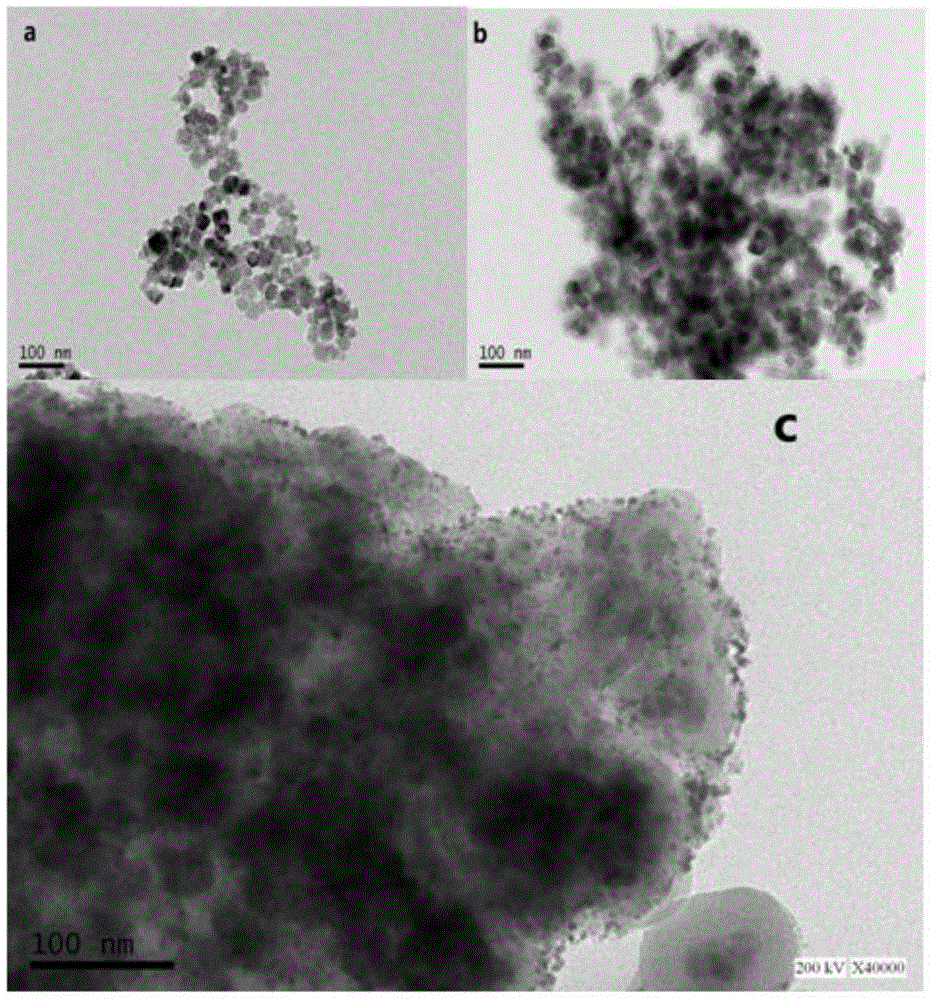
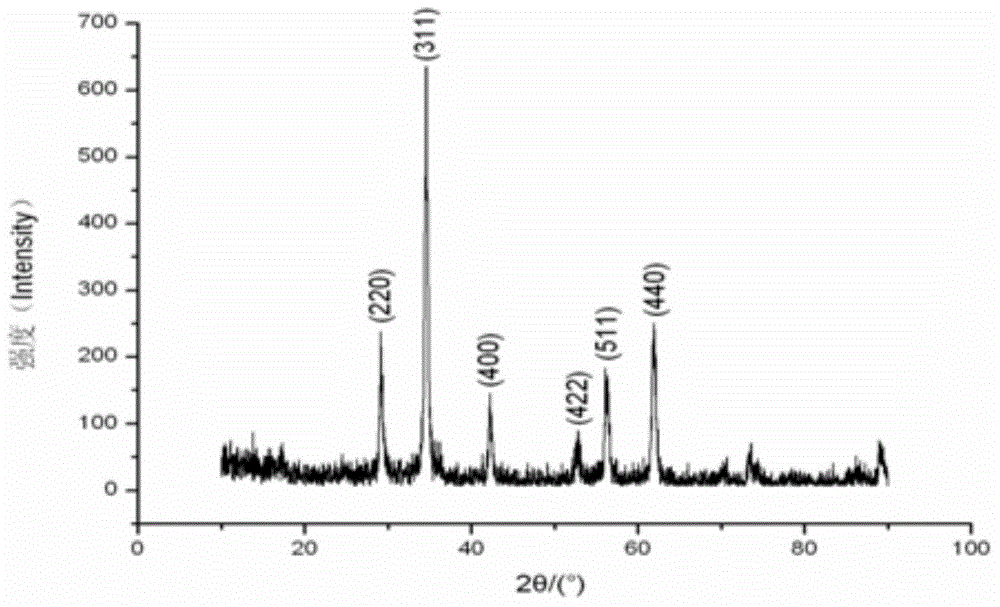
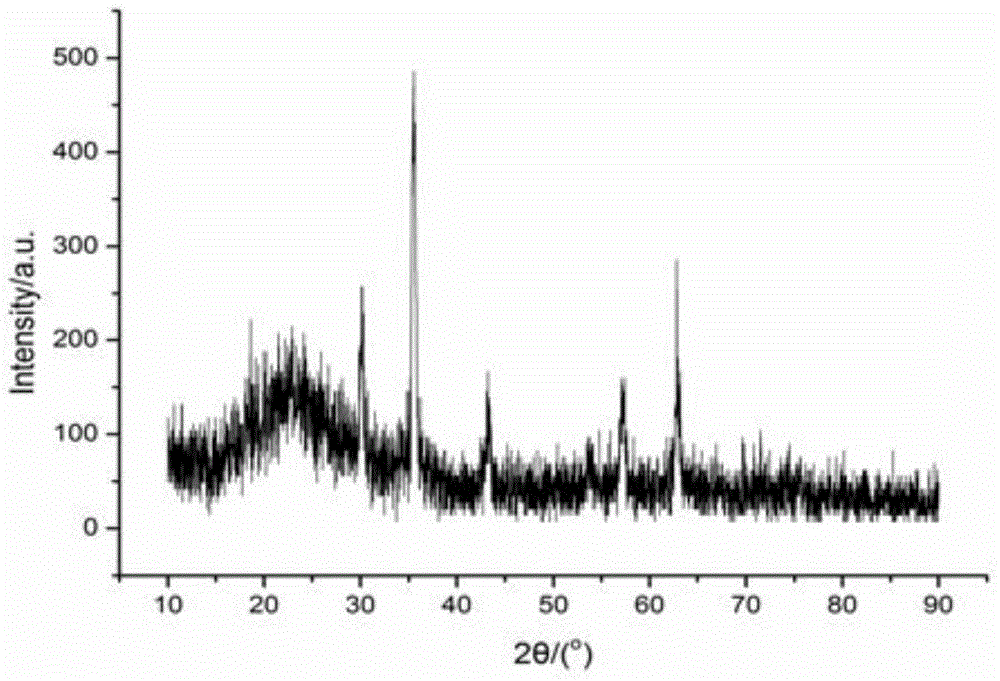
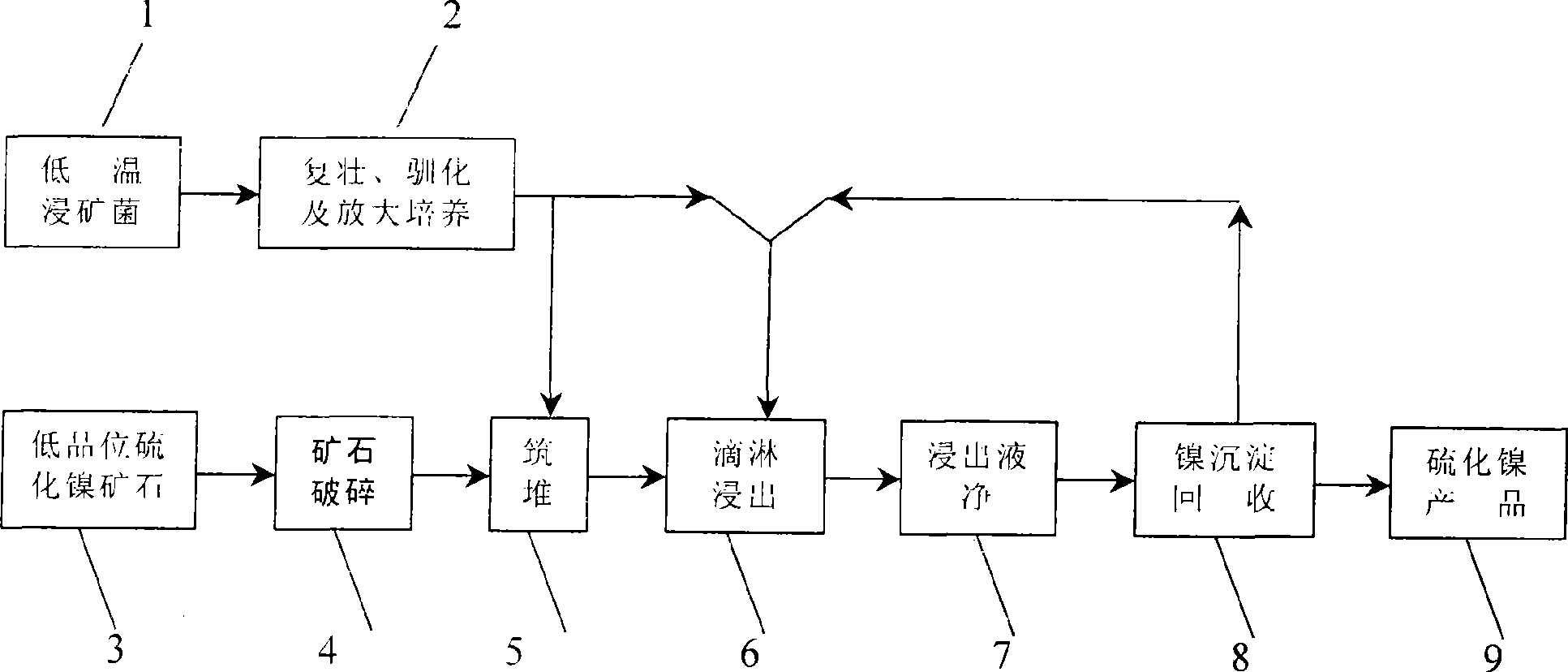
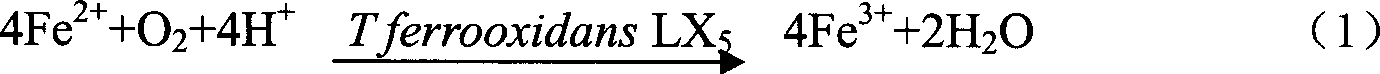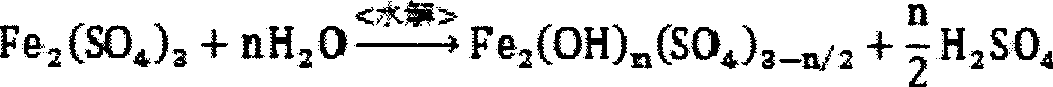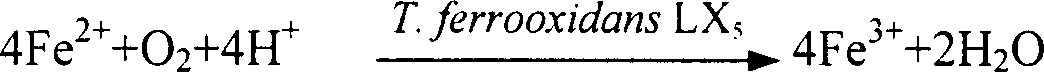Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
222 results about "Thiobacillus ferrooxidans" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
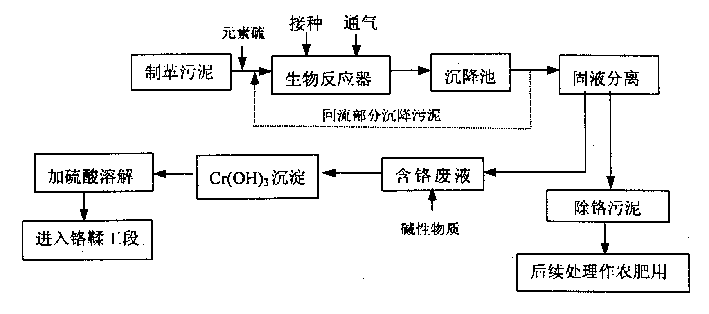
Thiobacillus thiooxidans and biological eliminating method of chromium in tanning sludge
InactiveCN1389564ALess value lossAchieve recyclingBacteriaSludge processingThiobacillus ferrooxidansSludge
The invention relates to sulfur oxide sulfur bacilli and biological eliminating method of chromium in tanning mud. Bacterial strain is named as TS6, preserve mark is CGMCCNO.0759. The method of eliminate chromium in tanning mud by above mentioned sulfur oxide sulfur bacilli is adding 1-3 g / L sulfur into tanning mud in biology reactor, inocualting 10-15% (v / v, the same below) TS6 bacteria strain, stirring, ventilating and subsiding; that 10-20% of subsiding mud backflow to reactor; dehydrating suprplus subsiding mud; adding basic material into liquid part to turn Cr3+ into Cr(OH)3 and subside, sediment is dissolved by sulfuric acid, then there is the tannage stage; solid part is neutralized to agriculture. The elimianting rate of Cr in mud is 95%-100%, reserving rate of nutrient in mud is above 80%.
