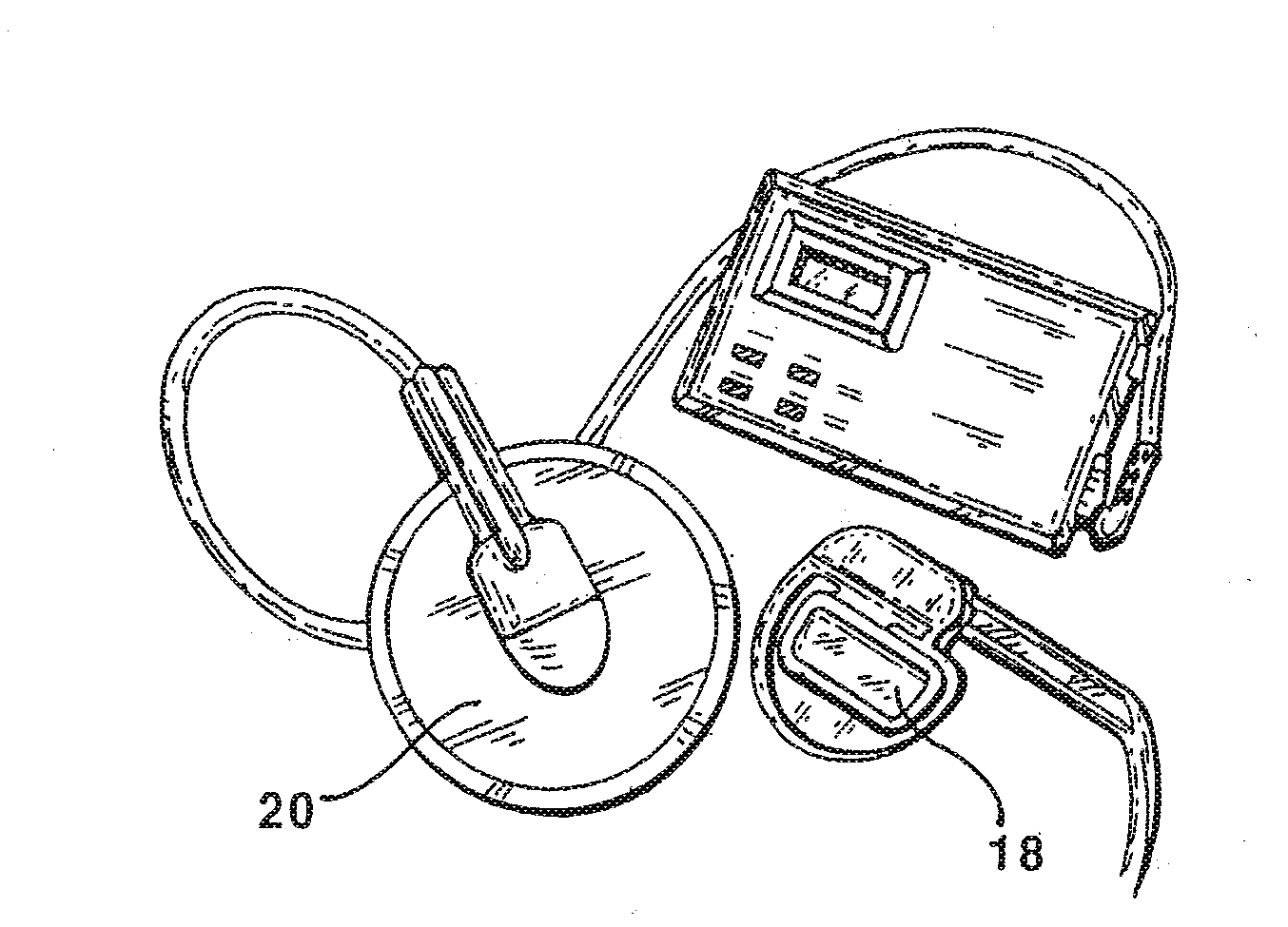
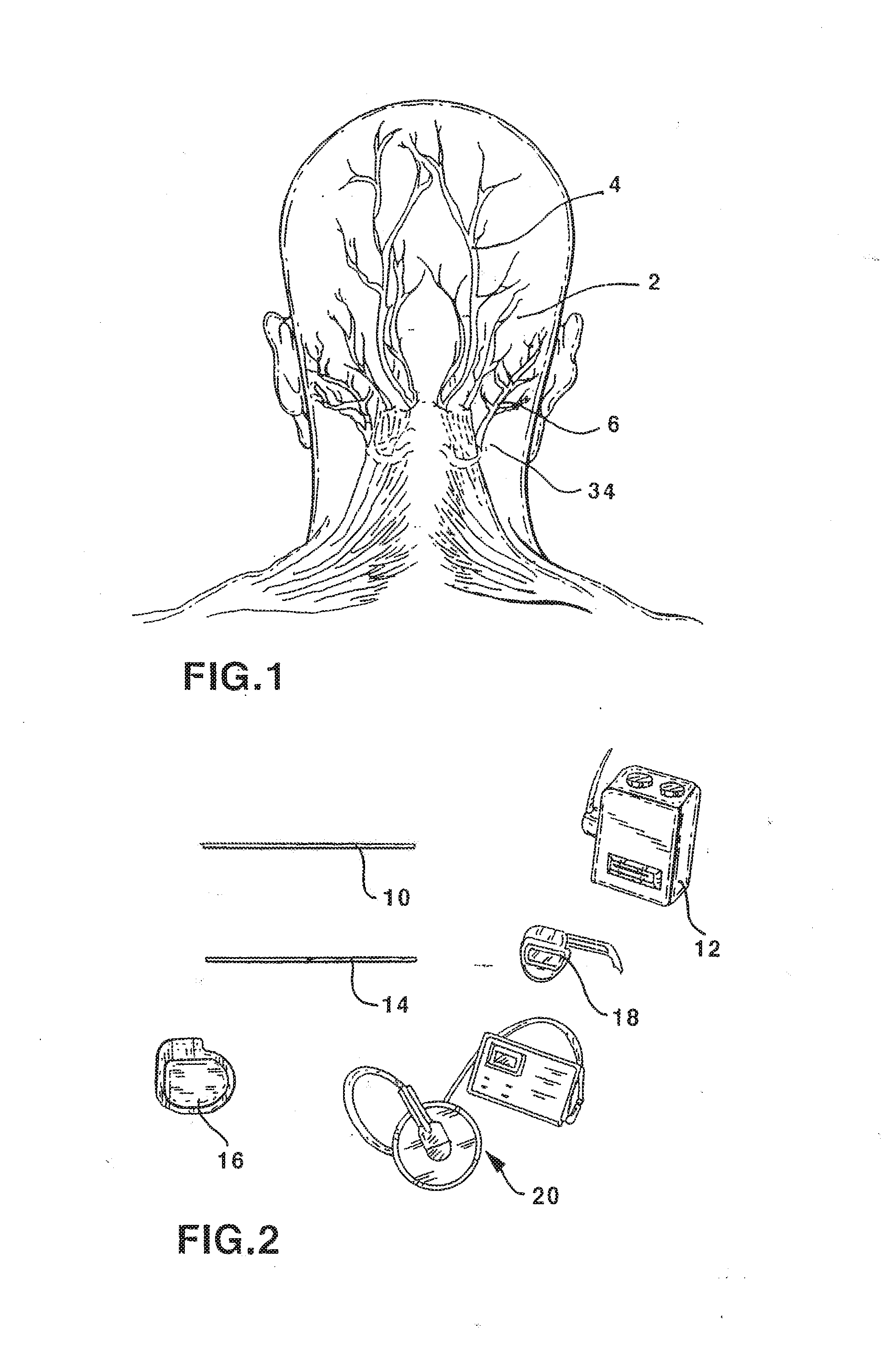
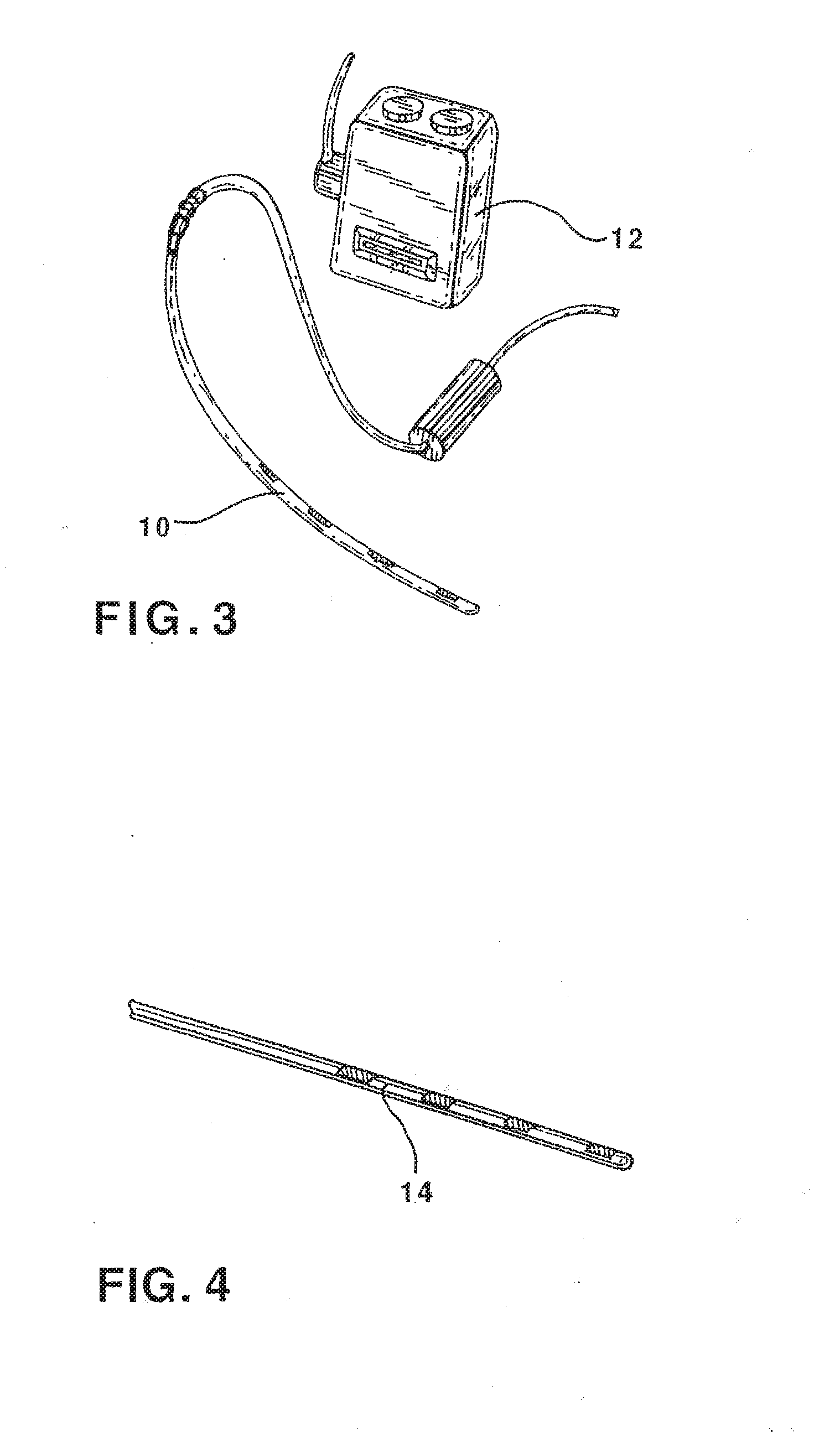
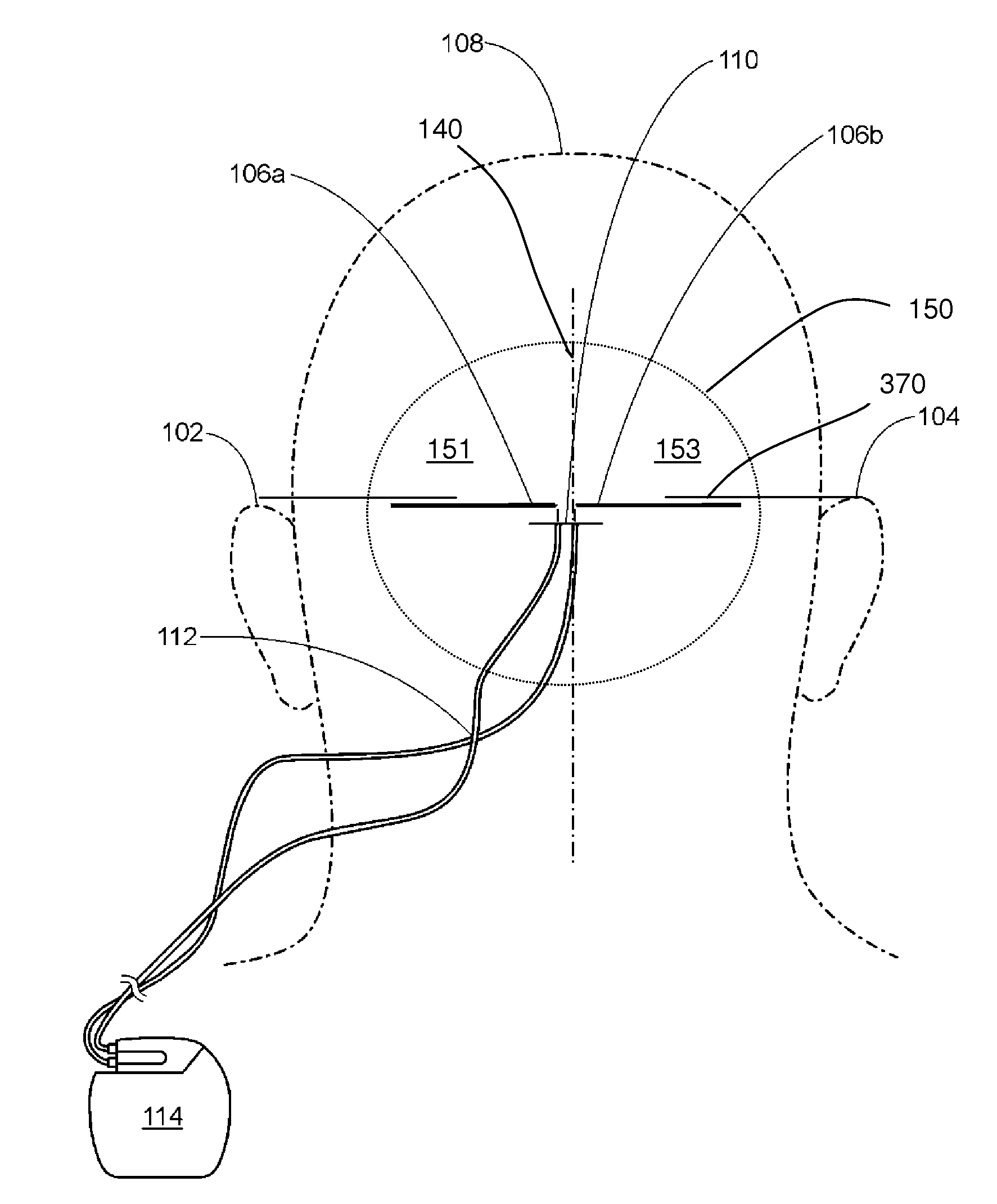
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
222results about "Subcutaneous electrodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
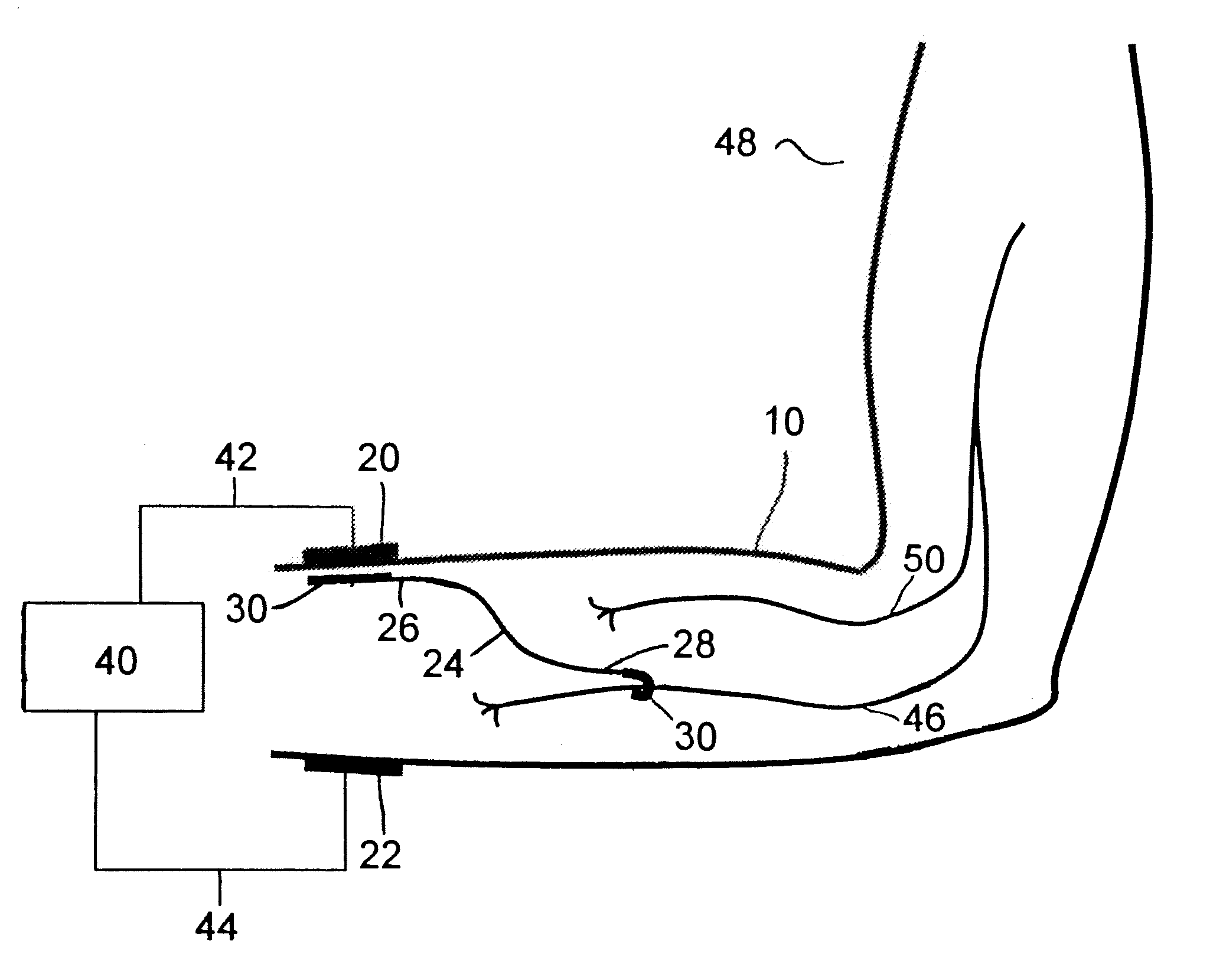
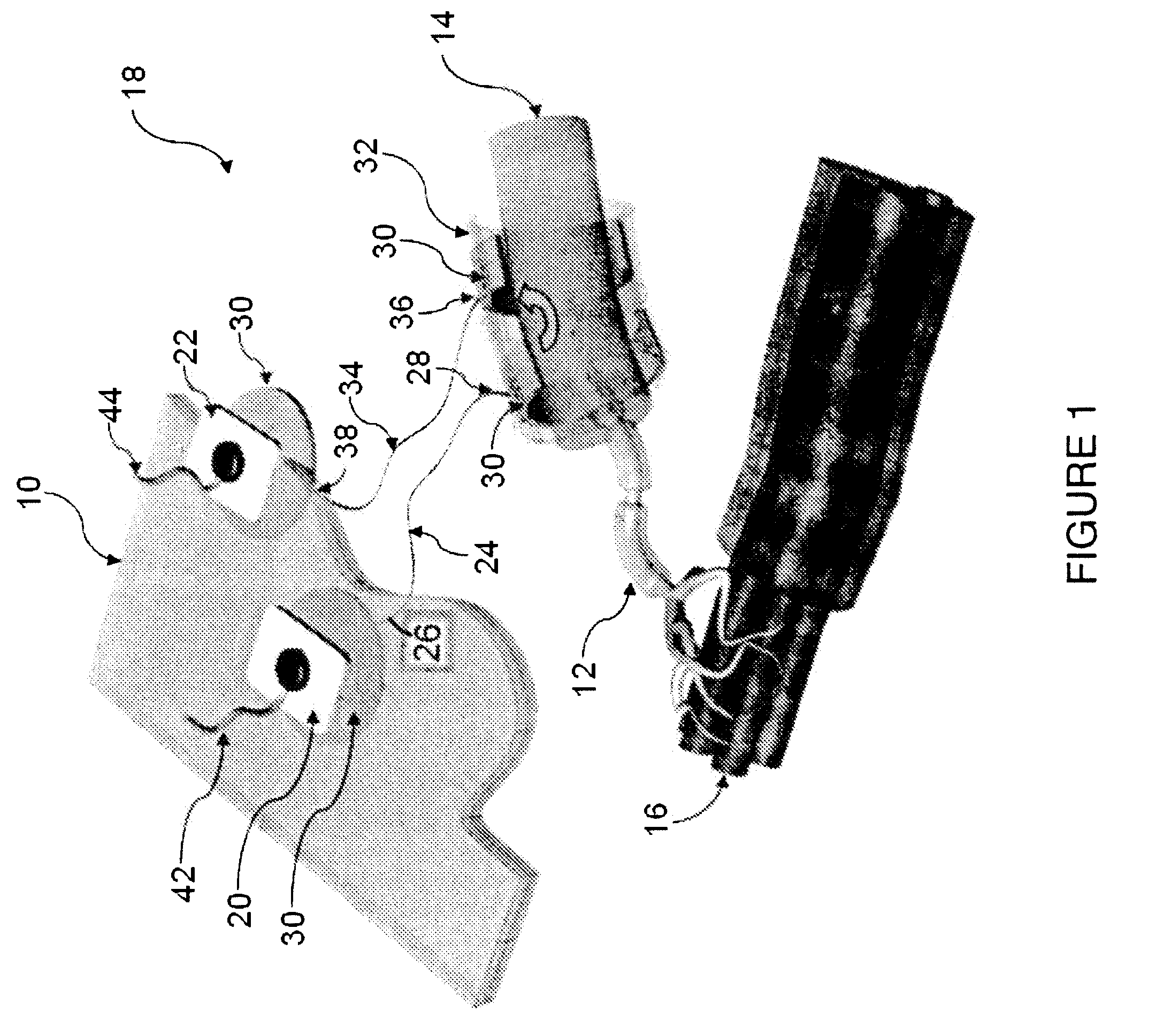
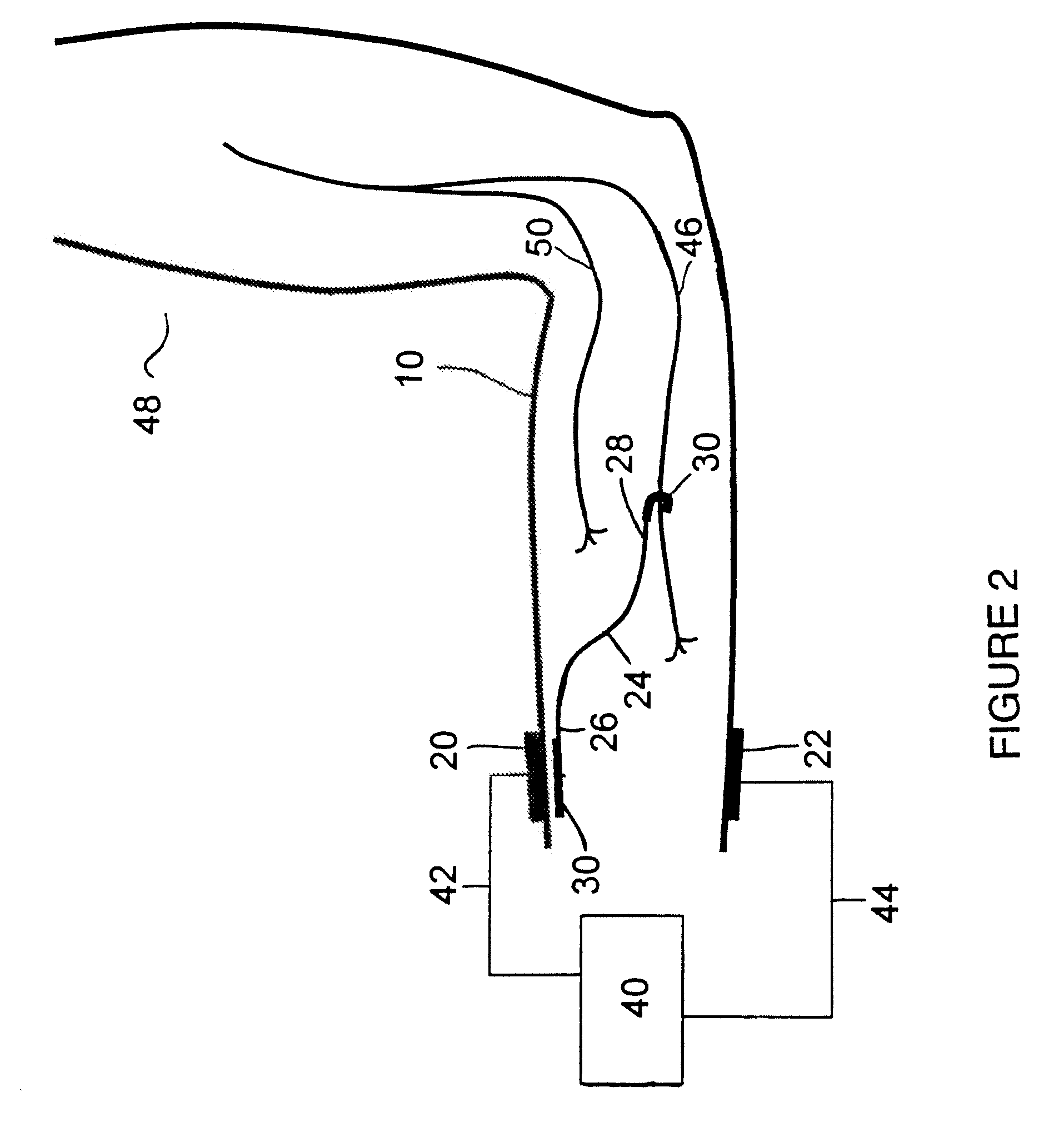
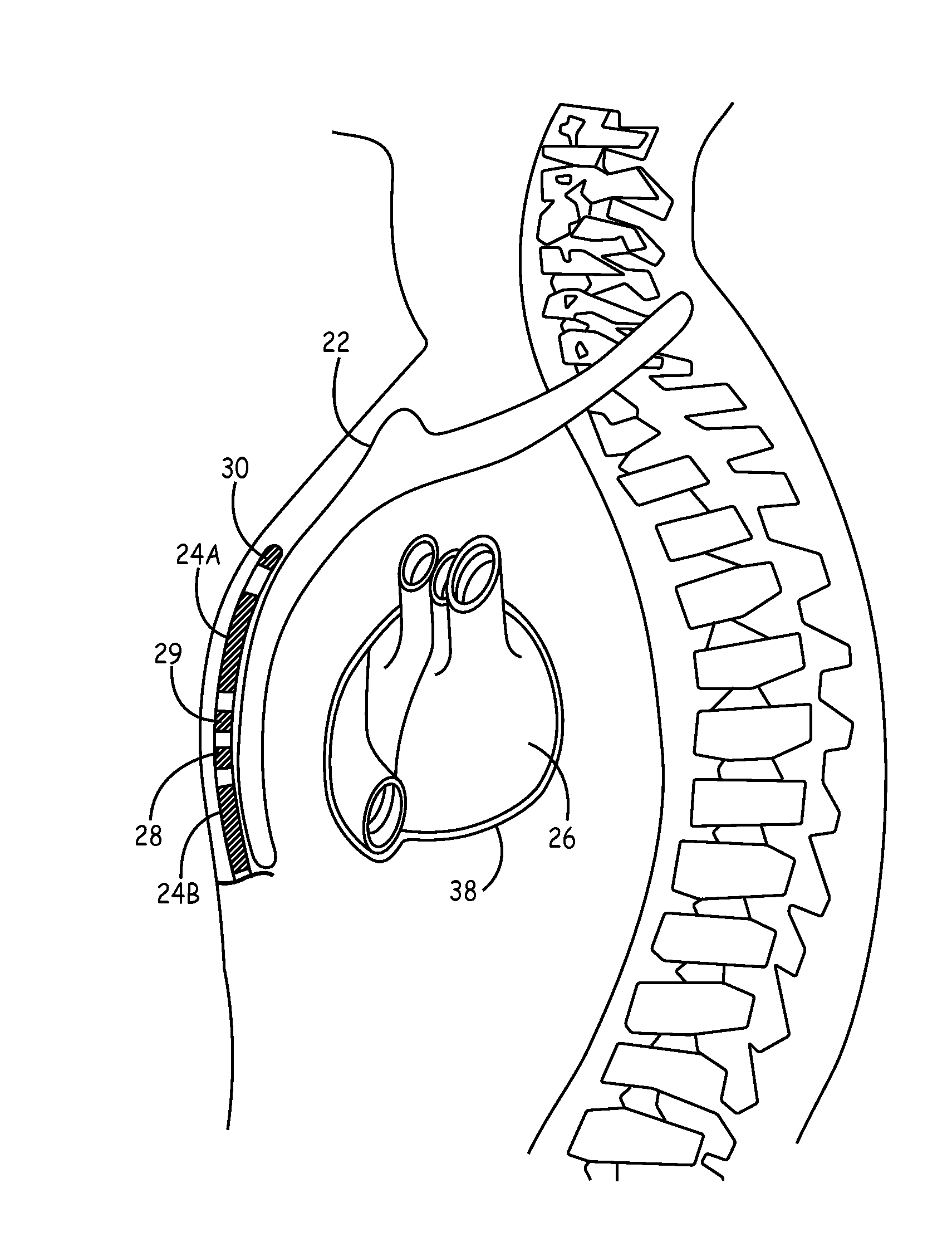
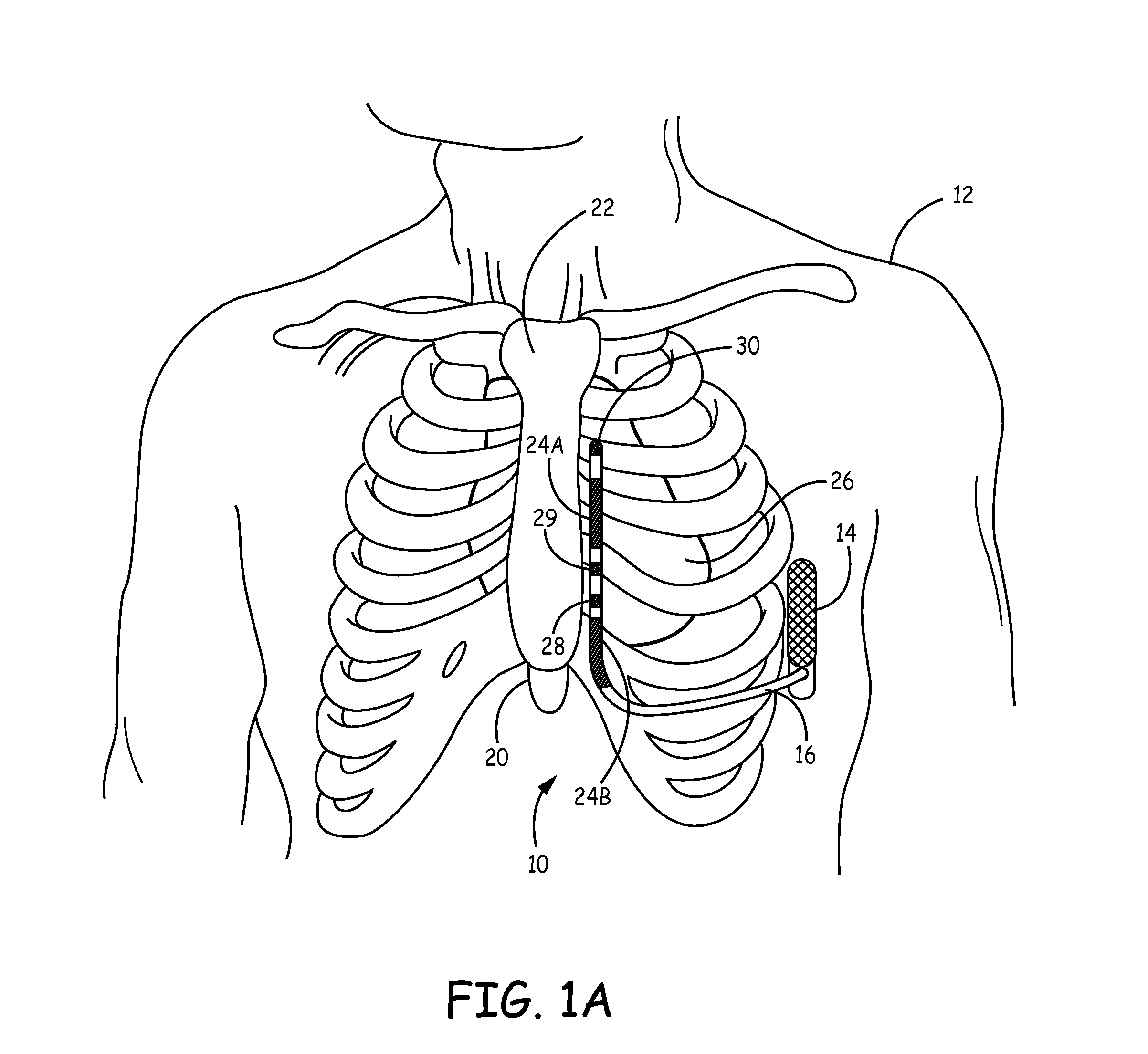
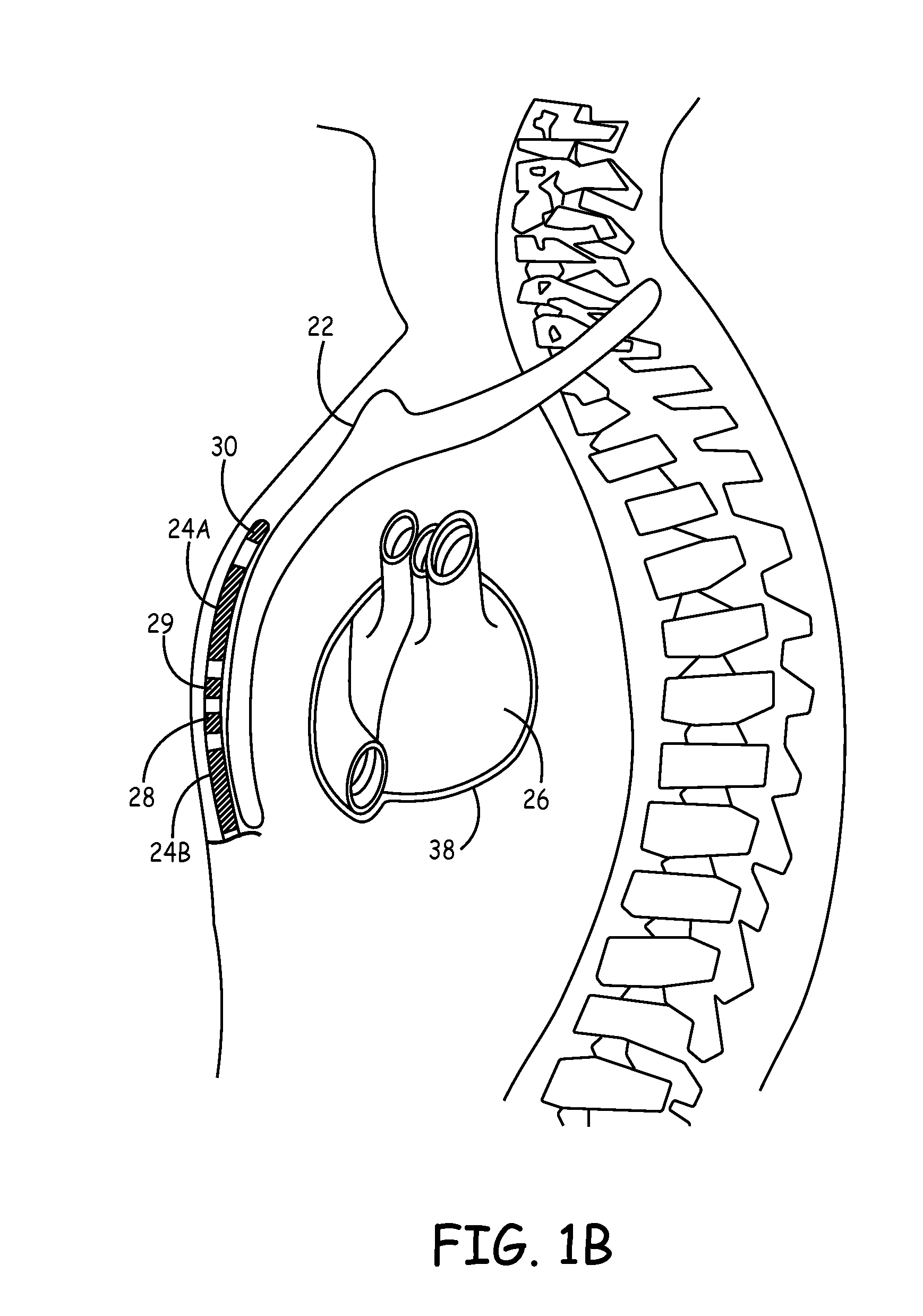
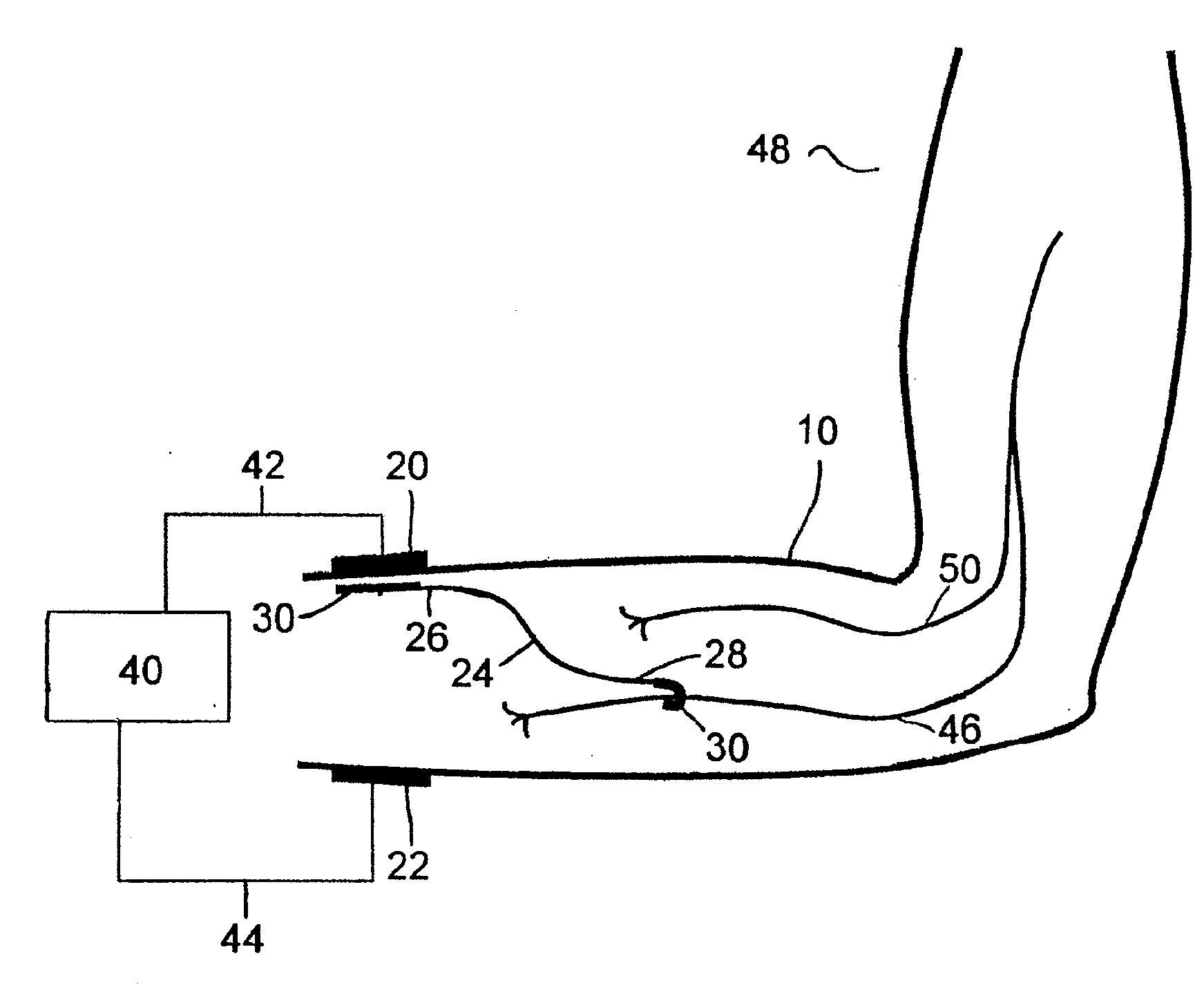
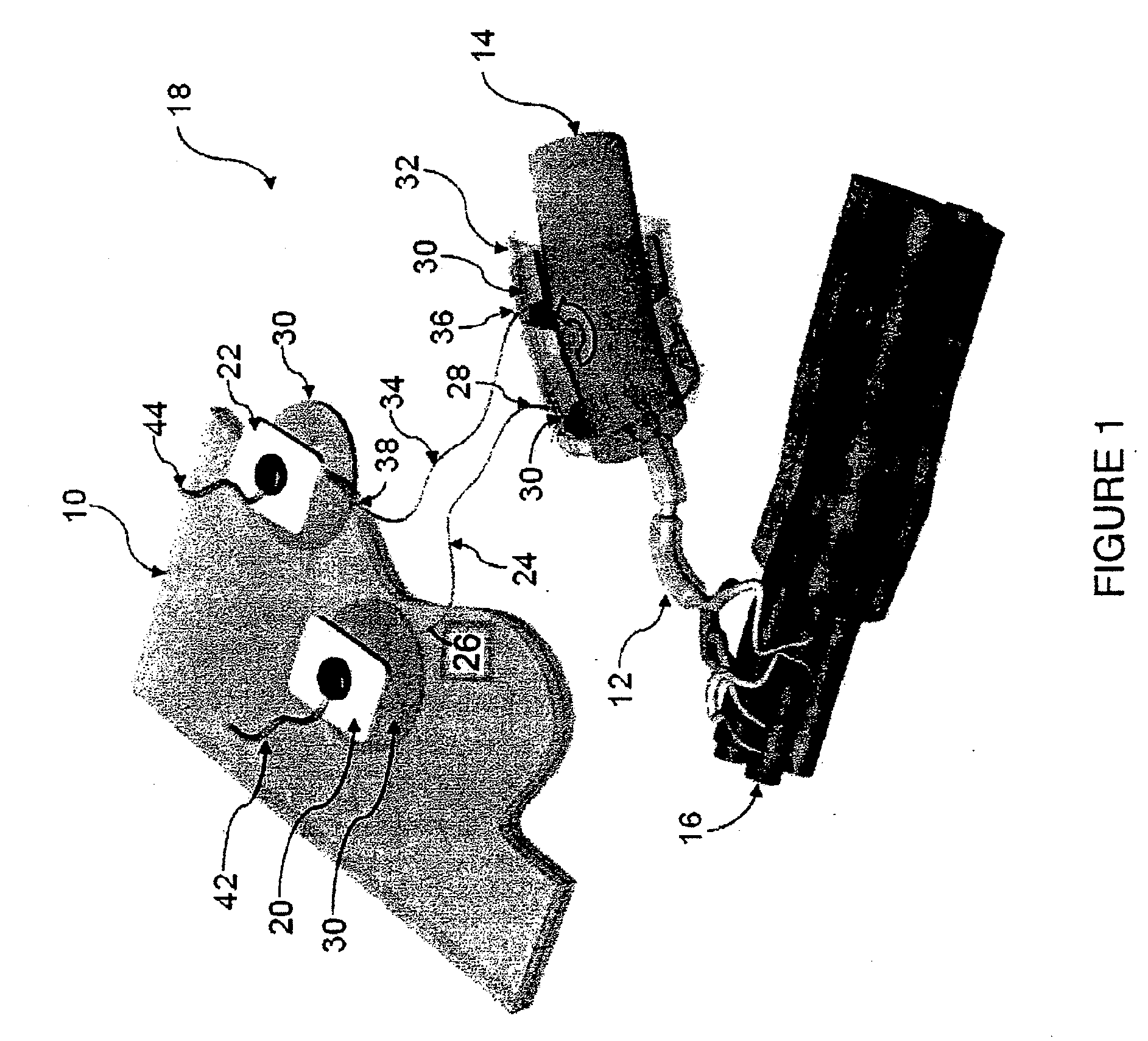
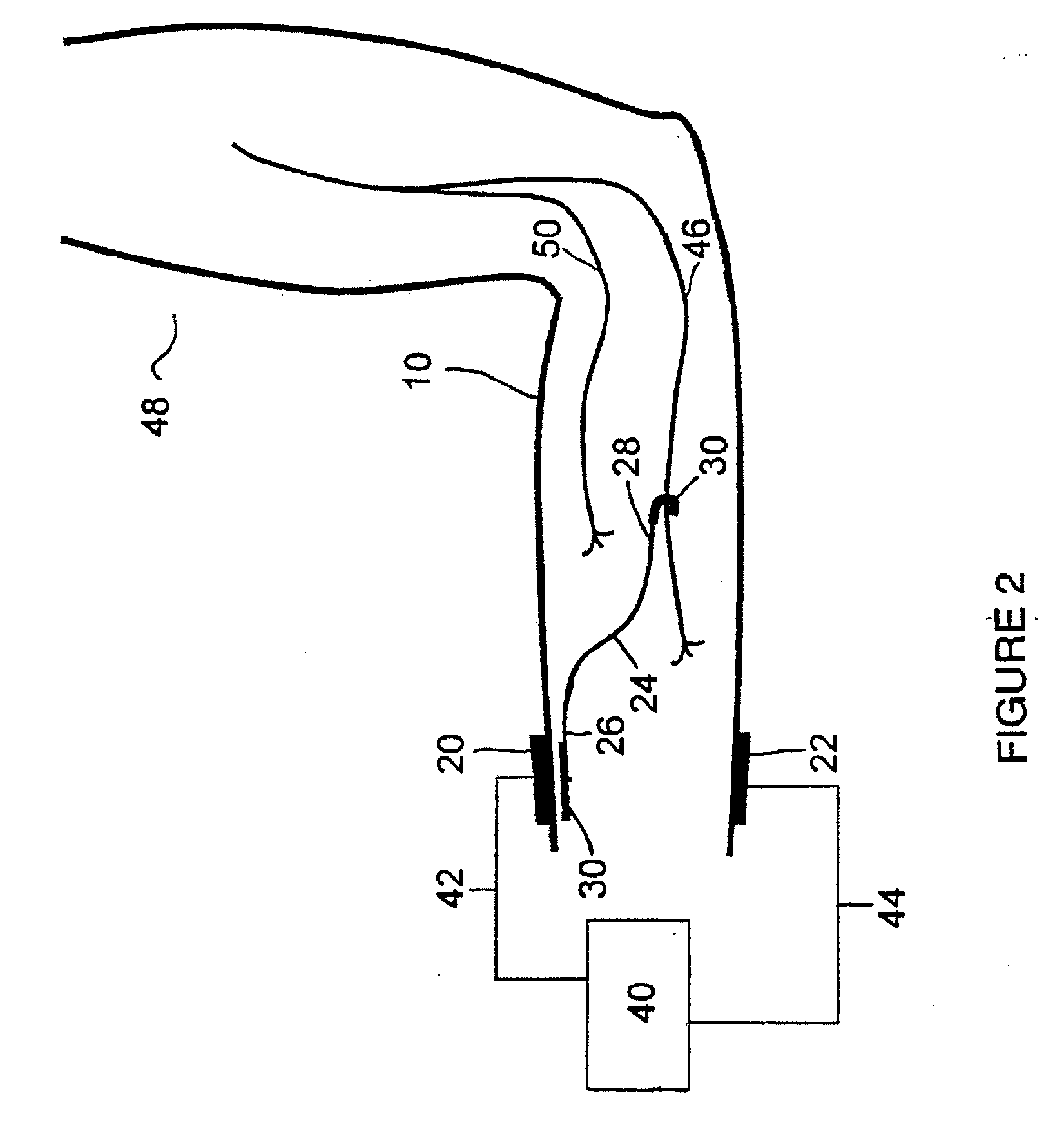
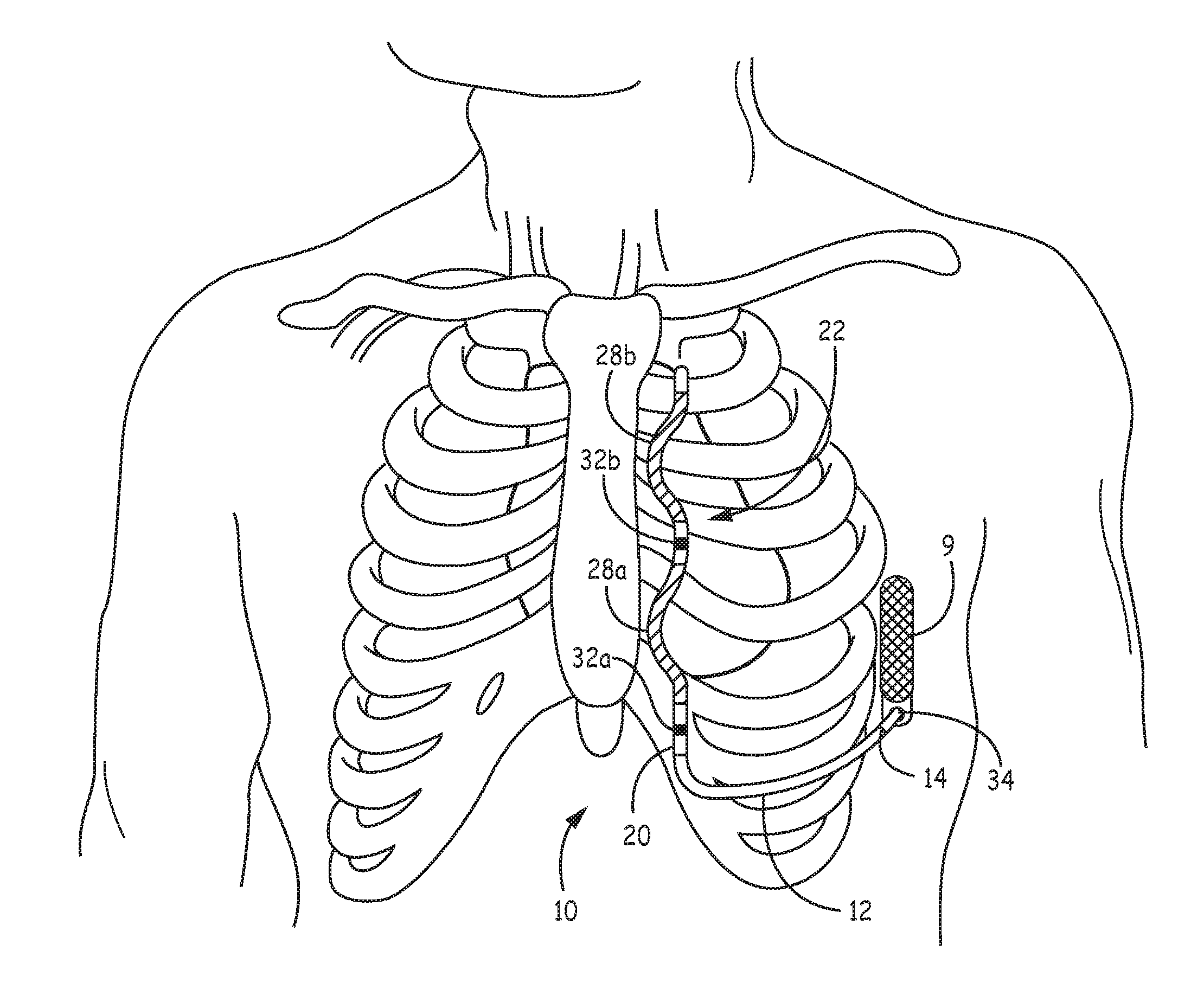
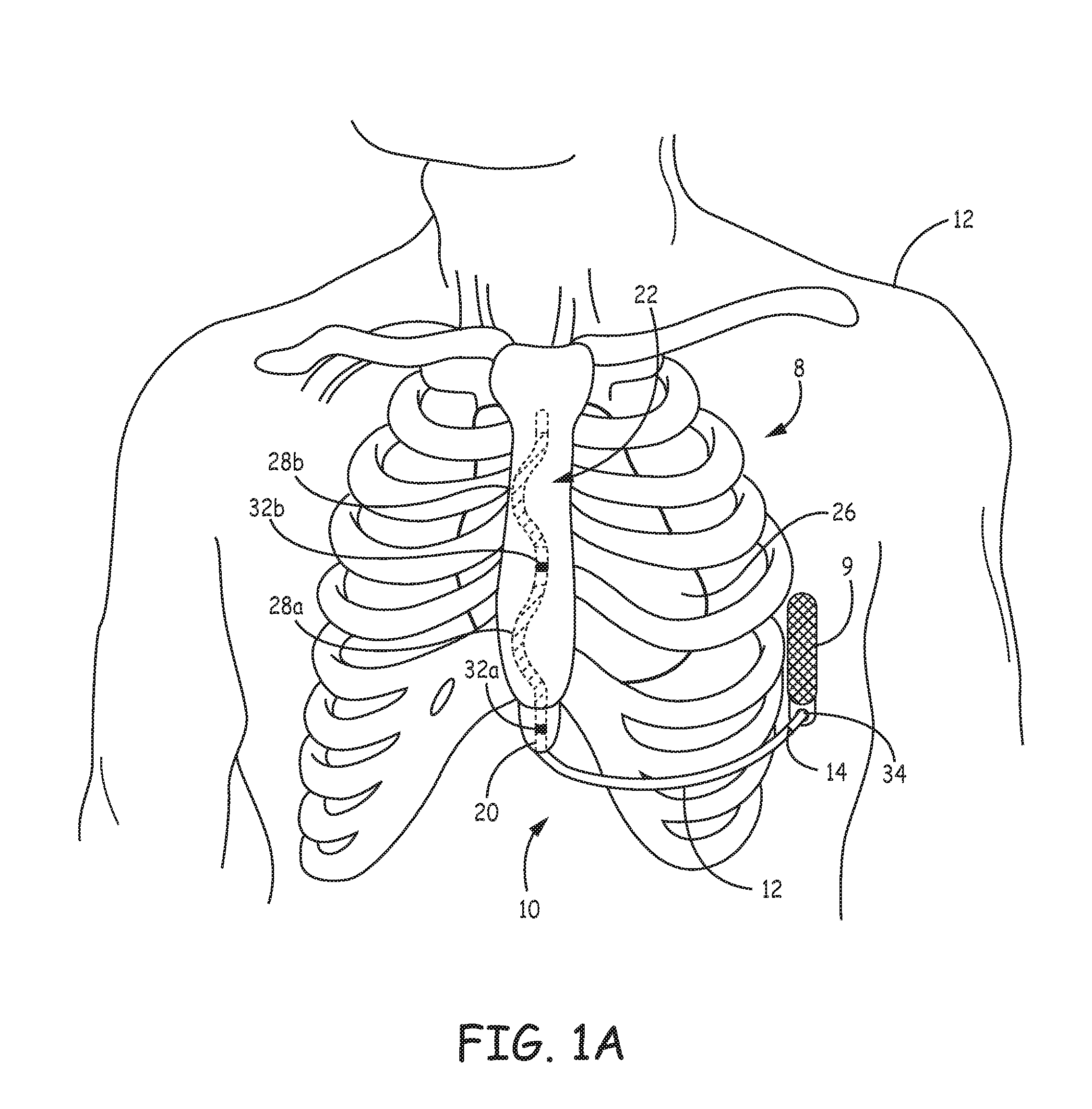
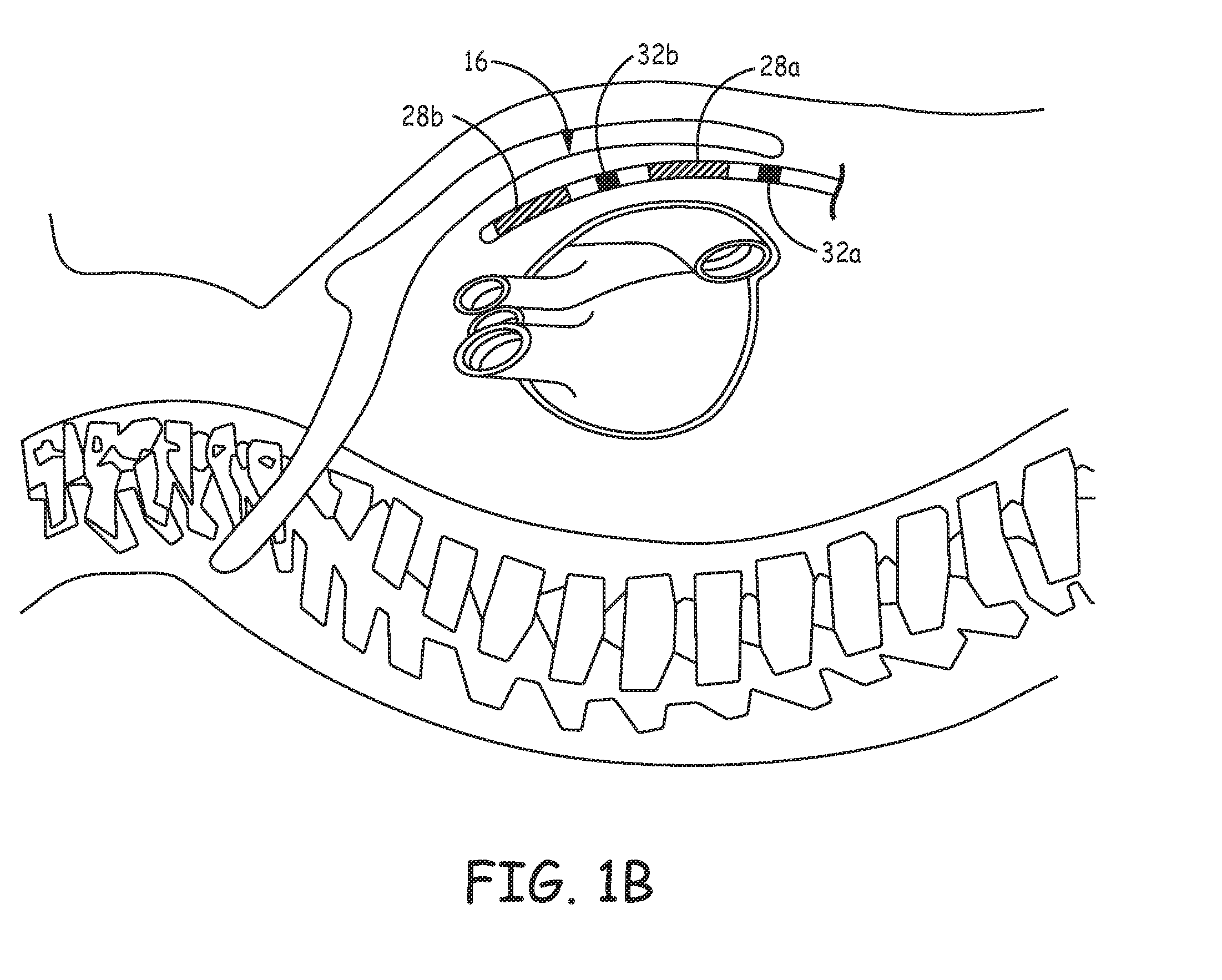
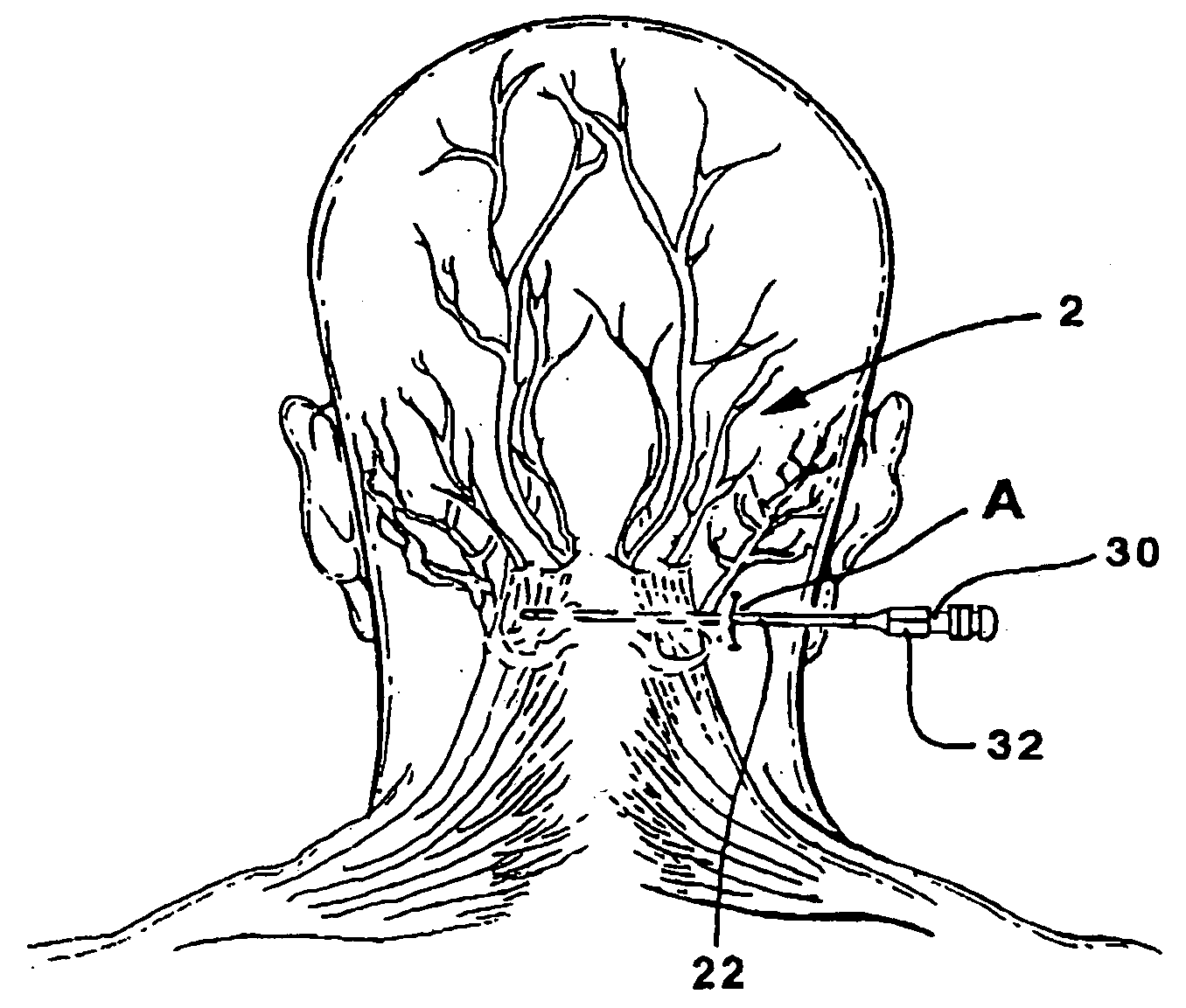
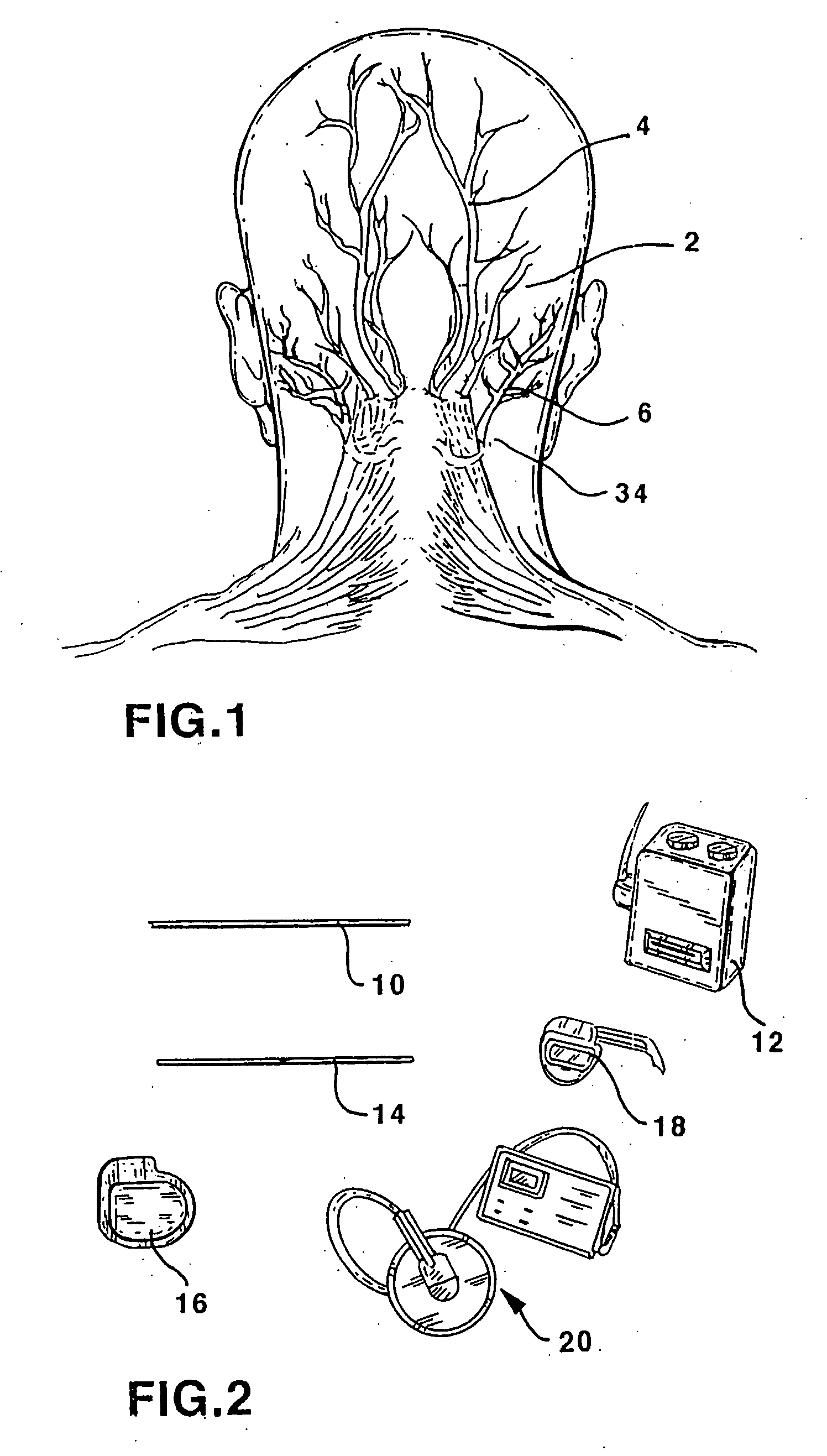
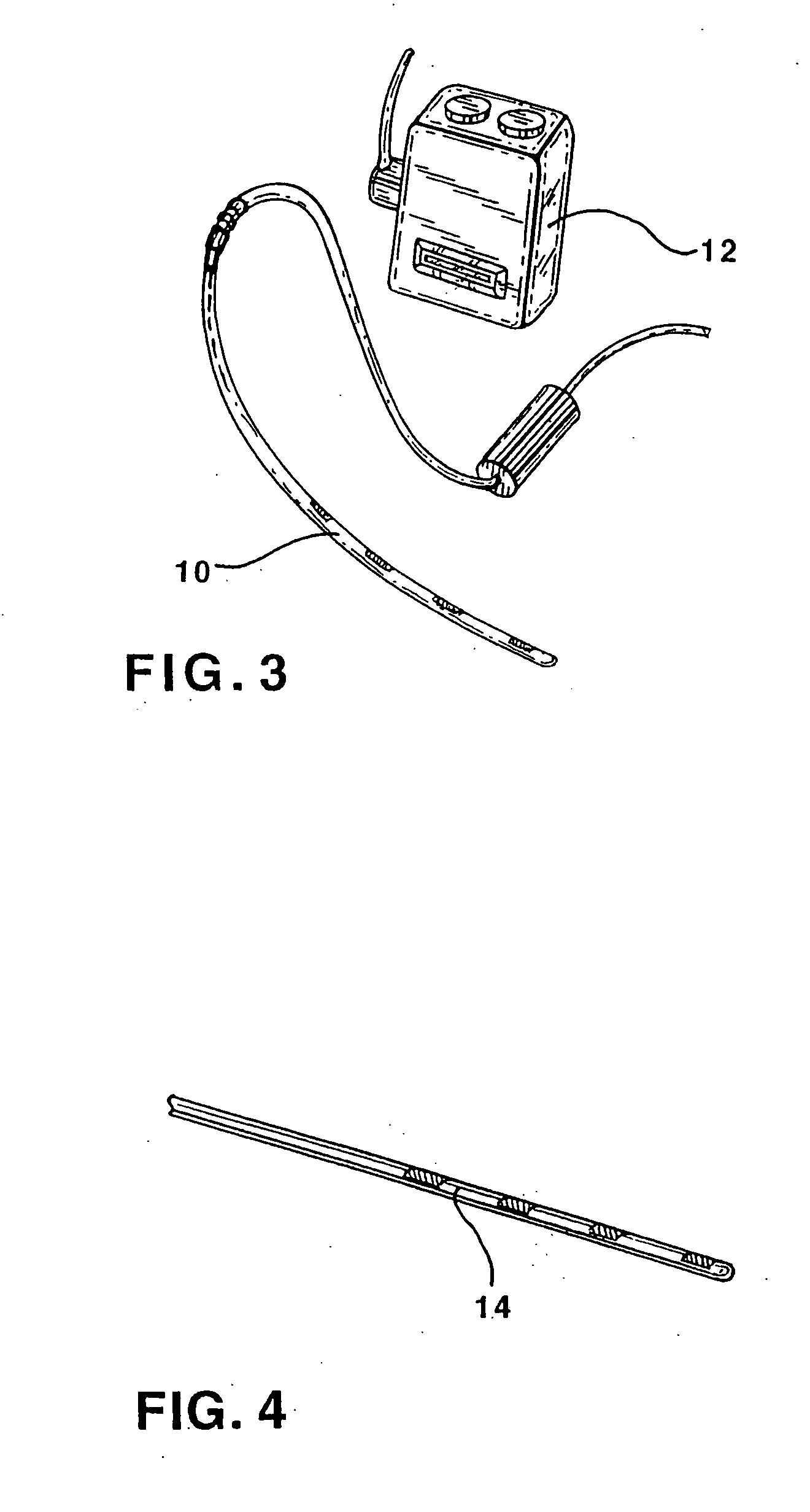
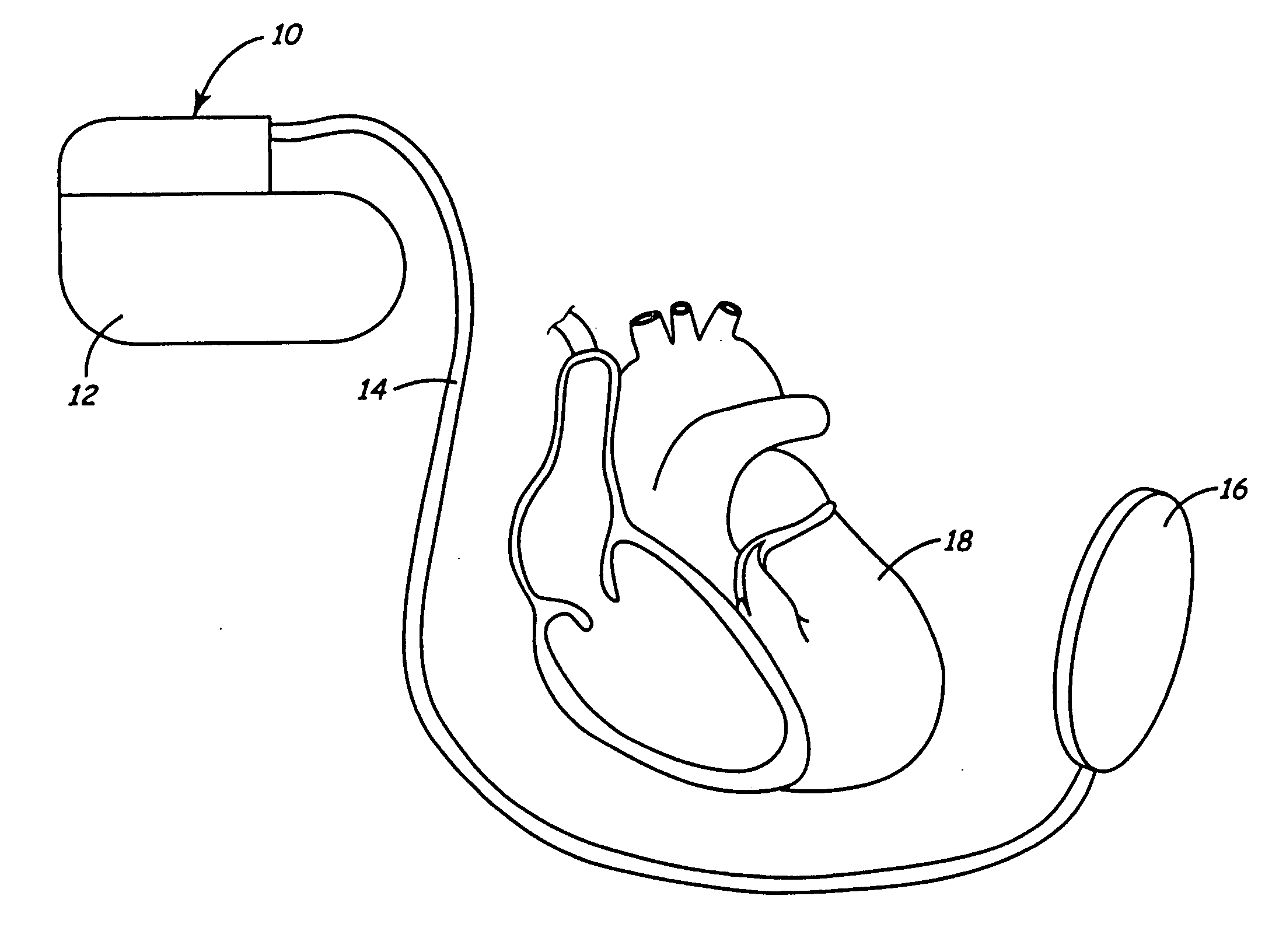
