Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
222 results about "Vagus nerve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
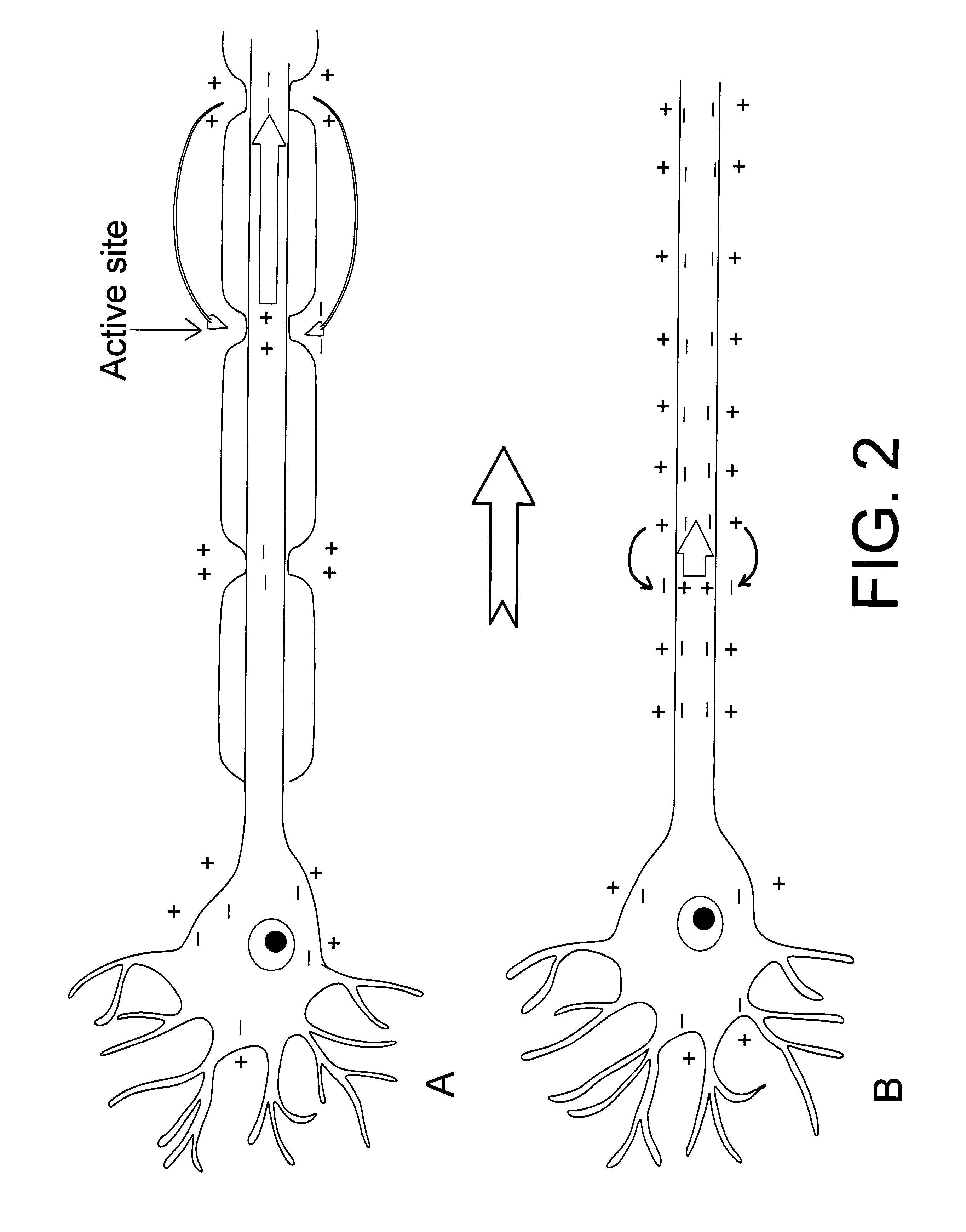
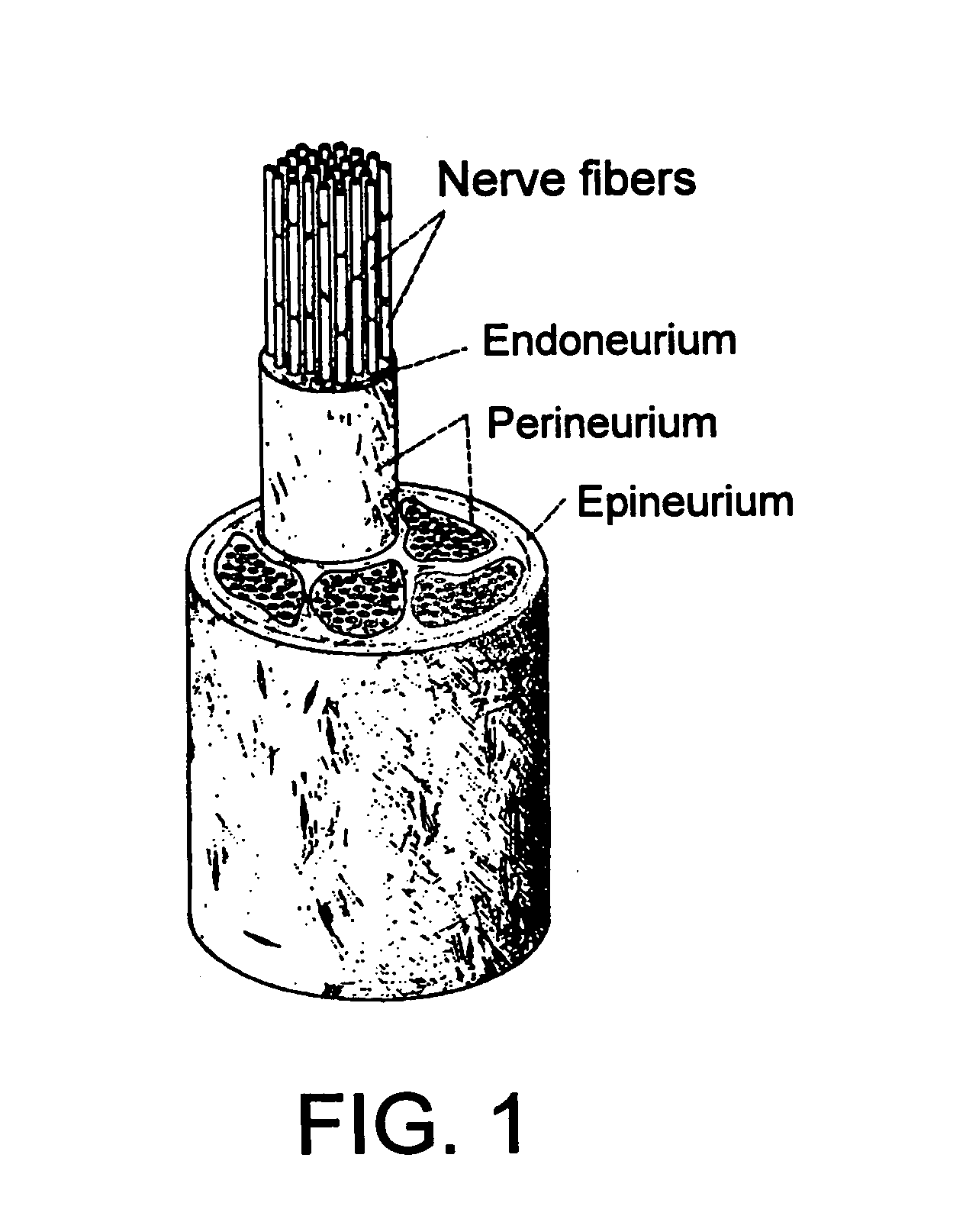
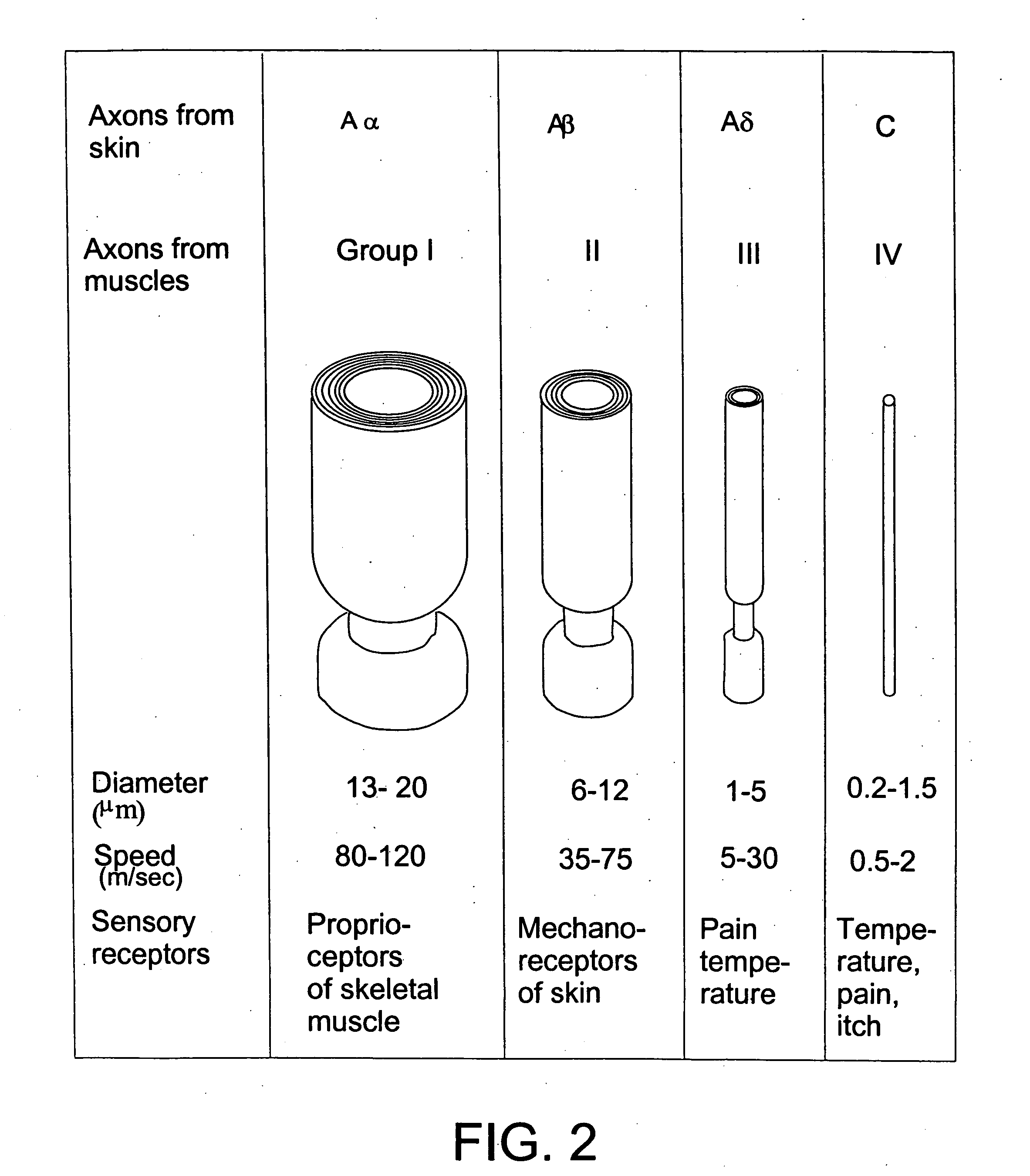
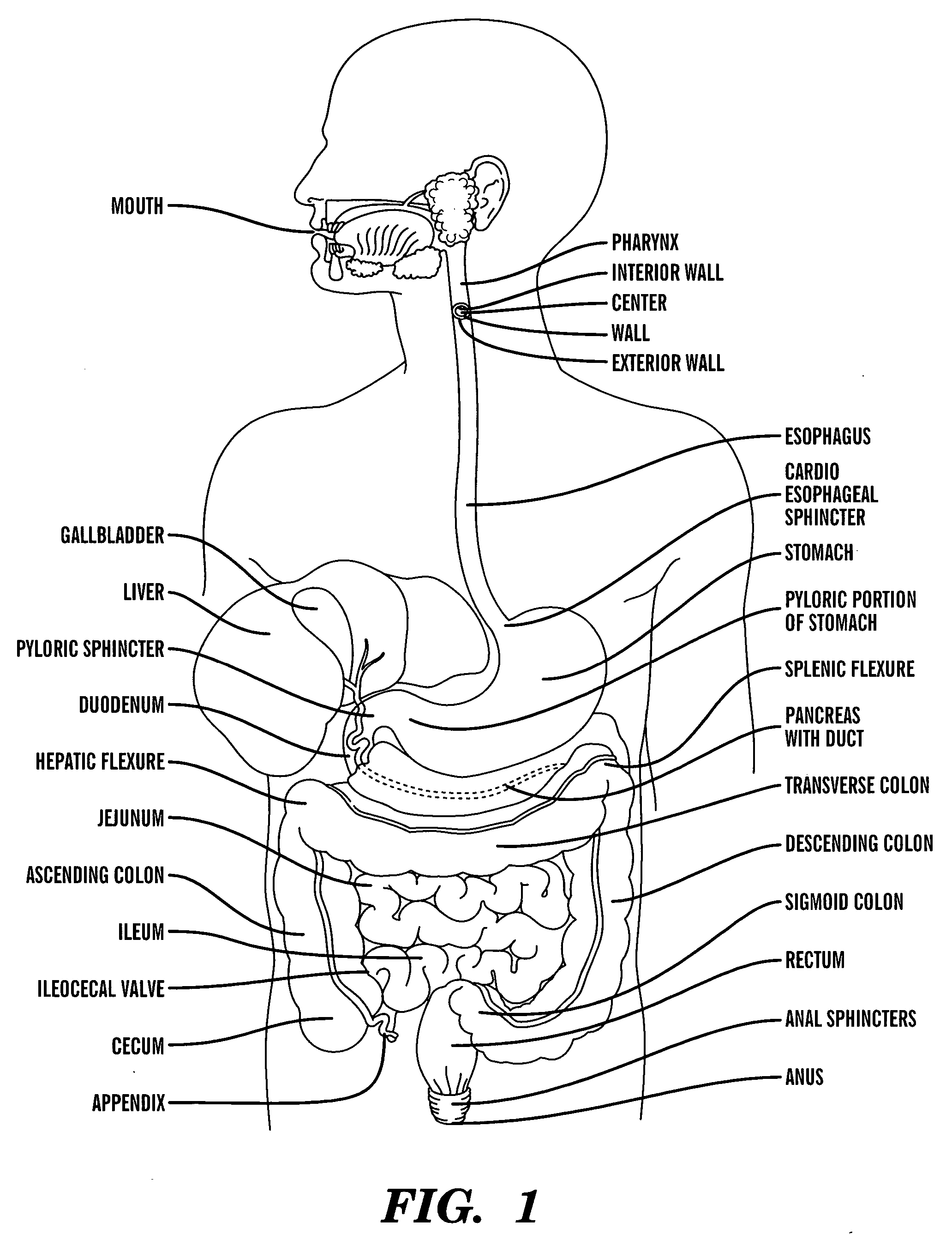
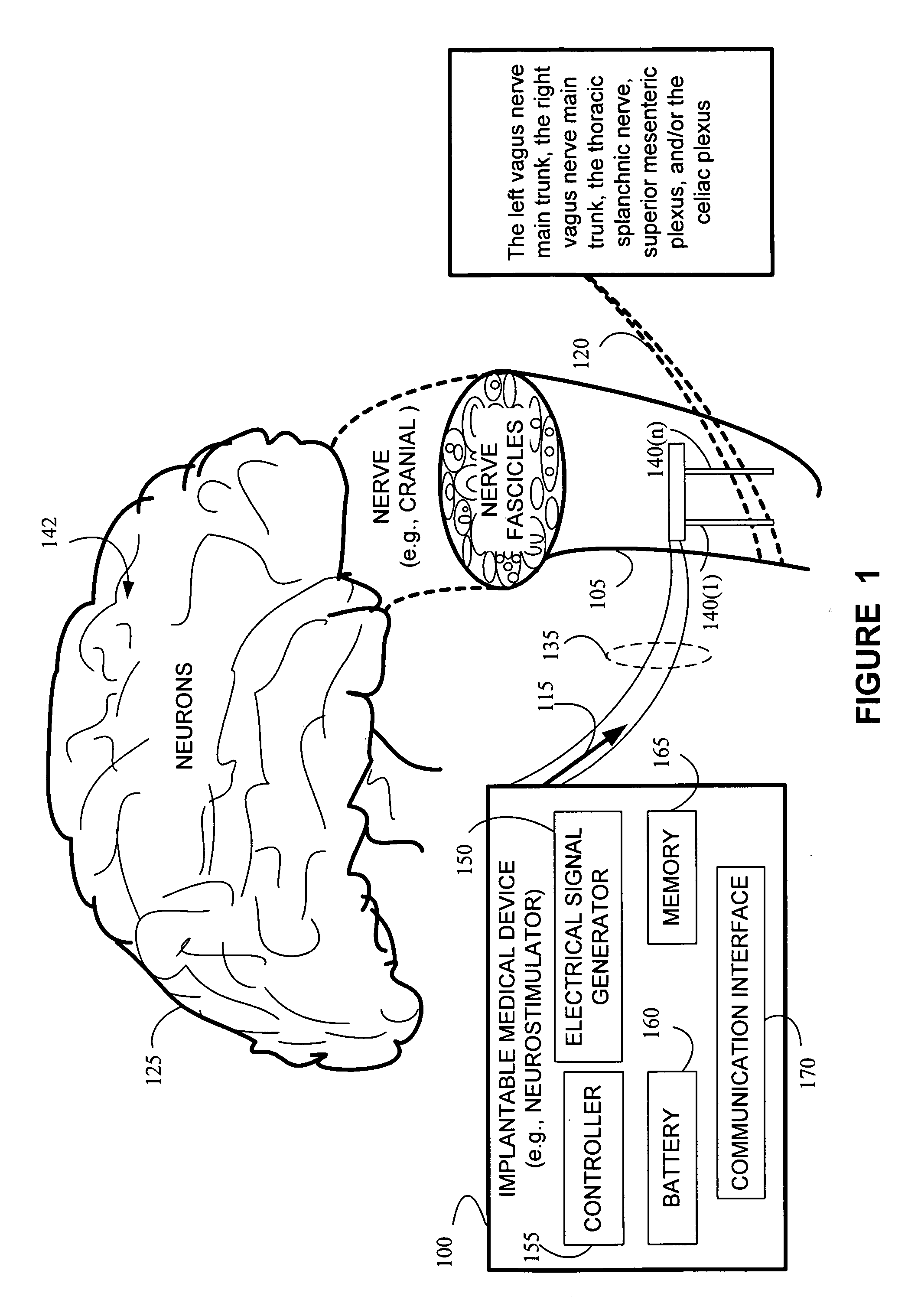
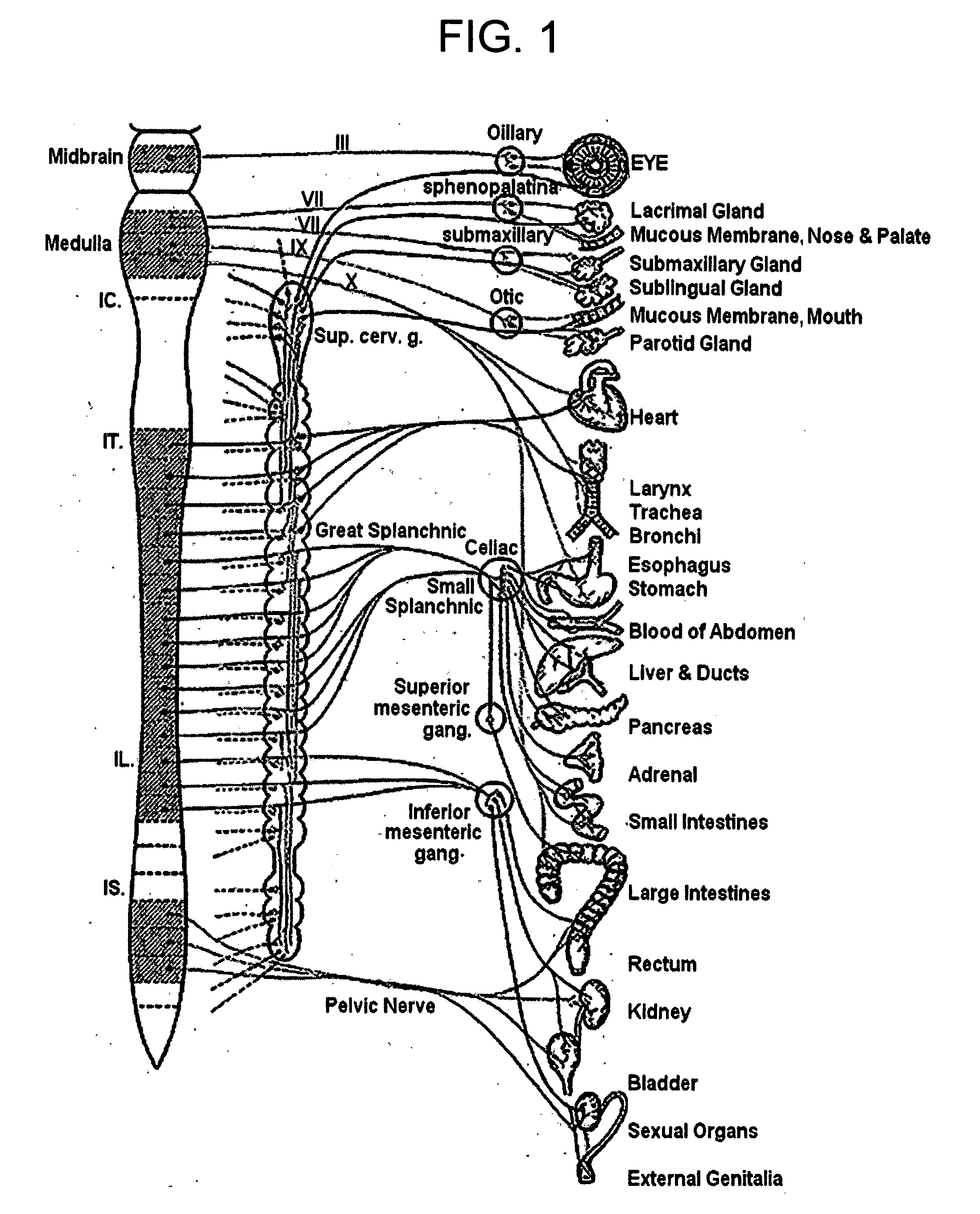
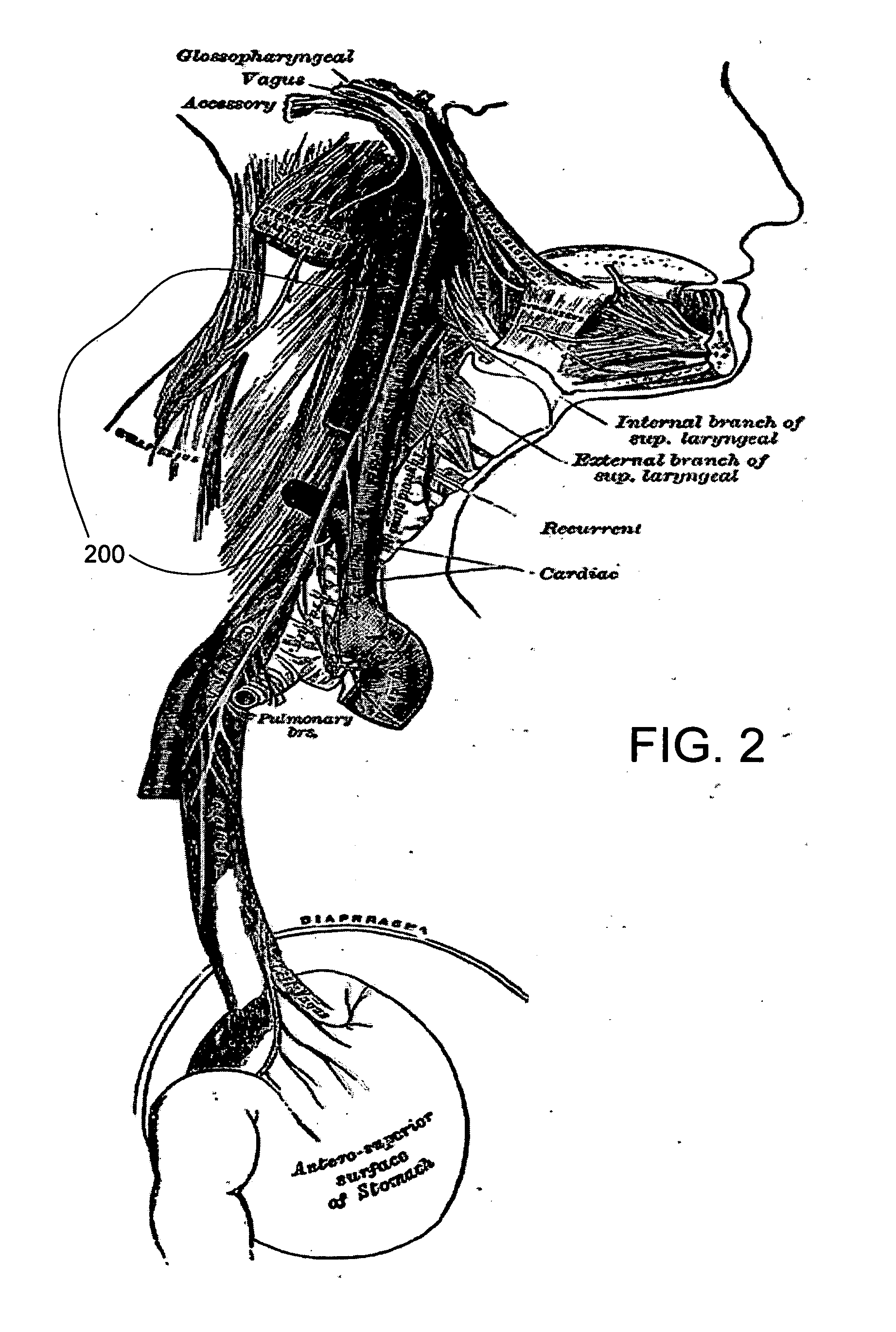
The vagus nerve (/ˈveɪɡəs/ VAY-gəs), historically cited as the pneumogastric nerve, is the tenth cranial nerve or CN X, and interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. The vagus nerves are paired but are normally referred to in the singular. It is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body. The ending part of vagus nerve is known as spinal accessory nucleus.
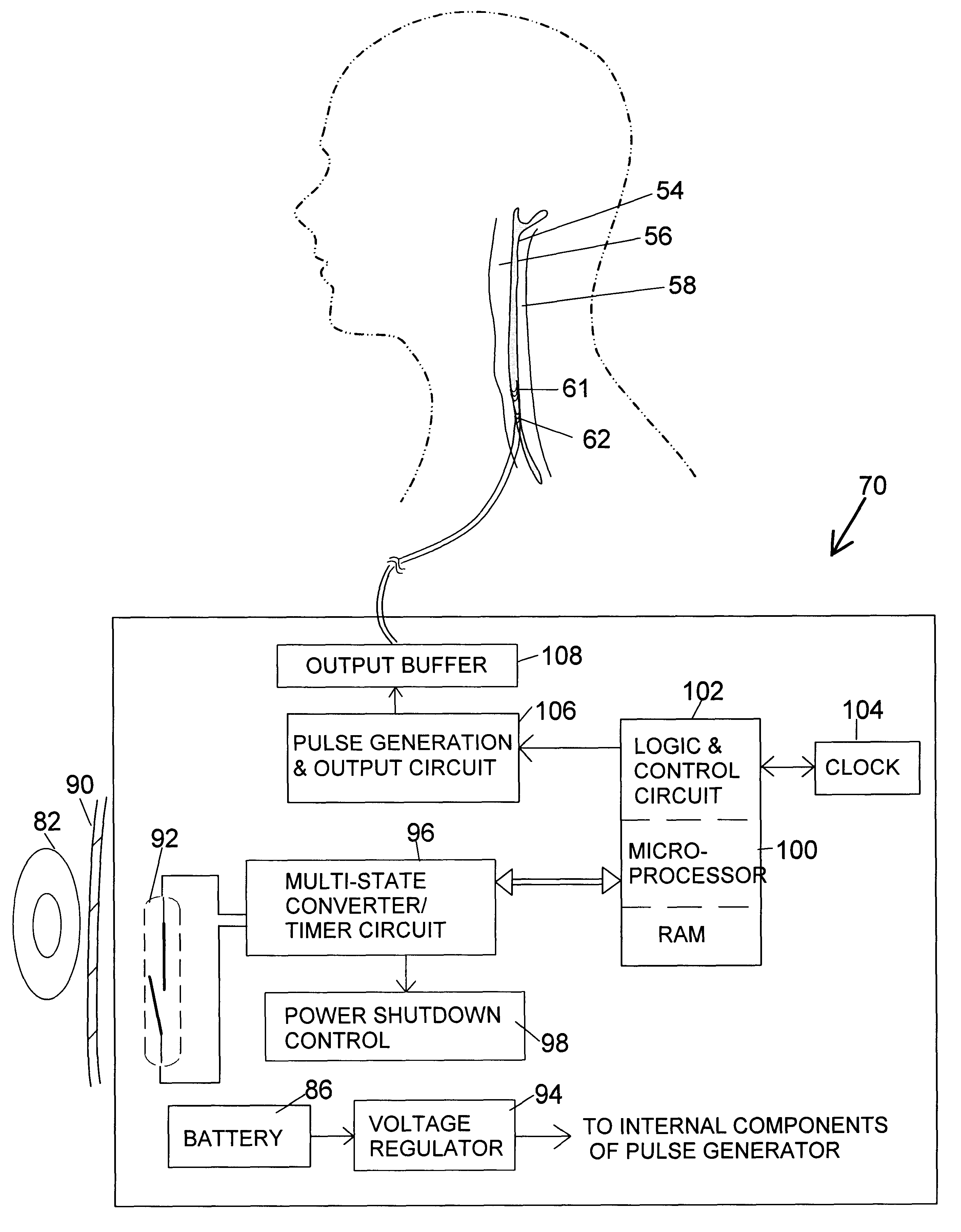
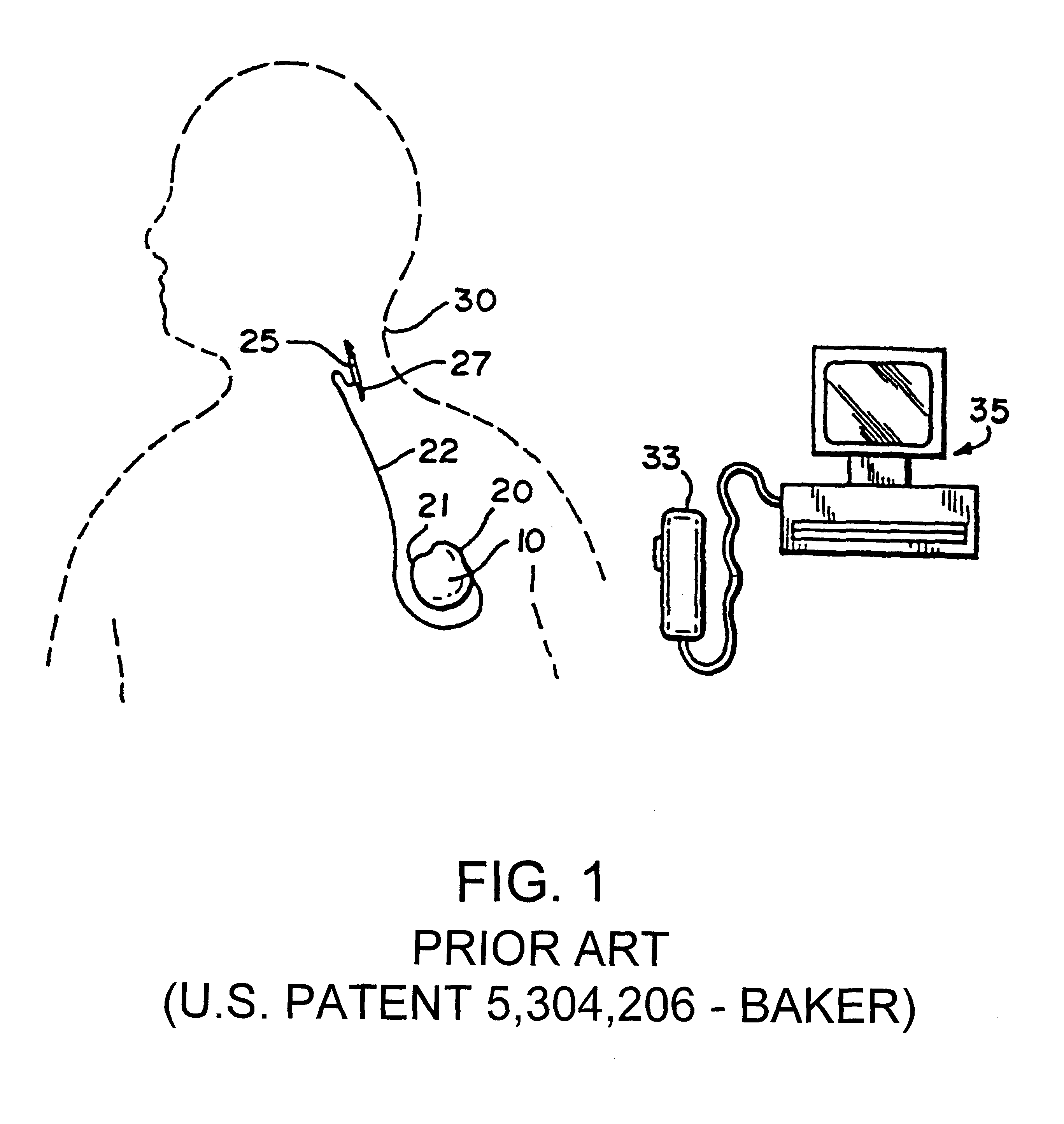
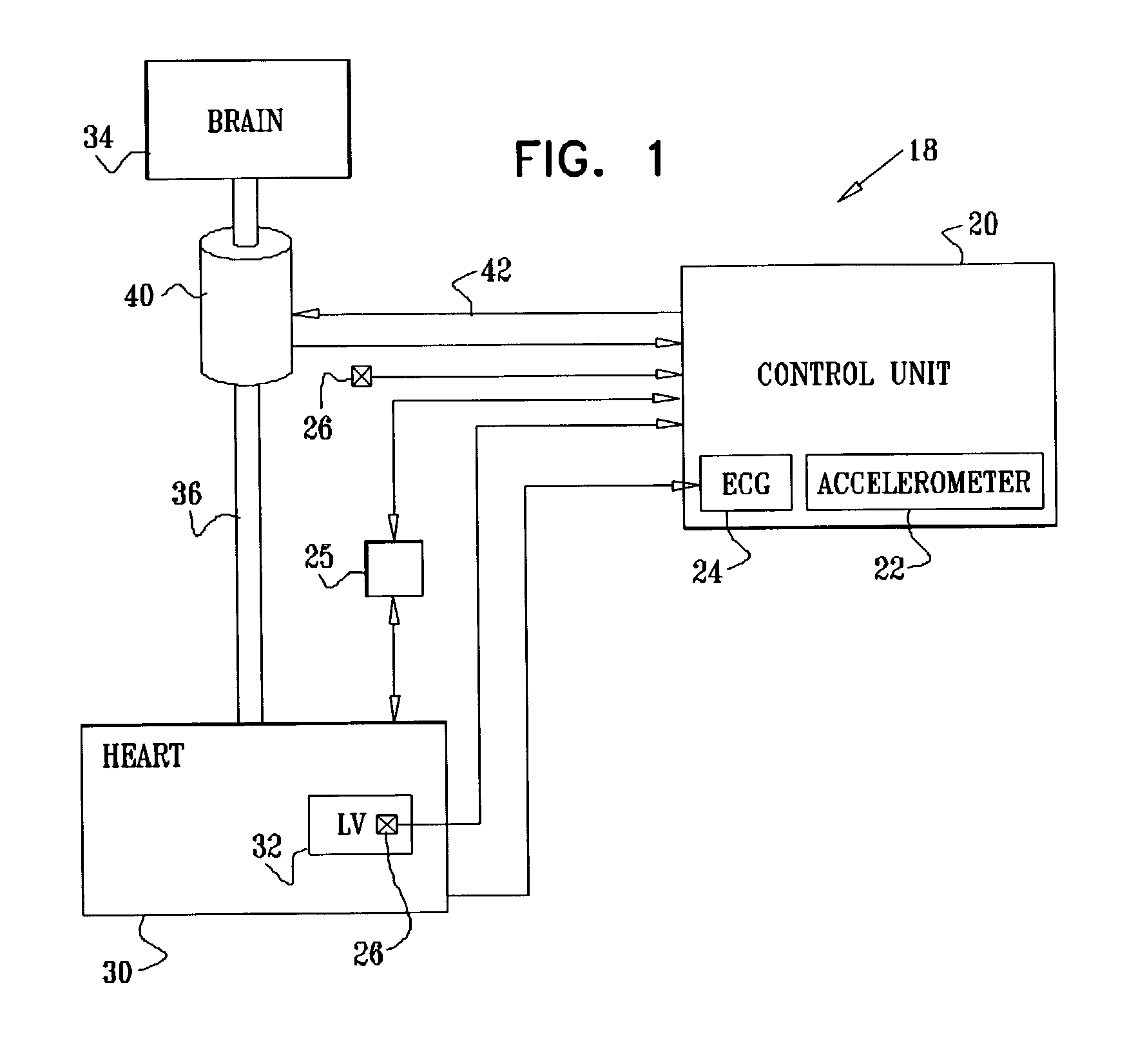
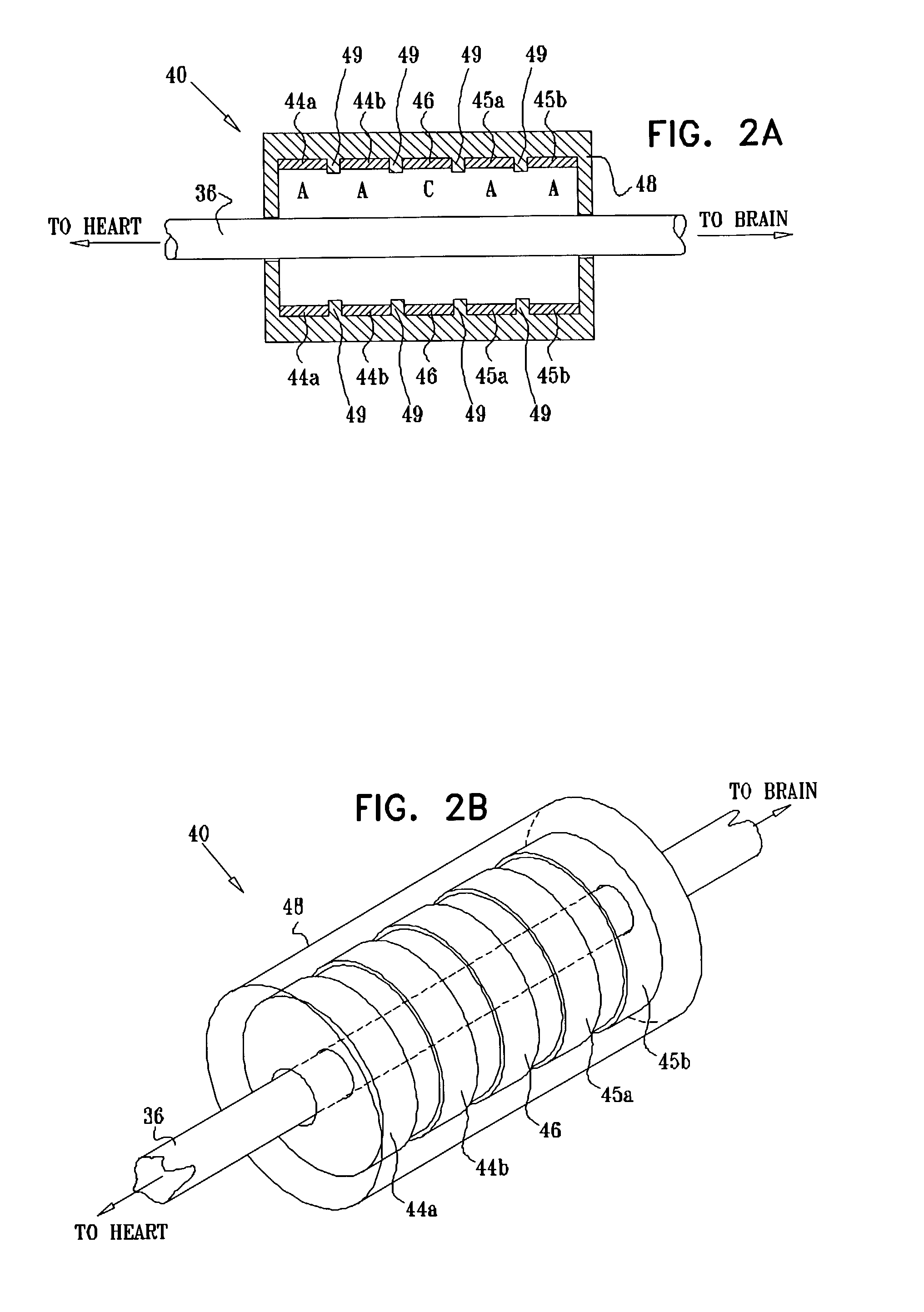
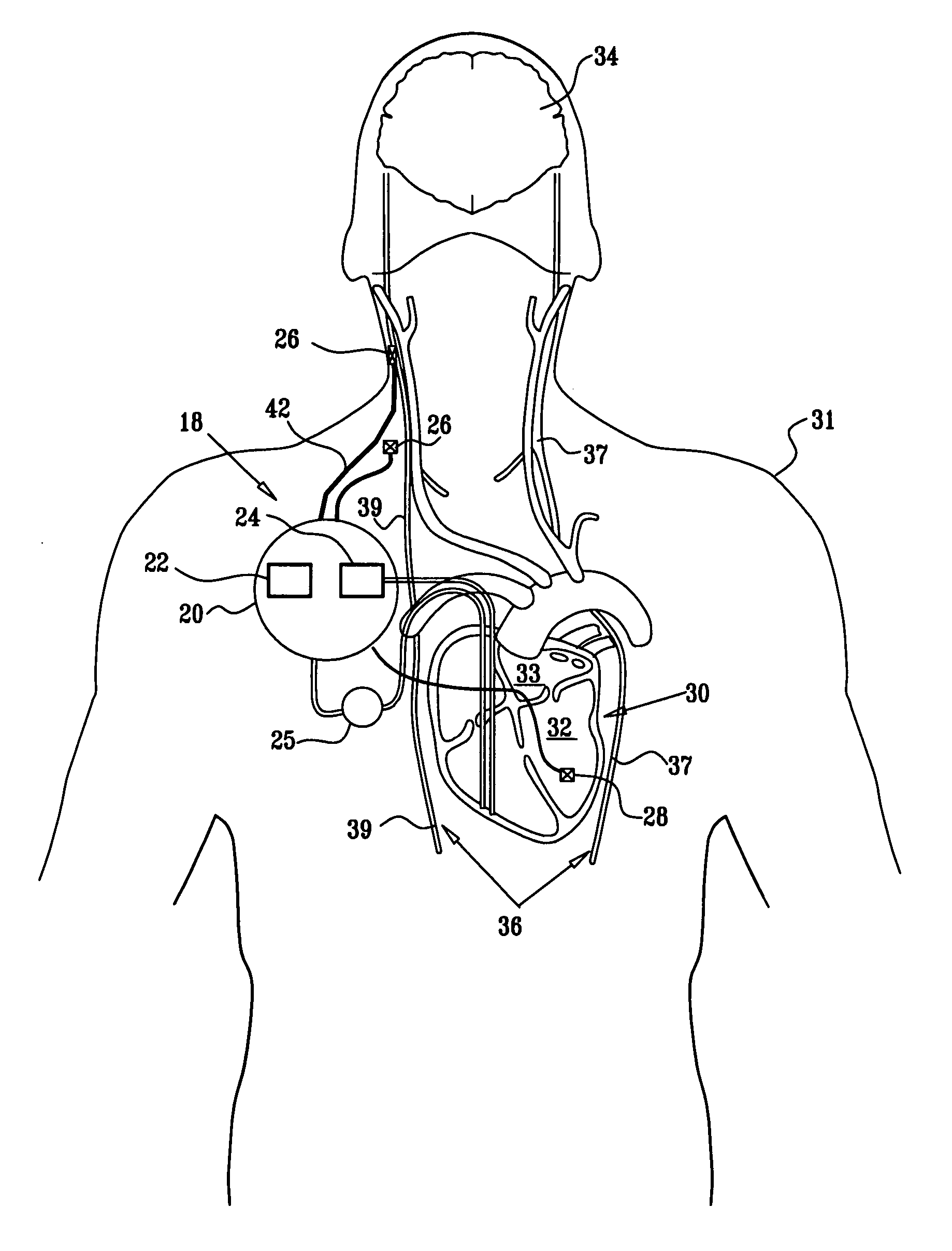
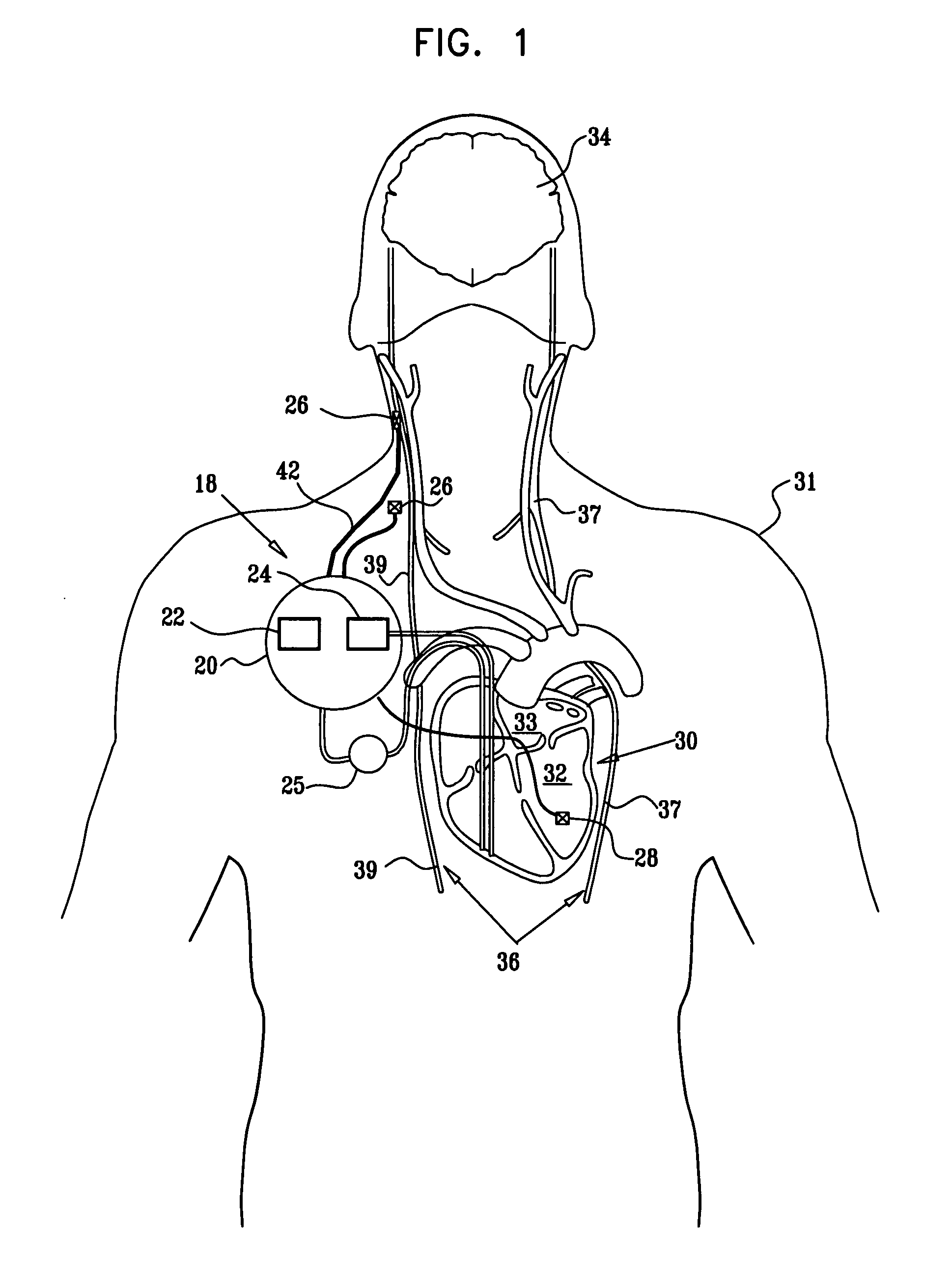
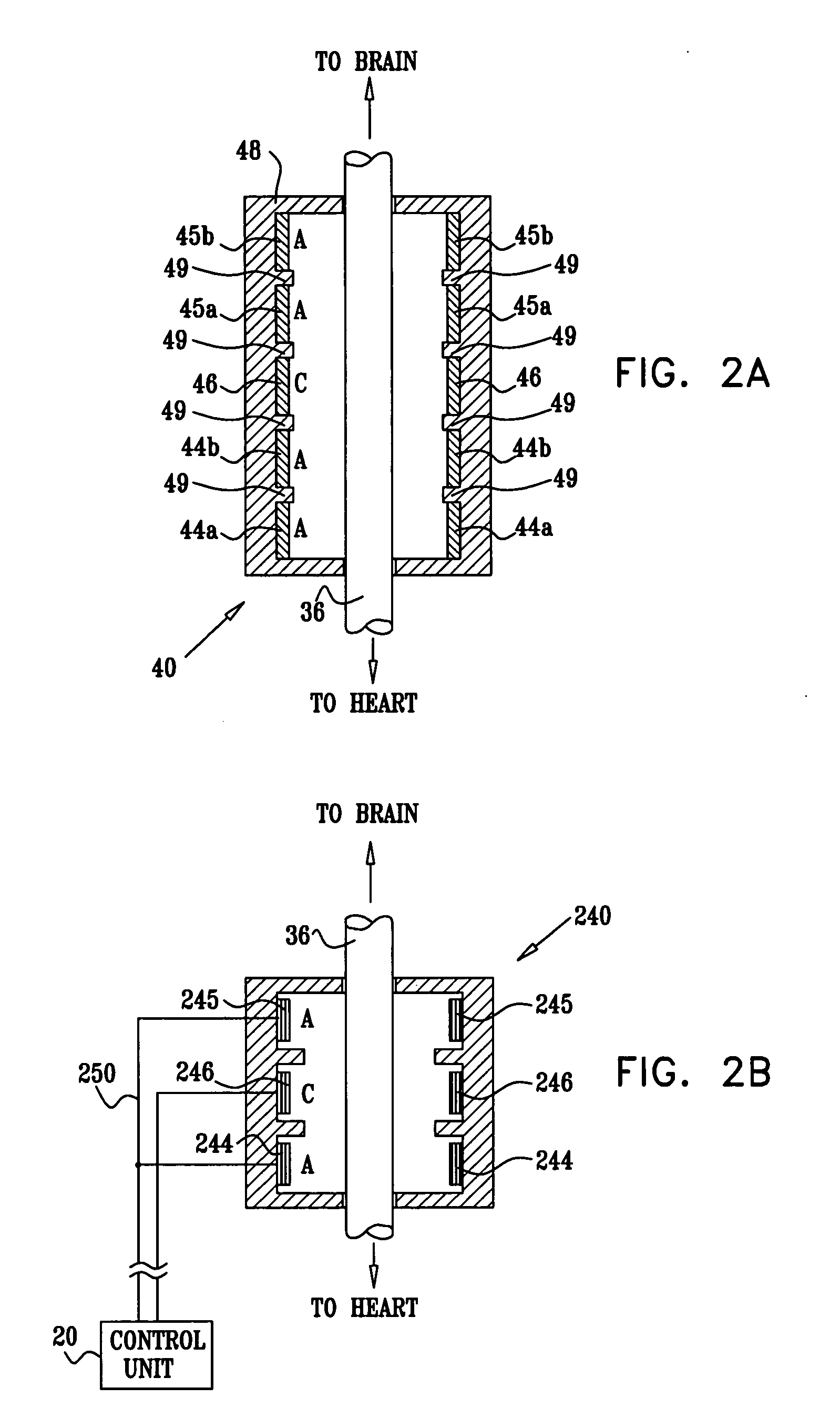
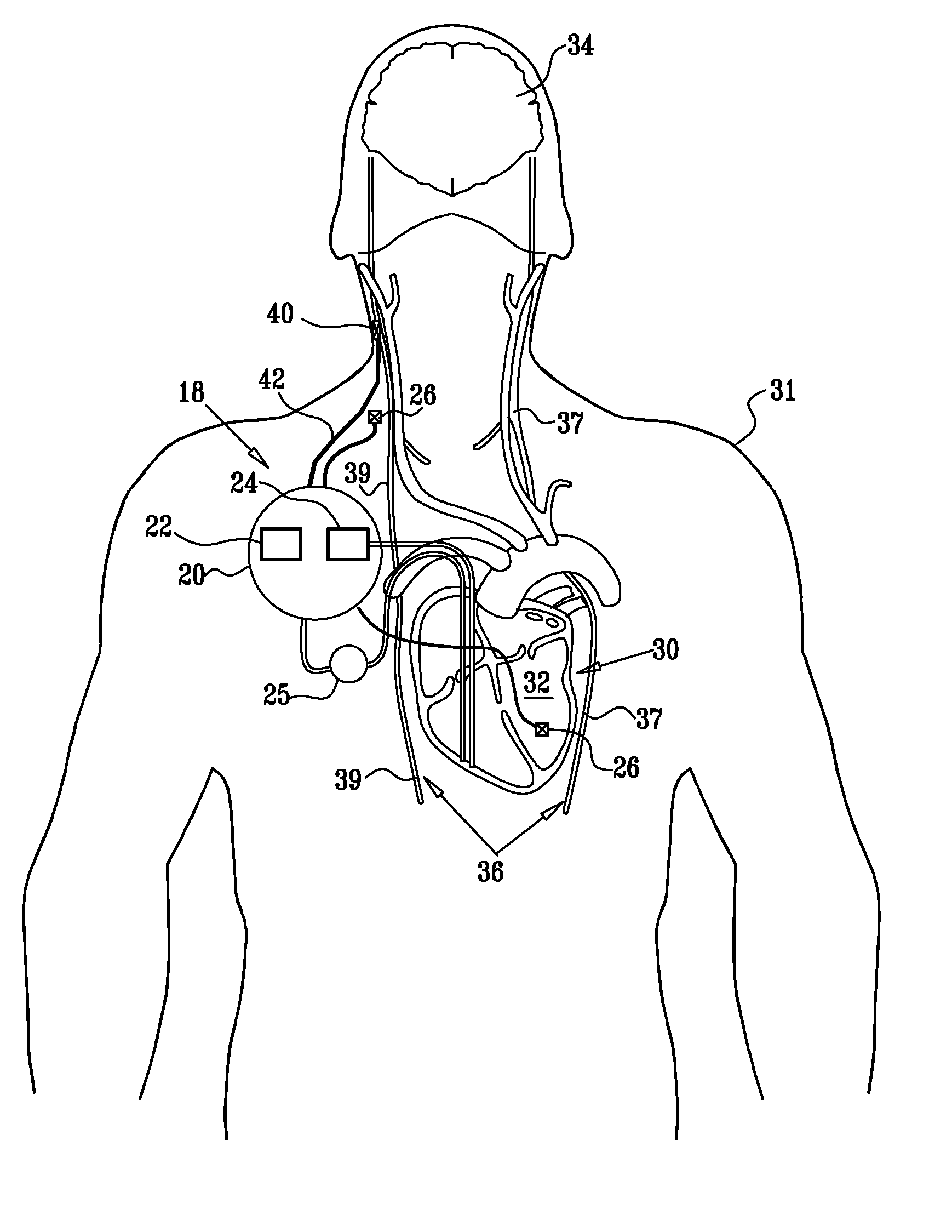
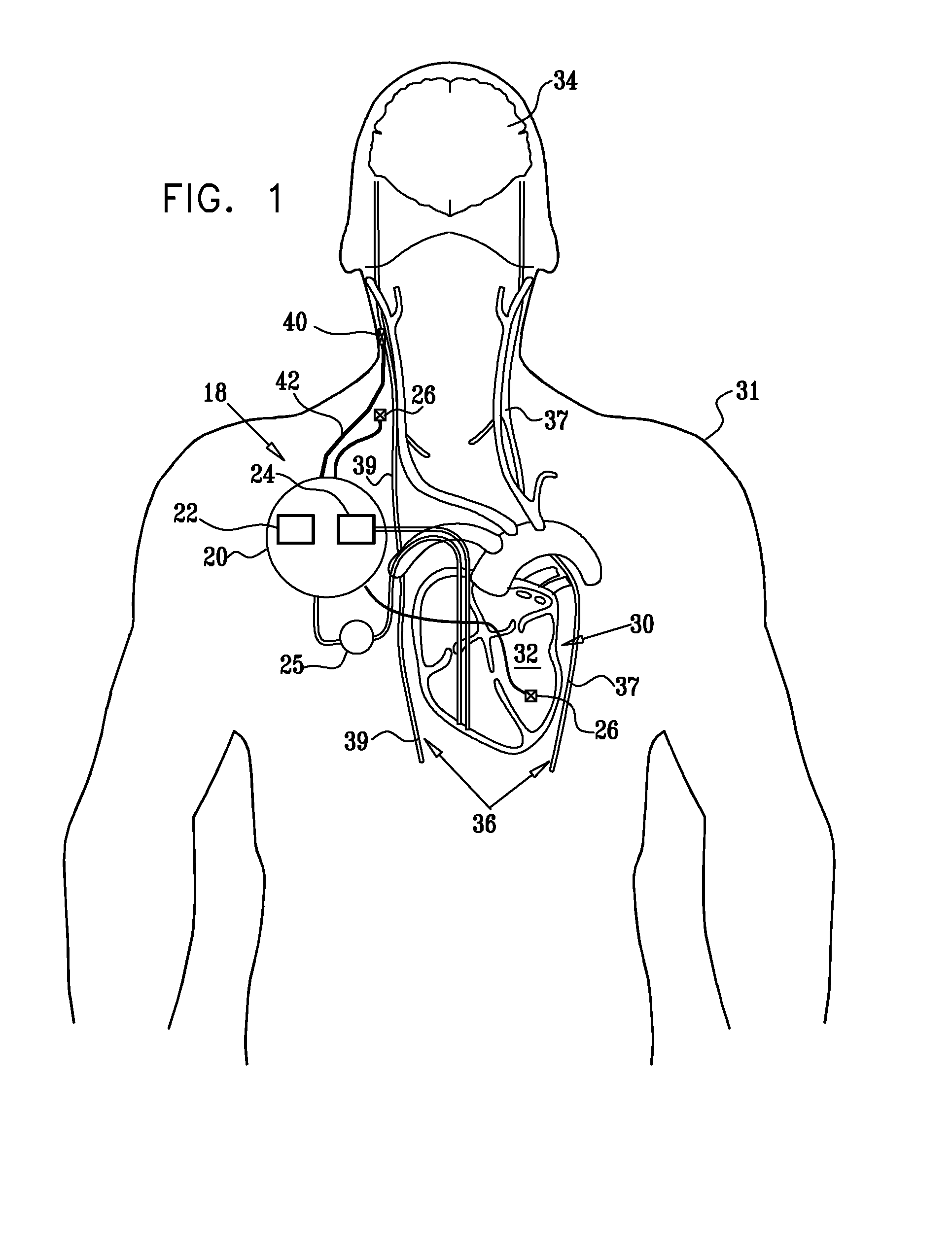
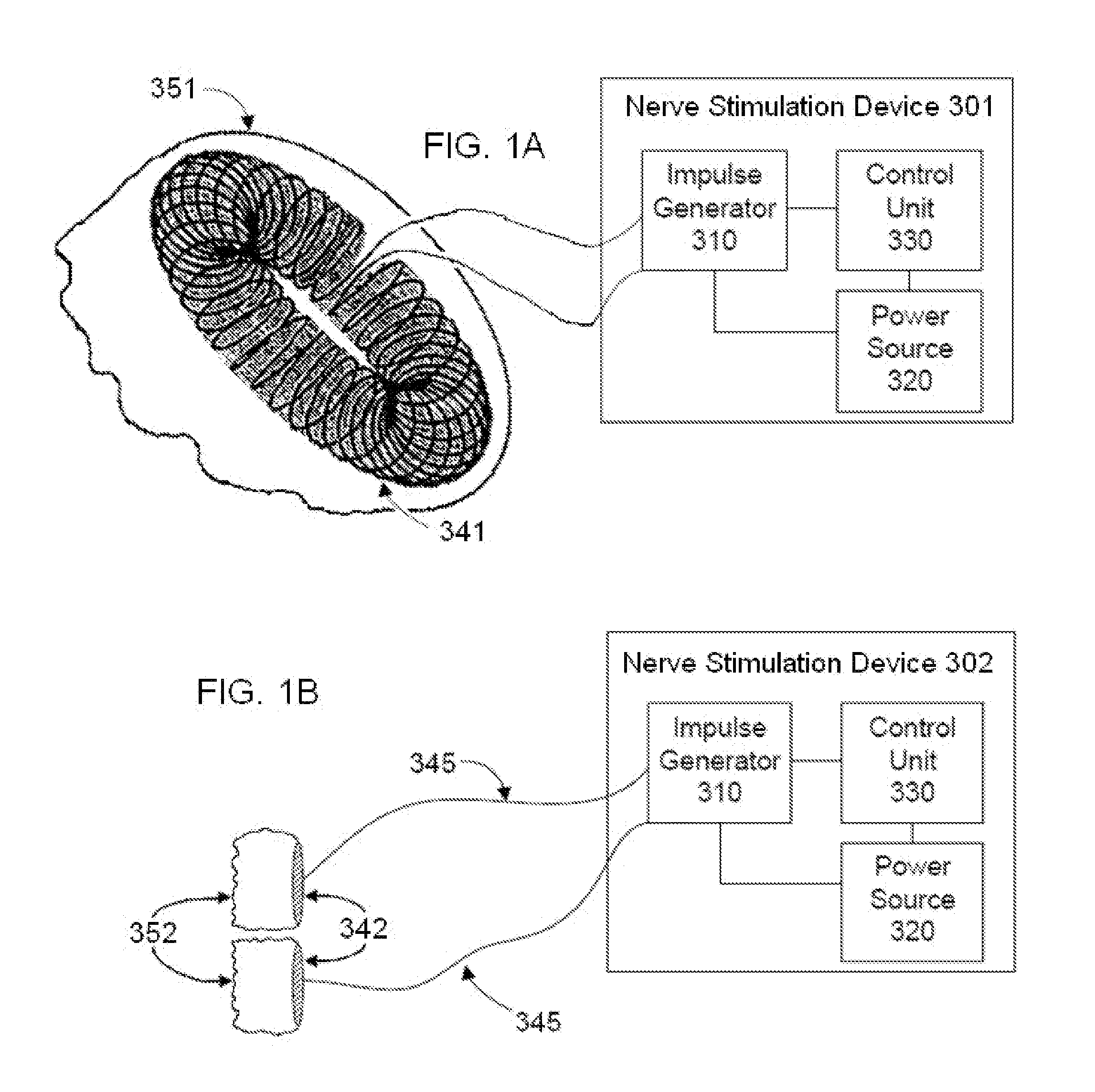
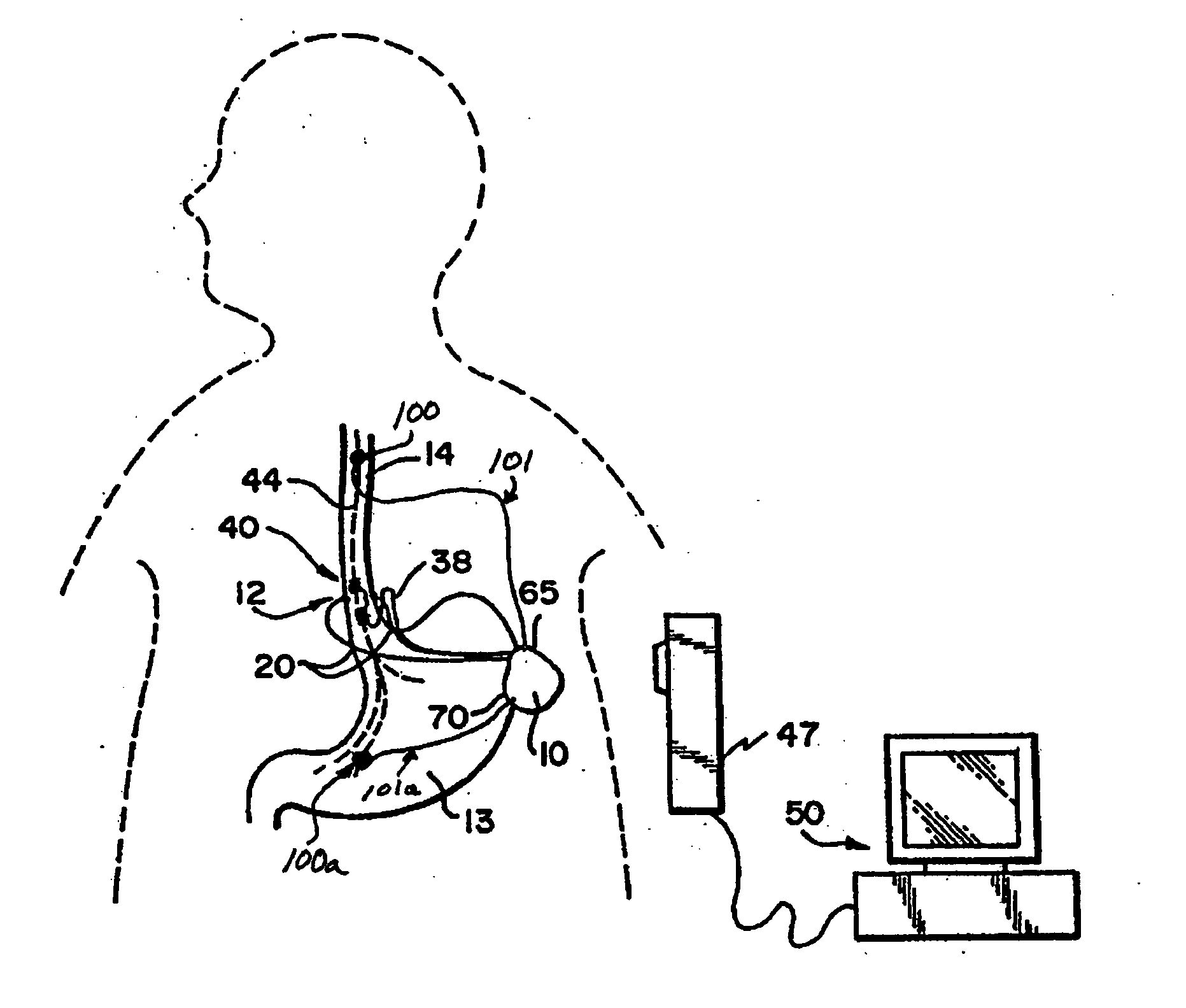
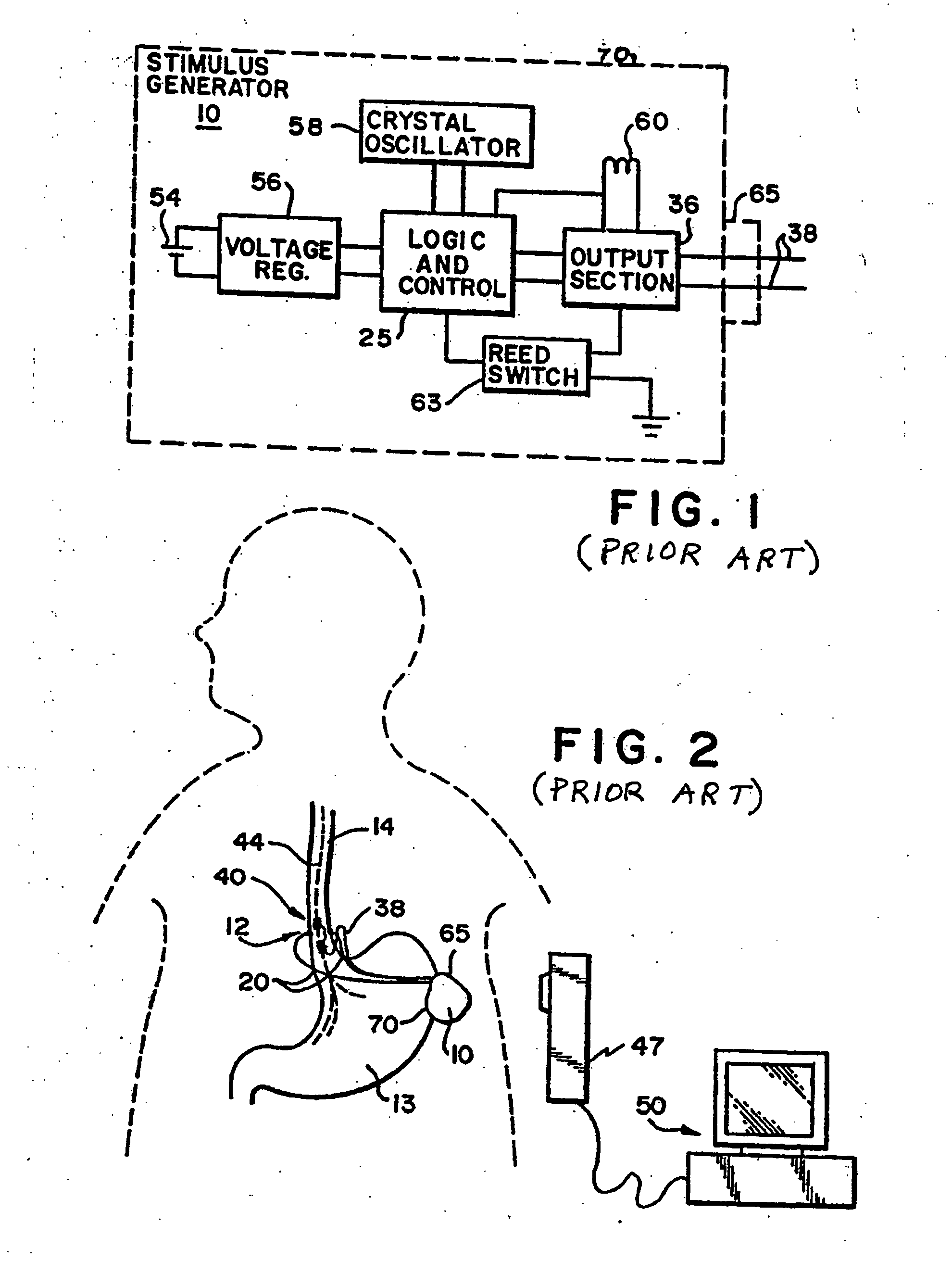
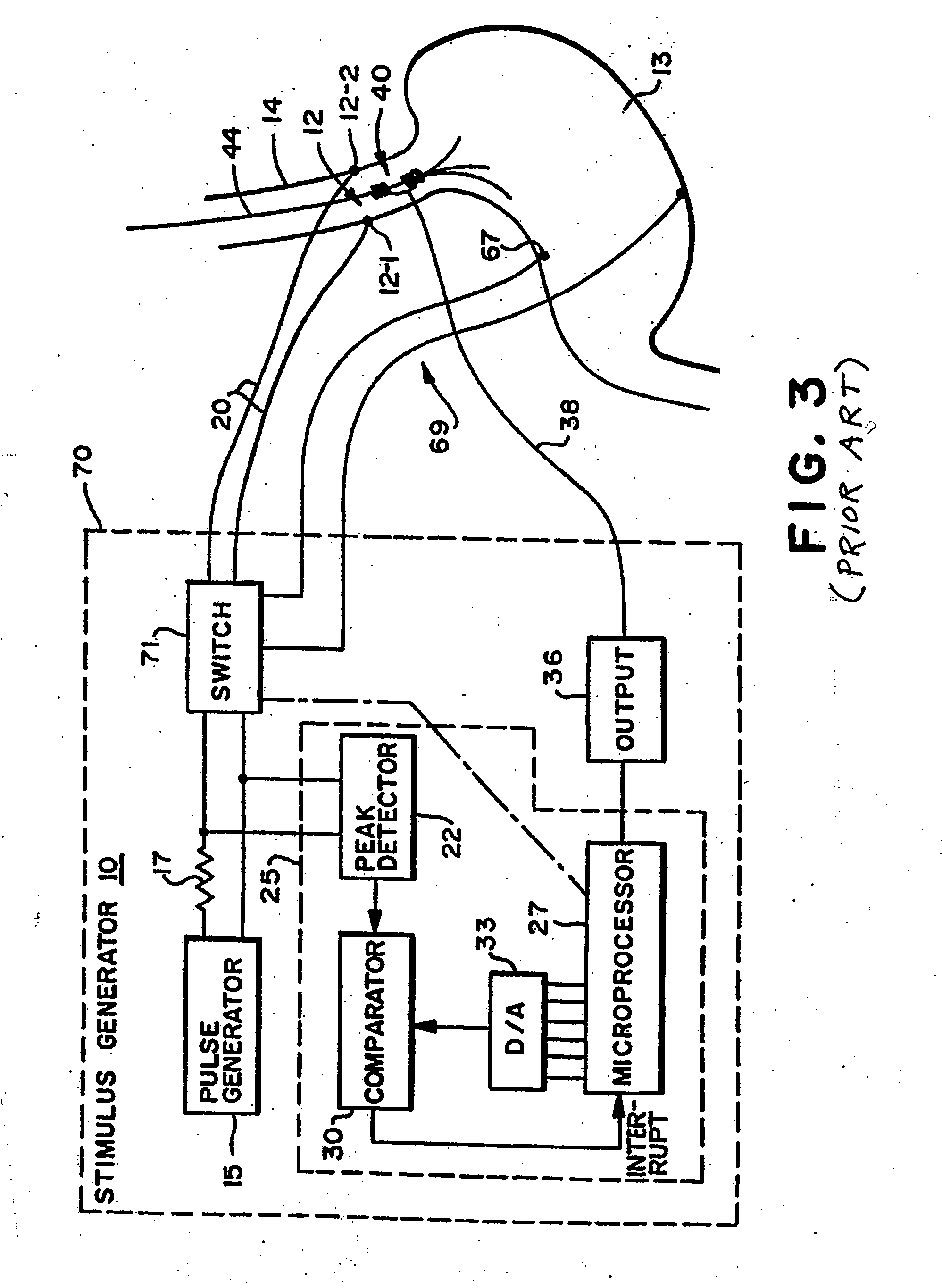
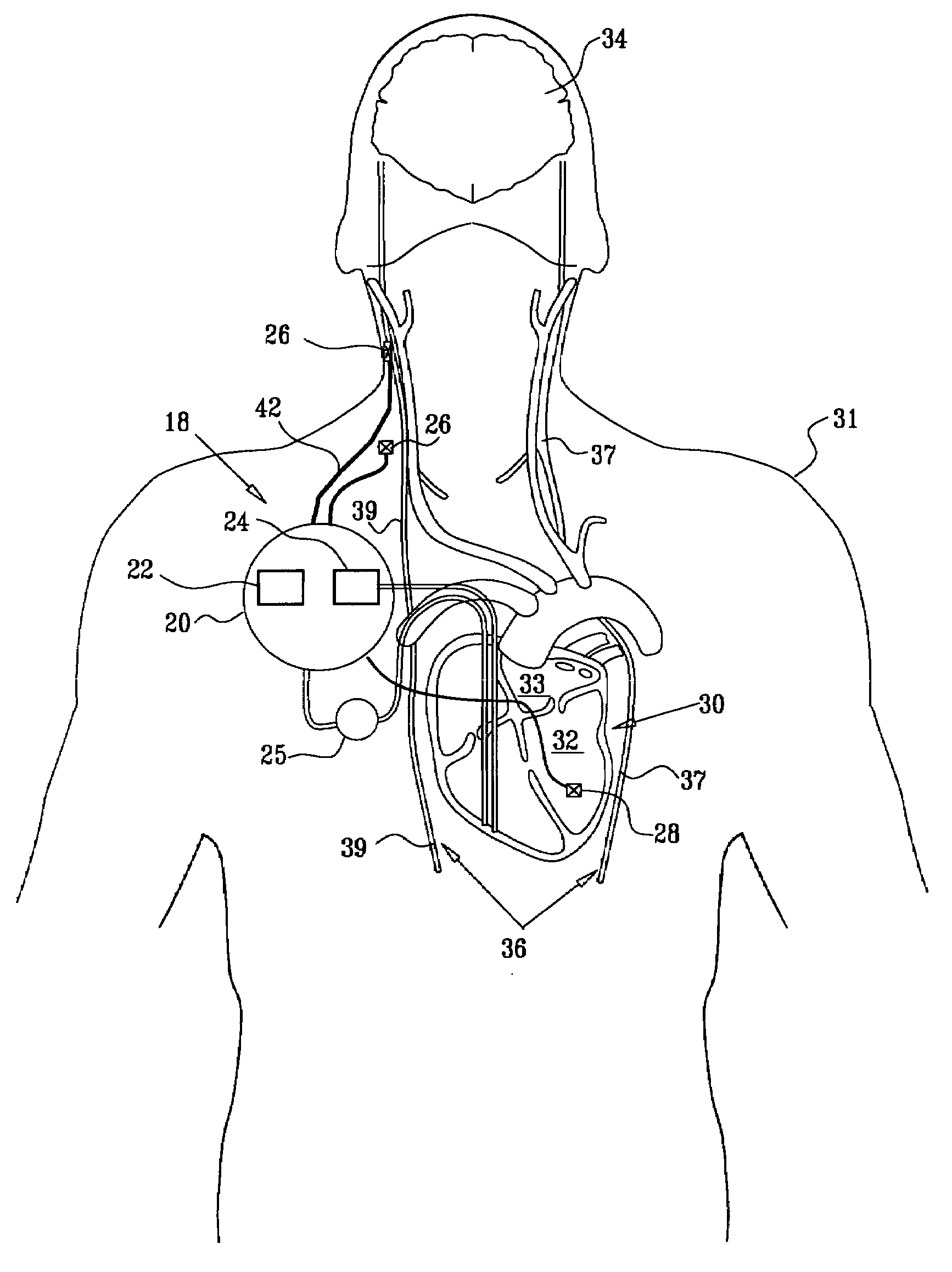
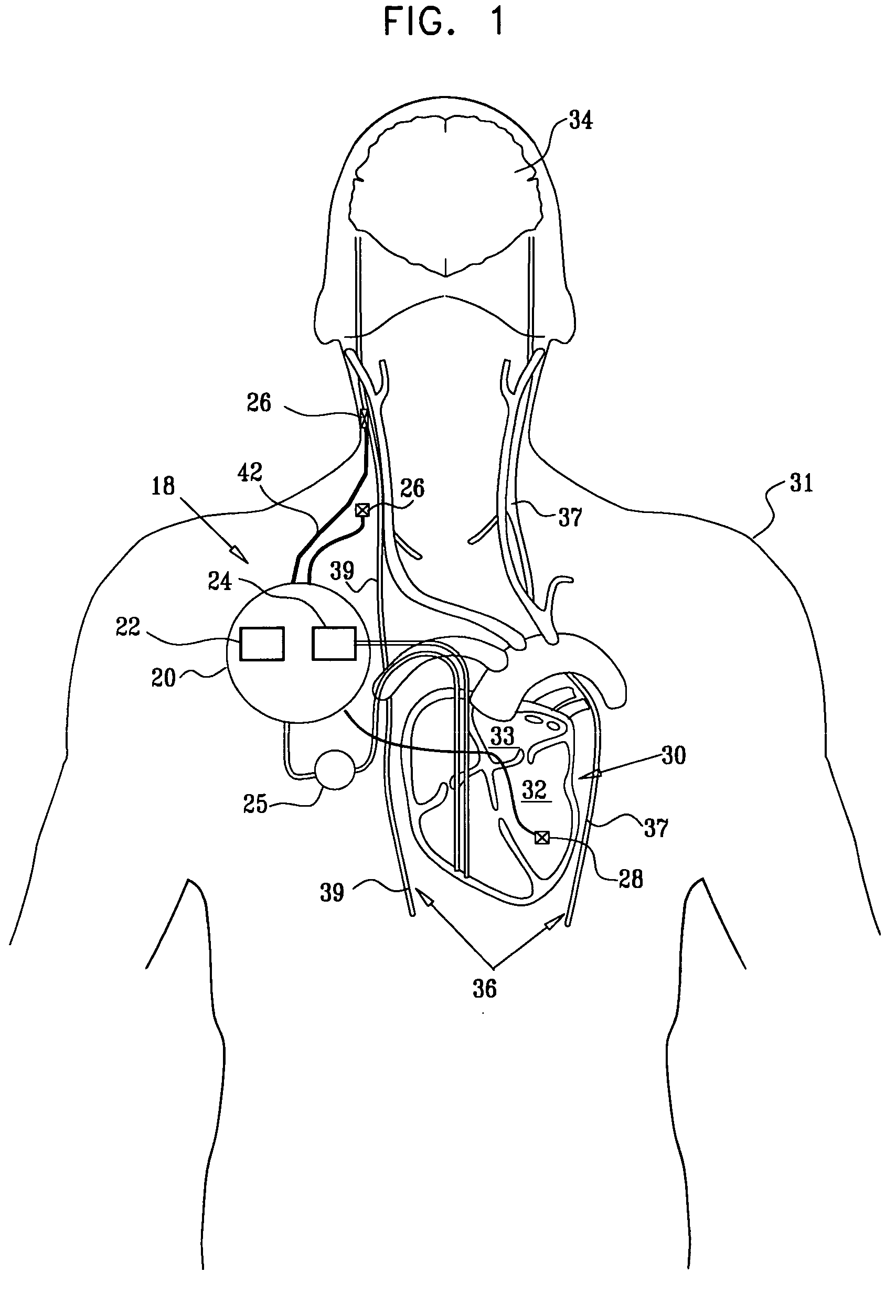
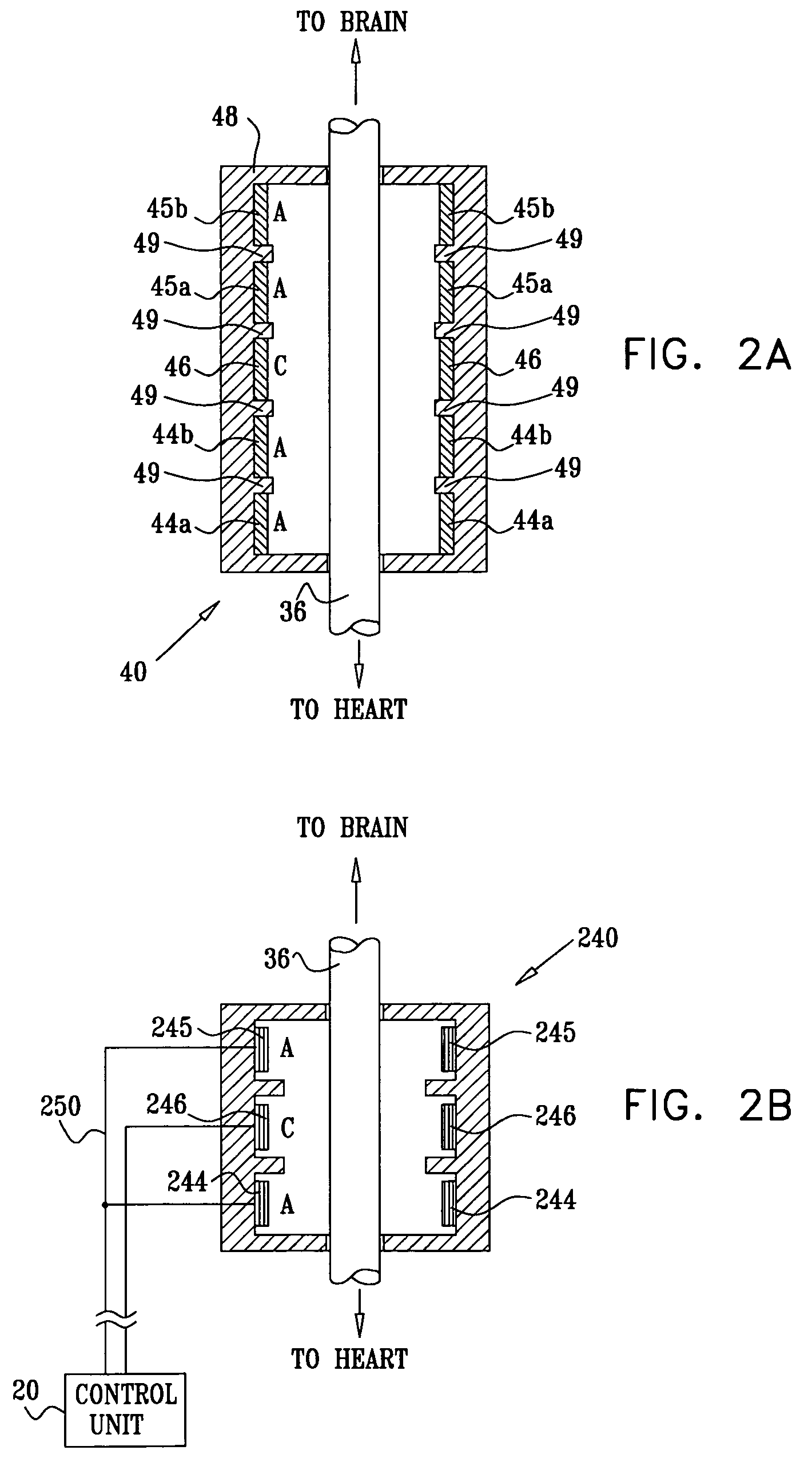
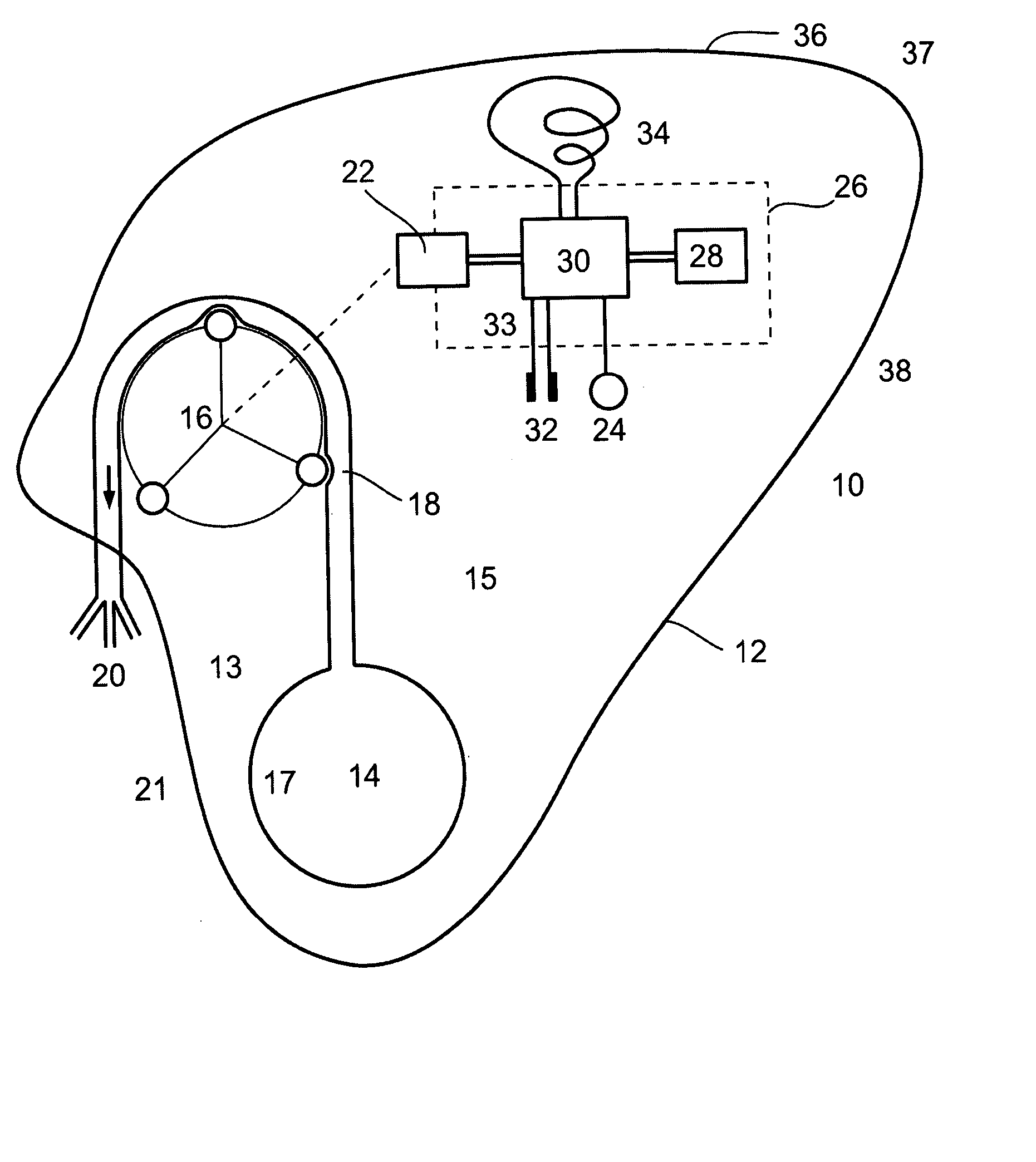
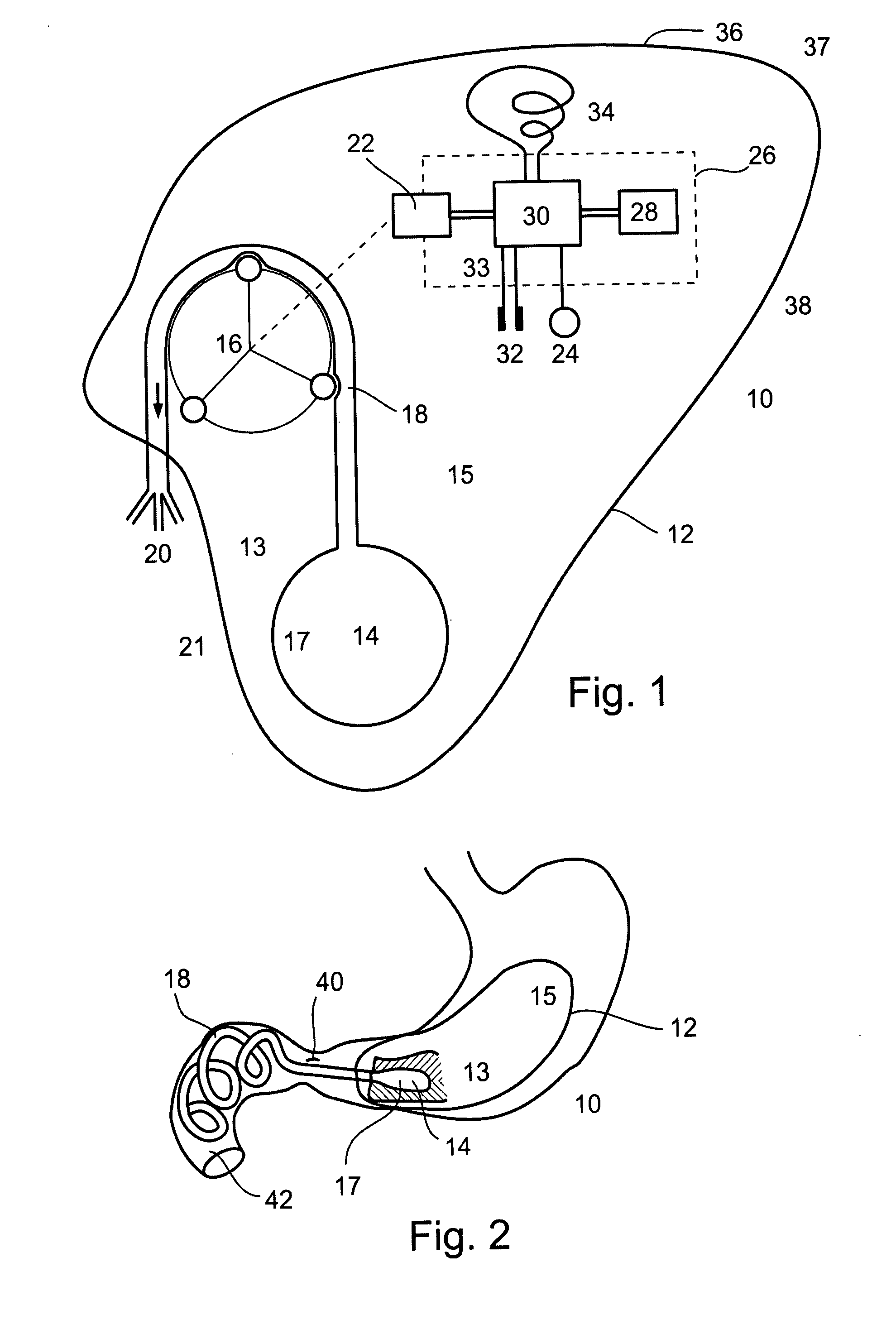
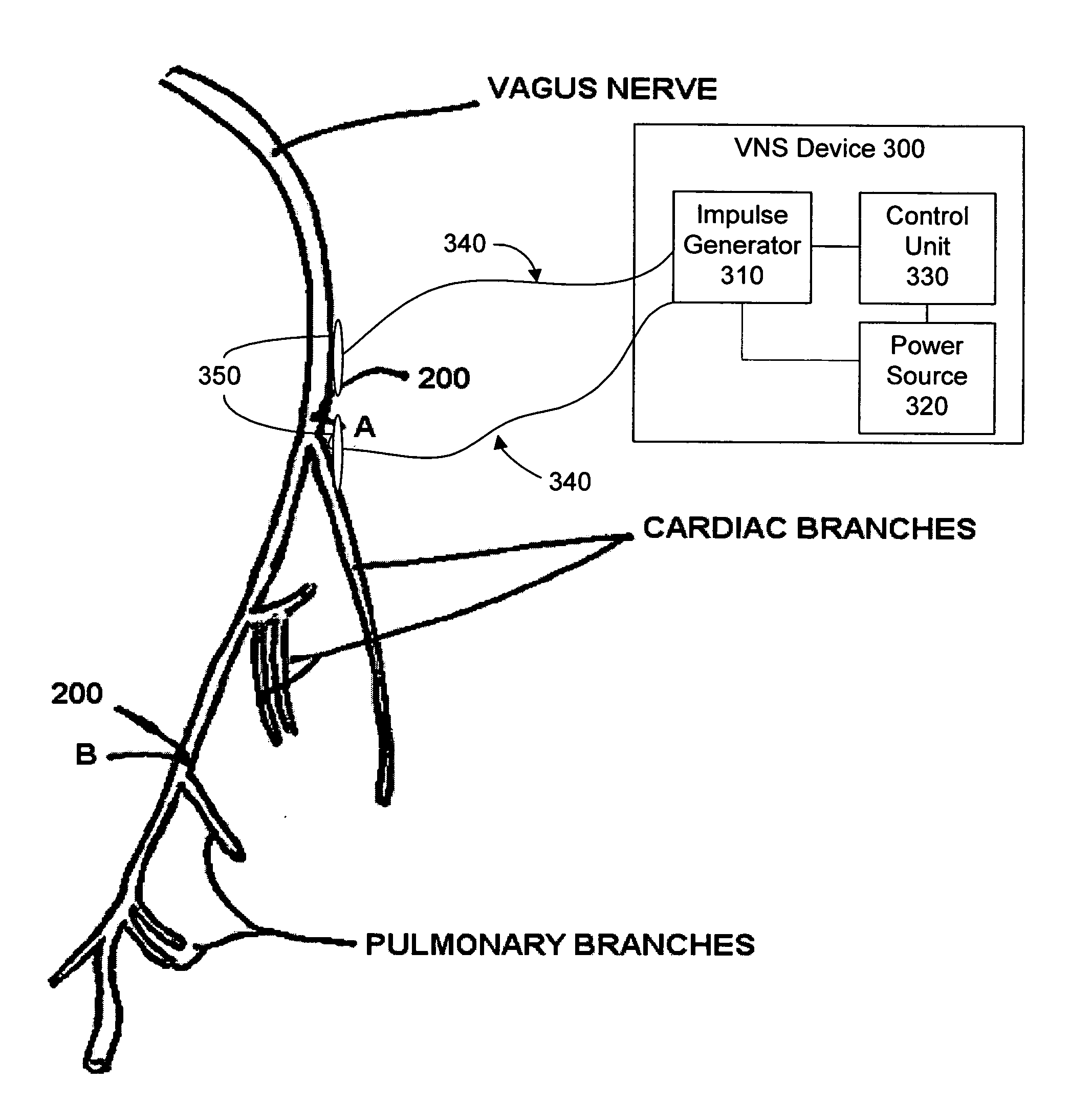
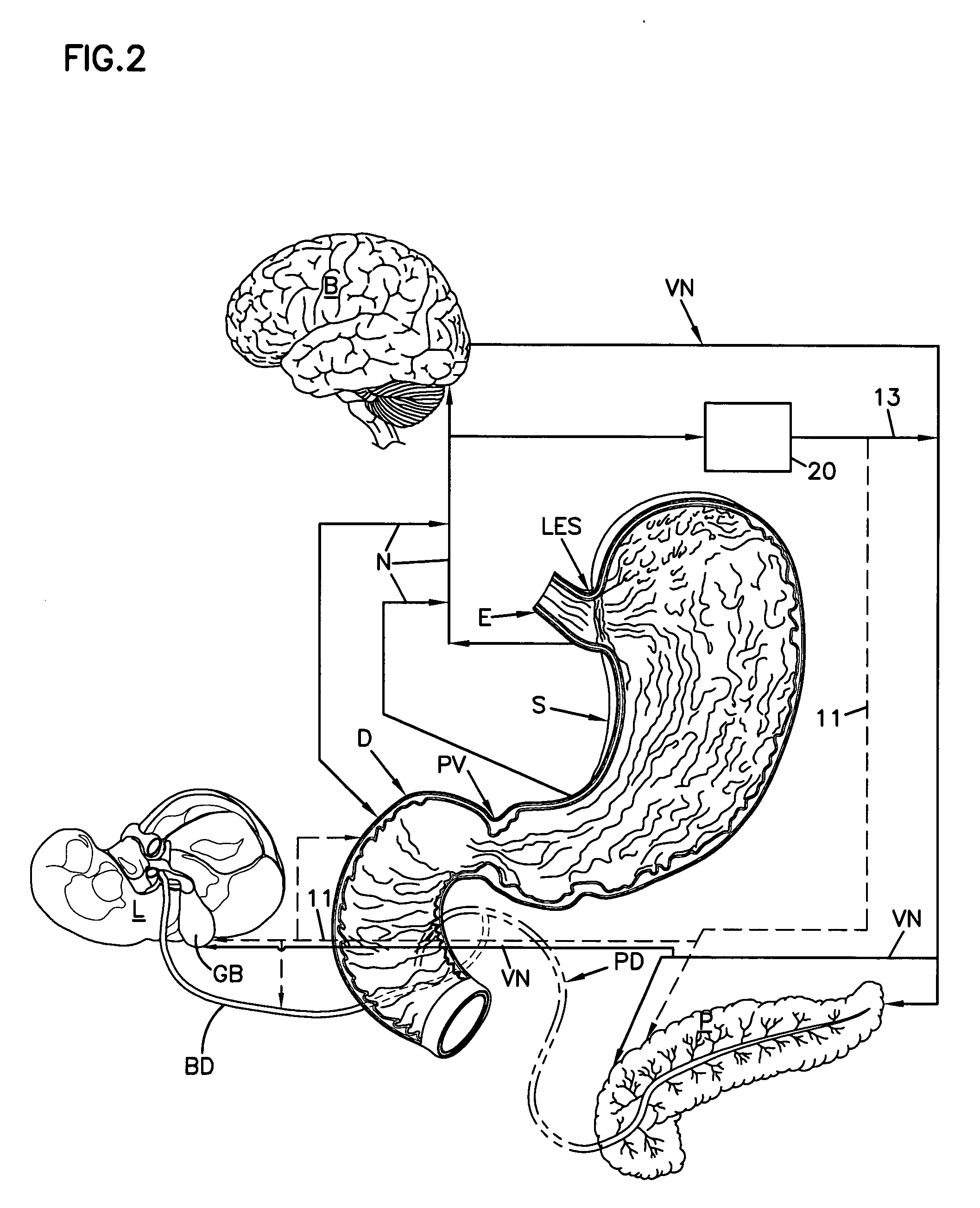
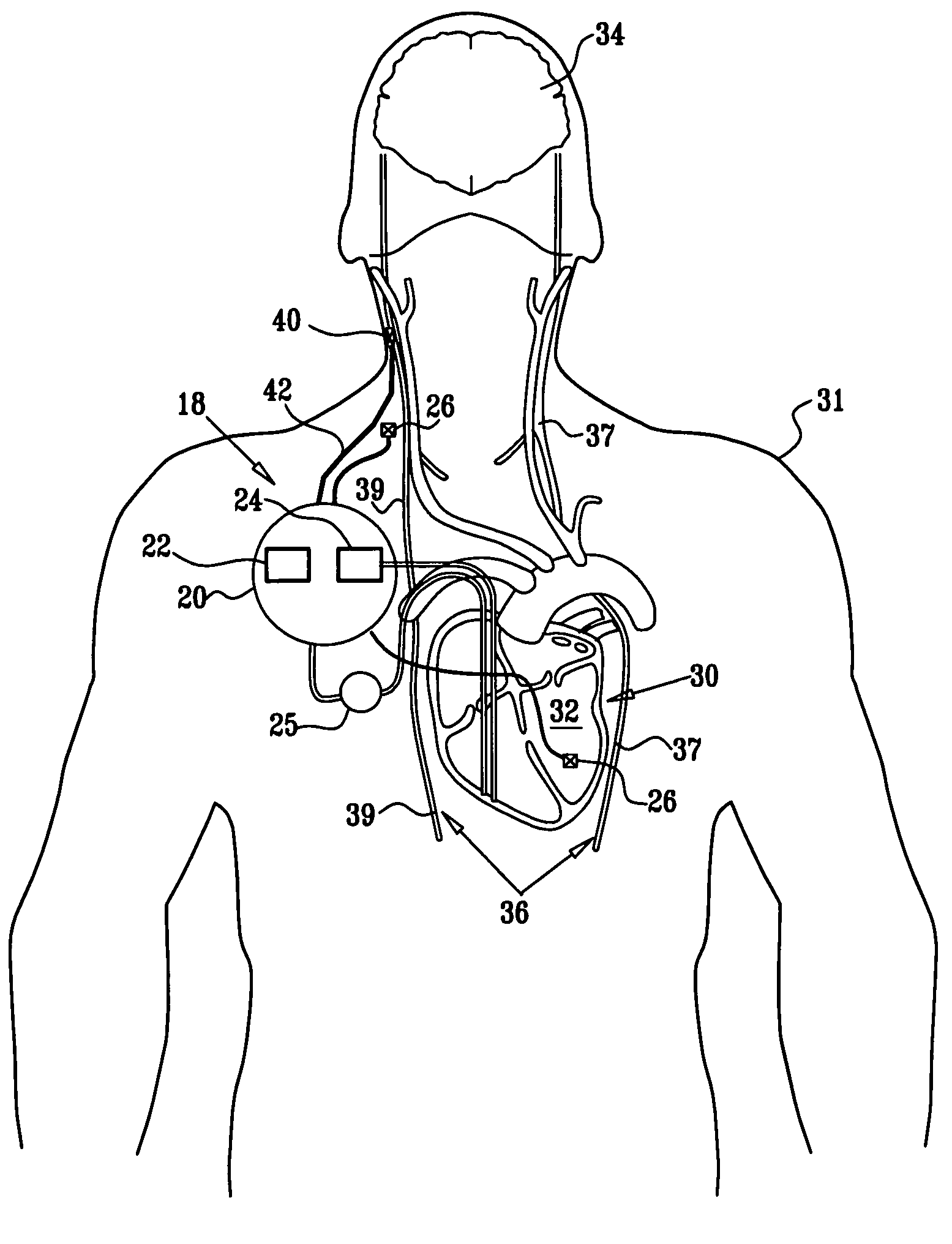
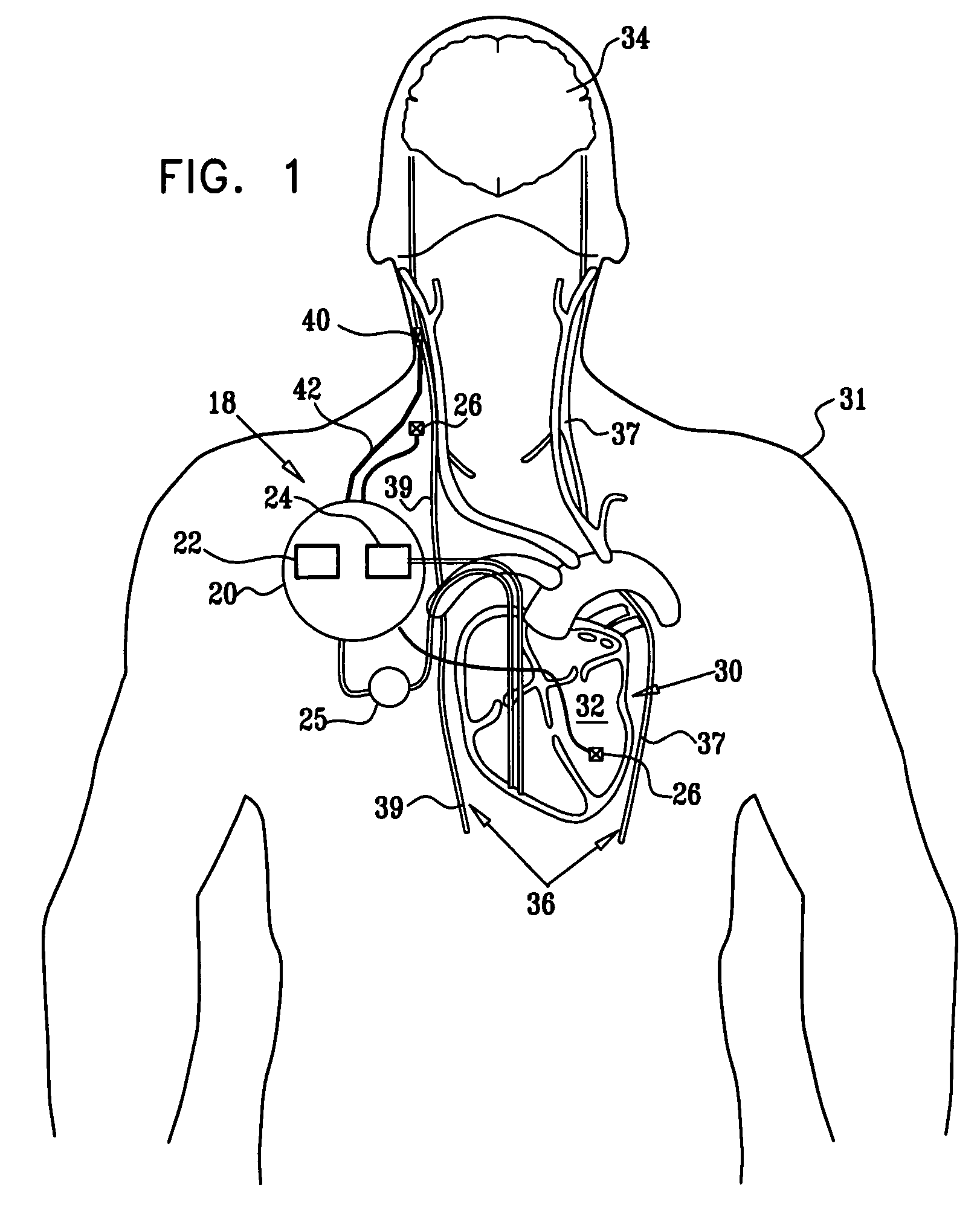
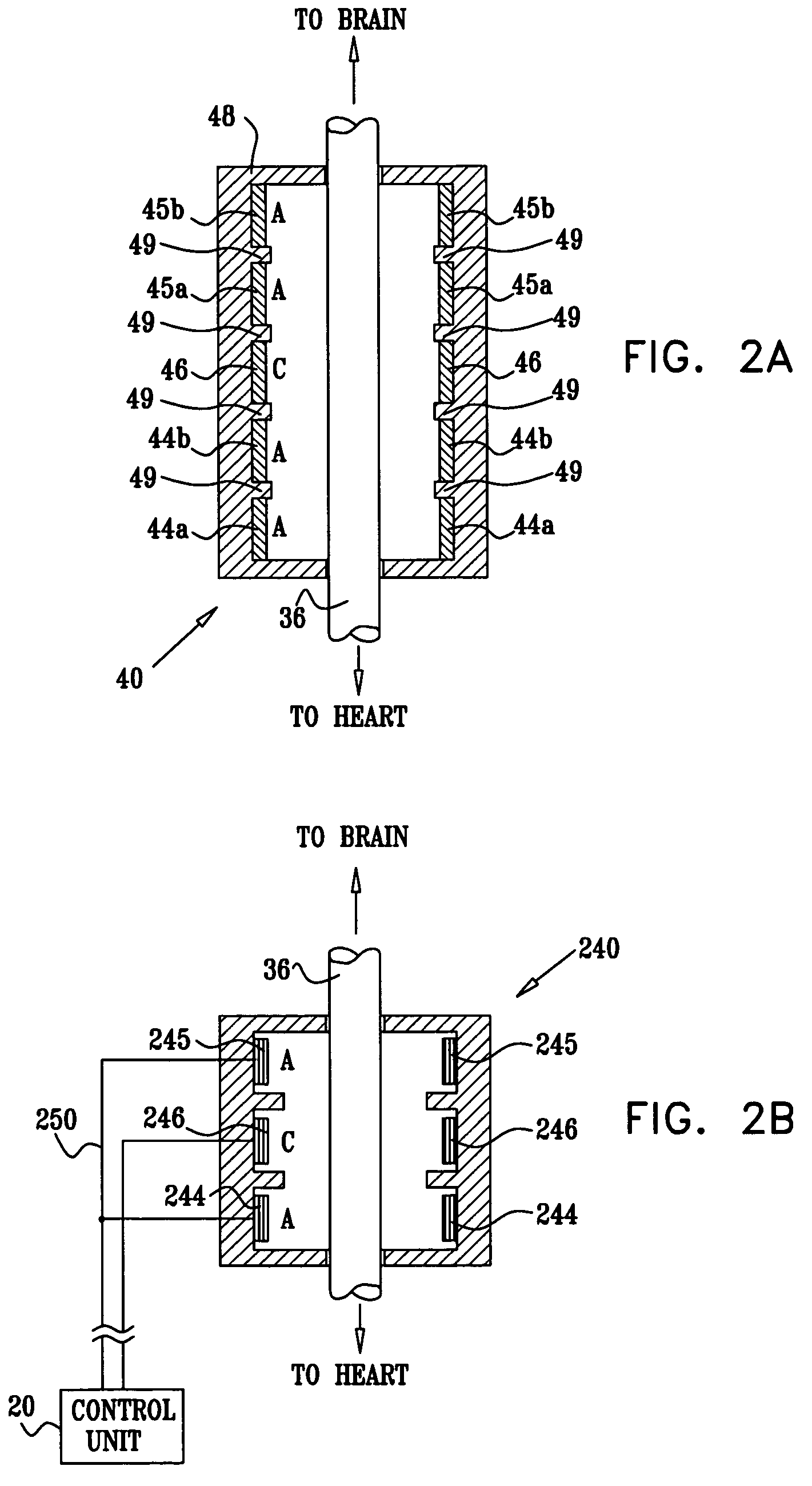
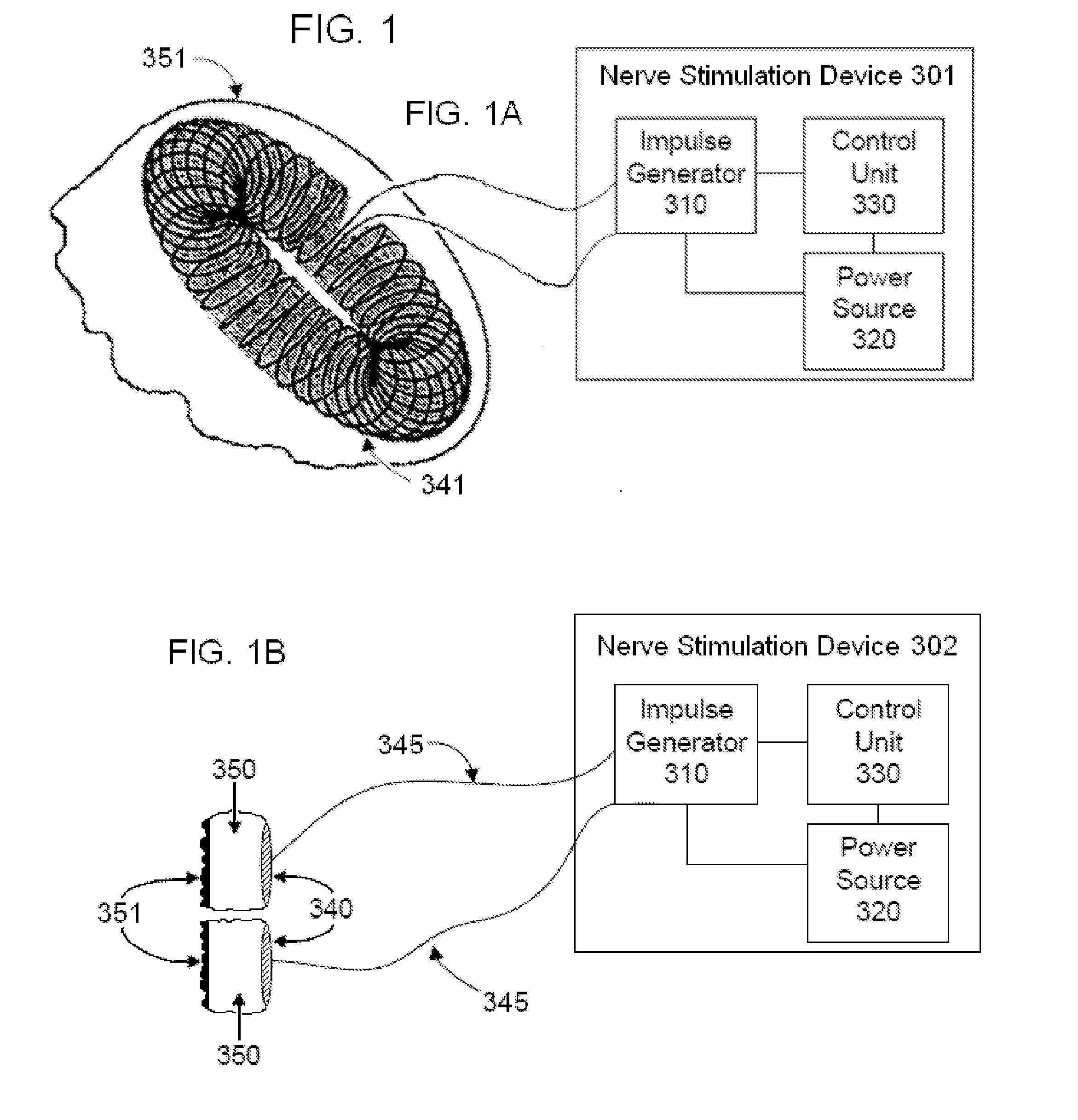
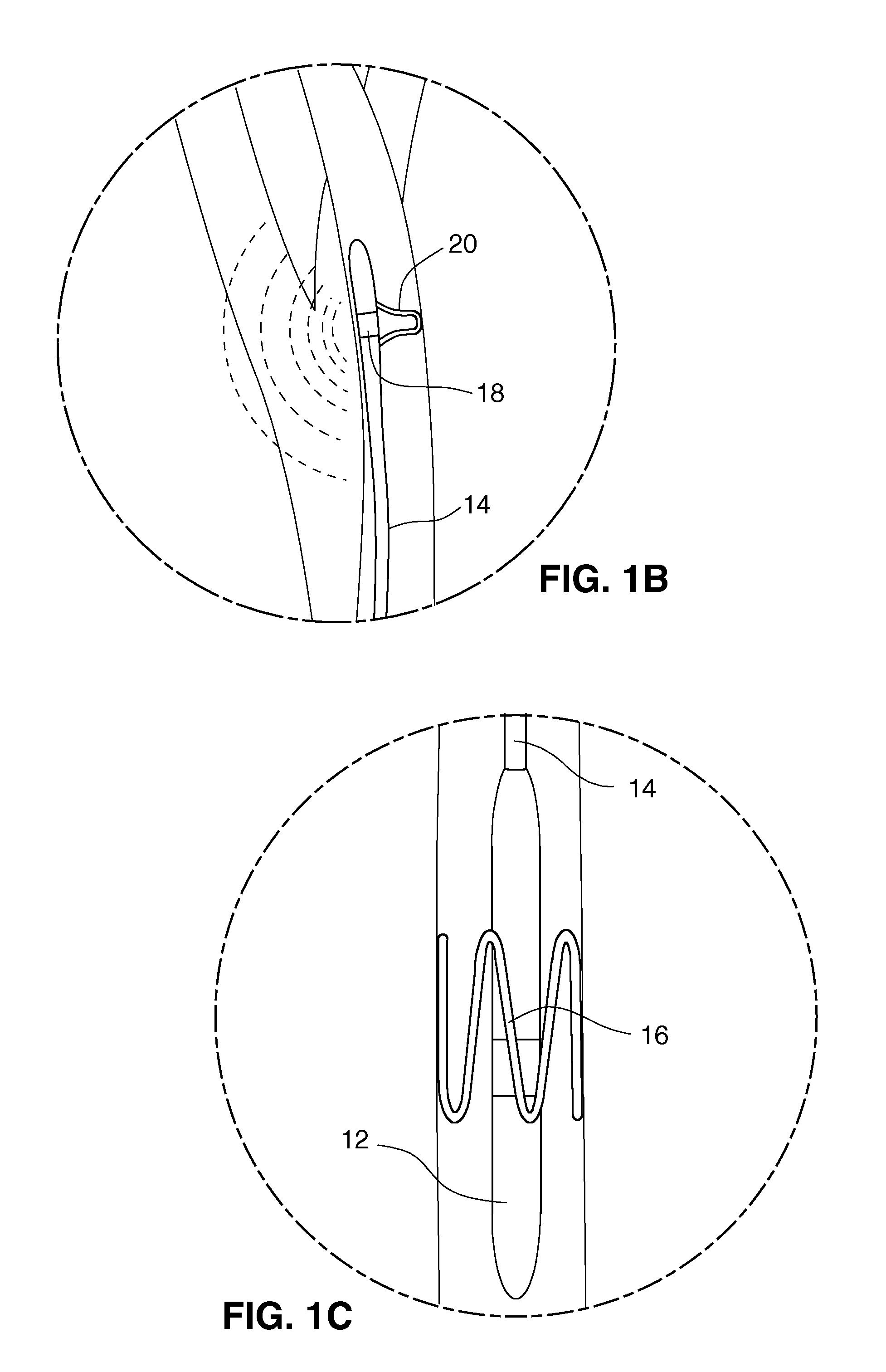
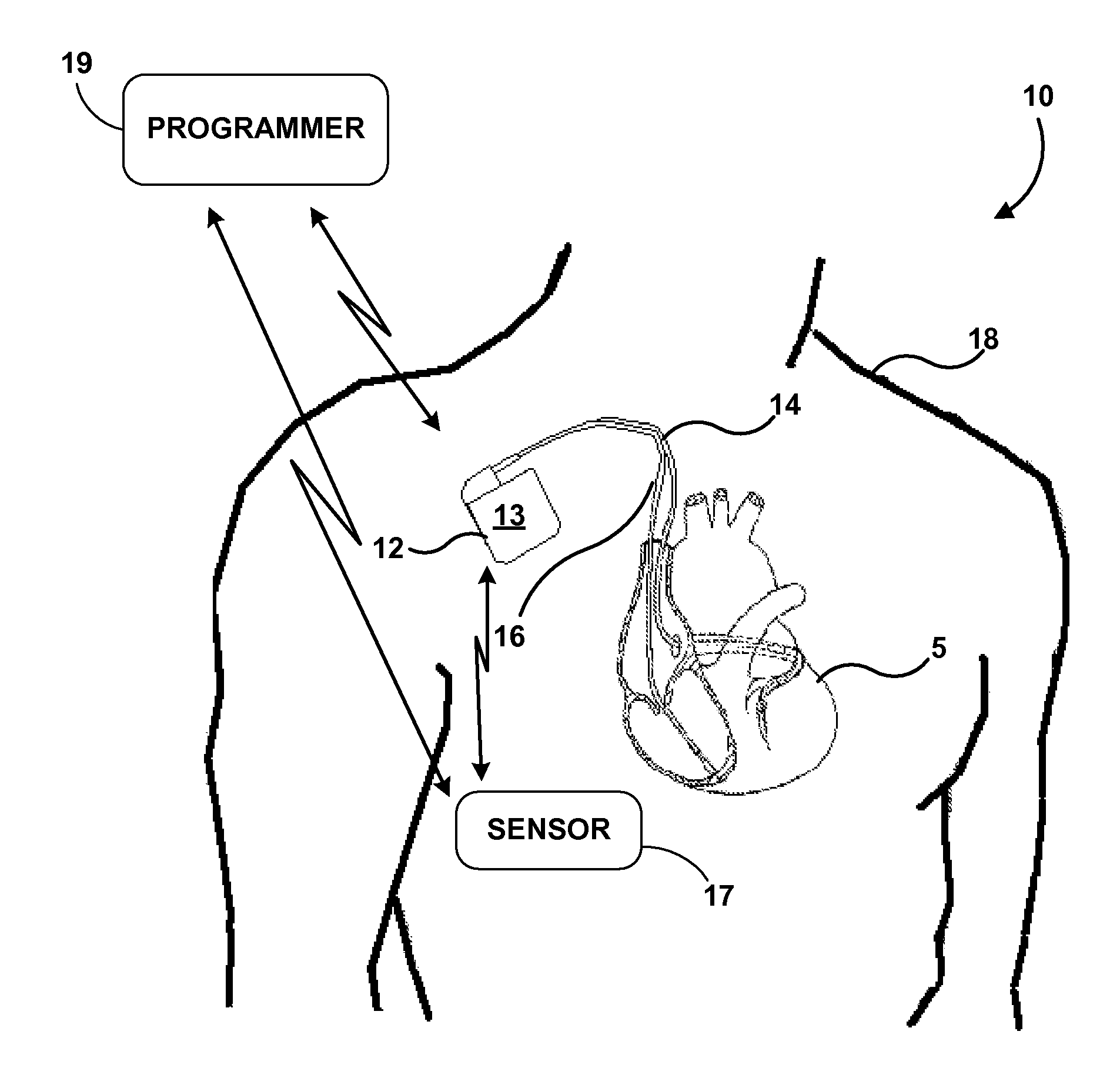
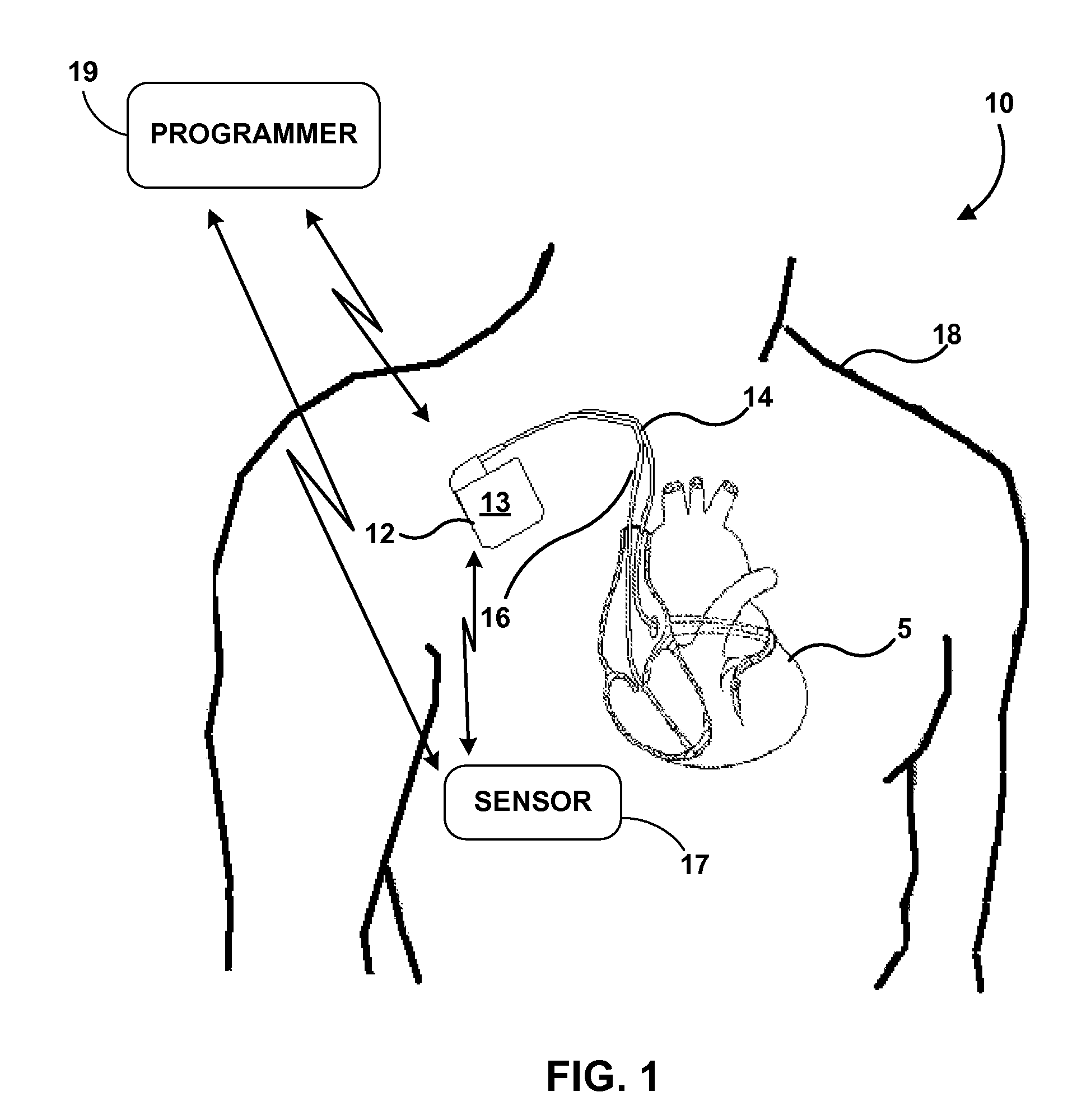
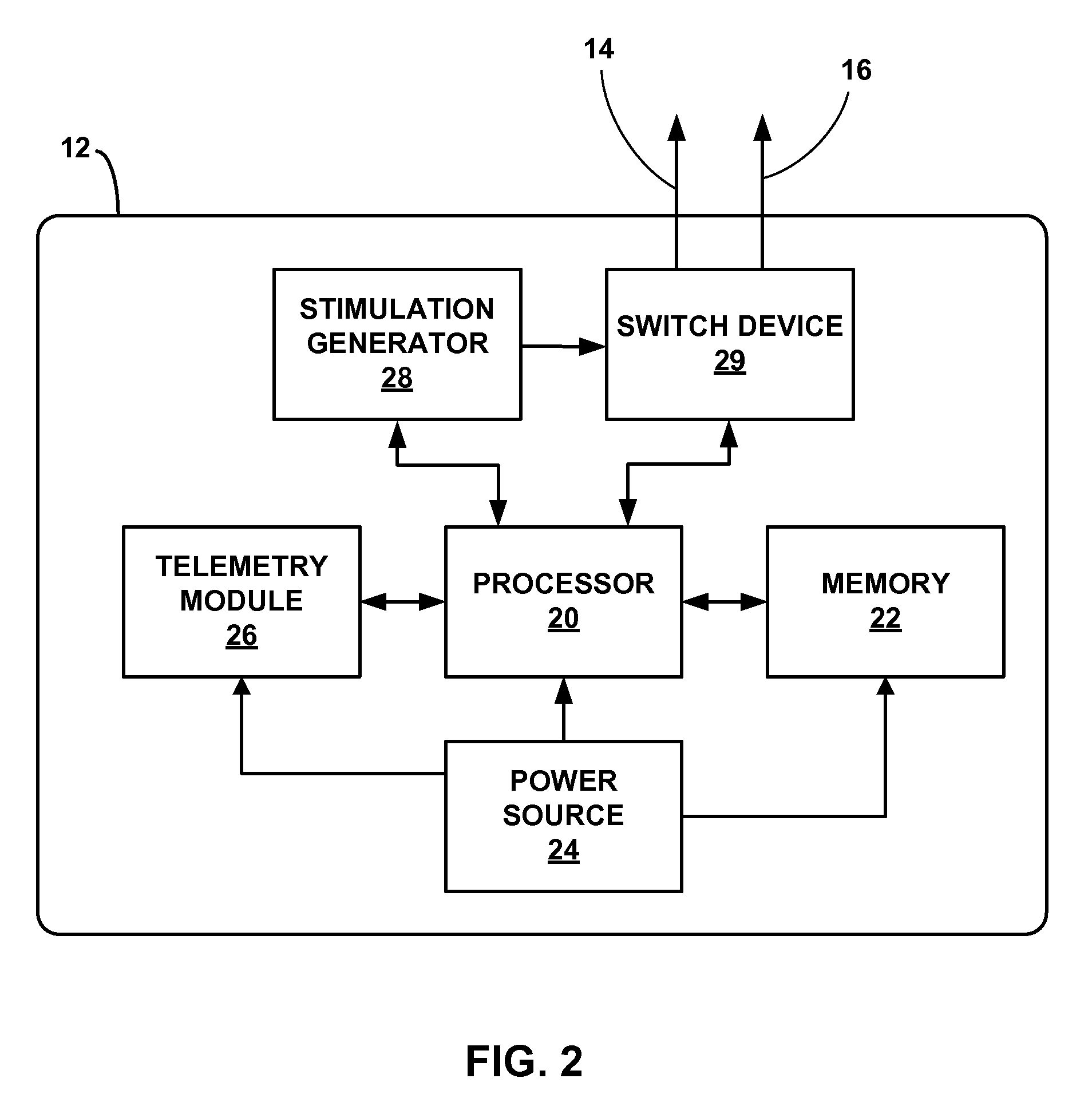
Apparatus and method for treatment of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders using programmerless implantable pulse generator system
InactiveUS6760626B1Internal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsCranial nervesElectrical stimulations
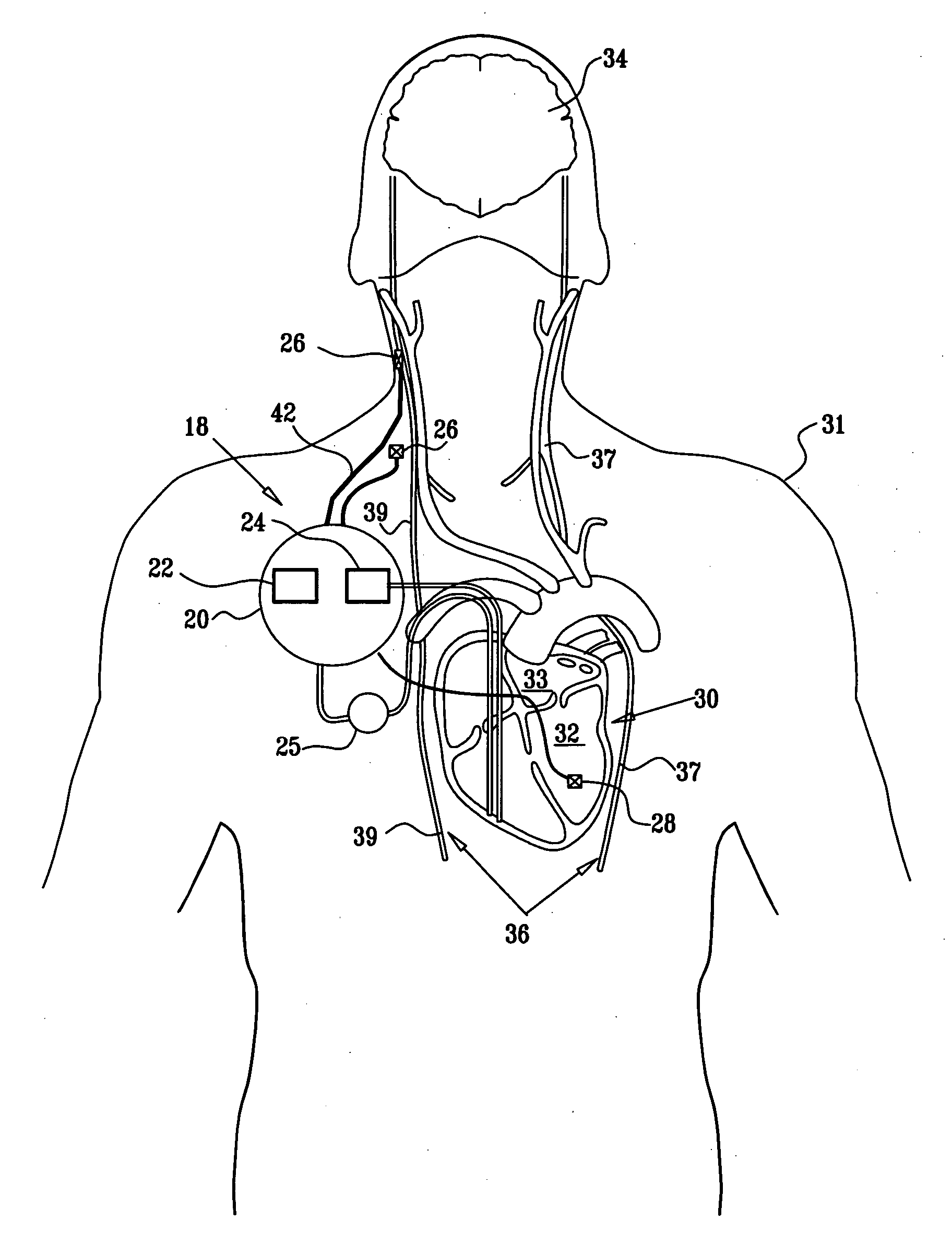
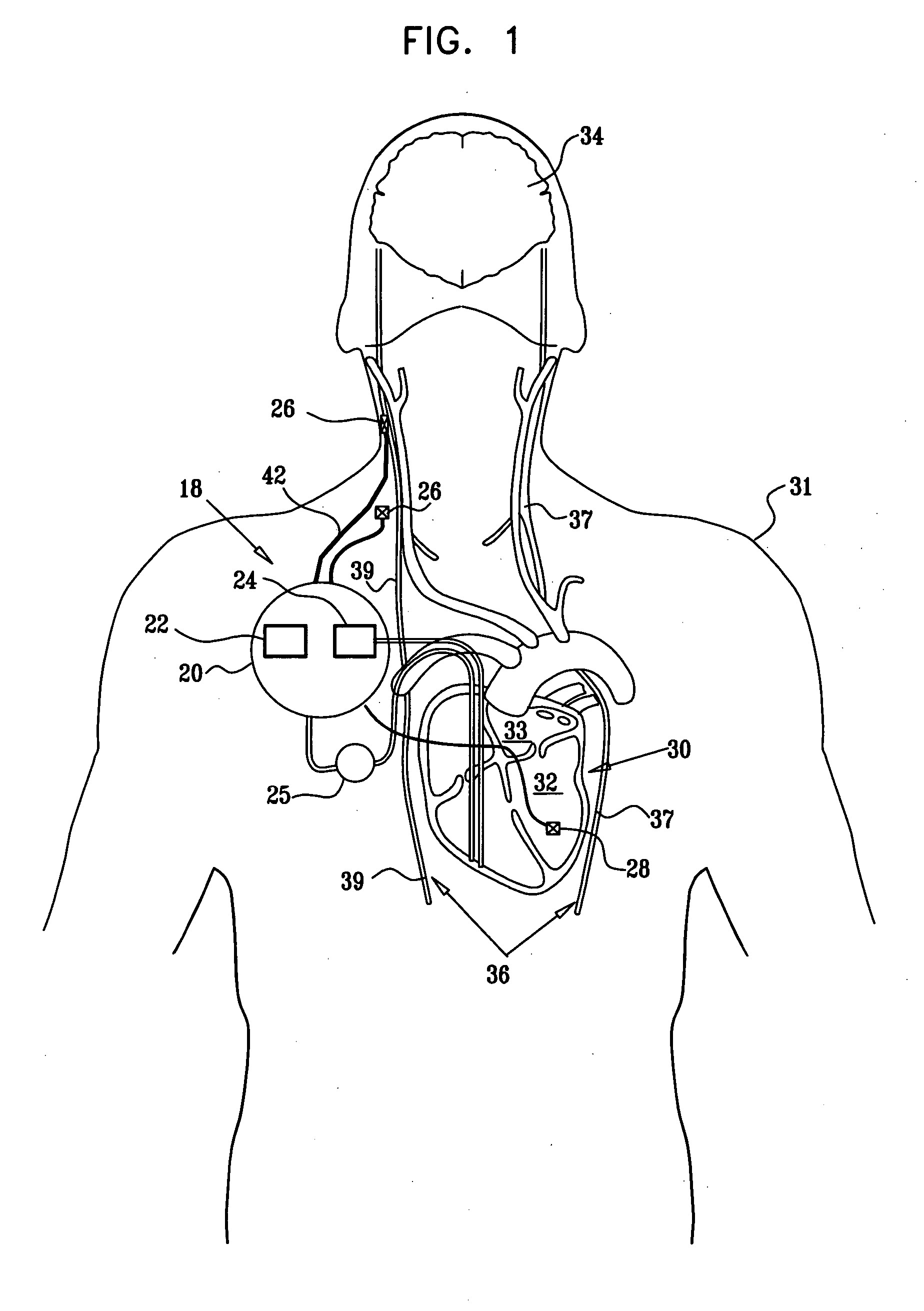
System and method for neuromodulation therapy of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders comprises an implantable lead and pulse generator system for providing the appropriate electrical stimulation to a cranial nerve such as the vagus nerve. The implantable pulse generator having prepackaged / predetermined programs stored in the memory of the pulse generator, and means for accessing these with an external magnet. The pulse generator adapted to selectively activate predetermined programs with the external magnet, thereby eliminating the need for an external programmer. The elimination of the external programmer resulting in significant cost reduction with essentially the same functionality.
