Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
98 results about "Unstable angina" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Unstable angina (UA) is a type of angina pectoris that is irregular. It is also classified as a type of acute coronary syndrome (ACS). It can be difficult to distinguish unstable angina from non-ST elevation (non-Q wave) myocardial infarction (NSTEMI). They differ primarily in whether the ischemia is severe enough to cause sufficient damage to the heart's muscular cells to release detectable quantities of a marker of injury (typically troponin T or troponin I). Unstable angina is considered to be present in patients with ischemic symptoms suggestive of an ACS and no elevation in troponin, with or without ECG changes indicative of ischemia (e.g., ST segment depression or transient elevation or new T wave inversion). Since an elevation in troponin may not be detectable for up to 12 hours after presentation, UA and NSTEMI are frequently indistinguishable at initial evaluation.
Method of treating acute coronary syndromes
InactiveUS20040266734A1Inhibitory activityInhibition amountBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsPhagocytic CellManagement of acute coronary syndrome
The present invention relates to methods and compositions designed for the treatment or management of acute coronary syndromes, particularly, unstable angina and acute myocardial infarction. The methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of a formulation containing one or more therapeutic agents which specifically decreases or inhibits the activity of phagocytic cells and / or eliminates or diminishes the amount of phagocytic cells including, but not limited to, macrophages and monocytes. The formulations are specifically targeted to phagocytic cells. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions of formulations containing one or more therapeutic agents of the invention for administration to subjects currently suffering from or having recently suffered an acute coronary syndrome such as unstable angina and acute myocardial infarction.
Owner:ZULI HLDG LTD
Diagnostic markers of acute coronary syndrome and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7358055B2Probability of future adverse outcomes in a patient may be rapidly and accurately determinedIncrease valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisTest sampleAngina
The present invention relates to methods for the diagnosis and evaluation of acute coronary syndromes. In particular, patient test samples are analyzed for the presence and amount of members of a panel of markers comprising one or more specific markers for myocardial injury and one or more non-specific markers for myocardial injury. A variety of markers are disclosed for assembling a panel of markers for such diagnosis and evaluation. In various aspects, the invention provides methods for the early detection and differentiation of stable angina, unstable angina, and myocardial infarction. Invention methods provide rapid, sensitive and specific assays that can greatly increase the number of patients that can receive beneficial treatment and therapy, reduce the costs associated with incorrect diagnosis, and provide important information about the prognosis of the patient.
Owner:BIOSITE INC
Methods and devices for targeting a site in a mammal and for removing species from a mammal
InactiveUS20050271653A1Improve stabilityImprove morbidityPowder deliveryOther blood circulation devicesTumor targetDisease
