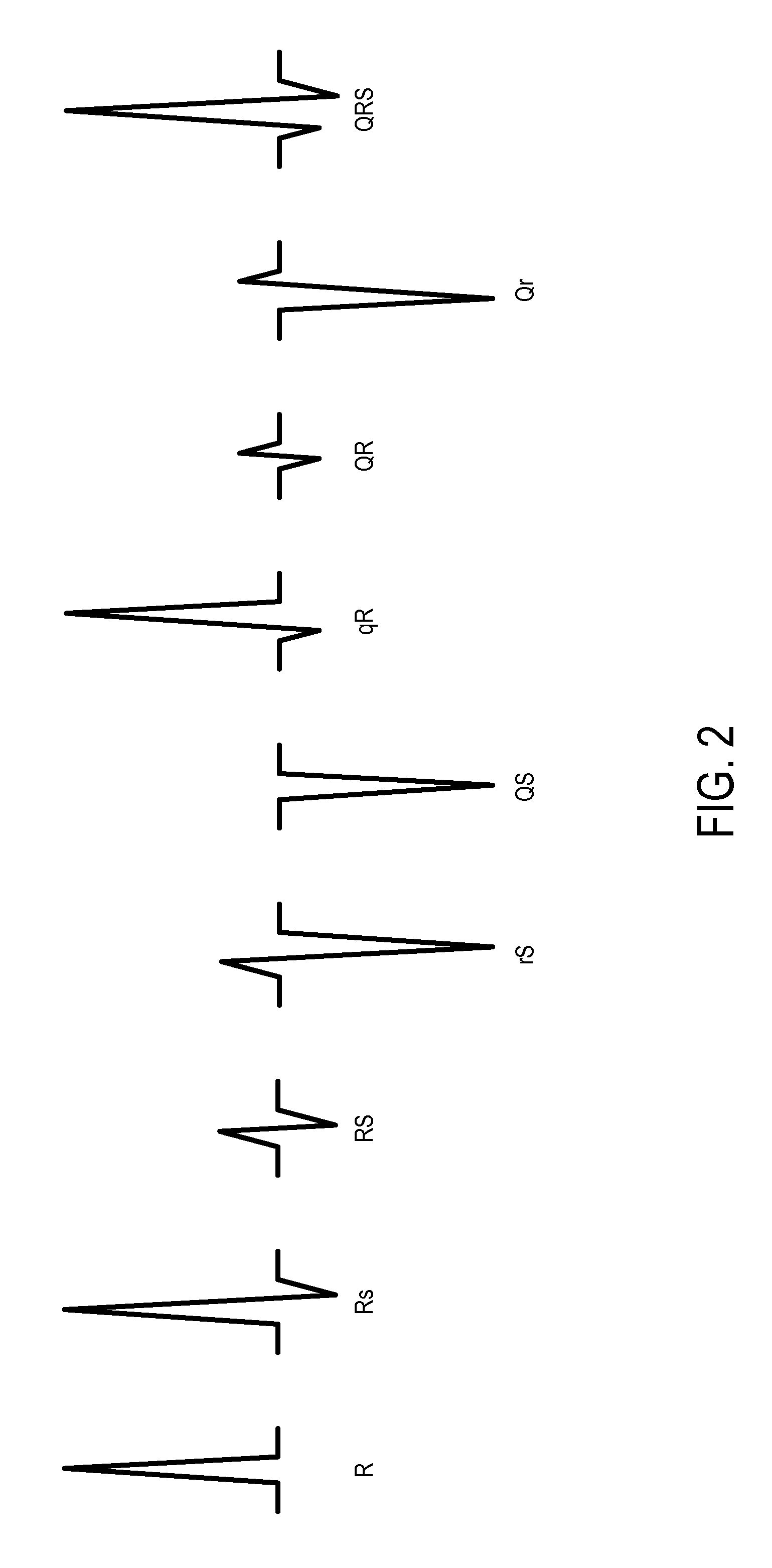
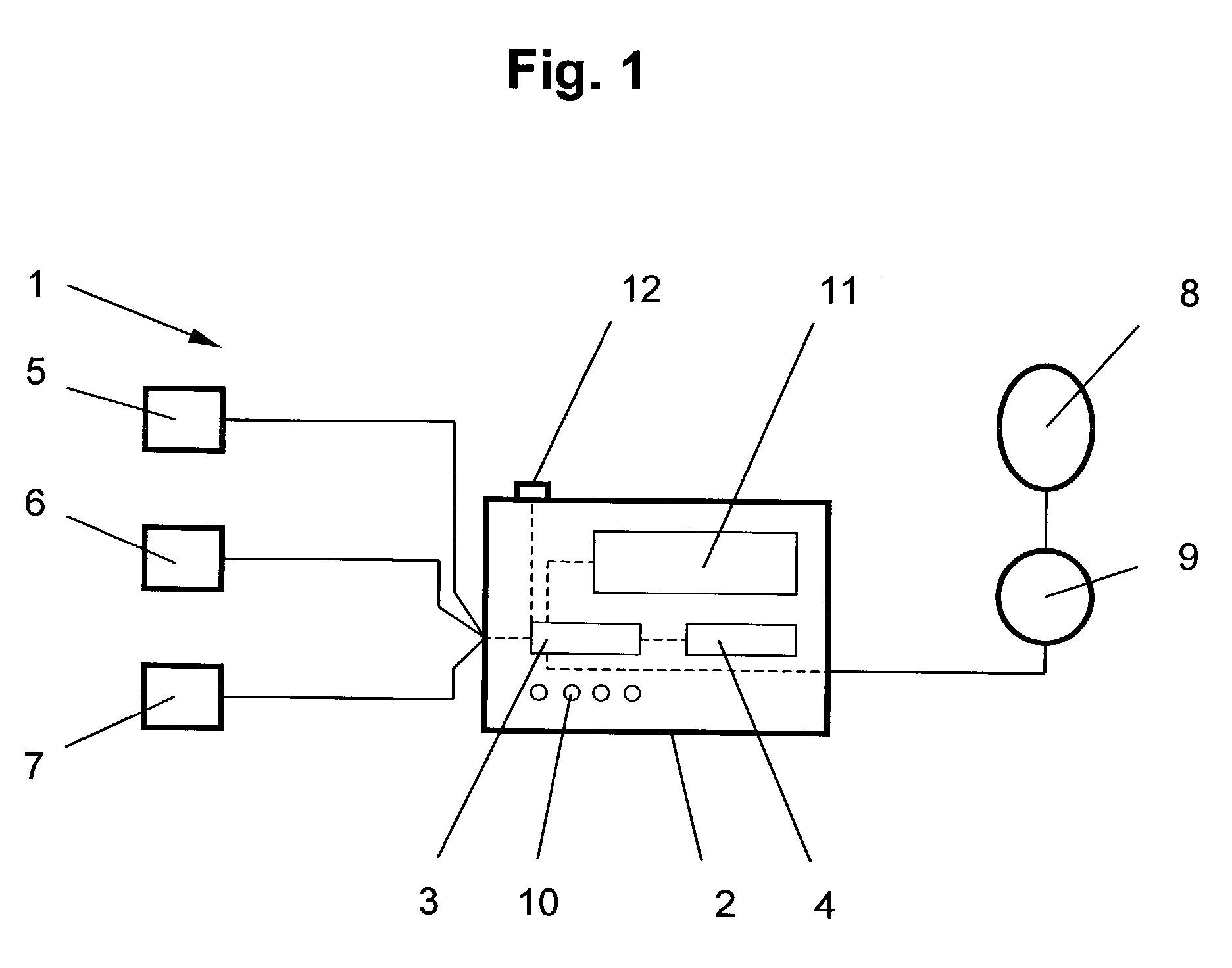
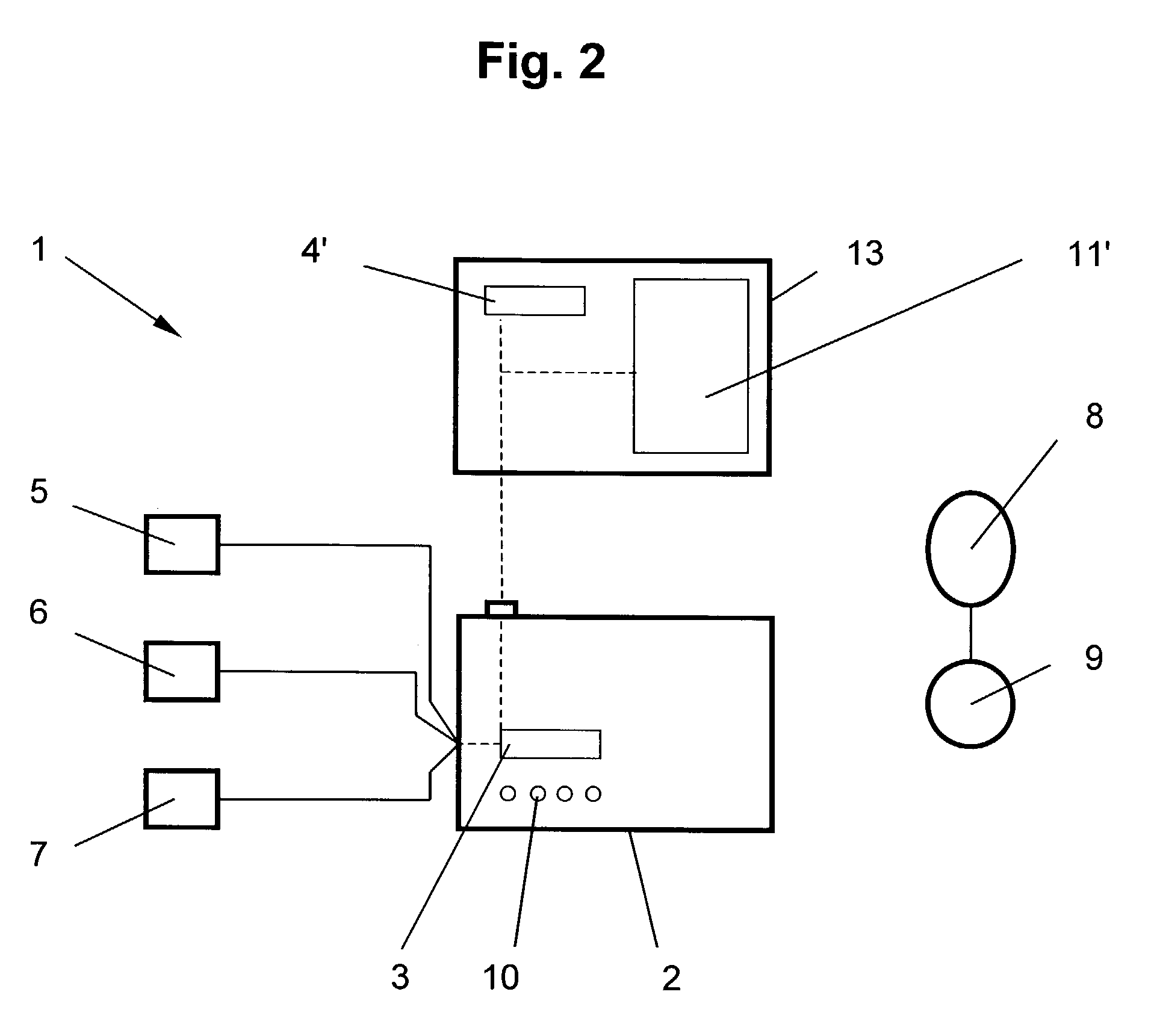
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
103 results about "Diastolic function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
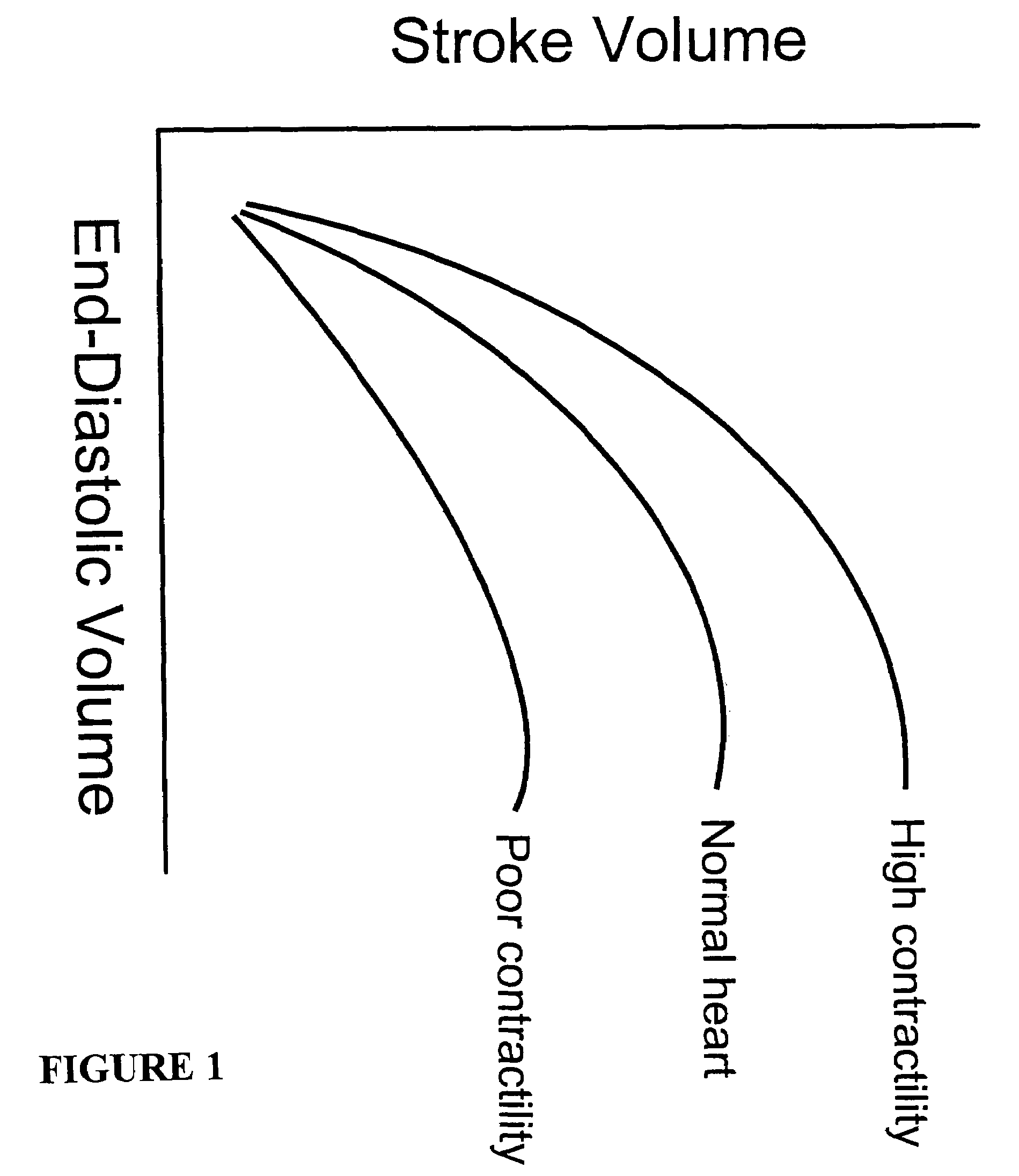
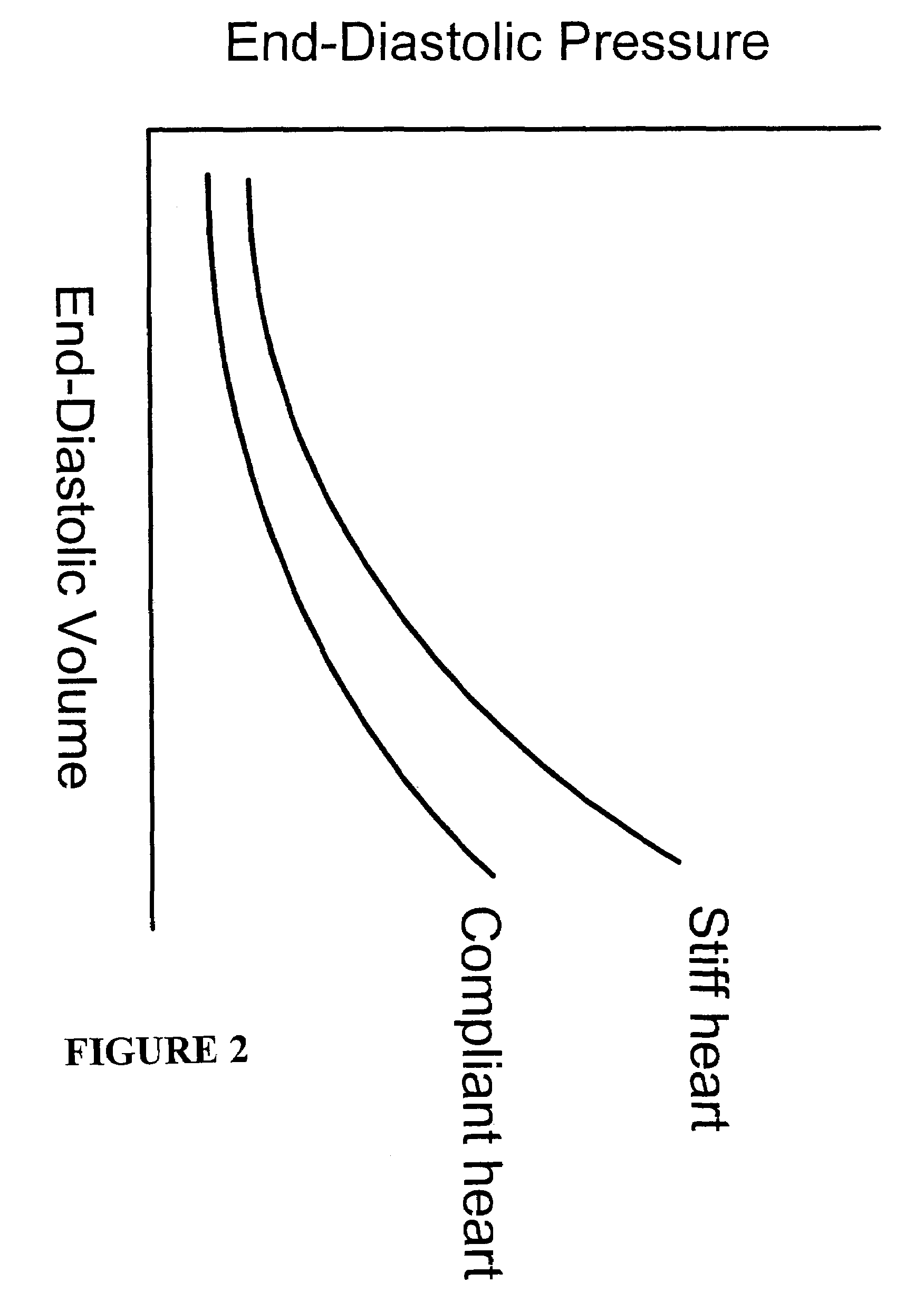
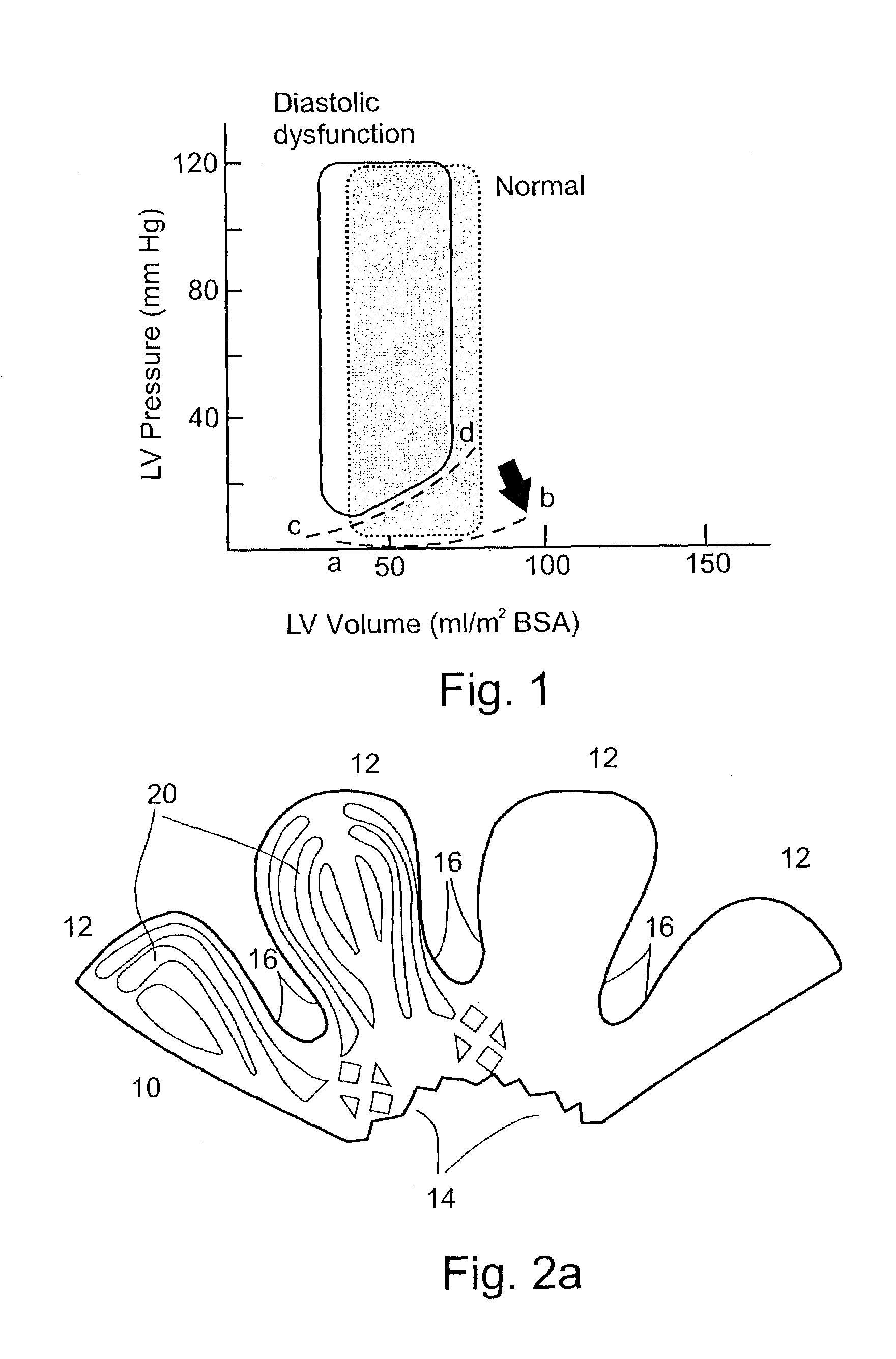
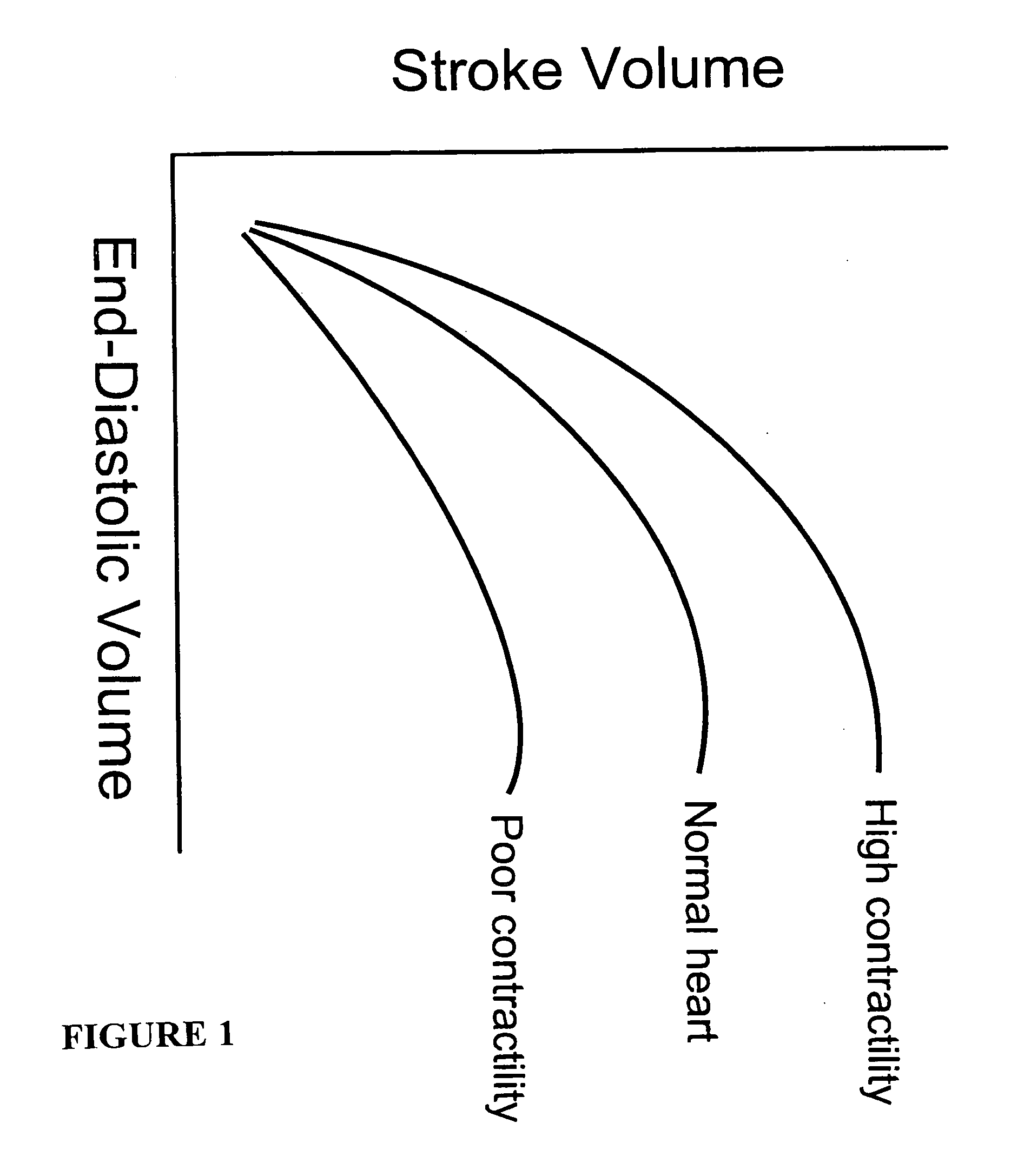
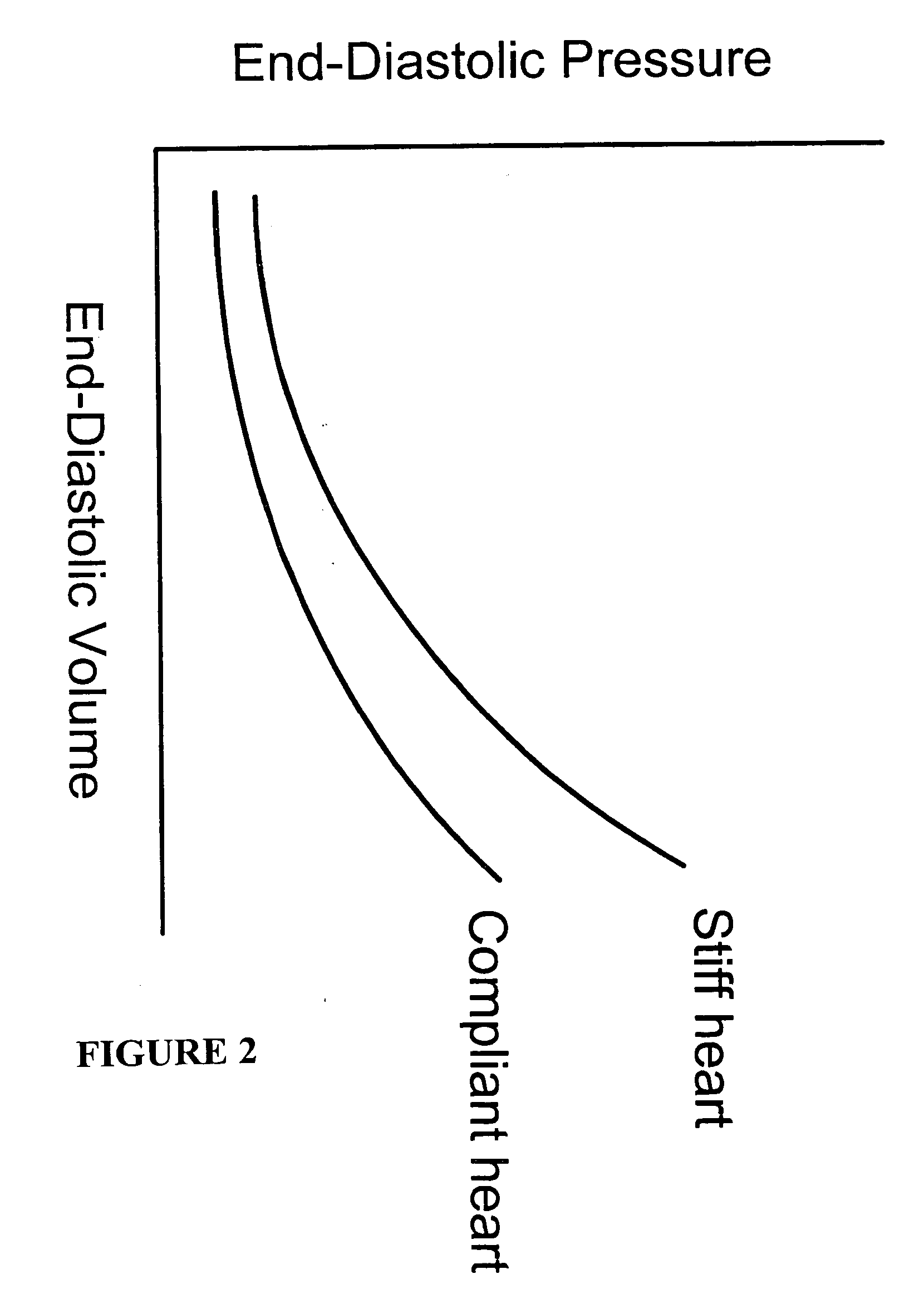
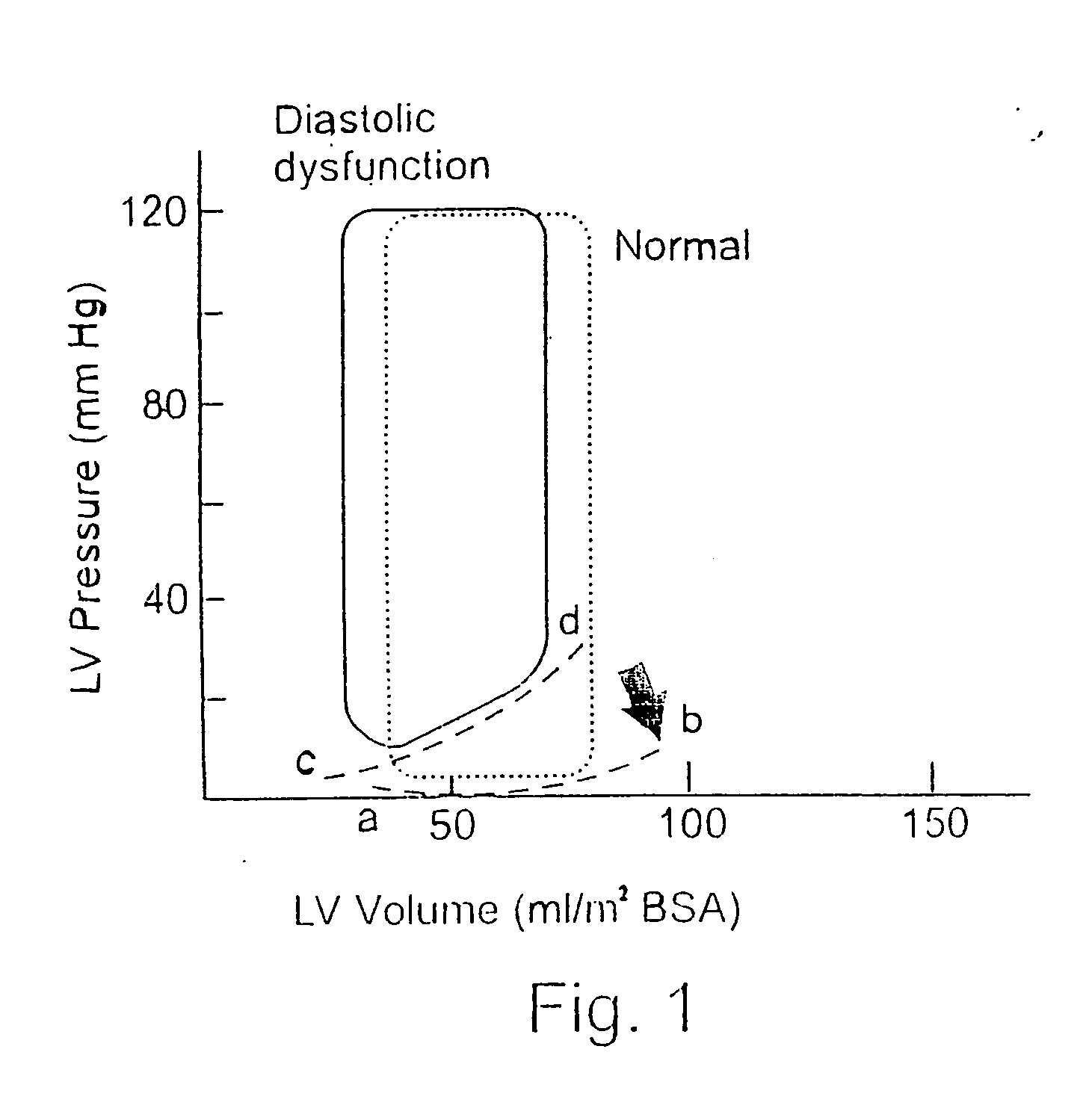
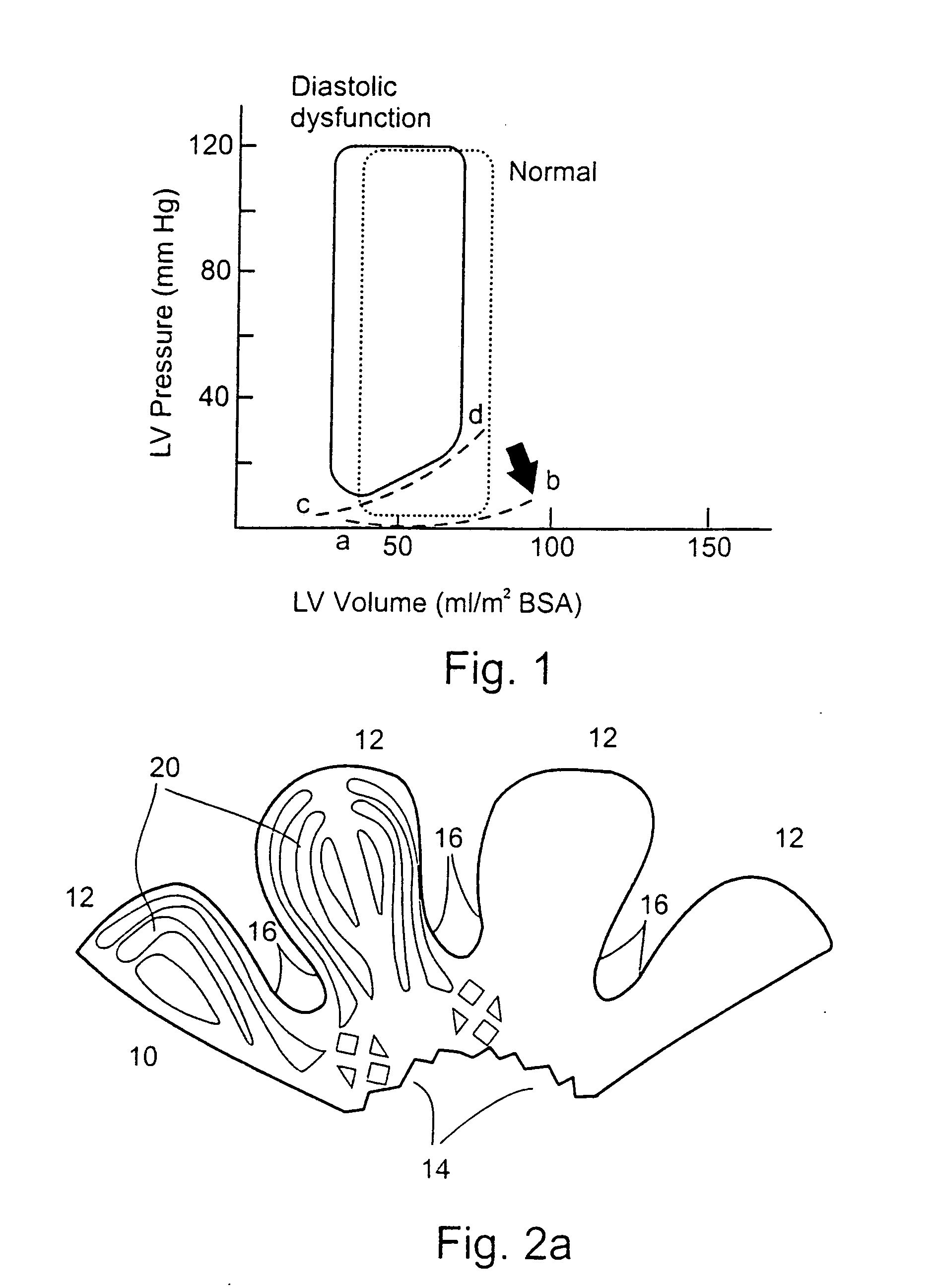
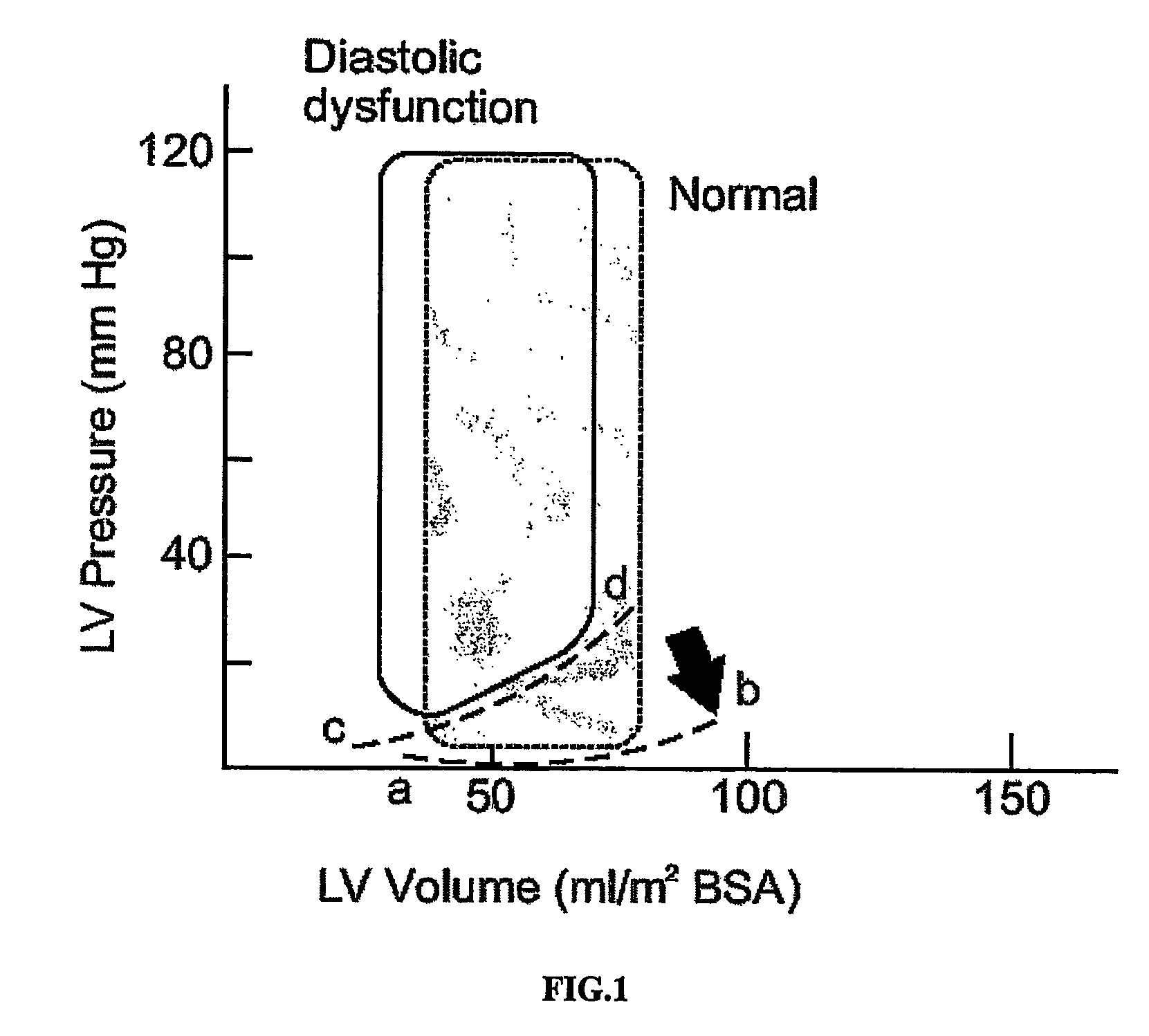
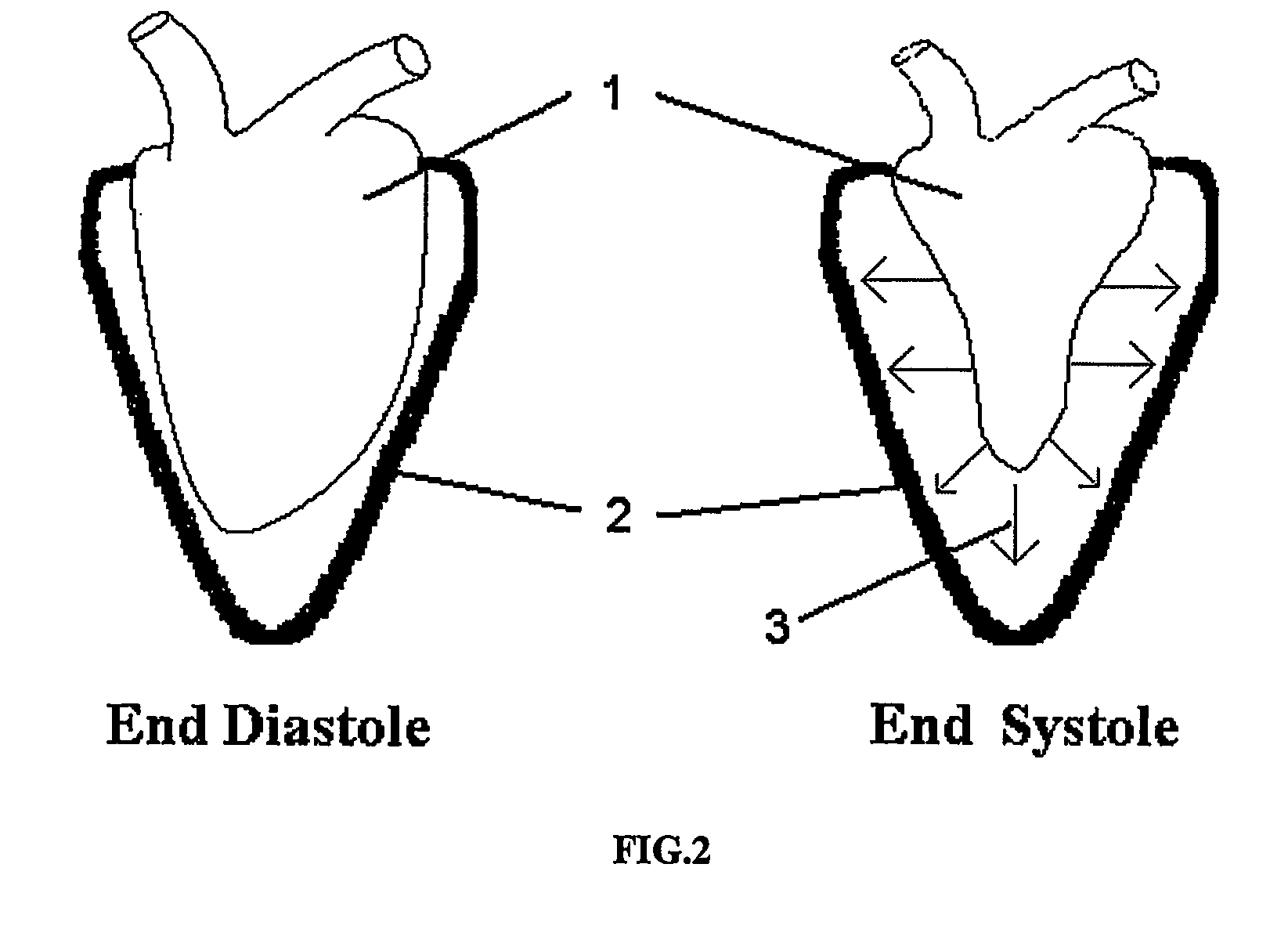
In clinical cardiology the term "diastolic function" is most commonly referred as how the heart fills. Parallel to "diastolic function", the term "systolic function" is usually referenced in terms of the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), which is the ratio of stroke volume and end-diastolic volume. Due to the epidemic of heart failure, particularly the cases determined as diastolic heart failure, it is