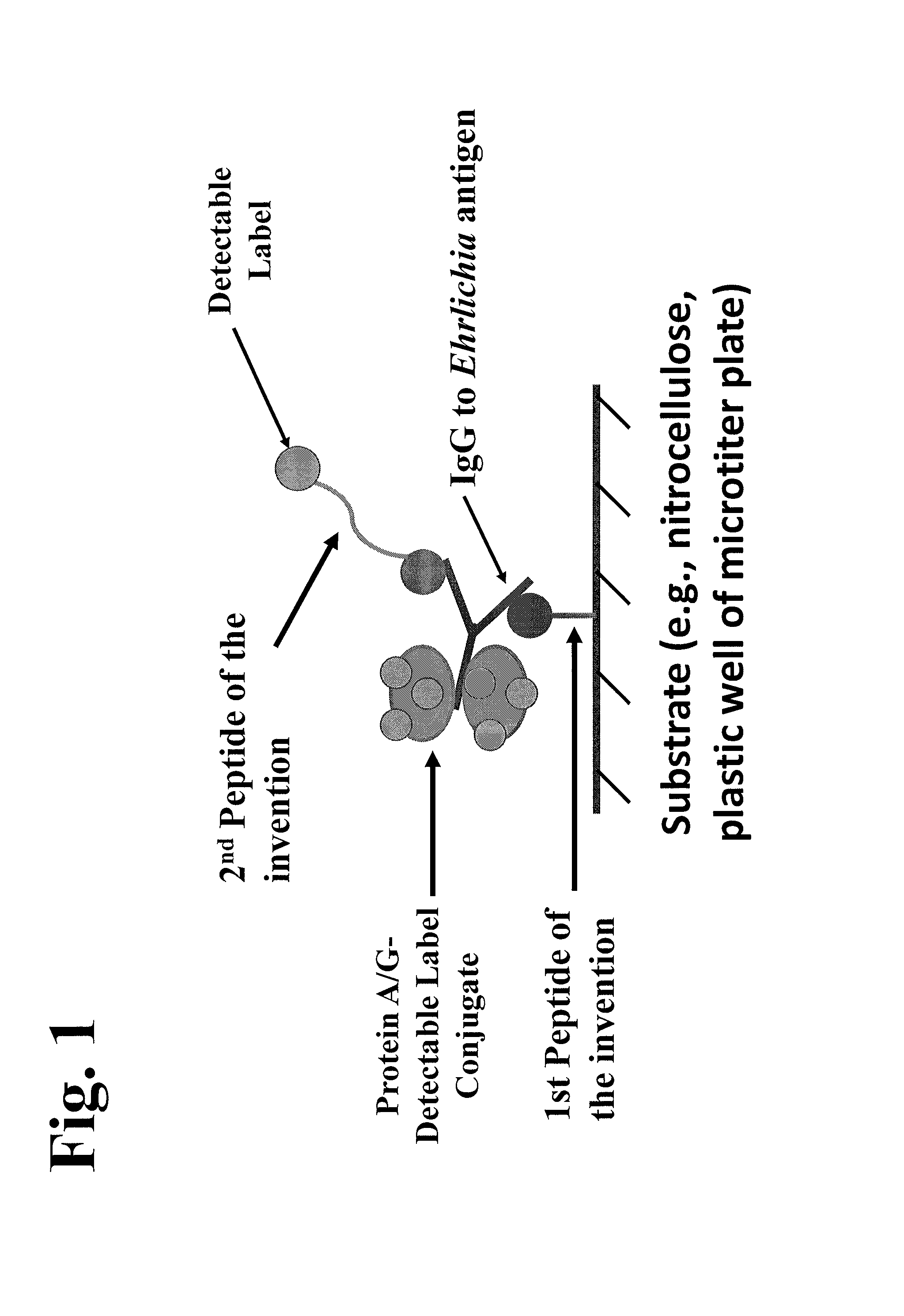
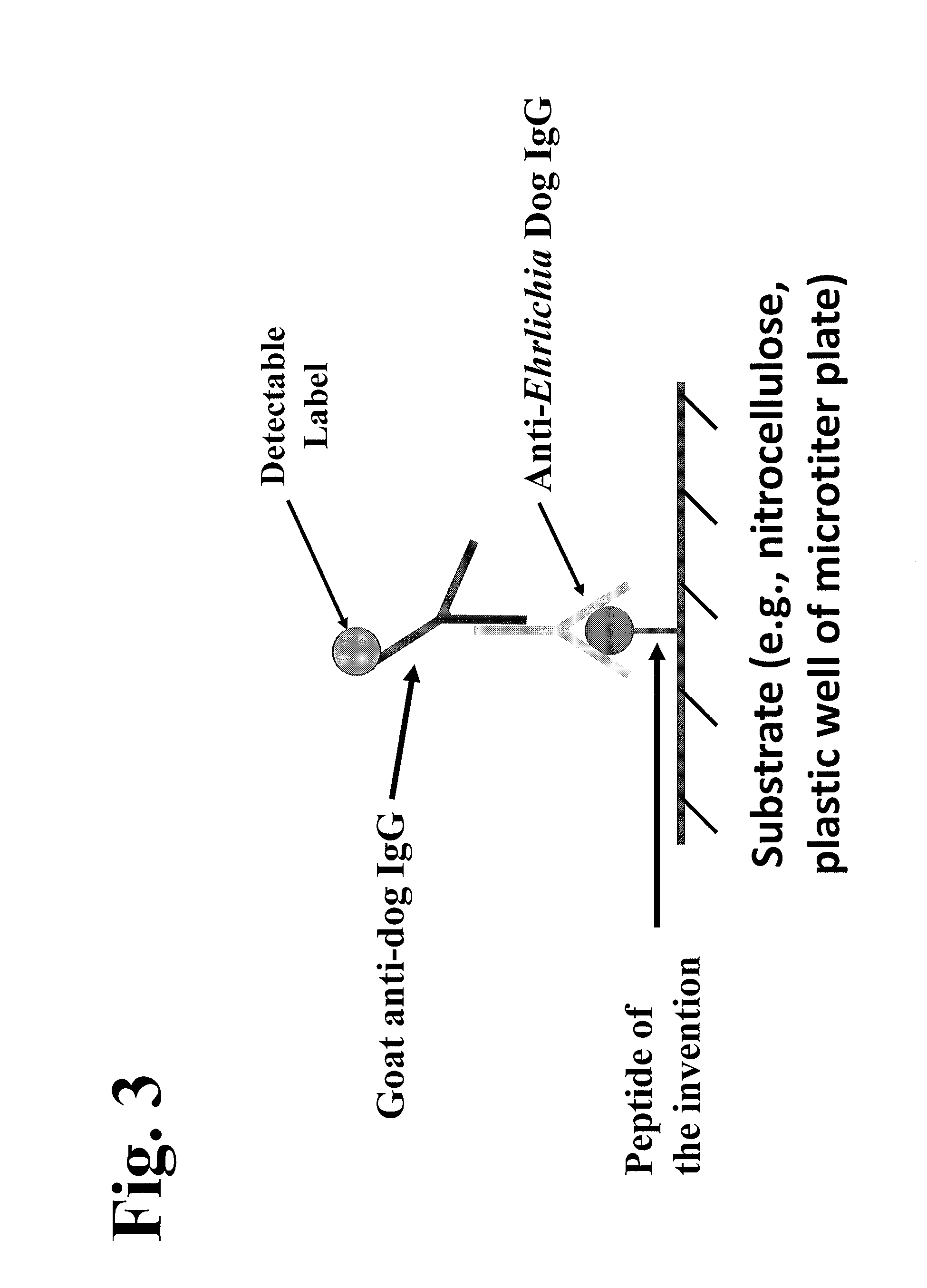
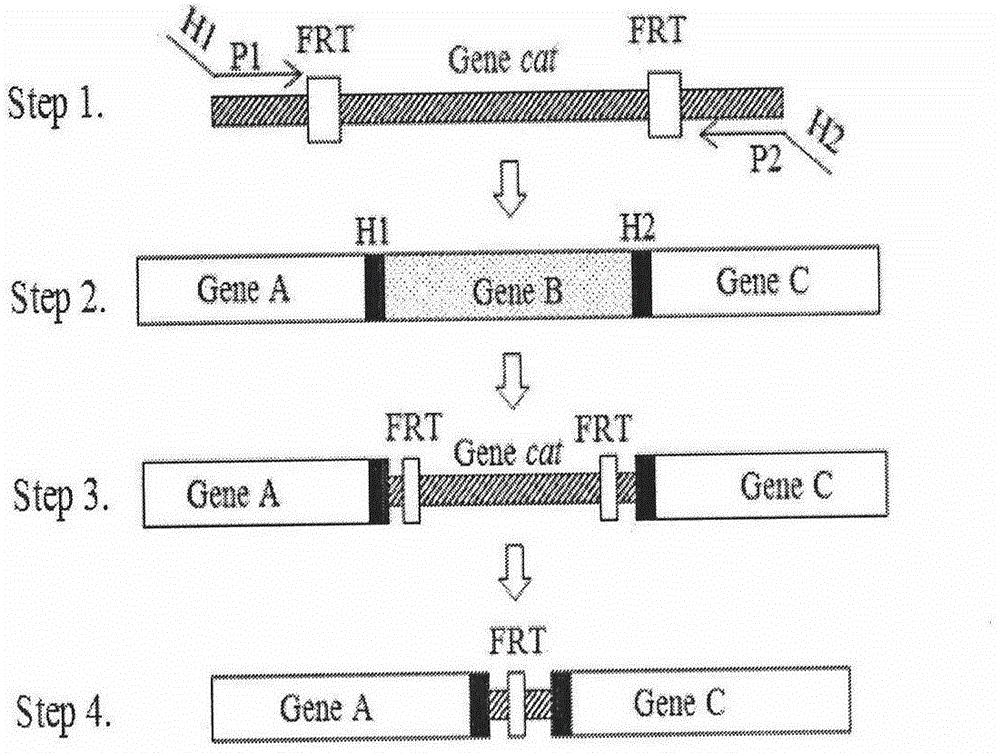
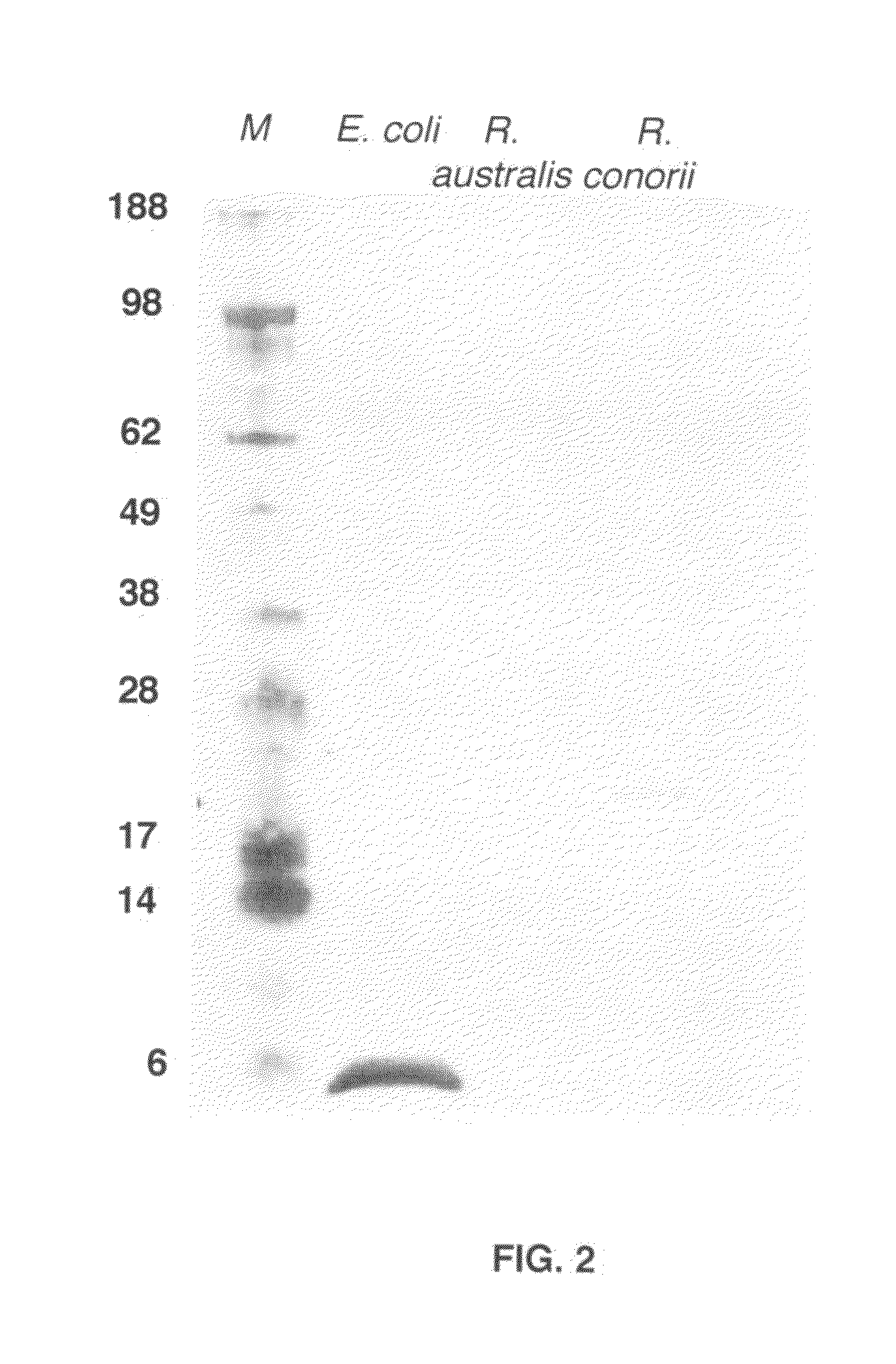
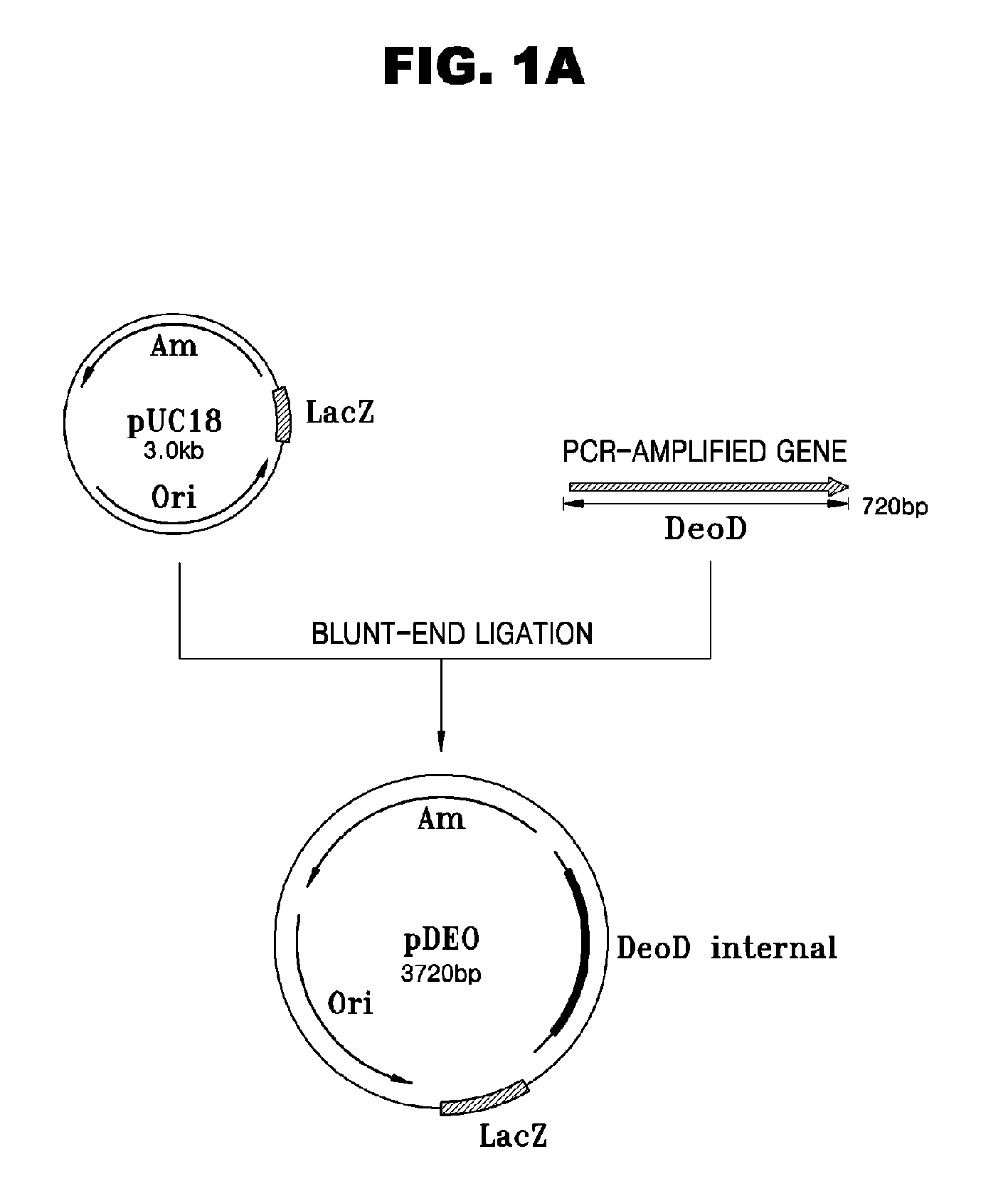
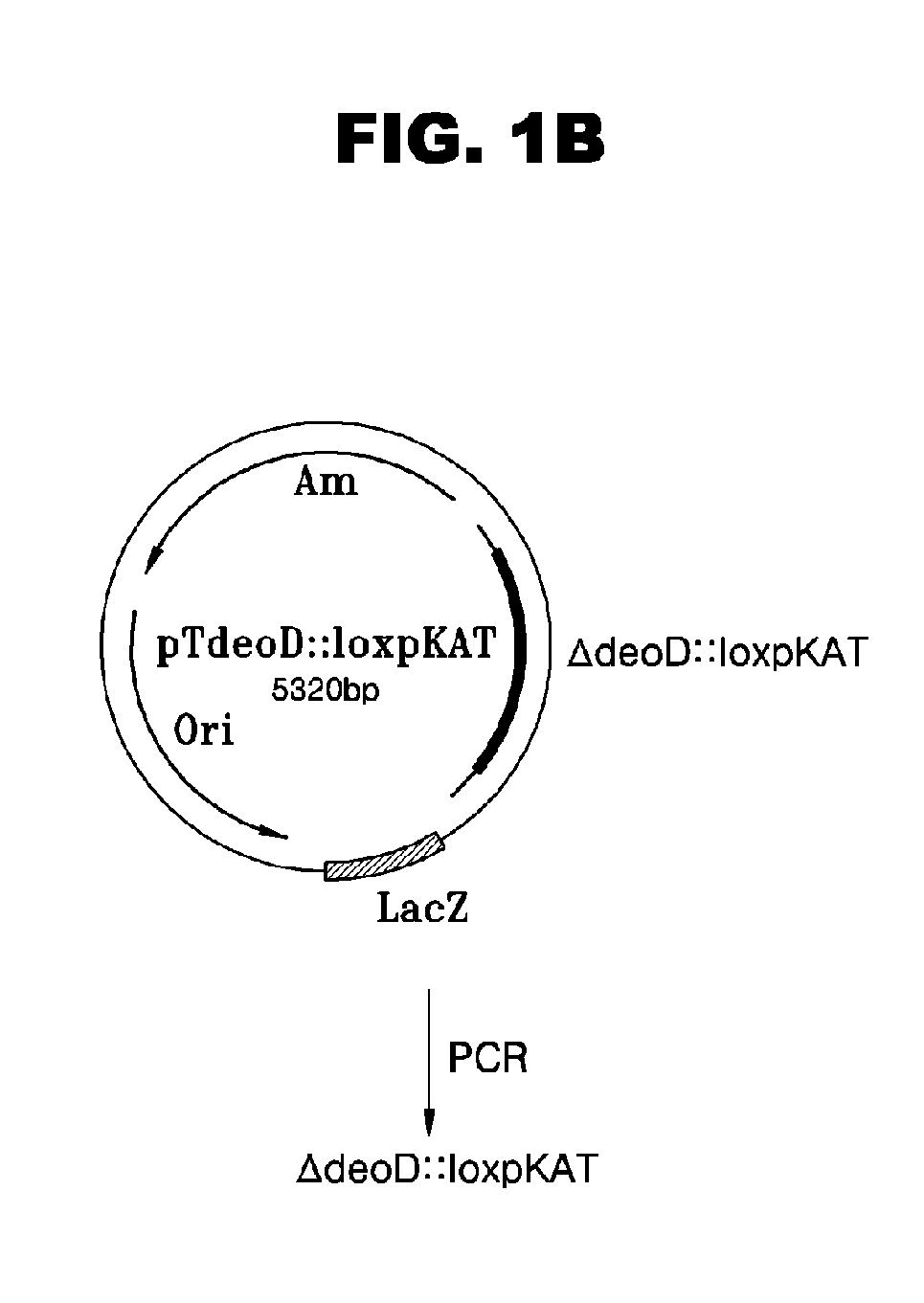
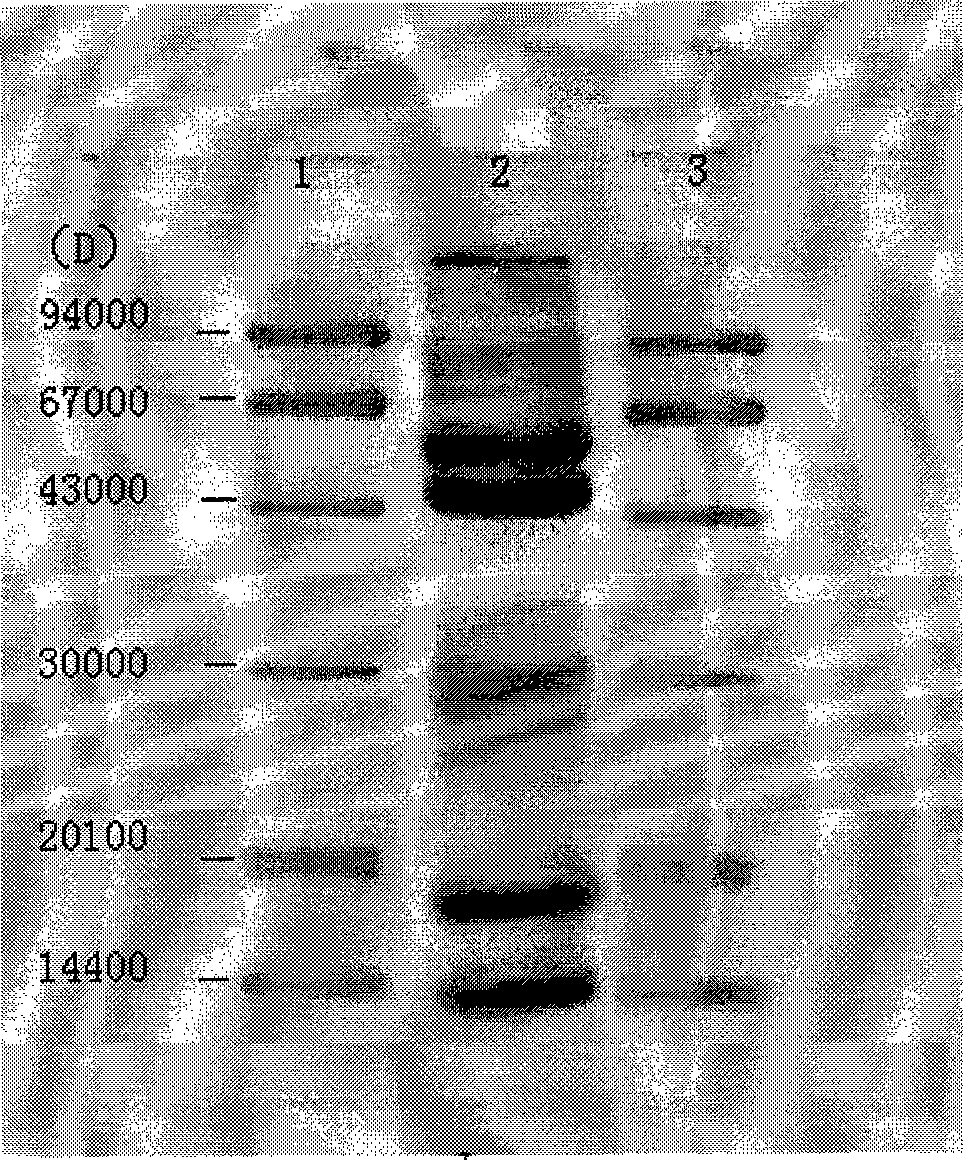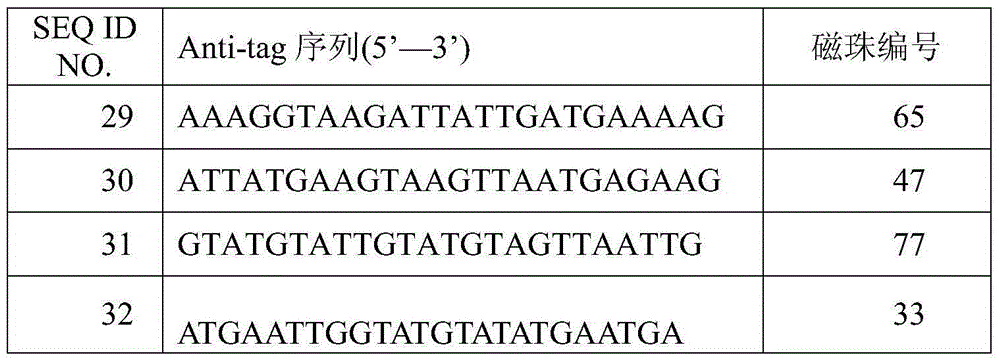Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Ehrlichia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ehrlichia is a genus of Rickettsiales bacteria that are transmitted to vertebrates by ticks. These bacteria cause the disease ehrlichiosis, which is considered zoonotic, because the main reservoirs for the disease are animals.
