Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
209 results about "Cytosol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cytosol, also known as intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix, or groundplasm, is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.
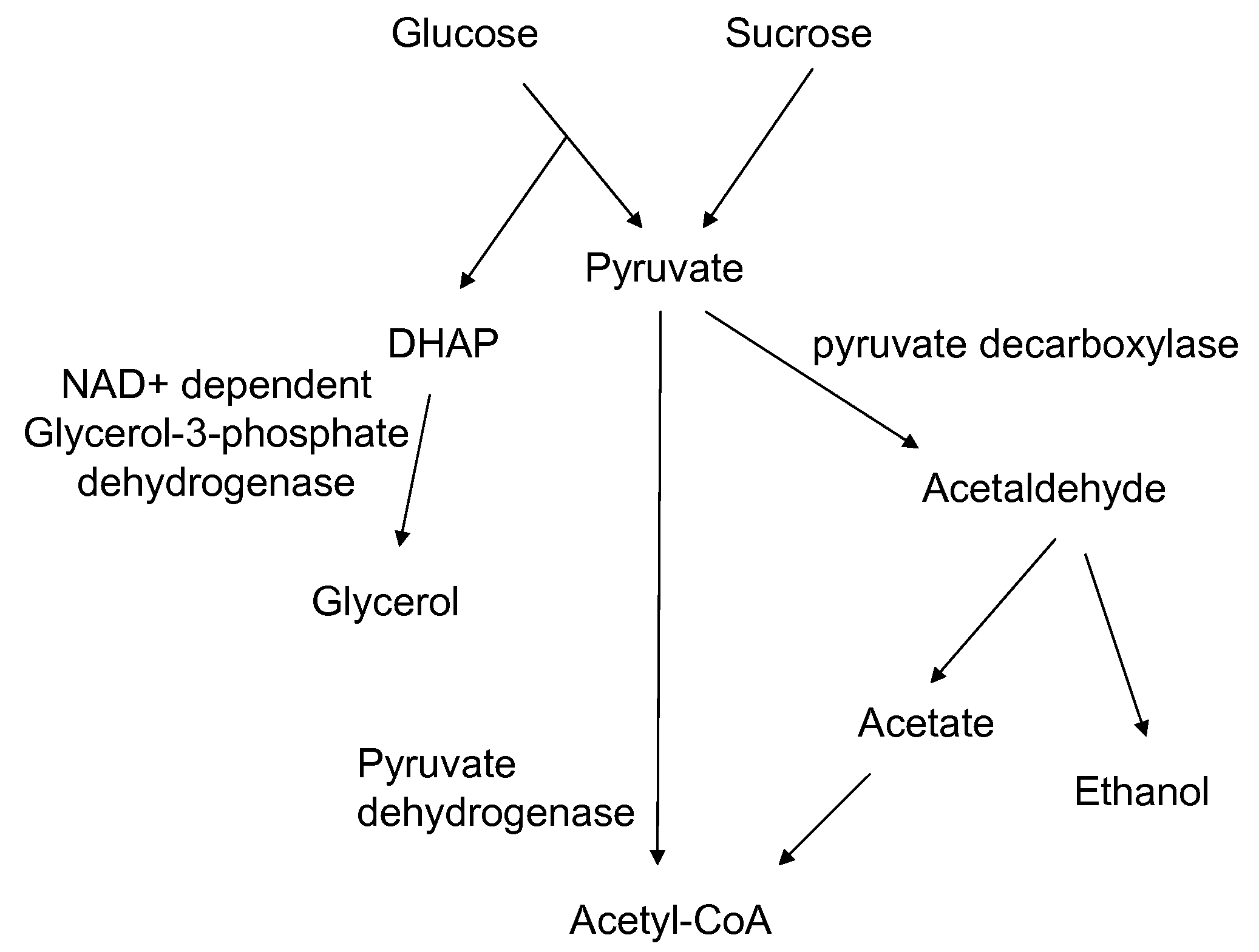
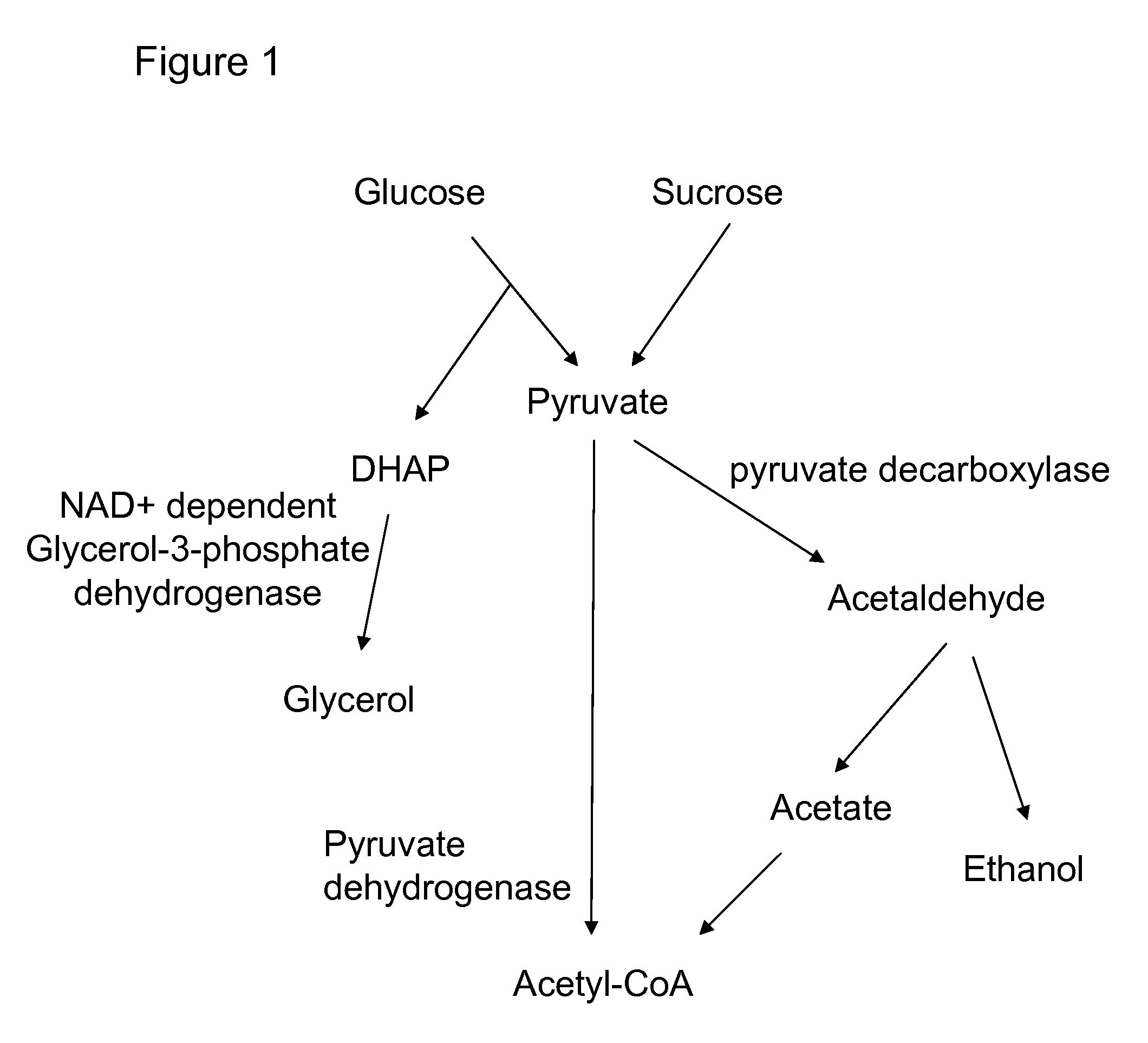
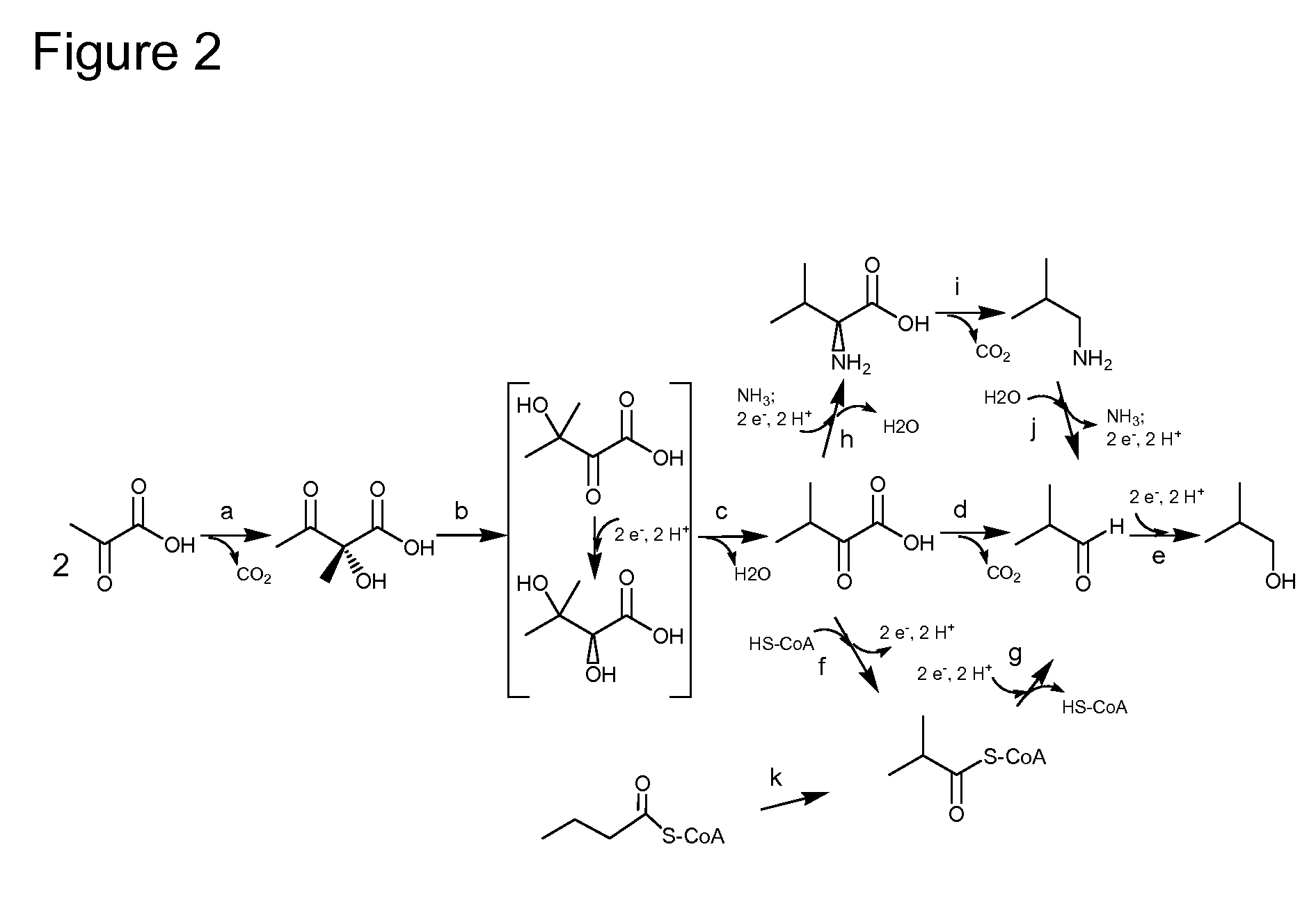
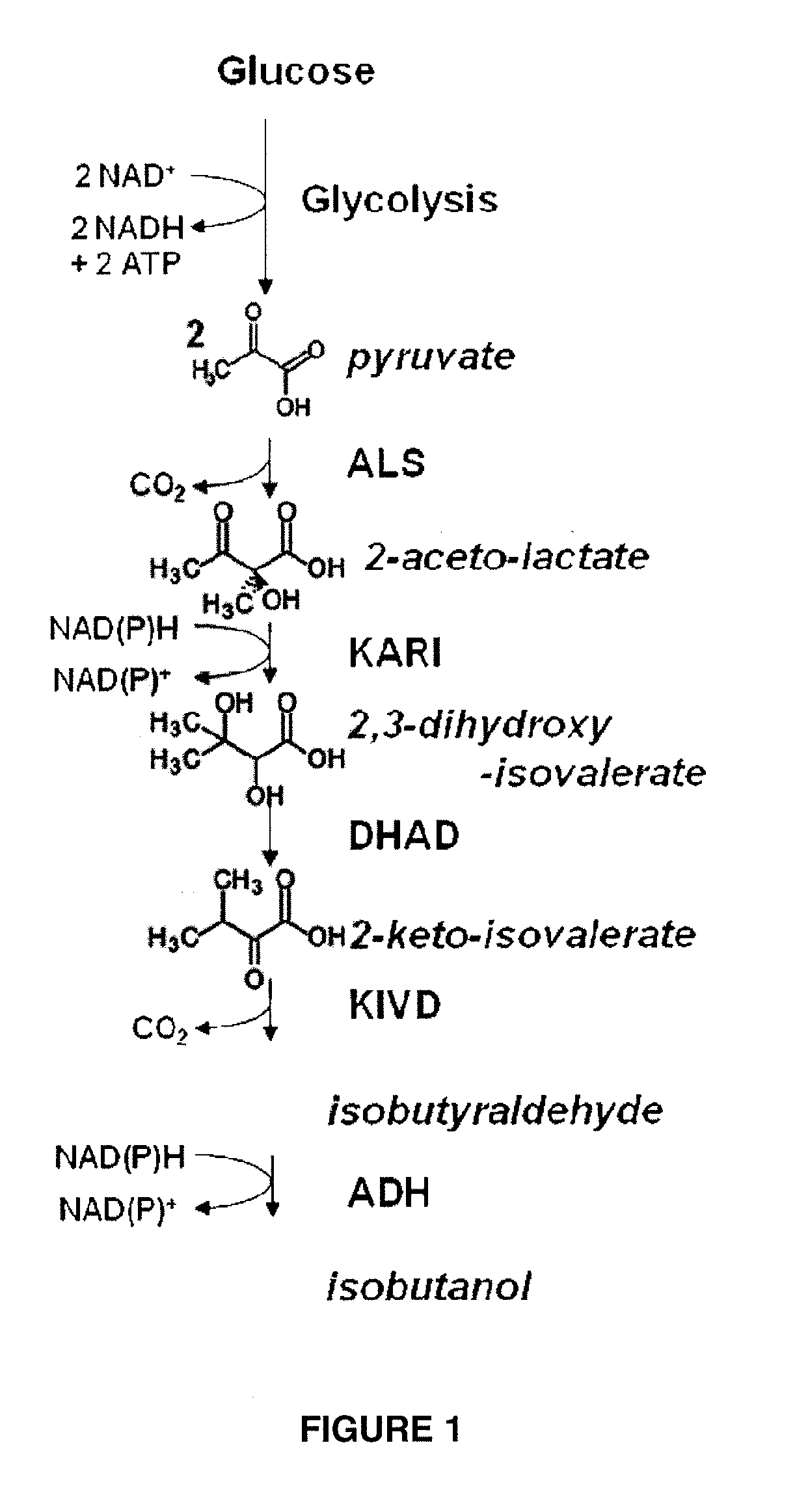
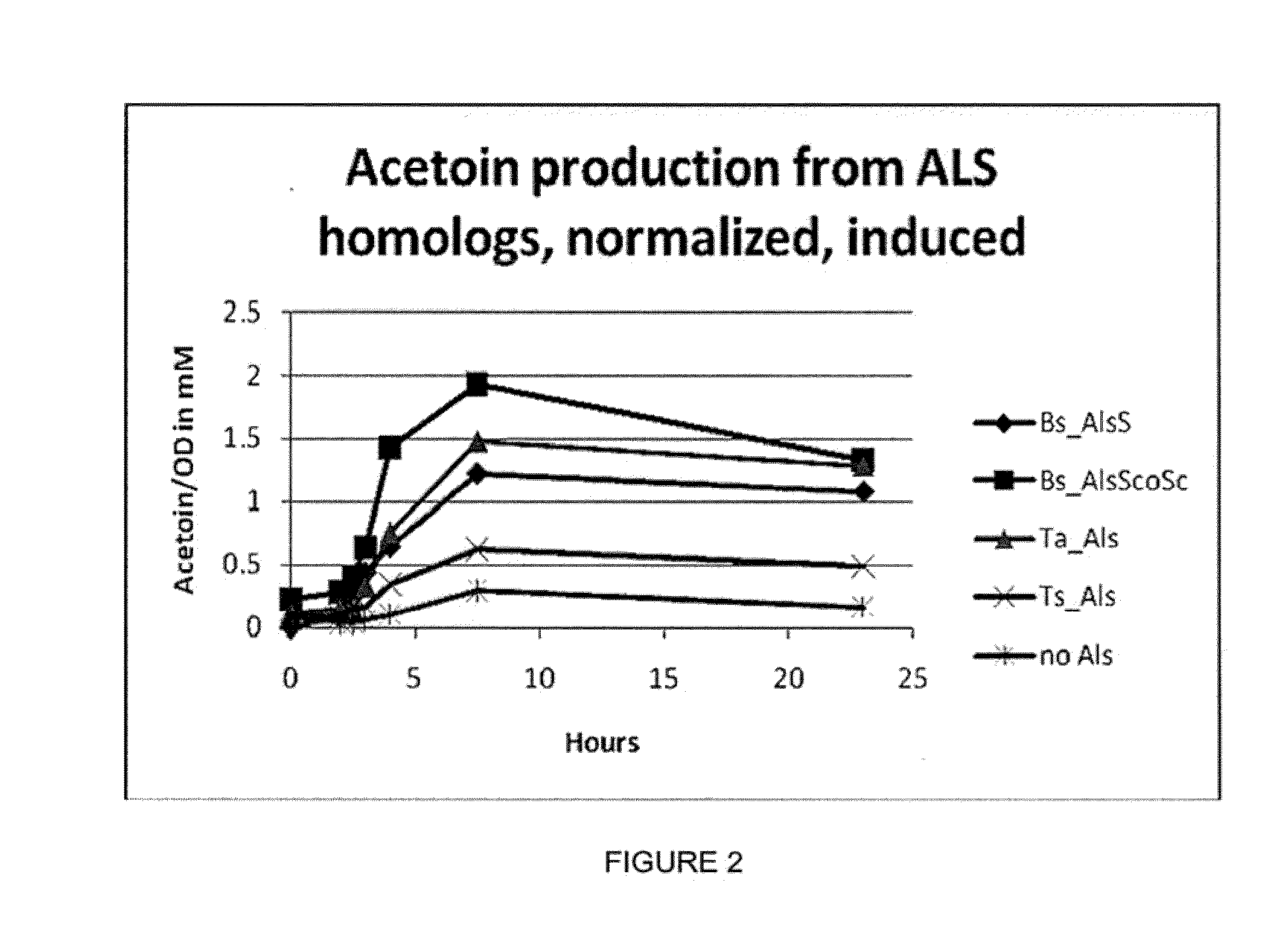
Enhanced pyruvate to acetolactate conversion in yeast
ActiveUS20090305363A1Improve throughputReduction of pyruvate decarboxylase activityFungiTransferasesYeastCytosol
A high flux in conversion of pyruvate to acetolactate was achieved in yeast through expression of acetolactate synthase in the cytosol in conjunction with reduction in pyruvate decarboxylase activity. Additional manipulations to improve flux to acetolactate are reduced pyruvate dehydrogenase activity and reduced glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. Production of compounds having acetolactate as an upstream intermediate benefit from the increased conversion of pruvate to acetolactate in the described strains.
Owner:GEVO INC
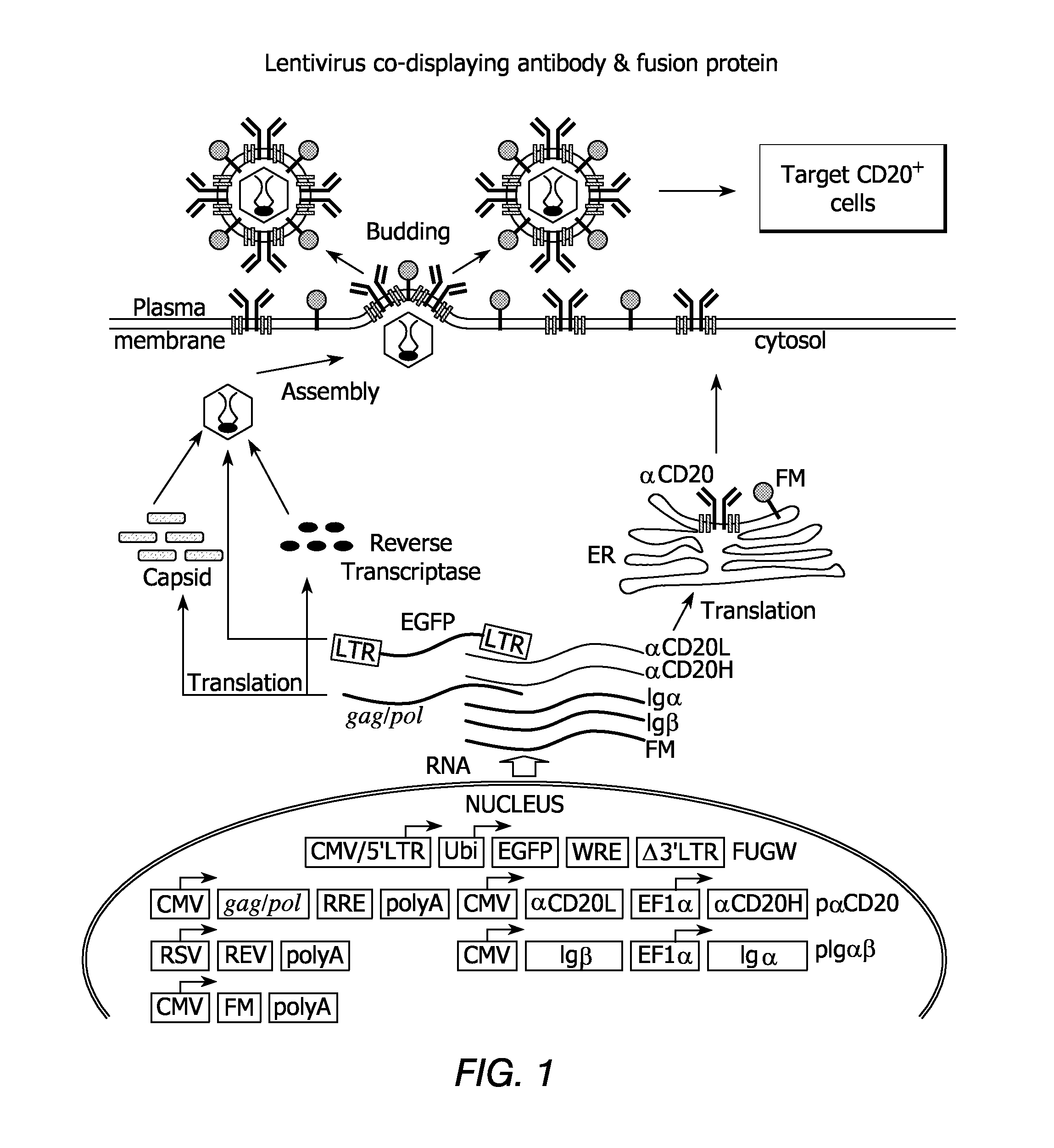
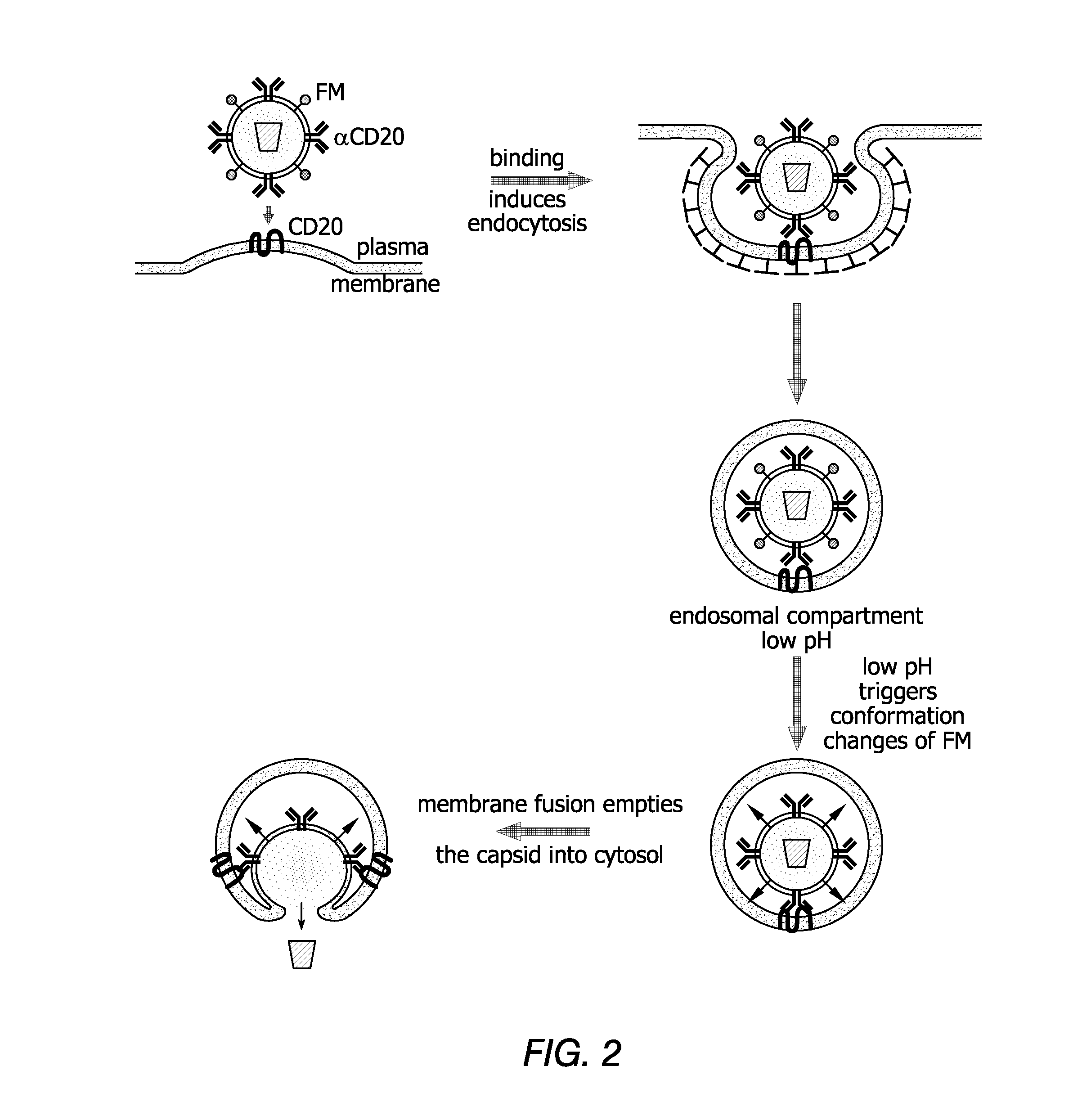
Method of targeted gene delivery using viral vectors
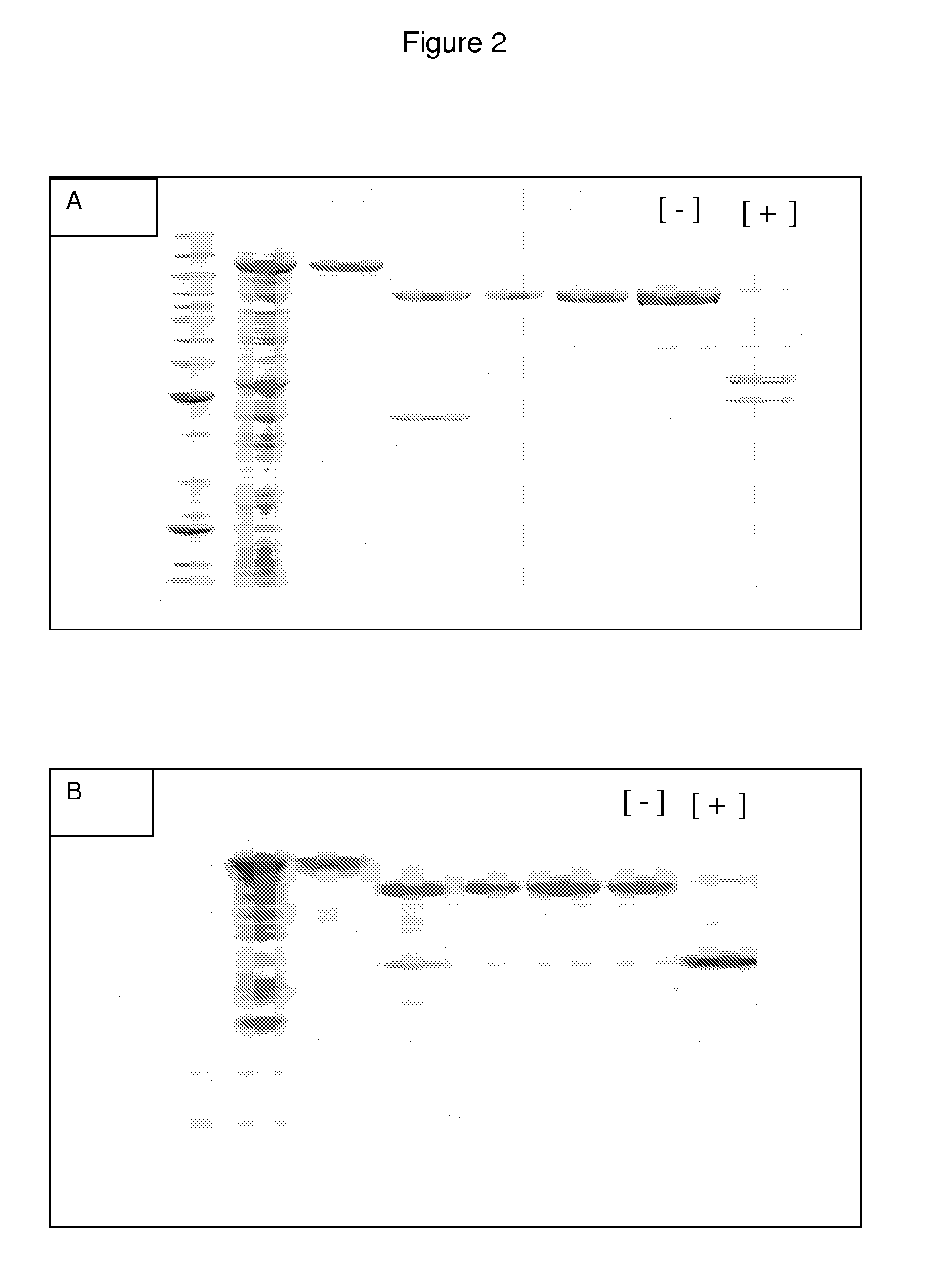
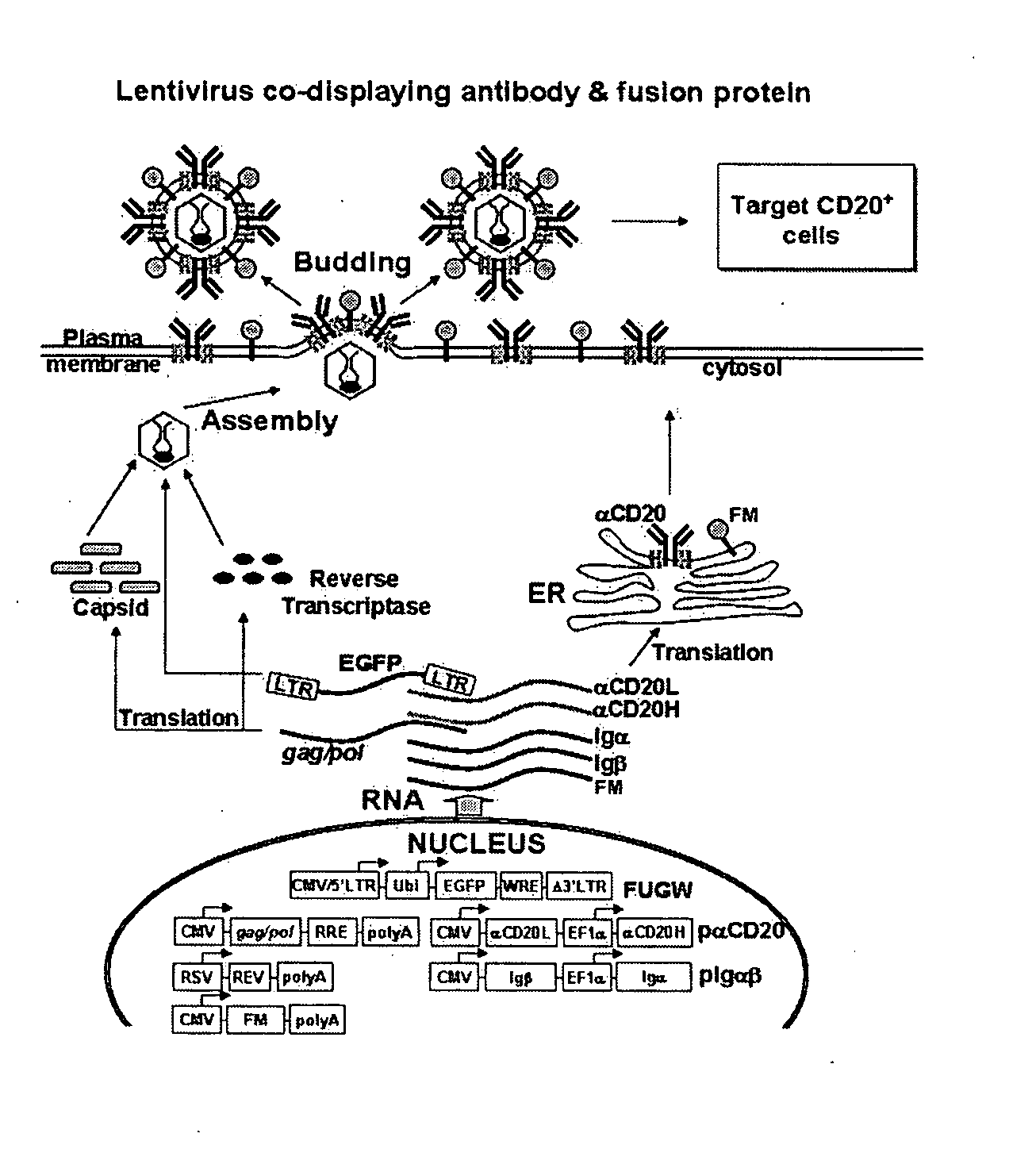
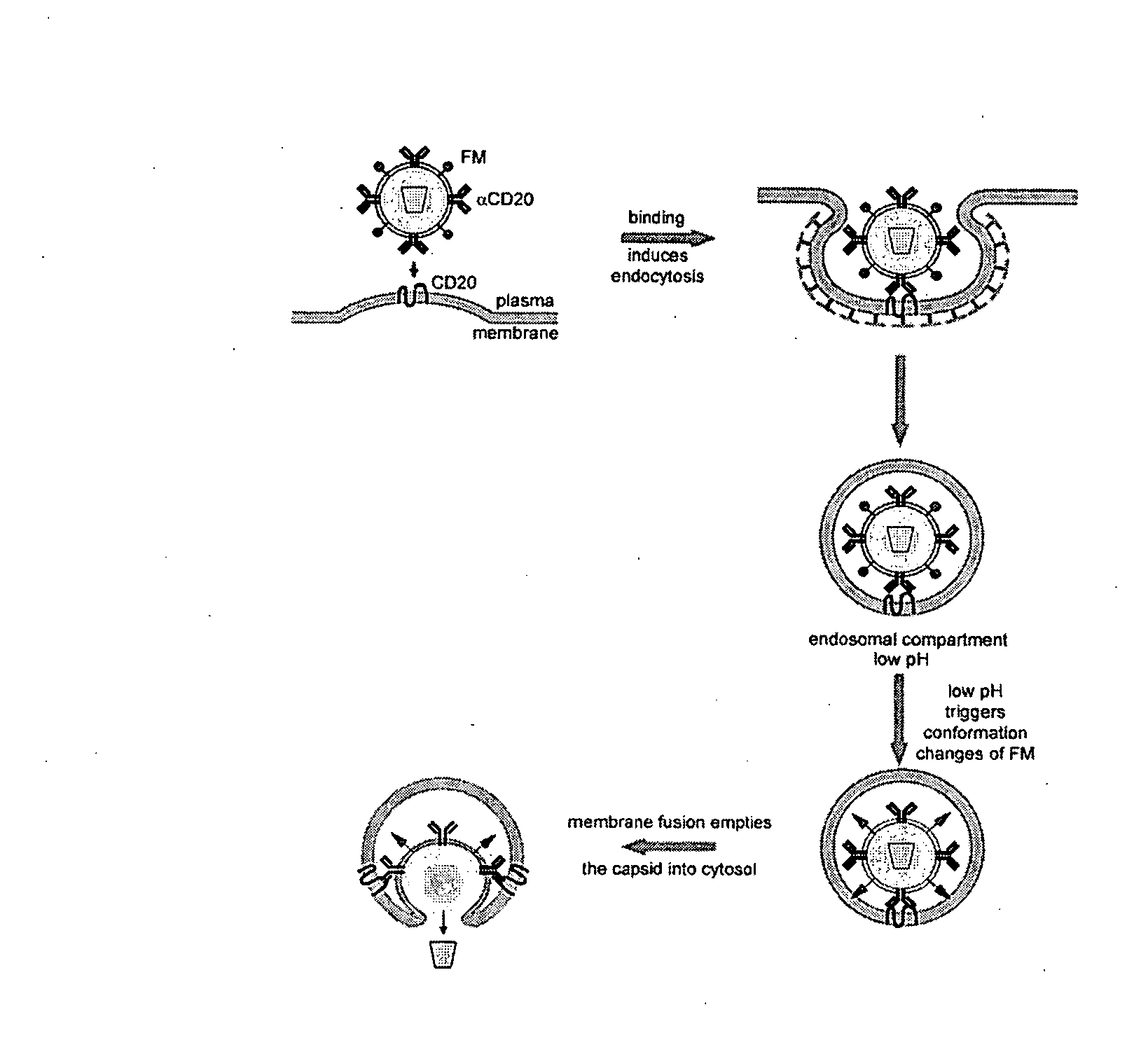
Methods and compositions are provided for delivering a polynucleotide encoding a gene of interest to a target cell using a virus. The virus envelope comprises a cell-specific binding determinant that recognizes and binds to a component on the target cell surface, leading to endocytosis of the virus. A separate fusogenic molecule is also present on the envelope and facilitates delivery of the polynucleotide across the membrane and into the cytosol of the target cell. The methods and related compositions can be used for treating patients having suffering from a wide range of conditions, including infection, such as HIV; cancers, such as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and breast cancer; and hematological disorders, such as severe combined immunodeficiency.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
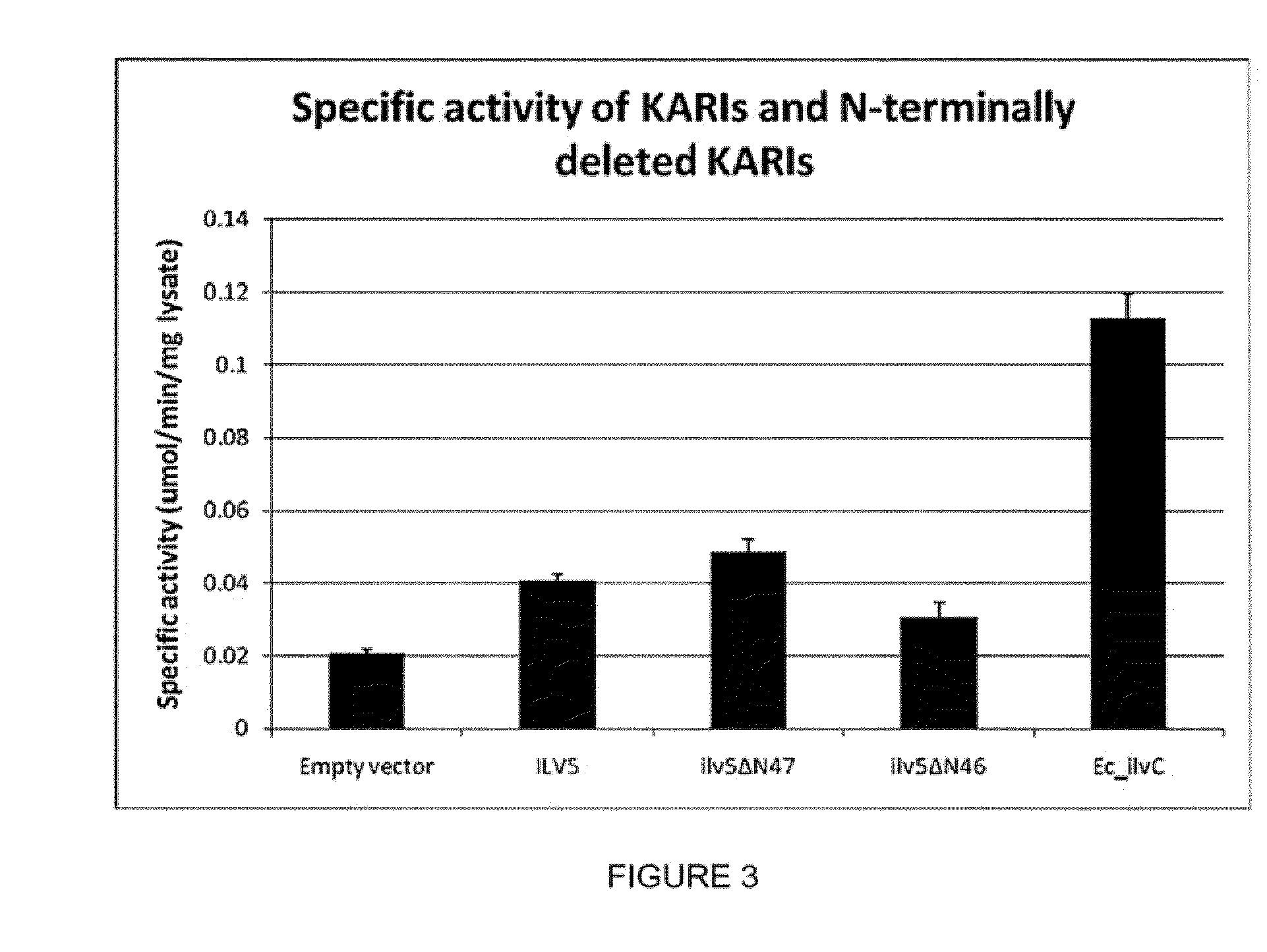
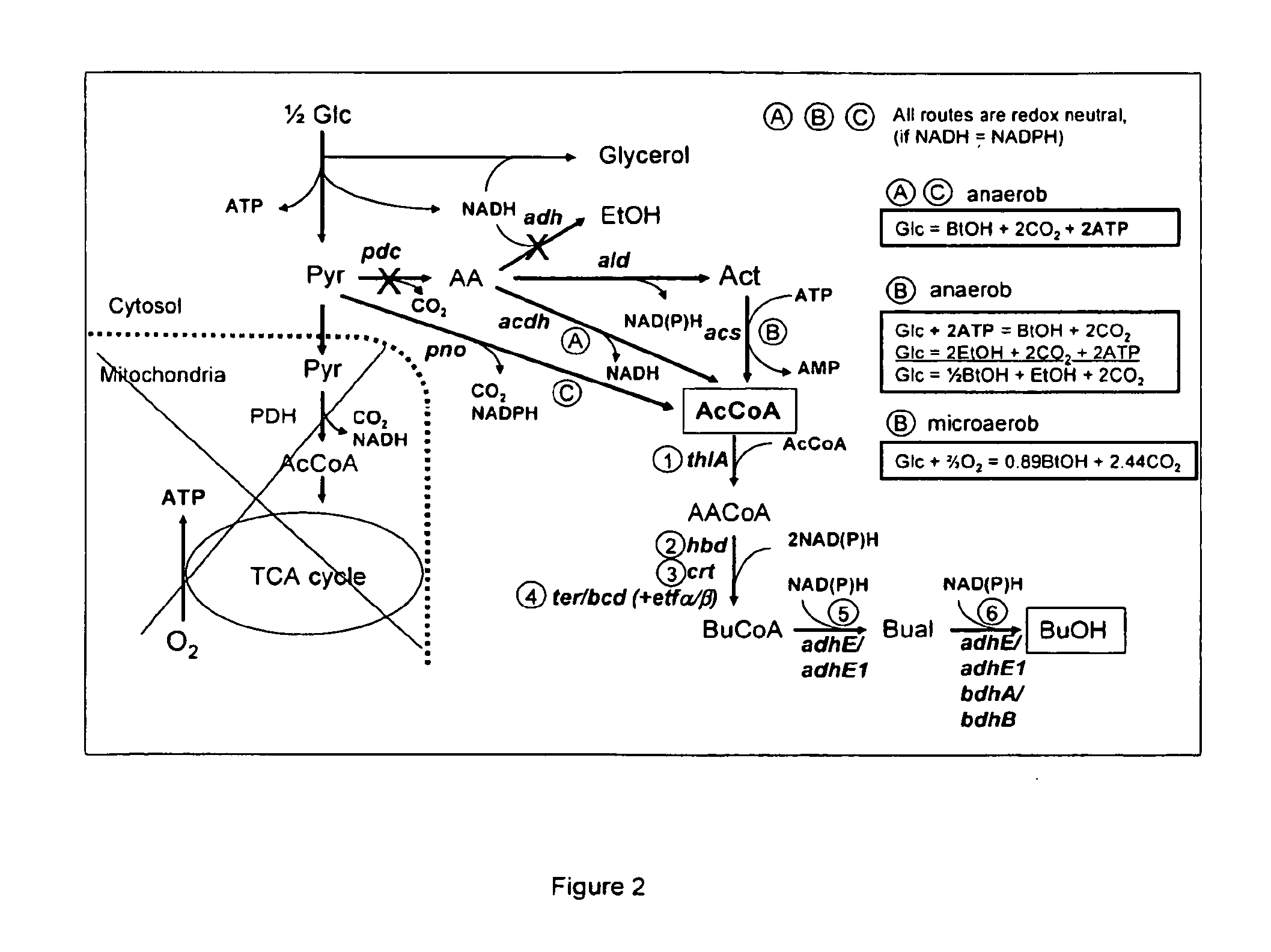
Cytosolic isobutanol pathway localization for the production of isobutanol
ActiveUS20110076733A1Increase cytosolic localizationIncrease cytosolic activityFungiBacteriaYeastIsobutanol
The present invention provides recombinant microorganisms comprising isobutanol producing metabolic pathway with at least one isobutanol pathway enzyme localized in the cytosol, wherein said recombinant microorganism is selected to produce isobutanol from a carbon source. Methods of using said recombinant microorganisms to produce isobutanol are also provided. In various aspects of the invention, the recombinant microorganisms may comprise a cytosolically active isobutanol pathway enzymes. In some embodiments, the invention provides mutated, modified, and / or chimeric isobutanol pathway enzymes with cytosolic activity. In various embodiments described herein, the recombinant microorganisms may be microorganisms of the Saccharomyces clade, Crabtree-negative yeast microorganisms, Crabtree-positive yeast microorganisms, post-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, pre-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, and non-fermenting yeast microorganisms.