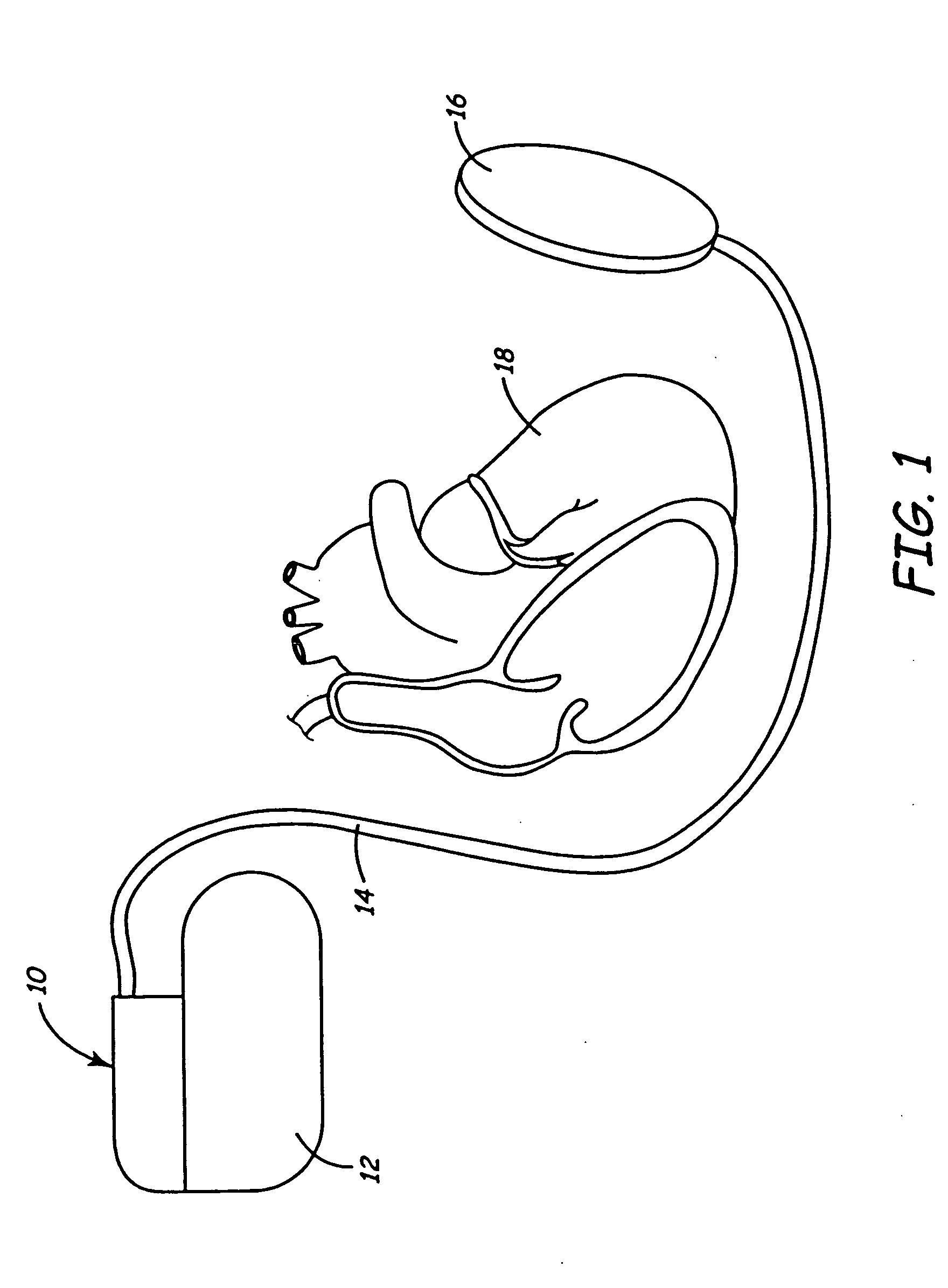
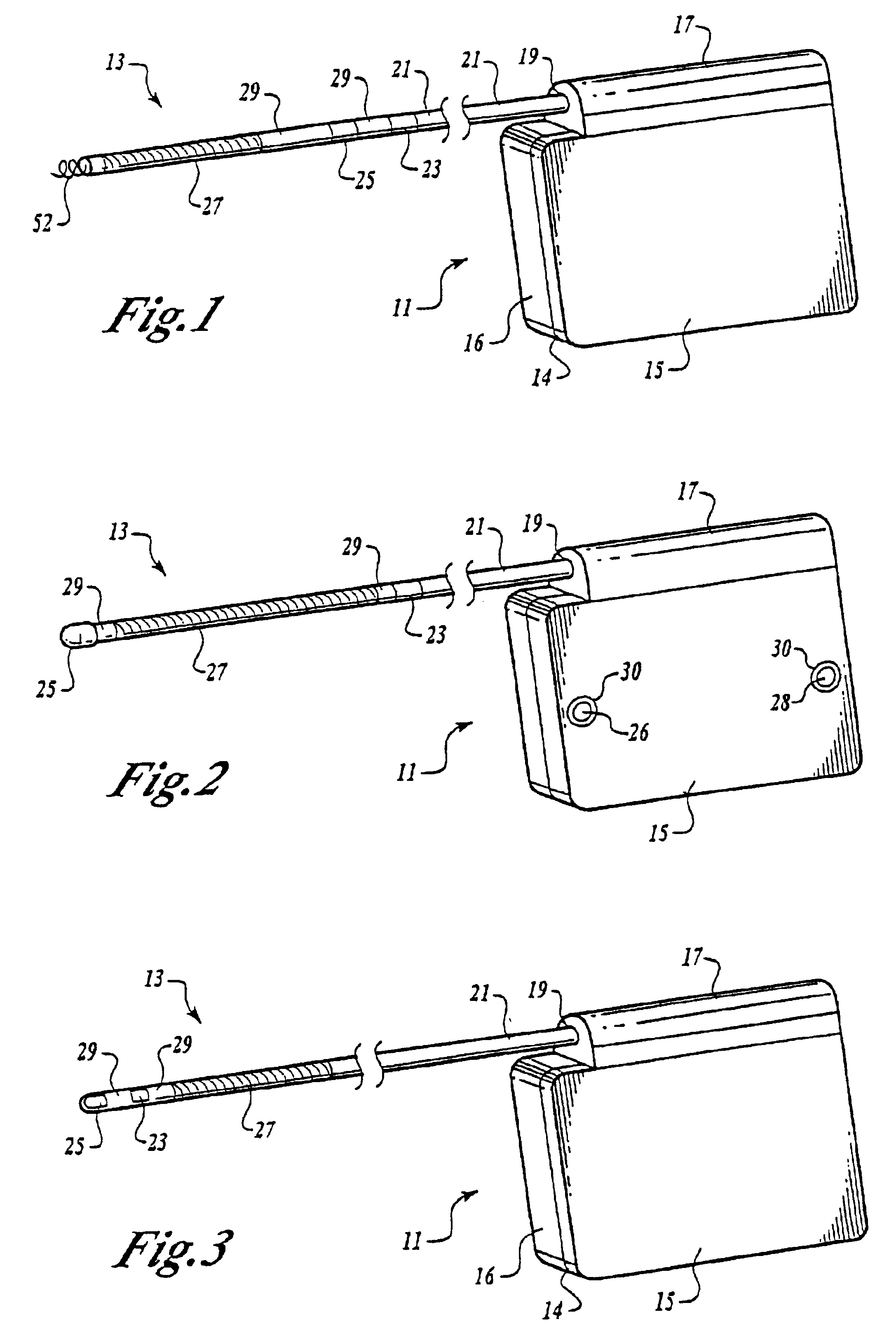
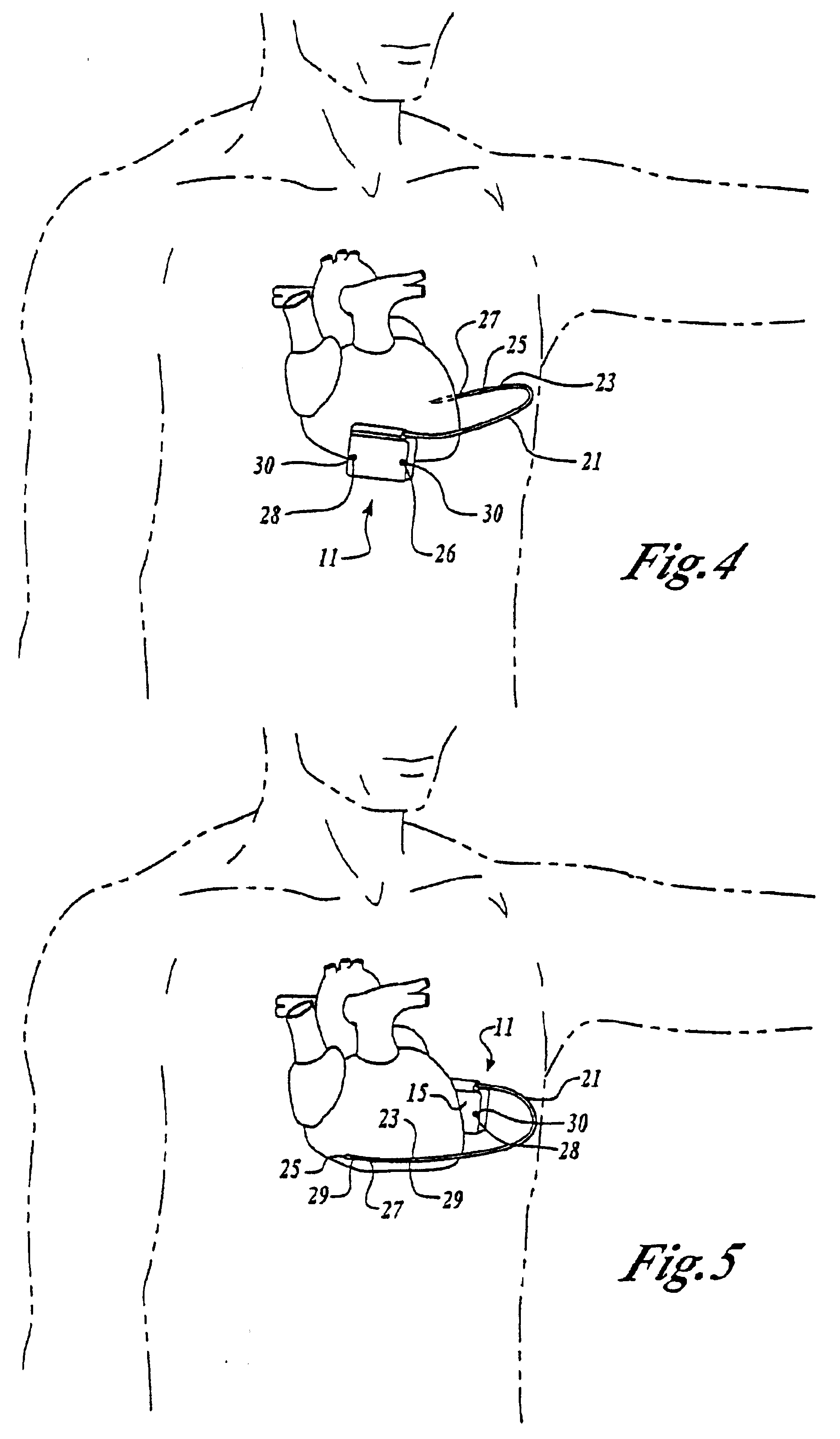
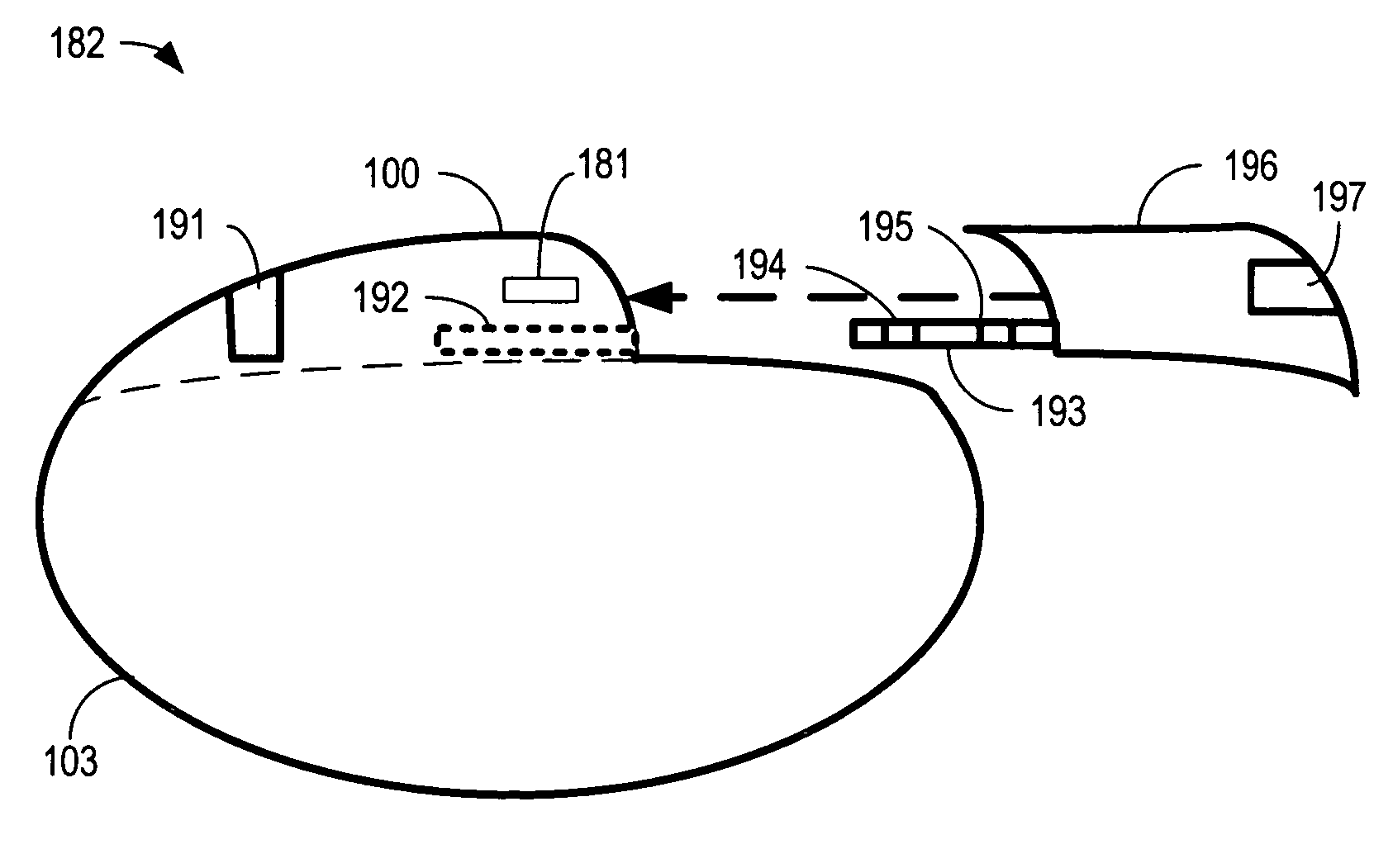
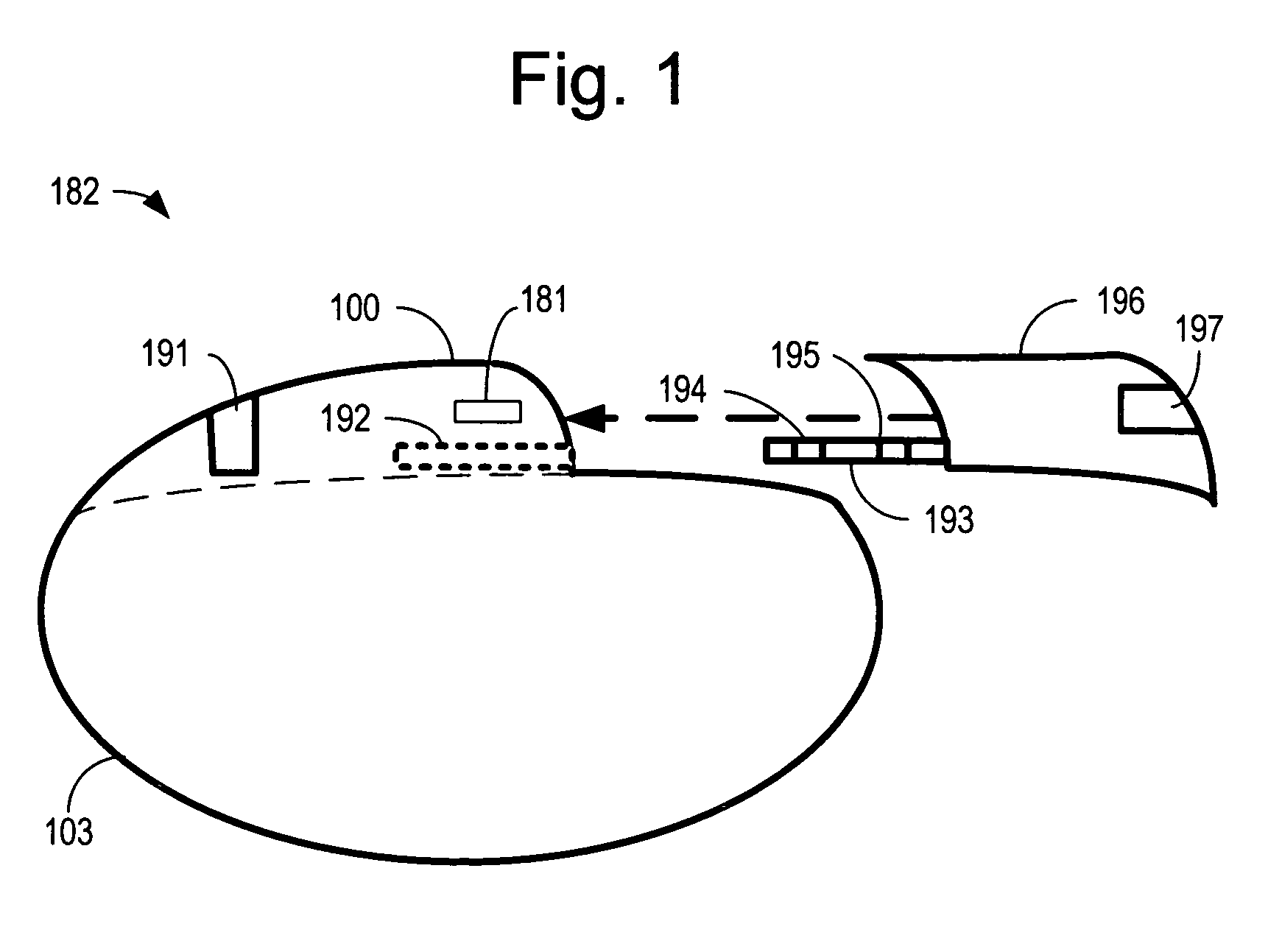
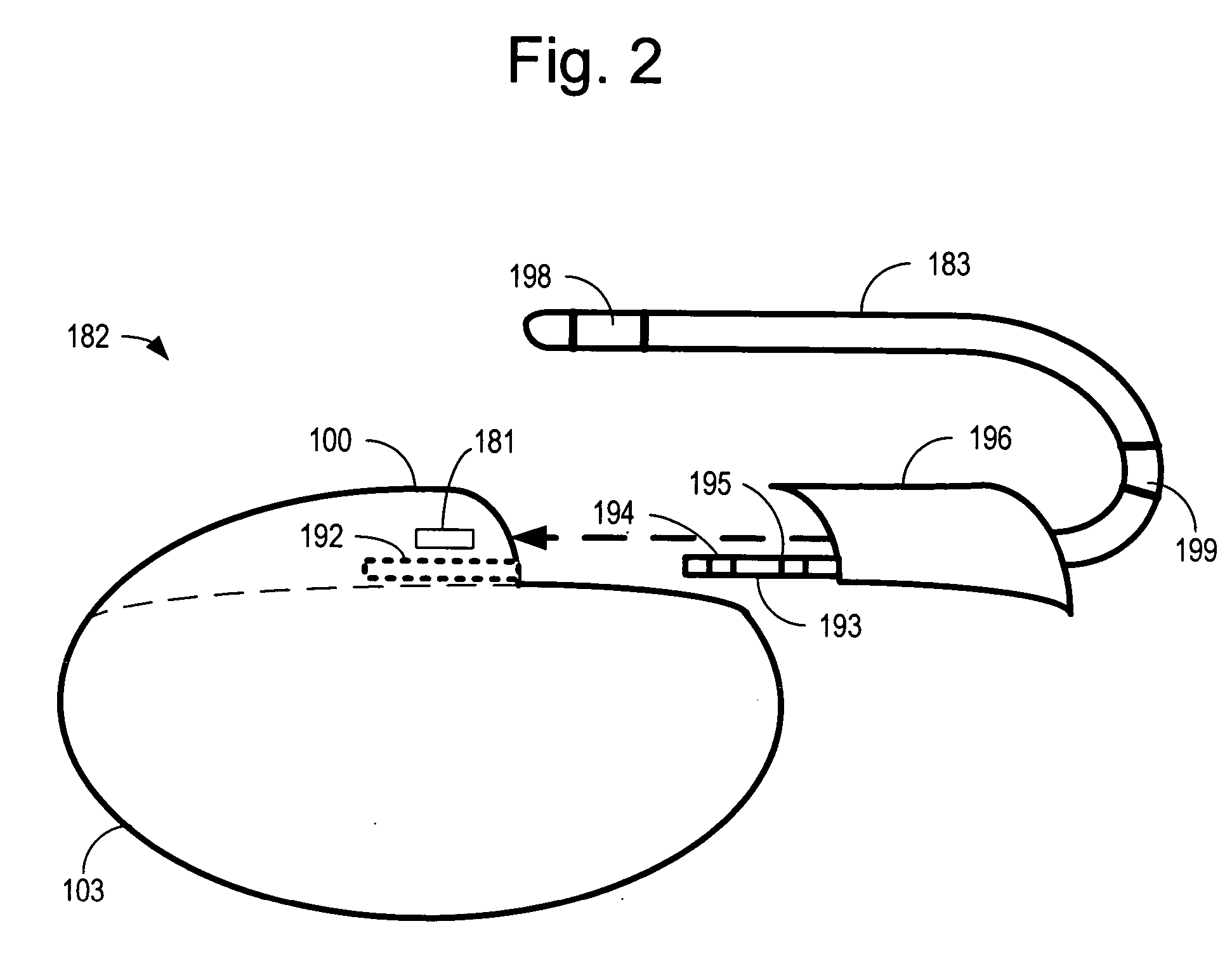
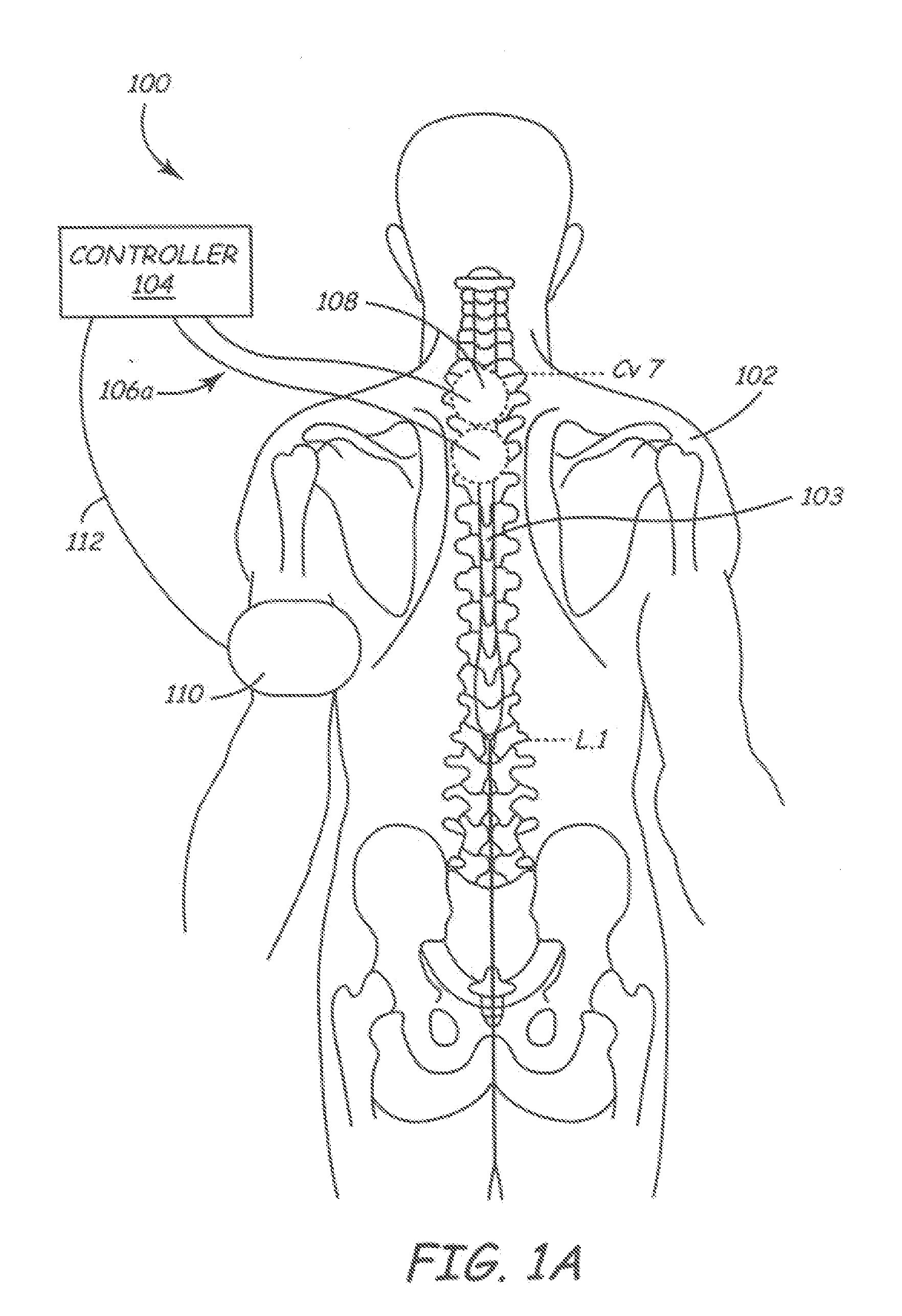
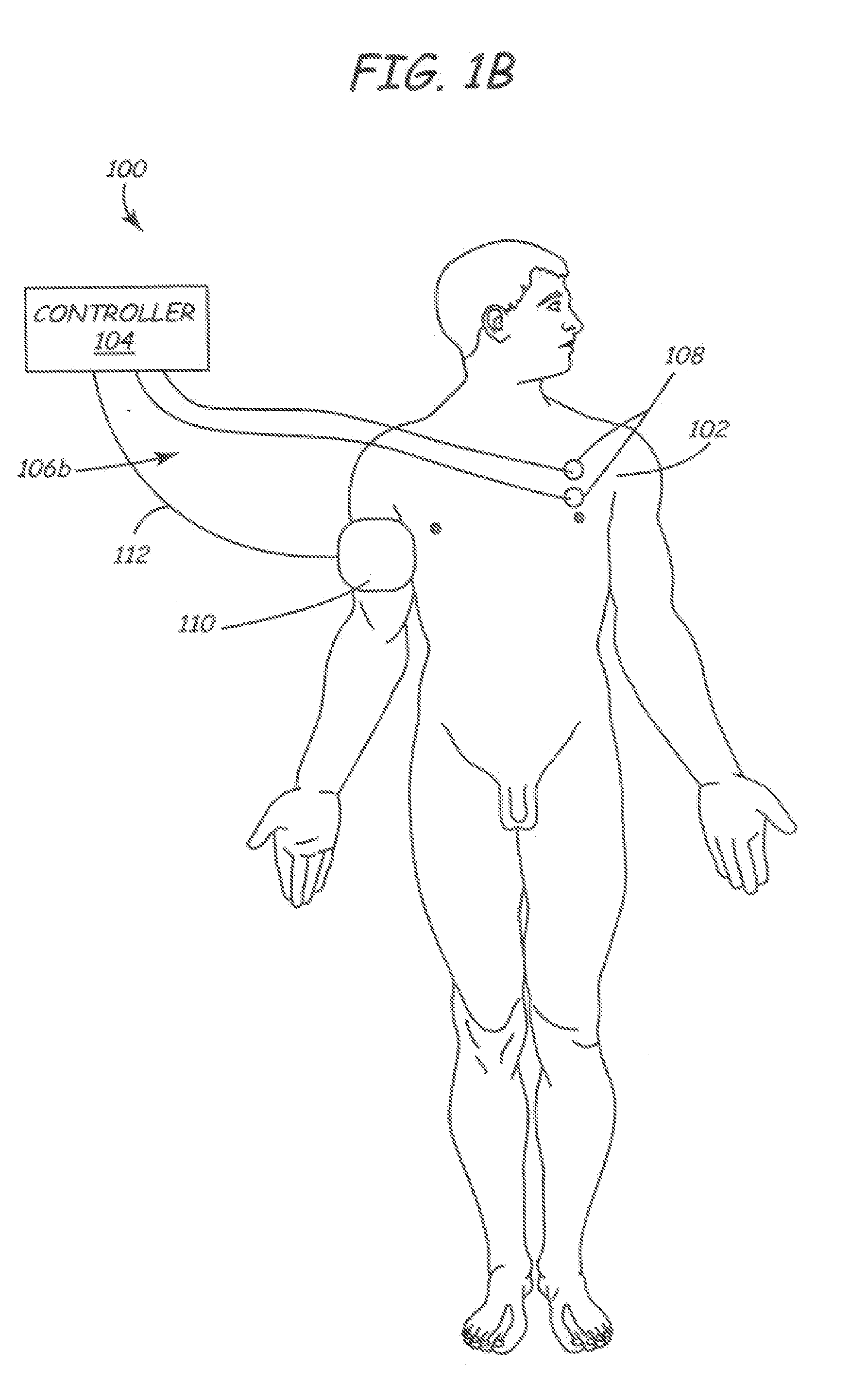
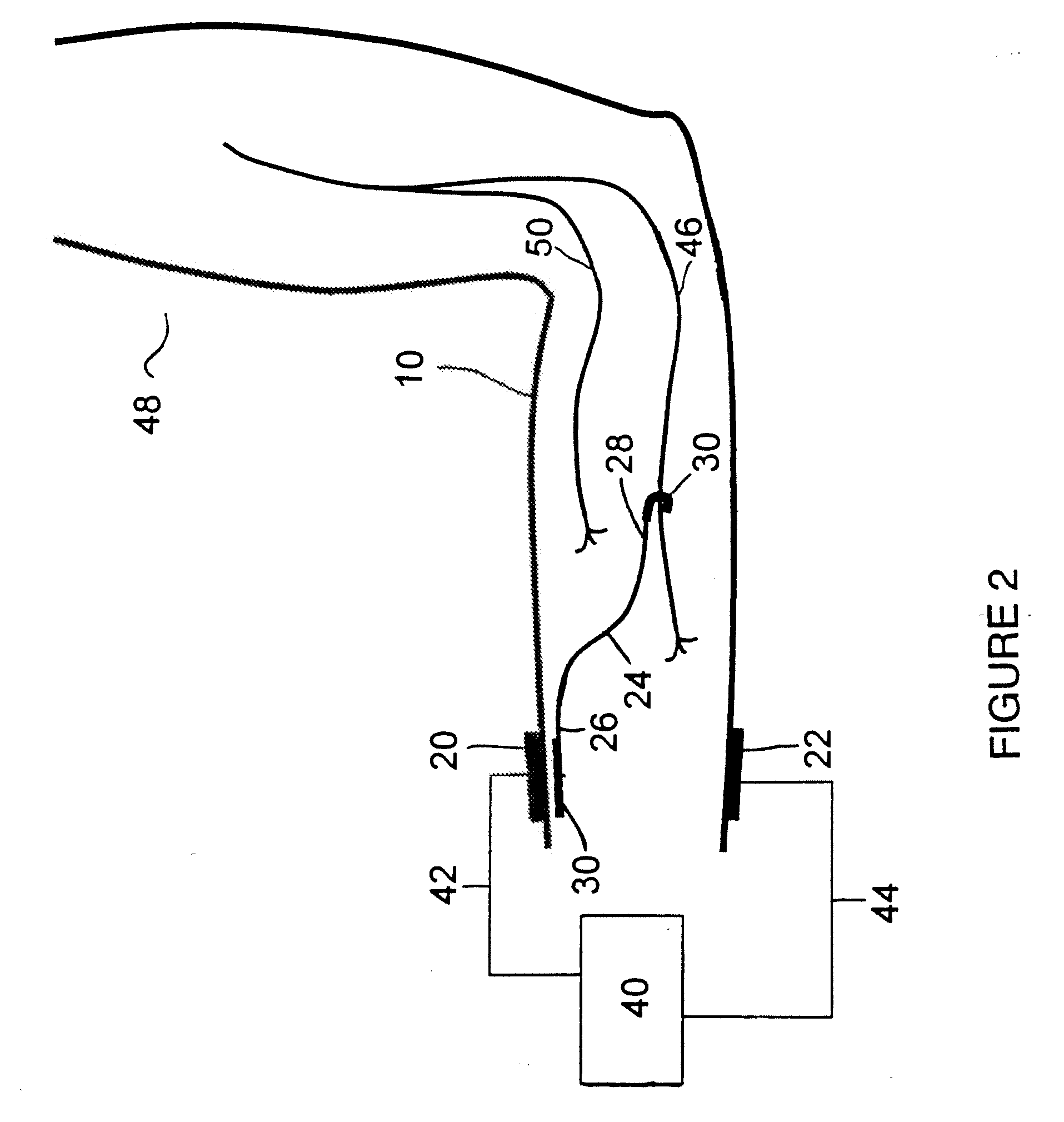
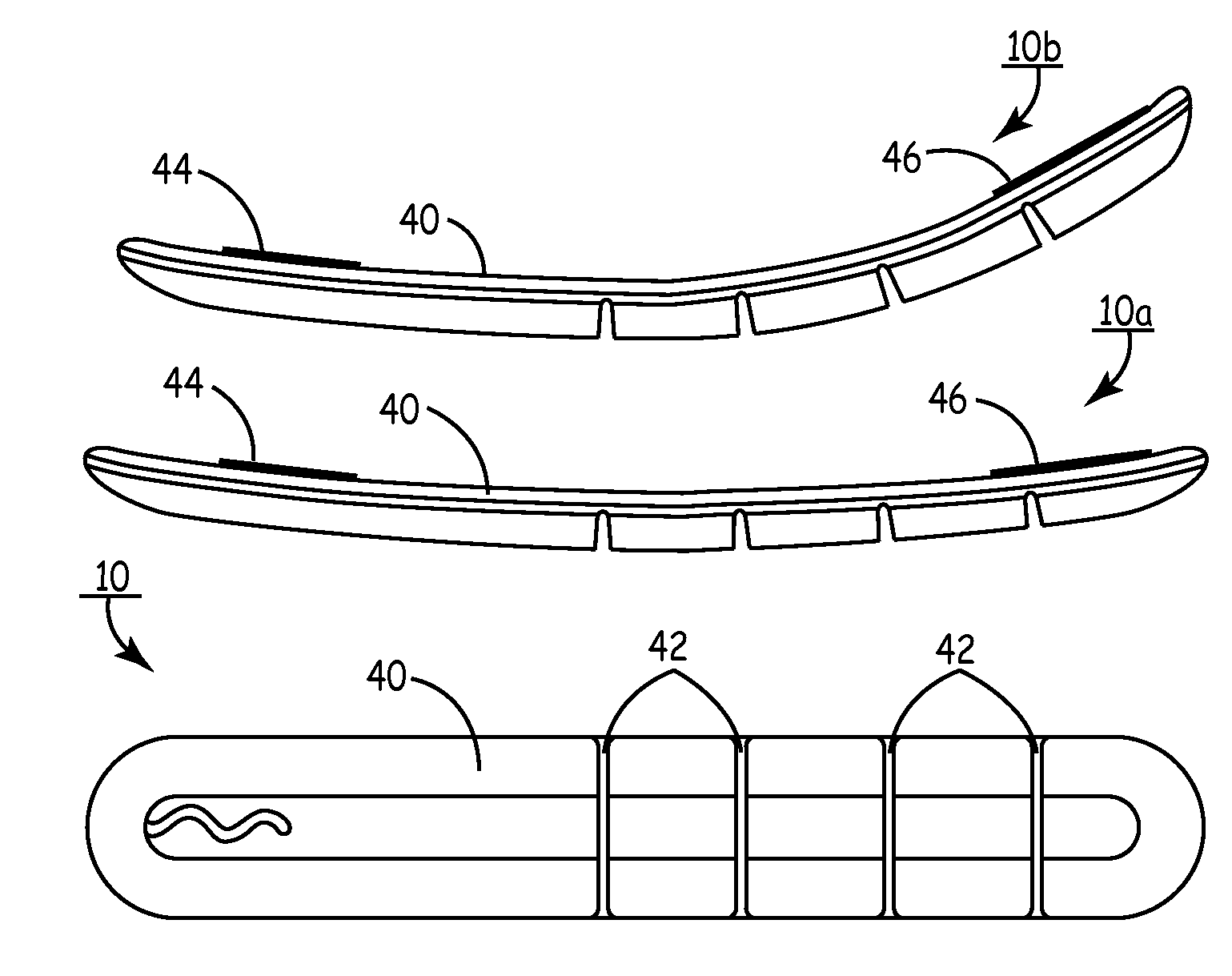
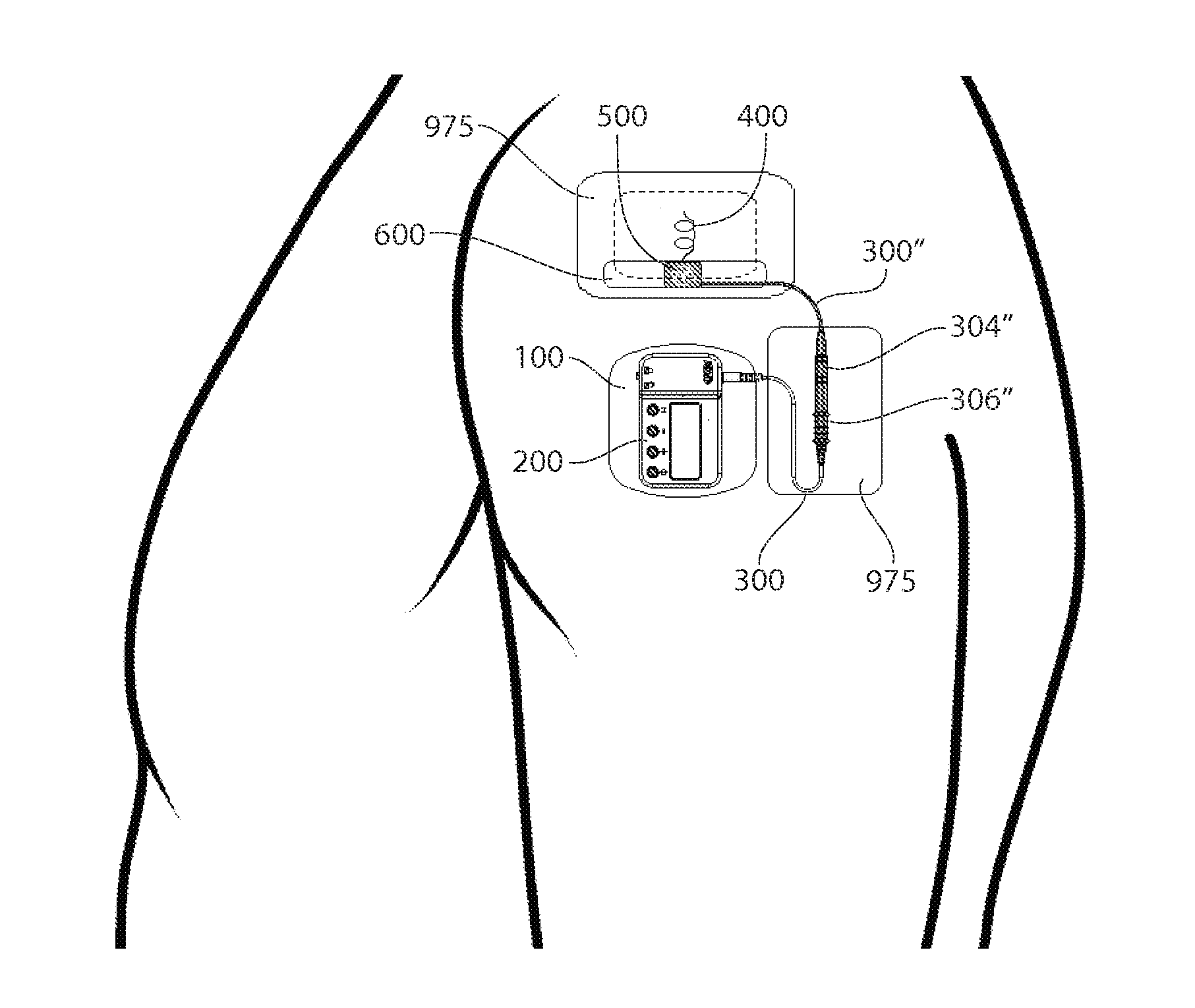
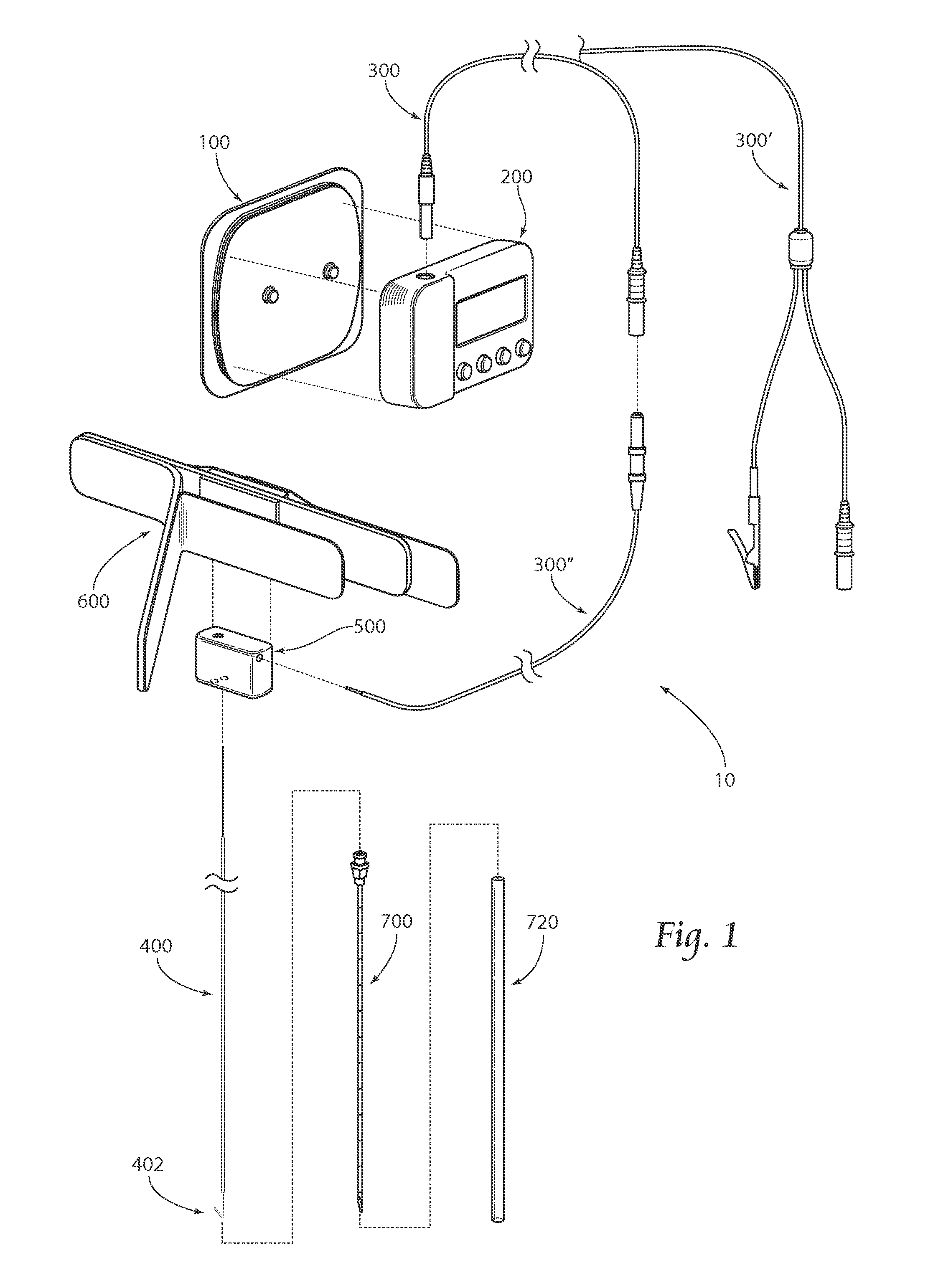
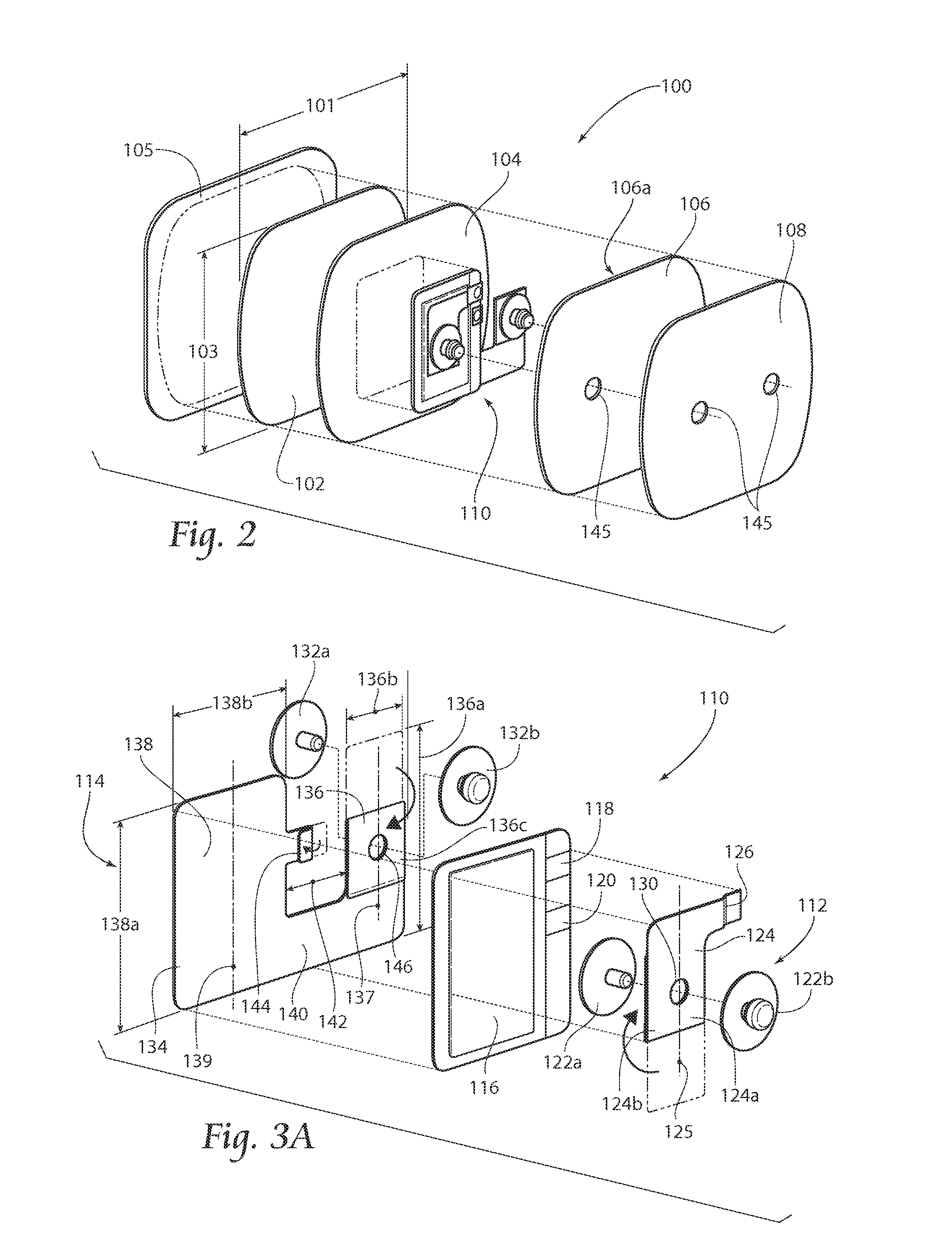
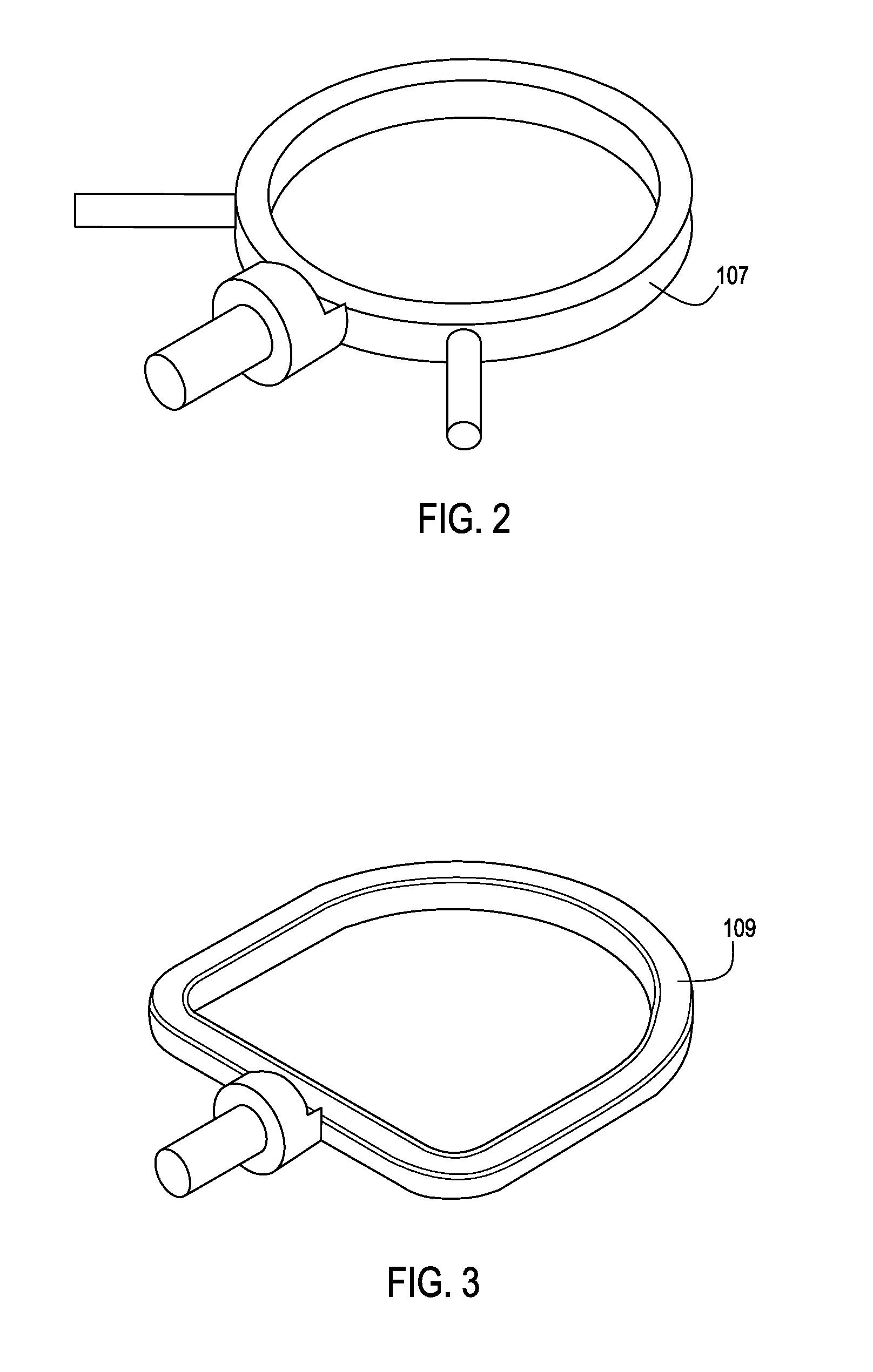
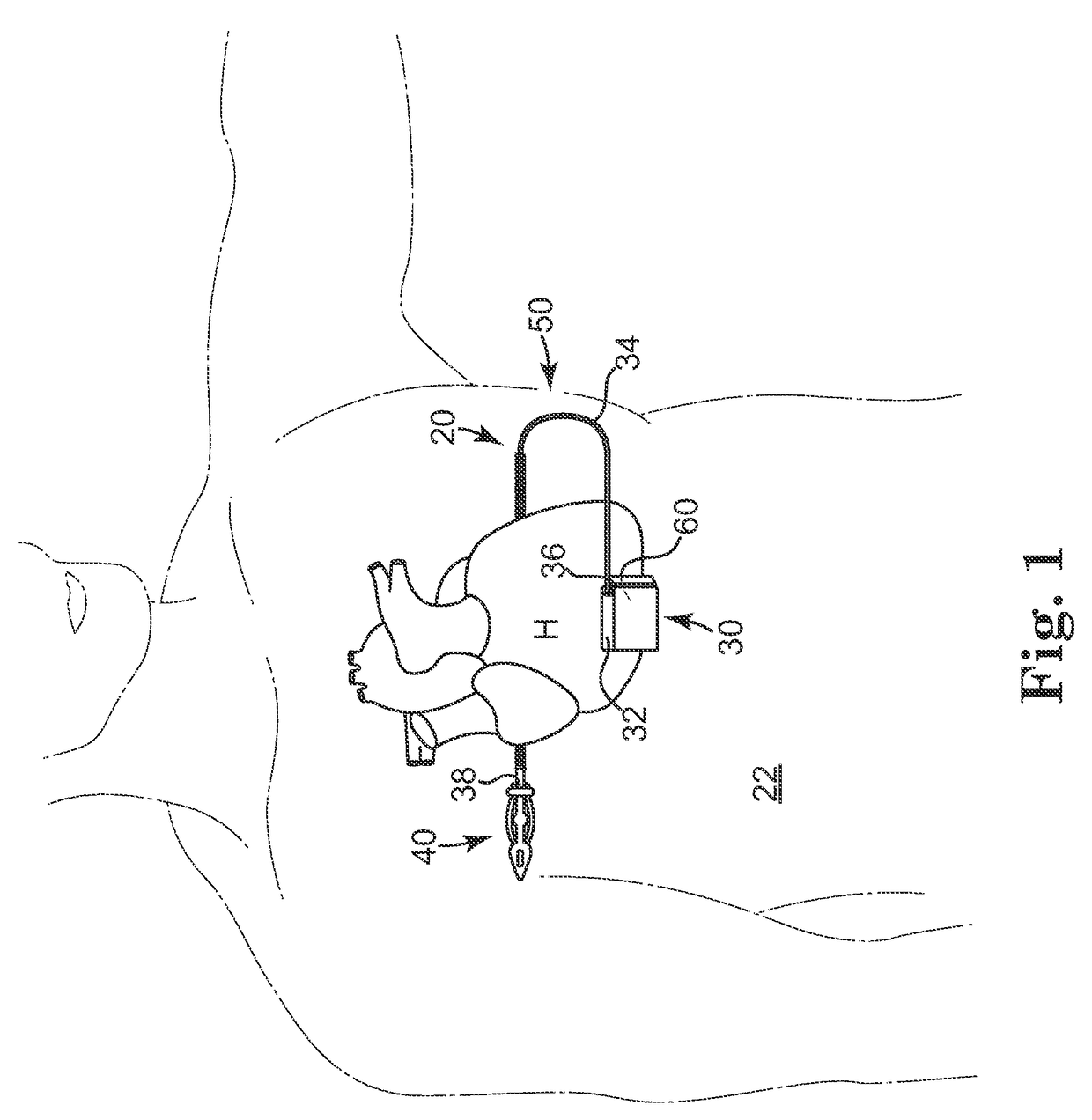
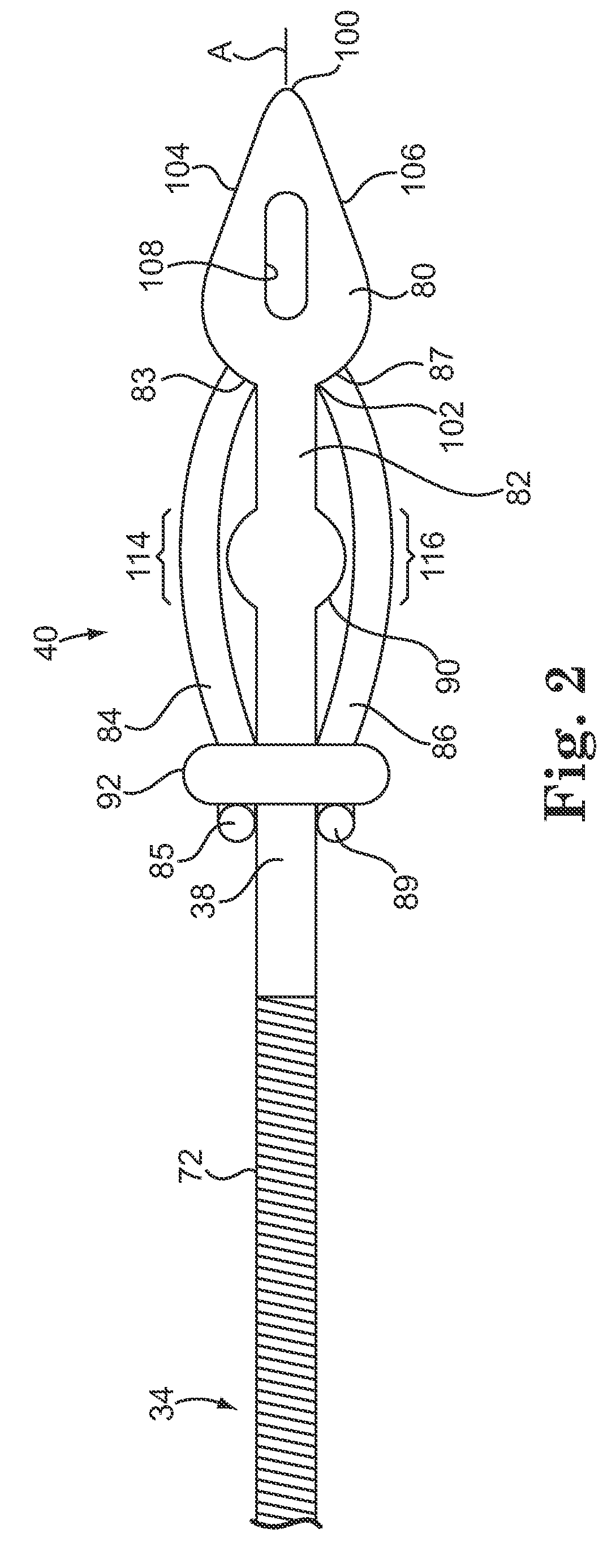
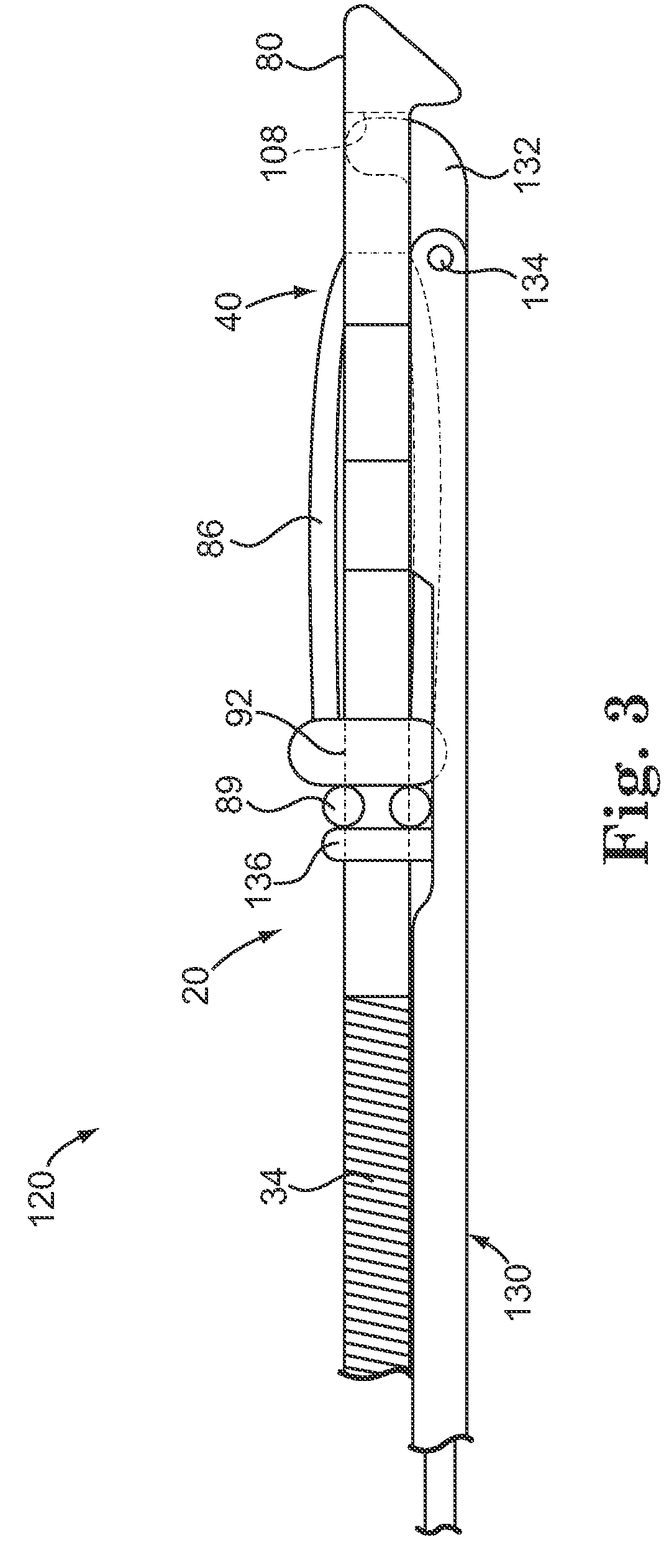
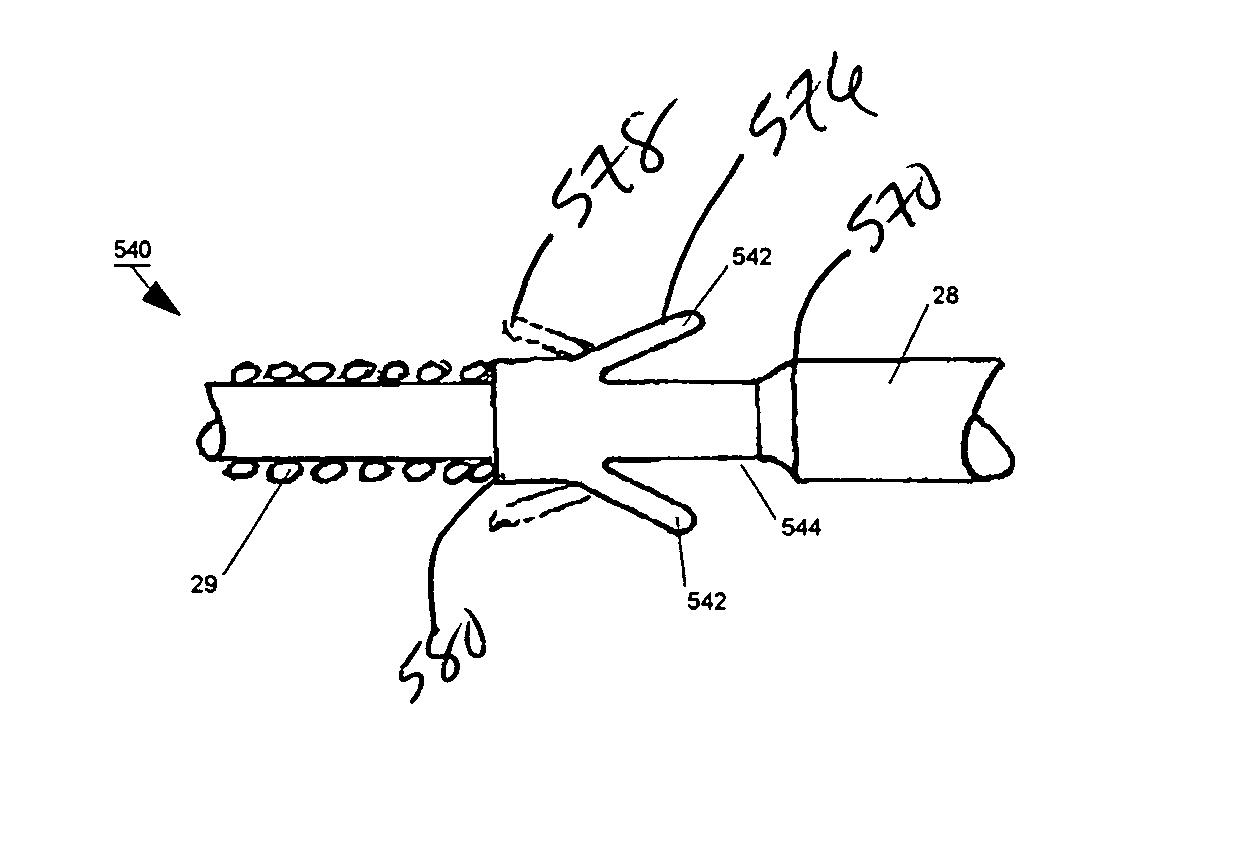
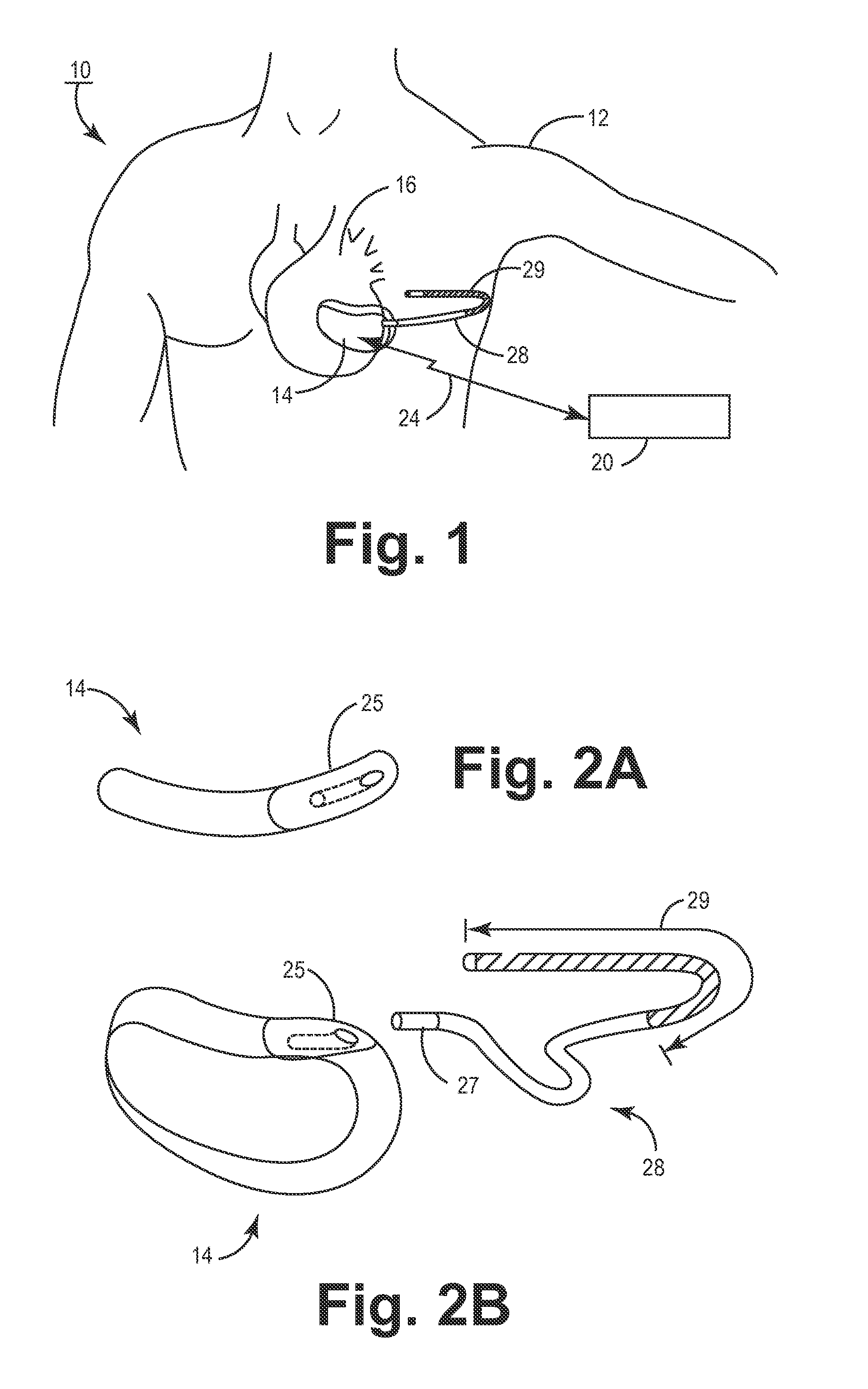
Method of routing electrical current to bodily tissues via implanted passive conductors
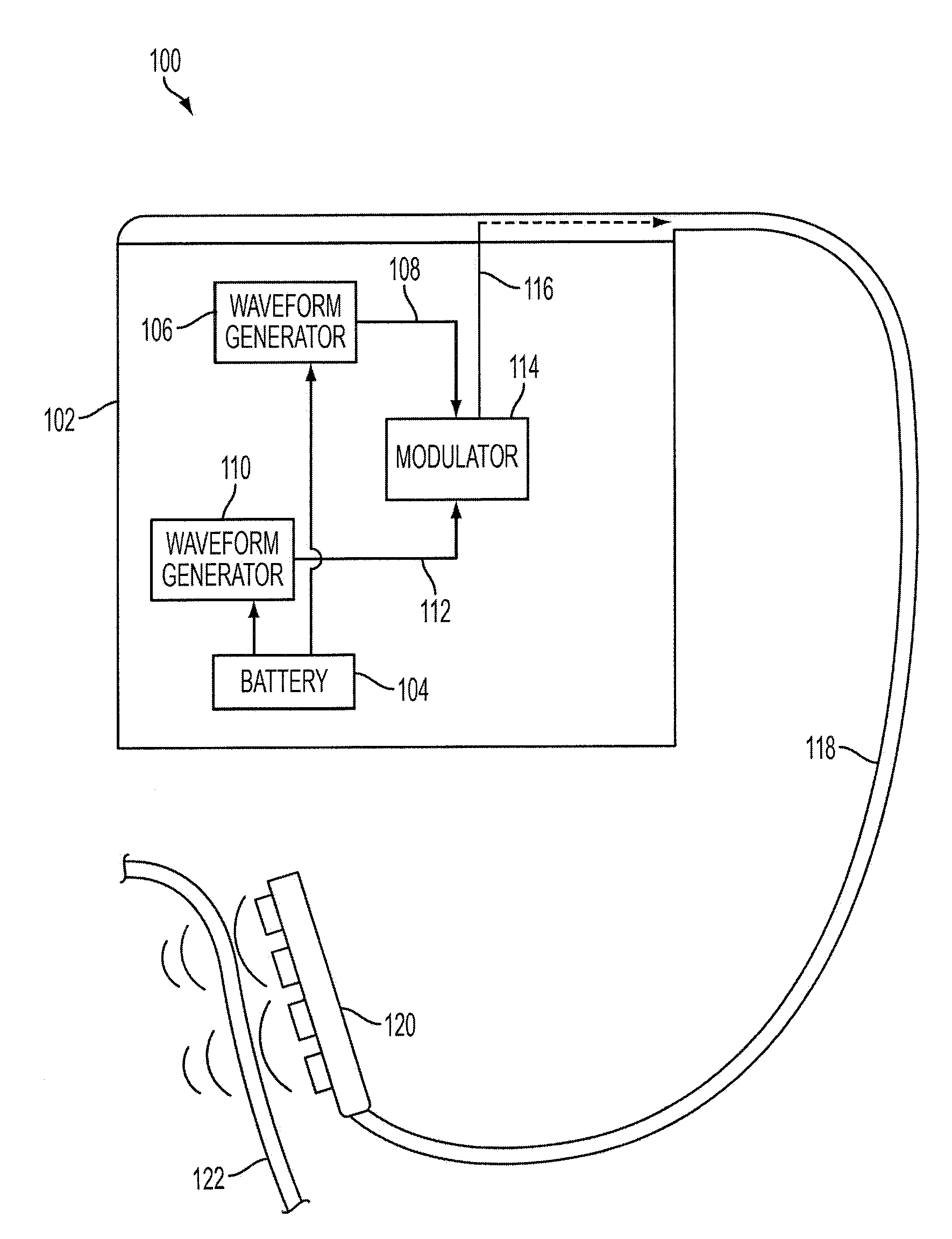
