Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Ventricular filling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
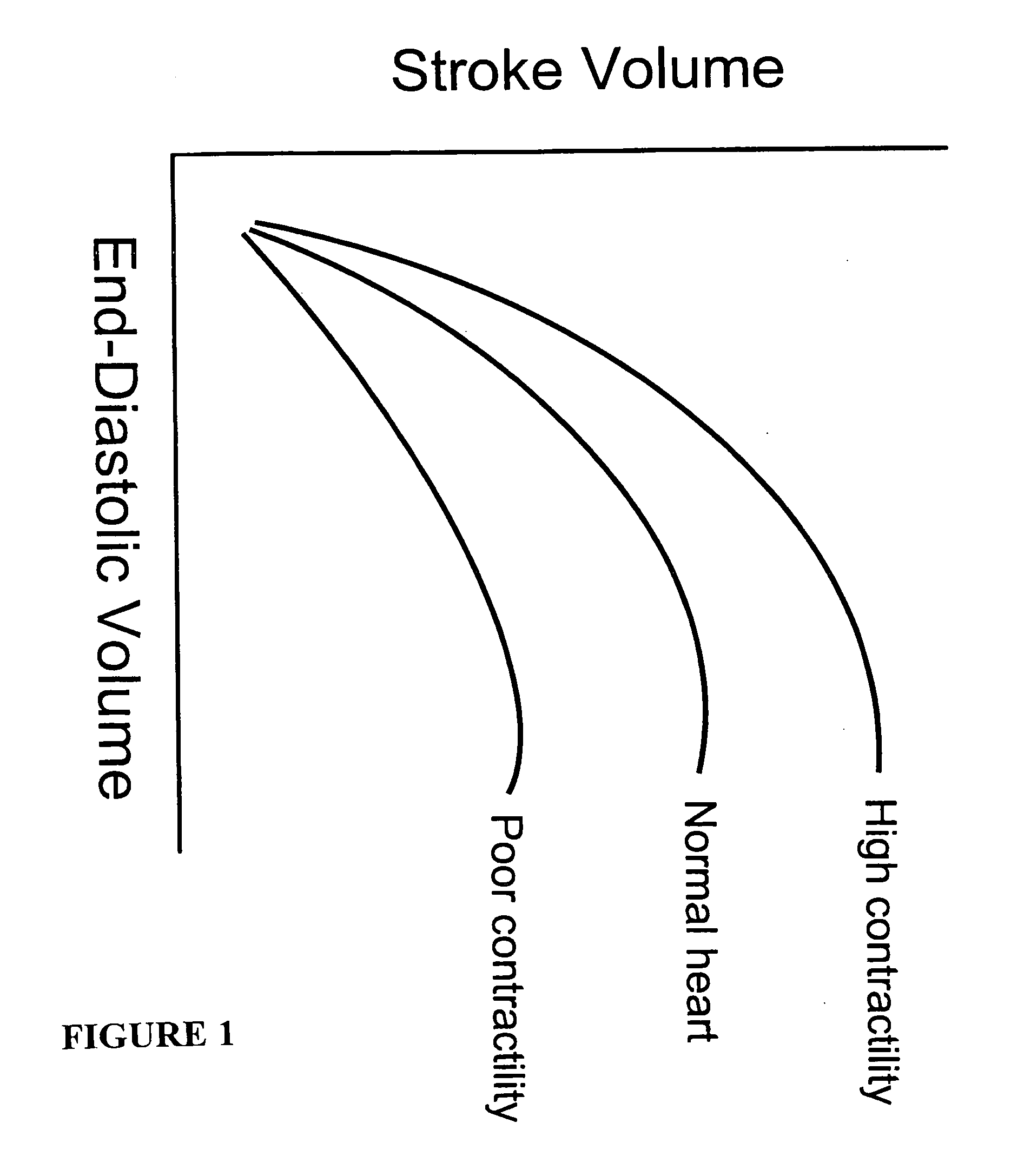
Ventricular filling is normally silent. When a third heart sound (S3) is audible during rapid ventricular filling, it may represent tensing of chordae tendineae and AV ring during ventricular relaxation and filling. This heart sound is normal in children; but is often pathological in adults and caused by ventricular dilation.
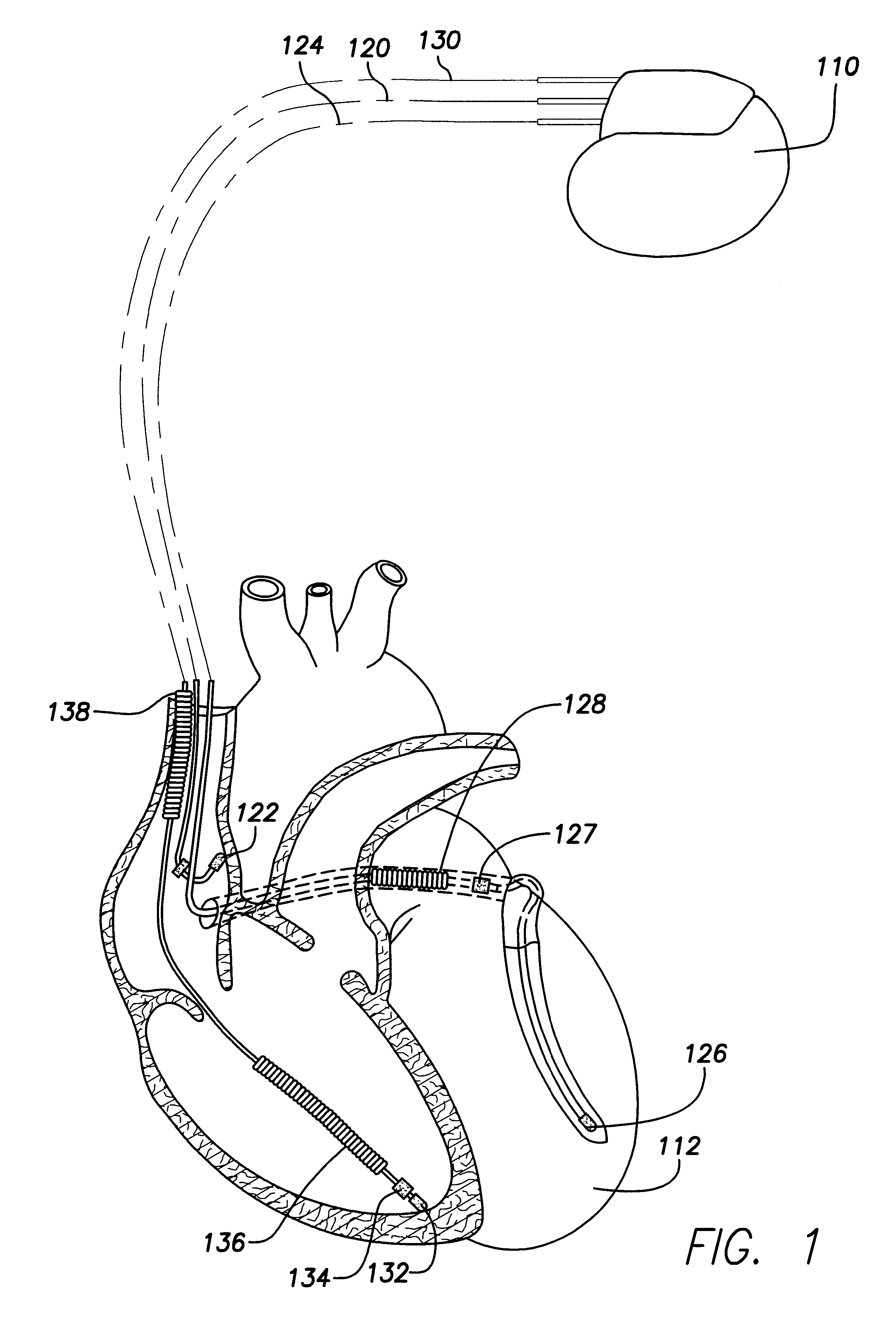
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS7022077B2Maximize tissue displacementEasy diagnosisBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound techniques
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
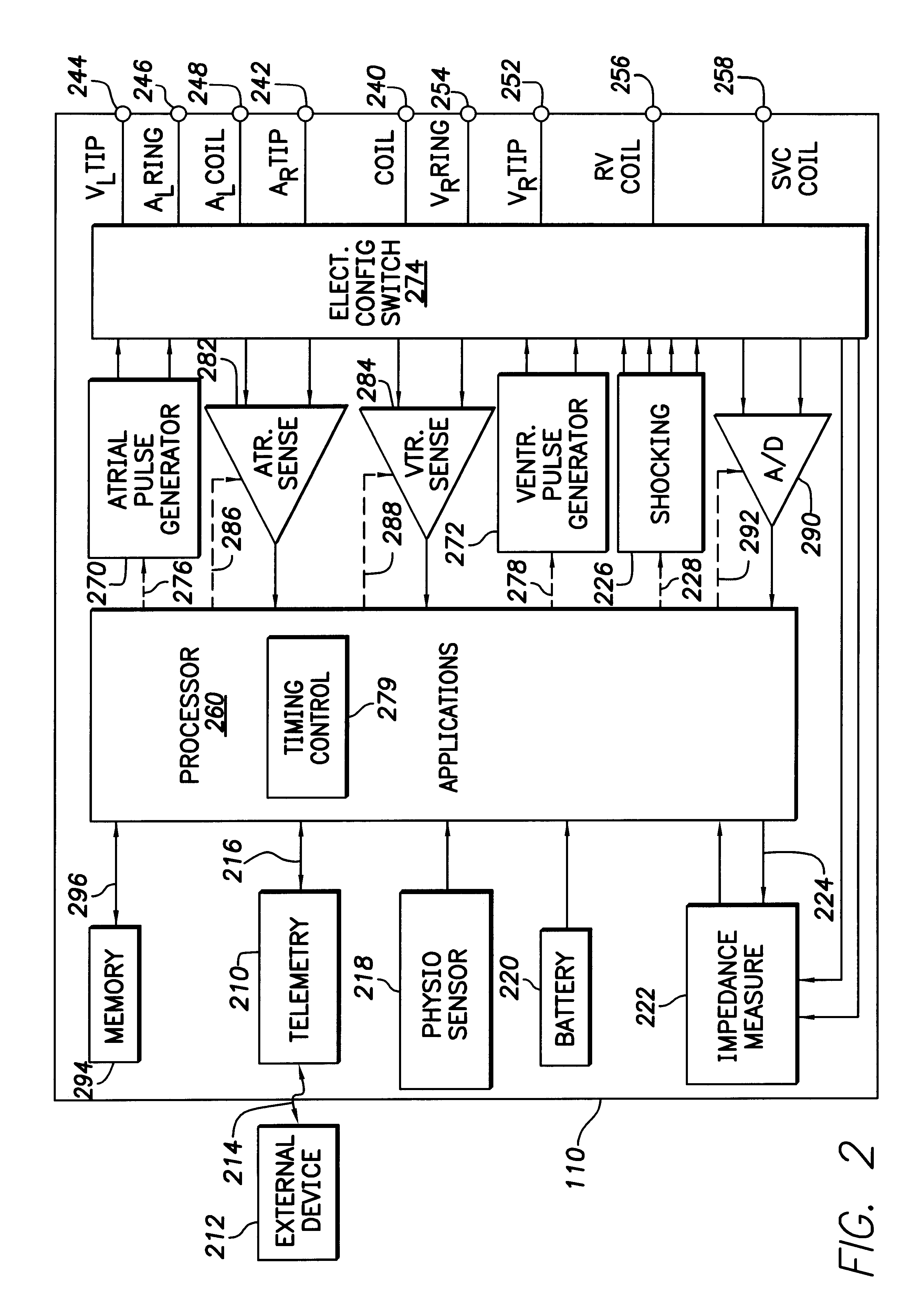
Evoked response variability as an indicator of autonomic tone and surrogate for patient condition
Modern implantable cardiac stimulation devices include processing and data storage capabilities that may be exploited to track myocardial condition and autonomic tone. Implantable devices have a capability to measure and store electrogram information over a period of time in a relatively large capacity memory, with advances in technology allowing increases in memory size. The evoked response varies in amplitude and morphology with changes in autonomic tone, ventricular filling, paced rate, and other parameters. The implantable cardiac device can be configured to sense and accurately quantify the evoked response, derive parameters from the quantified evoked response, store the parameters over long time periods, and derive variability statistics from the parameters to assist in tracking the patient's condition over time, and guiding the patient's therapy.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS20070016031A1Easy diagnosisLimited successBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationVentricular filling
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Atrioventricular delay adjustment
InactiveUS6882882B2Improved hemodynamic performanceMaintain performanceHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsAtrioventricular canalCardiac pacemaker electrode
