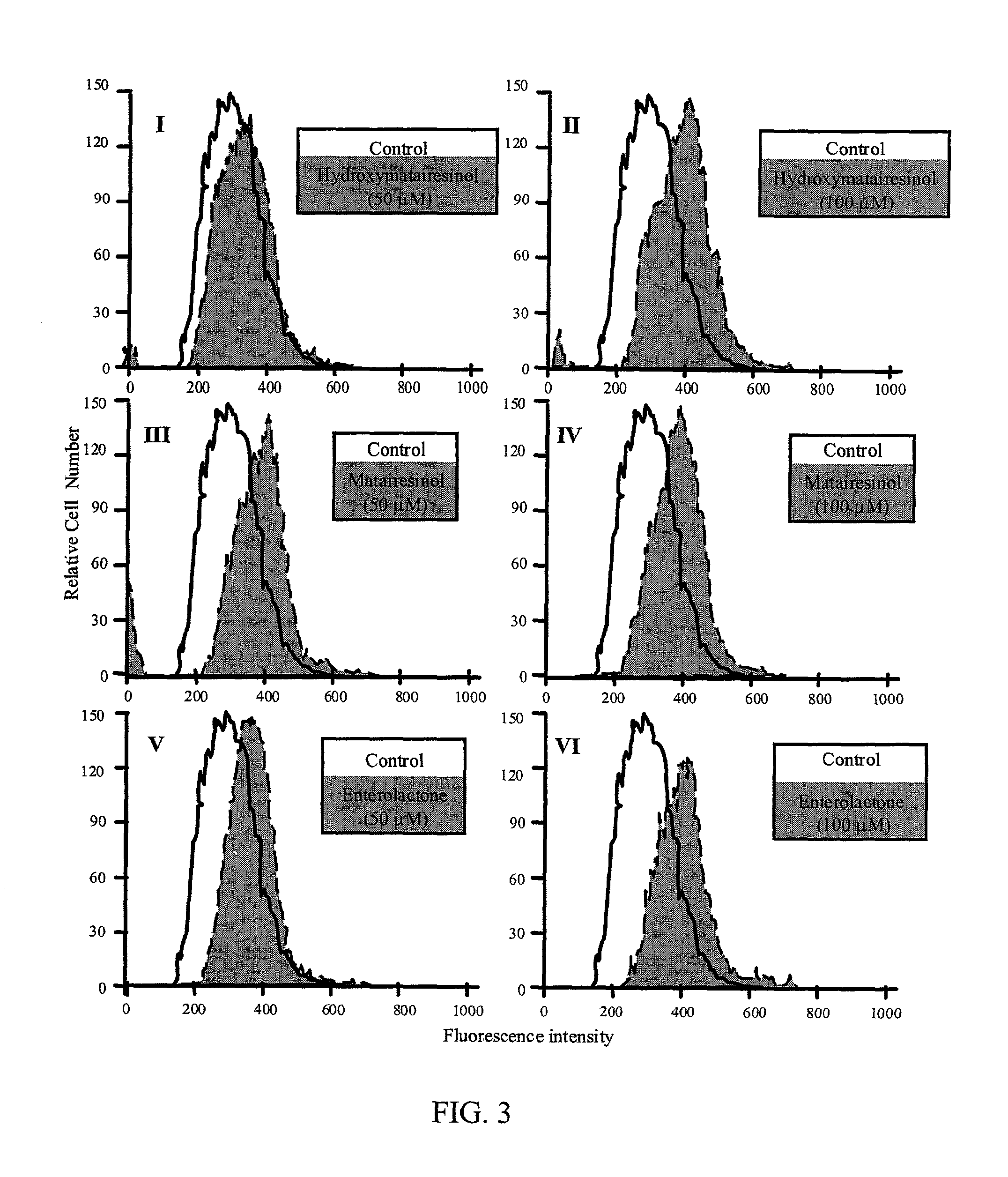
InactiveUS20030100514A1Reduce formationReduce riskBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsPhagocyteEnterolactone
This invention relates to a method of inhibiting the overactivity of phagocytes or lymphocytes in an individual by administering to said individual an effective amount of a lignan, wherein i) the phagocytes are neutrophils and the lignan is hydroxymatairesinol or matairesinol or mixtures thereof, or ii) the phagocytes are cells of myeloid origin and the lignan is enterolactone or hydroxymatairesinol or mixtures thereof, or iii) the lymphocytes are T-lymphocytes and the lignan is hydroxymatairesinol, matairesinol or enterolactone or mixtures thereof. Furthermore, this invention concerns a method of treating or preventing an acute ischemia-reperfusion injury or a chronic condition, caused by overactivity of phagocytes or lymphocytes in an individual, said method comprising decreasing the activity of phagocytes in an individual by administering to said individual an effective amount of a lignan.
Owner:HORMOS NUTRACEUTICAL
Method for obtaining transgenic bovine fetal fibroblast by using Cas9 cutting nuclease-mediated Ipr1 fixed point insertion
InactiveCN107619837AAvoid loss of activityAvoid lossGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementEmbryoUterus
