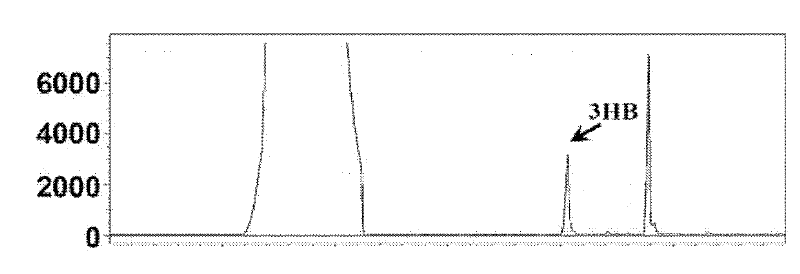
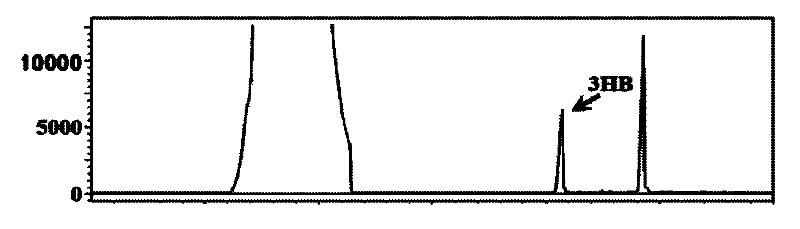
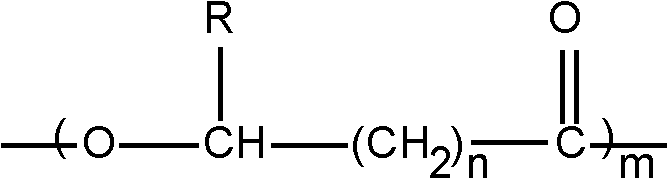
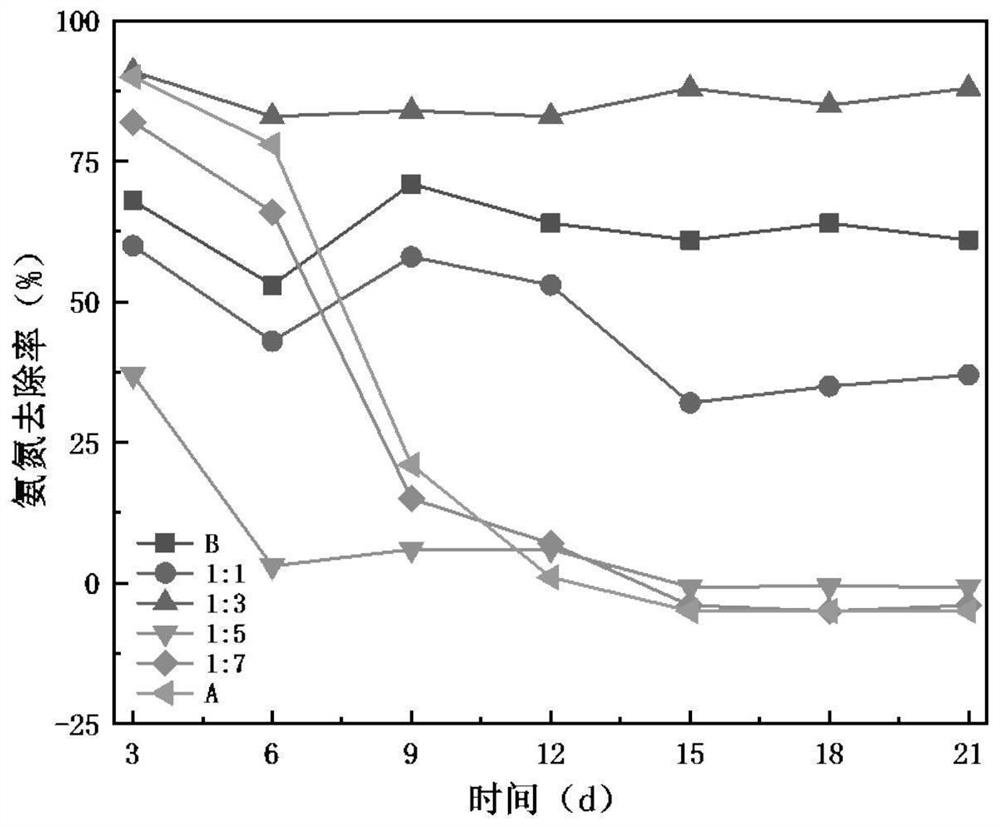
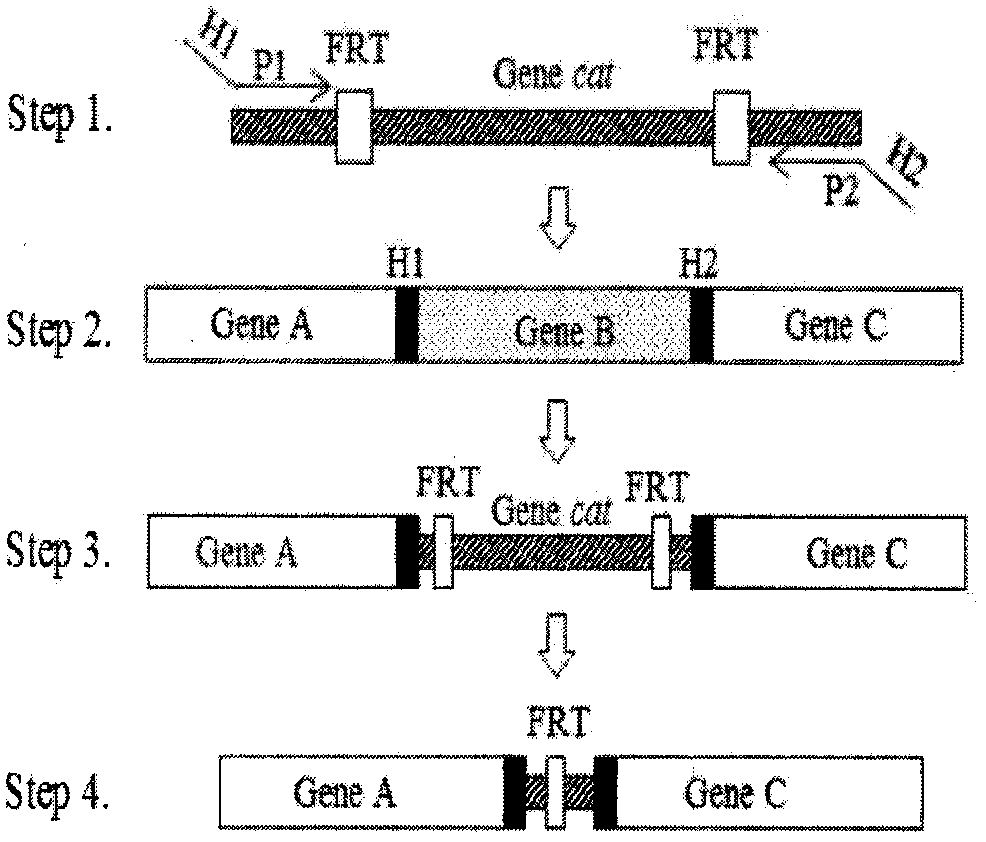
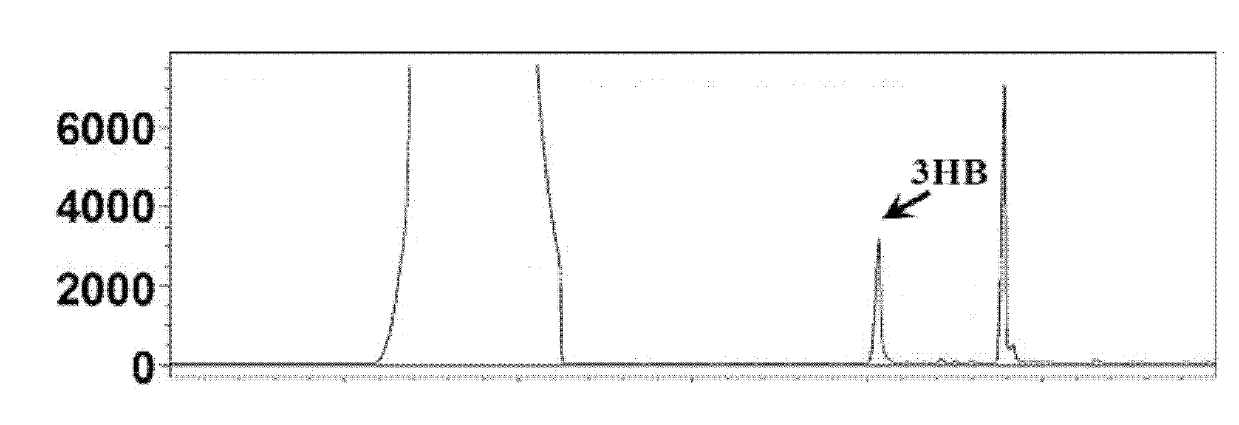
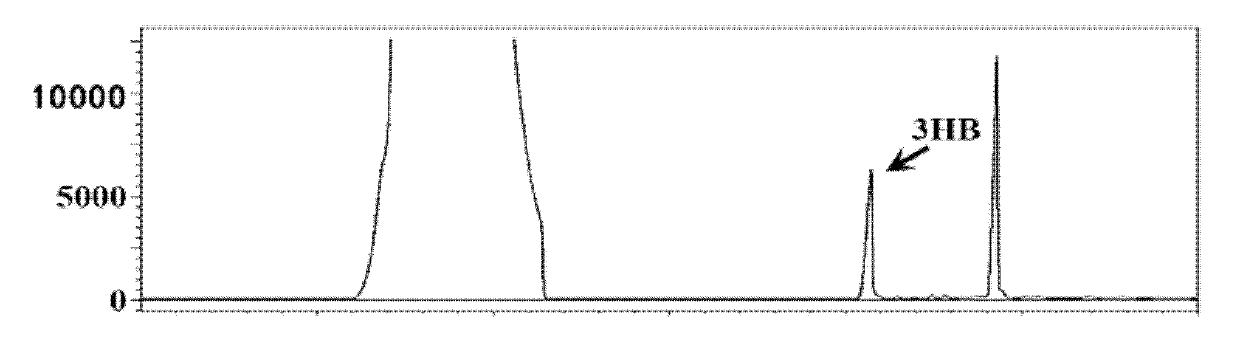
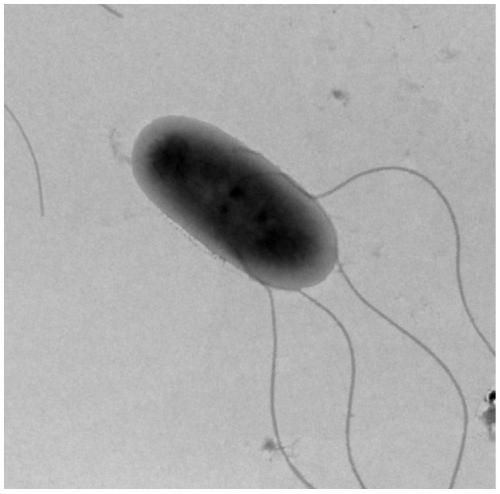
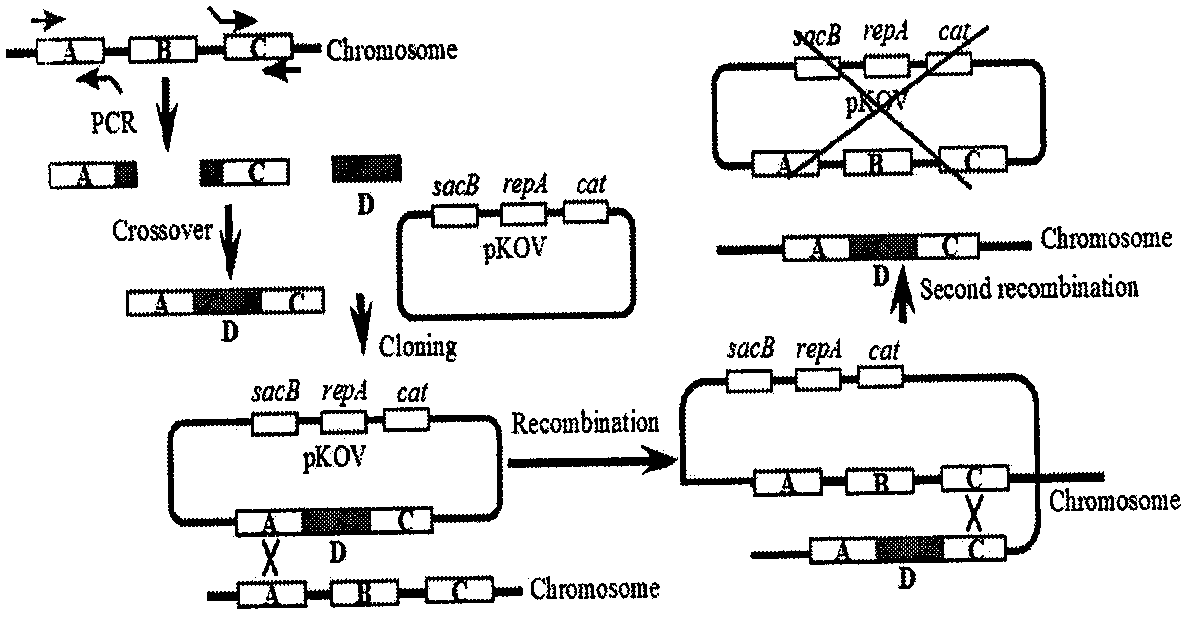
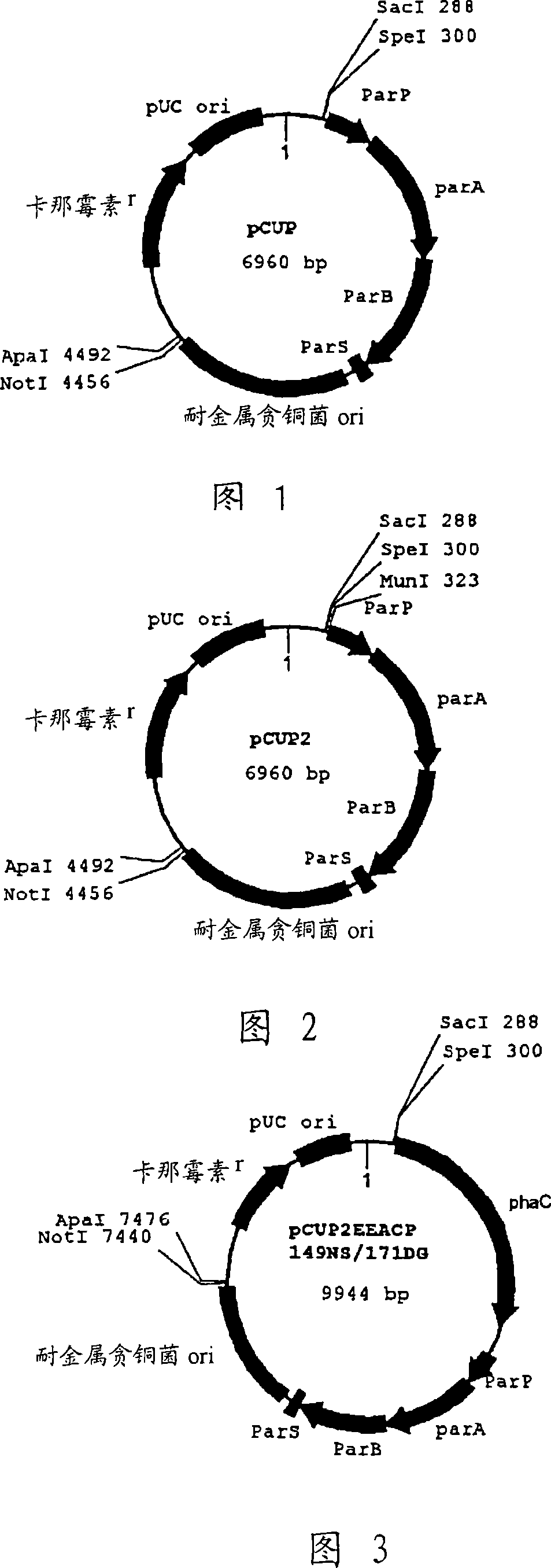
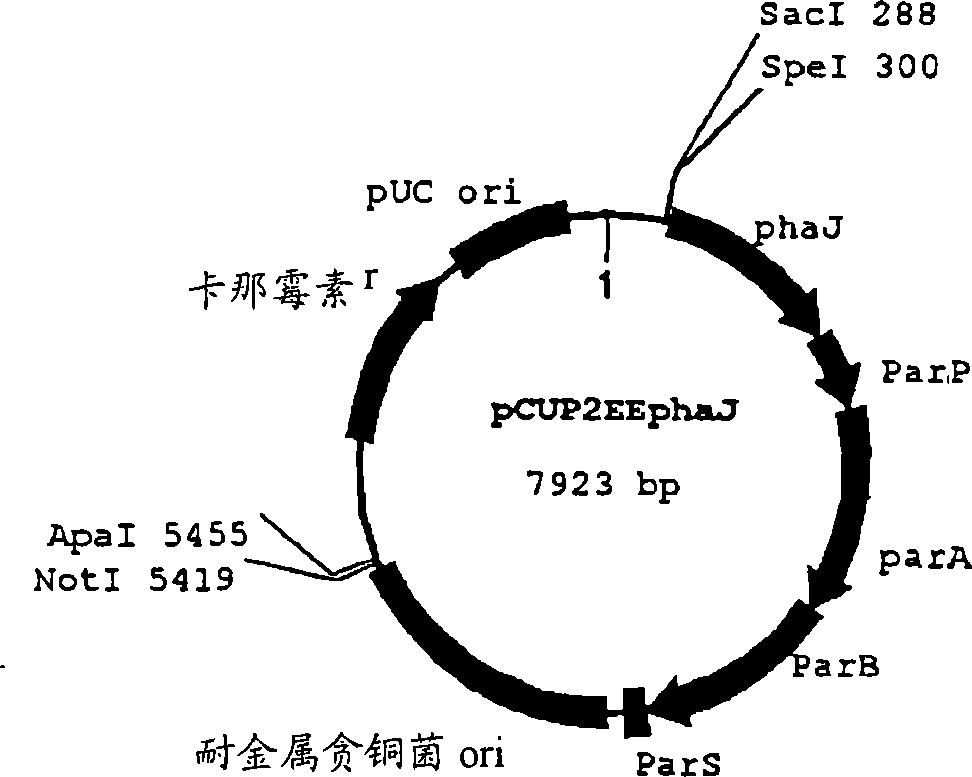
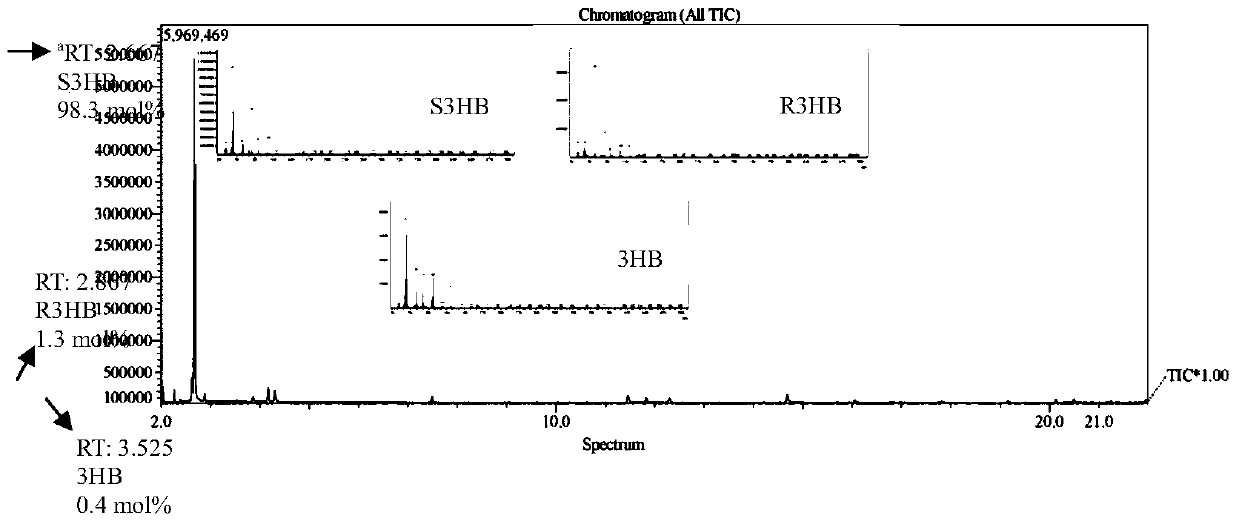
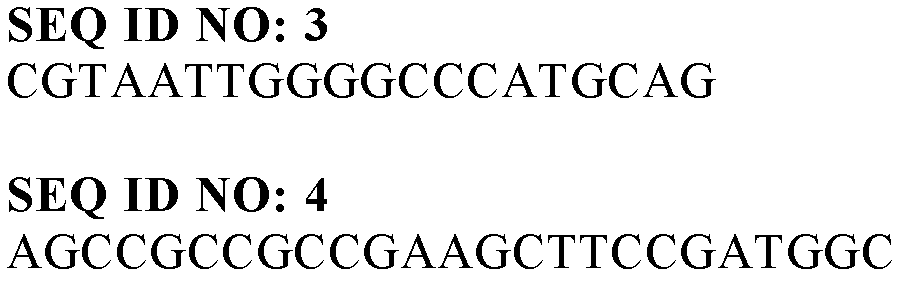Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Cupriavidus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
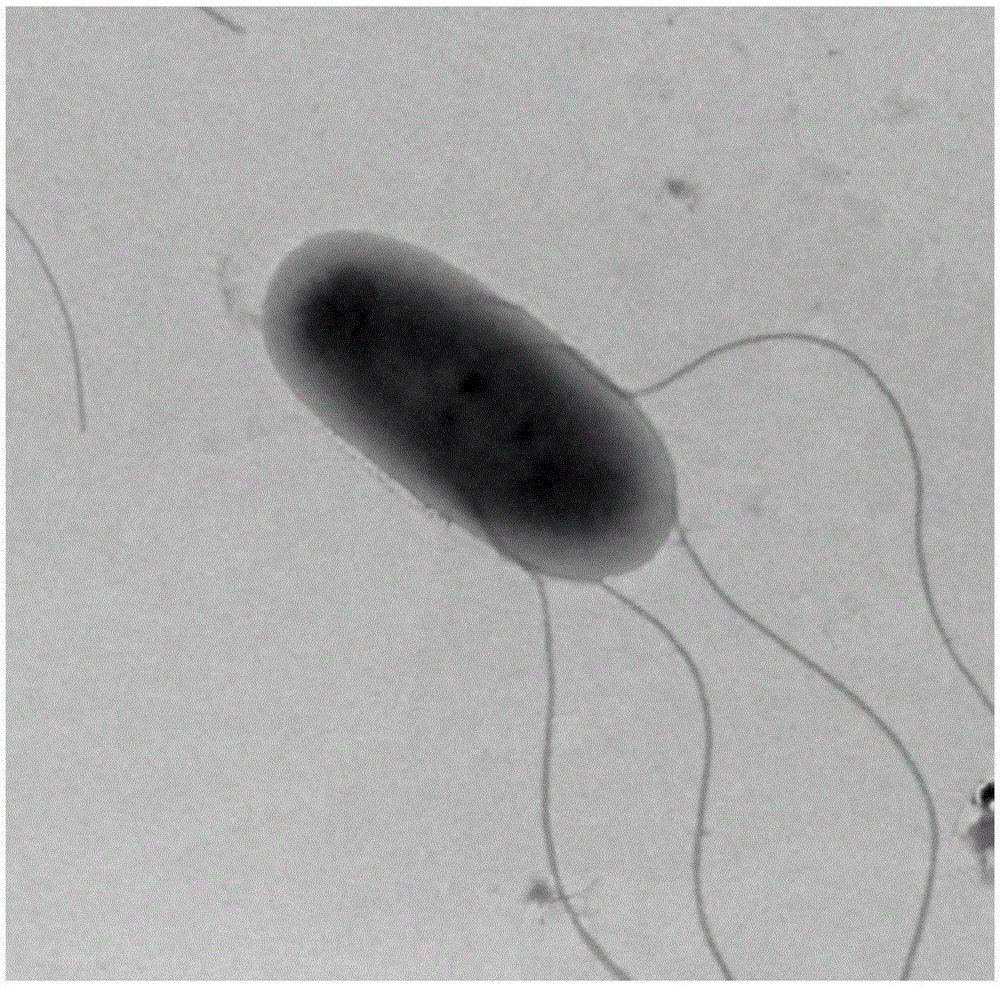
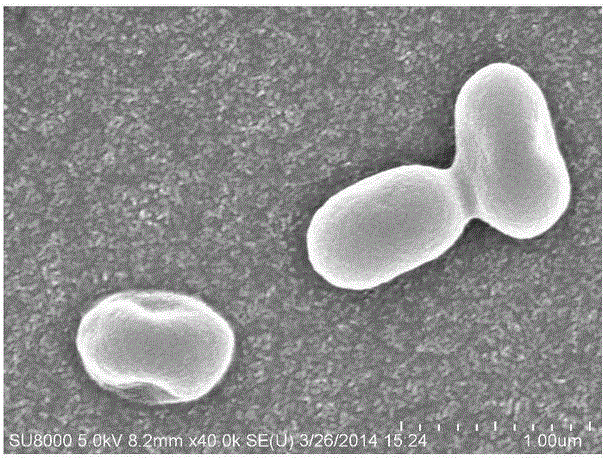
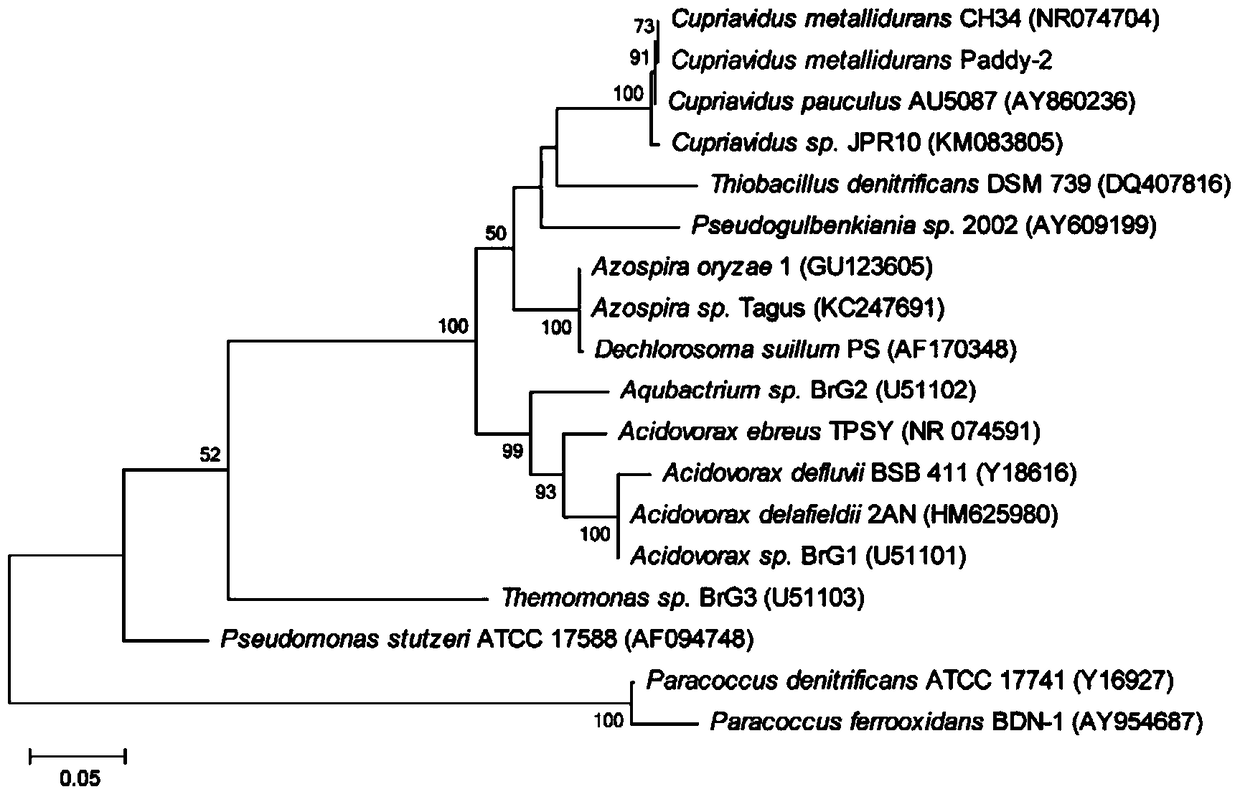
Cupriavidus is a genus of bacteria that includes the former genus Wautersia. They are characterized as Gram-negative, motile, rod-shaped organisms with oxidative metabolism. They possess peritrichous flagella, are obligate aerobic organisms, and are chemoorganotrophic or chemolithotrophic. Resistance to metals (including copper) has been described. These organisms have been found in both soil and in clinical isolates.
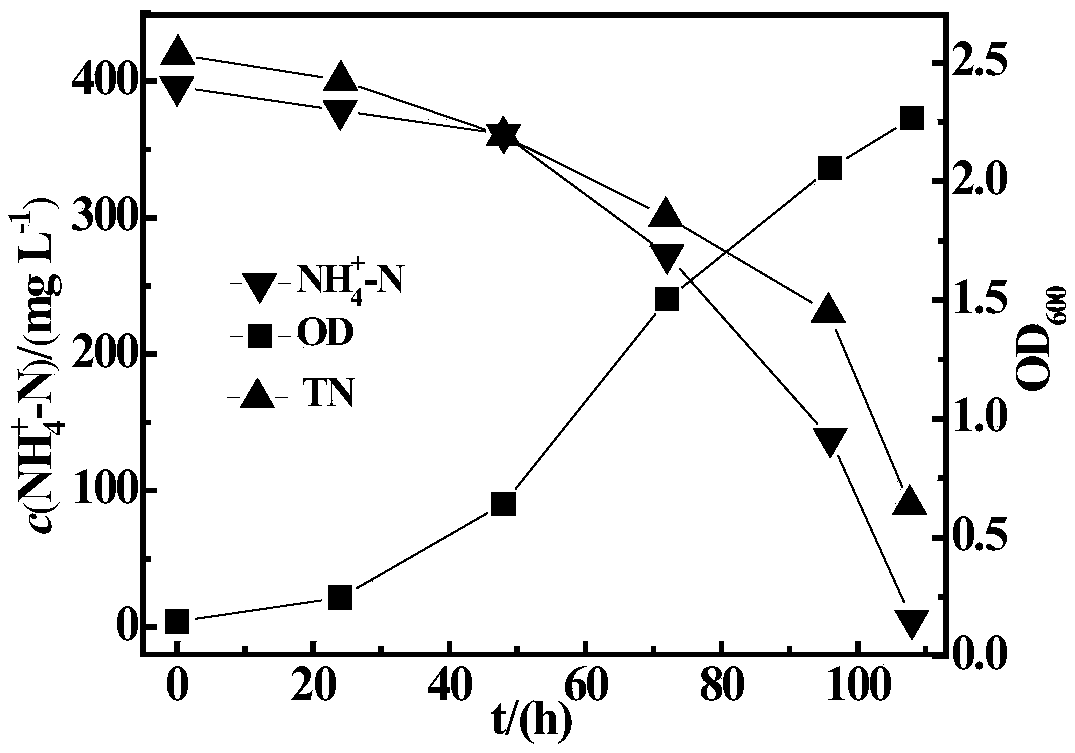
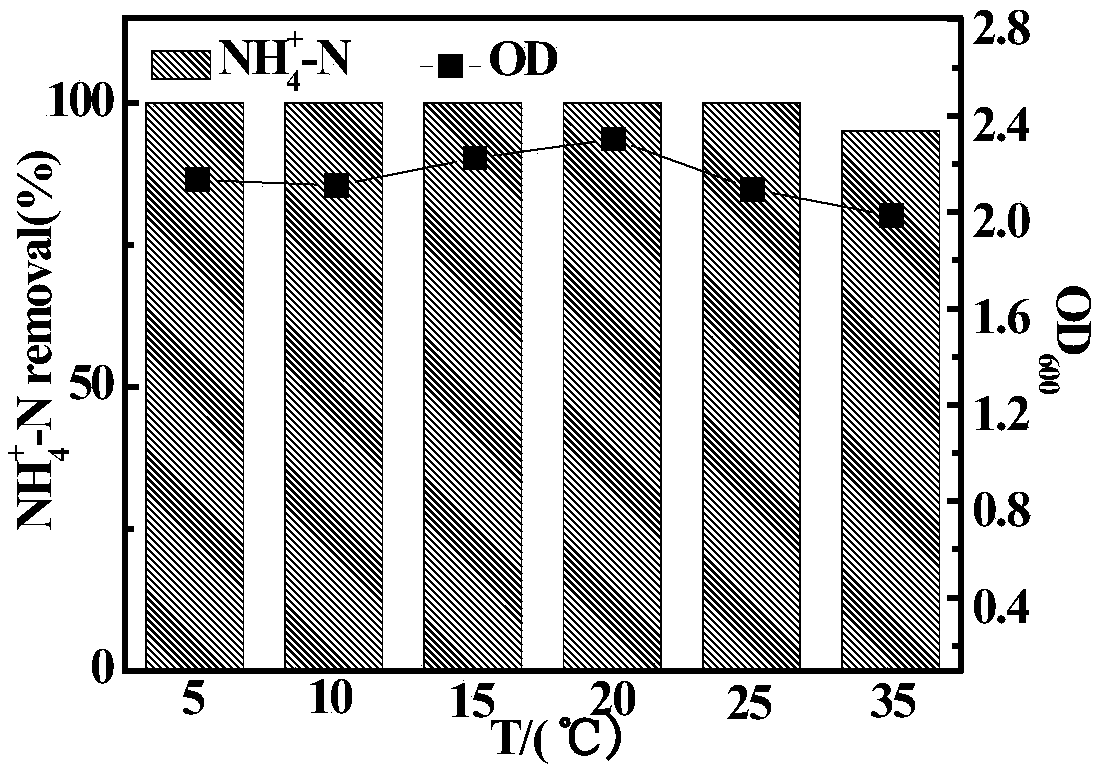
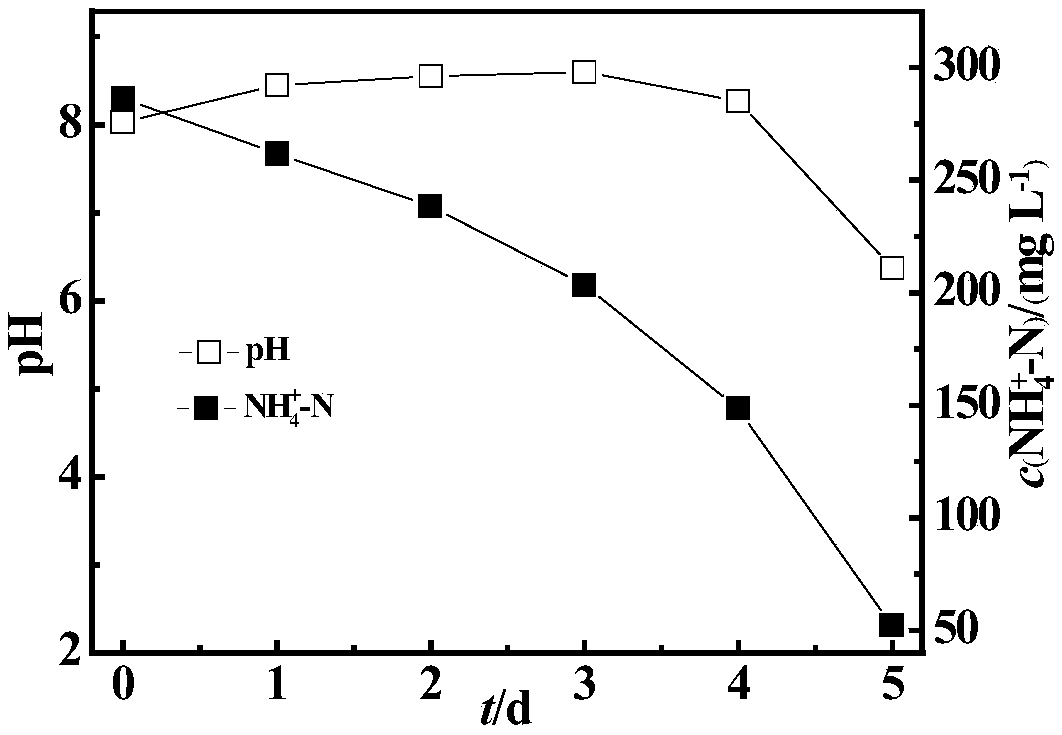
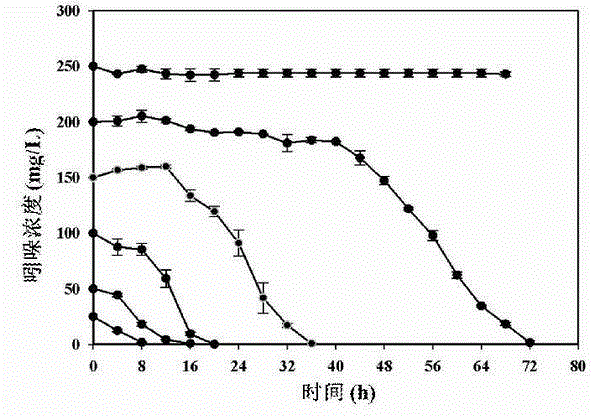
Heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification compound bacterial agent for low-temperature high ammonia-nitrogen removal and application
ActiveCN109082387AActivate cold resistanceGrow fastTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaMicroorganismCupriavidus
