Halomonas strain and application thereof
A technology for Halomonas and strains, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of difficulty in chemical synthesis, expensive tetrahydropyrimidine, etc., and achieves the effects of wide development and application prospects, short cycle and simple cultivation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
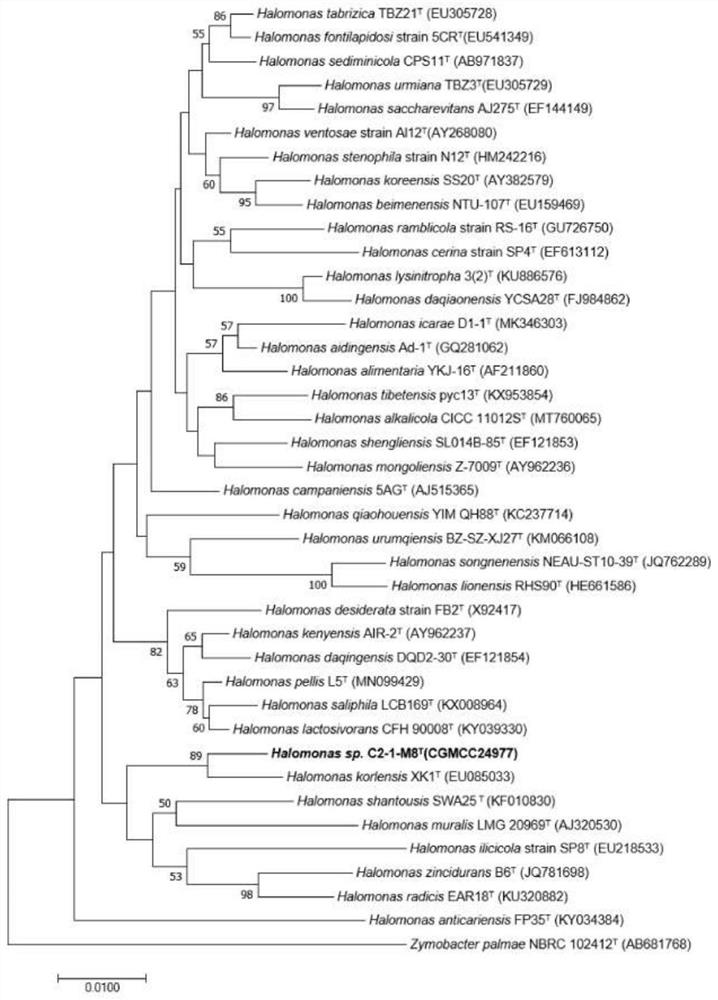
[0031] Example 1 Isolation and identification of Halomonas strain C2-1-M8
[0032] a. Soil sample collection: Soil was collected from the bank of Longmucuo in Ngari region of Tibet, placed at 4°C and brought back to the laboratory, and separated by plate dilution coating method.
[0033] b. The medium of the isolated strain is 2216 solid medium: peptone 5.0g, yeast extract 1.0g, citric acid 0.1g, sodium chloride 19.45g, magnesium chloride 8.8g, sodium sulfite 3.24g, calcium chloride 1.3g, chlorine Potassium 0.55g, sodium bicarbonate 0.16g, potassium bromide 0.08g, strontium chloride 34.0mg, boric acid 22mg, sodium silicate 4.0mg, sodium fluoride 2.4mg, ammonium nitrate 1.6mg, disodium hydrogen phosphate 8.0mg, Agar 15g, add distilled water to volume to 1000mL, pH 7.2-7.4, sterilize at 121°C for 20min.
