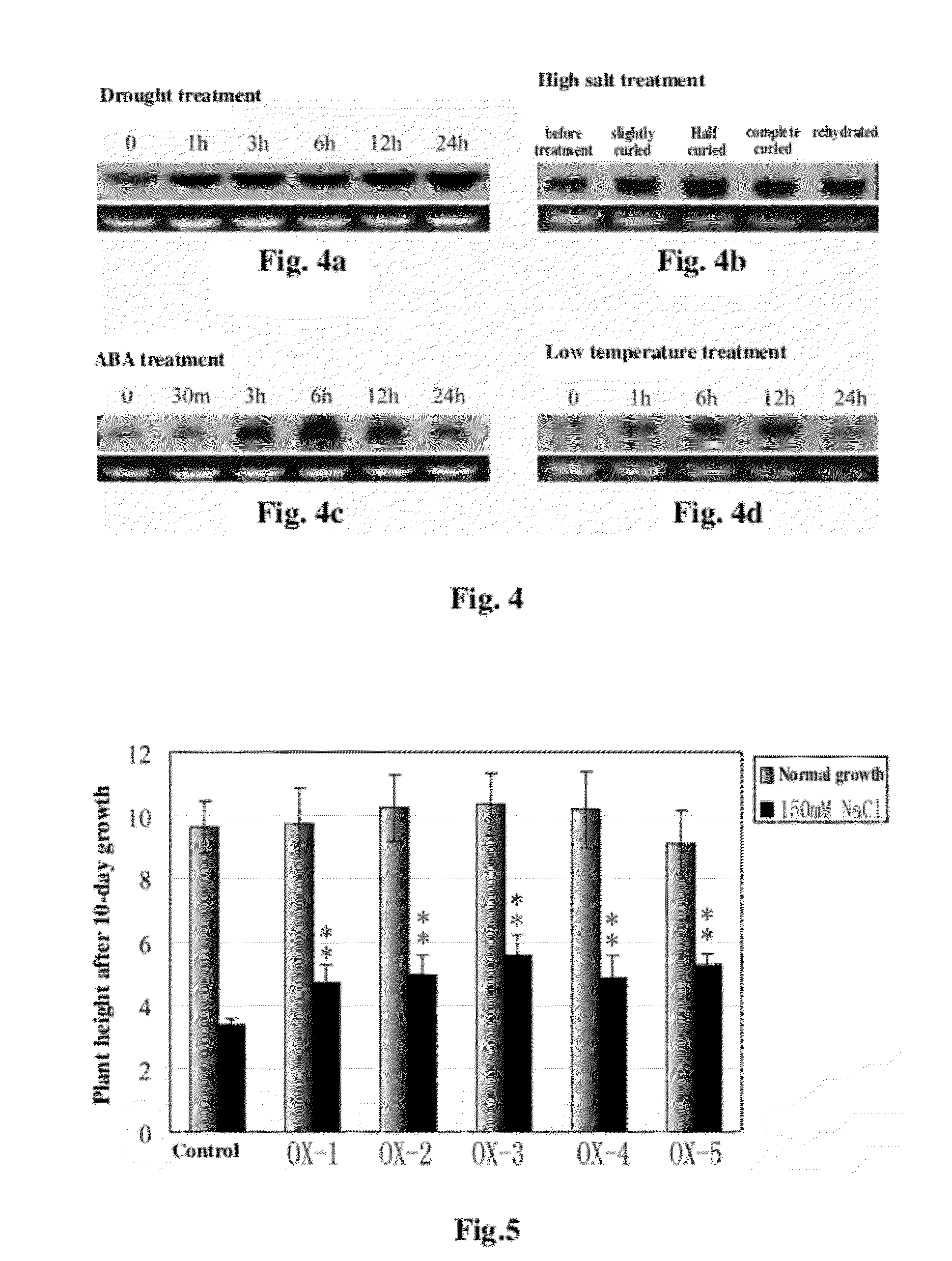
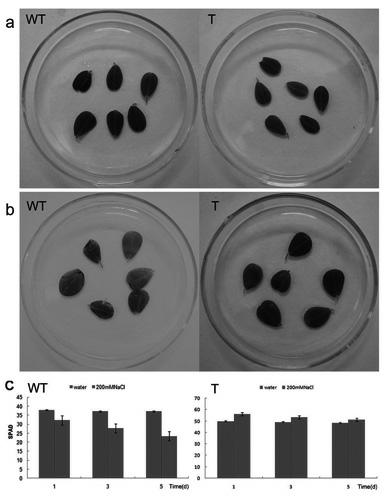
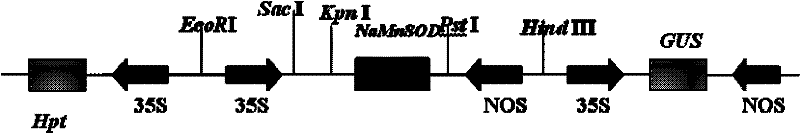Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
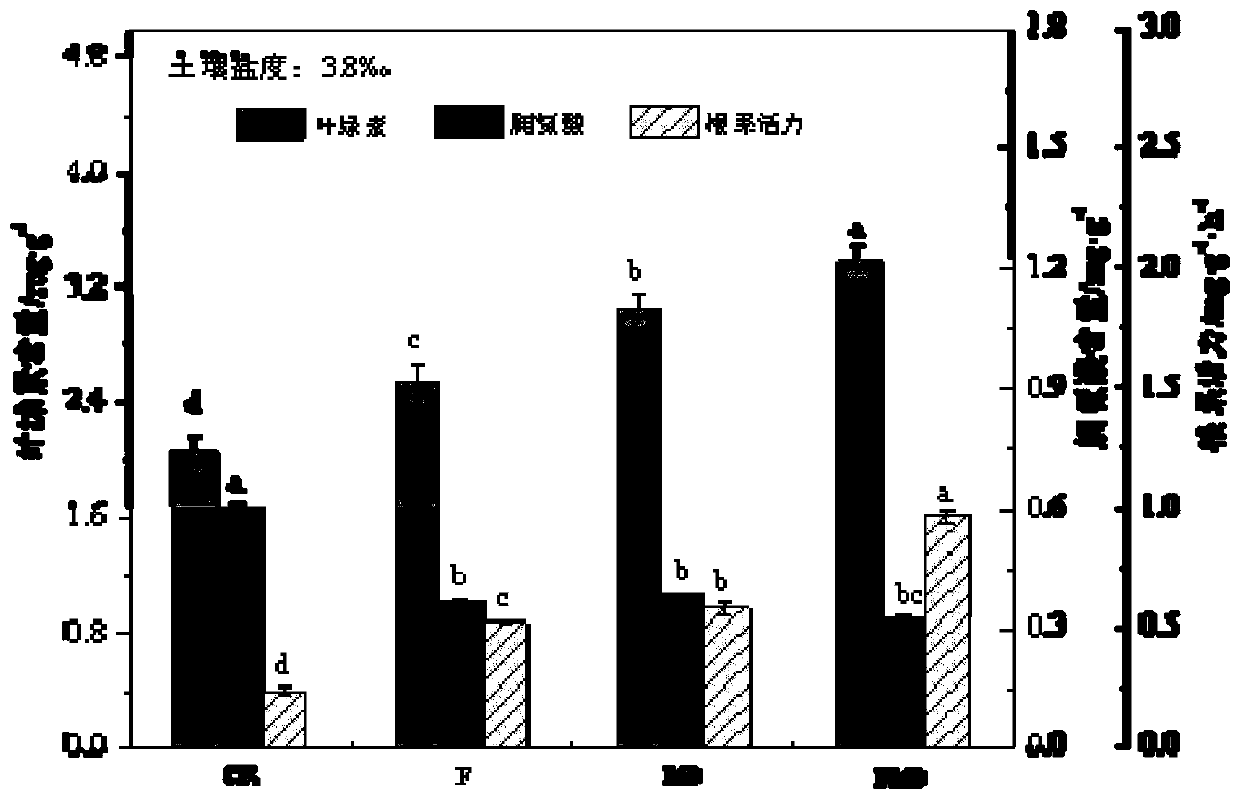
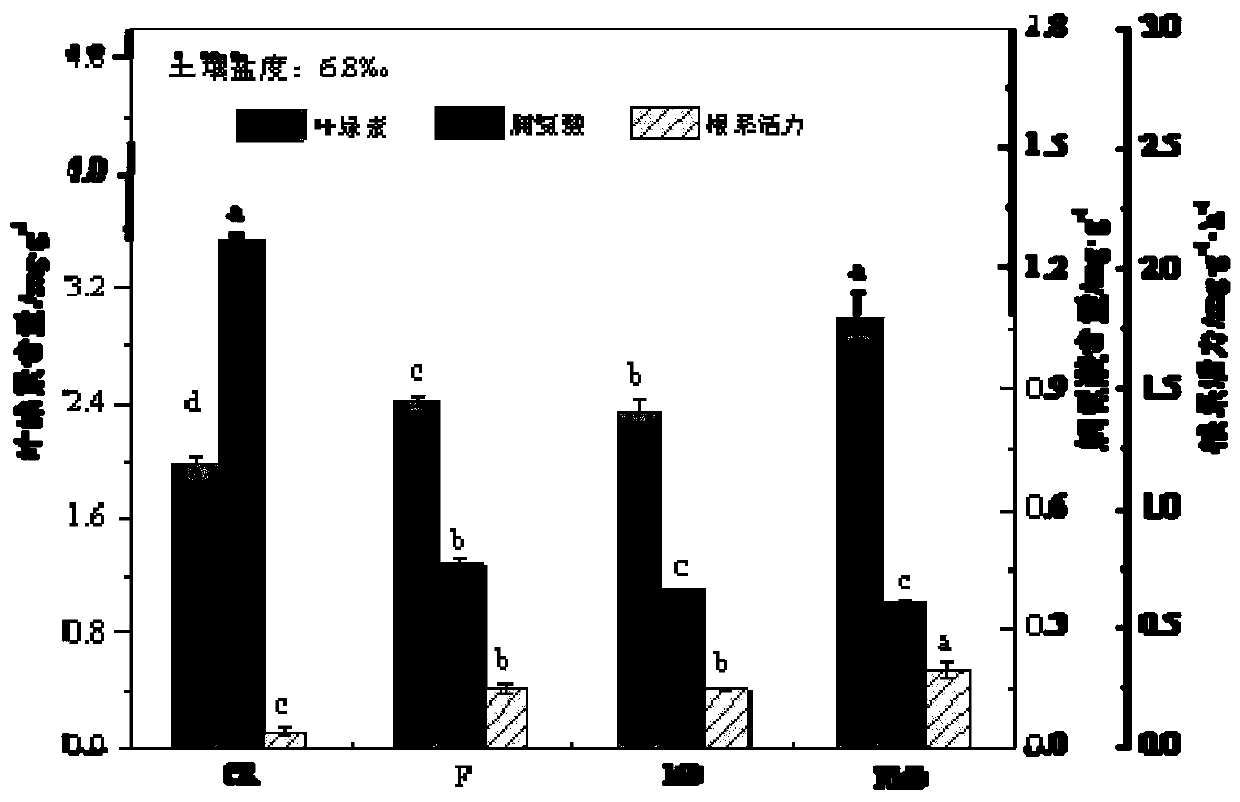
106 results about "Halotolerance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Halotolerance is the adaptation of living organisms to conditions of high salinity. Halotolerant species tend to live in areas such as hypersaline lakes, coastal dunes, saline deserts, salt marshes, and inland salt seas and springs. Halophiles are organisms that live in highly saline environments, and require the salinity to survive, while halotolerant organisms (belonging to different domains of life) can grow under saline conditions, but do not require elevated concentrations of salt for growth. Halophytes are salt-tolerant higher plants. Halotolerant microorganisms are of considerable biotechnological interest.
