Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1306 results about "Myocardial ischemia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A: Myocardial ischemia, also called cardiac ischemia, occurs when the blood flow to your heart is reduced. Causes for myocardial ischemia include coronary artery disease, blood clots, coronary artery spasm, etc. The most common sign or symptom is chest pressure or pain, especially on the left side of the body (angina pectoris).
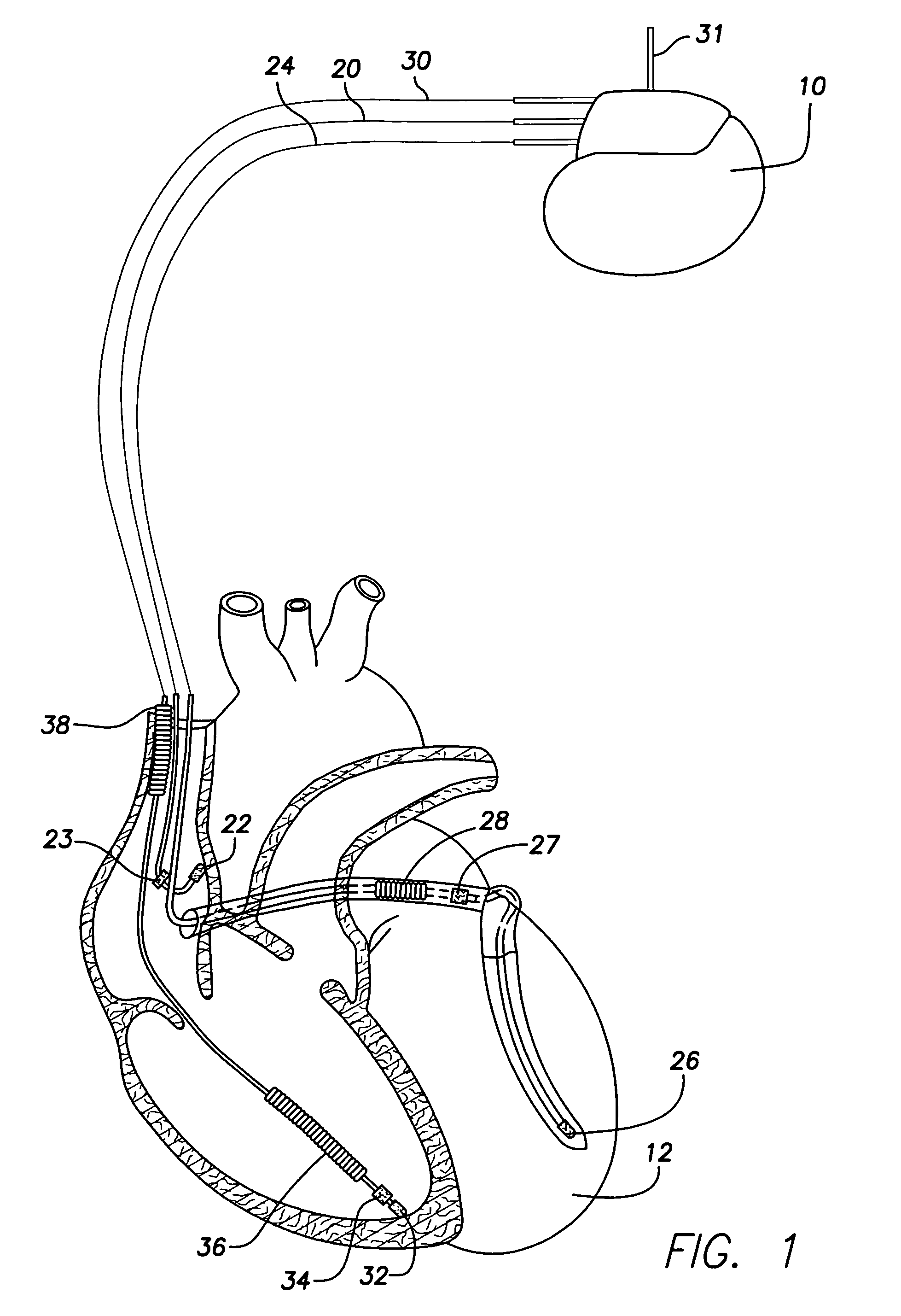
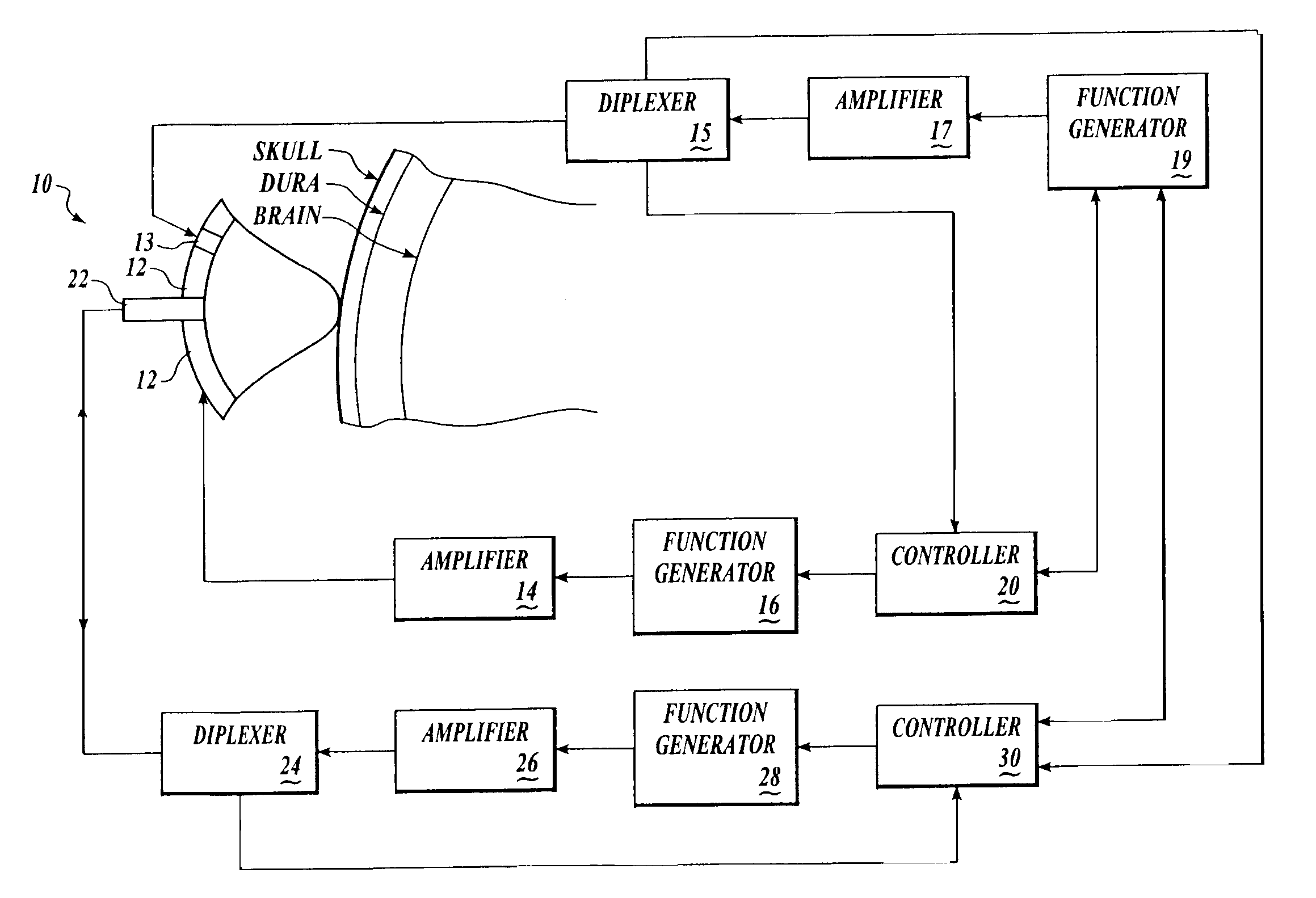
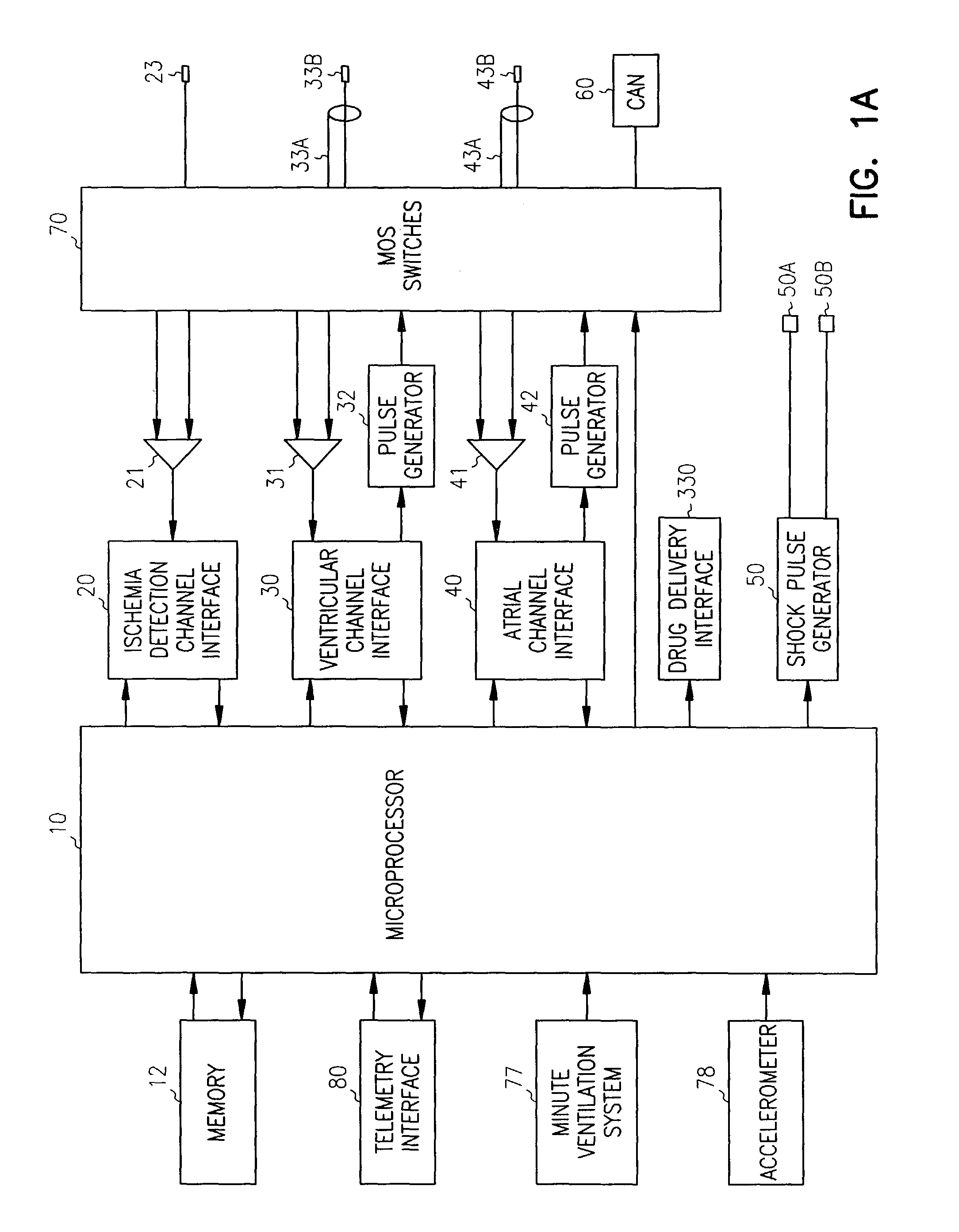
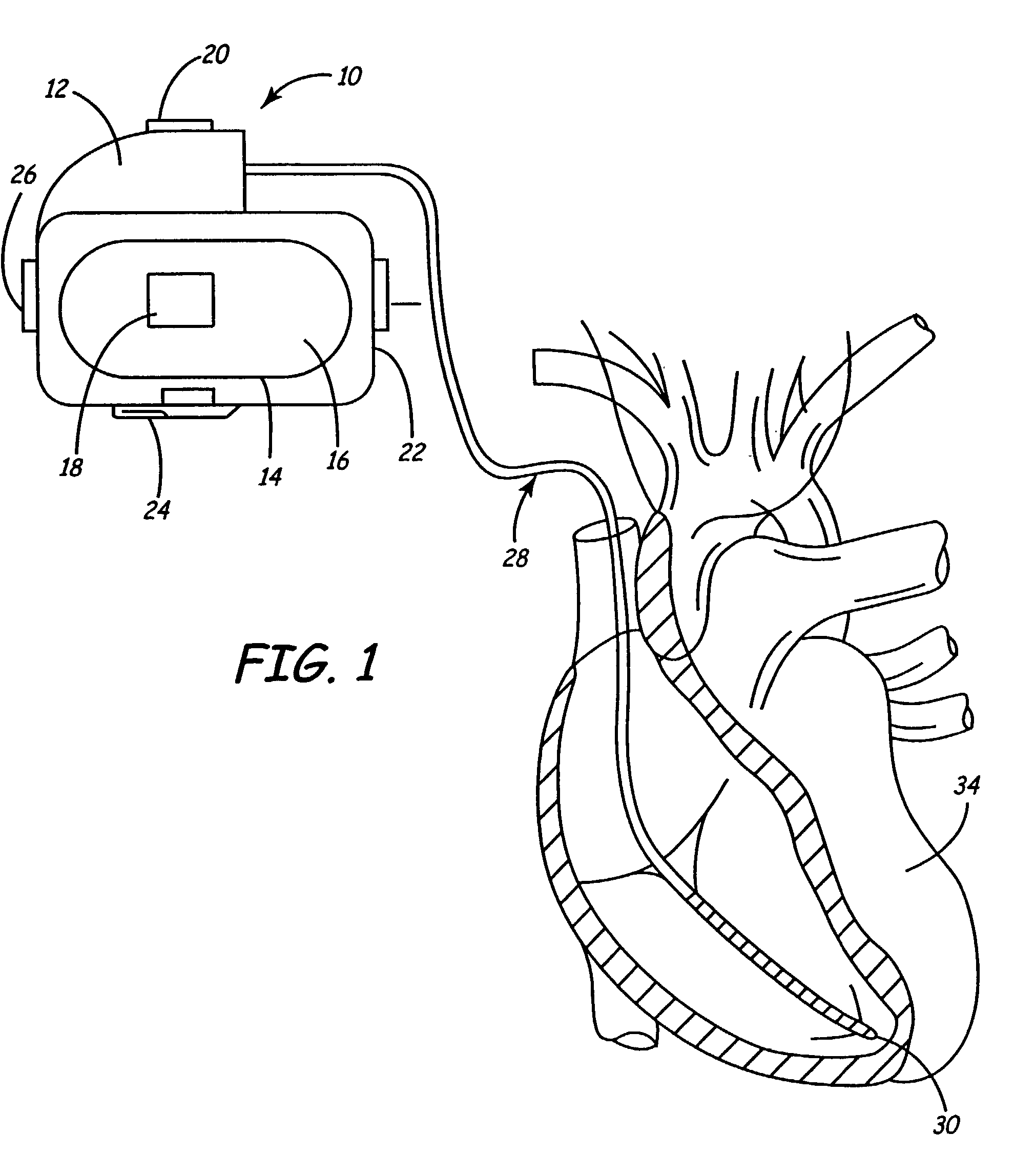
Myocardial ischemia and infarction analysis and monitoring method and apparatus
A cardiac monitoring and telemedicine method and system provides advanced ischemia and infarction analysis and monitoring. Advanced calculations are performed on ECG signals to obtain parameter values relating to myocardial ischemia and infarction. Dominant heart beats are averaged to form a smooth beat, which is analyzed to determine the parameter values continuously and in real-time. The device includes an entry portion for input of information data and a communication portion for bi-directional communication with a central unit.
Owner:ORTIVUS MEDICAL
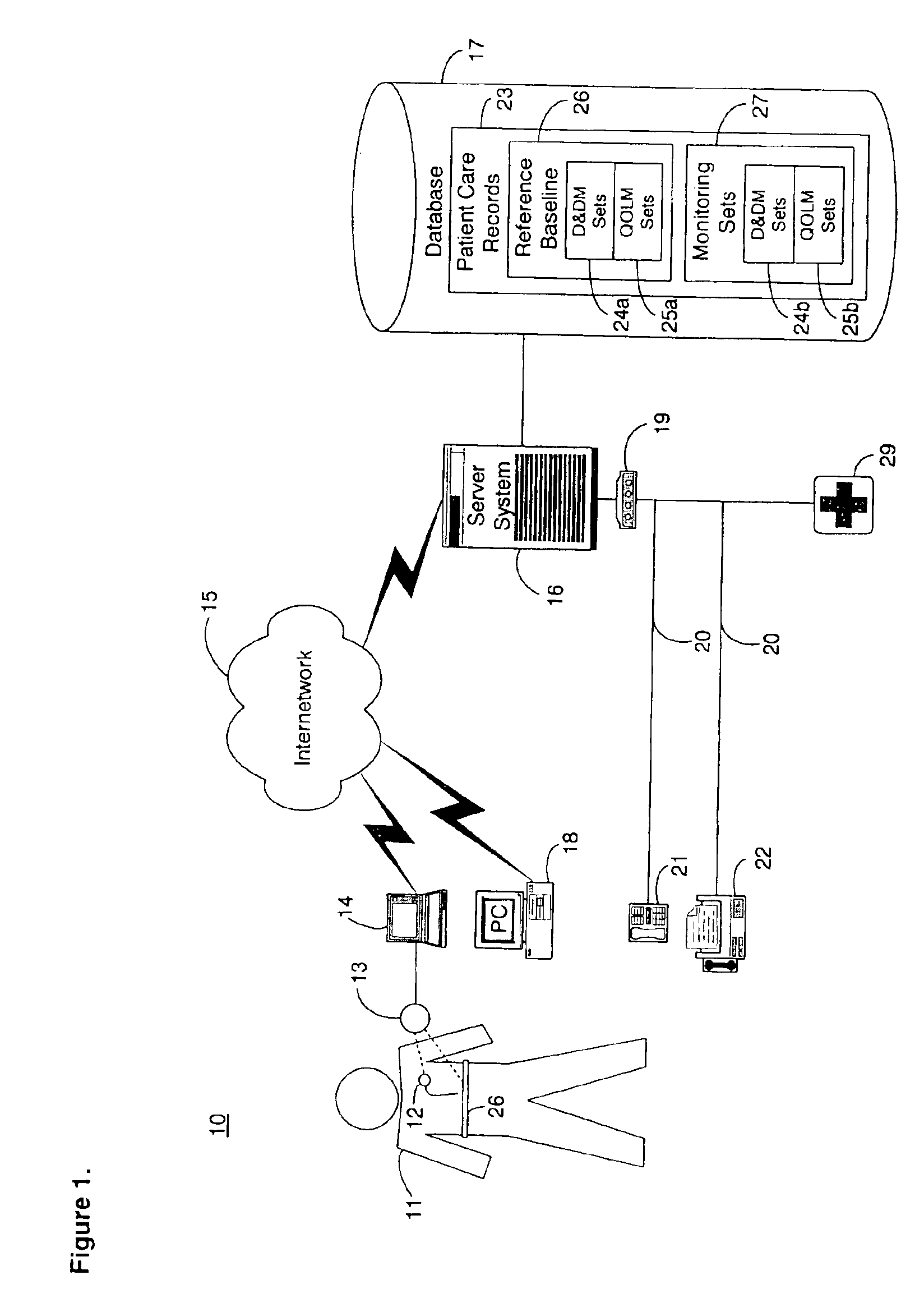
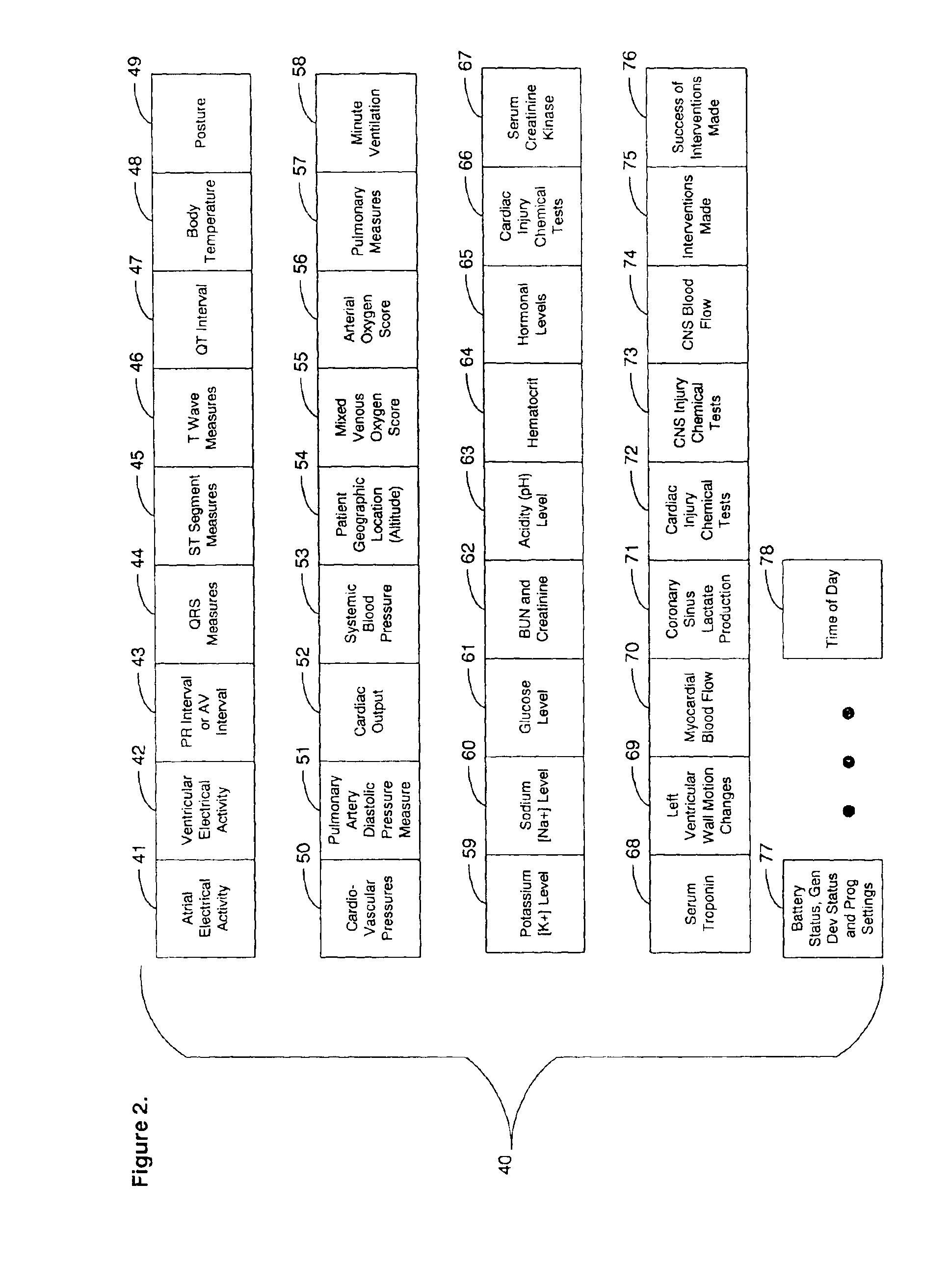
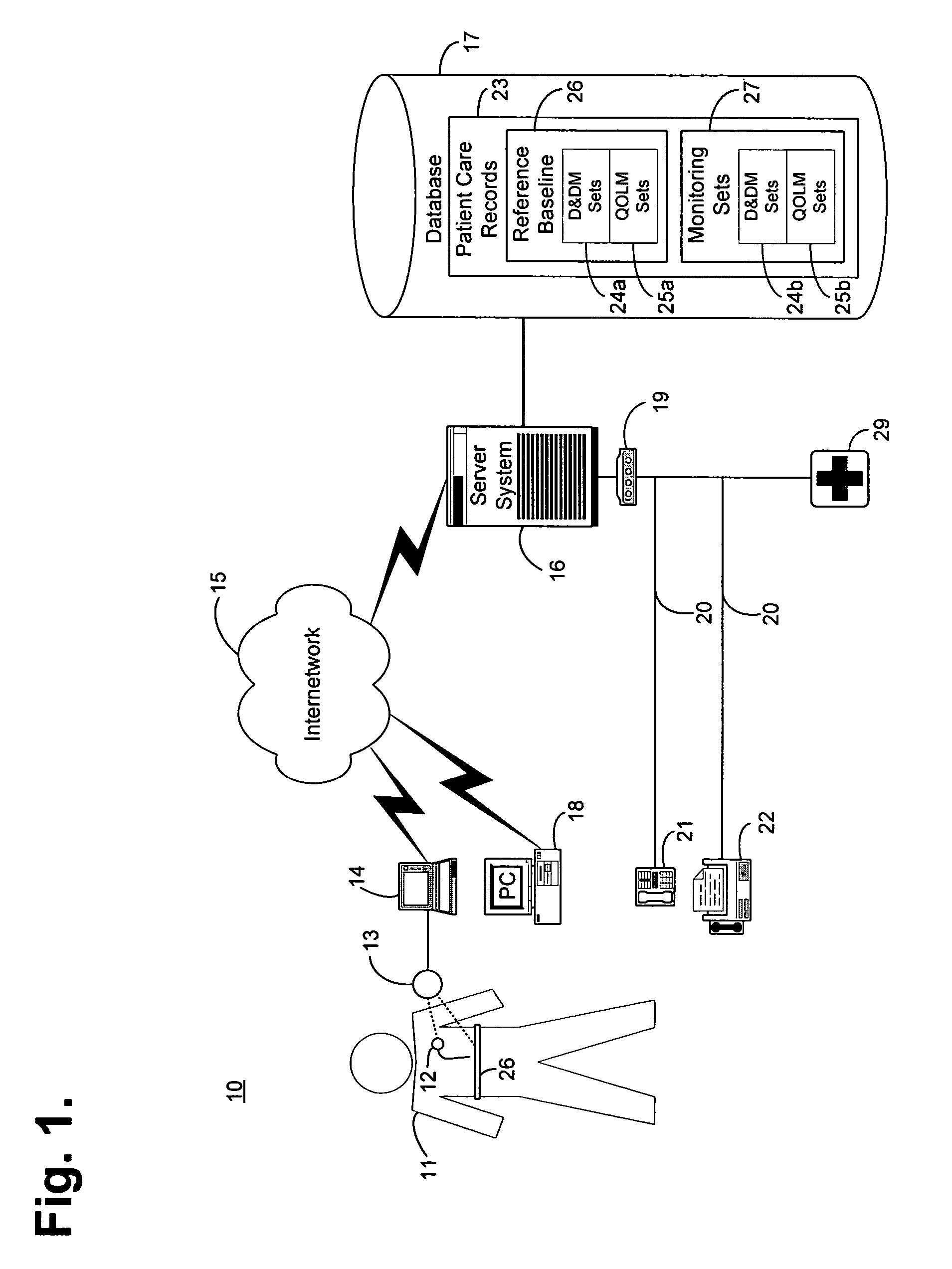
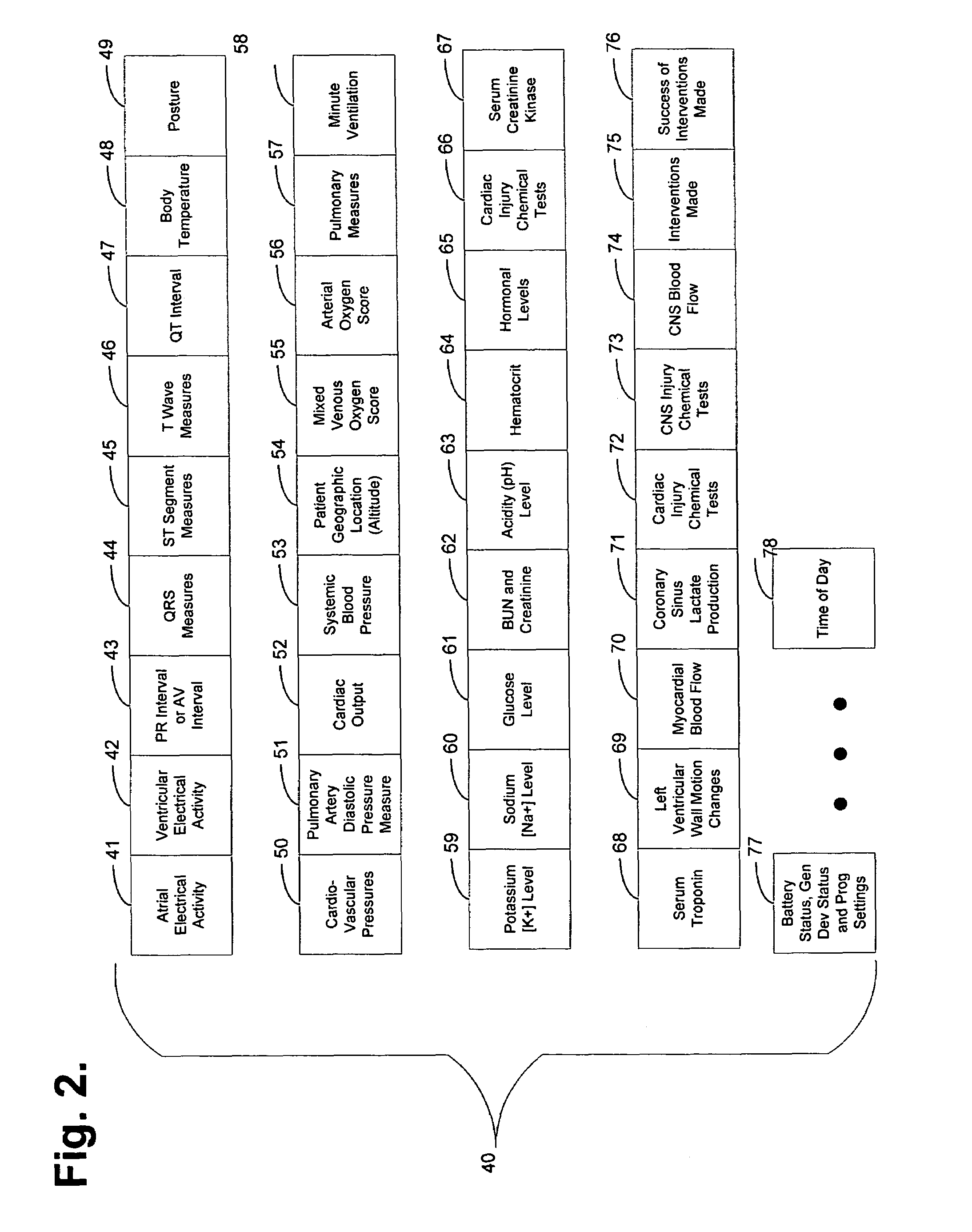
System and method for diagnosing and monitoring myocardial ischemia for automated remote patient care
InactiveUS6913577B2Increase productionIncreased serum creatinine kinaseElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesHysteresisHeart muscle extract
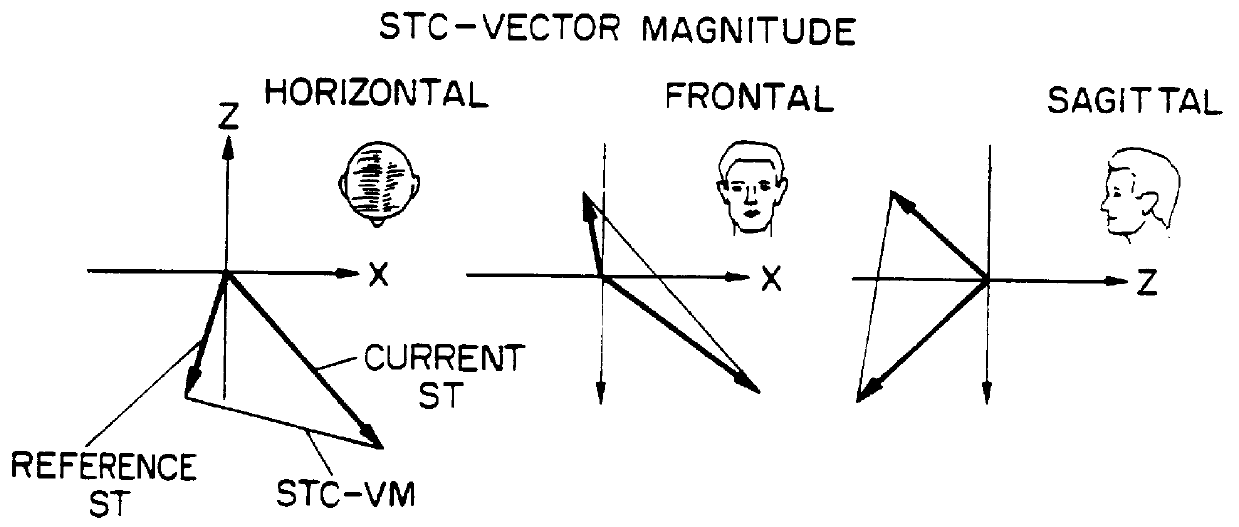
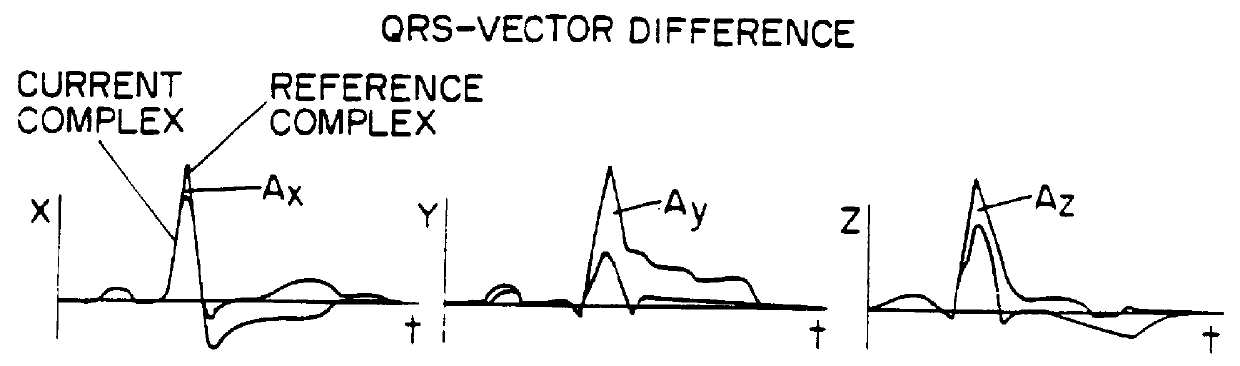
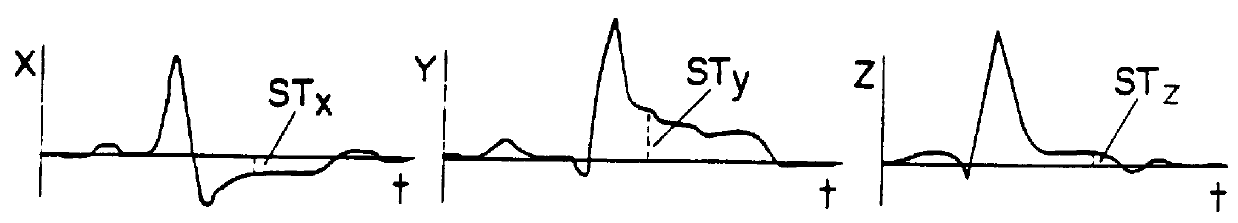
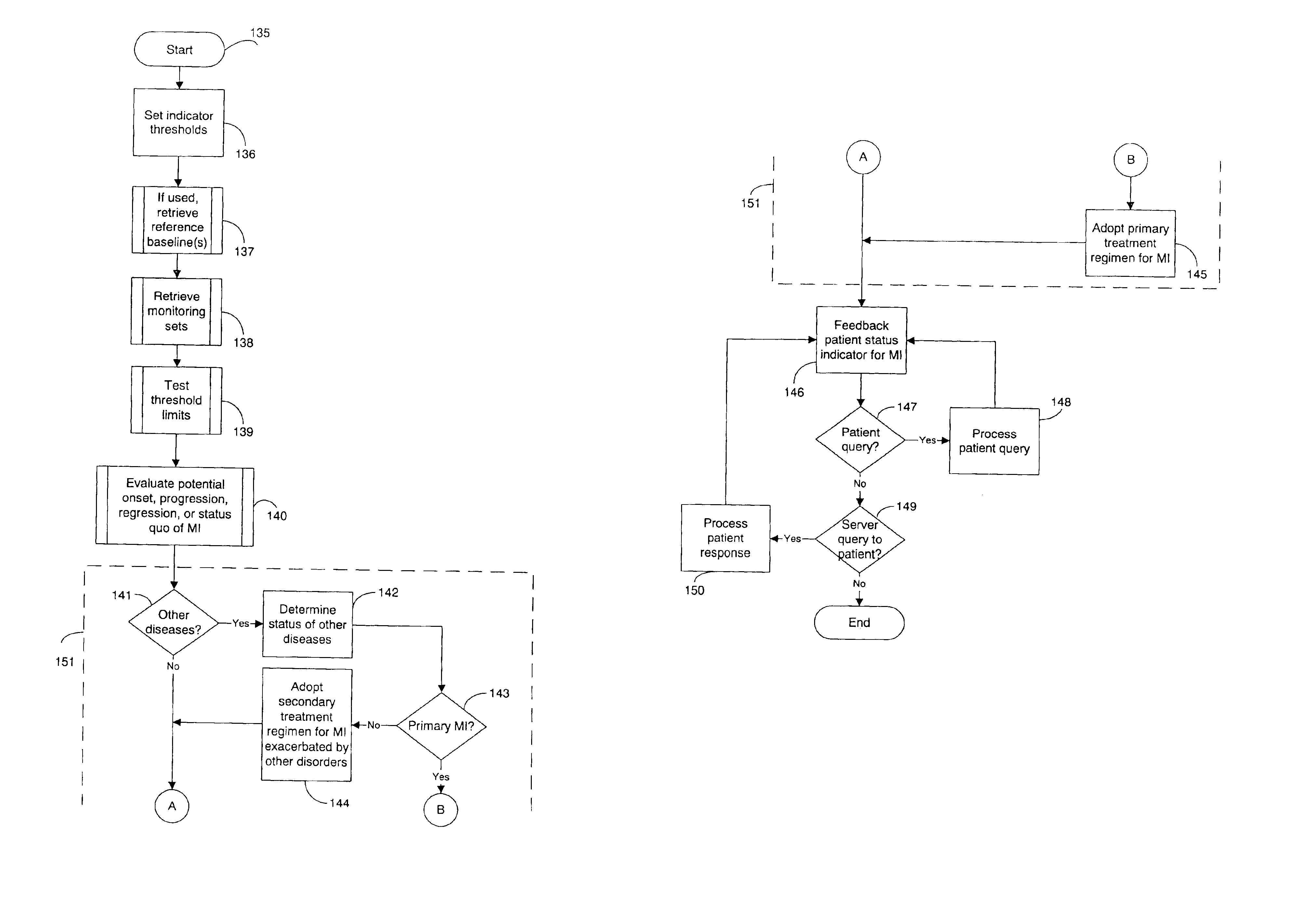
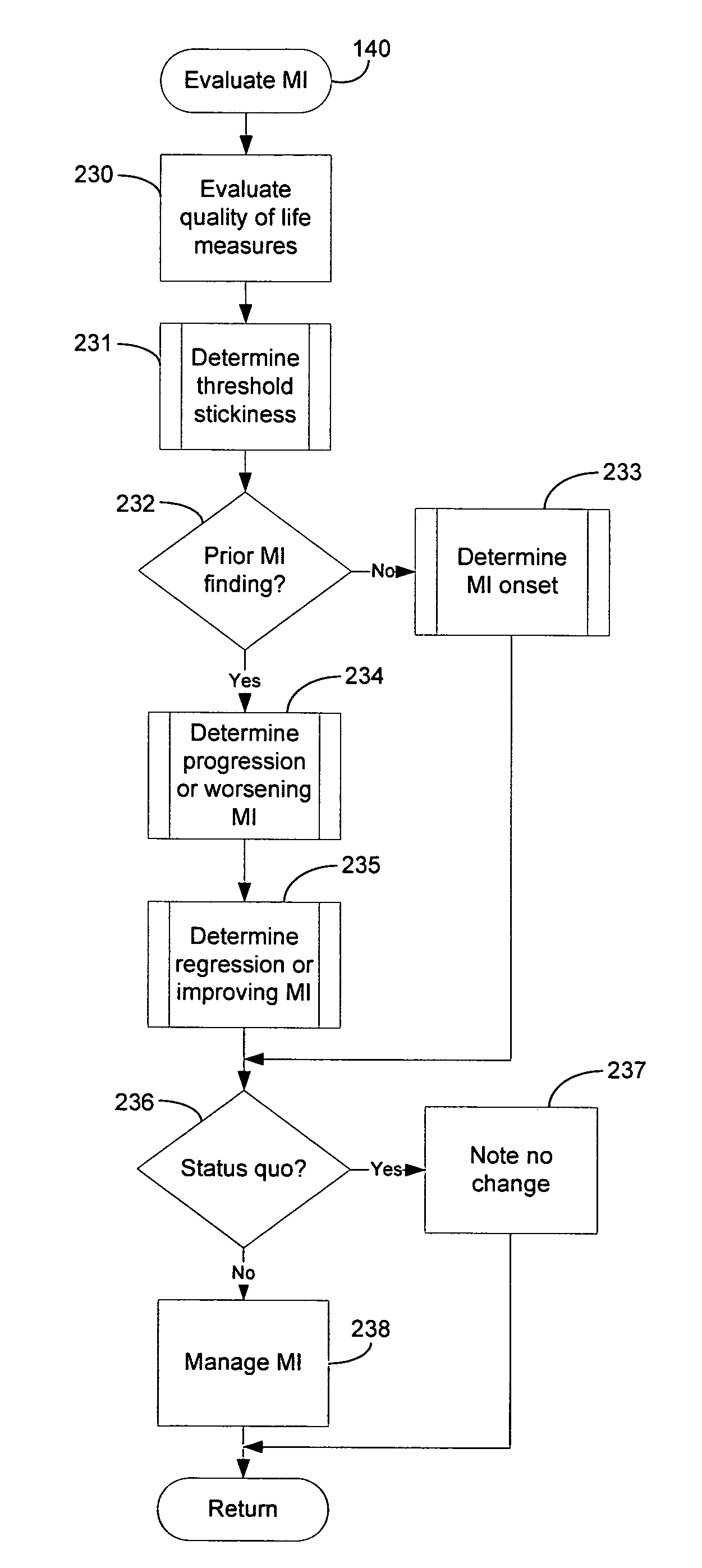
A system for diagnosing and monitoring myocardial ischemia for automated remote patient care is presented. A database stores monitoring sets containing recorded measures relating to patient information recorded on a substantially continuous basis. A server retrieving and processing the monitoring sets includes a comparison module determining a patient status change by comparing recorded measures and time from each of the monitoring sets to other recorded measures and time from another monitoring set with both recorded measures relating to a same type of patient information recorded at different times, and an analysis module testing each patient status change for, an onset, a progression, a regression, and a status quo of myocardial ischemia against a predetermined indicator threshold, including hysteresis threshold, corresponding to same type of patient information as the compared recorded measures.
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
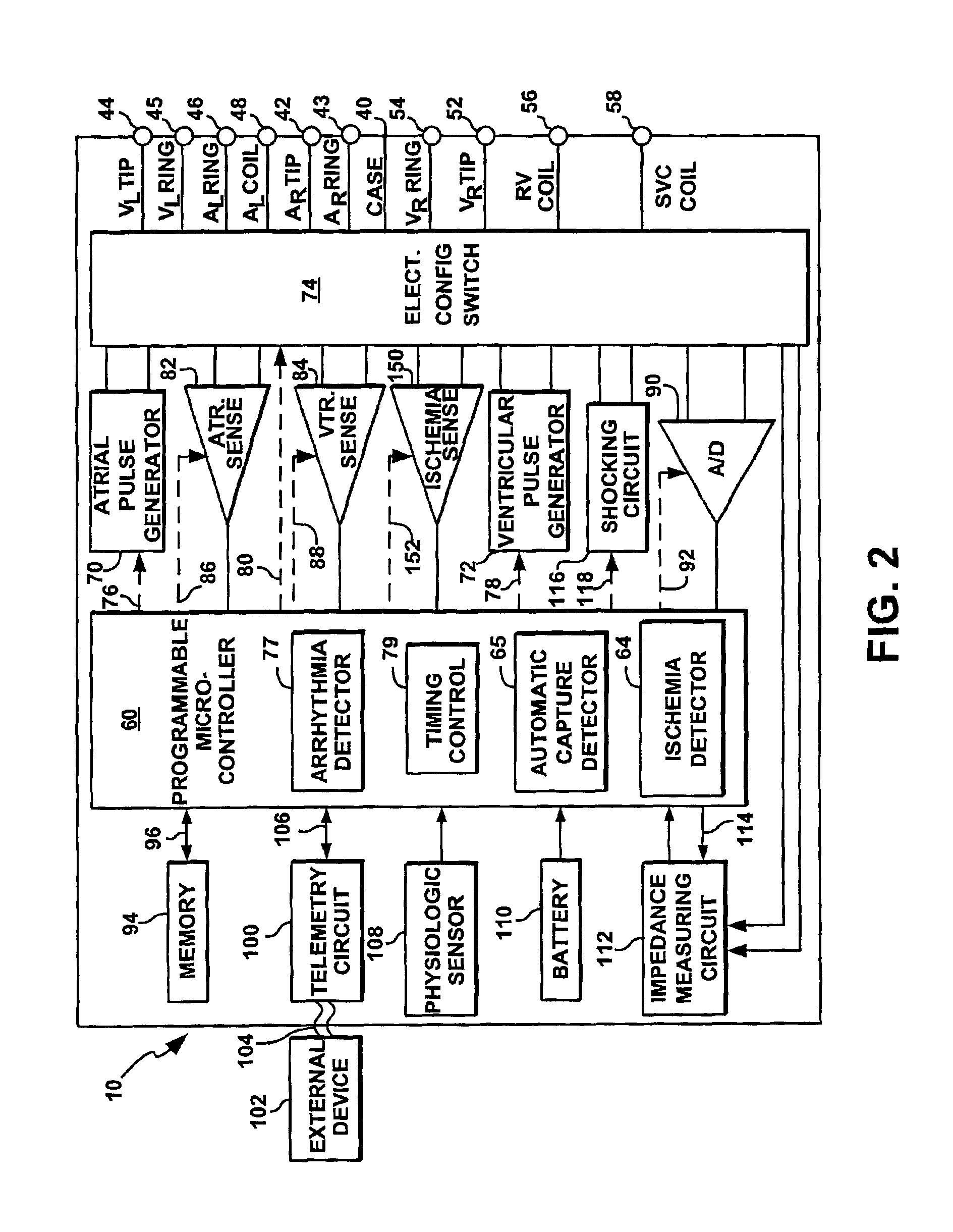
Cardiac stimulation device for optimizing cardiac output with myocardial ischemia protection
InactiveUS6865420B1Reduce demandReduce detectionHeart stimulatorsCardiac muscleIntracardiac Electrogram
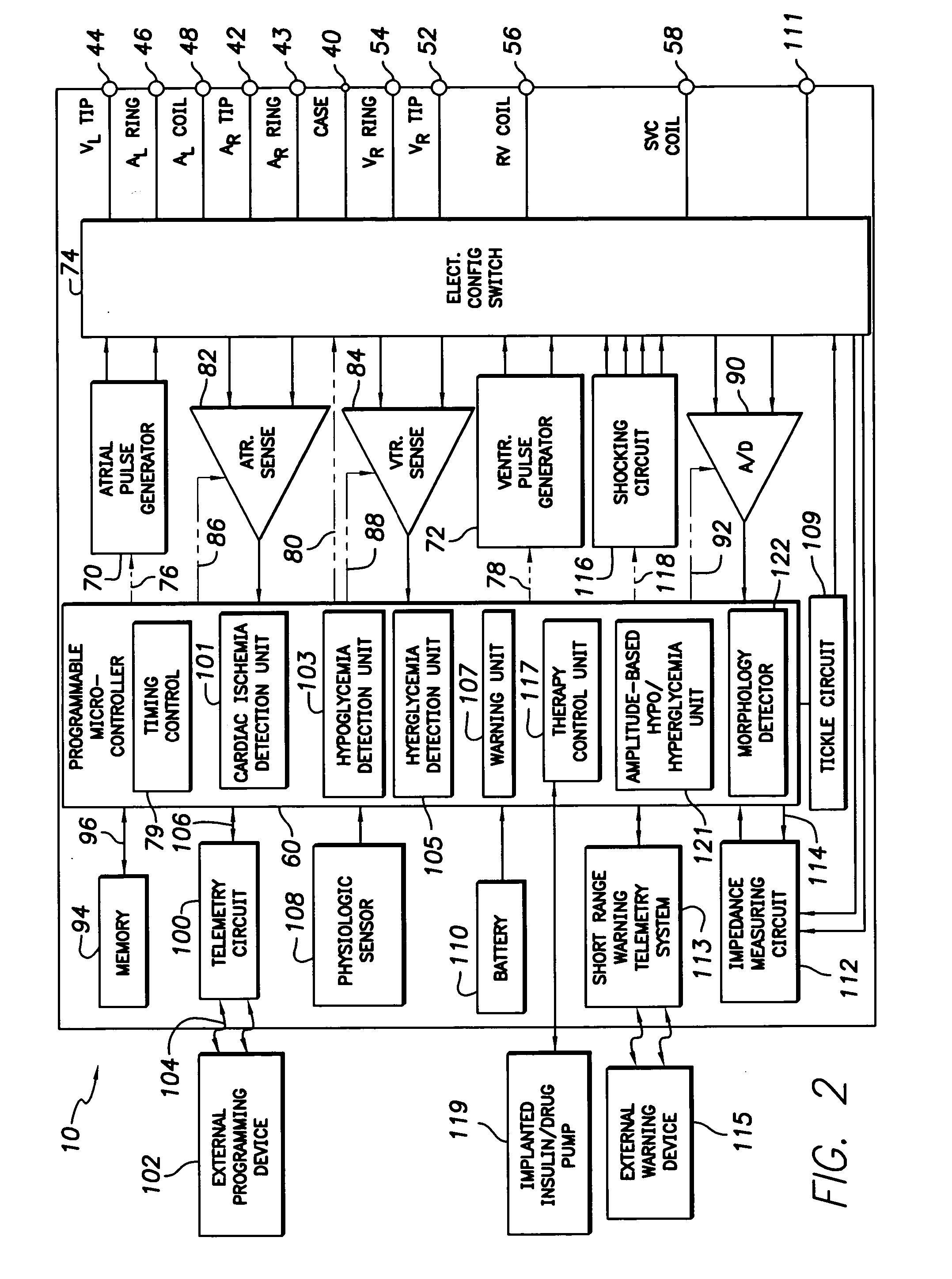
A cardiac stimulation device and method detect myocardial ischemia and provide a response for alleviating the ischemia. Myocardial ischemia is detected by identifying changes in the ST-segment of the intracardiac electrogram (EGM) sensed using large sensing electrode surfaces created by electrically coupling one or more cardiac electrodes or by using larger surface area shocking coils. Myocardial ischemia monitoring is performed when stimulation parameters are adjusted for increasing cardiac output, causing an increased metabolic demand to be placed on the myocardium itself. When myocardial ischemia is detected, stimulation parameters are re-adjusted to reduce the demand placed on the myocardium and thereby alleviate the ischemia.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