increasingly urgent and crucial to understand the meaning of “diastolic function”. Unlike "systolic function" which can be simply evaluated by LVEF, there are no established dimensionless parameter for "diastolic function" assessment. Hence to further study "diastolic function" the complicated and speculative physiology must be taken into consideration.
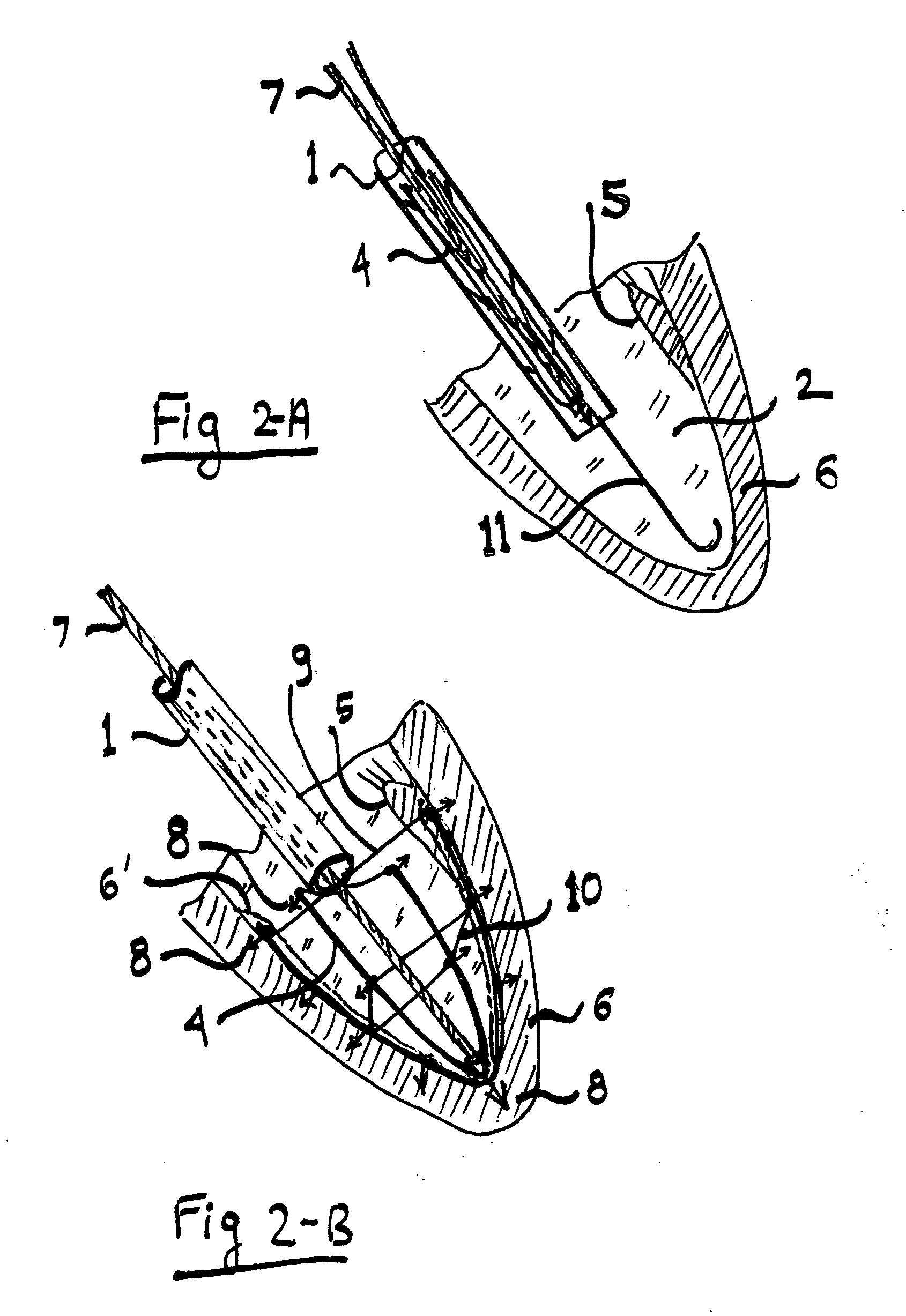
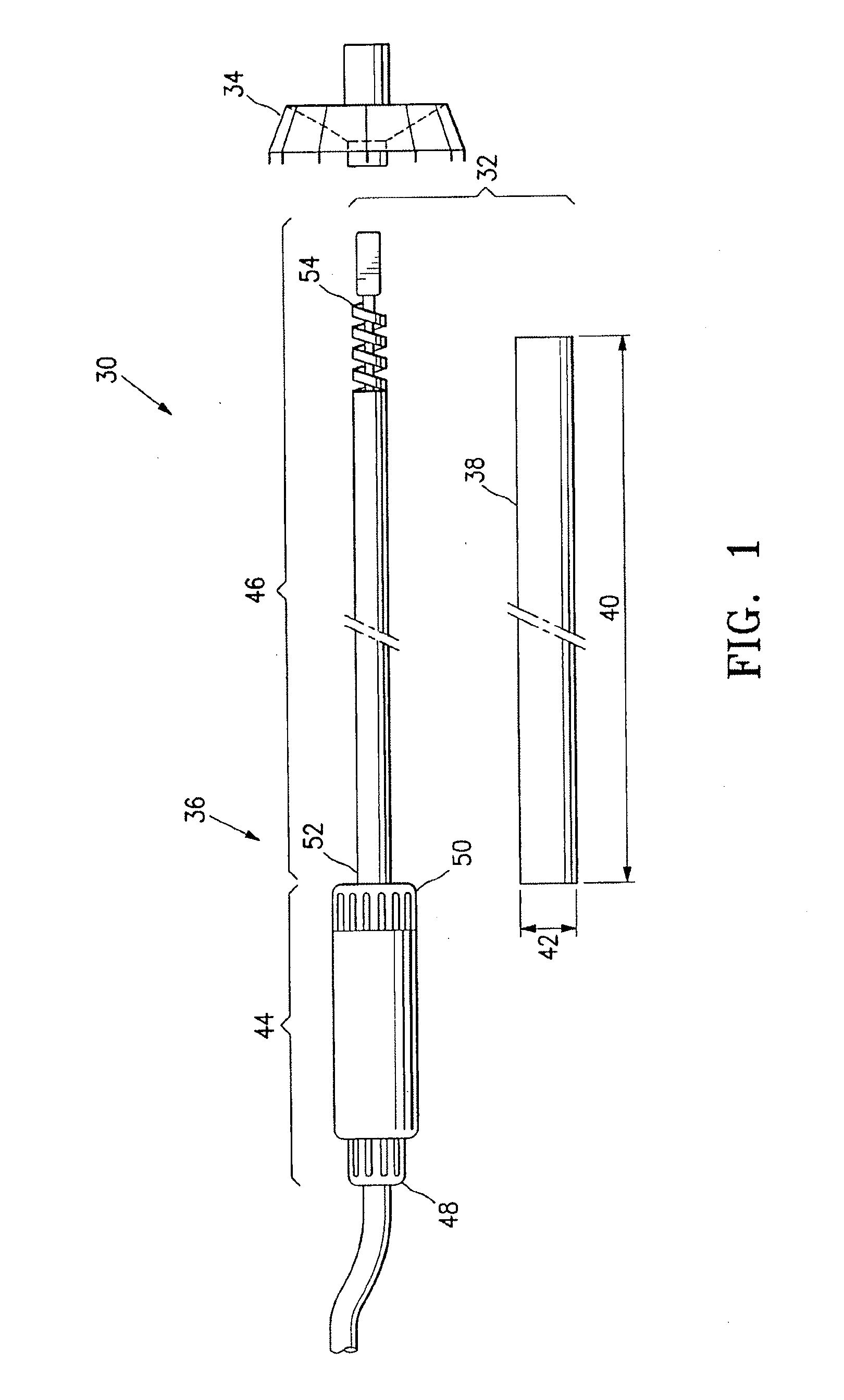
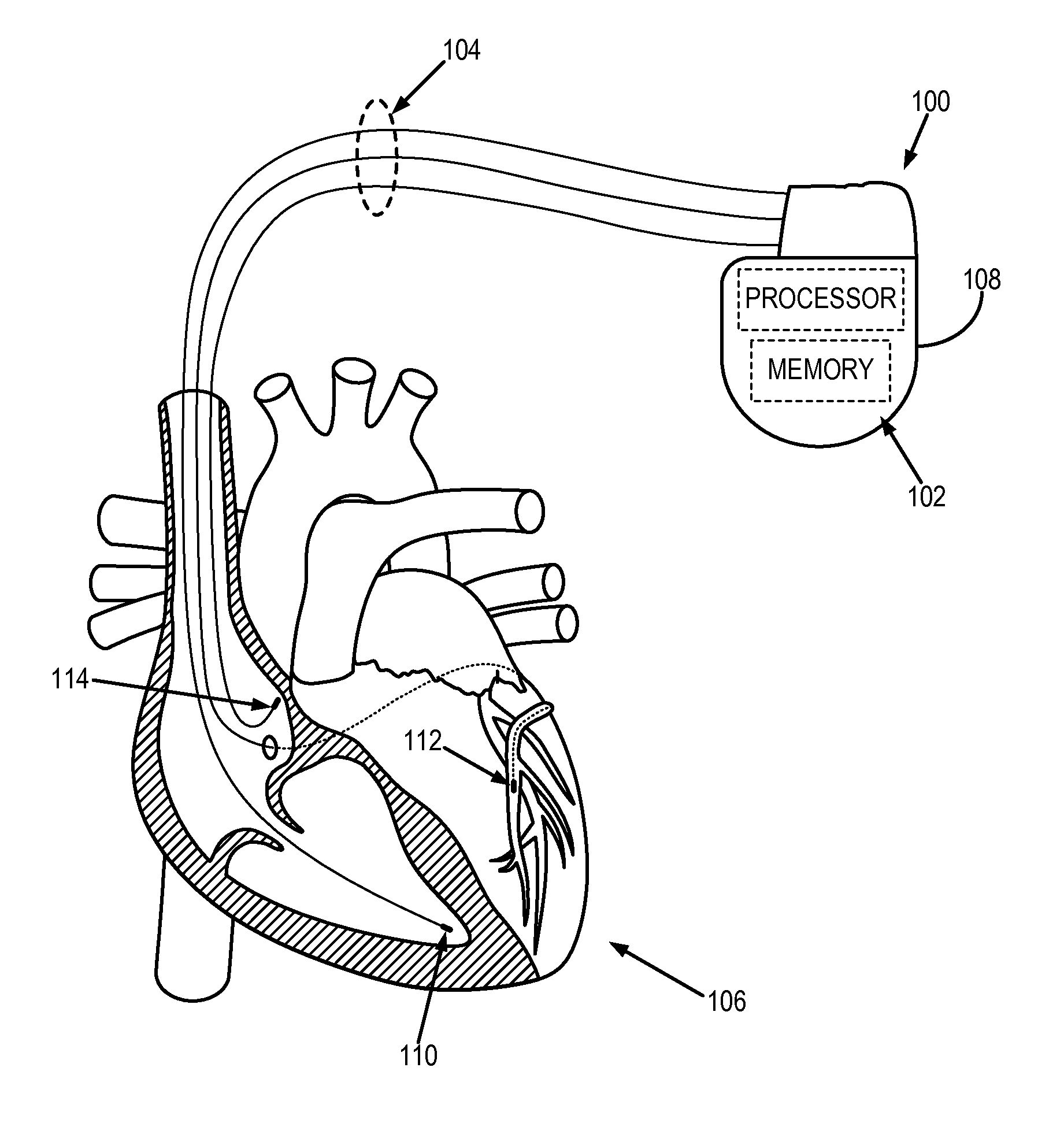
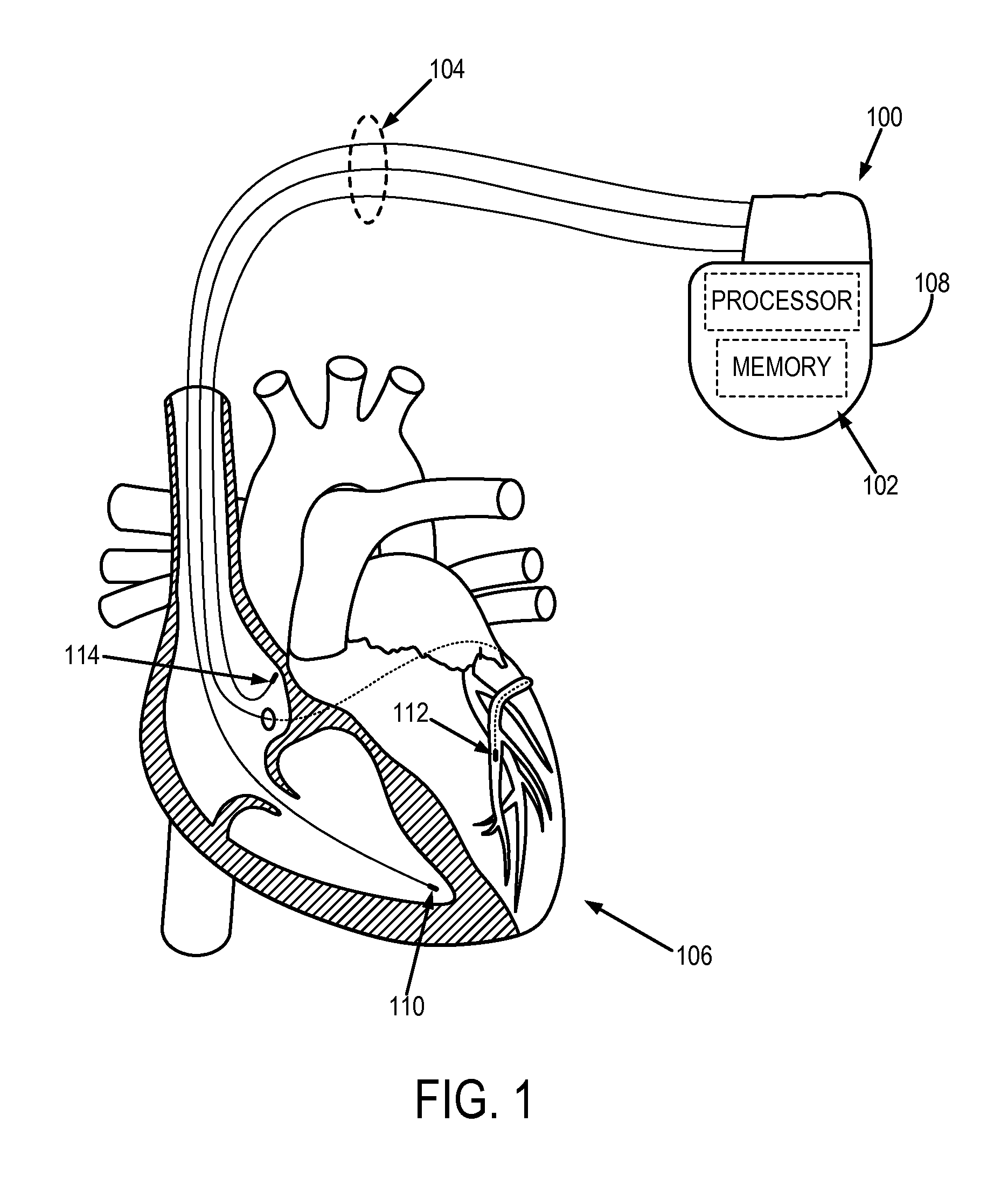
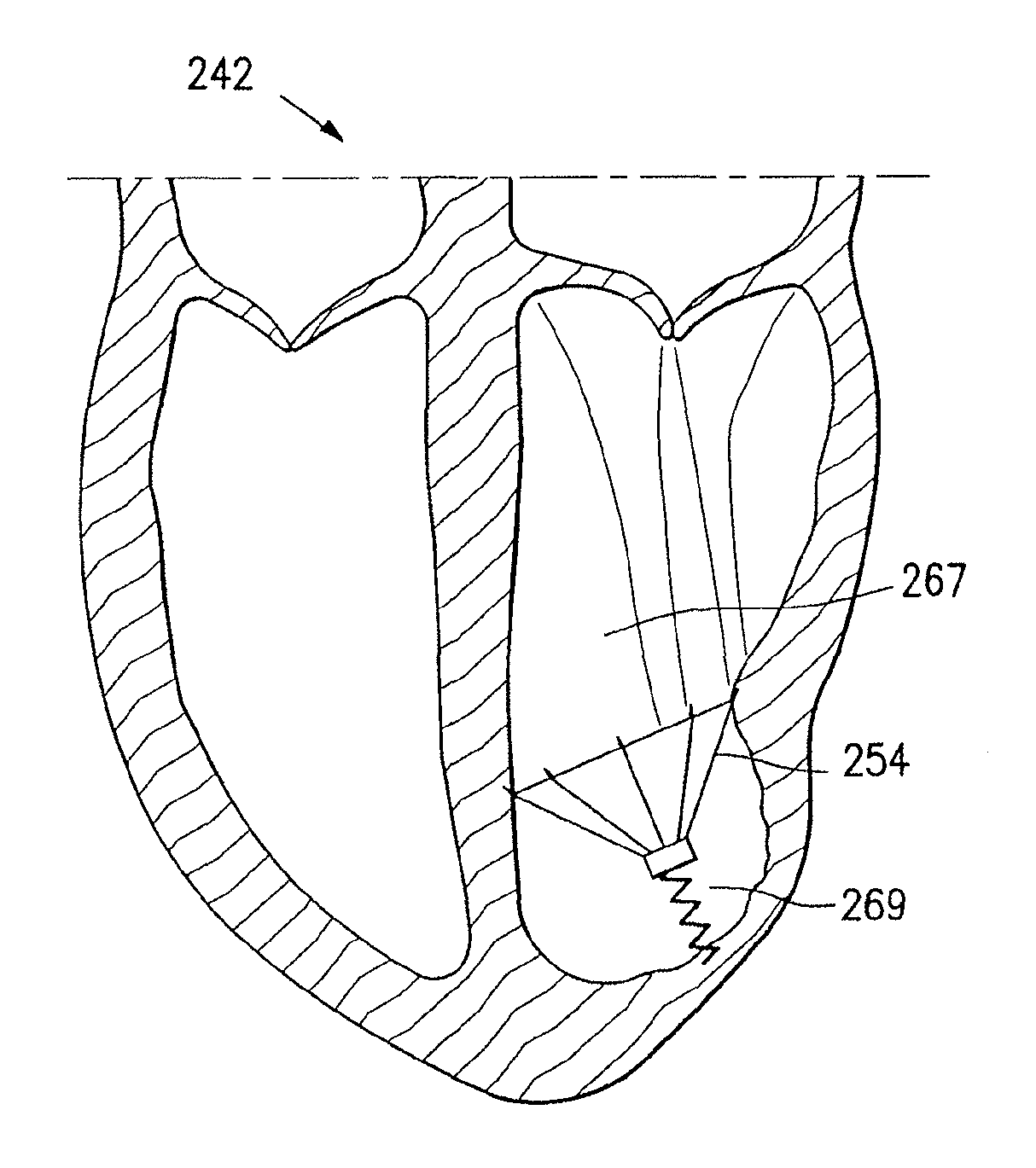
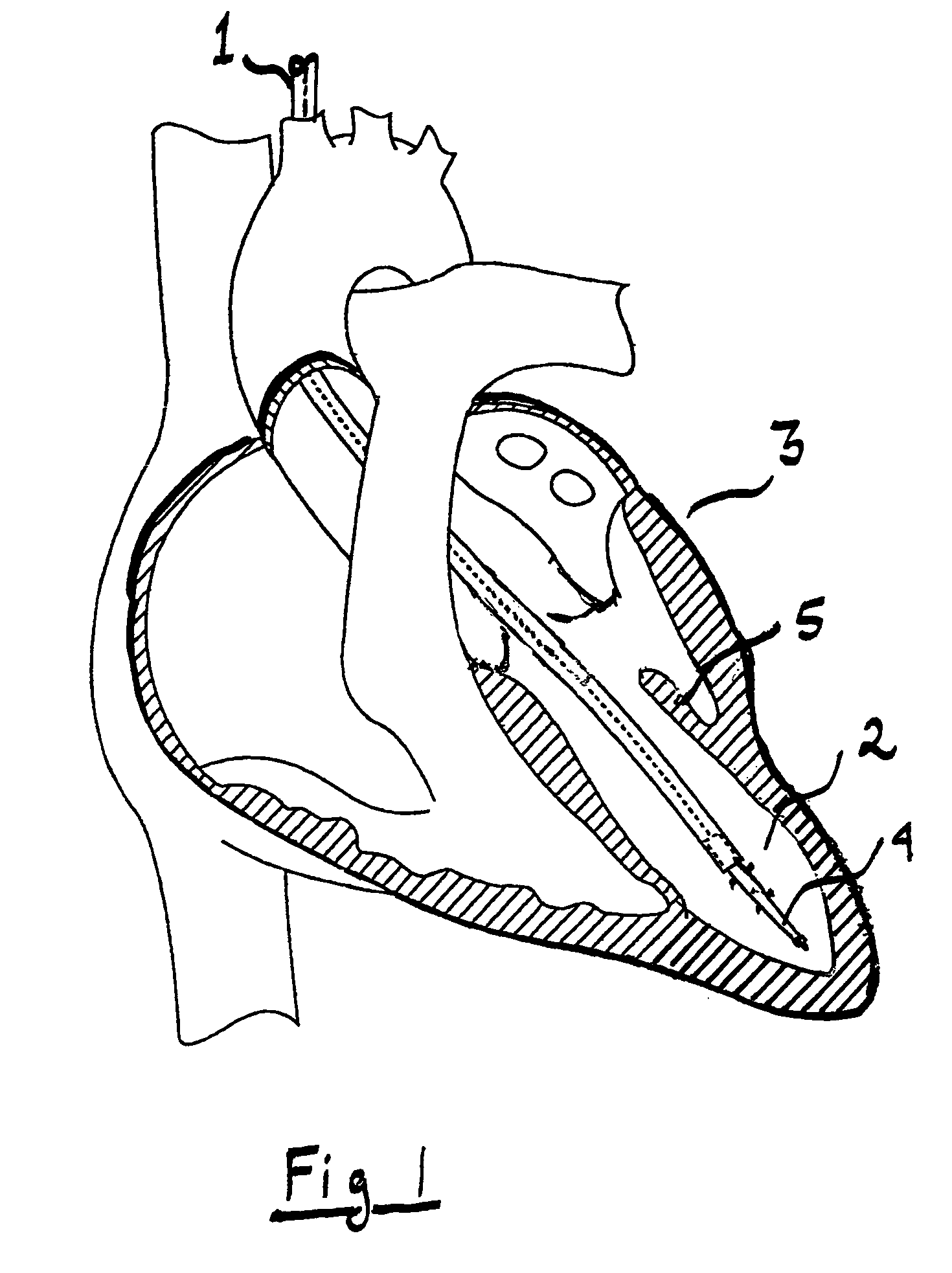
Cardiac device and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070161846A1Reduced elastic recoilShorten speedHeart valvesInternal electrodesCardiac deviceDiastolic function
Devices and methods are described herein which are directed to the treatment of a patient's heart having, or one which is susceptible to heart failure, to improve diastolic function.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
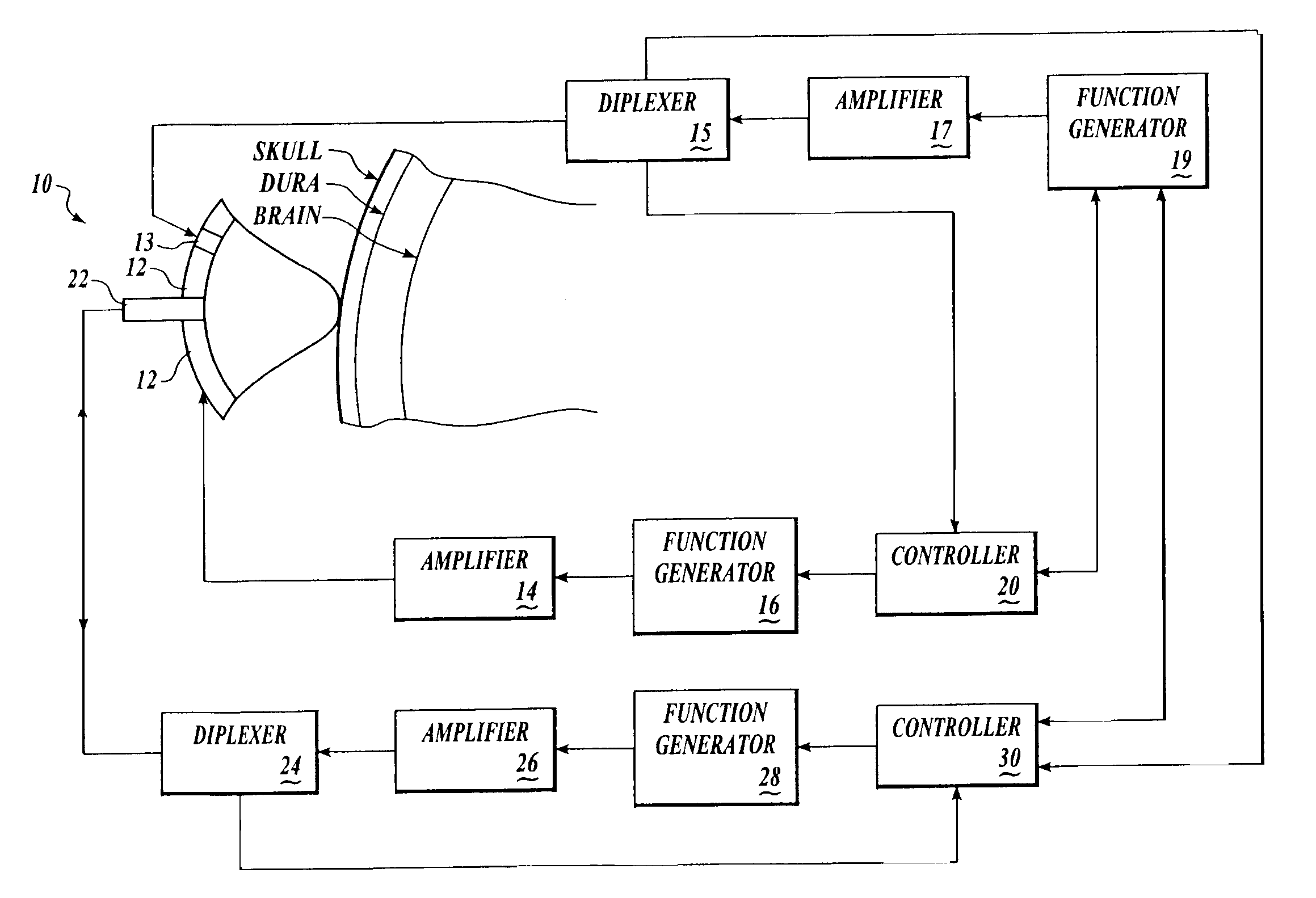
