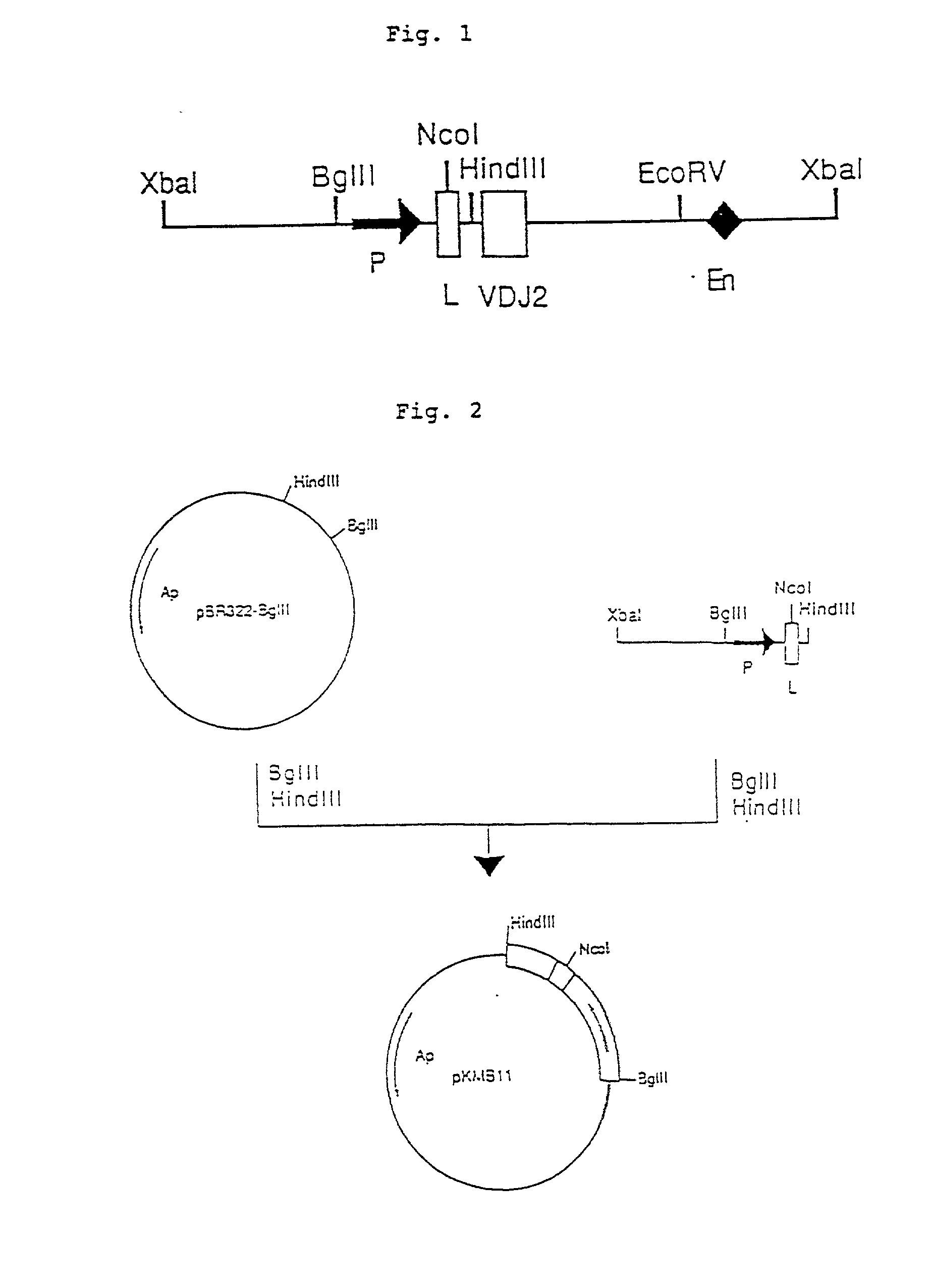
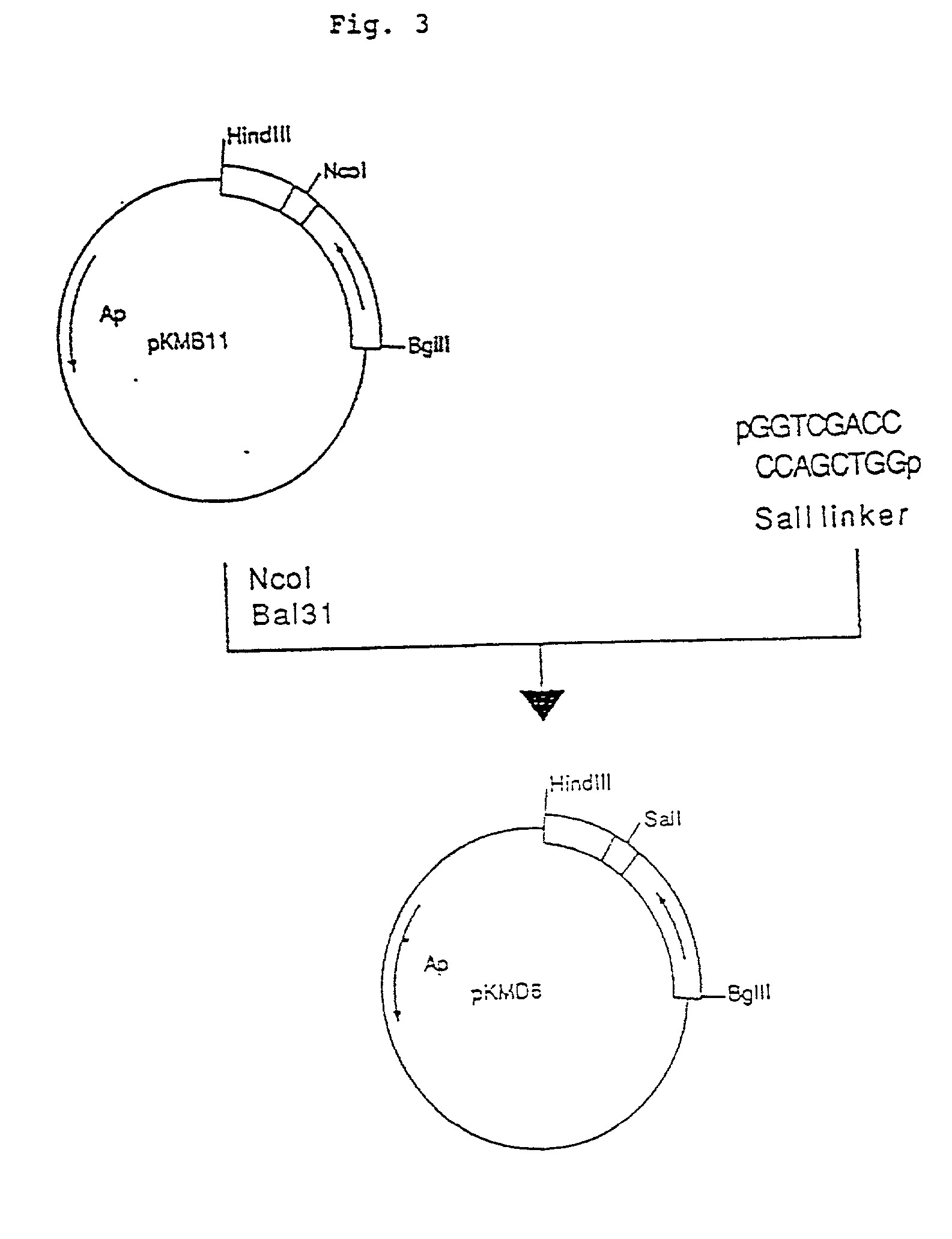
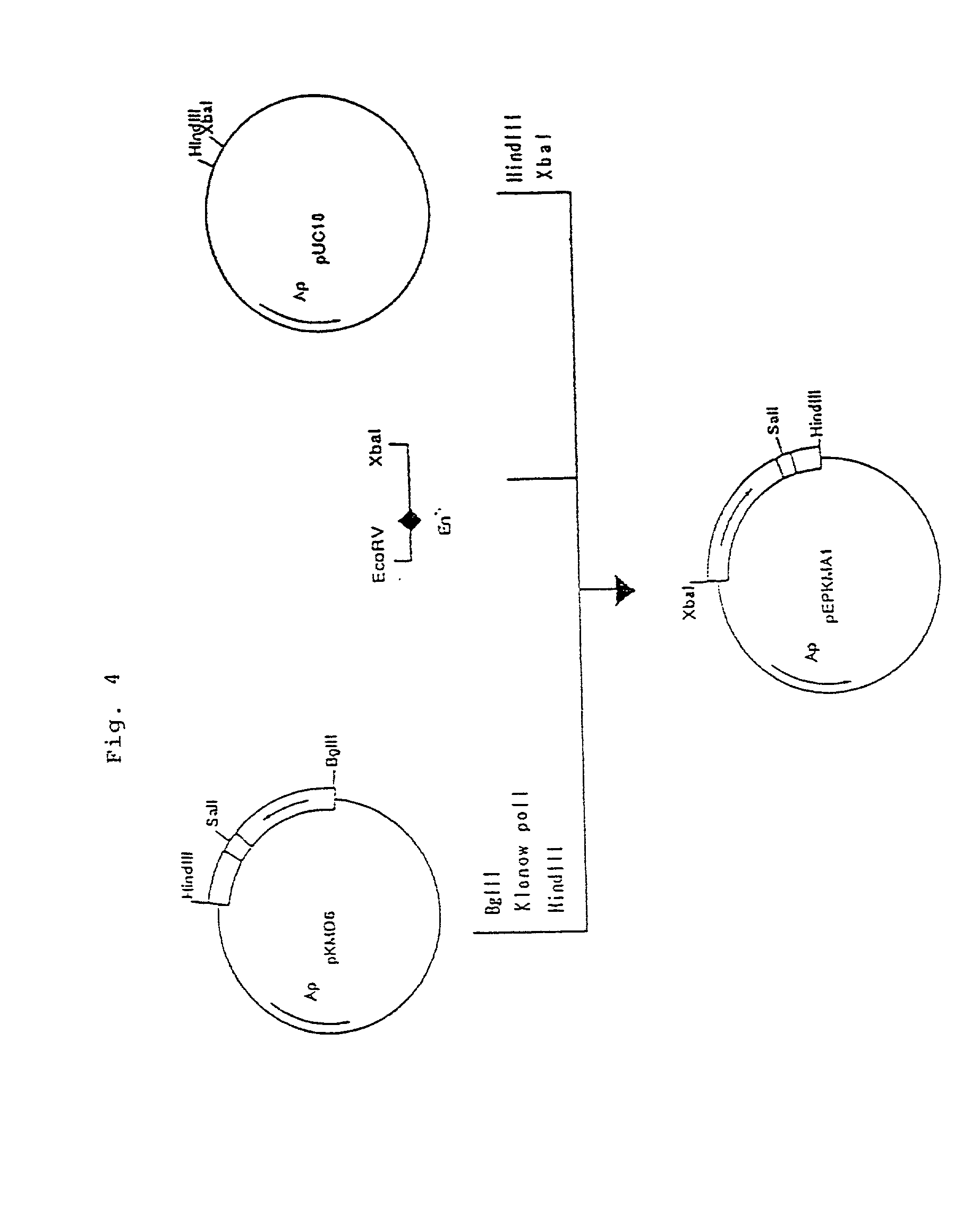
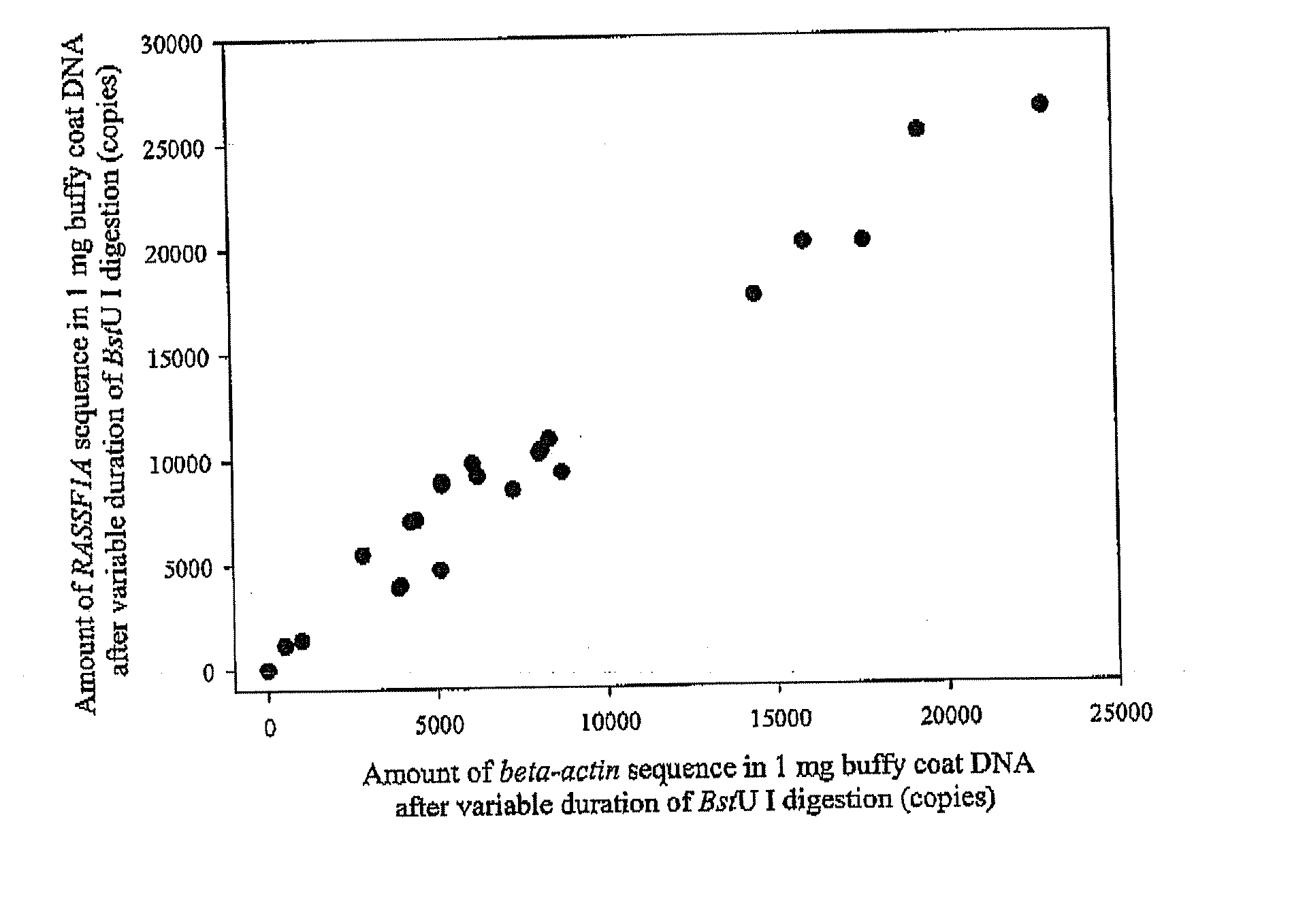
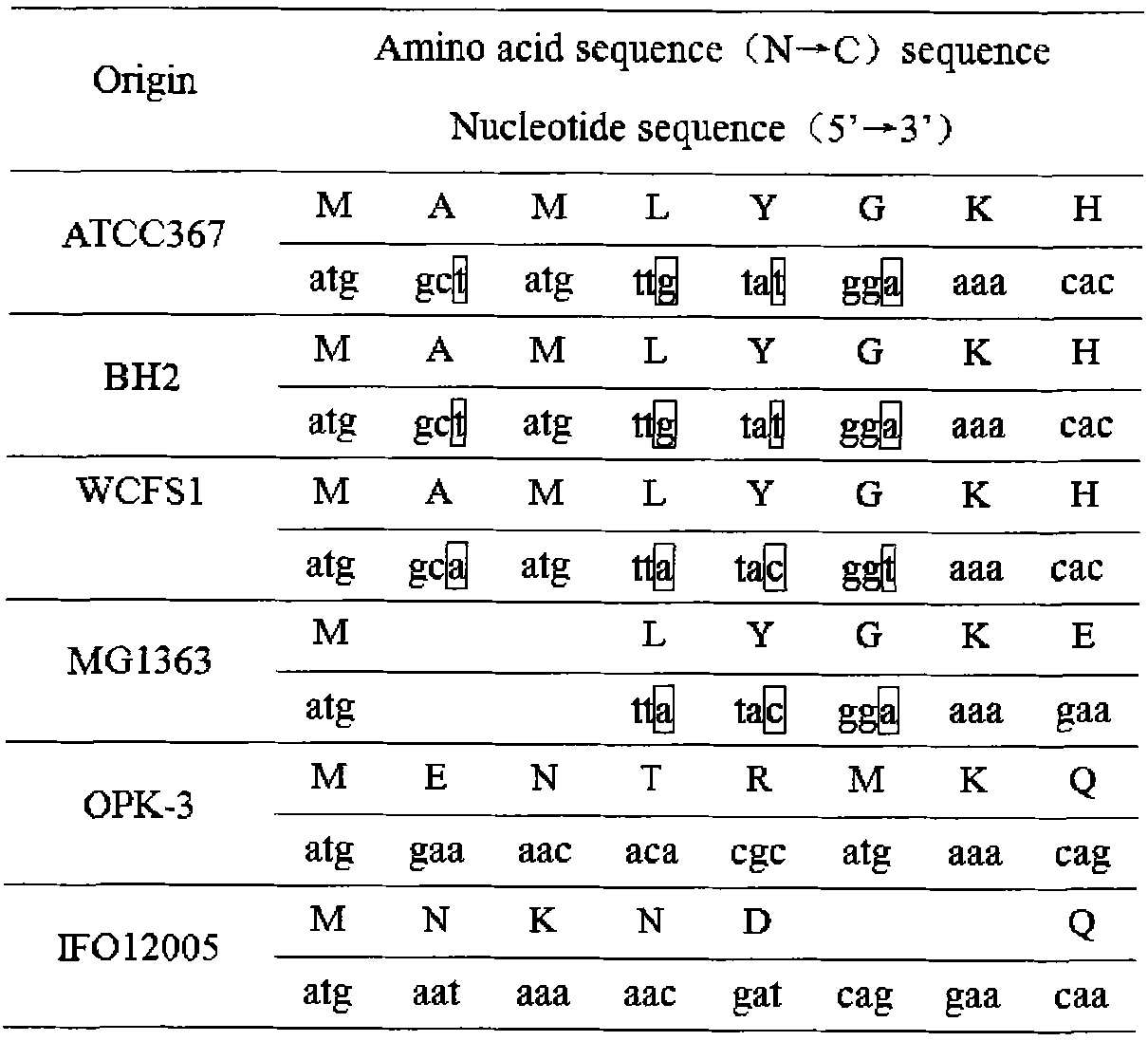
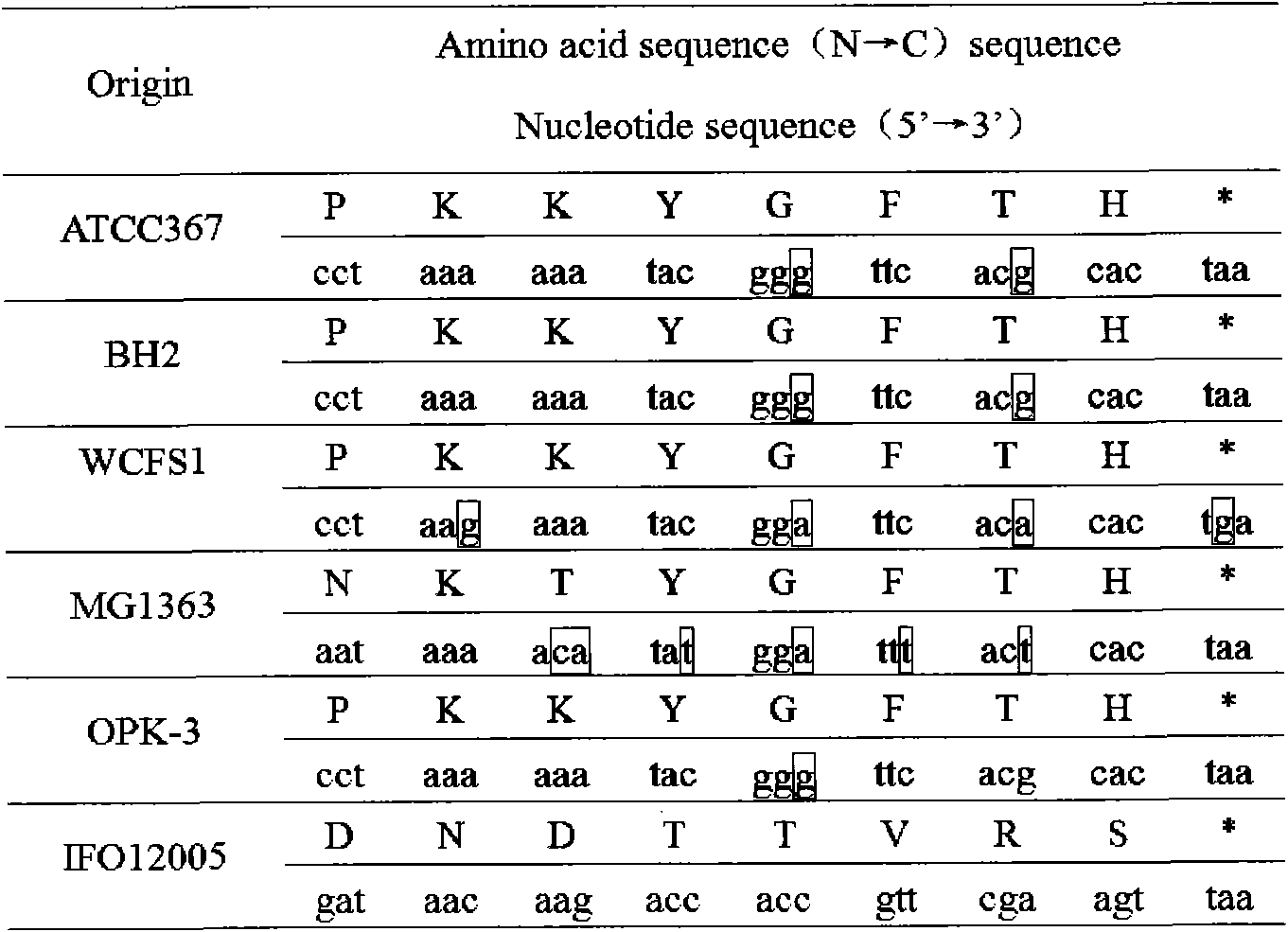
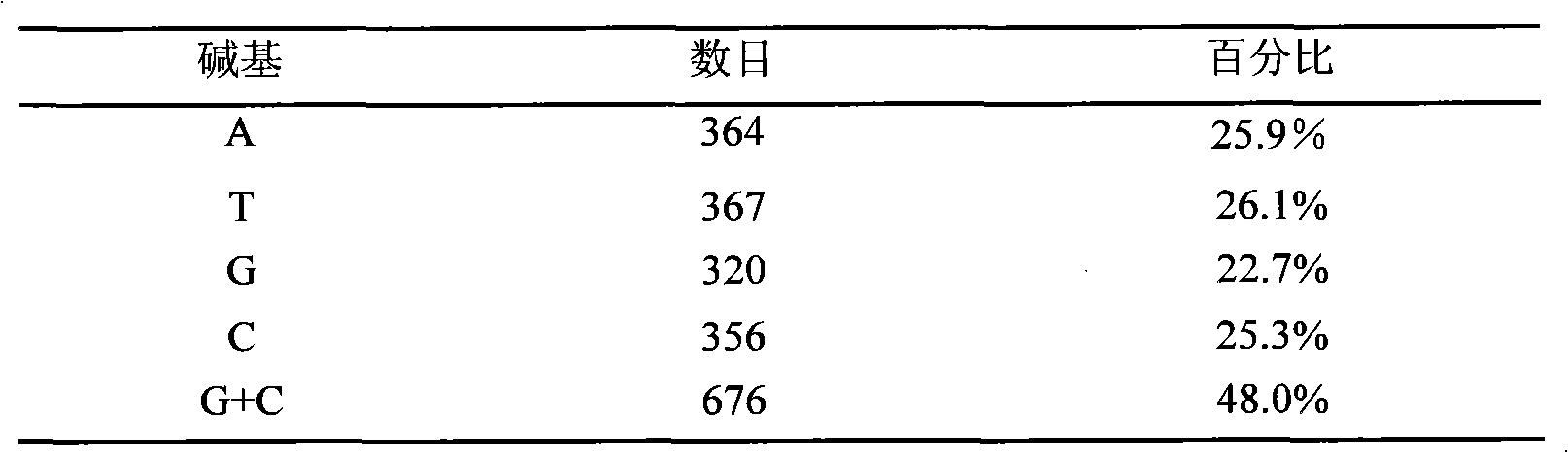
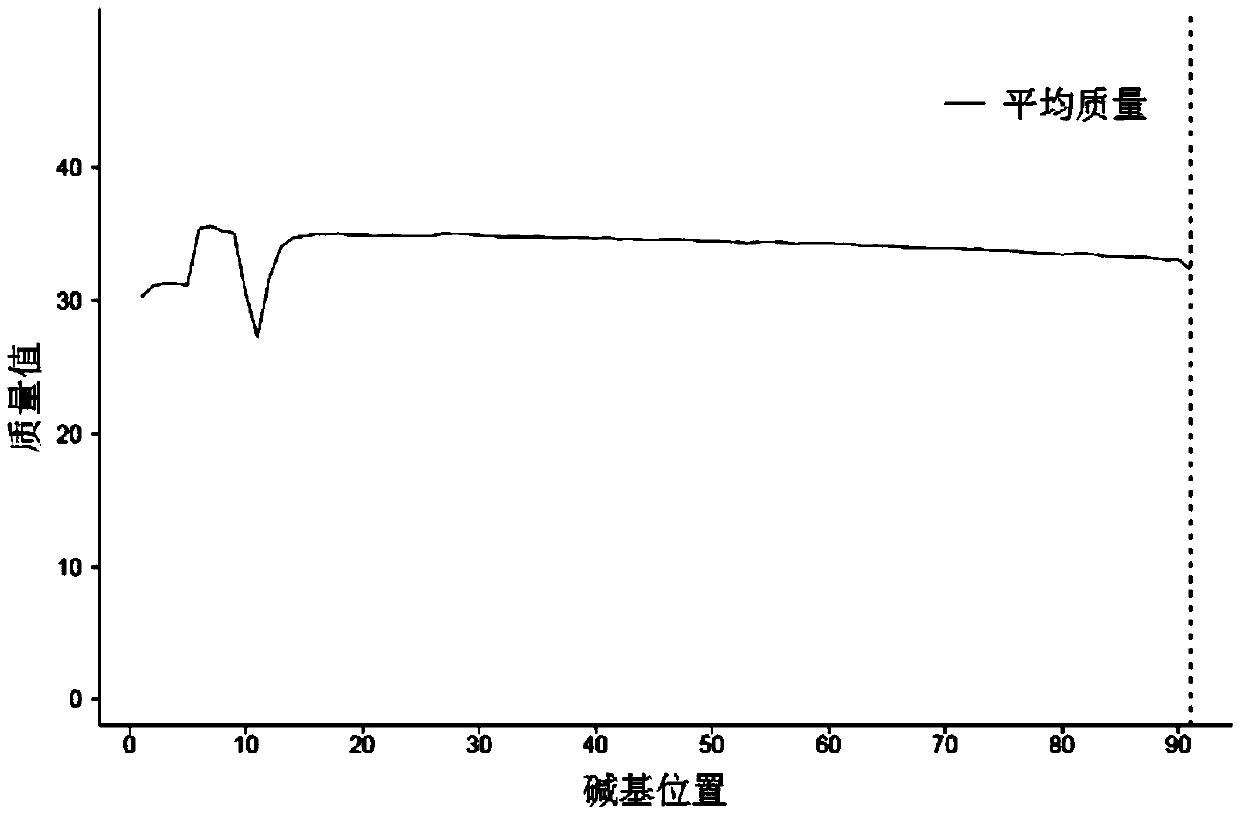
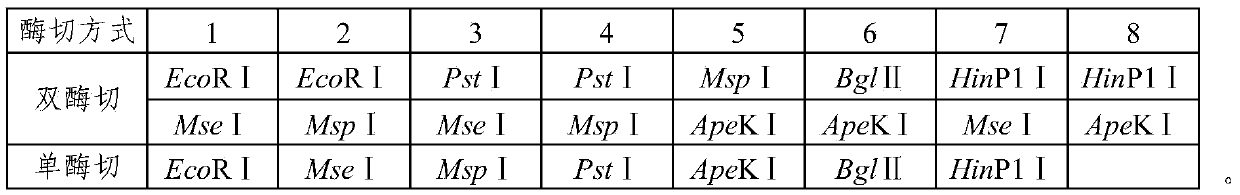
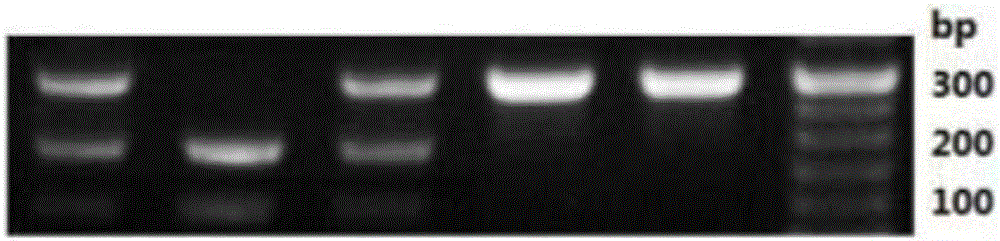
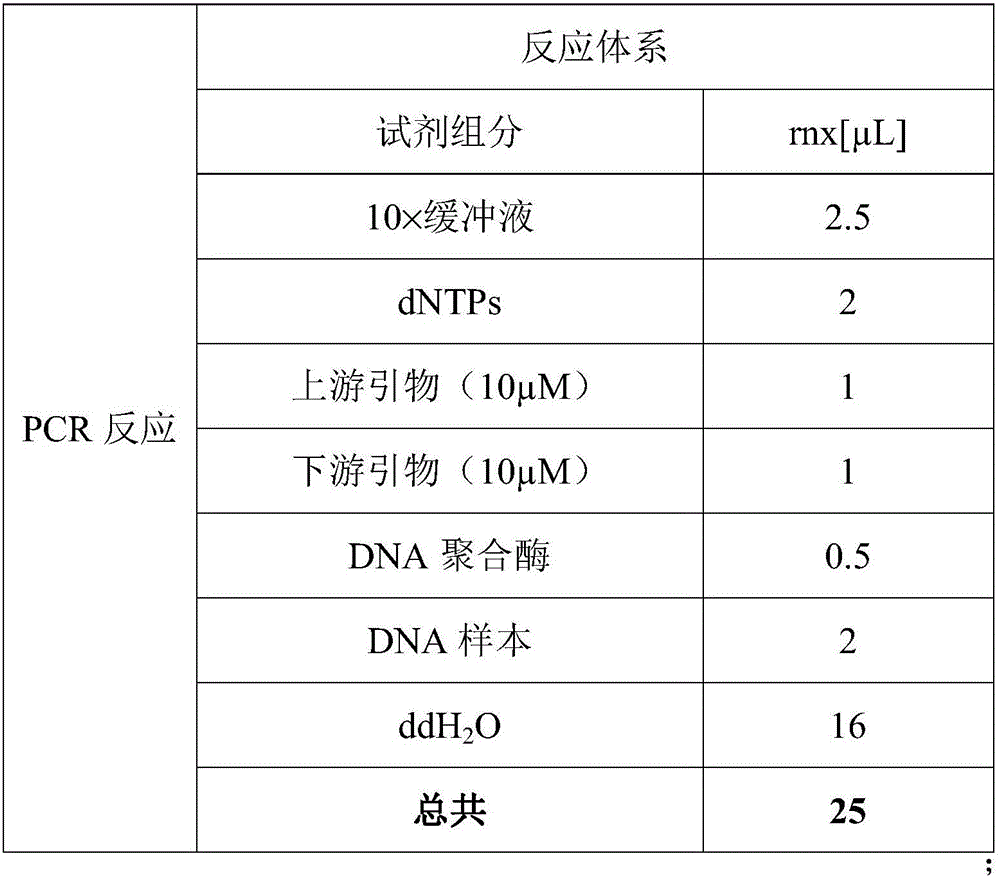
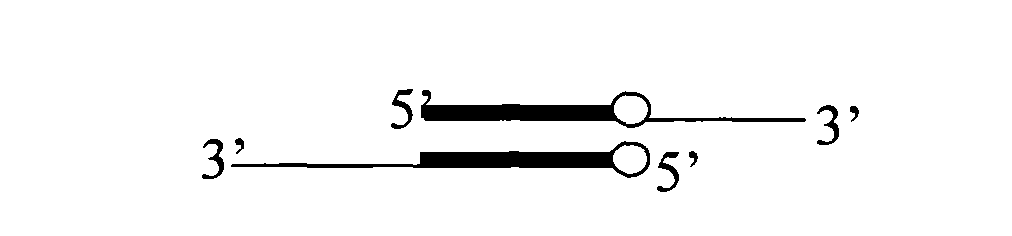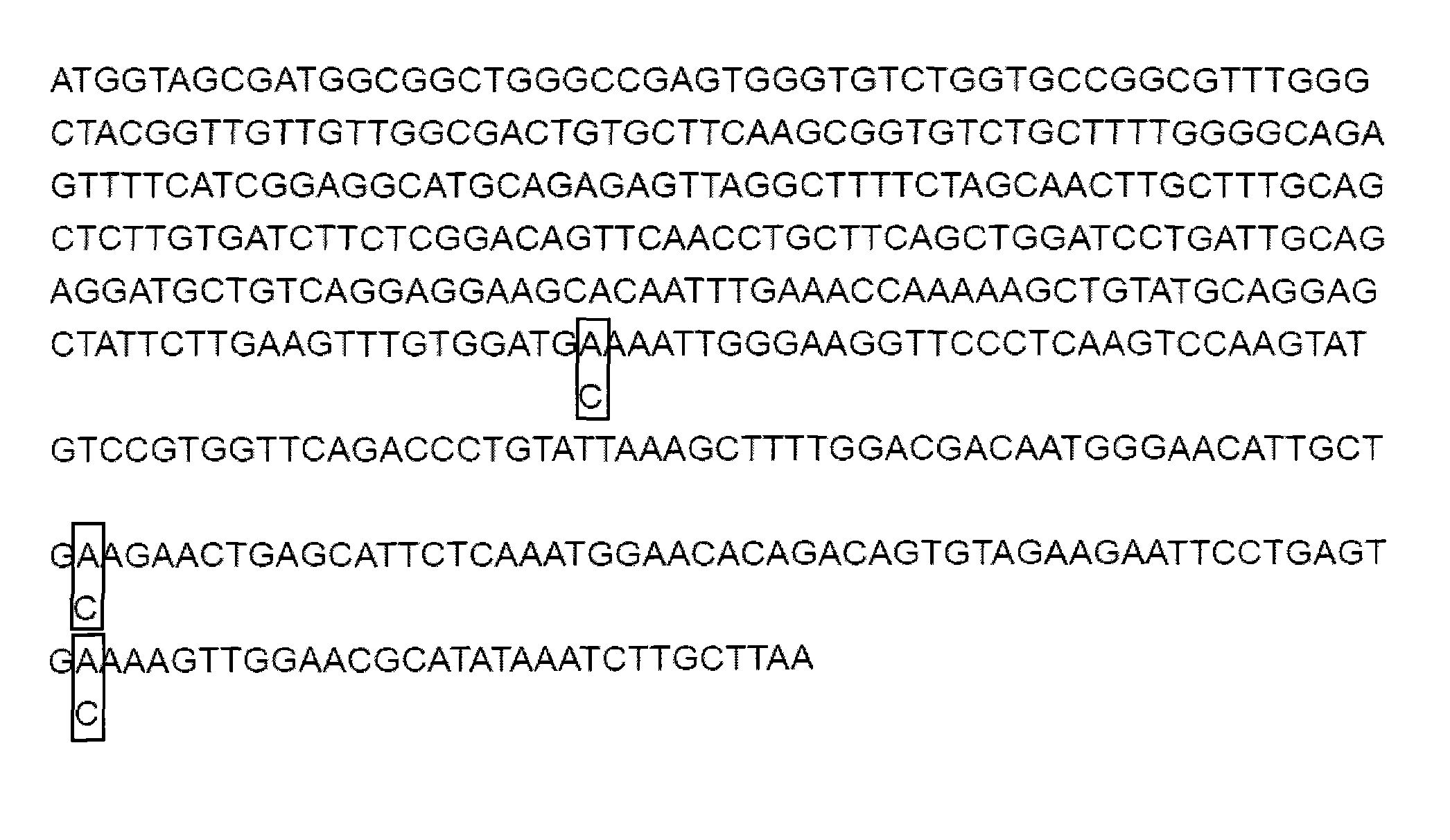Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
173 results about "Restriction enzyme digestion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
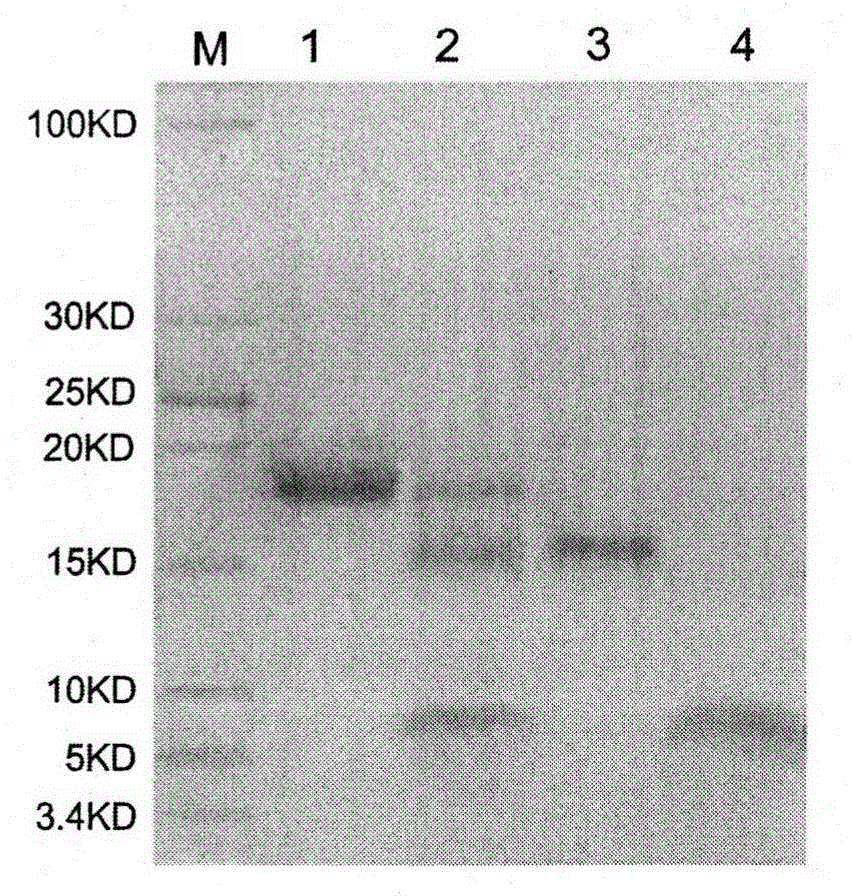
1 µL each restriction enzyme. 15 µL sterile water. Incubate the reaction at digestion temperature (usually 37°C) for 1 hour. Stop the digestion by heat inactivation (65°C for 15 minutes) or addition of 10mM final concentration EDTA. The digested DNA is ready for use in research applications.
Methods and kits for selectively amplifying, detecting or quantifying target DNA with specific end sequences
ActiveUS20090061425A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationPlasma samplesRestriction enzyme digestion
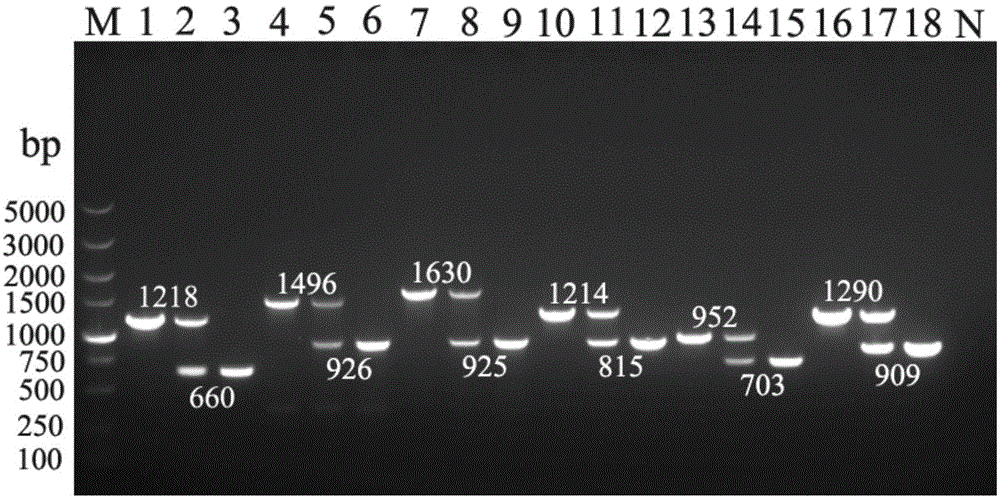
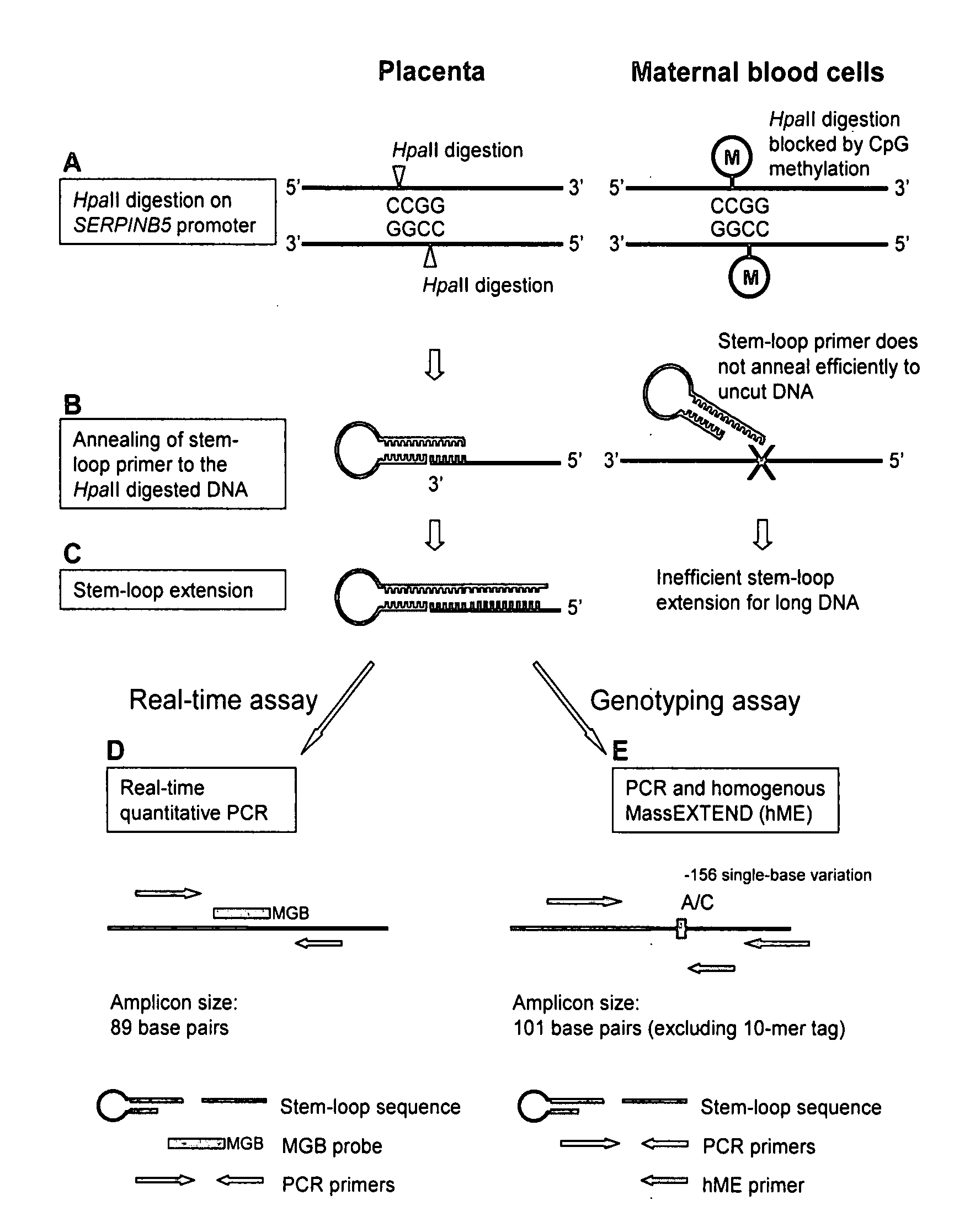
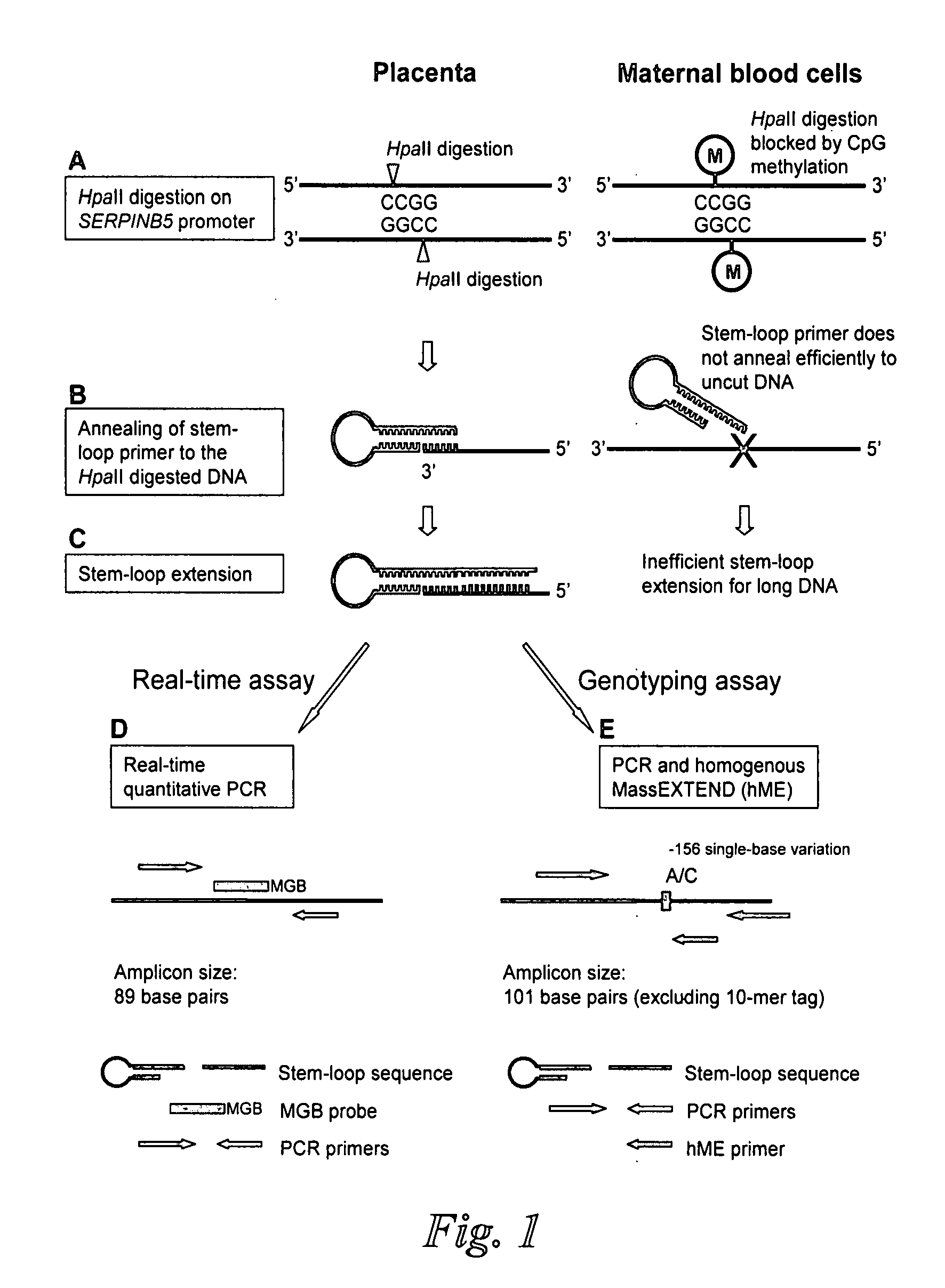
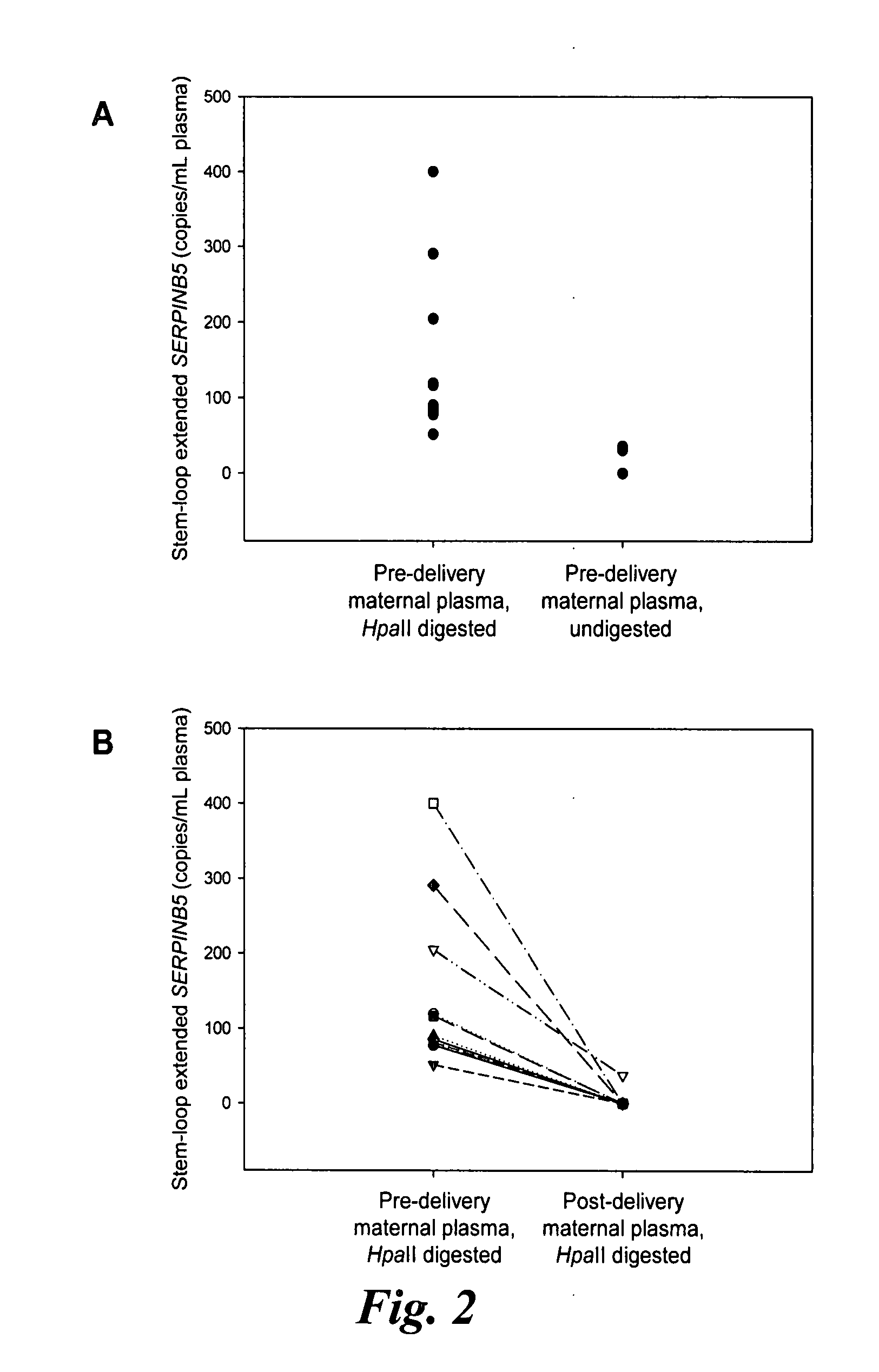
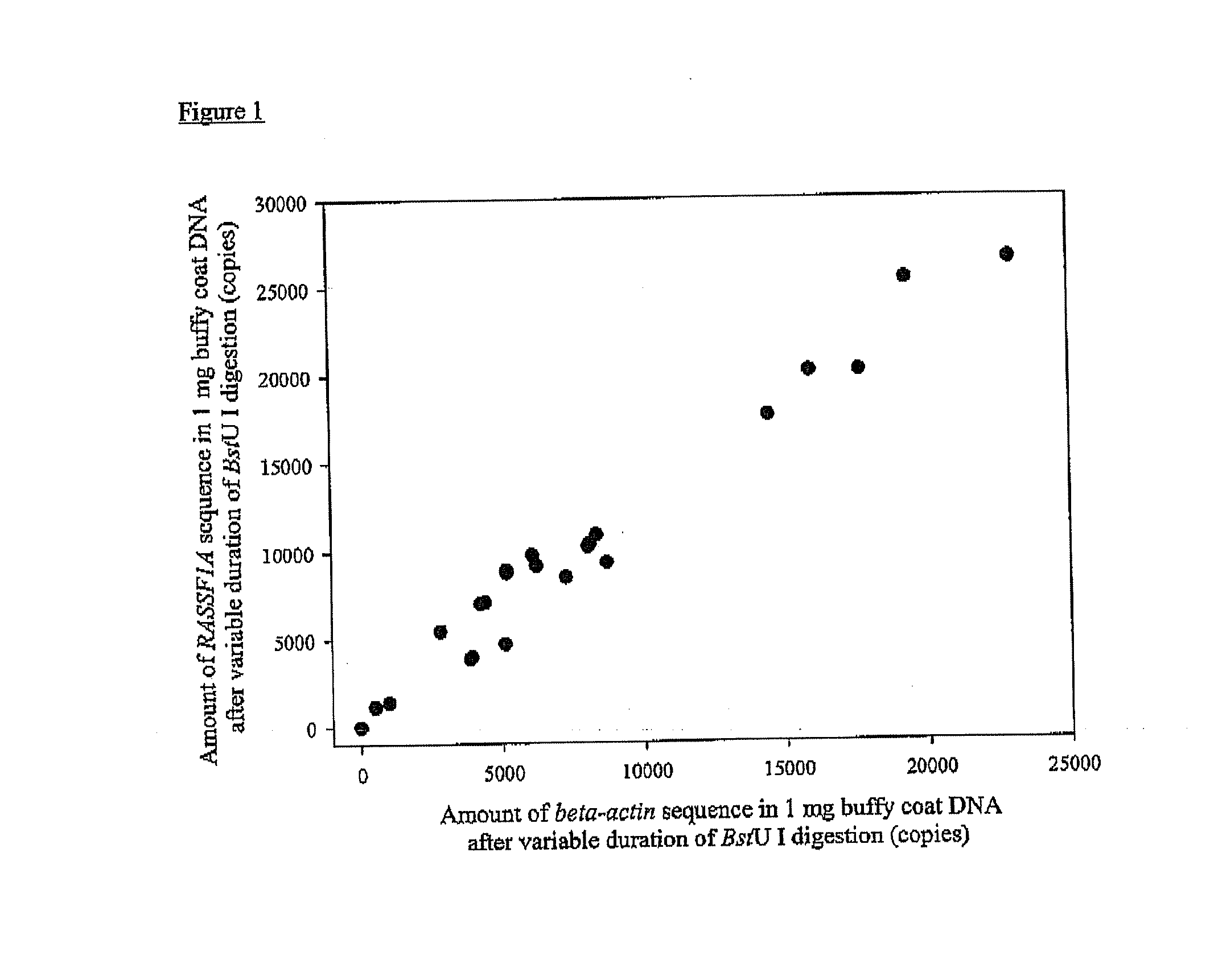
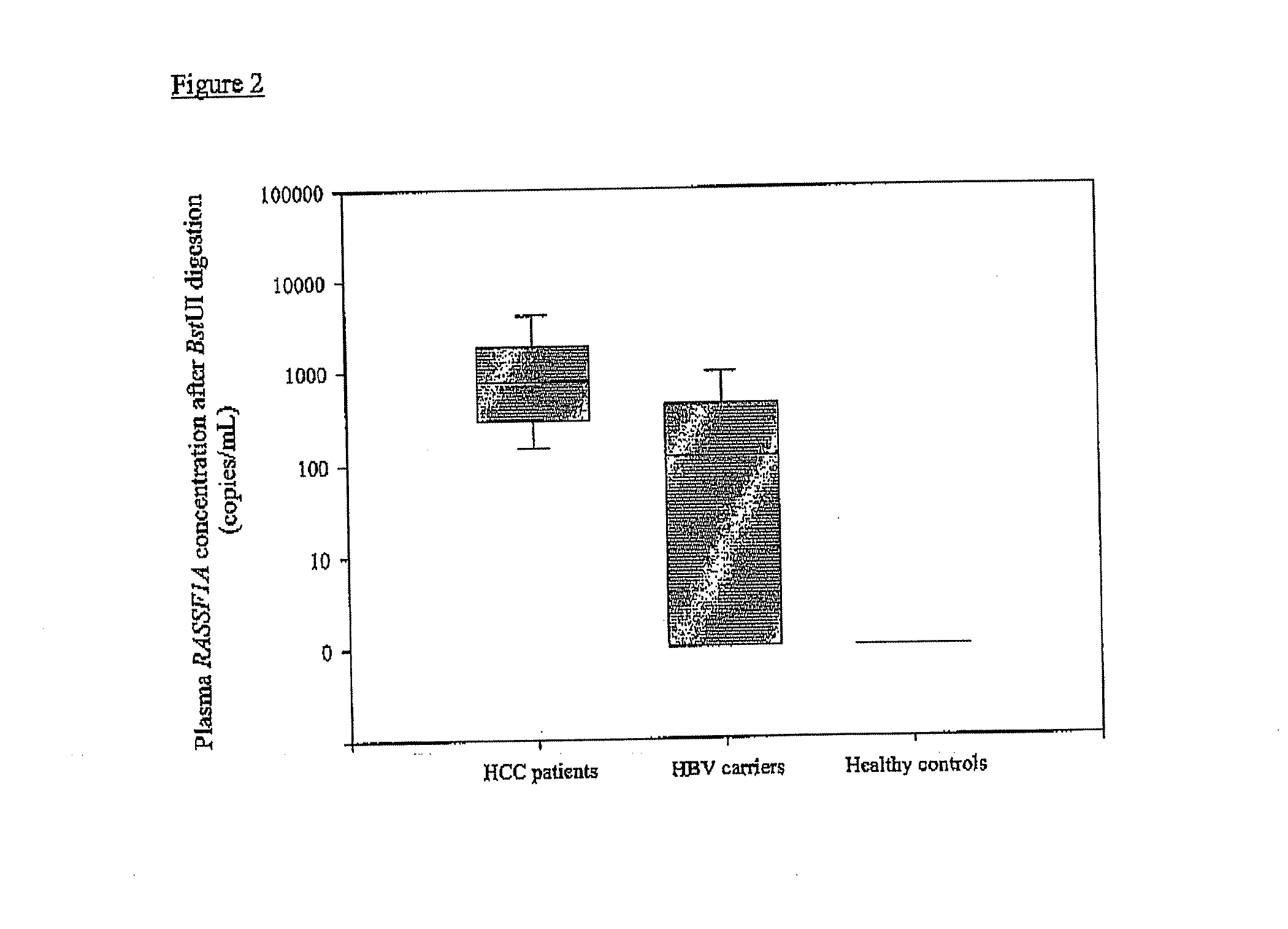
Disclosed herein are methods and kits for selectively amplifying, detecting or quantifying a DNA fragment with a specific end sequence, especially generated following restriction enzyme digestion. This method can be used, for example, to detect a hypomethylated DNA fragment. This methods and kits are especially useful in detecting or quantifying a hypomethylated fetal DNA fragment in a maternal plasma sample containing a corresponding hypermethylated maternal DNA fragment.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG +1
Circular chromosome conformation capture (4C)
ActiveUS8642295B2High throughput analysisAccurate mappingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionRestriction enzyme digestion
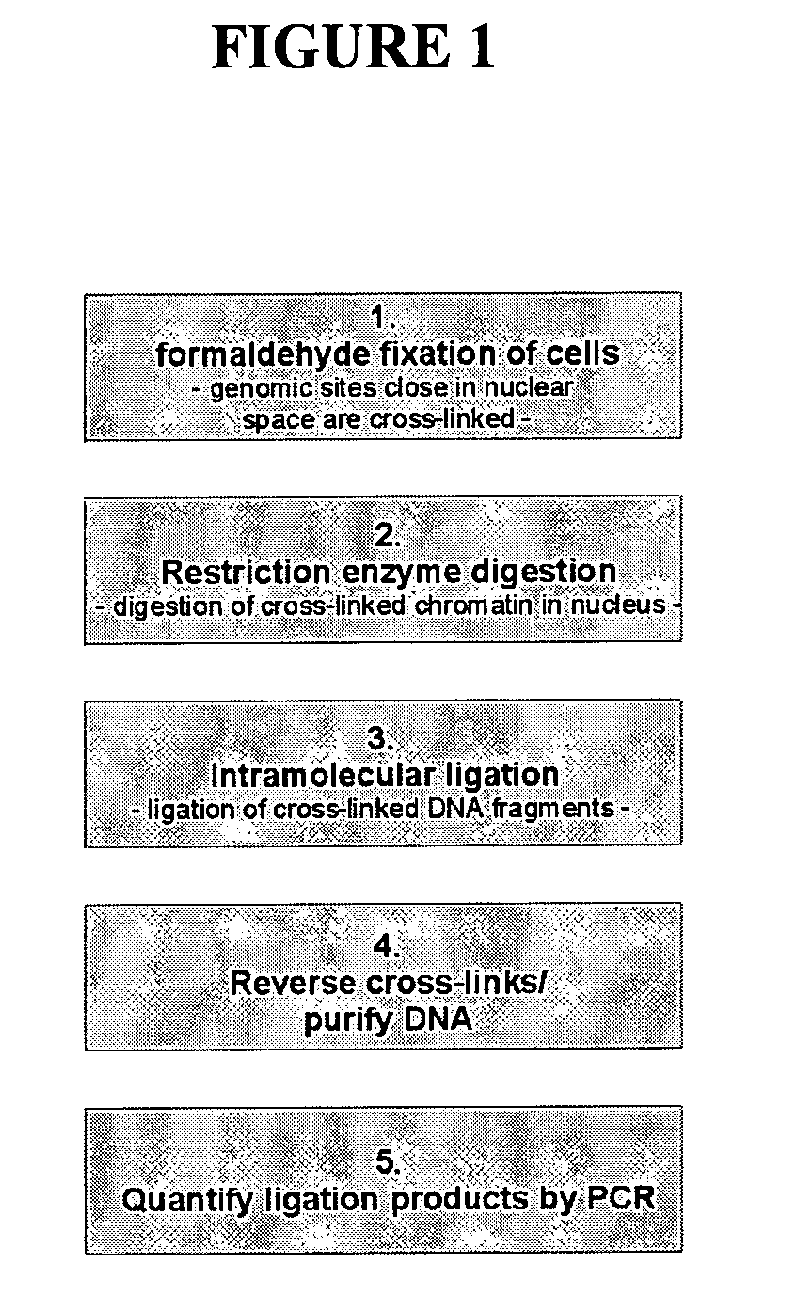
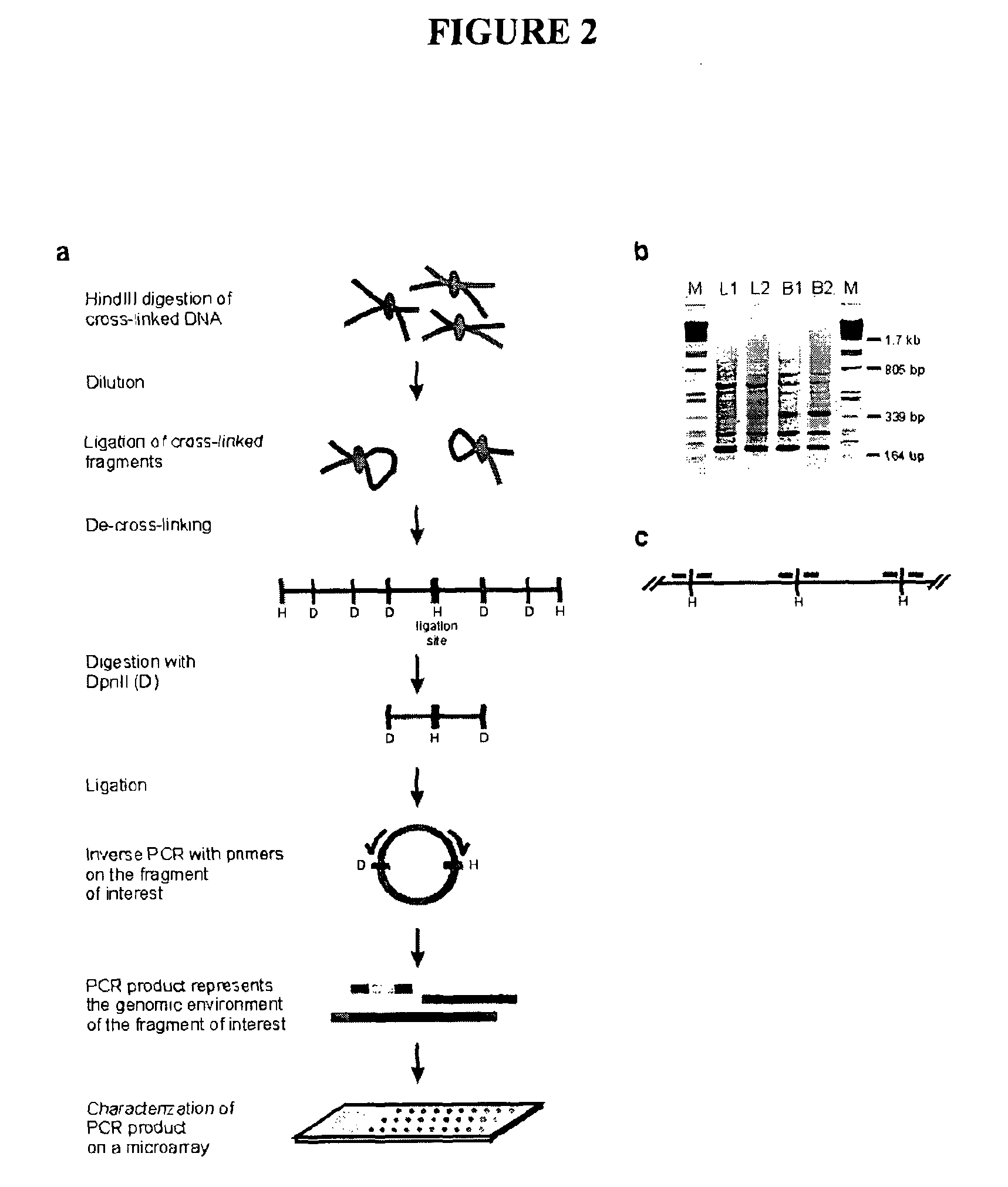
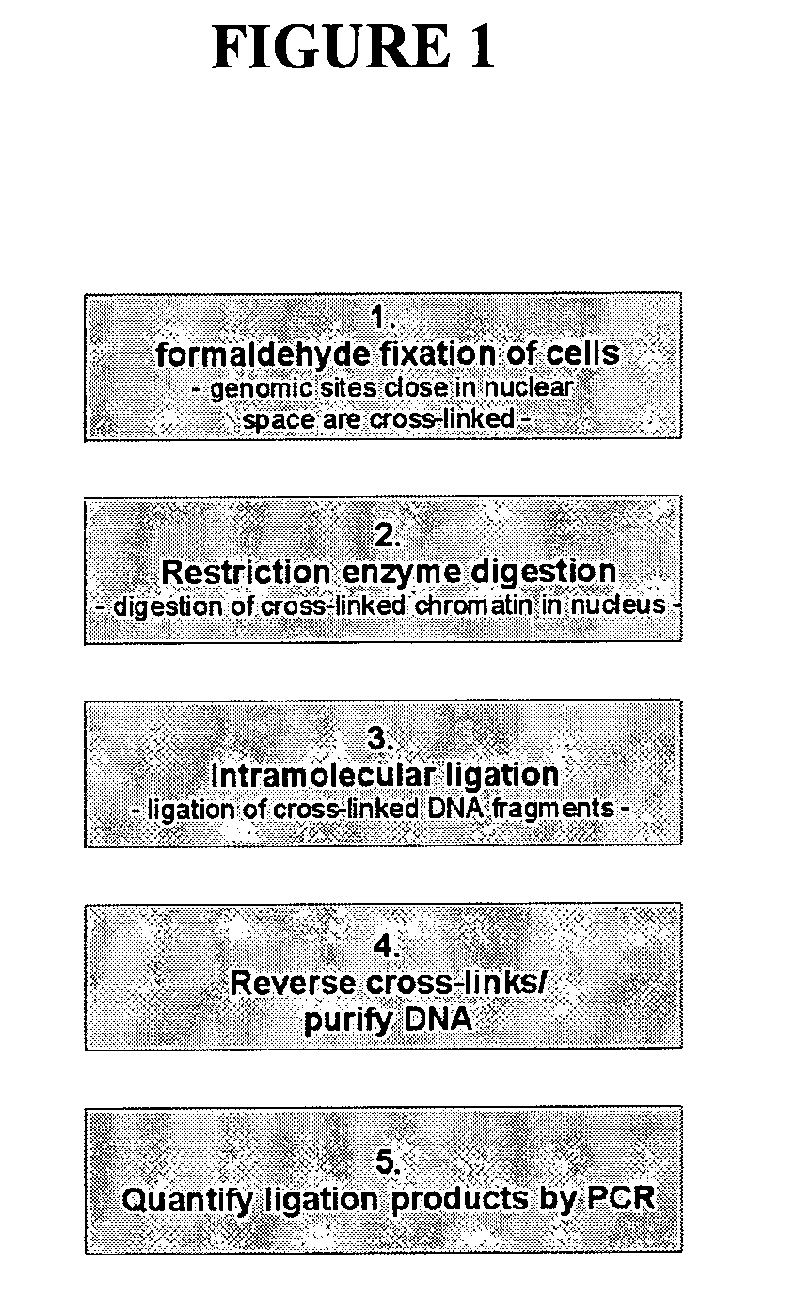
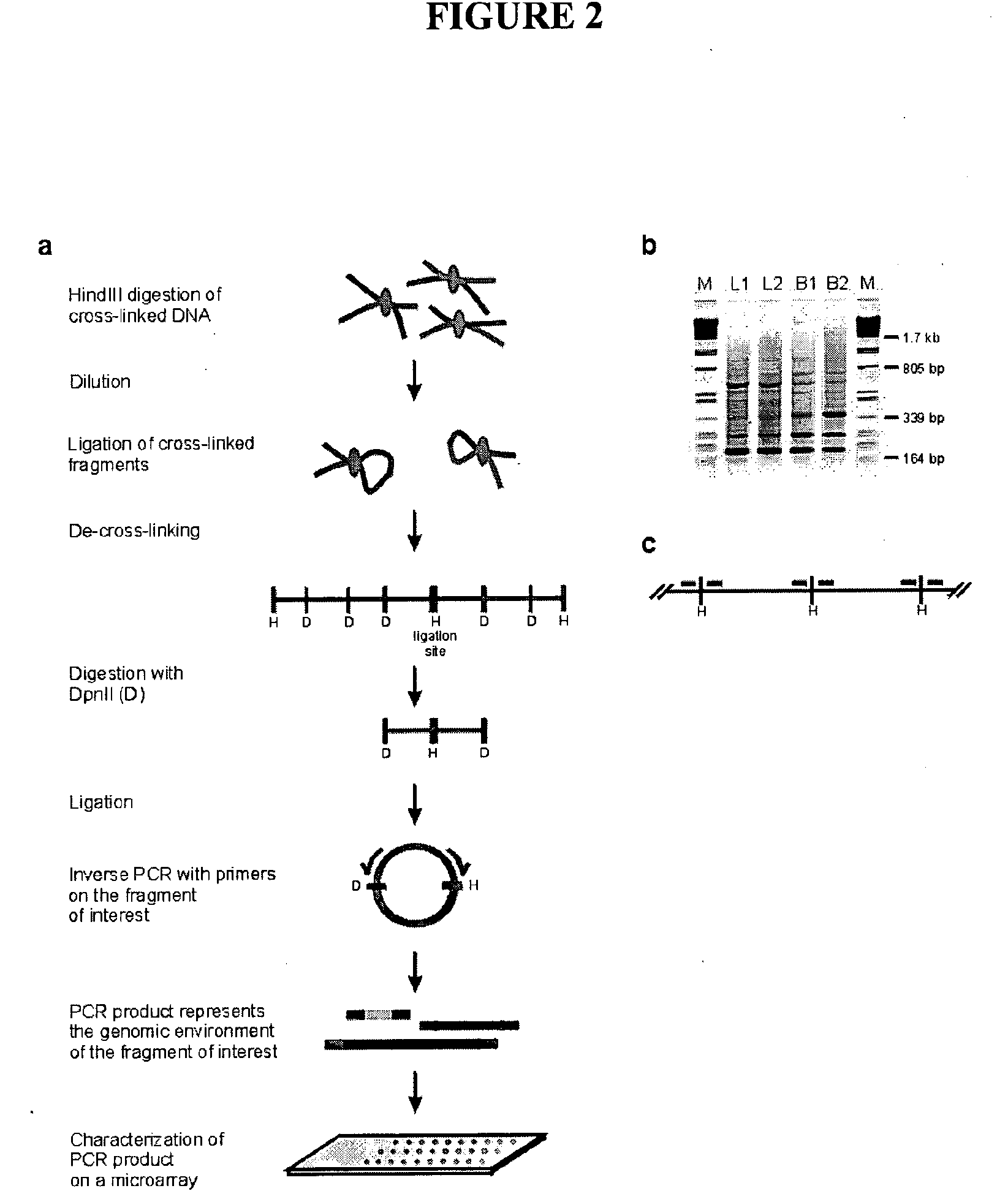
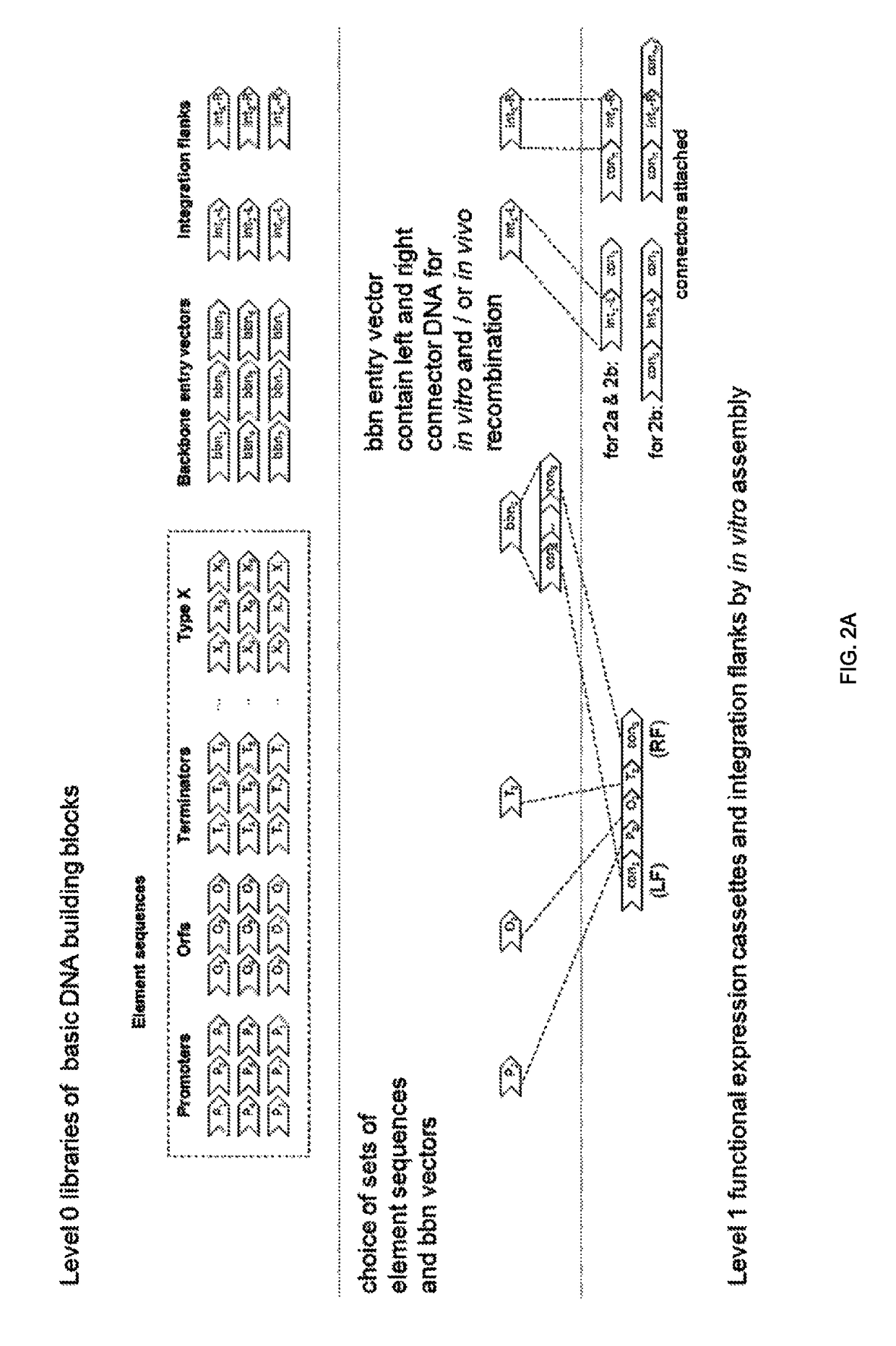
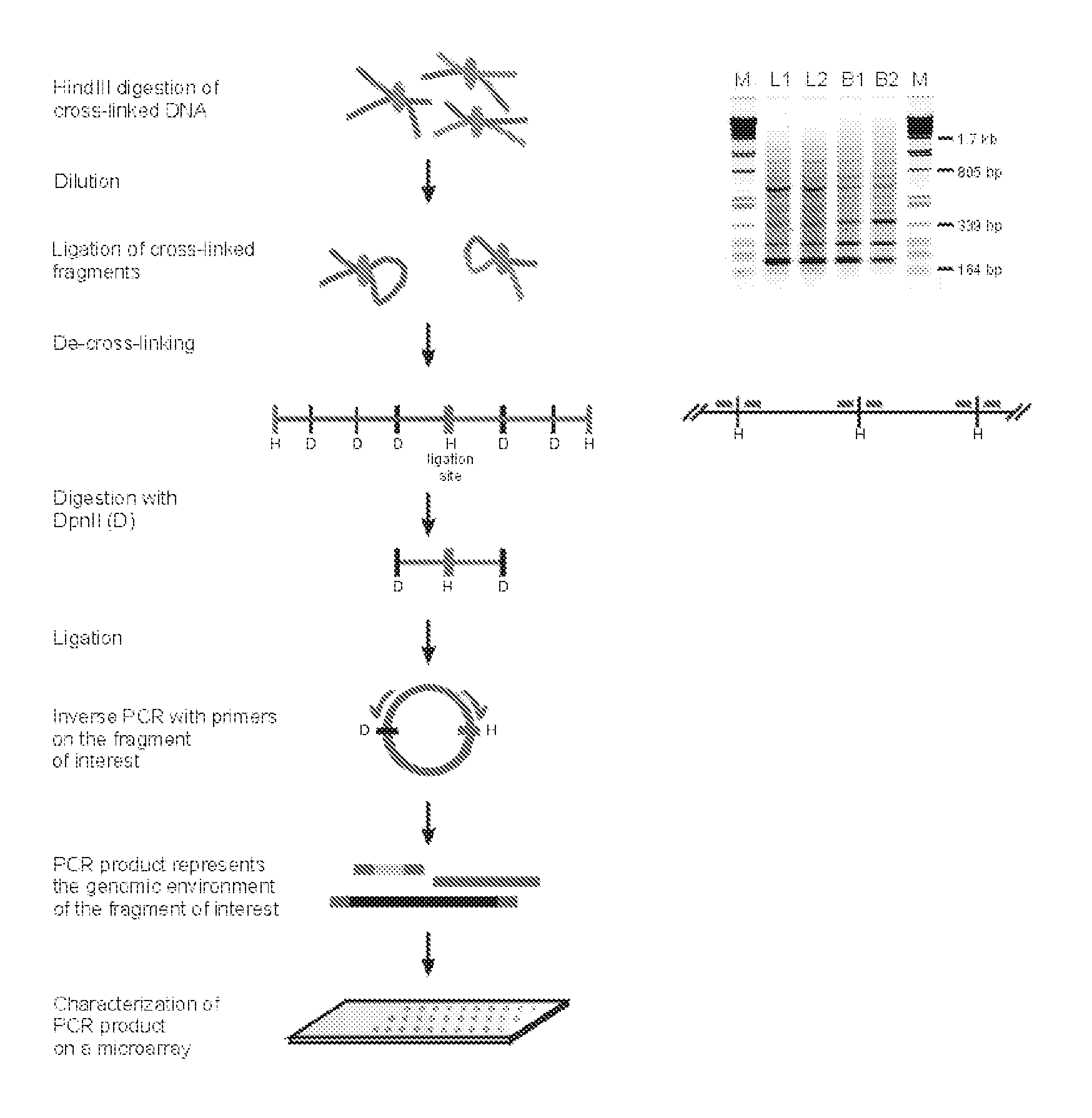
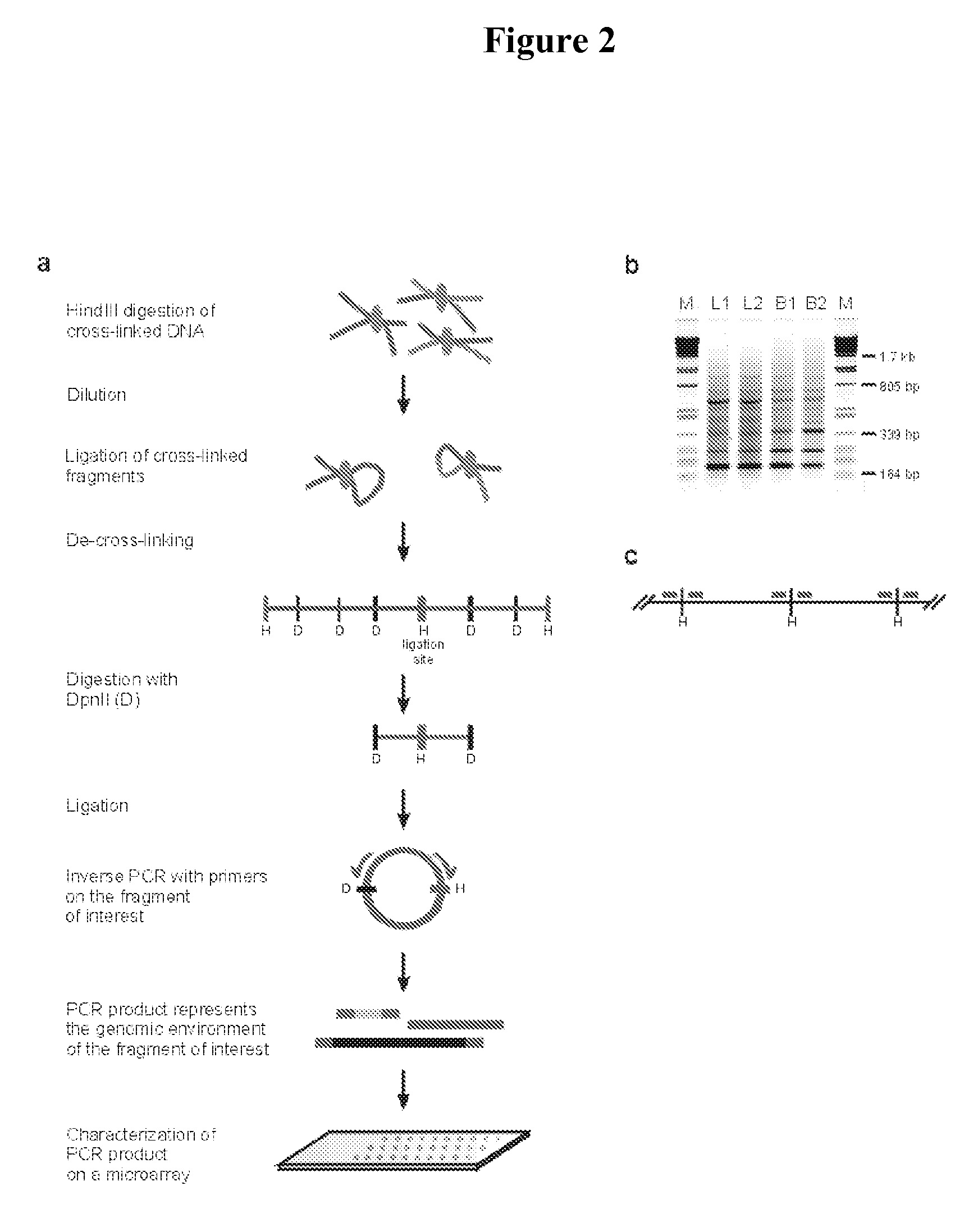
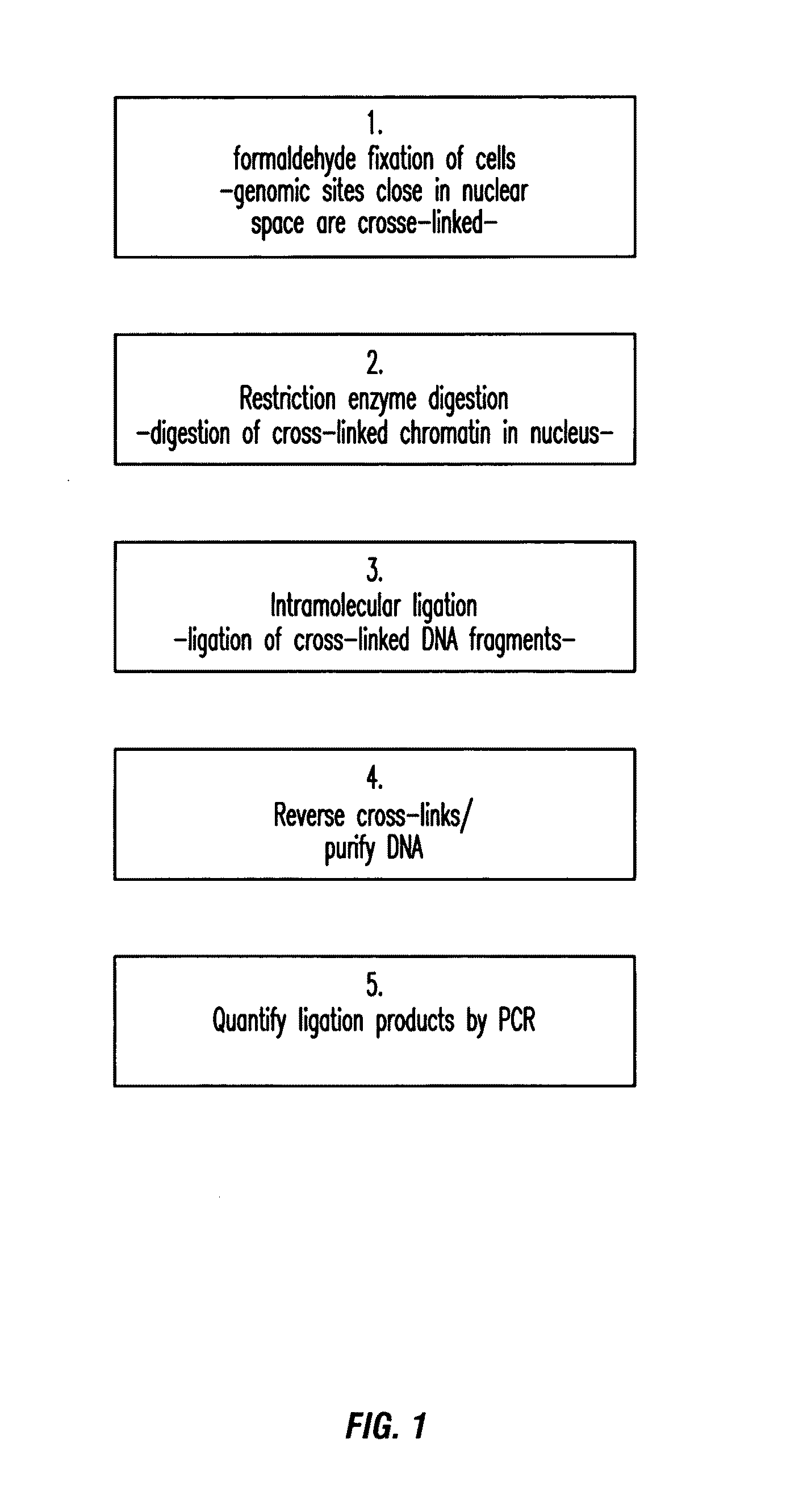
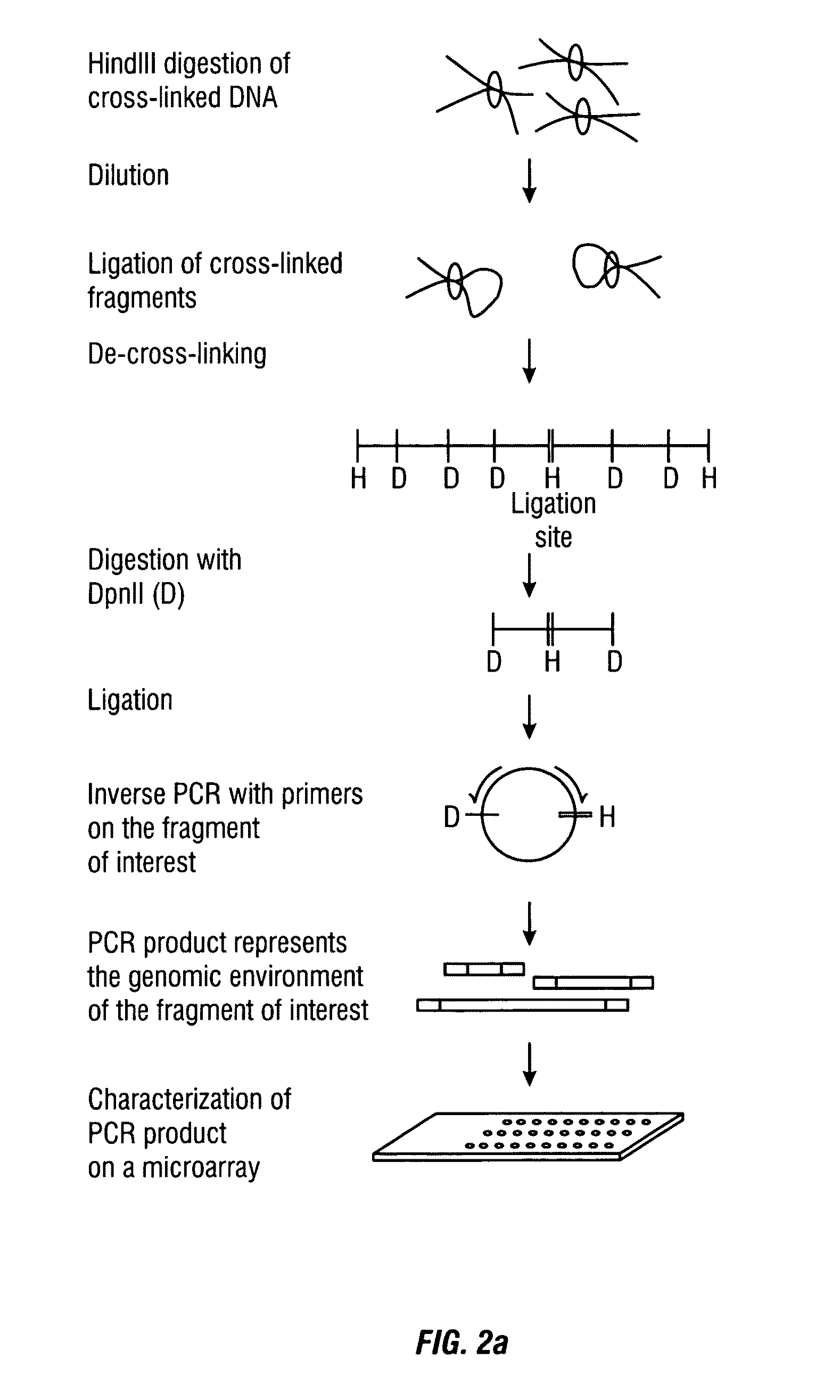
The present invention relates in one aspect to a method for analyzing the frequency of interaction of a target nucleotide sequence with one or more nucleotide sequences of interest (eg. one or more genomic loci) comprising the steps of: (a) providing a sample of cross-linked DNA; (b) digesting the cross-linked DNA with a primary restriction enzyme; (c) ligating the cross-linked nucleotide sequences; (d) reversing the cross linking; (e) optionally digesting the nucleotide sequences with a secondary