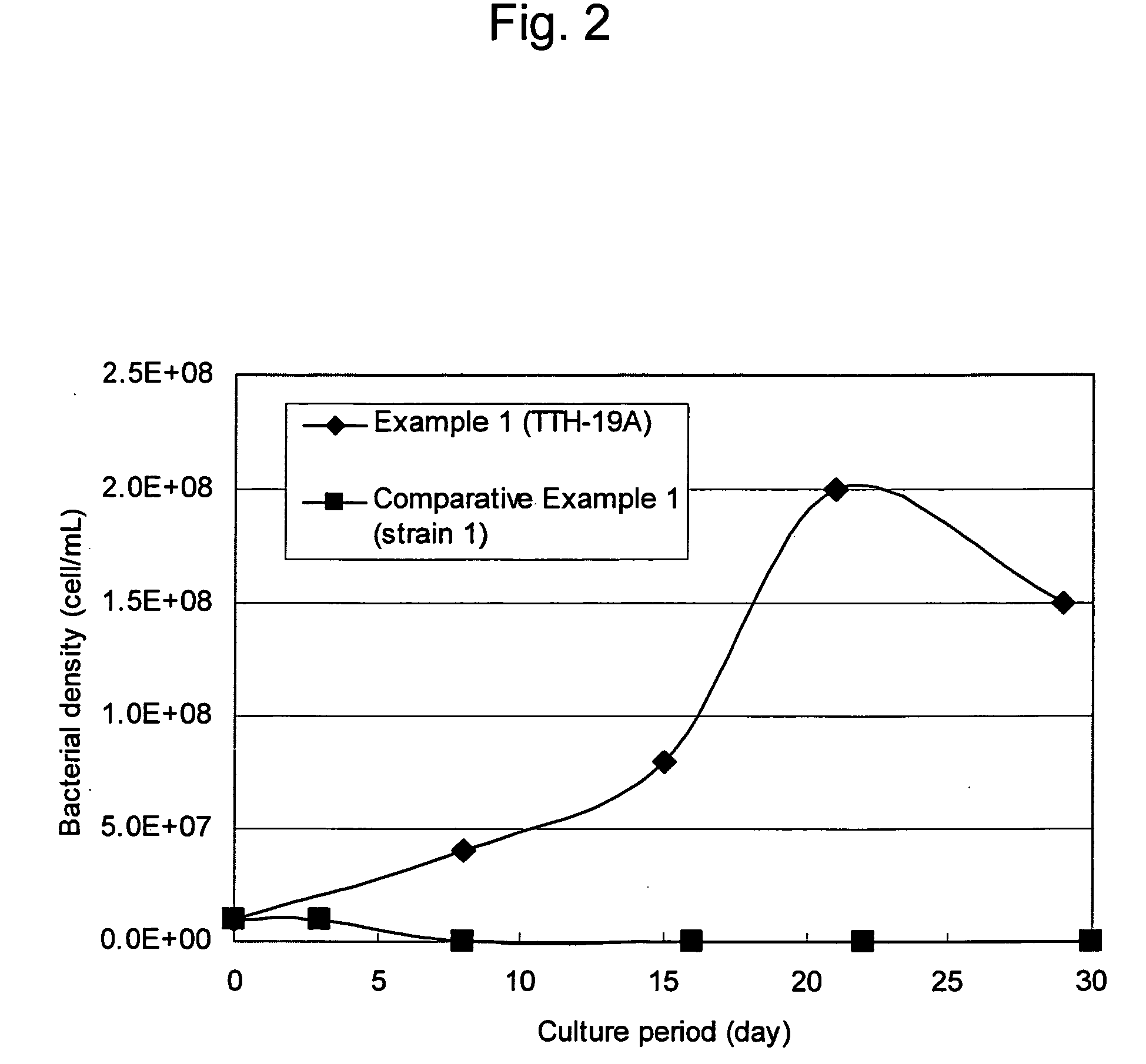
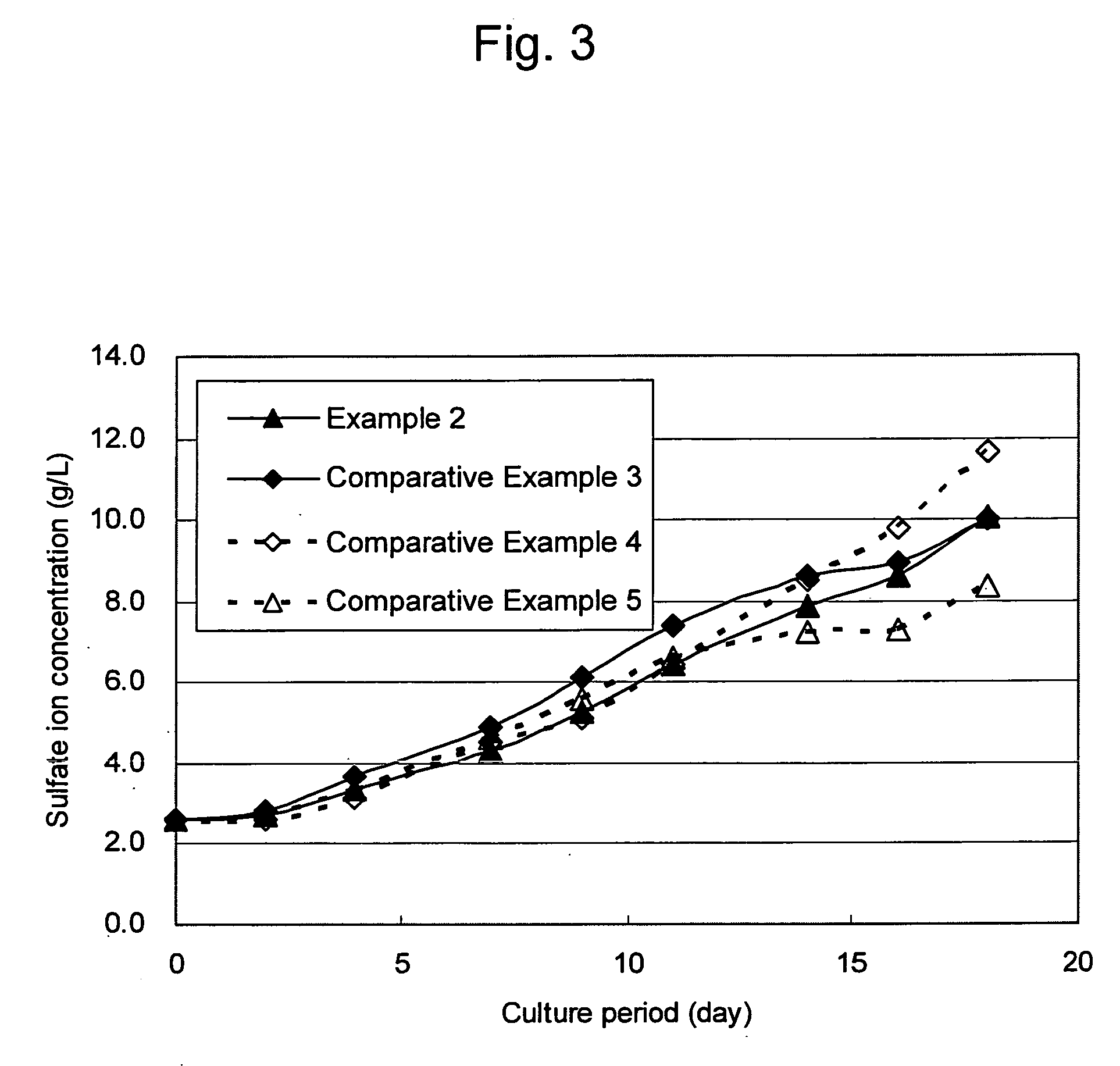
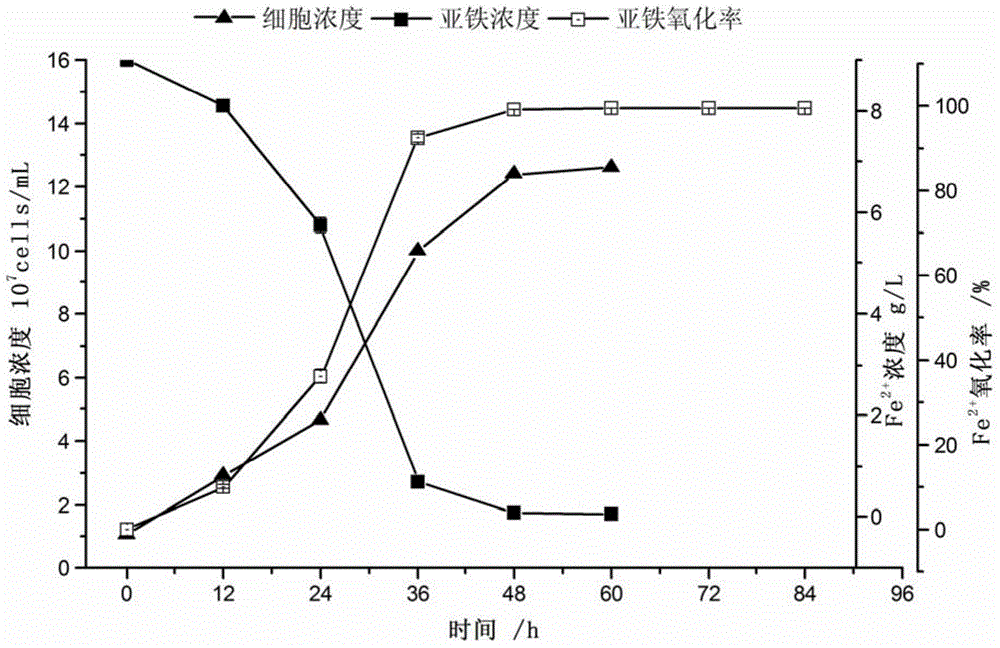
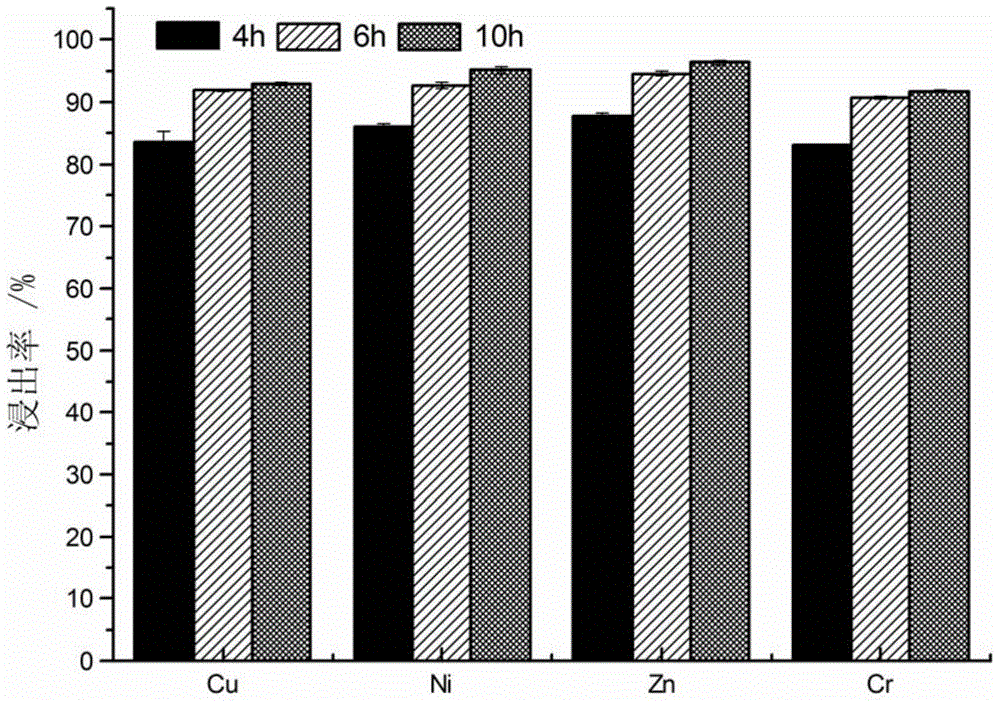
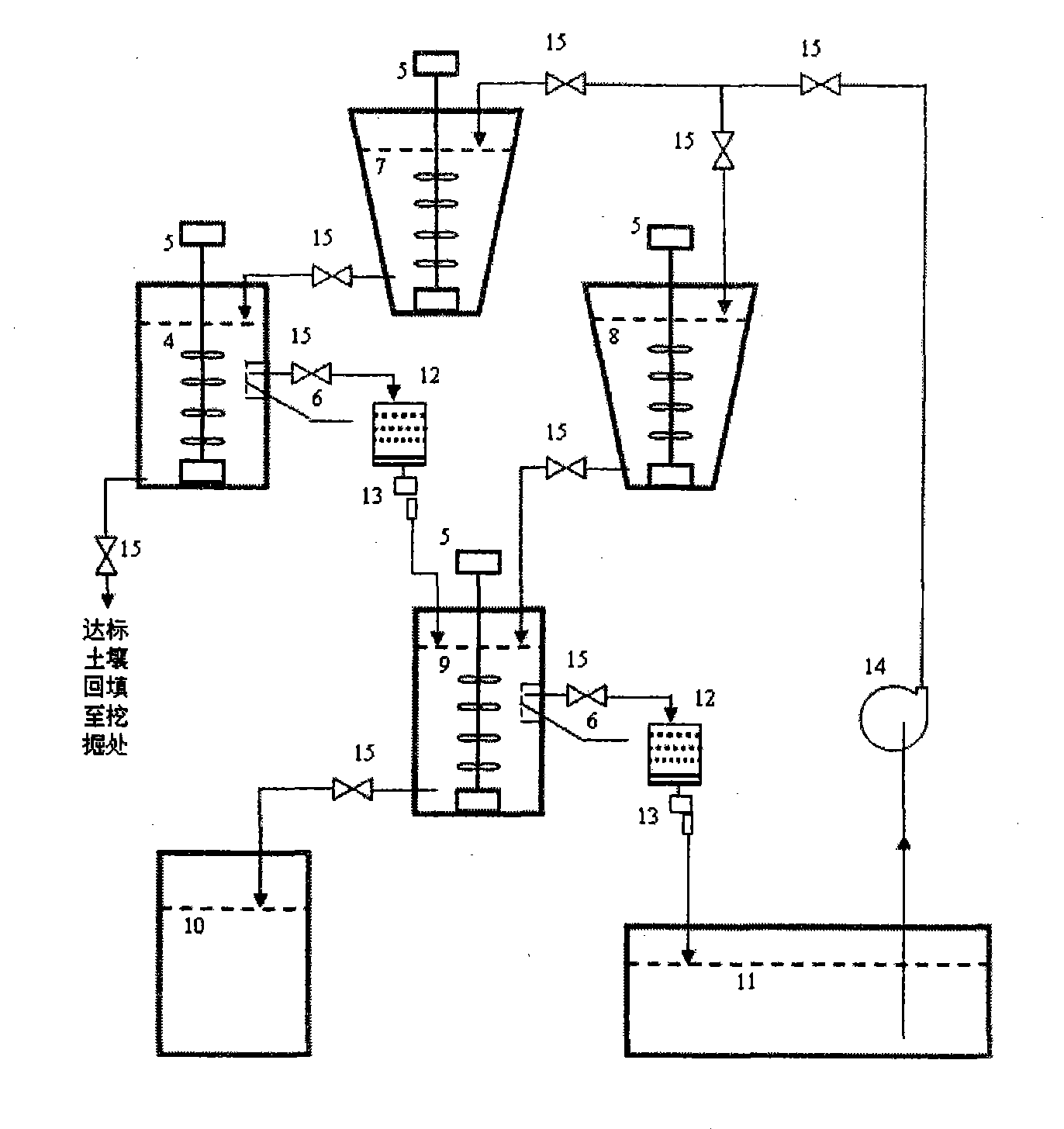
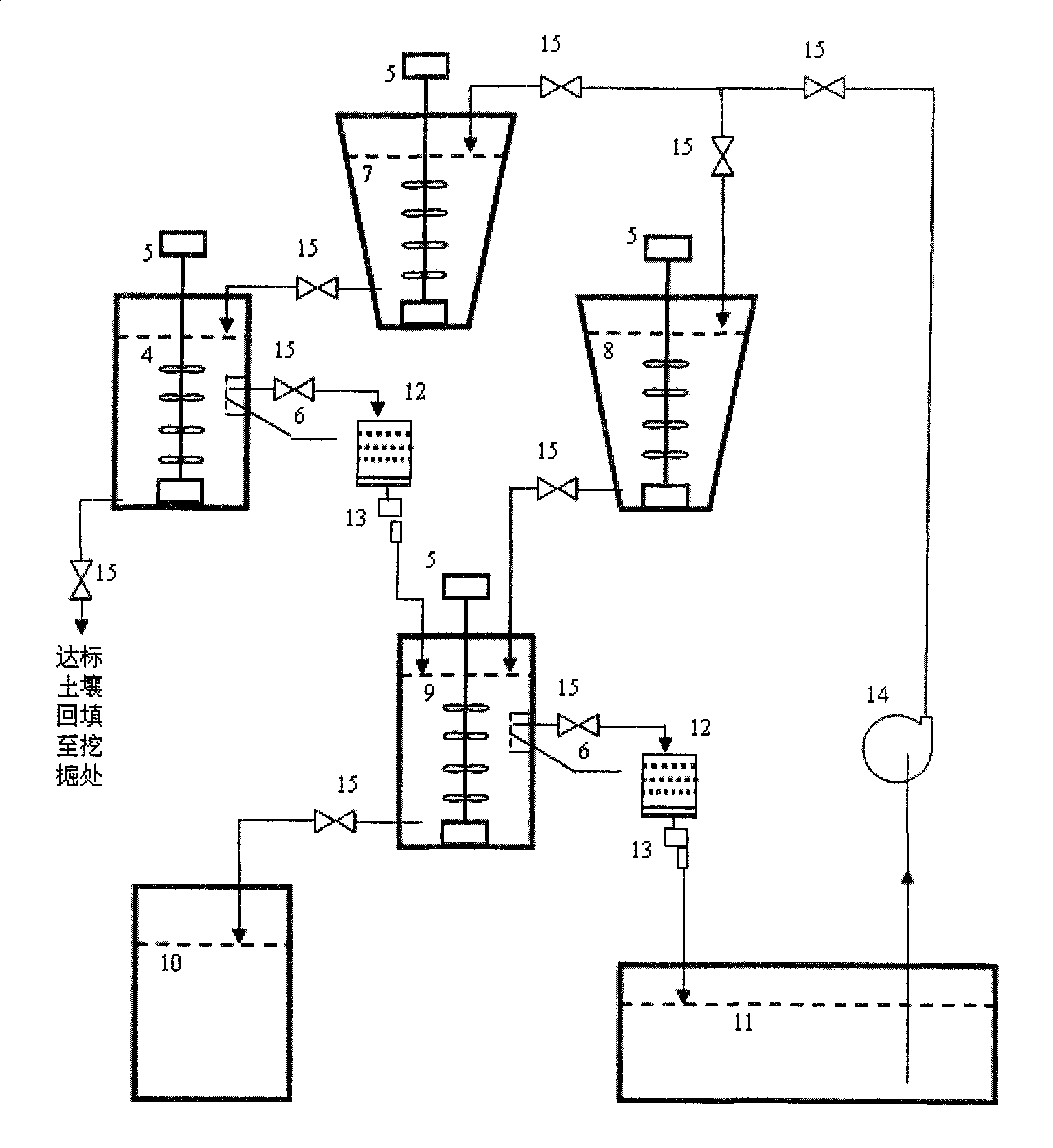
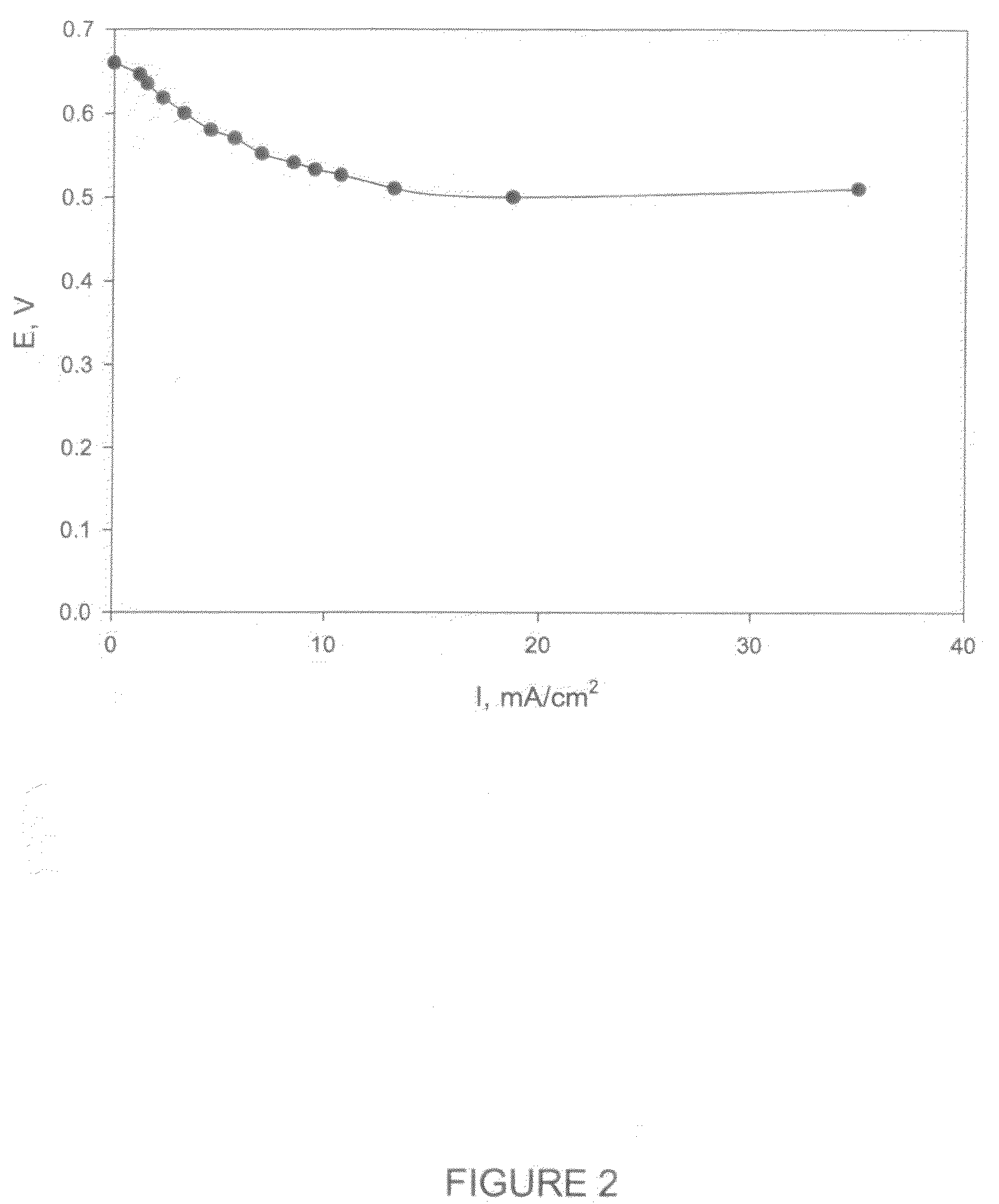
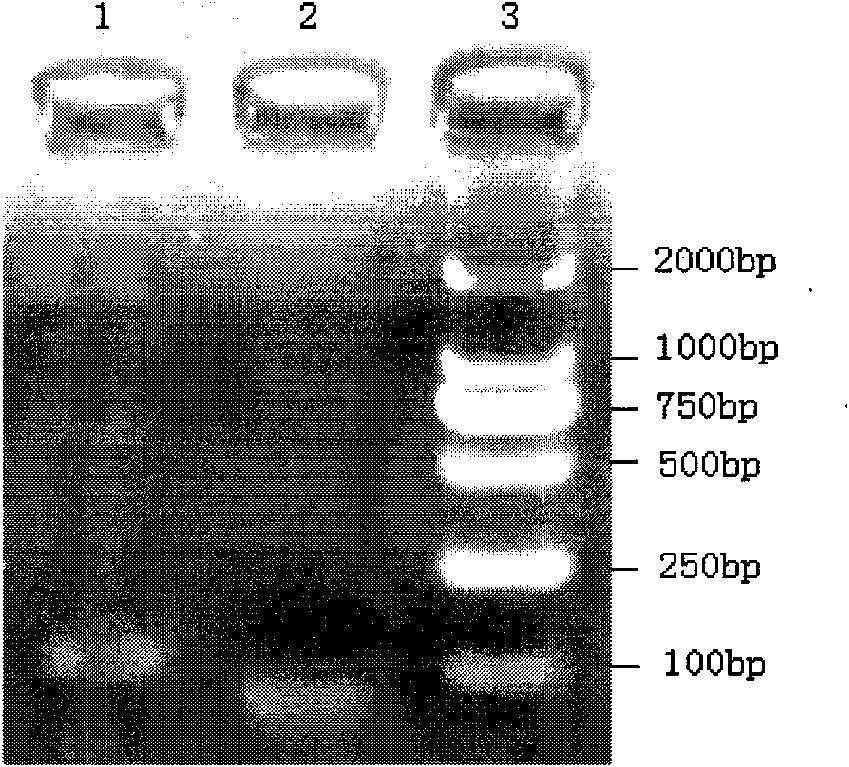Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53 results about "Acidithiobacillus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acidithiobacillus is a genus of the Acidithiobacillia in the "Proteobacteria". Like all "Proteobacteria", Acidithiobacillus spp. are Gram-negative. Some members of this genus were classified as Thiobacillus spp., before they were reclassified in 2000.
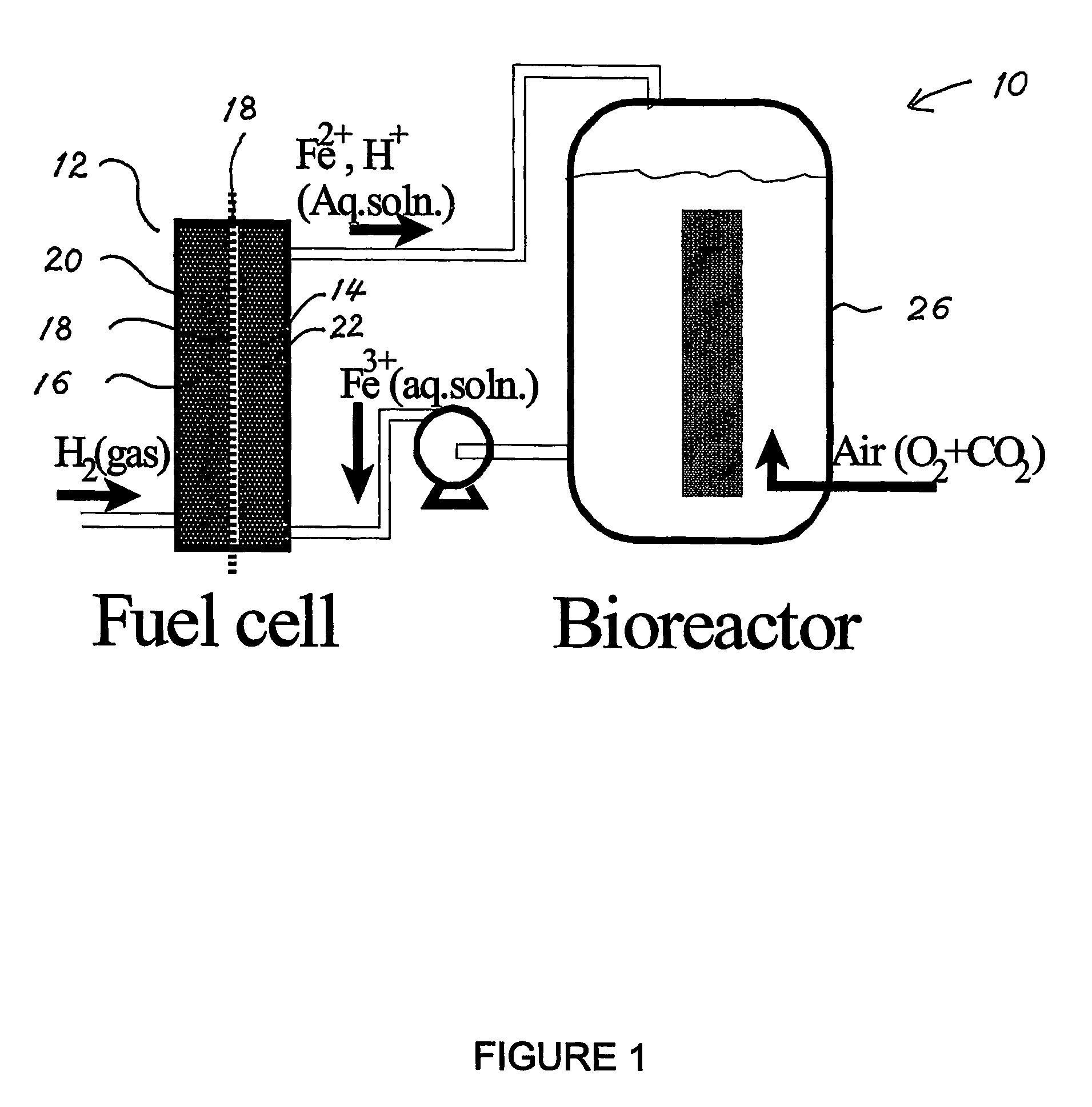
Biofuel cell
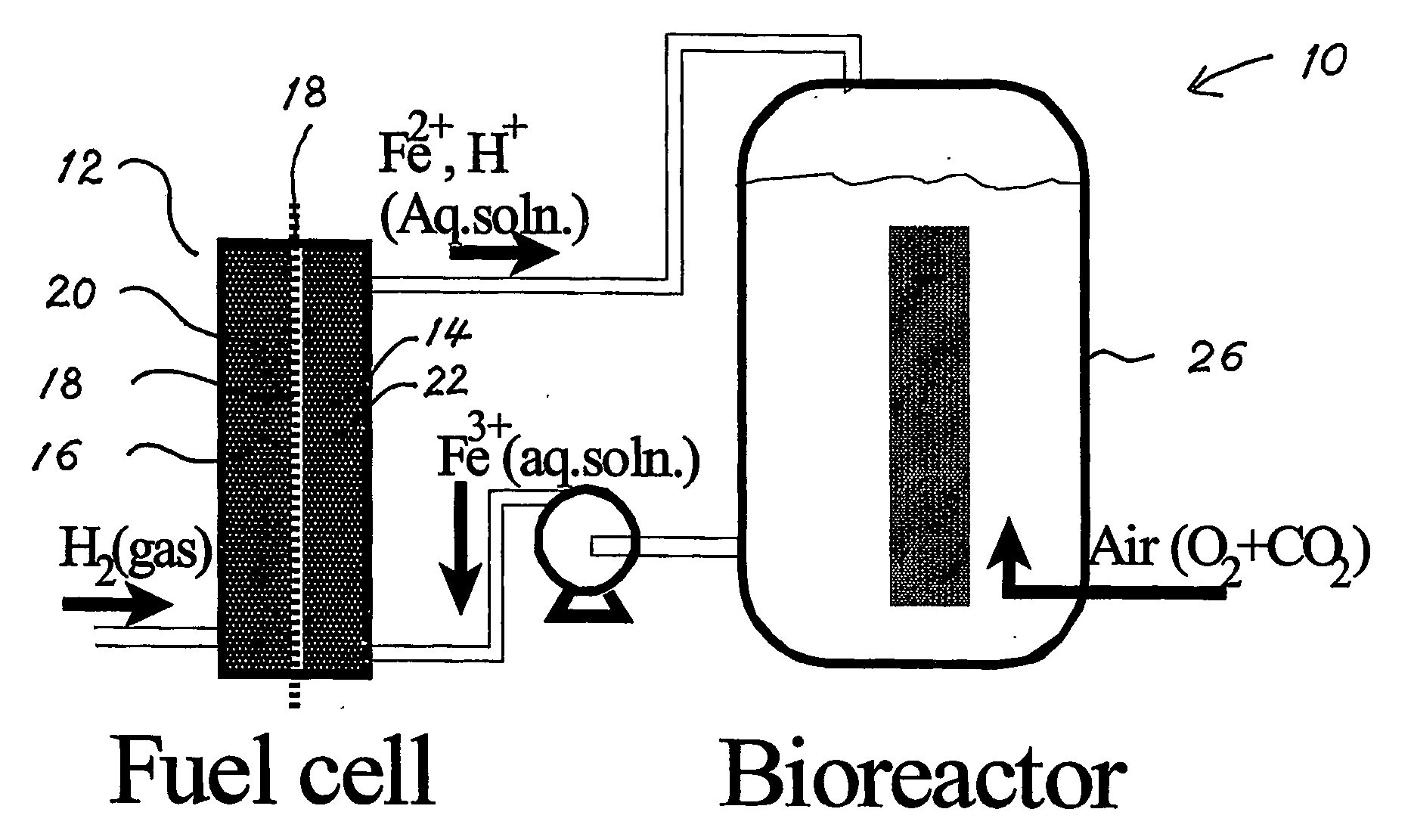
InactiveUS20060251959A1Promote growthElectrolyte holding meansRegenerative fuel cellsMicroorganismHydrogen
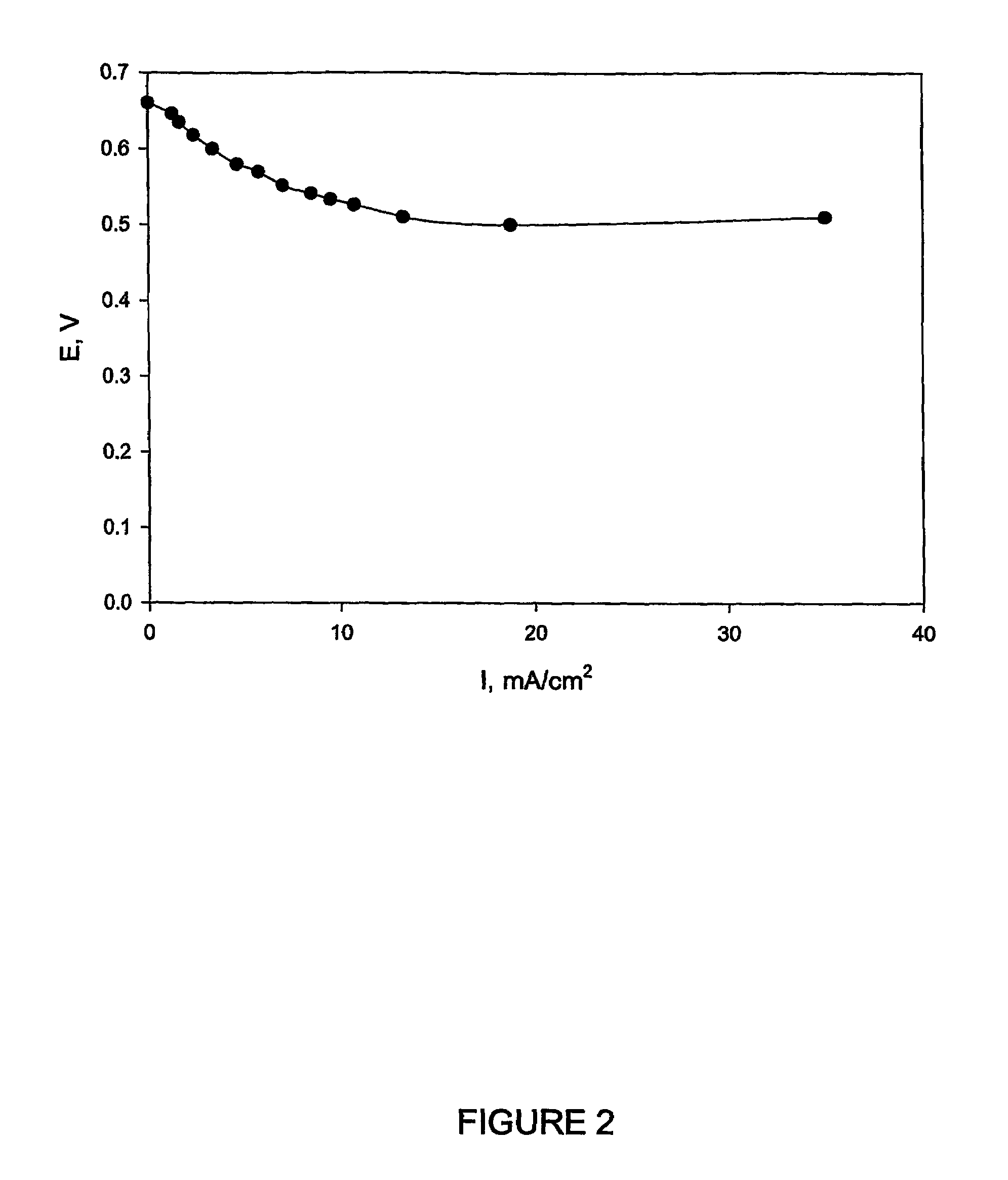
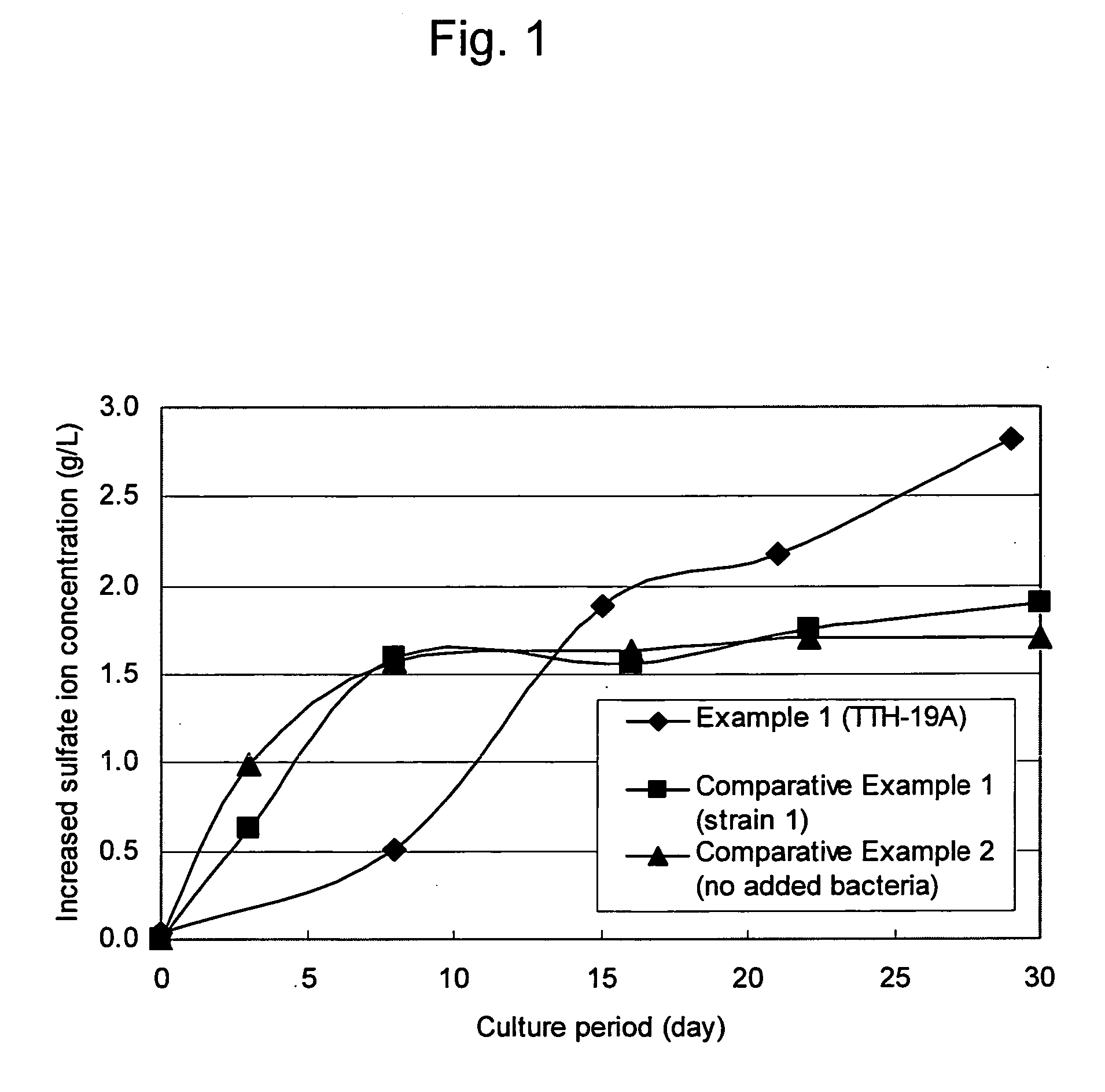
The present invention discloses a new type of biofuel cell, based on the microbial regeneration of the oxidant, ferric ions. The bio-fuel cell is based on the cathodic reduction of ferric to ferrous ions, coupled with the microbial regeneration of ferric ions by the oxidation of ferrous ions, with fuel (such as hydrogen) oxidation on the anode. The microbial regeneration of ferric ions is achieved by chemolithotrophic microorganisms such as Acidithiobacillus ferroxidans. Electrical generation is coupled with the consumption of carbon dioxide from atmosphere and its transformation into microbial cells, which can be used as a single-cell protein.