Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Halomonas sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Soil conditioning, fertility-increasing and salt-reducing agent for sulfate-type saline soil and application thereof to sculellaria barbata planting
InactiveCN105038807AReduce Sulfate LevelsReduce total salt contentSoil lifting machinesOther chemical processesAcrylonitrilePhosphogypsum
The invention discloses a soil conditioning, fertility-increasing and salt-reducing agent for sulfate-type saline soil. The soil conditioning, fertility-increasing and salt-reducing agent comprises the following ingredients by mass: 42-50 parts of phosphogypsum, 15-18 parts of fulvic acid, 6-10 parts of straw, 4-11 parts of medical stone, 7-9 parts of bagasse, 10-20 parts of coal ash, 6-9 parts of aluminium sulfate, 3-8 parts of bean cake, 2-3 parts of hawthorn fruit powder, 0.5-0.8 part of a water-retaining agent, 0.6-0.9 part of lauryl ethoxy ammonium sulfate, 10-16 parts of starch-acrylonitrile, 15-18 parts of hollyhock powder, 10-13 parts of fennel powder and 0.01-0.05 part of halomonas halophiles. The invention further discloses application of the soil conditioning, fertility-increasing and salt-reducing agent to sculellaria barbata planting. The soil conditioning, fertility-increasing and salt-reducing agent and the application thereof to sculellaria barbata planting have the benefits that 12 months after sculellaria barbata planting, sulfate in 100 g of soil has the milliequivalent of 0.09-0.13, the available phosphorus content and the organic matter content of soil are both increased, and the soil moisture permeability and the soil water-retaining capacity are improved.
Owner:WEIFANG YOURONG IND
Novel holomonas and method for producing tetrahydropyrimidine by novel holomonas
ActiveCN103451137ALow synthetic capacityReduce corrosionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIndustrial fermentationNitrogen source
The invention discloses novel halomonas sp. HS-2255 which can be used for producing tetrahydropyrimidine, and a mutant strain thereof. The preservation number of the novel halomonas sp. HS-2255 is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 6248. The invention further discloses a culture method of the strain and a method for producing the tetrahydropyrimidine by fermentation. The strain has a higher tetrahydropyrimidine yield in a culture medium with a carbon source and a nitrogen source which are assimilable, and lower NaCl content, and the content of a byproduct hydroxyl tetrahydropyrimidine is lower, and therefore, the novel halomonas sp. HS-2255 can be used for industrial fermentation production of tetrahydropyrimidine, and has good application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Construction and application of polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01
ActiveCN102816729AGood characterIncrease the molar ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnology3-Hydroxypentanoic acid
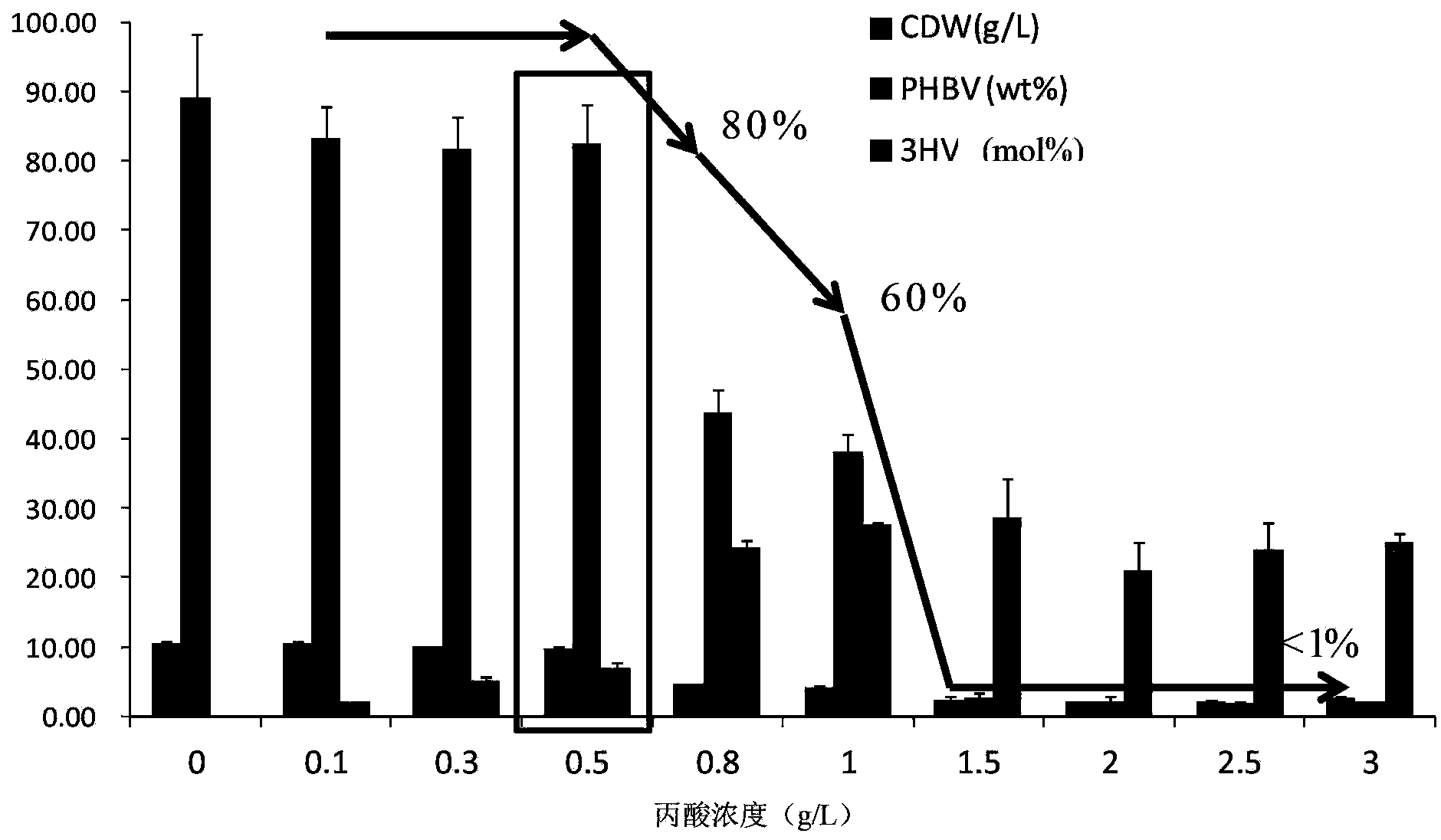
The invention discloses construction and application of a polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01. The invention provides a recombinant strain which is obtained by inactivating one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid in the Halomonas sp. TD01 used for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). The one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid are at least one selected from the group consisting of a coding gene for 2-methylcitrate synthetase, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 1, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 2 and a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 3. According to results of experiments in the invention, molecular modification is carried out on the Halomonas sp. TD01 to knock out 2-methylcitrate synthetase PrpC and three PHA digestive enzymes so as to obtain the novel recombinant strain, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) with more excellent material performance can be highly efficiently produced by utilizing propionic acid, and the proportion of 3-hydroxyvaleric acid monomers in the produced PHBV and the conversion rate of the substrate propionic acid are substantially improved.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD
Halomonas TF-1 and application thereof
ActiveCN105154367AEOR valueExtend hot wash cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesField testsFermentation
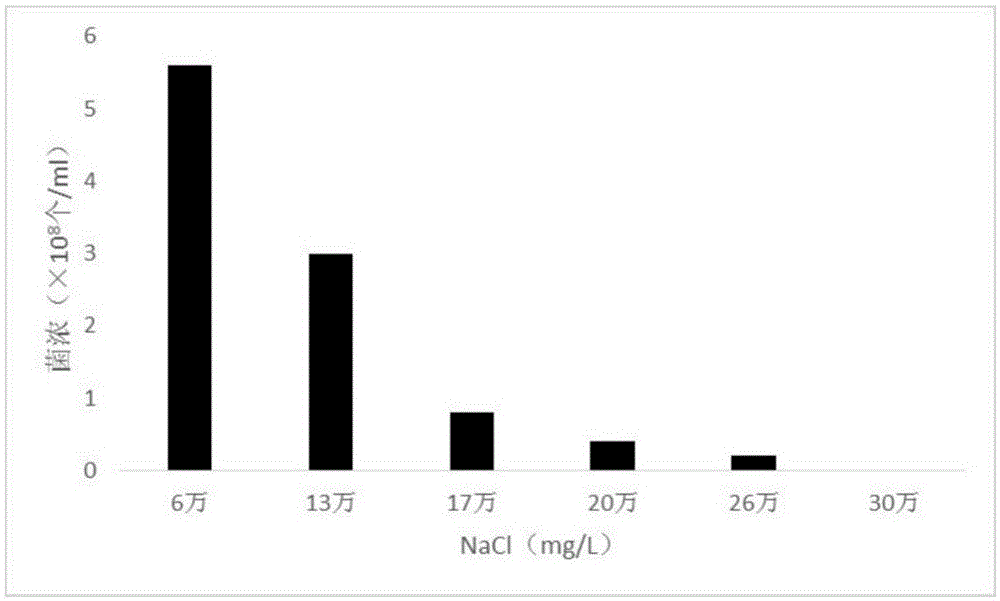
The invention discloses halomonas TF-1 and application thereof. The strain of the halomonas TF-1 is obtained from an oil-water well sample of the Shengli Oil Field under the conditions of 37 DEG C temperature and ordinary pressure by using a high-salt culture medium containing 6.0% of NaCl through enrichment culture screening, temperature-resistant salt-resistant performance investigation, repeated screening and passage, is named as halomonas sp.TF-1, and the preservation number of the halomonas TF-1 is CGMCC No.10619. The nutrient culture medium of the halomonas TF-1 is prepared from 0.3 mg / L of glucose, 0.3 mg / L of peptone, 0.3 mg / L of yeast powder, 0.27 mg / L of K2HPO4 and 6 mg / L sodium chloride, and a pH value is 7.0 -7.5. The halomonas TF-1 grows with crude oil as a carbon source, the bacterial concentration is greater than 5*108 per milliliter. The emulsification viscosity reduction rate of fermentation liquid is higher than 90%. The recovery ratio improved in a physical simulation experiment is higher than 15%. The average oil increase amount of microbial single well stimulation is more than 250 tons. An averagely prolonged hot washing period of microbial paraffin control is greater than 120d. Therefore, the halomonas TF-1 can be widely applied to a field test of microbial single well treatment.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Halomonas taeanensis and method for preparing flocculants by same
