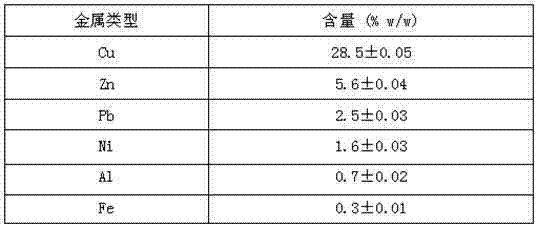
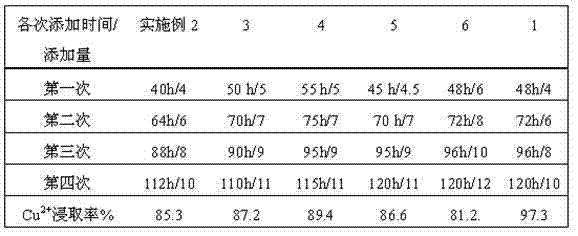
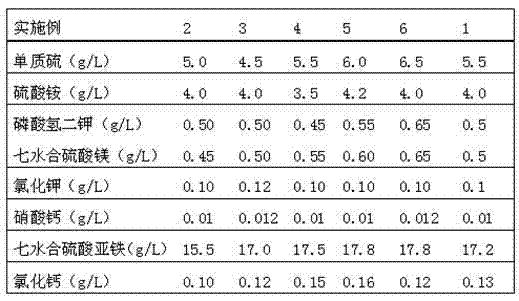
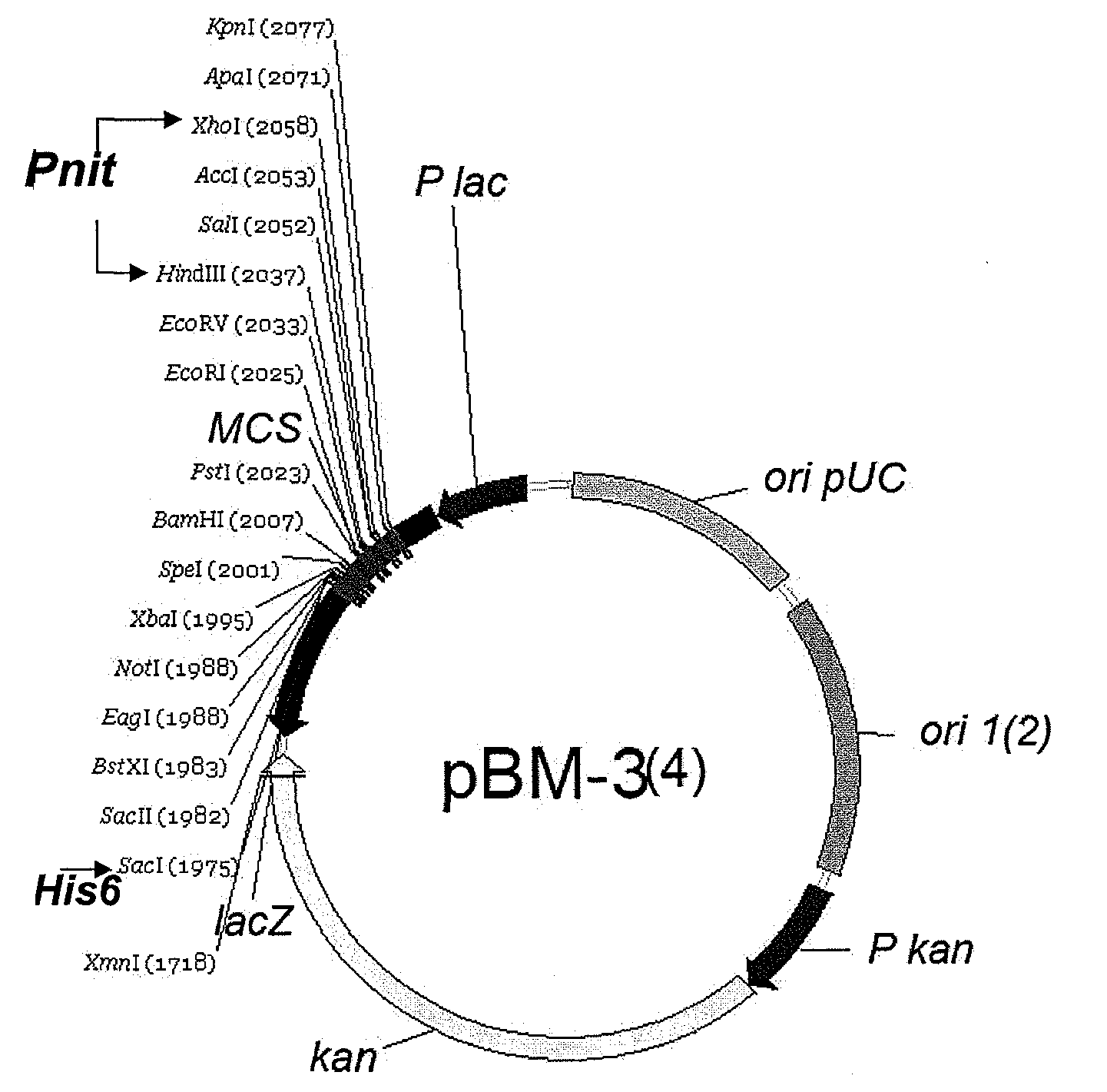
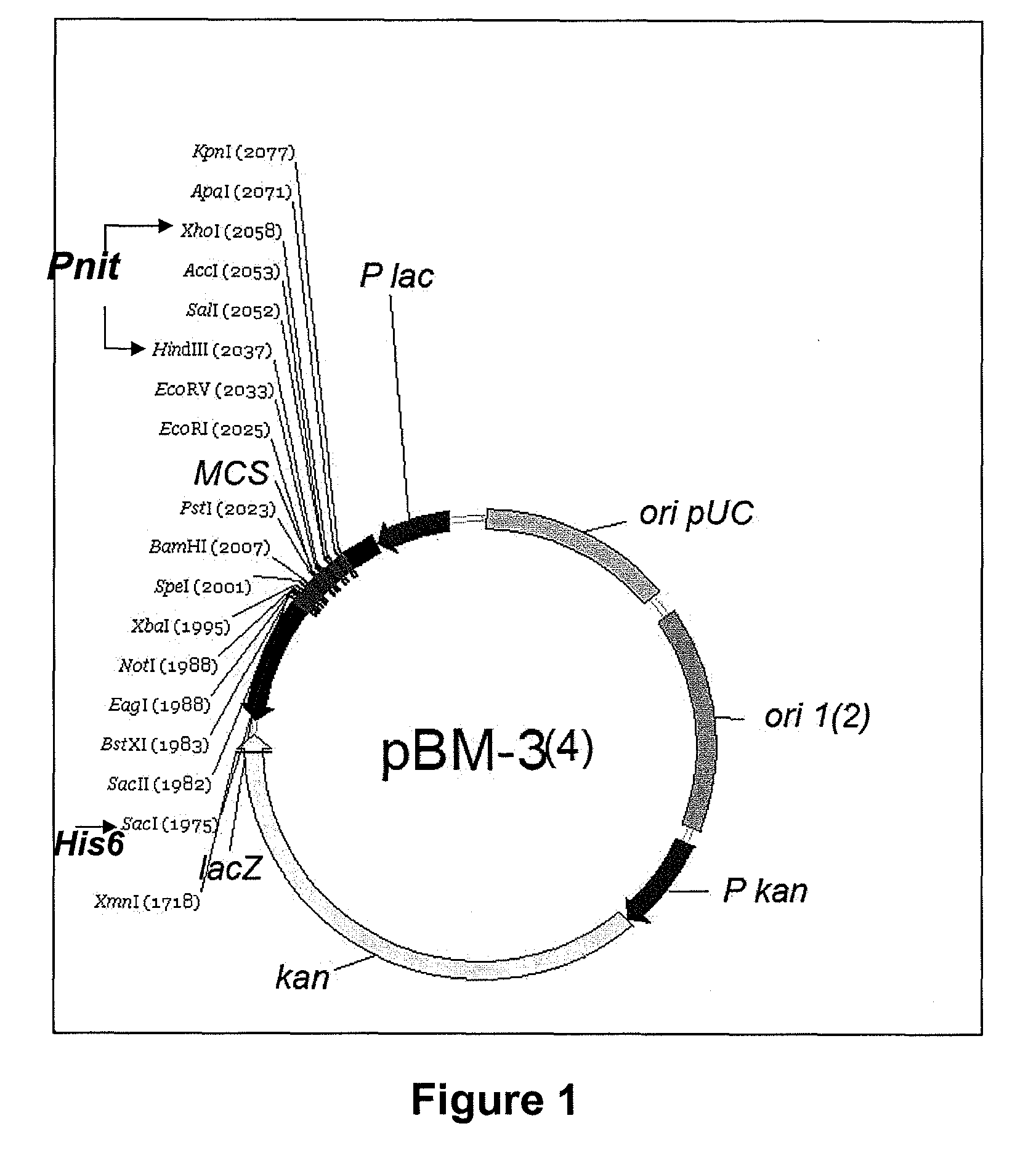
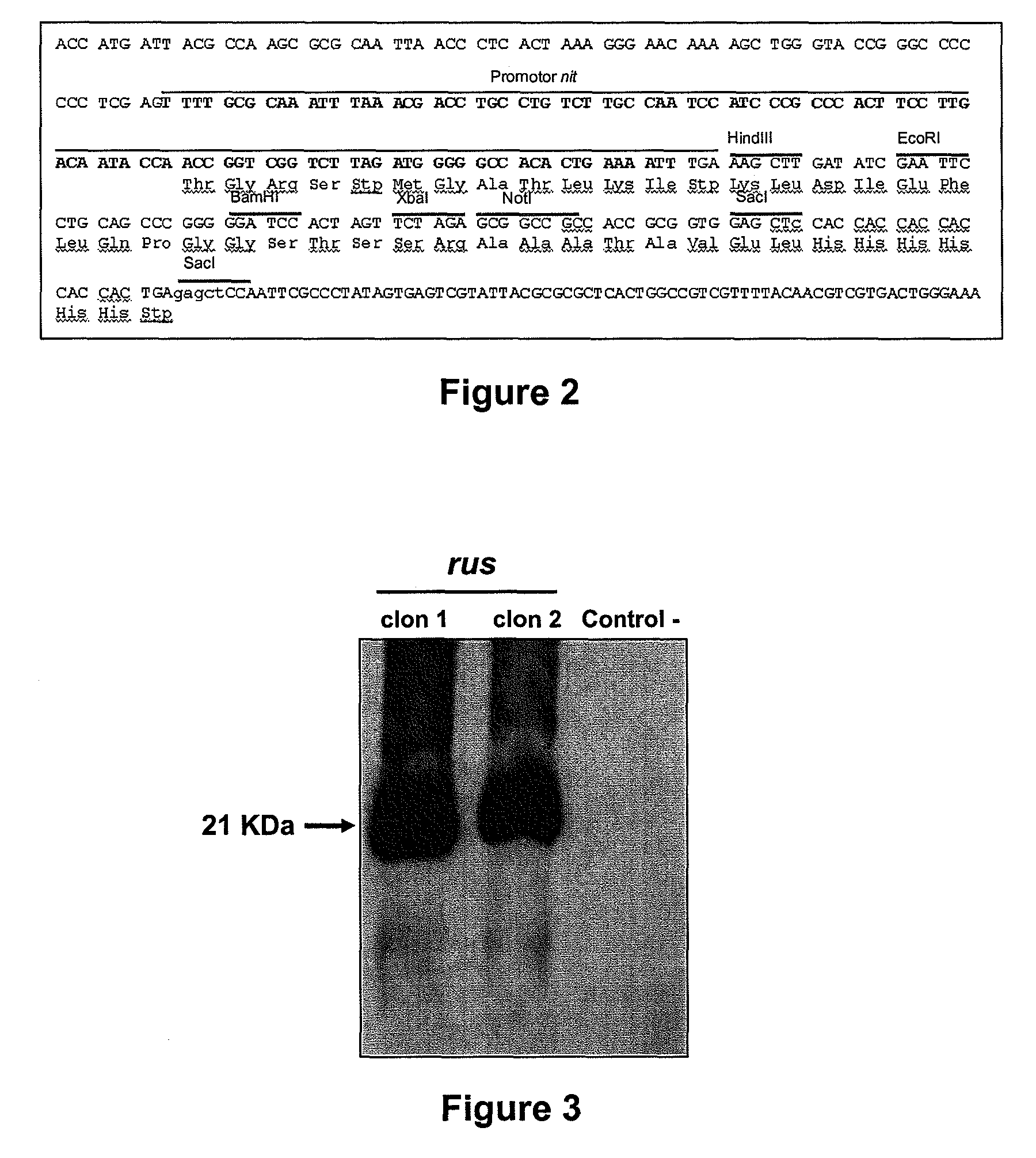
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, formerly known as Thiobacillus thiooxidans until its reclassification into the newly designated genus Acidithiobacillus of the gamma subclass of Proteobacteria, is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that uses sulfur as its primary energy source. It is mesophilic, with a temperature optimum of 28 °C. This bacterium is commonly found in soil, sewer pipes, and cave biofilms called snottites. A. thiooxidans is used in the mining technique known as bioleaching, where metals are extracted from their ores through the action of microbes.
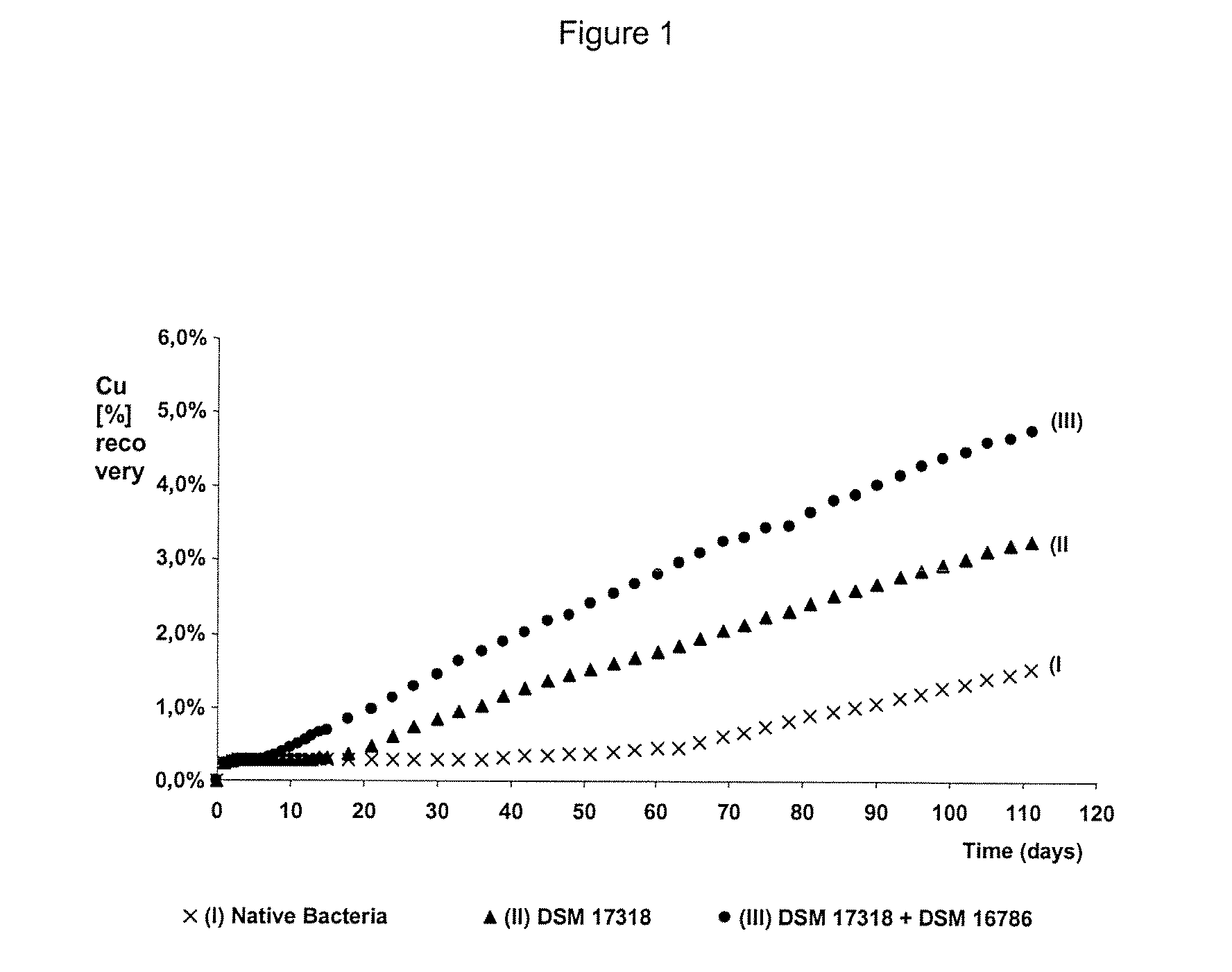
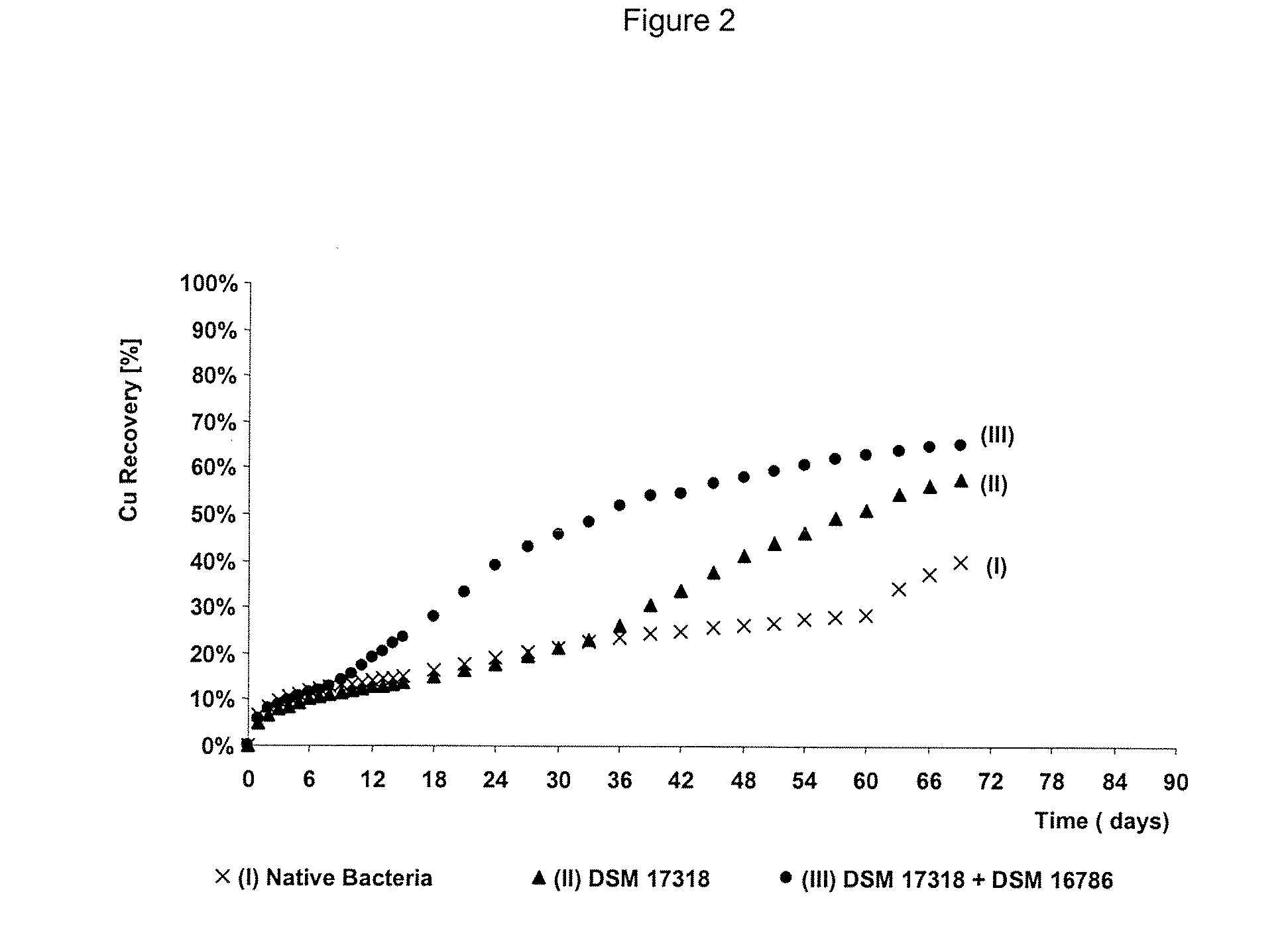
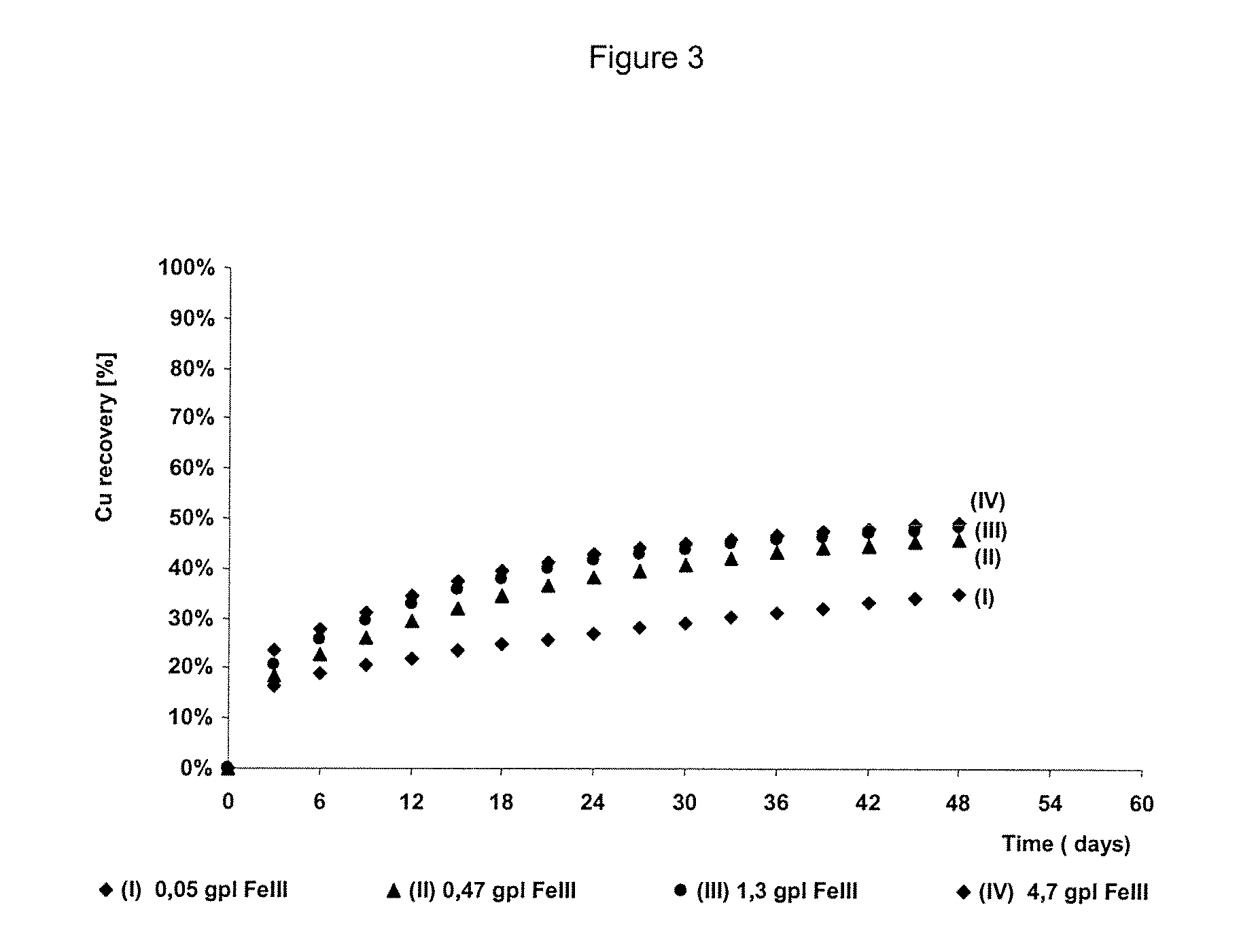
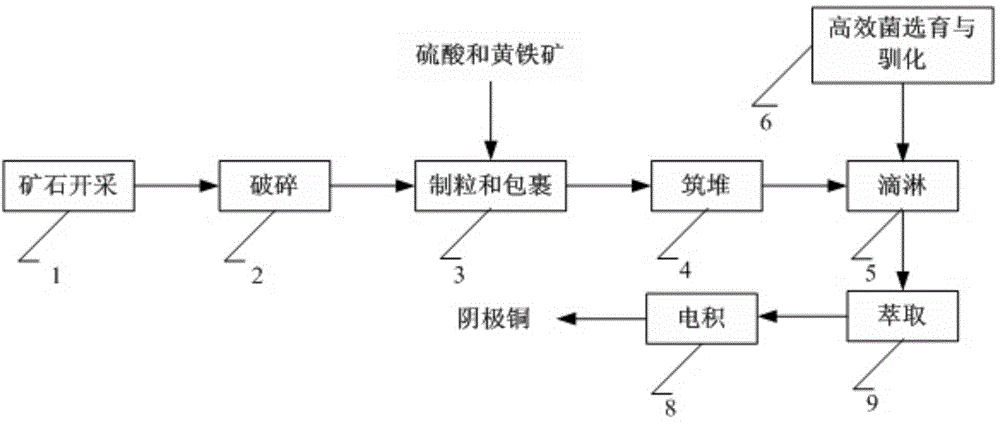
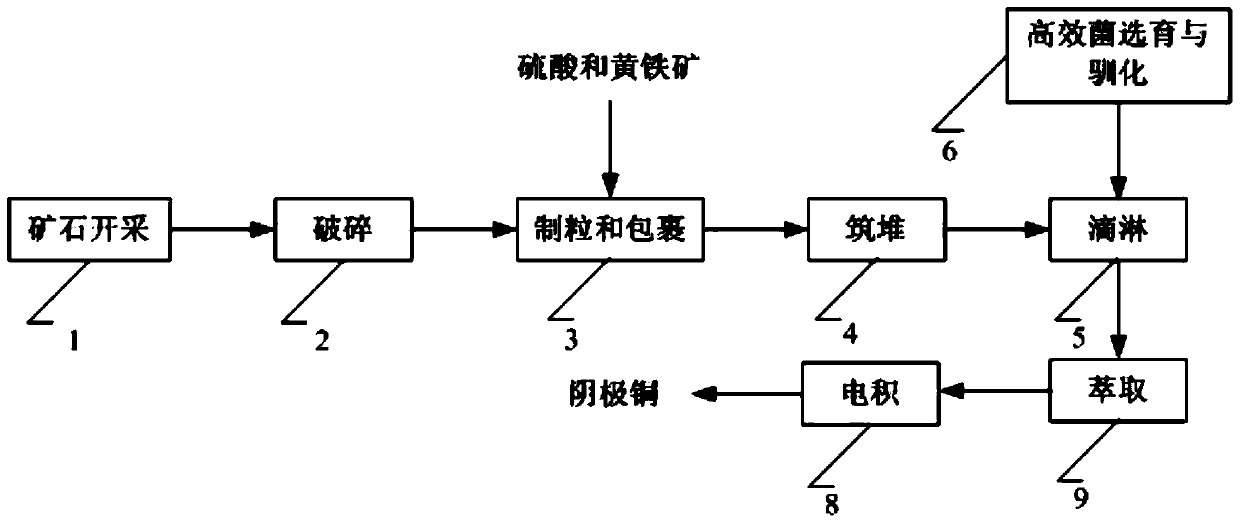
Process to increase the bioleaching speed of ores or concentrates of sulfide metal species, by means of continuous inoculation with leaching solution that contains isolated microorganisms, with or without presence of native microorganisms
ActiveUS20080127779A1Decrease ore bioleaching timeImprove bioleaching conditionSolvent extractionGold compoundsTailings damPotassium
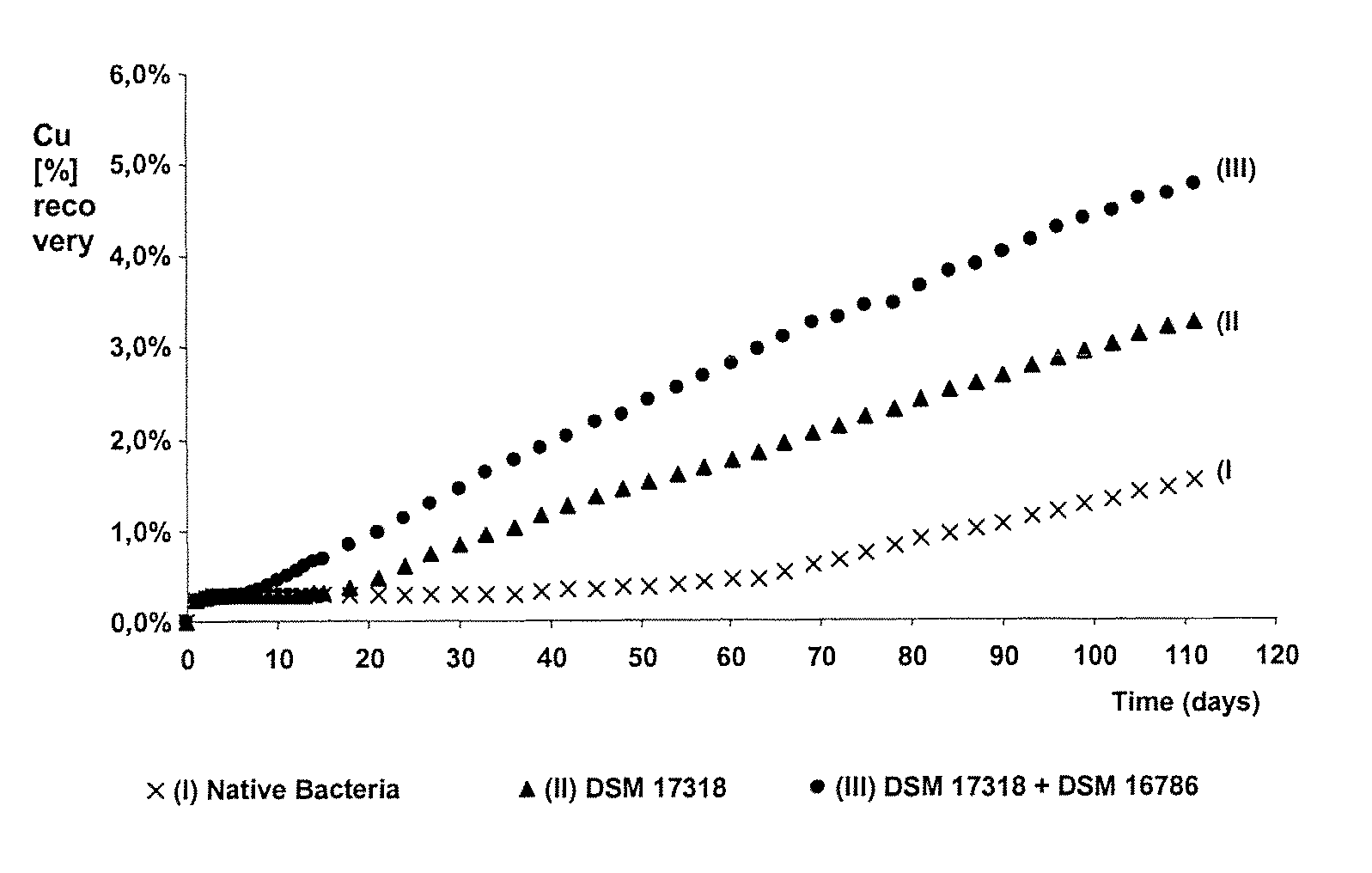
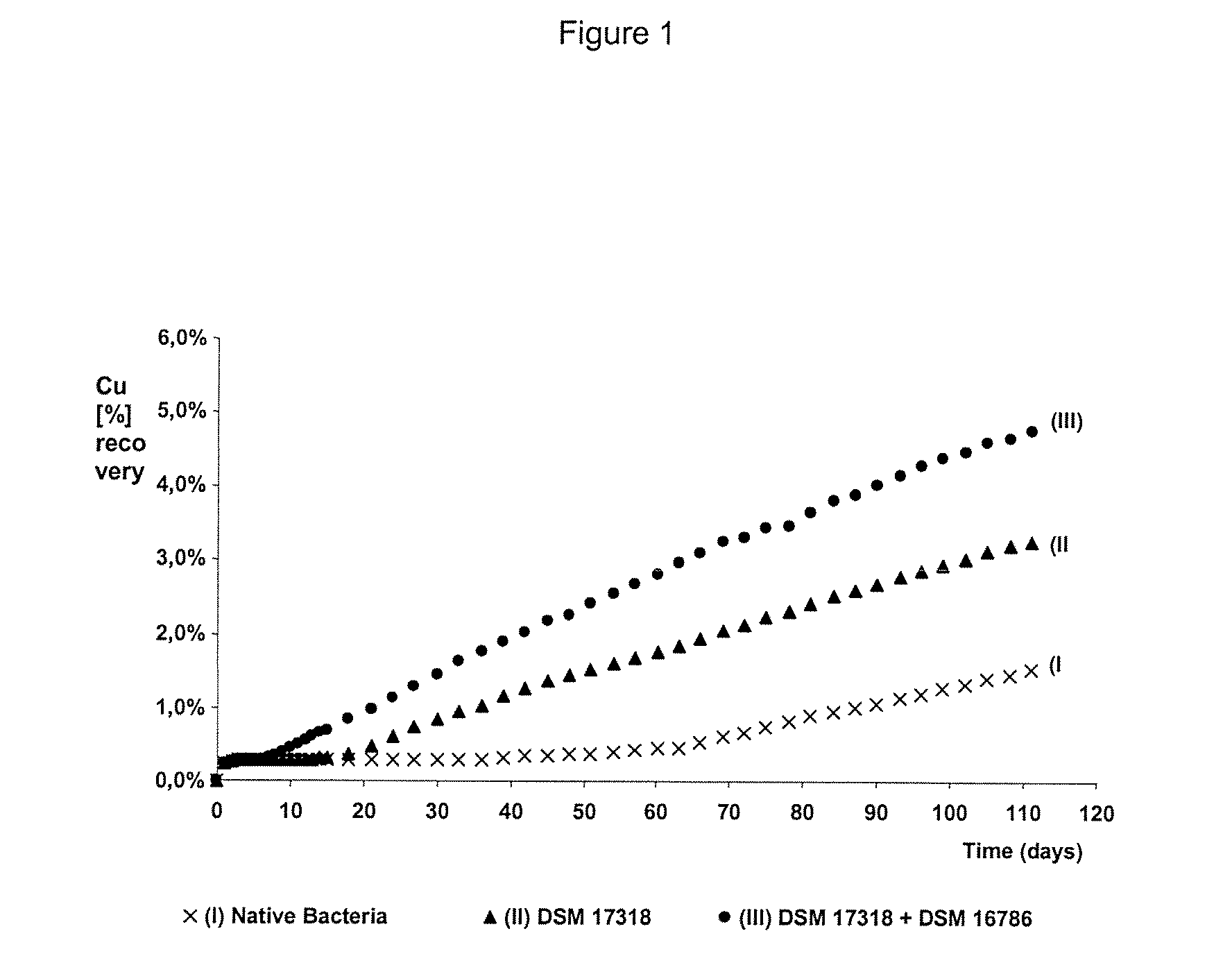
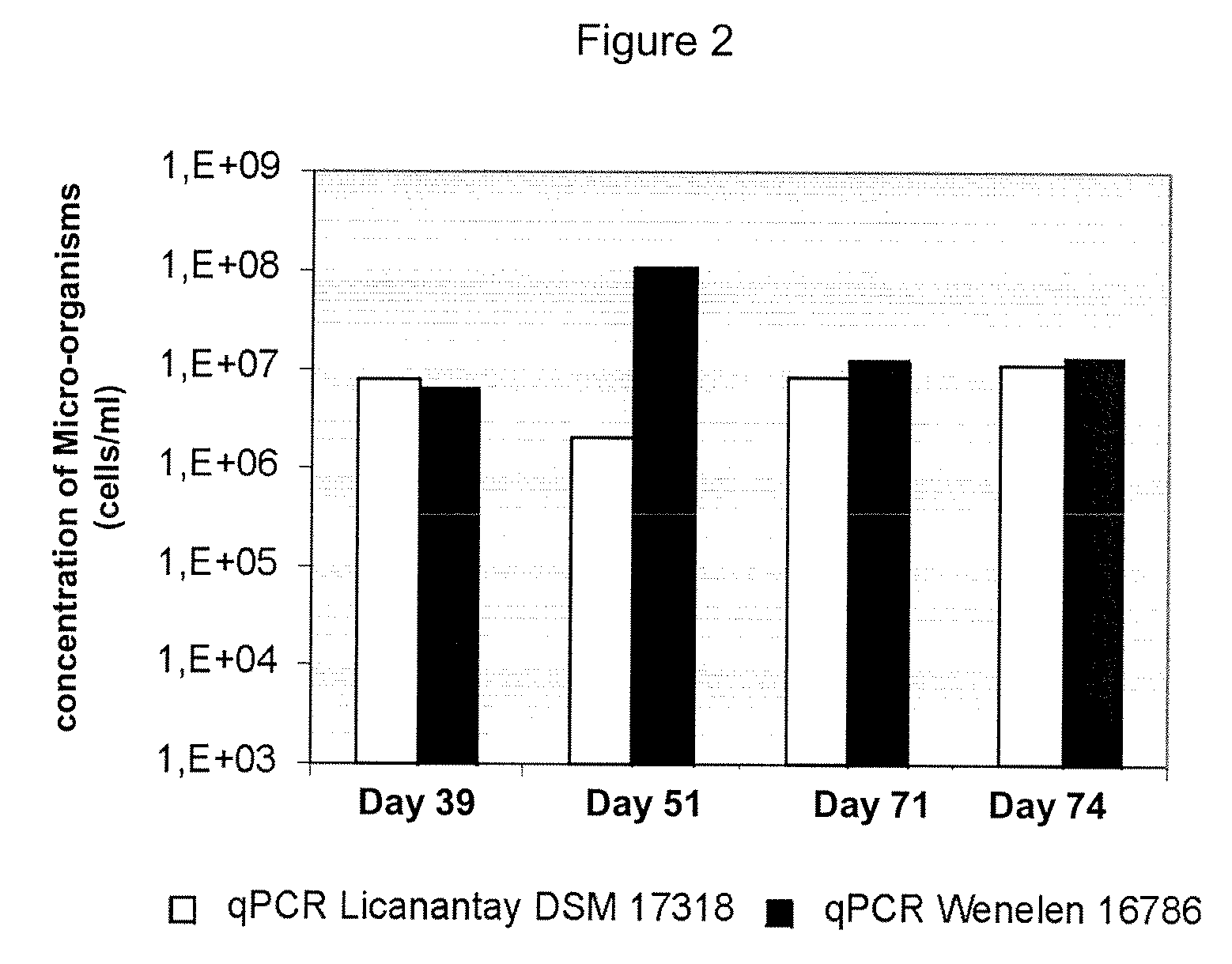
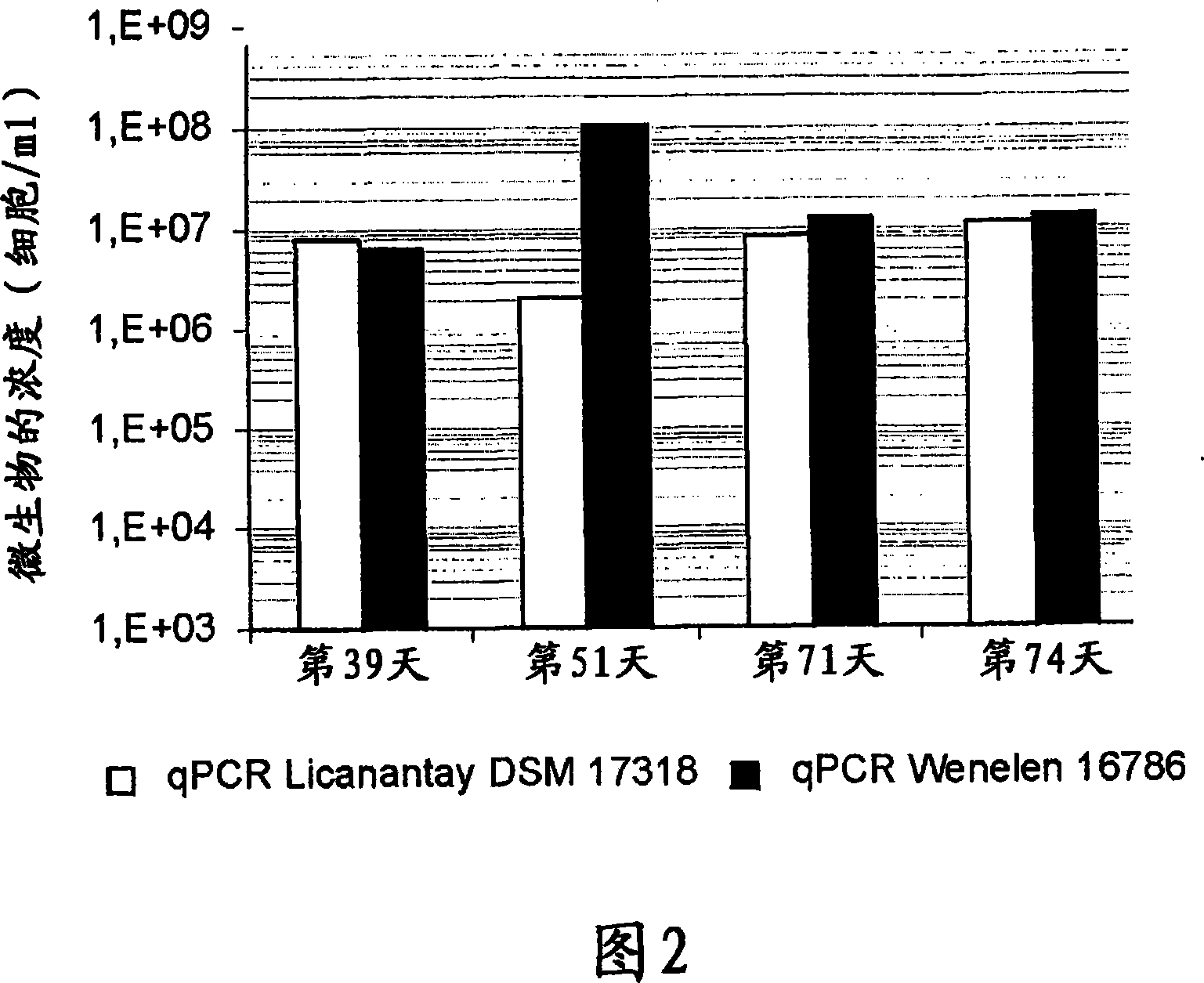