The invention discloses a method for obtaining transgenic bovine fetal fibroblast by using Cas9 cutting nuclease-mediated Ipr1 fixed point insertion. The bovine fetal fibroblast is cotransfected by adonor vector and a CRISPR / Cas0 expression vector for a target locus through an electroporation method, an MSR1 promoter in the donor vector can realize specific expression in full-time phagocytic cells, and after puromycin drug screening, the targeted positive clone cell is obtained through PCR authentication. The transgenic positive clone cell is used as a donor cell so as to obtain a transgenicclone embryo, the transgenic clone embryo is further transplanted into the uterus of a rutting acceptor calf, and finally a living Ipr1 fixed point insertion transgenic cloned calf is obtained.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Compositions and methods for selective phagocytosis of human cancer cells
ActiveUS20170151282A1Therapeutic effectEnhance phagocytic activityGenetically modified cellsMammal material medical ingredientsPhagocytic CellHuman cancer
The present invention relates to compositions and methods that provide novel therapies in cancer. The invention includes a phagocytic cell modified with a repressor of signal regulatory protein-alpha (SIRPα) and bound to a targeting antibody to enhance phagocytic activity of the phagocytic cell toward tumor tissue. Methods of enhancing phagocytic activity and treating a tumor are also included.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
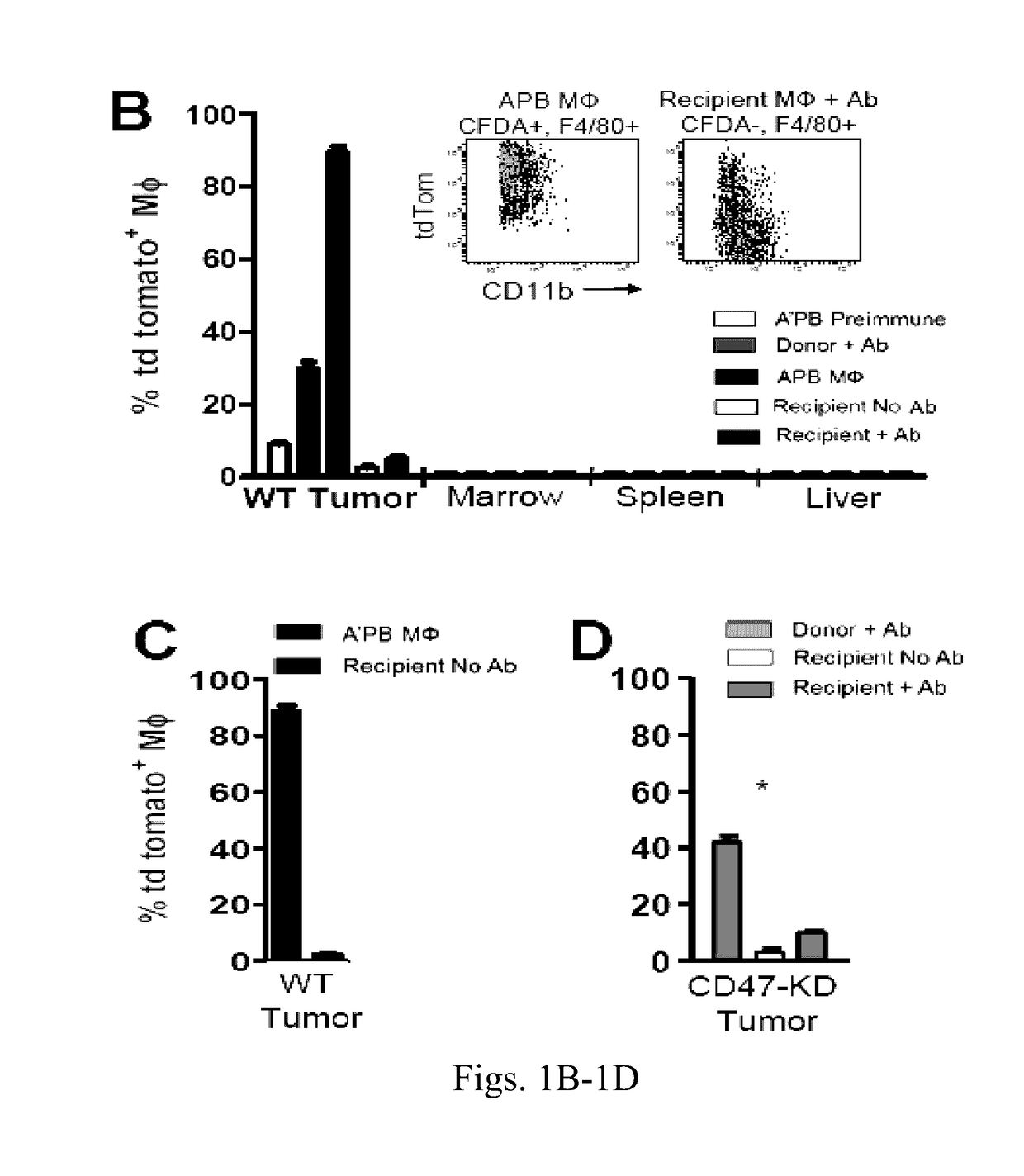
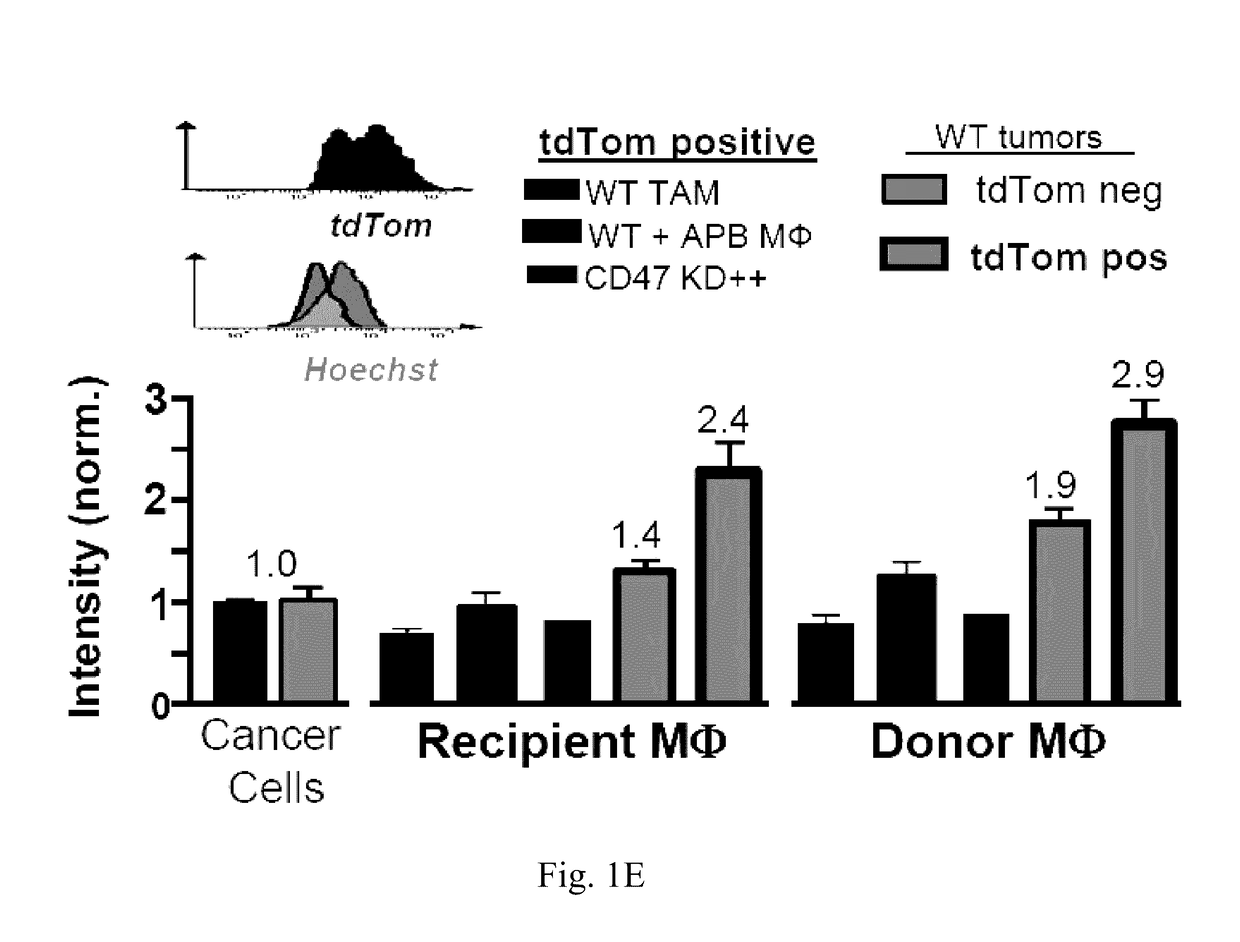
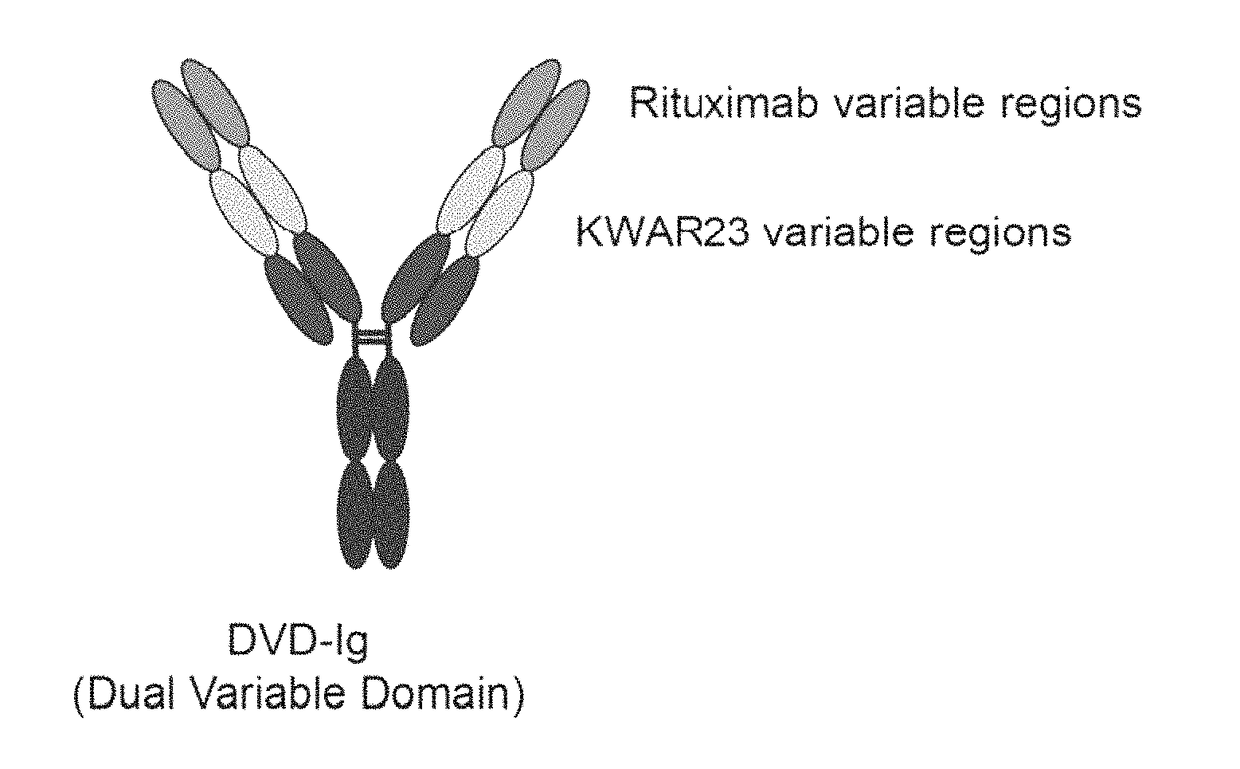
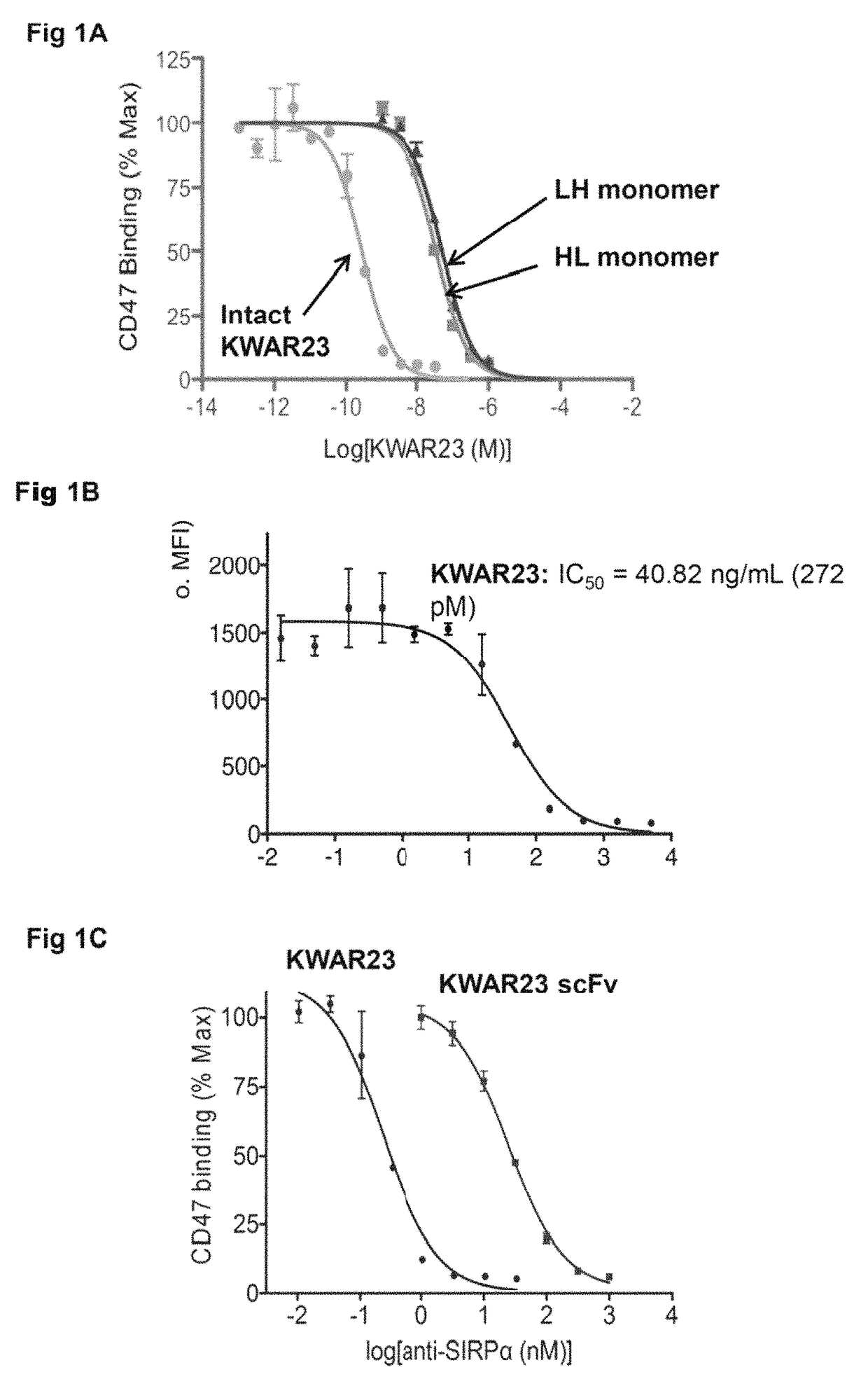