ActiveCN107641610AImprove flocculation abilityAccelerated settlementBacteriaMicroorganism based processesShort-necked clamSludge
The invention relates to the technical field of water treatment, in particular to Halomonas taeanensis and a method for preparing flocculants by the same. Bacterial strain Halomonas sp.GHF11 of the Halomonas taeanensis is separated and purified from sludge spitted by short-necked clams, cultures of the bacterial strain are subjected to amplification culture to obtain culture liquid, the culture liquid is subjected to fermenting culture to secrete exopolysaccharides, flocculation carriers are added into fermentation bacteria solutions in later period of fermentation to provide adhesion places for thalli, the thalli are adhered to cluster and settle, and the exopolysaccharides completely settle under the further action of ethyl alcohol. The exopolysaccharides secreted by the bacterial strainHalomonas sp.GHF11 has high flocculation effect; the carriers are added during preparation of the flocculants, exopolysaccharide sedimentation is accelerated, and consumption of the ethyl alcohol isreduced; the obtained flocculants have high flocculation capability and stable performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Halomonas sp. capable of degrading phenols and high-throughput screening method and application thereof
InactiveCN105087425ABacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPhenol
The invention discloses Halomonas sp. capable of degrading phenols and a high-throughput screening method and application thereof. The Halomonas sp. PH4-5 is preserved under CGMCC 10666. A bacterial liquid is cultured with a 48-pore deep-pore board, phenol concentration is measured by 96-pore microplate reader plate spectrophotometry based on 4-amino antipyrine colorimetry, moderately halophilic bacteria efficient in degrading phenols are screened from 43 environmental samples contaminated by high salinity and organics, the Halomonas sp. is separated and verified from an optimal flora E3, and a salt tolerant degrading mechanism of the Halomonas sp. is studied. Studying results show that quick screening of environmental degrading bacteria provides methodological basis and also provides technical support for the treatment of high-salinity phenolic wastewater.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for treating papermaking waste water by constructing artificial flora
InactiveCN101407362AHas the potential to develop applicationsWastewater dilutionWaste water treatment from plant processingBiological water/sewage treatmentFloraControllability
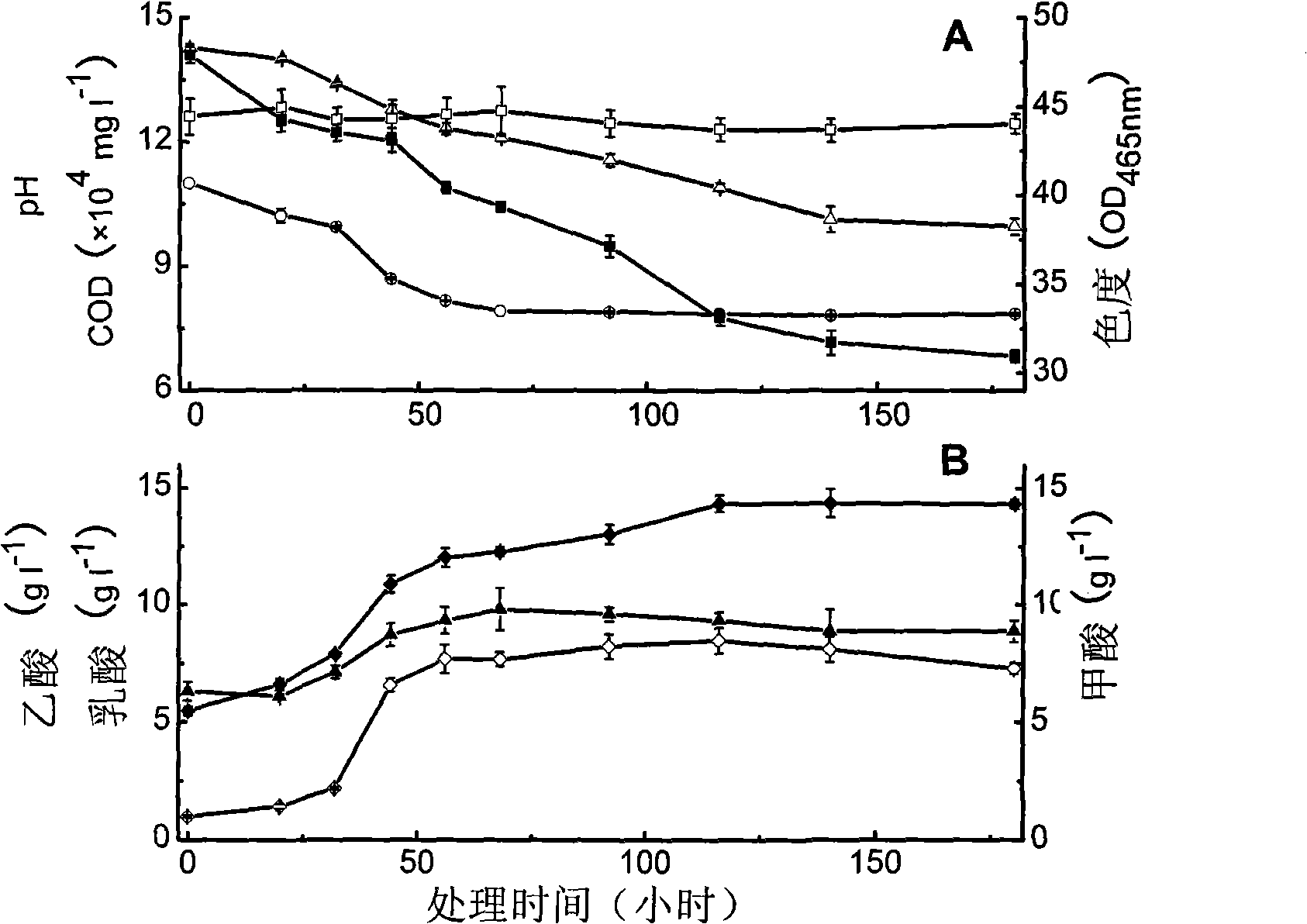
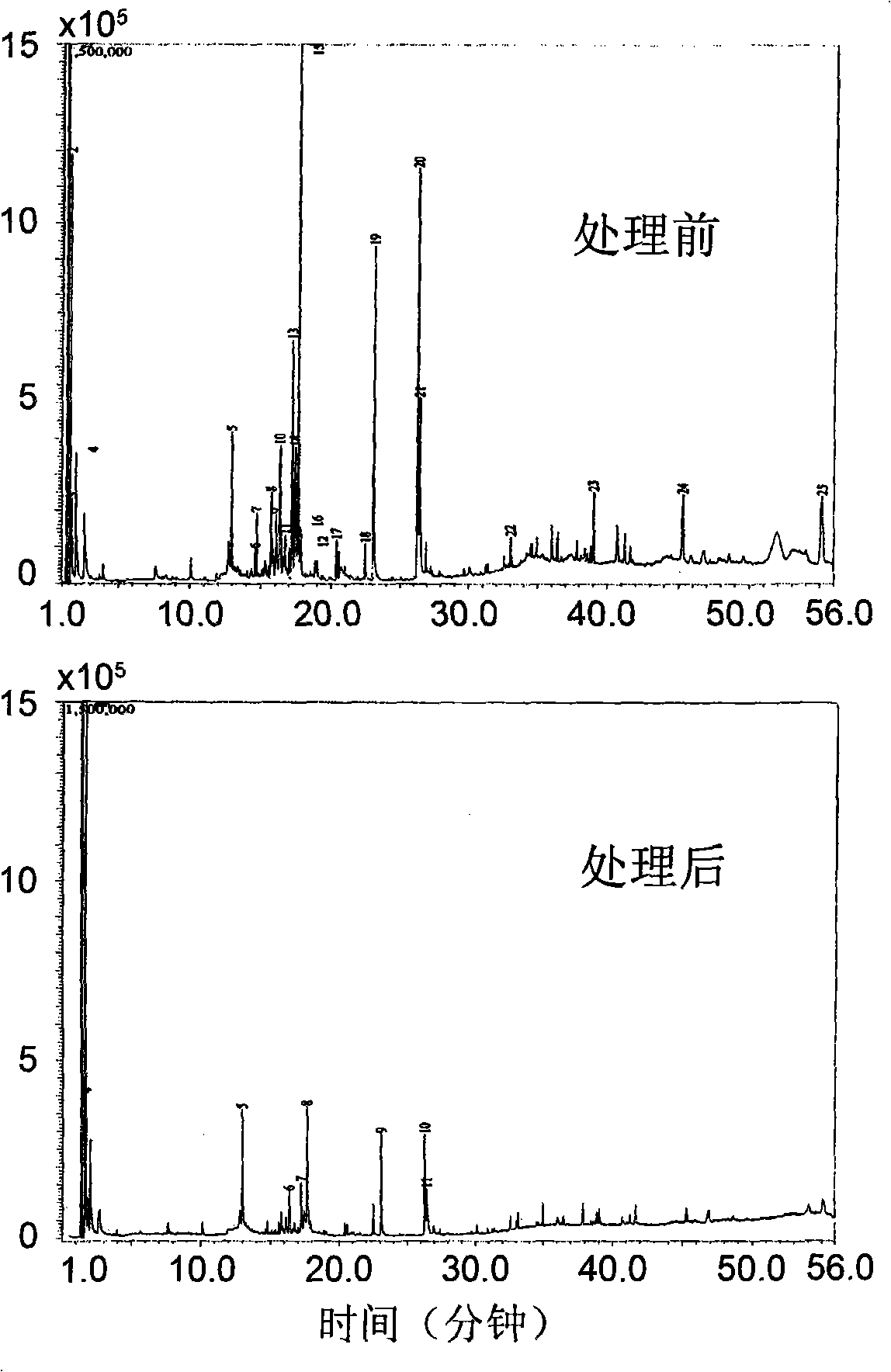
The invention discloses a method for processing paper-making waste water in the way of structuring artificial flora, including selecting more than two strains of Halomonas sp. flora and Bacillus sp. flora respectively for sterile culture to lead OD620nm to reach over 10.0 and then mixing the bacterial liquid by volume rate to structure the artificial flora; inoculating the paper-making waste water of pH being 9-11 and COD being 1,000-140,000mg l <-1> with the structured artificial flora, conducting stationary treatment for a certain time at 35-38 DEG C with intermittent stirring, in the treatment process, sampling at intervals to measure the pH, chroma and COD index of the paper-making waste water and finishing the treatment when the pH reduces to 7.0-8.8. The method is characterized by simple structure of the flora to be structured, obvious effect in direct treatment, strong controllability and repeatability and the like, and has great application prospect in the treatment aspects of waster water such as the control over the paper-making waste water.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for preparing heavy metal adsorbent by utilizing marine salt monoucleosis strains
ActiveCN107574184AImprove adsorption capacityImprove adsorption efficiencyOther chemical processesWater contaminantsAlcoholSorbent
The invention relates to the technical field of water treatment, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a heavy metal adsorbent by utilizing marine salt monoucleosis strains. The method comprises the following steps: performing enlarged cultivation and fermentation cultivation on the marine salt monoucleosis strains Halomonas sp.GHF11 to prepare fermented bacteria liquid; then, removing thalli from the fermented bacteria liquid, and performing centrifuging treatment to obtain supernatant; precipitating on two sides through ethyl alcohol to obtain high-purity exopolysaccharide; mixing the exopolysaccharide with agar and starch to obtain the heavy metal adsorbent. According to the method provided by the invention, the exopolysaccharide is produced by screening the marine salt monoucleosis strains Halomonas sp.GHF11; the adsorption capacity of the obtained exopolysaccharide is high; the exopolysaccharide is solidified through the agar and the starch to obtain the heavy metaladsorbent which can be directly added into drinking water; the heavy metal adsorbent is high in heavy metal adsorption efficiency and stable in performance, and is safe and harmless.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Moderate holophilic bacteria for degradation of phenylacetic acid and bacteria agent therefrom