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS7022077B2Maximize tissue displacementEasy diagnosisBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound techniques
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
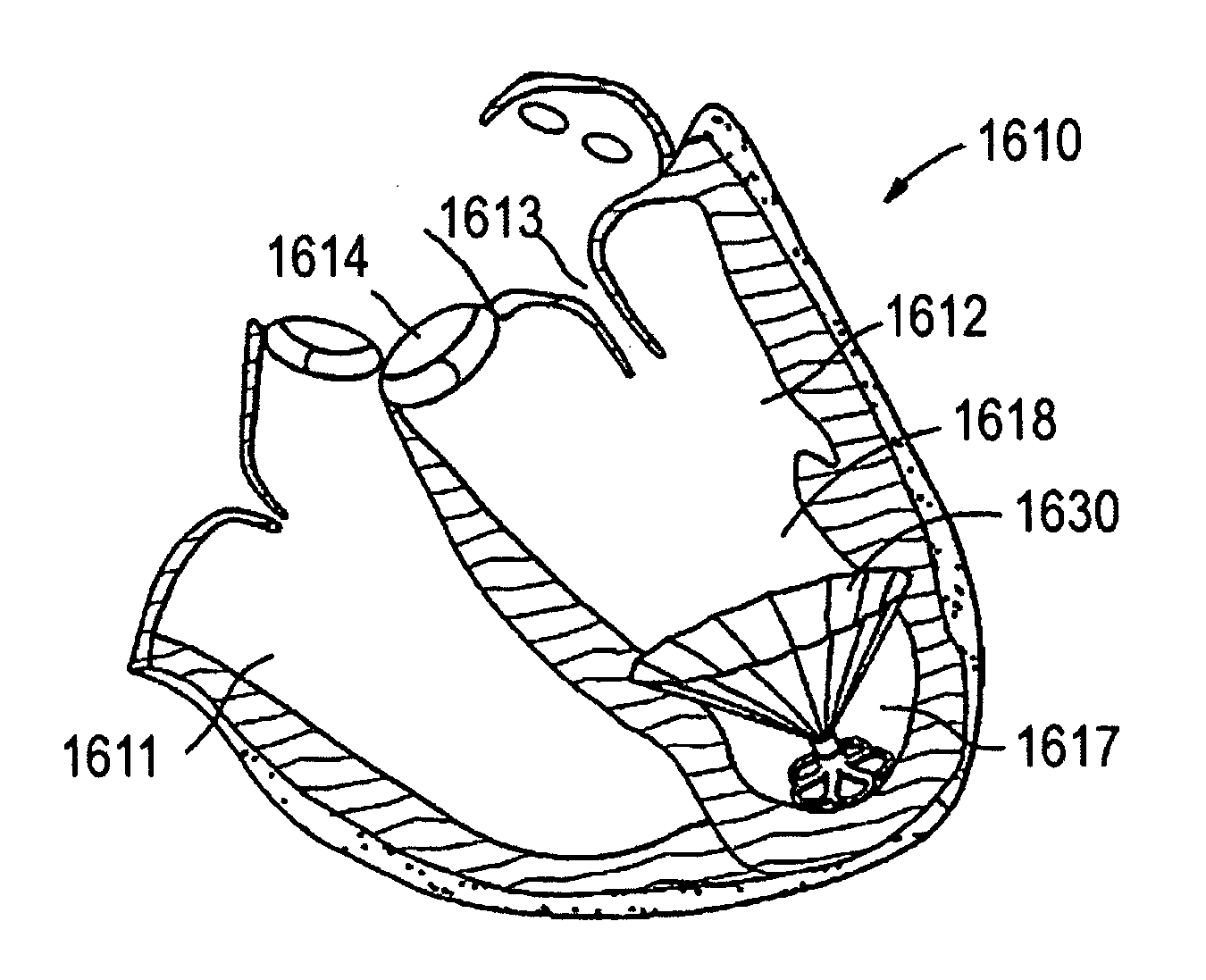
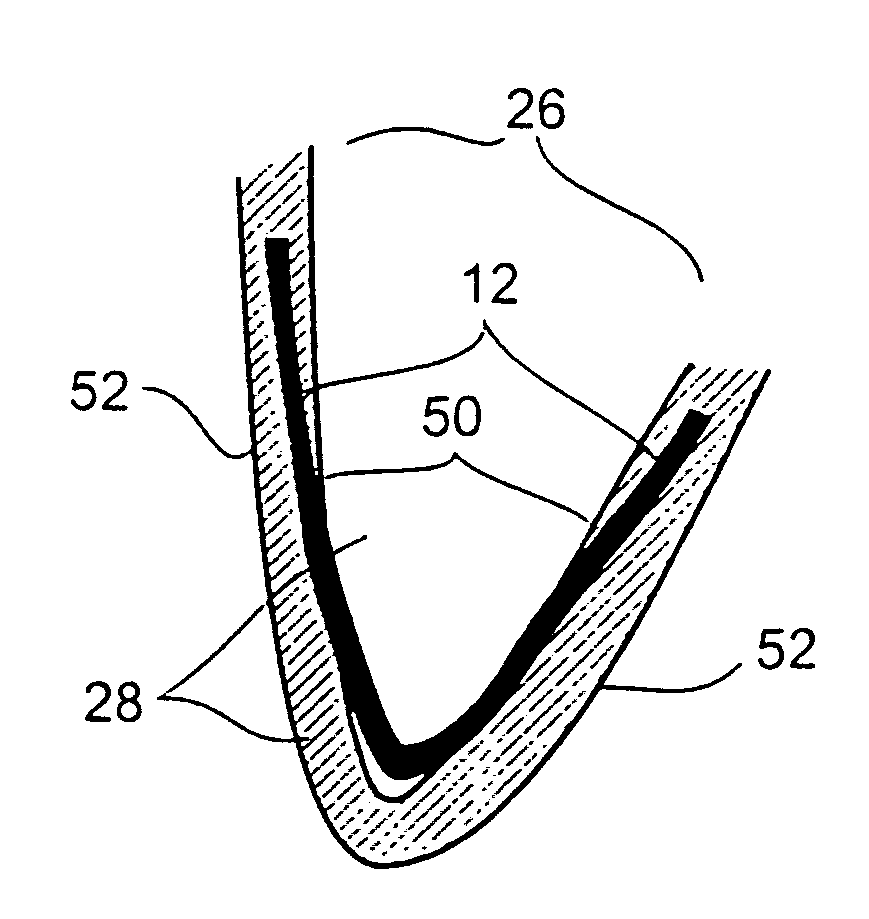
System for improving diastolic dysfunction
ActiveUS20080045778A1Affect performanceLimited effectHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsCongestive heart failure chfScar tissue
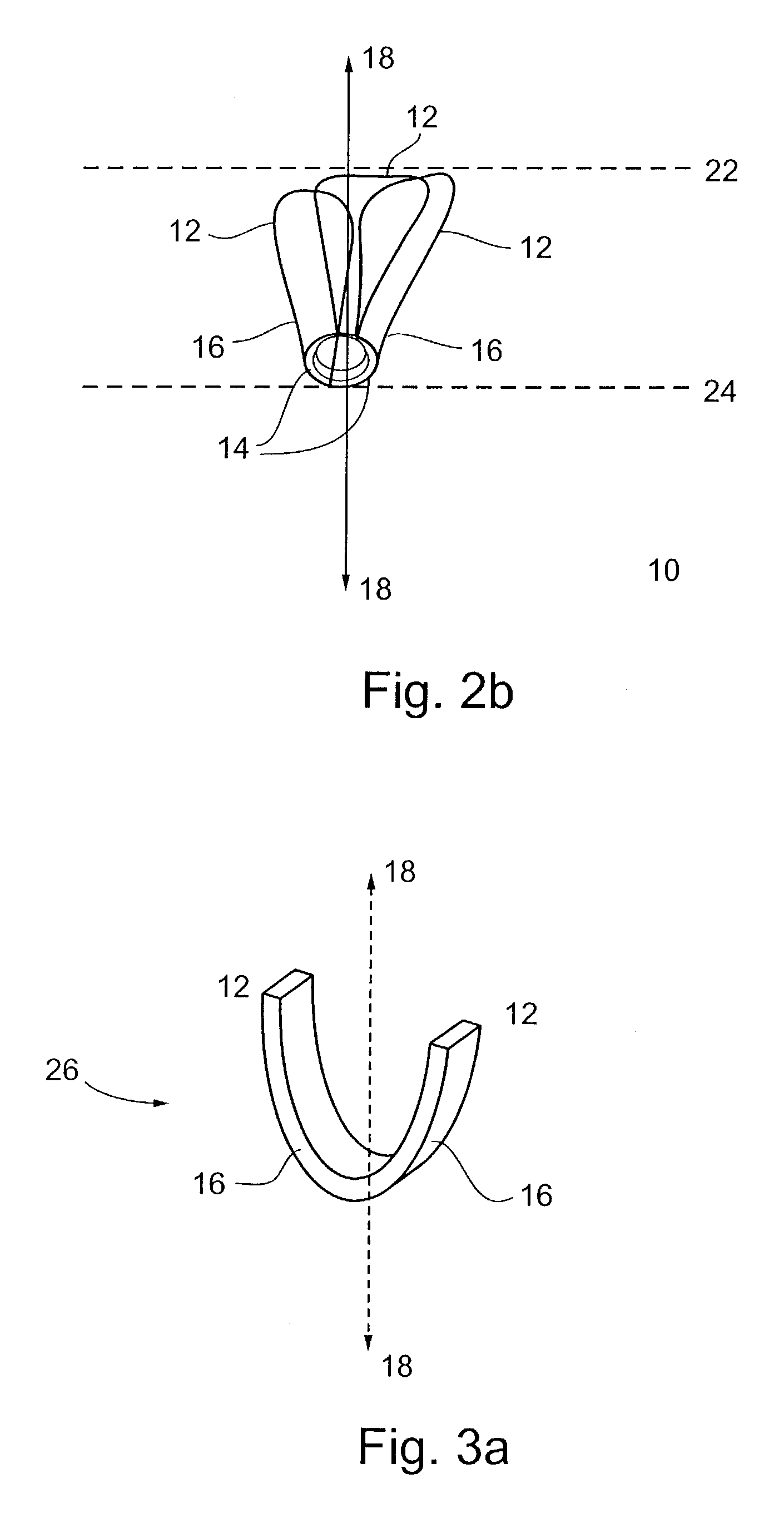
An elastic structure is introduced percutaneously into the left ventricle and attached to the walls of the ventricle. Over time the structure bonds firmly to the walls via scar tissue formation. The structure helps the ventricle expand and fill with blood during the diastolic period while having little affect on systolic performance. The structure also strengthens the ventricular walls and limits the effects of congestive heart failure, as the maximum expansion of the support structure is limited by flexible or elastic members.
