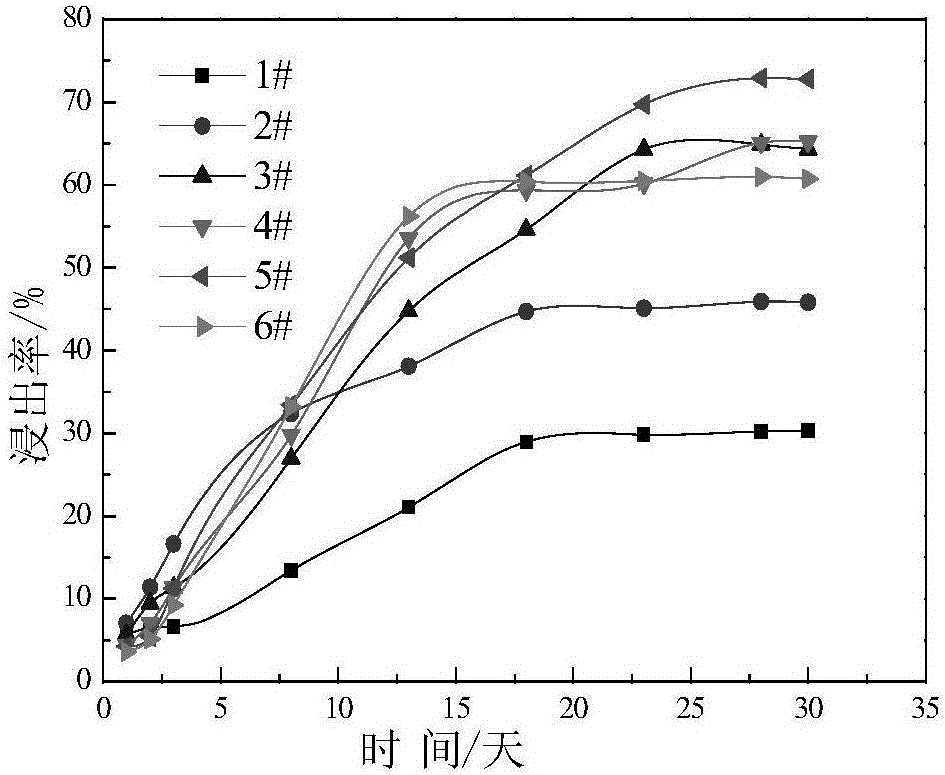
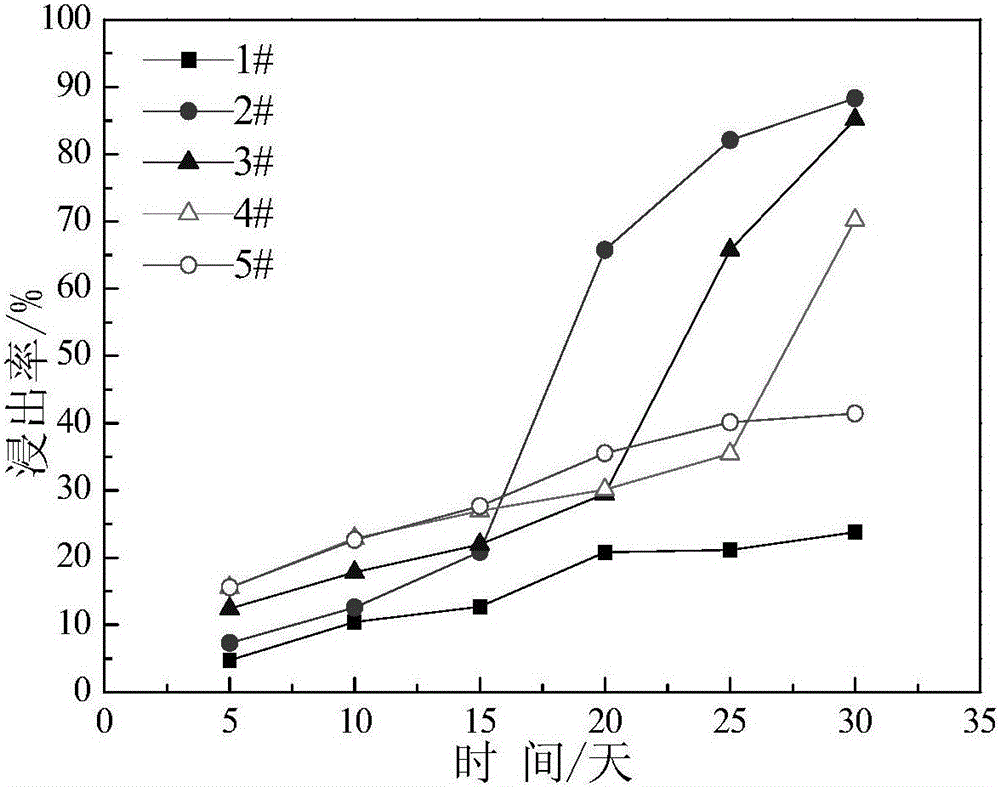
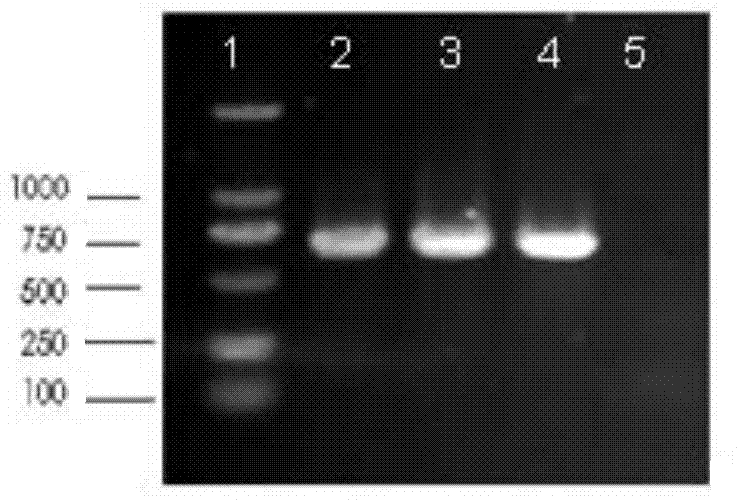
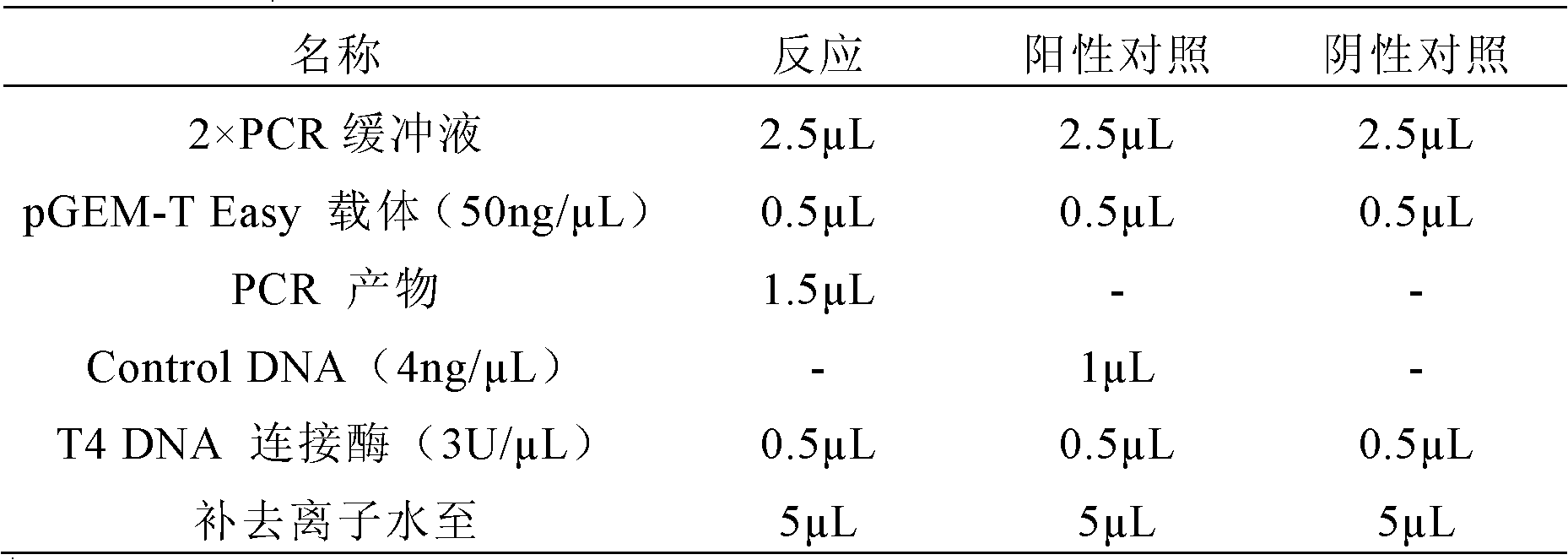
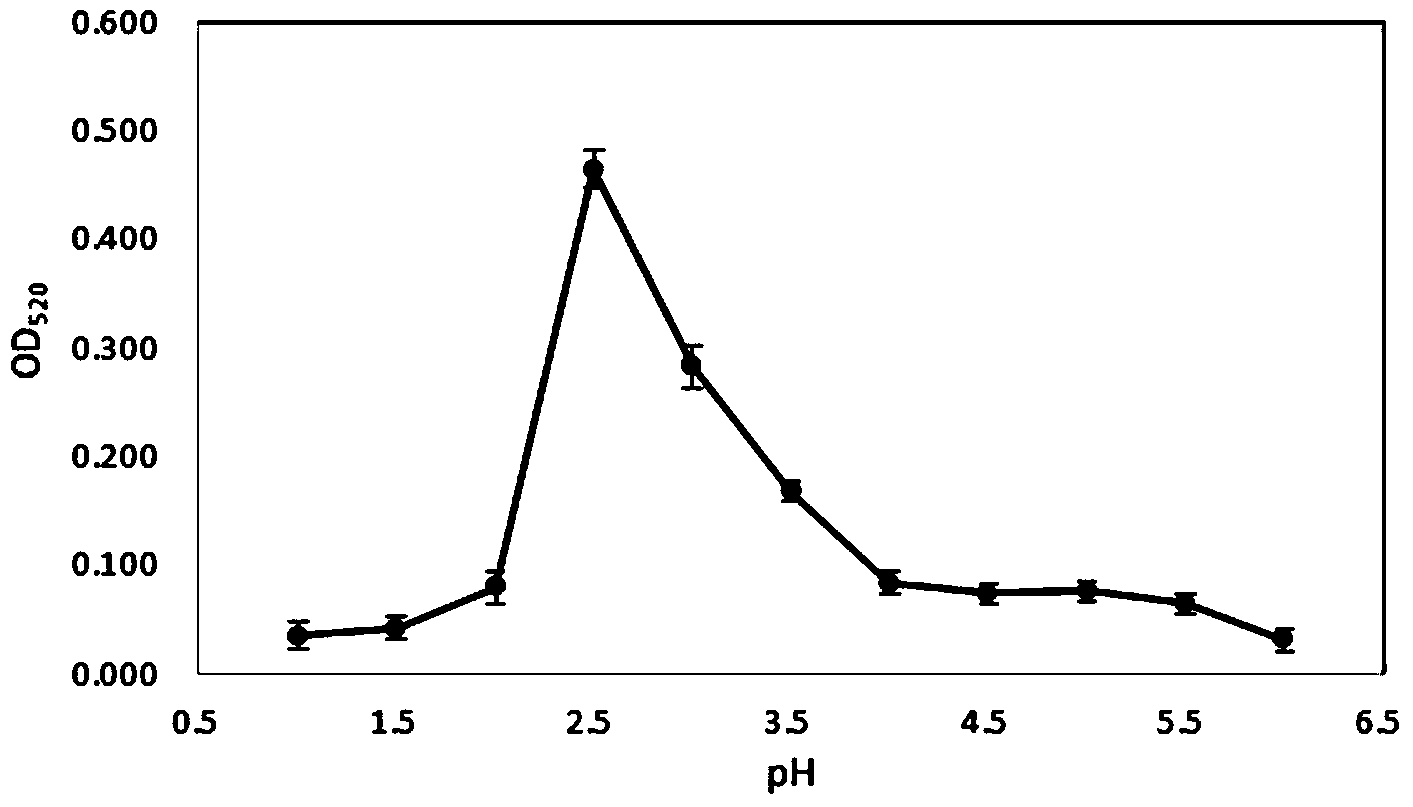
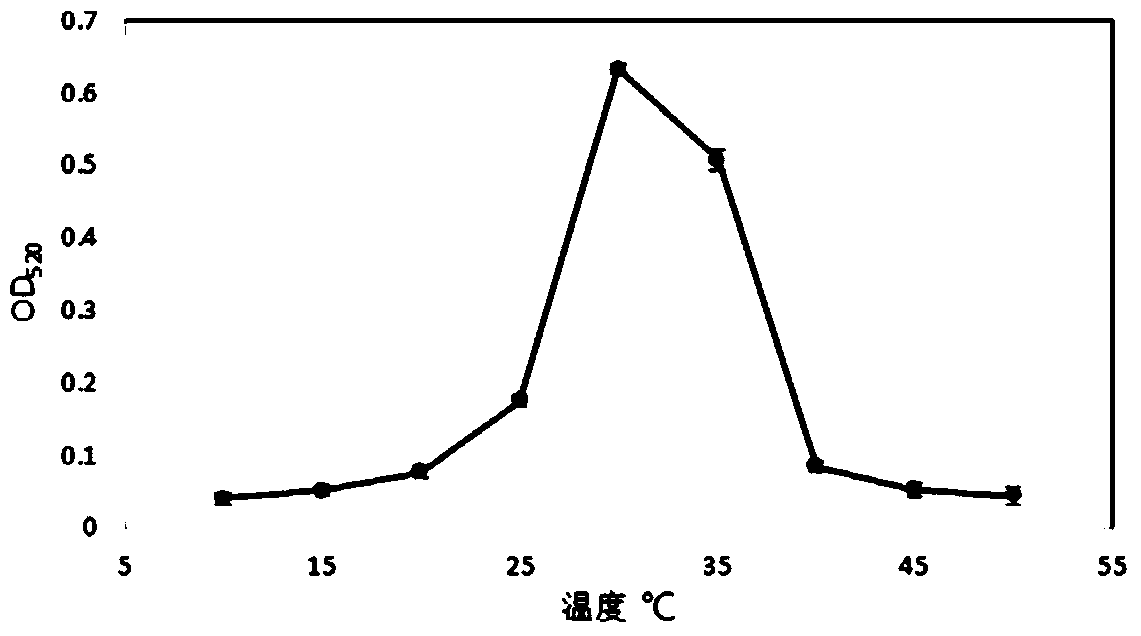
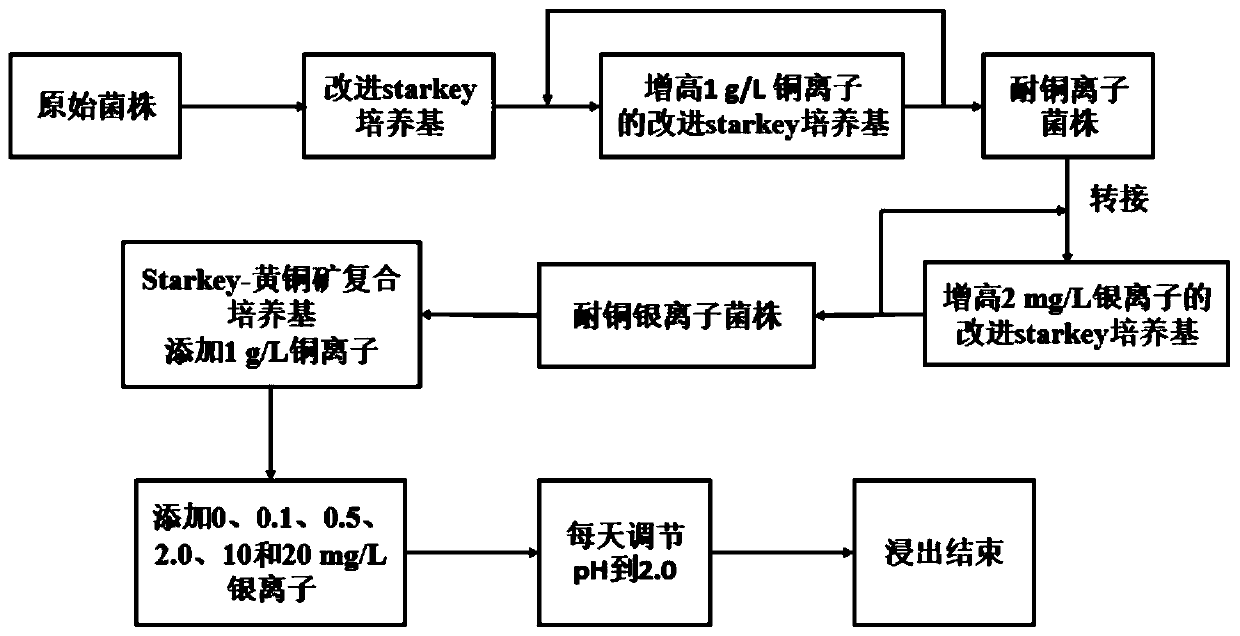
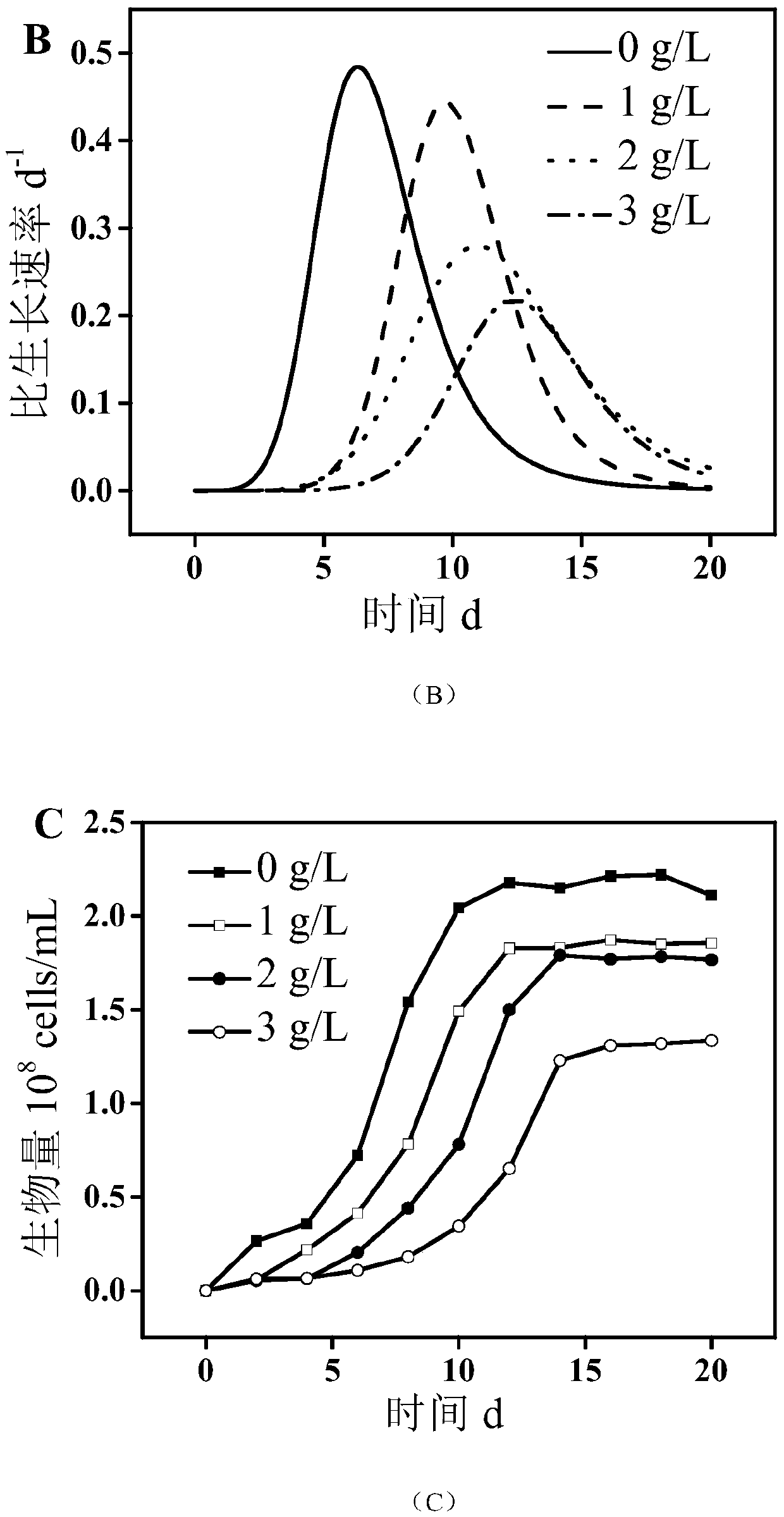
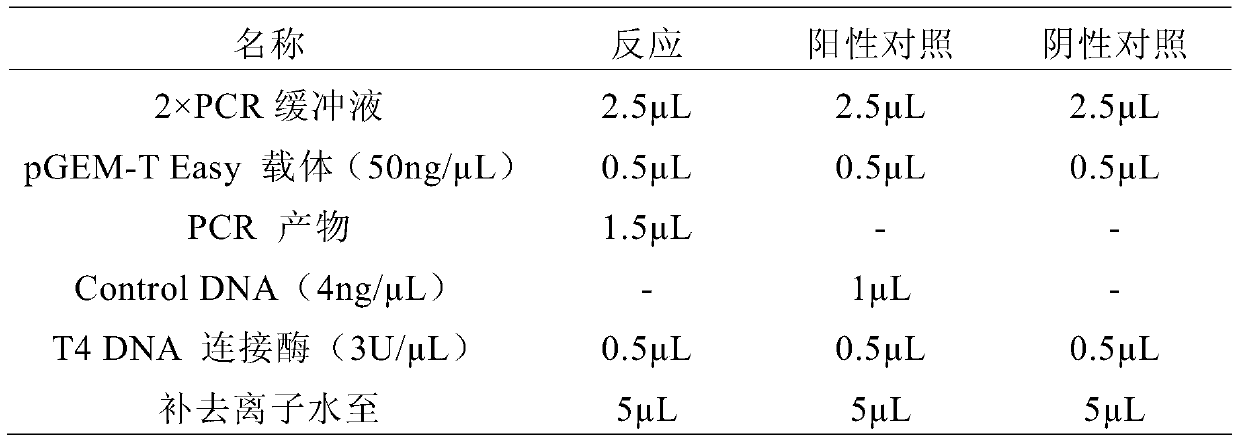
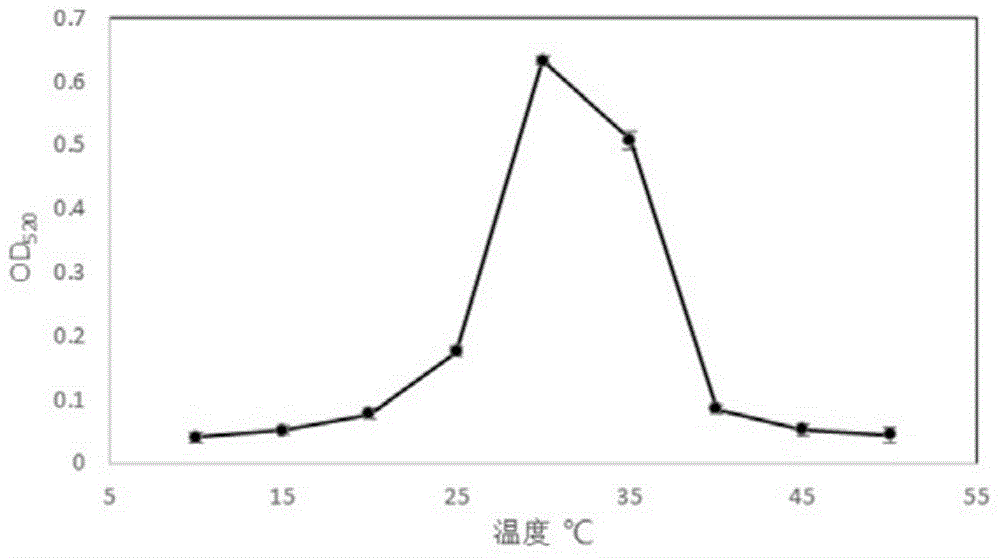
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Acidithiobacillus caldus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acidithiobacillus caldus formerly belonged to the genus Thiobacillus prior to 2000, when it was reclassified along with a number of other bacterial species into one of three new genera that better categorize sulfur-oxidizing acidophiles. As a member of the Gammaproteobacteria class of Proteobacteria, A. caldus may be identified as a Gram-negative bacterium that is frequently found in pairs. Considered to be one of the most common microbes involved in biomining, it is capable of oxidizing reduced inorganic sulfur compounds (RISCs) that form during the breakdown of sulfide minerals. The meaning of the prefix acidi- in the name Acidithiobacillus comes from the Latin word acidus, signifying that members of this genus love a sour, acidic environment. Thio is derived from the Greek word thios and describes the use of sulfur as an energy source, and bacillus describes the shape of these microorganisms, which are small rods. The species name, caldus, is derived from the Latin word for warm or hot, denoting this species' love of a warm environment.
