Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41results about How to "Inhibition of fibrillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
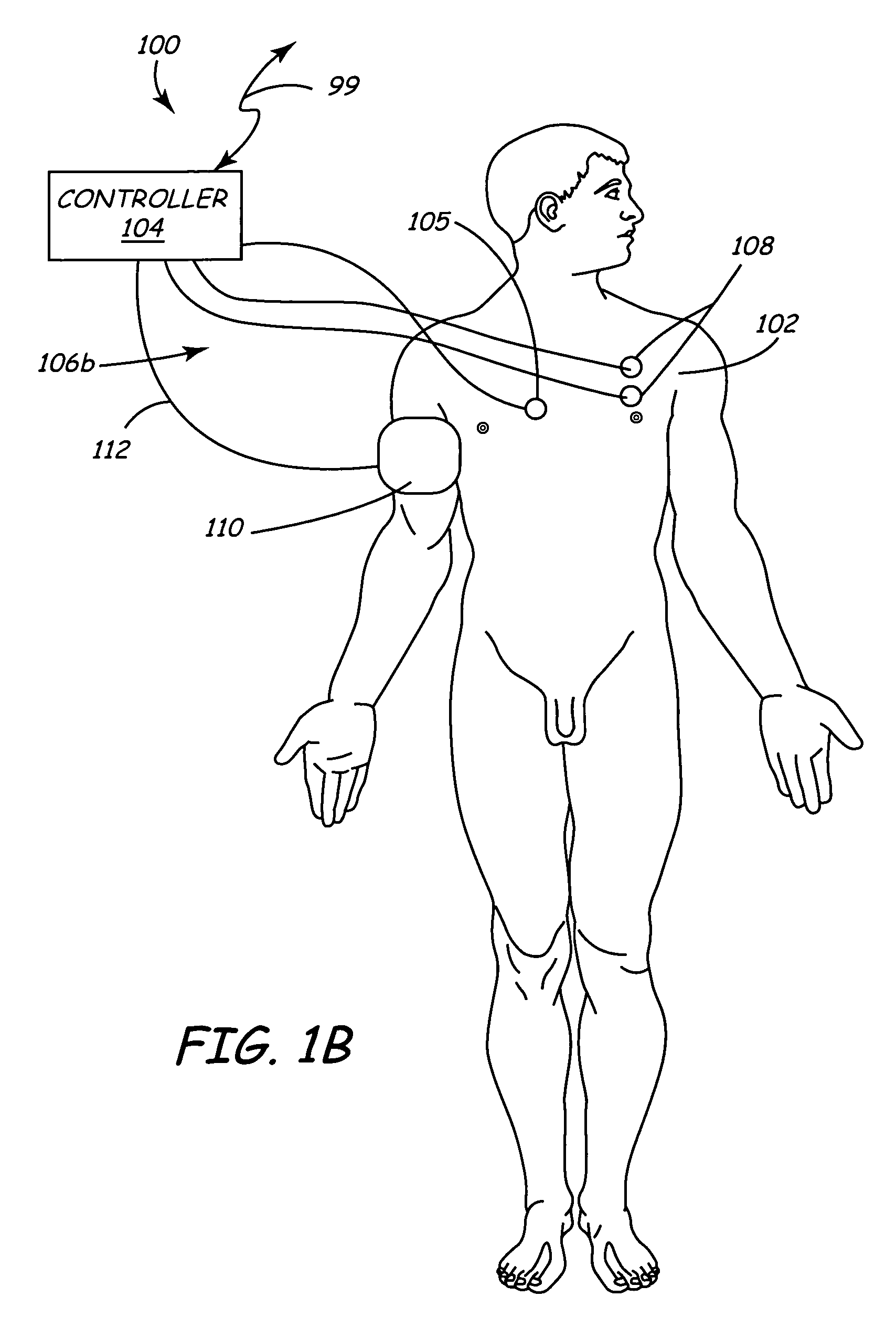
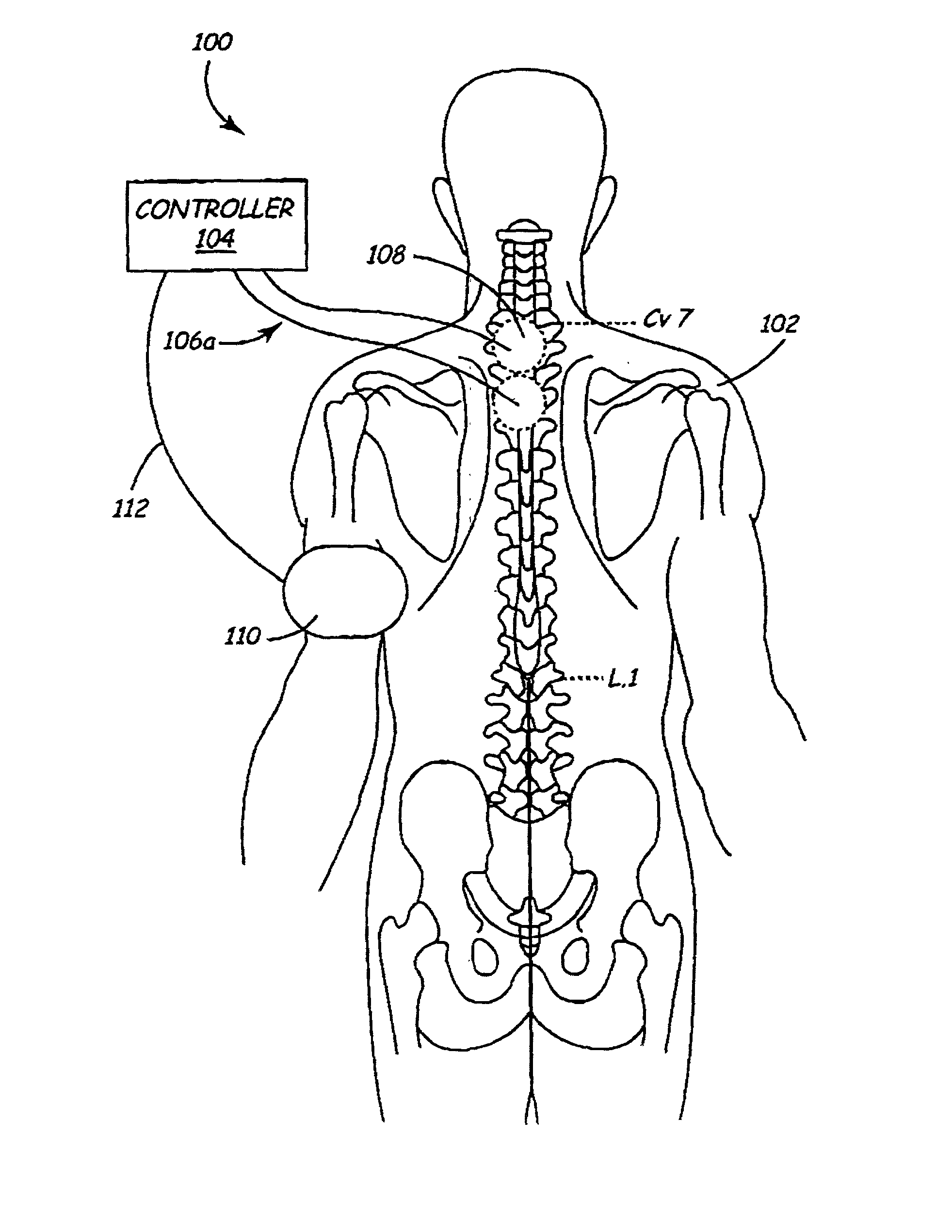
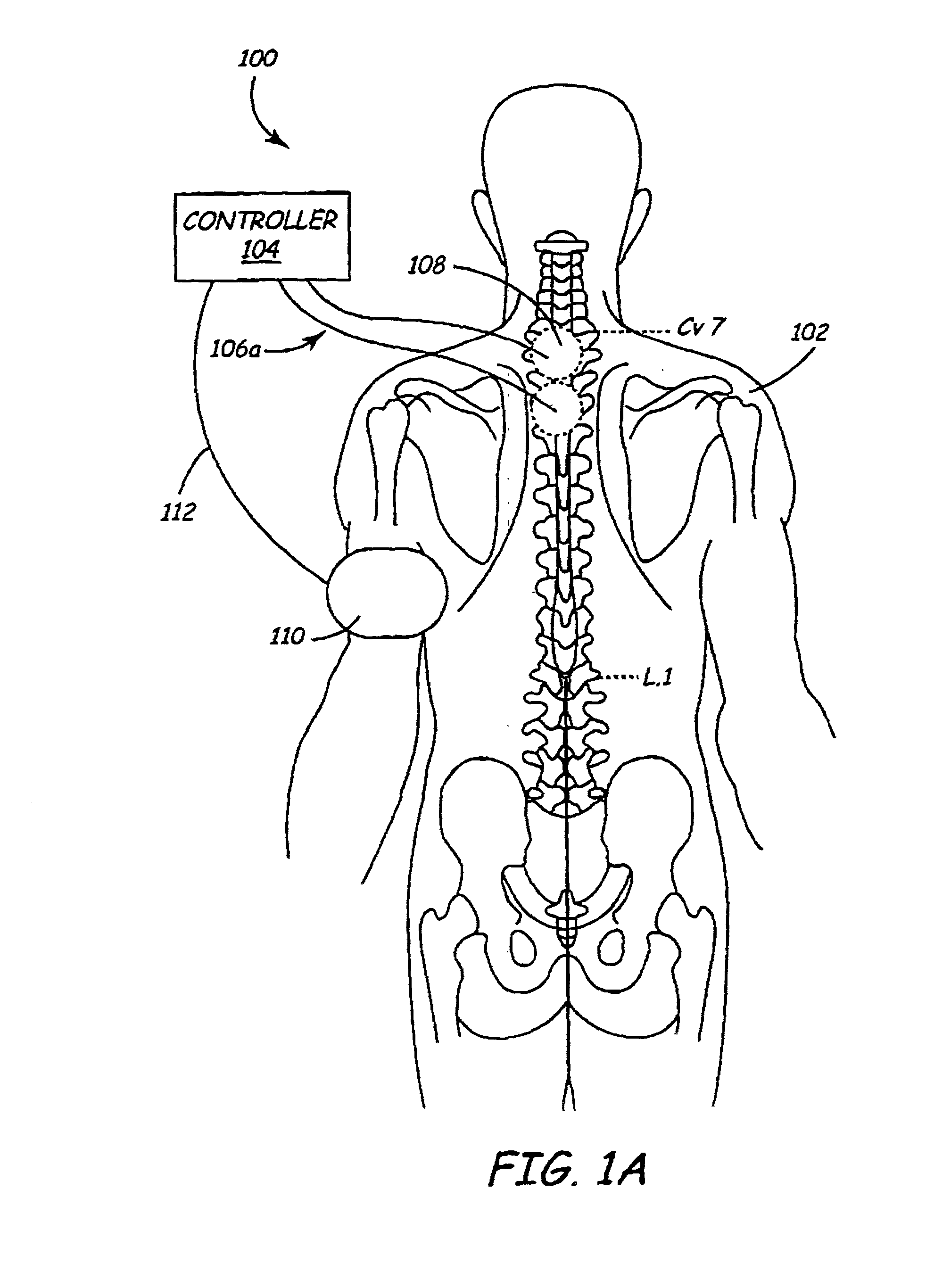
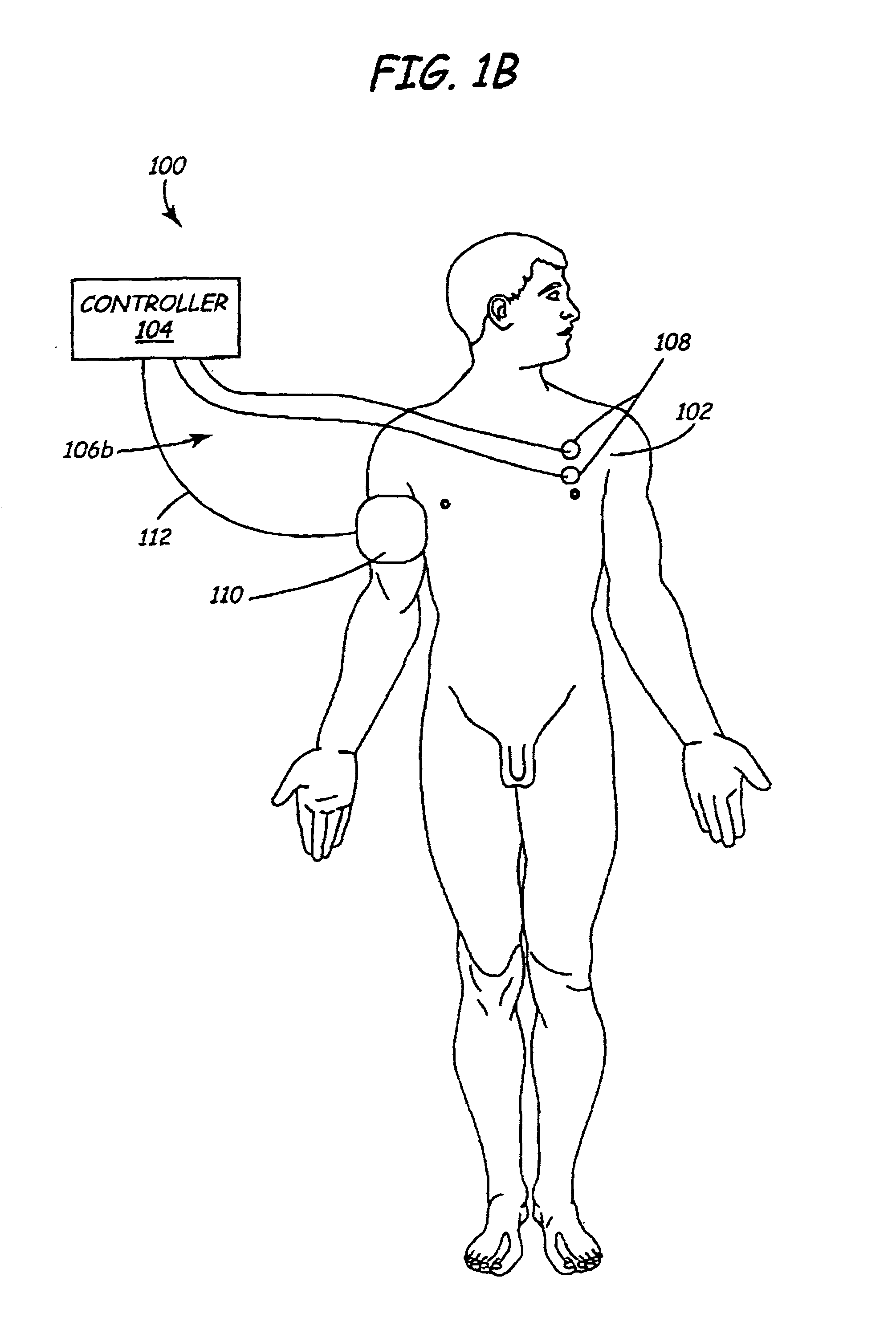
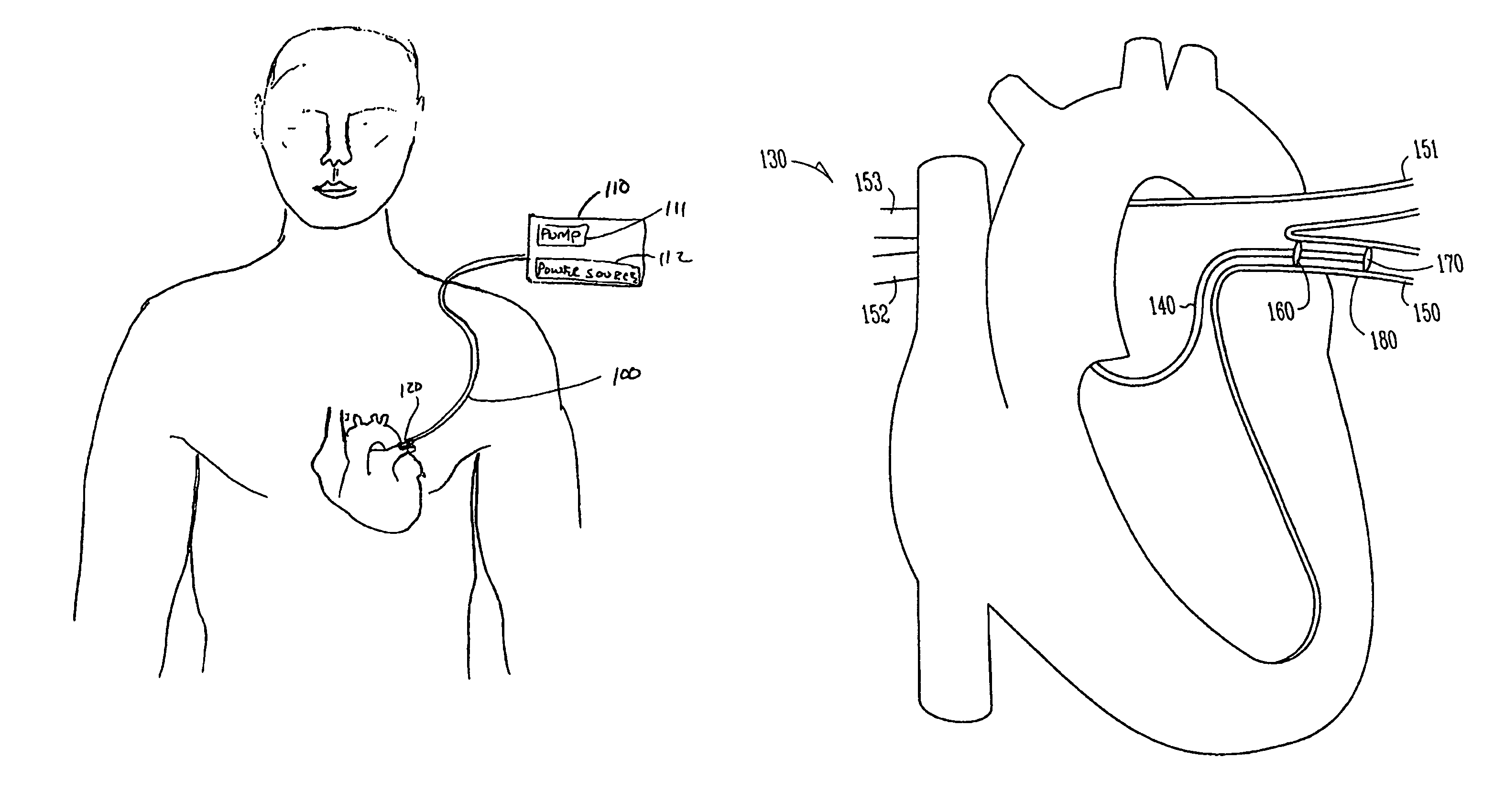
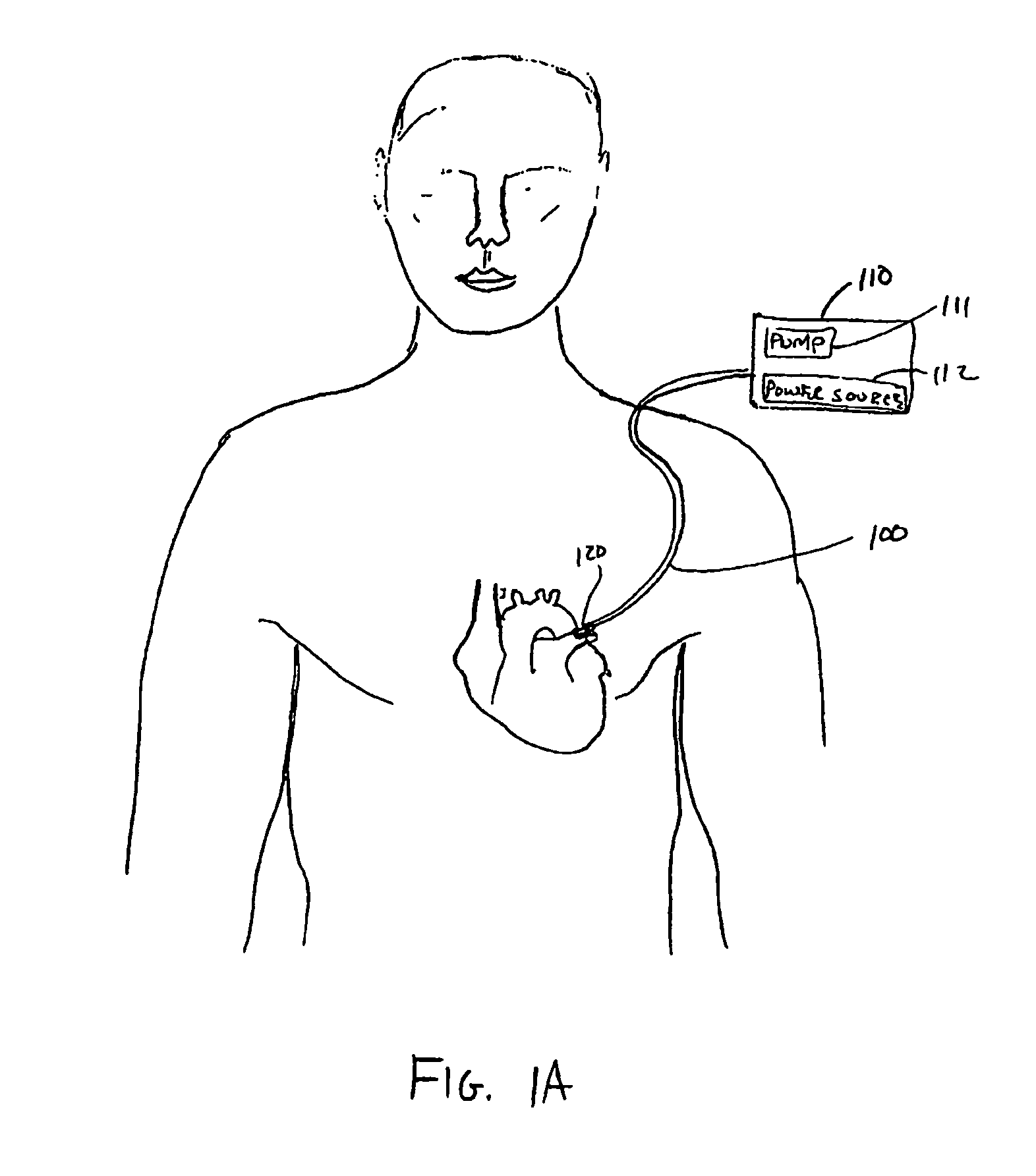
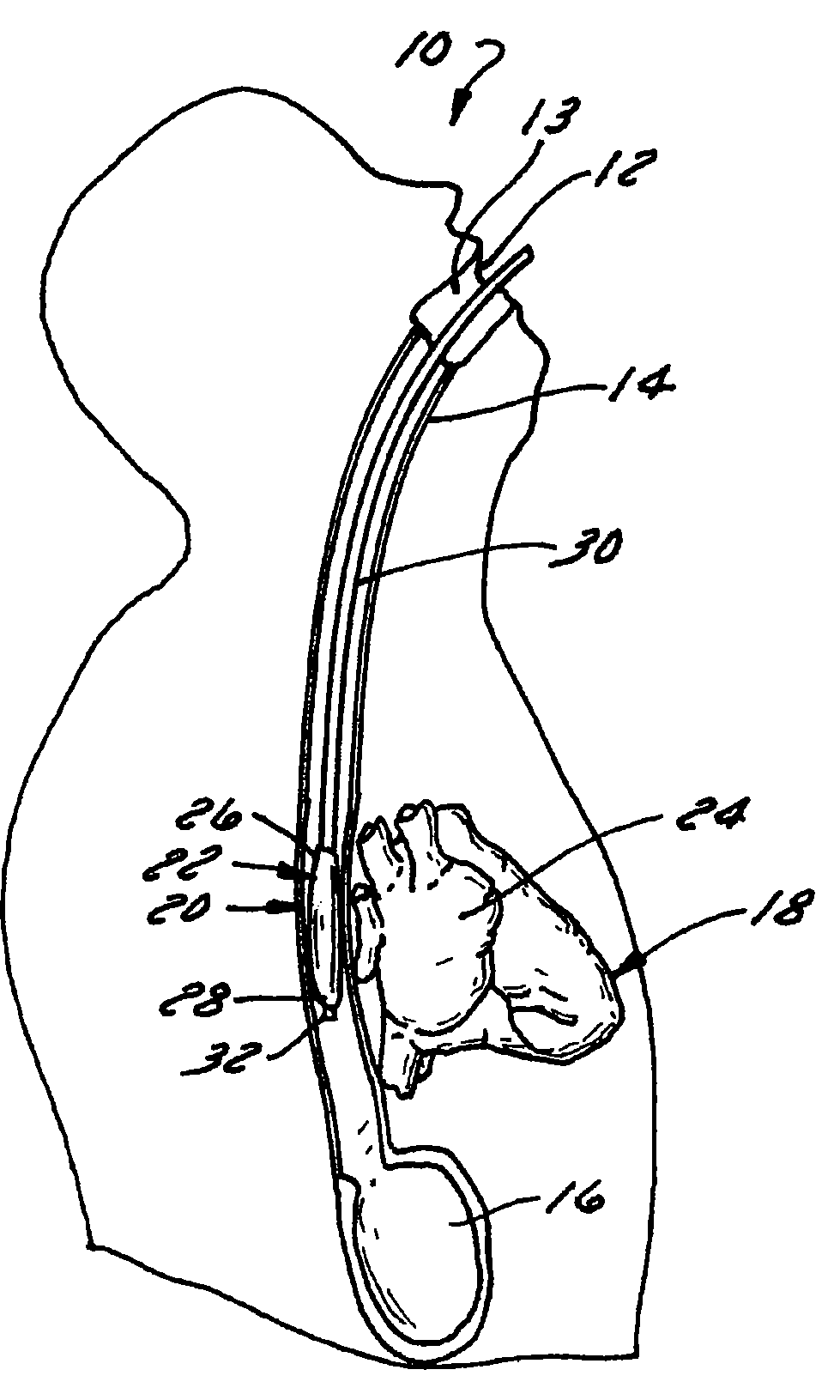
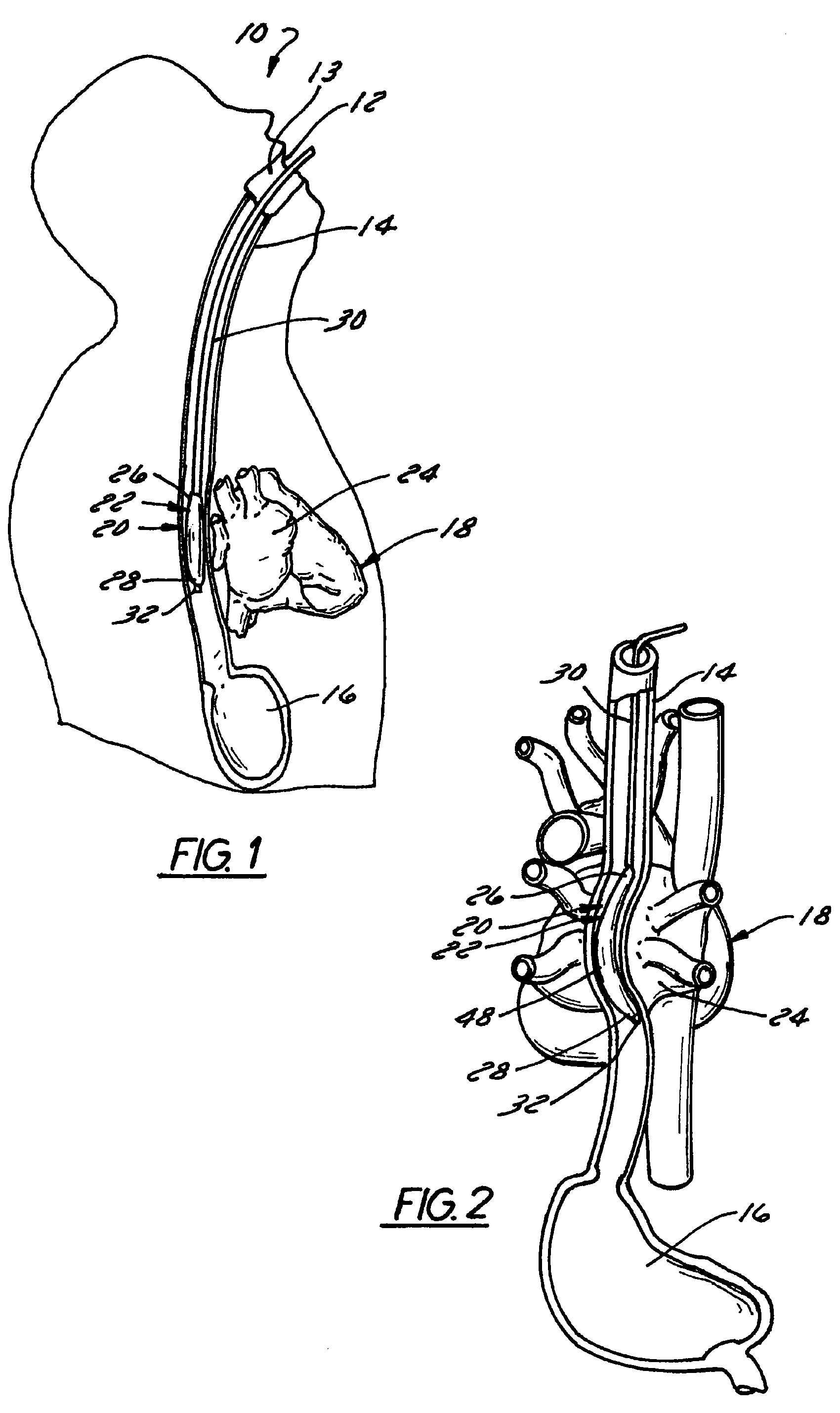
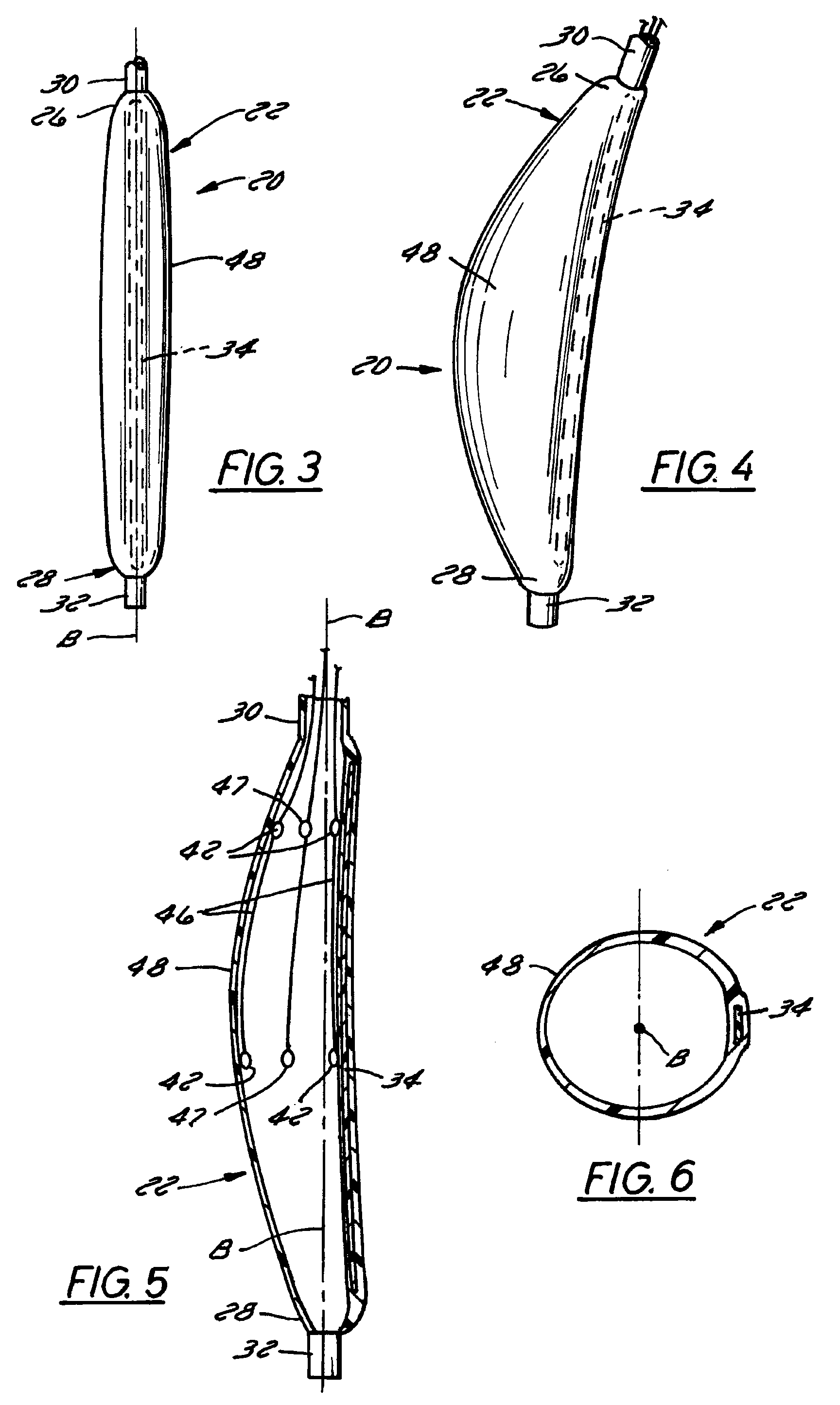
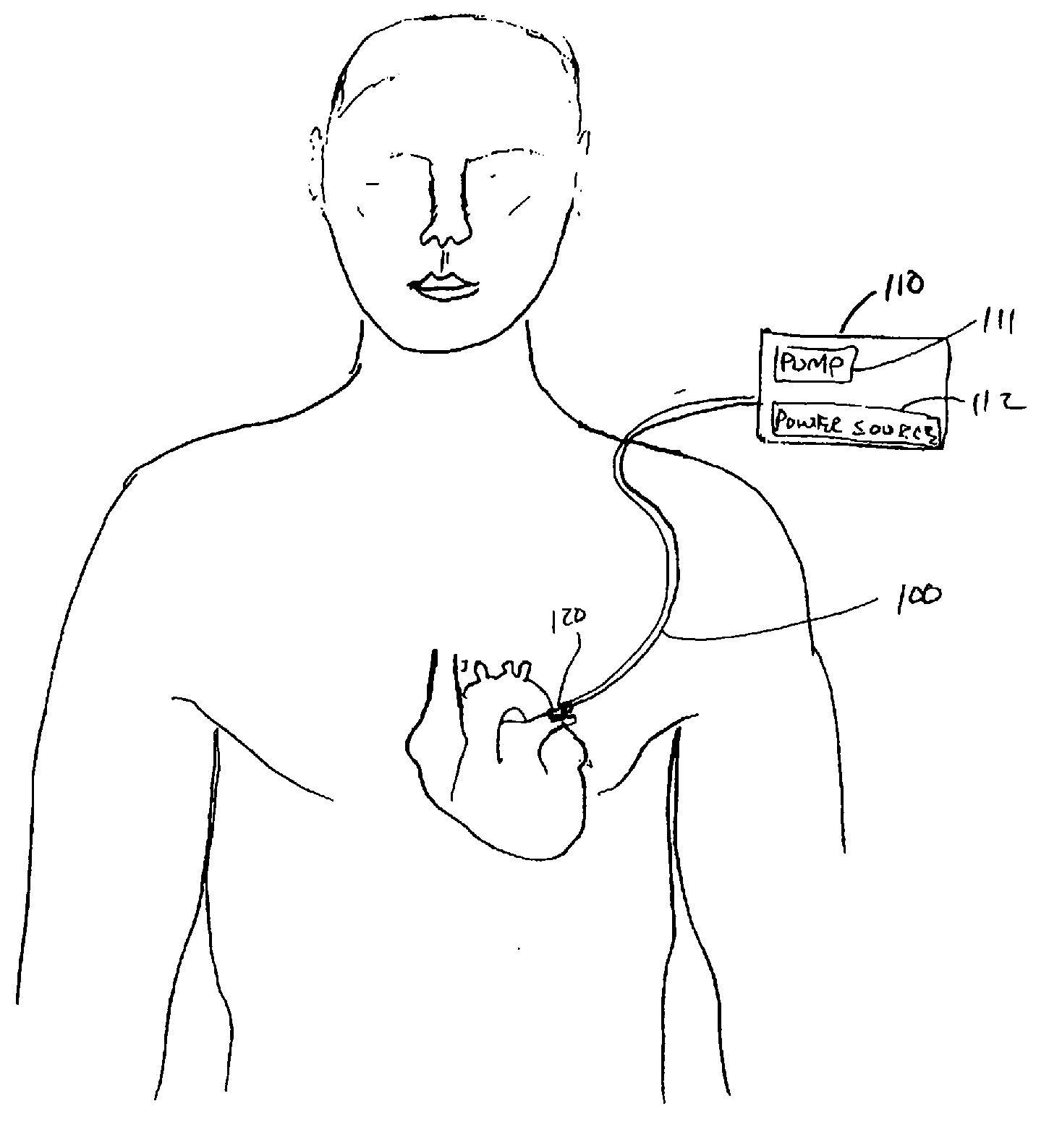
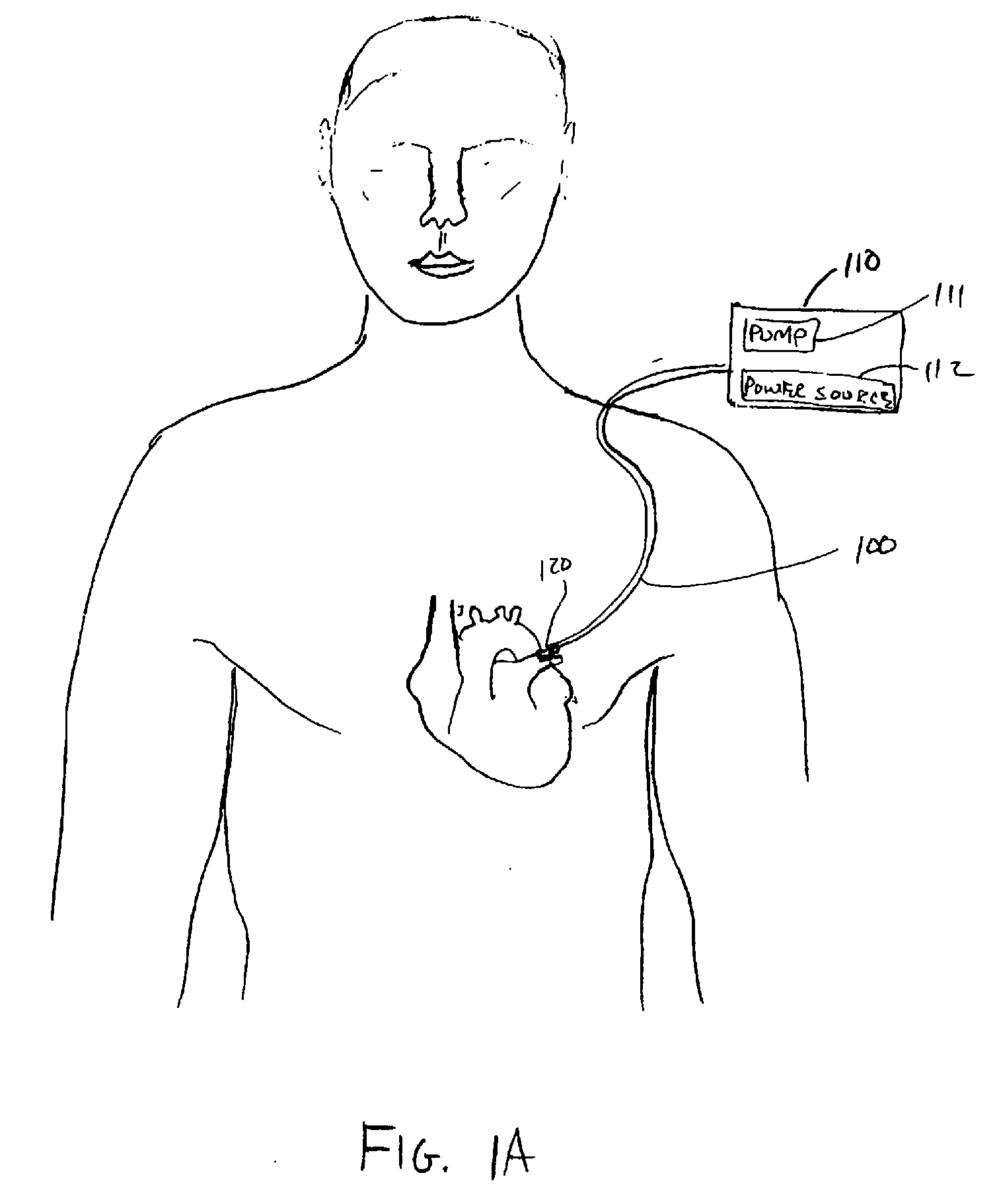
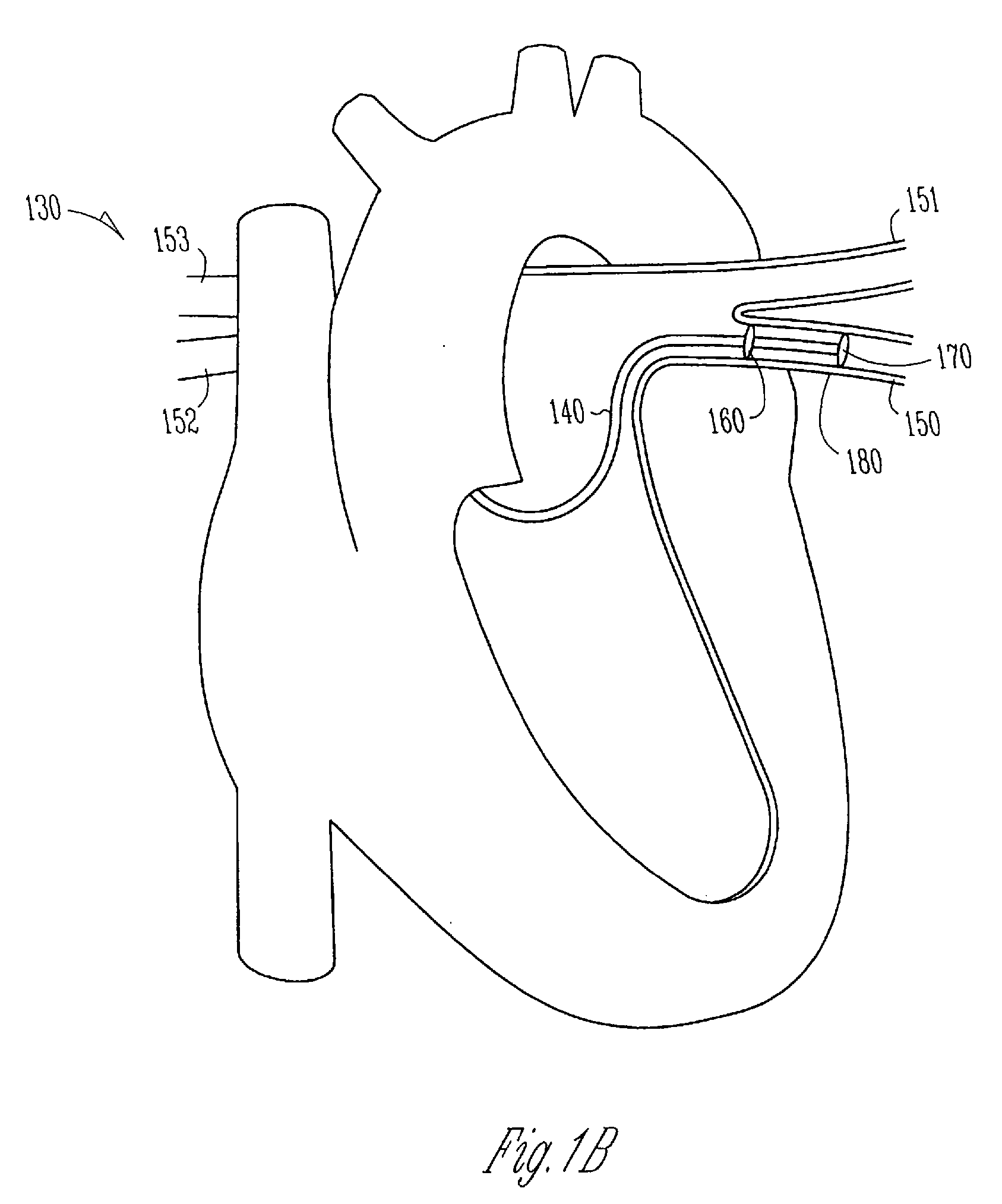
Method and apparatus to minimize effects of a cardiac insult
InactiveUS7010345B2Reduced activityImprove heart functionHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsHeart diseaseElectrical stimulations
A method and apparatus are provided for protecting cardiac tissue from insult. The method comprises identifying the occurrence of an insult, such as a heart attack, and delivering electrical stimulation to one or more predetermined nerves in a patient's body in response to identifying the occurrence of the insult. The stimulation may be provided at the spinal canal or on the chest wall of the patient through cutaneous electrodes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus to minimize effects of a cardiac insult
InactiveUS20020143369A1Reduced activityAvoid it happening againHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsHeart diseaseElectrical stimulations