The invention relates to a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification compound bacterial agent for low-temperature high ammonia-nitrogen removal and application. The compound bacterial agentis formed by compounding of 10-20% of cupriavidus SWA1, 5-20% of alcaligenes faecalis, 10-30% of acinetobacter and 20-50% of ochrobacterum TAC-2. The compound bacterial agent has advantages of high ammonia-nitrogen resistance, low-temperature resistance, heavy metal resistance and synchronous nitrification and denitrification; by synergistic effects of four microorganisms, efficient denitrification of high ammonia-nitrogen wastewater can be realized in an aerobic environment under low-temperature conditions.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Cupriavidus sp. IDO capable of aerobic degrading indole and application thereof
InactiveCN104099274AHigh similarityPromote degradationTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaBiotechnologyBacterial strain
The invention relates to a cupriavidus sp. IDO capable of aerobic degrading indole and the application thereof, and belongs to the field of microbial biotechnology. The bacterial strain is separated from soil samples at the seaside of Black Reef in Dalian City, Liaoning Province, China is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, CGMCC on June 4th, 2014, and the preservation number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC No.9265. The bacterial strain IDO is a Gram-negative bacterium and is in a short-rod shape, and through the determination of a 16SrRNA gene sequence, the bacterial strain IDO and the cupriavidus have higher likeness, so that the bacterium is classified and named as Cupriavidus sp. IDO, and the GenBank accession number of the16SrRNA gene sequence of the bacterial strain is KJ875862. The bacterial strain uses various aromatic compounds as a unique carbon source for growth, has a higher degrading capacity to the indole, also has better pH and temperature tolerance, and shows the application prospects in the treatment of wastewater containing high-concentration indole.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB)
The invention discloses a method for preparing polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), which is implemented by taking cupriavidus strains sh-1 (preservation No.: CGMCC No. 4815) as strains for preparing PHB. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating the strains in a slant culture medium, then culturing the strains for 24 hours at a temperature of 30 DEG C; taking slant cultures, then inoculating the slant cultures in a conical flask filled with a seed culture medium, and under the condition of shaking the conical flask at a rotating speed of 180 r / min, culturing the slant cultures for 24-36 hours at a temperature of 30 DEG C; inoculating the obtained seed liquid in a fermentation medium according to an inoculation quantity of 10%, and stirring the obtained product at a rotating speed of 300-500 r / min, then after fermenting the seed liquid 72 hours at a ventilatory capacity of 50-200 L / min and a fermentation temperature of 28-35 DEG C, stopping the operation of fermentation; and in the process of fermentation, when the dissolved oxygen content of the fermentation medium is increased to 80% of saturated dissolved oxygen content, adding a glucose solution (concentration: 10-300 g / L) into the fermentation medium, then when the dissolved oxygen content of the obtained solution drops to 50%, stopping the operation of adding. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the high-density fermentation and high yield of polyhydroxybutyrate can be realized.