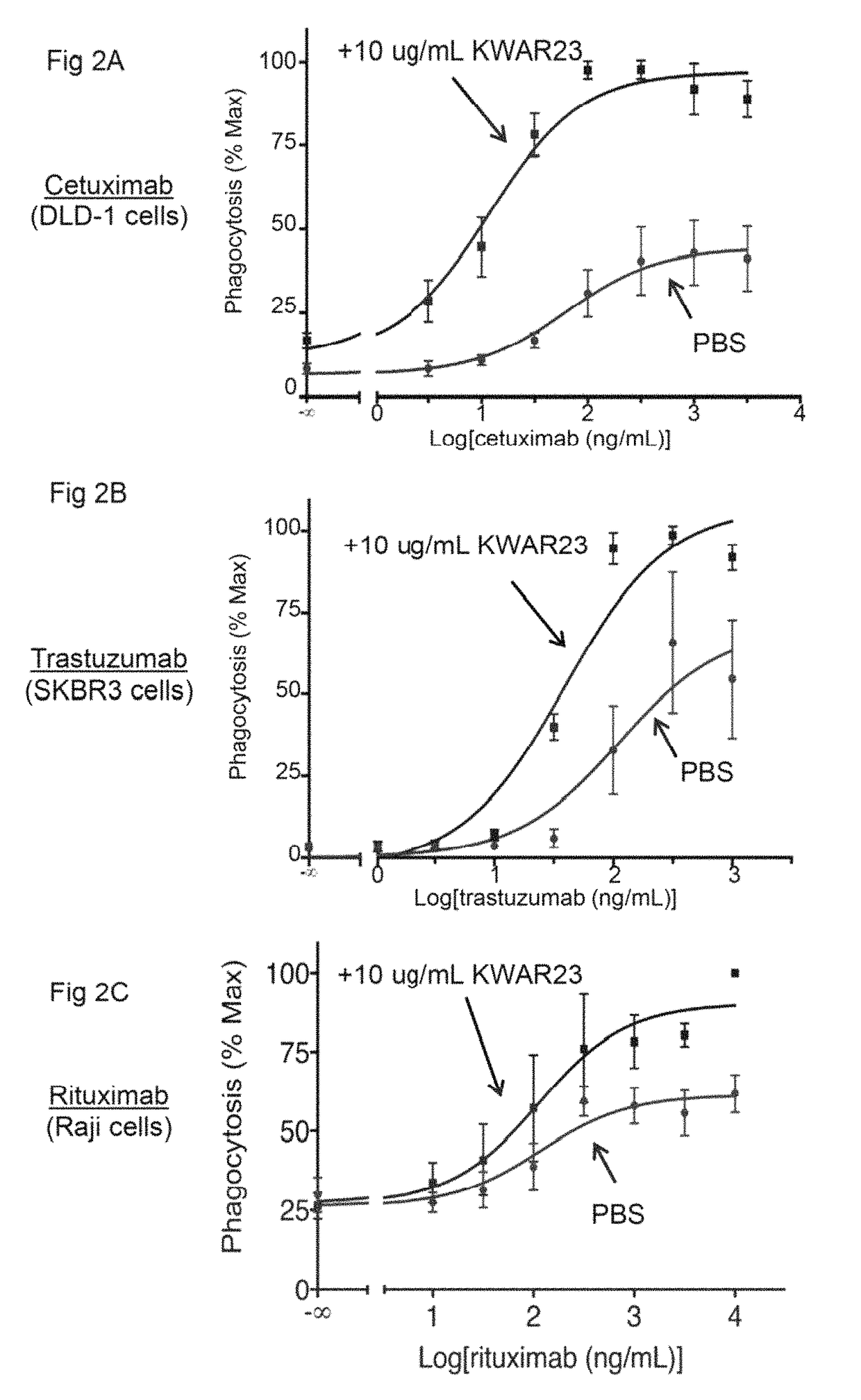
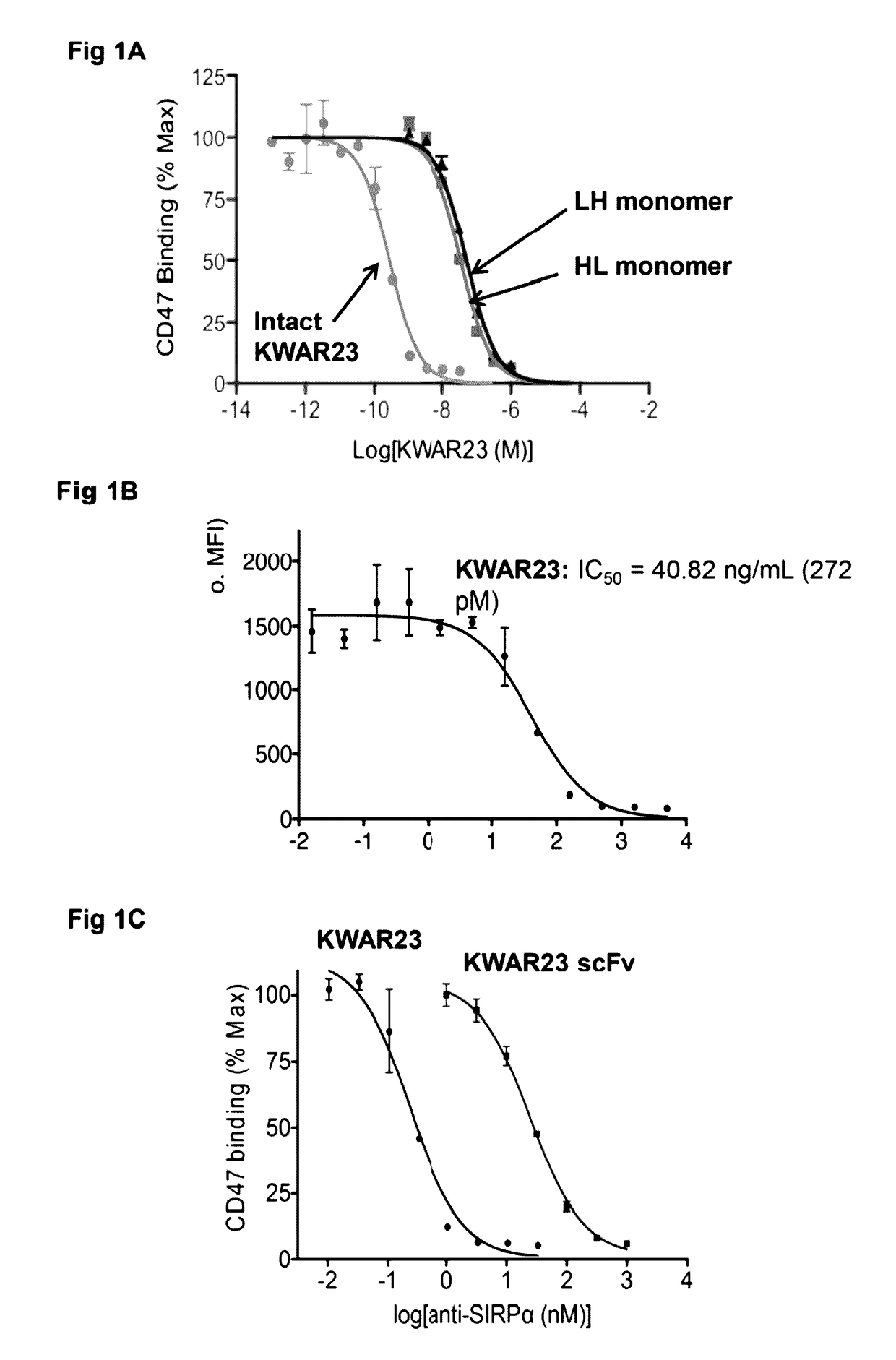
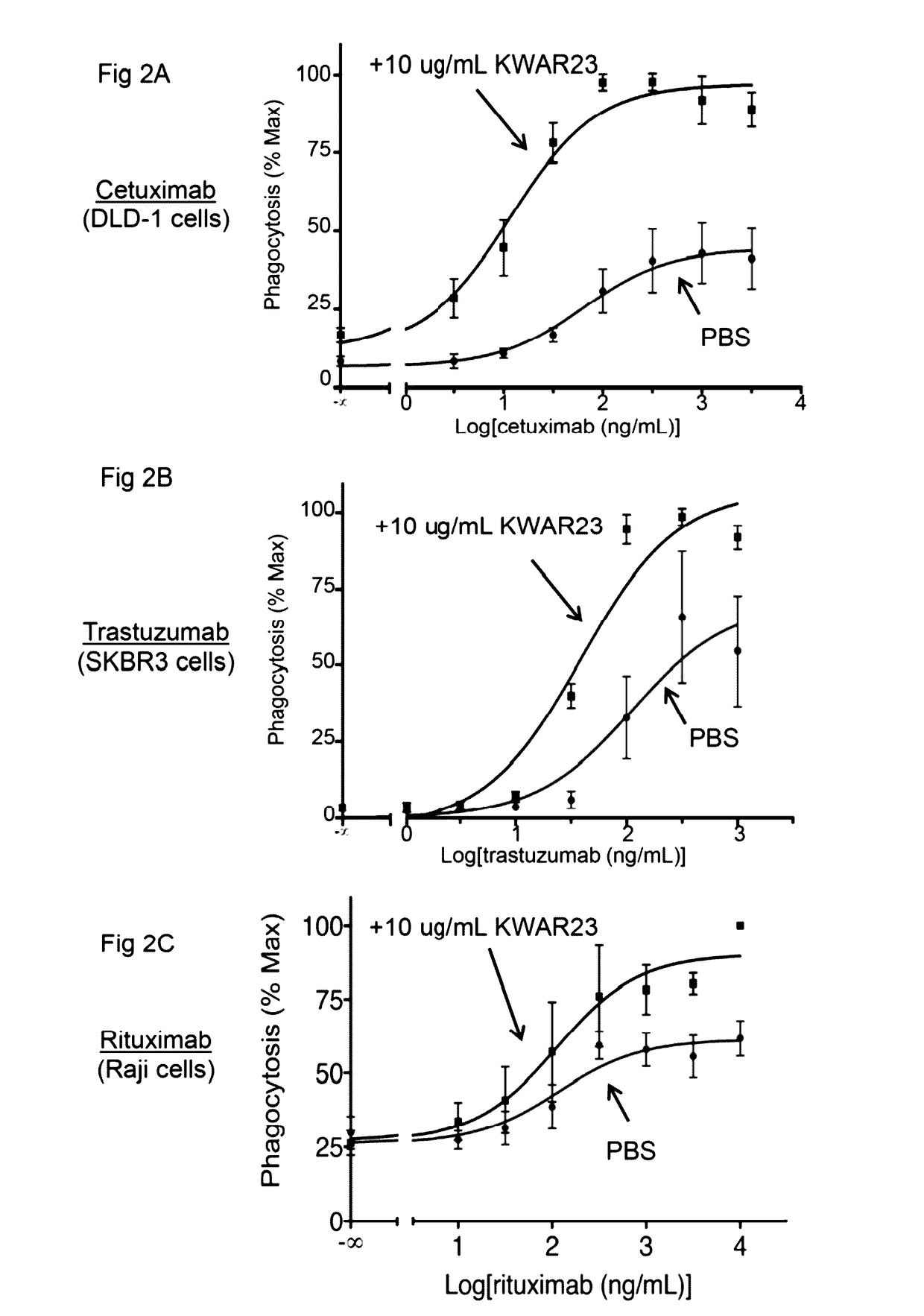
Anti-SIRP-alpha antibodies and bispecific macrophage enhancing antibodies
Anti-SIRPα antibodies, including multi-specific anti-SIRPα antibodies, are provided, as are related compositions and methods. The antibodies of the disclosure bind to SIRPα and can block the interaction of CD47 on one cell with SIRPα on a phagocytic cell. Antibodies that are bispecific for SIRPα and a second antigen are termed Bi-specific Macrophage Enhancing (BiME) antibodies and have emergent properties. The subject anti-SIRPα antibodies find use in various therapeutic methods. Embodiments of the disclosure include isolated antibodies and derivatives and fragments thereof, pharmaceutical formulations comprising one or more of the anti-SIRPα antibodies; and cell lines that produce the antibodies. Also provided are amino acid sequences of exemplary anti-SIRPα antibodies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Process for evaluating phagocytotic function and use thereof
InactiveUS20070059687A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsPhagocyteMicroorganism
A digested phagocyte prepared by contacting in vitro a phagocyte with a foreign microorganism and isolating the phagocyte so contacted; a process for producing the same; and a process and a kit in which these are utilized are disclosed. An experimental model, which enables in vitro evaluation of a phagocytotic function of phagocytes, is provided.