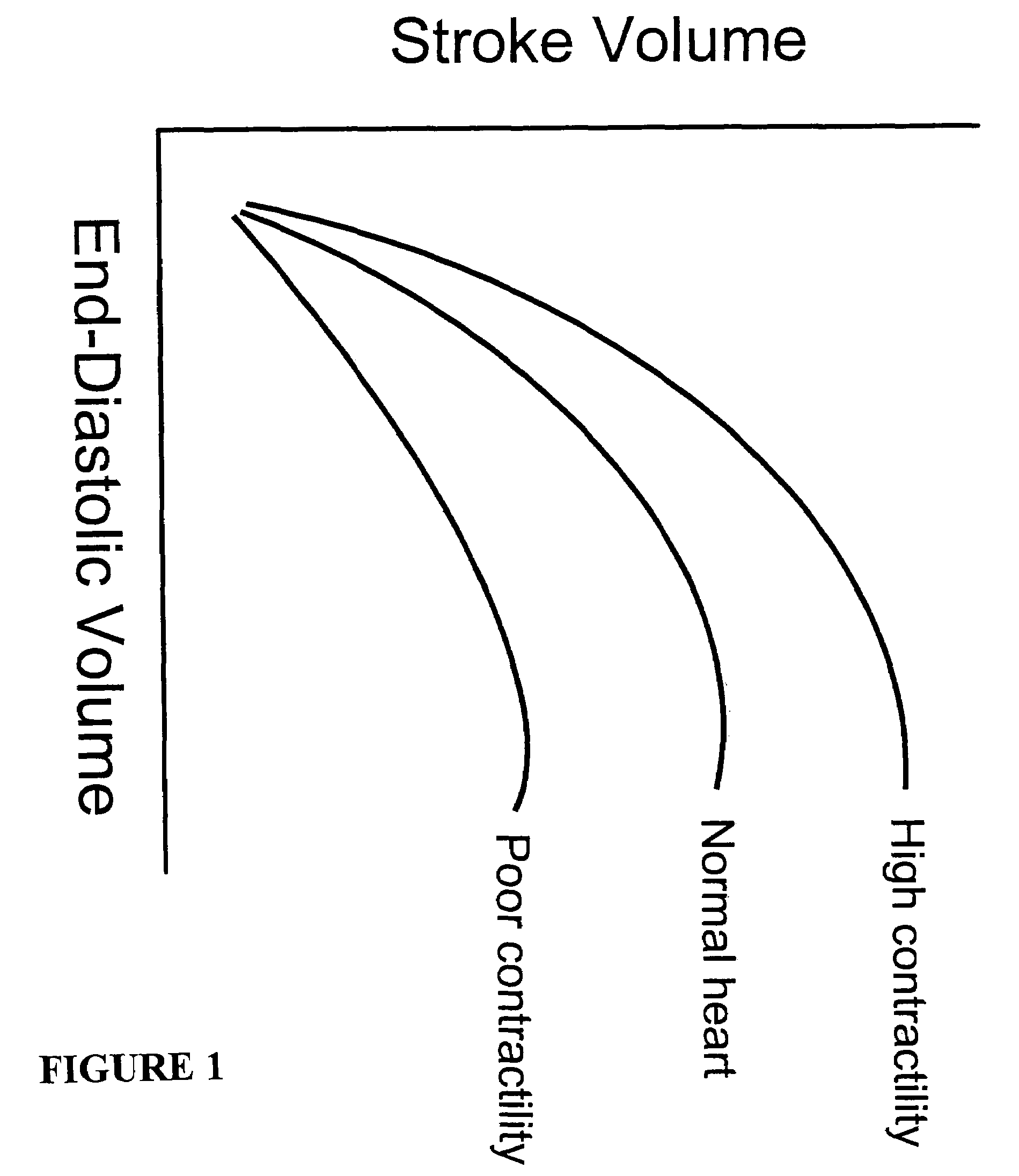
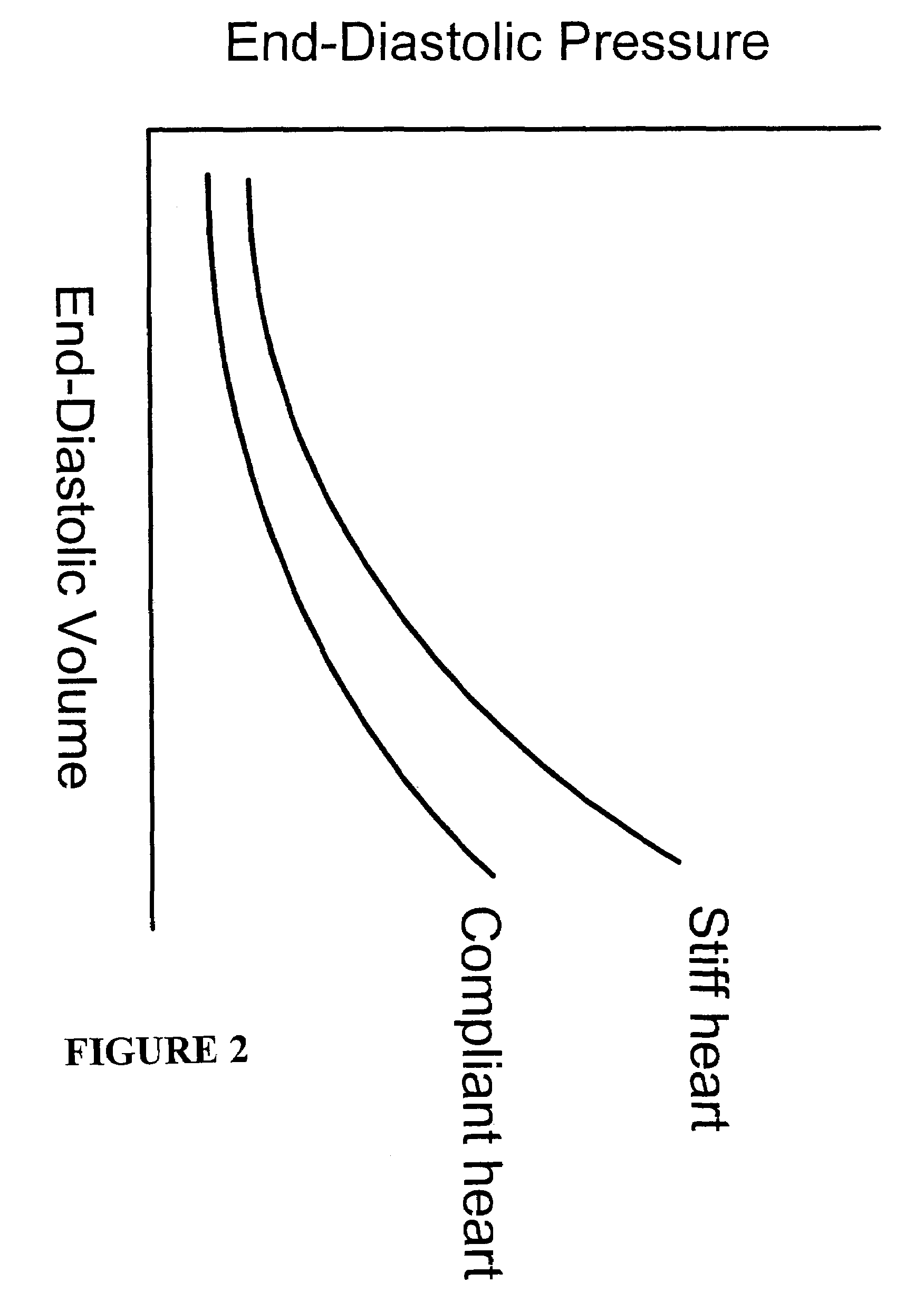
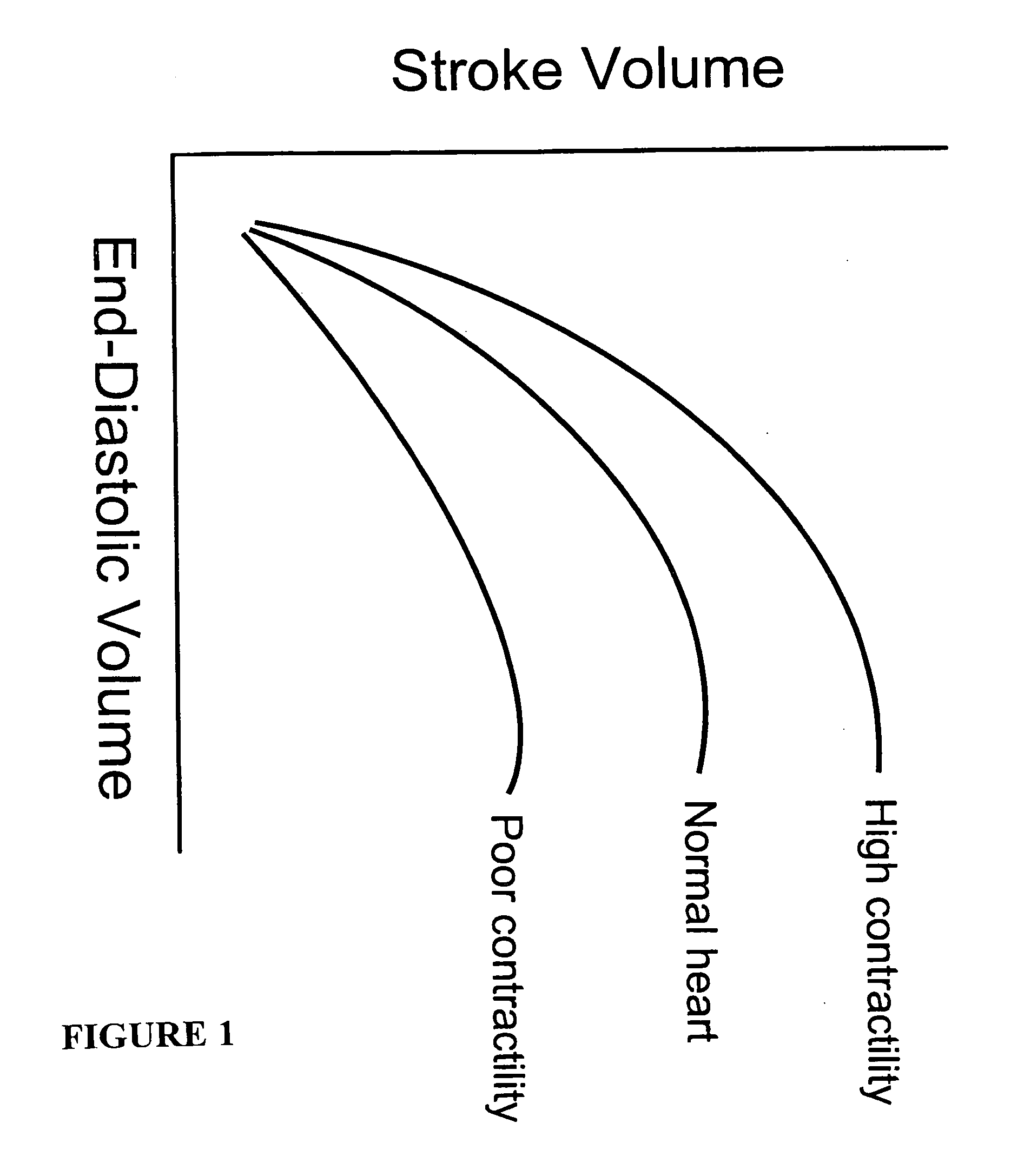
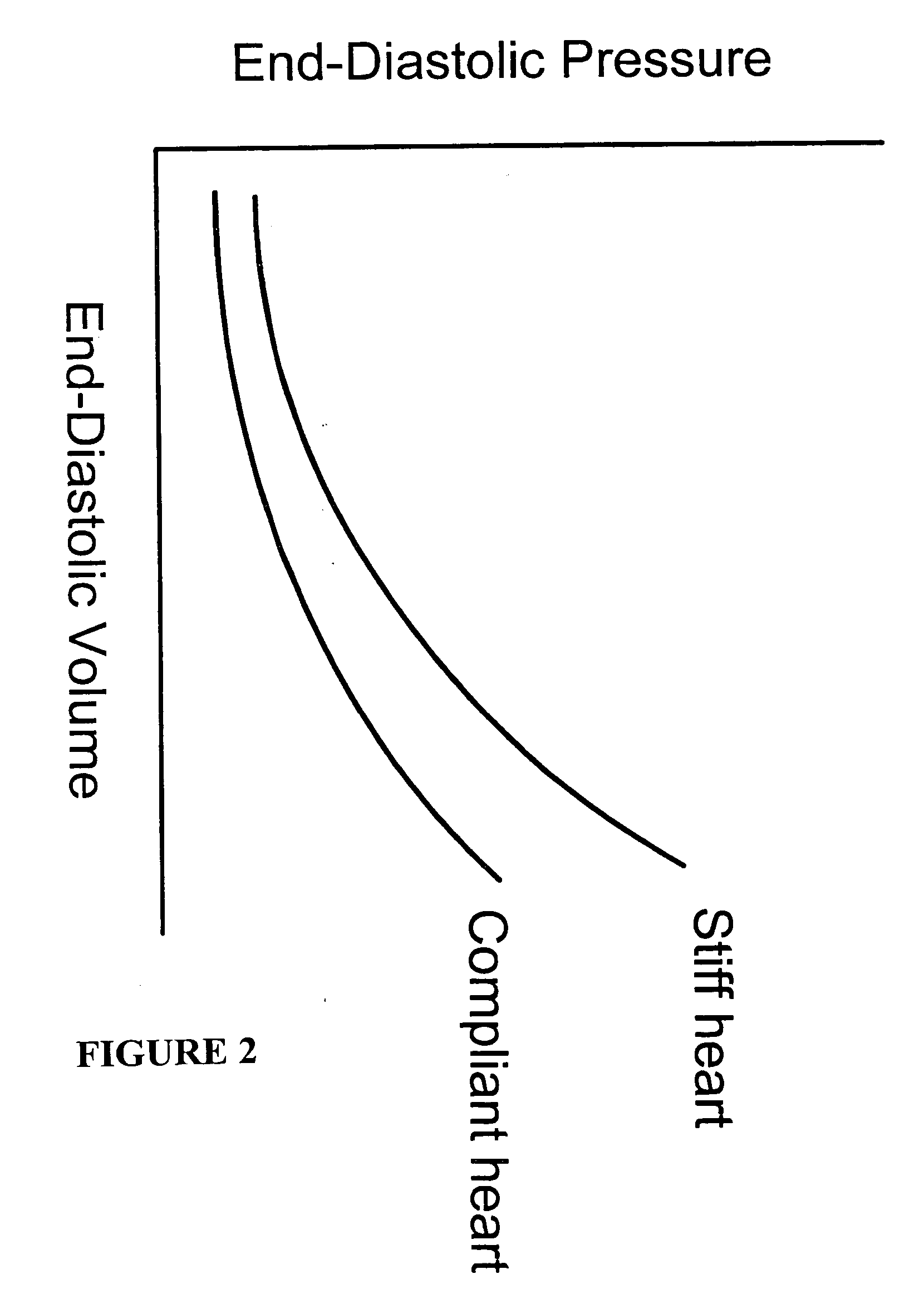
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS7022077B2Maximize tissue displacementEasy diagnosisBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound techniques
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Ischemia detection
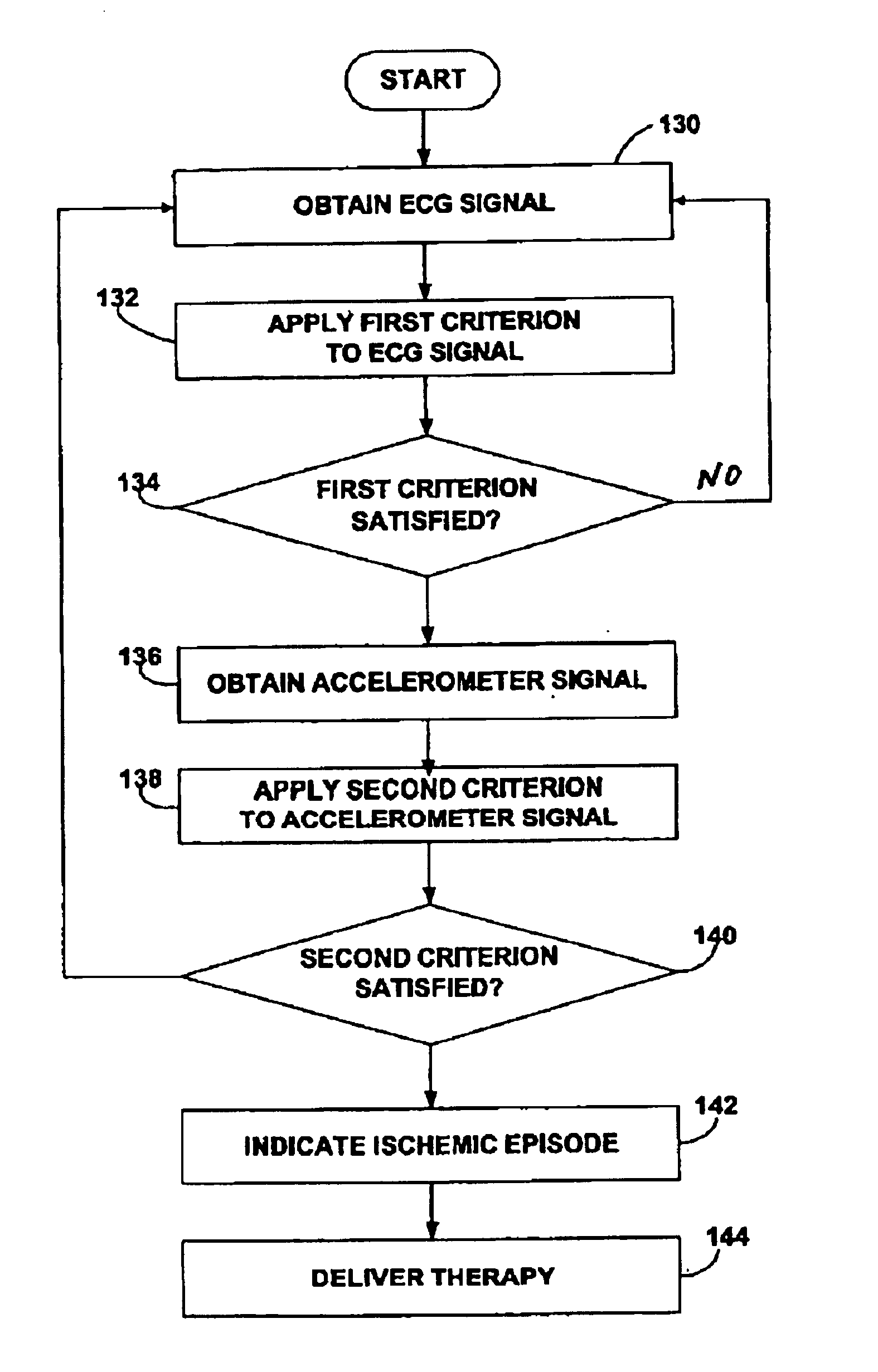
InactiveUS6937899B2Reliable detectionReliable treatmentElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsAccelerometerCardiac muscle
Techniques for detection and treatment of myocardial ischemia are described that monitor both the electrical and dynamic mechanical activity of the heart to detect and verify the occurrence of myocardial ischemia in a more reliable manner. The occurrence of myocardial ischemia can be detected by monitoring changes in an electrical signal such as an ECG or EGM, and changes in dynamic mechanical activity of the heart. Dynamic mechanical activity can be represented, for example, by a heart acceleration signal or pressure signal. The electrical signal can be obtained from a set of implanted or external electrodes. The heart acceleration signal can be obtained from an accelerometer or pressure sensor deployed within or near the heart. The techniques correlate contractility changes detected by an accelerometer or pressure sensor with changes in the ST electrogram segment detected by the electrodes to increase the reliability of ischemia detection.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cardiac activation sequence monitoring for ischemia detection
InactiveUS20060116593A1Convenient wireless communicationElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsImplantable ElectrodesCardiac cycle
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems that provide one or more of monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation, and pacing. Cardiac signal separation is employed to detect, monitor, track and / or trend ischemia using cardiac activation sequence information. Ischemia detection may involve sensing composite cardiac signals using implantable electrodes, and performing a signal separation that produces one or more cardiac activation signal vectors associated with one or more cardiac activation sequences. A change in the signal vector may be detected using subsequent separations. The change may be an elevation or depression of the ST segment of a cardiac cycle or other change indicative of myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction, or other pathological change. The change may be used to predict, quantify, and / or qualify an event such as an arrhythmia, a myocardial infarction, or other pathologic change. Information associated with the vectors may be stored and used to track the vectors.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
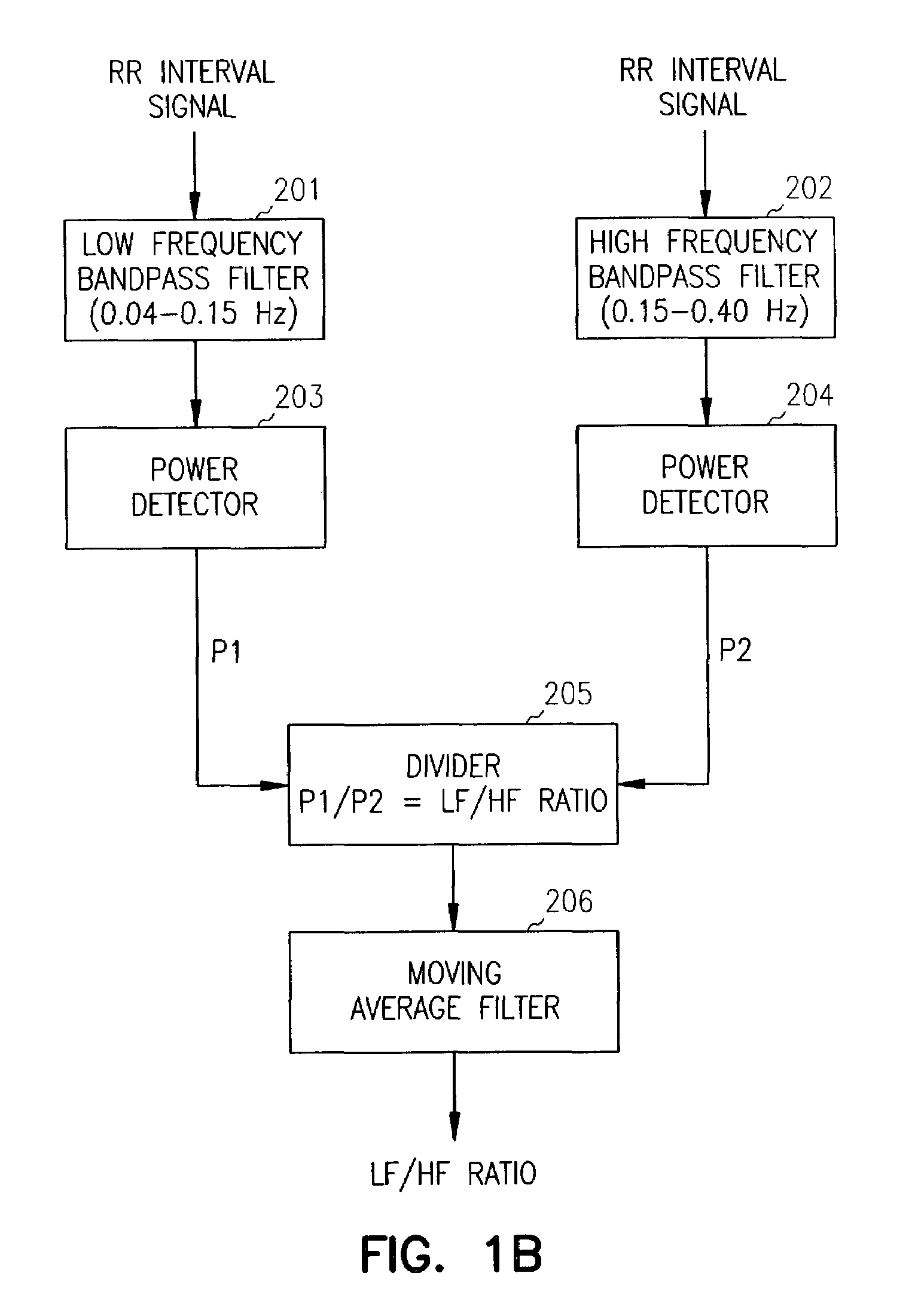
Method for monitoring autonomic tone
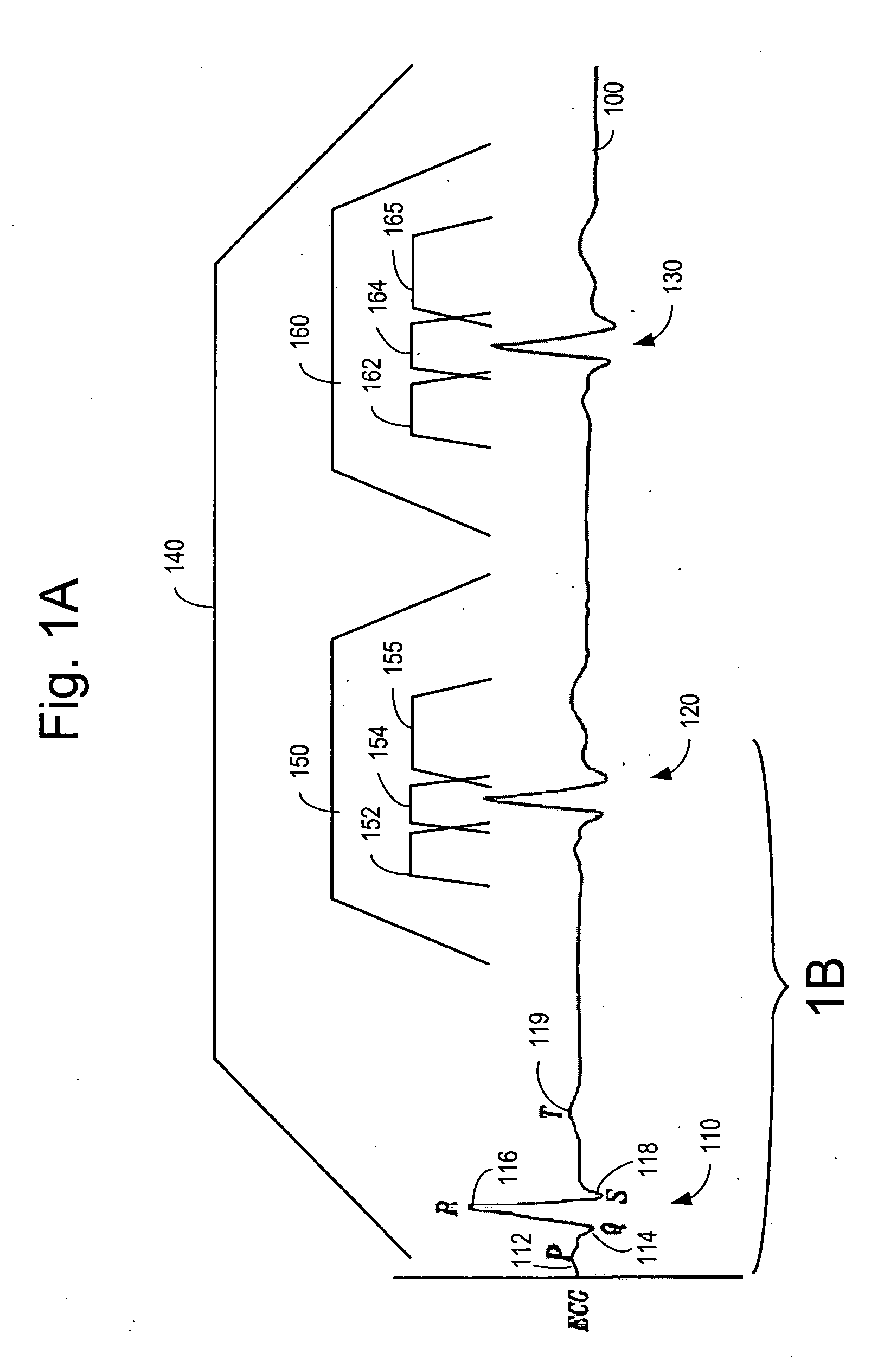
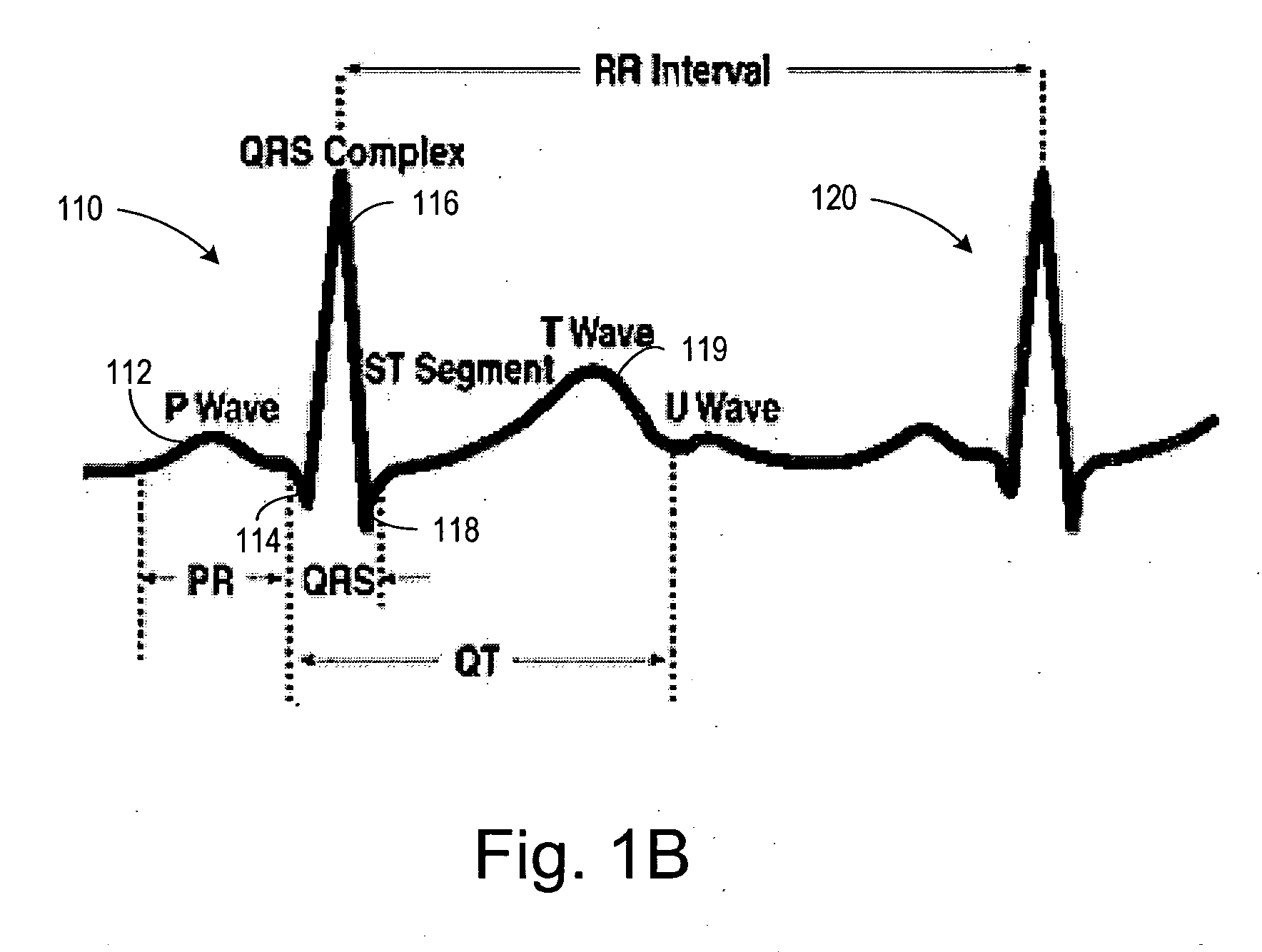
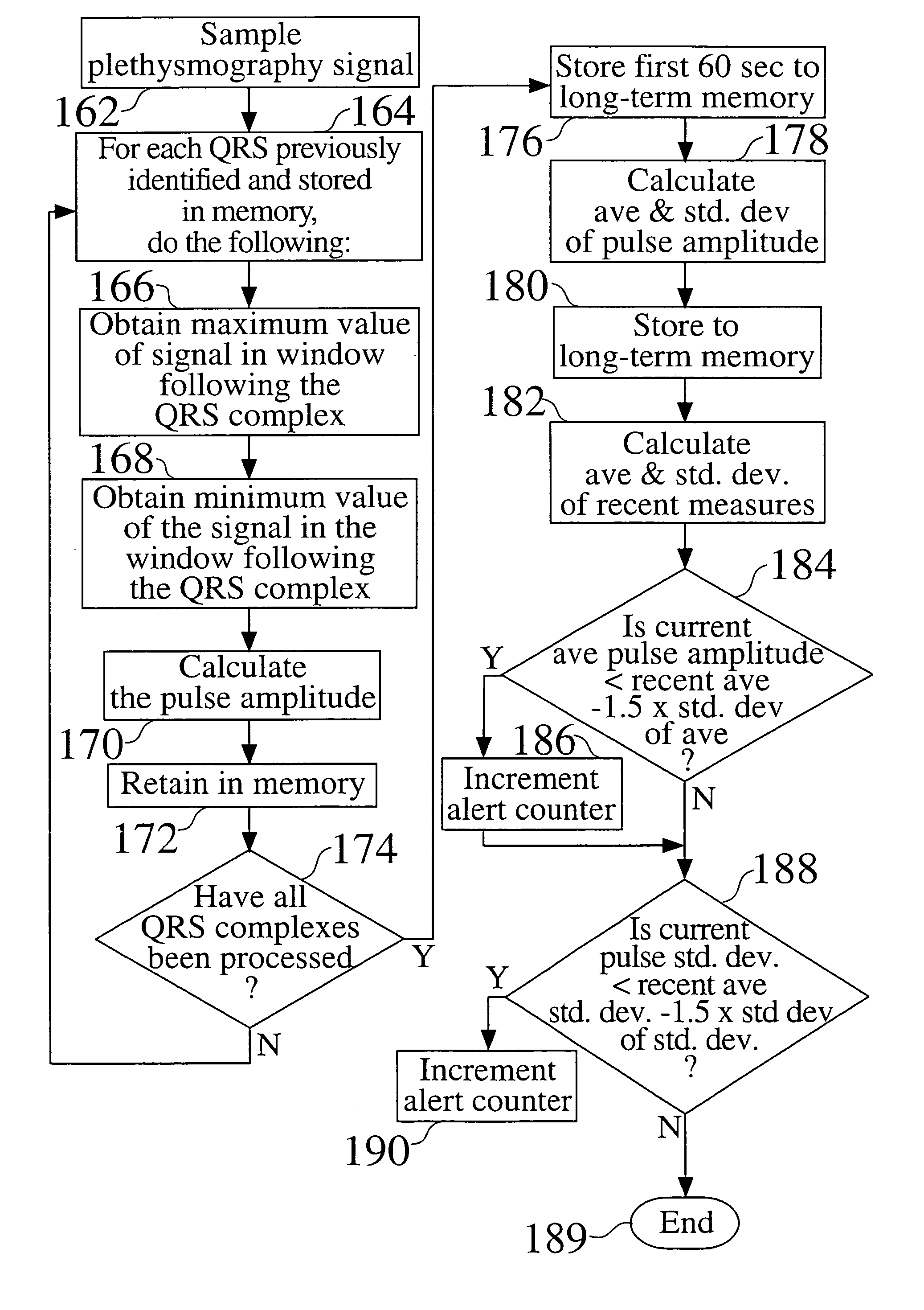
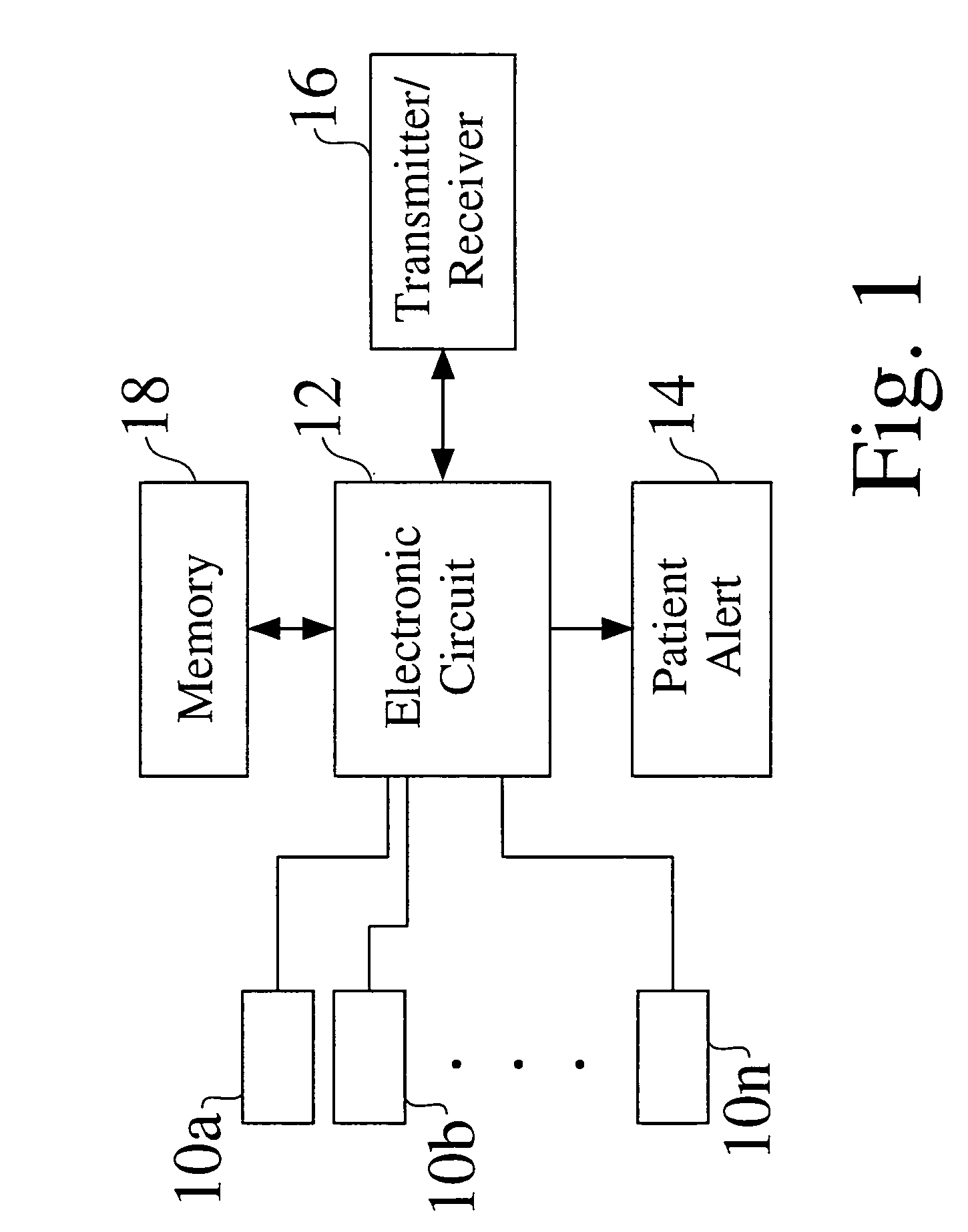