A method and apparatus are provided for protecting cardiac tissue from insult. The method comprises identifying the occurrence of an insult, such as a heart attack, and delivering electrical stimulation to one or more predetermined nerves in a patient's body in response to identifying the occurrence of the insult. The stimulation may be provided at the spinal canal or on the chest wall of the patient through cutaneous electrodes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
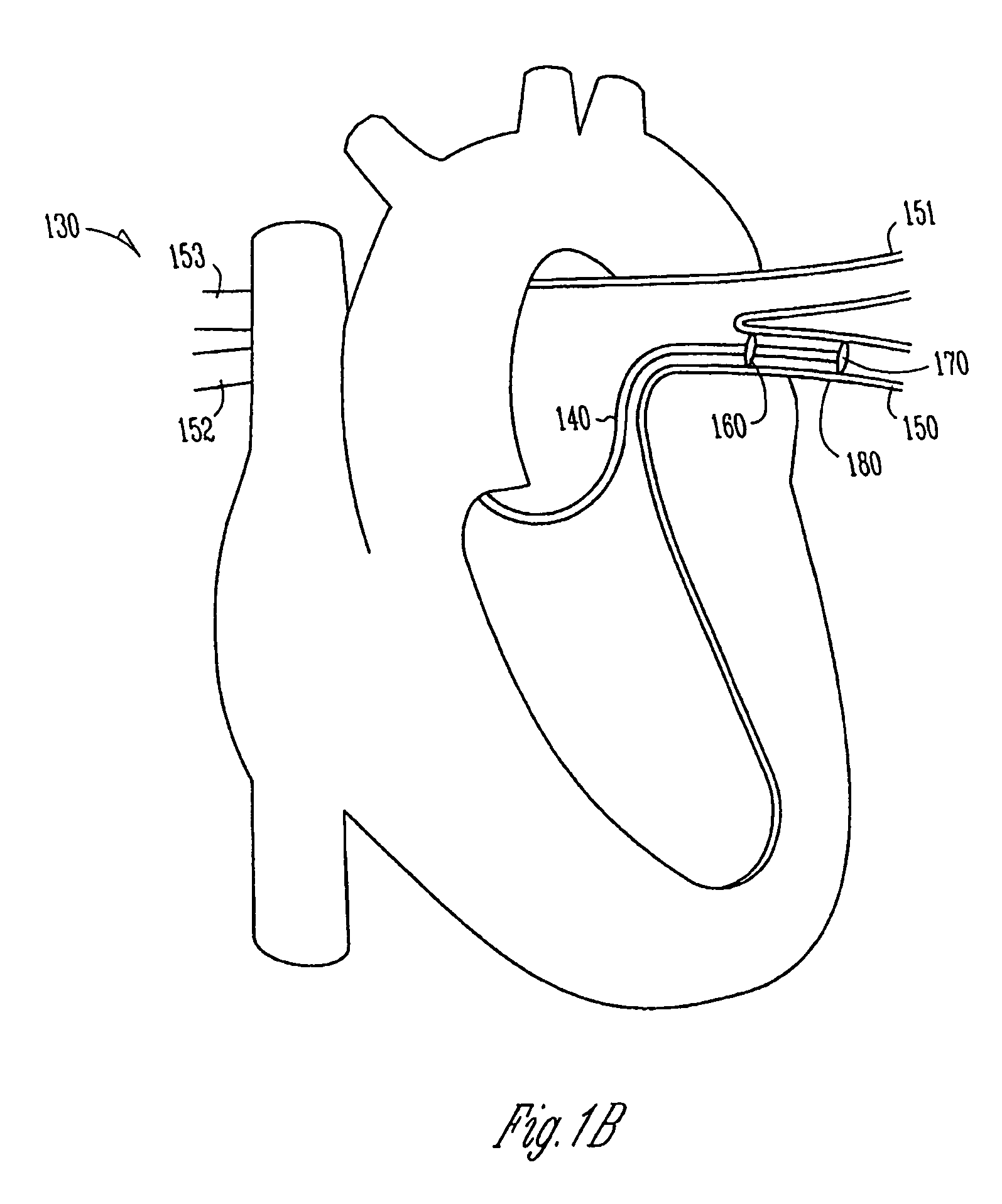
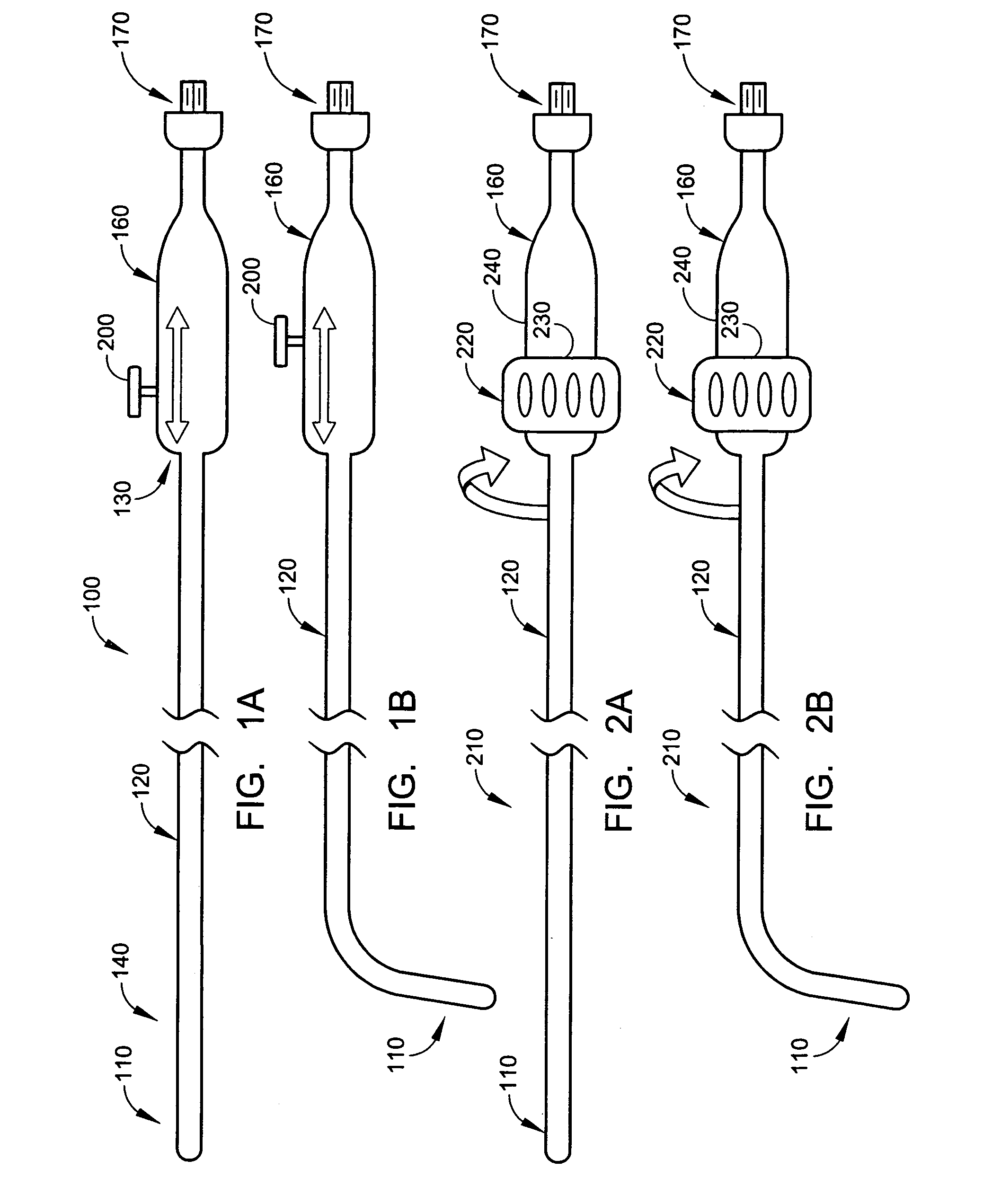
Radio-frequency-based catheter system with improved deflection and steering mechanisms
InactiveUS7004938B2Precise ablationPositioning is simple and fastElectrotherapyRadiating element housingsElectricityElectrical conductor
A RF catheter system includes a catheter with a proximal portion, a distal portion having a distal end and a lumen extending from the proximal portion to the distal portion. Inner and outer coaxially aligned conductors extend within the catheter and are coaxial with the lumen. A deflectable catheter guide is disposed within the catheter lumen and extends proximally within the catheter lumen and terminates distally of the distal end of the catheter to define a biological ablation pathway. A radio-frequency antenna is disposed at the distal portion of the catheter and is in electrical communication with the inner and outer coaxially aligned conductors. The radio-frequency antenna is adaptable to receive and transmit radio-frequency energy for ablating biological tissue along the ablation pathway.