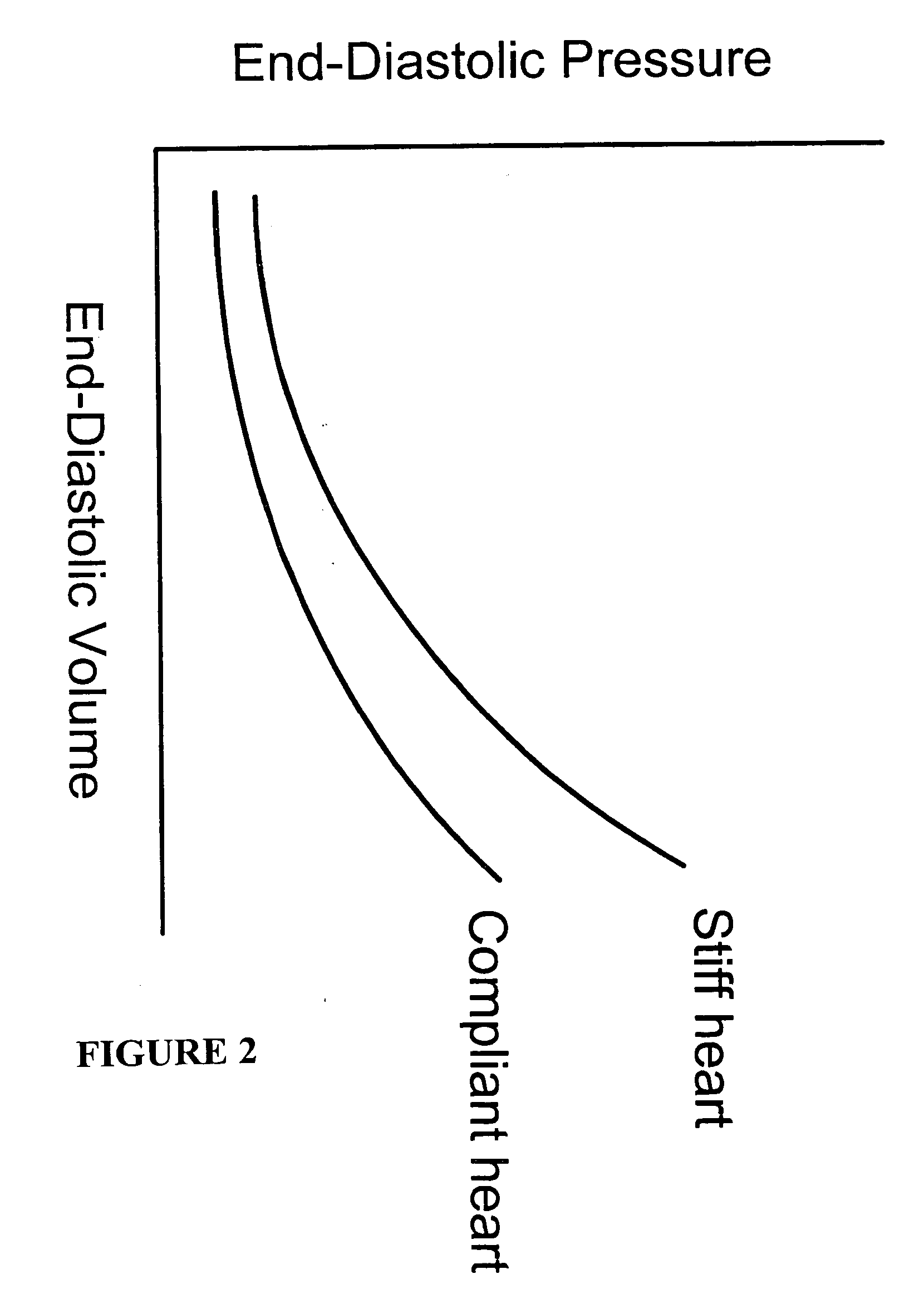
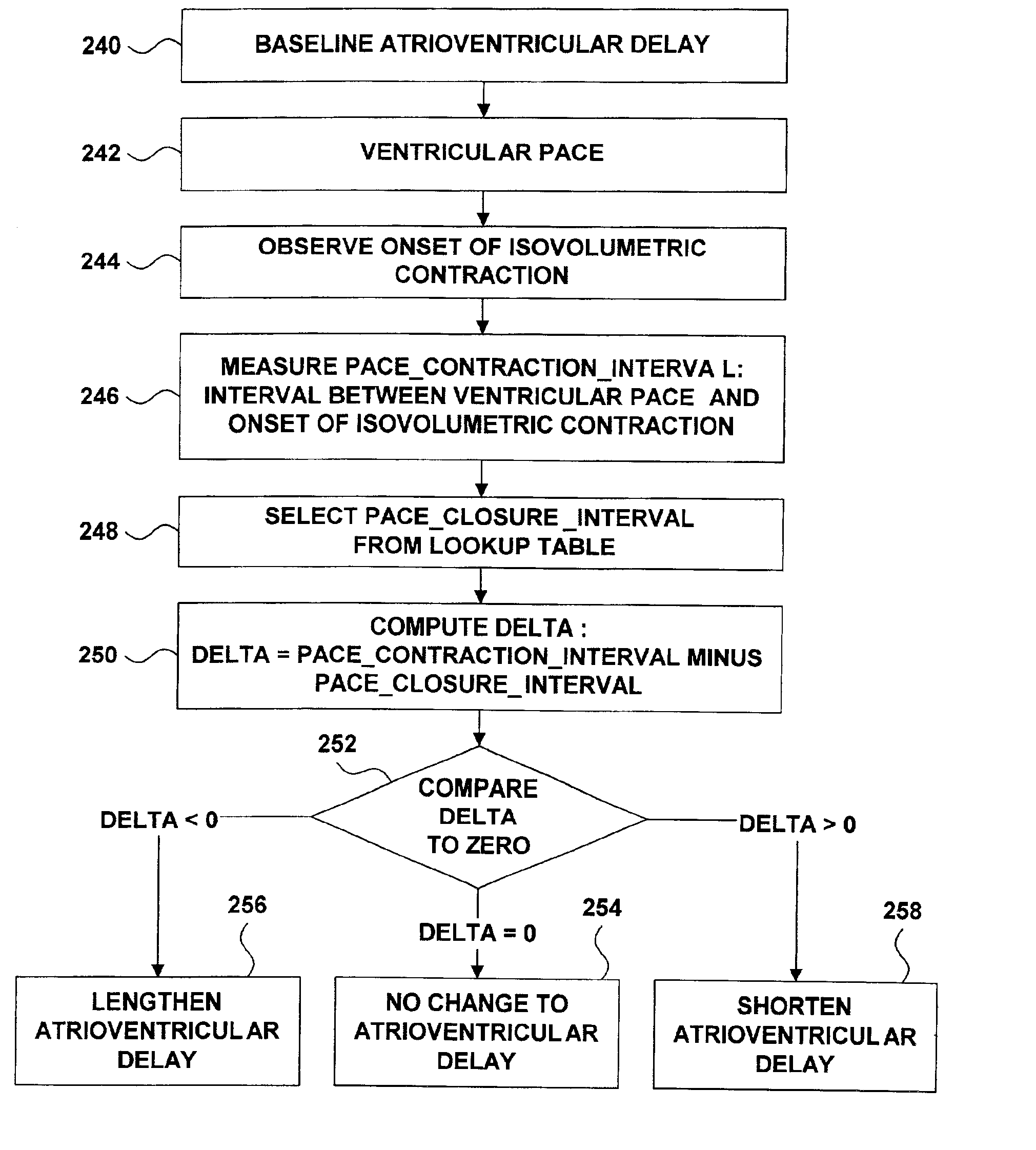
In a system that includes a ventricular pacemaker, the system adjusts an atrioventricular delay to synchronize the onset of isovolumetric contraction with the completion of ventricular filling. The system adjusts the atrioventricular delay as a function of electrical and pressure data from the heart. The system further adjusts the atrioventricular delay as a function of measurements of the time interval between a cardiac occurrence such as a ventricular pace and the completion of ventricular filling. The system may also adjust the atrioventricular delay as a function of the heart rate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for evaluating ventricular performance during isovolumic contraction
ActiveUS7233821B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyLeft ventricular sizeVentricular filling
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Predicting chronic optimal a-v intervals for biventricular pacing via observed inter-atrial delay
ActiveUS20080027488A1Maximize fillEasy to shrinkElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesAtrial cavityLeft ventricular size
Herein provided are methods for optimizing the atrio-ventricular (A-V) delay for efficacious delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy. The A-V delay is set such that pacing-induced left ventricular contraction occurs following completion of left atrial (LA) contraction. This maximizes left ventricular filling (preload) which theoretically results in optimal LV contraction via the Frank-Starling mechanism. In CRT devices, the programmed A-V delay starts with detection of electrical activity in the right atrium (RA). Thus, a major component of the A-V delay is the time required for inter-atrial conduction time (IACT) from the RA to the LA. This IACT can be measured during implantation as the time from the atrial lead stimulation artifact to local electrograms in a coronary sinus (CS) catheter. Assuming that the beginning of LA contraction closely corresponds with the beginning of LA electrical activity, the optimal AV delay should be related to the time between the start of RA electrical activity and the start of LA electrical activity plus the duration of LA atrial contraction. Thus the inventors hypothesized that during atrial pacing the IACT measured at implantation correlated with the echocardiographically defined optimal paced AV delay (PAV).