Methods and devices for improved targeting to a site in an organism, particularly to a tumor target site and for extracorporeal affinity adsorption, particularly in the treatment of cancer, atherosclerosis, including coronary artery disease, unstable angina, other acute ischemic syndromes and idiopathic dilated cardiac myopathy. In one aspect of the invention, a combination is provided comprising an extracorporeal device (1) having contained therein a binding compound (11) bound to a carrier (9), the binding compound having affinity for a binding partner, and a plurality of affinity binders (15), each of said affinity binders comprising a first portion (19) comprising the binding partner and a second portion (17) adapted to bind selectively with a species, the second portions of each of said affinity binders differing from each other.
Owner:STRAHILEVITZ MEIR
Therapeutic morpholino-substituted compounds
Morpholino-substituted pyridopyrimidine, quinolone, and benzopyranone derivatives inhibit phosphoinositide (PI) 3-kinase, an enzyme that regulates platelet-adhesion processes. As a consequence, the compounds in question have anti-thrombotic activity, as well as other pharmaceutical properties. The compounds claimed are represented by formula (I), (II) and (III). PI 3-kinase generates 3-phosphorylated PI second messengers which stimulate platelet adhesion under blood-flow conditions. Because platelet adhesion is a necessary step in the formation of a thrombus, inhibition by these compounds of PI 3-kinase under such conditions inhibits or prevents thrombus formation. The compounds are useful in treating PI 3-kinase-dependent conditions including cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery occlusion, stroke, acute coronary syndrome, acute myocardial infarction, vascular restenosis, atherosclerosis, and unstable angina; respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD), and bronchitis; inflammatory disorders; neoplasms including cancers such as glioma, prostate cancer, small cell lung cancer, and breast cancer, and diseases linked to disordered white blood cell function, such as autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
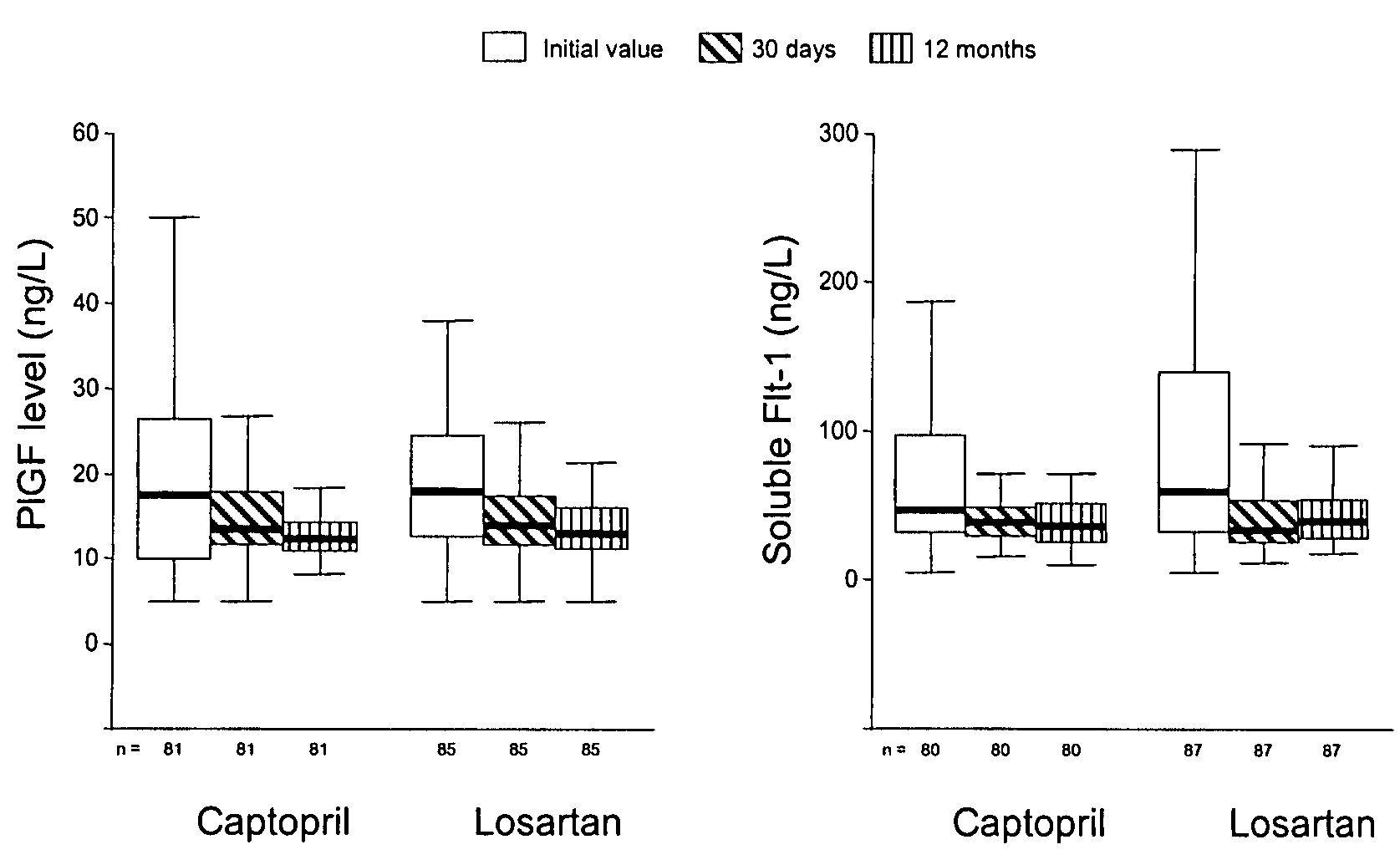
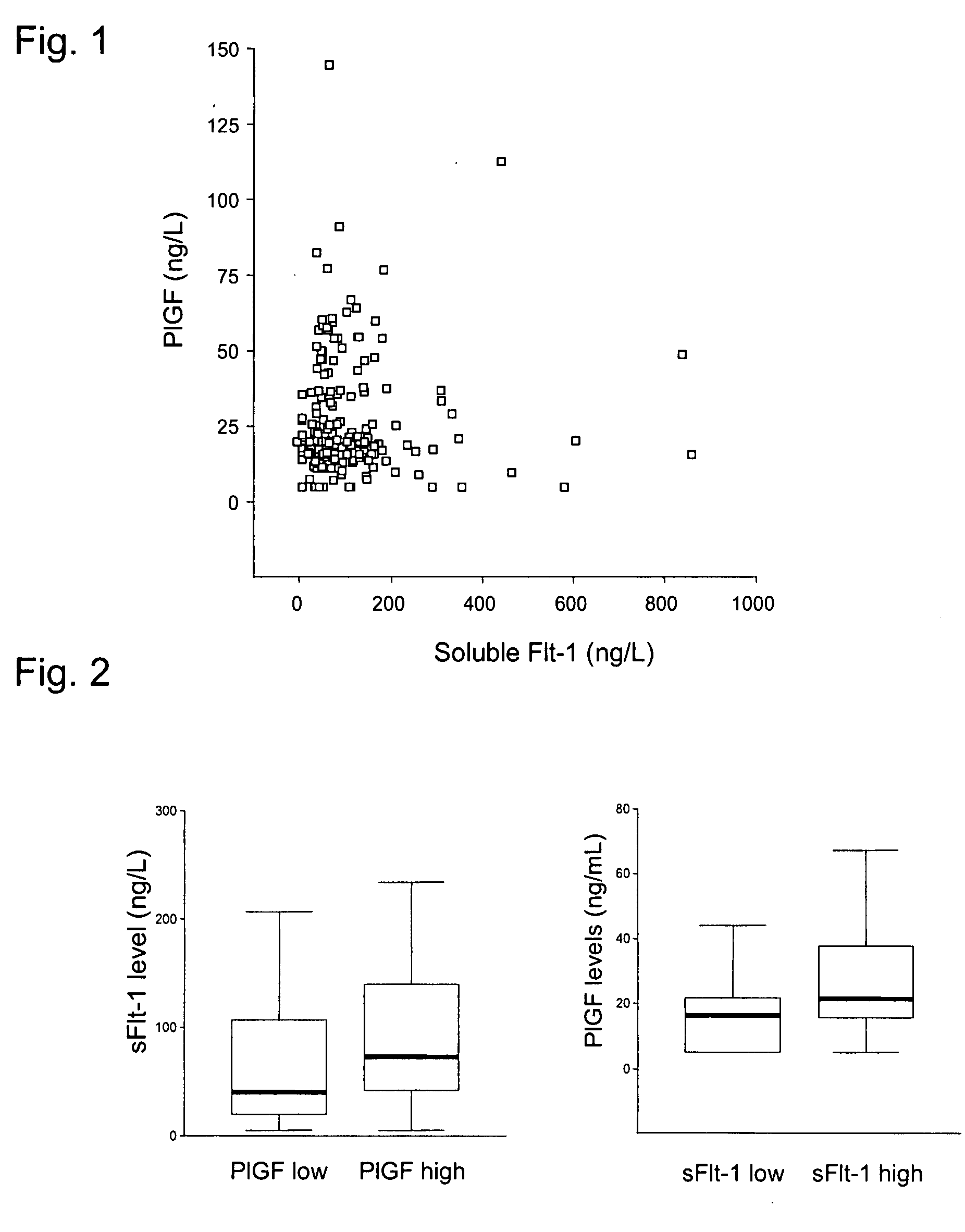
PIGF and FLT-1 as Prognostic Parameters for Cardiovascular Diseases
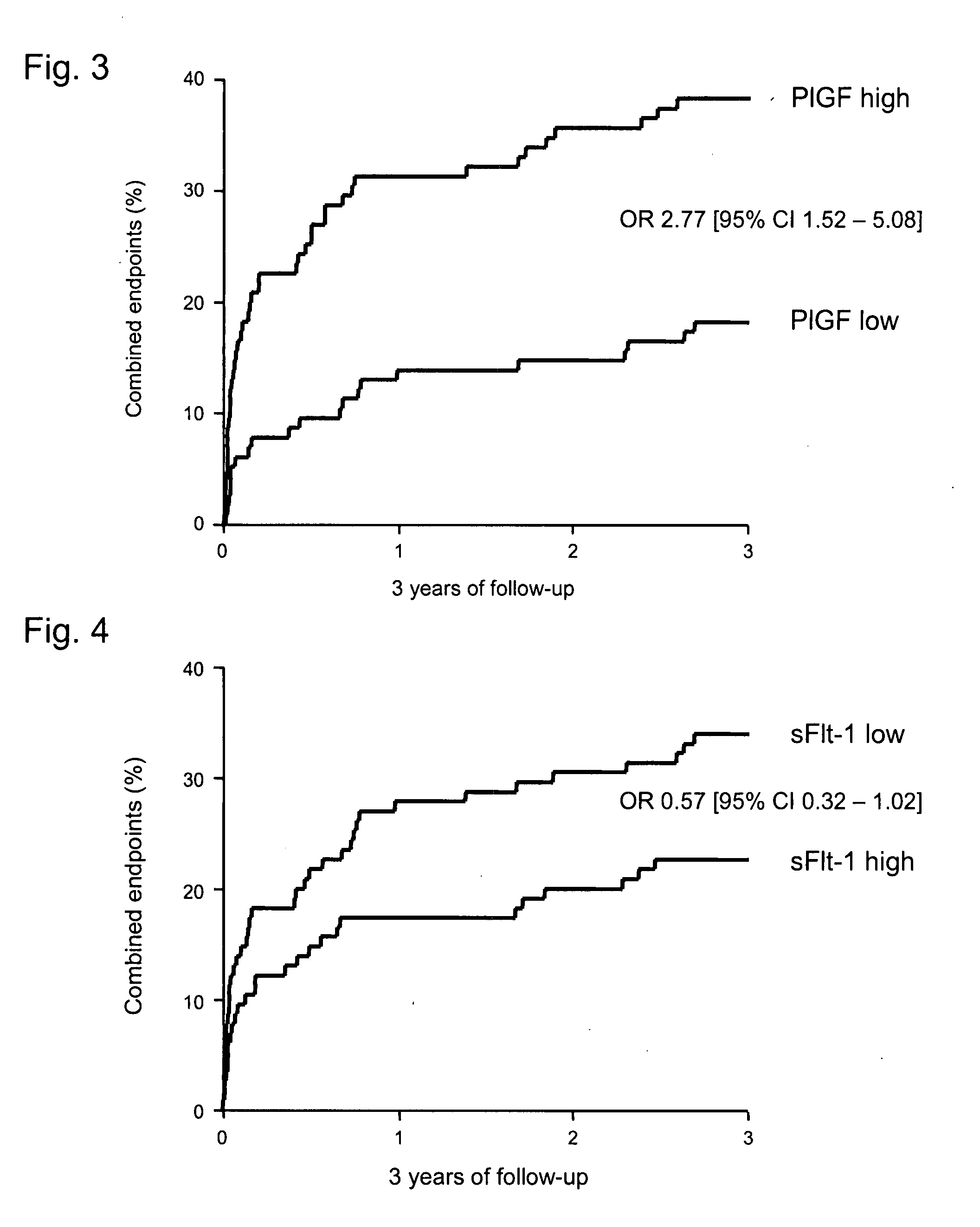
InactiveUS20090155827A1Reduce riskGood benefitMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisEtiologyAngina
The present invention refers to a use of an ex vivo method comprising the determination of PlGF and sFlt-1 in a sample for diagnosis, risk stratification and / or monitoring of a vascular disease with atherosclerotic etiology, in particular a coronary heart disease such a unstable angina pectoris or myocardial infarction, and / or for estimation of the probability of developing such a disease, as well as for identification of a patient supposed to benefit from a therapy by agents reducing the risk for a cardiovascular disease. In the method (i) a ratio of [PlGF=high:sFlt-1=low], and / or (ii) a PlGF concentration in the upper two tertiles of a reference collective, and an sFlt-1 concentration in the lower tertile of the reference collective, and / or (iii) a PlGF result above a PlGF reference value, and an sFlt-1 result below an sFlt-1-reference value indicate an elevated probability for an adverse event. The present invention also refers to the used method. The present invention further refers to a diagnostic kit and its use as well as to an assay element and its use.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS PRODS
Inhibition of platelet activation, aggregation and/or adhesion by hypothermia
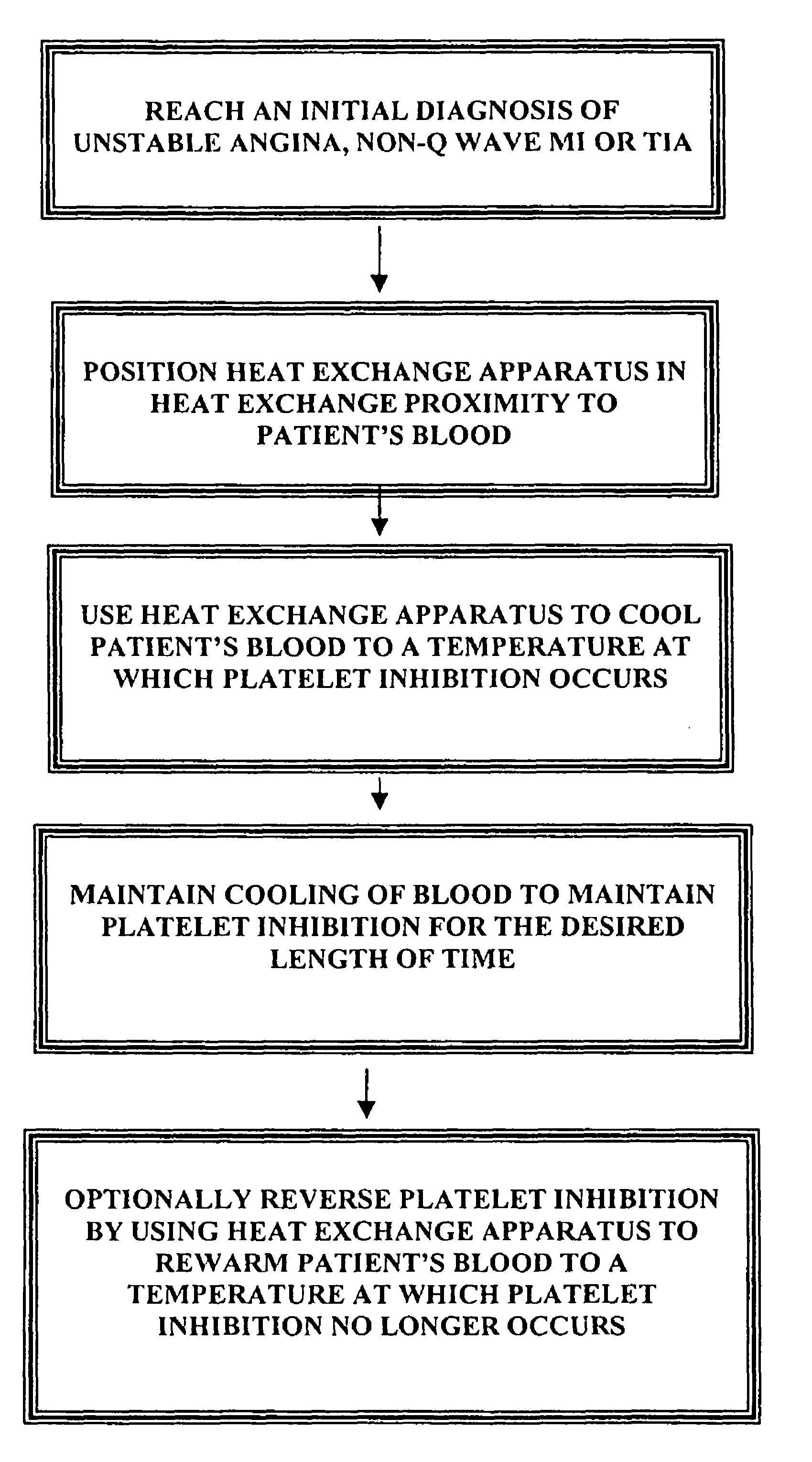
InactiveUS7846193B2Faster clearanceQuick effectTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingInstabilityACS - Acute coronary syndrome
