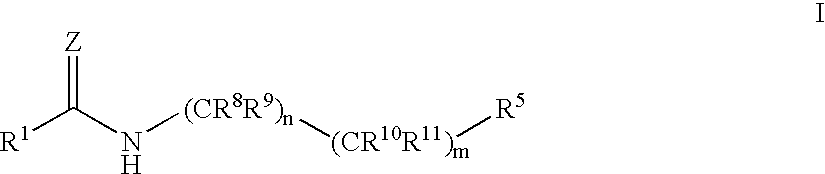
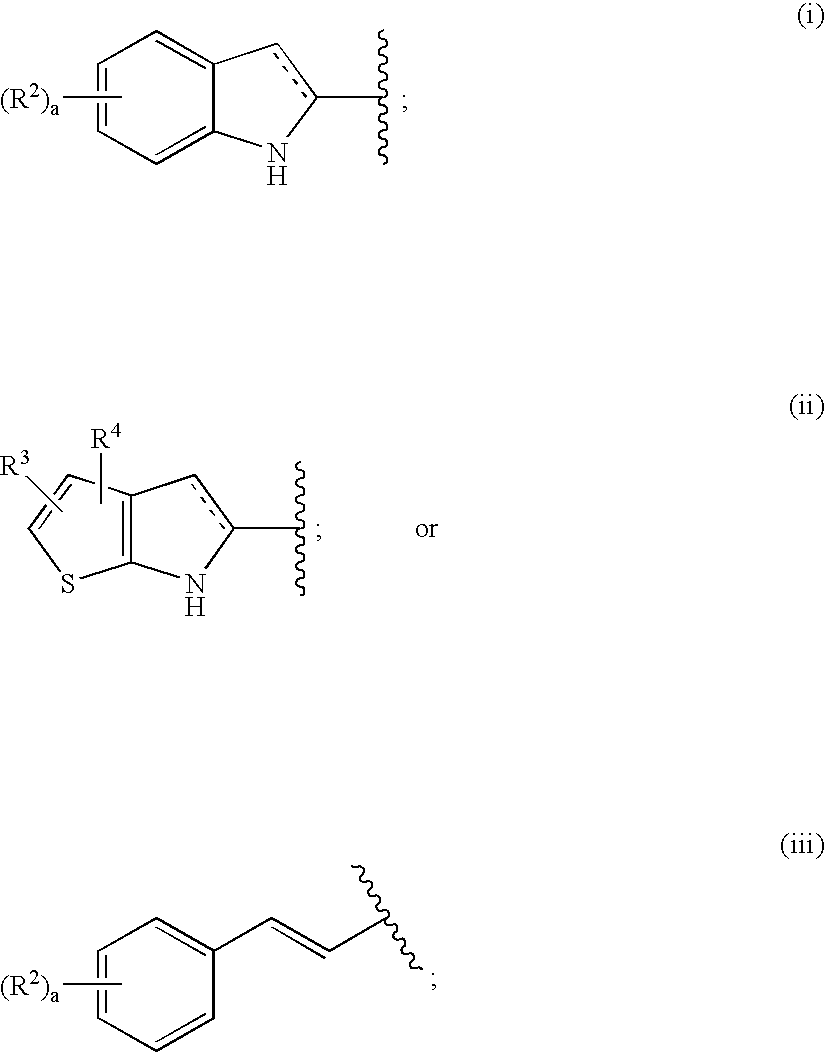
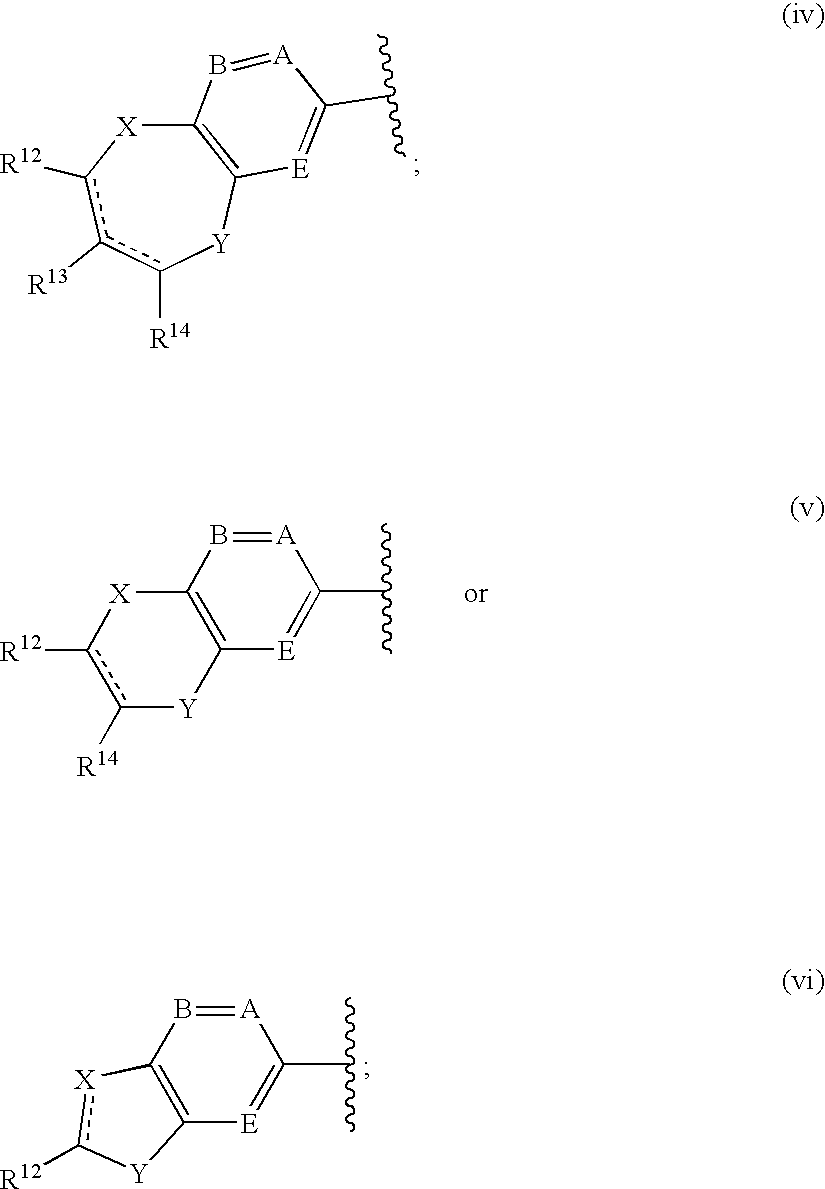
Antidiabetic agents
a technology of antidiabetic agents and antidiabetic drugs, applied in the field of antidiabetic agents, can solve the problems of limiting their use, hypoglycemic agents can have side effects, and the treatment of diabetes remains less than satisfactory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation 1
Methyl 2,3-dihydroxy benzoate
A mixture of 92.472 g (0.6 mol) of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid (FW 154.12; Aldrich cat.# 12,620-9; RSO # 9449), 100 mL of anhydrous methanol and 3 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid was heated to reflux for 36 hrs. After cooling down, reaction mixture was concentrated down to approximately ⅓ of its volume and poured on ice. A precipitate that formed was washed thoroughly with cold water, filtered off and dried in the desiccator over calcium sulfate. Yield 98.4 g of off-white solid (98%). This was used without further purification.
LC MS: AP+ 169, AP− 167.
preparation 2
3,4-Dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine-6-carboxylic acid methyl ester
A flame dried 1 L-flask was charged with 82.7 grams (0.6 mol) of finely ground and flame dried potassium carbonate and 200 mL of absolute dimethylformamide and kept under-nitrogen gas. This reaction mixture was then stirred and warmed up to 40° C. A 47.23 g (29.7 mL, 0.3 mol) of 1-bromo-3-chloropropane was then added to the reaction flask rapidly followed by 50.445 g (0.3 mol) of methyl 2,3-dihydroxy benzoate (C-2). The reaction was then heated to 