Owner:BIOCHEM ENG COLLEGE OF BEIJING UNION UNIV
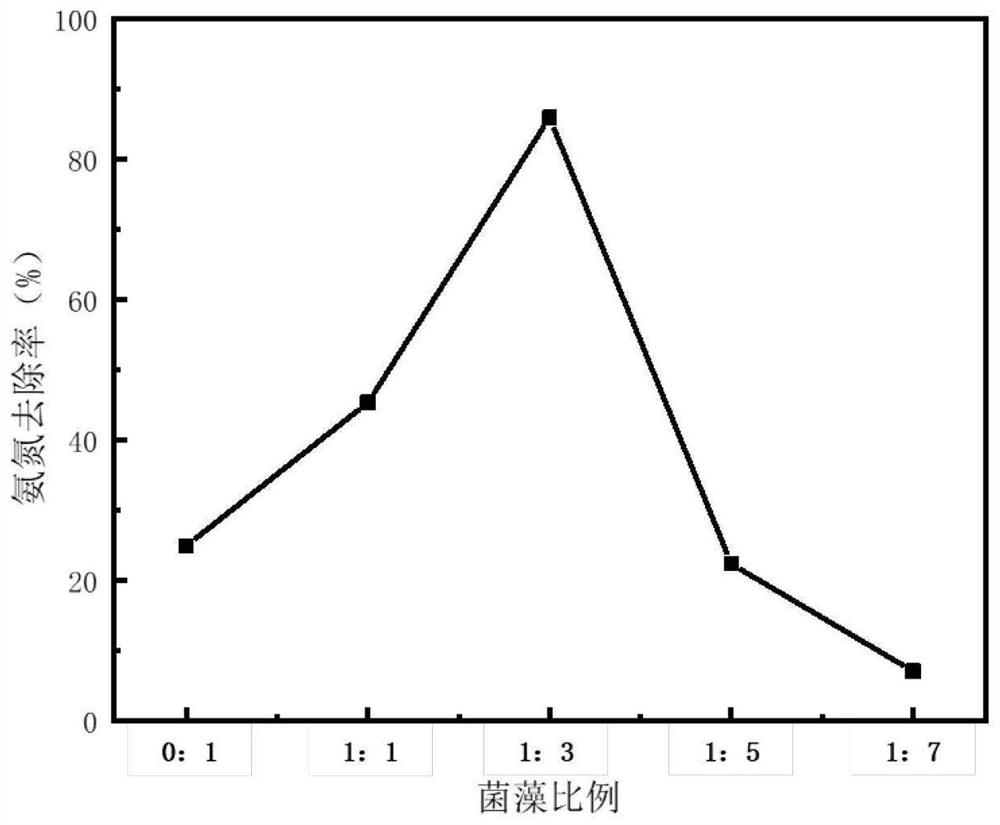
Bacteria-algae composition for synergistically degrading high-concentration ammonia nitrogen and phosphate as well as application and method thereof
PendingCN113003727AEfficient removalSolve the problem of not being able to remove phosphorusWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesTotal nitrogenP phosphate
The invention discloses a bacteria-algae composition for synergistically degrading high-concentration ammonia nitrogen and phosphate as well as application and a method thereof. The composition is prepared from a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification complex microbial inoculant and lesser chlorella, the complex microbial inoculant is formed by compounding cupriavidus, alcaligenes faecalis, acinetobacter and ochrobactrum TAC-2; chlorella is introduced into the complex microbial inoculant to form a bacterial-algae symbiotic system, chlorella generates oxygen through photosynthesis, dissolved oxygen is provided for denitrification of the complex microbial inoculant, the aeration energy consumption of the complex microbial inoculant system is reduced, and the complex microbial inoculant converts organic matters in wastewater into carbon dioxide through biological action to meet the growth requirement of chlorella. The method can improve the removal of ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen by the complex microbial inoculant, increase the phosphate removal capability, solve the problem that the complex microbial inoculant cannot remove phosphorus, and can be used for treating high-concentration ammonia nitrogen and phosphate wastewater.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
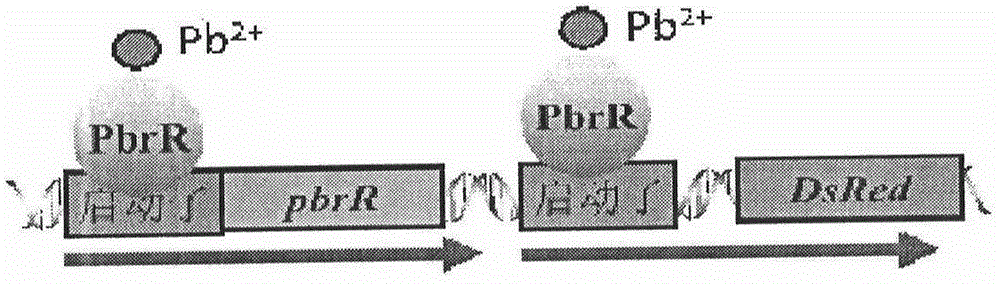
Escherichia coli for detecting lead
ActiveCN104805048AHigh sensitivityOvercome operabilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliLarge intestine
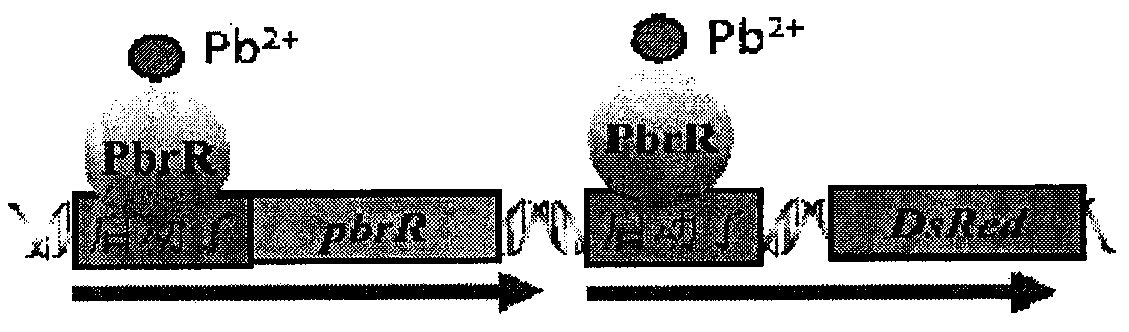
Escherichia coli for detecting lead is disclosed. Escherichia coli for detecting lead is disclosed. The invention provides a construction method of an escherichia coli engineered strain for detecting heavy metal lead and establishment of a method for detecting lead in a water body. The gene engineering strain is PpbrA-pbrR-PpbrA::DsRed-express2 / E.coli delta zntR delta zntA, named as E.coli WMC-008p CGMCC No.9748, wherein zntA and zntR genes undergo deletion mutation so as to be inactivated, and a pbr operon originated from a Cupriavidus metallidurans CH34 strain is knocked-in to express the red fluorescence protein DsRed-express2. In comparison with a reporter plasmid-containing E. coli reporter strain, the engineering strain provided by the invention has advantages of simple operation, low fluorescence background value, stable signal and the like. The engineering strain can reflect bio-availability of lead in a water body and provides a basis for objective evaluation of bio-toxicity effects of lead in a water body.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Cupriavidus strain capable of transforming heavy metals and application of strain
ActiveCN105400719AStrong oxidation abilityStrong reductionBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationCupriavidusMicroorganism
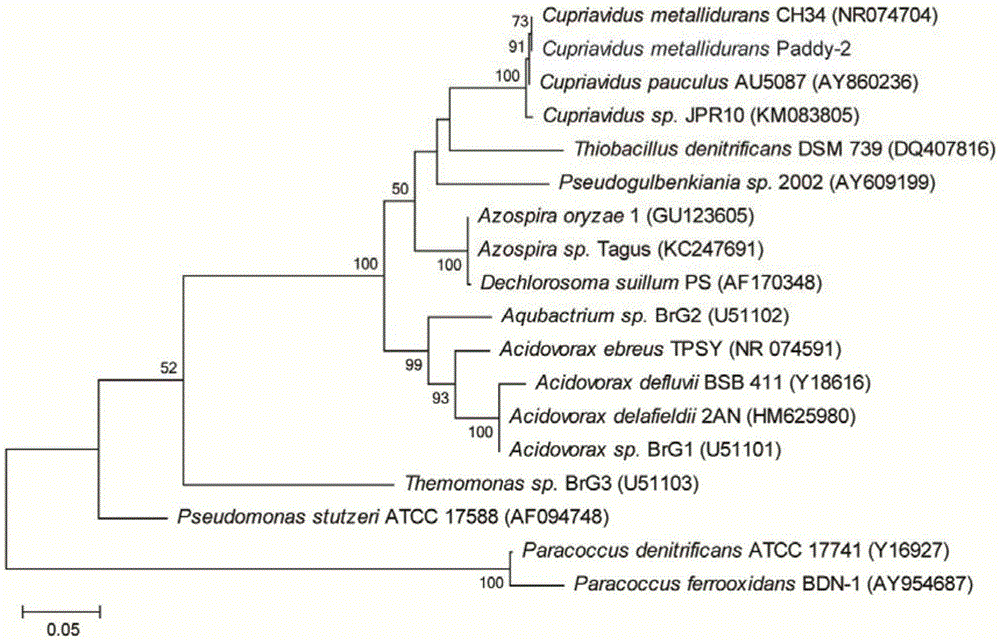
The invention discloses a cupriavidus strain capable of transforming heavy metals and application of the strain. The strain is named as cupriavidus metallidurans Paddy-2, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of Institute of Microbiology of Chinese Academy of Sciences on No.3, No. 1 Yard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing on June 9, 2015, with preservation number of CGMCC No. 11028. The strain, which has a relatively strong ferrous oxidization capacity and is capable of achieving mineralization by ferrous oxidization in a nitrate environment, is applicable to soil improvement; and the strain also has a relatively strong reduction effect on arsenic and the reduction effect on the arsenic is stronger under a condition free from nitrate and ferrous ions; therefore, the strain is suitable for repairing arsenic-contaminated soil.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Method for producing a polyhydroxyalkanoate using a microorganism belonging to the genus Cupriavidus
The present invention provides a microorganism that synthesizes a high-molecular-weight PHA, and a method for producing a high-molecular-weight PHA, which have a productivity of at least 100 g / L. The provision is achieved by controlling the specific activity of a PHA synthase in cells of a microorganism that belongs to the genus Cupriavidus and is capable of producing a PHA, to 0.1 U / mg-protein at most. The microorganism and the method enable industrially efficient production of a PHA with a weight average molecular weight of at least 4,000,000.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Novel microbial agent and soybean planting method
PendingCN112940969AImprove germination rateImprove seedling survival rateBacteriaSeed and root treatmentBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
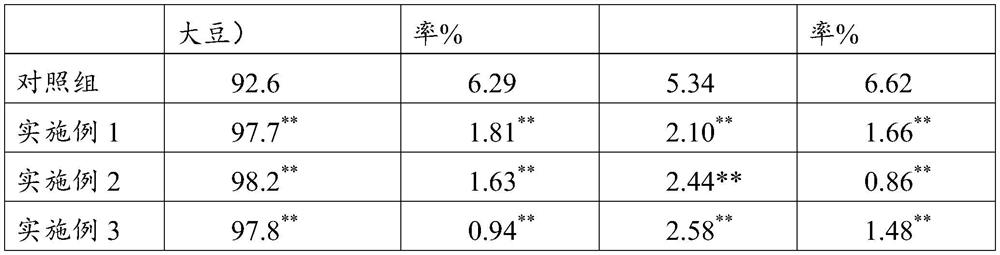
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, and particularly discloses a novel microbial agent and a soybean planting method. The novel microbial agent disclosed by the invention comprises the following strains: 1) one or more of corynebacterium, paracoccus, chromobacterium, achromobacter, acidithiobacillus, acidovorax, alcaligenes, arthrobacter, bacillus, cupriavidus, derxia, Herbaspirillum, hydrogenobacter, hydrogenophaga, pseudomonas, pseudonocardia, rhizobium, rhodococcus, rhodopseudomonas, rhodospirillum, thiocapsa, xanthomonas, flavobacterium and wautersia; and 2) azospirillum and azotobacter. The novel microbial agent can improve the emergence rate and the survival rate of soybeans, improve the growth of soybean seedlings, promote the accumulation of organic matter, improve the disease resistance of the soybeans to harmful bacteria and improve the nitrogen fertilizer utilization rate of the soybeans.