Owner:GEVO INC
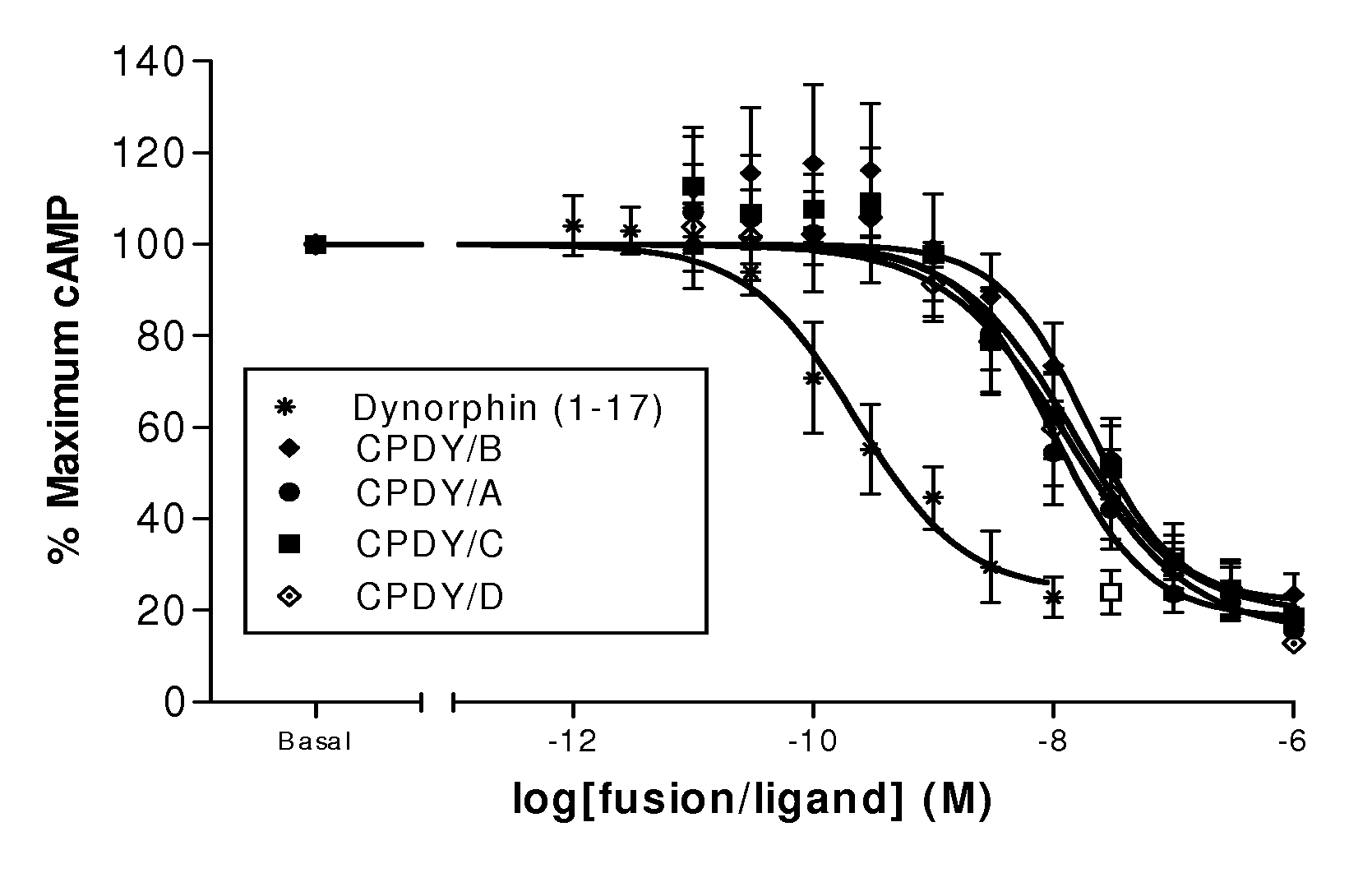
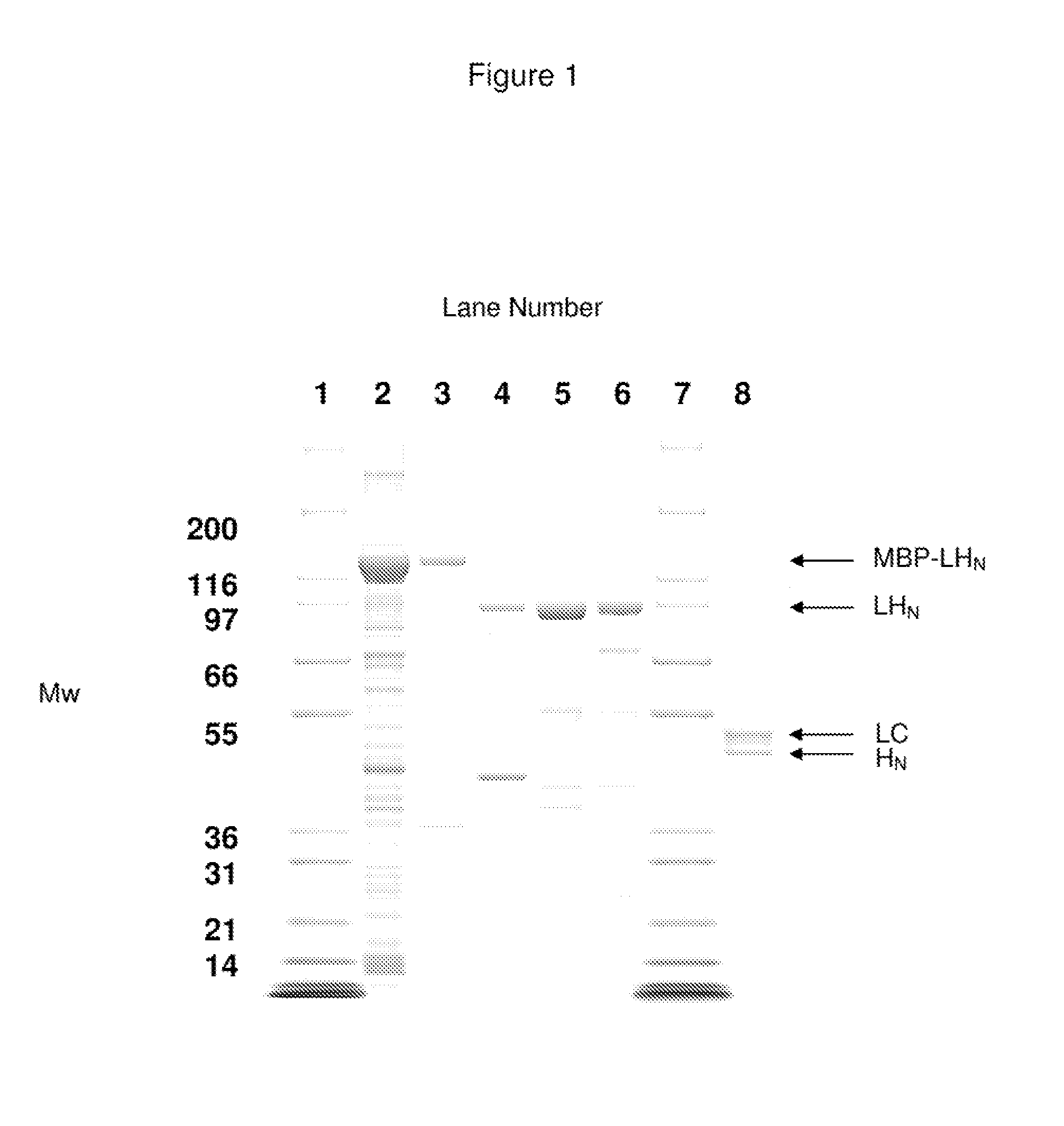
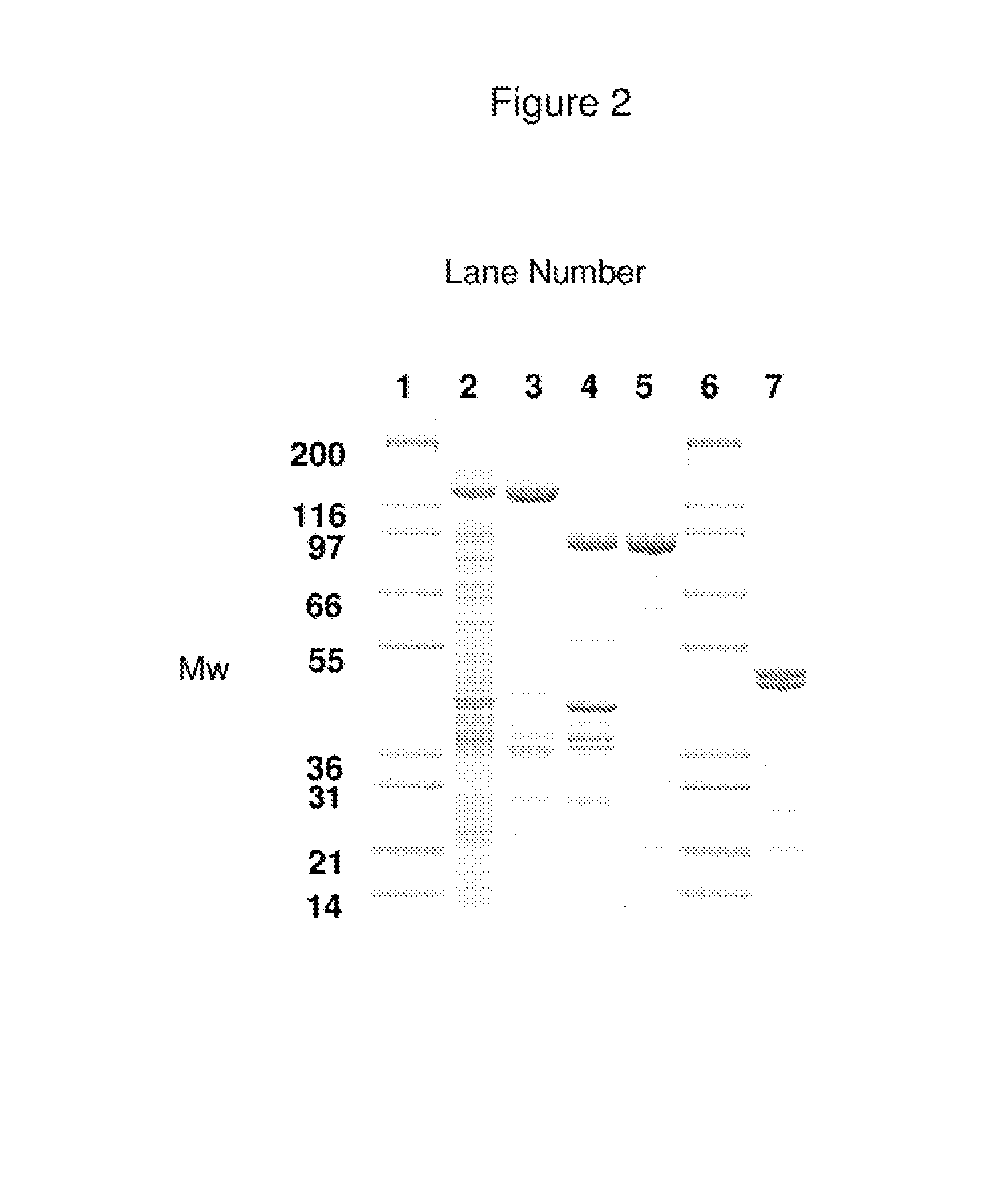
Fusion proteins
InactiveUS20110091437A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBinding siteCytotoxicity
A single chain, polypeptide fusion protein, comprising: a non-cytotoxic protease, or a fragment thereof, which protease or protease fragment is capable of cleaving a protein of the exocytic fusion apparatus of a nociceptive sensory afferent; a dynorphin Targeting Moiety that is capable of binding to a Binding Site on the nociceptive sensory afferent, which Binding Site is capable of undergoing endocytosis to be incorporated into an endosome within the nociceptive sensory afferent; a protease cleavage site at which site the fusion protein is cleavable by a protease, wherein the protease cleavage site is located between the non-cytotoxic protease or fragment thereof and the dynorphin Targeting Moiety; and a translocation domain that is capable of translocating the protease or protease fragment from within an endosome, across the endosomal membrane and into the cytosol of the nociceptive sensory afferent. Nucleic acid sequences encoding the polypeptide fusion proteins, methods of preparing same and uses thereof are also described.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY +1
Method of targeted gene delivery using viral vectors
Methods and compositions are provided for delivering a polynucleotide encoding a gene of interest to a target cell using a virus. The virus envelope comprises a cell-specific binding determinant that recognizes and binds to a component on the target cell surface, leading to endocytosis of the virus. A separate fusogenic molecule is also present on the envelope and facilitates delivery of the polynucleotide across the membrane and into the cytosol of the target cell. The methods and related compositions can be used for treating patients having suffering from a wide range of conditions, including infection, such as HIV; cancers, such as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and breast cancer; and hematological disorders, such as severe combined immunodeficiency.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Acetyl-coa producing enzymes in yeast
InactiveUS20100248233A1Increase productionFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousAcetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase
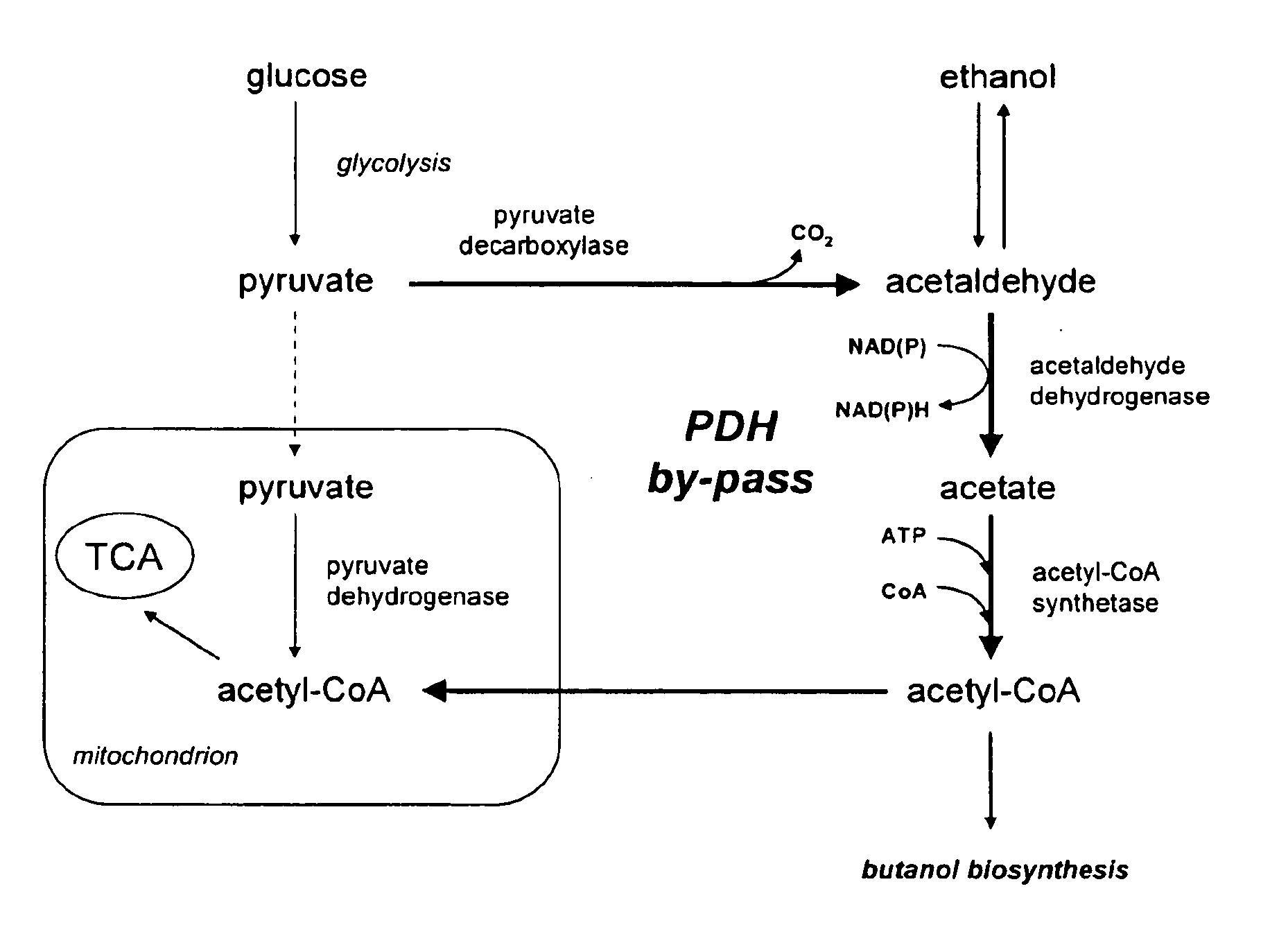
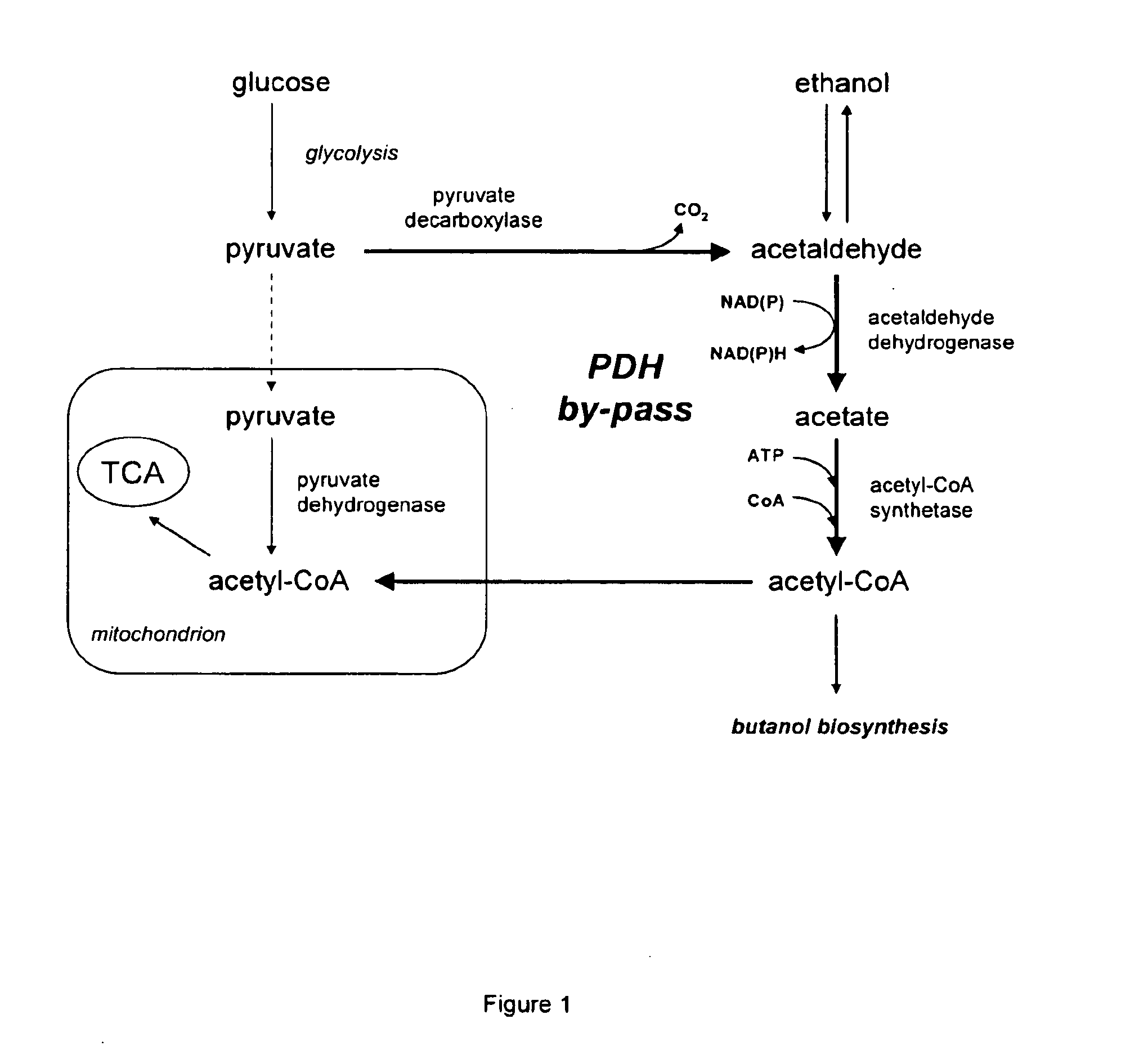
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a heterologous polypeptide having enzymatic activity for converting pyruvate, acetaldehyde or acetate into acetyl-CoA in (the cytosol of) a yeast cell comprising: a) providing a mutated yeast cell comprising a deletion of at least one gene of the (PDH) by-pass, selected from the genes encoding the enzymes pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC), acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (ALD), and acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACS); b) transforming said mutated yeast cell with