Owner:周立祥 +1
Composite microbial inoculum organic multielement compound fertilizer and production method thereof
ActiveCN102690151AImprove physicsGood biological propertiesFertilizer mixturesThiobacillus ferrooxidansBran
The invention discloses a composite microbial inoculum organic multielement compound fertilizer which is prepared from microbial inoculum, organic component and inorganic fertilizer. The microbial inoculum is a composite microbial inoculum which comprises the following three types of microbial inocula: resource type microbial inoculum, which contains Bacillus megaterium, thiobacillus thiooxidans, Bacillus mucilaginosus and Bacillus circulans; environment-friendly microbial inoculum, which contains Arthrobacter and Alcaligenes; and antibiotic microbial inoculum, which contains Streptomycs micuoflavus and Streptomyces jingyangensis. The organic component is one or more of cereal crop straw, subsidiary agricultural product dreg, sugar mill bagasse, bran coat, municipal and rural domestic waste, and livestock and poultry dung. The inorganic fertilizer is one or more of nitrogen fertilizer, phosphate fertilizer, potash fertilizer and medium / micro-nutrient element fertilizer. The weight proportion of microbial inoculum to organic constituent to inorganic fertilizer is (5-25):(18-28):(47-77).
Owner:赵大伟
Cyanidation aurum-extracting method for preprocessing high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by oxidation with arsenic resistant strains
InactiveCN101333599AIncrease growth temperatureStable temperatureProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansResistant strain
Disclosed is a cyaniding gold extraction method for pre-treating high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by arsenic-resistant bacteria oxidation, comprising five steps of arsenic-resistant bacteria culture, flotation concentrate mixing, bacterial oxidation of flotation concentrates, solid-liquid separation and cyaniding gold extraction. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts specific arsenic-resistant bacteria which are prepared by mixing Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Thiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, and conducts oxidation pretreatment of high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore. The high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic can be pretreated, and the arsenic removal rate is 85 to 98 percent. The leaching rate of gold is up to 90 to 95 percent after cyaniding leaching. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts unique bacteria for leaching ores, greatly saves cooling cost, conducts direct oxidation of high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic, and has advantages of being widely adaptable, simple in operation, environmentally friendly and remarkably beneficial.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for recycling heavy metal in electroplating sludge
ActiveCN102719657APhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method for recycling heavy metal in electroplating sludge. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out screening and acclimatizing to obtain thelloobacillus ferrooxidans and thiobacillus thiooxidans which have resistance of high-concentration heavy metal; under a certain condition, respectively stirring and mixing the thelloobacillus ferrooxidans and the thiobacillus thiooxidans with the electroplating sludge together; biologically leaching the mixture so as to obtain copper-contained leach liquor or nickel-contained leach liquor; and carrying out electrodeposition on the copper-contained leach liquor after removal of impurities, so as to recycle copper, and carrying out the electrodeposition on the nickel-contained leach liquor after the removal ofthe impurities, so as to recycle nickel.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Saline-alkali soil biological improved fertilizer based on high-sulfur gangue and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104788265ABreak the lattice structureIncrease the areaFertilizer mixturesThiobacillus ferrooxidansEcological environment
The invention discloses a saline-alkali soil biological improved fertilizer based on high-sulfur gangue. The saline-alkali soil biological improved fertilizer is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 50-60 parts of high-sulfur gangue microbial fermentation product, 20-30 parts of compost cow manure or chicken manure, 1-2 parts of citric acid, 1-2 parts of oxalic acid, 2-4 parts of urea, 2-4 parts of ammonium sulfate, 2-4 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 1-3 parts of potassium sulphate, 2-5 parts of ferrous sulfate, 1-2 parts of zinc sulfate, 1-2 parts of manganese sulfate and 1-10 parts of bentonite, wherein the high-sulfur gangue microbial fermentation product is a product obtained by performing activating treatment on the high-sulfur gangue by a compound microorganism bacterium solution composed of thiobacillus thiooxidans, bacillus subtilis, bacillus megatherium, bacillus mucilaginosus and enterococcus faecalis. The resource utilization of the high-sulfur gangue is realized, the improvement of the inland saline land can be promoted, the crop yield can be increased and the entironment can be improved.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCE SHANXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing and using polymeric flocculant polyferric silicate sulfate