Owner:NEURO & CARDIAC TECH
Selective nerve fiber stimulation for treating heart conditions
InactiveUS7778703B2Minimizing adverse side effectRegulate heart rateSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsNerve fiber bundleStimulus current
Apparatus for treating a heart condition of a subject is provided, including an electrode device, which is adapted to be coupled to a vagus nerve of the subject. A control unit is adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the vagus nerve a stimulating current, which is capable of inducing action potentials in a therapeutic direction in a first set and a second set of nerve fibers of the vagus nerve. The control unit is also adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the vagus nerve an inhibiting current, which is capable of inhibiting the induced action potentials traveling in the therapeutic direction in the second set of nerve fibers, the nerve fibers in the second set having generally larger diameters than the nerve fibers in the first set.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Techniques for applying, configuring, and coordinating nerve fiber stimulation
ActiveUS20050267542A1Decreased heart rateEliminate side effectsSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsCardiac arrhythmiaCarotid sinus
Apparatus is provided including an implantable sensor, adapted to sense an electrical parameter of a heart of a subject, and a first control unit, adapted to apply pulses to the heart responsively to the sensed parameter, the pulses selected from the list consisting of: pacing pulses and anti-arrhythmic energy. The apparatus further includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, and a jugular vein of the subject; and a second control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the site a current that increases parasympathetic tone of the subject and affects a heart rate of the subject. The first and second control units are not under common control. At least one of the control units is adapted to coordinate an aspect of its operation with an aspect of operation of the other control unit. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Treatment of movement disorders with drug therapy
ActiveUS7155279B2Increase excitementPrevent movementElectrotherapyDiagnosticsTherapeutic exerciseMedicine
Introducing one or more stimulating drugs to the vagus nerve and / or one or more branches of the vagus nerve to treat movement disorders uses at least one implantable system control unit (SCU) with an implantable pump with at least one infusion outlet. Optional electrical stimulation may additionally be supplied by an implantable signal / pulse generator (IPG) with one or more electrodes. In certain embodiments, a single SCU provides one or more stimulating drugs and the optional electrical stimulation. In some embodiments, one or more sensed conditions are used to adjust stimulation parameters.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Nerve stimulation techniques