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and method for hemodynamic-based optimization of cardiac pacing
InactiveUS20050234517A1Improves left ventricular filling pressureOptimal AV-delayHeart defibrillatorsCatheterSonificationLeft ventricular size
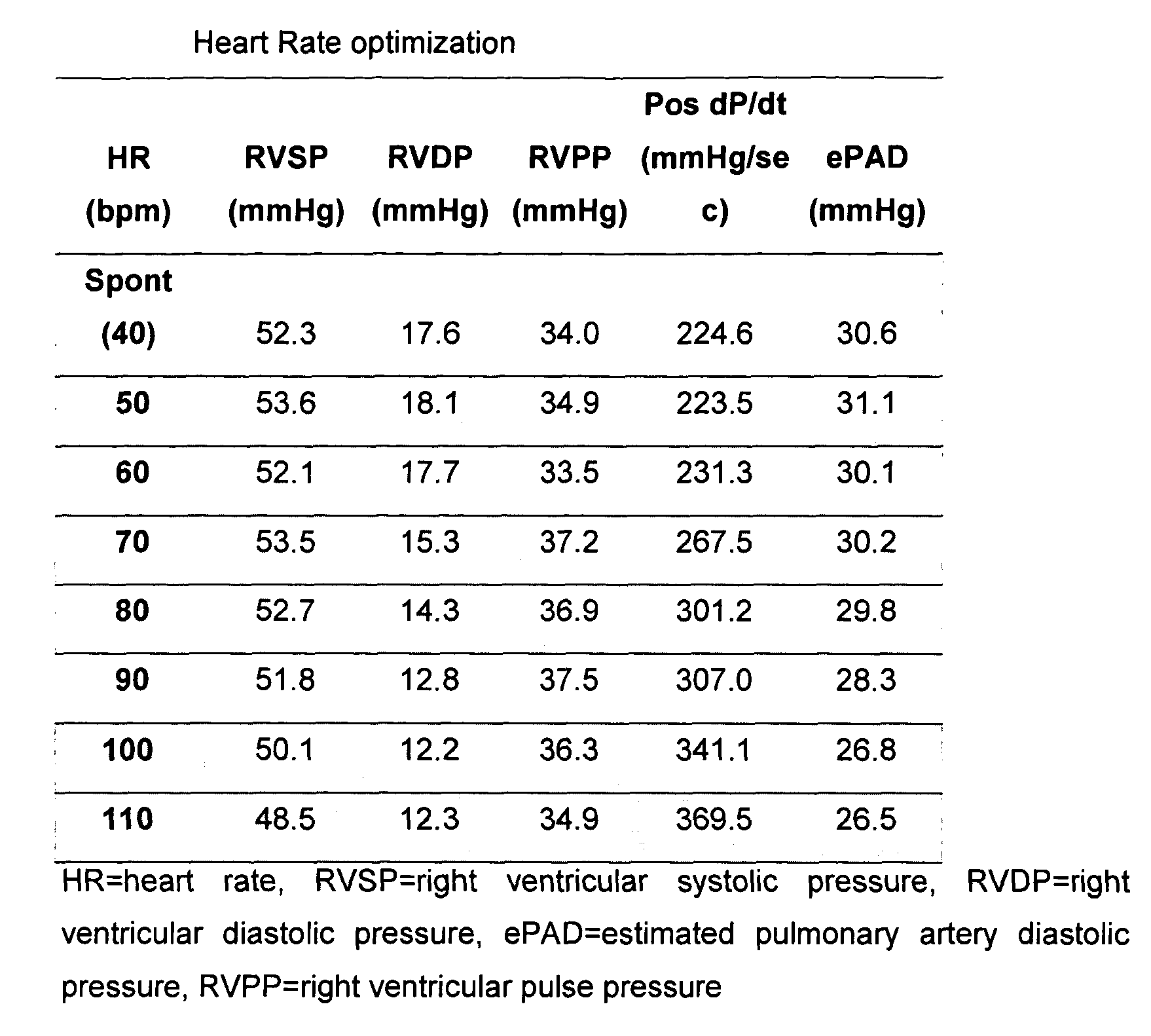
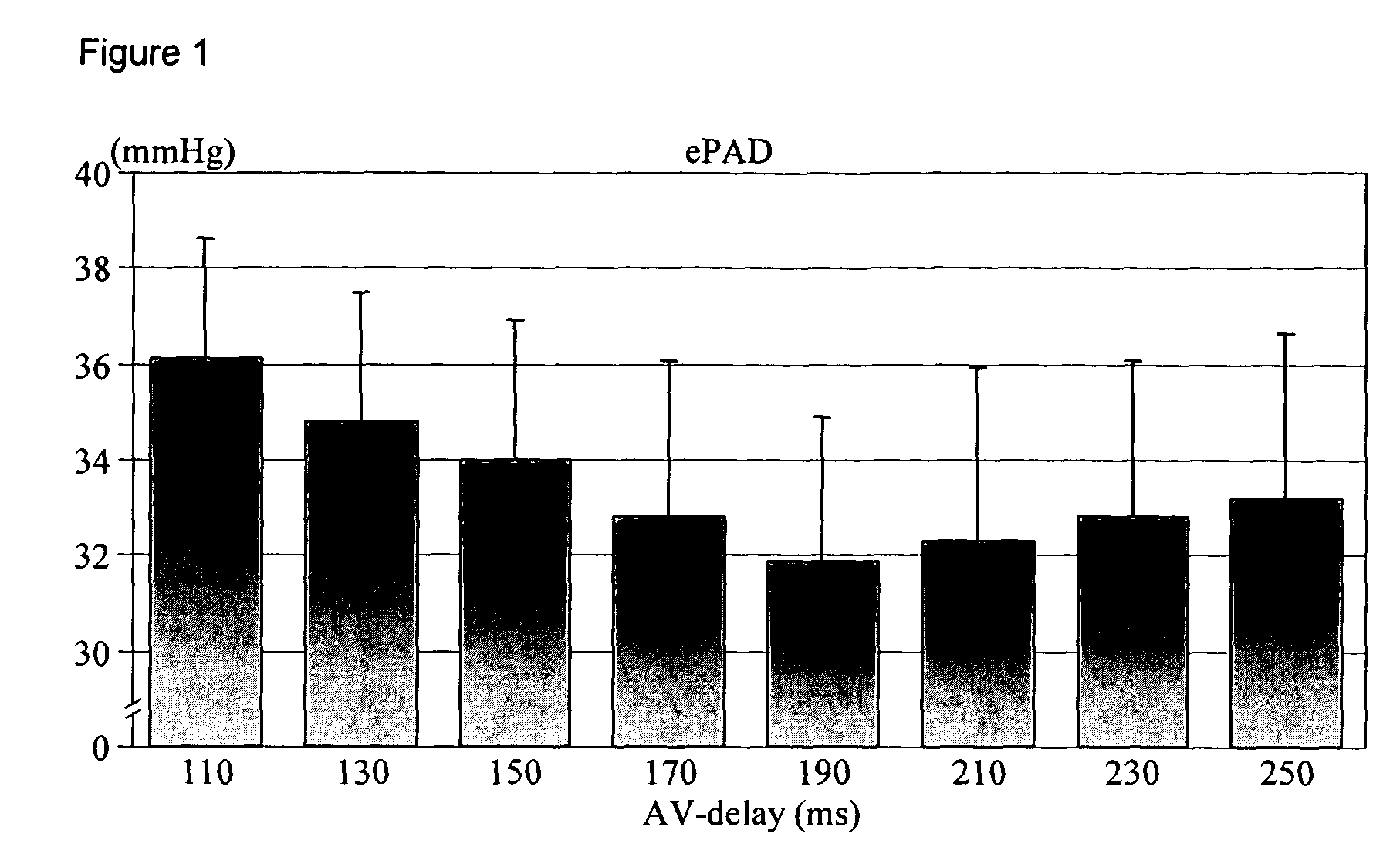
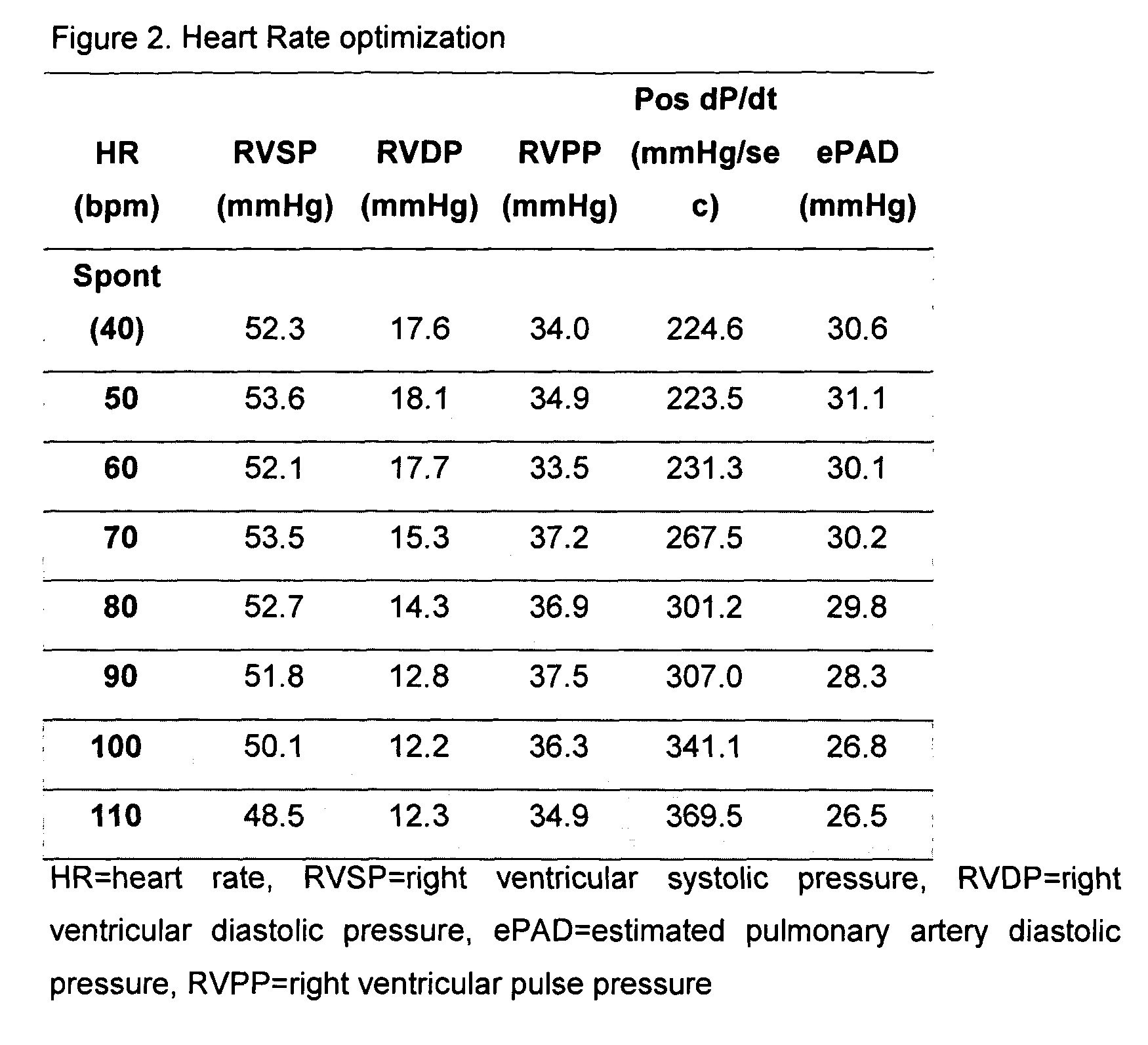
The present invention demonstrates that continuous hemodynamic monitoring can be used to identify the optimal AV-delay in a pacemaker-treated patient with end stage heart failure. The AV-delay determines the timing of late diastolic filling in relation to the onset of ventricular contraction and the duration of diastolic filling. An optimal tuning of the AV-delay improves left ventricular filling pressures in patients with a DDD-programmed pacemaker and is particularly important in the presence of a compromised left ventricular function. It has been discovered that using the lowest ePAD pressure, an indirect parameter of the left ventricular end-diastolic pressure, as an indicator for the optimal AV interval. Importantly, measurements of the ePAD revealed the same optimal AV-delay as echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular diastolic filling by standard echocardiographic methods. Importantly, the HR determined as optimal during the acute hemodynamic test did not turn out to be optimal during daily living activities.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and devices for diastolic assist
ActiveUS20120296153A1Increase volumeImprove heart functionIncision instrumentsBlood pumpsVentricular fillingBiomedical engineering
The devices and method described herein allow for therapeutic damage to increase volume in these hyperdynamic hearts to allow improved physiology and ventricular filling and to reduce diastolic filling pressure by making the ventricle less stiff.