A method for monitoring the progression of the hemodynamic status of a patient by tracking autonomic tone. For example, the method may be applied to patients suffering from heart failure, diabetic neuropathy, cardiac ischemia, sleep apnea and hypertension. An implantable or other ambulatory monitor senses a pulse amplitude signal such as a vascular plethysmography signal. Variations of the signal amplitude on a scale greater than the heartbeat to heartbeat scale are indicative of variations in autonomic tone. A significant reduction in pulse amplitude and pulse amplitude variability are indicative of a heart failure exacerbation or other disease state change. This information may be used to warn the patient or healthcare providers of changes in the patient's condition warranting attention.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
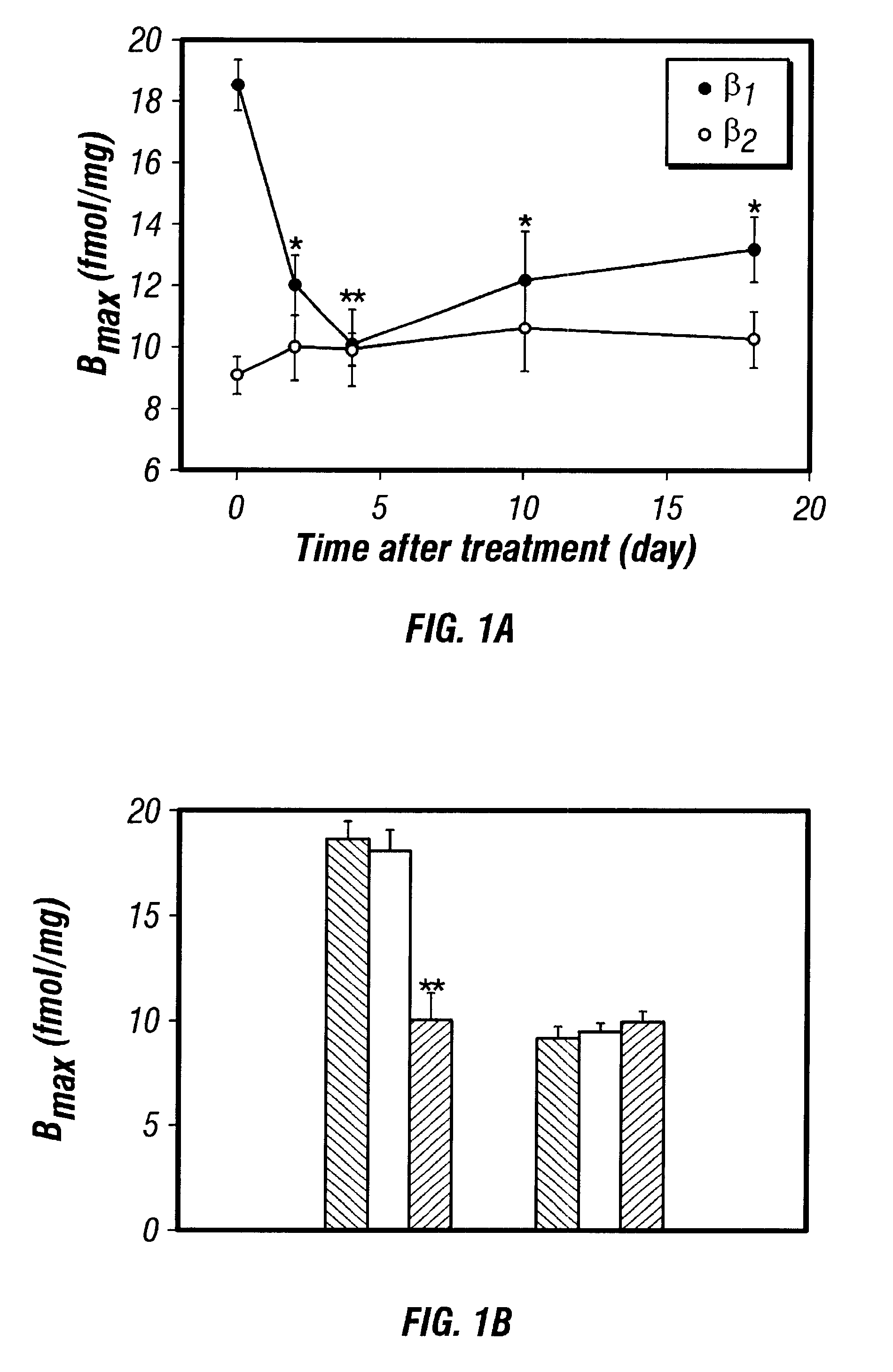
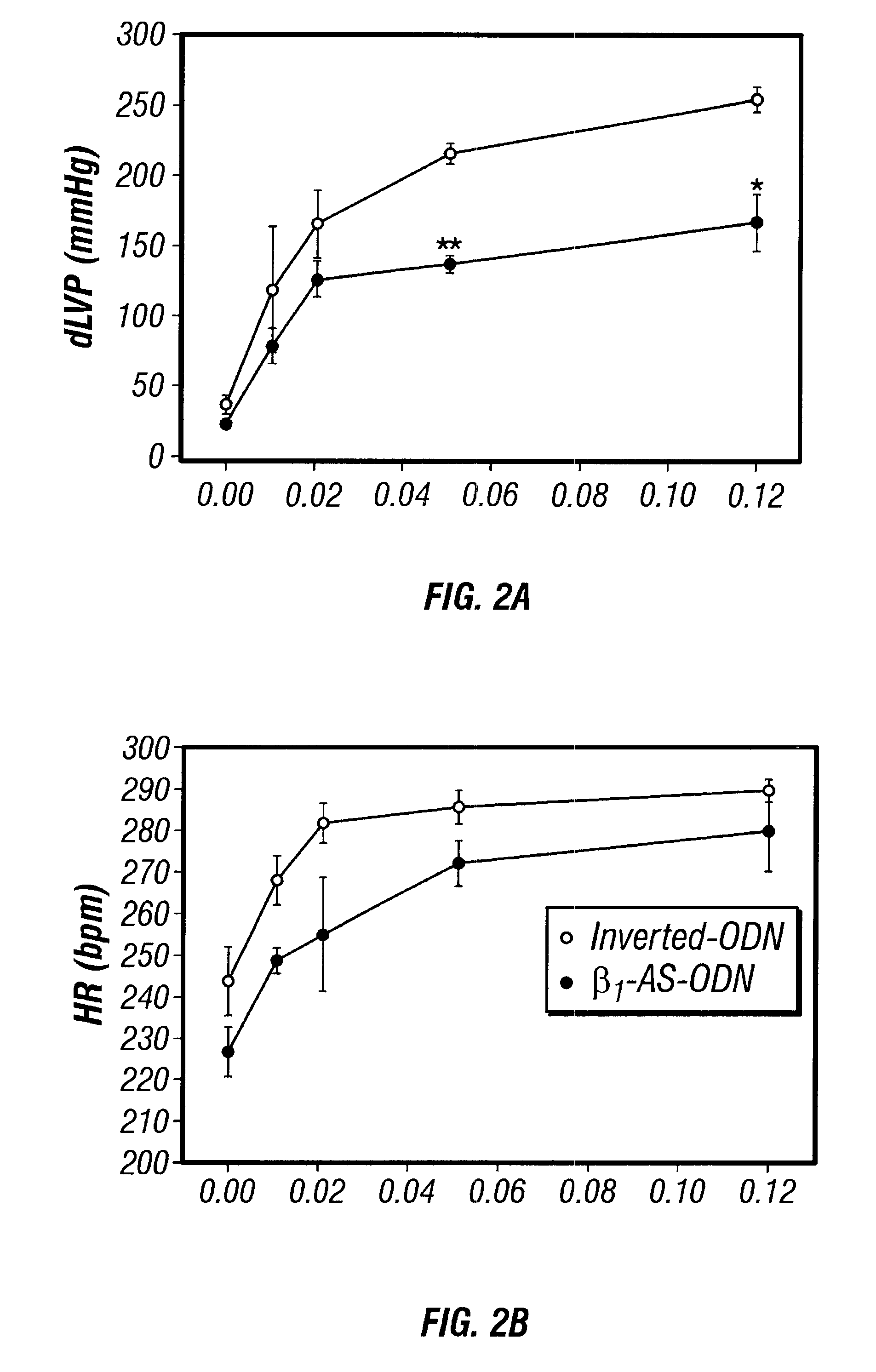
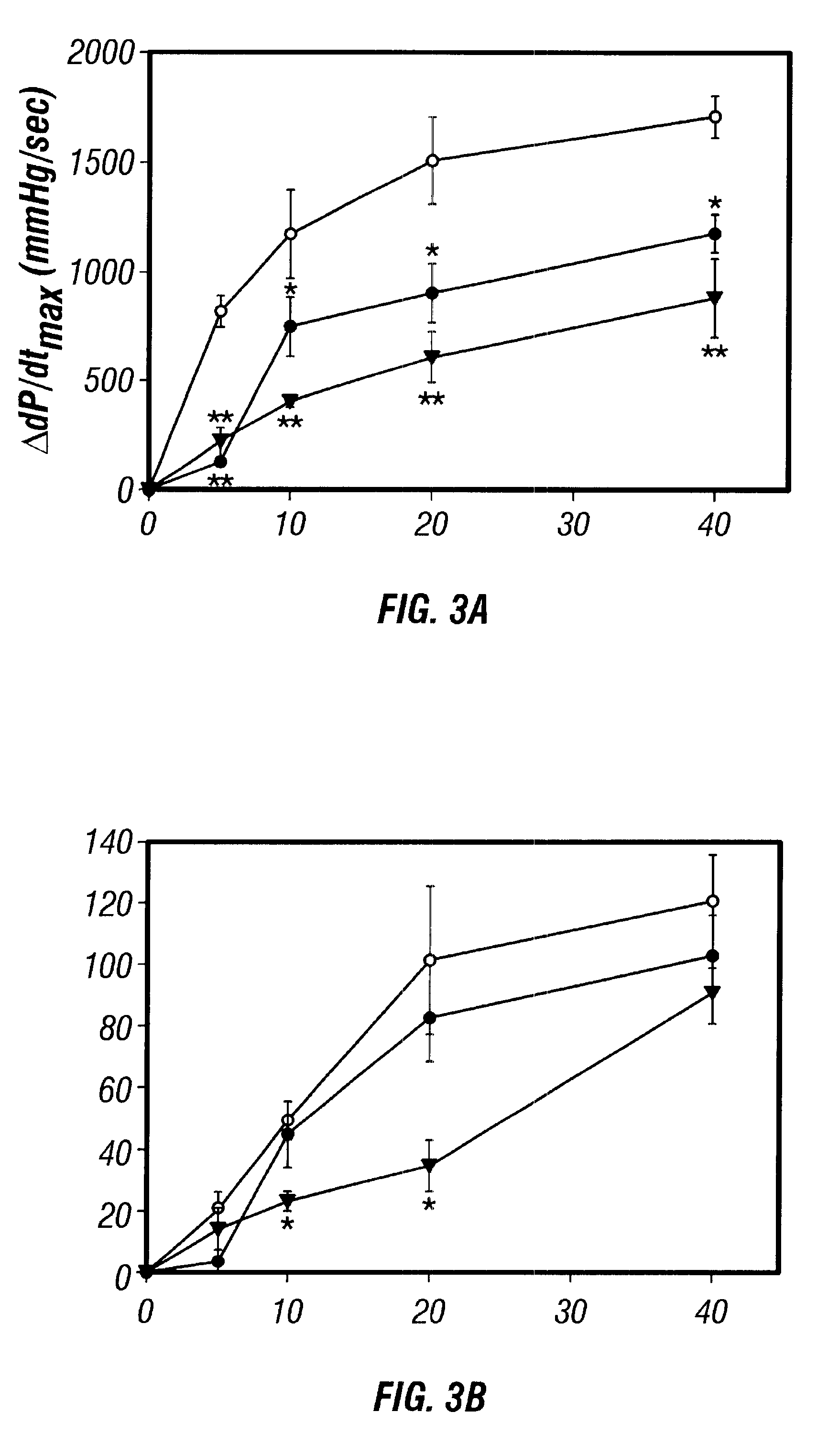
Antisense compositions targeted to beta1-adrenoceptor-specific mRNA and methods of use
InactiveUS6489307B1Reduce inhibitionInhibit and reduce expressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsEccentric hypertrophyMammal
Disclosed are antisense oligonucleotide, polynucleotide, and peptide nucleic acid compounds that specifically bind to mammalian mRNA encoding a beta1-adrenoceptor polypeptide and that are useful in the control and / or treatment of cardiac dysfunction, hypertension, hypertrophy, myocardial ischemia, and other cardiovascular diseases in an affected mammal, and preferably, in a human subject. The antisense compounds disclosed herein, and pharmaceutical formulations thereof, provide sustained control of beta1-adrenoceptor expression over prolonged periods, and achieve therapeutic effects from as little as a single dose. Administration of these antisense compositions to approved animal models resulted in a decrease in blood pressure, but no significant change in heart rate. Use of such antisense compositions in the reduction of beta1-adrenoceptor polypeptides in a host cell expressing beta1-adrenoceptor-specific mRNA, and in the preparation of medicaments for treating human and animal diseases, and in particular, hypertension and other cardiac dysfunction is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
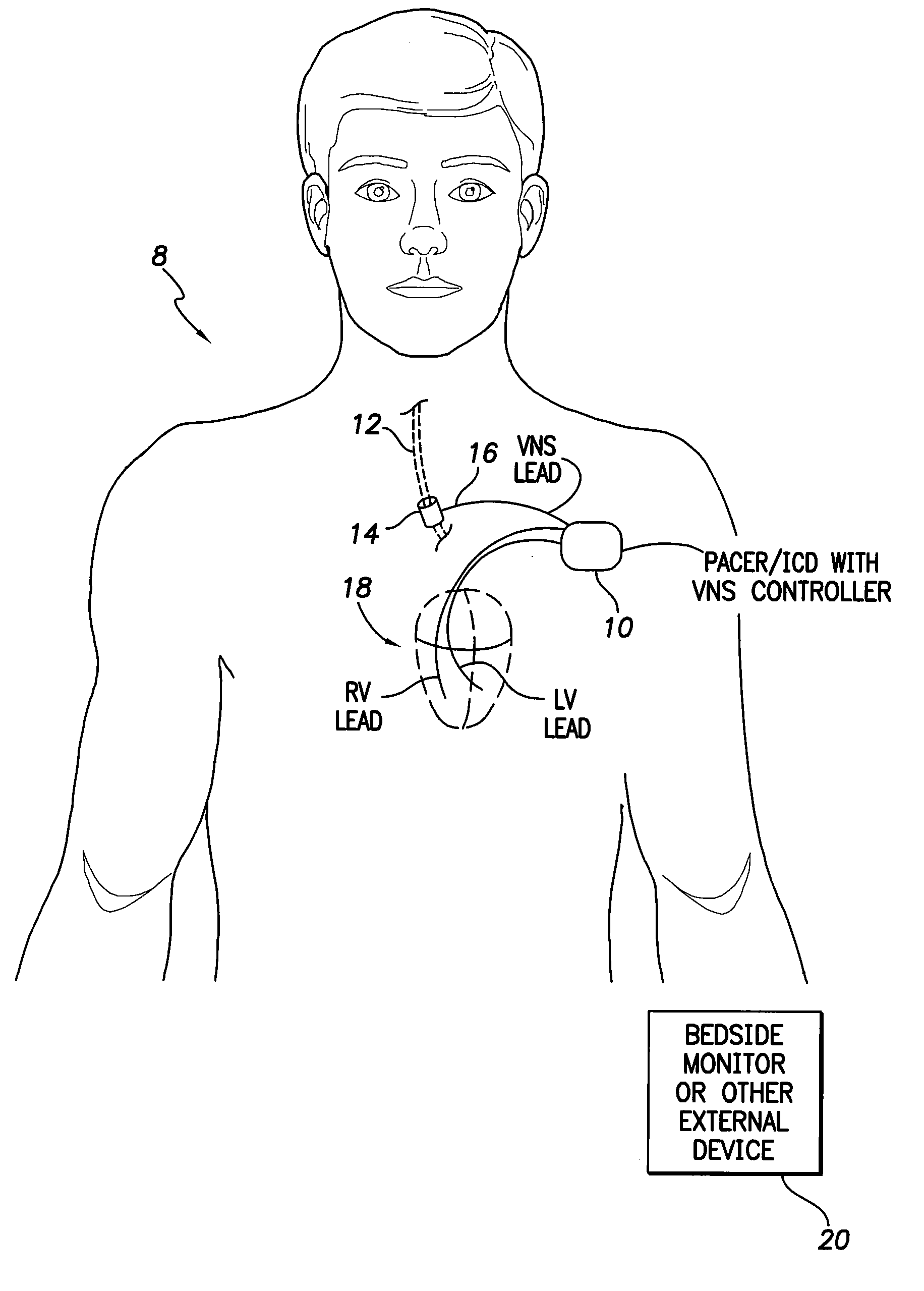
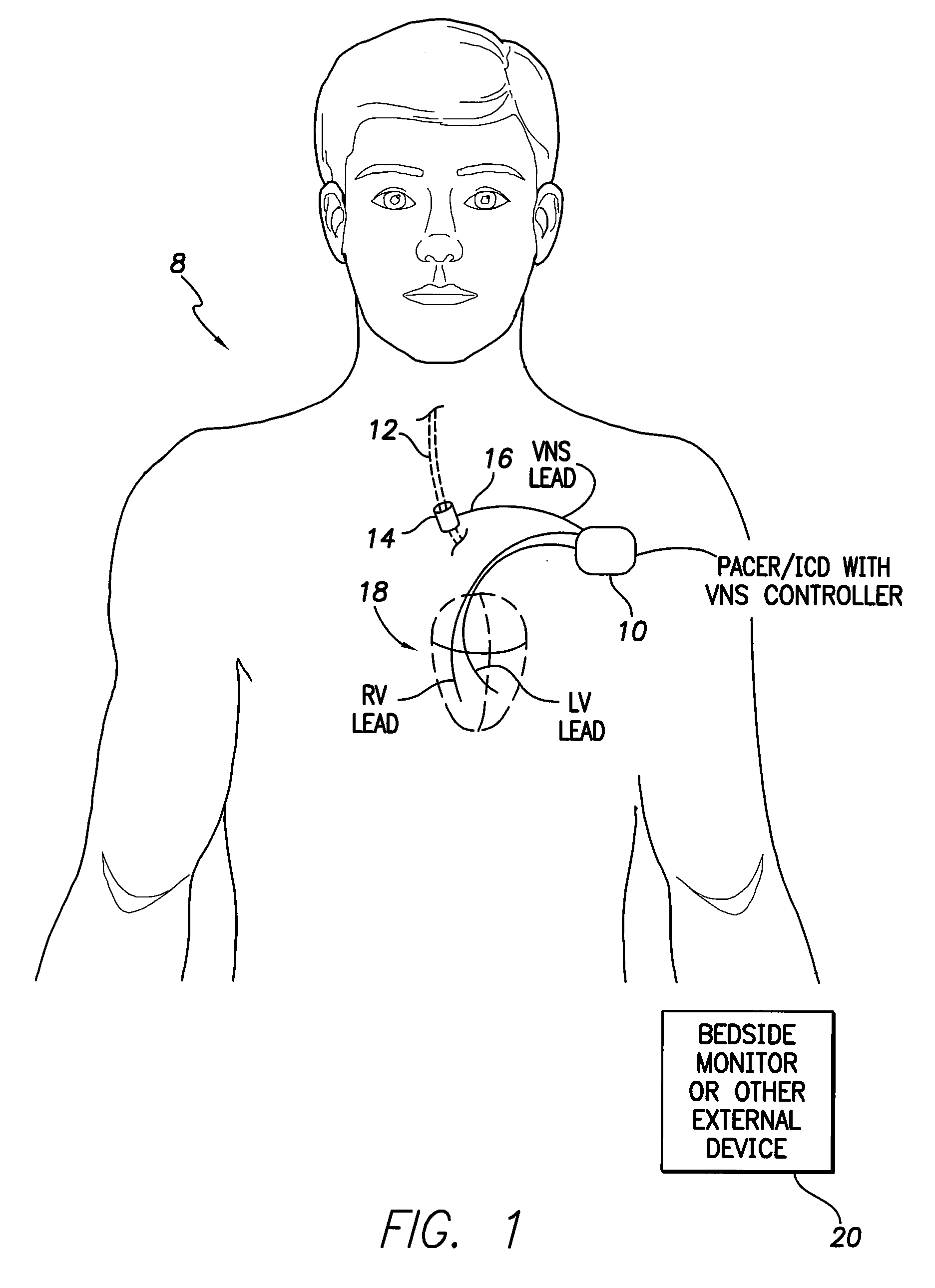
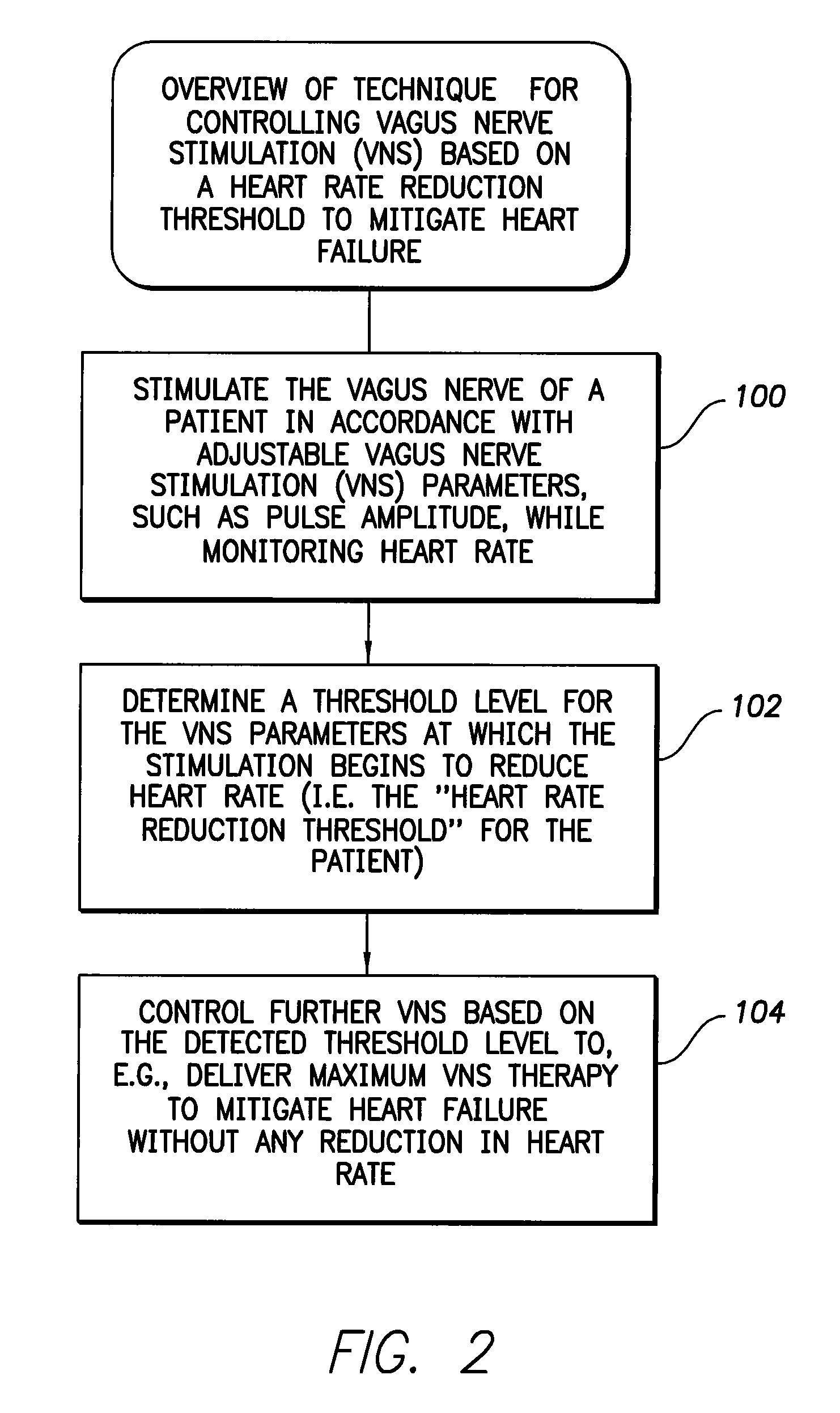
Systems and Methds for Use by an Implantable Medical Device for Controlling Vagus Nerve Stimulation Based on Heart Rate Reduction Curves and Thresholds to Mitigate Heart Failure
InactiveUS20100114227A1Slow down heart rateMitigate heart failureHeart stimulatorsMaximum levelCardiac muscle
Systems and techniques are provided for controlling vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) delivered by an implantable medical device for mitigating heart failure in a patient. In one mode, VNS therapy is set to levels just below a heart rate reduction threshold so as to deliver VNS near the highest stimulation levels that can be achieved without reducing patient heart rate. In this manner, a maximum level of heart failure mitigation can be achieved via VNS therapy without incurring the potentially adverse consequences of inducing bradycardia within the patient. In another mode, VNS therapy is instead controlled to deliver VNS above the threshold so as to mitigate heart failure while also selectively reducing heart rate, as may be appropriate in patients susceptible to cardiac ischemia. A controlled heart rate reduction curve may additionally or alternatively be determined for use in achieving target amounts of heart rate reduction.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