InactiveUS20110224749A1Minimize any unintended side effect of the signal applicationSuppresses afferent action potentialHeart stimulatorsMedicineCytokine
A method is provided for treating heart failure in a subject in need of such treatment, including applying a stimulating current to parasympathetic nervous tissue of the subject, selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve and an epicardial fat pad. The stimulating current is configured to inhibit release of at least one proinflammatory cytokine sufficiently to the treat heart failure of the subject. A level of the at least one proinflammatory cytokine is measured. Optionally, the stimulating current is configured to change a level of Connexin 43 of the subject, and the level of Connexin 43 is also measured. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Enteric rhythm management
InactiveUS20040176812A1Function increaseAltered autonomic balanceSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsBlocking nerveNerve impulse
Owner:RESHAPE LIFESCIENCES INC
Method and system for providing therapy for autism by providing electrical pulses to the vagus nerve(s)
InactiveUS20050187590A1Modulate its functionSpinal electrodesHead electrodesRechargeable cellImplanted device
A method and system to provide electrical pulses for neuromodulating vagus nerve(s) to provide therapy for autism, comprises implantable and external components. The pulsed electrical stimulation to vagus nerve(s) may be provided using one of the following stimulation systems, such as: a) an implanted stimulus-receiver with an external stimulator; b) an implanted stimulus-receiver comprising a high value capacitor for storing charge, used in conjunction with an external stimulator; c) a programmer-less implantable pulse generator (IPG) which is operable with a magnet; d) a microstimulator; e) a programmable implantable pulse generator; f) a combination implantable device comprising both a stimulus-receiver and a programmable implantable pulse generator (IPG); and g) an implantable pulse generator (IPG) comprising a rechargeable battery. In one embodiment, the external components such as the programmer or external stimulator may comprise a telemetry means for networking. The telemetry means therefore allows for interrogation or programming of implanted device, from a remote location over a wide area network.
Owner:NEURO & CARDIAC TECH
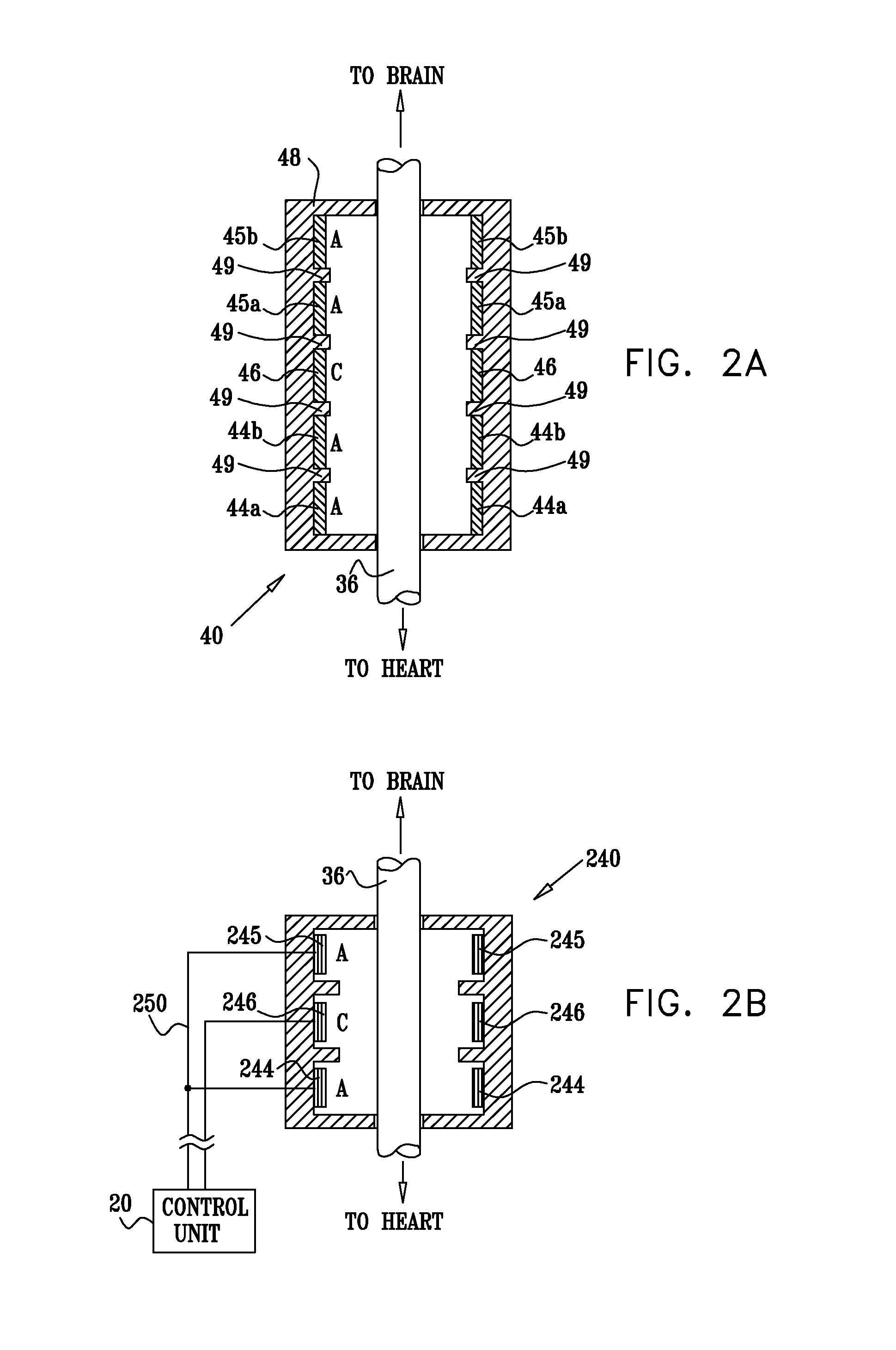
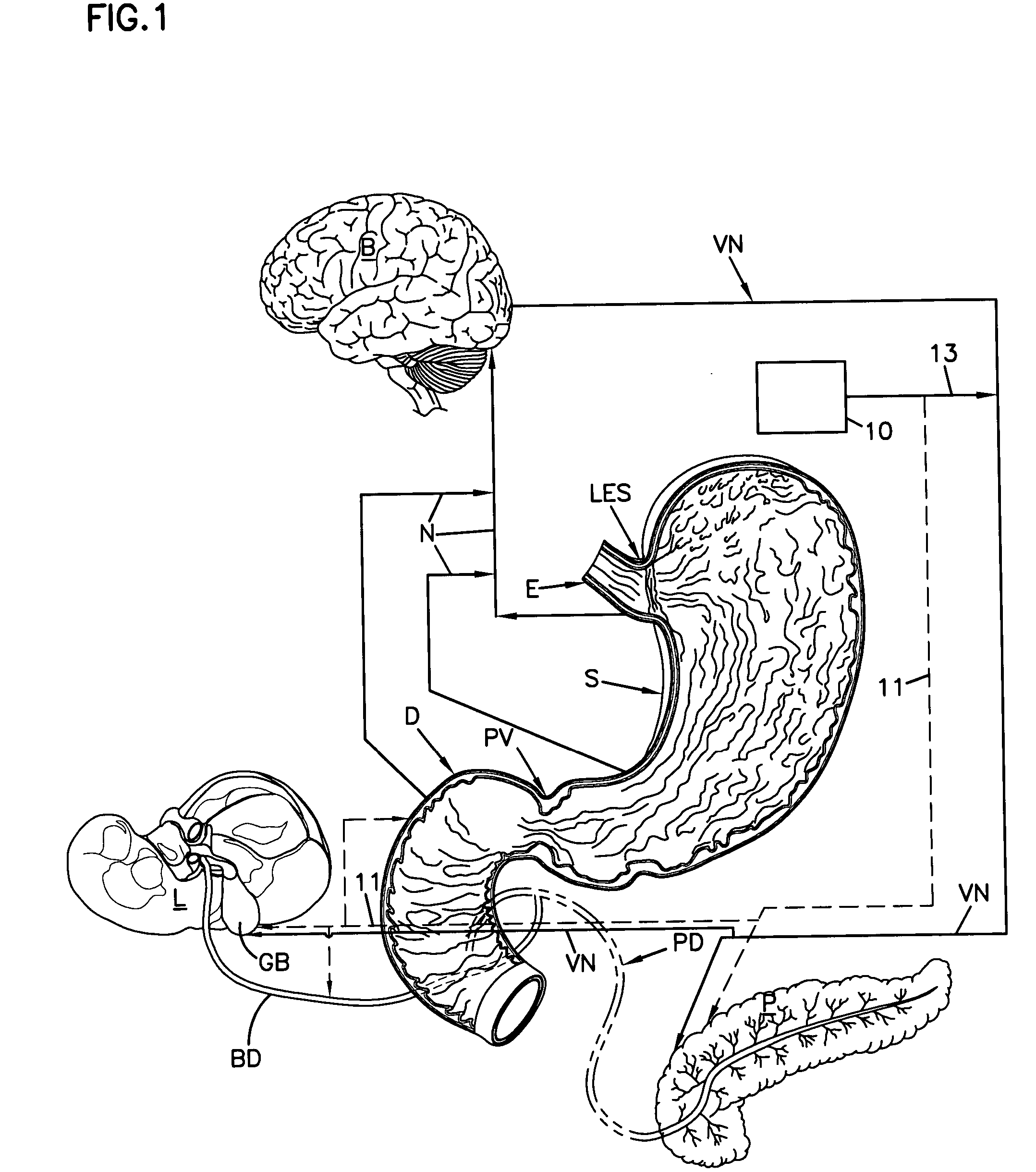
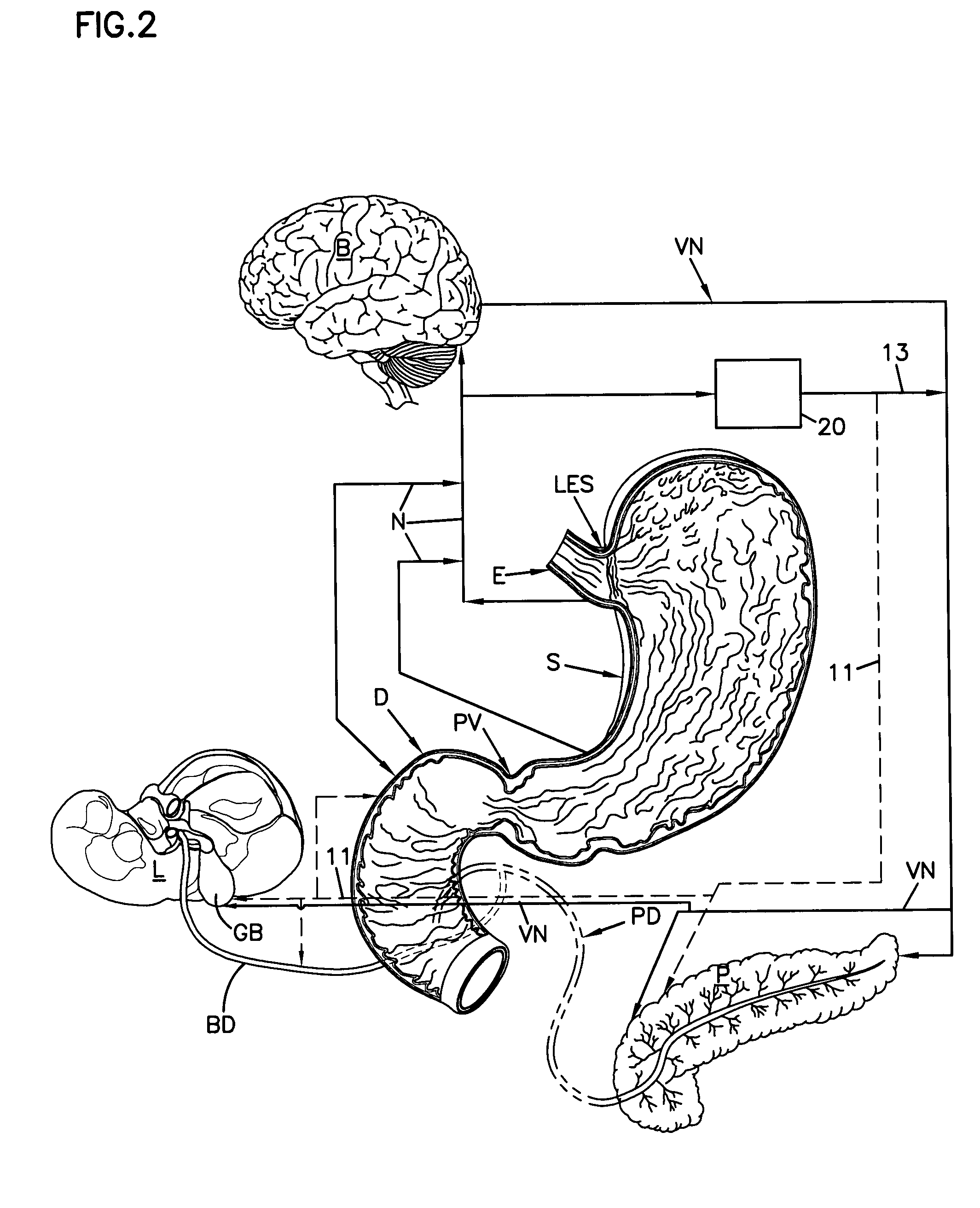