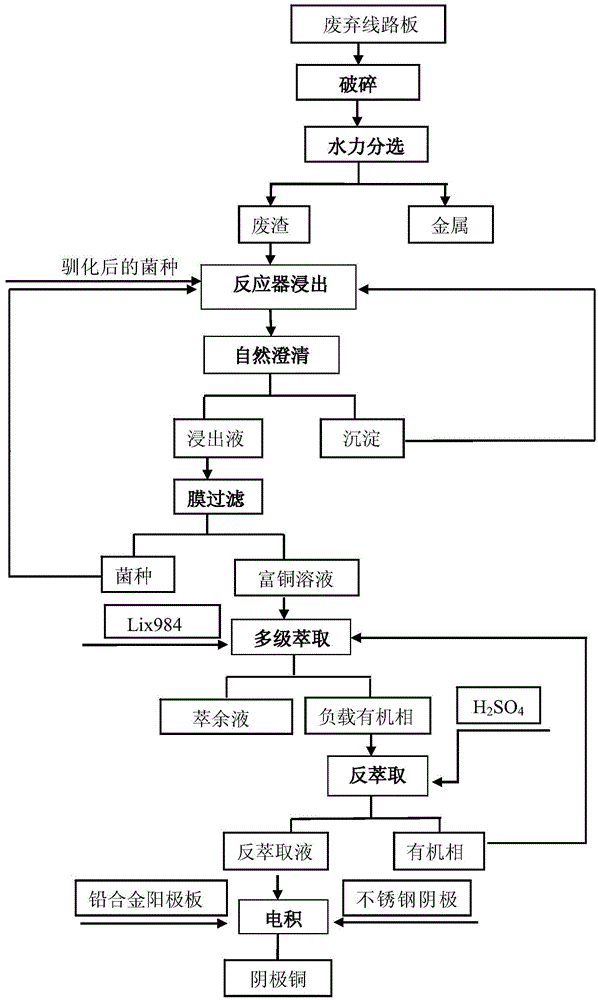
Method for extracting copper in waste printed circuit boards by virtue of moderately thermophilic bacteria
ActiveCN104328283AEfficient separationReduce processingProcess efficiency improvementRaffinateCulture mediums
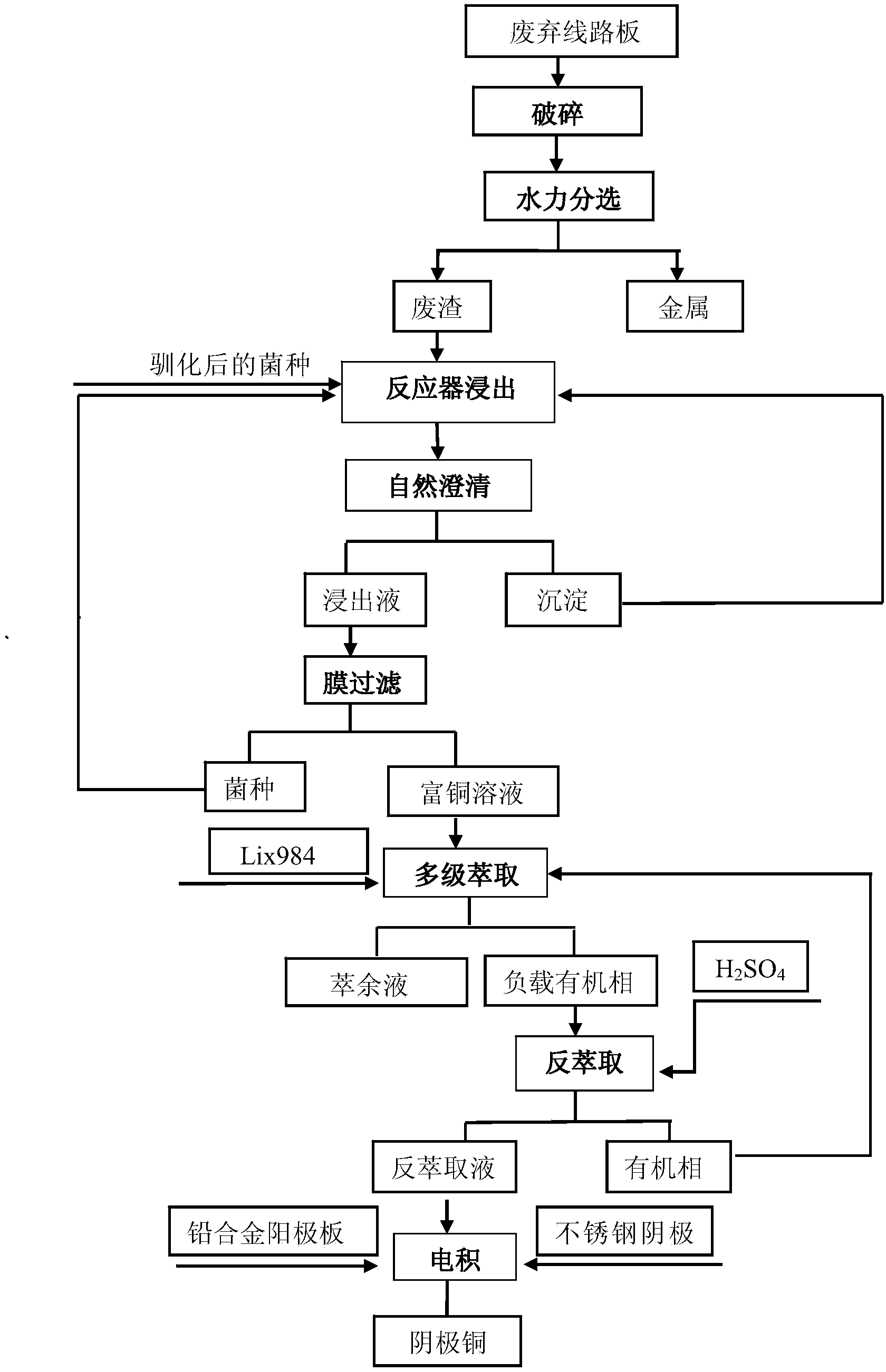
The invention relates to a method for extracting copper in waste printed circuit boards by virtue of moderately thermophilic bacteria. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out shaker hydraulic sorting on the artificially dismounted and pulverized waste printed circuit boards to obtain metal and waste residues; putting the waste residues into an improved 9K culture medium, adjusting the pH value to 2 and leaching with a mixed strain of leptospirillum ferriphilum, acidithiobacillus caldus, sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans and thermoacidiferriphile as a leaching strain to obtain a copper-enriched solution and leaching residues; filtering the copper-enriched solution with a hollow fiber membrane system to obtain the strain and a copper-containing filtrate and putting the strain again into the leaching system for repeatedly using; and extracting the copper-containing filtrate with hydroxy oxime and a hydroxy oxime complex Lix984 as extraction agents to obtain a copper-loaded organic phase and a raffinate, carrying out back extraction on the copper-loaded organic phase with a 10-30% sulfuric acid solution to obtain a back extract and a blank organic phase and carrying out electrodeposition on the back extract to obtain cathode copper and an electrodeposited barren liquid. By the method disclosed by the invention, the environment-friendly, economic and full-value recovery of the waste printed circuit boards is achieved and the method has the advantages of short flow, low investment, high efficiency and low treatment cost and is suitable for the recovery of all types of the waste printed circuit boards.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of performing traceless knockout and integration on gene of Acidithiobacillus caldus
InactiveCN102604929AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionRestriction enzyme digestionPlasmid Vector
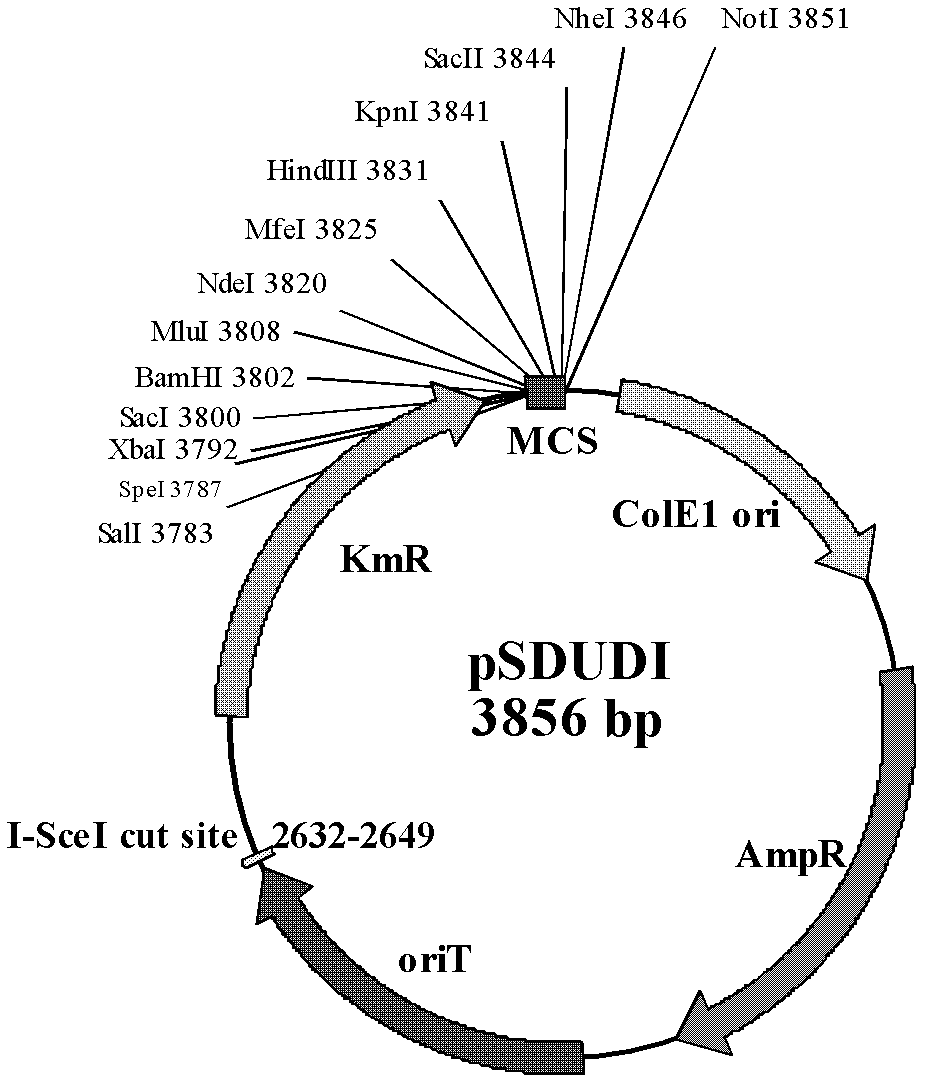
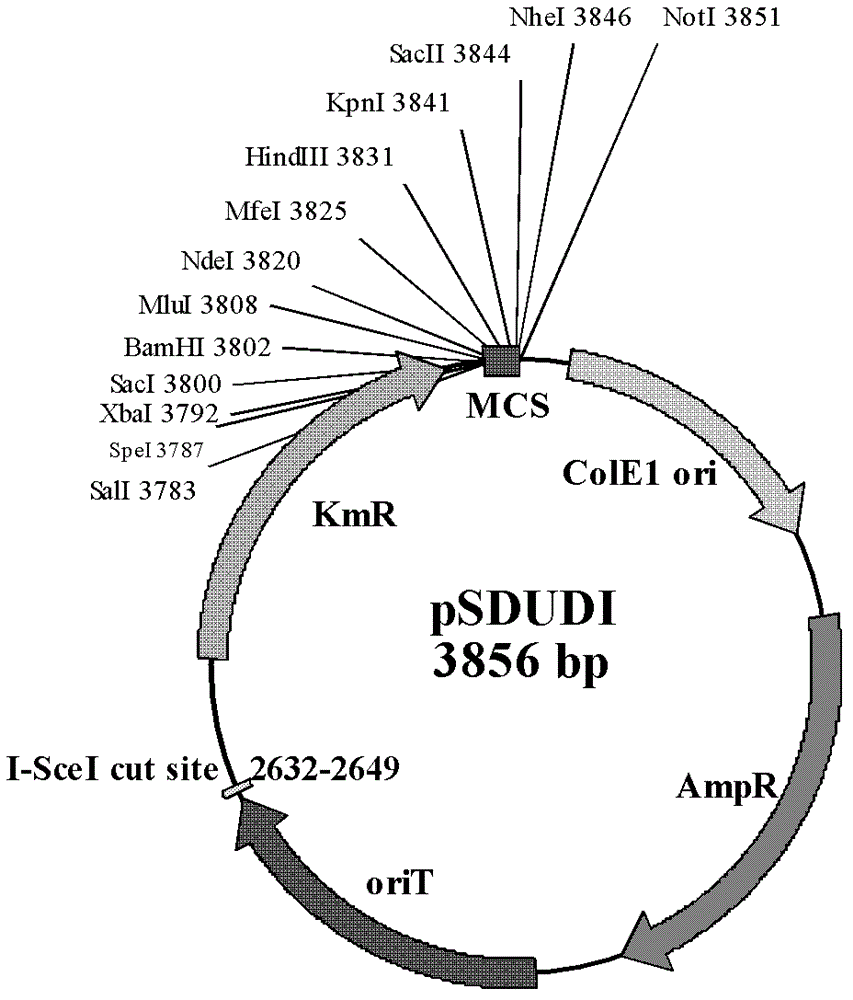
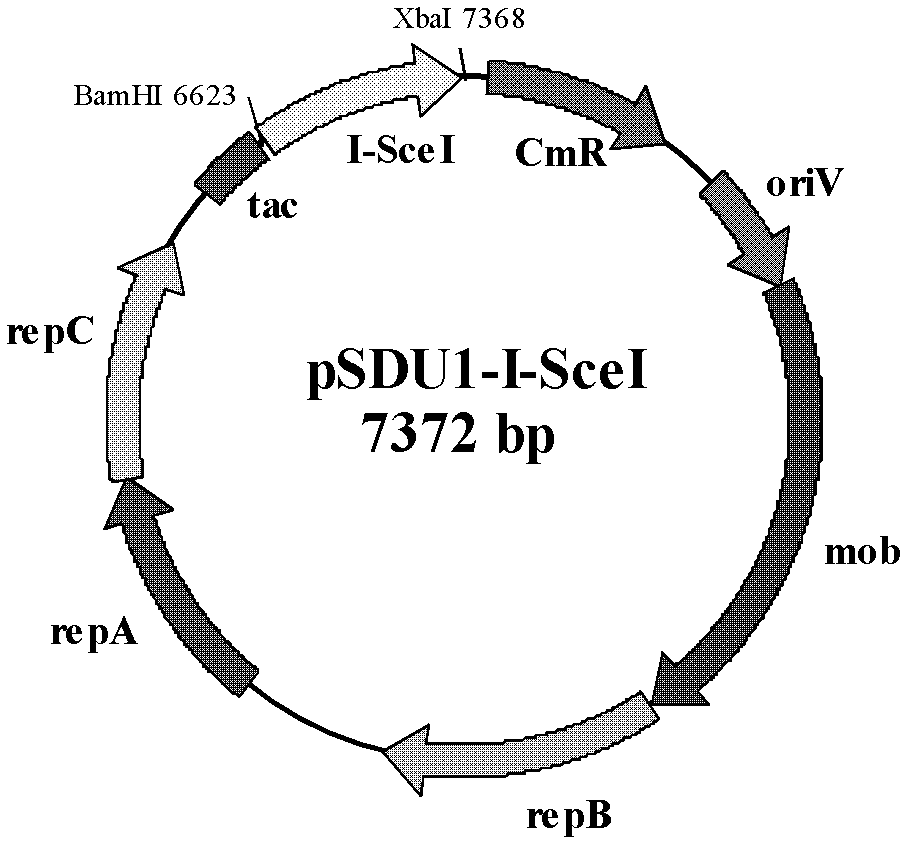
The invention discloses a method of performing traceless knockout on a chromogene or inserting an exogenous gene in a chromosome of Acidithiobacillus caldus. The method comprises the following steps: transferring a homologous recombinant plasmid containing plentiful restriction enzyme digestion sites of endonuclease I-SceI into the Acidithiobacillus caldus in a conjugation transfer manner, simultaneously, directionally inserting the homologous recombinant plasmid into the chromosome of Acidithiobacillus caldus by use of a homologous recombinant system of a cell itself, transferring a screenedsingle crossover to an I-SceI expression plasmid by an electroporation method, performing secondary homologous recombination on a single recon chromosome under a stress that the I-SceI enzyme cuts the chromosome, and optimizing and screening a double crossover bacterial strain to realize knockout and insertion of the gene. The invention also constructs a suicide type plasmid vector pSDUDI for homologous recombination and a plasmid pSDU1-I-SceI for expressing the I-SceI enzyme effectively, and provides convenience for the traceless knockout and the integration of the chromogene in the Acidithiobacillus caldus. The method provided by the invention provides a new way for intensive study on and modification of Acidithiobacillus caldus.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Plasmids for transforming bacteria of the acidithiobacillus spp. genus, and transformation method
The present invention discloses functional plasmids in bacteria of the Acidithiobacillus genus, such as the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Acidithiobacillus caldus species. And a method to successfully transform bacteria of the Acidithiobacillus genus, such as the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and Acidithiobacillus caldus species, with these plasmids.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Method for strengthening biological leaching of chalcopyrite and bornite
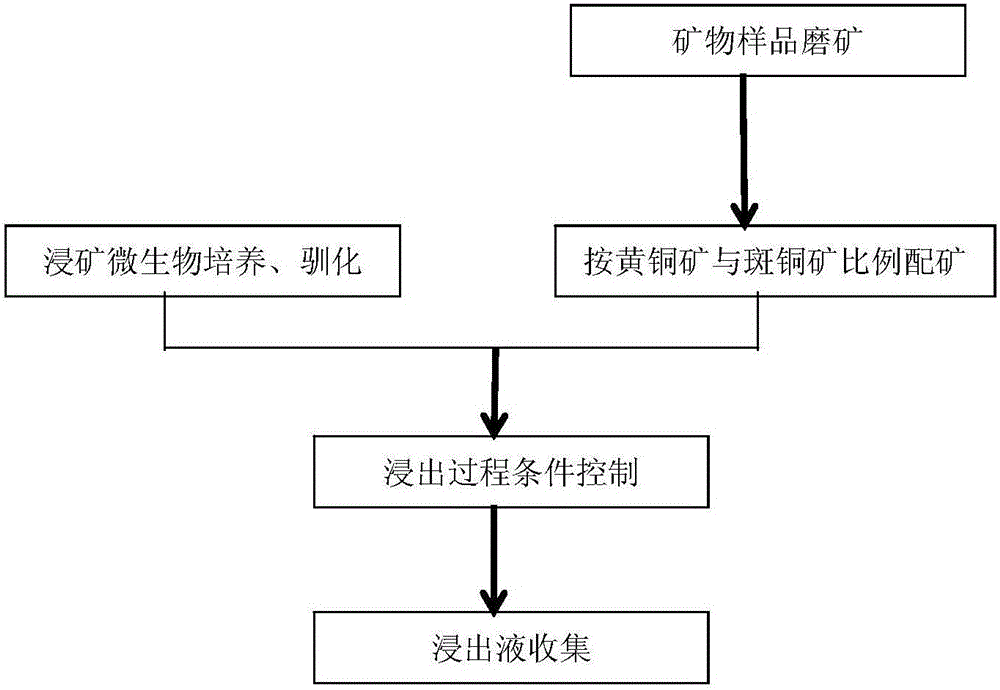
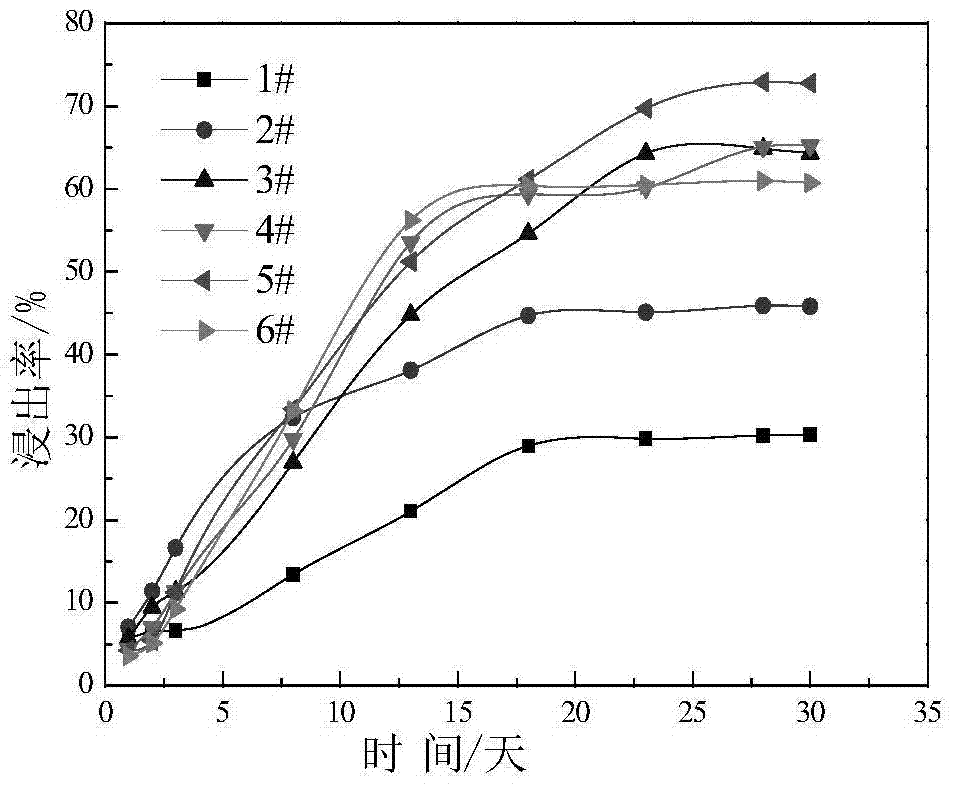
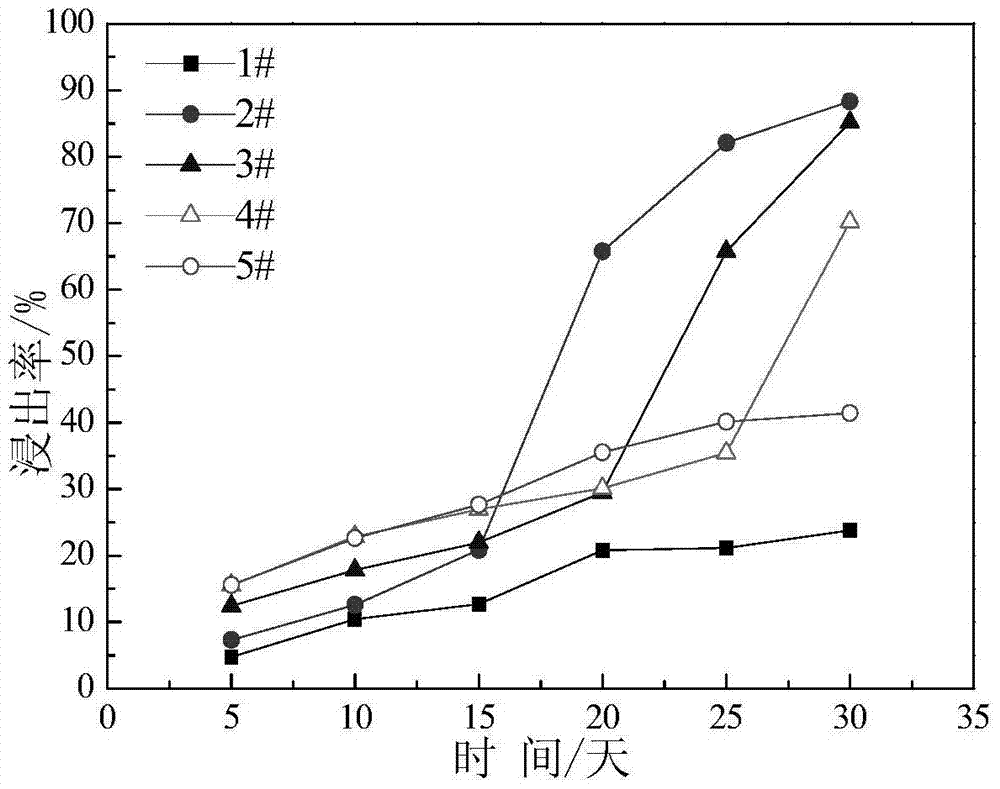
The invention provides a method for strengthening biological leaching of chalcopyrite and bornite. One or more of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, acidithiobacillus caldus and leptospirillum ferriphilum are used as mineral leaching microorganisms. The ratio of the chalcopyrite to the bornite is controlled to be 5:1-1:5. In the leaching process, the stirring speed is controlled to be 100-600 rpm. The pH value of a solution is controlled to be 1.5-2.5, the electric potential of the solution is 350-480 mV (Ag / AgCl is a reference electrode), the chalcopyrite and the bornite can be leached in a cooperative mode, and the Cu leaching rate is obviously increased. According to the method, through reasonable ore blending of the chalcopyrite and the bornite, proper leaching technological conditions are controlled, and the biological leaching efficiency of the chalcopyrite and the bornite is improved. The method is efficient, simple and easy to operate.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Acidithiobacillus caldus gene engineering strain and applications thereof
InactiveCN103571781AIncreased transcript levelsImprove abilitiesBacteriaDispersed particle separationMicroorganismSulfur
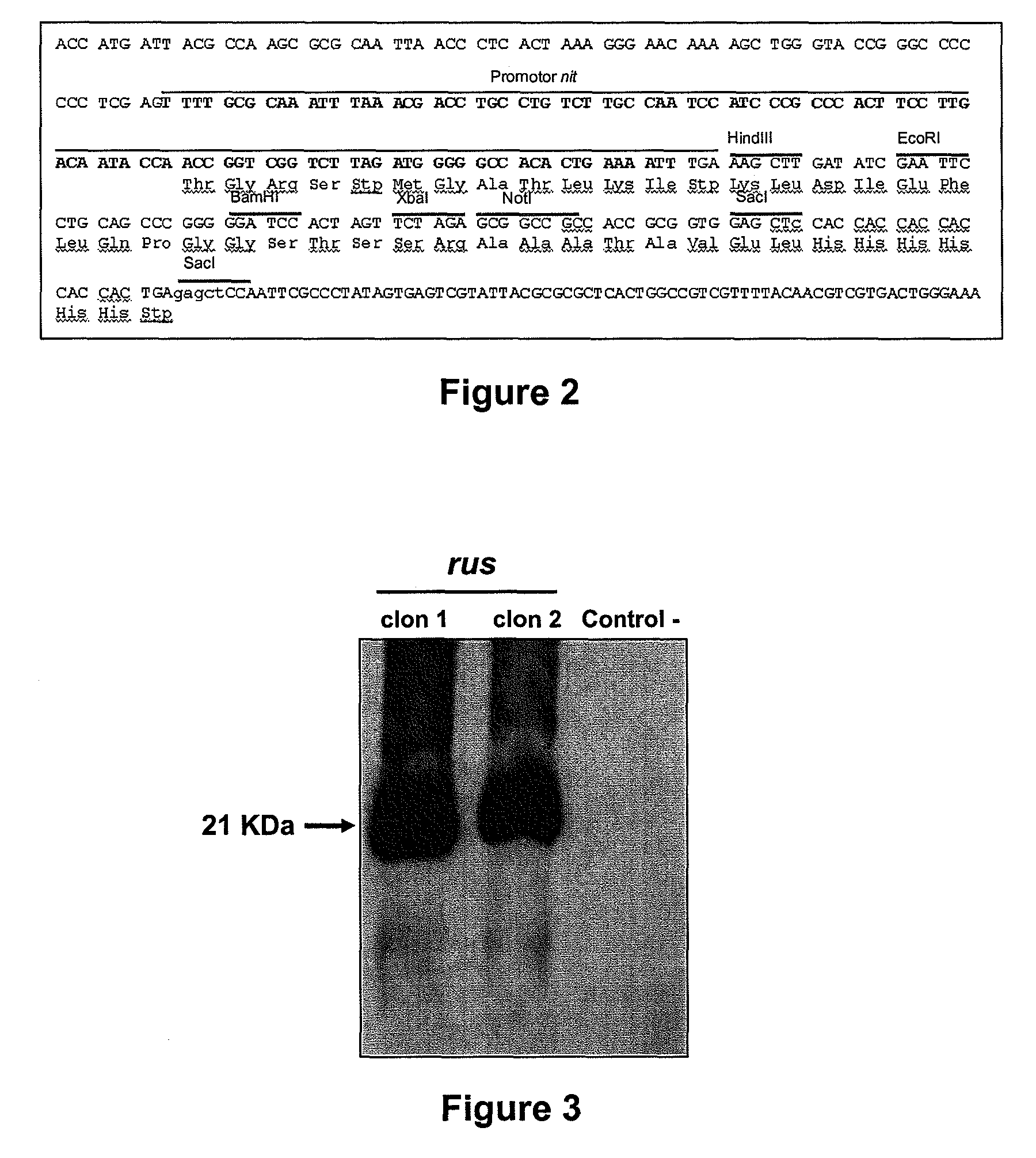