Plant cells and plants overexpressing vacuolar proton pyrophosphatases
InactiveUS8058515B2Increase planting yieldIncrease in sizeBryophytesClimate change adaptationHalotoleranceLeaf cell
The present invention relates to a transgenic plant, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which increases expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. Also encompassed by the present invention are transgenic progeny and seeds of the transgenic plants described herein. Progeny transgenic plants grown from seed are also described. Plant cells (e.g., root cells, stem cells, leaf cells) comprising exogenous nucleic acid which increases expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant cells are also the subject of the present invention. Also encompassed by the present invention are methods of making a transgenic plant described herein. The present invention also relates to a method of increasing the yield of a plant, a method of making a plant which is larger than its corresponding wild type plant, and a method of producing a transgenic plant with increased salt tolerance.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +2
Salt-tolerant microbial agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103374524ASimple compositionImprove the effect of biochemical treatmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus cohniiMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a salt-tolerant microbial agent and a preparation method thereof. The microbial agent contains staphylococcus cohnii FSND-C, arthrobacter creatinolyticus FDN-1, flavobacterium mizutaii FDN-2, paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3. The microbial agent can achieve removal of ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen and CODcr in the same reactor, has a good wastewater treatment effect, and can achieve short-cut nitrification and denitrification or simultaneous nitrification and denitrification while removing COD. Staphylococcus cohnii FSND-C can utilize various carbon sources, has certain salt tolerance, can be applied to the high-salinity wastewater treatment process, simultaneously can secrete a substance under environmental stimulus to enhance the flocculability of sludge, and further widens the application range of the microbial agent.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
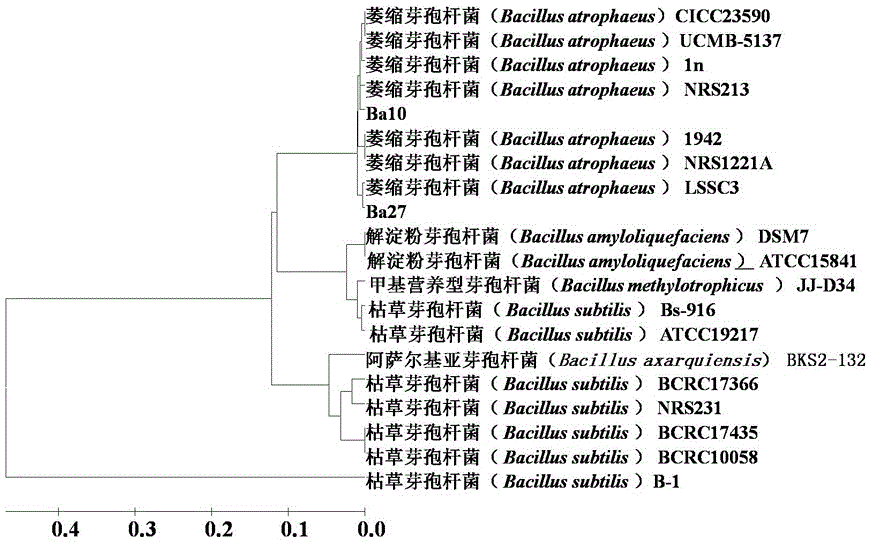
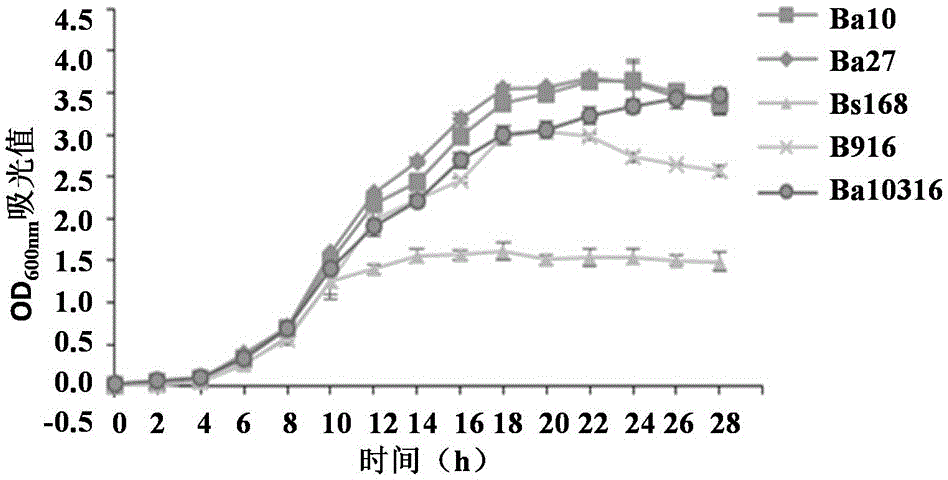
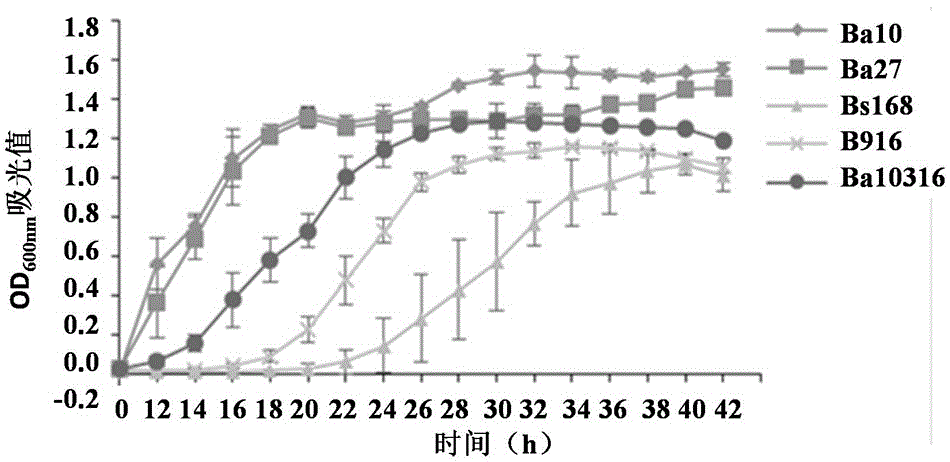
Bacillus strain and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of Bacillus, particularly a salt-tolerant Bacillus strain. The Bacillus is Bacillus atrophaeus. The Bacillus atrophaeus strain is selected from a strain named Ba10, the Ba10 is collected by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the collection number is CGMCC No.12053; and / or the Bacillus atrophaeus strain is selected from a strain named Ba27, the Ba27 is collected by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the collection number is CGMCC No.12054. The Bacillus atrophaeus strain can inhibit multiple pathogens from growth, and has tolerance to high-concentration salts.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for cultivating asparagus in seashore saline land
InactiveCN103858646AReduce salt contentReduce anti-saltFertilising methodsHorticultureHalotoleranceAlkali soil
The invention relates to a method for cultivating asparagus in the seashore saline land, and belongs to the field of vegetable cultivation. The specific method comprises the steps: choosing strong salt resistance asparagus varieties, such as ' Apollo' and 'Champion' asparagus varieties, taking saline-alkali soil with the salt content of 0.1%-0.2% as the matrix, growing seedlings in feeding pots in early August, and paving the wheat straw on ridge faces after planting to prevent accumulation of salt in the surface soil; carrying out field planting in late April the next year, and storing fresh water for leaching 15-20 days before field planting; ditching and carrying out field planting with the line spacing of 1-1.2m, and the row spacing of 25cm, digging deeply and burying shallowly, and harvesting rainwater in furrows for freshwater irrigation; after field planting, covering the mulching film between ridges to prevent accumulation of salt in the surface soil. The asparagus is harvested in a way that the stem is reserved and topping is carried out to prevent lodging when the stem is 1.5m. By applying the method for cultivating asparagus in the seashore saline land, the problems of seedling missing, seedlingless ridges and low survival rate in the traditional cultivation technique are solved, and the high and stable yield is realized . The technology is suitable for being applied in the seashore saline land with the soil salt content 0.4% to 0.8%, the survival rate is increased by more than 20% compared with that by the traditional cultivation technique, and the yield is increased by more than 30%.