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Domestic garbage harmful microorganism elimination deodorization liquid and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses domestic garbage harmful microorganism elimination deodorization liquid and a preparation method thereof. The domestic garbage harmful microorganism elimination deodorization liquid comprises probiotics components as follows: photosynthetic bacteria accounting for 11 to 17 parts, bacillus accounting for 9 to 13 parts, lactic acid bacteria accounting for 24 to 31 parts, saccharomycete accounting for 17 to 23 parts, nitrifiers accounting for 8 to 12 parts, acidithiobacillus accounting for 8 to 12 parts and ray fungi accounting for 10 to 15 parts. Meanwhile, the invention further discloses the preparation method of the domestic garbage harmful microorganism elimination deodorization liquid. The domestic garbage harmful microorganism elimination deodorization liquid performs self symbiotic propagation to generate group bacteria containing a plurality of beneficial bacteria that can achieve co-existence, co-prosperity and synergism; propagation can produce acid, so that the pH value is decreased to reach 3.6 to 4.8; and various beneficial derivatives for harmful microorganism elimination deodorization are generated. Various harmful microorganisms in domestic garbage can be inhibited so as to be eliminated, so that the generation of malodorous gas can be solved from the source of malodorous gas (hydrogen sulfide, ammonia gas and the like). The harmful microorganism elimination deodorization effect is good, the speed is high, and the suitability is strong. Meanwhile, toxic and harmful substances are converted to nontoxic and harmless substances facilitating growth and absorption of plants during the decomposing process of domestic garbage.
Owner:YULIN SHENGMINGBAO BIOTECH
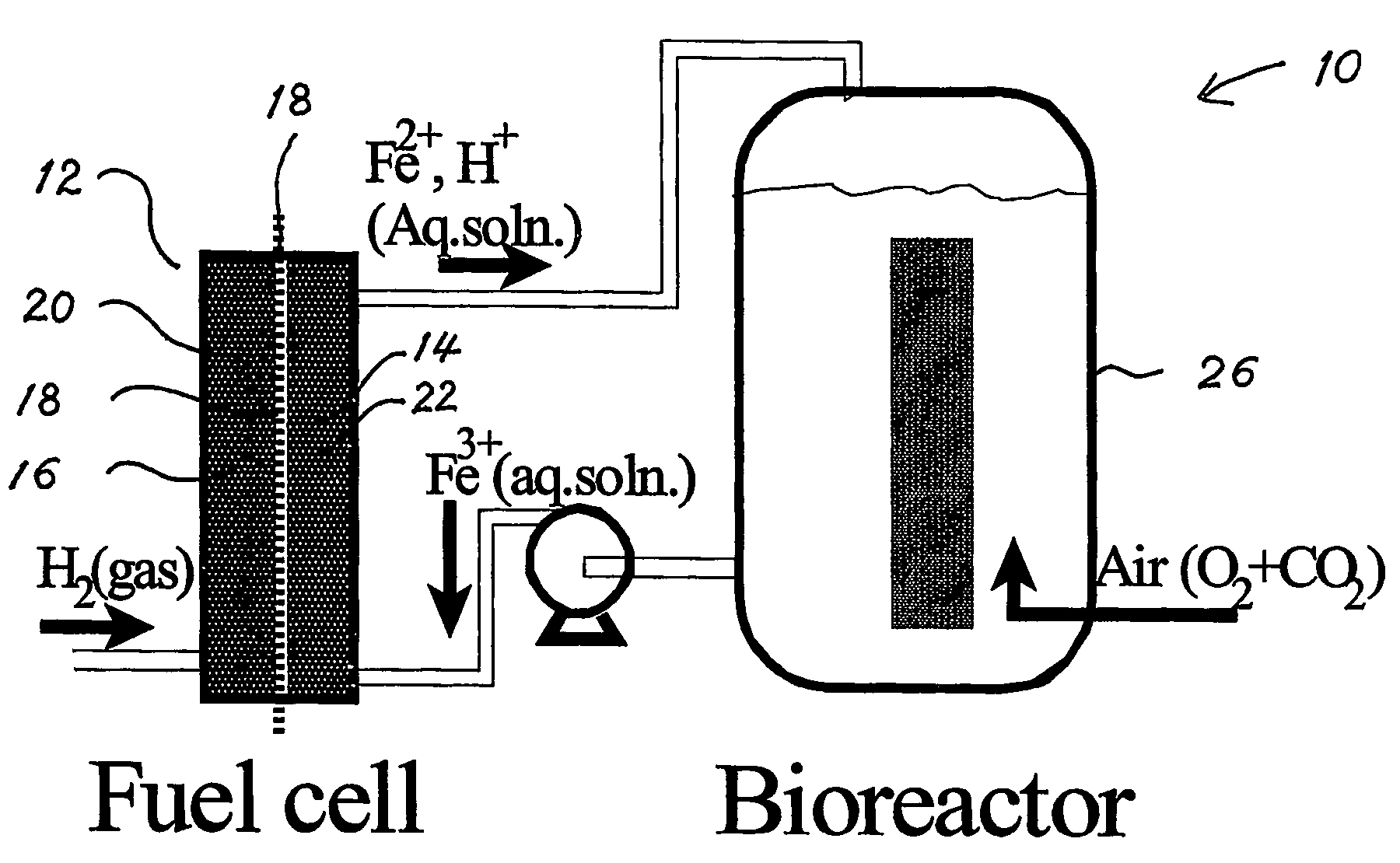
Biofuel cell
The present invention discloses a new type of biofuel cell, based on the microbial regeneration of the oxidant, ferric ions. The bio-fuel cell is based on the cathodic reduction of ferric to ferrous ions, coupled with the microbial regeneration of ferric ions by the oxidation of ferrous ions, with fuel (such as hydrogen) oxidation on the anode. The microbial regeneration of ferric ions is achieved by chemolithotrophic microorganisms such as Acidithiobacillus ferroxidans. Electrical generation is coupled with the consumption of carbon dioxide from atmosphere and its transformation into microbial cells, which can be used as a single-cell protein.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
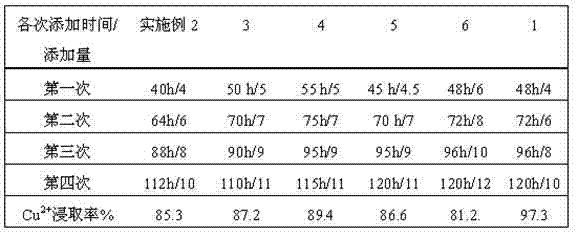
Method for leaching copper in waste printed circuit boards (PCBs) by mixed bacteria
ActiveCN103484680AEasy to addIncrease the amount addedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPre treatmentAcidithiobacillus
The invention discloses a method for leaching copper in waste PCBs by mixed bacteria. The waste PCBs are preprocessed for standby use; acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and acidithiobacillus thiooxidans are subjected to copper-resistant acclimation and culture respectively, and are mixed and cultured in a mixed bacteria culture solution; when the culture time reaches 40h-55h, powder of the PCBs is started to be added; then powder of the PCBs is added in additional dosage point by point at other time points; and bioleaching is performed. According to the method, when the mixed bacteria are cultured, the PH value of the culture solution is not required to be adjusted, two types of bacteria can grow in balance; at the same time, when the two types of bacteria grow, a large amount of sulfuric acid and Fe 3+ are generated and used for leaching copper in the powder of the waste PCBs in a later period; and in the whole process, the efficiency is high, and the energy is saved. A manner of low front, high rear and multipoint addition is adopted; and on the basis that the additive amount of the powder of the waste PCBs is increased, the copper leaching efficiency is improved remarkably, however, the bacteria growth inhibition degree is relatively small.