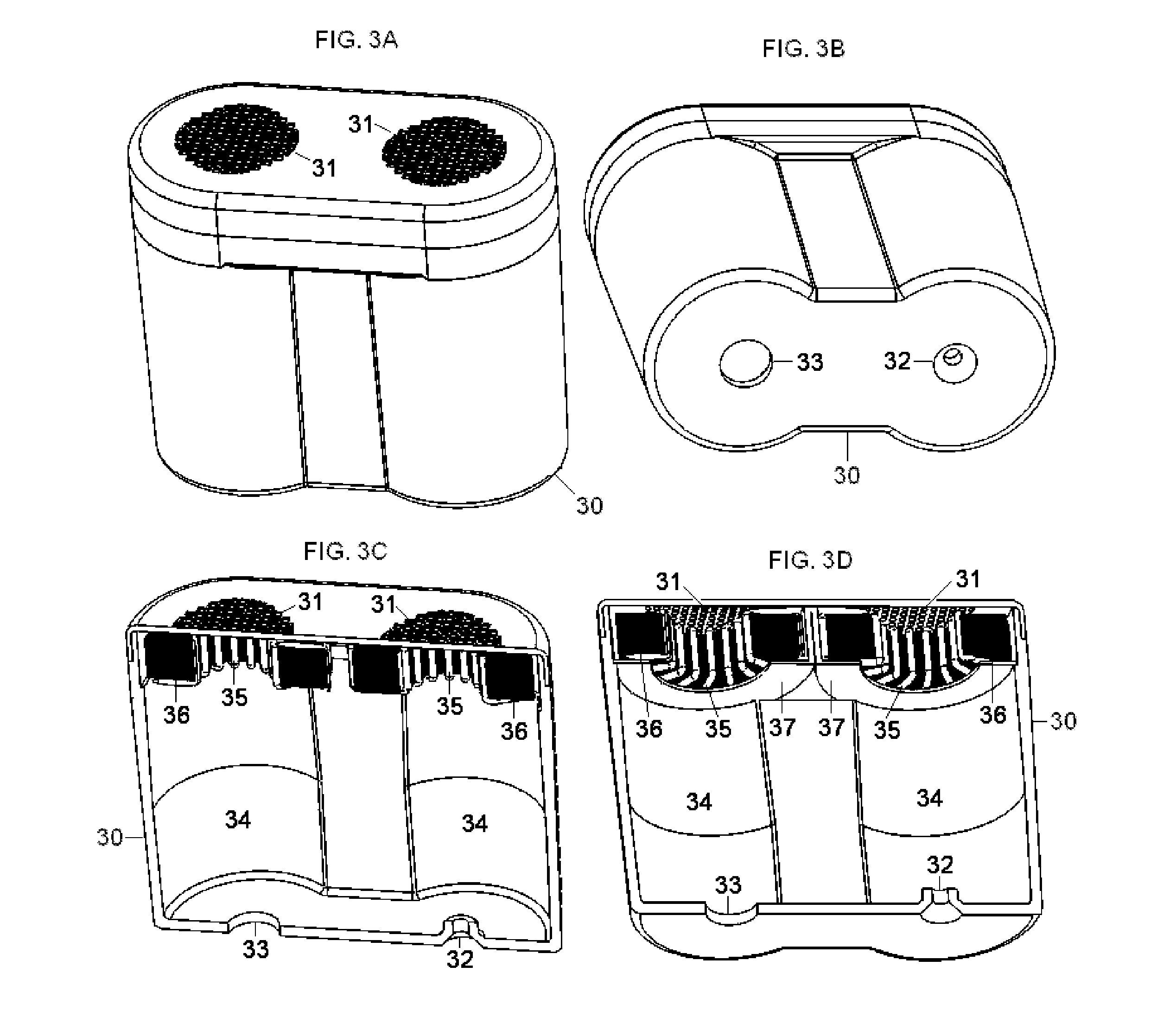
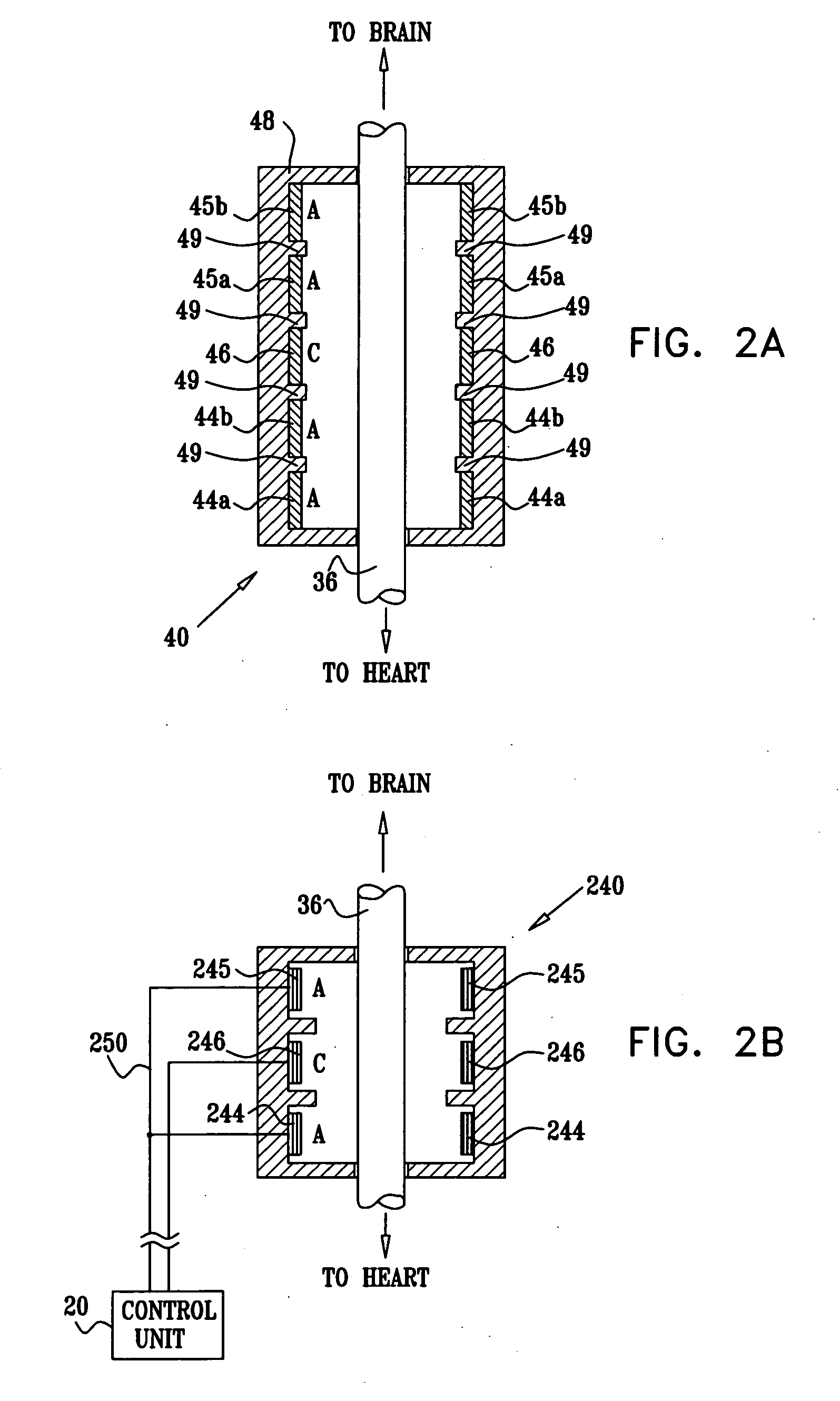
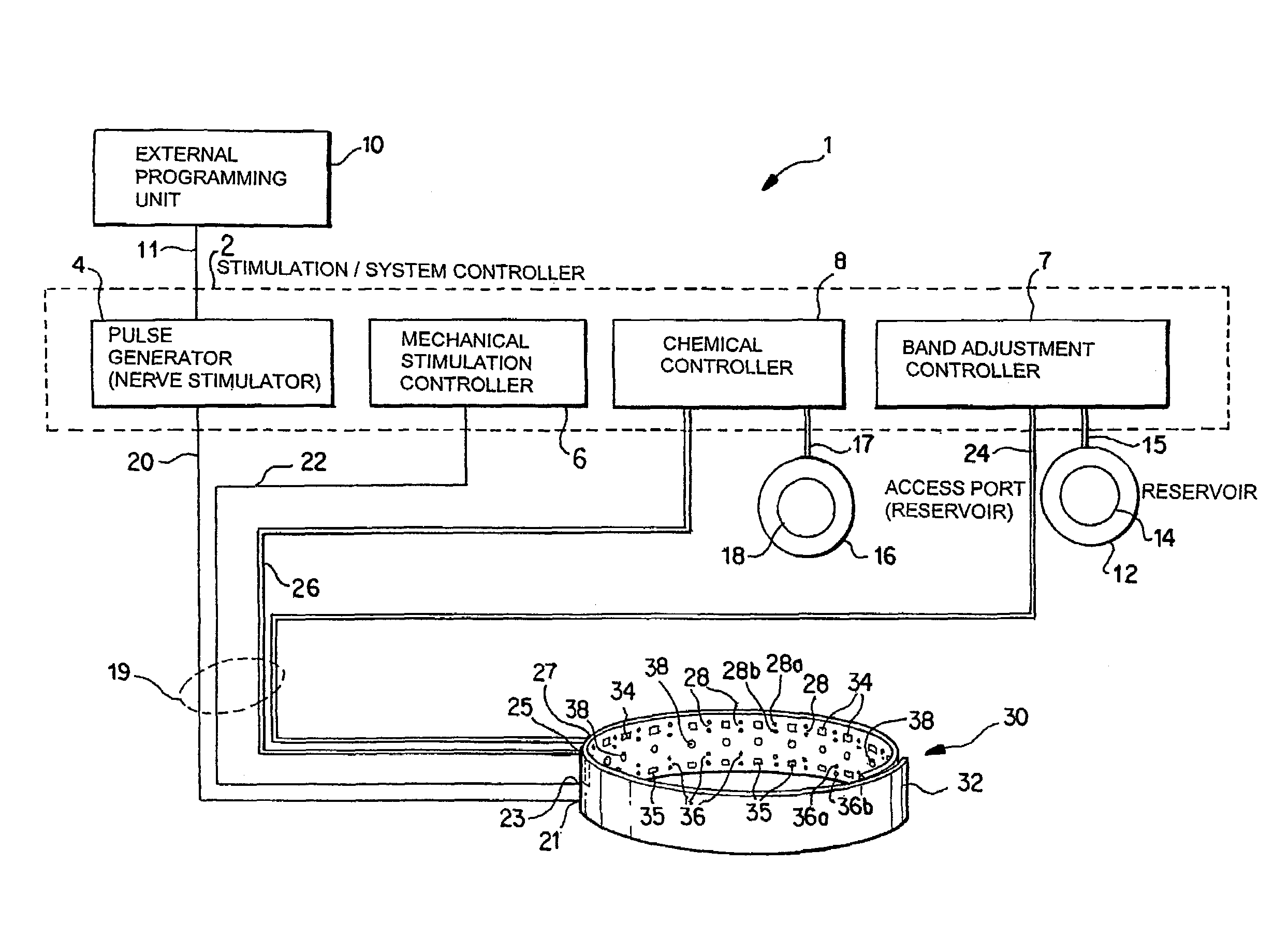
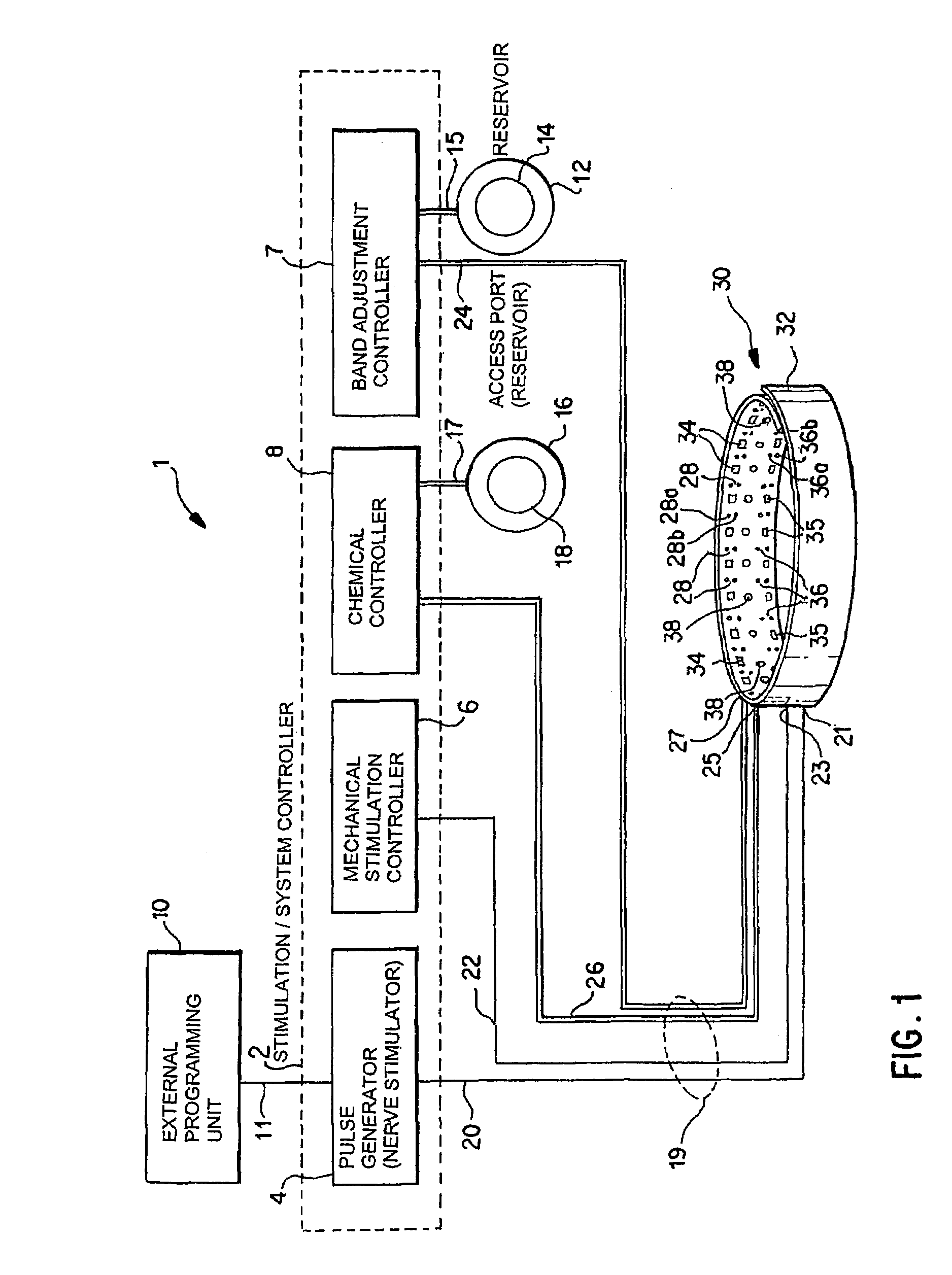
Noninvasively adjustable gastric band
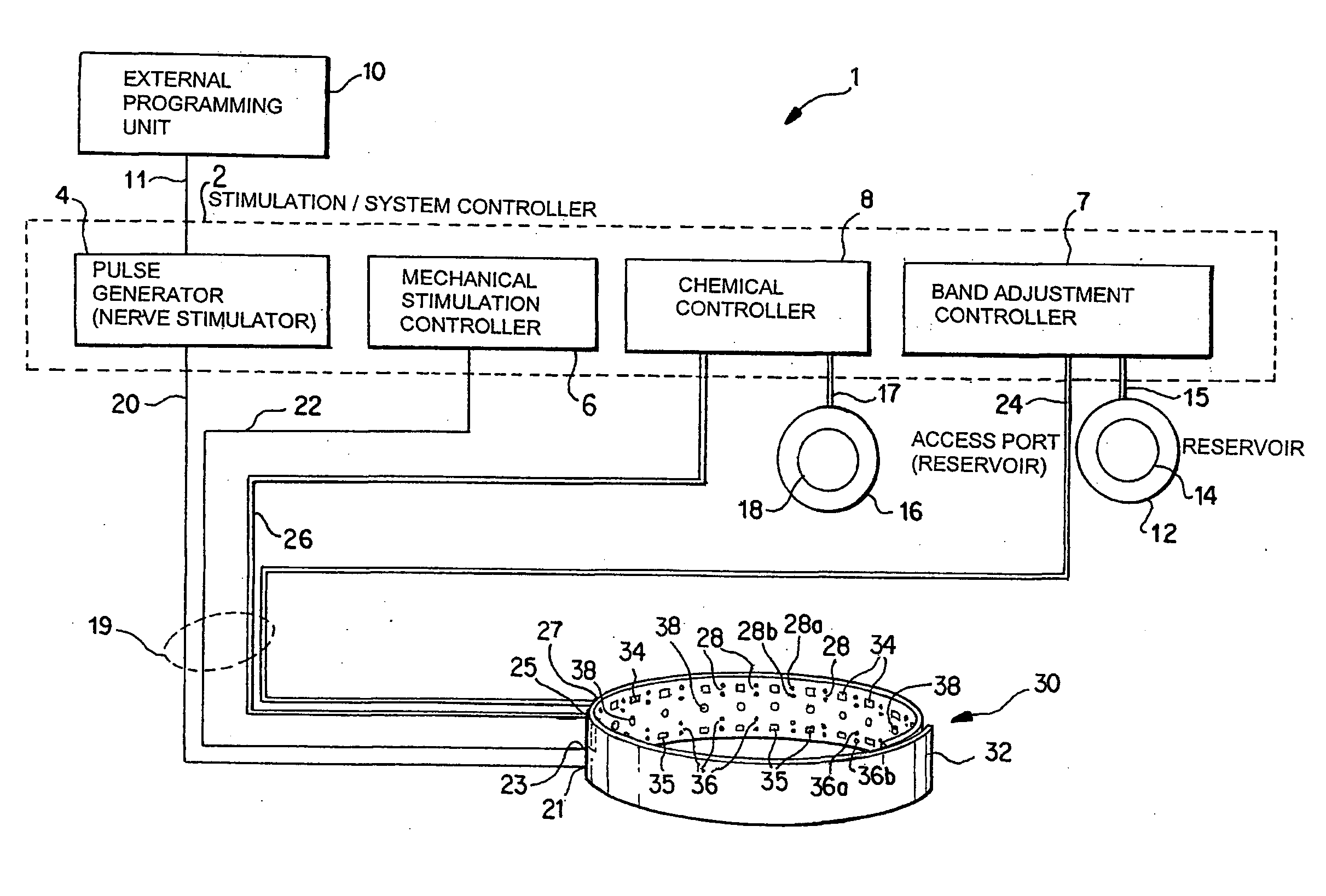
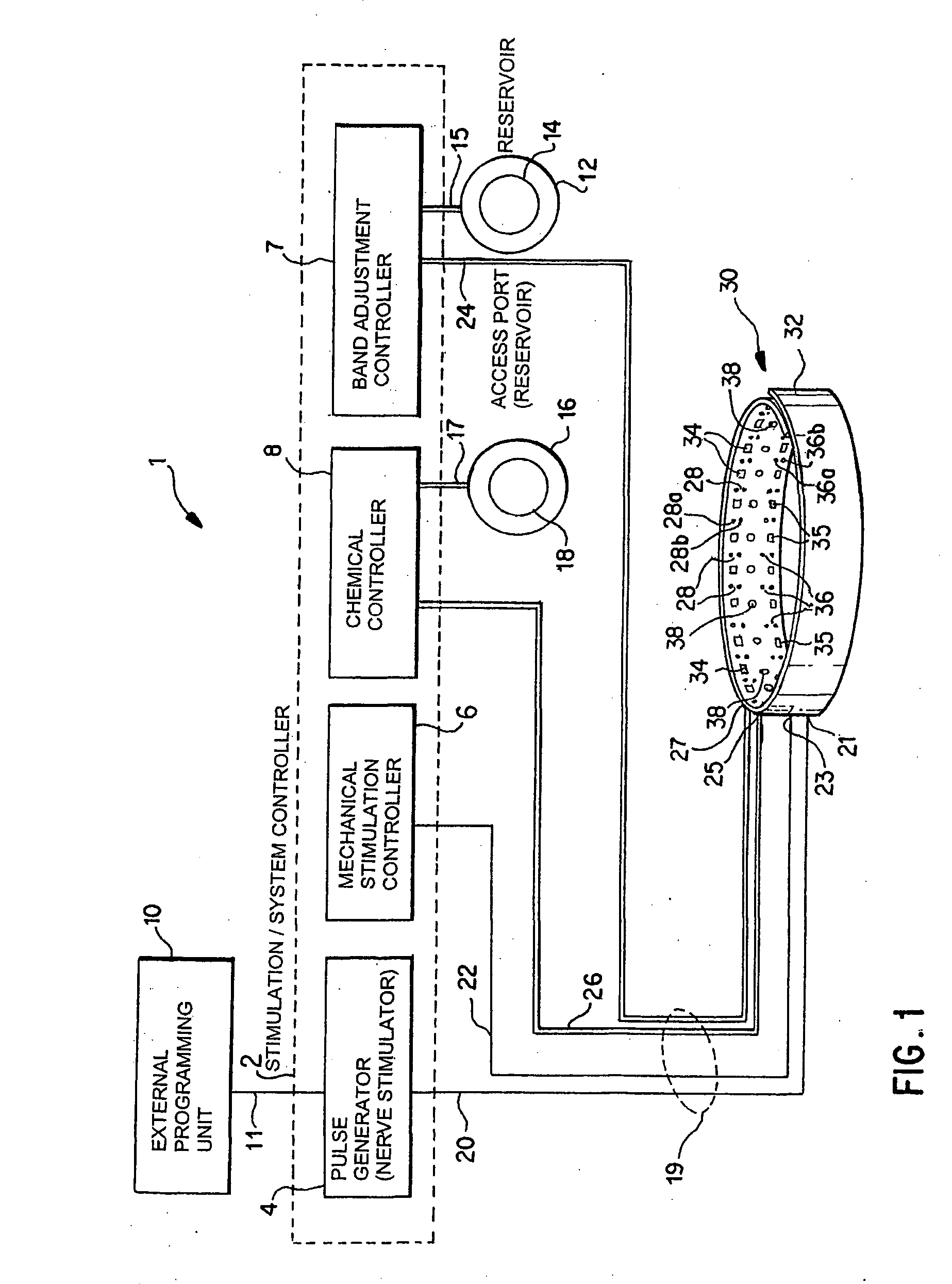
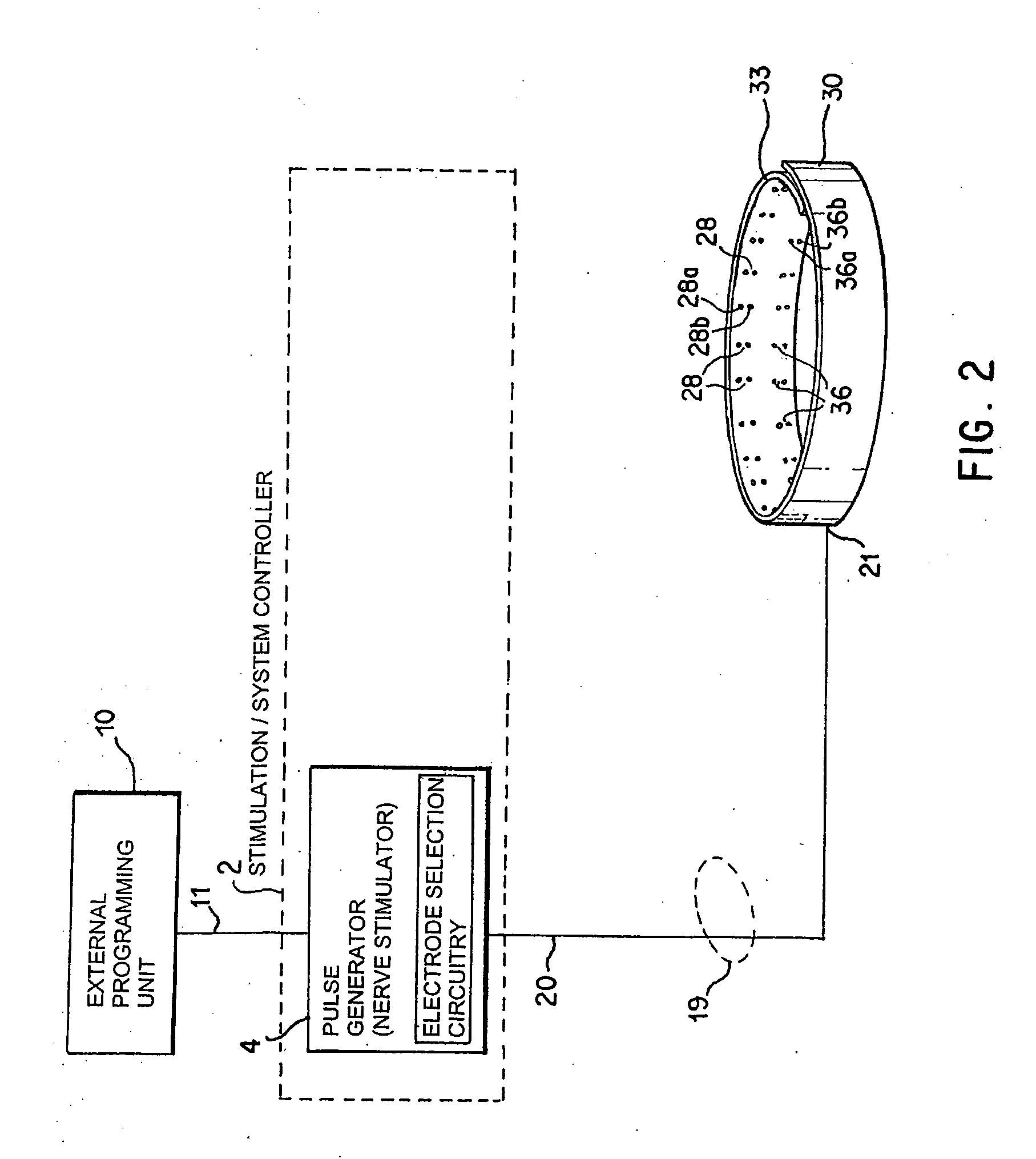
A method and apparatus for treatment of an eating disorder includes electrically, mechanically and / or pharmaceutically / chemically stimulating a of the vagus nerve of the lower esophagus, cardia, esophageal / cardia junction, cardia / fundus junction or upper stomach so as to induce afferent action potentials on the vagus nerve. The device may be noninvasively adjusted after implantation to provide increased or decreased restriction on the patient's gastrointestinal tract. Each stimulus may be administered as a series of programmed pulses of defined amplitude, duration and period, to evoke a responsive signal to the brain by the target nerve, effective for producing a temporary feeling of satiety in the person. An implantable stimulus generator may be operatively coupled to a nerve electrode, pressure device or chemical outlet to apply a defined signal to a selected nerve branch. The implantable stimulus generator is programmable to allow clinician programming of defined signal parameters effective to treat the eating disorder of the patient. Methods are also provided to identify electrodes nearest to a branch of the vagus nerve to apply an electrical stimulation signal with improved efficiency.
Owner:CYBERONICS INC
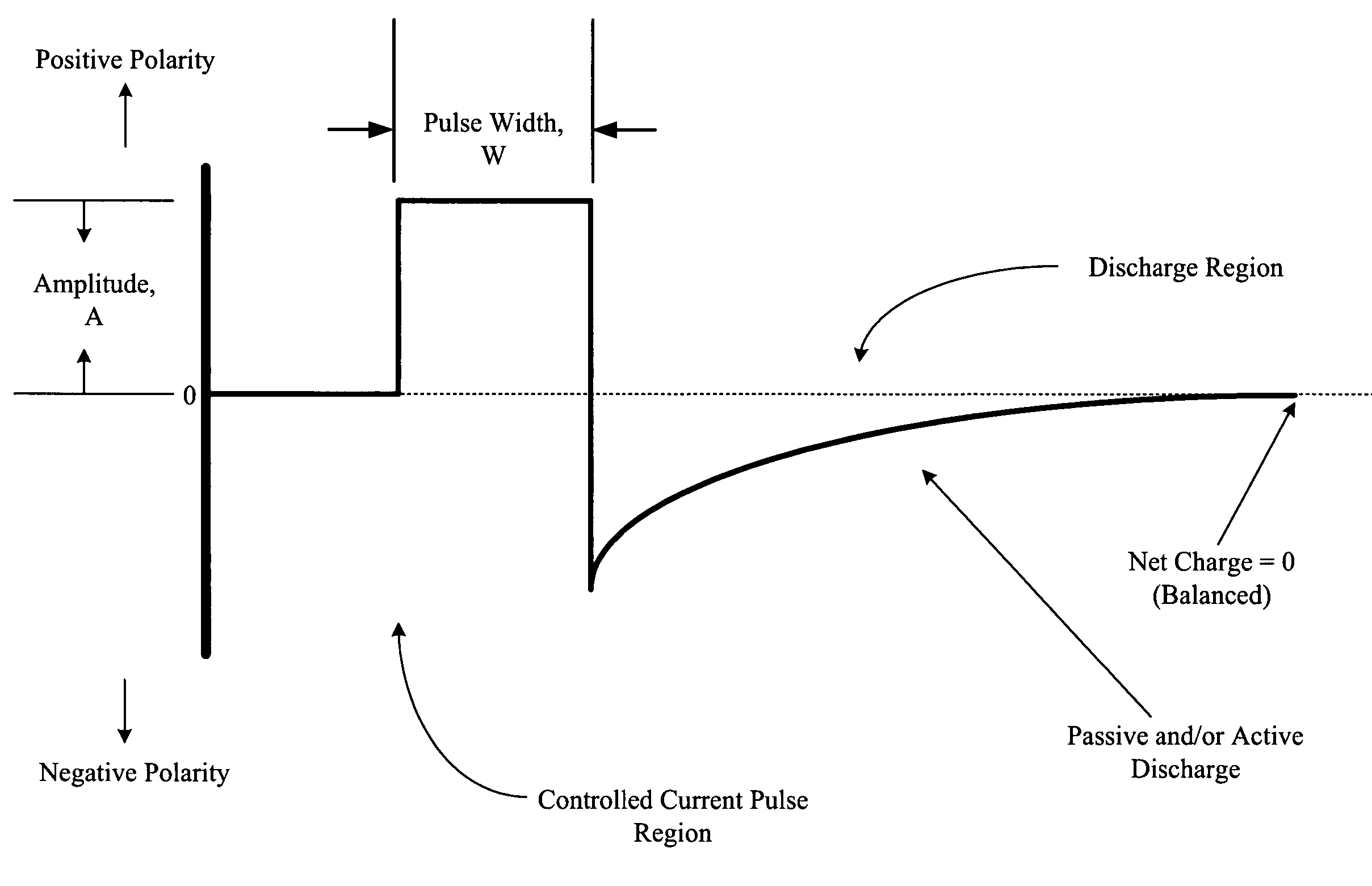
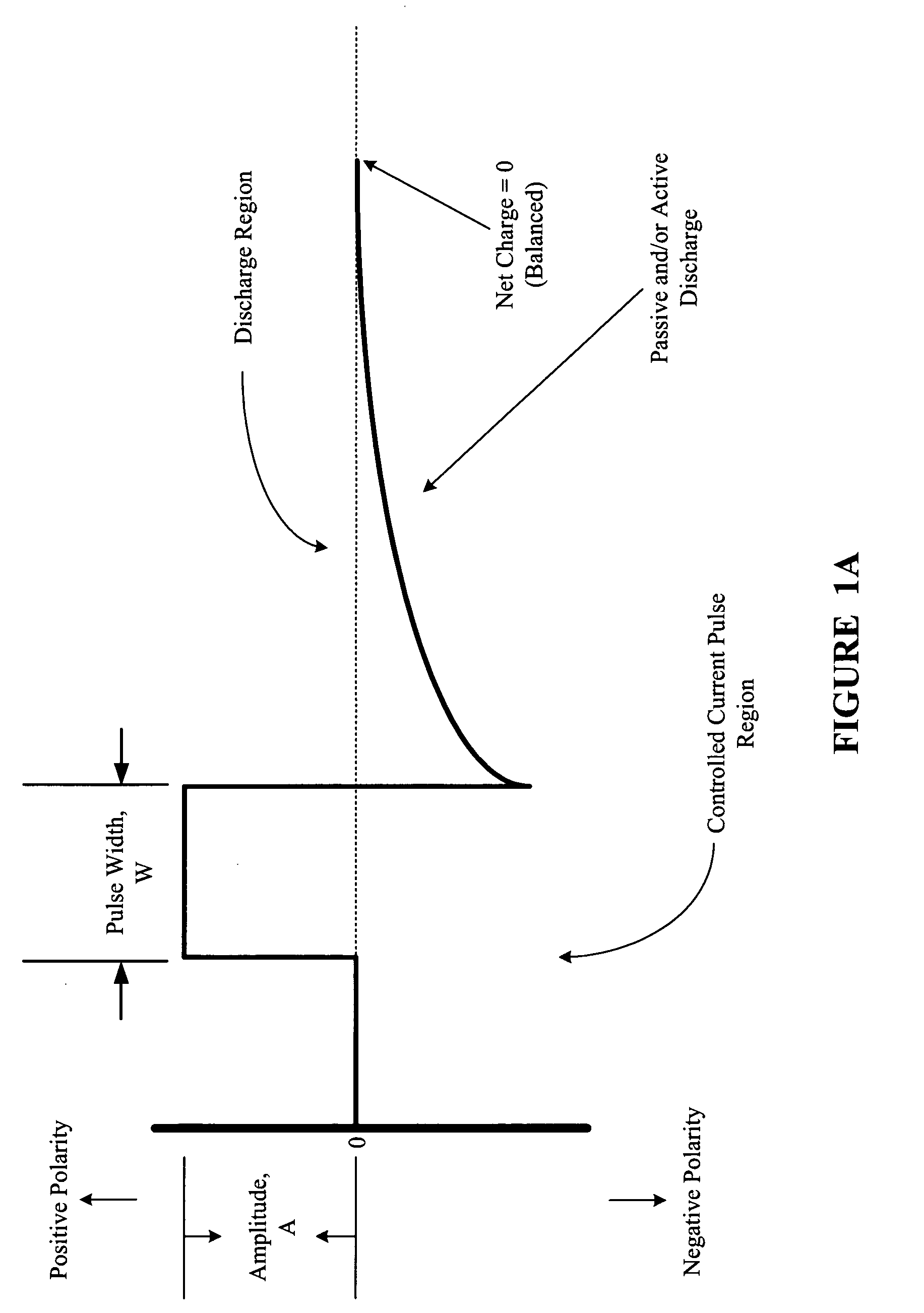
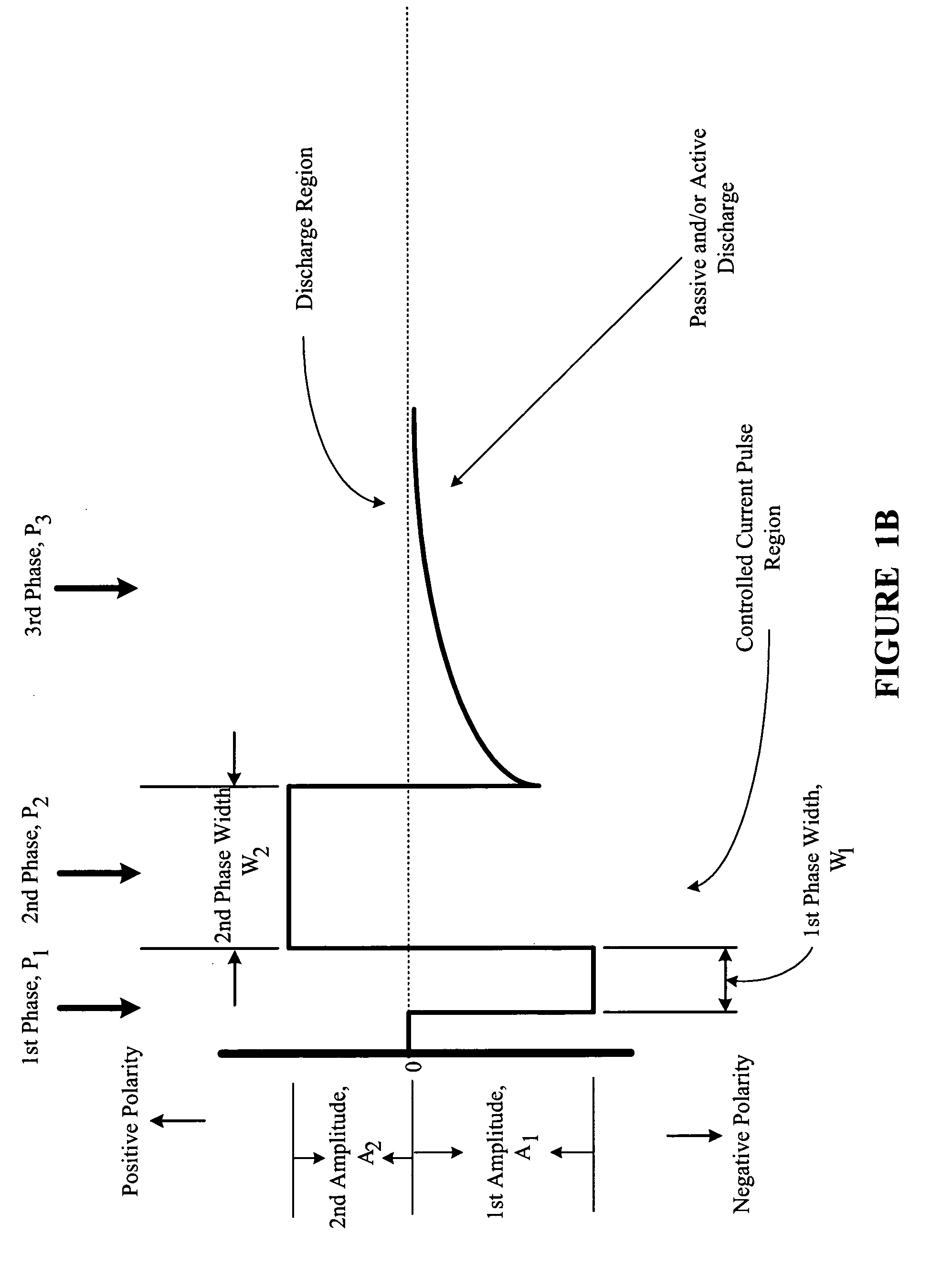
Multi-phasic signal for stimulation by an implantable device
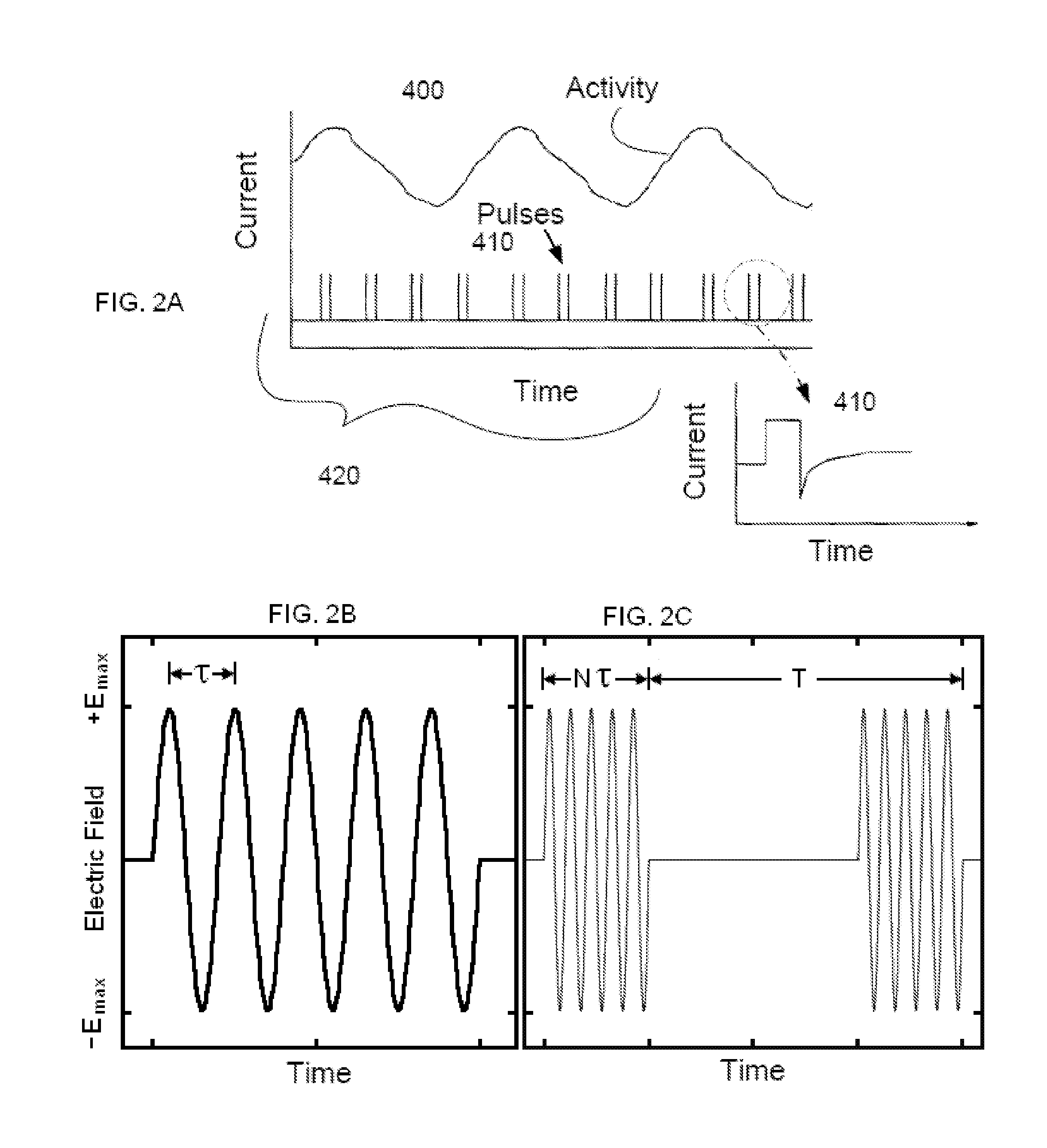
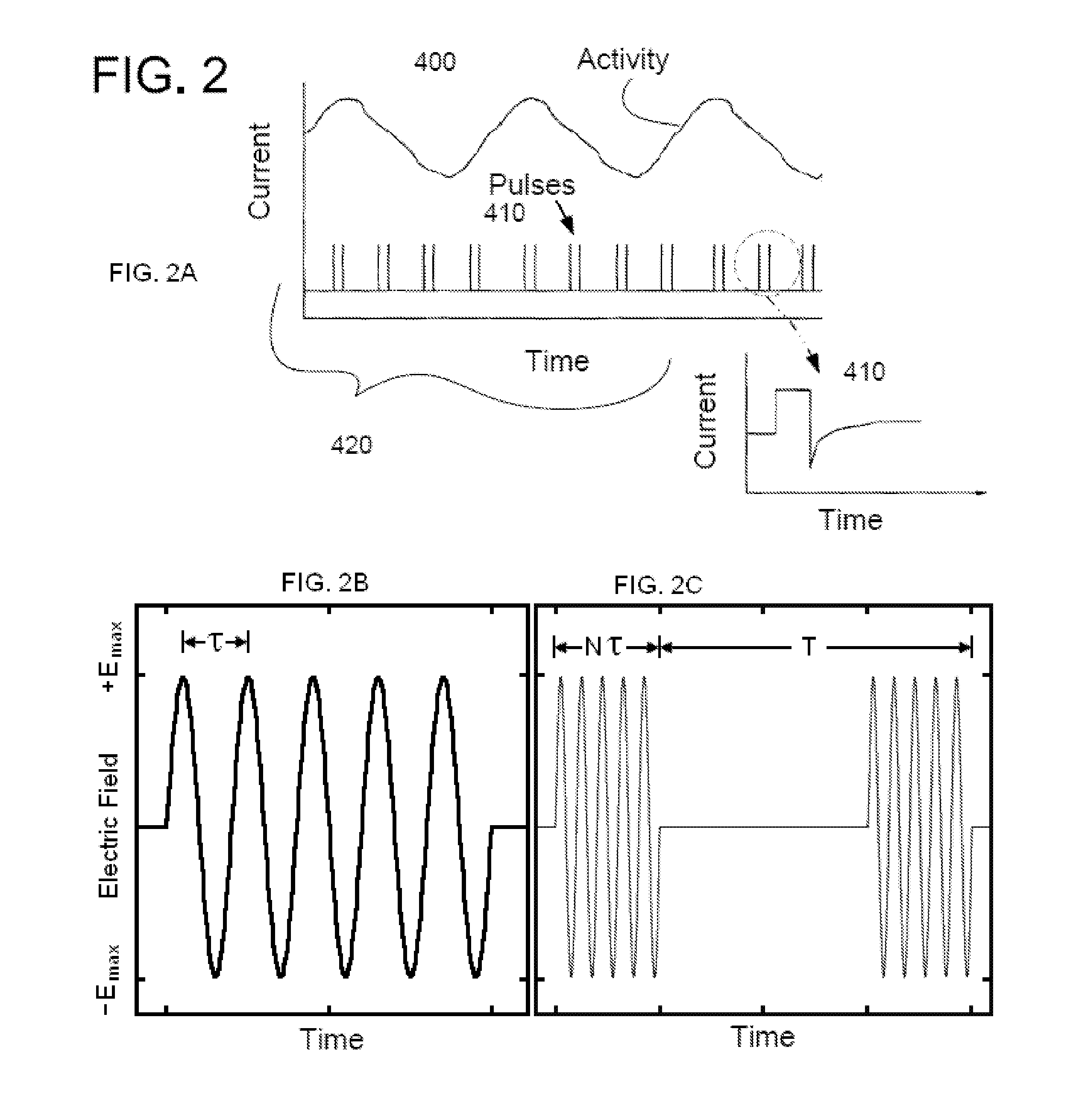
A method, system, and an apparatus for providing a multi-phasic stimulation signal for an implantable device are provided. An electrical pulse with a first characteristic that includes a first pulse width, a first pulse amplitude, a first pulse polarity, or a first pulse shape, is applied during a first time period to a portion of a vagus nerve using an implantable device. A controlled modification of the first characteristic of the electrical pulse is performed. The controlled modification is performed to provide a second characteristic for the electrical pulse during a second time period. The electrical pulse with the second characteristic is applied to the target portion of the vagus nerve.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
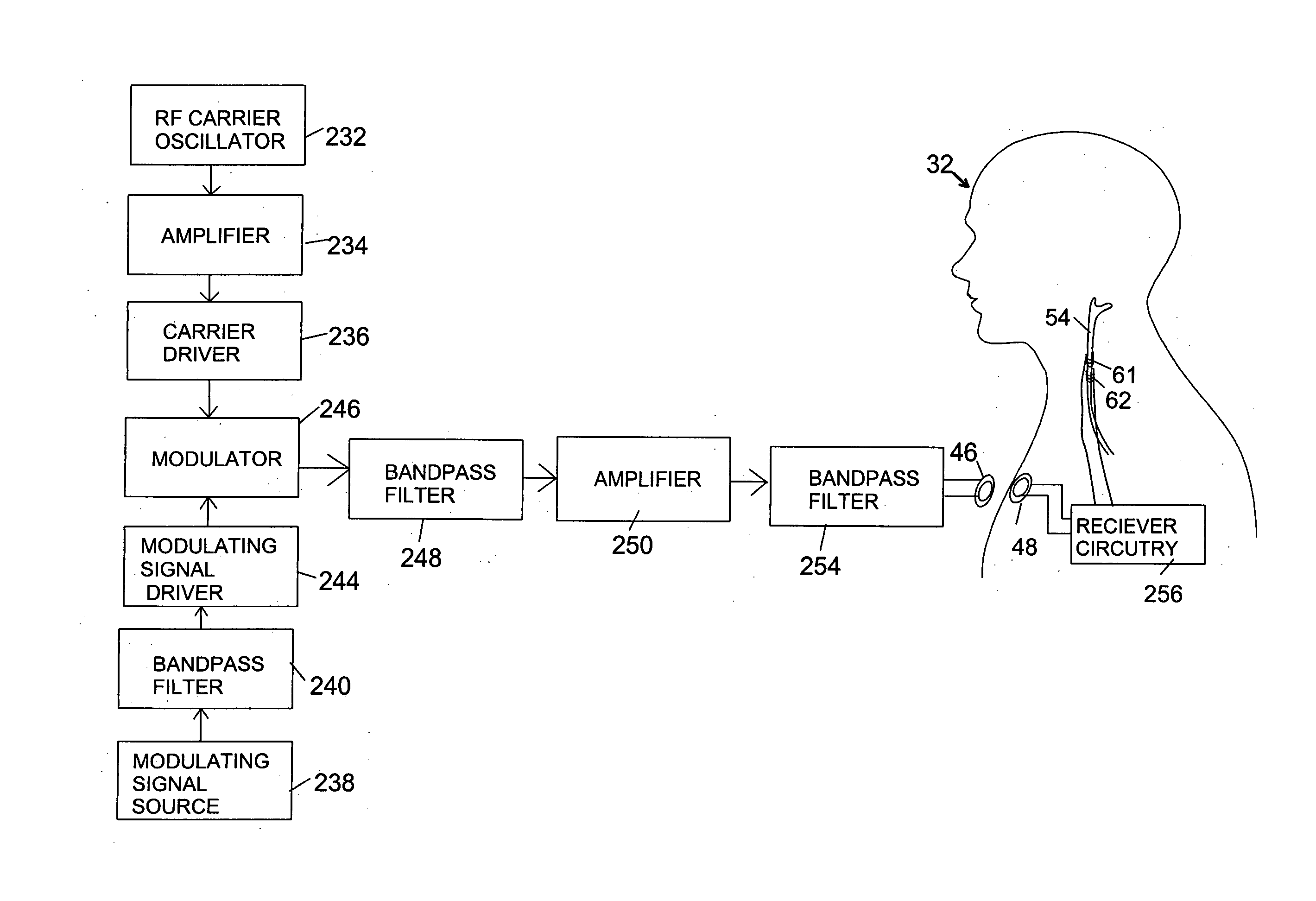
Electrical and magnetic stimulators used to treat migraine/sinus headache and comorbid disorders
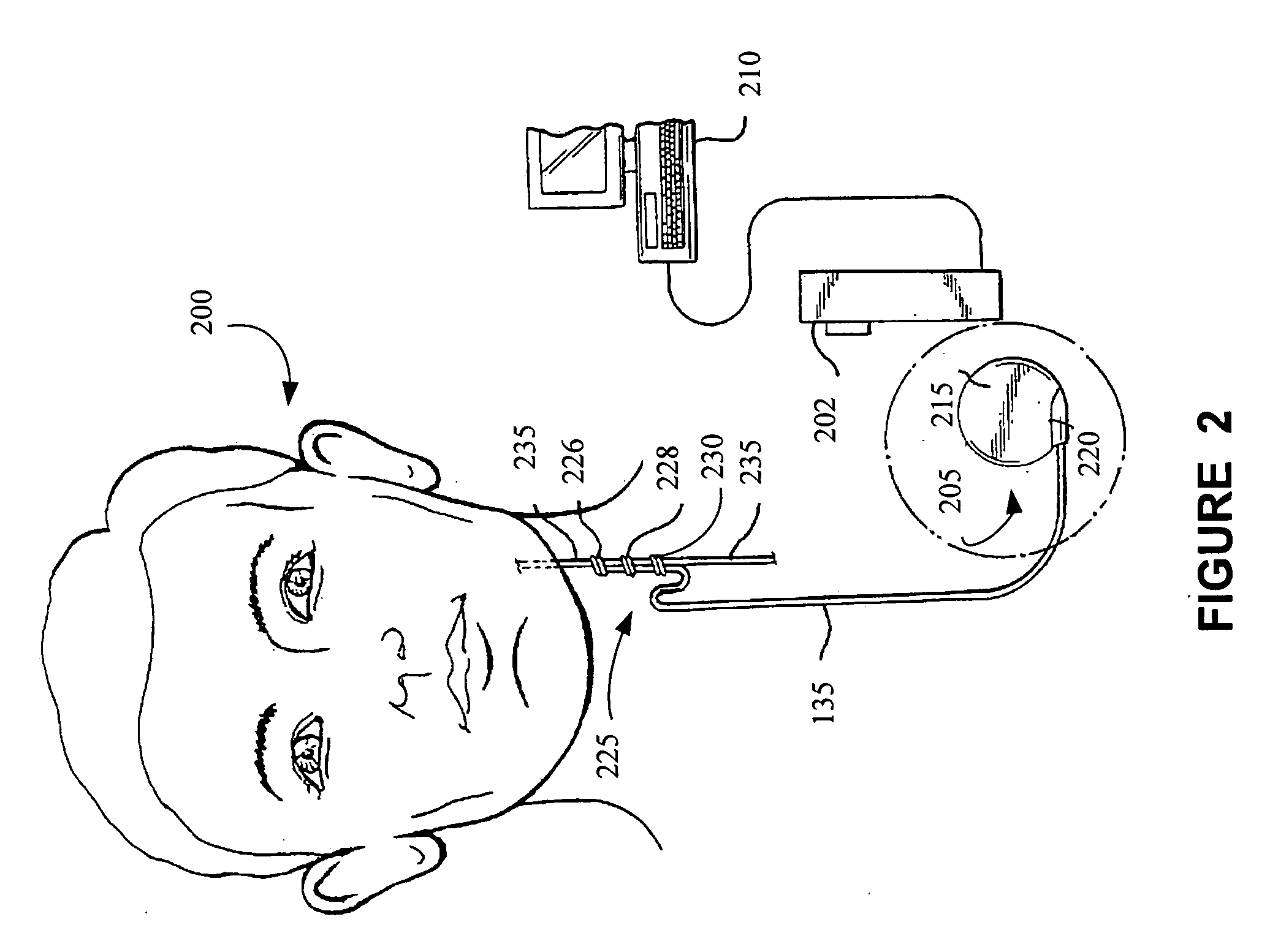
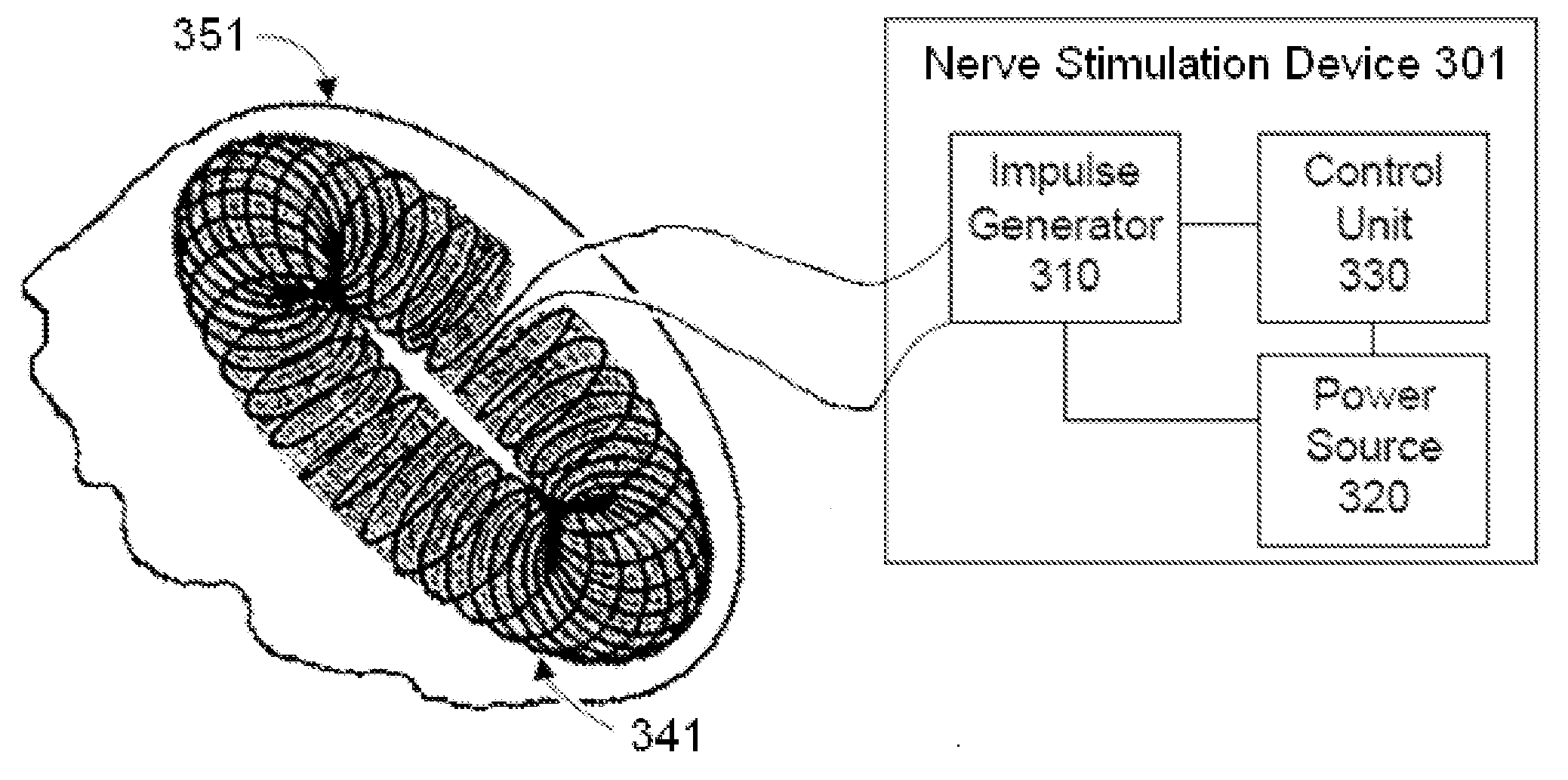