Owner:MEDWAVE INC
Neurotoxic agents and devices to treat atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS8052668B2Reduce riskInhibition of fibrillationTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgeryVeinNeurotoxicity
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Radio-frequency-based catheter system with improved deflection and steering mechanisms
ActiveUS7815637B2Precise ablationPositioning is simple and fastDiagnosticsMedical devicesElectricityElectrical conductor
A RF catheter system includes a catheter with a proximal portion, a distal portion having a distal end and a lumen extending from the proximal portion to the distal portion. Inner and outer coaxially aligned conductors extend within the catheter and are coaxial with the lumen. A deflectable catheter guide is disposed within the catheter lumen and extends proximally within the catheter lumen and terminates distally of the distal end of the catheter to define a biological ablation pathway. A radio-frequency antenna is disposed at the distal portion of the catheter and is in electrical communication with the inner and outer coaxially aligned conductors. The radio-frequency antenna is adaptable to receive and transmit radio-frequency energy for ablating biological tissue along the ablation pathway.
Owner:ORMSBY THEODORE C +2
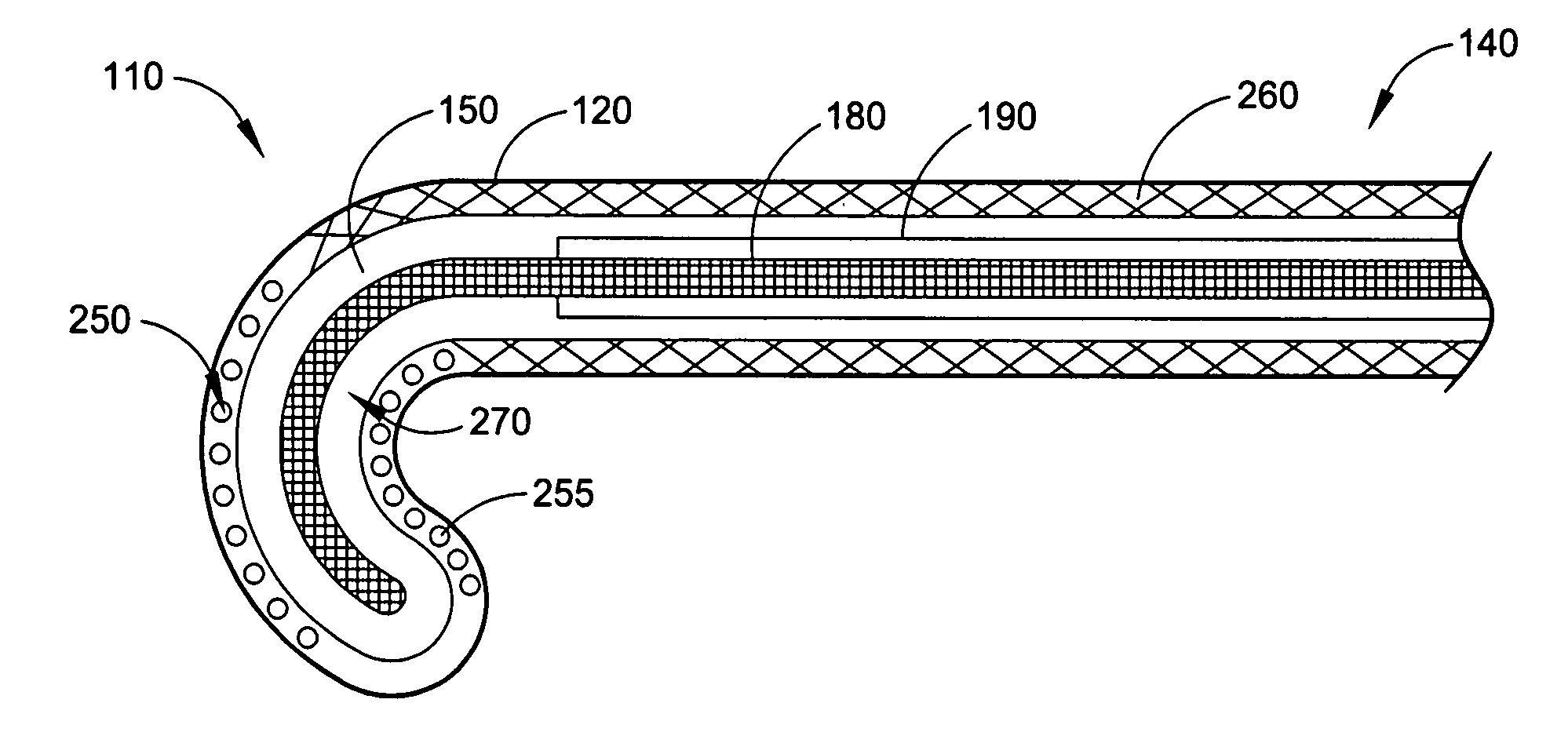
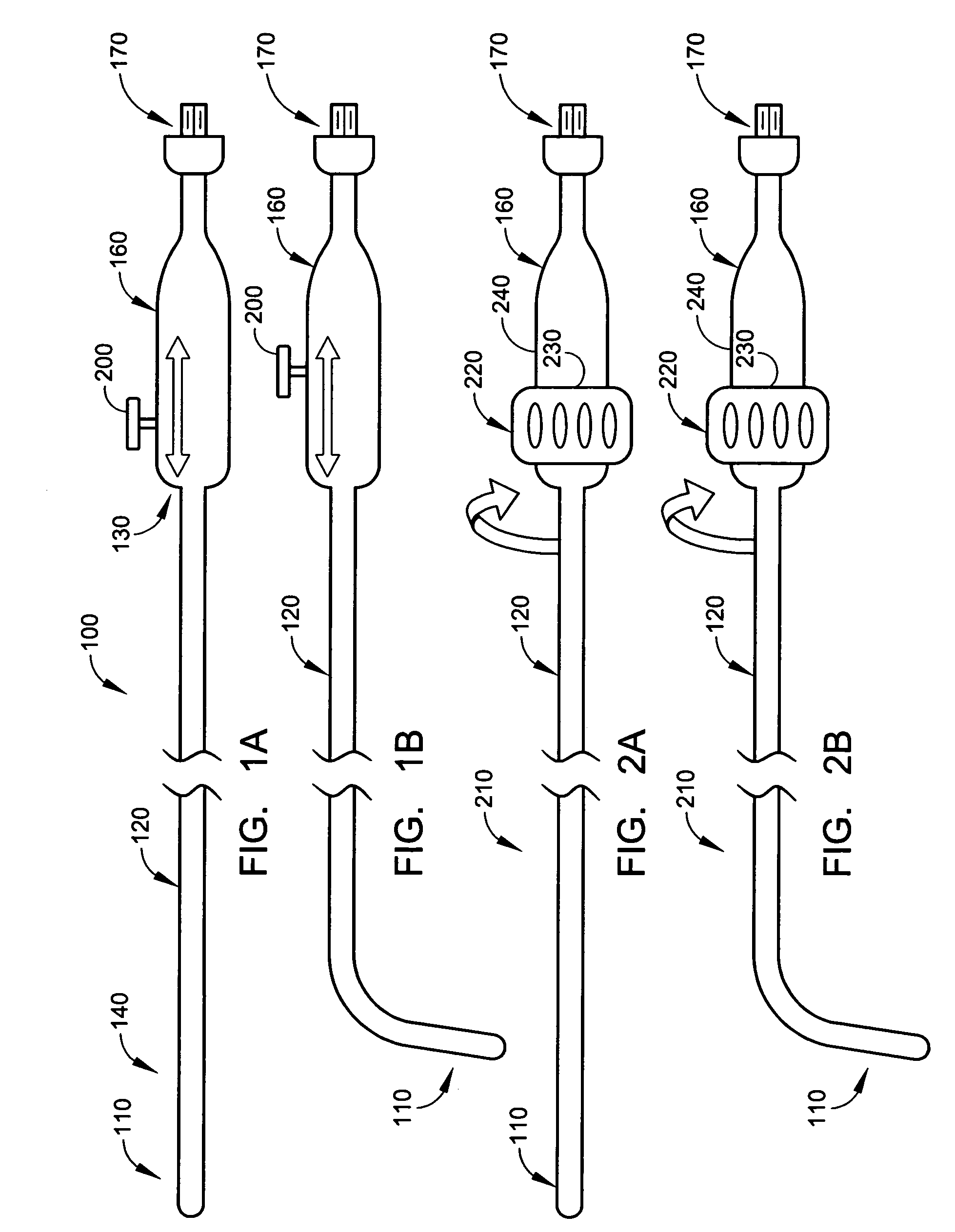
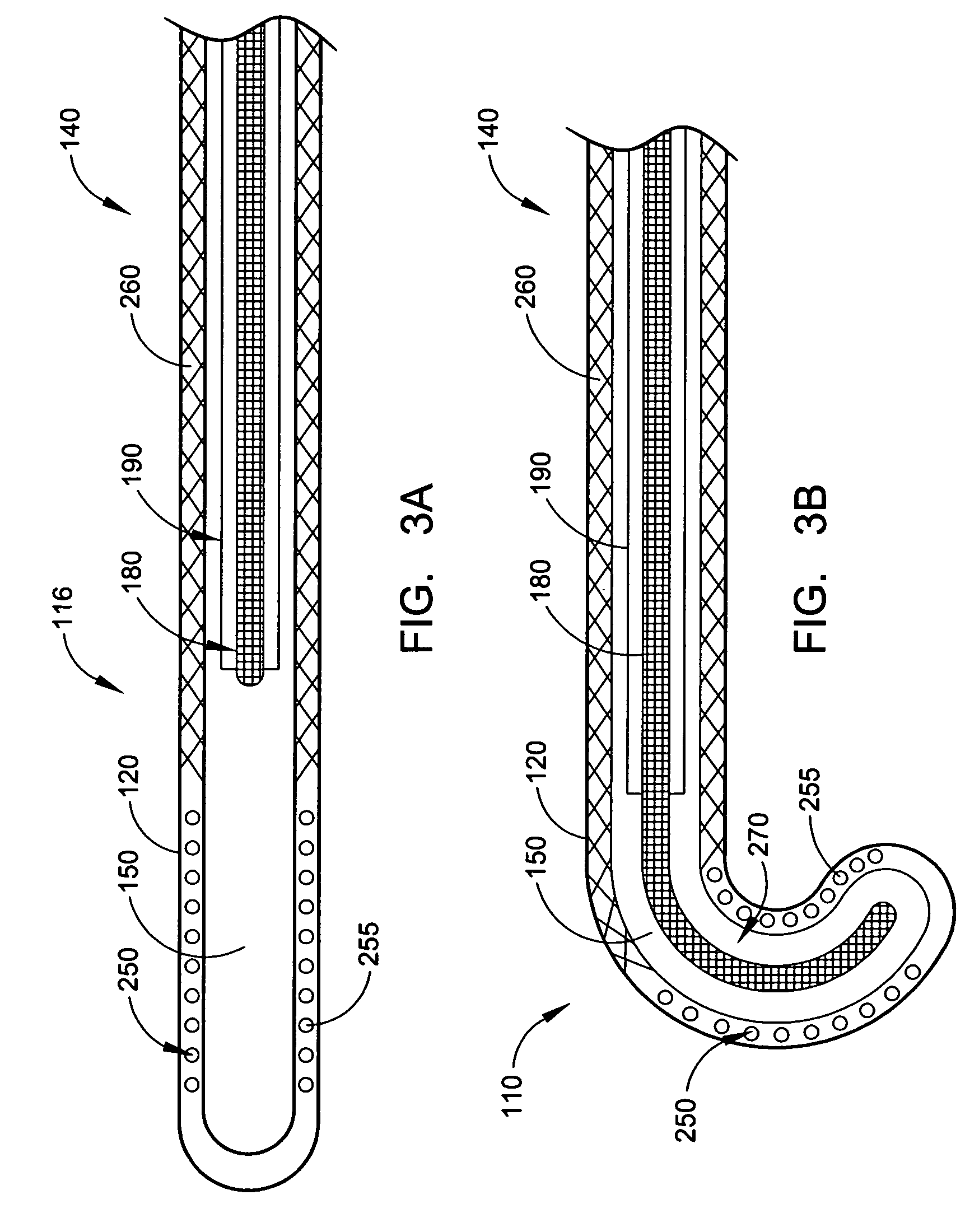
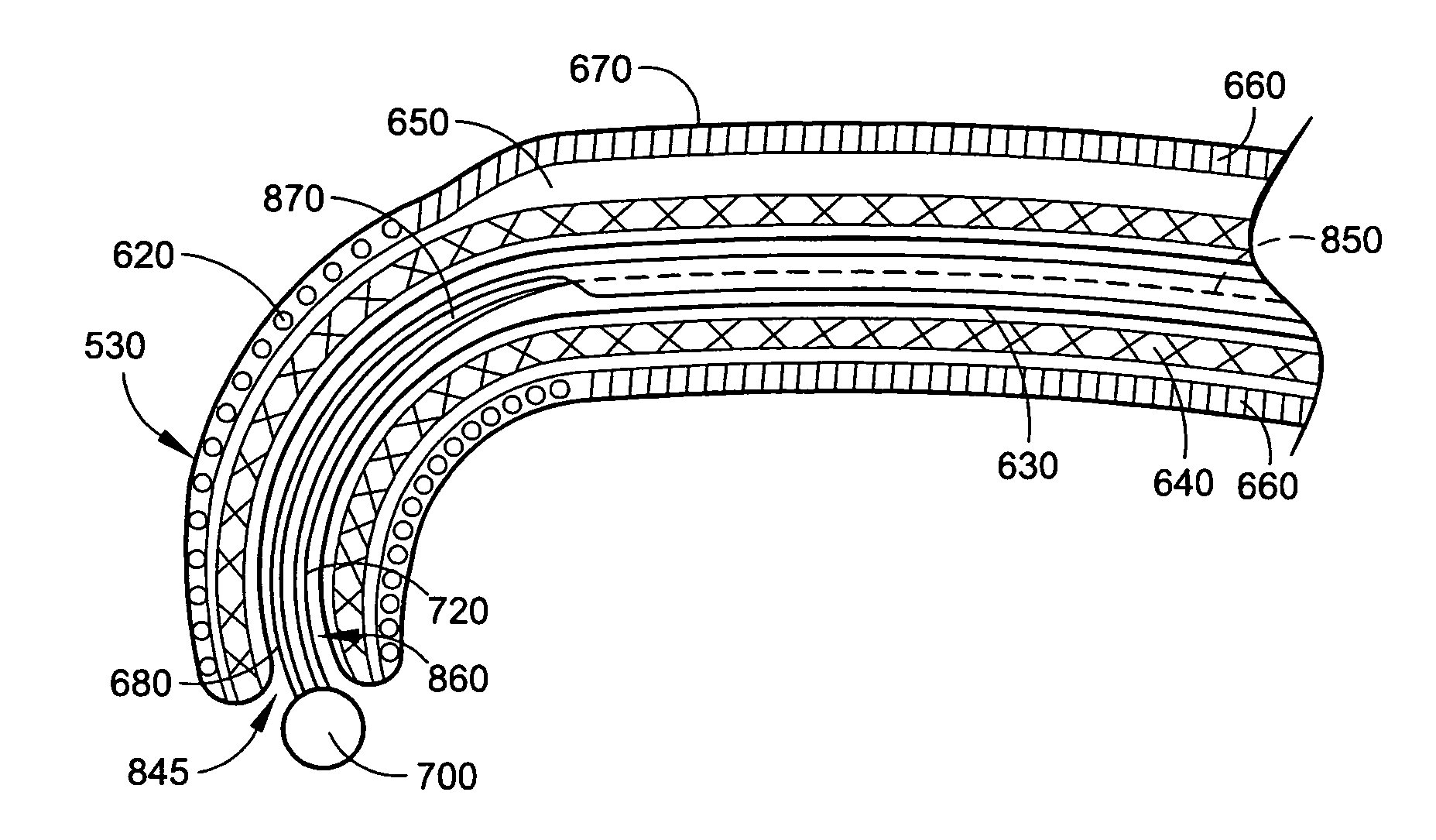
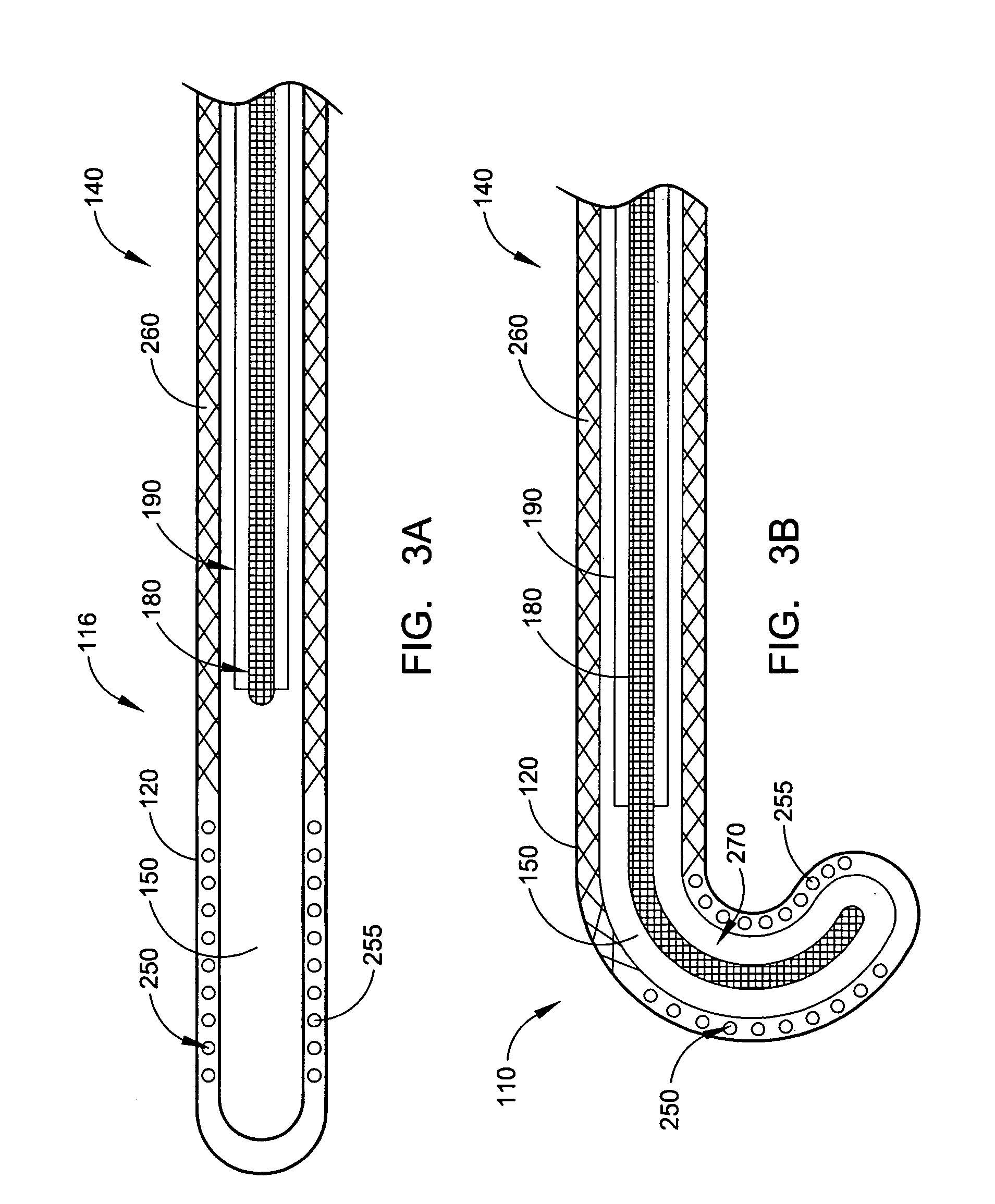
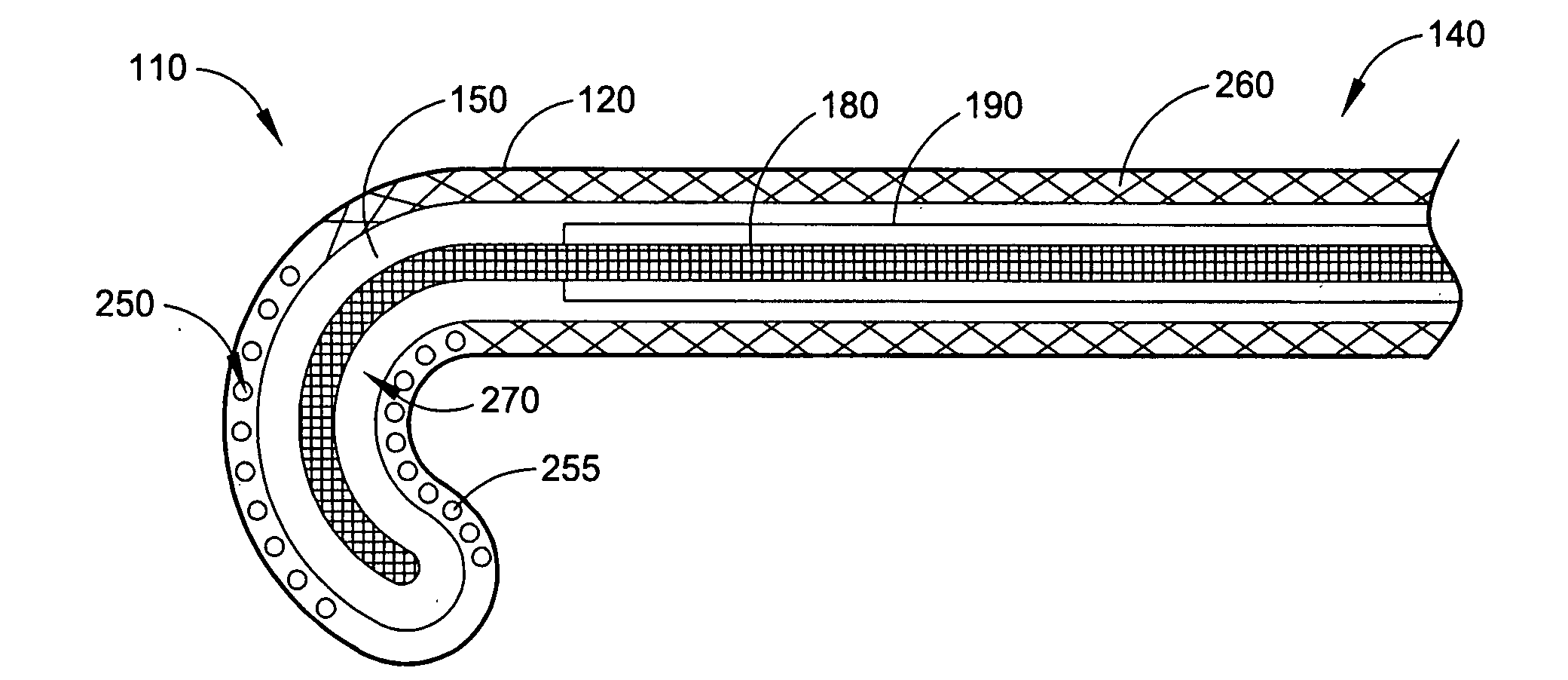
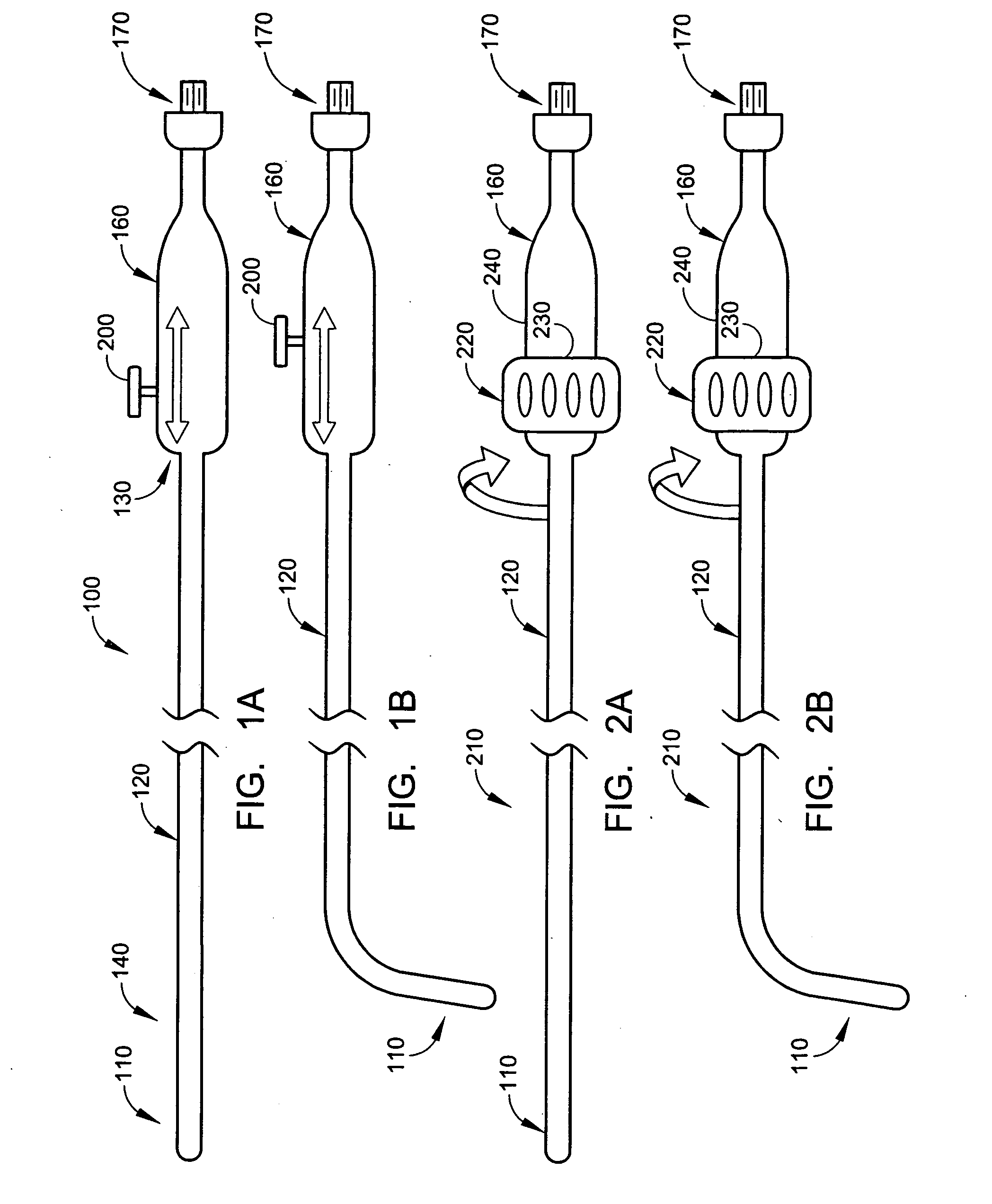
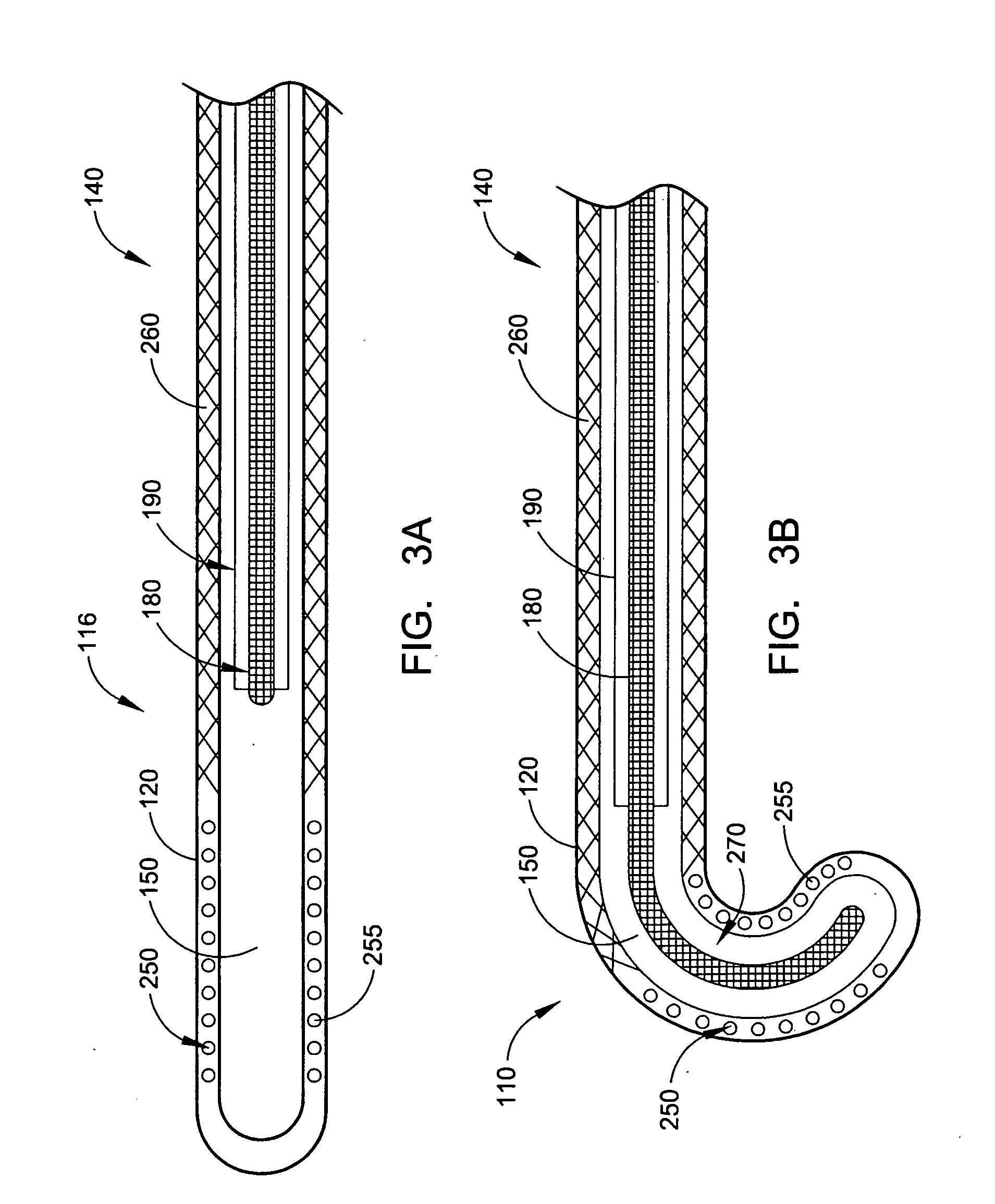
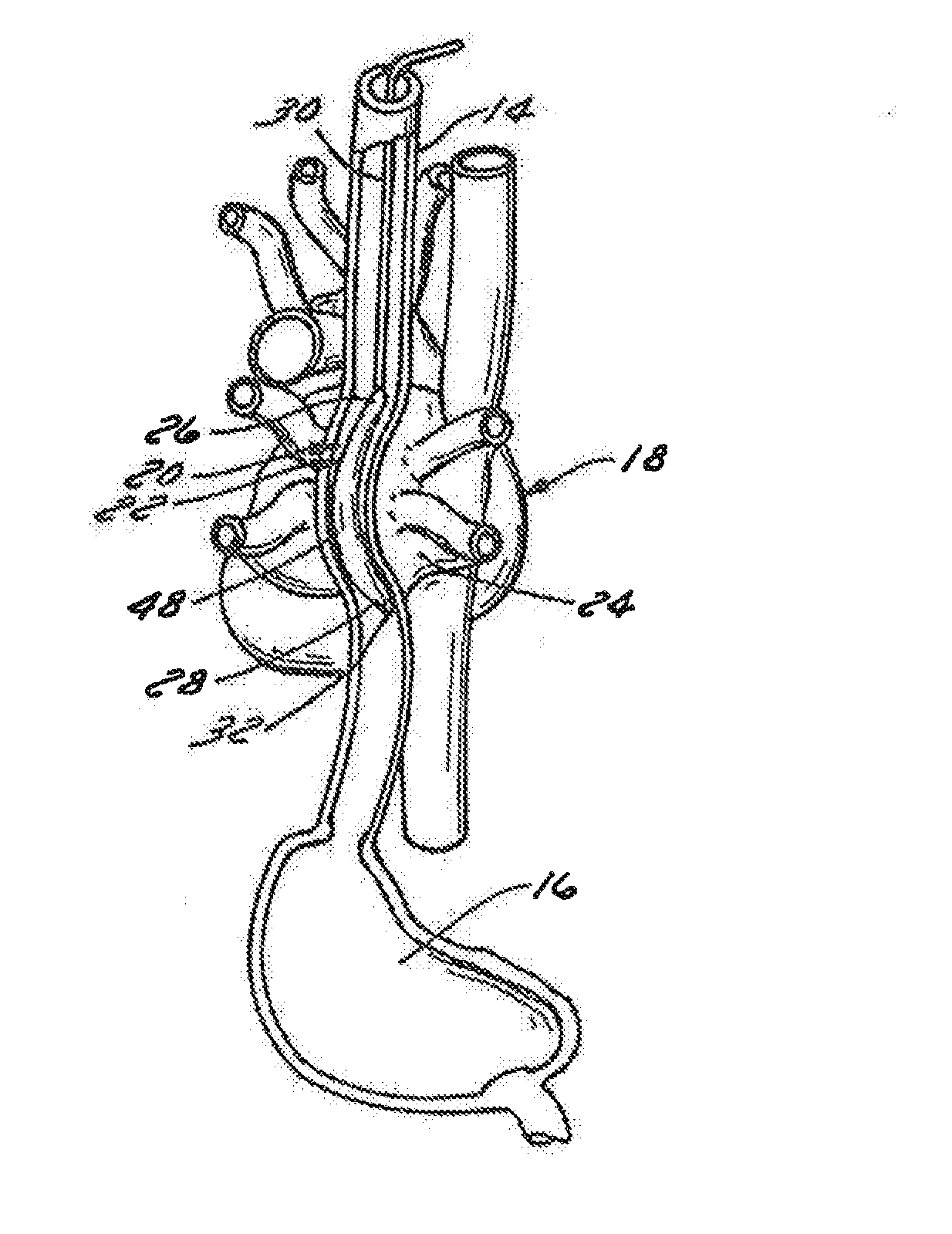
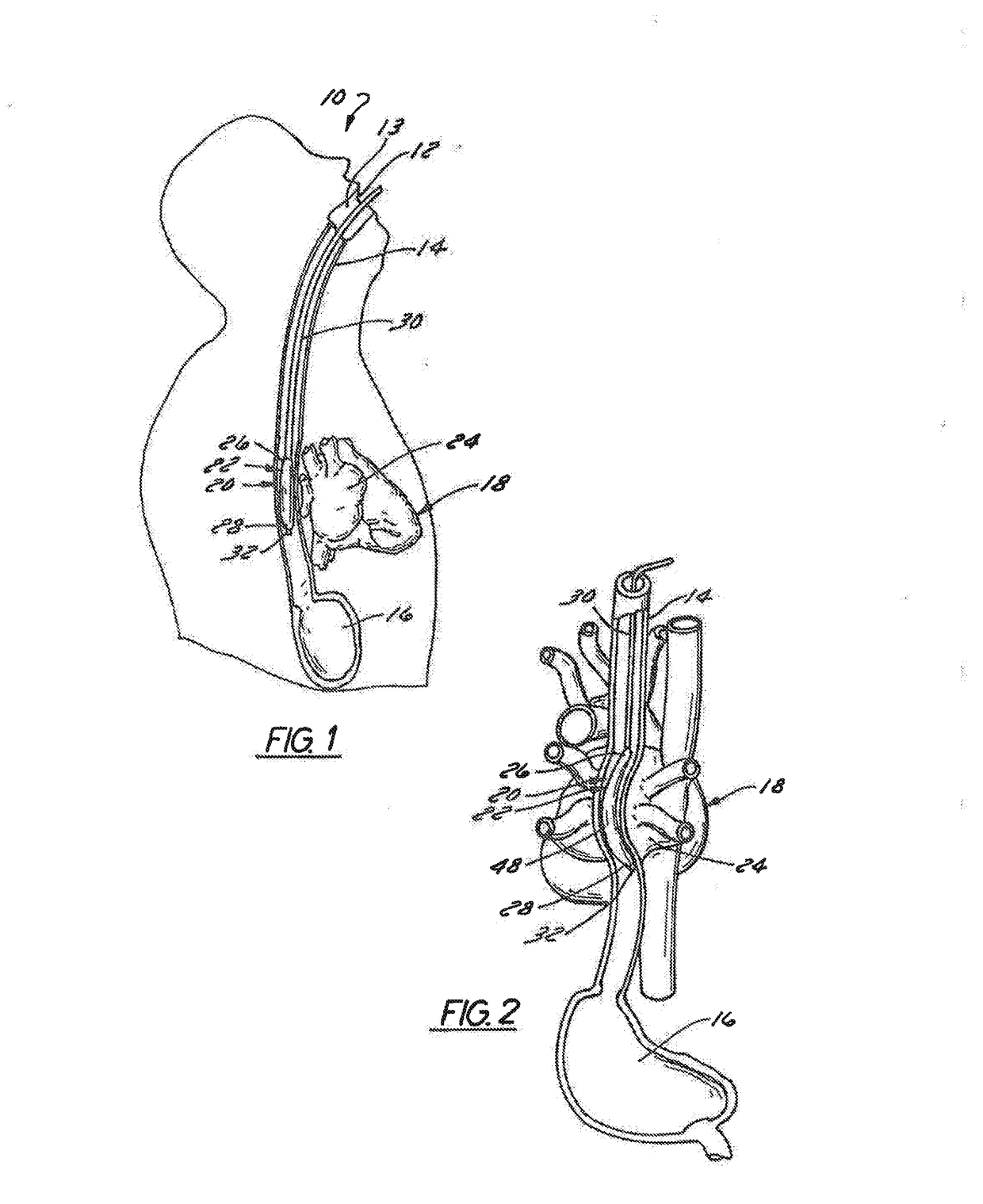
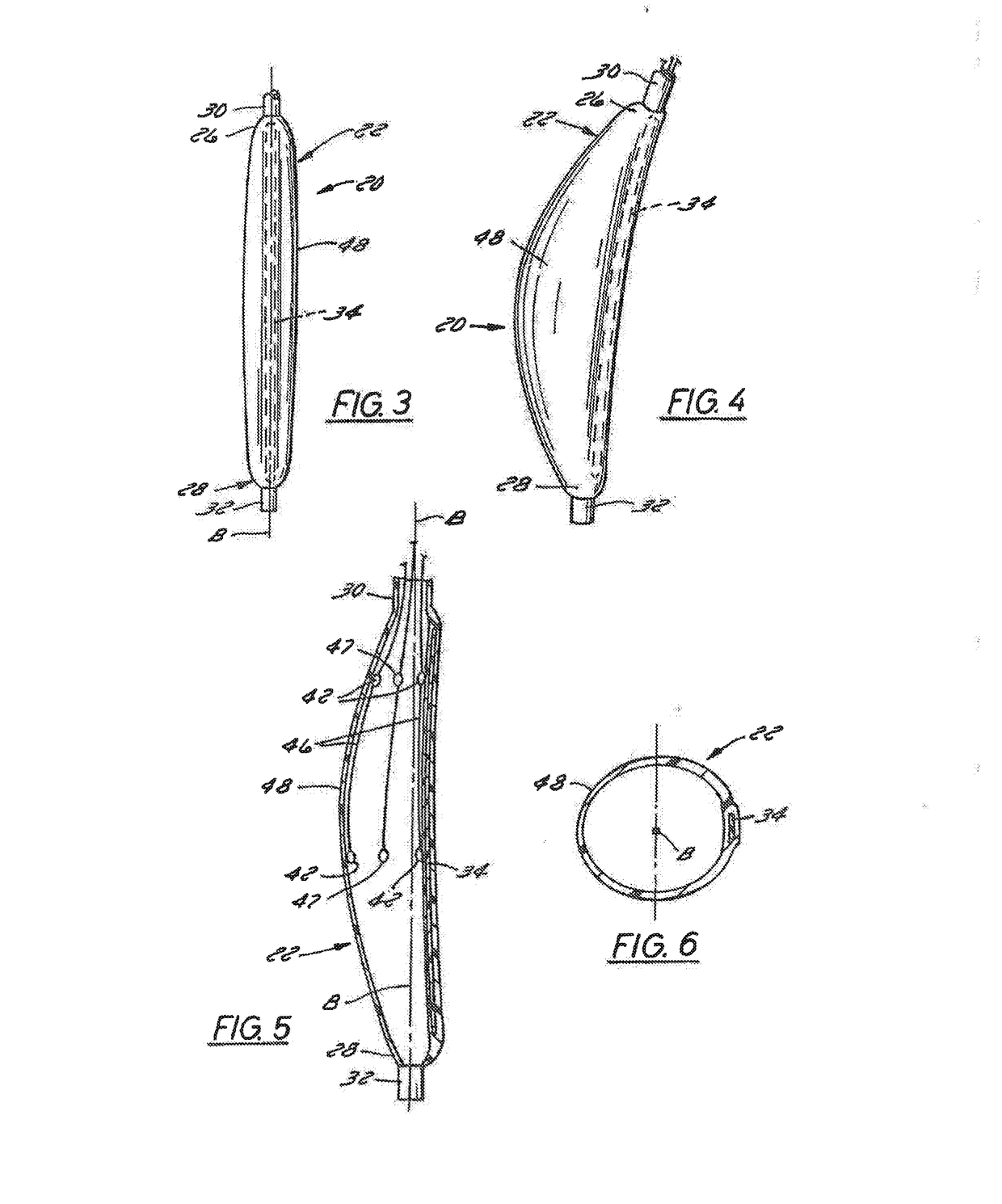
Intra-esophageal balloon system
ActiveUS20110082488A1Performed safelyInhibition of fibrillationBalloon catheterSurgeryLeft atriumHeat spreader