A degrading bacteria BYS-1 for degrading phenylacetic acid under hyperhaline condition is disclosed. It is halomonas sp, belongs to moderate halophil. Its characteristics are G-, nemaline, (0.8-1.0)X(1.5-2.5)mum, flagellate, opal, semi-transparent. Contact enzyme and oxidase are positive, and it can hydrolyze starch and ferment glucose, reduce NO3- and growth under condition of 0-3.4M NaCl. It can be used in waste water biochemical treating system by phenylacetic acid.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
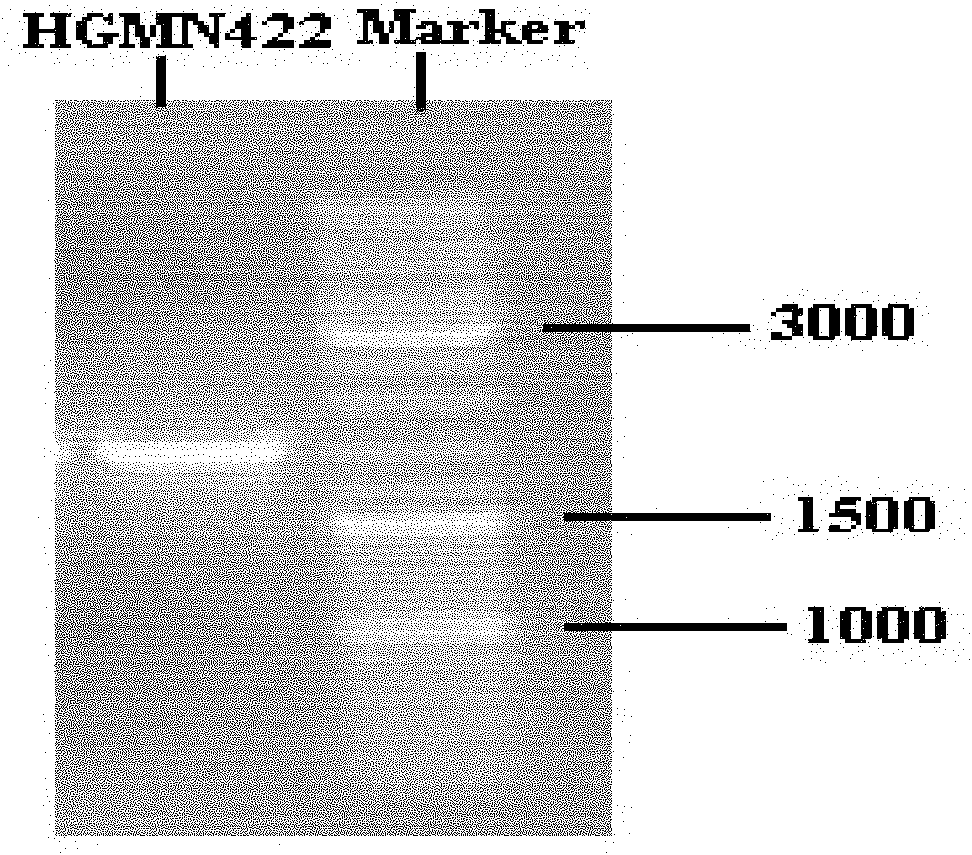
Marine aerobic denitrifying halomonas strain HGMN422 and application thereof
InactiveCN102154143AEfficient removalEfficient denitrification capacityBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesHigh concentrationMariculture
The invention discloses a marine aerobic denitrifying halomonas strain which belongs to the Halomonas (Halomonas sp.), wherein the preservation name of the marine aerobic denitrifying halomonas is Halomonas HGMN422; the preservation company of the marine aerobic denitrifying halomonas is the China center for type culture collection; the preservation data of the marine aerobic denitrifying halomonas is on Aug 28th in 2009; and the preservation number of the marine aerobic denitrifying halomonas is CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO.M209186. The strain has high-efficiency denitrifying capability under the aerobic condition, can be used for rapidly and effectively removing nitrite nitrogen (NO2--N) and nitrate nitrogen (NO3--N) in sea polluted by inorganic nitrogen, has no toxic and pathogenic effects on organisms cultured in the sea and has the characteristics of safety, environment protection and high efficiency for removing pollution of high-concentration inorganic nitrogen in the mariculture environment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for preparing flocculating agents by using compound strains
ActiveCN107641609AImprove flocculation abilityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFlocculationShort-necked clam
The invention relates to the technical field of water treatment, in particular to a method for preparing flocculating agents by using compound strains. The compound strains refer to Halomonas sp. GHF1and Psychrobacter sp. GHF2, the two strains are obtained through separation and purification from mud fluid spitted out by short-necked clam and are respectively subjected to amplification culture tobe prepared into two kinds of strain liquid, the strain liquid is mixed in a liquid medium for co-fermentation culture, flocculation carriers are added in fermented liquid in late fermentation, and exopolysaccharides is enabled to be settled completely by adding of ethyl alcohol. The strains are compounded and fermented and are cooperative with each other during fermentation, the strains are highin activity and yield of the exopolysaccharides, and the flocculation carriers are added in late fermentation; the strains are clumped on the flocculation carriers, settling of the exopolysaccharidesis promoted, use of the ethyl alcohol is reduced, and flocculation capacity of the flocculating agents is high and stable in performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Method for preparing heavy metal high-efficiency adsorbent by utilizing compound bacterial agent
ActiveCN107574219AVigorousIncrease productionOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSorbentSludge
The invention relates to the technical field of water treatment, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a heavy metal high-efficiency adsorbent by utilizing a compound bacterial agent. The compound bacterial agent comprises marine salt monoucleosis strains Halomonas sp.GHF11 and marine psychrobacter psychrophilus strains Psychrobacter sp .GHF2; the two types of strains are both obtained by separating and purifying sludge liquid which is spit by ruditapes philippinarum; the two types of the strains are compounded and fermented after being subjected to enlarged cultivation respectively; the two types of the strains are synergic to strengthen each other in fermenting and cultivating processes; the activity of the strains is high; the yield of produced exopolysaccharide is high; the exopolysaccharide is separated by dialyzing a fermented fermenting bacteria liquid, removing part of culture medium components, performing centrifuging and performing ethanol precipitation twice, and then is prepared into the heavy metal adsorbent by curing through agar and starch; the heavy metal adsorbent is good in adsorption effect, high in adsorption efficiency and stable in performance, is safe and harmless, and can be directly added into drinking water.
Owner:北京美胜同创科技发展有限公司
Salt-tolerant halomonas strain and application thereof in field of water purification
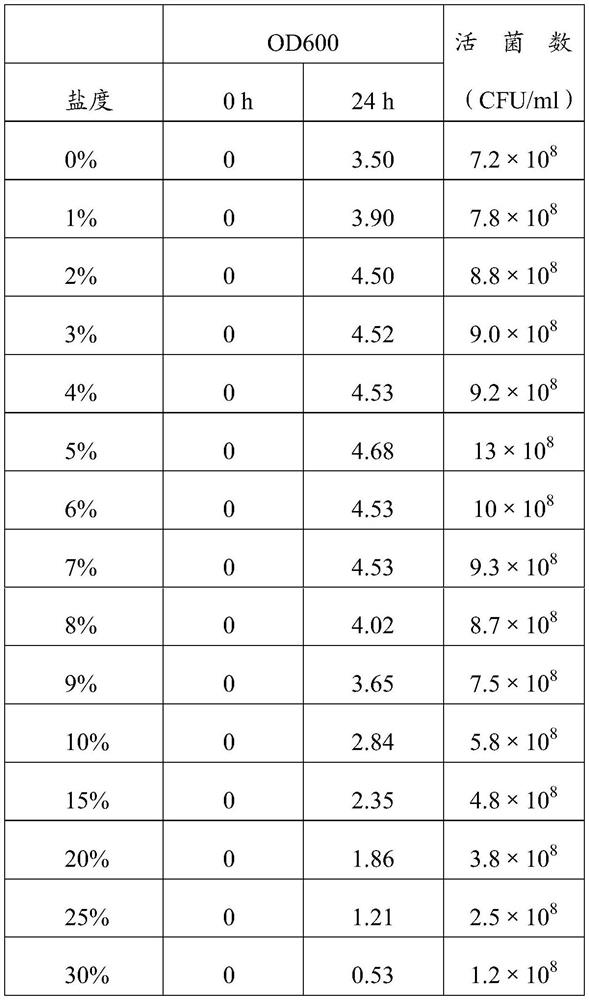
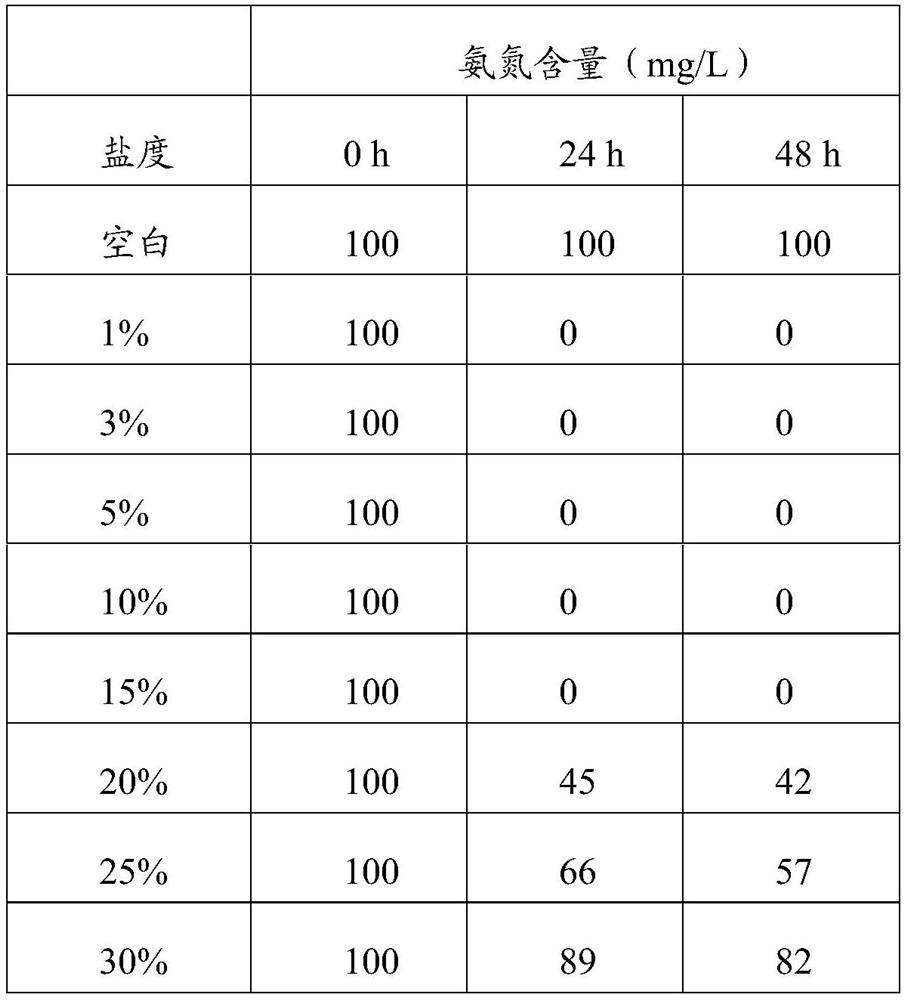
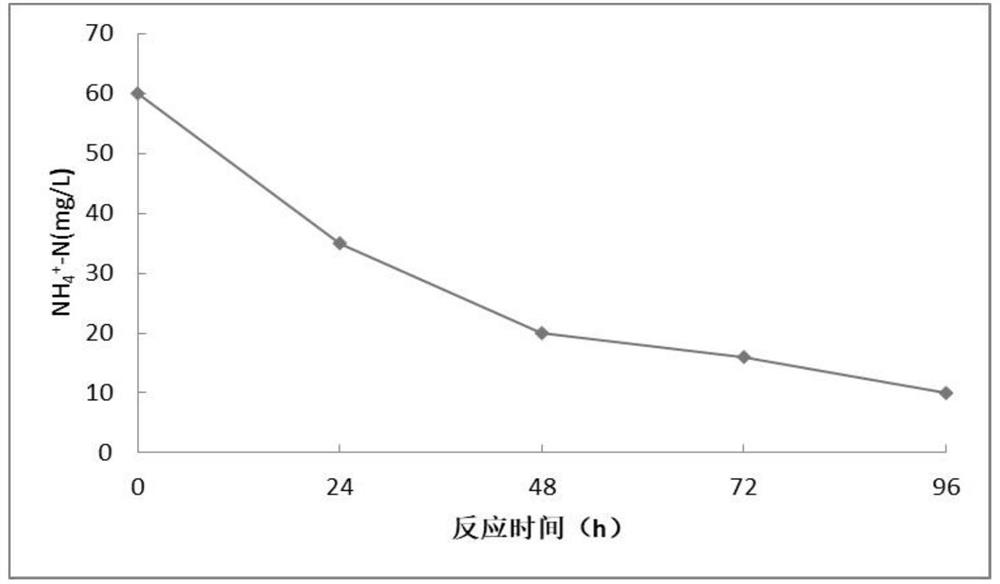
The invention relates to a salt-tolerant Halomonas sp. Strain and application thereof in the field of water purification, the strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), and the preservation number is CGMCC No.24127. The strain has good salt tolerance, the optimum growth salinity is 5%, under laboratory conditions, the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 100% in 24 h when the salinity is 15% or below, and the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 100% when the salinity is 15% or below. The strain can resist high ammonia nitrogen concentration and high temperature, the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 89.1% within 72 h for the ammonia nitrogen concentration of 3000 ppm, and when the initial ammonia nitrogen concentration is 100 ppm, the ammonia nitrogen degradation rate reaches 100% within 24 h at the temperature of 30-40 DEG C.
