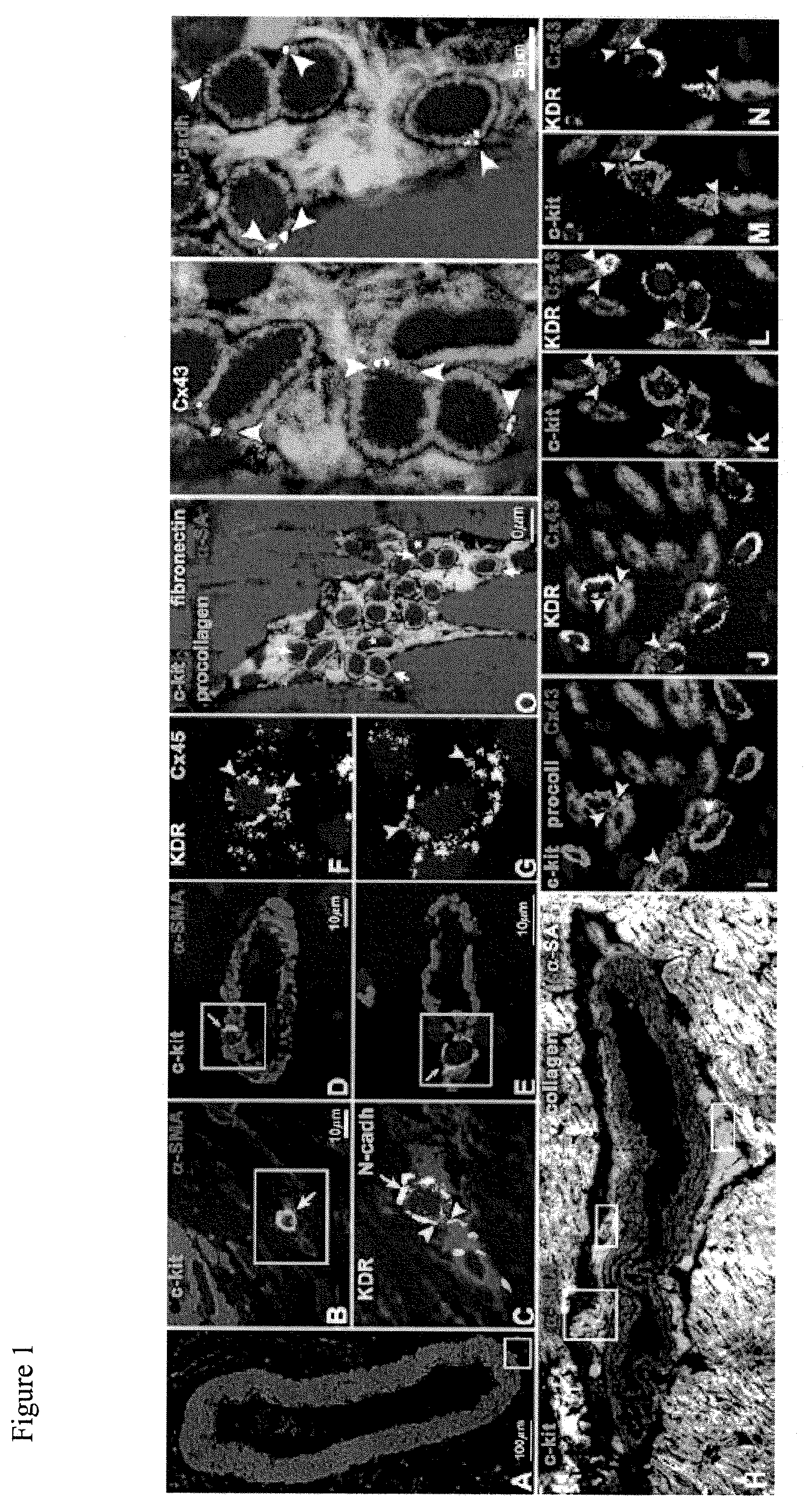
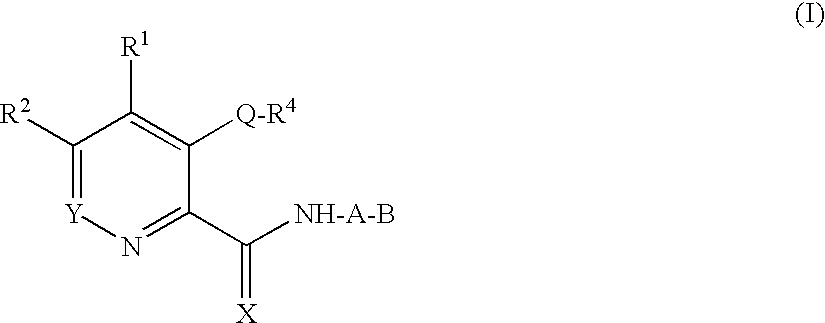Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
811results about How to "Improve heart function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
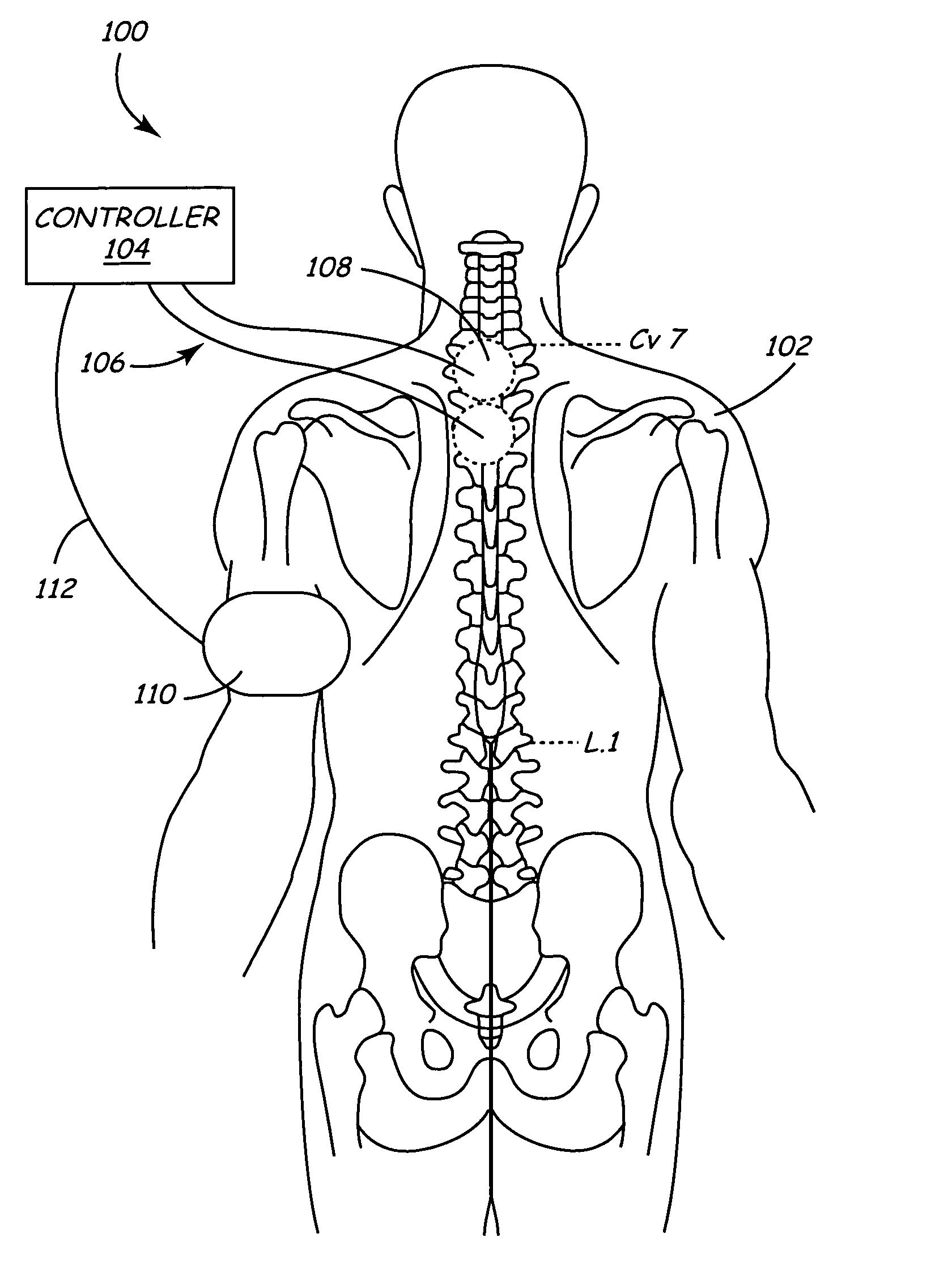
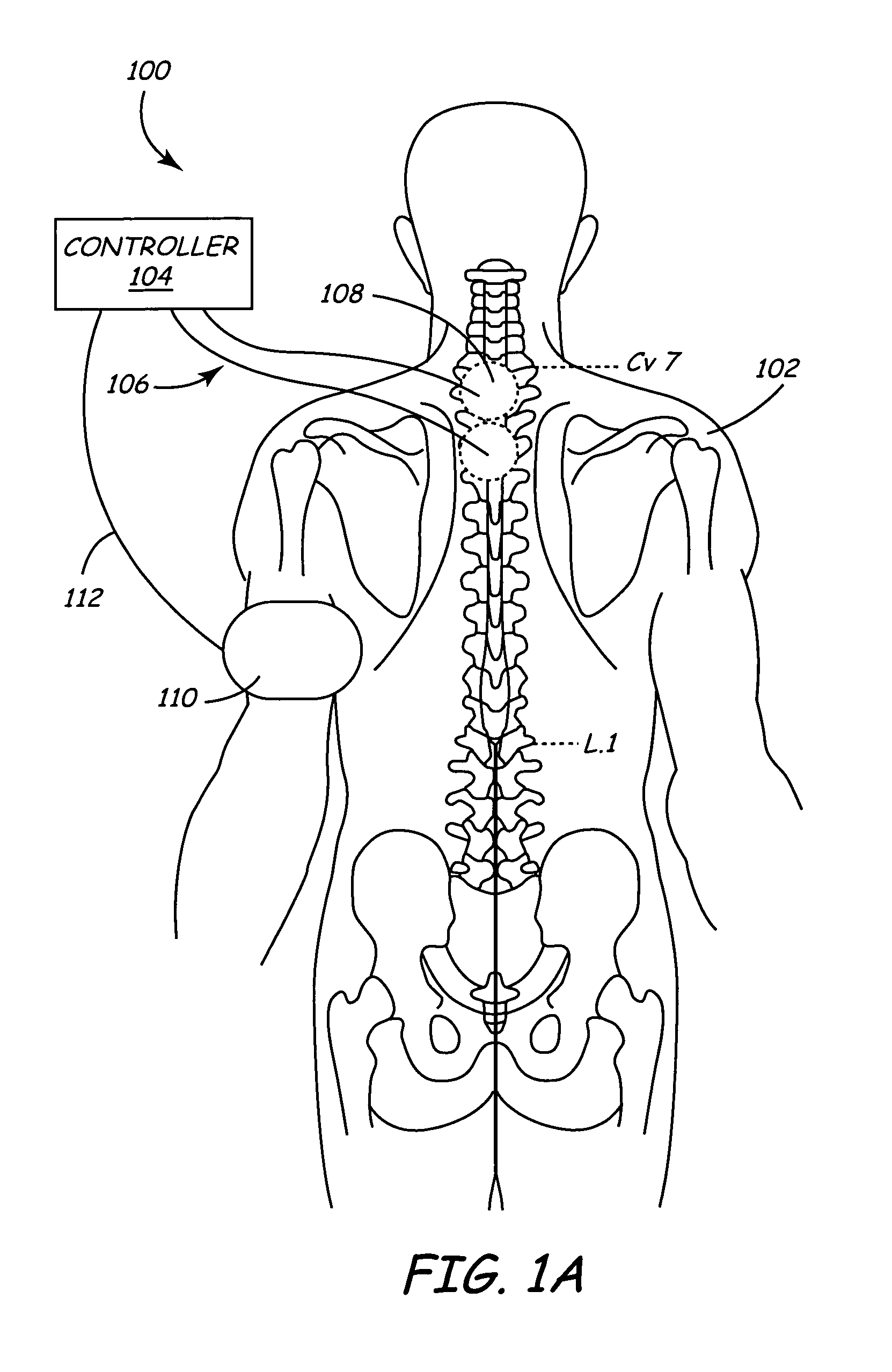
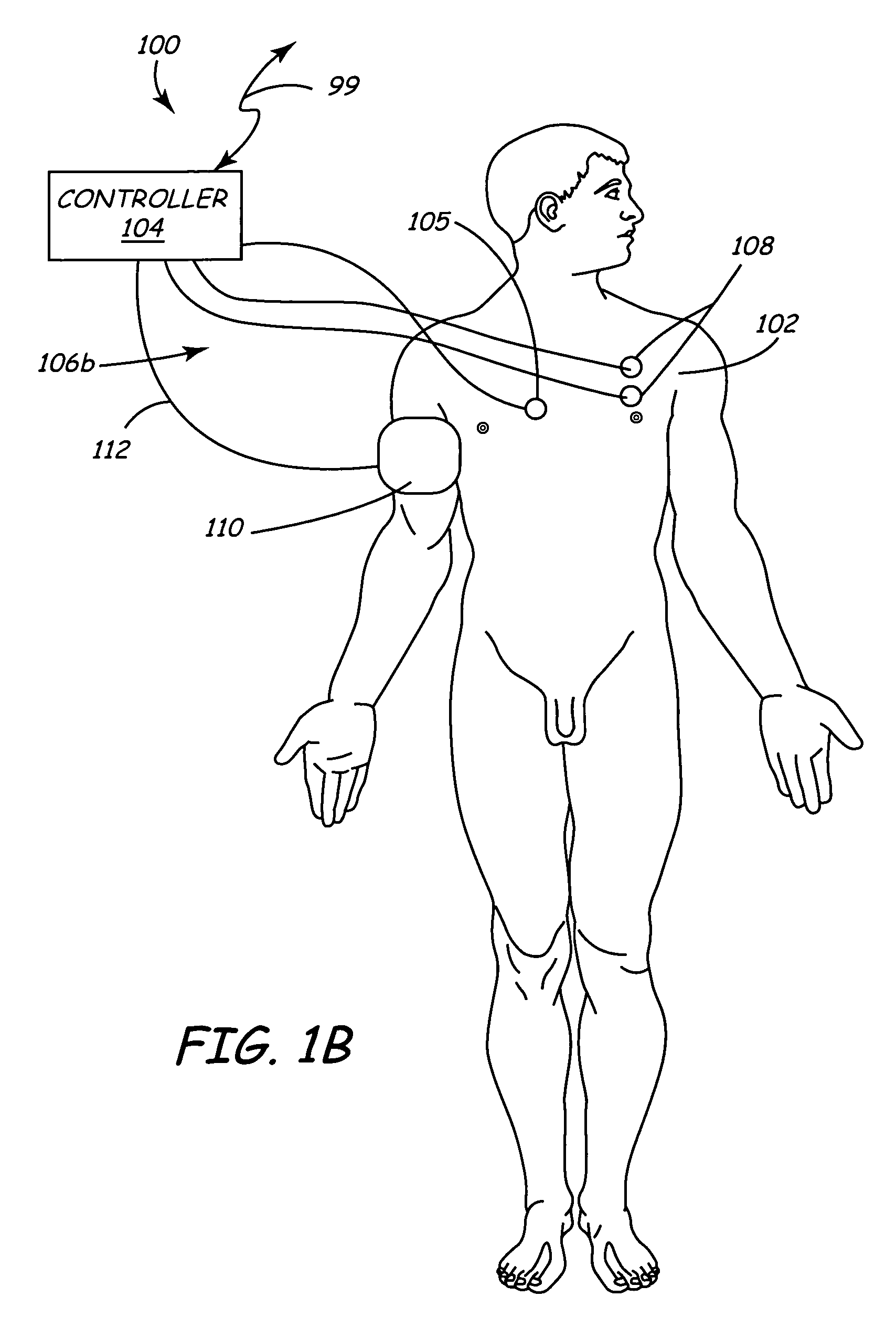
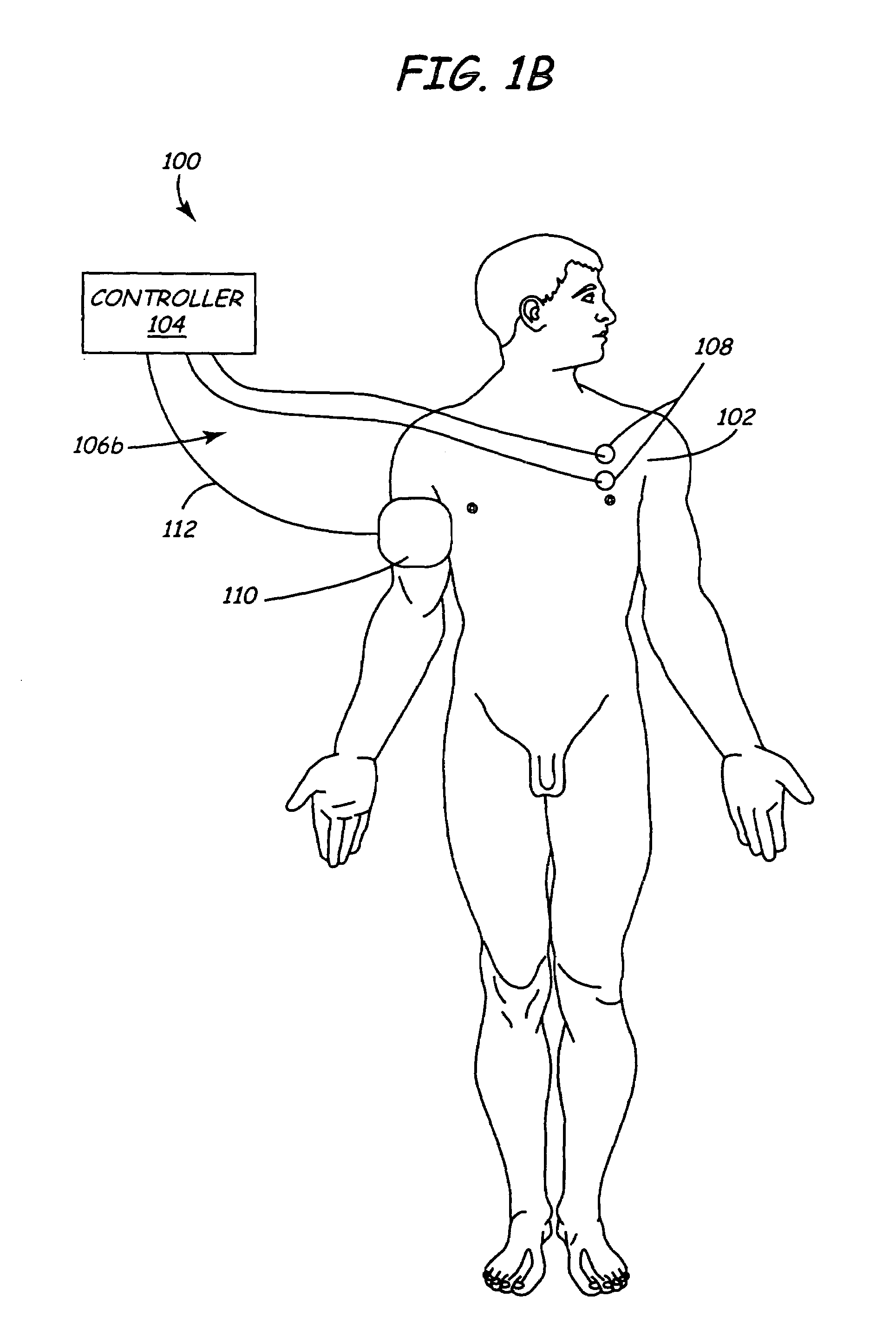
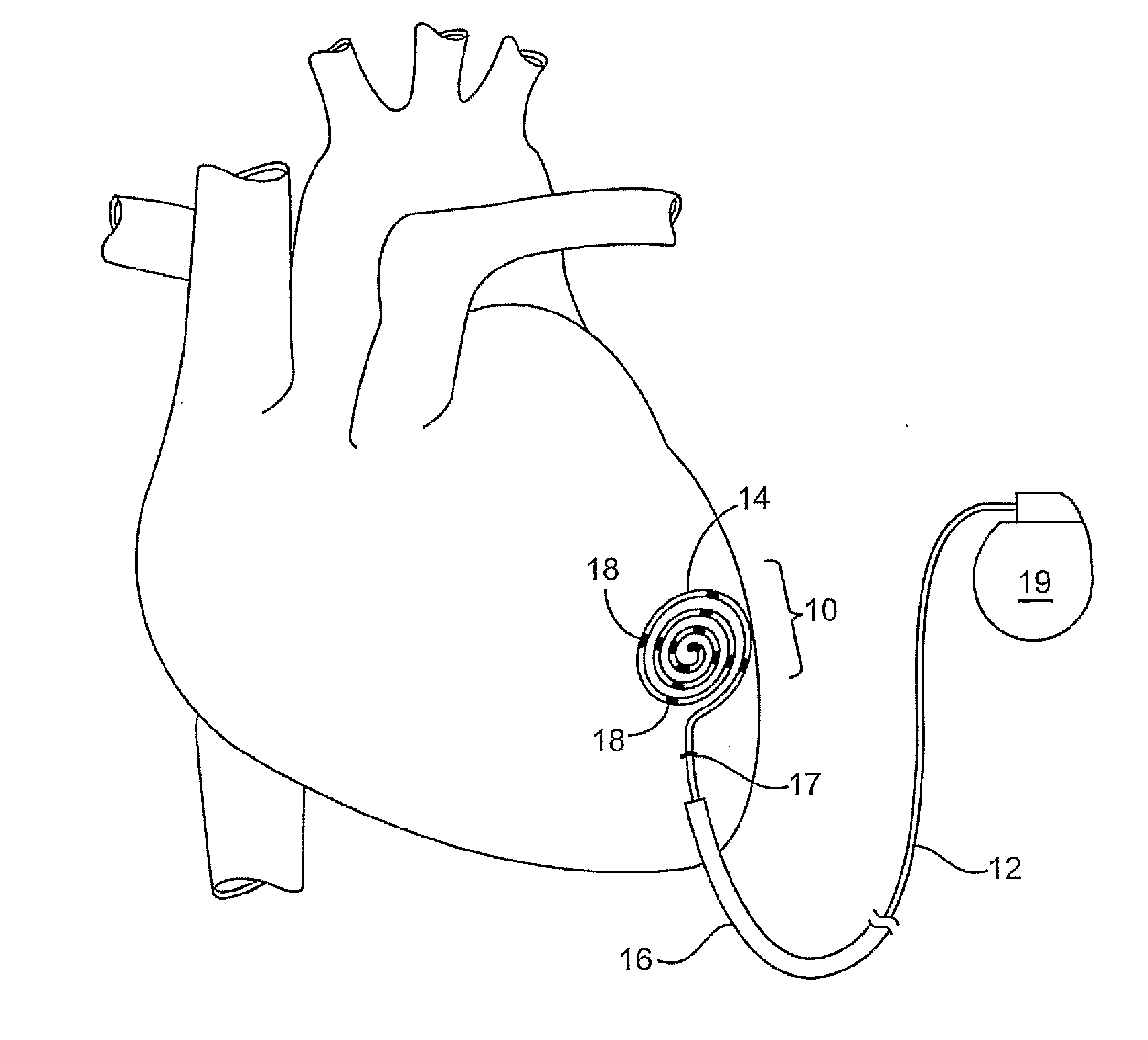
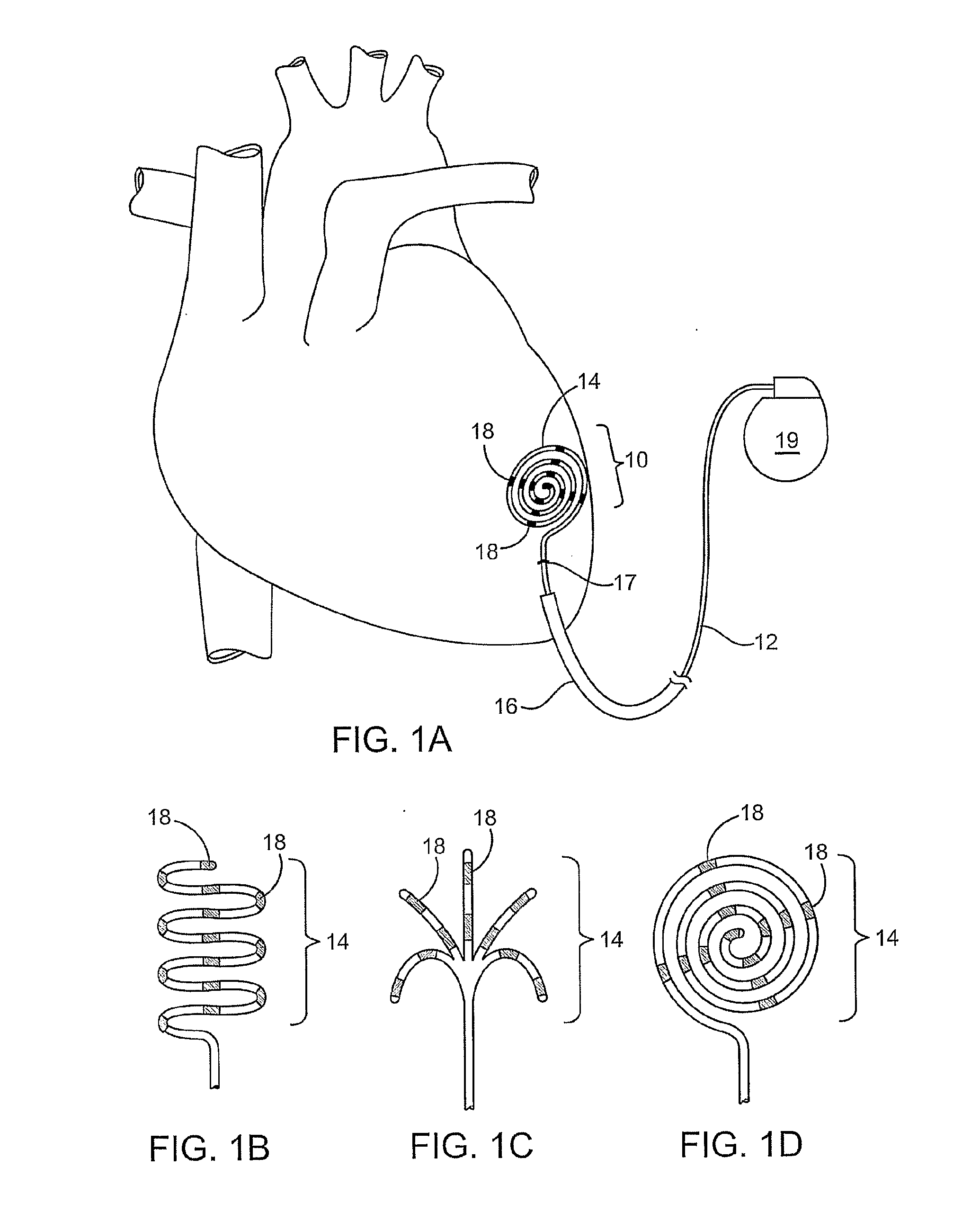
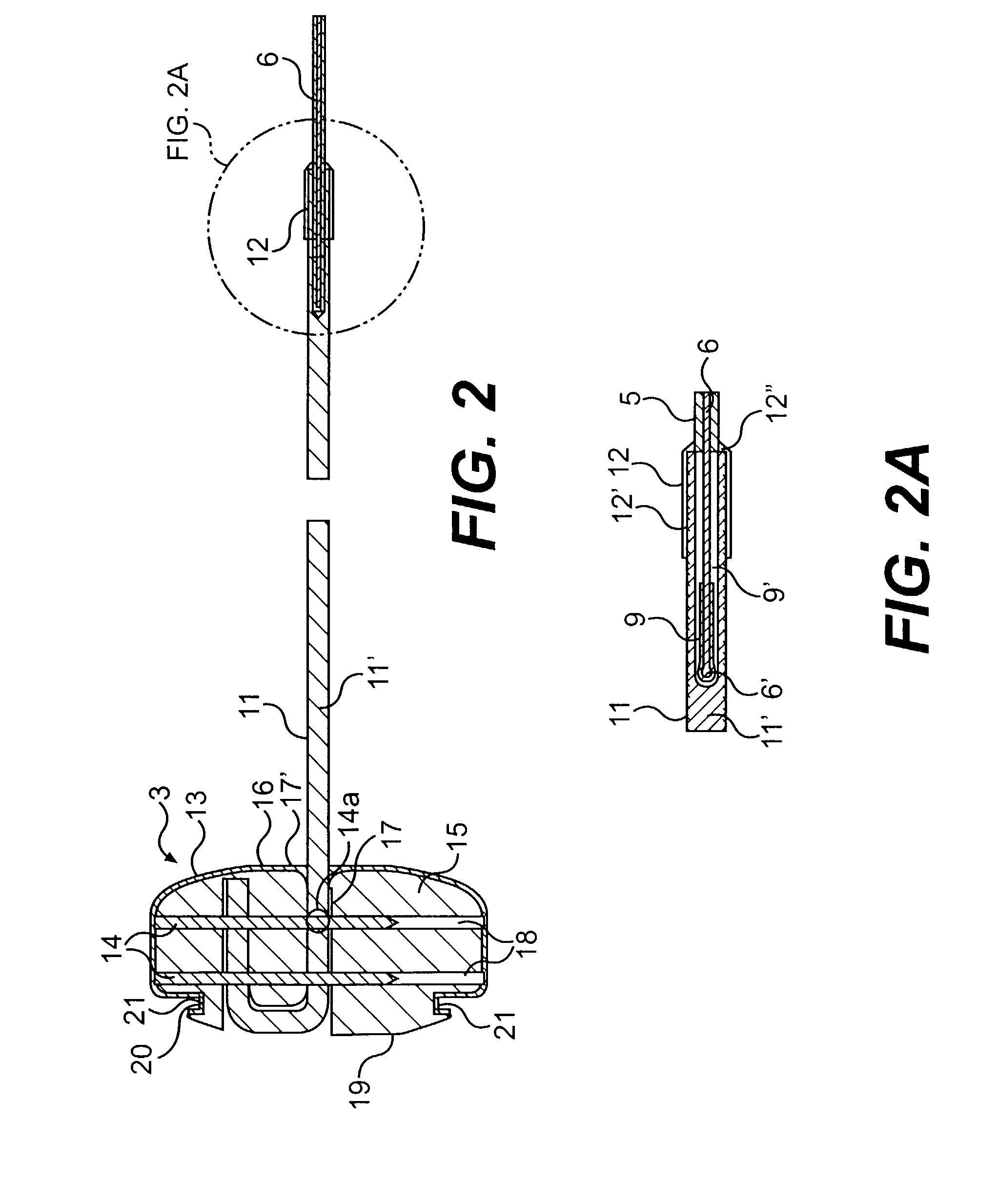
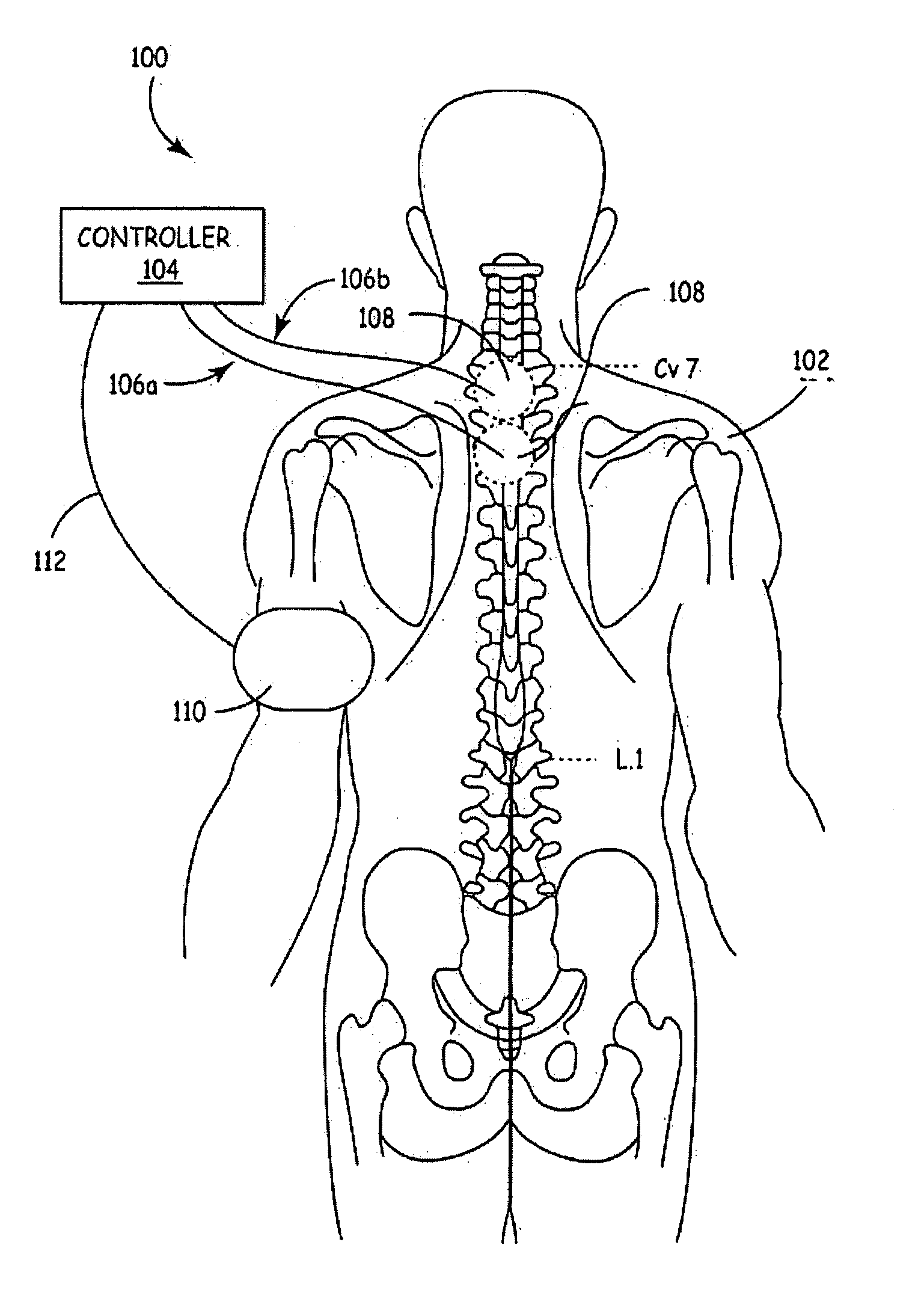
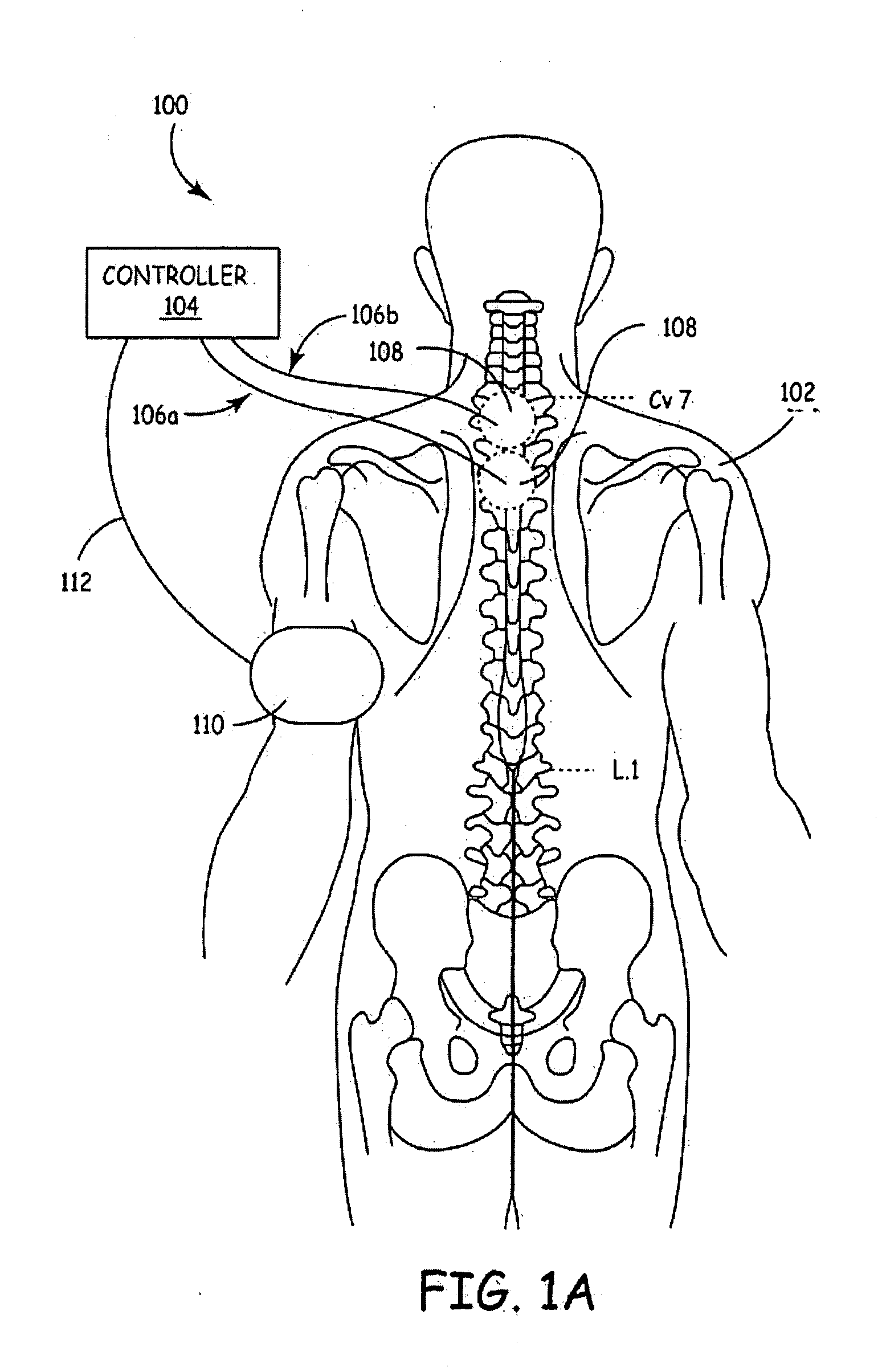
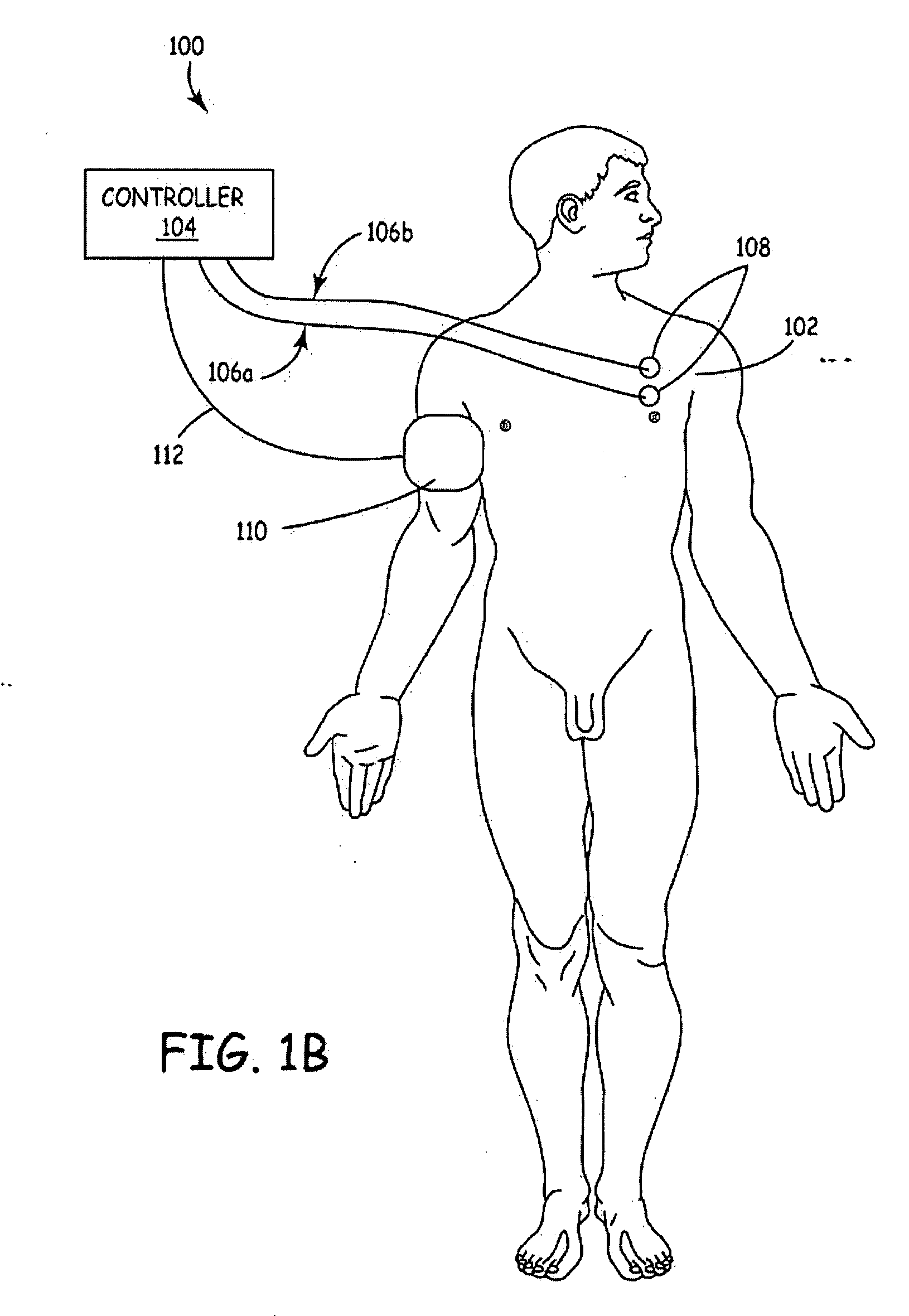
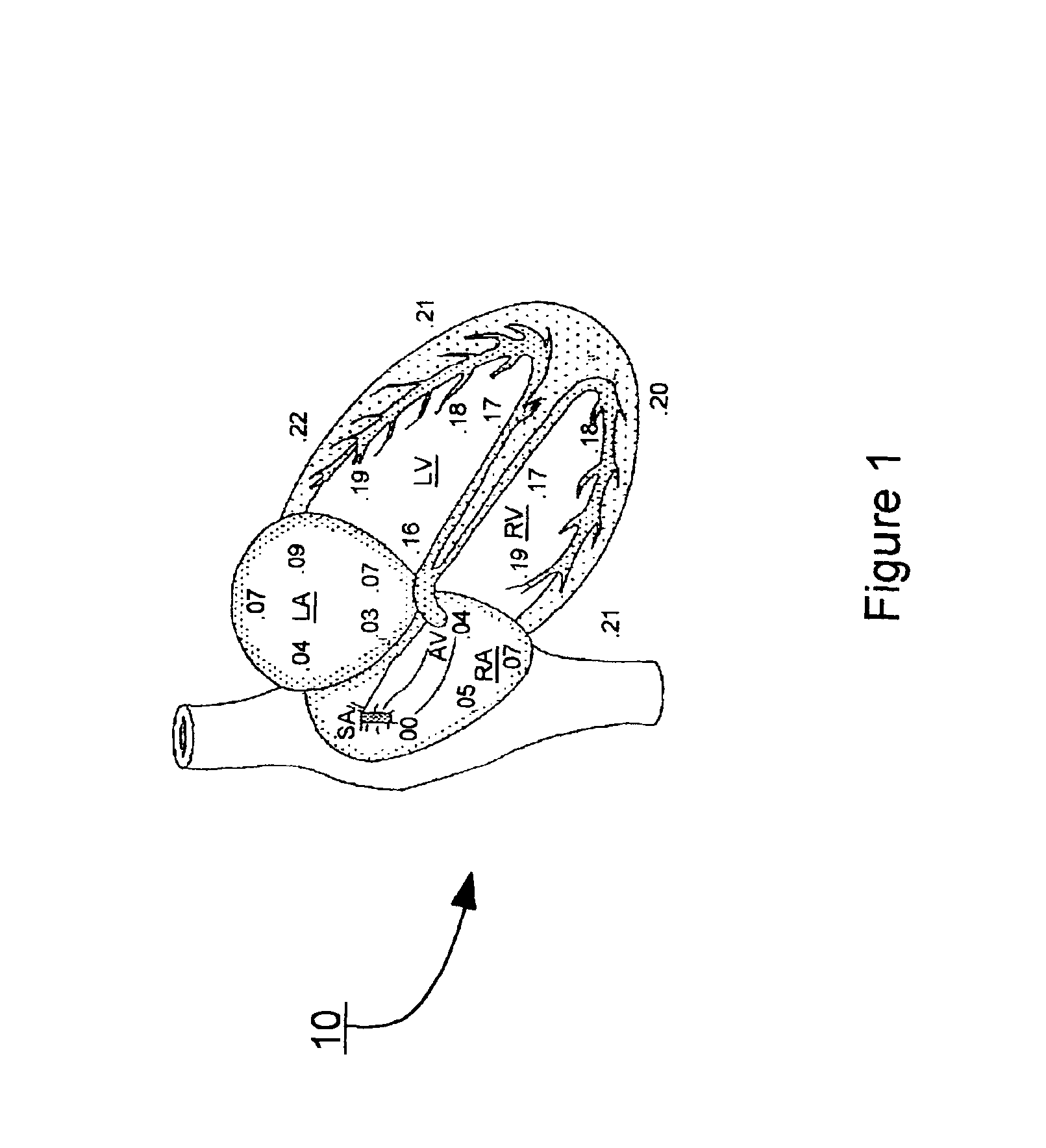
Method and apparatus to minimize effects of a cardiac insult
InactiveUS7010345B2Reduced activityImprove heart functionHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsHeart diseaseElectrical stimulations
A method and apparatus are provided for protecting cardiac tissue from insult. The method comprises identifying the occurrence of an insult, such as a heart attack, and delivering electrical stimulation to one or more predetermined nerves in a patient's body in response to identifying the occurrence of the insult. The stimulation may be provided at the spinal canal or on the chest wall of the patient through cutaneous electrodes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
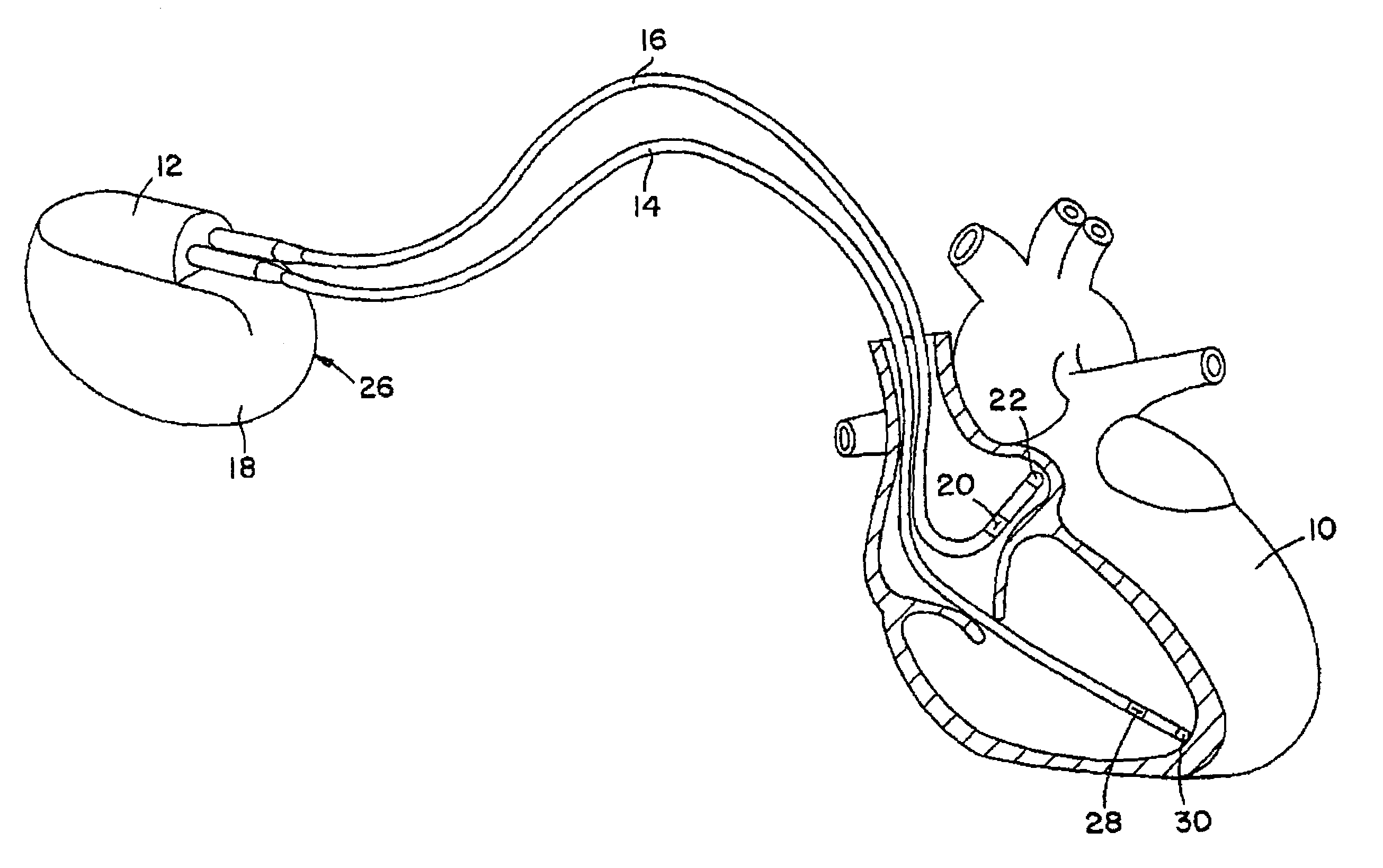
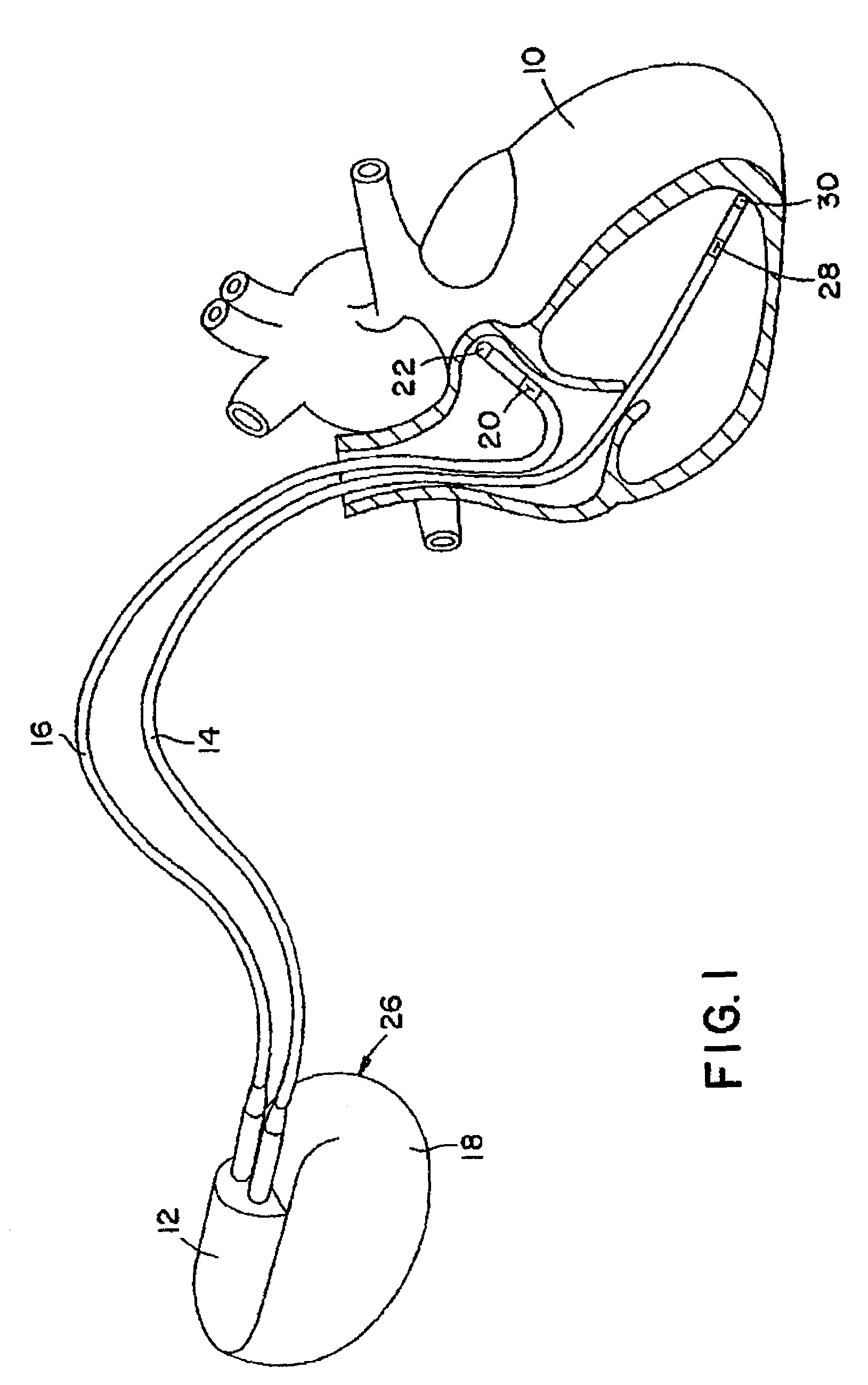
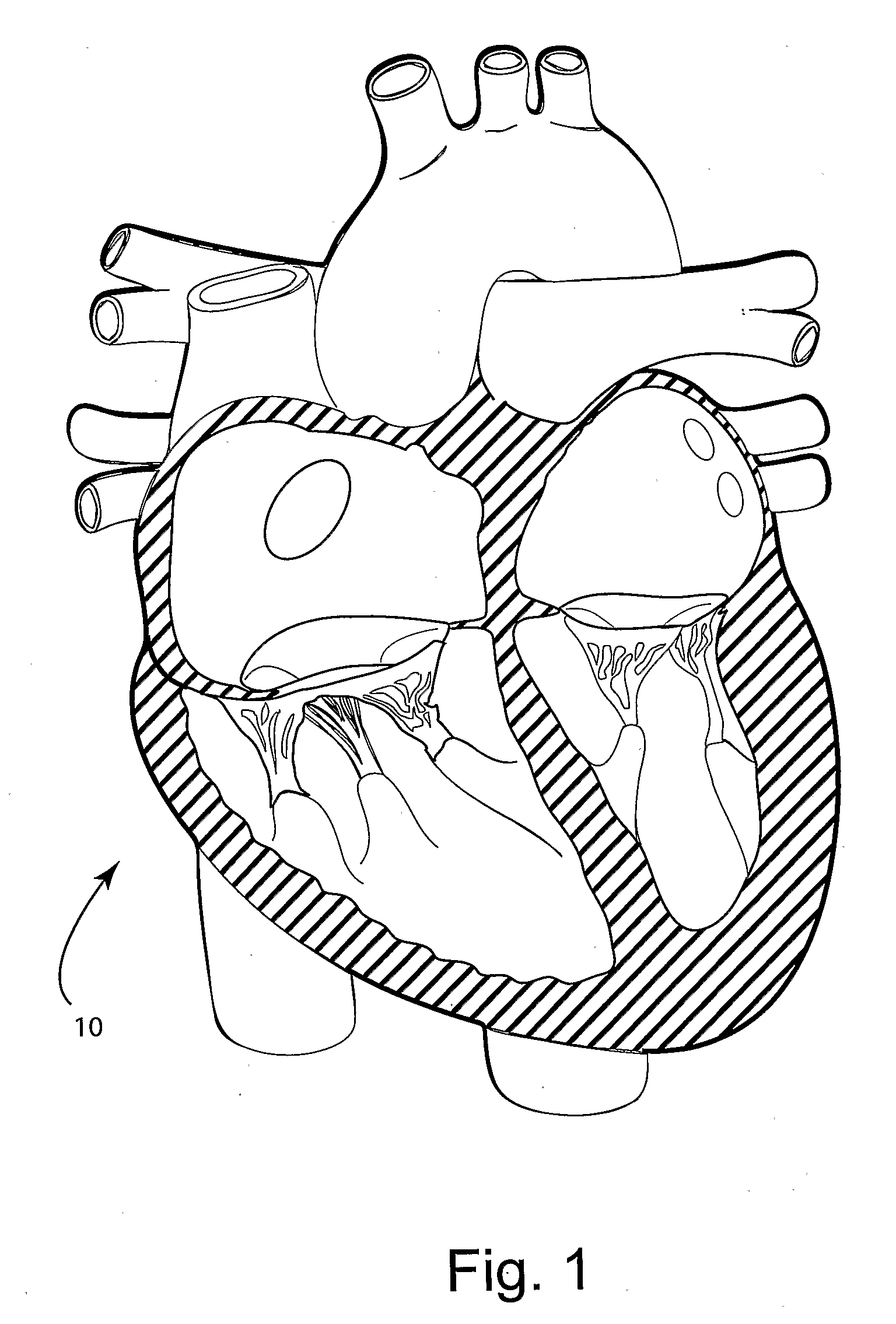
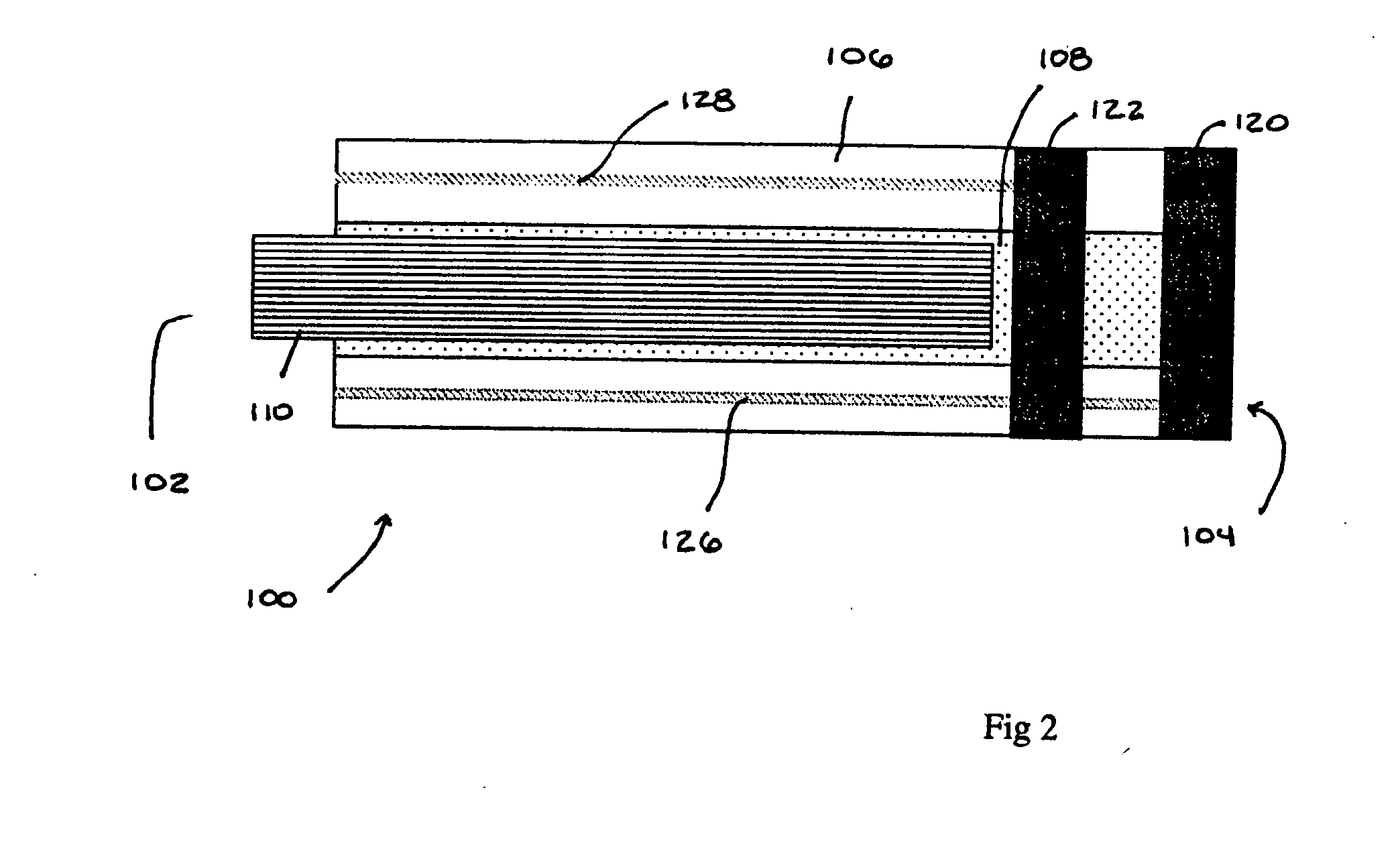
Method for improving cardiac function
A method and a device for improving cardiac function are provided. The device is packaged in a collapsed state in an end of a catheter. Portions of a frame construction of the device spring outwardly when the catheter is withdrawn from the device. Anchoring formations on the frame construction secure the frame construction to a myocardium of the heart. A membrane secured to the frame construction then forms a division between volumes of an endocardial cavity of the heart on opposing sides of the membrane.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Closed-loop neuromodulation for prevention and treatment of cardiac conditions
InactiveUS7218964B2Reduced activityImprove heart functionCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationClosed loop feedbackSpinal cord
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Prevention of myocardial infarction induced ventricular expansion and remodeling
ActiveUS20050080402A1Prevent further deteriorationInhibit swellingSuture equipmentsPowder deliveryCardiac muscleTherapeutic treatment
A method for direct therapeutic treatment of myocardial tissue in a localized region of a heart having a pathological condition. The method includes identifying a target region of the myocardium and applying material directly and substantially only to at least a portion of the myocardial tissue of the target region. The material applied results in a physically modification the mechanical properties, including stiffness, of said tissue. Various devices and modes of practicing the method are disclosed for stiffening, restraining and constraining myocardial tissue for the treatment of conditions including myocardial infarction or mitral valve regurgitation.
