Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1255 results about "Volume rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
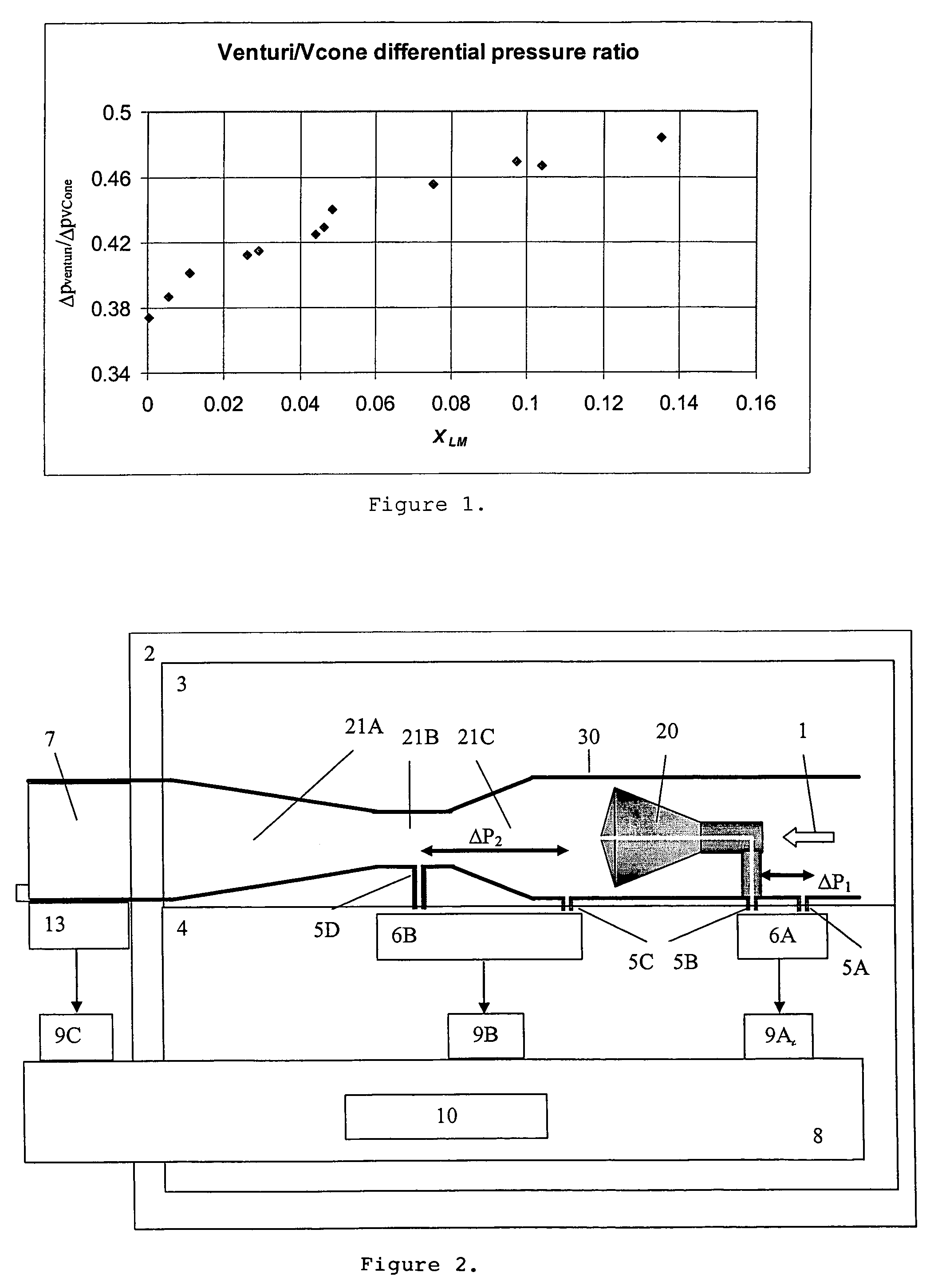
In physics and engineering, in particular fluid dynamics and hydrometry, the volumetric flow rate (also known as volume flow rate, rate of fluid flow or volume velocity) is the volume of fluid which passes per unit time; usually represented by the symbol Q (sometimes V̇). The SI unit is m3/s (cubic metres per second).
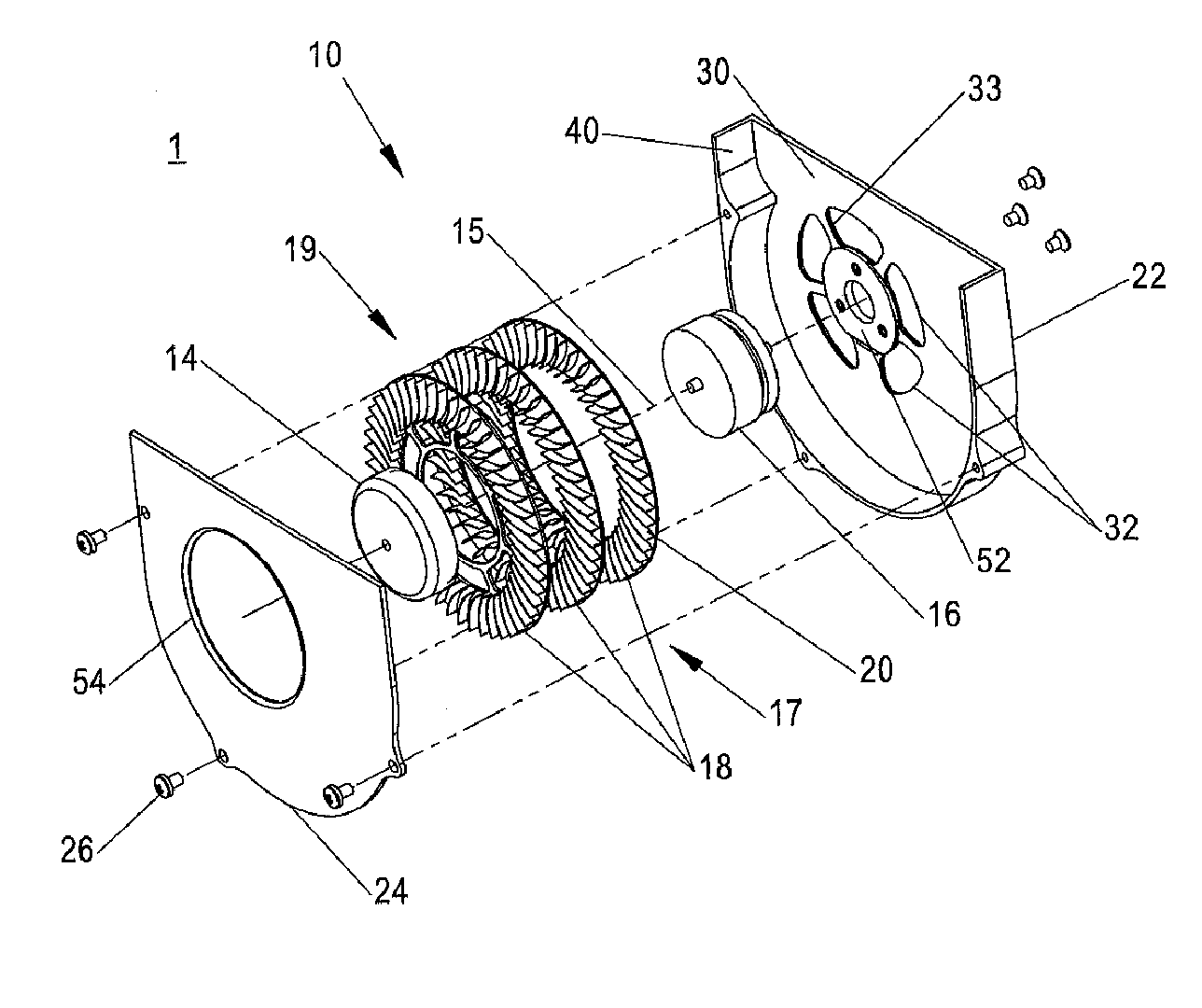
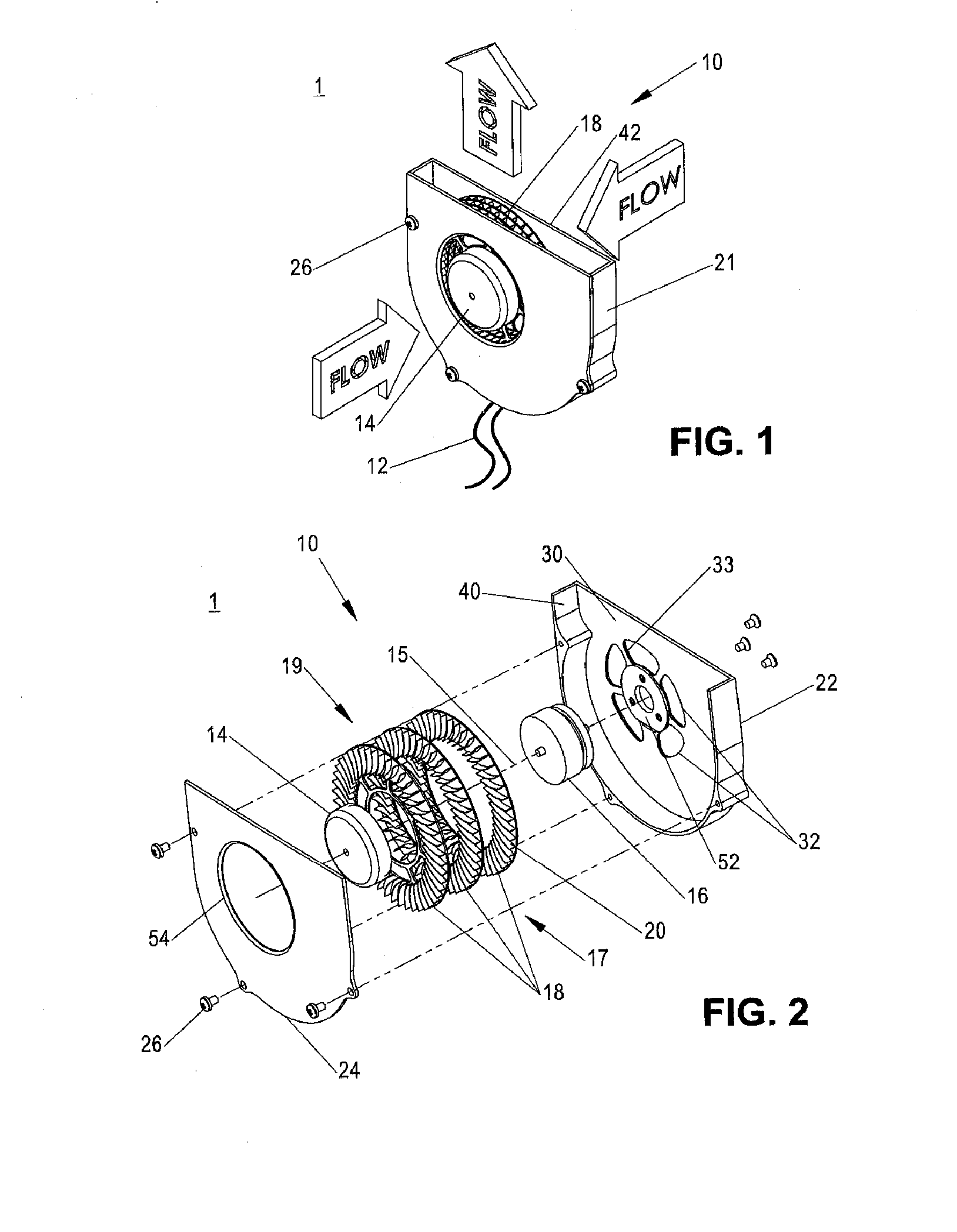
Flow meter
Various embodiments of the present invention provide a flow meter device having a laser Doppler anemometer (LDA) which measures the instantaneous center line velocity of fluid flow in a pipe. The flow meter may process the instantaneous velocity so obtained to compute the volumetric flow rate, mass rate, and / or other flow characteristics (e.g., as instantaneous quantities and / or integrated over a time interval) The flow meter may use an electronic processing method. The electronic processing method may provide essentially an exact solution to the Navier-Stokes equations for any periodically oscillating flow.
Owner:COMBUSTION DYNAMICS
Method for Depositing Conformal Amorphous Carbon Film by Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD)
ActiveUS20100093187A1Good shape retentionHighly conformalSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerNitrogen gas
Methods and apparatus for depositing an amorphous carbon layer on a substrate are provided. In one embodiment, a deposition process includes positioning a substrate in a substrate processing chamber, introducing a hydrocarbon source having a carbon to hydrogen atom ratio of greater than 1:2 into the processing chamber, introducing a plasma initiating gas selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, helium, argon, nitrogen, and combinations thereof into the processing chamber, with the hydrocarbon source having a volumetric flow rate to plasma initiating gas volumetric flow rate ratio of 1:2 or greater, generating a plasma in the processing chamber, and forming a conformal amorphous carbon layer on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
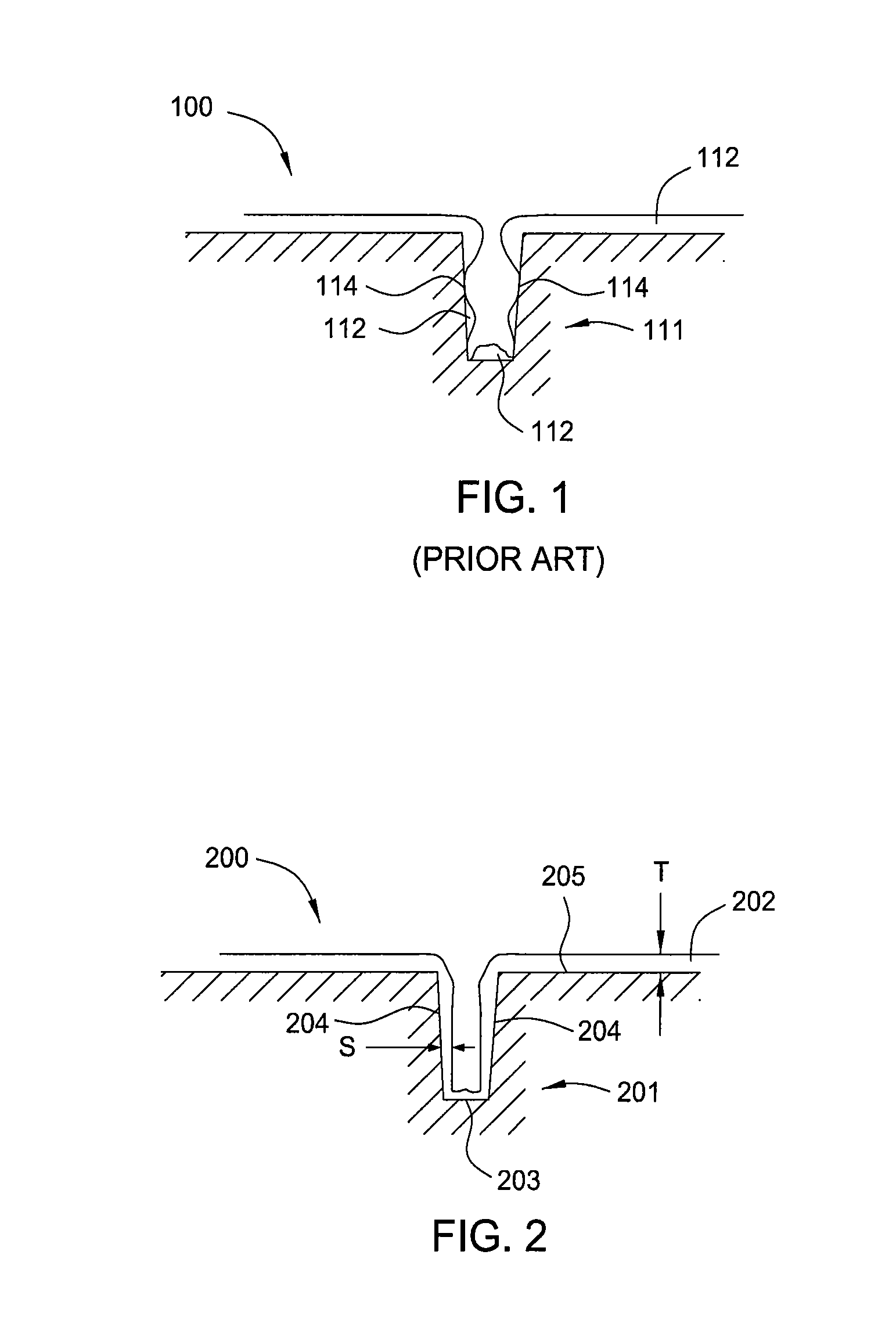
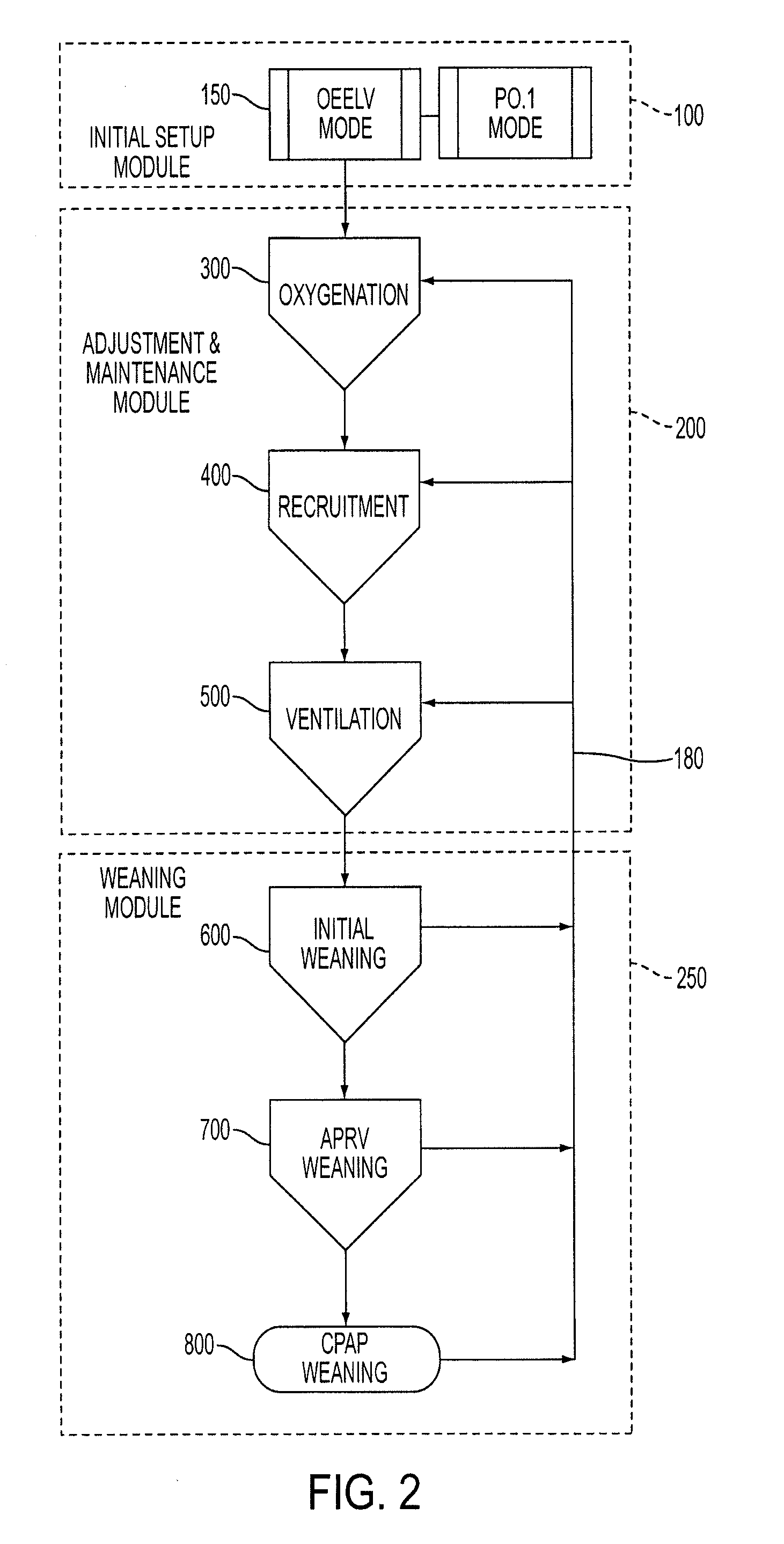
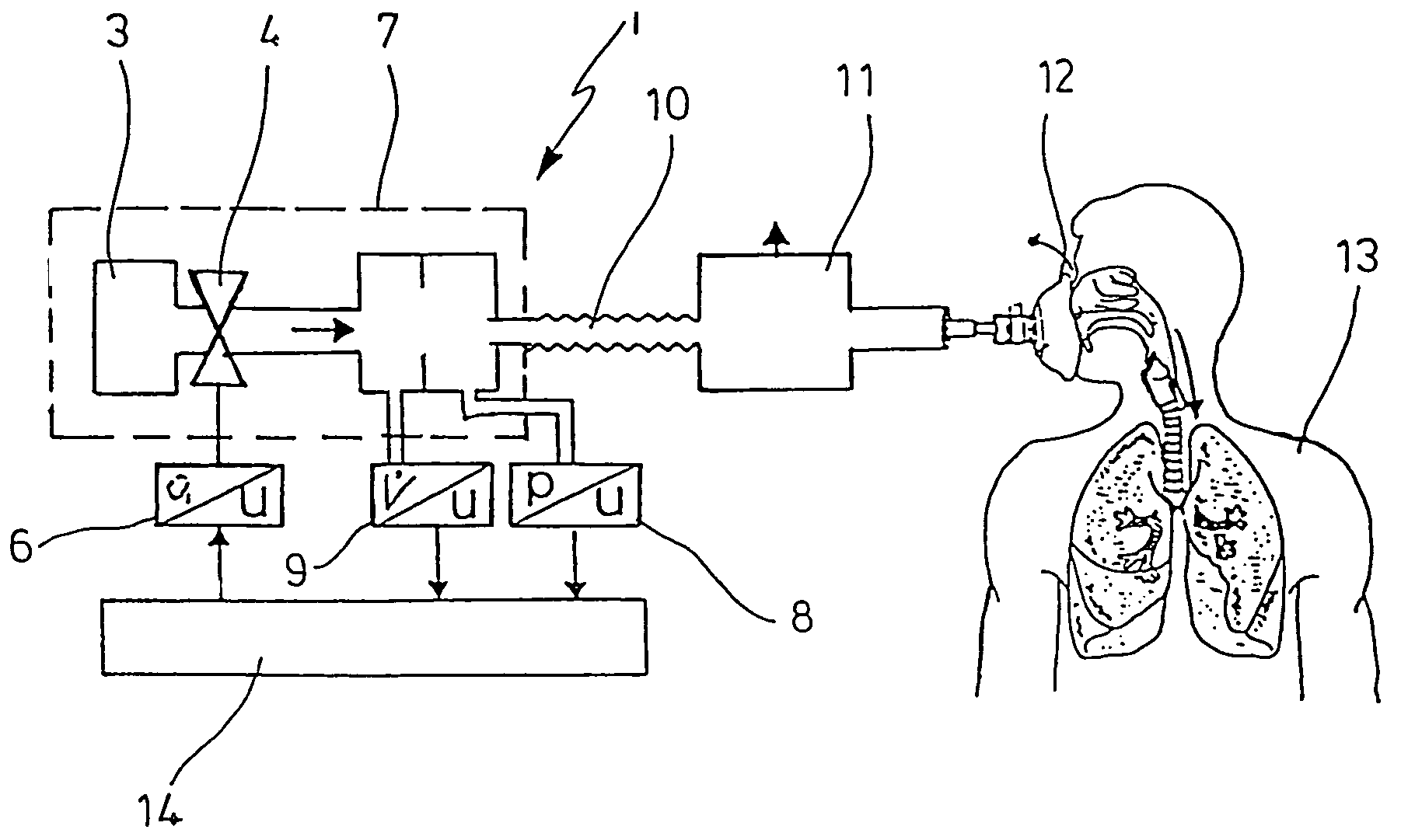
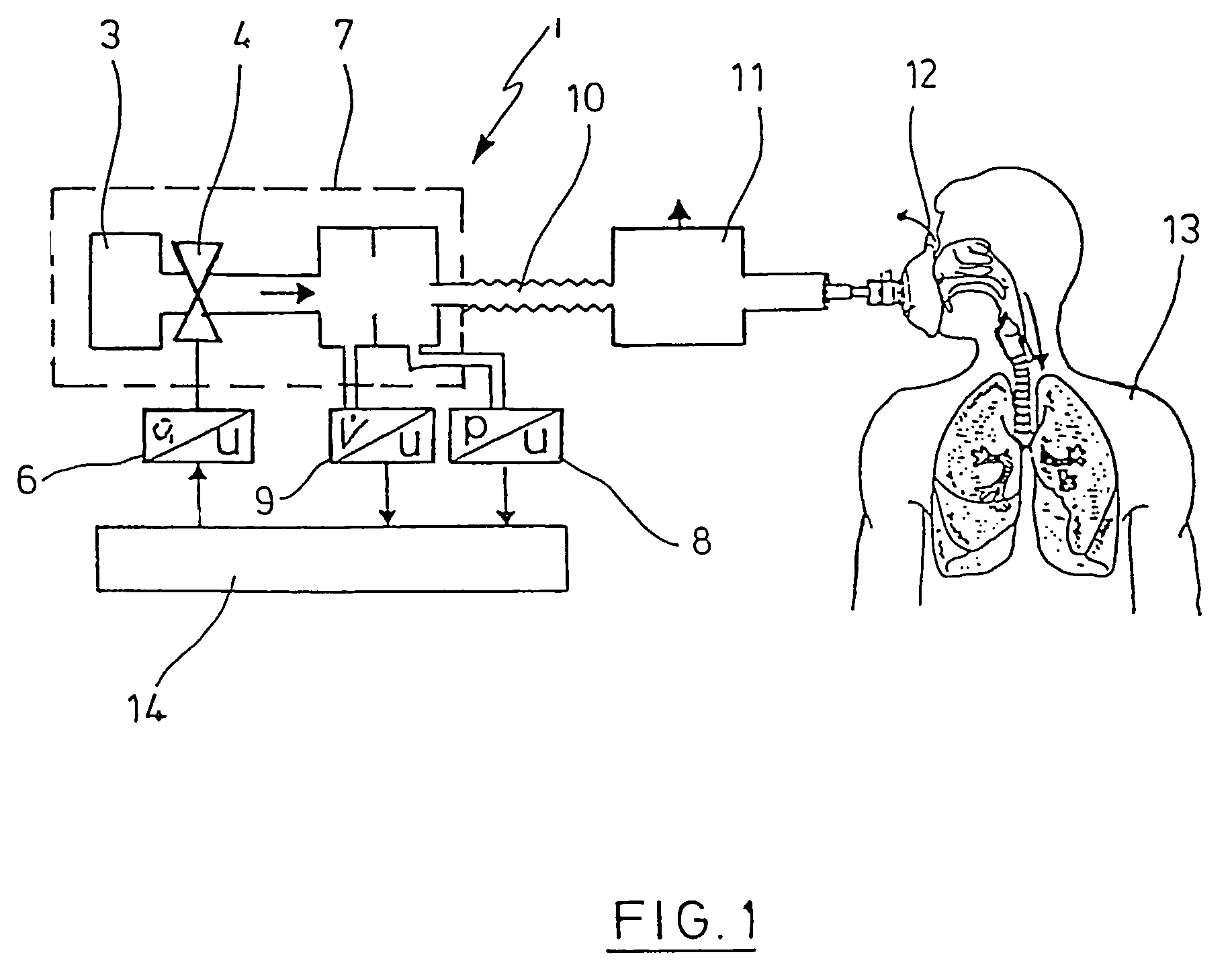
Ventilator Apparatus and System of Ventilation
InactiveUS20080295839A1Reduce dependenceRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDisplay deviceTransducer