restriction enzyme; (f) optionally ligating one or more DNA sequences of known nucleotide composition to the available secondary restriction enzyme digestion site(s) that flank the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest; (g) amplifying the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest using at least two oligonucleotide primers, wherein each primer hybridises to the DNA sequences that flank the nucleotide sequences of interest; (h) hybridising the amplified sequence(s) to an array; and (i) determining the frequency of interaction between the DNA sequences.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
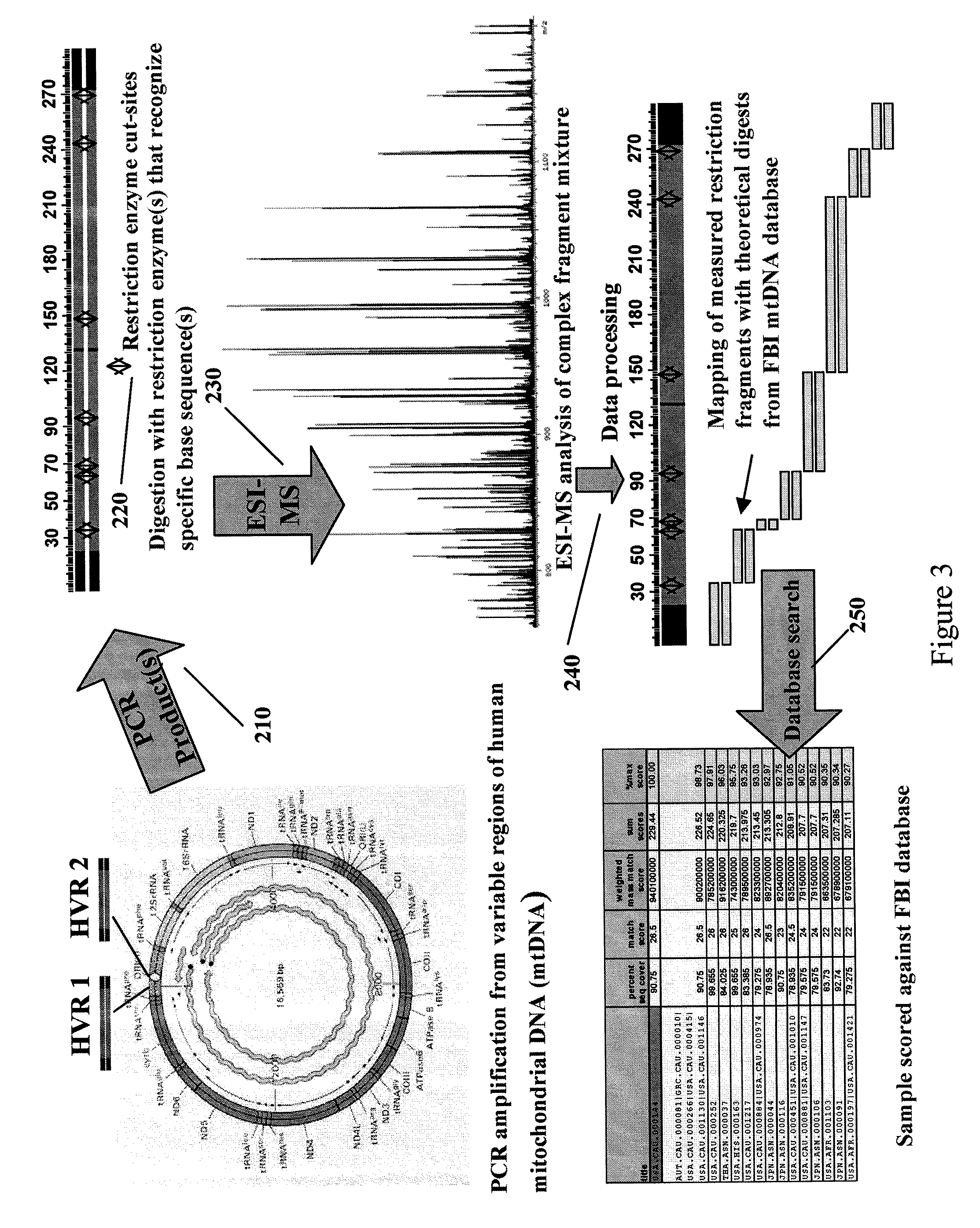
Methods For Rapid Forensic Analysis Of Mitochondrial DNA
InactiveUS20090125245A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionRestriction site
The present invention provides methods for rapid forensic analysis of mitochondrial DNA by amplification of a segment of mitochondrial DNA containing restriction sites, digesting the mitochondrial DNA segments with restriction enzymes, determining the molecular masses of the restriction fragments and comparing the molecular masses with the molecular masses of theoretical restriction digests of known mitochondrial DNA sequences stored in a database.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI +1
Process for producing humanized chimera antibody
InactiveUS20020026036A1Easy to produceEasy constructionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRestriction enzyme digestionSynthetic DNA
A process for the production of humanized chimera antibody, wherein the chimera antibody is produced easily without changing any of the amino acids of its mouse antibody variable region, which comprises the steps of: (1) constructing a cassette vector by inserting a cDNA coding for a heavy chain constant region of human antibody into an expression vector for animal cell use and establishing a cloning site in the upstream region of the heavy chain constant region of said cassette vector for inserting a cDNA which encodes a heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody; (2) digesting a cDNA coding for the heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody with restriction enzymes; (3) inserting said cDNA coding for the heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody into the cassette vector, using a synthetic DNA which comprises a base sequence corresponding to the 5'-end side of said heavy chain constant region of human antibody and a base sequence corresponding to the 3'-end side of said heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody and is possessed of the restriction enzyme recognition sites on both of its ends, thereby constructing a humanized chimera antibody heavy chain expression vector in which said cDNA coding for the heavy chain constant region of human antibody and said cDNA coding for the heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody are linked together through said synthetic DNA; (4) constructing a cassette vector by inserting a cDNA coding for a light