Non-invasive electrical nerve stimulation devices and magnetic stimulation devices are disclosed, along with methods of treating medical disorders using energy that is delivered noninvasively by such devices. The disorders comprise migraine and other primary headaches such as cluster headaches, including sinus symptoms that resemble an immune-mediated response (“sinus” headaches), irrespective of whether those symptoms arise from an allergy that is co-morbid with the headache. The disclosed methods may also be used to treat other disorders that may be co-morbid with migraine headaches, such as anxiety disorders. In preferred embodiments of the disclosed methods, one or both of the patient's vagus nerves are stimulated non-invasively. In other embodiments, parts of the sympathetic nervous system and / or the adrenal glands are stimulated.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Non-invasive treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
ActiveUS20110152967A1Reduce neuroinflammationReduce inflammationElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsRetinoidPostoperative cognitive dysfunction
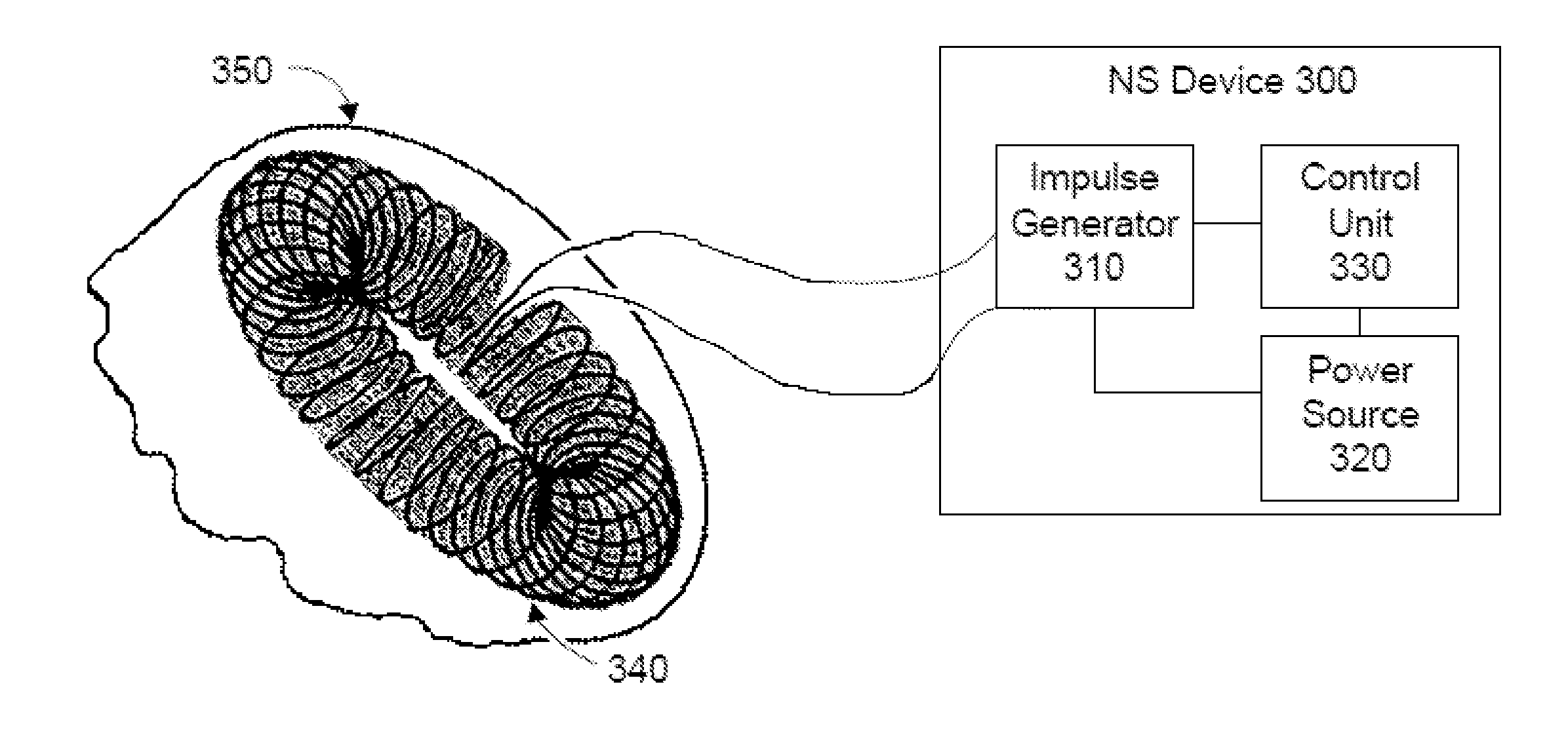
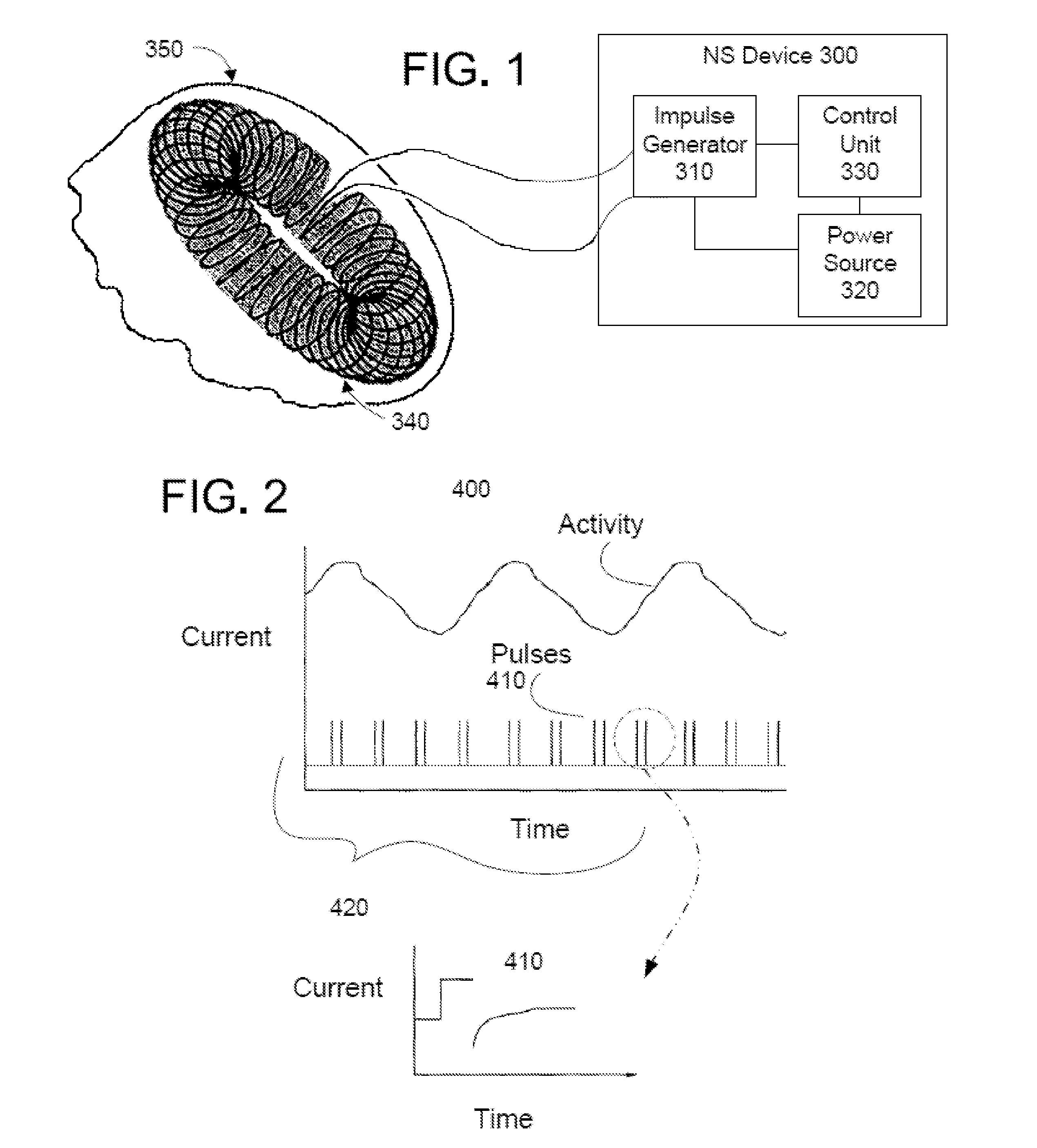
Methods and devices are disclosed for the non-invasive treatment of neurodegenerative diseases through delivery of energy to target nervous tissue, particularly the vagus nerve. The devices include a magnetic stimulator having coils with toroidal windings, which are in contact with an electrically conducting medium that is adapted to conform to the contour of a target body surface of a patient. The coils induce an electric current and / or an electric field within the patient, thereby stimulating nerve fibers within the patient. The stimulation brings about reduction of neuroinflammation in patients suffering from conditions comprising Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, postoperative cognitive dysfunction and postoperative delirium. Reduction in inflammation is effected by enhancing the anti-inflammatory competence of cytokines such as TGF-beta, wherein a retinoid or components of the retinoic acid signaling system provide an anti-inflammatory bias, by enhancing anti-inflammatory activity of a neurotrophic factor such as NGF, GDNF, BDNF, or MANF, and / or by inhibiting the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Obesity and eating disorder stimulation treatment with neural block
A method and apparatus for treating patients suffering from obesity or eating disorders by applying a predetermined stimulating signal to the patient's vagus nerve appropriate to alleviate the condition and by applying a neural conduction block to the vagus nerve at a blocking site with the neural conduction block selected to at least partially block nerve impulses on the vagus nerve at the blocking site.
Owner:RESHAPE LIFESCIENCES INC
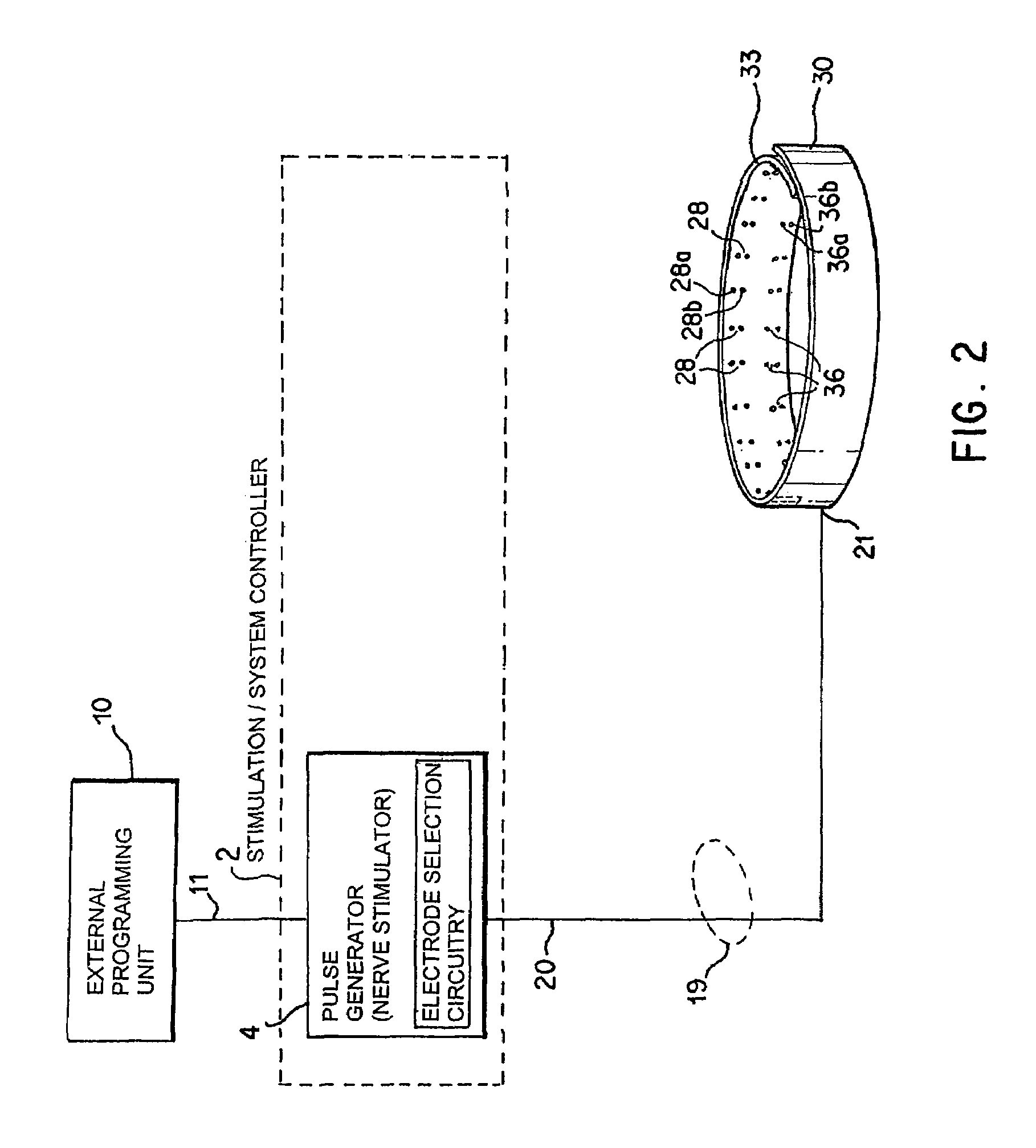