A ventilator (10) for use by a clinician in supporting a patient presenting pulmonary distress. A controller module (20) with a touch-screen display (26) operates a positive or negative pressure gas source (40) that communicates with the intubated or negative pressure configured patient through valved (46) supply and exhaust ports (42, 44). A variety of peripheral, central, and or supply / exhaust port positioned sensors (54) may be included to measure pressure, volumetric flow rate, gas concentration, transducer, and chest wall breathing work. Innovative modules and routines (30) are incorporated into the controller module enabling hybrid, self-adjusting ventilation protocols and models that are compatible with nearly every conceivable known, contemplated, and prospective technique, and which establish rigorous controls configured to rapidly adapt to even small patient responses with great precision so as to maximize ventilation and recruitment while minimizing risks of injury, atelectasis, and prolonged ventilator days.
Owner:HABASHI NADER M
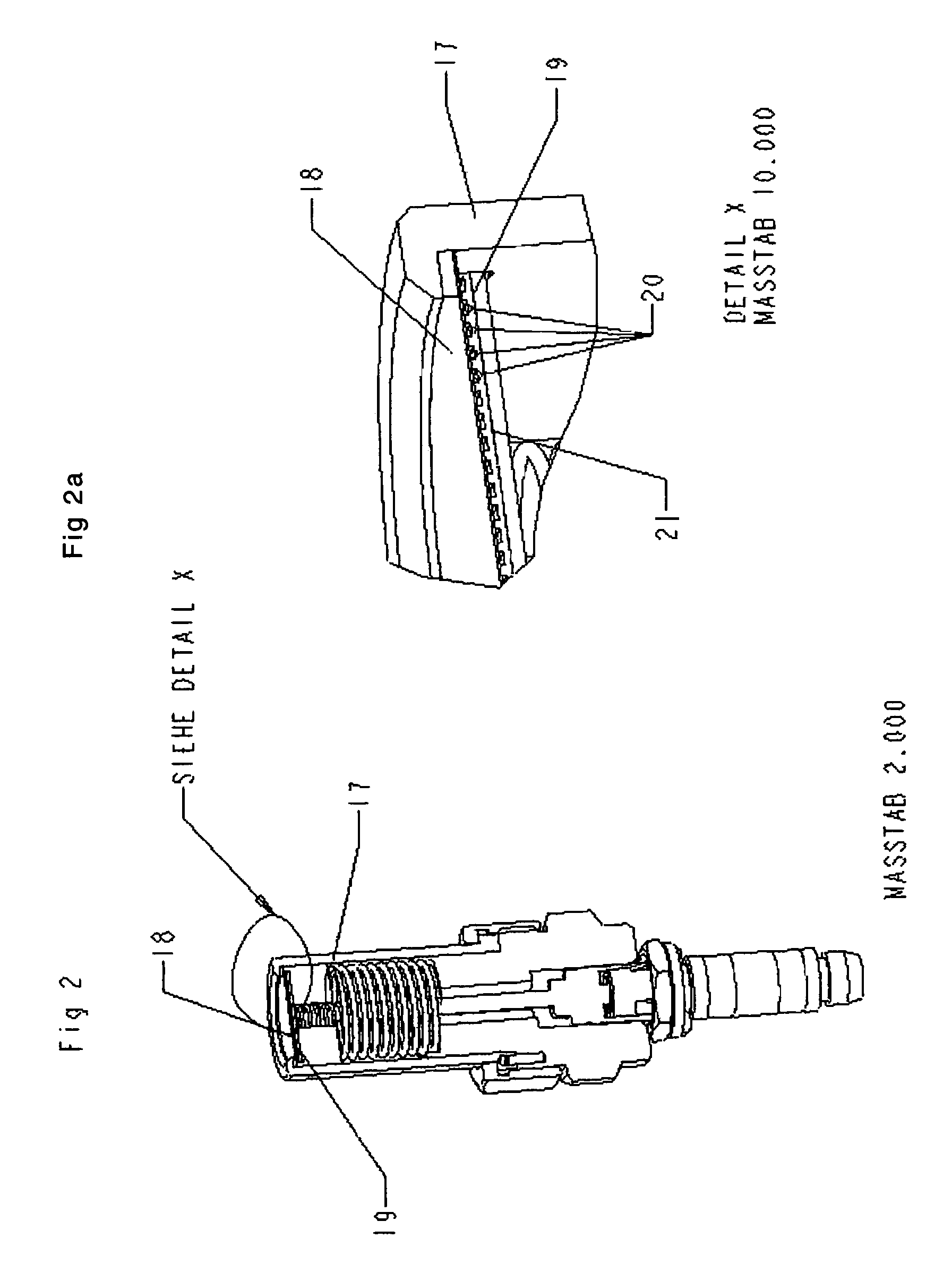
Method and device for painless injection of medication
InactiveUS7637891B2Simple and inexpensive to performSimple and inexpensive to and operateAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesMedication injectionMedical treatment
A device for painlessly injecting medications, and a method for providing a substantially painless injection of medication into a patient that does not require the use of an anesthetic, that does not require the medical personnel to spend a substantial amount of time performing the injection procedure, that is relatively simple and inexpensive to perform and operate, and that provides a relatively high degree of safety for both the medical personnel and for the patient. The injection needle can have an outside diameter greater than 0.20 mm and less than about 0.38 mm. The medicament can be injected painlessly through the needle and into the patient at a substantially constant volumetric flow rate of about 0.05 μL / s to about 50 μL / s.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
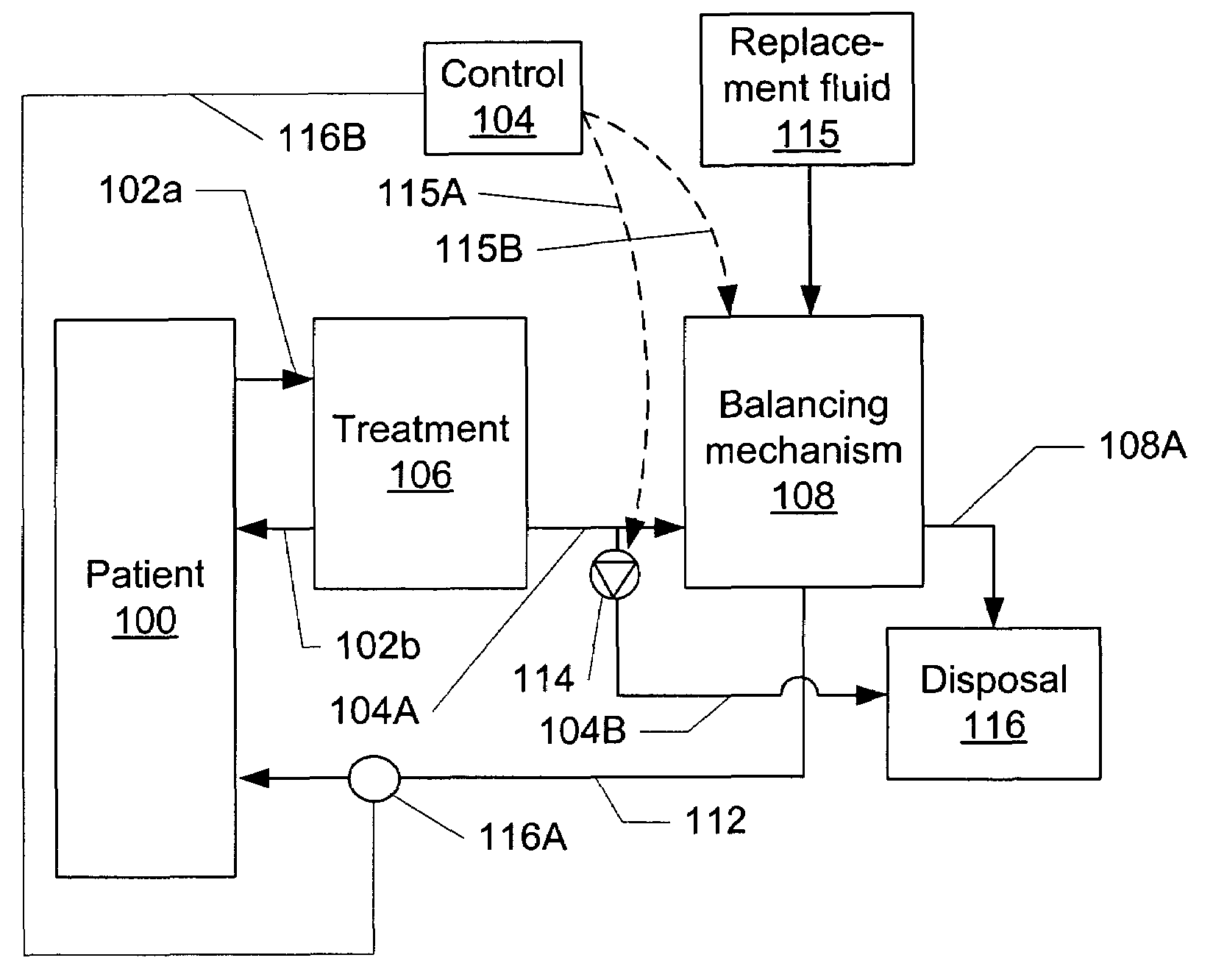
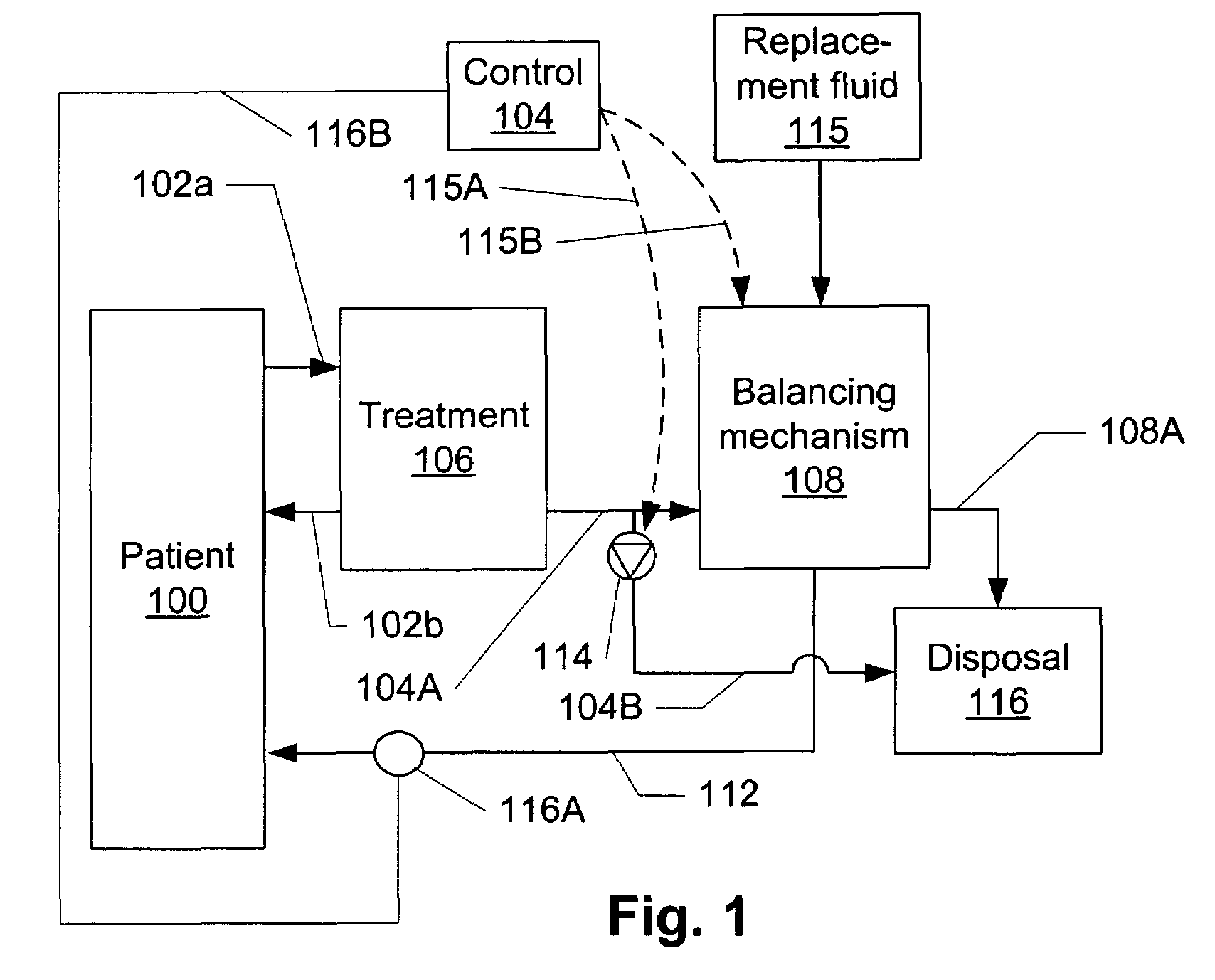
Volumetric fluid balance control for extracorporeal blood treatment
ActiveUS7112273B2Effective compensationDetectability of a fluid volume imbalanceHaemofiltrationSettling tanks feed/dischargeBlood treatmentsFluid balance
A method and device for adjusting a volumetric flow balancing system for an extracorporeal blood treatment system receives a pressure signal and calculates a compensation factor that is used to adjust the relative flow rates of the volumetrically balanced fluids. For example, in a hemofiltration system, the flow of waste and and replacement fluid may be balanced volumetrically. Ultrafiltrate may be pumped in a bypass circuit in such a system. The rate of ultrafiltrate flow may be adjusted by the compensation signal. The compensation signal may be empirically derived.