Owner:LAUFER MICHAEL D +2
Method and apparatus for evaluating ventricular performance during isovolumic contraction
ActiveUS20060224203A1Optimize ventricular performanceEvaluate and monitor performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterLeft ventricular sizeVentricular filling
A method of evaluating ventricular performance of a heart employing sensors to measure a ventricular dimension signal and deriving indices of ventricular performance therefrom. Premature Shortening (PS) and Isovolumic Lengthening (IL) comprise two indices of ventricular performance determined from analysis of the left ventricular dimension signal during the transition from ventricular filling to ventricular ejection. Measured values of PS and IL are compared to other measured values or reference values to determine if ventricular performance has improved (or worsened). In some embodiments, the dimension sensors may comprise piezoelectric sonomicrometer crystals that operate as ultrasound transmitters and receivers. The sensors may be mounted in relation to a ventricle of the heart either temporarily or permanently, and may be configured either separately from or integrally with cardiac pacing leads.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
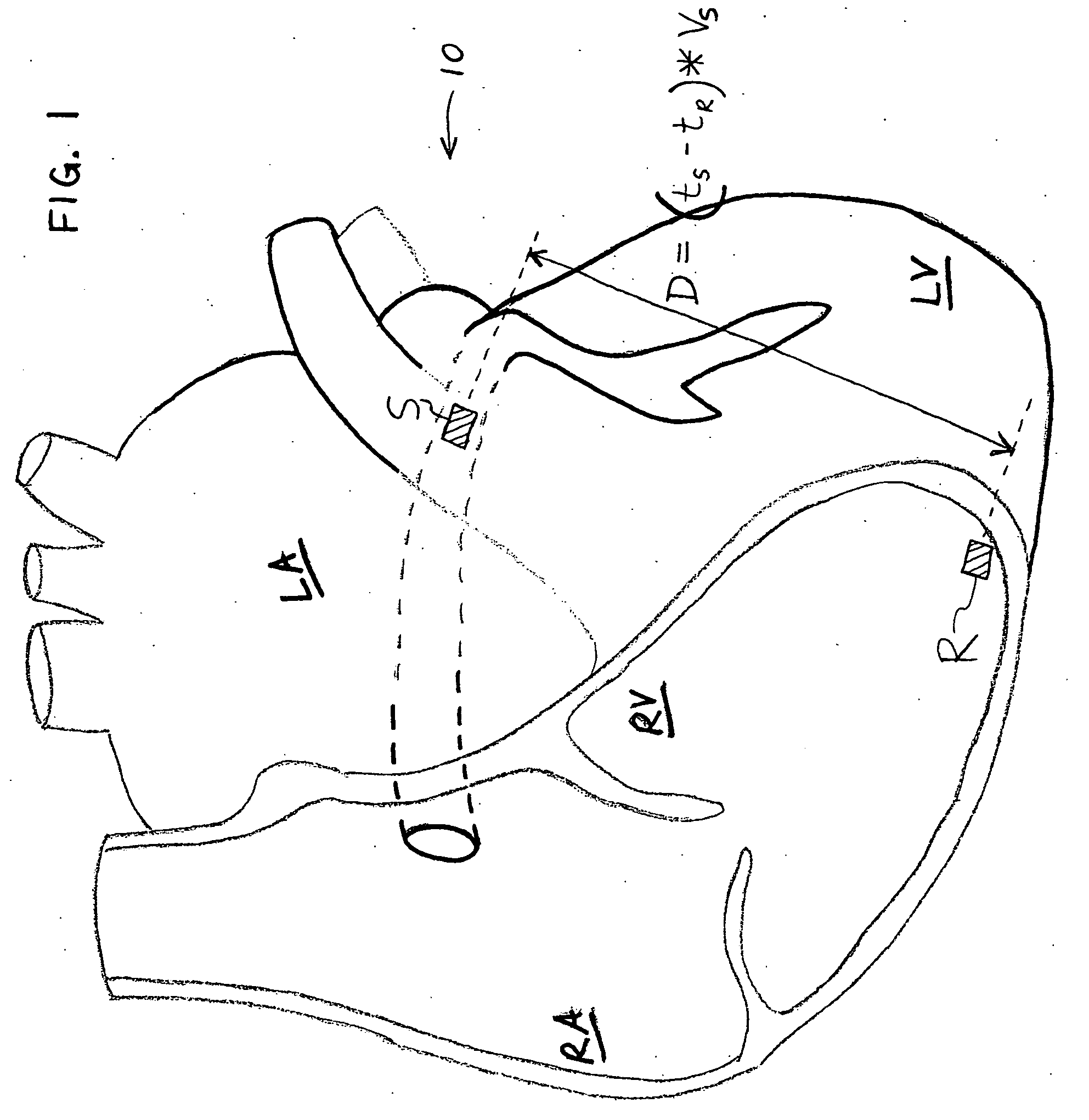
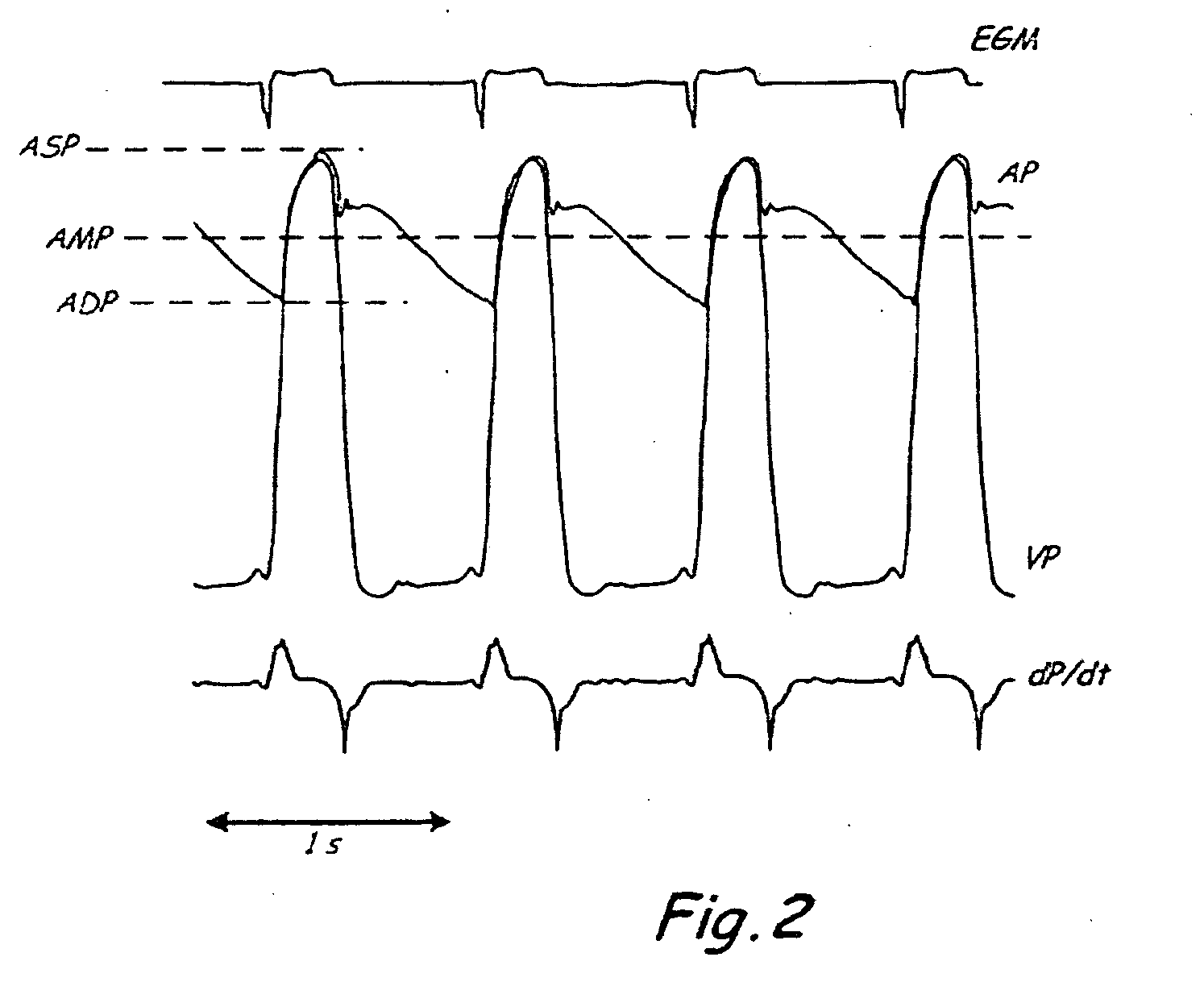
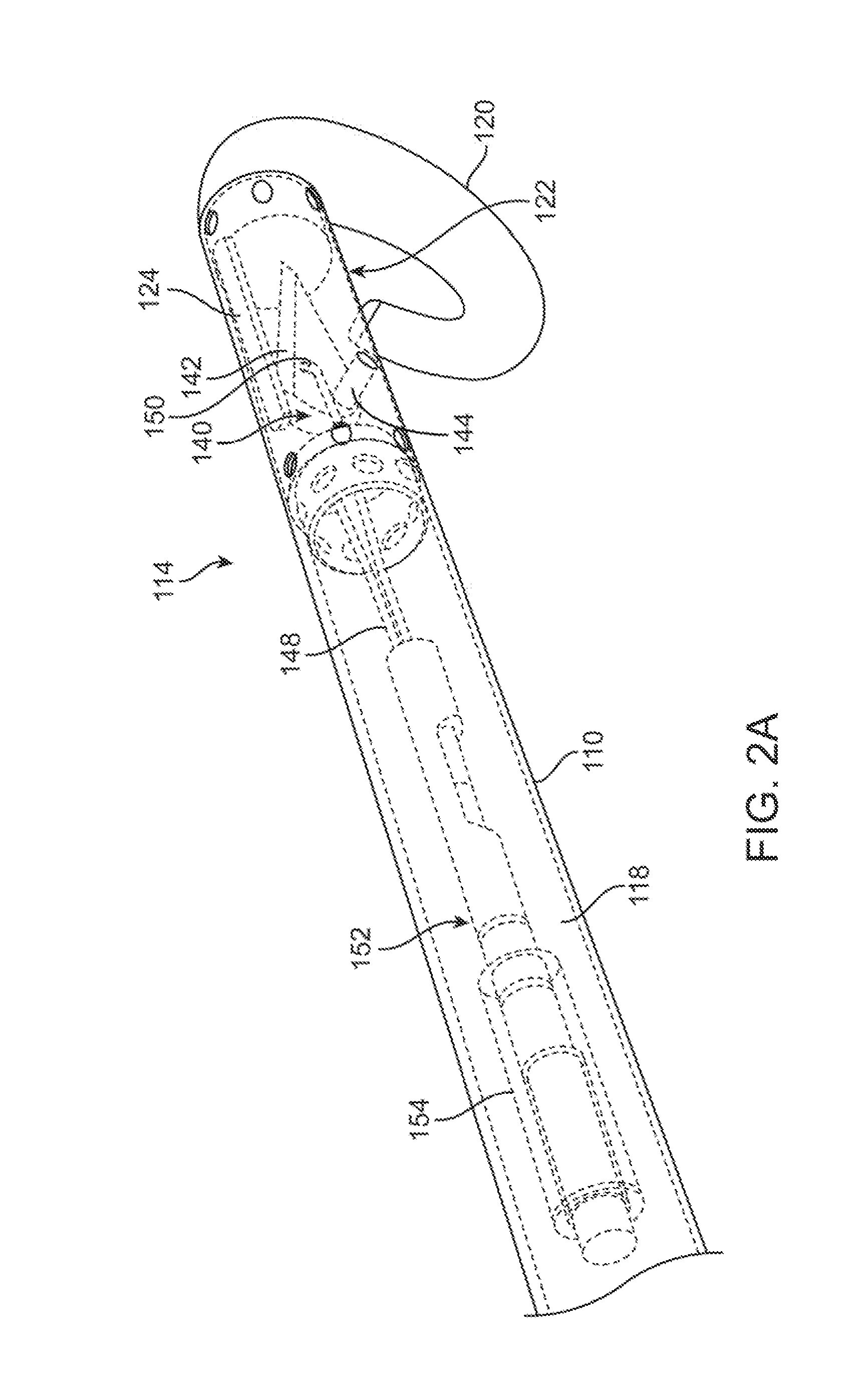
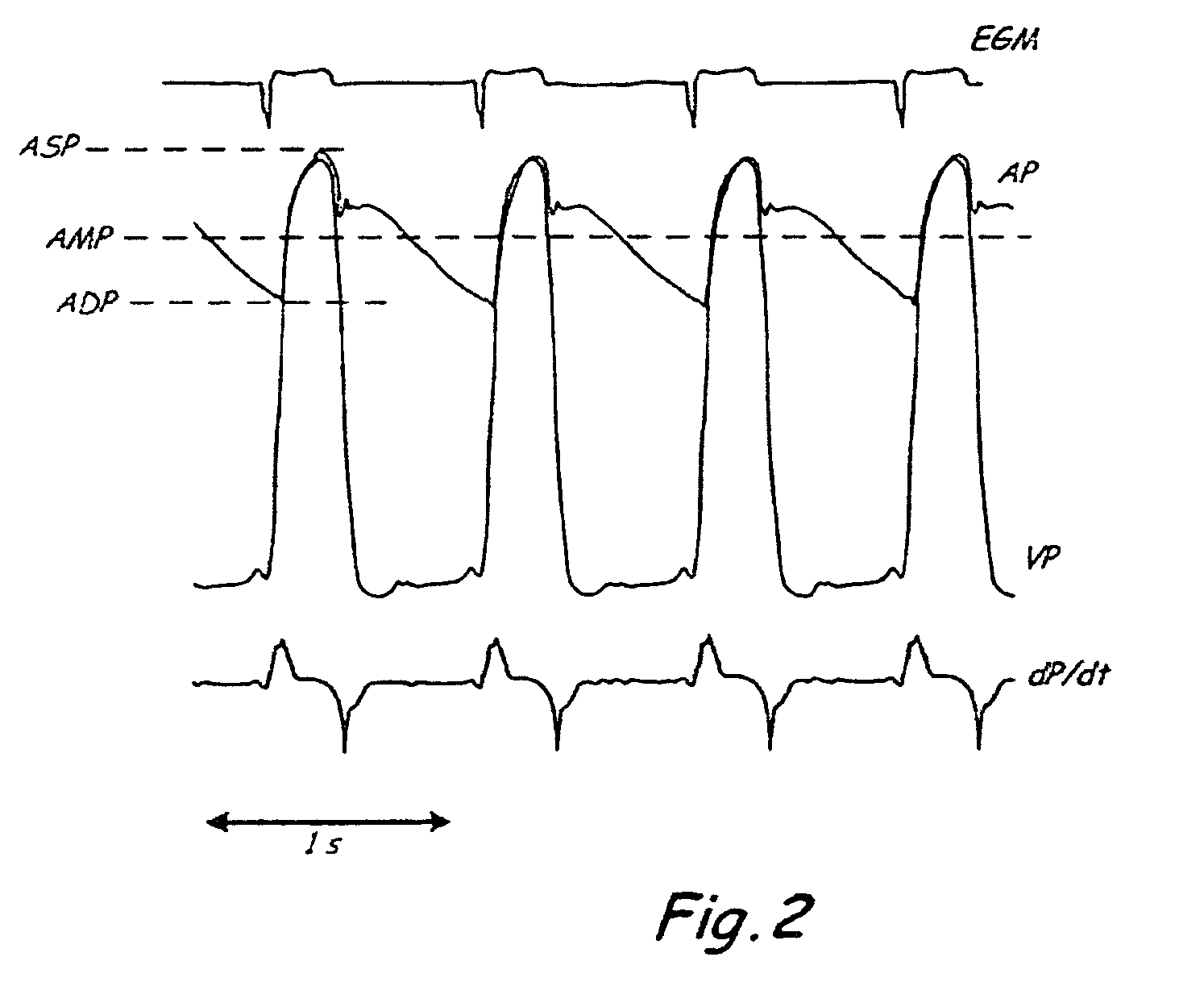
System and method of determining arterial blood pressure and ventricular fill parameters from ventricular blood pressure waveform data