A method for treating acute coronary syndromes (i.e., unstable angina or non-Q-wave MI) or transient ischemic attacks in a human or animal patient by placing a heat exchange apparatus in the patient's vasculature and using that heat exchange apparatus to cool the patient to a temperature (e.g. 30-36° C.) at which platelet inhibition (i.e., inhibition of platelet activation and / or aggregation and / or adhesion) occurs. Anti-shivering drugs or anesthesia may be administered to patients whose body temperature is cooled below that patient's shivering threshold (typically approximately 35.5 C). If it is determined that platelet inhibition is no longer desirable, such as when the patient is about to undergo a surgical or interventional procedure wherein bleeding could be problematic, the hypothermia-induced platelet inhibition may be rapidly reversed by using the intravascular heat exchange apparatus to re-warm the patient's body to normothermia or near normothermia.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
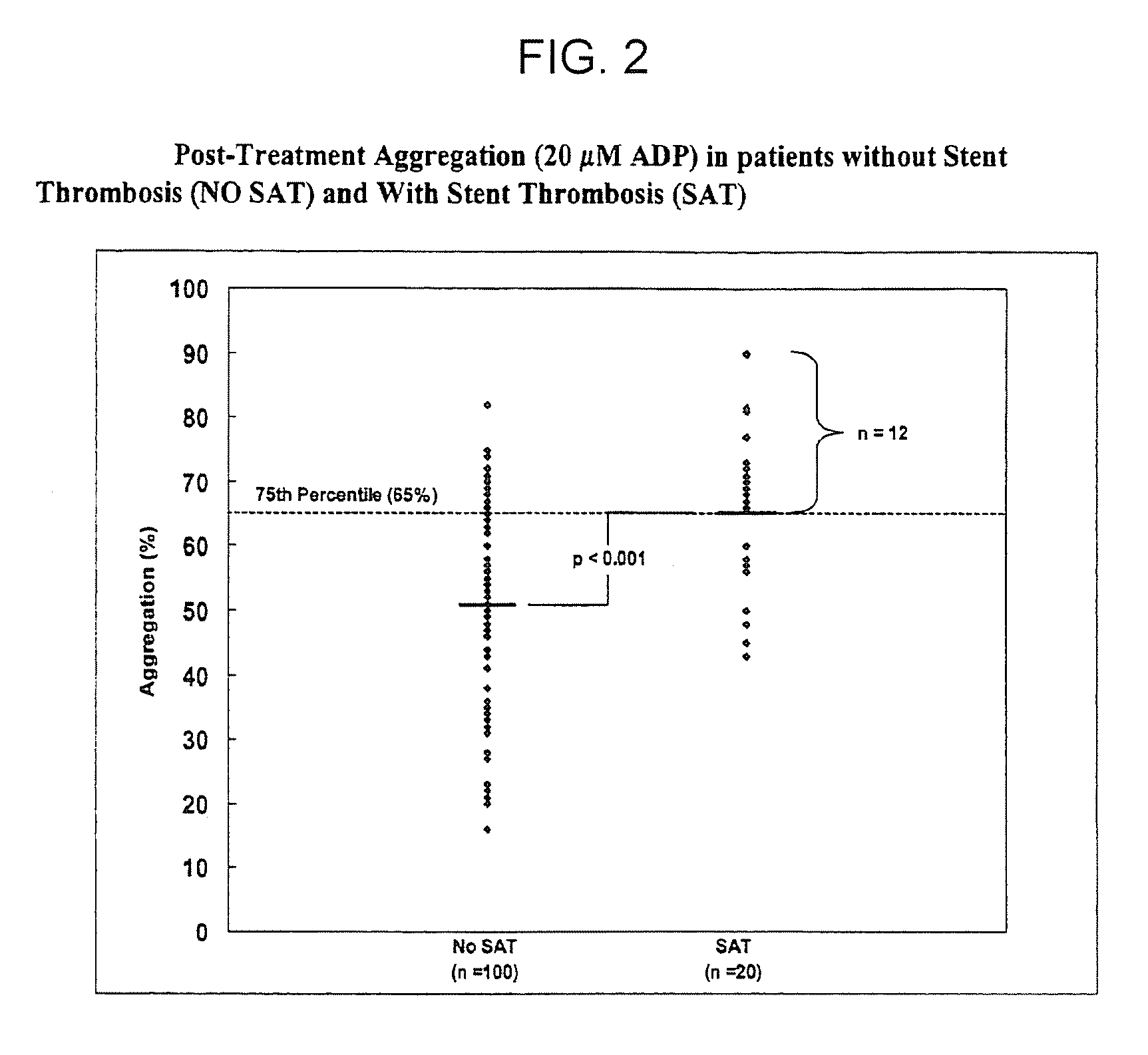
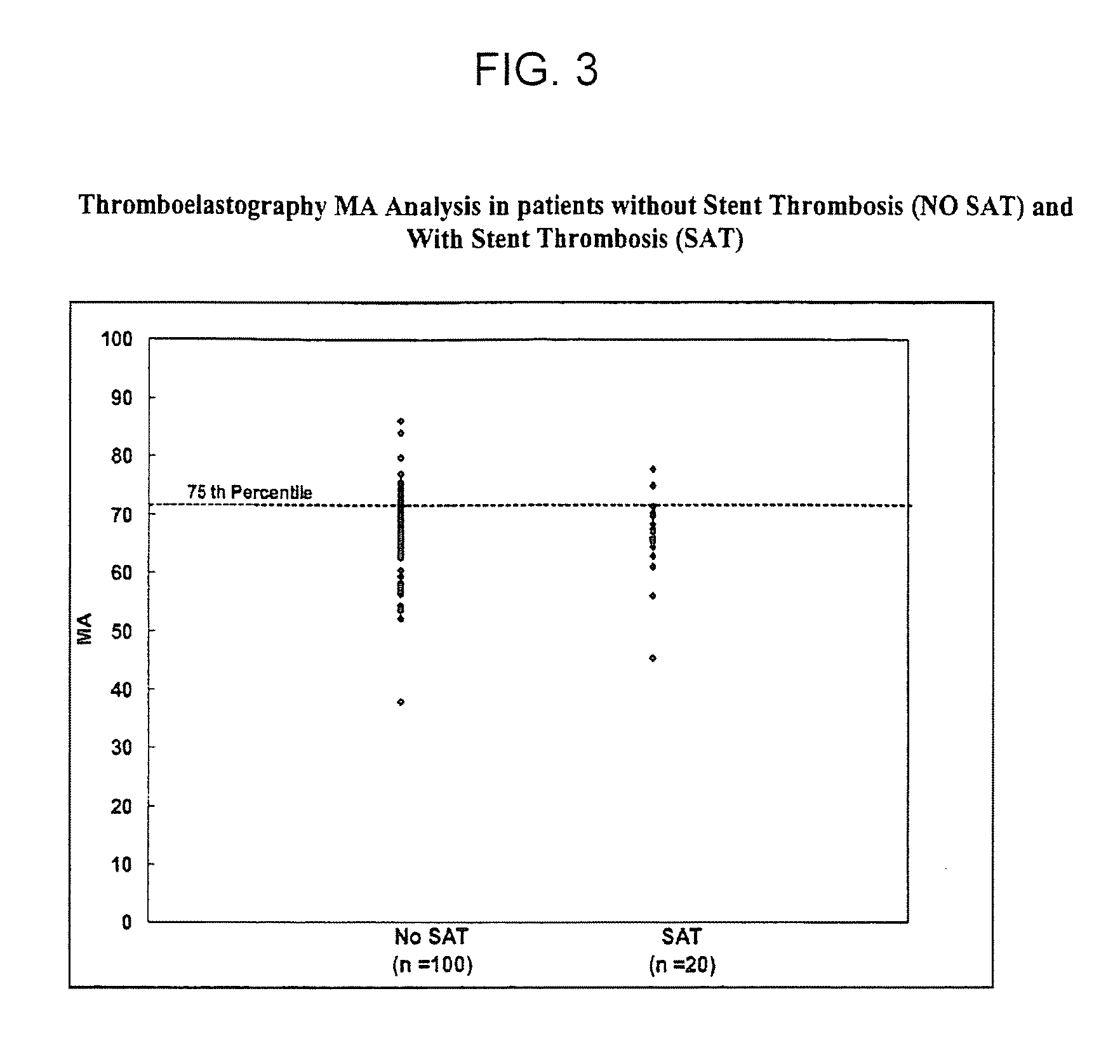
Assessment of cardiac health and thrombotic risk in a patient
ActiveUS20060199239A1Reduce riskRisk of the thrombotic event is assessedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseasePercent Diameter Stenosis
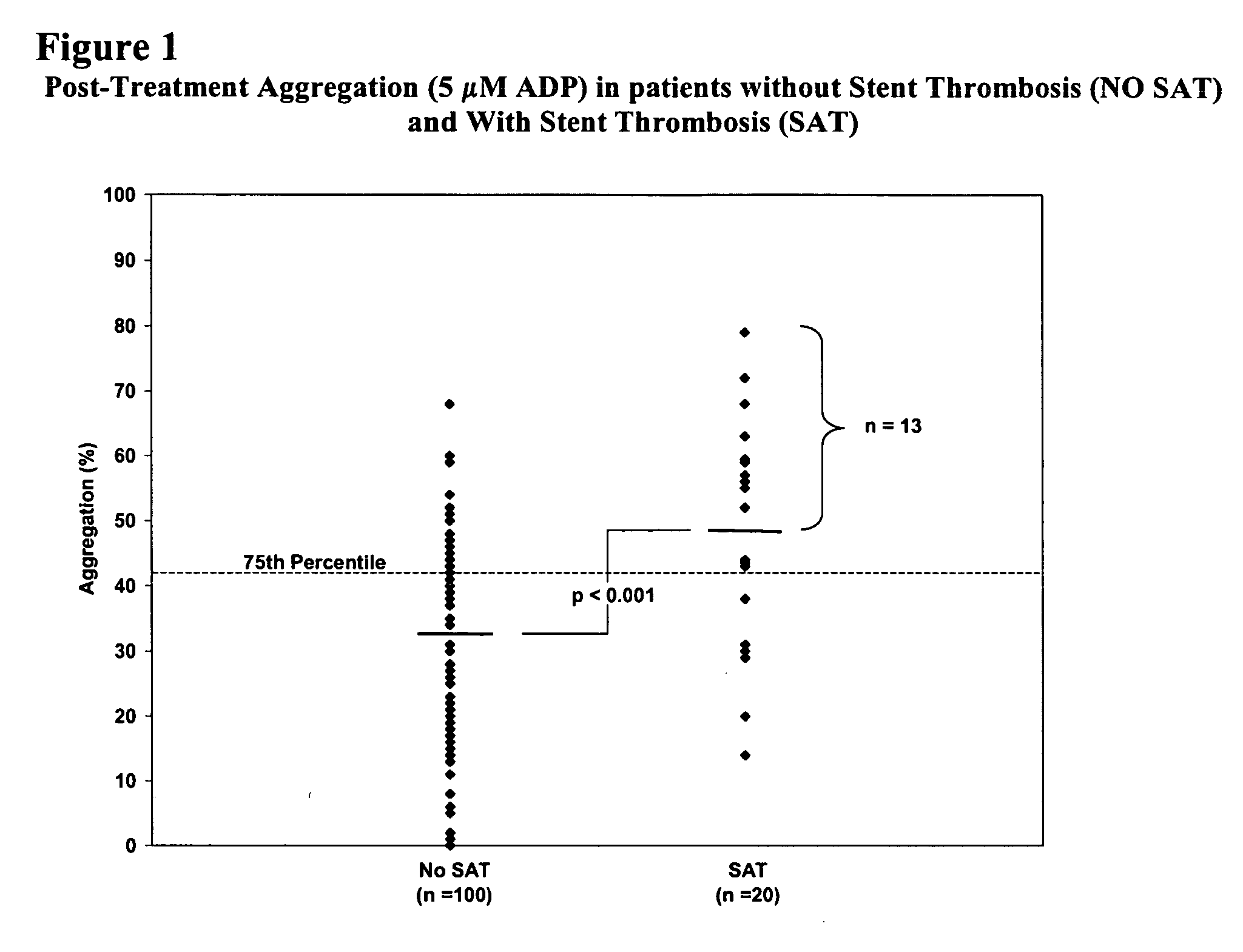
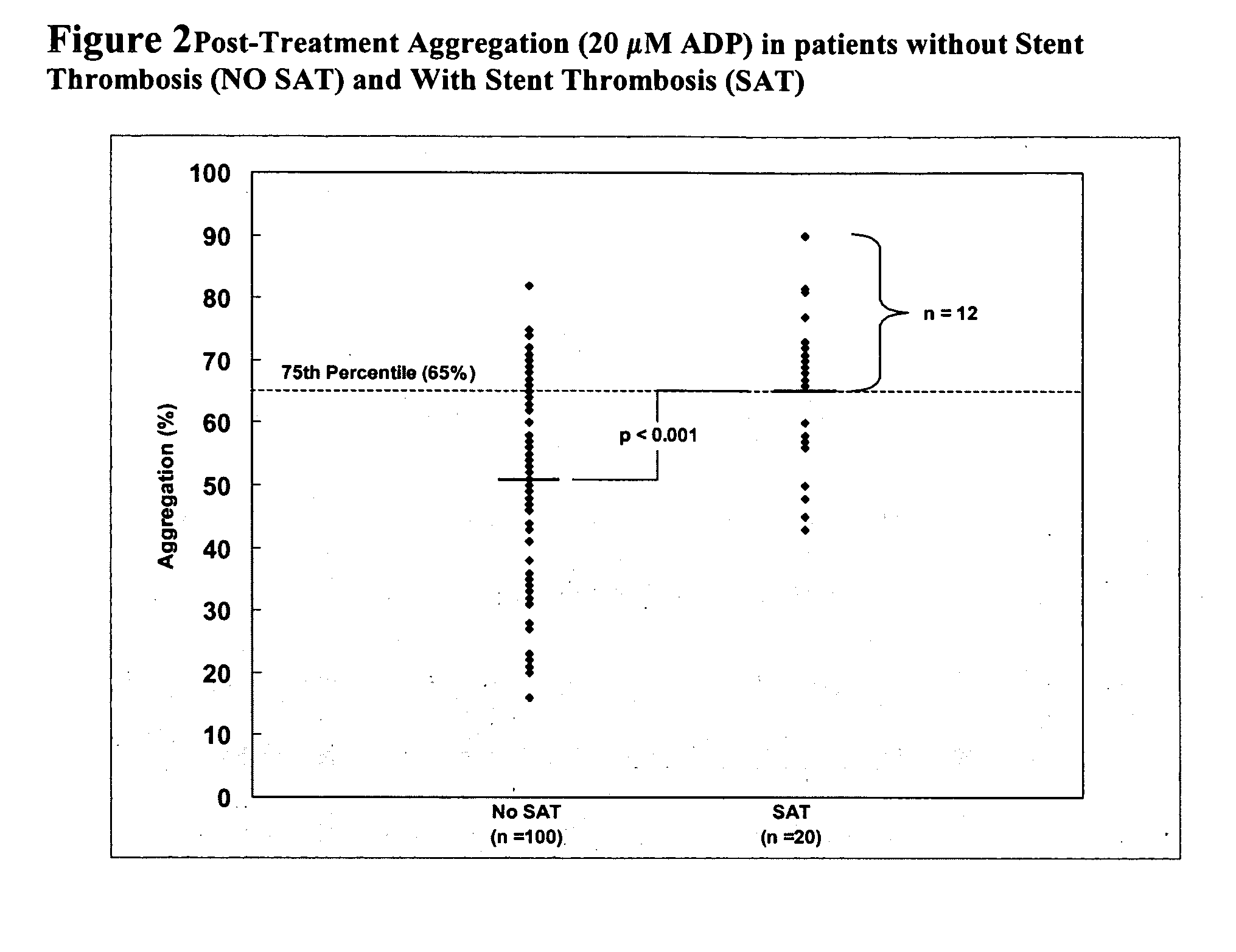
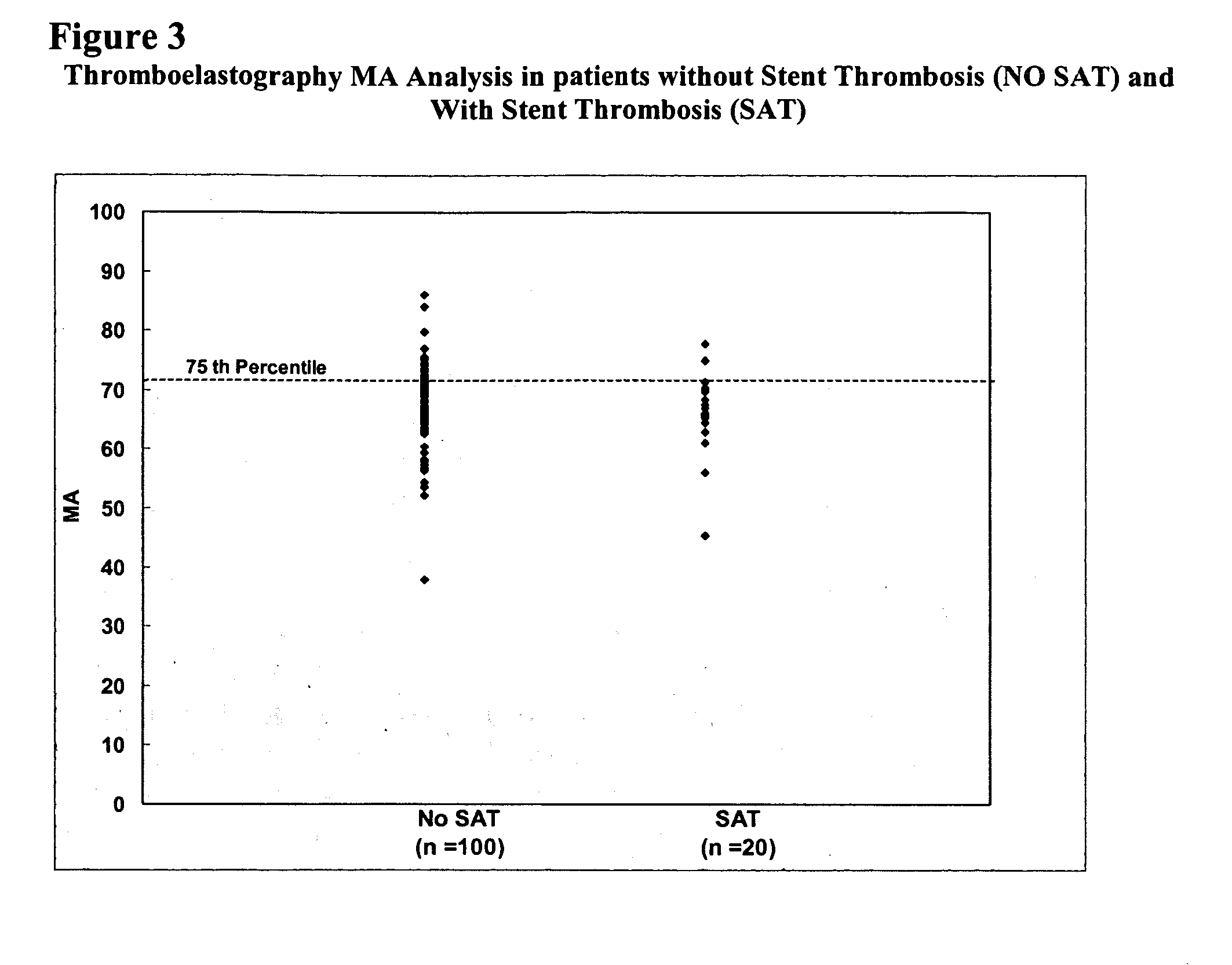
The invention features methods and compositions for assessing risk, particularly immediate risk, of thrombotic events in patients with suspected or known vascular disease, and more particularly to assessing risk of thrombotic events in patients with coronary artery disease, particularly acute myocardial infarction, stroke, unstable angina, stable angina, or restenosis. Risk of thrombosis can be assessed by analysis of platelet reactivity and / or velocity of thrombin or fibrin formation, and determining whether the patient has a score associated above a risk threshold value. In other embodiments, risk of thrombosis in a patient is evaluated in the context of a profile generated from values obtained from one or more assays that evaluate various factors associated with thrombosis and / or atherosclerosis.
Owner:GURBEL PAUL A
Selected dosage for the treatment of cardiovascular and related pathologies
Method is provided of treating or preventing hypertrophy, hypertension, myocardial ischemia, ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, organ ischemia, tissue ischemia, acute coronary syndrome, unstable angina, ischemia reperfusion injury, preventing death subsequent to myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, contractile dysfunction subsequent to myocardial infarction, or arrhythmia in a mammal with low doses of pyridoxine, pyridoxal-5′phosphate, pyridoxal or pyridoxamine. Compositions and kits for said method is also included.
Owner:MEDICURE INT INC
Future cardiac event biomarkers
ActiveUS20110059103A1Sure easyOrganic active ingredientsParticle separator tubesBiomarker (petroleum)ACS - Acute coronary syndrome
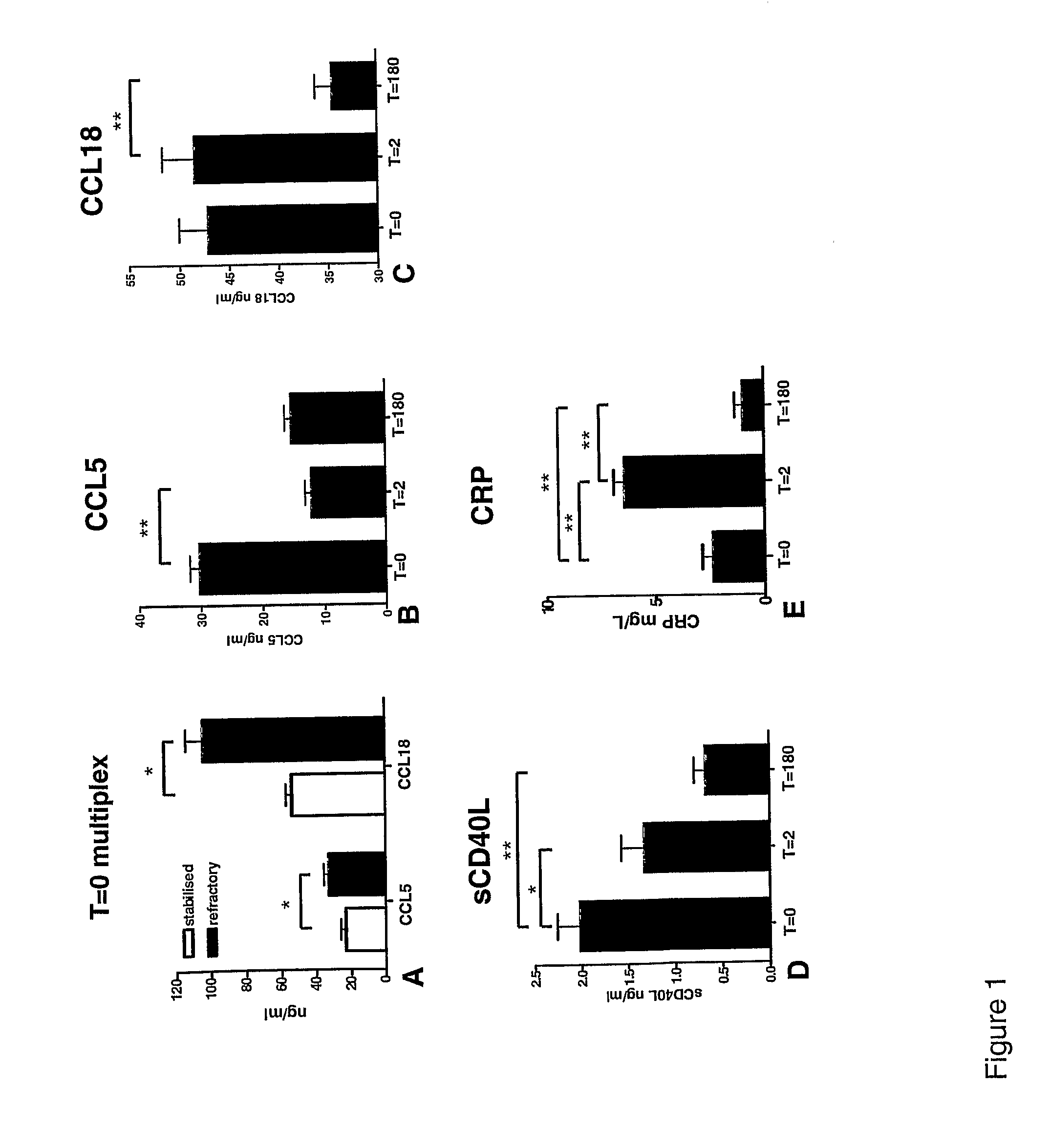
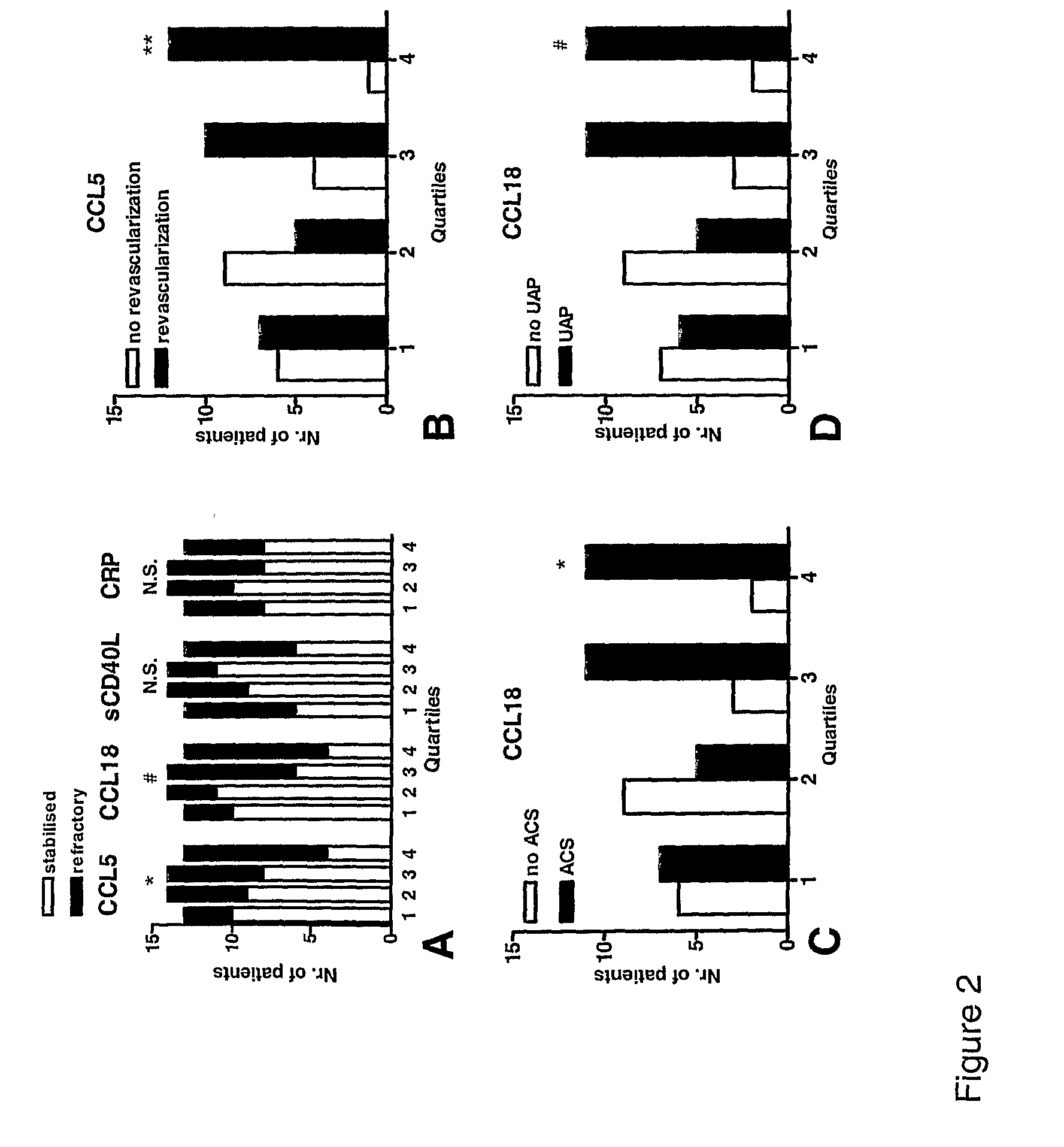
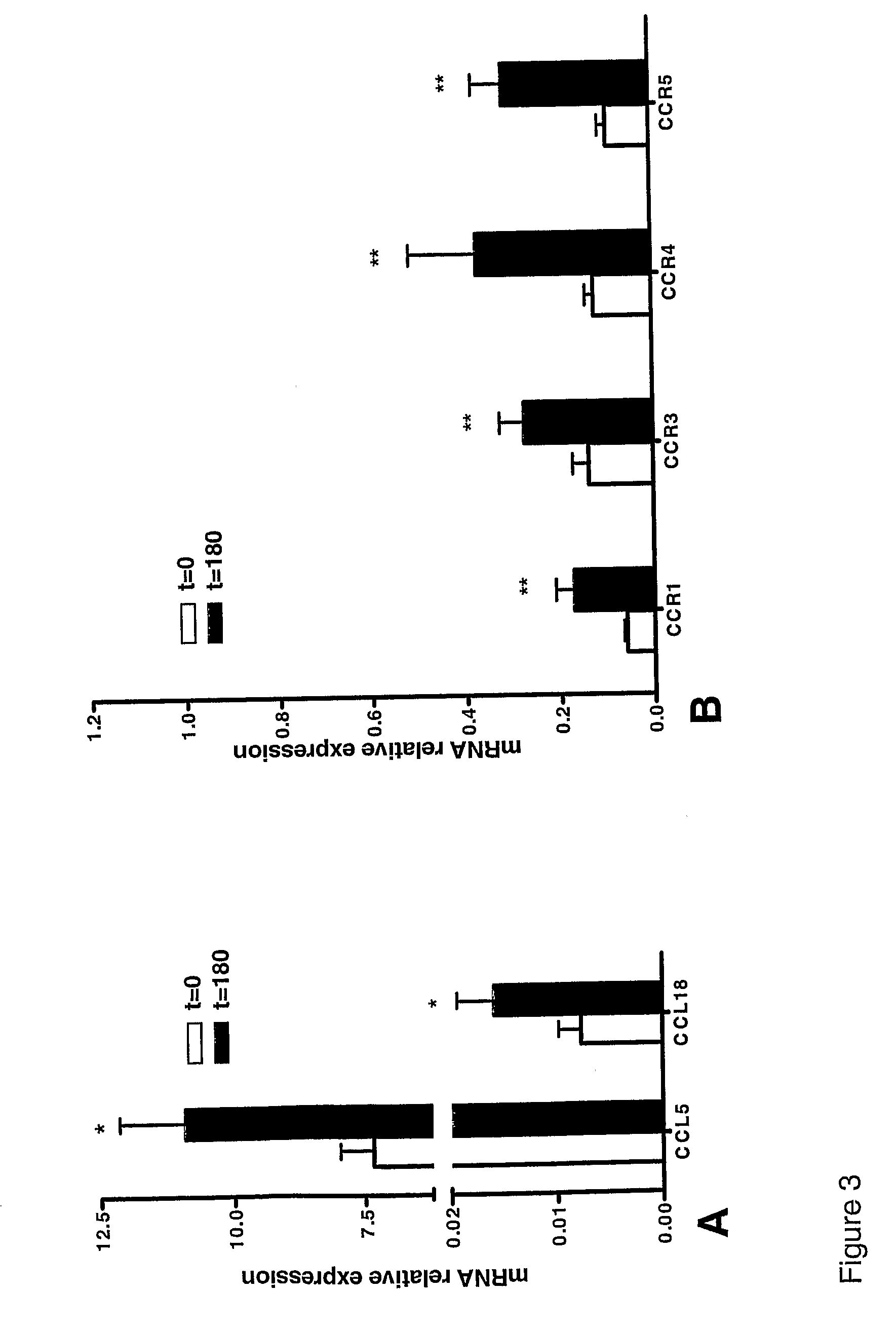
The present invention relates to the identification of chemokine biomarkers predictive of future acute coronary syndromes including unstable angina pectoris (UAP). The present invention also identifies particular chemokines as potential therapeutic targets for intervention in cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:LEIDEN UNIVERSITY +1
Diagnostic markers of acute coronary syndrome and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060063204A1Easy to analyzeProbability of future adverse outcomes in a patient may be rapidly and accurately determinedMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisTest sampleAngina
