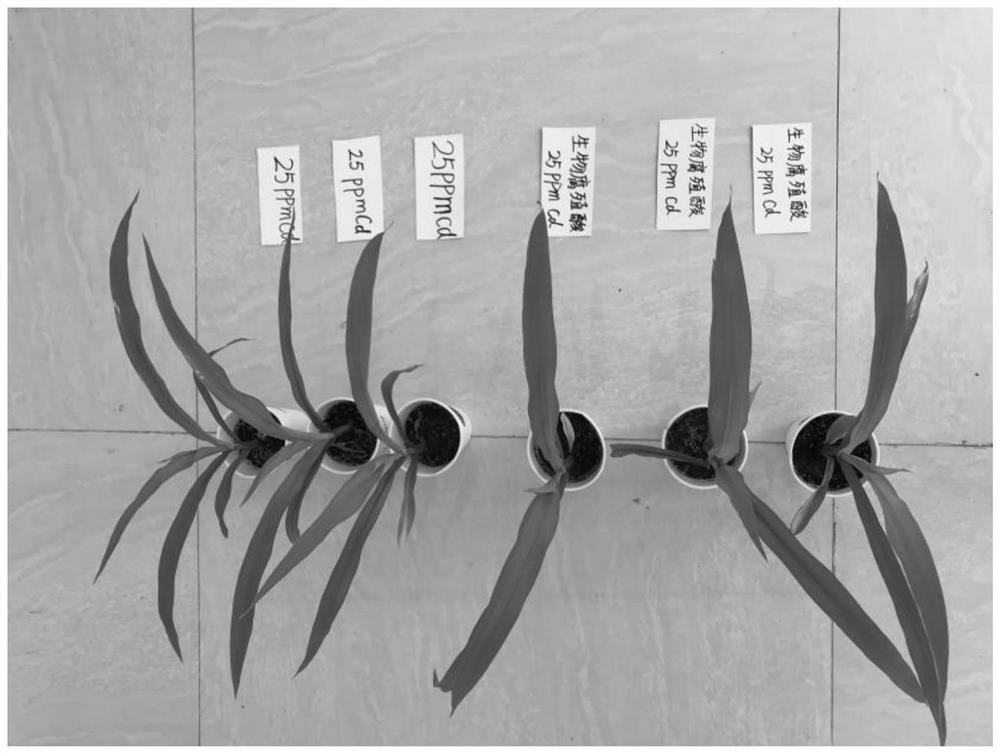
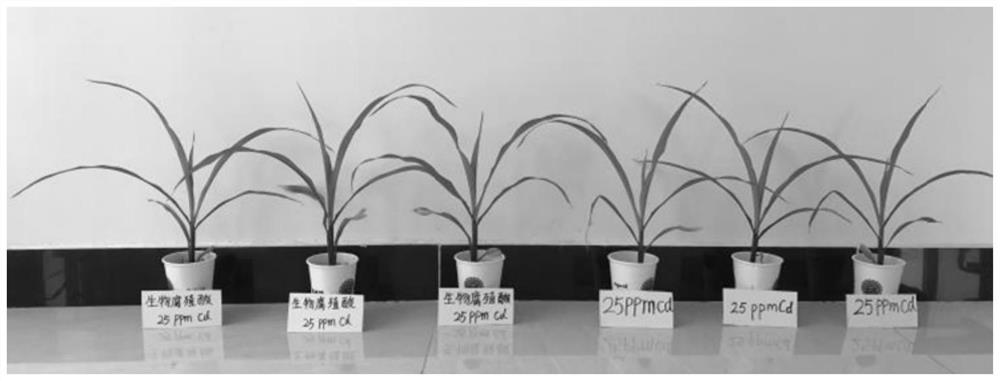
Basophilic Cupriavidus strain KY678 with functions of passivating heavy metal cadmium and promoting plant growth and application of basophilic Cupriavidus strain KY678
A technology to promote plant growth and copper greedy bacteria, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of reducing heavy metal activity and environmental risks, easily destroying soil structure, soil fertility decline, etc., to achieve the effect of alleviating poison, promoting plant growth and reducing absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: High-throughput screening of microbial strains with heavy metal resistance (cadmium (Cd)) function
[0036] 1.1 Soil sample collection
[0037] A total of more than 170 soil samples were collected from all over the country (especially in areas seriously polluted by heavy metal cadmium), including black soil, clay, red soil and other soil samples, respectively from forests, grasslands, wheat fields, rice fields, etc. These soil samples are marked with the collection place (province, city, county), collection time, and collection source (forest, grassland, wheat field, rice field, etc.).
[0038] 1.2 High-throughput enrichment screening of microbial strains resistant to heavy metals (cadmium (Cd))
[0039] Take five soil samples (0.2g for each soil sample) and mix them and place them in 50mL 250ppm cadmium liquid culture medium, shake and cultivate them at 200r / min at 30°C for 3 days, observe and record changes in the turbidity of the liquid medium ( 250ppm c...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2. Verify the ability of cadmium-tolerant microorganisms to passivate heavy metal cadmium in liquid
[0051] 2.1 Microbial method preliminary verification of the ability of cadmium-tolerant microorganisms to passivate heavy metal cadmium (Cd) in liquid
[0052] It is reported in the existing literature that the ability to passivate heavy metal cadmium (Cd) of microorganisms is mainly determined by atomic absorption spectrometry to determine the content of residual heavy metals in liquid or potted plants. The advantage of this method is mainly reflected in the fact that the cadmium content of heavy metal cadmium pollutants can be directly determined and the determination results are accurate. However, if the number of microorganisms to be verified to passivate heavy metal cadmium (Cd) reaches tens or even hundreds, this method has certain defects in screening efficiency. For example, flame atomic absorption spectrometry has high requirements on instruments and c...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3.KY678 strain identification-determination of 16s rDNA
[0085] 3.1 Preparation of DNA template
[0086] 3.1.1 Pick the purified single colony to the bottom of the EP tube, add 200 μL of 5% (w / v) BT-chelex 100 (distilled water configuration, sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes); ℃ or -80 ℃, then thawed at room temperature, centrifuged at 6000r / min for 3min, and 2μL of the supernatant was taken as a template.
[0087] 3.2 16S rDNA amplification
[0088] The 16S gene was amplified according to the 16S amplification system. The 16S PCR amplification system is as follows:
[0089]
[0090]
[0091] PCR amplification program:
[0092] Step 1: 95°C, 5min;
[0093] The second step: 94°C, 1min; 55°C, 1min; 72°C, 1.5min, 35 cycles.
[0094] Step 3: 72°C, 10min; store at 4°C.
[0095] The 16S rDNA sequence (SEQ ID No.1) of strain KY678 obtained is as follows:
[0096] TGGGGCCGCATGCTTACCATGCAGTCGAACGGCAGCGCGGGCTTCGG CCTGGCGGCGAGTGGCGAACGGGTGAGTAATACATCGGAACGTG...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com