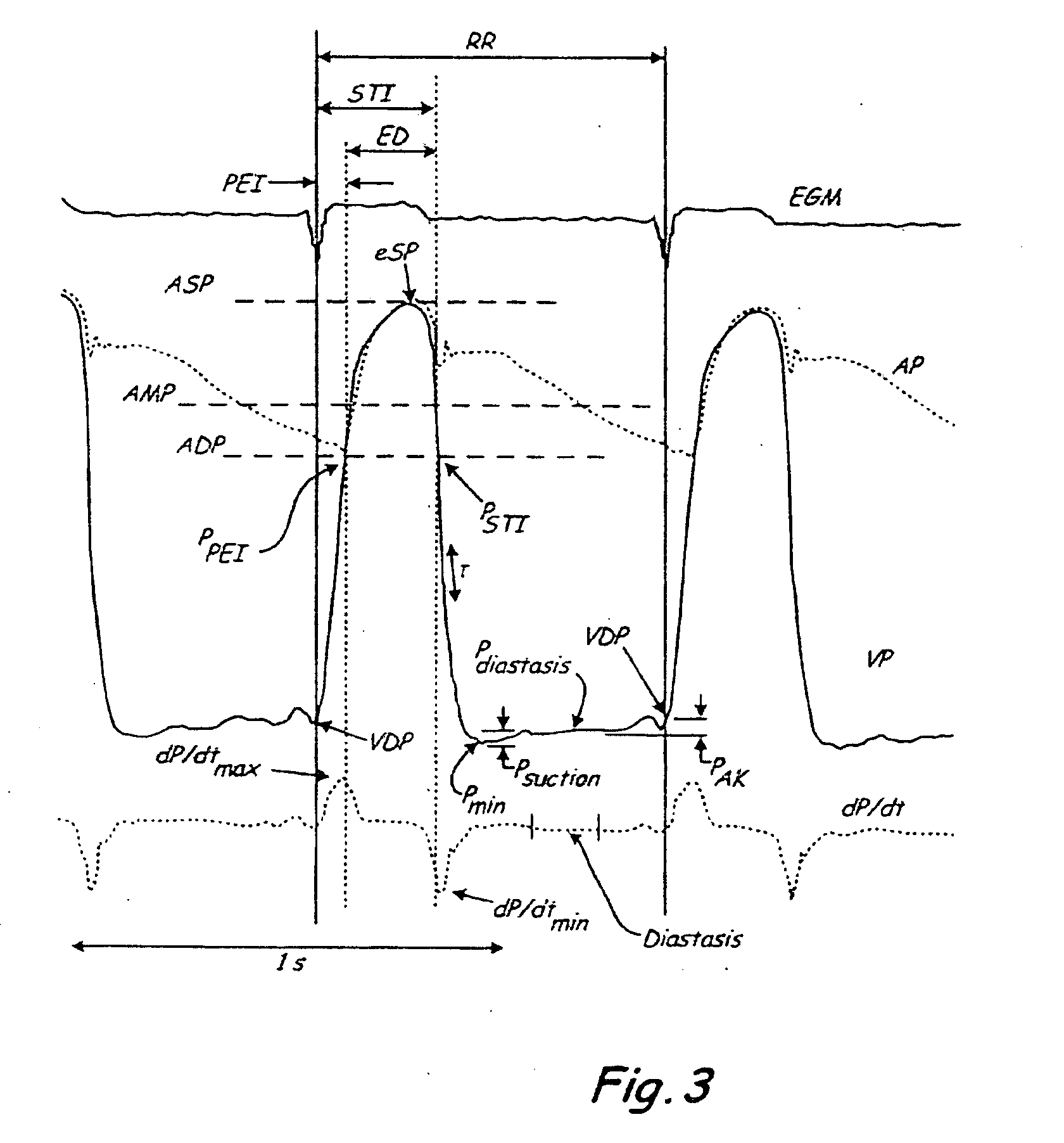
A system and method of determining hemodynamic parameters uses sensed ventricular blood pressure during a portion of ventricular pressure waveform following peak pressure. An estimated arterial diastolic pressure is based upon an amplitude of the sensed ventricular pressure corresponding to a time at which a first derivative of ventricular pressure as a function of time is at a minimum (dP / dtmin). Fill parameters such as isovolumetric relaxation constant, ventricular suction pressure, atrial kick pressure, and transvalve pressure gradient are derived from measured pressures representing minimum ventricular pressure, ventricular diastolic pressure, and diastasis pressure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Treatment Of Heart Failure By Controlled Adjustment Of The Atrioventricular And Interventricular Delays In An Active Implantable Medical Device
ActiveUS20100179608A1Improving AV-delayReduce delaysHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsSystoleLeft ventricular size
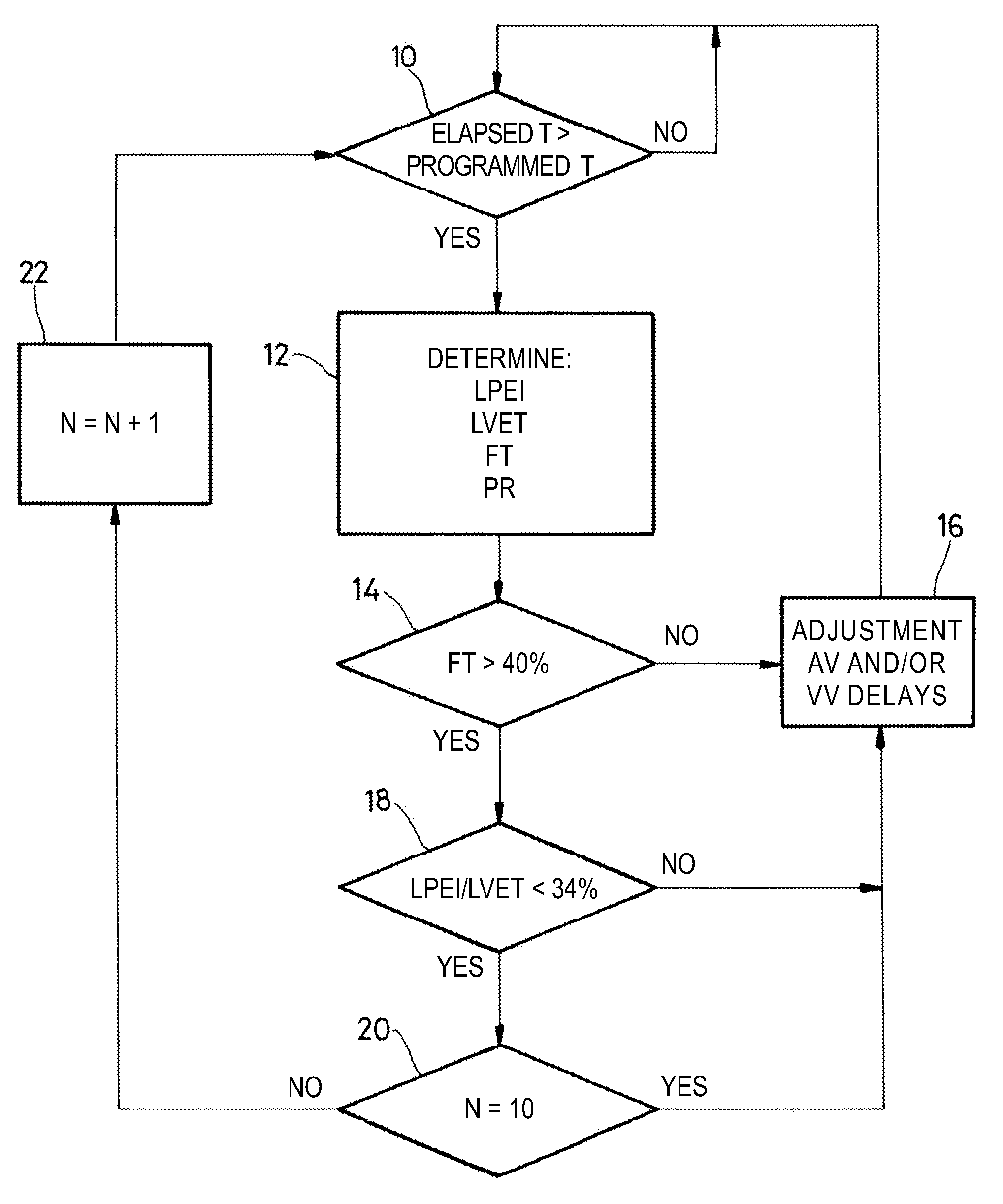
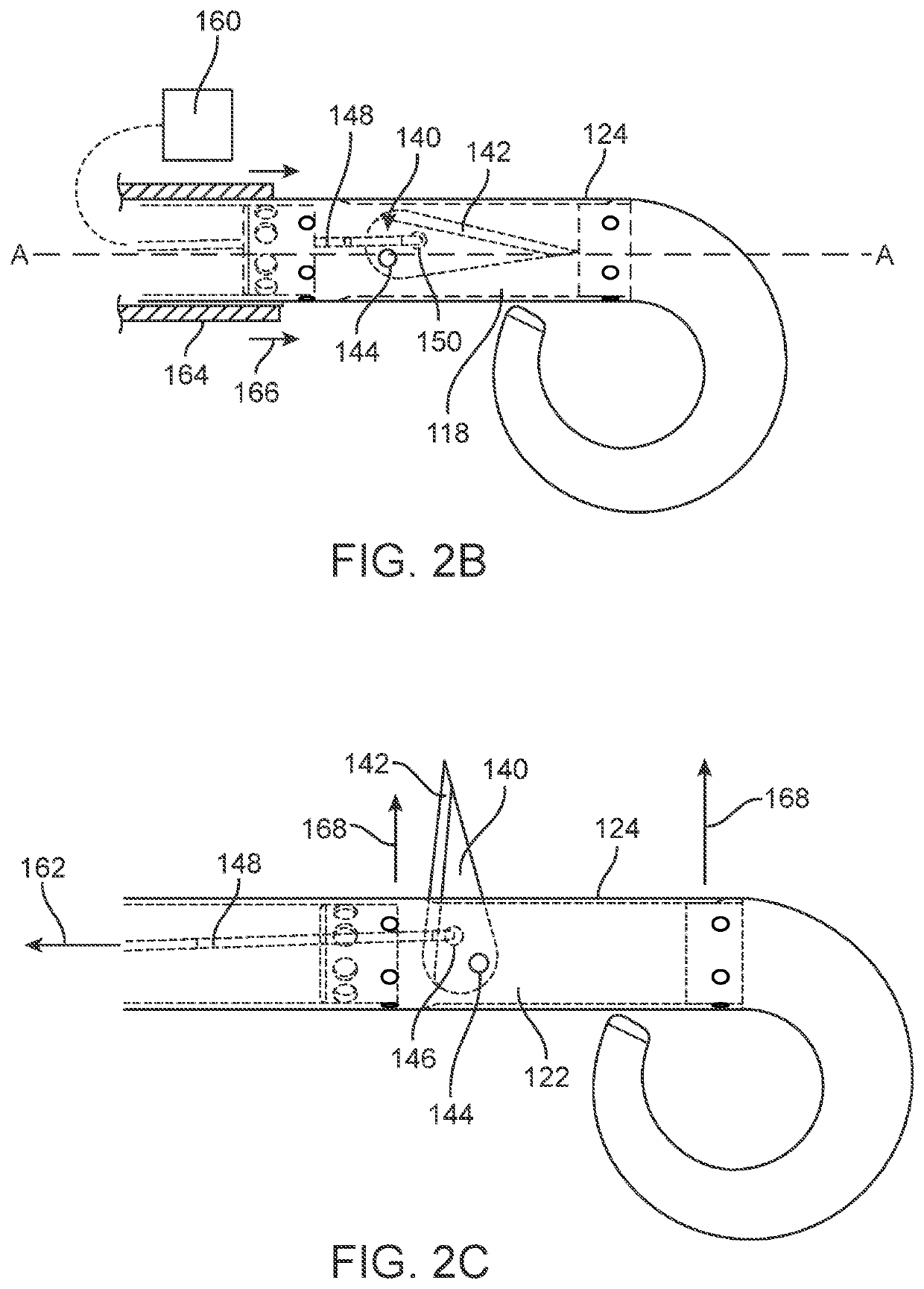
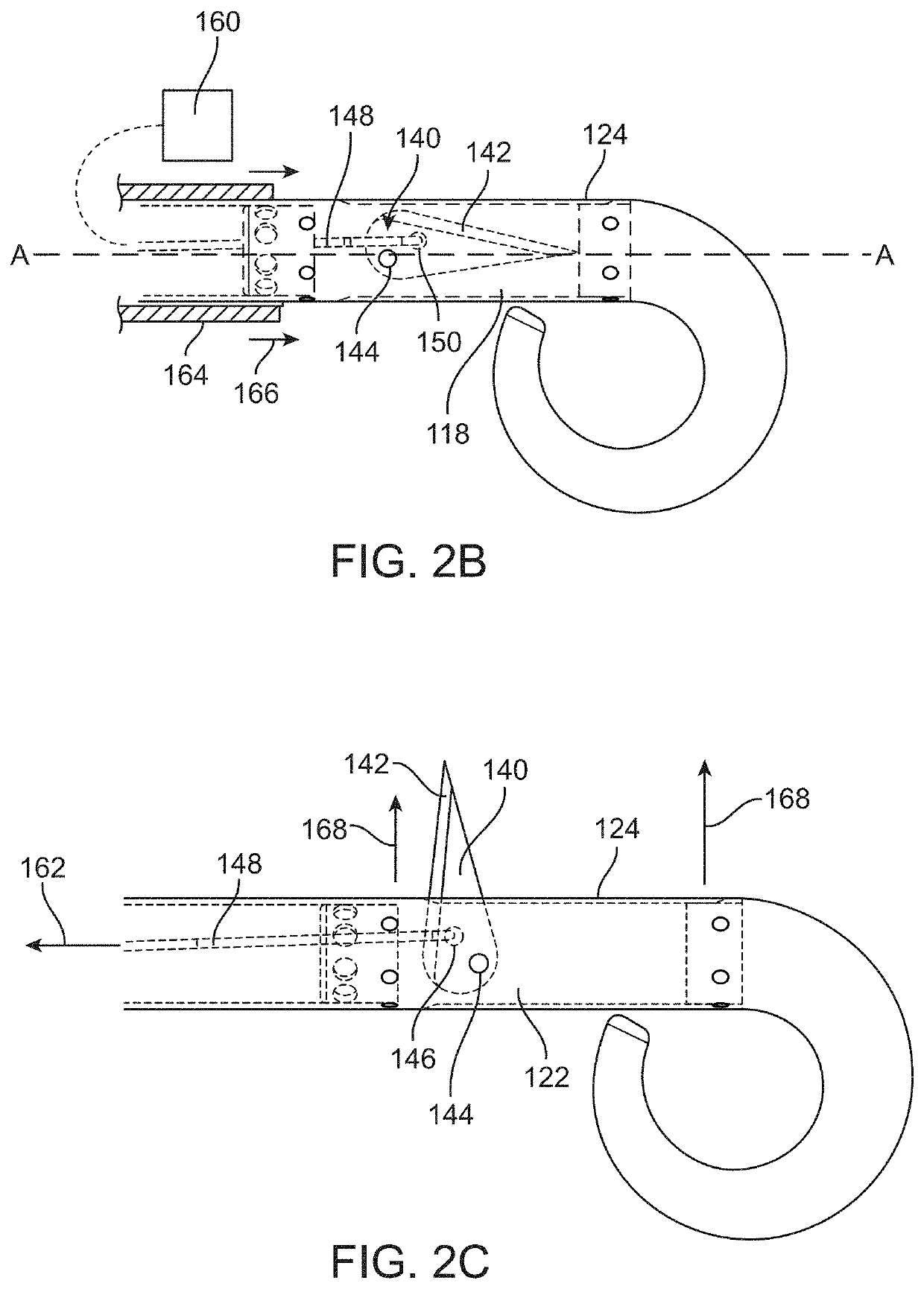
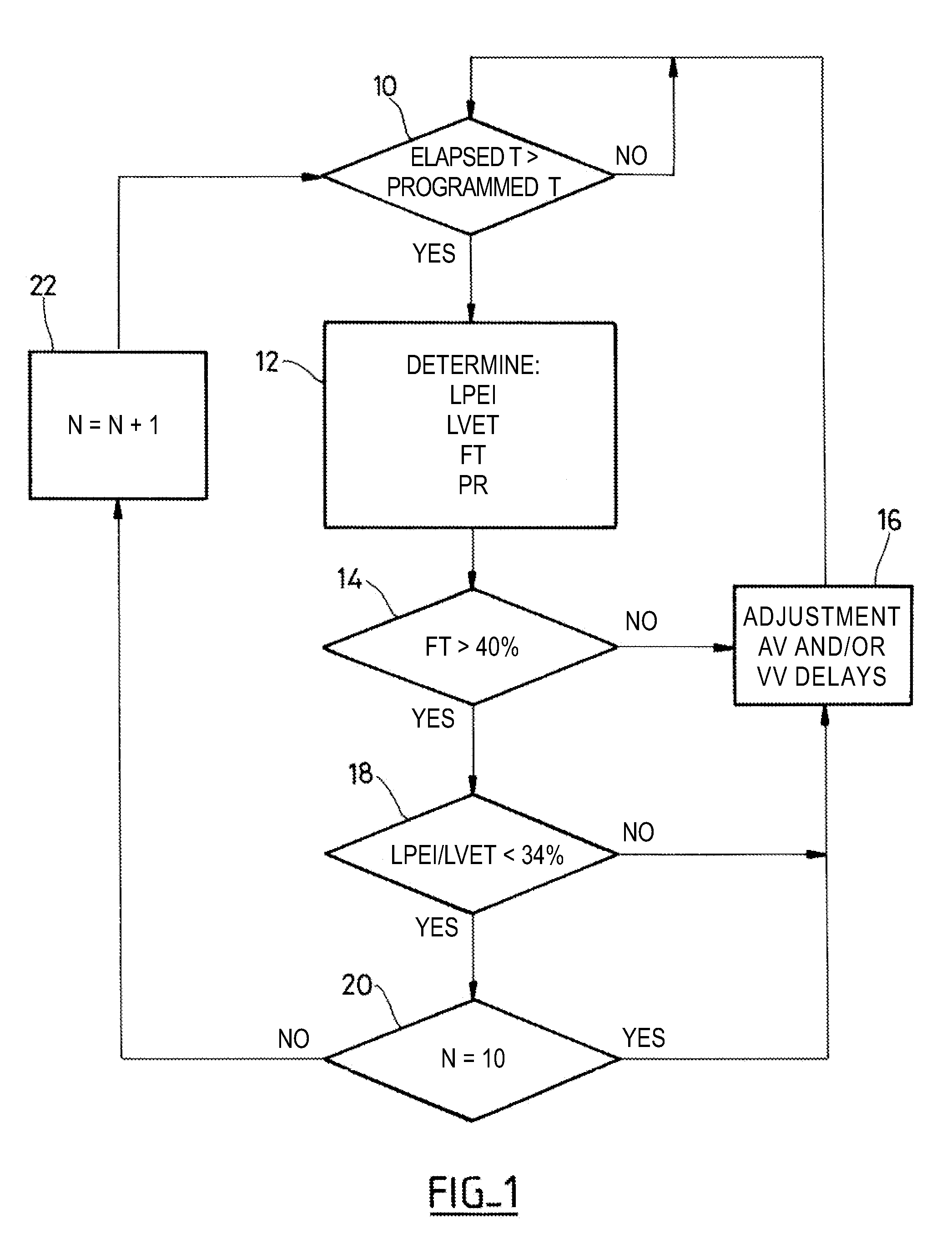
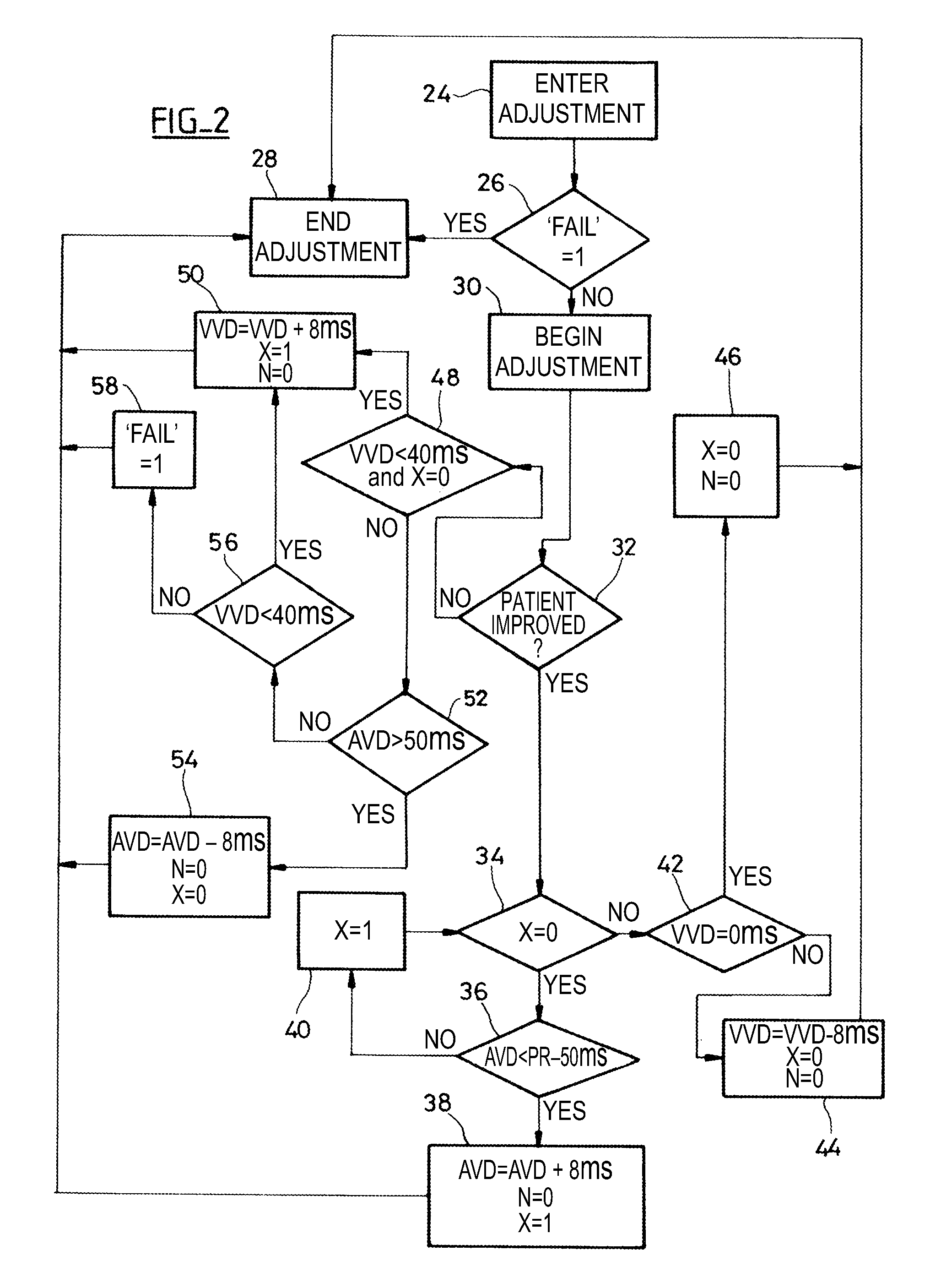
An active implantable medical device such as a cardiac prosthesis for the treatment of a heart failure by controlled adjustment of the atrioventricular and interventricular delays. The device provides atrioventricular and / or biventricular stimulation, a sensor delivering at least one hemodynamic parameter correlated with time intervals representative of the succession of the systolic and diastolic phases, and circuits to adjust the AV delay and / or VV delay. The device determines (12) during one cardiac cycle several parameters such as the left ventricular pre-ejection interval LPEI, the left ventricular ejection time LVET, the diastolic filling time FT and the conduction time PR. The device compares (14, 18) these parameters with at least one predetermined criterion. If a condition is met, the device readjusts (16) the AV delay and / or VV delay to maximize the ventricular filling and ejection.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Methods and devices for diastolic assist
ActiveUS8652025B2Increase volumeImprove heart functionIncision instrumentsDiagnosticsCardiac functioningCardiac muscle
The devices and method described herein allow for therapeutic damage to increase volume in these hyperdynamic hearts to allow improved physiology and ventricular filling and to reduce diastolic filling pressure by making the ventricle less stiff. For example, improving a diastolic heart function in a heart by creating at least one incision in cardiac muscle forming an interior heart wall of the interior chamber where the at least one incision extends into one or more layers of the interior heart wall without puncturing through the interior heart wall and the incision is sufficient to reduce a stiffness of the interior chamber to increase volume of the chamber and reduce diastolic filing pressure.