The present invention relates to methods for the diagnosis and evaluation of acute coronary syndromes. In particular, patient test samples are analyzed for the presence and amount of members of a panel of markers comprising one or more specific markers for myocardial injury and one or more non-specific markers for myocardial injury. A variety of markers are disclosed for assembling a panel of markers for such diagnosis and evaluation. In various aspects, the invention provides methods for the early detection and differentiation of stable angina, unstable angina, and myocardial infarction. Invention methods provide rapid, sensitive and specific assays that can greatly increase the number of patients that can receive beneficial treatment and therapy, reduce the costs associated with incorrect diagnosis, and provide important information about the prognosis of the patient.
Owner:BIOSITE INC
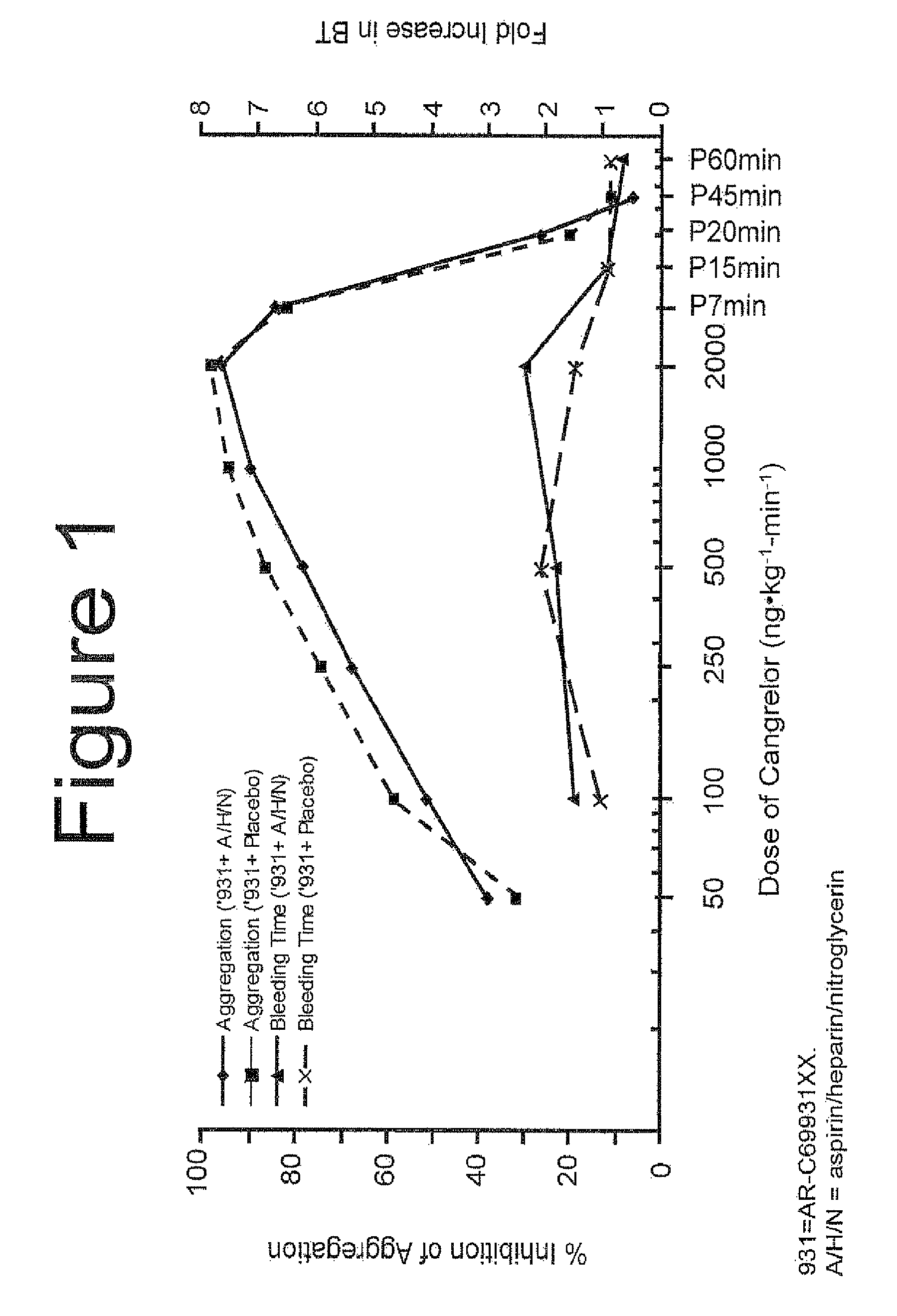
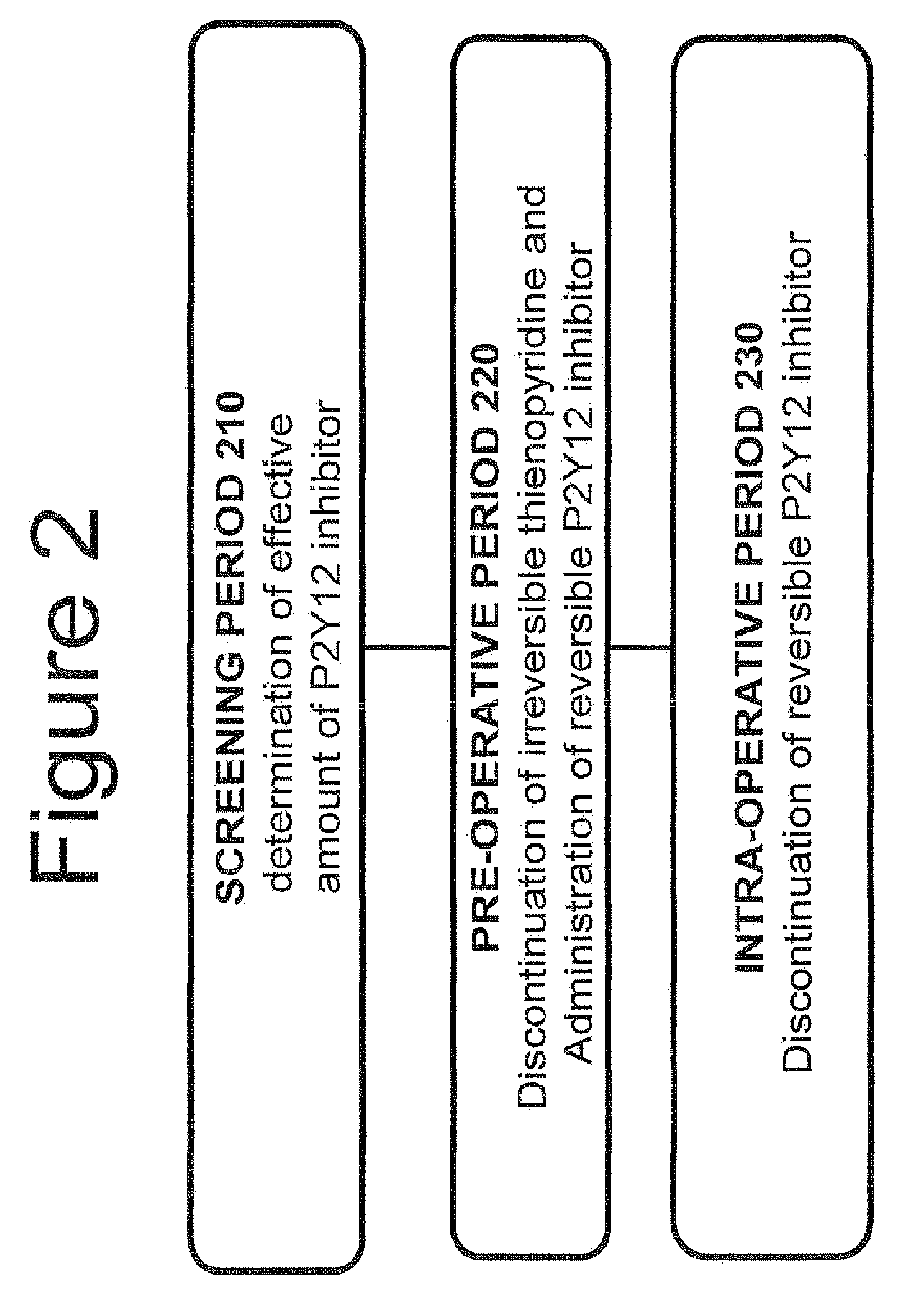
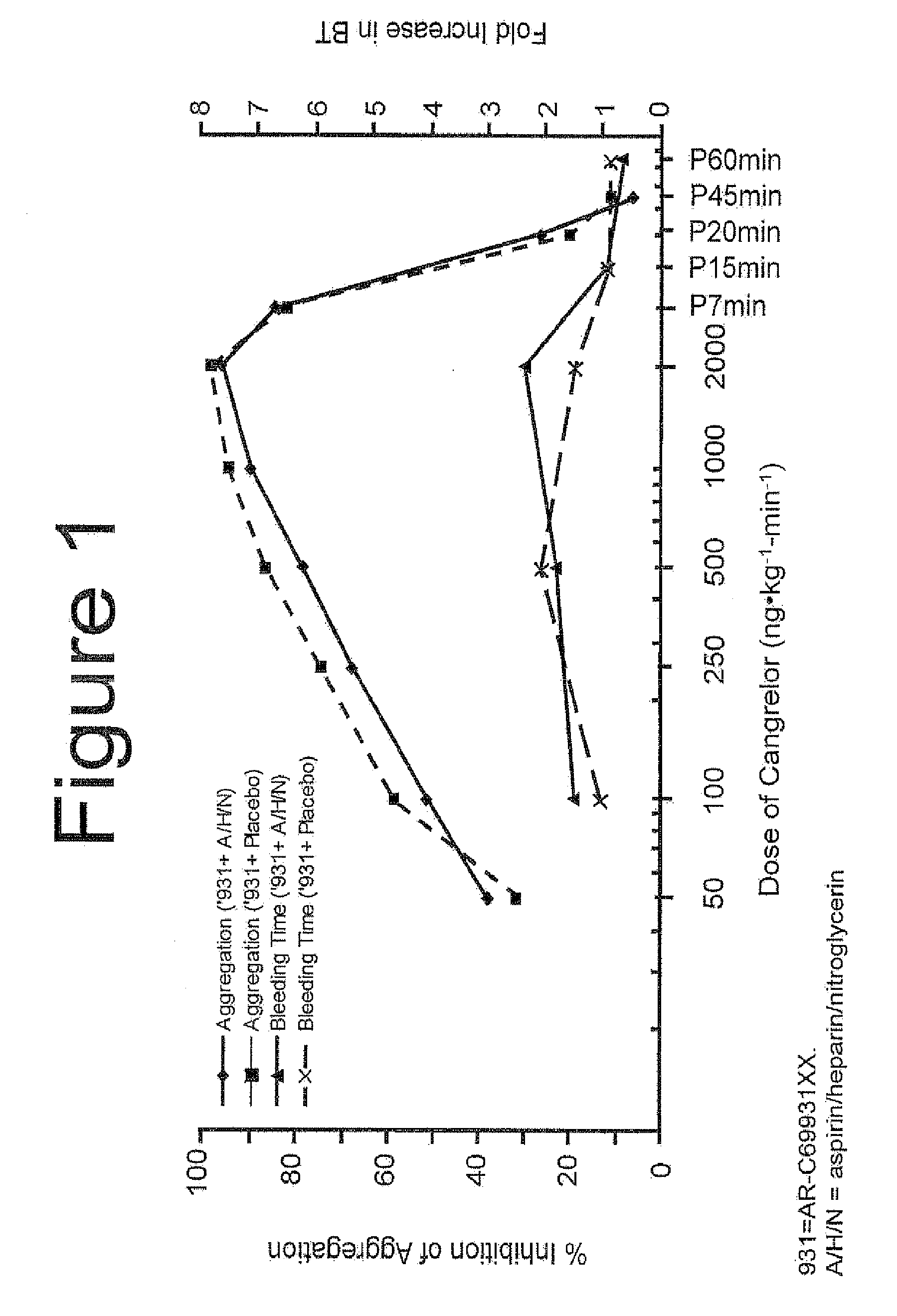
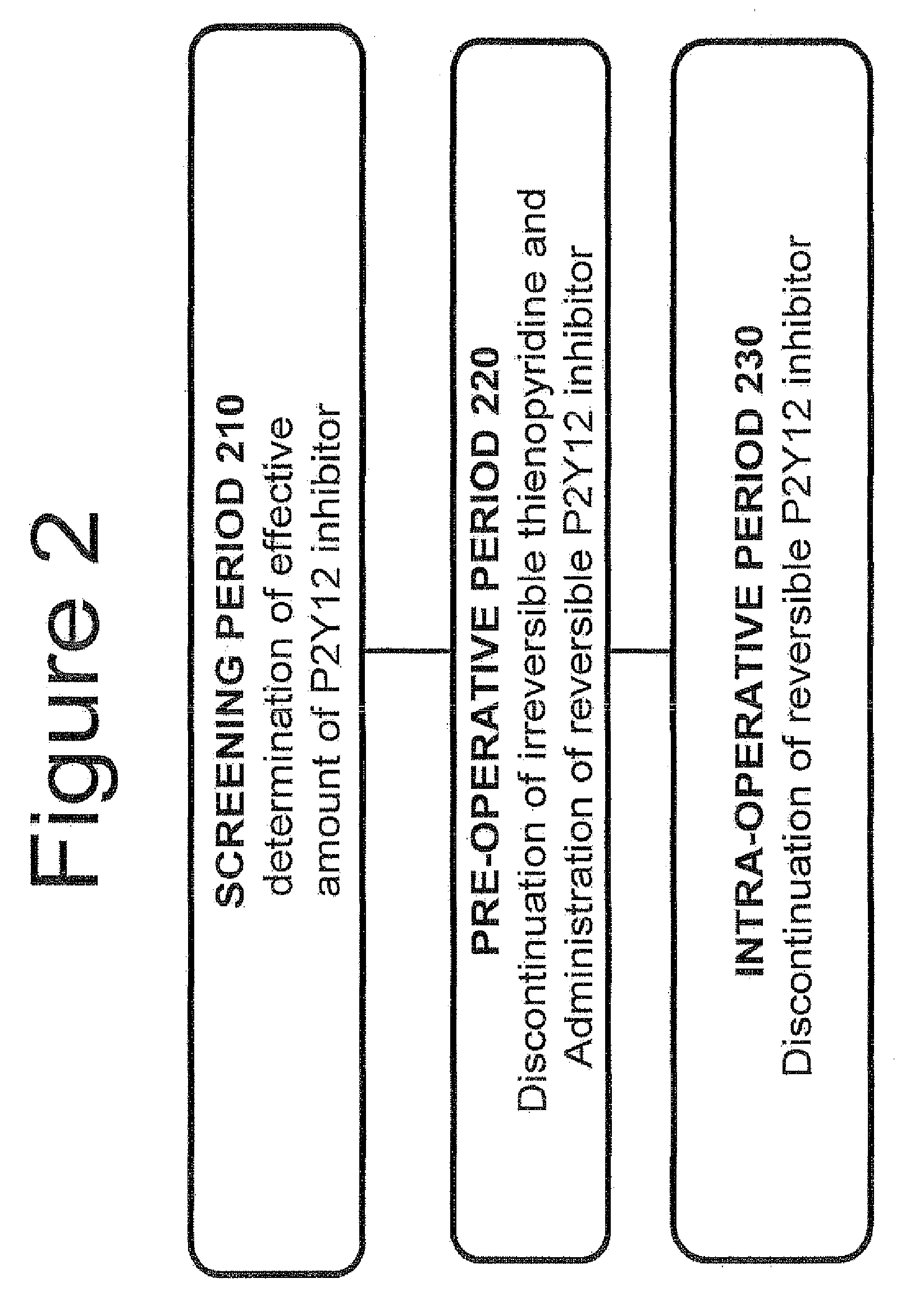
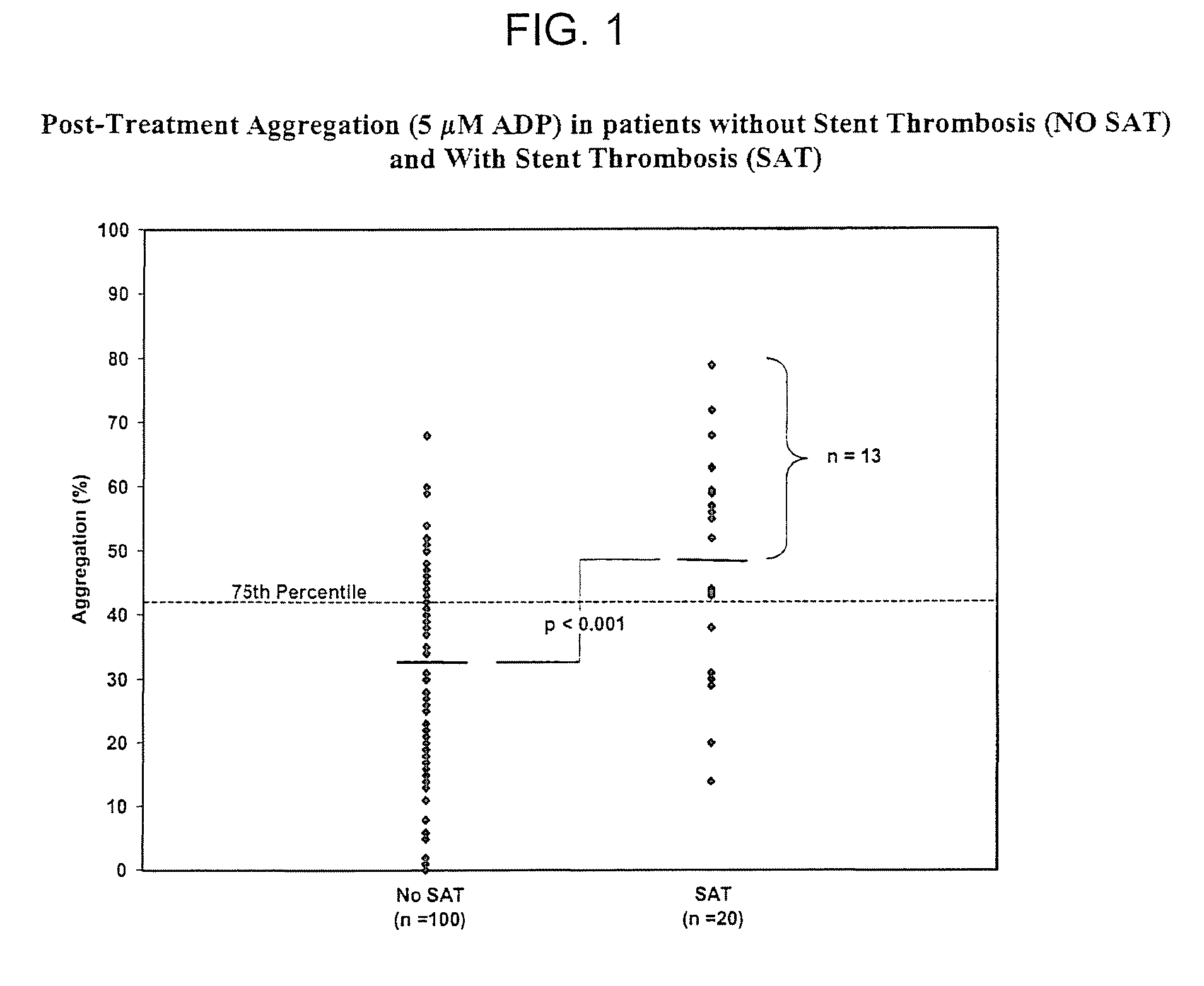
Maintenance of platelet inhibition during antiplatelet therapy
A method of treating or preventing a disease or condition in a subject that was previously treated with at least one thienopyridine is described. The method includes administering to the subject an effective amount of at least one reversible, short-acting P2Yi2 inhibitor. The described method can be used for subjects diagnosed with symptoms such as stable or unstable angina, vascular ischemic events, atherosclerosis, acute coronary syndrome, as well as STEMi or N-STEMI. The described method can also be used for patients having previously received a stent, such as a bare metal stent or a drug-eluting stent, and the treatment or prevention of stent thrombosis. The method can be used prior to, during, or after an invasive procedure such as coronary artery bypass grafting, percutaneous coronary intervention, or other general surgical procedure.
Owner:CHIESI FARM SPA
Use of probes for unbound metabolites
Methods of determining levels of unbound metabolites are disclosed. Probes derived from fatty acid binding protein muteins are described that bind preferentially to a number of unbound metabolites including oleate, stearate, linoleate, palmitate, arachidonate and unconjugated bilirubin. A profile for a patient is determined using one or more of the described probes. The profile is useful in diagnosis of disease, particularly myocardial infarction, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), diabetes, stroke, sepsis and neonatal jaundice. The responses of multiple probes to a test sample are used to classify the degree of acute coronary syndrome by comparison to multi-probe profiles generated from unstable angina, non ST elevation myocardial infarction, and ST elevation myocardial infarction.
Owner:KLEINFELD ALAN
Method for treatment of unstable coronary artery disease by an early revascularisation together with administration of a low molecular weight heparin
InactiveUS6258798B1Reduce riskPromote resultsOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderDiseaseCoronary artery disease
The invention relates to a method for treatment of unstable coronary artery disease, which is characterised by an early revascularisation together with administration of a low molecular weight heparin. Preferably the low molecular weight heparin is administered up to revascularisation. The methods are also useful for treatment of unstable angina and not worsening chest pain and for treatment of non-Q-wave myocardial infarction (mild heart attack).
Owner:PHARMACIA AB
Method for transdermal administration of GP IIb/IIIa antagonist
InactiveUS6322550B2Maintain stabilityImprove efficacyOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapySide effectLower risk
