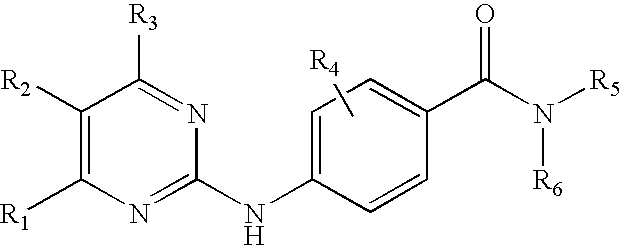
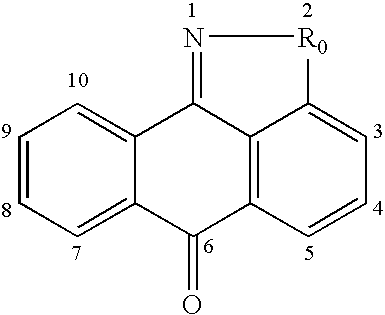
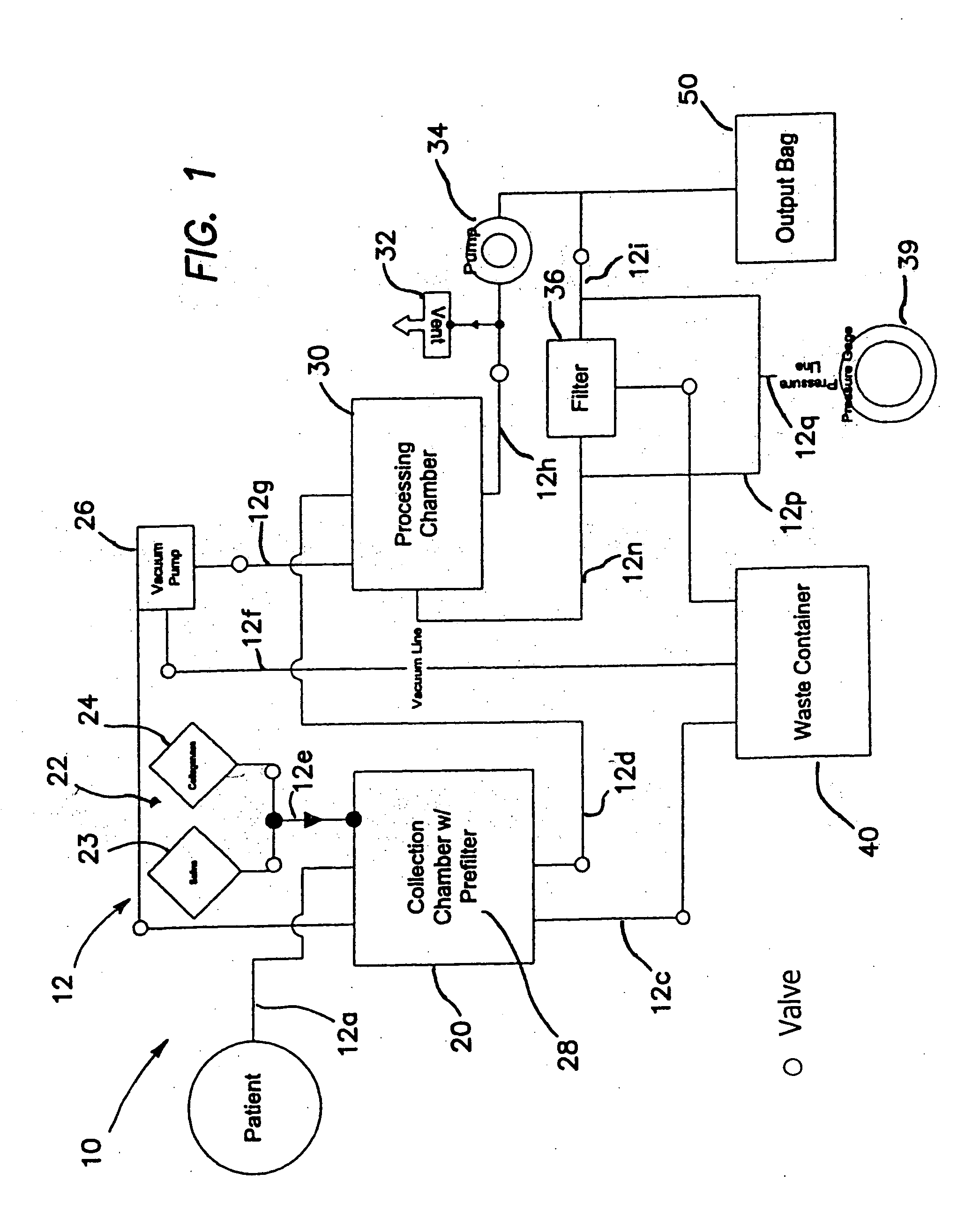
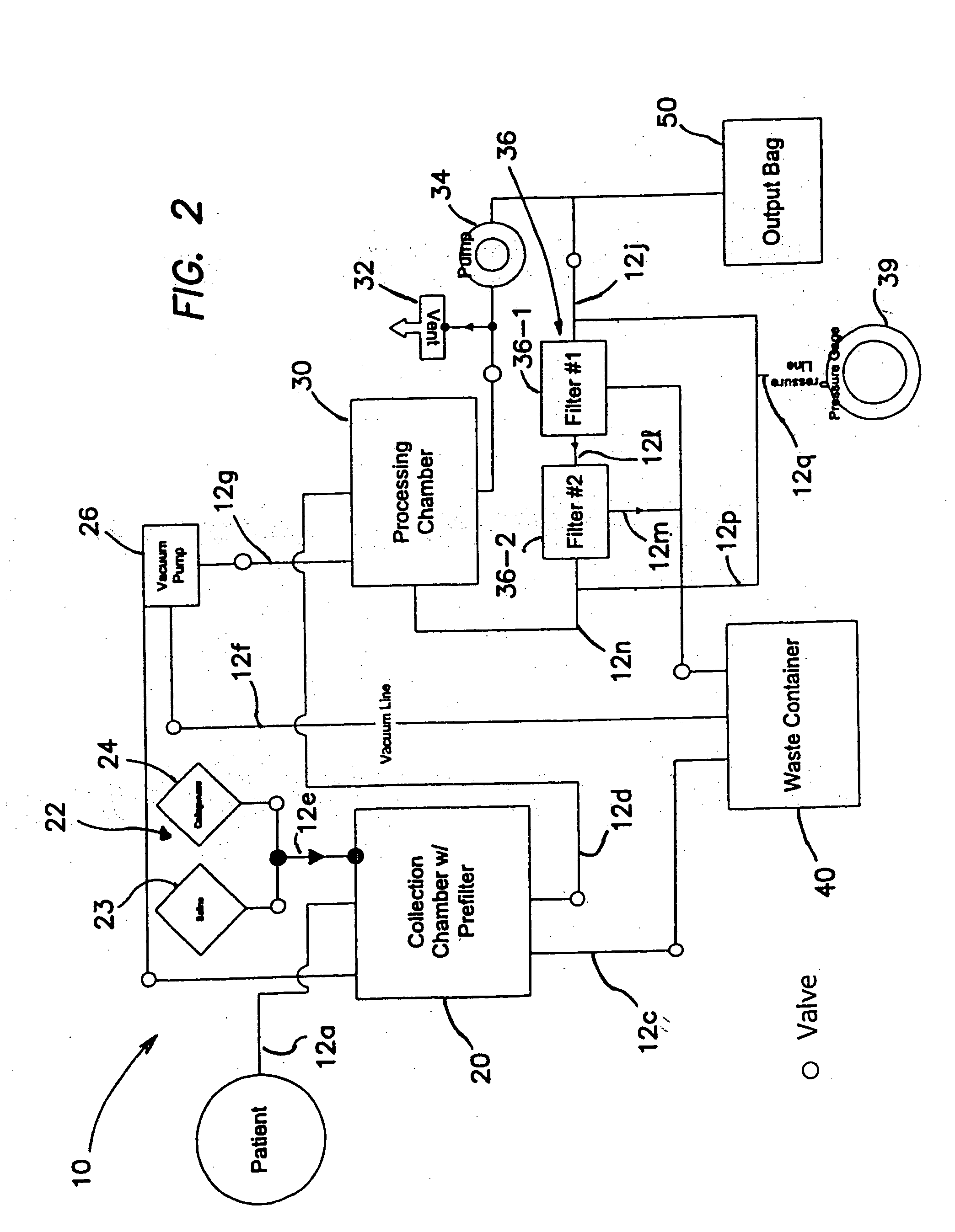
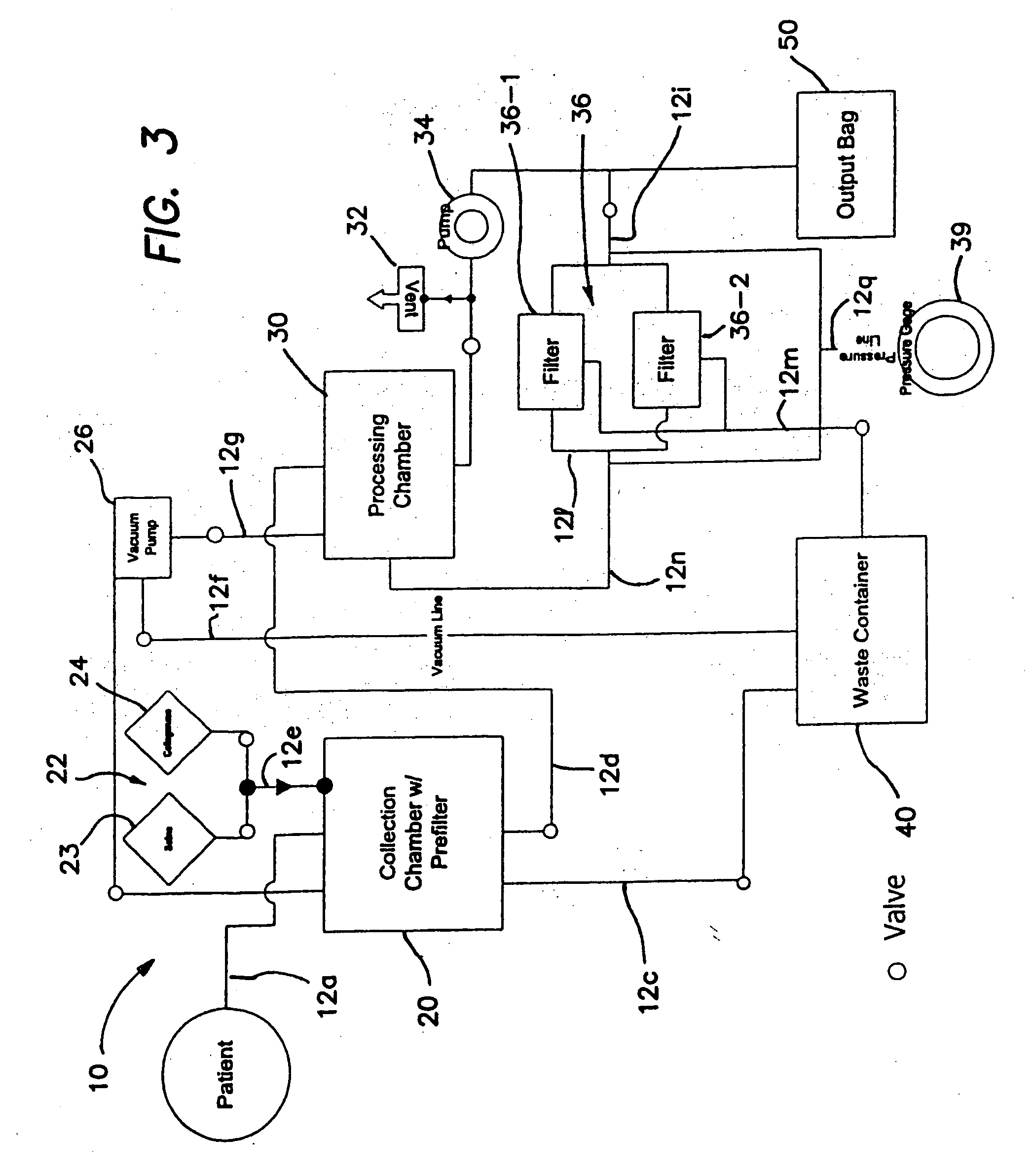
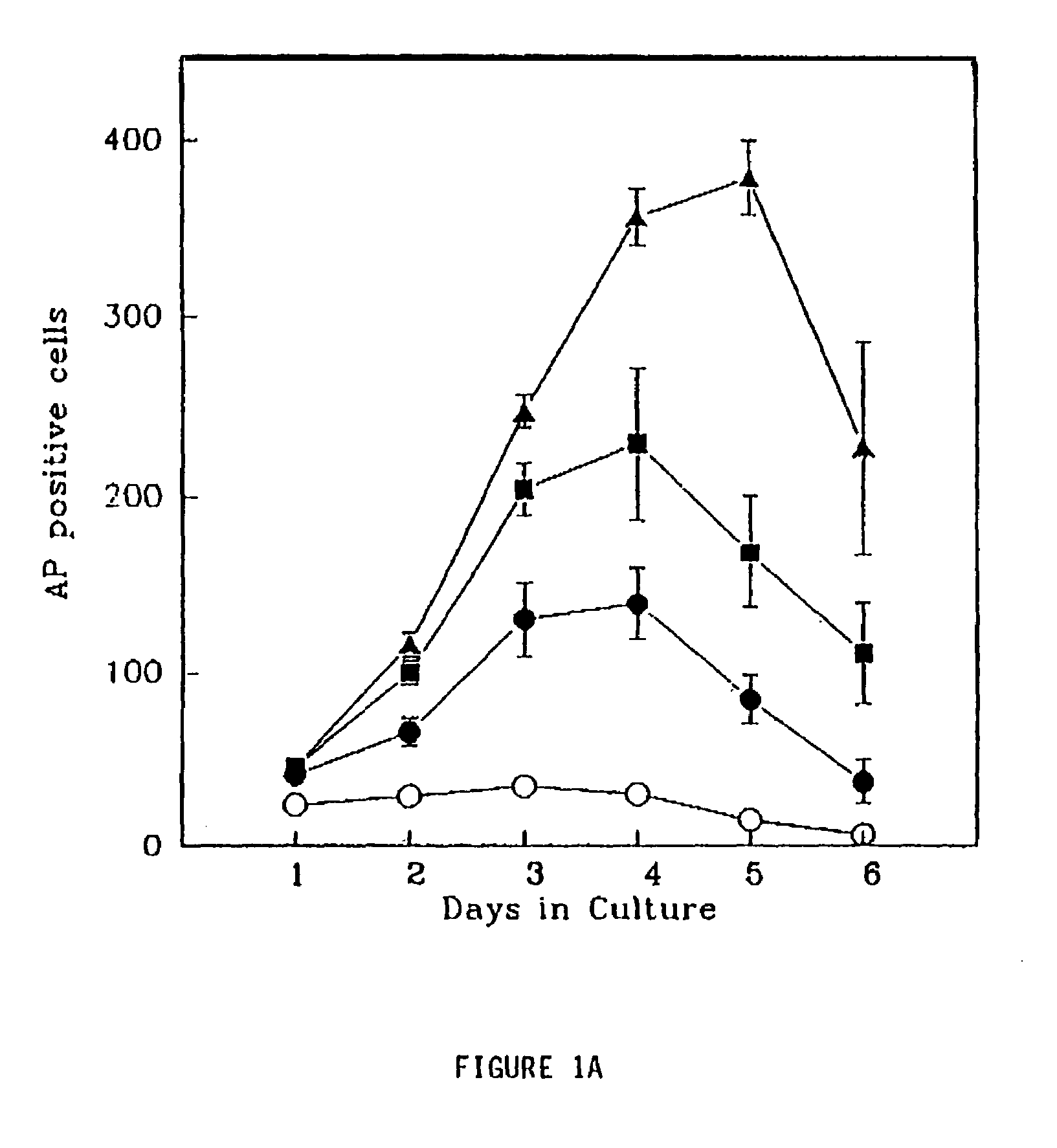
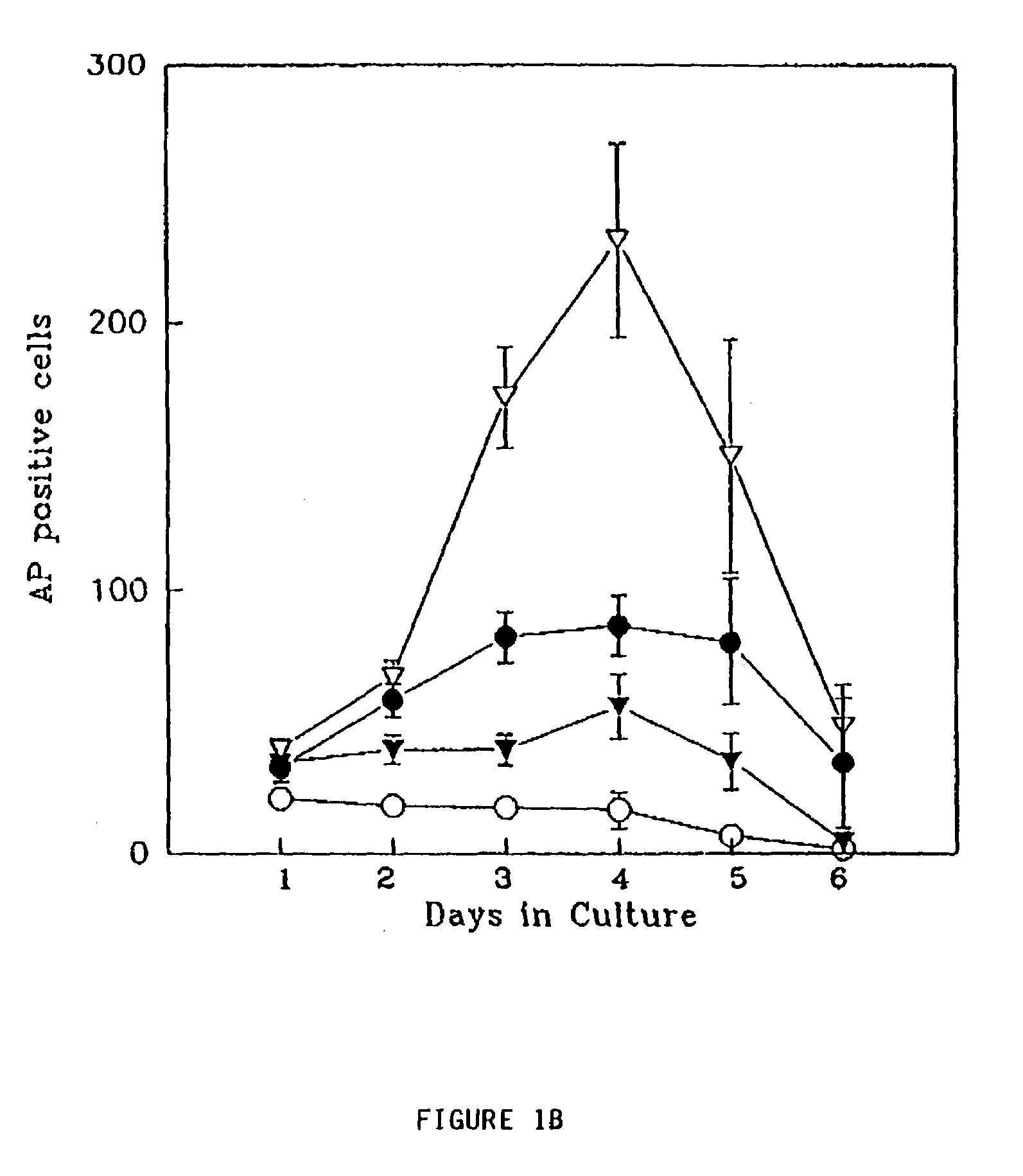
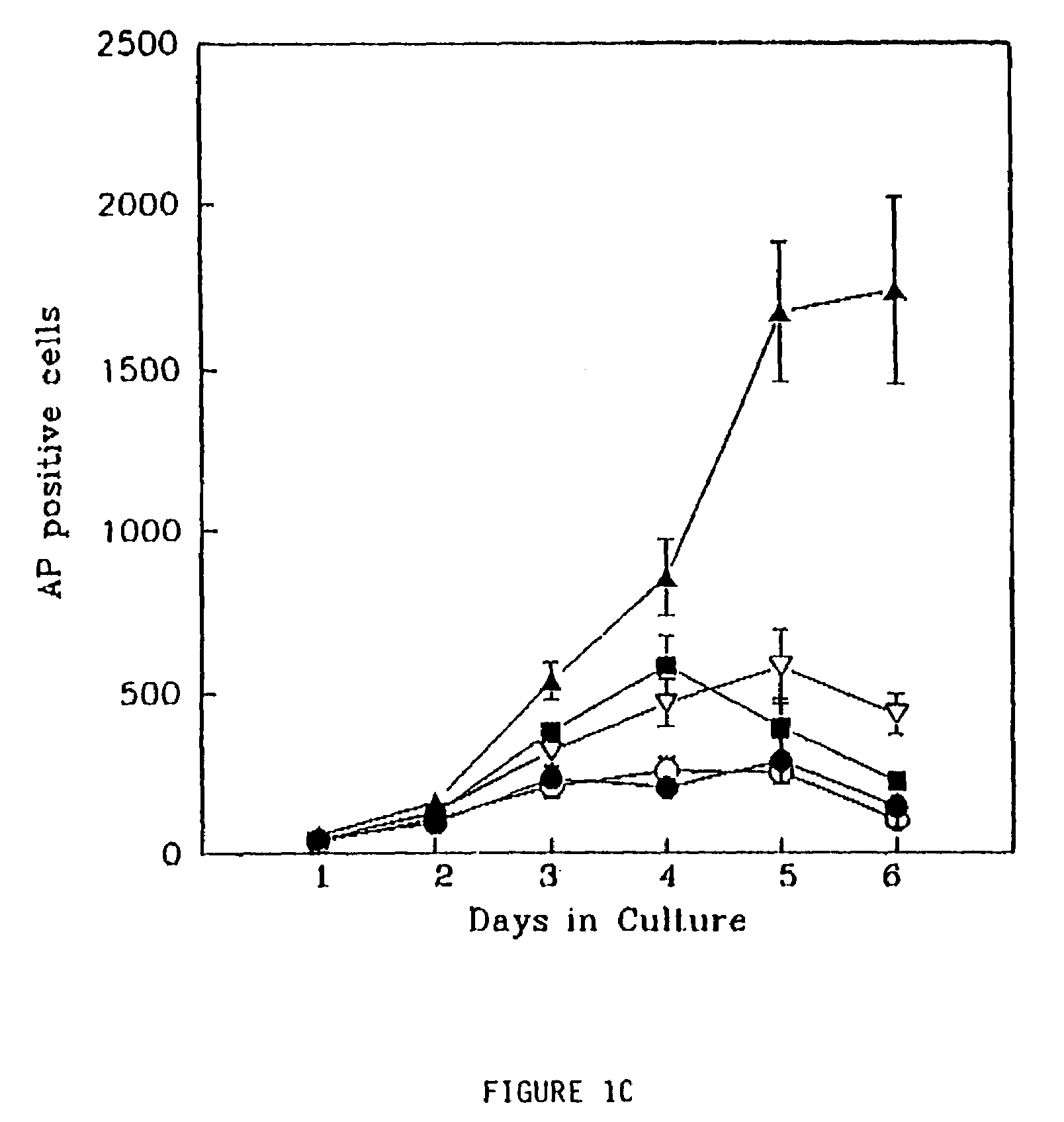
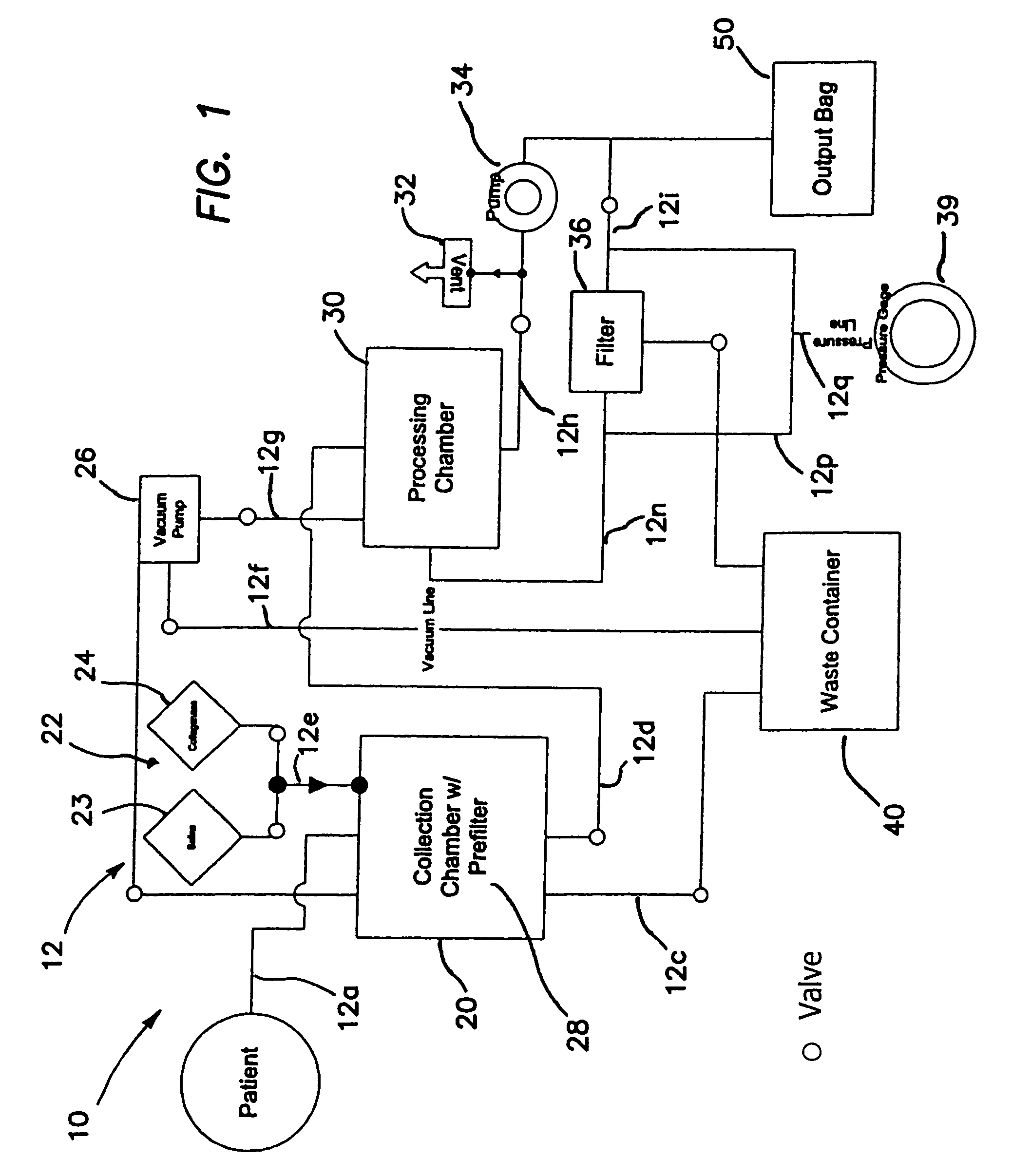
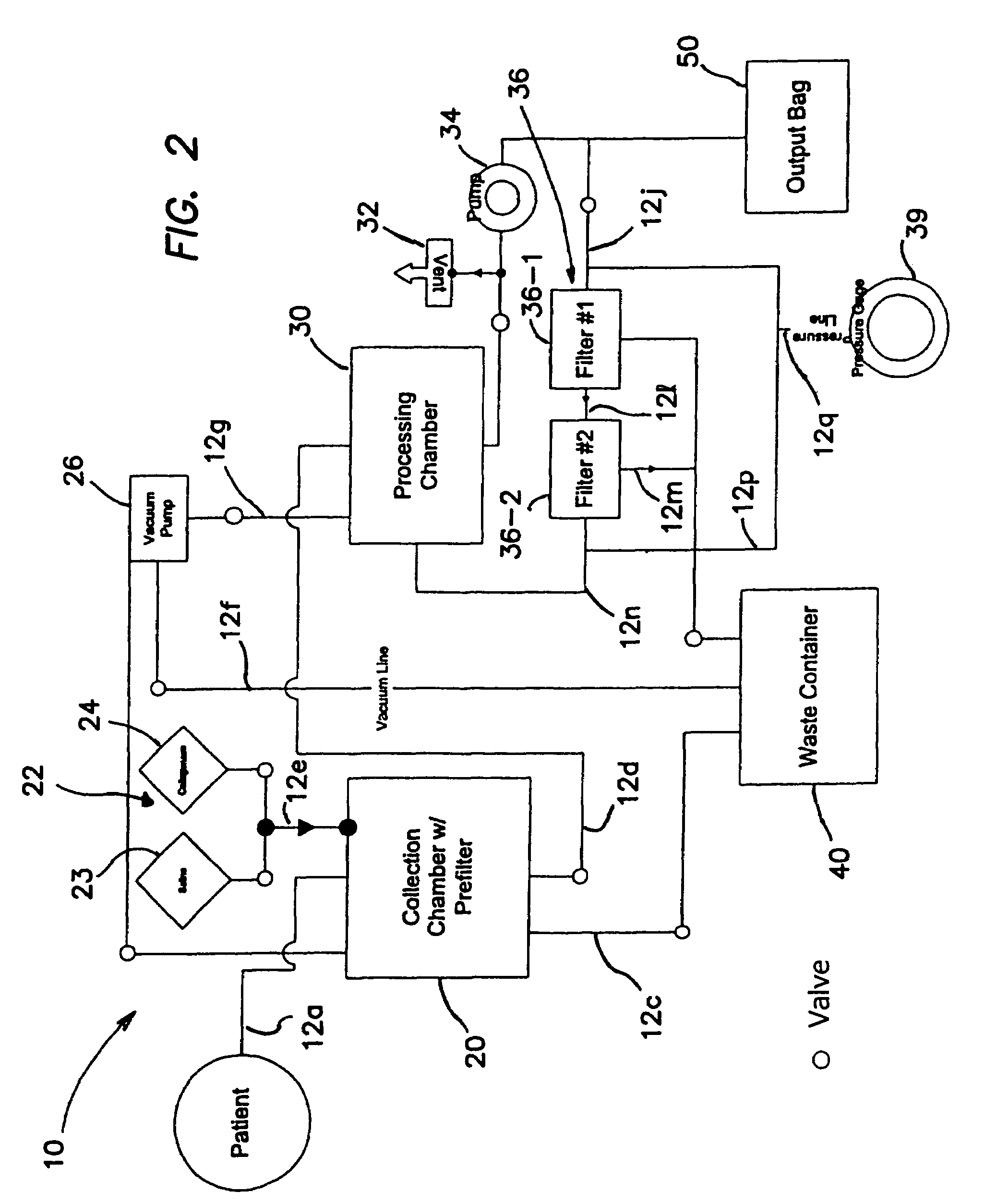
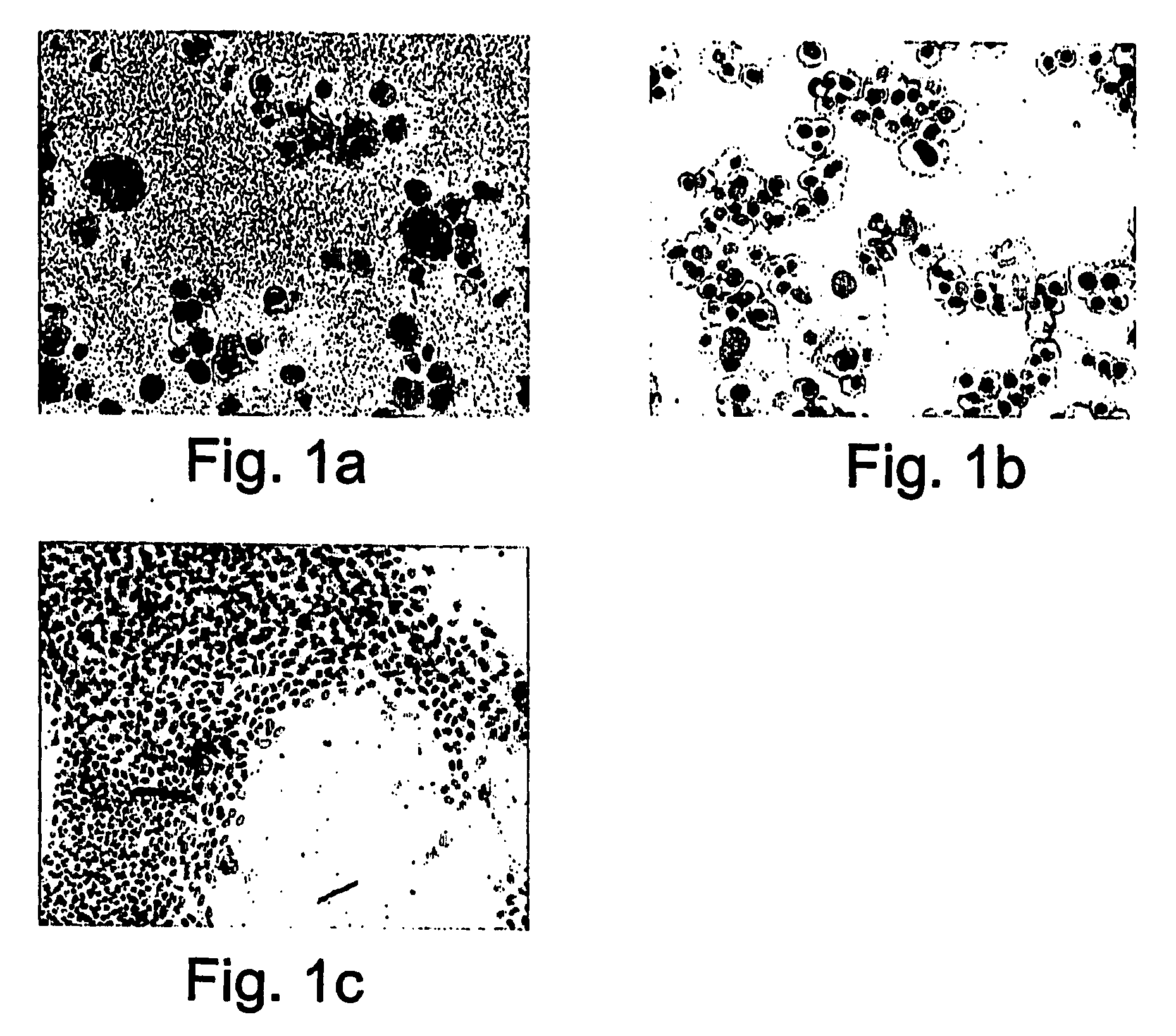
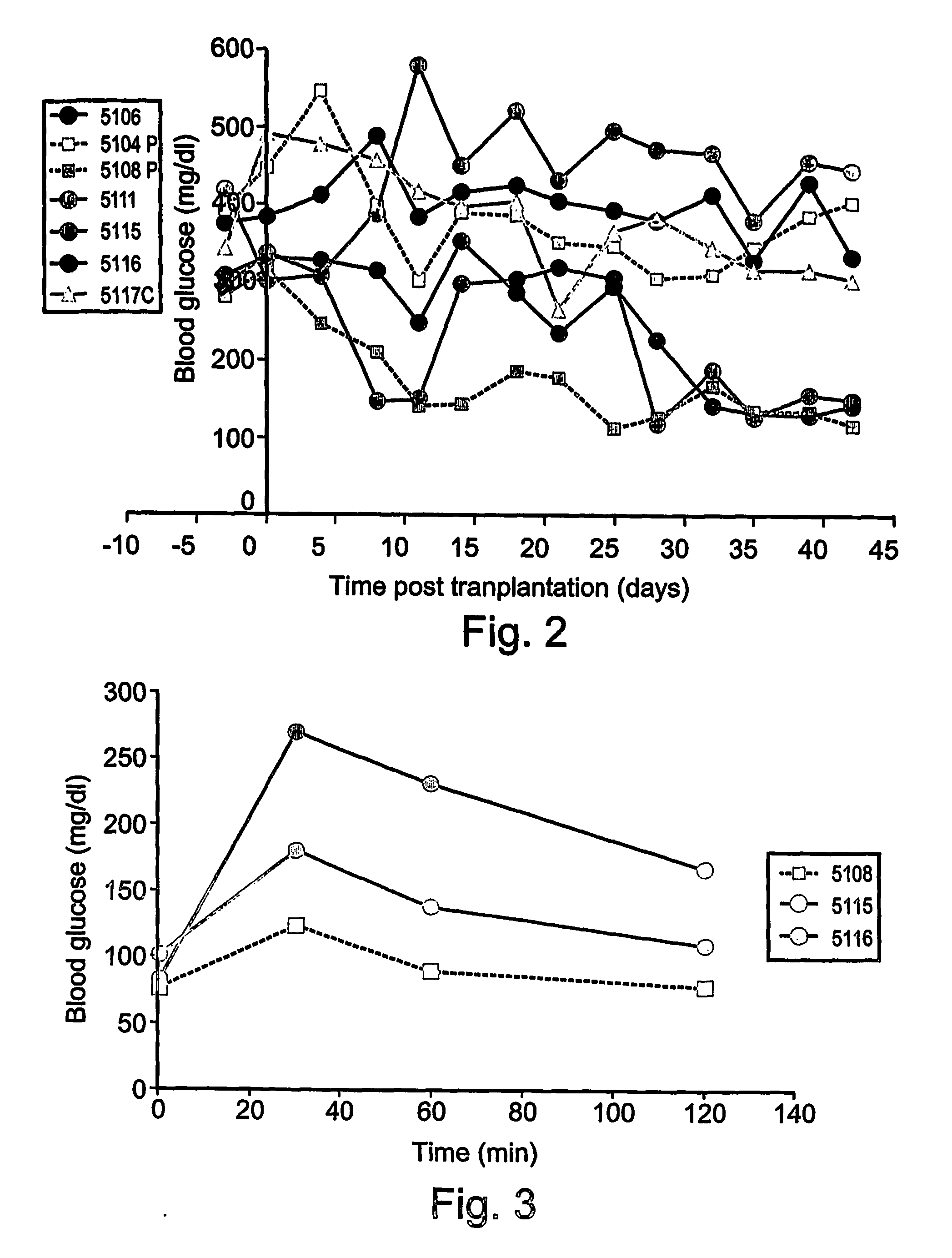
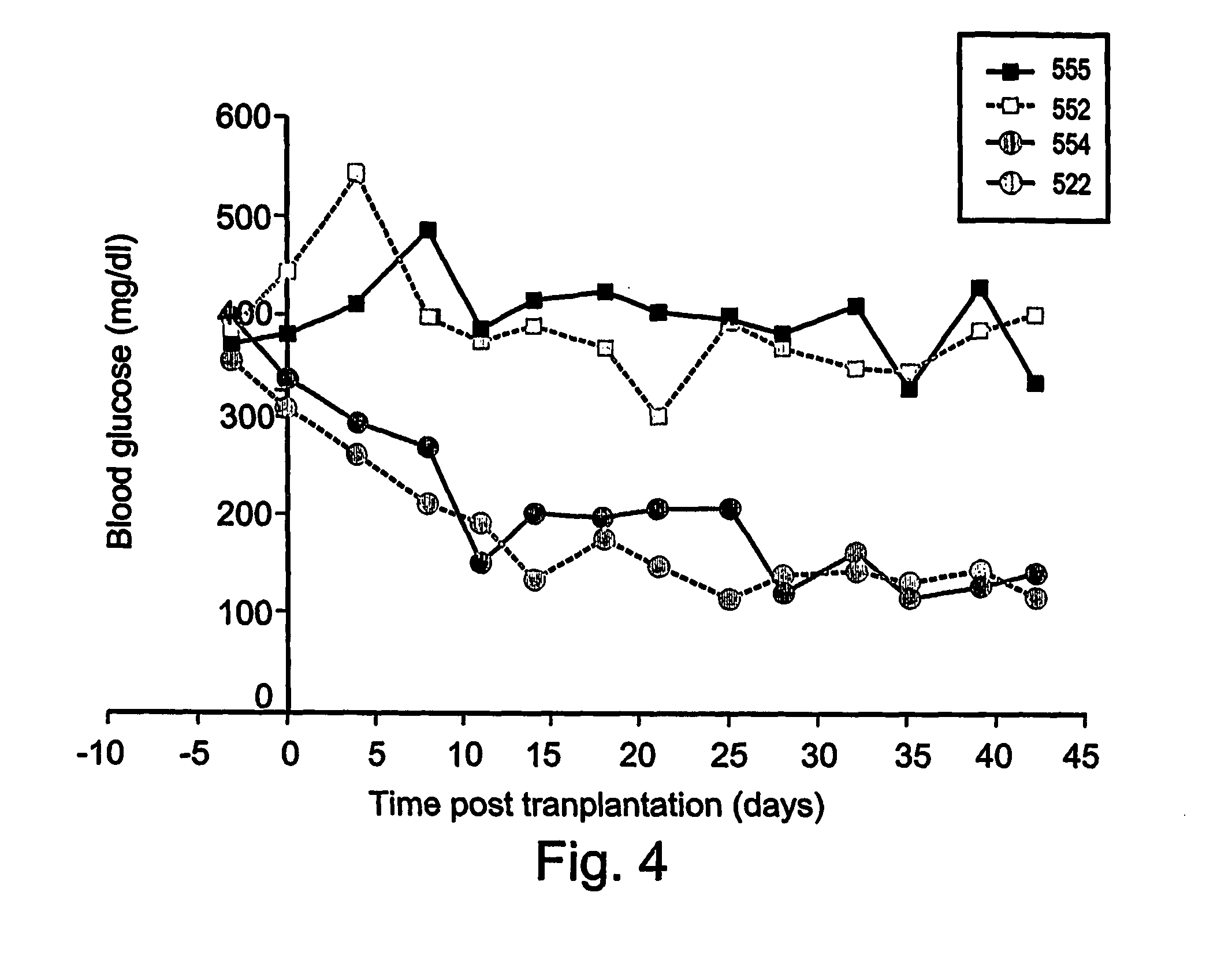
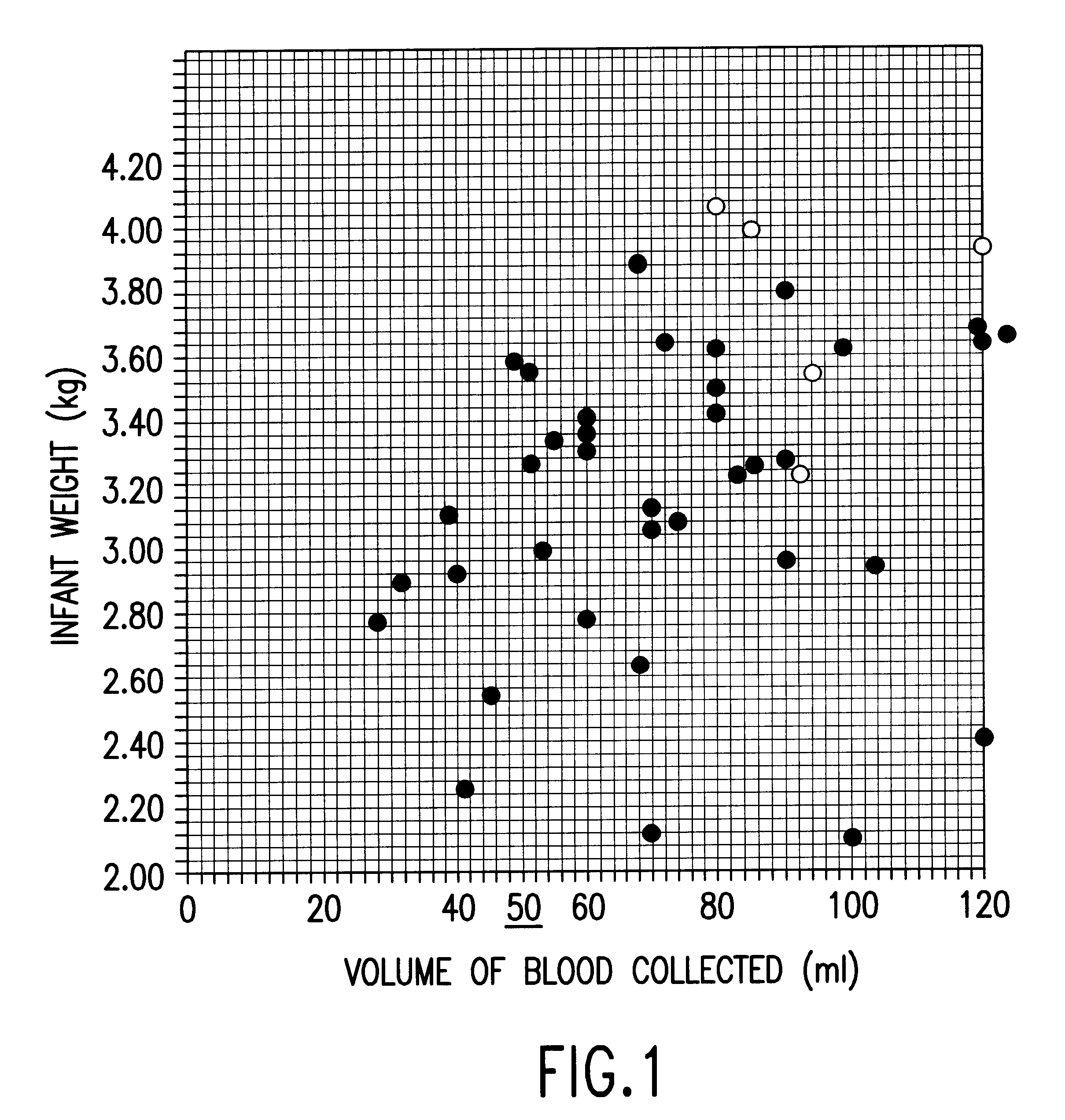
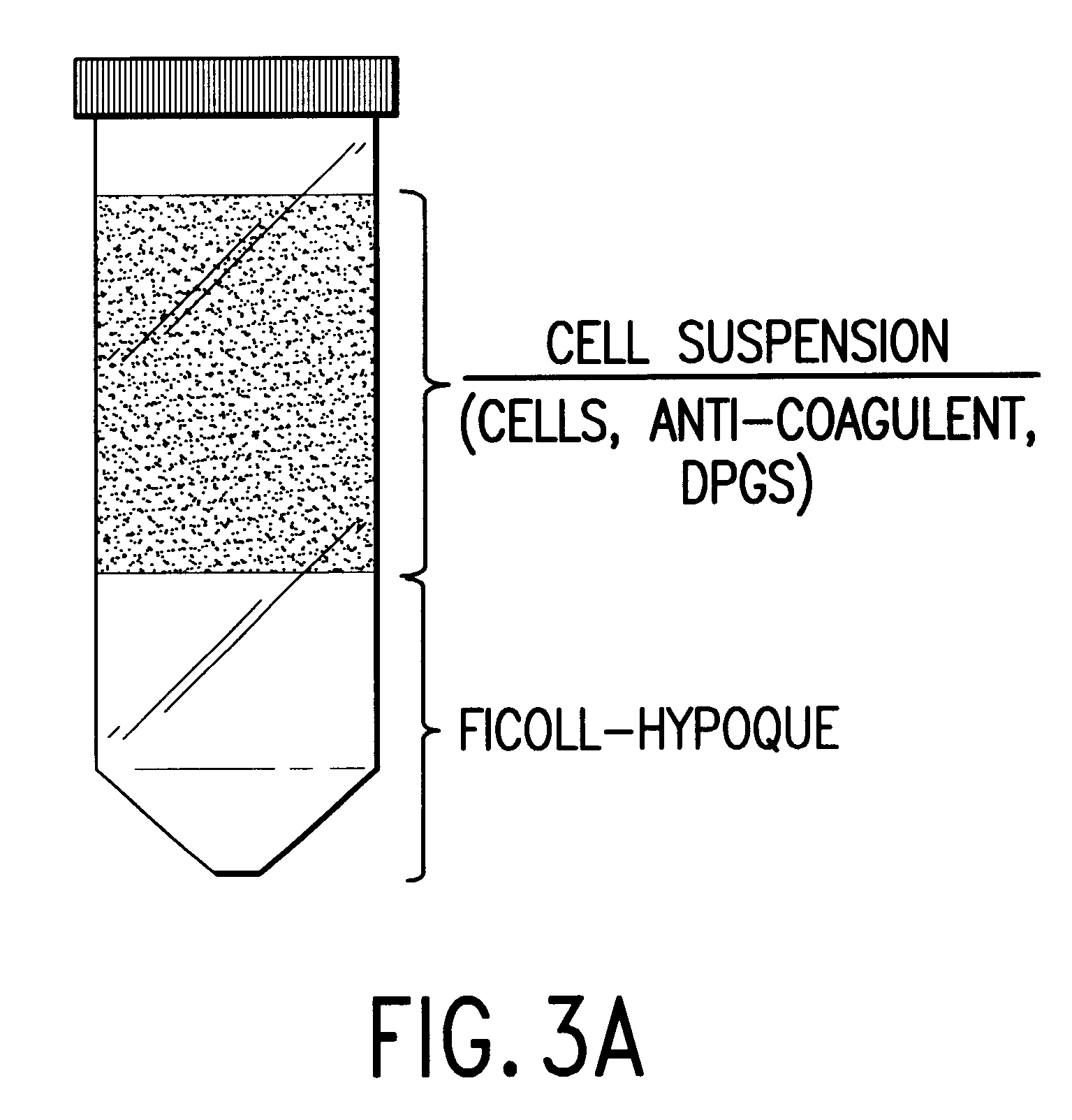
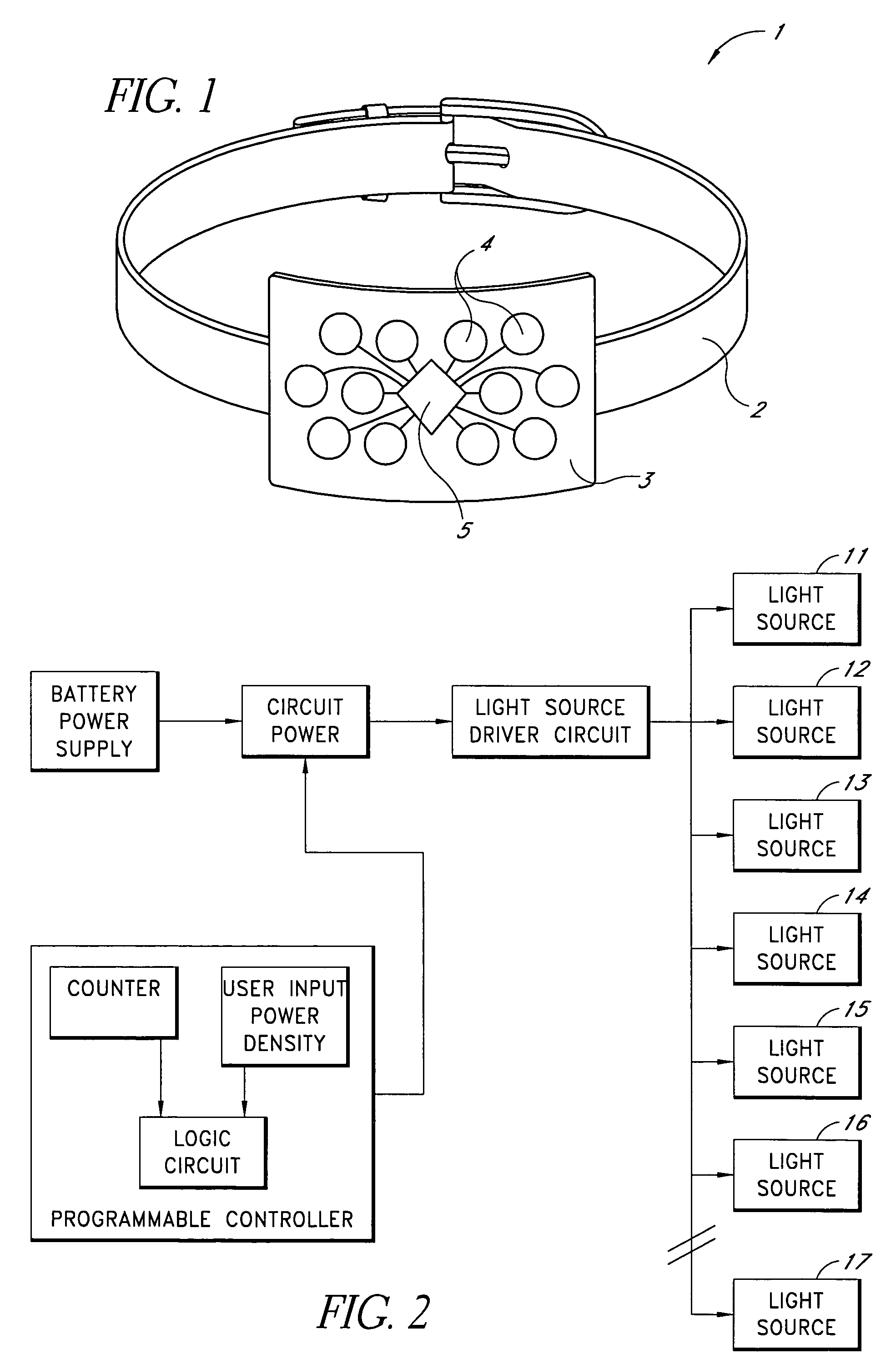
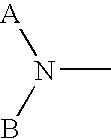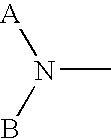Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
919 results about "Progenitor cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A progenitor cell is a biological cell that, like a stem cell, has a tendency to differentiate into a specific type of cell, but is already more specific than a stem cell and is pushed to differentiate into its "target" cell. The most important difference between stem cells and progenitor cells is that stem cells can replicate indefinitely, whereas progenitor cells can divide only a limited number of times. Controversy about the exact definition remains and the concept is still evolving.