ActiveCN101974566AWide variety of sourcesSimple production equipmentMicroorganism based processesFermentationThiobacillus ferrooxidansSilicic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing inorganic polymeric flocculant polyferric silicate sulfate and a wastewater treatment method. Ferrous sulfate is oxidized into polyferric sulfate through the acclimated thiobacillus ferrooxidans; polymerization reaction is conducted between the polyferric sulfate and the active polysilicic acid solution; and then the polymerization reaction product is left to stand and ageing to obtain the brownish red liquid polyferric silicate sulfate. The product brownish red liquid polyferric silicate sulfate is applicable to the purification of domestic sewage, printing and dyeing wastewater and heavy metal wastewater and COD removal rate, decoloring rate and heavy metal removal rate can reach more than 90%.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Efficient biological desulfurization method for coal
InactiveCN103937576AEffectively retain active ingredientsEasy to operateSolid fuelsThiobacillus ferrooxidansThiobacillus
The invention discloses an efficient biological desulfurization method for coal, which is characterized in that coal is crushed through a crusher until the particle size is below 150 meshes; and three bacteria, namely Thiobacillus thioxidans, Thiobacillus caldus and Pseudomonas stutzeri, are adopted. The desulfurization process comprises the following sequential steps: removing organic sulfur in the coal through the Pseudomonas stutzeri; after the primary desulfurization is finished, preparing the Thiobacillus thioxidans and the Thiobacillus caldus into a desulfurization solution according to a certain total bacterial count ratio, and removing inorganic sulfur of the coal; and washing the desulfurized coal with water, filtering, and drying. The total sulfur removal ratio of the desulfurized coal is up to 57.8%; and the method is simple to operate, mild in treatment conditions and low in cost, and effectively retains effective components in the coal, thus being a desulfurization technology having very wide market prospects.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Biosynthesis of obligate adsorbent and its usage in adsorbing to eliminate As and Cr from water
ActiveCN1772910AImprove catalytic oxidation efficiencyHigh purityFermentationWater/sewage treatment by sorptionThiobacillus ferrooxidansSorbent
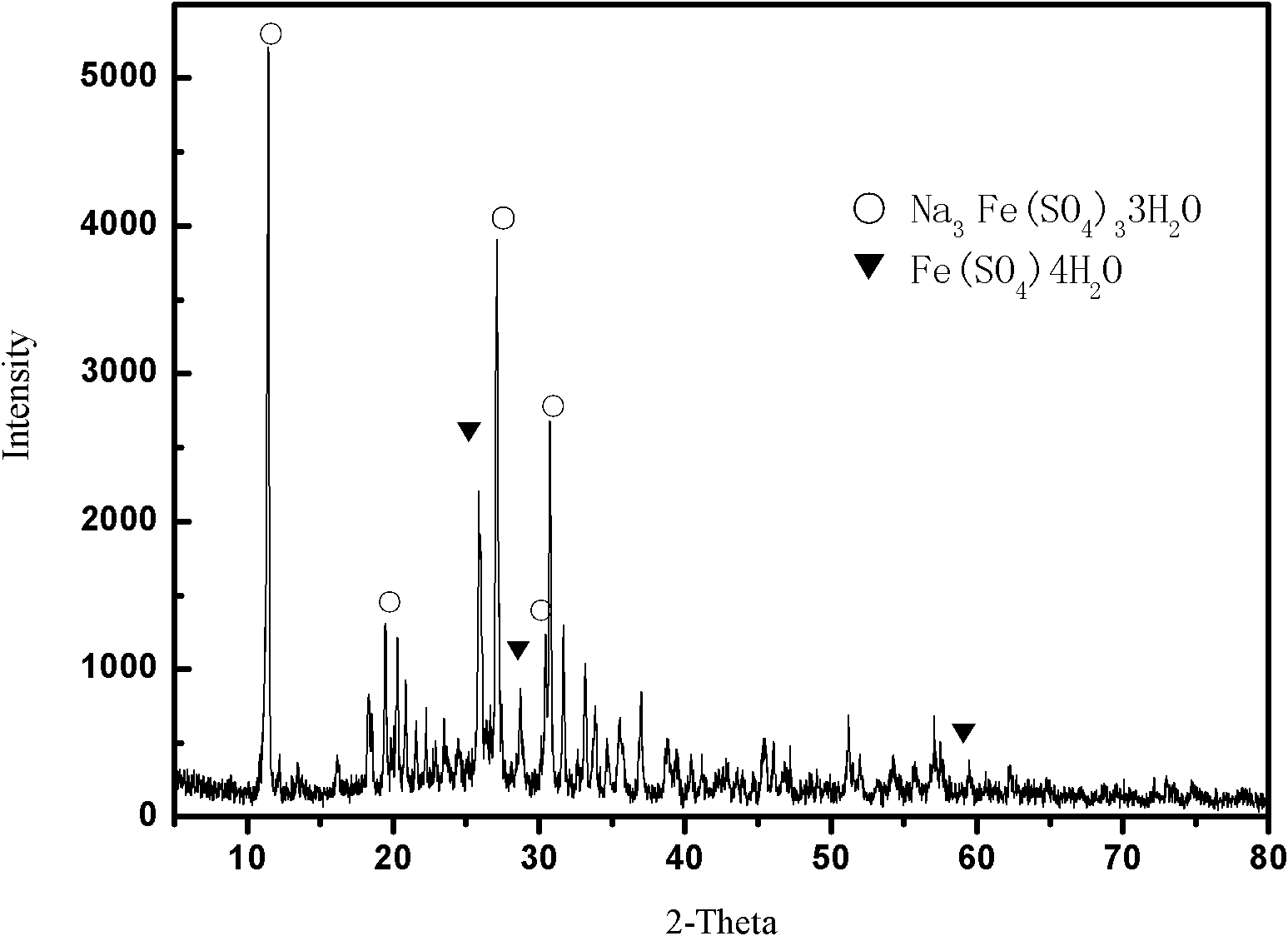
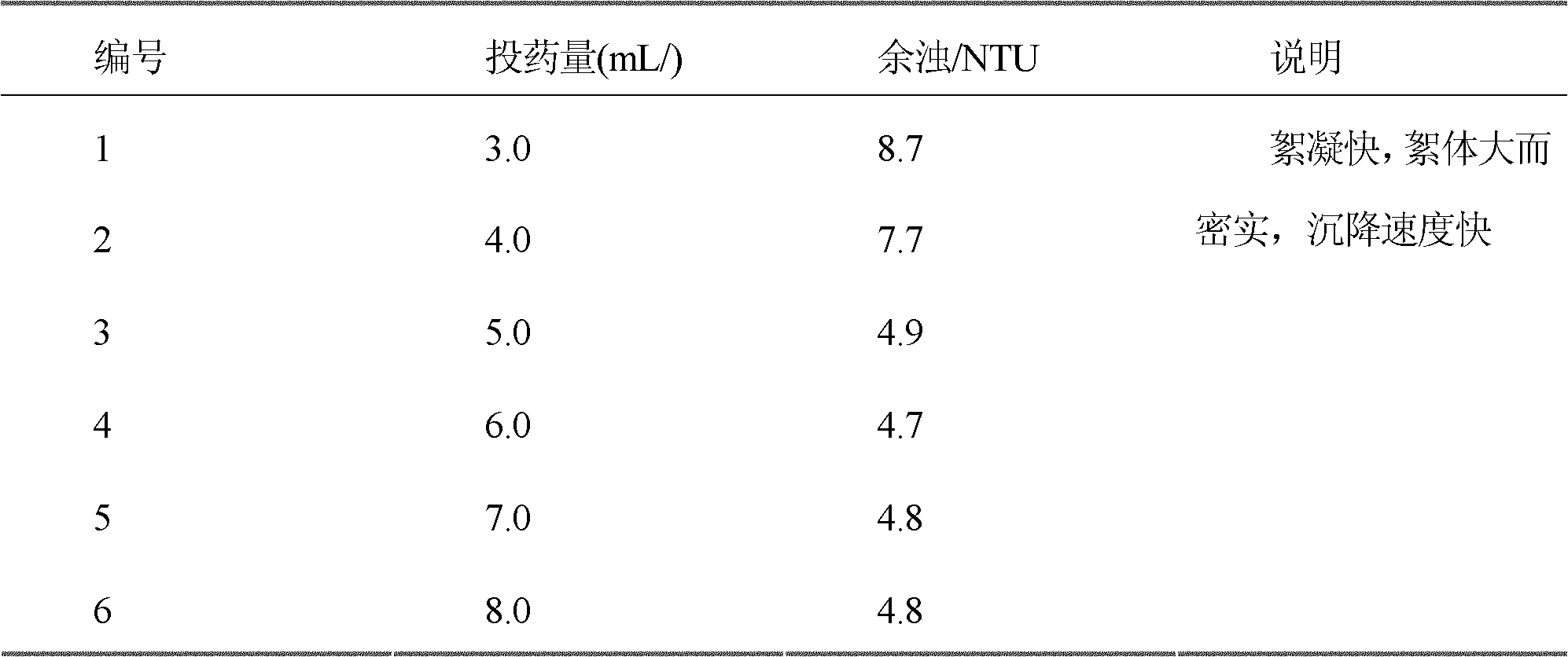
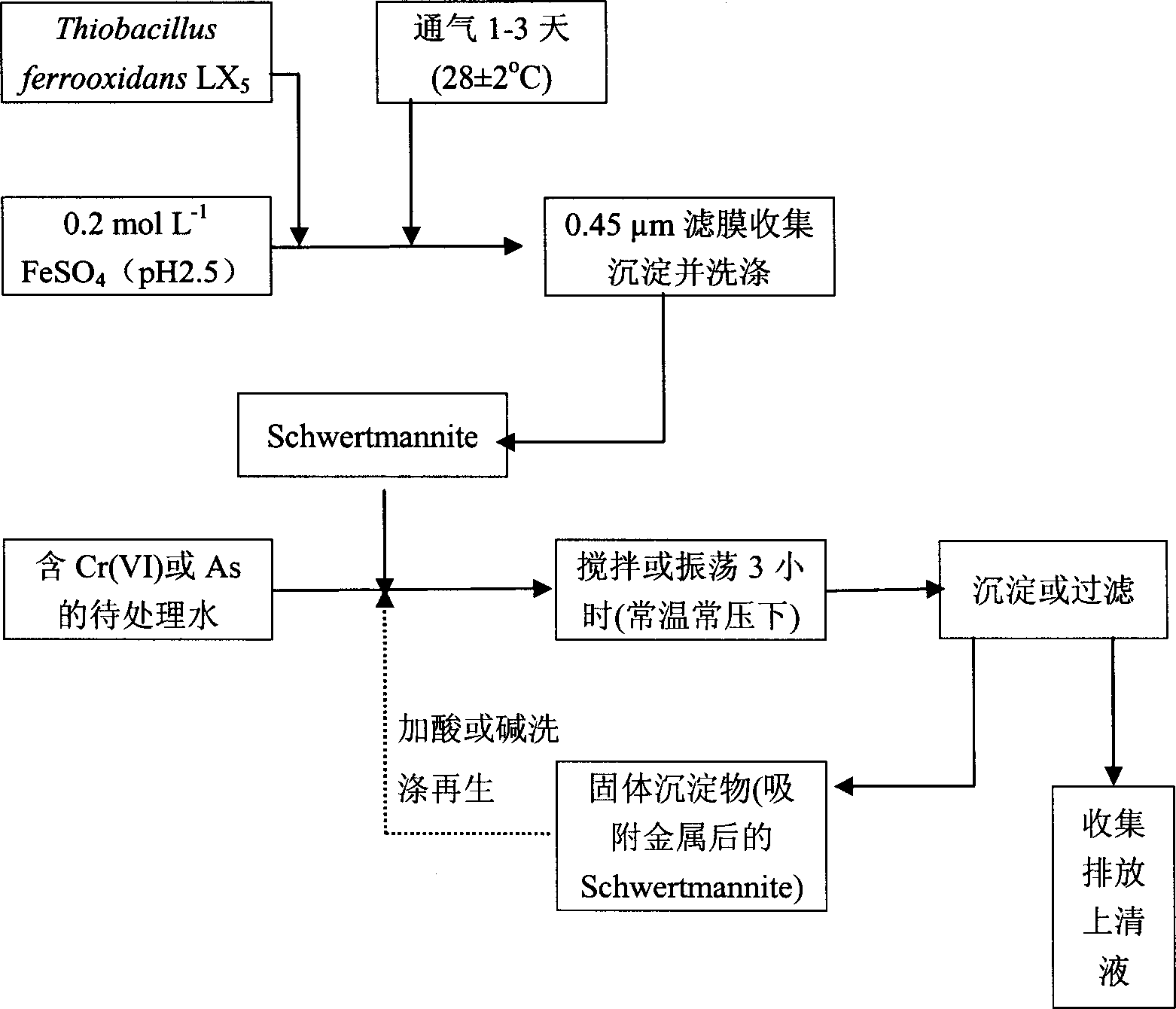
The present invention provides the biosynthesis of Schwertmannite as high efficiency adsorbent and its usage in adsorbing to eliminate Cr(VI) and As from waste water and underground water. Schwertmannite is prepared with ferrous sulfate as reactant, deionized water as reaction medium and Thiobacillus ferrooxidans LX5 as catalytic oxidant, and through stirring for 1-3 days, filtering to collect precipitate, washing with sulfuric acid acidified deionized water, washing with deionized water and stoving. Schwertmannite is added into water to be treated in the amount of 0.5 wt% or 0.02 wt%, dilute nitric acid is added into Cr(VI) containing system to regulate the pH value to 5.0-7.0 or sodium hydroxide is added into As containing system to regulate the pH value to 6.0-10.0, and the system is stirred for 3 hr and filtered to eliminate Cr(VI) and As. Schwertmannite has maximum adsorption amount on Cr(VI) and As of 55 mg / g and 65 mg / g separately.
Owner:南京贝克特环保科技有限公司
Method for leaching low-grade phosphorite with mixed bacillus of thiobacillus thioxidans and thiobacillus ferrooxidans
InactiveCN101891166AHigh activityReduce consumptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThiobacillus ferrooxidansAcid water
The invention relates to an ore extraction technology, in particular to a method for leaching low-grade phosphorite with mixed bacillus, wherein the mixed bacillus consists of a thiobacillus thioxidans At.t which is separated from soil sample of the Hubei tongshankou copper mine and a thiobacillus ferrooxidans At.f which is separated from acid water hole of the Hubei tonglushan copper mine. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) sampling from the soil sample of the Hubei tongshankou copper mine and the acid water hole of the Hubei tonglushan copper mine; 2) separating the thiobacillus thioxidans and the thiobacillus ferrooxidans in an enrichment way and domesticating; and 3) leading the phosphorus. The method has the beneficial effects of: 1. being high in the activity of mixed bacillus: the phosphorus leading rate is high up to 88.75%; 2. being low in cost: the cost of the 10% inoculum size is far lower than that of the 20%-30% inoculum size of the thiobacillus thiooxidans in the prior art, so that the cost for preparing culture solution with plenty of expensive medicaments is reduced; 3. being short in period and high in efficiency; and 4. being environment-friendly: the usage amount of the acid bacillus is small, thereby being good for reducing environment pollution.