The invention publishes a process to increase the bioleaching speed of ores or concentrates of sulfide metal species in heaps, tailing dams, dumps, or other on-site operations. The process is characterized by the continuous inoculation of the ores or concentrates with isolated microorganisms of the Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans type, together with isolated microorganisms of the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans type, with or without native microorganisms, in such a way that the total concentration of microorganisms in the continuous inoculation flow is of around 1×107 cells / ml to 5,6×107 cells / ml. In particular, the invention publishes the continuous inoculation of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans Licanantay DSM 17318 together with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Wenelen DSM 16786 microorganisms, or with other native microorganisms at a concentration higher than 5×107 cells / ml. In addition to the inoculation of isolated bacteria, the invention includes the addition of oxidizing agents such as the ferric ion produced externally, together with nutrients in the shape of salts of ammonium, magnesium, iron, potassium, as well as air enriched continuously with carbon dioxide to promote bacterial action in the bioleaching process of ores or concentrates.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
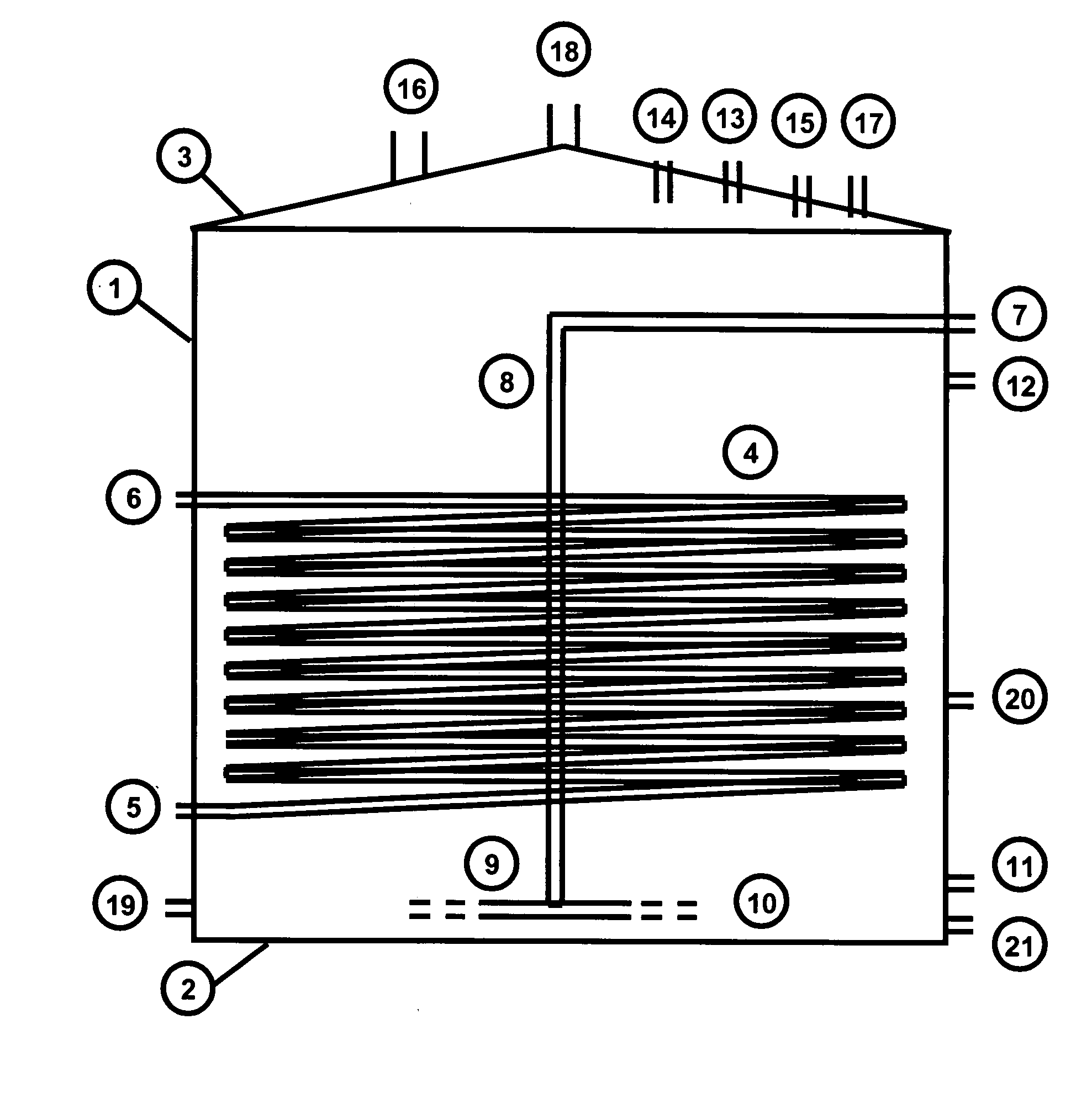
Reactor for the culture, biooxidation of solutions and/or large-scale propagation of isolated microorganisms and/or native microorganisms that are useful in ore leaching
InactiveUS20080102514A1Reducing average phasingIncrease concentrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrobiologyIsolate - microorganism
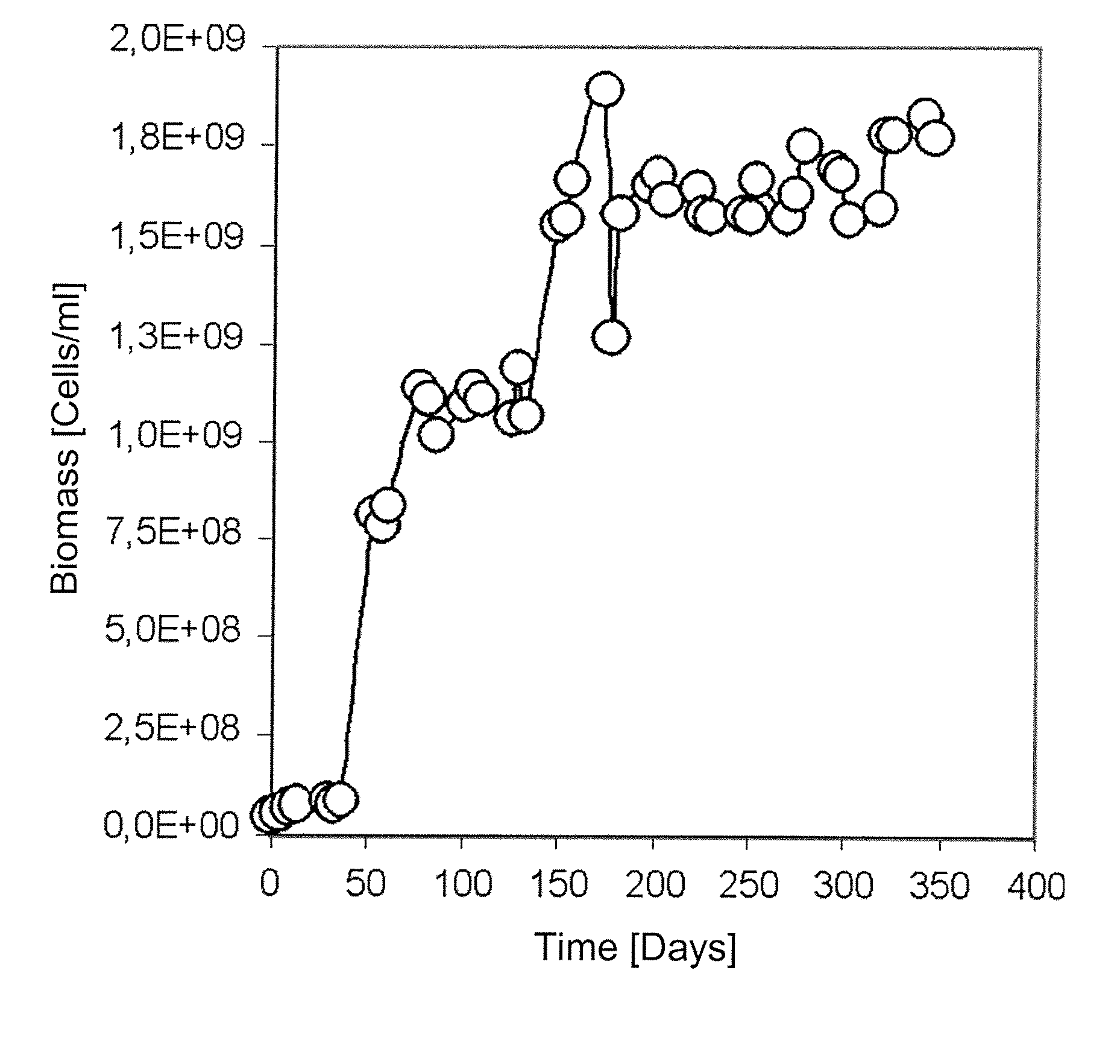
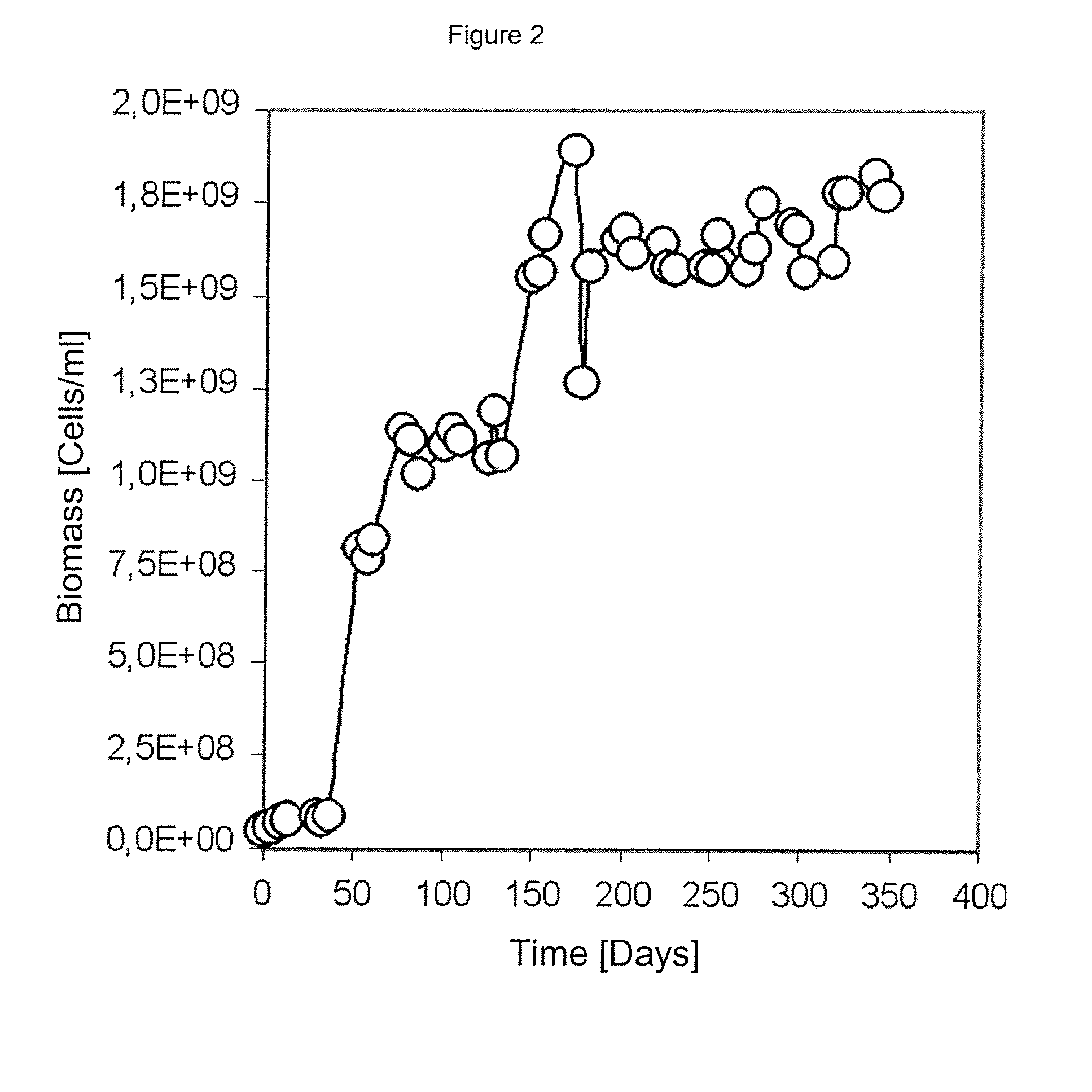
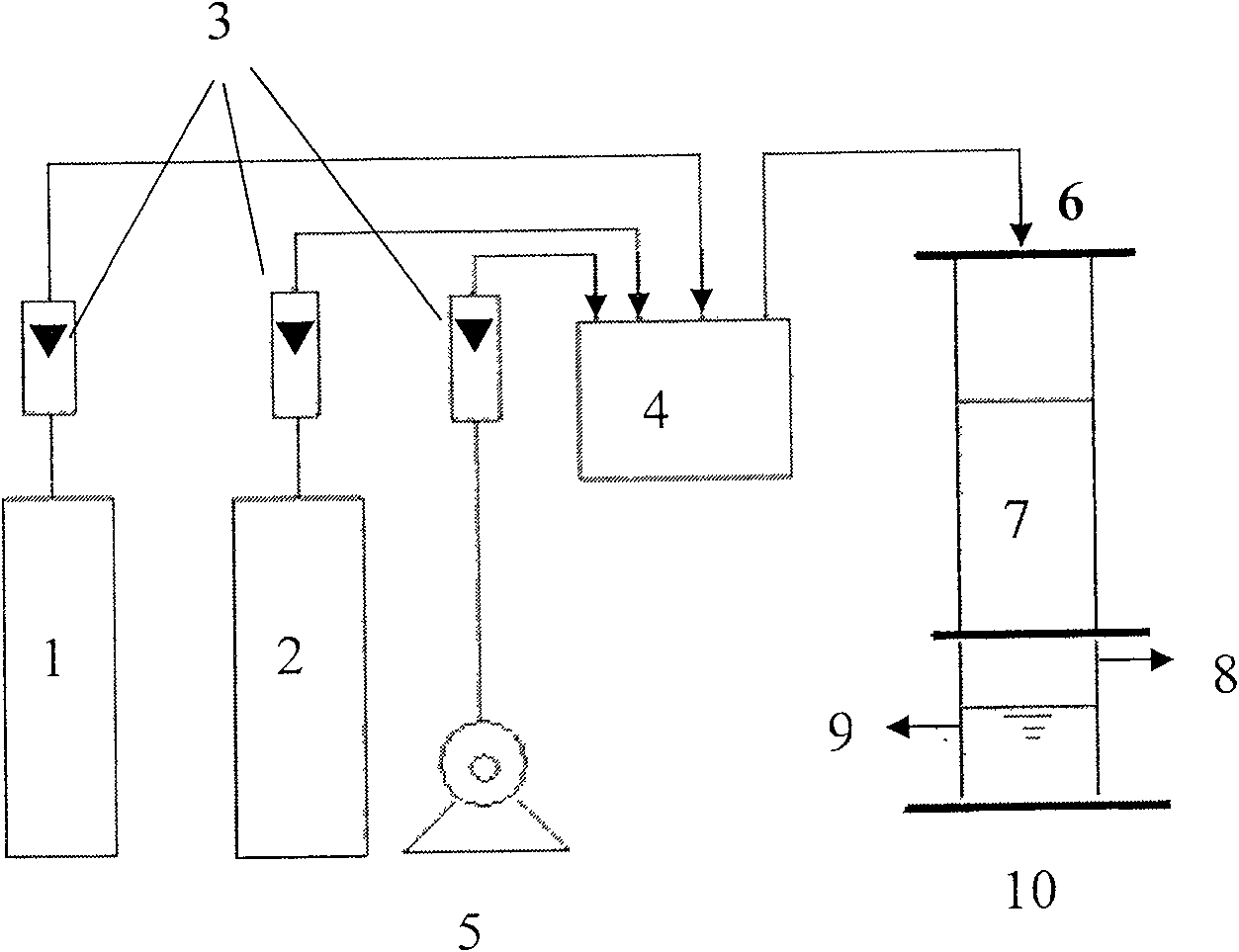