Owner:河北省农林科学院经济作物研究所
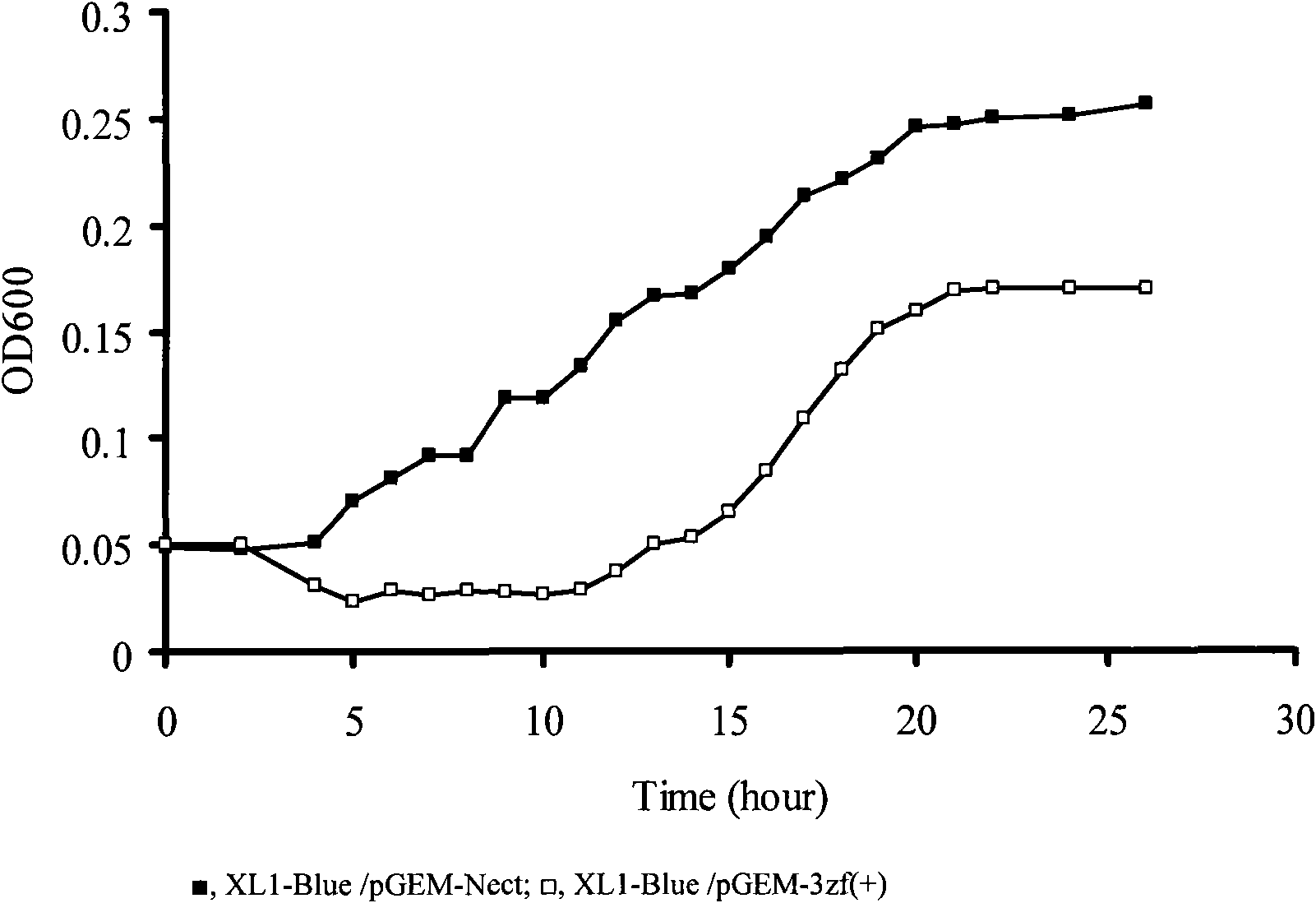
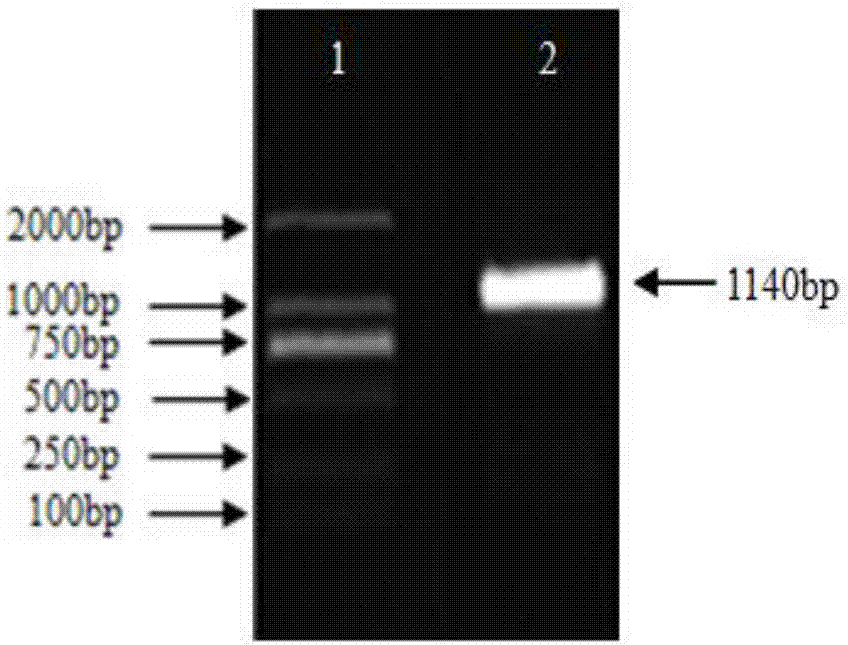
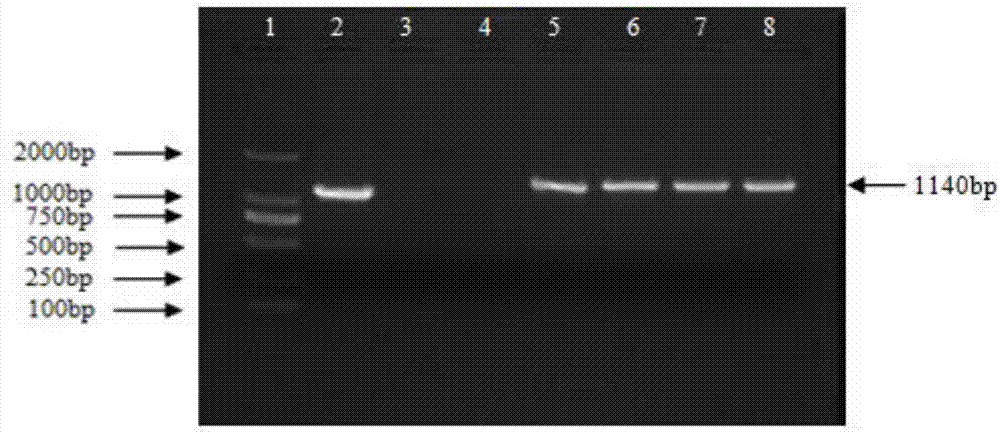
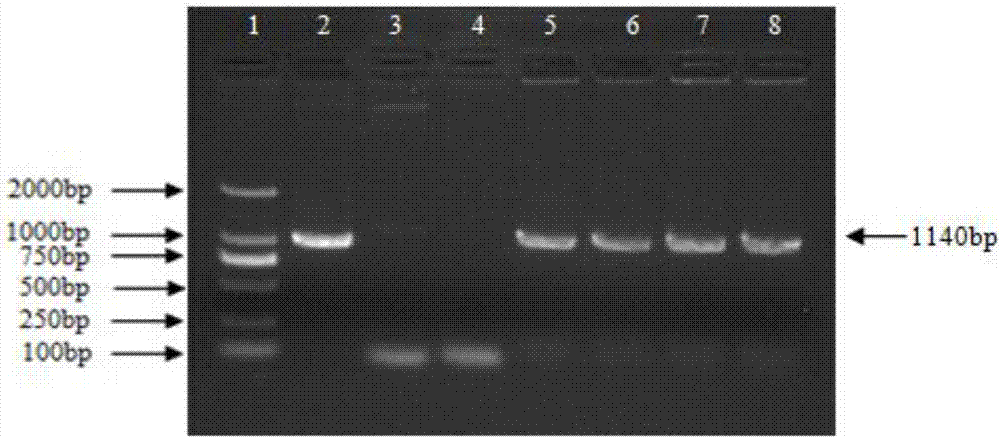
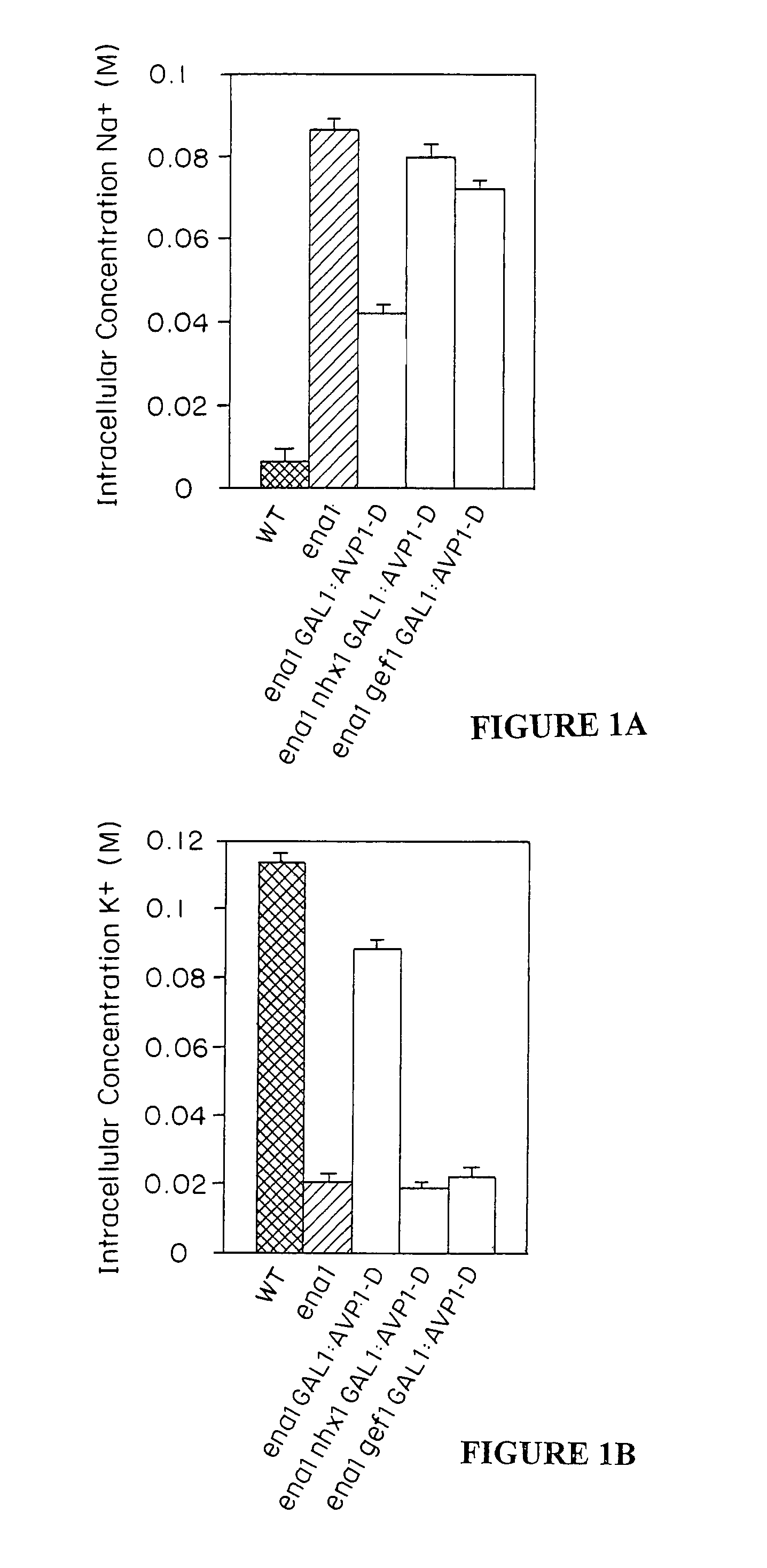
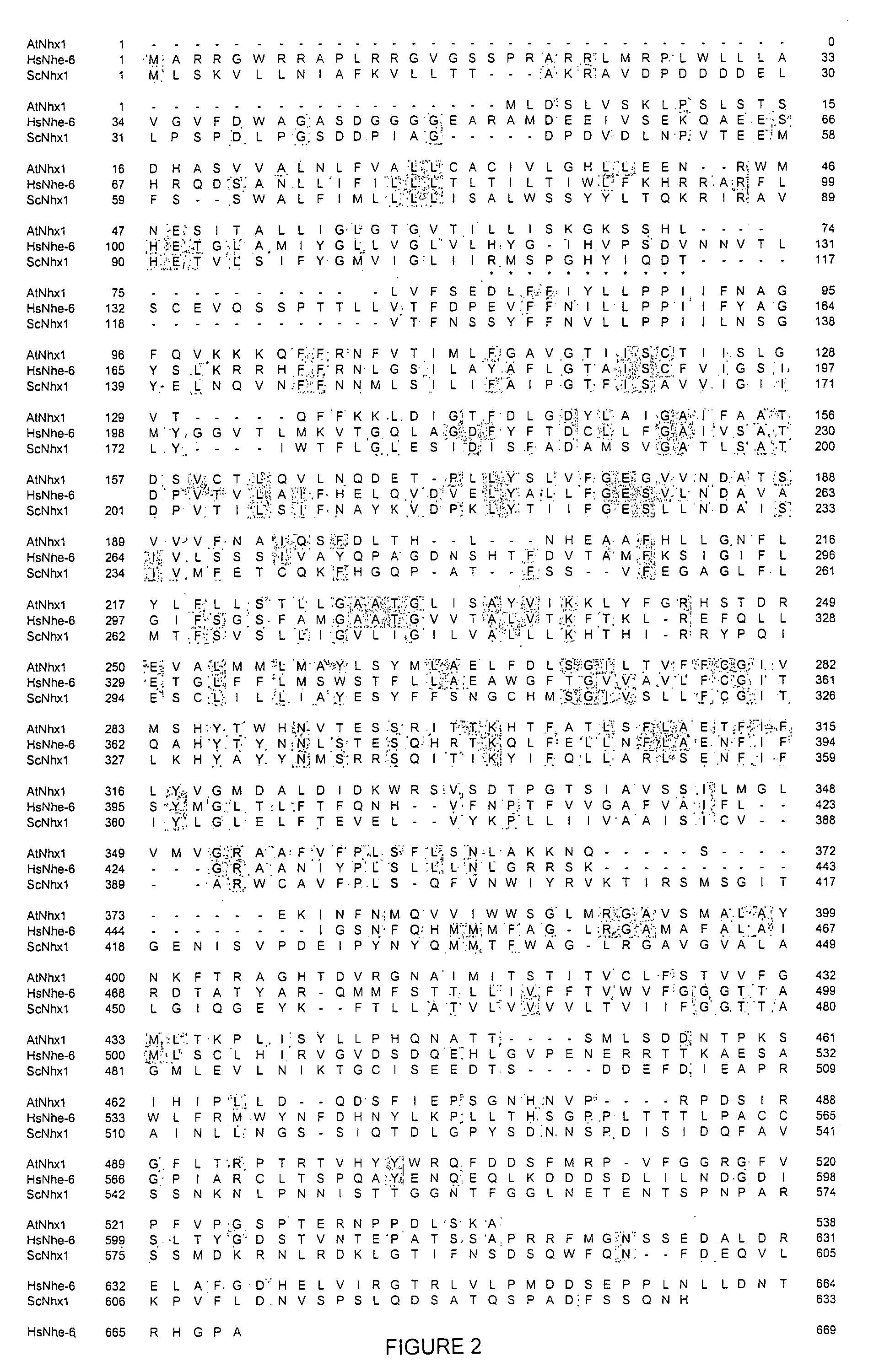
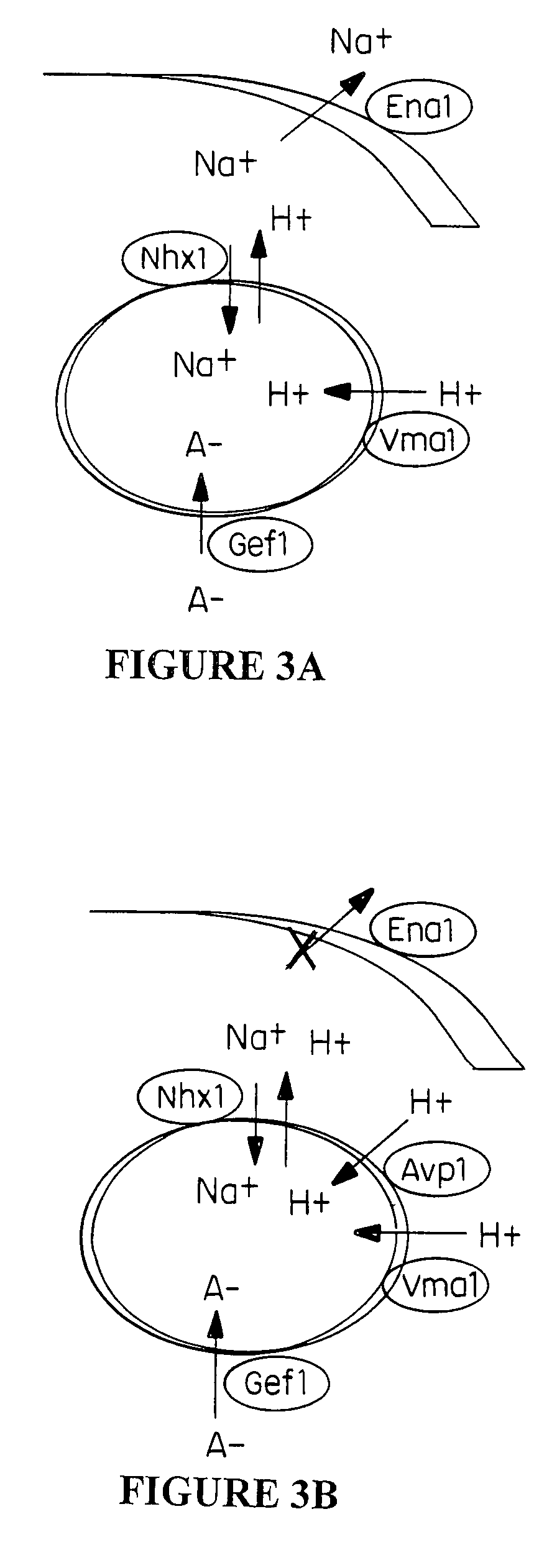
Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]
The invention is isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding Na+ / H+ exchanger polypeptides with 95% identity to a Na+ / H+ exchanger polypeptide from Arabidopsis thaliana for extrusion of monovalent cations from the cytosol of cells to provide the cell with increased salt tolerance. Crop species transformed with the nucleic acid molecule are capable of surviving in soil with high salt levels that would normally inhibit growth of the crop species.
Owner:BLUMWALD EDUARDO +1
Complex microbial agent for restoring coastline with heavy oil pollution, as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN104745511AImprove salt toleranceStrong competitive advantageBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationAchromobacter xylosoxidansSalt resistance
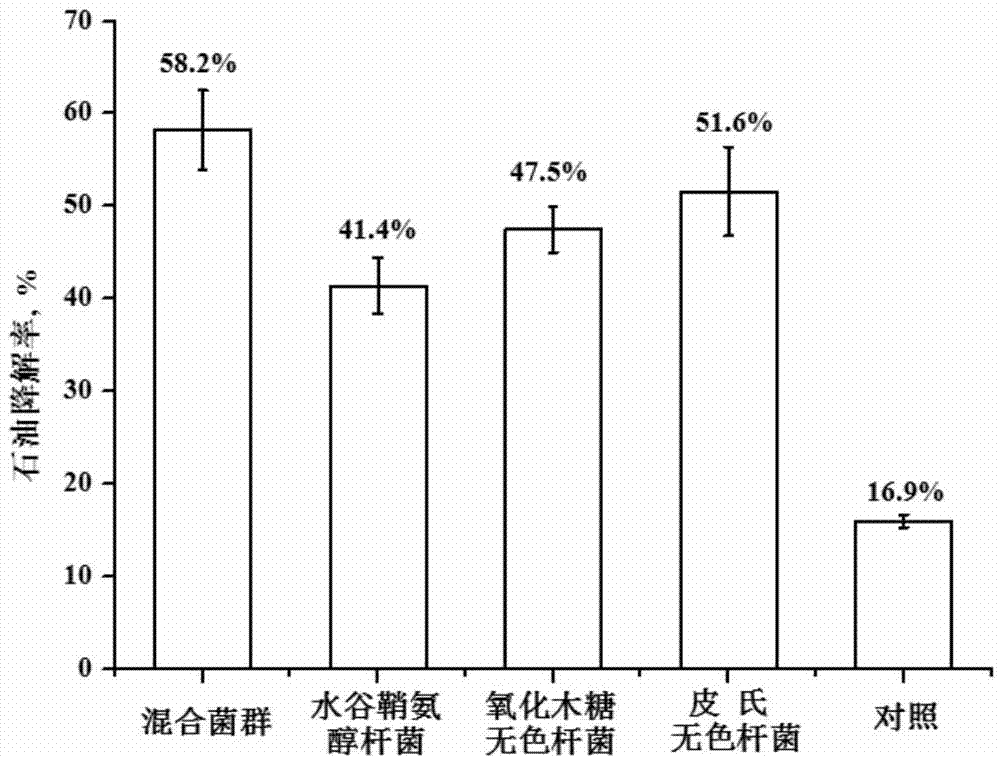
The invention relates to a complex microbial agent for restoring coastline with heavy oil pollution, as well as a preparation method and applications thereof. The complex microbial agent comprises Sphingobacterium mizutaii, Achromobacter xylosoxidans and Achromobacter piechaudii, furthermore, the collection number of the Sphingobacterium mizutaii is CGMCC No.800; the collection number of the Achromobacter xylosoxidans is CGMCC No.8022; and the collection number of Achromobacter piechaudii is CGMCC No.8021. The complex microbial agent is good in salt resistance property, prominent in competitive advantages, and has a high-efficiency restoration effect on the crude oil pollution of coastline, especially refractory heavy oil contamination through the synergistic effect of the three bacteria, and can also be applied to restoration of saline alkali soil with overflow oil contamination.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Genetic engineering salt tolerance in crop plants
InactiveUS20050204430A1Improve salt toleranceBiocideGenetic material ingredientsCytosolHalotolerance
The invention is isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding Na+ / H+ exchanger polypeptides with at least 95% homology to that of Arabidopsis thaliana for extrusion of monovalent cations from the cytosol of cells to provide the cell with increased salt tolerance. Crop species transformed with the nucleic acid molecule are capable of surviving in soil with high salt levels that would normally inhibit growth of the crop species.