Owner:兴安盟莱绅生物农业有限公司
Basophilic Cupriavidus strain KY678 with functions of passivating heavy metal cadmium and promoting plant growth and application of basophilic Cupriavidus strain KY678
ActiveCN114107091AImprove harmHazard mitigationBiocideAgriculture tools and machinesCupriavidusMicroorganism
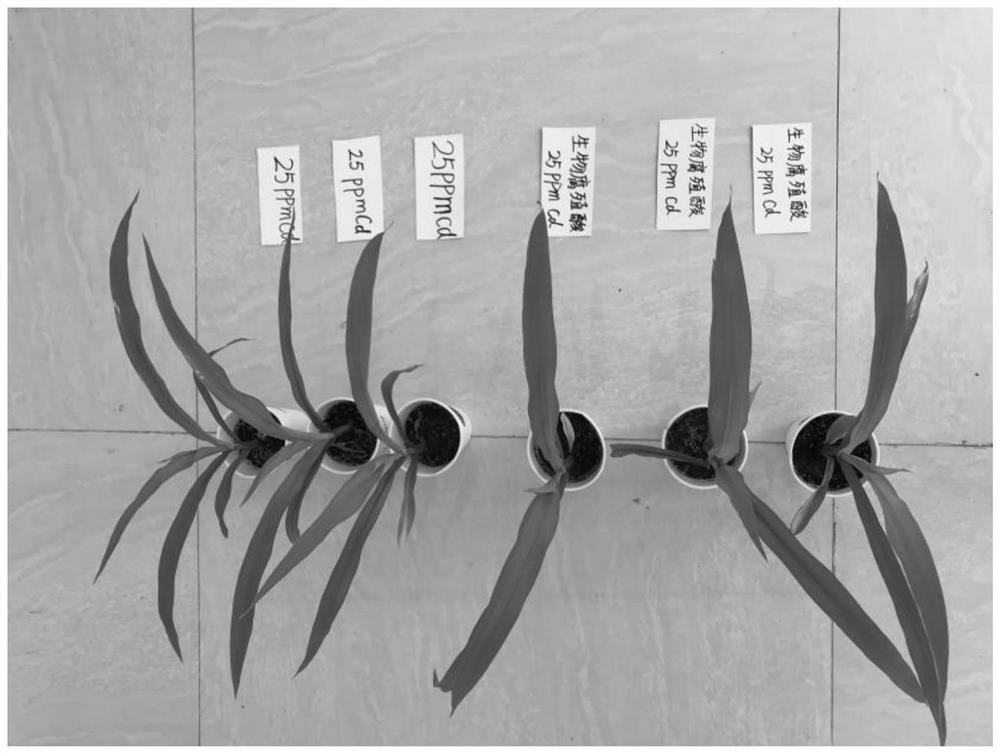
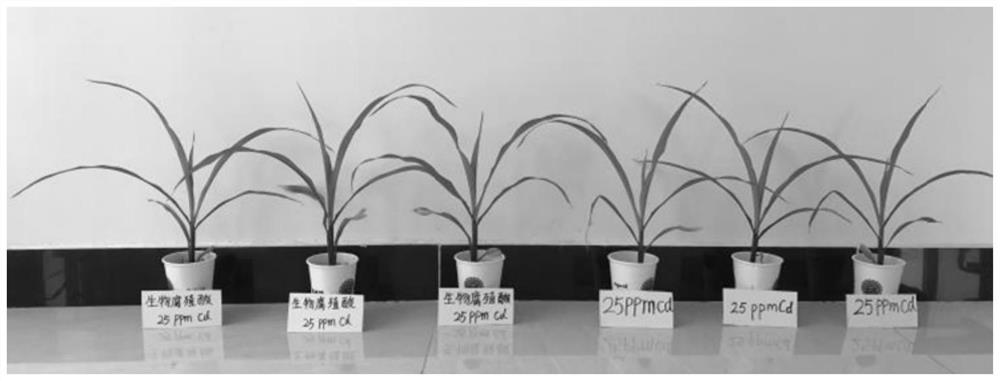
The invention provides Cupriavidus alkaliphilus (Cupriavidus alkaliphilus) with functions of passivating heavy metal cadmium and promoting plant growth and application of the Cupriavidus alkaliphilus (Cupriavidus alkaliphilus), and relates to the technical field of microorganisms. The basophilic Cupriavidus strain KY678 is separated and screened by using a high-throughput method, and the strain has a relatively high function of passivating heavy metal cadmium, can reduce the absorption of the heavy metal cadmium by plant root systems and stem and leaf parts, and remarkably reduces the harm of the heavy metal cadmium in soil to plants; in addition, the strain also has a function of promoting plant growth, and has good popularization and application values.
Owner:康生元(肇庆)生物科技有限公司
Microorganism producing high-molecular-weight pha
The present invention provides a microorganism that synthesizes a high-molecular-weight PHA, and a method for producing a high-molecular-weight PHA, which have a productivity of at least 100 g / L. The provision is achieved by controlling the specific activity of a PHA synthase in cells of a microorganism that belongs to the genus Cupriavidus and is capable of producing a PHA, to 0.1 U / mg-protein at most. The microorganism and the method enable industrially efficient production of a PHA with a weight average molecular weight of at least 4,000,000.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Cupriavidus and application thereof
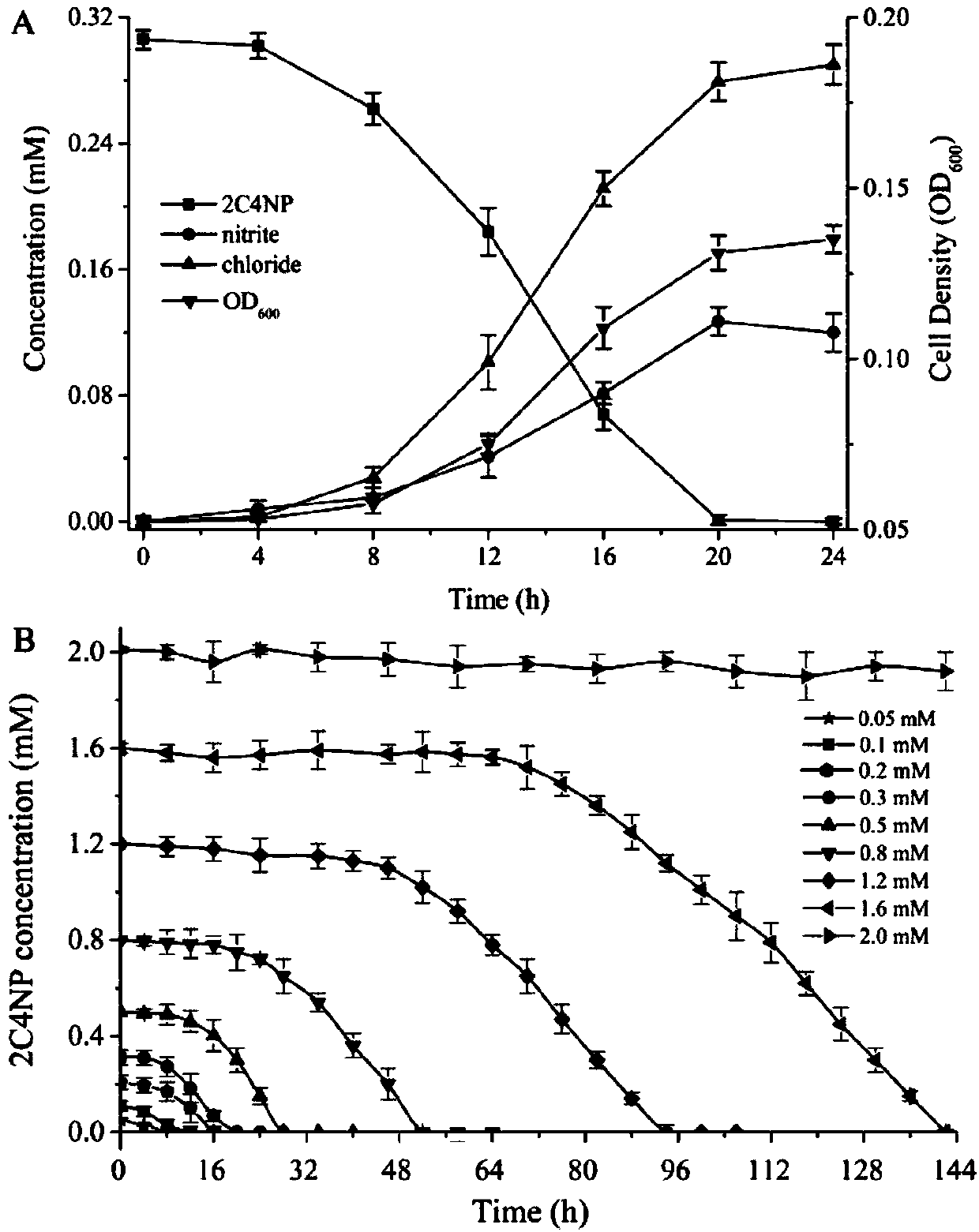
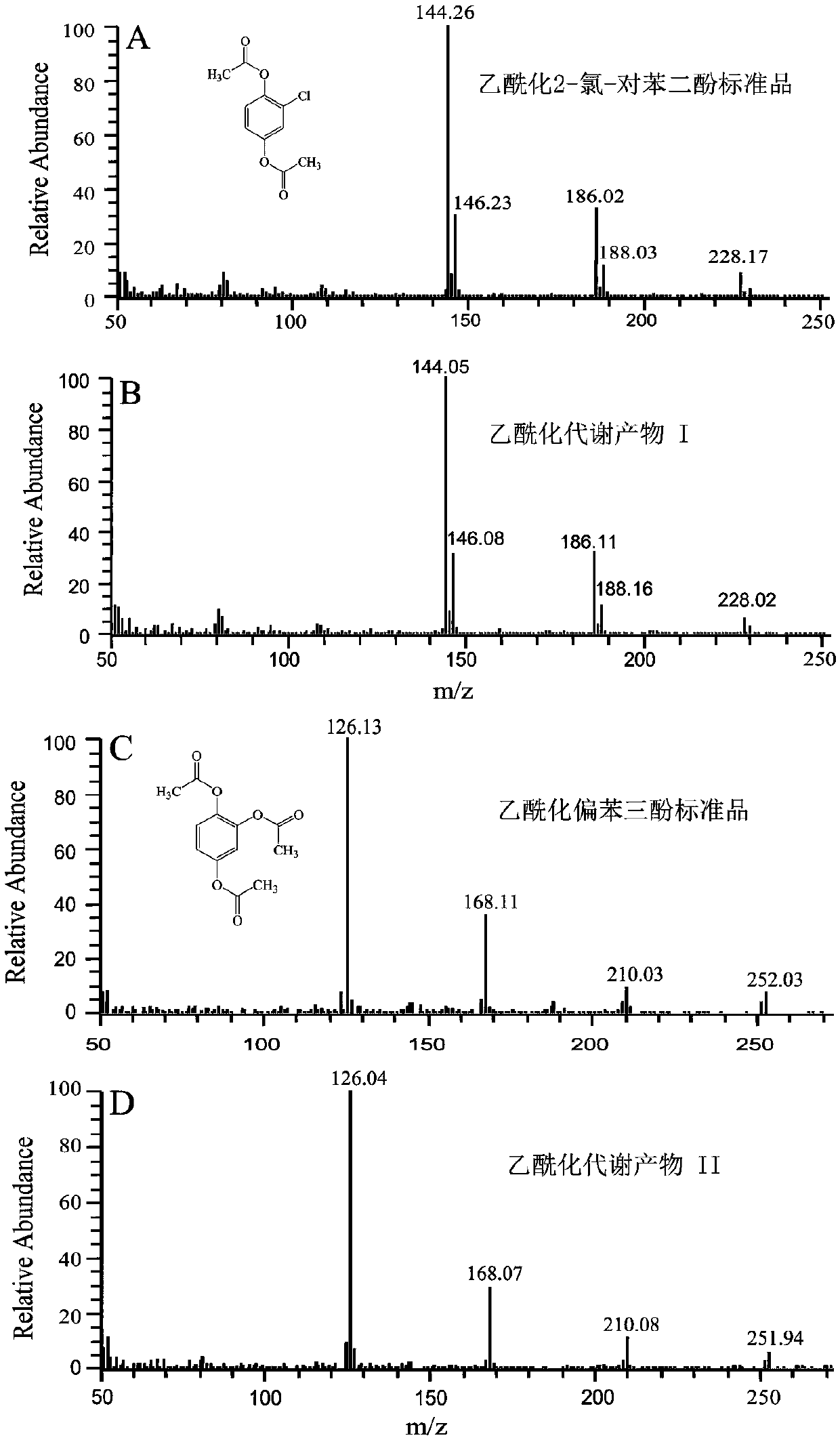
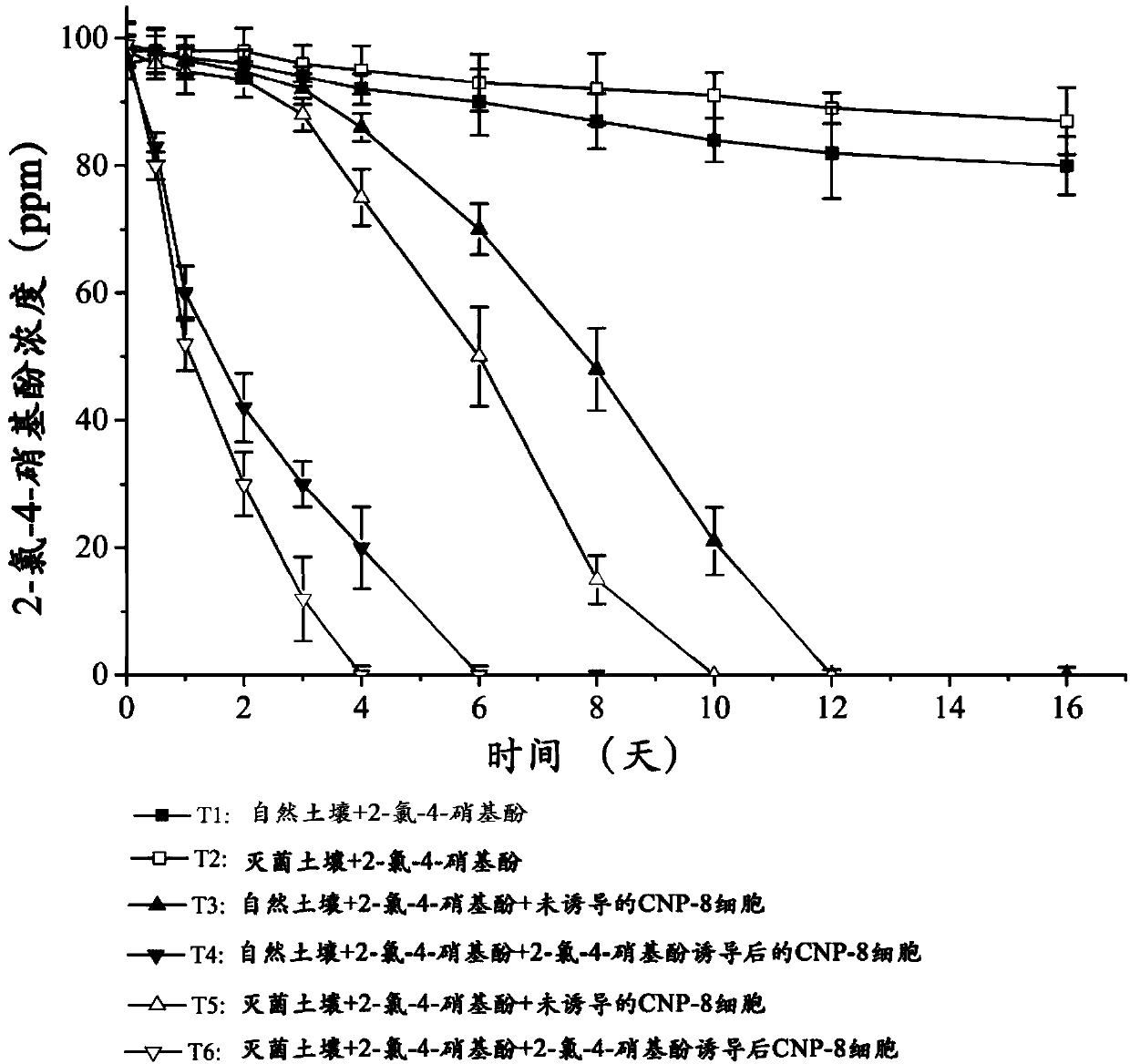
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to cupriavidus and application of the cupriavidus. The cupriavidus is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, the address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, the preservation date is September 25, 2017, and the preservation number is CCTCC M 2017546. Bacterial strain obtained by the invention can degrade 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol by taking phloroglucinol as a ring-opening substrate, and the strain provided by the invention is gram-negative bacteria capable of metabolizing 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol by a 1,2,4-benzenetriol way. On the other hand, the prepared remediation microbial inoculum can completely degrade 100 ppm of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol in contaminated soil within 12 days. Therefore, the strain has good application prospects in the biological treatment of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol pollution.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
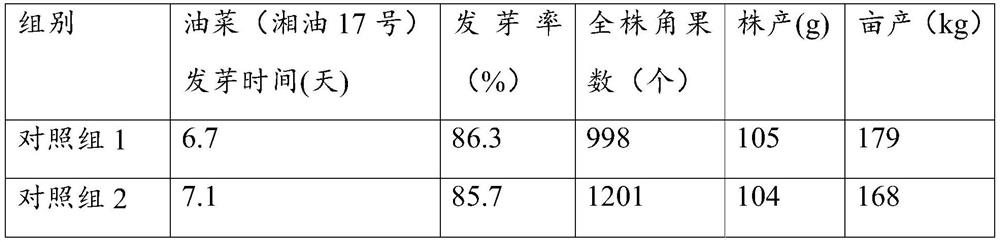
Microbial agent for promoting growth of oilseed rape and oilseed rape planting method thereof