Owner:WESTERN MINING CO LTD
Preparation of supported palladium catalyst Fe3O4/SiO2/Pd and application of supported palladium catalyst Fe3O4/SiO2/Pd in Suzuki reaction
InactiveCN104667945AImprove magnetic propertiesEasy to useOrganic chemistry methodsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsThiobacillus ferrooxidansPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a supported palladium catalyst Fe3O4 / SiO2 / Pd for Suzuki reaction, and a preparation method of the supported palladium catalyst Fe3O4 / SiO2 / Pd. The compound is a supported palladium catalyst material containing Fe3O4 / SiO2 / Pd, obtained by composite reaction of a precursor-based Fe3O4 / SiO2 composite particles and Pd; the supported palladium catalyst Fe3O4 / SiO2 / Pd has the molecular characteristics that the compound structure contains a magnetic nanometer material Fe3O4 and porous absorption materials SiO2 and Pd; the supported palladium catalyst has relatively good magnetism, is easy to recover and reuse, and is a relatively ideal material as the supported palladium catalyst. The supported palladium catalyst is simple in synthesis route, mild in reaction condition, relatively high in yield and convenient to apply; post-treatment is simple; meanwhile, a secondary resource generated in biological mineral separation preparation and simulation and coal biological desulphurization by adopting thiobacillus ferrooxidans as a raw material; and a reference is provided for a comprehensive utilization technology of developing a metallurgical tail liquid or a desulphurization waste solution.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
An strain of low temperature leaching-ore bacteria and process for using the same for low temperature heap leaching of nickel sulfide ore
ActiveCN101434920AGuaranteed leaching efficiency conditionsHigh recovery rateBacteriaProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansNickel sulfide
The invention provides a low-temperature mineral leaching bacterium and a low-temperature heap leaching technique of nickel sulfide ore that uses the low-temperature mineral leaching bacterium. The name of the low-temperature mineral leaching bacterium is Thiobacillus ferrooxidans Retech-L-I, the preservation registration number is CCTCC No. of M207157, the preservation date is October 16th, 2007, and the preservation unit is China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University. The low-temperature heap leaching technique of nickel sulfide ore comprises the working procedures of low-temperature mineral leaching bacterium rejuvenation, domestication and amplified cultivation, ore stacking, and spraying with a liquid containing the low-temperature mineral leaching bacterium, and a leaching liquid that is obtained by a leaching procedure is sent to working procedures of iron removing, arsenic removing and metal recycling. The low-temperature heap leaching technique of nickel sulfide ore that uses the low-temperature leaching bacterium has the advantages that the technique not only is environment-friendly, but also can be used for exploiting low-grade nickel ore resources that cannot be utilized by traditional picking metallurgy techniques, and the technique is particularly applicable to the exploit of nickel sulfide ore resources in highly cold low-temperature areas that cannot realize the engineering of biological normal temperature and high temperature heap leaching, enlarges the utilization range of nickel ore resources, and raises the synthetic nickel utilization rate.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Desulfur method of iron ore
InactiveCN1757769AImprove efficiencyLow costProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansThiobacillus
A process for desulfurizing iron ore concentrate includes such steps as culturing the mixture of thiobacillus ferro oxidans and thiobacillus sulfur oxidans in the non-Fe culture medium containing sulfur powder as energy source, adding the high-S iron ore concentrate containing pyrrhotite, naturalizing culture to obtain desulfurizing bacteria, putting them in water, immersing said high-S iron ore concentrate in it, vibrating in shaker for desulfurizing, washing and drying.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH +1
Arsenic-contaminated soil repairing and retaining agent based on microbe catalytic synthesis, and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN103773375APromote reproductionLow costAgriculture tools and machinesContaminated soil reclamationThiobacillus ferrooxidansSoil properties
The invention discloses an arsenic-contaminated soil repairing and retaining agent based on microbe catalytic synthesis, and a preparation and application method thereof. Currently, lots of fixing agents for repairing arsenic-contaminated soil can cause soil acidification and seriously destroy the soil property. Aiming at the problems, the fixing agent for repairing arsenic-contaminated soil is prepared from ferrous sulfate serving as raw material by steps of catalytically oxidizing thiobacillus ferrooxidans, collecting a precipitated product and performing aging modification to the precipitated product. The synthesized product is uniformly mixed with soil according to a certain proportion, the water-soluble arsenic in the contaminated soil is reduced by 99.8 percent, the effective-state arsenic is reduced by 75.4 percent, and the pH value of repaired soil is about 7. The fixing agent is simple in preparation process and low in cost, can be used for effectively reducing the mobility of arsenic and bio-availability in the soil, and hardly affects the pH value of soil. The repaired soil is good for crop growth.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Preparation method of magnetic nano Fe3O4 particles by biological catalysis and application of particles to treatment of uranium-containing wastewater
InactiveCN103877927AImprove adsorption capacityThe synthesis process is simpleOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesThiobacillus ferrooxidansIron(II) oxide
The invention provides an ecological and environment-friendly new method for preparing magnetic nano Fe3O4 particles by biological catalysis, and application of the particles to treatment of uranium-containing wastewater. The method comprises the following concrete steps: (1) culturing and domesticating thiobacillus ferrooxidans; (2) preparing bio-polymeric ferric sulfate; (3) synthesizing the magnetic nano Fe3O4 particles; (4) performing a test of adsorbing uranium in the uranium-containing wastewater by the magnetic nano Fe3O4 particles. The obtained magnetic nano Fe3O4 particles are simple in preparation synthesis route, mild in reaction condition and easy to operate; a biological catalysis oxidant is used for replacing a conventional chemical oxidant (nitrite), so that cancerogenic substances are prevented from being discharged to the environment and the environment-friendly effect is really achieved. Meanwhile, the obtained magnetic nano Fe3O4 particles can reduce the content of uranium in the low-concentration uranium-containing wastewater with the concentration of 0.45-0.50mg / L by more than 90% and have very important practical meaning in aspects of uranium-containing wastewater treatment, uranium recovery and the like in uranium mining and metallurgy.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
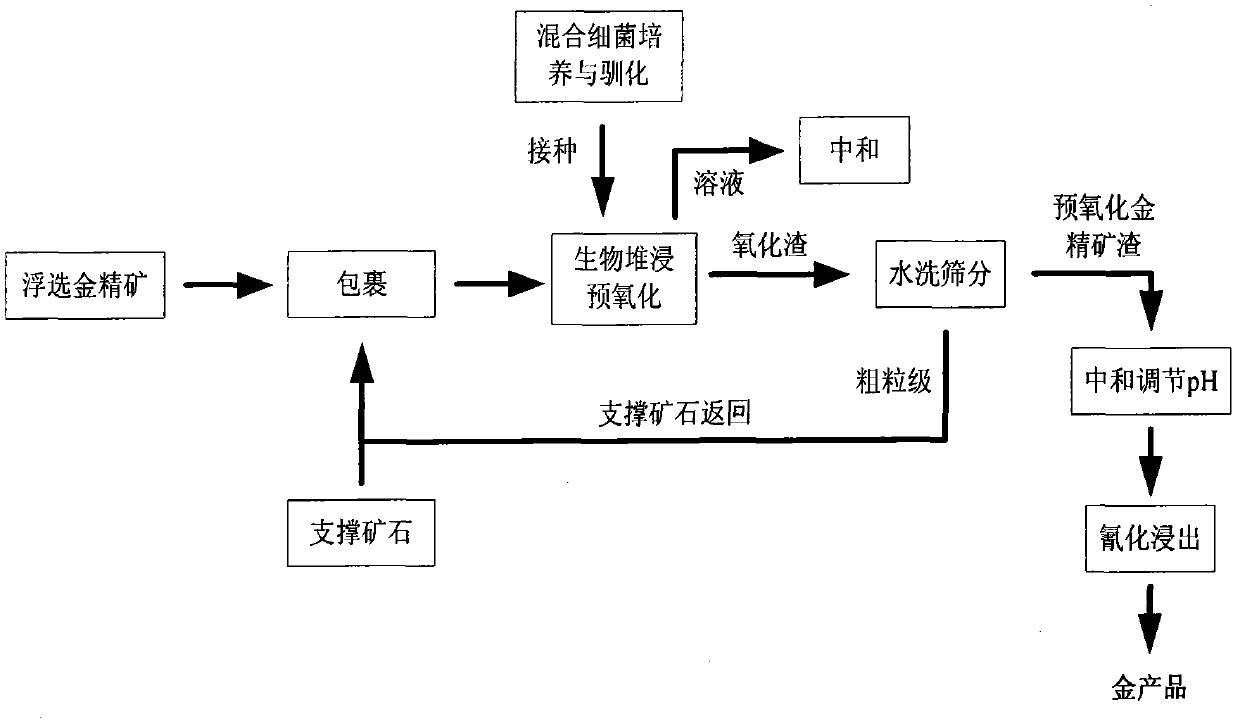
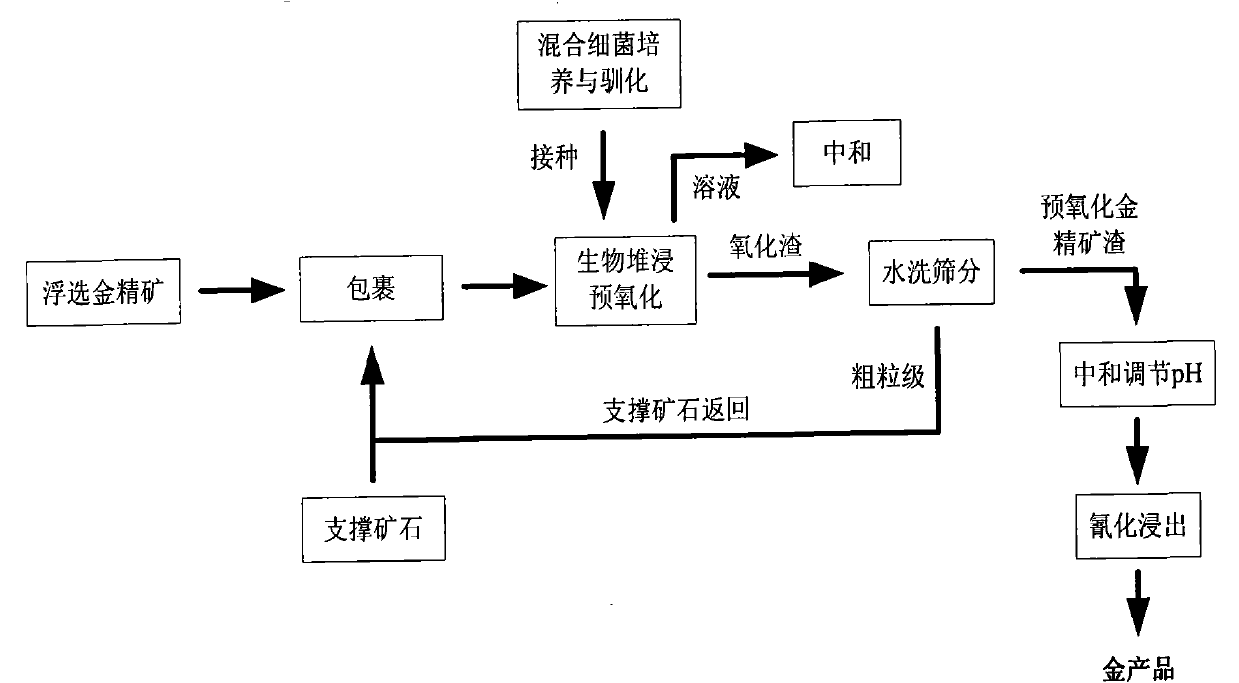
Biological pre-oxidation treatment process of low-grade refractory gold ores or ore concentrate