A device and system are disclosed for selective inflation of an inflatable body, such as a balloon, received through an oral cavity and into the esophagus of a patient. The inflatable body is operably coupled to a pressurized fluid source. The inflatable body has a relatively flexible portion and a relatively inflexible portion. When pressurized fluid is delivered to the body to inflate the body, the flexible portion expands more than the inflexible portion, resulting in asymmetrical expansion and movement of the esophagus away from the ablation site to avoid accidental injury while performing a procedure on the patient's left atrium. This movement may be opposite from or directly away from the heart or, alternatively, may be sideways relative to the heart to a location in which the esophagus is interposed between the ablation site and the phrenic nerve. The supplied fluid may be radio-opaque liquid to allow for imaging thereof to assist in positioning the balloon. The liquid may additionally be relatively cool as compared to the patient's body temperature so serve as a heat sink against heat applied to surrounding areas.
Owner:NIAZI PATENT HLDG LLC
Radio-frequency-based catheter system with improved deflection and steering mechanisms
ActiveUS20060142752A1Precise ablationPositioning is simple and fastElectrotherapyRadiating element housingsElectricityElectrical conductor
A RF catheter system includes a catheter with a proximal portion, a distal portion having a distal end and a lumen extending from the proximal portion to the distal portion. Inner and outer coaxially aligned conductors extend within the catheter and are coaxial with the lumen. A deflectable catheter guide is disposed within the catheter lumen and extends proximally within the catheter lumen and terminates distally of the distal end of the catheter to define a biological ablation pathway. A radio-frequency antenna is disposed at the distal portion of the catheter and is in electrical communication with the inner and outer coaxially aligned conductors. The radio-frequency antenna is adaptable to receive and transmit radio-frequency energy for ablating biological tissue along the ablation pathway.
Owner:ORMSBY THEODORE C +2
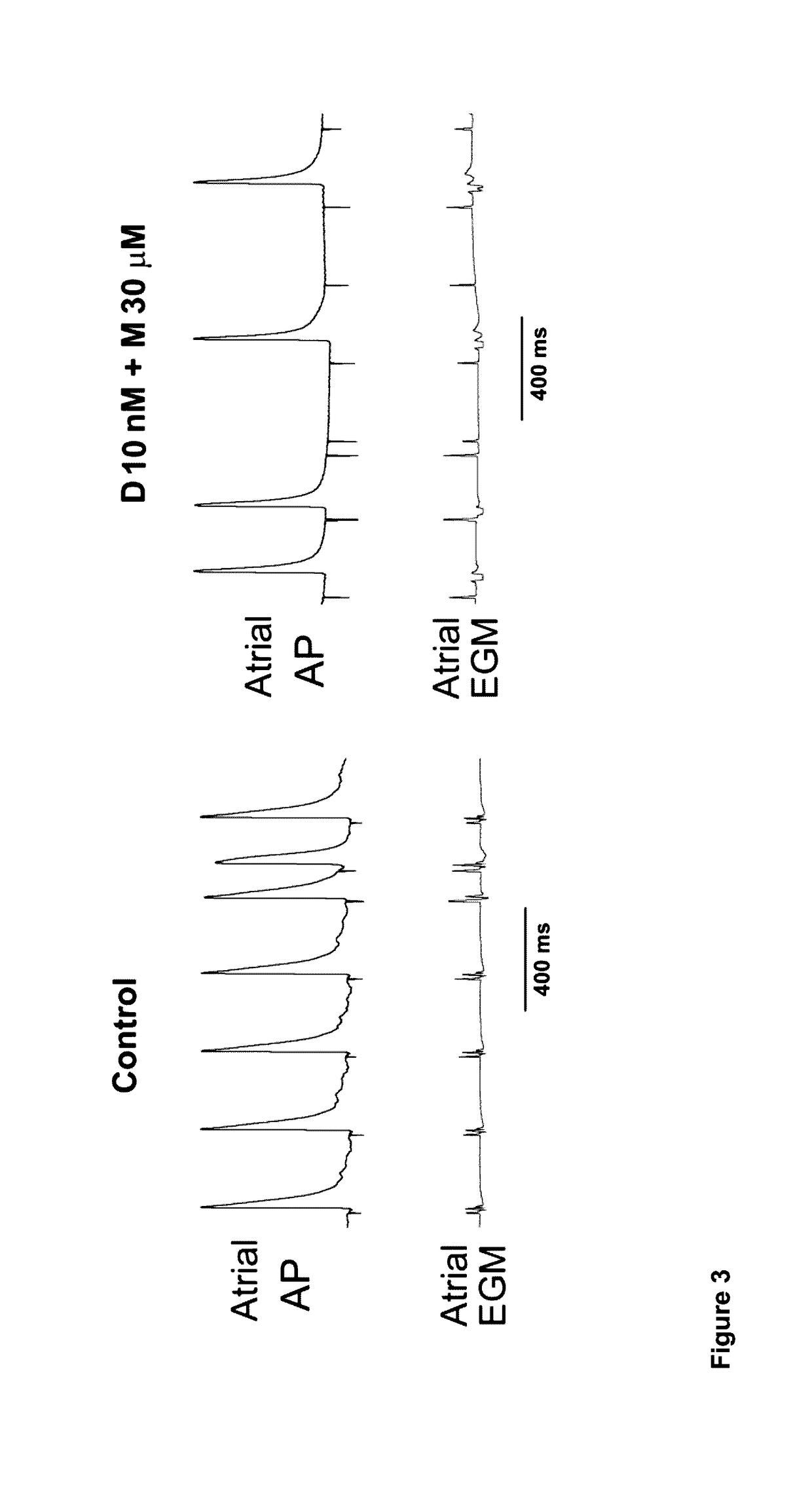
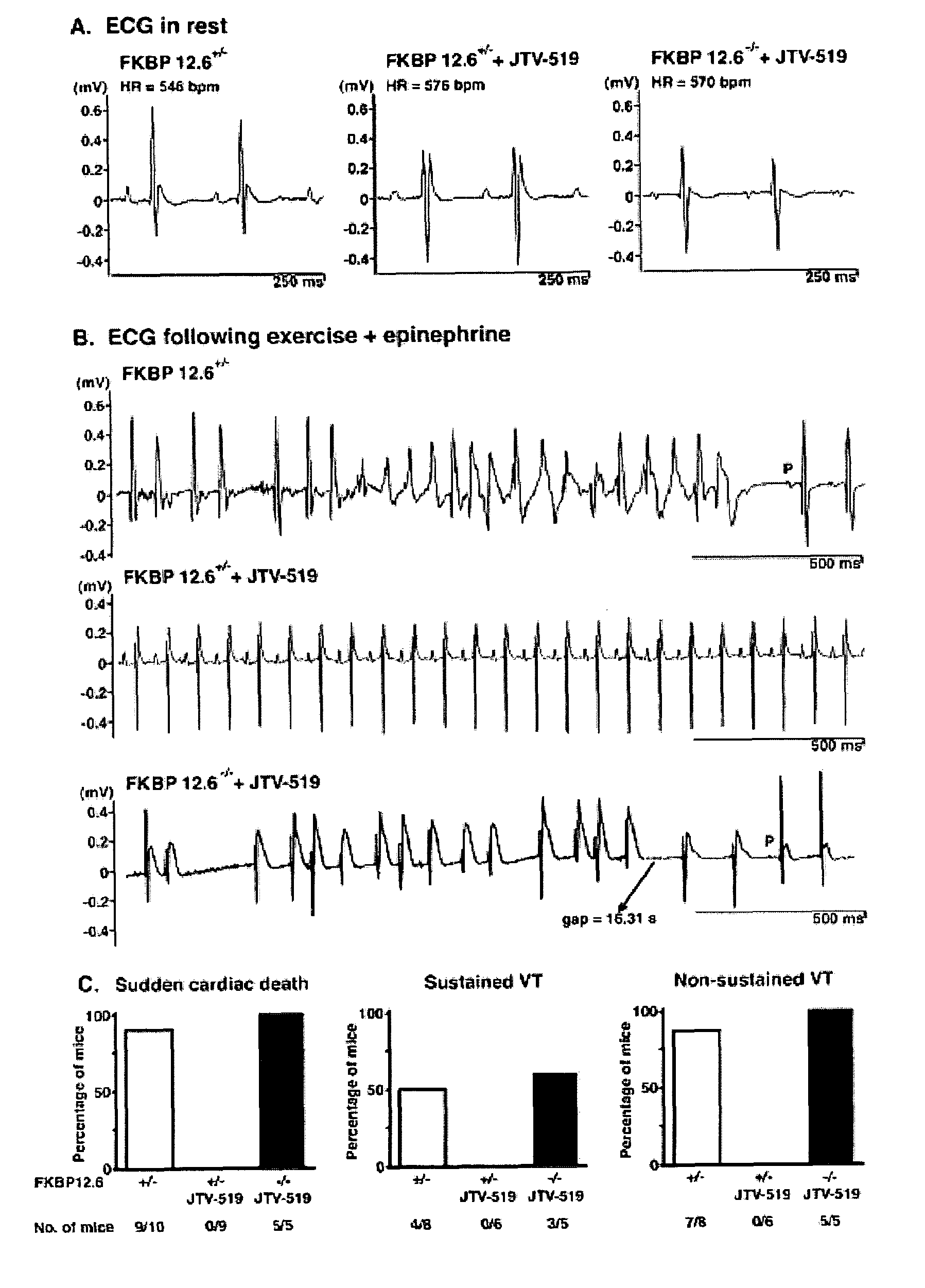
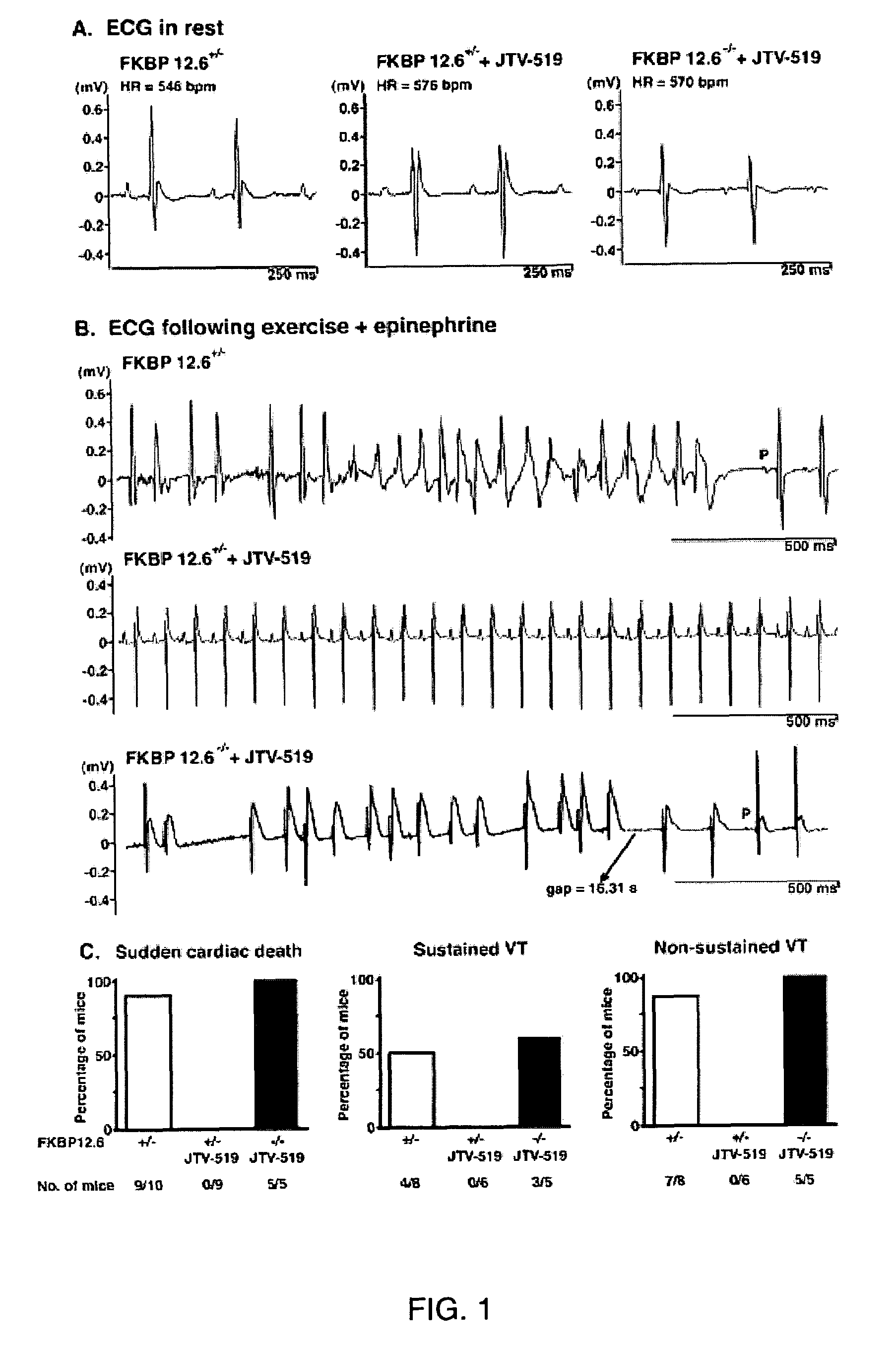