The invention publishes a reactor and method for the culture, biooxidation of cations in solution and / or large-scale propagation of jointly isolated microorganisms, with or without native microorganisms that are useful in sulfide metal ore bioleaching. The invention particularly publishes a reactor for the large-scale culture and / or propagation of an association of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans Licanantay DSM 17318 isolated microorganisms jointly with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Wenelen DSM 16786 with or without the presence of other microorganisms.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
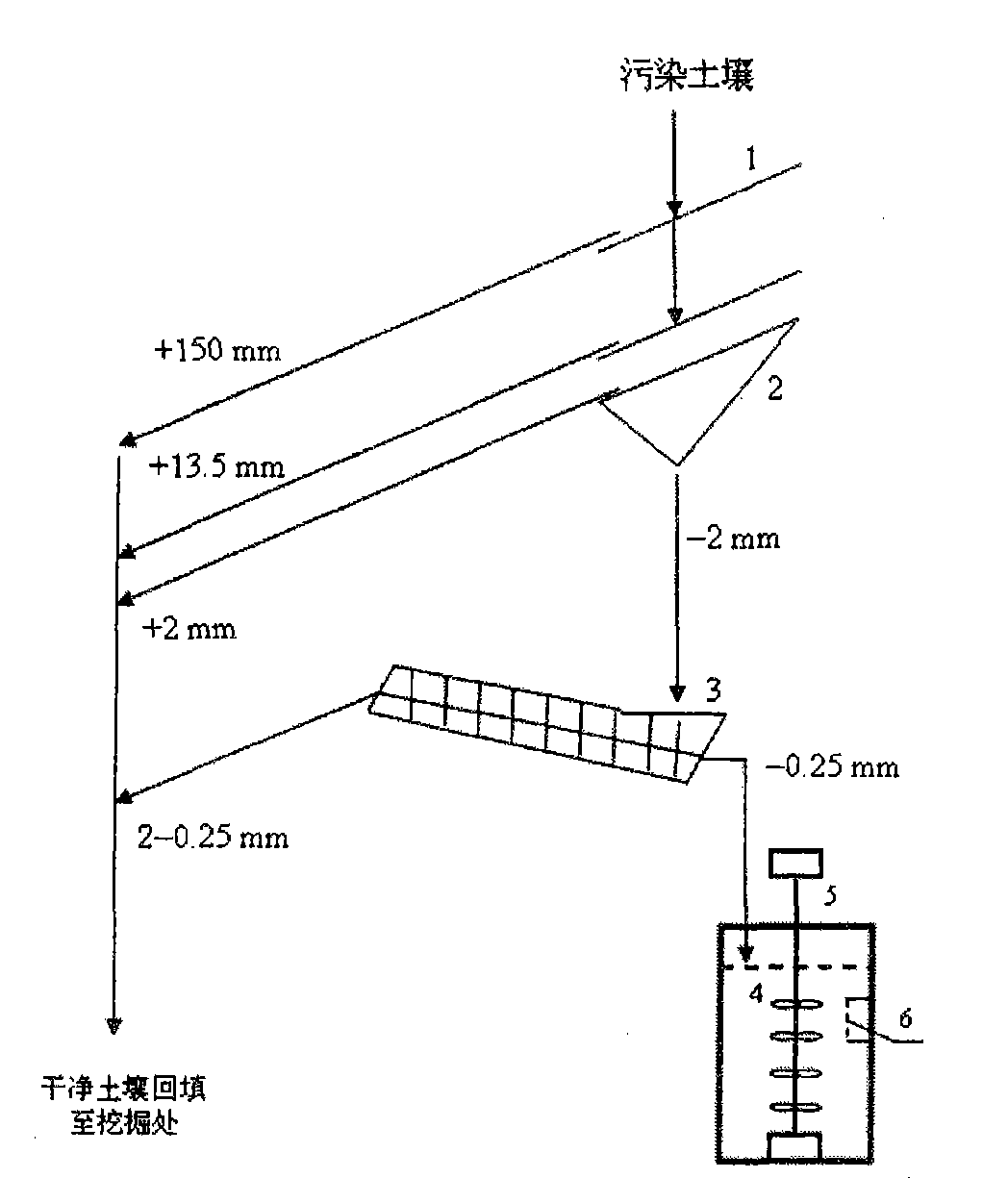
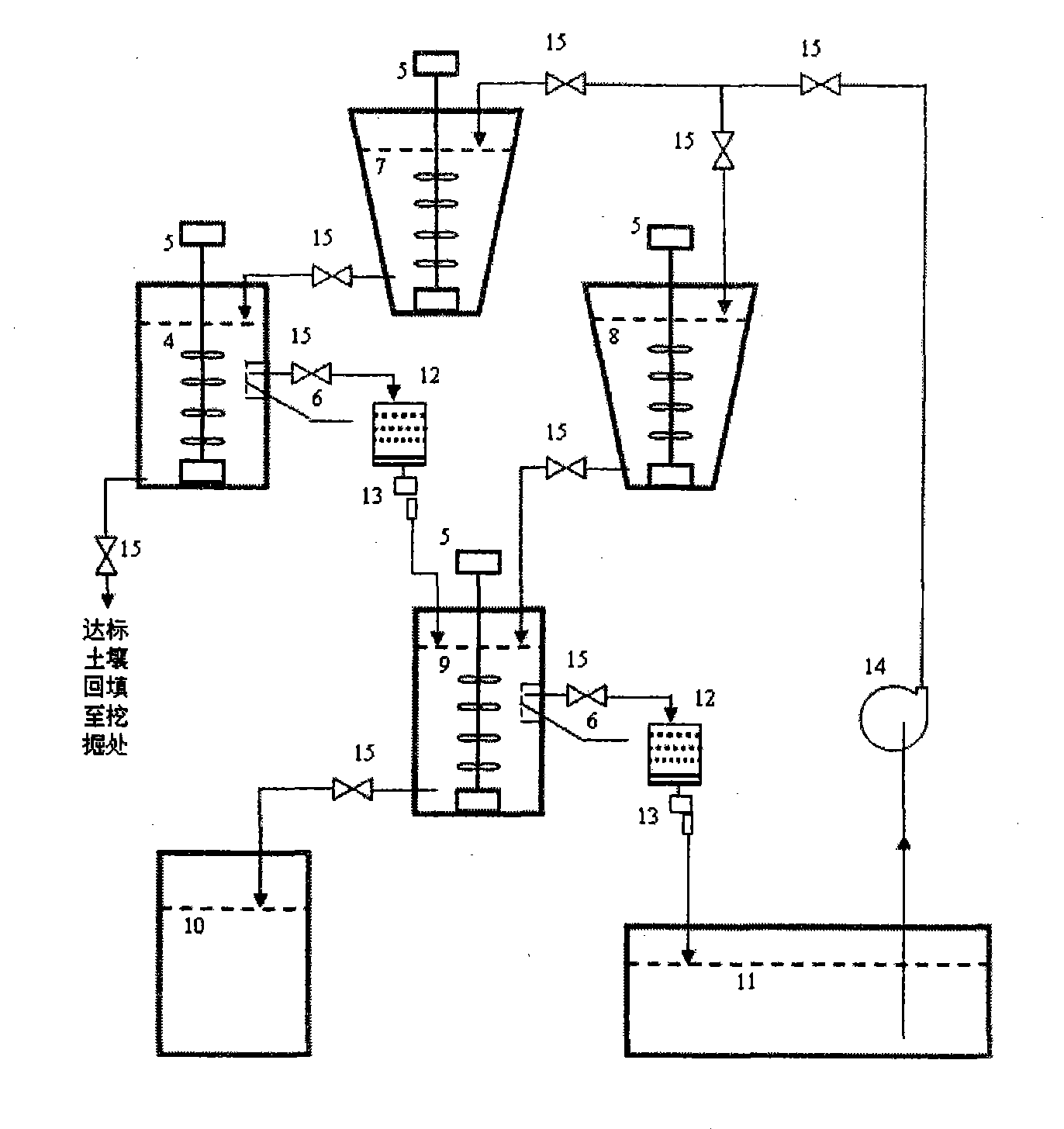
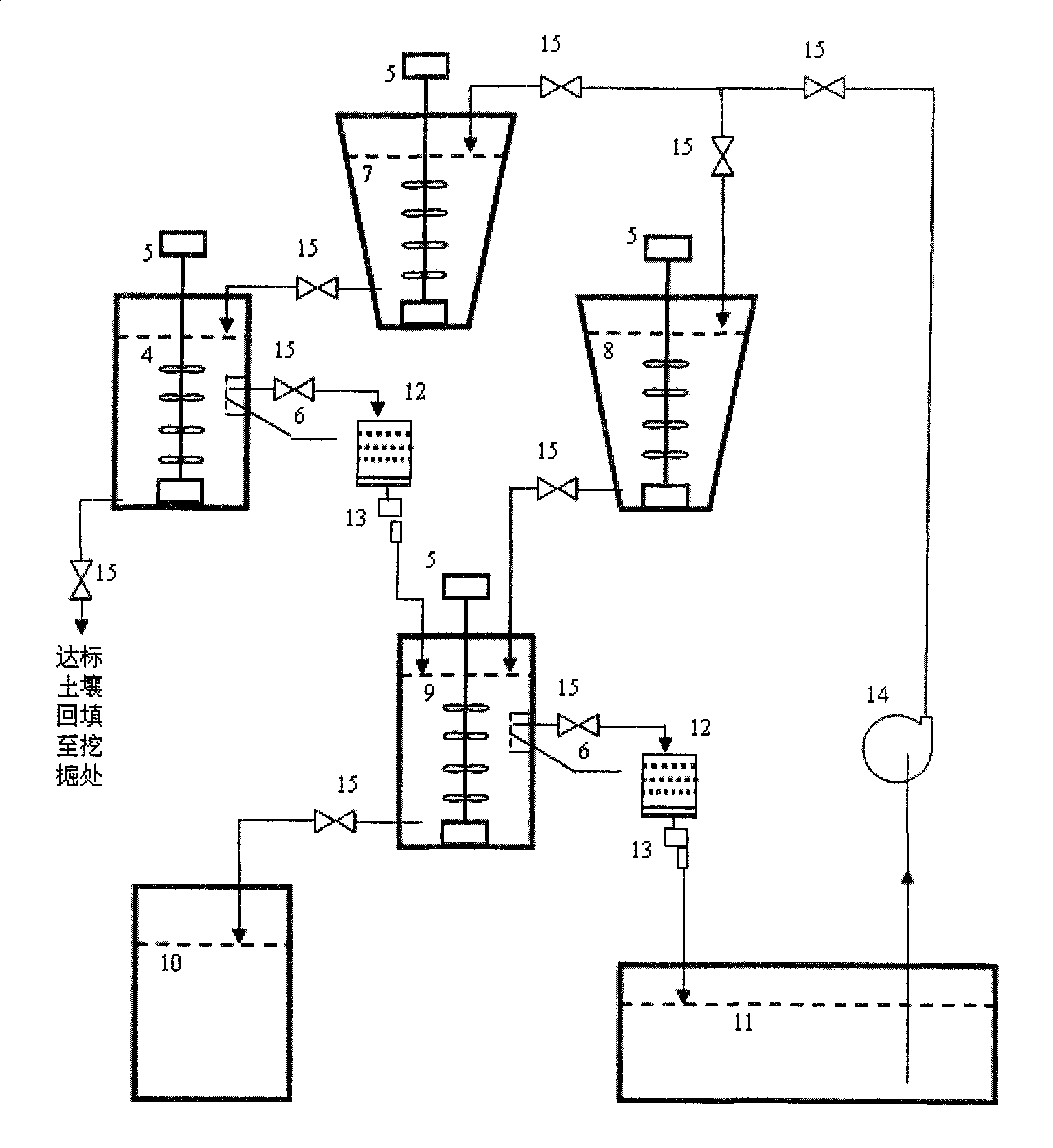
Method for treating plutonium or strontium polluted soil
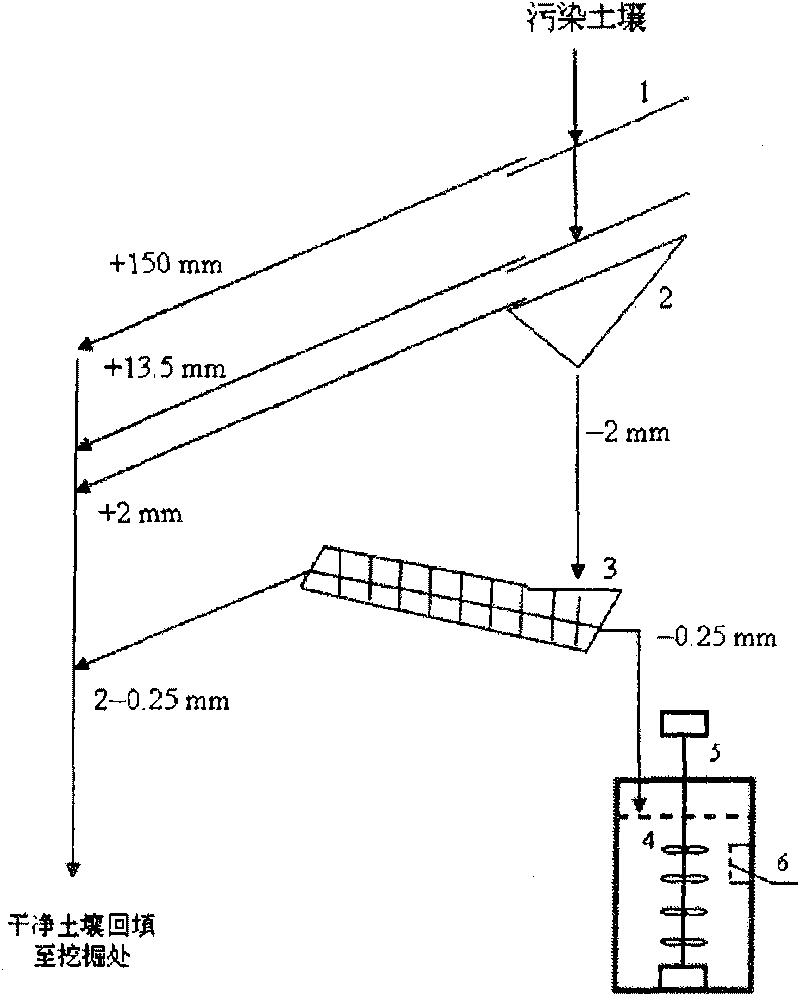
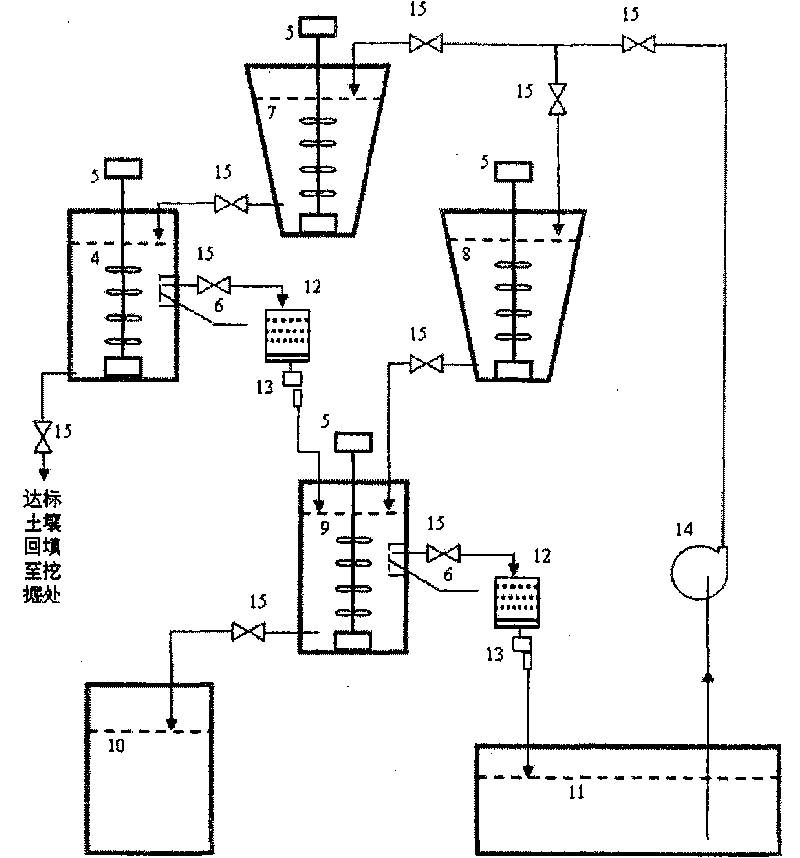
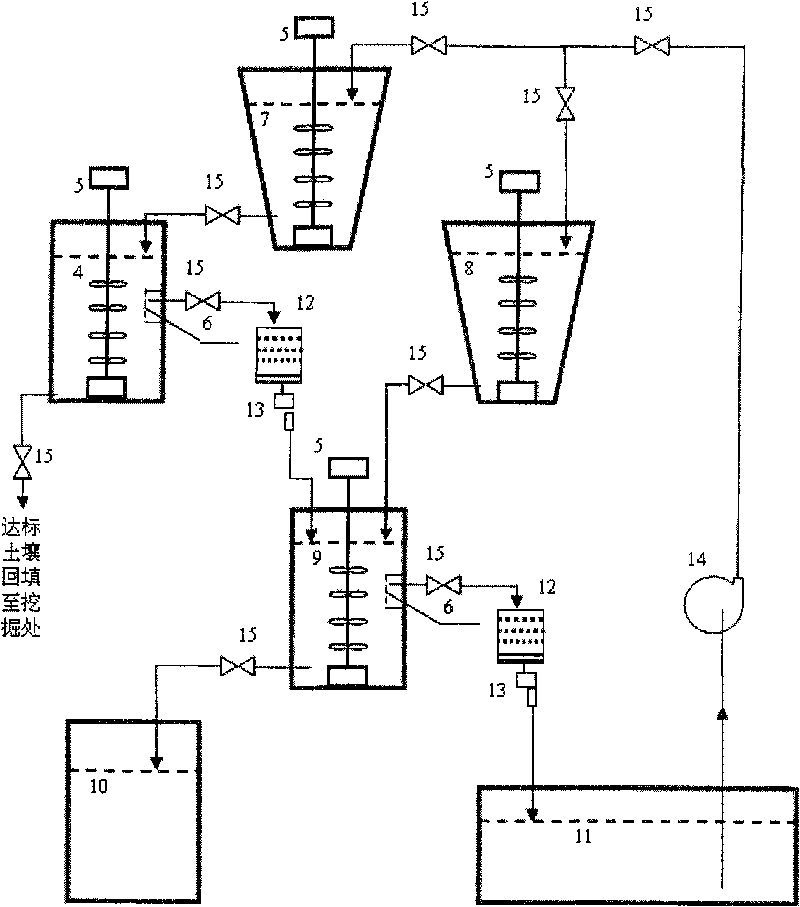
InactiveCN101745527AQuick removalEfficient removalBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationAcidithiobacillus thiooxidansPolluted soils
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbe, and particularly relates to a method for treating radionuclide plutonium or strontium polluted soil by microbe. The method comprises the following steps: screening the plutonium or strontium polluted soil by a bar screen, a double-plate screen and a spiral screen, wherein the soil grains with the granularity of more than 0.25 millimeter are clean soil grains and the soil grains with the granularity of less than 0.25 millimeter are plutonium or strontium polluted soil grains; and mixing the soil grains with the granularity of less than 0.25 millimeter and acidithiobacillus thiooxidans active solution, filtering the solution to obtain sediment which is clean soil, mixing the filtered solution and sulfate reducing bacteria active solution, settling plutonium or strontium, filtering and separating the solution, reclaiming the plutonium or the strontium, and recycling the water. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, economy and feasibility and high safety, has no secondary pollution, and can efficiently and quickly remove the plutonium or the strontium from the polluted soil.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Method for leaching copper in waste printed circuit boards (PCBs) by mixed bacteria
ActiveCN103484680AEasy to addIncrease the amount addedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPre treatmentAcidithiobacillus
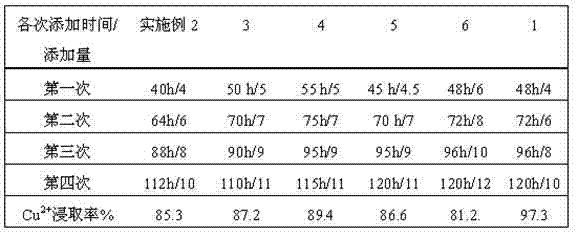
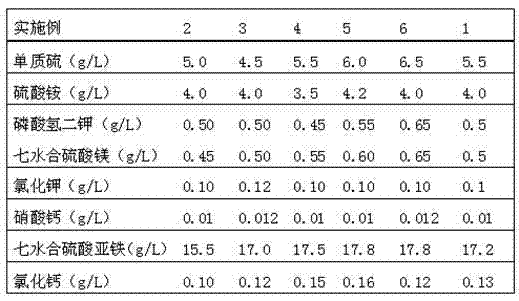
The invention discloses a method for leaching copper in waste PCBs by mixed bacteria. The waste PCBs are preprocessed for standby use; acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and acidithiobacillus thiooxidans are subjected to copper-resistant acclimation and culture respectively, and are mixed and cultured in a mixed bacteria culture solution; when the culture time reaches 40h-55h, powder of the PCBs is started to be added; then powder of the PCBs is added in additional dosage point by point at other time points; and bioleaching is performed. According to the method, when the mixed bacteria are cultured, the PH value of the culture solution is not required to be adjusted, two types of bacteria can grow in balance; at the same time, when the two types of bacteria grow, a large amount of sulfuric acid and Fe 3+ are generated and used for leaching copper in the powder of the waste PCBs in a later period; and in the whole process, the efficiency is high, and the energy is saved. A manner of low front, high rear and multipoint addition is adopted; and on the basis that the additive amount of the powder of the waste PCBs is increased, the copper leaching efficiency is improved remarkably, however, the bacteria growth inhibition degree is relatively small.