Owner:MYOMEND
Method for supplementing the diet
InactiveUS6579544B1Increased susceptibilityPrevent diseaseHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDietary supplementAlpha-Lipoic Acid
A dietary supplement blend composition is disclosed, the basic formulation of the composition containing vitamins, minerals, and carotenoids. The composition can also contain bioflavonoids, cartilage protectors such as glucosamine or chondroitin, alpha-lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10, and a source of omega-3 fatty acids such as flax seed oil. The composition is beneficial for improving health and preventing disease, particularly for degenerative conditions. A method for supplementing the diet is also disclosed, wherein the quantity of daily rations of the dietary supplement blend composition is determined based on the person's age, body weight, and quality of diet.
Owner:NUTRIEX
Method for improving cardiac function
A method and a device for improving cardiac function are provided. The device is packaged in a collapsed state in an end of a catheter. Portions of a frame construction of the device spring outwardly when the catheter is withdrawn from the device. Anchoring formations on the frame construction secure the frame construction to a myocardium of the heart. A membrane secured to the frame construction then forms a division between volumes of an endocardial cavity of the heart on opposing sides of the membrane.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
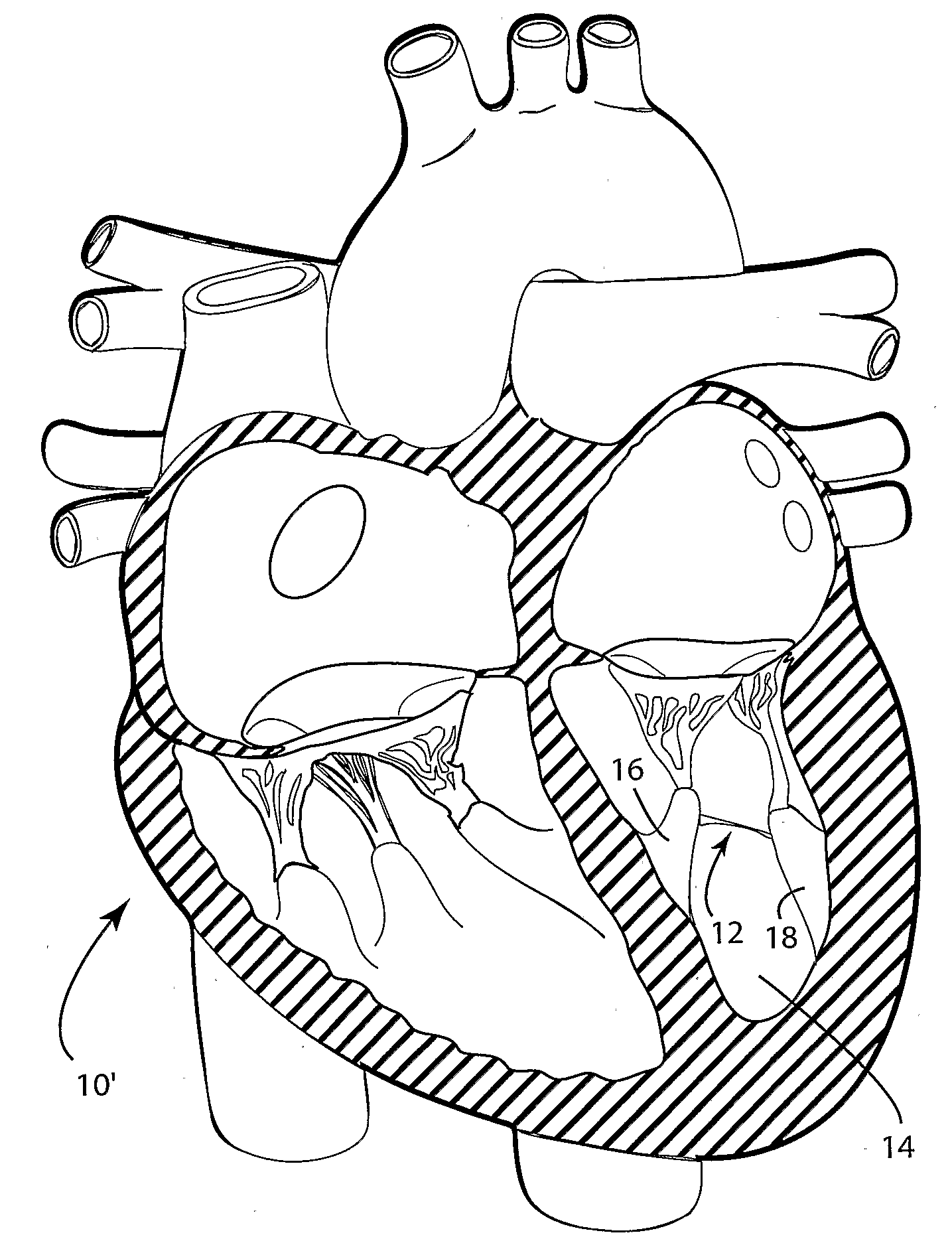
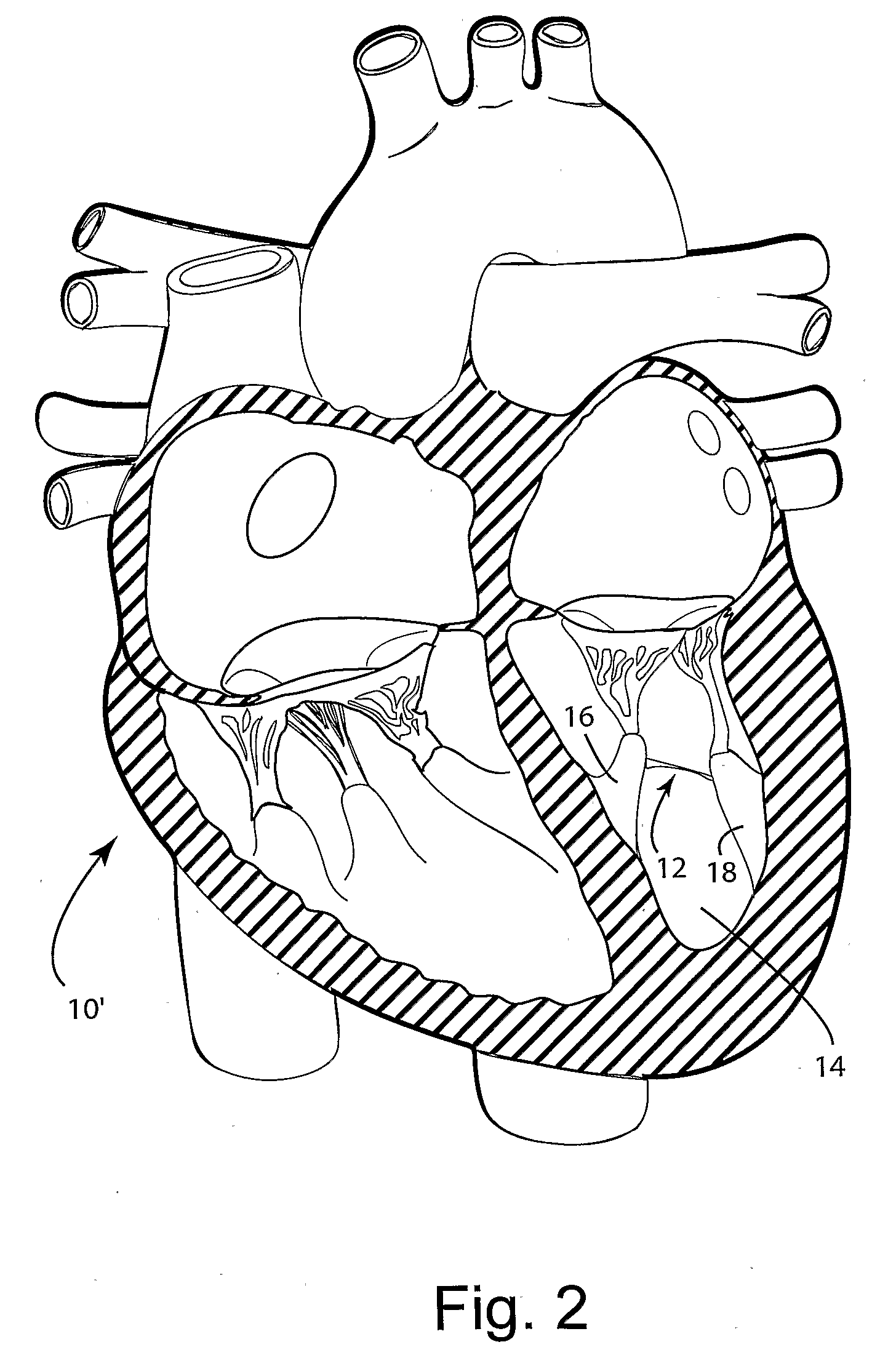
System for improving cardiac function
ActiveUS20060264980A1Improve heart functionOcculdersSurgical staplesCardiac functioningCardiac muscle
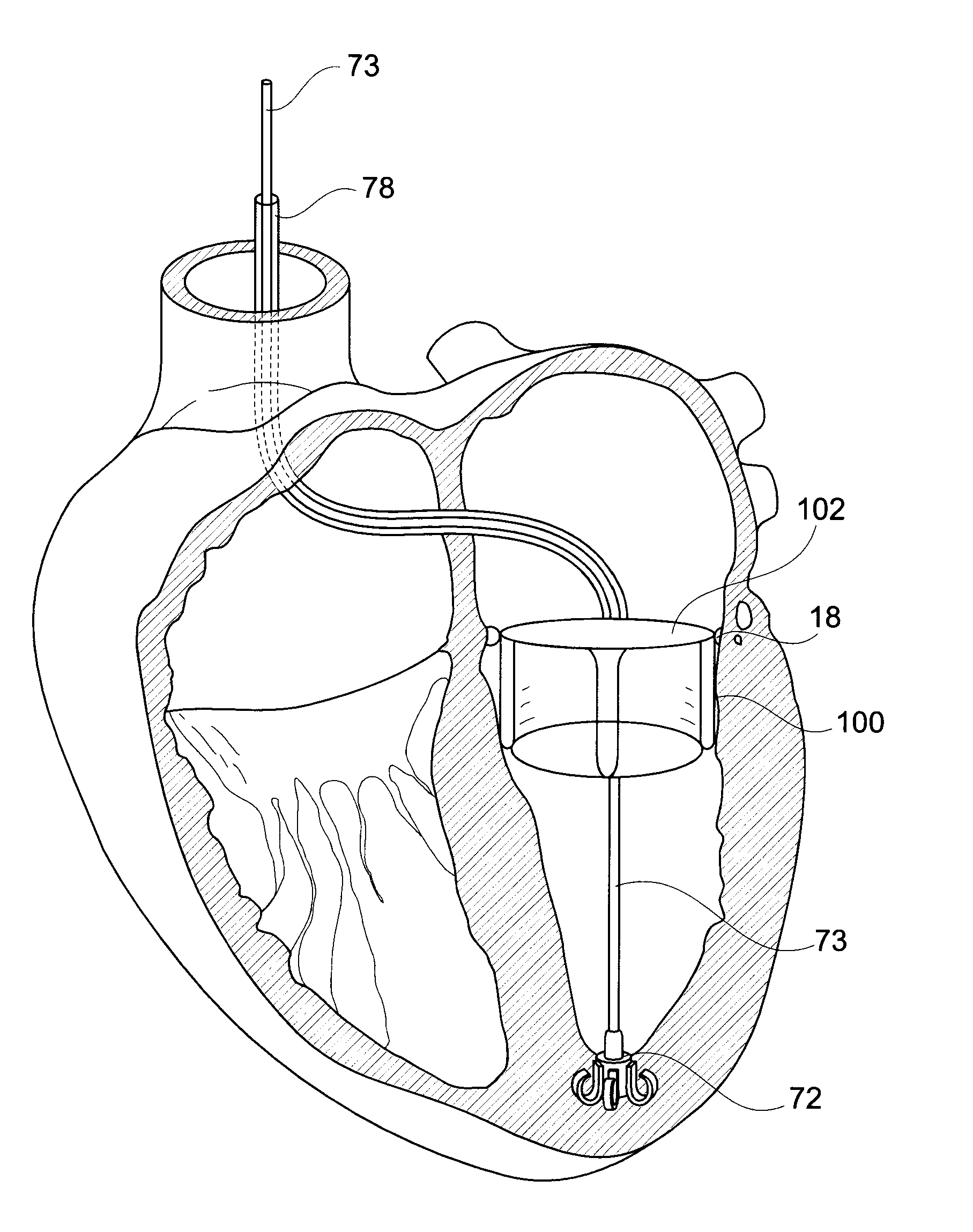
A system for improving cardiac function is provided. A foldable and expandable frame having at least one anchoring formation is attached to an elongate manipulator and placed in a catheter tube while folded. The tube is inserted into a left ventricle of a heart where the frame is ejected from the tube and expands in the left ventricle. Movements of the elongate manipulator cause the anchor to penetrate the heart muscle and the elongate manipulator to release the frame. The installed frame minimizes the effects of an akinetic portion of the heart forming an aneurysmic bulge.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
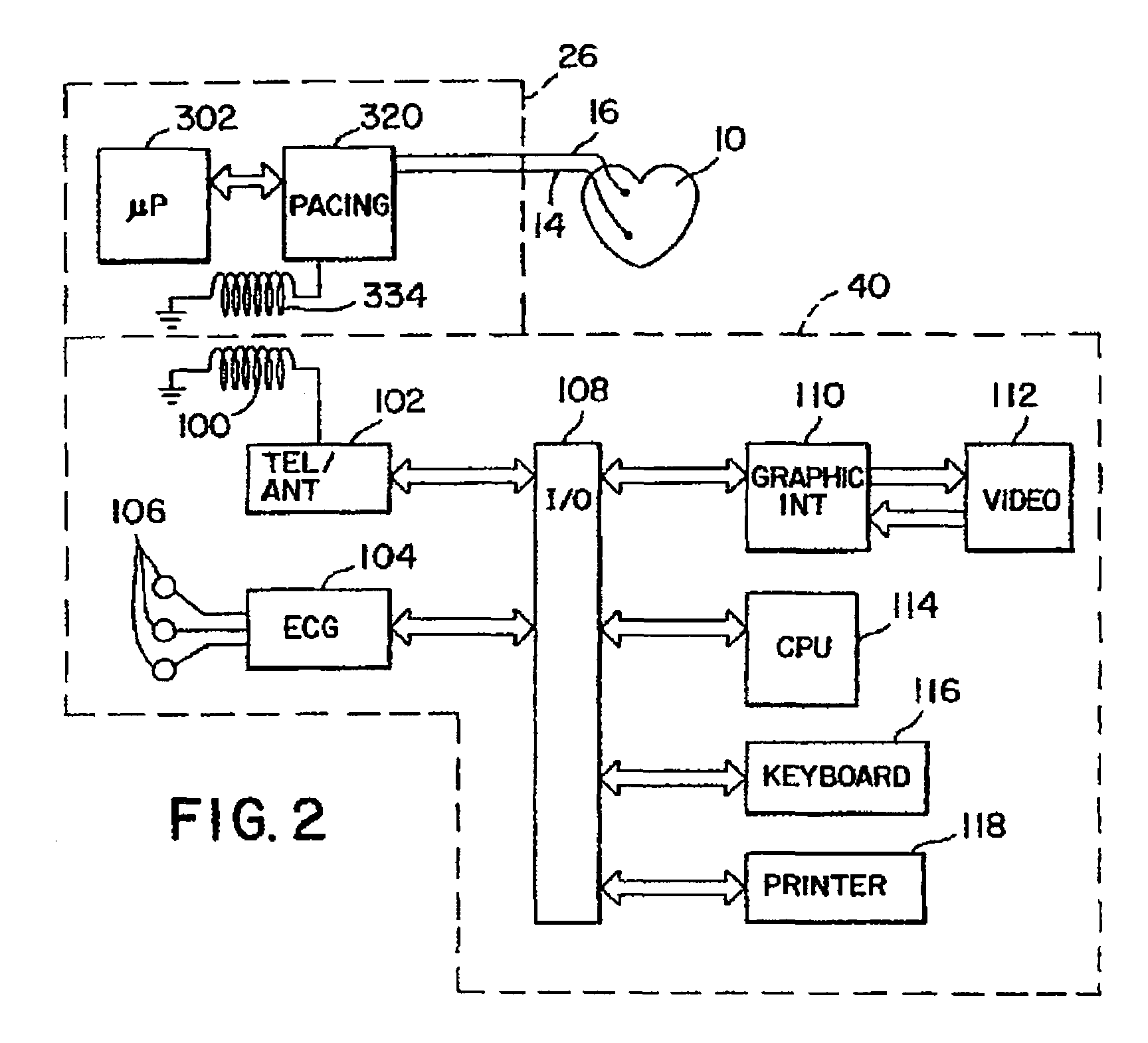
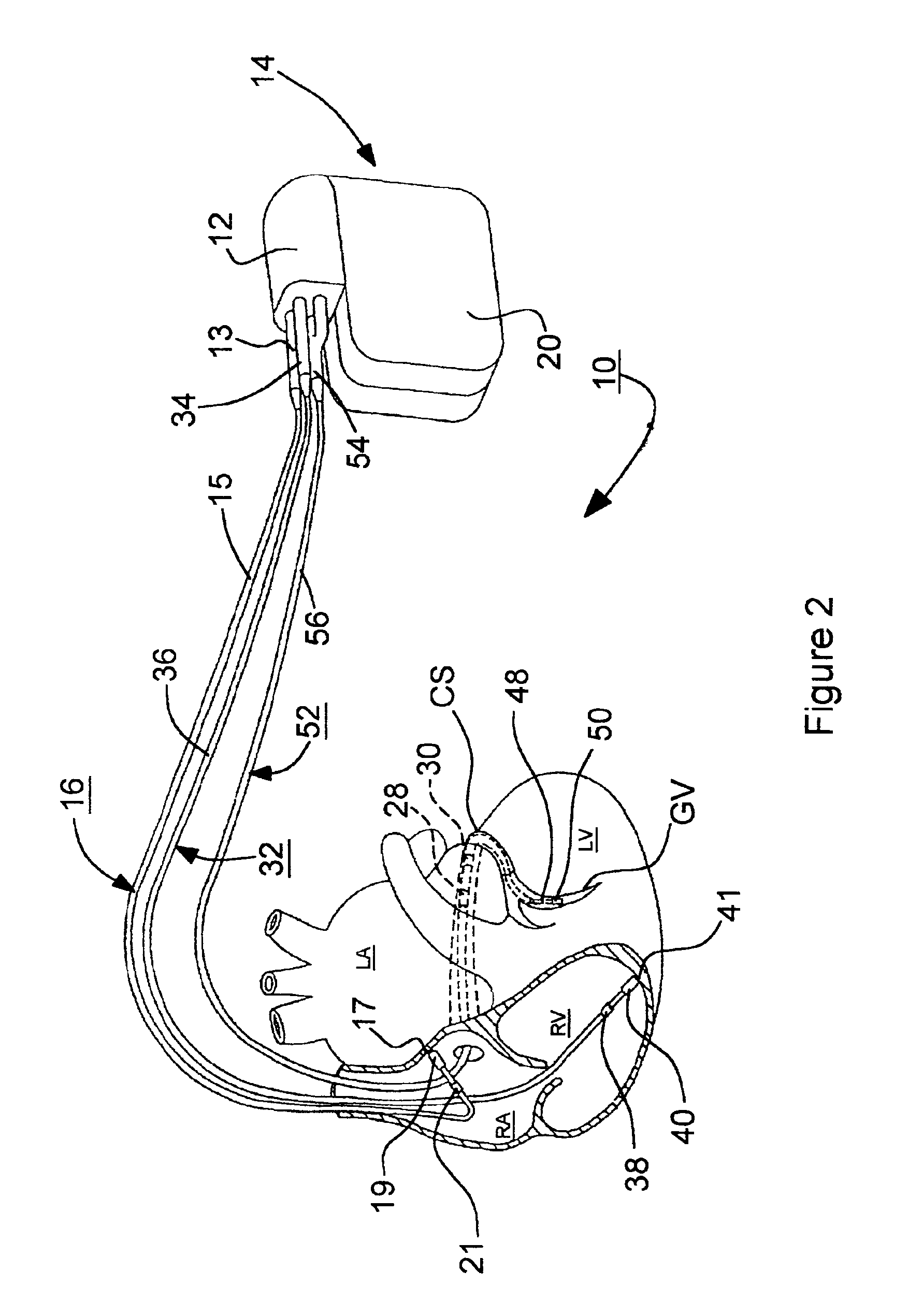
Cardiac pacing apparatus and method for continuous capture management
ActiveUS7831303B2Increase the number ofIncrease incidenceHeart stimulatorsHeart chamberCardiac stimulation
An implantable cardiac stimulation system and method having continuous capture management capabilities are provided. Continuous capture management is realized by continuously monitoring for secondary effects of loss of capture, thereby effectively providing continuous capture management in any heart chamber without encountering the limitations normally associated with evoked response sensing. A pacing threshold search is triggered upon detecting a secondary indicator of loss of capture. Secondary indicators of loss of capture may be lead-related changes, changes related to the occurrence of atrial sensed events, changes related related to the occurrence of ventricular sensed or paced events, and / or changes related to a monitored physiological condition.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
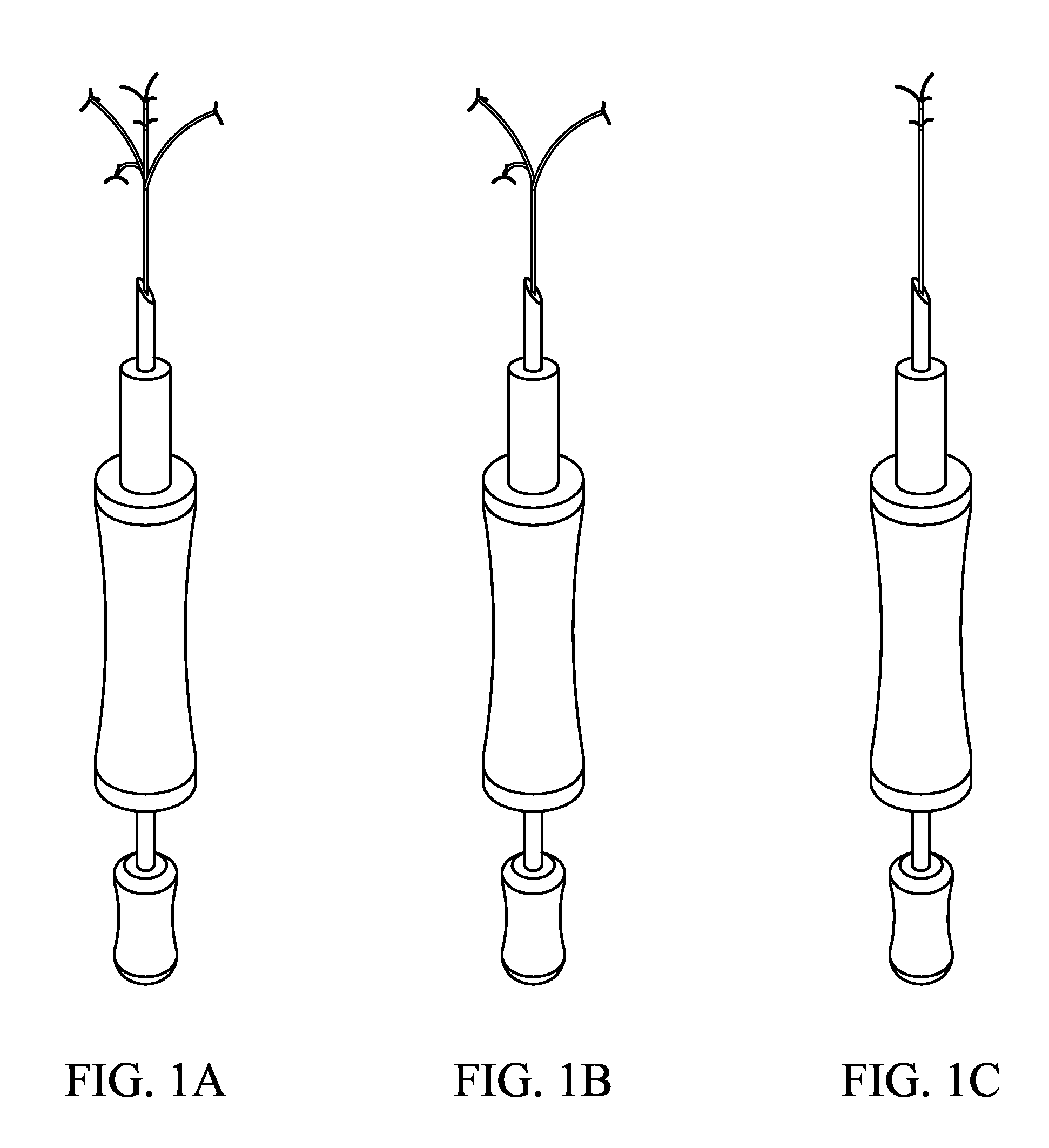
Deployable epicardial electrode and sensor array
InactiveUS20090299447A1Minimally invasiveRelieve stressEpicardial electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical controlSubxiphoid approach
Minimally invasive deployable epicardial array devices are provided. The devices include deployable platform comprising two or more effectors, such as sensors and actuators, where the devices are configured to be deployed at an epicardial location via a minimally invasive, e.g., sub-xiphoid approach. In embodiments of the present invention, at least one area of the electrode patch is an electrical control area that comprises a series of effectors, e.g., sensors and / or electrodes. Other embodiments provide localized physical constraint and dynamic mechanical stimulation of the heart to effectuate physical and biological responses. Still other embodiments provide both of these functions. Also provided are methods of using the devices, as well as systems and kits that include the devices.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
Stabilization of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) alpha
InactiveUS20030176317A1Improve heart functionPromote healingOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineBiochemistry
The present invention relates to methods of stabilizing the alpha subunit of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF). The invention further relates to methods of preventing, pretreating, or treating conditions associated with HIF, including ischemic and hypoxic conditions. Compounds for use in these methods are also provided.