Owner:NXSTAGE MEDICAL INC
Injection device for administering a vaccine
InactiveUS7670314B2Simple and inexpensive to prepareSimple and inexpensive to and operateAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesMedication injectionInjection device
A manually-powered injection device that self-administers a painless injection. The injection device provides a method for substantially painless injections of vaccine and other medication into a patient that does not require the use of an anesthetic, that does not require the medical personnel to spend a substantial amount of time performing the injection procedure, that is relatively simple and inexpensive to perform and operate, and that provides a relatively high degree of safety for both the medical personnel and for the patient. The injection needle can have an outside diameter greater than 0.10 mm and less than about 0.38 mm. The vaccine or other medicament can be injected painlessly through the needle and into the patient at a substantially constant volumetric flow rate of about 0.05 μL / s to about 50 μL / s, typically over a 3- to 5-minute period of time. The injection device is configured for easy handling, and is manually powered by the use of the hand or fingers of the medical technician, patient or other person.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Processes for converting oxygenates to olefins at reduced volumetric flow rates
InactiveUS20060020155A1Reduction in effluent volumetric flow rateMolecular sieve catalystCatalystsSyngasMolecular sieve
This invention provides processes for forming light olefins from methanol and / or from syngas through a dimethyl ether intermediate. Specifically, the invention is to converting methanol and / or syngas to dimethyl ether and water in the presence of a first catalyst, preferably comprising γ-alumina, and converting the dimethyl ether to light olefins and water in the presence of a second catalyst, preferably a molecular sieve catalyst composition.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
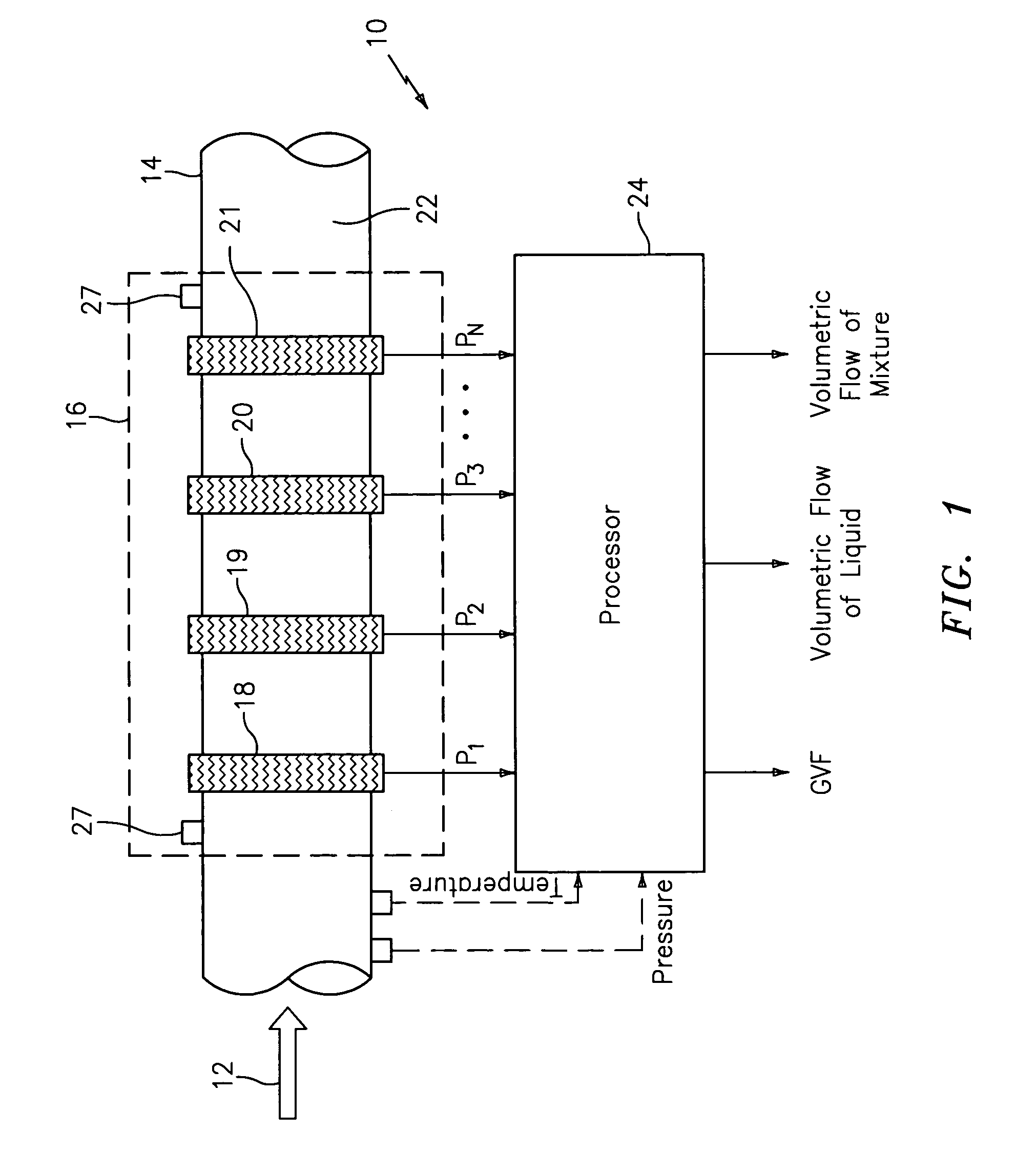
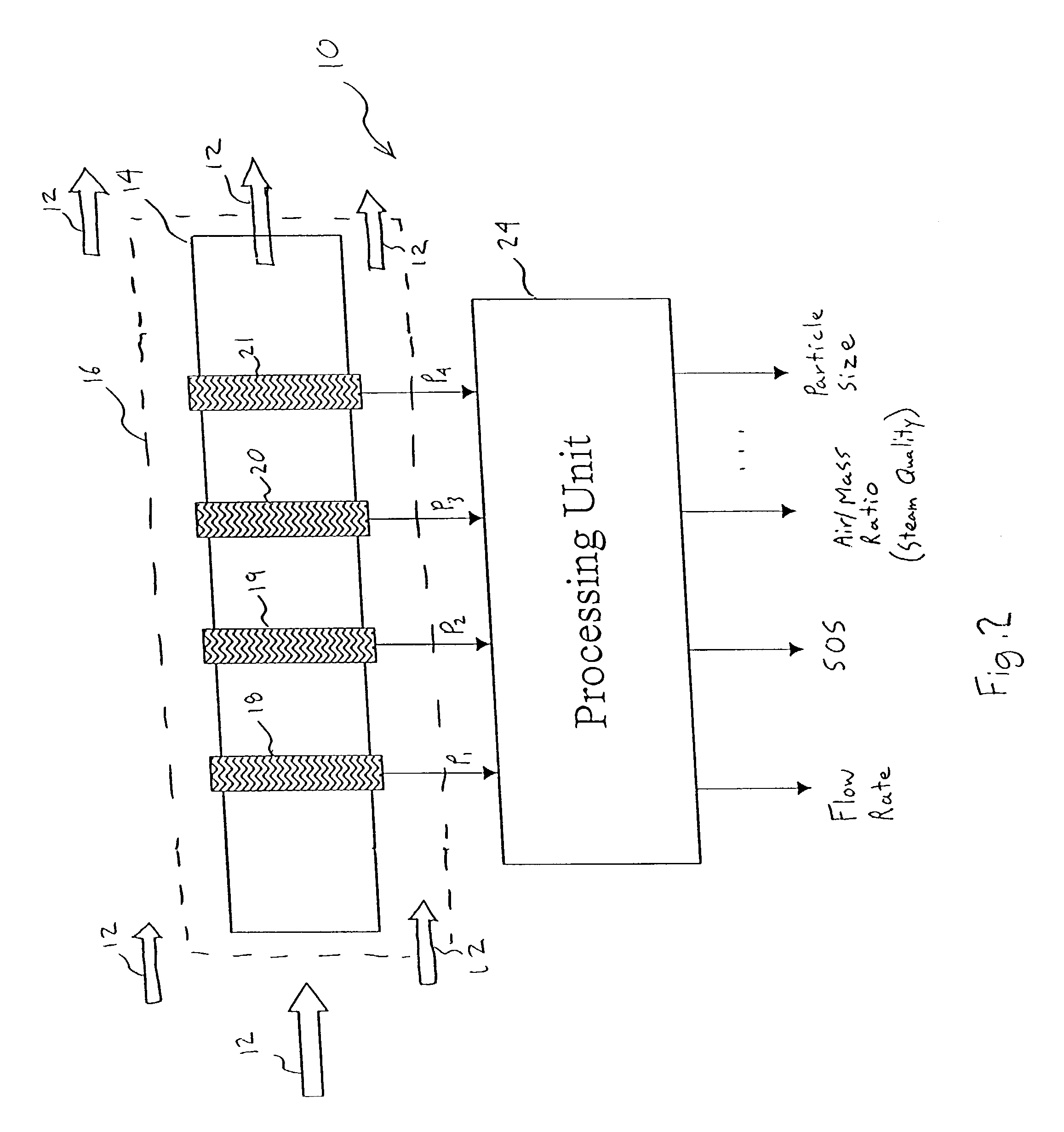
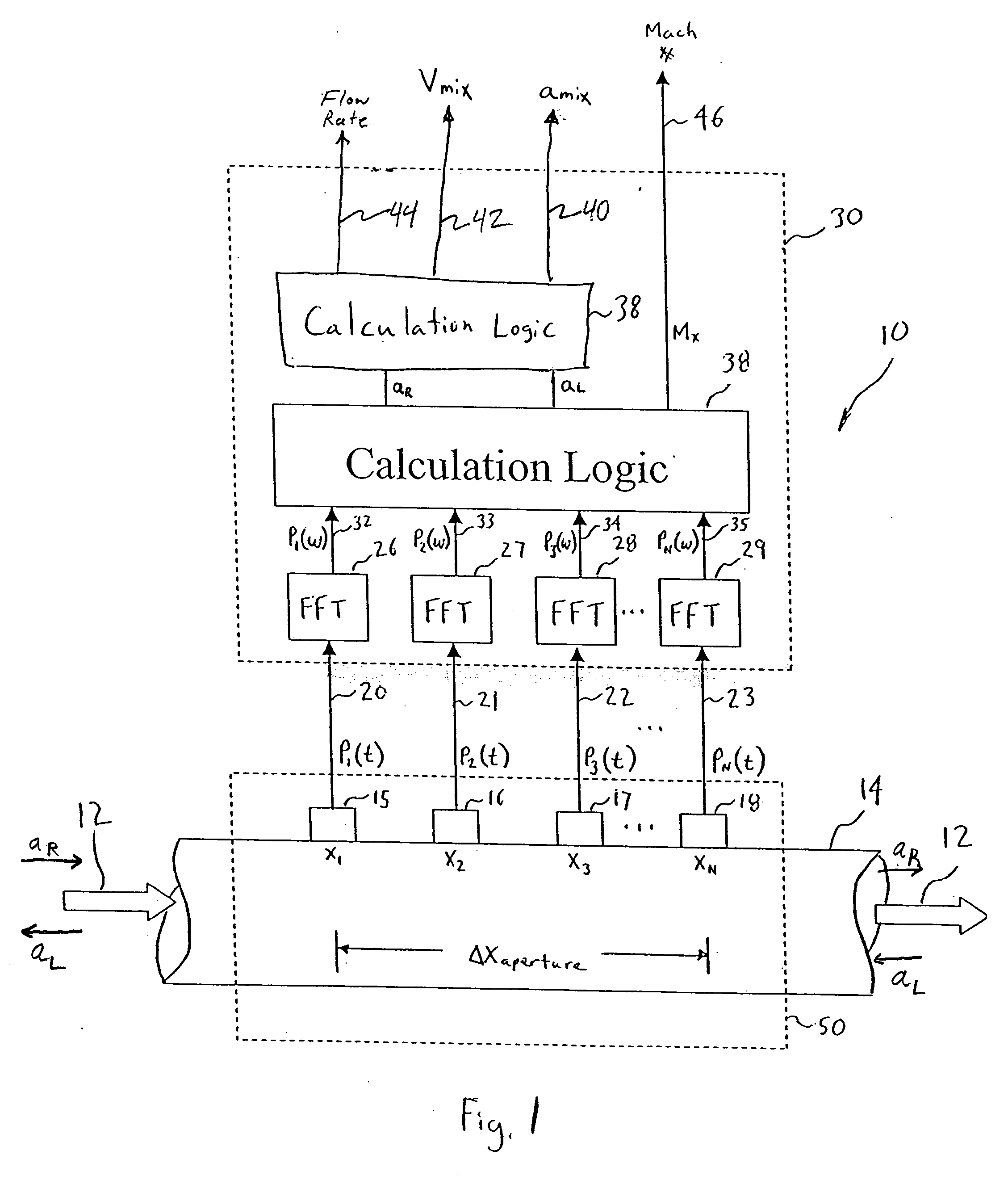
Apparatus for measuring parameters of a flowing multiphase mixture
ActiveUS7096719B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorMass ratio
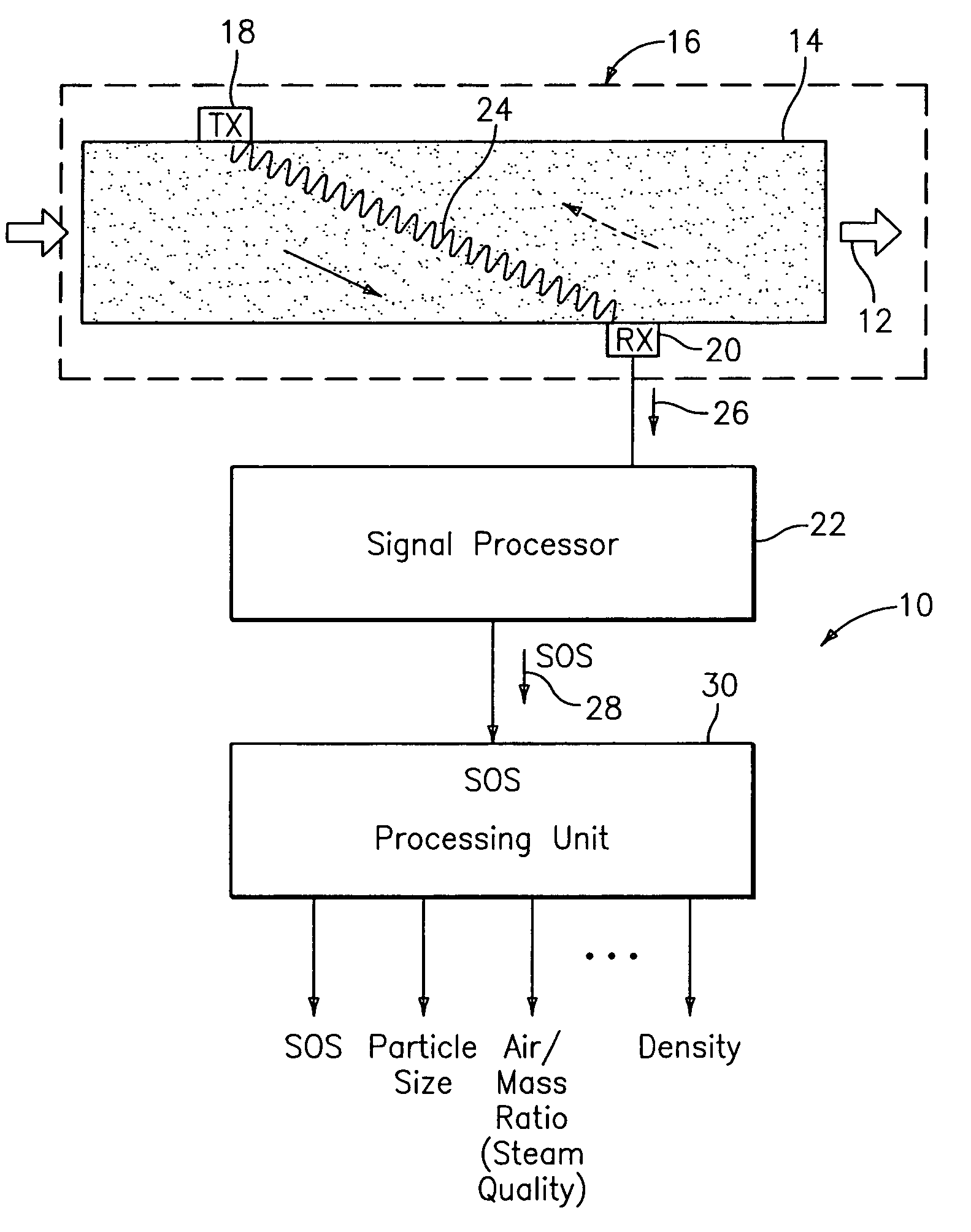
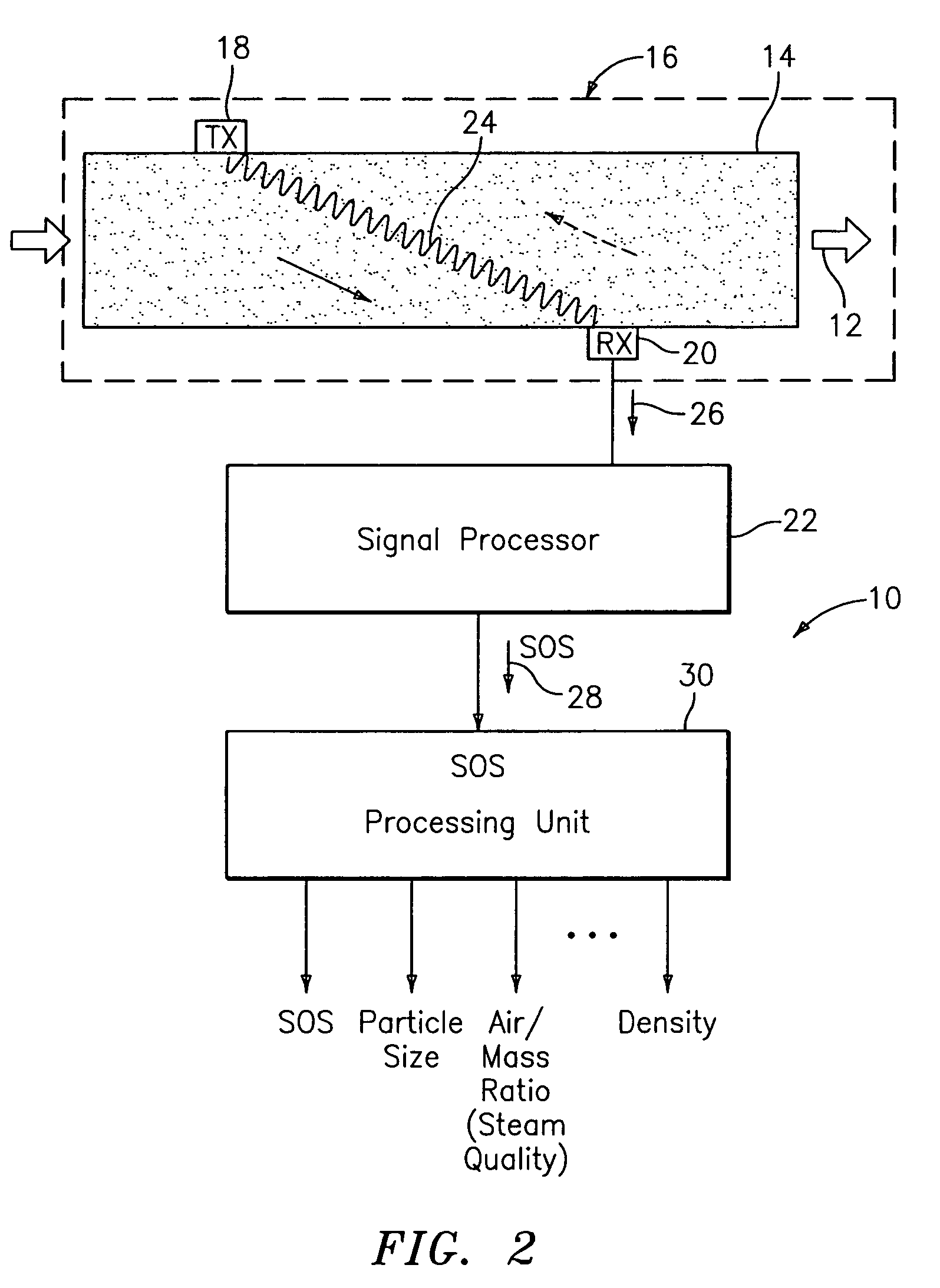
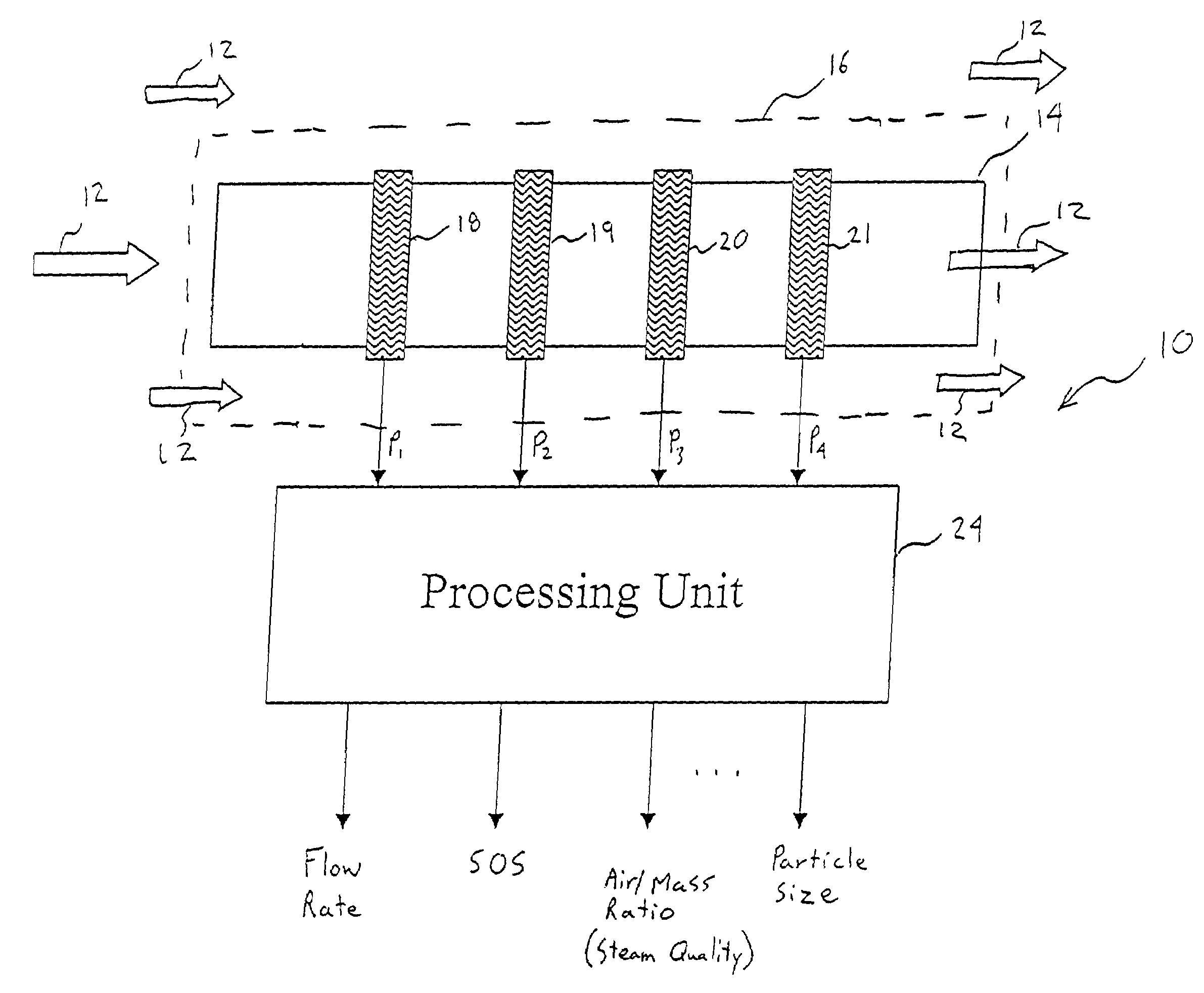
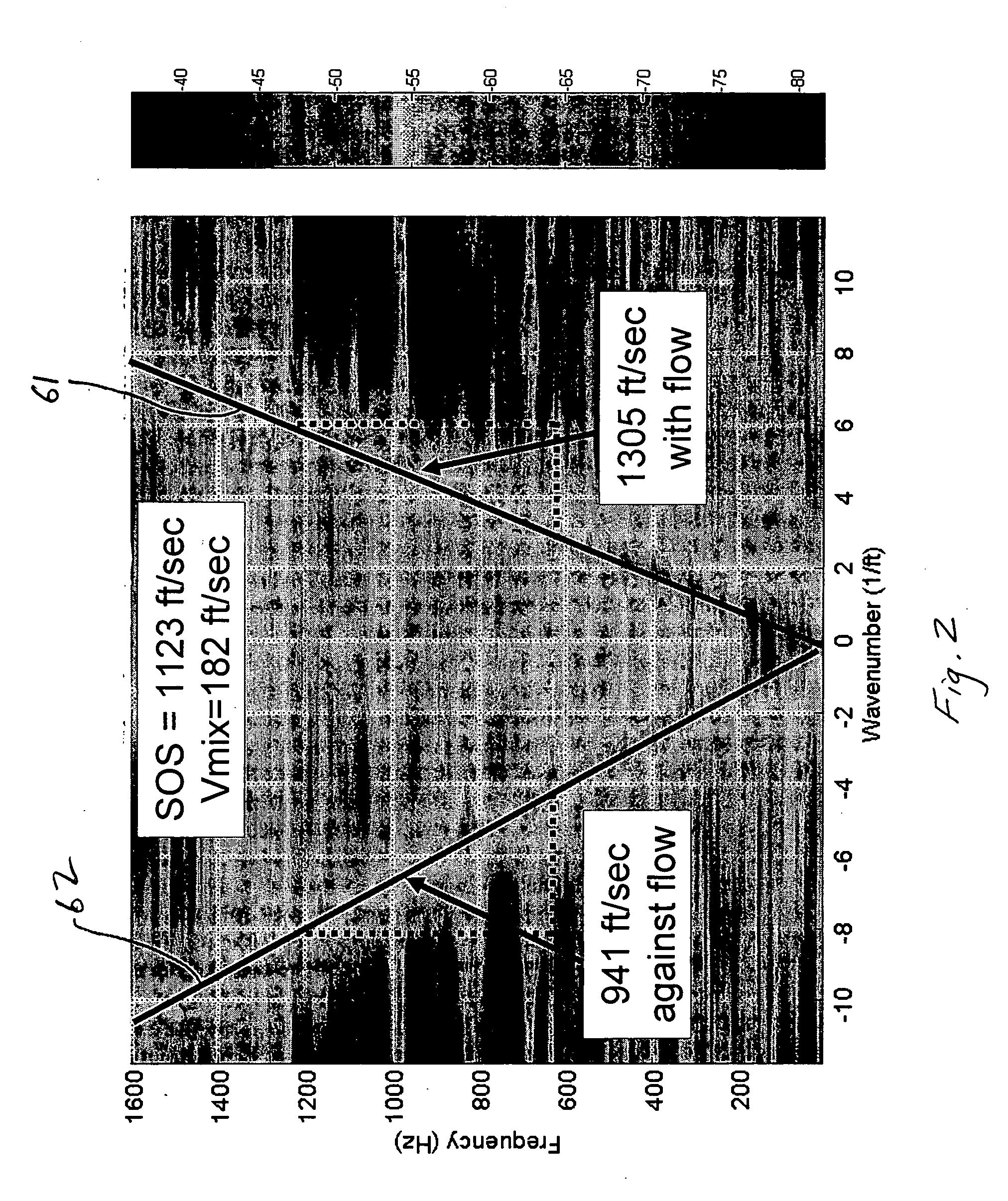
An apparatus 10 is provided that measures the speed of sound propagating in a multiphase mixture to determine parameters, such as mixture quality, particle size, vapor / mass ratio, liquid / vapor ratio, mass flow rate, enthalpy and volumetric flow rate of the flow in a pipe or unconfined space, for example, using acoustic and / or dynamic pressures. The apparatus includes a pair of ultrasonic transducers disposed axially along the pipe for measuring the transit time of an ultrasonic signal to propagate from one ultrasonic transducer to the other ultrasonic transducer. A signal