Owner:BLUMWALD EDUARDO +3
Salt-endurance related rice protein kinase gene clone and uses thereof
InactiveCN101225375AAffect normal growthAffect economyTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologyNormal growth
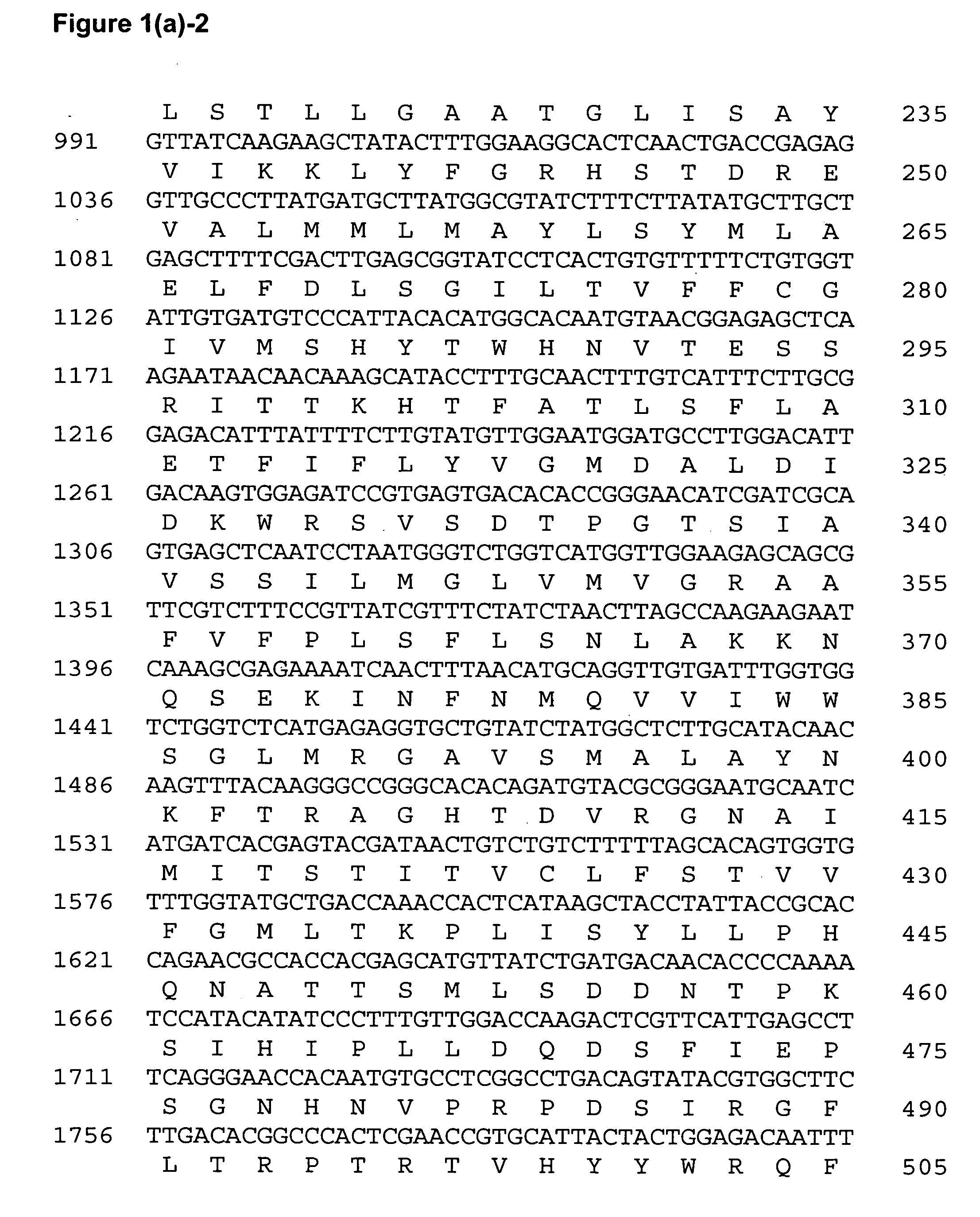
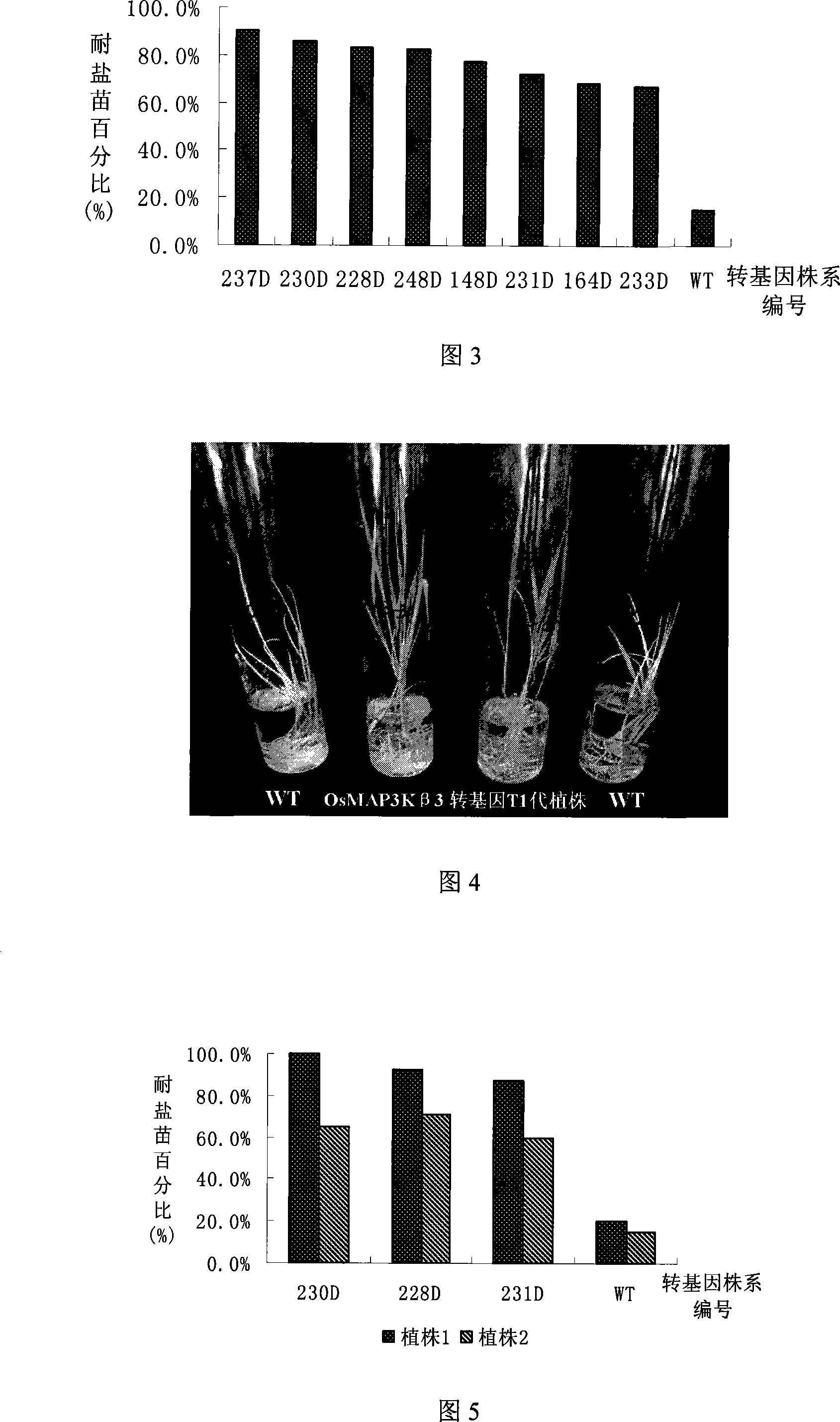
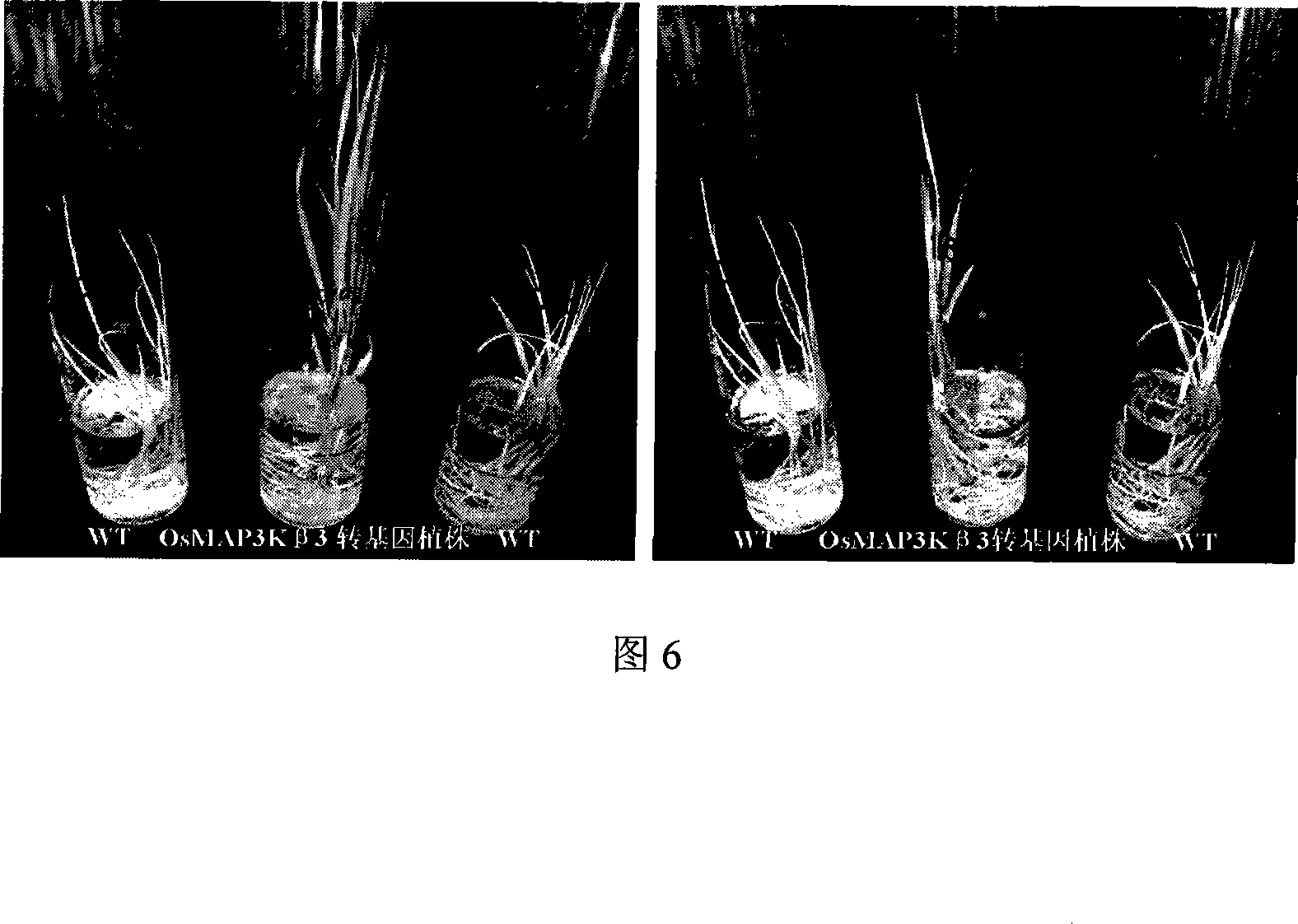
The invention relates to a cloned protein kinase gene of rice related to salt endurance and the application. The protein kinase gene codes a mitogen activating protein kinase (MAP3K), which is the following protein (i) or (ii): the amino acid sequence with SEQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence table; (ii) the protein derived from (i) with the function of controlling salt endurance of plants after replacing, missing or adding a to ten amino acid residues in the amino acid sequences limited by (i). The cloned protein kinase gene of rice related to salt endurance has the advantages that: the experiment proves that using the gene to transform the rice can significantly increase the salt endurance of rice without evidently influencing the normal growth and economic characters of the rice; the protein and the coding gene have important theoretical and practical significance to the improvement of salt endurance and related characters of the plant as well as the study on tolerance mechanism of the plant in adverse circumstances.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED
Halotolerant bacterium separation and purification method, saline-alkaline tolerant strain obtained from separation and application of saline-alkaline tolerant strain
ActiveCN106434481AGood energySignificant anti-saline effectAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaHalotoleranceMicroorganism
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and in particular to a halotolerant bacterium separation and purification method, a saline-alkaline tolerant strain obtained from separation and an application of the saline-alkaline tolerant strain. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, which is selected by the invention, is a microorganism which is extracted and screened from saline-alkali soil in Hetao area and is obvious in saline-alkaline tolerance, and the microorganism is excellent in capacity of improving soil activity in the Hetao area. According to the screening method provided by the invention, the microorganism, which is high in salt-tolerance capacity, is screened from a test soil sample by virtue of an enrichment and separation culture mode; the screening method has the effects of being strongly targeted and ideal in screening result, so as to guarantee saline-alkaline soil remediation which is short in cycle and rapid to take effects.