Owner:青岛蔚蓝赛德生物科技有限公司
Treatment method for radical curing black liquor of straw pulp from alkaline process
InactiveCN101003409AThe treatment process is feasibleThe process route is matureTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesWater/sewage treatment by heatingBacillus licheniformisPapermaking
This invention provides a method for treating black liquor from alkali-process straw pulp, and the application of the byproduct. The method comprises: sending fresh black liquor from alkali-process straw pulp (pH is 12-13) into an anaerobic bioreactor containing Bacillus licheniformis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Halomonas sp., performing anaerobic biochemical treatment for 10-15 h to obtain active black liquor (pH is 7.5-8.0), aerating, evaporating, concentrating, and spray-granulating to obtain additive for fertilizer and feed, or industrial byproduct of petrochemical industry and power generation industry. Alternatively, the active black liquor can be directly deodored, sterilized by heating, and sprayed onto crops for improving the quality and increasing the yield, or added into feed for breeding chicks and pigs for stimulating the growth and accelerating the breeding speed. Compared with the present technique, the method can eliminate the environmental pollution of black liquor discharged from papermaking industry, and brings profit to medium and small papermaking plants that use straw as the raw material.
Owner:王照华
Halomonas with aerobic denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation functions and application thereof
ActiveCN112551692AImprove recovery rateGrow fastWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesHalomonas salinaNitration
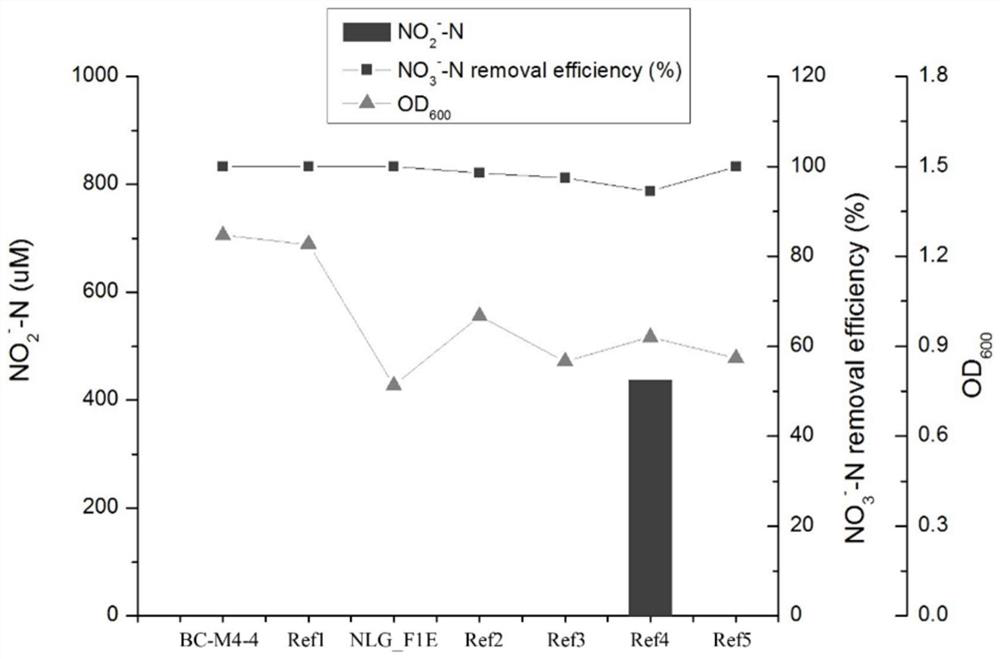
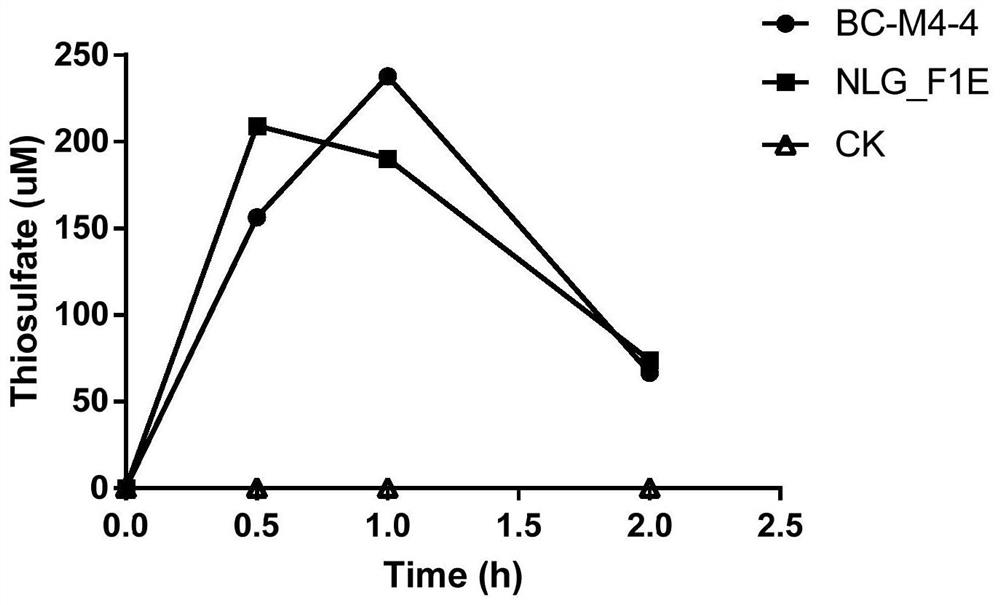
The invention discloses halomonas with aerobic denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation functions and application thereof , and belongs to the technical field of microorganism application. The invention provides two strains of halomonas sp. MCCC 1A17488 and MCCC 1A13718 with aerobic denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation functions, and the preservation numbers of the halomonas sp. MCCC 1A17488 and the MCCC 1A13718 are as follows: GDMCC No:60985 and GDMCC No:60984. The halomonas sp. MCCC 1A17488 and MCCC 1A13718 can be applied to nitrogen and sulfur removal, can be suitable for biological nitrogen removal treatment of various nitrogen-containing wastewater, has efficient denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation capacity under aerobic and anoxic conditions, can rapidly and efficiently remove nitrate, nitrite, ammonia nitrogen, sulfide and the like, and has good application prospects in the biological nitrogen and sulfur removal of sewage, sludge, sedimentsor culture water bodies.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MINIST OF NATURAL RESOURCES +1