process, responsive to said transit time signal, provides a signal representative of the speed of sound of the mixture. An SOS processing unit then provides an output signal indicative of at least one parameter of the mixture flowing through the pipe. The frequency of the ultrasonic signal is sufficiently low to minimize scatter from particle / liquid within the mixture. The frequency based sound speed is determined utilizing a dispersion model to determine the at least one parameter of the fluid flow and / or mixture.
Owner:CIDRA CORP SERVICES
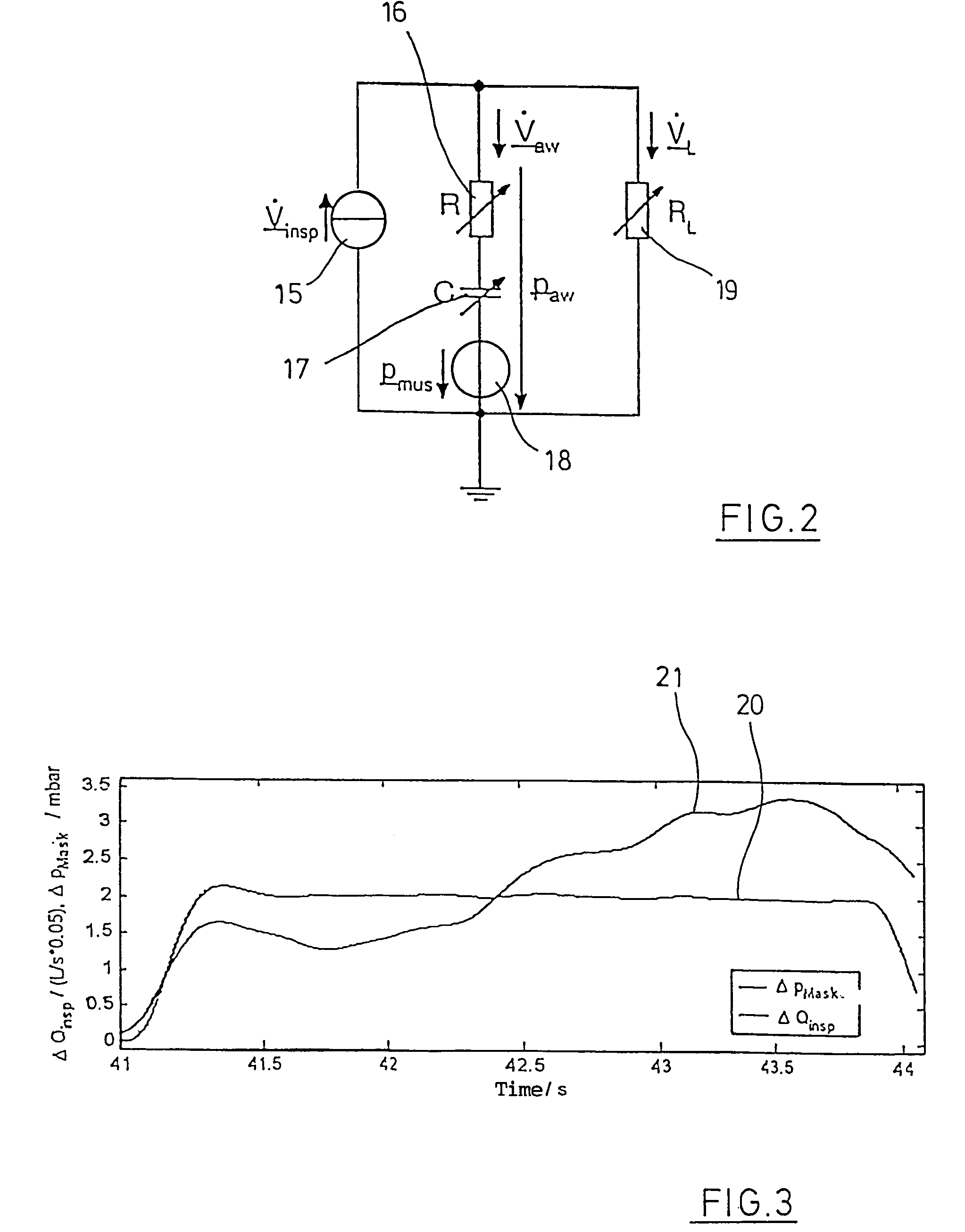
Method and device for detecting leaks in respiratory gas supply systems
ActiveUS7475685B2Eliminate the effects ofIncrease flow volumeRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesIntensive care medicineGas supply
The invention relates to a method and a device for detecting leaks in respiratory gas supply systems. Both the pressure and the volume flow of the respiratory gas are detected and the relevant values are supplied to an evaluation device. The evaluation device is used to calculate both the respiratory parameter resistance and compliance and the leak for at least two successive breathing cycles. At least one control parameter with different signal amplitudes is pre-determined for the successive breathing cycles. The leak resistance is determined from the resulting differential sequences of pressure and flow for the successive breathing cycles.
Owner:LOWENSTEIN MEDICAL TECH SA
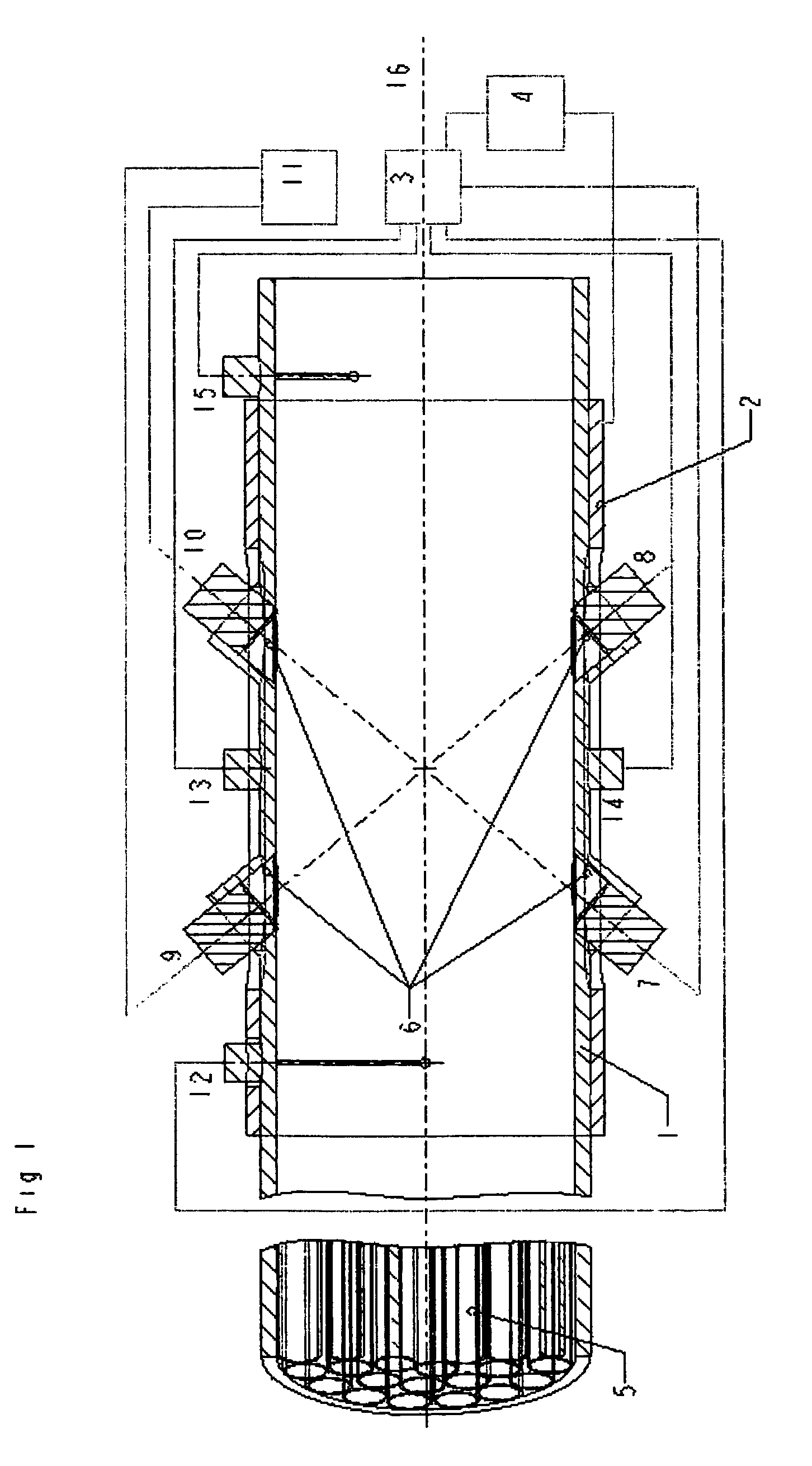
Ultrasonic gas flowmeter as well as device to measure exhaust flows of internal combustion engines and method to determine flow of gases
ActiveUS7093502B2Level gas temperature profileMinimize impactVolume/mass flow measurementVolume variation compensation/correction apparatusUltrasonic sensorDischarge measurements
An ultrasonic gas flowmeter includes a measuring pipe with flowing gas, transmitting and receiving sound transducers, transmission and reception electronics, and evaluation electronics. The sound transducers (7, 8, 9, 10) are designed as capacitive electro-acoustic ultrasonic transducers to construct a flowmeter with improved capacity, especially in view of temperature stability and the reduction and consideration of a temperature profile. Devices (5, 6) are provided to level the gas temperature profile and to minimize the influence of the temperature profile on the flow measurement. A more accurate and dependable detection of the volume flow or the mass flow of gases is to be achieved, especially in highly dynamic flows, for the method of determining the flow of gases whereby the mean flow velocity is determined and the flowing gas quantity is determined with highly synchronized resolution from the two transit times of two acoustic signals. In addition, an assessed value is computed (35) for the flow after the determination of the transit times and the assessed value is corrected at least by means of a characteristic temperature of the gas and the temperature of the wall of the measuring pipe (36).