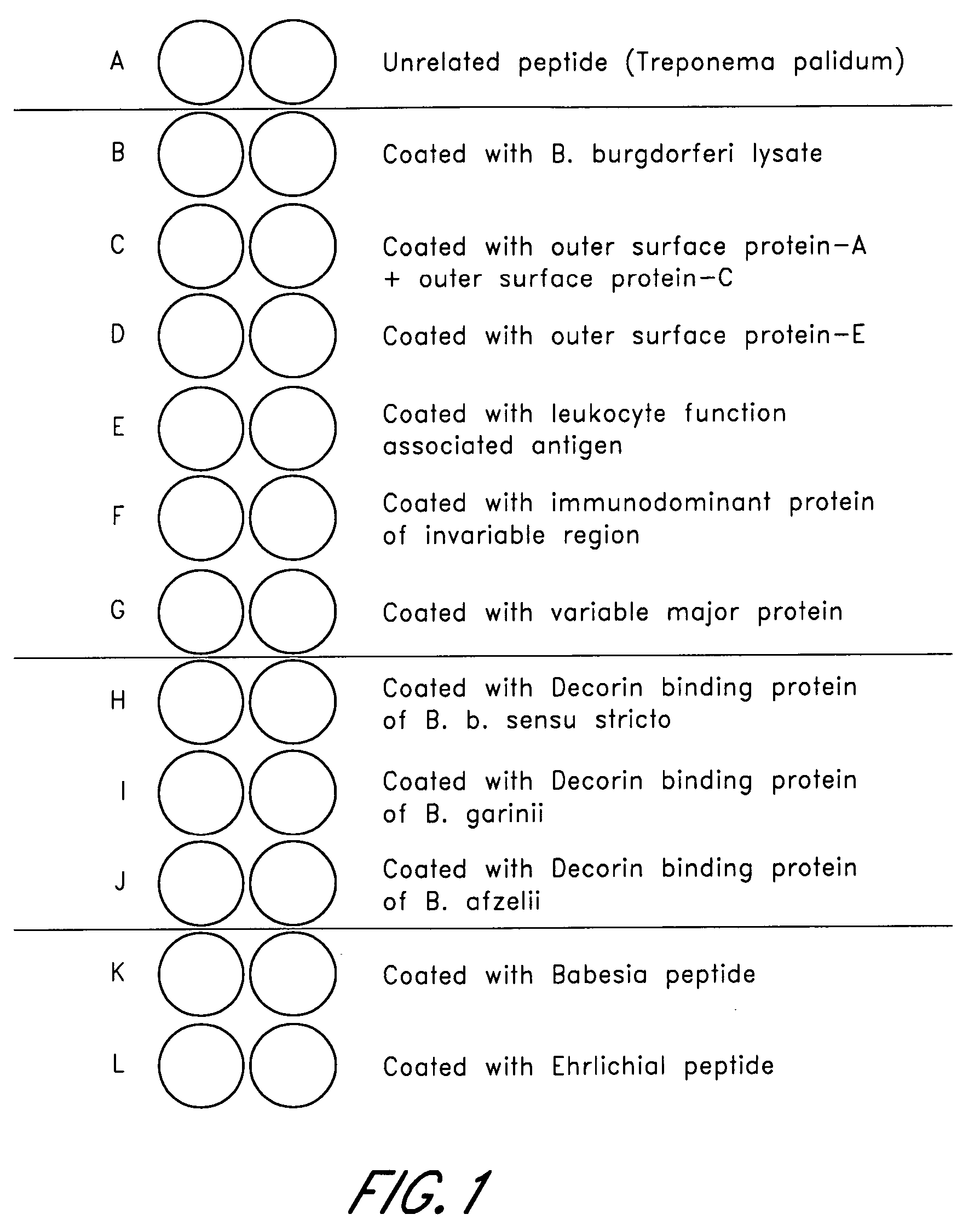
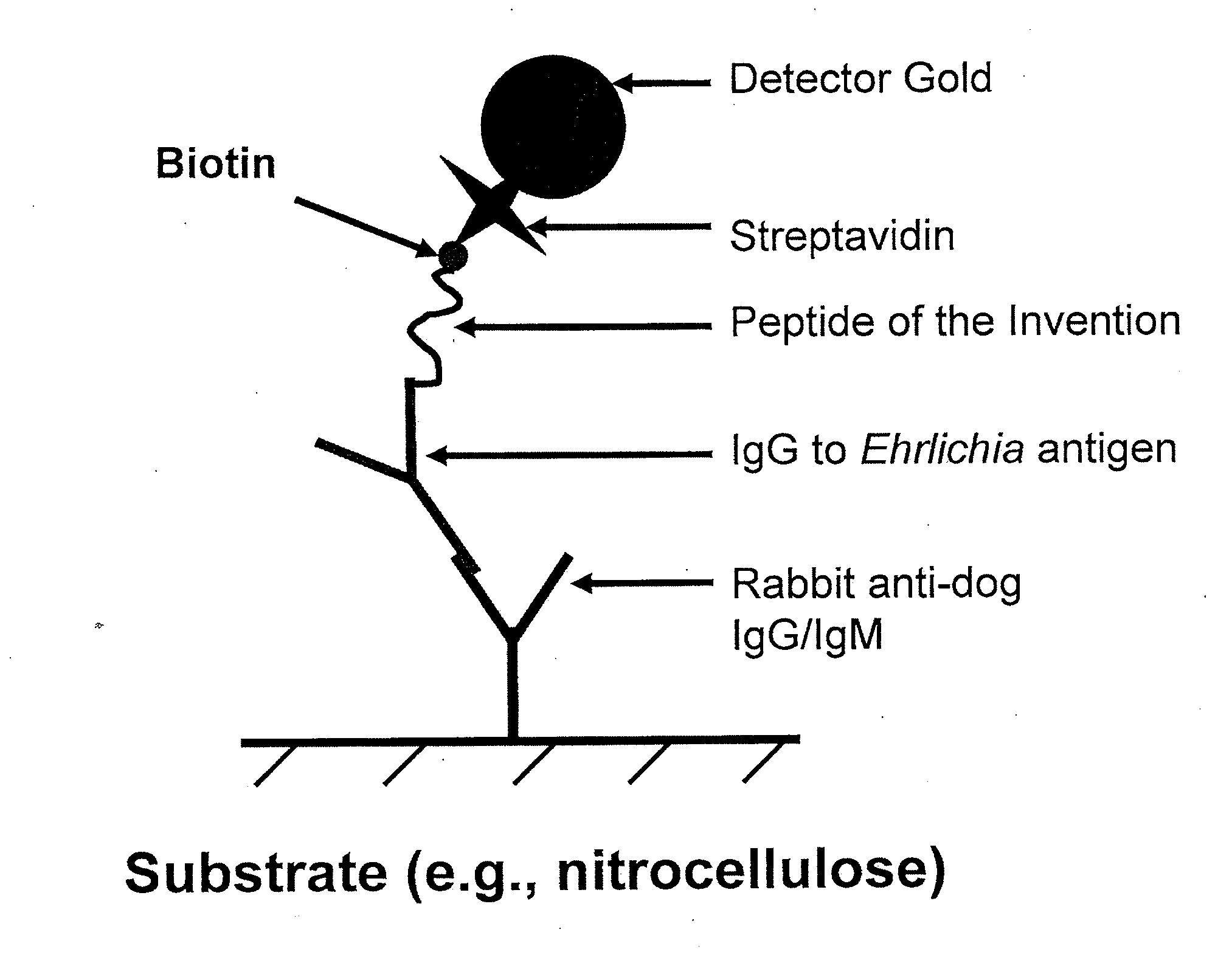
Peptides for detection of antibody to Anaplasma phagocytophilum
InactiveUS20050124015A1High sensitivityStrong specificityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody fragmentsAnaplasma phagocytophilum DNA
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
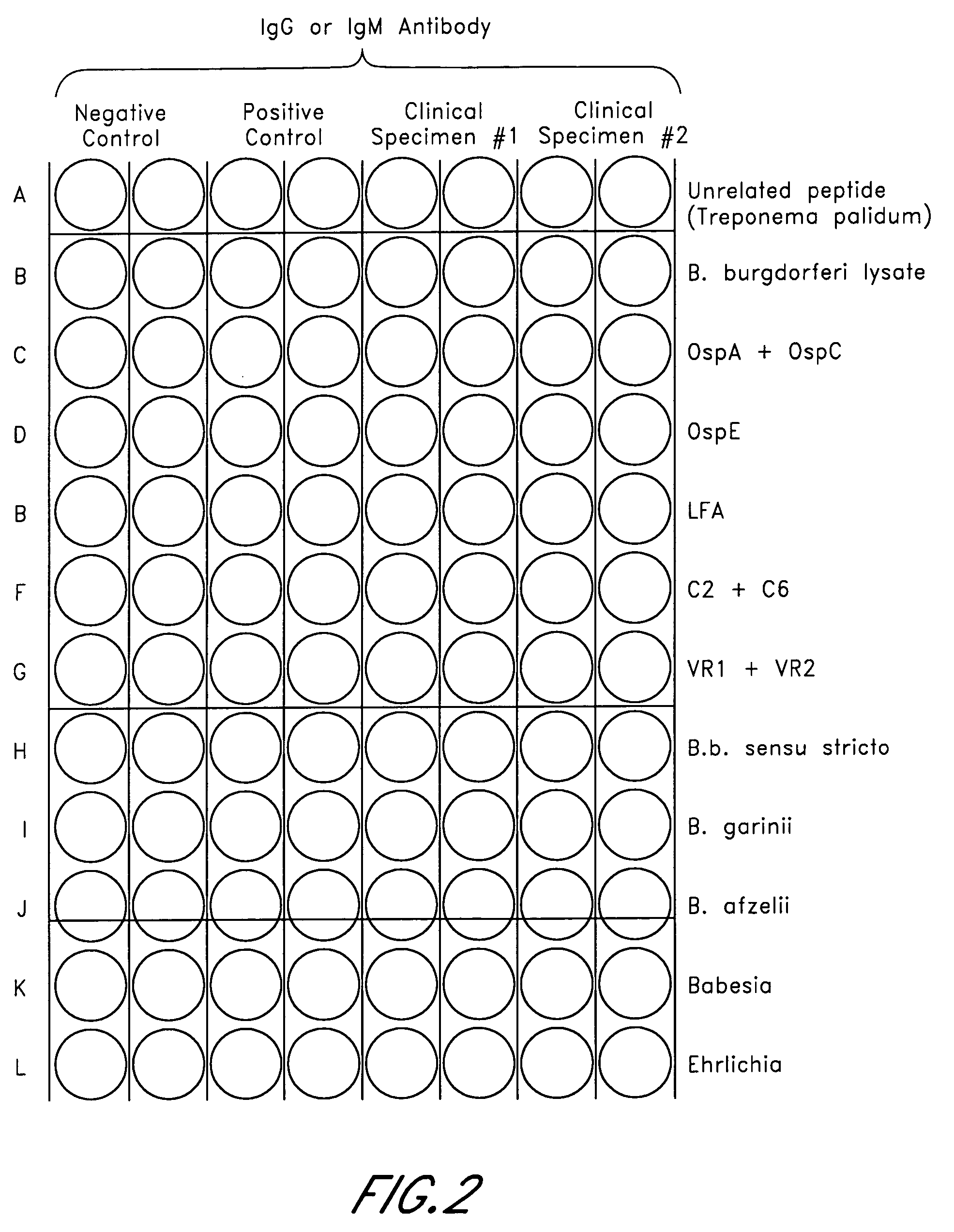
Peptides, devices, and methods for the detection of ehrlichia antibodies
ActiveUS20140121125A1Robust detectionUseful in detectionPeptide librariesLibrary screeningCell Membrane ProteinsMonocyte
The invention provides peptide compositions and mixtures useful for the detection of antibodies that bind to Ehrlichia antigens. The peptide compositions and mixtures comprise polypeptide sequences based on an immunogenic fragment of the Ehrlichia Outer Membrane Protein 1 (OMP-1) protein. The invention also provides devices, methods, and kits comprising such peptide compositions and mixtures useful for the detection of antibodies that bind to Ehrlichia antigens and the diagnosis of monocytic and / or granulocytic ehrlichiosis.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Peptides, devices, and methods for the detection of ehrlichia antibodies
ActiveUS8828675B2Simple and inexpensive and rapid and sensitive and accurate detectionAvoid serologic cross-reactivityPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisCell Membrane ProteinsMonocyte
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Methods and kit for diagnosing tick borne illnesses
InactiveUS7390626B2High sensitivityStrong specificitySamplingAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionDiseaseLeukocyte function
Owner:IMMUNOSCI LAB
Peptides, devices, and methods for the detection of ehrlichia antibodies
ActiveUS20140212898A1Simple inexpensive rapid sensitive accurate detectionAvoid serologic cross-reactivityCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesBiological testingMonocyteCell Membrane Proteins
The invention provides peptide compositions and mixtures useful for the detection of antibodies that bind to Ehrlichia antigens. The peptide compositions and mixtures comprise polypeptide sequences based on an immunogenic fragment of the Ehrlichia Outer Membrane Protein 1 (OMP-1) protein. The invention also provides devices, methods, and kits comprising such peptide compositions and mixtures useful for the detection of antibodies that bind to Ehrlichia antigens and the diagnosis of monocytic and / or granulocytic ehrlichiosis.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