Owner:YANGZHOU NINGDA NOBLE METAL CO LTD
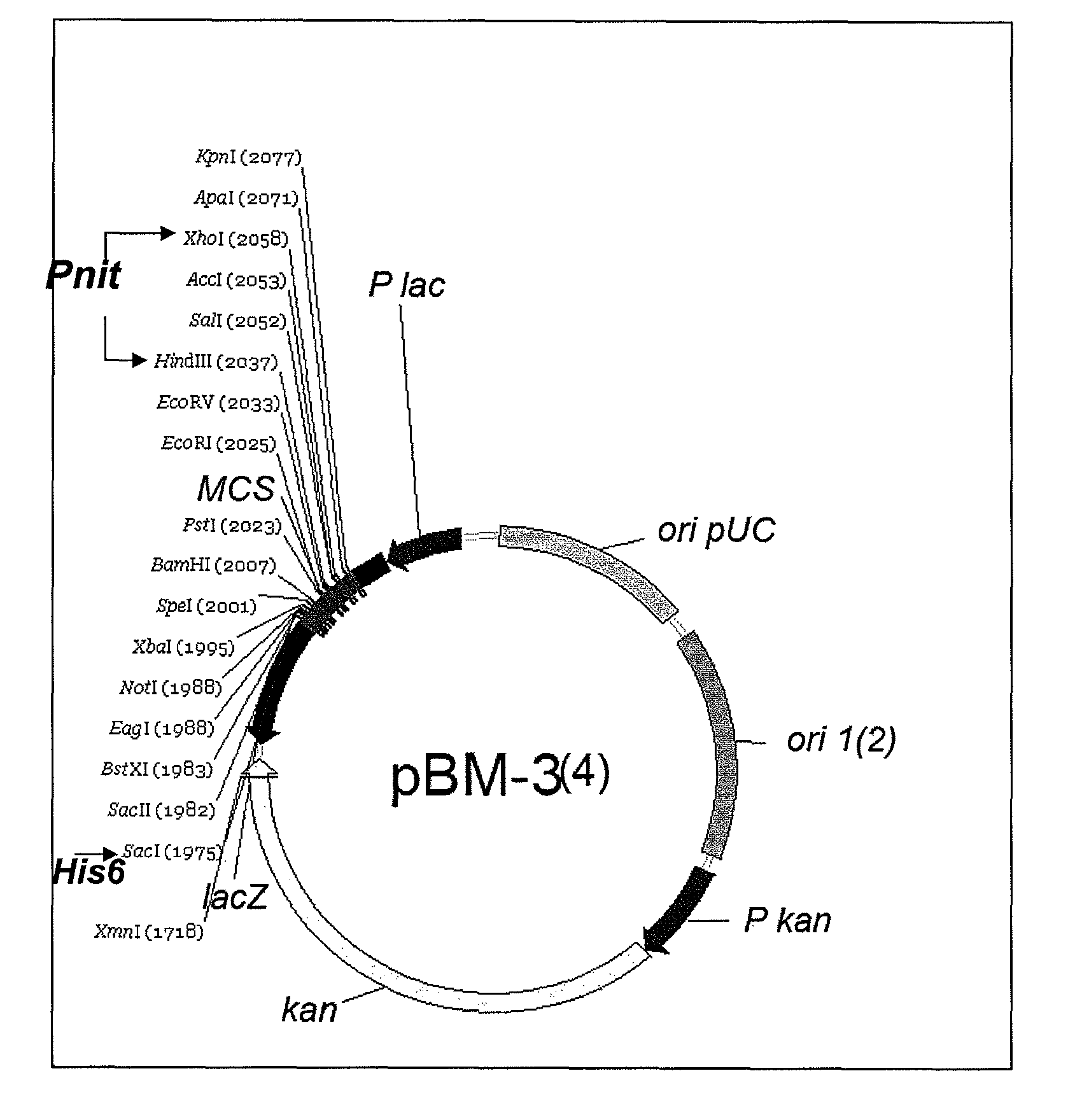
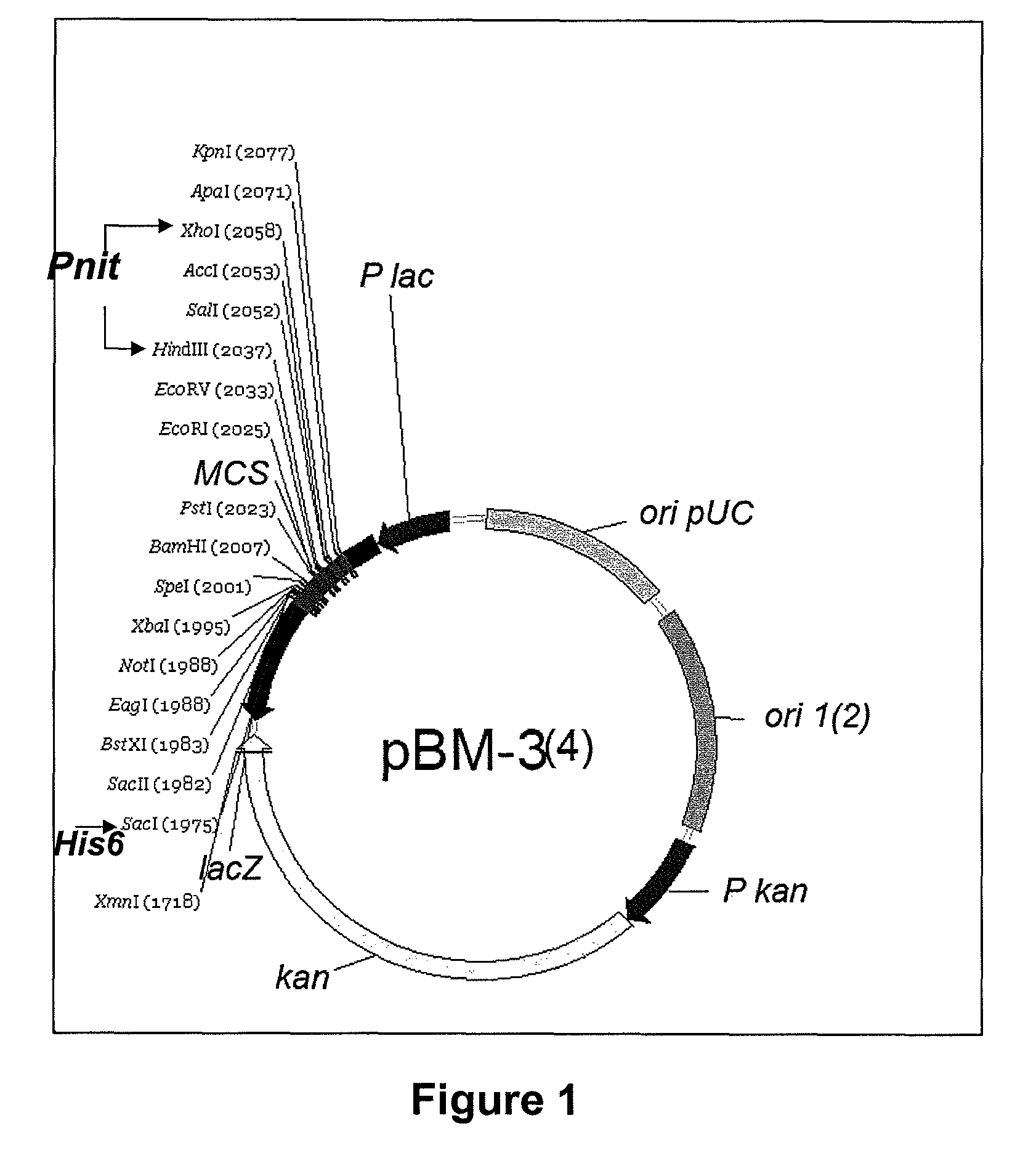
Plasmids for transforming bacteria of the acidithiobacillus spp. genus, and transformation method
The present invention discloses functional plasmids in bacteria of the Acidithiobacillus genus, such as the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Acidithiobacillus caldus species. And a method to successfully transform bacteria of the Acidithiobacillus genus, such as the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Acidithiobacillus caldus species, with these plasmids.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Process to increase the bioleaching speed of ores or concentrates of sulfide metal species, by means of continuous inoculation with leaching solution that contains isolated microorganisms, with or without presence of native microorganisms
ActiveUS7837760B2Shorten the timeImprove bioleaching conditionSolvent extractionGold compoundsTailings damPotassium
The invention publishes a process to increase the bioleaching speed of ores or concentrates of sulfide metal species in heaps, tailing dams, dumps, or other on-site operations. The process is characterized by the continuous inoculation of the ores or concentrates with isolated microorganisms of the Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans type, together with isolated microorganisms of the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans type, with or without native microorganisms, in such a way that the total concentration of microorganisms in the continuous inoculation flow is of around 1×107 cells / ml to 5,6×107 cells / ml. In particular, the invention publishes the continuous inoculation of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans Licanantay DSM 17318 together with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Wenelen DSM 16786 microorganisms, or with other native microorganisms at a concentration higher than 5×107 cells / ml. In addition to the inoculation of isolated bacteria, the invention includes the addition of oxidizing agents such as the ferric ion produced externally, together with nutrients in the shape of salts of ammonium, magnesium, iron, potassium, as well as air enriched continuously with carbon dioxide to promote bacterial action in the bioleaching process of ores or concentrates.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Sulfur oxide thiobacillus and application thereof in heavy metal removal
InactiveCN106906173ALess investmentLow running costBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationThiobacillus ferrooxidansOptimal growth
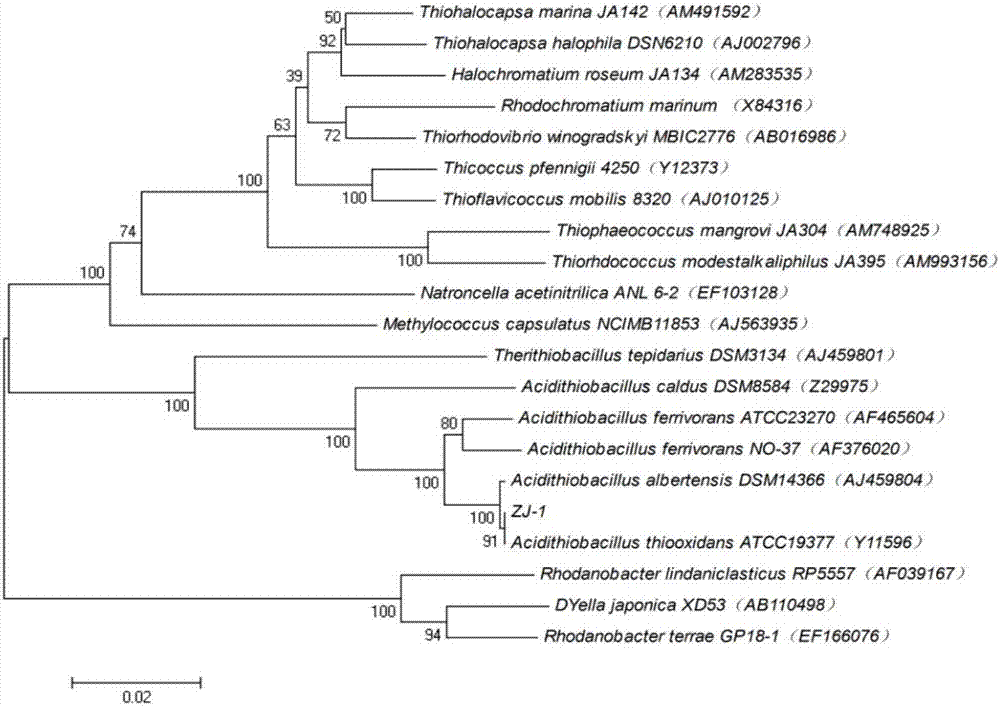
The invention relates to a sulfur oxide thiobacillus Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans ZJ-1 and an application thereof in heavy metal removal. The bacterial strain is preserved in the China Microbial Culture Preservation Management Committee General Microbiology Center, the preservation number is CGMCC No. 12387. The optimum growth temperature of the bacterial strain ZJ-1 is 28 DEG C, and the optimal growth pH value is 3.0. The bacterial strains can separate out the heavy metals in all kinds of wastes, can be used for the removal of heavy metals in all kinds of wastes and has an important function for preventing the secondary pollution of heavy metals.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Reactor for large scale continuous cultivating and/or reproducing microorganism capable of being used for ore biology lixiviation separated under natural microorganism or without natural microorganism
InactiveCN101168718ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention publishes a reactor and method for the culture, biooxidation of cations in solution and / or large-scale propagation of jointly isolated microorganisms, with or without native microorganisms that are useful in sulfide metal ore bioleaching. The invention particularly publishes a reactor for the large-scale culture and / or propagation of an association of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans Licanantay DSM 17318 isolated microorganisms jointly with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Wenelen DSM 16786 with or without the presence of other microorganisms.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Mixotroph-type functional microbial flora capable of removing acid-soluble cadmium and reducible-status cadmium in cadmium-polluted soil, and preparation method and application method thereof
ActiveCN108102970AReduced effectivenessHigh removal rateFungiBacteriaAcidithiobacillus thiooxidansTrichoderma
The invention discloses a mixotroph-type functional microbial flora capable of removing acid-soluble cadmium and reducible-status cadmium in cadmium-polluted soil, and a preparation method and an application method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial treatment of heavy metal polluted soil. In the invention, the mixotroph-type functional microbial flora, which can high-effectively remove the acid-soluble cadmium and reducible-status cadmium soil, is prepared by compounding autotrophic and heterotrophic microorganisms, i.e., the flora not only includes heterotrophic microorganisms, such as Geobacter metallireducens, Alicyclo bacillus, Acetobacter diazotrophicus, Anaeromyxobacter and trichoderma, but also includes autotrophic microorganisms, such as Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, Thiobacillus caldus and bacillusacidoohilus. The invention solves the problems that compound functional microbial flora is poor in adaptability and is difficult to colonize when being appliedto polluted soil. The functional microbial flora guarantees high removal rate of the acid-soluble cadmium and reducible-status cadmium in the polluted soil, significantly reduces bioavailability of cadmium and plant availability, and lays a certain fundament for promotion and application of microbial treatment of the cadmium-polluted soil.