Owner:AVL LIST GMBH
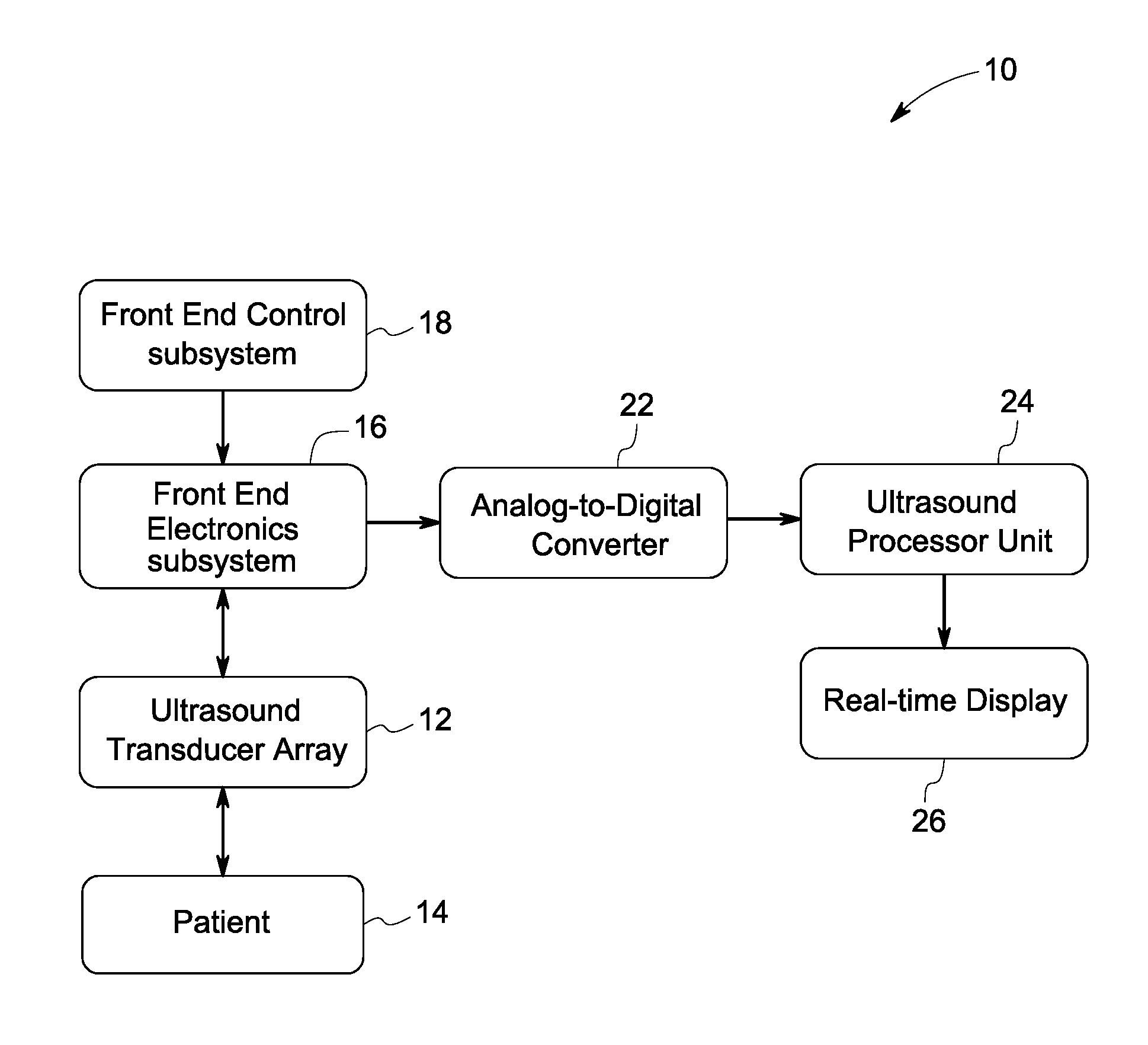
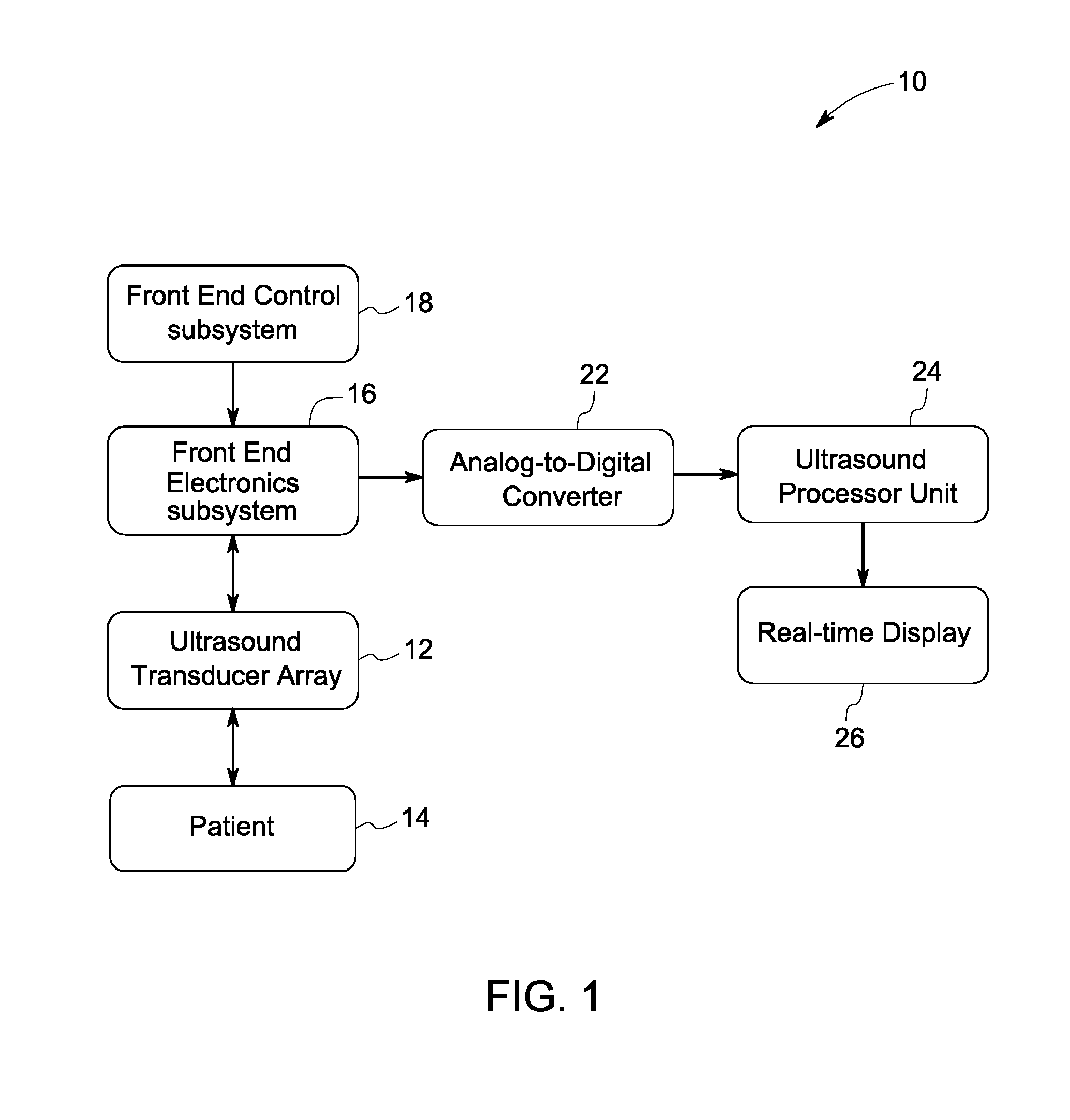
Method and system for non-invasive monitoring of patient parameters
ActiveUS20120078106A1Reduce noiseBlood flow measurement devicesHealth-index calculationUltrasonic sensorTransducer
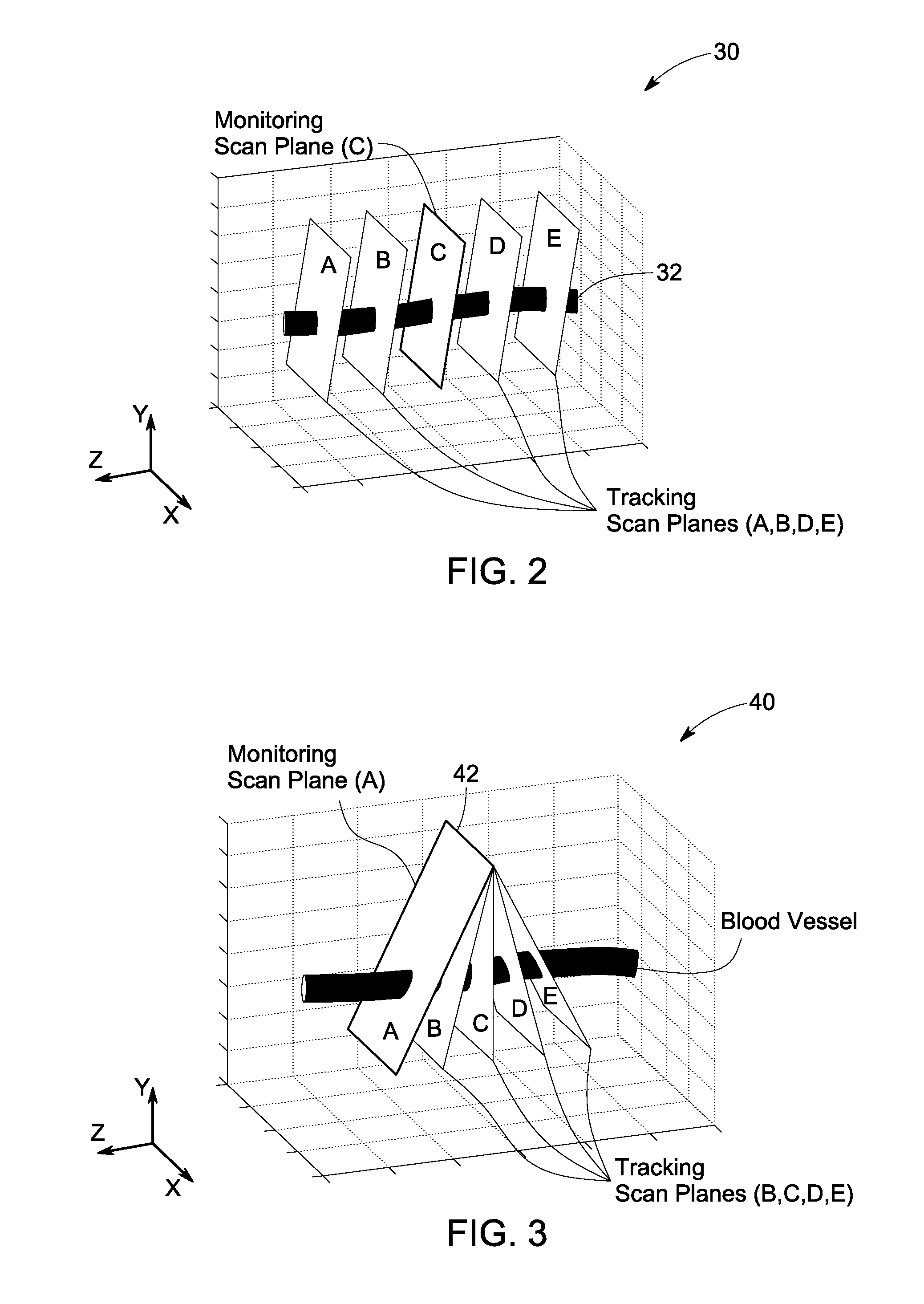
A method for continuous non-invasive monitoring of multiple arterial parameters of a patient is provided. The method includes continuously acquiring ultrasound data via an ultrasound transducer attached to the patient for detecting a blood vessel using color flow processing within a monitoring scan plane. Further, the method includes processing the continuously acquired ultrasound data to generate continuous quantitative waveforms based on an estimated cross-sectional area of the blood vessel and an estimated volumetric flow rate of blood through the vessel and displaying the generated continuous quantitative waveforms for monitoring the arterial parameters of the patient in real-time.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
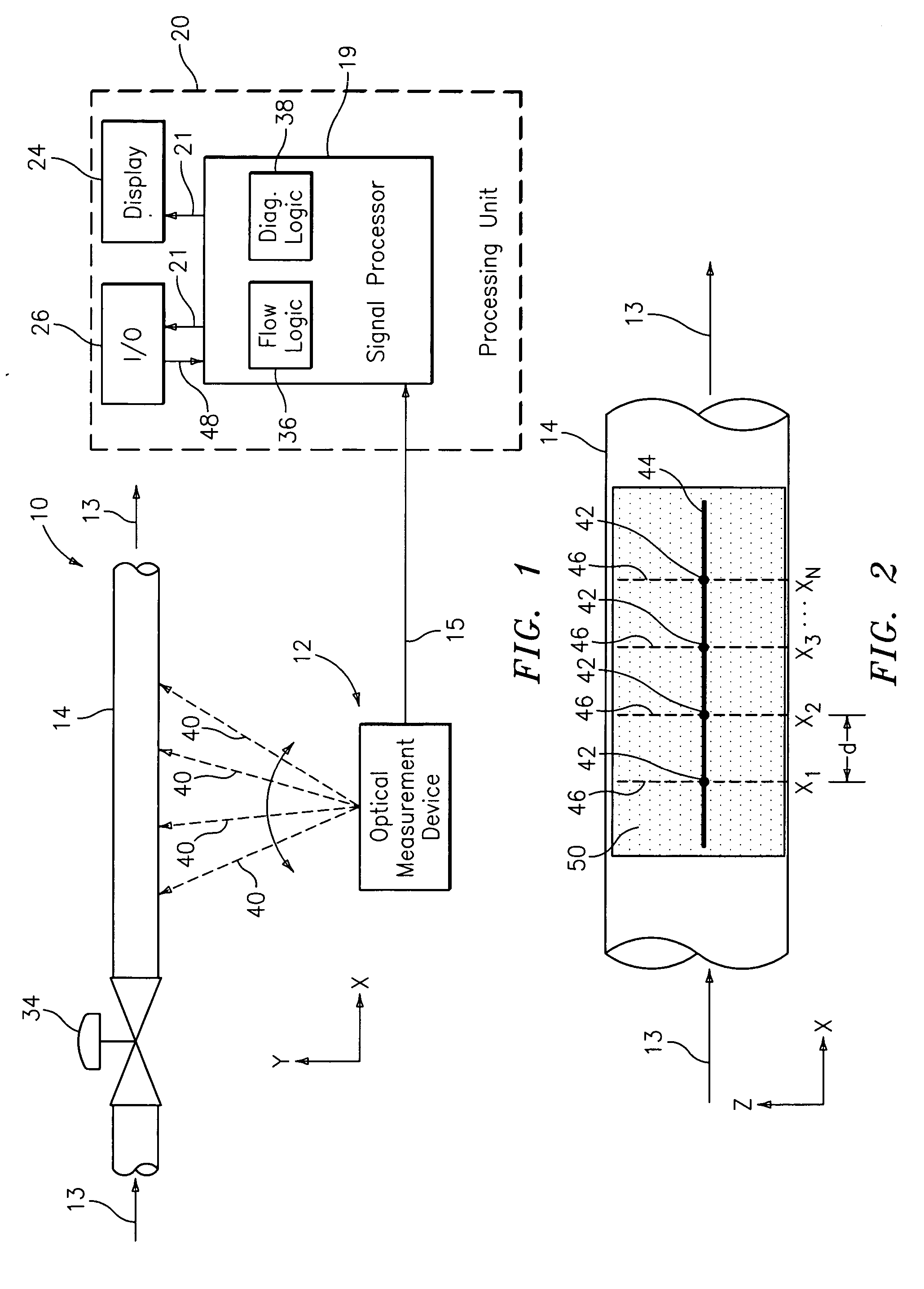
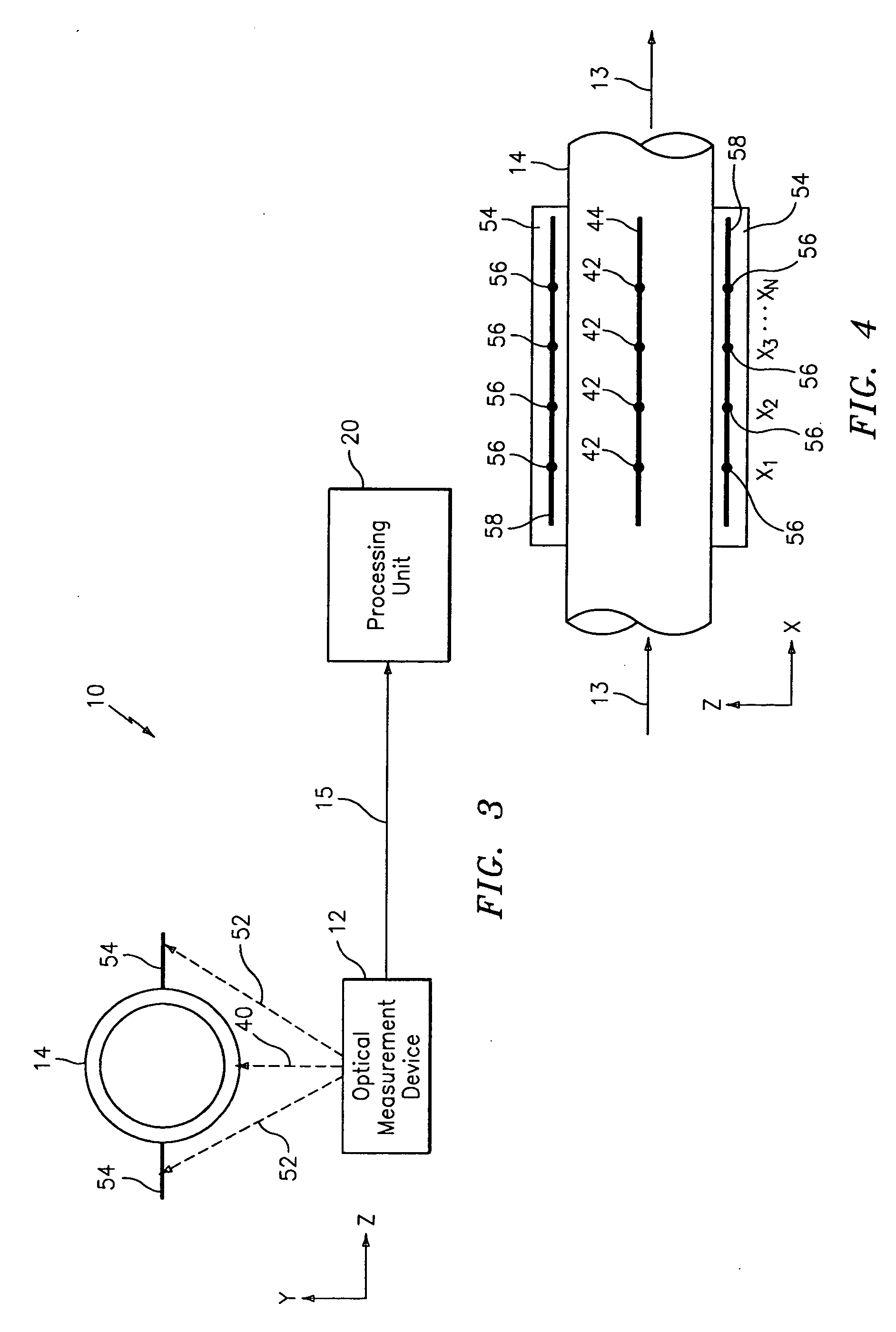
Characterizing unsteady pressures in pipes using optical measurement devices
ActiveUS20050012935A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementVolume/mass flow measurementLaser vibrometryEngineering
An apparatus for measuring at least one parameter associated with a fluid flowing within a pipe comprises an optical measurement device and a signal processor. The optical measurement device provides output signals indicative of unsteady pressures within the fluid at two or more axial locations along the pipe in response to light reflected from an outer surface of the pipe. The signal processor provides an output signal indicative of at least one parameter associated with the fluid in response to the output signals. The optical measurement device may include, for example, an electronic speckle pattern interferometer, a Fabry-Perot