A method for transdermal administration of a GP IIb / IIIa antagonist by iontophoresis, comprising plural electric current application steps, progressively reduced in current density. The method insures excellent pharmacologic efficacy with a low risk for side effects in the prevention and therapy of (1) angina pectoris, (2) unstable angina and (3) ischemic complications and coronary arterial reocclusion or restenosis associated with PTCA or coronary thrombolysis.
Owner:HISAMITSU PHARM CO INC
Organic compounds
ActiveUS20100150913A1Increased riskInhibiting fibrinogen bindingSalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideInstabilityVascular surgery
The present invention relates to compounds and compositions useful for inhibiting and / or reducing platelet deposition, adhesion and / or aggregation. The present invention also relates to methods for screening compounds and compositions useful for inhibiting or reducing platelet deposition, adhesion and / or aggregation. The present invention further relates to methods for the treatment or prophylaxis of thrombotic disorders, including stroke, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, peripheral vascular disease, abrupt closure following angioplasty or stent placement and thrombosis as a result of vascular surgery.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine enteric oral liquor using leech extractive as active component, and its preparation method
InactiveCN1911250AAnthropod material medical ingredientsPill deliveryMedicinal herbsUpper gastrointestinal
An orally taken enteric Chinese medicine in the form of tablet, capsule, dripping pill, or soft capsule for treating unstable angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction, cerebral haemorrhage, etc and preventing deep phlebothrombosis is prepared from leech. Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:BEIJING RUNDEKANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Non-invasive method for measuring changes in vascular reactivity
A method is disclosed for measuring changes in vascular reactivity that seeks to overcome the aforementioned shortcomings. The method is non-invasive and allows for continuous or sustained monitoring of blood vessels. By measuring changes in vascular reactivity, information on endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation may be provided. Parameters such as skin temperature, heat flux, ambient temperature, movement, galvanic response and / or body acceleration may be monitored to indicate changes in vascular reactivity and to provide information concerning endothelical function of patients. Other information such as patient response to blood pressure medications and other types of medications, onset of congestive heart failure and other types of medical complications, and the occurrence of unstable angina may also be obtained.
Owner:GORDON LINDA
Maintenance of platelet inhibition during antiplatelet therapy
A method of treating or preventing a disease or condition in a subject that was previously treated with at least one thienopyhdine is described. The method includes administering to the subject an effective amount of at least one reversible, short-acting P2Yi2 inhibitor. The described method can be used for subjects diagnosed with symptoms such as stable or unstable angina, vascular ischemic events, atherosclerosis, acute coronary syndrome, as well as STEMi or N-STEMI. The described method can also be used for patients having previously received a stent, such as a bare metal stent or a drug-eluting stent, and the treatment or prevention of stent thrombosis. The method can be used prior to, during, or after an invasive procedure such as coronary artery bypass grafting, percutaneous coronary intervention, or other genera! surgical procedure.