Owner:YANGZHOU NINGDA NOBLE METAL CO LTD
Acidithiobacillus and application thereof
ActiveCN102174425AStrong molybdenum resistancePromote growthBacteriaProcess efficiency improvementSulfideAcidithiobacillus
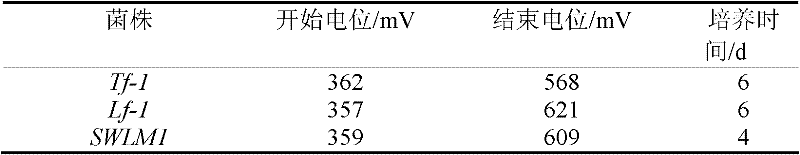
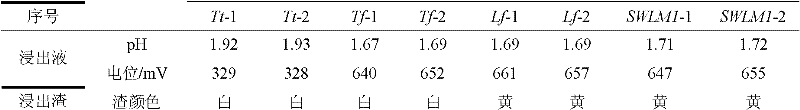
The invention relates to an acidithiobacillus and application thereof. The preserving number of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans SWLM1 of the acidithiobacillus is CGMCC No.3265. The invention also provides the application of the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans in metallurgy, particularly the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is applied to the leaching of molybdenum ore containing Fe2<+> or sulfides. In the invention, the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is added into the molybdenum ore pulp containing the Fe2<+>, the leaching temperature is between 28 DEG C and 32 DEG C, the leaching pH is between 1 and 3, and the Fe2<+> is oxidized into Fe3<+>; the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is also added into the molybdenum ore pulp containing Fe2<+> and sulfides, the leaching temperature is between 28 DEG C and 32 DEG C, the leaching pH is between 1 and 3, and the Fe2<+> and the sulfides are oxidized into Fe3<+> and sulfuric acid or sulfate respectively. The acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans provided by the invention has a stronger molybdenum resisting characteristic, can also grow well when the content of the molybdenum is 1.6 g / L, and can be widely applied to the leaching of molybdenum-bearing minerals.
Owner:BEIJING RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND METALLURGY
Chloride ion-resistant sulfur-oxidizing bacteria
A microorganism having an ability to oxidize sulfur even at high chloride ion concentration is provided. Specifically, a microorganism belonging to the genus Acidithiobacillus having the ability to oxidize sulfur even at high chloride ion concentration is provided. A method for bacterial leaching of copper sulfide ores and a method for improving alkaline soil using the microorganism are also provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Acidophilic iron-oxidizing composite microbial agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104862250AAchieve leachingAchieve recyclingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSludgeMicrobial agent
The invention discloses an acidophilic iron-oxidizing composite microbial agent which comprises the following communities: a ferroplasma acidiphilum-containing strain, an acidithiobacillus ferrivorans-containing strain, an acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans-containing strain, a leptospirillum ferriphilum-containing strain and a sulfobacillus acidophilus-containing strain, wherein a preparation method of the composite microbial agent comprises the following steps: the aforementioned five strains are placed in a specific basic iron salt / nutrient-containing culture medium, and are subjected to the temperature gradient compounding culture, tolerance mixed-heavy-metal gradient pressure type domestication, temperature cycling gradient type domestication, ferrous oxidation activity improvement and tolerance high-iron domestication, so as to obtain the acidophilic iron-oxidizing composite microbial agent. According to the invention, the acidophilic iron-oxidizing composite microbial agent is simple in formulation, economical, adaptable, versatile and efficient, and can be used for the efficient extraction of heavy metals in electroplating sludge.
Owner:HUNAN AIGE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Microorganism detoxification, and solidification and hazard-free treatment method for metal substrate sludge
InactiveCN101898861ARealize closed loopReduce energy consumptionSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesLiquid wasteSulfate-reducing bacteria
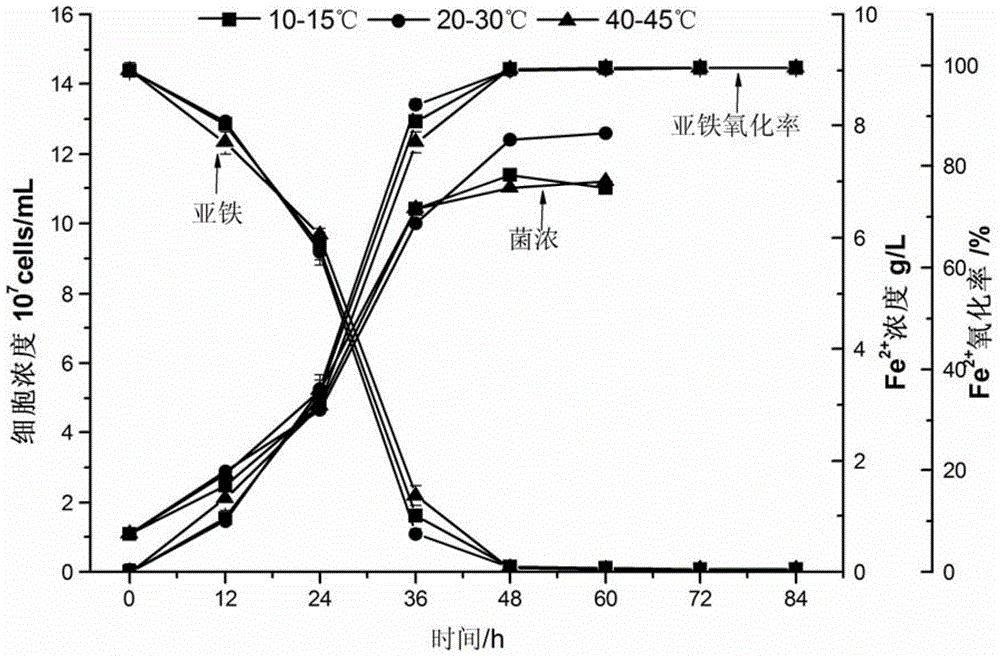
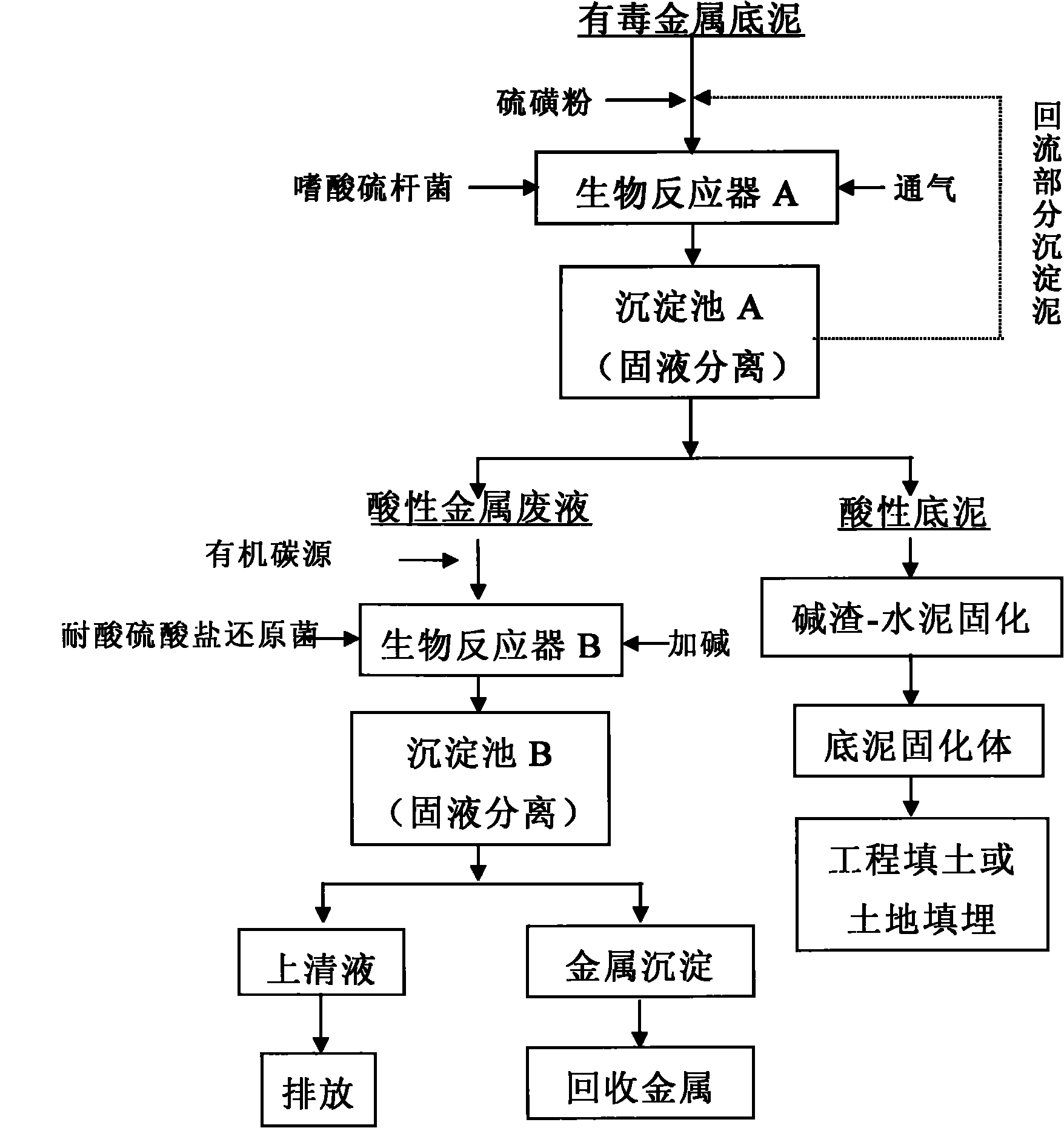
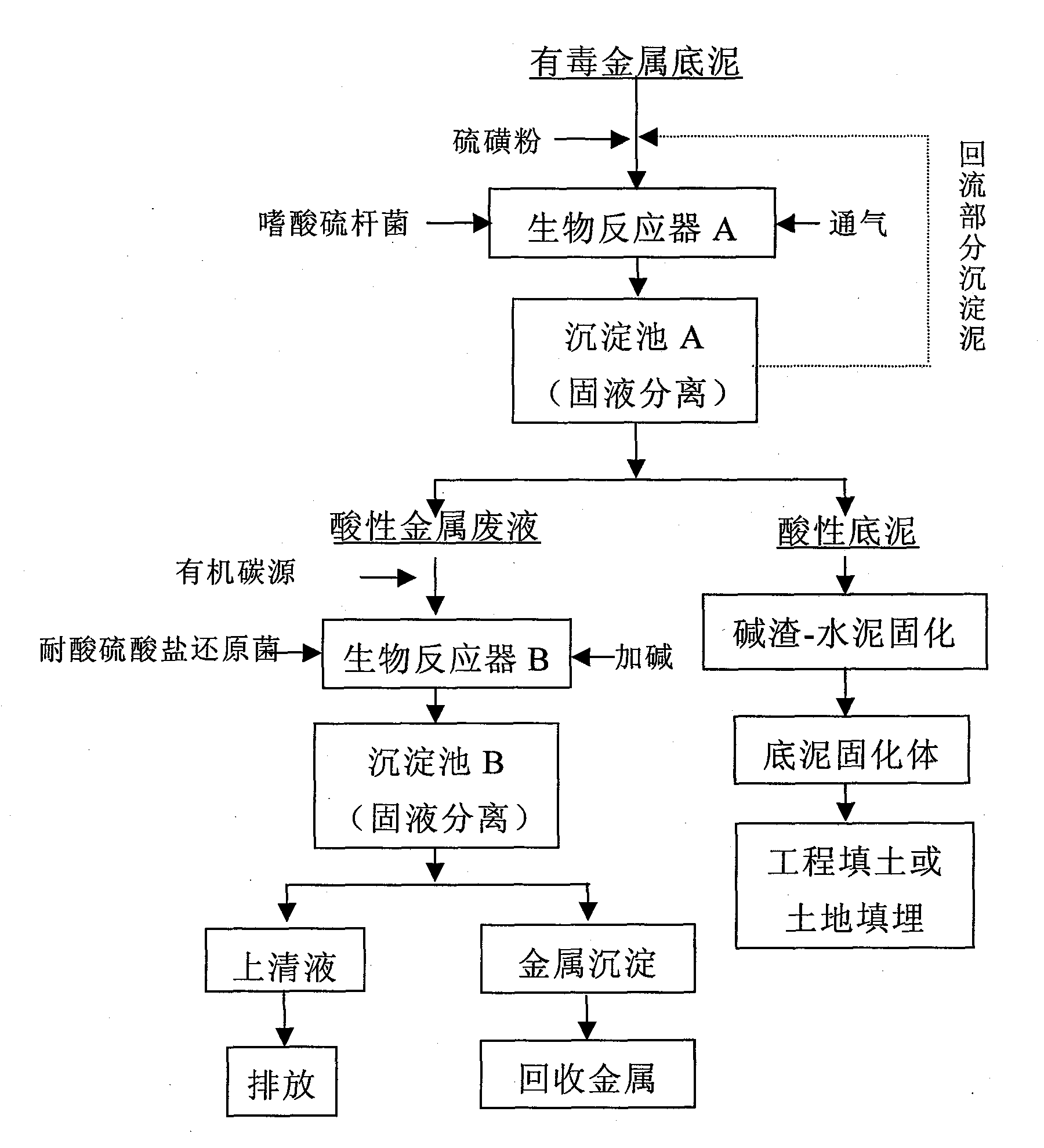
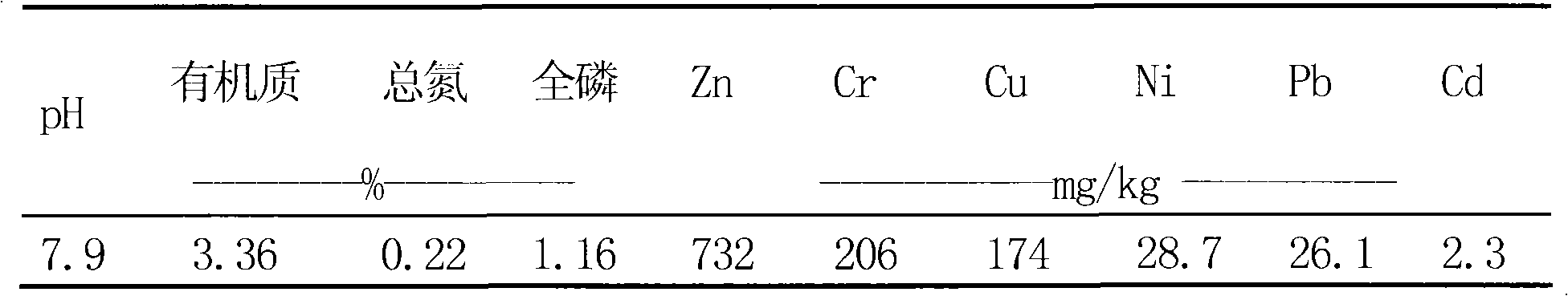
The invention relates to a microorganism detoxification, and solidification and hazard-free treatment method for metal substrate sludge. The method comprises the following steps of: lowering the pH value of the substrate sludge to be 2.5 to 3.0 under the action that sulfuric acid is generated by microbial oxidation of acidithiobacillus spp.; dissolving toxic metal from a solid phase of the substrate sludge into a liquid phase; and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain acid toxic metal waste solution and solid-phase acid substrate sludge which hardly contains toxic metal, and in the liquid-phase part, reacting microbial reduction product H2S of acid-resisting sulfate reducing bacteria with toxic metal ions to obtain metal sulfide deposit to realize standard emission; and performing solidification treatment on the solid-phase part by using caustic sludge as a modifier and using cement as a curing agent to finally finish full detoxification and hazard-free treatment of the toxic metal substrate sludge, wherein the treated substrate sludge meets the requirements of engineering filling and landfill. The method of the invention has the advantages of full detoxification, no secondary pollution, a few process devices, low energy consumption and suitability for industrial operation.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Preparation method of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidian genetic engineering strain with quick growth speed and strong uranium and heat resistance capacities as well as application thereof
InactiveCN101659962AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionAcidithiobacillusGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a preparation method of an acidithiobacillus ferrooxidian genetic engineering strain with quick growth speed and strong uranium and heat resistance capacities as well as the application thereof, wherein the strain is Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans QEY-6(pJRD215-PT-rcs), CCTCCM 209156; and the preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, augmenting a T5 promoter and a T0 terminator of pQE30, and establishing a shuttle expression vector pJRD215-PT together with pJRD 215; secondly, augmenting and cloning a micrococcus luteus rpf gene, a caulobacter crescentuscc3302 gene and a sulfolobus shibatae ss10b gene to a T vector; thirdly, establishing a recombined shuttle expression vector pJRD215-PT-rcs; and fourthly, establishing the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidian genetic engineering strain which fusedly expresses rpf, cc3302 and ssh10b genes. The invention has simple operation and good repeatability, and can shorten the uranium leaching period, improve theleaching rate and reduce the acid-consuming rate.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Microbial soil remediation agent and soil remediation method