Owner:KARDIUM
Cardiac device and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7674222B2Lower the volumeImprove pressure-volume relationshipHeart valvesInternal electrodesCardiac deviceHeart disease
Devices and methods are described herein which are directed to the treatment of a patient's heart having, or one which is susceptible to heart failure, to improve diastolic function.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
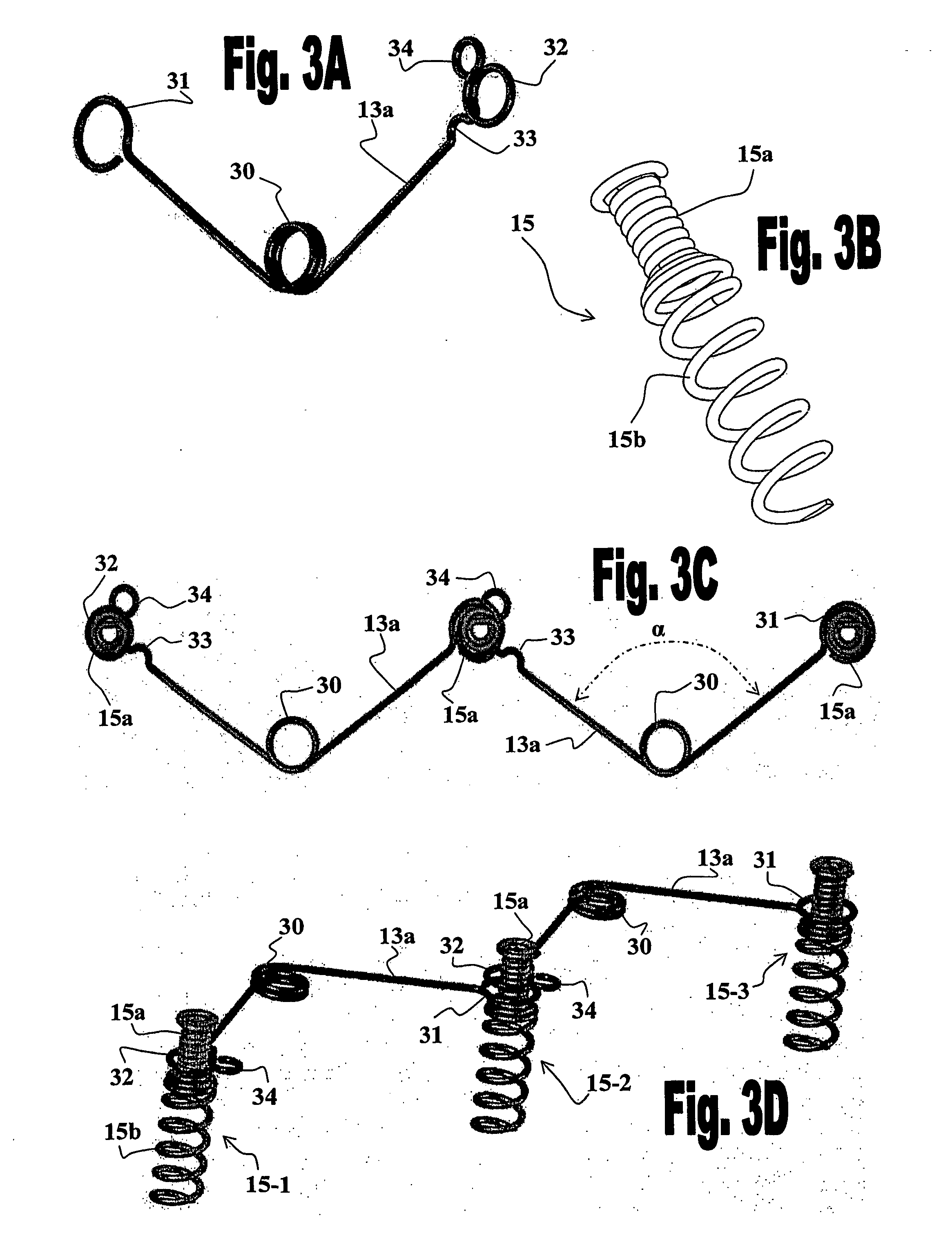
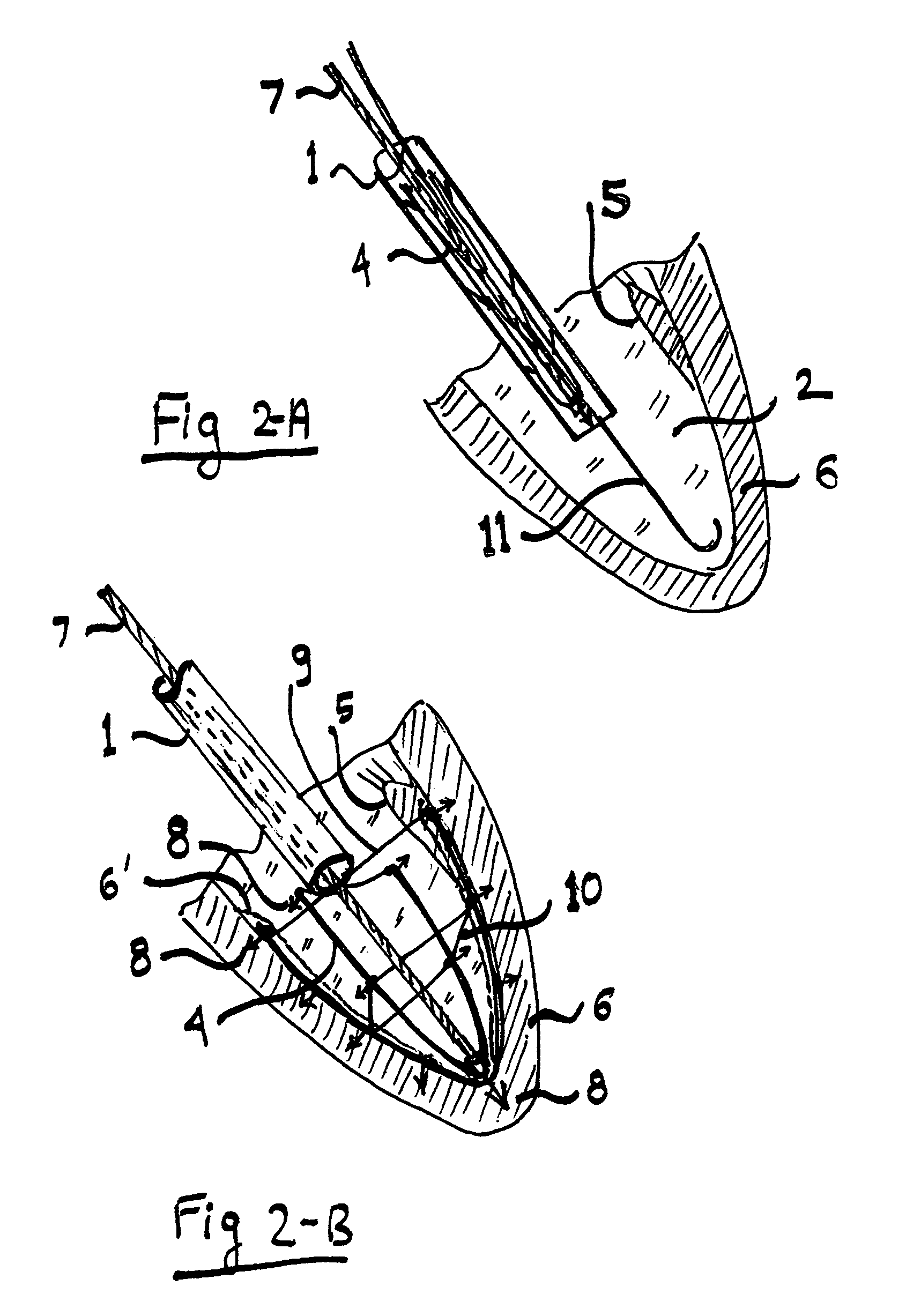
In-vivo method and device for improving diastolic function of the left ventricle
InactiveUS7186210B2Function increaseReduce hydrostatic pressureSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLeft ventricular sizeCardiac cycle
A method and device featuring at least one component providing a potential to kinetic converted elastic, magnetic repulsion, or, an elastic and magnetic repulsion, pushing, pulling, or, pulling and pushing, type of radially outward expansive force or pressure to an inner, outer, intermediate, and, combination thereof, wall region of the left ventricle, for reducing intraluminal hydrostatic pressure of the left ventricle (LV filling pressure) during the ventricular diastolic stage of the cardiac cycle, thereby, improving diastolic function of the left ventricle of the heart in subjects having a condition of diastolic heart failure (DHF), while minimally disturbing systolic function of the heart. The expansive force or pressure is in a range of about 5–40 mm Hg, whereby, left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP) is reduced down to the normal range of about 6–12 mm Hg, during ventricular diastole of the heart.
Owner:RELAXIS
Method and system for improving diastolic function of the heart
ActiveUS20100022821A1Avoid restrictionsEnabling modularitySuture equipmentsHeart valvesVentricular FunctionsDiastolic function
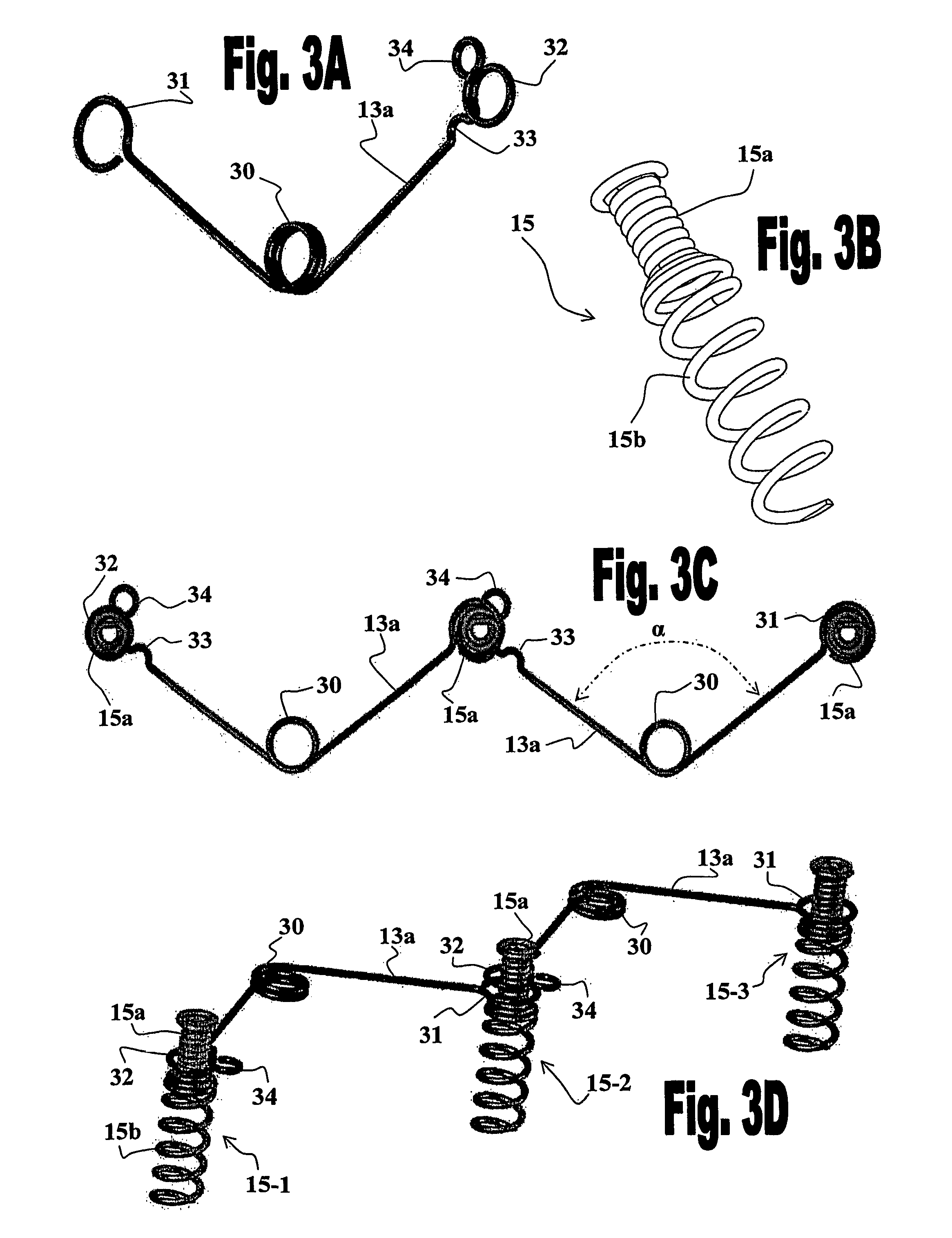
The present invention provides a system for improving diastolic function of the heart comprising elastic elements and attachment elements, wherein said elastic elements and said attachment elements are configured such that they are capable of being interconnected to form a chain formed of an alternating series of said elastic elements and said attachment elements, and wherein said attachment elements are adapted to be anchored in the wall of the heart and with option for drug delivery to the wall of the heart. The invention further provides devices, methods and kits, for mounting the ventricular function assisting device of the invention.
Owner:CORASSIST CARDIOVASCULAR LTD
Systems and methods for making noninvasive assessments of cardiac tissue and parameters
InactiveUS20070016031A1Easy diagnosisLimited successBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationVentricular filling
Systems and methods for noninvasive assessment of cardiac tissue properties and cardiac parameters using ultrasound techniques are disclosed. Determinations of myocardial tissue stiffness, tension, strain, strain rate, and the like, may be used to assess myocardial contractility, myocardial ischemia and infarction, ventricular filling and atrial pressures, and diastolic functions. Non-invasive systems in which acoustic techniques, such as ultrasound, are employed to acquire data relating to intrinsic tissue displacements are disclosed. Non-invasive systems in which ultrasound techniques are used to acoustically stimulate or palpate target cardiac tissue, or induce a response at a cardiac tissue site that relates to cardiac tissue properties and / or cardiac parameters are also disclosed.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS +1
Soluble guanylate cyclase activators
A compound having the structureuseful for treatment or prevention of cardiovascular diseases, endothelial dysfunction, diastolic dysfunction, atherosclerosis, hypertension, angina pectoris, thromboses, restenoses, myocardial infarction, strokes, cardiac insufficiency, pulmonary hypertonia, erectile dysfunction, asthma bronchiale, chronic kidney insufficiency, diabetes, or cirrhosis of the liver in a human or animal patient.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Systems and methods for improving cardiac function
InactiveUS20140179993A1Improve heart functionImprove complianceHeart valvesMedical devicesCardiac muscleHeart disease
A system for improving cardiac function is provided. A foldable and expandable frame having at least one anchoring formation is attached to an elongate manipulator and placed in a catheter tube while folded. The tube is inserted into a left ventricle of a heart where the frame is ejected from the tube and expands in the left ventricle. Movements of the elongate manipulator cause the anchor to penetrate the heart muscle and the elongate manipulator to release the frame. The installed frame minimizes the effects of an akinetic portion of the heart forming an aneurysmic bulge. Devices and methods are described herein which are directed to the treatment of a patient's heart having, or one which is susceptible to heart failure, to improve diastolic function.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
System and method for automated adjustment of cardiac resynchronization therapy control parameters
ActiveUS20120310297A1Accurate representationEasy to adjustElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsCvd riskControl parameters
A system and method for cardiac resynchronization therapy in which pacing control parameters are automatically adjusted by comparison of local electrograms acquired by a cardiac implantable electrical device with a model of cardiac electrical activity derived from surface-lead electrocardiograph measurements under baseline and paced conditions is provided. The adjusted pacing control parameters guarantee substantially maximum evidence of ventricular activation wavefront fusion while reducing the risk of compromising diastolic function. Atrioventricular intervals (AVIs] are measured and utilized to constrain the adjustment of pacing control parameters such that diastolic dysfunctions are not induced in the patient's heart.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
In vivo device for improving diastolic ventricular function
InactiveUS20060241334A1Easy to adaptReduce construction costsSuture equipmentsHeart valvesElastic componentVentricular Functions
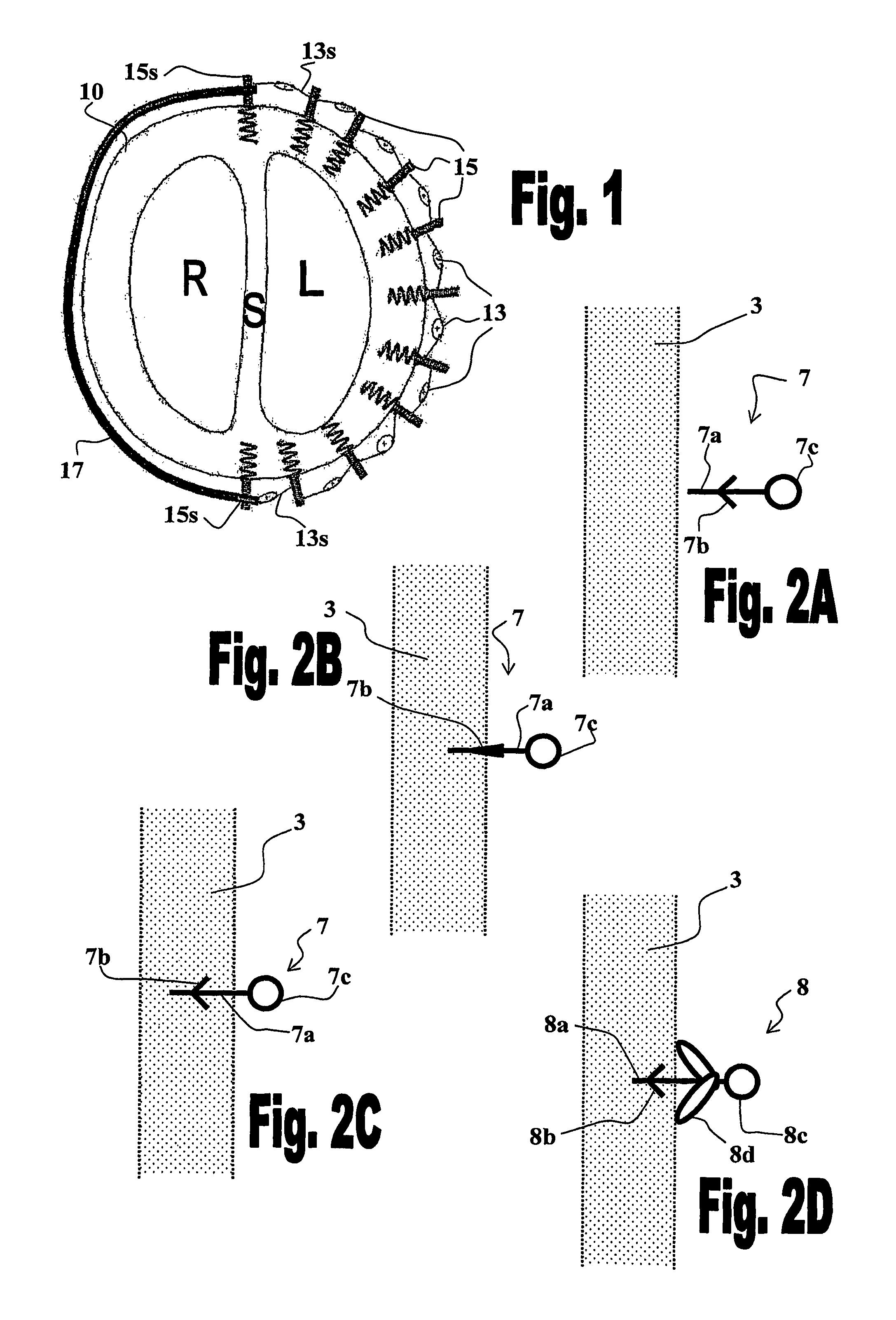
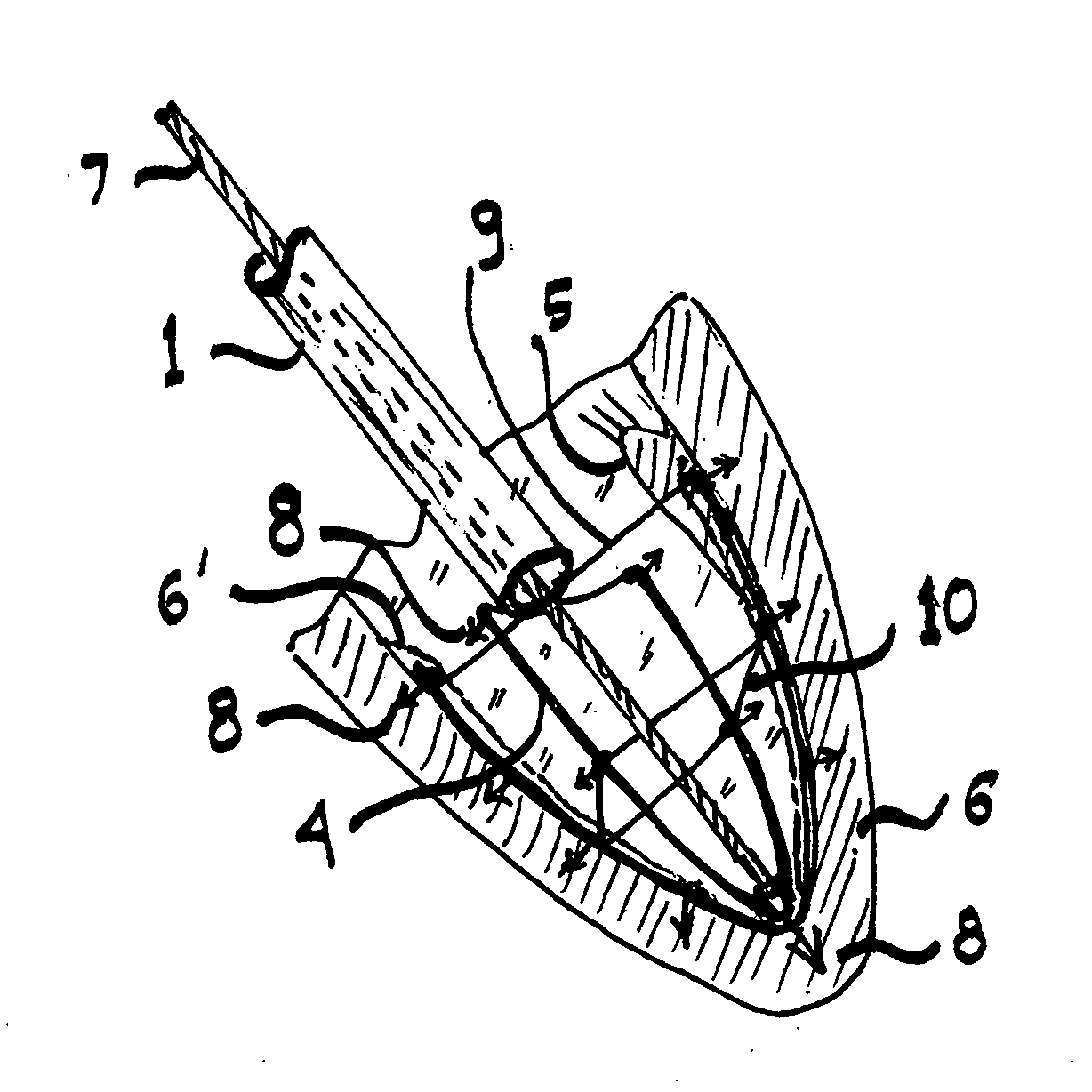
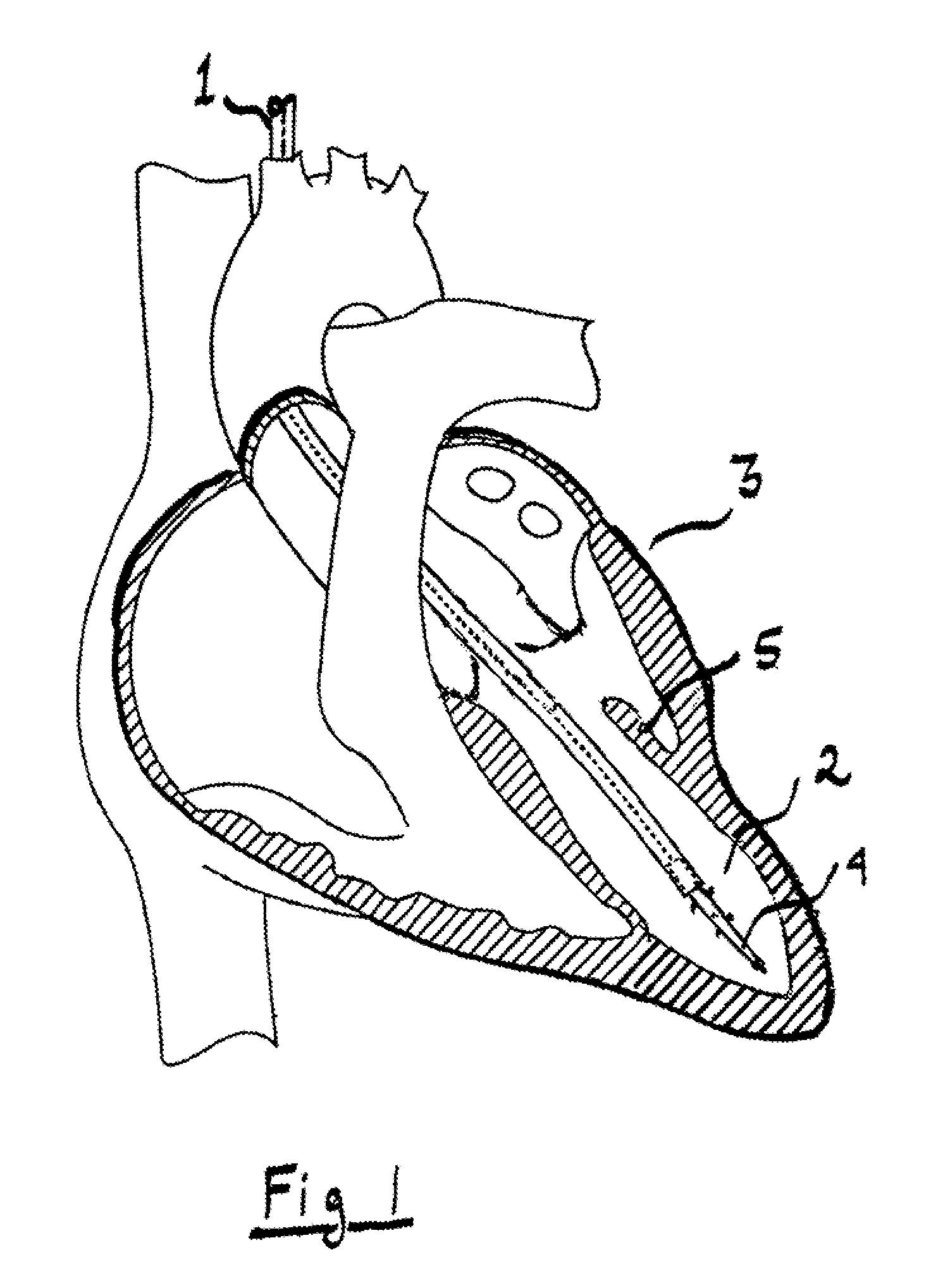
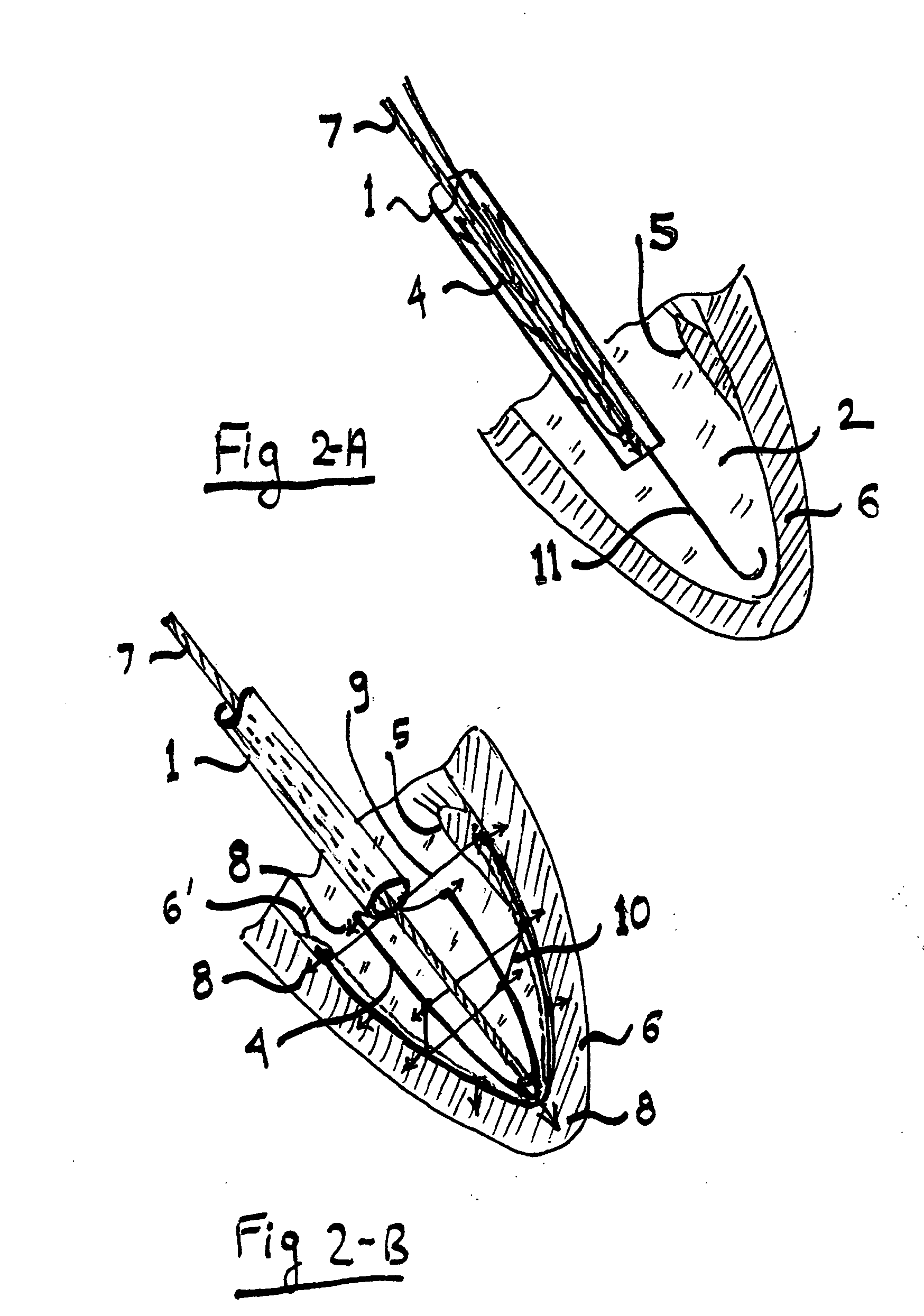
The present invention provides an in vivo device for improving diastolic function of the heart, comprising: at least one elastic component that may be operatively connected to the external surface of the left or right ventricle of the heart by means of connecting elements, wherein said elastic component comprises essentially longitudinal members arranged such that the lateral separation therebetween may be increased or decreased in response to elastic deformation of said elastic component, and wherein said essentially longitudinal members are arranged such that said elastic component is curved in both the vertical and horizontal planes, such that its inner surface may be adapted to the curvature of the external ventricular surface of the heart, such that said elastic component is capable of exerting both radially outward expansive and tangentially-directed forces on the external surface of the cardiac ventricle.
