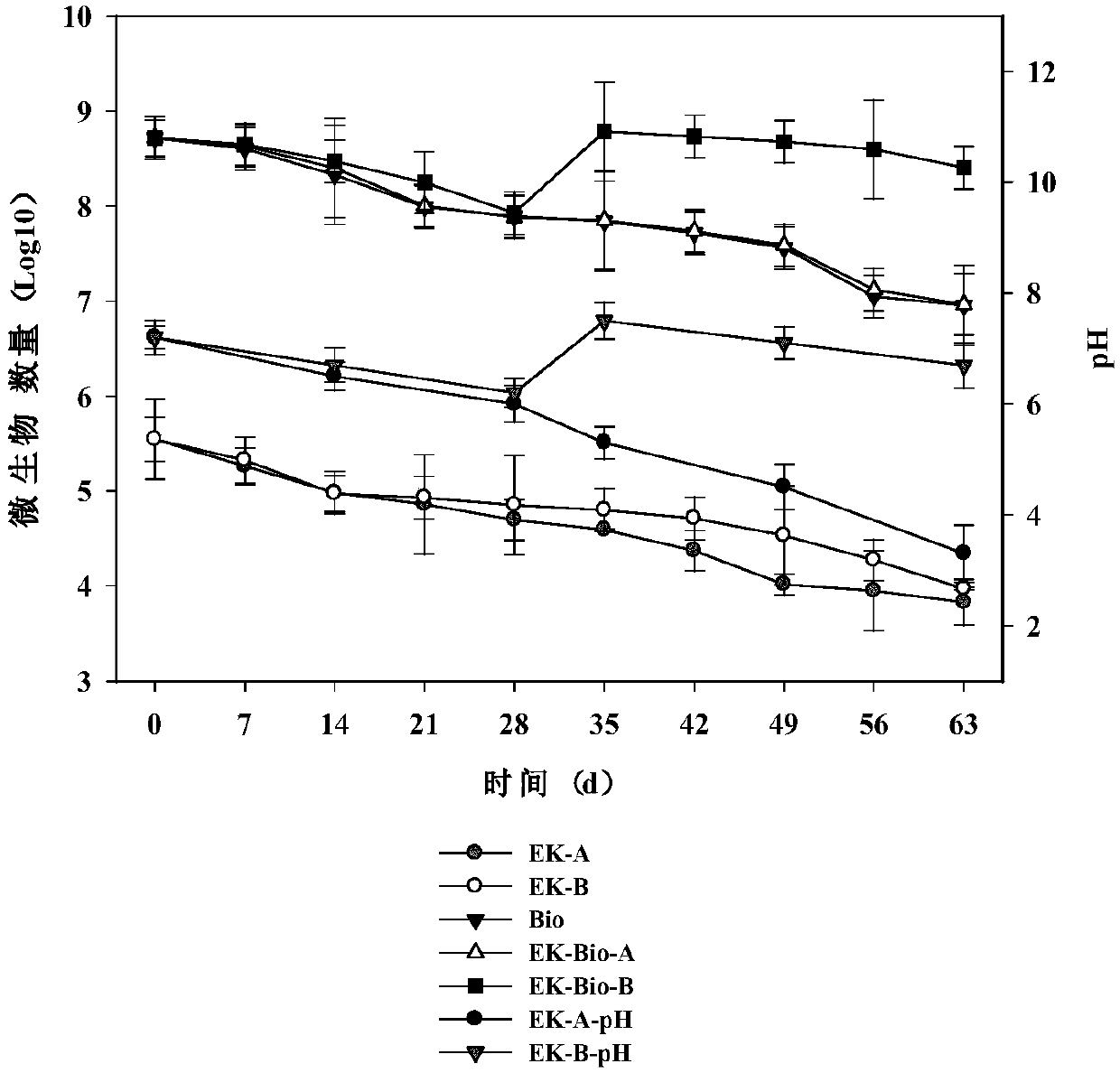
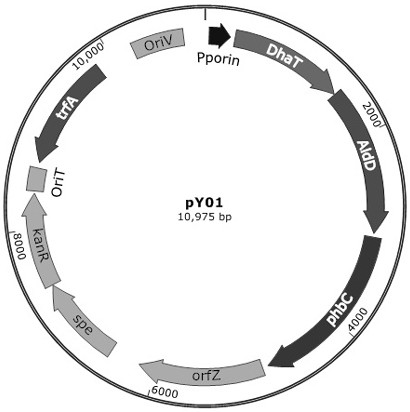
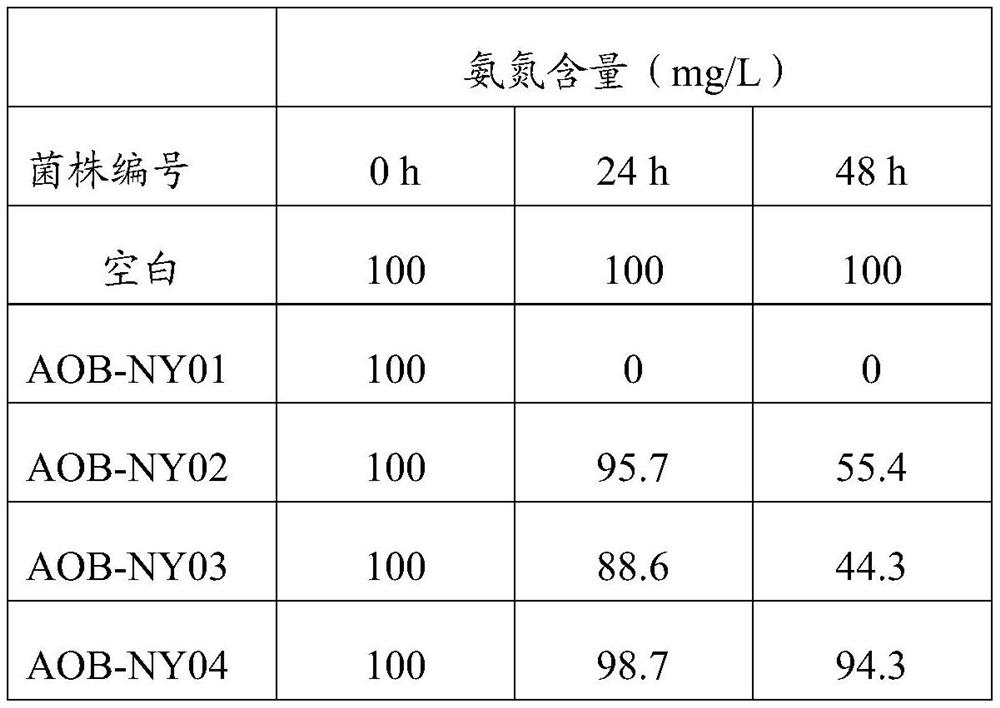
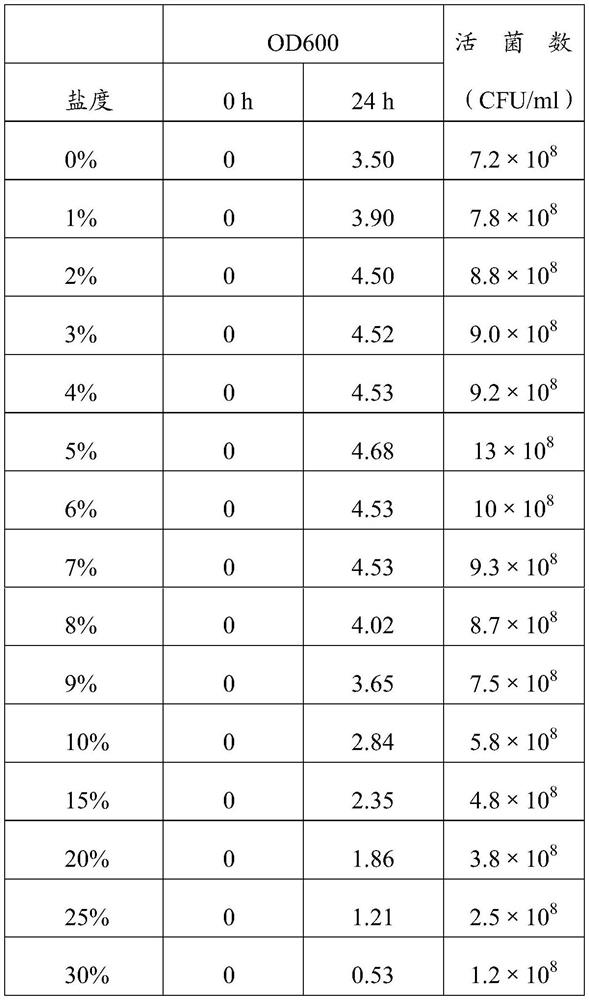
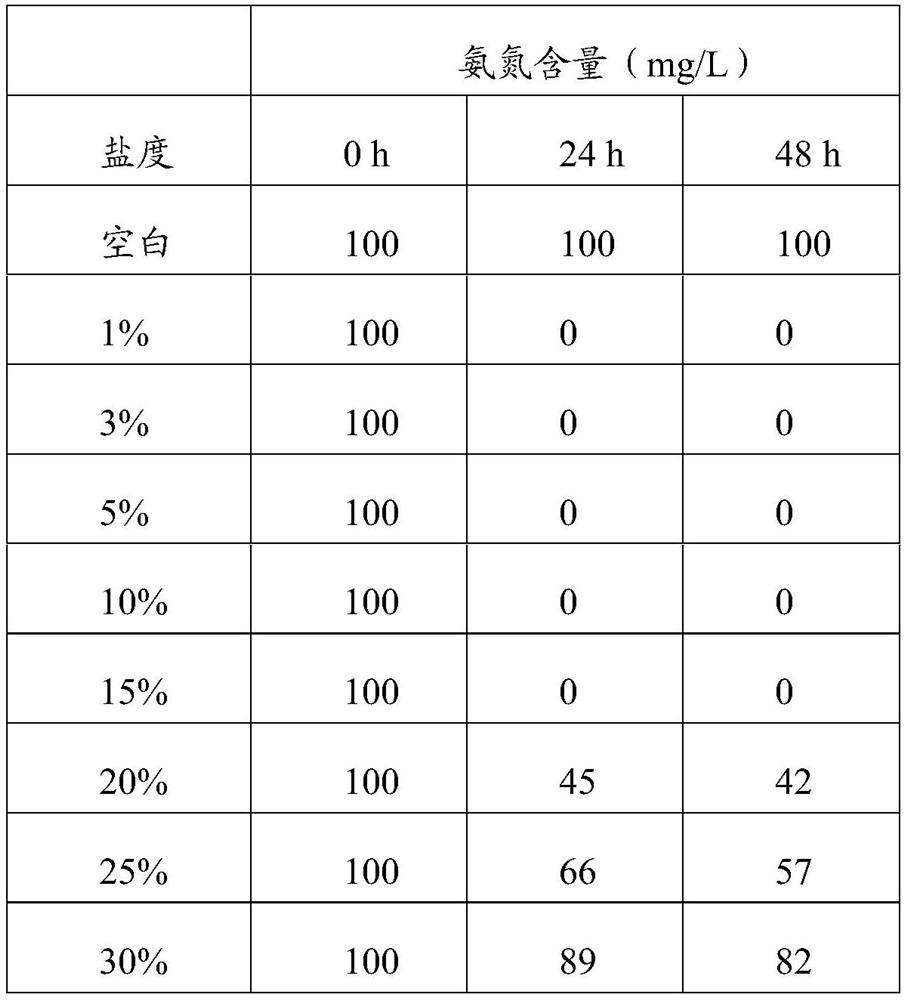
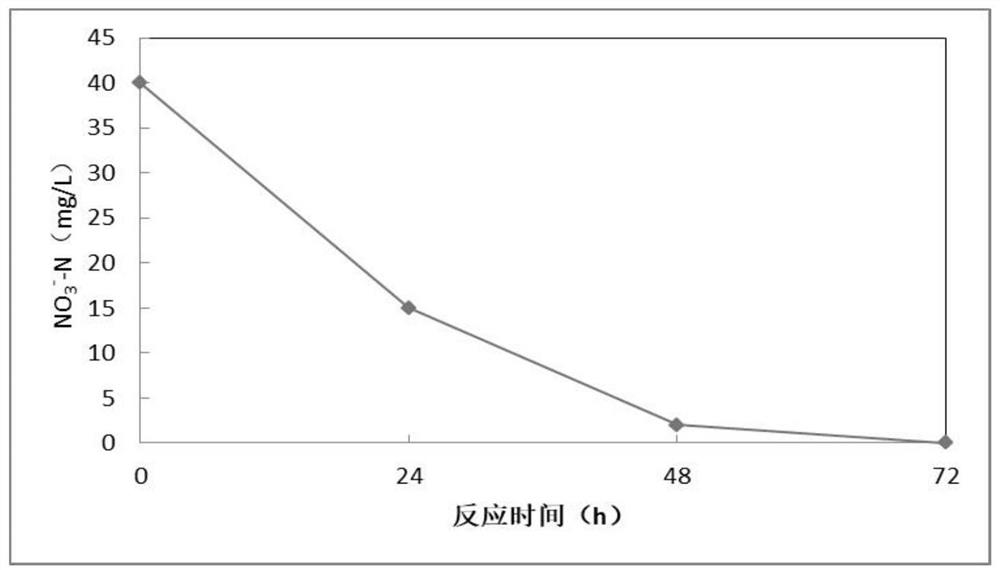
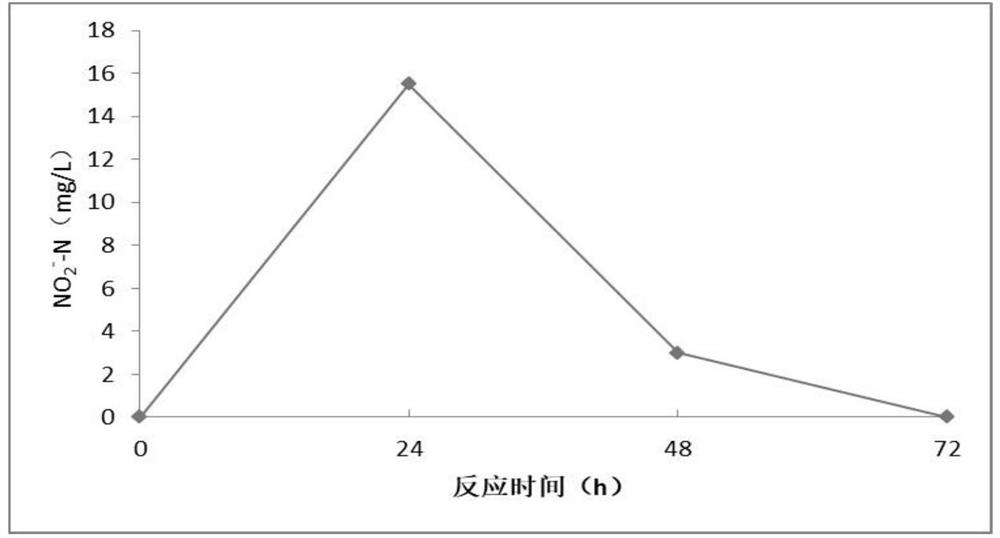
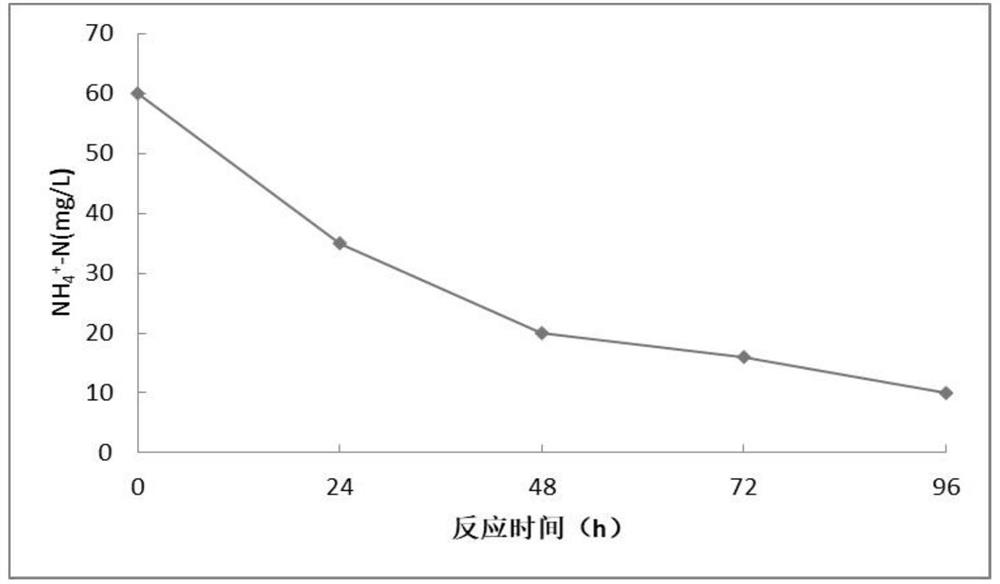
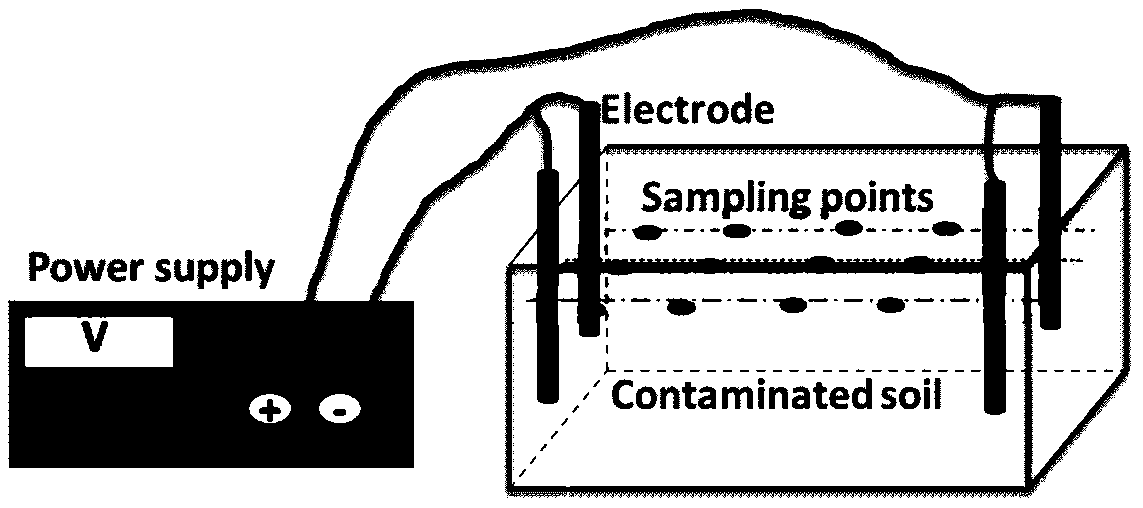
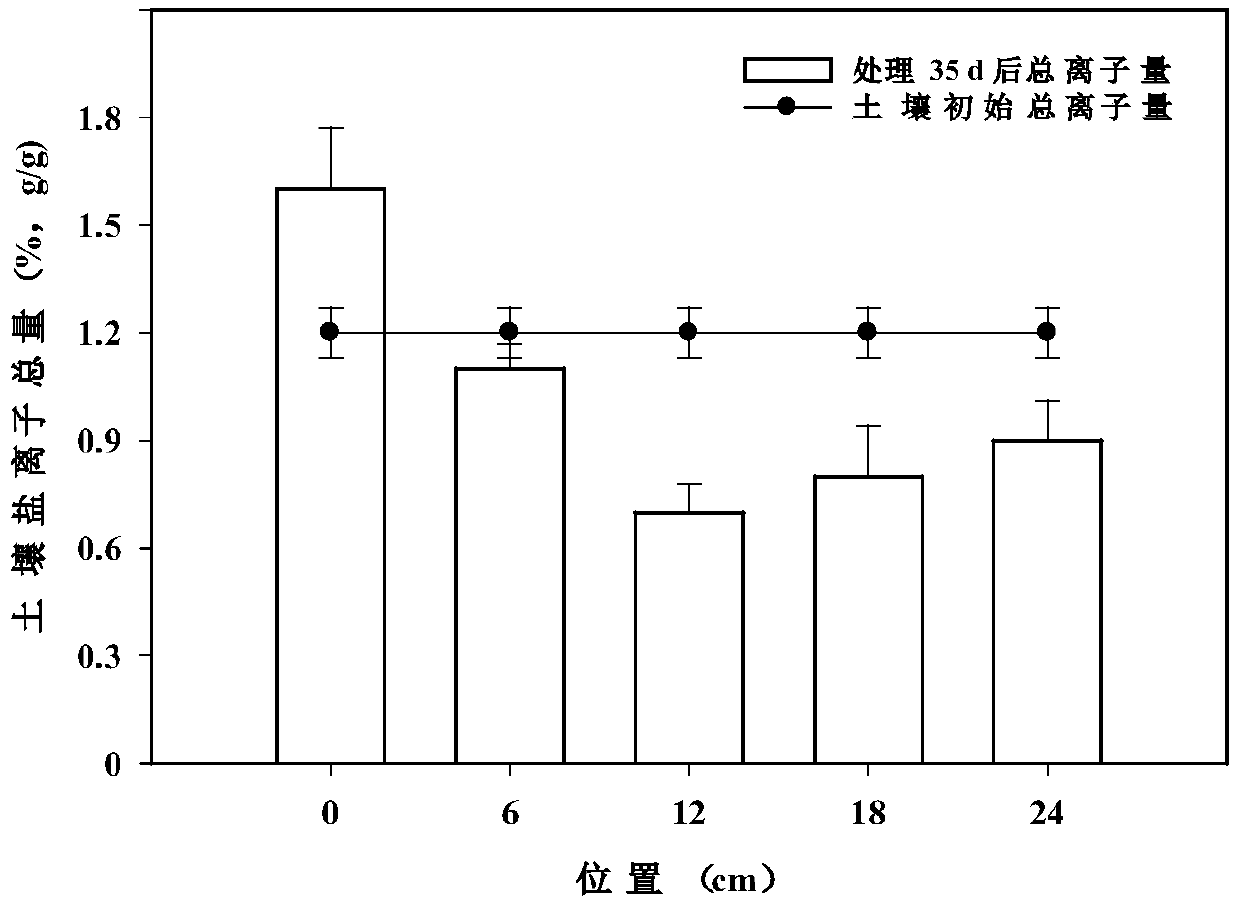
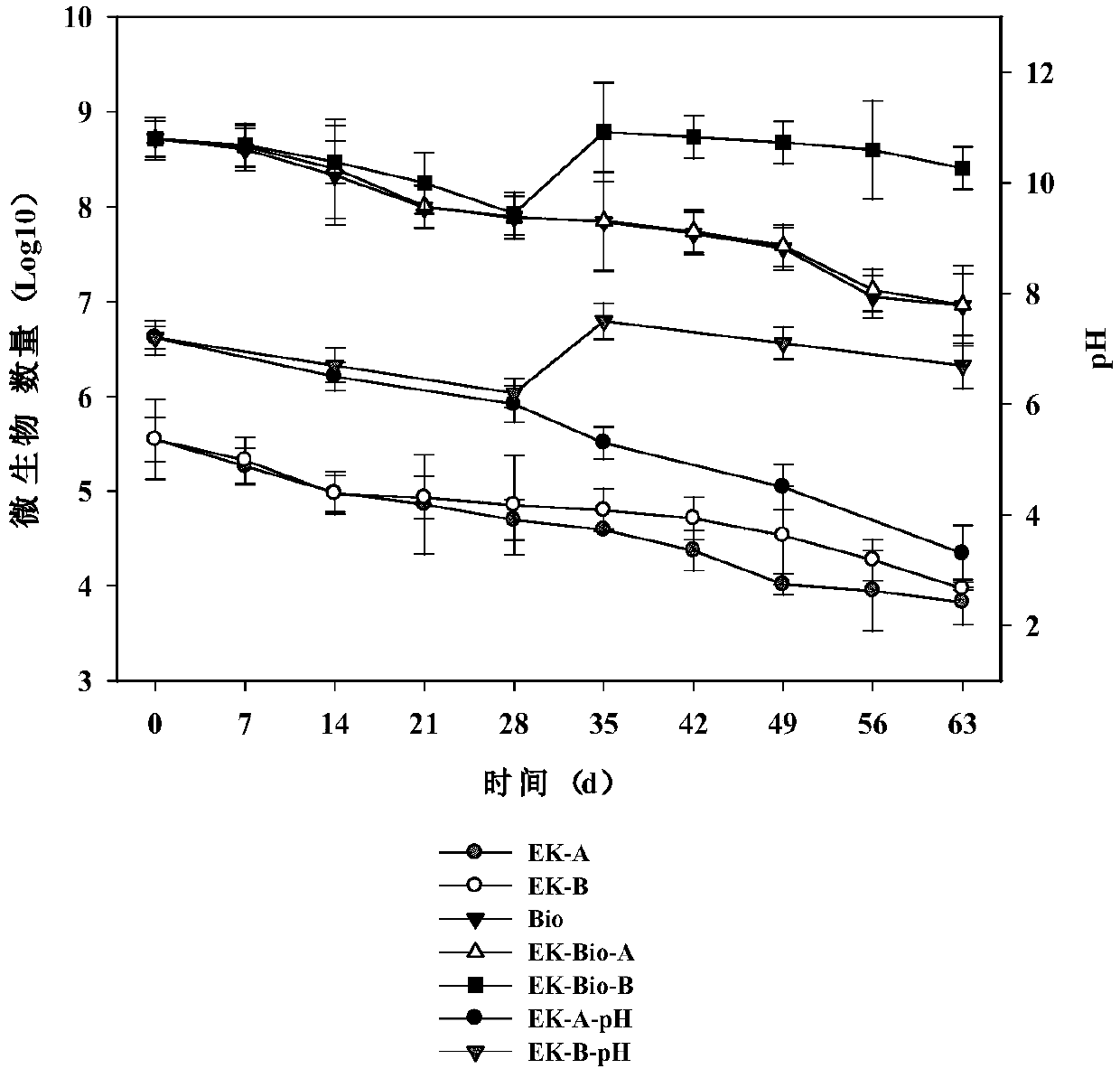
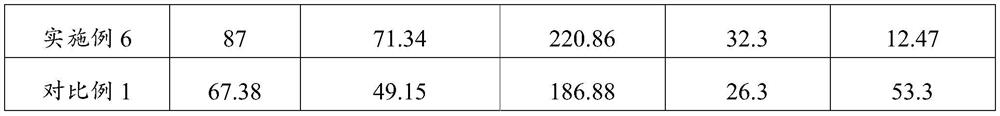
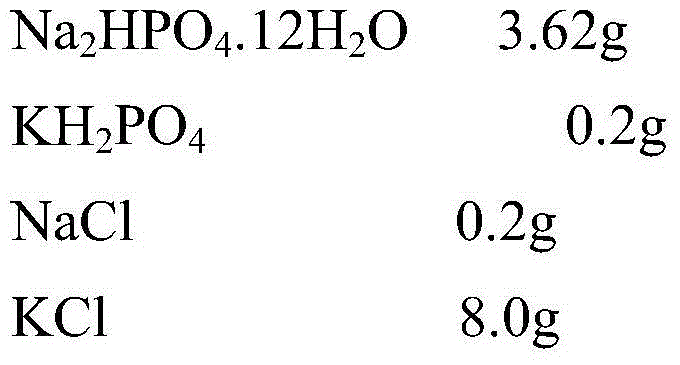Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "Halomonas salina" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Halophilic bacterial agent and preparation method thereof as well as biological treatment system fixed with bacterial agent and application thereof
ActiveCN102146342AShort processEasy to operateBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyHalomonas salina
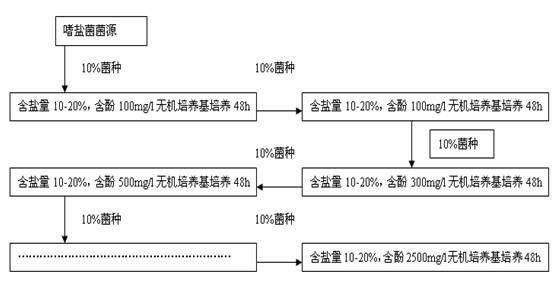
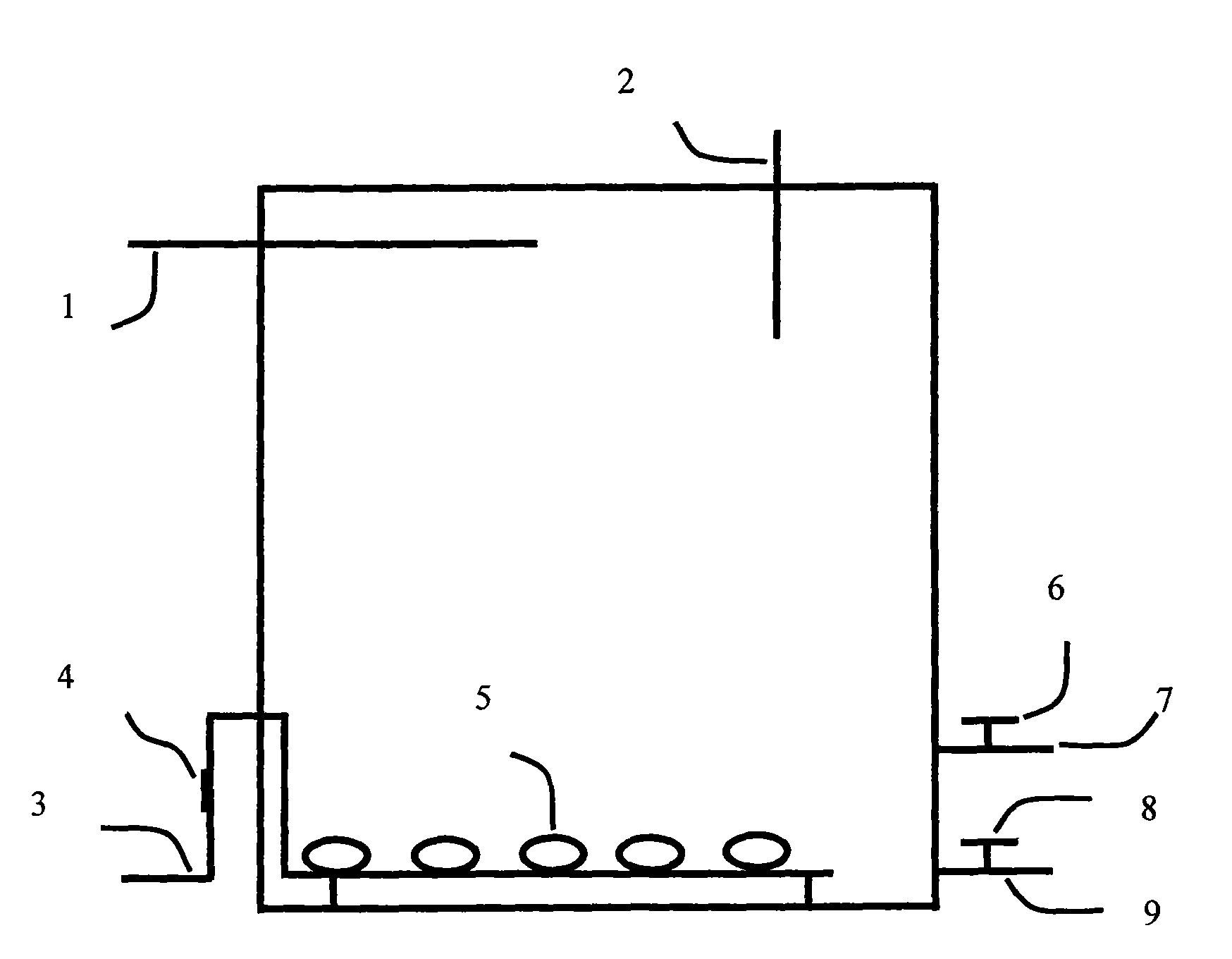
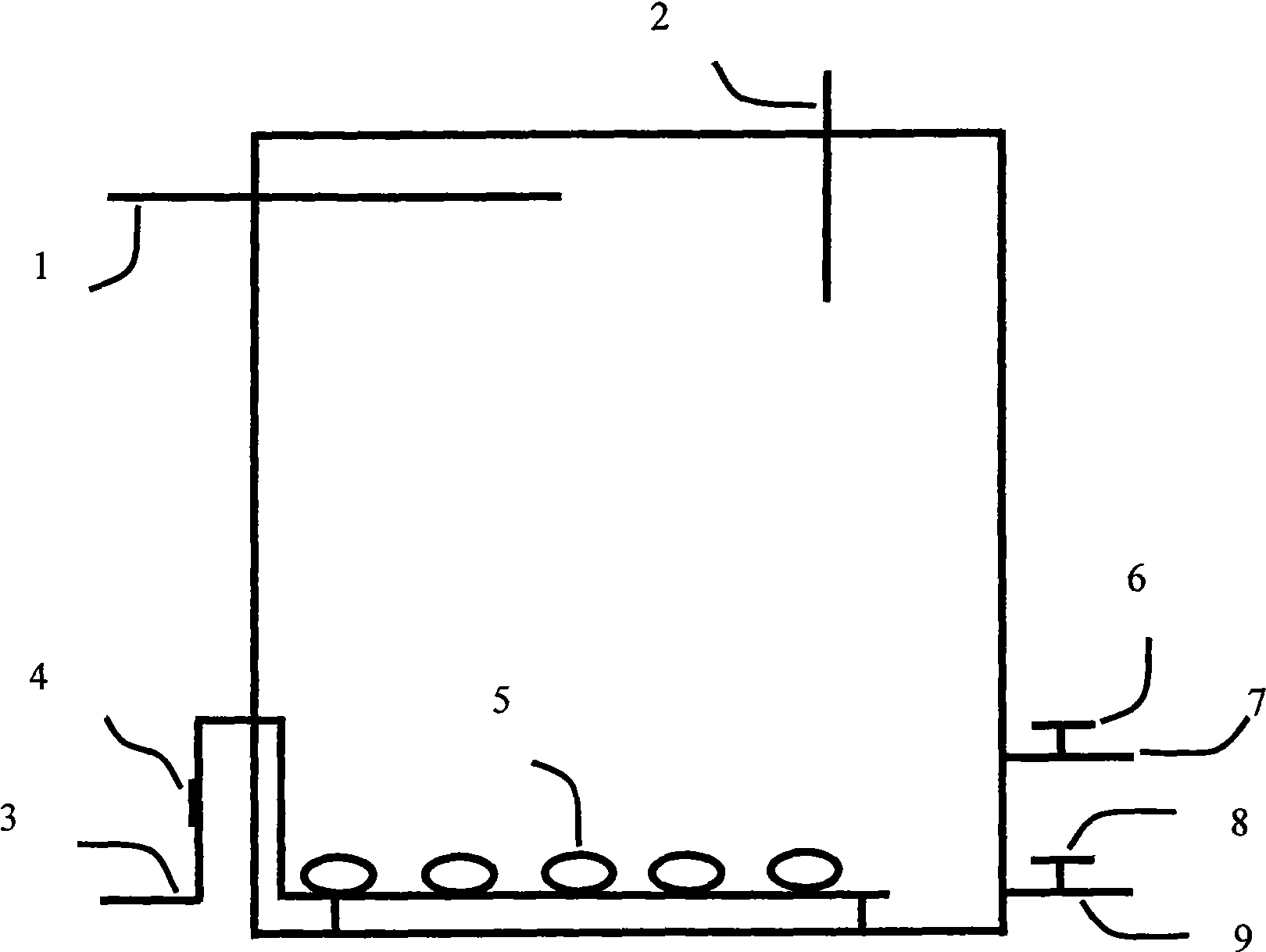
The invention discloses a halophilic bacterial agent and a preparation method thereof as well as a biological treatment system fixed with the bacterial agent and application thereof. In the invention, strains are screened from sewage, sludge and soil to be prepared into a bacterial agent, wherein the bacterial agent comprises four strains including Providenciasp. CJ-4, Oceanobcillussp. CJ-10, Brevibacterium epidermidis CJ-12 and Halomonassp. CJ-13. The invention also provides the biological treatment system fixed with the bacterial agent and a method for treating waste water by using the same. The bacterial agent disclosed by the invention has stronger degradation capability on phenolic wastewater, can adapt to high-salt environments and has very good degradation effects under an environment with the salt content of 2-25% and the phenol concentration of 2500 mg / l; and compared with the traditional active sludge method, the bacterial agent has obvious advantages in the performance of degrading phenolic compounds, and the degradation effect on the phenolic compounds in water can reach more than 99.9%.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIFANG RAINBOW CHEM
Construction and application of polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01
ActiveCN102816729AGood characterIncrease the molar ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnology3-Hydroxypentanoic acid
The invention discloses construction and application of a polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01. The invention provides a recombinant strain which is obtained by inactivating one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid in the Halomonas sp. TD01 used for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). The one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid are at least one selected from the group consisting of a coding gene for 2-methylcitrate synthetase, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 1, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 2 and a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 3. According to results of experiments in the invention, molecular modification is carried out on the Halomonas sp. TD01 to knock out 2-methylcitrate synthetase PrpC and three PHA digestive enzymes so as to obtain the novel recombinant strain, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) with more excellent material performance can be highly efficiently produced by utilizing propionic acid, and the proportion of 3-hydroxyvaleric acid monomers in the produced PHBV and the conversion rate of the substrate propionic acid are substantially improved.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD
Method for processing preserved szechuan pickle waste water by compound bacterial flora
The invention discloses a method for processing preserved szechuan pickle waste water by halophilic (haloduric) bacteria, which uses a compound bacterial flora mainly including microzyme, marinobacter and bacillus and combines an SBR technology to process the preserved szechuan pickle waste water so as to realize COD removing rate more than 90 percent within 24 hours. The method for processing the preserved szechuan pickle waste water has simple technology, stable water outflow and good load impact resistance and can realize the high-efficiency processing of the processing preserved szechuan pickle waste water with lower cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Salt-resistant denitriding composite inoculant, and preparation method and use method thereof
ActiveCN103589669AImprove denitrification effectGood removal effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHalomonas salinaAmmoniacal nitrogen
The invention belongs to the biotechnical field, and concretely relates to a salt-resistant denitriding composite inoculant, and a preparation method and a use method thereof. The salt-resistant denitriding composite inoculant is obtained by mixing Halomonas having a denitrification characteristic and having nitrite accumulation in the denitriding process, Halomonas having a denitrification characteristic and having no nitrite accumulation in the denitriding process, bacillus having a denitrification characteristic, and Halomonas having a salt resisting characteristic according to a volume ratio of 1:1:(10-20):(60-85); and by adopting the salt-resistant denitriding composite inoculant to denitride high salinity wastewater, the denitriding rate is not lower than 95%, and the treated water is discharged in a standard reaching manner. Four microbes in the composite denitriding interact with each other and influence each other, the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogenof the inoculant is higher than that of the individual use of the microbes; and the impact tolerance of the composite inoculant is stronger than that of a purified strain, so the synchronous implementation of nitration and denitrification is effectively promoted, and the denitriding effect of the high salinity wastewater is obviously improved.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
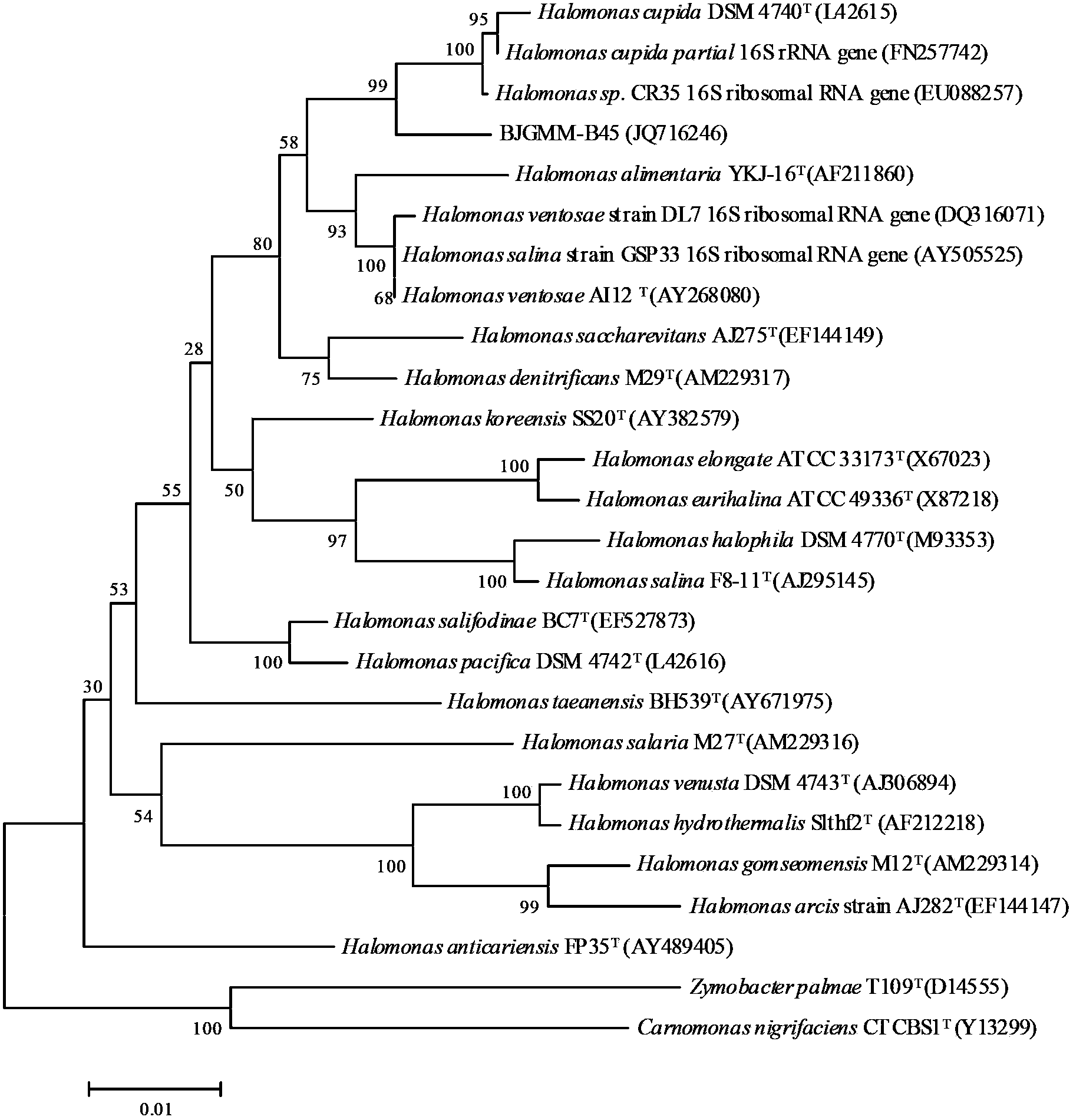
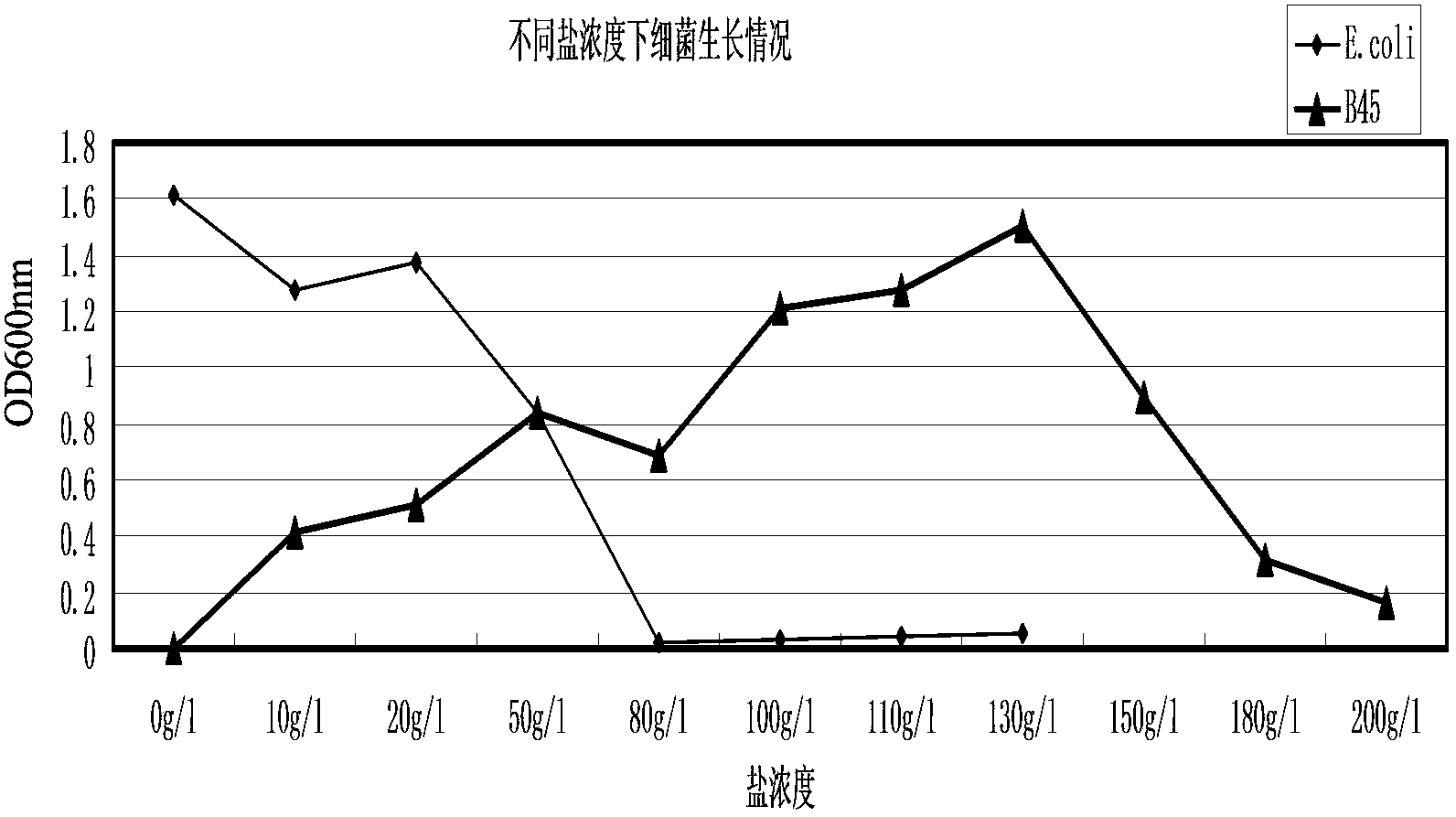
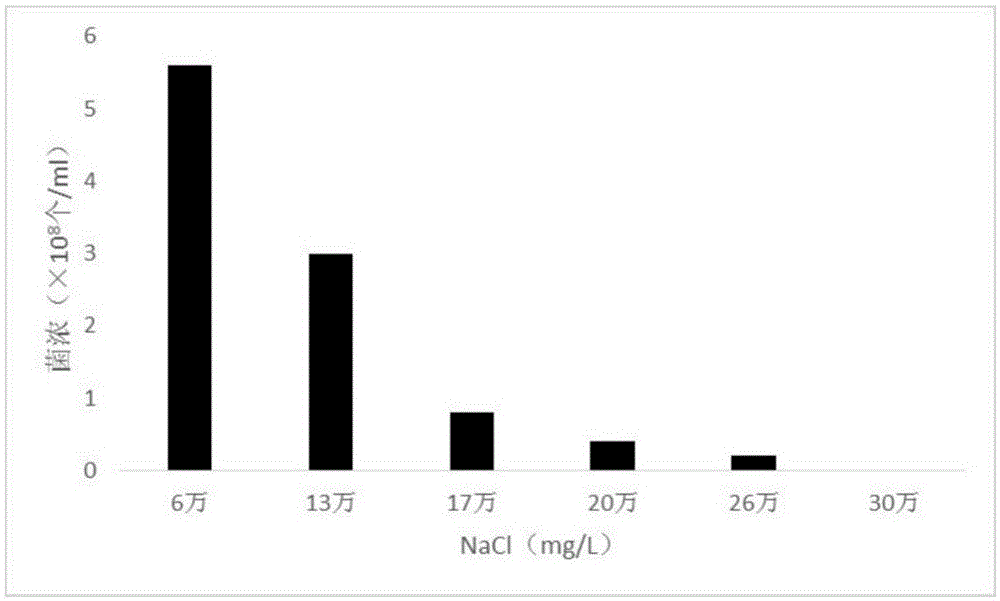
Halomonas huanghegensis BJGMM-B45 and application thereof
InactiveCN103805531AGood characterImproved stress resistance traitsAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaBiotechnologyAlkali soil
The invention provides a bacteria halomonas huanghegensis BJGMM-B45, which has excellent salt tolerance. The preservation number of the halomonas huanghegensis BJGMM-B45 is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO.7022. The bacteria not only can be directly used as functional bacteria for improvement of saline-alkali soil, but also can be used as a gene donor of a novel transgenic organism; the organism can obtain excellent stress resistance if an excellent salt tolerance gene is transferred into the organism; in addition, the bacteria also can be used as a novel gene engineering bacteria, and can obtain more excellent properties by accepting other foreign excellent genes; furthermore, more mutant strains with excellent properties can be obtained through improvement of properties by traditional mutation breeding manner.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Halomonas TF-1 and application thereof