chain constant region of human antibody into an expression vector for animal cell use and establishing a cloning site in the upstream region of the light chain constant region of said cassette vector for inserting a cDNA which encodes a light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody; (5) digesting a cDNA coding for the light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody with restriction enzymes; (6) inserting said cDNA coding for a light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody into the cassette vector using a synthetic DNA which comprises a base sequence corresponding to the 5'-end side of said light chain constant region of human antibody and a base sequence corresponding to the 3'-end side of said light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody and is possessed of the restriction enzyme recognition sites on both of its ends, thereby constructing a humanized chimera antibody light chain expression vector in which said cDNA coding for the light chain constant region of human antibody and said cDNA coding for the light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody are linked together through said synthetic DNA; (7) introducing these expression vectors into host cells to obtain a transformant; and (8) culturing said transformant in an appropriate culture medium, thereby allowing the transformant to produce and accumulate a humanized chimera antibody, and collecting said humanized chimera antibody from the resulting culture broth.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Diagnostic Method
ActiveUS20080081338A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionA-DNA
The present invention concerns a method for the detection or monitoring of cancer using a biological sample selected from blood, plasma, serum, saliva, urine from an individual, said method comprising: (a) obtaining DNA from the said biological sample; (b) digesting the DNA sample with one or more methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes; (c) quantifying or detecting a DNA sequence of interest after step (b), wherein the target sequence of interest contains at least two methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme recognition sites; and (d) comparing the level of the DNA sequence from the individual to a normal standard, to detect, prognosticate or monitor cancer.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Differential PCR-RFLP assay for detecting and distinguishing between nonpathogenic PCV-1 and pathogenic PCV-2
InactiveUS20050147966A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionNucleotide
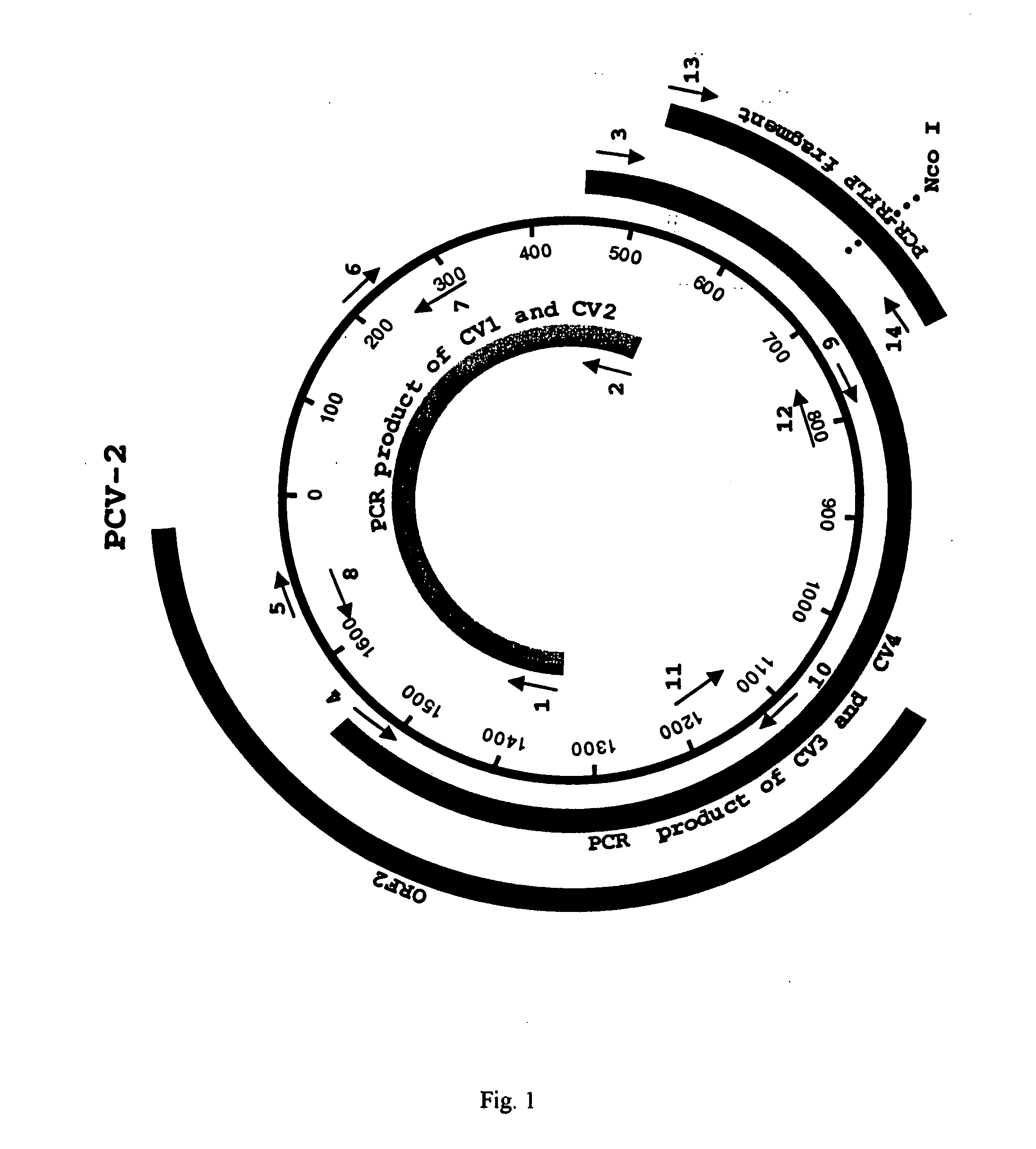
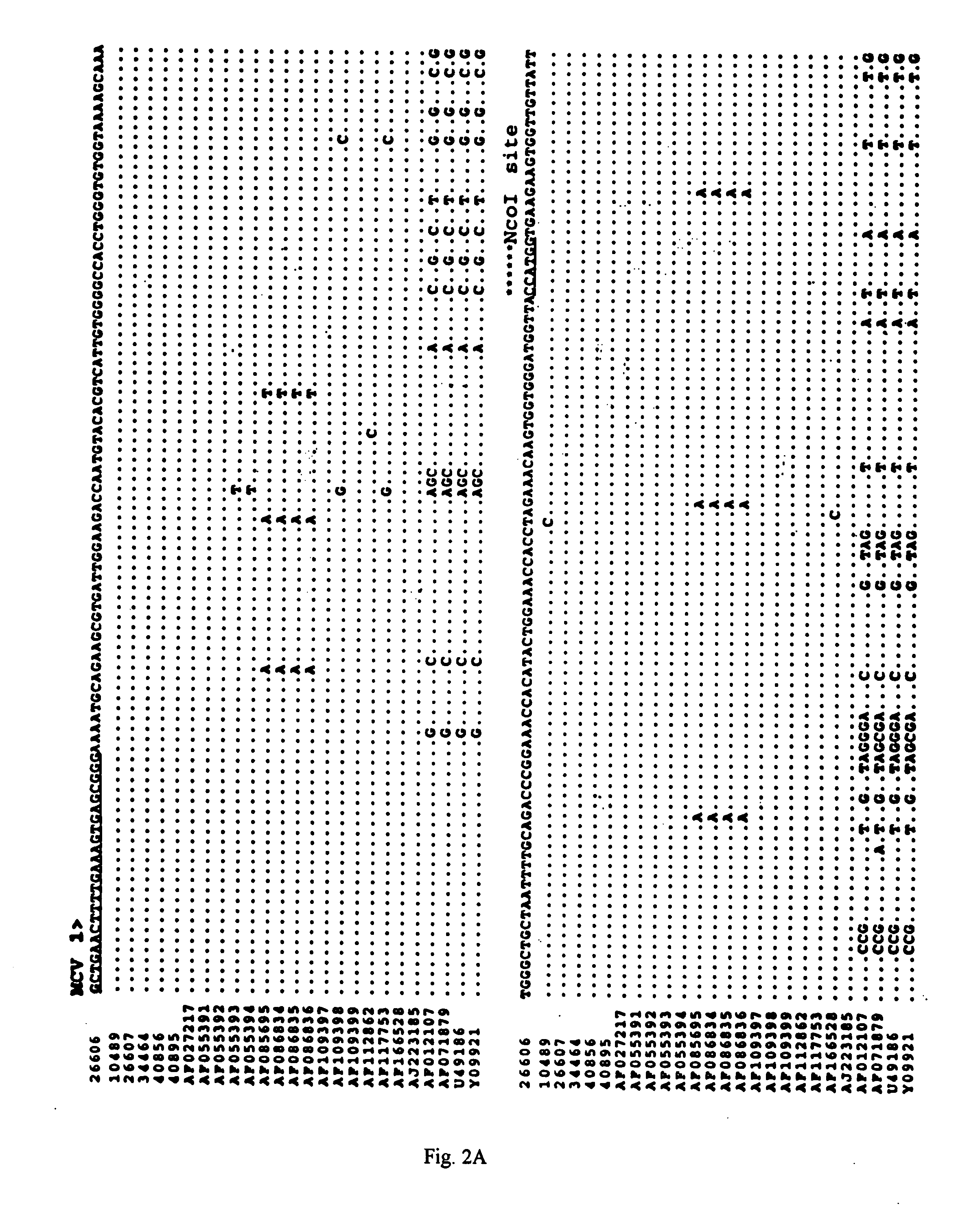
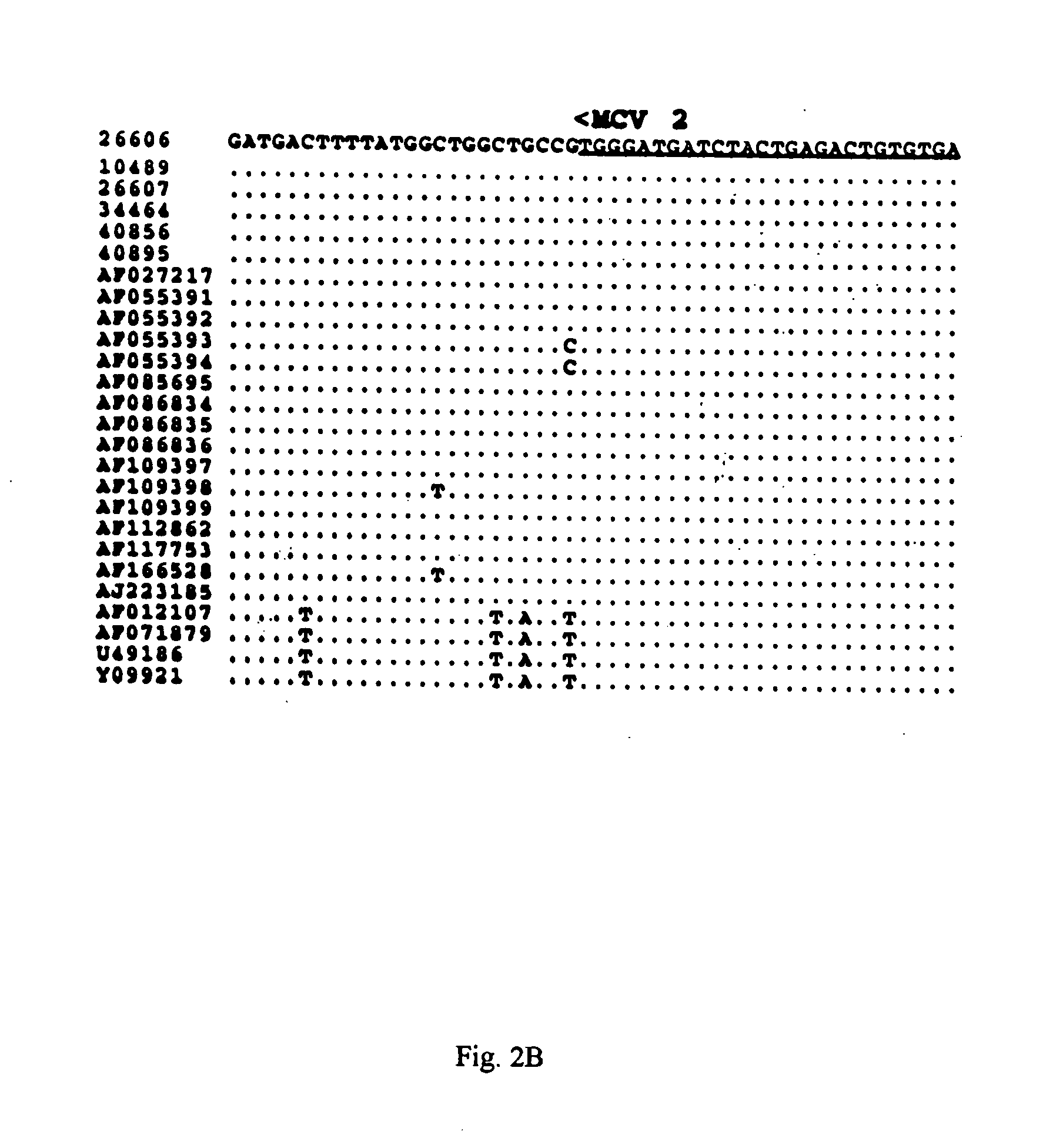