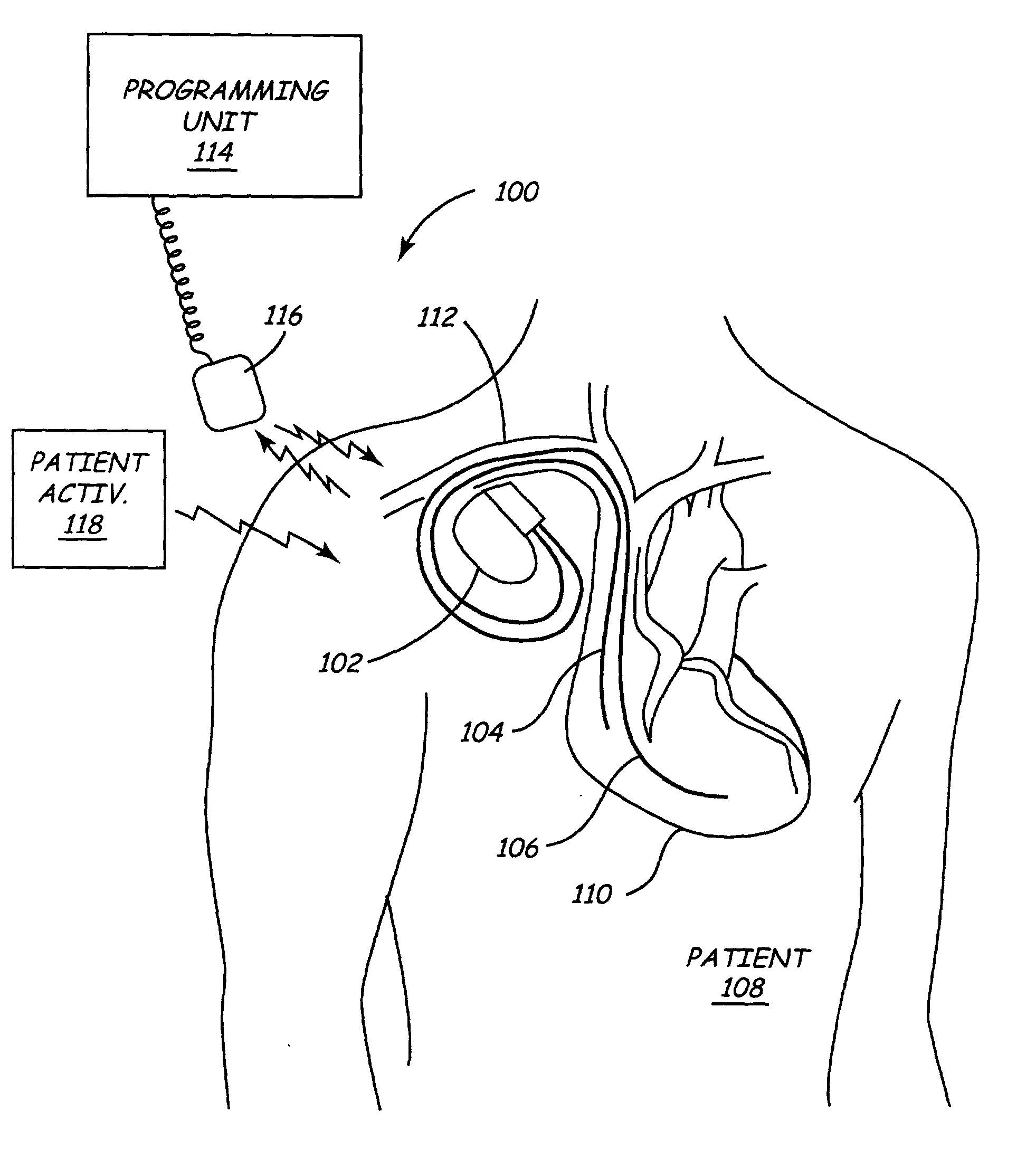
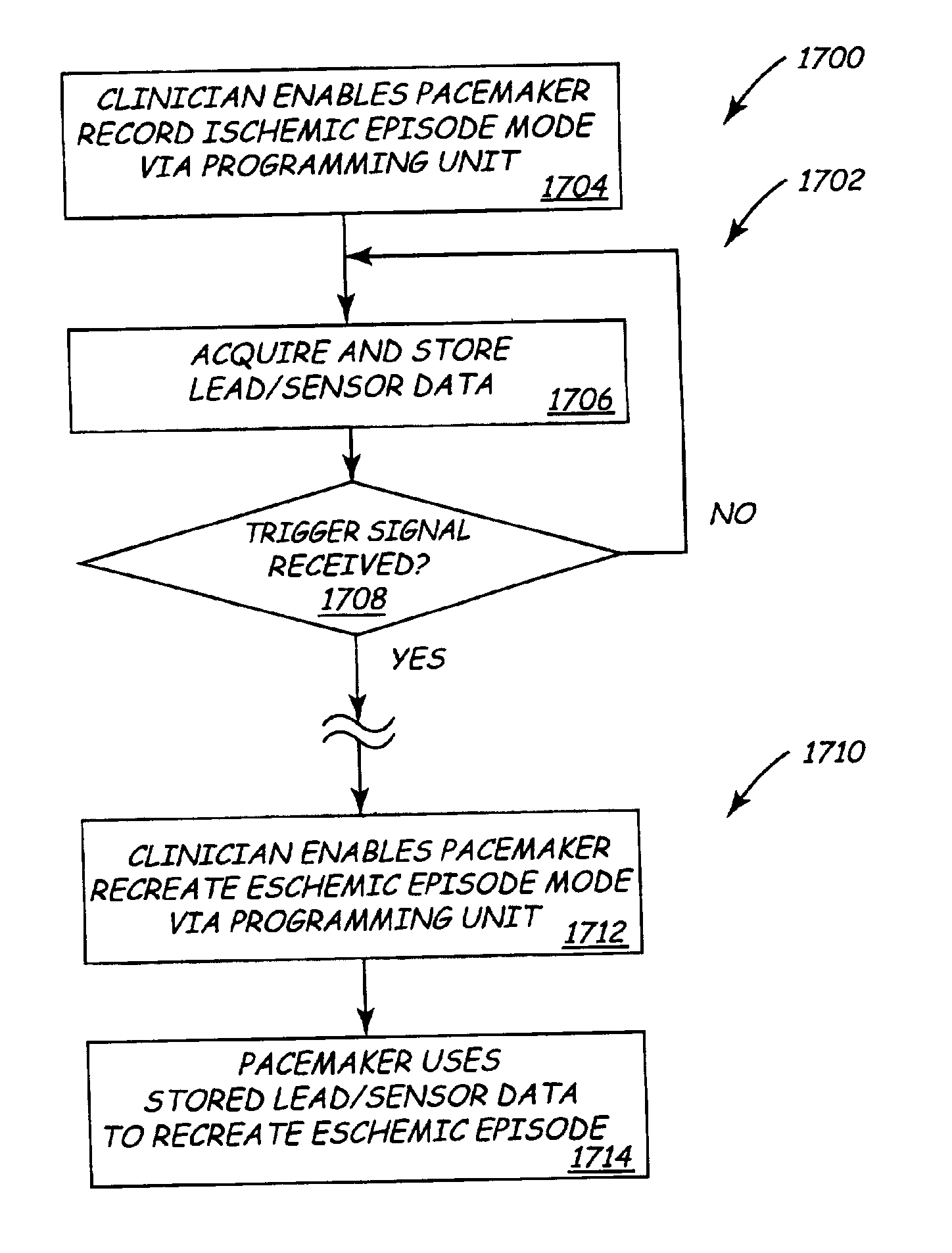
Implantable medical device (IMD) system configurable to subject a patient to a stress test and to detect myocardial ischemia within the patient
Various implantable medical devices (IMDs) are disclosed for implantation in a patient. The IMD includes pacing circuitry configured to selectively produce pacing pulses at a programmable pacing rate. In one embodiment, the IMD is configurable to subject a patient to a stress test. The IMD may be configurable to subject the patient to the stress test at the time specified by stored timing information, or in response to a signal (e.g., from a patient activator). Another embodiment of the implantable medical device (IMD) includes sensor circuitry, a memory for storing data, and a control unit. The sensor circuitry produces sensor data relating to cardiac condition. The control unit is configurable to store the sensor data in the memory until a trigger signal is received. Methods are described for performing a stress test in a patient with an IMD, and for subsequently reproducing cardiac operational states.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for predicting recurring ventricular arrhythmias
ActiveUS6922585B2High sensitivityStrong specificityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaVentricular fibrillation
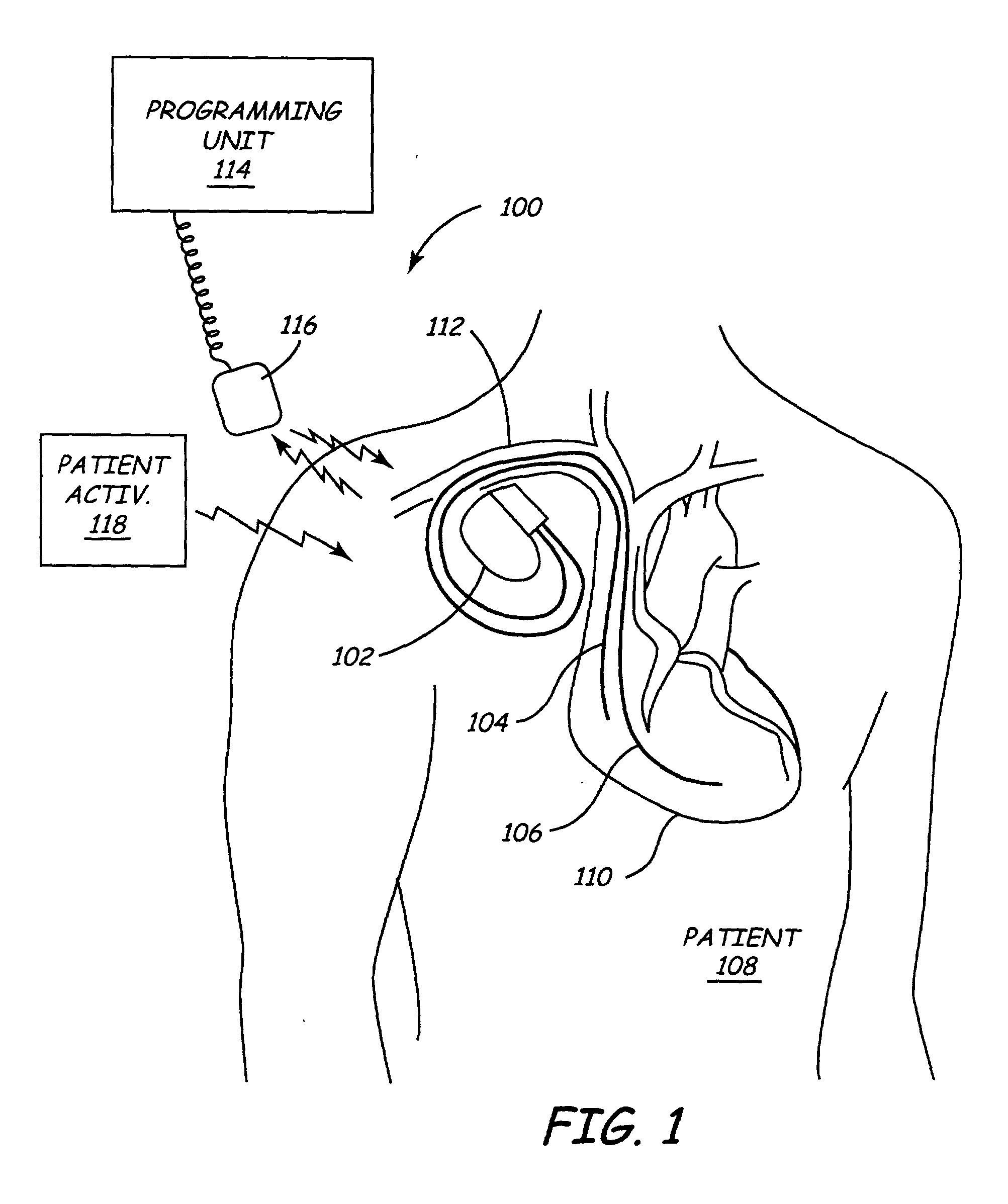
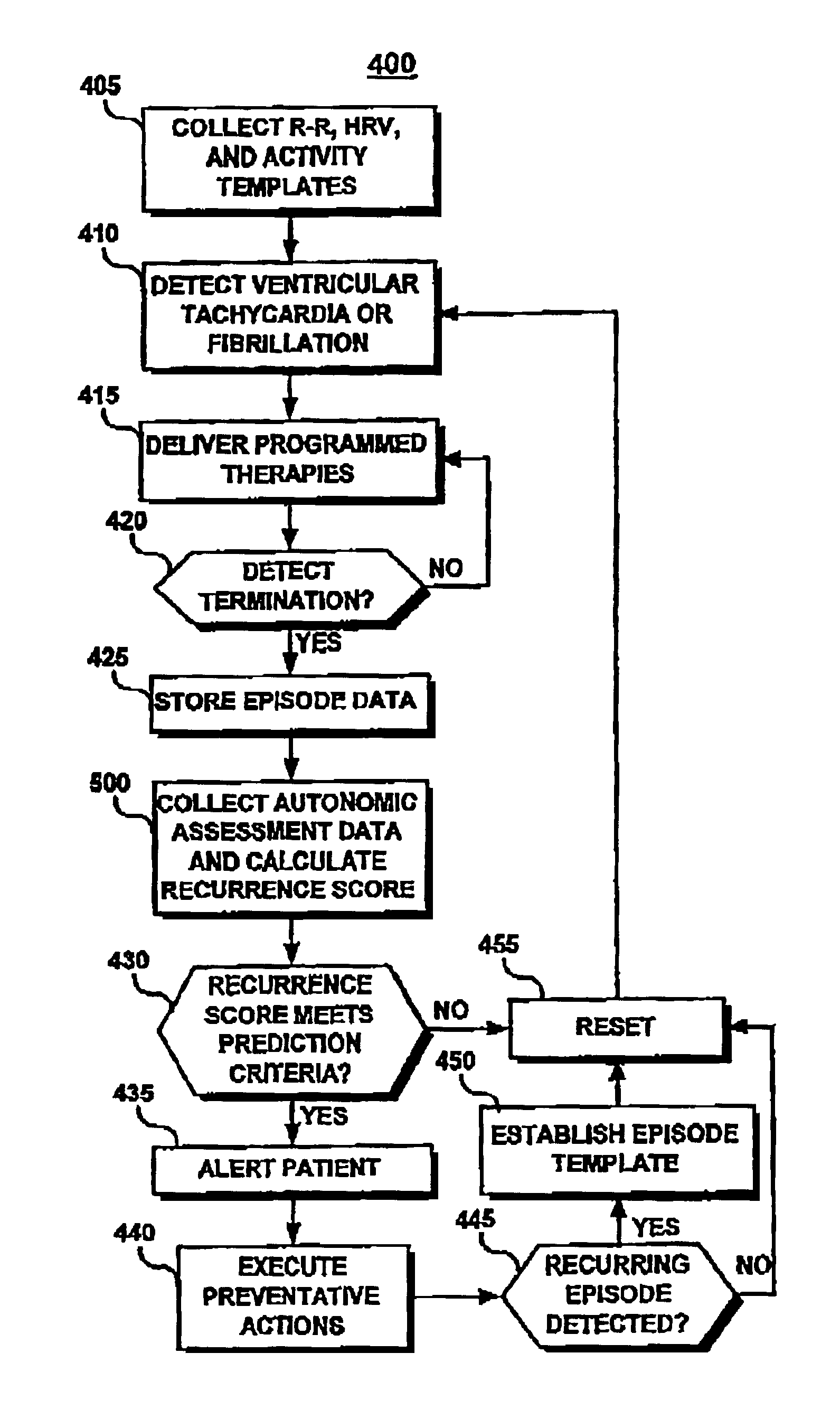
An implantable medical device and method are provided for assessing autonomic tone and risk factors associated with arrhythmias and, based on this assessment, an early recurrence of ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation is predicted. Specifically, changes in R—R interval, heart rate variability, patient activity, and myocardial ischemia are measured prior to and after a detected an arrhythmia episode. A recurrence score is calculated as a weighted sum of measured parameters and compared to a prediction criterion. The prediction criterion may be a preset threshold score or an individualized episode template based on previously calculated recurrence scores associated with recurring episodes. Stored parameters and episode-related data may be downloaded for offline analyses for optimizing prediction criteria and monitoring patient status.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
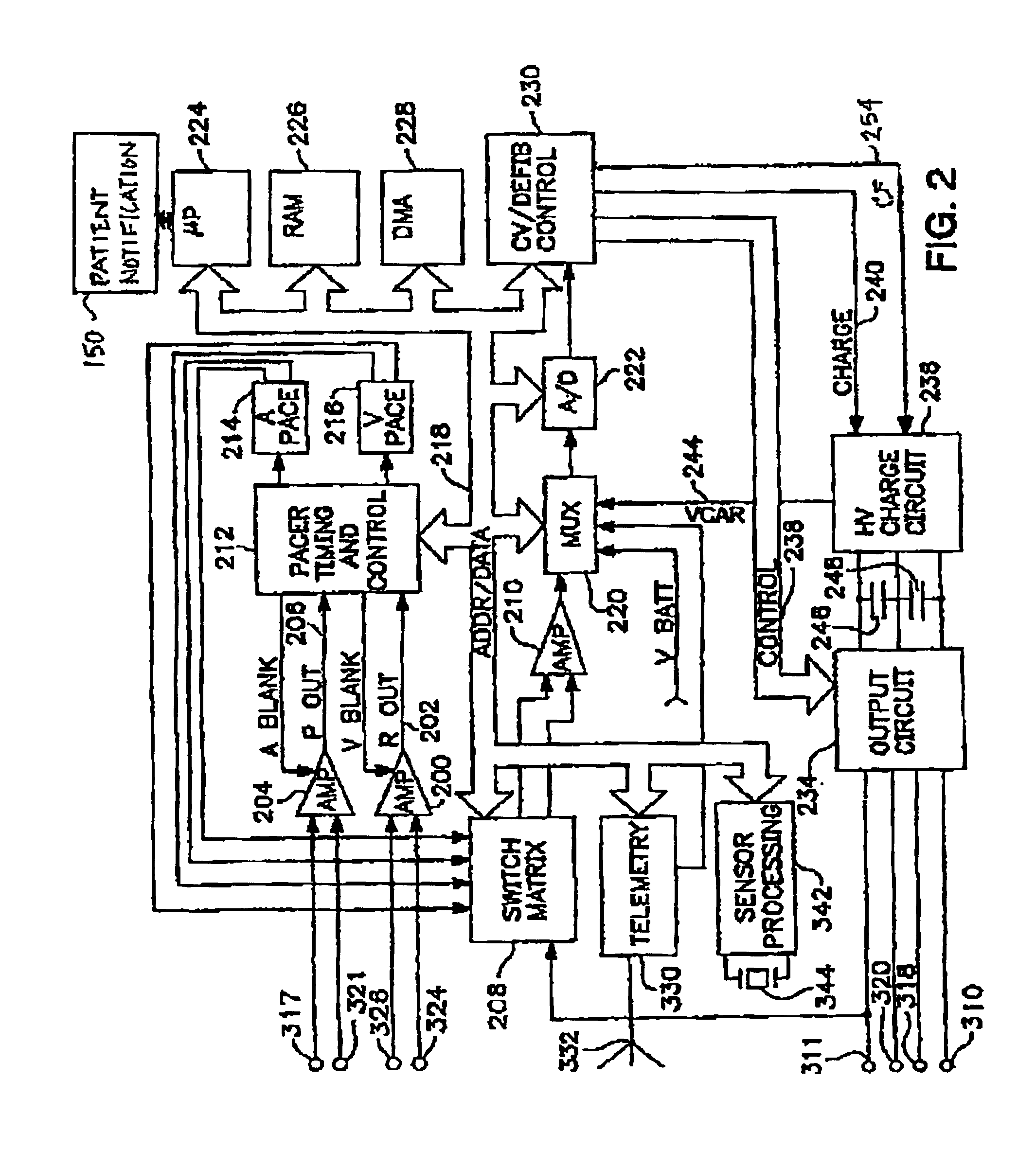
Implantable multi-parameter sensing system and method
A system and method of sensing multiple parameters. The method may include implanting an implantable sensor in a patient and reading an output from at least one of the implantable sensing elements. The implantable sensor may have a housing within which are disposed a plurality of implantable sensing elements. At least one of the implantable sensing elements may respond to lactate. In addition, a medical professional may administer to the patient for myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction angina, sepsis based on the output read. A medical professional may also administer to the patient having an implantable cardiovascular defibrillator or who is receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. The method may be used in a surgical or intensive care environment.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
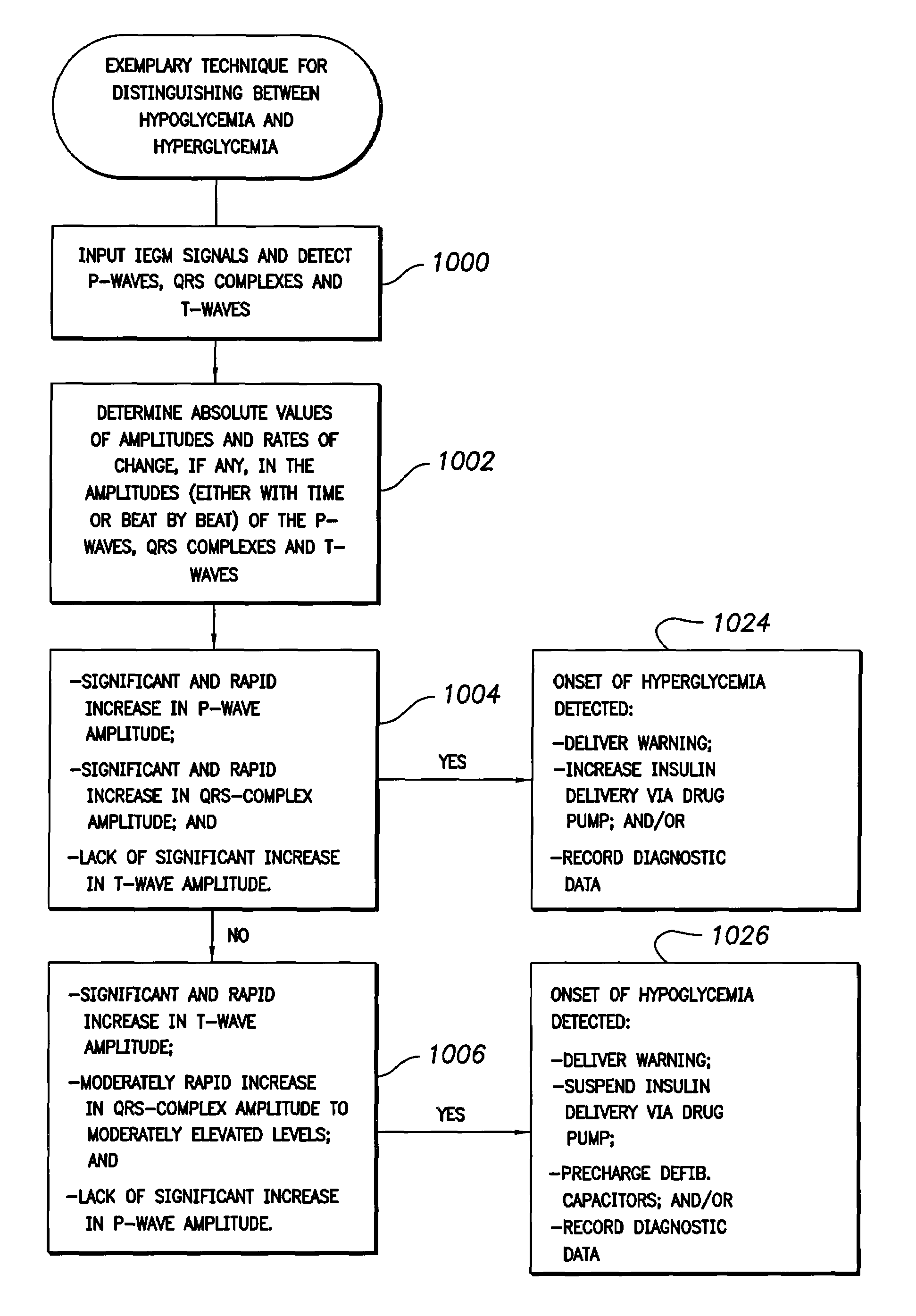
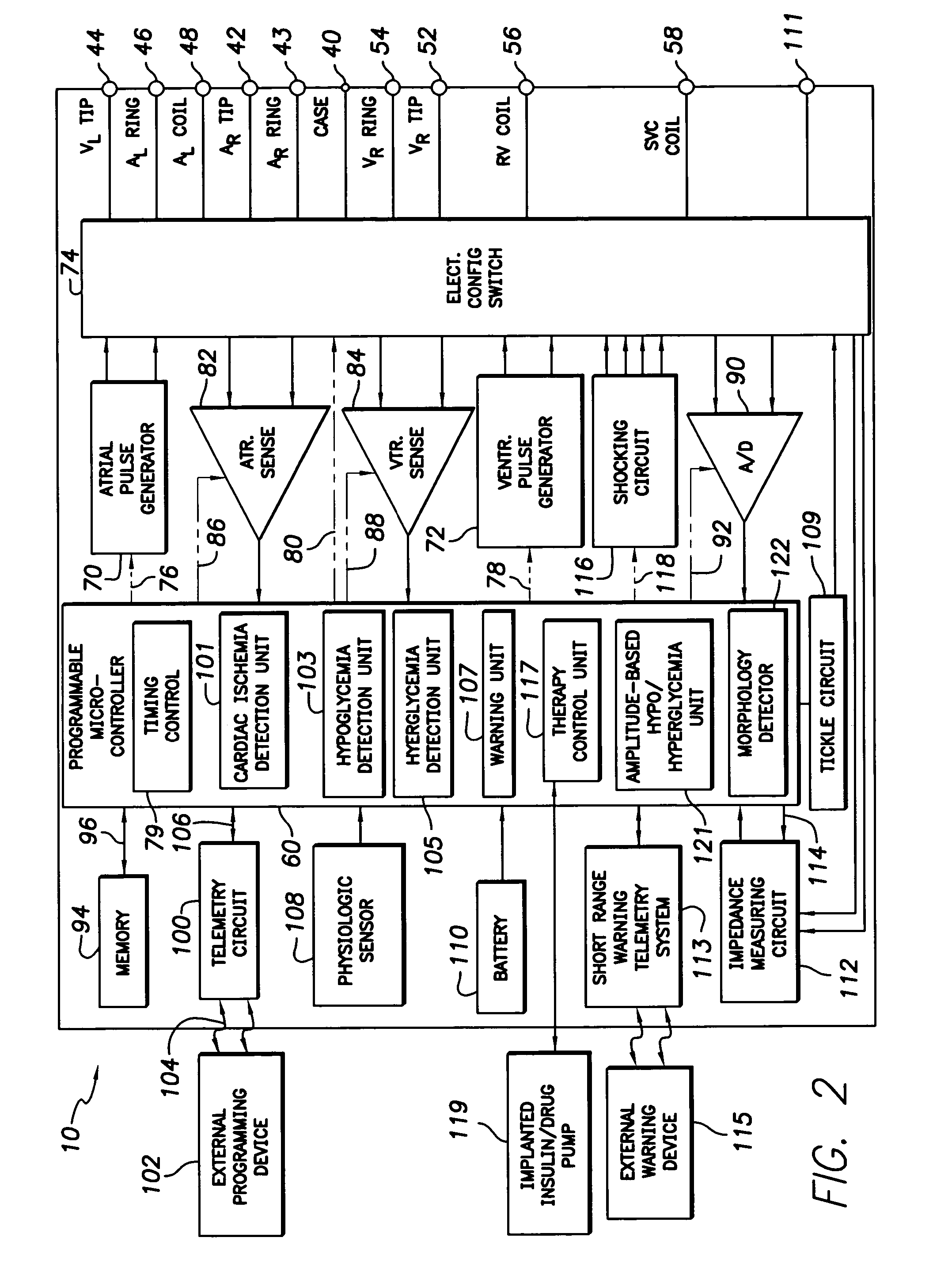
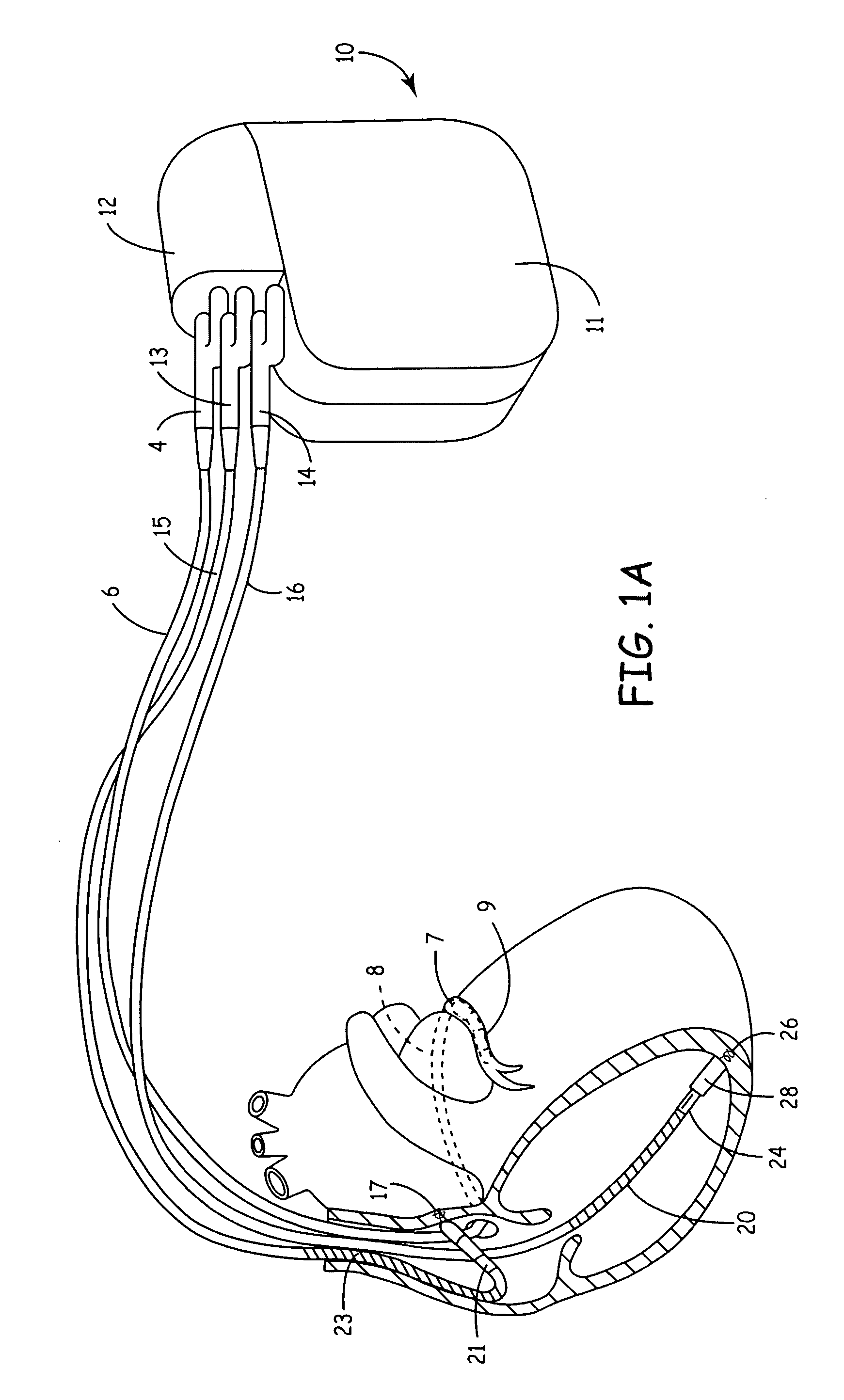
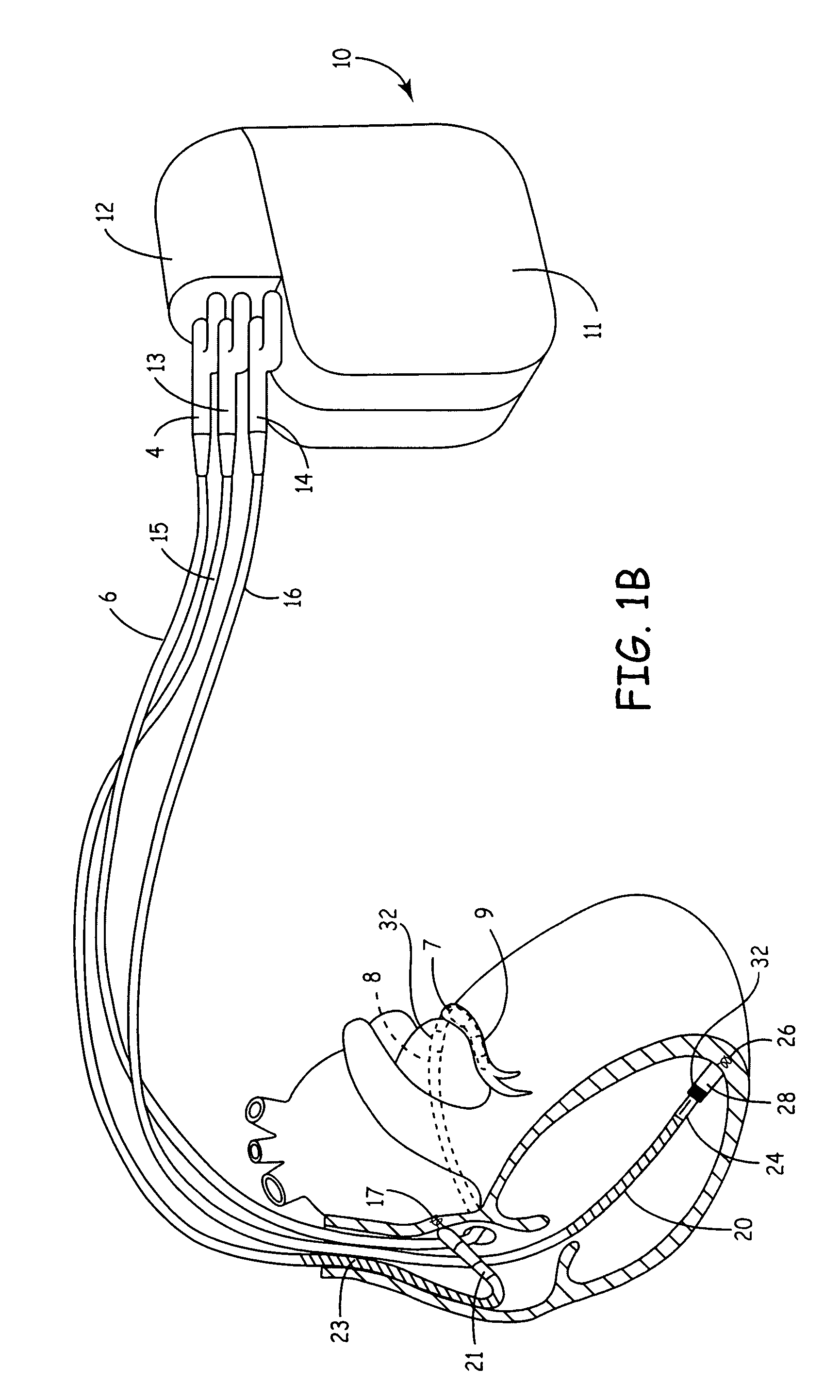
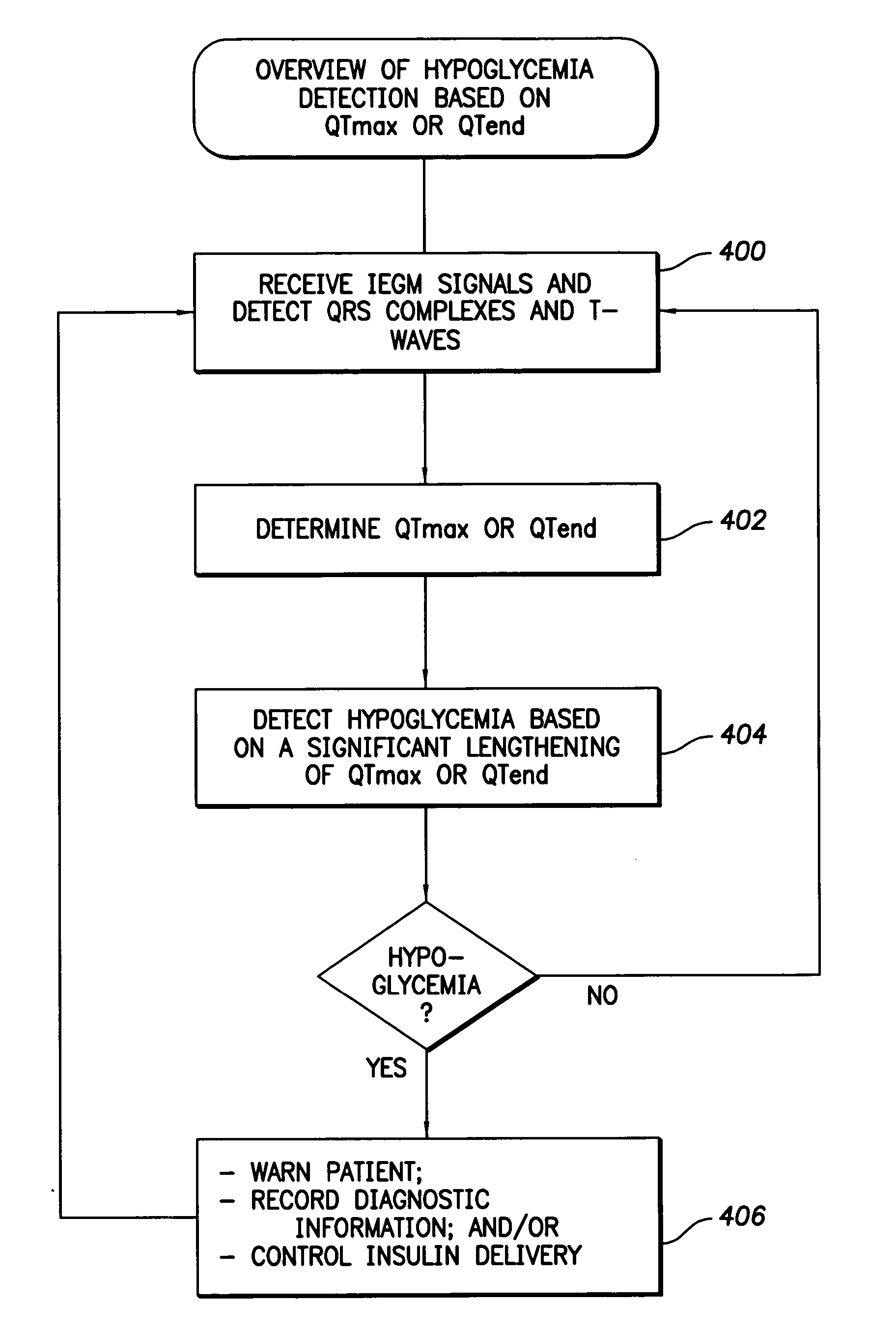
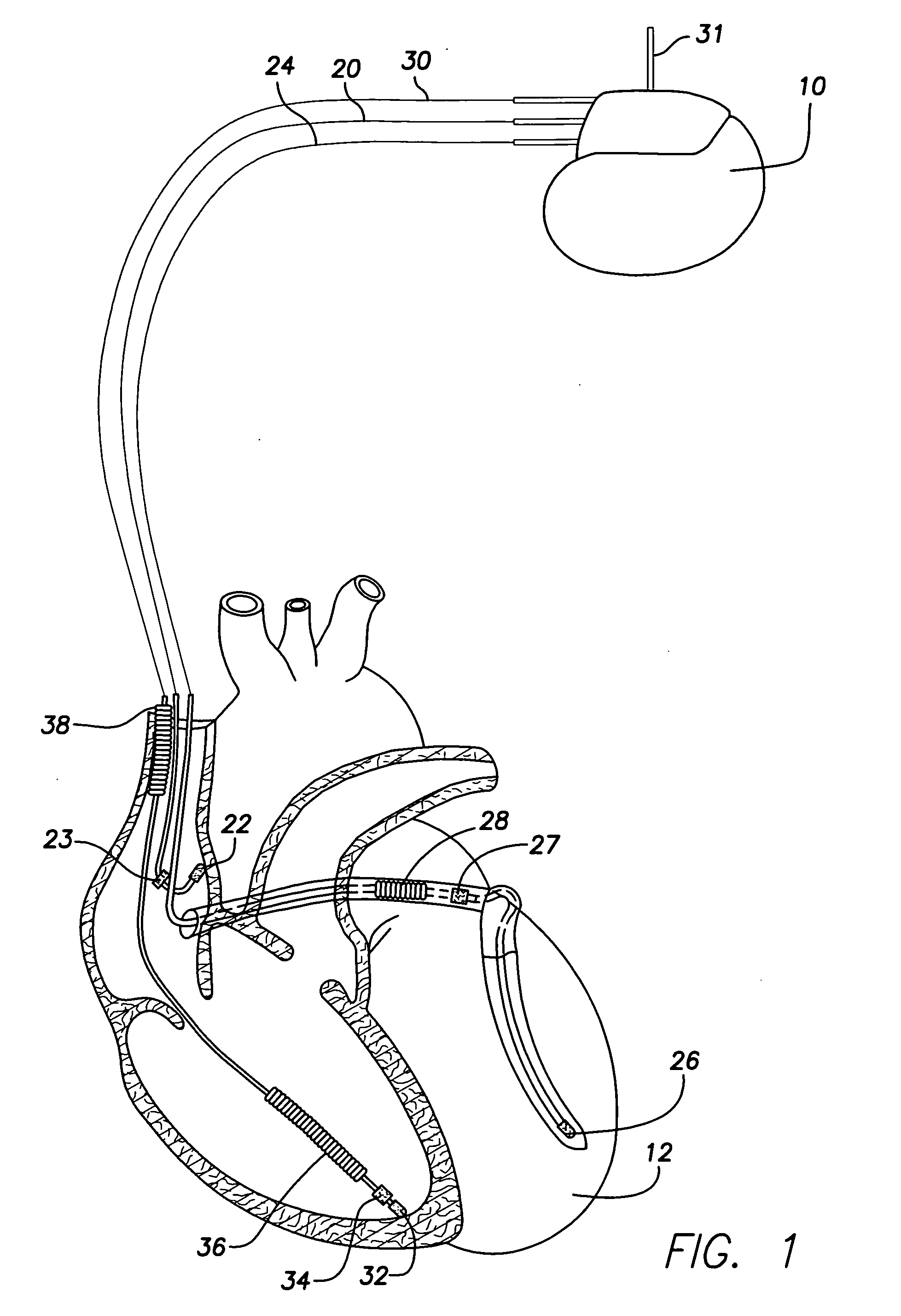