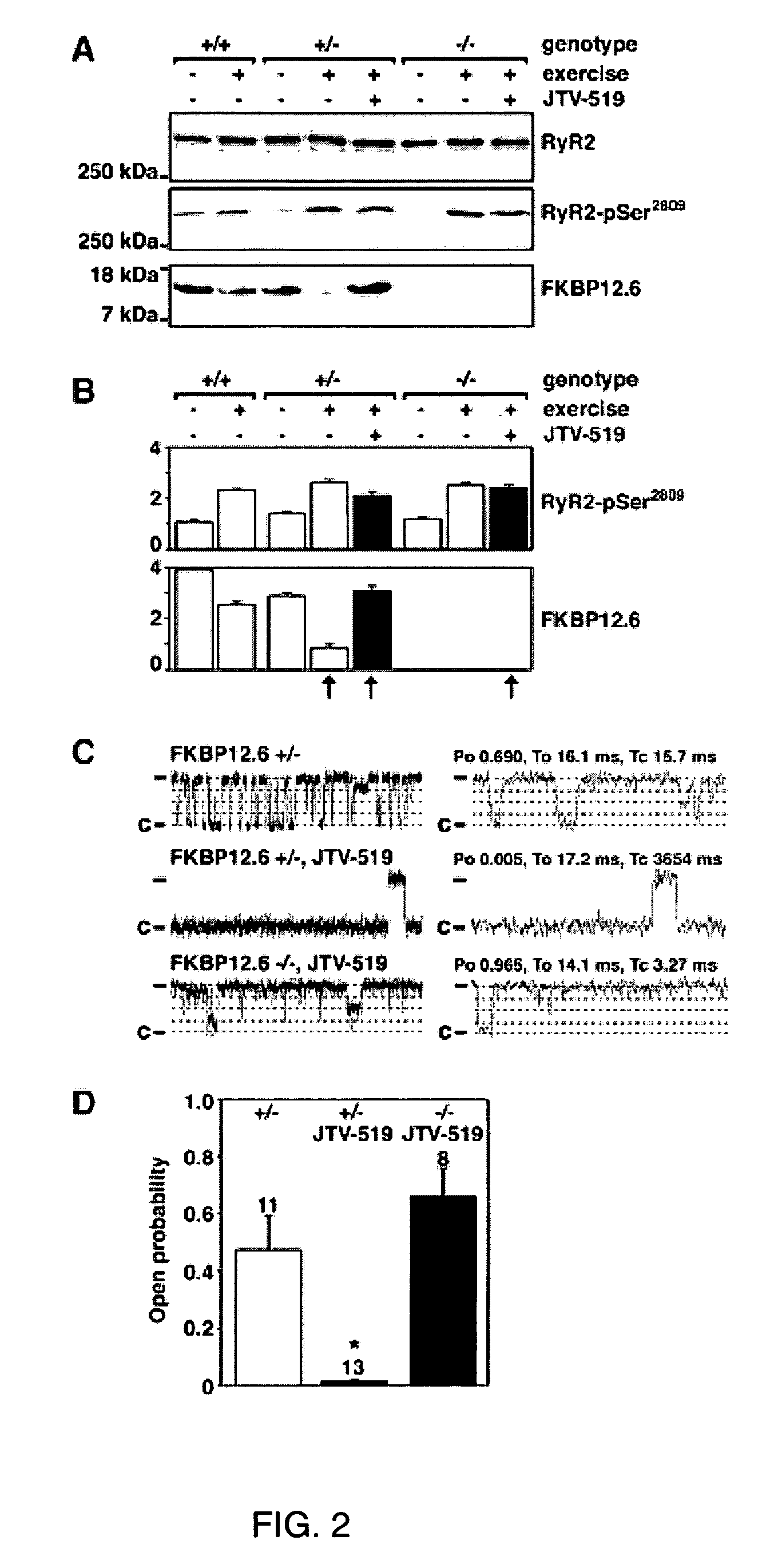
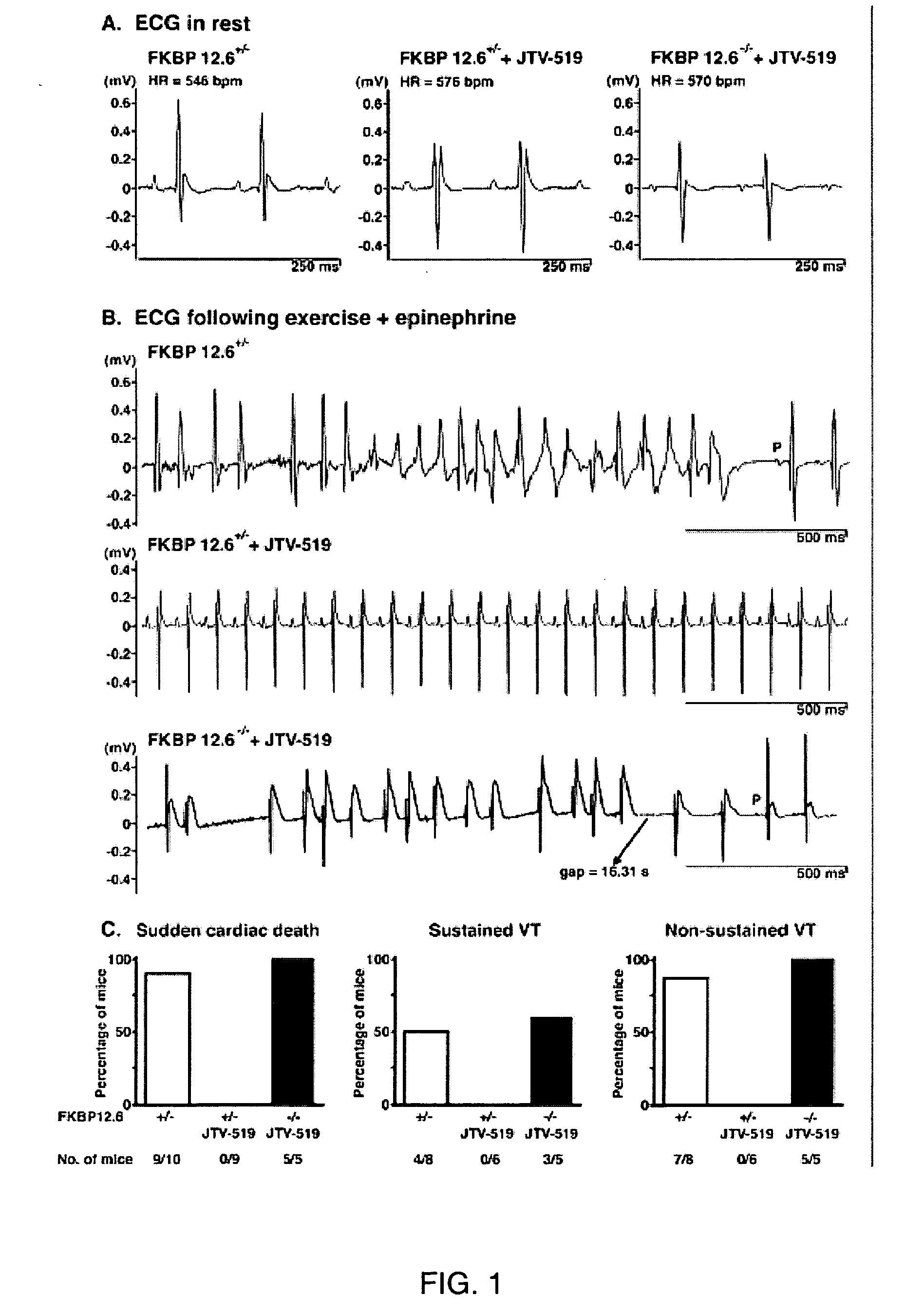
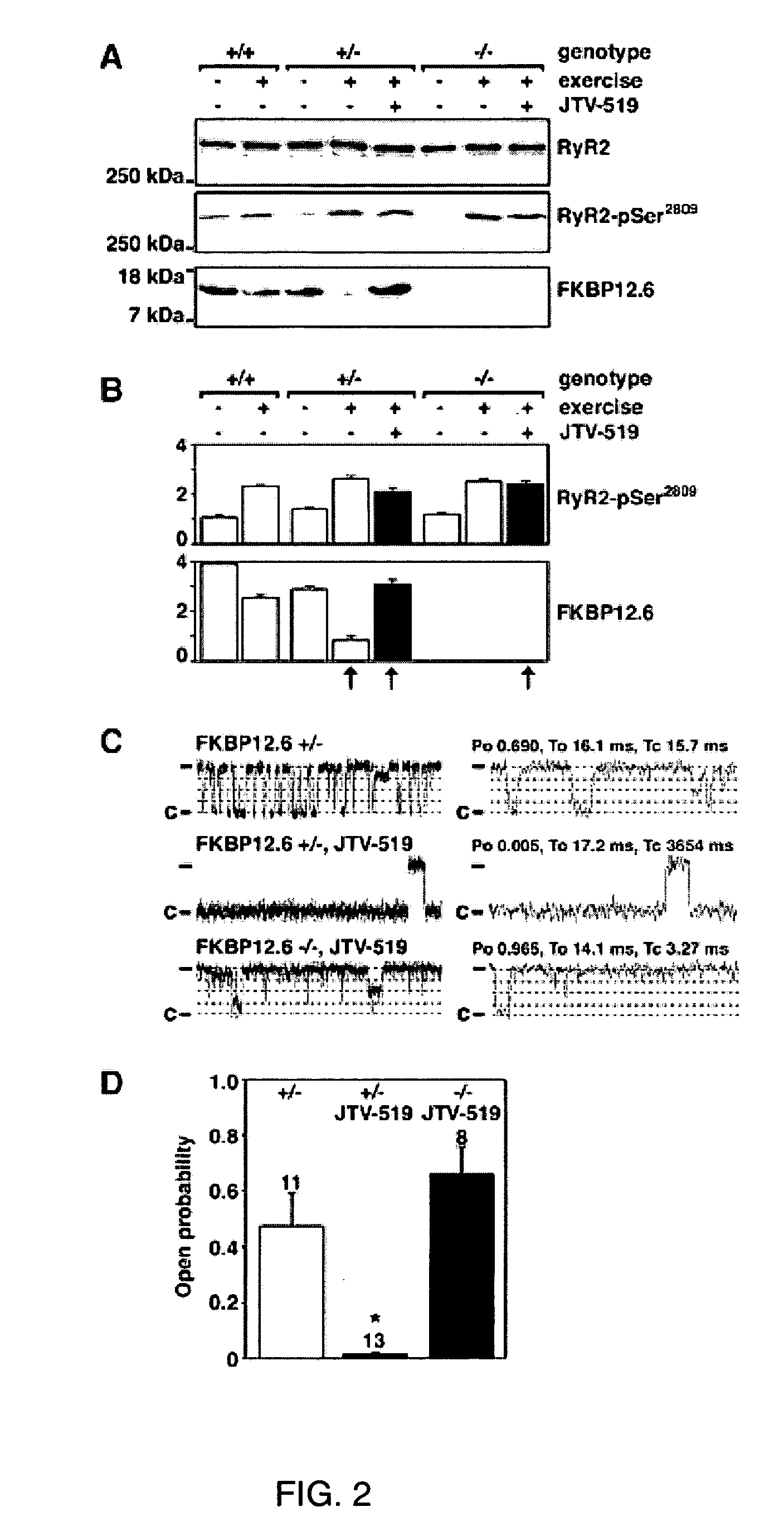
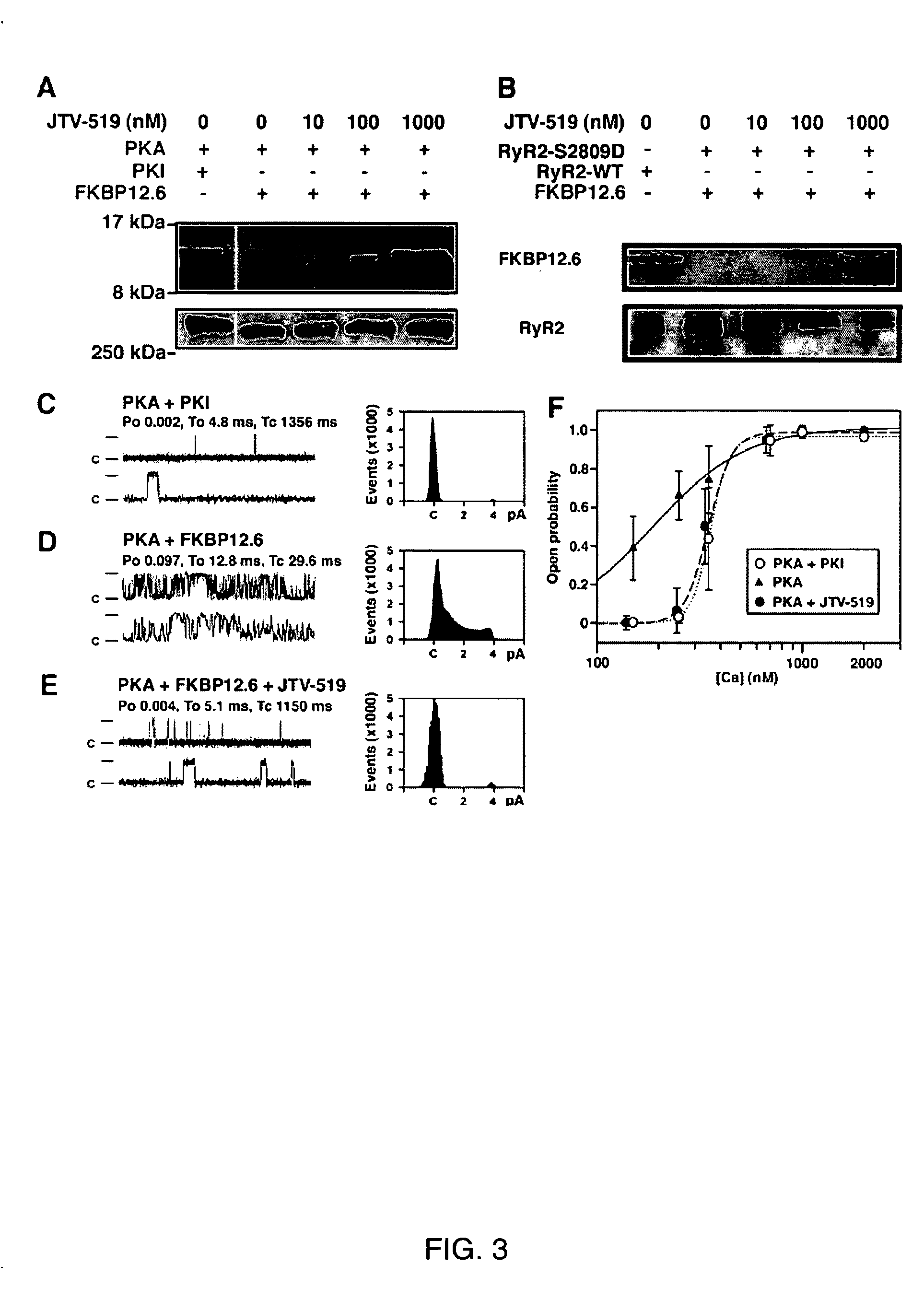
Novel anti-arrhythmic and heart failure drugs that target the leak in the ryanodine receptor (RyR2) and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050215540A1Inhibition of fibrillationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsVentricular dysrhythmiaRyanodine receptor
The present invention provides methods for limiting or preventing a decrease in the level of RyR2-bound FKBP12.6 in a subject. The present invention further provides methods for treating and preventing atrial and ventricular cardiac arrhythmias, heart failure, and exercise-induced sudden cardiac death in a subject. Additionally, the present invention provides use of JTV-519 in a method for limiting or preventing a decrease in the level of RyR2-bound FKBP12.6 in a subject who has, or is a candidate for, atrial fibrillation. Also provided are uses of 1,4-benzothiazepine derivatives in methods for treating and preventing atrial and ventricular cardiac arrhythmias and heart failure in a subject, and for preventing exercise-induced sudden cardiac death. The present invention also provides methods for identifying agents for use in treating and preventing atrial fibrillation and heart failure, and agents identified by these methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
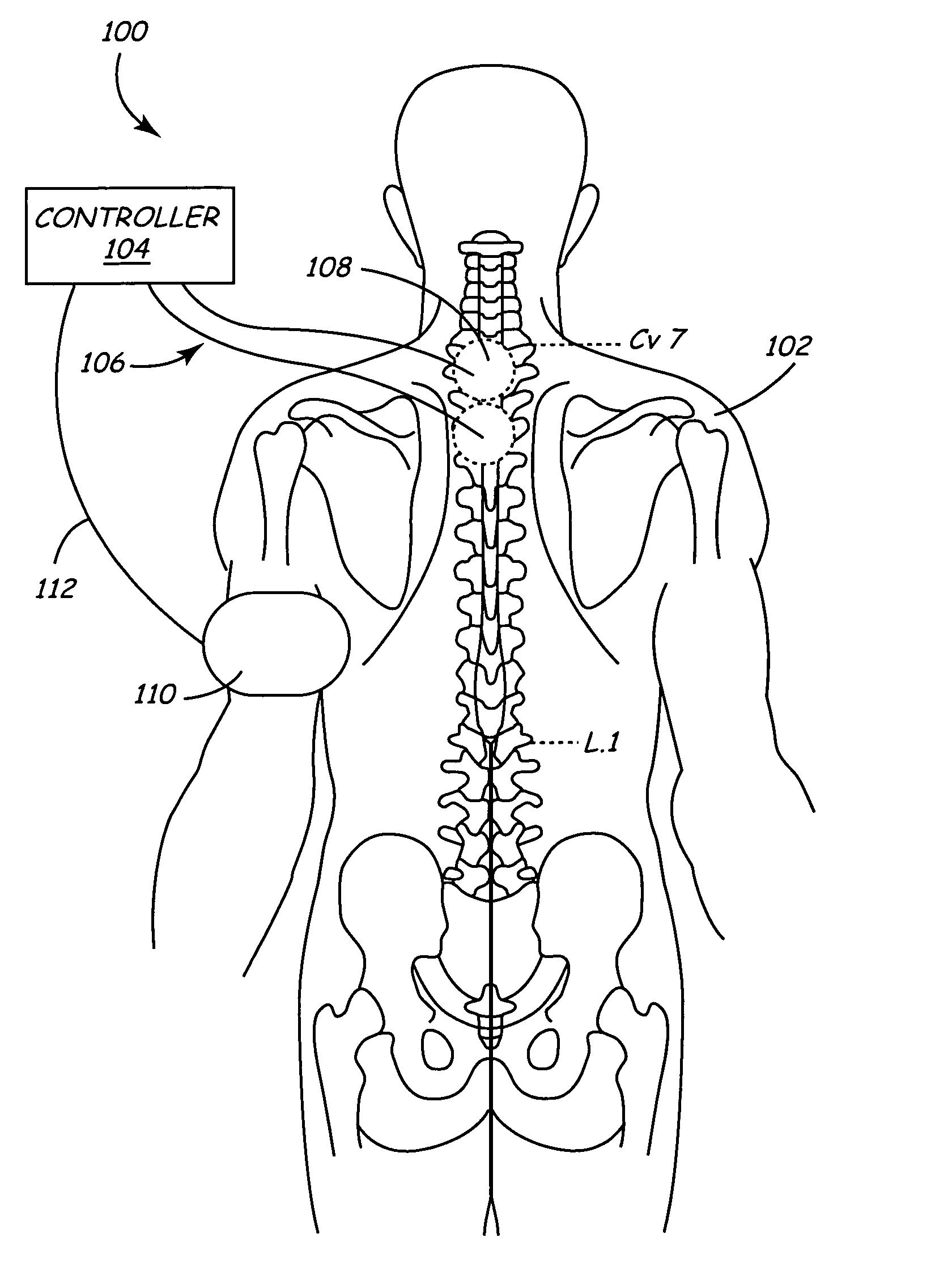
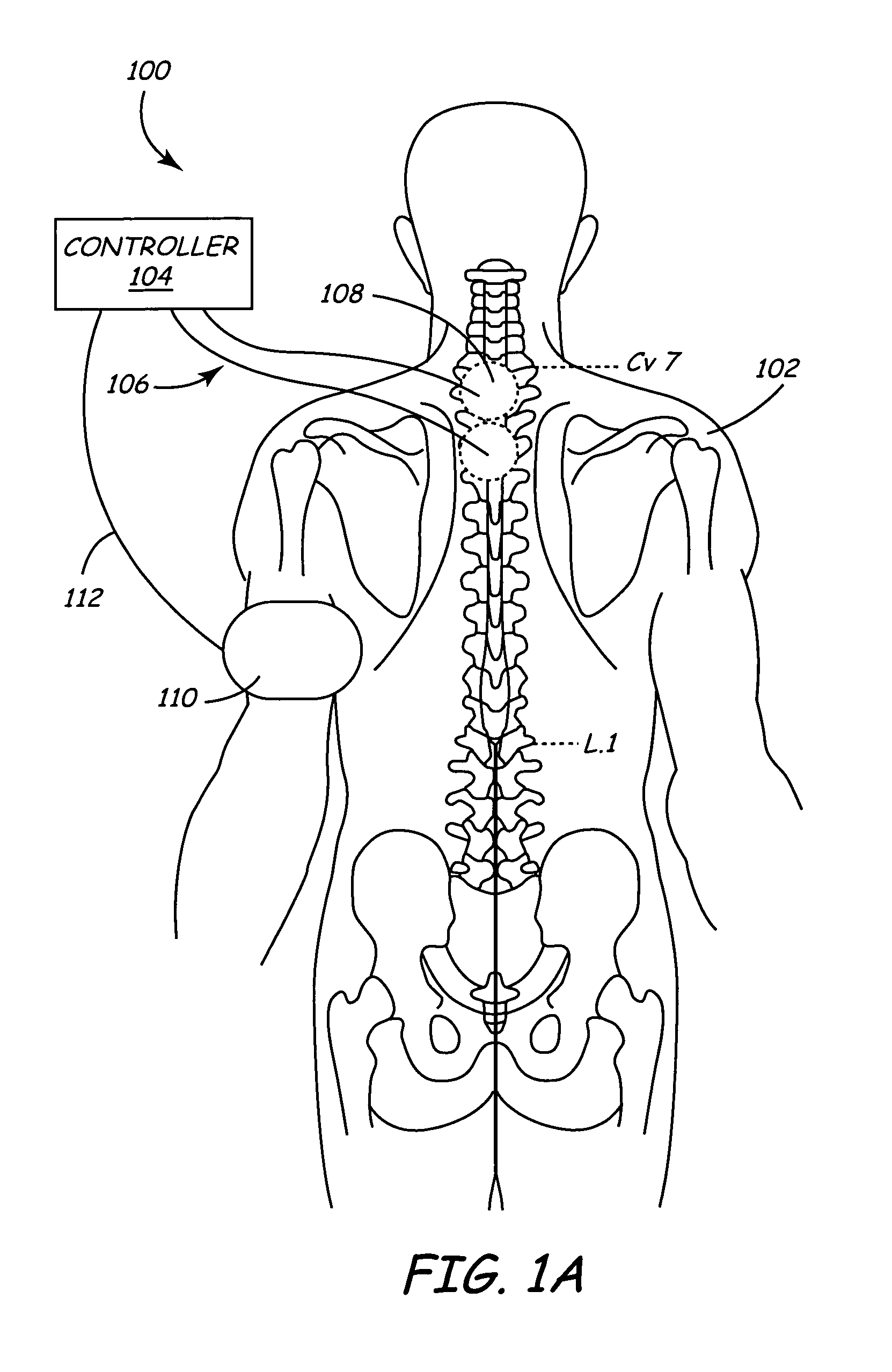
Electrical Conduction Block Implant Device
InactiveUS20090171431A1Safely and effectively block aberrant electrical signalMinimallyStentsHeart valvesElectrical resistance and conductanceImplanted device
The present invention provides an electrical block implant sized and shaped for securement at the perimeter of the pulmonary ostium of the left atrium. By utilizing various expandable ring designs and optional anchoring mechanisms, the present invention causes even, circular scarring around the perimeter of the pulmonary ostium, achieving reliable blocking of aberrant electrical signals responsible for atrial fibrillation.