Owner:本农合众科技有限公司
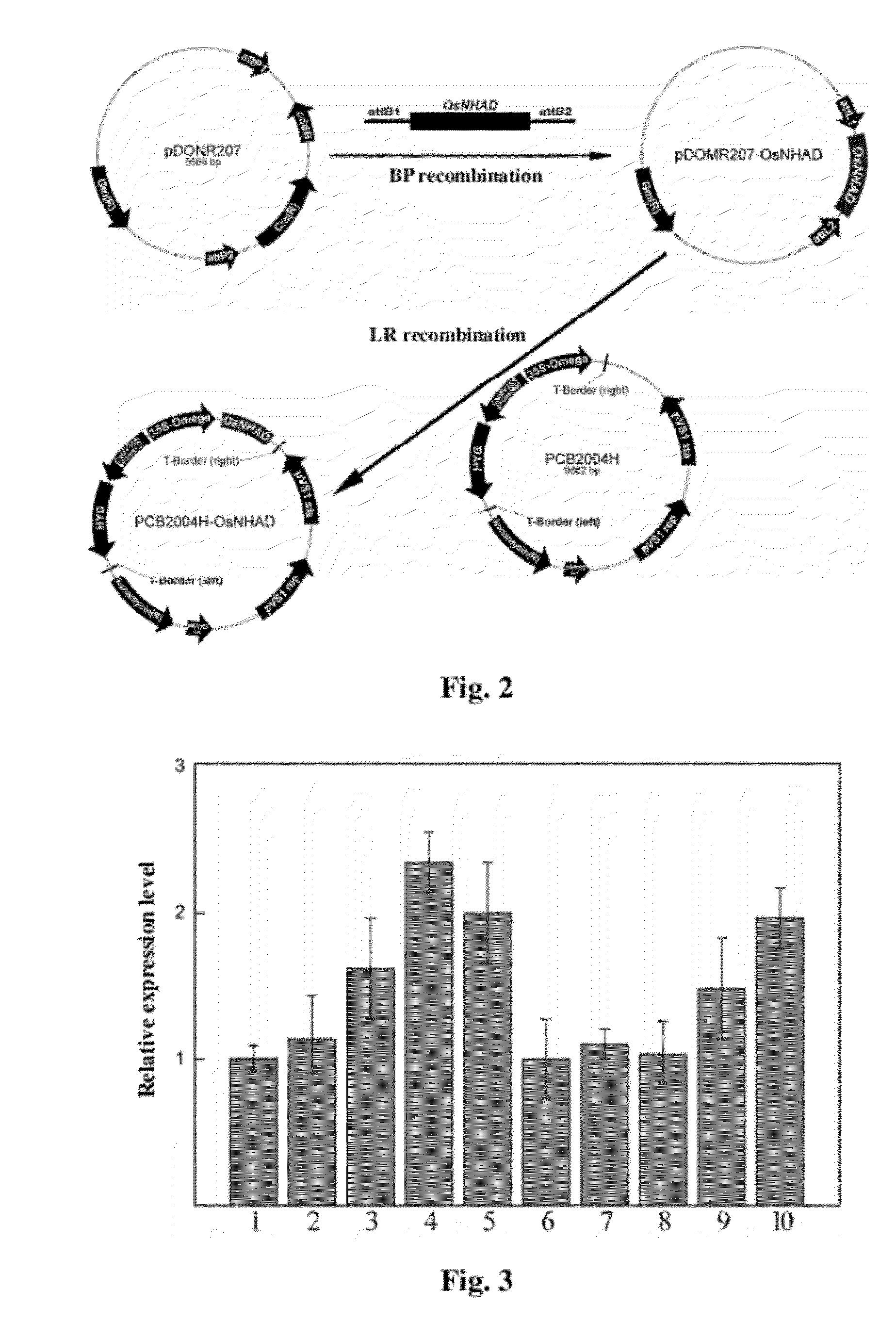
Enhancing Salt Tolerance of Plants with Rice OsNHAD Gene
InactiveUS20120102591A1Improve toleranceOther foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesGenetically modified riceRice plants
The present invention pertains to the field of rice genetic engineering. Specifically, the present invention relates to a rice OsNHAD gene that enhances tolerance to salt stress, which was obtained through gene isolation, cloning and function verification, and also to use of the gene in genetic improvement of salt tolerance of rice. Said gene is selected from one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) the nucleotide sequence from positions 60 to 1649 of SEQ NO: 1 in the Sequence Listing; or 2) a nucleotide sequence that encodes the same protein as that encoded by 1). Transgenic rice plants obtained by introducing into rice the nucleotide sequence comprising OsNHAD gene operably ligated with exogenous promoter had enhanced salt tolerance.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Peanut salt-tolerant associated gene Rab7 and application thereof to improvement of salt tolerance
InactiveCN102604967AMorphologically normalImprove salt toleranceBacteriaPlant peptidesEscherichia coliHalotolerance
The invention provides a peanut salt-tolerant associated gene Rab7 (AhRab7) and an Rab7 (RabG3f) protein generated by encoding the gene. The amino acid sequence similarity of the protein to AtRabG3f in arabidopsis thaliana is 92 percent. After the gene is excessively expressed in a peanut, a transgenic plant of which the salt tolerance is obviously improved is obtained. After the gene is expressed in escherichia coli, the salt tolerance of a recombinant bacterium is obviously improved. The tolerance of the peanut and the escherichia coli to high-salt stress can be obviously improved through the over expression of the AhRab7 gene, and the normal growth and the economic character of the peanut are not obviously affected. The protein and the gene encoding the protein have an important theoretic and practical significance in study on the salt-tolerant mechanism of plants and the improvement of associated characters of the plants. The protein and the gene have an important effect in the improvement of salt-tolerant genetic engineering of the plants and have wide application prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
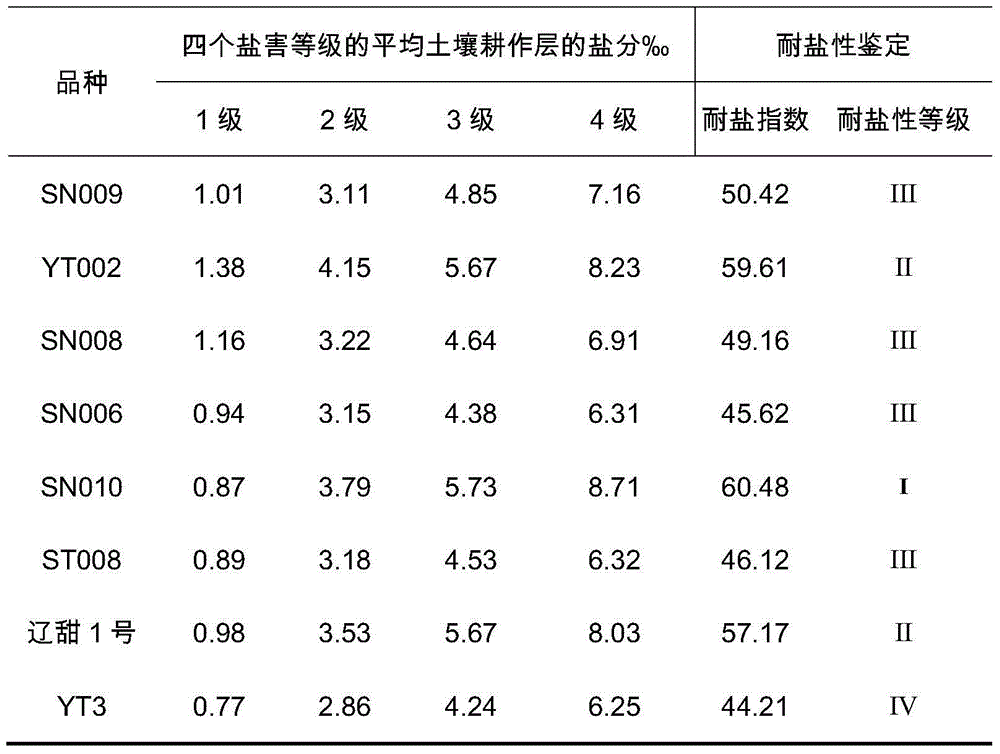
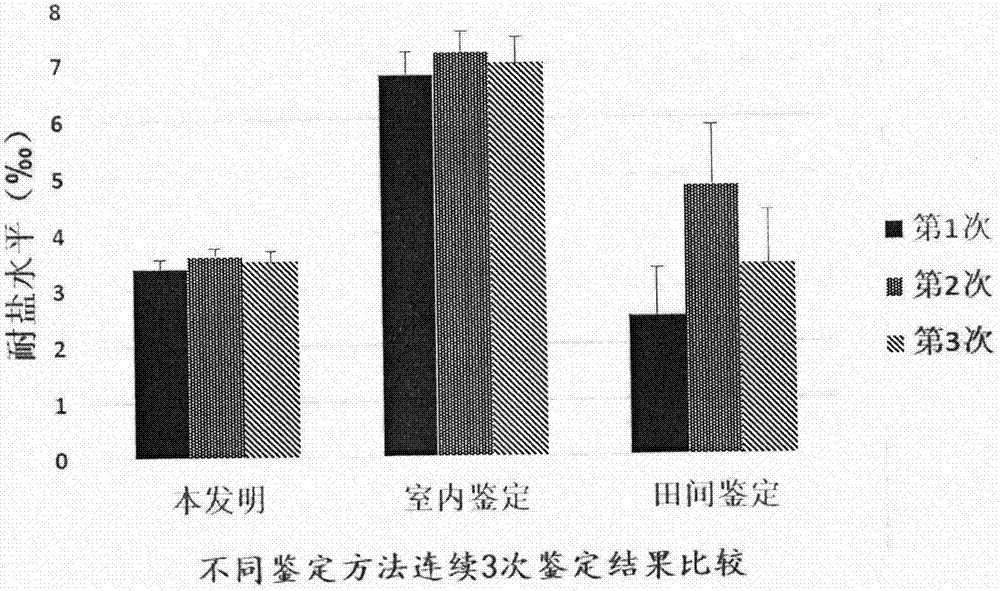
Salt-tolerant sorgo germplasm identification method
InactiveCN104604554ALow efficiencyAvoid lack of salt toleranceSeed and root treatmentPlant cultivationSoil salinityPlough
The invention provides a salt-tolerant sorgo germplasm identification method and relates to the technical field of agriculture. Land parcels with soil plough layers with the light salinity being smaller than 0.3%, the medium salinity between 0.3% and 0.6% and the heavy salinity being larger than 0.6% are selected on a coastal mud flat. Materials to be identified are sown in the land parcels with the soil plough layers with the light salinity, the medium salinity and the heavy salinity. The materials are divided into four grades during mature seedling and milk-ripe stages according to the salt damage degrees of seedlings, and the salinity average values of the 5 cm portions, the 10 cm portions, the 15 cm portions and the 20 cm portions of the soil plough layers where the root of each seedling is located are measured by means of a soil salinity meter when the materials are in different salt damage degrees. The salt tolerance index is calculated according to the average salinity of the soil plough layers for the sampled seedlings in the four salt damage degrees of the materials, and the materials which are high in salt tolerance are selected based on the identified salt tolerance in the mature seedling and milk-ripe stages. By the adoption of the method, the tolerance of sorgos can be identified in a short period of time, operation is easy and visual, cost is low, and reliability is high.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of vacuolar Na+/H+ transporters
The invention is isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding Na+ / H+ exchanger polypeptides for extrusion of monovalent cations from the cytosol of cells to provide the cell with increased salt tolerance. Crop species transformed with the nucleic acid molecule are capable of surviving in soil with high salt levels that would normally inhibit growth of the crop species.