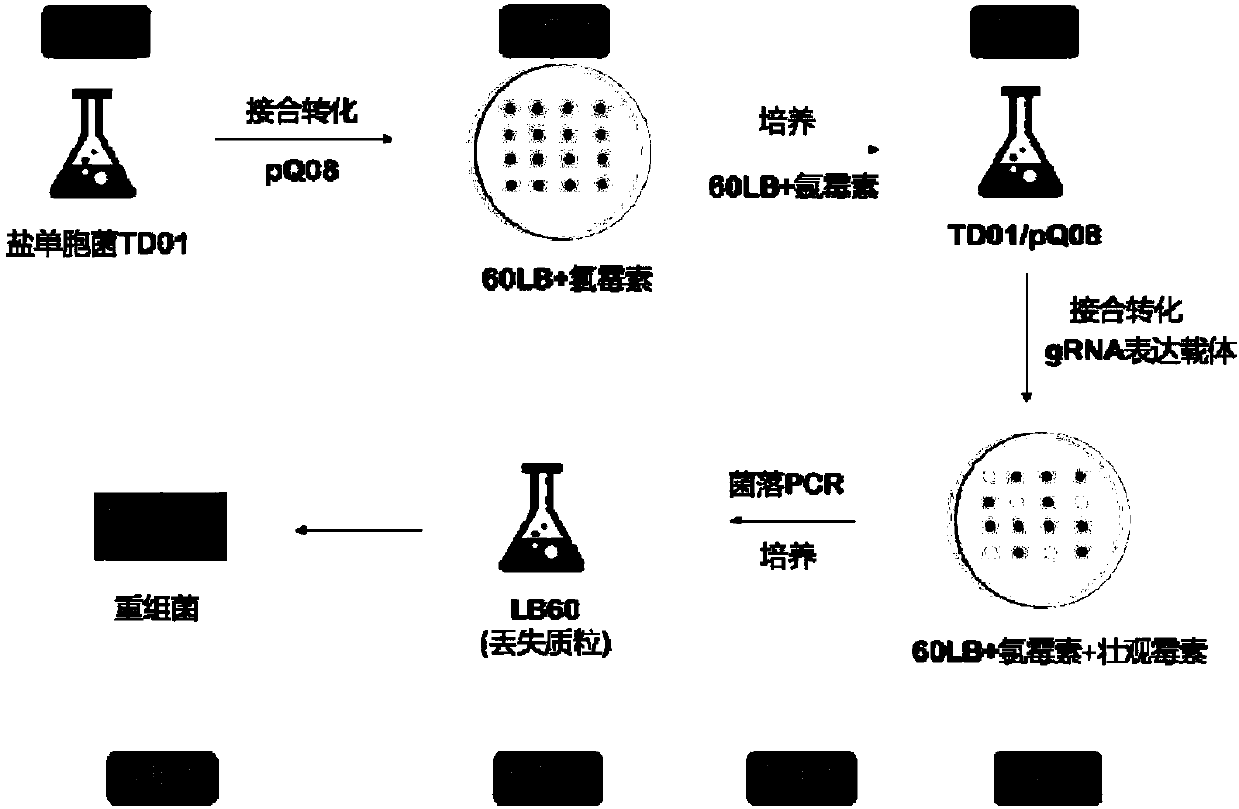
Vector combination for quick gene editing of halomonas sp. and application of vector combination
ActiveCN109971778AImprove transformation efficiencySimplify the step-by-step processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlasmid VectorRecombinase
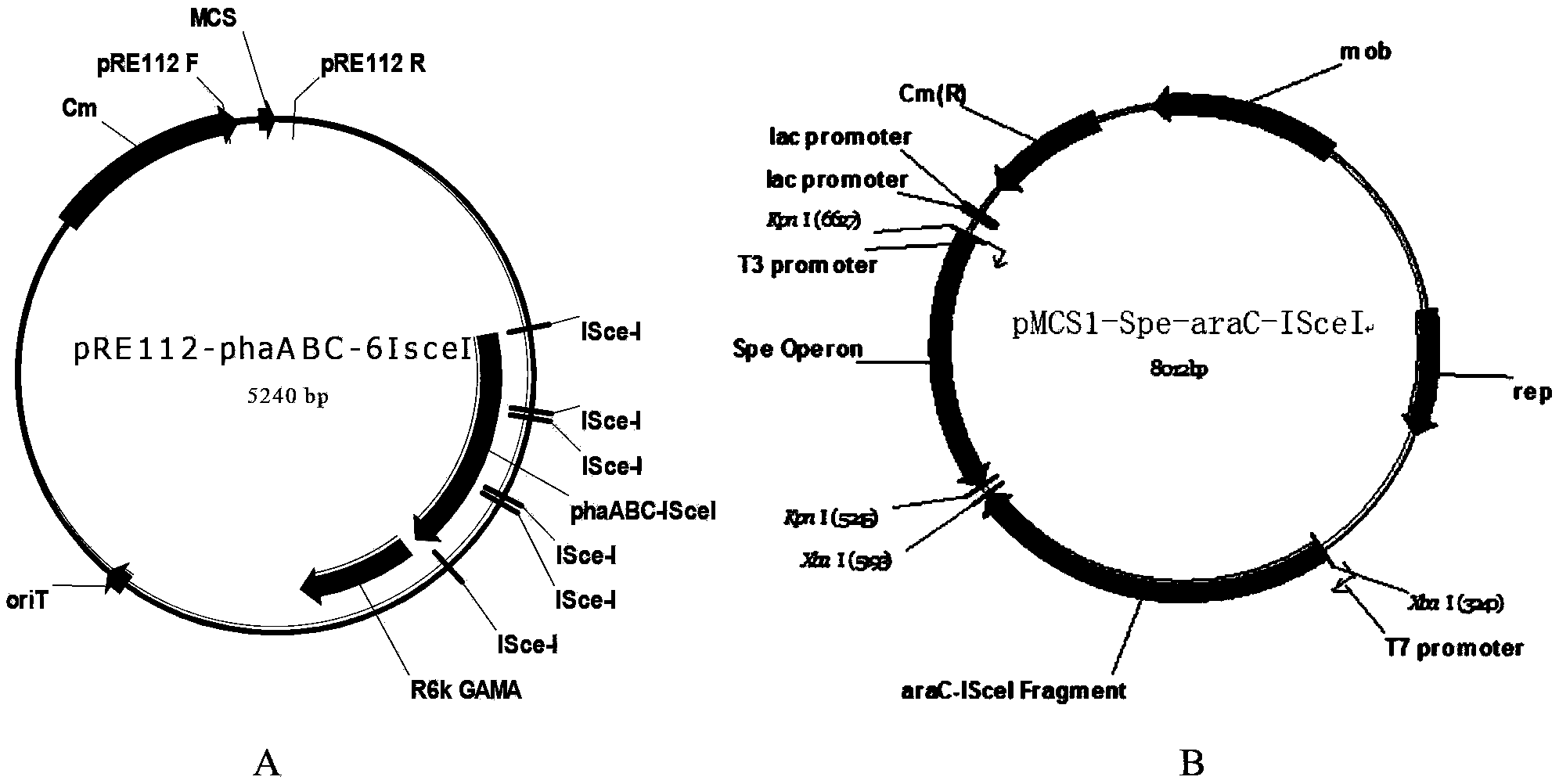
The invention provides a vector combination for quick gene editing of halomonas sp. and an application of the vector combination. The vector combination comprises a cas9 expression vector and an sgRNAexpression vector, wherein the cas9 expression vector is obtained by introducing cas9 genes into a plasmid vector, and the cas9 expression vector does not contain lambda-RED recombinase genes. Compared with a conventional gene editing means for halomonas sp., the vector combination is quicker, only 8 days are needed for the flow for performing gene editing once, and the reforming efficiency of the halomonas sp. is greatly improved. In addition, the vector combination is used for the halomonas sp., and a gene editing method based on CRISPR / Cas9 is used for performing continuous editing (knockout and insertion) of a plurality of genes, so that the required time can be greatly shortened.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD +1
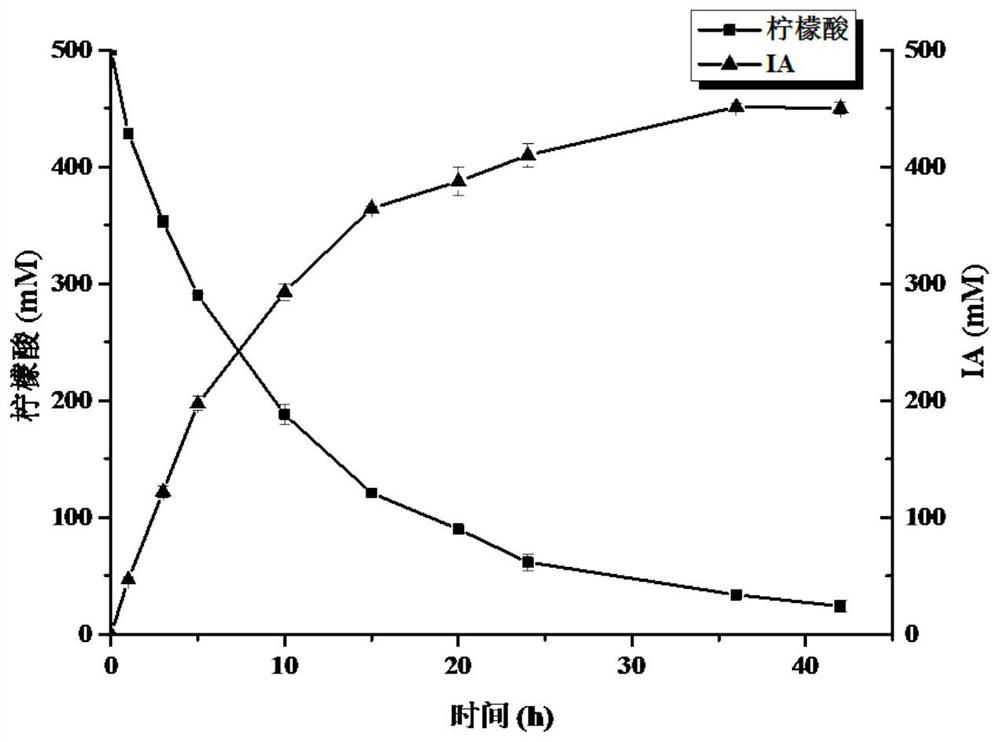
Recombinant halomonas, construction method of recombinant halomonas and application of recombinant halomonas in preparation of itaconic acid by catalyzing citric acid
ActiveCN113481136AEasy to purifyShort reaction cycleBacteriaTransferasesHalomonas salinaItaconic acid
The invention discloses recombinant halomonas, a construction method of the recombinant halomonas and application of the recombinant halomonas to preparation of itaconic acid by catalyzing citric acid. The construction method of the recombinant halomonas is characterized by comprising the following steps of: integrating an Mmp1 RNA polymerase expression unit on a wild type halomonas sp. TD01 genome, and replacing an initiation codon ATG of an icd gene of the genome with TTG to obtain Halomonas sp. TD2.0; sequentially introducing a high-copy expression vector pN59-PMmp1-RBS-cadA-acn and a low-copy expression vector pN85-PMmp1-RBS-GroESL-PMmp1-RBS-acn into the Halomonas sp. TD2.0; and obtaining the recombinant halomonas sp. IA02. The itaconic acid can be efficiently prepared through cell catalysis of the bacterium. The recombinant halomonas is short in period, simple, convenient and high in yield.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
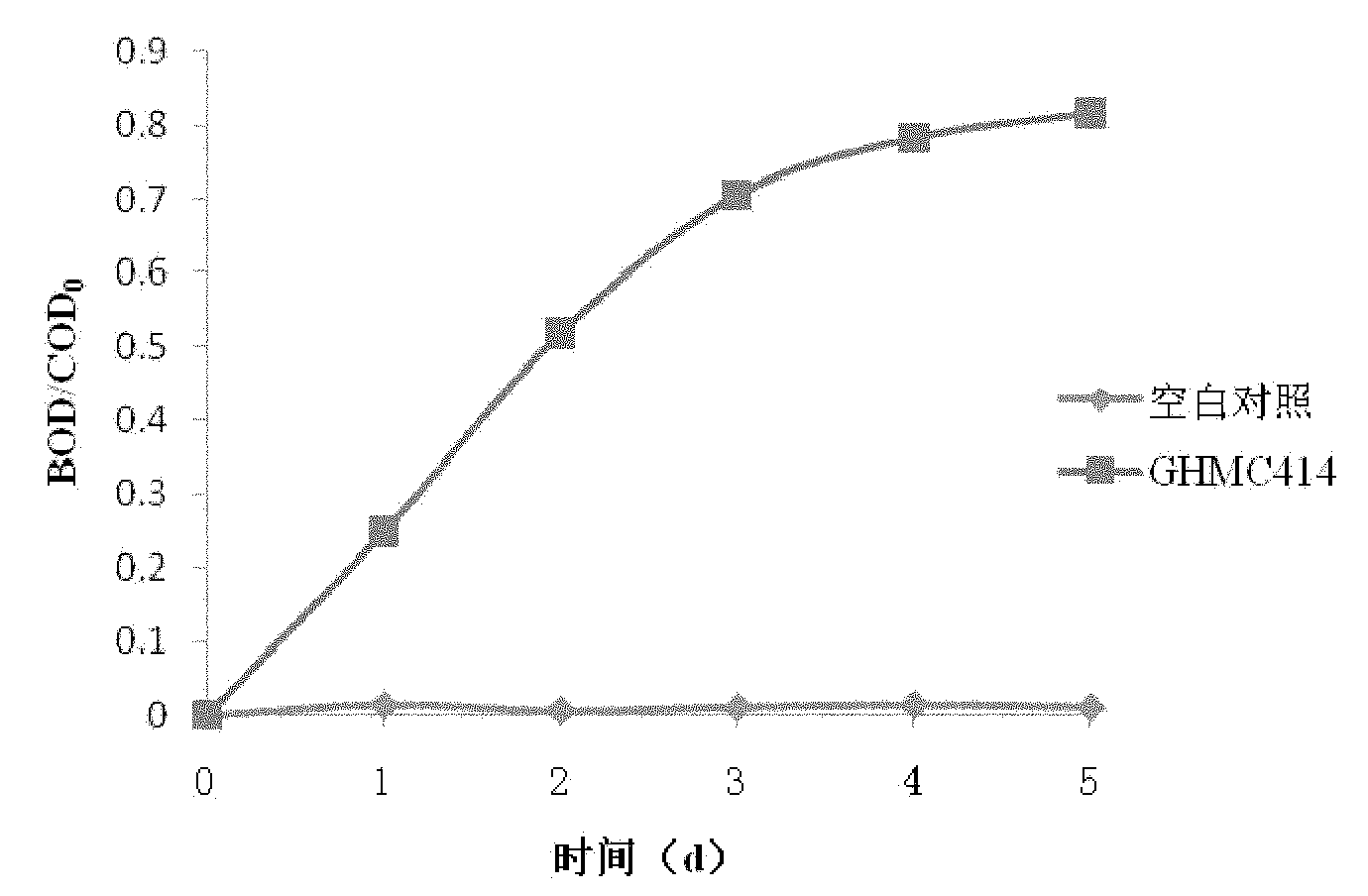
Marine organic matter degradation Halomonas sp. strain GHMC414 and application thereof
InactiveCN102168031APromote degradationBacteriaSeawater treatmentHigh concentrationMarine aquaculture