InactiveCN110355196AHigh organic contentEliminate compactionAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesPhylum CyanobacteriaSulfate-reducing bacteria
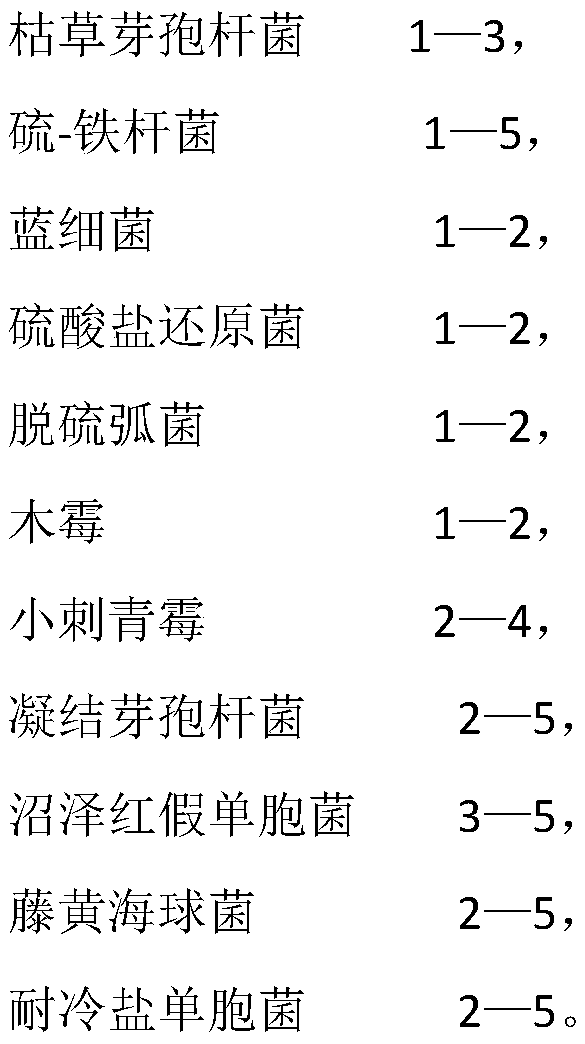
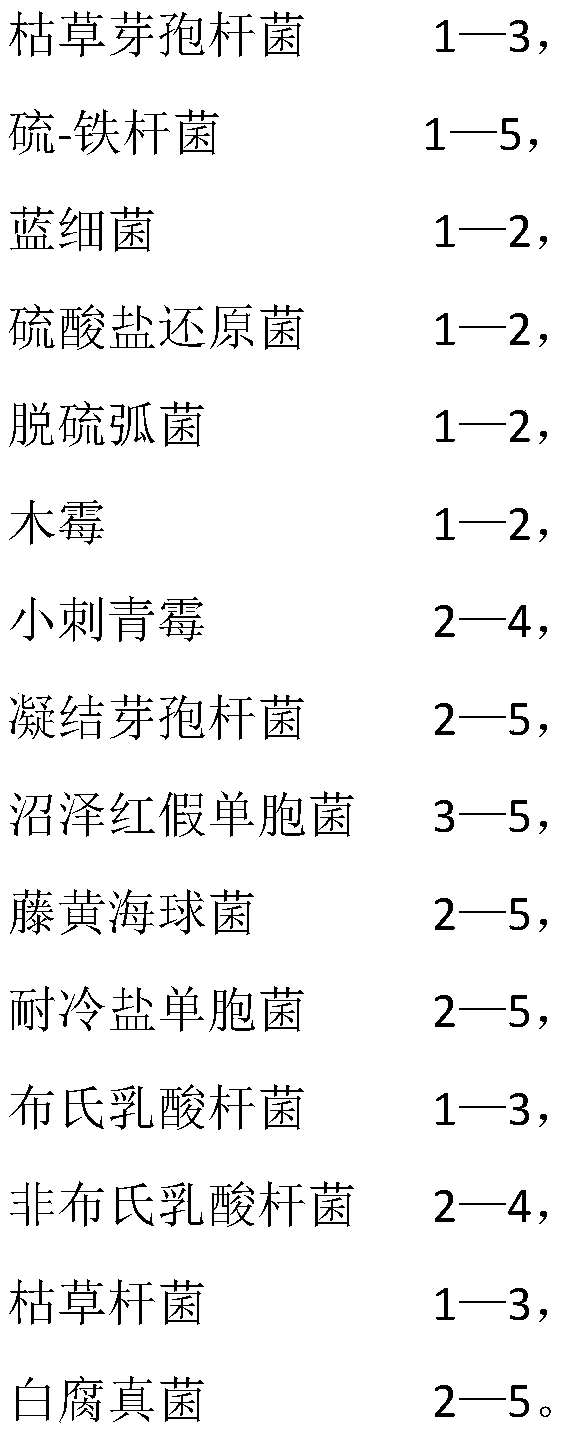
In order to solve the problem that conventional soil remediation technology has a single remediation function, can only remedy soil hardening and salinization and cannot reduce the content of heavy metal, the invention provides a microbial soil remediation agent and a soil remediation method. The microbial soil remediation agent is composed of the following substances, by mass: 1-3 parts of bacillus subtilis, 1-5 parts of acidithiobacillus ferooxidans, 1-2 parts of cyanobacteria, 1-2 parts of sulfate reducing bacteria, 1-2 parts of desulfovibrio desulfuricans, 1-2 parts of trichoderma, 2-4 parts of penicillium spinulosum, 2-5 parts of bacillus coagulans, 3-5 parts of rhodopseudomonas palustris, 2-5 parts of garcinococci, and 2-5 parts of cold salt tolerant gingivalis. The microbial soil remediation agent and the soil remediation method of the invention can effectively reduce the heavy metal content of oil, adjust the pH of the soil, reduce the cadmium content of crops and increase theyield of the crops.
Owner:重庆丰衣谷农业科技有限公司
Preoxidation treating method for leaching arsenic golden ores by using drum type reactor organisms
InactiveCN101899570AOvercoming high mass transferOvercoming the Paradox of Low ShearProcess efficiency improvementHigh concentrationSlurry
The invention relates to a preoxidation treating method for leaching arsenic golden ores by using drum type reactor organisms. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) rinsing arsenic golden concentrate ores; (2) filtering, drying, grinding, activating and acid presoaking the rinsed arsenic golden concentrate ores; (3) acclimating and culturing the induced bacteria of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, and amplifying and culturing to prepare induced mixing bacteria; (4) inoculating the induced mixed bacteria into the drum type reactor to leach the organisms of high-concentration arsenic golden ores; and (5) cyanizing and extracting golden from the arsenic golden ores leached residues. The drum type reactor comprises a gas distributor, wherein the gas distributor comprises a gas inlet pipe, a gas guide branch pipe, a gas distributing pipe and a gas outlet pipe. The gas distributor realizes the gas predispersing and sufficient gas and liquid contact and mixing, and promotes the sufficient gas and liquid mass transfer and dissolved oxygen supply. The invention fundamentally solves the problems of high mass transfer rate and low shearing in high ore slurry concentration, and realizes the high-efficiency biology preoxidation of arsenic golden ores.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Complex acidophilic microbial agent as well as preparation method and application thereof in treating waste copper-clad plate flotation residue
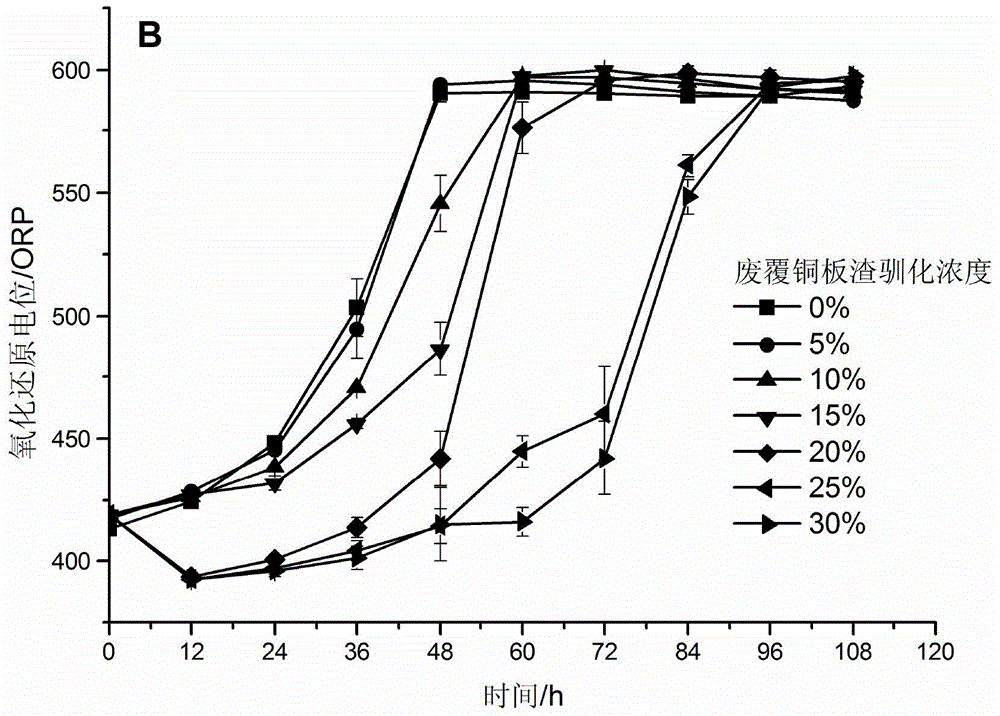
ActiveCN105132319AEasy to prepareLow costBacteriaProcess efficiency improvementMicrobial agentSlurry
The invention discloses a complex acidophilic microbial agent, wherein the colony consists of five strains, namely ferroplasma thermophilum, leptospirillum ferriphilum, sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, acidithiobacillus ferrivorans, acidithiobacillus ferroxidans and the like. The preparation method of the complex microbial agent sequentially comprises steps of proportional compounding of microbial agent, temperature gradient complex culture, waste copper-clad plate residue tolerance domestication and the like; and by virtue of the complex acidophilic microbial agent disclosed by the invention, valuable metallic copper in high-grade or low-grade waste copper-clad plate residue can be leached, which can be specifically achieved by an operating process as follows: mixing the complex microbial agent with waste copper-clad plate residue and iron-containing basic salt / nutrient medium so as to obtain mixed slurry; and continuously stirring and leaching at room temperature until a leaching operation is completed, and meanwhile ventilating in the bottom. The complex microbial agent and the application thereof disclosed by the invention have the advantages of being simple in formula, good in economical efficiency, strong in adaptability, efficient and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
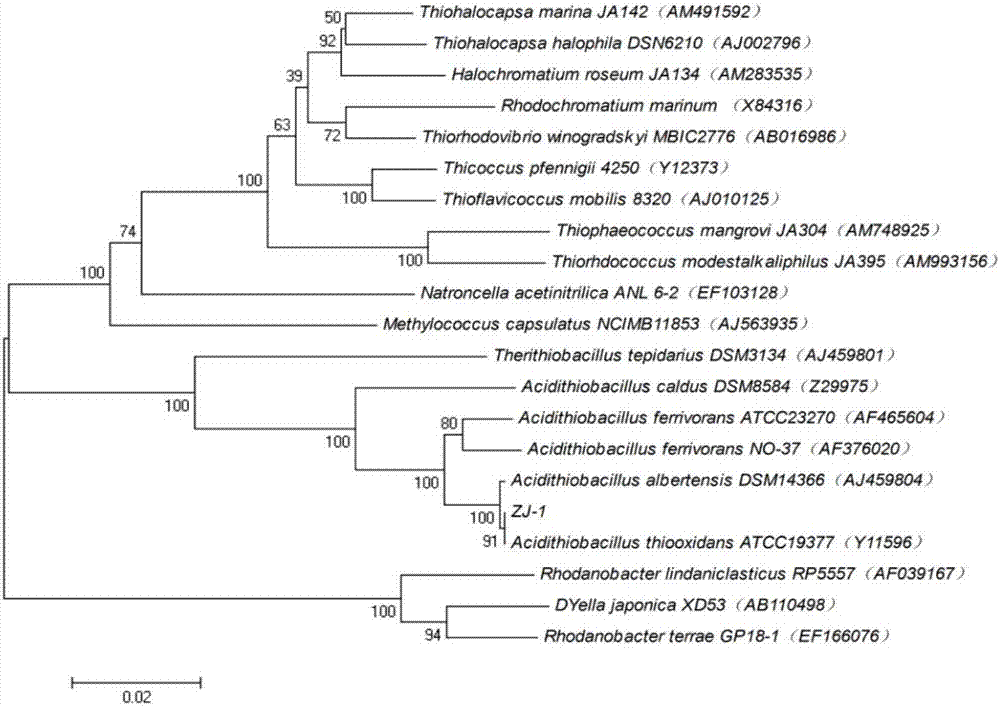
Sulfur oxide thiobacillus and application thereof in heavy metal removal
InactiveCN106906173ALess investmentLow running costBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationThiobacillus ferrooxidansOptimal growth
The invention relates to a sulfur oxide thiobacillus Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans ZJ-1 and an application thereof in heavy metal removal. The bacterial strain is preserved in the China Microbial Culture Preservation Management Committee General Microbiology Center, the preservation number is CGMCC No. 12387. The optimum growth temperature of the bacterial strain ZJ-1 is 28 DEG C, and the optimal growth pH value is 3.0. The bacterial strains can separate out the heavy metals in all kinds of wastes, can be used for the removal of heavy metals in all kinds of wastes and has an important function for preventing the secondary pollution of heavy metals.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Bacterial leaching way of vanadium in high-sulfur vanadium stone-like coal
InactiveCN101760649AReduce energy consumptionReduce usageProcess efficiency improvementSulfurGranularity
The invention discloses a novel bacterial leaching way of vanadium in high-sulfur vanadium stone-like coal, mainly utilizing the characteristic that acidithiobacillus thiooxidans generates sour, and the vanadium of the stone-like coal mineral is leached out. The stone-like coal mineral is crushed and grinded until granularity is less than 0.10mm, and then the stone-like coal mineral is mixed with leaching agent containing with acidithiobacillus thiooxidans for finishing the leaching process under room temperature (15-25 DEG C). After a period for leaching, leaching agent with vanadium is gotten. The invention has the following beneficial effects that 1, the invention is a biological metallurgy way and belongs to the cleaning productive technology; 2, the invention has simple operation and small investment; 3, the characteristic that the acidithiobacillus thiooxidans generates sour is utilized, thus avoiding using a lot of vitriol.