ActiveCN105154367AEOR valueExtend hot wash cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesField testsFermentation
The invention discloses halomonas TF-1 and application thereof. The strain of the halomonas TF-1 is obtained from an oil-water well sample of the Shengli Oil Field under the conditions of 37 DEG C temperature and ordinary pressure by using a high-salt culture medium containing 6.0% of NaCl through enrichment culture screening, temperature-resistant salt-resistant performance investigation, repeated screening and passage, is named as halomonas sp.TF-1, and the preservation number of the halomonas TF-1 is CGMCC No.10619. The nutrient culture medium of the halomonas TF-1 is prepared from 0.3 mg / L of glucose, 0.3 mg / L of peptone, 0.3 mg / L of yeast powder, 0.27 mg / L of K2HPO4 and 6 mg / L sodium chloride, and a pH value is 7.0 -7.5. The halomonas TF-1 grows with crude oil as a carbon source, the bacterial concentration is greater than 5*108 per milliliter. The emulsification viscosity reduction rate of fermentation liquid is higher than 90%. The recovery ratio improved in a physical simulation experiment is higher than 15%. The average oil increase amount of microbial single well stimulation is more than 250 tons. An averagely prolonged hot washing period of microbial paraffin control is greater than 120d. Therefore, the halomonas TF-1 can be widely applied to a field test of microbial single well treatment.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Mixed microbial agent suitable for electric-microbiology collaborative remediation of soil contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbon as well as preparation and application of mixed microbial agent
ActiveCN107828684AHas the characteristic of high salt toleranceSuitable for Restoration ApplicationsBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacillus licheniformisHalomonas salina
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric-microbiology collaborative remediation of soil contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbon, and particularly relates to a mixed microbial agent suitable for electric-microbiology collaborative remediation of high-salinity soil contaminated by the petroleum hydrocarbon as well as preparation and application of the mixed microbial agent. The microbial agent is obtained by respectively fermenting and mixing halomonas xianhensis, bacillus licheniformis and bacillus cereus. The combined microbial agent disclosed by the invention is applied to an electric-microbiology collaborative remediation technology; the remediation bottleneck of the high-salinity state of the soil, formed by the remediation process, is broken, functional microbial agent resources are reasonably utilized, degradation of the petroleum hydrocarbon in petroleum oil is effectively realized, and the toxicity of petroleum hydrocarbon organic pollutants in the soil is reduced.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Halomona with aerobic denitrification function, and application of halomona
InactiveCN110760470AStrong salt toleranceImprove denitrification effectBacteriaSeawater treatmentHalomonas salinaNitrogen removal
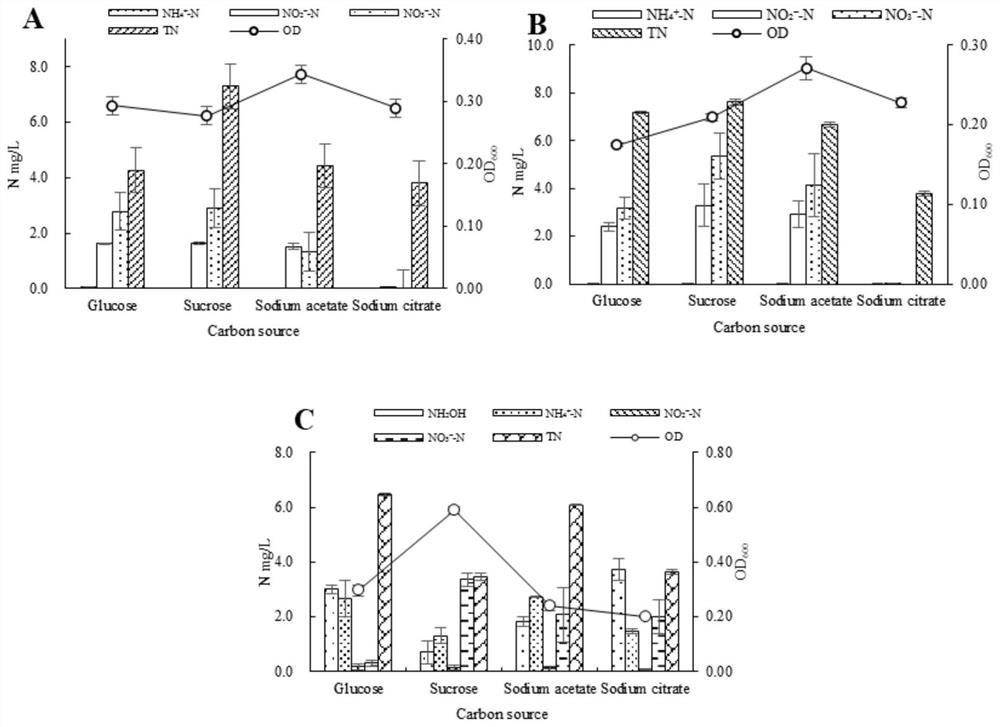