Owner:FUSO PHARMA INDS
Anti SIRP-alpha Antibodies and Bi-specific Macrophage Enhancing Antibodies
Anti-SIRPα antibodies, including multi-specific anti-SIRPα antibodies, are provided, as are related compositions and methods. The antibodies of the disclosure bind to SIRPα and can block the interaction of CD47 on one cell with SIRPα on a phagocytic cell. Antibodies that are bispecific for SIRPα and a second antigen are termed Bi-specific Macrophage Enhancing (BiME) antibodies and have emergent properties. The subject anti-SIRPα antibodies find use in various therapeutic methods. Embodiments of the disclosure include isolated antibodies and derivatives and fragments thereof, pharmaceutical formulations comprising one or more of the anti-SIRPα antibodies; and cell lines that produce the antibodies. Also provided are amino acid sequences of exemplary anti-SIRPα antibodies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Microparticle-drug conjugates for biological targeting
InactiveUS20060008461A1Control releasePowder deliveryTripeptide ingredientsAntimicrobial drugMicroparticle
This invention provides novel methods and reagents for specifically delivering biologically active compounds to phagocytic mammalian cells. The invention also relates to specific uptake of such biologically active compounds by phagocytic cells and delivery of such compounds to specific sites intracellularly. The invention specifically relates to methods of facilitating the entry of antiviral and antimicrobial drugs and other agents into phagocytic cells and for targeting such compounds to specific organelles within the cell. The invention specifically provides compositions of matter and pharmaceutical embodiments of such compositions comprising conjugates of such antimicrobial drugs and agents covalently linked to particulate carriers generally termed microparticles. In particular embodiments, the antimicrobial drug is covalently linked to a microparticle via a cleavable linker moiety that is non-specifically cleaved in a phagocytic cell. In additional embodiments, the biologically-active compound is provided in an inactive, prodrug form that is activated by a chemical or enzymatic activity specific for cells infected by a microorganism, particularly a pathological or disease-causing microorganism. Thus, the invention provides cell targeting of drugs wherein the targeted drug is only activated in cells infected with a particular microorganism. Alternative embodiments of such specific drug delivery compositions also contain polar lipid carrier molecules effective in achieving intracellular organelle targeting in infected phagocytic mammalian cells. Particular embodiments of such conjugates comprise antimicrobial drugs covalently linked both to a microparticle via a cleavable linker molecule and to a polar lipid compound, to facilitate targeting of such drugs to particular subcellular organelles within the cell. Also provided are porous microparticles impregnated with antiviral and antimicrobial drugs and agents wherein the surface or outside extent of the microparticle is covered with a degradable coating that is degraded within a phagocytic mammalian cell. Also provided are nonporous microparticles coated with an antiviral or antimicrobial drug and further coated wherein the surface or outside extent of the microparticle is covered with a degradable coating that is degraded within a phagocytic mammalian cell. Methods of inhibiting, attenuating, arresting, combating and overcoming microbial infection of phagocytic mammalian cells in vivo and in vitro are also provided.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
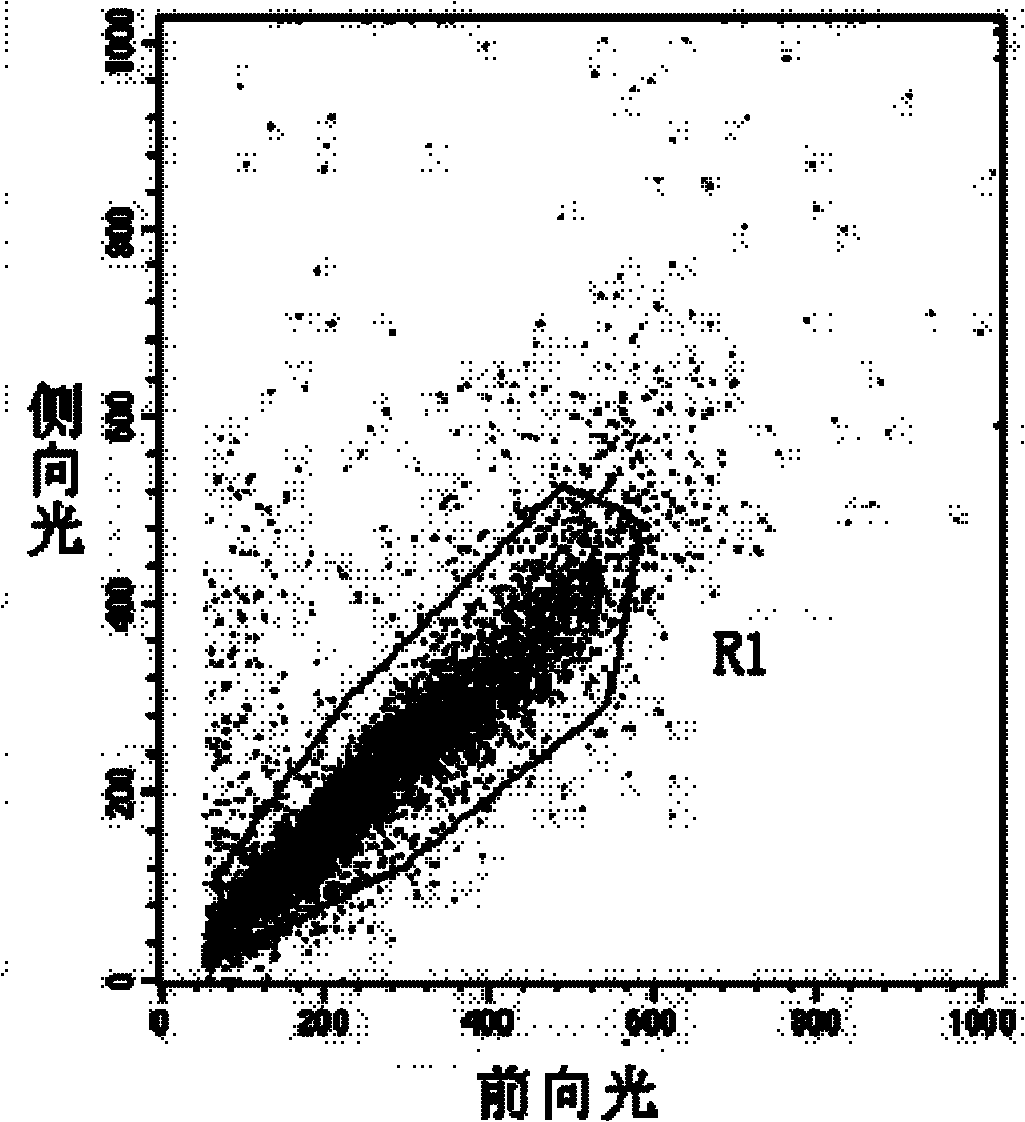
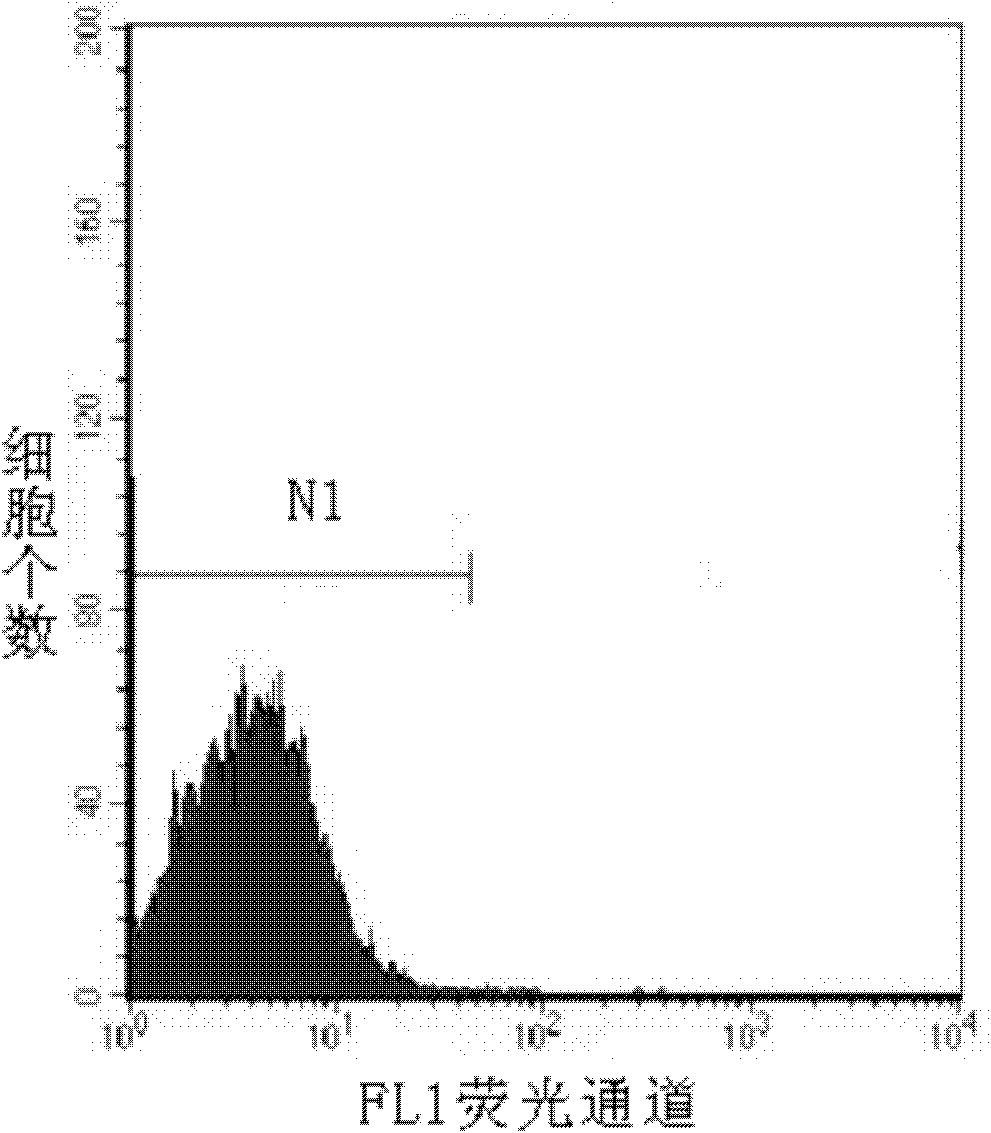
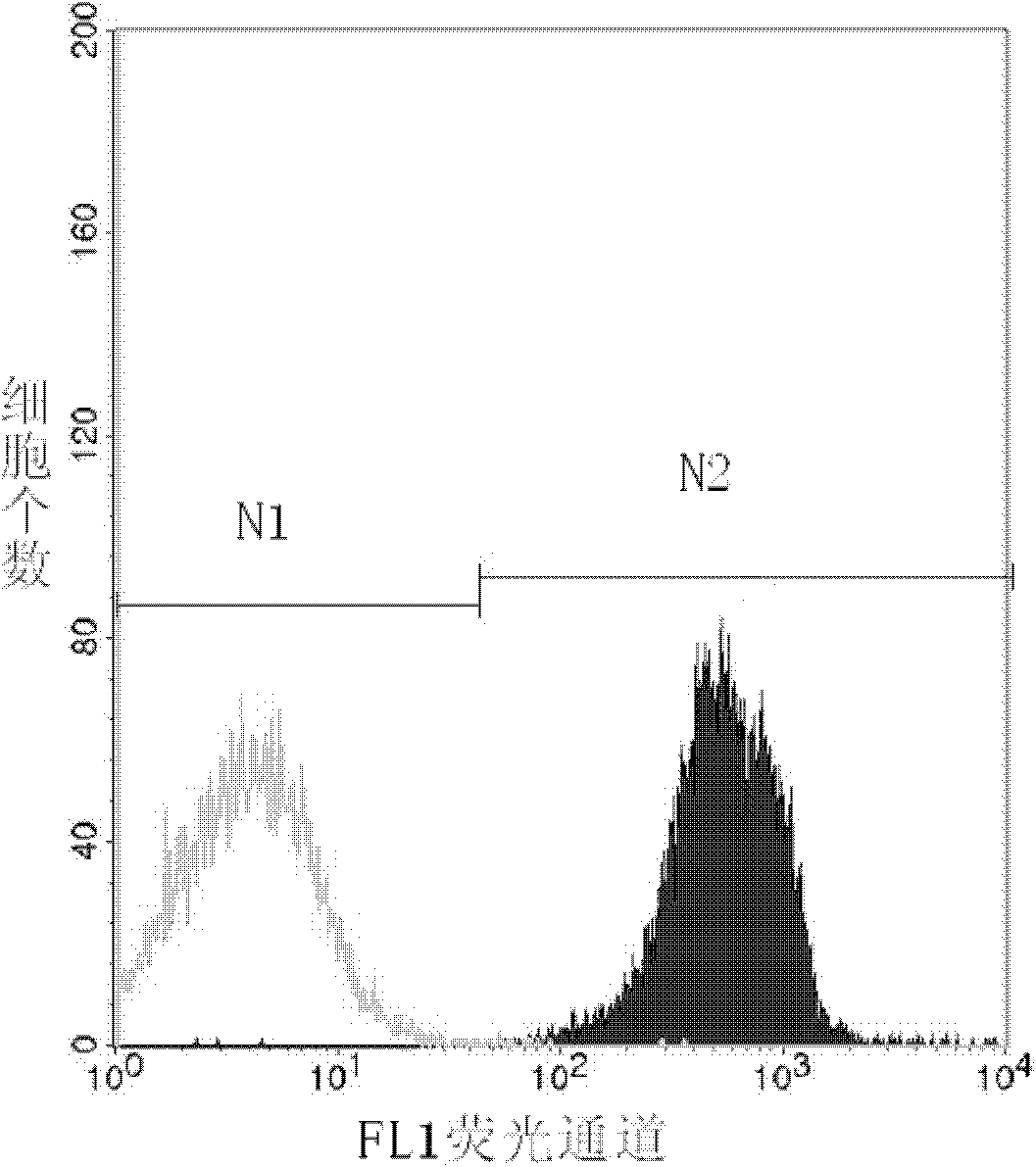
Method for detecting activity of abdominal cavity phagocytic cells by flow cytometry
InactiveCN101846626AEliminate the effects ofAccurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationFreeze-dryingFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for detecting the activity of abdominal cavity phagocytic cells by a flow cytometry, which aims at providing a method for fast, accurately, simply and easily detecting the activity of the phagocytic cells through the quantitative analysis on the number of phagocytic yeasts of the phagocytic cells on the basis of eliminating the influence of unendocytosed fluorescence yeast cells on the analysis results. The method comprises the following steps: preparing beer yeast cell freeze-dried powder; using FITC to mark the beer yeast cells; carrying out incubation on the suspension liquid of the fluorescence marked beer yeast cells and the blood serum of the mice at the room temperature; adding the suspension liquid of the abdominal cavity phagocytic cells into a hole of a culture plate; adding the fluorescence marked beer yeast cells after the incubation with the blood serum of the mice and the identical suspension liquid of the abdominal cavity phagocytic cells into the rest holes in the cell culture plate; carrying out wall adherence incubation on the cell culture plate; and using the flow cytometry to obtain data and carrying out analysis on the data. The method of the invention accurately measures the phagocytic rate and the phagocytic index, and has good repetitiveness.