Owner:SWANSON WILLIAM +2
Electrical conduction block implant device
InactiveUS9398967B2Safely and effectively block aberrant electrical signalMinimallyStentsBlood vesselsElectrical resistance and conductanceAtrial cavity
The present invention provides an electrical block implant sized and shaped for securement at the perimeter of the pulmonary ostium of the left atrium. By utilizing various expandable ring designs and optional anchoring mechanisms, the present invention causes even, circular scarring around the perimeter of the pulmonary ostium, achieving reliable blocking of aberrant electrical signals responsible for atrial fibrillation.
Owner:SYNTACH AG
Neurotoxic agents and devices to treat atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS20060282120A1Reduce riskInhibition of fibrillationTransvascular endocardial electrodesMedical devicesVeinNeurotoxic agents
Devices and methods to treat atrial fibrillation via inhibition of nerves which innervate the pulmonary vein are provided.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Composite comprising heat-resistant fiber and siloxane polymer
InactiveUS20050165154A1Improve heat resistanceImprove toughnessEngine sealsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceHeat resistance
The present invention provides a fiber-reinforced glass having excellent heat resistance and toughness, or a composite comprising a heat-resistant fiber and a siloxane polymer, which has a modified surface structure and is useful as a heat-resistant fiber.
Owner:IWAMIYA YOKO
Composite comprising heat-resistant fiber and siloxane polymer
InactiveUS7332196B2Increase resistanceImprove toughnessEngine sealsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceHeat resistance
The present invention provides a fiber-reinforced glass having excellent heat resistance and toughness, or a composite comprising a heat-resistant fiber and a siloxane polymer, which has a modified surface structure and is useful as a heat-resistant fiber.
Owner:IWAMIYA YOKO
Electrical conduction block implant device
InactiveUS20060178725A1Safely and effectively block aberrant electrical signalMinimallyStentsBlood vesselsAtrial cavityImplanted device
The present invention provides an electrical block implant sized and shaped for securement at the perimeter of the pulmonary ostium of the left atrium. By utilizing various expandable ring designs and optional anchoring mechanisms, the present invention causes even, circular scarring around the perimeter of the pulmonary ostium, achieving reliable blocking of aberrant electrical signals responsible for atrial fibrillation.
Owner:SYNTACH AG
Method of Using an Intra-Esophageal Balloon System
ActiveUS20180050181A1Performed safelyInhibition of fibrillationBalloon catheterSurgeryOesophageal tubeLeft atrium
Owner:NIAZI PATENT HLDG LLC
Combination of dofetilide and mexiletine for the prevention and treatment of atrial fibrillation
ActiveUS9597302B1Inhibition is effectiveConvenient treatmentAmide active ingredientsCapsule deliveryCombined useCvd risk
Effective and safe pharmaceutical composition and method for treating atrial fibrillation are described. The combined use of dofetilide and mexiletine resulted in an enhanced efficacy in the prevention and treatment of atrial fibrillation with markedly reduced risk of the life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia TdP.
Owner:FB HRS LLC
Methods and compositions for treating atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS20140241988A1Prevents AF-inducedIncreases percentage of spontaneous terminationCompounds screening/testingBiocideAtrial cavityFibrillation
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the prevention and treatment of atrial fibrillation. In particular, the present invention provides therapeutic agents for the treatment and prevention of persistent and permanent atrial fibrillation and prevention of progression of atrial fibrillation to permanent atrial fibrillation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Electrical Conduction Block Implant Device
InactiveUS20090171445A1Safely and effectively block aberrant electrical signalMinimallyStentsHeart valvesElectrical resistance and conductanceImplanted device