ActiveCN112980732AIncrease productionIncrease harvestPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, and particularly discloses a microbial agent for promoting growth of oilseed rape and an oilseed rape planting method thereof. The microbial agent provided by the invention comprises the following bacteria: a) at least one of corynebacterium, paracoccus, chromobacterium, achromobacter, acidithiobacillus, acidovorax, alcaligenes, arthrobacter, bacillus, cupriavidus, derxia, herbaspirillum, hydrogenobacter, hydrogenophaga, pseudomonas, pseudonocardia, rhizobium, rhodococcus, rhodopseudomonas, rhodospirillum, thiocapsa, xanthobacter, flavobacterium and wautersia; B) acetobacter, and c) azospirillum. The microbial agent provided by the invention improves the yield of oilseed rape, and is matched with a specific oilseed rape planting method to increase the yield of oilseed rape per mu, reduce the nitrogen fertilizer demand, reduce harmful germs, restore the number of microorganisms in soil and increase the diversity of the microorganisms.
Owner:GUANGDONG RICHHOLD BIOLOGICAL AGRI CO LTD
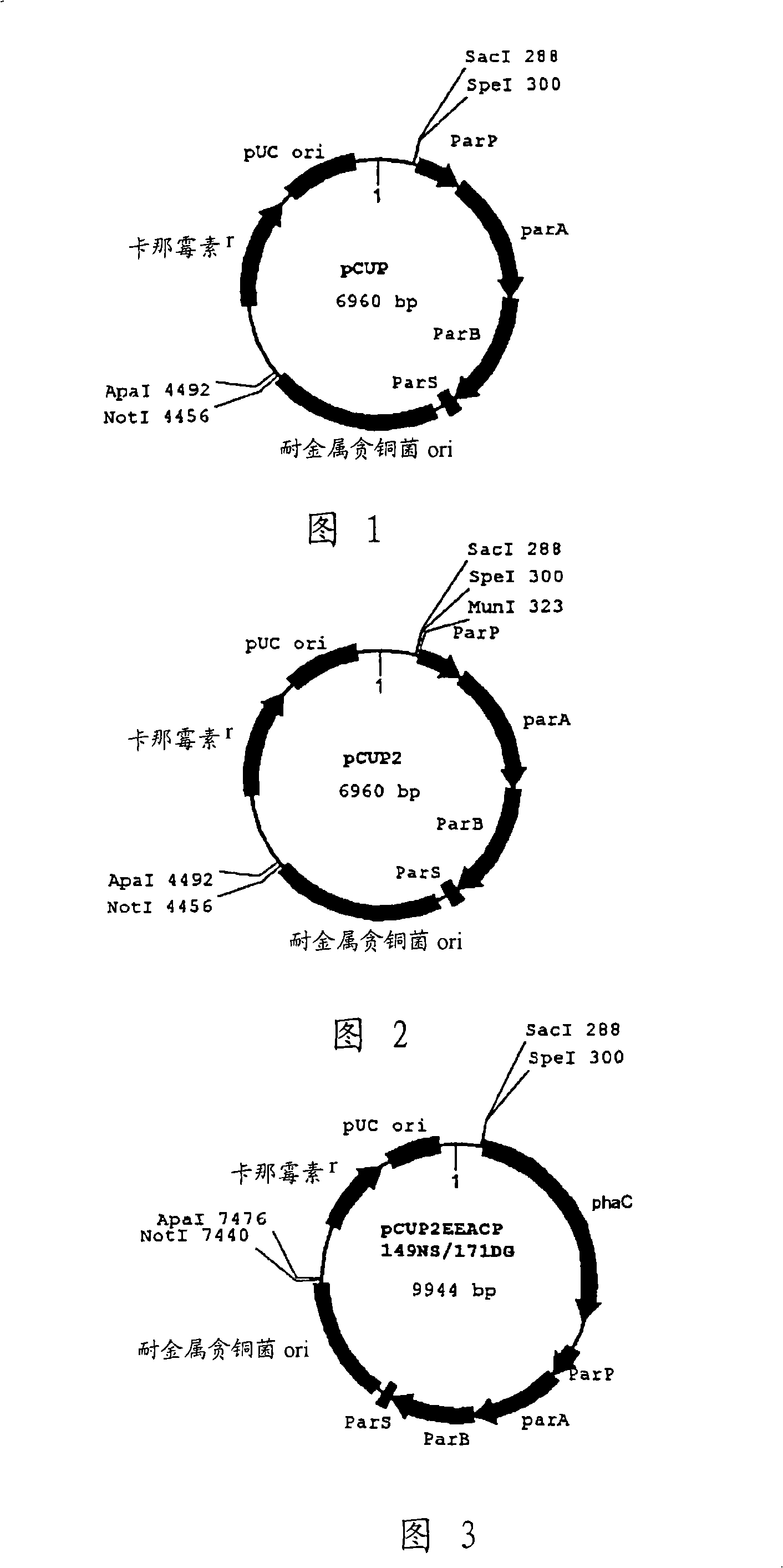
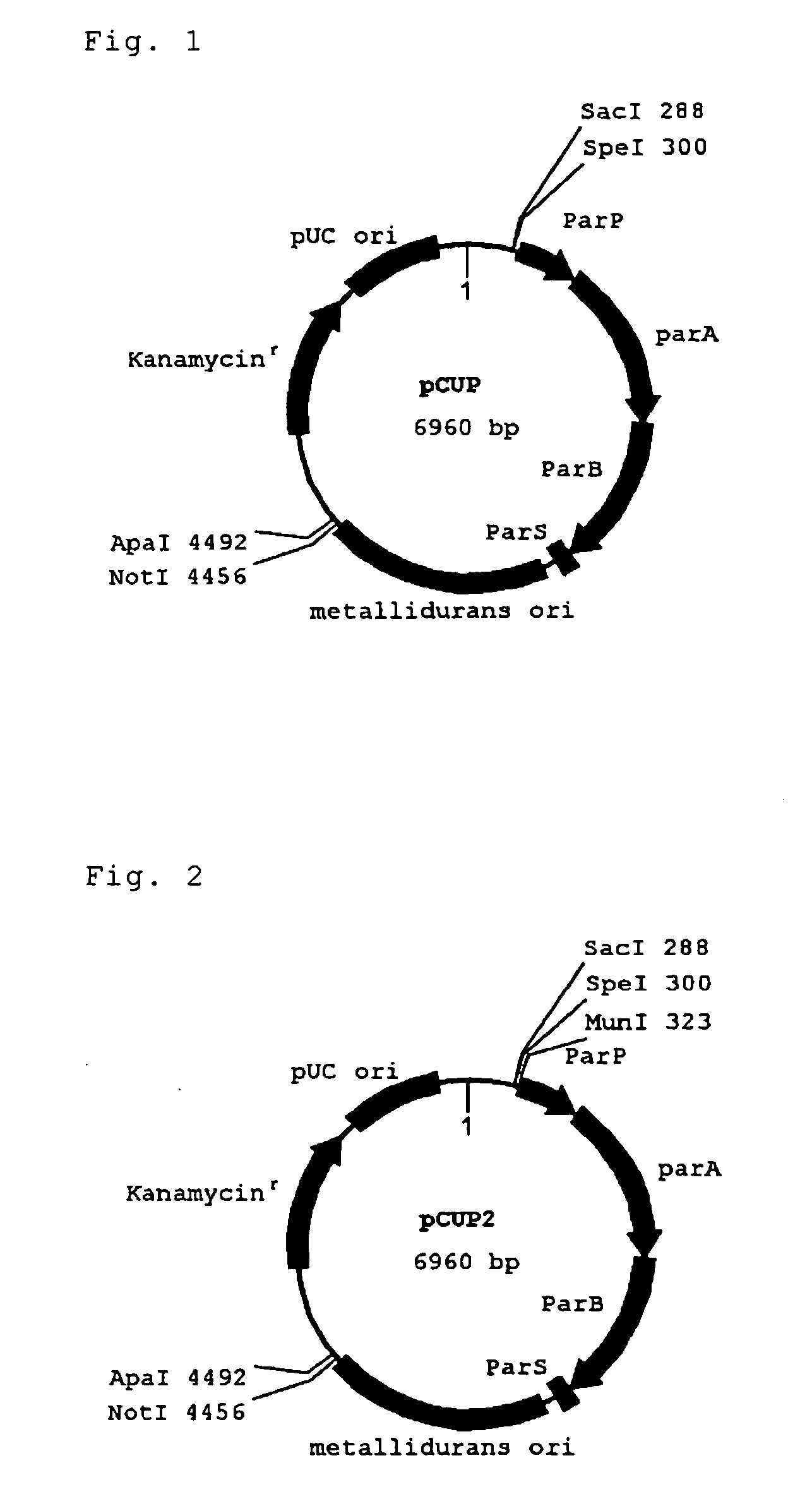
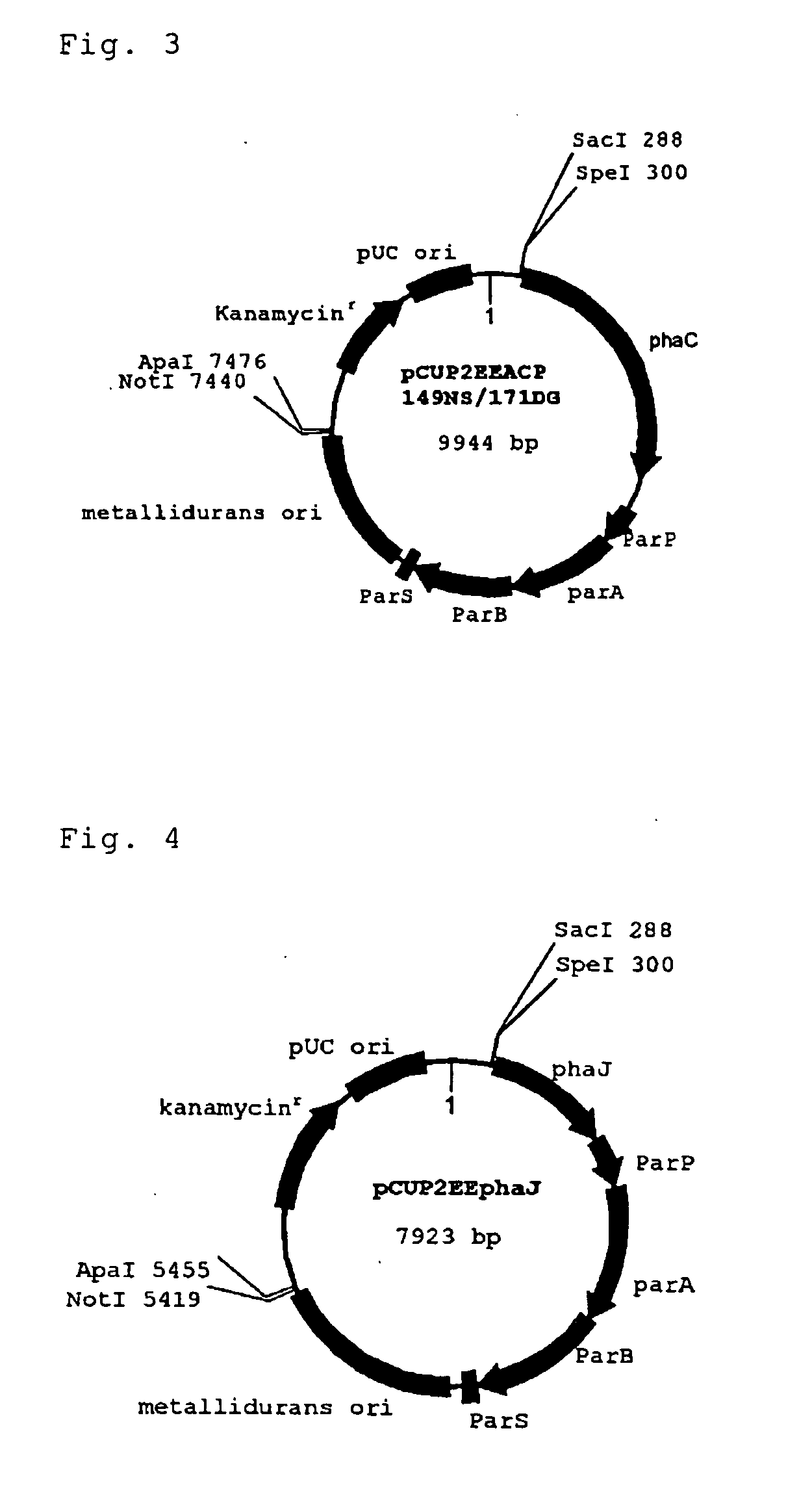
Novel plasmid vector and transformant capable of carrying plasmid stably
The object is to develop: a novel vector, preferably a novel vector which can be carried in a cell of a bacterium belonging to the genus Ralstonia, Cupriavidus or Wautersia stably in the absence of selection pressure for an antibiotic and has no conjugal transfer property; a strain capable of stably producing a polyhydroxyalkanoate using the vector; and a method for production of a polyhydroxyalkanoate using the strain. Disclosed is a novel recombinant vector having a DNA replication initiation segment which can function in a cell of a bacterium belonging to the genus Ralstonia, Cupriavidus or Wautersia, particularly a recombinant vector having both a DNA replication initiation segment which can function in a cell of a bacterium belonging to the genus Ralstonia, Cupriavidus or Wautersia and a segment which can stabilize the recombinant vector (a par segment). By using a transformant produced using the vector, the vector can be carried in a bacterium stably and a polyhydroxyalkanoate can be produced with good efficiency.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Microbial agent and planting method for promoting sesamum indicum growth
PendingCN113215041AIncrease vitalityIncrease planting densityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly discloses a microbial agent and a planting method for promoting sesamum indicum growth. The microbial agent comprises the following bacteria of a) at least one of corynebacterium, paracoccus, chromobacterium, achromobacter, acidothiobacter, acidovorax, alcaligenes, arthrobacter, bacillus, cupriavidus, derxia, herbaspirillum, hydrogenobacter, hydrogenophaga, pseudomonas, pseudonocardia, rhizobium, rhodococcus, rhodopseudomonas, rhodospirillum, thiocapsa, xanthobacter, flavobacterium and wautersia; and b) Frankia, and c) xanthobacter. The microbial agent provided by the invention can improve the vitality of sesamum indicum root systems, increase the mass production of sesamum indicum and improve the disease resistance of sesamum indicum; and the planting method can improve the planting density of the sesamum indicum and reduce the dependence of excessive fertilizer application.
Owner:GUANGDONG RICHHOLD BIOLOGICAL AGRI CO LTD
A strain of copper greedy bacteria for aerobic degradation of indole and its application
InactiveCN104099274BHigh similarityPromote degradationTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaBiotechnologyCupriavidus
The invention relates to a copper greedy bacterium which aerobically degrades indole and its application, belonging to the field of microbial biotechnology. The strain was isolated from the seaside soil sample of Heishijiao, Dalian, and was deposited in the China General Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center on June 4, 2014, with the preservation number CGMCC No. 9265. The strain IDO is a Gram-negative bacterium with a short rod shape. It has a high similarity with Cupriavidus as determined by the 16S rRNA gene sequence, so the strain is named Cupriavidussp. IDO, and the GenBank accession number of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of the strain is KJ875862. The strain uses a variety of aromatic compounds as the sole carbon source for growth, and has a high ability to degrade indole. The strain also has good pH and temperature tolerance, showing its application in the treatment of wastewater containing high concentrations of indole prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Gene encoding polymer synthase and a process for producing polymer
InactiveCN102459601AAchieve the purpose of the inventionEnzymesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidChromobacterium sp.
Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase gene (SEQ ID NO:2) isolated from fresh water Chromobacterium sp. USM2, its amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 1) and its use to produce polymers incorporating C3 to C7 monomer units, including poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) random copolymer P(3HB-co-3HHx), poly(3- hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxycalerate) random copolymer P(3HB-co-3HV) and P(3HB-co-3HV-co-3HHx) terpolymer. Production of polymer by expression of SEQ ID NO:2 in recombinant hosts including microorganisms such as Cupriavidus or Pseudomonas.
Owner:UNIVERSITI SAINS MALAYSIA
Reutilization method for domestic waste resources
InactiveCN109279922AImprove denaturationPromote decompositionClimate change adaptationOrganic fertilisersBacillus megateriumDecomposition
The invention relates to the technical field of resource regeneration, specifically to a reutilization method for domestic waste resources. The reutilization method comprises the following steps: manually classifying domestic wastes into combustion products and decomposition auxiliary agents, mixing the combustion products with sea sand, putting an obtained mixture into an incinerator, and carrying out incineration, wherein the weight ratio of the combustion products to the sea sand is 100: 7; preheating a next batch of the combustion products with heat energy generated by combustion, whereinresidual heat is used for supplying heat; pouring discharged ash produced by combustion into a reaction pool; mixing the decomposition auxiliary agents with bacillus megaterium, metal-resistant cupriavidus metallidurans and yeast, and pouring an obtained mixture into the reaction pool; and taking two thirds of a mixture out of the reaction pool after three hundred days. According to the invention,through further treatment to the ash of the incinerator, the ash is turned into a nutrient-rich inorganic fertilizer for planting, so the recycling value of the domestic wastes is greatly improved; the domestic wastes have economic values in heat supplying and power generation, so the requirement of the domestic wastes for thermal energy values is reduced, and the construction cost of the incinerator can be reduced.