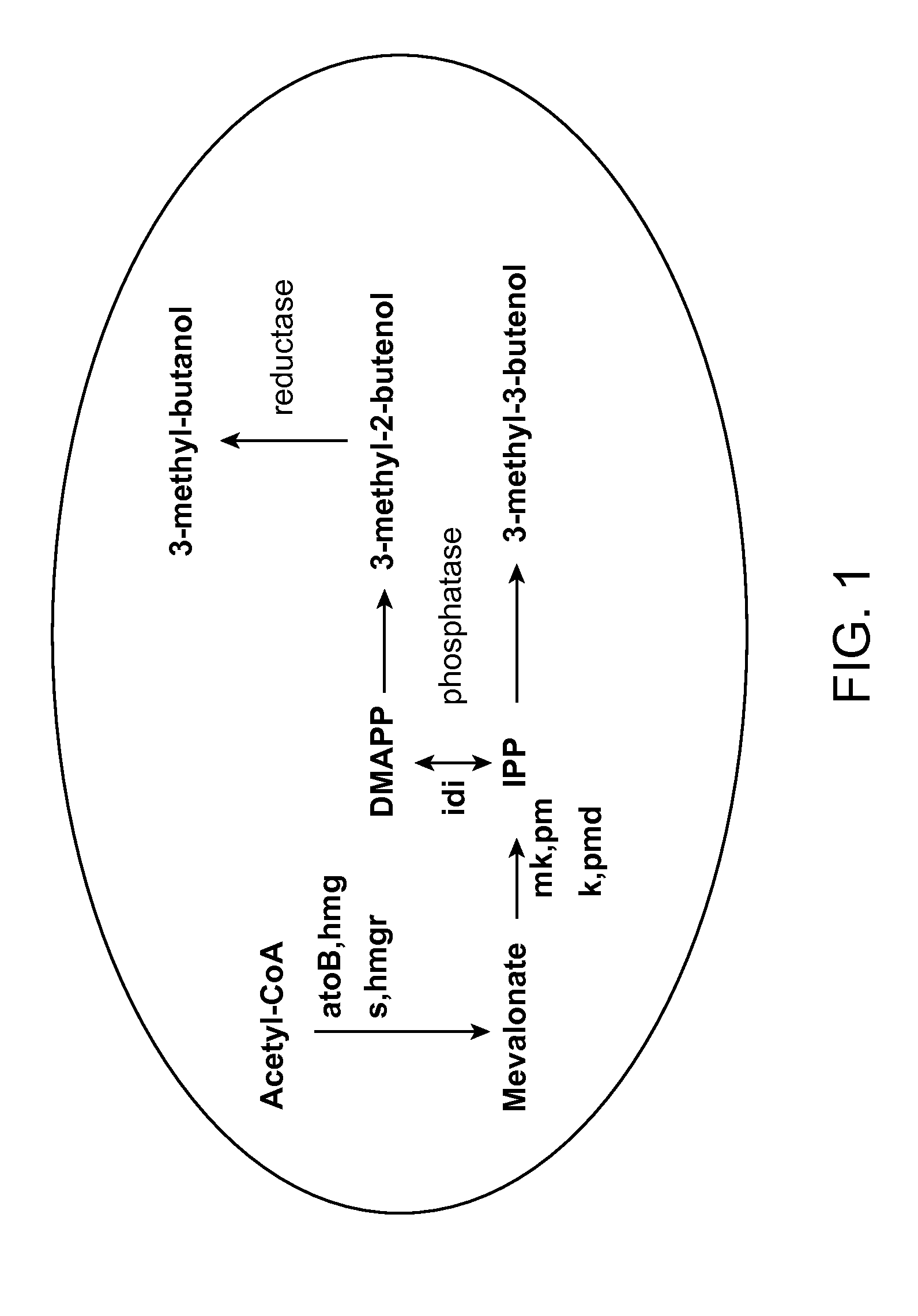
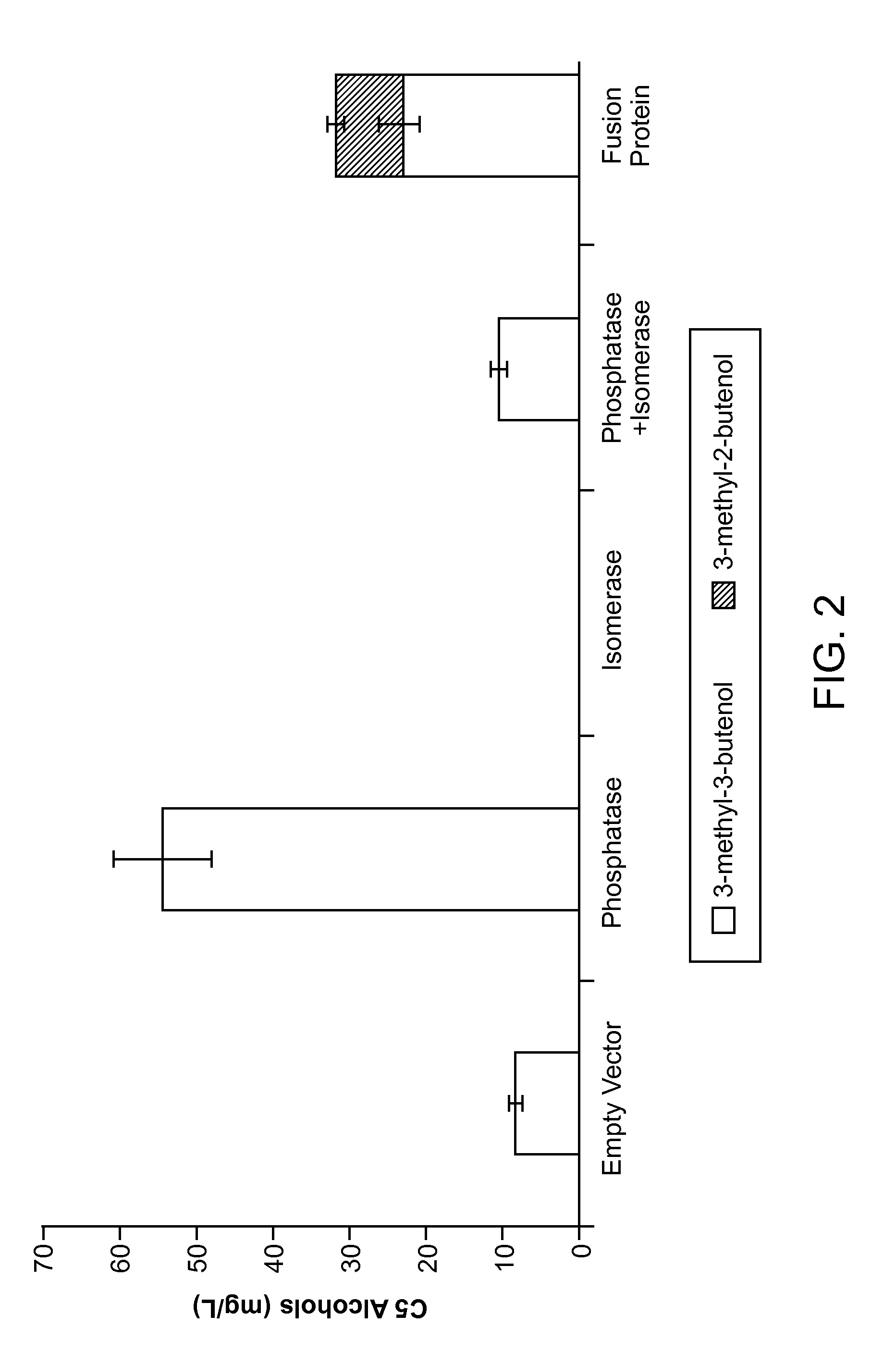
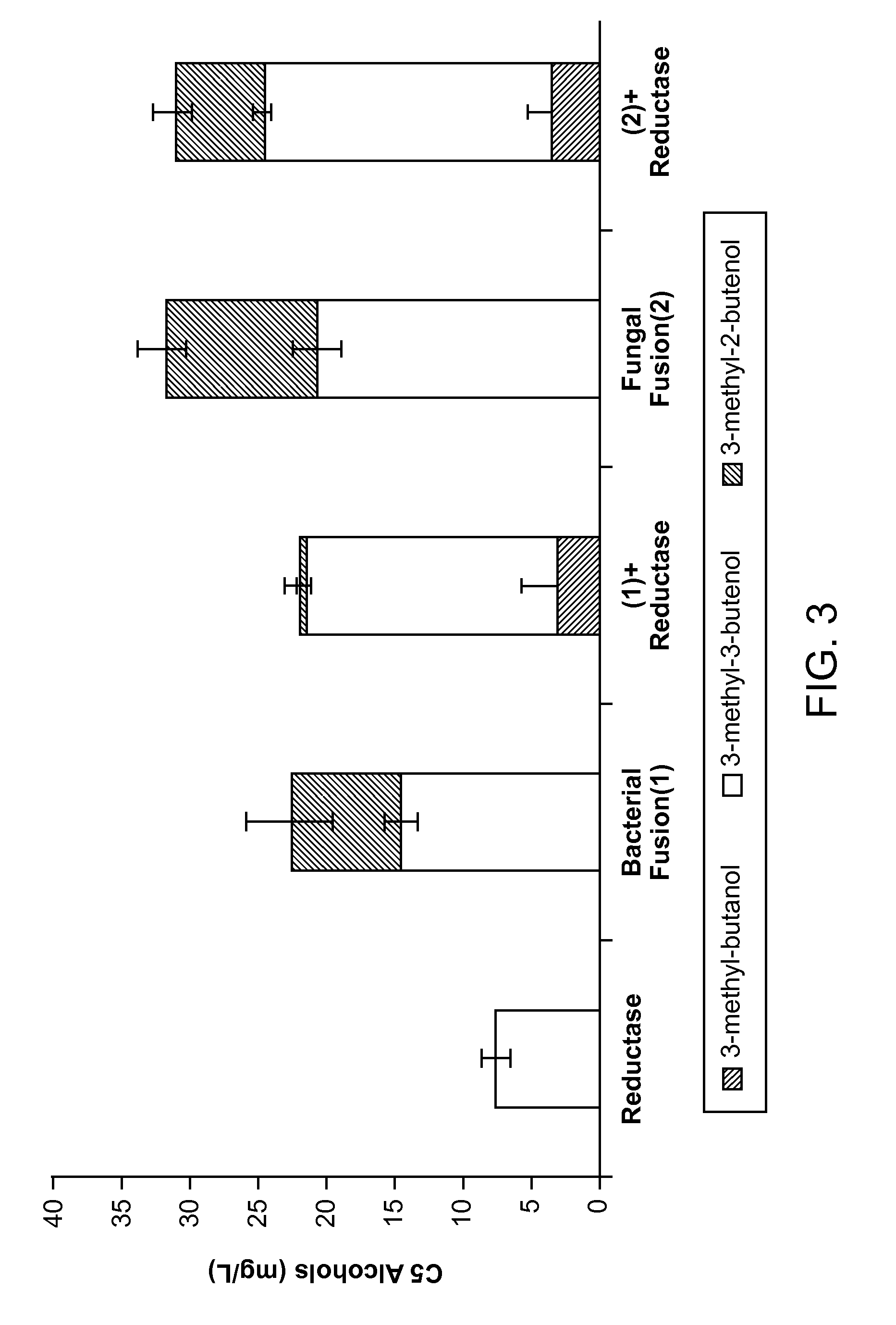
Methods for increasing production of 3-methyl-2-butenol using fusion proteins
The invention relates, in part, to nucleic acid constructs, genetically modified host cells and methods employing such constructs and host cells to increase the production of 3-methyl-2-butenol from IPP. Thus, in some aspects, the invention provides a genetically modified host cell transformed with a nucleic acid construct encoding a fusion protein comprising a phosphatase capable of catalyzing the dephosphorylation of dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) linked to an IPP isomerase capable of converting IPP to DMAPP, wherein the nucleic acid construct is operably linked to a promoter. In some embodiments, the genetically modified host cell 5 further comprises a nucleic acid encoding a reductase that is capable of converting 3-methyl-2-butenol to 3-methyl-butanol. In some embodiments, the reductase is encoded by a nucleic acid construct introduced into the cell. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is a Type I isomerase. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is a Type II isomerase. In some embodiments, the host cell is selected from a group of taxonimcal classes consisting of 20 Escherichia, Enterobacter, Azotobacter, Erwinia, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, Proteus, Salmonella, Serratia, Shigella, Rhizobia, Vitreoscilla, Synechococcus, Synechocystis, and Paracoccus taxonomical classes. In some embodiments, the host cell is an Escherichia coli cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is a fungal cell, such as a yeast cell. In some embodiments, the yeast cell is a Saccharomyces sp. cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is an algal, insect or mammalian cell line. In some embodiments, the phosphatase is nudB from E. coli. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is encoded by an idi gene from E. coli or idil gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Fluorescent quantitation PCR detection of Ehrlichia bacterium and typing primer, probe and kit
InactiveCN103060468AEfficient detectionEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPositive sampleFluorescence