Owner:HUNAN AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT +2
Use of mining waste and concentrates containing pyrite, in the culture of iron-oxidizing and sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms as an energy source for bacterial growth
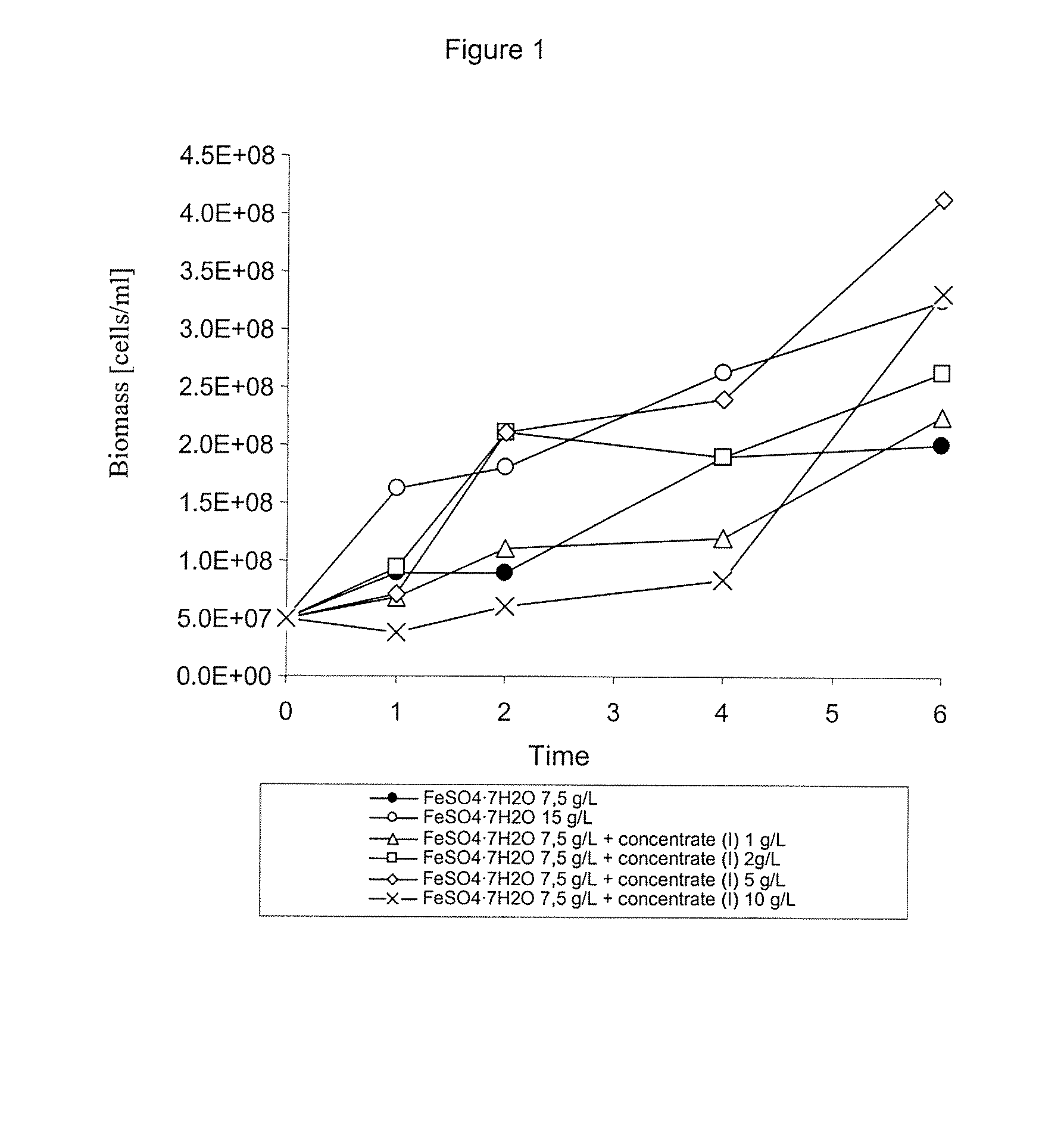
The invention publishes the use of mining products and sub-products that contain pyrite, such as copper concentrates, and waste from the process in which these concentrates are obtained, known as scavenger tail, as an energy source for the large-scale culture of an association of microorganisms that are useful for ore bioleaching, and that includes both isolated microorganisms, and native microorganisms from the worked ores. In particular, the invention publishes the use of mining waste known as scavenger tail from the flotation process, in the culture of an association of isolated microorganisms of the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans y Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans type together, with or without other native microorganisms from the worked ores.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
PROCESS FOR THE JOINT CULTURE OF AN ASSOCIATION OF MICROORGANISM, USING PYRITE (FeS2) AS AND ENERGY SOURCE
The invention publishes a process for the joint culture of an association of microorganisms using pyrite (FeS2) as an energy source. This invention particularly publishes the use of a pyrite ore as an energy source in the joint culture of an association of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans type isolated microorganisms known as Wenelen DSM 16786 and Licanantay DSM 17318 respectively.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
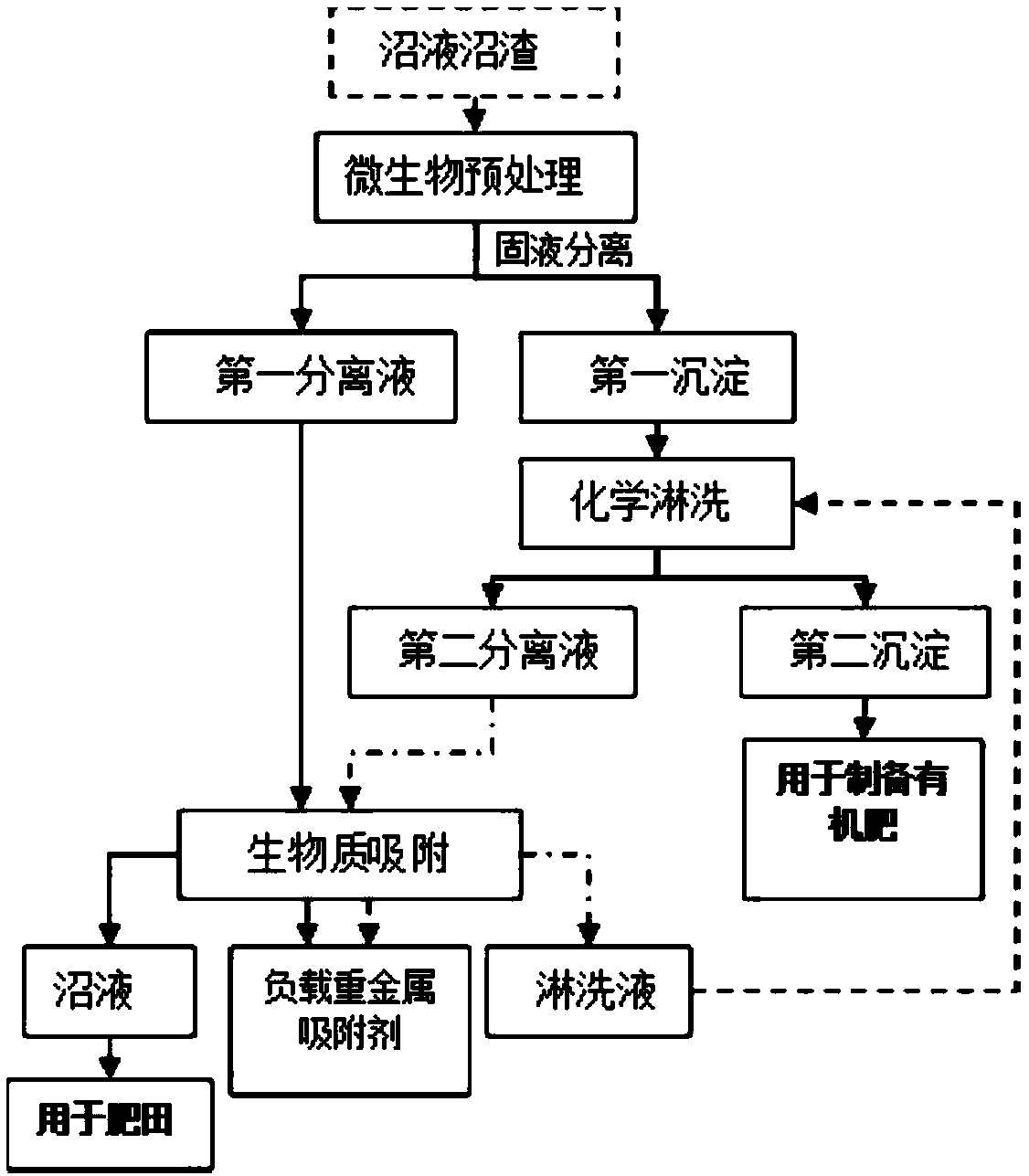
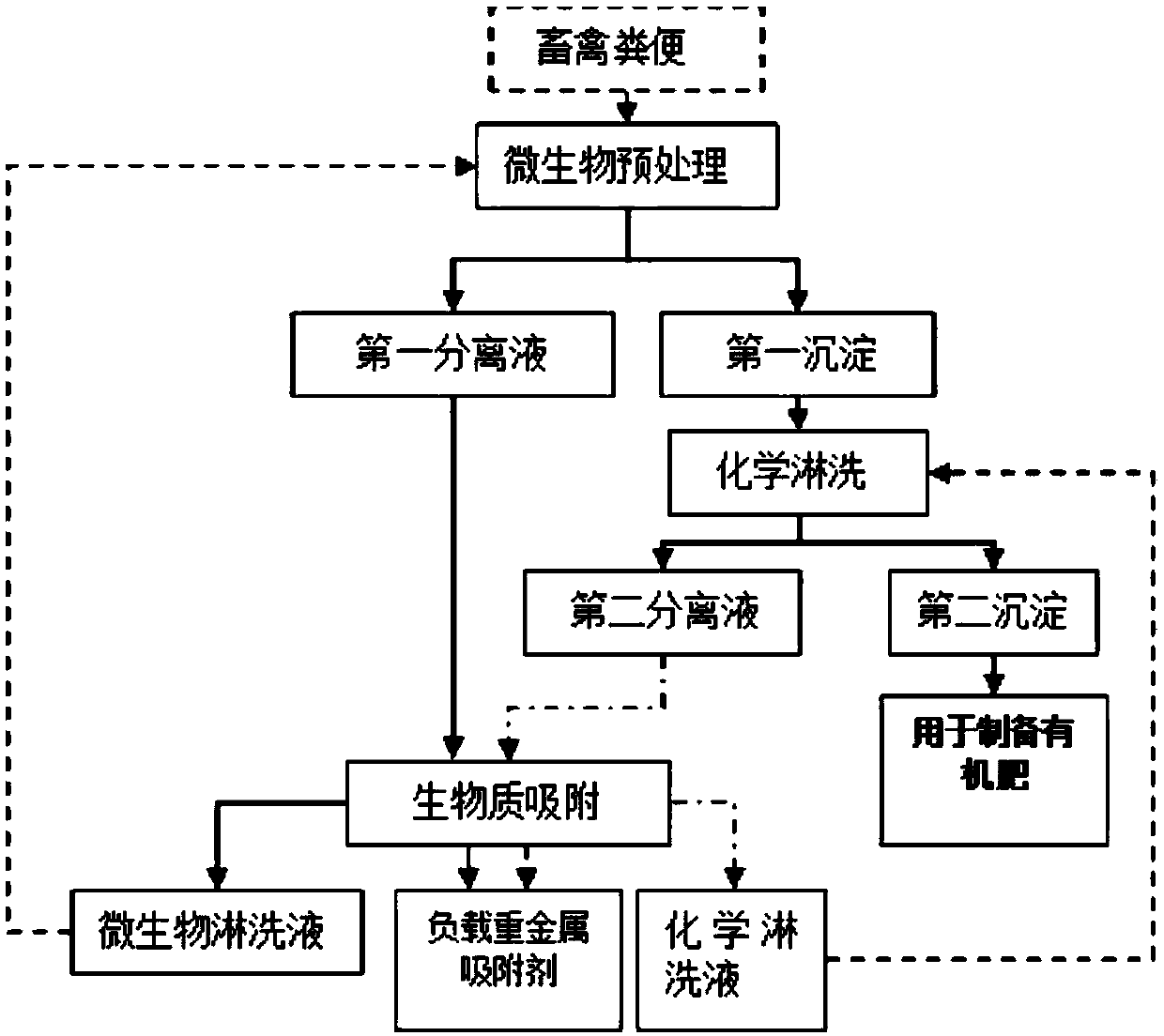
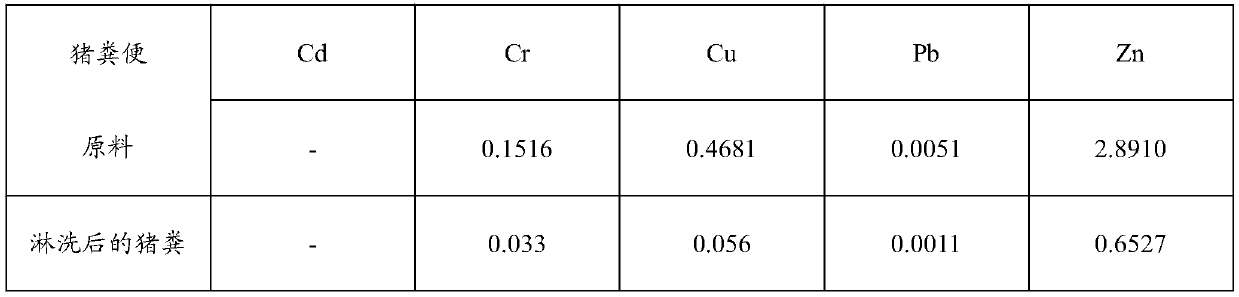
Method for removing heavy metals of livestock and poultry wastes
InactiveCN109250882AEfficient removalAchieve concentrated recoveryWater contaminantsBiological sludge treatmentWaste treatmentAcidithiobacillus
The invention provides a method for removing heavy metals of livestock and poultry wastes, and belongs to the technical field of waste treatment, wherein the method includes the steps: cultivating anddomesticating a culture solution with acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans or acidithiobacillus thiooxidans as a dominant strain; mixing the culture solution with the livestock and poultry wastes, and carrying out solid-liquid separation, to obtain a first separation liquid and a first precipitate; mixing the first precipitate with an acid solution, and carrying out solid-liquid separation, to obtain asecond separation solution and a second precipitate; and mixing the first separation solution and the second separation solution with an adsorbent, and adsorbing to remove heavy metals from the separation solution, so as to realize the removal of the heavy metals of the livestock and poultry wastes. The method provided by the invention can efficiently remove the heavy metals Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb and Znfrom the livestock and poultry wastes.
Owner:JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for extracting copper out of waste printed circuit board by employing mixed bacteria
ActiveCN104726714AEasy to addIncrease the amount addedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCopperPre treatment
The invention discloses a method for extracting copper out of waste printed circuit boards by employing mixed bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: pre-treating waste printed circuit boards (PCBs) for later use; respectively carrying out copper-resistant domesticated incubation on acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, carrying out mixed cultivation in mixed bacteria culture liquid, and adding PCBs powder when the culture time reaches 40-55 hours; and adding the PCBs powder at other time points point by point in increase quantity, and carrying out biological extraction. Two bacteria can grow in balance without adjusting the pH value of the culture liquid in mixed bacterial cultivation; meanwhile, when the two bacteria grow, a lot of sulfuric acid and Fe<3+> are generated for extracting copper out of the waste PCBs powder in the later period; the overall process is high in efficiency; and energy sources are saved. In a front-low and rear-high multi-point adding manner, the extraction rate of copper is significantly improved on the basis of improving the adding amount of the waste PCBs powder; and the inhibition degree on bacterial cell growth is relatively low.
Owner:YANGZHOU NINGDA NOBLE METAL CO LTD
Application of microbial preparation for efficiently converting heavy metal cadmium in polluted soil
The invention discloses an application of a microbial preparation for efficiently converting heavy metal cadmium in polluted soil. The microbial preparation is prepared by performing enriched cultivation on the following two mixed floras: (1) candida mycoderma bacteria, aspergillus monicus, rhodosporidium toruloides and cryptococcus which form a flora 1; and (2) acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, leptospirillum ferrooxidans, acidithiobacillus caldus, sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and thermos ferric bacteria which form a flora 2. By using the microbial preparation to treat the cadmium polluted soil, the metal cadmium is converted from being indissolvable into being soluble and the removal rate is 70-82%. The microbial preparation disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being high in conversion efficiency, short in period, low in cost, free of secondary pollution, easy to popularize and the like.
Owner:HUNAN AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT +1
Efficient sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and rapid heating method for low-sulfur copper mine leaching process in Alpine region
ActiveCN105779324AImprove permeabilityIncrease oxidation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSulfurInitial rate
The invention discloses an efficient sulfur-oxidizing bacteria with a strain name of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans Retech DW-II. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, Institute of Microbiology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, Court No.1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing on September 10, 2014, and has accession number of CGMCCNo. 9625. The invention also provides a rapid heating method for low-sulfur copper mine leaching process in Alpine region. The method comprises the steps of: crushing ore to -50mm, mixing with pyrite powder, conducting sulfuric acid slaking and granulation to improve the permeability of the stock heap and provide sufficient energy for bacteria; and finally adding the efficient sulfur-oxidizing bacteria CGMCC No. 9625. The method speeds up the initial rate of oxidation of the pyrite ore heap, and provides sufficient heat for the stock heap, so that temperature of the stock heap rapidly increases to above 40 DEG C.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
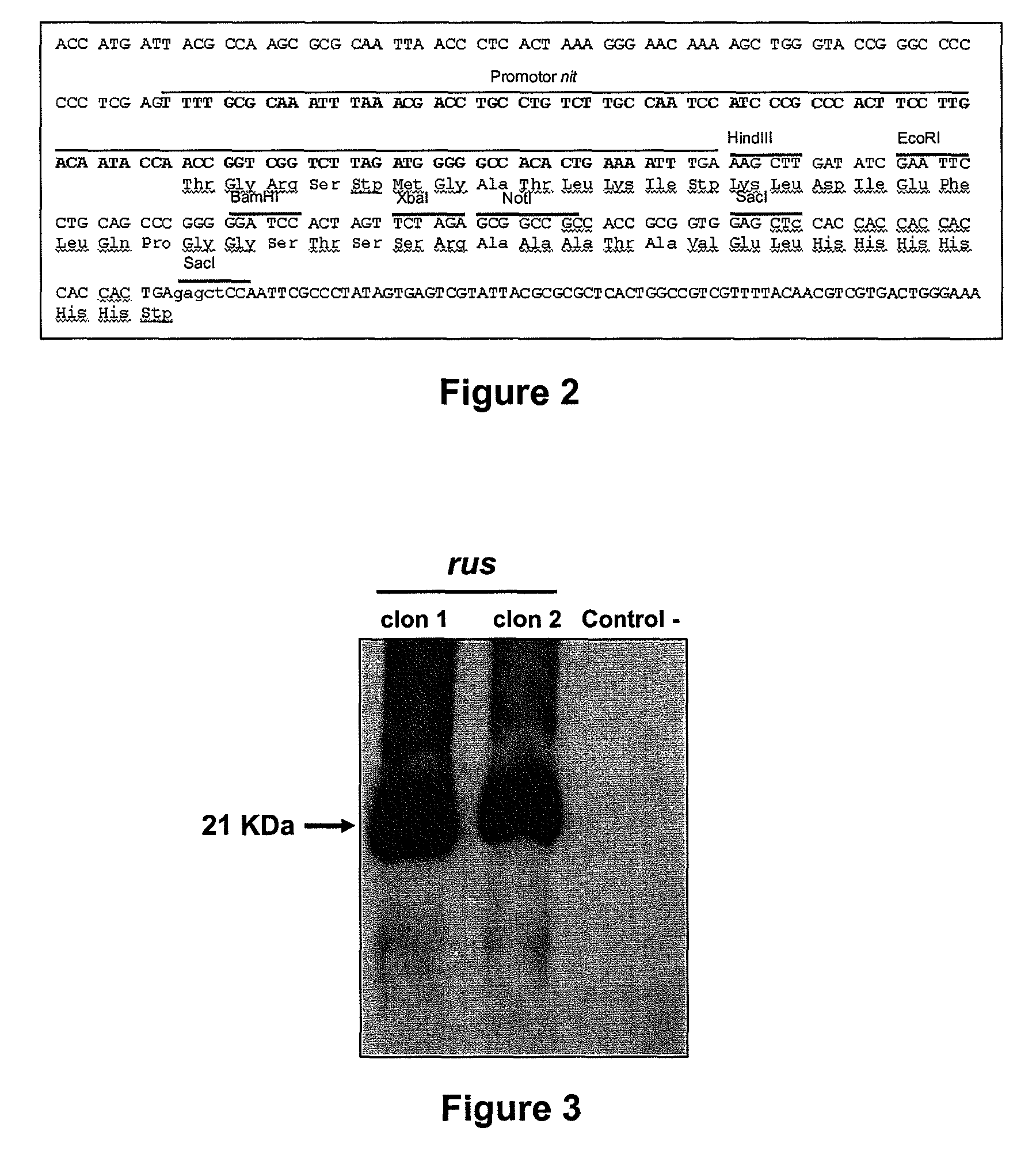
Method for screening unmarked gene knockout bacterial strain of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans
ActiveCN103232994AEfficient knockoutEasy to exploreMicrobiological testing/measurementHybrid cell preparationThiobacillus ferrooxidansBeta-Galactosidases
The invention discloses a method for screening an unmarked gene knockout bacterial strain of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. The method comprises introducing a knockout plasmid for construction of a target gene and an induction plasmid carrying an I-SceI gene into acidithiobacillus thiooxidans by conjugational transfer, carrying out single recon screening by a resistance maker, and carrying out double recon preliminary screening by blue-white selection. The method discloses the method for unmarked gene knockout of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans first, utilizes beta-galactosidase blue-white selection for double recon screening, can fast, stably and efficiently knock out a target gene, solves the problem that in the existing unmarked gene knockout process, selective pressure lacks so that screening is difficult, shortens double recon screening time, improves screening efficiency, reduces a screening cost and provides a novel method for stable genetic modification of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
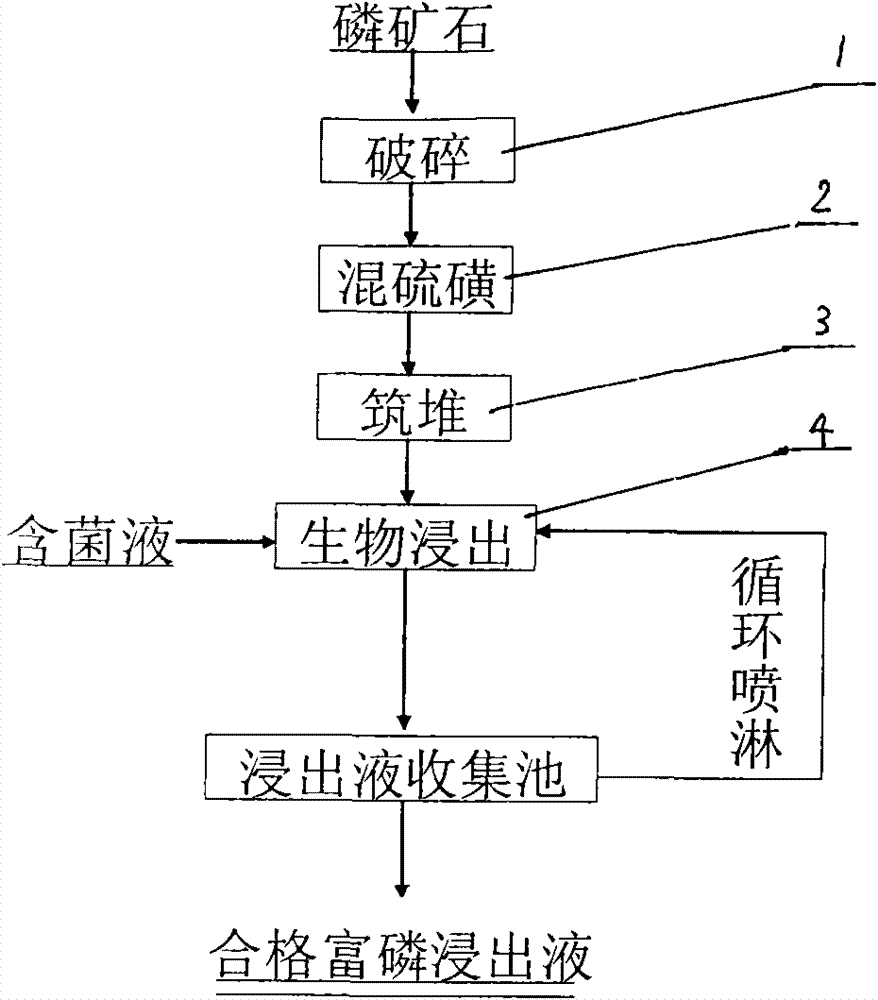
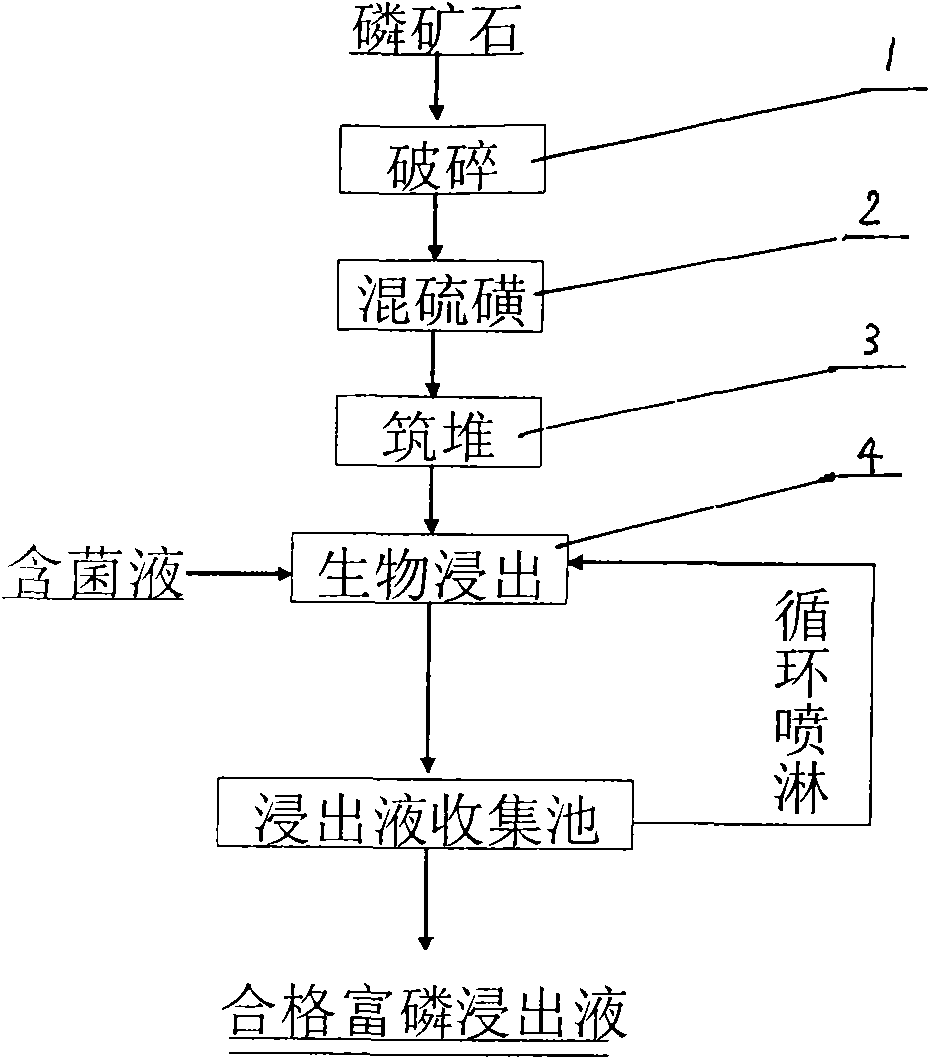
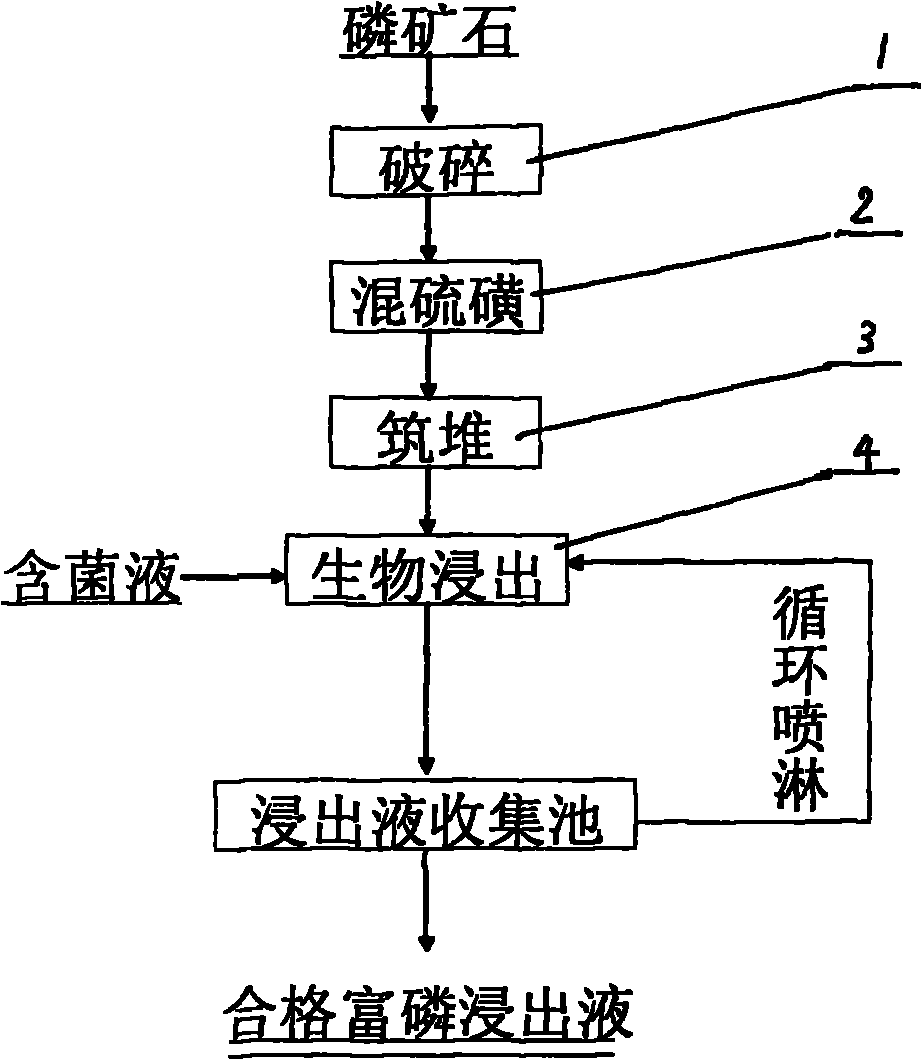
Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and heap leaching technology using same of middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore
ActiveCN102102085BReduce pollutionReduce the cost of beneficiationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesO-Phosphoric AcidAcidithiobacillus