The present invention relates to a method for detecting and differentiating PCV infections in a biological sample taken from a pig which involves amplifying a fragment from an extracted nucleic acid; digesting the fragment with a suitable restriction enzyme such as the unique NcoI restriction enzyme; forming a restriction fragment length polymorphism pattern; and then detecting the presence or absence of a PCV isolate. The invention further concerns the new oligonucleotide primers for differentiating PCV infections comprising a nucleotide sequence selected from the group consisting of MCV1 having a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1 and MCV2 having a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:2. Moreover, this invention provides a novel kit for detecting and distinguishing PCV infections that includes the new oligonucleotide primers and the suitable restriction enzyme.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Goat CDK2 (Cyclin-dependent kinases 2) gene knockout vector and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106834347AThe method is simple and fastHigh knockout efficiencyNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliRestriction enzyme digestion
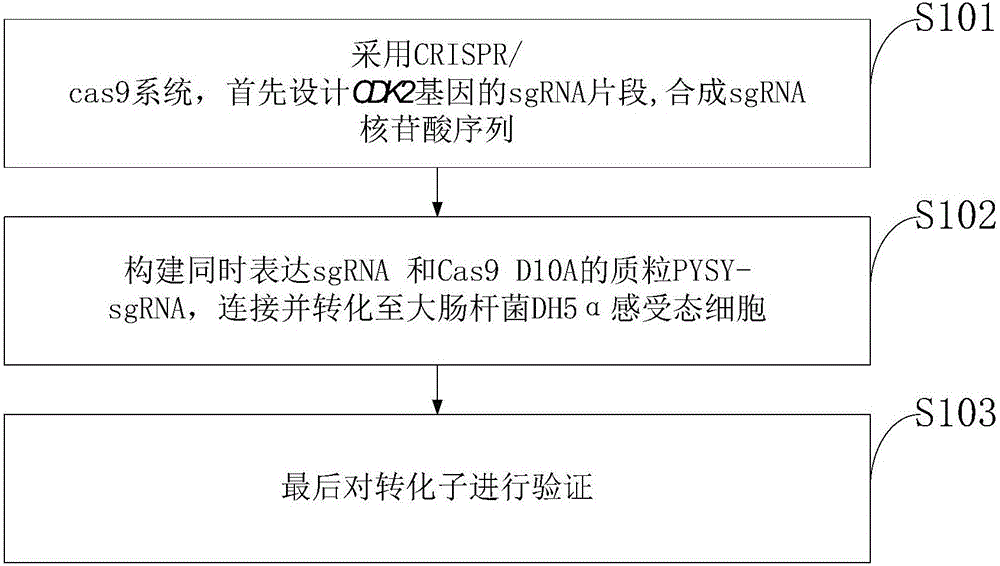
The invention discloses a goat CDK2 (Cyclin-dependent kinases 2) gene knockout vector and a construction method thereof. A CRISPR / Cas9 system is adopted; an SgRNA segment of a CDK2 gene is designed at first and an SgRNA nucleotide sequence is synthesized; a plasmid PYSY-sgRNA for expressing SgRNA and Cas9D10A at the same time is constructed; the plasmid PYSY-sgRNA is connected and transformed to an escherichia coli DH5alpha competent cell; finally, a transformant is verified; restriction enzyme digestion and sequencing identification prove that the construction of the CDK2 gene knockout vector is accurate. The vector constructed by CRISPR / Cas9 is adopted, and a theoretical basis is provided for subsequently obtaining a goat CDK2 gene deletion type cell line and researching a molecular mechanism of cell apoptosis molecules triggered by mycoplasma pneumonia infection.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Genome signature tags
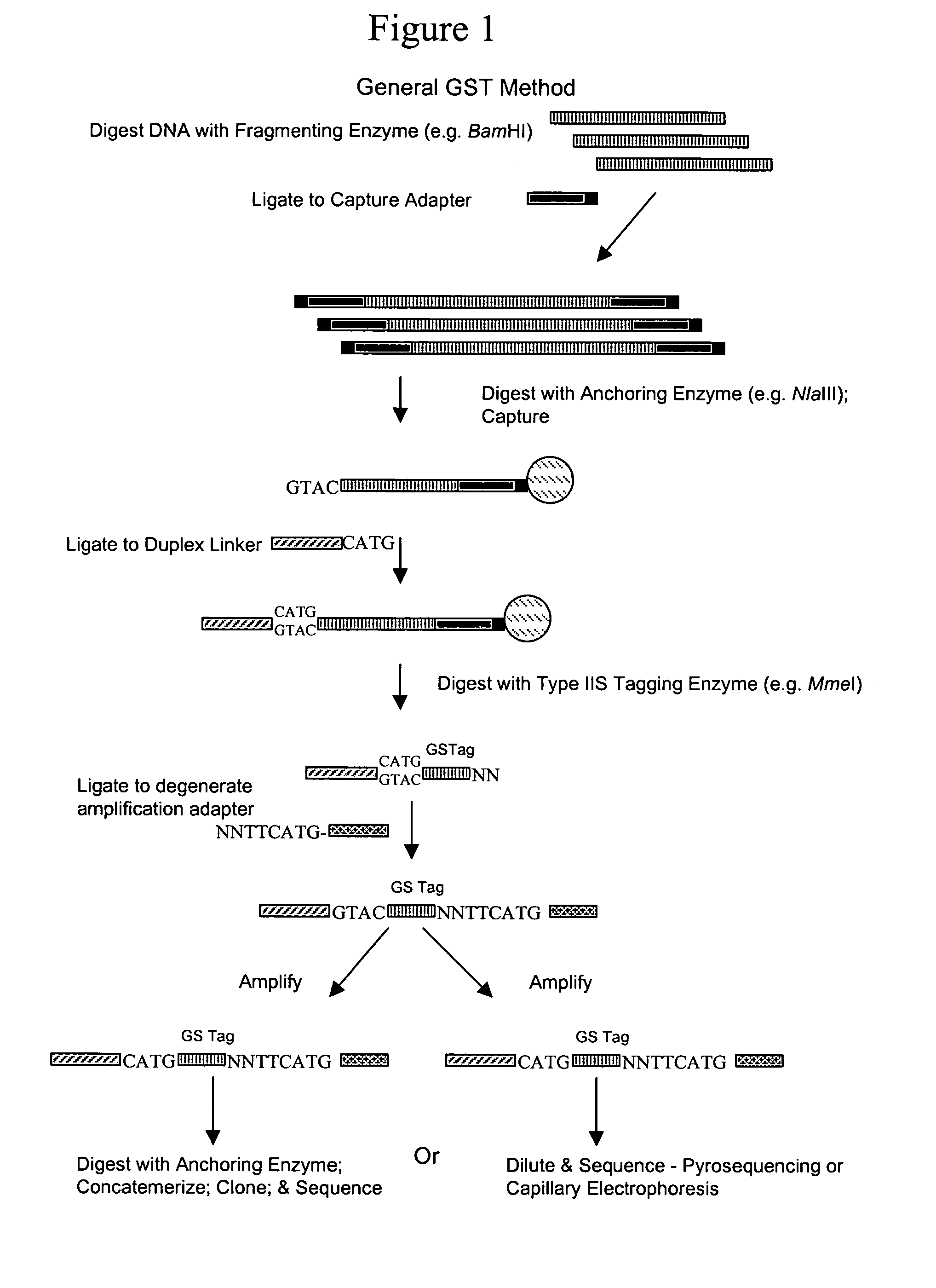
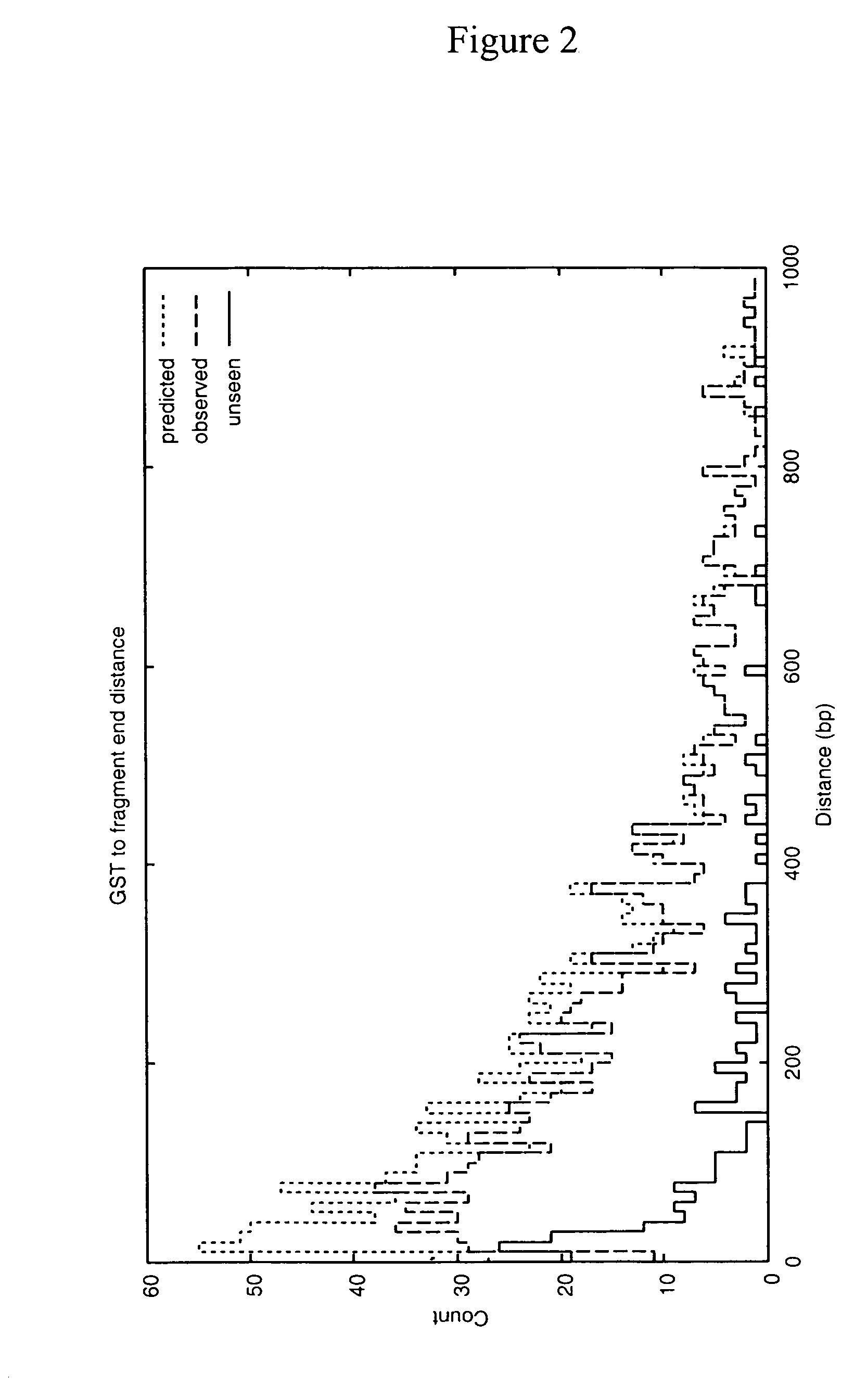
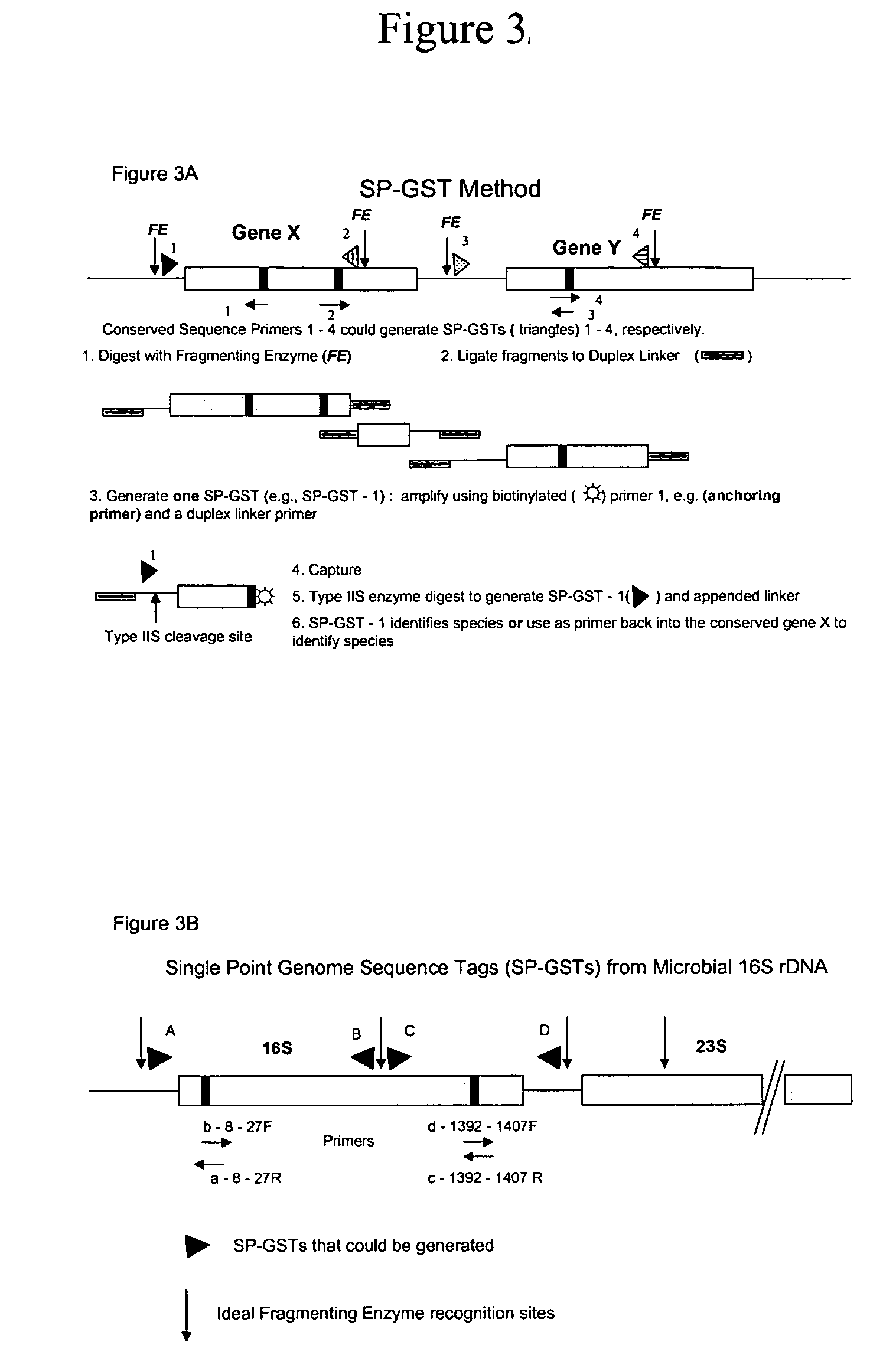
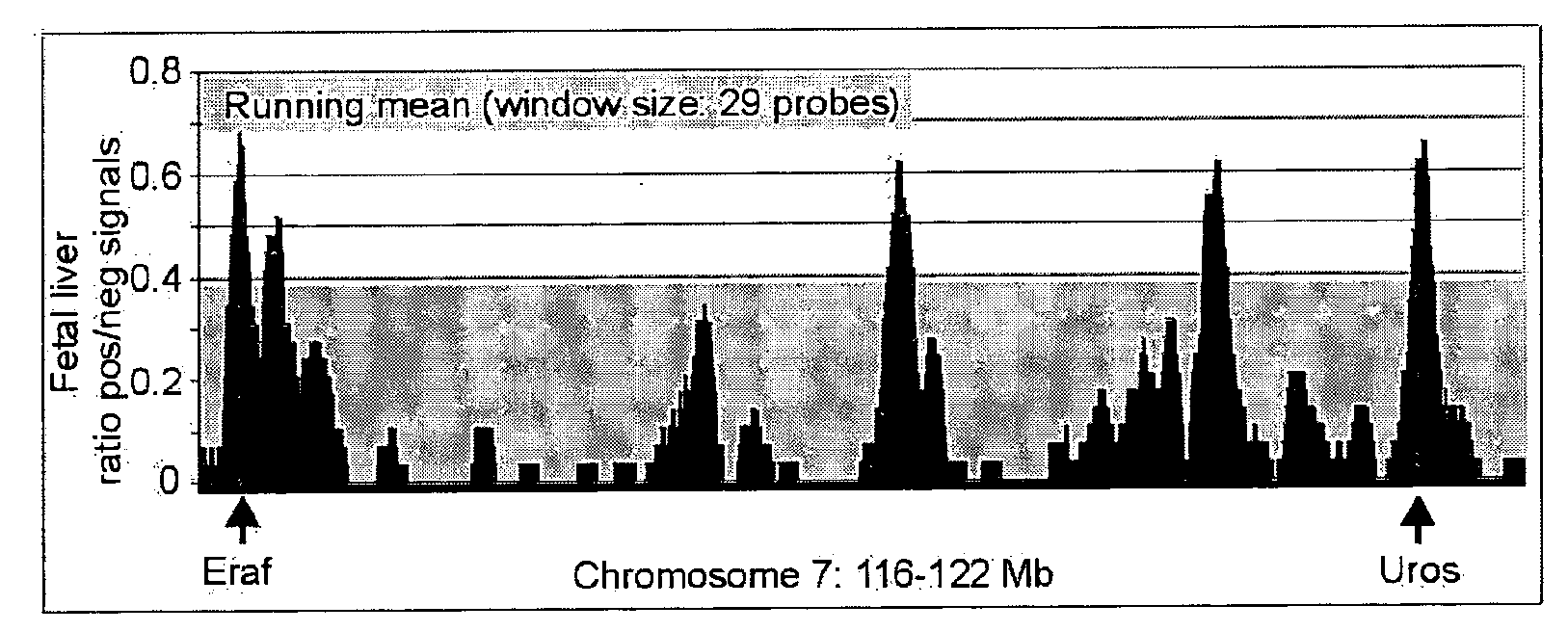
InactiveUS7323306B2Additional versatility and utilityMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionDigestion
Disclosed is a method for analyzing the organismic complexity of a sample through analysis of the nucleic acid in the sample. In the disclosed method, through a series of steps, including digestion with a type II restriction enzyme, ligation of capture adapters and linkers and digestion with a type IIS restriction enzyme, genome signature tags are produced. The sequences of a statistically significant number of the signature tags are determined and the sequences are used to identify and quantify the organisms in the sample. Various embodiments of the invention described herein include methods for using single point genome signature tags to analyze the related families present in a sample, methods for analyzing sequences associated with hyper- and hypo-methylated CpG islands, methods for visualizing organismic complexity change in a sampling location over time and methods for generating the genome signature tag profile of a sample of fragmented DNA.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Circular chromosome conformation capture (4C)