an expression vector comprising a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a candidate polypeptide having potential enzymatic activity for converting pyruvate, acetaldehyde or acetate into acetyl-CoA; c) testing said recombinant mutated yeast cell for its ability to grow on minimal medium containing glucose as sole carbon source, and d) identifying said candidate polypeptide as a heterologous polypeptide having enzymatic activity for converting pyruvate, acetaldehyde or acetate into acetyl-CoA in (the cytosol of) said yeast cell when growth of said cell is observed. The invention further relates to a method of producing a fermentation production such as butanol.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
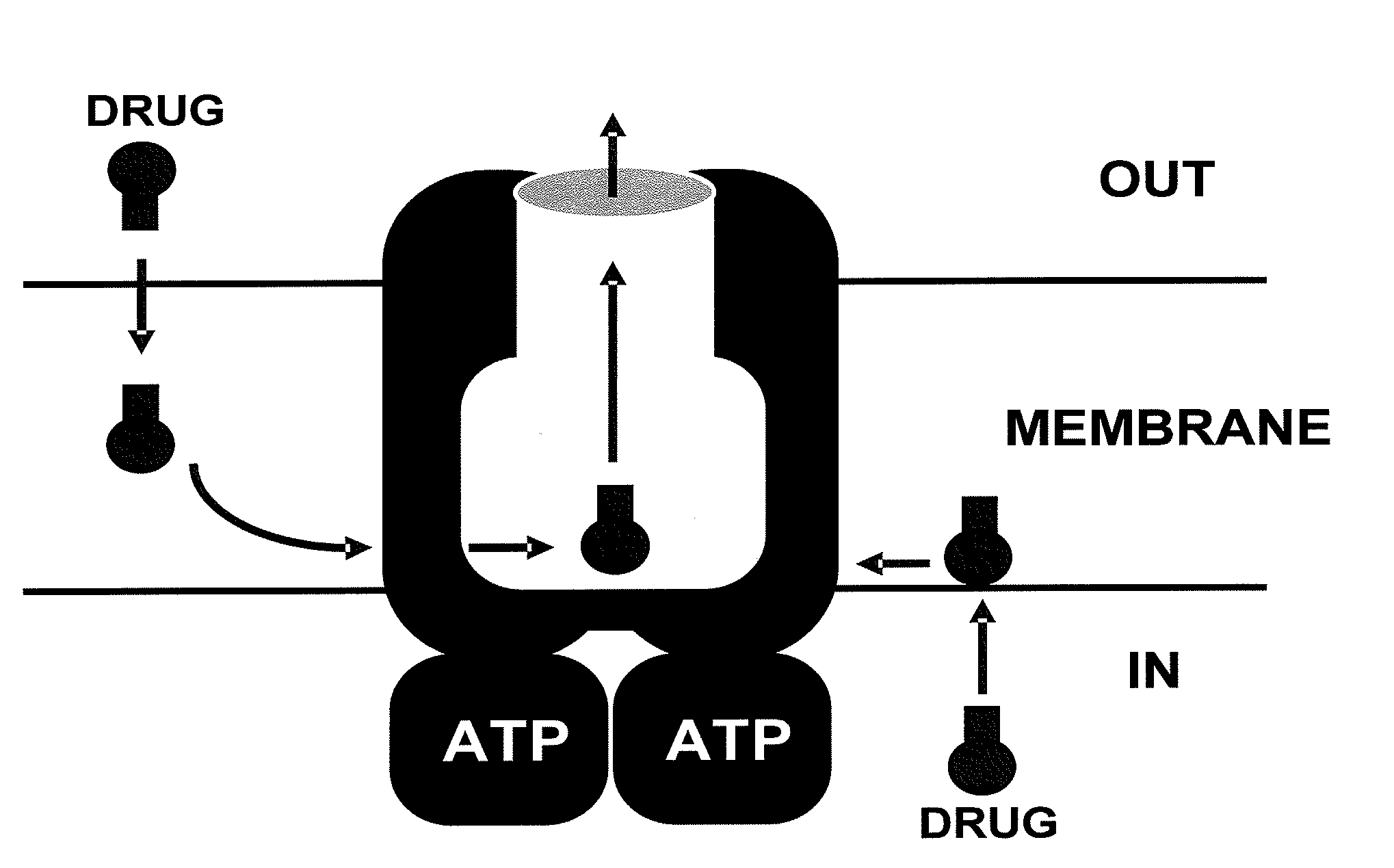
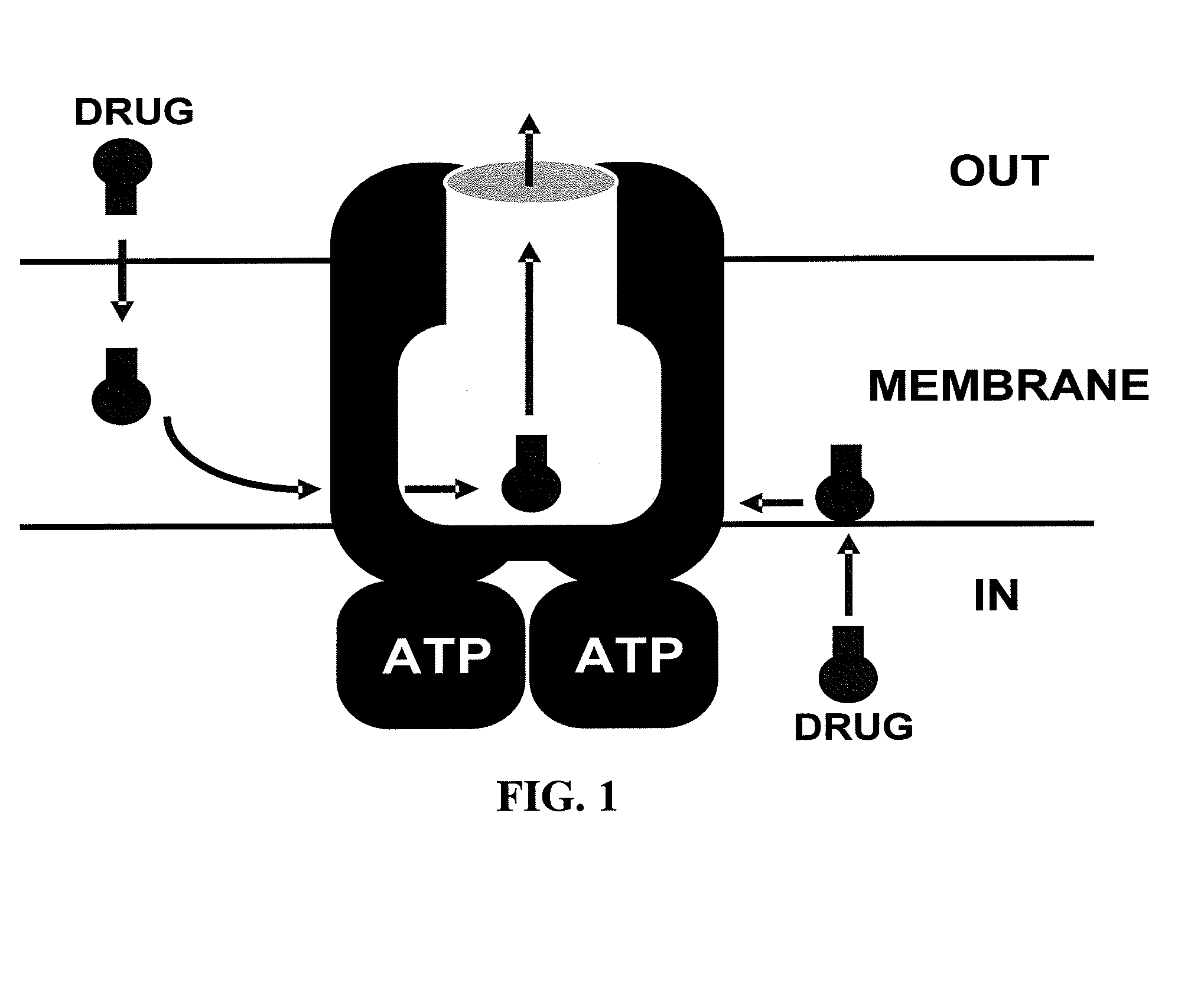
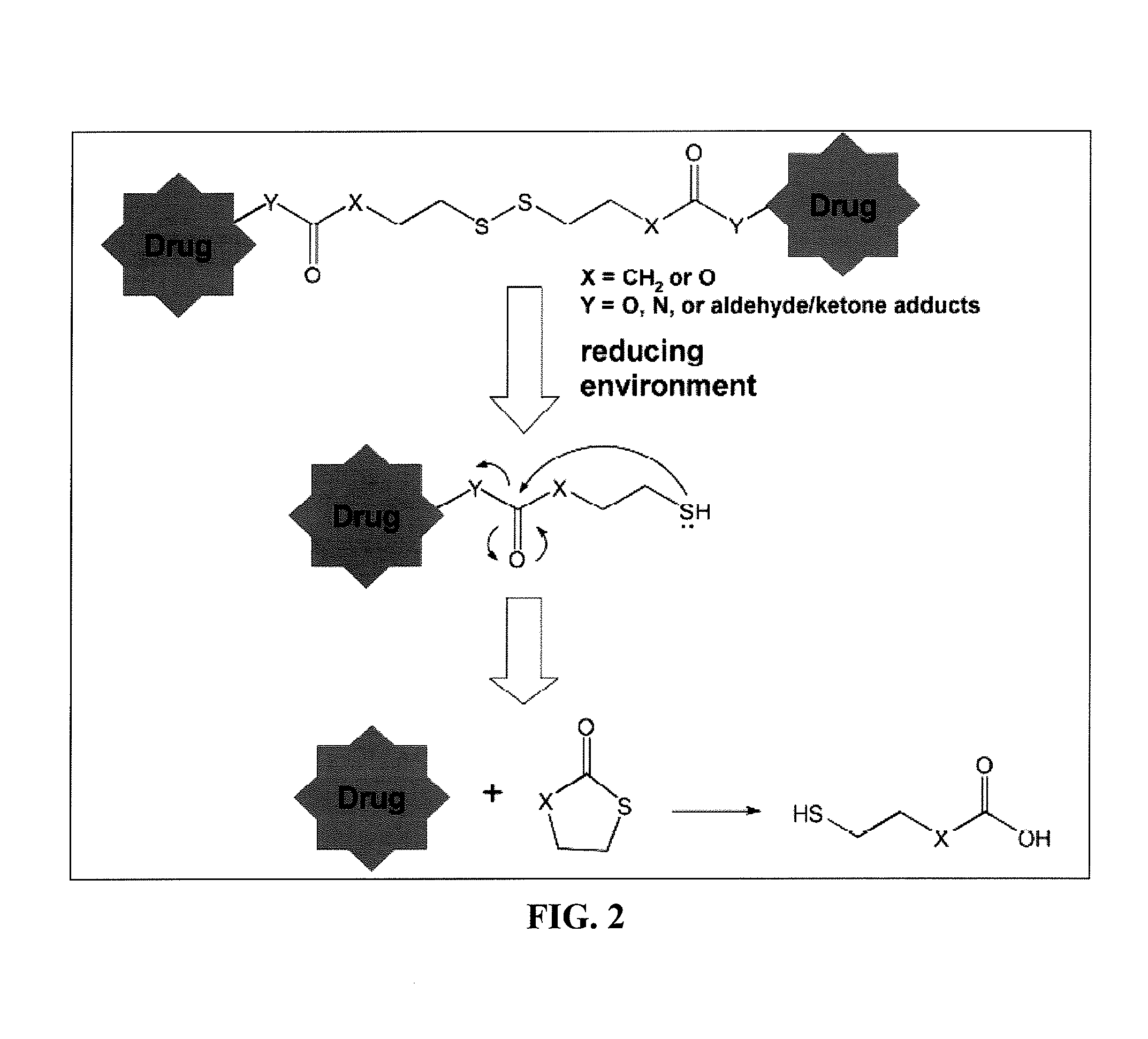
Methods and compositions for reversing p-glycoprotein medicated drug resistance
A method for inhibiting therapeutic drug resistance within a cell over-expressing a membrane protein is provided. The method comprises synthesizing a dimeric prodrug inhibitor of a monomeric therapeutic agent; administering the dimeric prodrug inhibitor to the membrane protein together with the monomeric therapeutic agent; and occupying at least one substrate binding site of the membrane protein with the synthesized dimeric prodrug to allow the monomeric therapeutic agent to accumulate within the cell. The dimeric prodrug inhibitor contains a crosslinking agent that is adapted to breakdown under reducing conditions within the cytosol of the cell to cause the dimeric prodrug to revert back to a form equivalent to the monomeric therapeutic agent.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
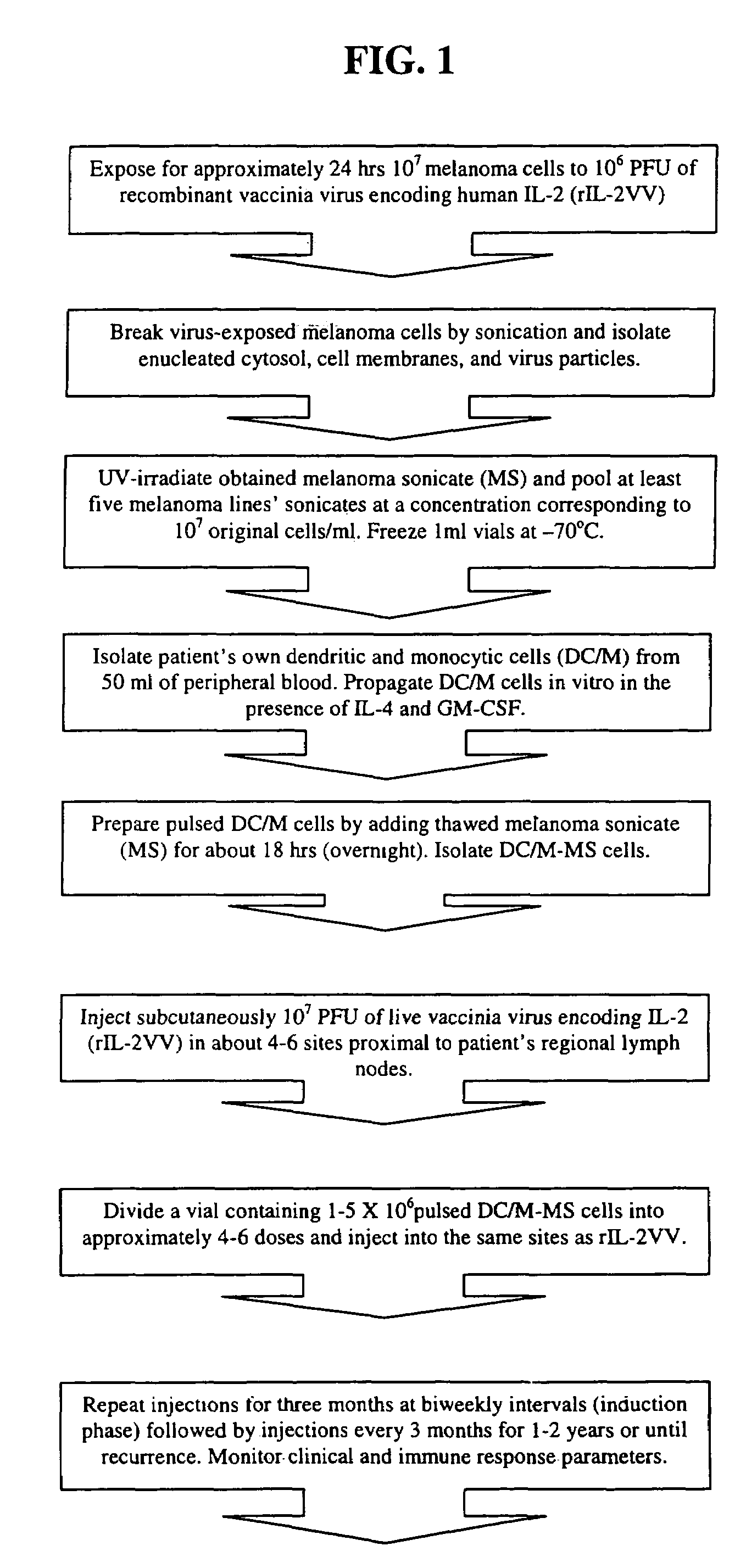
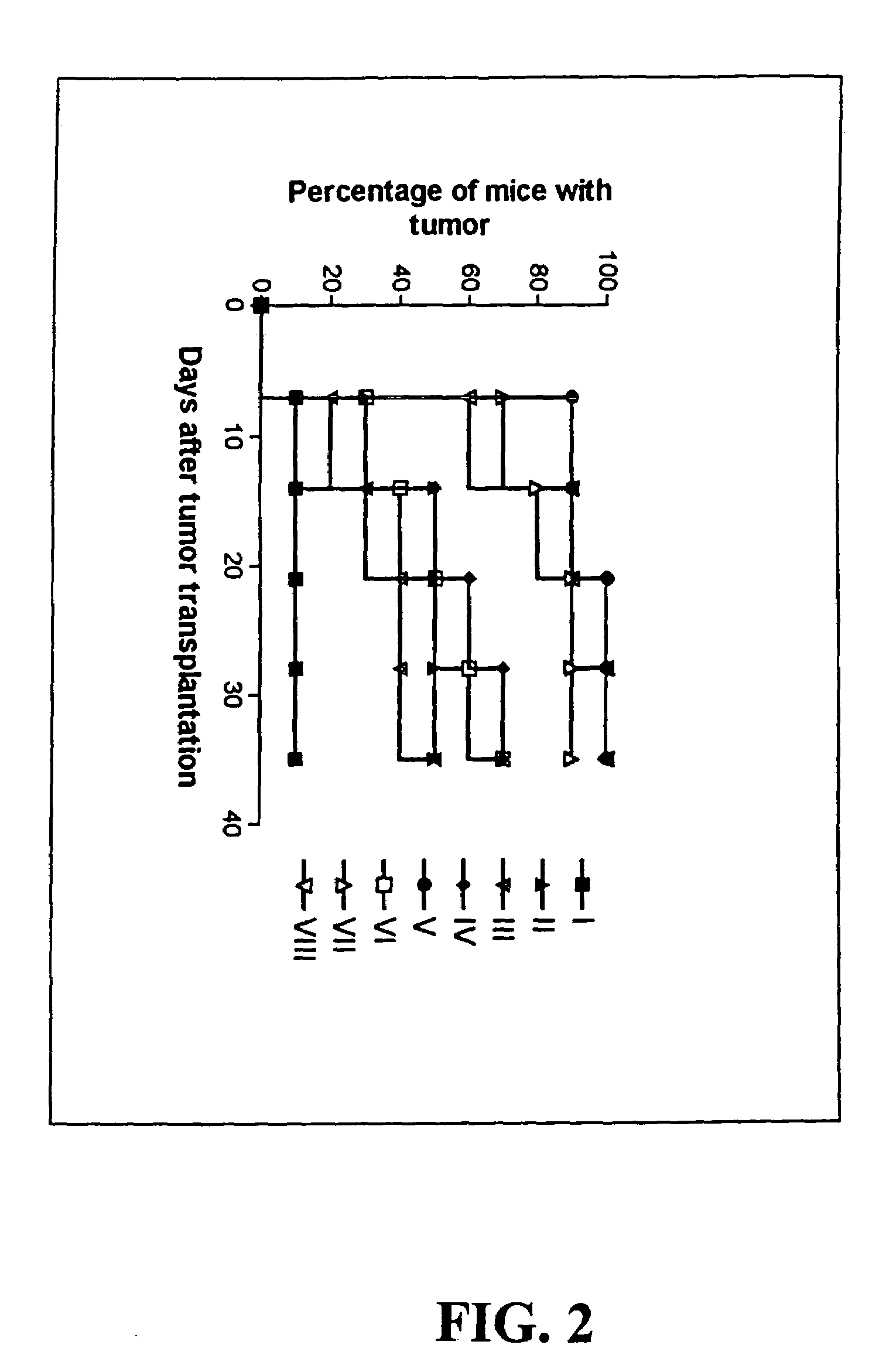
Melanoma vaccine and methods of making and using same
Owner:WALLACK MARC K
Delivery System and Conjugates For Compound Delivery Via Naturally Occurring Intracellular Transport Routes
InactiveUS20120258104A1Improve efficiencyLow toxicityFungiSpecial deliveryCytosolEndoplasmic reticulum
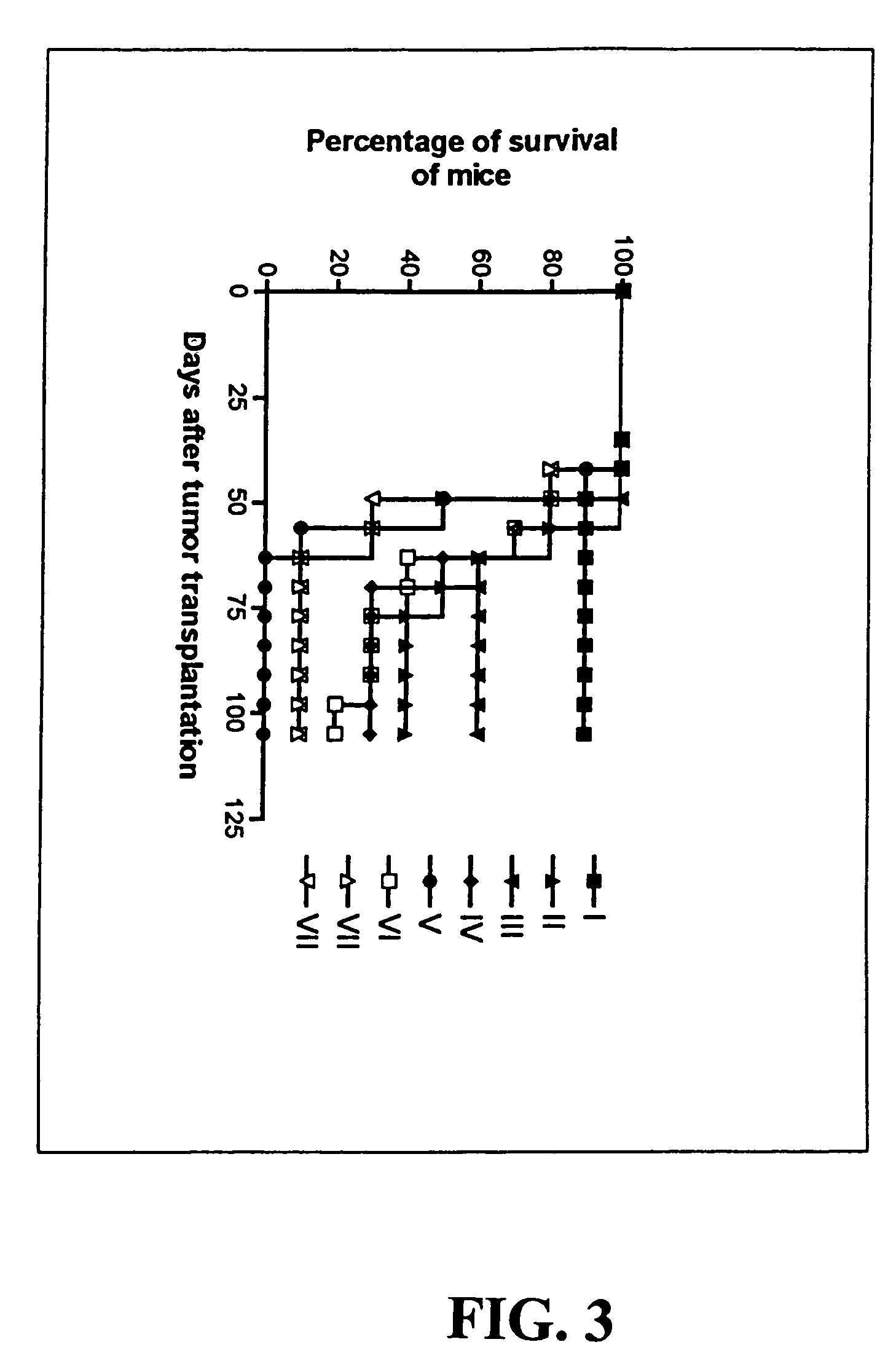
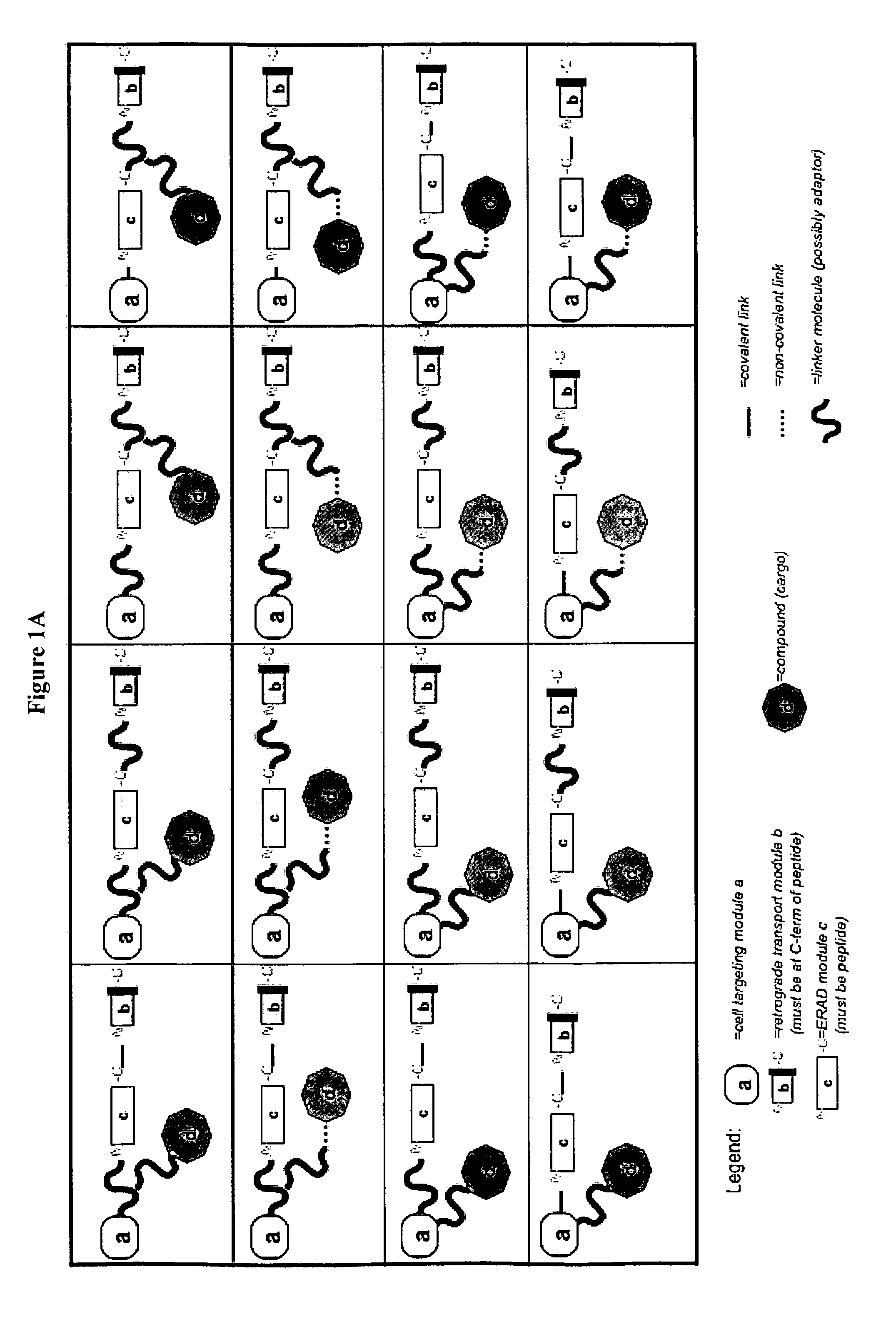
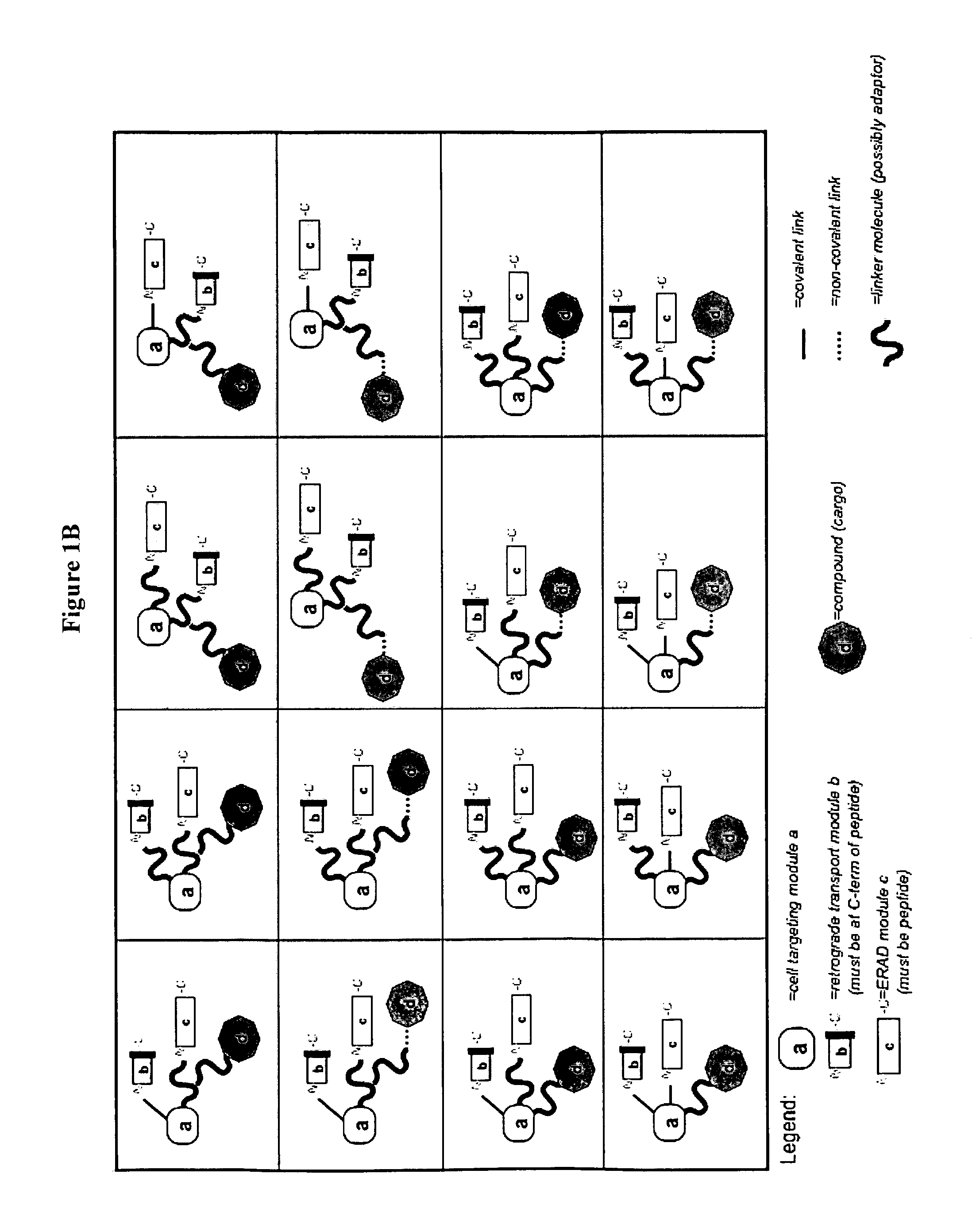
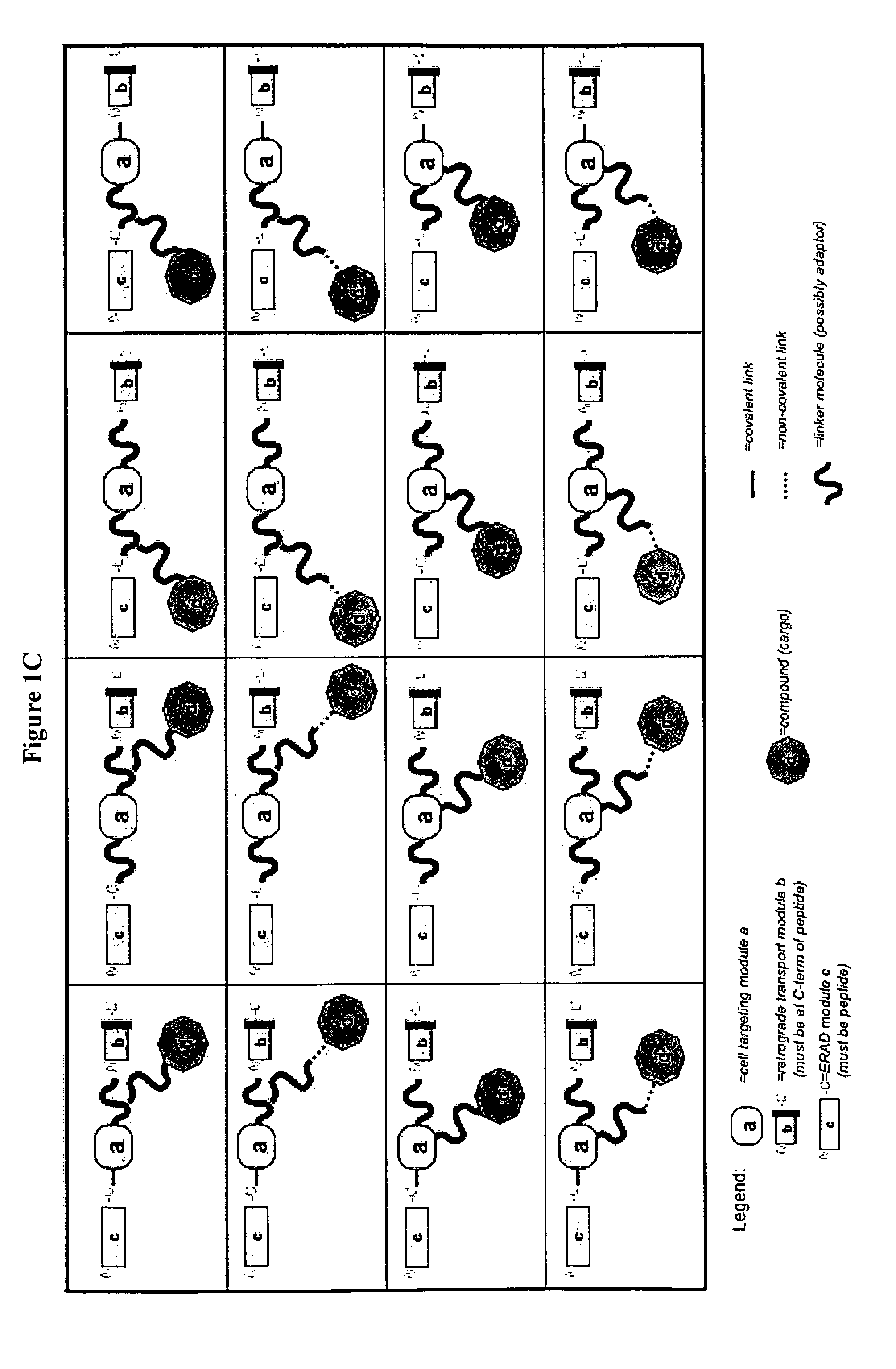
The present invention relates to a delivery system that comprises a conjugate that facilitates the delivery of a compound such as a biologically-active macromolecule, a nucleic acid or a peptide in particular, into a cell. The present invention also relates to said conjugate for delivery of a compound, such as a biologically-active macromolecule, a nucleic acid or a peptide, into a cell. The present invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising said conjugate and to its use. The present invention also relates to a method of delivering a compound to a cell or an organism, preferably a patient. The conjugates comprise: (a) at least one module that mediates cell targeting and facilitates cellular uptake, (b) at least one module that facilitates transport to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), (c) at least one module that mediates translocation from the ER to the cytosol, and (d) at least one compound to be delivered wherein the modules (a) to (c) and the compound (d) are linked to each other in any arrangement.