Owner:LAUFER MICHAEL D +2
Methods and devices for diastolic assist
ActiveUS20150094715A1Increase volumeImprove heart functionDiagnosticsTransvascular endocardial electrodesMedicineVentricular filling
The devices and method described herein allow for therapeutic damage to increase volume in these hyperdynamic hearts to allow improved physiology and ventricular filling and to reduce diastolic filling pressure by making the ventricle less stiff.
Owner:LAUFER MICHAEL D +1
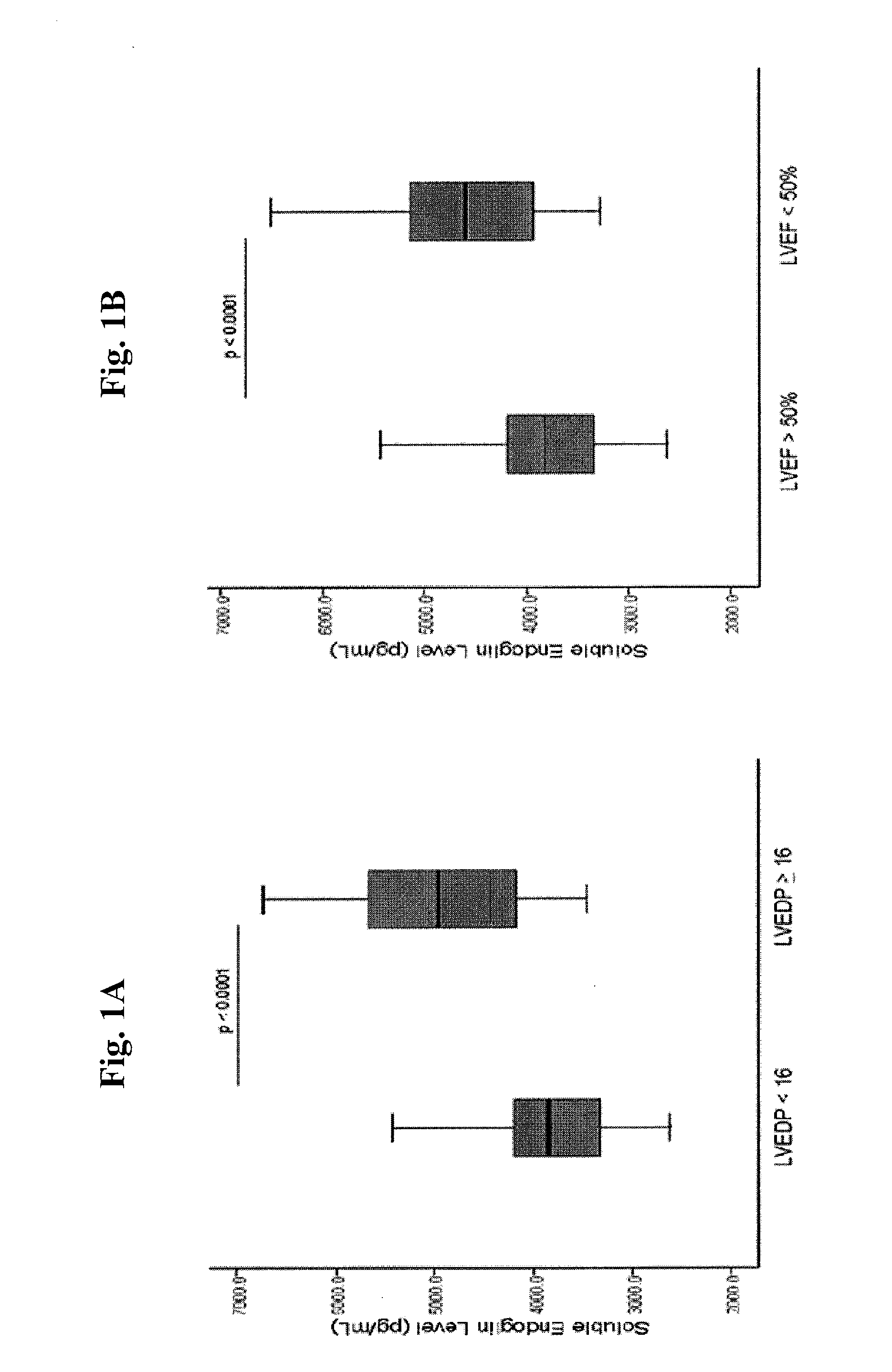
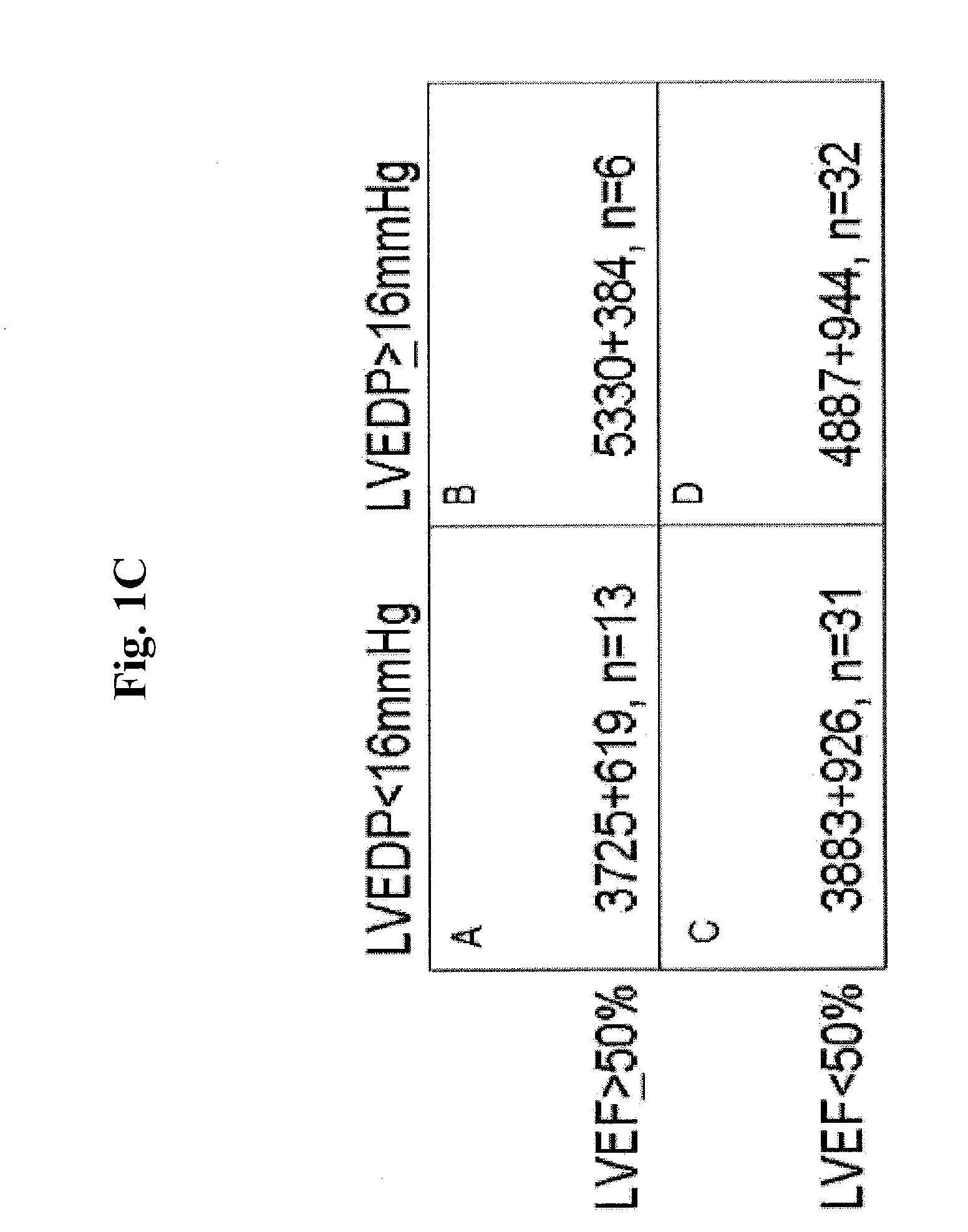
Methods for diagnosing elevated right or left ventricular filling pressure
InactiveUS20120115175A1Increase filling pressureImprove the level ofDisease diagnosisBiological testingLeft ventricular sizeVentricular filling
Owner:TUFTS MEDICAL CENTER INC
Methods and apparatus for optimizing cardiac output, preventing backward heart failure, and minimizing diastolic myocardial wall stress by controlling left ventricular filling
InactiveUS20120172944A1Less timeIncrease heart rateElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsIncreased heart rateCardiac pacemaker electrode
Apparatus for diastole trimming including a controller for producing a diastole ending signal, and one or more leads connected to the controller, for carrying the signal to lead connections to a heart, characterized by the controller detecting when a left ventricle (LV) of the heart is mostly full, and producing the diastole ending signal such that the diastole duration is trimmed. Apparatus for diastole trimming including a controller for producing a diastole ending signal, and a connection to a pacemaker, characterized by the controller having decision rules for indicating to the pacemaker when to fire and end the diastole. A method of programming a pacemaker characterized by increasing cardiac output by trimming duration of diastole. A method for increasing cardiac output including producing a signal to trim diastole duration, thereby increasing heart rate (HR) and increasing a product of stroke volume (SV) times HR. Related apparatus and methods are also described.
Owner:D H S MEDICAL
Method of defining continuous heart rate vs AV delay values and sensed to paced AV delay offset in patients undergoing cardiac resynchronization therapy
A method of data management for optimizing the patient outcome from the provision of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is described. A regression equation is constructed using 3 data points on a plot of AV delay vs. HR. The x-axis consist of the three points consist of resting HR, HR at the optimal AV delay value during light exercise, and the upper tracking or paced HR. The y-values associated with the three points consist of the AV delay values computed using an equation for ventricular filling time and the optimally determined AV delay value. Also described is a process for determining the sensed to paced AV delay offset. The combined processes yield 4 (the three constant values in the polynomial regression equation Y=b2X2+b1X+a and the sensed to paced AV delay offset) which can be stored on the patient's pacemaker for determining dynamically the AV delay value which is physiologically fine-tuned for each patient from resting HR to the upper tracking or paced HR. In combination with visual observation and computer-assisted ranking of the dependent variables, a physician can utilize the resulting information to render decisions on the optimal choice of the programming biventricular pacemakers / ICDs and DDDR pacemakers for individual patients.