InactiveCN102560110AFully oxidizedImprove pre-oxidation rateProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansSlag
The invention provides a biological pre-oxidation treatment process of low-grade refractory gold ores or ore concentrate, which is a new process comprising the following steps: wrapping low-grade refractory ore concentrate on the surface of supporting ore particles, performing biological heap leaching preoxidation, washing and screening the slag, returning large particles to supplement supporting materials, and extracting gold from the gold ore concentrate-wrapped and pre-oxidized slag by cyanation. Bacteria are mixed bacteria mainly comprising Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Thiobacillus thioxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, and the temperature is 30-45 DEG C; the particle sizes of the ore concentrate and the supporting ore are respectively 80-400 meshes and 10-30mm, and the wrapping thickness of the ore concentrate is less than 2mm; and the preoxidation period is 30-90 days, the preoxidation rate is increased to 50-70%, and the recovery rate of gold is up to 80-95%. Compared with biological stirring preoxidation and complete heap leaching preoxidation, the preoxidation treatment process provided by the invention solves the problems of long preoxidation period and low gold recovery rate, and has remarkable economic benefits. The process of the invention is especially suitable for gold ores with high content of pyrite, is environment-friendly, and is in line with the development of low-carbon economy in nonferrous metallurgy industry.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
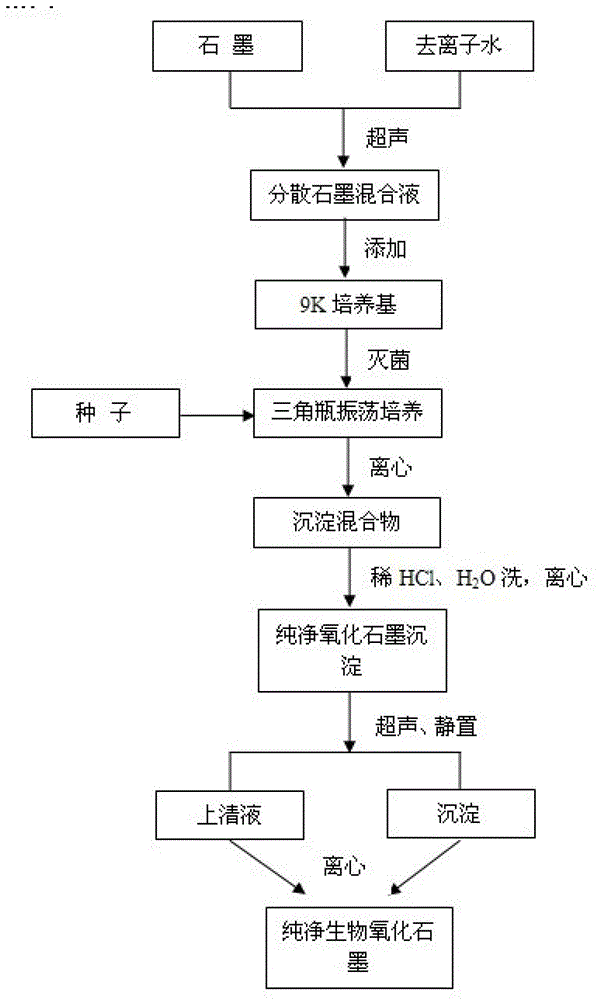
Biological oxidation graphite and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses biological oxidation graphite and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes dispersing the graphite in water to form a graphite mixed liquor with a good dispersion, adding the graphite mixed liquor into a ferrous oxide thiobacillus culture medium, sterilizing, cooling, inoculating Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, culturing for several days, so that an oxygen containing group is introduced and the dispersed graphite is oxidized under the action of the microorganismThiobacillus ferrooxidans, removing minerals and other ions which are generated in the oxidation process after the culturing is finished, until the potential of hydrogen (pH) is neutral, and vacuum drying to obtain the pure biological oxidation graphite. According to the biological oxidation graphite and the preparation method thereof, the microorganism Thiobacillus ferrooxidans capable of oxidizing minerals is used as a strain, and the ultrasonic dispersed graphite is subjected to a biological oxidation. Compared with traditional chemical oxidation methods for graphite, the preparation method has the advantages that the reaction condition is mild and controllable, the reaction process is environment-friendly and pollution-free, the prepared biological oxidation graphite has few defects, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
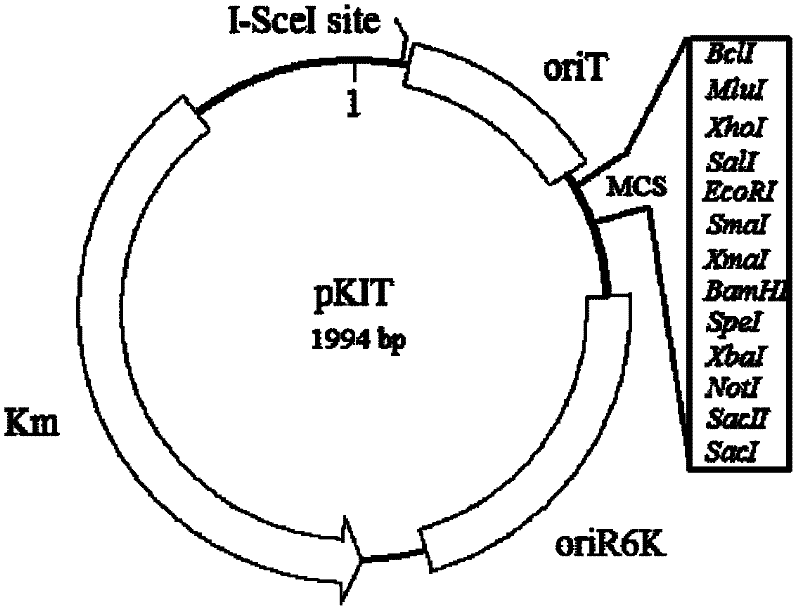
A marker-free gene knockout method for extreme acidophilic Thiobacillus ferrooxidans
ActiveCN102260699ARapid knockoutEfficient knockoutMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionThiobacillus ferrooxidansBiotechnology
The invention discloses an unmarked gene knock-out method of extremely acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans based on the principle of homologous recombination. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing initial plasmids, suicide plasmids containing homologous fragments at upstream and downstream parts of target genes to be knocked out, and induction plasmids containing yeast endonuclease I-SceI genes; jointing and transferring the suicide plasmids and the induction plasmids to acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans; and screening and identifying single commutators generating homologous recombination for the first time and double-exchange mutant strains generating homologous recombination for the second time. The method disclosed by the invention realizes the unmarked gene knock-out of acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans for the first time, can realize the purpose of quickly, stably and efficiently knocking out the genes of the thiobacillus ferrooxidans, and can be used for researching the functional and metabolic mechanisms of the genes of the thiobacillus ferrooxidans, improving the genetic characters and constructing efficient bioleaching engineering bacteria; and moreover, the obtained mutant strain does not carry any resistance gene, thus the obtained mutant strain not only can be used as an original strain to knock out and improve genes in subsequent different sites, but also can be safely used for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for microorganism-pelleting heap leaching of earthy oxide copper ores
InactiveCN101781705AIncrease throughputReduce ore washingProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansHydrometallurgy
The invention relates to a method for leaching earthy oxide copper ores, in particular to a method for microorganism-pelleting heap leaching, and belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy. The method is characterized in that: the earthy ores are directly screened, and fine ores with the granularity of 1.5mm are added with strain acid water and cement to prepare ore pellets with the diameter between 10 and 20 mm for heap leaching, wherein the mass concentration of sulphuric acid in the strain acid water is 3 to 10 percent, strains are mixed strains of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Thiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, the mass ratio of the three is 4.0-5.5:2.5-3.5:1.5-2.5, the bacterial load ratio is 105 and 108 / ml, the cement amount is 15 to 30kg / ton of ores; and leachate in the leaching is sprayed for closed cycle production. The method has the advantages of low investment, low energy consumption, good leaching effect, and no discharge of closed cycle, solves the problem of leaching the low-grade earthy oxide copper ores (including sulphide and oxide blend ores) by microorganism heap leaching, and overcomes the defects of long flow and high cost of agitation leaching.
Owner:王宣明
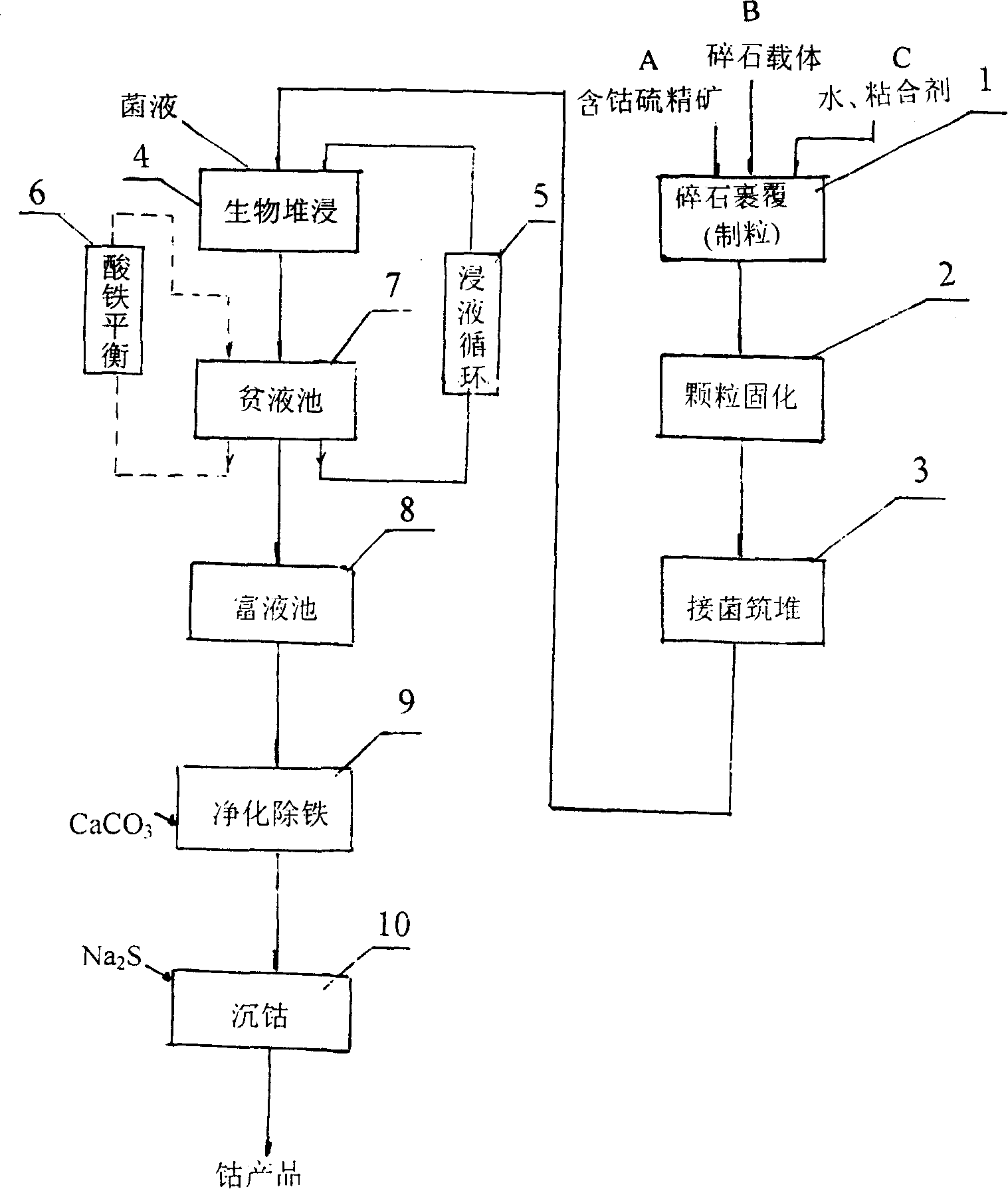
Mesophilic acidophilic bacteria and biological heap leaching technique for low-grade cobalt-containing sulfur concentrate
InactiveCN101191122AEfficient recyclingLow investment costBacteriaProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansCobalt sulphate