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
Preparation and application of rickettsia discrimination detection gene chip
InactiveCN104651498AImprove throughputStrong specificityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide chipAnaplasma phagocytophilum DNA
The invention relates to preparation and application of a rickettsia discrimination detection gene chip. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing universal and specific primers, preparing seven rickettsia nucleic acid typing probes, preparing an oligonucleotide chip, establishing a multiplex PCR (polymerase chain reaction) system, and establishing a hybridization system. The gene chip can simultaneously discriminate seven important rickettsiae, including rickettsia prowazeki, rickettsia mooseri, spotted fever group rickettsia, Coxiella burnetii, Orientia tsutsugamushi, Ehrlichia chaffeensis and Anaplasma phagocytophilum. The gene chip has the advantages of high speed, high accuracy, high flux and high specificity, and can provide a novel detection means for clinical diagnosis and epidemiological investigation of rickettsia infection.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Compositions and methods for enhancing phagocytosis or phagocyte activity
ActiveUS8198020B2Better targets for phagocytosisEnhances and incites phagocytosisSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWhite blood cellCell type specific
The present invention provides a system for enhancing clearance or destruction of undesirable cells or noncellular molecular entities by tagging such cells or noncellular molecular entities with a marker that targets the cells or noncellular molecular entities for phagocytosis (phagocytic marker). The target cells can be, for example, endothelial cells, tumor cells, leukocytes, or virus-infected cells. In certain embodiments of the invention the tagging is accomplished by administering a composition comprising an antibody or ligand linked to the phagcytotic marker, wherein the antibody or ligand binds to a cell type specific marker present on or in the cell surface of a target cell. In preferred embodiments of the invention, the phagocytic marker comprises phosphatidylserine or a group derived from phosphatidylserine, thrombospondin-1, annexin I, or a derivative of any of these.
Owner:APELLIS PHARMA
Implantable liposome embedded matrix composition, uses thereof, and polycaprolactone particles as scaffolds for tissue regeneration
In various embodiments, the present invention describes materials and methods for the local reprogramming of cells in a location where the treatment is applied. The invention can be used to replace lost cells or to restore function to tissue damaged due to disease, injury or genetic defect. In various embodiments, the treatment includes a semisolid hydrogel embedded with liposomes. The liposomes can contain an effector molecule or molecules. When phagocytic cells such as monocytes infiltrate the hydrogel, they encounter the liposomes and incorporate the liposomes carrying the effector molecules into the cells. In some embodiments, the effector molecules can be genetic material encoding the expression of specific proteins such as transcription factors, the expression of which can initiate the reprogramming of the cells. In other embodiments, the effector molecules can induce angiogenesis. In other embodiments, the effector molecules are tumor antigens. The matrix can contain other effector molecules designed to attract specific cells to the matrix. The cells can be released from the matrix as the matrix degrades or by active migration from the matrix. The cells can also remain in the matrix and secret molecules such as proteins and hormones that will diffuse through the matrix material to the surrounding tissue.
Owner:SCHUBERT HLDG
Method for detecting and identifying microorganism causative of infection
InactiveUS20060234219A1Microbiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringPhagocytePathogenic microorganism