The invention relates to Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and a heap leaching technology using same of the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore. The name of the bacteria is Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans RETECH-PS1; the bacteria are conserved in the China center for type culture collection of which address is the Wuhan University; the conservation date is April 25, 2009; and the CCTCC NO is 209088. The biological heap leaching technology of the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore comprises the following steps: ores are crushed to less than 15mm, sulfur is added to mix and build up leaching heap; (2) the Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in the claim 1 which is conserved at low temperature is activated and propagated step by step to reach the bacterium solution volume for spraying, finally the bacteria are inoculated in the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore heap mixed with sulfur; and (3) leachate is collected by a collection pool and pumped by a pump to a spraying system for circular spraying. The invention has the following advantages: the process flow is simple, the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore is used without adopting ore dressing and enrichment; sulfuric acid is not added in the production process of phosphoric acid, thus reducing the cost and avoiding the environmental pollution problem caused by the production of sulfuric acid; the production scale can be large or small; and the technology is especially suitable for the collophanite resource which accounts for 70% of Chinese phosphorus resources and is difficult to treat through traditional ore dressing, thus increasing the comprehensive utilization rate of Chinese phosphorus resources.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Autotrophic and heterotrophic compound ore-leaching flora FIM-Z4 and application thereof
ActiveCN105199990AImprove leaching rateImprove leaching reaction kineticsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLeaching rateAcidithiobacillus thiooxidans
The invention discloses autotrophic and heterotrophic compound ore-leaching flora FIM-Z4 and application thereof and provides a mixed culture FIM-Z4 of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and acidiphiliu acidophilum; the preservation number of the mixed culture FIM-Z4 is CGMCC No.11190. Through synergistic effect, the leaching reaction kinetics is improved obviously, the reaction speed is increased, the leaching period is shortened, and the leaching rate and leaching yield of metal (copper and nickel) ions in target ore are increased. The heterotrophic compound ore-leaching flora FIM-Z4 is a compatible whole, and the population ecology keeps relatively stable in a long-term domestication process. The heterotrophic compound ore-leaching flora FIM-Z4 is applied to biological metallurgy and has a better leaching effect on copper ions in low-grade copper sulphide ore and nickel ions in low-grade nickel ore.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
Specific primers for detection of mRNA expression level of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans sor gene
InactiveCN105925667AEffectively reflect the expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleotide sequencingAcidithiobacillus
The invention provides specific primers for detection of mRNA expression level of an Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans sor gene. The nucleotide sequences are as follows: an upstream primer sequence of 5'-AAGCCCGTGCCTAAAGTG-3', and a downstream primer sequence of 5'-CTGCCATAGTTGGTGTTGT-3'. The specific primers can detect the transcription level of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans sor gene, and hace the advantages of high sensitivity and good specificity in detecting mRNA gene expression level. Through the real-time monitoring of mRNA expression level of sor gene in sulfur oxidation process, the primers are used to explain the sulfur oxidation mechanism of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and heap leaching technology using same of middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore
ActiveCN102102085AReduce pollutionReduce the cost of beneficiationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesO-Phosphoric AcidAcidithiobacillus
The invention relates to Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and a heap leaching technology using same of the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore. The name of the bacteria is Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans RETECH-PS1; the bacteria are conserved in the China center for type culture collection of which address is the Wuhan University; the conservation date is April 25, 2009; and the CCTCC NO is 209088. The biological heap leaching technology of the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore comprises the following steps: ores are crushed to less than 15mm, sulfur is added to mix and build up leaching heap; (2) the Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in the claim 1 which is conserved at low temperature is activated and propagated step by step to reach the bacterium solution volume for spraying, finally the bacteria are inoculated in the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore heap mixed with sulfur; and (3) leachate is collected by a collection pool and pumped by a pump to a spraying system for circular spraying. The invention has the following advantages: the process flow is simple, the middle-grade and low-grade phosphate ore is used without adopting ore dressing and enrichment; sulfuric acid is not added in the production process of phosphoric acid, thus reducing the cost and avoiding the environmental pollution problem caused by the production of sulfuric acid; the production scale can be large or small; and the technology is especially suitable for the collophanite resource which accounts for 70% of Chinese phosphorus resources and is difficult to treat through traditional ore dressing, thus increasing the comprehensive utilization rate of Chinese phosphorus resources.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Method for treating plutonium or strontium polluted soil
InactiveCN101745527BQuick removalEfficient removalBacteriaSulfate-reducing bacteriaAcidithiobacillus
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbe, and particularly relates to a method for treating radionuclide plutonium or strontium polluted soil by microbe. The method comprises the following steps: screening the plutonium or strontium polluted soil by a bar screen, a double-plate screen and a spiral screen, wherein the soil grains with the granularity of more than 0.25 millimeter areclean soil grains and the soil grains with the granularity of less than 0.25 millimeter are plutonium or strontium polluted soil grains; and mixing the soil grains with the granularity of less than 0.25 millimeter and acidithiobacillus thiooxidans active solution, filtering the solution to obtain sediment which is clean soil, mixing the filtered solution and sulfate reducing bacteria active solution, settling plutonium or strontium, filtering and separating the solution, reclaiming the plutonium or the strontium, and recycling the water. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, economy and feasibility and high safety, has no secondary pollution, and can efficiently and quickly remove the plutonium or the strontium from the polluted soil.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Bacterial cultures of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and their use in the treatment of materials containing sulfur-compounds
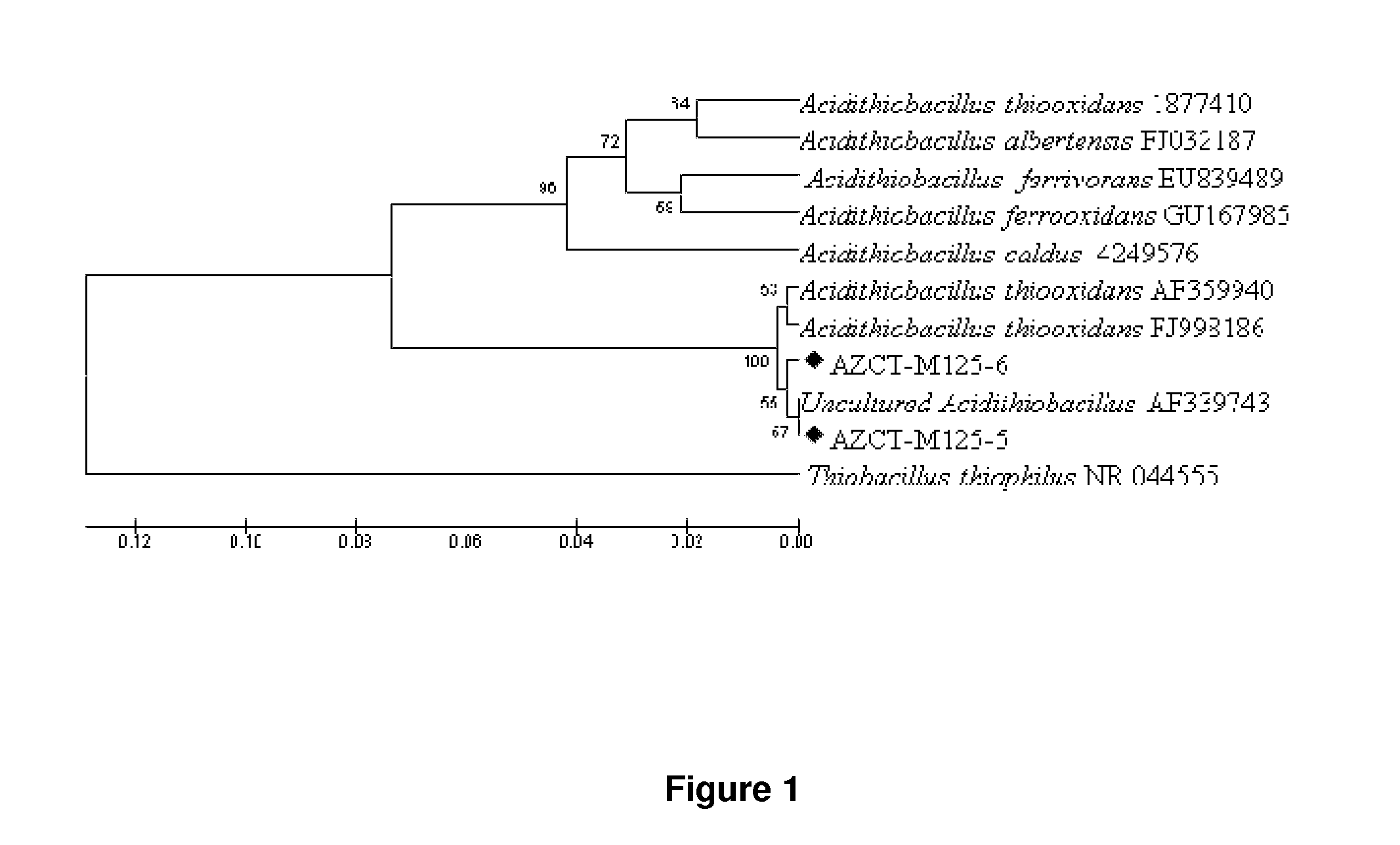
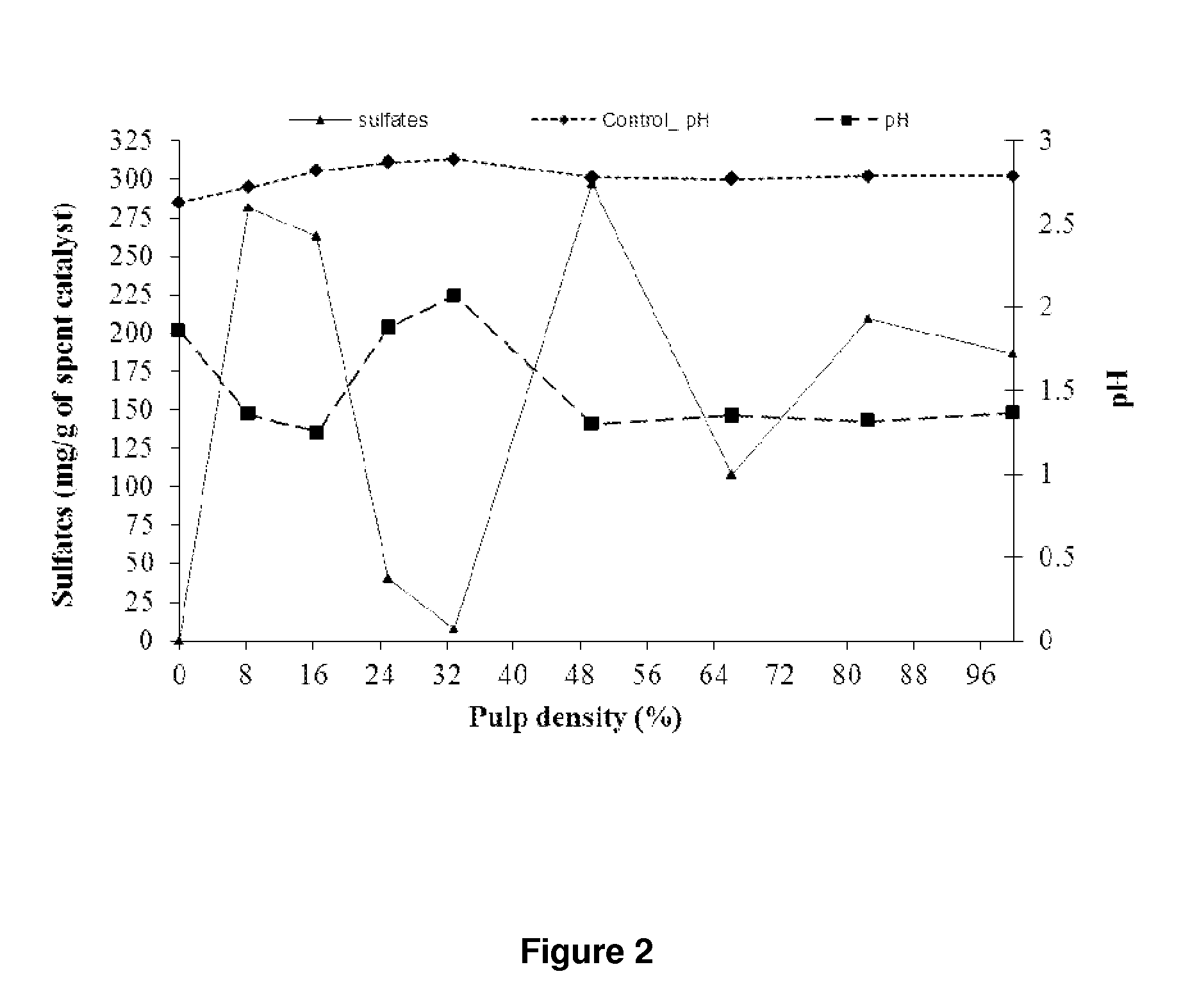
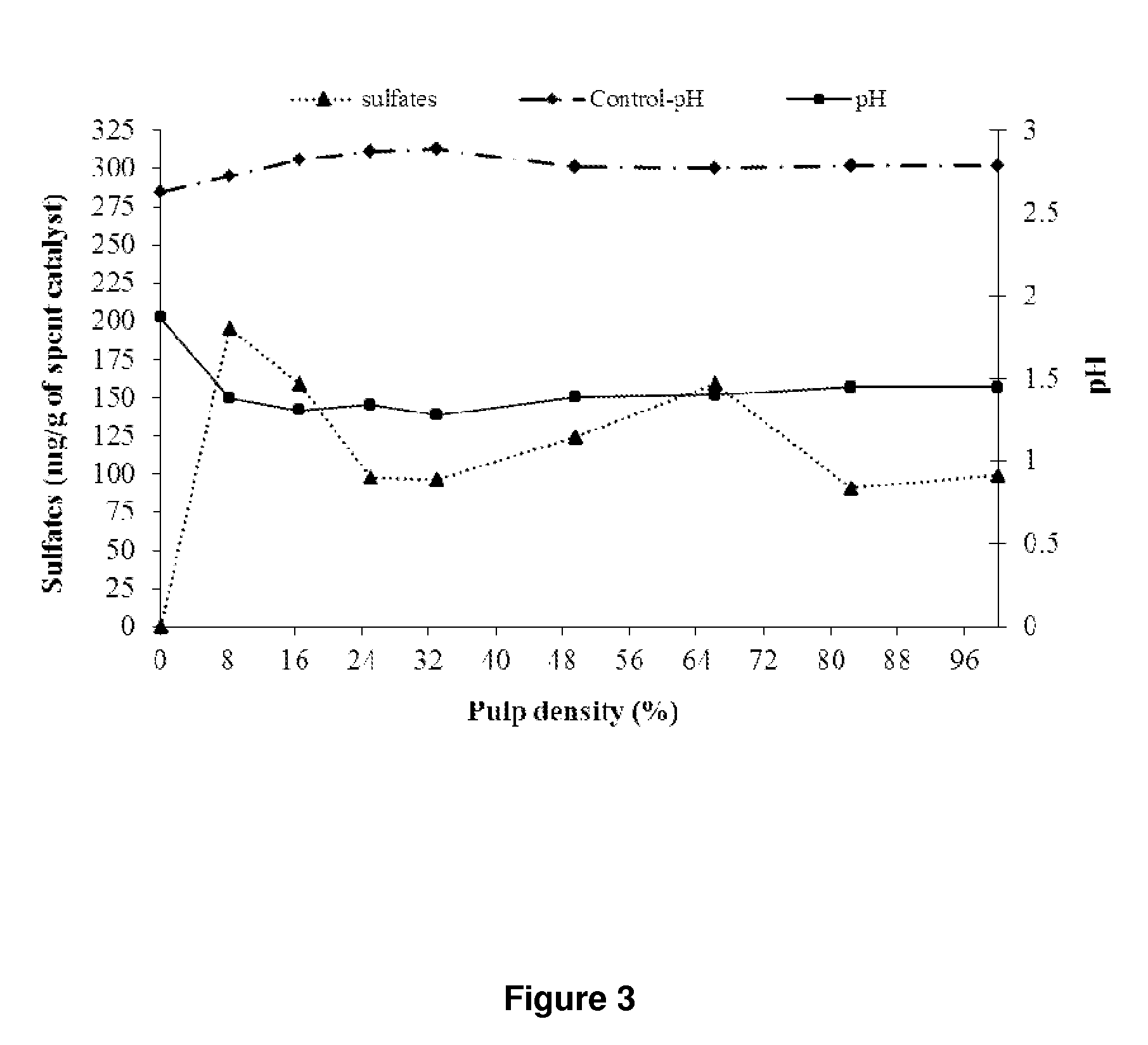
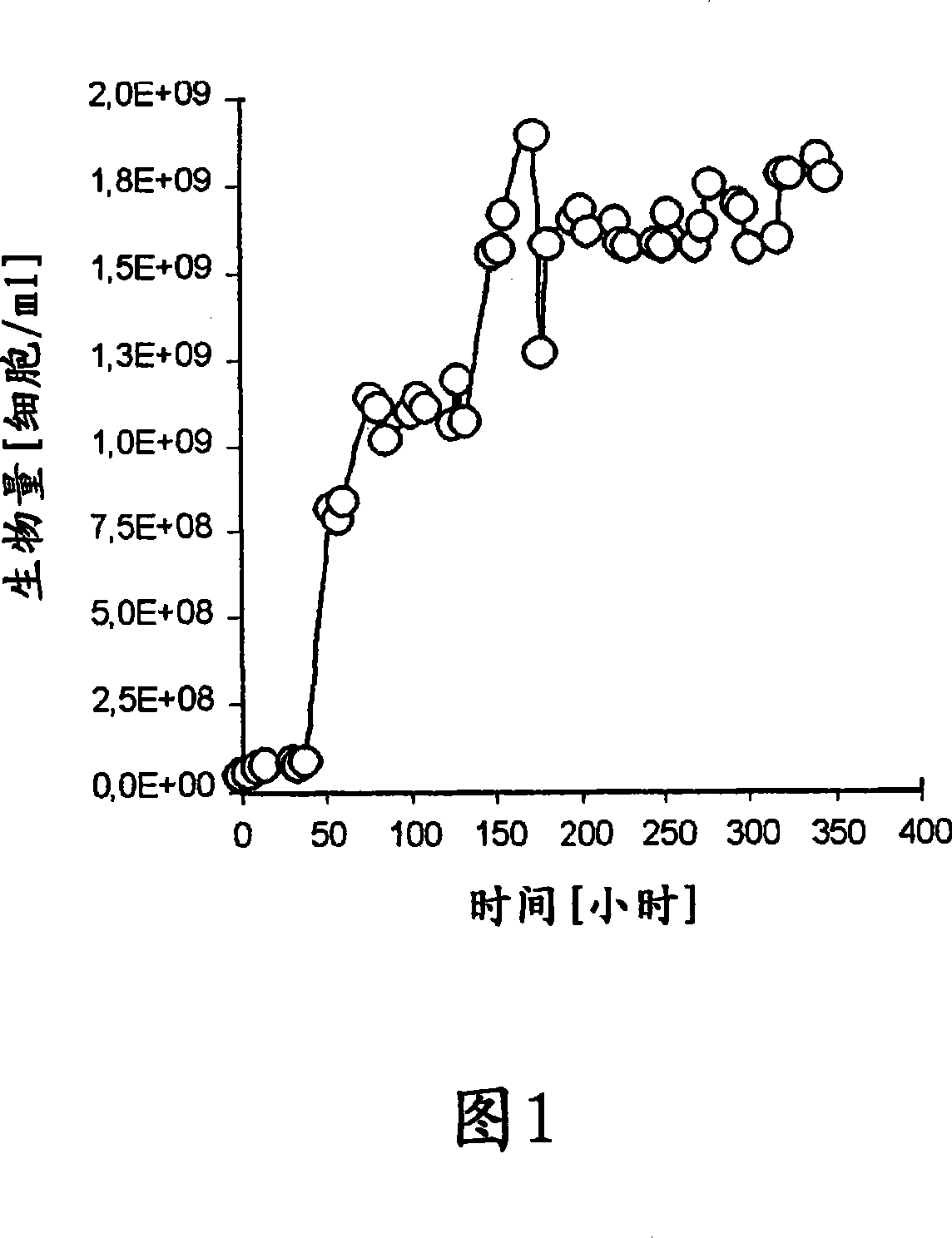
Bacterial cultures of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans are isolated, maintained and identified and used in the treatment of materials containing sulfur-compounds, such as contaminated and / or spent catalysts with elemental sulfur (S). Bacterial cultures of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans exhibit sulfur-oxidizing activity particularly useful in the transformation of elemental sulfur (S) to sulfates (SO4), a compound soluble in water (H2O) and usable in industry. The bacterial cultures of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans are mainly used as a biological or biotechnological procedure for the treatment of contaminated and / or spent catalysts with elemental sulfur (S) hazardous contaminated wastes that are mainly, but not exclusively, from the Claus process that operates at environmental conditions; does not impact the environment or ecosystem; and recovers 91-100% of the elemental sulfur (S) in sulfate form (SO4).