The invention relates to an acidithiobacillus caldus gene engineering strain and applications thereof. The acidithiobacillus caldus MTH-04(pJRD215-tac-sor) gene engineering strain is preserved in the general microbiology centre of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on June 28, 2013, address: Institute of Microbiology Chinese Academy of Sciences, NO.3, NO.1 yard, beichen west road, Beijing chaoyang district. The strain preservation number: CGMCC NO.7388. Compared with the acidithiobacillus caldus MTH-04, the acidithiobacillus caldus MTH-04(pJRD215-tac-sor) gene engineering strain has the advantages that the capability of sulfur oxide is enhanced, and the bacteria biomass, sulfur and oxygen reductase enzyme activity and the transcriptional level of key enzyme of a sulfur oxidation system are increased.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Intermediate-temperature mineral leaching composite microbial system for leaching copper pyrites
InactiveCN103173356AImprove environmental adaptabilityEasy to trainBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyriteFerroplasma
The invention provides an intermediate-temperature mineral leaching composite microbial system for leaching copper pyrites. The composite microbial system is named Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans 6Y-1, is preserved in the China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) in Wuhan University in November 10th 2010, and has a preservation number of CCTCC M2010297. The composite microbial system consists of 77% of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, 5% of Acidithiomicrobium sp, 12% of Acidithiobacillus caldus and 6% of Ferroplasma sp. The microbial system has high copper pyrite leaching efficiency.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Method for increasing metal ore leaching rate, and special strain thereof
ActiveCN103667131AAcid resistantEliminate passivationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetallurgical slagAlicyclobacillus pohliae
The present invention discloses a method for increasing a metal ore leaching rate, and a special strain thereof. According to the present invention, Alicyclobacillus sp. SJ-68 is provided, the preservation number is CGMCC No.7682, and a bacterial agent for leaching the target metal from metal ore is further provided, and comprises Alicyclobacillus sp. SJ-68 described in the claim 1 and Acidithiobacillus caldus SM-1 described in the claim 1; and experiment results prove that the Alicyclobacillus sp. SJ-68CGMCC No.7682 can be separately used for leaching the valuable metal in the sulphide ore or be synergistically used with other strains so as to co-leach the valuable metal in the sulphide ore, can be used for deepening extraction of noble metals or rare metals in sulphide ore concentrates, abandoned mine, lean ore, metallurgical slag and difficultly-treated complex sulphide ores, and has important industrial application prospects in the biological mineral leaching field.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Shuttle expression vector with broad hosts
ActiveCN102876702ABroad host capabilityHigh splicing transfer frequencyMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionConjugated proteinPlasmid
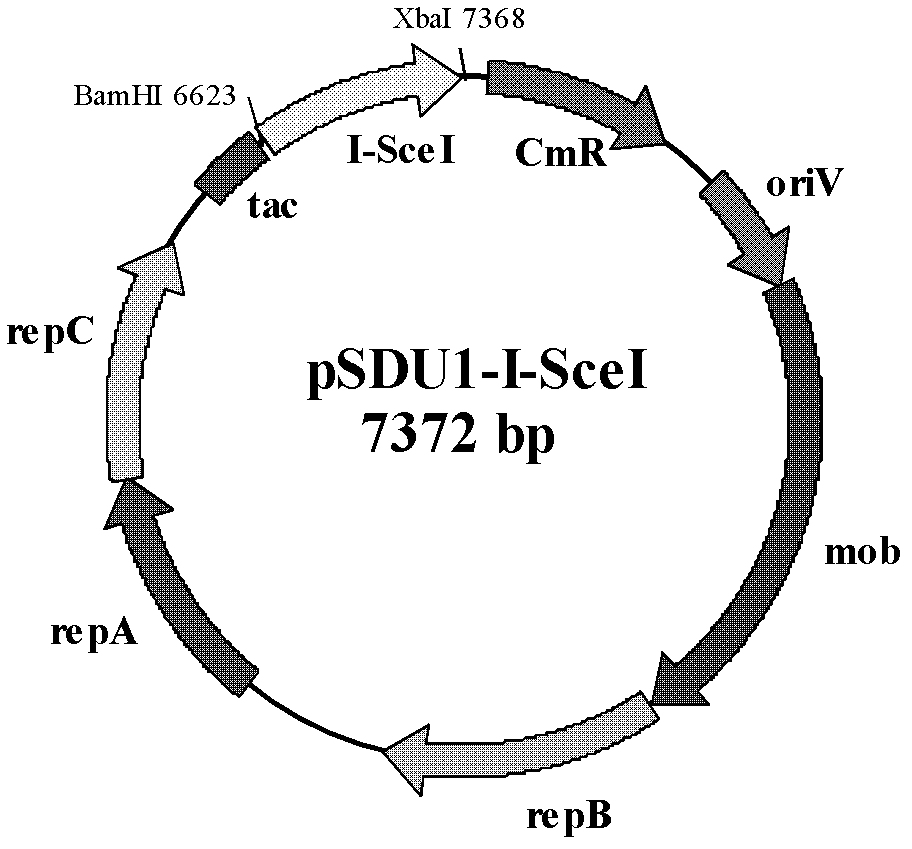
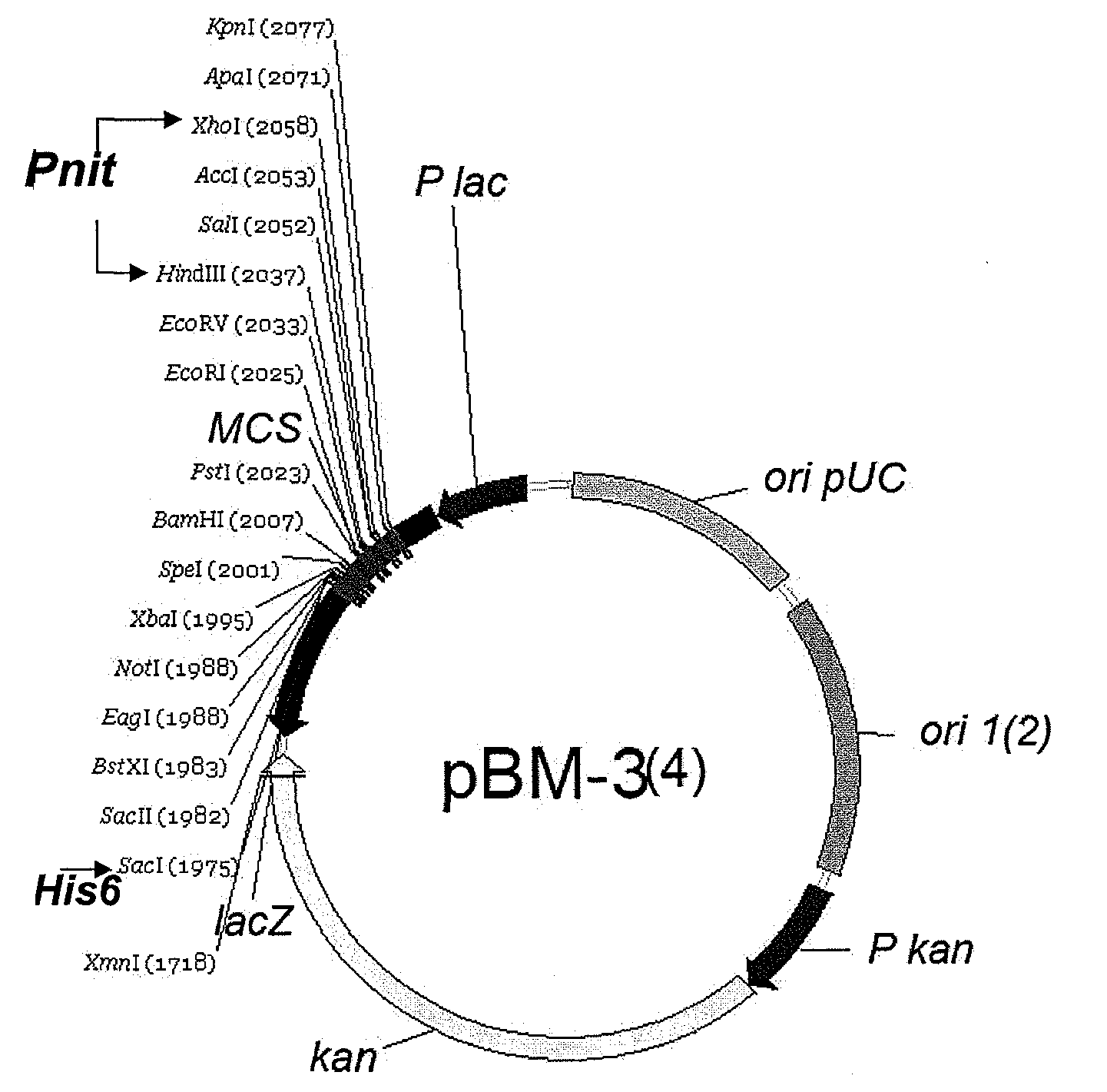
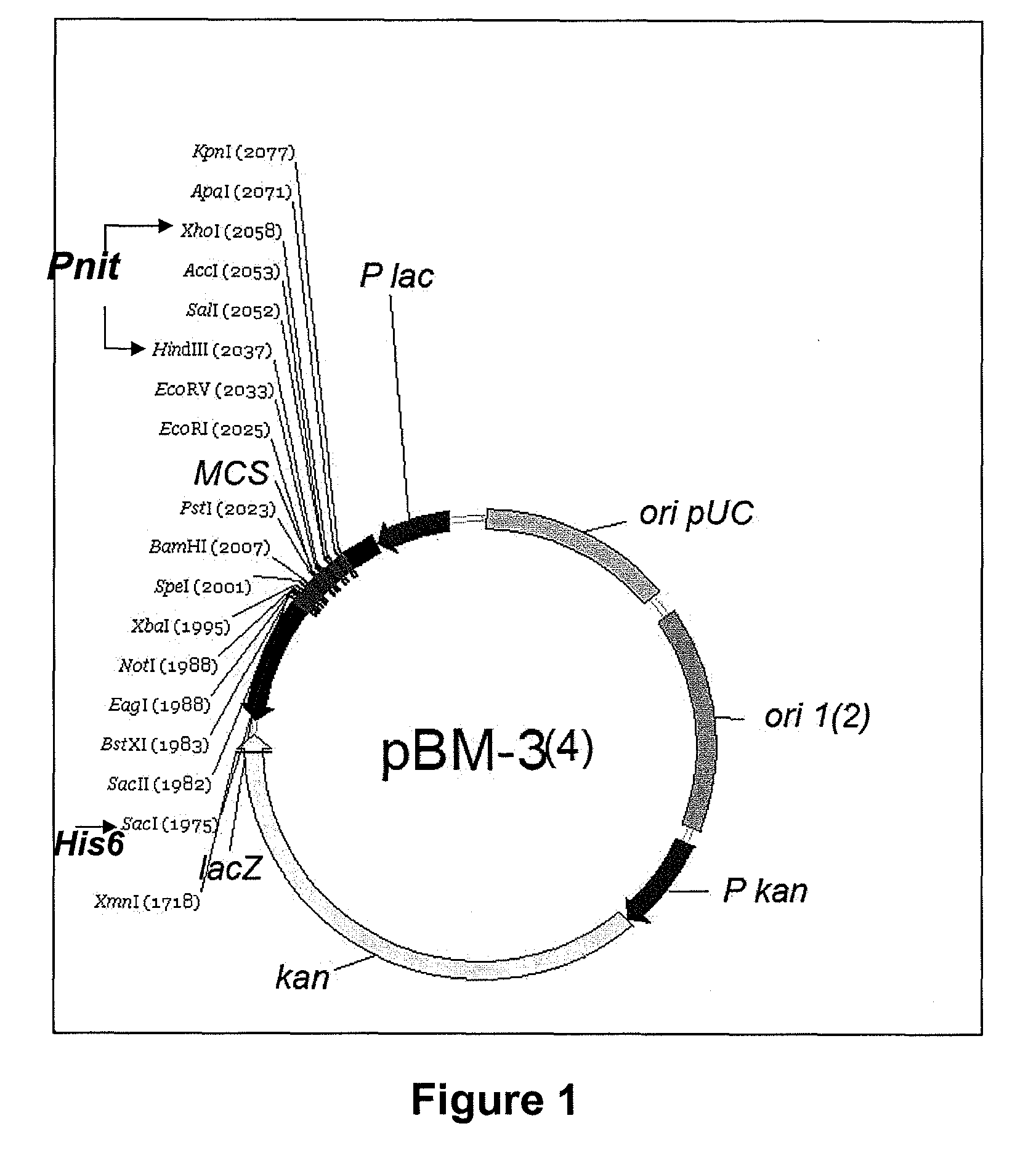
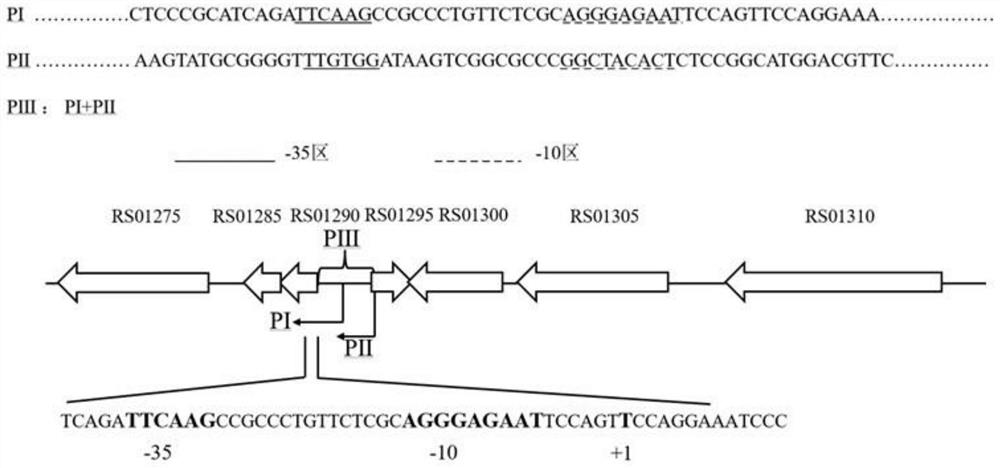
The invention discloses a shuttle expression vector with broad hosts and provides a plasmid. The plasmid comprises the following components: a replication origin oriV, a gene for encoding replication protein Rep, a conjugation origin oriT, a gene for encoding conjugated protein Mob, an antibiotic selective marker gene and a foreign gene expression cassette, wherein the foreign gene expression cassette sequentially comprises a promoter, a multiple cloning endonuclease site in which a foreign gene is inserted, and a transcription termination sequence from upstream to downstream. The plasmid has a broad host ability, can be stably replicated in hosts and has high transconjugative frequency. The shuttle expression vector has great value for the genetic transformation of Acidithiobacillus caldus.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electroporation method of thermophilic thiobacillus
InactiveCN101372695AConvenient gene transfer methodRapid and efficient gene delivery methodBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionGene deliveryCapacitance
The invention discloses an electro-transformation method for inducing a constructed plasmid containing exogenous genes to acidithiobacillus caldus. The method comprises the following steps: the constructed plasmid containing the exogenous genes is extracted and the concentration of the plasmid is corrected; the competent cells of the acidithiobacillus caldus are cultured and collected; the electro-transformation and plate screening are carried out, and positive transformants are identified and detected; wherein, the electro-transformation parameters are as follows: the voltage is 10,500V / cm, the resistance is 400 omega and the capacitance is 25muF. By adopting the method, the electro-transformation of the acidithiobacillus caldus is realized for the first time, and a recovery culture scheme and a screening method for the cidithiobacillus caldus are established, which provides a convenient, quick and high-efficiency gene delivery method for the studies of genetic engineering breeding, genetics and molecular biology of the acidithiobacillus caldus.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
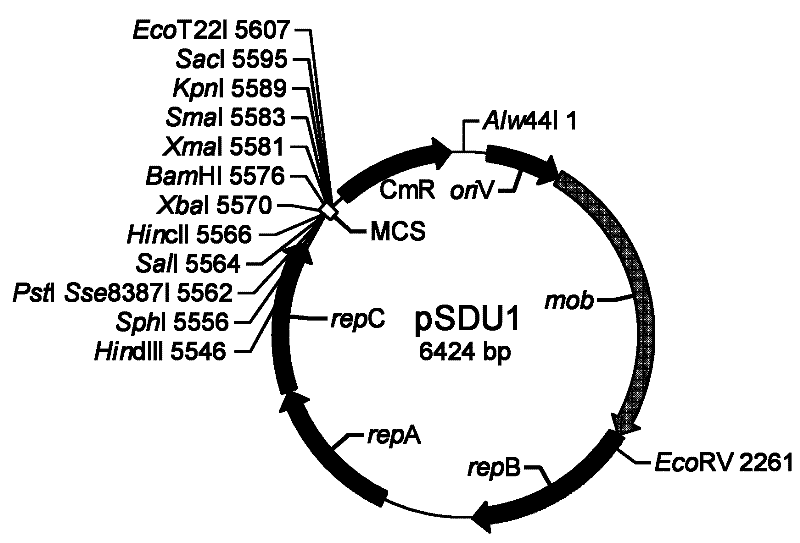
Small shuttle plasmid pSDU1 with chloramphenicol resistant gene for Acidithiobacillus caldus
InactiveCN102250939AGreat application potentialImprove carrying capacityVector-based foreign material introductionTransformation efficiencyCloning Site