System and method for distinguishing between hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS7524287B2Improve blood sugar controlReduce deliveryElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyAcute hyperglycaemiaT wave
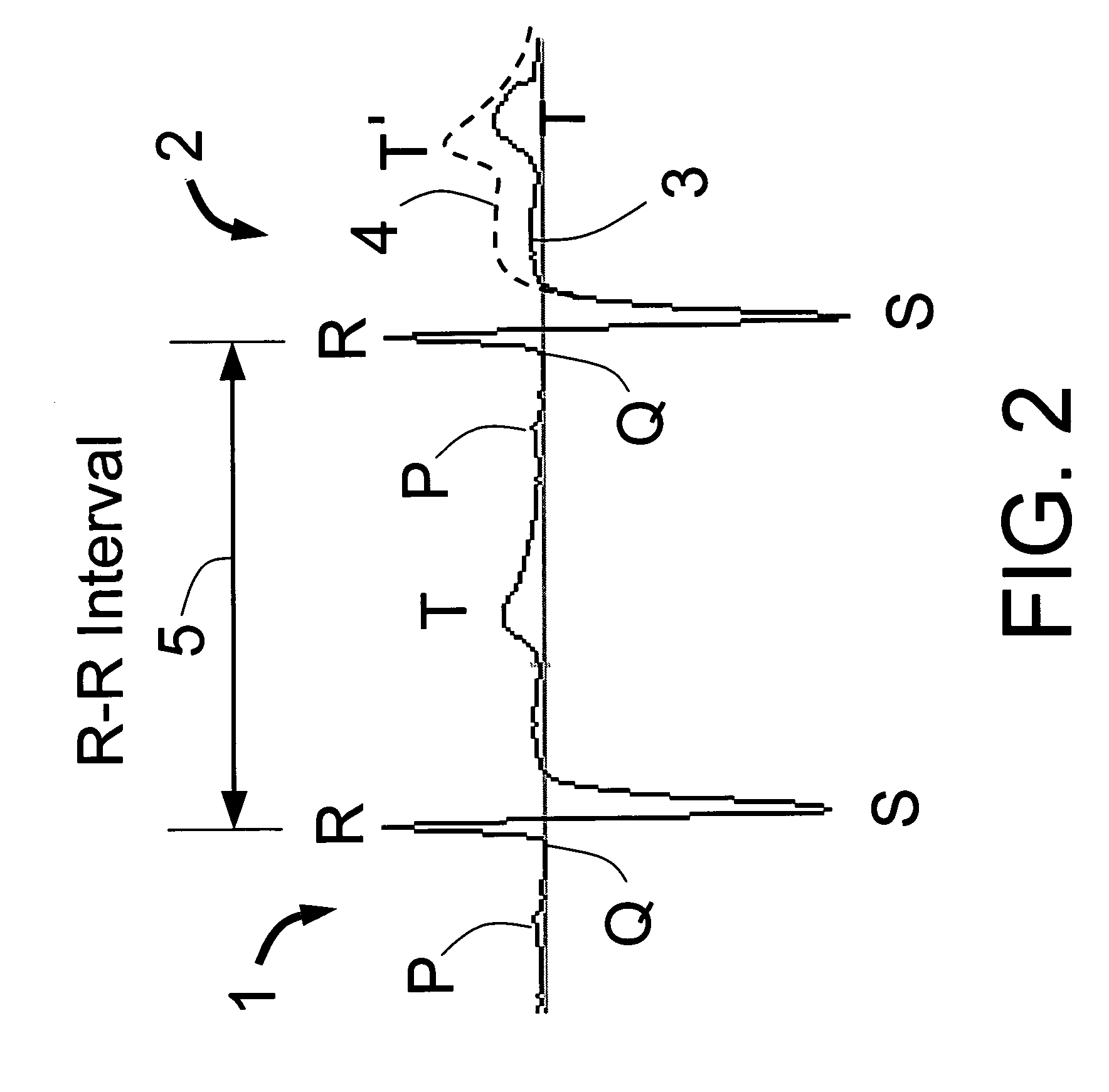
Techniques are described for detecting and distinguishing among ischemia, hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia based on intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals. In one technique, these conditions are detected and distinguished based on an analysis of: the interval between the QRS complex and the peak of a T-wave (QTmax), the interval between the QRS complex and the end of a T-wave (QTend), alone or in combination with a change in ST segment elevation. By exploiting QTmax and QTend in combination with ST segment elevation, changes in ST segment elevation caused by hypo / hyperglycemia can be properly distinguished from changes caused by cardiac ischemia. In another technique, hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are predicted, detected and / or distinguished from one another based on an analysis of the amplitudes of P-waves, QRS-complexes and T-waves within the IEGM. Appropriate warning signals are delivered and therapy is automatically adjusted.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
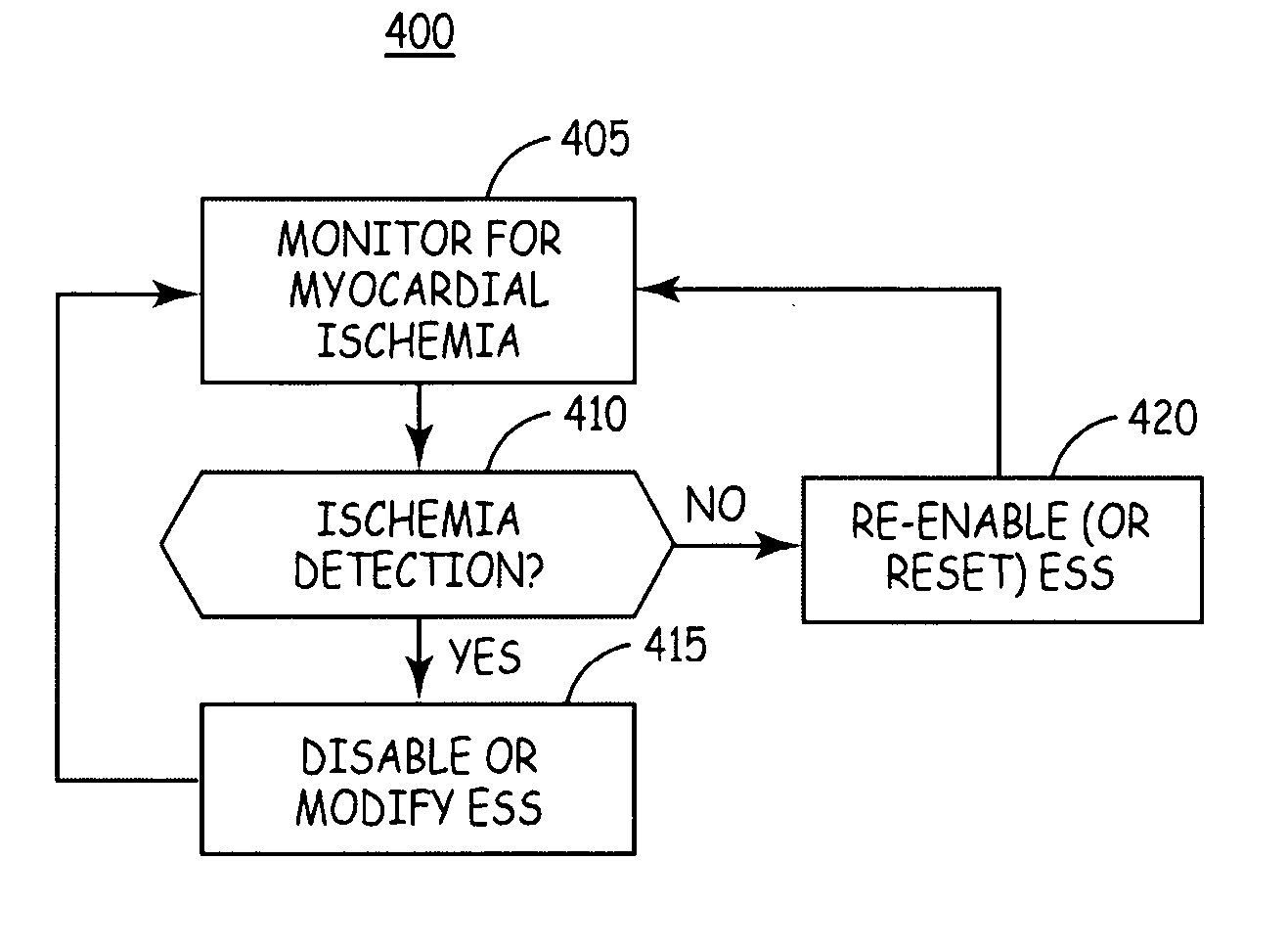
Method and apparatus for controlling extra-systolic stimulation (ESS) therapy using ischemia detection
InactiveUS20050075673A1Achieve effectRisk is exacerbatedHeart stimulatorsCardiac muscleMyocardial ischemia
An implantable cardiac stimulation device capable of delivering ESS, monitoring for myocardial ischemia and responding to the detection of myocardial ischemia by modifying the delivery of ESS. Modification of ESS delivery may include disabling ESS, initiating ESS, and / or modifying ESS control parameters.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for distinguishing between hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20060167365A1Improve blood sugar controlReduce deliveryElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyAcute hyperglycaemiaT wave
Techniques are described for detecting and distinguishing among ischemia, hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia based on intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals. In one technique, these conditions are detected and distinguished based on an analysis of: the interval between the QRS complex and the peak of a T-wave (QTmax), the interval between the QRS complex and the end of a T-wave (QTend), alone or in combination with a change in ST segment elevation. By exploiting QTmax and QTend in combination with ST segment elevation, changes in ST segment elevation caused by hypo / hyperglycemia can be properly distinguished from changes caused by cardiac ischemia. In another technique, hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are predicted, detected and / or distinguished from one another based on an analysis of the amplitudes of P-waves, QRS-complexes and T-waves within the IEGM. Appropriate warning signals are delivered and therapy is automatically adjusted.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
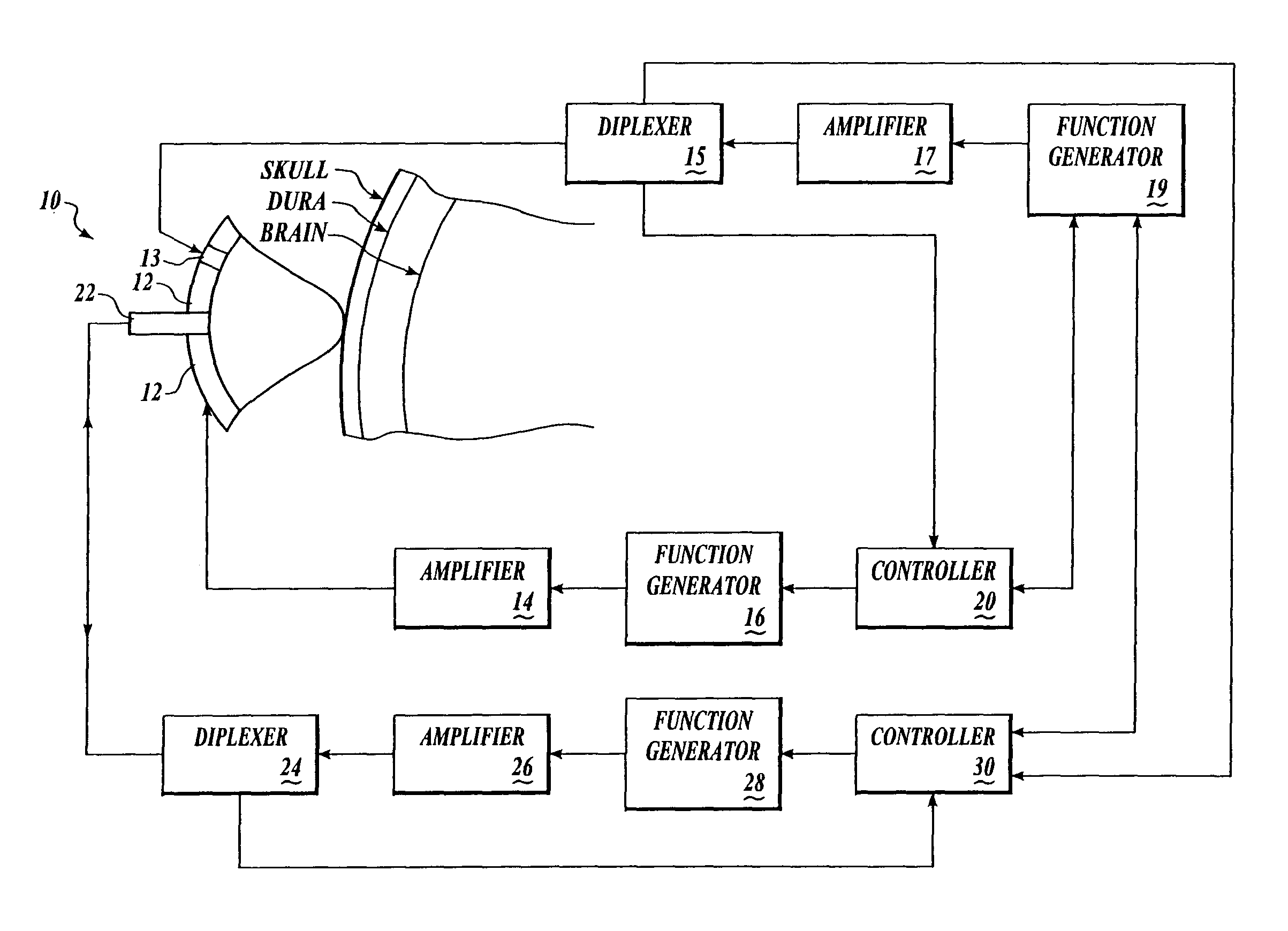
Ultrasound energy driven intraventricular catheter to treat ischemia
InactiveUS7901359B2Minimizes injuryMinimizes to riskUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCurve shapeCardiac muscle
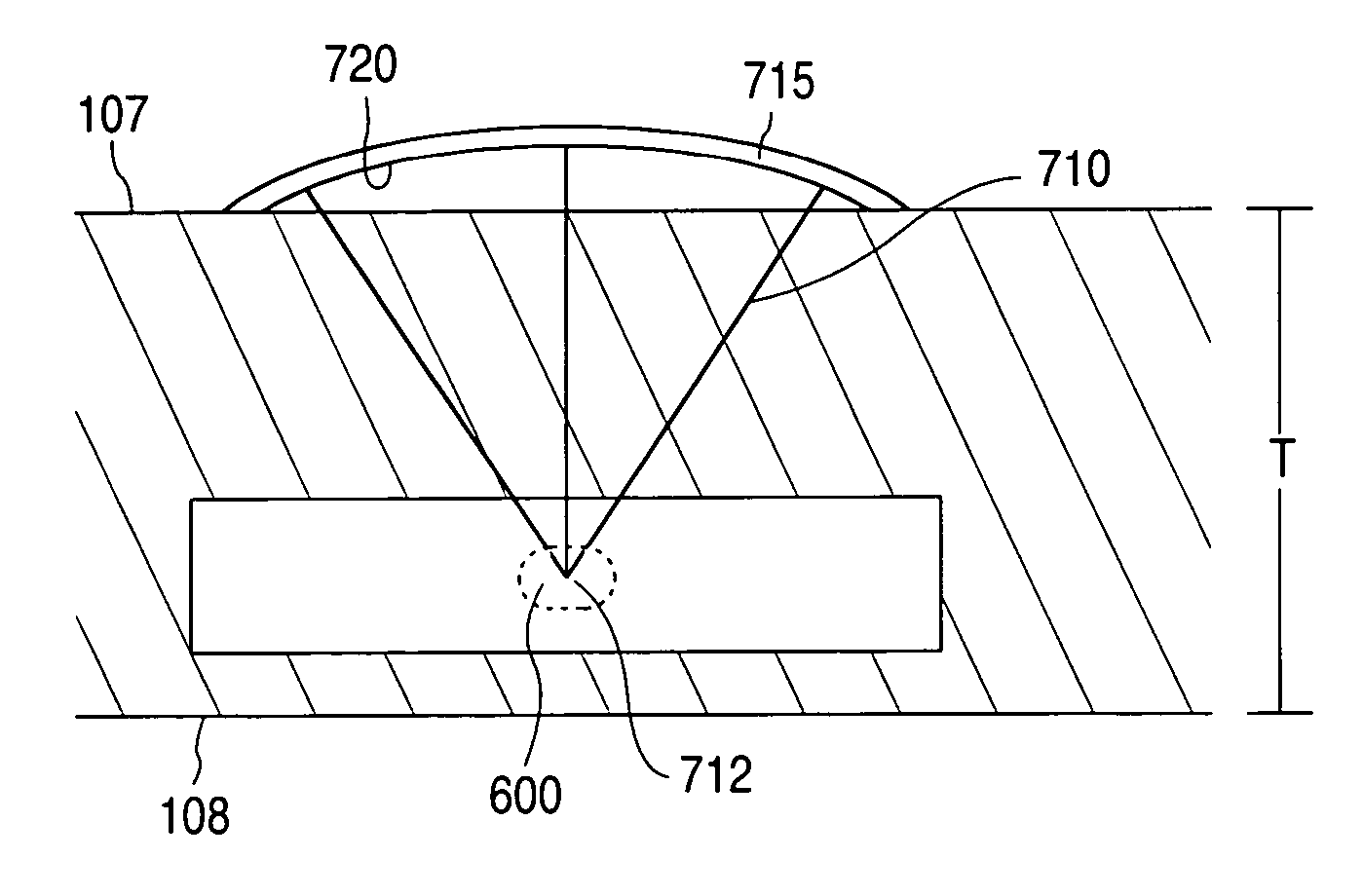