ActiveUS20100062947A1High throughput analysisAccurate mappingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionRestriction enzyme digestion
The present invention relates in one aspect to a method for analysing the frequency of interaction of a target nucleotide sequence with one or more nucleotide sequences of interest (eg. one or more genomic loci) comprising the steps of: (a) providing a sample of cross-linked DNA; (b) digesting the cross-linked DNA with a primary restriction enzyme; (c) ligating the cross-linked nucleotide sequences; (d) reversing the cross linking; (e) optionally digesting the nucleotide sequences with a secondary restriction enzyme; (f) optionally ligating one or more DNA sequences of known nucleotide composition to the available secondary restriction enzyme digestion site(s) that flank the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest; (g) amplifying the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest using at least two oligonucleotide primers, wherein each primer hybridises to the DNA sequences that flank the nucleotide sequences of interest; (h) hybridising the amplified sequence(s) to an array; and (i) determining the frequency of interaction between the DNA sequences.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
Cloning method
ActiveUS9738890B2Improve versatilityIncrease flexibilityStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorRestriction enzyme digestionGenetics
The present invention relates to a method based on the use of restriction enzyme digestion and ligation via cleavage sites, thereby to prepare two or more standardized expression cassettes.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
4c
UndeterminedUS20070231817A1High throughput analysisLow costSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionRestriction enzyme digestion
The present invention relates in one aspect to a method for analysing the frequency of interaction of a target nucleotide sequence with one or more nucleotide sequences of interest (eg. one or more genomic loci) comprising the steps of: (a) providing a sample of cross-linked DNA; (b) digesting the cross-linked DNA with a primary restriction enzyme; (c) ligating the cross-linked nucleotide sequences; (d) reversing the cross linking; (e) digesting the nucleotide sequences with a secondary restriction enzyme; (f) ligating one or more DNA sequences of known nucleotide composition to the available secondary restriction enzyme digestion site(s) that flank the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest; (g) amplifying the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest using at least two oligonucleotide primers, wherein each primer hybridises to the DNA sequences that flank the nucleotide sequences of interest; (h) hybridising the amplified sequence(s) to an array or sequencing the amplified sequences; and (i) determining the frequency of interaction between the DNA sequences.