Identification of electrodes for nerve stimulation in the treatment of eating disorders
A method and apparatus for treatment of an eating disorder includes electrically, mechanically and / or pharmaceutically / chemically stimulating a of the vagus nerve of the lower esophagus, cardia, esophageal / cardia junction, cardia / fundus junction or upper stomach so as to induce afferent action potentials on the vagus nerve. The device may be noninvasively adjusted after implantation to provide increased or decreased restriction on the patient's gastrointestinal tract. Each stimulus may be administered as a series of programmed pulses of defined amplitude, duration and period, to evoke a responsive signal to the brain by the target nerve, effective for producing a temporary feeling of satiety in the person. An implantable stimulus generator may be operatively coupled to a nerve electrode, pressure device or chemical outlet to apply a defined signal to a selected nerve branch. The implantable stimulus generator is programmable to allow clinician programming of defined signal parameters effective to treat the eating disorder of the patient. Methods are also provided to identify electrodes nearest to a branch of the vagus nerve to apply an electrical stimulation signal with improved efficiency.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Method and system for providing therapy for bulimia/eating disorders by providing electrical pulses to vagus nerve(s)
InactiveUS20050192644A1Increase valueSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical impulseElectrical stimulations
A method and system to provide pre-determined electrical pulses for neuromodulating vagus nerve(s) or its branches to provide therapy for bulimia / eating disorders, comprises implantable and external components. The electrical pulses to vagus nerve(s) may be stimulating and / or blocking. The pulsed electrical stimulation / blocking to vagus nerve(s) may be provided using one of the following stimulation systems, such as: a) an implanted stimulus-receiver with an external stimulator; b) an implanted stimulus-receiver comprising a high value capacitor for storing charge, used in conjunction with an external stimulator; c) a programmer-less implantable pulse generator (IPG) which is operable with a magnet; d) a microstimulator; e) a programmable implantable pulse generator; f) a combination implantable device comprising both a stimulus-receiver and a programmable implantable pulse generator (IPG); and g) an implantable pulse generator (IPG) comprising a rechargeable battery. In one embodiment, the external components such as the programmer or external stimulator may comprise a telemetry means for networking. The telemetry means therefore allows for interrogation or programming of implanted device, from a remote location over a wide area network.