The invention discloses halomona with an aerobic denitrification function, and application of the halomona. The halomona is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on17th September, 2019 with a collection number of CGMCC No.18499. The halomona can carry out aerobic denitrification nitrogen removal under a high-salinity environment and can comprise the following steps of: 1) preparing a high-salinity nitrogen-containing liquid culture medium, wherein salinity is 31; and 2) taking a halomona strain, inoculating the halomona strain in the culture medium accordingto an inoculum size a, and culturing for 24-48h under conditions of 90-150 rpm, 20-40 DEG C and pH of 7.0+ / -0.5, wherein a is greater than or equal to 1% and less than or equal to 3%. When the halomona is used for processing the nitrogen-containing waste water of seawater, a removal rate for NO3<->-N at 48h is 92%, a removal rate for TOC (Total Organic Carbon) and a removal rate for TN (Total Nitrogen) are independently 69.4% and 65.6%, and the halomona performs efficient nitrogen removal performance in high-salinity nitrogen-containing wastewater processing.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Method for efficiently producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid(3HP) and derivatives thereof based on halophilic bacteria
A 3-hydroxypropionic acid(3HP) degradation way of halophilic bacteria is analyzed for the first time by a transcriptomics method, the inventor finds that the 3-hydroxypropionic acid can degrade genesdddA and dddC, and recombination halophilic bacteria TD delta dddA which cannot degrade 3HP is obtained. Based on this, an alcohol dehydrogenase gene AdhP and an aldehyde dehydrogenase gene AldDTD, which are from the halophilic bacteria endogenous and responsible for production and metabolism of the 3HP are further utilized, and a synthetizing biology means is taken for adjusting and controlling the expression level of the metabolic way. Through screening, the recombination halophilic bacteria high in yield of the 3HP is obtained, and the yield and the productivity are respectively 0.93g / g ofthe 1,3-propylene glycol(PDO) and 2.4g / L / h, which are the highest 3HP yield and productivity reported so far.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Immobilized microorganism preparation and method for treating high-salinity waste water of pickled vegetable by adopting immobilized microorganism preparation
ActiveCN103232990ASolve pollutionIncrease concentrationMicroorganism based processesWaste water treatment from food industryHalomonas salinaMicroorganism
The invention discloses an immobilized microorganism preparation. The immobilized microorganism preparation is prepared by adopting the steps of: S1, cultivating and collecting halophilic monads, huge bacilli and deep red yeasts; and S2, preparing the immobilized microorganism preparation, namely mixing bacteria, then adding the mixed bacteria into an embedding agent, fully and uniformly mixing, dropwise adding the mixture into a calcium chloride solution at a constant speed, standing and solidifying at room temperature, and carrying out vacuum freeze drying, so that the immobilized microorganism preparation is obtained. The invention also discloses a method for treating high-salinity waste water of the pickled vegetable by adopting the immobilized microorganism preparation, and the method comprises the step of adding the immobilized microorganism preparation into the high-salinity waste water of the pickled vegetable with the pH regulated to be 6.5-7.5 in a ratio of 3-5%(w / v). The immobilized microorganism preparation has the beneficial effects that multiple pollutants in the waste water can be degraded, a degrading speed is fast, degrading capacity is strong, treatment efficiency is high, stability is good, a technological operation is simple, and production cost is low, so that the immobilized microorganism preparation is an effective manner for solving the problem of pollution of the waste water of the pickled vegetable.