Owner:浙江豪美钒业有限公司
Method for achieving plant-microorganism combined remediation on soil of coal mining area
ActiveCN108160685AImprove repair efficiencyImprove repair effectContaminated soil reclamationGlomus coronatumBioremediation
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil bioremediation, particularly relates to a method for remedying soil of a coal mining area, and discloses a method for achieving plant-microorganismcombined remediation on soil of a coal mining area. According to the method, trisetum bifidum seeds are exposed to the sun, soaked and sprouted, then the sprouted trisetum bifidum seeds are sown in aplug containing a seedling grow matrix for emerging and seedling grow, then a mixed bacterium agent formed by acidithiobacillus ferrooxins, trametes versicolor and glomus coronatum is applied, afterthe polluted soil of the mining area is leveled, improved and ditched, seedlings are buried in ditches for soil return seedling covering, field management is carried out, and after growing for 90-120days, the seedlings are harvested. Through the method, after one or more times of planting, the physicochemical indexes of the soil of the coal mining area can be obviously improved to reach the normal standard, a new way is provided for soil control of wide coal mining areas, and wide application prospects are achieved.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Copper sulphide leaching in ferrous chloride medium with bacteria
InactiveUS20170335275A1Inhibition formationBacteriaProcess efficiency improvementIron sulphateSulfide
A method for leaching secondary and primary sulphides of copper in a ferrous chloride medium with iron-oxidising bacteria adapted from the crushing of the mineral from the mine, includes steps of: mixing the mineral from the crushing with concentrated sulphuric acid; transporting the material mixed with sulphuric acid by means of a belt; adding a liquid leaching solution at an intermediate point during transport on the belt, the solution consisting of: iron (II) sulphate to reduce the redox potential of the solution-mineral mixture to values less than 550 mV Ag / AgCl; iron (III) sulphate; bacteria and archaea of the mesophile- and thermophile-type belonging to the genera Acidithiobacillus, Leptospirillum and Sulfulobos; and sodium chloride to produce a chlorinated environment in solutions. The method also comprises the subsequent steps of: heaping the material on heap pads; during the resting step, injecting air warmed by a liquid / air exchange system; and leaching the heaped material.
Owner:COMPANIA MINERA ZALDIVAR SPA
Method for removing heavy metals of livestock and poultry wastes
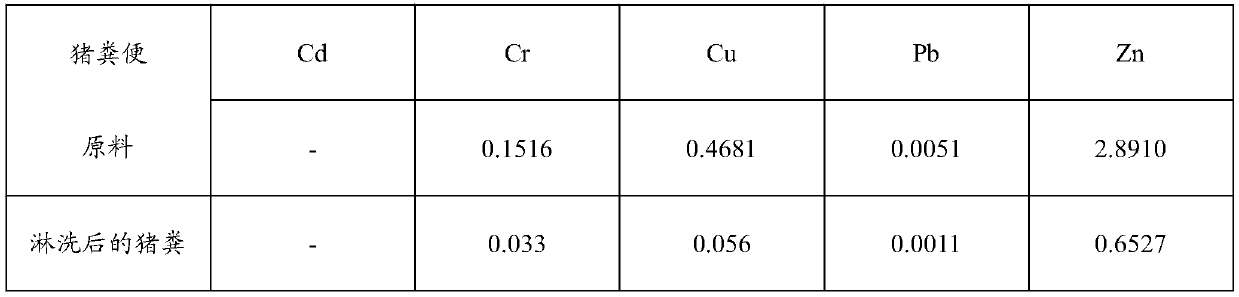
InactiveCN109250882AEfficient removalAchieve concentrated recoveryWater contaminantsBiological sludge treatmentWaste treatmentAcidithiobacillus
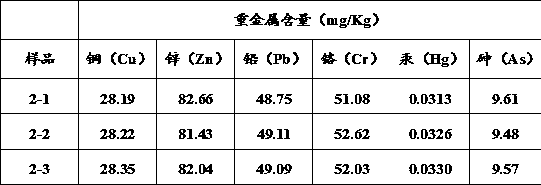
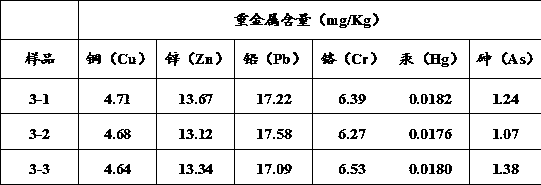
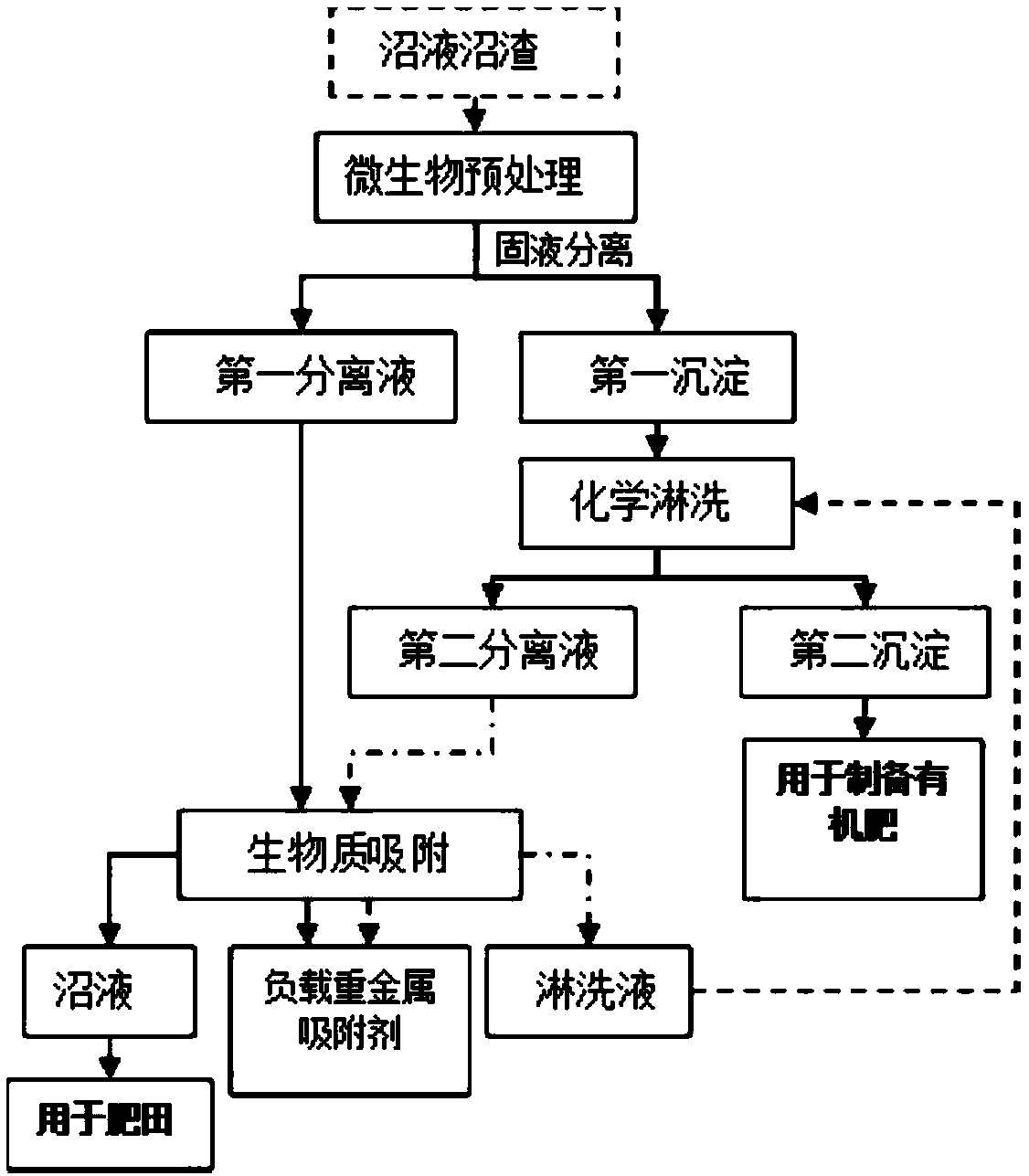
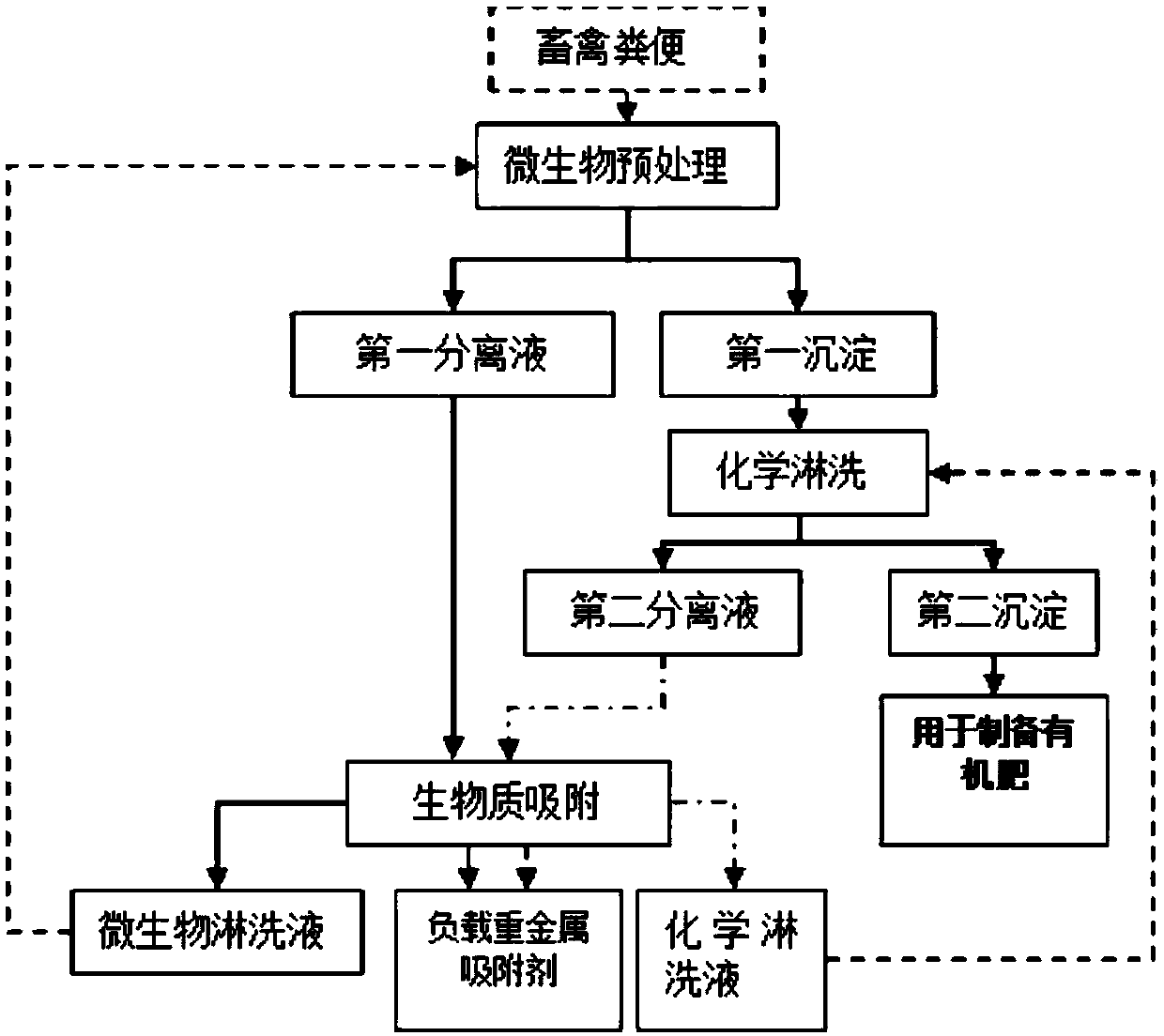
The invention provides a method for removing heavy metals of livestock and poultry wastes, and belongs to the technical field of waste treatment, wherein the method includes the steps: cultivating anddomesticating a culture solution with acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans or acidithiobacillus thiooxidans as a dominant strain; mixing the culture solution with the livestock and poultry wastes, and carrying out solid-liquid separation, to obtain a first separation liquid and a first precipitate; mixing the first precipitate with an acid solution, and carrying out solid-liquid separation, to obtain asecond separation solution and a second precipitate; and mixing the first separation solution and the second separation solution with an adsorbent, and adsorbing to remove heavy metals from the separation solution, so as to realize the removal of the heavy metals of the livestock and poultry wastes. The method provided by the invention can efficiently remove the heavy metals Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb and Znfrom the livestock and poultry wastes.
Owner:JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
Mercury removal agent for treating waste water containing mercury
InactiveCN102476860AHigh selectivityWill not cause secondary pollutionWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSodium bicarbonateIron sulfate
The invention discloses mercury removal agent for treating waste water containing mercury, which is formed by compounding engineering bacillus, inorganic matters and organic aldehyde. The engineering bacillus includes one or two of engineering acidithiobacillus, iron-oxidizing bacteria, mercury removal bacillus and pseudomonas cepacia, the inorganic matters include one or two of sodium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, sodium bisulfate and ferrous sulfate, and the organic aldehyde includes one or two of cyclohexyl formaldehyde, trioxymethylene, O-phthalic aldehyde and p-fluoro benzaldehyde. Undera condition with a pH (potential of hydrogen) value ranging from 6.0 to 8.0, the composite mercury removal agent is added into waste water with mercury concentration ranging from 50mg / L to 1000mg / L, the mass ratio of the fed mercury removal agent to the waste water ranges from 1:100 to 1:500, fermentation is carried out for 24 to 48 hours under an anaerobic condition, mercury in the waste water can be converted into mercury steam, the mercury steam is absorbed by hydrogen sulfide gas to generate precipitated mercuric sulfide, and accordingly the purpose of removing the mercury is achieved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU YAHUAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Method for extracting copper out of waste printed circuit board by employing mixed bacteria
ActiveCN104726714AEasy to addIncrease the amount addedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCopperPre treatment
The invention discloses a method for extracting copper out of waste printed circuit boards by employing mixed bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: pre-treating waste printed circuit boards (PCBs) for later use; respectively carrying out copper-resistant domesticated incubation on acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, carrying out mixed cultivation in mixed bacteria culture liquid, and adding PCBs powder when the culture time reaches 40-55 hours; and adding the PCBs powder at other time points point by point in increase quantity, and carrying out biological extraction. Two bacteria can grow in balance without adjusting the pH value of the culture liquid in mixed bacterial cultivation; meanwhile, when the two bacteria grow, a lot of sulfuric acid and Fe<3+> are generated for extracting copper out of the waste PCBs powder in the later period; the overall process is high in efficiency; and energy sources are saved. In a front-low and rear-high multi-point adding manner, the extraction rate of copper is significantly improved on the basis of improving the adding amount of the waste PCBs powder; and the inhibition degree on bacterial cell growth is relatively low.