The invention discloses a fluorescent quantitation PCR detection of Ehrlichia bacterium and a typing primer, a probe and a kit. The sequence of the primer is shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and 2; the probe is shown in SEQ ID No. 3 and 4. The primer and the probe are adopted to carry out the PCR amplification for the bacterium to be detected and amplify 210bp band, and the fluorescent detection enhanced in 640 nanometers wavelength is positive samples of Ehrlichia bacterium; and then the Ehrlichia bacterium are typed according to the melting temperature. The invention has obvious technical advantages, high specificity and high sensitiveness, can conveniently detect all kinds of Ehrlichia bacteria, can be used for diagnosing and treating human and various animals (cattle, dogs and sheep) and Ehrlichia chafeensis diseases, and has good economic benefits.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Gene recombinant vaccine for preventing enterovirus 71 infection and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a gene recombinant vaccine for preventing enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection and a preparation method thereof. The inflection comprises multiple diseases related with the nervous system such as hand-foot-and-mouth disease, paralytic diseases of sterile meningitis, cephalitis and poliomyelitis and the like. Escherichia coli labile enterotoxin B subunit (LTB) is used as an immunological enhancement adjuvant, two fragments of linear neutralizing epitope SP55 and SP70 in EV71 virus coat protein VP1 are used as antigens, prokaryotic expression plasmids of LTB-SP55-SP70 fusion genes are constructed by using gene engineering technology, the plasmids are expressed in escherichia coli, and a recombinant expression product is purified for preparing the EV71 virus gene engineering vaccine.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所 +1
Recombinant escherichia coli for expression of adenomethionine synthetase
ActiveCN101392230AHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliS-Adenosylmethionine Synthetase
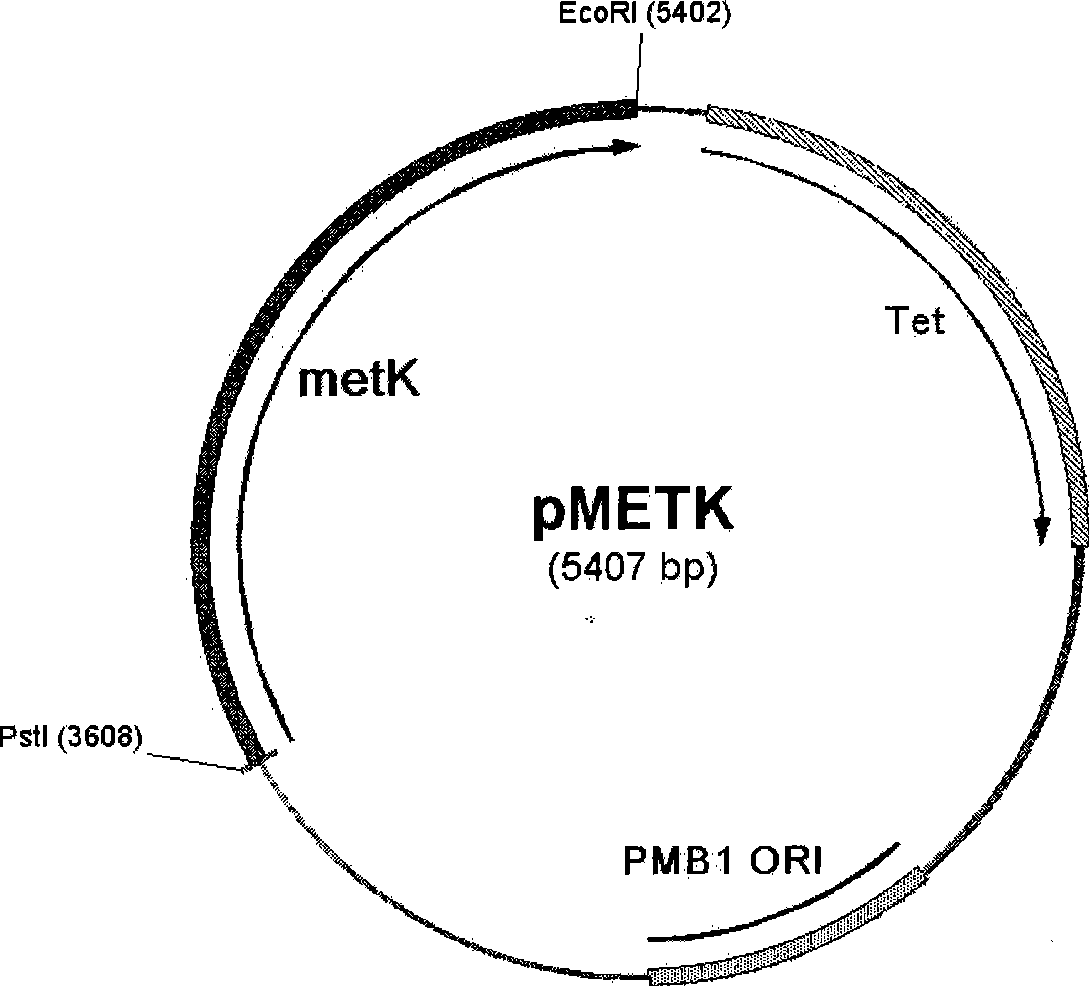
The invention provides a recomposed large intestine Escherichia coli expressing adenosine methionine synthetase with CGMCC No. 2299 and the composition method of the recomposed large intestine Escherichia coli. The invention further provides a recomposed expression carrier pMETK of adenosine methionine synthetase. In the recomposed large intestine Escherichia coli expressing adenosine methionine synthetase with CGMCC No. 2299, the expression quantity of the adenosine methionine synthetase accounts for 31.36 percent of soluble albumen of the strain, the activity of the adenosine methionine synthetase expressed is as high as 7.38U / ml, far higher than that of wild type strains.