Owner:CENIX BIOSCI
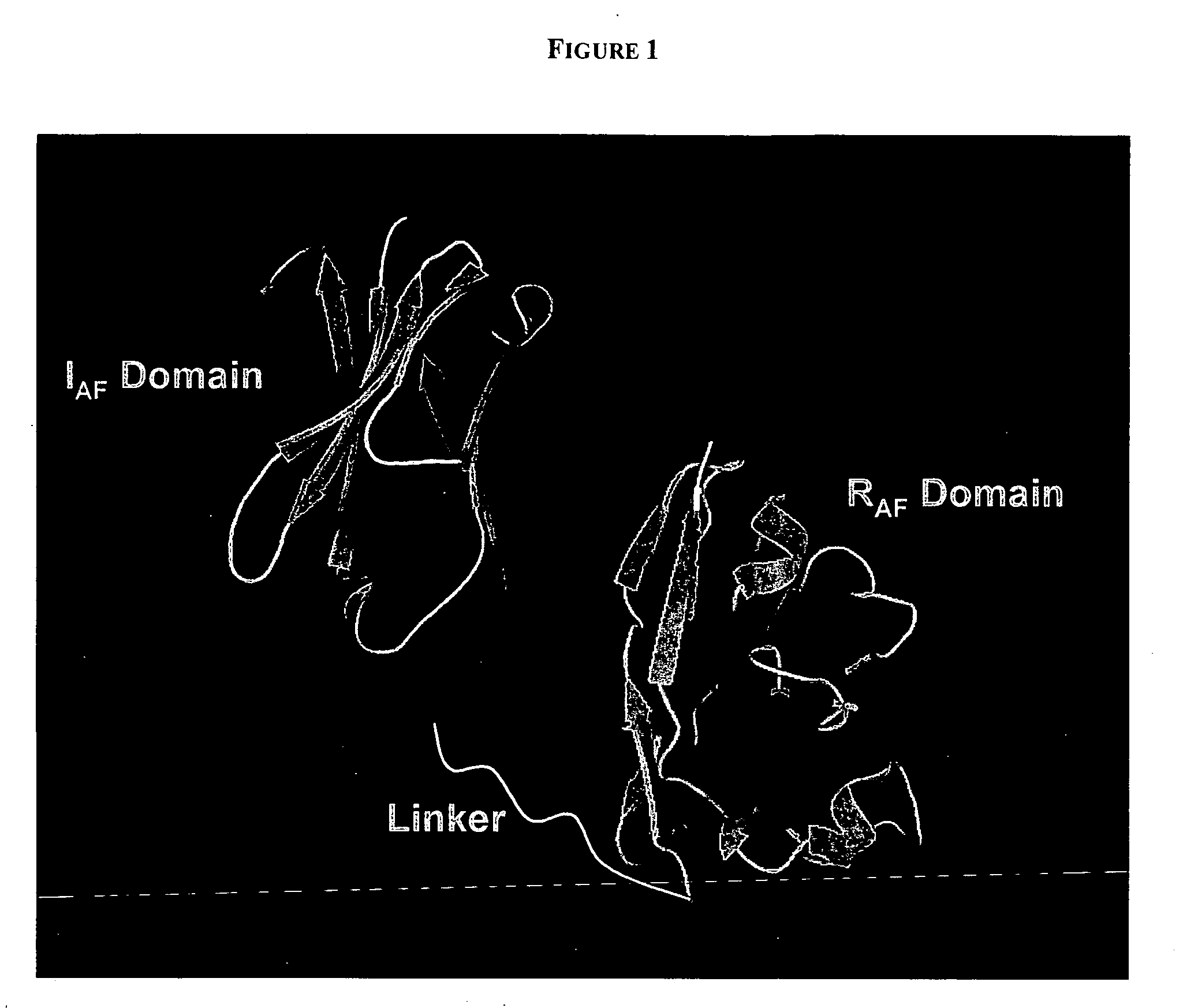
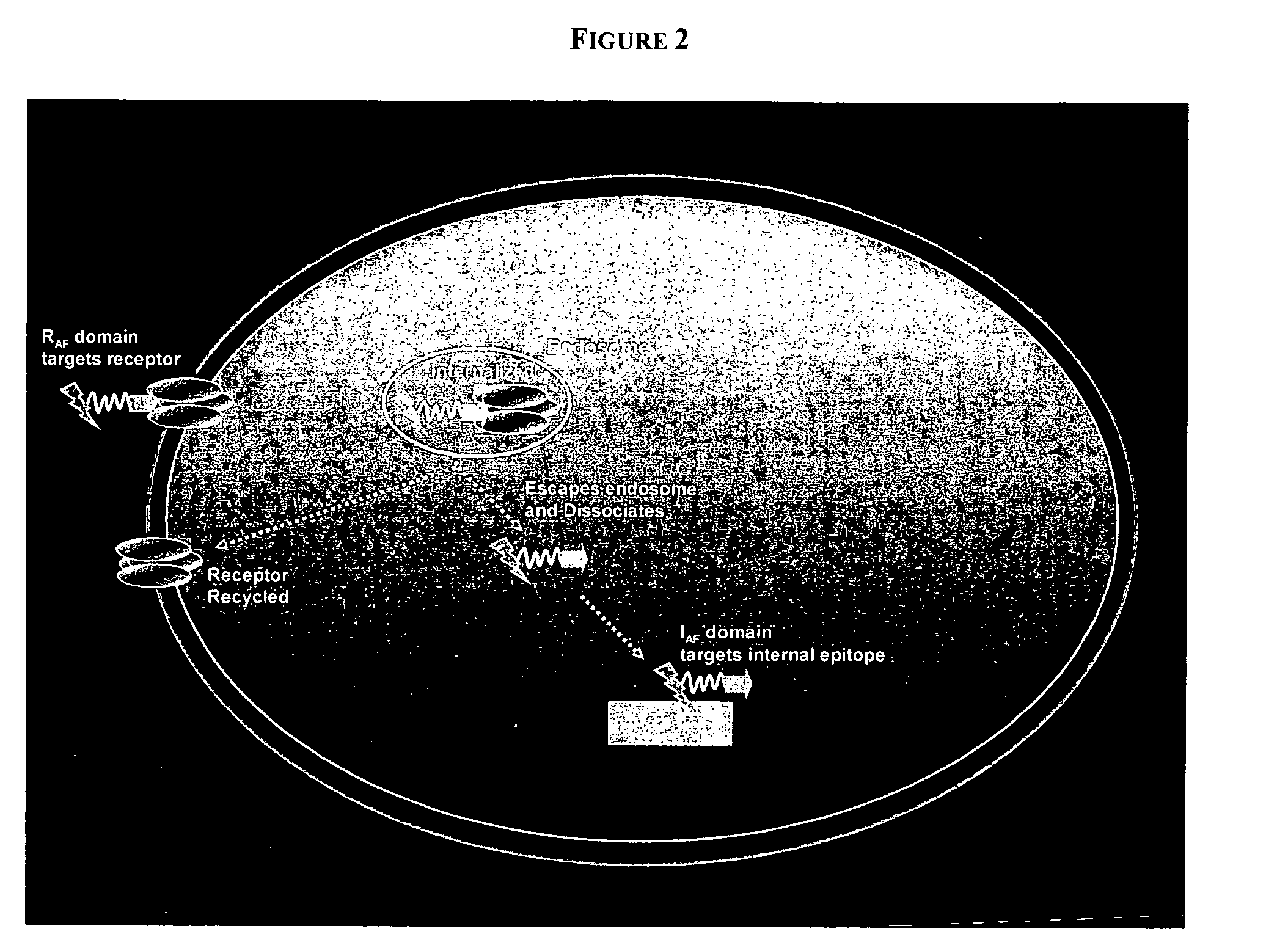
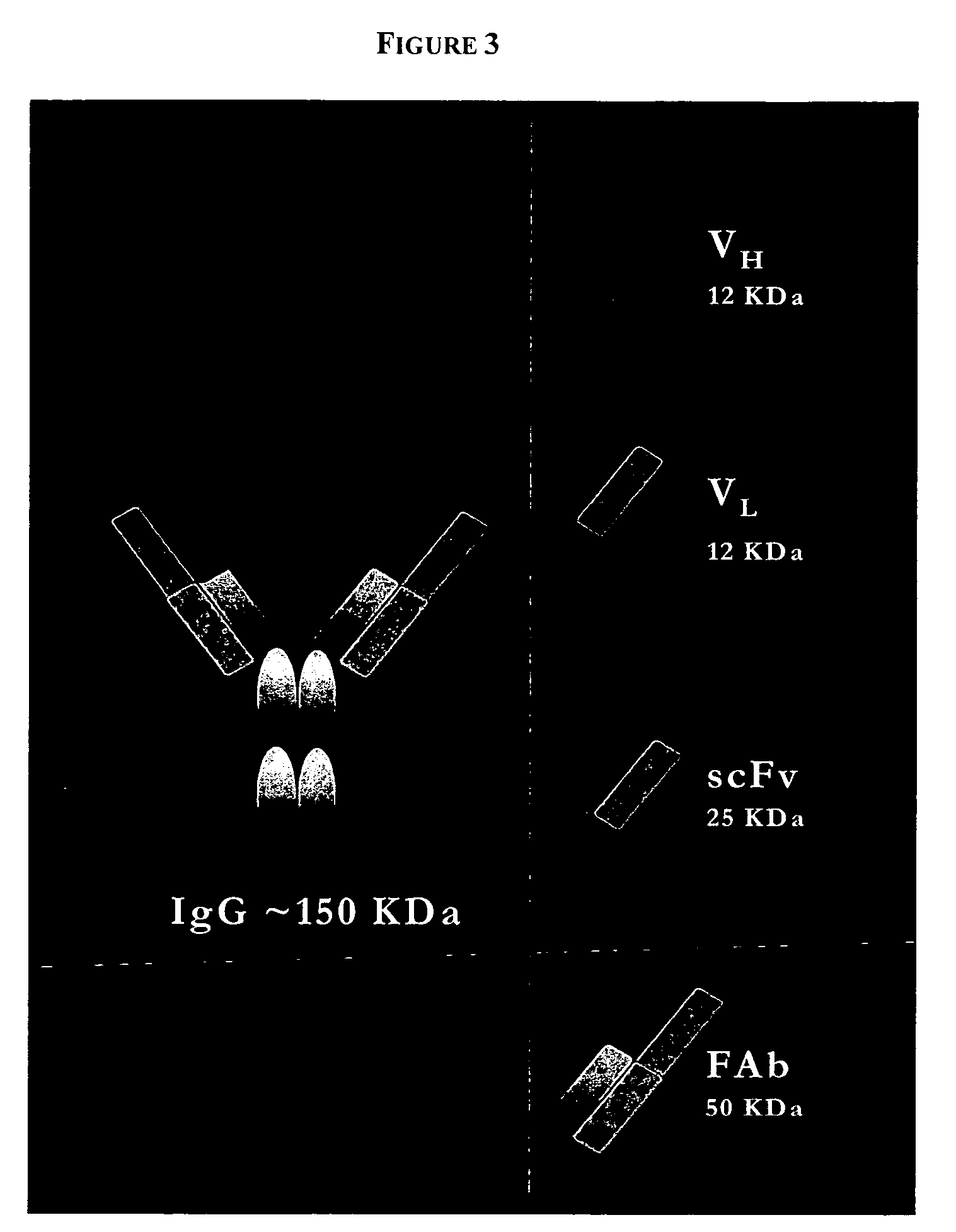
PenetraBodies: receptor-mediated targeted delivery of functionally-active human antibody fragments into cytosol for the treatment of chronic infections and diseases
InactiveUS20060147997A1Small sizeBinding property is not compromisedPeptide librariesBacterial antigen ingredientsCytosolAntibody fragments
The present invention relates to methods of making and using chimeric antibody molecules comprised of at least two domains, namely RAF, and IAF, linked by a flexible peptide linker.
Owner:VIROSYS PHARMA
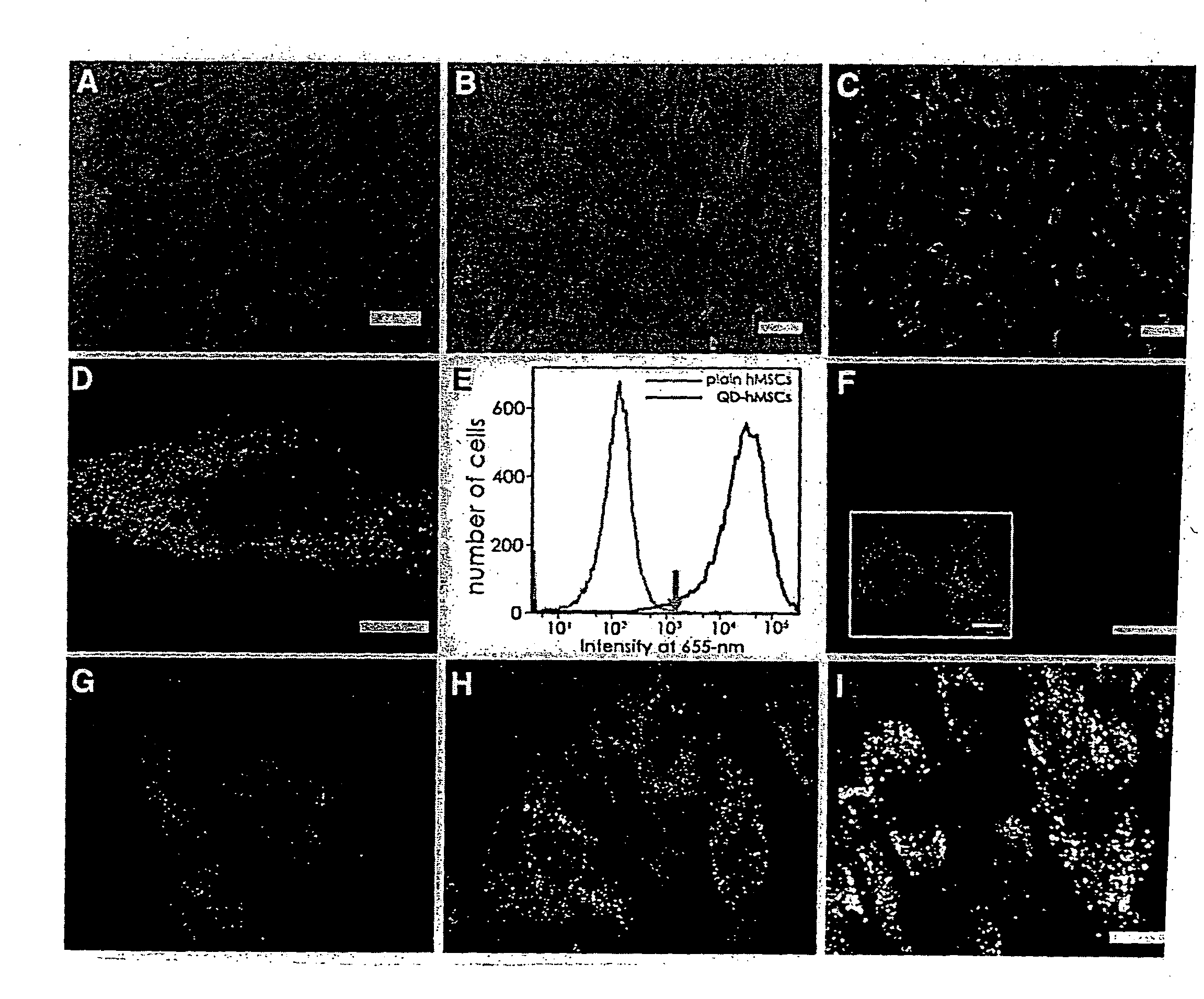
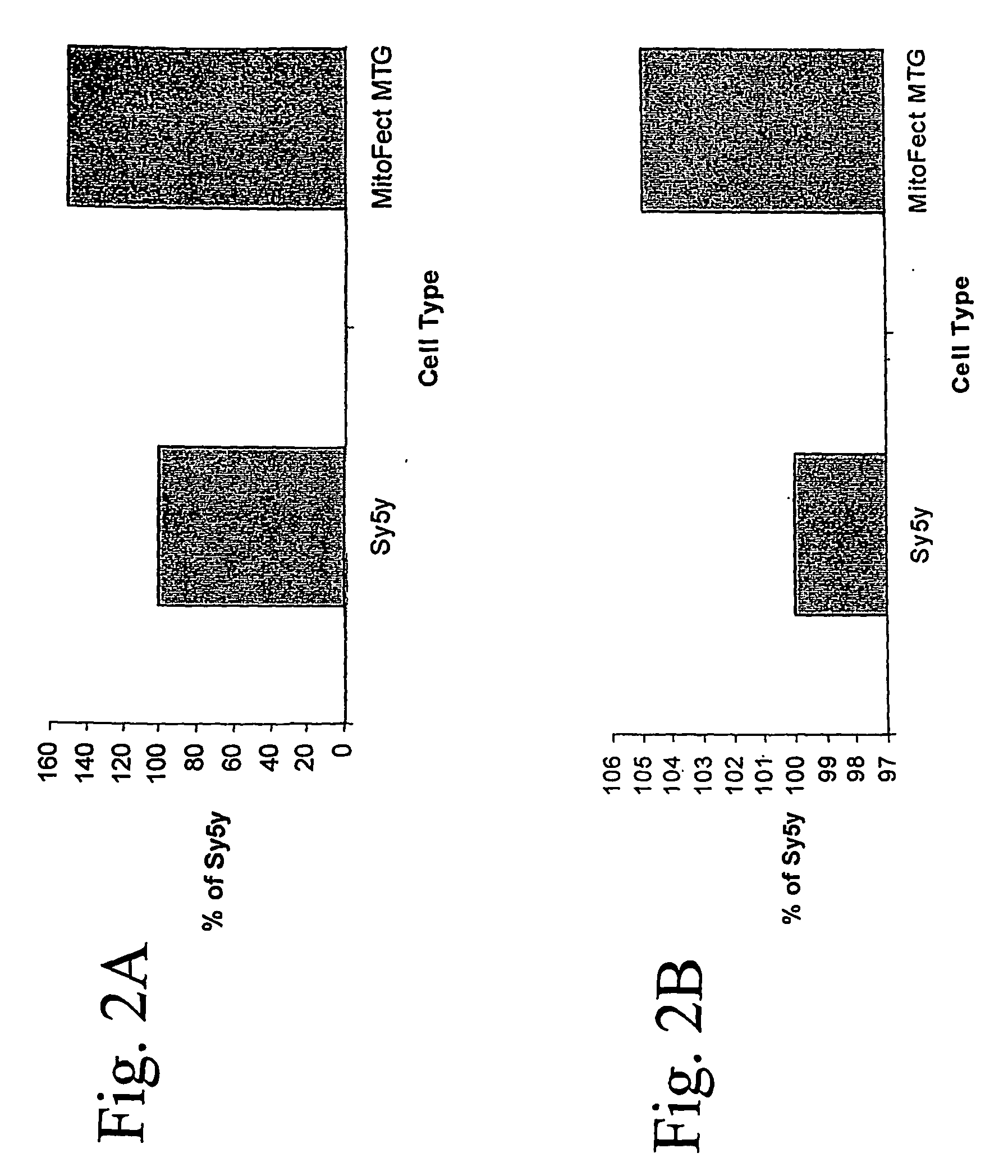
Quantum dot labeled stem cells for use in cardiac repair
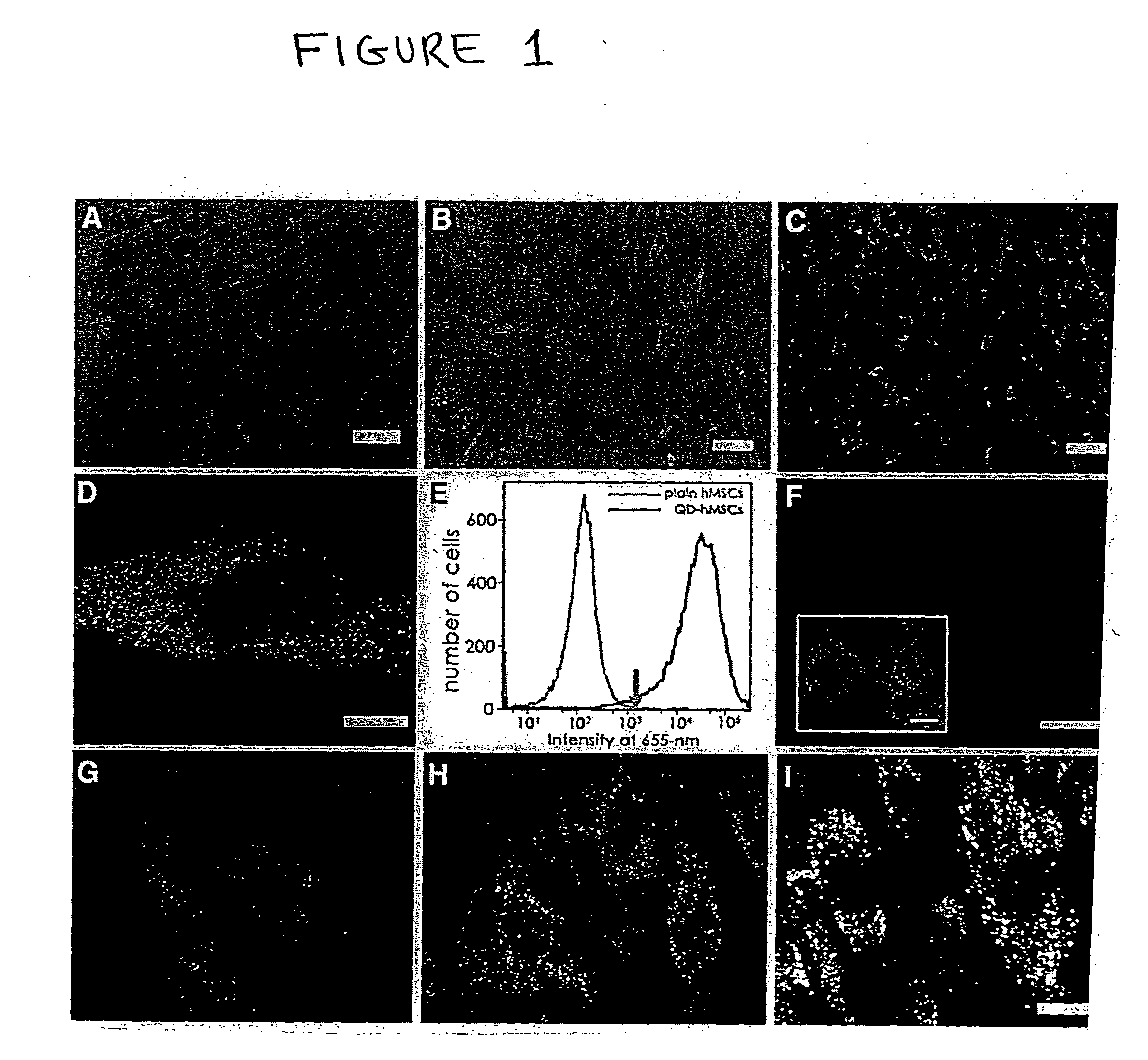
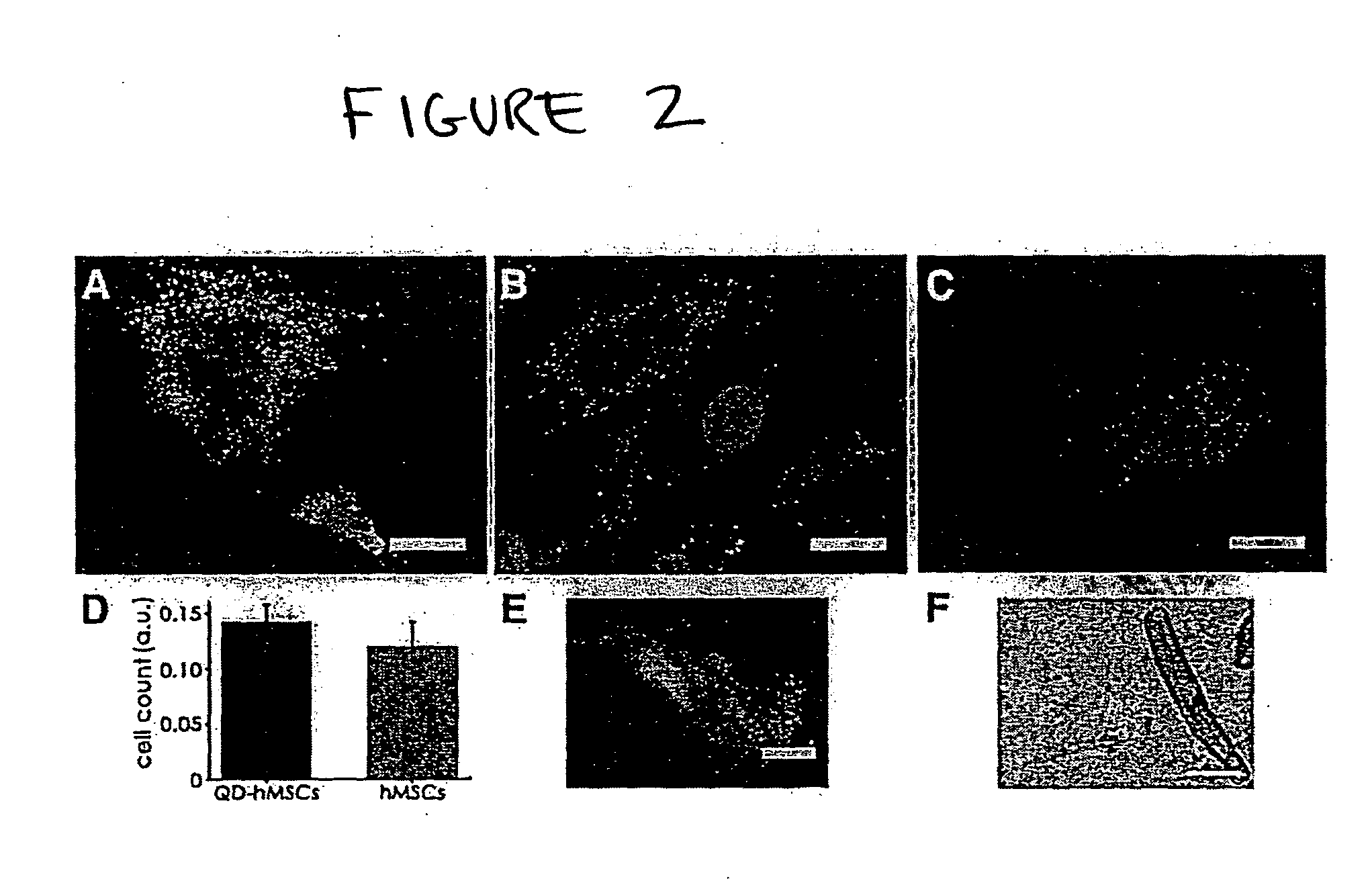
InactiveUS20100158805A1Easy to useLack of cellular toxicityBiocidePowder deliveryCytosolFluorescence
The present invention provides methods and compositions relating to the labeling of target cells with quantum dots (QDs). Specifically, a delivery system is disclosed based on the use of negatively charged QDs for delivery of a tracking fluorescent signal into the cytosol of target cells via a passive endocytosis-mediated delivery process. In a specific embodiment of the invention the target cell is a stem cell, preferably a mesenchymal stem cell (MSC). Such labeled MSCs provide a means for tracking the distribution and fate of MSCs that have been administered to a subject to promote cardiac repair. The invention is based on the discovery that MSCs can be tracked in vitro for up to at least 6 weeks. Additionally, QDs delivered in vivo can be tracked for up to at least 8 weeks, thereby permitting for the first time, the complete 3-D reconstruction of the locations of all MSCs following administration into a host.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
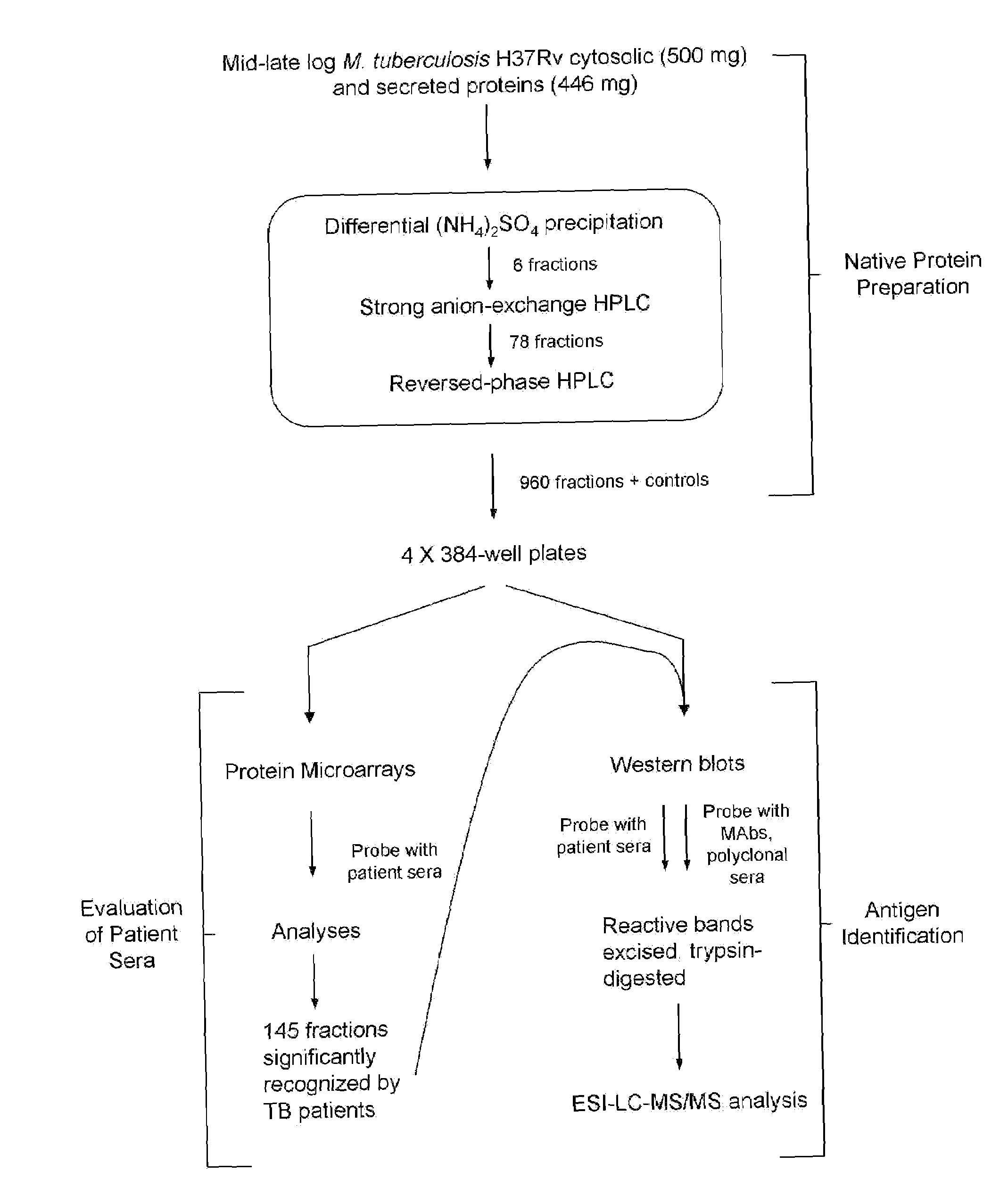
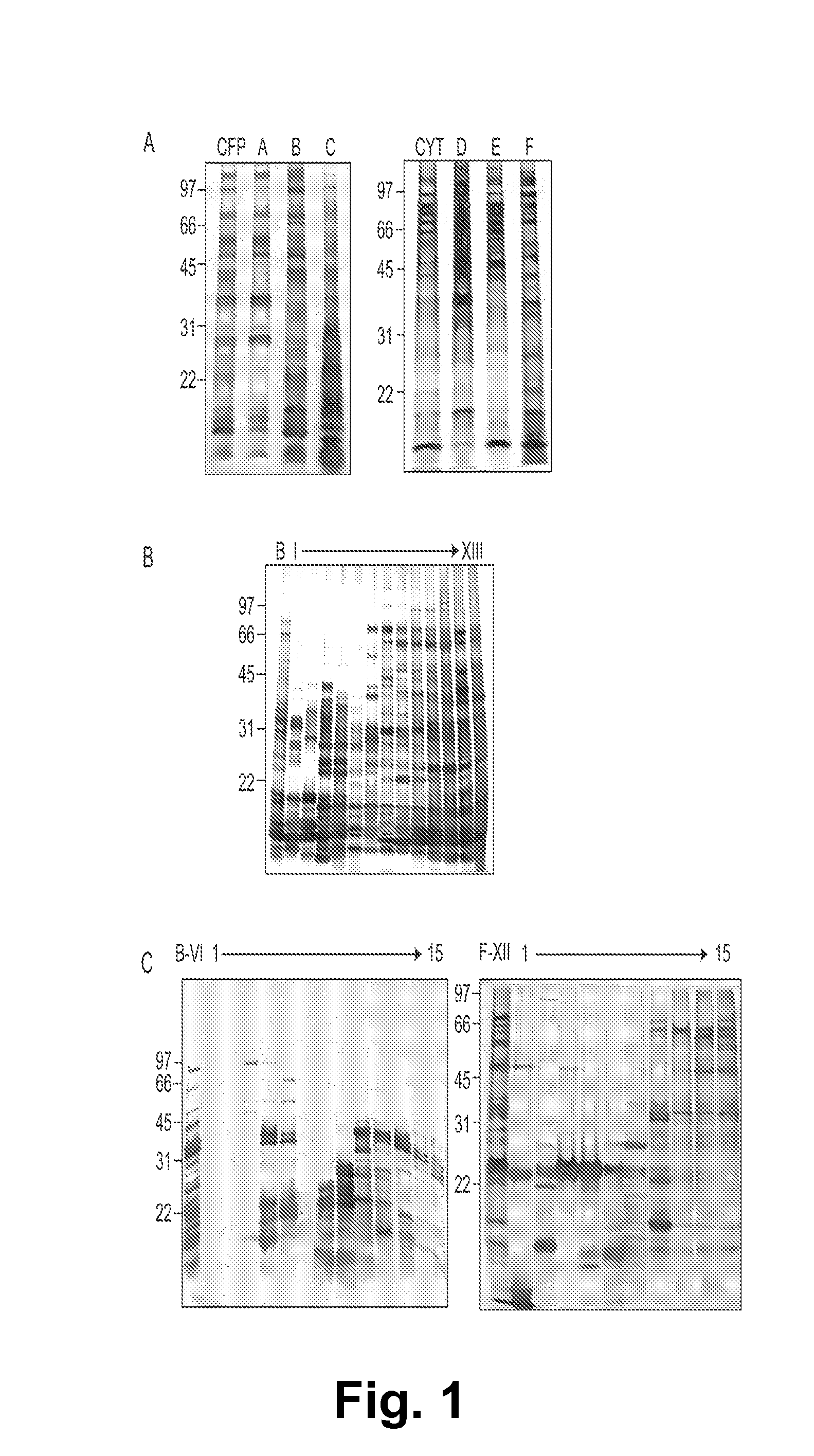
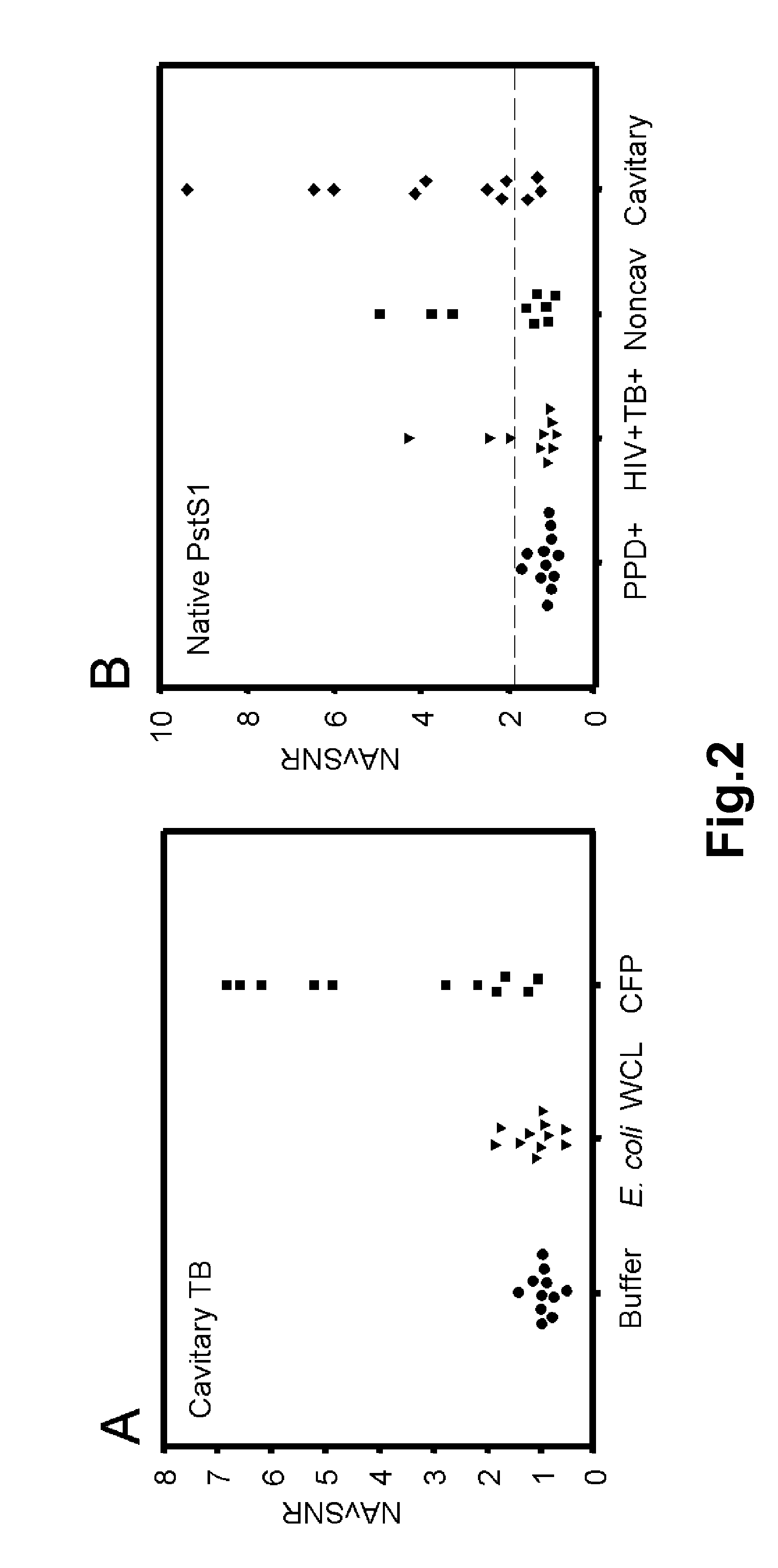
Biomarkers of tuberculosis that distinguish disease categories: use as serodiagnostic antigens
Mycobacterial proteins from culture filtrate or cytosol are disclosed as being useful B cell antigens for early diagnosis of mycobacterial disease, particularly in humans. These proteins include four that had not previously been recognized as B cell antigens (LppZ protein encoded by Mtb gene Rv3006; SodC protein encoded by Mtb gene Rv0432; BfrB protein encoded by Mtb gene Rv3841 and TrxC protein encoded byMtb gene Rv3914). Antigenic compositions include these proteins and / or peptide fragments thereof, in various combinations with each other or with one or more of a set of 10 additional Mtb proteins known to be antigens (in paricular early antigens. Methods and kits for using these antigenic composition for early diagnosis of mycobacterial infection and disease are also disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Delivery of biomolecules to immune cells
ActiveUS20180142198A1Elicit T cell responseGenetically modified cellsCulture processCytosolAntigen delivery
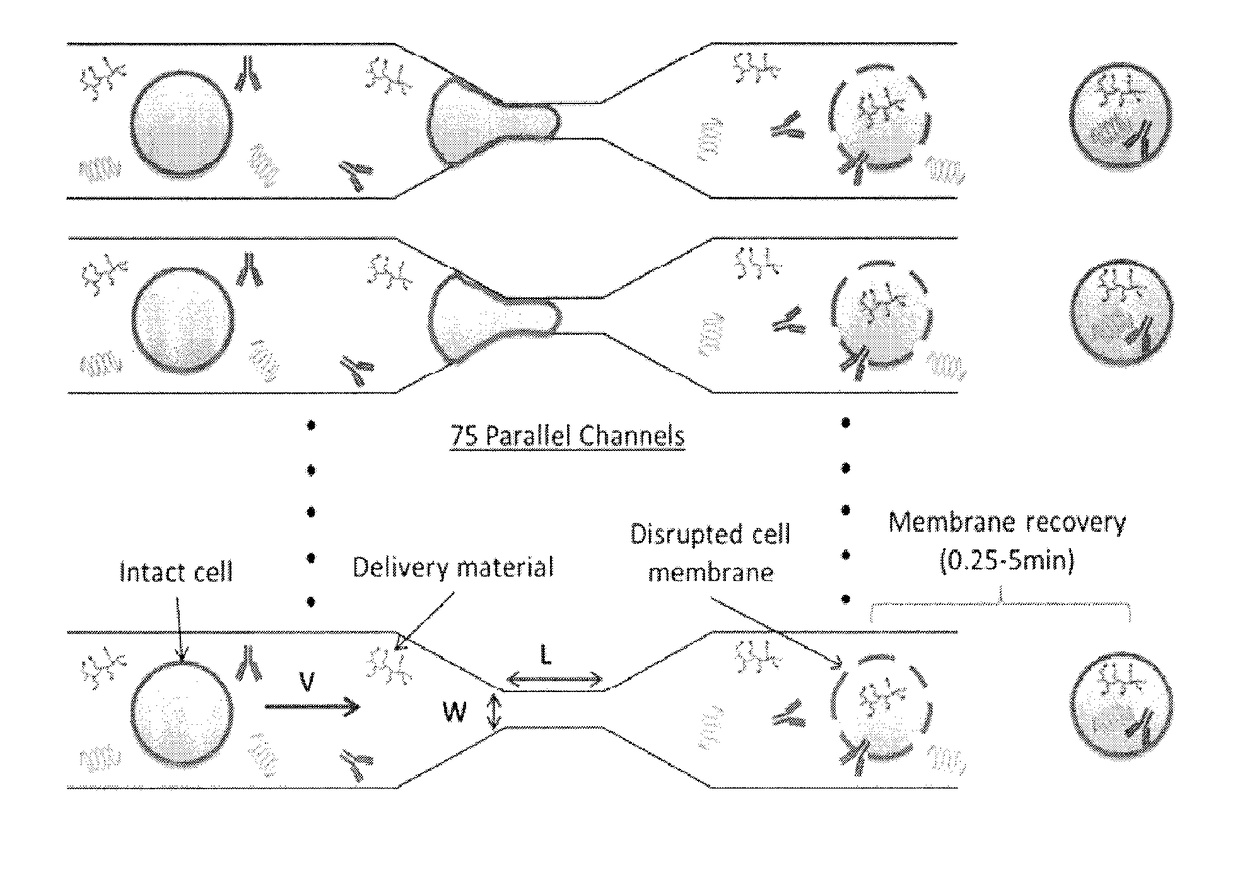
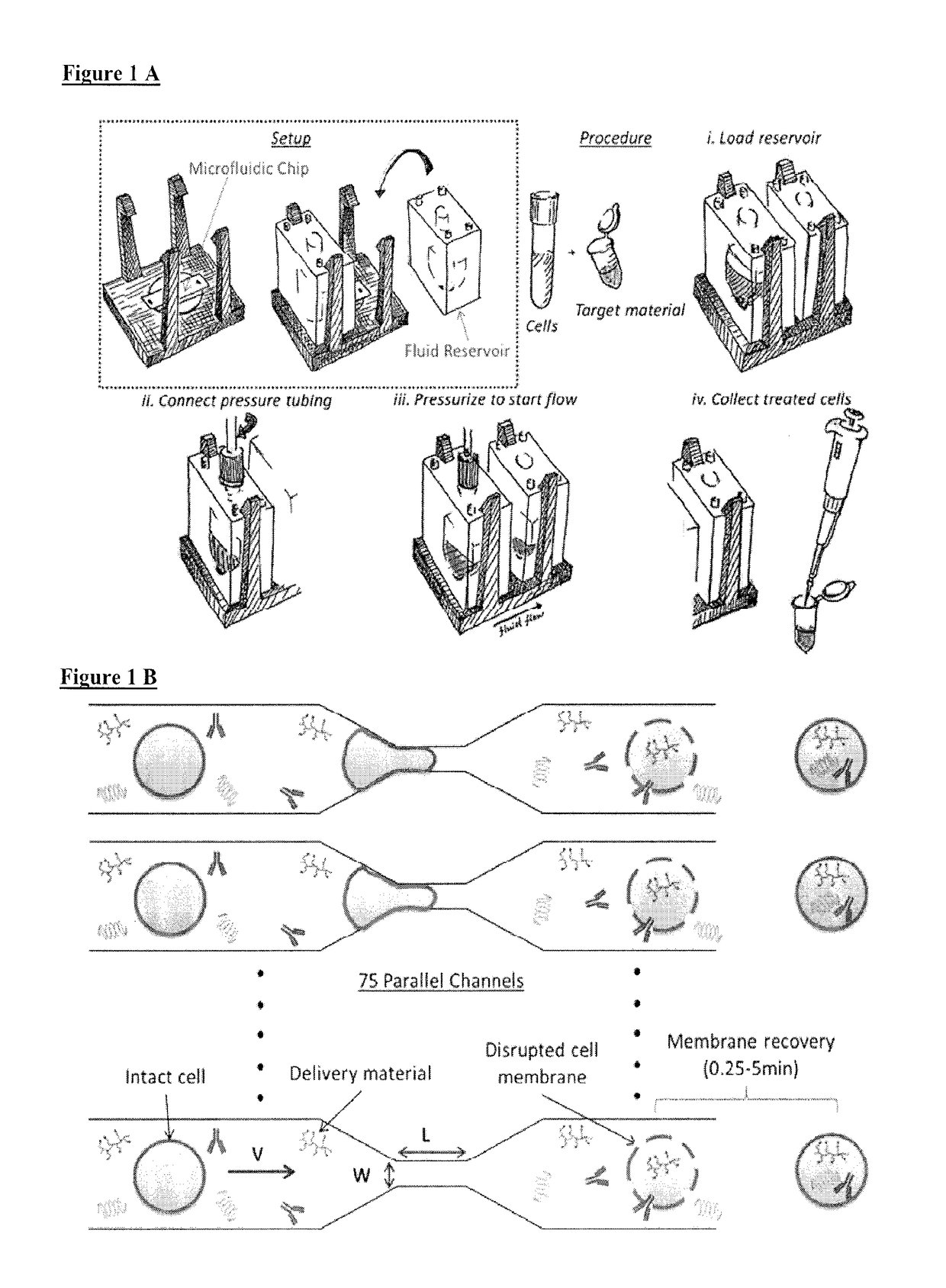
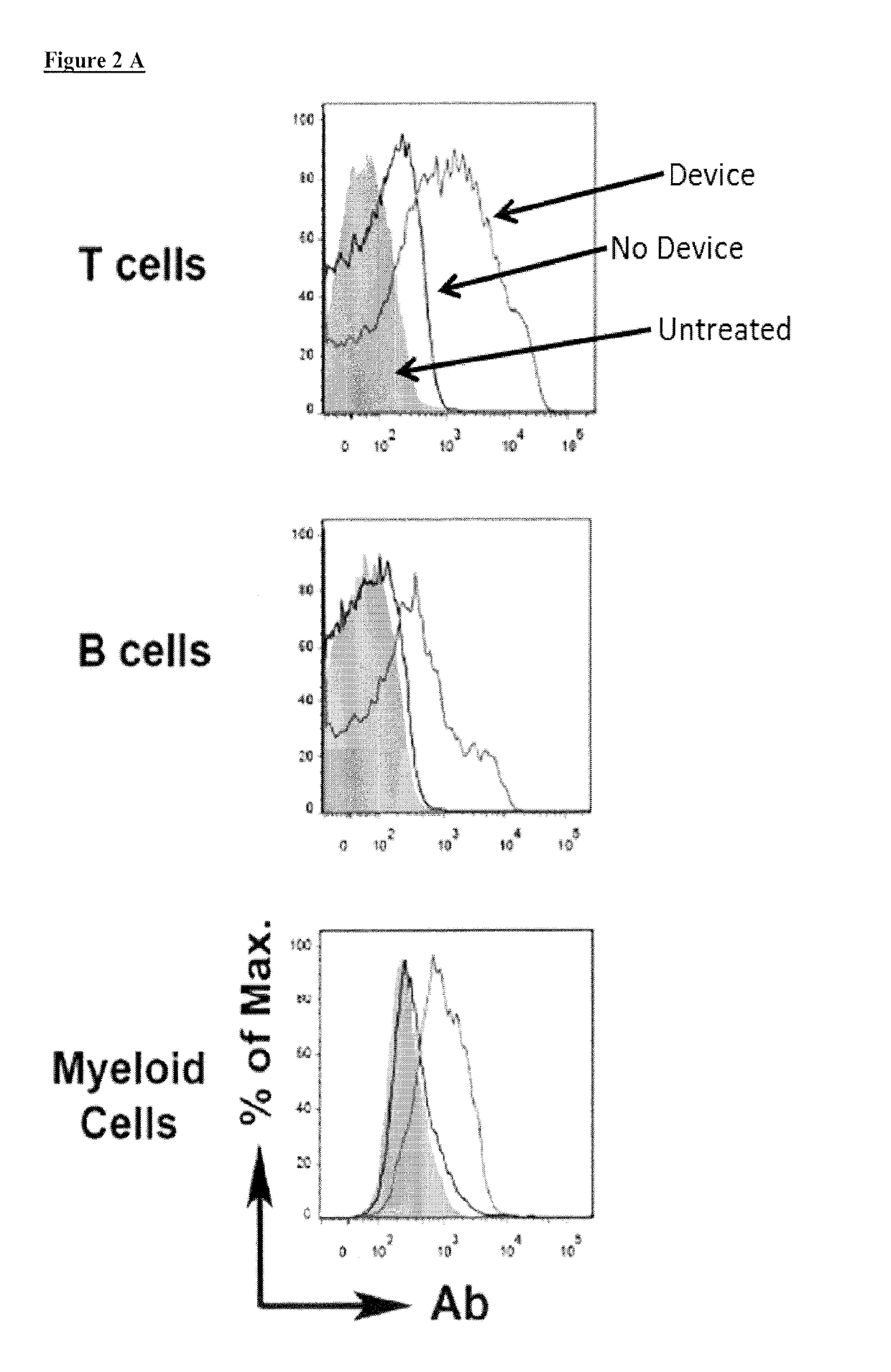
A method and device for preferentially delivering a compound such as an antigen to the cytosol of an immune cell. The method comprises passing a cell suspension comprising the target immune cell through a microfluidic device and contacting the suspension with the compound(s) or payload to be delivered.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for delivering agents into cells using bacterial toxins
The invention provides compositions and methods for delivering a bioactive moiety comprising at least one non-natural component into a cell cytosol of an eukaryotic cell. The bioactive moiety is linked to an A component of a bacterial toxin, a functional wild-type or modified fragment thereof, or an A component surrogate or mimetic. For delivery, the cell is contacted with the linked bioactive moiety and a corresponding B component of the bacterial toxin or a functional fragment thereof.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
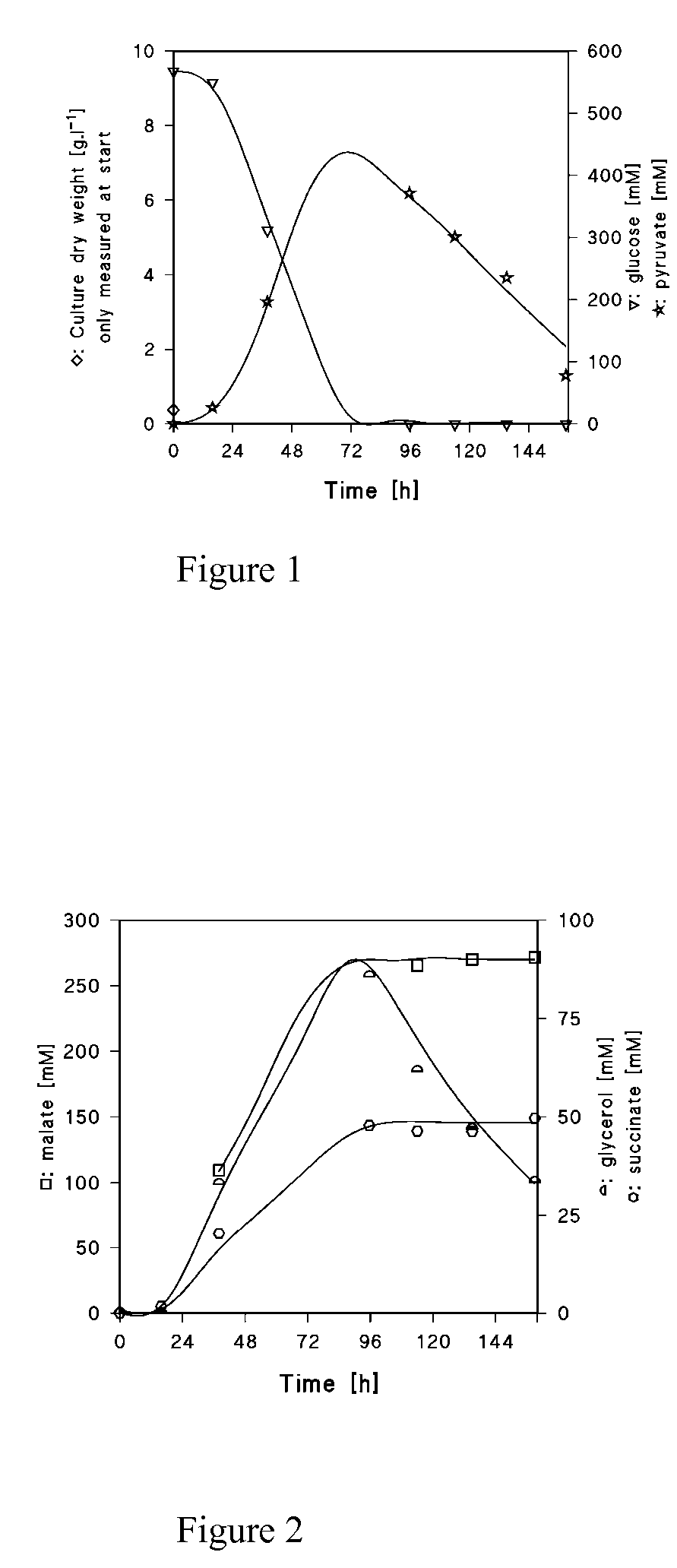
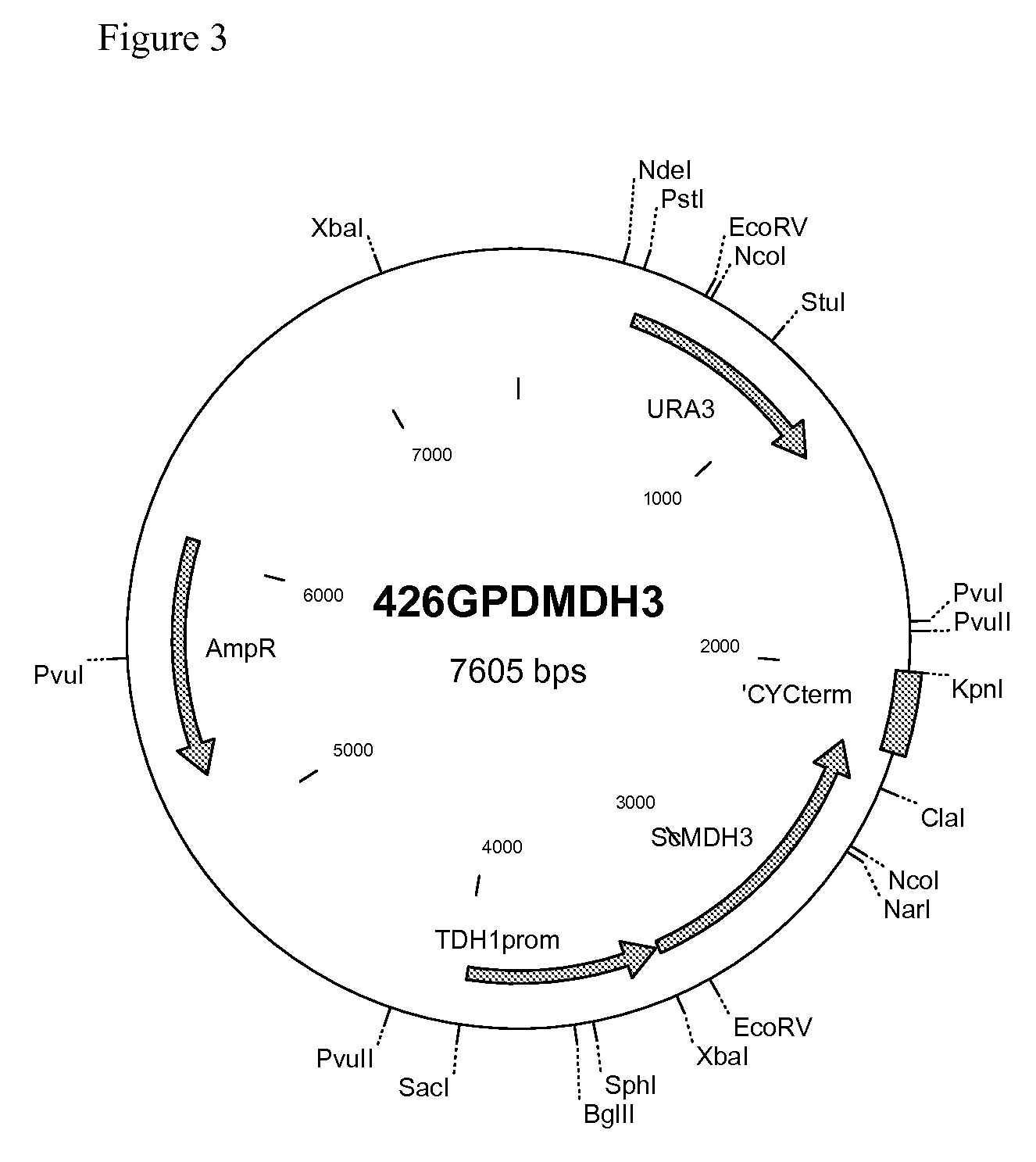
Malic Acid Production in Recombinant Yeast
We disclose a recombinant yeast, wherein the yeast is pyruvate decarboxylase enzyme (PDC) activity negative (PDC-negative) and is functionally transformed with a coding region encoding a pyruvate carboxylase enzyme (PYC) wherein the PYC is active in the cytosol, a coding region encoding a malate dehydrogenase enzyme (MDH) wherein the MDH is active in the cytosol and is not inactivated in the presence of glucose, and a coding region encoding a malic acid transporter protein (MAE). We also disclose a method of producing malic acid by culturing such a yeast in a medium comprising a carbon source and a carbon dioxide source and isolating malic acid from the medium.