The invention provides an implant, system and method for electrically stimulating a target tissue to either activate or block neural impulses. The implant provides a conductive pathway for a portion of electrical current flowing between surface electrodes positioned on the skin and transmits that current to the target tissue. The implant has a passive electrical conductor of sufficient length to extend from subcutaneous tissue located below a surface cathodic electrode to the target tissue. The conductor has a pick-up end which forms an electrical termination having a sufficient surface area to allow a sufficient portion of the electrical current to flow through the conductor, in preference to flowing through body tissue between the surface electrodes, such that the target tissue is stimulated to either activate or block neural impulses. The conductor also has a stimulating end which forms an electrical termination for delivering the current to the target body tissue.
Owner:2249020 ALBERTA LTD
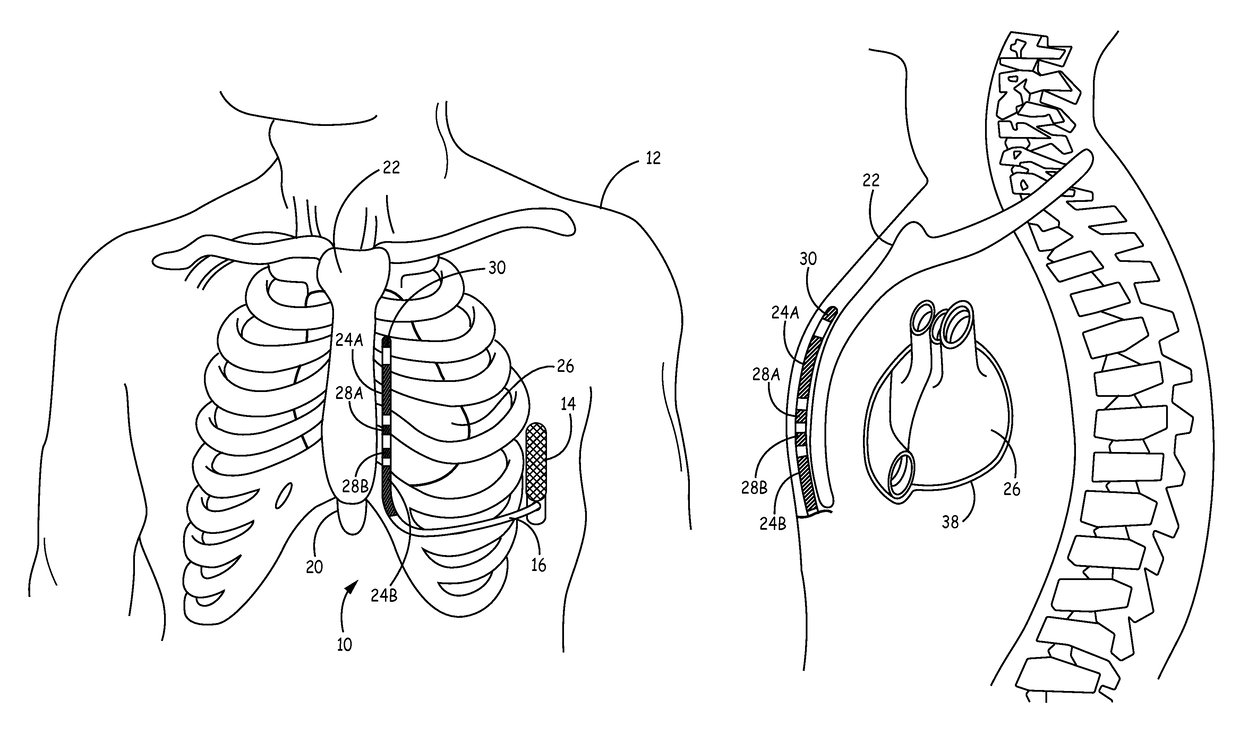