Owner:SHAPE MEDICAL SYST
Methods and devices for diastolic assist
ActiveUS20160206345A1Increase volumeImprove heart functionIncision instrumentsTransvascular endocardial electrodesVentricular fillingBiomedical engineering
The devices and method described herein allow for therapeutic damage to increase volume in these hyperdynamic hearts to allow improved physiology and ventricular filling and to reduce diastolic filling pressure by making the ventricle less stiff.
Owner:CORDYNAMIX
System and method of determining arterial blood pressure and ventricular fill parameters from ventricular blood pressure waveform data
A system and method of determining hemodynamic parameters uses sensed ventricular blood pressure during a portion of ventricular pressure waveform following peak pressure. An estimated arterial diastolic pressure is based upon an amplitude of the sensed ventricular pressure corresponding to a time at which a first derivative of ventricular pressure as a function of time is at a minimum (dP / dtmin). Fill parameters such as isovolumetric relaxation constant, ventricular suction pressure, atrial kick pressure, and transvalve pressure gradient are derived from measured pressures representing minimum ventricular pressure, ventricular diastolic pressure, and diastasis pressure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and devices for diastolic assist
ActiveUS10765447B2Increase volumeImprove heart functionIncision instrumentsTransvascular endocardial electrodesVentricular fillingRat heart
The devices and method described herein allow for therapeutic damage to increase volume in these hyperdynamic hearts to allow improved physiology and ventricular filling and to reduce diastolic filling pressure by making the ventricle less stiff.
Owner:CORDYNAMIX
Methods and devices for diastolic assist
ActiveUS10772678B2Increase volumeImprove heart functionTransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnosticsVentricular fillingRat heart
The devices and method described herein allow for therapeutic damage to increase volume in these hyperdynamic hearts to allow improved physiology and ventricular filling and to reduce diastolic filling pressure by making the ventricle less stiff.
Owner:LAUFER MICHAEL D +1
Heart failure detecting medical device
InactiveUS20110028855A1Increase opportunitiesIncreased risk of failureMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesElectrocardiographyVentricular fillingIncreased risk
An implantable medical device has an event detector that detects a predetermined cardiac event during a heart cycle of a subject. A reference time is assigned to this detected cardiac event. An onset detector detects the onset of ventricular filling of the heart during the heart cycle. The relative time of the detected filling onset is determined based on the assigned time reference. An increased risk of heart failure of the subject is automatically determined based on the determined relative time for the filling onset. Generally, a reduction in the relative time, as determined at different points in time, indicates an increased heart failure risk or the presence of a heart failure condition.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP +1
Methods and devices for diastolic assist
ActiveUS10864014B2Increase volumeImprove heart functionElectrocardiographyIncision instrumentsVentricular fillingRat heart
The devices and method described herein allow for therapeutic damage to increase volume in these hyperdynamic hearts to allow improved physiology and ventricular filling and to reduce diastolic filling pressure by making the ventricle less stiff.
Owner:CORDYNAMIX
Methods and devices for diastolic assist
PendingUS20210128190A1Increase volumeImprove heart functionElectrocardiographyIncision instrumentsVentricular fillingRat heart
The devices and method described herein allow for therapeutic damage to increase volume in these hyperdynamic hearts to allow improved physiology and ventricular filling and to reduce diastolic filling pressure by making the ventricle less stiff.
Owner:CORDYNAMIX
Treatment of heart failure by controlled adjustment of the atrioventricular and interventricular delays in an active implantable medical device
An active implantable medical device such as a cardiac prosthesis for the treatment of a heart failure by controlled adjustment of the atrioventricular and interventricular delays. The device provides atrioventricular and / or biventricular stimulation, a sensor delivering at least one hemodynamic parameter correlated with time intervals representative of the succession of the systolic and diastolic phases, and circuits to adjust the AV delay and / or VV delay. The device determines (12) during one cardiac cycle several parameters such as the left ventricular pre-ejection interval LPEI, the left ventricular ejection time LVET, the diastolic filling time FT and the conduction time PR. The device compares (14, 18) these parameters with at least one predetermined criterion. If a condition is met, the device readjusts (16) the AV delay and / or VV delay to maximize the ventricular filling and ejection.
Owner:SORIN CRM
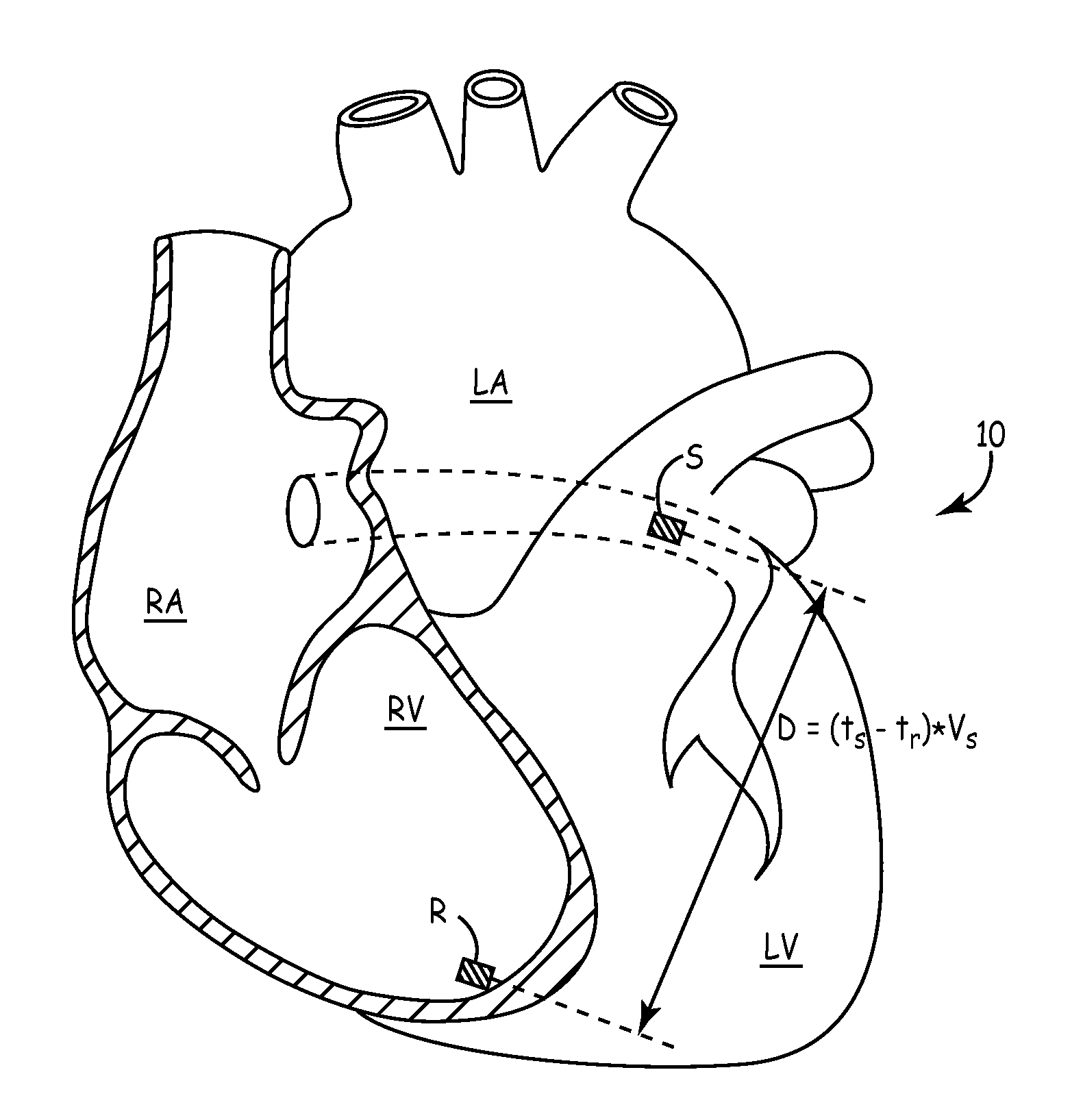
Methods and systems for detecting atrial contraction timing fiducials during ventricular filling from a ventricularly implanted leadless cardiac pacemaker
A ventricularly implantable medical device that includes a sensing module that is configured to detect an artifact during ventricular filling and to identify an atrial event based at least on part onthe detected artifact. Control circuitry of the implantable medical device is configured to deliver a ventricular pacing therapy to a patient's heart, wherein the ventricular pacing therapy is time dependent, at least in part, on the identified atrial event.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Methods and devices for diastolic assist
ActiveUS20210007773A1Increase volumeImprove heart functionIncision instrumentsTransvascular endocardial electrodesMedicineVentricular filling
The devices and method described herein allow for therapeutic damage to increase volume in these hyperdynamic hearts to allow improved physiology and ventricular filling and to reduce diastolic filling pressure by making the ventricle less stiff.
Owner:CORDYNAMIX
Diastolic heart failure treatment
ActiveUS11357629B1Lower the volumeEasy to fillSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsCardiac cyclePapillary muscle
A method of treating diastolic heart failure includes implanting a cardiac implant in a heart of a subject diagnosed as suffering from diastolic heart failure. A superior portion of a flexible tether of the cardiac implant is anchored to one or more left-atrial sites of one or more walls of the left atrium. An inferior portion of the flexible tether is anchored to a site of a wall of a mid third of the left ventricle, of a wall of an apical third of the left ventricle, and / or of a papillary muscle of the left ventricle. As a result, the flexible tether reduces a volume of the left atrium during at least a portion of ventricular diastole of each cardiac cycle, thereby enhancing ventricular filling. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:GROSS YOSSI
Methods and systems for analyzing valve related timing and monitoring heart failure
A method and system are provided to analyze valve related timing and monitor heart failure. The method and system comprise collecting cardiac signals associated with an atrial chamber of interest; collecting dynamic impedance (DI) data along an atria-function focused (AFF) vector to form a DI data set, the DI data set including information corresponding to a mechanical function (MF) of a valve associated with the atrial chamber of interest; identifying, from the cardiac signals, an intra-atrial conduction timing (IACT) associated with the atrial chamber of interest; estimating an MF landmark at which the mechanical function of the valve occurs based on the DI data set; analyzing a timing delay between the MF landmark and the IACT; and adjusting a therapy, based on the timing delay, to encourage atrial contribution to ventricular filling.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method of Defining Continuous Heart Rate vs AV Delay Values and Sensed to Paced AV Delay Offset in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
InactiveUS20120123493A1Optimizing patient outcomeHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeVentricular filling
A method of data management for optimizing the patient outcome from the provision of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is described. A regression equation is constructed using 3 data points on a plot of AV delay vs. HR. The x-axis consist of the three points consist of resting HR, HR at the optimal AV delay value during light exercise, and the upper tracking or paced HR. The y-values associated with the three points consist of the AV delay values computed using an equation for ventricular filling time and the optimally determined AV delay value. Also described is a process for determining the sensed to paced AV delay offset. The combined processes yield 4 (the three constant values in the polynomial regression equation Y=b2X2+b1X+a and the sensed to paced AV delay offset) which can be stored on the patient's pacemaker for determining dynamically the AV delay value which is physiologically fine-tuned for each patient from resting HR to the upper tracking or paced HR. In combination with visual observation and computer-assisted ranking of the dependent variables, a physician can utilize the resulting information to render decisions on the optimal choice of the programming biventricular pacemakers / ICDs and DDDR pacemakers for individual patients.
Owner:SHAPE MEDICAL SYST
Heart failure detecting medical device
InactiveUS8457726B2Increase opportunitiesIncreased risk of failureMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesElectrocardiographyVentricular fillingIncreased risk
An implantable medical device has an event detector that detects a predetermined cardiac event during a heart cycle of a subject. A reference time is assigned to this detected cardiac event. An onset detector detects the onset of ventricular filling of the heart during the heart cycle. The relative time of the detected filling onset is determined based on the assigned time reference. An increased risk of heart failure of the subject is automatically determined based on the determined relative time for the filling onset. Generally, a reduction in the relative time, as determined at different points in time, indicates an increased heart failure risk or the presence of a heart failure condition.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com