Causative microorganisms of infectious diseases are detected and / or identified rapidly and high-sensitively by taking phagocytes from the clinical specimens containing active phagocytes, immobilizing the phagocytes so taken, treating the phagocytes to improve cell membrane permeabilities thereof, further treating the phagocytes to bare DNA in the causative microorganisms which might be existed in the phagocytes, and detecting the causative microorganisms with DNA probes which can hybridize with such DNA under stringent conditions.
Owner:FUSO PHARMA INDS
Flow cytometric detection method of coelomocyte phagocytic activity of Apostichopus japonicus
The invention discloses a flow type cell detection method for phagocytic activity of coelomic cells of a stichopus japonicus, belonging to the technical field of halobios. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly separating and preparing phagocytic cells in coelomic fluid of the stichopus japonicus; labeling heat-inactivated yeast cells by using fluorescein isothiocyanate (FIFC); co-incubating the labeled yeast cells and the phagocytic cells of the stichopus japonicus; and finally measuring the phagocytic activity by using flow cytometry. The method has high accuracy and good repeatability and is simple and convenient and fast to operate, and a method basis is provided for researching the phagocytic function of the coelomic cells of the stichopus japonicus.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV AT WEIHAI
Targeted gene delivery to non-phagocytic mammalian cells via bacterially derived intact minicells
ActiveUS9169495B2High expressionFunction increaseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroencapsulation basedGene deliveryPhagocytic Cell
A method of targeting bacterially-derived, intact minicells to specific, non-phagocytic mammalian cells employs bispecific ligands to deliver nucleic acids efficiently to the mammalian cells. Bispecific ligands, comprising (i) a first arm that carries specificity for a bacterially-derived minicell surface structure and (ii) a second arm that carries specificity for a non-phagocytic mammalian cell surface receptor are useful for targeting minicells to specific, non-phagocytic mammalian cells and causing endocytosis of minicells by non-phagocytic cells.
Owner:ENGENEIC MOLECULAR DELIVERY PTY LTD
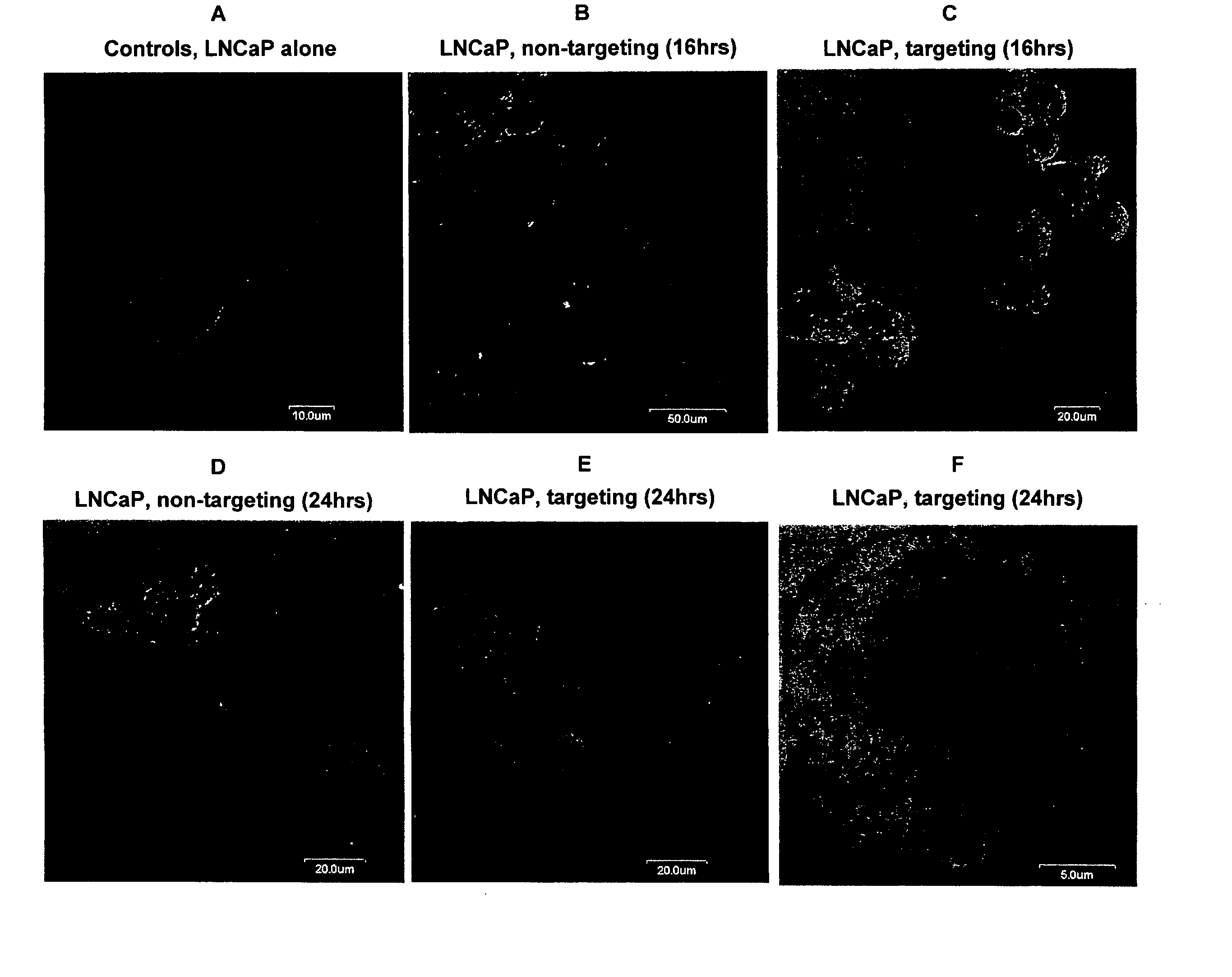
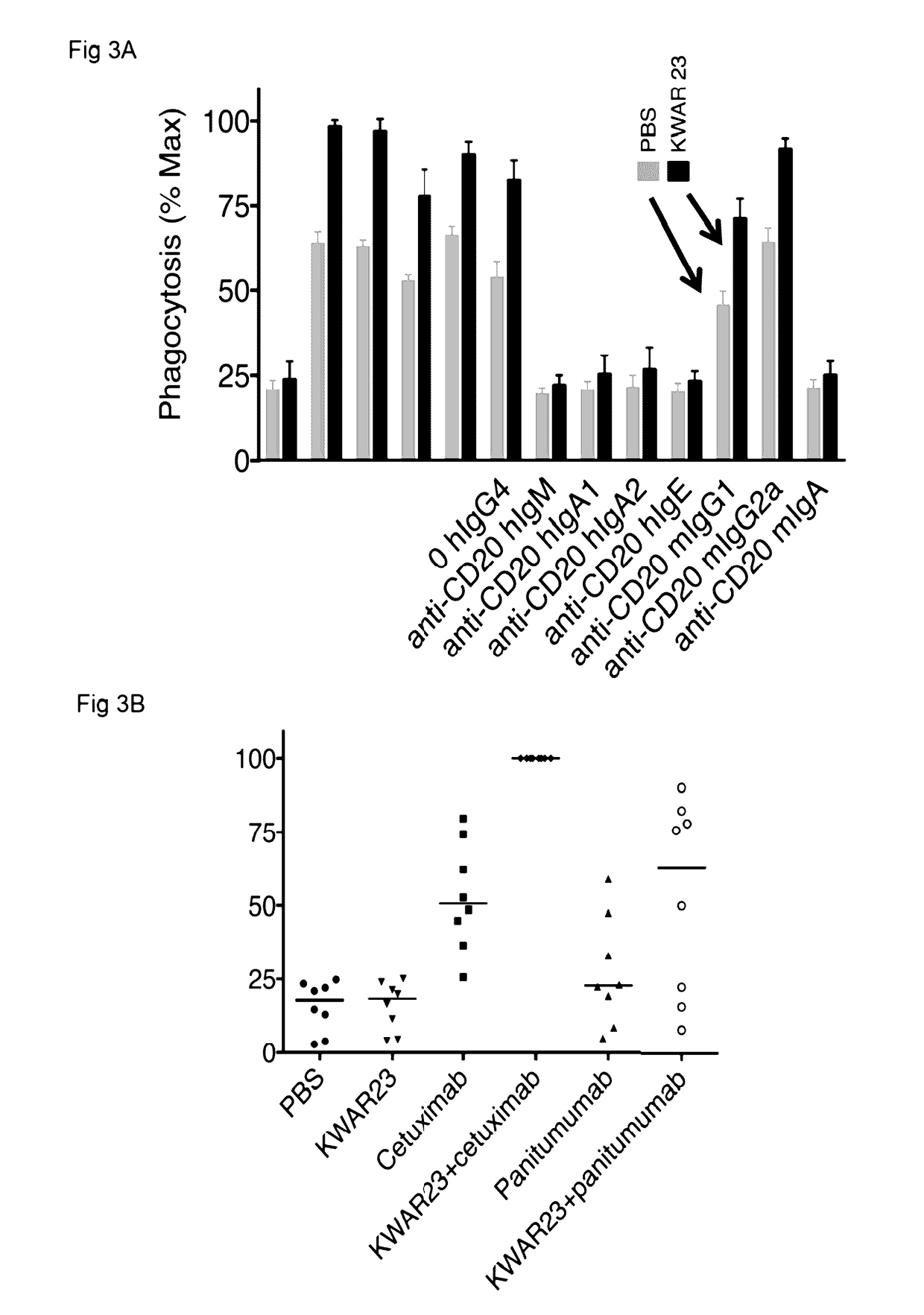
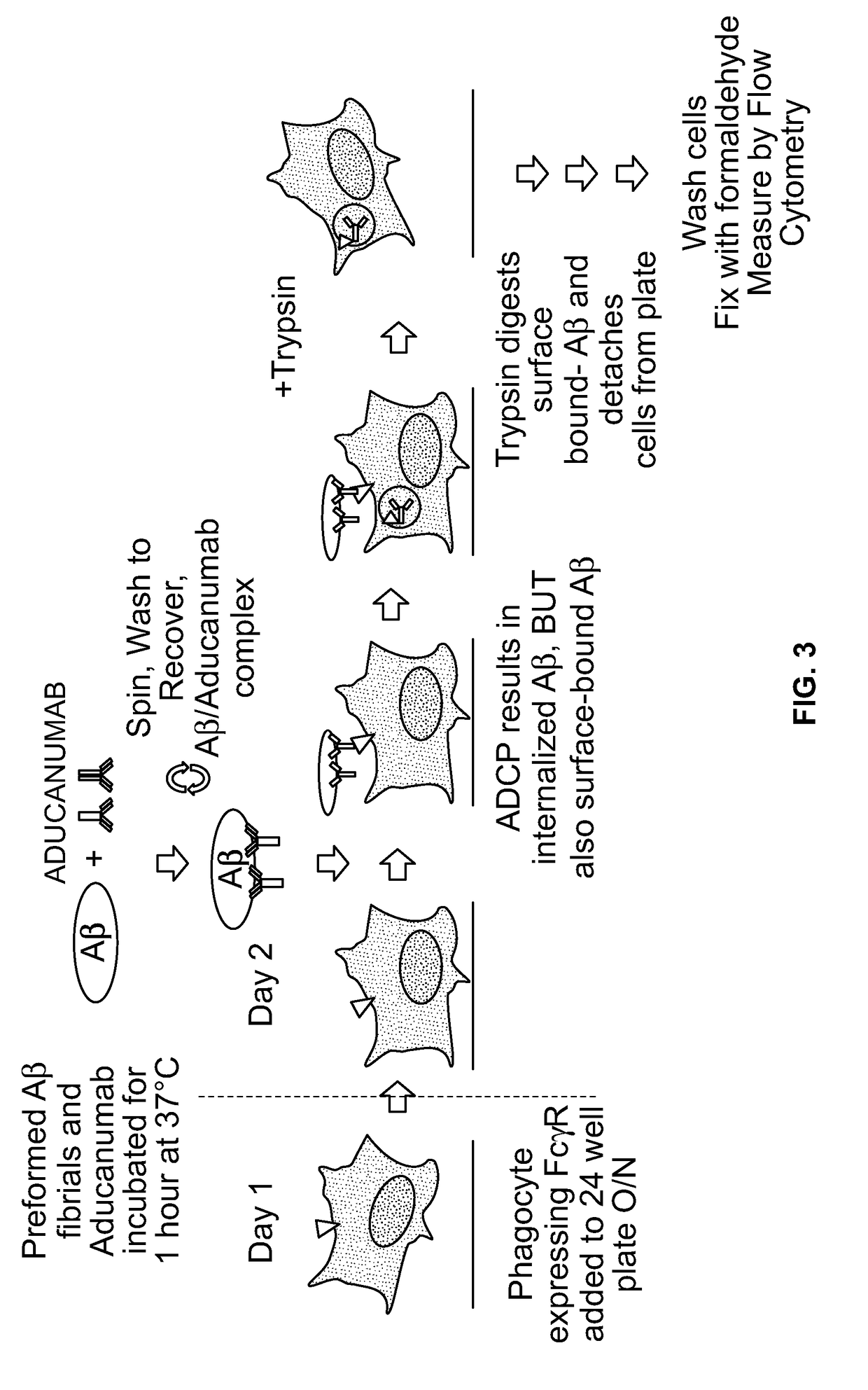
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis assay for reliably measuring uptake of aggregated proteins
ActiveUS20190079077A1High throughput analysisCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPhagocytic CellProtein insertion
The present disclosure provides methods of assaying for antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP). In some embodiments, the methods include monomerizing and labeling a protein, contacting the protein with a protein-specific antibody to form an antibody-protein complex, contacting the antibody-protein complex with a phagocytic cell to permit phagocytosis, and assessing the amount of internalized fluorescence.
Owner:BIOGEN INT NEUROSCI
Application of antradiacomphora extract capsule for protecting liver and promoting body immune regulation function
InactiveCN101785793AEnhance immune regulation functionHigh activityFungi medical ingredientsBiological testingAbnormal tissue growthPhagocyte
The invention tests liver protection and immune regulation functions by feeding a rat and a mouse with an antradiacomphora capsule which is prepared by adopting a special process and solid-state culture, wherein a liver protection test comprises the following steps of: inducing chronic hepatitis of the rat by using carbon tetrachloride twice a week for eight weeks, and measuring GPT and GOT, water content of liver, spleen and liver, liver protein and hydroxyproline content. The antradiacomphora capsule can lighten the rat chronic hepatitis induced by the carbon tetrachloride. A specific immunity test: the test matter is fed to the BALB / c mouse and egg albumen is injected, thereby accelerating the immune cell proliferation capacity and the effect of the immune regulation function generated by an antibody with serological specificity. A non-specific immunity test comprises the following step of: doing an oral test for consecutive six weeks by means of the BALB / c mouse. The invention accelerates the abdominal cavity phagocyte activity, regulates the anti-tumor cytohormone secretion and promotes the effect of the immune regulation function generated by a serological antibody.