The invention discloses a marine organic matter degradation Halomonas sp. strain which belongs to Halomonas sp. The preservation name is Halomonas sp. GHMC414, the preservation unit is the China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation date is August 28th, 2009, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M209183. The strain has efficient organic matter degradation ability, can be used for quickly and efficiently removing organic matters in organic matter polluted sea water and does not have toxic or pathogenic actions on marine aquaculture organisms. The Halomonas sp. strain has the characteristics of safety, environmental protection and high efficiency for removing high-concentration organic matters in the marine aquaculture environment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
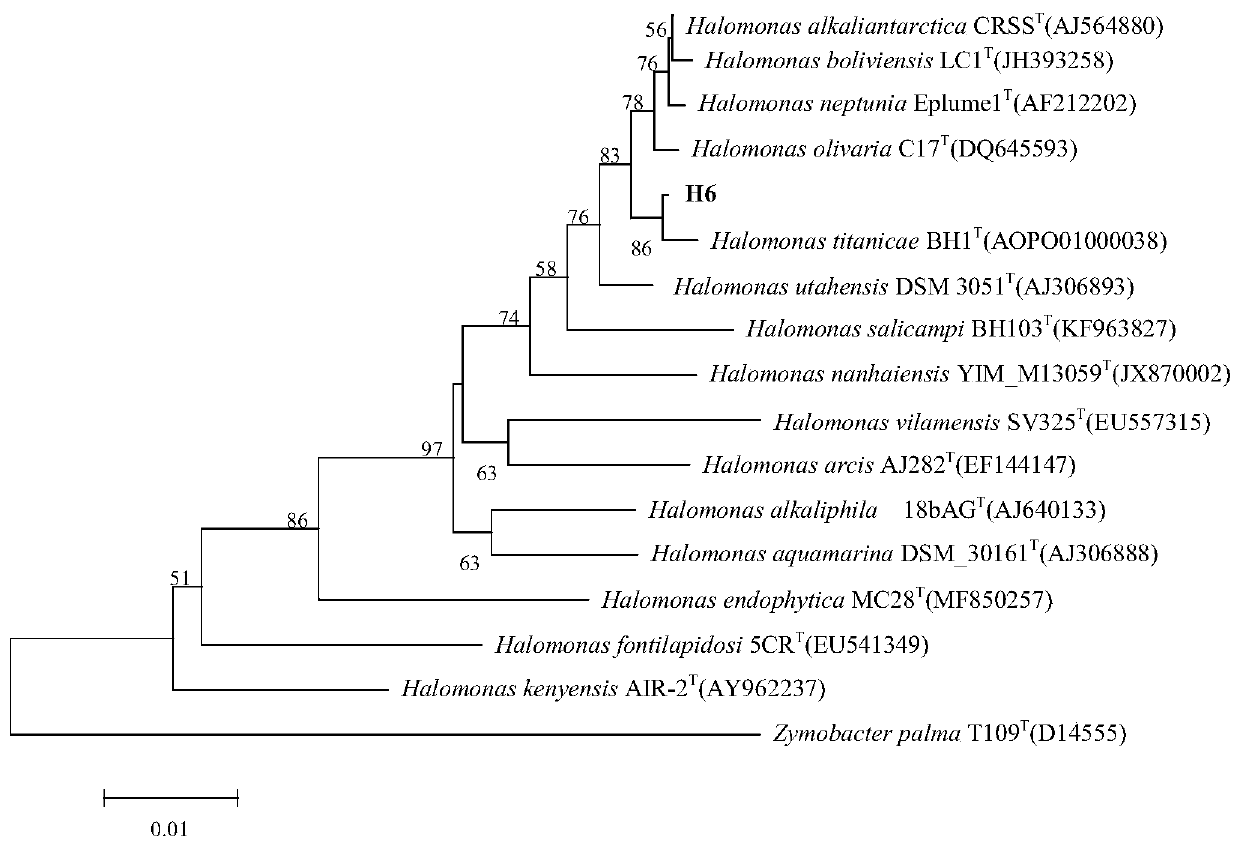
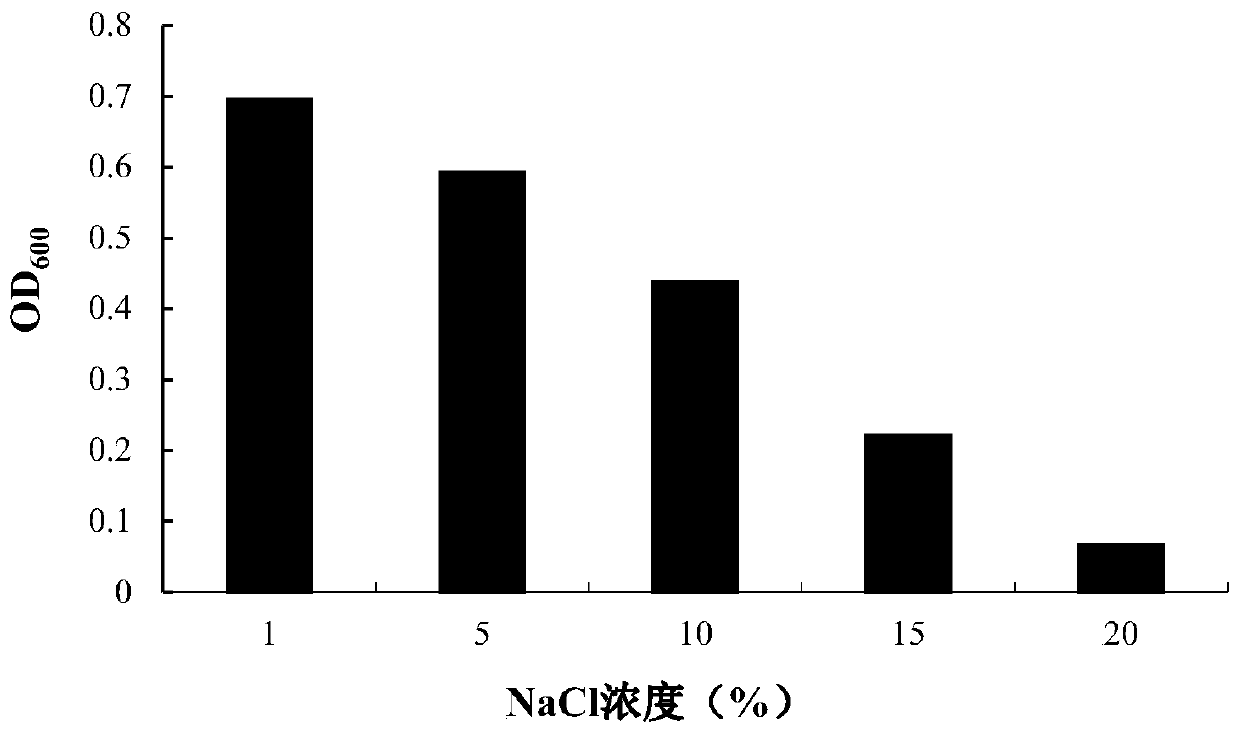
Halomonas strain H6, composition and application thereof in salt tolerance and growth promoting
ActiveCN109929777AAddressing Adaptive IssuesGood effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyPesticide pollution
The invention relates to a novel strain of Halomonas sp. obtained by isolation and screening, which has the ability to secrete indoleacetic acid and produce ACC deaminase. The strain can grow well under low temperature or high temperature and salt and alkali conditions. The composition of the strain and a microbial fertilizer prepared by a liquid fermentation technique alleviate the salt-alkali stress caused by the salt on the crops and promote the growth of the crop under salt stress. The novel strain or the composition provided by the invention is suitable for special geographical and climatic conditions and improves the physical and chemical properties of the soil and the ability to fertilize, effectively utilizes environmental resources and reduces pesticide pollution. The novel strainor the composition has the characteristics of good effect, short cycle and good environmental compatibility, and has important practical value for solving the current soil salinization.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
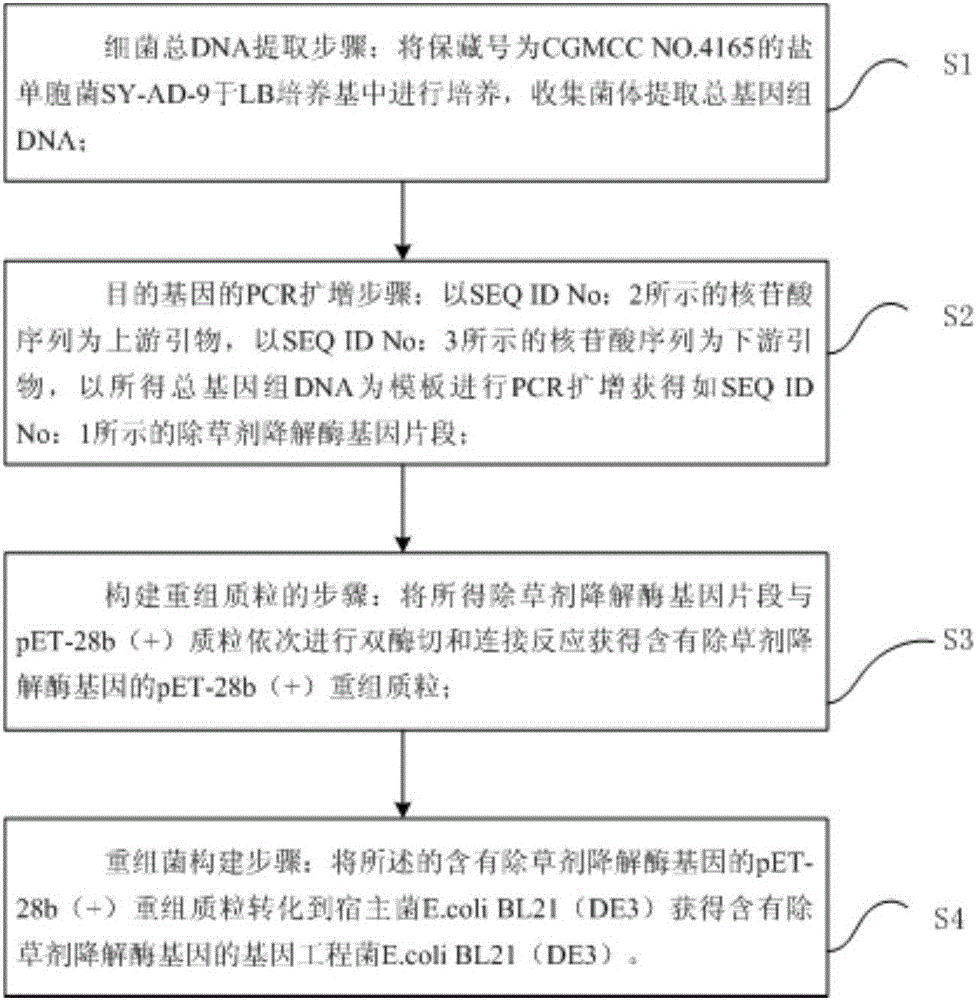
Herbicide degrading enzyme gene, engineering bacterium and application of engineering bacterium
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, and in particular to an atrazine herbicide degrading enzyme gene, an engineering bacterium comprising the same and application of the engineering bacterium. The herbicide degrading enzyme gene is derived from Halomonas sp.SY-AD-9 of efficiently-degraded atrazine, and triazine hydrolase, an expression product of the herbicide degrading enzyme gene can degrade the atrazine efficiently. The engineering bacterium comprising the herbicide degrading enzyme gene can express herbicide degrading enzymes (the triazine hydrolase) efficiently and can be applied to environmental bioremediation.