Owner:FIBROGEN INC
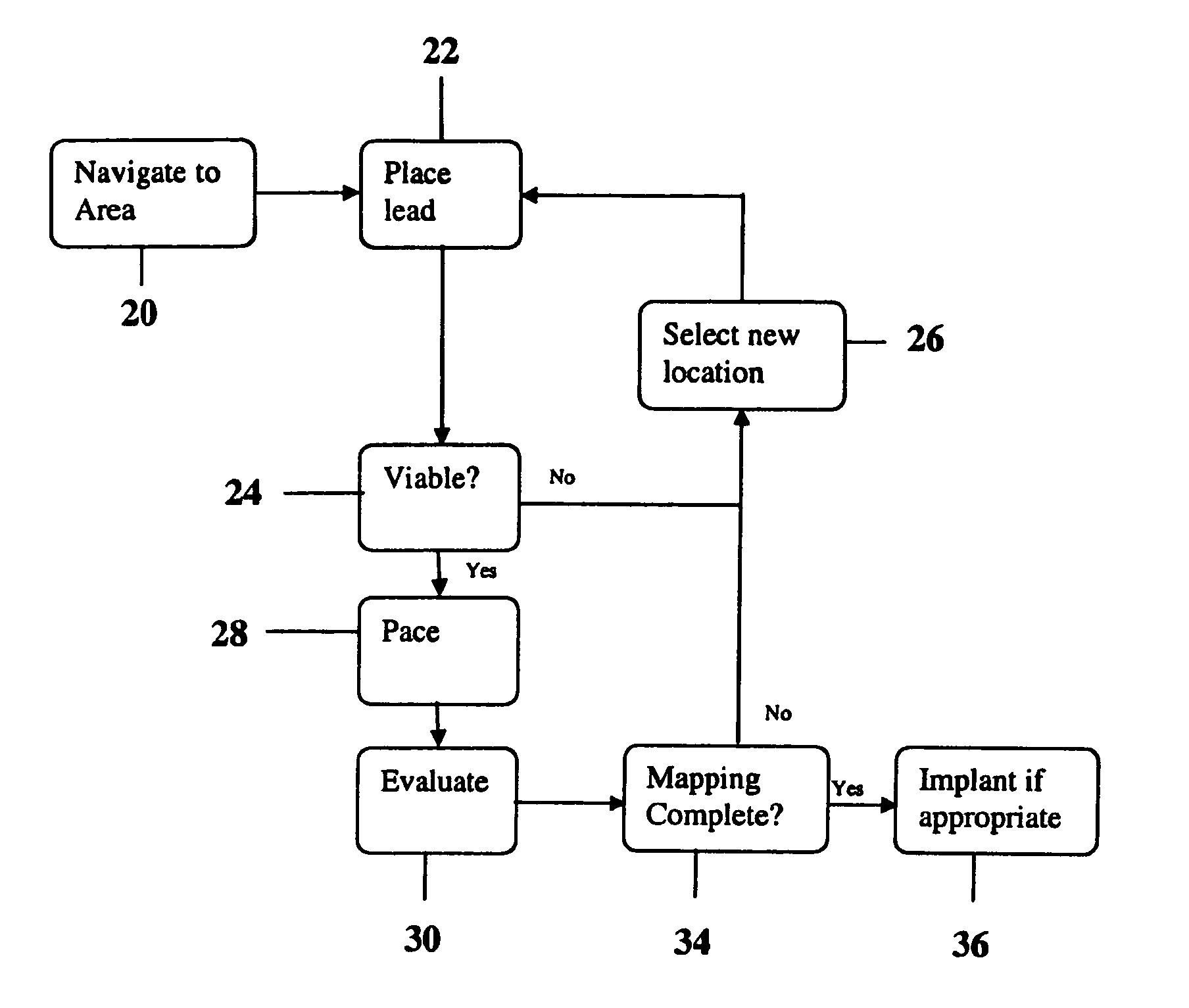
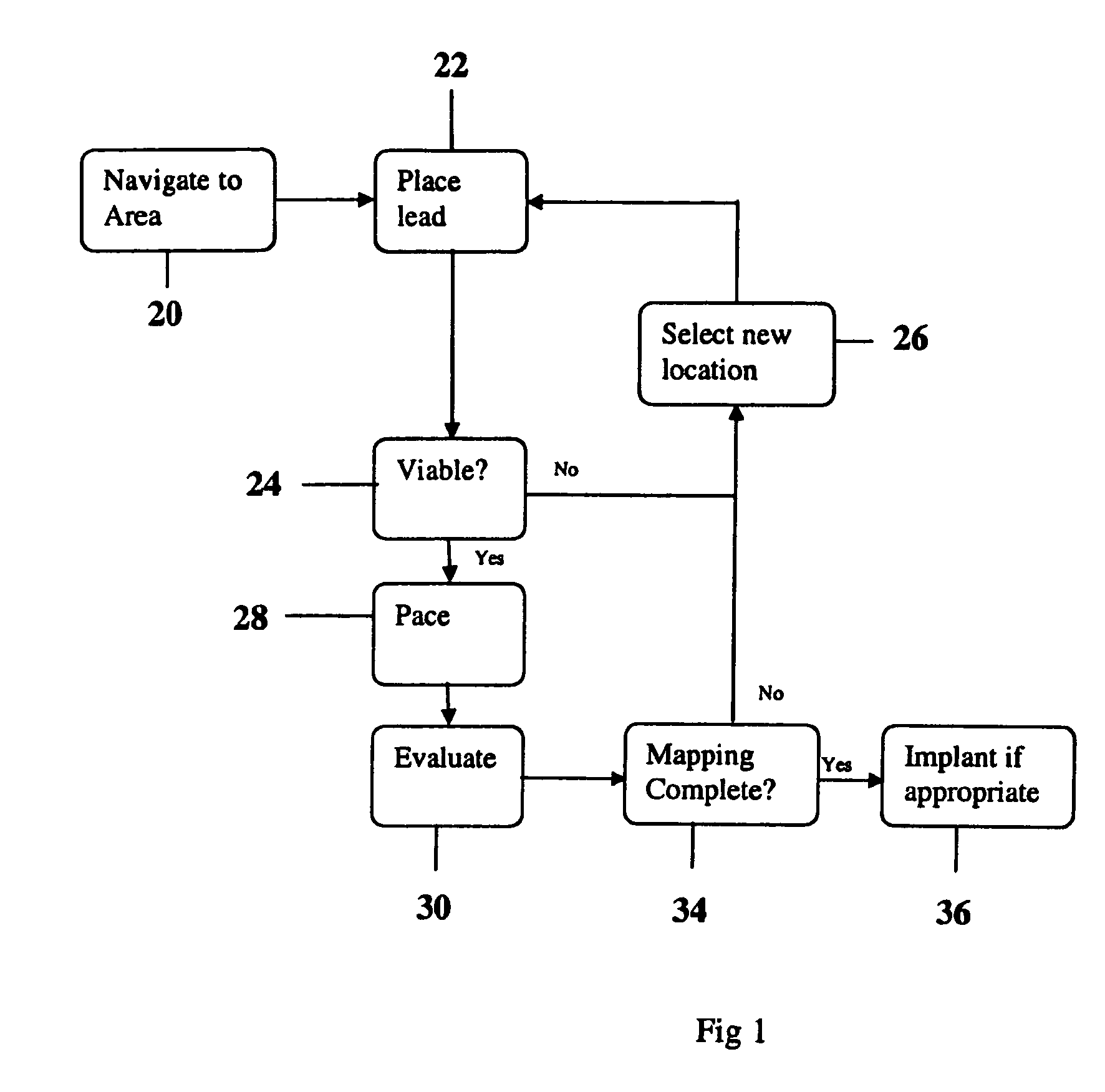
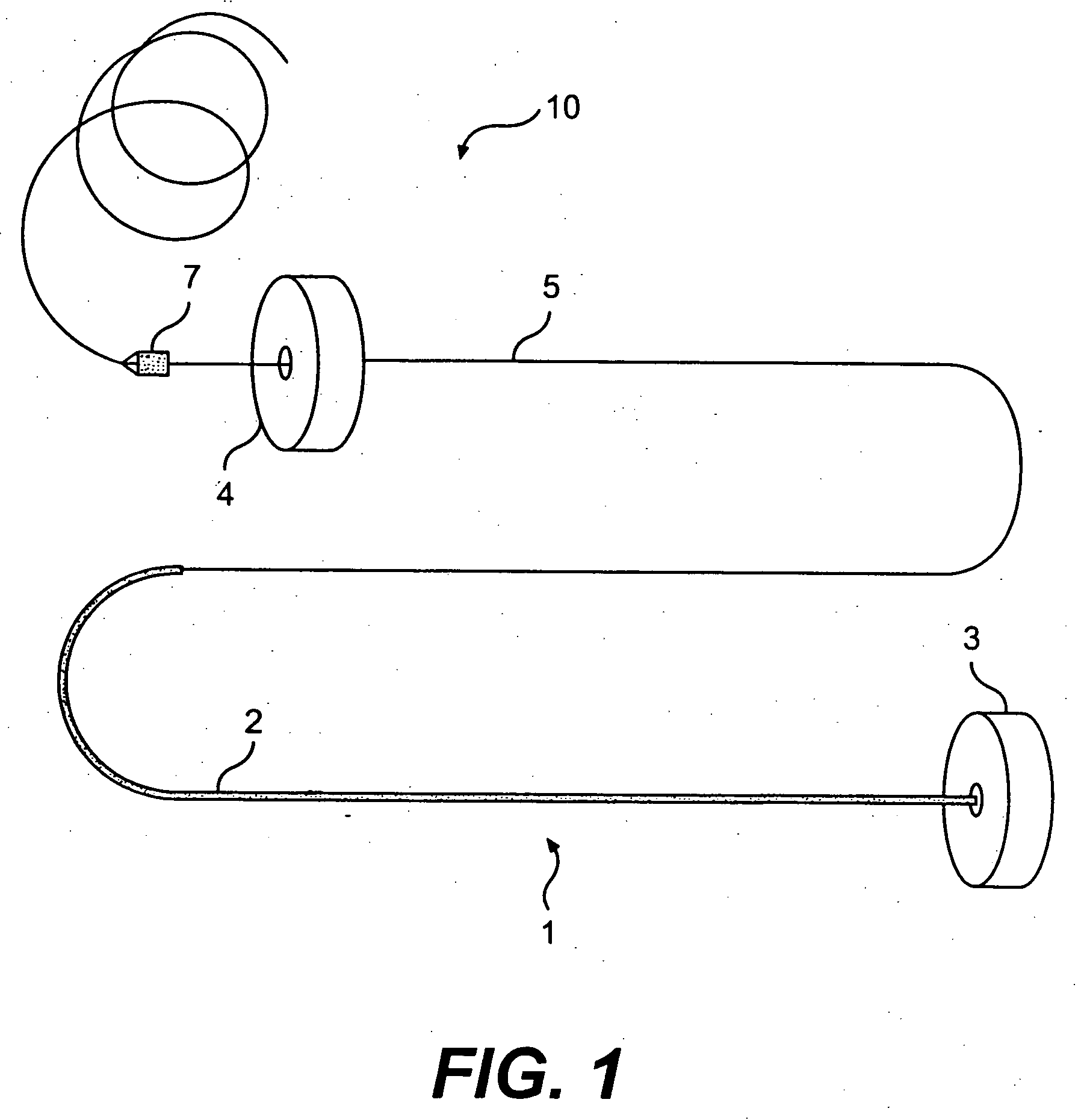
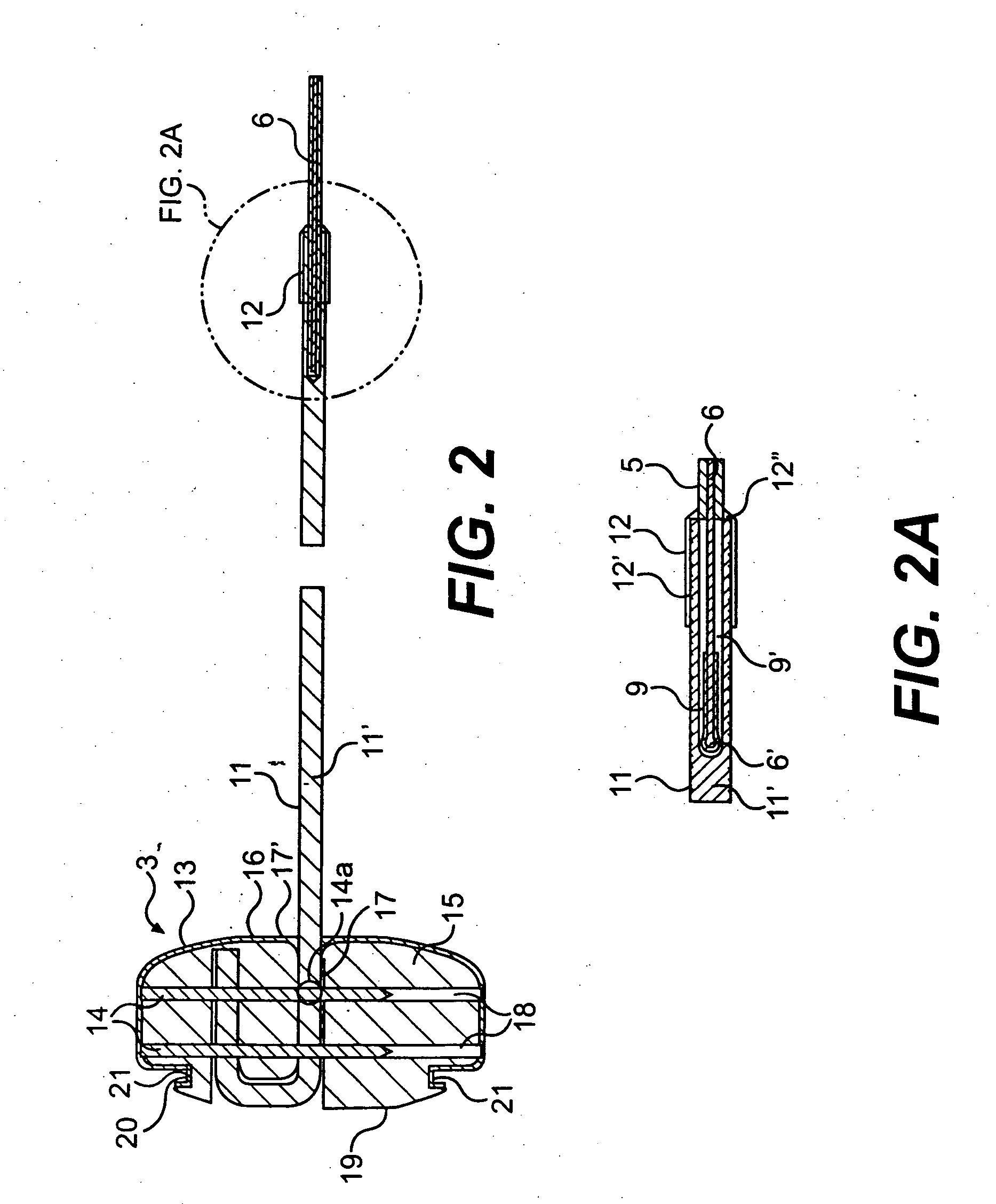
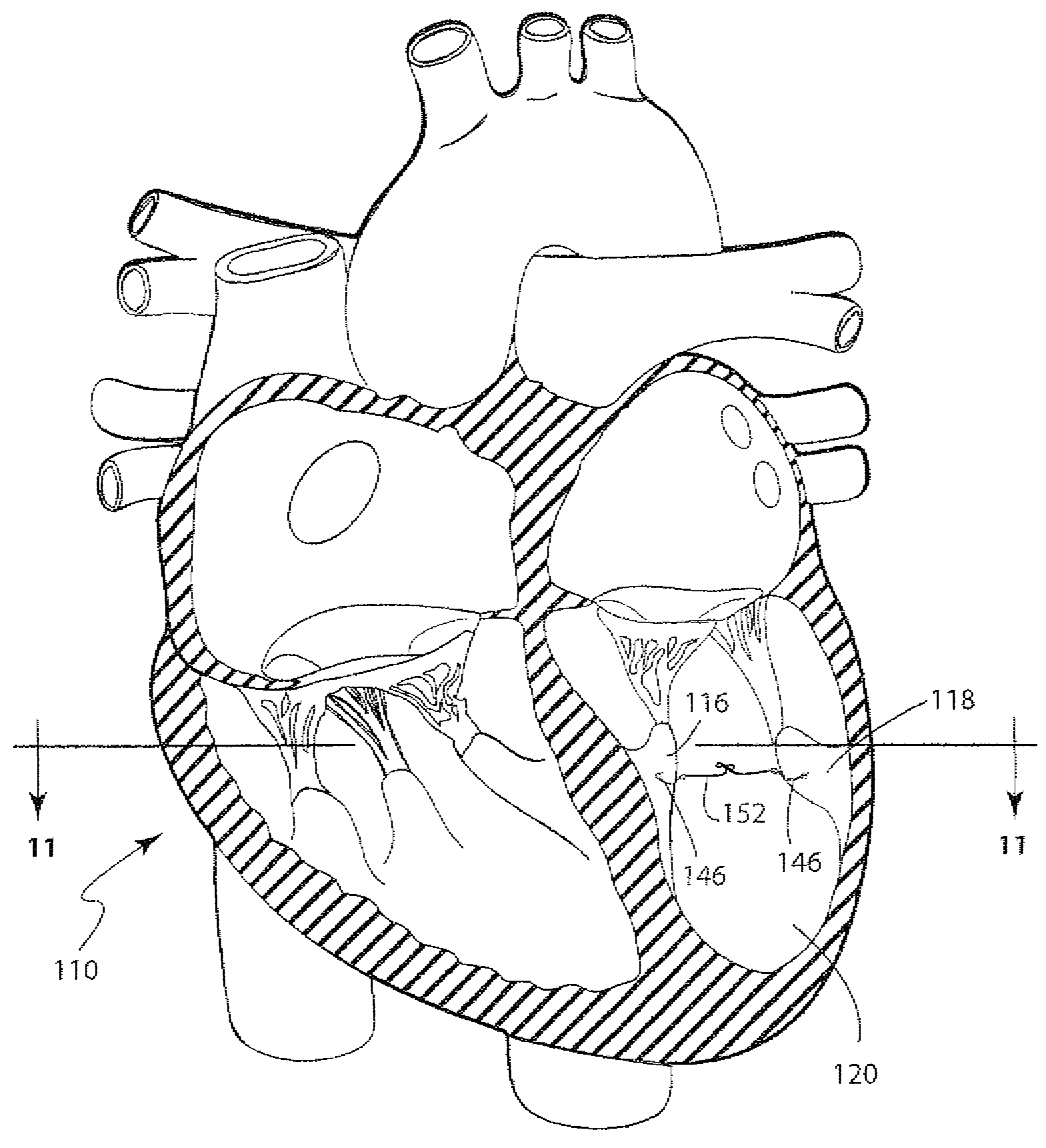
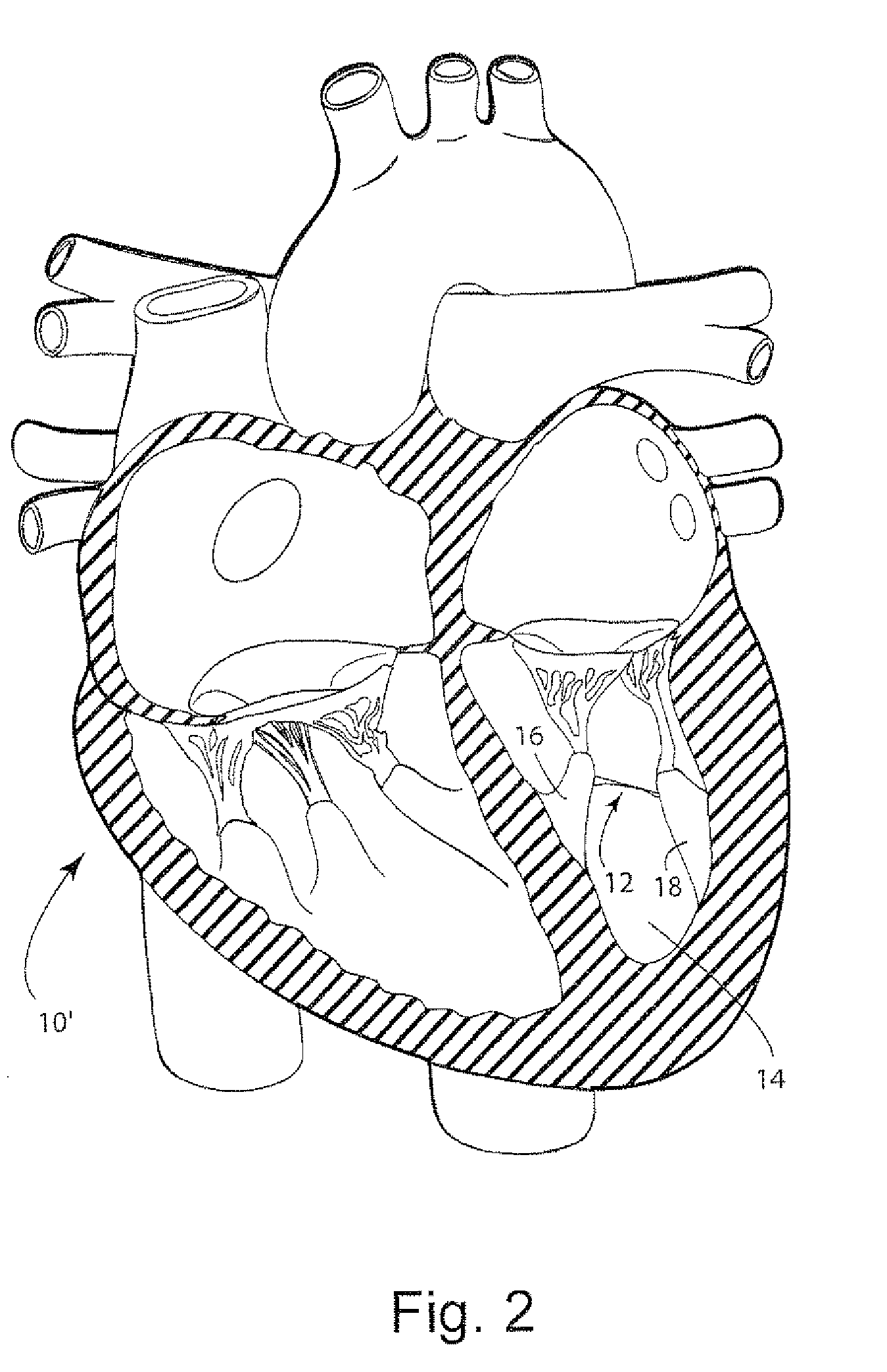
Methods and devices for mapping the ventricle for pacing lead placement and therapy delivery
InactiveUS20070060992A1Easy to placeImprove heart functionInternal electrodesSurgical instrument detailsLead PlacementCatheter device
A method of placing a pacing lead in the heart includes moving an electrode catheter successively to a plurality of possible placement sites. The viability of the tissue at each site is determined. If the tissue at the site is viable, a pacing signal is applied to the tissue at the site, and the effectiveness of the pacing from the site is measured. After the area has been mapped in this fashion, at least one pacing lead is placed from at least one of the sites which exceeded a predetermined level of pacing effectiveness.