Owner:BEIJING KAWIN TECH SHARE HLDG
Amplification primer for detecting food-borne pathogenic microorganisms and liquid chip kit
InactiveCN105316398AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImplement parallel detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerEscherichia coli
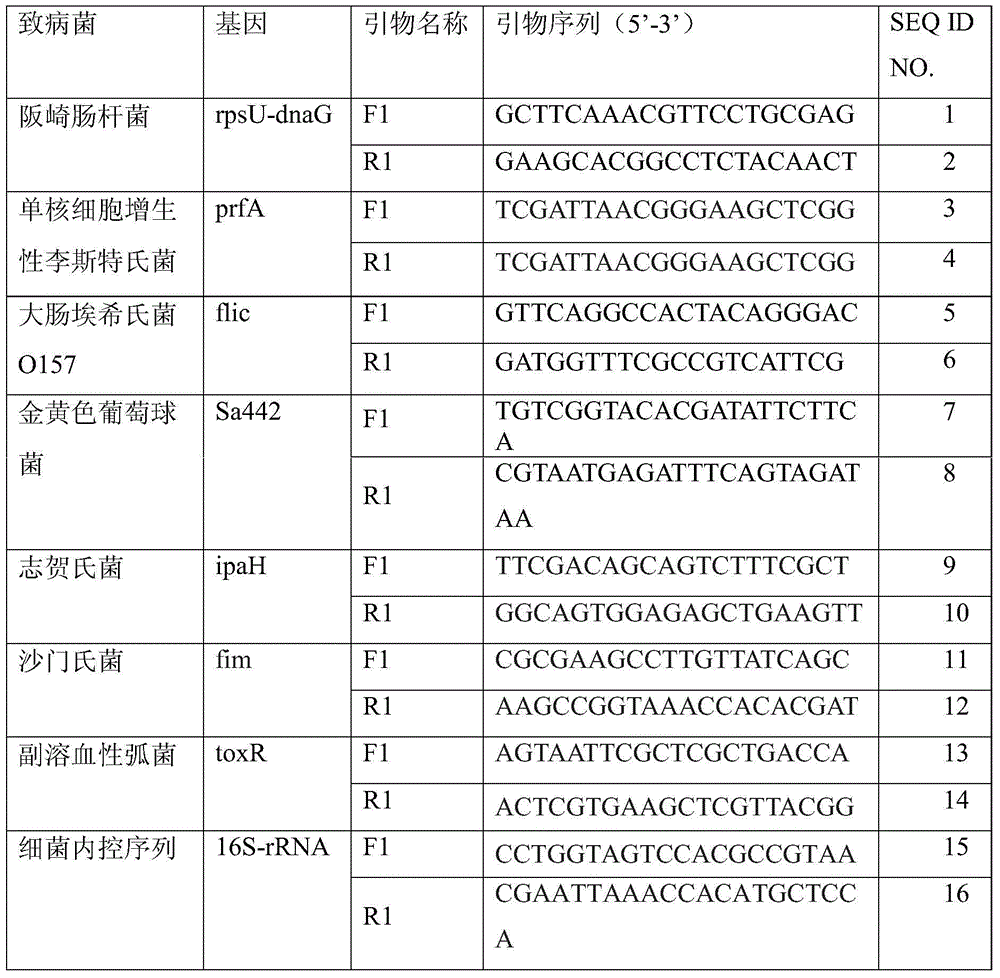
The invention discloses an amplification primer for detecting food-borne pathogenic microorganisms and a liquid chip kit. The kit comprises an amplification primer pair designed for microorganism genes to be detected; and a forward primer and a reverse primer of microorganisms to be detected comprise at least one pair of SEQ ID NO. 1 and SEQ ID NO. 2 for enterobacter sakazakii, SEQ ID NO. 3 and SEQ ID NO. 4 for monocyte listeria monocytogenes, SEQ ID NO. 5 and SEQ ID NO. 6 for escherichia coli O157, SEQ ID NO. 7 and SEQ ID NO. 8 for staphylococcus aureus, SEQ ID NO. 9 and SEQ ID NO. 10 for shigella, SEQ ID NO. 11 and SEQ ID NO. 12 for salmonella, and SEQ ID NO. 13 and SEQ ID NO. 14 for vibrio parahaemolyticus, and magnetic beads coated with Anti-tag sequences. The amplification primer designed by the invention has excellent specificity, and can accurately distinguish and specifically amplify gene segments corresponding to various target detection pathogenic microorganisms. In addition, the sensibility of the detecting kit designed by the invention is greatly improved. An experiment result shows that sensibility of detection of seven food-borne pathogenic microorganisms can reach 10 CFU / mL.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Construction and applications of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide auxotroph escherichia coli
InactiveCN102925398ACapable of transmembrane transportIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousEscherichia coli
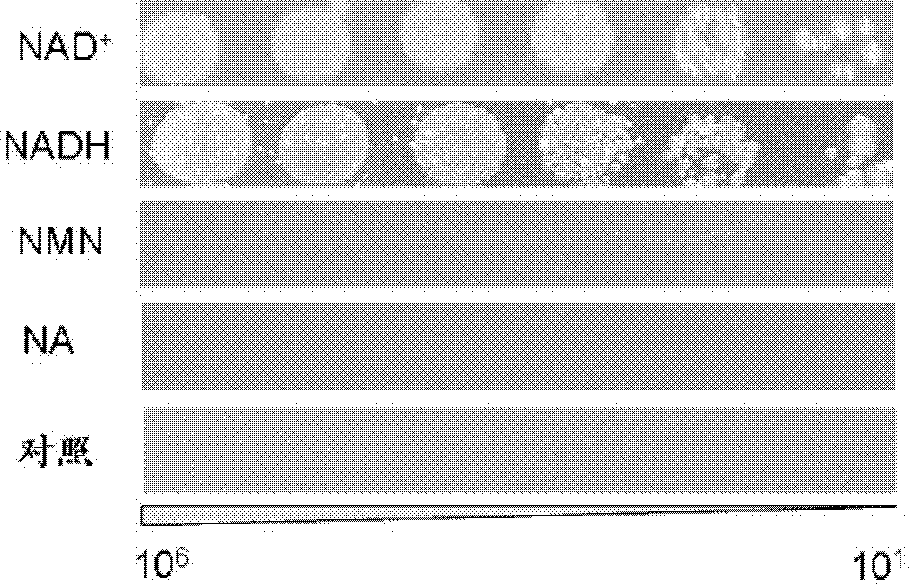
The present invention discloses construction and applications of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) auxotrophic Escherichia microbe, wherein NAD transporter protein is introduced to the Escherichia microbe, an intracellular NAD biosynthesis pathway is blocked, and the Escherichia engineered bacteria growing dependent on exogenous pyridine nucleotide coenzyme is constructed. The NAD auxotrophic Escherichia can be used in the field of bio-technology, and can be provided for screening inhibition drugs for pyridine nucleotide coenzyme metabolism, improving oxidation reduction biotransformation efficiency, and establishing non-antibiotic screening platforms for gene cloning and protein heterogenesis expression.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microorganism of Escherichia Sp, or Corynebacterium Sp, Comprising Foreign Nadp Dependent Glyceraldehyde-3-Phospate Dehydrogenase Gene and Method For Prodicing L-Lysine Using the Same
InactiveUS20080138882A1Improve productivityBacteriaSugar derivativesEscherichia coliCorynebacterium efficiens
Provided are an Escherichia species microorganism and Corynebacterium species microorganism that are transformed with a foreign NADP dependent glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and have the ability to produce L-lysine and a method of producing L-lysine using the microorganisms.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Peptides, devices, and methods for the detection of ehrlichia antibodies
ActiveUS20150024417A1Simple and inexpensive and rapid and sensitive and accurate detectionAvoid serologic cross-reactivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMonocyteCell Membrane Proteins
The invention provides compositions (e.g., peptide compositions) useful for the detection of antibodies that bind to Ehrlichia antigens. The peptide compositions comprise polypeptide sequences based on an immunogenic fragment of the Ehrlichia Outer Membrane Protein 1 (OMP-1) protein. The invention also provides devices, methods, and kits comprising such peptide compositions and useful for the detection of antibodies that bind to Ehrlichia antigens and the diagnosis of monocytic ehrlichiosis.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Treatment for leukemia and idiopathic aplastic anemia
A process for treating a patient with leukemia or an aplastic anemia having cells with inclusions that stain with anti-E. canis antibodies or antibodies to other Ehrlichia or Anaplasma is disclosed. That process comprises administering to the patient (i) an antibacterial amount of a rifamycin, (ii) an antibacterial amount of a quinolone, or a mixture of (i) and (ii).
Owner:SPHINGOMONAS RES PARTNERS
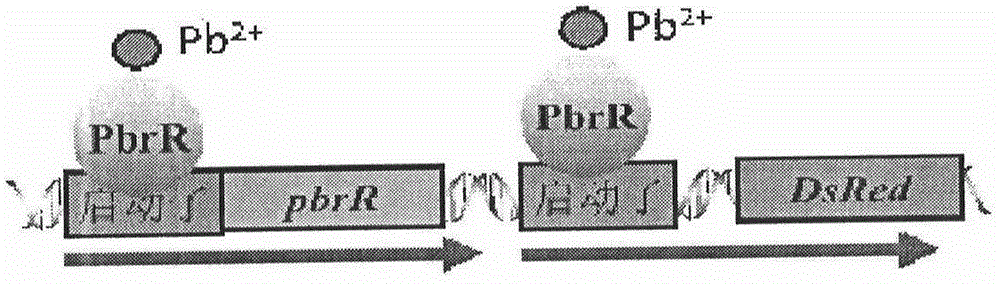
Escherichia coli for detecting lead
ActiveCN104805048AHigh sensitivityOvercome operabilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliLarge intestine
Escherichia coli for detecting lead is disclosed. Escherichia coli for detecting lead is disclosed. The invention provides a construction method of an escherichia coli engineered strain for detecting heavy metal lead and establishment of a method for detecting lead in a water body. The gene engineering strain is PpbrA-pbrR-PpbrA::DsRed-express2 / E.coli delta zntR delta zntA, named as E.coli WMC-008p CGMCC No.9748, wherein zntA and zntR genes undergo deletion mutation so as to be inactivated, and a pbr operon originated from a Cupriavidus metallidurans CH34 strain is knocked-in to express the red fluorescence protein DsRed-express2. In comparison with a reporter plasmid-containing E. coli reporter strain, the engineering strain provided by the invention has advantages of simple operation, low fluorescence background value, stable signal and the like. The engineering strain can reflect bio-availability of lead in a water body and provides a basis for objective evaluation of bio-toxicity effects of lead in a water body.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
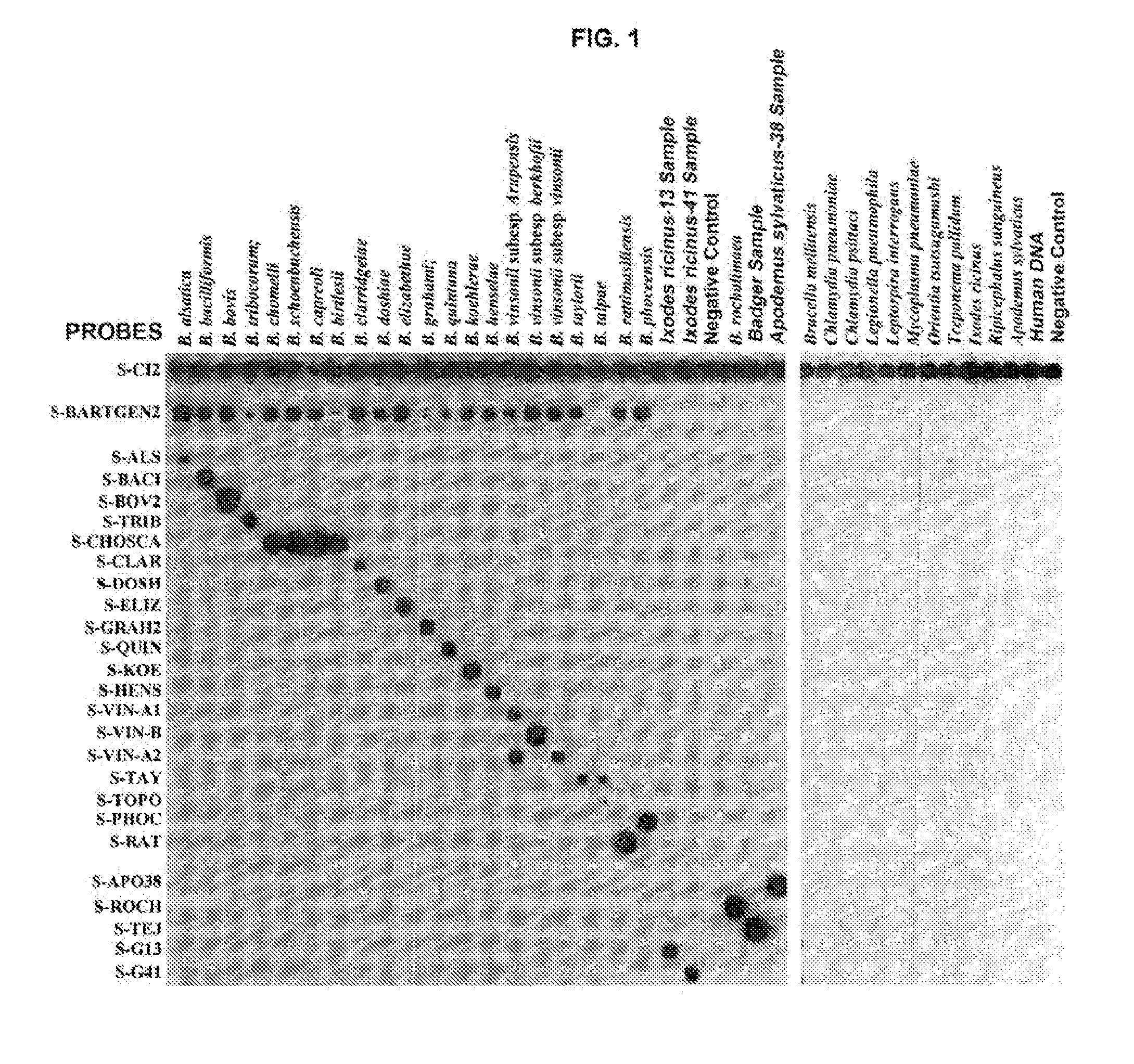
Method for the detection of bacterial species of the genera anaplasma/ehrlichia and bartonella
The present invention relates to a method for the detection and identification of bacterial species belonging to the genera Anaplasma / Ehrlichia and Bartonella, and also provides triggers and probes required for its application, as well as associated kits.