The invention discloses a small shuttle plasmid pSDU1 with a chloramphenicol resistant gene for Acidithiobacillus caldus, which consists of a replicor oriV, an auto-replicating protein gene rep, a conjugational transfer gene mob, a chloramphenicol resistance selection gene cat and a multiple cloning site (MCS). The plasmid pSDU1 uses chloramphenicol resistance as a selection marker and has higher conversion efficiency; the multiple cloning sites of the plasmid pSDU1 are introduced, and the use is convenient; the oriV, rep and mob parts of the plasmid pJRD 215 is used, so higher stability is achieved; and the length of the plasmid is only 6.4kbp and the bearing capacity of the plasmid is higher, which indicate the plasmid has a huge application potential in molecular biological research and genetic engineering modification of the Acidithiobacillus caldus.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Sulfide ore flame retardant method based on microorganism-inhibitor comprehensive effect
ActiveCN114263492APrevent spontaneous combustionReduce surface sulfur contentDust removalFire preventionSpontaneous combustionMicroorganism
The invention discloses a sulfide ore flame-retardant method based on a microorganism-inhibitor comprehensive effect. The sulfide ore flame-retardant method comprises the following steps: 1, culturing acidophilic Acidithiobacillus caldus; 2, mixing the sulfide ore and the cultured bacterial liquid, adding a leaching aid, putting the mixture into a sealed container, and carrying out desulfurization treatment in a shaking table; 3, mixing a foaming agent, a foam stabilizer and a stopping agent to obtain a foam stopping agent; and 4, mixing the desulfurized sulfide ore with a foam inhibitor, and carrying out flame retardance on the sulfide ore. The sulfur content on the surface of the sulfide ore is reduced through the microbial action, surface oxidation of the sulfide ore and heat accumulation caused by oxidation heat release are reduced, so that the spontaneous combustion tendency of the sulfide ore is reduced, the sulfide ore is covered with the foam stopping agent, generated foam tightly covers the surface of the sulfide ore, and the spontaneous combustion tendency of the sulfide ore is reduced. Oxygen is isolated to interrupt the spontaneous combustion process, the spontaneous combustion tendency of the sulfide ore is reduced, and the sulfide ore spontaneous combustion prevention purpose under the comprehensive action of internal and external factors is achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
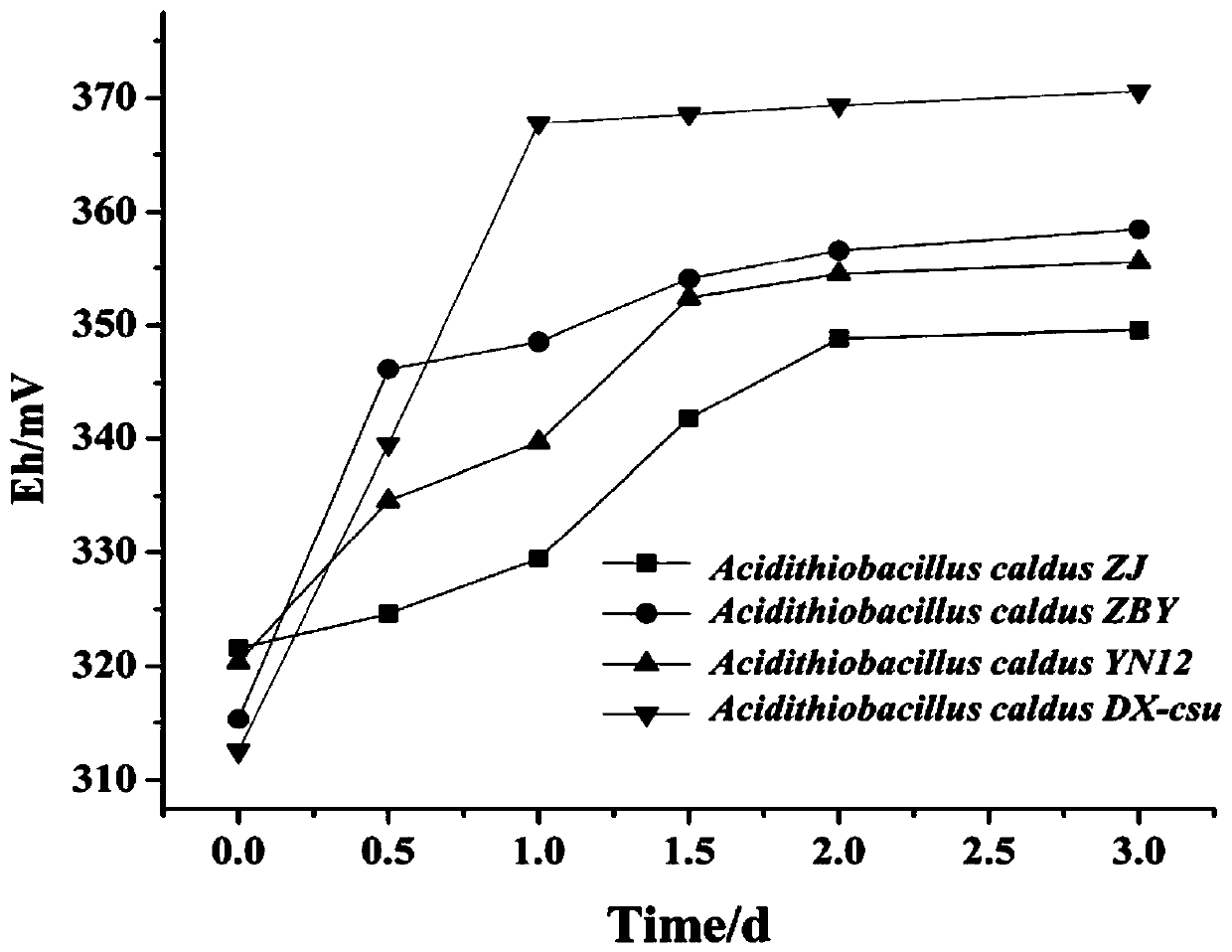
Application of acidithiobacillus caldus
ActiveCN107090423APromote growthIncrease acidityBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismMetal leaching
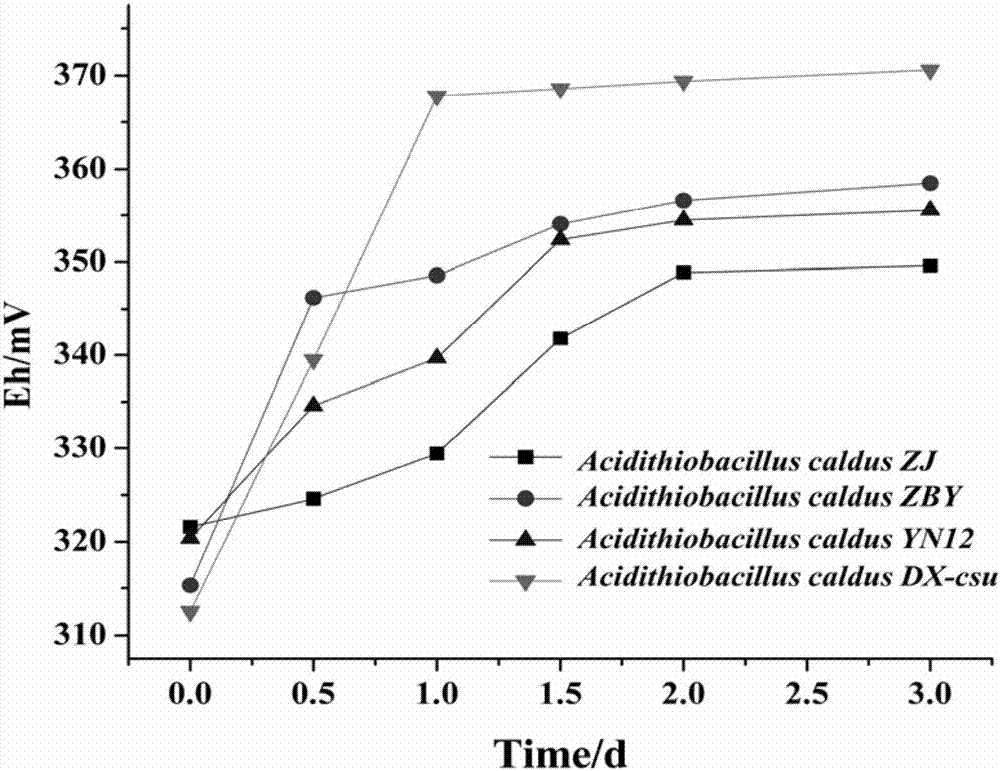
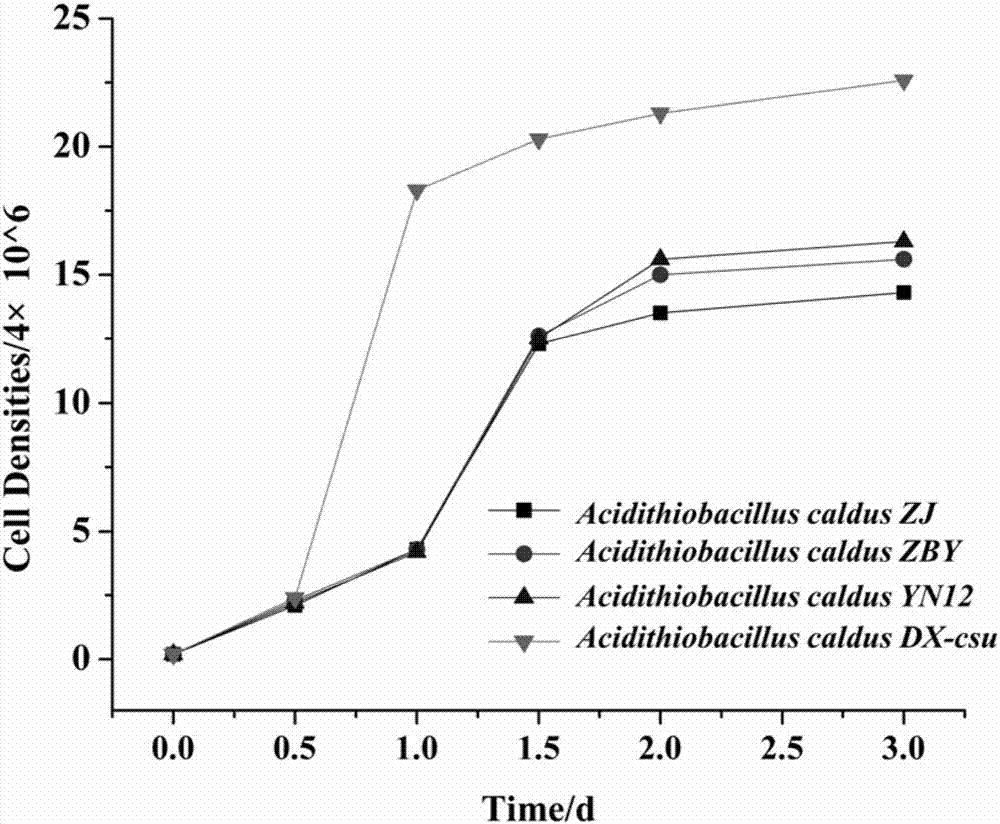
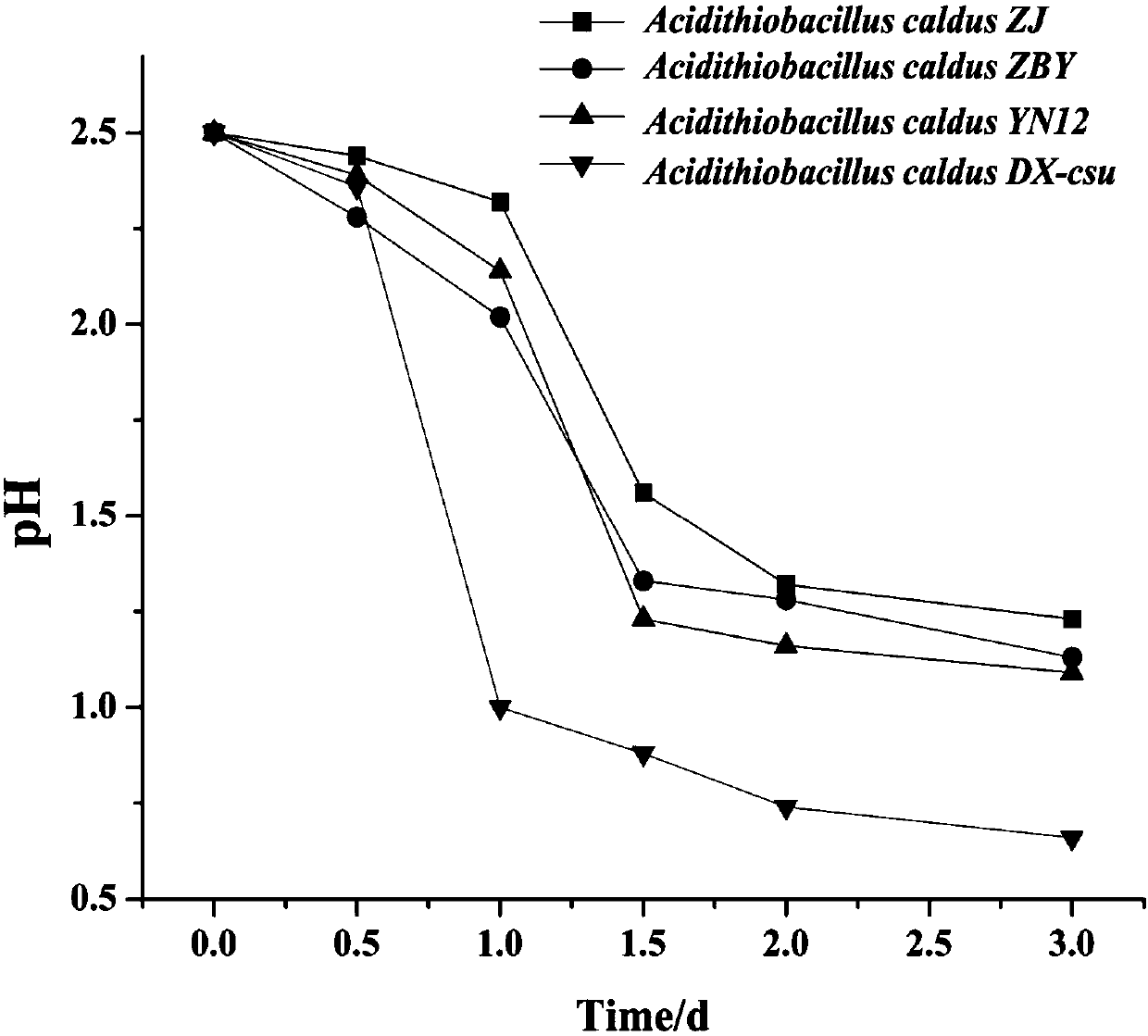
The invention belongs to the technical field of treating heavy metal pollution with microorganisms, discloses application of acidithiobacillus caldus and particularly discloses application of a new bacterial strain DX-csu in the acidithiobacillus caldus. A preservation number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC No. 14008 and the bacterial strain is named acidithiobacillus caldus. The acidithiobacillus caldus disclosed by the invention has good biotransformation action to iron and manganese-bond cadmium in soil and provides technical guidance for efficient metal leaching with the microorganisms, environmental treatment and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
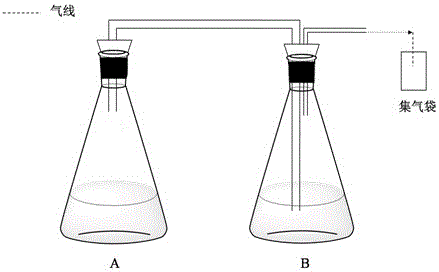
Method for removing hydrogen sulfide in biogas through combination of iron-containing compound and Acidithiobacillus caldus
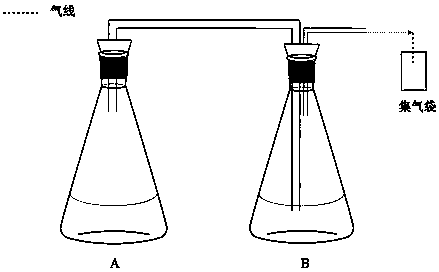
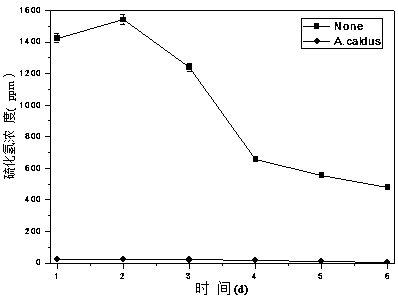
The invention discloses a method for removing hydrogen sulfide in biogas through combination of an iron-containing compound and Acidithiobacillus caldus. The method comprises 1) iron-containing compound desulfurization: adding an iron-containing compound along with fed materials into a biogas production reactor and carrying out synchronous biogas raw material fermentation and iron-containing compound desulfurization, and 2) biological desulfurization: feeding the biogas subjected to iron-containing compound desulfurization into the fermentation liquid of Acidithiobacillus caldus, detecting hydrogen sulfide content of the biogas and collecting the biogas when the hydrogen sulfide content satisfies the standard. The method has high desulfurization efficiency and reduces the cost and workload of later desulfurization processes. After the combined removal, the hydrogen sulfide content of the biogas is less than 5ppm and more preferably less than 1ppm so that it is proved that the hydrogen sulfide is substantially completely removed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Acidithiobacillus caldus-sourced EpsRAc transcriptional regulation factor and application thereof in copper oxidation tolerance
ActiveCN113896777AImprove copper resistanceBacteria peptidesProcess efficiency improvementEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention discloses an Acidithiobacillus caldus-sourced EpsRAc transcriptional regulation factor and application thereof in copper oxidation tolerance, and belongs to the field of biochemistry and molecular biology. According to the present invention, the promoter sequence derived from the Acidithiobacillus caldus transcriptional regulation factor EpsRAc and the heavy metal specificity participating in the regulation of the transcriptional regulation factor EpsRAc are analyzed; through heterologous expression in Escherichia coli, the effect of EpsRAc on the aspect of copper ion tolerance is proved.The co-purification of the EpsRAc protein and the copper ions shows that the copper ions may indirectly regulate and control the EpsRAc protein so as to achieve the purpose of transcriptional regulation and control. According to the method, a foundation is laid for improving the copper resistance of the acidithiobacillus caldus through metabolic means such as transcriptional regulation and the like in the later period, so that the biological leaching of heavy metal ions of copper ore is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Medium-temperature ore-leaching composite microbial system used for leaching of chalcopyrite and ore leaching process