100° C. (110° C. was the temp. of an oil bath) under reflux condenser for 6 hrs. After cooling, the reaction was filtered to remove all the solids, solids washed with 50 mL of, DMF and filtrate concentrated on the rotary evaporator. The residue was then partitioned between water and ethyl acetate. The organic layer was then washed with 200 mL of 1N NaOH to remove any starting material, followed by 5% HCl, 5% NaHCO3, water and brine. Dried with magnesium sulfate. Filtered...
preparation 3
8-Nitro-3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine-6-carboxylic acid methyl ester (C-4) and 9- Nitro-3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine-6-carboxylic acid methyl ester (C-5)
A 17.15 g (0.0825 mol) of (3,4-Dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine-6-carboxylic acid methyl ester; C-3) was dissolved in a mixture of 65 mL of glacial acetic acid and 65 mL of acetic anhydride. The reaction mixture was heated to 45° C. and treated with a solution of 12 mL of 90% HNO3 (fuming) inl2 mL of glacial acetic acid dropwise. The reaction was then heated to 45-50° C. for 4 hours under reflux condenser. When cooled down, the reaction mixture was poured on a mix of ice and water and the yellow precipitate collected on a filter. Washed with water and dried on air. Crude 17.6 grams (this product was a mixture of the meta- (about 30%). and paranitration (about 60%) products. This was used without further purification. LC MS: AP− 253 (for the mixture)
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| color | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| blood pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com