Modulation of stem and progenitor cell differentiation, assays, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20030235909A1Modulate their differentiationIncrease speedOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderAssayPlacenta
The present invention relates to methods of modulating mammalian stem cell and progenitor cell differentiation. The methods of the invention can be employed to regulate and control the differentiation and maturation of mammalian, particularly human stem cells along specific cell and tissue lineages. The methods of the invention relate to the use of certain small organic molecules to modulate the differentiation of stem or progenitor cell populations along specific cell and tissue lineages, and in particular, to the differentiation of embryonic-like stem cells originating from a postpartum placenta or for the differentiation of early progenitor cells to a granulocytic lineage. Finally, the invention relates to the use of such differentiated stem or progenitor cells in transplantation and other medical treatments.
Owner:SIGNAL PHARMA LLC +2
Methods of using JNK or MKK inhibitors to modulate cell differentiation and to treat myeloproliferative disorders and myelodysplastic syndromes
InactiveUS20040028660A1Increase productionPromote recoveryBiocideGenetic material ingredientsCord blood stem cellMyeloproliferative Disorders
The present invention provides methods of modulating mammalian, particularly human, stem cell and progenitor cell differentiation to regulate and control the differentiation and maturation of these cells along specific cell and tissue lineages. The methods of the invention relate to the use of certain small organic molecules to modulate the differentiation of stem cell populations along specific cell and tissue lineages, particularly embryonic-like stem cells originating from a postpartum placenta or stem cells isolated form sources such as cord blood. The invention also relates to the treatment or prevention of myelodysplastic syndrome or myeloproliferative syndrome, or symptoms thereof, comprising administration of JNK or MKK inhibitors, alone or in combination, as well as with or without the use of unconditioned cells or cells conditioned in accordance with other aspects of the invention. Finally, the invention relates to the use of such differentiated stem cells in transplantation and other medical treatments.
Owner:ANTHROGENESIS CORP +1
Systems and methods for separating and concentrating regenerative cells from tissue
ActiveUS20050084961A1High yieldImprove consistencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiocideBiomedical engineeringAdipose tissue
Systems and methods are described that are used to separate cells from a wide variety of tissues. In particular, automated systems and methods are described that separate regenerative cells, e.g., stem and / or progenitor cells, from adipose tissue. The systems and methods described herein provide rapid and reliable methods of separating and concentrating regenerative cells suitable for re-infusion into a subject.
Owner:LOREM VASCULAR PTE LTD
Isolation, cultivation and uses of stem/progenitor cells
The present invention relates to a method for isolating stem / progenitor cells from the amniotic membrane of umbilical cord, wherein the method comprises separating the amniotic membrane from the other components of the umbilical cord in vitro, culturing the amniotic membrane tissue under conditions allowing cell proliferation, and isolating the stem / progenitor cells from the tissue cultures. The isolated stem cell cells can have embryonic stem cell-like properties and can be used for various therapeutic purposes. In one embodiment, the invention relates to the isolation and cultivation of stem cells such as epithelial and / or mesenchymal stem / progenitor cells under conditions allowing the cells to undergo mitotic expansion. Furthermore, the invention is directed to a method for the differentiation of the isolated stem / progenitor cells into epithelial and / or mesenchymal cells.
Owner:CELLRESEARCH CORP PTE LTD
Pluripotential embryonic stem cells and methods of making same
The present invention provides a non-mouse, including human, pluripotential embryonic stem cell which can:(a) be maintained on feeder layers for at least 20 passages; and(b) give rise to embryoid bodies and multiple differentiated cell phenotypes in monolayer culture.The invention further provides a method of making a pluripotential embryonic stem cell comprising culturing germ cells and germ cell progenitors in a composition comprising a growth enhancing amount of basic fibroblast growth factor, leukemia inhibitory factor, membrane associated steel factor, and soluble steel factor to primordial germ cells under cell growth conditions, thereby making a pluripotential embryonic stem cell.Also provided are compositions useful to produce the pluripotent embryonic stem cells and methods of screening associated with the method of making the embryonic stem cell.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Method for processing and using adipose-derived stem cells
The present invention relates to a device comprising a cell carrier portion containing regenerative cells, e.g., stem and progenitor cells, and a cell carrier containment portion. The device is useful for the treatment of bone related disorders, including spinal fusion related disorders and long bone or flat bone related defects. The device may be used in conjunction with disclosed automated systems and methods for separating and concentrating regenerative cells.
Owner:LOREM VASCULAR PTE LTD
Ultrasound Therapy Resulting in Bone Marrow Rejuvenation
A method and system for treating a patient to repair damaged tissue which includes exposing a selected area of bone marrow of a patient to ultrasound waves or ultra shock waves so that cells comprising stem cells, progenitor cells or macrophages are generated in the area of the bone marrow of the patient due to the ultrasound, converting the cells from the bone marrow of the patient and reducing the damaged tissue in the bone marrow of the patient by repairing the damaged tissue.
Owner:JOHNSON LANNY L
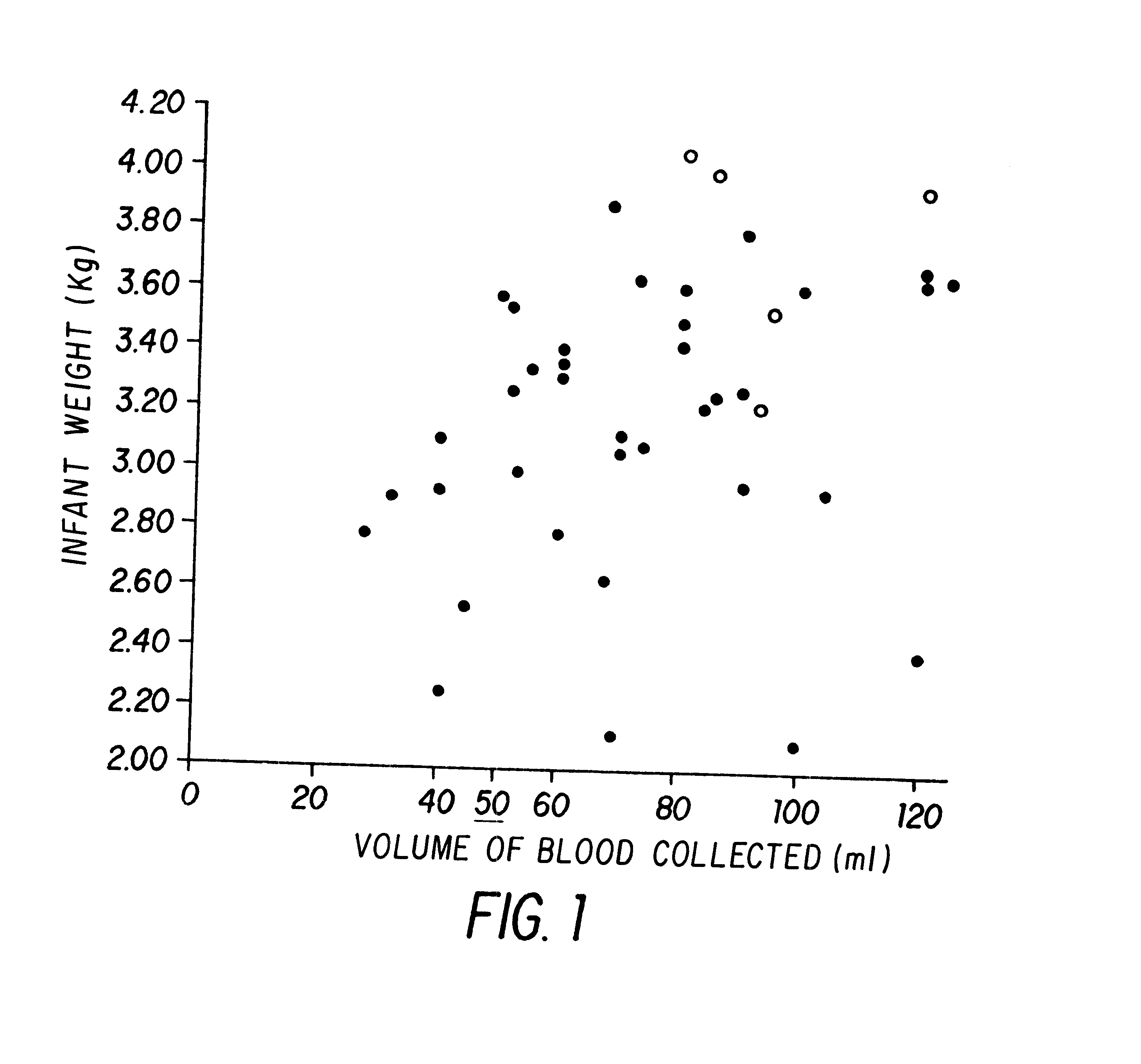
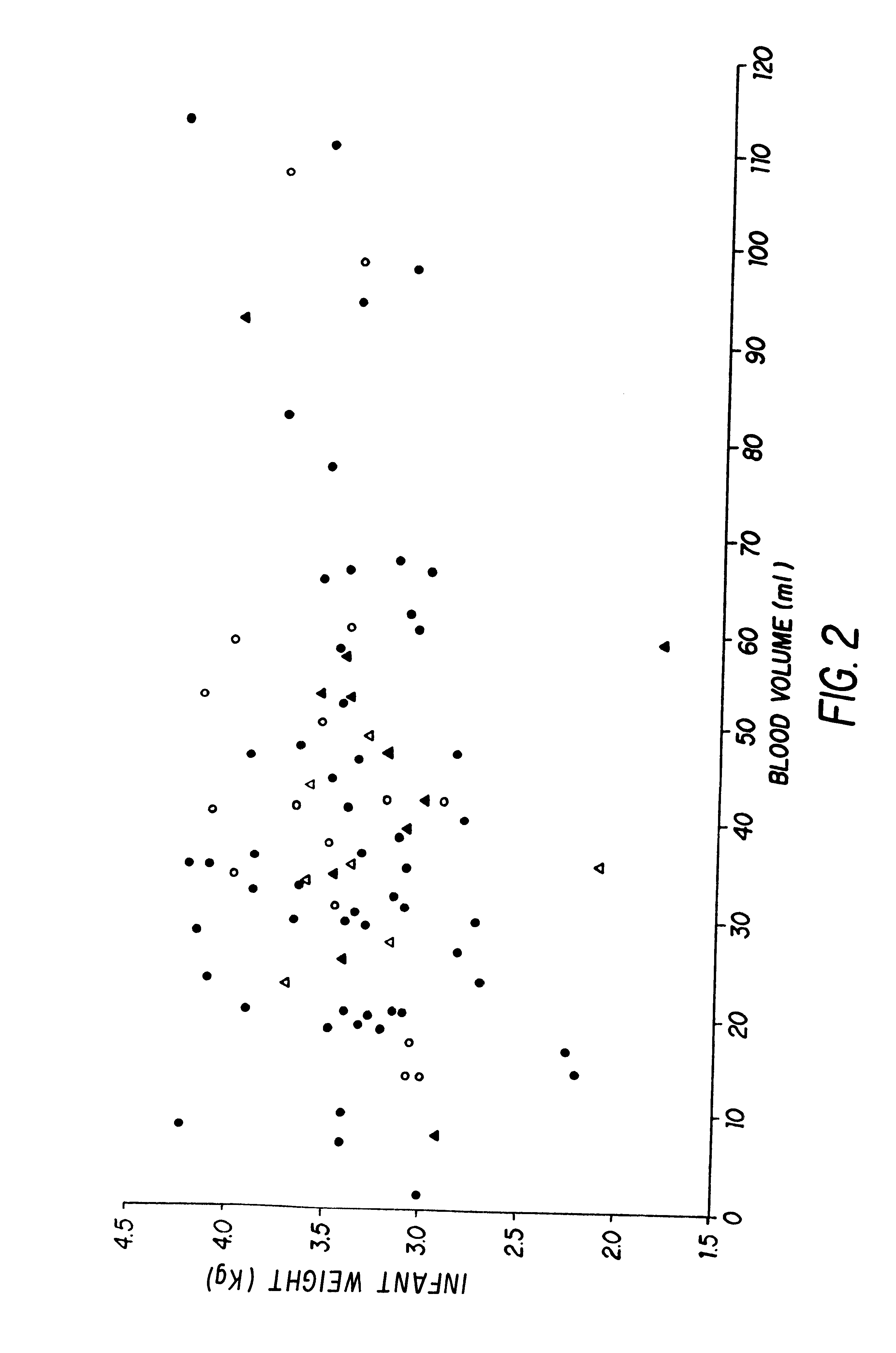
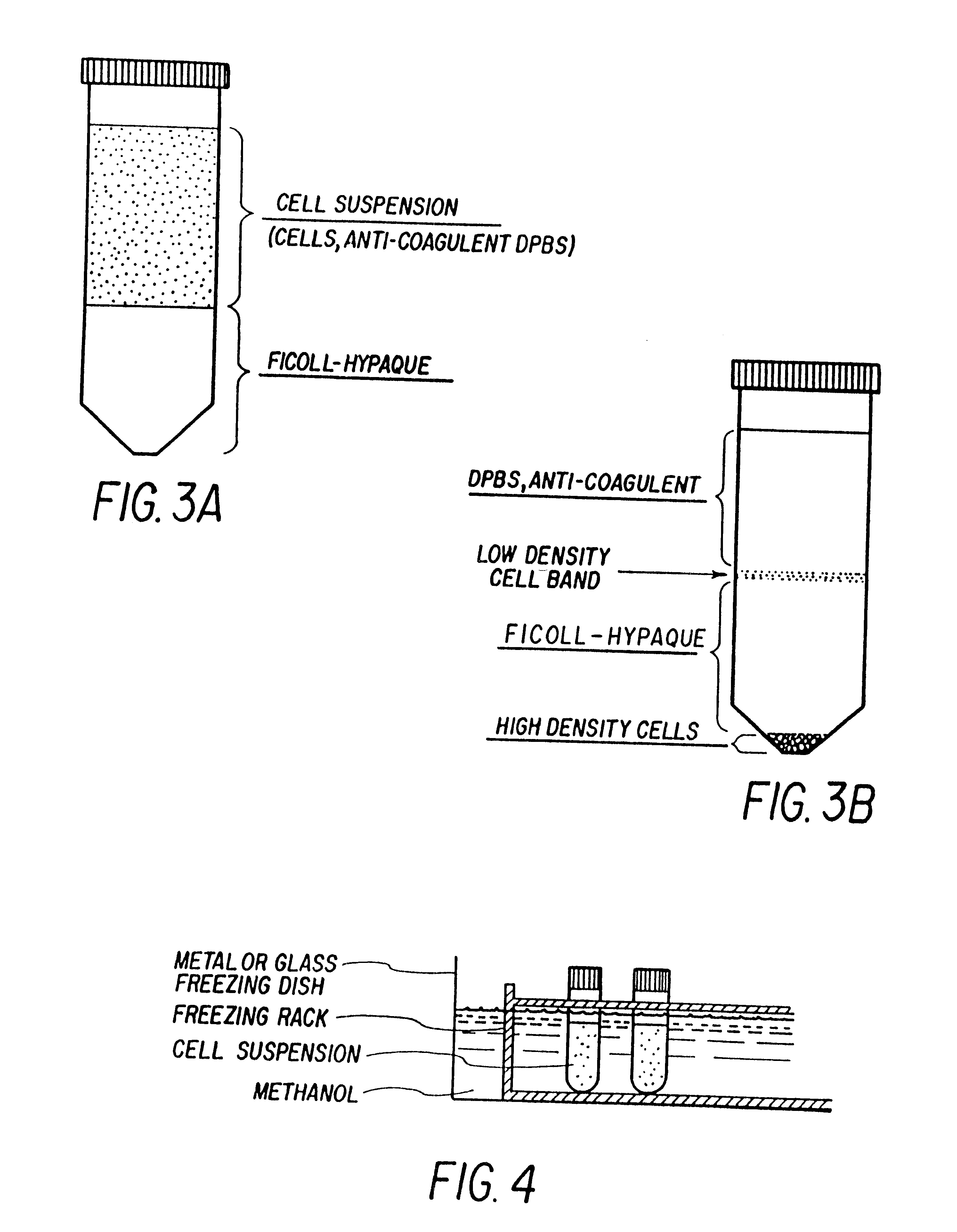
Isolation and preservation of fetal and neonatal hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells of the blood
The present invention relates to hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells of neonatal or fetal blood that are cryopreserved, and the therapeutic uses of such stem and progenitor cells upon thawing. In particular, the present invention relates to the therapeutic use of fetal or neonatal stem cells for hematopoietic (or immune) reconstitution. Hematopoietic reconstitution with the cells of the invention can be valuable in the treatment or prevention of various diseases and disorders such as anemias, malignancies, autoimmune disorders, and various immune dysfunctions and deficiencies. In another embodiment, fetal or neonatal hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells which contain a heterologous gene sequence can be used for hematopoietic reconstitution in gene therapy. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, neonatal or fetal blood cells that have been cryopreserved and thawed can be used for autologous (self) reconstitution.