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
Fusion proteins
A single chain, polypeptide fusion protein, comprising: a non-cytotoxic protease, or a fragment thereof, which protease or protease fragment is capable of cleaving a protein of the exocytic fusion apparatus of a nociceptive sensory afferent; a dynorphin Targeting Moiety that is capable of binding to a Binding Site on the nociceptive sensory afferent, which Binding Site is capable of undergoing endocytosis to be incorporated into an endosome within the nociceptive sensory afferent; a protease cleavage site at which site the fusion protein is cleavable by a protease, wherein the protease cleavage site is located between the non-cytotoxic protease or fragment thereof and the dynorphin Targeting Moiety; and a translocation domain that is capable of translocating the protease or protease fragment from within an endosome, across the endosomal membrane and into the cytosol of the nociceptive sensory afferent. Nucleic acid sequences encoding the polypeptide fusion proteins, methods of preparing same and uses thereof are also described.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Multi-level specific targeting of cancer cells with IL-13
A compound comprising, in combination: a cell surface binding ligand or internalizing factor, such as an IL-13Rα2 binding ligand; at least one effector molecule (e.g., one, two, three or more effector molecules); optionally but preferably, a cytosol localization element covalently coupled between said binding ligand and said at least one effector molecule; and a subcellular compartment localization signal element covalently coupled between said binding ligand and said at least one effector molecule (and preferably with said cytosol localization element between said binding ligand and said subcellular compartment localization signal element). Methods of using such compounds and formulations containing the same are also described.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Non-cytotoxic protein conjugates
The present invention is directed to non-cytotoxic protein conjugates for inhibition or reduction of exocytic fusion in a nociceptive sensory afferent cell. The protein conjugates comprise: (i) a galanin Targeting Moiety (TM), wherein the TM is an agonist of a receptor present on a nociceptive sensory afferent cell, and wherein the receptor undergoes endocytosis to be incorporated into an endosome within the nociceptive sensory afferent cell; (ii) a non-cytotoxic protease or a fragment thereof, wherein the protease or protease fragment is capable of cleaving a protein of the exocytic fusion apparatus of the nociceptive sensory afferent cell; and (iii) a Translocation Domain, wherein the Translocation Domain translocates the protease or protease fragment from within the endosome, across the endosomal membrane, and into the cytosol of the nociceptive sensory afferent cell. Nucleic acid sequences encoding the protein conjugates, methods of preparing same and uses thereof are is also described.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Compounds and molecular complexes comprising multiple binding regions directed to transcytotic ligands
InactiveUS20060134103A1Simple processIncrease ratingsSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsExocytosisActive agent
Disclosed herein are multimeric molecular complexes and compounds that are multivalent, i.e., they have two or more targeting elements directed to a ligand that confers paracellular transporting properties and / or transcytotic properties to complexes and compounds to which it is bound. The complexes and compounds have properties that are different from the properties of monomers, complexes and compounds having only one targeting element directed to a paracellular and / or transcytotic ligand. The complexes and compounds of the invention undergo endocytosis, transcytosis and exocytosis; following endocytosis, the complexes or compounds may be transported into the cytosol or an organelle of a cell. In polarized cells, transcytosis can proceed in a “forward” or “reverse” direction. Reverse transcytosis is used for the non-invasive delivery of biologically active agents from the lumen of, e.g., the gastrointestinal tract or the airways of lungs, to the circulatory system. The complexes and compounds are incorporated in various compositions and medical devices suitable for medicinal or veterinary use.