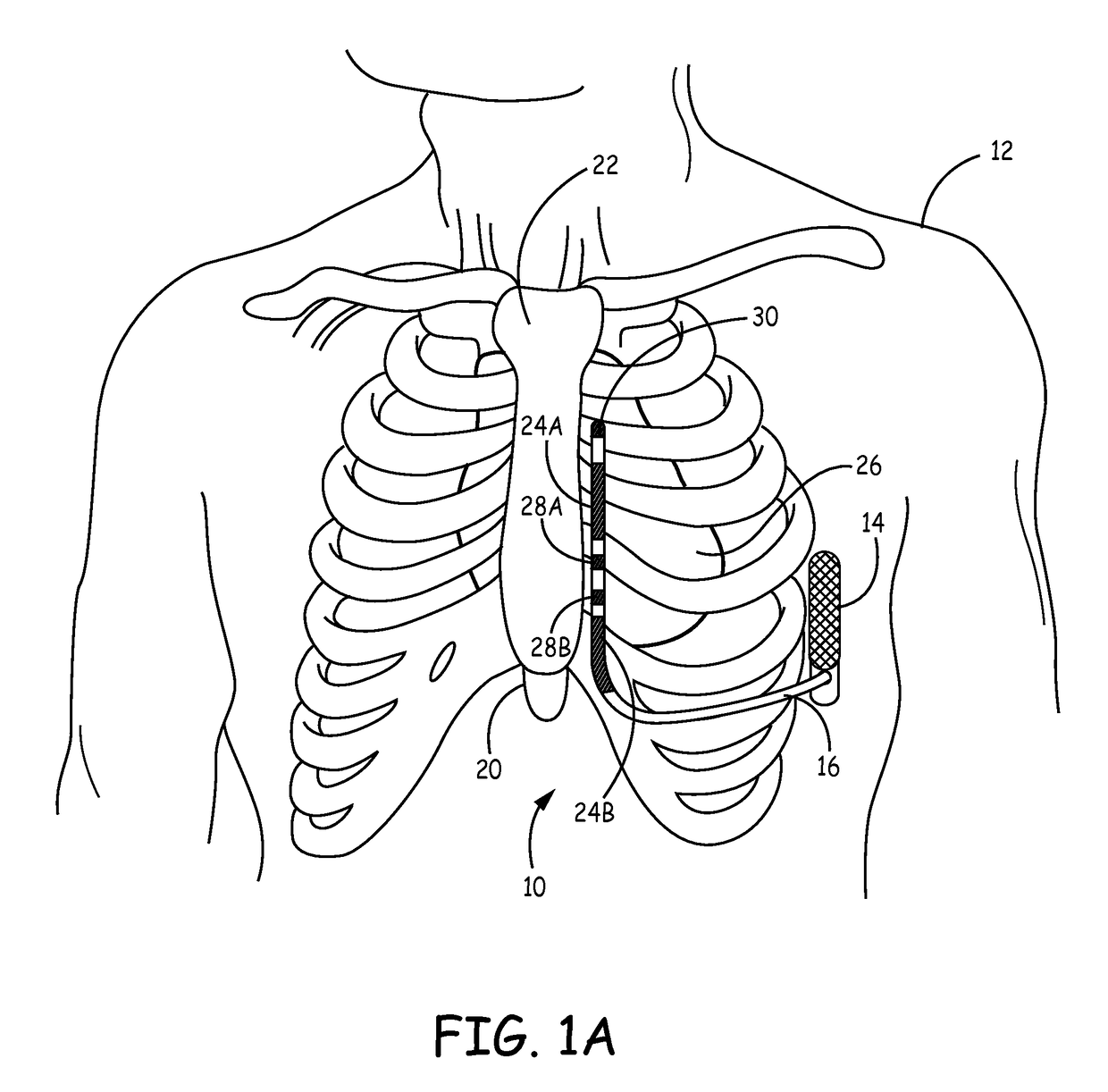
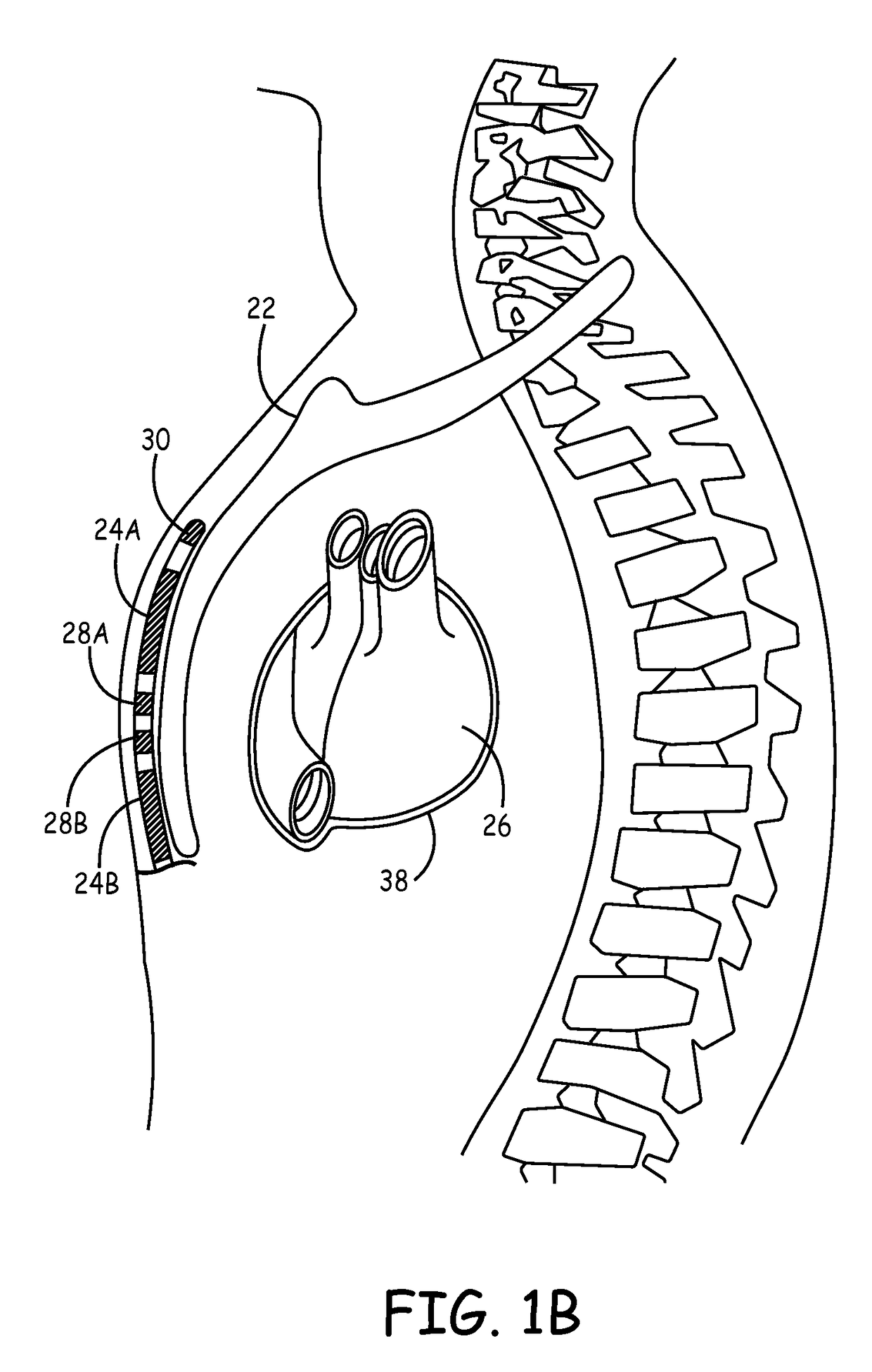
Implantable extravascular electrical stimulation lead having improved sensing and pacing capability
InactiveUS20150306375A1Heart defibrillatorsSubcutaneous electrodesElectrical conductorDistal portion
Implantable medical electrical leads having electrodes arranged such that a defibrillation coil electrode and a pace / sense electrode(s) are concurrently positioned substantially over the ventricle when implanted are described. The leads include an elongated lead body having a distal portion and a proximal end, a connector at the proximal end of the lead body, a defibrillation electrode located along the distal portion of the lead body, wherein the defibrillation electrode includes a first segment and a second segment proximal to the first segment by a distance, a first electrical conductor extending from the proximal end of the lead body and electrically coupling to the first segment and the second segment of the defibrillation electrode, and at least one pace / sense electrode located between the first segment and the second segment of the defibrillation electrode.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and system for controlled nerve ablation
InactiveUS20100016929A1Simple procedureSpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringPower flowAnatomy
The invention provides a system and method for treating a subject having unwanted or overactive nerve activity. The method involves applying one or more of direct current, charge imbalanced time varying current and pulsatile current to a target nerve; and controlling the amplitude and the duration of the current such that there is a net charge delivered to the target nerve at a sufficient charge density to cause controlled ablation to the target nerve until unwanted or overactive nerve activity is reduced in one or both of the target nerve and a target body tissue innervated by the target nerve.