Owner:四会市华永兴再生资源有限公司
Hydrolysis saccharification process of alternanthera philoxeroides
ActiveCN108315373AReduce the content of metal ionsOptimizing Fermentation ConditionsFermentationCupriavidus speciesCobalt
Owner:JINING UNIV
A dsf quorum sensing signal molecule quenching bacterium and its application in plant disease control
ActiveCN109082396BAddress abuseAddressing drug resistanceBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyPesticide residue
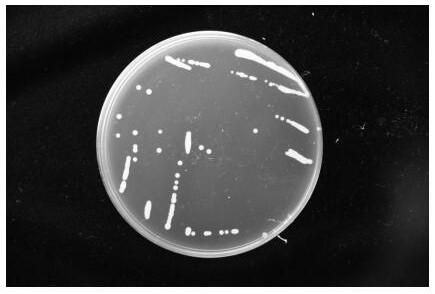
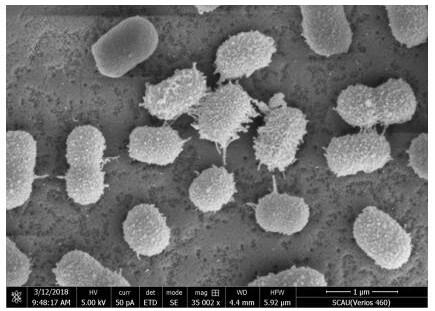
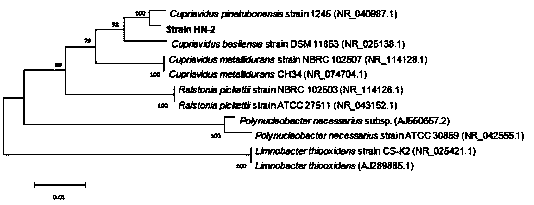
The invention discloses a DSF quorum sensing signal molecule quenching bacterium and its application in plant disease control. The present invention studies and finds copper greedy bacteria ( Cupriavidus sp.) can grow and reproduce with DSF as the sole carbon source, nitrogen source and energy source, and has a significant degradation effect on higher concentrations of DSF; at the same time, the present invention also provides a strain HN-copper greedy bacteria that efficiently degrades DSF 2. The strain was deposited in the Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on August 13, 2018, with the preservation number GDMCC NO: 60432. Copper greedy bacteria HN‑2 has significant degradative activity on quorum sensing signal molecules in plant pathogens, and is environmentally friendly, and has great applications in the control of pathogenic plant pathogens mediated by DSF and / or DSF signal molecule analogs At the same time, the invention can reduce the problem of antibiotic abuse and pesticide residue pollution, reduce environmental pressure, provide a new idea for biological control of plant diseases, and has great application value and broad application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
A Microbiological Method for Detecting Heavy Metal Lead in Water
ActiveCN104946682BHigh sensitivityThe detection signal is stableBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliOperon
The invention provides a construction method of an Escherichia coli engineering strain for detecting heavy metal lead and a method for detecting lead in a water body. The gene engineering strain provided by the invention is PpbrA-pbrR-PpbrA:DsRed-express2 / E.colideltazntRdeltazntA named as E.coli WMC-008p CGMCC No.9748, wherein zntA and zntR genes are subjected to deletion mutation and inactivation, and a pbr operon from a cupriavidus metallidurans CH34 strain is input to express a red fluorescence protein DsRed-express2. Compared with an Escherichia coli reporter strain containing a reporter plasmid, the engineering strain provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, low fluorescence background value, stable signal and the like. The engineering strain provided by the invention can reflect the bioavailability of lead in the water body and can provide the basis for objectively evaluating the biotoxicity effect of lead in the water body.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Method for preparing polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB)
Owner:BIOCHEM ENG COLLEGE OF BEIJING UNION UNIV
A strain of the genus Curaporia bacterium capable of transforming heavy metals and its application
ActiveCN105400719BStrong oxidation abilityStrong reductionBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationCupriavidus speciesMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses a cupriavidus strain capable of transforming heavy metals and application of the strain. The strain is named as cupriavidus metallidurans Paddy-2, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of Institute of Microbiology of Chinese Academy of Sciences on No.3, No. 1 Yard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing on June 9, 2015, with preservation number of CGMCC No. 11028. The strain, which has a relatively strong ferrous oxidization capacity and is capable of achieving mineralization by ferrous oxidization in a nitrate environment, is applicable to soil improvement; and the strain also has a relatively strong reduction effect on arsenic and the reduction effect on the arsenic is stronger under a condition free from nitrate and ferrous ions; therefore, the strain is suitable for repairing arsenic-contaminated soil.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
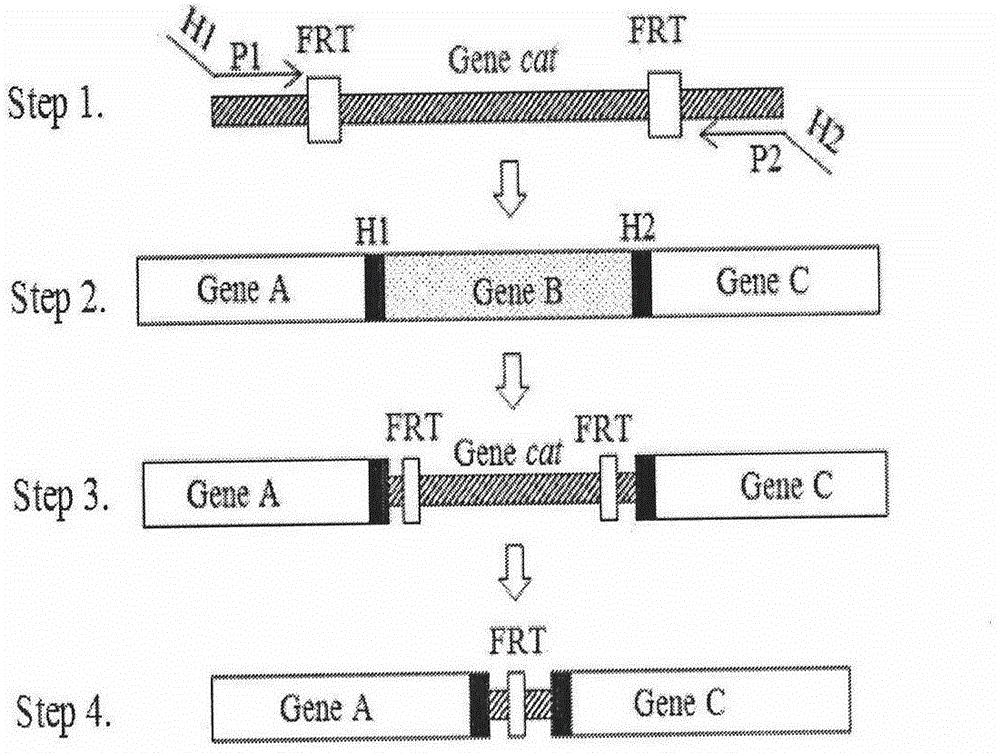
Method for improving electric transformation efficiency of genus cupriavidus bacteria with high GC content
ActiveCN109371052AEfficient removalEfficient manufacturingVector-based foreign material introductionPectinaseGlycerol
The invention provides a method for improving the electric transformation efficiency of genus cupriavidus bacteria with high GC content. The method comprises the following steps: after activating thegenus cupriavidus bacteria with high GC content, inoculating into a diluted eutrophic culture medium containing a surfactant and pectinase; after culturing for a period of time, centrifuging and collecting thalli; then re-suspending and washing with sterile de-ionized water for a plurality of times; centrifuging and collecting thallus sediment; re-suspending in a pre-cooled glycerol water solutionto prepare competent cells and carrying out electric transformation. According to the method provided by the invention, the culture medium is improved to find out that extracellular polymers of the genus cupriavidus bacteria can be effectively reduced by reducing the content of nutrient substances in the culture medium and adding a proper amount of the surfactant and pectinase, so that the electric transformation efficiency of the competent cells is greatly improved. The invention develops a stable and efficient electric transformation method aiming at the characteristics of the genus cupriavidus bacteria with high GC content, and provides powerful technical supports for deeply researching and analyzing the genus cupriavidus bacteria.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Plasmid vector and transformant stably retaining plasmid
ActiveUS9051589B2Retention stabilityIncrease productivityBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyBacteroides
Owner:KANEKA CORP
A strain of Escherichia coli that detects lead
ActiveCN104805048BHigh sensitivityThe detection signal is stableBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliLarge intestine
Escherichia coli for detecting lead is disclosed. Escherichia coli for detecting lead is disclosed. The invention provides a construction method of an escherichia coli engineered strain for detecting heavy metal lead and establishment of a method for detecting lead in a water body. The gene engineering strain is PpbrA-pbrR-PpbrA::DsRed-express2 / E.coli delta zntR delta zntA, named as E.coli WMC-008p CGMCC No.9748, wherein zntA and zntR genes undergo deletion mutation so as to be inactivated, and a pbr operon originated from a Cupriavidus metallidurans CH34 strain is knocked-in to express the red fluorescence protein DsRed-express2. In comparison with a reporter plasmid-containing E. coli reporter strain, the engineering strain provided by the invention has advantages of simple operation, low fluorescence background value, stable signal and the like. The engineering strain can reflect bio-availability of lead in a water body and provides a basis for objective evaluation of bio-toxicity effects of lead in a water body.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Novel plasmid vector and transformant capable of carrying plasmid stably
It is an object of the present invention to develop a novel vector. Preferably, the object is to develop a novel vector which can be stably retained in bacteria of the genus Ralstonia, Cupriavidus or Wautersia without any antibiotic-due selective pressure and has no transferability by conjugation. Another object is to provide a strain which can stably produce polyhydroxyalkanoate using the vector, and a method for producing a polyhydroxyalkanoate using the strain. The present invention provides a novel recombinant vector which contains an origin of DNA replication functioning in bacteria of the genus Ralstonia, Cupriavidus or Wautersia . Particularly, the transformant, which is obtained by using a recombinant vector which contains the origin of DNA replication functioning in bacteria of the genus Ralstonia, Cupriavidus or Wautersia and contains a region for a recombinant vector stabilization (par region) can make the vector to be stably retained in bacteria, and can efficiently produce a polyhydroxyalkanoate.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
A method for synthesizing bioplastic precursor polyhydroxyalkanoate by utilizing lignin-degrading bacteria
ActiveCN106190907BLow costSimple fermentation conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCupriavidusEthylene Homopolymers
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Novel plasmid vector and transformant stably retaining plasmid
ActiveUS20070099281A1Increase productivityRetention stabilityBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyOrigin of replication
It is an object of the present invention to develop a novel vector. Preferably, the object is to develop a novel vector which can be stably retained in bacteria of the genus Ralstonia, Cupriavidus or Wautersia without any antibiotic-due selective pressure and has no transferability by conjugation. Another object is to provide a strain which can stably produce polyhydroxyalkanoate using the vector, and a method for producing a polyhydroxyalkanoate using the strain. The present invention provides a novel recombinant vector which contains an origin of DNA replication functioning in bacteria of the genus Ralstonia, Cupriavidus or Wautersia. Particularly, the transformant, which is obtained by using a recombinant vector which contains the origin of DNA replication functioning in bacteria of the genus Ralstonia, Cupriavidus or Wautersia and contains a region for a recombinant vector stabilization (par region) can make the vector to be stably retained in bacteria, and can efficiently produce a polyhydroxyalkanoate.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Preparation method of sodium alginate immobilized bacterial combination for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution remediation
InactiveCN109370962AOvercome the difficult problem of easily causing secondary pollutionBacteriaWater contaminantsCupriavidusPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
The invention discloses a preparation method of sodium alginate immobilized bacterial combination for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution remediation. According to the method, benzo[a]pyrene isselected as a representative model of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, sodium alginate pellets are adopted as carriers for immobilizing eight bacteria including rhodobacter P1, flavobacterium P2, rhizobium P3, Mucilaginibacter P4, flavobacterium P5, cupriavidus P6, cupriavidus P7 and cupriavidus P8, the sodium alginate pellets containing the eight bacteria are mixed in a mass ratio of P1, P2, P3,P4, P5, P6, P7 and P8 being 1:1:1:1:1:12:12:1, and a bacterial combination is obtained. The bacterial combination is obtained with a method of first immobilization and later mixing, and a ratio of strains in the bacteria combination is guaranteed while polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is prevented from being introduced in a culture process; bacteria are immobilized with a sodium alginate embeddingmethod, an antagonistic effect among the strains in the bacterial combination is reduced, and the efficiency of degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon by the bacteria combination is improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A kind of cupriavidus and its application
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to a cupriavidus and its application. Cupriavidus has been preserved. Deposit unit: China Type Culture Collection Center, address: China. Wuhan. Wuhan University, deposit date: September 25, 2017, deposit number: CCTCC M 2017546. The bacterial strain obtained in the present invention degrades 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol with pyroglucinol as the ring-opening substrate, and the bacterial strain of the present invention is a Gram-negative drug that metabolizes 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol through the pyroglucinol pathway. bacteria. On the other hand, 100ppm of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol in the polluted soil can be completely degraded within 12 days by using the prepared restoration bacteria agent. Therefore, the strain has a good application prospect in the biological treatment of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol pollution.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com