Owner:HAWLEY STEPHEN +4
Microorganisms as carriers of nucleotide sequences coding for antigens and protein toxins, process of manufacturing and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110287037A1Patient compliance is goodSuitable for oralAntibacterial agentsBacteriaCell specificMutated protein
The invention relates to a microorganism as a carrier of nucleotide sequences coding for antigens and protein toxins comprising the following components: (I) at least one nucleotide sequence coding for at least one complete or partial antigen of at least one wild-type or mutated protein; and (II) at least one nucleotide sequence coding for at least one protein toxin and / or at least one protein toxin subunit; and (III) a) at least one nucleotide sequence coding for at least one transport system which enables the expression of the expression products of component (I) and component (II) on the outer surface of the microorganism and / or enables the secretion of the expression products of component (I) and component (II); and / or coding for at least one signal sequence which enables the secretion of the expression products of component (I) and component (II); and / or (III) b) optionally, at least one nucleotide sequence coding for at least one protein for lysing the microorganism in the cytosol of mammalian cells and for intracellularly releasing plasmids or expression vectors, which are contained in the lysed microorganism; and (IV) at least one nucleotide sequence for at least one activation sequence for the expression of one or more of components (I) to (III), wherein said activation sequence can be activated in the microorganism and / or is tissue cell-specific, tumor cell-specific, macrophage-specific, dendrite-specific, lymphocyte-specific, function-specific or non-cell-specific”; wherein any of components (I) to (IV) can be present either once or several times and either identical or different. Also disclosed are a process of manufacturing thereof, corresponding plasmids or expression vectors and uses of the microorganism as a medicament.
Owner:SOCIUM THERAPEUTICS INC
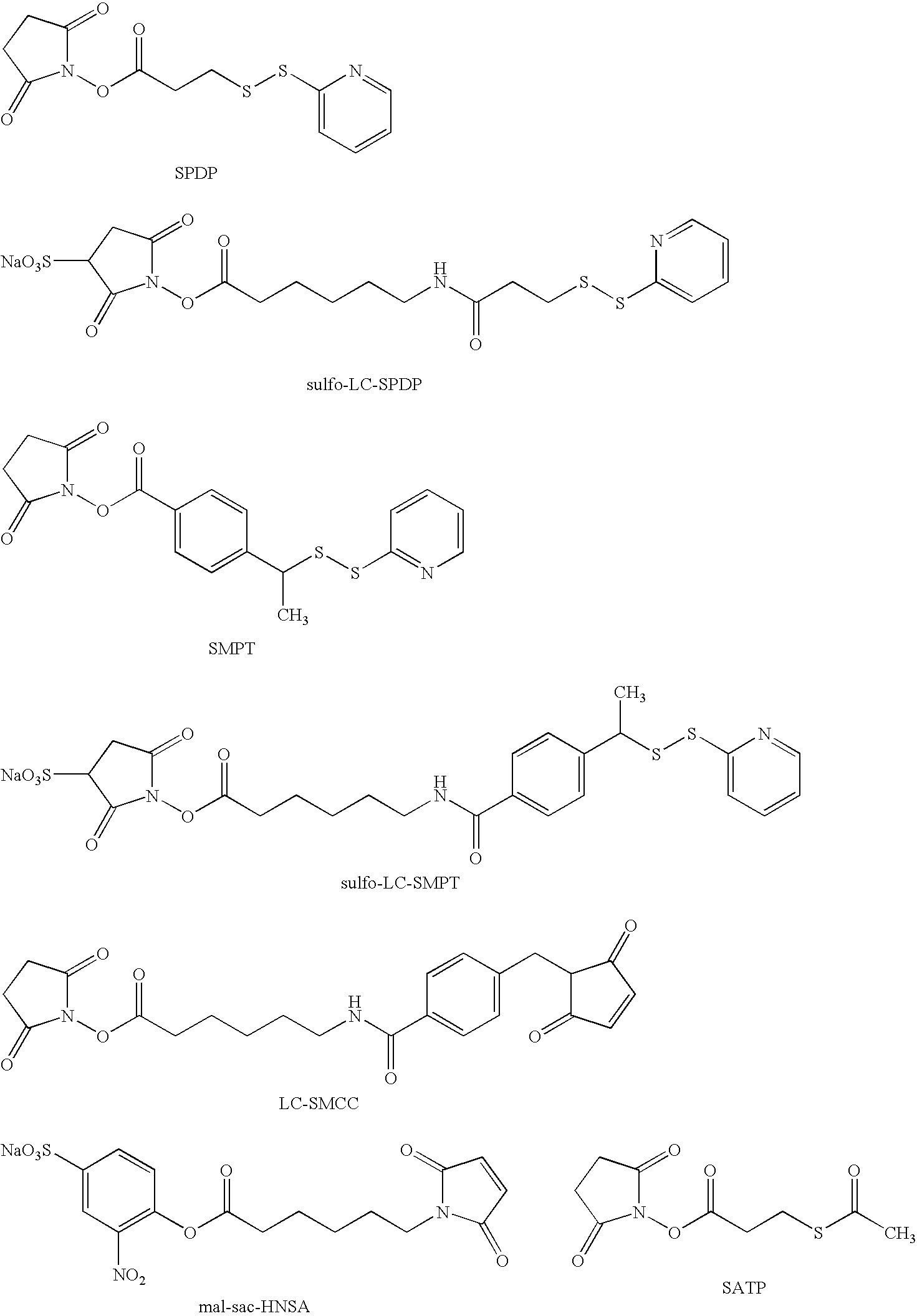
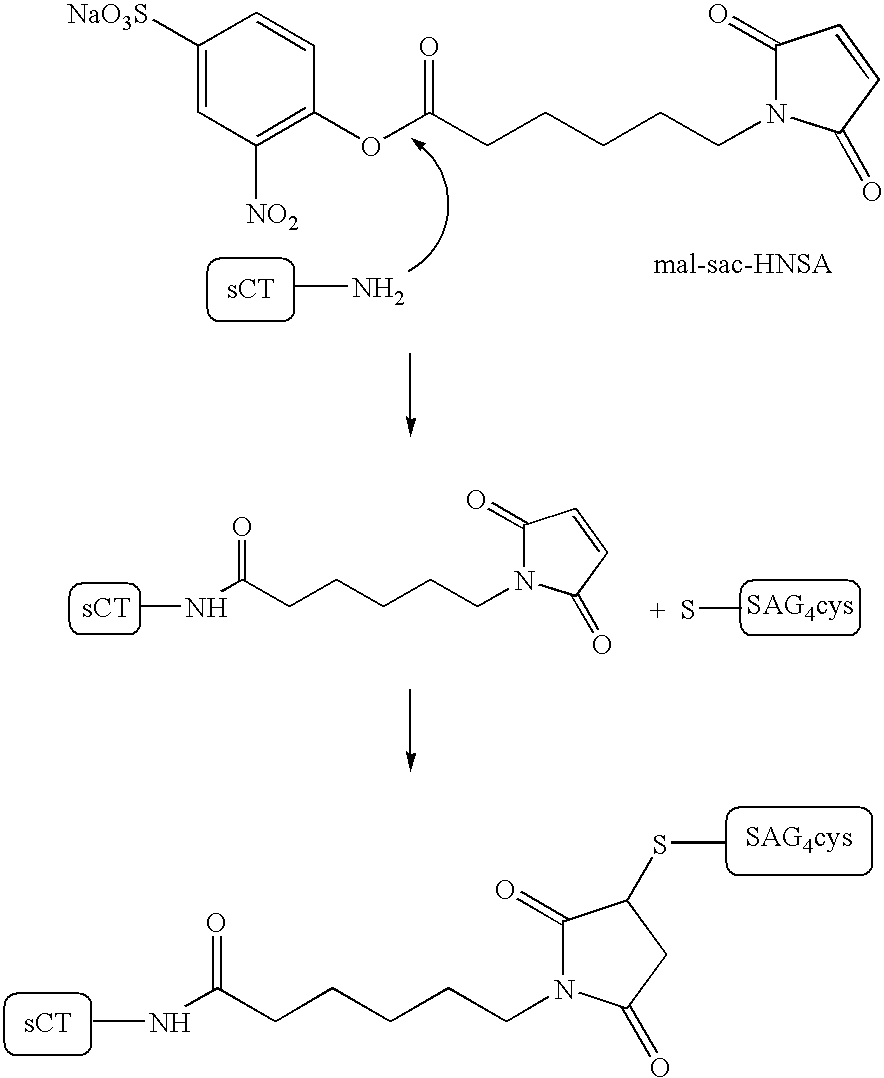
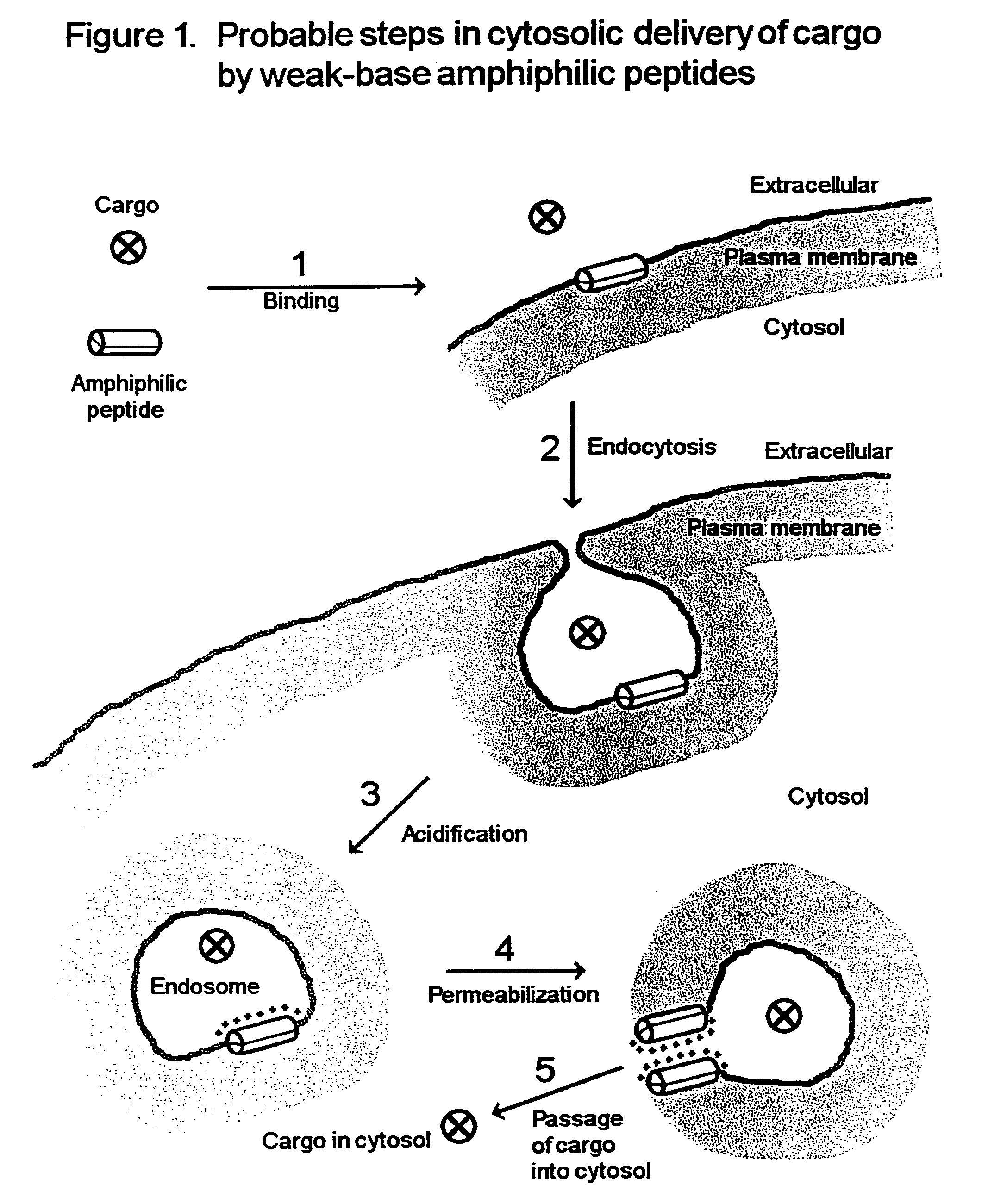
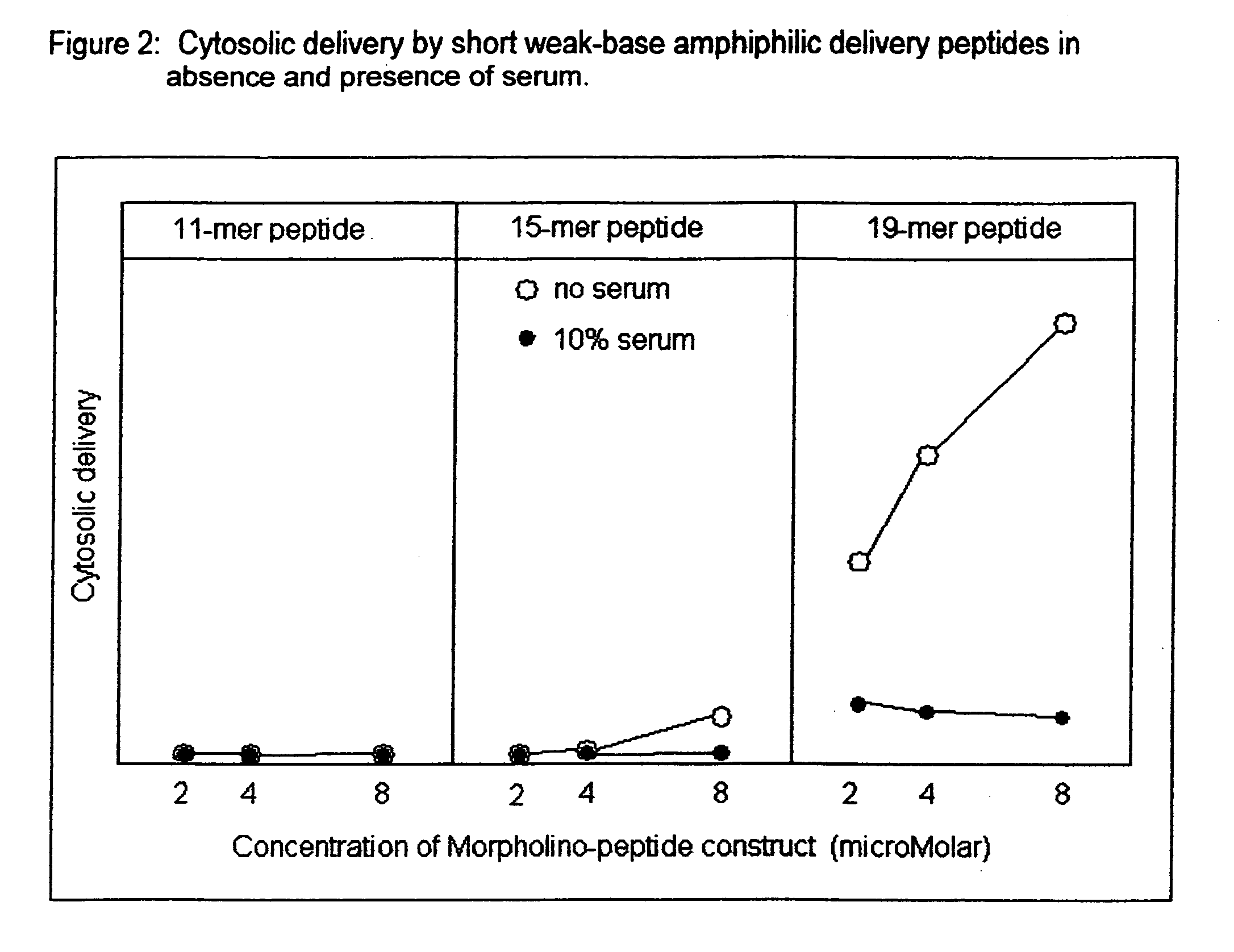
Peptide composition and method for delivering substances into the cytosol of cells
InactiveUS7084248B2Little and no toxicityEasy to useSsRNA viruses negative-sensePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCytosolNeutral ph
Weak-base amphiphilic delivery peptide compositions are described for use in delivering large polar substances (cargo) into the cytosol of animal cells via an indirect endocytosis-mediated delivery process. The delivery peptides, which are predominantly non-ionic at neutral pH, bind but do not permeabilize cell membranes. After endocytosis of both delivery peptides and cargo, acidification of the endosome converts the delivery peptides to their polycationic form, whereupon they permeabilize the endosomal membrane and allow co-endocytosed cargo to pass from the endosome to the cytosol of the cell.
Owner:GENE TOOLS
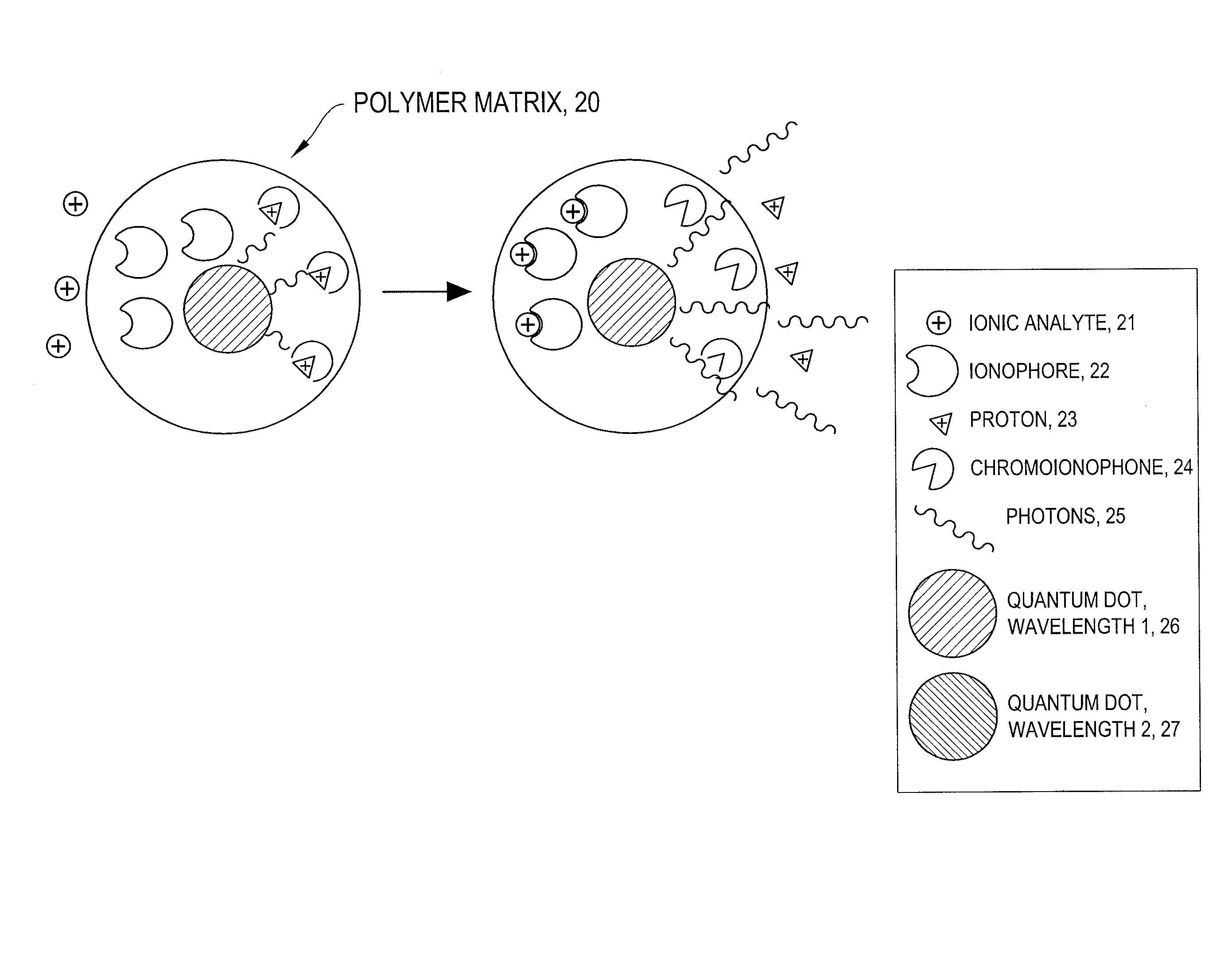
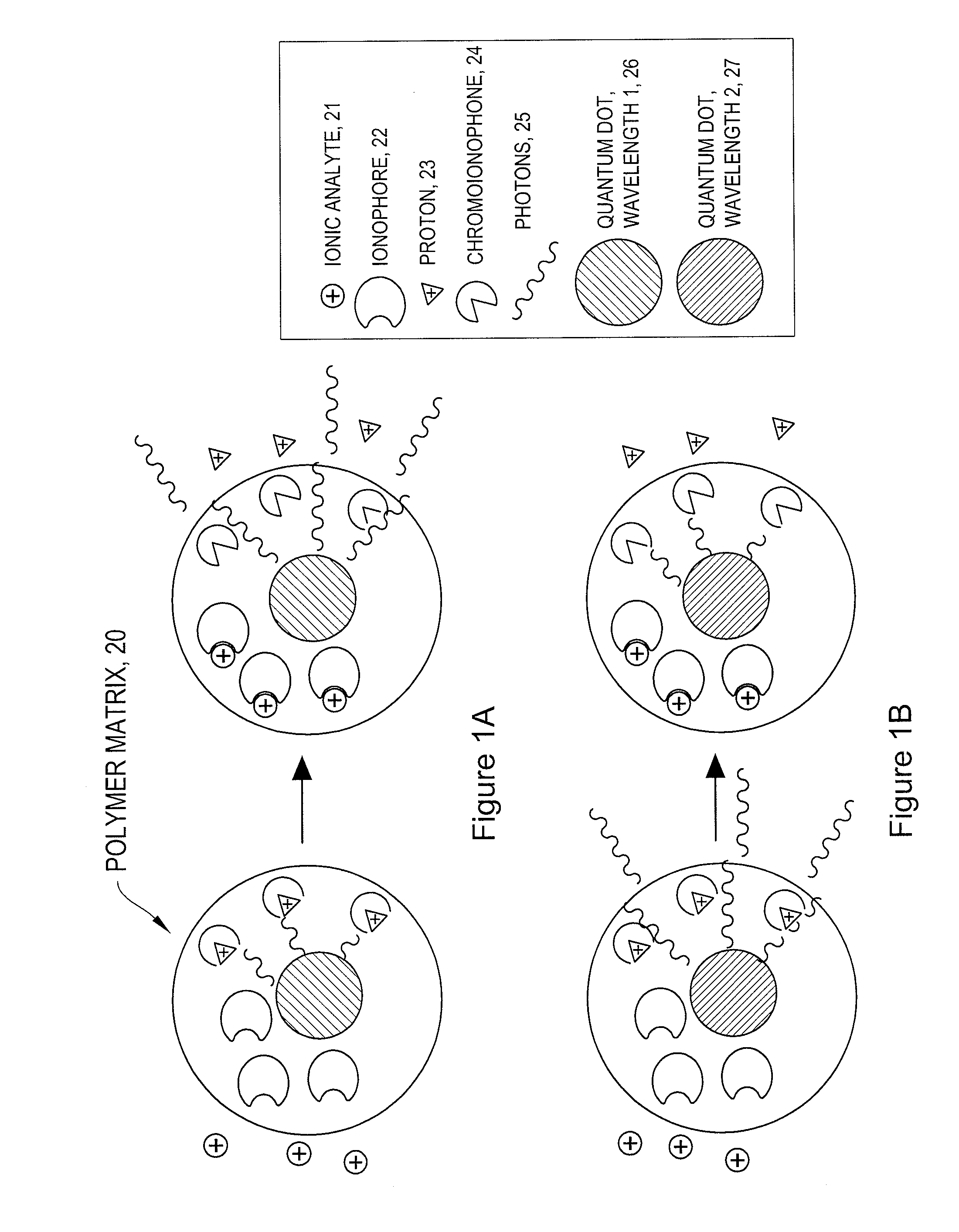
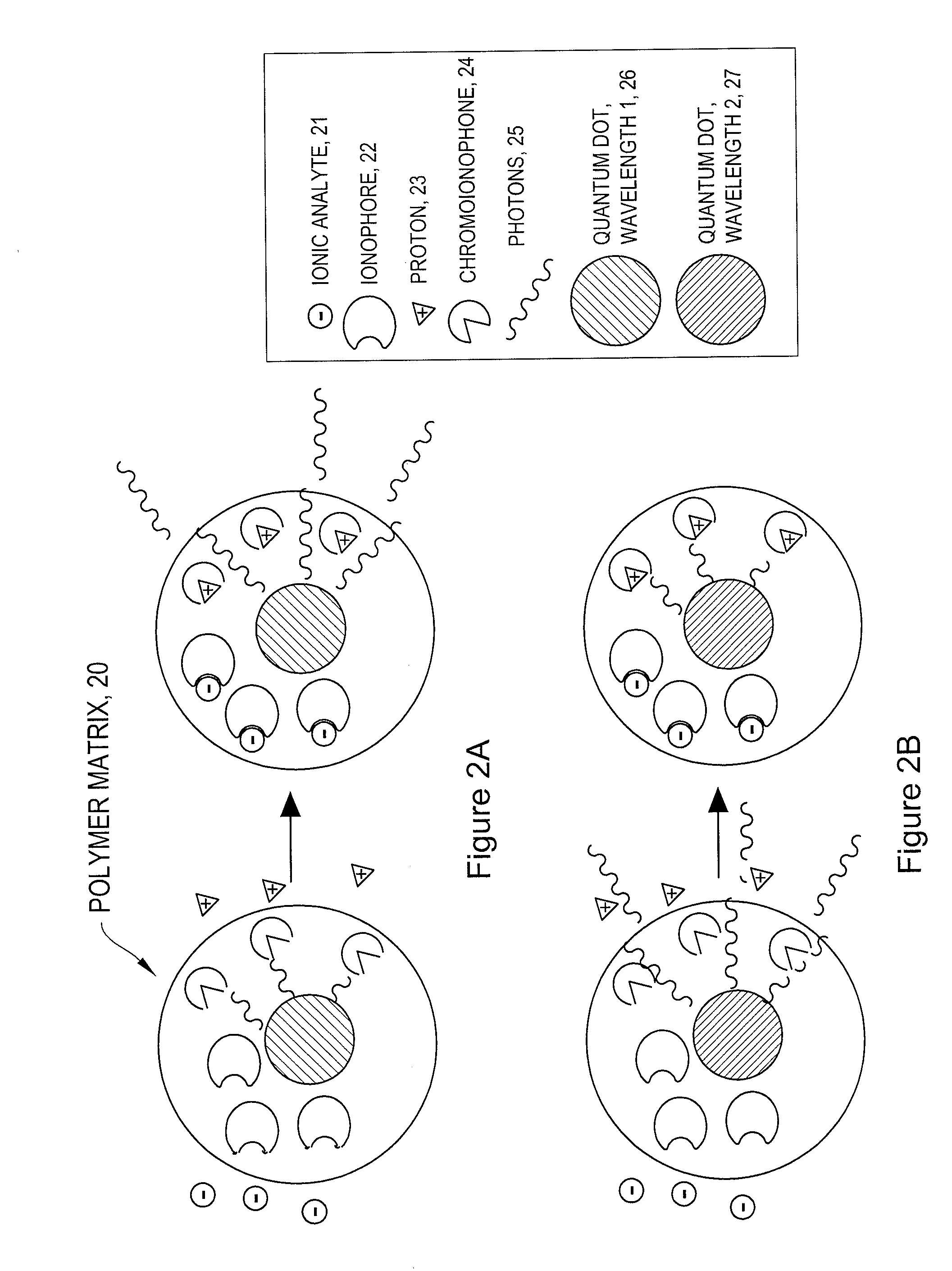
Intracellular nanosensors and methods for their introduction into cells
InactiveUS8263358B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFluorescenceAbsorbance
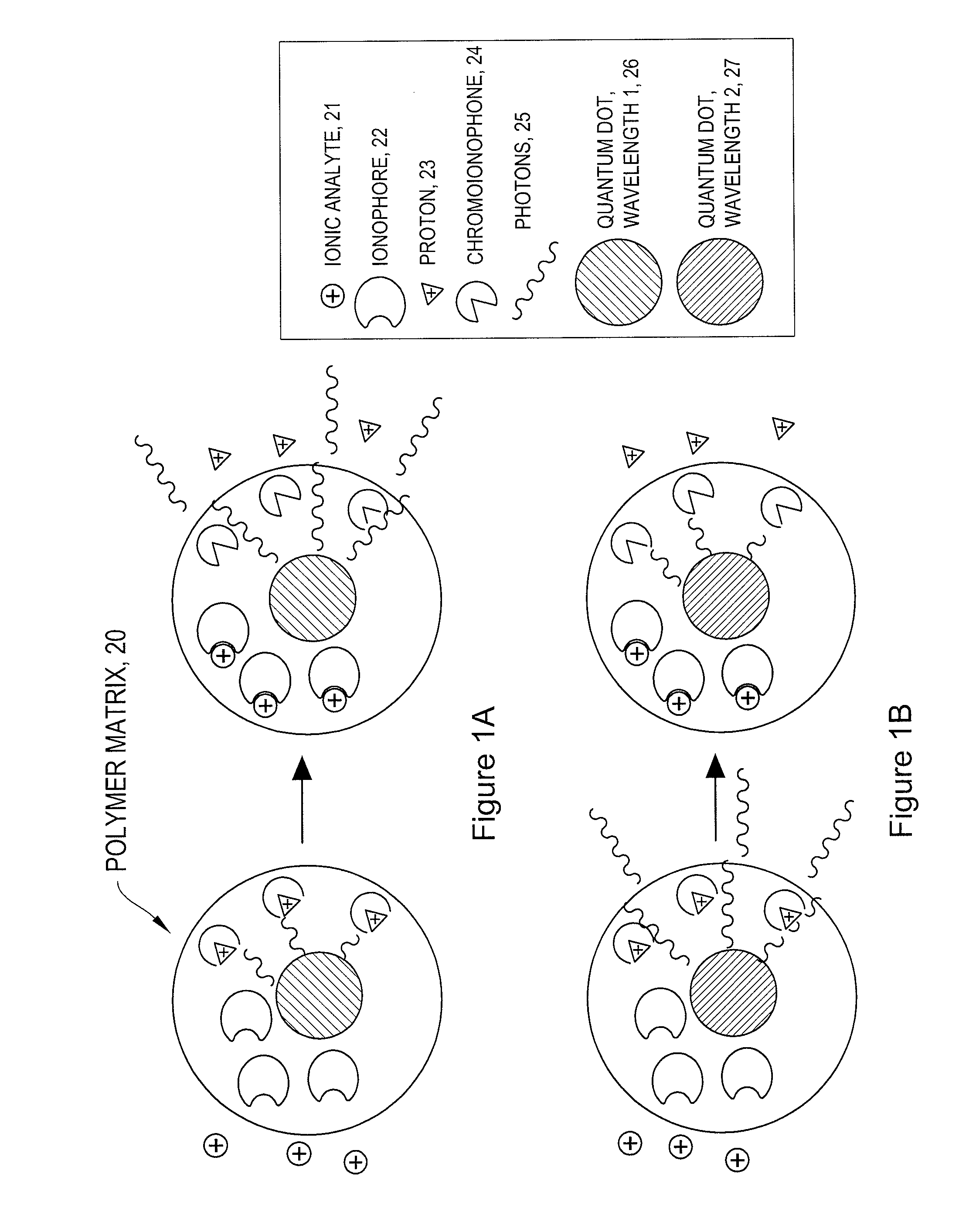
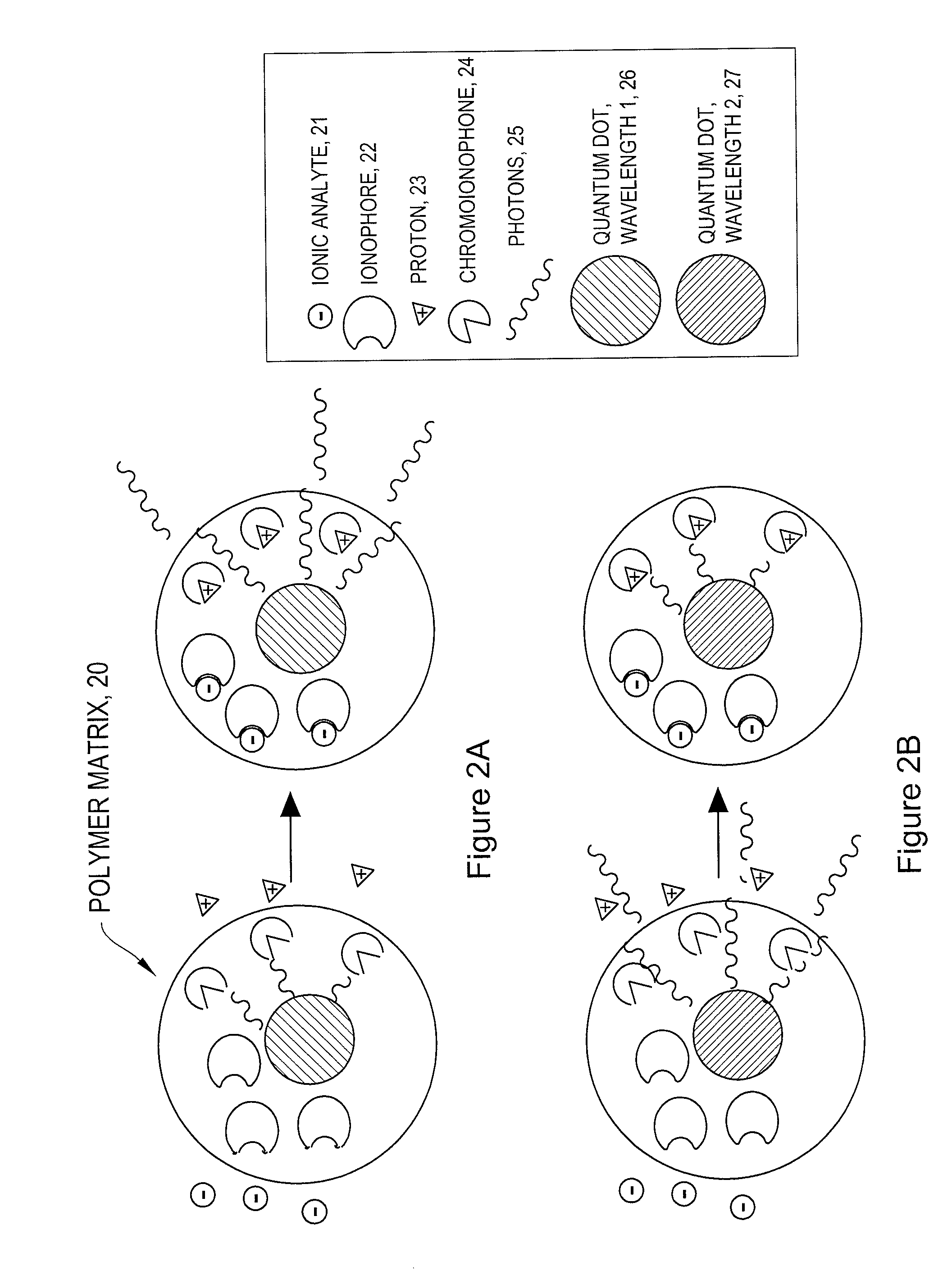
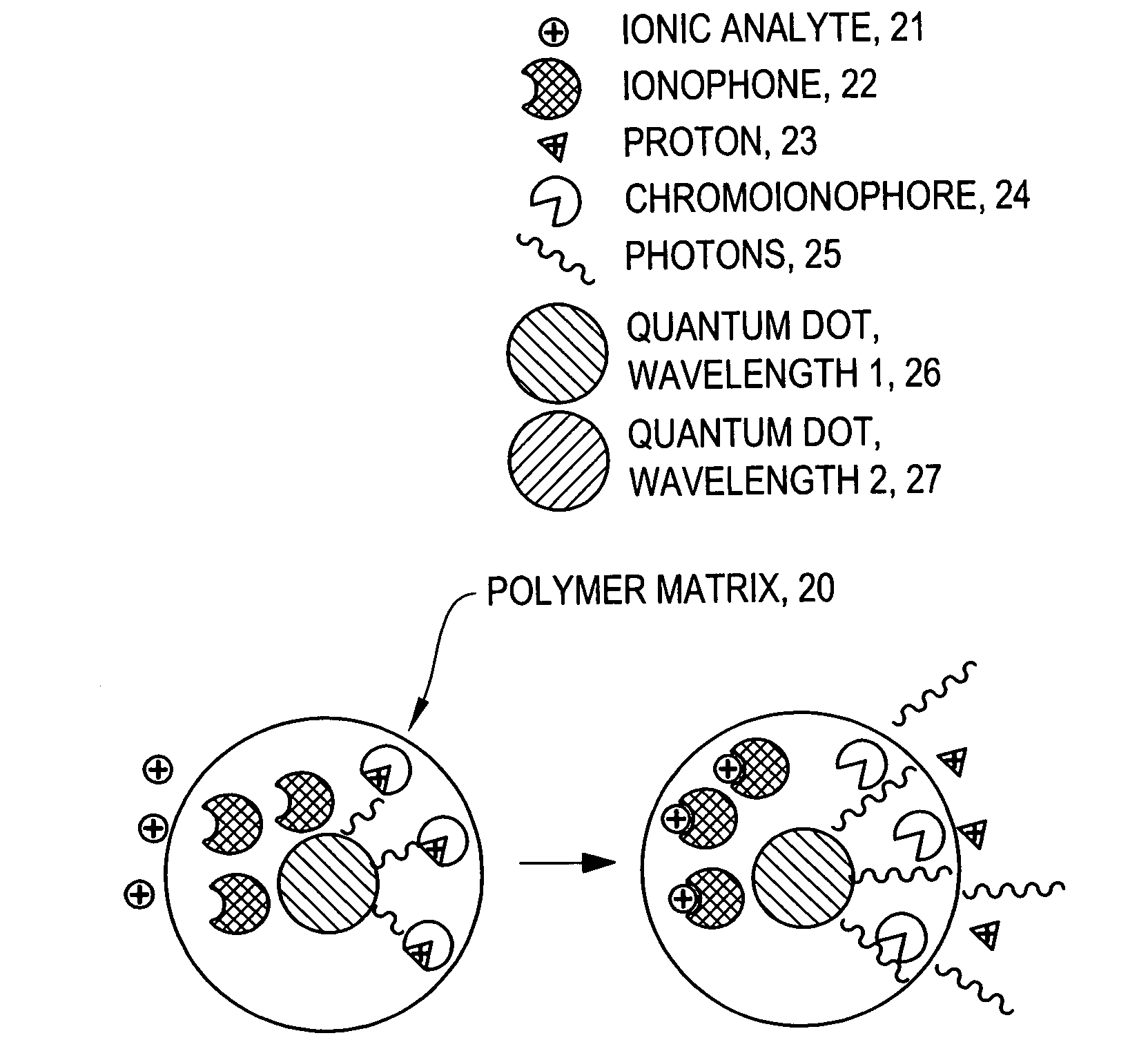
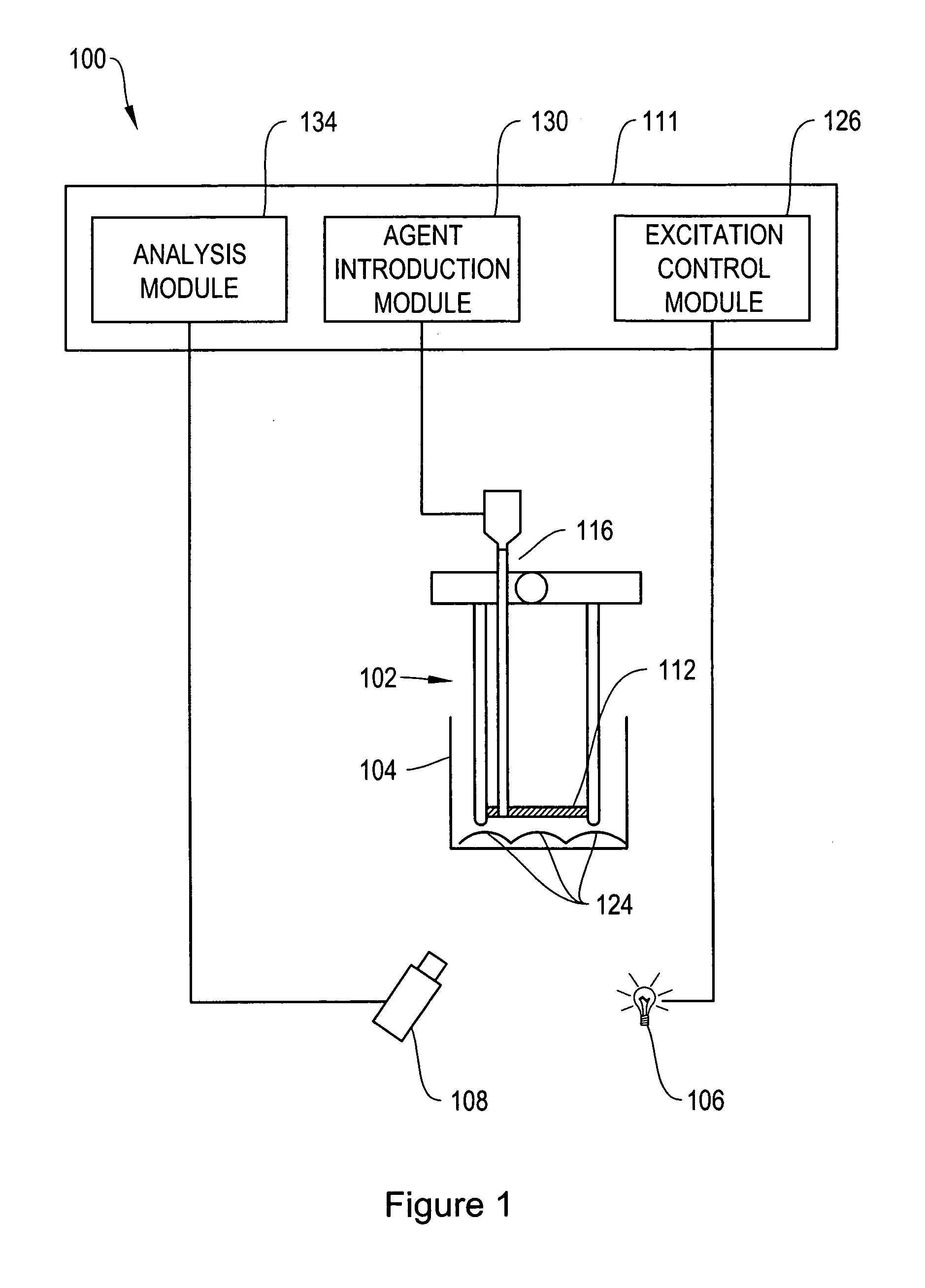
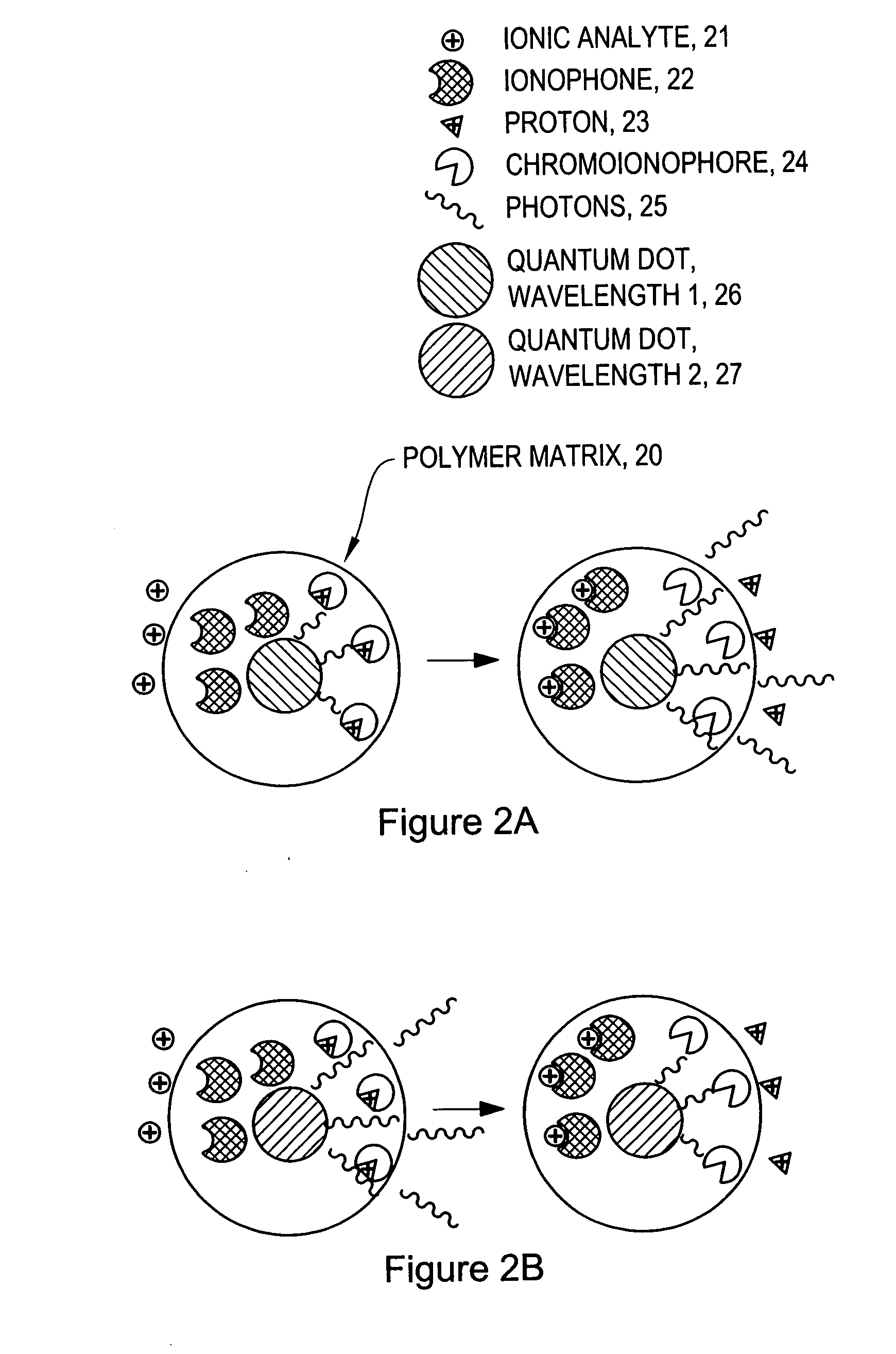
The invention provides ion-selective sensors capable of selectively measuring ions, e.g., Na+, K+, Cl−, etc., in the cytosol of a single living cell. The sensor comprises one or more quantum dots or a fluorescent dye, a pH-sensitive dye, and optionally an ion-selective component such as an ionophore. These elements may, for example, be disposed in a polymer matrix. The polymer matrix comprises an internalizing moiety which enables the sensor to localize within the cytosol of a cell. The internalizing moiety comprises a small molecule or peptide such as an amine, antepennepedia, mastoparan, or melittin that react under acidic conditions to release a sensor from the confines of a endosome. Once in the cytosol the sensors may detect ionic analytes by selective ion extraction by the polymer, thereby inducing a pH change within the sensor which in turn changes the absorbance of the pH-sensitive dye. The change of absorbance may in turn attenuate the intensity of detectable emissions, e.g., fluorescence, from the quantum dot or dye by directly absorbing its fluorescence emission.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Non-cytotoxic protein conjugates