Owner:GUANGHAN HANGJIA FOOD CO LTD
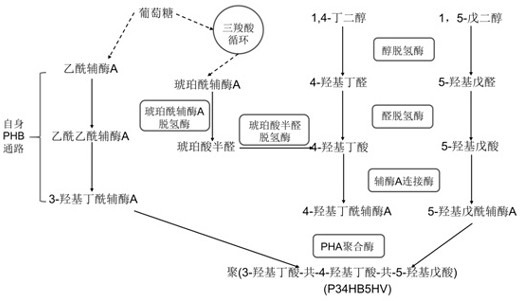
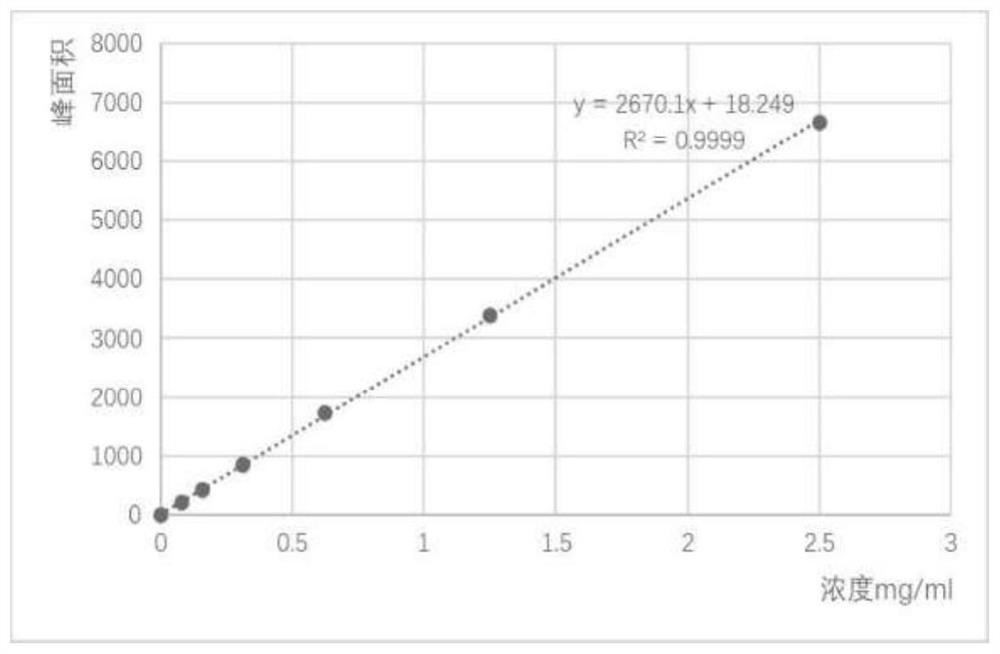
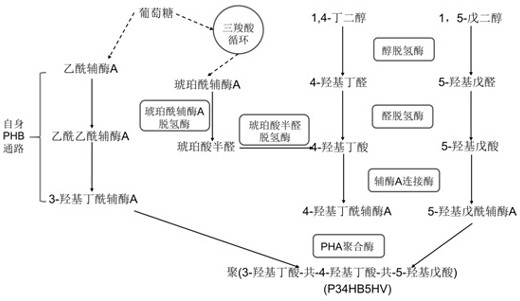
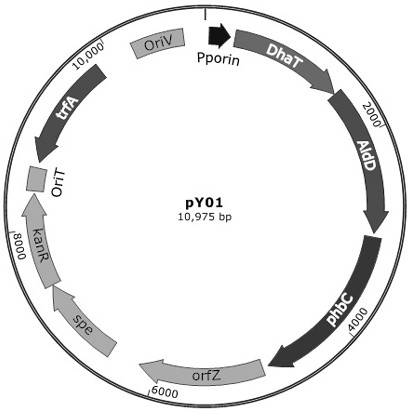
Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-4-hydroxybutyrate-5-hydroxyvalerate) tripolymer and construction of microbial production strain thereof
The invention provides a novel polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) tripolymer poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-4-hydroxybutyrate-5-hydroxyvalerate) and construction of a recombinant bacterium for its production, and particularly relates to a microorganism which can be any bacterium, in particular to halomonas. By constructing halomonas for producing the terpolymer, a specific substrate is selected, and the degradable PHA terpolymer is produced through fermentation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Salt-tolerant denitrifying bacteria, strain preparation method thereof and application of bacteria
ActiveCN110129224ASimple processThorough denitrificationBacteriaWater contaminantsNitrate nitrogenHigh concentration
The invention discloses salt-tolerant denitrifying bacteria, a strain preparation method thereof and an application of the bacteria, and belongs to the field of environmental microorganisms. The bacteria are named as Halomonas stevensii and belong to anaerobic denitrifying bacteria strains, and the collection number of the denitrifying bacteria is CGMCC NO. 15311. The Halomonas stevensii has highsalt-tolerant and denitrification characteristics, denitrification rate reaches 98% or more, high-concentration nitrate nitrogen in water can be reduced into harmless nitrite-free nitrogen under the condition of sodium chloride salinity lower than 10%, the denitrifying bacterium is applied into a denitrifying denitrification reactor, denitrification is effective and stable, secondary pollution isavoided, a start period can be shortened, and the denitrifying bacteria can be widely applied to denitrification treatment of industrial wastewater.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Salt-tolerant halomonas strain and application thereof in field of water purification
The invention relates to a salt-tolerant Halomonas sp. Strain and application thereof in the field of water purification, the strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), and the preservation number is CGMCC No.24127. The strain has good salt tolerance, the optimum growth salinity is 5%, under laboratory conditions, the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 100% in 24 h when the salinity is 15% or below, and the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 100% when the salinity is 15% or below. The strain can resist high ammonia nitrogen concentration and high temperature, the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 89.1% within 72 h for the ammonia nitrogen concentration of 3000 ppm, and when the initial ammonia nitrogen concentration is 100 ppm, the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 100% within 24 h at the temperature of 30-40 DEG C.