The invention relates to mesophilic acidophilic bacteria and a biological heap leaching technology for low-grade cobaltiferous sulfide ore concentrates. The mesophilic acidophilic bacteria have a name of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans Retech V and a collection registration number of CCTCC NO: M202039, and has been stored and collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (in Wuhan University). The biological heap leaching technology is that: mineral grains which are suitable for biological heap leaching are obtained after coating of crushed stones and solidification of the mineral grains of the low-grade cobaltiferous sulfur-bearing ore concentrates. Cobalt sulphates are obtained through procedures of embankment, heap leaching and trickling by adoption of bacteria with two different growth temperatures, lixivium circulation, purification and deferrization of cobalt pregnant solution, cobalt settlement and so on of the mineral grains. The temperature of 10 to 55 DEG C, the PH value of 1.2 to 1.8 and the adequate Fe concentration of a storage yard in a heap leaching system during the leaching out process are favorable for activity of leaching bacteria. The invention has the advantages of capability of fully utilizing low-grade cobaltiferous sulfide ore resources in old mines, improvement of comprehensive utilization level of mines, conservation of cost, and improvement of profit. The invention is applied in developing cobaltiferous sulfide ore resources in remote areas.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
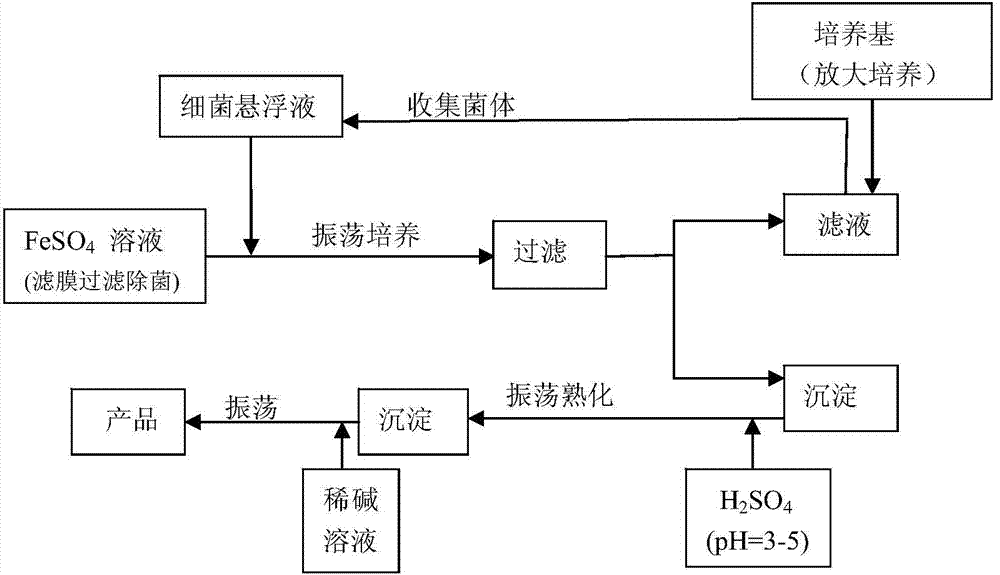
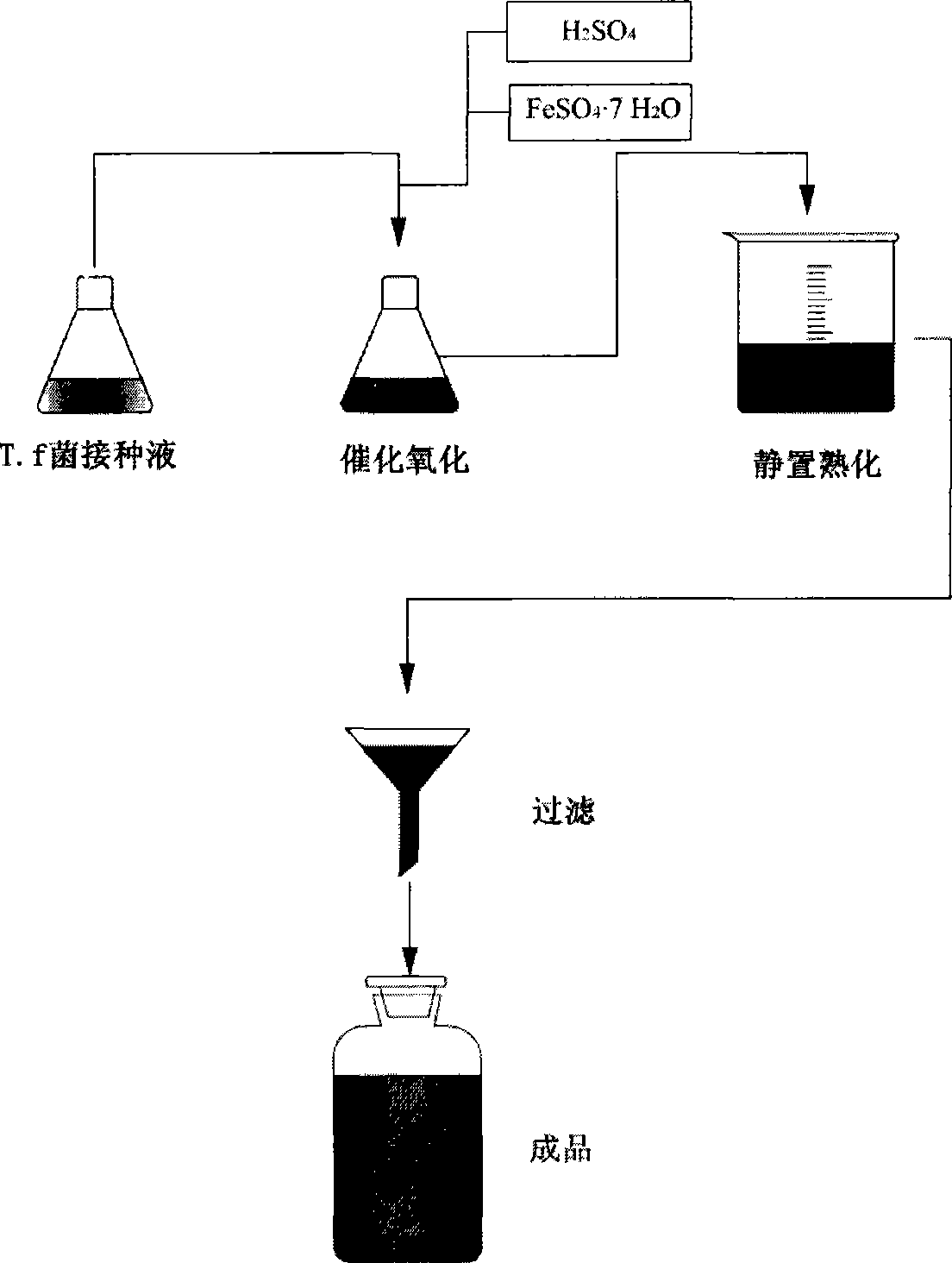
Method for synthesizing polymeric ferric sulfate by microbial catalysis
InactiveCN101503710AGive up dependenceProduction environmental protectionMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismThiobacillus ferrooxidans
The invention provides a method for synthesizing polymeric ferric sulfate through microbial catalysis. The method comprises the steps of taking ferrous sulphate and water as main raw materials, performing aerobic culture on the raw materials for 2 to 4 days at normal temperature and normal pressure through the catalysis of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, preparing a polymeric ferric sulfate solution through oxidation, hydrolysis, polymerization and other processes, keeping the solution stand to cure the solution for 3 to 4 weeks, filtering the cured solution and obtaining a product. The product is a homogeneous red brown polymeric ferric sulfate solution, of which the base saturation degree can reach 14.0 percent, and cannot deteriorate after long-term storage. The method for preparing polymeric ferric sulfate has the advantages of convenient operation, economic viability, safety, reliability, energy conservation and environmental protection, and is a novel method for preparing polymeric ferric sulfate with high efficiency and convenience.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
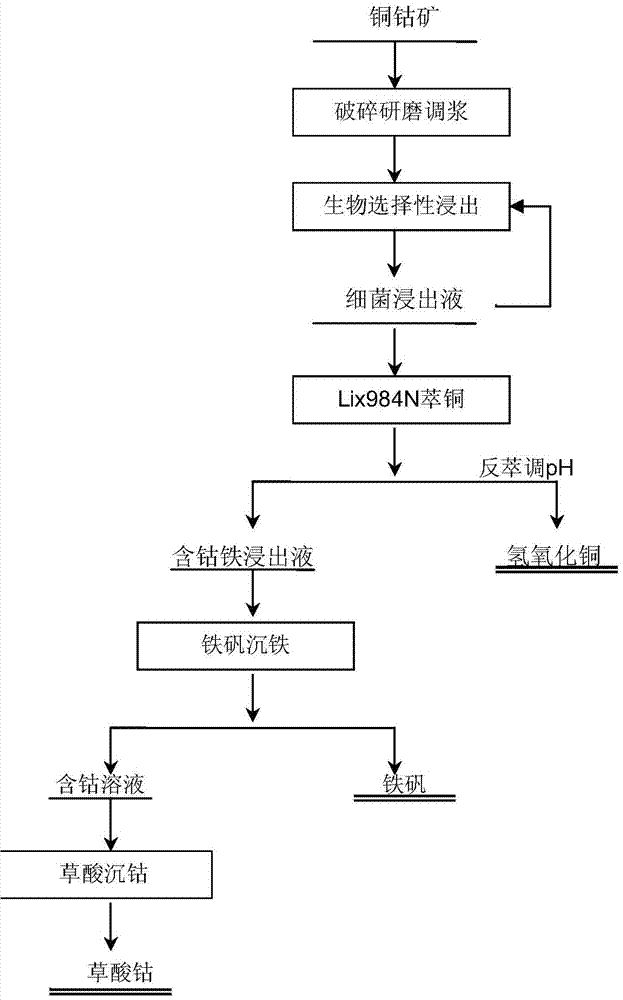
Biological selectivity leaching method of low-grade copper-cobalt ore
ActiveCN103572050AAchieve separationEfficient recyclingProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansCobalt
The invention discloses a biological selectivity leaching method of low-grade copper-cobalt ore, and belongs to the field of microbial metallurgy. The biological selectivity leaching method comprises the following steps: the copper-cobalt ore is crushed and grinded; a mixed bacterium liquid containing ferrous oxide micro spirilla, acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans and acidophilic thiobacillus thiooxidans is introduced to a 9 K of culture medium for cultivating to obtain a bacterium culture solution. The copper-cobalt ore is added to the bacterium culture solution to conduct bacterium leaching on the cobalt concentrate; when the leaching rate of cobalt in the bacterium leaching liquid reaches above 97%, the leaching liquid containing valuable metal ions such as cobalt and copper is separated from the leaching residue; then Lix984N extraction agent is adopted to extract copper to obtain a copper product; the raffinate from which the copper is extracted is subjected to precipitation and iron removing treatment by a jarosite process to obtain an iron product; cobalt-containing liquid after being subjected to iron removal is crystallized to obtain a cobalt oxalate product. The biological selectivity leaching method has the advantages of short technique flow, easy operation, simple equipment, low energy consumption, no high-temperature smelting, no emission of pollutant smoke and poisonous gas, and quick achievement of separation and efficient recovery of cobalt and other valuable metals.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for removing heavy metal in solid organic waste compost
ActiveCN101624300AImprove qualityReduce heavy metal concentrationClimate change adaptationOrganic fertilisersThiobacillus ferrooxidansYeast
The invention relates to a method for removing heavy metal in solid organic waste compost, which comprises the following steps: (1) adding sulfur powder into solid organic waste compost according to a use amount of 10-150 g of sulfur powder for one 1kg of compost; (2) adding ferrous sulfate heptahydrate solution into the compost; (3) inoculating microorganism compound bacteria including thiobacillus ferrous oxide, thiobacillus thiooxidans, white rot fungi, yeast and penicillium according to a use amount of 1g of compound bacteria for 1 kg of compost; (4) spraying and leaching the inoculated compost which is arranged on a stacking bed and keeping water content in the stacking bed to be not lower than 65 percent; (5) during leaching time of 4-14 days, monitoring the concentration of heavy metal of leaching liquid in real time till the concentration of heavy metal meets the national standard; and (6) adding slaked lime into the compost to adjust pH value to 7 after the leaching is finished. The invention has the advantages that the removal rate of heavy metal in leaching reaches over 90 percent, the lose rate of nutrient elements such as N, P and the like is lower than 5 percent, and the method has simple operation and low running cost.
Owner:安徽徽粮生物科技有限公司
Microbial-catalytic synthesizing method of pyrite ammonia alum
InactiveCN1438318AHigh puritySimple particlesFermentationThiobacillus ferrooxidansCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a microbial catalytic synthesizing method of pyrites vanadium. It uses ferrosi sulfate and one of potassium sulfate, sodium sulfate and ammonia sulfate as the reaction matters, distilled water as reaction medium, and Thiobacillus ferrooxidans LX5 as catalytic oxidizer, blends by ventilating for 1-3 days to make reaction, filters and collects the deposit, washes by the acidified distilled water by vitriol, then washes by distilled water, and at least dries to get the pyrites vanadium. The reaction is at ordinary temperature and pressure.
Owner:南京贝克特环保科技有限公司
Method for leaching phosphorus from low-grade phosphate ore by thiobacillus thiooxidans
InactiveCN101837962AReduce joinEasy to joinBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThiobacillus ferrooxidansResource development
The invention relates to microbial leaching technology, in particular to a microbial leaching method for low-grade phosphate ore by thiobacillus thiooxidans separated from a copper ore soil sample in Tongshankou in Hubei Province. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) sampling; 2) enrichment, separation and domestication of bacterial strain; and 3) leaching method for phosphorus. The bacterial strain which is obtained by screening and domesticating makes the phosphorus leaching rate over 30 percent higher than that in the conventional reports. By using pyrite as a leaching aid, the leaching method reduces the addition of a great amount of expensive phosphorous compounds and monomer sulfur, is favorable for cycle and high-efficiency utilization of accompanying resources in the phosphorite, reduces the environmental pollution and the investment cost, has lower production cost, and can realize sustainable development of the resource development and environmental protection.