The present invention is directed to non-cytotoxic protein conjugates for inhibition or reduction of exocytic fusion in a nociceptive sensory afferent cell. The protein conjugates comprise: (i) a dynorphin Targeting Moiety (TM), wherein the TM is an agonist of a receptor present on a nociceptive sensory afferent cell, and wherein the receptor undergoes endocytosis to be incorporated into an endosome within the nociceptive sensory afferent cell; (ii) a non-cytotoxic protease or a fragment thereof, wherein the protease or protease fragment is capable of cleaving a protein of the exocytic fusion apparatus of the nociceptive sensory afferent cell; and (iii) a Translocation Domain, wherein the Translocation Domain translocates the protease or protease fragment from within the endosome, across the endosomal membrane, and into the cytosol of the nociceptive sensory afferent cell. Nucleic acid sequences encoding the protein conjugates, methods of preparing same and uses thereof are also described.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
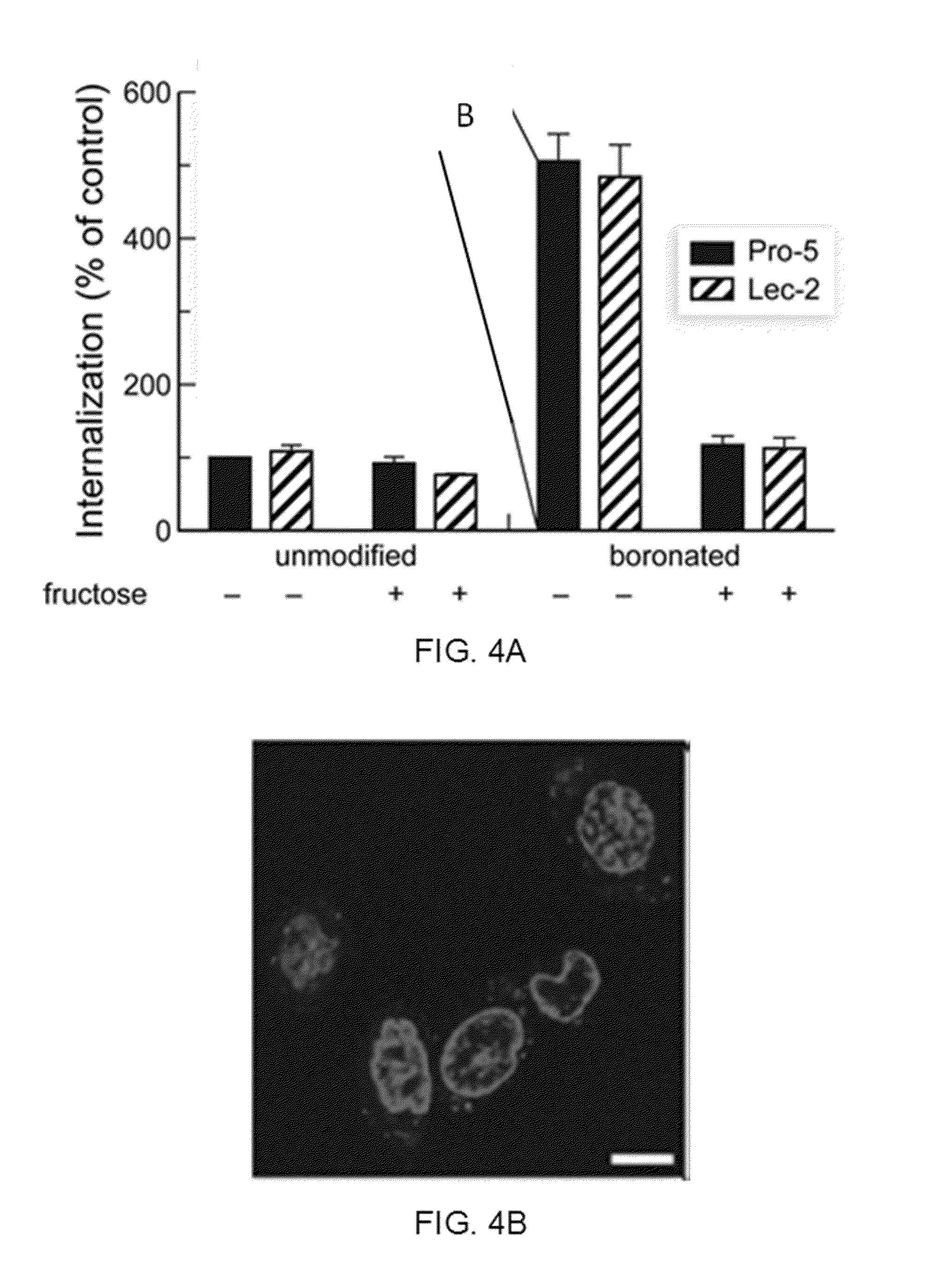
Boronate-Mediated Delivery of Molecules into Cells
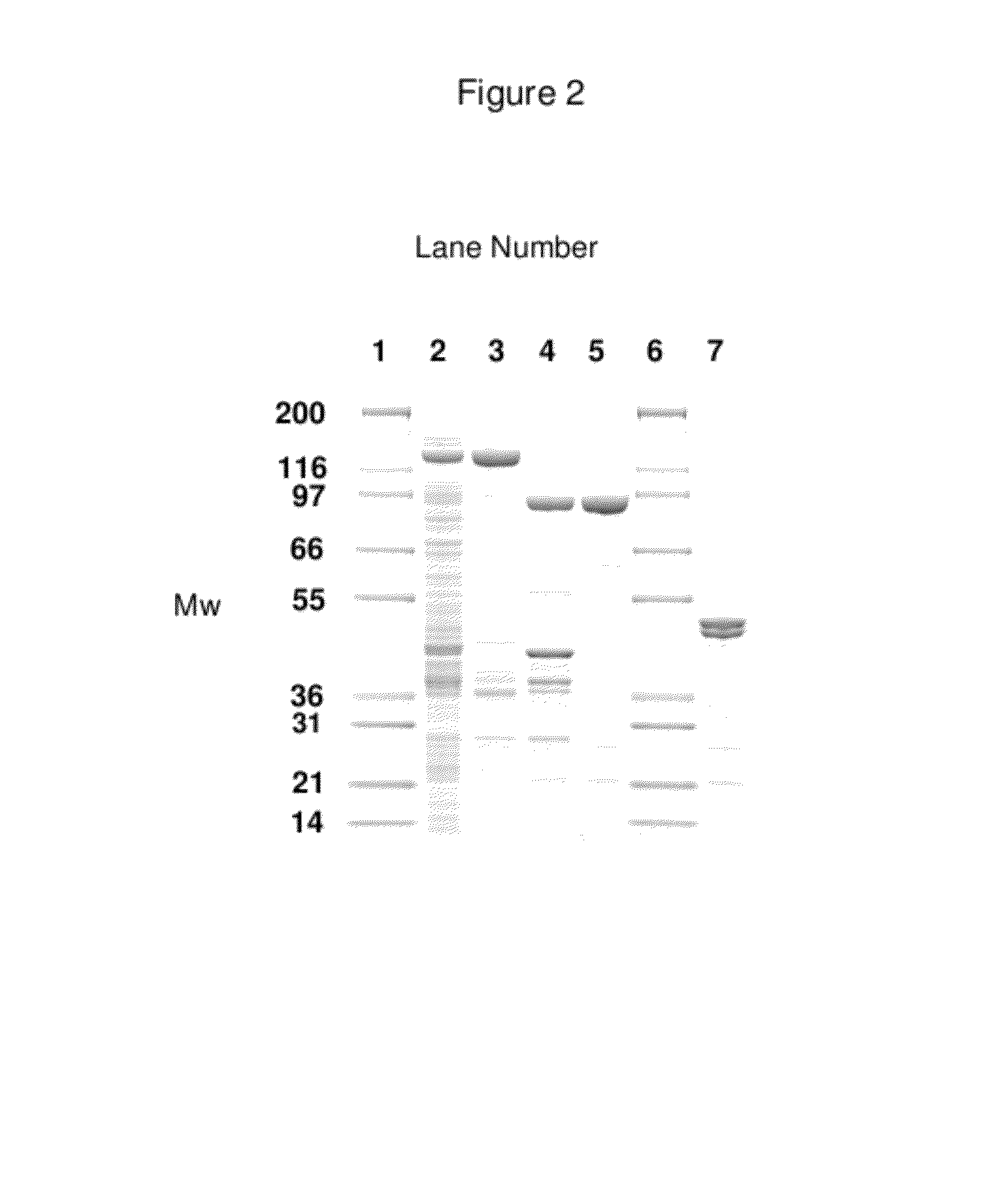
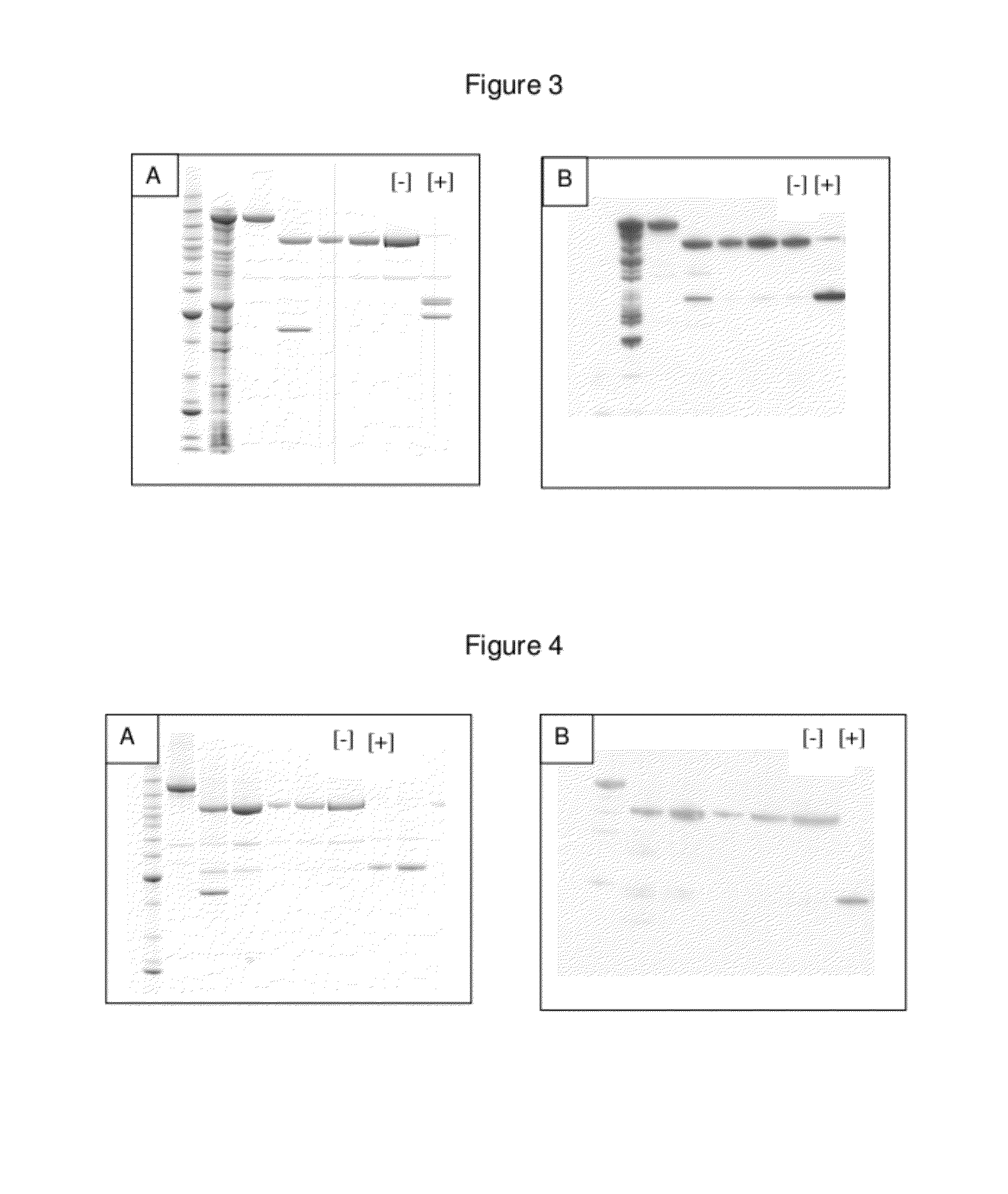
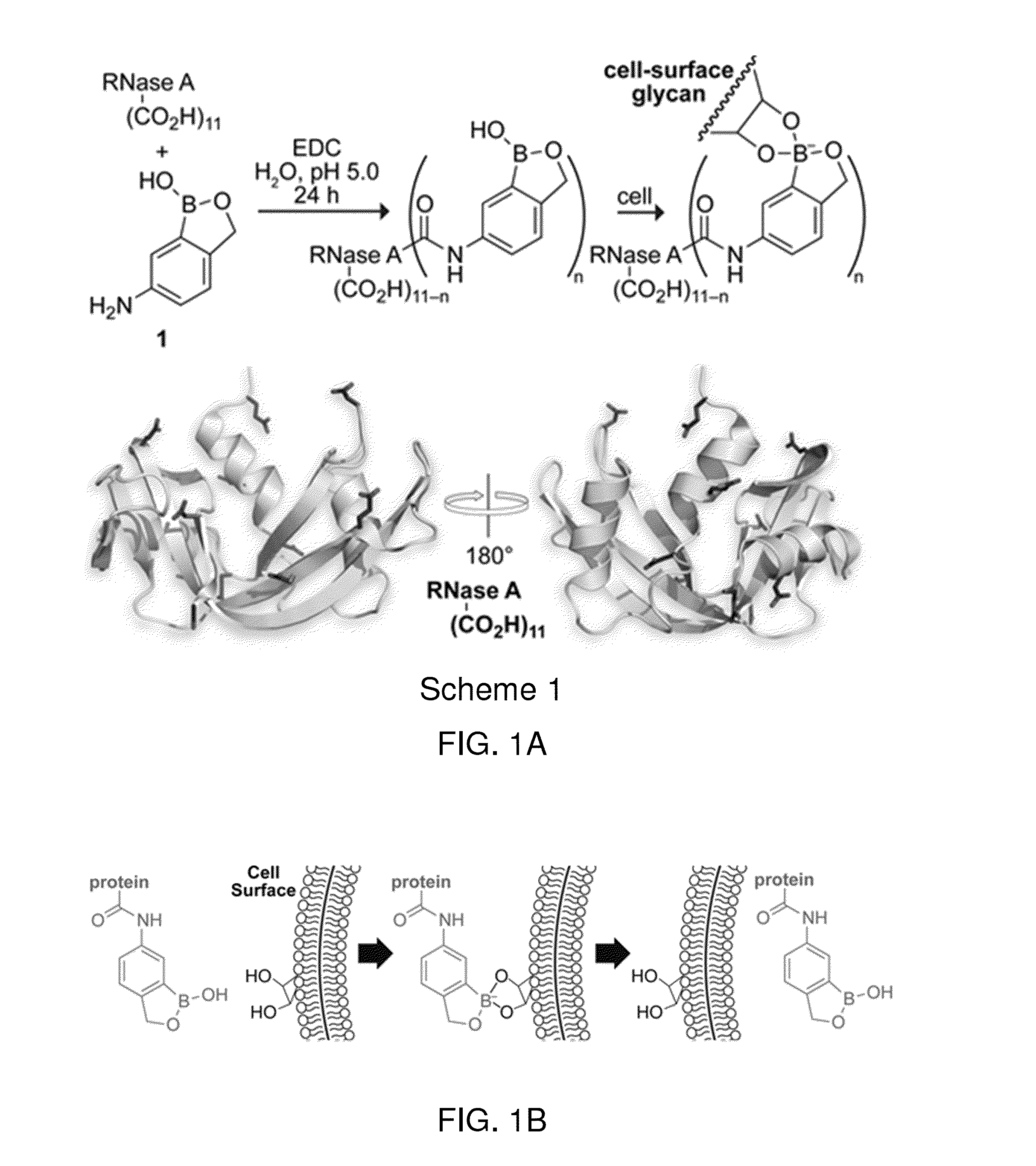
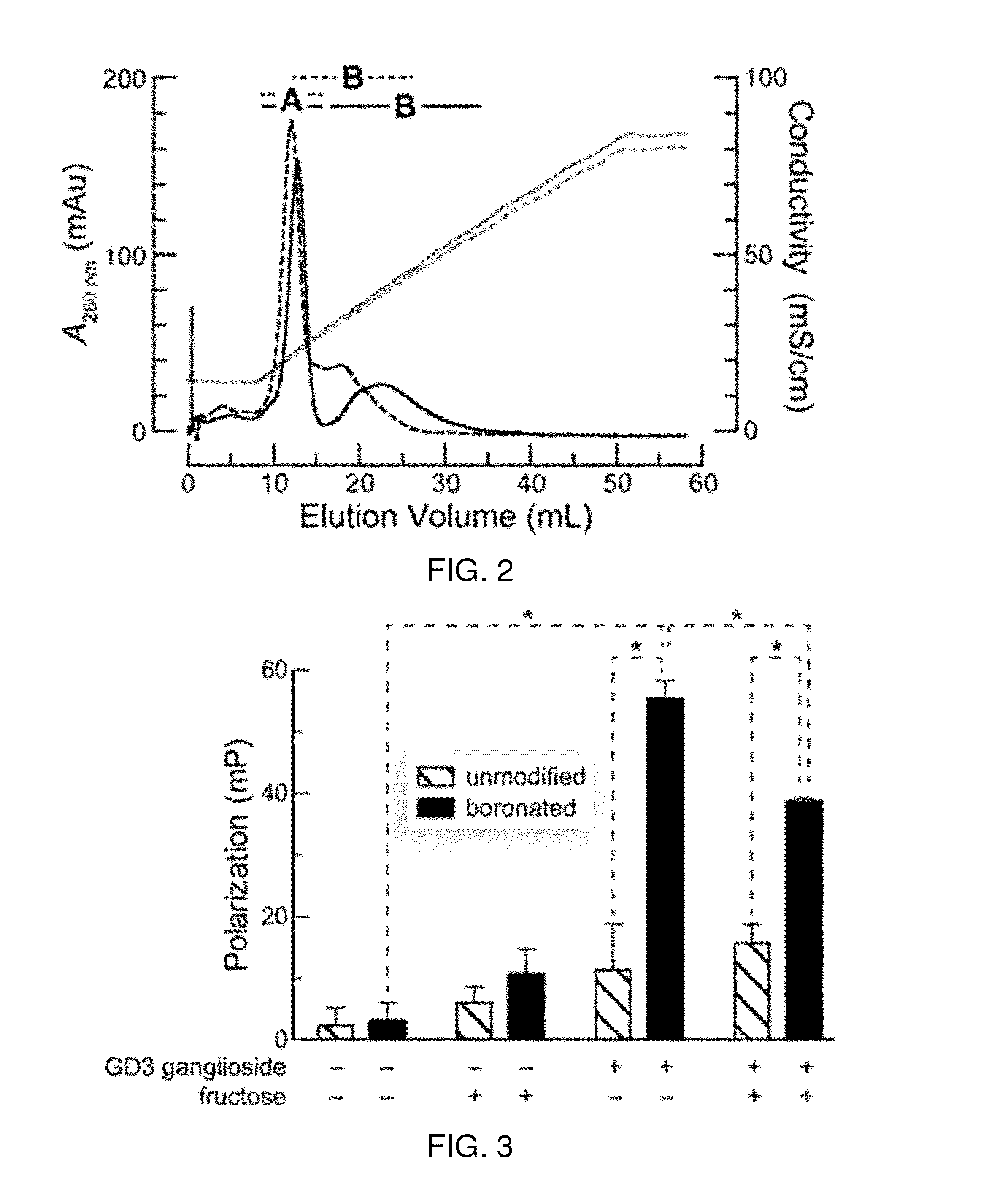
Methods for enhancing cellular uptake of cargo molecules by boronating the cargo molecule, particularly with one or more phenylboronic acid groups. Cellular uptake includes at least partial uptake into the cytosol. Boronation includes ligating, crosslinking or otherwise bonding one or more phenylboronic acids substituted to contain a reactive group to a cargo molecule. Boronation also includes ligating, crosslinking or otherwise bonding a phenylboronated oligopeptide to a cargo molecule. The phenylboronate groups are optionally conjugated to the cargo molecule via linking moieties that can be selectively cleaved, such cleavable linkers can allow the phenylboronate groups to be removed from the cargo molecule after the boronated cargo molecule is introduced into the cell. The invention includes certain phenylboronates which are boronation reagents, certain boronated oligopeptides and certain boronated peptides and proteins. The invention also includes kits for enhancing cellular uptake of cargo molecules by boronation with one or more phenylboronates or boronated oligopeptides.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Intracellular nanosensors and methods for their introduction into cells
InactiveUS20090142274A1Reduce intensityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAbsorbanceFluorochrome Dye
The invention provides ion-selective sensors capable of selectively measuring ions, e.g., Na+, K+, Cl−, etc., in the cytosol of a single living cell. The sensor comprises one or more quantum dots or a fluorescent dye, a pH-sensitive dye, and optionally an ion-selective component such as an ionophore. These elements may, for example, be disposed in a polymer matrix. The polymer matrix comprises an internalizing moiety which enables the sensor to localize within the cytosol of a cell. The internalizing moiety comprises a small molecule or peptide such as an amine, antepennepedia, mastoparan, or melittin that react under acidic conditions to release a sensor from the confines of a endosome. Once in the cytosol the sensors may detect ionic analytes by selective ion extraction by the polymer, thereby inducing a pH change within the sensor which in turn changes the absorbance of the pH-sensitive dye. The change of absorbance may in turn attenuate the intensity of detectable emissions, e.g., fluorescence, from the quantum dot or dye by directly absorbing its fluorescence emission.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Ion-selective quantum dots
ActiveUS20080131909A1Improve photostabilityIncrease brightnessBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceAbsorbance
The invention provides ion-selective sensors comprising quantum dots capable of selectively measuring ions, e.g., Na+, K+, Cl−, etc., in various environments, including in the cytosol of a living cell. Quantum dots are attractive probes for microscopy due to their photophysical advantages over fluorescent dyes, including prolonged photostability, brightness and quantum efficiency. In certain embodiments, a sensor comprises one or more quantum dots, a pH-sensitive dye, and optionally an ion-selective component such as an ionophore. These elements may, for example, be disposed in a polymer matrix. In certain embodiments, the sensors may detect ionic analytes by selective ion extraction by the polymer, thereby inducing a pH change within the sensor which in turn changes the absorbance of the pH-sensitive dye. The change of absorbance may in turn attenuate the intensity of detectable emissions, e.g., fluorescence, from the quantum dot by directly absorbing its fluorescence emission.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Vector mediated organelle transfection
ActiveUS20070011759A1High expressionFunction increaseSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsEucaryotic cellDNA construct
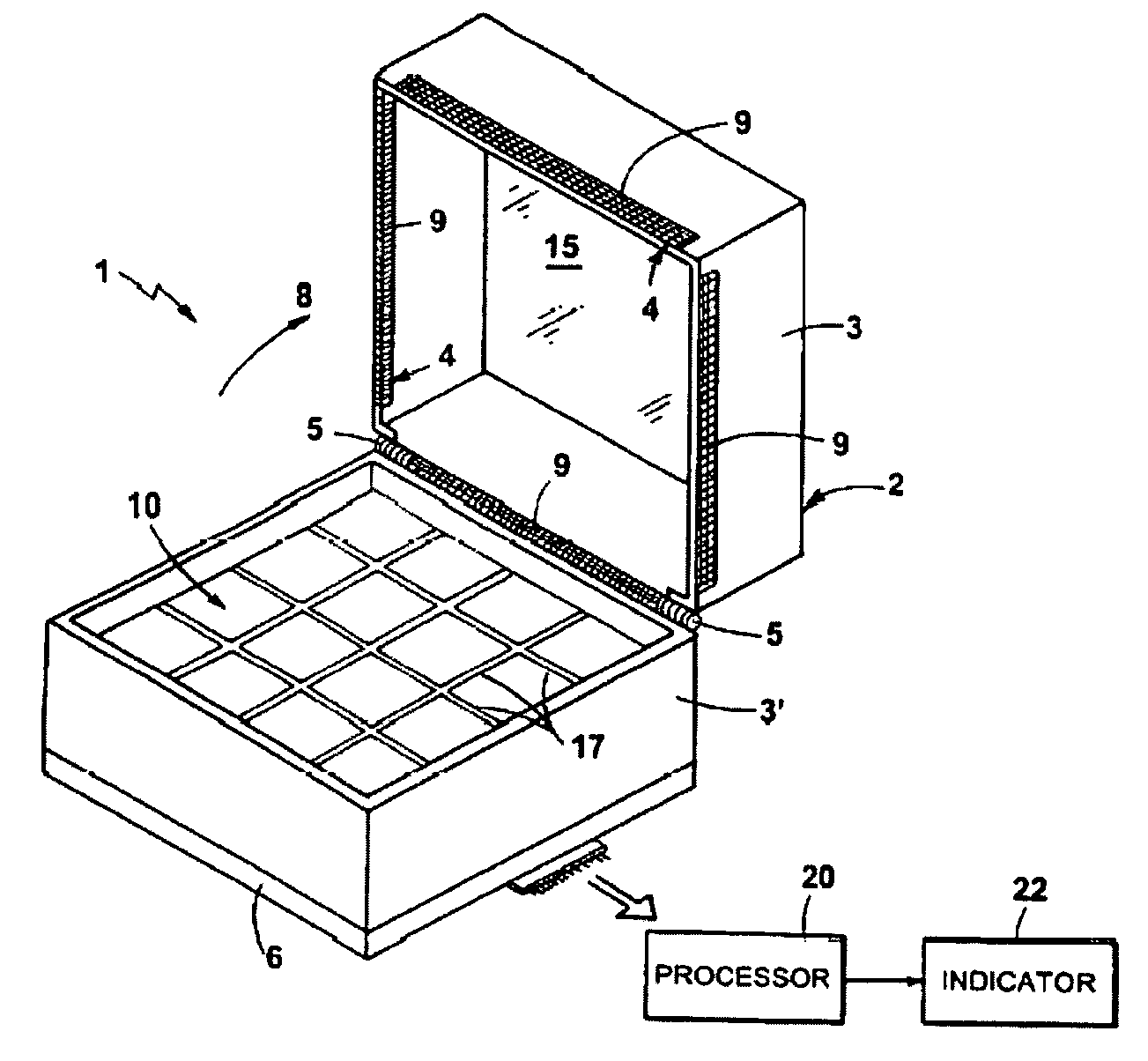
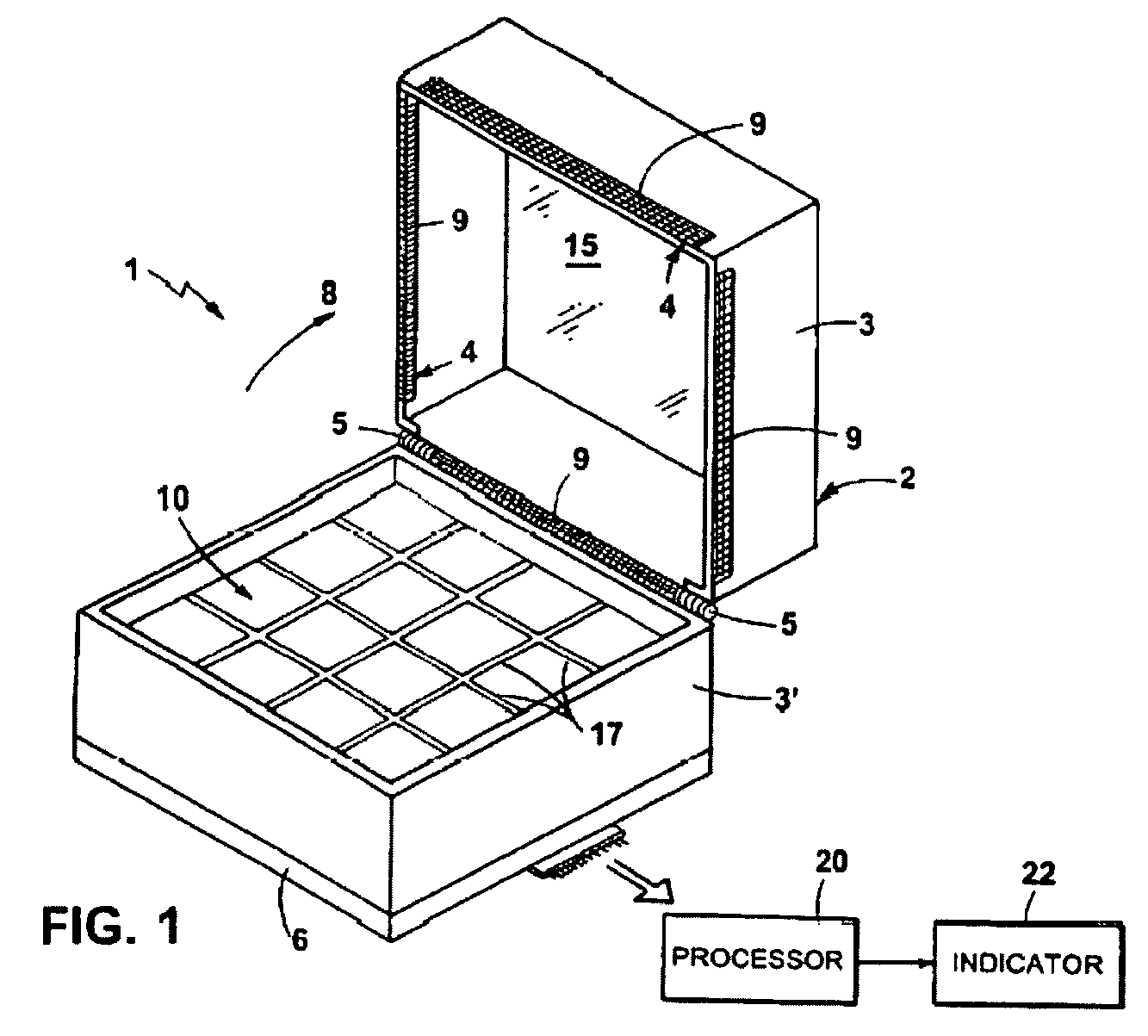
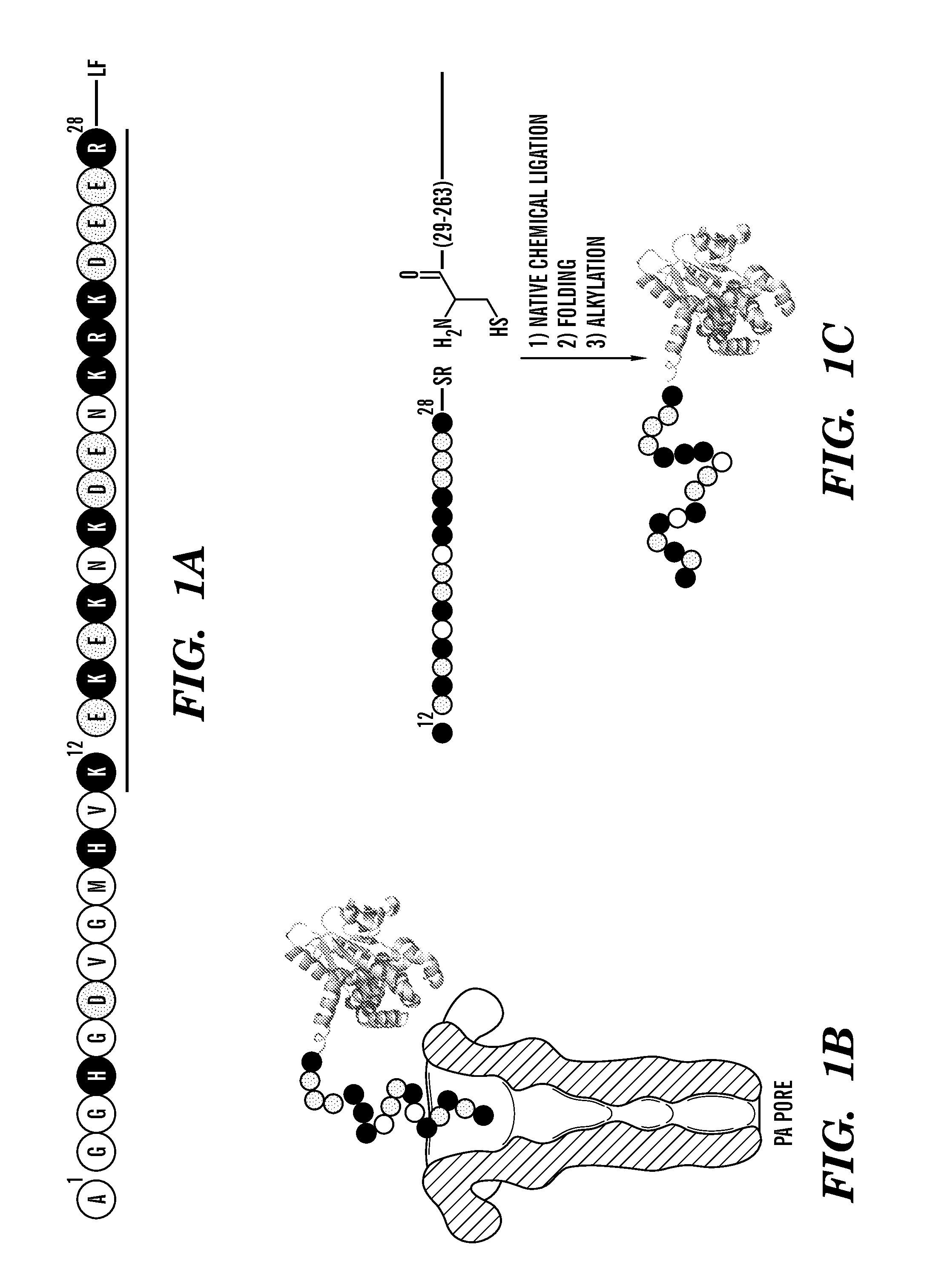
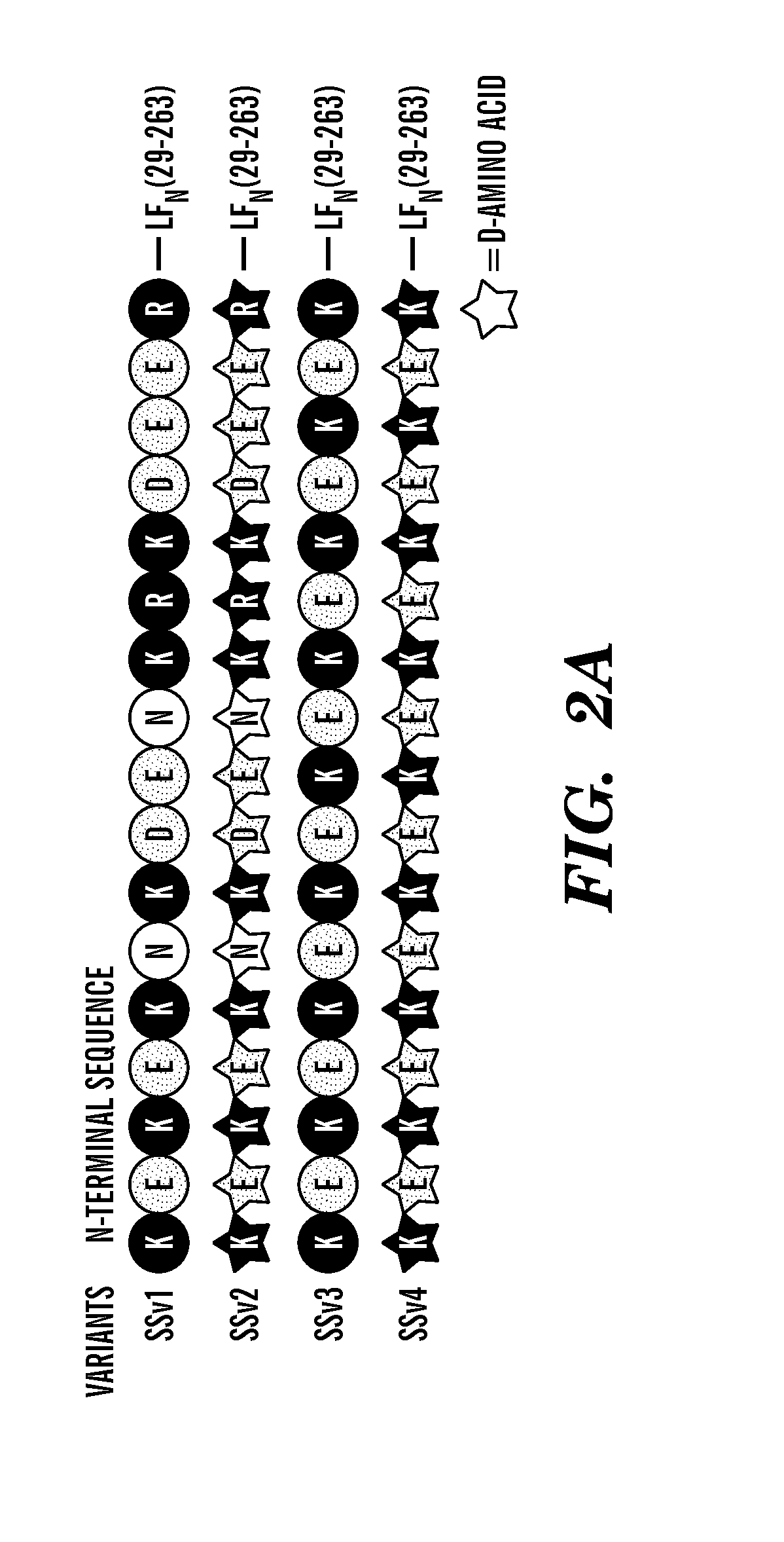
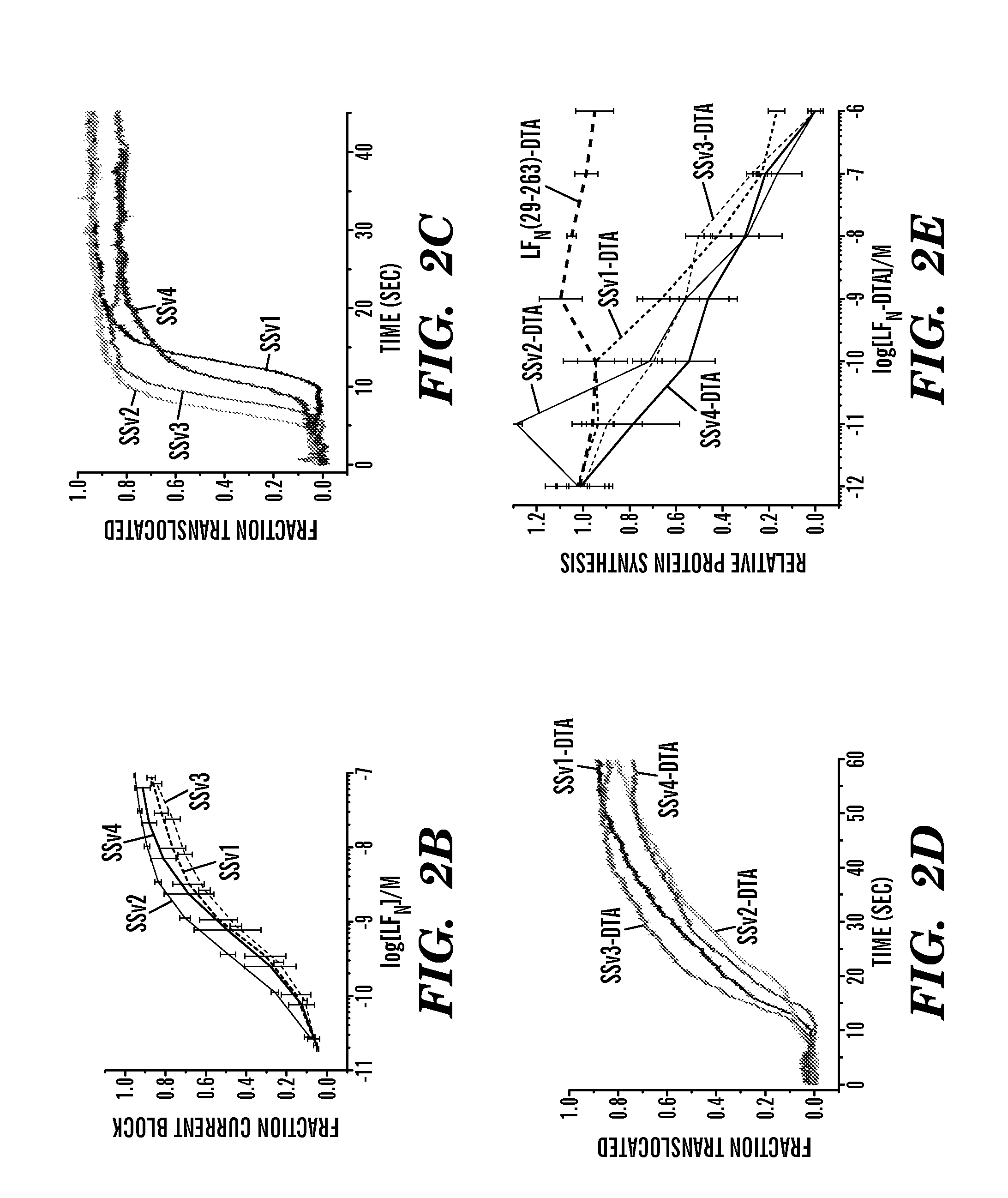
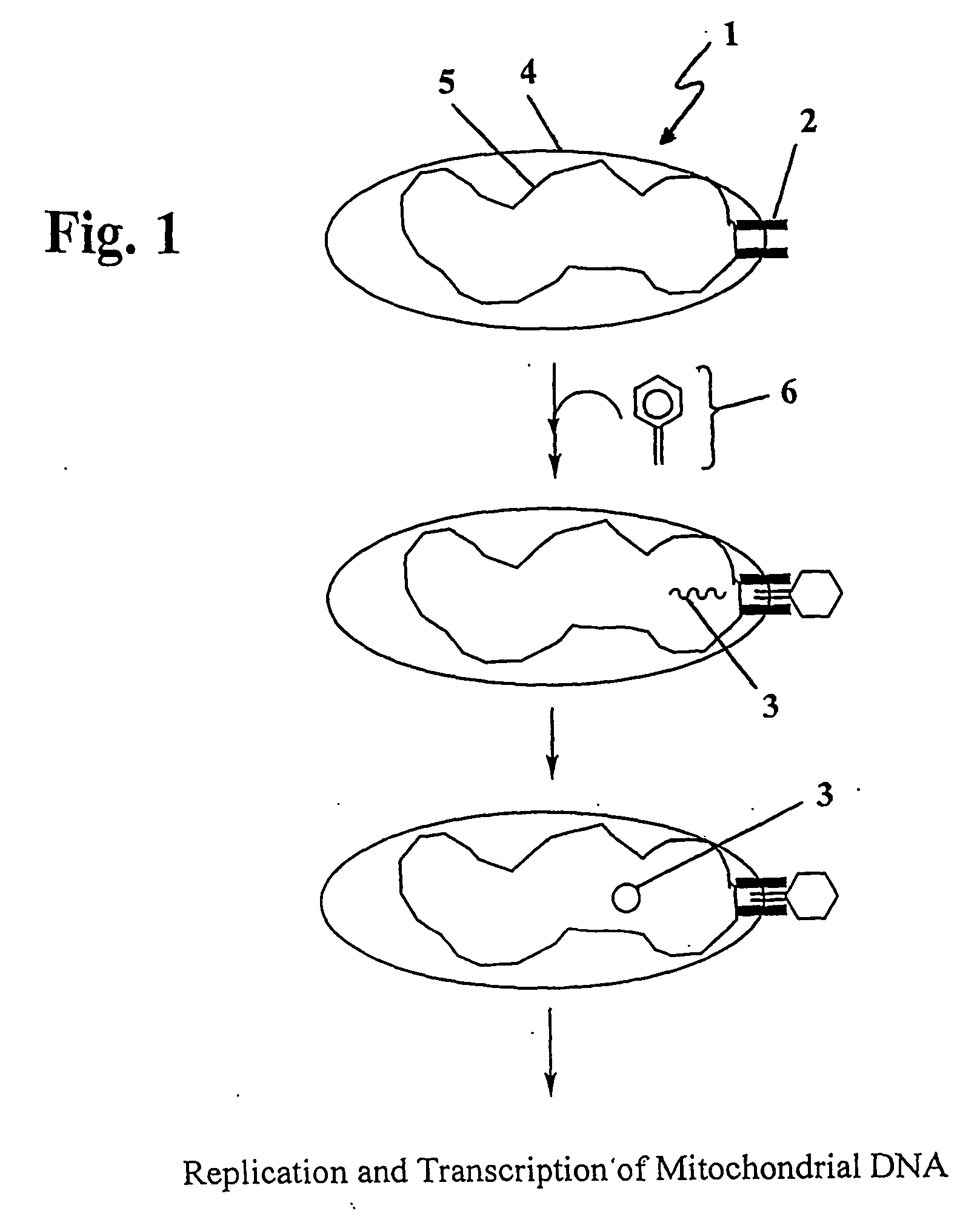
The present invention provides compositions and methods for direct transfection of mitochondria and chloroplast DNA in living cells. More particularly, the present invention is based on the use of viral vectors that specifically bind to receptors uniquely found on the target organelle. In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 1, a eukaryotic cell containing an organelle (1) that has been modified to express a viral receptor (2) on the organelle's surface is provided. A viral vector (6) comprising a desired recombinant DNA construct (3) is introduced into the cytosol of the cell, wherein the viral vector binds to its receptor and introduces the recombinant DNA into the interior of the organelle.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]
The invention is isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding Na+ / H+ exchanger polypeptides with 95% identity to a Na+ / H+ exchanger polypeptide from Arabidopsis thaliana for extrusion of monovalent cations from the cytosol of cells to provide the cell with increased salt tolerance. Crop species transformed with the nucleic acid molecule are capable of surviving in soil with high salt levels that would normally inhibit growth of the crop species.
Owner:BLUMWALD EDUARDO +1
Optoelectronic sensor
InactiveUS7090988B2Avoid pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenCytosol
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
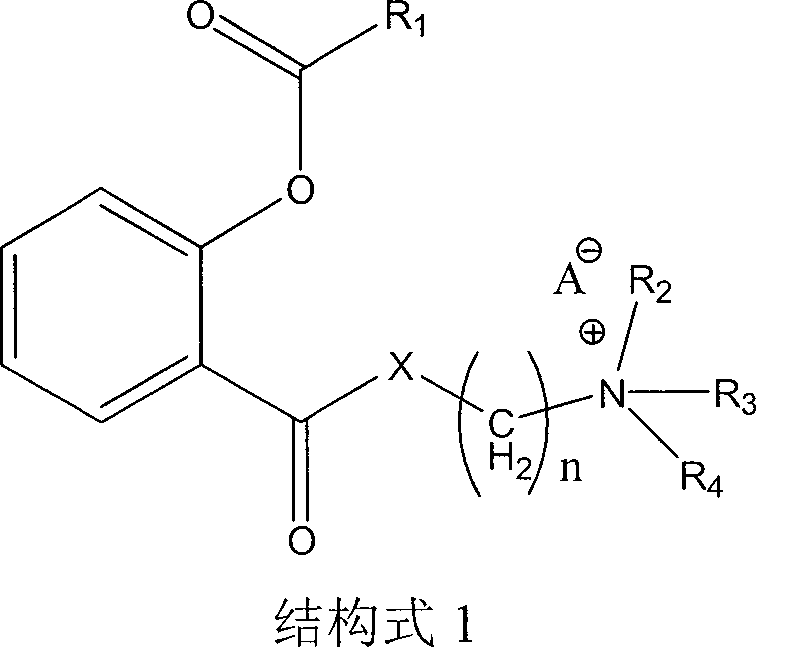
Positively charged water-soluble prodrugs of aspirin
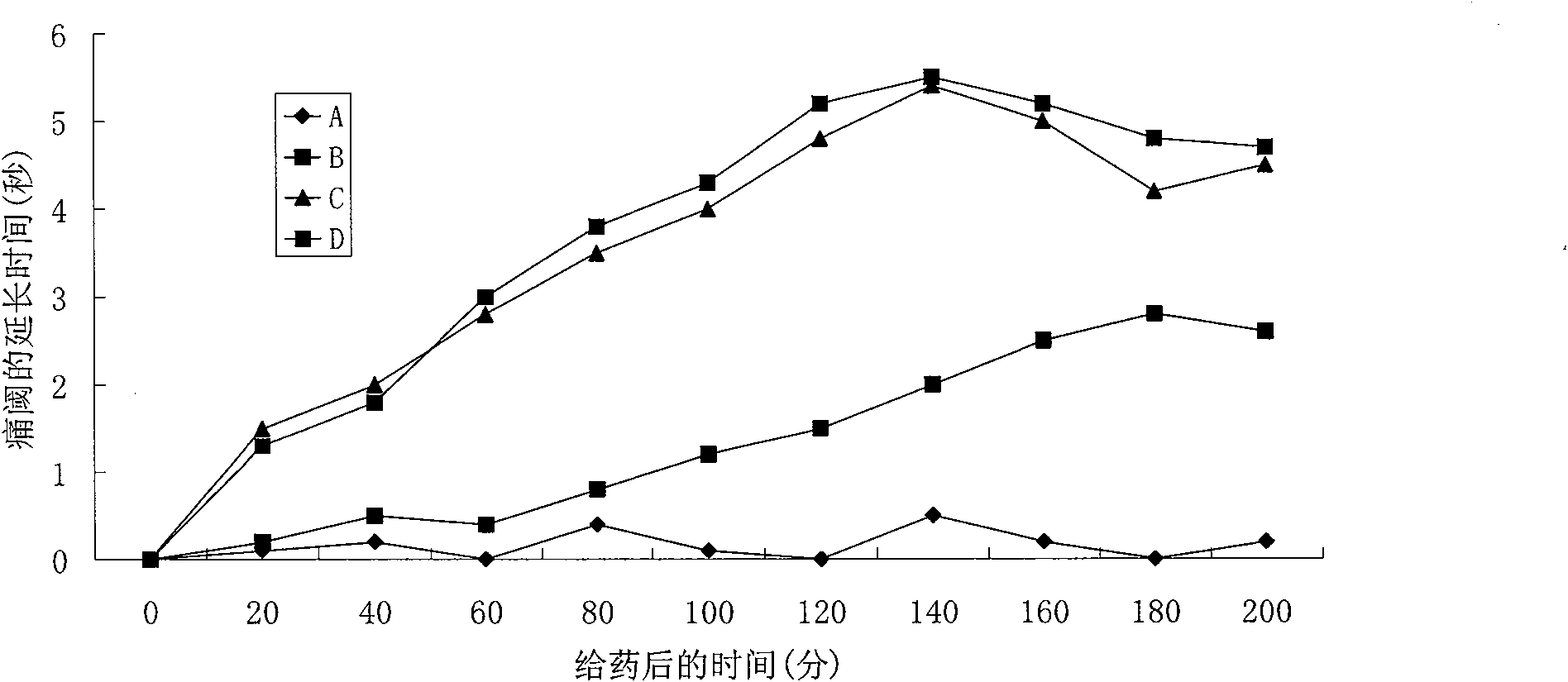
InactiveCN101484415BFast in vivo penetrationAvoid side effectsSenses disorderNervous disorderDiethylaminoethyl acetylsalicylateAspirin
The novel positively charged prodrugs of acetylsalicylic acid and its analogues in the general formula(1) 'Structure 1' were designed and synthesized. The compounds of the general formula(1) 'Structure 1' indicated above can be prepared from functional derivatives of ASA or its analogues,(for example acid halides or mixed anhydrides), by reaction with suitable alcohols, thiols, or amines. The positively charged amino groups of these pro-drugs not only largely increases the solubility of the drugs, but also bonds to the negative charge on the phosphate head group of membranes and push the pro-drug into the cytosol. The experiment results suggest that the pro-drug, diethylaminoethyl acetylsalicylate. AcOH, diffuses through human skin -400 times faster than acetylsalicylic acid itself and ˆ¼100 times faster than ethyl acetylsalicylate. In plasma, 80% of these pro-drugs can change back to the drug in a few minutes. The pro-drugs can be used medicinally in treating any aspirin-treatable conditions in humans or animals and be administered not only orally, but also transdermally for any kind of medical treatments and avoid most of the side effects of aspirin, most notably GI disturbances such as dyspepsia, gastroduodenal bleeding, gastric ulcerations, and gastritis. Controlled transdermal administration systems of the prodrug enables the aspirin to reach constantly optimal therapeutic blood levels to increase effectiveness and reduce the side effects of aspirin.
Owner:于崇曦 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com






![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00001.png)
![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00002.png)
![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00003.png)