Owner:INST DE SALUD CARLOS III
Characterization of granulocytic Ehrlichia and methods of use
The present invention relates, in general, to granulocytic ehrlichia (GE) proteins. In particular, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules coding for GE S2, S7, S22, S23, C6.1, C6.2, S11, E8, E46#1, and E46#2 proteins; purified GE S2, S7, S22, S23, C6.1, C6.2, S11, E8, E46#1, and E46#2 proteins and polypeptides; recombinant nucleic acid molecules; cells containing the recombinant nucleic acid molecules; antibodies having binding affinity specifically to GE S2, S7, S22, S23, C6.1, C6.2, S11, E8, E46#1, and E46#2 proteins and polypeptides; hybridomas containing the antibodies; nucleic acid probes for the detection of nucleic acids encoding GE S2, S7, S22, S23, C6.1, C6.2, S11, E8, E46#1, and E46#2 proteins; a method of detecting nucleic acids encoding GE S2, S7, S22, S23, C6.1, C6.2, S11, E8, E46#1, and E46#2 proteins or polypeptides in a sample; kits containing nucleic acid probes or antibodies; bioassays using the nucleic acid sequence, protein or antibodies of this invention to diagnose, assess, or prognose a mammal afflicted with ehrlichiosis; therapeutic uses, specifically vaccines comprising S2, S7, S22, S23, C6.1, C6.2, S11, E8, E46#1, and E46#2 proteins or polypeptides or nucleic acids; and methods of preventing or inhibiting ehrlichiosis in an animal.
Owner:ANTIGENICS
Nontoxic killer of E. coli and other problem microorganisms
The present invention provide a composition of non-toxic low-cost ingredients that effectively kill pathologic bacteria and methods for use of the composition. The present invention comprises novel compositions and methods for controlling enteric pathogens and spoilage organisms such as Salmonella, Escherichia, Campylobacter, Listeria, Pseudomonas and Enterobacteracae on the surface of meat products and food preparation surfaces.
Owner:MARVEL TECH USA
Inactivated vaccine for poultry pathogenic escherichia coli and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104774796AAvoid infectionOptimal immune doseAntibacterial agentsBacteriaESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENSerum ige
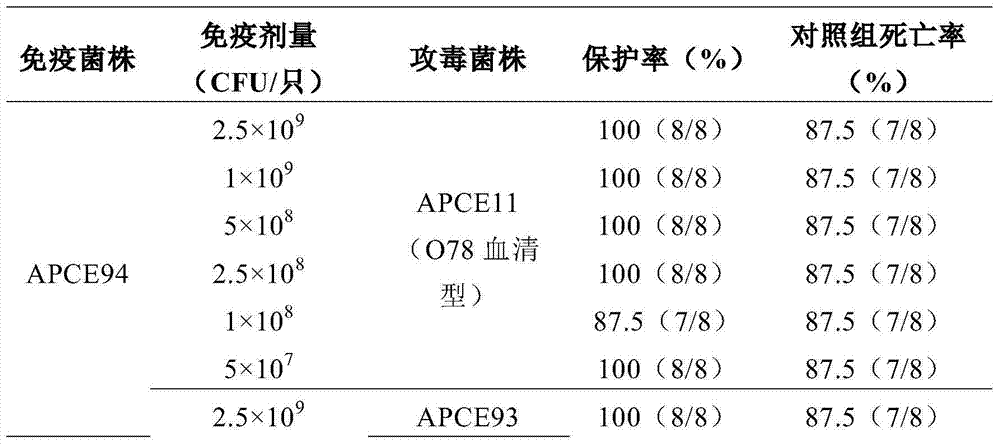
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention provides poultry pathogenic escherichia coli strain, the strain is Escherichia coli, and the preservation number is CGMCC 10602. The invention further provides inactivated vaccine for the poultry pathogenic escherichia coli, and the inactivated vaccine for the poultry pathogenic escherichia coli is O 78 serotype poultry escherichia coli inactivate whole bacterial and adjuvant. The immune protective rates of the inactivated vaccine for the poultry pathogenic escherichia coli to the serotype O78 poultry pathogenic escherichia coli virulent strain challenge all reach over 90 percents. The inactivated vaccine for the poultry pathogenic escherichia coli has great immune protective effect on the O 78 serotype poultry escherichia coli strain infection.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Escherichia coli for arsenic detection
ActiveCN104894042AReduce the background valueHigh background valueBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliFluorescence
The invention relates to a microorganism method for detecting metallic-arsenic-like in water, in particular to an escherichia coli report bacterial strain culturing method improved through genetic engineering, and an escherichia coli culturing method for detecting arsenic in water. The detection bacterial strain is obtained by adopting a Red recombination system to knockout arsenic resistant arsB genes of wild type escherichia coli MC4100, and then adopting the gene knockin technology to substitute pars-arsR-gfpmut2 report genes to the positions of araB coding genes. The biological detection bacterial strain is named as E.coli WMC-011p. The lowest arsenic detection range meets the Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard of GB8978-1996. The bacterial strain overcomes the shortcomings of high fluorescence background value, unstable detection signals, inaccurate results and the like of a biological detection bacterial strain based on a plasmid vector, and has the advantages of high specificity, high sensitivity, low cost and the like.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Microorganism of Escherichia Sp, or Corynebacterium Sp, comprising foreign NADP dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and method for producing L-lysine using the same
InactiveUS7566553B2Improve productivitySugar derivativesBacteriaCorynebacterium efficiensGlyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Gene
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
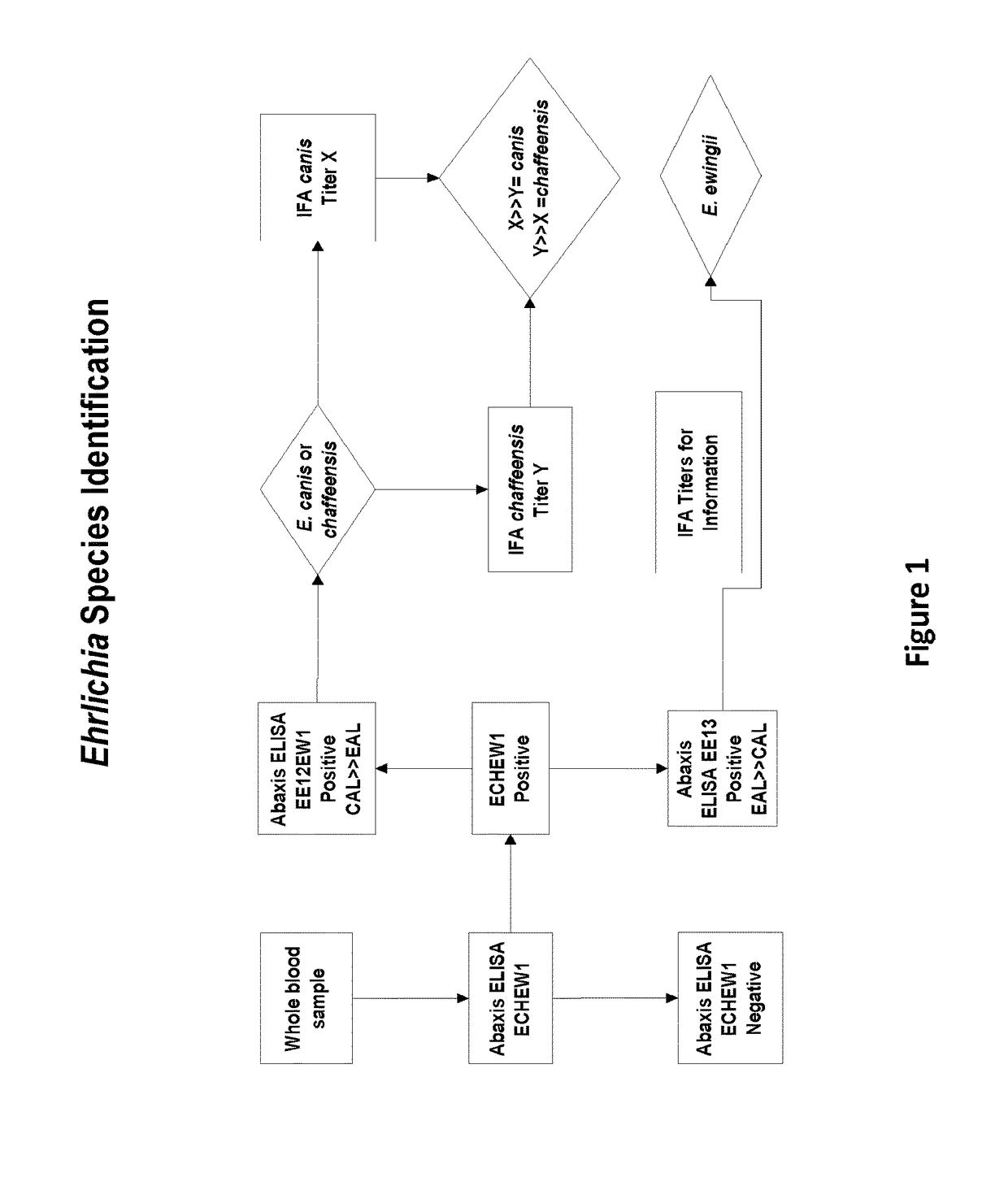
Compositions and methods for identifying Ehrlichia species
The invention provides methods, kits, compositions, and devices useful for detection of antibodies that bind to Ehrlichia antigens and / or for differentiation of certain Ehrlichia species from others. In particular, the invention provides methods and kits useful for identifying species of Ehrlichia using populations of isolated peptides.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Method of diagnosing and treating Ehrlichia
ActiveUS20110117130A1Induce network cross reactivityEnhanced antibodyAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPositive reactionAmino acid
The present invention provides an isolated and purified heat shock protein 60 (Hsp60) peptide having the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:2. The instant invention is also directed to a vaccine against Ehrlichia comprising a peptide homologous to the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:2. The instant invention is also directed to an antibody directed against a peptide homologous to the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:2. The instant invention is also directed to a method of determining whether a subject is infected with Ehrlichia, comprising the steps of: contacting a sample from a subject with the antibody described herein; and detecting a resulting antibody reaction, wherein a positive reaction indicates the subject is infected with Ehrlichia.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF TEXAS SYST THE
Escherichia Strain Capable of Converting Xmp to Gmp and Maintaining the Inactivated State of Gene(s) Associated with Gmp Degradation and Methods of Using the Same