Owner:青岛蔚蓝赛德生物科技有限公司
Halomonas with aerobic denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation functions and application thereof
ActiveCN112551692AImprove recovery rateGrow fastWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesHalomonas salinaNitration
The invention discloses halomonas with aerobic denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation functions and application thereof , and belongs to the technical field of microorganism application. The invention provides two strains of halomonas sp. MCCC 1A17488 and MCCC 1A13718 with aerobic denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation functions, and the preservation numbers of the halomonas sp. MCCC 1A17488 and the MCCC 1A13718 are as follows: GDMCC No:60985 and GDMCC No:60984. The halomonas sp. MCCC 1A17488 and MCCC 1A13718 can be applied to nitrogen and sulfur removal, can be suitable for biological nitrogen removal treatment of various nitrogen-containing wastewater, has efficient denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation capacity under aerobic and anoxic conditions, can rapidly and efficiently remove nitrate, nitrite, ammonia nitrogen, sulfide and the like, and has good application prospects in the biological nitrogen and sulfur removal of sewage, sludge, sedimentsor culture water bodies.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MINIST OF NATURAL RESOURCES +1
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain for synthesizing ectoine through fermentation
PendingCN113151024AEfficient synthesisFungiMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHalomonas salina
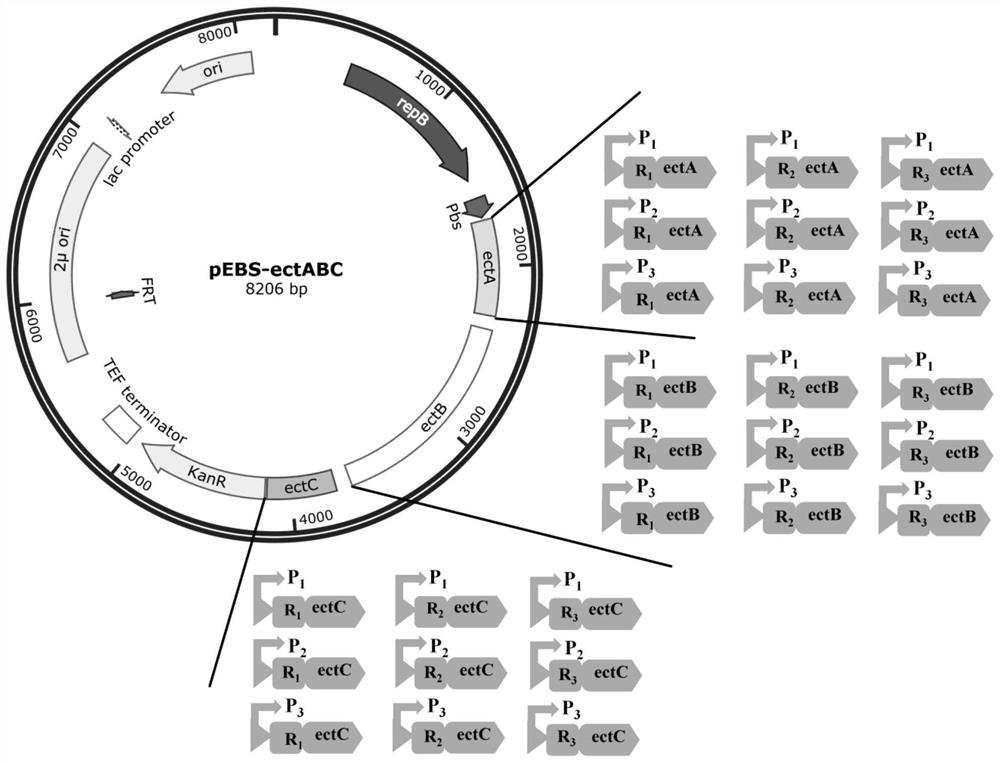
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain for synthesizing ectoine through fermentation, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. According to the invention, saccharomyces cerevisiae is taken as a host, a triple shuttle plasmid pEBS of bacillus subtilis, escherichia coli and saccharomyces cerevisiae is taken as an expression vector, an ectABC gene cluster derived from halomonas elongata is introduced into the saccharomyces cerevisiae, then strategies such as ectA, ectB and ectC single-gene RBS optimization, promoter optimization, single-gene RBS and promoter double optimization and the like are carried out, and efficient biosynthesis of ectoine is realized. The ectoine accumulation amount is up to 2.3 g / L when the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain constructed by the invention is cultured for 96 hours on a shake flask, and the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain has potential and wide application value in industry.
Owner:RAYTING BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Halomonas taeanensis for degradation of phenol
ActiveCN107164277AImprove salt resistanceImprove economyBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyHalomonas salina
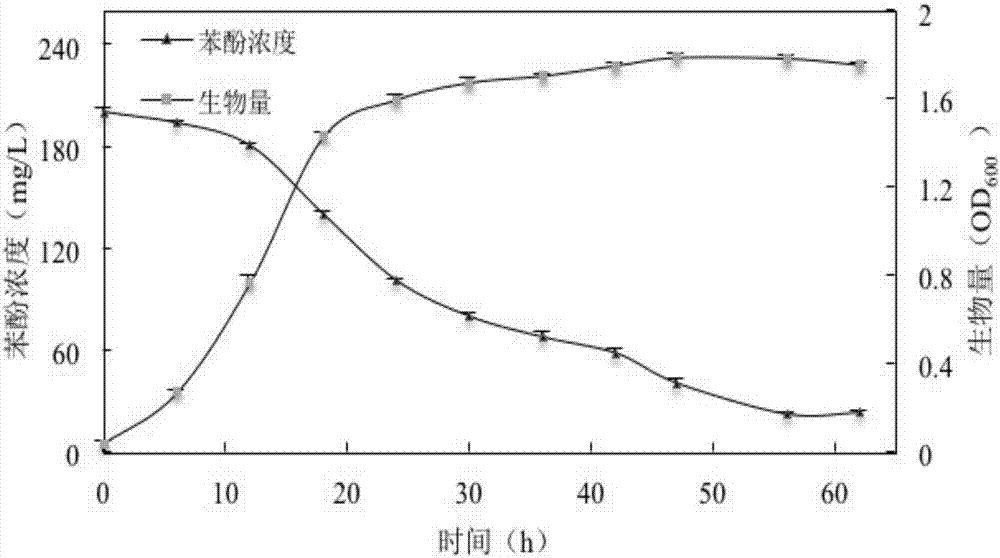
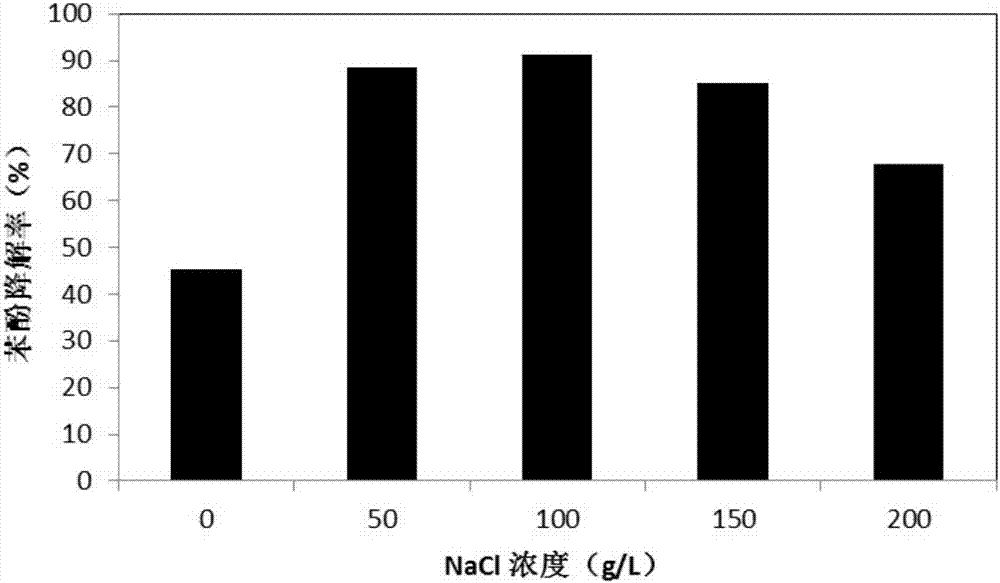
The invention provides a strain of Halomonas taeanensis and an application thereof. The bacterial strain is named H17 and is assigned the accession number CCTCC No: M2016306. The bacterial strain can degrade phenol in a liquid culture medium containing 200 mg / L of phenol within 50 h by more than 90%. 1L of the liquid culture medium includes 10 g of MgSO4.7H2O, 0.2 g of CaCl2.2H2O, 2-5 g of KCl, 2.5 g of tryptone, 10 g of yeast extract, 10% of NaCl, and distilled water added to 1000 ml, wherein pH value is regulated to about 7.2 and sterilization is carried out at 121 DEG C for 15 min. The Halomonas taeanensis H17 has strong capability of degrading phenol, can be used for biological recovery of phenol polluted environments and has excellent economic value and application prospect.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Recombinant halomonas, construction method of recombinant halomonas and application of recombinant halomonas in preparation of itaconic acid by catalyzing citric acid