Owner:PHARMASTEM THERAPEUTICS
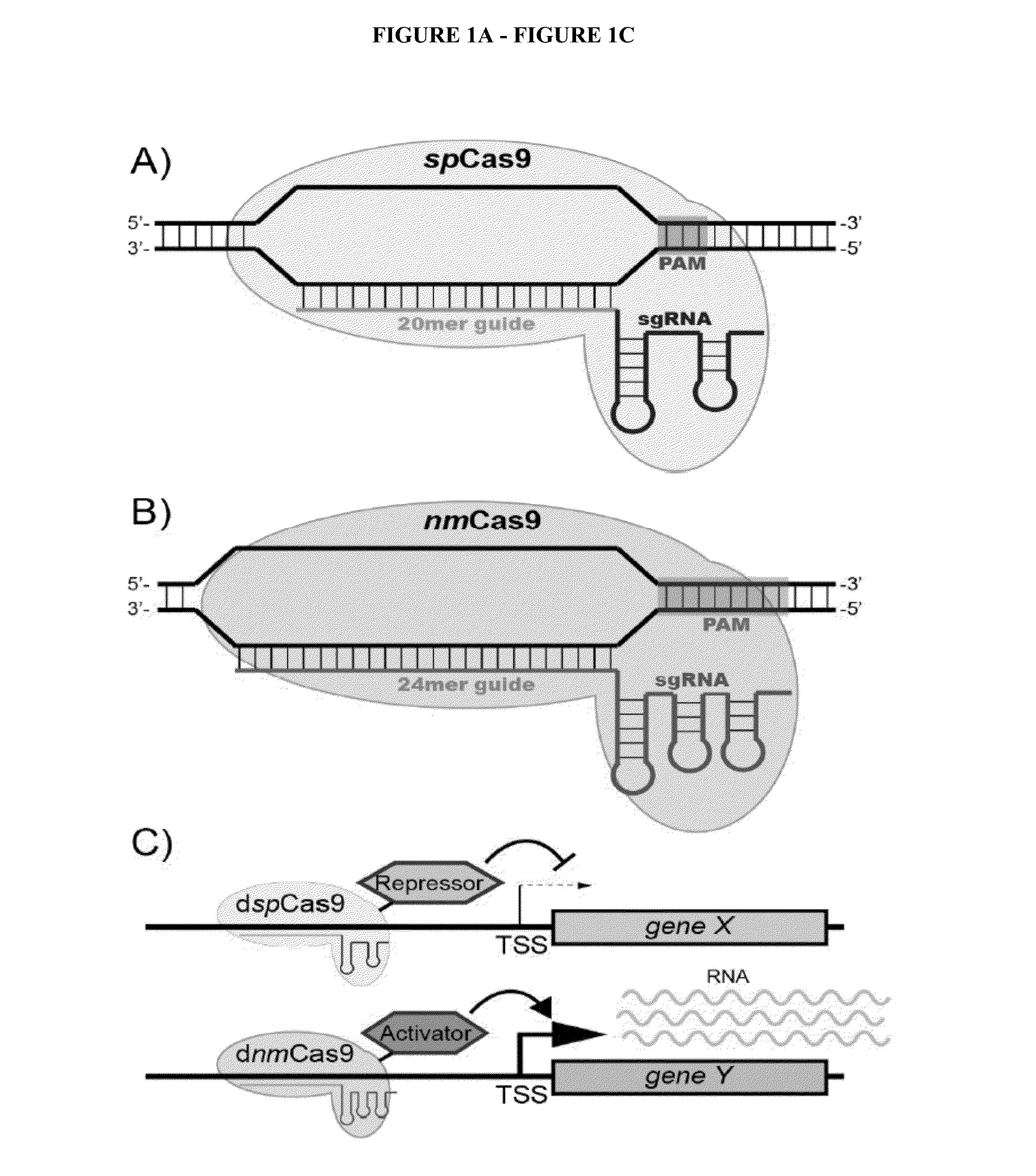
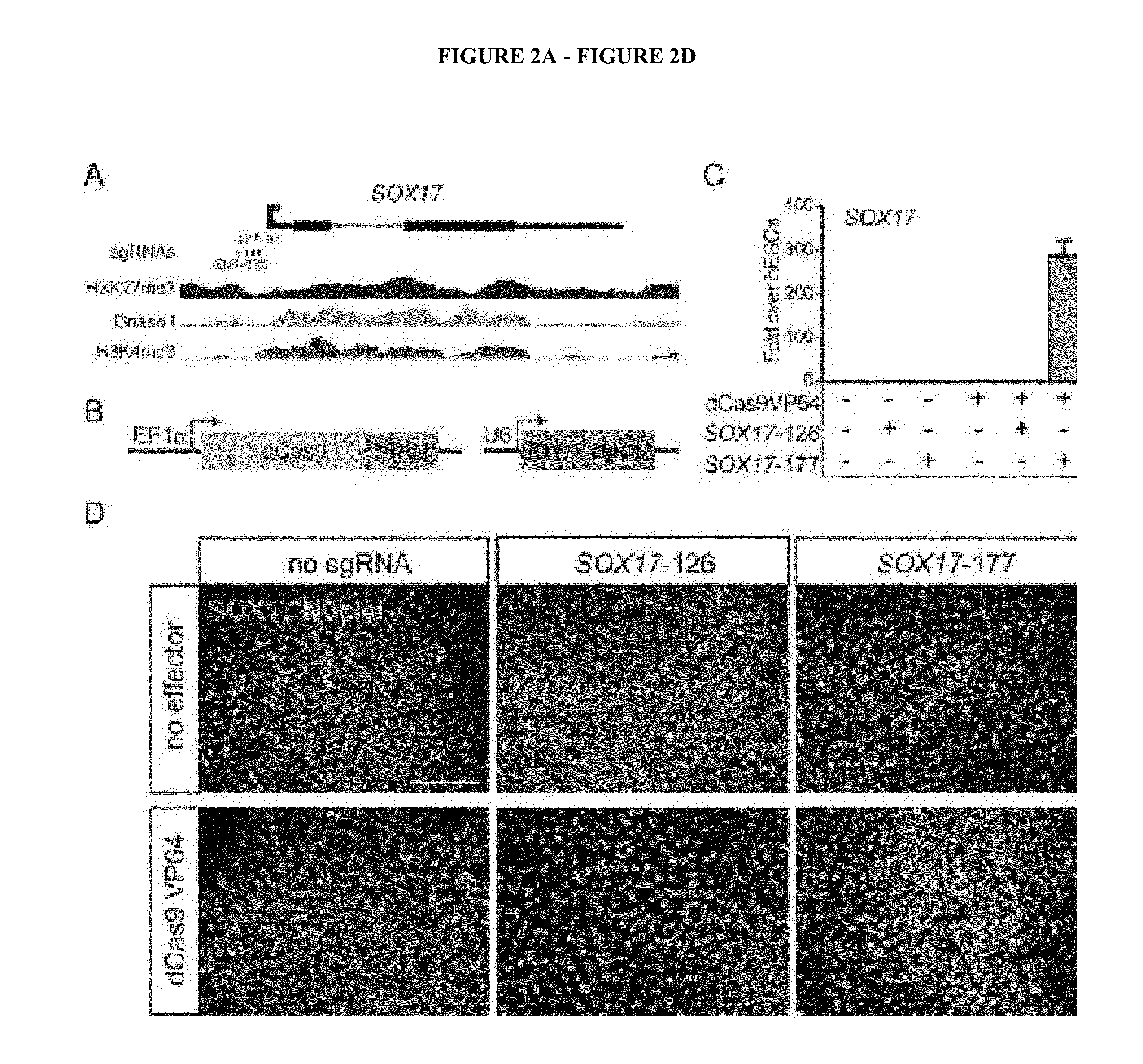
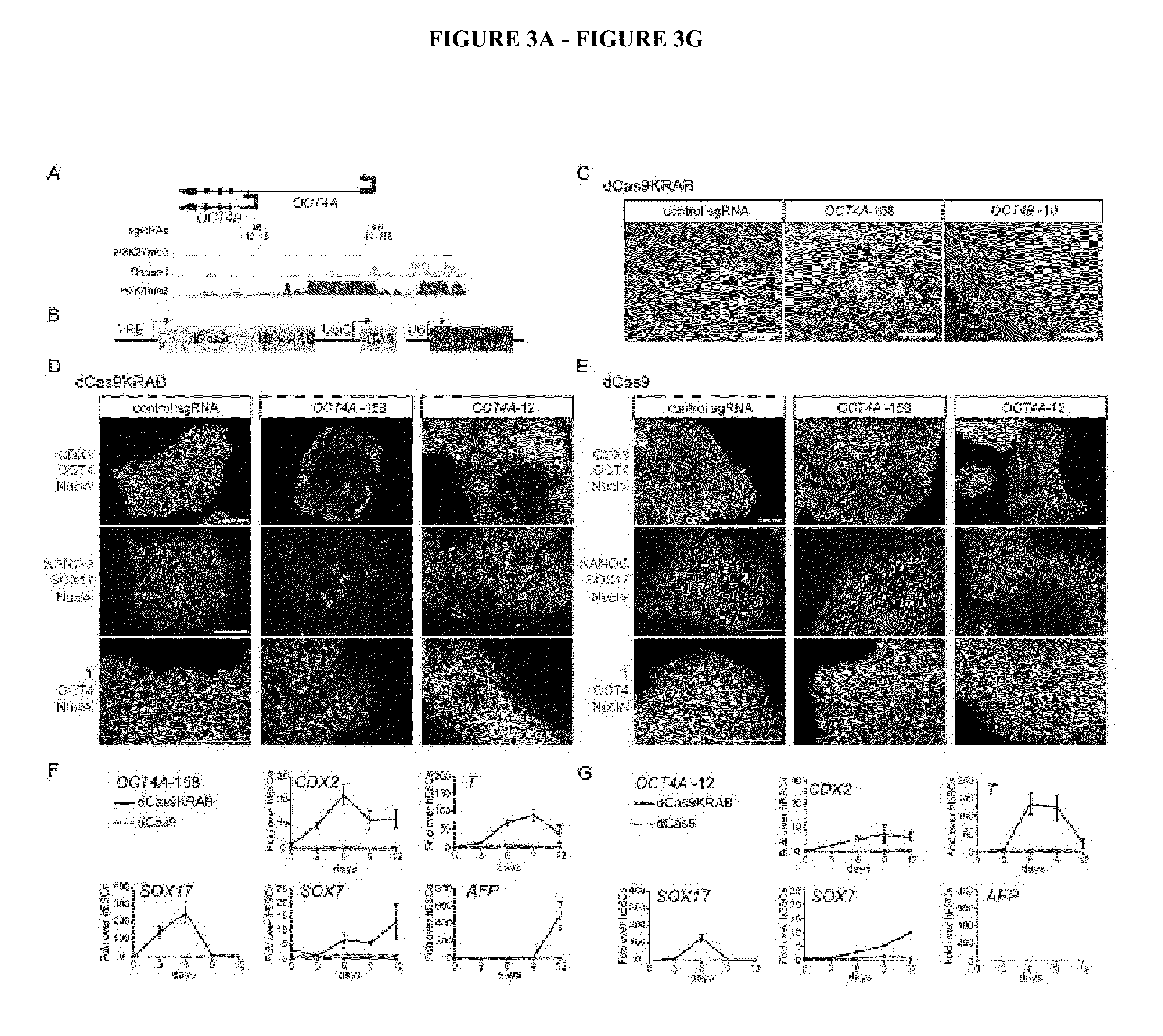
Cas9 effector-mediated regulation of transcription, differentiation and gene editing/labeling
InactiveUS20150191744A1Prevent degradationHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementProgenitorReprogramming
The present disclosure relates to methods of and systems for modifying the transcriptional regulation of stem or progenitor cells to promote their differentiation or reprogramming of somatic cells. Further, the labeling and editing of human genomic loci in live cells with three orthogonal CRISPR / Cas9 components allow multicolor detection of genomic loci with high spatial resolution, which provides an avenue for barcoding elements of the human genome in the living state.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Methods of ex vivo progenitor and stem cell expansion by co-culture with mesenchymal cells
Methods of ex-vivo expansion and at the same time inhibiting differentiation of stem cells by co-culture with mesenchymal cells, transplantable populations of renewable progenitor and stem cells expanded thereby, and their uses in therapeutic applications.
Owner:GAMIDA CELL
Ex vivo human lung/immune system model using tissue engineering for studying microbial pathogens with lung tropism
A method for studying scaffold-based tissue engineering approaches in combination with the use of progenitor or stem cells to generate new lung tissue in an in vitro system. The engineered tissue system of this invention is used to monitor lung and immune system exposure of pathogen and / or toxins. The method involves growing engineered lung / immune tissue from progenitor cells in a bioreactor and then exposing the engineered lung / immune tissue to a pathogen and / or toxin. Once exposed, response of the engineered tissue is monitored to determine the effects of exposure to the immune component of the tissue and to lung component of the tissue. This invention also involves development of mixed engineered tissues including a first fully functional engineered tissue such as lung tissue and a second fully functional engineered tissued such as immune tissue from a single animal donor. The mixed systems can include more than two engineered tissues.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT TEXAS UNIV SYST
Ex vivo progenitor and stem cell expansion for use in the treatment of disease of endodermally-derived organs
Methods of ex-vivo expansion of endodermally-derived and non-endodermally-derived progenitor and stem cells, expanded populations of renewable progenitor and stem cells and to their uses in therapeutic applications such as the production of endocrine hormones and the prevention and treatment of liver and pancreatic disease.
Owner:GAMIDA CELL
Deposition of calcium-phosphate (CaP) and calcium-phosphate with bone morphogenic protein (CaP+BMP) coatings on metallic and polymeric surfaces
InactiveUS20080097618A1Reduce the amount of solutionHigh densityImpression capsBone implantPolymeric surfaceSolubility
The invention is a medical implantable device which is coated by the method according to the invention. The surface of the substrate used for the implantable device, in the raw condition, following a cleaning regime and physiochemical pretreatments, is coated using a biomimetic process in a supersaturated calcium phosphate solution (SCPS) to obtain the desired coating coverage and morphology maintaining a ratio of calcium to phosphorus pH, as well as solution temperature plays a major role in yielding precipitation of the proper phase of CaP so that composition, morphologies, crystal structures, and solubility characteristics are optimal for the deposition process. The biomimetic coating adds the attribute of osteoconductivity to the implant device. To maximize bone growth, the implant must also induce bone growth, or possess the attribute of osteoinductivity. This attribute is acquired by the use of therapeutic agents, i.e. bone morphogenic proteins (BMP), growth factors, stem cells, etc. The preparation of the SCPS solution is slightly altered so that during the immersion of the implant in the SCPS, the therapeutic agents are co-precipitated and bonded with the CaP directly on the underlying surface of the implant device. A final dipping process into a BMP solution provides an initial burst of cellular activity. For delivering stem and / or progenitor cell, after drying the dipped solution of BMP, the cells are cultured on the surface of the implant.
Owner:HERKOWITZ HARRY N
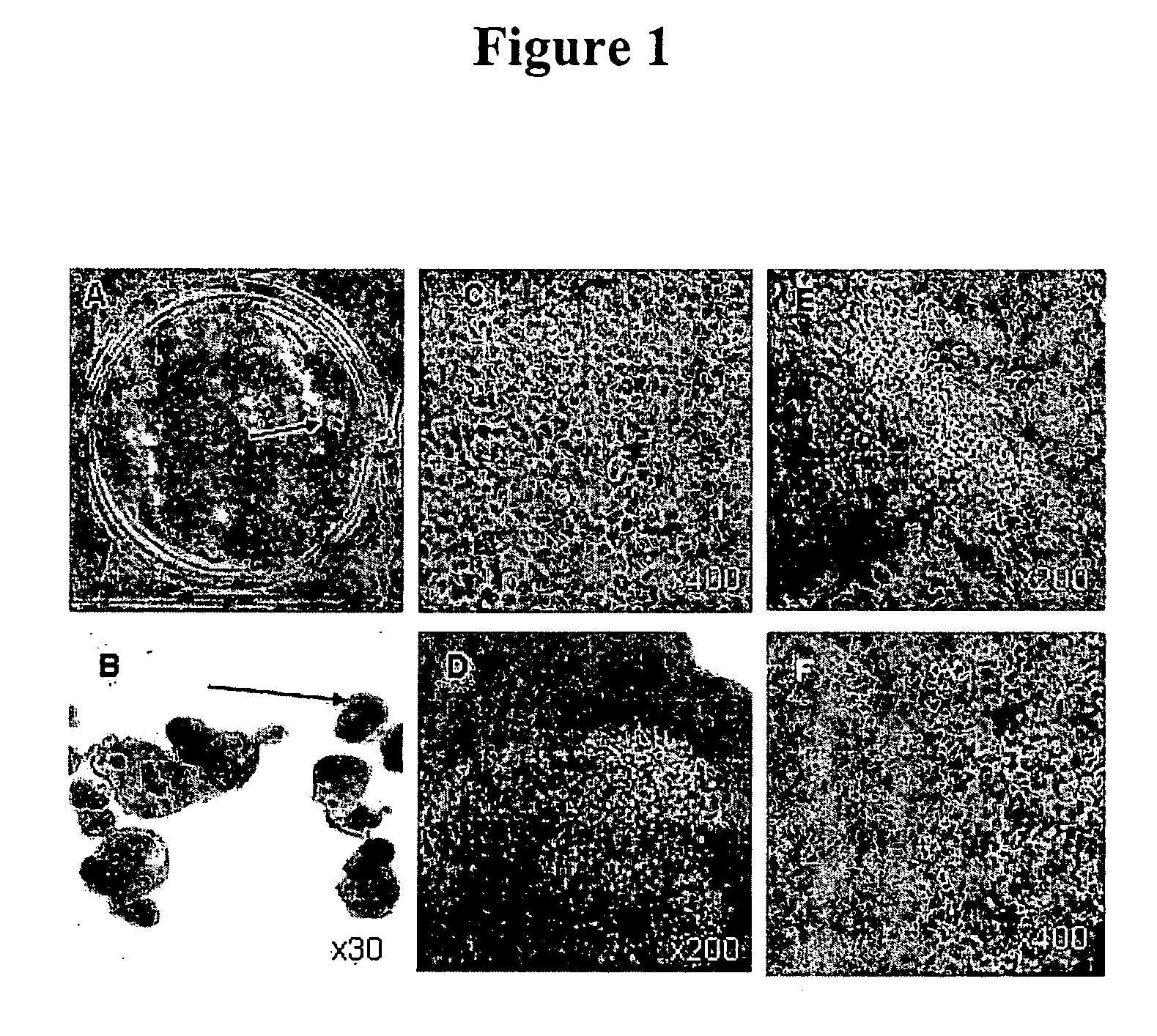
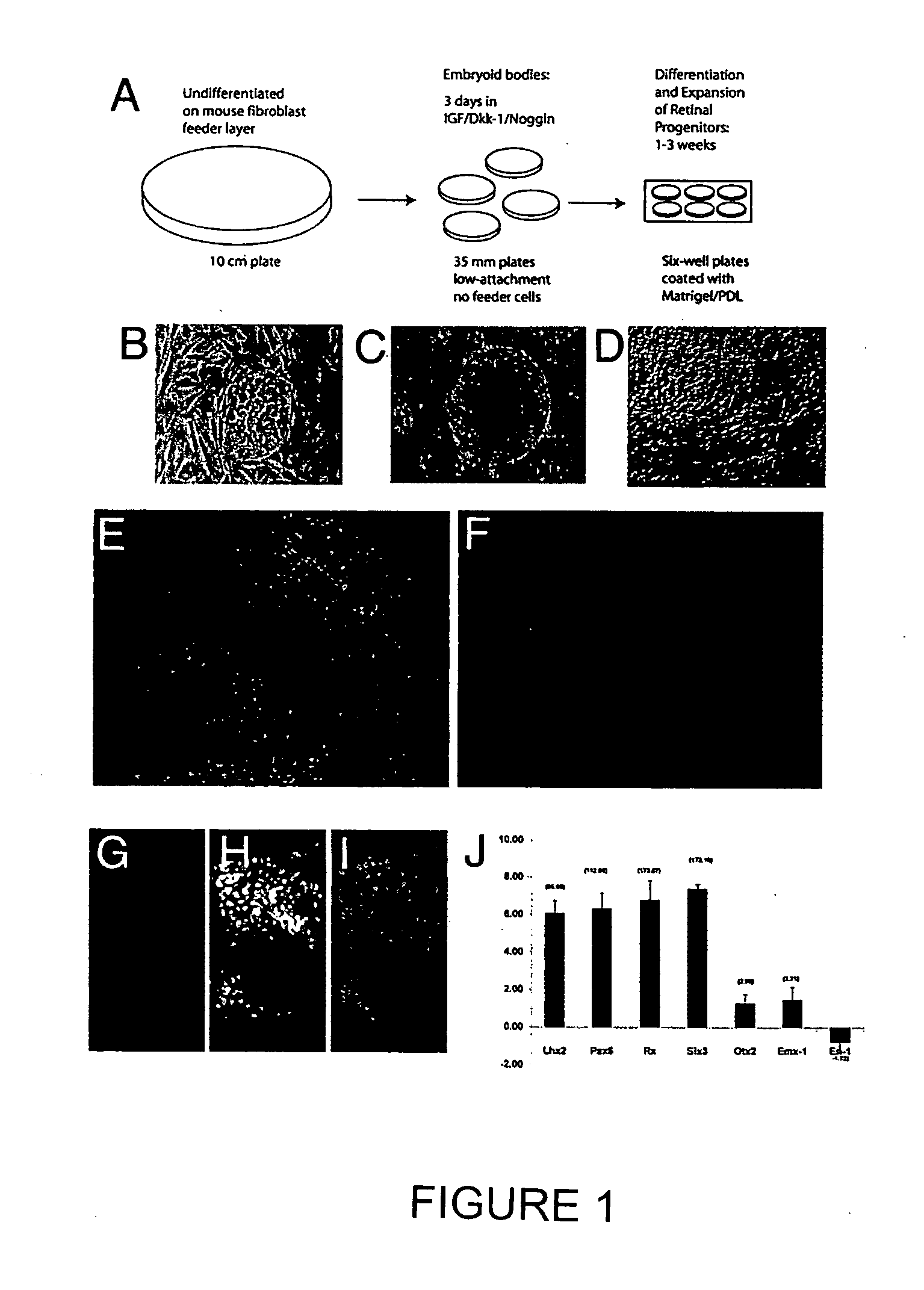
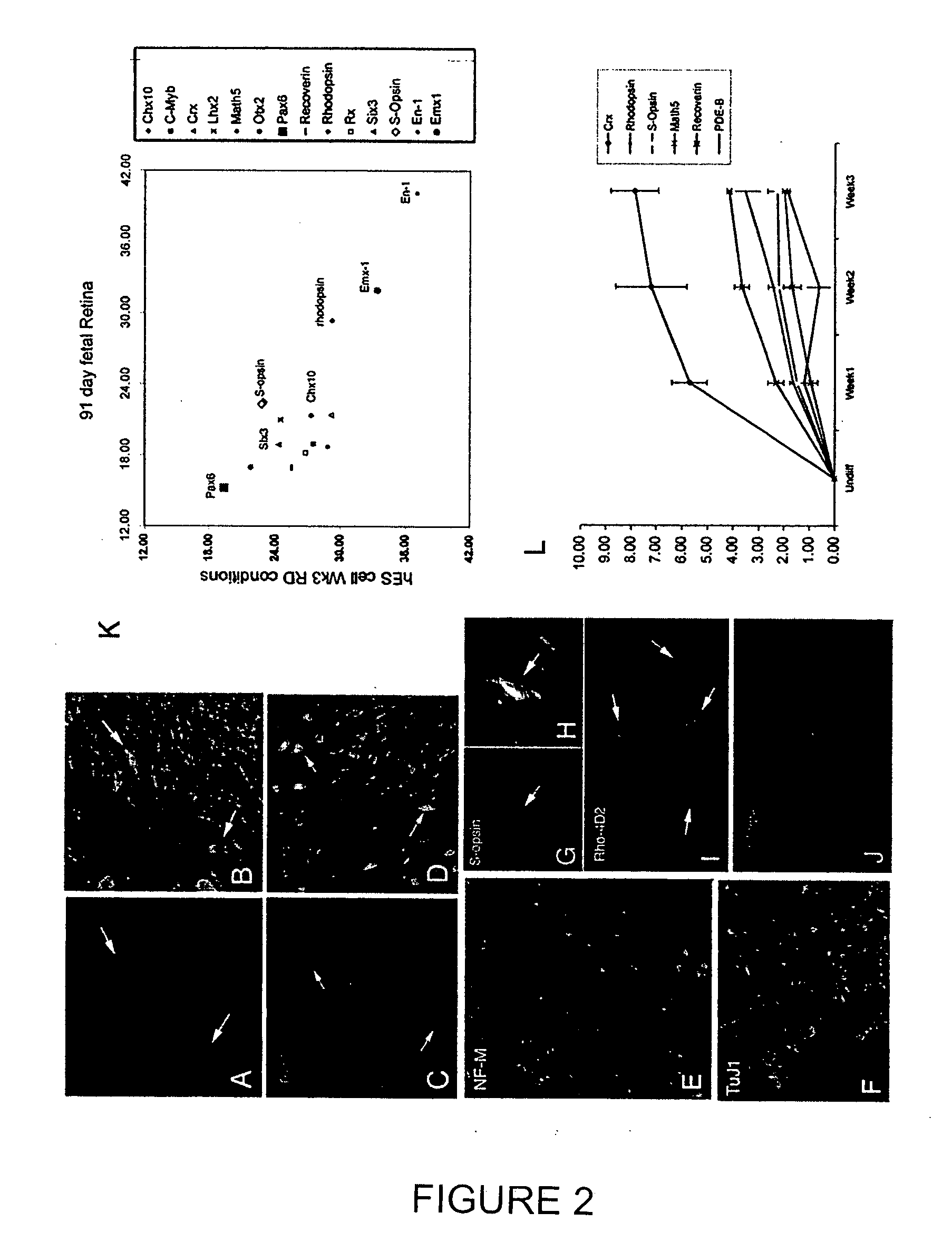
Method of generating human retinal progenitors from embryonic stem cells
Methods are provided for the in vitro differentiation of human retinal progenitor cells from embryonic stem cells.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Use of bioactive glass compositions to stimulate osteoblast production
InactiveUS20040009598A1Expand the populationRapid apoptosisSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture supports/coatingOsteoblastMammal
Compositions comprising bioactive glass compositions or extracts thereof which include ions in an appropriate concentration and ratio that they enhance osteoblast production, and methods of preparation and use thereof, are disclosed. The compositions can be included in implantable devices that are capable of inducing tissue formation in autogeneic, allogeneic and xenogeneic implants, for example as coatings and / or matrix materials. Examples of such devices include prosthetic implants, sutures, stents, screws, plates, tubes, and the like. Aqueous extracts of the bioactive glass compositions, which extracts are capable of stimulating osteoblast production, are also disclosed. The compositions can be used, for example, to induce local tissue formation from a progenitor cell in a mammal, for accelerating allograft repair in a mammal, for promoting in vivo integration of an implantable prosthetic device to enhance the bond strength between the prosthesis and the existing target tissue at the joining site, and for treating tissue degenerative conditions.
Owner:NOVATHERA
Isolation and preservation of fetal and neonatal hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells of the blood
The present invention relates to hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells of neonatal or fetal blood that are cryopreserved, and the therapeutic uses of such stem and progenitor cells upon thawing. In particular, the present invention relates to the therapeutic use of fetal or neonatal stem cells for hematopoietic (or immune) reconstitution. Hematopoietic reconstitution with the cells of the invention can be valuable in the treatment or prevention of various diseases and disorders such as anemias, malignancies, autoimmune disorders, and various immune dysfunctions and deficiencies. In another embodiment, fetal or neonatal hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells which contain a heterologous gene sequence can be used for hematopoietic reconstitution in gene therapy. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, neonatal or fetal blood cells that have been cryopreserved and thawed can be used for autologous (self) reconstitution.
Owner:PHARMASTEM THERAPEUTICS
Low level light therapy for enhancement of neurologic function
ActiveUS7534255B1Improve neurological functionIncreases ATP productionDiagnosticsSurgeryLight energyRisk stroke
Therapeutic methods for enhancing neurologic function such as may be desired in individuals having motor and / or cognitive impairment, including that resulting from Alzheimer's disease, dementia, head trauma, mental disease such as depression, stroke and neurodegeneration, as well as in healthy individuals are described, the methods including delivering a cognitive enhancing effective amount of light energy having a wavelength in the visible to near-infrared wavelength range to a target area of the brain. The neurologic function enhancing effective amount of light energy, in accordance with a preferred embodiment, is a predetermined power density (mW / cm2) at the level of the brain tissue being treated, and is delivered by determining a surface power density of the light energy that is sufficient to deliver the predetermined power density of light energy to the target brain tissue. In one embodiment, progenitor cells are treated using light energy and implanted into the central nervous system of a patient.