Owner:PAPPONE CARLO
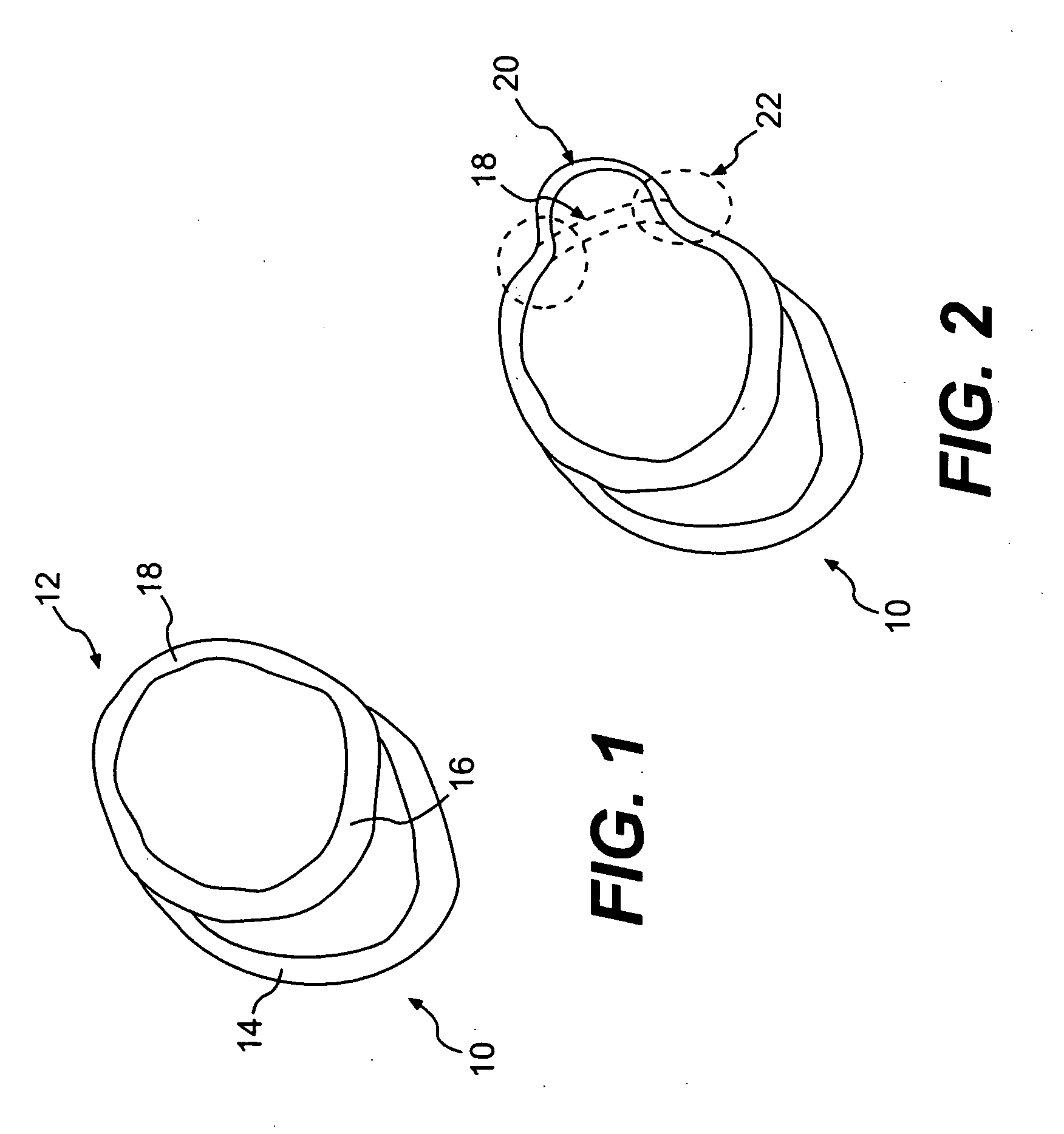
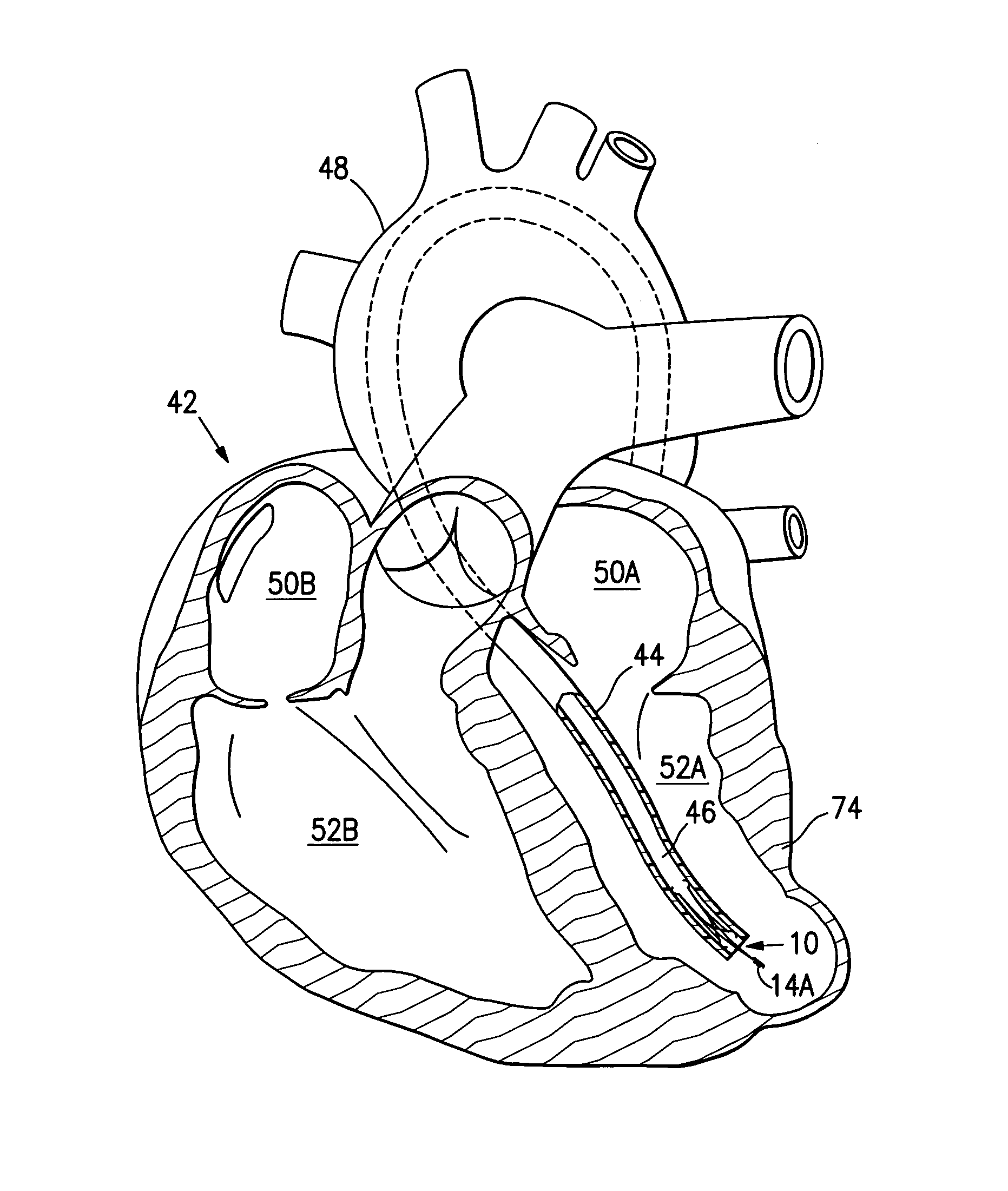
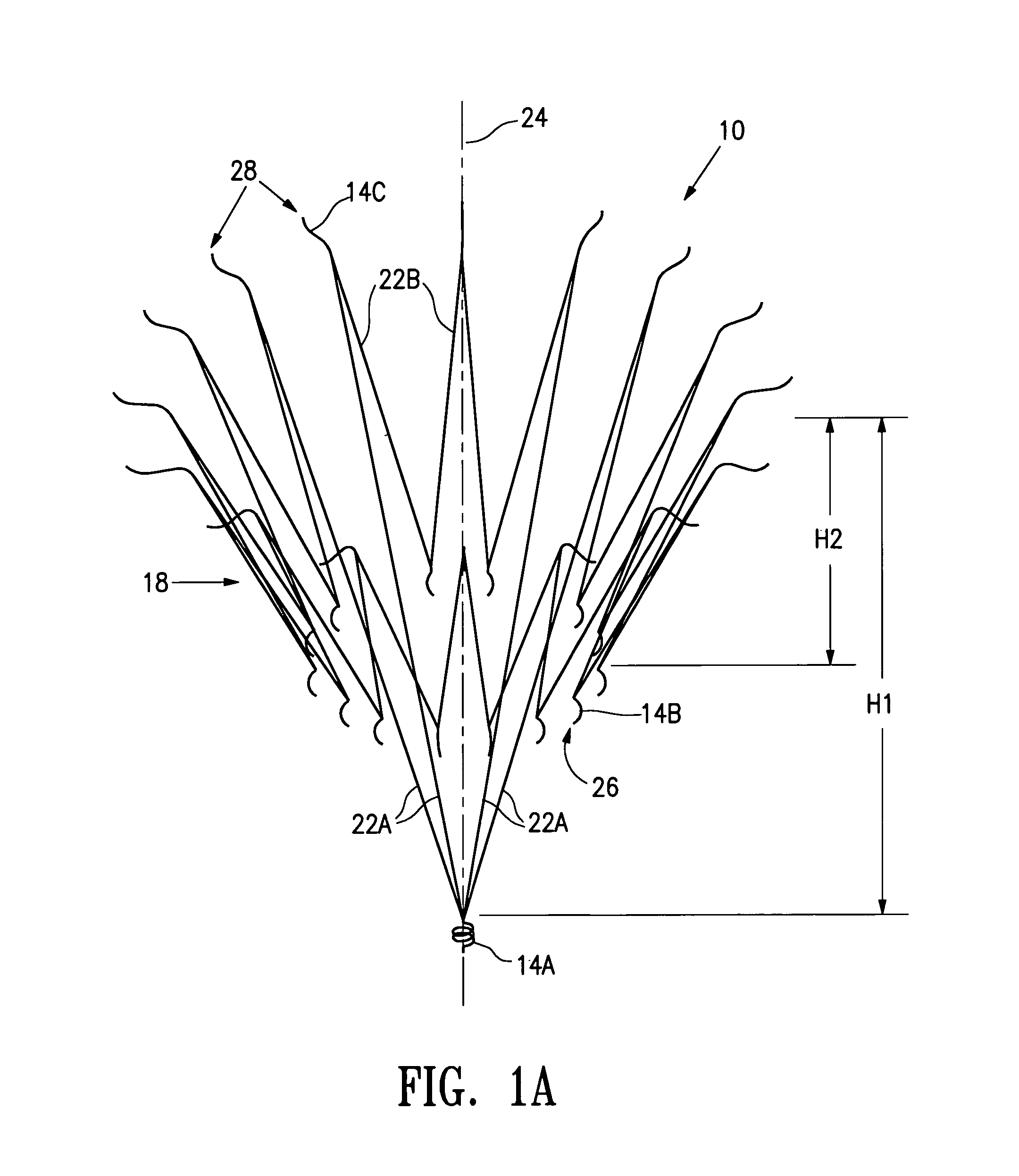
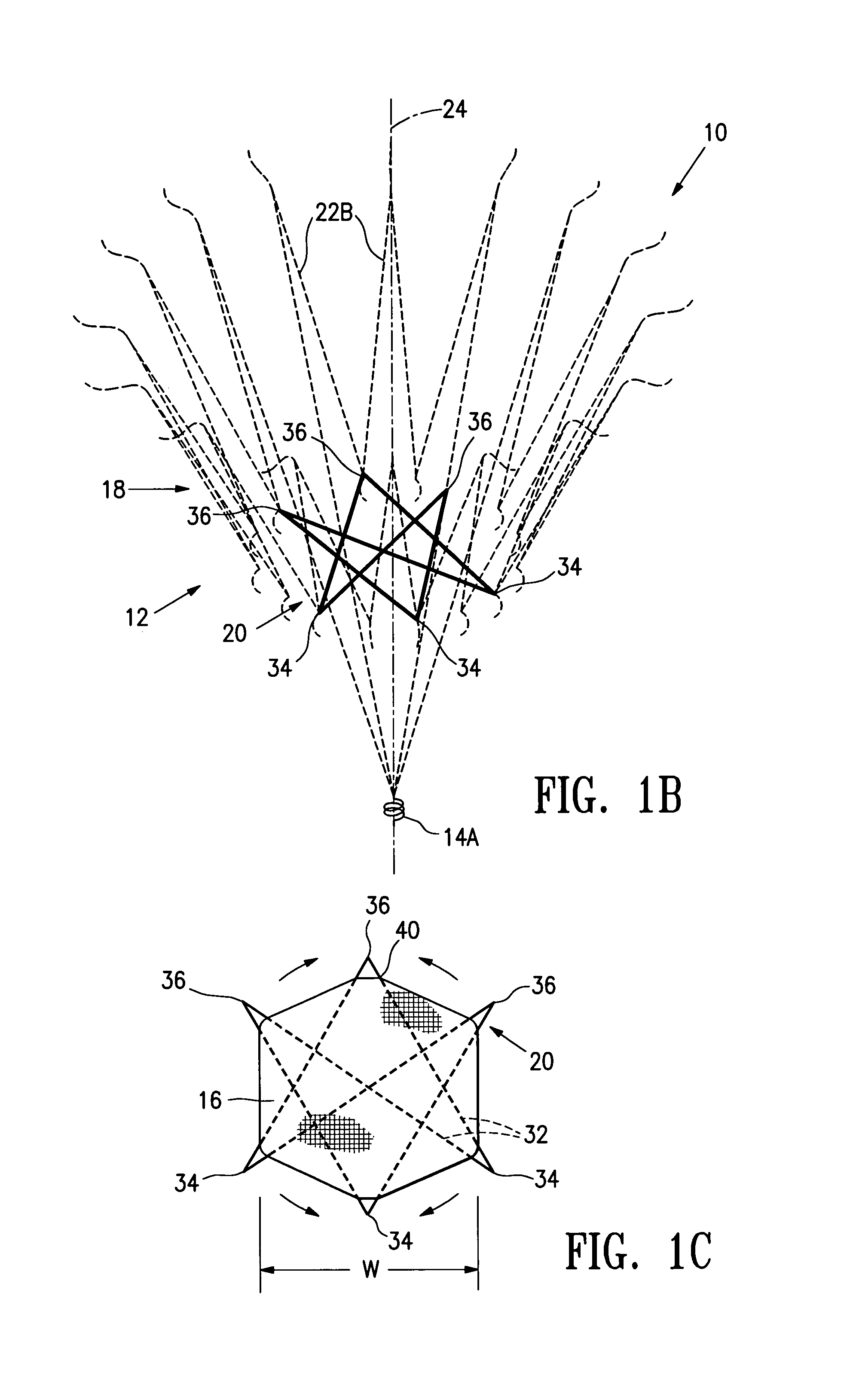
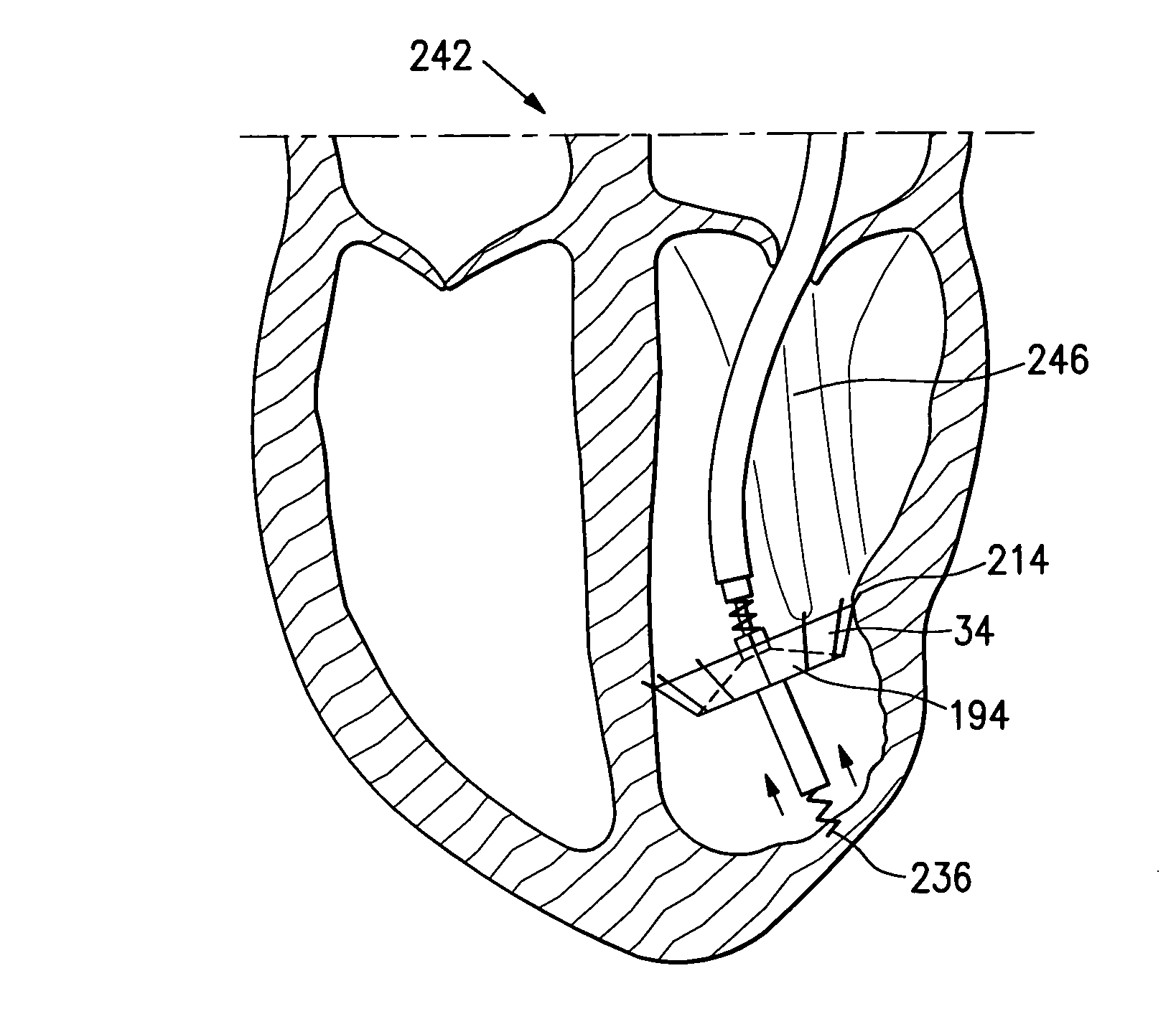
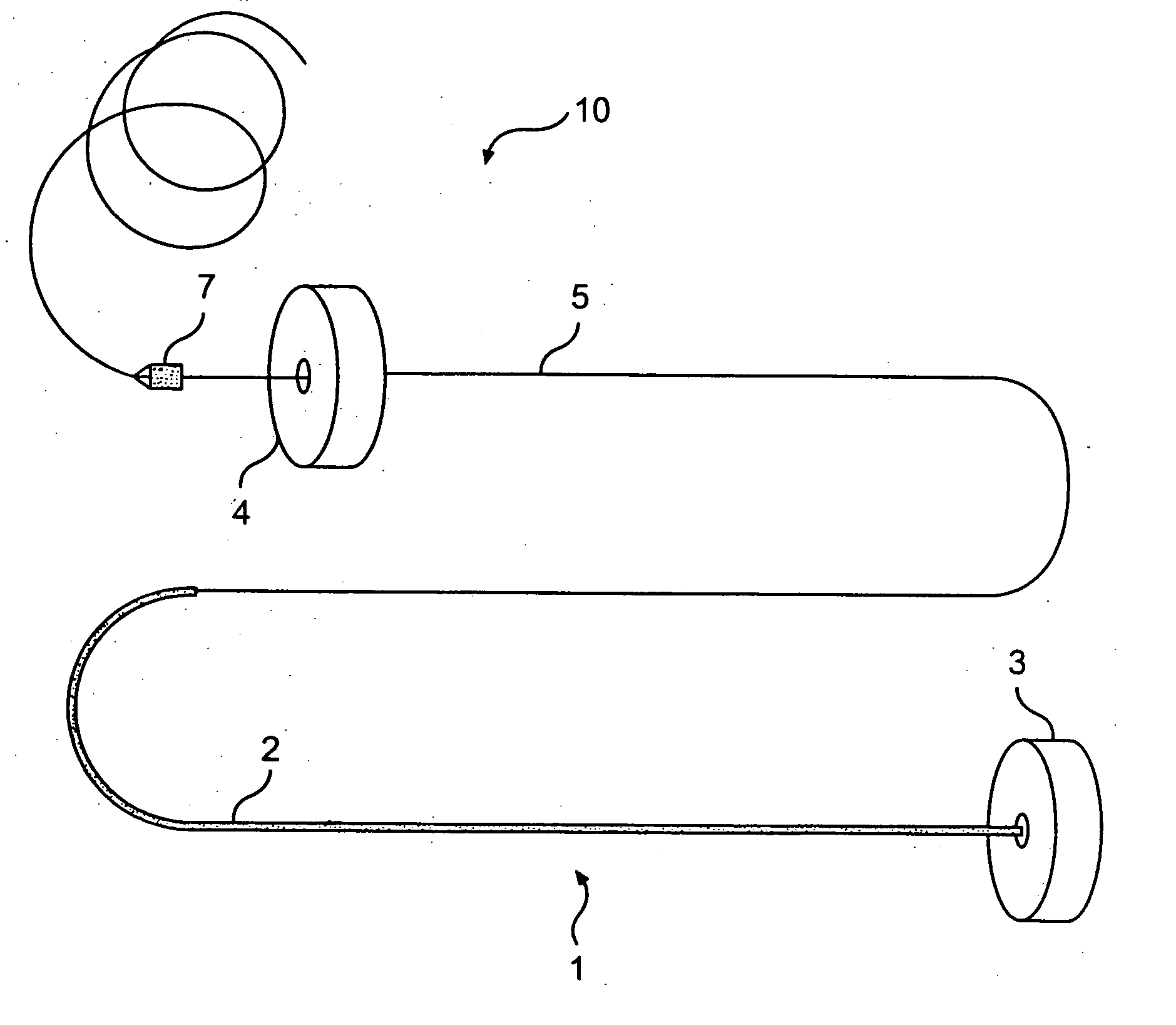
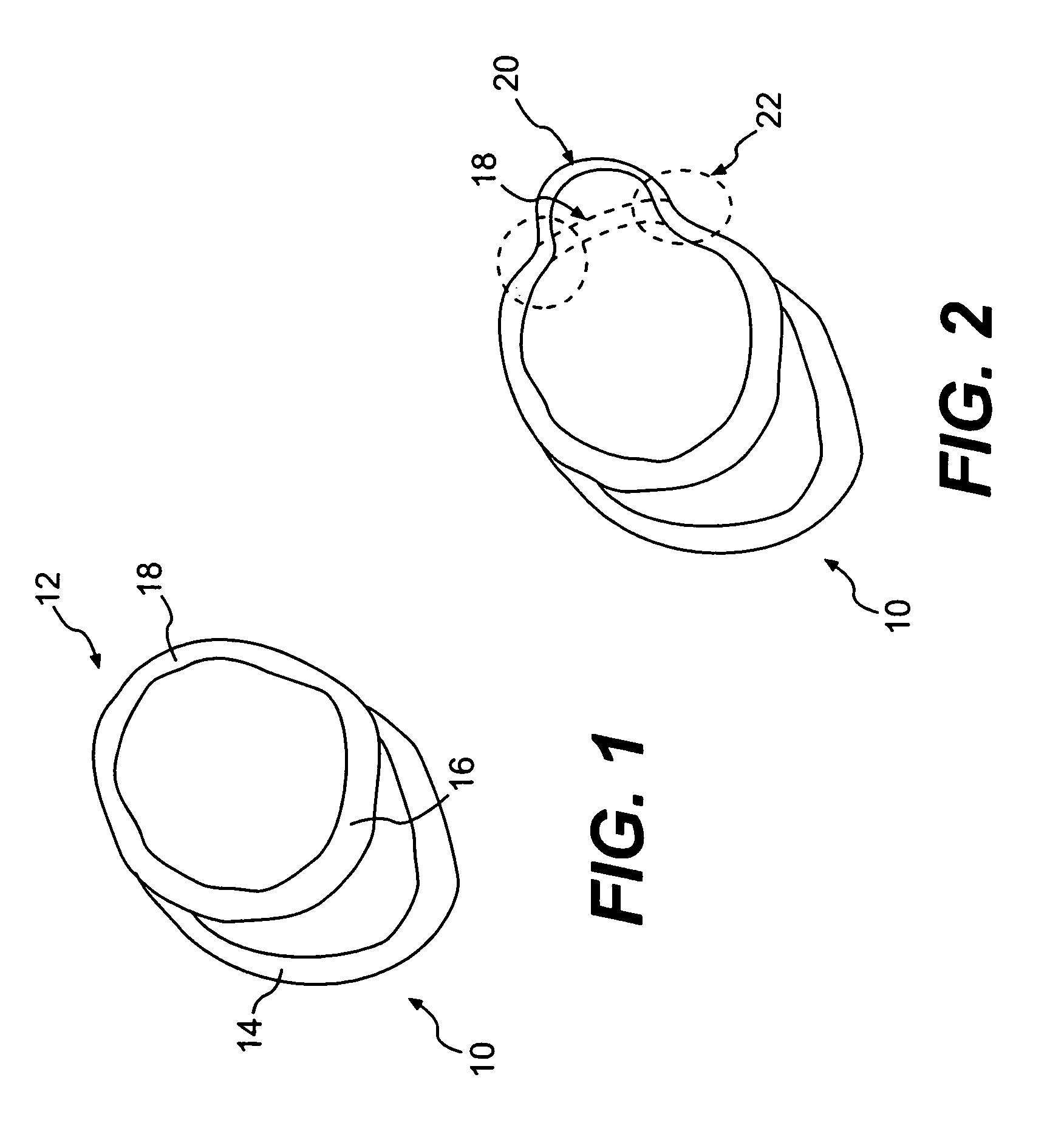
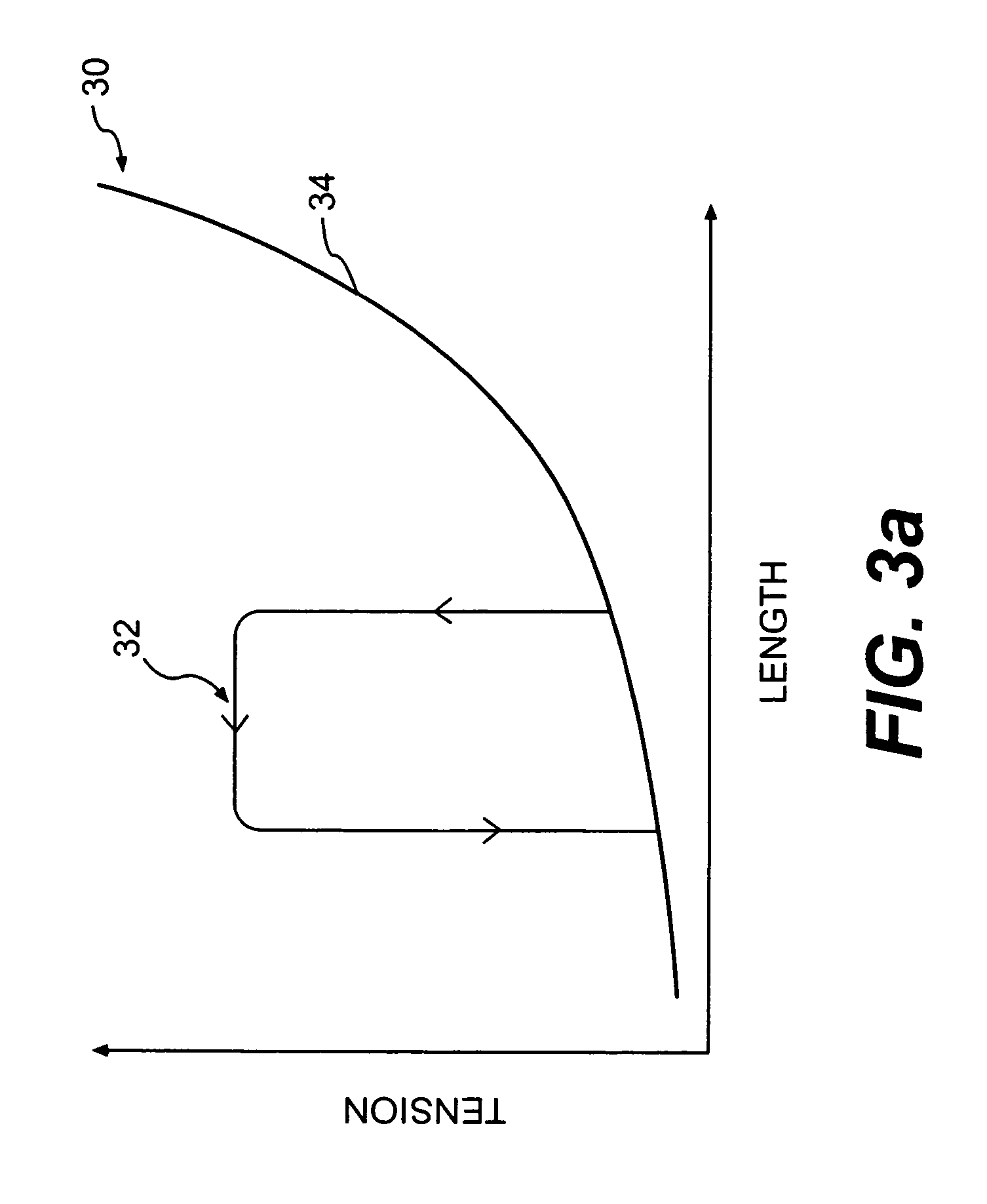
Splint assembly for improving cardiac function in hearts, and method for implanting the splint assembly
InactiveUS7044905B2Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberTension member
A splint assembly for placement transverse a heart chamber to reduce the heart chamber radius and improve cardiac function has a tension member formed of a braided cable with a covering. A fixed anchor assembly is attached to one end of the tension member and a leader for penetrating a heart wall and guiding the tension member through the heart is attached to the other end. An adjustable anchor assembly can be secured onto the tension member opposite to the side on which the fixed pad assembly is attached. The adjustable anchor assembly can be positioned along the tension member so as to adjust the length of the tension member extending between the fixed and adjustable anchor assemblies. The pad assemblies engage with the outside of the heart wall to hold the tension member in place transverse the heart chamber. A probe and marker delivery device is used to identify locations on the heart wall to place the splint assembly such that it will not interfere with internal heart structures. The device delivers a marker to these locations on the heart wall for both visual and tactile identification during implantation of the splint assembly in the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
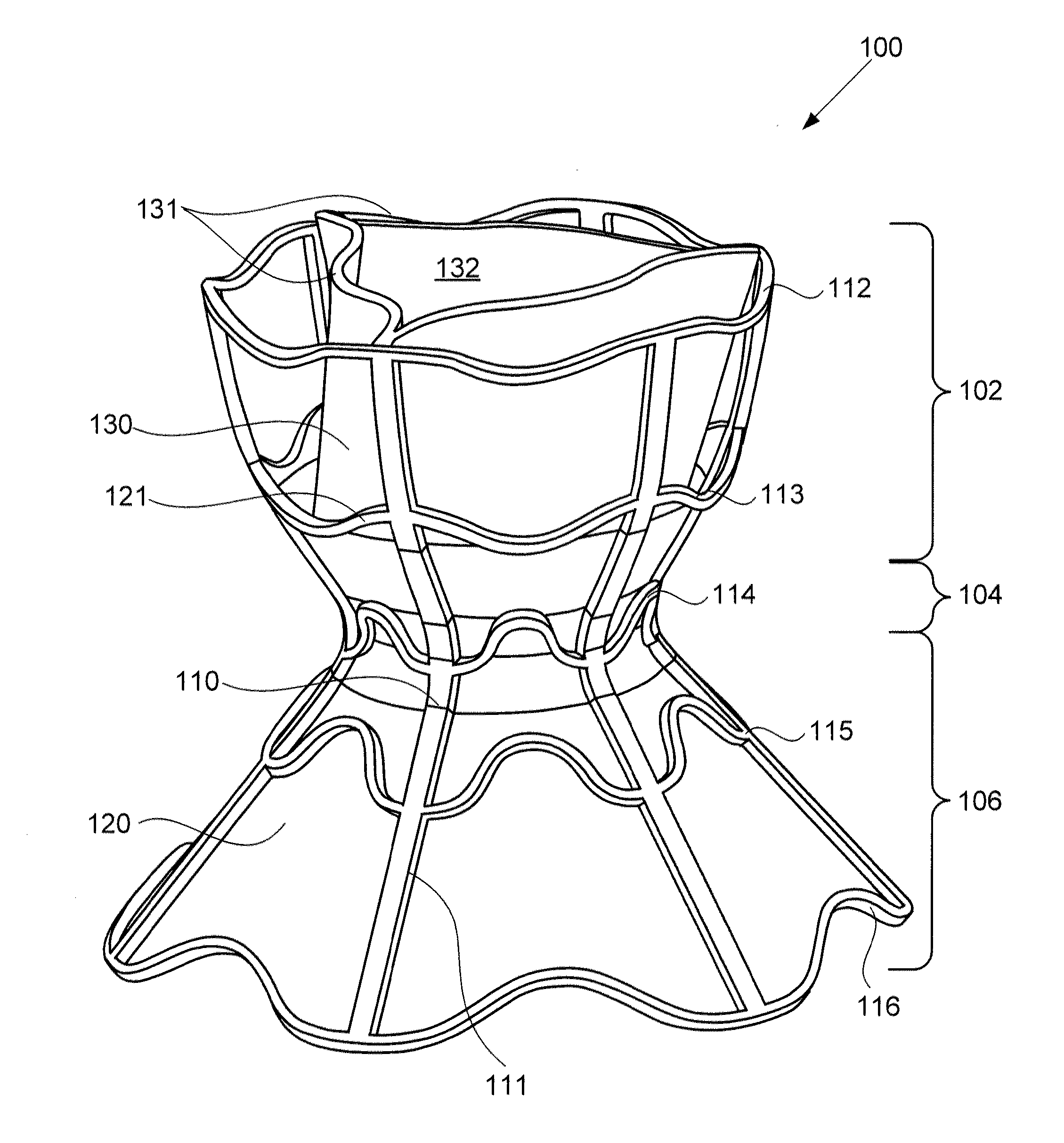
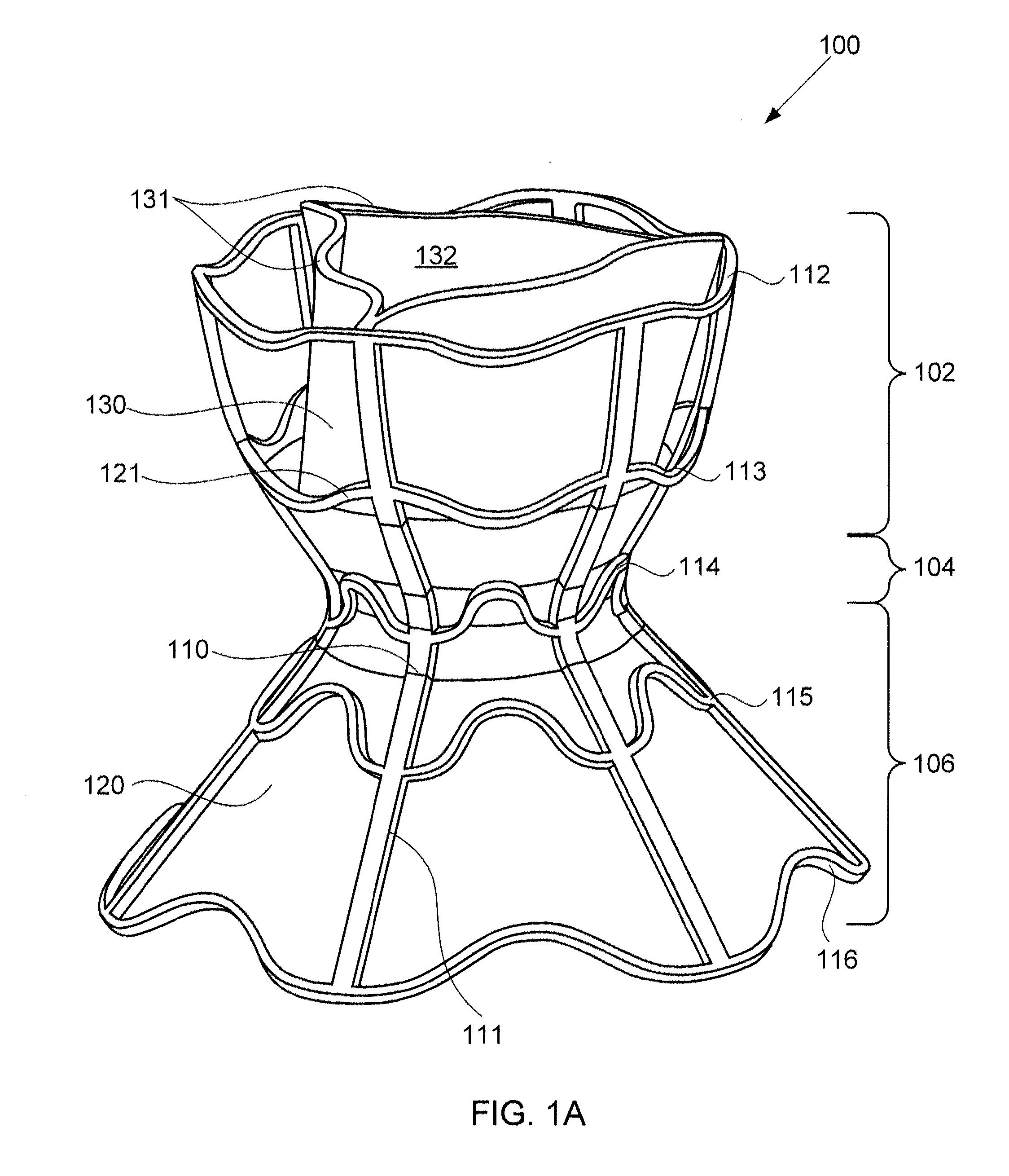
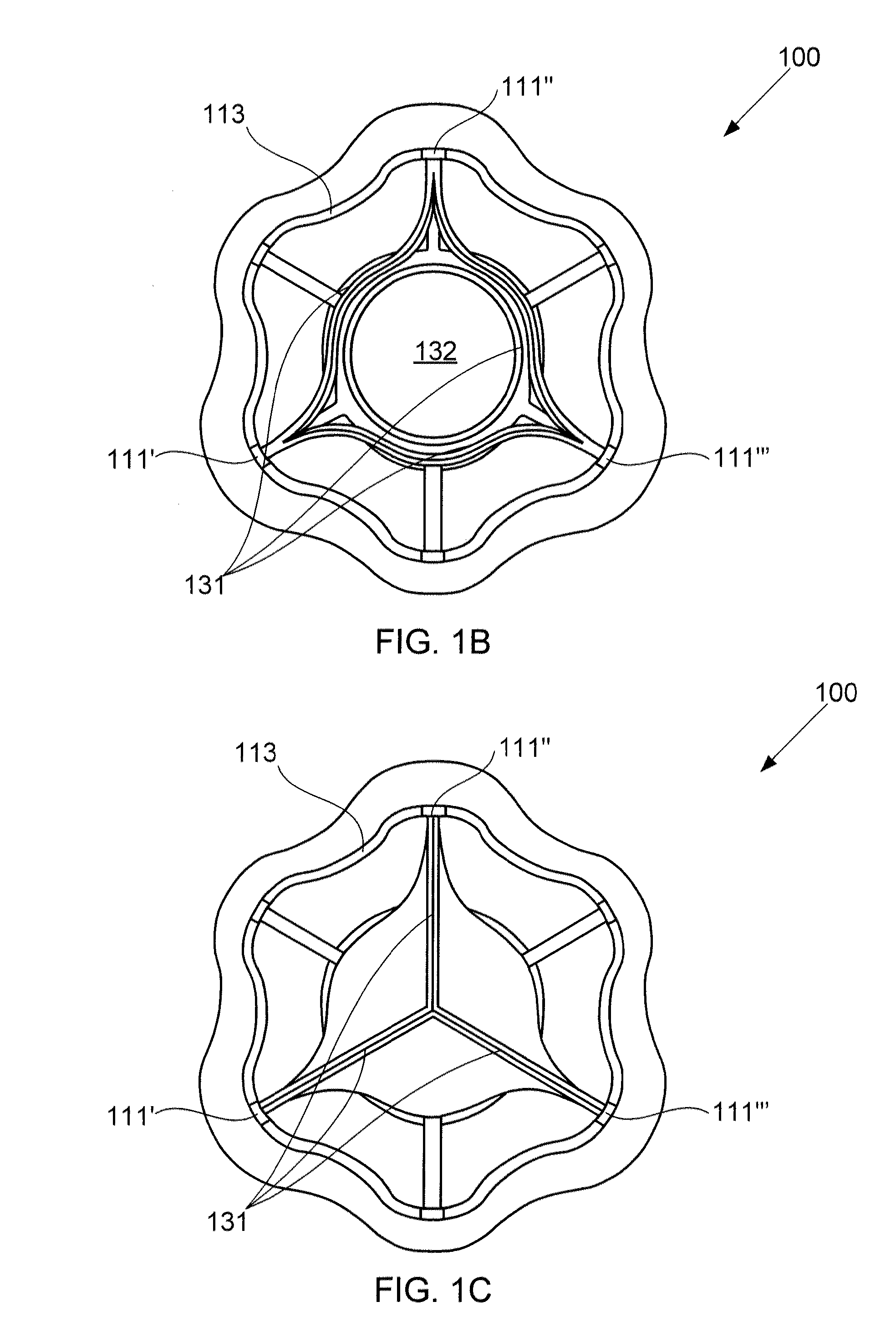
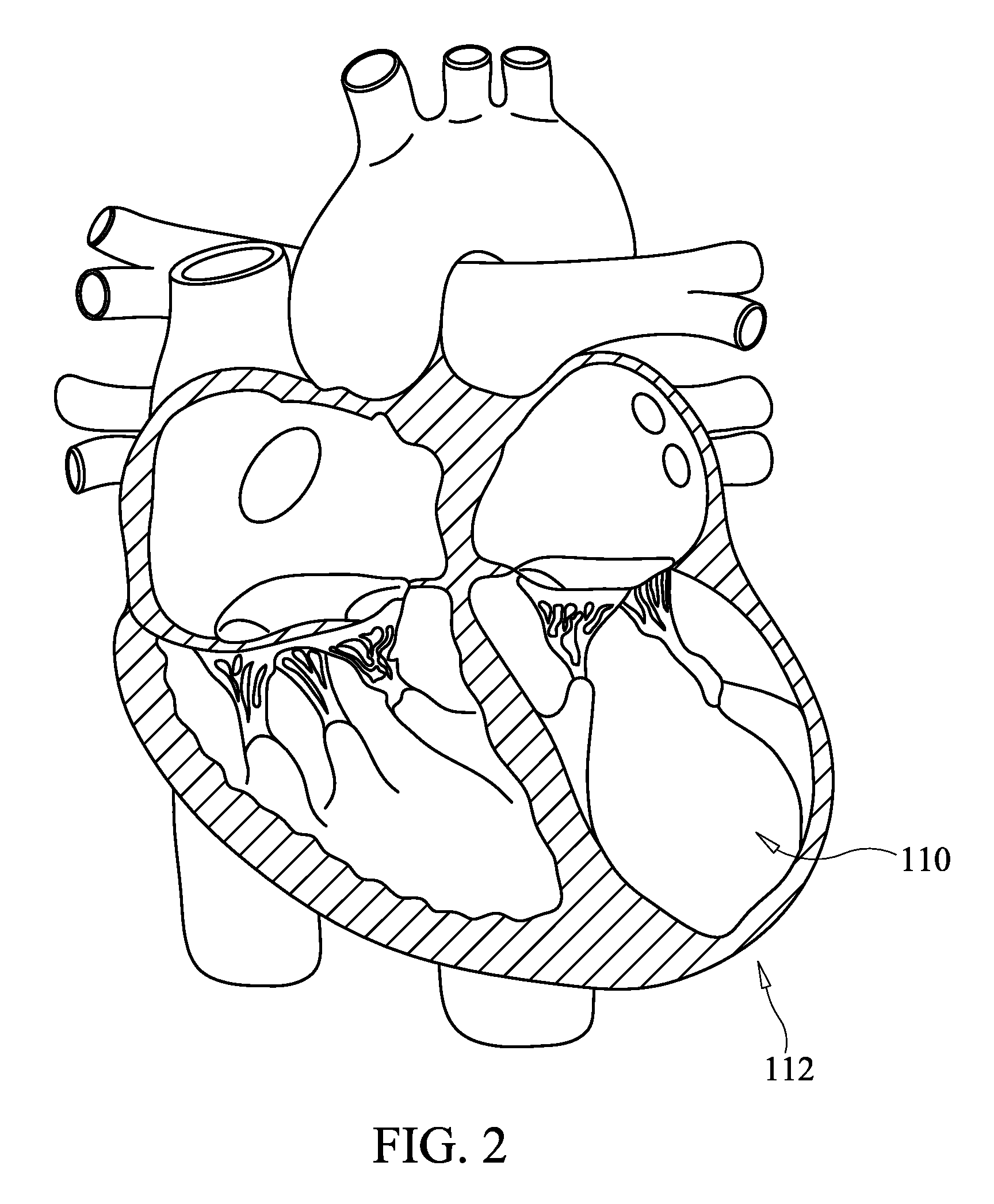
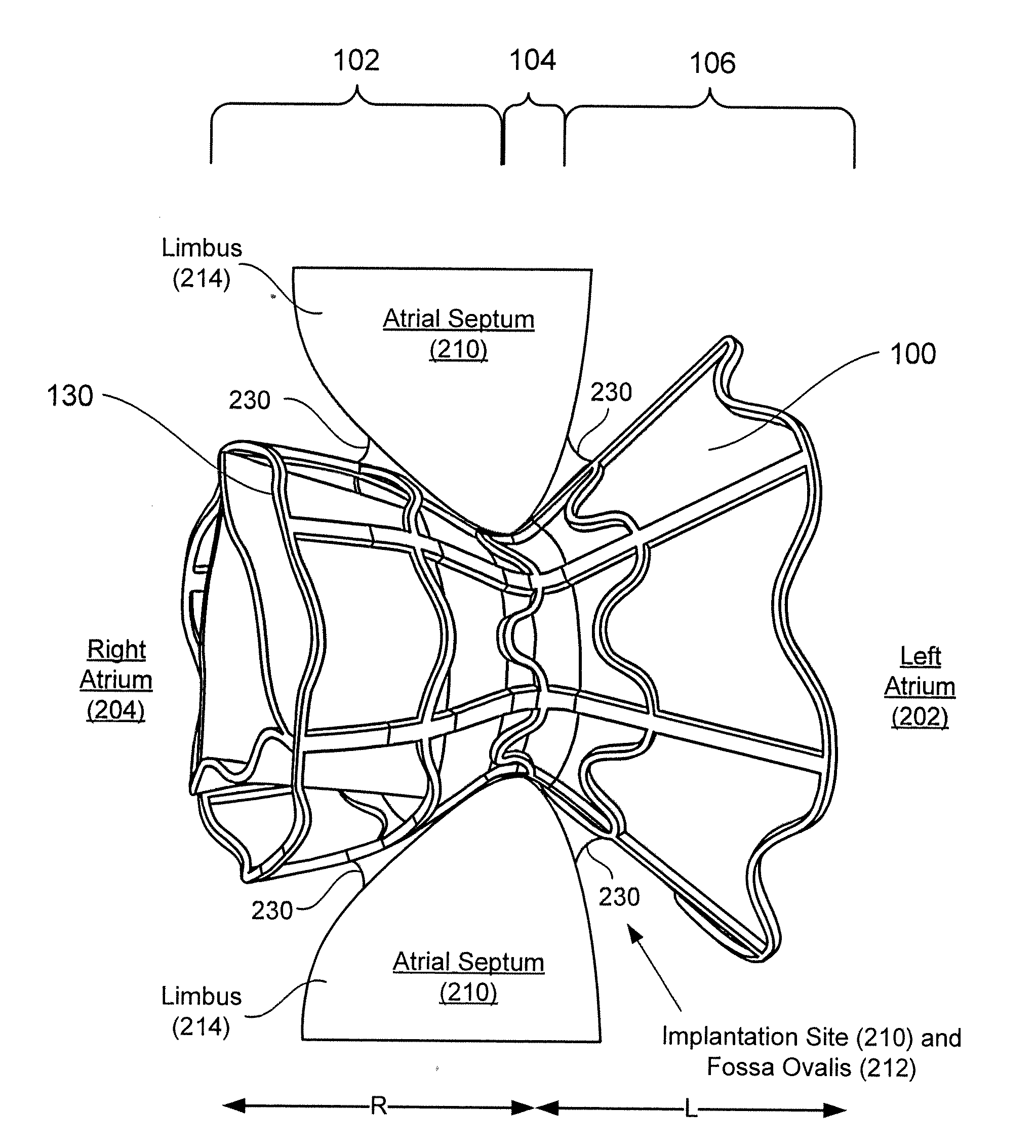
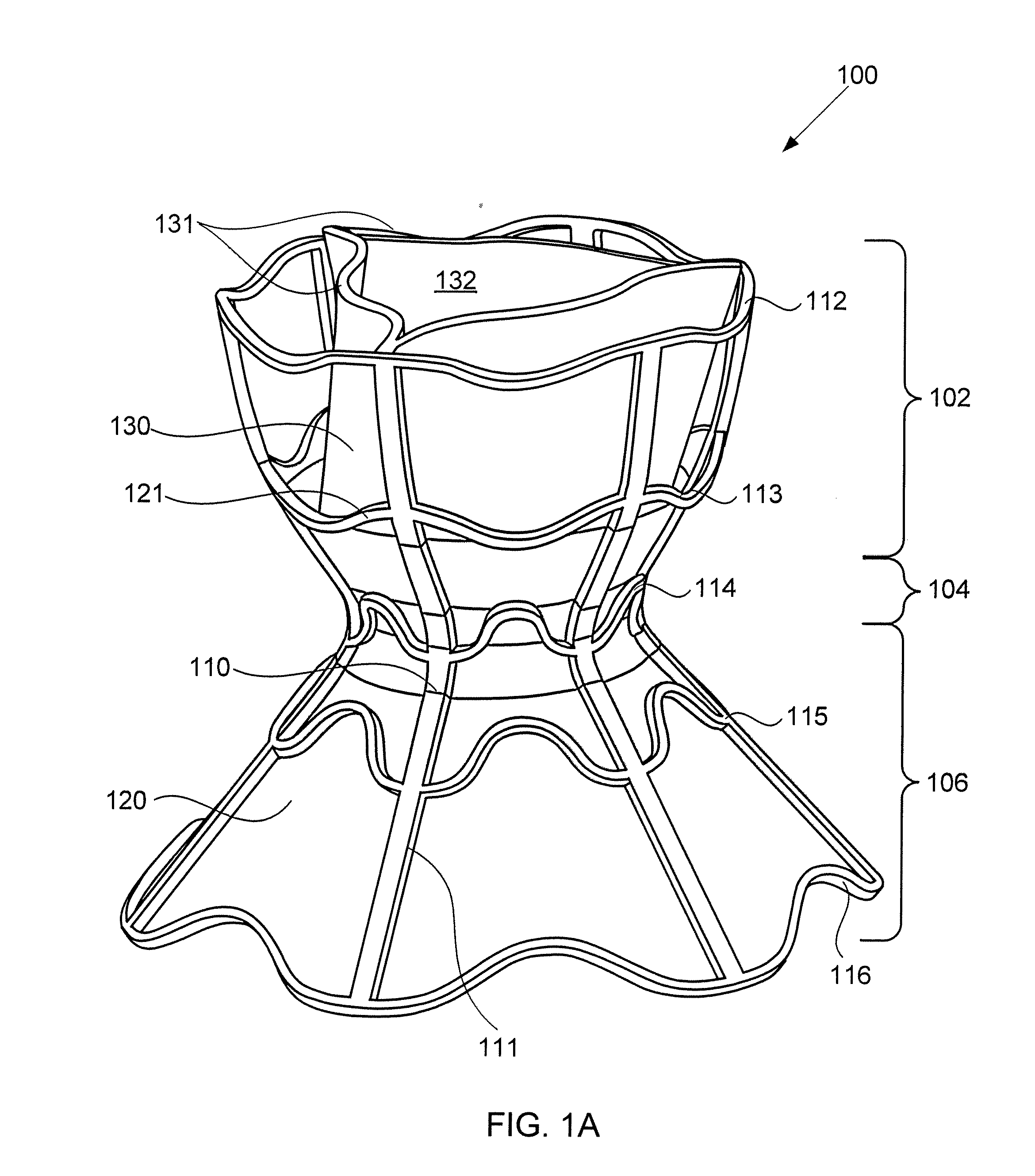
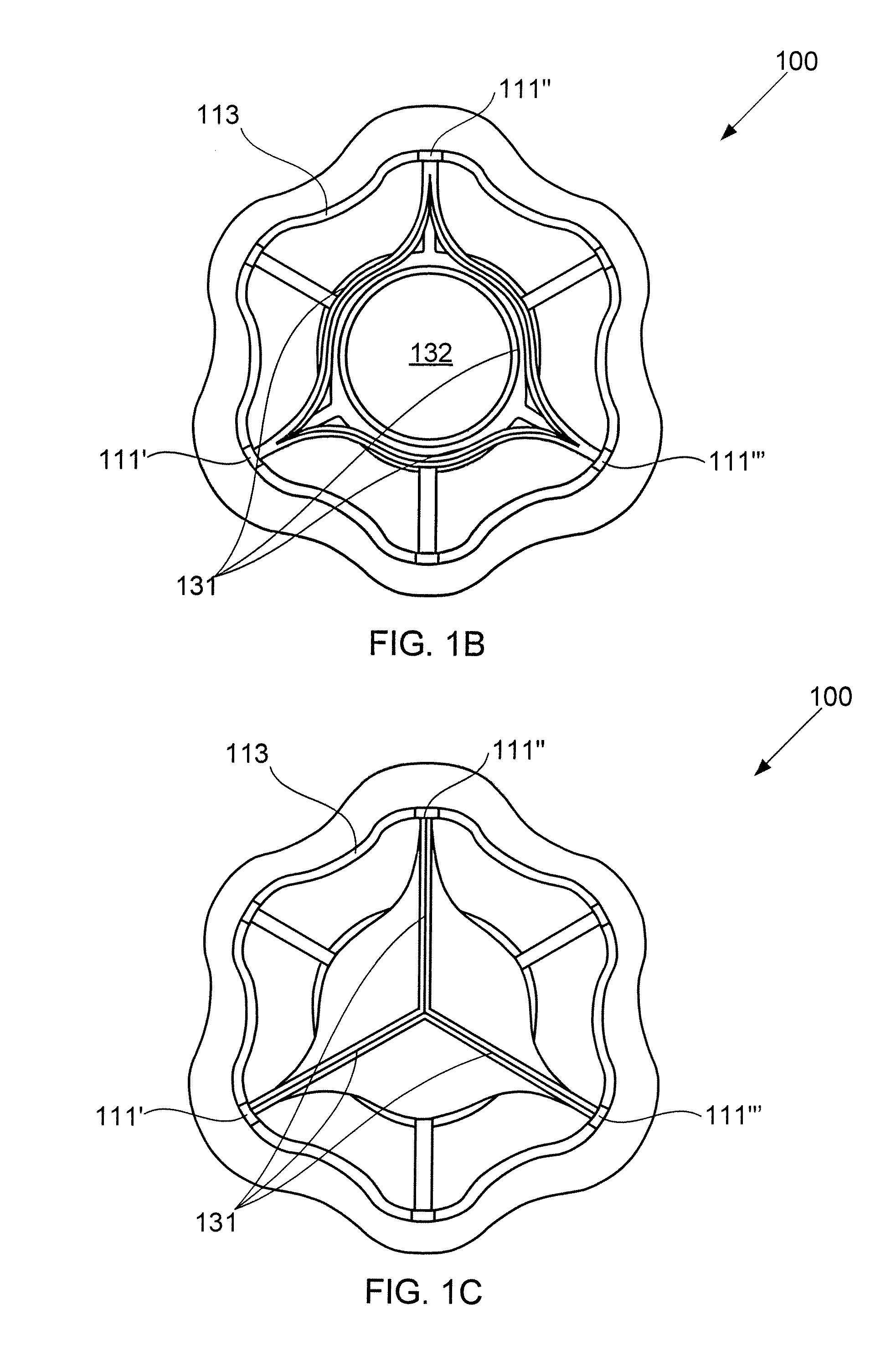
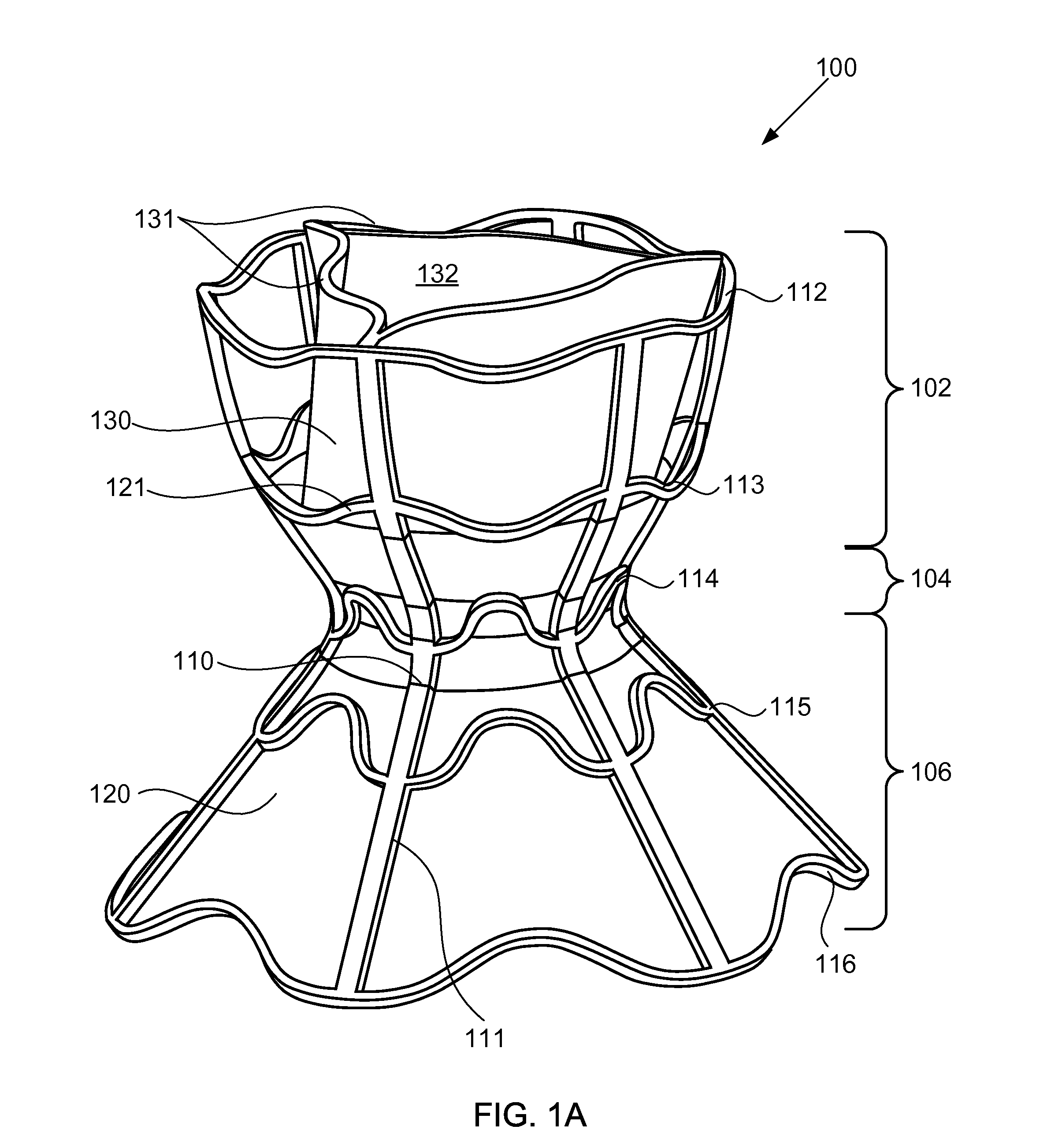
Devices for reducing left atrial pressure, and methods of making and using same
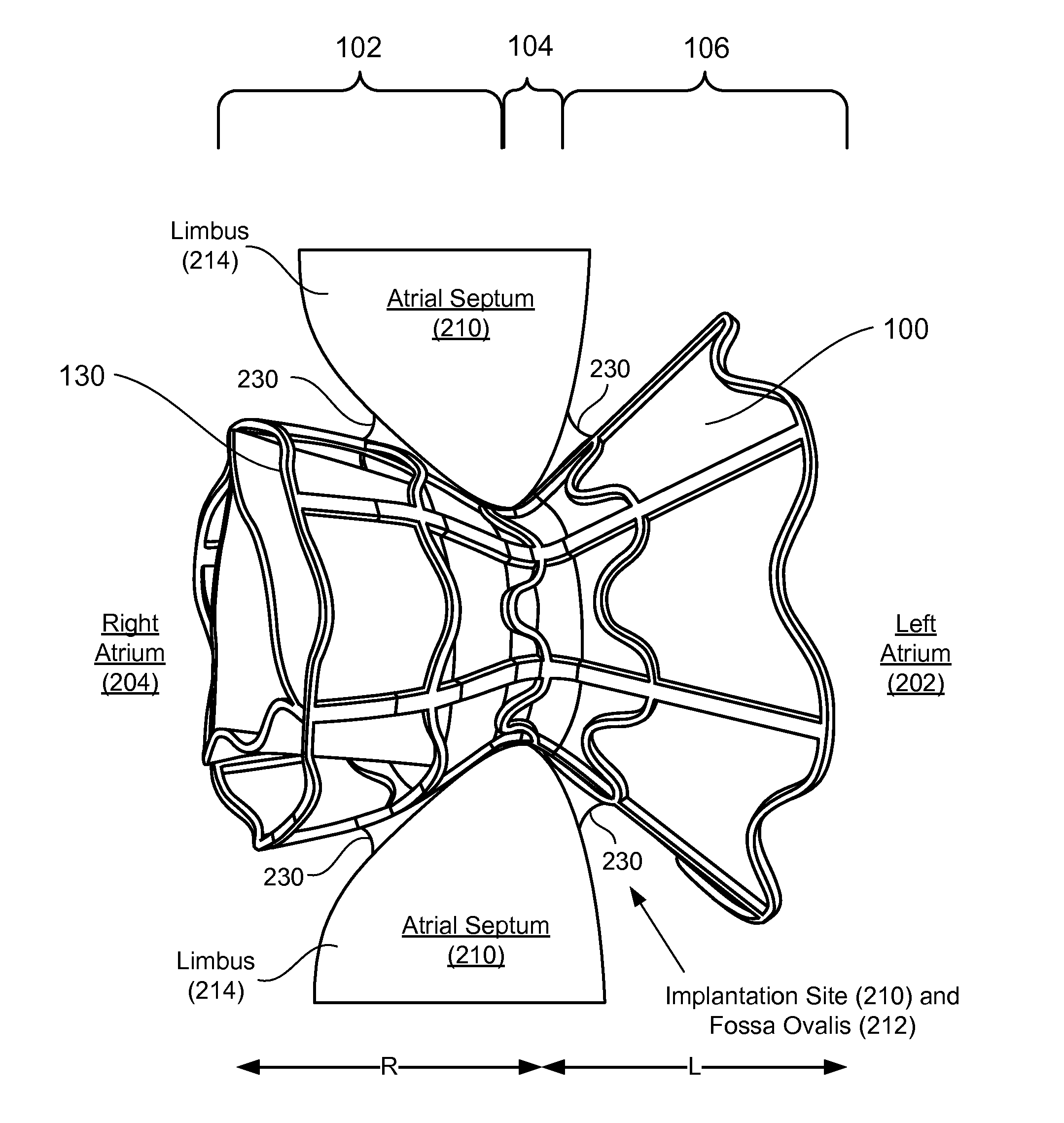
ActiveUS20120165928A1Reducing left atrial pressureIncrease cardiac outputHeart valvesSurgeryLeft ventricular sizeLeft atrial pressure