The present invention provides an electrical block implant sized and shaped for securement at the perimeter of the pulmonary ostium of the left atrium. By utilizing various expandable ring designs and optional anchoring mechanisms, the present invention causes even, circular scarring around the perimeter of the pulmonary ostium, achieving reliable blocking of aberrant electrical signals responsible for atrial fibrillation.
Owner:SYNTACH AG
Use of D-ribose to treat cardiac arrhythmias
ActiveUS20080176809A1Preventing atrial fibrillationInhibition of fibrillationBiocideSugar derivativesRiboseAtrial fibrillation
D-ribose, given in doses of five to 15 grams daily, reduces or prevents the occurrence of atrial fibrillation in persons experiencing atrial fibrillation.
Owner:BIOENERGY INC
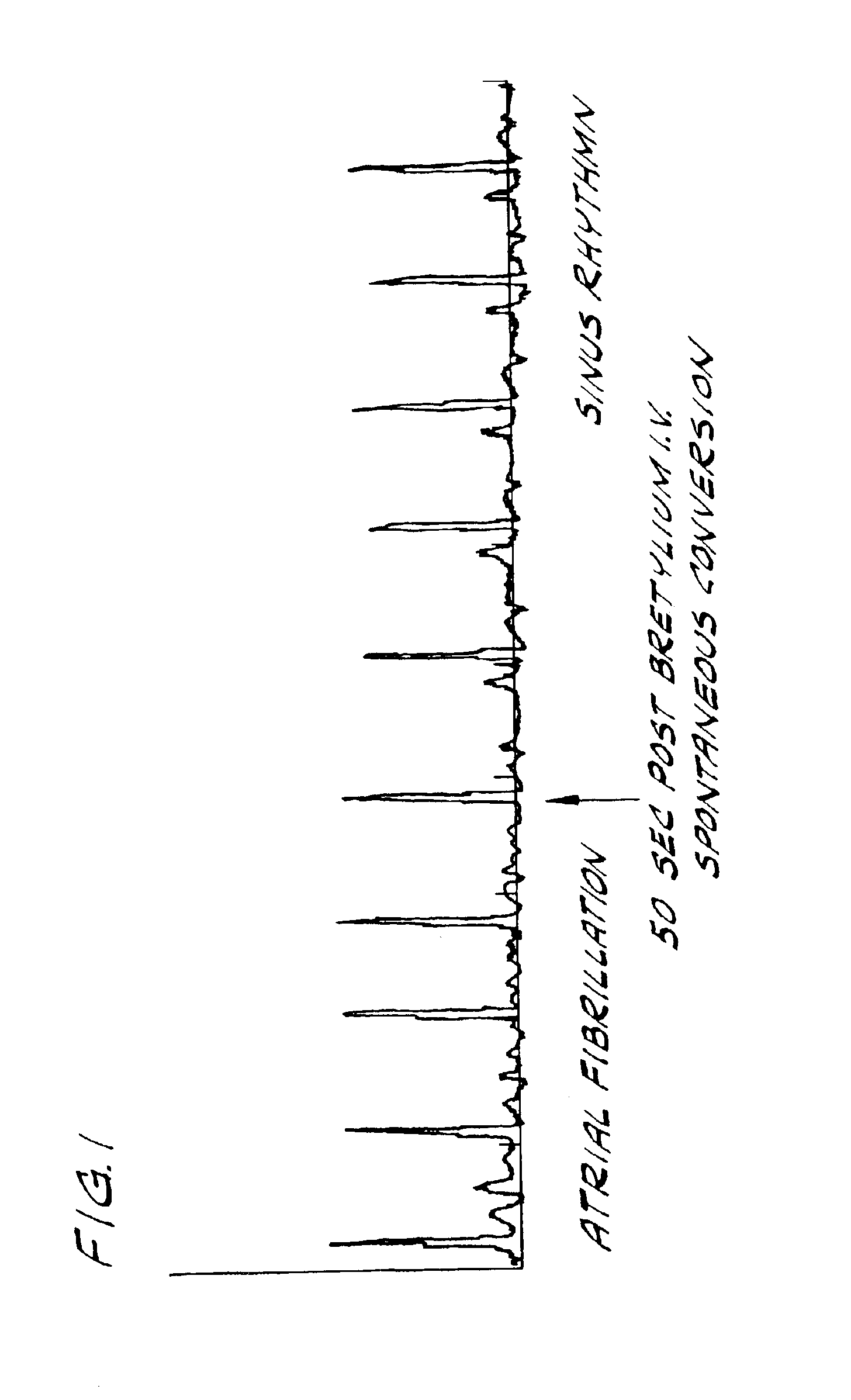
Bretylium compositions and kits and their use in preventing and treating cardiovascular conditions
InactiveUS6884792B2High activityImprove effectivenessBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsPharmaceutical drugBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention is directed to novel pharmaceutical combinations including compositions and kits comprising bretylium as the active ingredient, as well as methods for preventing and / or treating conditions related to the cardiovascular system using such novel pharmaceutical combinations.
Owner:BACANER MARVIN B +1
Electrical Conduction Block Implant Device
InactiveUS20100211155A1Safely and effectively block aberrant electrical signalMinimallyStentsHeart valvesElectrical resistance and conductanceImplanted device
Owner:SYNTACH AG
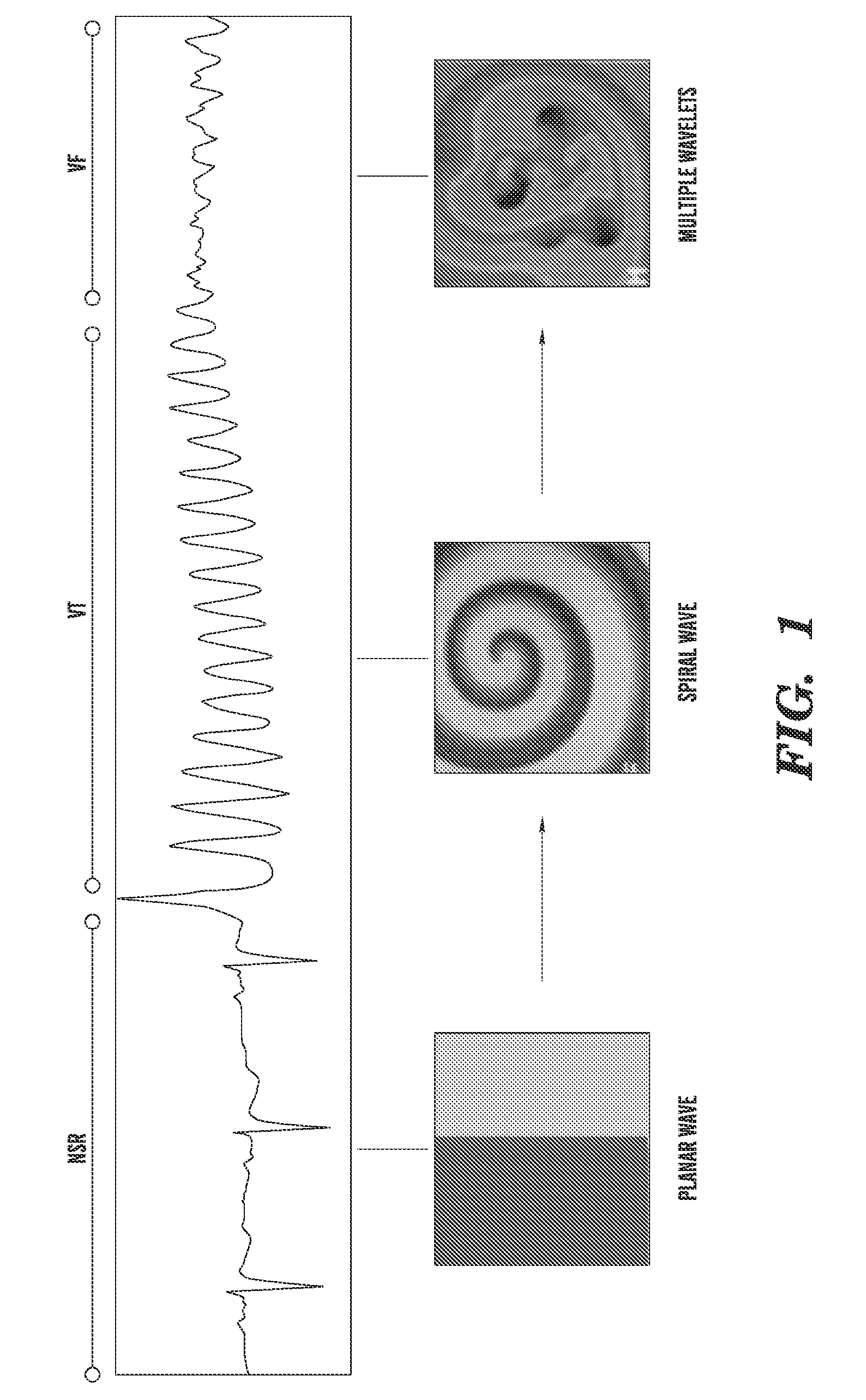
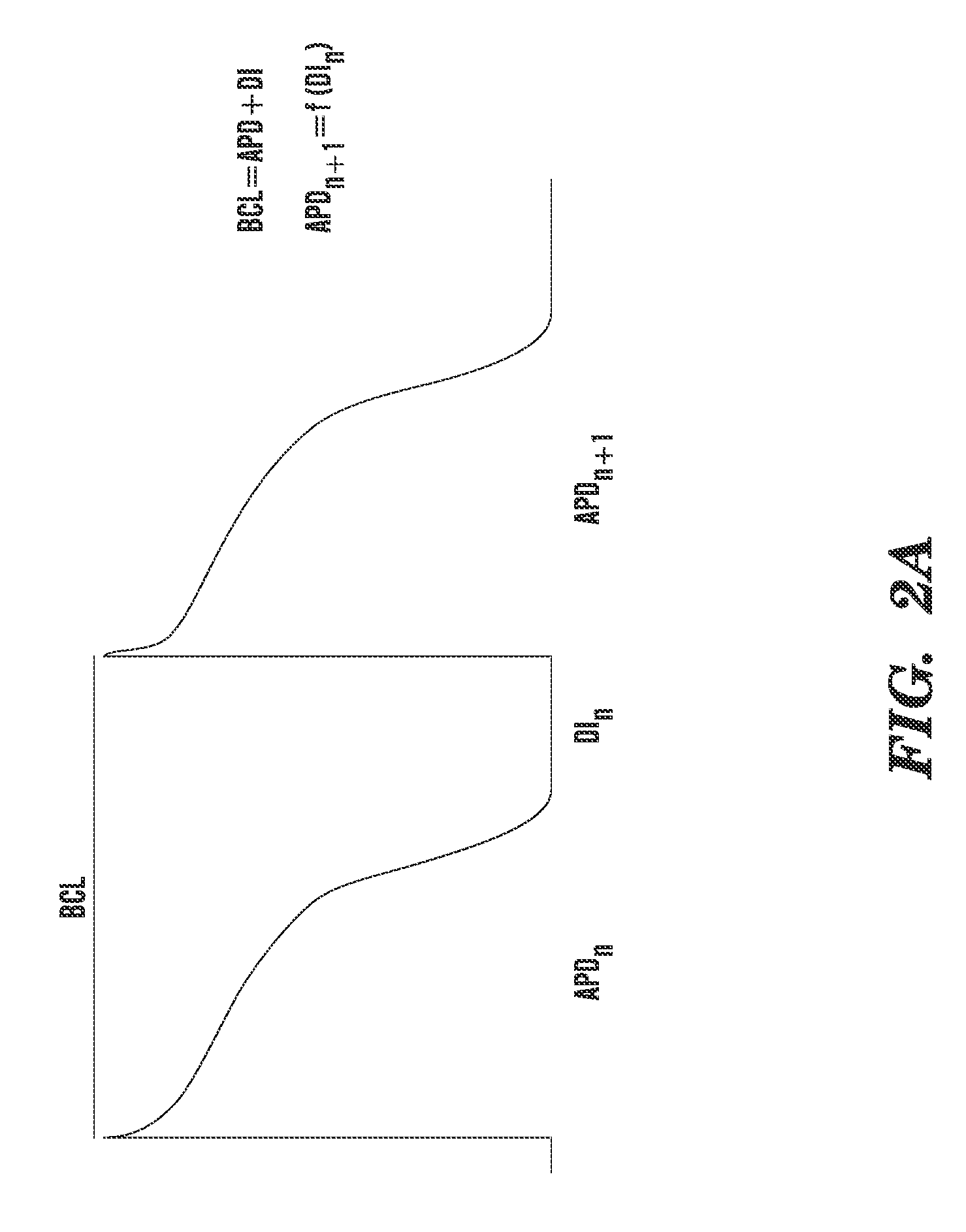
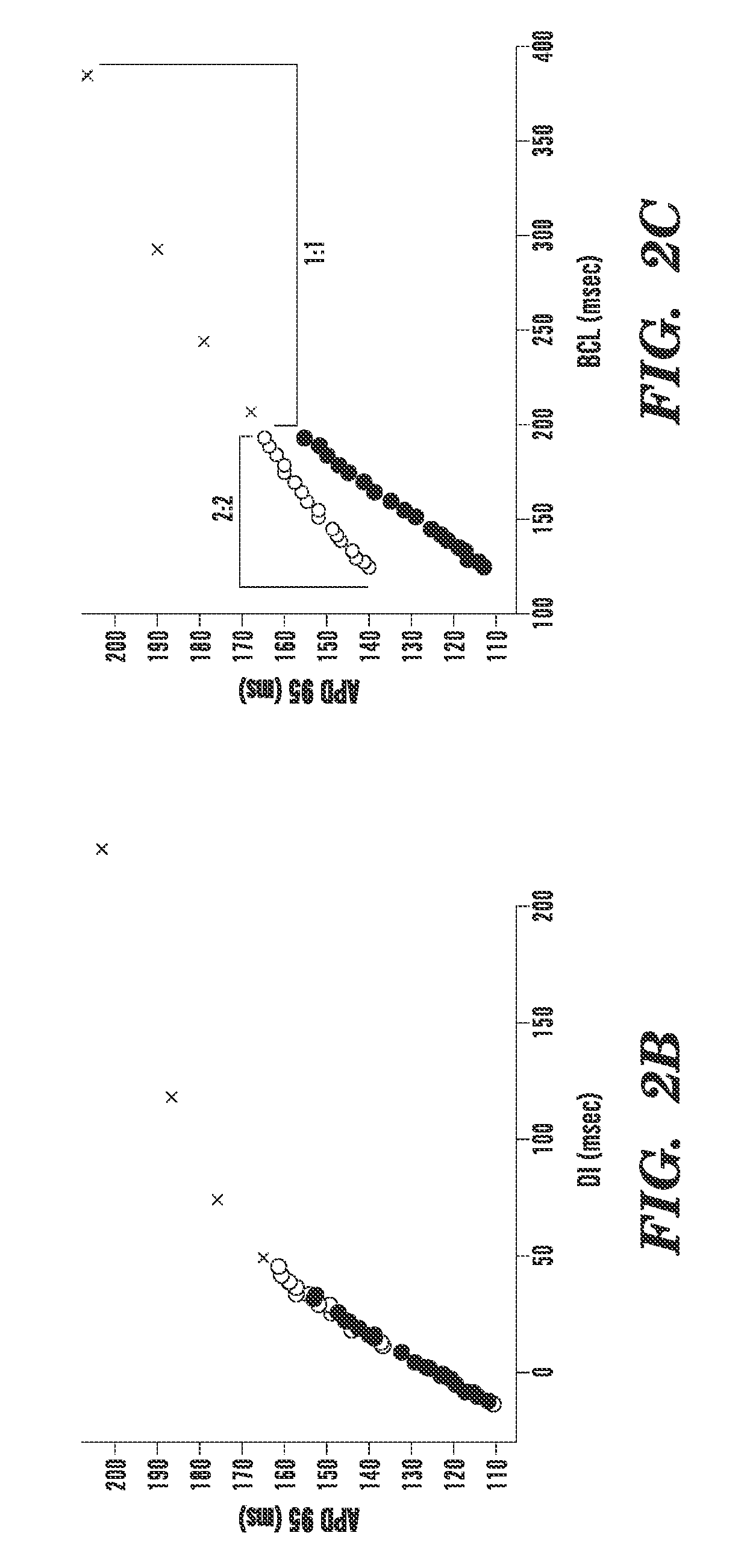
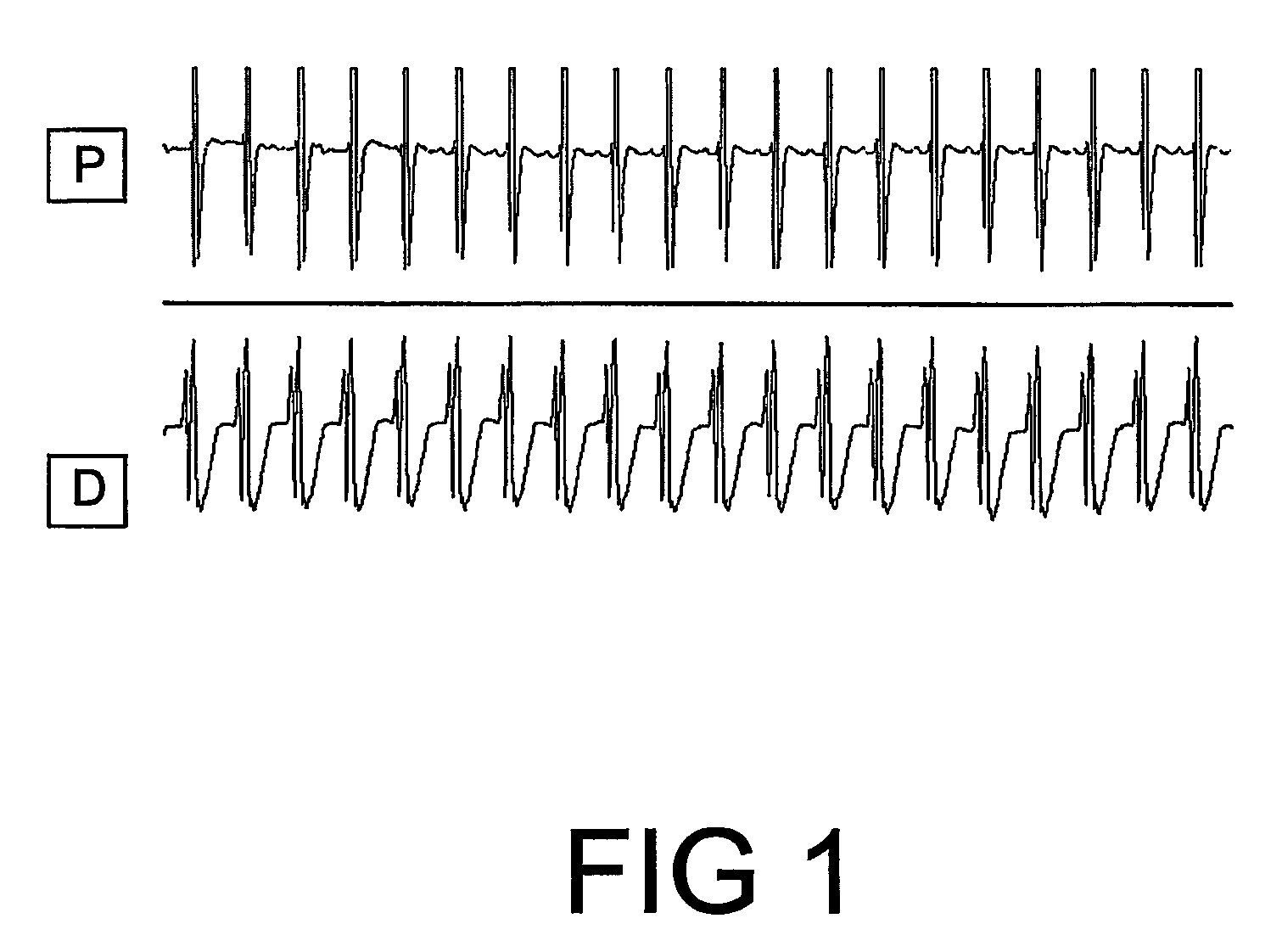
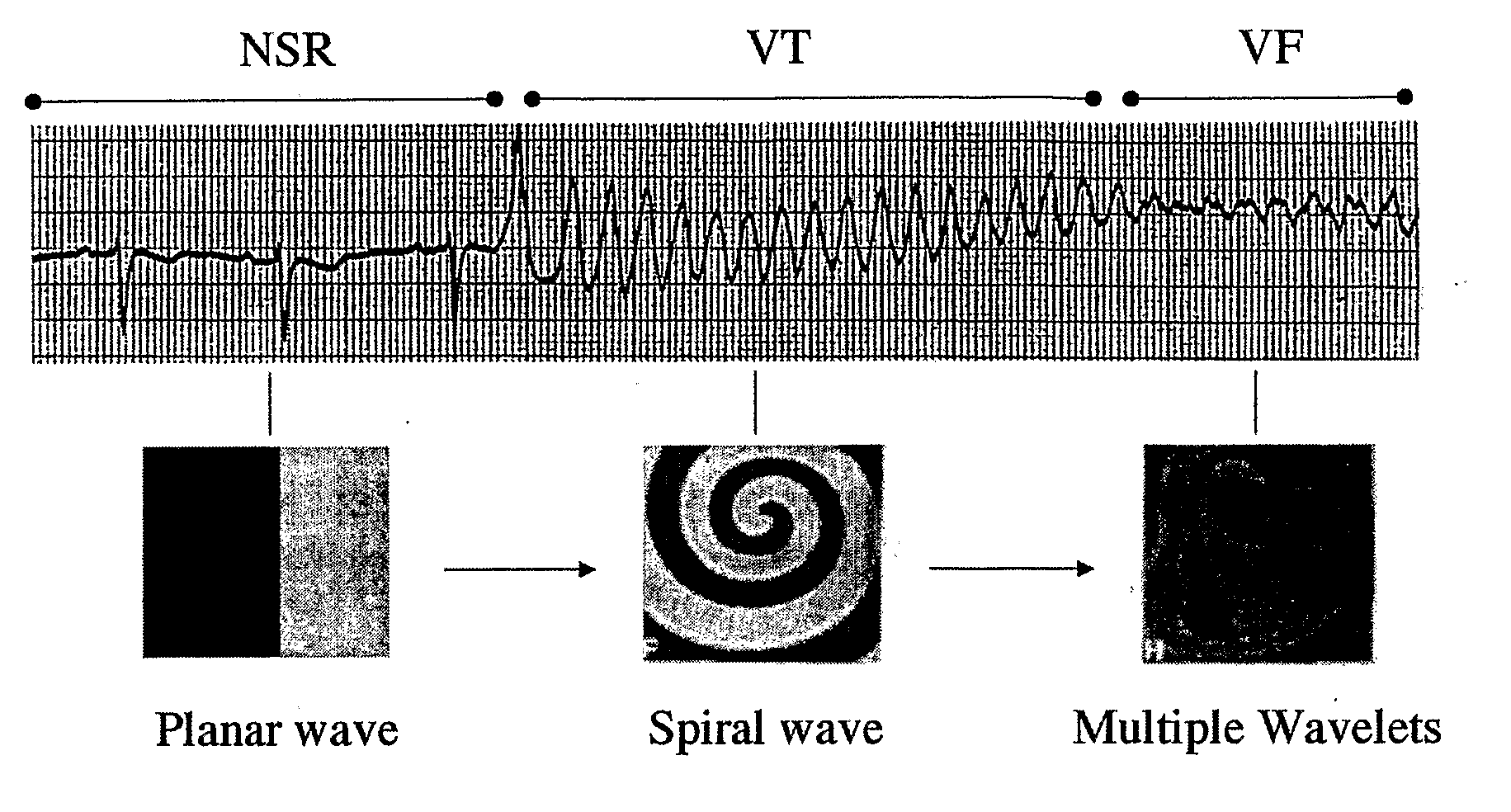
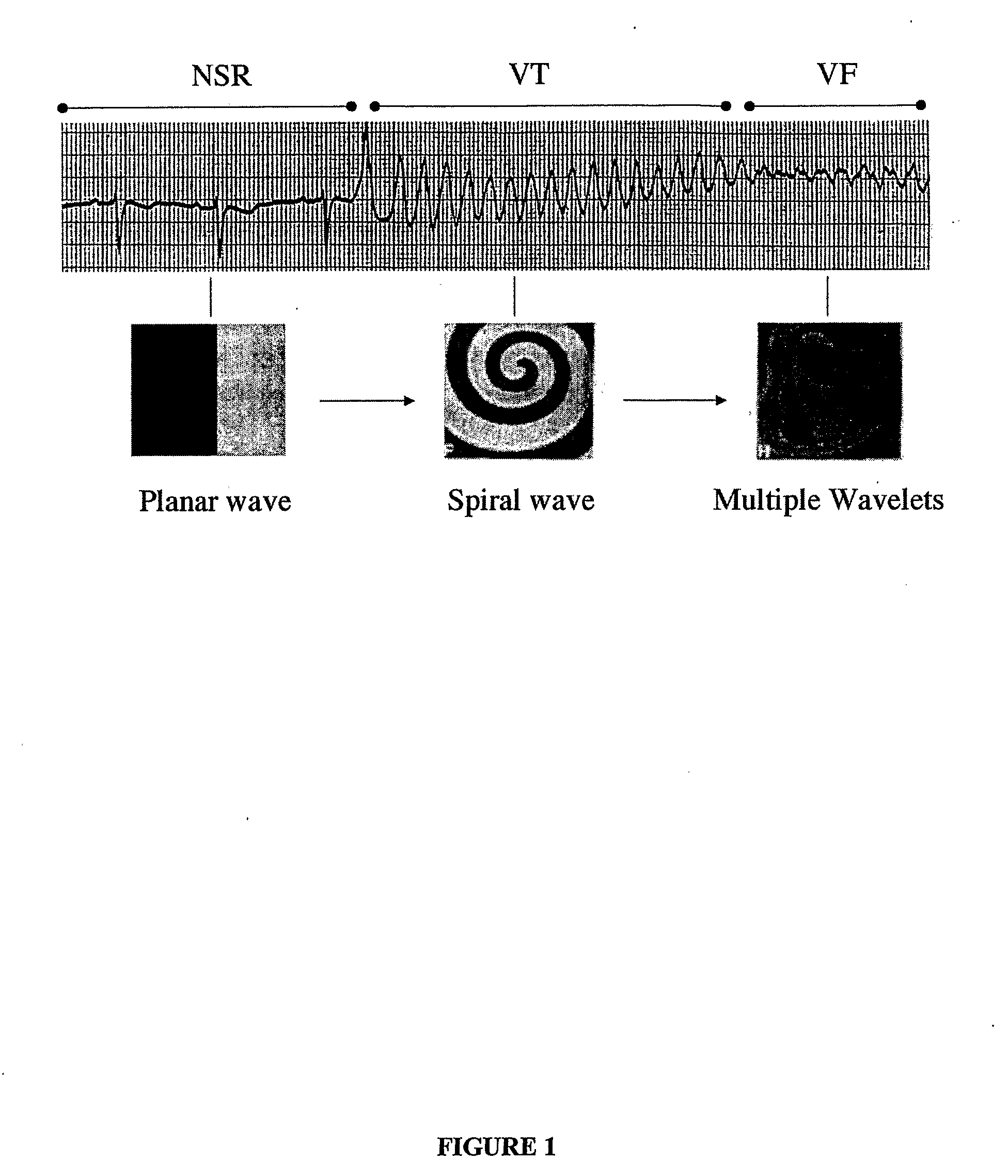
Method of Identifying Strategies for Treatment or Prevention of Ventricular Fibrillation and Ventricular Tachycardia
InactiveUS20070249948A1Prevention of ventricular fibrillationNovel methodElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsVentricular tachycardiaVentricular fibrillation
The present invention relates to evaluating the effect of physiological conditions on the occurrence of ventricular fibrillation, identifying strategies for treatment or prevention of ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, and evaluating a subject for induction of ventricular fibrillation from a condition of ventricular tachycardia.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
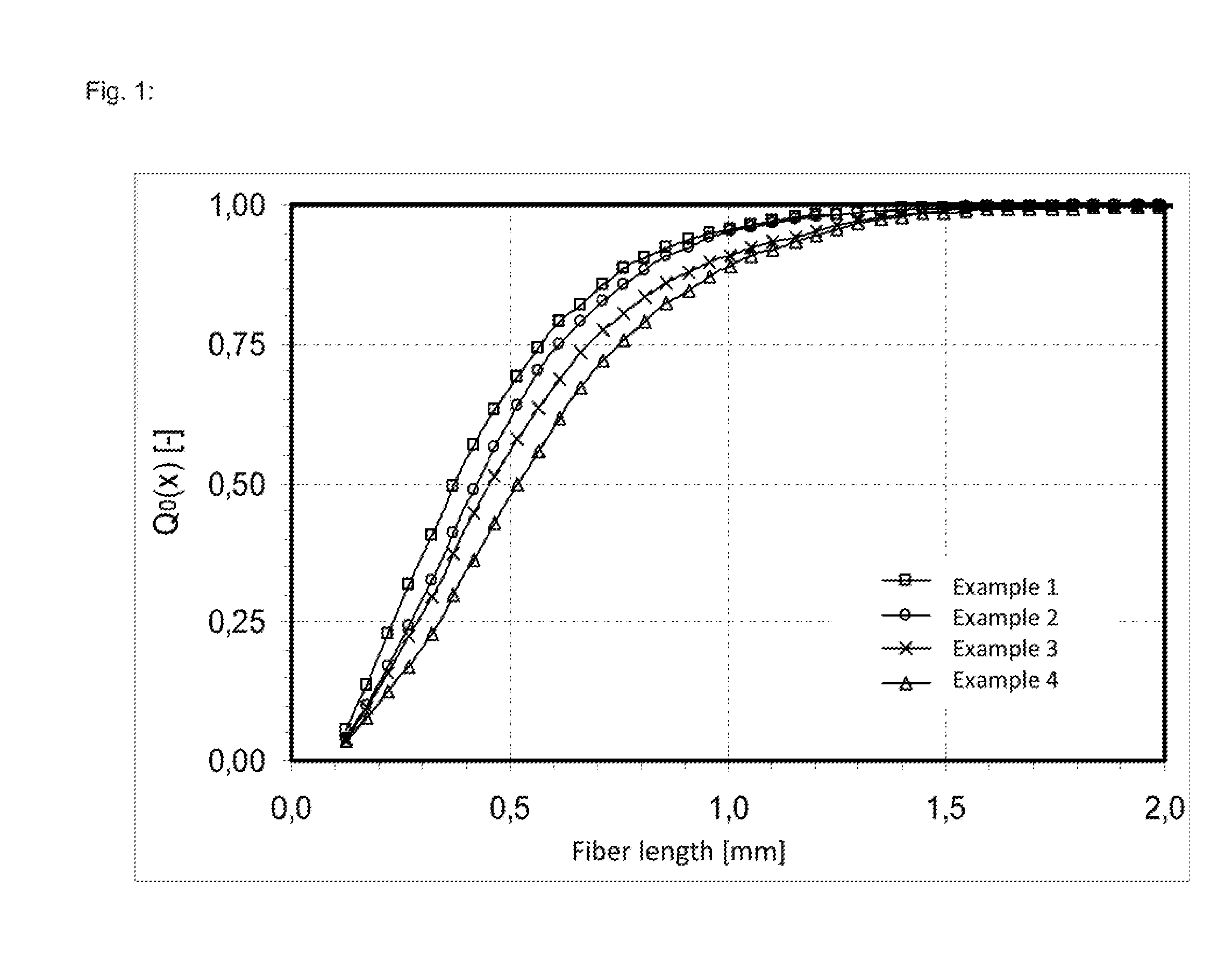
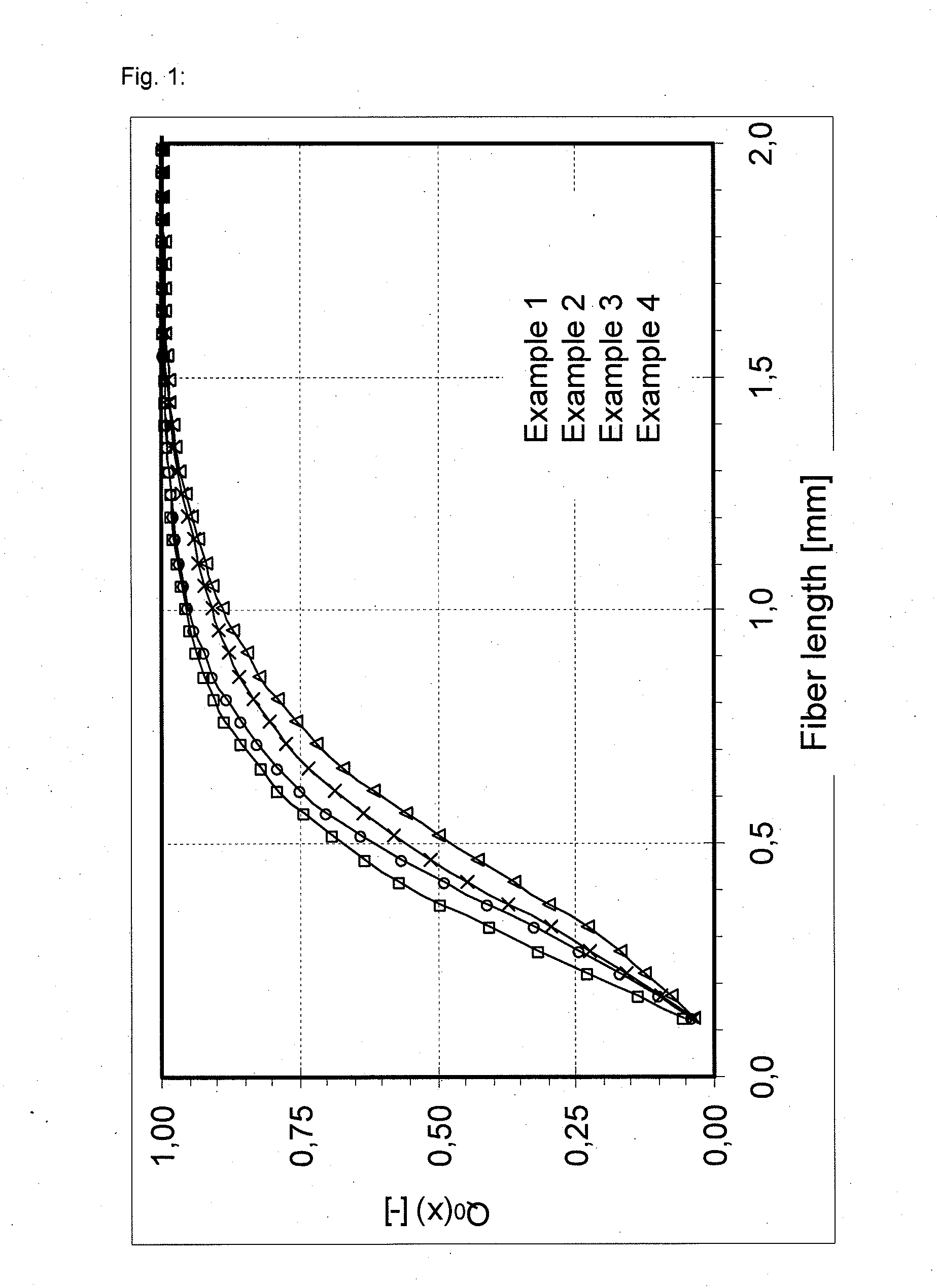
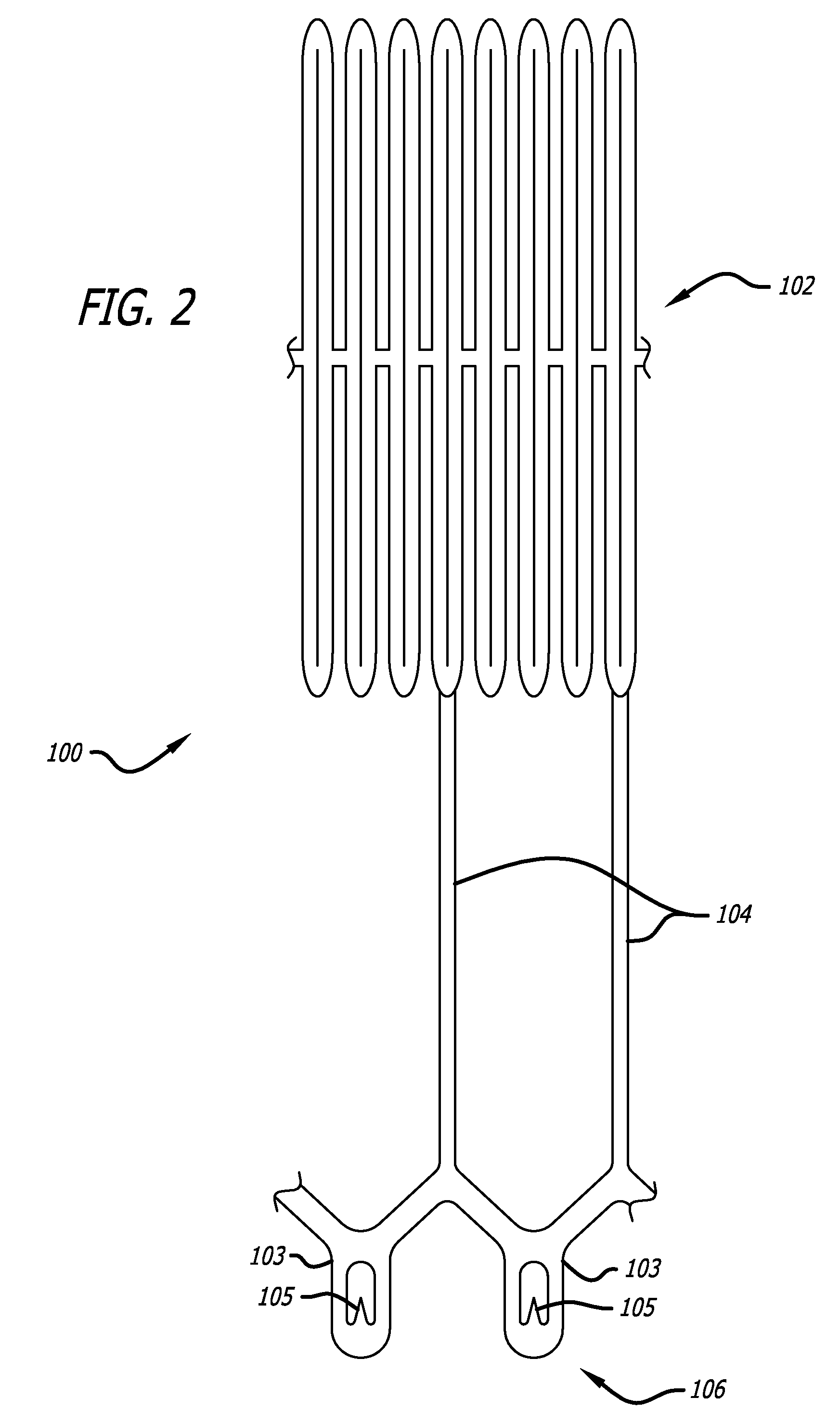
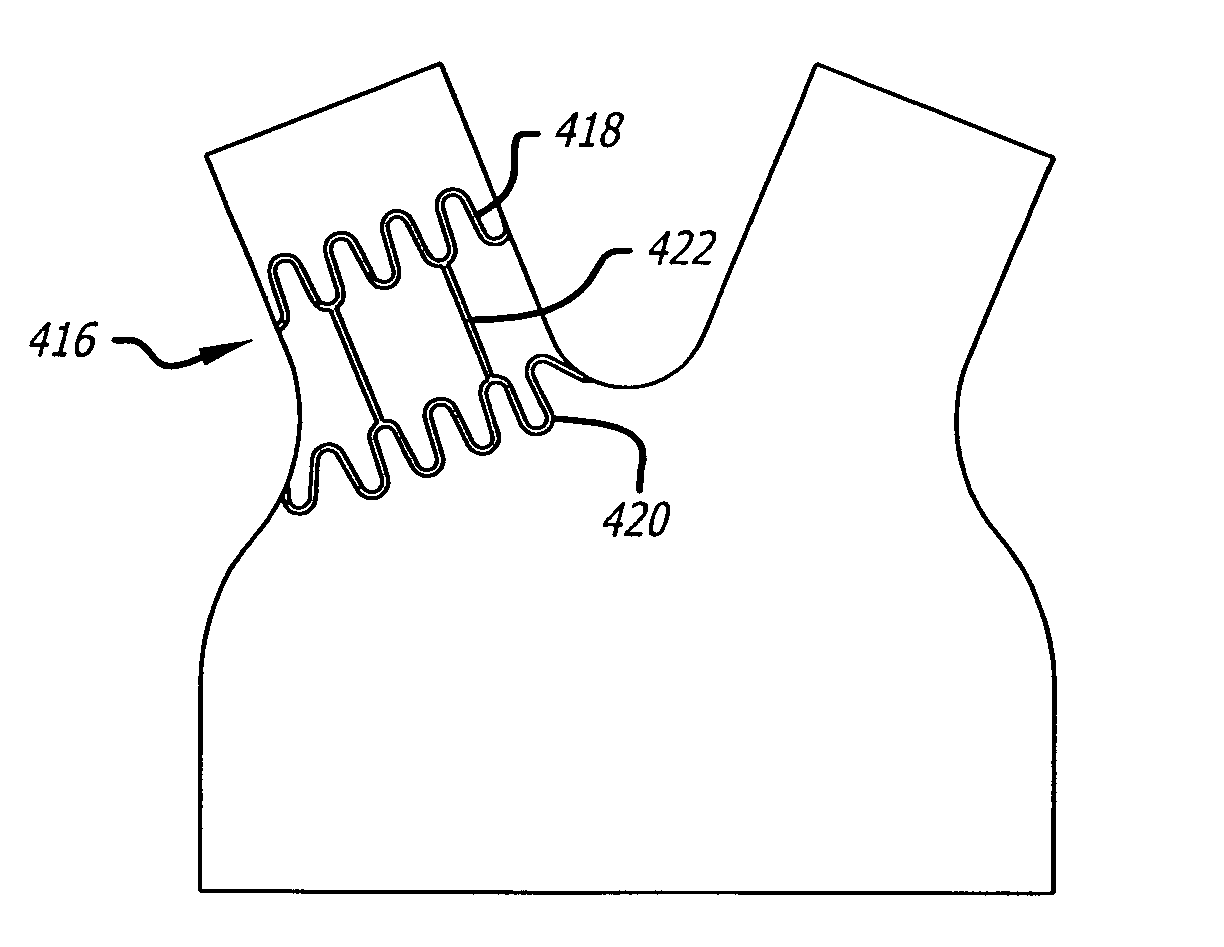
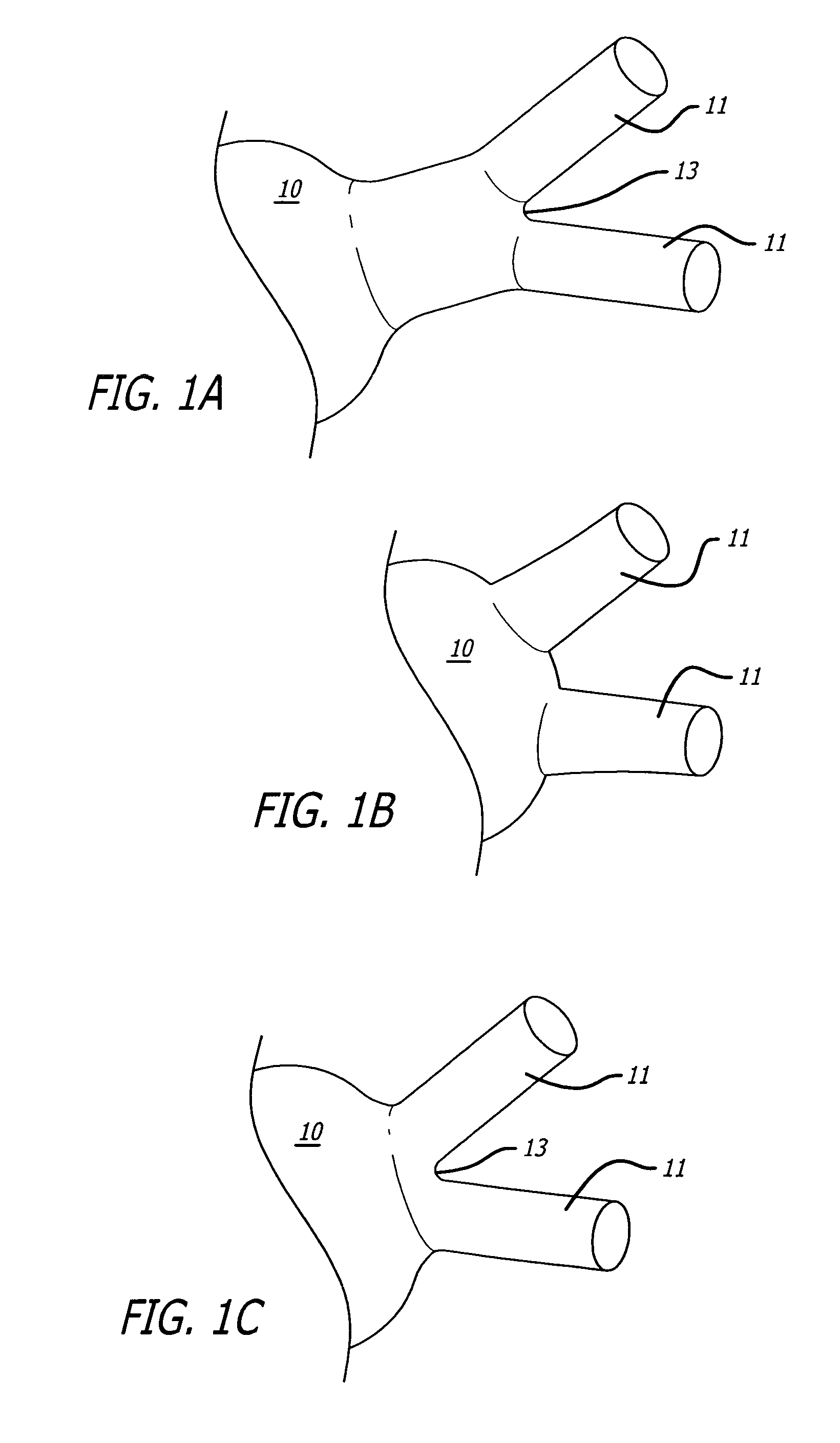
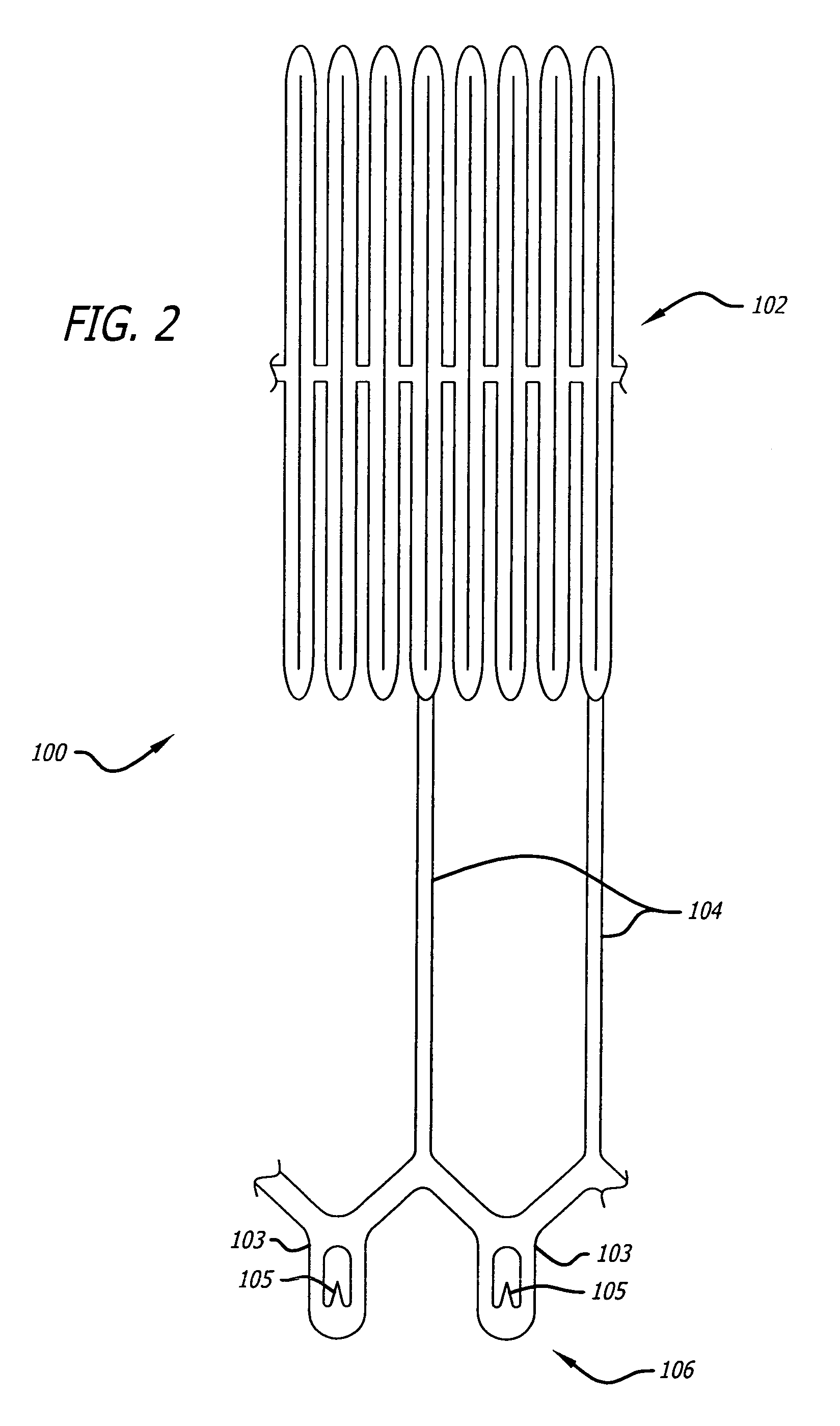
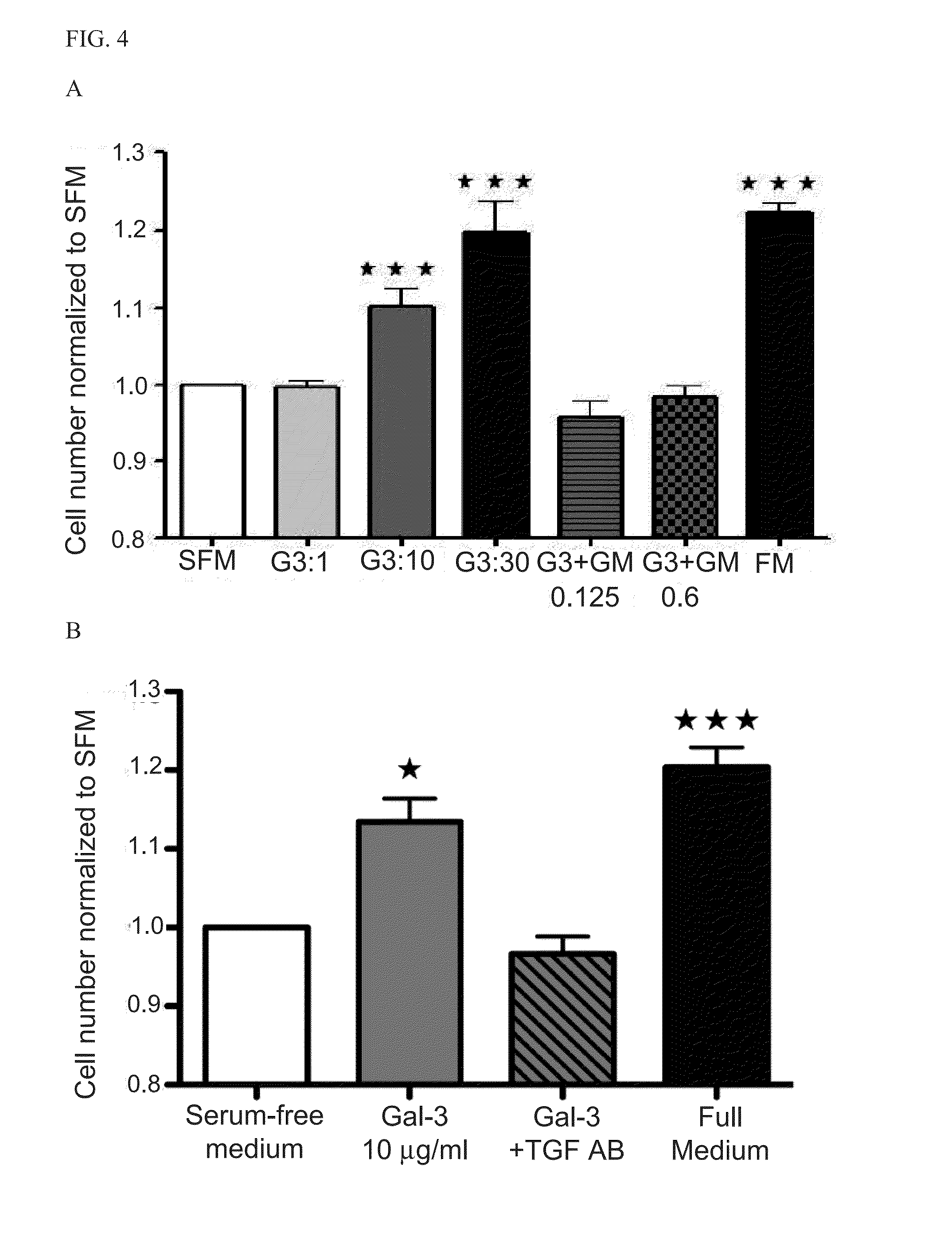
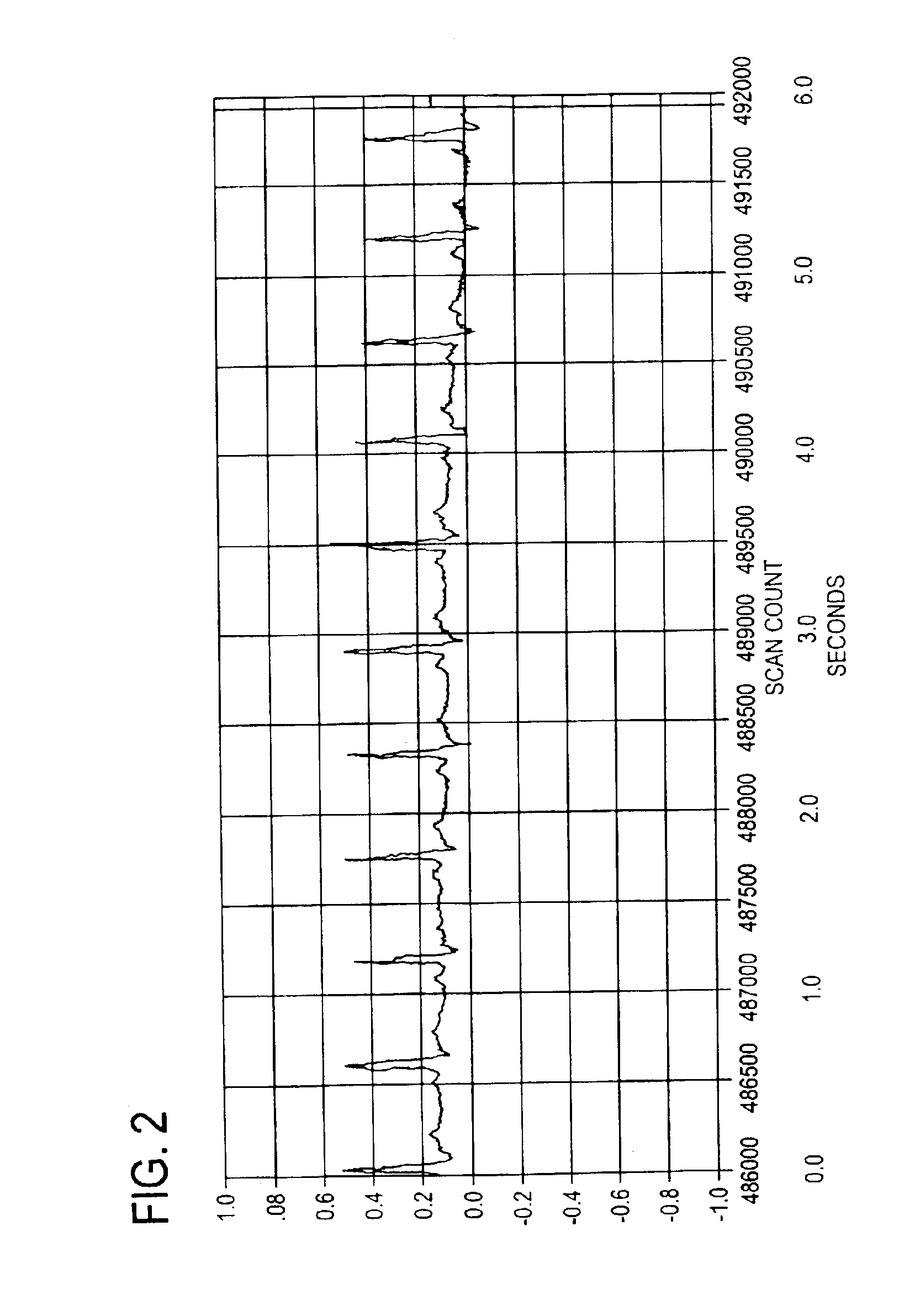
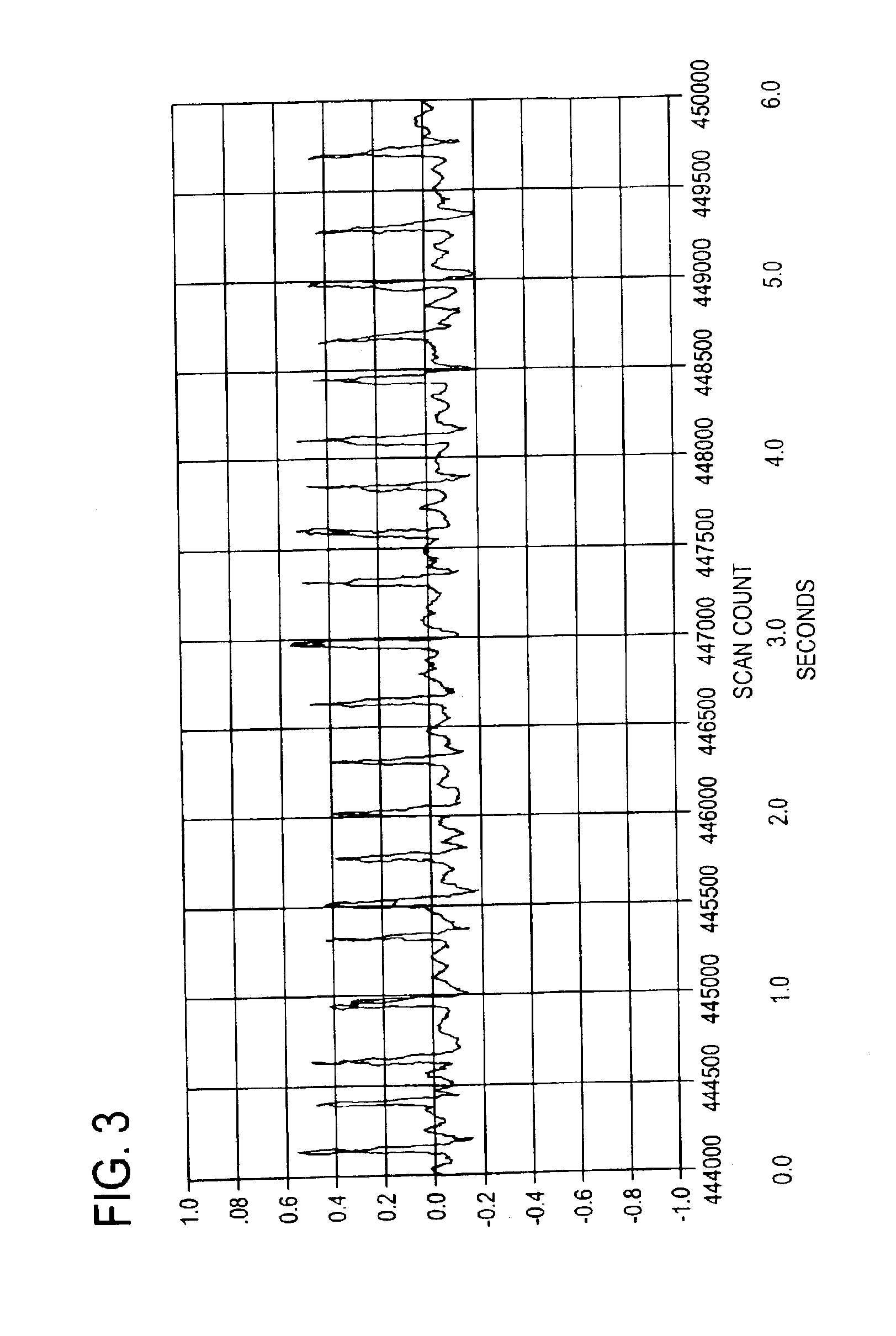
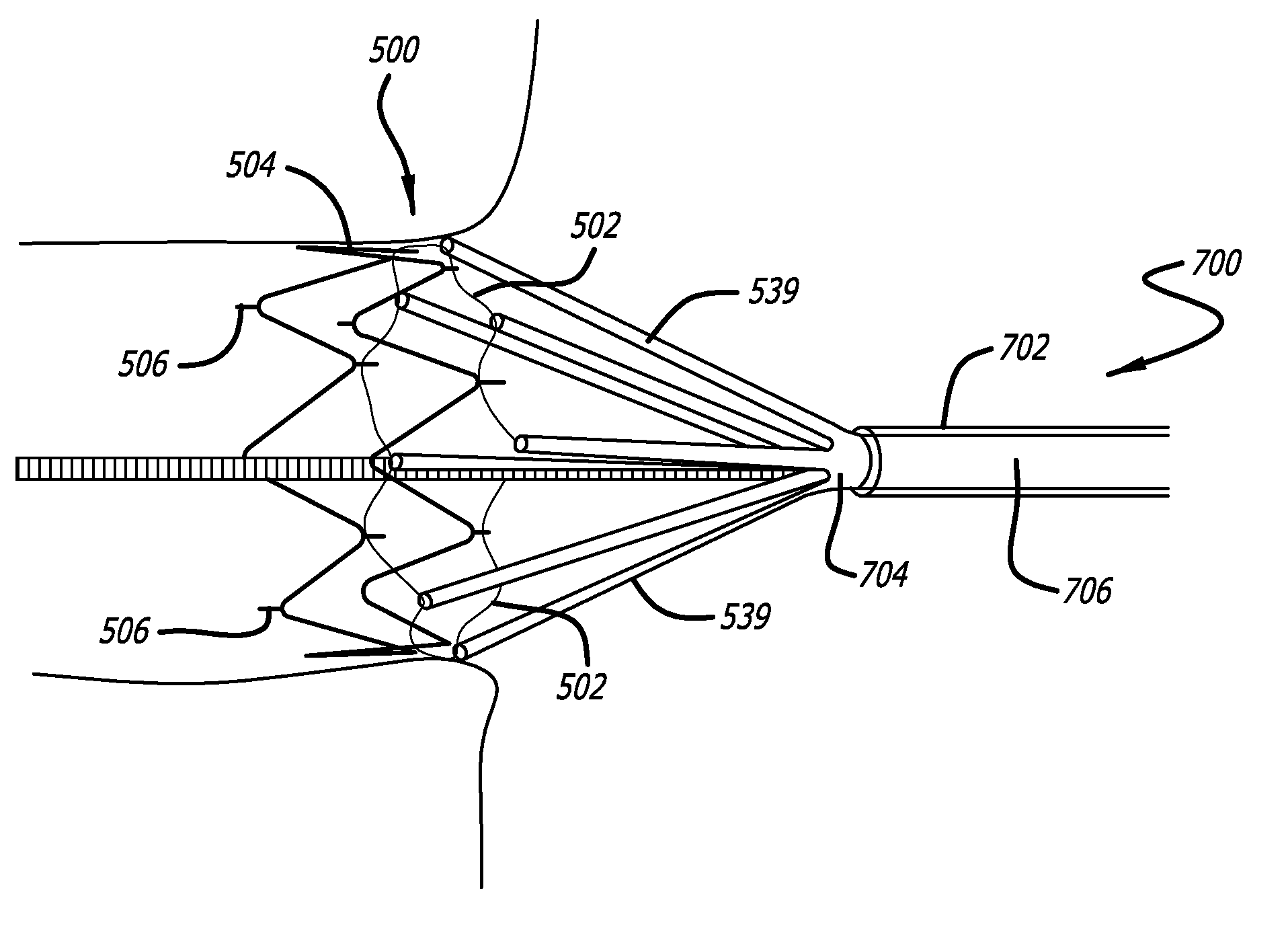
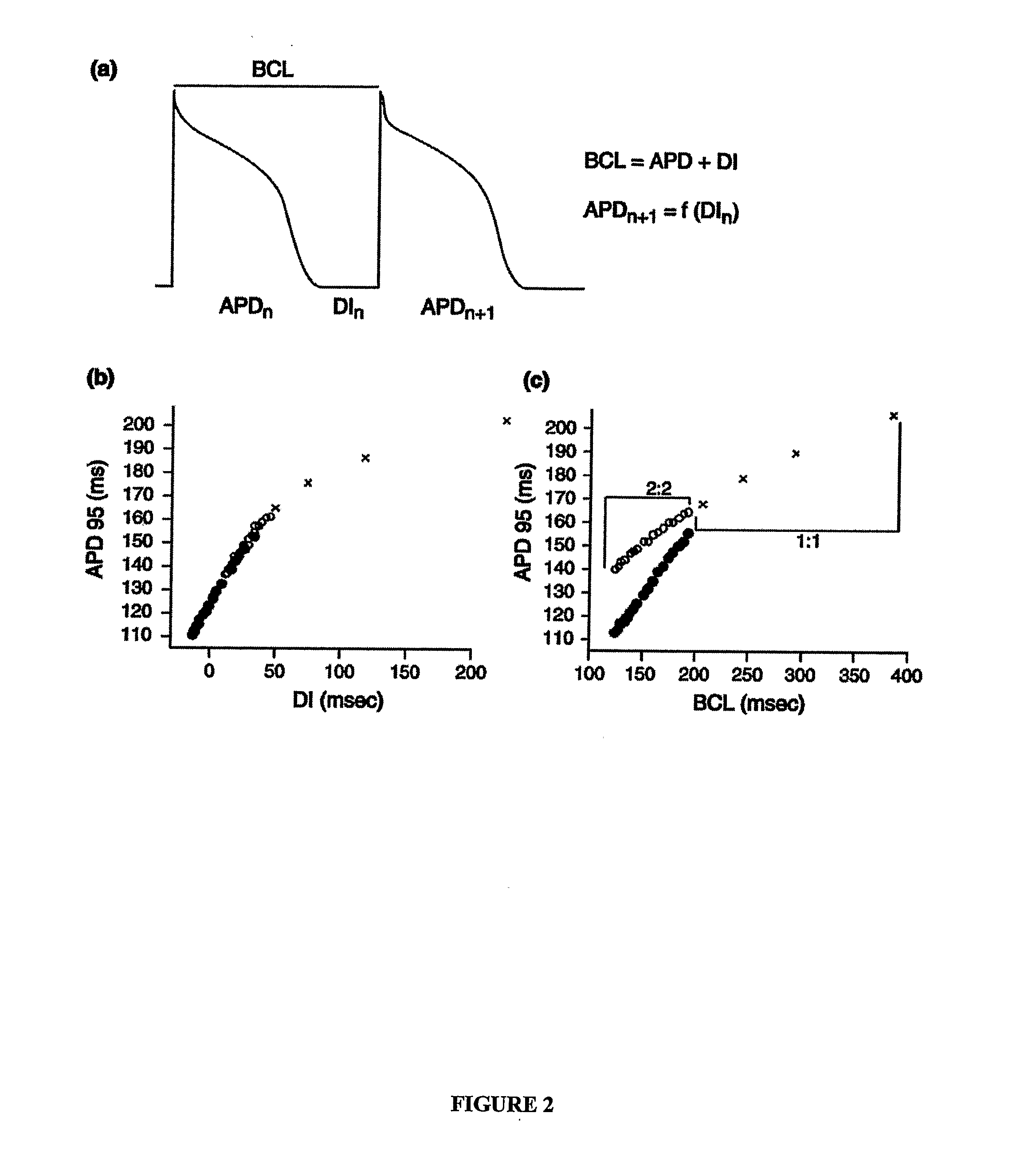
Polymeric complements to [beta]-amyloid peptides
InactiveCN103260743AInhibition of fibrillationSuppress or suppress neurotoxicityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsOther chemical processesAmyloidPolymer
Owner:伯耶·塞勒格伦
Method of identifying strategies for treatment or prevention of ventricular fibrilation and ventricular tachycardia
ActiveUS20100233088A1Inhibition of fibrillationNovel methodElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsVentricular tachycardiaVentricular fibrillation
The present invention relates to evaluating the effect of physiological conditions on the occurrence of ventricular fibrillation, identifying strategies for treatment or prevention of ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, and evaluating a subject for induction of ventricular fibrillation from a condition of ventricular tachycardia.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Pharmeceutical composition comprising plant material or trichilia sp. alone or in association with other plant extracts for the reversion/combat and/or prevention of ventricular fibrillation
ActiveUS20060286179A1Recovery effectInhibition of fibrillationBiocideAnimal repellantsTrichiliaZingiberaceae