Owner:WESTERN MINING CO LTD
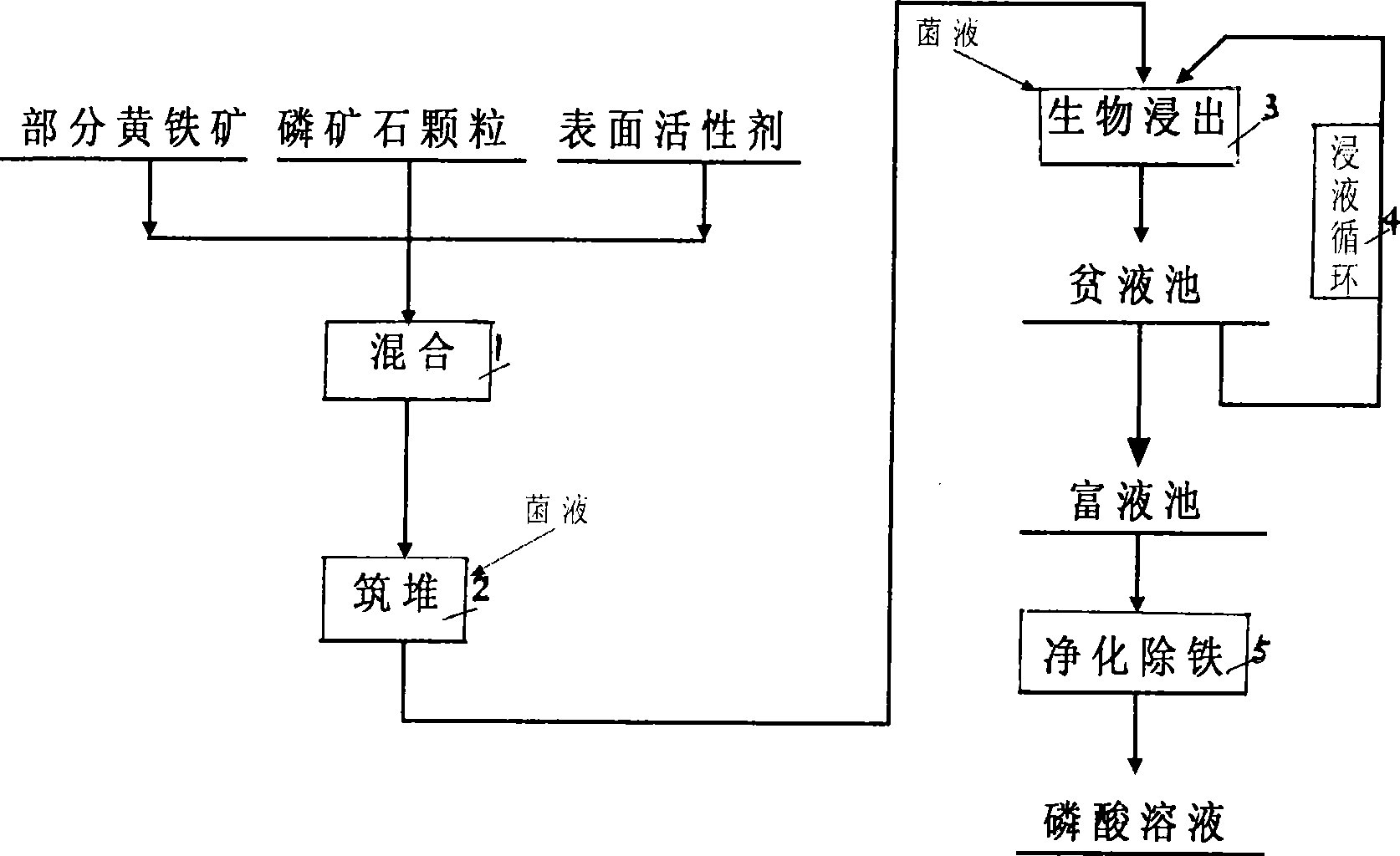
Acidophilic leaching-ore bacteria, heap bioleaching process for low grade phosphate ore by using the same
InactiveCN101434917AEfficient recyclingTake advantage ofBacteriaProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansSurface-active agents
The invention relates to acidophilic mineral leaching bacteria and a biological heap leaching technique of middle-grade and low-grade phosphorite that uses the acidophilic leaching bacteria. The acidophilic mineral leaching bacteria is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University and named Thiobacillus ferrooxidans Retech V, the preservation date is October 21st, 2002, and the preservation registration number is CCTCC NO. of M202039. The biological heap leaching technique smashes raw ores and mixes the ores with proper amount of iron pyrites and surface active agent, thus greatly improving phosphorus leaching rate. A leaching liquid with iron removed has the phosphorus (according to P2O5) content more than 30 percent and can be directly used for phosphate fertilizer production. The biological heap leaching technique has short procedure, simple equipment, saved investment, low cost, no pollution, high recycling rate and flexible production scale, can be used for treating the resources of middle-grade and low-grade phosphate rocks which are hard to be treated by traditional picking metallurgy techniques, and can raise the utilization rate of phosphorus resources.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
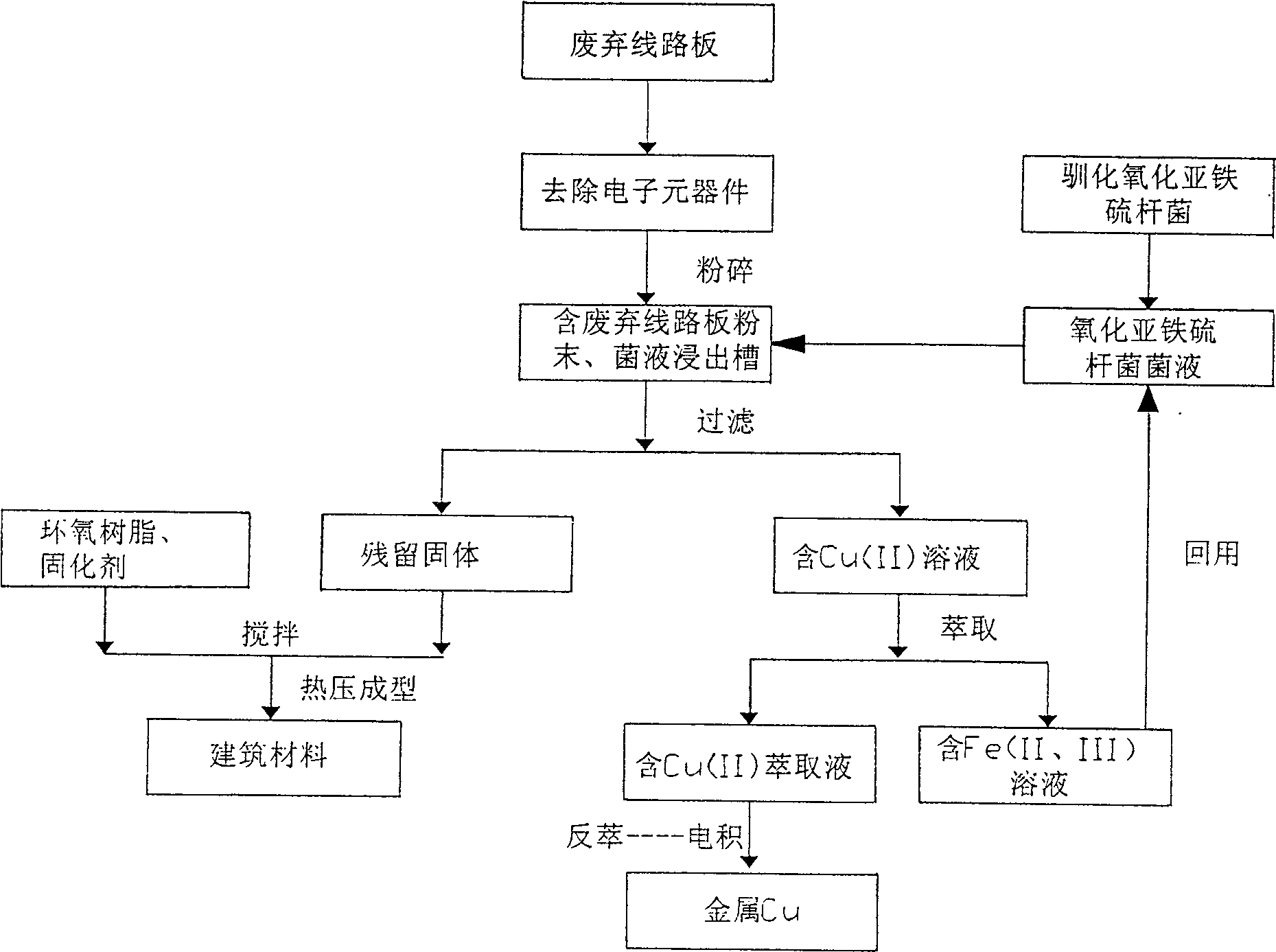
Comprehensive resources treatment method of waste circuit board
InactiveCN100510126CHigh recovery rateRealize cleaner productionPhotography auxillary processesBacteriaThiobacillusWastewater
The invention relates to a method that combines microbial, metallurgical, material and other technologies to extract metallic copper from waste circuit boards and comprehensively utilize other remaining materials. This invention draws on the principles of microbial hydrometallurgy, uses Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and the like to leaching and recovering the metallic Cu in the waste circuit boards, and at the same time recycles the residual solids after leaching the Cu, achieving a completely comprehensive resource utilization of the waste circuit boards. deal with. This method realizes full resource treatment of waste circuit boards, does not discharge waste water, waste residue or waste gas to the environment, realizes clean production in the whole process, has the characteristics of low investment, low cost, high metal recovery rate, no pollution, green ecology, etc. Advantages: It has good social, economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
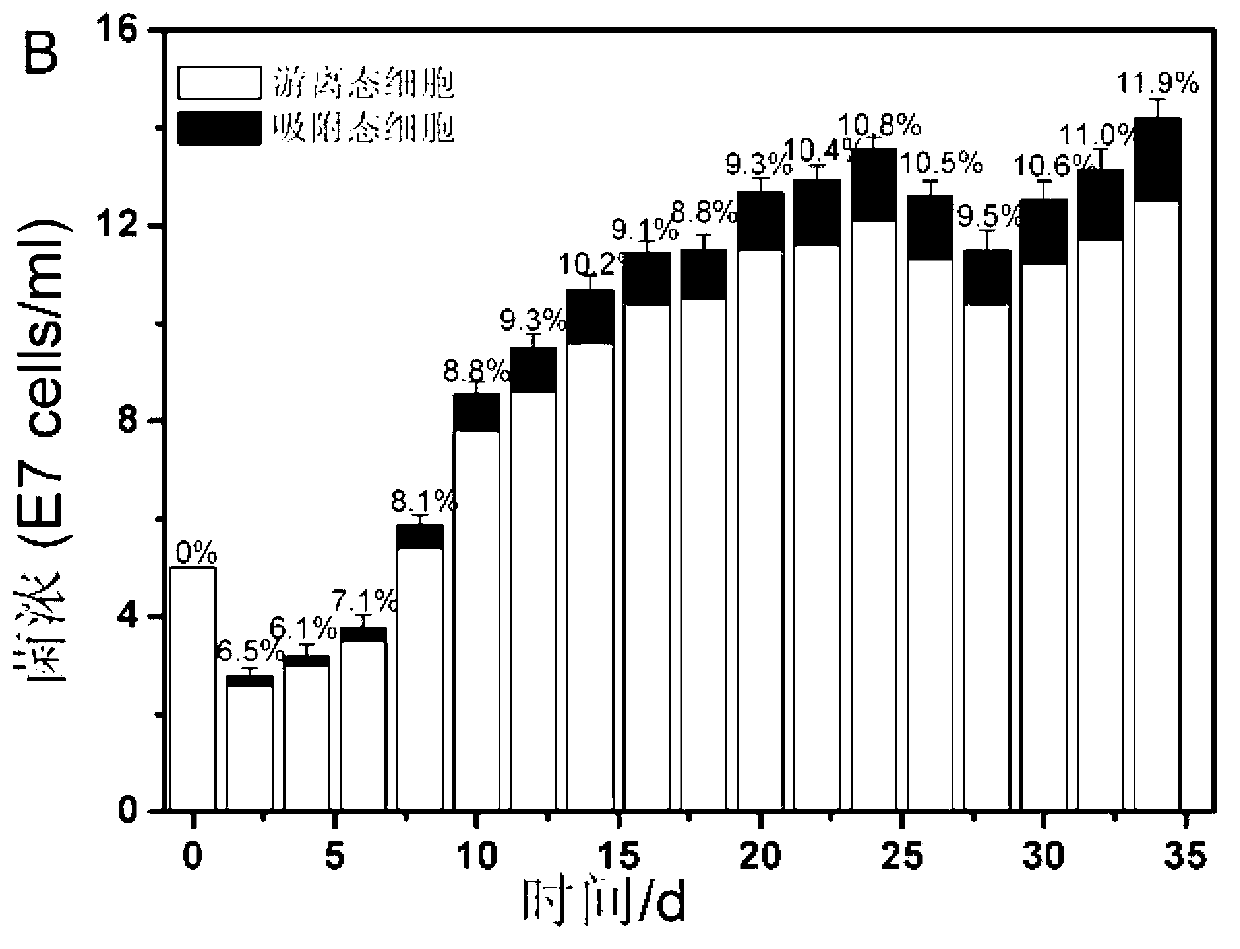
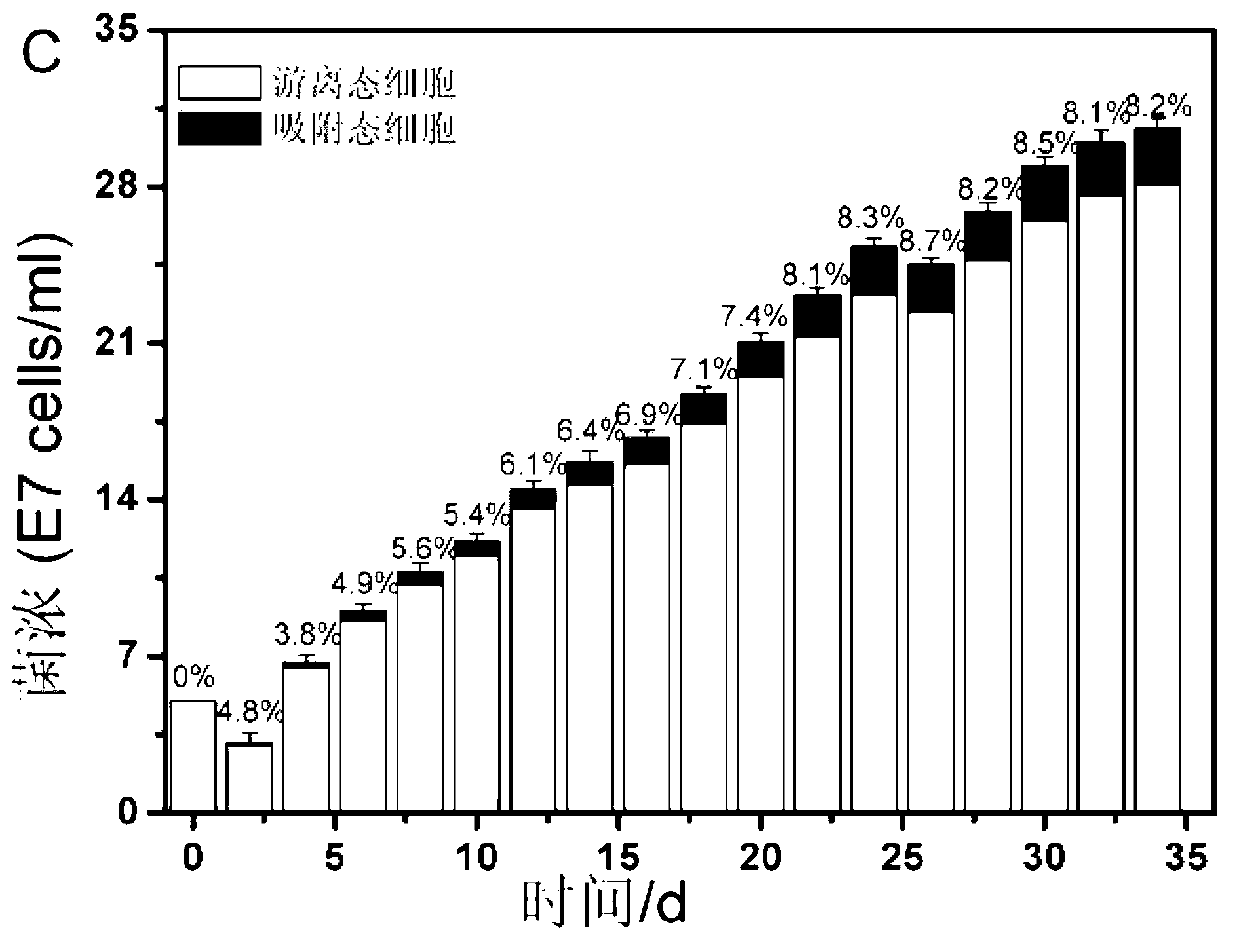
Method for detecting adsorbed-state microorganism in chalcopyrite biological leaching process
ActiveCN103276079AEffective detection of concentrationGood stability in three parallel testsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesThiobacillus ferrooxidansMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for detecting an adsorbed-state microorganism in a chalcopyrite biological leaching process, and belongs to the technical field of biological leaching. The method disclosed by the invention comprises a washing method applied to an absorbed strain on the mineral surface, the calculation of total concentration of absorbed-state bacteria, and qualitative and quantitative detection method applied to the microorganism in a mixed bacteria system. Three different leaching systems applied to the chalcopyrite biological leaching, namely a pure thiobacillus ferrooxidans CUMT-1 system, a pure thiobacillus thiooxidans ZJJN-1 system and a mixed thiobacillus ferrooxidans and thiobacillus thiooxidans system (number concentration 1:1), are used as examples for verification, and the verification results prove that the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple and easy operation implementation, low requirements for equipment, good specificity and high stability in the detection of the mixed system, and the like, can fast achieve the qualitative and quantitative detection on the absorbed-state microorganism in the biological leaching process, provides basic technical measures for improving the leaching rate, and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