A device for regulating blood pressure between a patient's left atrium and right atrium comprises an hourglass-shaped stent comprising a neck region and first and second flared end regions, the neck region disposed between the first and second end regions and configured to engage the fossa ovalis of the patient's atrial septum; and a one-way tissue valve coupled to the first flared end region and configured to shunt blood from the left atrium to the right atrium when blood pressure in the left atrium exceeds blood pressure in the right atrium. The inventive devices may reduce left atrial pressure and left ventricular end diastolic pressure, and may increase cardiac output, increase ejection fraction, relieve pulmonary congestion, and lower pulmonary artery pressure, among other benefits. The inventive devices may be used, for example, to treat subjects having heart failure, pulmonary congestion, or myocardial infarction, among other pathologies.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
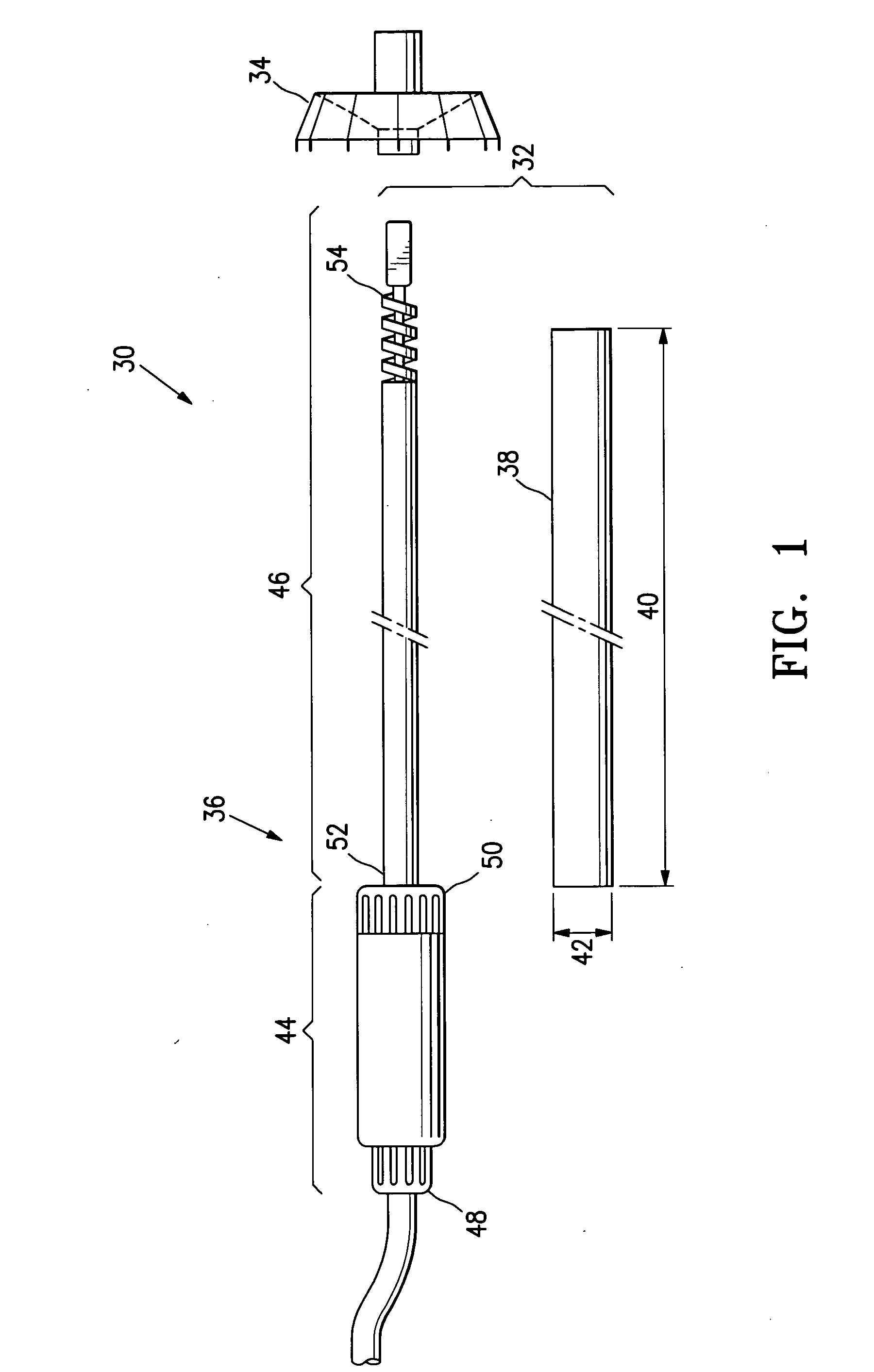
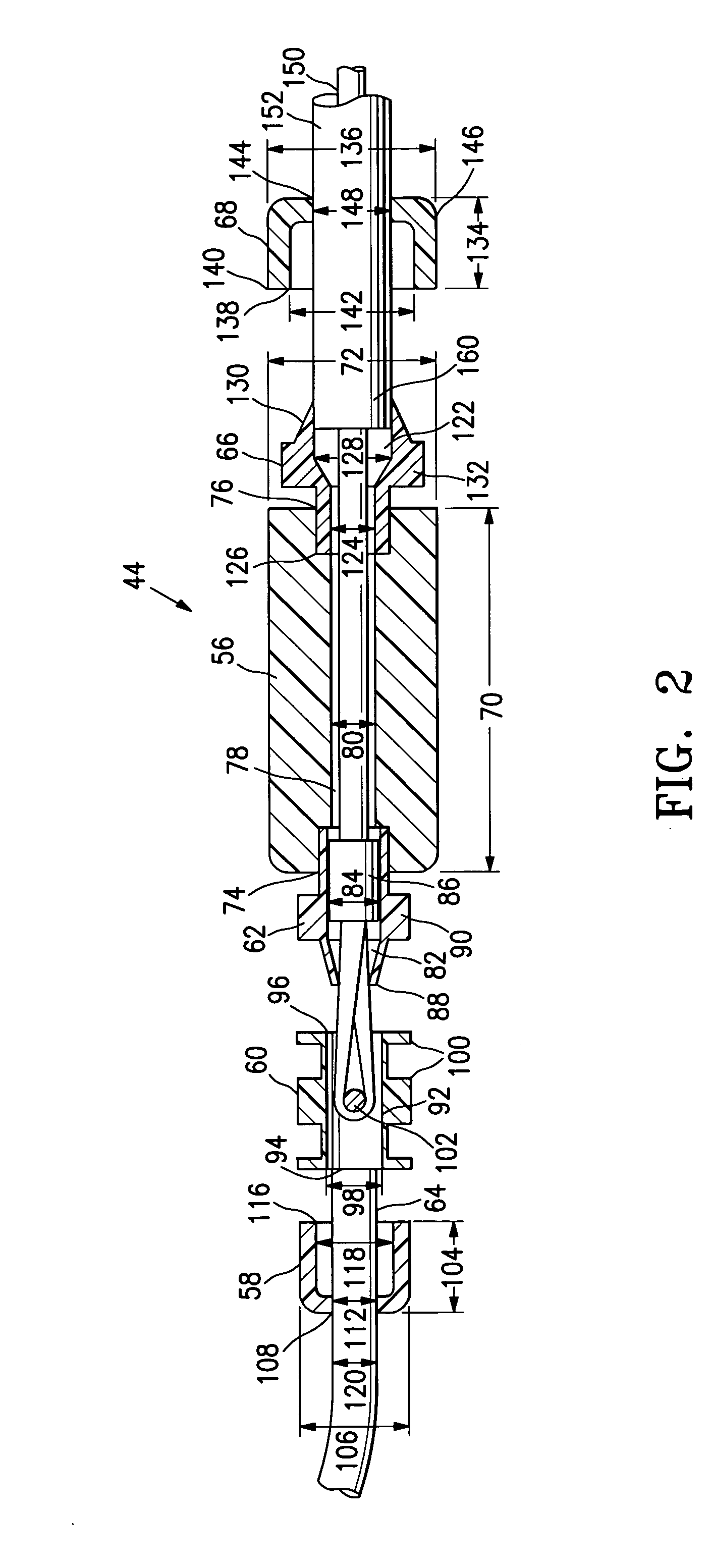
Method and apparatus to minimize the effects of a cardiac insult
InactiveUS20070276453A1Reduced activityImprove heart functionSubcutaneous electrodesArtificial respirationPeripheral neuronPeripheral nerve
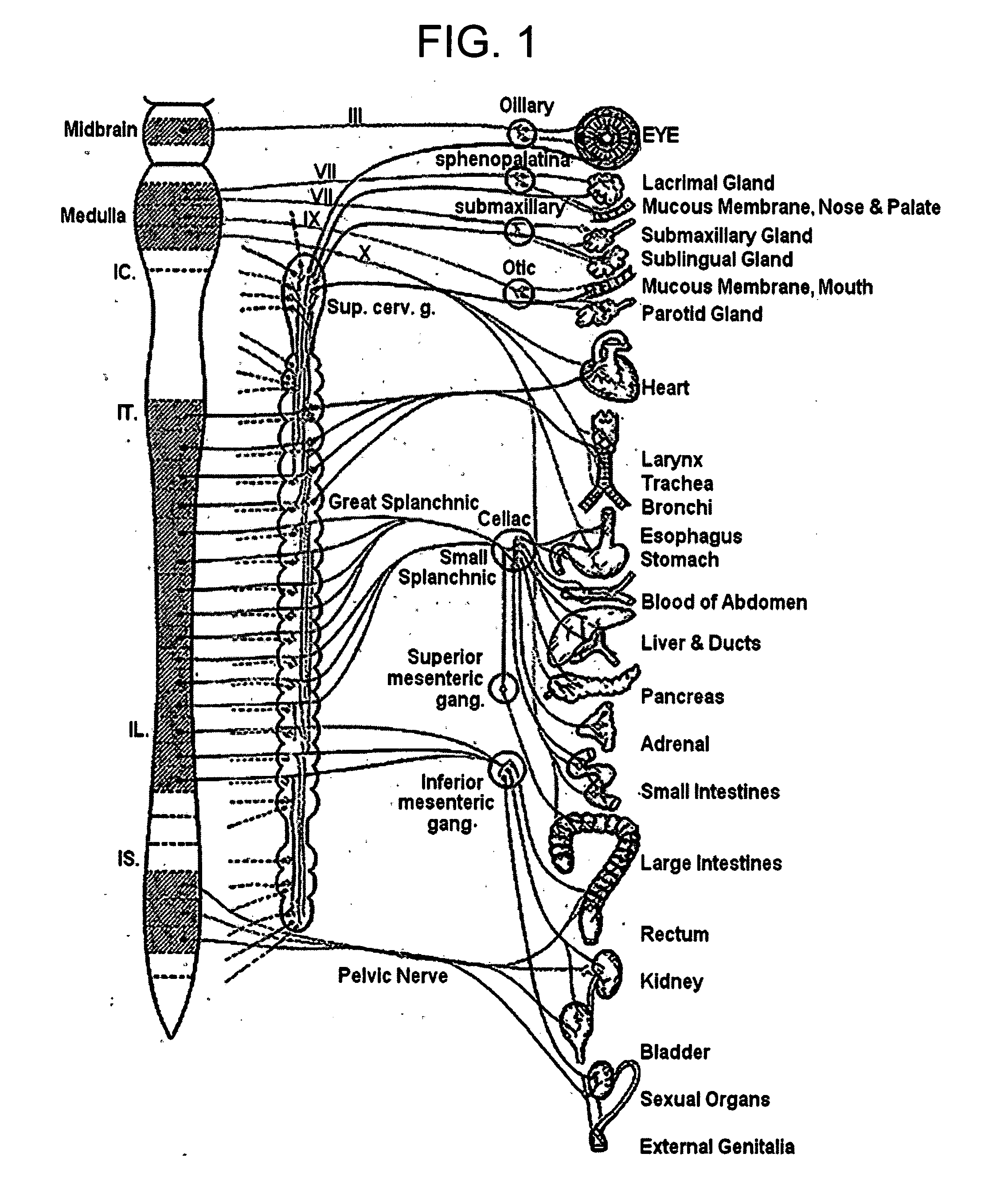
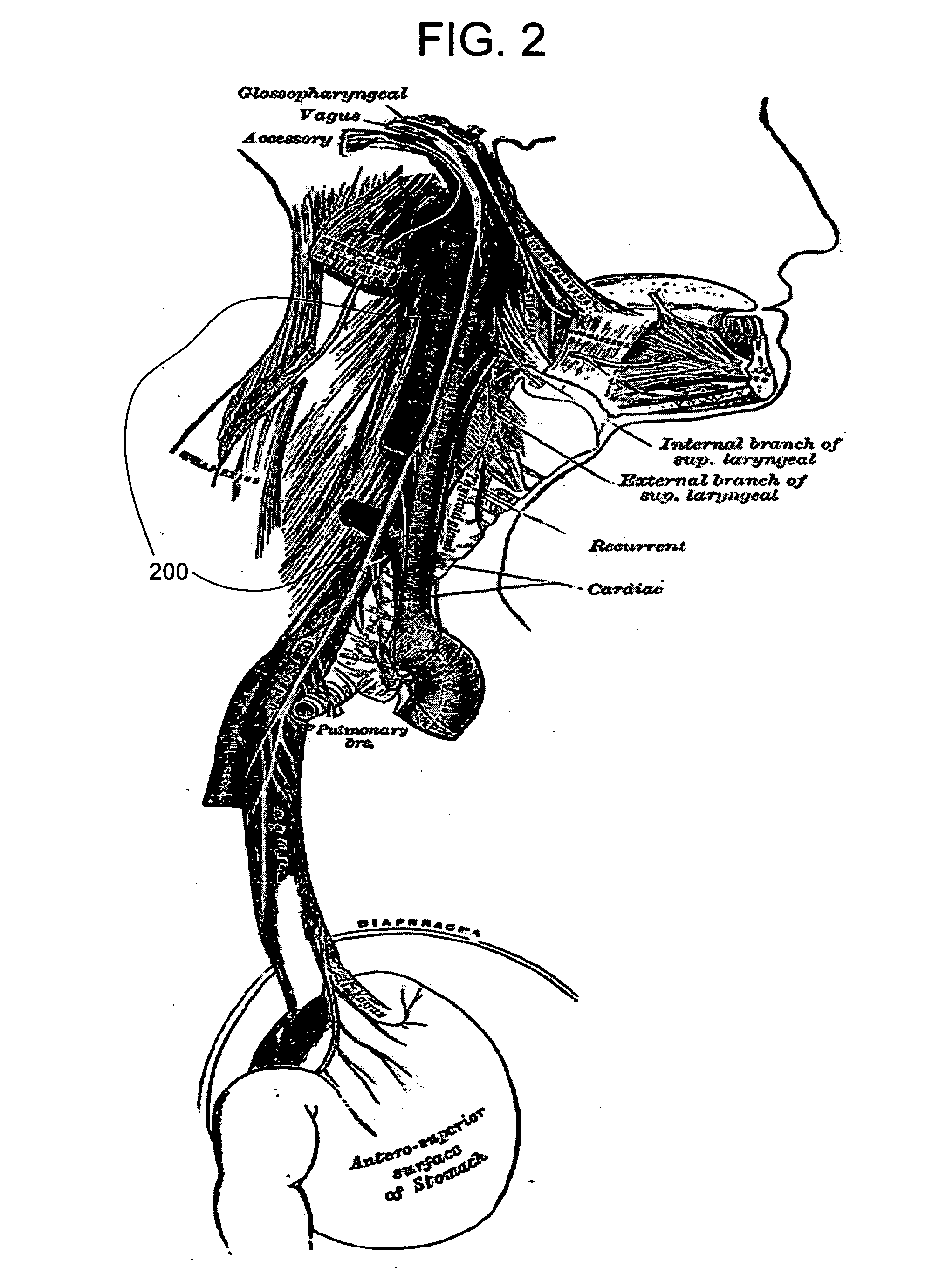
A method and apparatus are provided for protecting cardiac tissue from insult. The method comprises identifying the occurrence of an insult, such as a heart attack, and delivering electrical stimulation to one or more predetermined nerves in a patient's body in response to identifying the occurrence of the insult. The stimulation may be provided to peripheral nerves, intrinsic cardiac nerves, sympathetic ganglia, cranial nerves, and may generally be directed to the vertebral column, or within the chest wall of the patient.
Owner:HILL MICHAEL +4
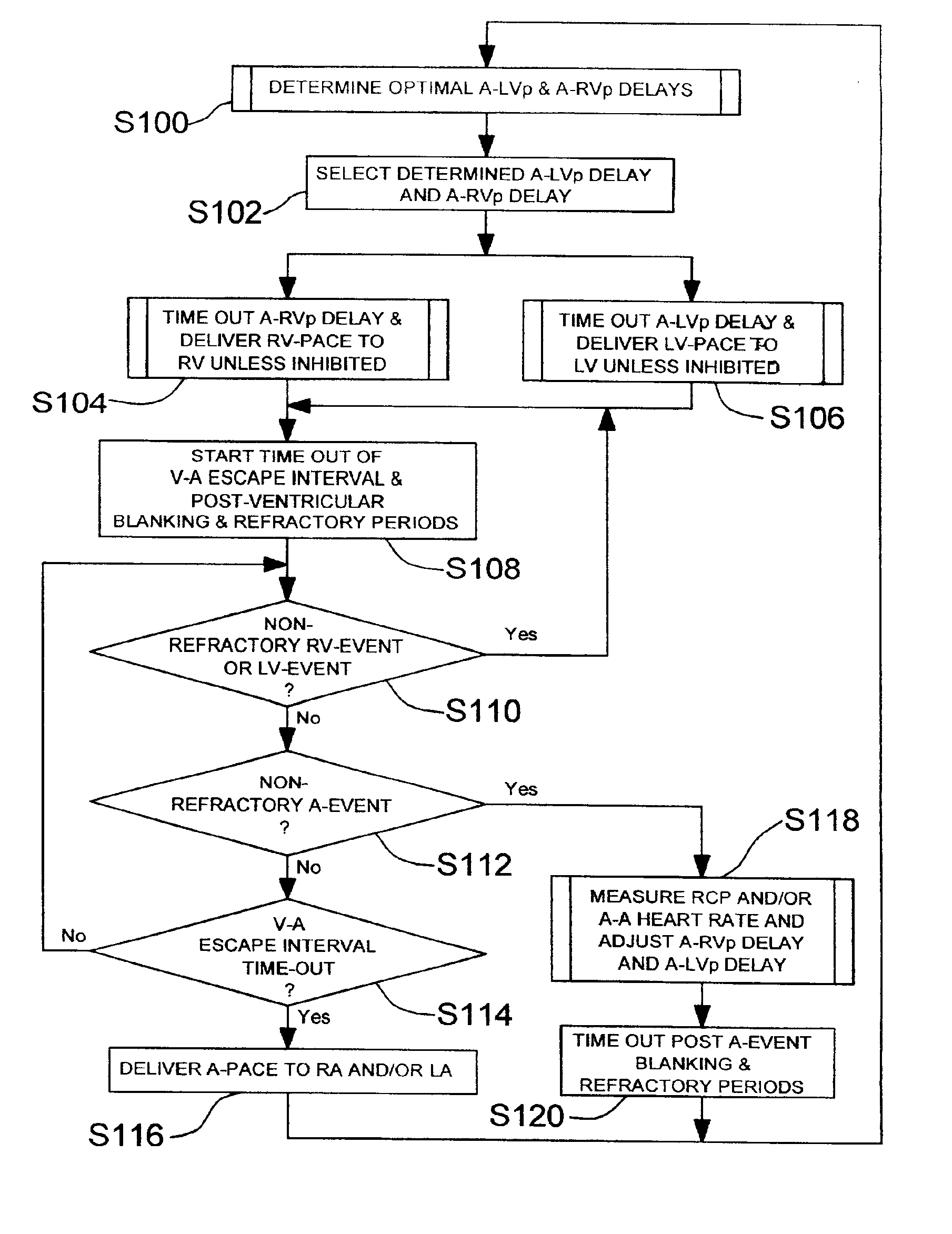
System and method for bi-ventricular fusion pacing
Bi-ventricular cardiac pacing systems and systems for improving cardiac function for heart failure patients that pace and sense in right and left ventricles of the heart and particularly pace in one of the right and left ventricles after an AV delay timed from a preceding atrial event and after a spontaneous depolarization in the other of the right and left ventricles to achieve fusion pacing. An A-RVp delay and an A-LVp delay are each determined from an intrinsic sensed A-RVs delay and an intrinsic A-LVs delay. If the derived A-LVp delay becomes substantially equal to or shorter than the intrinsic A-RVs delay, then the A-RVp delay is decremented to be shorter than the A-LVp delay. Bi-ventricular pacing of the RV and LV is then established closely timed to the intrinsic RV and LV depolarizations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apical Papillary Msucle Attachment for Left Ventricular Reduction
InactiveUS20100185278A1Improve heart functionLower the volumeSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLeft ventricular sizePapillary muscle