Owner:BLUMWALD EDUARDO +1
Plant salt tolerance identification pond and use method thereof
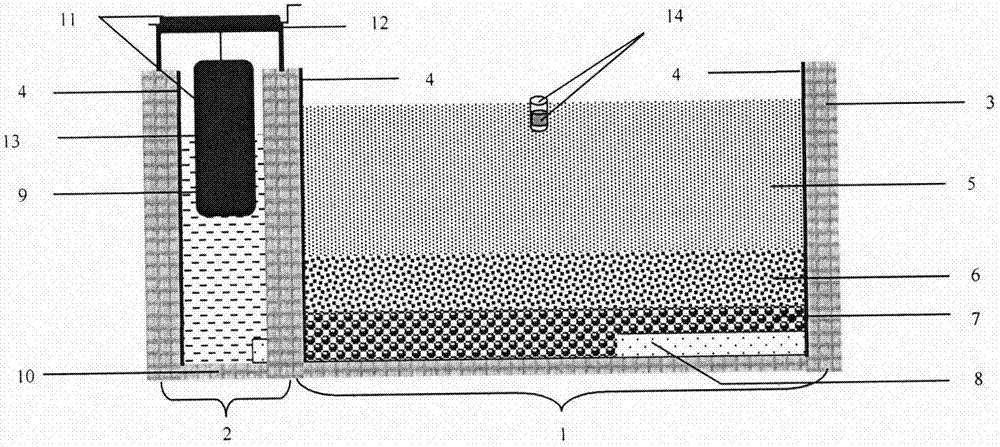
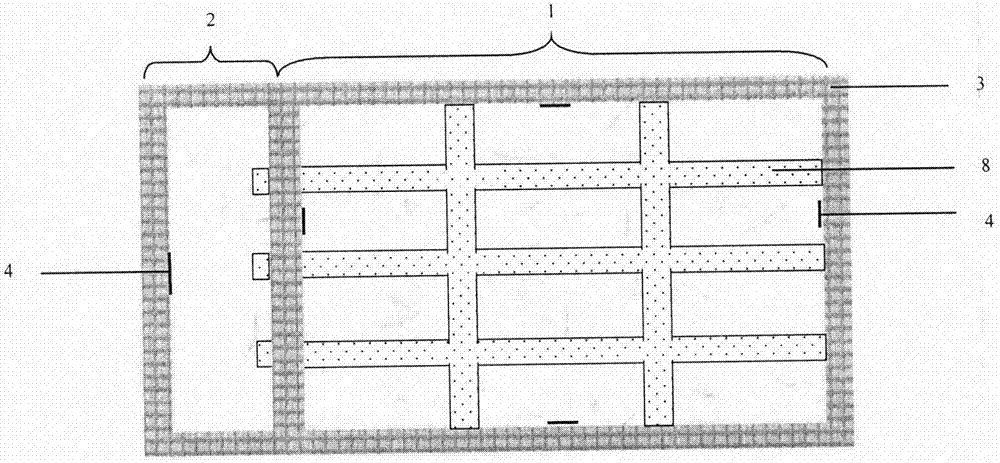
ActiveCN107114103ASimulated coercionObjective and Accurate Evaluation of Salt ToleranceHorticulture methodsSaline waterHalotolerance
The invention discloses a plant salt tolerance identification pond and a use method thereof. The plant salt tolerance identification pond structurally comprises a salt tolerance identification pond and a salinity regulating pond. The salt tolerance identification pond internally comprises a saline soil layer, a sand layer, a stone layer and a water seepage pipeline from top to bottom. A water level observation pipe is arranged on the top of the saline soil layer, saline water is contained in the salinity regulating pond, and a water level regulating device is arranged above the salinity regulating pond. Graduated scales with the minimum scale of 0.5 mm are marked in the pond walls of the salt tolerance identification pond and the salinity regulating pond. The saline water can be formed by diluting seawater or extracting saline-alkali soil or is manually prepared. The use method of the plant salt tolerance identification pond includes the steps of salt tolerance identification pond land leveling and plastic film mulching, salinity regulating pond saline water adding, plant material preparation, soil salinity regulating and keeping and salt damage evaluation. The defects that an existing salt pond is uncontrollable in soil salt content and poor in stability are overcome, and the accuracy of a plant salt tolerance qualification test is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU COASTAL AREA AGRI SCI RES INST +1
Application of rice GT transcription factor family gene OsGT gamma-1 in controlling salt tolerance of rice
The invention relates to the technical field of rice genetic engineering, in particular to the application of a GT transcription factor family gene OsGT gamma-1 in controlling the salt tolerance of rice. By functional analysis and identification, the gene OsGT gamma-1 for controlling the salt tolerance of rice is obtained, and the application of the gene in adverse resistance genetic improvement of the salt tolerance of rice is verified. The gene OsGT gamma-1 is one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) the nucleotide sequence shown from 475th to 1707th in a sequence table SEQ NO: 1; or the nucleotide sequence of protein with the same code as that of the protein encoded by 1). The nucleotide sequence containing the gene OsGT gamma-1 is transferred to rice after being connected with an exogenous promoter, and the salt tolerance of the transgenic rice is obviously enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Salt-tolerant sinorhizobium meliloti NSM18 and special gene cluster thereof
InactiveCN101875940AExcellent nodulation nitrogen fixation abilityImprove salt toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGene clusterMicrobiology
The invention discloses salt-tolerant sinorhizobium meliloti NSM18 and a special gene cluster thereof. The gene cluster is expressed as a sequence 1 in a sequence table. The gene cluster is transferred to sinorhizobium meliloti to construct an engineering strain NSM18. Salt-tolerant experiments show that the engineering strain can tolerate the salt concentration conditions of 1.4mol / L NaCl, 1.5mol / L KCl and 0.6mol / L LiCl; and the engineering strain can be grown at the temperature of 42 DEG C, while a contrast cannot be grown, and the engineering strain shows high-temperature resistance. Moreover, apart from the advantages, the engineering strain NSM18 still keeps good nodulation and nitrogen fixation capabilities.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A BpSPL9 gene of betula platyphylla Suk., an encoding protein thereof and applications of the gene
InactiveCN106868018AImprove the ability to resist adversity and stressHigh activityPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringHalotoleranceBetula platyphylla
The invention relates to a BpSPL9 gene of betula platyphylla Suk., an encoding protein thereof and applications of the gene and discloses the BpSPL9 gene of betula platyphylla Suk., the encoding protein thereof and the applications of the gene. The objective of the invention is to provide the BpSPL9 gene of betula platyphylla Suk., the encoding protein thereof and the applications of the gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table, and an amino sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:2 in the sequence table. The gene can enhance adversity stress resistance of plants. An agrobacterium-tumefaciens-mediated leaf disc transformation method is utilized to perform genetic transformation of the betula platyphylla Suk., obtained transgenic betula platyphylla Suk. plants are subjected to salt resistance and drought tolerance analysis, and results show that the gene can enhance salt resistance and drought tolerance of the betula platyphylla Suk.. Through the gene, the encoding protein and the applications, a novel BpSPL9-transgenic betula platyphylla Suk. variety that is salt-resistant and drought-tolerant can be cultivated. The gene, the encoding protein and the applications are applied in the field of forest tree molecular breeding.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Kandelia candel (L.) druce ERF (ethylene-responsive element binding factor) transcription factor as well as encoding gene, expression vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a kandelia candel (L.) druce ERF (ethylene-responsive element binding factor) transcription factor as well as an encoding gene, an expression vector and application thereof. In the invention, the nucleic acid sequence of the ERF transcription factor cDNA separated from mangrove plant kandelia candel (L.) druce is as shown in SEQ ID No.1. After the ERF transcription factor cDNA is transformed to tobacco, the contents of osmoregulation substances (such as proline) of a transgenic plant are obviously increased, and the salt tolerance of the transgenic plant is obviously improved. An experimental result indicates that the ERF transcription factor can response an adverse signal, thereby effectively improving environmental stress resistances of the plant such as salt andbase resistance, diseases and pets resistance and the like.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
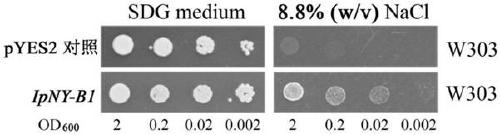
Drought-resistant and salt-tolerant gene IpNY-B1 as well as encoding protein and application thereof
The invention relates to a drought-resistant and salt-tolerant gene IpNY-B1 as well as an encoding protein and an application thereof. The gene IpNY-B1 is obtained by cloning from Ipomoea pes-caprae as an important wild plant in sand beach, and drought resistance and salt tolerance of plants can be improved by transferring the gene into cells, tissue or individuals of host plants; resistance of engineered strains to high salinity and oxidative stress can be improved by transferring the gene into saccharomyces cerevisiae; the gene has remarkable application prospects in the field of improvementof resistance of the plants and the engineered strains.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GY30 and preparation and application of bacterium powder thereof
ActiveCN108148778AWide range of antibacterialGood stabilityBiocideBacteriaFertilizerBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention discloses an ocean-originated bacillus amyloliquefaciens GY30 strain. The preservation number of the ocean-originated bacillus amyloliquefaciens GY30 strain is CGMCC NO. 14480. The invention also discloses a spore production fermentation medium composition and a culture method of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens GY30 strain and a method for preparing bacterium power through the bacillus amyloliquefaciens GY30 strain. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens GY30 strain has the advantages of being high in salt tolerance, low in growth temperature, good in antibacterial effects, wide in antibacterial range and easy to culture, which do not exist in terrigenous microorganisms. The spore production fermentation medium composition and the culture method of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens GY30strain are simple, applied raw materials are mainly agricultural product leftovers, thereby being low in price, extensive in resources, high in strain growth speed, low in fermentation temperature, short in fermentation time, easy to control in fermentation conditions, high in spore fermentation yield and capable of reducing raw material costs and fermentation energy consumption and improving thefermentation production efficiency; bacterium powder prepared through the spore production fermentation medium composition and a culture method of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens GY30 strain is high ineffects on processing microorganism fertilizers or rice sheath blight disease preventing pesticides.
Owner:JIANGSU GENGYUN CHEM CO LTD
Salt-tolerant halomonas strain and application thereof in field of water purification
The invention relates to a salt-tolerant Halomonas sp. Strain and application thereof in the field of water purification, the strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), and the preservation number is CGMCC No.24127. The strain has good salt tolerance, the optimum growth salinity is 5%, under laboratory conditions, the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 100% in 24 h when the salinity is 15% or below, and the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 100% when the salinity is 15% or below. The strain can resist high ammonia nitrogen concentration and high temperature, the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 89.1% within 72 h for the ammonia nitrogen concentration of 3000 ppm, and when the initial ammonia nitrogen concentration is 100 ppm, the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 100% within 24 h at the temperature of 30-40 DEG C.