InactiveCN105802869AImprove environmental adaptabilityEasy to trainBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChalcopyriteFerroplasma
The invention provides a medium-temperature ore-leaching composite microbial system used for leaching of chalcopyrite and an ore leaching process. The medium-temperature ore-leaching composite microbial system is Acidithiobacillus caldus 0Y which has been preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), Wuhan University, China, on January 20th, 2011, with an accession number of CCTCC No. M2010356. The medium-temperature ore-leaching composite microbial system is composed of Acidithiomicrobium ferrooxidans (81%), Acidithiobacillus caldus (13%) and Ferroplasma sp (6%). The composite microbial system has high leaching efficiency and especially has good commercial application prospects in dump leaching processes for low-grade copper sulphide like chalcopyrite.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Method of performing traceless knockout and integration on gene of Acidithiobacillus caldus
InactiveCN102604929BMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionRestriction enzyme digestionPlasmid Vector
The invention discloses a method of performing traceless knockout on a chromogene or inserting an exogenous gene in a chromosome of Acidithiobacillus caldus. The method comprises the following steps: transferring a homologous recombinant plasmid containing plentiful restriction enzyme digestion sites of endonuclease I-SceI into the Acidithiobacillus caldus in a conjugation transfer manner, simultaneously, directionally inserting the homologous recombinant plasmid into the chromosome of Acidithiobacillus caldus by use of a homologous recombinant system of a cell itself, transferring a screened single crossover to an I-SceI expression plasmid by an electroporation method, performing secondary homologous recombination on a single recon chromosome under a stress that the I-SceI enzyme cuts the chromosome, and optimizing and screening a double crossover bacterial strain to realize knockout and insertion of the gene. The invention also constructs a suicide type plasmid vector pSDUDI for homologous recombination and a plasmid pSDU1-I-SceI for expressing the I-SceI enzyme effectively, and provides convenience for the traceless knockout and the integration of the chromogene in the Acidithiobacillus caldus. The method provided by the invention provides a new way for intensive study on and modification of Acidithiobacillus caldus.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
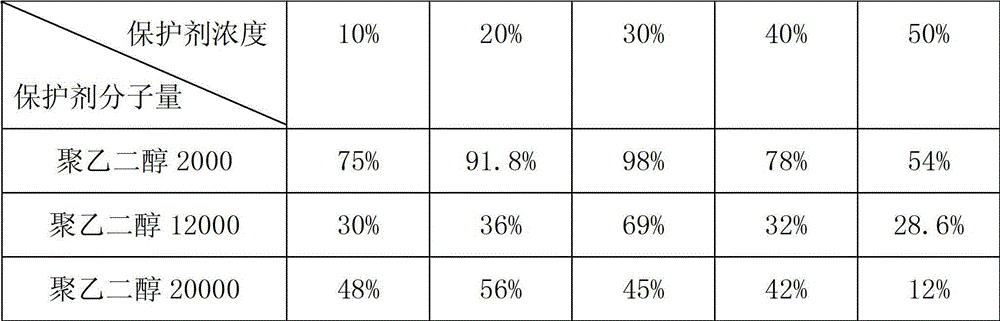
Application method of polyethylene glycol as acidithiobacillus caldus cryoprotectant
InactiveCN103074229AImprove survival rateMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationPolymer scienceGlycerol
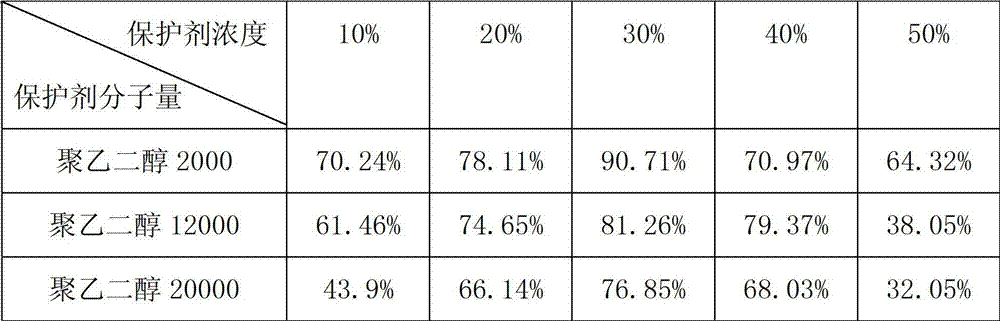
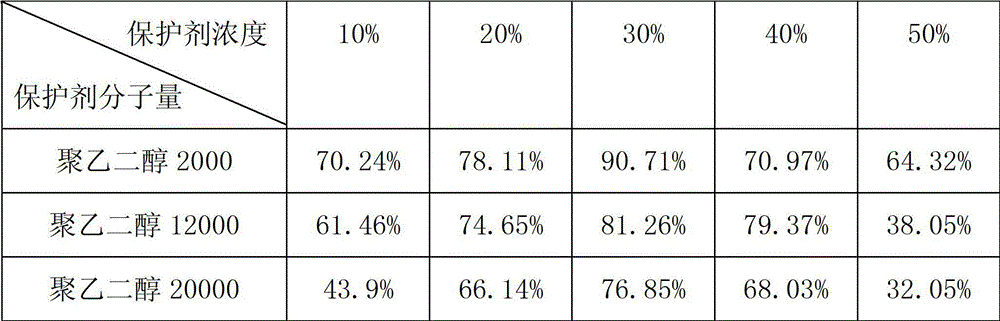
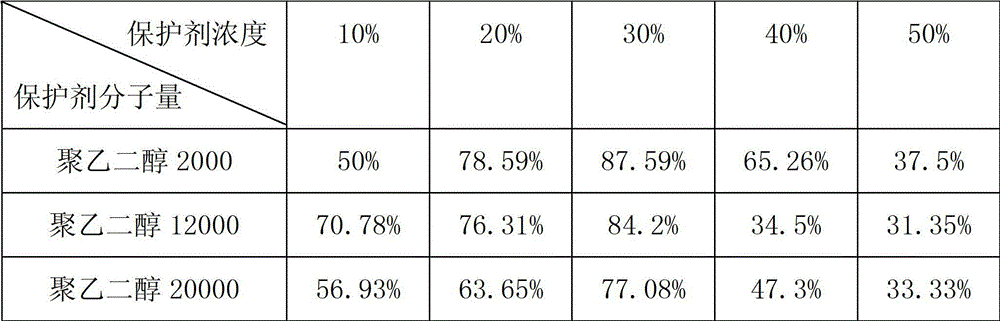
The invention discloses an application method of polyethylene glycol as an acidithiobacillus caldus cryoprotectant, belonging to the technical field of bacteria preservation. The application method disclosed herein is characterized by mixing a polyethylene glycol solution and an acidithiobacillus caldus bacterium suspension to obtain a mixed solution for cryopreservation, wherein the molecular weight of polyethylene glycol is 2000, 12000 or 20000, and the concentration of polyethylene glycol in the mixed solution is in a range of 10-50%(w / v). According to the invention, when acidithiobacillus caldus is subjected to liquid nitrogen preservation, the preservation effect of polyethylene glycol as the protector is obviously better than that of glycerol, and thus when acidithiobacillus caldus is subjected to liquid nitrogen preservation, polyethylene glycol as the protector can effectively improve a survival rate of acidithiobacillus caldus.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Strain of Acidithiobacillus caldus and culture medium and culture method thereof
ActiveCN107699511APromote growthIncrease acidityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMetal leaching
The invention belongs to the technical field of using microbes to treat heavy metal pollution, and discloses a novel strain (DX-csu) of Acidithiobacillus caldus, and a culture medium and a culture method thereof. The preservation number of Acidithiobacillus caldus DX-csu is CGMCC No.14008. The culture process has the advantages of low equipment requirements and simple and convenient operation. Thestrain has the advantages of quick growth and strong acid producing performance. The strain can well biologically convert cadmium that is combined with iron and manganese in soil and can be applied to high efficient metal leaching performed by microbes and environmental governance.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
A bioleaching method for strengthening chalcopyrite and bornite