Owner:PHOTOTHERA IP HLDG
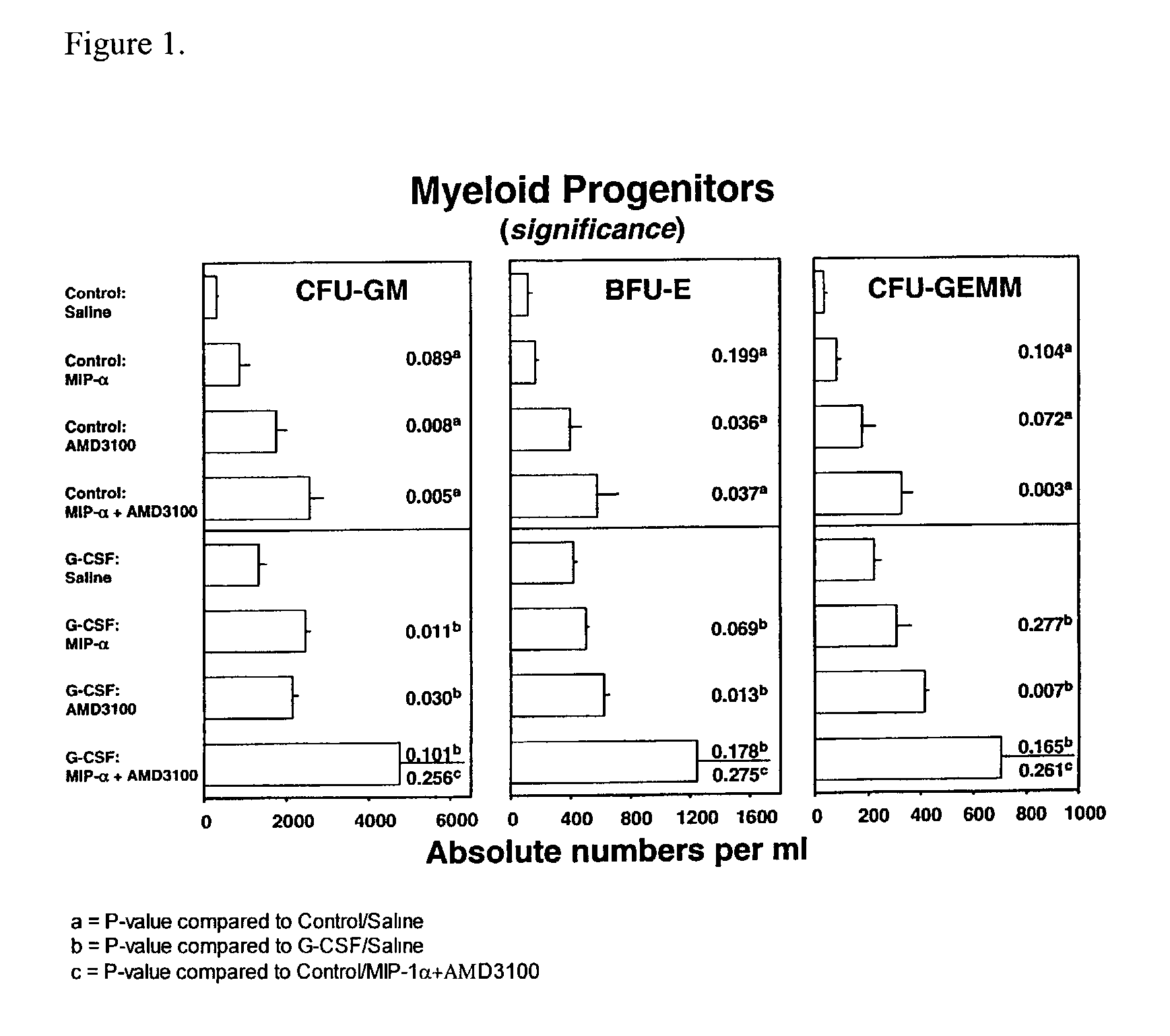
Methods to mobilize progenitor/stem cells
Certain nitrogen-containing compounds that bind the chemokine receptor CXCR4 are able to mobilize progenitor and / or stem cells into the peripheral blood to permit harvesting them for stem cell transplantation.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
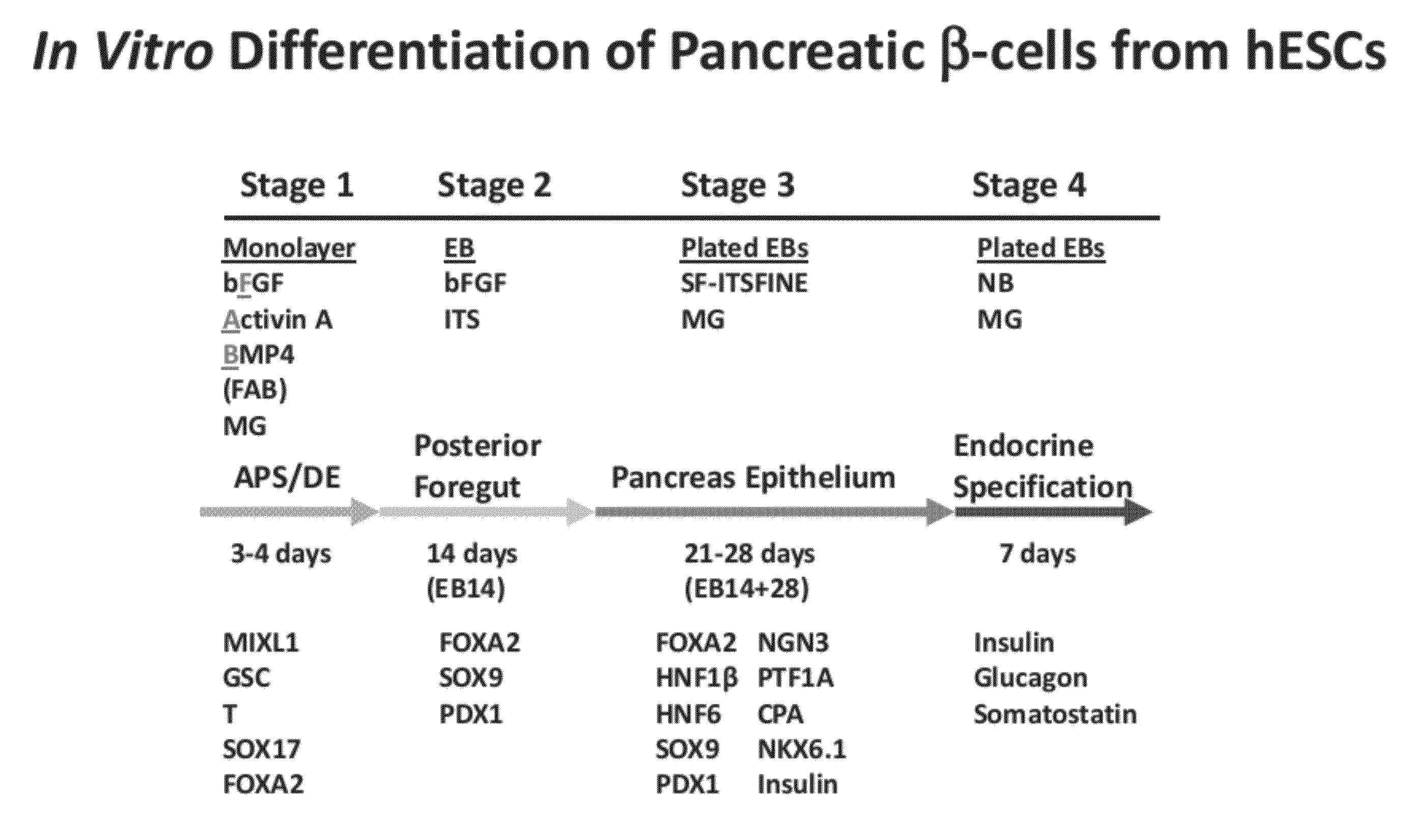
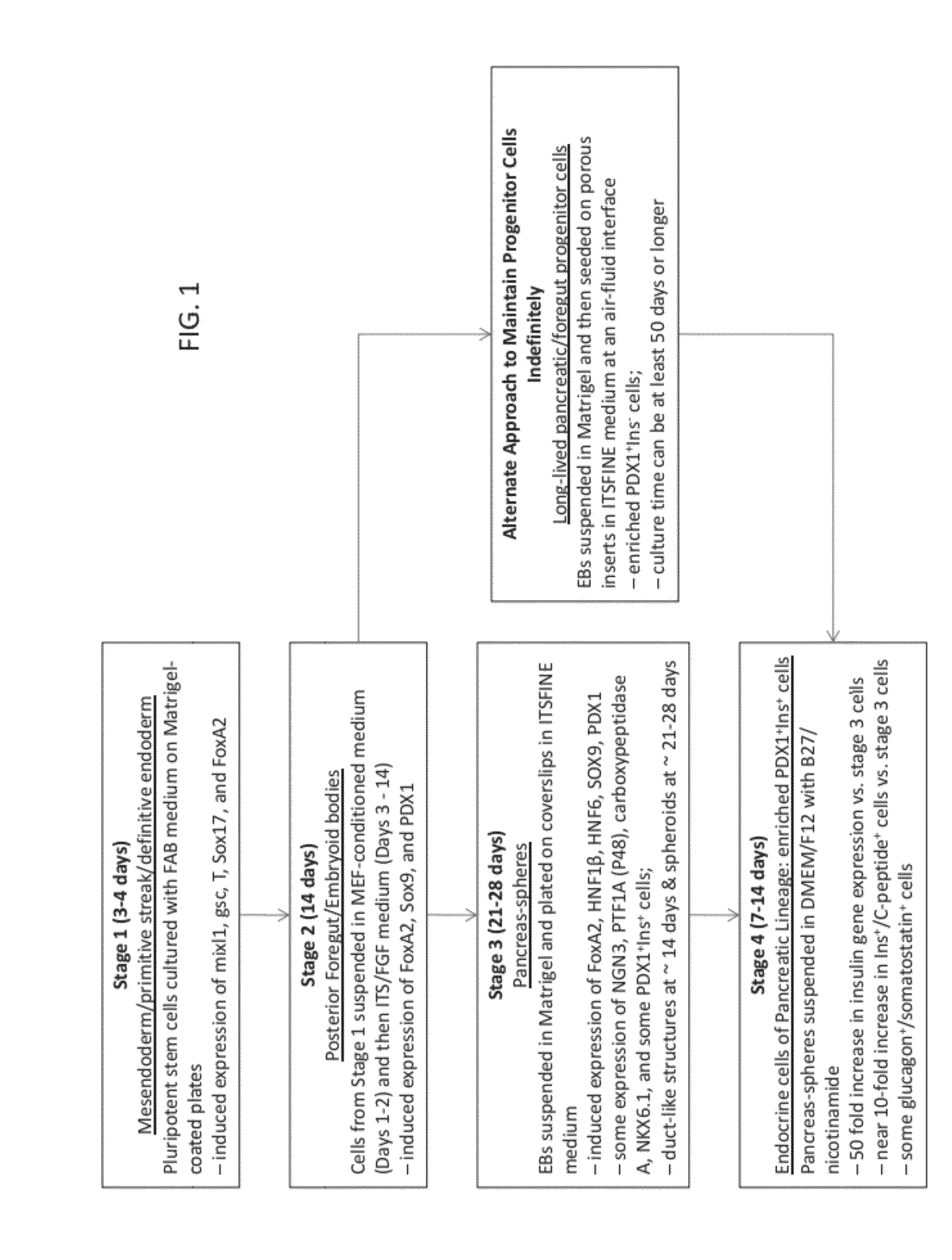
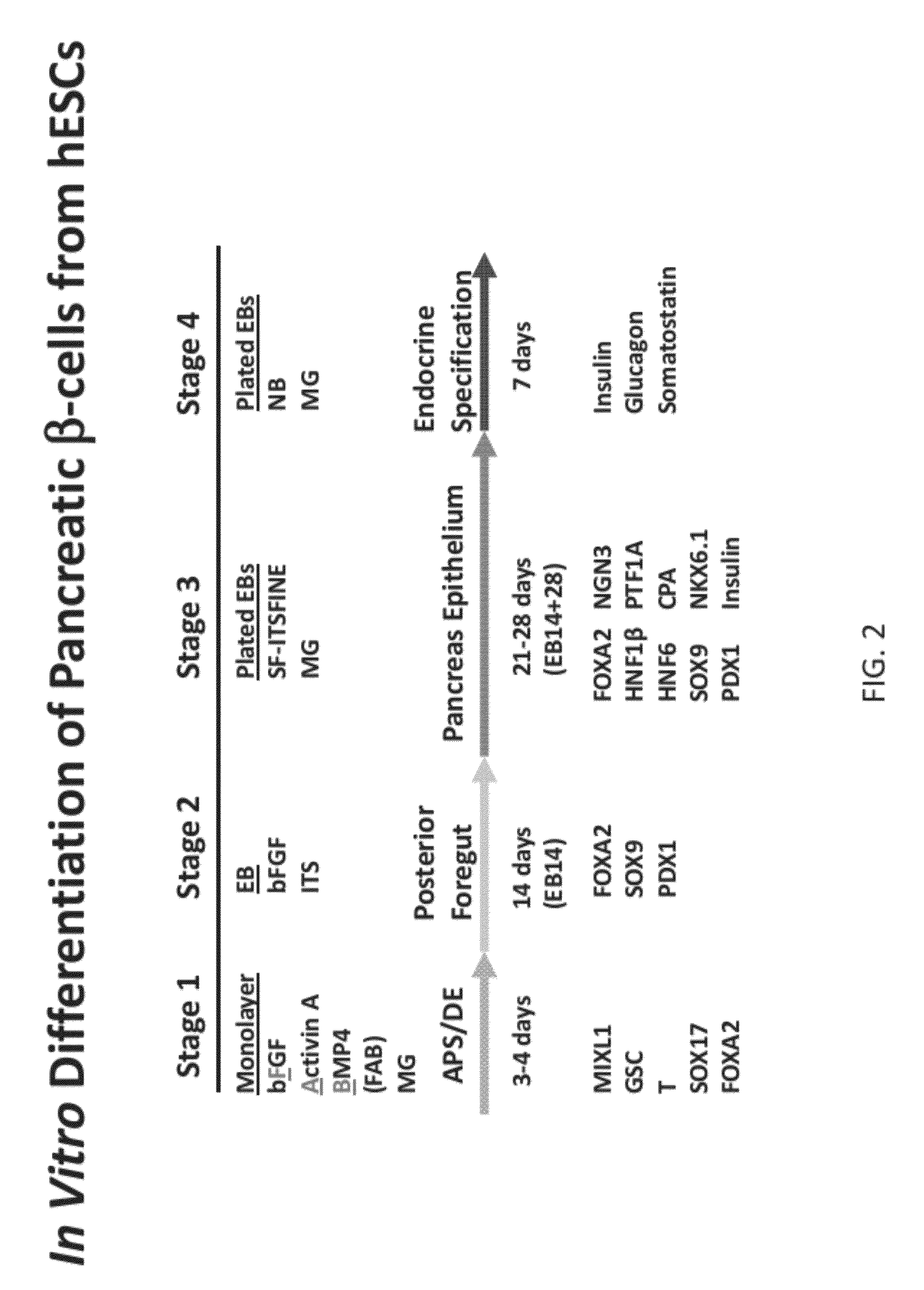
Methods and devices for differentiating pluripotent stem cells into cells of the pancreatic lineage
Methods and devices for culturing human pluripotent stem cells to produce cells of the pancreatic lineage are disclosed. The methods include steps of culturing the stem cells under conditions that induce the expression of mesendoderm / primitive streak and definitive endoderm markers in a chemically defined medium including an effective amount of i) fibroblast growth factor, ii) Activin A, and iii) bone morphogenetic protein. The methods further include the steps of culturing cells under conditions favoring the formation of at least one of intact embryoid bodies and pancreatic progenitor PDX1+ Ins− cells.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
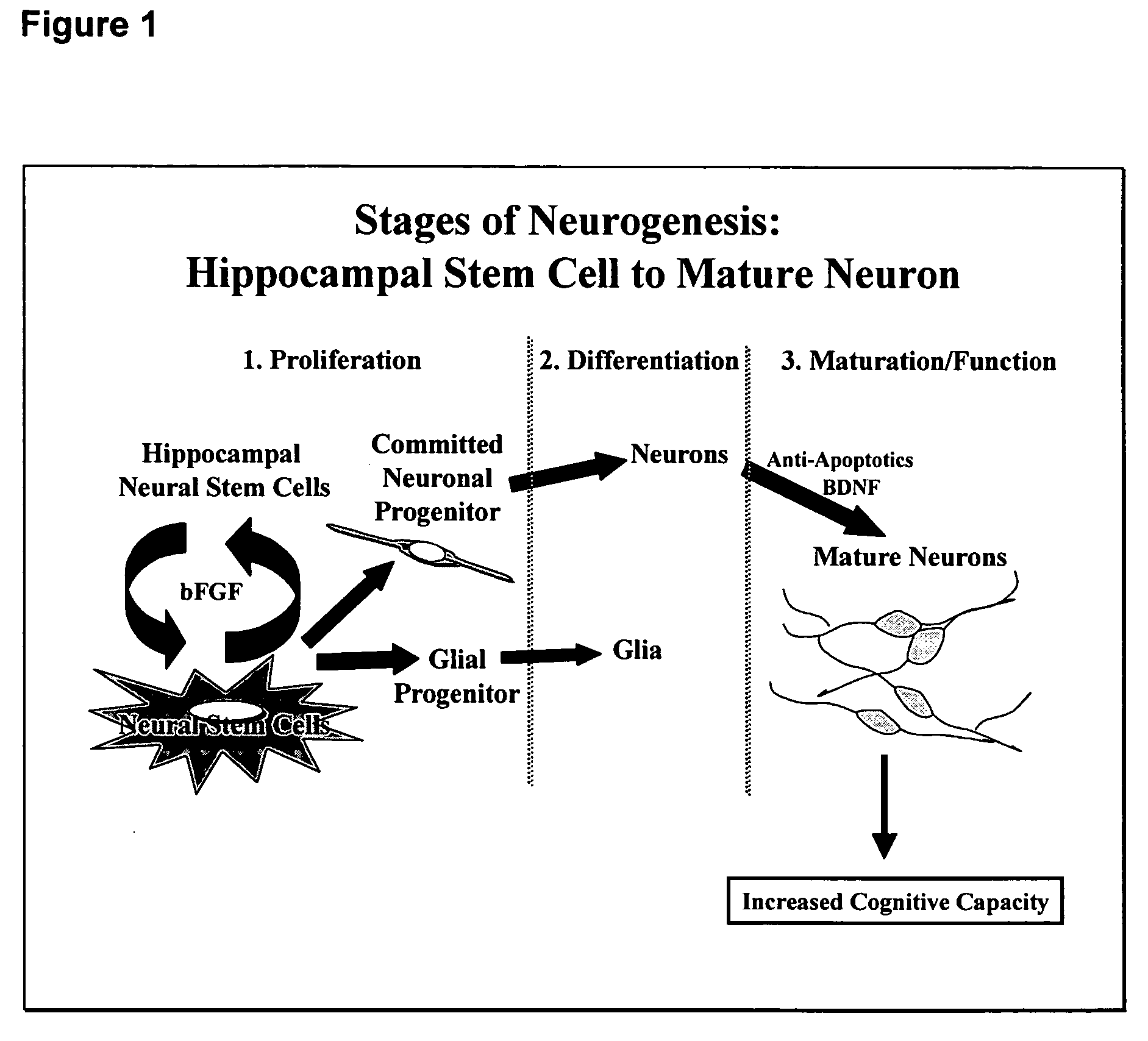
Method for discovering neurogenic agents
A method for discovering neurogenic drugs is revealed. The method allows for systematic screening of test agents such as libraries of compounds. The method consists of exposing test agents to cultures of differentiating neural progenitor cells and measuring their effects on increasing the overall cell number and / or the number of neurons.