device, and / or a laser vibrometer. The at least one parameter may include at least one of: density of the fluid, volumetric flow rate of the fluid, mass flow rate of the fluid, composition of the fluid, entrained air in the fluid, consistency of the fluid, size of particles in the fluid, and health of a device causing the unsteady pressures to be generated in the pipe.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
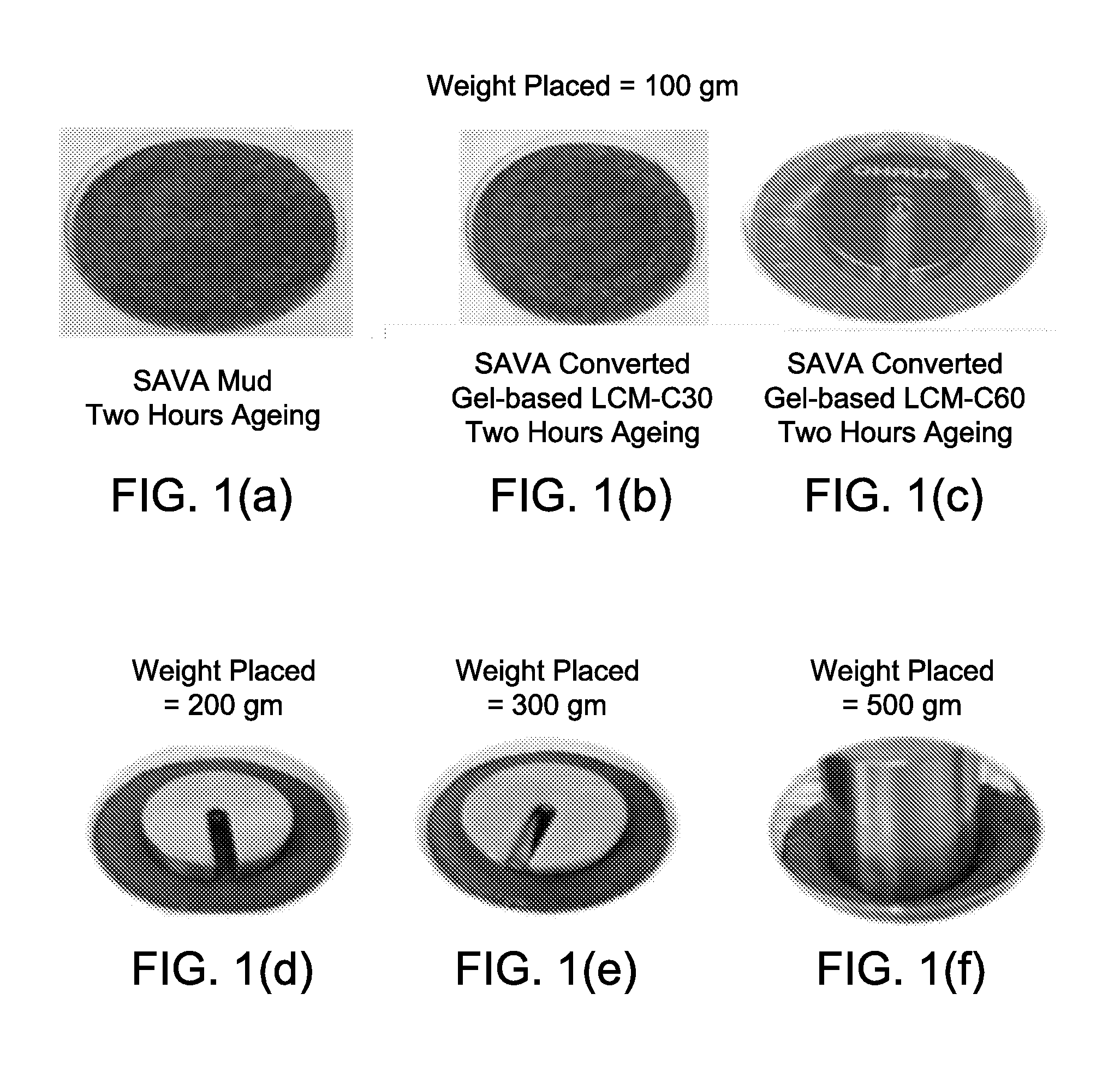
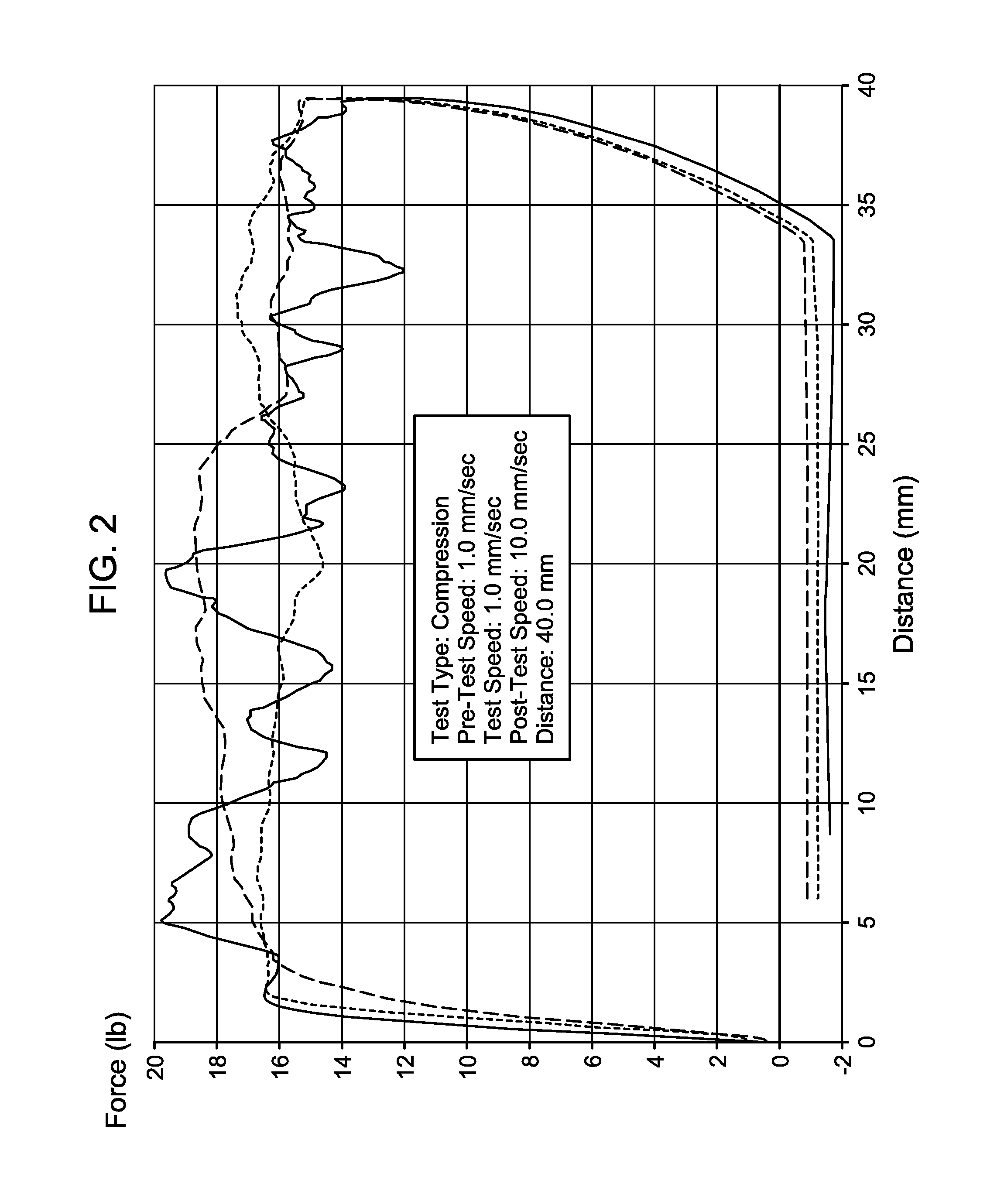
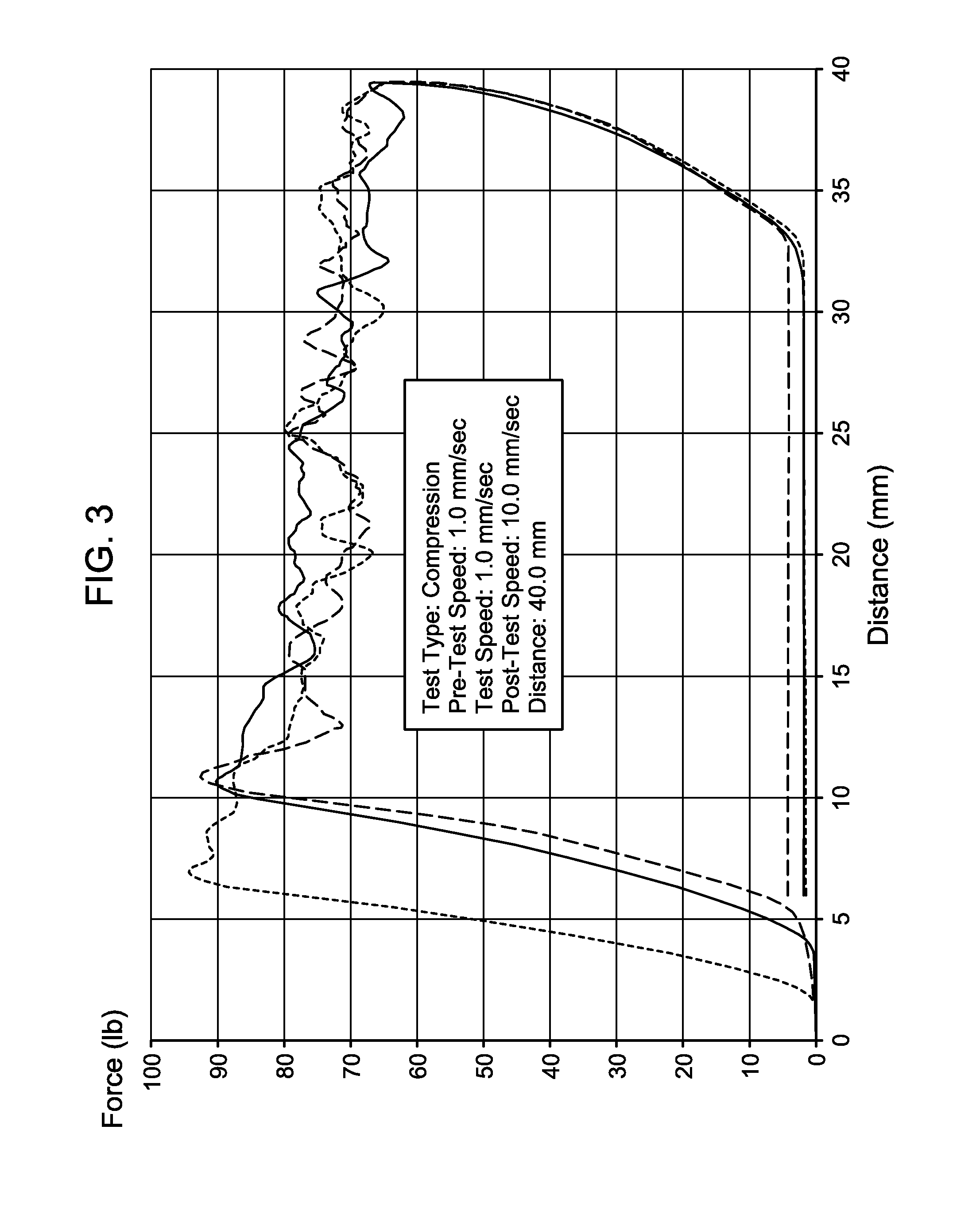
Method of Conversion of a Drilling Mud to a Gel-Based Lost Circulation Material to Combat Lost Circulation During Continuous Drilling
A method of conversion of a water-based mud to a gel-based LCM quickly to control lost circulation in a lost circulation zone in a wellbore during continuous drilling with a drilling mud, the drilling mud comprises a volcanic ash, water, a de-foamer, a pH buffer, and a polymer. The method comprises the steps of entering the lost circulation zone, determining a lost circulation volumetric flow rate, metering a first amount of a binder into the drilling mud to create a binder containing mud, pumping the binder containing drilling mud into the wellbore, and suspending metering of the first amount of the binder to the drilling mud after a pre-defined regulating period of time effective to permit the binder containing drilling mud to create a gel-based LCM operable to alter the lost circulation zone.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
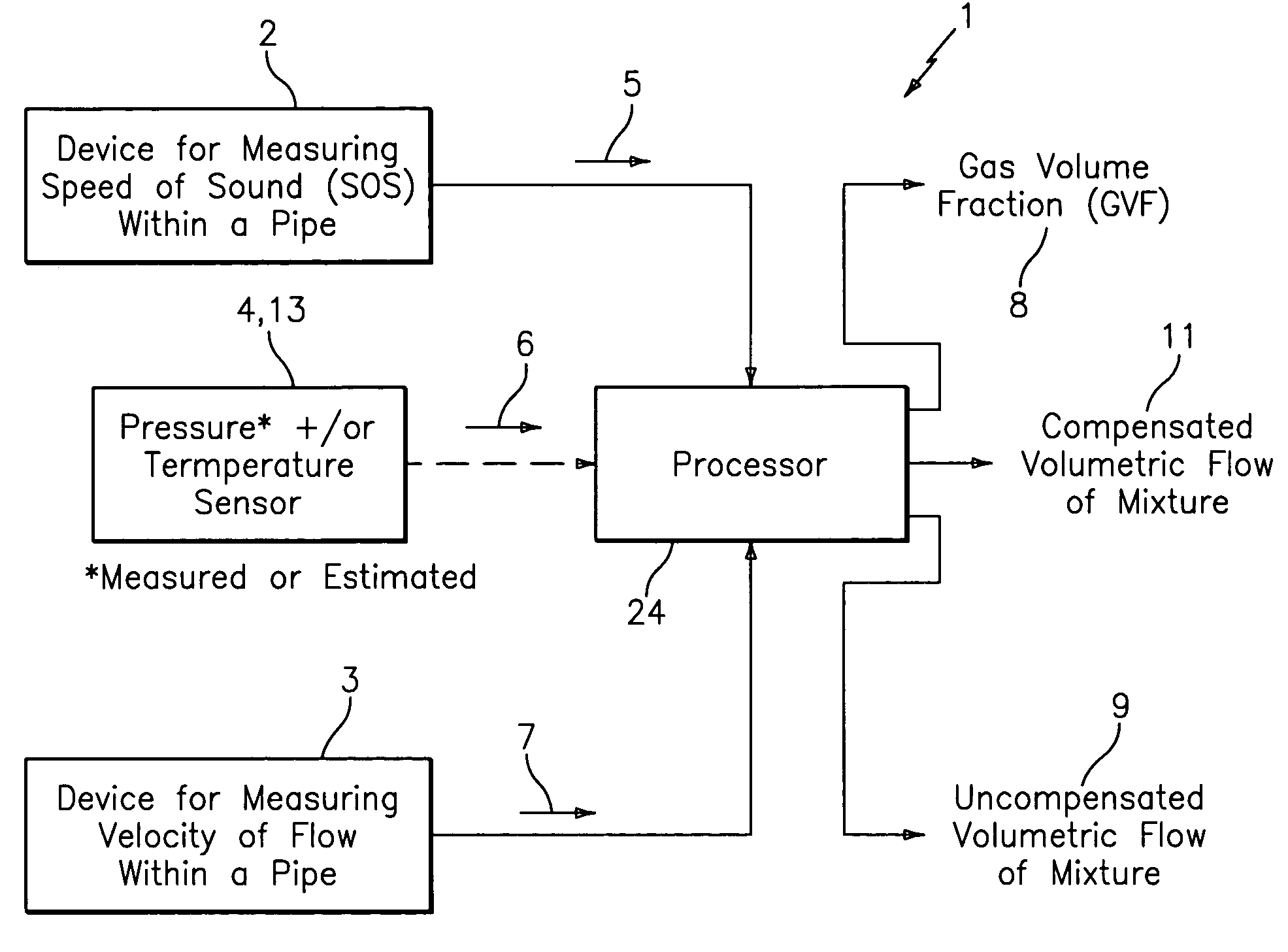
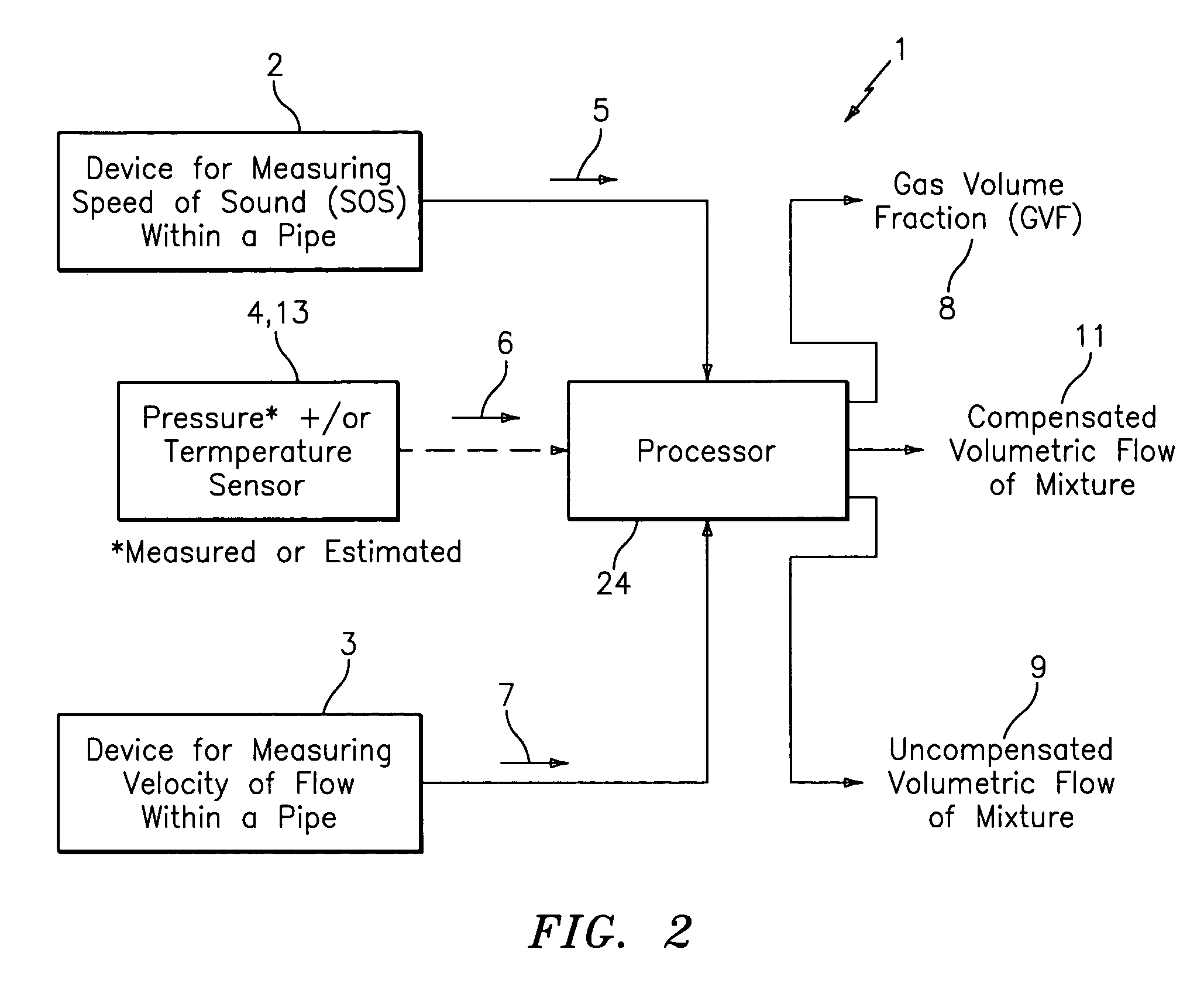
Apparatus and method for providing a flow measurement compensated for entrained gas
ActiveUS7165464B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using microwave meansSensor arrayAir entrainment