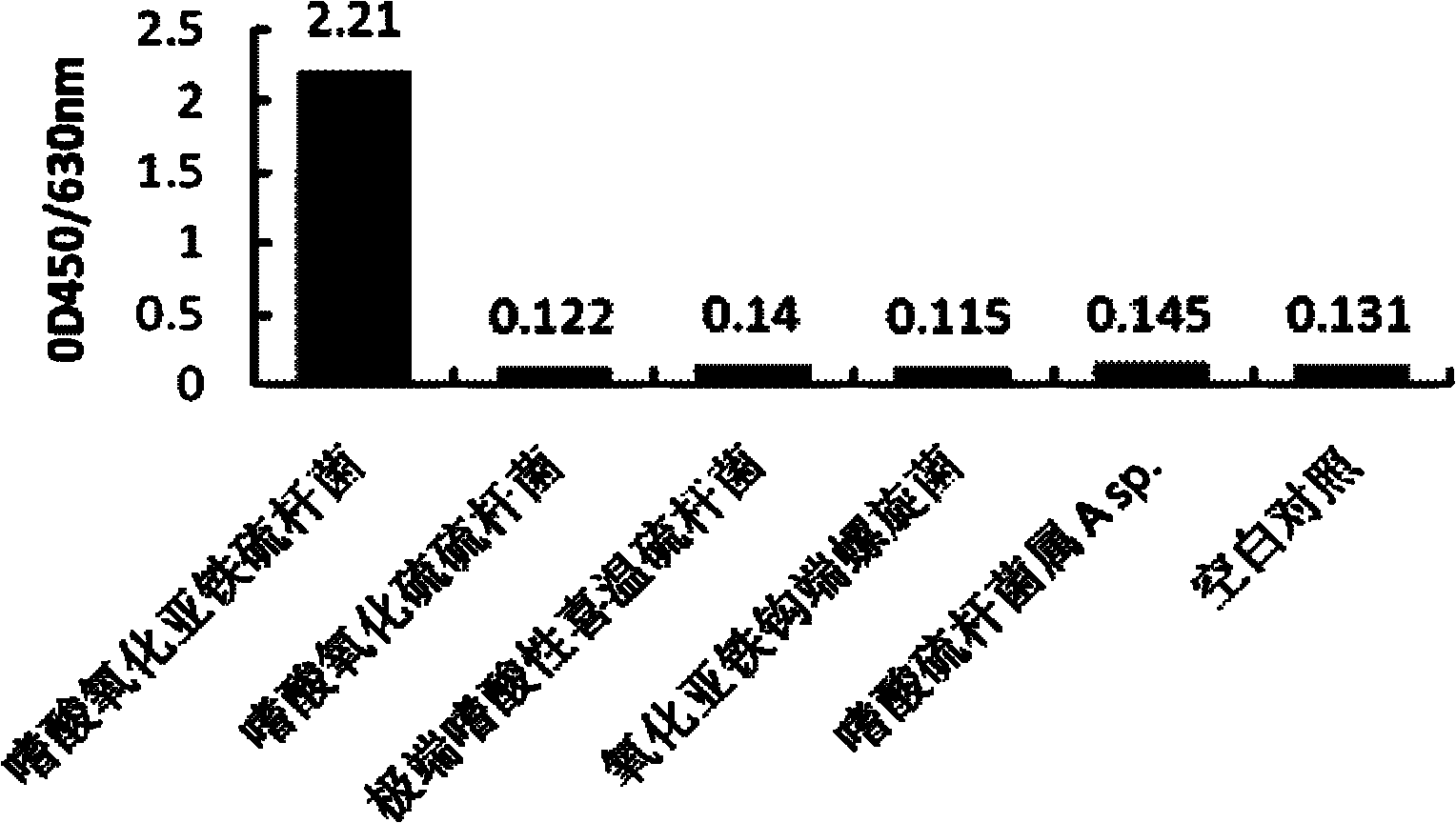
Thiobacillus ferrooxidans detection probe composition and related detection method
ActiveCN102839210AStrong specificityImprove detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationThiobacillus ferrooxidansProtein markers
The invention relates to a thiobacillus ferrooxidans detection probe composition comprising an analysis probe used to be specifically combined with the rRNA of the thiobacillus ferrooxidans, a capturing probe used to be combined on a carrier and is used to be specifically combined with the analysis probe, and a signal probe used to be specifically combined with the analysis probe. The signal probe has protein markers. Preferably, the analysis probe has a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 1, the capturing probe has a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No.2 and has biotin markers, and the signal probe has a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 3. The protein markers are fluorescein markers. The invention also provides a thiobacillus ferrooxidans detection method. The thiobacillus ferrooxidans detection probe composition provided by the invention is inelegantly designed. With the detection probe composition, thiobacillus ferrooxidans can be rapidly quantitatively and qualitatively detected. The detection method has the advantages of simple operation and good repeatability. The method is suitable for large-scale popularization.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of treatment and composition for inhibiting the production of toxic free radical and reactive oxygen species using metalloproteins found in bacteria
PendingUS20050267015A1Preventing tissueAvoid cell damageBiocideSenses disorderThiobacillus ferrooxidansMetalloprotein
Compositions and methods for treating, reducing the risk of, or slowing the onset of a neurological disorder or pathological condition in a subject are provided. An inhibitor of the formation of free radical or reactive oxygen species is administered in an effective amount to the subject and the inhibitor prevents tissue and cellular damage and / or necrosis by inhibiting the release of free radicals or reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can cause such damage in the subject. The inhibitor may be a bacterial metalloprotein. An exemplary free radical production inhibitor is the metalloprotein rusticyanin, a type I blue-copper metalloprotein found in the aerobic acidophilic iron-oxidizing bacterium Thiobacillus ferrooxidan. A composition containing the inhibitor of the formation of free radical or reactive oxygen species includes a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:BATARSEH KAREEM I
Method for removing heavy metal in excess activated sludge
InactiveCN101050047AEasy to operateShort removal timeWater contaminantsBiological sludge treatmentThiobacillus ferrooxidansActivated sludge
This invention discloses method and apparatus for removing heavy metals. The method comprises: inoculating Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and eosinophilic heterotrophic bacteria (3.0-8.0%) into residual active sludge for biological reaction, automatically flowing the reaction solution by a constant flow pump into a precipitation barrel, precipitating heavy metals in the supernatant with heavy metal chelating agent or CaO, and refluxing the eosinophilic heterotrophic bacteria by the constant flow pump to the reaction barrel. Since Thiobacillus ferrooxidans is sensitive to soluble organic matters, inoculation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans together with eosinophilic heterotrophic bacteria can reduce the contents of soluble organic matters in the reaction solution, thus can shorten the growth period of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and improve the removal effect of heavy metals. When the method and apparatus are utilized for biological reaction for 5-7 days, the removal effect of heavy metals in residual sludge is obvious. The apparatus has such advantages as high heavy metal removal efficiency and easy operation. The method has such advantages as easy operation, and good effect.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com