Owner:REHABTRONICS INC
Implantable extravascular electrical stimulation lead having improved sensing and pacing capability
Implantable medical electrical leads having electrodes arranged such that a defibrillation coil electrode and a pace / sense electrode(s) are concurrently positioned substantially over the ventricle when implanted as described. The leads include an elongated lead body having a distal portion and a proximal end, a connector at the proximal end of the lead body, a defibrillation electrode located along the distal portion of the lead body, wherein the defibrillation electrode includes a first electrode segment and a second electrode segment proximal to the first electrode segment by a distance. The leads may include at least one pace / sense electrode, which in some instances, is located between the first defibrillation electrode segment and the second defibrillation electrode segment.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Extravascular implantable electrical lead having undulating configuration
ActiveUS20160158567A1ElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectricityDistal portion
This disclosure describes an implantable medical electrical lead and an ICD system utilizing the lead. The lead includes a lead body defining a proximal end and a distal portion, wherein at least a part of the distal portion of the lead body defines an undulating configuration. The lead includes a defibrillation electrode that includes a plurality of defibrillation electrode segments disposed along the undulating configuration spaced apart from one another by a distance. The lead also includes at least one electrode disposed between adjacent sections of the plurality of defibrillation sections. The at least one electrode is configured to deliver a pacing pulse to the heart and / or sense cardiac electrical activity of the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
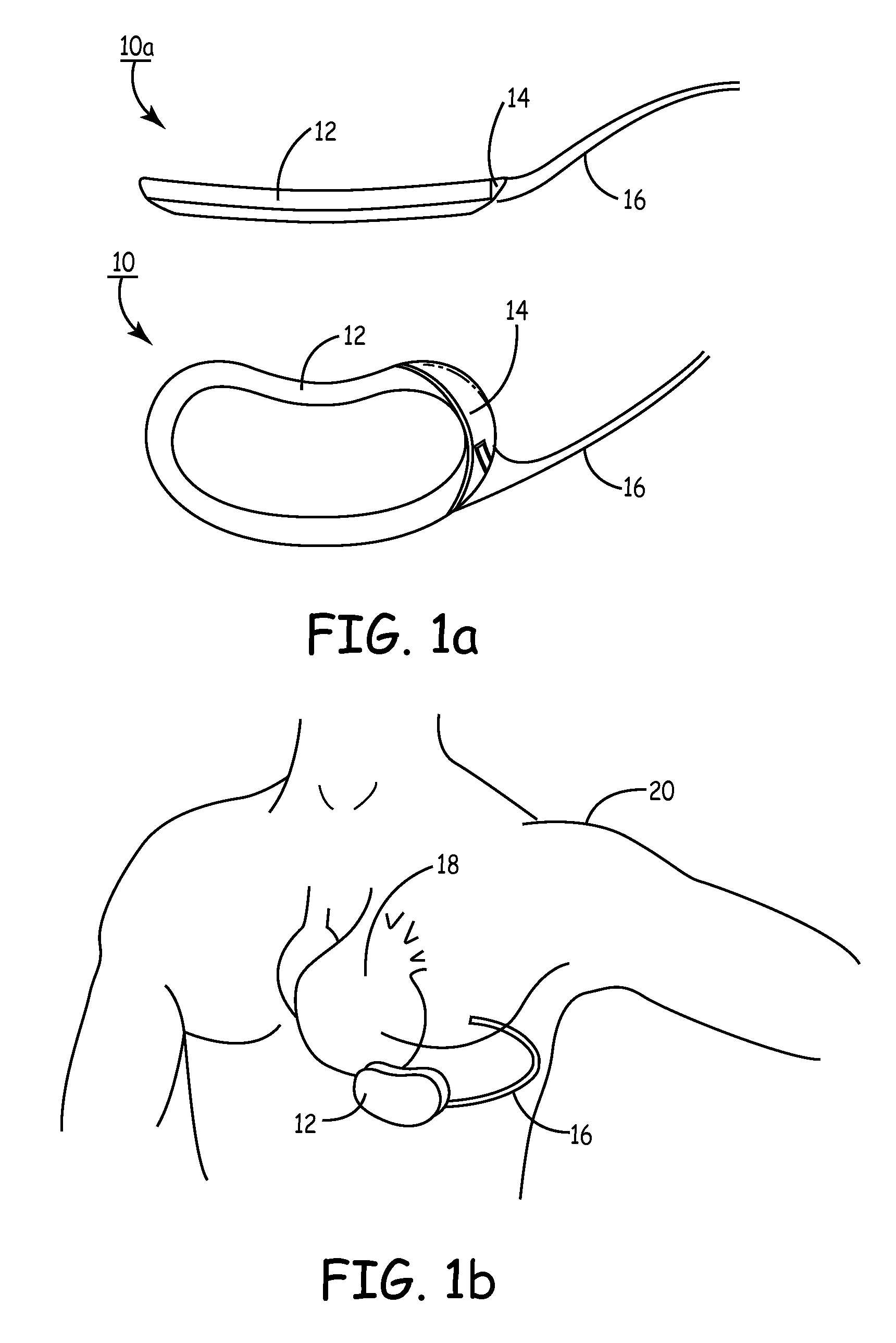
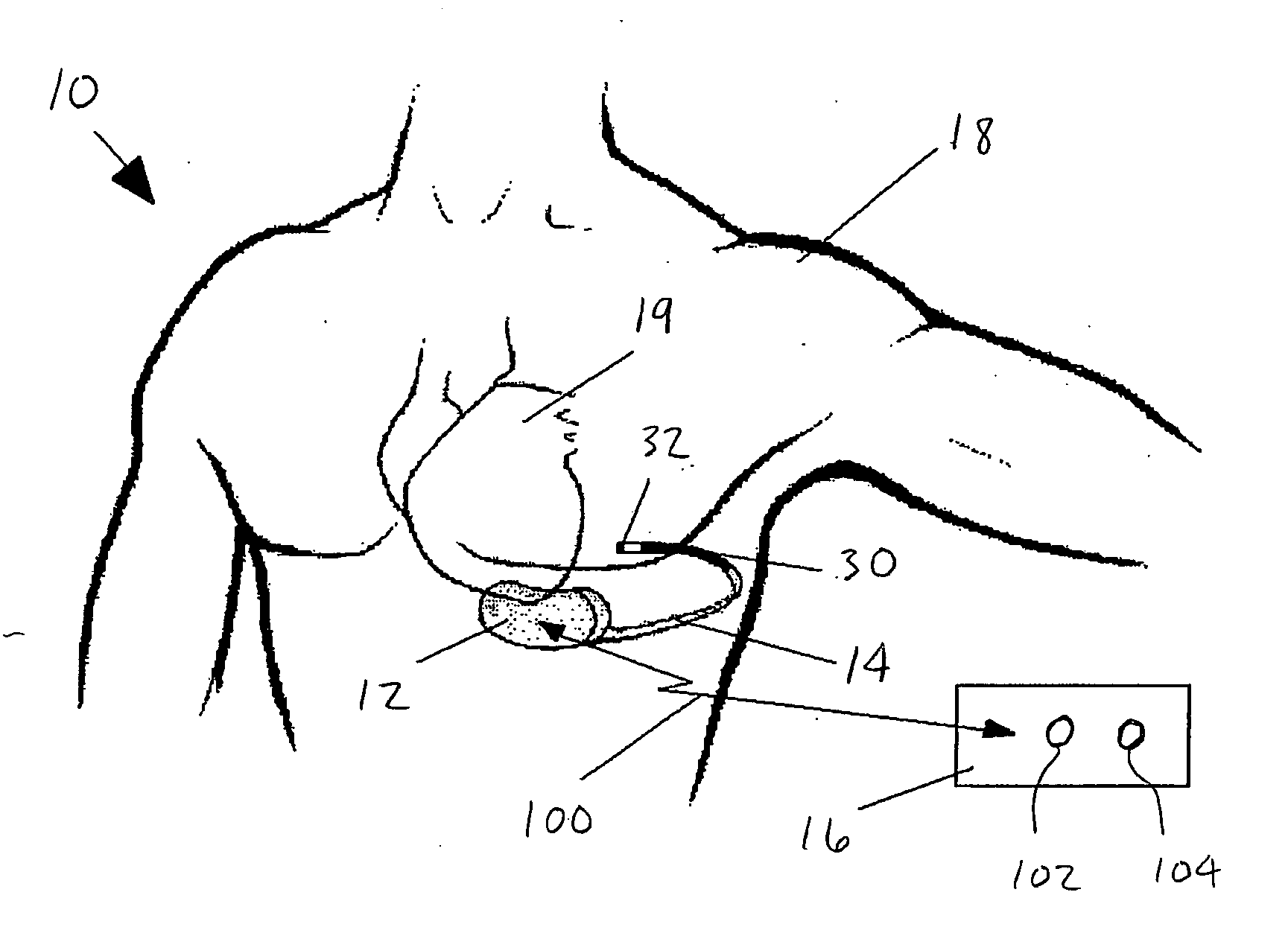
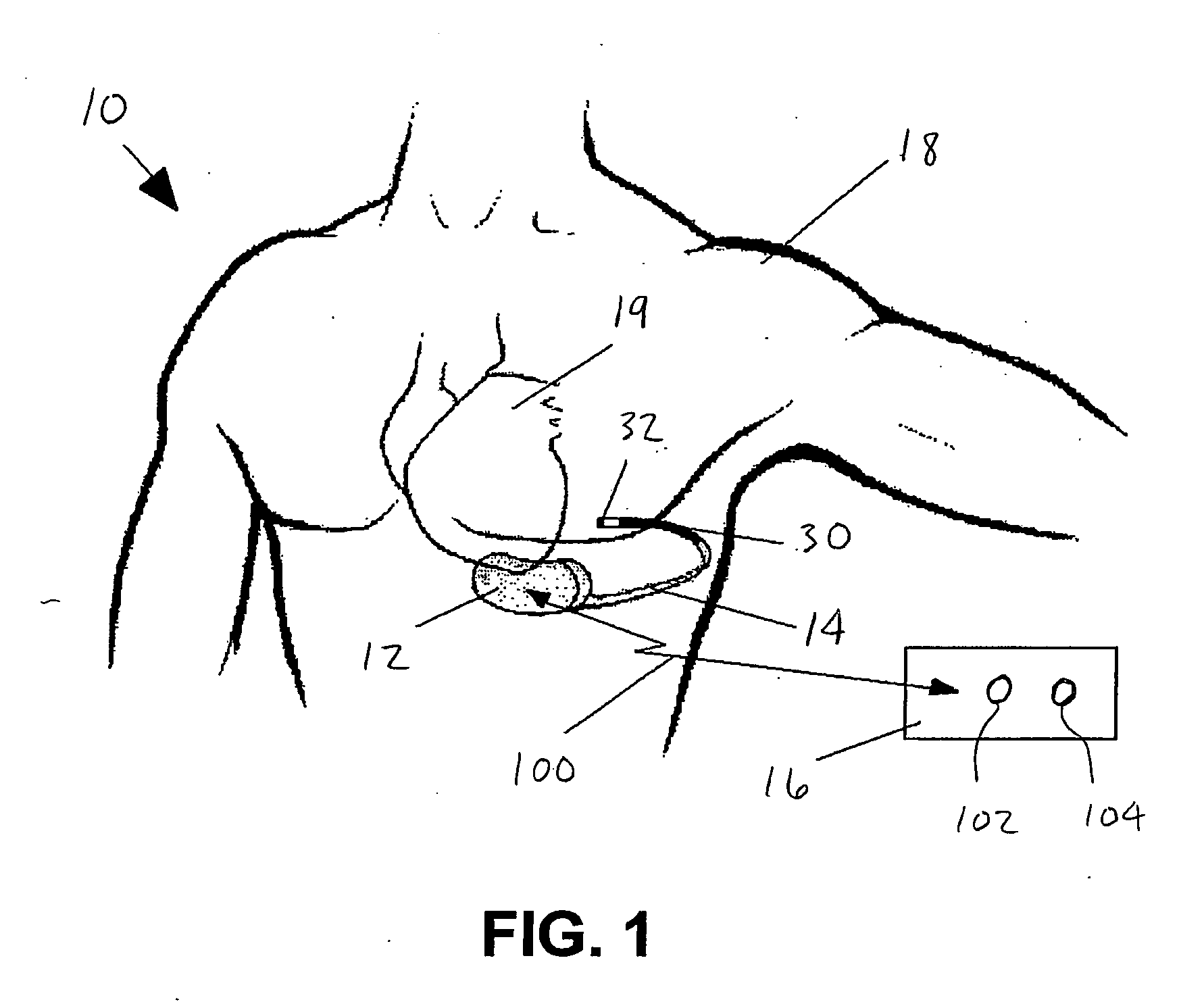
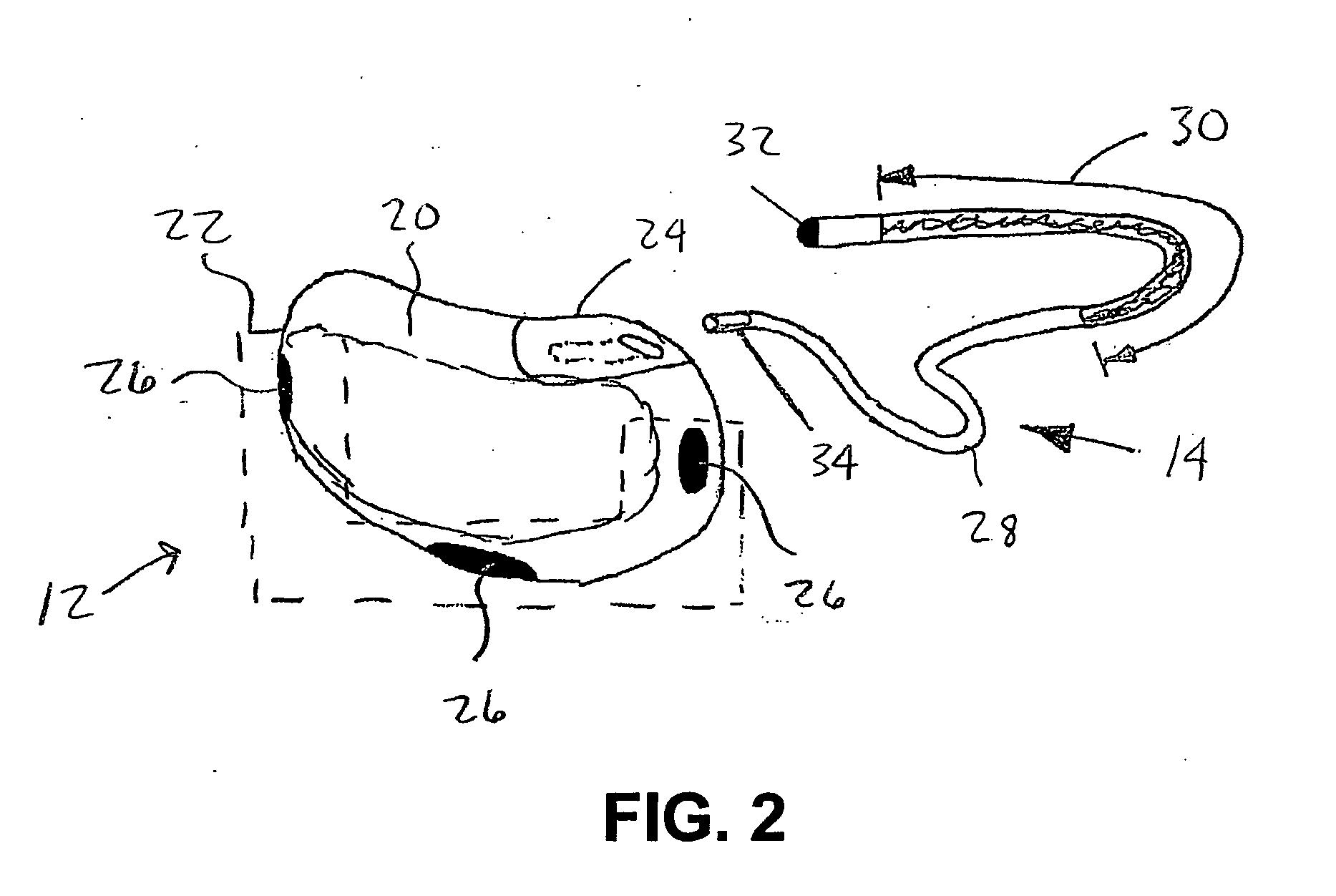
Peripheral nerve stimulation
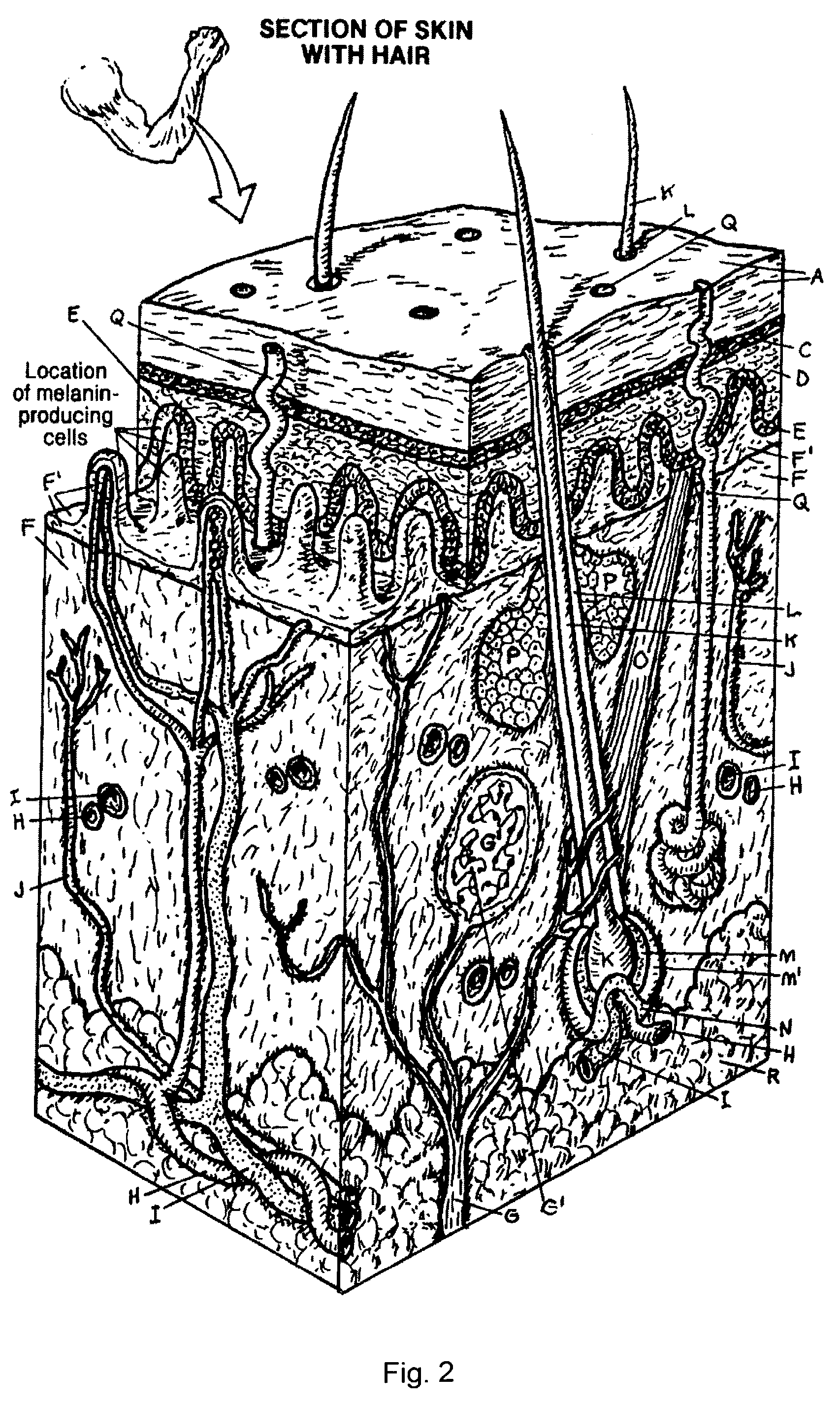
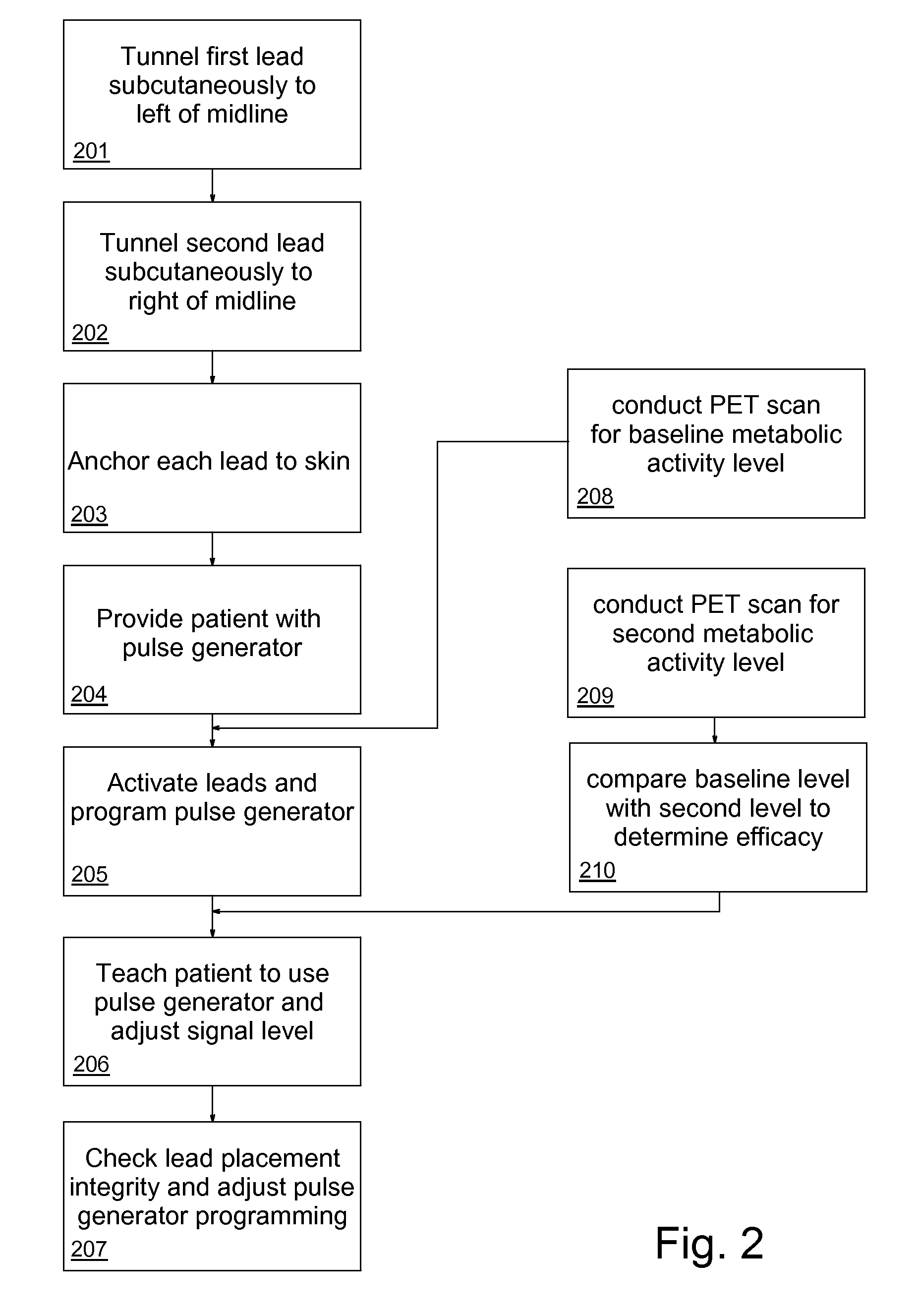
An apparatus for treating pain by electrical stimulation is disclosed. A lead is placed subcutaneously in the region of pain. The subcutaneous tissue is electrically stimulated to cause paresthesia. The method encompasses subcutaneous placement of an electrical lead near the region of pain and subsequent electrical stimulation of the tissue to cause paresthesia. In particular, an apparatus for treating intractable occipital neuralgia using percutaneous electrostimulation techniques is disclosed.
Owner:WEINER RICHARD L
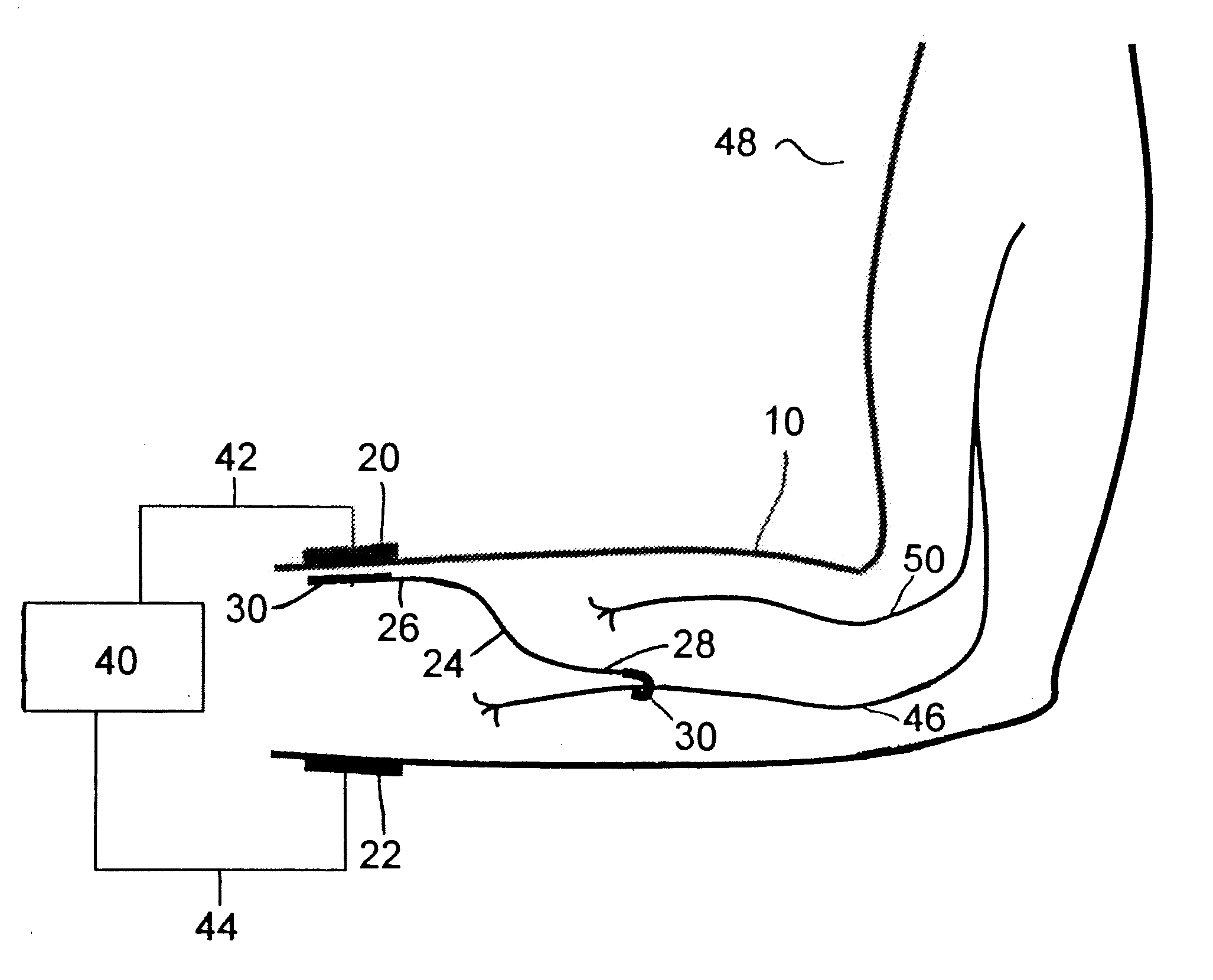
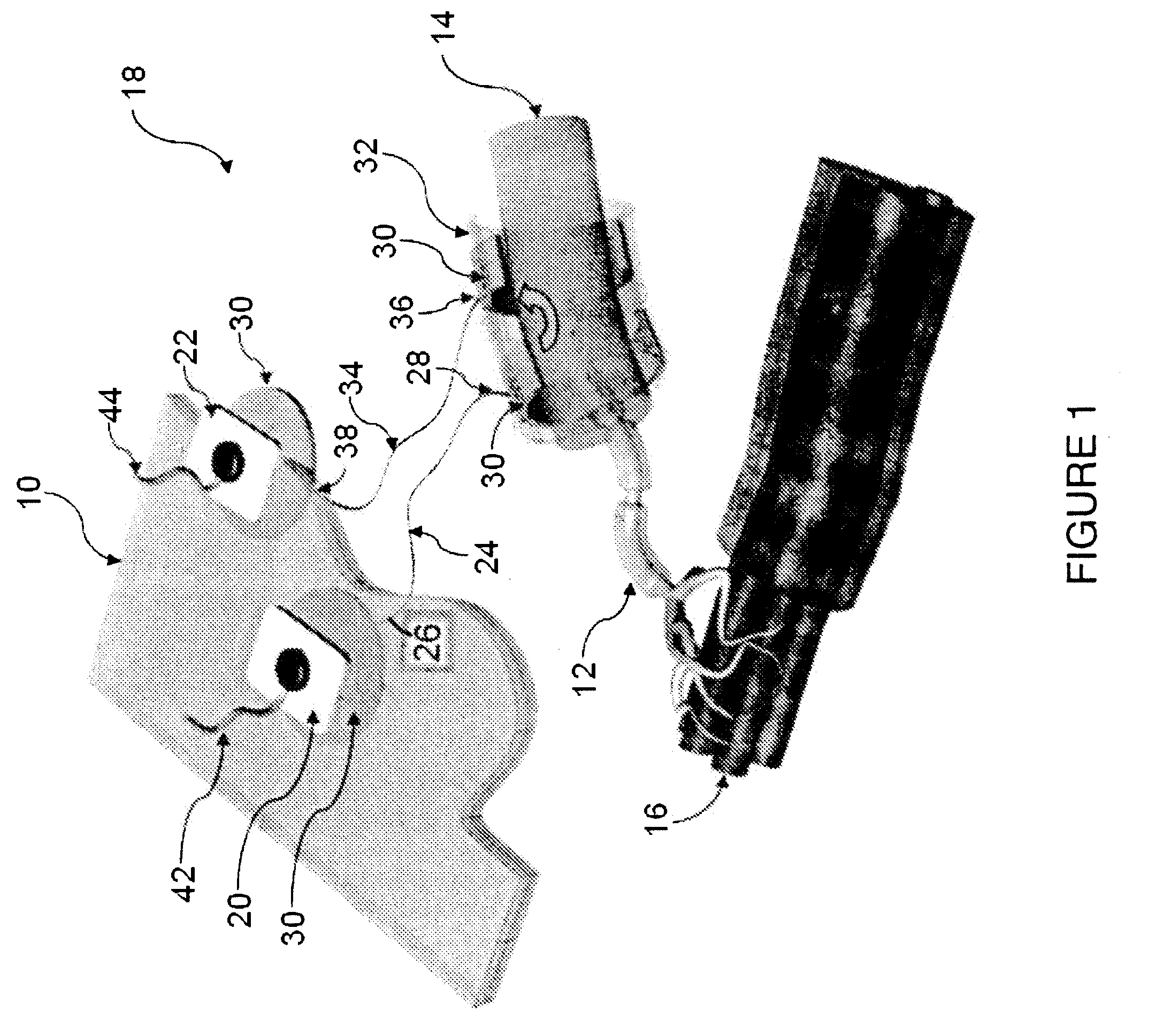
Subcutaneous cardiac stimulator with small contact surface electrodes
InactiveUS7194302B2Reducing electrode interface resistanceReduce energy consumptionHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac activityCardiac device
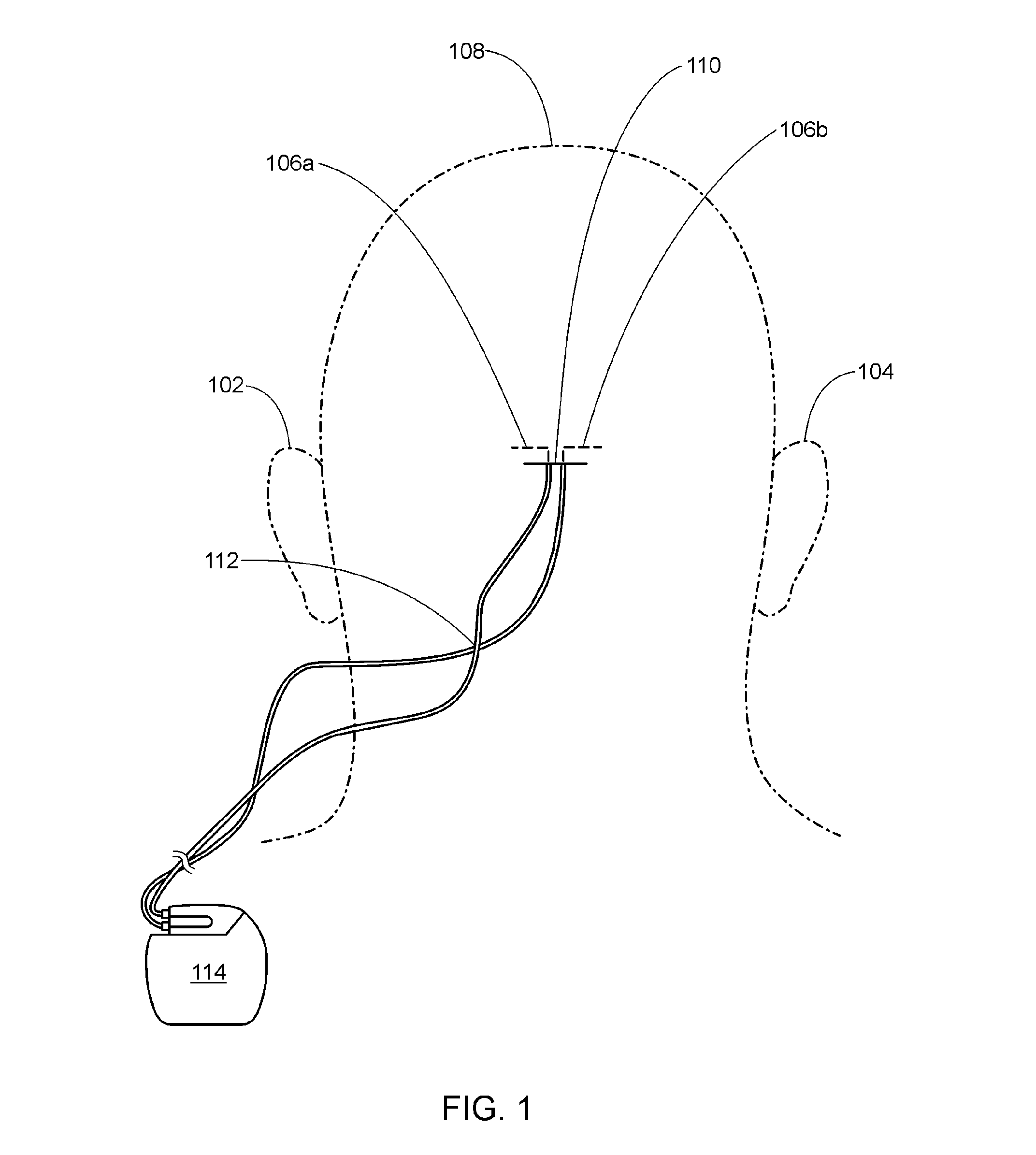
A subcutaneous cardiac device includes two electrodes and a stimulator that generates a pulse to the electrodes. The electrodes are implanted between the skin and the rib cage of the patient and are adapted to generate an electric field corresponding to the pulse, the electric field having a substantially uniform voltage gradient as it passes through the heart. The shapes, sizes, positions and structures of the electrodes are selected to optimize the voltage gradient of the electric field, and to minimize the energy dissipated by the electric field outside the heart. More specifically, the electrodes have contact surfaces that contact the patient tissues, said contact surfaces having a total contact area of less than 100 cm2. In one embodiment, one or both electrodes are physically separated from the stimulator. In another embodiment a unitary housing holds the both electrodes and the stimulator. Sensor circuitry may also includes in the stimulator for detecting intrinsic cardiac activity through the same electrodes.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Antitachycardia Pacing Pulse from a Subcutaneous Defibrillator
Devices and methods for single therapy pulse (STP) therapy for tachyarrythmia are disclosed. The STP therapy can be delivered from a far-field position to allow a “global” capture approach to pacing. Due to the global capture in STP, a series of pulses, which is indicative of conventional anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) delivered by transvenous systems, becomes unnecessary. One to four pulses at most are needed for STP, and after delivery of the one to four pulses, therapy delivery can be interrupted to determine whether the previously delivered therapy has been successful.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
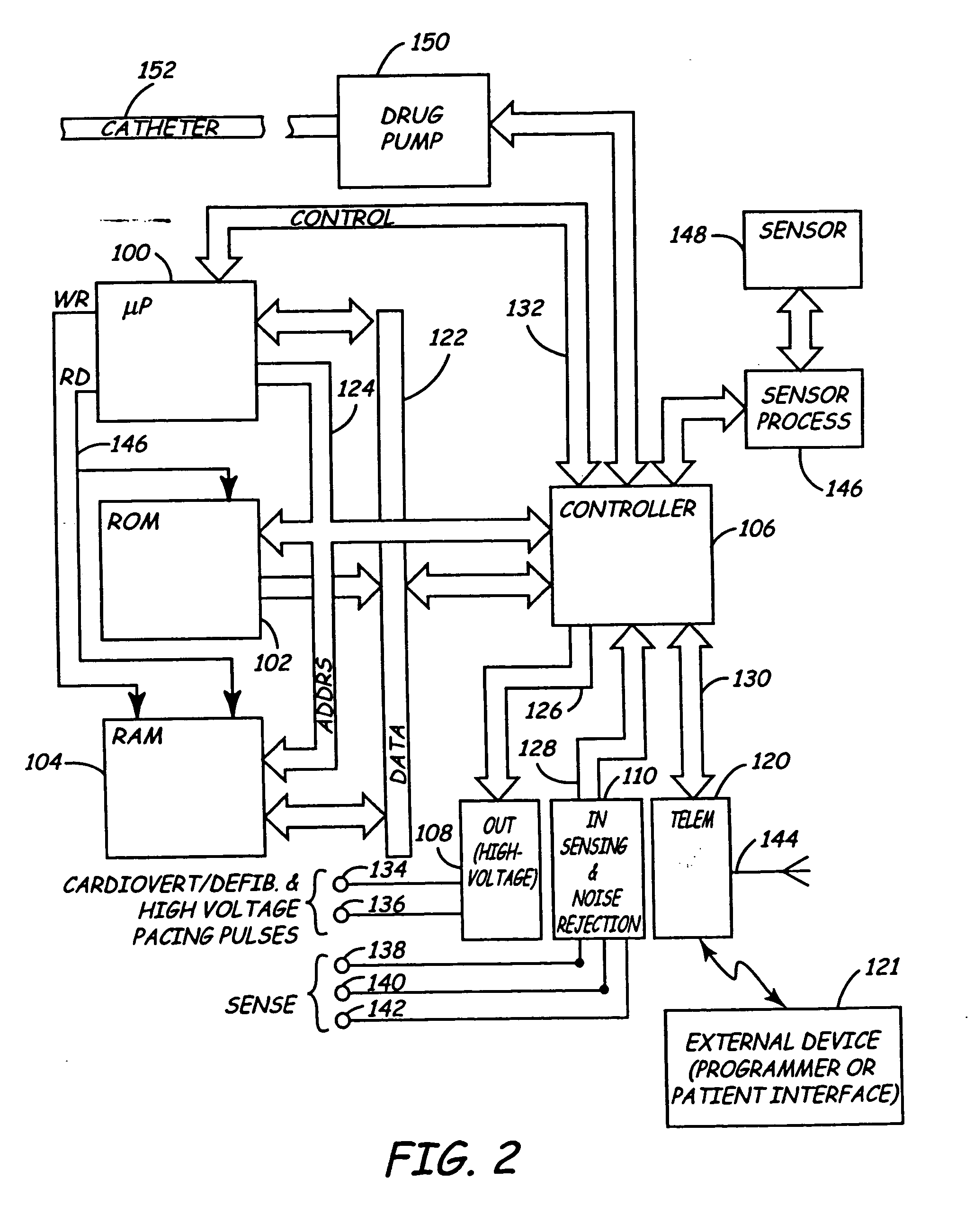
Apparatus for detecting and treating ventricular arrhythmia
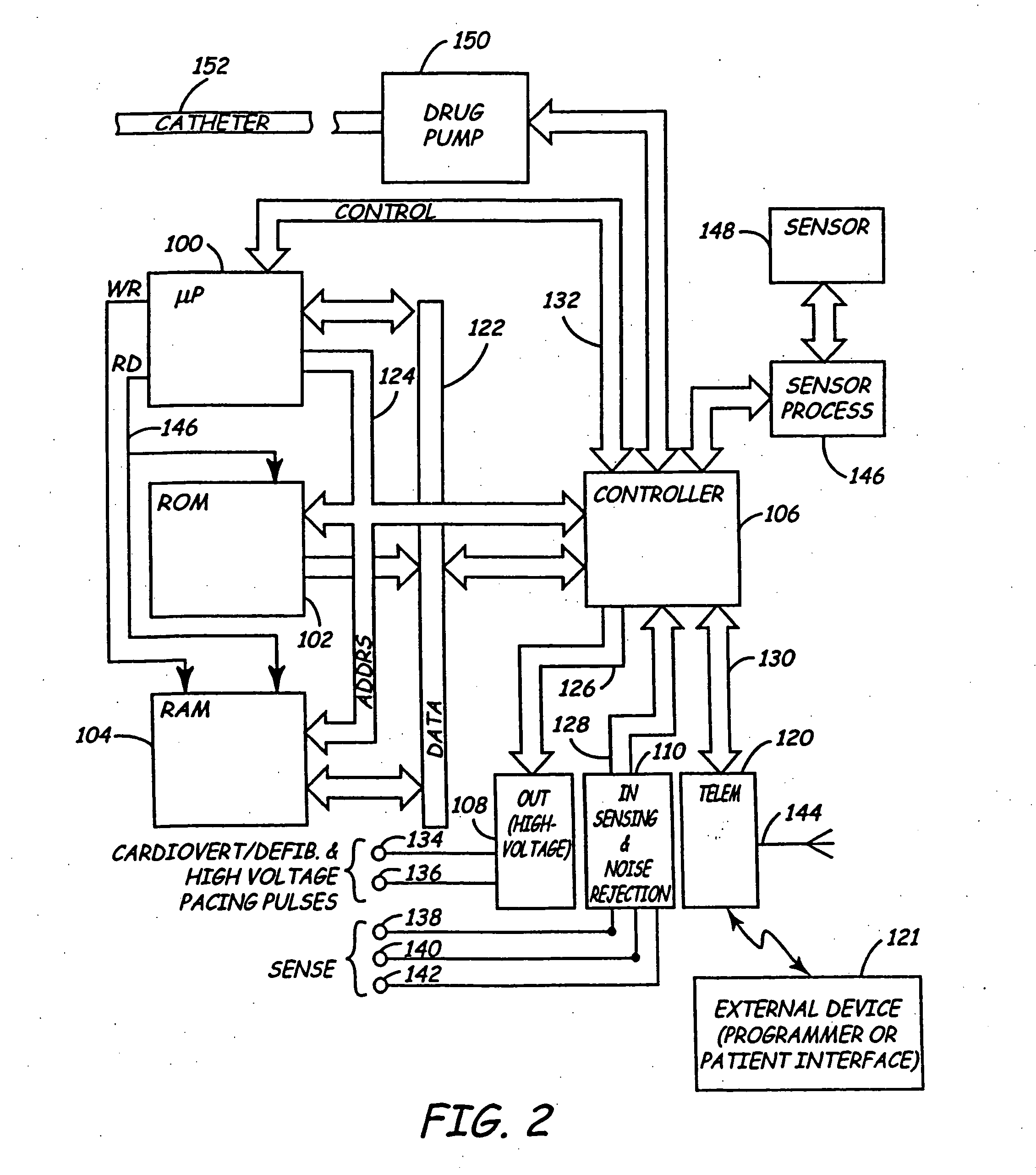
A system and method for long-term monitoring of cardiac conditions such as arrhythmias is disclosed. The invention includes a pulse generator including means for sensing an arrhythmia. The pulse generator is coupled to at least one subcutaneous electrode or electrode array for providing electrical stimulation such as cardioversion / defibrillation shocks and / or pacing pulses. The electrical stimulation may be provided between multiple subcutaneous electrodes, or between one or more such electrodes and the housing of the pulse generator. In one embodiment, the pulse generator includes one or more electrodes that are isolated from the can. These electrodes may be used to sense cardiac signals.