Owner:KELLEHER ANDERSSON JUDITH +1
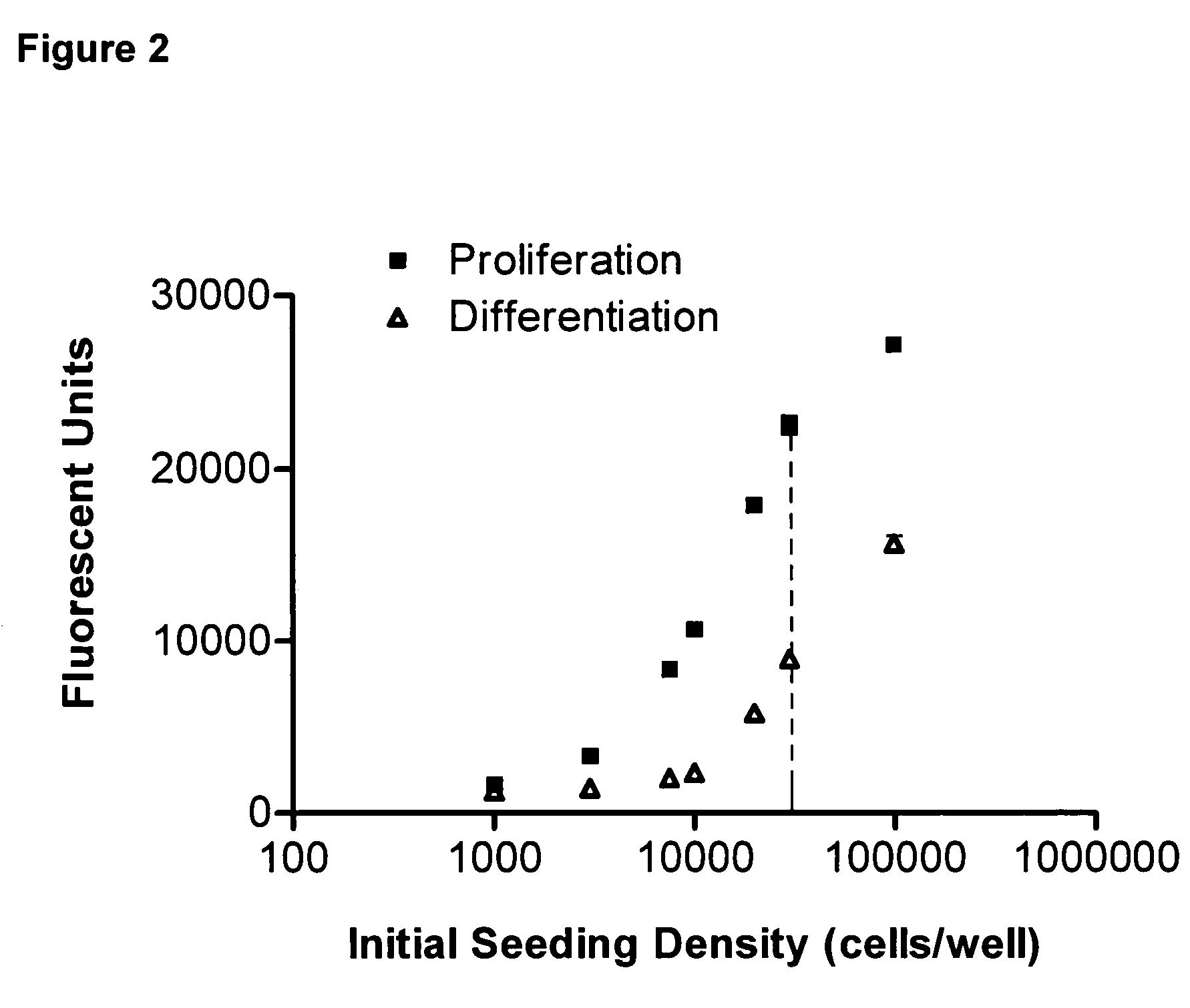
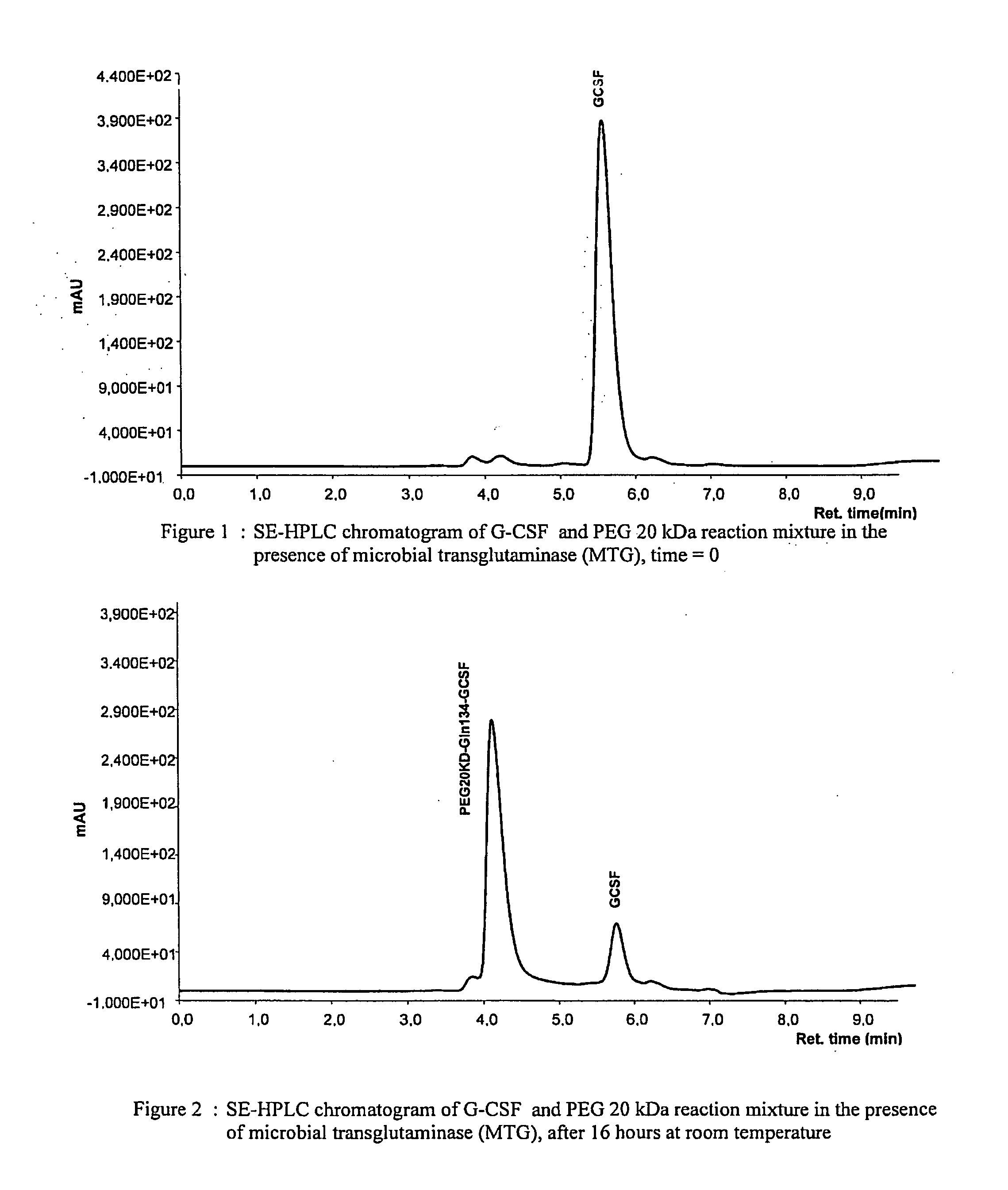
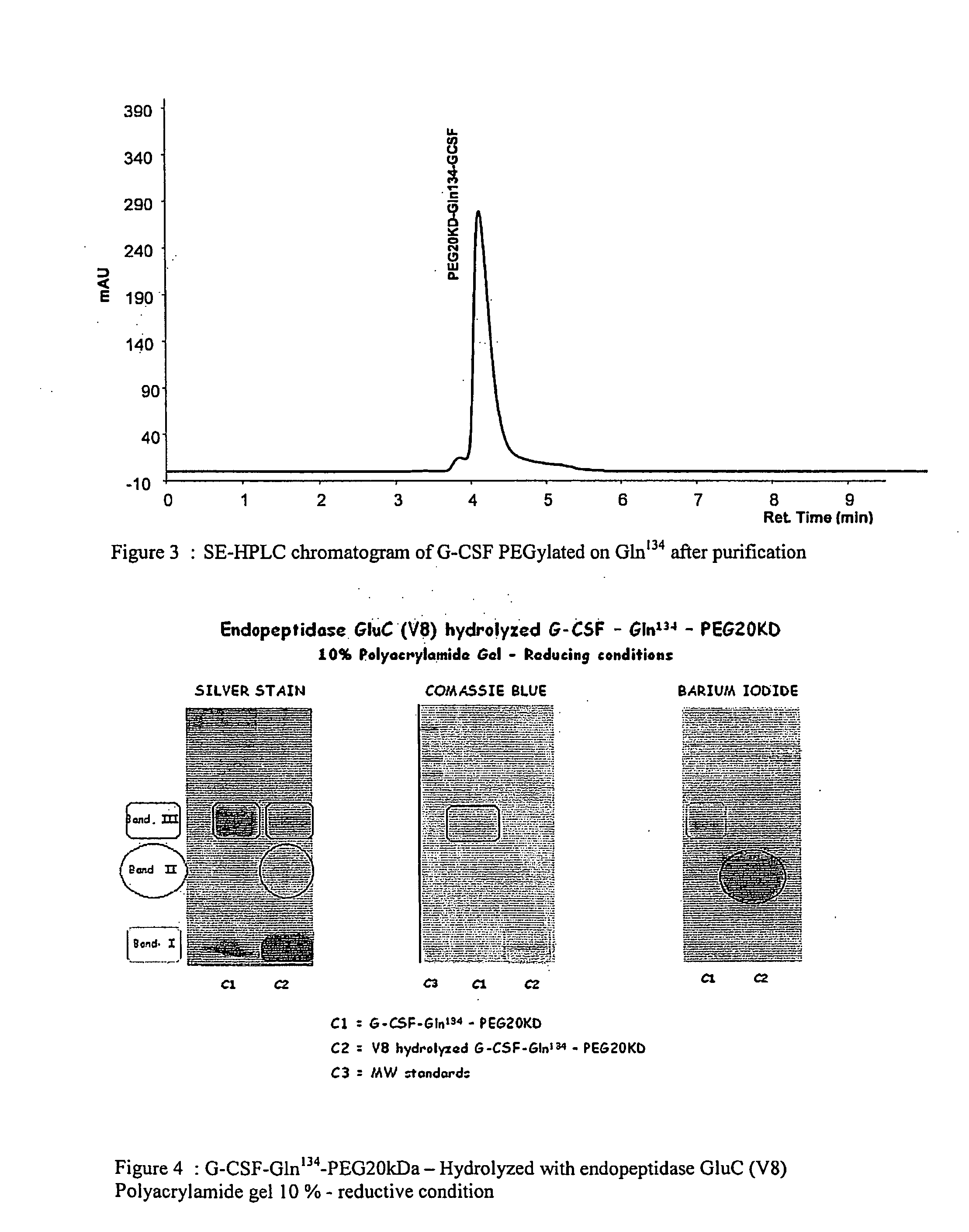
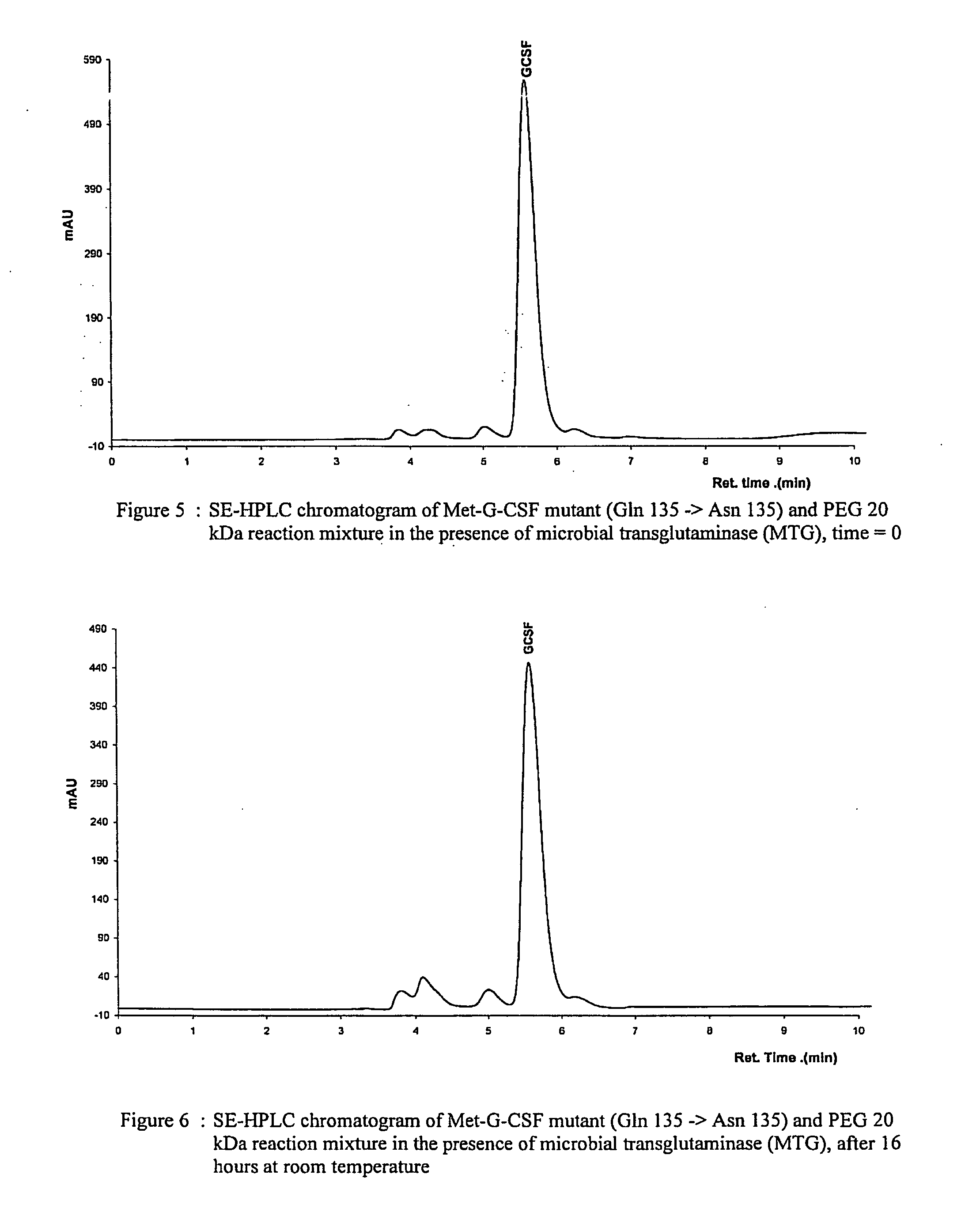
G-csf site-specific mono-conjugates
Novel site-specific mono-conjugates of Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) are hereby described, with analogues and derivatives thereof, which stimulate proliferation and differentiation of progenitor cells to mature neutrophiles. These conjugates have been obtained using transglutaminase to covalently and site-specifically bind a hydrophilic, non-immunogenic polymer to a single glutamine residue of the human G-CSF native sequence and analogues thereof. These novel site-specific mono-conjugated derivatives are recommended for therapeutic use since they are stable in solution and exhibit significant biological activity in vitro and a longer bloodstream half-life, as compared to the non-conjugated protein, with a consequent prolonged pharmacological activity.
Owner:BIO KER
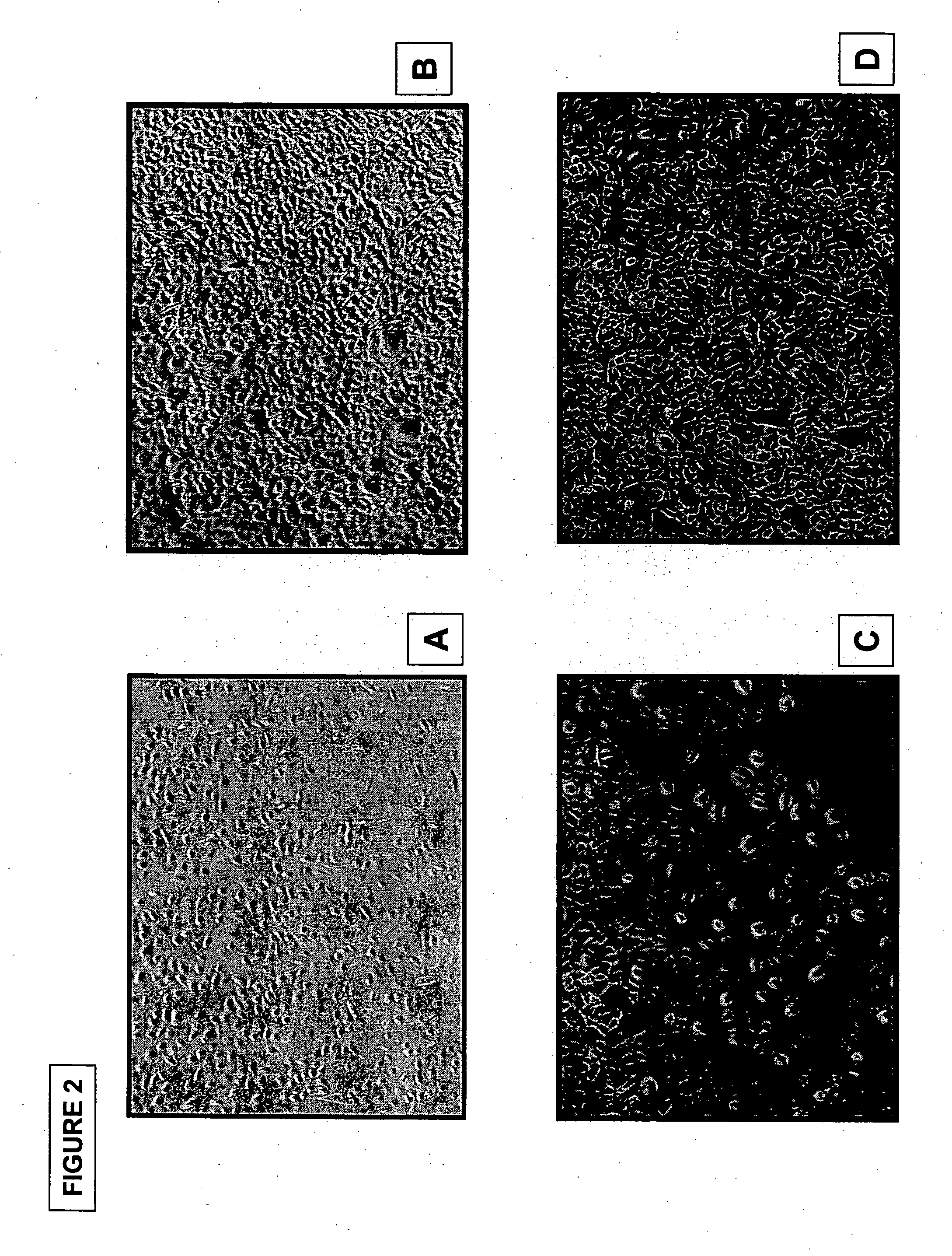
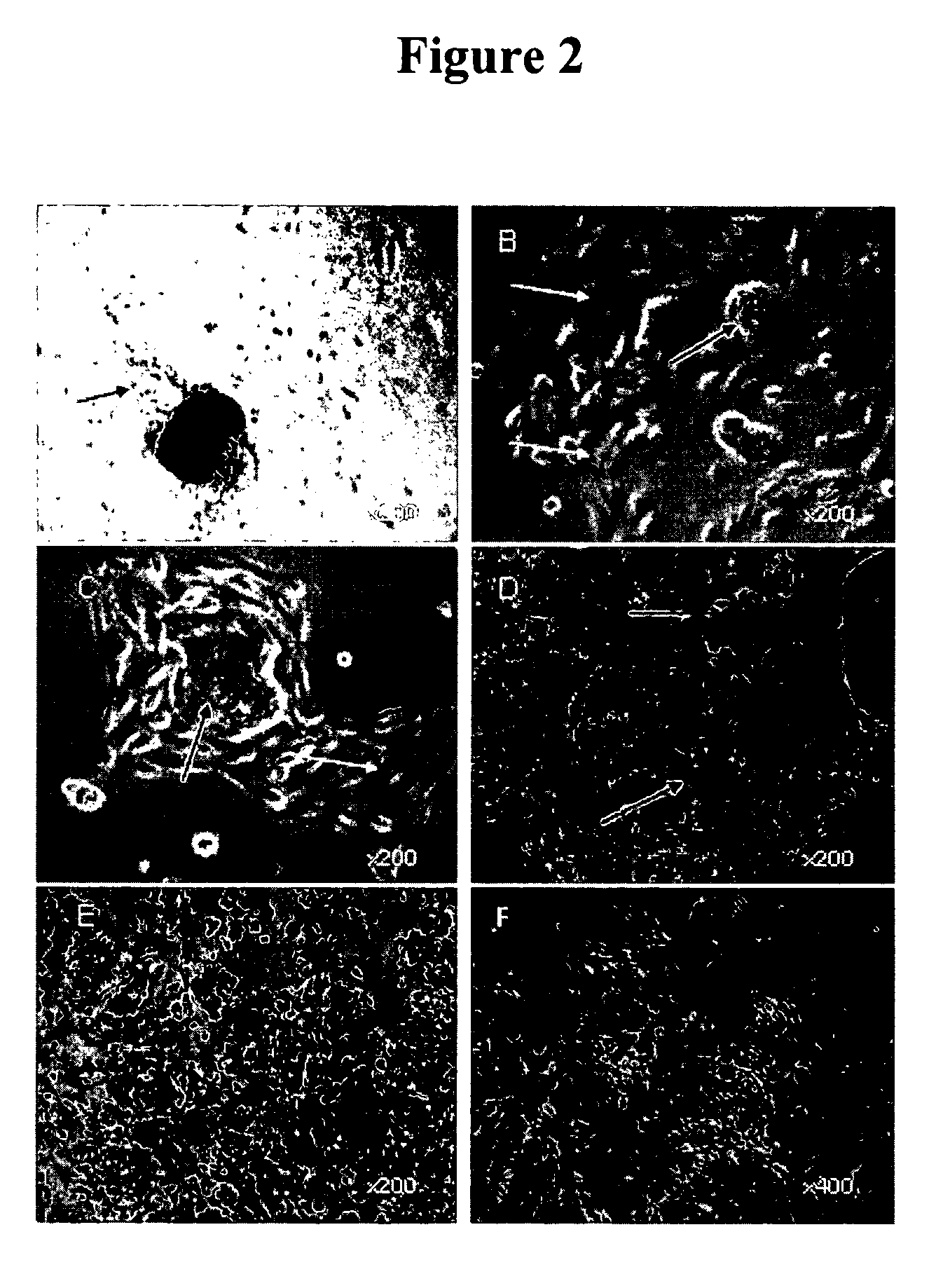
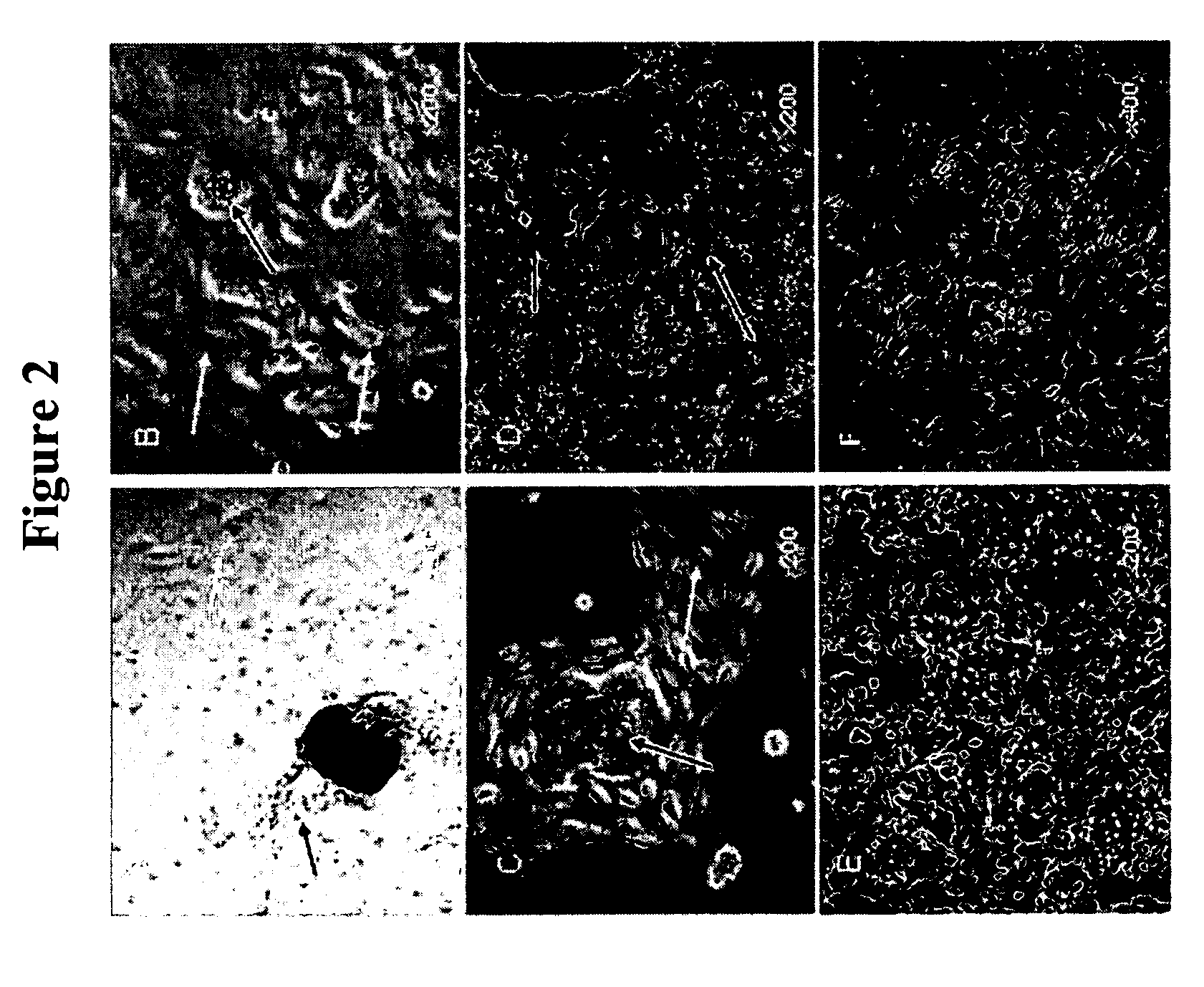
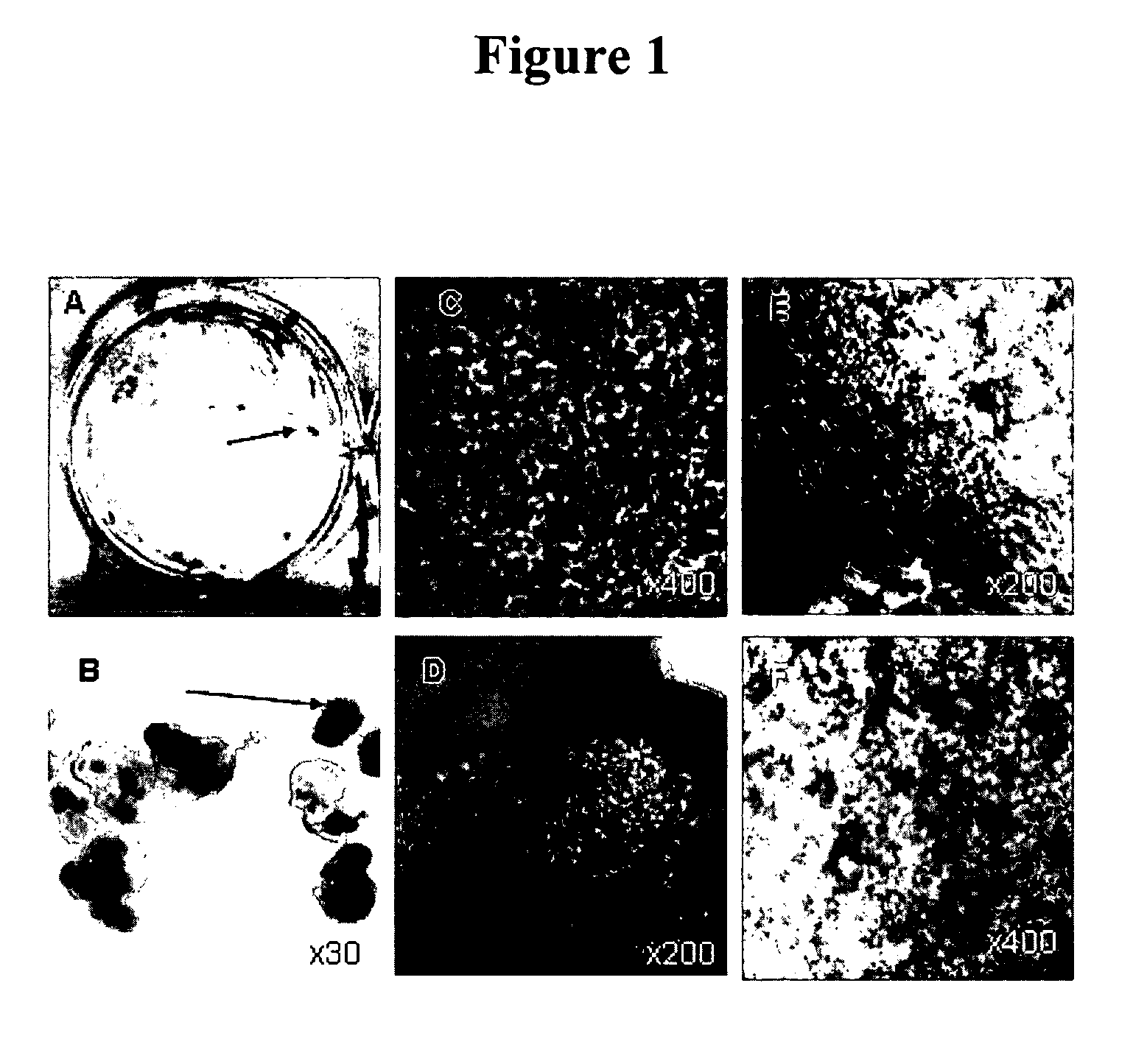
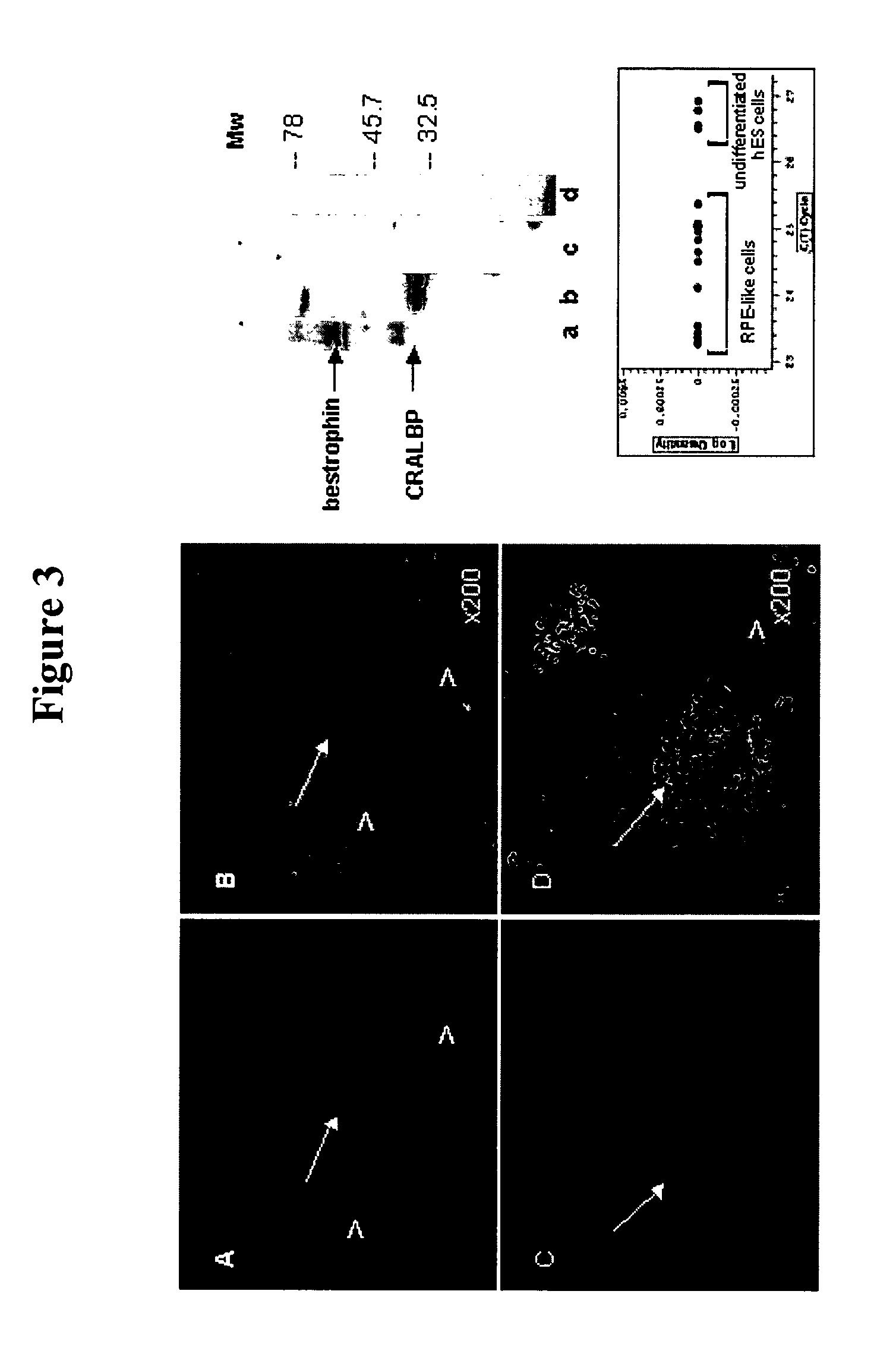
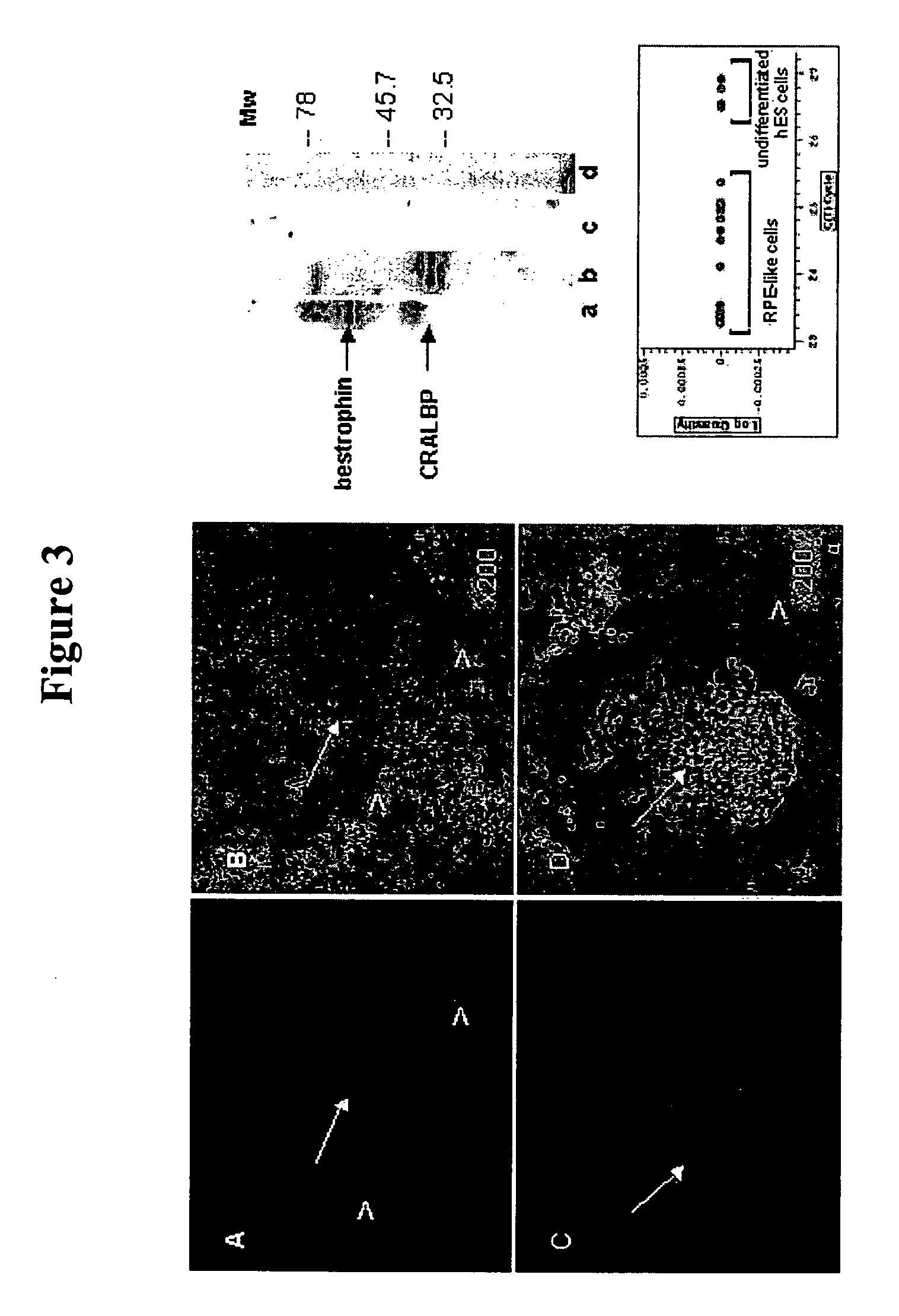
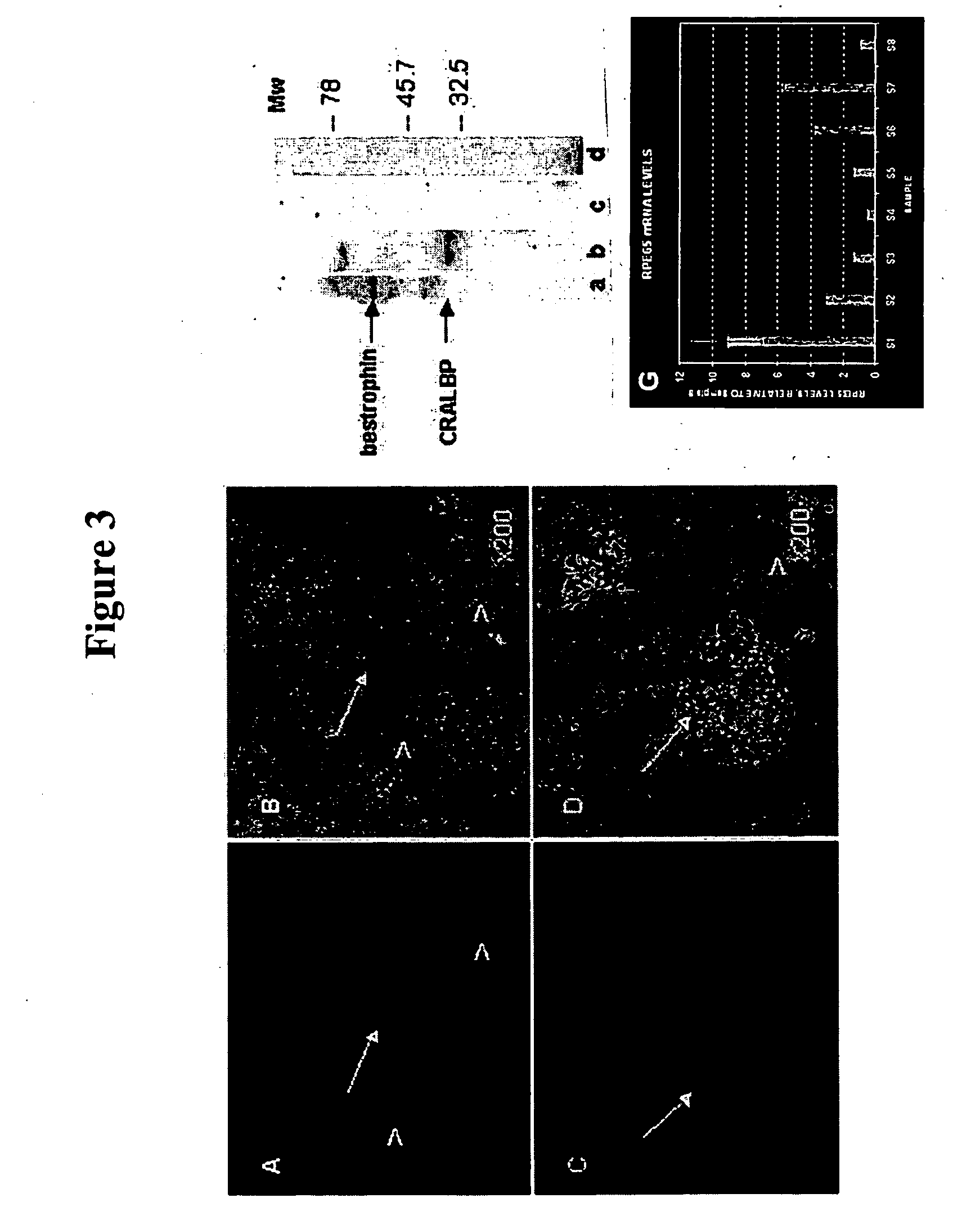
Methods for producing enriched populations of human retinal pigment epithelium cells for treatment of retinal degeneration
ActiveUS7794704B2Quality improvementReduce complexityBiocideSenses disorderMedicineRetinal progenitor
This invention relates to methods for improved cell-based therapies for retinal degeneration and for differentiating human embryonic stem cells and human embryo-derived into retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells and other retinal progenitor cells.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Neuronal progenitors from feeder-free human embryonic stem cell culture
The present invention relates to methods for producing feeder cell-free neuroprogenitor cells (preferably adherent) from embryonic stems cells, preferably human embryonic stem cells, the feeder cell-free neuroprogenitor cells, preferably human cells themselves, as well as methods for producing feeder cell-free samples of neuronal cells, preferably adherent human neuronal cells and the feeder cell-free neuronal cells themselves. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating neurodegenerative diseases as well as the use of the described cells in assay systems is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Method for protecting implantable sensors and protected implantable sensors
InactiveUS20050124896A1Conducive to survivalImprove scalabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterAntigenCell-Extracellular Matrix