Owner:DE LAAT WOUTER +1
4c
ActiveUS20100075861A1High throughput analysisLow costSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesCross-linkRestriction enzyme digestion
The present invention relates in one aspect to a method for analyzing the frequency of interaction of a target nucleotide sequence with one or more nucleotide sequences of interest (e.g., one or more genomic loci) comprising the steps of: (a) providing a sample of cross-linked DNA; (b) digesting the cross-linked DNA with a primary restriction enzyme; (c) ligating the cross-linked nucleotide sequences; (d) reversing the cross linking; (e) digesting the nucleotide sequences with a secondary restriction enzyme; (f) ligating one or more DNA sequences of known nucleotide composition to the available secondary restriction enzyme digestion site(s) that flank the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest; (g) amplifying the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest using at least two oligonucleotide primers, wherein each primer hybridises to the DNA sequences that flank the nucleotide sequence of interest; (h) hybridising the amplified sequence(s) to an array; and (i) determining the frequency of interaction between the DNA sequences.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
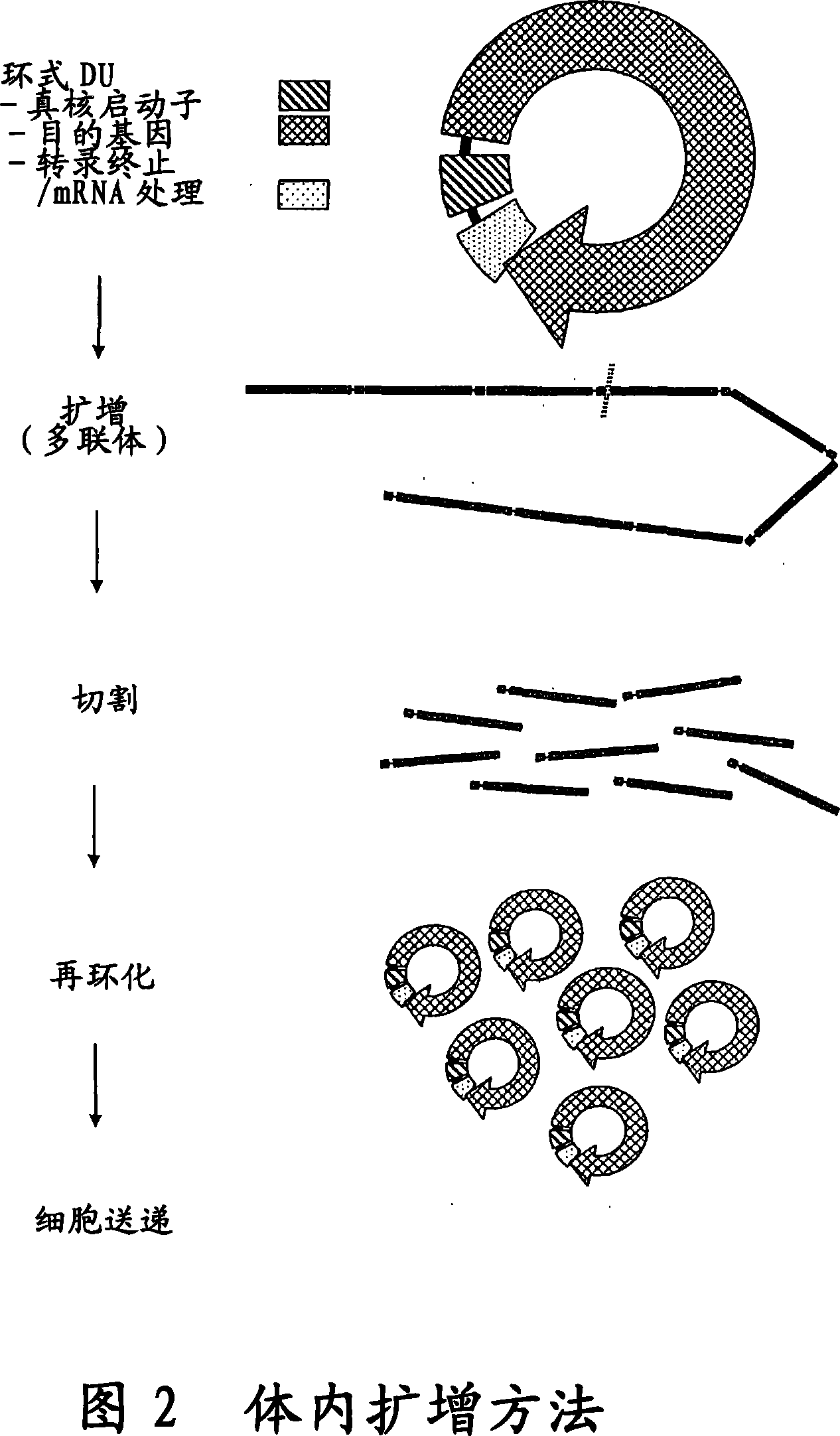
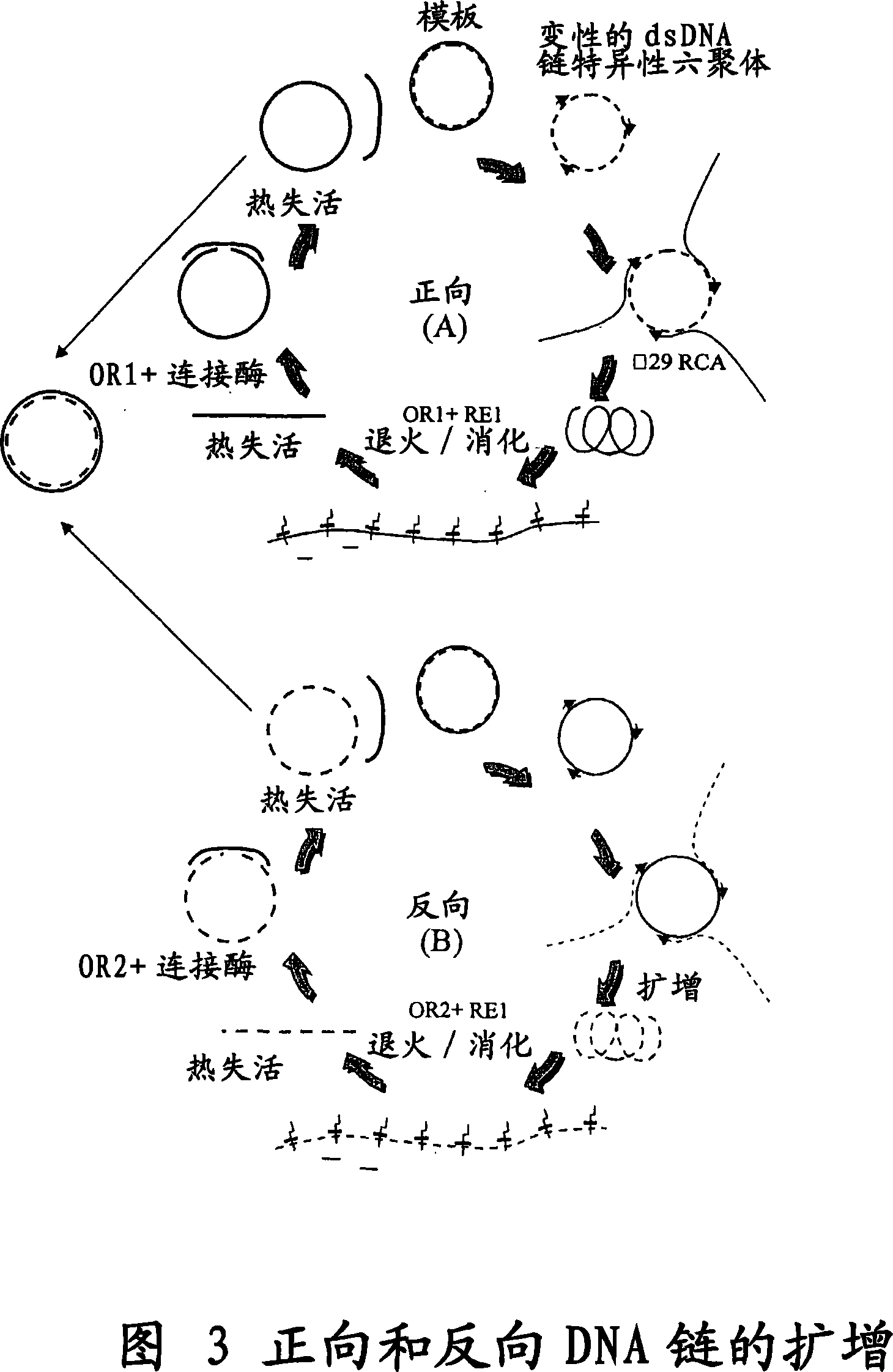
Cell Free Biosynthesis of High-Quality Nucleic Acid and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080305142A1Short timeSmall volumeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCell freeRestriction enzyme digestion
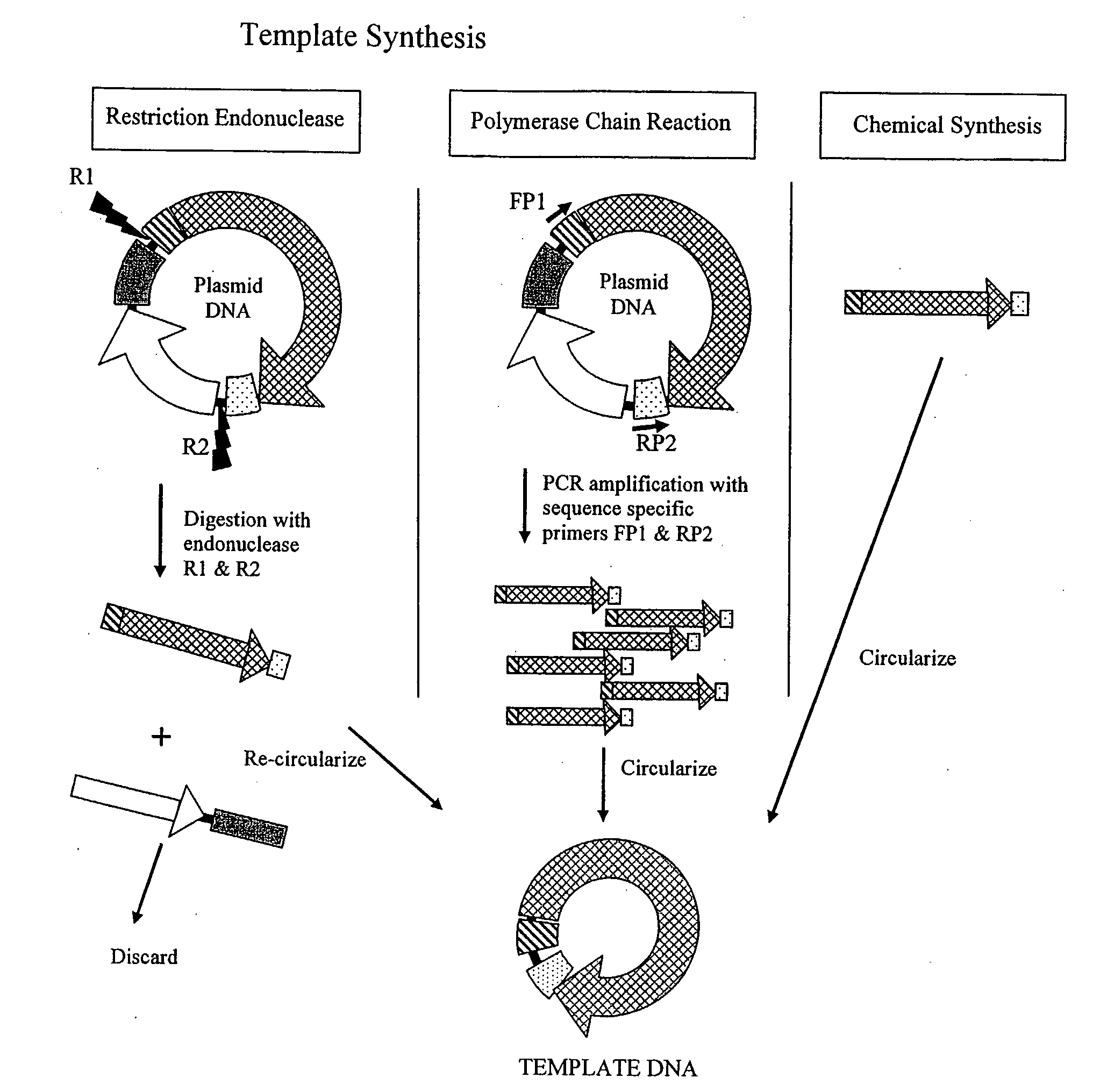
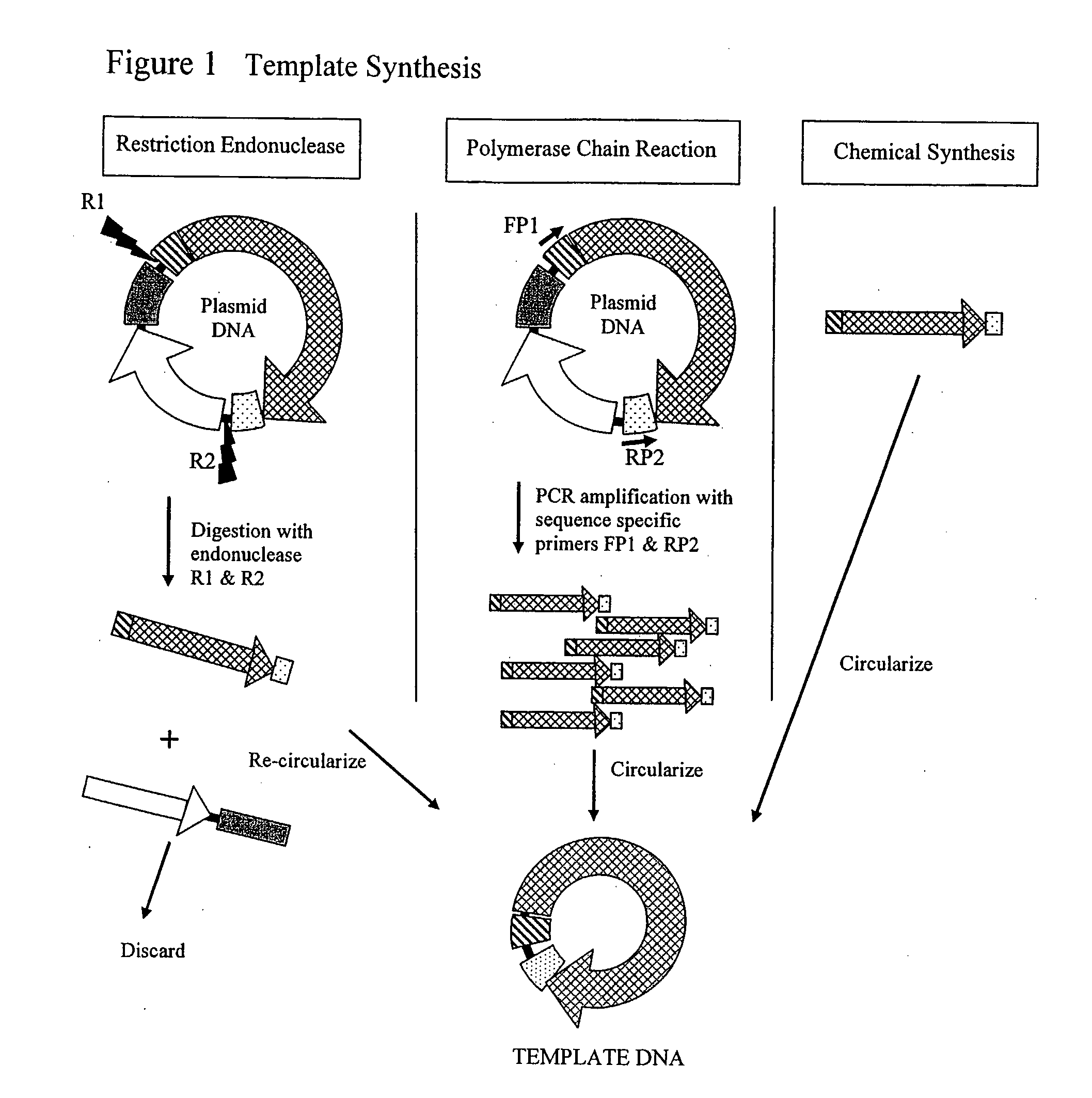
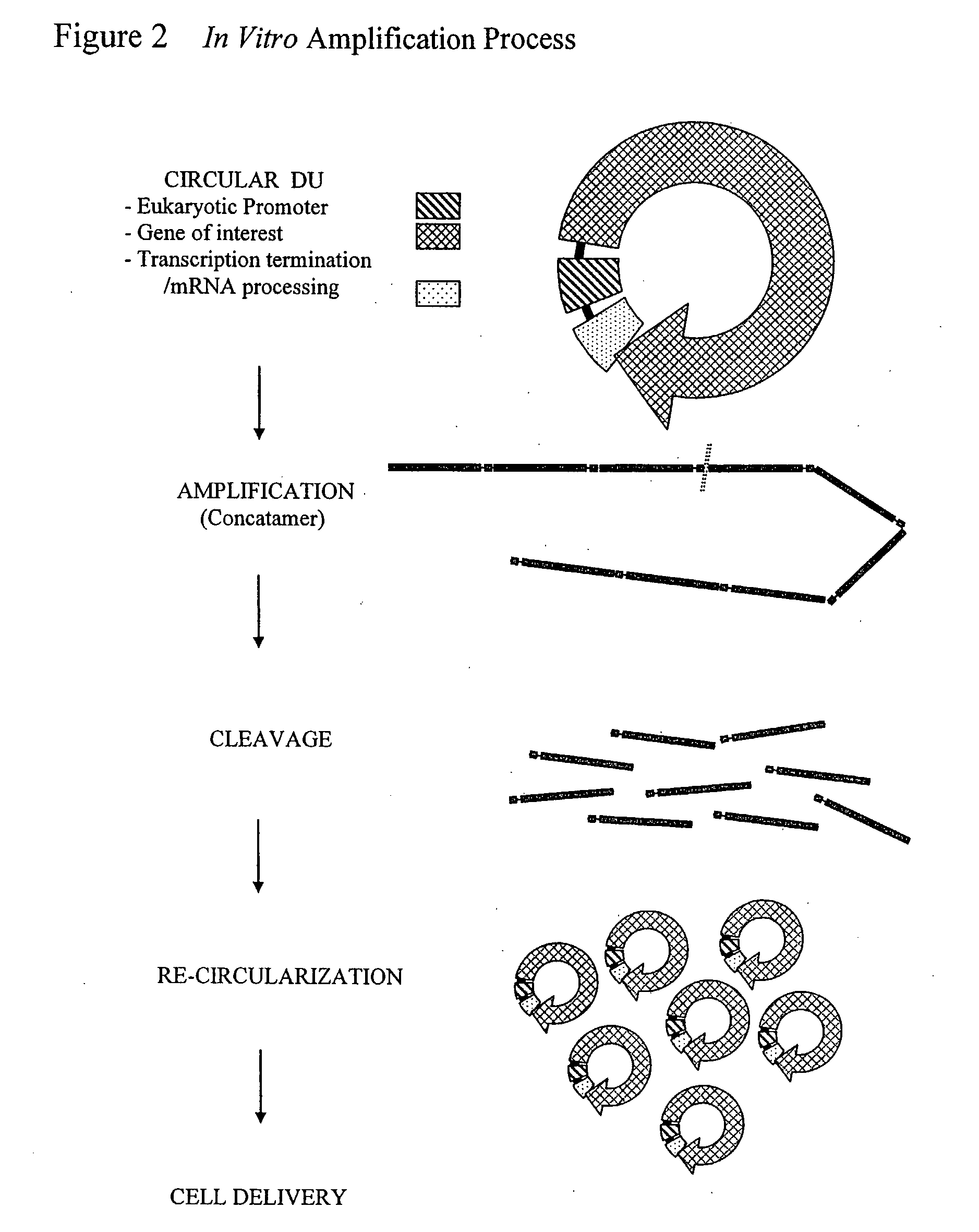
The invention provides an improved cell free amplification method capable of producing large quantities of therapeutic-quality nucleic acids and methods of using the synthesized nucleic acid in research, therapeutic and other applications—The methods combine several different state-of-the-art procedures and coordinate their applications to affordably synthesize nucleic acids for therapeutic purposes. It combines in vitro rolling circle amplification, high fidelity polymerases, high affinity primers, and streamlined template specifically designed for particular applications. For expression purposes, the templates contain an expression cassette including a eukaryotic promoter, the coding sequence for the gene of interest, and a eukaryotic termination sequence. Following amplification, concatamers are subsequently processed according to their intended use and may include: restriction enzyme digestion for the production of short expression cassettes (SECs); ligation steps to circularize the SEC (CNAs); and / or supercoiling steps to produce sCNAs. The final product contains nearly non-detectable levels of bacterial endotoxin.