Owner:CORASSIST CARDIOVASCULAR LTD
In-vivo method and device for improving diastolic function of the left ventricle
InactiveUS20060276683A1Function increaseReduce hydrostatic pressureSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac cycleLeft ventricular size
A method and device featuring at least one component providing a potential to kinetic converted elastic, magnetic repulsion, or, an elastic and magnetic repulsion, pushing, pulling, or, pulling and pushing, type of radially outward expansive force or pressure to an inner, outer, intermediate, and, combination thereof, wall region of the left ventricle, for reducing intraluminal hydrostatic pressure of the left ventricle (LV filling pressure) during the ventricular diastolic stage of the cardiac cycle, thereby, improving diastolic function of the left ventricle of the heart in subjects having a condition of diastolic heart failure (DHF), while minimally disturbing systolic function of the heart. The expansive force or pressure is in a range of about 5-40 mm Hg, whereby, left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP) is reduced down to the normal range of about 6-12 mm Hg, during ventricular diastole of the heart.
Owner:CORASSIST CARDIOVASCULAR LTD
Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activators
A compound having the structureuseful for treatment or prevention of cardiovascular diseases, endothelial dysfunction, diastolic dysfunction, atherosclerosis, hypertension, angina pectoris, thromboses, restenoses, myocardial infarction, strokes, cardiac insufficiency, pulmonary hypertonia, erectile dysfunction, asthma bronchiale, chronic kidney insufficiency, diabetes, or cirrhosis of the liver in a human or animal patient.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
System and method for automated adjustment of cardiac resynchronization therapy control parameters
ActiveUS9265951B2Accurate representationEasy to adjustElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsControl parametersVentricular activation
A system and method for cardiac resynchronization therapy in which pacing control parameters are automatically adjusted by comparison of local electrograms acquired by a cardiac implantable electrical device with a model of cardiac electrical activity derived from surface-lead electrocardiograph measurements under baseline and paced conditions is provided. The adjusted pacing control parameters guarantee substantially maximum evidence of ventricular activation wavefront fusion while reducing the risk of compromising diastolic function. Atrioventricular intervals (AVIs] are measured and utilized to constrain the adjustment of pacing control parameters such that diastolic dysfunctions are not induced in the patient's heart.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
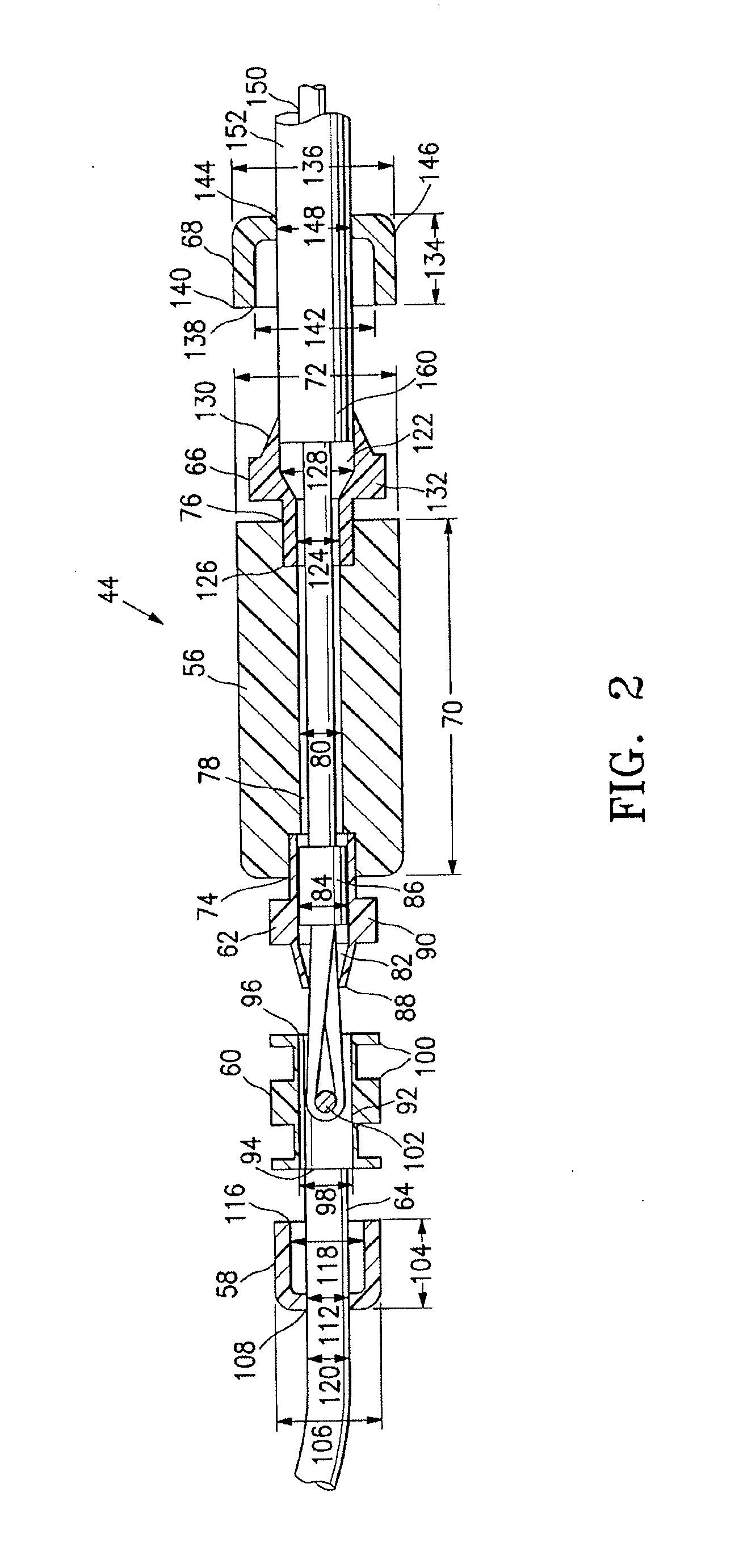
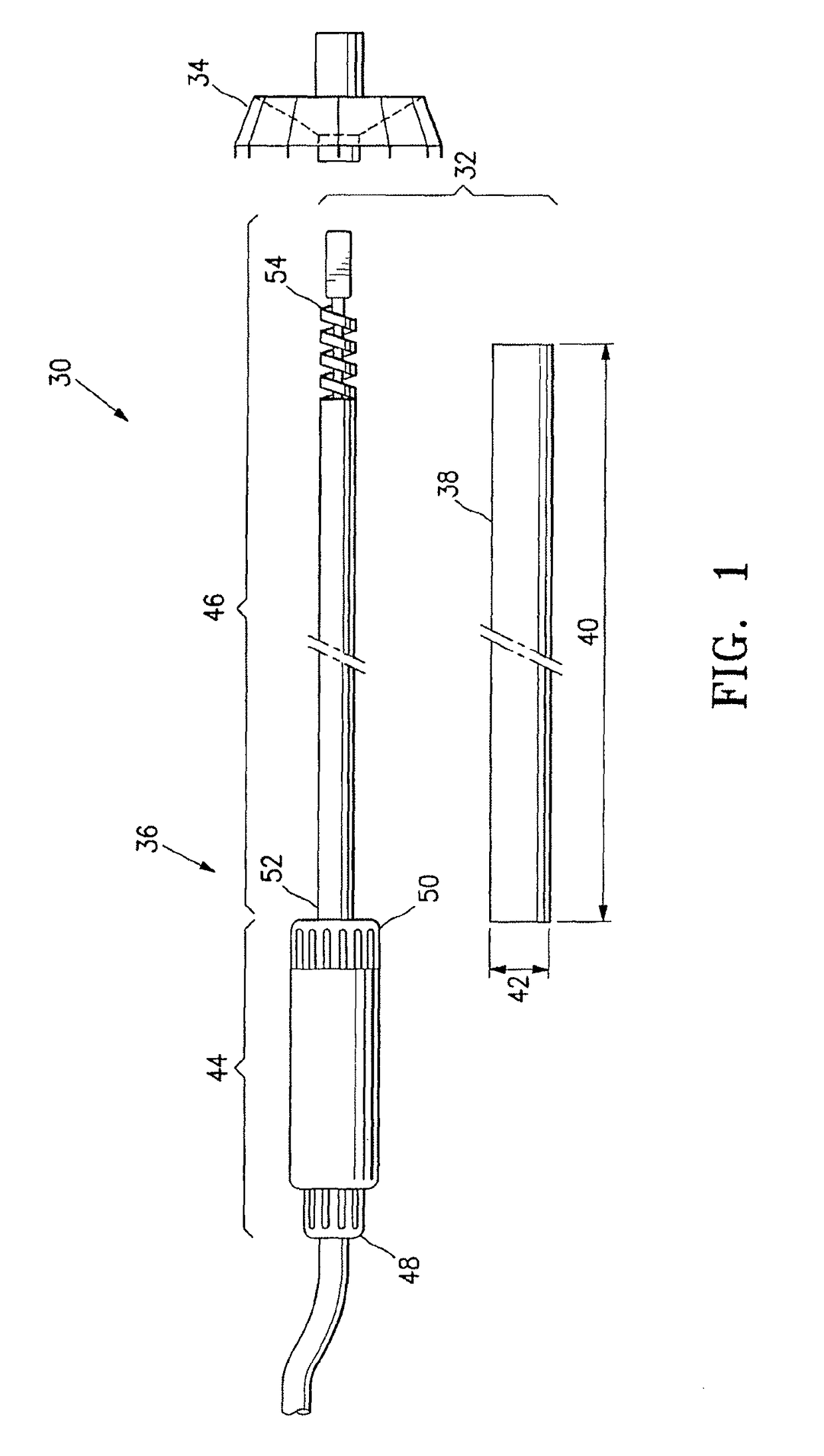
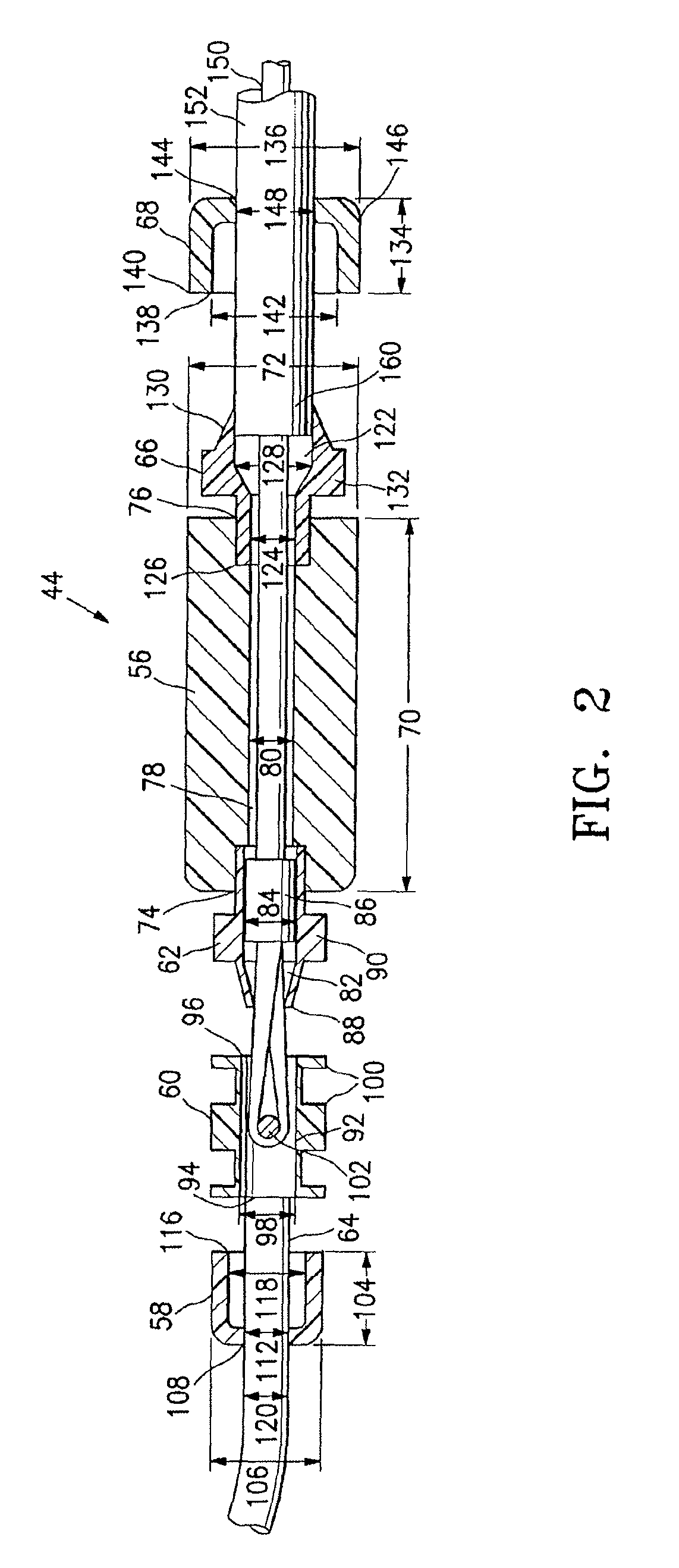
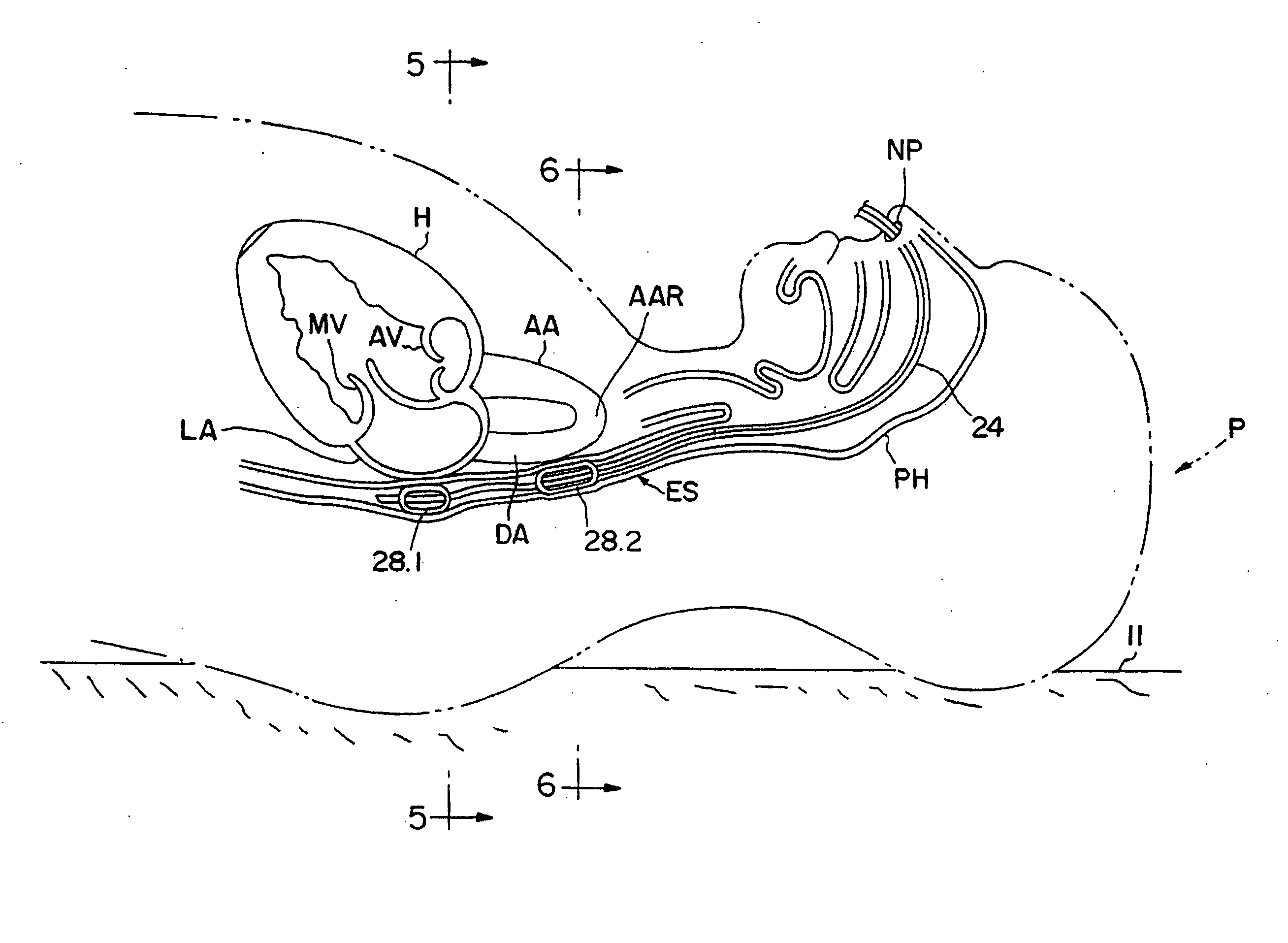
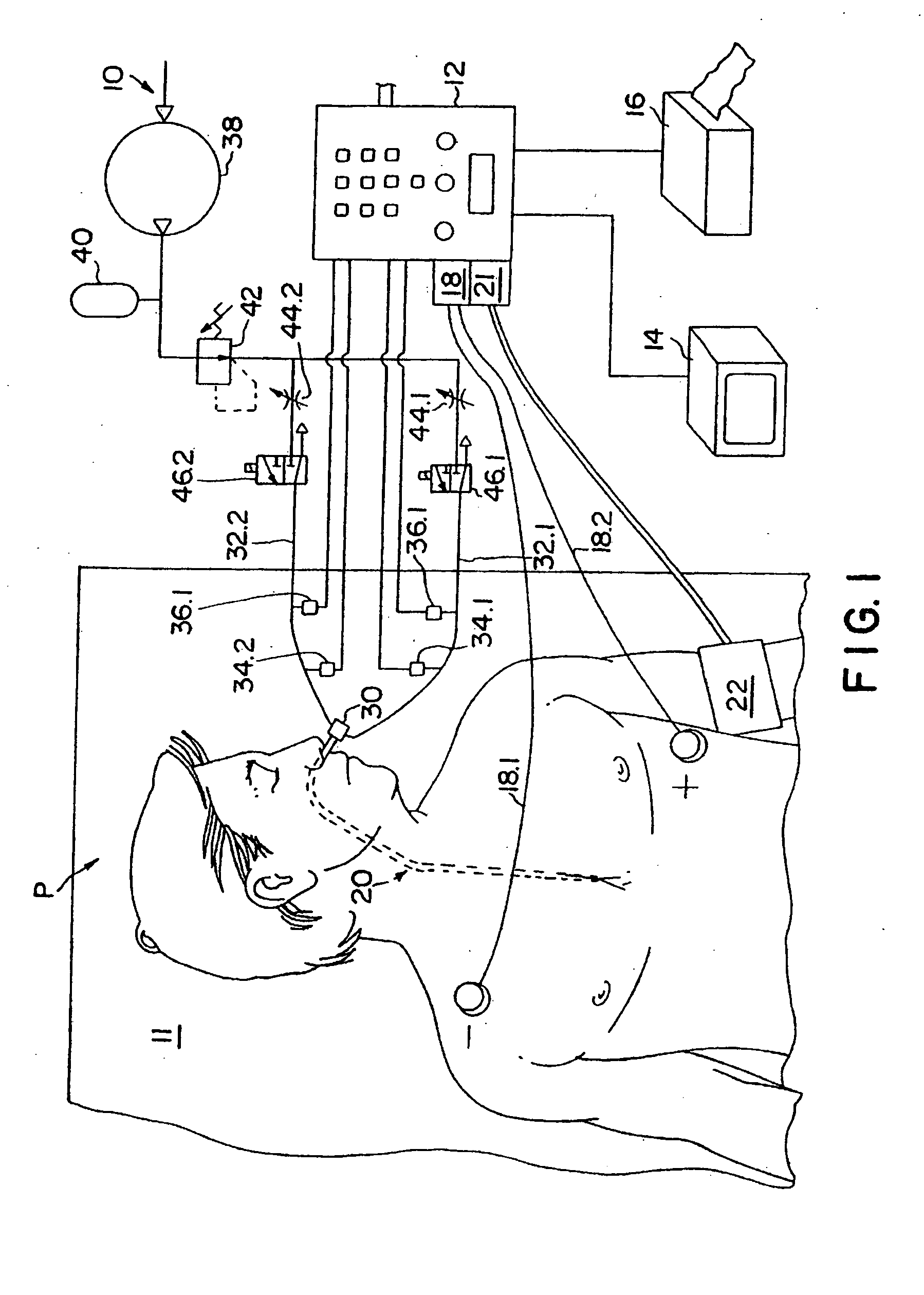
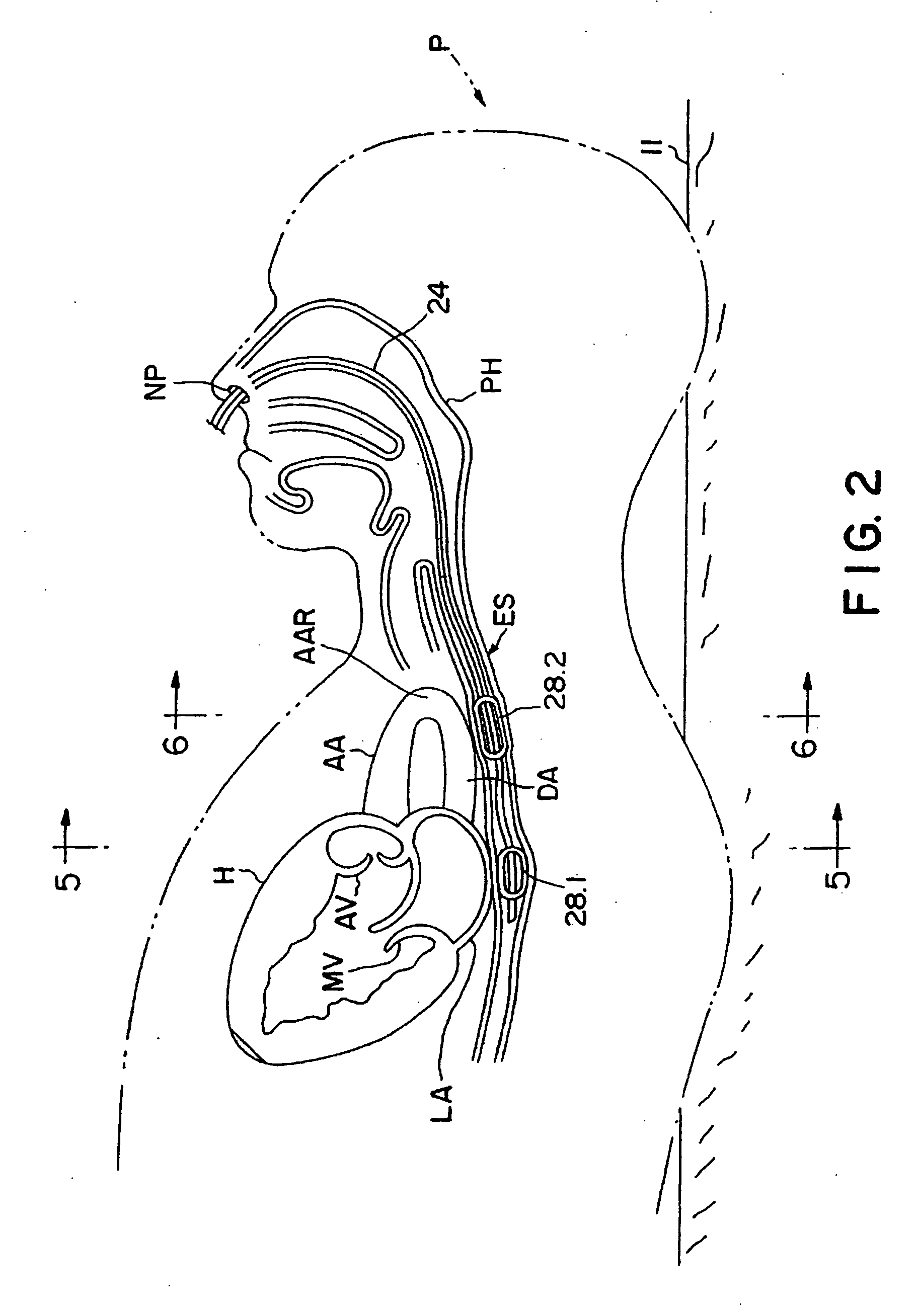
Device for and method of rapid noninvasive measurement of parameters of diastolic function of left ventricle and automated evaluation of the measured profile of left ventricular function at rest and with exercise
ActiveUS7107095B2Information can be usedSafe and convenient modalityEvaluation of blood vesselsAuscultation instrumentsLeft ventricular sizeHeart disease
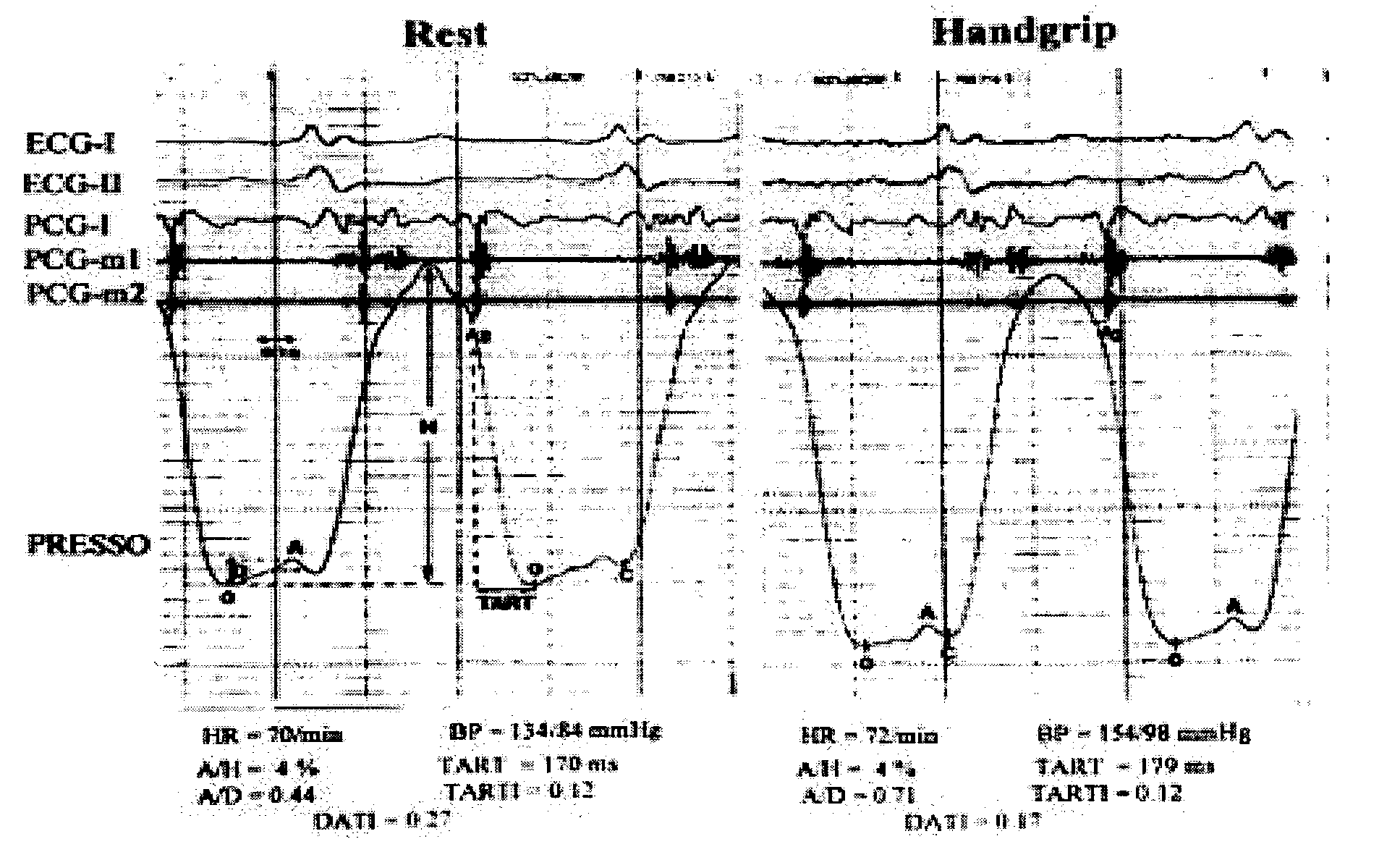
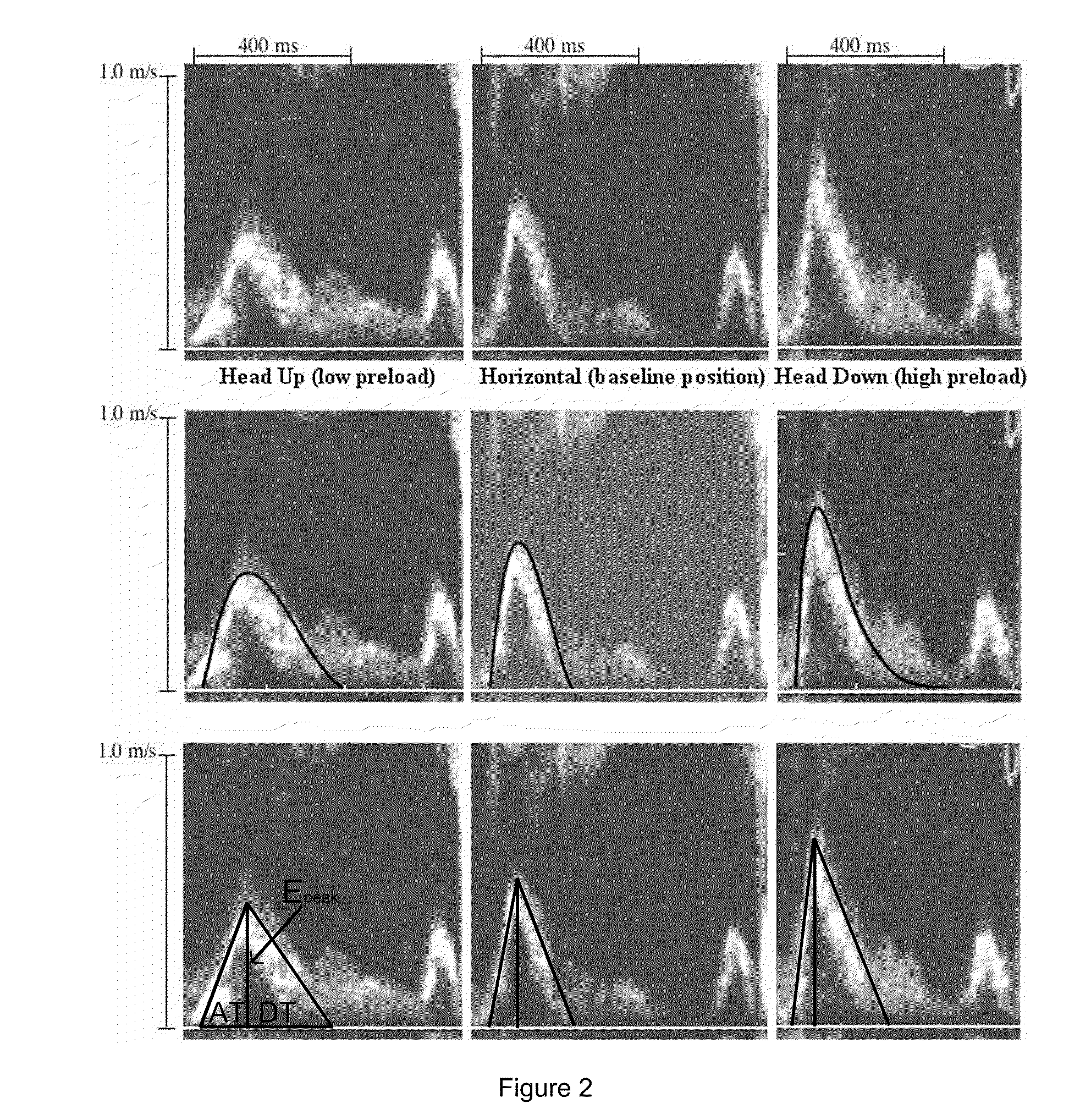
In a method of noninvasive measurement of parameters of diastolic function of left ventricle and automated evaluation of the measured profile at rest and with exercise, a patient performs an isometric exercise. An external pressure sensor and heart sounds microphone are applied in a non-invasive manner on the thoracic wall to obtain a left ventricular pressure mirroring curve (pressocardiogram) and simultaneously the heart sounds (phonocardiogram). An external unit determines and calculates characteristic diastolic parameters derived from the pressocardiographic curve and phonocardiogram at rest, during and after exercise, converts each said pressocardiogram into a digital waveform in the time domain, and automatically categorizes the mentioned characteristic parameters based on exact categorization criteria for defining several differentialforms of diastolic dysfunction of left ventricle in human beings.
Owner:MANOLAS JAN
Systems and methods for improving cardiac function
InactiveUS9694121B2Improve heart functionImprove complianceHeart valvesMedical devicesCatheterIliac Aneurysm