The invention provides a method for strengthening biological leaching of chalcopyrite and bornite. One or more of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, acidithiobacillus caldus and leptospirillum ferriphilum are used as mineral leaching microorganisms. The ratio of the chalcopyrite to the bornite is controlled to be 5:1-1:5. In the leaching process, the stirring speed is controlled to be 100-600 rpm. The pH value of a solution is controlled to be 1.5-2.5, the electric potential of the solution is 350-480 mV (Ag / AgCl is a reference electrode), the chalcopyrite and the bornite can be leached in a cooperative mode, and the Cu leaching rate is obviously increased. According to the method, through reasonable ore blending of the chalcopyrite and the bornite, proper leaching technological conditions are controlled, and the biological leaching efficiency of the chalcopyrite and the bornite is improved. The method is efficient, simple and easy to operate.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A kind of method for removing hydrogen sulfide in biogas by thermophilic acid thiobacillus
ActiveCN106635210BStrong oxidation abilityLess quantityGas treatmentBacteriaMicroorganismLiving cell
The invention discloses a method for removing hydrogen sulfide in methane by acidithiobacillus caldus. The method comprises the following steps of introducing to-be-treated methane into fermenting liquid of the acidithiobacillus caldus; removing the hydrogen sulfide in the methane by the fermenting of the acidithiobacillus caldus, wherein the fermenting temperature is 40 to 45 DEG C; the acidithiobacillus caldus is No. 1.7296 strain in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center; the number of live cells of strain in the fermenting liquid of the acidithiobacillus caldus is 2.0*10<6> to 10.0*10<6> per mL. The method has the advantages that the operation is convenient, the technological process is simple, the utilization value of resources is improved, the cost is reduced, the desulfurizing efficiency is high, and the like; the hydrogen sulfide in the methane is stably and efficiently removed, the utilization level of the methane is favorably improved, and the desulfurizing problem of the methane is solved.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Application method of polyethylene glycol as acidithiobacillus caldus cryoprotectant
InactiveCN103074229BImprove survival rateMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationPolymer sciencePolyethylene glycol
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A method for combined removal of hydrogen sulfide from biogas with iron-containing compound and mesophilic acidophilic thiobacterium
The invention discloses a method for removing hydrogen sulfide in biogas through combination of an iron-containing compound and Acidithiobacillus caldus. The method comprises 1) iron-containing compound desulfurization: adding an iron-containing compound along with fed materials into a biogas production reactor and carrying out synchronous biogas raw material fermentation and iron-containing compound desulfurization, and 2) biological desulfurization: feeding the biogas subjected to iron-containing compound desulfurization into the fermentation liquid of Acidithiobacillus caldus, detecting hydrogen sulfide content of the biogas and collecting the biogas when the hydrogen sulfide content satisfies the standard. The method has high desulfurization efficiency and reduces the cost and workload of later desulfurization processes. After the combined removal, the hydrogen sulfide content of the biogas is less than 5ppm and more preferably less than 1ppm so that it is proved that the hydrogen sulfide is substantially completely removed.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Electroporation method of thermophilic thiobacillus
InactiveCN101372695BEfficient electroconversion methodBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionCapacitanceGene delivery
The invention discloses an electro-transformation method for inducing a constructed plasmid containing exogenous genes to acidithiobacillus caldus. The method comprises the following steps: the constructed plasmid containing the exogenous genes is extracted and the concentration of the plasmid is corrected; the competent cells of the acidithiobacillus caldus are cultured and collected; the electro-transformation and plate screening are carried out, and positive transformants are identified and detected; wherein, the electro-transformation parameters are as follows: the voltage is 10,500V / cm, the resistance is 400 omega and the capacitance is 25muF. By adopting the method, the electro-transformation of the acidithiobacillus caldus is realized for the first time, and a recovery culture scheme and a screening method for the cidithiobacillus caldus are established, which provides a convenient, quick and high-efficiency gene delivery method for the studies of genetic engineering breeding, genetics and molecular biology of the acidithiobacillus caldus.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A Strain of Acidophilus Thiobacillus and Its Application
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of medium-temperature leaching ore composite bacterial system and leaching process for chalcopyrite leaching
InactiveCN105802869BImprove environmental adaptabilityEasy to trainBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChalcopyriteMetallurgy
The invention provides a medium-temperature ore-leaching composite microbial system used for leaching of chalcopyrite and an ore leaching process. The medium-temperature ore-leaching composite microbial system is Acidithiobacillus caldus 0Y which has been preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), Wuhan University, China, on January 20th, 2011, with an accession number of CCTCC No. M2010356. The medium-temperature ore-leaching composite microbial system is composed of Acidithiomicrobium ferrooxidans (81%), Acidithiobacillus caldus (13%) and Ferroplasma sp (6%). The composite microbial system has high leaching efficiency and especially has good commercial application prospects in dump leaching processes for low-grade copper sulphide like chalcopyrite.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
A method for improving metal ore leaching rate and its special bacterial strain