A apparatus 10,110 is provided that measures the speed of sound and / or vortical disturbances propagating in a fluid or mixture having entrained gas / air to determine the gas volume fraction of the flow 12 propagating through a pipes and compensating or correcting the volumetric flow measurement for entrained air. The GVF meter includes and array of sensor disposed axially along the length of the pipe. The GVF measures the speed of sound propagating through the pipe and fluid to determine the gas volume fraction of the mixture using array processing. The GVF meter can be used with an electromagnetic meter and a consistency meter to compensate for volumetric flow rate and consistency measurement respective, to correct for errors due to entrained gas / air.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Flow regulated pressure swing adsorption system
InactiveUSRE38493E1Satisfactory operationGas treatmentIsotope separationSystem pressureProcess engineering
Pressure swing adsorption (PSA) separation of a gas mixture is performed in an apparatus with a plurality of adsorbent beds. The invention provides rotary multiport distributor valves to control the timing sequence of the PSA cycle steps between the beds, with flow controls cooperating with the rotary distributor valves to control the volume rates of gas flows to and from the adsorbent beds in blowdown, purge, equalization and repressurization steps.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
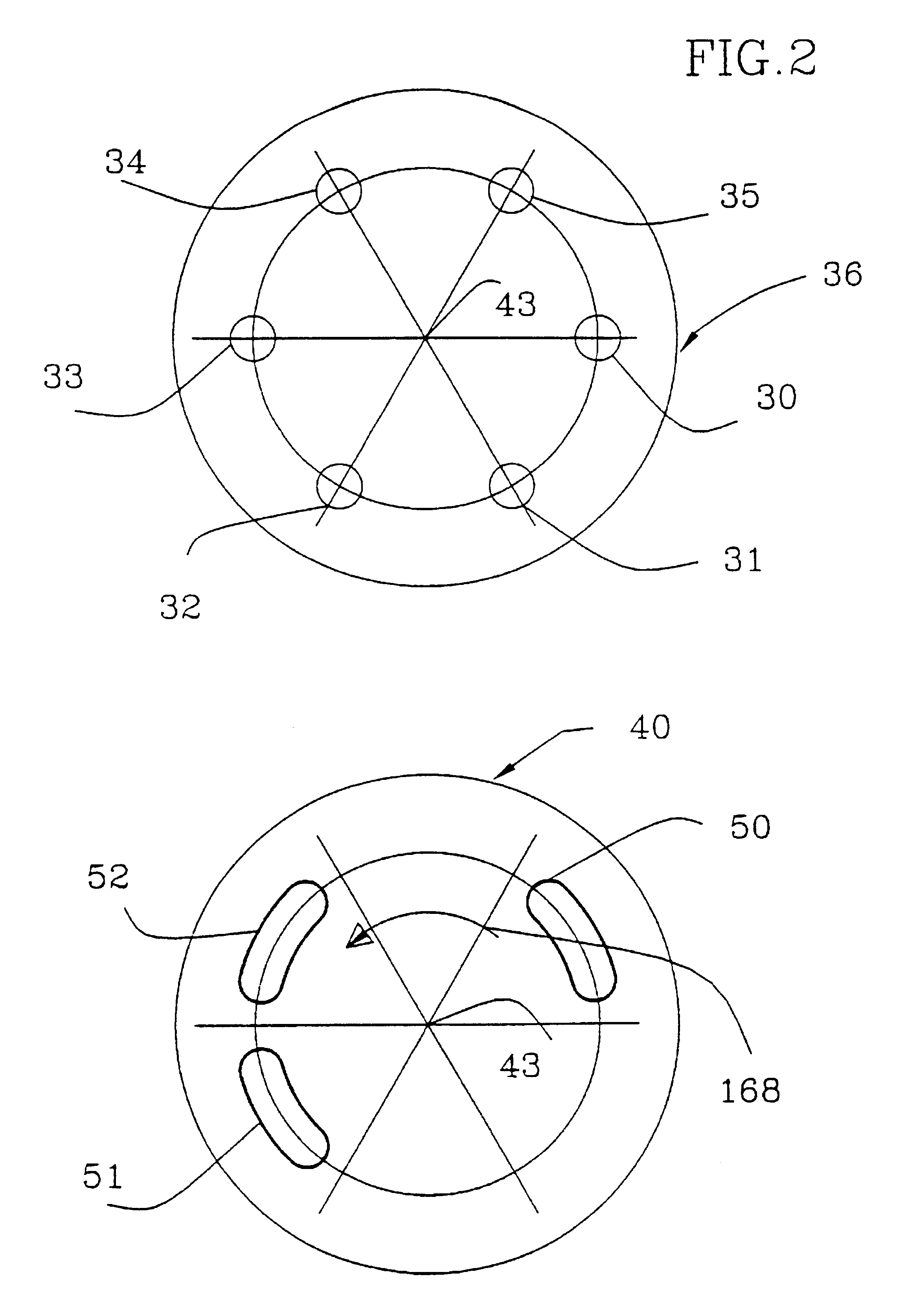
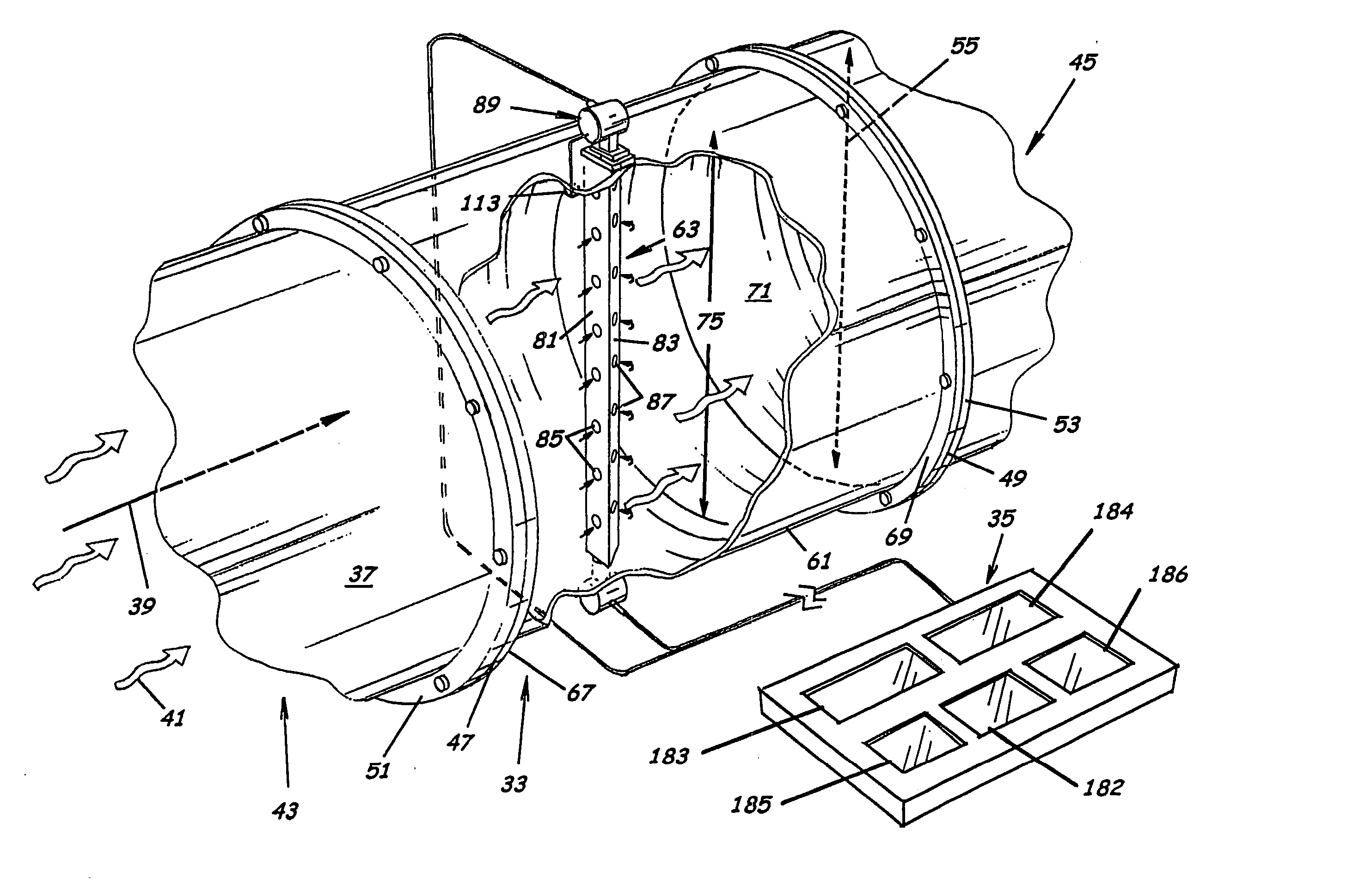
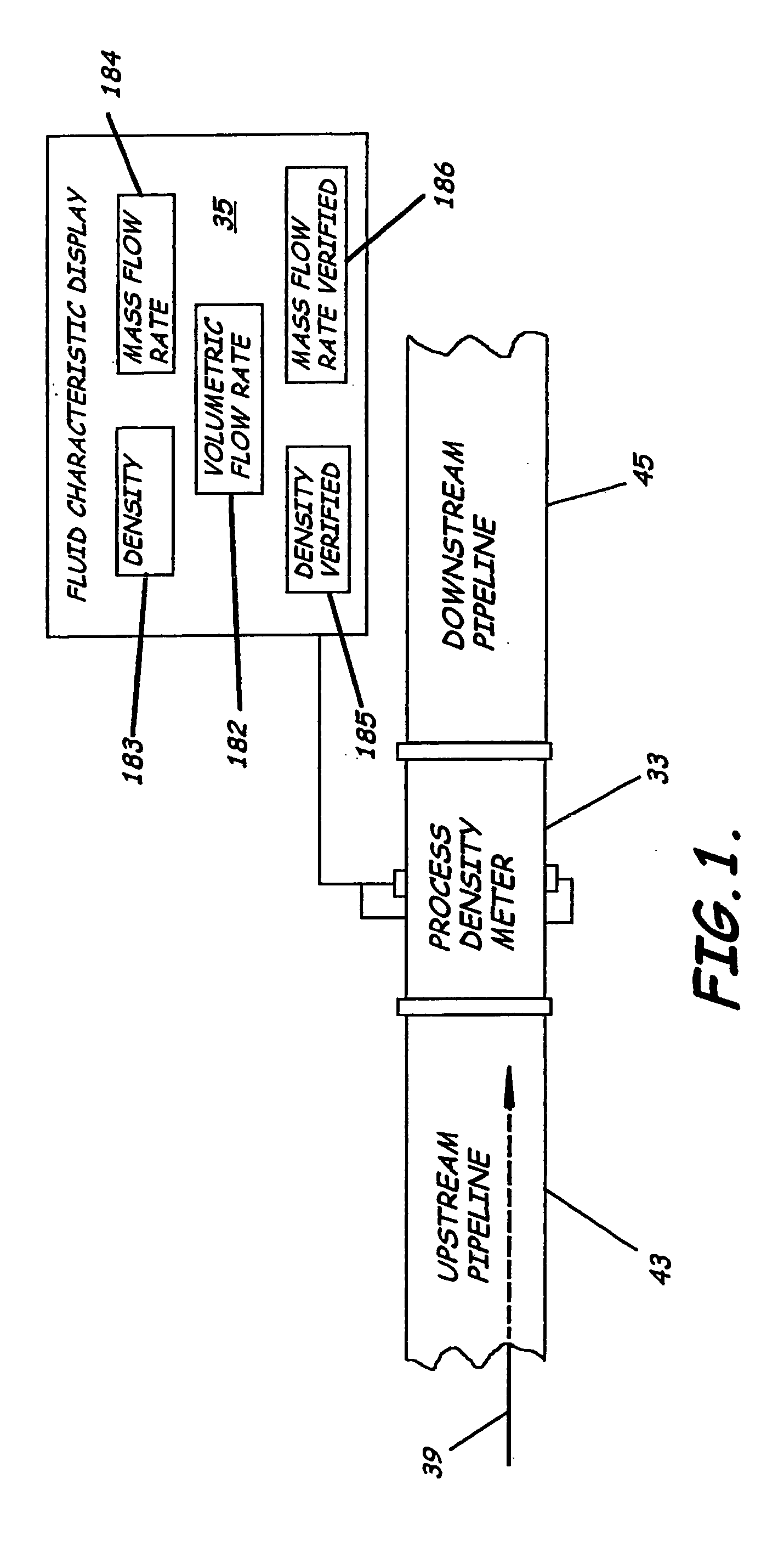
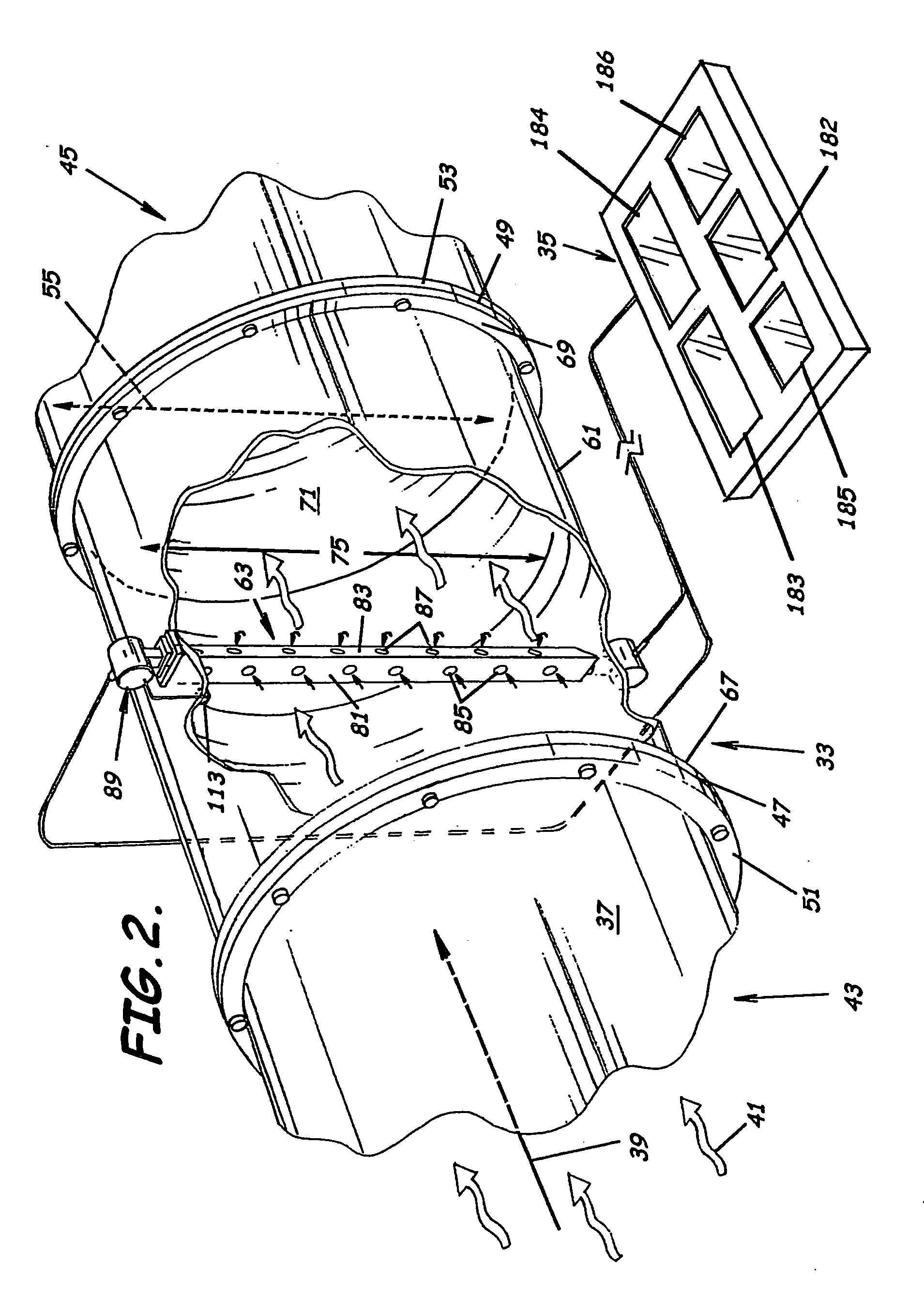
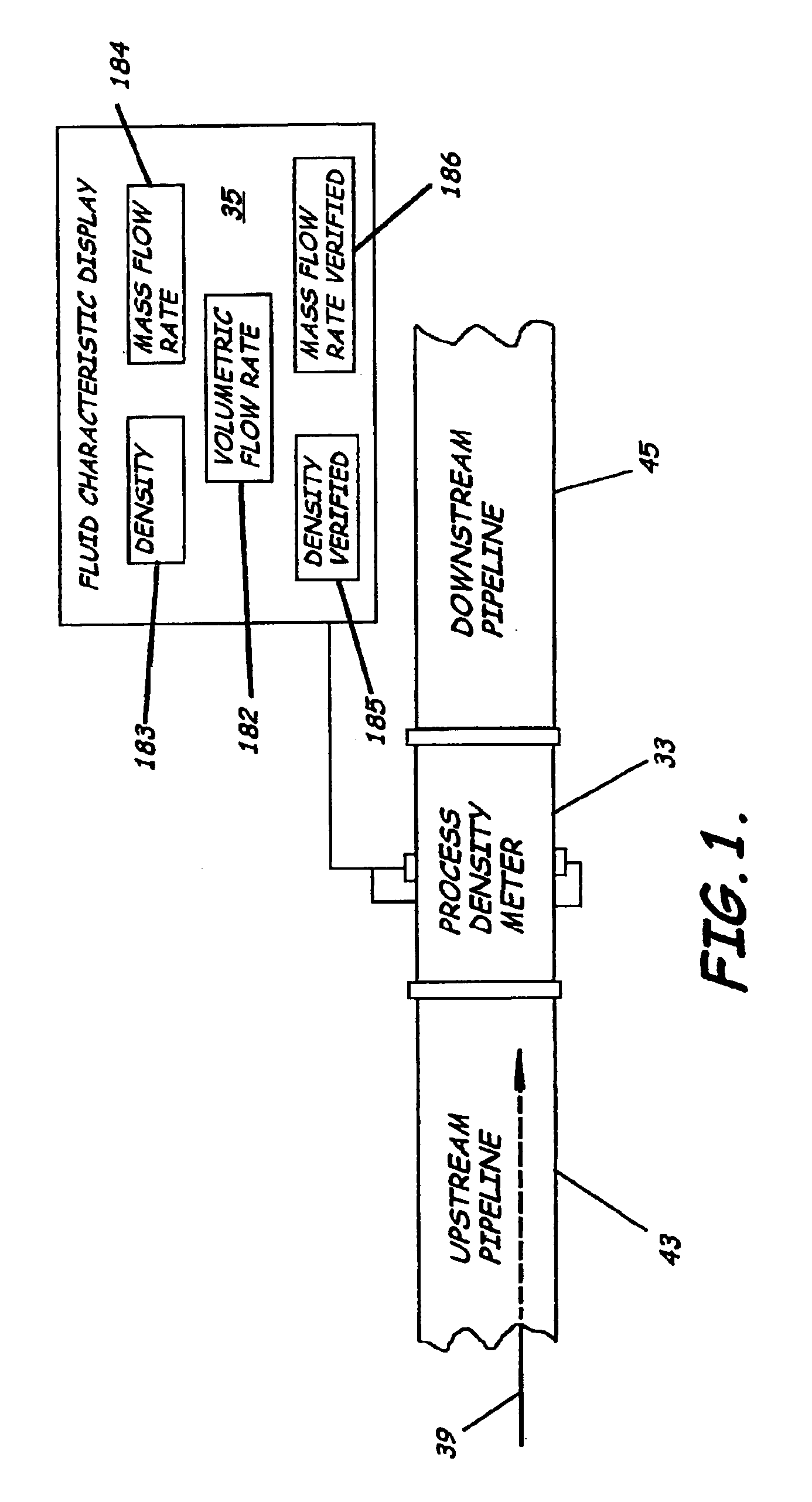
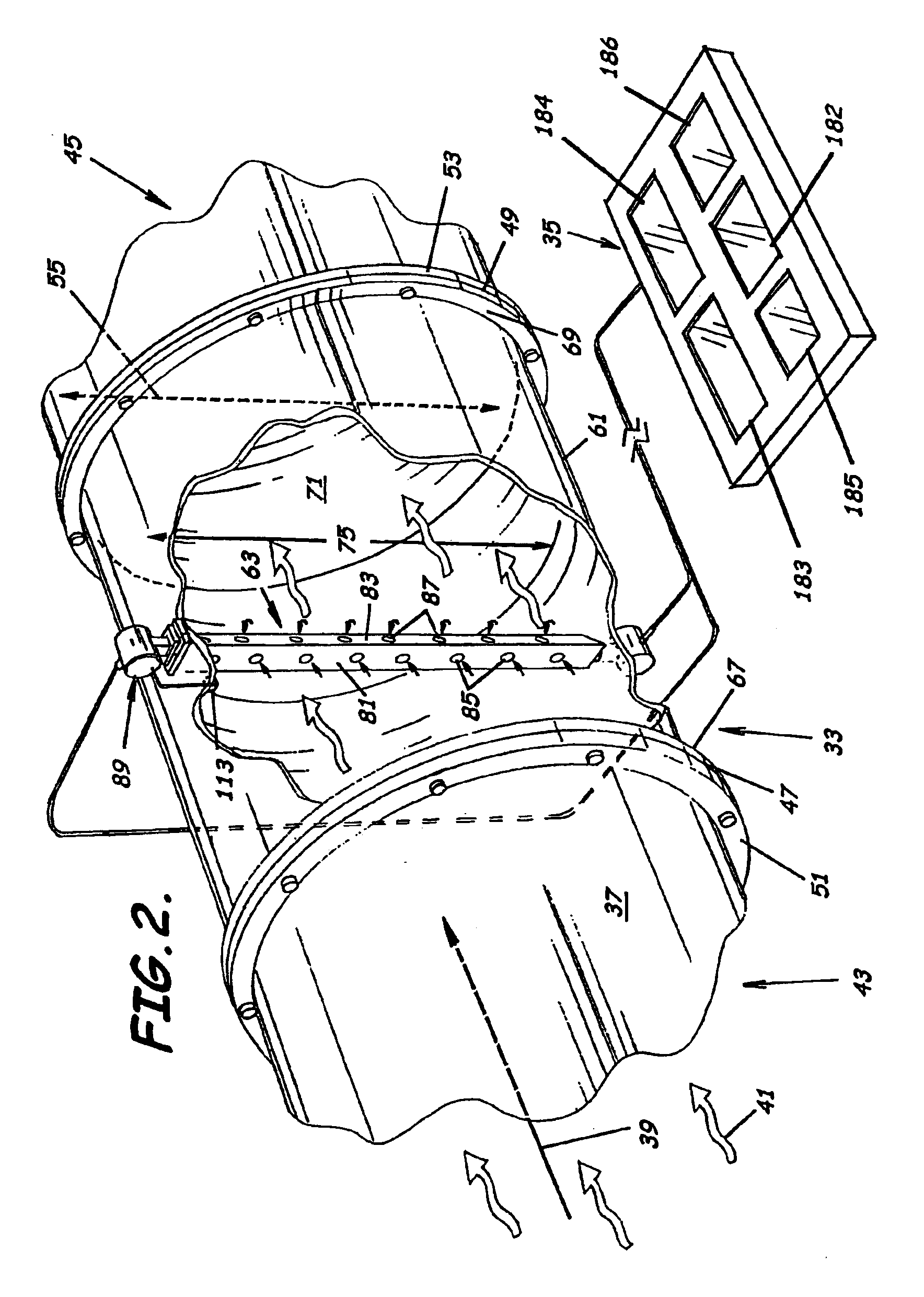
System to measure density, specific gravity, and flow rate of fluids, meter, and related methods
ActiveUS20050034535A1Little maintenanceMinimization needsVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectDifferential pressureDisplay device