The present invention relates to the use of a plant material of the species Trichilia sp., alone or in association with one or more of the following plants: Paullinia cupana (Sapindaceae), Croton moritibensis (Euphorbiaceae) and Zingiber officinale (Zingiberaceae) in the treatment, reversion, combat and / or prevention of ventricular fibrillation. A product particularly embraced by the present invention comprises the plant material of the species Trichilia sp., alone or in association with extracts from other plants. The invention also refers to the use of one or more fractions of plant extract from such plant material, particularly of Trichilia catigua A. Juss, and of one or more subfractions of said fractions in the treatment, combat, prevention and / or reversion of ventricular fibrillation.
Owner:LAB CATARINENSE
Combination of dofetilide and mexiletine for the prevention and treatment of atrial fibrillation
ActiveUS20170087105A1Increase rangeReduce riskAmide active ingredientsCapsule deliveryVentricular dysrhythmiaPharmaceutical drug
Effective and safe pharmaceutical composition and method for treating atrial fibrillation are described. The combined use of dofetilide and mexiletine resulted in an enhanced efficacy in the prevention and treatment of atrial fibrillation with markedly reduced risk of the life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia TdP.
Owner:FB HRS LLC
Anti-arrhythmic and heart failure drugs that target the leak in the ryanodine receptor (RyR2) and uses thereof
InactiveUS7718644B2Inhibition of fibrillationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBenzothiazepine derivativesMedicine
The present invention provides methods for limiting or preventing a decrease in the level of RyR2-bound FKBP12.6 in a subject. The present invention further provides methods for treating and preventing atrial and ventricular cardiac arrhythmias, heart failure, and exercise-induced sudden cardiac death in a subject. Additionally, the present invention provides use of JTV-519 in a method for limiting or preventing a decrease in the level of RyR2-bound FKBP12.6 in a subject who has, or is a candidate for, atrial fibrillation. Also provided are uses of 1,4-benzothiazepine derivatives in methods for treating and preventing atrial and ventricular cardiac arrhythmias and heart failure in a subject, and for preventing exercise-induced sudden cardiac death. The present invention also provides methods for identifying agents for use in treating and preventing atrial fibrillation and heart failure, and agents identified by these methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Cellulose fibers with an enhanced metering capability, processes for their production of these and their use to reinforce compound materials
InactiveUS20160244576A1Significant positive effectQuality improvementFibre mixingMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentCellulose fiberPolymer chemistry
The present invention relates to cellulose fibers with an enhanced metering capability, a process for the production of these and the use of these for the reinforcement of compound materials, in particular thermoplastic polymers.
Owner:LENZING AG
Use of D-ribose to treat cardiac arrhythmias
D-ribose, given in doses of five to 15 grams daily, reduces or prevents the occurrence of atrial fibrillation in persons experiencing atrial fibrillation.
Owner:BIOENERGY INC
Cellulose fibers with an enhanced metering capability, processes for their production and their use to reinforce compound materials
InactiveUS20120178856A1Reduce throughputLarge caliberFibre mixingMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentPolymer scienceCellulose fiber
The present invention relates to cellulose fibers with an enhanced metering capability, a process for the production of these and the use of these for the reinforcement of compound materials, in particular thermoplastic polymers.
Owner:LENZING AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
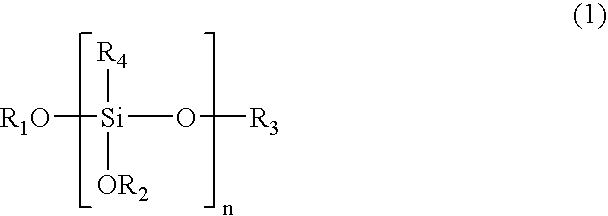
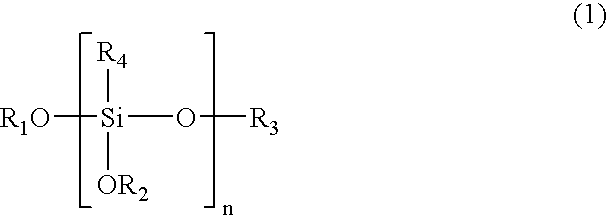
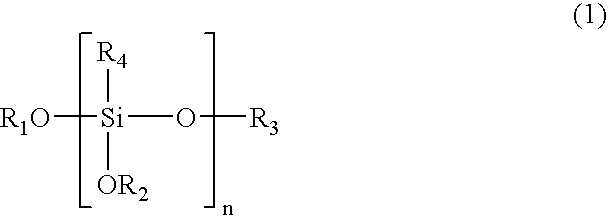
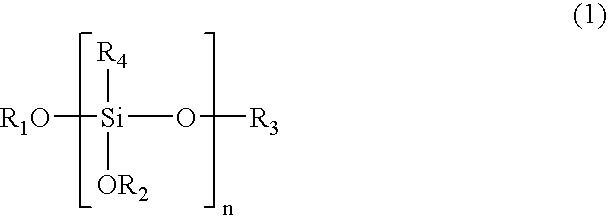
![Polymeric complements to [beta]-amyloid peptides Polymeric complements to [beta]-amyloid peptides](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/c9217c4f-152f-44c8-b928-7c6d05a836a9/HDA00002999260100011.PNG)
![Polymeric complements to [beta]-amyloid peptides Polymeric complements to [beta]-amyloid peptides](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/c9217c4f-152f-44c8-b928-7c6d05a836a9/HDA00002999260100012.PNG)
![Polymeric complements to [beta]-amyloid peptides Polymeric complements to [beta]-amyloid peptides](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/c9217c4f-152f-44c8-b928-7c6d05a836a9/HDA00002999260100021.PNG)