A method and apparatus for improving blood flow to an ischemic region (e.g., myocardial ischemia) a patient is provided. An ultrasonic transducer is positioned proximate to the ischemic region. Ultrasonic energy is applied at a frequency at or above 1 MHz to create one or more thermal lesions in the ischemic region of the myocardium. The thermal lesions can have a gradient of sizes. The ultrasound transducer can have a curved shape so that ultrasound energy emitted by the transducer converges to a site within the myocardium, to create a thermal lesion without injuring the epicardium or endocardium.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS20070016031A1Easy diagnosisLimited successBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationVentricular filling
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Methods and devices providing transmyocardial blood flow to the arterial vascular system of the heart
InactiveUS20050043781A1Increase blood flowMinimize flowStentsHeart valvesCoronary atherosclerosisCoronary revascularization
This invention relates to methods and devices providing transmyocardial blood flow or coronary revascularization for the treatment of coronary atherosclerosis and resulting myocardial ischemia by increasing the flow of blood from one or more oxygenated blood sources within the patient to one or more sites selected in the arterial vascular system of the heart using a channel for maintaining and regulating blood flow therebetween. A valved conduit or a self-maintained channel is created between the left ventricle reservoir of oxygenated blood and the coronary artery distal to an area of obstruction by surgical and percutaneous methods. Preferably, the conduit or self-maintained channel integrally regulates the flow of blood between the oxygenated blood source and the site selected in the arterial vascular system of the heart wherein an increase in blood flow is desired.
Owner:FOLEY MARK
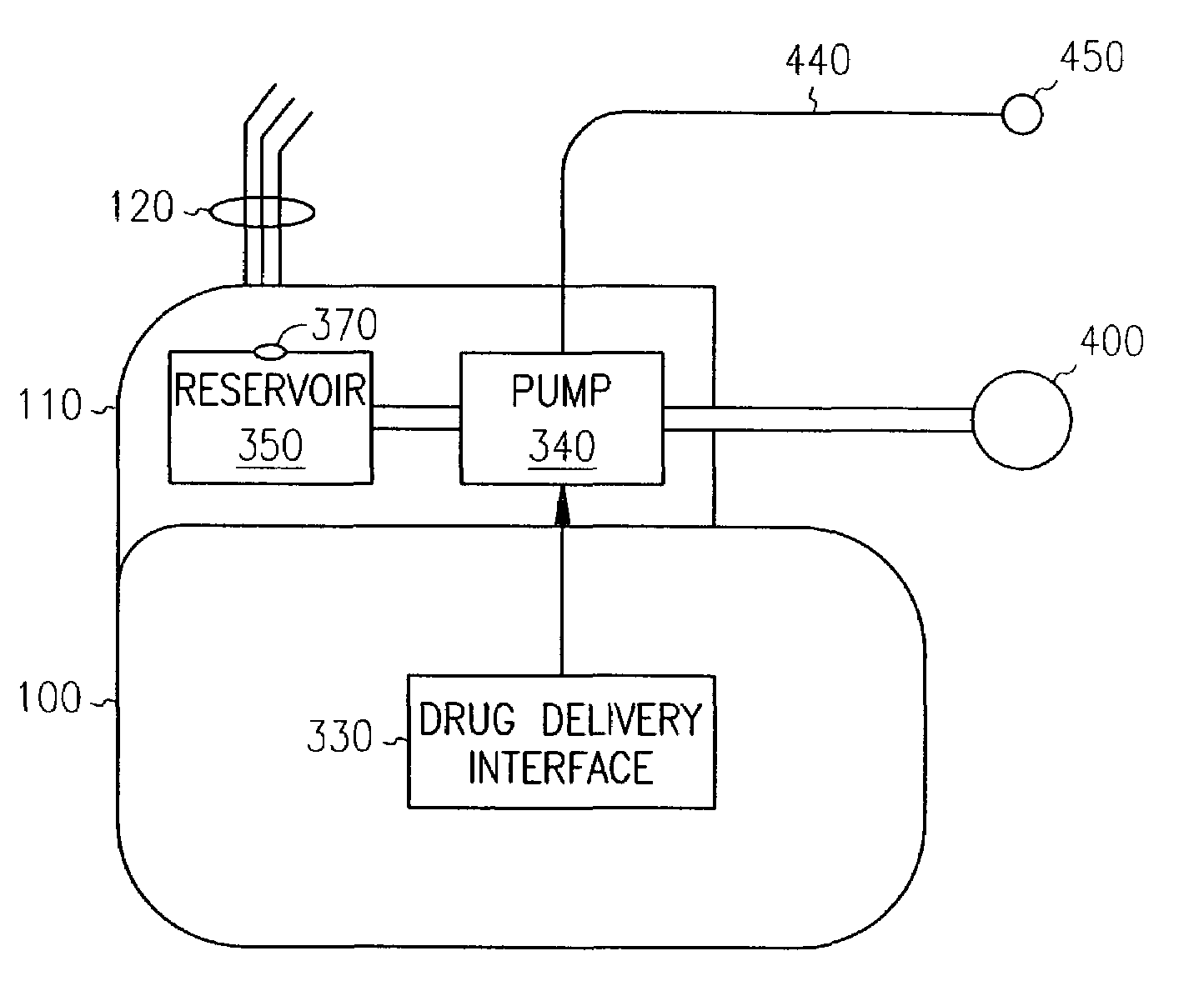
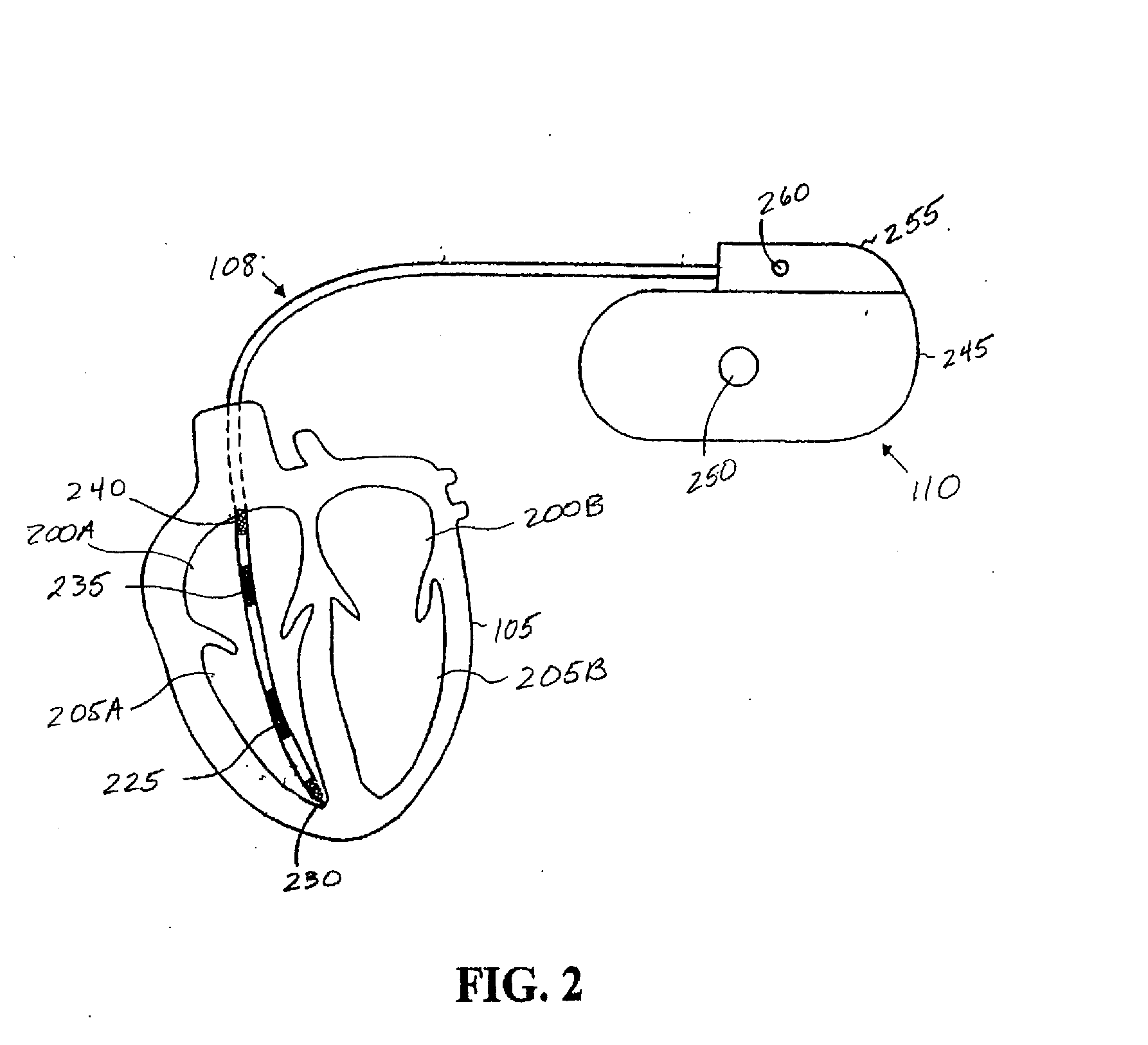
Implantable device for delivering cardiac drug therapy
An implantable medical device in which an electrogram is recorded and analyzed in order to detect changes indicative of cardiac ischemia. Cardiac ischemia may be detected by recording an electrogram from a sensing channel of the device and comparing the recorded electrogram with a reference electrogram. If cardiac ischemia is detected, a cardiac drug such as a thrombolytic agent is delivered.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Detection of myocardial ischemia from the time sequence of implanted sensor measurements
A system including a plurality of implantable sensors, a processor, and a response circuit. Each sensor produces an electrical sensor signal related to physiologic cardiovascular events of a subject. The processor includes an event sequence detector to permit real-time detection of a time-wise sequential cascade of physiologic cardiovascular events related to myocardial ischemia of a subject and a decision module. The time-wise cascade includes at least first, second, and third physiologic cardiovascular events. The decision module declares whether an ischemic event occurred using at least one rule applied to a temporal relationship of the first, second, and third physiologic cardiovascular events. The response circuit provides a specified response if the ischemic event is declared.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Implantable medical device (IMD) system configurable to subject a patient to a stress test and to detect myocardial ischemia within the patient