Owner:HEINRICH STEPHEN D +1
Current waveforms for anti-tachycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter- defibrillator
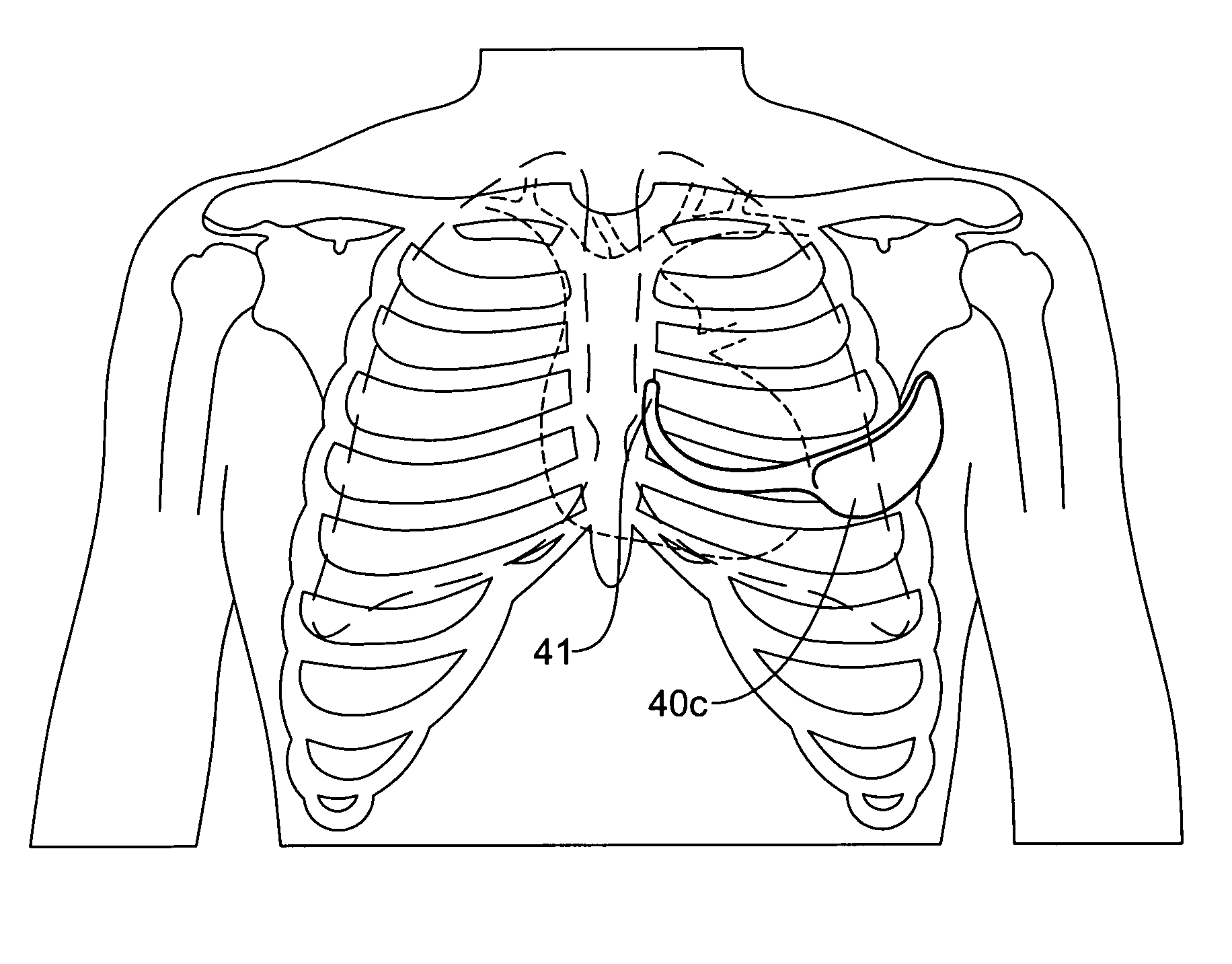
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathoracic blood vessels and for providing anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
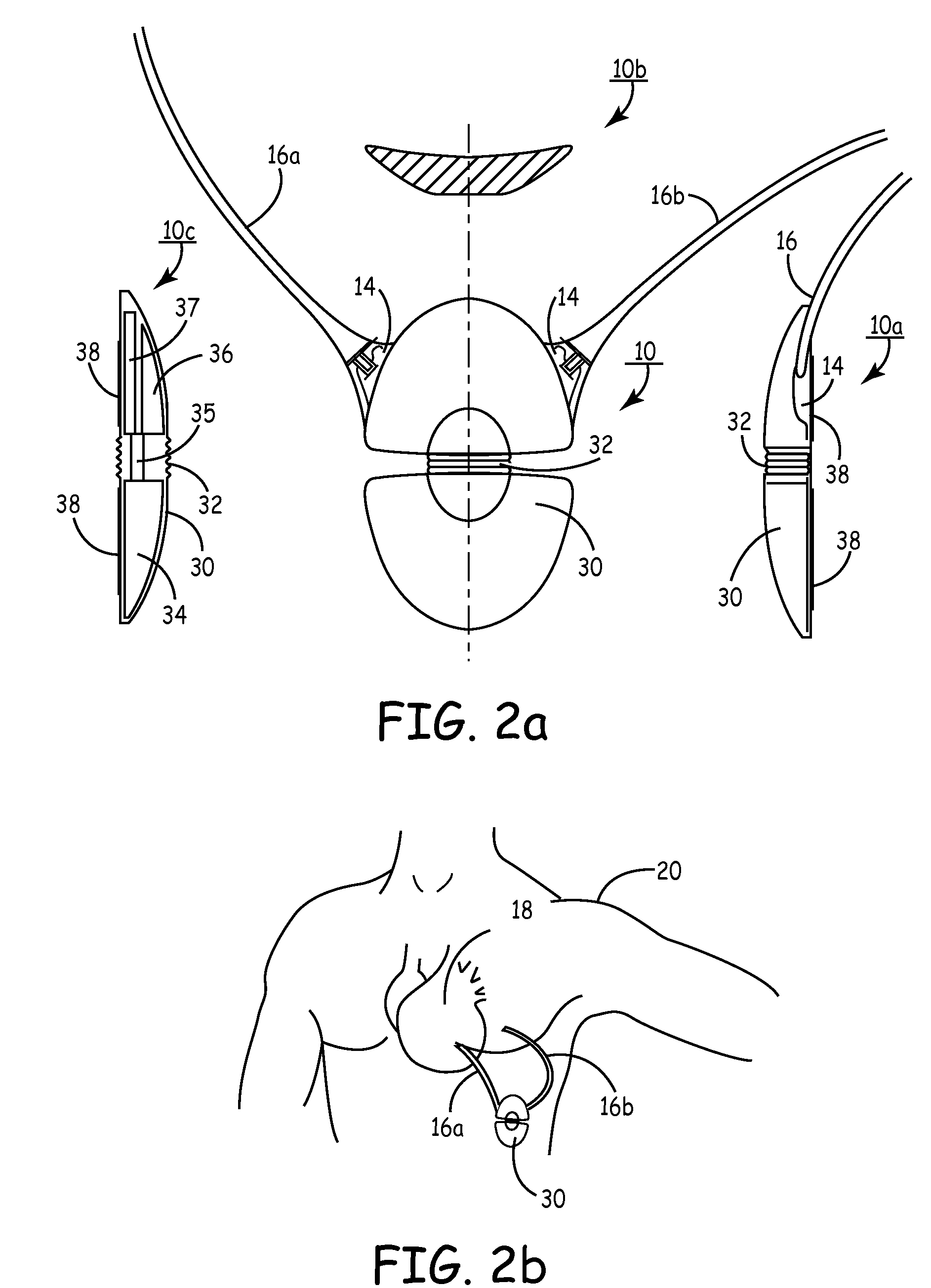
Devices and Methods for Screening of Vagal Nerve Stimulation
InactiveUS20100286553A1Good effectElectroencephalographySensorsRight carotid sheathSacral nerve stimulation
The present disclosure provides systems and methods for screening vagus nerve stimulation to determine the potential efficacy of permanent stimulation systems. In one aspect, the system includes temporary electrode assemblies adapted for temporary placement on or in the body adjacent the vagus nerve. In another aspect, a method is provided to place a stimulating electrode adjacent the posterior of the carotid sheath.
Owner:DECAF
Charge-enhanced neural electric stimulation system
InactiveUS20130035745A1Stimulating effectiveness of communicationPromote effectivenessSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsElectricityElectrical polarity
A system and method to treat neural communication impairment is provided. The neural communication impairment is present in a neural pathway, which can be a cortico-neuromuscular pathway, an intra-brain neural pathway, or in a sensory-cortico pathway. A synchronized external stimulation is applied to a first point in proximity to a first neural component at one end of the neural pathway and to a second point in proximity to a second neural component at the other end of the neural pathway. Two induced neural handshake signals contemporaneously arrive at a neural communication impairment point in the neural pathway, triggering and stimulating a rehabilitation process by which the neural connection is permanently improved. The synchronized applied electrical signals applied to the first and second points may have an opposite polarity in dipolar neural stimulation, or may have identical polarity and waveform in in-phase neural stimulation.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
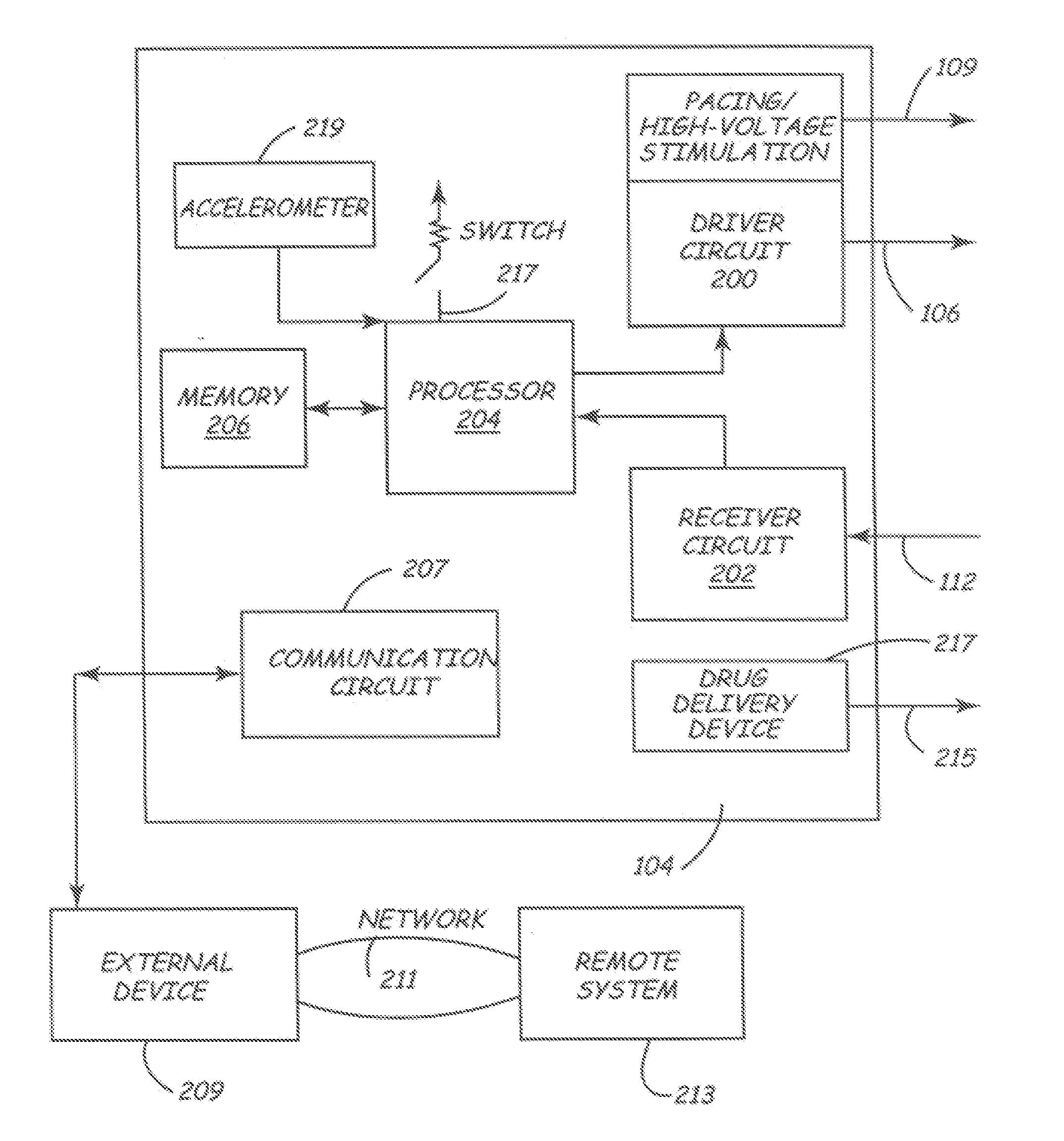
Reconfigurable implantable cardiac monitoring and therapy delivery device
Methods and systems for implantable cardiac monitors reconfigurable to cardiac therapy devices. A device includes a housing with electrodes configured for cardiac activity sensing when the device is operated in monitoring mode, and sensing and energy delivery when operated in an energy delivery mode. A header may be configured to receive a cardiac lead, and may be associated with a switch to switch the device between monitoring and therapy modes in response to connecting one or more leads to the header. The device may include a transceiver that transmits the contents of the memory to a patient-external device. A method involves providing an implantable cardiac device configured to operate in a first mode as a loop recorder for monitoring cardiac activity and storing selected cardiac events, and operating in the second mode to monitor cardiac activity and provide cardiac stimulation therapy when the second mode is enabled.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
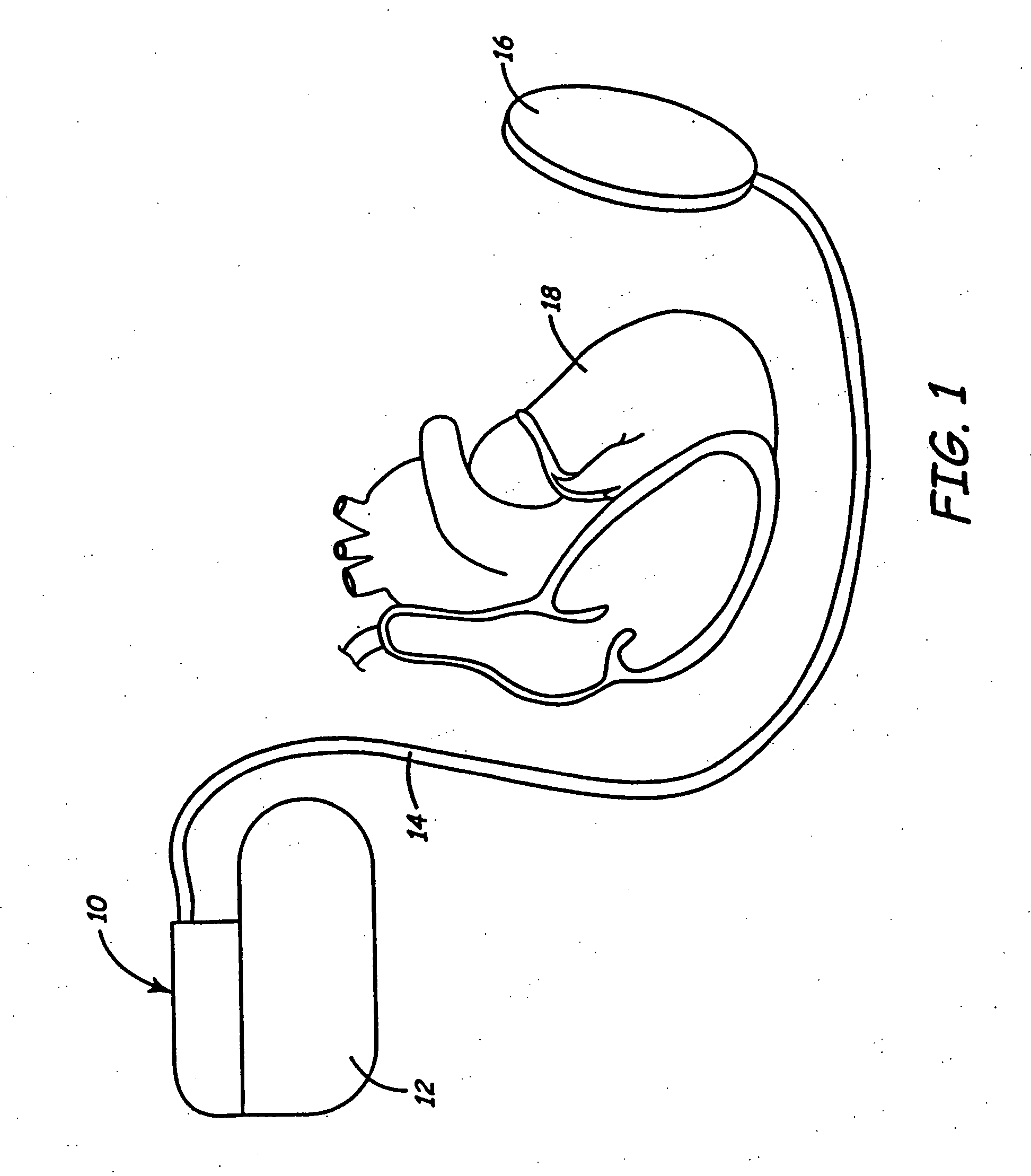
Closed-Loop Neuromodulation for Prevention and Treatment of Cardiac Conditions
InactiveUS20070213773A1Improve heart functionLimit ischemic attackSubcutaneous electrodesNervous systemClosed loop feedback
A method and apparatus to provide therapy to a patient for protecting cardiac tissue from insult is disclosed. The method comprises delivering electrical stimulation to one or more predetermined portions of the nervous system in a patient's body; and monitoring one or more physiologic indices of the body to determine whether the delivered therapy is effective. That is, a closed-loop feedback controller is used to apply electrical stimulation to preselected regions of the patient's body, and then the physiologic response of the patient is monitored to determine the efficacy of the stimulation.
Owner:HILL MICHAEL R S +3
Method of routing electrical current to bodily tissues via implanted passive conductors
The invention provides an implant, system and method for electrically stimulating a target tissue to either activate or block neural impulses. The implant provides a conductive pathway for a portion of electrical current flowing between surface electrodes positioned on the skin and transmits that current to the target tissue. The implant has a passive electrical conductor of sufficient length to extend from subcutaneous tissue located below a surface cathodic electrode to the target tissue. The conductor has a pick-up end which forms an electrical termination having a sufficient surface area to allow a sufficient portion of the electrical current to flow through the conductor, in preference to flowing through body tissue between the surface electrodes, such that the target tissue is stimulated to either activate or block neural impulses. The conductor also has a stimulating end which forms an electrical termination for delivering the current to the target body tissue.
Owner:2249020 ALBERTA LTD
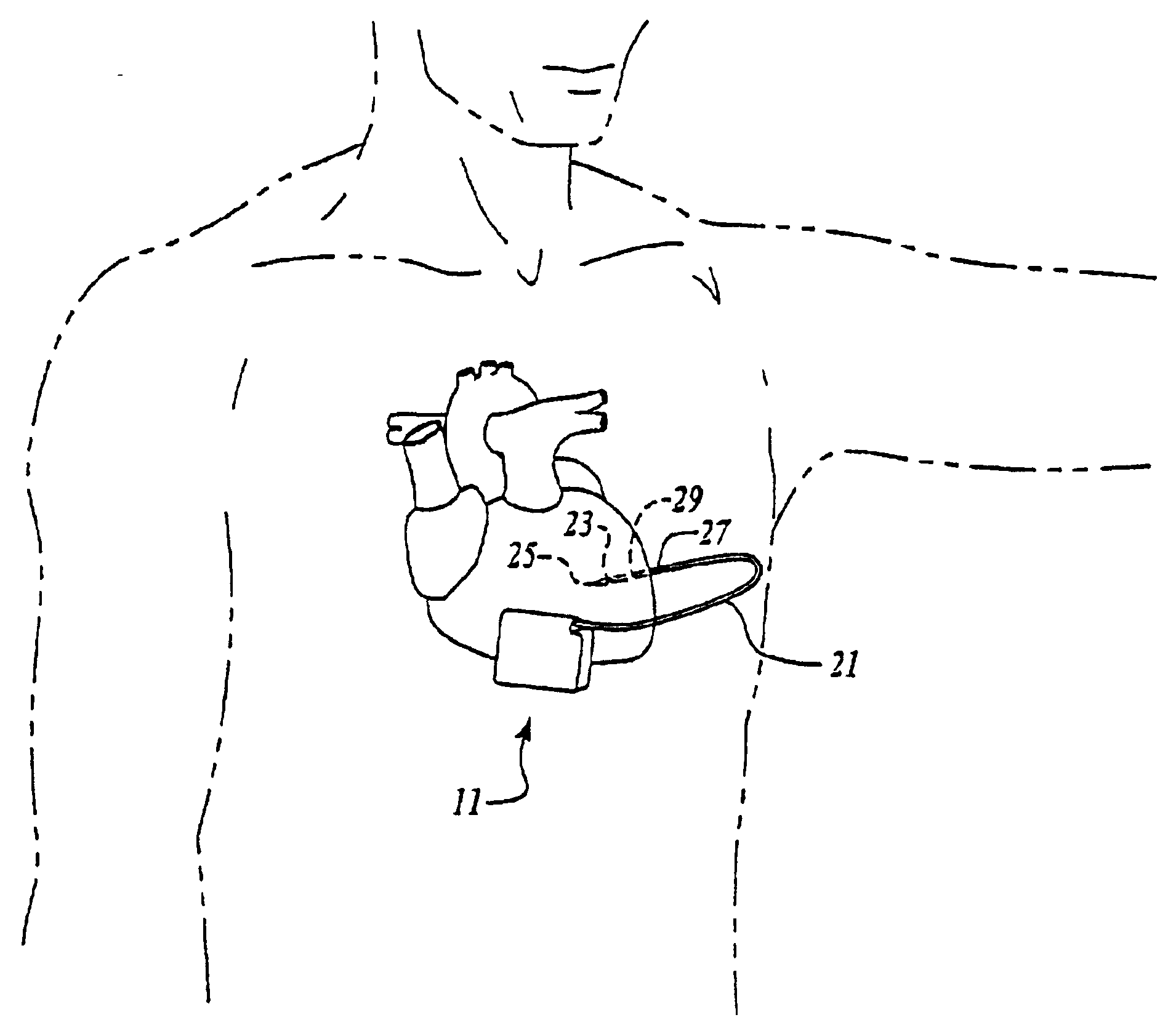
Subcutaneous cardioverter-defibrillator
SubQ ICDs are disclosed that are entirely implantable subcutaneously with minimal surgical intrusion into the body of the patient and provide distributed cardioversion-defibrillation sense and stimulation electrodes for delivery of cardioversion-defibrillation shock and pacing therapies across the heart when necessary. Configurations include one hermetically sealed housing with 1 or, optionally, 2 subcutaneous sensing and cardioversion-defibrillation therapy delivery leads or alternatively, 2 hermetically sealed housings interconnected by a power / signal cable. The housings are generally dynamically configurable to adjust to varying rib structure and associated articulation of the thoracic cavity and muscles. Further the housings may optionally be flexibly adjusted for ease of implant and patient comfort.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Systems and methods for percutaneous electrical stimulation
InactiveUS20130197615A1Easy to break awayLine/current collector detailsSubcutaneous electrodesElectricityPhysical therapy
Systems and methods according to the present invention relate to a substantially extracorporeal pulse generator system for electrical stimulation of one or more target nerve or their branches using one or more preferably percutaneous leads each having one or more electrodes implanted in, on, around, or near the target nerve. Improved systems include a patch assembly configured to be adhesively mounted to a patient's skin and an electrical stimulation assembly configured to be mechanically mounted to the patch assembly. A preferred patch assembly, in addition to provide mechanical mounting of the stimulation assembly, provides a power source for the stimulation assembly, and may further serve as a return electrode. Associated system components and methods of use are also provided.
Owner:NDI MEDICAL
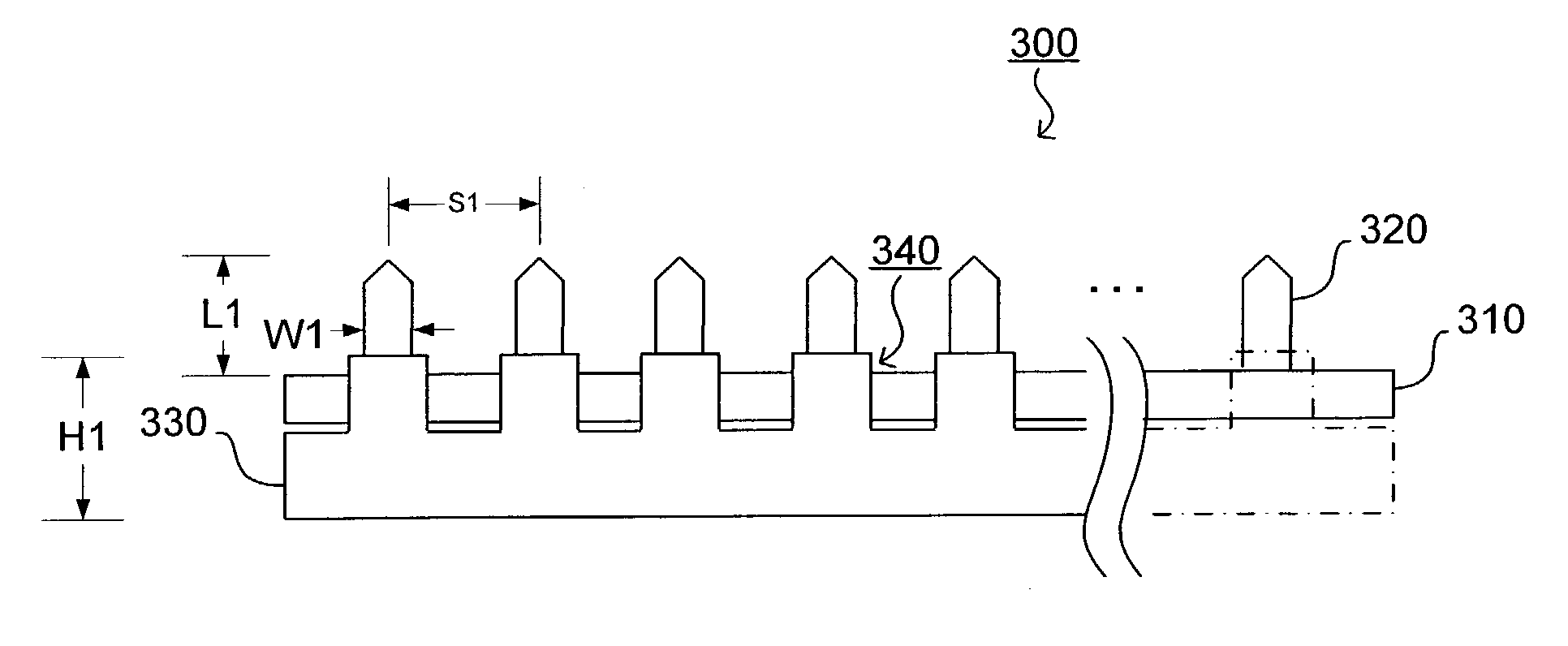
Percutaneous electrode array
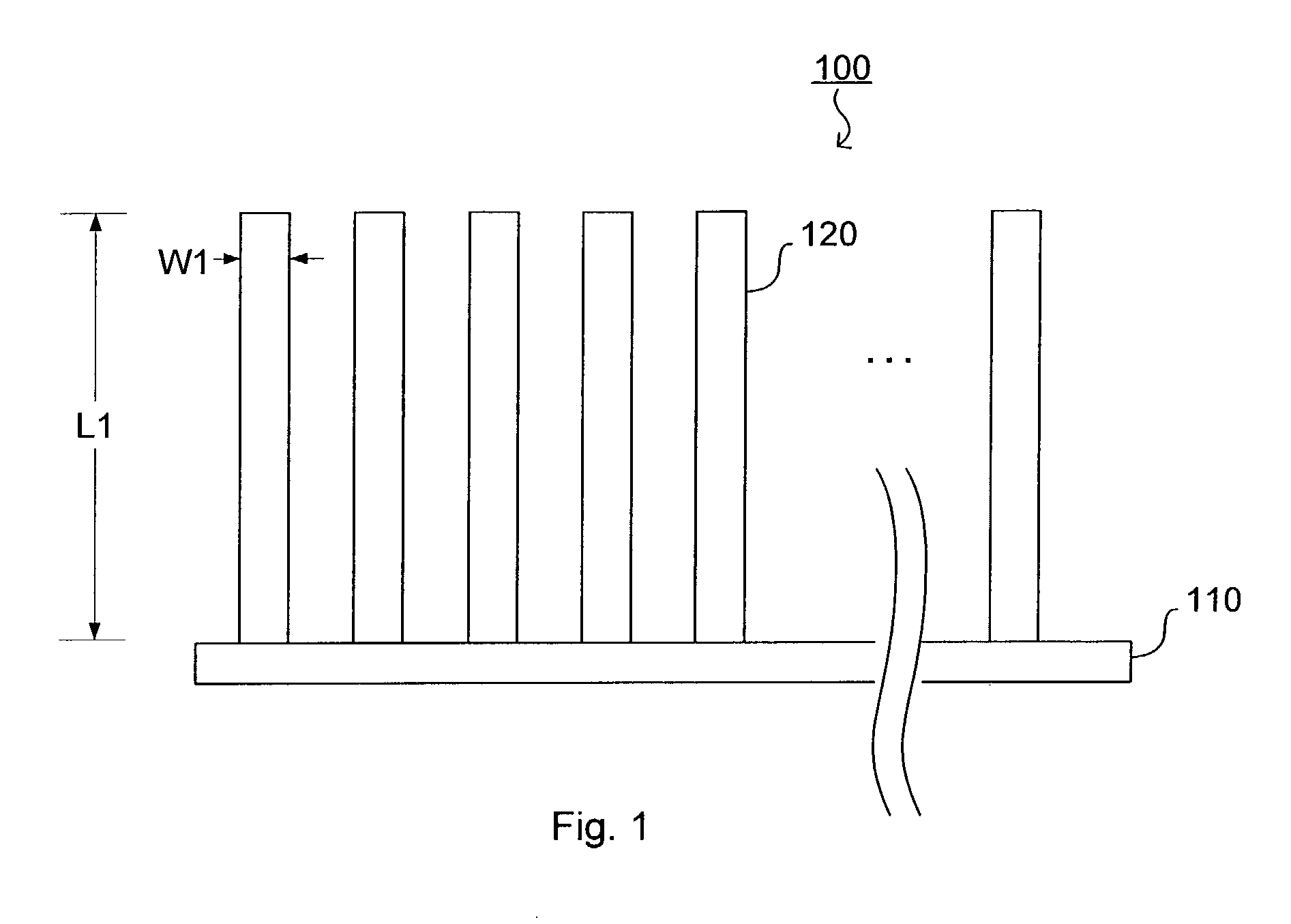
InactiveUS7013179B2Improve securitySubcutaneous electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical resistance and conductanceProper treatment
A percutaneous electrode array is disclosed for applying therapeutic electrical energy to a treatment site in the body of a patient. The array comprises a plurality of electrode microstructures which are inserted into the epidermis, thereby overcoming the inherent electrical impedance of the outer skin layers and obviating the need to prepare the skin surface prior to an electro-therapy treatment. The array preferably includes an adhesion layer to help keep the electrode microstructures inserted into the epidermis during the duration of the therapeutic treatment, and temperature and condition monitoring devices to ensure proper treatment and enhance patient safety.