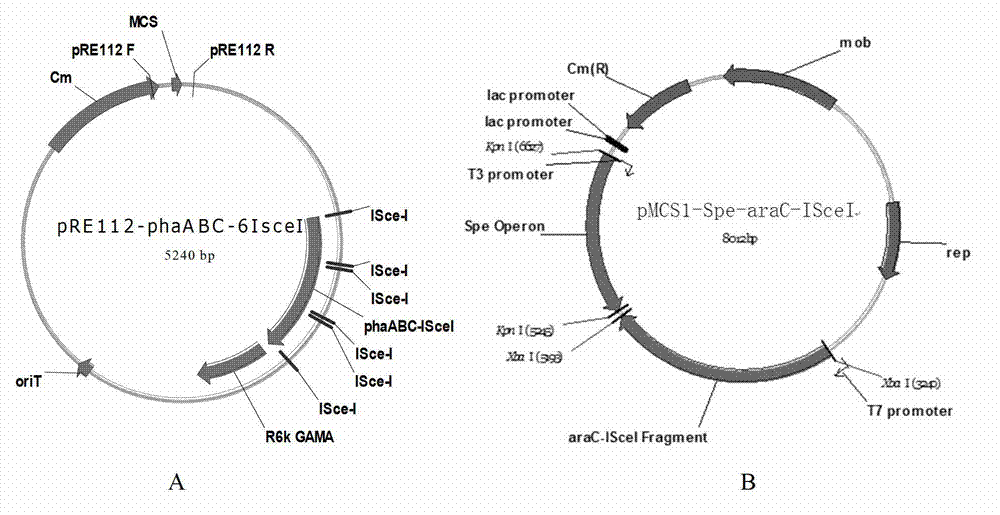
ActiveCN113481136AEasy to purifyShort reaction cycleBacteriaTransferasesHalomonas salinaItaconic acid
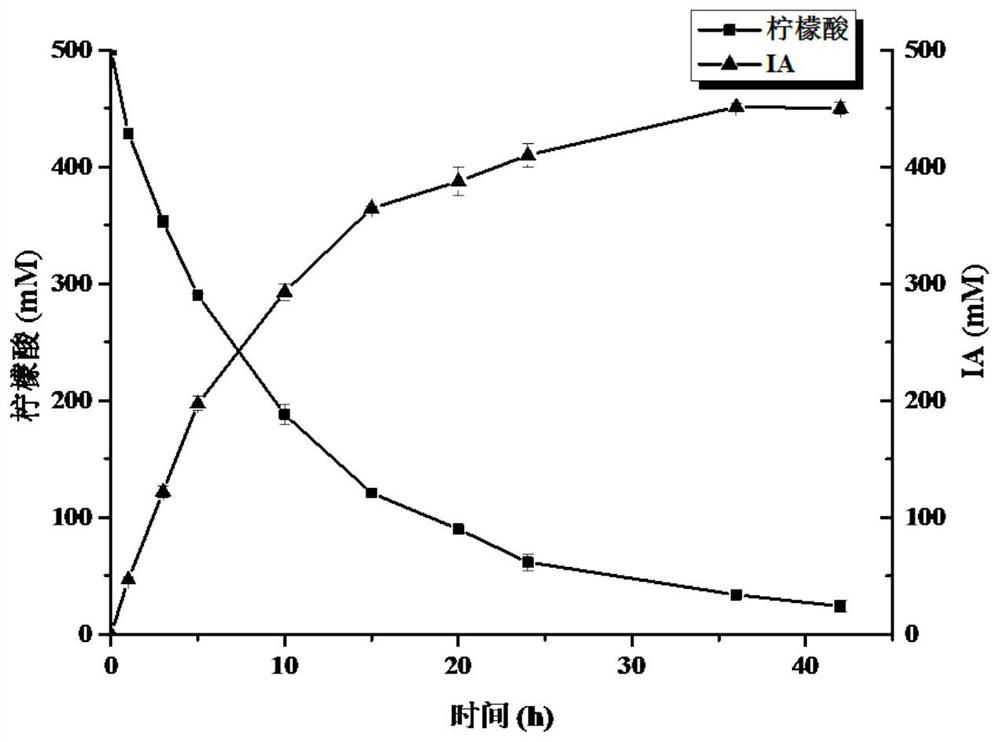
The invention discloses recombinant halomonas, a construction method of the recombinant halomonas and application of the recombinant halomonas to preparation of itaconic acid by catalyzing citric acid. The construction method of the recombinant halomonas is characterized by comprising the following steps of: integrating an Mmp1 RNA polymerase expression unit on a wild type halomonas sp. TD01 genome, and replacing an initiation codon ATG of an icd gene of the genome with TTG to obtain Halomonas sp. TD2.0; sequentially introducing a high-copy expression vector pN59-PMmp1-RBS-cadA-acn and a low-copy expression vector pN85-PMmp1-RBS-GroESL-PMmp1-RBS-acn into the Halomonas sp. TD2.0; and obtaining the recombinant halomonas sp. IA02. The itaconic acid can be efficiently prepared through cell catalysis of the bacterium. The recombinant halomonas is short in period, simple, convenient and high in yield.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
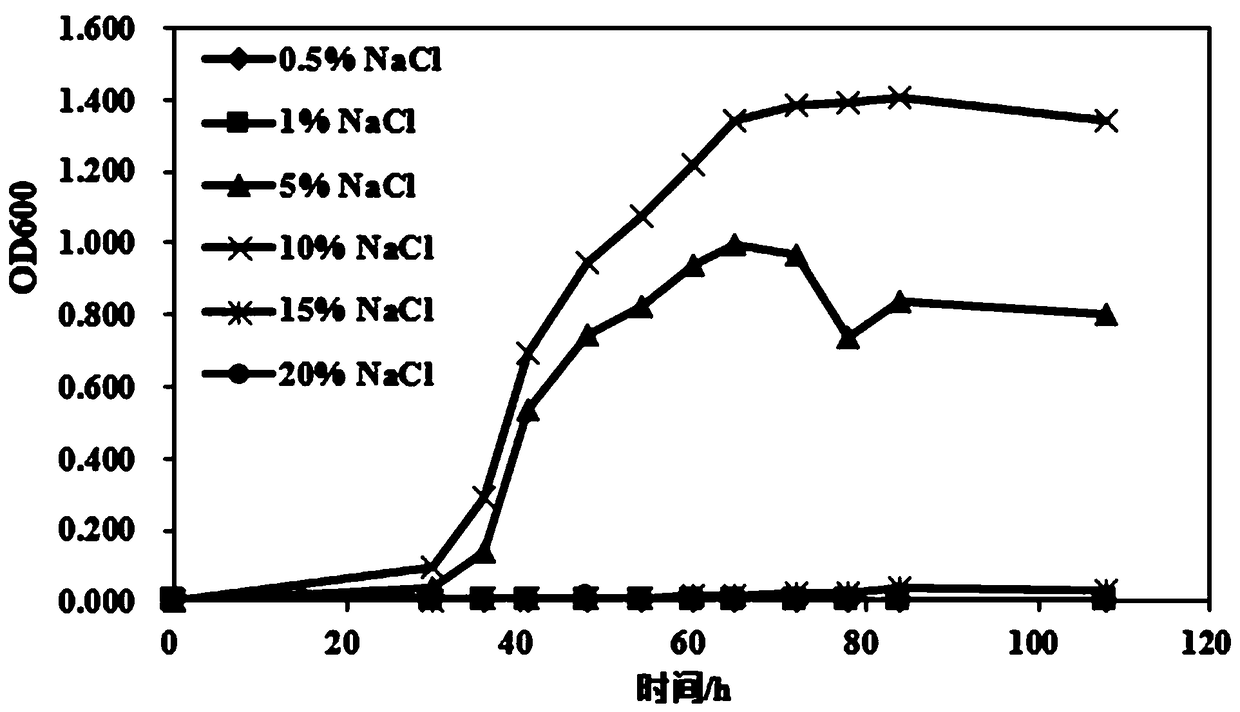
Halomonas ventosae strain JPT10-1 for improving salt-tolerance capability of corns as well as bacterium agent and application of halomonas ventosae strain JPT10-1
ActiveCN109486709AStable traitsEasy to trainPlant growth regulatorsBiocideHalomonas ventosaeNutrient
The invention provides a halomonas ventosae strain JPT10-1 for improving the salt-tolerance capability of corns as well as a bacterium agent and application of the halomonas ventosae strain JPT10-1. The strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on August 17, 2018, with the preservation number of CCTCC M 2018548. The strain can resist high-concentration NaCl and can grow in the environment with the salt concentration of 3000mmol / L, and the growth speed is relatively rapid. The invention further discloses the bacterium agent prepared from the strain and the application of the bacterium agent to the improvement of the salt-tolerance capability of the corns. A bacterium suspension solution of the strain is inoculated into corn seedlings under salt stress, so thatbiomasses including the root length, the plant height and the like, and various physiological indexes including the vitality of a root system, a photosynthetic rate, an anti-oxidization enzyme systemand the like can be remarkably improved. Meanwhile, the vitality of part of a soil enzyme can be changed through the strain, so that the fertility of the soil and the utilization rate of plants on nutrient elements are improved. The strain provided by the invention has important application value on reduction of the stress on the growth of the corns in a saline and alkaline land.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
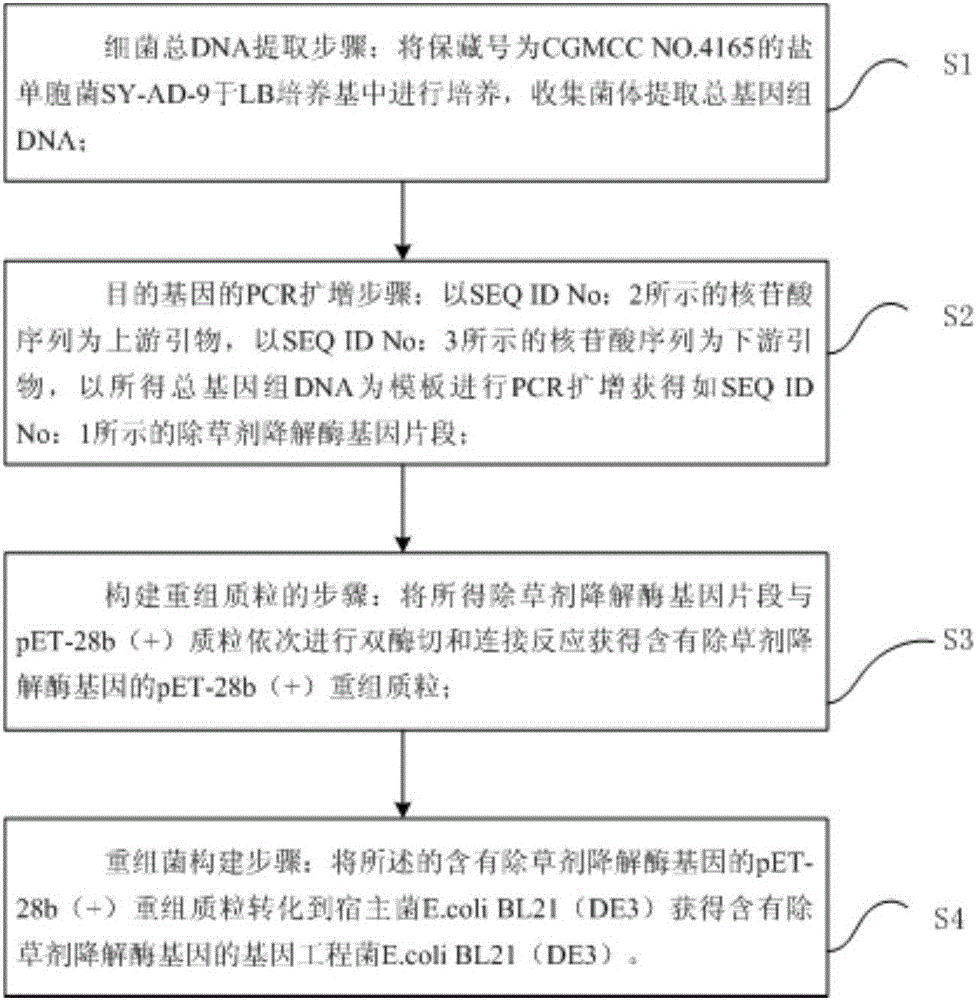
Herbicide degrading enzyme gene, engineering bacterium and application of engineering bacterium
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, and in particular to an atrazine herbicide degrading enzyme gene, an engineering bacterium comprising the same and application of the engineering bacterium. The herbicide degrading enzyme gene is derived from Halomonas sp.SY-AD-9 of efficiently-degraded atrazine, and triazine hydrolase, an expression product of the herbicide degrading enzyme gene can degrade the atrazine efficiently. The engineering bacterium comprising the herbicide degrading enzyme gene can express herbicide degrading enzymes (the triazine hydrolase) efficiently and can be applied to environmental bioremediation.