This invention relates to devices and methods for the therapeutic changing of the geometry of the left ventricle of the human heart. Specifically, the invention relates to the apical introduction of an anchoring device to align the papillary muscles.
Owner:TENDYNE MEDICAL
Medicine for preventing and treating coronary heart disease and angina pectoris and its prepn and other use
InactiveCN1348815AGood curative effectLess frequent seizuresNervous disorderMetabolism disorderSalvia miltiorrhizaCoronary artery disease
The present invention relates to traditional Chinese medicine for treating coronary heart disease and stenocardia is made from (by wt.%) salvia root 50-97%, notoginseng 2-48% and borneol 0.2-3%, in which the salvia root and notoginseng and hot extracted with water, then filtering, concentrating, alcohol precipitating, standing still, recovering ethyl alcohol, concentrating, into extractum, further blended with borneol and adjuvant polyglycol-6000 to form into product.
Owner:TIANJIN TASLY PHARMA CO LTD
Devices for reducing left atrial pressure having biodegradable constriction, and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS20130030521A1Reducing left atrial pressureIncrease cardiac outputHeart valvesSurgeryLeft ventricular sizeLeft atrial pressure
A device for regulating blood pressure between a patient's left atrium and right atrium comprises an hourglass-shaped stent comprising a neck region and first and second flared end regions, the neck region disposed between the first and second end regions and configured to engage the fossa ovalis of the patient's atrial septum; and a one-way tissue valve coupled to the first flared end region and configured to shunt blood from the left atrium to the right atrium when blood pressure in the left atrium exceeds blood pressure in the right atrium. The inventive device may include a biodegradable material that biodegrades to offset flow changes caused by tissue ingrowth. The inventive device may reduce left atrial pressure and left ventricular end diastolic pressure, and may increase cardiac output, increase ejection fraction, relieve pulmonary congestion, and lower pulmonary artery pressure, among other benefits.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
Papillary Muscle Attachment for Left Ventricular Reduction
InactiveUS20090099410A1Reduce transventricular dimensionShorten the lengthSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsLeft ventricular sizePapillary muscle
The surgical implantation of a link, which may be in the form of a tether or a looped band, is proposed to connect and reduce the spacing between papillary muscles, to reduce dilation of the left ventricle. The implanted link thus improves heart function by reducing left ventricular failure.