Owner:青岛蔚蓝赛德生物科技有限公司
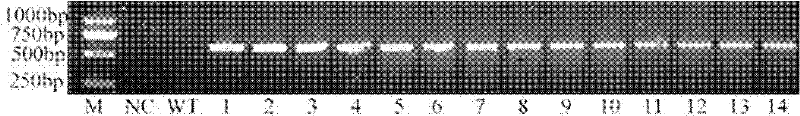
Application of extremely halophilic archaea NaSOD gene in improving rice salt tolerance
InactiveCN102399816AHigh ROS scavenging abilityImprove salt toleranceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHalotoleranceGenetically modified rice
The invention discloses an application of an extremely halophilic archaea (Natrinema altunense sp.) NaSOD gene in improving rice salt tolerance. The base sequence of the extremely halophilic archaea NaSOD is shown by SEQ ID NO.3. The over-expression NaSOD genetically modified rice has the advantages of higher ROS scavenging capability and capability of reducing membrane lipid peroxidation caused by salt treatment so that higher photosynthetic rate can be guaranteed. According to the invention, the extremely halophilic archaea NaSOD gene is transferred into the rice so that the salt tolerance of the rice can be obviously improved.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV +2
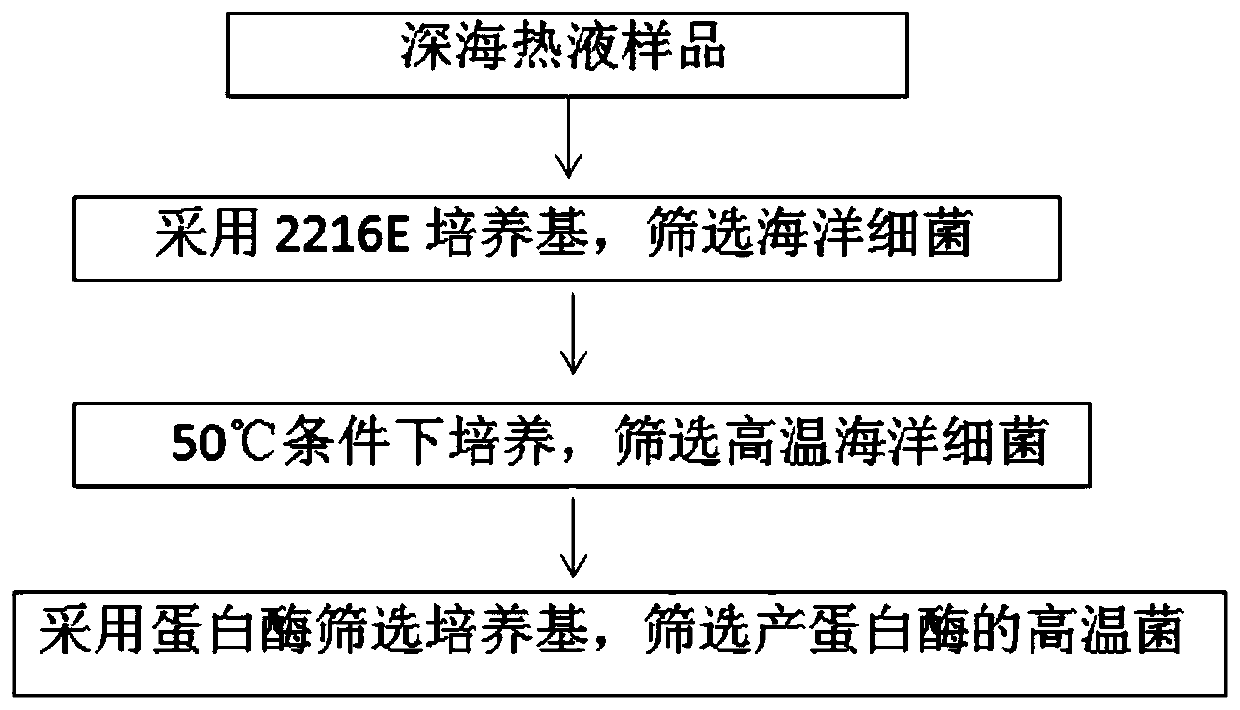
Exiguobacterium profundum and application thereof
ActiveCN111019868AGrowth inhibitionIncreased energy costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFish paste
The invention provides an exiguobacterium profundum. The preservation number of the exiguobacterium profundum is CGMCC No.18990. The exiguobacterium profundum P-47-3 strain provided by the invention is used for fermenting fish paste. The strain P-47-3 used in the method is separated from a deep sea hydrothermal solution extreme environment; spores are produced, and the growth temperature ranges from 10 DEG C to 65 DEG C; growth and propagation can be performed under the salt concentration of 0 to 14%; general high-temperature bacteria mainly come from land environments such as hot spring and the like, are poor in salt resistance, can not grow at high salt conditions, and has great limitation in marine biological product fermentation, while the strain P-47-3 has halophilicity, so that the strain P-47-3 is not only suitable for marine organism fermentation, but also can consume salt in a metabolic process, the salt concentration in a fermentation product is further reduced, and the quality of the fermentation product is improved.
Owner:浙江亿丰海洋生物制品有限公司
Preparation method and application of immobilized agent bag of efficient denitrifier
ActiveCN109402107AHigh governance costImprove repair effectTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaSeawaterEnvironmental chemistry
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of an immobilized agent bag of an efficient denitrifier. The preparation method of the agent bag comprises the steps of screening out efficient heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacteria at first, and then carrying out salt-tolerant domestication on the efficient heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacteria to obtain salt-tolerant heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacteria; adsorbing the immobilized salt-tolerant heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacteria by using modified zeolite to obtain immobilized salt-tolerant heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacteria zeolite; and then flatly laying the obtain immobilized salt-tolerant heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacteria zeolite in a cloth bag to obtain the final product. The bacterial density of zeolite particles in the cloth bag is 1* 109-5* 109 CFU / mL. The prepared immobilized agent bag is widely used in shallow sea aquatic farms and aquaculture ponds, and efficient removal in a high-salinity environment is realized; and moreover, the agent bag can be reused, the cost is greatly reduced, the shortcoming that free microbial flora which are directly used easily flow along with tides of seawater, cannot accurately position bacteria and cannotbe in full contact with the bacteria is overcome effectively, threatening to the quality of aquaculture products due to introduction of alien microbes is also avoided, ecological safety of water of aseawater aquaculture region is protected, and the immobilized agent bag is expected to be widely used.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Composite microbial agent and application thereof
ActiveCN111073831AStrong salt toleranceEasy to manufactureAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to a composite microbial agent and an application thereof in improving soda saline-alkali soil. The composite microbial inoculum is prepared by mixing bacillus licheniformis witha concentration of 1*10<6>-9*10<7> CFU / ml and pseudomonas zhaodongensis with a concentration of 1*10<6>-9*10<7> CFU / ml according to a volume ratio of 1:(0.45-0.55). The composite microbial inoculum is added into saline-alkali soil according to a usage amount of 1800-2000ml per square meter, and then plowing is performed by 20-30cm for application in improving the saline-alkali soil. The compositemicrobial agent disclosed by the invention is strong in salt tolerance, and can improve high alkalinity, loosen soil structure, reduce viscosity and promote plant growth. In addition, the preparationmethod is convenient, the process is simple and economic, and the composite microbial agent has good popularization and application values.
Owner:ANSTEEL GRP MINING CO LTD
Biological seaweed fertilizer, bacterial liquid for biological fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112358345AExtended storage timePromote absorptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPseudomonas
The invention provides a biological seaweed fertilizer. The biological seaweed fertilizer is obtained by culturing a seaweed water extracting solution and a bacterial solution, wherein the bacterial liquid comprises halomonas, shewanella, Marinobacter, pseudomonas and nitrate reducing bacteria. Compared with the prior art, the microbial preparation is added into the seaweed water extracting solution for culture, plants can be promoted to absorb nutrient substances in the seaweed water extracting solution, then the quality of fruits and vegetables is improved, the content of soluble solids andVC is increased, fruit coloring is promoted, and the salt tolerance of the plants is improved; the preservation time of the biological seaweed fertilizer can be prolonged, and tropical agricultural areas are convenient to use.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY +1
Method for improving salinity tolerance
The invention relates to a specific method for improving the tolerance to salinity of living organisms and eliminating sodium (Na+) from water, soil, sludge or any other medium containing said element, using isolated nucleic acid sequence that codes for the phytochelatin synthase of Nicotiana glauca
Owner:NAVARRO AVINO JUAN PEDRO
Bacillus thuringiensis strain YN-2-2 and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacillus thuringiensis strain YN-2-2 CGMCC No.19316, which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on Jan.17,2020, wherein the accession number is CGMCC No.19316, the preservation date is Jan.17,2020, and the address of the preservation unit is No.3, Yard 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The bacillus thuringiensis strain YN-2-2 provided by the invention has the advantages of simple culture, short period, no ecological toxicity, abundant available carbon sources, high salt tolerance, wide tolerable PH range and capability of effectively inhibiting growth of pathogenic bacteria of potato deep scab.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY +1
Membrane biofilm culturing and domesticating process and membrane biofilm reaction device for treating high-salinity wastewater
ActiveCN111018101AReduce infrastructure costsSmall footprintSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentBiofilmMicroorganism
The invention discloses a membrane biofilm culturing and domesticating process and a membrane biofilm reaction device for treating high-salinity wastewater. The membrane biofilm culturing and domesticating process provided by the invention comprises a secondary circulating biofilm culturing stage and a salt tolerance domesticating stage. The membrane biofilm reaction device comprises: a reaction vessel; a gas separation membrane, which is arranged in the reaction vessel and is provided with an inner cavity; a biofilm, which is positioned on the outer side of the gas separation membrane; a water inlet pipeline and a water outlet pipeline, which are communicated with the interior of the reaction vessel; and a gas inlet assembly and a gas outlet assembly, which are communicated with an innercavity of the gas separation membrane, wherein wastewater entering the reaction vessel sequentially passes through the gas outlet end and the gas inlet end of the gas separation membrane. The membranebiofilm reaction device has the advantages of low capital construction cost, small occupied area, low energy consumption, simple operation, high oxygen utilization rate and the like, also has the advantage of capacity of improving the attachment stability of microorganisms, enhancing the pollutant removal capability of the microorganisms and the like, and realizes an efficient sludge reduction effect.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
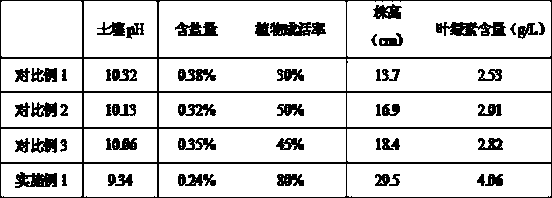
Composite biological soil conditioner, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111187102ASolve Alkaline ProblemsImprove adsorption capacityClimate change adaptationCarbon preparation/purificationAlkali soilNutrition
The invention provides a composite biological soil conditioner, and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The composite biological soil conditioner provided by the invention can solve the problems that charcoal is alkaline and is limited in saline-alkali soil improvement, antagonism exists between bacterial manure and indigenous microorganisms and the like in the preparation of conventional composite soil conditioners. According to a technical scheme in the invention, the composite biological soil conditioner comprises the following components in parts by weight: 70-80 parts of modified charcoal and 20-30 parts of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus bacterial fertilizer. The composite biological soil conditioner is prepared through the steps of preparing the modified charcoal, preparing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus bacterial fertilizer, conducting mixing and the like, and is used for improving light and medium saline-alkali soil. The modifiedcharcoal and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus bacterial fertilizer produce a synergistic effect; and the charcoal can directly improve the physicochemical properties of saline alkali soil, reduce the salinity of surface soil, provide nutrition sources and refuges for microorganisms and ensure the survival rate of microorganisms in the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus bacterial manure, so the bacterial manure is used for improving the salt tolerance of plants, promoting plant growth and improving the saline alkali soil.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00001.png)
![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00002.png)
![Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s] Increasing salt tolerance in plants by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ transporter[s]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d91cdd0d-3efd-4cb2-8c59-845405780aee/US06936750-20050830-D00003.png)