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF CHEM IND
Composite flora for regulating and controlling prawn culture water body
ActiveCN112725217AEfficient nitrogen reduction effectGive full play to the synergistic effectBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyHalomonas salina
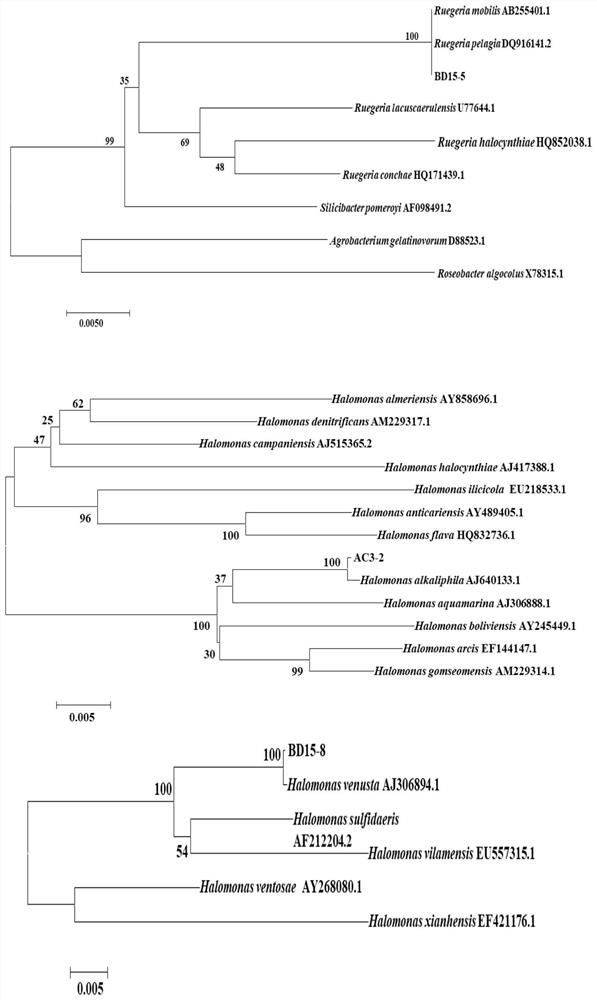
The invention provides a composite flora for regulating and controlling a prawn culture water body. The composite flora comprises a halomonas basophila AC3-2 strain, a Lugeria BD15-5 strain and a Halomonas dahurica BD15-8 strain, and the composite flora also contains strains for inhibiting common vibrios in the prawn culture process. On the basis of screening out strains which are safe to prawns and have an efficient nitrogen reduction effect from a prawn biofloc culture system, the screened strains are compounded to obtain the composite flora disclosed by the invention, so that the synergistic effect among the strains is fully exerted, the treatment effect on a culture water body is improved, and the anti-pathogenic vibrio capability of the cultured object is improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Cheap synthesis of biodegradable mulching film from straws and illegal cooking oil by using halomonas sp ZY-1
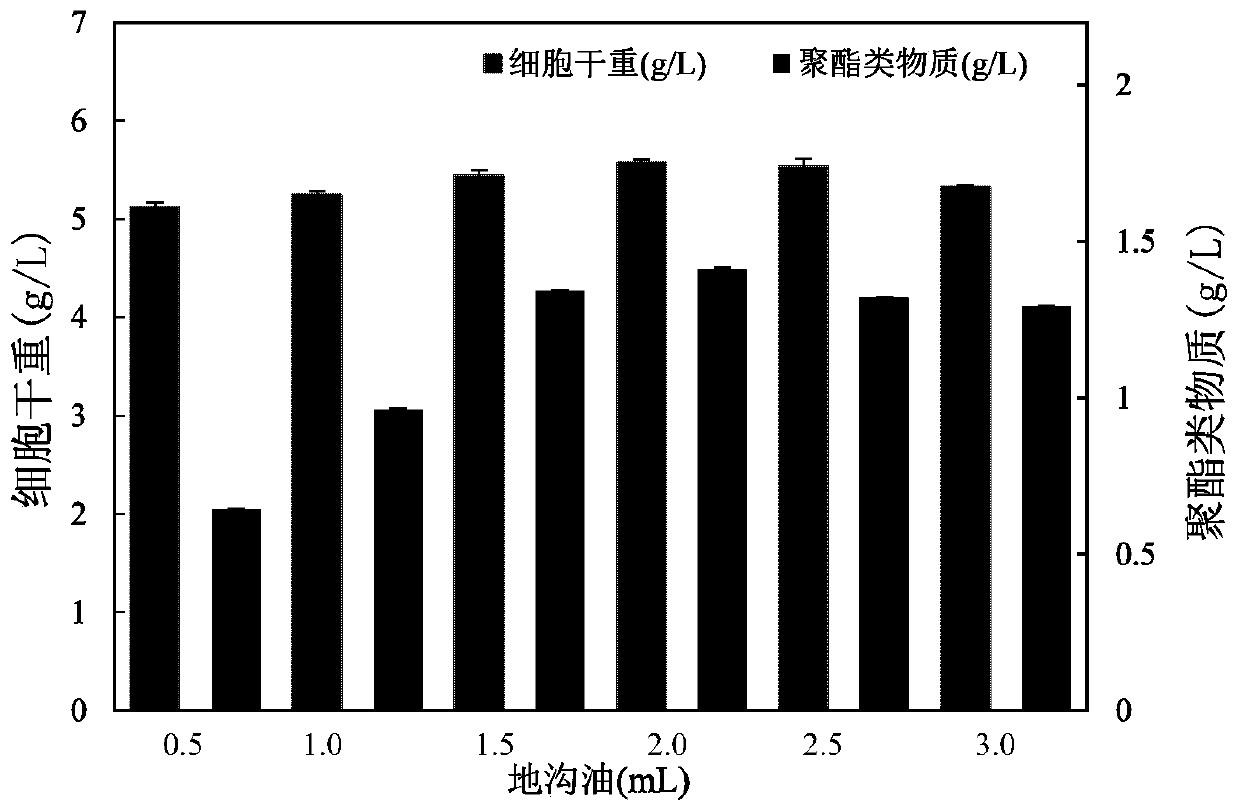
PendingCN111378254AReduce manufacturing costPromote degradationBacteriaClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyHalomonas salina
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a biodegradable mulching film from straws and illegal cooking oil by using halomonas sp.ZY-1 under an open and non-sterile condition. Straws are treated to obtain a straw supernatant, and an MS culture medium with the volume ratio of the straw supernatant to illegal cooking oil being 35: 1-40: 1 is prepared. In a sequencing batch reactor (SBR), Halomonas sp.ZY-1 is subjected to aerobic culture with the unsterilized straw supernatant and illegal cooking oil MS culture medium to obtain thalli, and intracellular polyester substances are extracted.Polyester substances are further modified to obtain the mulching film with the tensile strength of 16-18 MPa, the mulching film is deeply buried in cultivated land soil with the depth of 20-30 cm, the 35d weight reduction rate is 40%-50%, and the 35d weight reduction rate is 0.3%-0.5% when the mulching film is placed in dry air. Under the condition that halophilic bacteria are not sterilized, wastes are utilized to synthesize the biological mulching film, so that the production cost is reduced to the maximum extent, and technical support is provided for realizing green ecological cycle and agricultural sustainable development.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for processing preserved szechuan pickle waste water by compound bacterial flora
InactiveCN101629153BAccelerated settlementSimple processFungiBacteriaHalomonas salinaEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a method for processing preserved szechuan pickle waste water by halophilic (haloduric) bacteria, which uses a compound bacterial flora mainly including microzyme, marinobacter and bacillus and combines an SBR technology to process the preserved szechuan pickle waste water so as to realize COD removing rate more than 90 percent within 24 hours. The method for processing the preserved szechuan pickle waste water has simple technology, stable water outflow and good load impact resistance and can realize the high-efficiency processing of the processing preserved szechuan pickle waste water with lower cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Halomonas with nitrification and denitrification effects and application thereof
ActiveCN111925960AImprove denitrification activityBacteriaWater contaminantsHalomonas salinaMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of nitrogen pollution, and provides halomonas DY-S025GC05 with nitrification and denitrification effects and application of the halomonas DY-S025GC05. TheLatin of the halomonas DY-S025GC05 with nitrification and denitrification effects is Halomonas sp., the strain has been preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, Yard 1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the preservation date is May 19th, 2020, and the preservation number is CGMCCNO.19847. The halomonas DY-S025GC05 provided by the invention has double activities of nitrification and denitrification at the same time, and the conversion of nitrification and denitrification functions can be realized by adjusting the oxygen content.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA +1
It is suitable for electrokinetic-microbial synergistic remediation of mixed bacterial agent in petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil and its preparation and application
ActiveCN107828684BDegradation toxicityAchieving synergistic co-metabolismBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacillus licheniformisHalomonas salina
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric-microbiology collaborative remediation of soil contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbon, and particularly relates to a mixed microbial agent suitable for electric-microbiology collaborative remediation of high-salinity soil contaminated by the petroleum hydrocarbon as well as preparation and application of the mixed microbial agent. The microbial agent is obtained by respectively fermenting and mixing halomonas xianhensis, bacillus licheniformis and bacillus cereus. The combined microbial agent disclosed by the invention is applied to an electric-microbiology collaborative remediation technology; the remediation bottleneck of the high-salinity state of the soil, formed by the remediation process, is broken, functional microbial agent resources are reasonably utilized, degradation of the petroleum hydrocarbon in petroleum oil is effectively realized, and the toxicity of petroleum hydrocarbon organic pollutants in the soil is reduced.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantitative detection method for halomonas strains by adopting indirect enzyme-linked immunosordent assay
ActiveCN104655842AStrong nitrite degradation abilityPlay a role in promotingMaterial analysisSerum igeAquatic product
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Preparation method and application of polyhydroxyalkanoate
ActiveCN114277066ASuitable for growthImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHalomonas salina
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of polyhydroxyalkanoate, and discloses a preparation method and application of polyhydroxyalkanoate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: inoculating a fermentation culture medium with a halomonas strain for fermentation culture; after the fermentation culture is performed for 6-10 hours, the mass percent of the carbon source is controlled to be 1.3-1.6%, and the mass percent of the nitrogen source is controlled to be 0.015-0.05%; after the fermentation is performed for 30 to 40 hours, the mass percent of the nitrogen source is controlled to be 0.01 to 0.015 percent; and after the fermentation culture time is 45-50 hours, stopping controlling the concentration of the nitrogen source. By controlling the concentration of the carbon source, the concentration of the nitrogen source, the adding time and other factors, the preparation method of the polyhydroxyalkanoate improves the conversion rate of the polyhydroxyalkanoate, reduces the usage amount of sodium hydroxide, and also has the advantages of being simple and easy to industrialize.
Owner:MEDPHA CO LTD
Halophilic bacterial agent and preparation method thereof as well as biological treatment system fixed with bacterial agent and application thereof
ActiveCN102146342BShort processEasy to operateBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyHalomonas salina
The invention discloses a halophilic bacterial agent and a preparation method thereof as well as a biological treatment system fixed with the bacterial agent and application thereof. In the invention, strains are screened from sewage, sludge and soil to be prepared into a bacterial agent, wherein the bacterial agent comprises four strains including Providenciasp. CJ-4, Oceanobcillussp. CJ-10, Brevibacterium epidermidis CJ-12 and Halomonassp. CJ-13. The invention also provides the biological treatment system fixed with the bacterial agent and a method for treating waste water by using the same. The bacterial agent disclosed by the invention has stronger degradation capability on phenolic wastewater, can adapt to high-salt environments and has very good degradation effects under an environment with the salt content of 2-25% and the phenol concentration of 2500 mg / l; and compared with the traditional active sludge method, the bacterial agent has obvious advantages in the performance of degrading phenolic compounds, and the degradation effect on the phenolic compounds in water can reach more than 99.9%.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIFANG RAINBOW CHEM
Halomonas strain and application thereof
The invention discloses a Halomonas strain and an application thereof. The strain is a new species in Halomonas, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO.24977. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the Halomonas strain. The strain C2-1-M8 obtained by separation in the invention is a new species different from a known species of Halomonas, and can be used for synthesizing ectoine (Ectoine) in cells. The strain C2-1-M8 can utilize substrates such as D-fructose, glycerol, D-fructose-6-phosphoric acid, L-alanine, L-histamine, L-serine, D-galacturonic acid, D-glucuronic acid, glucosamide, L-lactic acid, D-malic acid, L-malic acid, Tween 40 and the like, and has a broad-spectrum property of the substrates. According to physiological and biochemical experiments, the growth temperature of the strain C2-1-M8 ranges from 4 DEG C to 30 DEG C, the NaCl concentration needed by growth ranges from 1.0% to 17.0%, and the growth pH value ranges from 5.0 to 7.5. Meanwhile, the yield of tetrahydropyrimidine synthesized by the strain C2-1-M8 under the conditions that the temperature is 30 DEG C, the NaCl concentration is 5.0%-9.0% and the pH is 5.5-7.0 is optimal. The strain has a very wide application prospect in biological preparation of ectoine.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A salt-tolerant denitrification compound bacterial agent and its preparation and use method
ActiveCN103589669BImprove denitrification effectGood removal effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHalomonas salinaTotal nitrogen
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a salt-tolerant and denitrification compound bacterial agent and its preparation and application method. Salt-resistant denitrification compound bacterial agent consists of Halomonas with denitrification characteristics and nitrous nitrogen accumulation in the denitrification process, Halomonas with denitrification characteristics and no nitrite nitrogen accumulation in the denitrification process, and Nitrification The specific Bacillus and Halomonas with salt-tolerant characteristics are mixed according to the volume ratio of 1:1:(10~20):(60~85). Nitrogen treatment, the denitrification rate is at least 95%, and the effluent water quality meets the standard discharge. In the composite bacterial agent of the present invention, the four kinds of microorganisms interact and influence each other, and the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen is higher than that of any microorganism used alone. Because the impact resistance of the composite bacterial agent is stronger than that of purified bacterial strains, it can effectively Promote simultaneous nitrification and denitrification, so that the denitrification effect of high-salt wastewater is significantly improved.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-4-hydroxybutyrate-5-hydroxyvaleric acid) terpolymer and construction of its microbial production strain
The present invention provides a novel polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) trimer poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid-4-hydroxybutyric acid-5-hydroxyvaleric acid), and the construction of recombinant bacteria for its production, specifically related to The microorganism may be any bacterium, especially Halomonas. By constructing Halomonas bacteria producing the above-mentioned trimer, selecting a specific substrate, and fermenting and producing the degradable PHA trimer.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com