ActiveUS20080299620A1Avoid difficult choicesReduced activityBacteriaHydrolasesGMP degradationMicrobiology
Provided are mutant strains derived from Escherichia sp. GPU1114 (Accession No. KCCM-10536), having cumulative inactivation of deoD, aphA, appA, and hprt genes, and methods of using the same.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
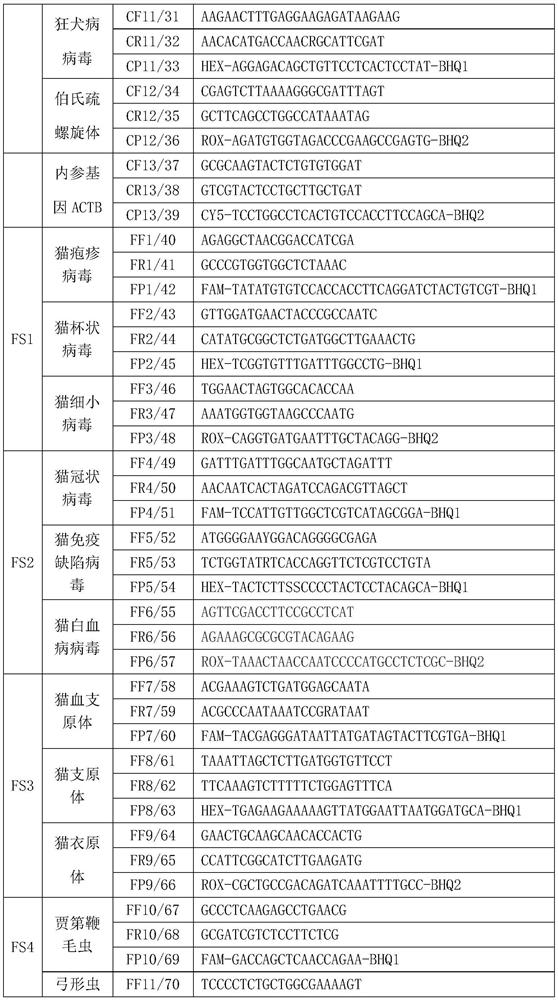
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for cat and/or dog pathogens, detection method and application
PendingCN114277189AShorten detection timeSave human resourcesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFeline parvovirusLeucosis
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biomedicine, in particular to a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for cat and / or dog pathogens, a detection method and application. The kit is used for detecting canine distemper virus, canine influenza A virus, canine parainfluenza virus, canine parvovirus, canine coronavirus, canine rotavirus, canine babesia, canine ascaris, canine Ehrlichia, canine brucella, rabies virus, borrelia burgdorferi, reference gene ACTB, feline herpes virus, feline calicivirus and feline parvovirus. The kit comprises primers and probes of feline coronavirus, feline immunodeficiency virus, feline leukemia virus, feline mycoplasma, feline mycoplasma, feline chlamydia, giardia, toxoplasma, bartonella and reference gene GAPDH, collected DNA and RNA are added into the kit, a real-time fluorescence PCR instrument is adopted for PCR reaction, FAM, HEX, ROX and CY5 fluorescence signals are collected in each cycle, analysis of related pathogens is carried out, and the kit can be used for detecting the feline and the canine. Compared with a traditional detection method, the method has the advantages of higher specificity and higher sensitivity.
Owner:北京迈基诺基因科技股份有限公司
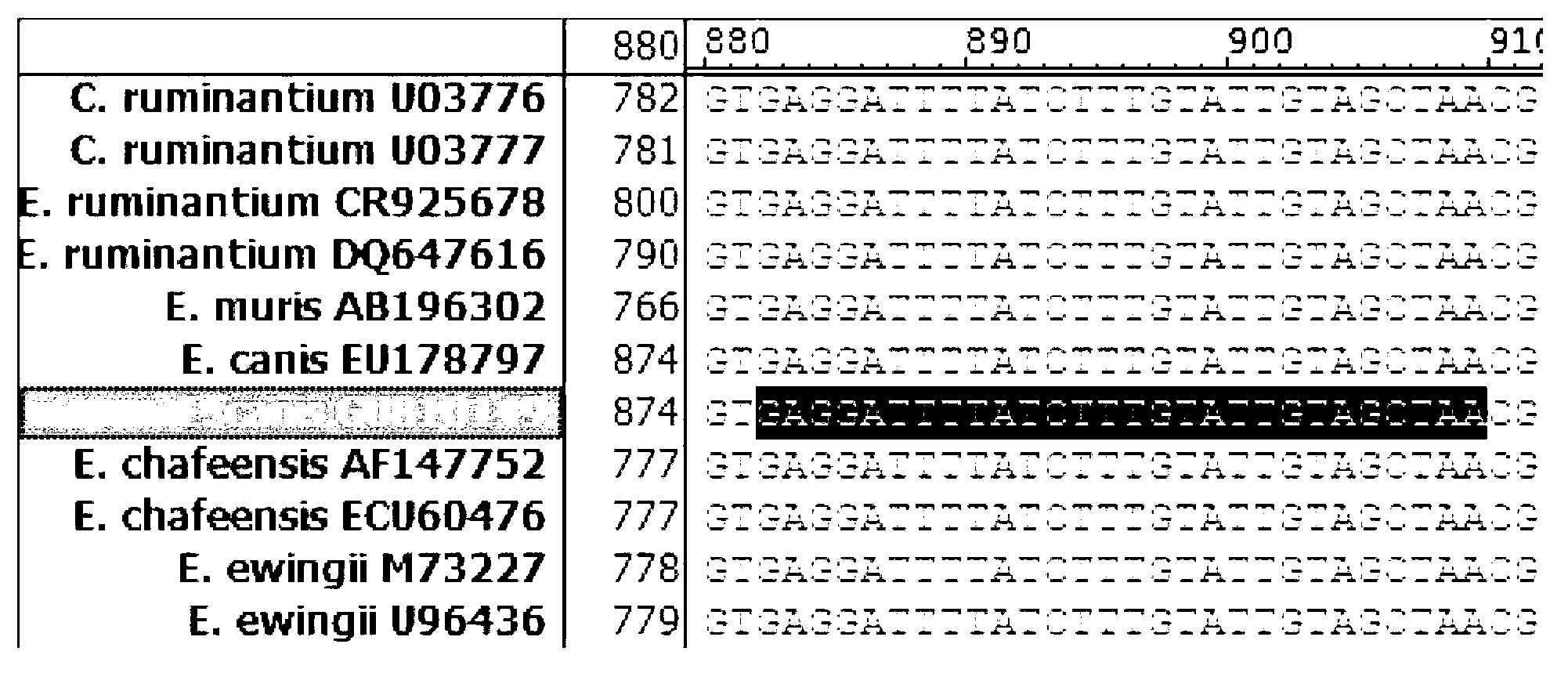
Methods for detecting Ehrlichia canis and Ehrlichia chaffensis in vertebrate and invertebrate hosts
Tools and methods for detecting the presence of E. canis and E. chaffeensis in a sample obtained from an animal are provided. The methods employ a polymerase chain reaction and primer sets that are based on the p30 gene of E. canis and the p28 gene of E. chaffeensis. The present invention also relates to the p30 and the p28 primer sets. Each p30 primer set comprises a first primer and the second primer, both of which are from 15 to 35 nucleotides in length. The first p30 primer comprises a sequence which is complementary to a consecutive sequence, within the following sequence: CCA AGTGTCTCAC ATTTTGGTAG CTTCTCAGCT AAAGAAGAAA GCAAATCAAC TGTTGGAGTTTTTGGATTAA AACATGATTG GGATGGAAGT CCAATACTTA AGAATAAACA CGCTGACTTTACTGTTCCAA AC. SEQ ID NO.1. The second p30 primer comprises a sequence which is complementary to the inverse complement of a consecutive sequence contained within the following sequence: GTTACT CAATGGGTGG CCCAAGAATA GAATTCGAAA TATCTTATGA AGCATTCGAC GTAAAAAGTC CTAATATCAA TTATCAAAAT GACGCGCACA GGTACTGCGC TCTATCTCAT CACACATCGG CAGCCAT, SEQ ID NO.2. The first p28 comprises a sequence which is complementary to a consecutive sequenc, within the following sequence: A GTTTTCATAA CAAGTGCATT GATATCACTA ATATCTTCTC TACCTGGAGT ATCATTTTCC GACCCAACAG GTAGTGGTAT TAACGG, SEQ ID NO. 3. The second p28 primercomprises a sequence which is complementary to the inverse complement of a consecutive sequencewithin one of the following two sequences: CAT TTCTAGGTTT TGCAGGAGCT ATTGGCTACT CAATGGATGG TCCAAGAATA GAGCTTGAAG TATCTTATGA, SEQ ID NO. 4, or C AAGGAAAGTT AGGTTTAAGC TACTCTATAA GCCCAGA, SEQ ID NO. 5.
Owner:STICH ROGER +1
Treatment for leukemia and idiopathic aplastic anemia
A process for treating a patient with leukemia or an aplastic anemia having cells with inclusions that stain with anti-E. canis antibodies or antibodies to other Ehrlichia or Anaplasma is disclosed. That process comprises administering to the patient (i) an antibacterial amount of a rifamycin, (ii) an antibacterial amount of a quinolone, or a mixture of (i) and (ii).
Owner:SPHINGOMONAS RES PARTNERS
Recombinant microorganisms of Escherichia with L-threonine productivity and method of producing L-threonine using the same
The present invention relates to an E. coli mutant strain having enhanced L-threonine productivity, which is obtained by introducing the permease of Corynebacterium origin, and to method of producing L-threonine using the E. coli mutant strain.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Compositions of and method of using heat shock protein peptides
The present invention provides an isolated and purified heat shock protein 60 (Hsp60) peptide having the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:2. The instant invention is also directed to a vaccine against Ehrlichia comprising a peptide homologous to the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:2. The instant invention is also directed to an antibody directed against a peptide homologous to the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:2. The instant invention is also directed to a method of determining whether a subject is infected with Ehrlichia, comprising the steps of: contacting a sample from a subject with the antibody described herein; and detecting a resulting antibody reaction, wherein a positive reaction indicates the subject is infected with Ehrlichia.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Recombinant escherichia coli for expression of adenomethionine synthetase
ActiveCN101392230BHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliS-Adenosylmethionine Synthetase
The invention provides a recomposed large intestine Escherichia coli expressing adenosine methionine synthetase with CGMCC No. 2299 and the composition method of the recomposed large intestine Escherichia coli. The invention further provides a recomposed expression carrier pMETK of adenosine methionine synthetase. In the recomposed large intestine Escherichia coli expressing adenosine methionine synthetase with CGMCC No. 2299, the expression quantity of the adenosine methionine synthetase accounts for 31.36 percent of soluble albumen of the strain, the activity of the adenosine methionine synthetase expressed is as high as 7.38U / ml, far higher than that of wild type strains.
Owner:BEIJING KAWIN TECH SHARE HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com