Owner:NEURO & CARDIAC TECH
Parasympathetic pacing therapy during and following a medical procedure, clinical trauma or pathology
ActiveUS20060206155A1Increase parasympathetic toneReduced responseSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsParasympathetic ganglionPathology diagnosis
A treatment method is provided, including identifying a subject as one who is selected to undergo an interventional medical procedure, and, in response to the identifying, reducing a likelihood of a potential adverse effect of the procedure by applying an electrical current to a parasympathetic site of the subject selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a jugular vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, a parasympathetic ganglion of the subject, and a parasympathetic nerve of the subject.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
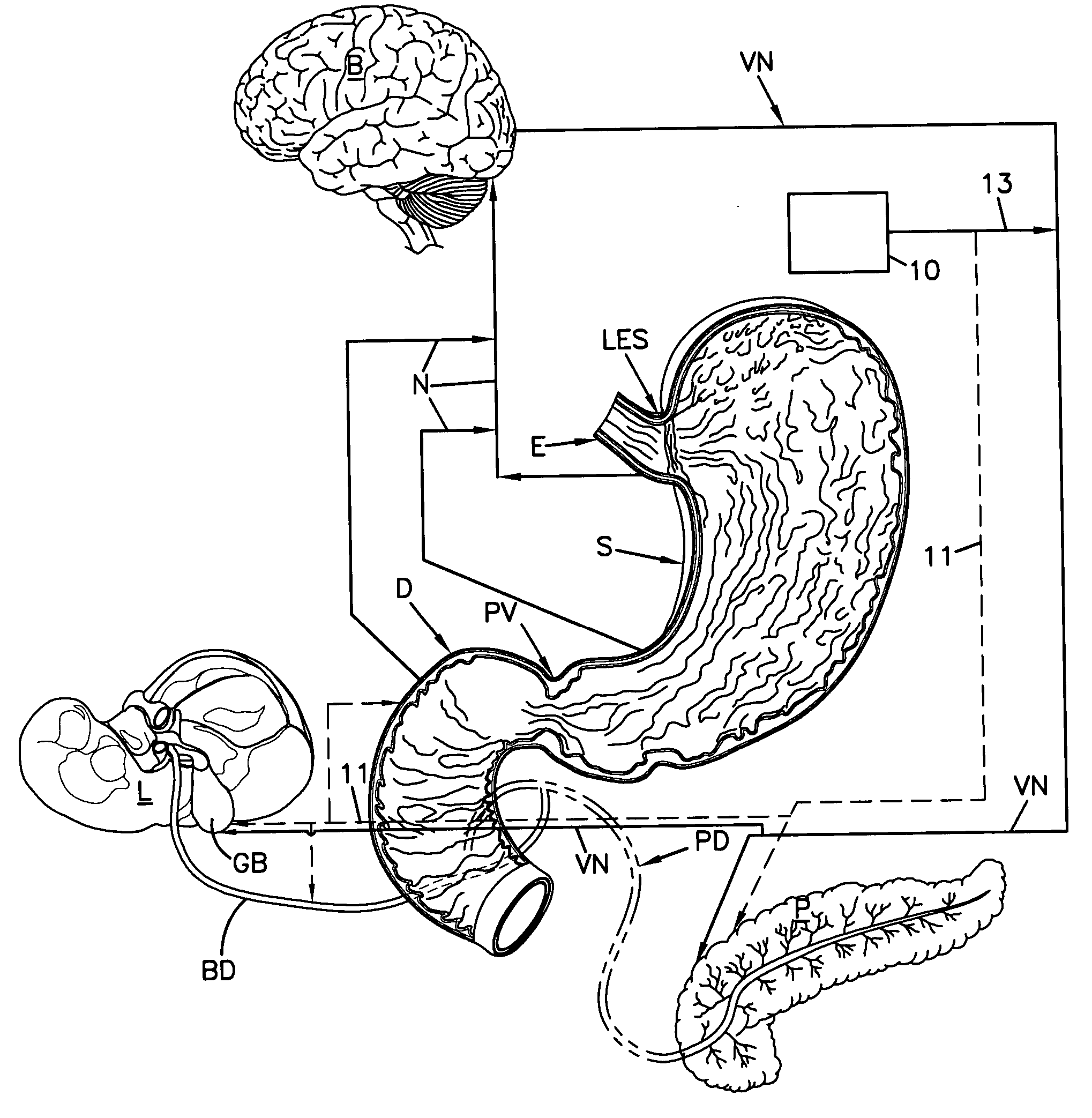
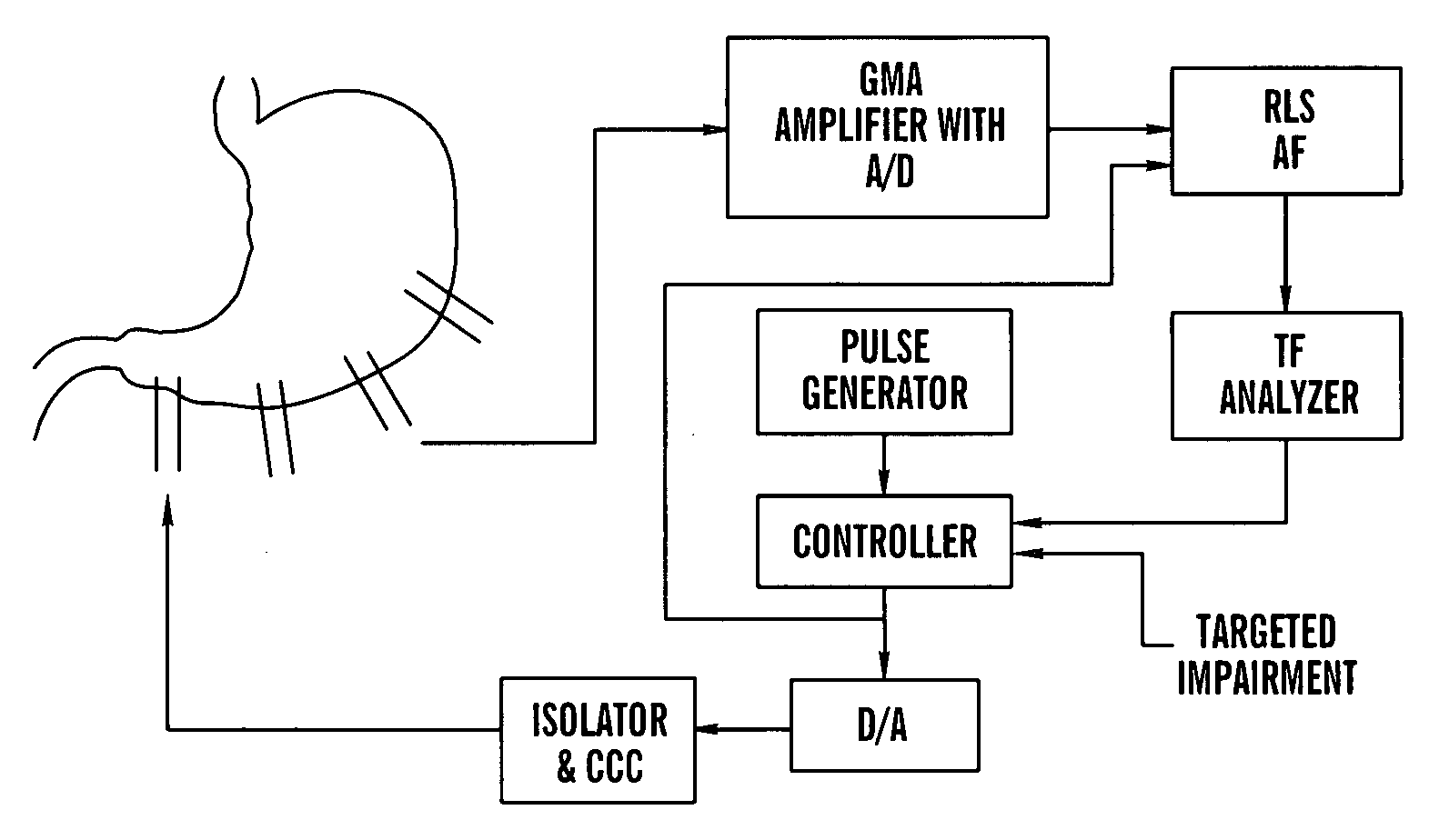
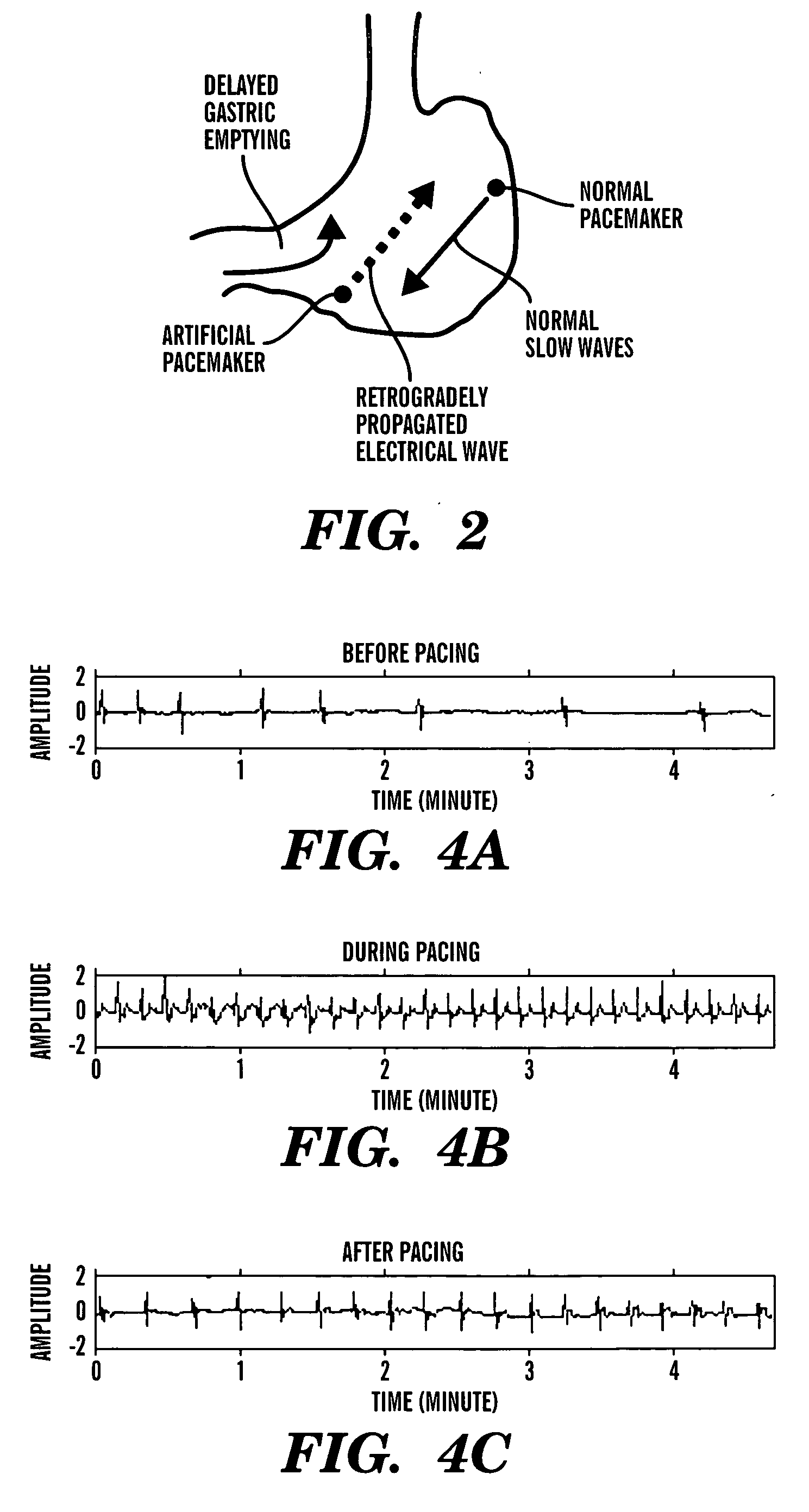
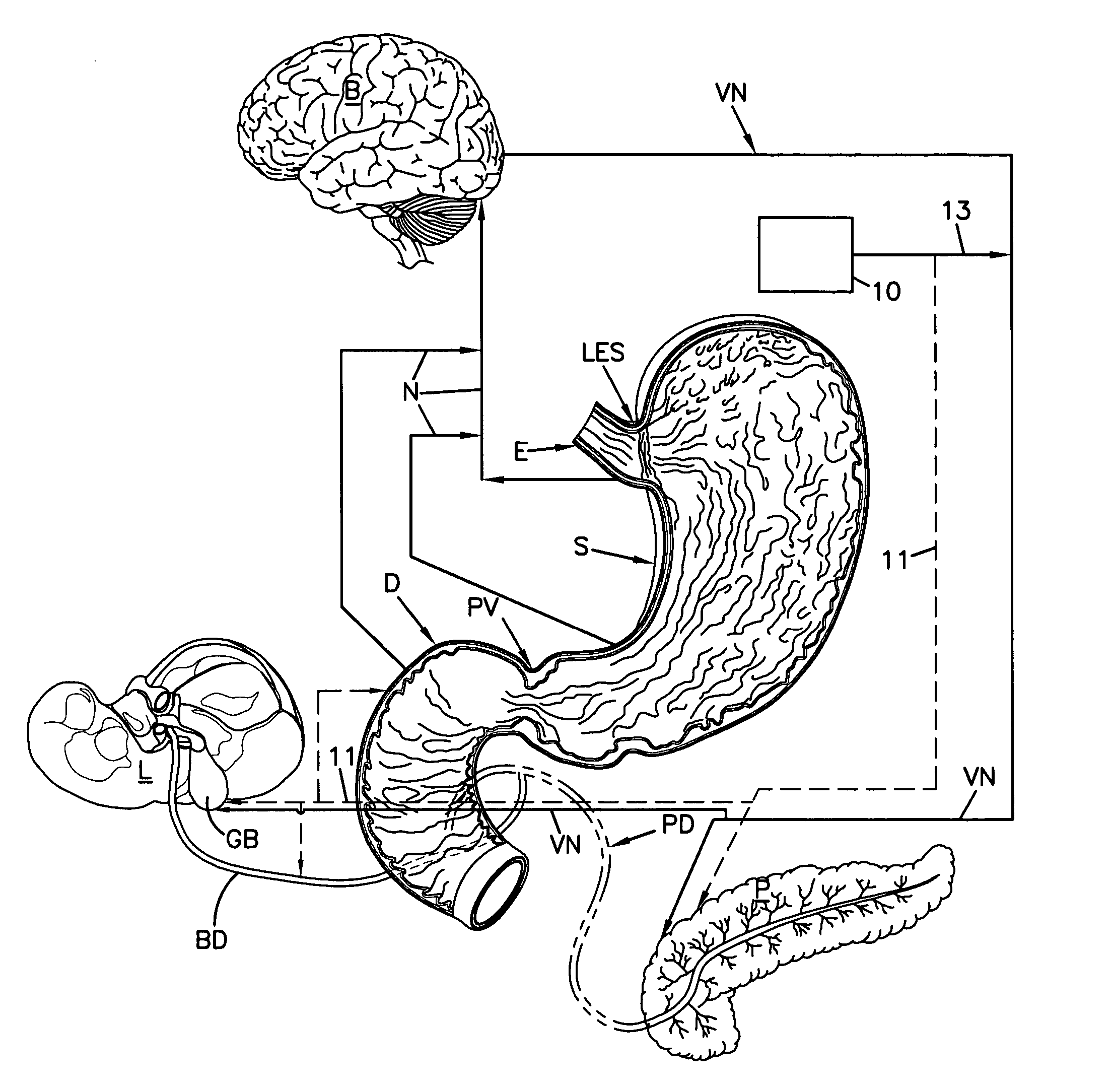
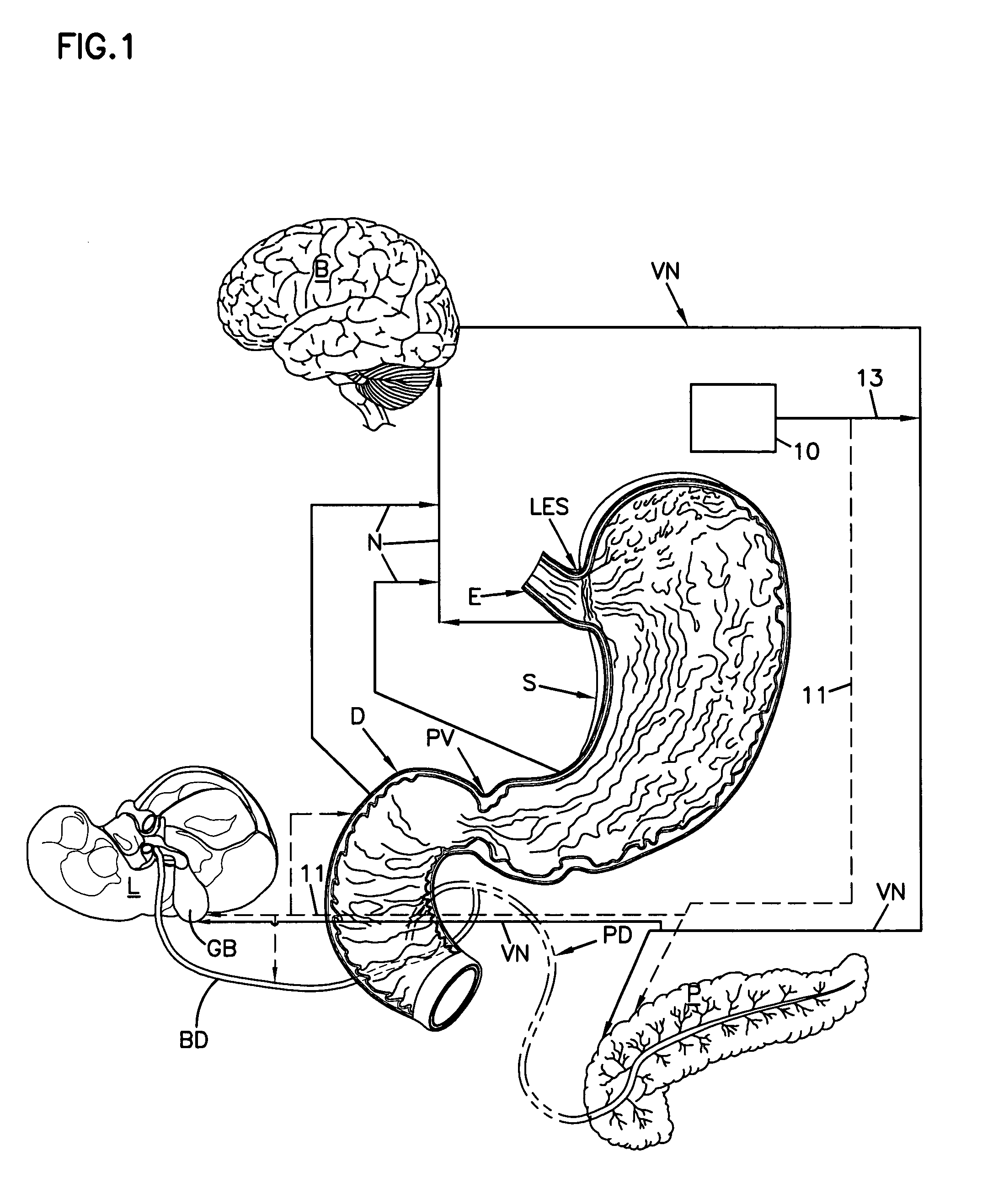
Gastrointestinal electrical stimulation
The present invention is directed to a method of regulating gastrointestinal action in a subject using a stimulatory electrode and a sensor to provide retrograde feedback control of electrical stimulation to the GI tract. The invention is further directed to a method for reducing weight in a subject, again using a stimulatory electrode and a sensor to provide retrograde feedback control of electrical stimulation to the stomach. The invention is further directed to a method of providing electrical field stimulation to a gastrointestinal organ, as well as a method of providing an electrical potential gradient in a gastrointestinal organ. Further provided is a method of stimulating the vagus nerve of a subject. Additionally provided is a method of placing a device in the gastrointestinal tract or wall of a subject from the exterior of the subject, using a needle to insert the device.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Techniques for reducing pain associated with nerve stimulation
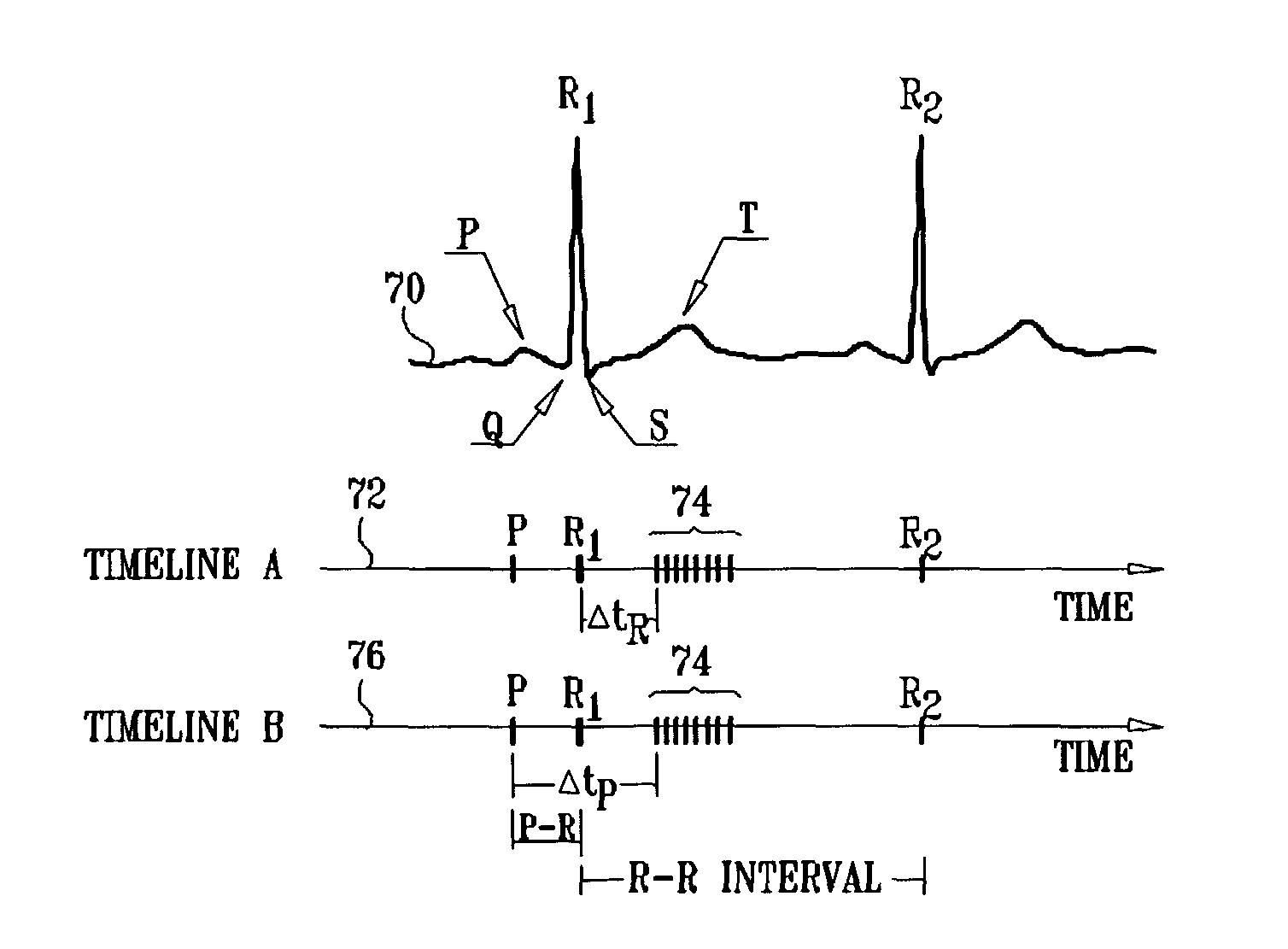
Apparatus is provided including an electrode device and a control unit. The electrode device is configured to be coupled to a site of a subject selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve, an epicardial fat pad, a pulmonary vein, a carotid artery, a carotid sinus, a coronary sinus, a vena cava vein, a right ventricle, a right atrium, and a jugular vein. The control unit is configured to drive the electrode device to apply to the site a current in at least first and second bursts, the first burst including a plurality of pulses, and the second burst including at least one pulse, and set (a) a pulse repetition interval (PRI) of the first burst to be on average at least 20 ms, (b) an interburst interval between initiation of the first burst and initiation of the second burst to be less than 10 seconds, (c) an interburst gap between a conclusion of the first burst and the initiation of the second burst to have a duration greater than the average PRI, and (d) a burst duration of the first burst to be less than a percentage of the interburst interval between, the percentage being less than 67%. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Device and Method for Treating Weight Disorders
An apparatus and a method for treating a weight disorder in a subject are provided. The apparatus comprising an implantable device such as an inflatable balloon and electrodes capable of sensing a physiological change associated with food ingestion or hunger and a mechanism adapted for directly stimulating a region such as the duodenum which is responsive to a gastrointestinal satiety agent, such a mechanism can be a drug reservoir containing a drug such as CCK or analogs thereof which is contained within an inflatable balloon being implantable in a stomach of the subject. The apparatus and method provided here combine synergistic approaches to limiting meal size, i.e., chemo and mechano receptor activation of vagal satiety stimuli, electric stimulation of specific vagal pathways and limitations of gastric space.
Owner:DUOCURE
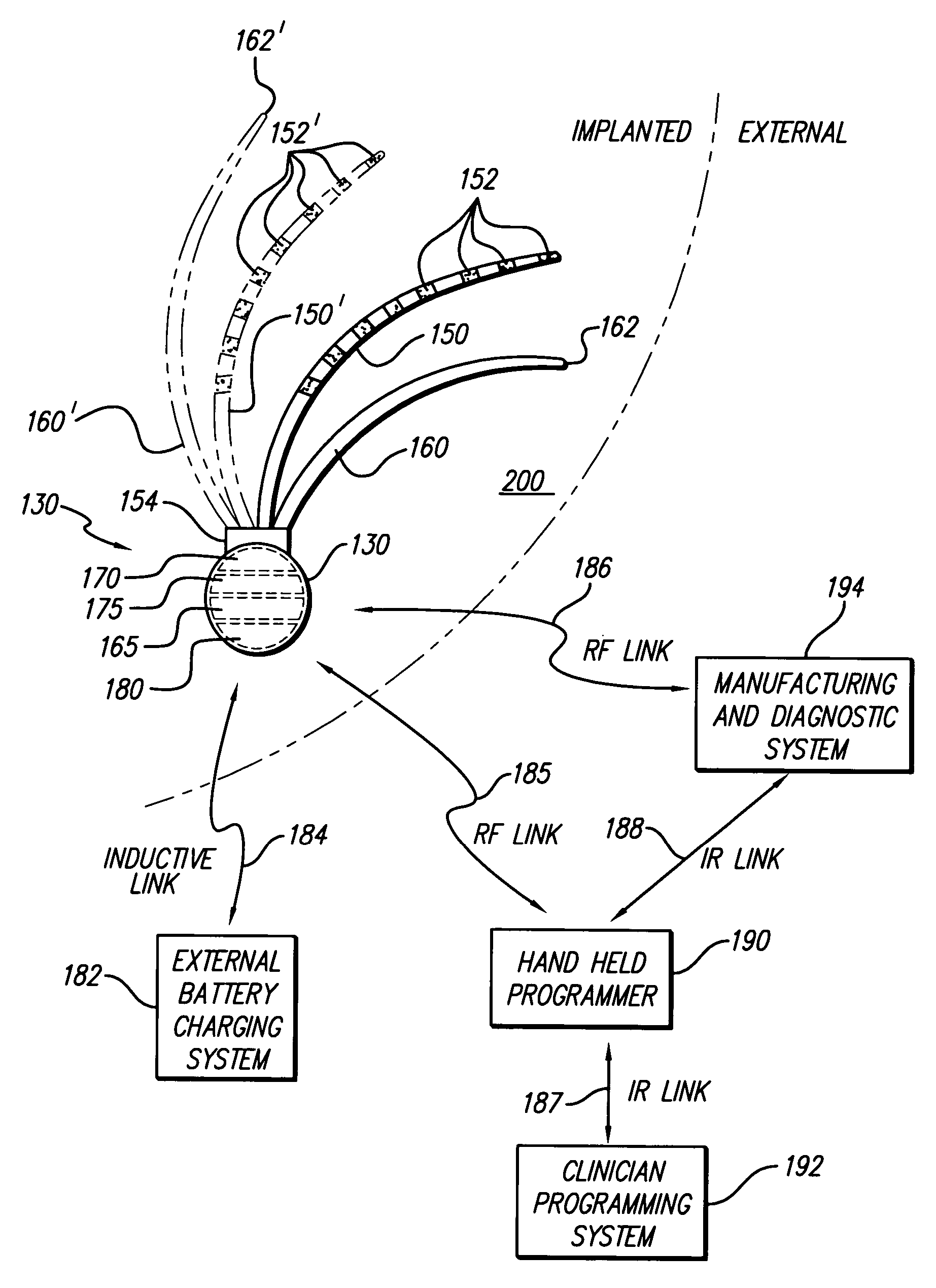
Neural stimulation devices and systems for treatment of chronic inflammation
ActiveUS20110190849A1Reduce communication errorsLimited amountSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsMedicineDose delivery
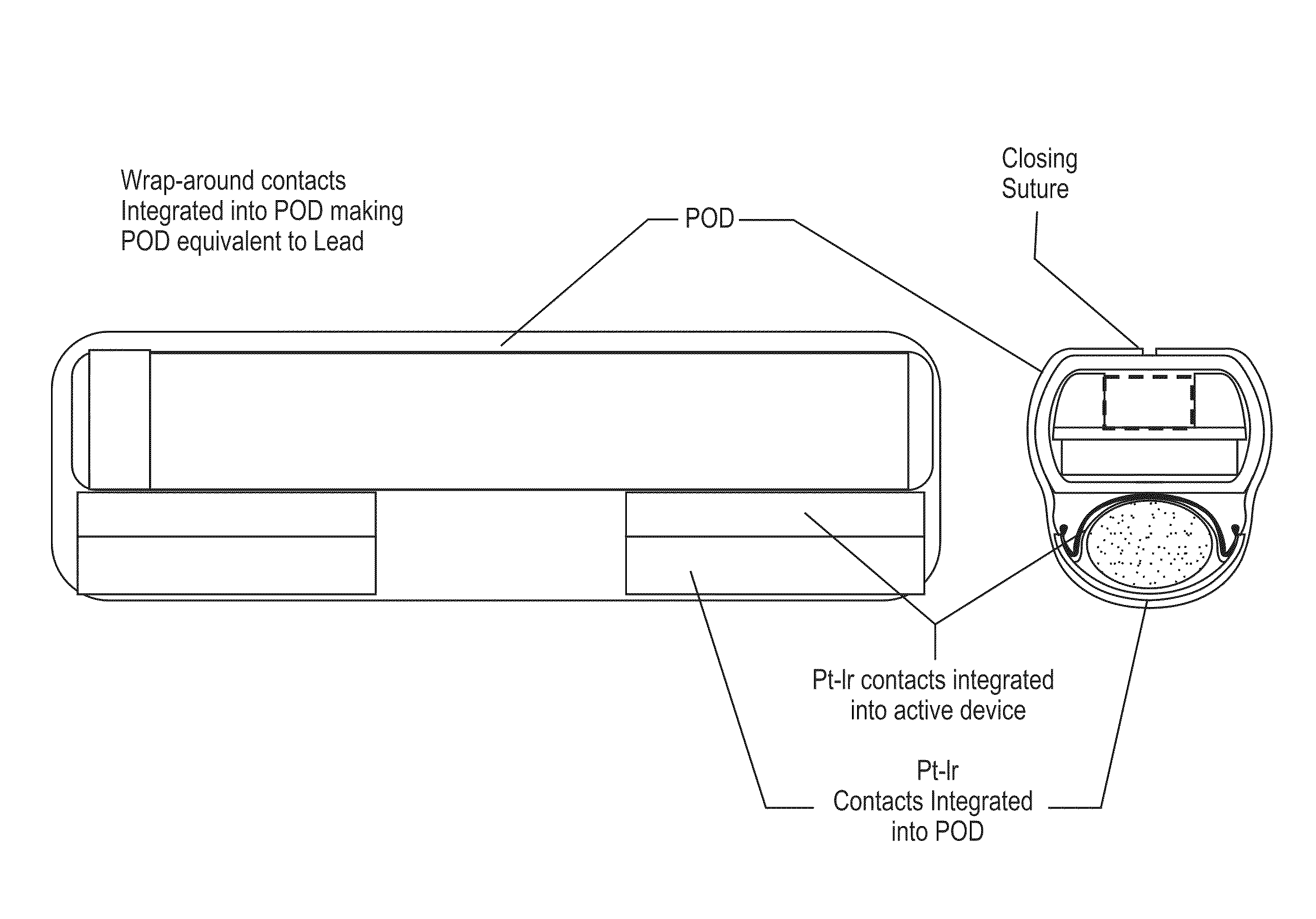
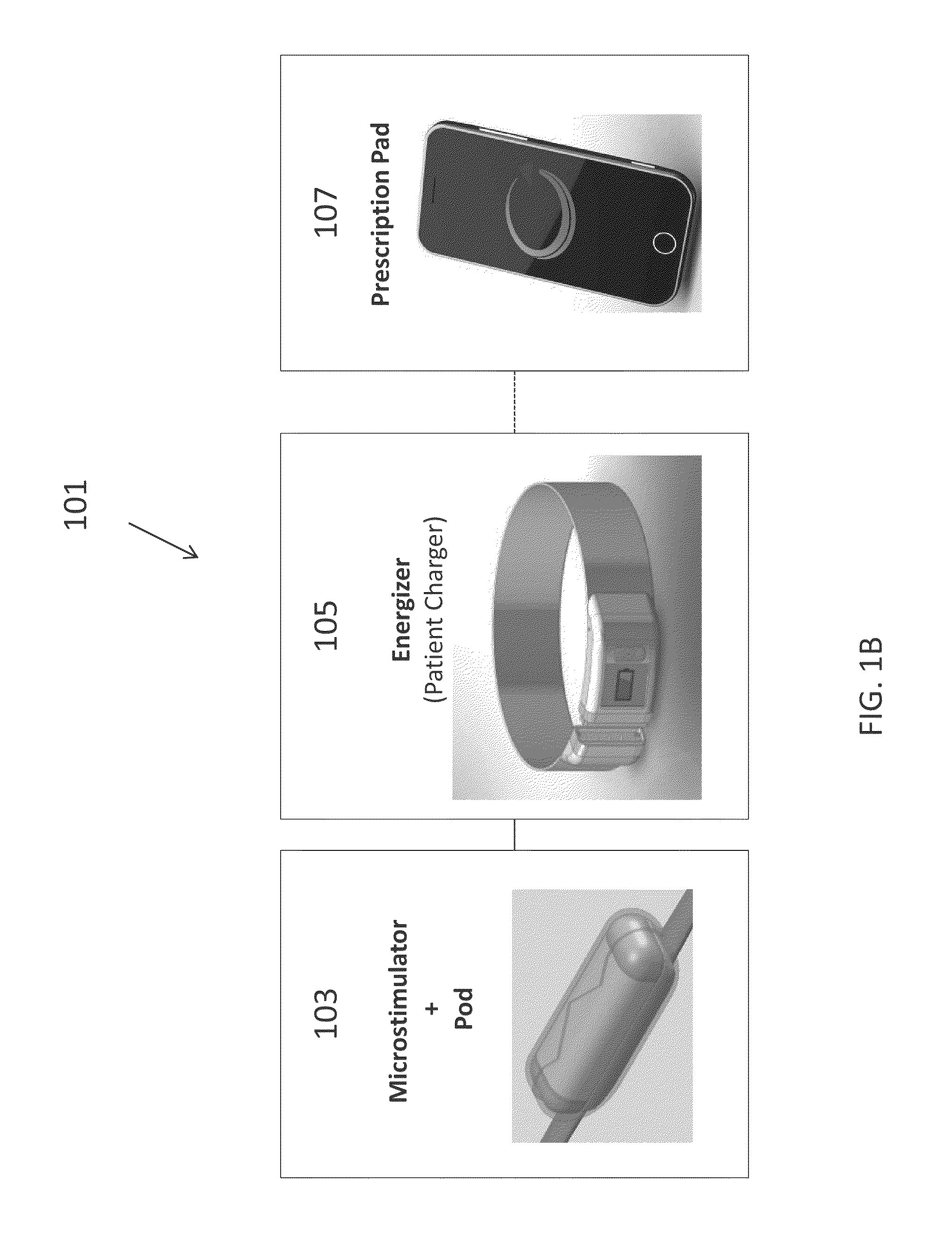
A system for treating chronic inflammation may include an implantable microstimulator, a wearable charger, and optionally an external controller. The implantable microstimulator may be implemented as a leadless neurostimulator implantable in communication with a cervical region of a vagus nerve. The microstimulator can address several types of stimulation including regular dose delivery. The wearable charger may be worn around the subject's neck to rapidly (<10 minutes per week) charge an implanted microstimulator. The external controller may be configured as a prescription pad that controls the dosing and activity of the microstimulator.
Owner:SETPOINT MEDICAL CORP
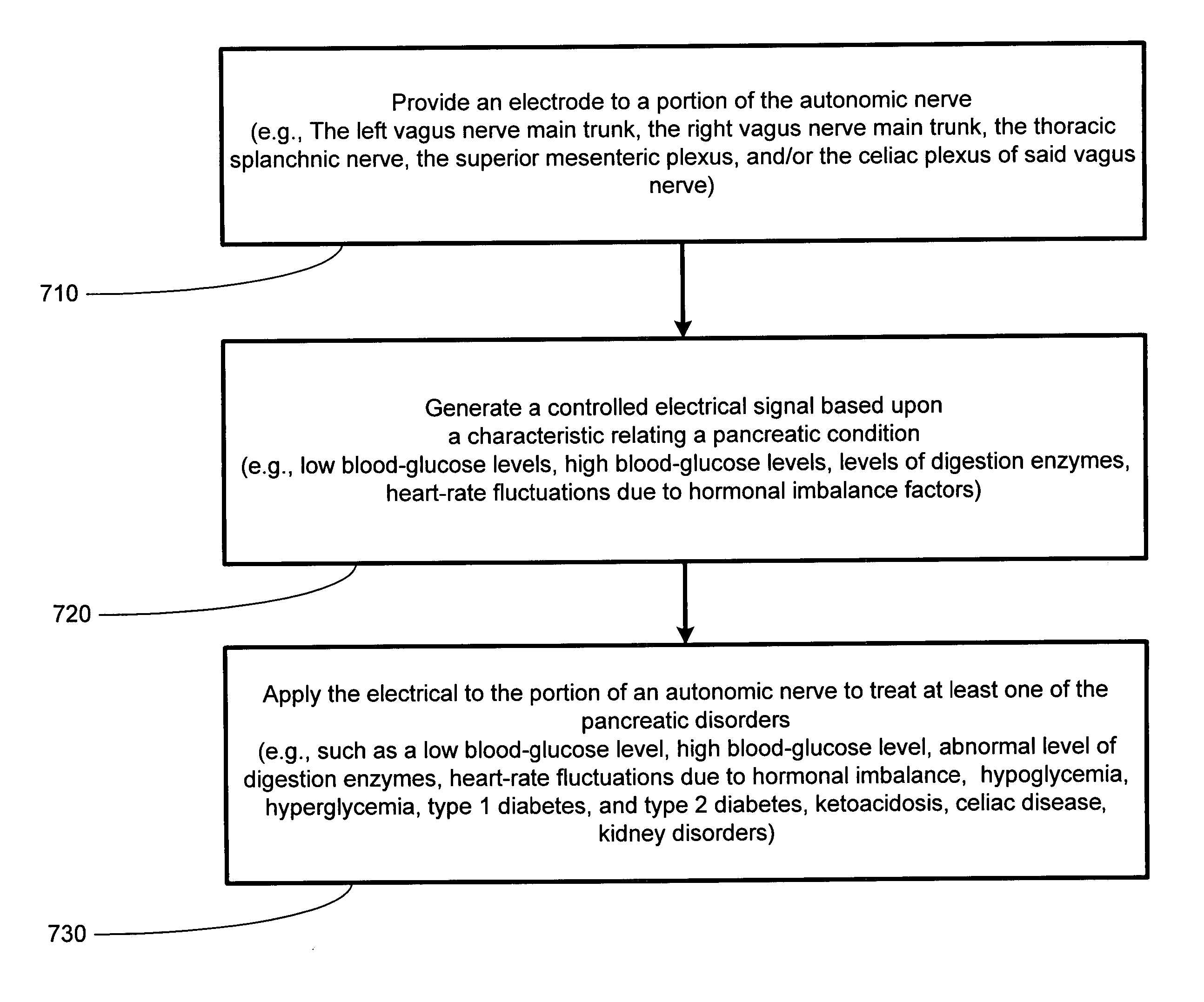
Autonomic nerve stimulation to treat a pancreatic disorder
A method for stimulating a portion of a vagus nerve of a patient to treat a pancreatic disorder is provided. At least one electrode is coupled to at least one portion of an autonomic nerve of the patient. The portion may include a celiac plexus, a superior mesenteric plexus, and a thoracic splanchnic. An electrical signal is applied to the portion of the vagus nerve using the electrode to treat the pancreatic disorder.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Electrical stimulation treatment of bronchial constriction
ActiveUS20070106339A1Avoid hard activationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationRadiologyElectrical impulse
Methods and devices for treating bronchial constriction related to asthma and anaphylaxis wherein the treatment includes providing an electrical impulse to a selected region of the vagus nerve and / or the lungs of a patient suffering from bronchial constriction.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Identification of electrodes for nerve stimulation in the treatment of eating disorders
A method and apparatus for treatment of an eating disorder includes electrically, mechanically and / or pharmaceutically / chemically stimulating a of the vagus nerve of the lower esophagus, cardia, esophageal / cardia junction, cardia / fundus junction or upper stomach so as to induce afferent action potentials on the vagus nerve. The device may be noninvasively adjusted after implantation to provide increased or decreased restriction on the patient's gastrointestinal tract. Each stimulus may be administered as a series of programmed pulses of defined amplitude, duration and period, to evoke a responsive signal to the brain by the target nerve, effective for producing a temporary feeling of satiety in the person. An implantable stimulus generator may be operatively coupled to a nerve electrode, pressure device or chemical outlet to apply a defined signal to a selected nerve branch. The implantable stimulus generator is programmable to allow clinician programming of defined signal parameters effective to treat the eating disorder of the patient. Methods are also provided to identify electrodes nearest to a branch of the vagus nerve to apply an electrical stimulation signal with improved efficiency.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Nerve conduction block treatment
InactiveUS20040172086A1Function increaseAltered autonomic balanceSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsDiseaseBlocking nerve
At least one of a plurality of disorders of a patient are treated where the disorders are associated with a gastrointestinal tract of a patient where the disorders are characterized at least in part by hyper-tonal vagal activity innervating at least one of a plurality of alimentary tract organs of the patient at an innervation site. The treatment includes applying a neural conduction block to a vagus nerve of the patient at a blocking site proximal to the innervation site. The neural conduction block is selected to at least partially block nerve impulses on the vagus nerve at the blocking site. A treatment apparatus has an electrically controllable neural conduction electrode adapted to be placed on a vagus nerve of a patient at a blocking site proximal to an innervation site.