Various implantable medical devices (IMDs) are disclosed for implantation in a patient. The IMD includes pacing circuitry configured to selectively produce pacing pulses at a programmable pacing rate. In one embodiment, the IMD is configurable to subject a patient to a stress test. The IMD may be configurable to subject the patient to the stress test at the time specified by stored timing information, or in response to a signal (e.g., from a patient activator). Another embodiment of the implantable medical device (IMD) includes sensor circuitry, a memory for storing data, and a control unit. The sensor circuitry produces sensor data relating to cardiac condition. The control unit is configurable to store the sensor data in the memory until a trigger signal is received. Methods are described for performing a stress test in a patient with an IMD, and for subsequently reproducing cardiac operational states.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Ischemia detection
InactiveUS20030158492A1Reliable indicationAvoid false indicationsCatheterHeart stimulatorsAccelerometerCardiac muscle
Techniques for detection and treatment of myocardial ischemia are described that monitor both the electrical and dynamic mechanical activity of the heart to detect and verify the occurrence of myocardial ischemia in a more reliable manner. The occurrence of myocardial ischemia can be detected by monitoring changes in an electrical signal such as an ECG or EGM, and changes in dynamic mechanical activity of the heart that are sensed by an accelerometer sensor. The heart acceleration signal can be obtained from an single- or multiple-axis accelerometer and / or a pressure sensor deployed within or near the heart. The techniques correlate contractility changes detected by an accelerometer or pressure sensor with changes in the ST electrogram segment detected by the electrodes to increase the reliability of ischemia detection.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and device for early detection of heart attack
A device and method for heart performance characterization and abnormality detection is disclosed herein. The device and method analyze and characterize cardiac electrophysiological signals which help in the diagnosis of myocardial ischemia in advance of a heart attack.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Multimeric VLA-4 antagonists comprising polymer moieties
InactiveUS20060013799A1Minimize degradationSenses disorderNervous disorderLymphatic SpreadWhite blood cell
Disclosed are conjugates which bind VLA-4. Certain of these conjugates also inhibit leukocyte adhesion and, in particular, leukocyte adhesion mediated by VLA-4. Such conjugates are useful in the treatment of inflammatory diseases in a mammalian patient, e.g., human, such as asthma, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis, AIDS dementia, diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, tissue transplantation, tumor metastasis and myocardial ischemia. The conjugates can also be administered for the treatment of inflammatory brain diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
Owner:ELAN PHARM INC
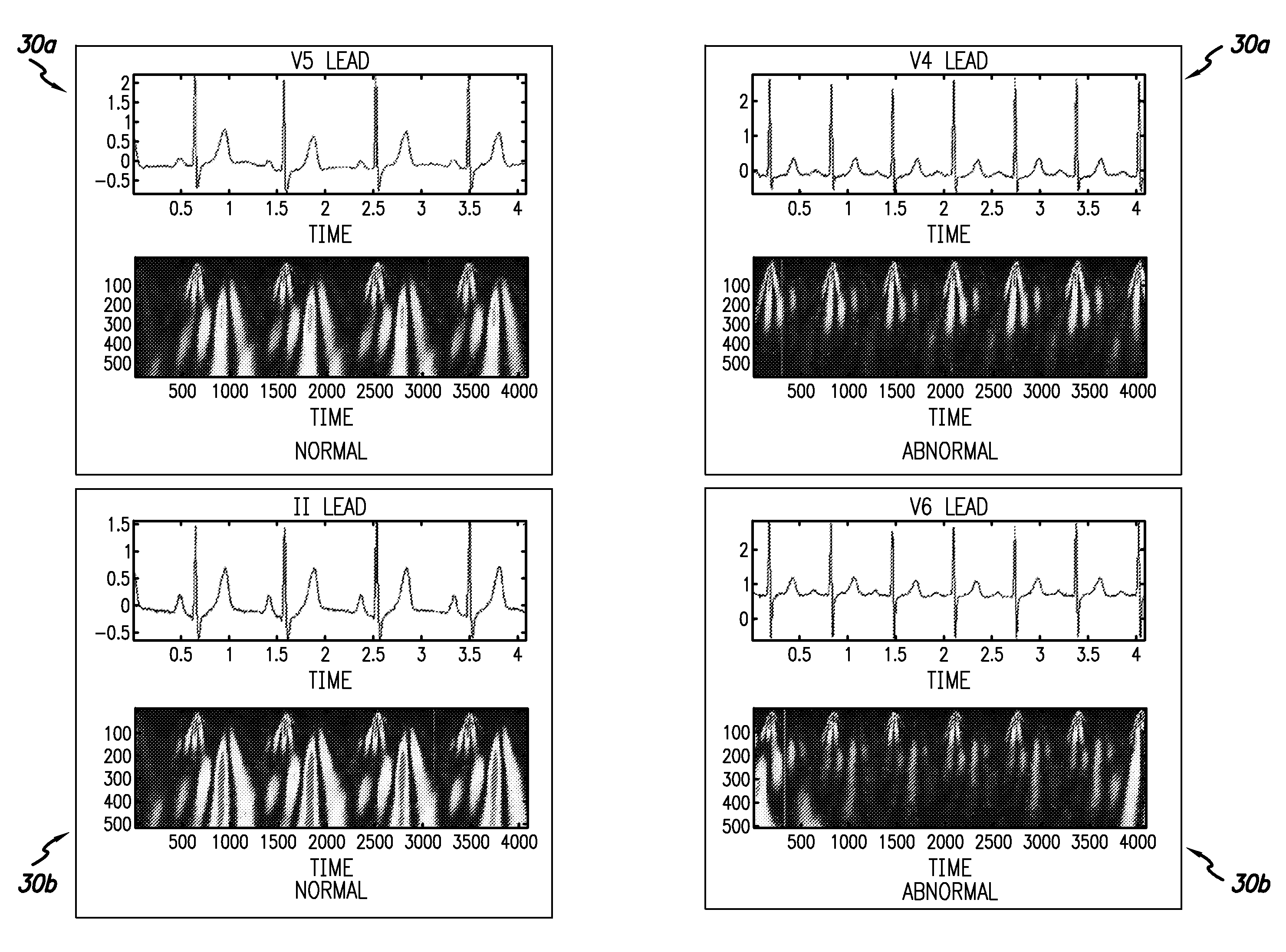
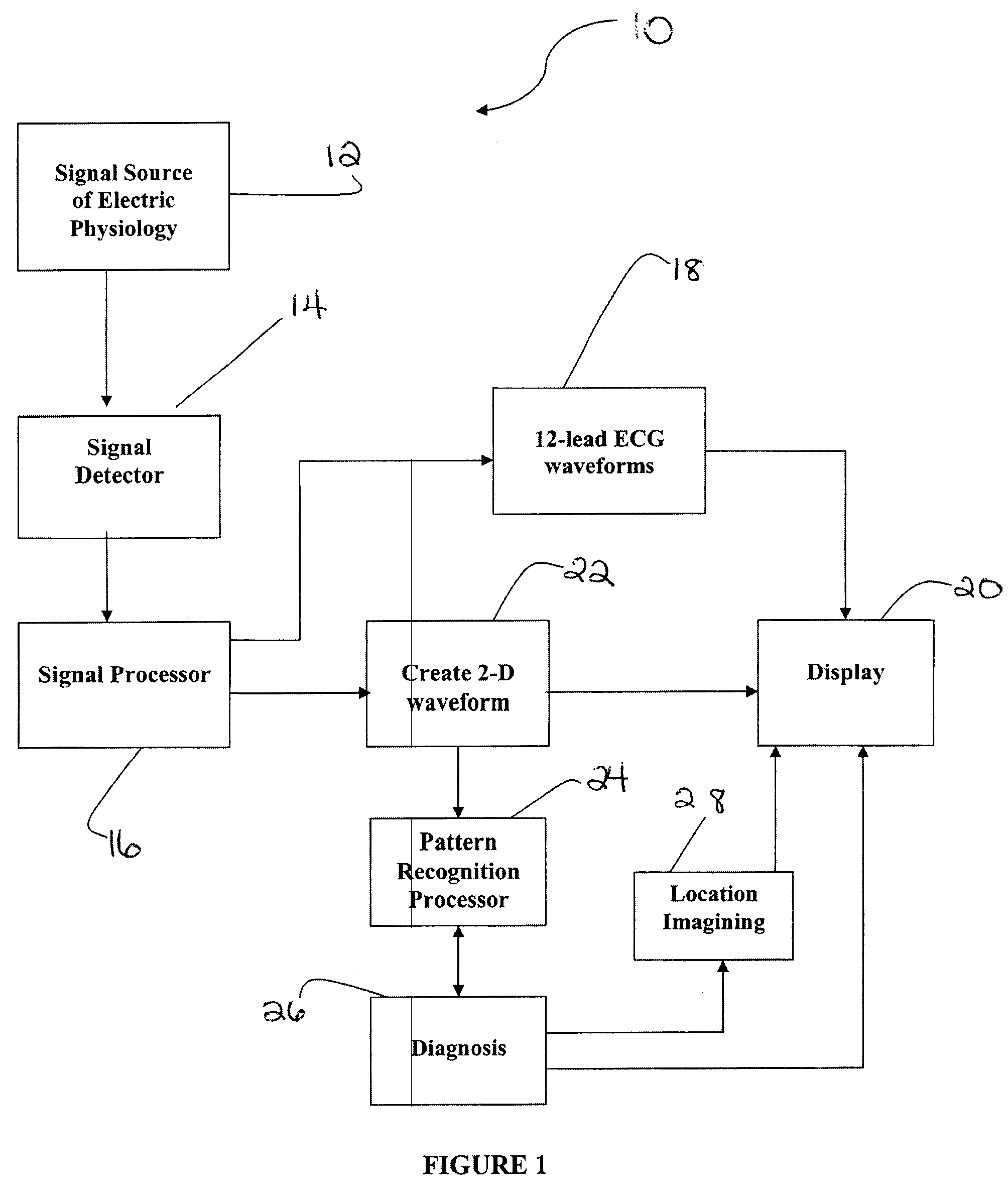
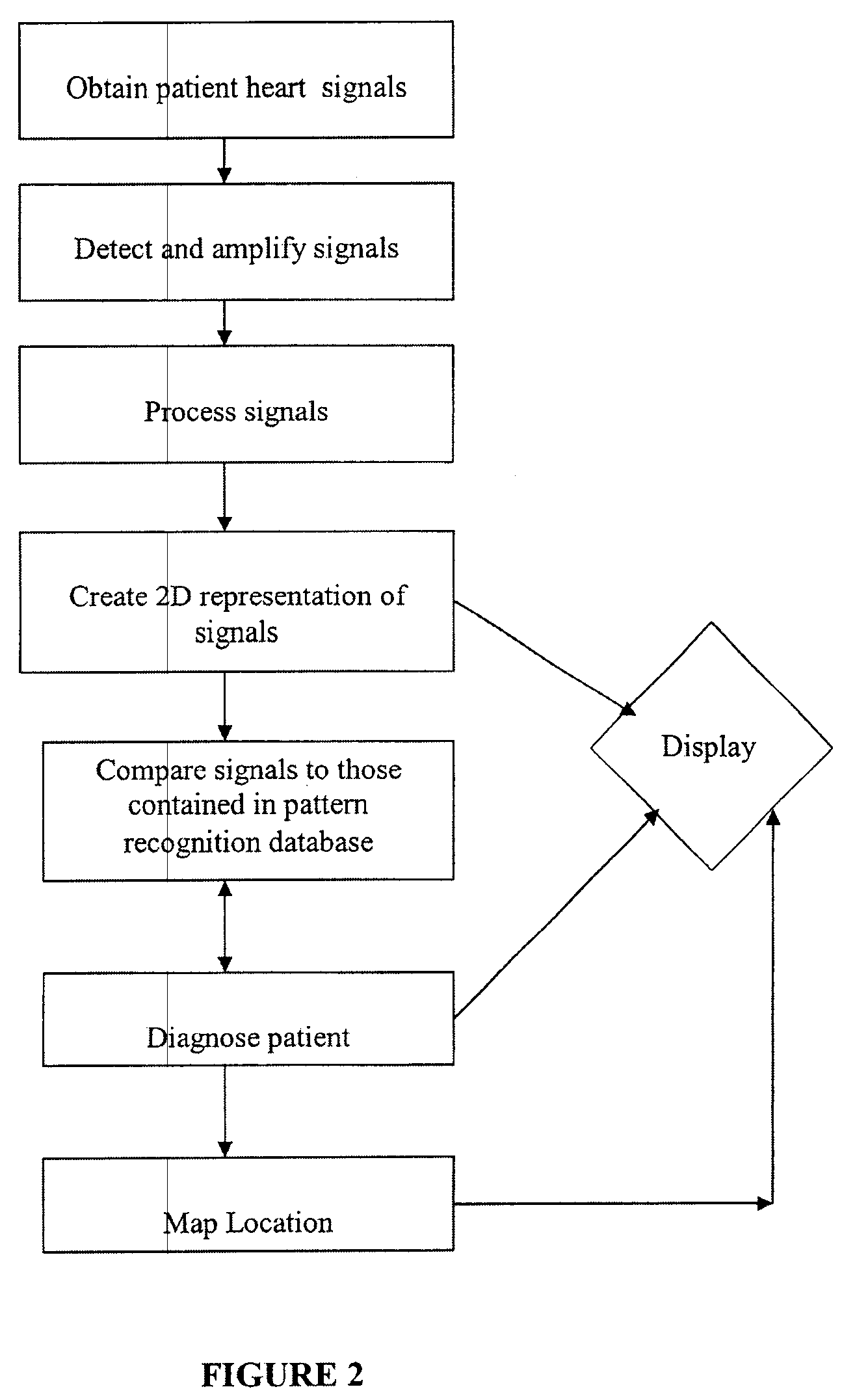
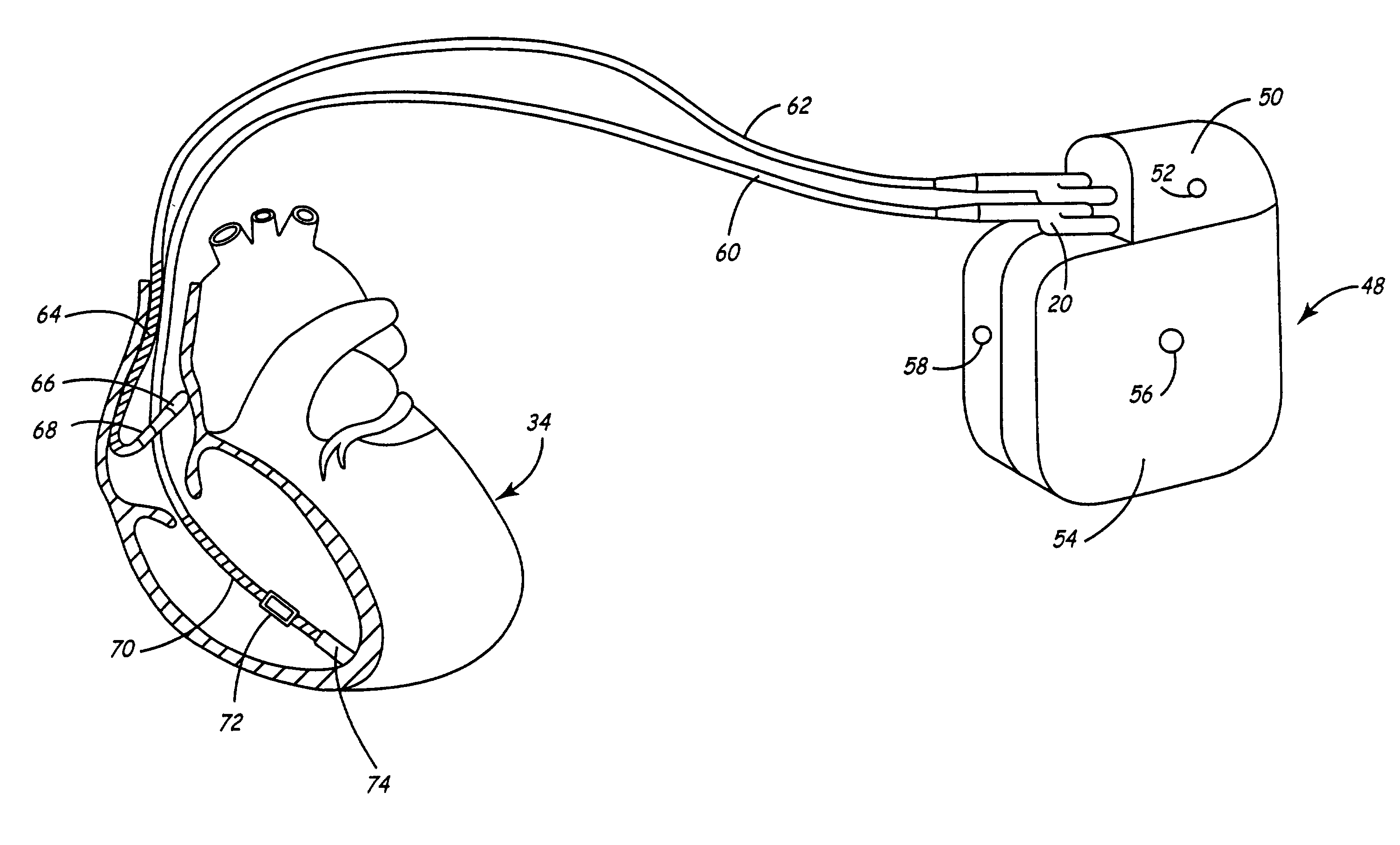
System and method for scanning the heart