Owner:STAR BIOLOGICS
Biological method for producing resveratrol
InactiveCN102605006ADe novo synthesisResolve source issuesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhenylalanine hydroxylase
The invention discloses a biological method for producing resveratrol, which comprises the following steps: ligating target genes obtained by restriction enzyme digestion to an expression vector, wherein the target genes include the sequences of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL) 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase (4CL) and resveratrol synthase (RS); transforming the constructed expression vector into a strain to obtain a recombinant engineered strain; and fermenting the recombined engineered strain. Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme provided by the invention uses the genetically engineered strain for fermentation to produce resveratrol, so as to realize denovo synthesis of resveratrol with no need of adding substrates. The method disclosed by the invention solves the source problem of resveratrol, and at the same time, reduces the production cost in a maximum extent, and is beneficial for industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Bacillus subtilis strain for excreting nattokinase at high efficiency and preparation technology of high-purity nattokinase
InactiveCN107058204AIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRestriction enzyme digestionDigestion
The invention relates to a bacillus subtilis strain for excreting nattokinase at high efficiency. An aprN gene of bacillus subtilis NK is amplified by a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technique; codons of initial thirty amino acids are optimized according to the codon preference of the bacillus subtilis, a recombination expression plasmid pHT01-aprN is established, and the correctness is verified through the restriction enzymes digestion, PCR amplification and sequencing. The recombination expression plasmid pHT01-aprN is imported into the bacillus subtilis 168 by an electric shocking method, and is performed with resistance screening by adopting chloramphenicol, so as to obtain engineering bacteria. After the fermenting condition is optimized, and the expression is induced by IPTG, the highest enzyme activity in a shake culture fermenting liquid is 289U / ml; the highest enzyme activity in a high-density fermenting liquid is 7778U / ml; the highest enzyme activity of a nattokinase preparation prepared by affinity column chromatography is 981731U / g.
Owner:上海诺金科生物科技有限公司
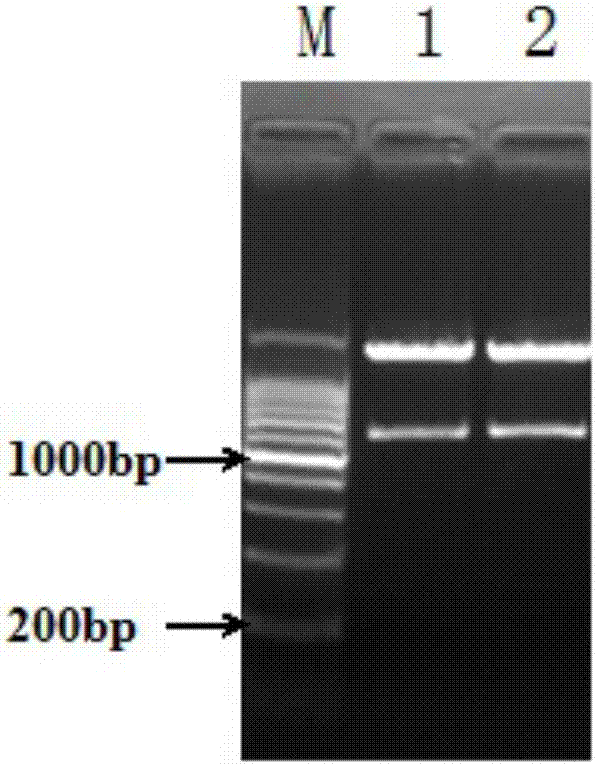
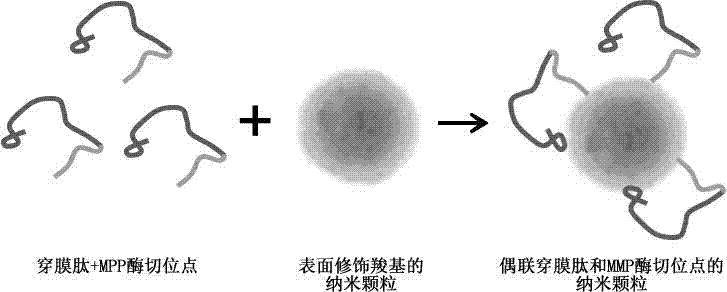
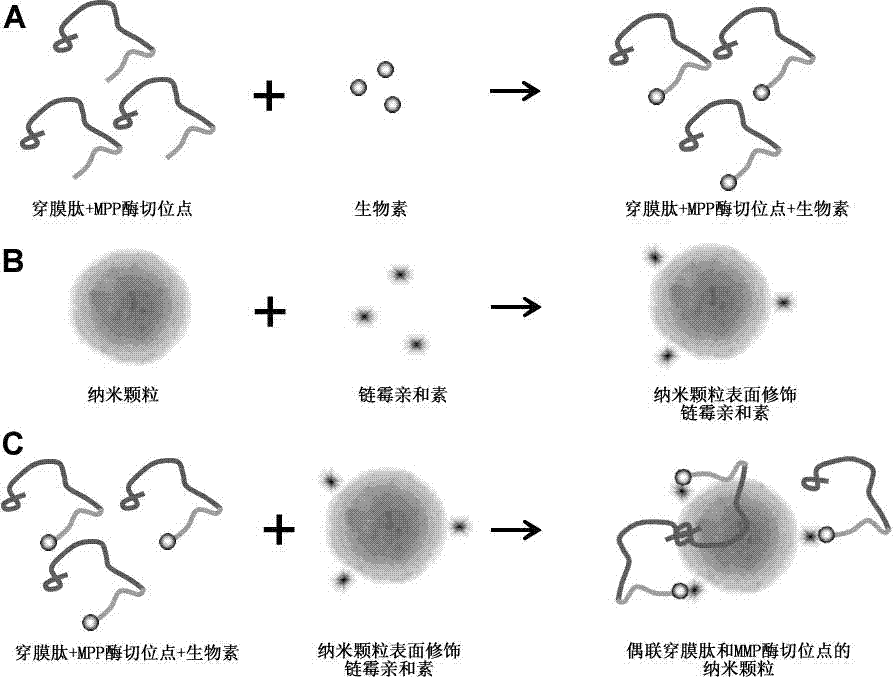
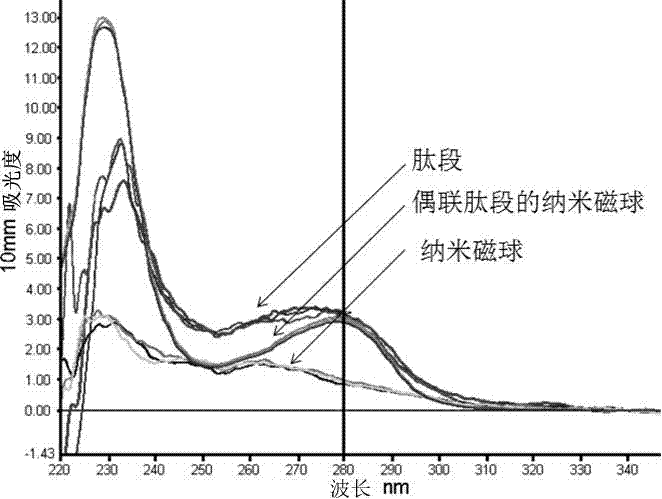
Nanoparticle coupled with coupling cell-penetrating peptide and metal matrix proteinase (MMP) restriction enzyme digestion site
InactiveCN103784406APowder deliveryEnergy modified materialsRestriction enzyme digestionCarboxyl radical
The invention relates to a nanoparticle coupled with a coupling cell-penetrating peptide and a metal matrix proteinase (MMP) restriction enzyme digestion site. The cell-penetrating peptide and the MMP restriction enzyme digestion site are distributed outside the surface-modified carboxyl or streptavidin nanoparticle; the cell-penetrating peptide and the MMP restriction enzyme digestion site are ligated via a chemical bond, and the amino group of the last amino acid residue of the restriction enzyme digestion site sequence is ligated with the carboxyl group on the surface of the nanoparticle by condensation reaction; or the last amino acid residue of the restriction enzyme digestion site sequence is ligated with biotin, the surface of the nanoparticle is modified with streptavidin, and a peptide fragment is ligated with the nanoparticle by use of the biotin-streptavidin affinity reaction. According to the invention, an MMP restriction enzyme digested peptide segment is innovatively utilized to couple the coupling cell-penetrating peptide and the nanoparticle, and the cell-penetrating peptide is separated from the nanoparticle by the fact that the activity of MMP inside or around a target cell is higher than the activity of MMP inside or around a normal cell, and physical or drug therapy, imaging and other treatment are performed on the target cell and tissue by use of the specific physiological environment inside or around the target cell or the surrounding auxiliary physical environment and the characteristics of the nanoparticle.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Cloning, expression and application of Lactobacillus brevis glutamate decarboxylase gene
InactiveCN102080090AOvercoming rateOvercome the cycleFermentationLyasesEscherichia coliRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention discloses cloning, expression and application of a Lactobacillus brevis glutamate decarboxylase gene. The gene is derived from Lactobacillus brevis CGMCC No.1306, and is obtained by amplifying a Lactobacillus brevis genome DNA through PCR (polymerase chain reaction); and the full length of the gene is 1407bp. BamH I and EcoRI restriction enzyme recognition sequences are respectively added to both ends of the gene; and the gene is connected with pET-28a(+) which is digested by the same restriction enzymes, and is converted into colibacillus expression host bacteria BL21 (DE3), thereby realizing the recombinant expression in the colibacillus; and the molecular weight of the expression product glutamate decarboxylase is 53538.6Da. The recombinant glutamate decarboxylase, or the engineering bacteria for expressing the recombinant glutamate decarboxylase can convert L-glutamic acid or salt thereof into gamma-aminobutyric acid by decarboxylation, and has the advantages of high conversion efficiency, high product purity and high production efficiency.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Method of performing traceless knockout and integration on gene of Acidithiobacillus caldus
InactiveCN102604929AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionRestriction enzyme digestionPlasmid Vector
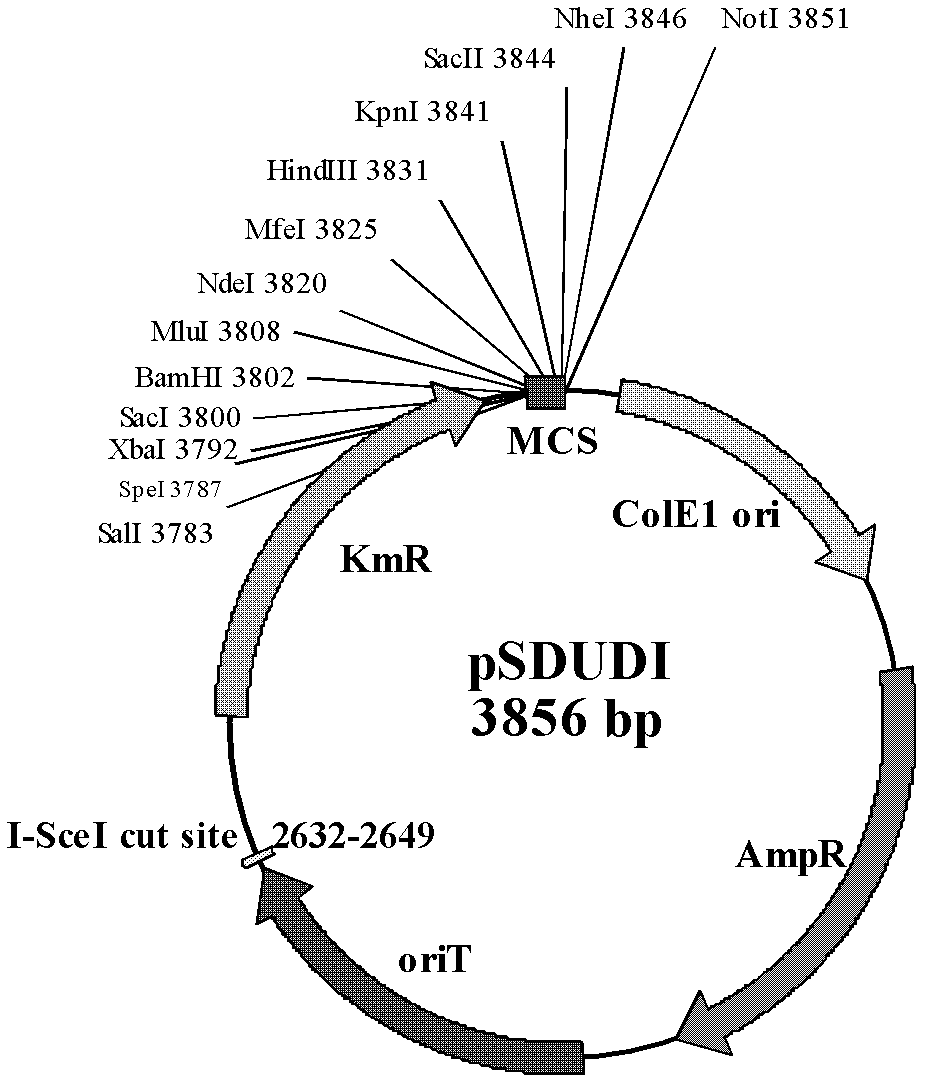
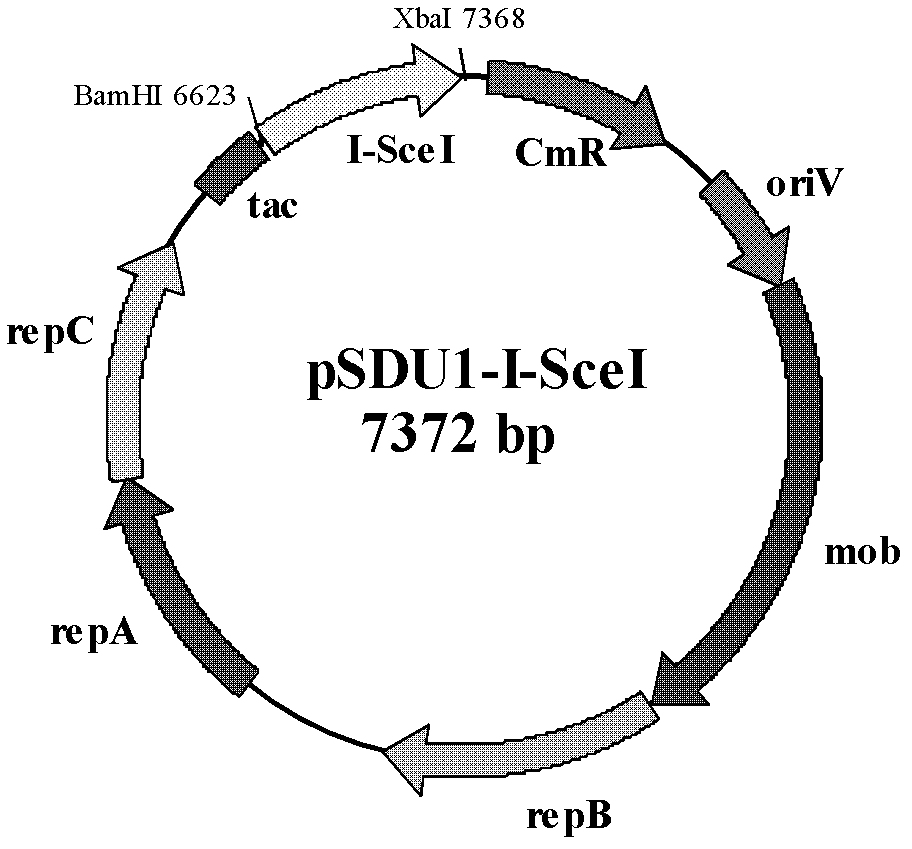
The invention discloses a method of performing traceless knockout on a chromogene or inserting an exogenous gene in a chromosome of Acidithiobacillus caldus. The method comprises the following steps: transferring a homologous recombinant plasmid containing plentiful restriction enzyme digestion sites of endonuclease I-SceI into the Acidithiobacillus caldus in a conjugation transfer manner, simultaneously, directionally inserting the homologous recombinant plasmid into the chromosome of Acidithiobacillus caldus by use of a homologous recombinant system of a cell itself, transferring a screenedsingle crossover to an I-SceI expression plasmid by an electroporation method, performing secondary homologous recombination on a single recon chromosome under a stress that the I-SceI enzyme cuts the chromosome, and optimizing and screening a double crossover bacterial strain to realize knockout and insertion of the gene. The invention also constructs a suicide type plasmid vector pSDUDI for homologous recombination and a plasmid pSDU1-I-SceI for expressing the I-SceI enzyme effectively, and provides convenience for the traceless knockout and the integration of the chromogene in the Acidithiobacillus caldus. The method provided by the invention provides a new way for intensive study on and modification of Acidithiobacillus caldus.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
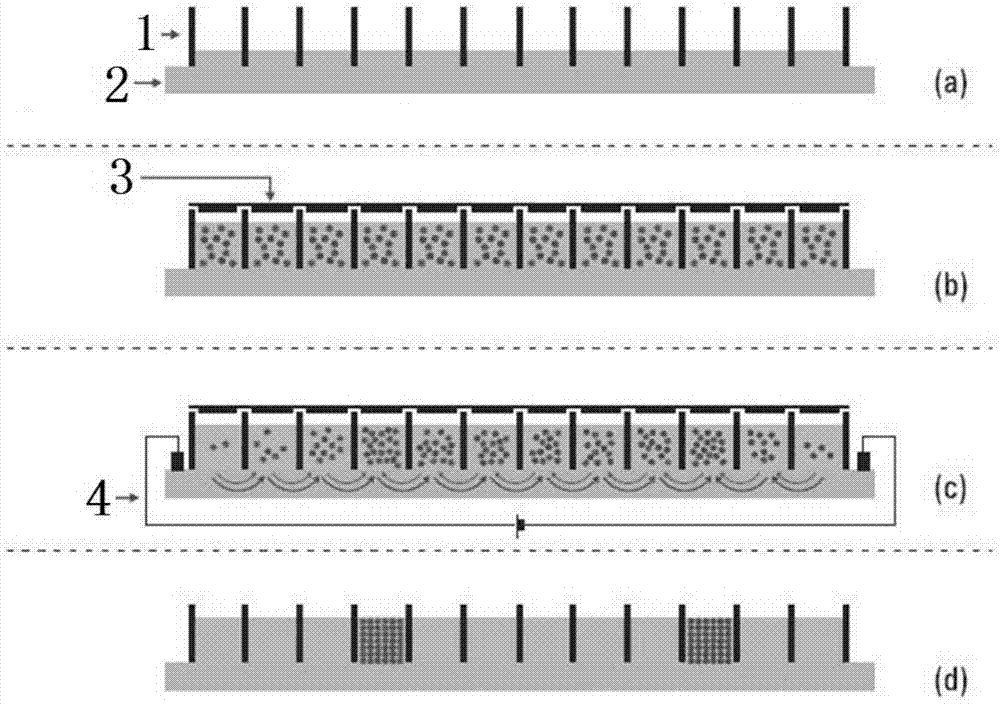
Reduced-representation genome library building method based on type IIB restriction enzyme digestion
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology, and discloses a reduced-representation genome library building method based on type IIB restriction enzyme digestion. The method comprises steps as follows: (1), digestion is performed on genome DNA by means of BsaXI enzyme; (2), an adaptor I and an adaptor II are connected for an enzyme-digested product; (3), a connected product is purified; (4), PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed on the purified product; (5), a PCR product is purified to obtain a sequencing library, and two adaptors of the step (2) are synthesized through hybridization of two nucleotide fragments represented by sequences SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2 as well as two nucleotide fragments represented by sequences SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 2 respectively. The library building method is simple, fast and low in library building cost, the built library has high accuracy, and high-throughput sequencing can be more effectively performed.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Clone, expression and application for lactic acid bacteria glutamic acid decarboxylase gene
InactiveCN101063144AOvercome the disadvantage of low yieldNot easy to polluteGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention discloses a colony, expression and appliance of lactic acid bacteria aminoglutaric acid decarboxylase gene in food industry biotechnics domain, which is characterized by the following: coming from spittle streptococcus thermophilic subspecies (Streptococcus thermophilus) with length at 1380bp; augmenting from gene group DNA through PCR; adding NcoI and EcoRI on the two ends of the gene; limiting enzyme identification sequence; connecting to pET-DsbA of same limited enzyme alimentary; transforming expressing host bacteria BL21(DE3)pLysS of bacillus coli; realizing retooling expression in bacillus coli; getting glutamic acid decarboxylase molecule with molecular weight at 52. 4kDa; transforming L- glutamic acid decarboxylase to gamma-aminobutyric acid with retooling enzyme; providing a great amount of and high active rough enzyme for enzymatical synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid; decreasing cost of enzymatical synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid. This method possesses warm condition, which belongs to biological synthesis method.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Universal gene-knockout suicide vector for vibrios and application thereof
InactiveCN105063073AStrong lethal effectWide range of lethal objectsBacteriaHybrid cell preparationAgricultural scienceRestriction enzyme digestion
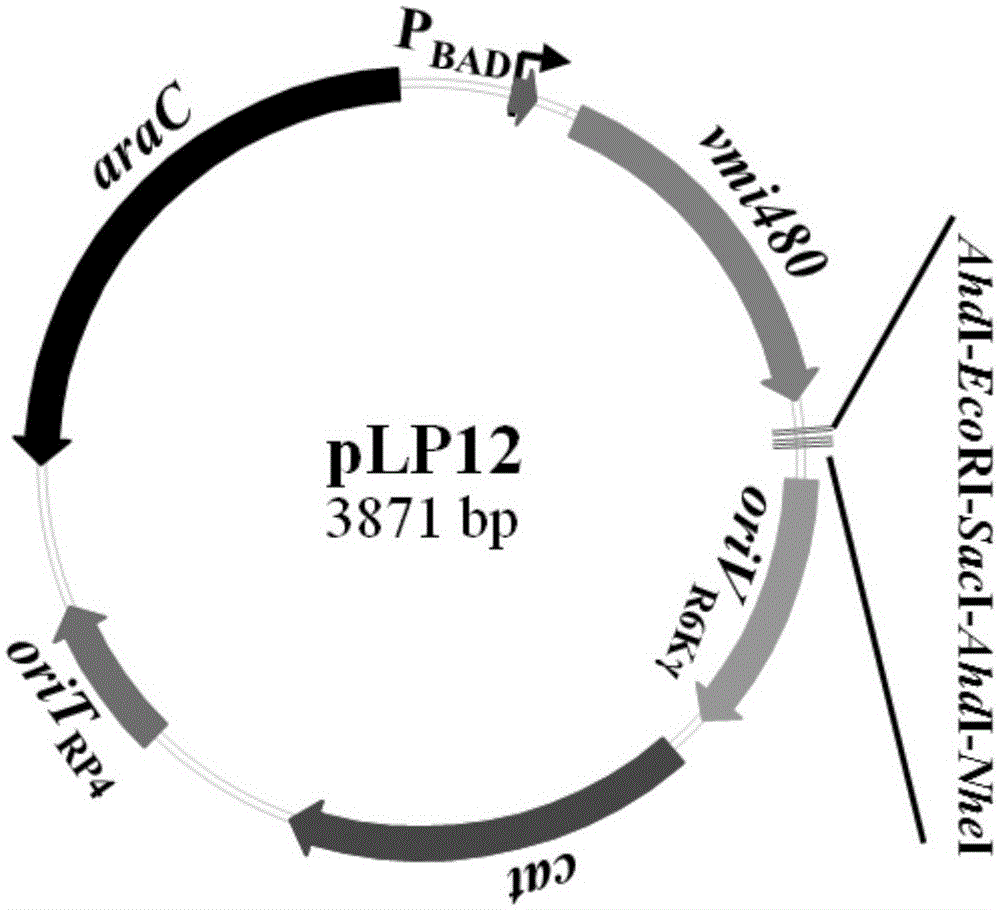
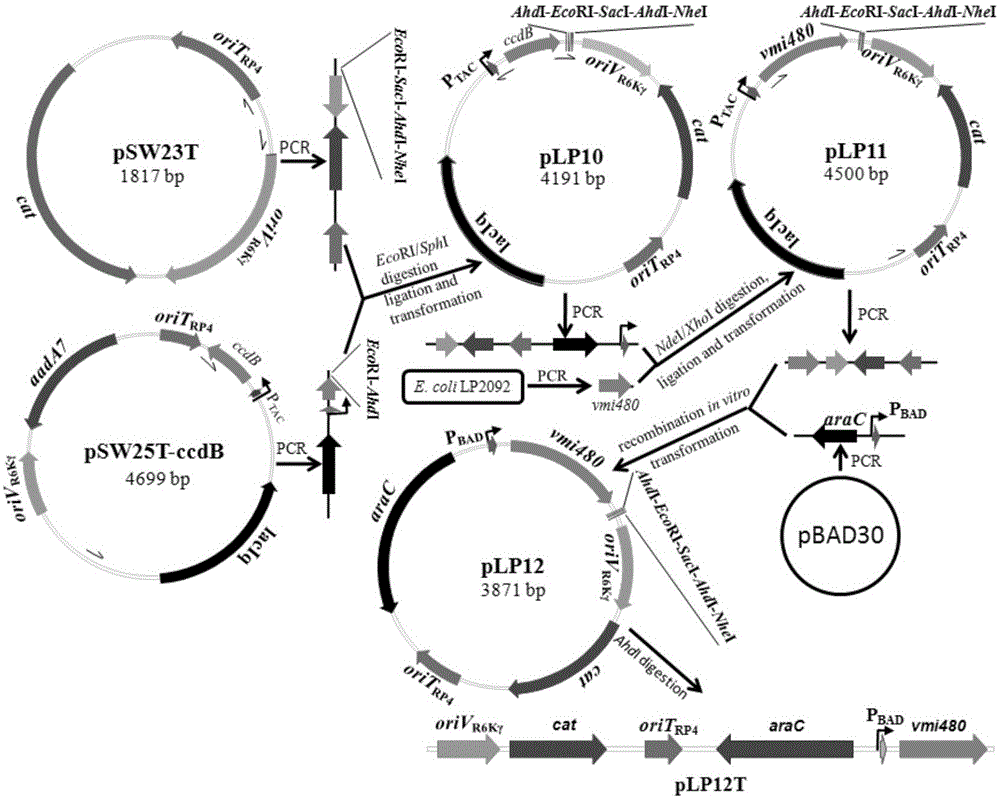
The invention discloses a universal gene-knockout suicide vector for vibrios and a construction method theroef and provides an application thereof in gene knockout of the vibrios. The universal gene-knockout suicide vector pLP12 is a ring-shaped vector and comprises a PBAD promoter, a repressor protein gene araC, an RP4 transferring initiation site, a chlorampenicol resistant gene, an R6K duplicating initiation site, a multiple-cloning-site area and a lethal gene vmi480; the multiple-cloning-site area at least contains two AhdI restriction enzyme digestion sites; the suicide vector pLP12 is subject to AhdI restriction enzyme digestion to form linearized suicide vector pLP12T. The universal gene-knockout suicide vector adopts entirely-new reverse selection genes vmi480 and is used for replacing the common sacB gene. Foreign fragments carried by the pLP12T are transferred to vibrio cells to be mutated by a jointing mode, under the pressure of antibiotics and reverse selection of products of lethal gene vmi480, first-time homologous recombination and second-time homologous recombination are carried out on the vibrios successively, and finally the mutant strain with deletion of target genes is generated.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electrotransformation method for introducing shuttle plasmid into corynebacterium acetoacidophilum
InactiveCN103160535AReduce hindranceAvoid cutsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAmpicillin
The invention provides an electrotransformation method for introducing shuttle plasmid into corynebacterium acetoacidophilum. The method is mainly used for rapidly and effectively introducing shuttle-expression recombinant plasmid in escherichia coli and corynebacterium acetoacidophilum into corynebacterium acetoacidophilum through electrotransformation. Through controlling composition of a culture medium, cell culture time, ampicillin processing time, methylation of the plasmid, heat shock time and temperature and electric shock conditions, a high efficiency electrotransformation competent cell is prepared, a blocking effect of the cell wall of corynebacterium acetoacidophilum on the shuttle plasmid is weakened, restriction enzyme digestion of corynebacterium acetoacidophilum on the shuttle plasmid is reduced, so the shuttle plasmid can be highly efficiently introduced into corynebacterium acetoacidophilum through electrotransformation, and electrotransformation efficiency reaches 6.4 * 10<4> cfu / mu g DNA.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of preparing recombinant small molecular protein or polypeptide with hirudin as fusion partner
InactiveCN103819546APlant peptidesFusions for enhanced expression stability/foldingFusion Protein ExpressionProtein target
The invention provides a new method of fusion expressing a small molecular protein (polypeptide). The new method is characterized by comprising the following steps: using hirudin as a fusion partner (label), splicing the protein (polypeptide) with a small molecular mesh to the downstream of the hirudin as the fusion partner to carry out fusion expression, designing a connecting peptide (which contains protease or a chemical cutting site or intein as a self-cuttable protein intron) between the fusion partner and a target protein (polypeptide), and releasing the target protein (polypeptide) by restriction enzyme digestion or chemical cutting or induced self cutting after fusion protein expression. The new method has the advantages that (1) as the hirudin as the fusion partner (label) is smaller (with the molecular weight of 7Kd), the rate of the protein (polypeptide) with the small molecular mesh accounting for a fusion protein can be effectively increased, and the yield of the target small molecular protein (polypeptide) is finally increased; (2) the hirudin still has the anticoagulant activity after being fused as the fusion partner (label), and the expression and the purification of the fusion protein can be conveniently detected and traced in real time.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Polypeptide mixture isoelectric focusing separation method for proteomics analysis
InactiveCN103926301AAvoid lossAvoid degradationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRestriction enzyme digestionIon exchange
The invention discloses a polypeptide mixture isoelectric focusing separation method for proteomics analysis. The method comprises the following steps: performing restriction enzyme digestion on a total protein mixture of a biological sample completely to obtain relatively short peptide fragment mixtures; re-dissolving the peptide fragment mixtures by using a peptide fragment isoelectric focusing buffer solution; performing isoelectric focusing electrophoresis in a loading manner by adopting a loading cup, so as to realize the effective separation of a complex peptide fragment mixture; performing desalination on a taken polypeptide mixture pre-separated from each groove and performing mass spectrometry analysis so as to obtain more polypeptide signals, higher peptide fragment covering rate and higher protein identification number compared with those obtained when a conventional method is adopted. The method is precise, efficient and low in cost, can be used in multidimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrum identification technology systems of total proteins of the various biological samples, can replace a conventional ion exchange chromatography pre-separation method so as to realize the efficient pre-separation of the peptide fragment mixtures, and avoids the lost of peptide fragments, and therefore, proteome expression profile information with the high covering rate can be established.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for separating short interspersed repeated segments based on magnetic bead probe complexes
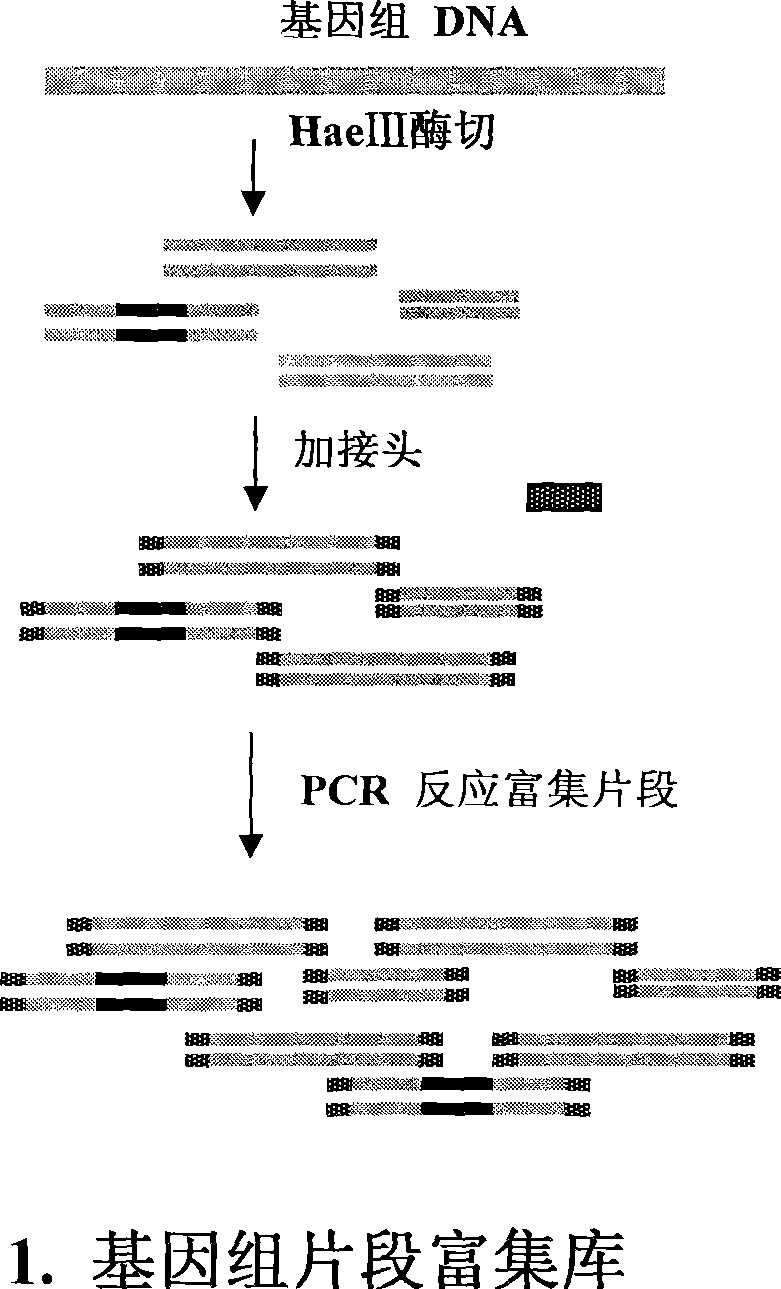
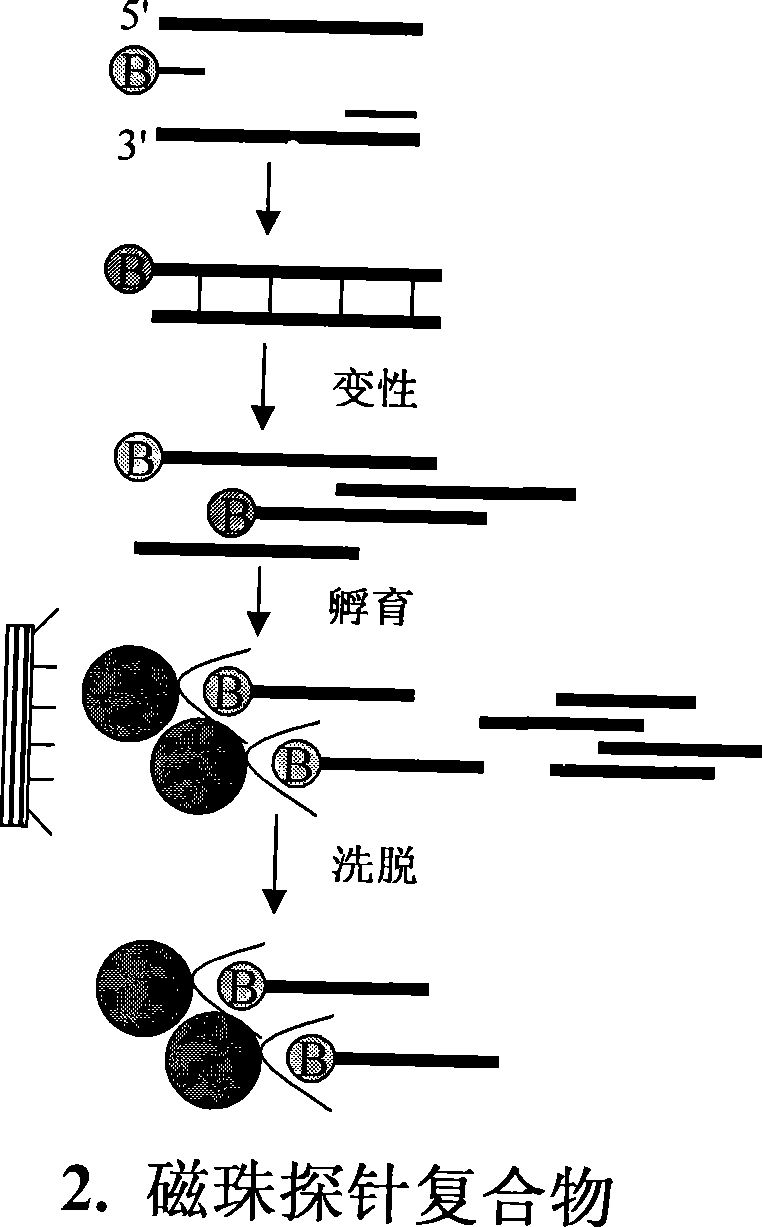
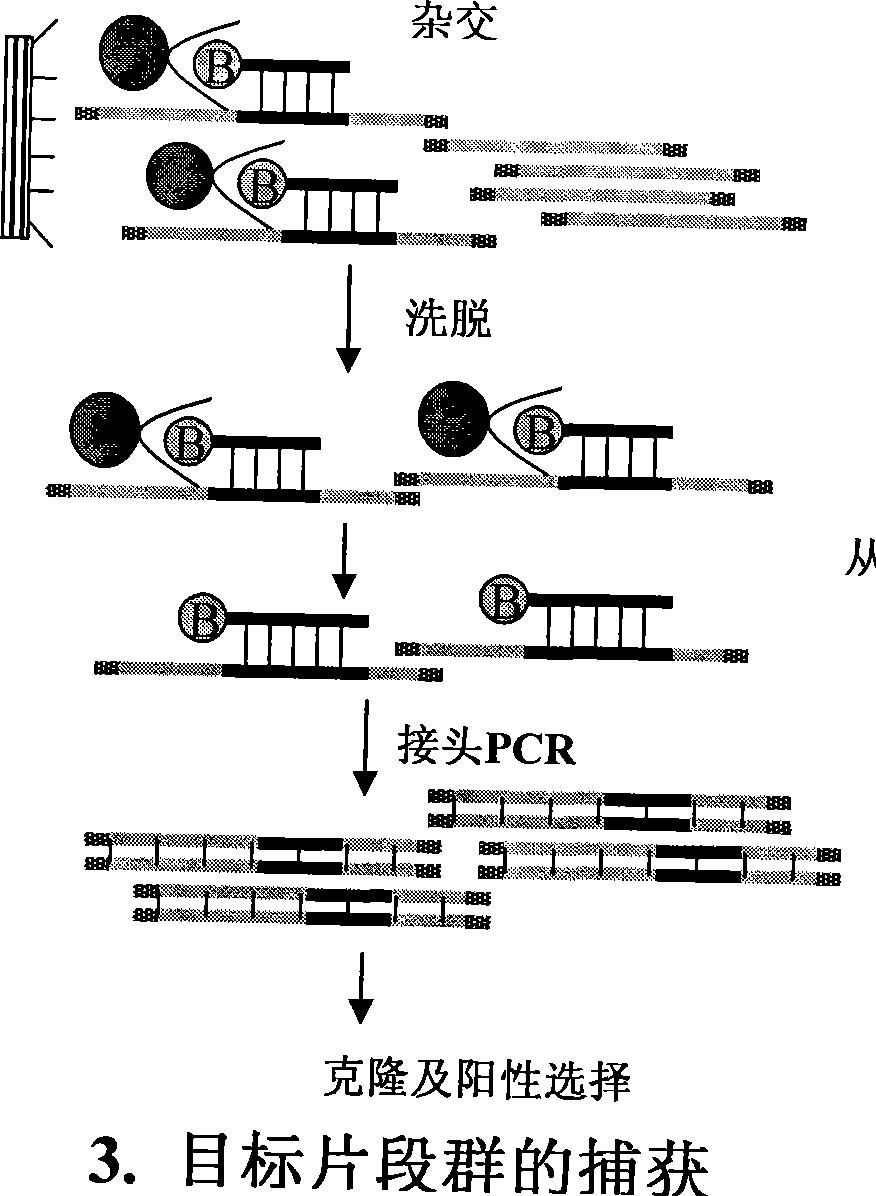
InactiveCN101381724AShort experiment cycleReduce consumption costDNA preparationPositive selectionGenomic Segment
The invention discloses a method for separation, dispersion and sequence repetition of a bead-probe complex. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the preparation of a genome fragment enriched library, which is to perform restriction enzyme digestion on a genome, to recover fragments with adequate dimensions, to add linkers on T4 ligase, and to perform cyclic amplification of the genome fragment library after restriction enzyme digestion through PCR of a small number of linkers; secondly, the preparation of the bead-probe complex, which is to realize biotin labeled DNA probes by the primer amplification method, and to bind biotin labeled single-chain probes on beads; and thirdly, acquisition of a target fragment group, which is to perform crossover on the bead-probe complex and the genome library, to acquire a target fragment, to separate and clone the target fragment, and to perform positive selection on the target fragment. The method is simple, high-efficiency and quick, shortens the experimental period, reduces the cost consumption, greatly improves the efficiency, and does not require special experimental equipment.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Cell free biosynthesis of high-quality nucleic acid and uses thereof
InactiveCN101103122ASimple purification stepsImprove fidelityFermentationCell freeRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention provides an improved cell free amplification method capable of producing large quantities of therapeutic-quality nucleic acids and methods of using the synthesized nucleic acid in research, therapeutic and other applications- The methods combine several different state-of-the-art procedures and coordinate their applications to affordably synthesize nucleic acids for therapeutic purposes. It combines in vitro rolling circle amplification, high fidelity polymerases, high affinity primers, and streamlined template specifically designed for particular applications. For expression purposes, the templates contain an expression cassette including a eukaryotic promoter, the coding sequence for the gene of interest, and a eukaryotic termination sequence. Following amplification, concatamers are subsequently processed according to their intended use and may include: restriction enzyme digestion for the production of short expression cassettes (SECs); ligation steps to circularize the SEC (CNAs); and / or supercoiling steps to produce sCNAs. The final product contains nearly non-detectable levels of bacterial endotoxin.
Owner:CYTOGENIX INC
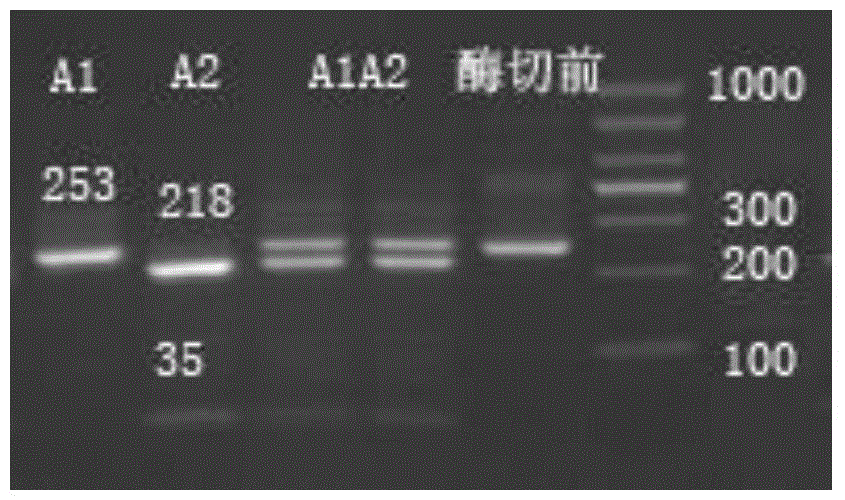
Method for detecting beta-casein genotype on basis of restriction enzyme digestion
The invention discloses a method for detecting beta-casein genotype on the basis of restriction enzyme digestion. The method comprises the following steps of designing a primer by which amplified fragments of an A1 type beta-casein gene contain TaqI cleavage sites but amplified fragments of an A2 beta-casein gene do not generate TaqI cleavage sites according to a base sequence of the beta-casein gene; performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on a to-be-detected dairy cow genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) by using the primer; performing digestion on amplified products by using restriction enzyme TaqI; and judging according to a result of agarose gel electrophoresis. The amplified products which contain A1 beta-casein can generate a 218 bp fragment and a 35 bp small fragment after digestion; and the amplified products of the A2 beta-casein gene cannot generate the TaqI digestion sites, cannot be cut off by TaqI, and are still 253 bp bands. By the method for detecting the beta-casein genotype on the basis of restriction enzyme digestion, different genotypes of the beta-casein can be detected, so that milk consumed by people contains A1 type beta-casein.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Determining method for sequencing enzyme digestion combination in sequencing genotyping technology
ActiveCN105368930AGuaranteed accuracyLow parting costMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionSpecific enzyme
The invention provides a determining method for sequencing enzyme digestion combination in a sequencing genotyping technology. The determining method comprises the following steps that 1, restriction enzyme digestion site predicting is performed on a target genome, and the number of enzyme digestion segments obtained through different enzyme digestion modes is counted; 2, a joint sequence and a PCR amplification primer sequence at the two ends of each enzyme digestion segment are designed according to the predicted enzyme digestion segments in the various enzyme digestion modes in the step 1; 3, sequencing libraries are constructed through a GBS technology for the different enzyme digestion modes; 4, sequencing is performed through the sequencing libraries constructed in the step 3; 5, SNP marker sites are obtained according to sequencing results; 6, the specific enzyme digestion combination for the target genome is determined according to the number of the SNP marker sites and the enzyme digestion segment sizes which are obtained through different enzyme digestion combinations.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Amplification primer for detecting polymorphism of children's calcium absorption genes and application of amplification primer
InactiveCN106755532AImprove accuracyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRestriction enzyme digestionNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection medical molecules, and relates to an amplification primer for detecting polymorphism of children's calcium absorption genes and application of the amplification primer, in particular to a detection primer used for polymorphism of a nucleotide at a FokI (rs2228570) SNP site. The amplification primer comprises a specific primer which is designed according to polymorphism of a mononucleotide at a FokI (rs2228570) site. According to the method, a restriction enzyme digestion method adopted to detect a VDR gene is high in accuracy, results are visual, specificity is good and a false positive and false negative rate is low, and therefore, the method is a simple novel method for judging children's calcium absorption. Besides, the PCR amplification primer for detecting polymorphism of children's calcium absorption genes, a detection kit and a detecting method thereof have a very high application value, are simple and convenient to operate, are low in equipment requirement, are wide in adaptation and are especially suitable for being popularized and applied.
Owner:天津脉络医学检验有限公司
Gene site-directed multi-site mutation method
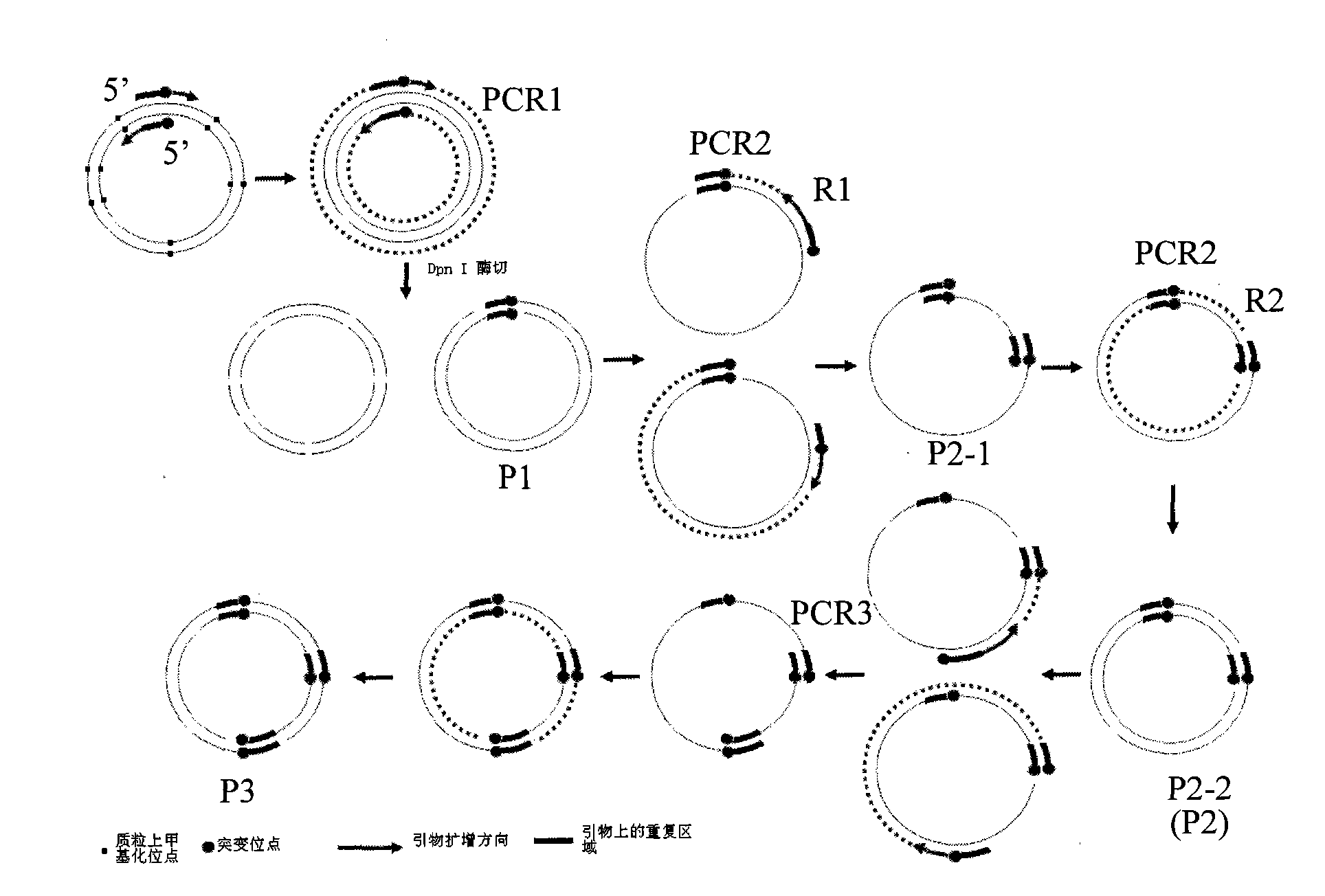
ActiveCN101580829ALow costShorten the timeRecombinant DNA-technologyFermentationForward primerMulti site
The invention relates to a gene site-directed multi-site mutation method, which comprises the following steps of: respectively designing a forward mutation primer and a reverse mutation primer according to sites of sequences where mutated bases are located, wherein the mutation sites are positioned in the middle of the forward primer and the position close to 5' end of the reverse primer; designing the same pairs of mutation primers according to the number of the mutation sites; taking a plasmid containing methylated sites as a template, carrying out the first round of PCR reaction on the first pair of primers with high fidelity polymerase for amplifying a gene fragment containing the first mutation base; adopting DpnI enzyme for carrying out the restriction enzyme digestion on the gene fragment, removing the template plasmid, obtaining a ring plasmid with a target mutation site and an opening; then taking the ring plasmid as the template and sequentially adding the residual mutation primers for PCR reaction for obtaining a ring plasmid with a plurality of mutation sites and an opening. The method utilizes a complementary region of the primers to complete the polymerase chain reaction of the ring plasmid template with the opening, thereby introducing the site-directed mutation with more than one site.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com