Owner:CHIESI FARM SPA
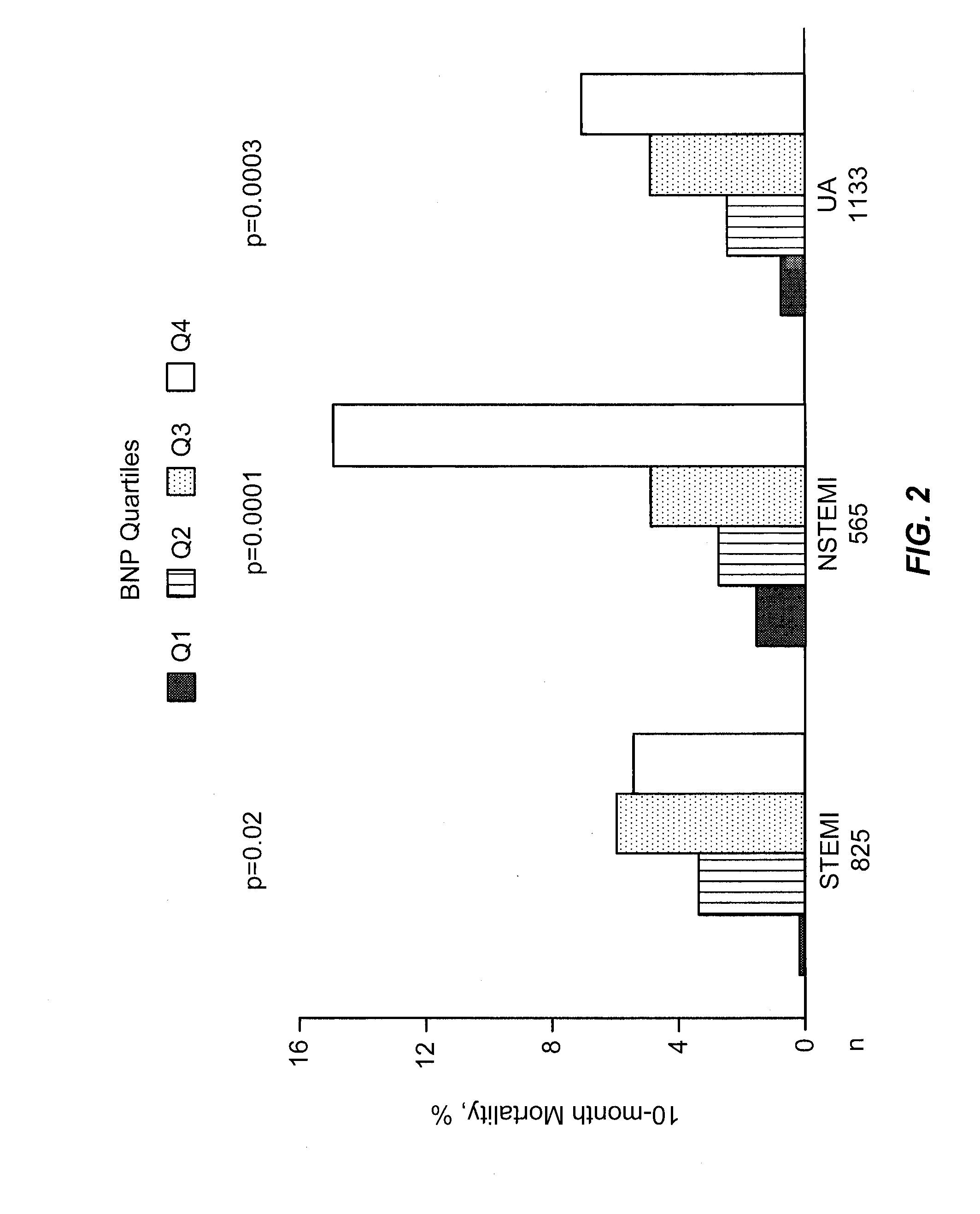
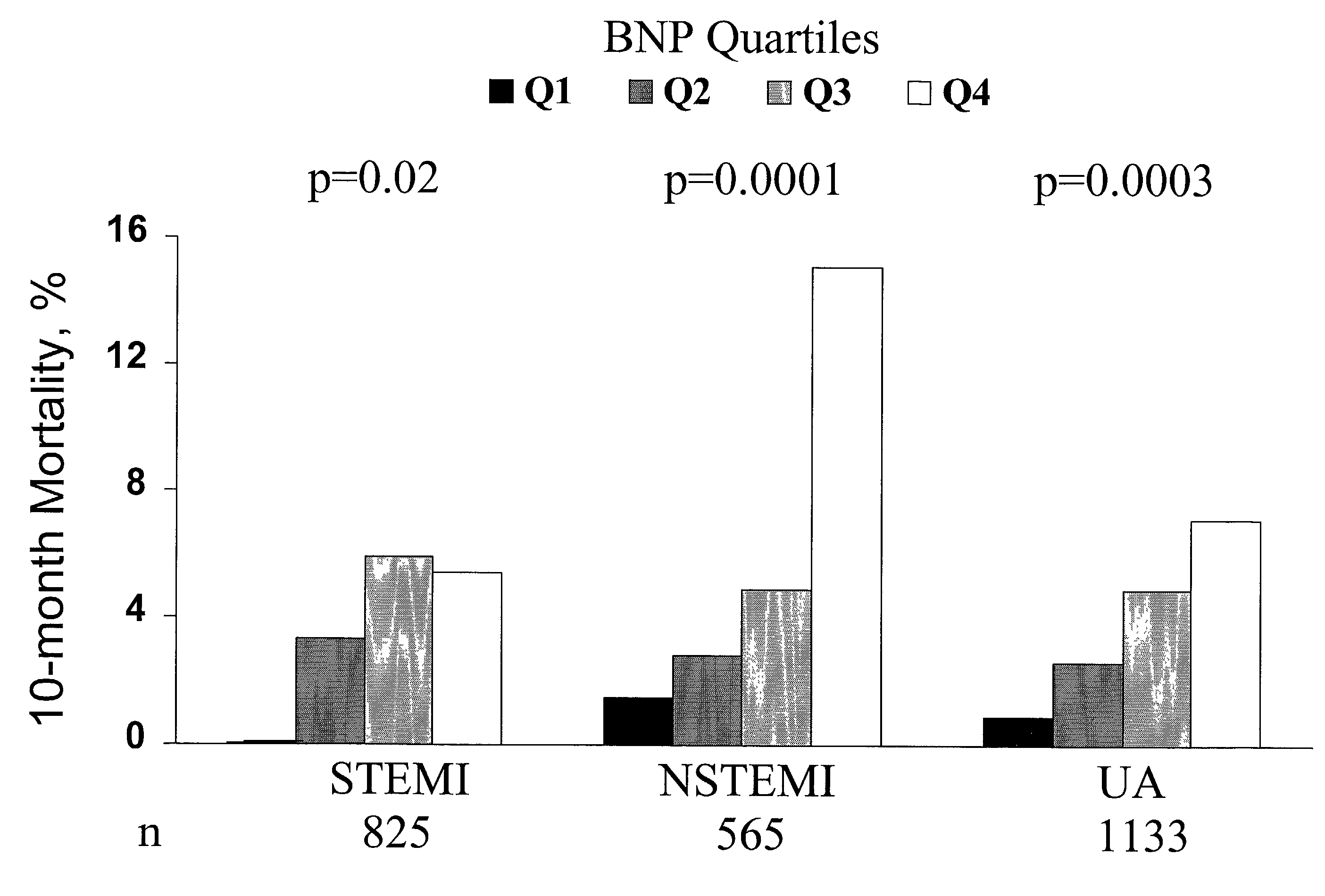
Use of B-type natriuretic peptide as a prognostic indicator in acute coronary syndromes
The present invention relates to materials and procedures for evaluating the prognosis of patients suffering from acute coronary syndromes. In particular, the level of BNP, or a marker related to BNP, in a patient sample, alone or in combination with one or more other prognostic markers, provides prognostic information useful for predicting near-term morbidity and / or mortality across the entire spectrum of acute coronary syndromes, including unstable angina, non-ST-elevation non-Q wave myocardial infarction, ST-elevation non-Q wave MI, and transmural (Q-wave) MI.
Owner:BIOSITE INC
Assessment of cardiac health and thrombotic risk in a patient
ActiveUS7381536B2Reduce riskRisk of the thrombotic event is assessedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPercent Diameter StenosisThrombus
The invention features methods and compositions for assessing risk, particularly immediate risk, of thrombotic events in patients with suspected or known vascular disease, and more particularly to assessing risk of thrombotic events in patients with coronary artery disease, particularly acute myocardial infarction, stroke, unstable angina, stable angina, or restenosis. Risk of thrombosis can be assessed by analysis of platelet reactivity and / or velocity of thrombin or fibrin formation, and determining whether the patient has a score associated above a risk threshold value. In other embodiments, risk of thrombosis in a patient is evaluated in the context of a profile generated from values obtained from one or more assays that evaluate various factors associated with thrombosis and / or atherosclerosis.
Owner:GURBEL PAUL A
Detection and determination of the stages of coronary artery disease
A method having clinically sufficient degree of diagnostic accuracy for detecting the presence of coronary artery disease in a human patient from the general population and for distinguishing between the stages of the disease in that patient is disclosed. The stages are, first, the non-acute stage, which is either asymptomatic coronary artery disease or stable angina, second, the acute stage known as unstable angina, and, third, the acute stage known as acute myocardial infarction. The diseased state (as opposed to the non-diseased state) is indicated by the clinically significant presence of a first marker in a sample from the patient. The presence of one of the two acute stages, unstable angina or acute myocardial infarction, is indicated by the clinically significant presence of a second marker in a sample from the patient. The presence of the more severe acute stage known as acute myocardial infarction is indicated by the clinically significant presence of a third marker in a sample from the patient. Preferably the first marker comprises OxLDL, the second marker comprises MDA-modified LDL, and the third marker is a troponin. Preferably the OxLDL and MDA-modified LDL are detected using monoclonal antibodies that can detect the presence of those markers in undiluted human plasma at concentrations as low as 0.02 milligrams / deciliter.
Owner:LEUVEN RES & DEV VZW
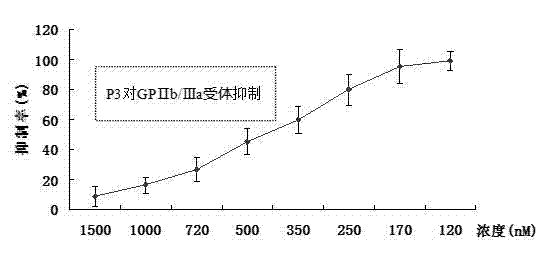
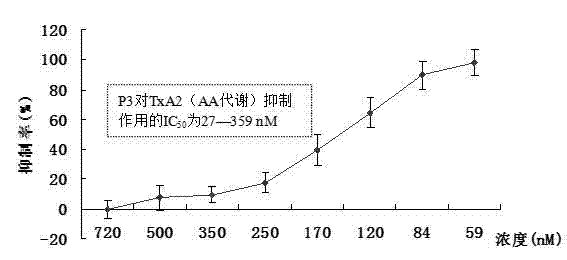
Polypeptide used for prevention and treatment of acute coronary syndrome and anticoagulation antithrombotic therapy and application thereof
ActiveCN102241735ATetrapeptide ingredientsTripeptide ingredientsHuman plateletFemoral artery thrombosis
Owner:SHAANXI MICOT TECH LTD
Alpha-IIB-beta-3 inhibitors and uses thereof
ActiveUS8173661B2Increased riskInhibiting fibrinogen bindingBiocideOrganic active ingredientsInstabilityPercutaneous angioplasty
The present invention relates to compounds and compositions useful for inhibiting and / or reducing platelet deposition, adhesion and / or aggregation. The present invention also relates to methods for screening compounds and compositions useful for inhibiting or reducing platelet deposition, adhesion and / or aggregation. The present invention further relates to methods for the treatment or prophylaxis of thrombotic disorders, including stroke, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, peripheral vascular disease, abrupt closure following angioplasty or stent placement and thrombosis as a result of vascular surgery.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Medicine composition of trifusal and clopidogrel
InactiveCN1887284AExcellent in combinationSuitable for long-term useOrganic active ingredientsPill deliveryDiseaseVascular disease
The medicine composition has synergistic active components trifusal and clopidogrel, and its clopidogrel exists in free state or pharmaceutically acceptable salt. The medicine composition is used in treating stable or unstable angina pectoris and other cardiac and cerebral vascular diseases. Pharmaceutical experiments prove the synergistic effect of trifusal and clopidogrel in the medicine composition and the medicine composition has blood platelet inhibiting rate superior to that of aspirin-clopidogrel composition and high safety suitable for long -term taking.