A system for improving cardiac function is provided. A foldable and expandable frame having at least one anchoring formation is attached to an elongate manipulator and placed in a catheter tube while folded. The tube is inserted into a left ventricle of a heart where the frame is ejected from the tube and expands in the left ventricle. Movements of the elongate manipulator cause the anchor to penetrate the heart muscle and the elongate manipulator to release the frame. The installed frame minimizes the effects of an akinetic portion of the heart forming an aneurysmic bulge. Devices and methods are described herein which are directed to the treatment of a patient's heart having, or one which is susceptible to heart failure, to improve diastolic function.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method and system for improving diastolic function of the heart
ActiveUS8382653B2Wear minimizationPrevent accidental releaseSuture equipmentsTorsion springsVentricular FunctionsCardiology
The present invention provides a system for improving diastolic function of the heart comprising elastic elements and attachment elements, wherein said elastic elements and said attachment elements are configured such that they are capable of being interconnected to form a chain formed of an alternating series of said elastic elements and said attachment elements, and wherein said attachment elements are adapted to be anchored in the wall of the heart and with option for drug delivery to the wall of the heart. The invention further provides devices, methods and kits, for mounting the ventricular function assisting device of the invention.
Owner:CORASSIST CARDIOVASCULAR LTD
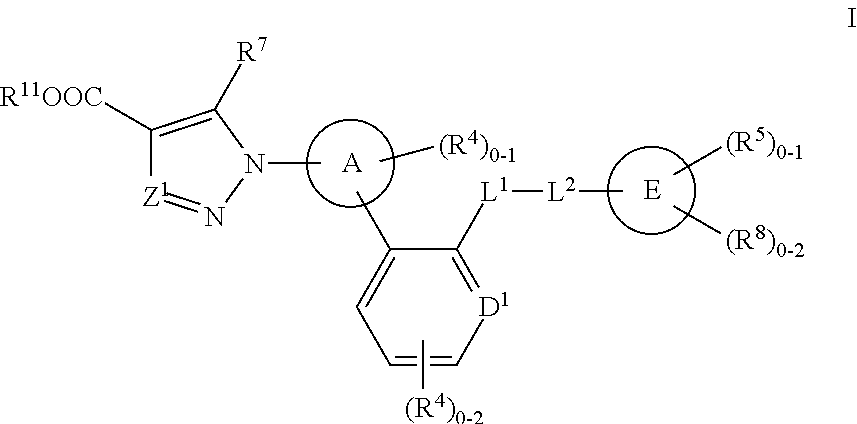
Organic Compounds
InactiveUS20090076062A1Avoid actionReduce formationBiocideSenses disorderIntra ocular pressureCardiac fibrosis
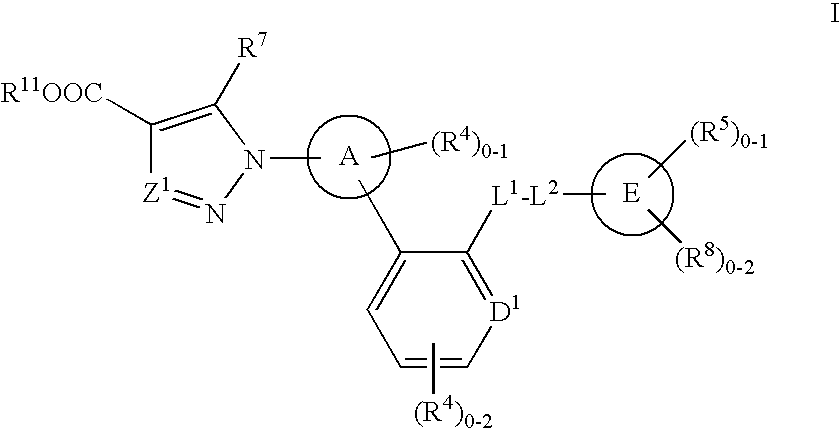
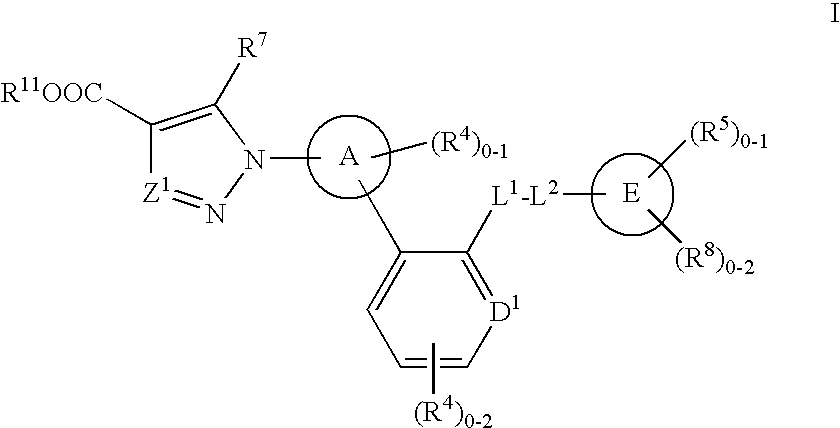
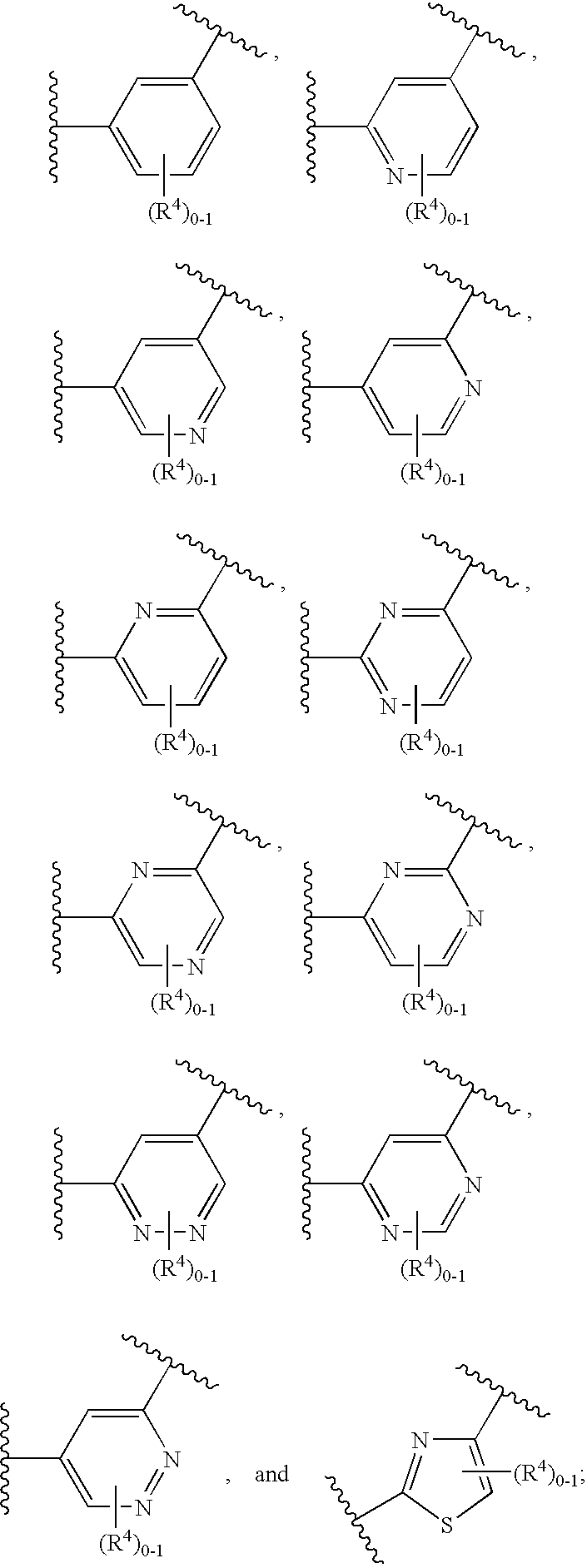
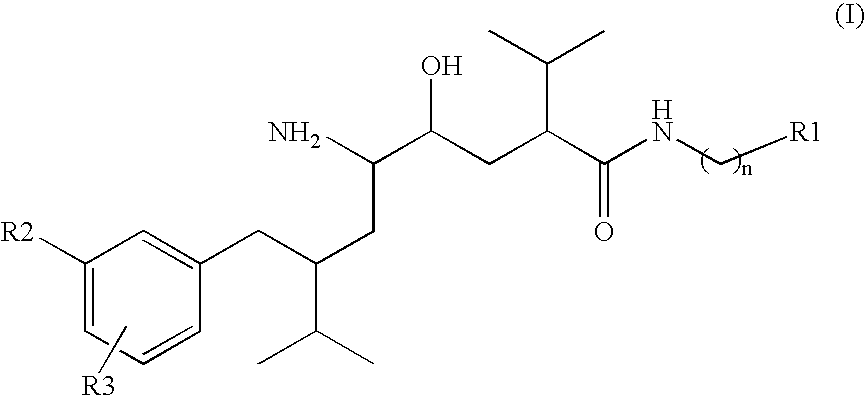
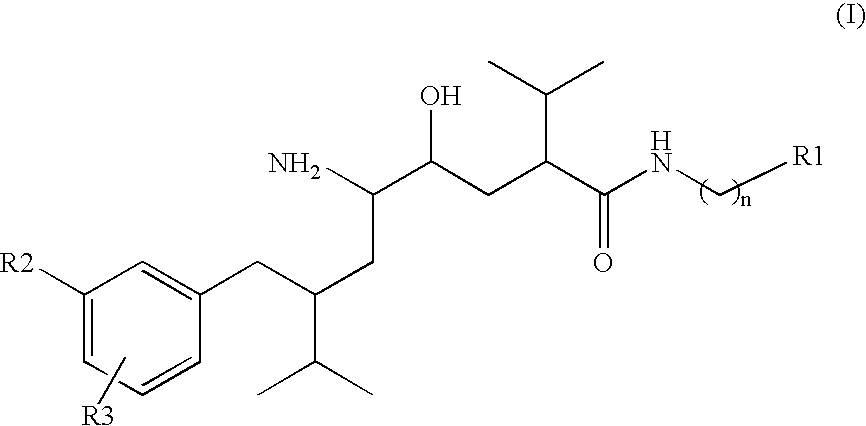
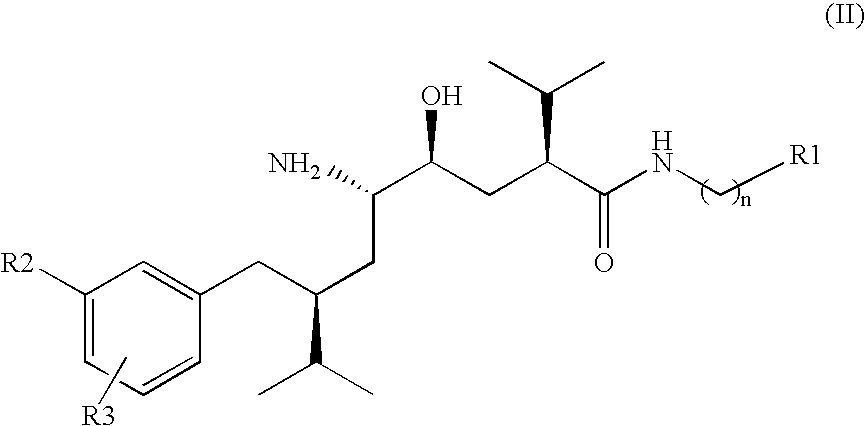
Disclosed are δ-amino-γ-hydroxy-ω-aryl-alkanoic acid amide compounds of formula (I)and the salts thereof, having renin-inhibiting properties. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds and methods of administering them for the treatment of hypertension, atherosclerosis, unstable coronary syndrome, congestive heart failure, cardiac hypertrophy, cardiac fibrosis, cardiomyopathy postinfarction, unstable coronary syndrome, diastolic dysfunction, chronic kidney disease, hepatic fibrosis, complications resulting from diabetes, such as nephropathy, vasculopathy and neuropathy, diseases of the coronary vessels, restenosis following angioplasty, raised intra-ocular pressure, glaucoma, abnormal vascular growth, hyperaldosteronism, cognitive impairment, alzheimers, dementia, anxiety states and cognitive disorders.
Owner:MAIBAUM JUERGEN KLAUS +2
Method of determining cardiac indicators
ActiveUS20060287604A1Effective therapyImproved ventricular functionElectrocardiographyStethoscopeLeft ventricular sizeLeft atrial
Methods for determining indicators of left ventricular diastolic function are disclosed. The indicators may include the left ventricular isovolumetric relaxation time and the negative slope of a left atrial “V” wave.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Cardiac device and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20100121132A1Lower the volumeImprove pressure-volume relationshipHeart valvesInternal electrodesHeart diseaseCardiac device
Devices and methods are described herein which are directed to the treatment of a patient's heart having, or one which is susceptible to heart failure, to improve diastolic function.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
In Vivo Device for Assisting and Improving Diastolic Ventricular Function
InactiveUS20080071134A1Easy to adaptLow costHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsElastic componentVentricular function
The present invention is primarily directed towards an anatomically-compatible and physiologically-compatible in vivo device for improving diastolic function of either the left or right ventricle of the heart, wherein said device comprises at least one elastic component in the form of a lattice capable of being arranged in a curved conformation such that one surface of said lattice may be adapted to the curvature of the external ventricular surface of the heart, or a portion thereof, and wherein said at least one elastic component is capable of being operatively connected to the external ventricular surface of the heart by means of one or more connecting elements.