Owner:WEI CHENG BIOTECH
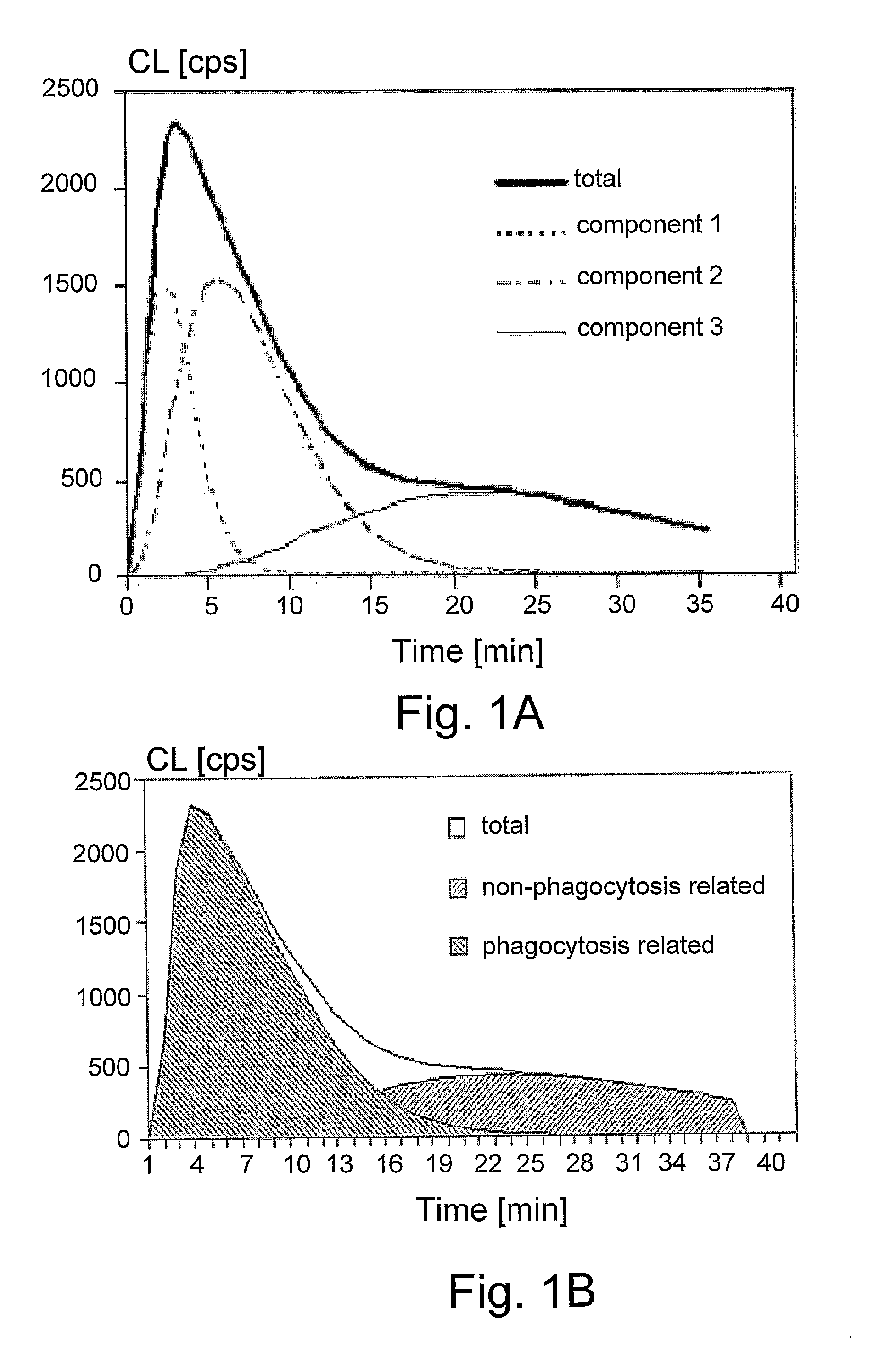
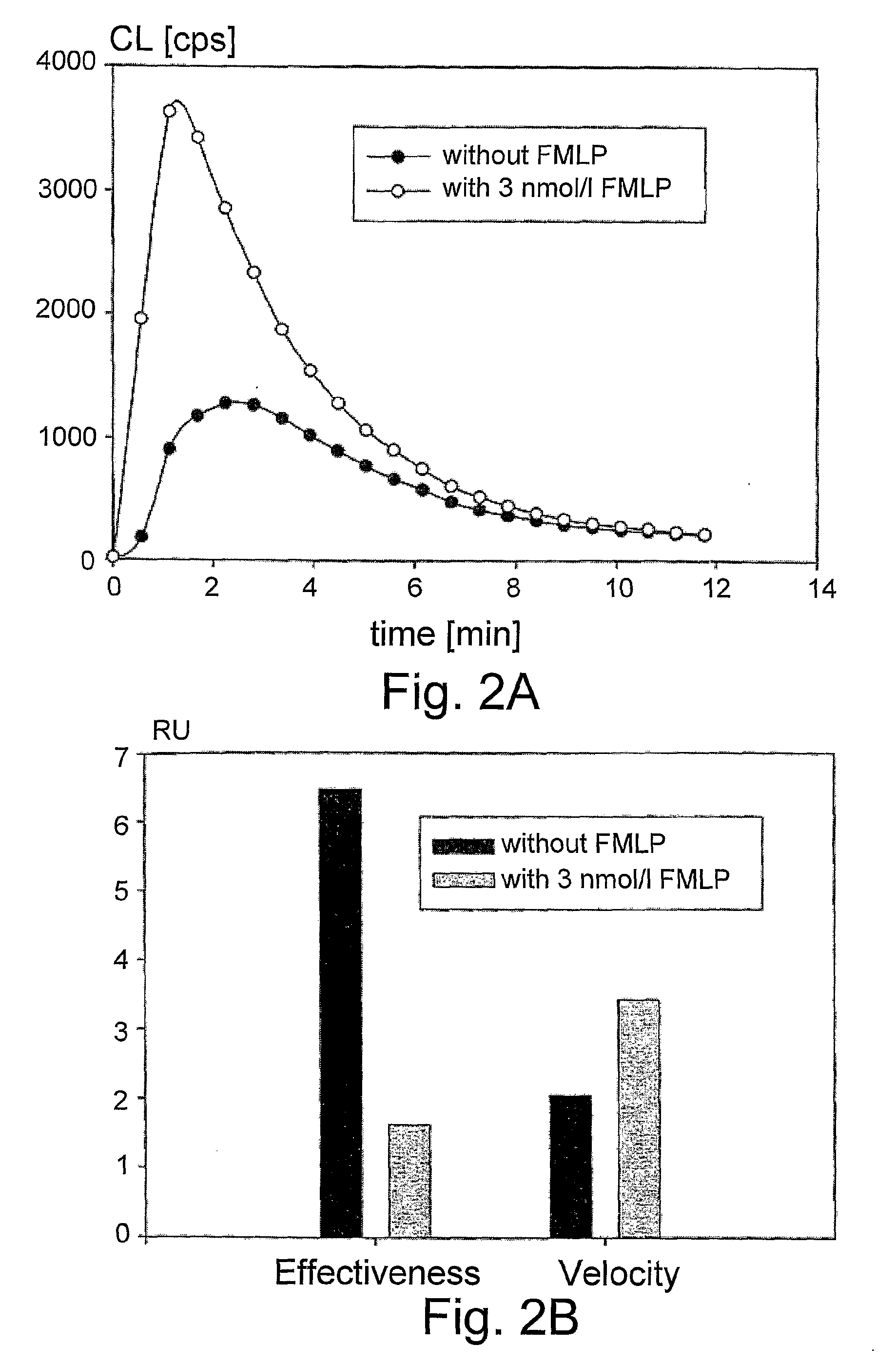
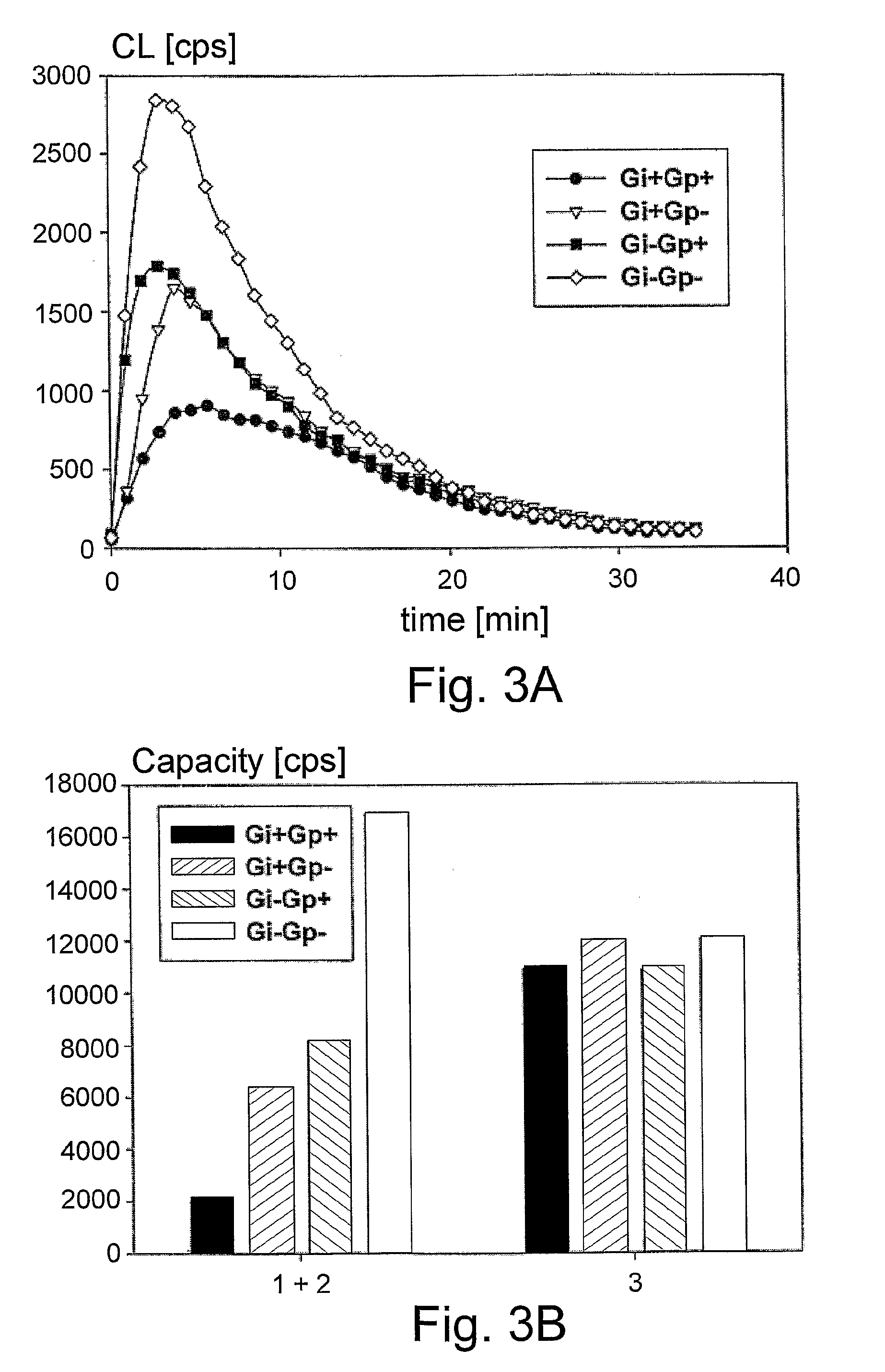
Chemiluminescent Method and Device for Evaluating the In Vivo Functional State of Phagocytes
InactiveUS20090053751A1High sensitivityMinimal signal lossBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhagocyteOxygen
A method of assessing the in vivo state of phagocytes in a patient, possibly indicating diagnostically important states such as inflammation or infection, which method utilizes chemiluminescent (CL) light emitted during the reaction in vitro between a CL substrate and the reactive oxygen species (ROS) formed in a fluid sample obtained from the patient. The measurement is performed in two or more portions of the sample, with stimulated phagocytes affected by one or more priming agents which shift the functional state of the phagocytes, providing a plurality of measurements, which are analyzed so as to distinguish intracellular and extracellular contributions to the CL kinetics. The results are compared with a range of control measurements performed with patients suffering from various diagnostic conditions.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
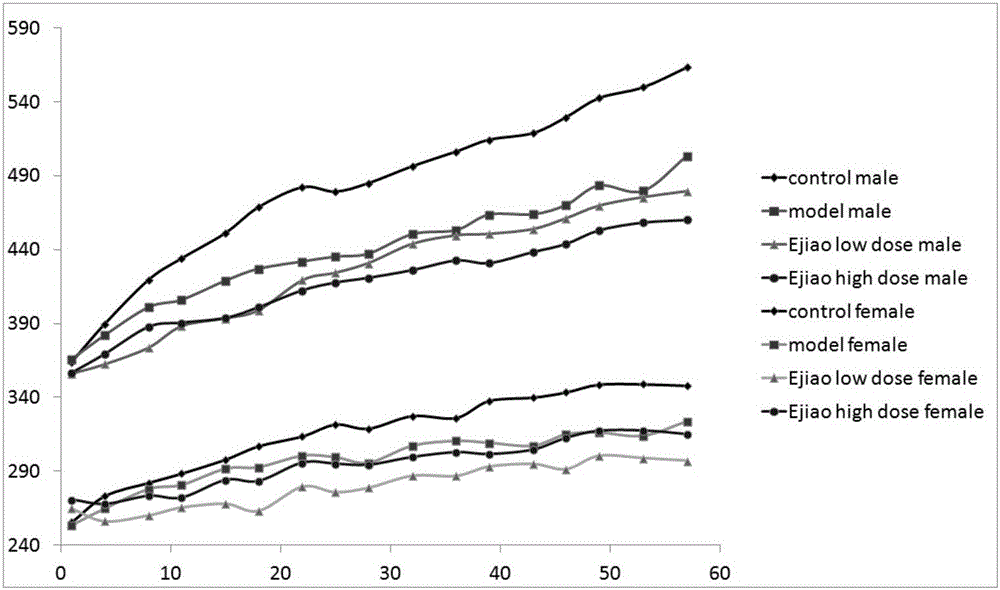
Application of donkey-hide gelatins to preparation of medicament or healthcare product for treating respiratory injury caused by fine air particulate matters
InactiveCN105726572AAvoid damageProtectiveUnknown materialsRespiratory disorderInhaled airPharmaceutical Substances
The invention discloses application of donkey-hide gelatins to preparation of a medicament or healthcare product for treating respiratory injury caused by fine air particulate matters, and belongs to the field of novel medicinal uses of donkey-hide gelatins. SD rats continuously inhale the fine air particulate matters for 8 weeks, and are given by gavage with different dosages of donkey-hide gelatin solutions for medicinal intervention at the same time of contamination, researches on an injury mechanism caused by toxicity and a protection mechanism of the donkey-hide gelatins for respiratory injury caused by the fine air particulate patterns are made from weights, organ coefficients and pulmonary functions in combination with the aspects of the hematology, blood biochemical index measurement, respiratory functions, histopathological examination, oxidative damage and the like, and experimental results show that the donkey-hide gelatins can be used for effectively reducing the content of malondialdehyde and the number of pulmonary alveolar phagocytes and increasing the content of glutathione peroxidase, have an exact improvement effect on rat pulmonary function and pulmonary pathological changes caused by the fine air particulate matters and can be applied to preparation of the medicament or healthcare product for treating respiratory injury caused by the fine air particulate matters.