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF CHEM IND
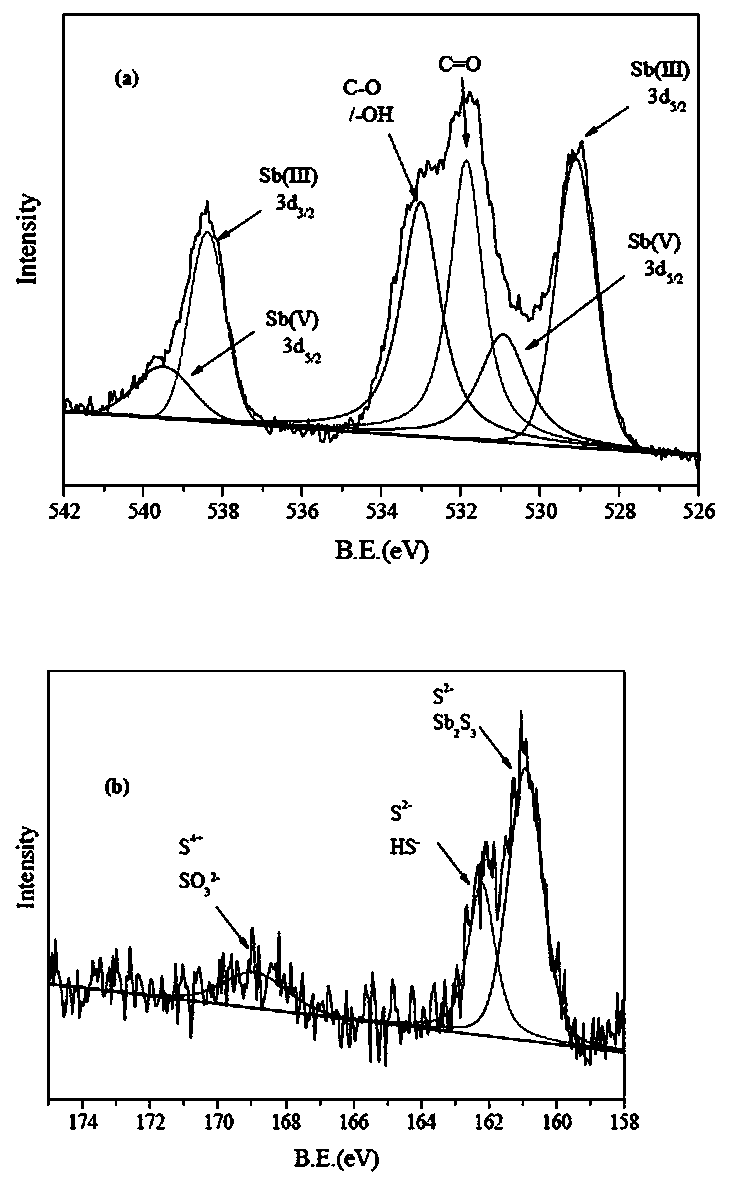
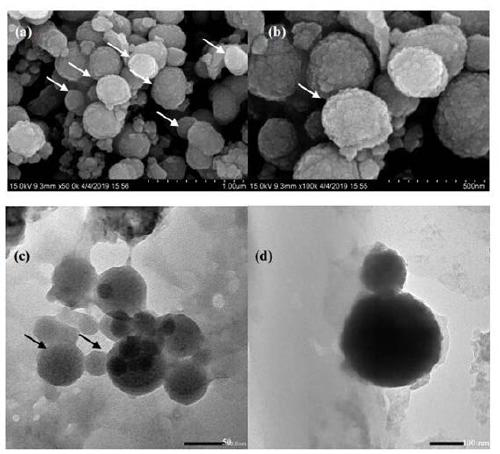
Microorganism for preparing broccoli-shaped antimony sulfide and application of microorganism
ActiveCN110257311AAccelerated photodegradationLow technical costBacteriaWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSulfite saltSodium sulfite
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental engineering water treatment and particularly relates to a microorganism for preparing broccoli-shaped antimony sulfide and application of the microorganism. The microorganism refers to marine Halomonas sp.X3 which is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection located in Wuhan University on May 30, 2019, and a preservation number is CCTCC M 2019409. The strain is an indigenous microorganism screened from marine sediments and can be used for preparing nano antimony sulfide by adopting potassium pyroantimonate and sodium thiosulfate or sodium sulfite as precursors. Nano antimony sulfide prepared from the microorganism is broccoli shaped and can serve as a photocatalyst for accelerating light degradation of azo dye compounds. Currently, antimony sulfide is prepared according to chemical methods mostly. Shaped-controllable antimony sulfide is prepared from the microorganism for the first time, and high innovativeness is realized.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Marine-microbe-sourced low-temperature beta-galactosidase, and coding gene thereof and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of marine biotechnology, and provides a marine-microbe-sourced low-temperature beta-galactosidase, which is obtained by fermentation culturing and purification of a marine halomonas sp. strain P6009-1 obtained by the applicant previously. The marine halomonas sp. strain P6009-1 is cultured and separated from seawater in East China Sea areas, and has a collection number of CCTCC No: M2011001. Under a temperature of 0 DEG C, a capacity of the enzyme in catalyzing lactose hydrolysis is 20% of a maximal activity, such that good low-temperature performance is shown. The invention further provides a coding gene of beta-galactosidase, and an application of beta-galactosidase in decomposing milk lactose.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Improvement agent for red mud in-situ soil and application method thereof
PendingCN114015455AAchieve improvementLower pHCalcareous fertilisersAgriculture tools and machinesMicroorganismMicrobial agent
The invention provides an improvement agent for red mud in-situ soil and an application method thereof, the improvement agent comprises a main agent and an auxiliary agent, the main agent comprises inorganic acid waste and organic acid waste; the auxiliary agent comprises an organic fertilizer, an inorganic fertilizer and a microbial agent; the microbial agent comprises halomonas, Nesterensis and bacillus. The application method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a premix; step S2, preparing a neutralized substance; s3, forming a red mud improvement layer; and S4, activating and diluting the microbial agent, and spraying the microbial agent on the red mud improvement layer. The red mud environment in which plants can normally grow and develop is established, positive evolution of the red mud towards the soil direction is promoted, and thus ecological restoration and ecological reconstruction of the red mud storage yard are achieved, and the problem that the red mud storage yard returns alkali and salt to hinder vegetation growth is solved.