Owner:陈文展
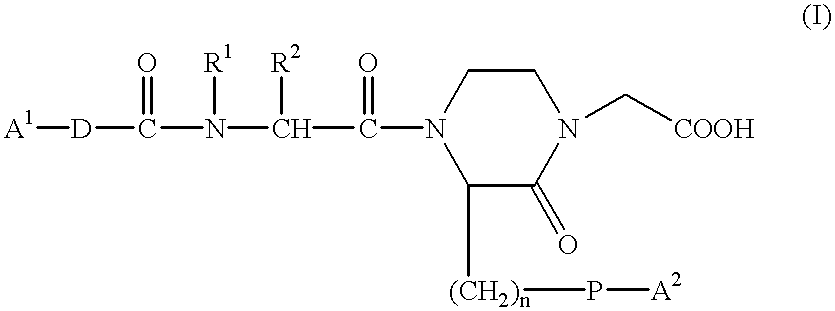
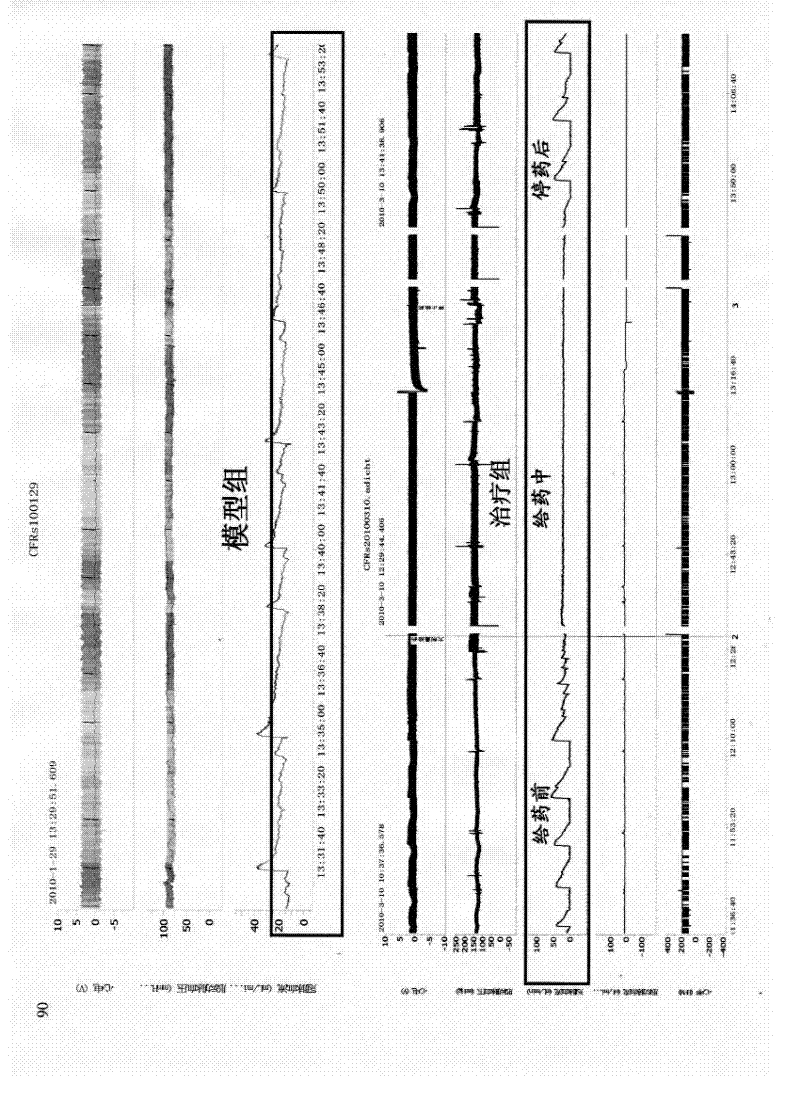
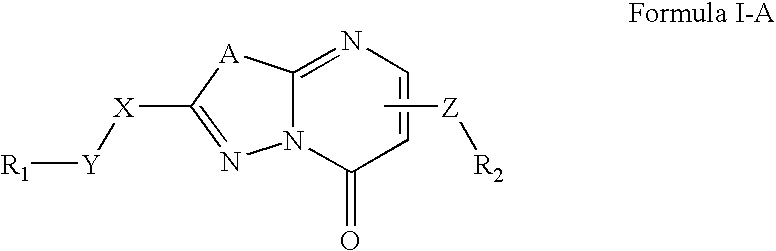
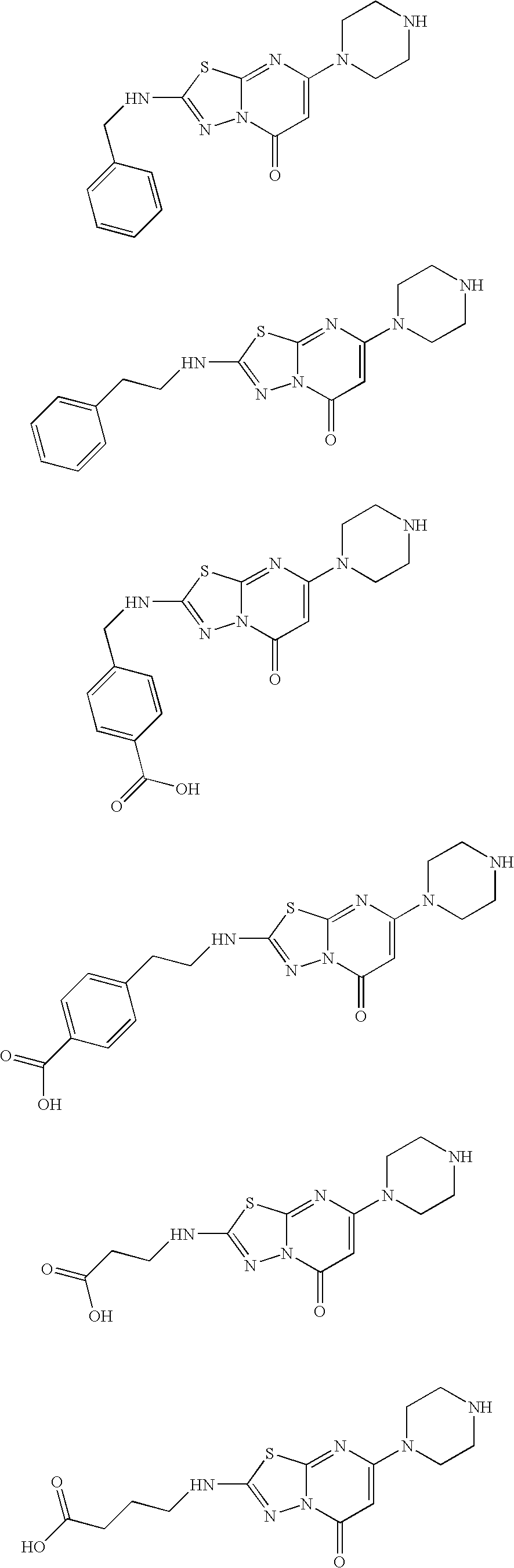
7-(piperazin-1-yl)-5H-[1,3,4]thiadiazolo[3,2-A]pyrimidin-5-ones for the treatment of thrombotic disorders
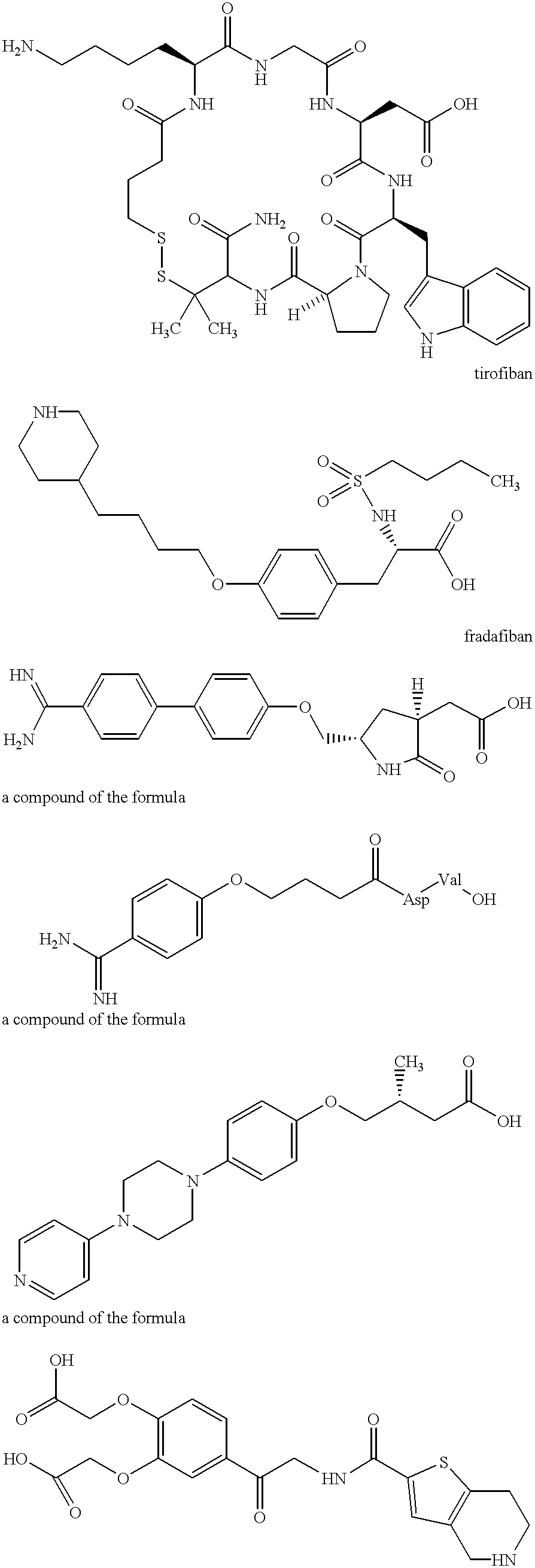
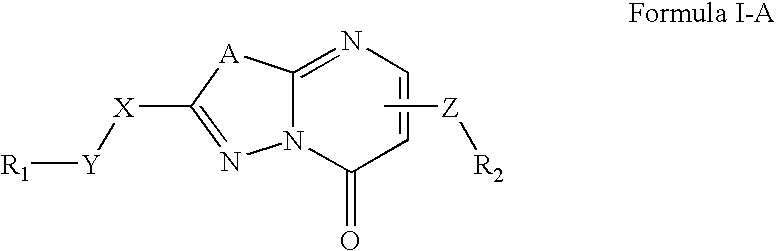
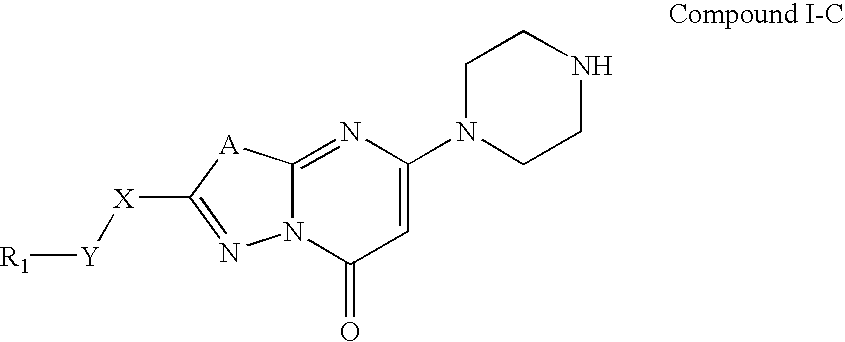
The present invention relates to compounds and compositions of Formula P useful for inhibiting and / or reducing platelet deposition, adhesion and / or aggregation. The definitions of variables A, B, R2, R3, R4, Ra, Ra′, Rb, Rb′, Rc, Rd, Rd′, Re, and Re′ are provided in the disclosure. The present invention further relates to methods for the treatment or prophylaxis of thrombotic disorders, including stroke, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, peripheral vascular disease, abrupt closure following angioplasty or stent placement and thrombosis as a result of vascular surgery.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV +2
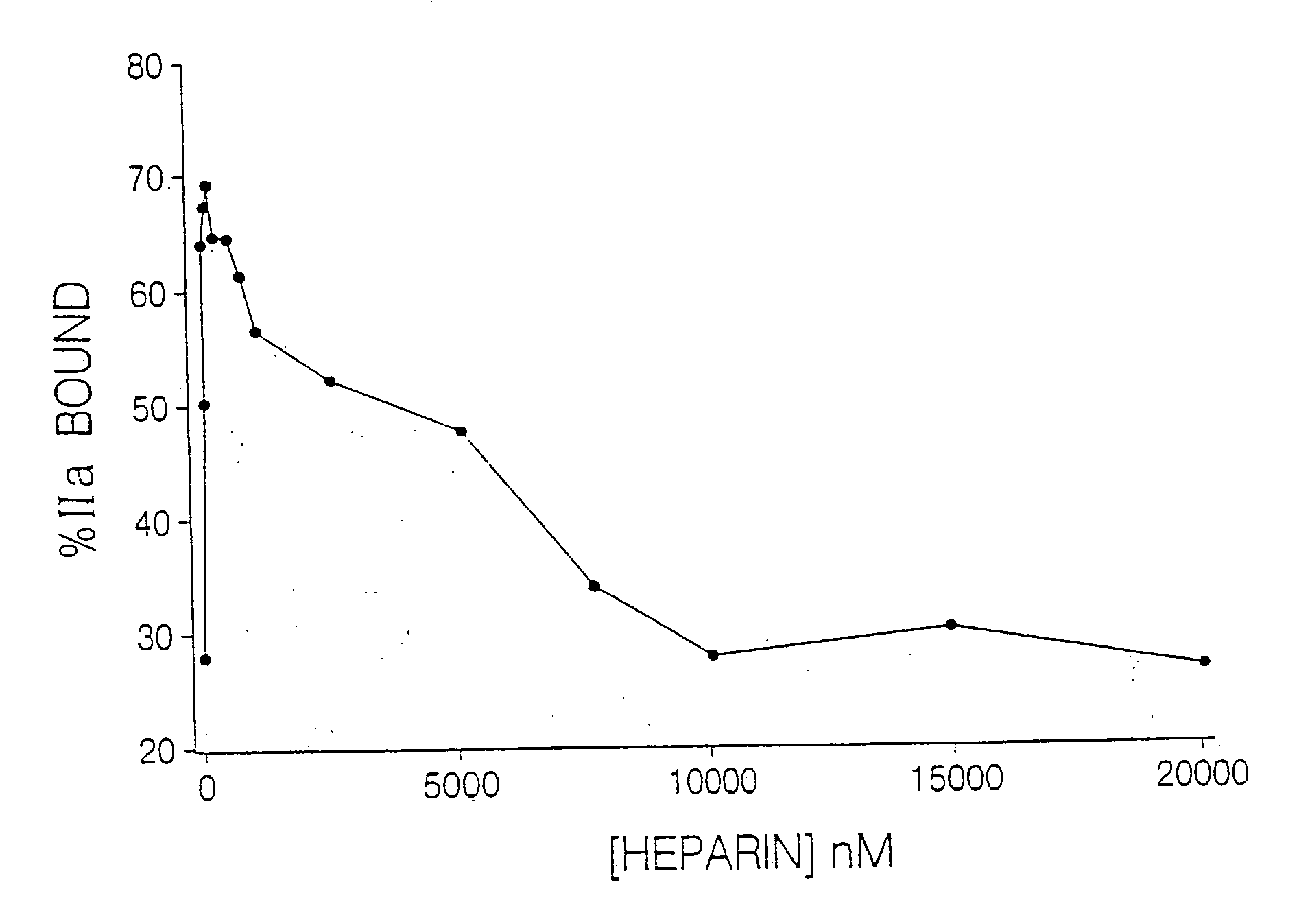
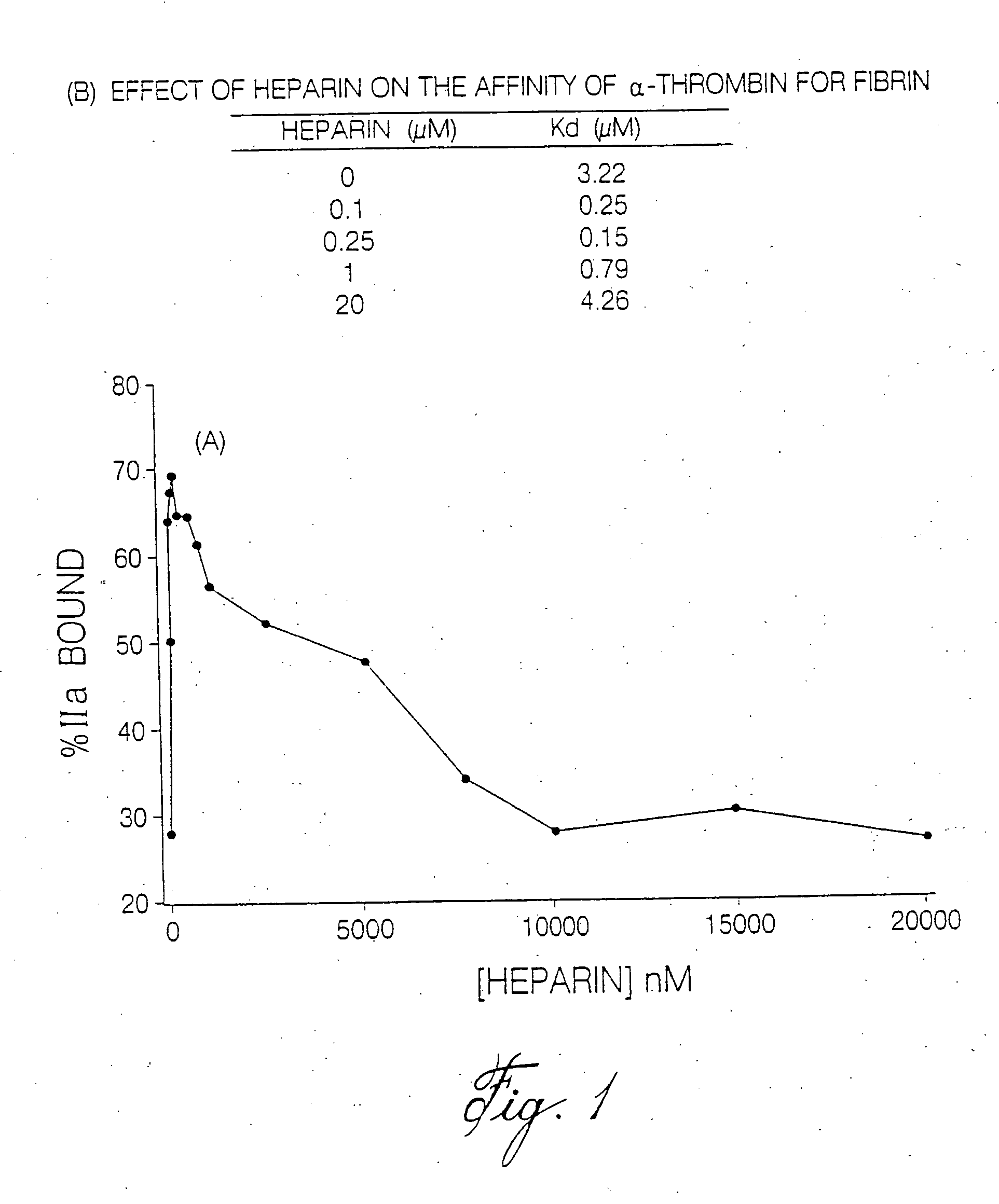
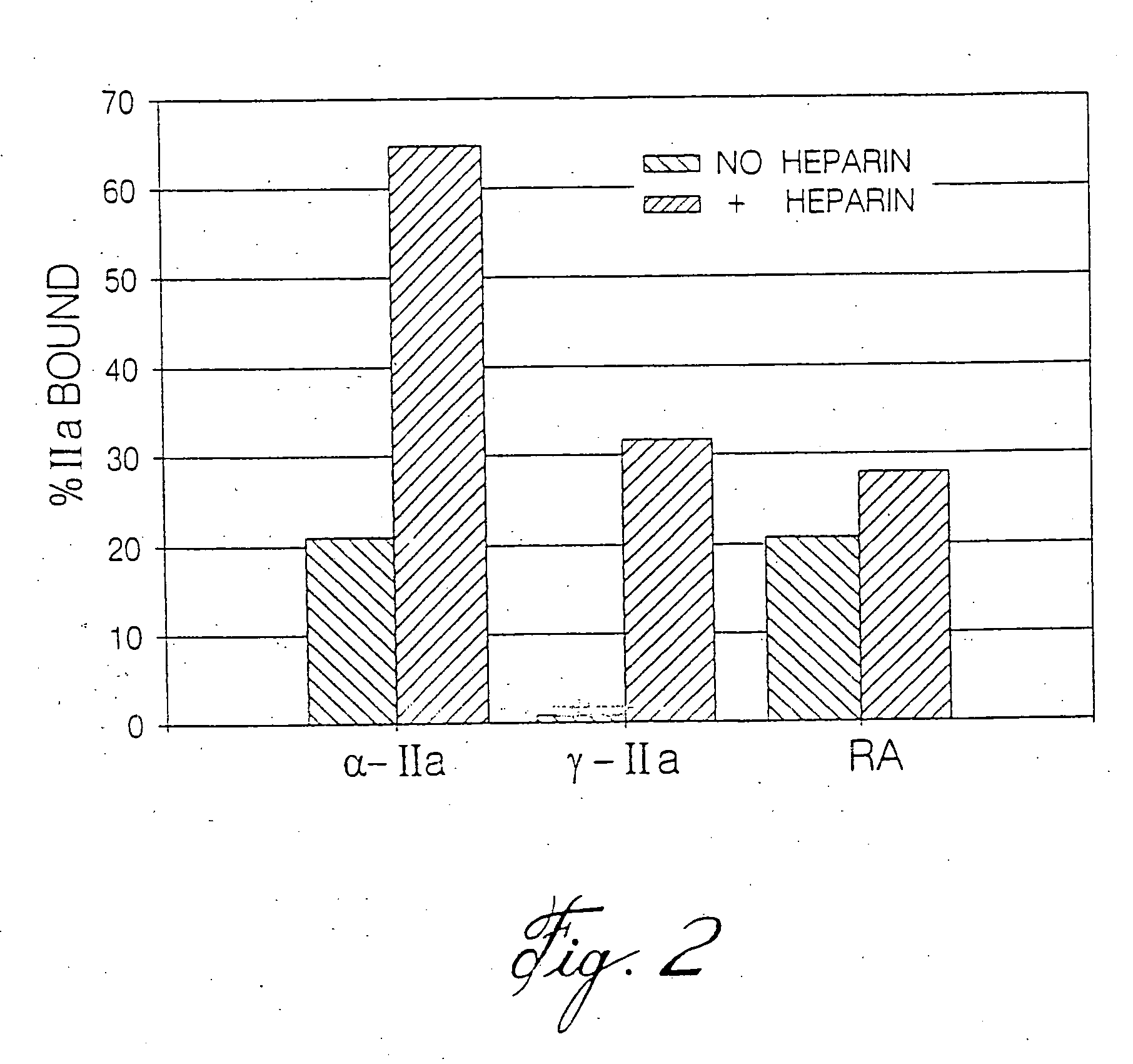
Heparin compositions that inhibit clot associated coagulation factors
InactiveUS20080119438A1Prevent reactivationAvoid generatingOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderVenous bloodAngina
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. More particularly, the present invention relates to modifying thrombus formation by administering an agent which, inter alia, is capable of (1) inactivating fluid-phase thrombin and thrombin which is bound either to fibrin in a clot or to some other surface by catalyzing antithrombin; and (2) inhibiting thrombin generation by catalyzing factor Xa inactivation by antithrombin III (ATIII). The compositions and methods of the present invention are particularly useful for preventing thrombosis in the circuit of cardiac bypass apparatus and in patients undergoing renal dialysis, and for treating patients suffering from or at risk of suffering from thrombus-related cardiovascular conditions, such as unstable angina, acute myocardial infraction (heart attack), cerebrovascular accidents (stroke), pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, arterial thrombosis, etc.
Owner:WEITZ JEFFREY I +1
Method for transdermal administration of gp iib/iiia antagonist
InactiveUS20010018568A1Excellent pharmacological efficacyReduce riskOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapySide effectLower risk
A method for transdermal administration of a GP IIb / IIIa antagonist by iontophoresis, comprising plural electric current application steps, progressively reduced in current density. The method insures excellent pharmacologic efficacy with a low risk for side effects in the prevention and therapy of (1) angina pectoris, (2) unstable angina and (3) ischemic complications and coronary arterial reocclusion or restenosis associated with PTCA or coronary thrombolysis.
Owner:HISAMITSU PHARM CO INC
Metabolic marker for diagnosing and distinguishing unstable angina pectoris and acute myocardial infarction
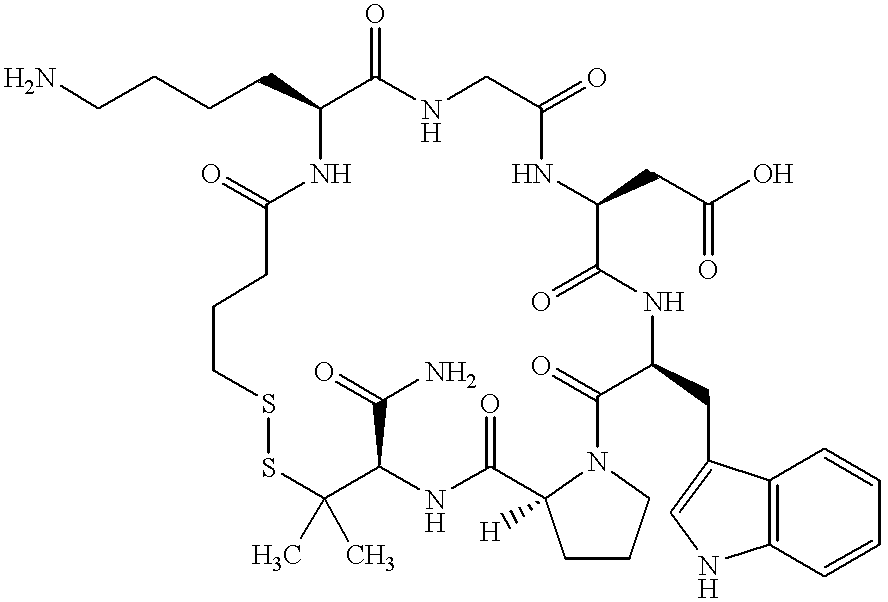
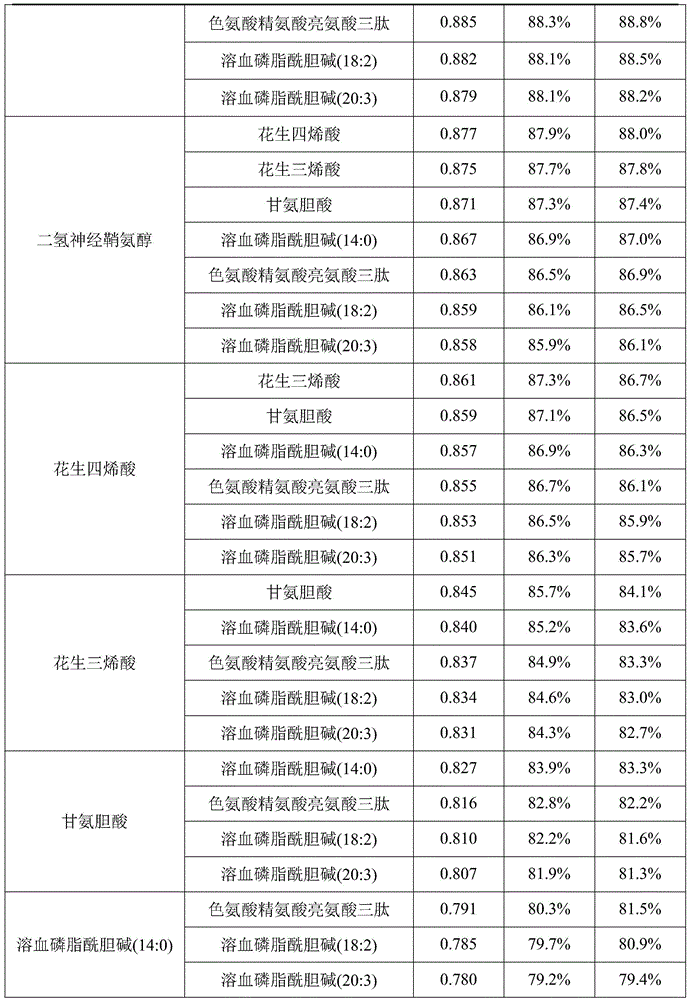
The invention discloses a metabolic marker for diagnosing and distinguishing unstable angina pectoris and acute myocardial infarction, comprising one or more of N-phenylalanyl-L-glutamine, sphinganine, arachidonic acid, eicosatrienoic acid, glycocholic acid, lysophosphatidylcholine (14:0), tryptophan-arginine-leucine tripeptide, lysophosphatidylcholine (18:2), and lysophosphatidylcholine (20:3). In the single use of diagnosing and distinguishing patients with acute myocardial infarction and patients with unstable angina pectoris, each ROC (receiver operating characteristic) AUC (area under the curve) is greater than 0.7, and clinical diagnostic significance is provided; in the joint use for diagnosis, AUC further increases as a joint quantity increases, a highest AUC up to 0.991 is obtained in a case of nine members jointed, and sensitivity and specificity are respectively 99.2% and 98.9% under an optimal cutoff value. The metabolic marker can accurately diagnose and distinguish unstable angina pectoris and acute myocardial infarction, with high accuracy and high sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:齐炼文