Owner:RESHAPE LIFESCIENCES INC
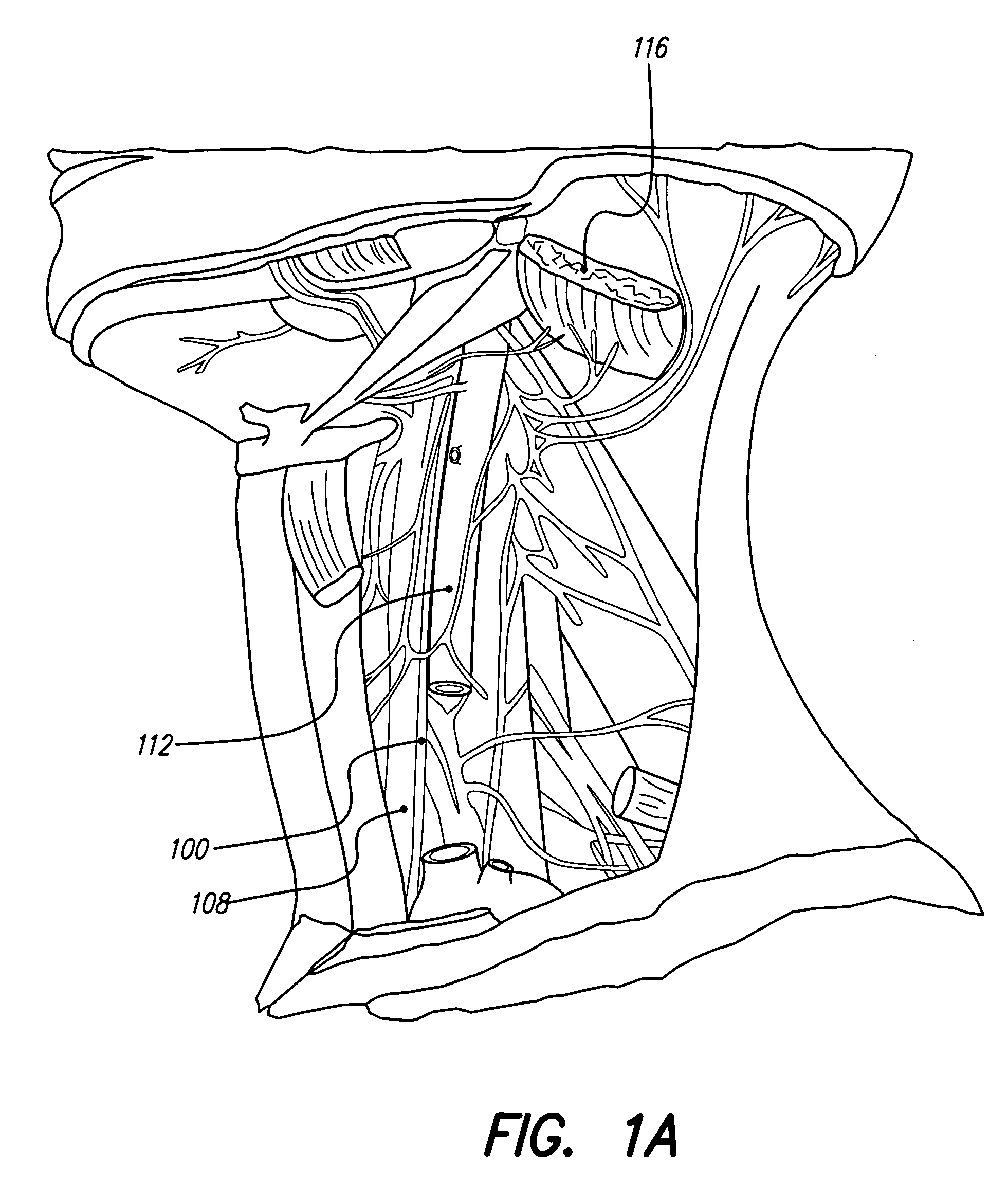
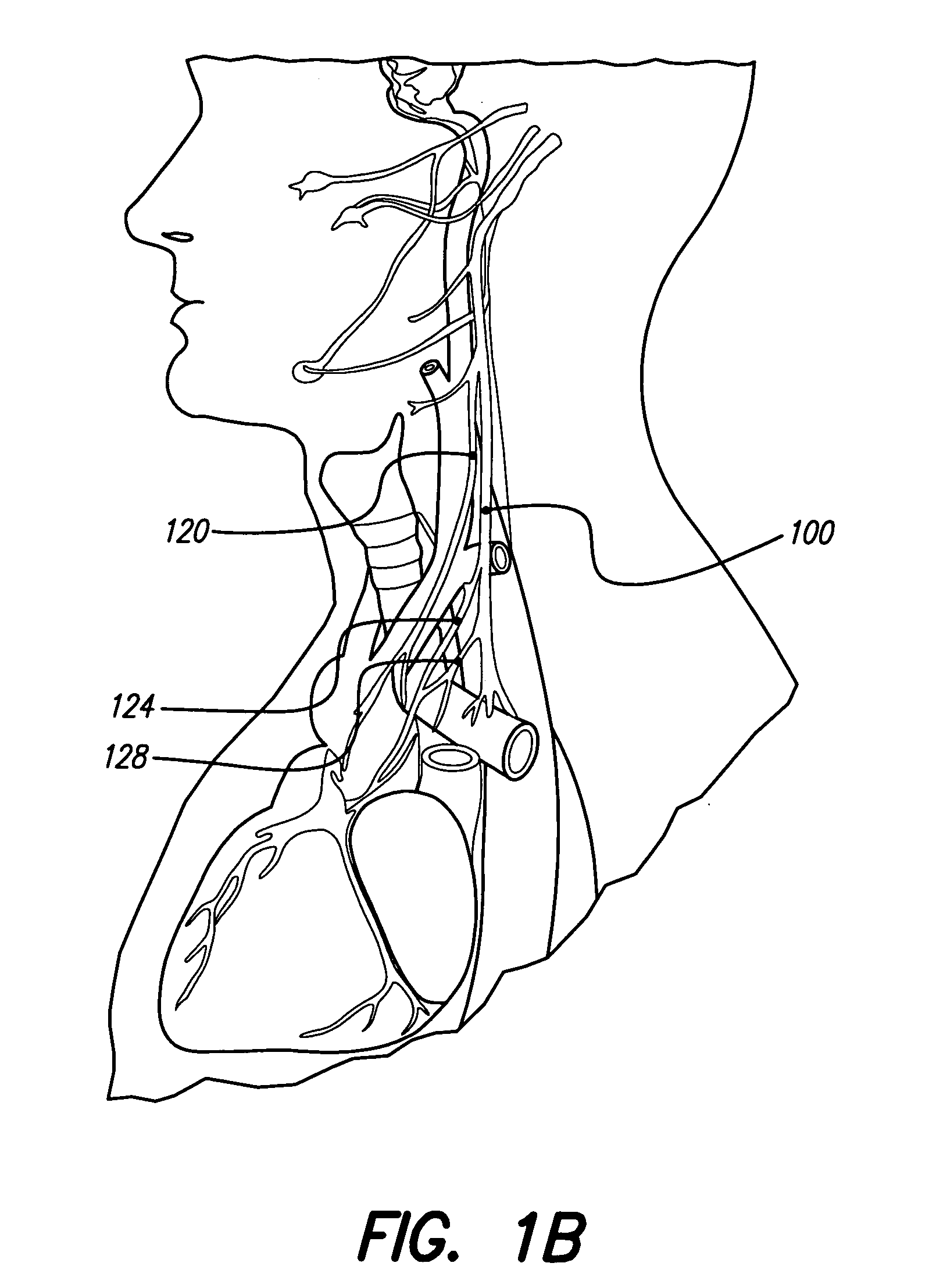
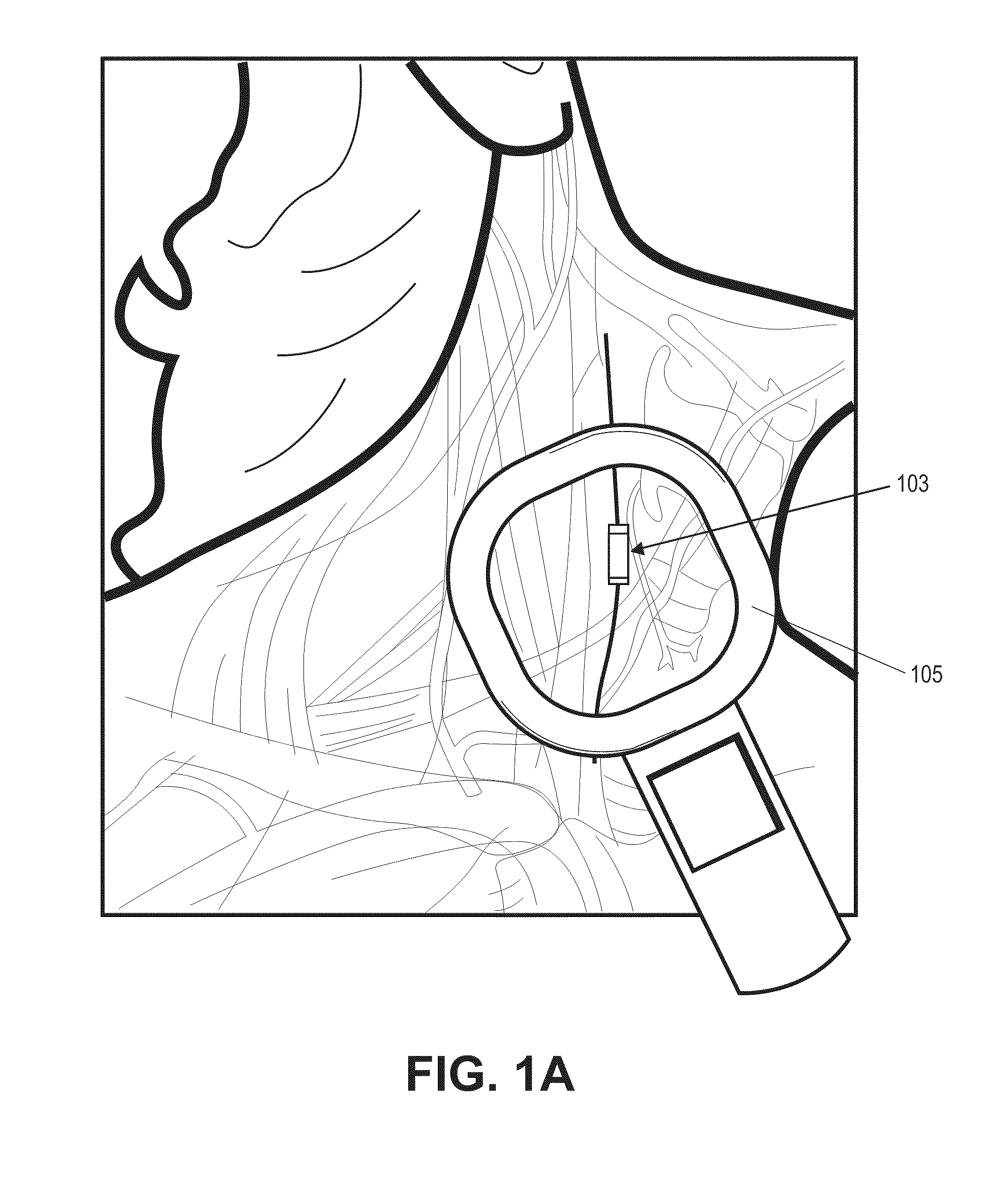
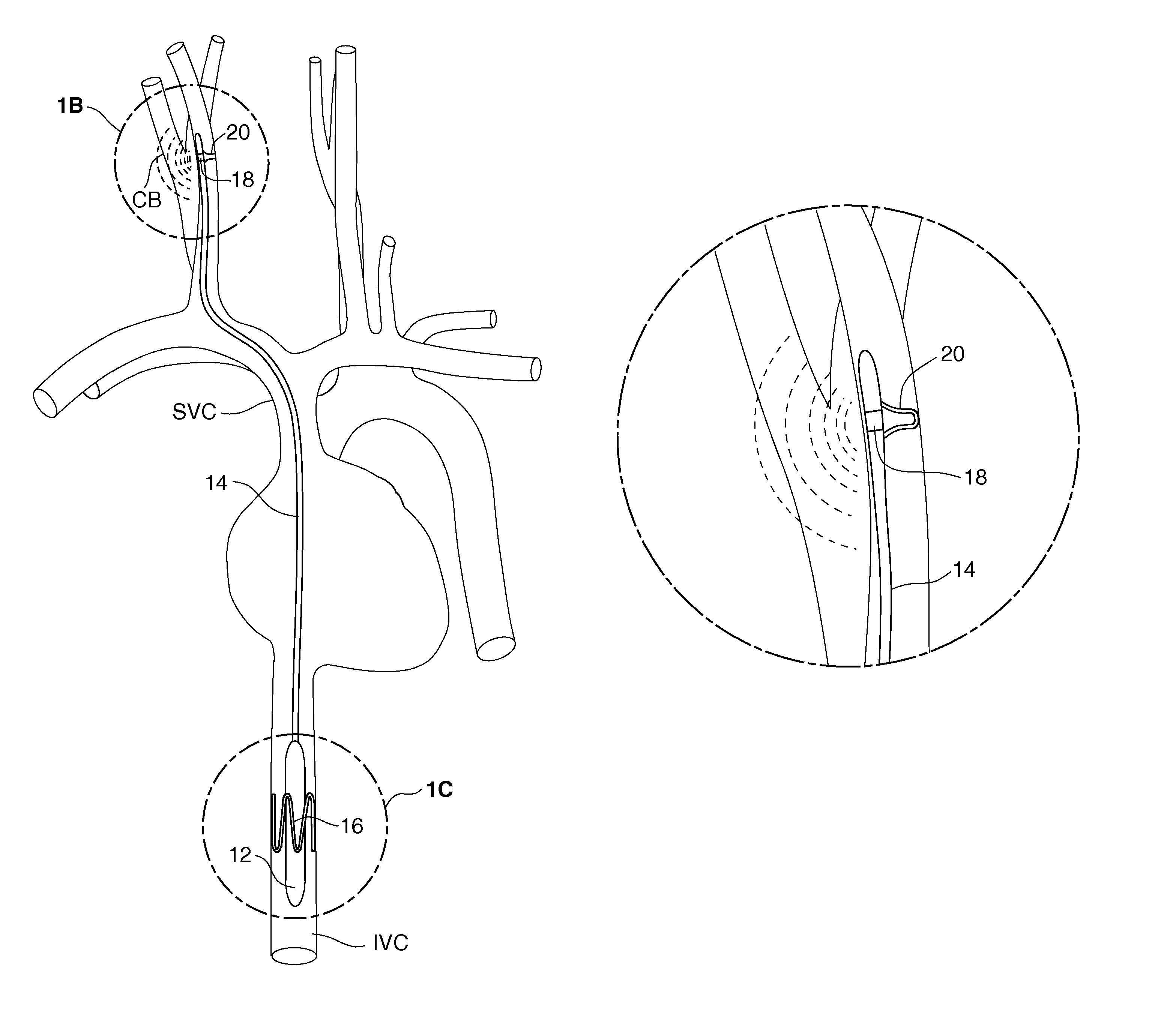
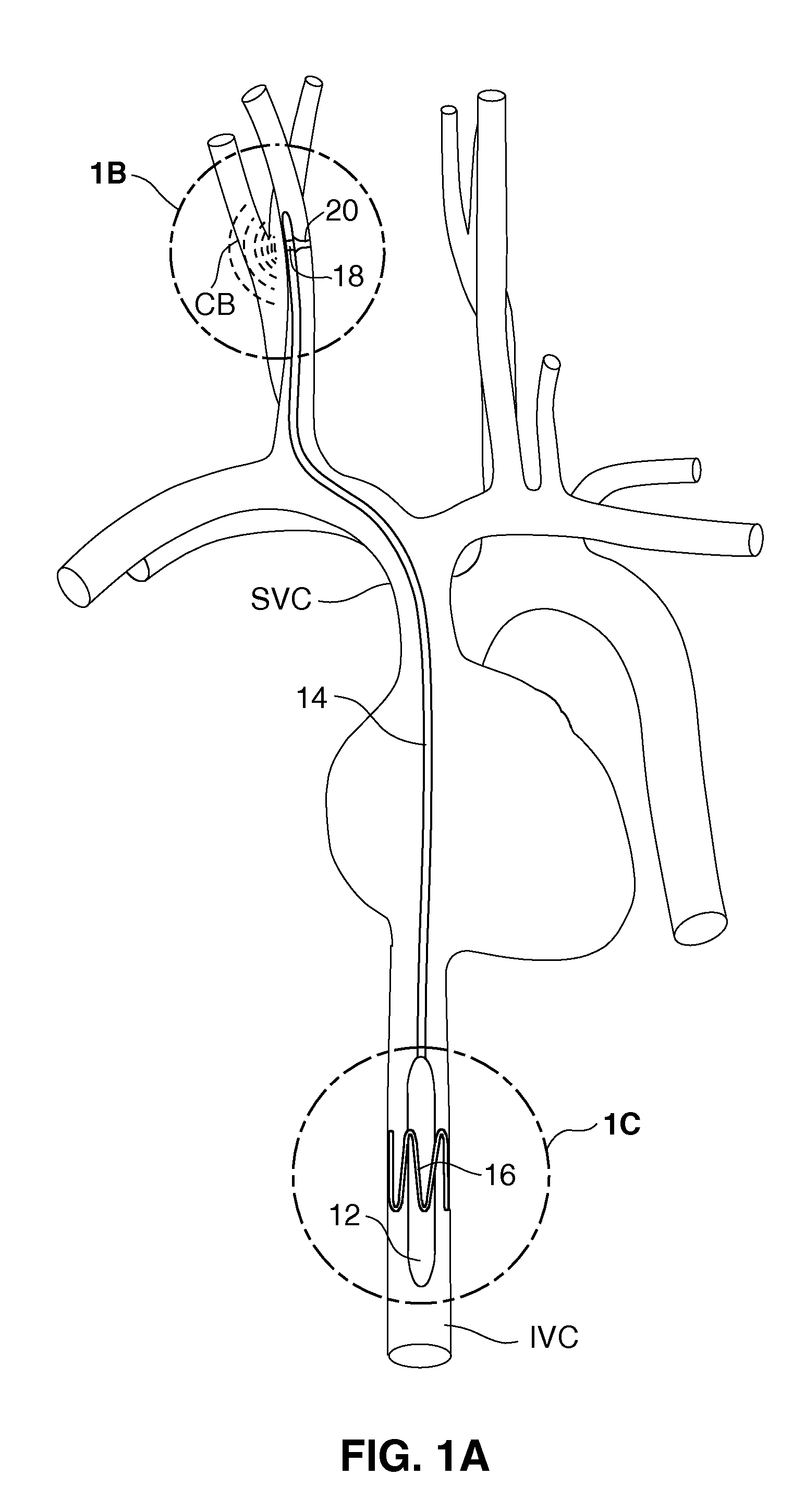
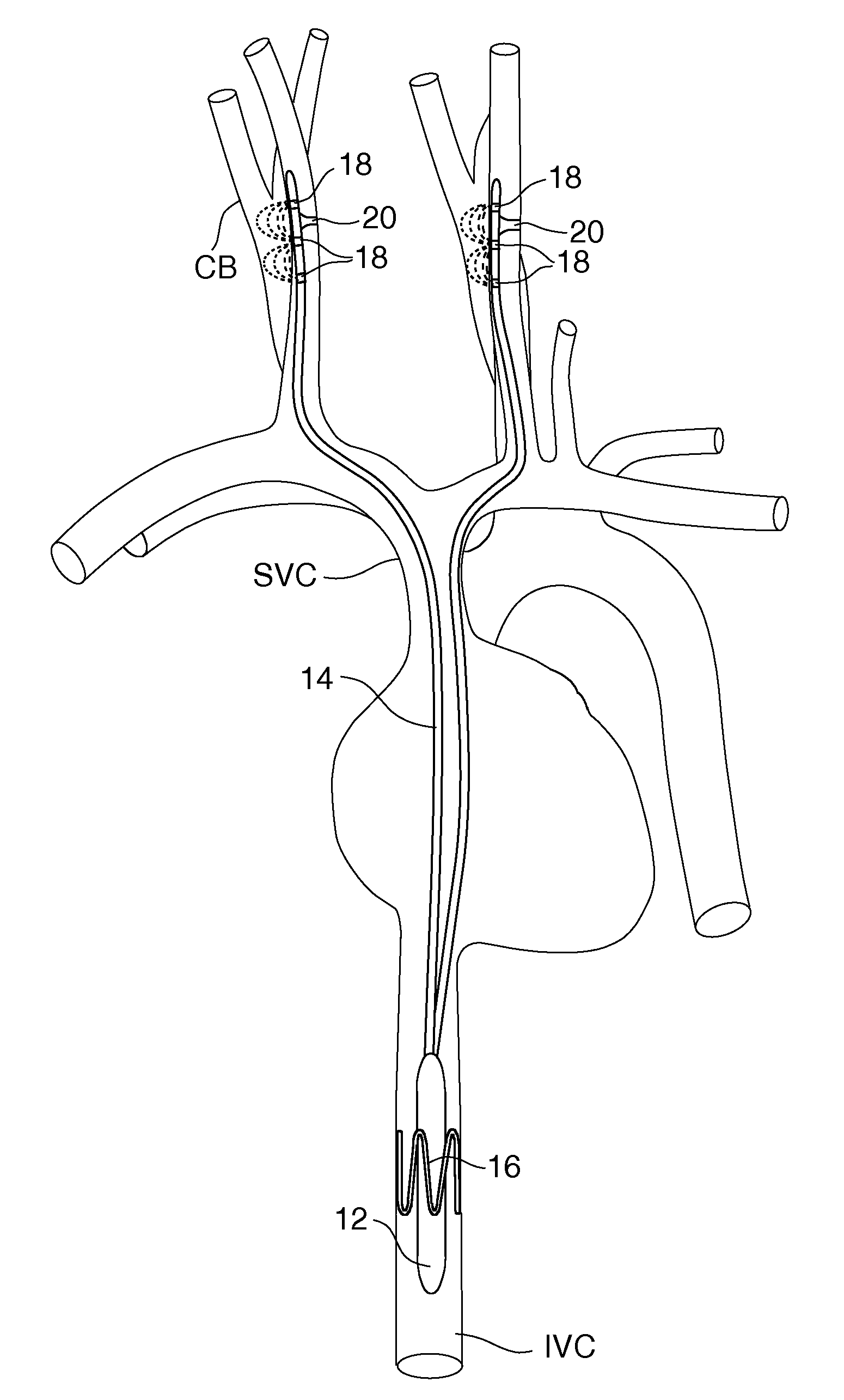
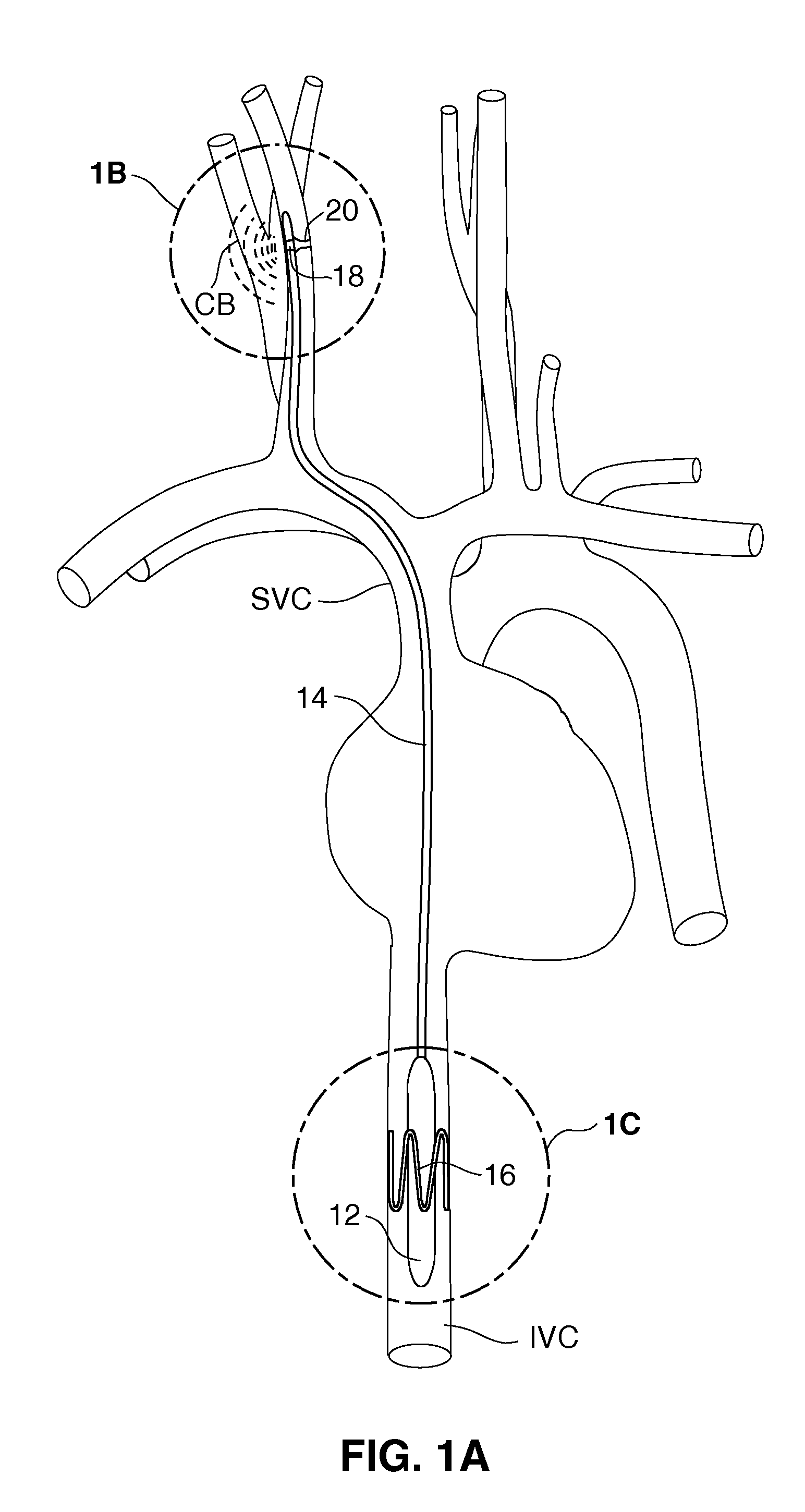
System and method for transvascularly stimulating contents of the carotid sheath
Methods and systems are disclosed for stimulating contents of the carotid sheath using an intravascular pulse generator and lead. The lead carries an energy delivery device such as an electrode, which is anchor within the portion of the internal jugular vein that is disposed within the carotid sheath. The energy delivery device is energized to transvenously direct energy to target contents of the carotid sheath external to the internal jugular vein. Such target contents may include nervous system elements associated with the carotid sinus baroreceptors, the carotid sinus nerve and associated nerve branches, and or the vagus nerve and associated nerve branches. The system may be used to control blood pressure and / or to lower heart rate and may be suitable for treatment of hypertension, heart failure, or other conditions.
Owner:NUXCEL2 LLC
Selective nerve fiber stimulation for treating heart conditions
ActiveUS20050187586A1Modify heart rate variabilityReduce heart rate variabilitySpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsNerve fiber bundleRR interval
Apparatus is provided that includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a vagus nerve of a subject, and a control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the vagus nerve a current that reduces heart rate variability of the subject. Also provided is a method comprising applying to a vagus nerve of a subject a current that reduces heart rate variability of the subject.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Nerve stimulation methods for averting imminent onset or episode of a disease
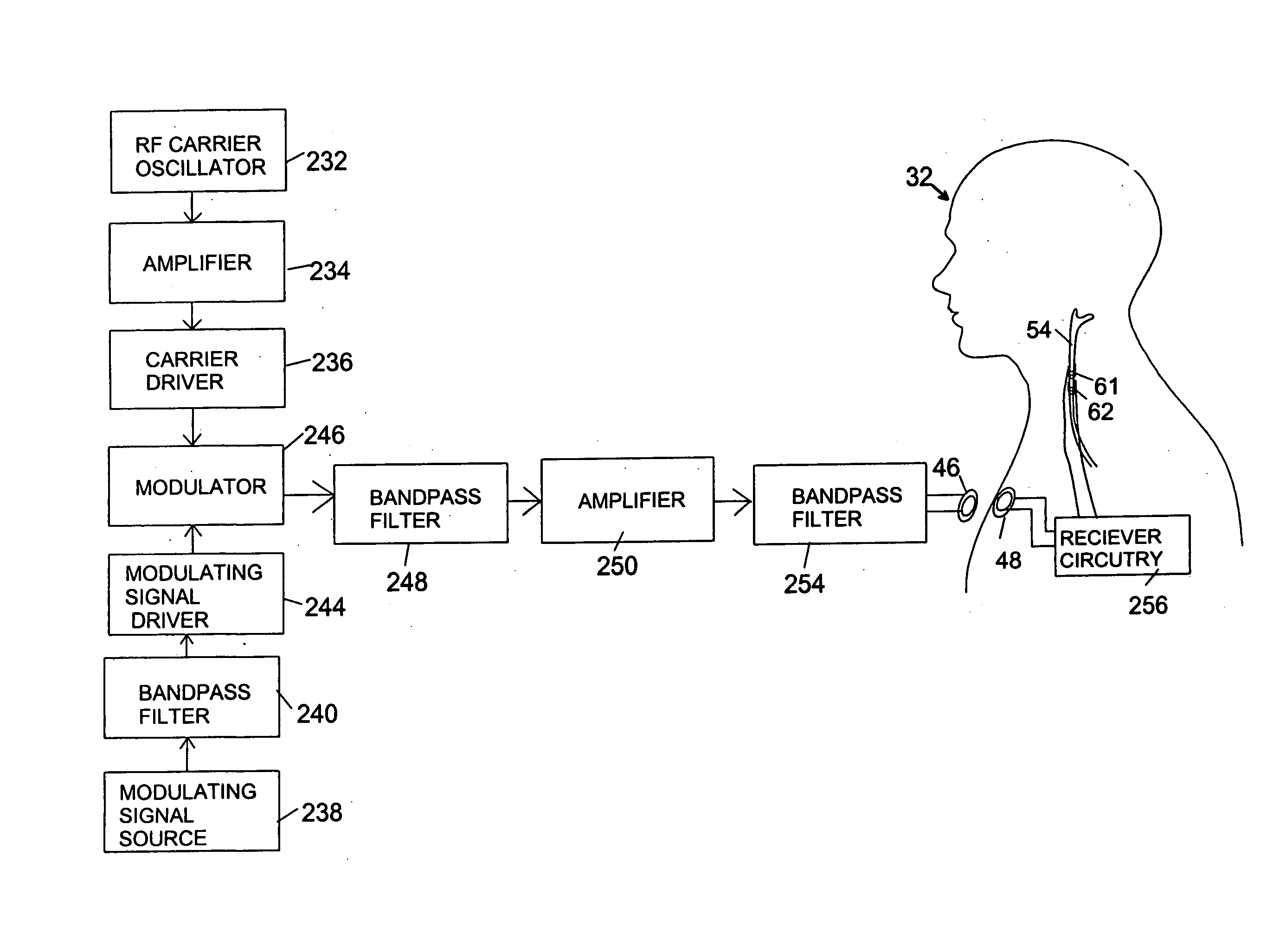
Transcutaneous electrical and magnetic nerve stimulation devices are disclosed, along with methods of averting imminent medical attacks using energy that is delivered noninvasively by the devices. The attacks comprise asthma attack, epileptic seizure, attacks of migraine headache, transient ischemic attack or stroke, onset of atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, onset of ventricular fibrillation or tachycardia, panic attack, and attacks of acute depression. The imminence of an attack is forecasted using grey-box or black-box models as used in control theory. In preferred embodiments of the disclosed methods, a vagus nerve in the neck of a patient is stimulated noninvasively to avert the attack.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
System and method for transvascularly stimulating contents of the carotid sheath
Methods and systems are disclosed for stimulating contents of the carotid sheath using an intravascular pulse generator and lead. The lead carries an energy delivery device such as an electrode, which is anchor within the portion of the internal jugular vein that is disposed within the carotid sheath. The energy delivery device is energized to transvenously direct energy to target contents of the carotid sheath external to the internal jugular vein. Such target contents may include nervous system elements associated with the carotid sinus baroreceptors, the carotid sinus nerve and associated nerve branches, and or the vagus nerve and associated nerve branches. The system may be used to control blood pressure and / or to lower heart rate and may be suitable for treatment of hypertension, heart failure, or other conditions.
Owner:NUXCEL2 LLC
Evaluating therapeutic stimulation electrode configurations based on physiological responses
A medical system comprises a plurality of electrodes; at least one sensor configured to output at least one signal based on at least one physiological parameter of a patient; and a processor. The processor is configured to control delivery of stimulation to the patient using a plurality of electrode configurations. Each of the electrode configurations comprises at least one of the plurality of electrodes. For each of the electrode configurations, the processor is configured to determine a first response of target tissue to the stimulation based on the signals, and a second response of non-target tissue to the stimulation based on the signals. The processor is also configured to select at least one of the electrode configurations for delivery of stimulation to the patient based on the first and second responses for the electrode configurations. As examples, the target tissue may be a left ventricle or vagus nerve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cranial nerve stimulation to treat a vocal cord disorder
Disclosed is a method of treating a patient having a vocal cord disorder, comprising coupling at least one electrode to at least one cranial nerve of the patient, wherein the cranial nerve is selected from the group consisting of a vagus nerve, a trigeminal nerve, and a glossopharyngeal nerve, and applying an electrical signal to the cranial nerve using the electrode to treat the vocal cord disorder. The electrode may be coupled to a branch of the vagus nerve selected from the group consisting of a recurrent laryngeal nerve, the external branch of a superior laryngeal nerve, the internal branch of a superior laryngeal nerve, and a pharyngeal plexus. Also disclosed is a computer readable program storage device encoded with instructions that, when executed by a computer, perform the method, and a medical device and a vocal cord disorder treatment system that may be used in performance of the method.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
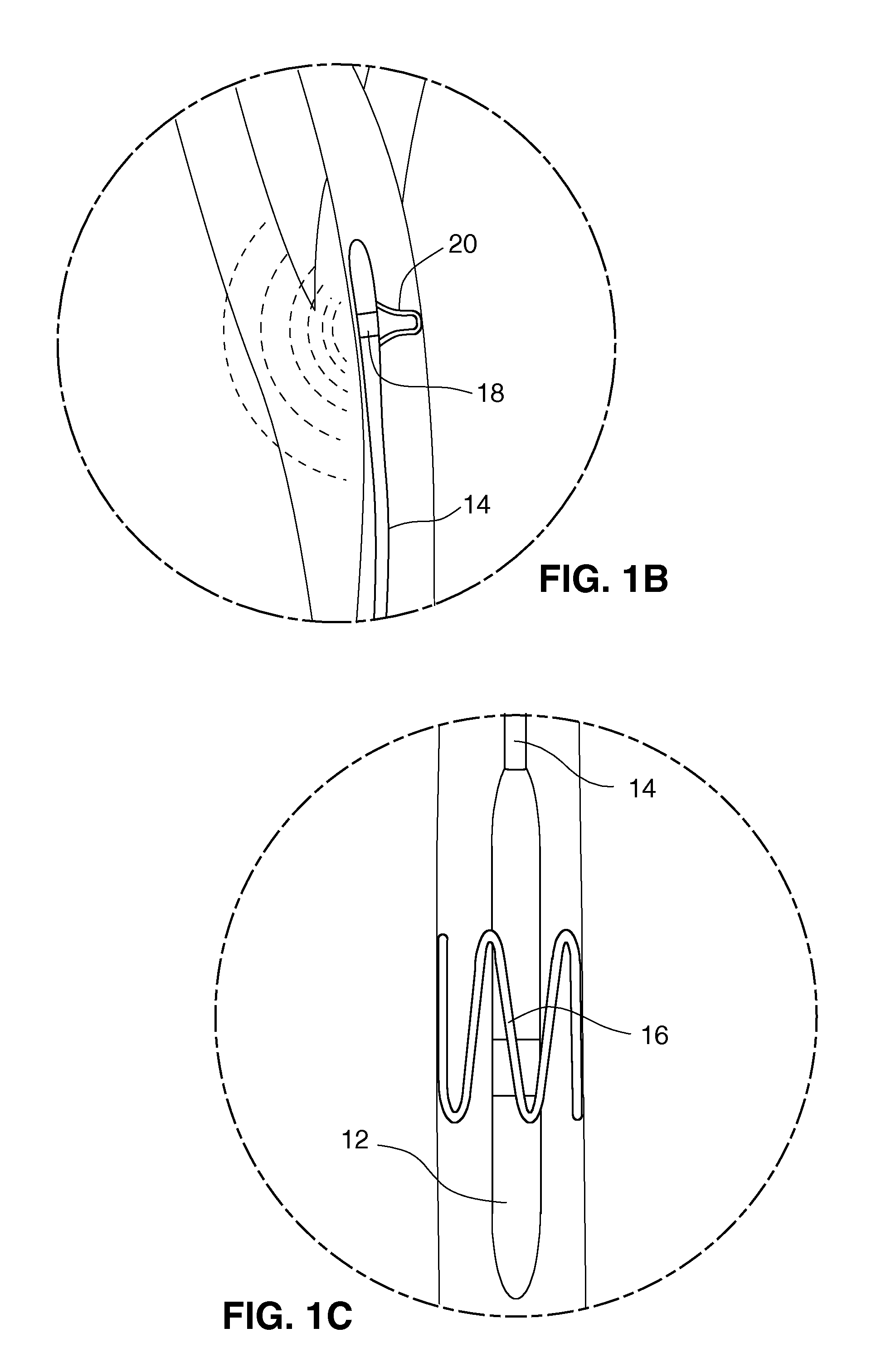
Endovascular lead for chronic nerve stimulation
A lead of the present invention comprises an electrode array adapted to be stably anchored at a selected location within the vena cava of a human patient. The electrode array may take various shapes, including helical, annular and linear. The electrode array is connectable to an electrical stimulation means such as an implantable pulse or signal generator. Electrical stimulation applied to a selected region of the vena cava and across the wall of the vein, that is, transvascularly, to the vagus nerve or branches thereof, depolarizes the nerve to thereby effect control of the heart rate.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com