Owner:CHINA NONFERROUS METAL CHANGSHA SURVEY & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Cheap synthesis of biodegradable mulching film from straws and illegal cooking oil by using halomonas sp ZY-1
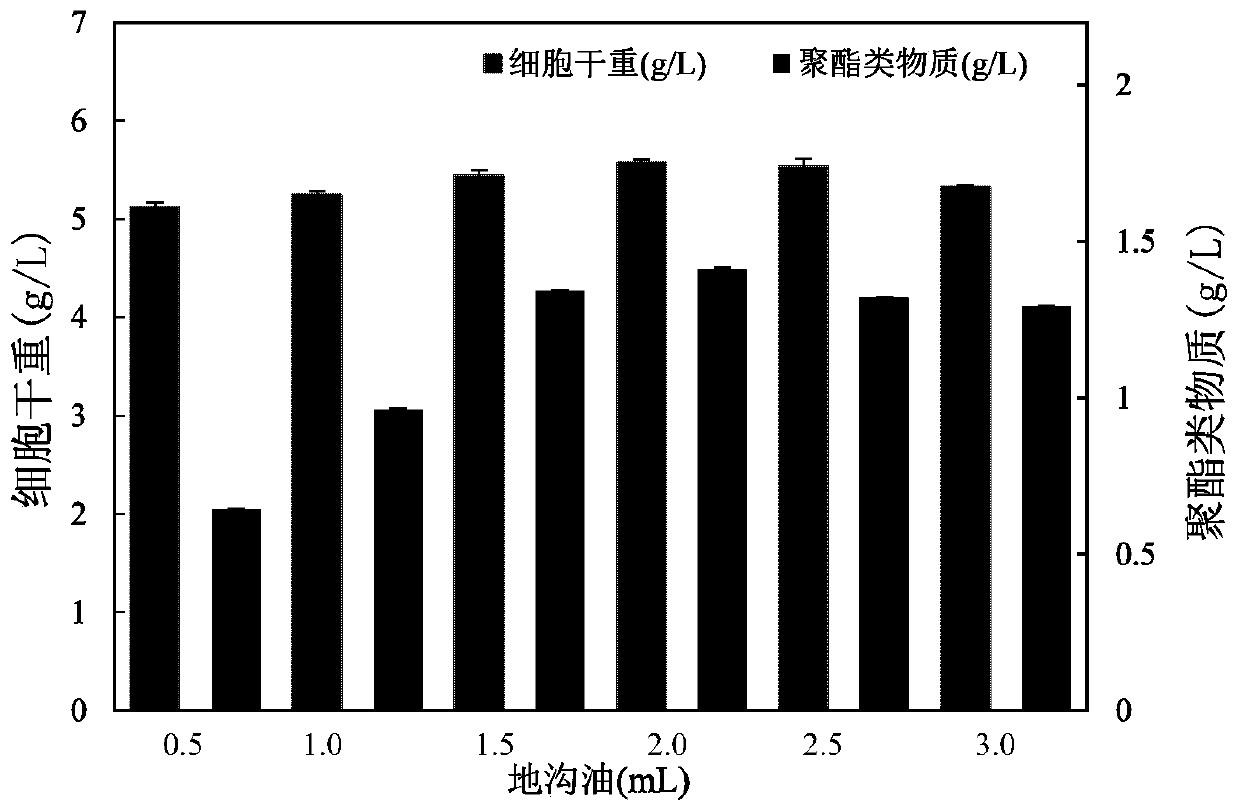
PendingCN111378254AReduce manufacturing costPromote degradationBacteriaClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyHalomonas salina
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a biodegradable mulching film from straws and illegal cooking oil by using halomonas sp.ZY-1 under an open and non-sterile condition. Straws are treated to obtain a straw supernatant, and an MS culture medium with the volume ratio of the straw supernatant to illegal cooking oil being 35: 1-40: 1 is prepared. In a sequencing batch reactor (SBR), Halomonas sp.ZY-1 is subjected to aerobic culture with the unsterilized straw supernatant and illegal cooking oil MS culture medium to obtain thalli, and intracellular polyester substances are extracted.Polyester substances are further modified to obtain the mulching film with the tensile strength of 16-18 MPa, the mulching film is deeply buried in cultivated land soil with the depth of 20-30 cm, the 35d weight reduction rate is 40%-50%, and the 35d weight reduction rate is 0.3%-0.5% when the mulching film is placed in dry air. Under the condition that halophilic bacteria are not sterilized, wastes are utilized to synthesize the biological mulching film, so that the production cost is reduced to the maximum extent, and technical support is provided for realizing green ecological cycle and agricultural sustainable development.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Halomonas 100-16-2 and method for preparing poly-3-hydroxybutyrate with same
The invention provides a halomonas 100-16-2 and method for preparing poly-3-hydroxybutyrate with the same and relates to technical field of production of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate. The halomonas 100-16-2has a Latin name of Halomonas sp. with a preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 13730. Through gradually amplified cultivation, the halomonas 100-16-2 finally achieves fermentation at 2000-4000 L, and after fermentation is completed, the content of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate is 80% of the dry weight of stain cells, and the dry weight of fermented bacteria is 30 g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Compound microbial agent and preparation method therefor and treatment method for high-salinity nitrogen-containing wastewater
The invention belongs to the field of microbial engineering, in particular to a compound microbial agent and a preparation method therefor and a treatment method for high-salinity nitrogen-containingwastewater. The compound microbial agent comprises mixed bacteria, a microbial growth promoter and an adsorption carrier; the mixed bacteria and the microbial growth promoter are loaded onto the adsorption carrier; and the mixed bacteria include monilia tropicalis, pichia pastoris, bacillus badius, bacillus cereus, nitrobacteriaceae and halomonas sp. The compound microbial agent can obviously theresistance of biology to salinity, can be used for improving the effect of biochemical treatment of the high-salinity nitrogen-containing wastewater, and has a very broad application prospect.
Owner:山东海景天环保科技股份公司
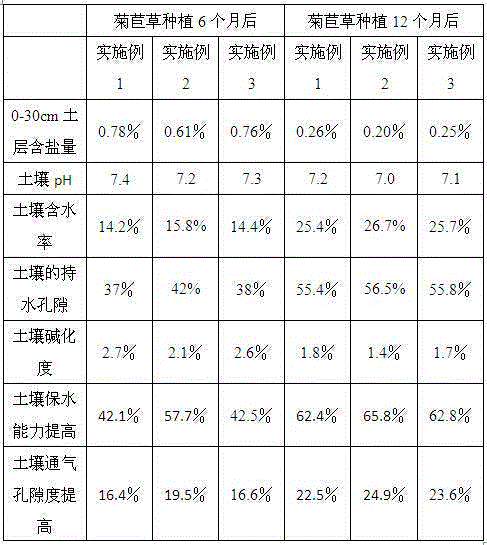
Halophilic bacteria-containing soil modifier for saline land, and applications of halophilic bacteria-containing soil modifier in cichorium intybus l planting
InactiveCN105018096AReduce salt contentLower pHOther chemical processesOrganic fertilisersAlkali soilSalicylic acid
The present invention discloses a halophilic bacteria-containing soil modifier for saline land, wherein the raw materials comprise, by mass, 8-13 parts of fulvic acid, 4-6 parts of emulsified asphalt, 0.2-0.5 part of salicylic acid, 1-3 parts of malic acid, 5-10 parts of hullessbarley residue, 5-10 parts of bentonite, 5-10 parts of a urea-formaldehyde resin, 1-5 parts of stachybotrys atra, 3-7 parts of halomonas halophilic bacteria, 0.5-1.2 parts of halophilic methane bacteria, 4-6 parts of melilotus officinalis l powder, 7-12 parts of puccinelia chinampoensis, and 0.5-0.9 part of a water retention agent. The invention further discloses applications of the modifier in cichorium intybus l planting. According to the present invention, 12 months after the cichorium intybus l is planted, the salt content in the 0-30 cm soil layer is 0.20-0.26%, the water content and the water holding porosity of the soil respectively are 25.4-26.7% and 55.4-56.5%, and the water retention capacity and the aeration porosity of the soil are significantly improved.
Owner:WEIFANG YOURONG IND
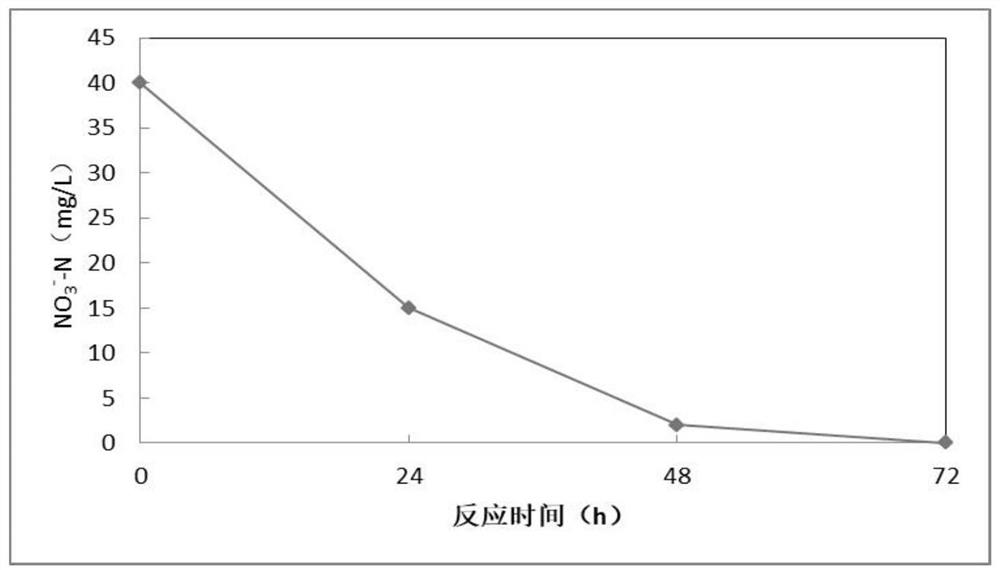
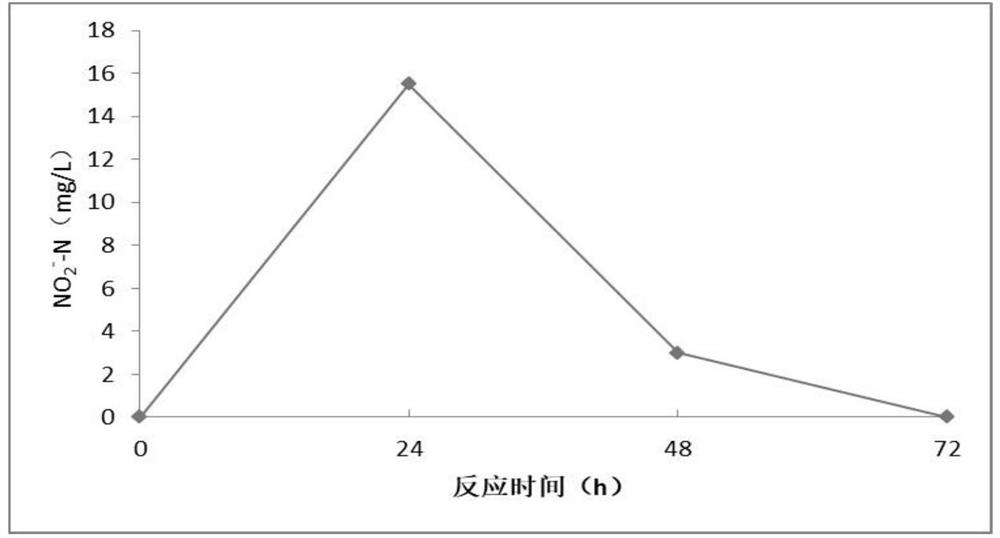
Halomonas with nitrification and denitrification effects and application thereof
ActiveCN111925960AImprove denitrification activityBacteriaWater contaminantsHalomonas salinaMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of nitrogen pollution, and provides halomonas DY-S025GC05 with nitrification and denitrification effects and application of the halomonas DY-S025GC05. TheLatin of the halomonas DY-S025GC05 with nitrification and denitrification effects is Halomonas sp., the strain has been preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, Yard 1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the preservation date is May 19th, 2020, and the preservation number is CGMCCNO.19847. The halomonas DY-S025GC05 provided by the invention has double activities of nitrification and denitrification at the same time, and the conversion of nitrification and denitrification functions can be realized by adjusting the oxygen content.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA +1
Construction and application of polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01
ActiveCN102816729BGood characterIncrease the molar ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxybutyric acidBiotechnology
The invention discloses construction and application of a polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01. The invention provides a recombinant strain which is obtained by inactivating one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid in the Halomonas sp. TD01 used for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). The one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid are at least one selected from the group consisting of a coding gene for 2-methylcitrate synthetase, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 1, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 2 and a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 3. According to results of experiments in the invention, molecular modification is carried out on the Halomonas sp. TD01 to knock out 2-methylcitrate synthetase PrpC and three PHA digestive enzymes so as to obtain the novel recombinant strain, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) with more excellent material performance can be highly efficiently produced by utilizing propionic acid, and the proportion of 3-hydroxyvaleric acid monomers in the produced PHBV and the conversion rate of the substrate propionic acid are substantially improved.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD
Application of Liyun type fructan
ActiveCN114271277AFood production safetyNo pollution in the processBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyOrganosolv
The invention provides an application of a Liyun type fructan. The fructosan provided by the invention is a Liyun type fructosan synthesized from Halomonas sp. AAD6 (T), and the fructosan is non-toxic and harmless, does not have antibacterial activity, but can activate the immunity of plants so as to improve the capability of resisting gibberellic disease and banded sclerotial blight. Meanwhile, the Liyun type fructan can be dissolved in water, no organic solvent needs to be added when the Liyun type fructan is used, and the requirement of green pesticides is met.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com