Owner:CORASSIST CARDIOVASCULAR LTD
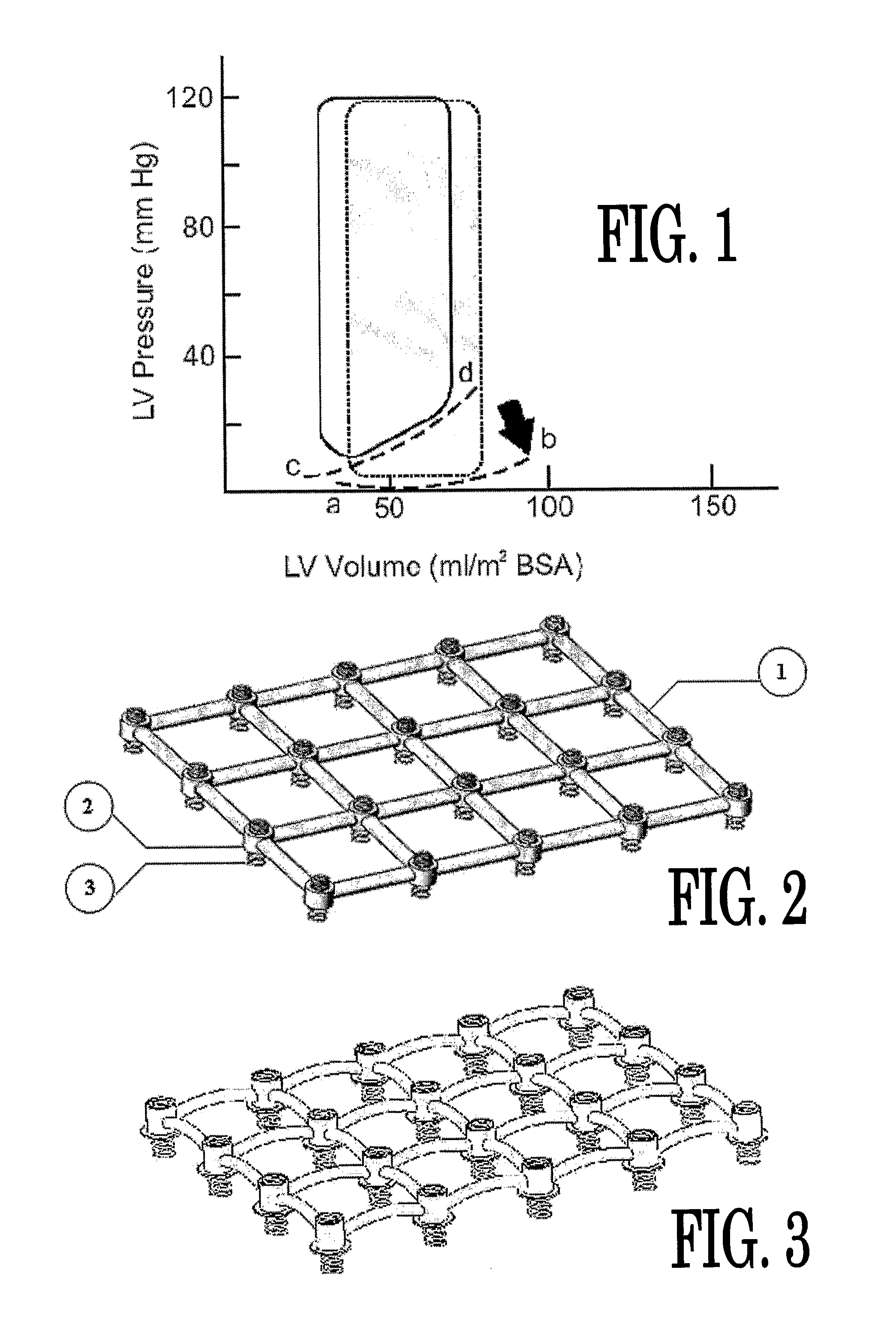
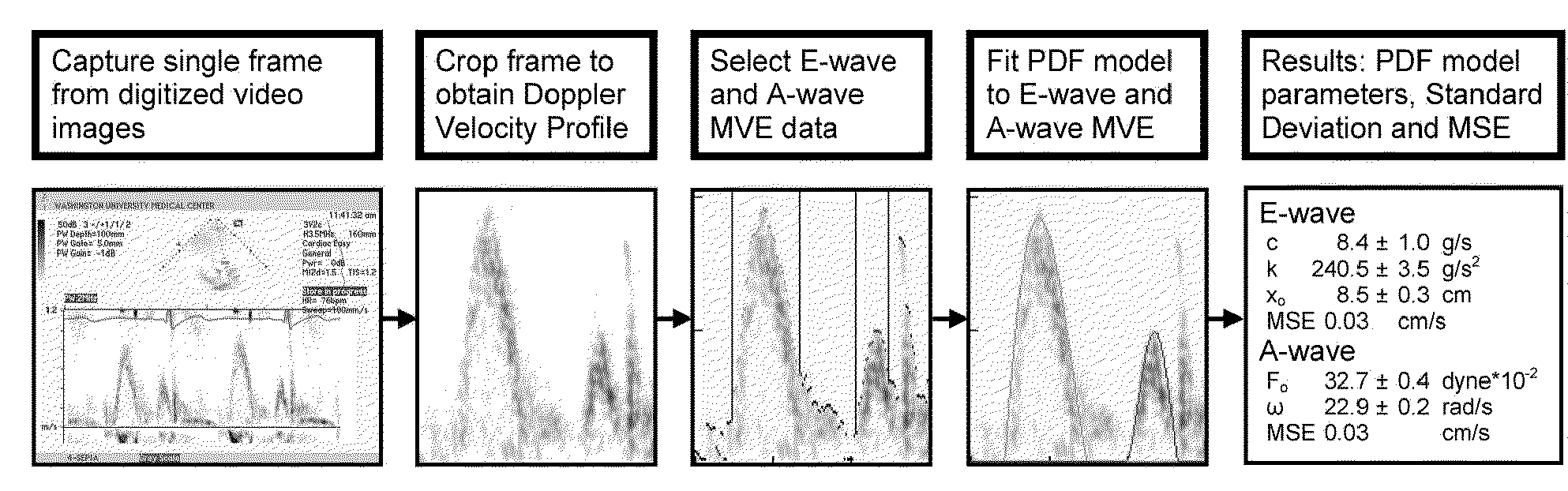
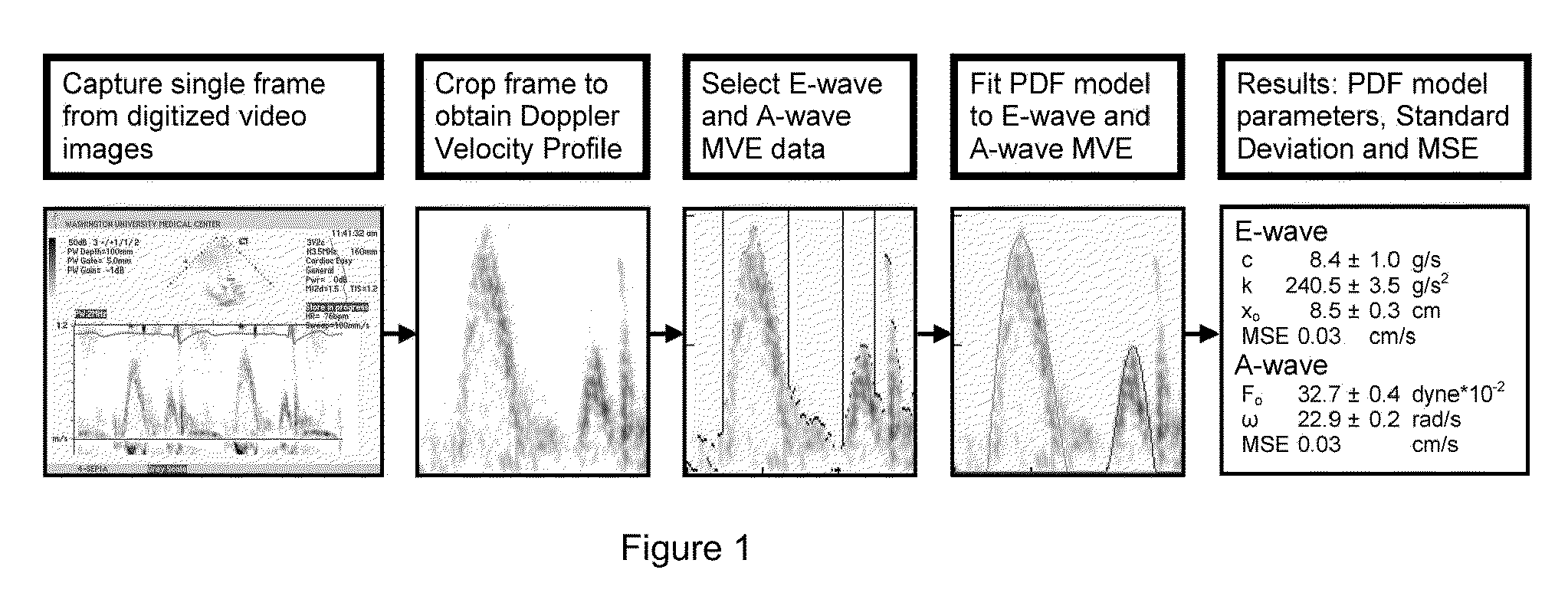
Load independent index of diastolic function
Methods and related apparatus and systems for determining a load-independent index of diastolic function in the heart are described.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
System for improving diastolic dysfunction
ActiveUS20110087203A1Avoid expansionSolve the real problemHeart valvesSurgical instrument detailsBLOOD FILLEDCongestive heart failure chf
An elastic structure is introduced percutaneously into the left ventricle and attached to the walls of the ventricle. Over time the structure bonds firmly to the walls via scar tissue formation. The structure helps the ventricle expand and fill with blood during the diastolic period while having little affect on systolic performance. The structure also strengthens the ventricular walls and limits the effects of congestive heart failure, as the maximum expansion of the support structure is limited by flexible or elastic members.
Owner:KARDIUM
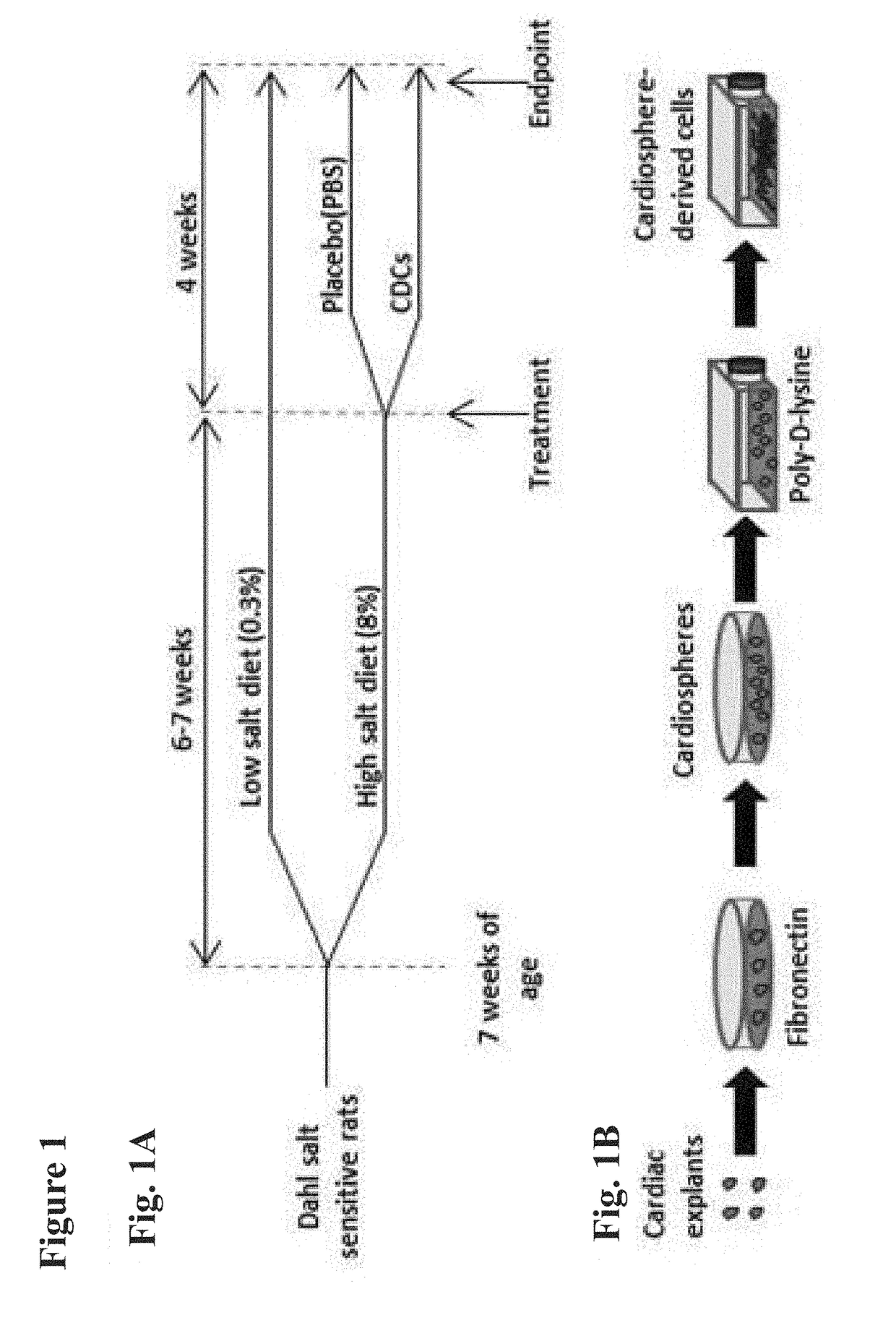
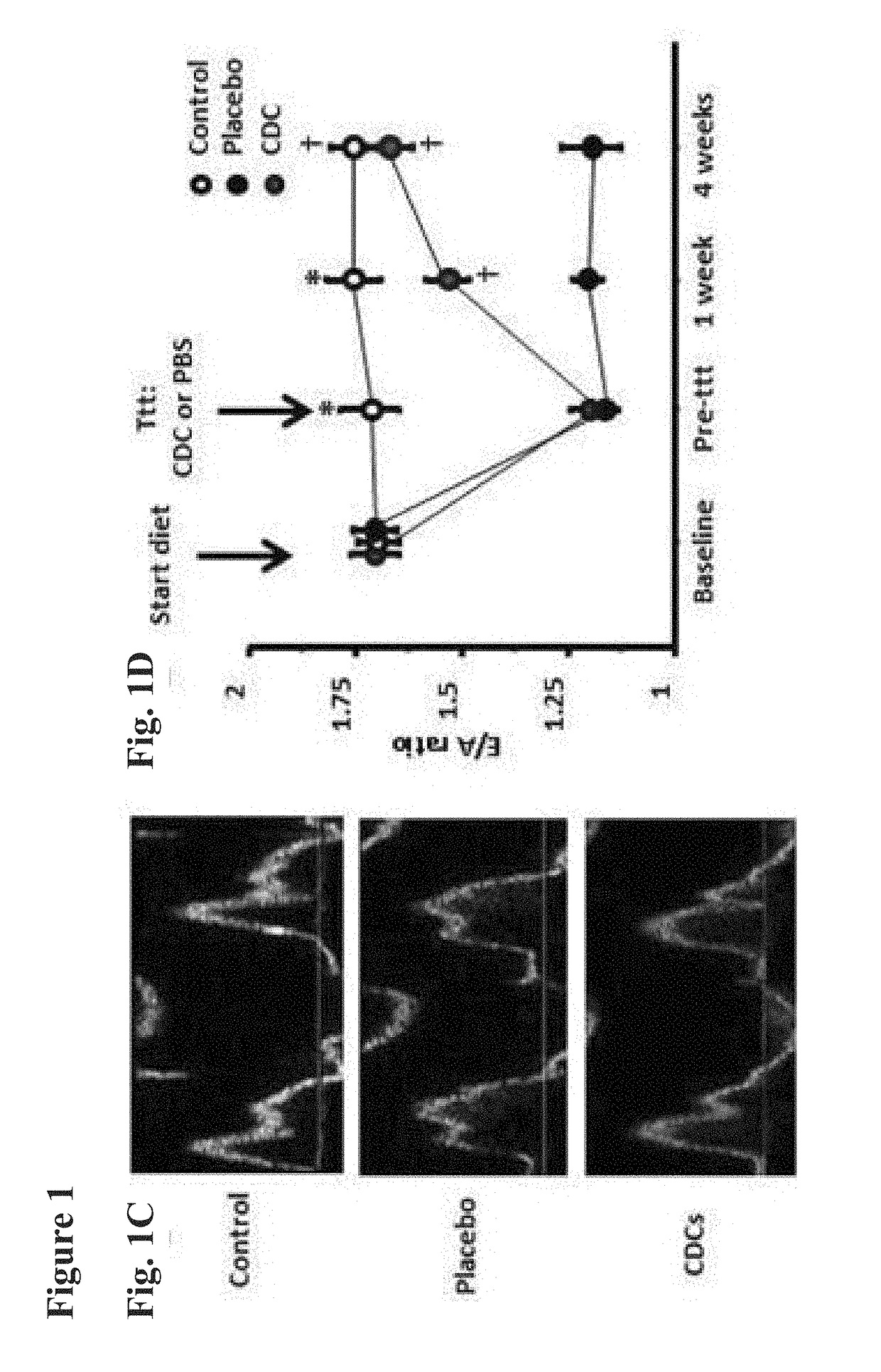
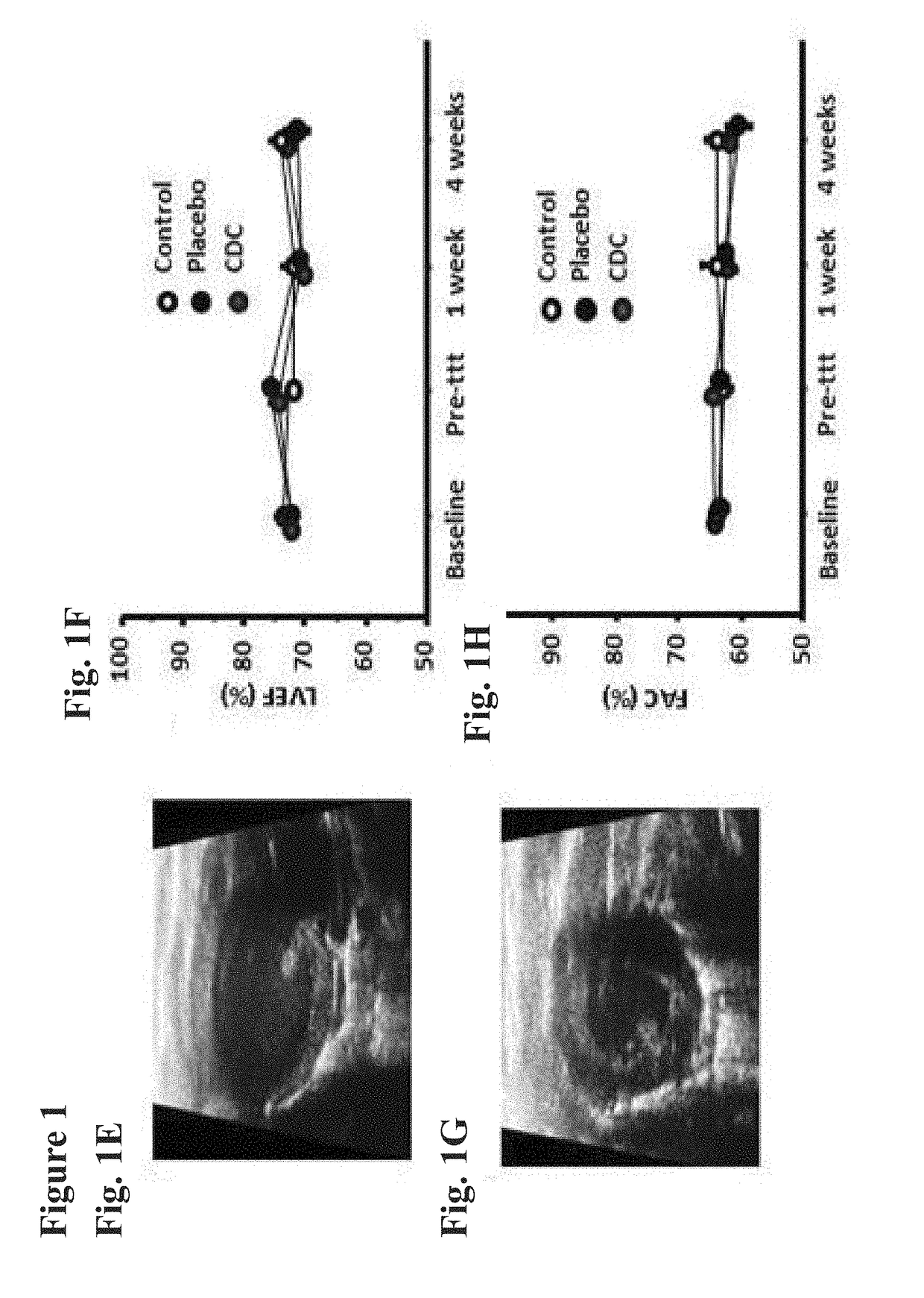
Cardiosphere-derived cells and exosomes secreted by such cells in the treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
ActiveUS20190000888A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismSkeletal/connective tissue cellsLower riskMortality rate
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a disease condition characterized by heart failure (HF) signs and symptoms, but with normal or near normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and is not responsive to standard therapy for treatment of HF. Described herein are compositions and methods related to use of cardiosphere derived cells (CDCs) and their exosomes to improve left ventricular structure, function and overall outcome. Administration of CDCs led to improved LV relaxation, lower LV end-diastolic pressure, decreased lung congestion and enhanced survival. Lower risk of arrhythmias in HFpEF was also observed following CDC administration. Improvement of diastolic dysfunction following administration of CDC-derived exosomes was observed, along with decreased mortality. In view of these salutary effects, CDCs and CDC-derived exosomes are beneficial in the treatment of HFpEF.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
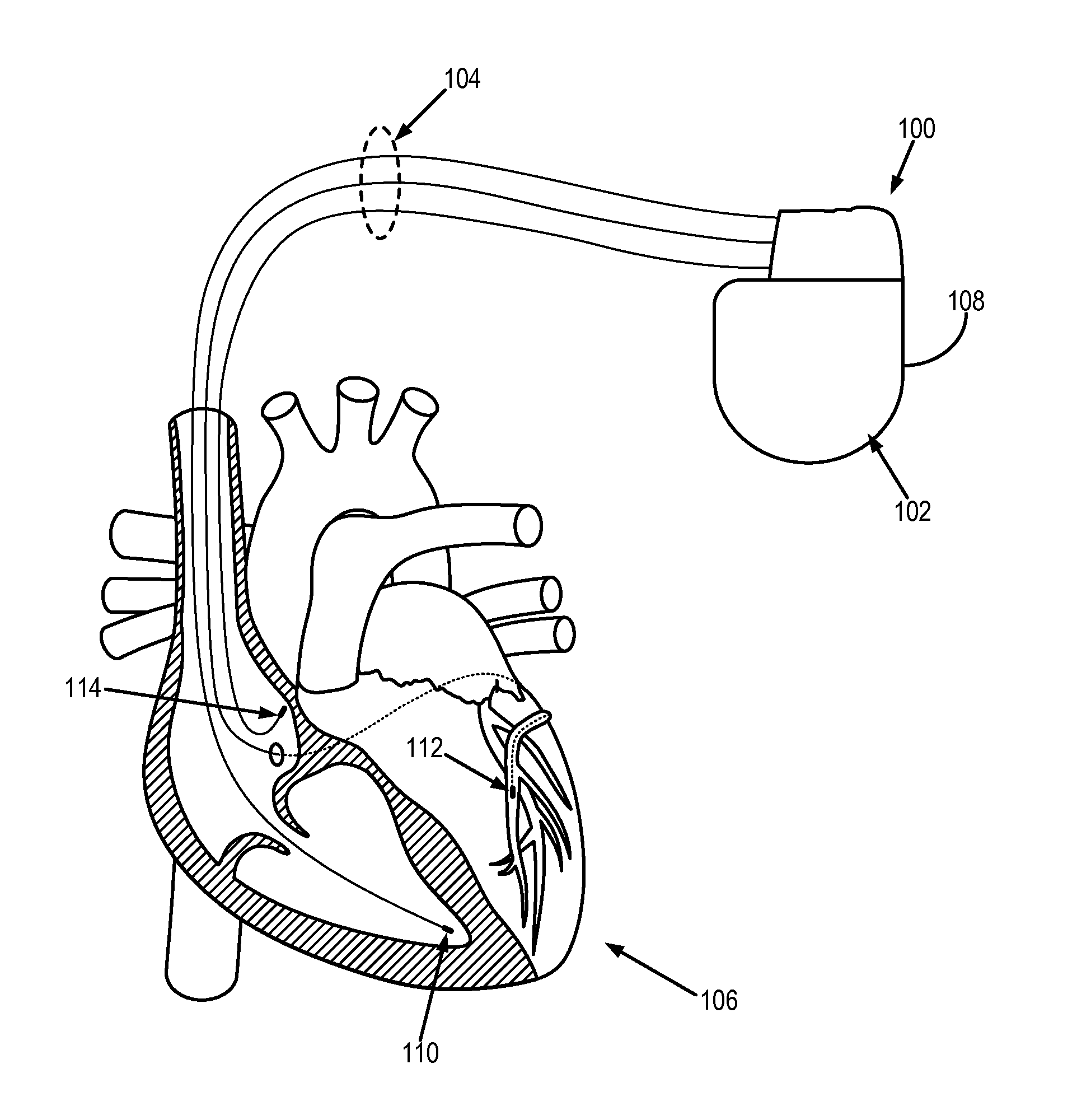
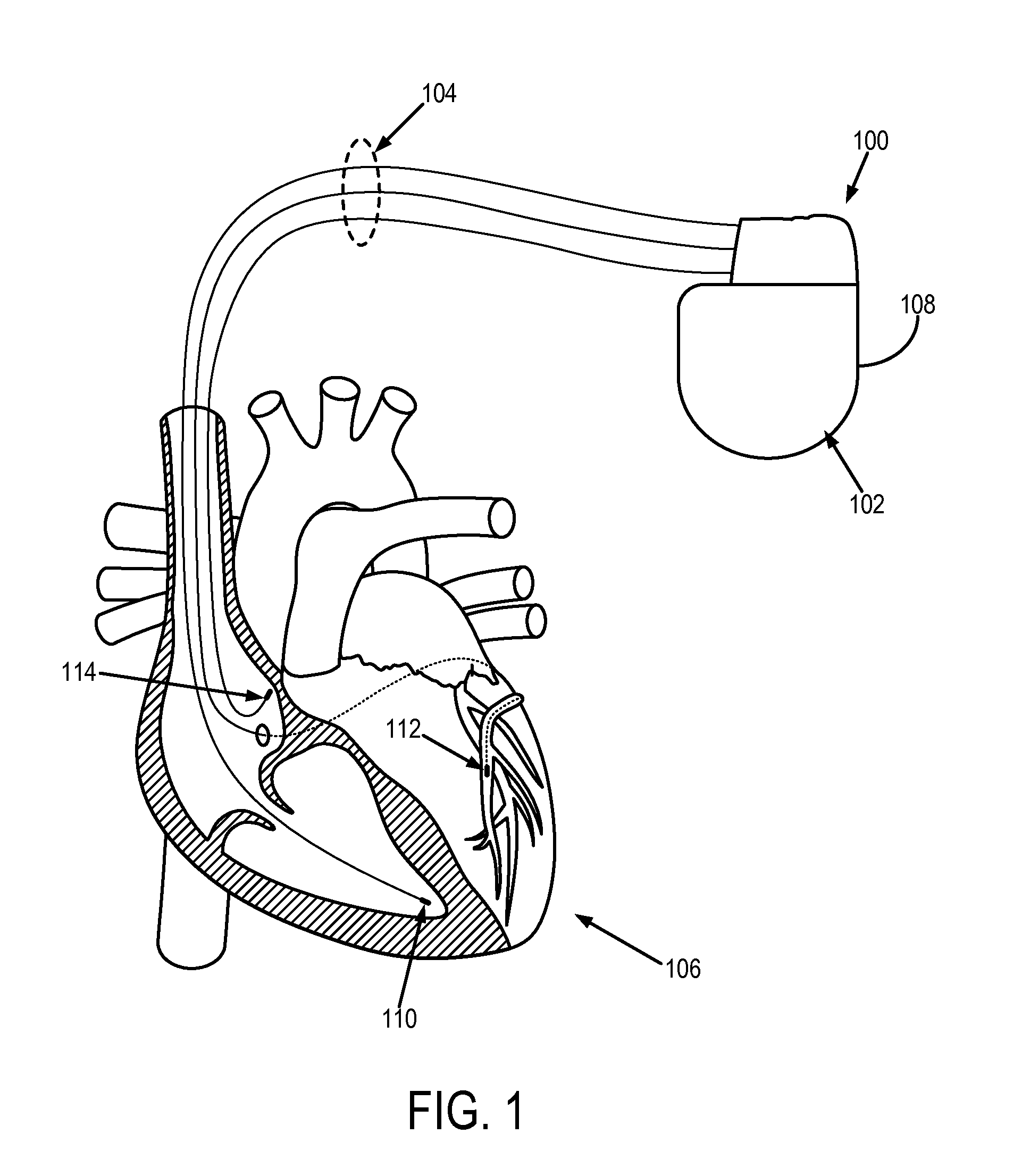
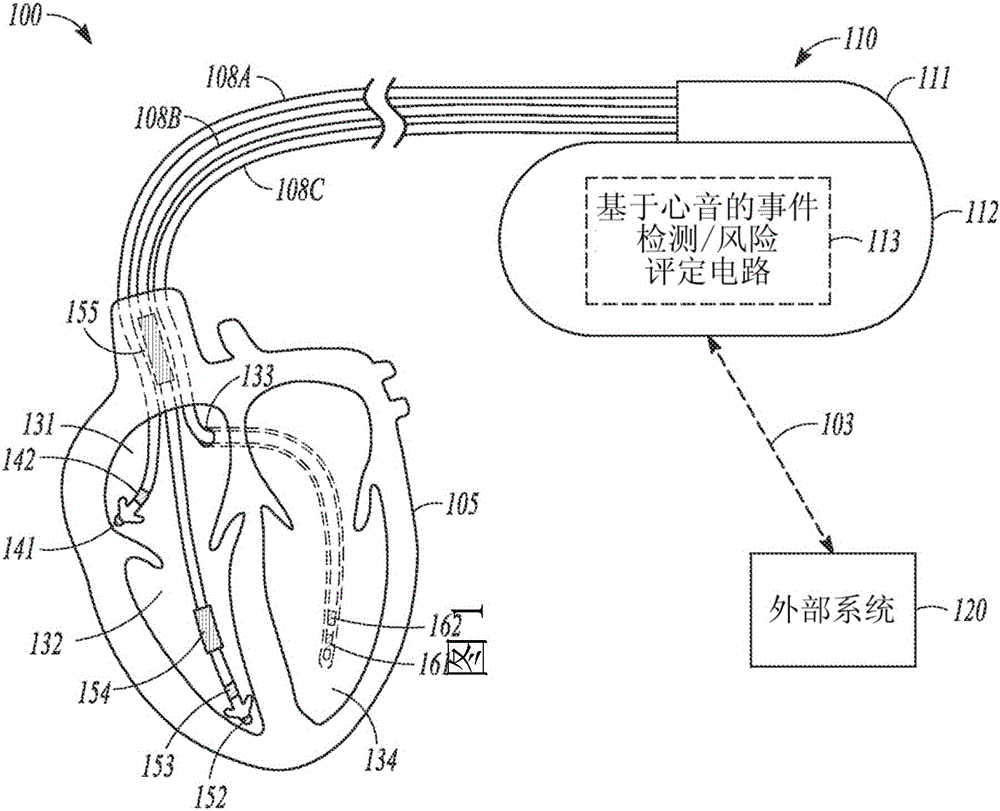
Heart failure detection and risk stratification system
InactiveCN105873499APrevent exacerbation of HFSafety managementHealth-index calculationStethoscopeGuidelineHeart sounds
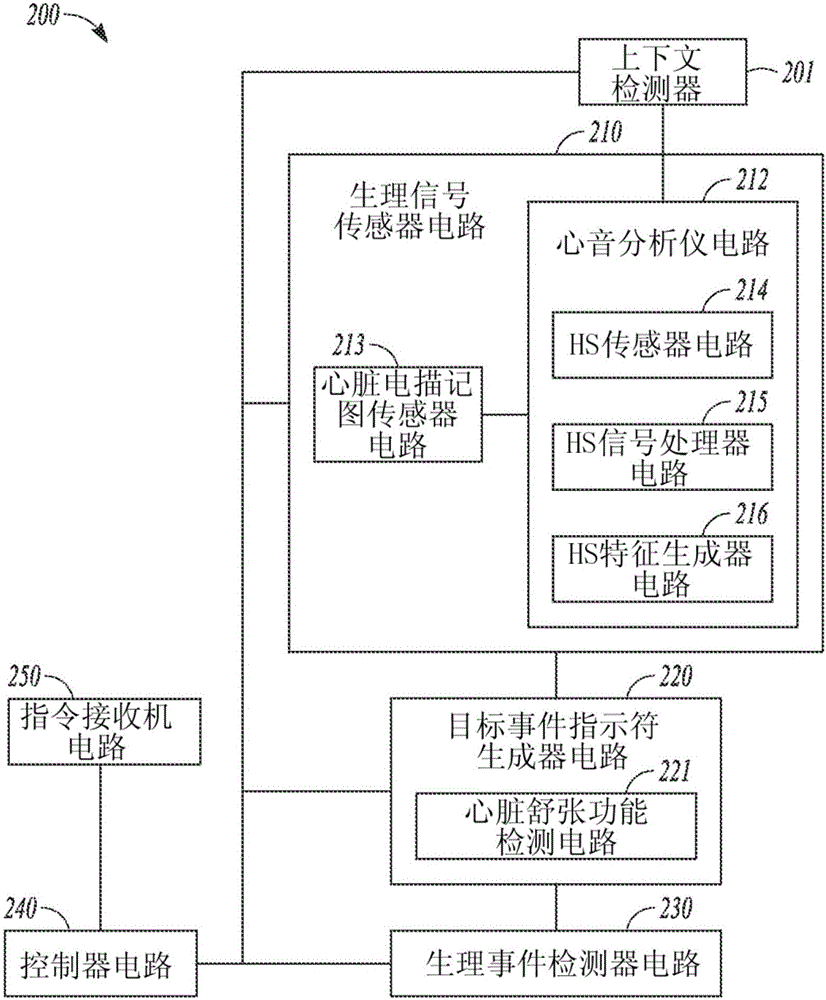
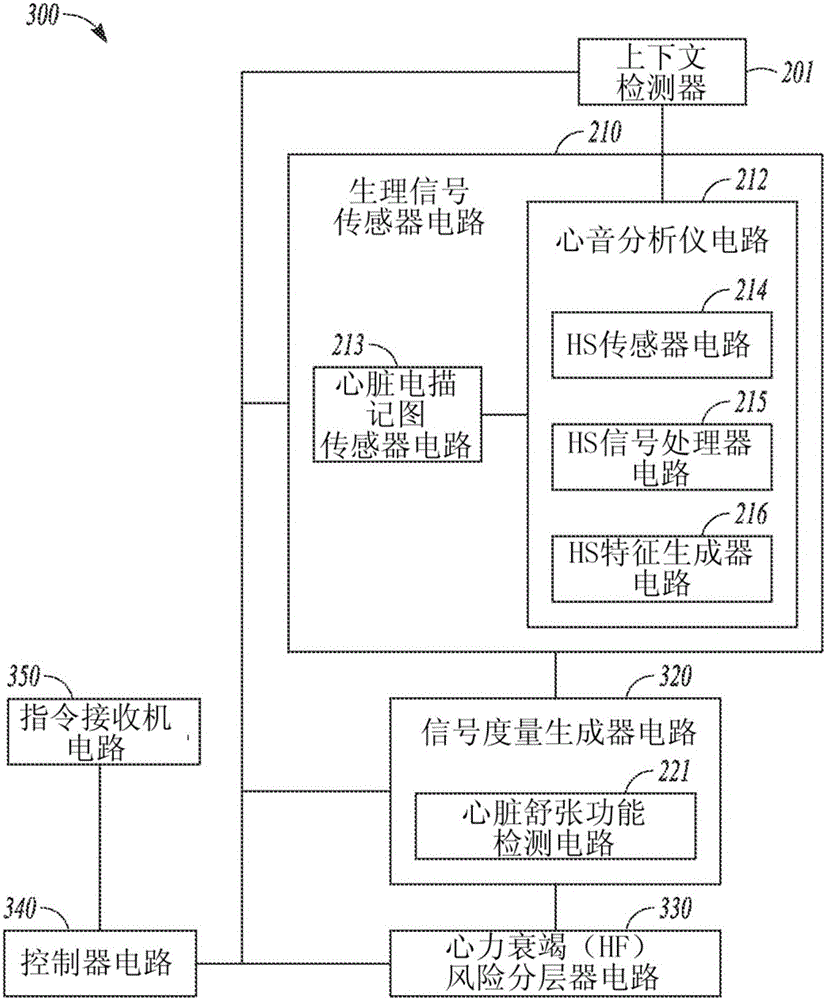
Devices and methods for detecting heart failure (HF) events or identifying patient at elevated risk of developing future HF events are described. A medical device can detect contextual condition associated with a patient, such as an environmental context or a physiologic context, sense a heart sound signal, and perform multiple measurements of heart sound features in response to the detected patient contextual condition meeting specified criterion. The contextual condition includes information correlating to or indicative of a change in metabolic demand of a patient. The medical device can use the physiologic signals to calculate one or more signal metrics indicative of diastolic function of the heart such as a trend of the heart sound features. The medical device can use the signal metrics to detect an HF event or to predict the likelihood of the patient later developing an HF event.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
In vivo for improving diastolic ventricular function