Owner:BIOWAVE CORP
Apparatus for detecting and treating ventricular arrhythmia
A system and method for long-term monitoring of cardiac conditions such as arrhythmias is disclosed. The invention includes a pulse generator including means for sensing an arrhythmia. The pulse generator is coupled to at least one subcutaneous electrode or electrode array for providing electrical stimulation such as cardioversion / defibrillation shocks and / or pacing pulses. The electrical stimulation may be provided between multiple subcutaneous electrodes, or between one or more such electrodes and the housing of the pulse generator. In one embodiment, the pulse generator includes one or more electrodes that are isolated from the can. These electrodes may be used to sense cardiac signals.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
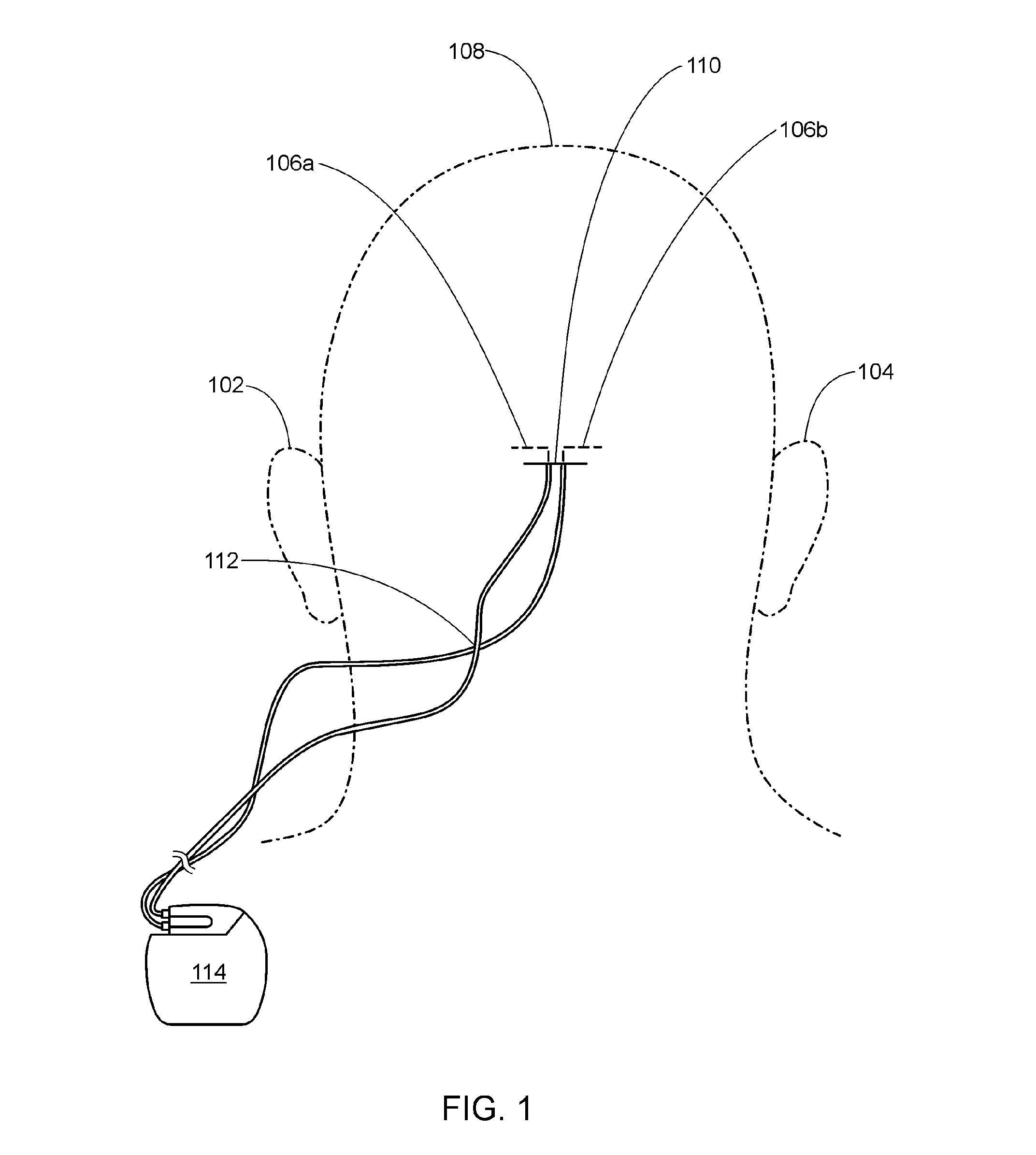
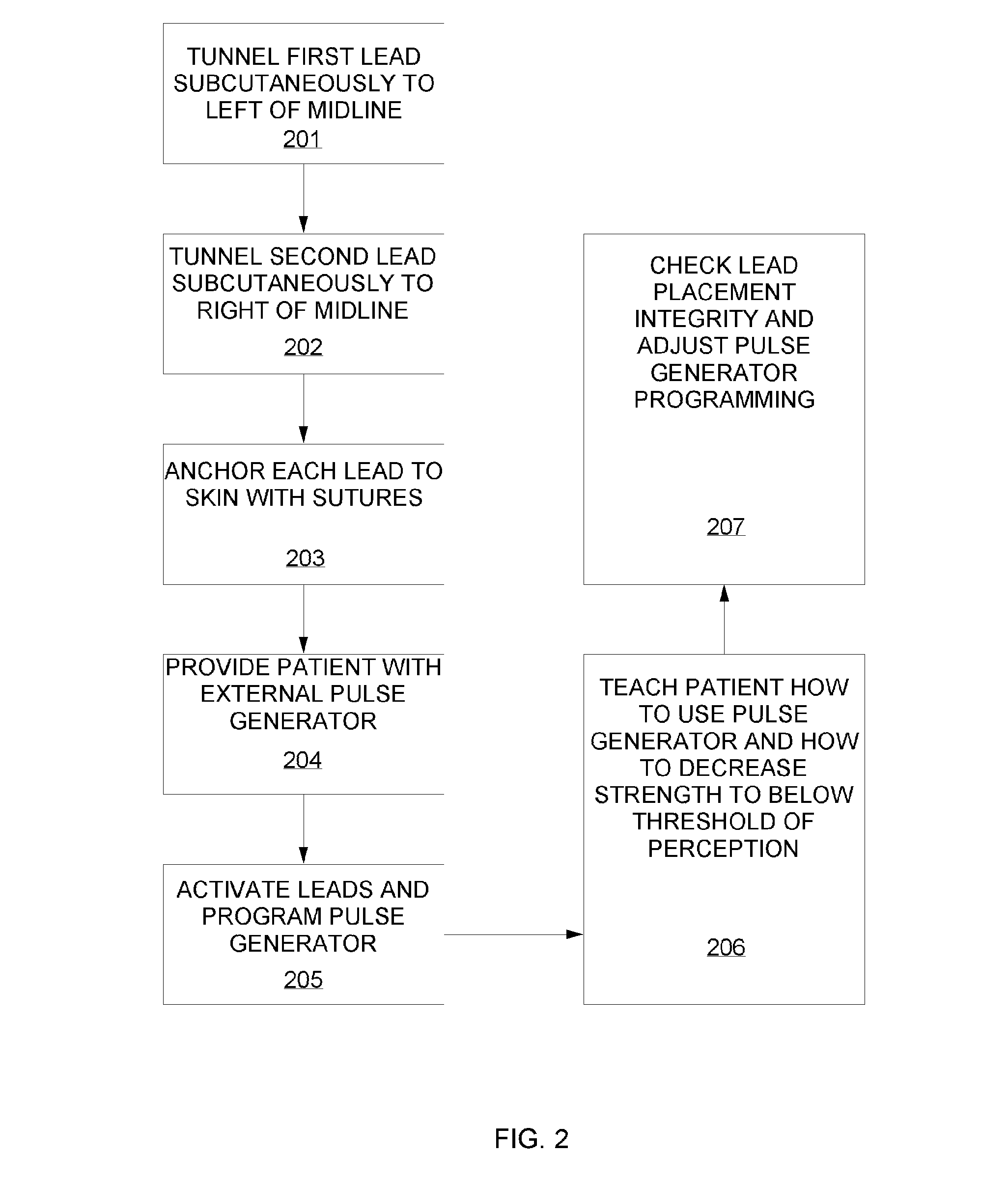
Occipital neuromodulation
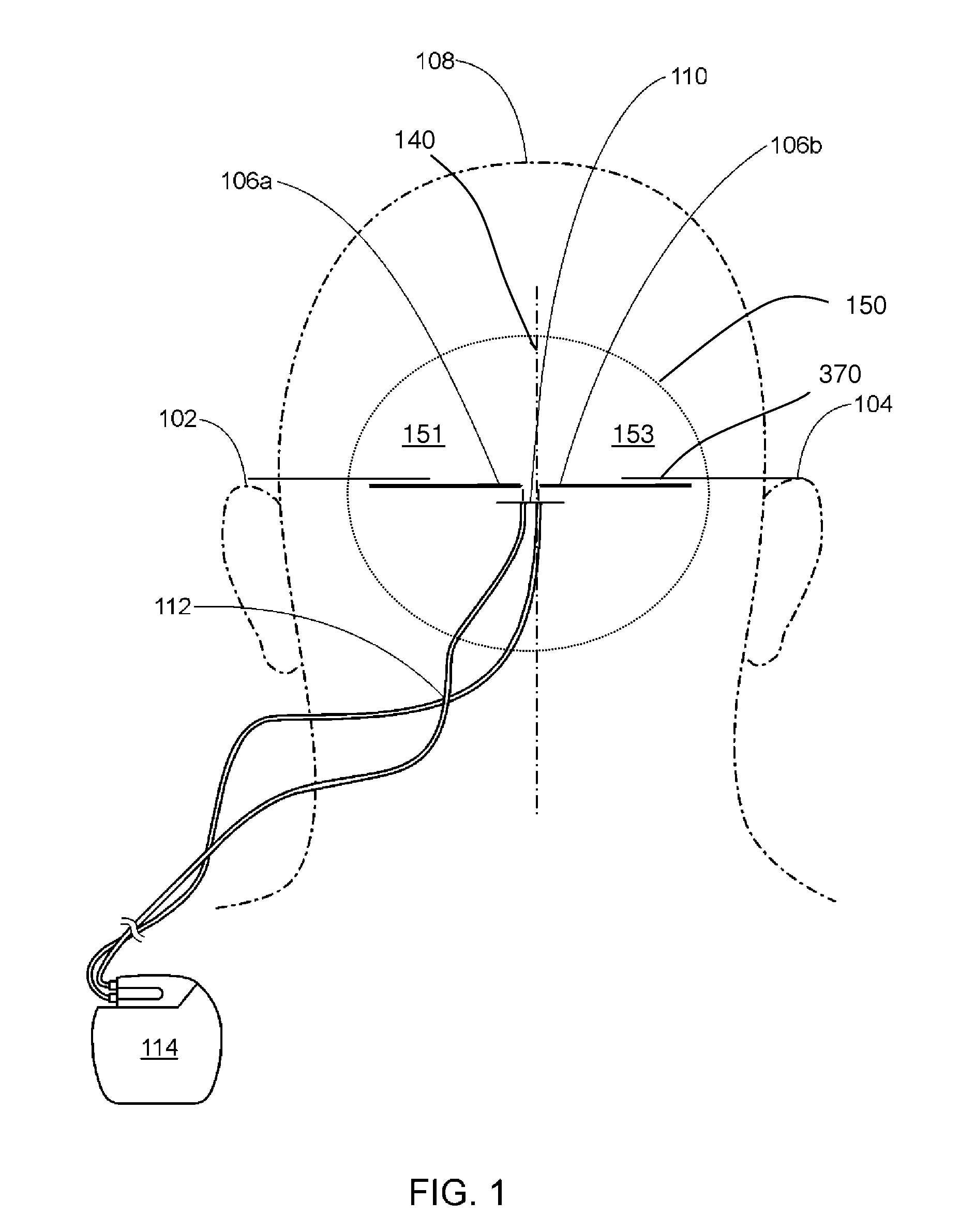
A method of treating chronic pain in a subject by positioning a lead containing electrodes subcutaneously in the occipital region of a subject's skull at the height of an imaginary line connecting the tops of the ears; and energizing the lead with an electrical signal effective to suppress pain, and below the level where the subject can feel the lead being energized. Typically the procedure involves a trial phase and a permanent implant phase. The procedure is known as occipital neuromodulation.
Owner:THE KING OF PAIN
Peripheral Nerve Stimulation
Owner:WEINER RICHARD L
Occipital neuromodulation method
InactiveUS20130023951A1Satisfies needRelief the painHead electrodesSubcutaneous electrodesOccipital nerveOccipital bone
A method of treating pain in a subject includes the step of positioning a tip of one or more leads subcutaneously in the occipital region of a subject's scalp, where the leads are configured to conduct an electrical signal along an occipital nerve into the brain. The leads are energized to conduct the electrical signal along the occipital nerve and the electrical signal is adjusted to a level effective to decrease the subject's pain over time and so that the subject cannot feel the lead being energized.
Owner:GREENSPAN JOSHUA
Methods and devices for activating brown apidose tissue using electrical energy
ActiveUS20110270360A1Increased energy expenditureImplantable neurostimulatorsSubcutaneous electrodesElectricityMicrochiroptera
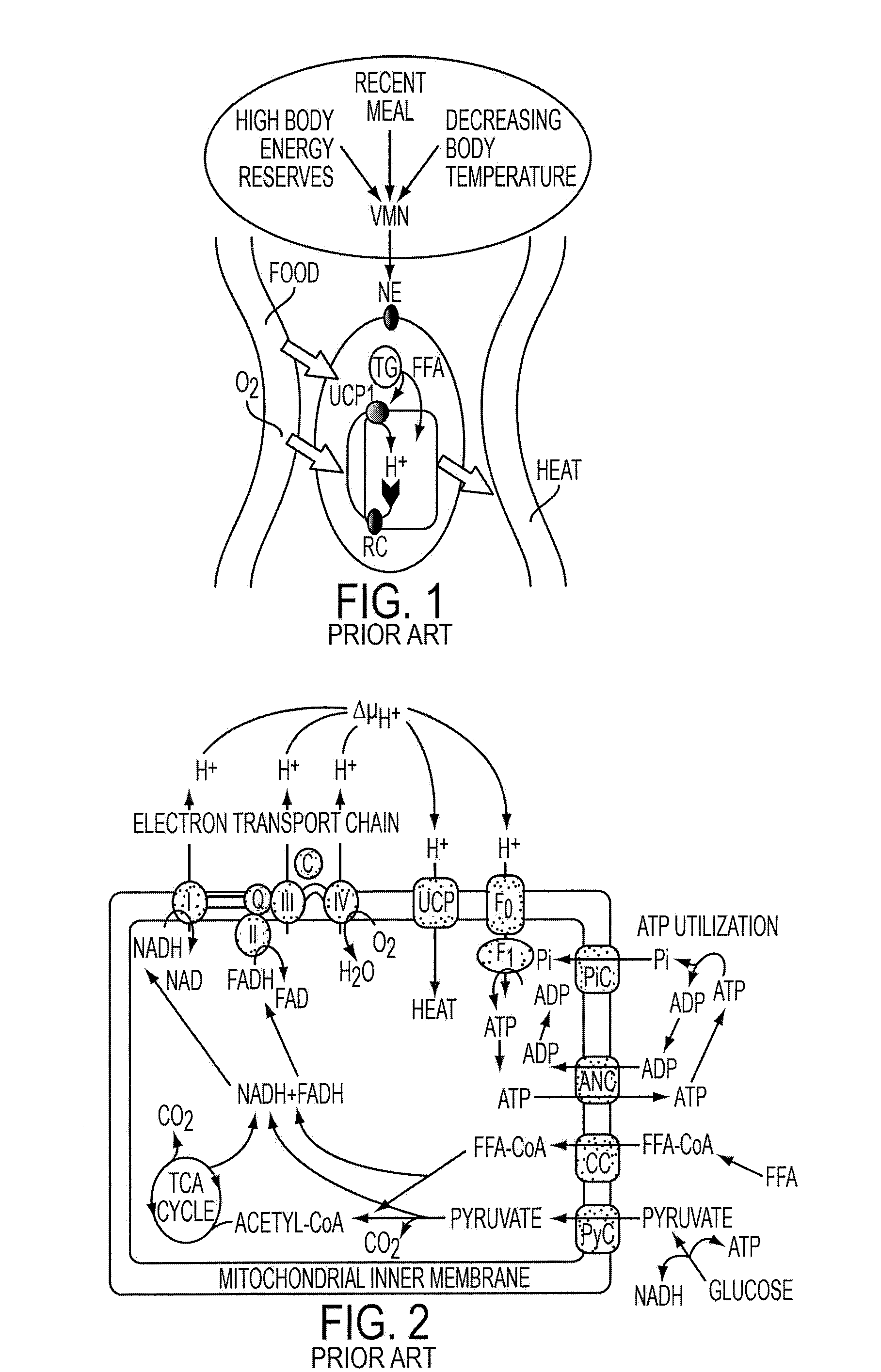
Methods and devices are provided for activating brown adipose tissue (BAT). Generally, the methods and devices can activate BAT to increase thermogenesis, e.g., increase heat production in the patient, which over time can lead to weight loss. In one embodiment, a medical device is provided that activates BAT by electrically stimulating nerves that activate the BAT and / or electrically stimulating brown adipocytes directly, thereby increasing thermogenesis in the BAT and inducing weight loss through energy expenditure.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
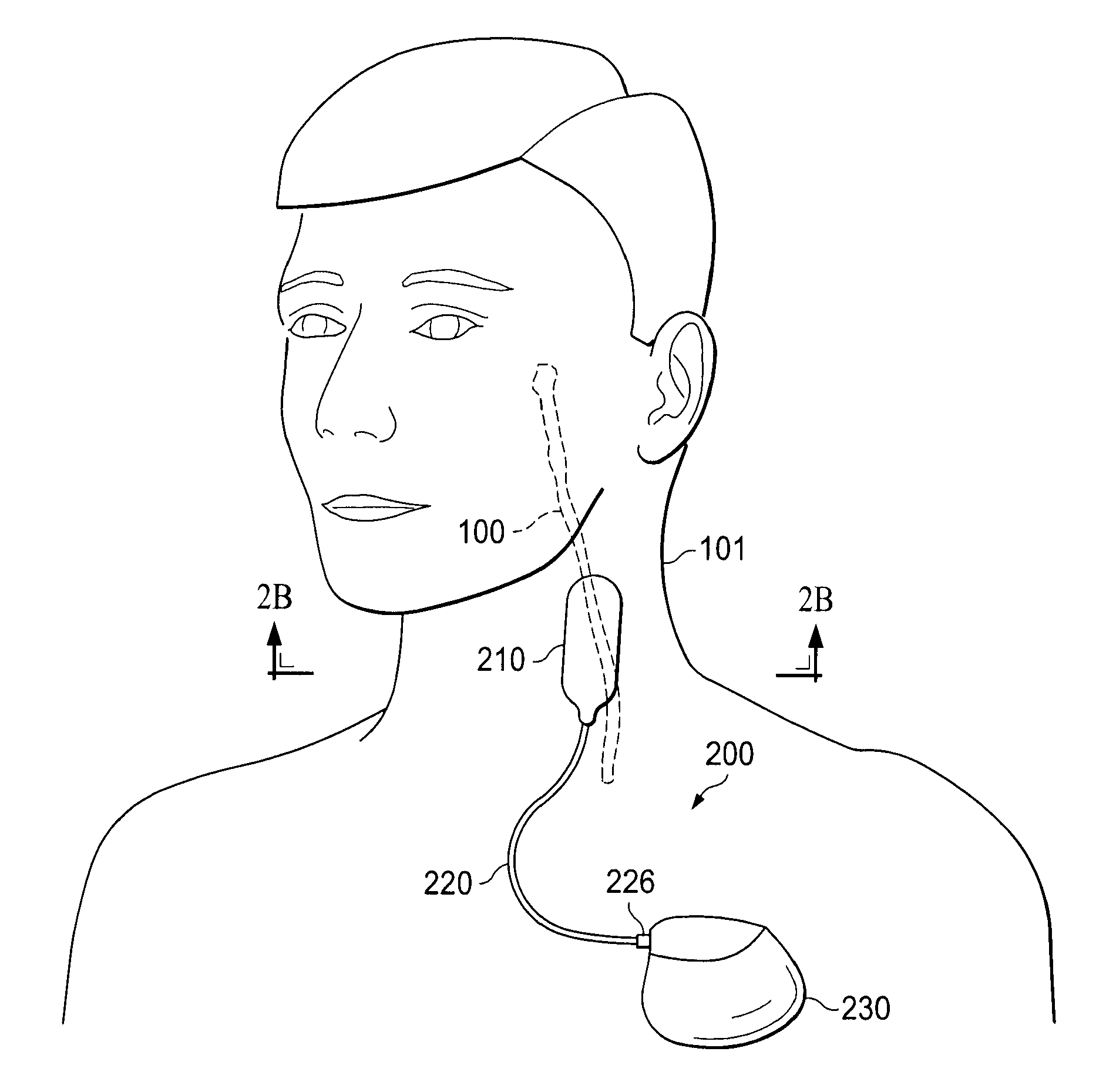
Self-Tunneling Lead
ActiveUS20130238067A1Easy to understandSpinal electrodesSubcutaneous electrodesSubcutaneous tissueBiomedical engineering
An implantable medical lead includes (i) a proximal end portion including a contact and having a proximal end; and (ii) a distal end portion including an electrode and having a distal end. The electrode is electrically coupled to the contact. The distal end portion is generally flat and sufficiently stiff to be pushed through subcutaneous tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable extravascular electrical stimulation lead having improved sensing and pacing capability
Implantable medical electrical leads having electrodes arranged such that a defibrillation coil electrode and a pace / sense electrode(s) are concurrently positioned substantially over the ventricle when implanted as described. The leads include an elongated lead body having a distal portion and a proximal end, a connector at the proximal end of the lead body, a defibrillation electrode located along the distal portion of the lead body, wherein the defibrillation electrode includes a first electrode segment and a second electrode segment proximal to the first electrode segment by a distance. The leads may include at least one pace / sense electrode, which in some instances, is located between the first defibrillation electrode segment and the second defibrillation electrode segment.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Occipital neuromodulation
InactiveUS20100069993A1Satisfies needHead electrodesSubcutaneous electrodesPermanent implantMedicine
A method of treating chronic pain in a subject by positioning a lead containing electrodes subcutaneously in the occipital region of a subject's skull at the height of an imaginary line connecting the tops of the ears; and energizing the lead with an electrical signal effective to suppress pain, and below the level where the subject can feel the lead being energized. Typically the procedure involves a trial phase and a permanent implant phase. The procedure is known as occipital neuromodulation.
Owner:THE KING OF PAIN
Methods, Tools, and Assemblies for Implantation of Medical Leads Having Distal Tip Anchors
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
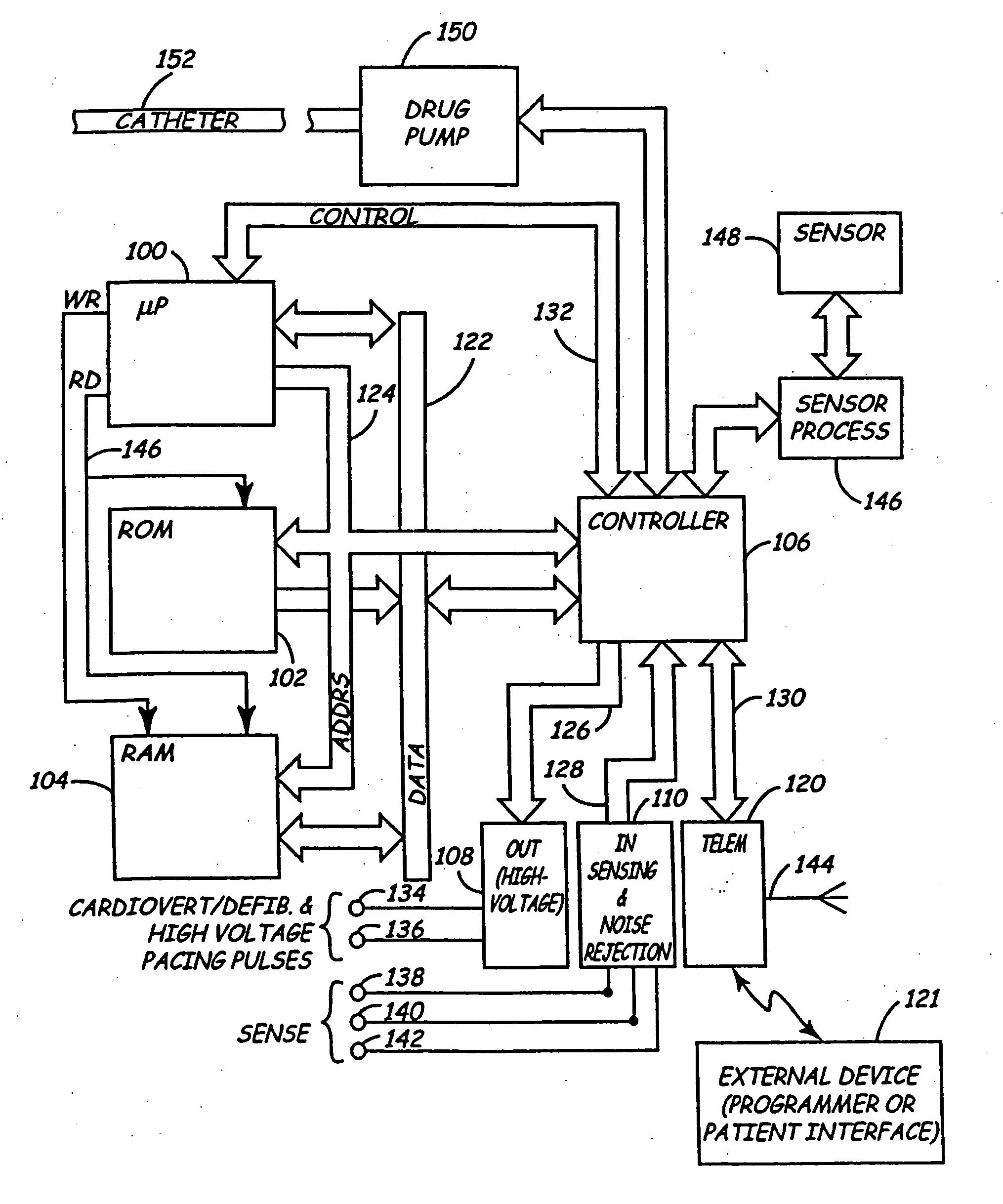
Method and system for aborting cardiac treatments
A method and system for aborting cardiac treatments are provided. An arrhythmia in a heart of a patient is detected with at least one electrode, which is located outside the heart of the patient. An alarm signal is generated after said detection of the arrhythmia to alert a user of an impending cardiac treatment. The cardiac treatment is cancelled if an abort signal is provided by the user within a predetermined amount of time.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
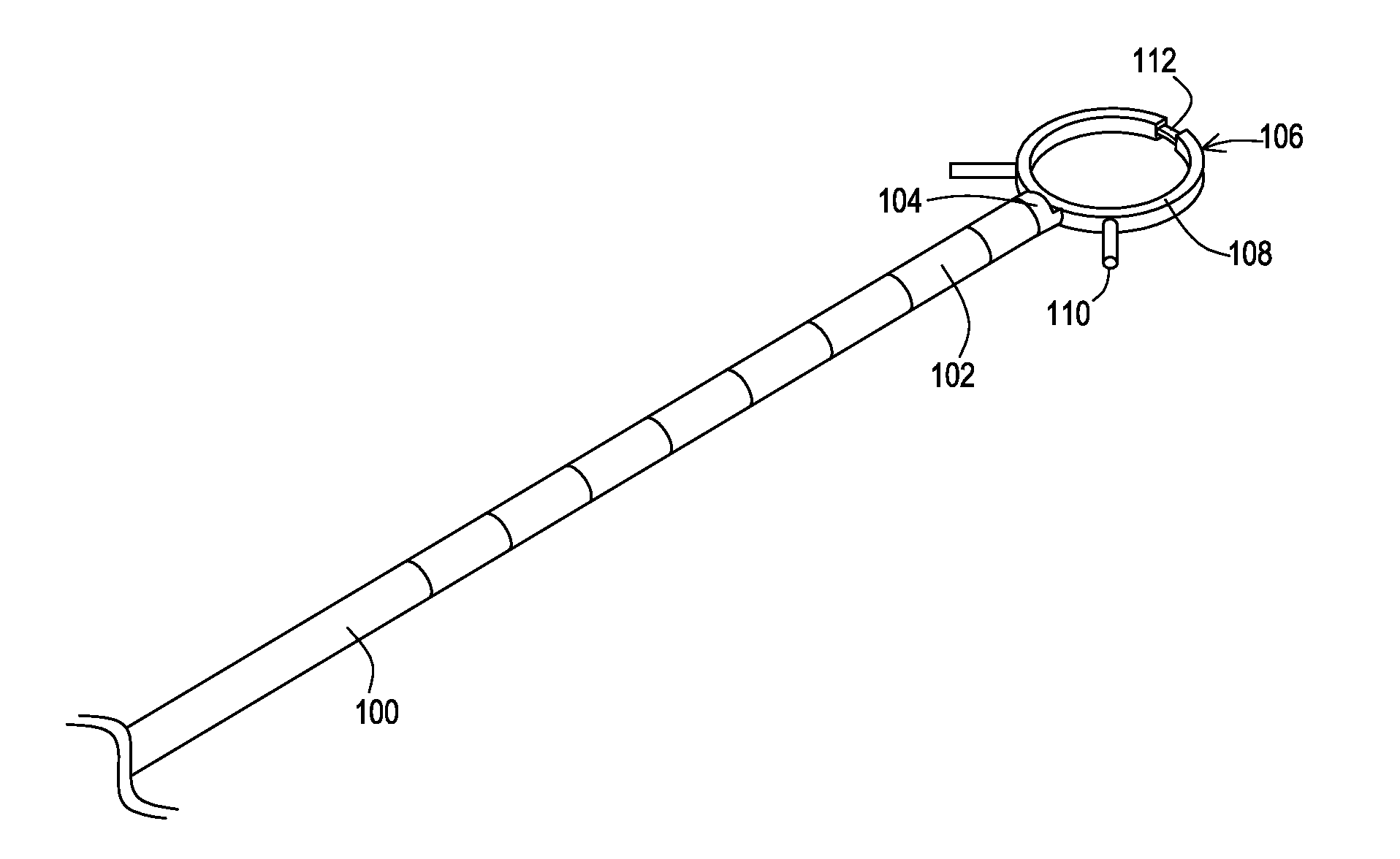
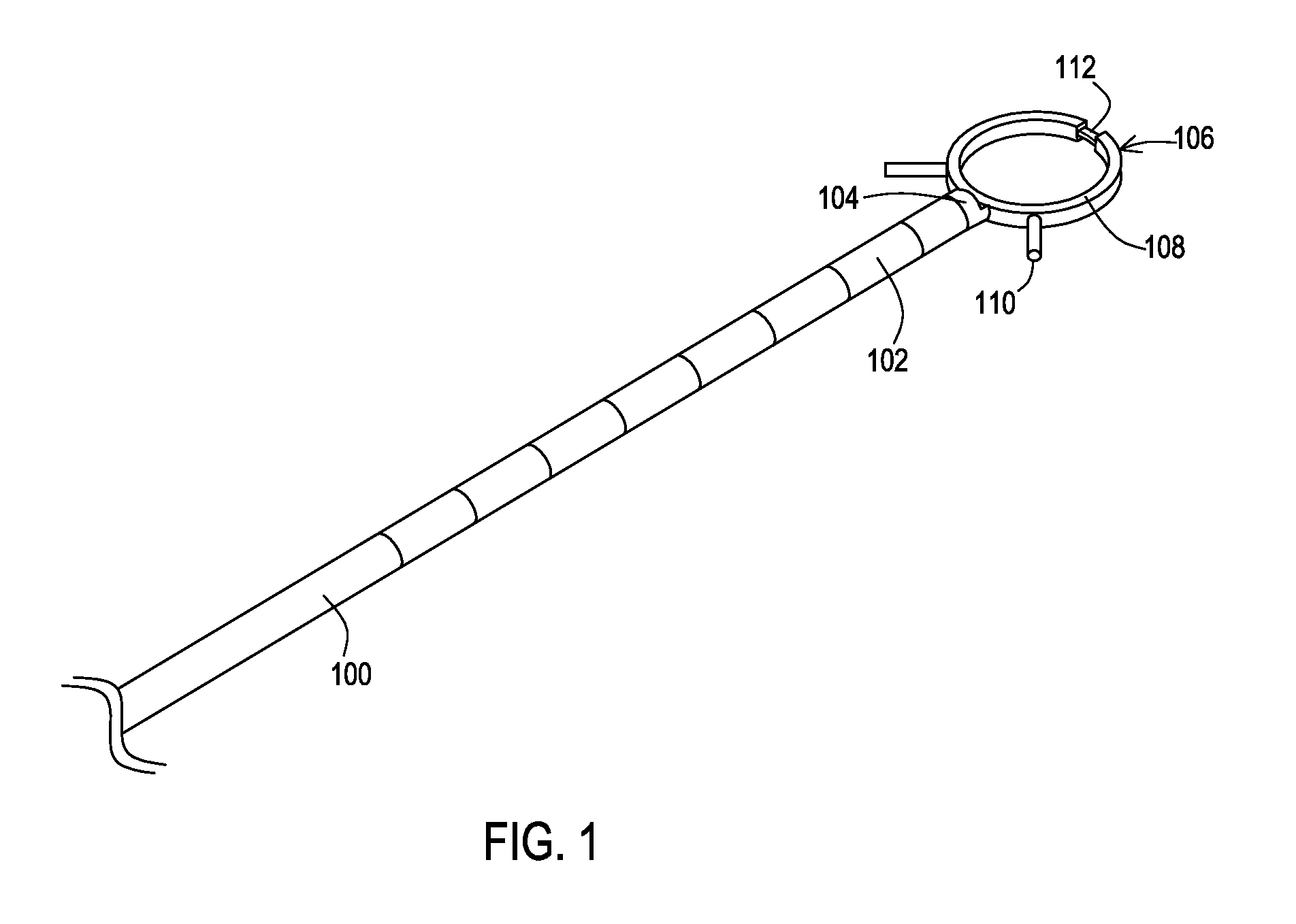
Subcutaneously implantable lead including distal fixation mechanism
InactiveUS7908015B2Transvascular endocardial electrodesSubcutaneous electrodesDistal fixationSubcutaneous implant
A subcutaneously implantable lead includes a coil disposed along a portion of the lead, and a lead tip coupled to a distal end of the lead. The lead tip includes at least one component that is movable relative to the distal end of the lead and configured to anchor the lead tip in subcutaneous tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Subcutaneous lead fixation mechanisms
ActiveUS20070203556A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesSubcutaneous electrodesSurgeryMedical device
A medical device that includes a lead having a lead body extending from a proximal end to a distal end, and a housing having a connector block for receiving the proximal end of the lead body. A fixation mechanism is positioned proximal to an electrode coil located at the distal end of the lead body, and a fixation member or a plurality of fixation members extend from the fixation mechanism from a fixation member proximal end to a fixation member distal end. The fixation members are advanceable from a first position corresponding to the fixation member distal end being positioned along the lead during subcutaneous placement of the lead, to a second position corresponding to the fixation member distal end being positioned away from the lead to fixedly engage the lead at a target site.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com