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO +1
Mining waste containing pyrite, in the culture of iron-oxidizing and sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Method for efficient conversion of soil weak-acid-bound cadmium by compoundbacterial agent
The invention relates to a method for efficient conversion of soil weak-acid-bound cadmium by compoundbacterial agent. The compound bacterial agent is obtained by mixing and enrichment culture of two floras as follows: (1) aflora I comprising candida, phialemonium,rhodosporidium toruloides and cryptococcus; (2) a flora II comprising acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, leptospirillum ferrooxidans, acidithiobacillus caldus,sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, acidithiobacillus ferrooxidansand ferroplasma thermophilum. The obtained compoundbacterial agent is guided into cadmium polluted soil after culture, cadmium is fully reacted after stirring for a certain time, and cadmium can be efficiently converted into soil weak-acid-bound cadmium.
Owner:HUNAN AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT +1
A method for desulfurizing high-sulfur iron ore with low-temperature and high-efficiency sulfur-oxidizing bacteria
ActiveCN105779761BIncrease oxidation rateShorten the removal cycleProcess efficiency improvementLoss rateMicroorganism
The invention discloses a low-temperature efficient sulfur-oxidizing bacterium. The name of the bacterium is acidithiobacillus thiooxidans Retech DW-II; the preservation institution is General Microbe Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms; the address is Institute of Microbiology of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, Yard 1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing; the preservation date is September 10, 2014; the preservation number is CGMCC No.9625. The invention also provides a method for efficiently desulfurating high-sulfur iron ores. The method comprises the following steps of crushing ores until the size of the ores is -0.074mm, adding the low-temperature efficient sulfur-oxidizing bacterium CGMCC No.9625, accelerating the oxidizing rate of sulfur in the iron ores at the low temperature, and enabling the removal rate of the inorganic sulfur in the iron ores to be greater than or equal to 85%. The method is low in investment, low in production cost, free of emission of SO2 gas and free of pollution to the environment, has the advantage of low iron loss rate, and provides technical support for large-scale development of the sulfur-containing iron ores.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Bacterial leaching way of vanadium in high-sulfur vanadium stone-like coal
InactiveCN101760649BReduce energy consumptionReduce usageProcess efficiency improvementSulfurGranularity
The invention discloses a novel bacterial leaching way of vanadium in high-sulfur vanadium stone-like coal, mainly utilizing the characteristic that acidithiobacillus thiooxidans generates sour, and the vanadium of the stone-like coal mineral is leached out. The stone-like coal mineral is crushed and grinded until granularity is less than 0.10mm, and then the stone-like coal mineral is mixed withleaching agent containing with acidithiobacillus thiooxidans for finishing the leaching process under room temperature (15-25 DEG C). After a period for leaching, leaching agent with vanadium is gotten. The invention has the following beneficial effects that 1, the invention is a biological metallurgy way and belongs to the cleaning productive technology; 2, the invention has simple operation and small investment; 3, the characteristic that the acidithiobacillus thiooxidans generates sour is utilized, thus avoiding using a lot of vitriol.
Owner:浙江豪美钒业有限公司
Method for screening unmarked gene knockout bacterial strain of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans
ActiveCN103232994BEfficient knockoutEasy to exploreMicrobiological testing/measurementHybrid cell preparationThiobacillus ferrooxidansBacterial strain
The invention discloses a method for screening an unmarked gene knockout bacterial strain of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. The method comprises introducing a knockout plasmid for construction of a target gene and an induction plasmid carrying an I-SceI gene into acidithiobacillus thiooxidans by conjugational transfer, carrying out single recon screening by a resistance maker, and carrying out double recon preliminary screening by blue-white selection. The method discloses the method for unmarked gene knockout of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans first, utilizes beta-galactosidase blue-white selection for double recon screening, can fast, stably and efficiently knock out a target gene, solves the problem that in the existing unmarked gene knockout process, selective pressure lacks so that screening is difficult, shortens double recon screening time, improves screening efficiency, reduces a screening cost and provides a novel method for stable genetic modification of acidithiobacillus thiooxidans.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Microorganism synchronously removing ammonia and sulfureted hydrogen foul gas and method for preparing the same
InactiveCN100560715CEfficient removalSuitable operating conditionsBacteriaDispersed particle separationDipotassium hydrogen phosphateActivated sludge
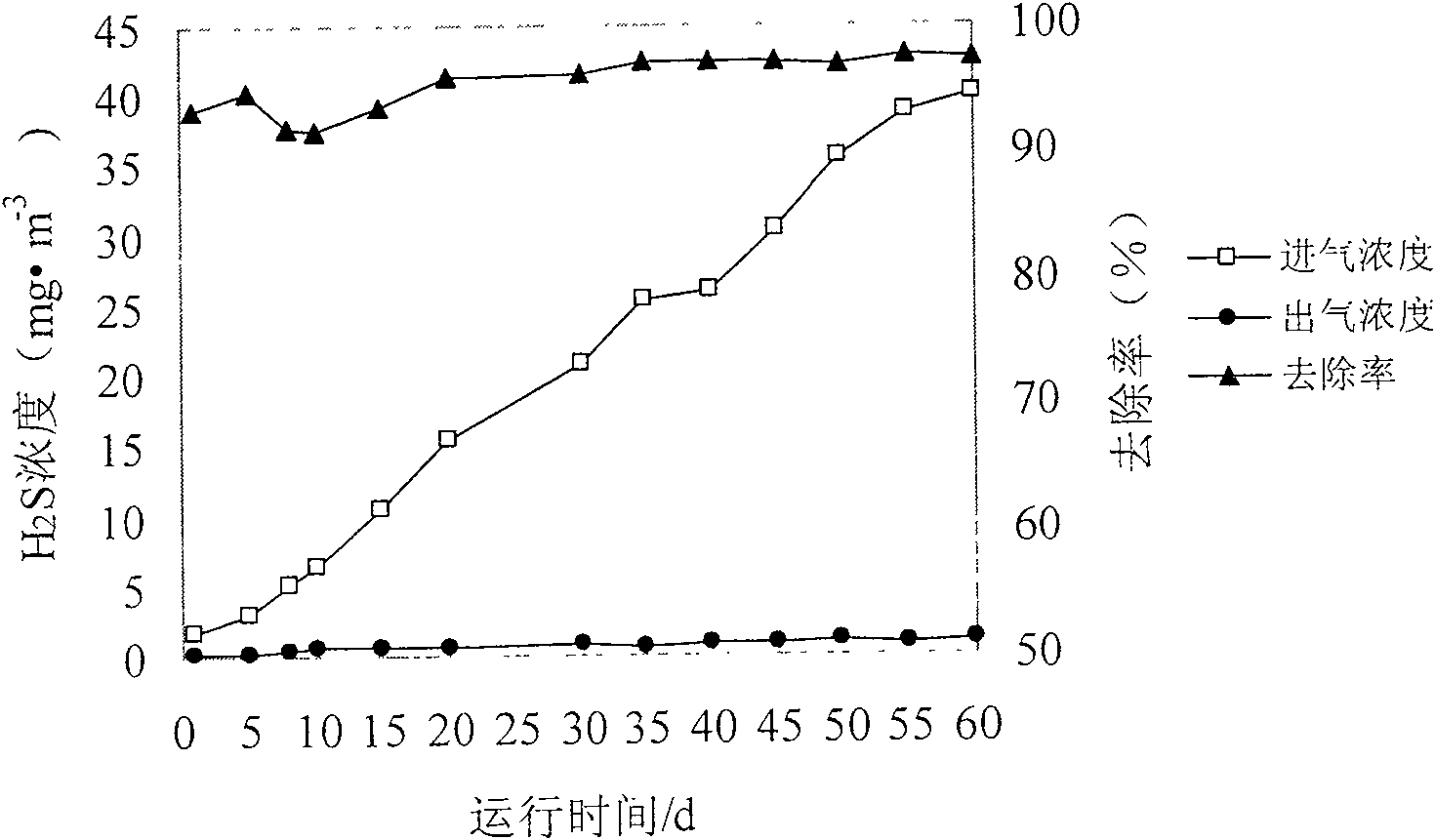
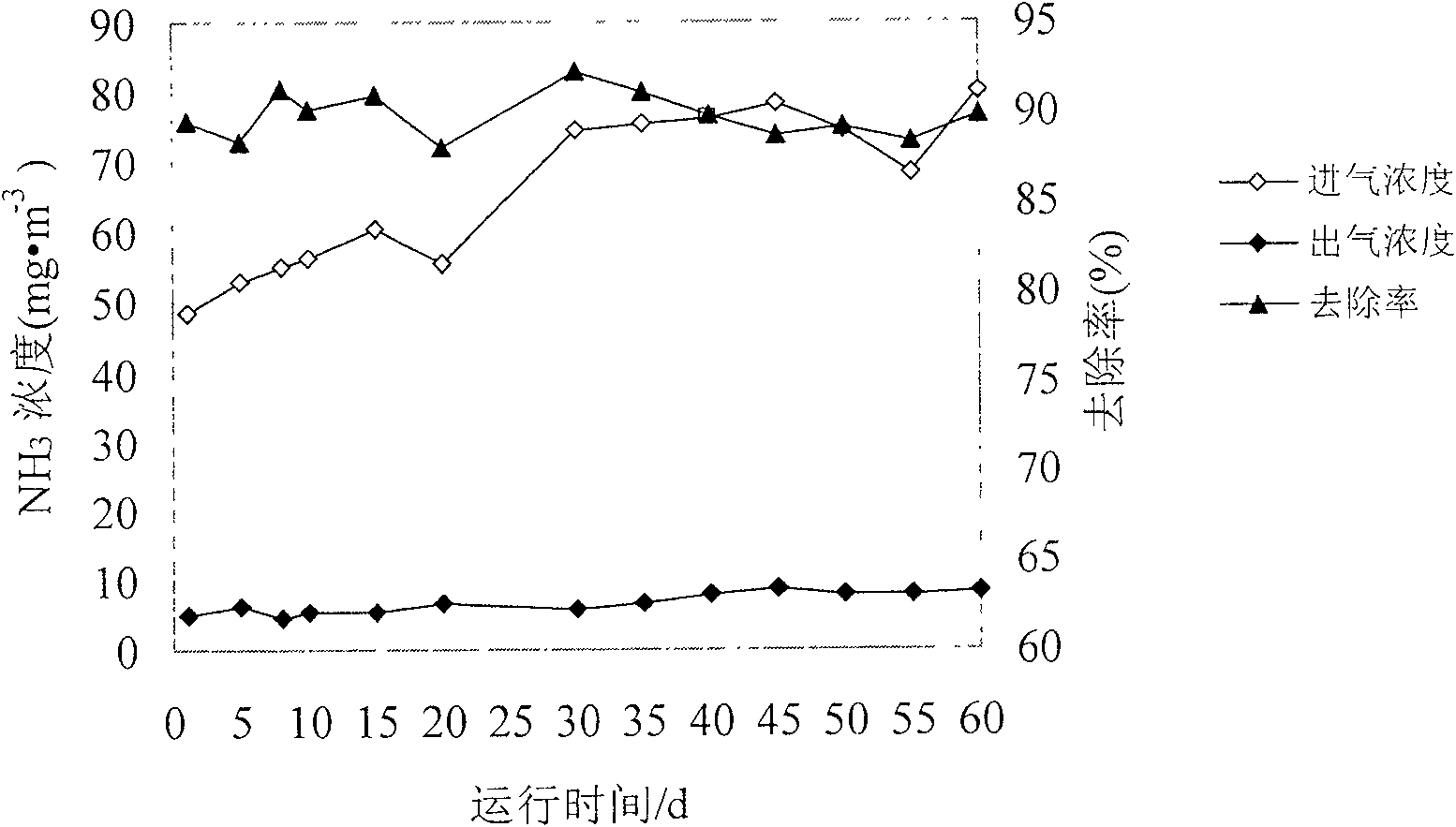
A microorganism which can remove the malodorous gas of NH3 and H2S synchronously and a preparation method thereof relate to the microorganism technical field and in particular to an efficient deodorization microorganism of the mixed malodorous gas in a sewage collecting and disposing establishment and the preparation method thereof. An acidithiobacillus thiooxidans CCW-Y2 strain provided by the present invention is conserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collections of Microorganisms, and the conversing serial number CGMCC No. is 2158. The strain is ammonium sulfate tolerant type and is obtained by sieving and separating from the activated sludge of the living sewage disposal factory. The culture conditions of the acidithiobacillus thiooxidans CCW-Y2 strain of the present invention are as follows: firstly, SOB culture medium is adopted, and the components of the culture medium are the dipotassium hydrogen phosphate of 2g / L, the potassium dihydrogen phosphate of 2g / L, the magnesium chloride (MgCl2 / 7H2O) of 0.2g / L, the ammonium sulfate of 10g / L, the ferrous sulfate (FeSO4 / 7H2O) of 0.01g / L and the powdered sulfur of 10g / L; secondly, the culture condition is the temperature of 28 DEG C to 32 DEG C and 180 circles per minute; thirdly, a carrier is water, and dilute sulfuric acid (or hydrochloric acid) is added for adjusting pH value to be 2.0 to 3.0. The acidithiobacillus thiooxidans CCW-Y2 strain of the present invention can be directly inoculated into a waste gas disposing establishment (such as a biological filtration tower) and can synchronously remove the mixed malodorous gas of the H2S and the NH3 efficiently, which simplifies the operation condition of the waste gas disposing establishment and ensures that the operation is more simple.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Plasmids for transforming bacteria of the acidithiobacillus spp. genus, and transformation method
The present invention discloses functional plasmids in bacteria of the Acidithiobacillus genus, such as the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Acidithiobacillus caldus species. And a method to successfully transform bacteria of the Acidithiobacillus genus, such as the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Acidithiobacillus caldus species, with these plasmids.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
High-efficiency sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and a process for rapid heating of low-sulfur copper ore leaching in alpine regions
ActiveCN105779324BImprove permeabilityIncrease oxidation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismSulfur
The invention discloses an efficient sulfur-oxidizing bacteria with a strain name of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans Retech DW-II. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, Institute of Microbiology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, Court No.1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing on September 10, 2014, and has accession number of CGMCCNo. 9625. The invention also provides a rapid heating method for low-sulfur copper mine leaching process in Alpine region. The method comprises the steps of: crushing ore to -50mm, mixing with pyrite powder, conducting sulfuric acid slaking and granulation to improve the permeability of the stock heap and provide sufficient energy for bacteria; and finally adding the efficient sulfur-oxidizing bacteria CGMCC No. 9625. The method speeds up the initial rate of oxidation of the pyrite ore heap, and provides sufficient heat for the stock heap, so that temperature of the stock heap rapidly increases to above 40 DEG C.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com