[0034]c. Use the plate dilution coating method for separation: fully mix the collected soil samples, weigh 10 g, put it into a triangular flask with an appropriate amount of g...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The preparation of embodiment 2 Halomonas C2-1-M8 fermentation broth
[0038] a. Bacterial activation: pick strains and streak inoculation to 2216 solid medium (5.0 g of peptone, 1.0 g of yeast extract, 0.1 g of citric acid, 19.45 g of sodium chloride, 8.8 g of magnesium chloride, 3.24 g of sodium sulfite, 3.24 g of sodium chloride Calcium 1.3g, Potassium Chloride 0.55g, Sodium Bicarbonate 0.16g, Potassium Bromide 0.08g, Strontium Chloride 34.0mg, Boric Acid 22mg, Sodium Silicate 4.0mg, Sodium Fluoride 2.4mg, Ammonium Nitrate 1.6mg, Hydrogen Phosphate Disodium 8.0mg, agar 15g, add distilled water to dilute to 1000mL, pH 7.2-7.4, sterilize at 121°C for 20min), incubate at 30°C for 14-20h;
[0039] b. Preparation of seed liquid: pick the activated strain and inoculate it in 2216 liquid medium (2216 liquid medium: formula and preparation are the same as above-mentioned 2216 solid medium, without adding agar), at 30° C., 150rpm shaking culture for 16-24 Liquid seeds are ob...
Embodiment 3
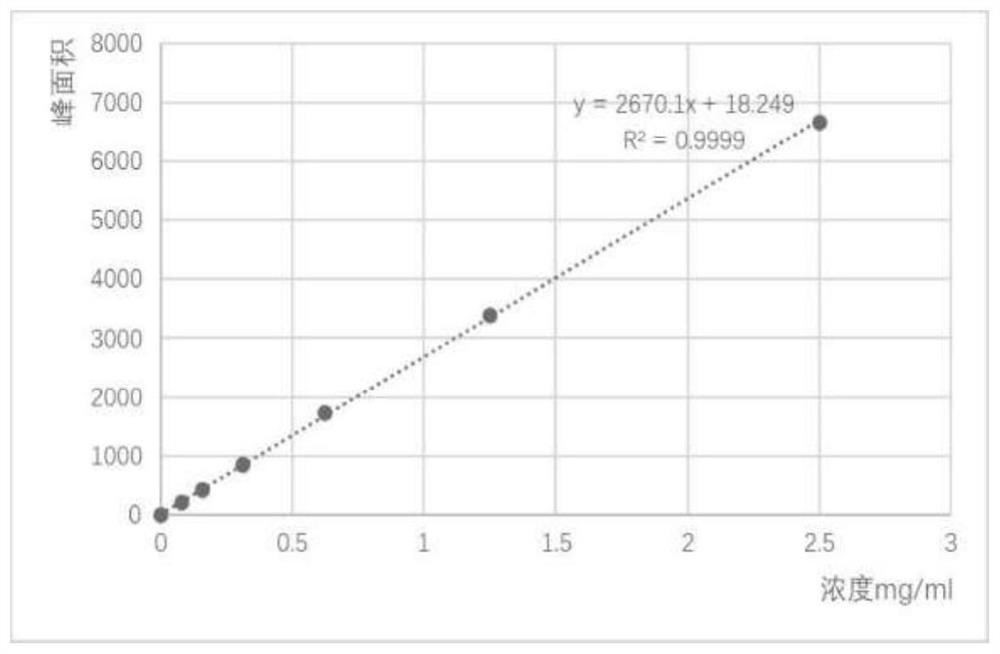
[0042] Example 3 Extraction of tetrahydropyrimidine from aseptic fermentation broth of Halomonas strain C2-1-M8
[0043] a. Centrifuge the fermentation broth in Example 2 at 12,000 rpm for 15 min, discard the supernatant, and collect the precipitated cells.
[0044] b. Wash the cells with dipotassium hydrogen phosphate-potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer (pH 7.0).
[0045] c. Centrifuge the liquid in b at 12000 rpm for 15 min, discard the supernatant, and collect the precipitate.
[0046] d. Add 2 ml of 80% ethanol to the precipitate obtained in c to suspend, and shake at room temperature overnight.
[0047] e. Centrifuge the overnight suspension in d for 15min under the condition of 12000rpm, collect the supernatant, the supernatant contains tetrahydropyrimidine, and the supernatant is determined by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) in the next step. sample.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com