Owner:MIAMI THE UNIV OF
Splint assembly for improving cardiac function in hearts, and method for implanting the splint assembly
InactiveUS20060149123A1Reduce tensionReduce consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberCardiac wall
A splint assembly for placement transverse a heart chamber to reduce the heart chamber radius and improve cardiac function has a tension member formed of a braided cable with a covering. A fixed anchor assembly is attached to one end of the tension member and a leader for penetrating a heart wall and guiding the tension member through the heart is attached to the other end. An adjustable anchor assembly can be secured onto the tension member opposite to the side on which the fixed pad assembly is attached. The adjustable anchor assembly can be positioned along the tension member so as to adjust the length of the tension member extending between the fixed and adjustable anchor assemblies. The pad assemblies engage with the outside of the heart wall to hold the tension member in place transverse the heart chamber. A probe and marker delivery device is used to identify locations on the heart wall to place the splint assembly such that it will not interfere with internal heart structures. The device delivers a marker to these locations on the heart wall for both visual and tactile identification during implantation of the splint assembly in the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
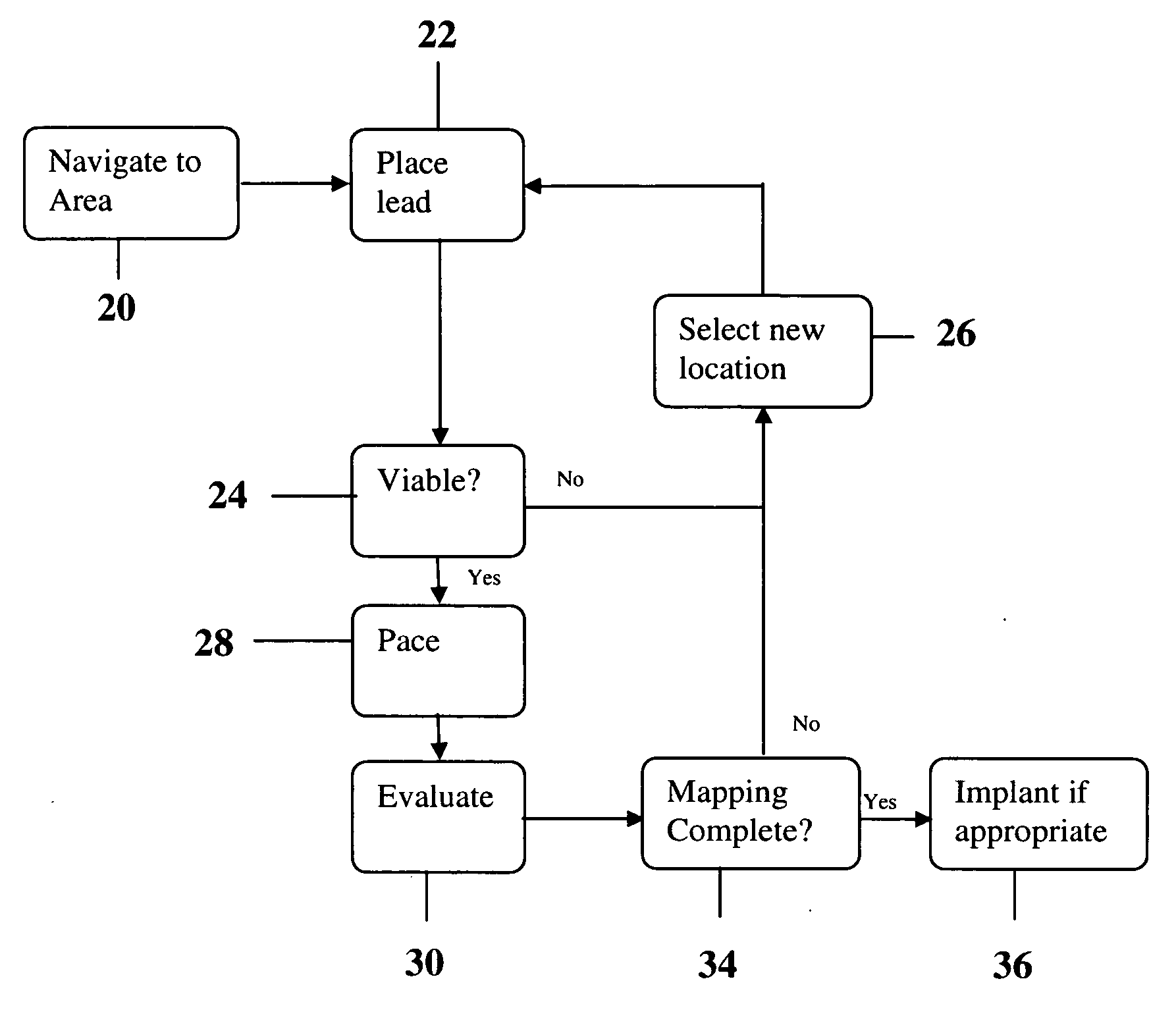
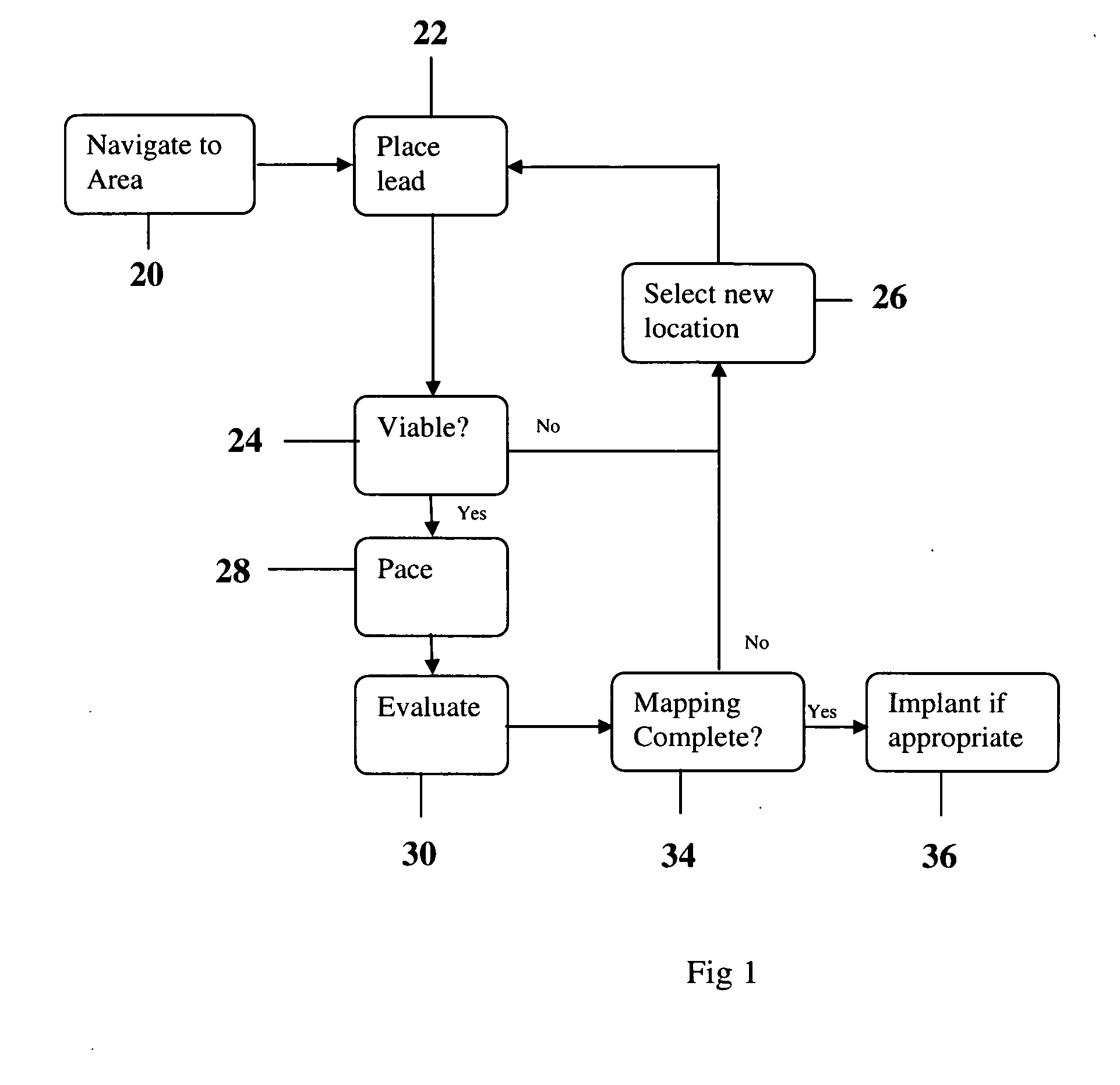
Methods and devices for mapping the ventricle for pacing lead placement and therapy delivery
InactiveUS20060276867A1Easy to placeImprove heart functionDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsLead PlacementCatheter device
A method of placing a pacing lead in the heart includes moving an electrode catheter successively to a plurality of possible placement sites. The viability of the tissue at each site is determined. If the tissue at the site is viable, a pacing signal is applied to the tissue at the site, and the effectiveness of the pacing from the site is measured. After the area has been mapped in this fashion, at least one pacing lead is placed from at least one of the sites which exceeded a predetermined level of pacing effectiveness.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Method of treating cardiomyopathy
InactiveUS20090082619A1Reduced dimensionShorten the lengthSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLeft ventricle wallTethered Cord
The surgical implantation of a link, which may be in the form of a tether or a looped band, is proposed to connect and reduce the spacing between facing walls of the left ventricle, to reduce dilation of the left ventricle. Decreasing the distance between the facing portions of the ventricle may also more appropriately align the chordal apparatus to decrease mitral regurgitation. The implanted link thus improves heart function by reducing left ventricular failure.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Prevention of myocardial infarction induced ventricular expansion and remodeling
InactiveUS7988727B2Limited elongationReduce the abnormal geometry and wall stressSuture equipmentsPowder deliveryCardiac muscleTherapeutic treatment
A method for direct therapeutic treatment of myocardial tissue in a localized region of a heart having a pathological condition. The method includes identifying a target region of the myocardium and applying material directly and substantially only to at least a portion of the myocardial tissue of the target region. The material applied results in a physically modification the mechanical properties, including stiffness, of said tissue. Various devices and modes of practicing the method are disclosed for stiffening, restraining and constraining myocardial tissue for the treatment of conditions including myocardial infarction or mitral valve regurgitation.
Owner:MYOMEND
Cardiac muscle function and manipulation
InactiveUS7226907B1Augment PE-mediated cardiac muscle cell differentiationImprove heart functionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCardiomyocyte growthNeuregulin
Owner:ZENSUN (SHANGHAI) SCI & TECH CO LTD
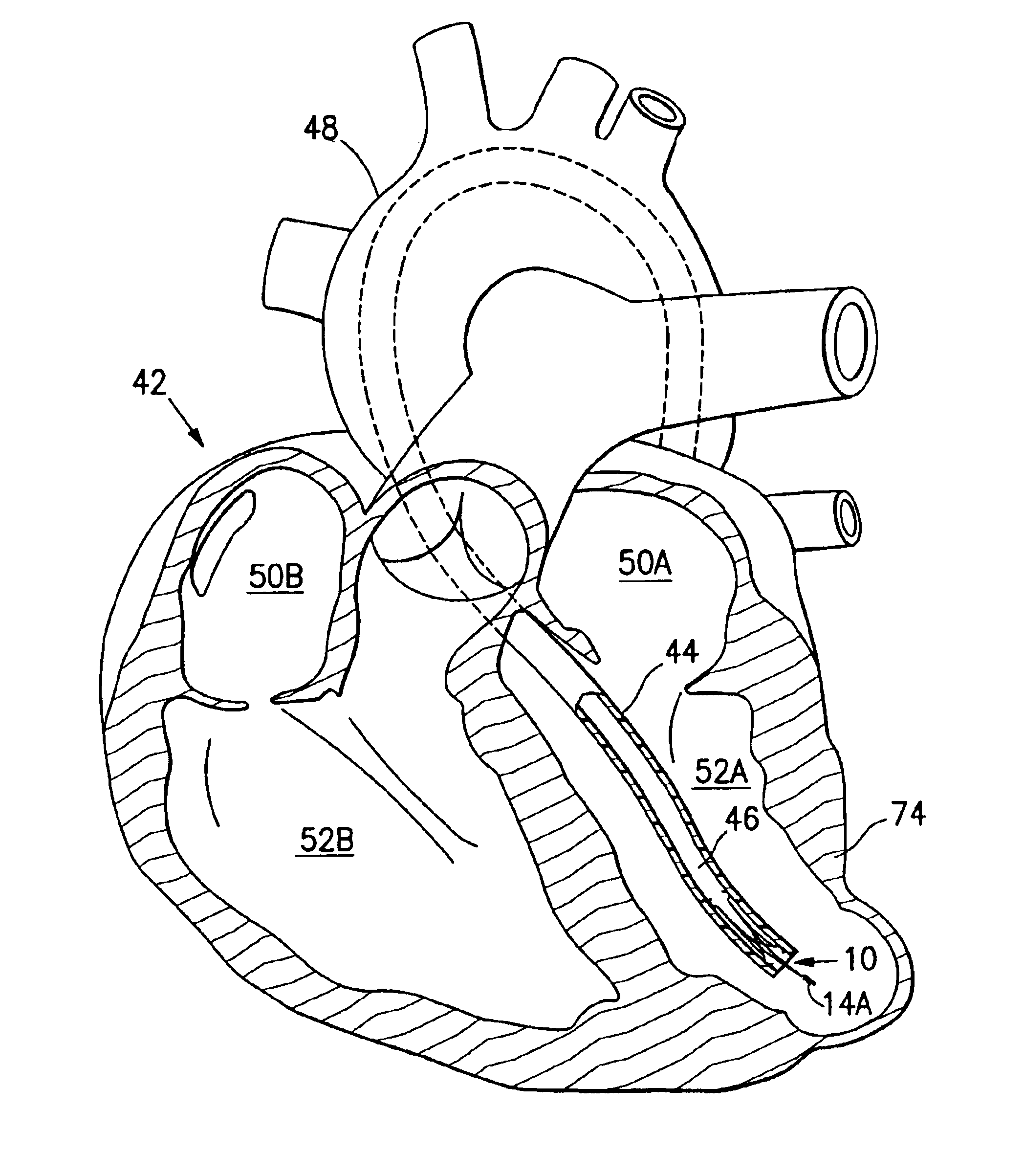
Transvalvular intraannular band for valve repair
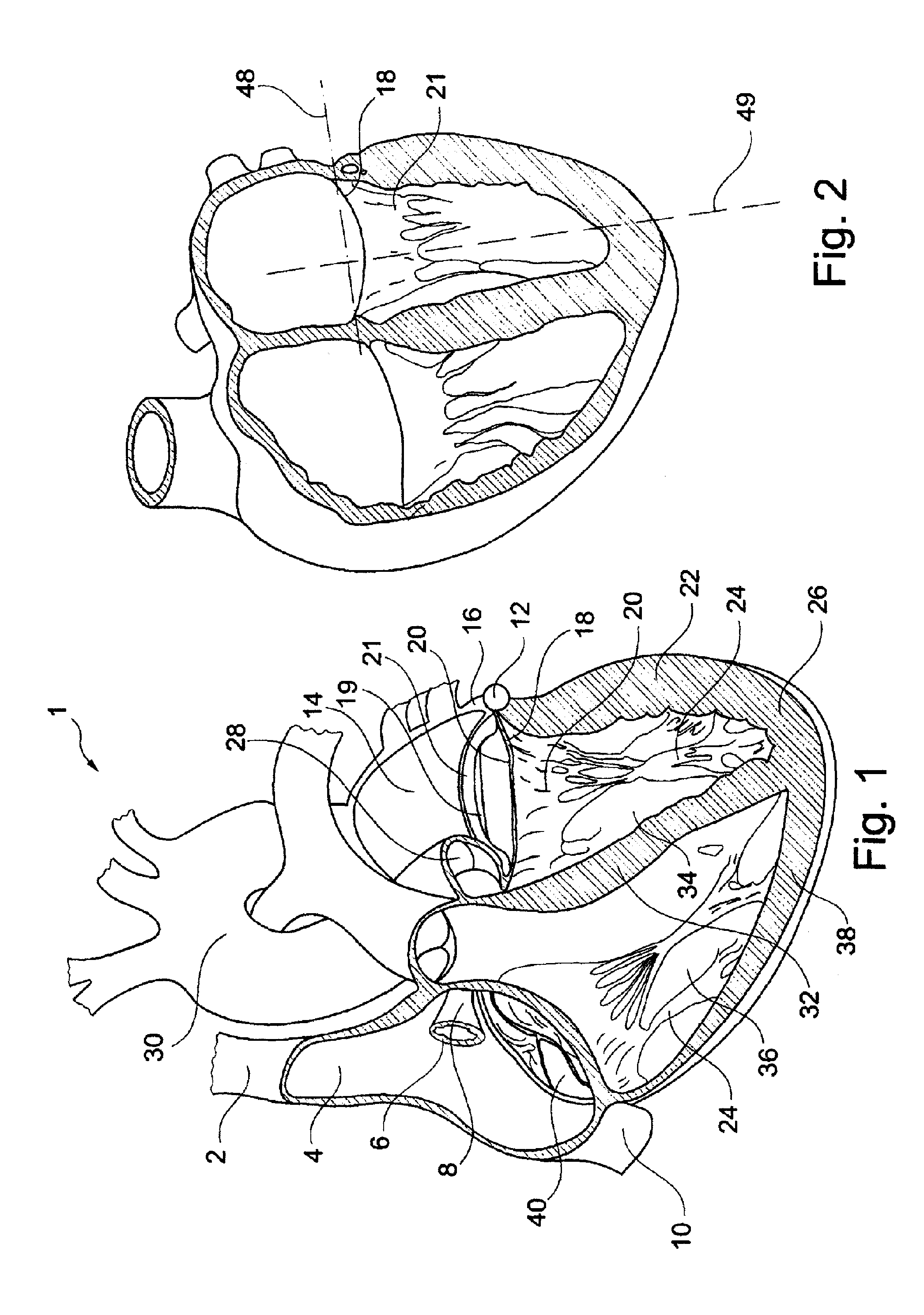
Mitral valve prolapse and mitral regurgitation can be treating by implanting in the mitral annulus a transvalvular intraannular band having an elongate and arcuate body. The elongate and arcuate body has a first end, a first anchoring portion located proximate the first end, a second end, a second anchoring portion located proximate the second end, and a central portion. The central portion is displaced from the plane containing the first end and the second end. The transvalvular band is positioned so that it extends transversely across a coaptive edge formed by the closure of the mitral valve leaflets and the central portion is displaced towards the left ventricle relative to the first anchoring portion and the second anchoring portion. The ventricular direction displacement moves coaption to an earlier point in the cardiac cycle.
Owner:HEART REPAIR TECH INC
Intracardiac pressure guided pacemaker
InactiveUS20040172081A1Optimize pacing settingFunction increaseHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodePulse rate
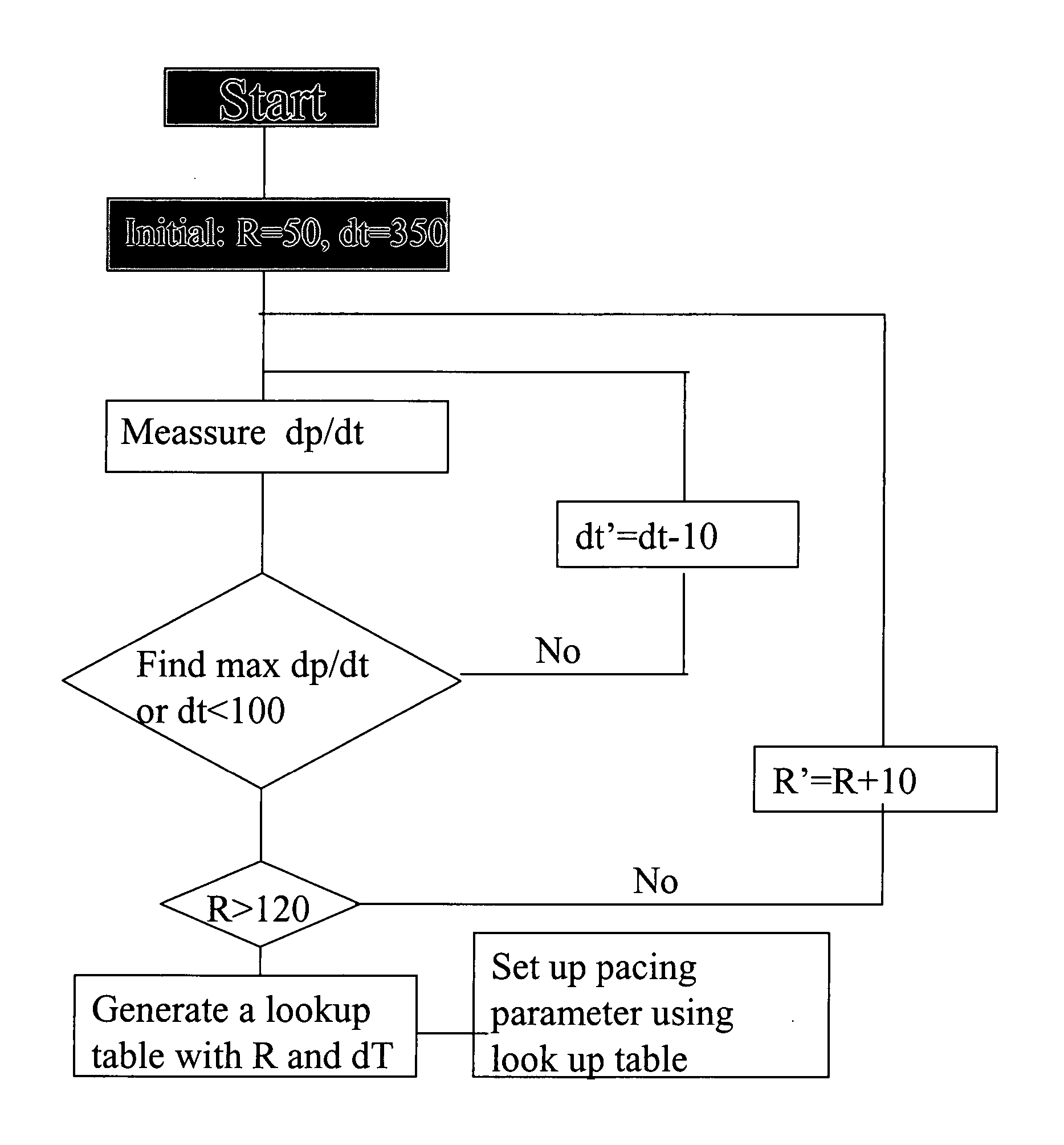
The current invention is an intracardiac pressure guided pacemaker. It has a sensor in pacemaker lead to sense intracardiac pressure, which is used to find the best pacing location in the cardiac chamber and to adjust the timing of pacing signal. It will optimize pacing location and pacing timing and, therefore, optimize resychronization of the contraction of myocardium and interaction between different cardiac chambers. This will improve cardiac function at the same working condition without increase in oxygen demand from myocardium. The pacemaker has a computer program, which, based on intracardiac pressure, can adjust pacing parameters of the pacemaker to optimize resynchronization of the myocardium and interaction between different cardiac chambers automatically at different heart rate and in certain time interval specified by care provider. This also can be achieved by using an interrogator manually. The pacemaker can also store profiles of pacing parameter and intracardiac pressure, which can be retrieved for review to help optimize cardiac performance.
Owner:WANG DAI YUAN
Apparatus and methods for delivering devices for reducing left atrial pressure
ActiveUS20140350565A1Reduce pressureHigh outputEar treatmentHeart valvesAtrial cavityLeft ventricular size
A device for regulating blood pressure between a patient's left atrium and right atrium, and apparatus for delivery the device, are provided. The delivery apparatus may include one or more latching legs, a release ring, a pull chord, and a catheter wherein the latching legs are configured to engage the device for delivery. The inventive devices may reduce left atrial pressure and left ventricular end diastolic pressure, and may increase cardiac output, increase ejection fraction, relieve pulmonary congestion, and lower pulmonary artery pressure, among other benefits. The inventive devices may be used, for example, to treat subjects having heart failure, pulmonary congestion, or myocardial infarction, among other pathologies.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
Compositions comprising HDAC inhibitors and methods of their use in restoring stem cell function and preventing heart failure
InactiveUS20090162329A1Improve heart functionRelieve symptomsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsProgenitorHeart failure
The invention provides compositions of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors and progenitor cells useful for treating heart failure in a subject. The invention also provides methods of restoring progenitor cell function to aged progenitor cells and methods for enhancing progenitor cell proliferation and / or differentiation using HDAC inhibitors.
Owner:NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE
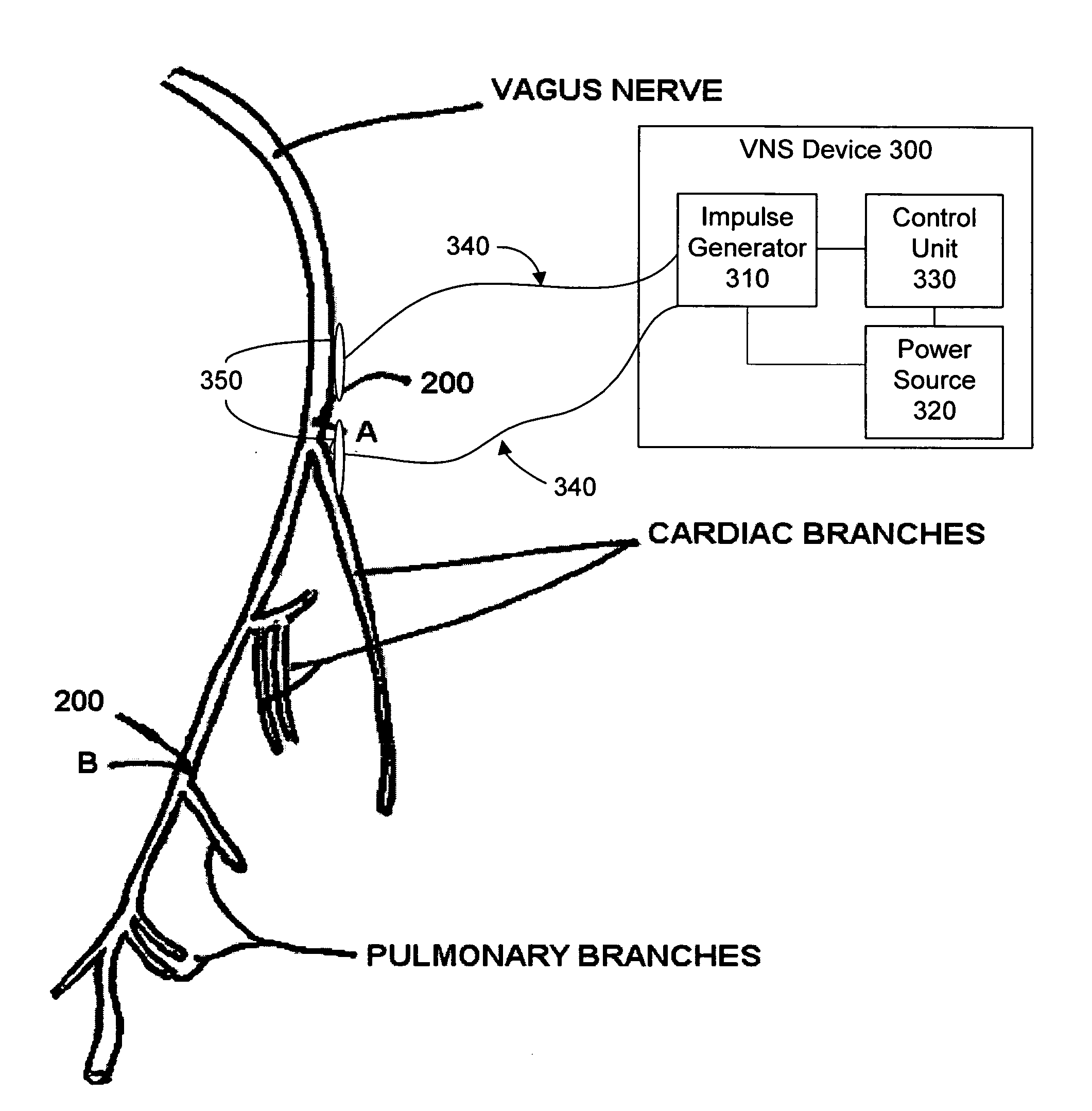
Methods and apparatus for treating anaphylaxis using electrical modulation
ActiveUS20070191902A1Improve heart functionIncrease pressureSpinal electrodesBronchial tubeAnesthesia
Methods and devices for treating anaphylaxis, anaphylactic shock, bronchial constriction, and / or asthma include providing an electrical impulse to a selected region of the vagus nerve of a patient suffering from anaphylaxis to block and / or modulate nerve signals that would regulate the function of, for example, myocardial tissue, vasodilation / constriction and / or pulmonary tissue.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Device And A Method For Augmenting Heart Function
ActiveUS20130289717A1Improve heart functionBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsAtrial cavityLeft ventricular size
A device, a kit and a method are presented for permanently augmenting the pump function of the left heart. The basis for the presented innovation is an augmentation of the physiologically up and down movement of the mitral valve during each heart cycle. By means of catheter technique, minimal surgery, or open heart surgery implants are inserted into the left ventricle, the mitral valve annulus, the left atrium and adjacent tissue in order to augment the natural up and down movement of the mitral valve and thereby increasing the left ventricular diastolic filling and the piston effect of the closed mitral valve when moving towards the apex of said heart in systole and / or away from said apex in diastole.
Owner:SYNTACH AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com