The present invention relates to a protected implantable sensor and methods of making the same. Sensors of the present invention are protected from deposition of extraneous materials or tissue by a non-biological or biological barrier. In embodiments where the sensor is protected by a non-biological barrier, the protected sensor includes a compliant member that forms part of one or more chambers that includes a substantially non-compressible medium disposed within the chamber(s). The medium is in contact with a surface of the sensor and with a second side of the compliant member. In embodiments where the sensor is protected by a biological barrier, the protected sensor is covered entirely or in part by a layer of endothelial cells. The endothelial cells may be attached to the sensor via interaction with an antibody, antigen binding fragment thereof, or small molecule that specifically binds to a ligand on the cell membrane or cell surface of endothelial cells and / or their progenitor cells or one or more extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules to which the desired cells naturally adhere. In specific embodiments, the implantable sensor to be protected a resonating sensor comprising at least one vibratable member.
Owner:MICROTECH MEDICAL TECH
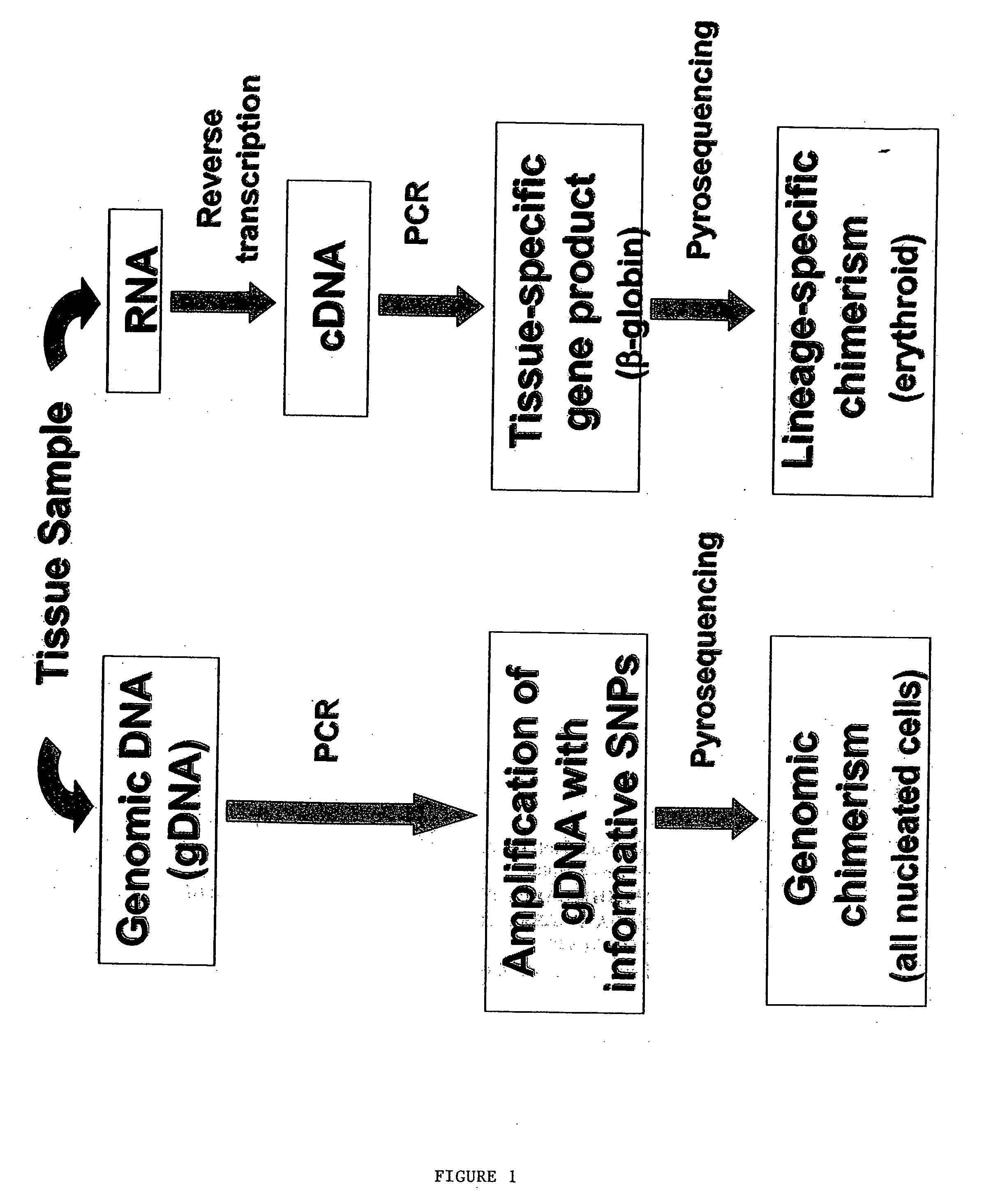
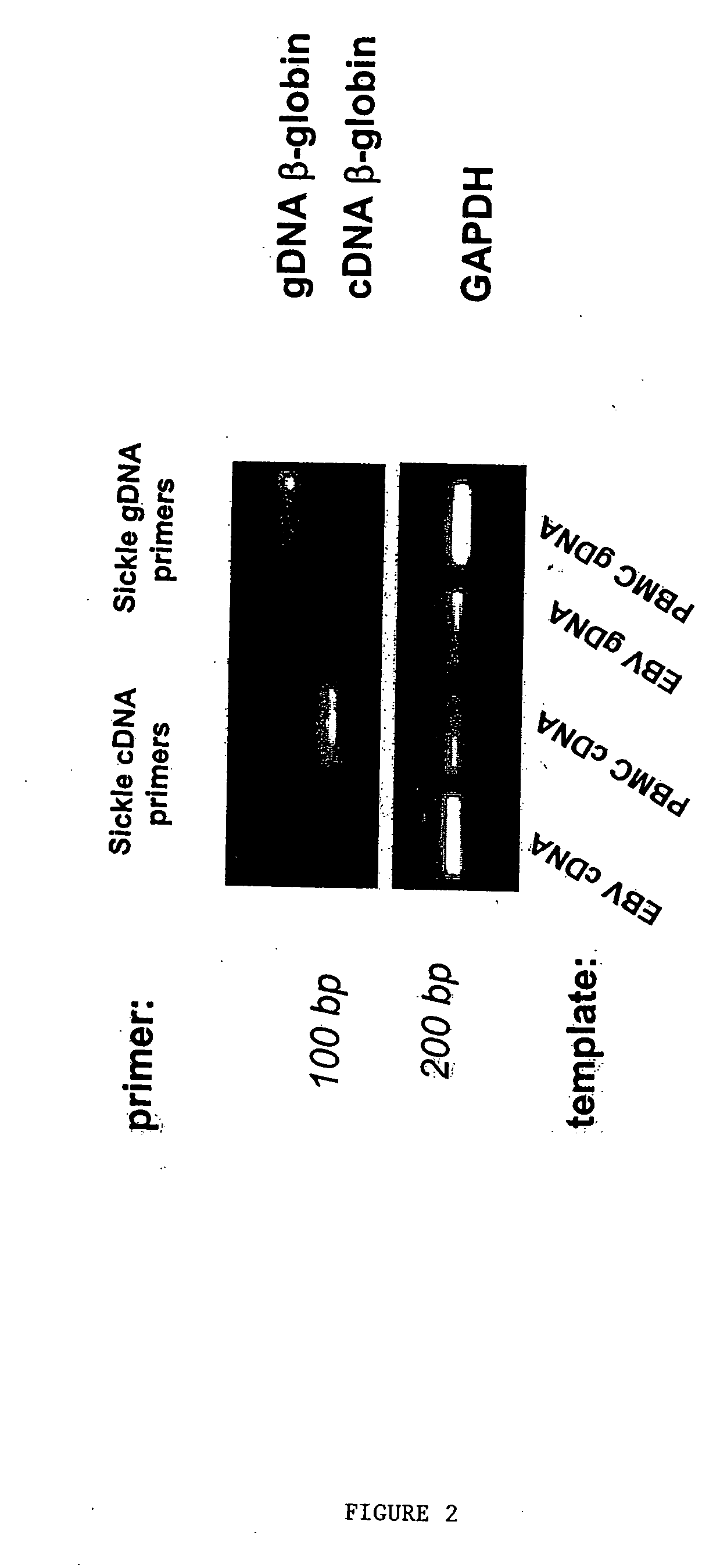
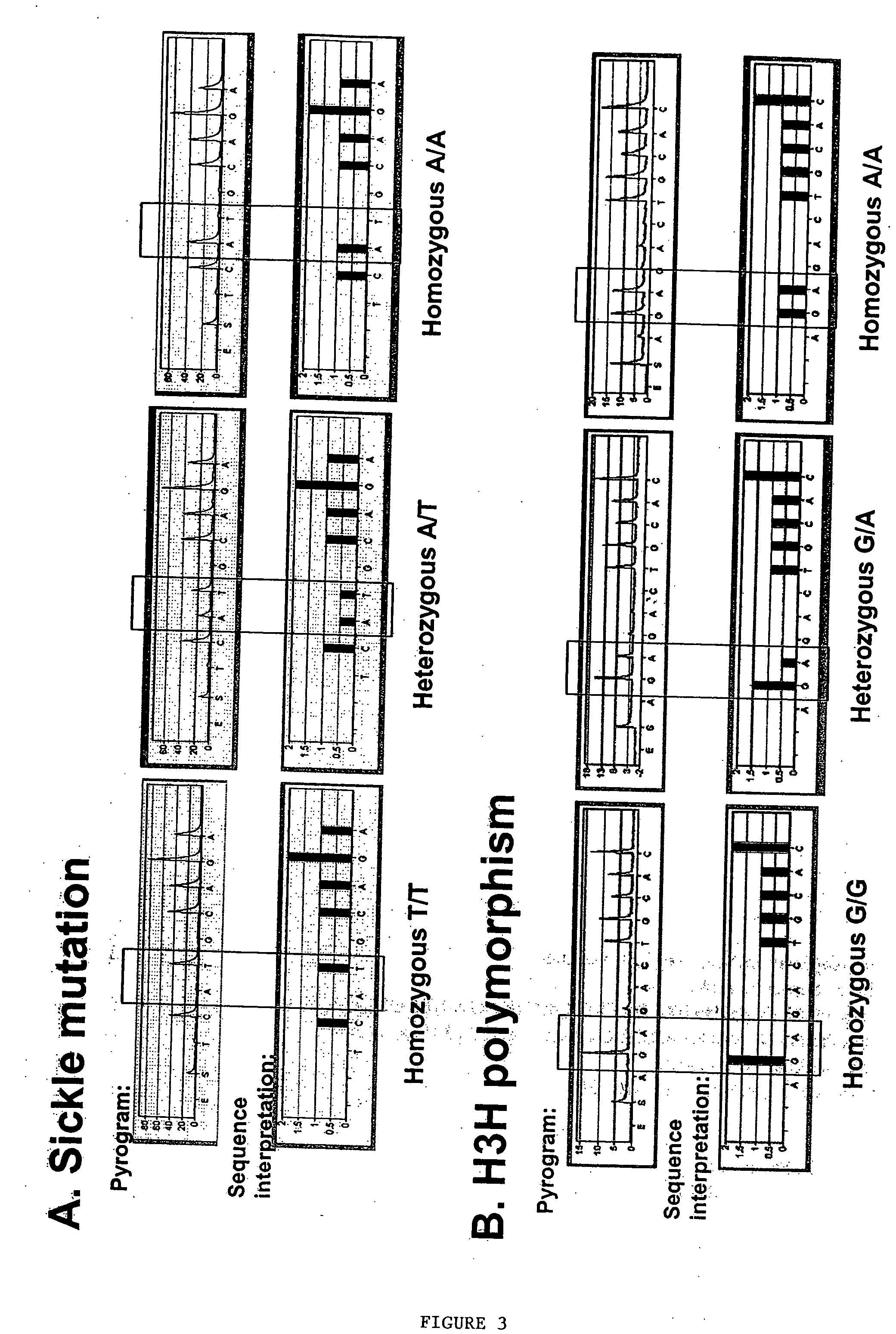
Methods to detect lineage-specific cells
The present invention is based, at least in part, on methods to identify and quantify lineage-specific cells. The present invention provides methods of detecting lineage-specific cells in a biological sample, and monitoring the effectiveness of progenitor cell transfer in a subject. The invention further provides methods of determining an effective dose of progenitor cell transfer in a subject and methods of quantifying progenitor cell transfer in a subject. Additionally, methods are provided to identify allelic variants in lineage-specific cells.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Modalities for the treatment of degenerative diseases of the retina
ActiveUS20070031386A1Quality improvementReduce complexityBiocideSenses disorderCell basedRetinal progenitor
This invention relates to methods for improved cell-based therapies for retinal degeneration and for differentiating human embryonic stem cells and human embryo-derived into retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells and other retinal progenitor cells.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
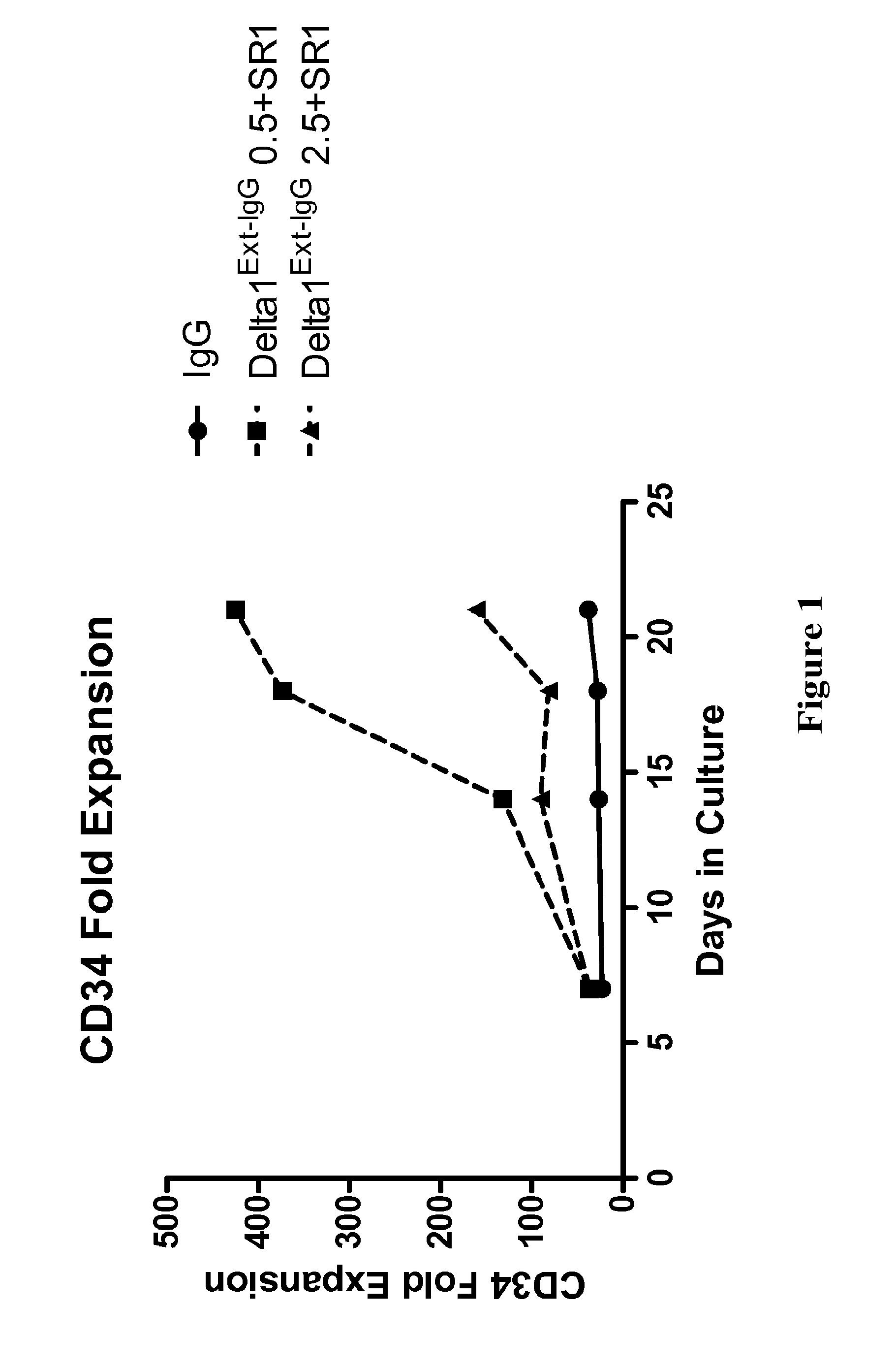
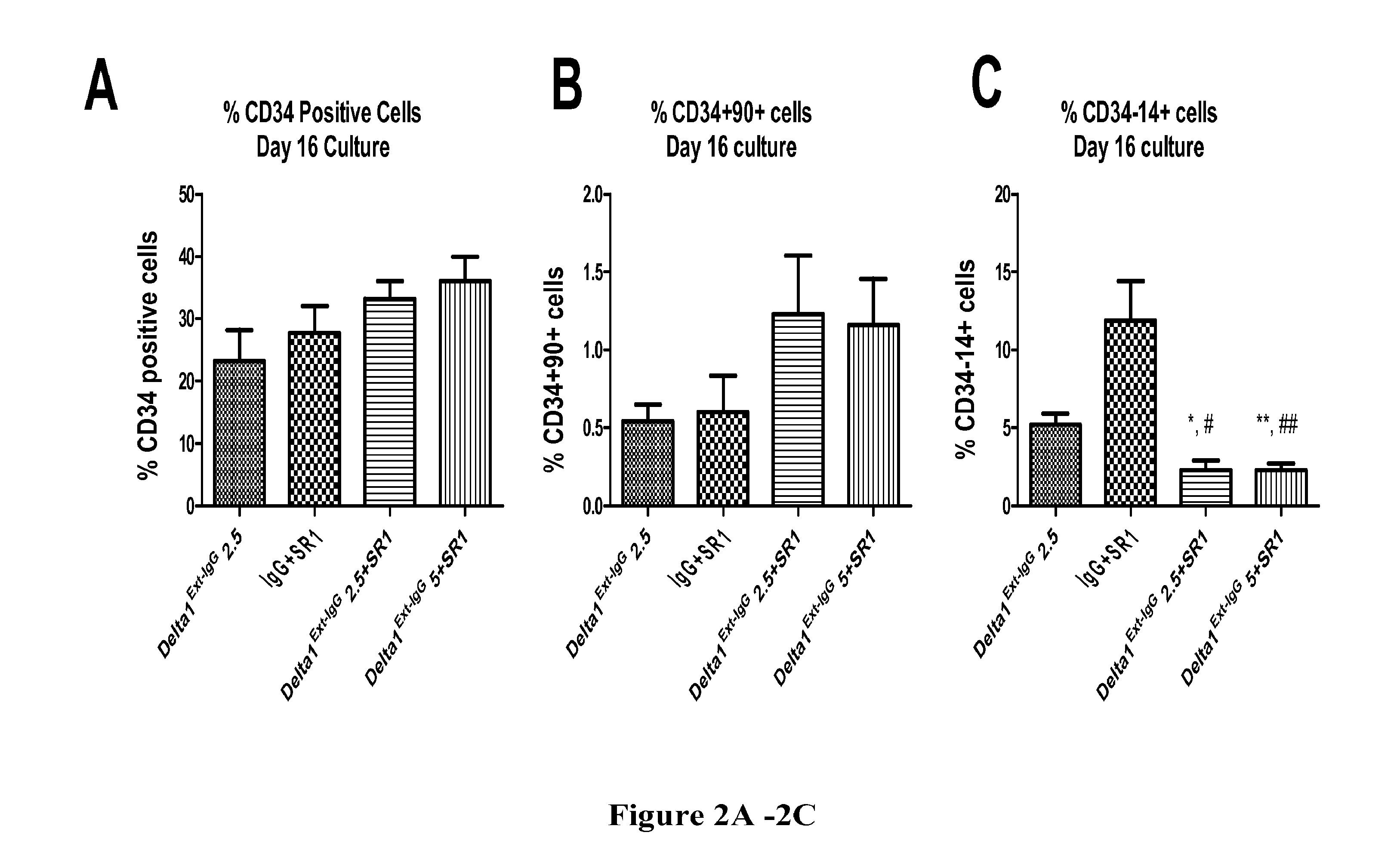
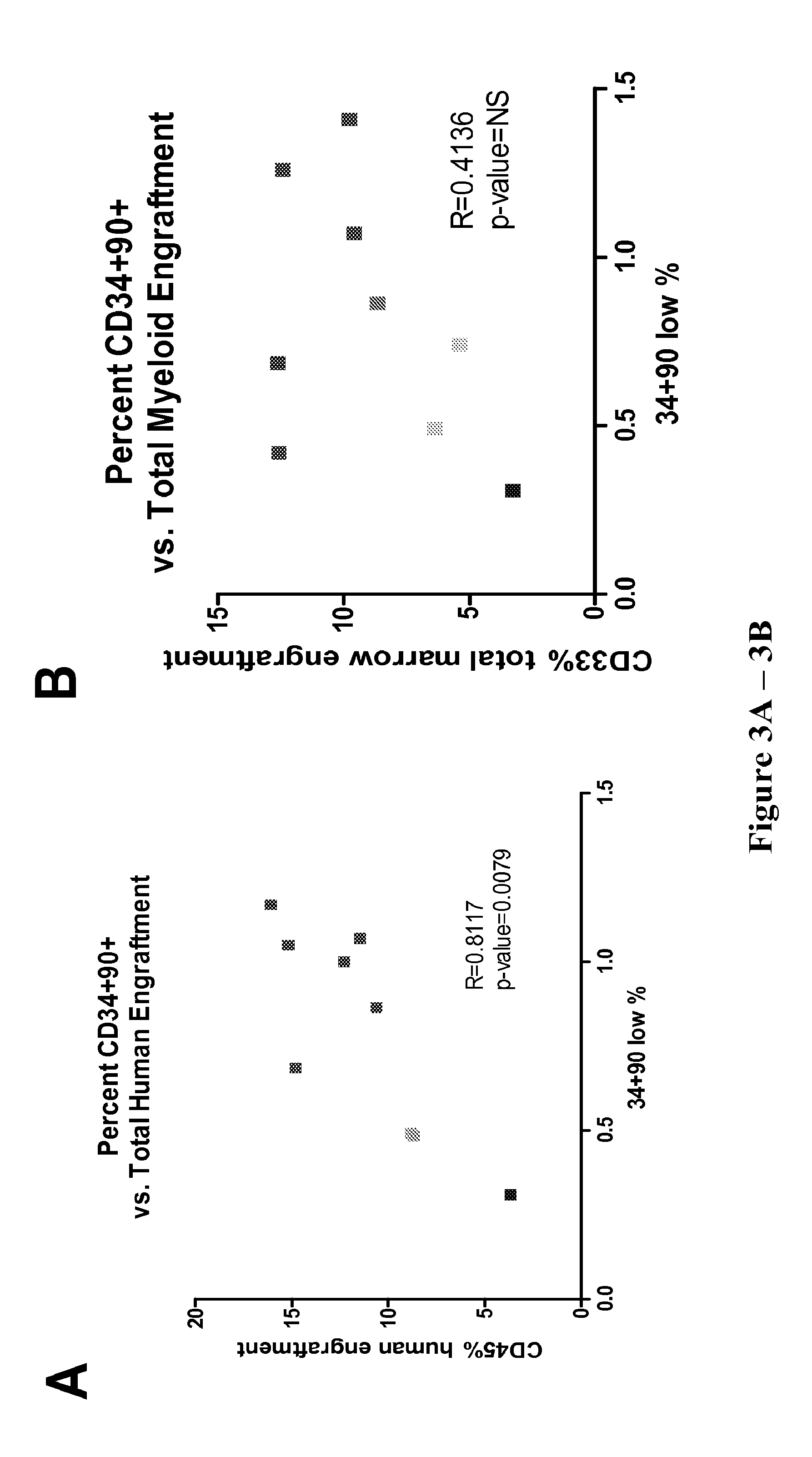
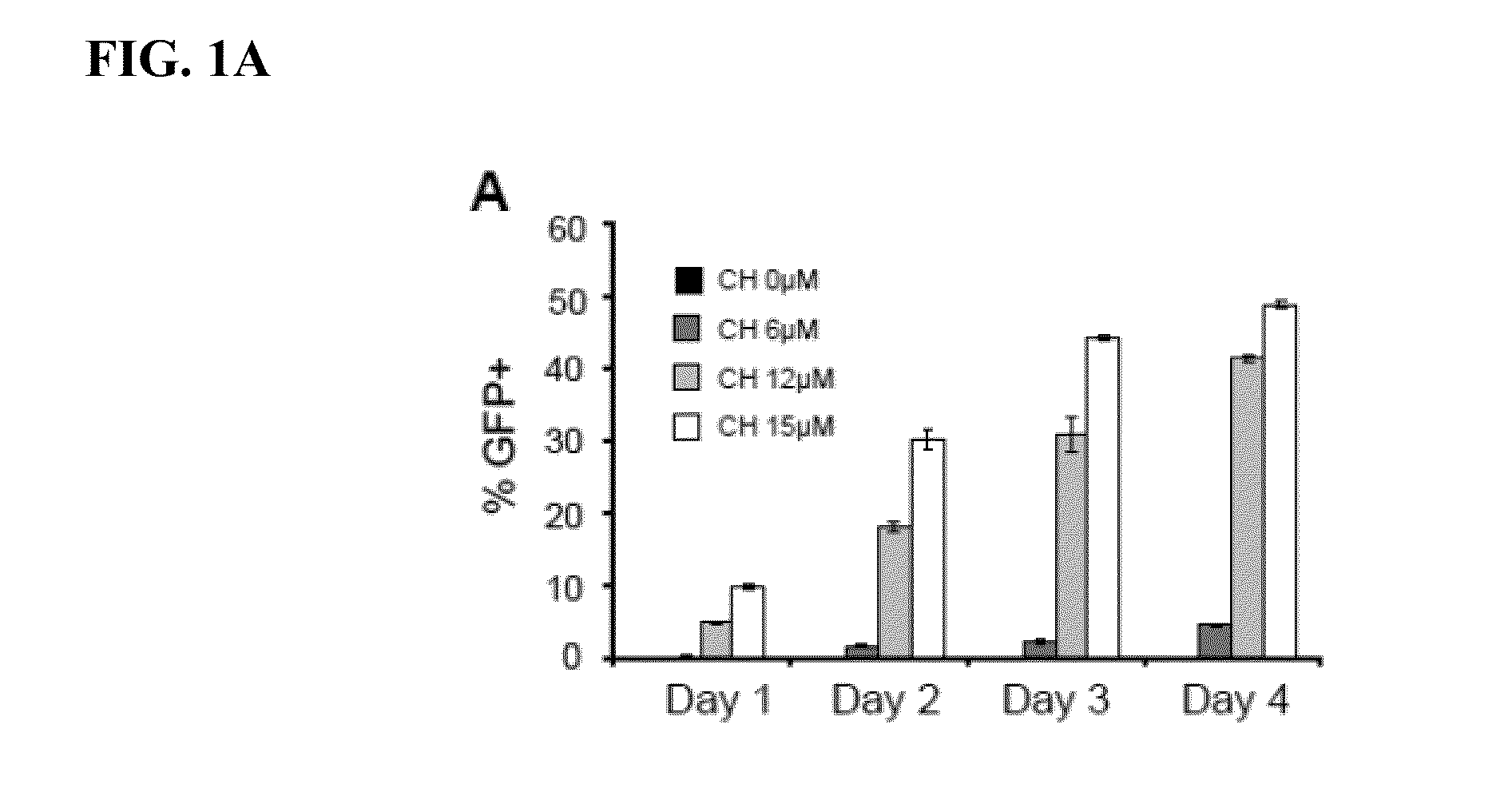
Compositions and methods for enhanced generation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells
The present invention relates to methods, kits and compositions for expansion of hematopoietic stem / progenitor cells and providing hematopoietic function to human patients in need thereof. In one aspect, it relates to kits and compositions comprising a Notch agonist and an aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonist. Also provided herein are methods for expanding the hematopoietic stem / progenitor cells using kits and compositions comprising a Notch agonist and an aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonist. The hematopoietic stem / progenitor cells expanded using the disclosed kits, compositions and methods include human umbilical cord blood stem / progenitor cells, placental cord blood stem / progenitor cells and peripheral blood stem cells. The present invention also relates to administering hematopoietic stem / progenitor cells expanded using a combination of a Notch agonist and an aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonist to a patient for short-term and / or long-term in vivo repopulation benefits.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
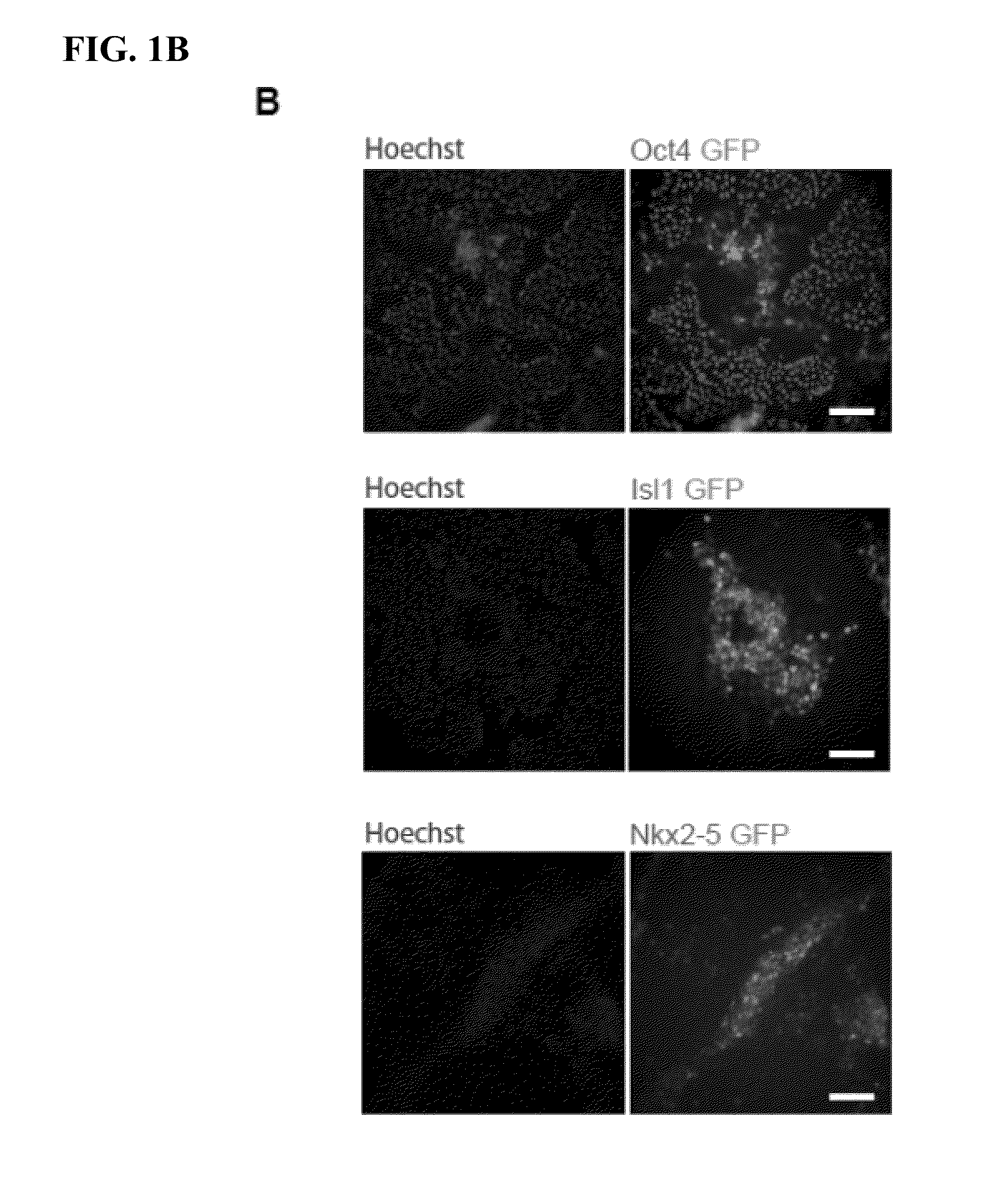
Use of islet 1 as a marker for isolating or generating stem cells
InactiveUS20060246446A1Enhance expressionGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementStem cell populationCardiac repair
The present invention provides in vitro methods of expansion and propagation of undifferentiated progenitor cells and more specifically undifferentiated progenitor cells containing Islet1, a marker apparently unique to proliferating cardiac stem cells. Methods are described for isolation of stem cell populations as well as for provoking expansion and propagation of undifferentiated progenitor cells without differentiation, to provide cardiac repair or improve cardiac function, for example.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
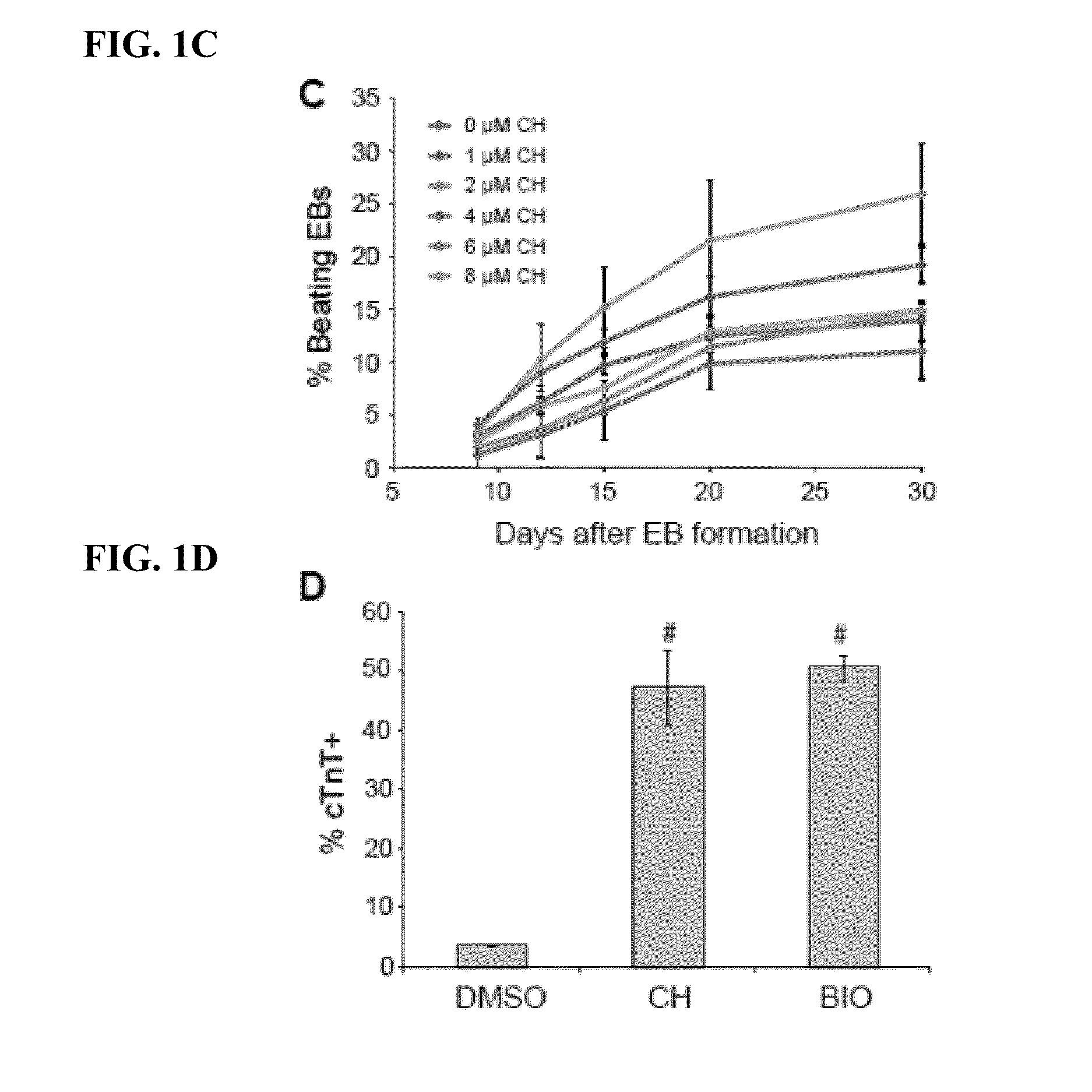
Generation of cardiomyocytes from human pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20130189785A1Artificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProgenitorInduced pluripotent stem cell
Methods for generating high-yield, high-purity cardiomyocyte progenitors or cardiomyocytes from pluripotent cells are described. Wnt / β-catenin signaling is first activated in pluripotent cells, e.g., by inhibition of Gsk-3 to obtain a first population of cells. Wnt / β-catenin signaling is then inhibited in the first cell population to induce cardiogenesis under fully defined, growth factor free culture conditions.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Modalities for the treatment of degenerative diseases of the retina
ActiveUS20060018886A1Quality improvementReduce complexityBiocideSenses disorderEmbryoRetinal progenitor
This invention relates to methods for improved cell-based therapies for retinal degeneration and for differentiating human embryonic stem cells and human embryo-derived into retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells and other retinal progenitor cells.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com