Use of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide as a Prognostic Indicator in Acute Coronary Syndromes
The present invention relates to materials and procedures for evaluating the prognosis of patients suffering from acute coronary syndromes. In particular, the level of BNP, or a marker related to BNP, in a patient sample, alone or in combination with one or more other prognostic markers, provides prognostic information useful for predicting near-term morbidity and / or mortality across the entire spectrum of acute coronary syndromes, including unstable angina, non-ST-elevation non-Q wave myocardial infarction, ST-elevation non-Q wave MI, and transmural (Q-wave) MI.
Owner:DAHLEN JEFFREY R +2
Nifedipine medicine composition and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102370644AHigh dissolution ratePromote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsChronic stable anginaPeripheral resistance
The invention discloses a nifedipine medicine composition and a preparation method thereof. The nifedipine medicine composition contains nifedipine, hydroxymethyl propyl cellulose and microcrystalline cellulose. The hydroxymethyl propyl cellulose is used as slow-releasing framework material; the weight ratio of the nifedipine and the hydroxymethyl propyl cellulose is 2:1-1:1; and the weight ratio of the nifedipine and the microcrystalline cellulose is 1:4-1:3; and lactose, starch, calcium hydrophosphate and glucose can be also added. The method for preparing the nifedipine medicine composition comprises the following steps of: (1) crushing and screening; (2) drying; and (3) tabletting. According to the invention, the dissolution rate of the nifedipine in the water can be increased, the coronary arteries in the normal blood supply area and the ischemic area are relaxed while the absorption rate of the nifedipine in the body is increased so that coronarospasm and is released and prevented and myocardial contraction is inhibited; myocardial oxygen consumption is reduced; the peripheral resistance is released; after load of heart is reduced; sinus node function and atrioventricular conduction of the isolated heart are slowed down; and the nifedipine medicine composition is applicable to variant angina pectoris, unstable angina pectoris and chronic stable angina pectoris.
Owner:JILIN AODONG GROUP DALIAN PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
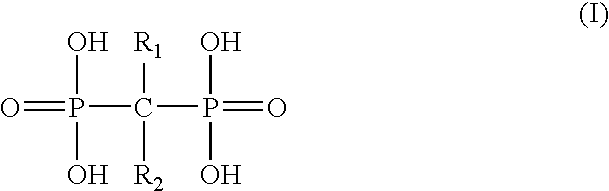
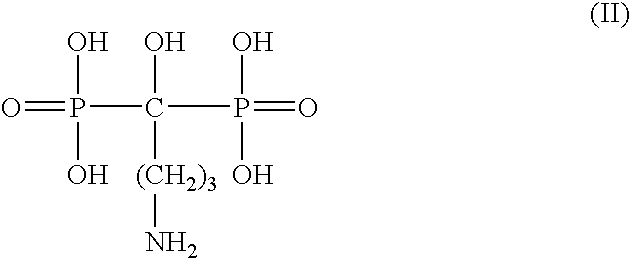
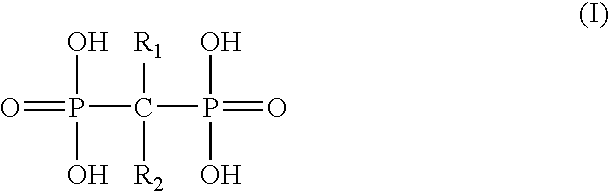








![7-(piperazin-1-yl)-5H-[1,3,4]thiadiazolo[3,2-A]pyrimidin-5-ones for the treatment of thrombotic disorders 7-(piperazin-1-yl)-5H-[1,3,4]thiadiazolo[3,2-A]pyrimidin-5-ones for the treatment of thrombotic disorders](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/22727a3f-0a6e-4689-9062-ab34e575059d/US09303044-20160405-C00001.PNG)
![7-(piperazin-1-yl)-5H-[1,3,4]thiadiazolo[3,2-A]pyrimidin-5-ones for the treatment of thrombotic disorders 7-(piperazin-1-yl)-5H-[1,3,4]thiadiazolo[3,2-A]pyrimidin-5-ones for the treatment of thrombotic disorders](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/22727a3f-0a6e-4689-9062-ab34e575059d/US09303044-20160405-C00002.PNG)
![7-(piperazin-1-yl)-5H-[1,3,4]thiadiazolo[3,2-A]pyrimidin-5-ones for the treatment of thrombotic disorders 7-(piperazin-1-yl)-5H-[1,3,4]thiadiazolo[3,2-A]pyrimidin-5-ones for the treatment of thrombotic disorders](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/22727a3f-0a6e-4689-9062-ab34e575059d/US09303044-20160405-C00003.PNG)