Owner:YANGZHOU NINGDA NOBLE METAL CO LTD
Application of microbial preparation for efficiently converting heavy metal cadmium in polluted soil
The invention discloses an application of a microbial preparation for efficiently converting heavy metal cadmium in polluted soil. The microbial preparation is prepared by performing enriched cultivation on the following two mixed floras: (1) candida mycoderma bacteria, aspergillus monicus, rhodosporidium toruloides and cryptococcus which form a flora 1; and (2) acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, leptospirillum ferrooxidans, acidithiobacillus caldus, sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and thermos ferric bacteria which form a flora 2. By using the microbial preparation to treat the cadmium polluted soil, the metal cadmium is converted from being indissolvable into being soluble and the removal rate is 70-82%. The microbial preparation disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being high in conversion efficiency, short in period, low in cost, free of secondary pollution, easy to popularize and the like.
Owner:HUNAN AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT +1
Method for screening unmarked gene knockout bacterial strain of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans
ActiveCN103232994AEfficient knockoutEasy to exploreMicrobiological testing/measurementHybrid cell preparationThiobacillus ferrooxidansBeta-Galactosidases
The invention discloses a method for screening an unmarked gene knockout bacterial strain of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. The method comprises introducing a knockout plasmid for construction of a target gene and an induction plasmid carrying an I-SceI gene into acidithiobacillus thiooxidans by conjugational transfer, carrying out single recon screening by a resistance maker, and carrying out double recon preliminary screening by blue-white selection. The method discloses the method for unmarked gene knockout of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans first, utilizes beta-galactosidase blue-white selection for double recon screening, can fast, stably and efficiently knock out a target gene, solves the problem that in the existing unmarked gene knockout process, selective pressure lacks so that screening is difficult, shortens double recon screening time, improves screening efficiency, reduces a screening cost and provides a novel method for stable genetic modification of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A kind of acidophilic ferric oxidizing microbial composite bacterial agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104862250BEasy to prepareLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIron saltsMicrobial agent
The invention discloses an acidophilic iron-oxidizing composite microbial agent which comprises the following communities: a ferroplasma acidiphilum-containing strain, an acidithiobacillus ferrivorans-containing strain, an acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans-containing strain, a leptospirillum ferriphilum-containing strain and a sulfobacillus acidophilus-containing strain, wherein a preparation method of the composite microbial agent comprises the following steps: the aforementioned five strains are placed in a specific basic iron salt / nutrient-containing culture medium, and are subjected to the temperature gradient compounding culture, tolerance mixed-heavy-metal gradient pressure type domestication, temperature cycling gradient type domestication, ferrous oxidation activity improvement and tolerance high-iron domestication, so as to obtain the acidophilic iron-oxidizing composite microbial agent. According to the invention, the acidophilic iron-oxidizing composite microbial agent is simple in formulation, economical, adaptable, versatile and efficient, and can be used for the efficient extraction of heavy metals in electroplating sludge.
Owner:HUNAN AIGE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
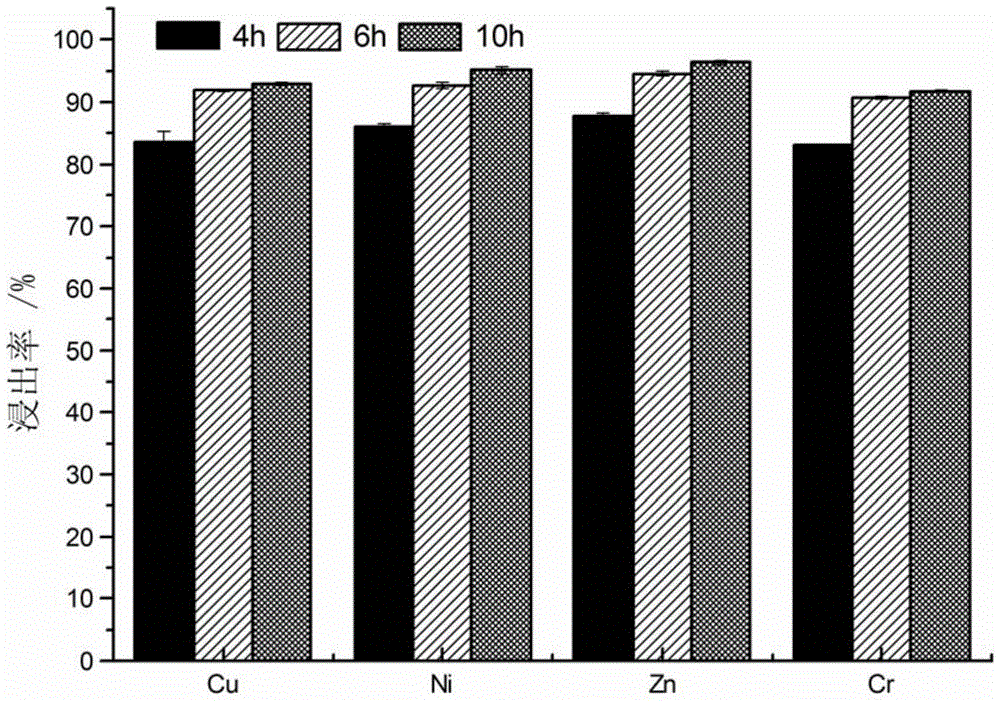
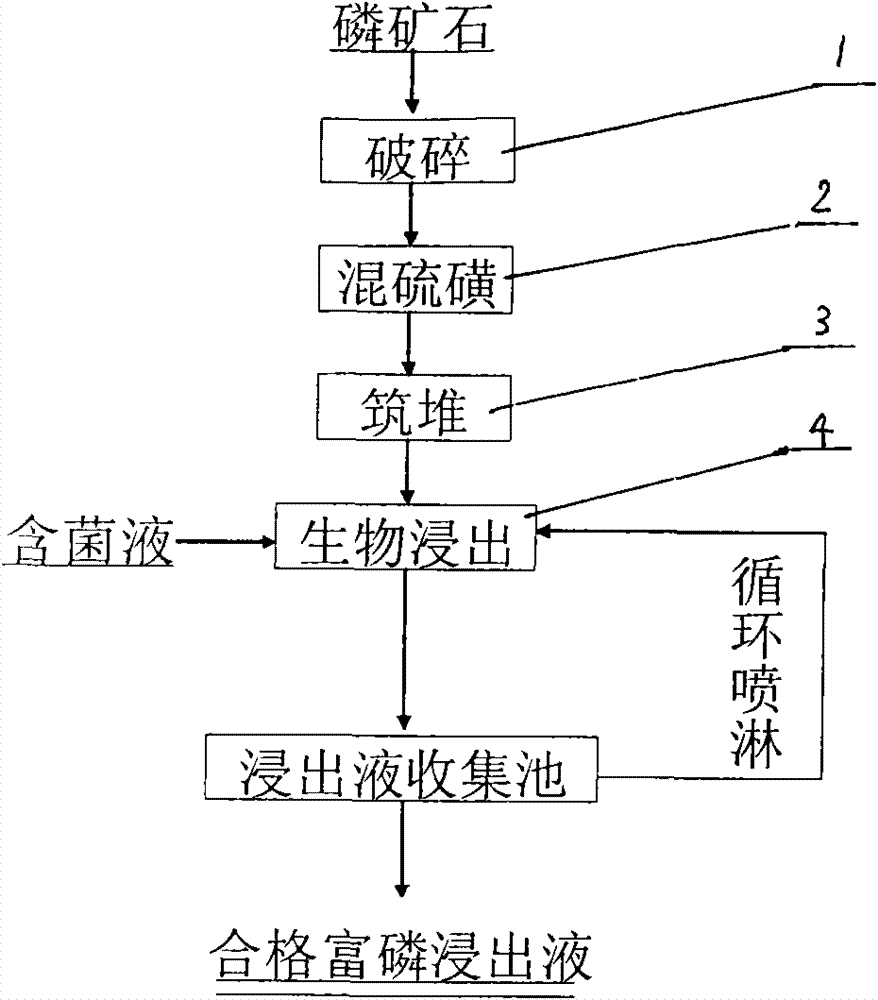
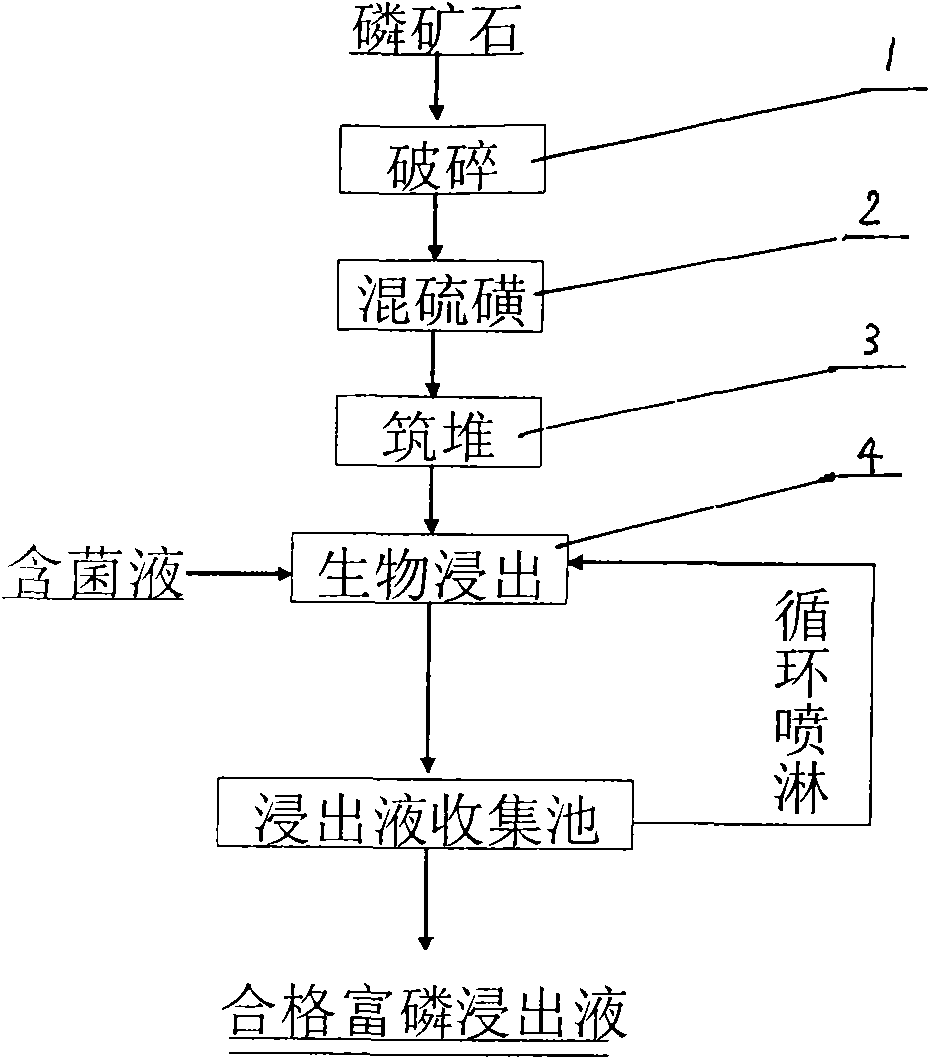
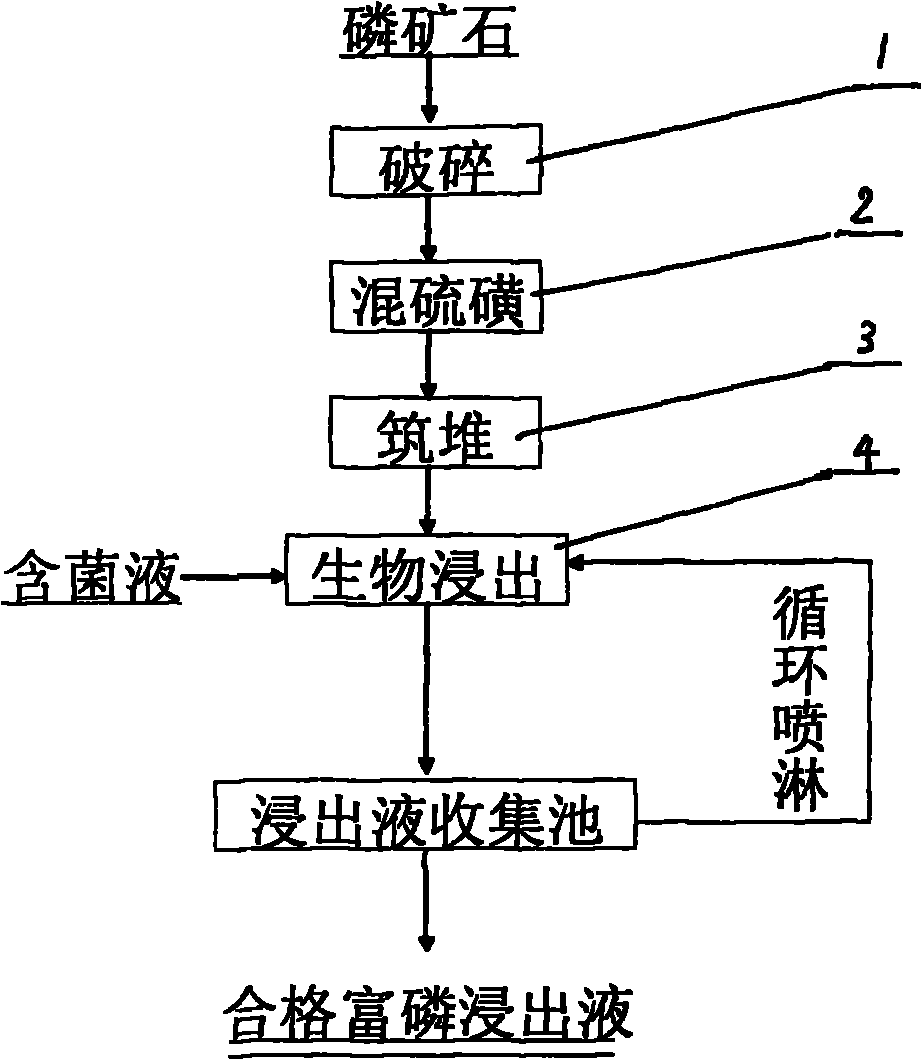
Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and heap leaching technology using same of middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore
ActiveCN102102085BReduce pollutionReduce the cost of beneficiationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesO-Phosphoric AcidAcidithiobacillus
The invention relates to Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and a heap leaching technology using same of the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore. The name of the bacteria is Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans RETECH-PS1; the bacteria are conserved in the China center for type culture collection of which address is the Wuhan University; the conservation date is April 25, 2009; and the CCTCC NO is 209088. The biological heap leaching technology of the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore comprises the following steps: ores are crushed to less than 15mm, sulfur is added to mix and build up leaching heap; (2) the Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in the claim 1 which is conserved at low temperature is activated and propagated step by step to reach the bacterium solution volume for spraying, finally the bacteria are inoculated in the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore heap mixed with sulfur; and (3) leachate is collected by a collection pool and pumped by a pump to a spraying system for circular spraying. The invention has the following advantages: the process flow is simple, the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore is used without adopting ore dressing and enrichment; sulfuric acid is not added in the production process of phosphoric acid, thus reducing the cost and avoiding the environmental pollution problem caused by the production of sulfuric acid; the production scale can be large or small; and the technology is especially suitable for the collophanite resource which accounts for 70% of Chinese phosphorus resources and is difficult to treat through traditional ore dressing, thus increasing the comprehensive utilization rate of Chinese phosphorus resources.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
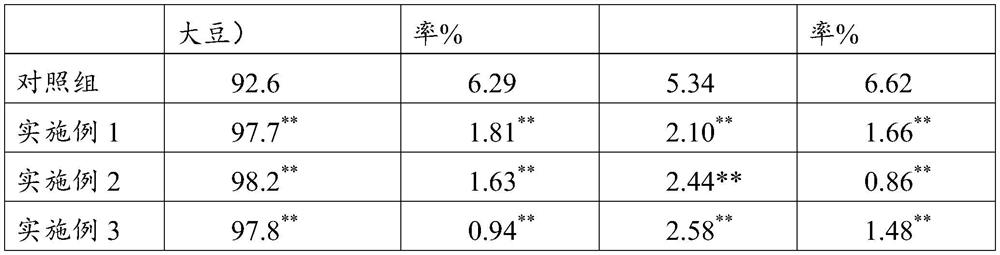
Novel microbial agent and soybean planting method
PendingCN112940969AImprove germination rateImprove seedling survival rateBacteriaSeed and root treatmentBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, and particularly discloses a novel microbial agent and a soybean planting method. The novel microbial agent disclosed by the invention comprises the following strains: 1) one or more of corynebacterium, paracoccus, chromobacterium, achromobacter, acidithiobacillus, acidovorax, alcaligenes, arthrobacter, bacillus, cupriavidus, derxia, Herbaspirillum, hydrogenobacter, hydrogenophaga, pseudomonas, pseudonocardia, rhizobium, rhodococcus, rhodopseudomonas, rhodospirillum, thiocapsa, xanthomonas, flavobacterium and wautersia; and 2) azospirillum and azotobacter. The novel microbial agent can improve the emergence rate and the survival rate of soybeans, improve the growth of soybean seedlings, promote the accumulation of organic matter, improve the disease resistance of the soybeans to harmful bacteria and improve the nitrogen fertilizer utilization rate of the soybeans.