A system and method of testing a patient for coronary disease in the patient's heart is disclosed that comprises a microprocessor which contains a signal processor and a pattern recognition processor; means to detect the electrical signals of the heart whereby the signals are processed to create a pattern that represents the patient's heart. The pattern may be further processed by repeatedly comparing it to patterns stored within the pattern recognition processor whereby certain coronary diseases such as myocardial ischemia in the patient's heart may be diagnosed. During each heartbeat, at least a million different electrical impulses are collected and the results of the test are displayed on a screen. The results may include the diagnosis, computer generated image of the patient's heart identifying areas of any coronary disease that has been detected and / or a two dimensional waveform representing the electrical impulses of the patient's heart will be shown. In a further embodiment, the system will also generate ECG waveforms. to create vectors which represent the different directions of the muscle activity of the heart.
Owner:GUANGREN CHEN CO TAYLOR DUNHAM & RODRIGUEZ LLP
Ischemia detection
InactiveUS7181268B2Reduce morbidityReliable indicationCatheterHeart stimulatorsAccelerometerCardiac muscle
Techniques for detection and treatment of myocardial ischemia are described that monitor both the electrical and dynamic mechanical activity of the heart to detect and verify the occurrence of myocardial ischemia in a more reliable manner. The occurrence of myocardial ischemia can be detected by monitoring changes in an electrical signal such as an ECG or EGM, and changes in dynamic mechanical activity of the heart that are sensed by an accelerometer sensor. The heart acceleration signal can be obtained from an single- or multiple-axis accelerometer and / or a pressure sensor deployed within or near the heart. The techniques correlate contractility changes detected by an accelerometer or pressure sensor with changes in the ST electrogram segment detected by the electrodes to increase the reliability of ischemia detection.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
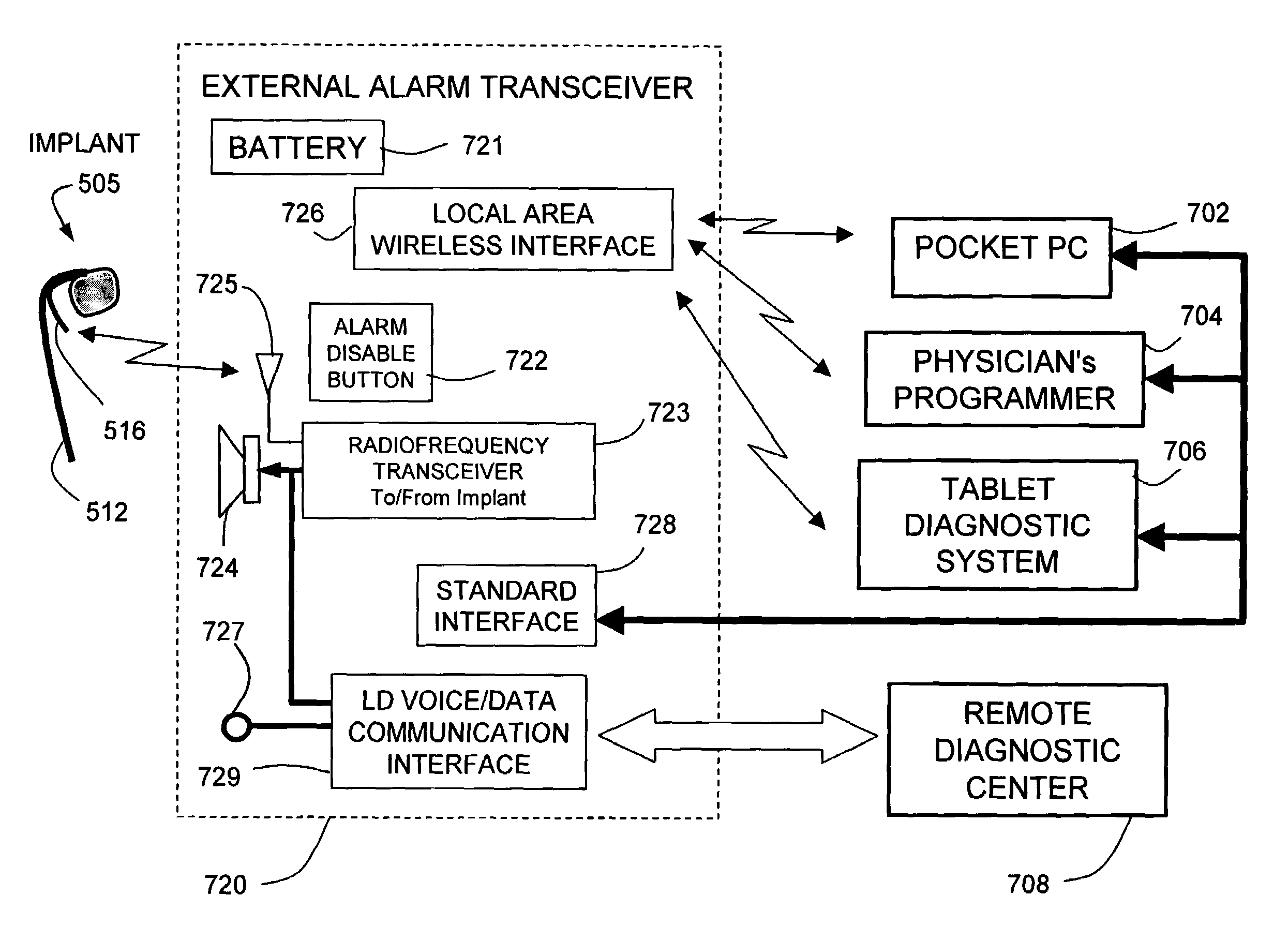
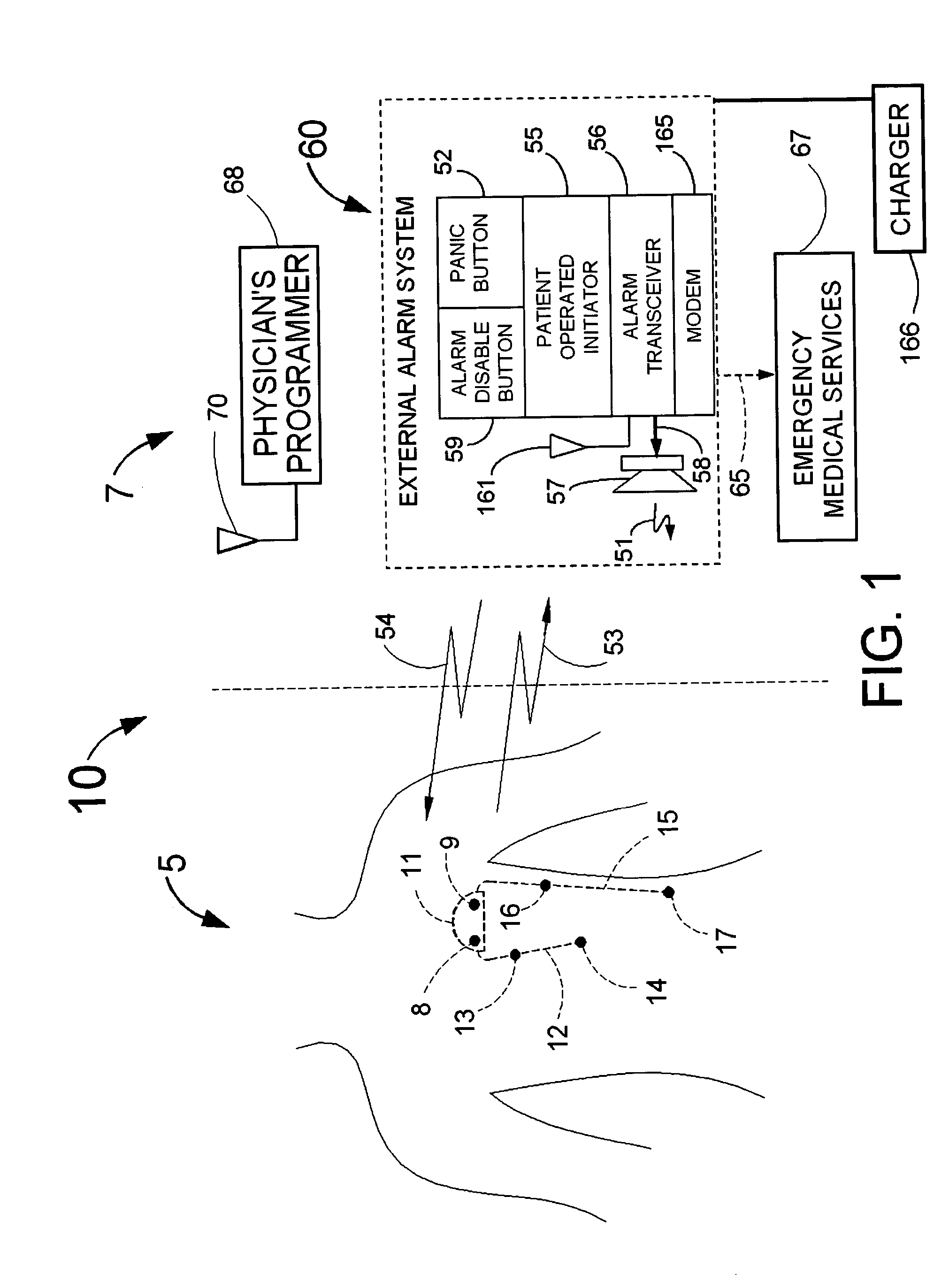
Means and method for the detection of cardiac events
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Implantable myocardial ischemia detection, indication and action technology
InactiveUS7277745B2Reduce capacityReduce mechanical performance requirementsElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsThoracic structureCardiac muscle
One embodiment enables detection of MI / I and emerging infarction in an implantable system. A plurality of devices may be used to gather and interpret data from within the heart, from the heart surface, and / or from the thoracic cavity. The apparatus may further alert the patient and / or communicate the condition to an external device or medical caregiver. Additionally, the implanted apparatus may initiate therapy of MI / I and emerging infarction.
Owner:INFINITE BIOMEDICAL TECH
Antidiabetic agents
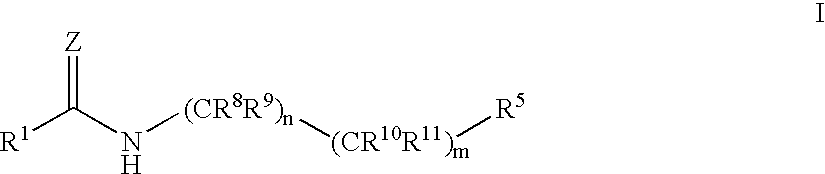
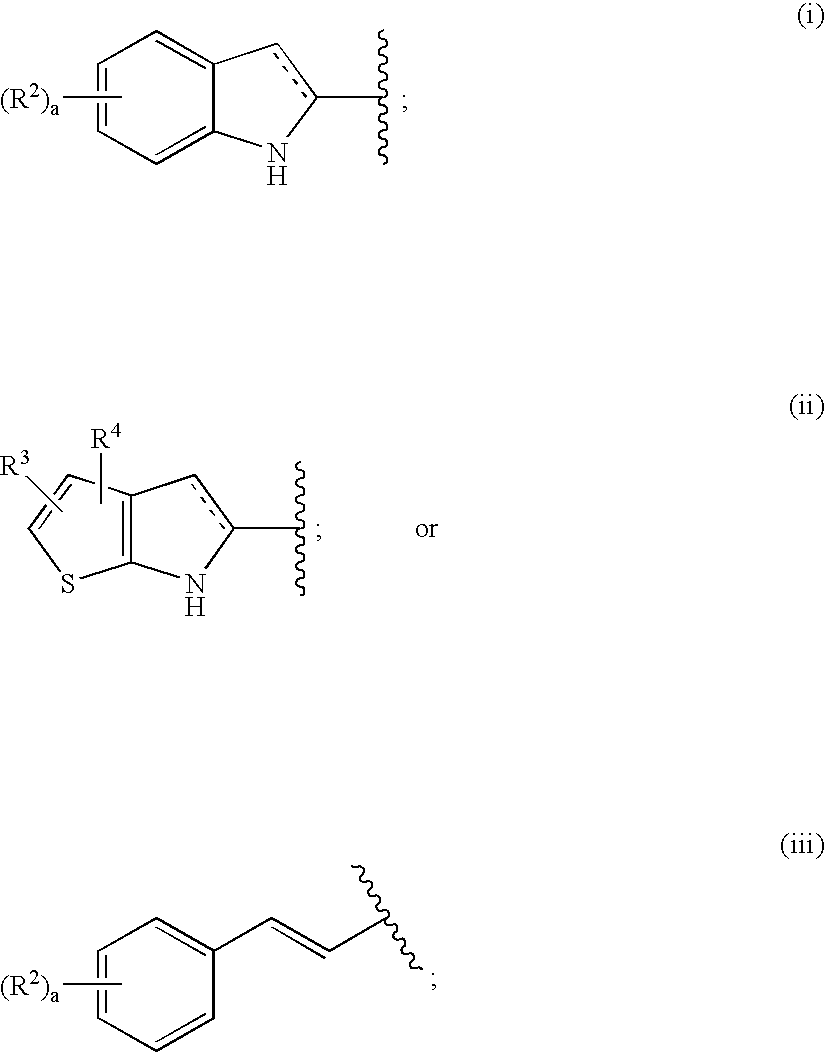
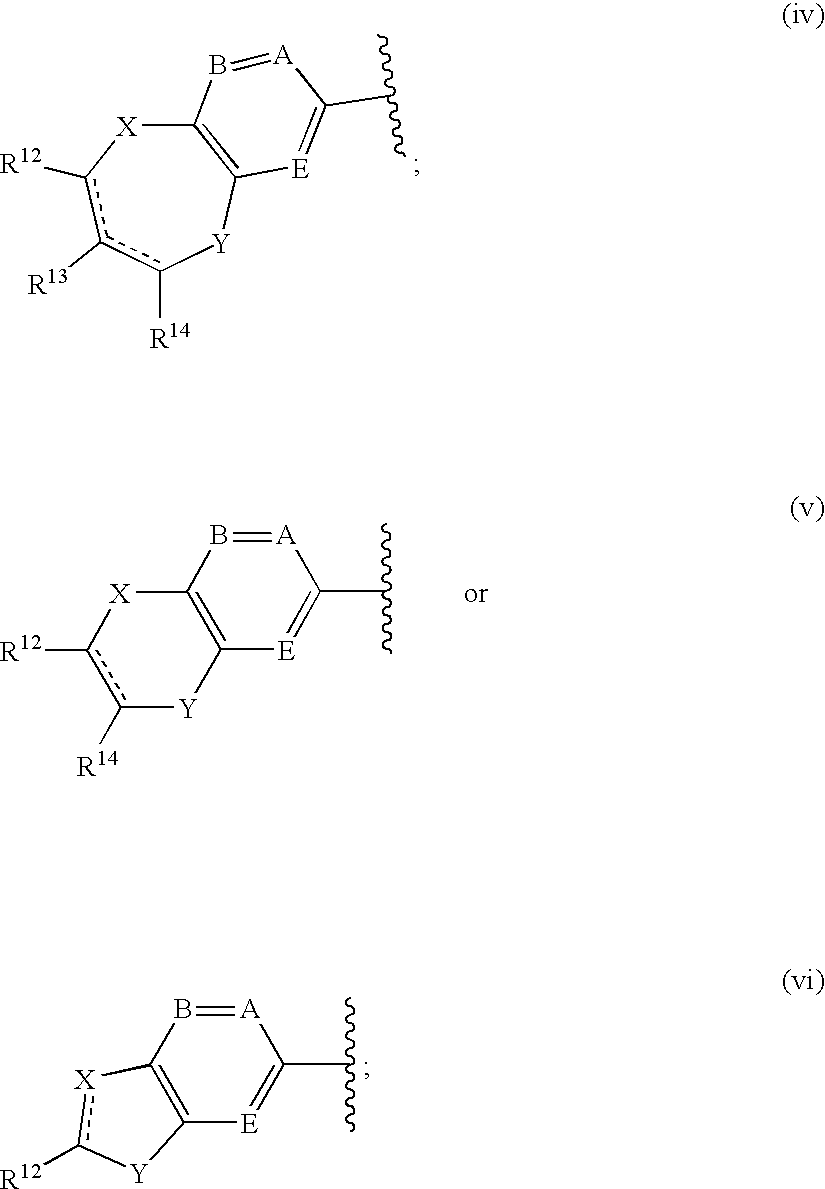
A compound of the formula wherein R1 is: R5 is: and n, m, Z, R8, R9, R10 and R11 are as defined herein, useful in the treatment of diabetes, insulin resistance, diabetic neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, hyperinsulinemia, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis, and tissue ischemia, particularly, myocardial ischemia.
Owner:GAMMILL RONALD B
System and method for analyzing a patient status for myocardial ischemia for use in automated patient care
InactiveUS7299087B2Increase productionIncreased serum creating kinaseElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPhysiologic StatesCardiac muscle
Owner:CARDIAC INTELLIGENCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com