Owner:SHAN DONG DONG E E JIAO
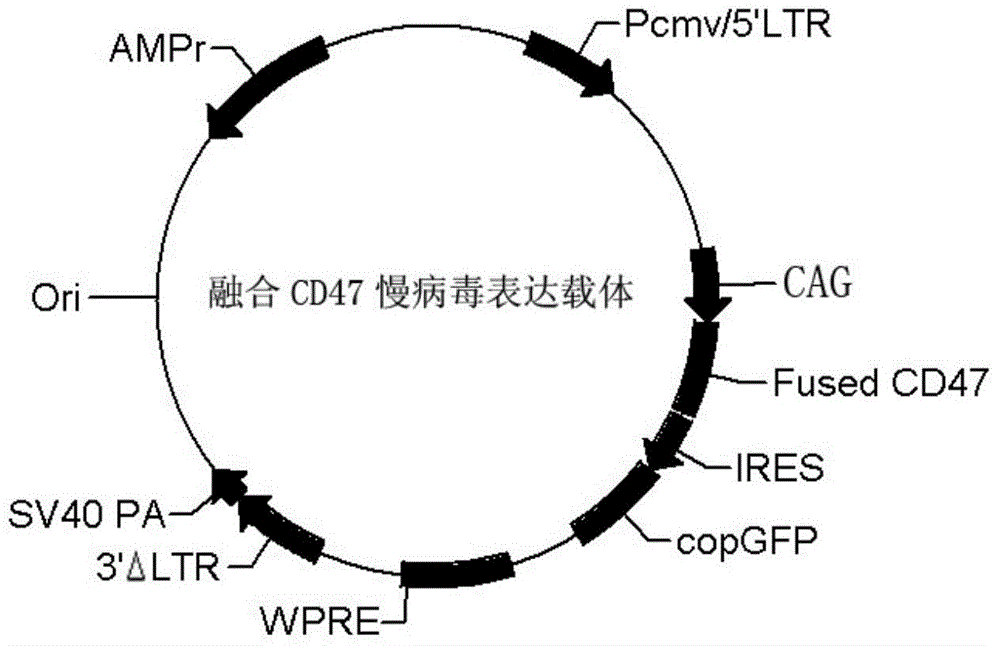
Humanized mouse
The invention discloses a humanized mouse. A mouse-human fusion CD47 gene is expressed on humanized cells of the humanized mouse and is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; an extracellular portion of the gene is a mouse CD47 sequence, and a transmembrane portion and an intracellular portion are human CD47 sequence; or the extracellular portion and the transmembrane portion are mouse CD47 amino acid sequences, and the intracellular portion is a human CD47 amino acid sequence. The humanized mouse has the humanized cells of the mouse-human fusion CD47 gene, extracellular information in an in-vivo environment of the mouse can be transmitted to the humanized cells and can be perceived by the humanized cells and the humanized cells have corresponding responses under the condition that the humanized cells are not swallowed by phagocytic cells, and the humanized cells in the humanized mouse grow and develop normally and play functions.
Owner:杭州正因生物技术有限公司
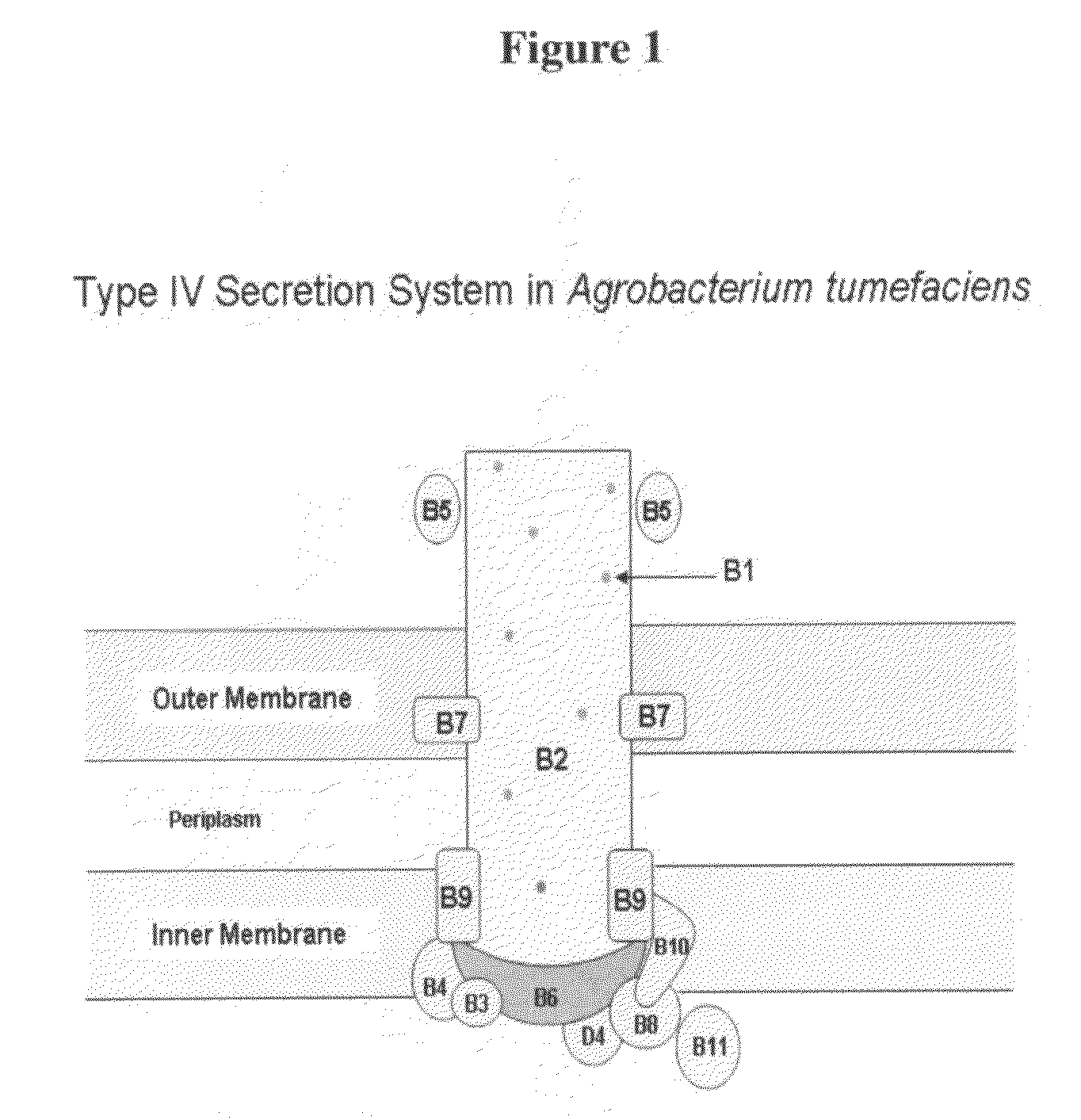
Type IV secretion system proteins in sero-detection of Anaplasma phagocytophium
Disclosed are two (2) proteins in the Type IV Secretion System (TIVSS) in Anaplasma phagocytophilum (namely, virB 10 and virB11) useful in the ELISA detection of Anaplasma pathogen. The recombinant expression of virB 10 and virB 11 and their use as kits for ELISA are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
Nucleic acid ligands capable of binding to internalin B or internalin A
The present disclosure relates to the isolation of a novel reagent selected for its binding characteristics to the proteins internalin B or internalin A. InIB is a surface-localized protein of Listeria monocytogenes that binds and activates the receptor tyrosine kinase Met. InIB promotes invasion of a number of cells including hepatocytes, endothelial and epithelial cell lines and causes activation of the actin-mediated internalization of the bacterium. InIA belongs to a large group of surface-localized leucine-rich repeat (LRR) proteins identified in the Listeria genome. InIA enables Listeria monocytogenes to invade non-phagocytic cells such as those of the human intestinal epithelium and is sufficient for adhesion to and inducing uptake into epithelial cells. The disclosed nucleic acid ligands to internalin B and internalin A may be useful for determining the presence or absence of internalin B, internalin A, or Listeria in food, clinical or environmental samples; they may also be useful as an agent for combating Listeria infection by binding to and inactivating the infection-promoting inlB or inlA proteins. One object is to incorporate these nucleic acid ligands into an in vitro diagnostic or biosensor platform designed to detect the presence or absence of internalin B, internalin A, or Listeria in food, clinical or environmental samples. Another object is to employ these nucleic acid ligands in methods for treating or preventing Listeria infection.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION +1
Implantable liposome embedded matrix composition, uses thereof, and polycaprolactone particles as scaffolds for tissue regeneration
ActiveUS20150050332A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMononuclear cell infiltration
Owner:BONUS CELLORA LTD
Compositions for transfection of biomolecules into cells
ActiveUS20130095124A1Prevents premature breakdown and releaseEnhanced interactionOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticLipid formationAntioxidant
The present invention is directed to new compositions that are described for the simultaneous, controlled dose delivery of a variety of biomolecules into phagocytic cells. Such a composition is a biologically active composition comprising: (1) at least one of the following biologically active components: (a) a nucleic acid or a derivative thereof; (b) a nucleoside, nucleotide, or a derivative of a nucleoside or nucleotide; (c) a peptide, protein, or a derivative of a peptide or protein; (d) a lipopolysaccharide or a derivative thereof; (e) a peptidoglycan or a derivative thereof; (f) a carbohydrate or a derivative thereof; (g) a lipid or a derivative thereof; (h) a lipopeptide or a derivative thereof; (i) a metal ion; (j) a thiol; (k) an antibiotic or a derivative thereof; (I) a vitamin or a derivative thereof; (m) a bioflavonoid or a derivative thereof; (n) an antioxidant or a derivative thereof; (o) an immune response modifier; (p) an antibody; (q) a biologically active nonmetal; (r) histamine or an antihistamine; and (s) a kinase inhibitor; and (2) at least one carrier effective to deliver the composition to a phagocytic cell such that the biologically active component is taken up by the phagocytic cell and influences its biological activity.
Owner:SZATHMARY SUSAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com