The present invention provides an anatomically-compatible and physiologically-compatible in vivo device for improving diastolic function of either the left or right ventricle of the heart, comprising at least one air-impermeable sheet that is capable of being operatively connected to the external ventricular surface of the heart using one or more connecting elements, such that said at least one air-impermeable sheet is capable of creating a sub-atmospheric pressure within said closed empty space as a consequence of changes in the volume of said space during the course of the cardiac cycle, thereby exerting an outward and normally directed force on the external ventricular surface of the heart.
Owner:CORASSIST CARDIOVASCULAR LTD
Bioactive implant for myocardial regeneration and ventricular chamber restoration
InactiveUS20130116789A1Limit chronic dilationRestore native elliptical shapeHeart valvesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProsthesisCardiac muscle
Bioactive implant for myocardial regeneration and ventricular chamber support including an elastomeric microporous membrane. The elastomeric microporous membrane being at least one non-degradable polymer and at least one partially degradable polymer. The non-degradable polymer is selected from polyethylacrylate and polyethylacrylate copolymerized with a hydroxyethylacrylate comonomer. The partially degradable polymer is selected from caprolactone 2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl ester and caprolactone 2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl ester copolymerized with ethylacrylate. The elastomeric microporous membrane further includes a nanofiber hydrogel, and cells. The bioactive implant, having one or two helical loops, contributes to the restauration of the heart conical shape. Cardiac wrapping by ventricular support bioprostheses of the present invention, having reinforcement bands spatially distributed as helicoids, recovers the sequential contraction of the myocardium resulting in the successive shortening and lengthening of the ventricles, therefore improving the ejection (systolic function) and suction of blood (diastolic function).
Owner:INSTITUT QUIMIC DE SARRIA +3
Kv1.5-BLOCKER FOR THE SELECTIVE INCREASE OF ATRIAL CONTRACTILITY AND TREATMENT OF CARDIAC INSUFFICIENCY
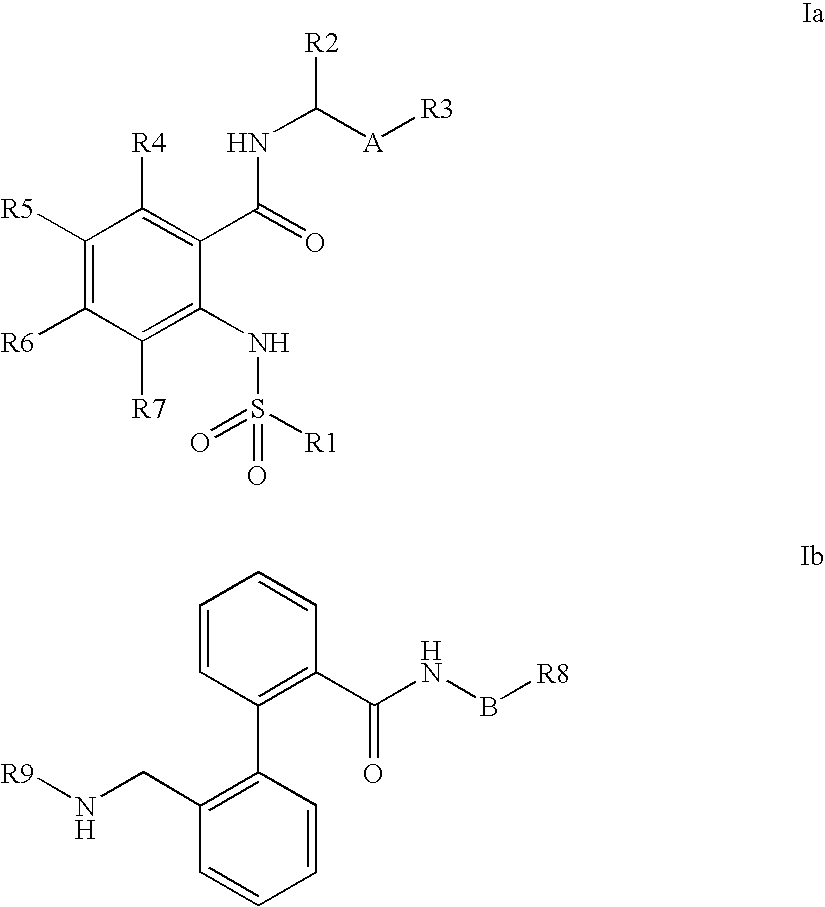
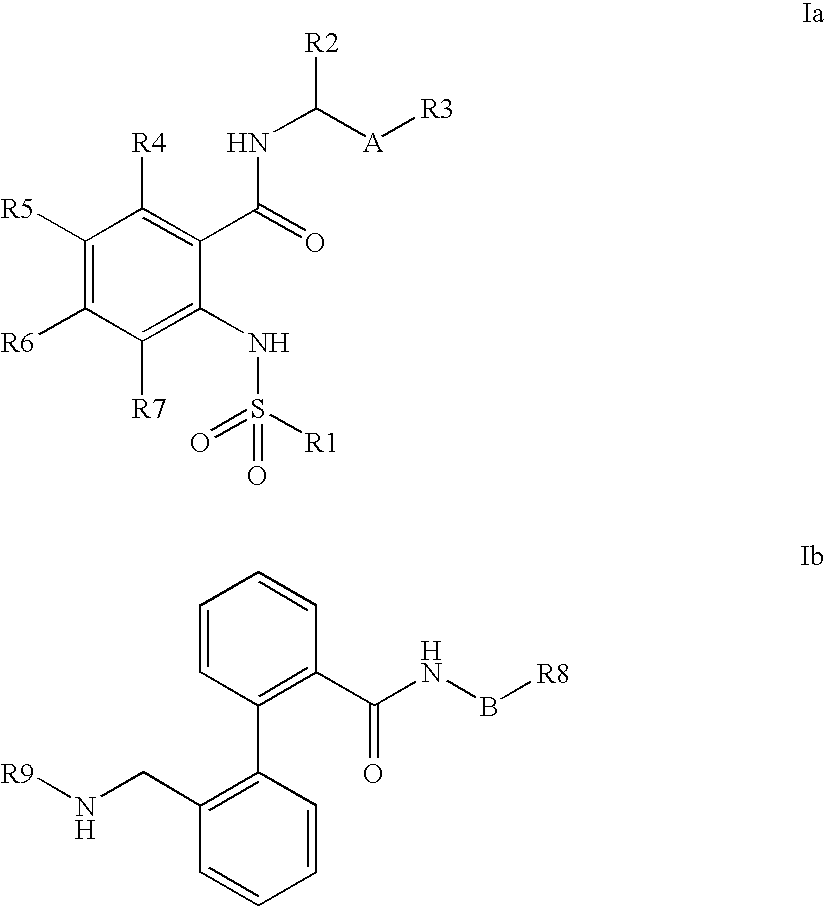
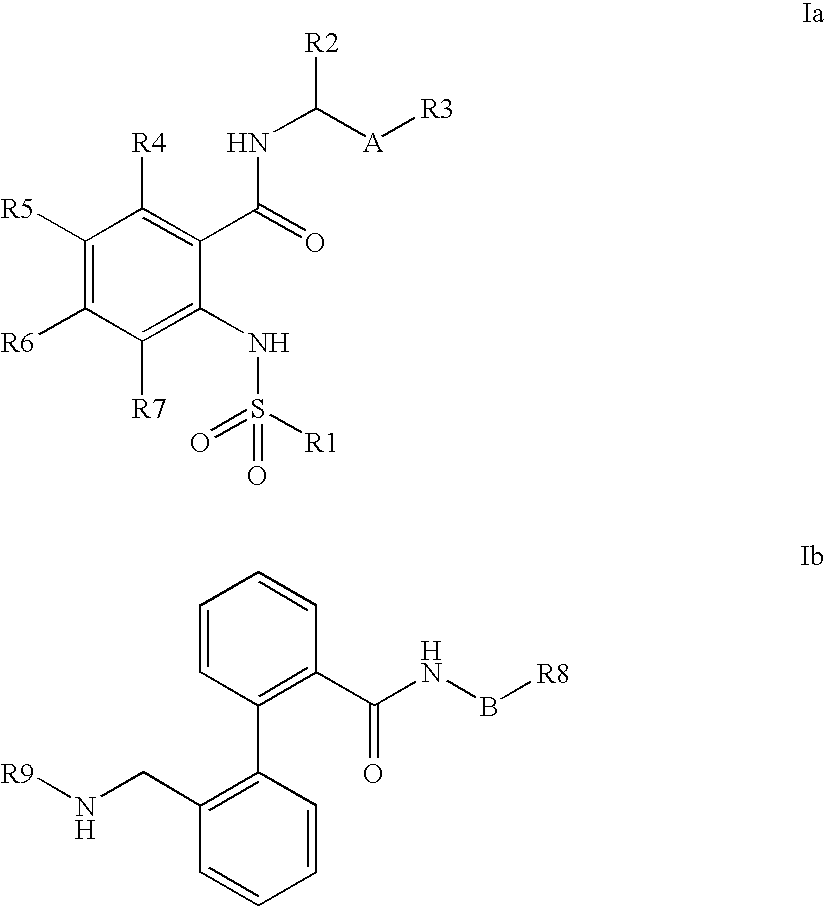
The invention relates to the atrial contractility-increasing effect of Kv1.5 blockers, especially phenylcarboxamides of the formulae Ia or Ib or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, for treating reduced atrial contractility and heart failure, especially heart failure caused by diastolic dysfunction.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
System for improving diastolic dysfunction
ActiveUS7837610B2Avoid expansionSolve the real problemHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsCongestive heart failure chfScar tissue
Owner:KARDIUM
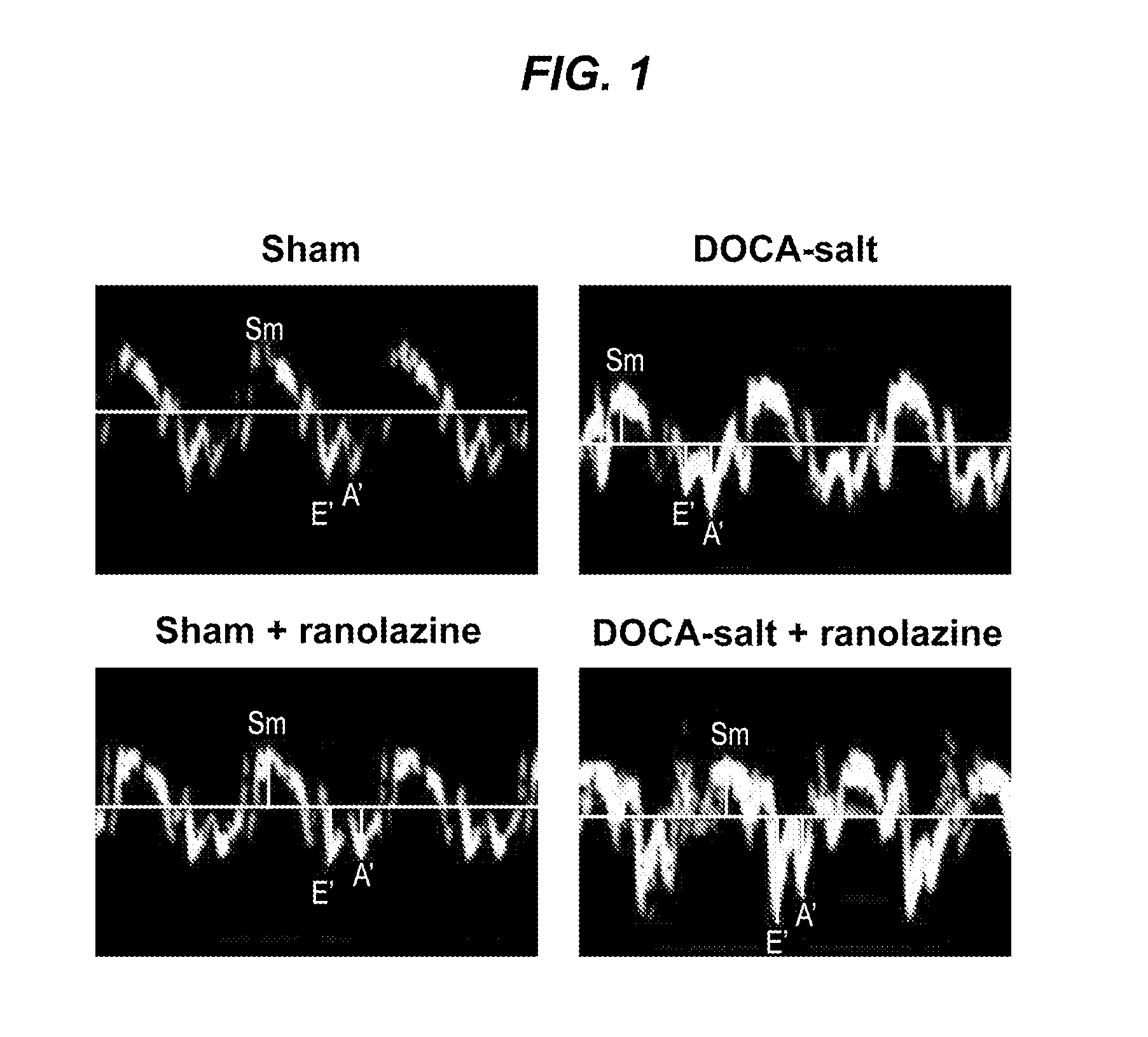
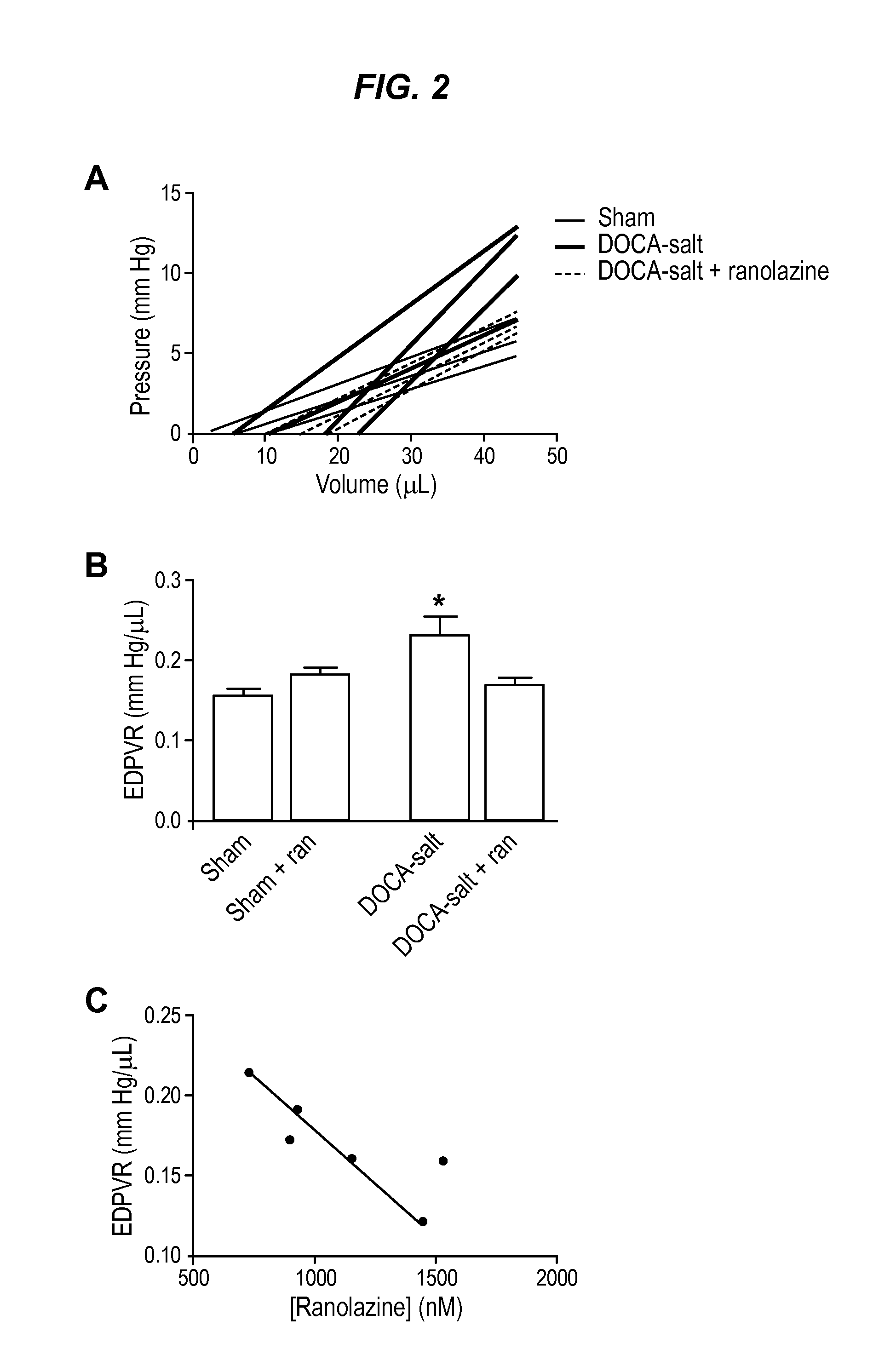
Methods of treating diastolic dysfunction and related conditions
InactiveUS20120214818A1Organic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderHeart failure with preserved ejection fractionAcute decompensated heart failure
The invention provides a method of treating diastolic dysfunction, e.g., diastolic dysfunction with preserved ejection fraction, in a subject. The method comprises administering to the subject in an amount effective to treat the diastolic dysfunction a cardiac metabolic modifier, as described herein. In some embodiments, the diastolic dysfunction is characterized by (i) a lack of increased late INa in cardiomyocytes, (ii) an increase in myofilament calcium sensitivity, or (iii) a combination thereof. In some embodiments, the subject does not suffer from a cardiac injury or a structural heart disease, as described herein. Further provided are a method of treating heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in a subject, a method of treating acute decompensated heart failure, a method of modulating myofilament calcium sensitivity in a subject, and a method of treating a condition associated with or caused by increased myofilament calcium sensitivity.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com