Owner:兴安盟莱绅生物农业有限公司
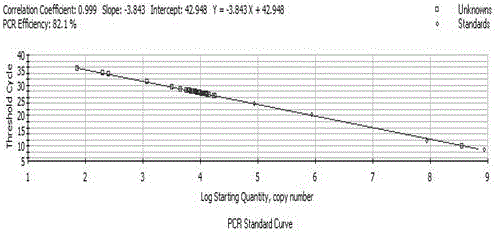
Specific primers for detection of mRNA expression level of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans sor gene
InactiveCN105925667AEffectively reflect the expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleotide sequencingAcidithiobacillus
The invention provides specific primers for detection of mRNA expression level of an Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans sor gene. The nucleotide sequences are as follows: an upstream primer sequence of 5'-AAGCCCGTGCCTAAAGTG-3', and a downstream primer sequence of 5'-CTGCCATAGTTGGTGTTGT-3'. The specific primers can detect the transcription level of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans sor gene, and hace the advantages of high sensitivity and good specificity in detecting mRNA gene expression level. Through the real-time monitoring of mRNA expression level of sor gene in sulfur oxidation process, the primers are used to explain the sulfur oxidation mechanism of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and heap leaching technology using same of middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore
ActiveCN102102085AReduce pollutionReduce the cost of beneficiationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesO-Phosphoric AcidAcidithiobacillus
The invention relates to Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and a heap leaching technology using same of the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore. The name of the bacteria is Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans RETECH-PS1; the bacteria are conserved in the China center for type culture collection of which address is the Wuhan University; the conservation date is April 25, 2009; and the CCTCC NO is 209088. The biological heap leaching technology of the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore comprises the following steps: ores are crushed to less than 15mm, sulfur is added to mix and build up leaching heap; (2) the Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in the claim 1 which is conserved at low temperature is activated and propagated step by step to reach the bacterium solution volume for spraying, finally the bacteria are inoculated in the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore heap mixed with sulfur; and (3) leachate is collected by a collection pool and pumped by a pump to a spraying system for circular spraying. The invention has the following advantages: the process flow is simple, the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore is used without adopting ore dressing and enrichment; sulfuric acid is not added in the production process of phosphoric acid, thus reducing the cost and avoiding the environmental pollution problem caused by the production of sulfuric acid; the production scale can be large or small; and the technology is especially suitable for the collophanite resource which accounts for 70% of Chinese phosphorus resources and is difficult to treat through traditional ore dressing, thus increasing the comprehensive utilization rate of Chinese phosphorus resources.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Microbial agent for promoting growth of oilseed rape and oilseed rape planting method thereof
ActiveCN112980732AIncrease productionIncrease harvestPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, and particularly discloses a microbial agent for promoting growth of oilseed rape and an oilseed rape planting method thereof. The microbial agent provided by the invention comprises the following bacteria: a) at least one of corynebacterium, paracoccus, chromobacterium, achromobacter, acidithiobacillus, acidovorax, alcaligenes, arthrobacter, bacillus, cupriavidus, derxia, herbaspirillum, hydrogenobacter, hydrogenophaga, pseudomonas, pseudonocardia, rhizobium, rhodococcus, rhodopseudomonas, rhodospirillum, thiocapsa, xanthobacter, flavobacterium and wautersia; B) acetobacter, and c) azospirillum. The microbial agent provided by the invention improves the yield of oilseed rape, and is matched with a specific oilseed rape planting method to increase the yield of oilseed rape per mu, reduce the nitrogen fertilizer demand, reduce harmful germs, restore the number of microorganisms in soil and increase the diversity of the microorganisms.
Owner:GUANGDONG RICHHOLD BIOLOGICAL AGRI CO LTD
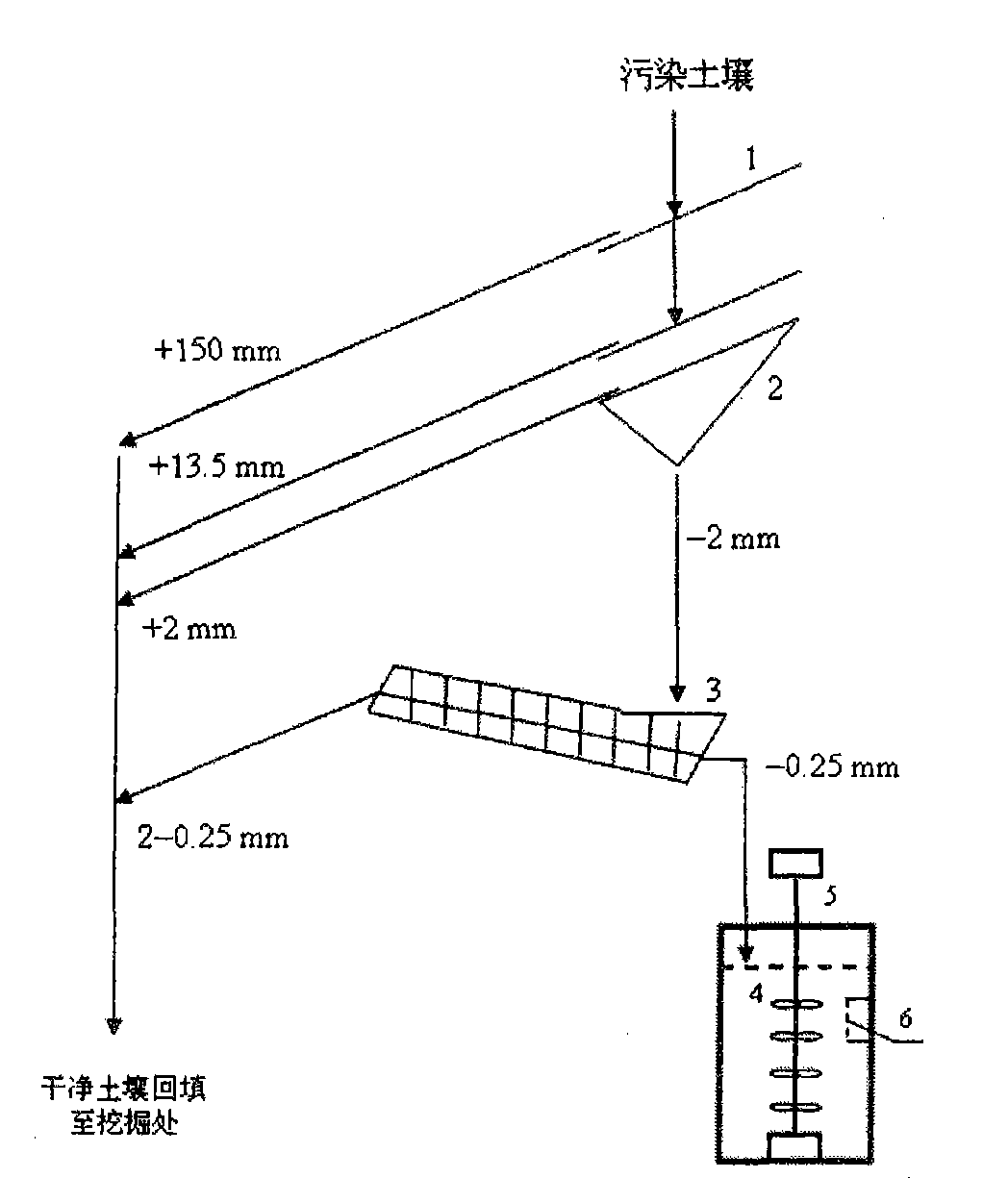
Method for treating plutonium or strontium polluted soil
InactiveCN101745527BQuick removalEfficient removalBacteriaSulfate-reducing bacteriaAcidithiobacillus
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbe, and particularly relates to a method for treating radionuclide plutonium or strontium polluted soil by microbe. The method comprises the following steps: screening the plutonium or strontium polluted soil by a bar screen, a double-plate screen and a spiral screen, wherein the soil grains with the granularity of more than 0.25 millimeter areclean soil grains and the soil grains with the granularity of less than 0.25 millimeter are plutonium or strontium polluted soil grains; and mixing the soil grains with the granularity of less than 0.25 millimeter and acidithiobacillus thiooxidans active solution, filtering the solution to obtain sediment which is clean soil, mixing the filtered solution and sulfate reducing bacteria active solution, settling plutonium or strontium, filtering and separating the solution, reclaiming the plutonium or the strontium, and recycling the water. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, economy and feasibility and high safety, has no secondary pollution, and can efficiently and quickly remove the plutonium or the strontium from the polluted soil.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Preparation method of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidian genetic engineering strain with quick growth speed and strong uranium and fluorine resistance capacities as well as application thereof
InactiveCN101659961AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceAcidithiobacillus
The invention discloses a preparation method of an acidithiobacillus ferrooxidian genetic engineering strain with quick growth speed and strong uranium and fluorine resistance capacities as well as the application thereof, wherein the strain is Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans QEY-6(pJRD215-PT-rcf), CCTCCM 209156; and the preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, augmenting a T5 promoter and a T0 terminator of pQE30, and establishing a shuttle expression vector pJRD215-PT together with pJRD215; secondly, augmenting and cloning a micrococcus luteus rpf gene, a caulobacter crescentus cc3302 gene and a caenorhabditis elegans flr-4 gene to a T vector; thirdly, establishing a recombined shuttle expression vector pJRD215-PT-rcs; and fourthly, establishing the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidian genetic engineering strain which fusedly expresses rpf, cc3302 and flr-4 genes. The invention has simple operation and good repeatability, and can improve the tolerance of ores containing uranium and fluorine, shorten the uranium leaching period, improve the leaching rate and reduce the acid-consuming rate.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
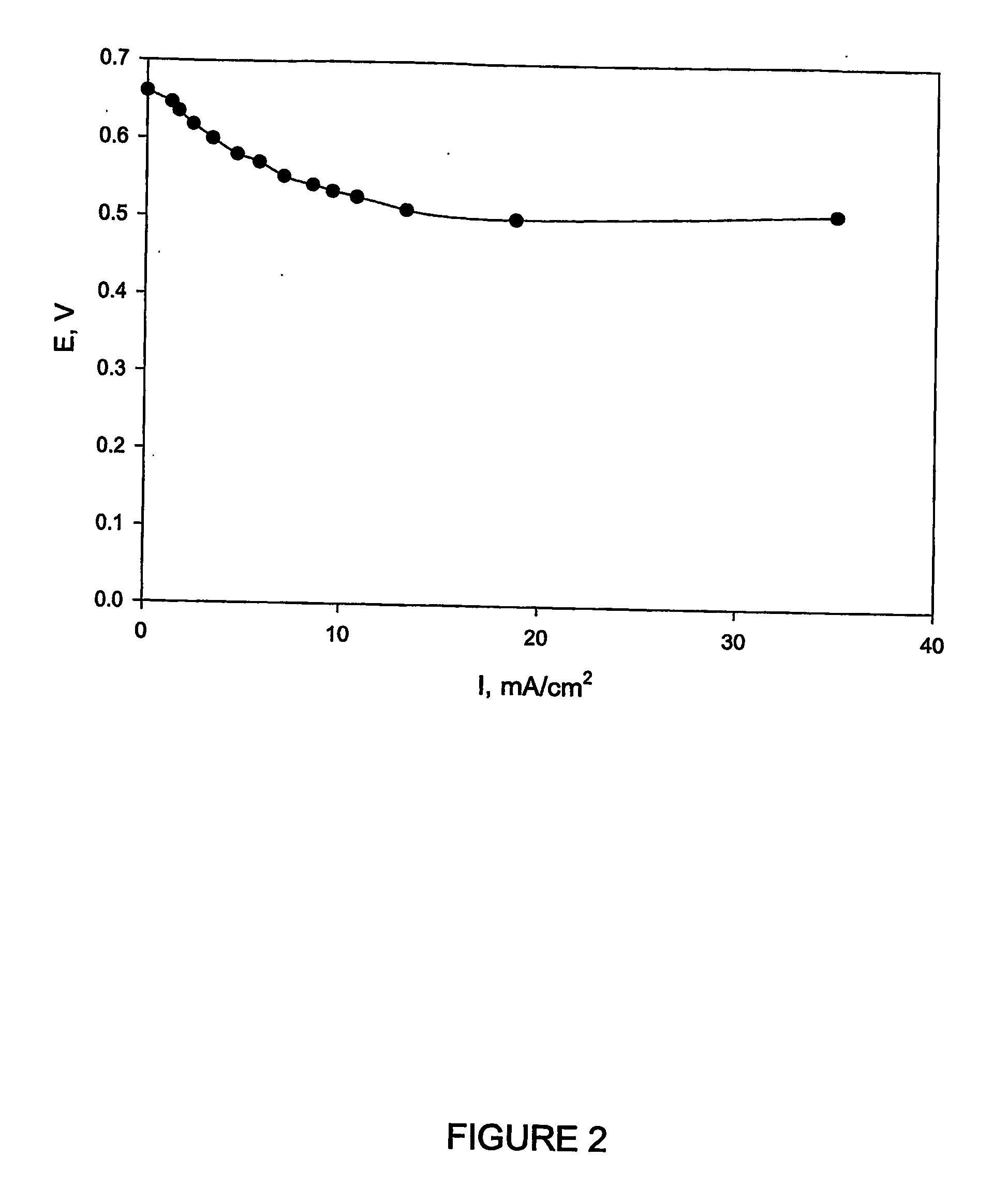
Method for generating electricity
InactiveUS20100035089A1Promote growthElectrolyte holding meansCell electrodesBiotechnologySingle-cell protein
The present invention discloses a method of generating electricity which uses a new type of biofuel cell. The method is based on the microbial regeneration of the oxidant, ferric ions. The bio-fuel cell is based on the cathodic reduction of ferric to ferrous ions, coupled with the microbial regeneration of ferric ions by the oxidation of ferrous ions, with fuel (such as hydrogen) oxidation on the anode. The microbial regeneration of ferric ions is achieved by chemolithotrophic microorganisms such as Acidithiobacillus ferroxidans. Electrical generation is coupled with the consumption of carbon dioxide from atmosphere and its transformation into microbial cells, which can be used as a single-cell protein.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com