ActiveCN103667131BAcid resistantEliminate passivationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetallurgical slagAlicyclobacillus sp.
The present invention discloses a method for increasing a metal ore leaching rate, and a special strain thereof. According to the present invention, Alicyclobacillus sp. SJ-68 is provided, the preservation number is CGMCC No.7682, and a bacterial agent for leaching the target metal from metal ore is further provided, and comprises Alicyclobacillus sp. SJ-68 described in the claim 1 and Acidithiobacillus caldus SM-1 described in the claim 1; and experiment results prove that the Alicyclobacillus sp. SJ-68CGMCC No.7682 can be separately used for leaching the valuable metal in the sulphide ore or be synergistically used with other strains so as to co-leach the valuable metal in the sulphide ore, can be used for deepening extraction of noble metals or rare metals in sulphide ore concentrates, abandoned mine, lean ore, metallurgical slag and difficultly-treated complex sulphide ores, and has important industrial application prospects in the biological mineral leaching field.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for extracting copper from waste circuit boards by using moderately thermophilic bacteria
ActiveCN104328283BEfficient separationReduce processingProcess efficiency improvementRaffinateCulture mediums
The invention relates to a method for extracting copper in waste printed circuit boards by virtue of moderately thermophilic bacteria. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out shaker hydraulic sorting on the artificially dismounted and pulverized waste printed circuit boards to obtain metal and waste residues; putting the waste residues into an improved 9K culture medium, adjusting the pH value to 2 and leaching with a mixed strain of leptospirillum ferriphilum, acidithiobacillus caldus, sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans and thermoacidiferriphile as a leaching strain to obtain a copper-enriched solution and leaching residues; filtering the copper-enriched solution with a hollow fiber membrane system to obtain the strain and a copper-containing filtrate and putting the strain again into the leaching system for repeatedly using; and extracting the copper-containing filtrate with hydroxy oxime and a hydroxy oxime complex Lix984 as extraction agents to obtain a copper-loaded organic phase and a raffinate, carrying out back extraction on the copper-loaded organic phase with a 10-30% sulfuric acid solution to obtain a back extract and a blank organic phase and carrying out electrodeposition on the back extract to obtain cathode copper and an electrodeposited barren liquid. By the method disclosed by the invention, the environment-friendly, economic and full-value recovery of the waste printed circuit boards is achieved and the method has the advantages of short flow, low investment, high efficiency and low treatment cost and is suitable for the recovery of all types of the waste printed circuit boards.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Intermediate-temperature mineral leaching composite microbial system for leaching copper pyrites
InactiveCN103173356BImprove environmental adaptabilityEasy to trainBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyriteFerroplasma
The invention provides an intermediate-temperature mineral leaching composite microbial system for leaching copper pyrites. The composite microbial system is named Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans 6Y-1, is preserved in the China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) in Wuhan University in November 10th 2010, and has a preservation number of CCTCC M2010297. The composite microbial system consists of 77% of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, 5% of Acidithiomicrobium sp, 12% of Acidithiobacillus caldus and 6% of Ferroplasma sp. The microbial system has high copper pyrite leaching efficiency.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Rust remover and use method thereof
PendingCN114250476AReduce storageReduce riskBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThiobacillus ferrooxidans
The invention discloses a rust remover and a use method thereof. The rust remover comprises (a) metabolites of microorganisms; or (b) a microorganism and a microorganism culture solution; wherein the microorganisms comprise thiobacillus thiooxidans and / or acidithiobacillus caldus. According to the scheme, the metabolite produced by culturing the microorganisms in the microorganism culture solution contains sulfuric acid, the sulfuric acid can react with the metal oxide and the corrosion layer, so that the metal oxide and the corrosion layer generate ions to be dissolved, and compared with direct use of the sulfuric acid, three wastes produced by mass production of the sulfuric acid are avoided; therefore, the pollution to the environment and the danger of storage and transportation of sulfuric acid are reduced.
Owner:HUBEI ENG UNIV
Application of a Strain of Thermophilic Thiobacillus
ActiveCN107090423BPromote growthIncrease acidityBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismManganese binding
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial control of heavy metal pollution, and discloses the application of a thermophilic acid thiobacillus, specifically the application of a new strain DX-csu in Acidithiobacillus caldus. The preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.14008; naming For Acidithiobacillus caldus. The Acidithiobacillus caldus bacterium of the invention has a good biotransformation effect on the cadmium in the iron-manganese bonded state in the soil, and provides technical guidance for efficient metal leaching by microorganisms, environmental treatment and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com