A system to measure fluid flow characteristics in a pipeline, meter, and methods includes a pipeline having a passageway to transport flowing fluid therethrough, a process density meter including at least portions thereof positioned within the pipeline to provide flowing fluid characteristics including volumetric flow rate, fluid density, and mass flow rate of the flowing fluid, and a fluid characteristic display to display the fluid characteristics. The process density meter includes a vortex-shedding body positioned within the pipeline to form vortices and a vortex meter having a vortex frequency sensor to measure the frequency of the vortices and to determine the volumetric flow rate. The process density meter further includes a differential pressure meter positioned adjacent the vortex-shedding body to produce a differential pressure meter flow rate signal indicative of the density of fluid when flowing through the pipeline. The process density meter also includes a thermal flow meter positioned adjacent the vortex-shedding body to produce a mass flow rate signal indicative of the mass flow rate of fluid when flowing through the pipeline. The process density meter produces an output of a volumetric flow rate, a flowing fluid density, and a mass flow rate to be displayed by the fluid characteristic display.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Flow regulated pressure swing adsorption system
Pressure swing adsorption (PSA) separation of a gas mixture is performed in an apparatus with a plurality of adsorbent beds. The invention provides rotary multiport distributor valves to control the timing sequence of the PSA cycle steps between the beds, with flow controls cooperating with the rotary distributor valves to control the volume rates of gas flows to and from the adsorbent beds in blowdown, purge, equalization and repressurization steps.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
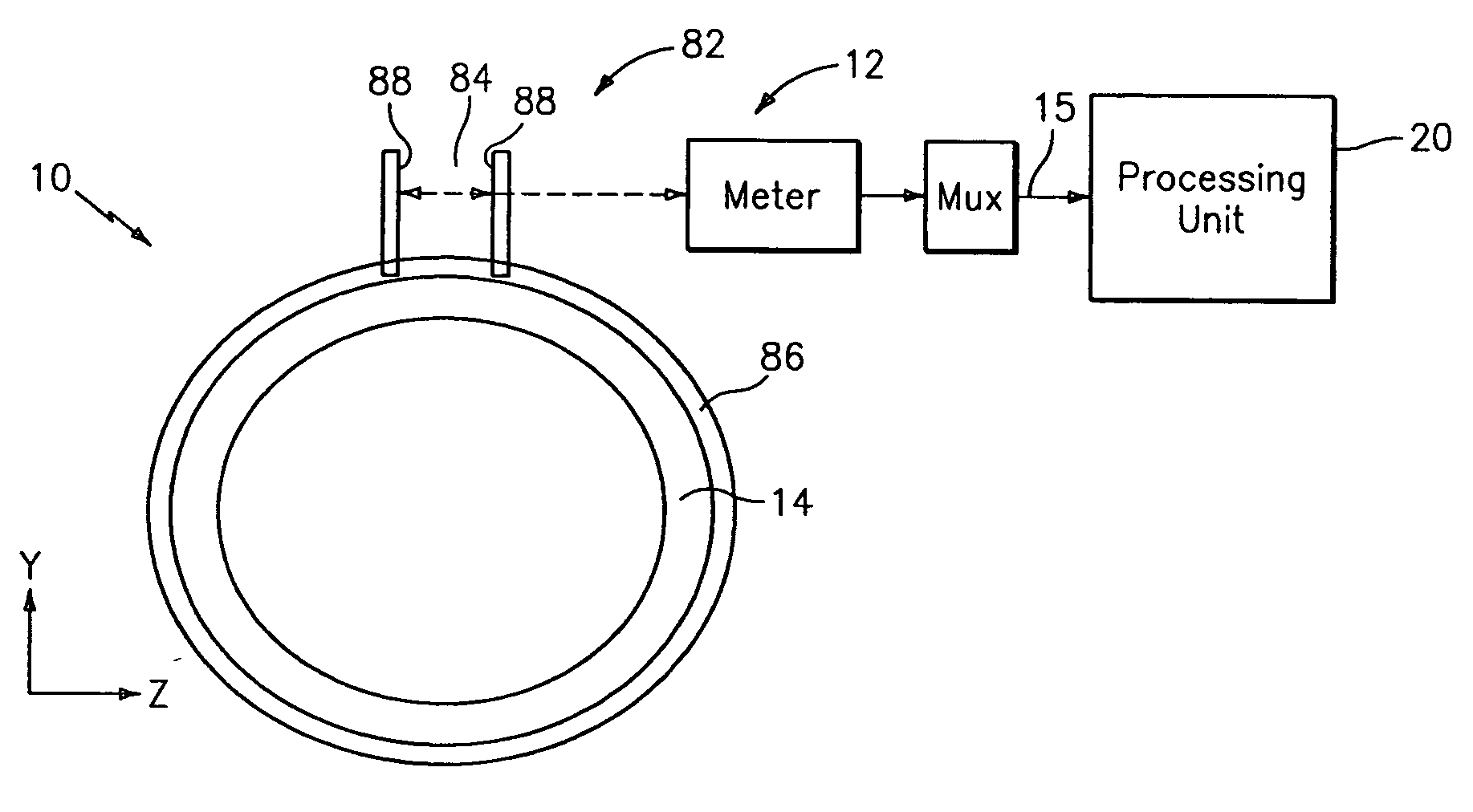
Flow meter
ActiveUS20050188771A1Specific gravity by measuring pressure differencesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLiquid stateDifferential pressure
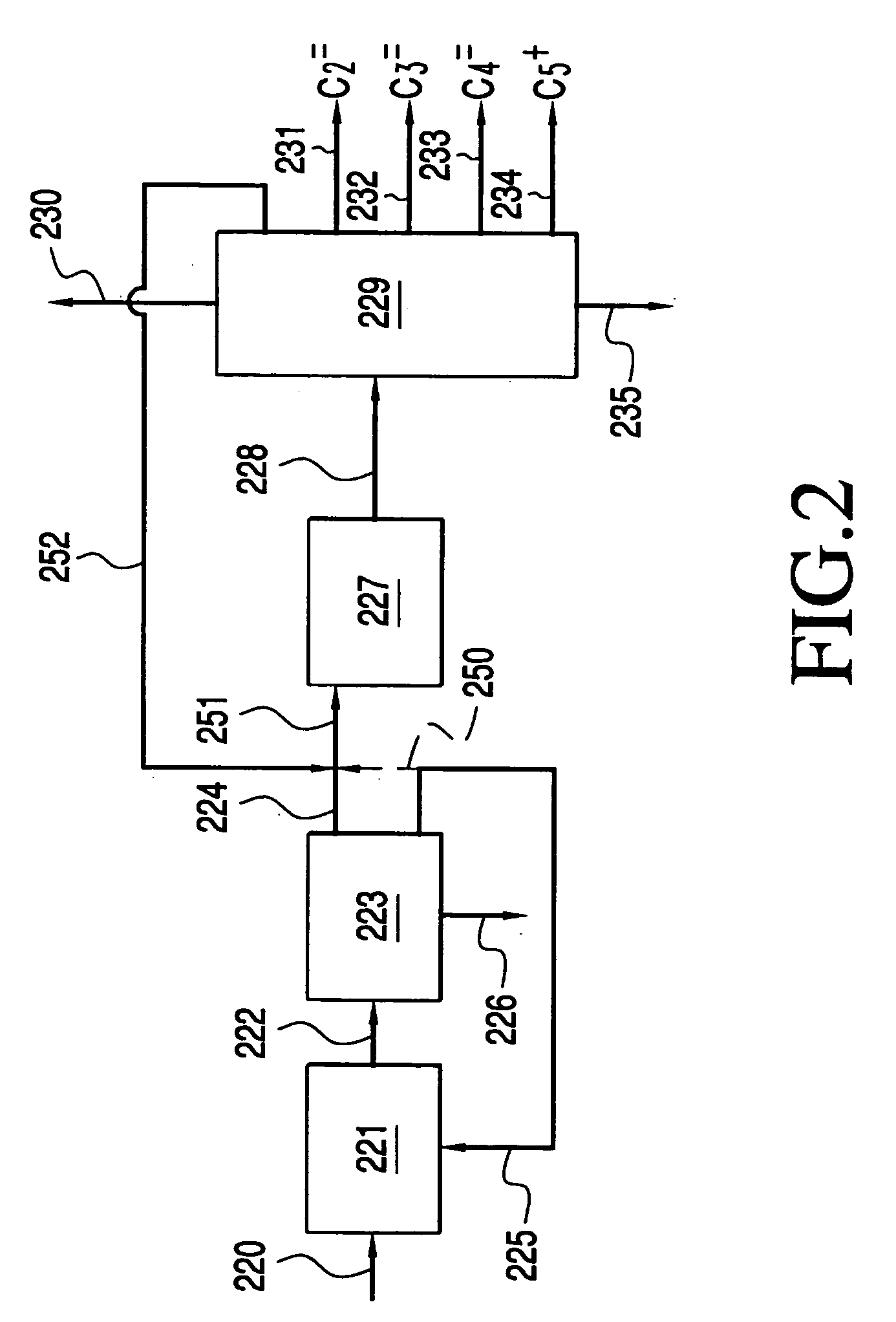
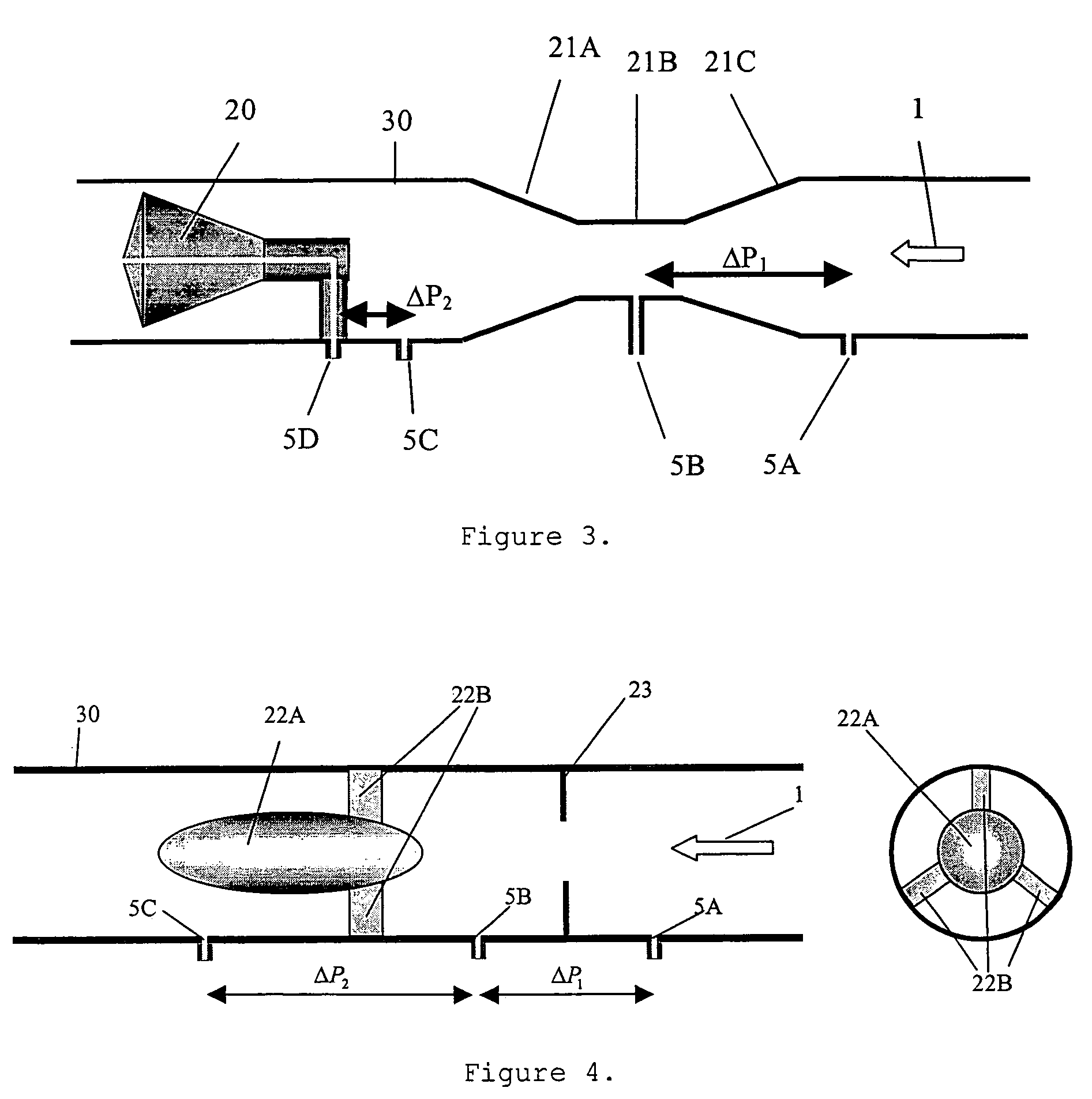
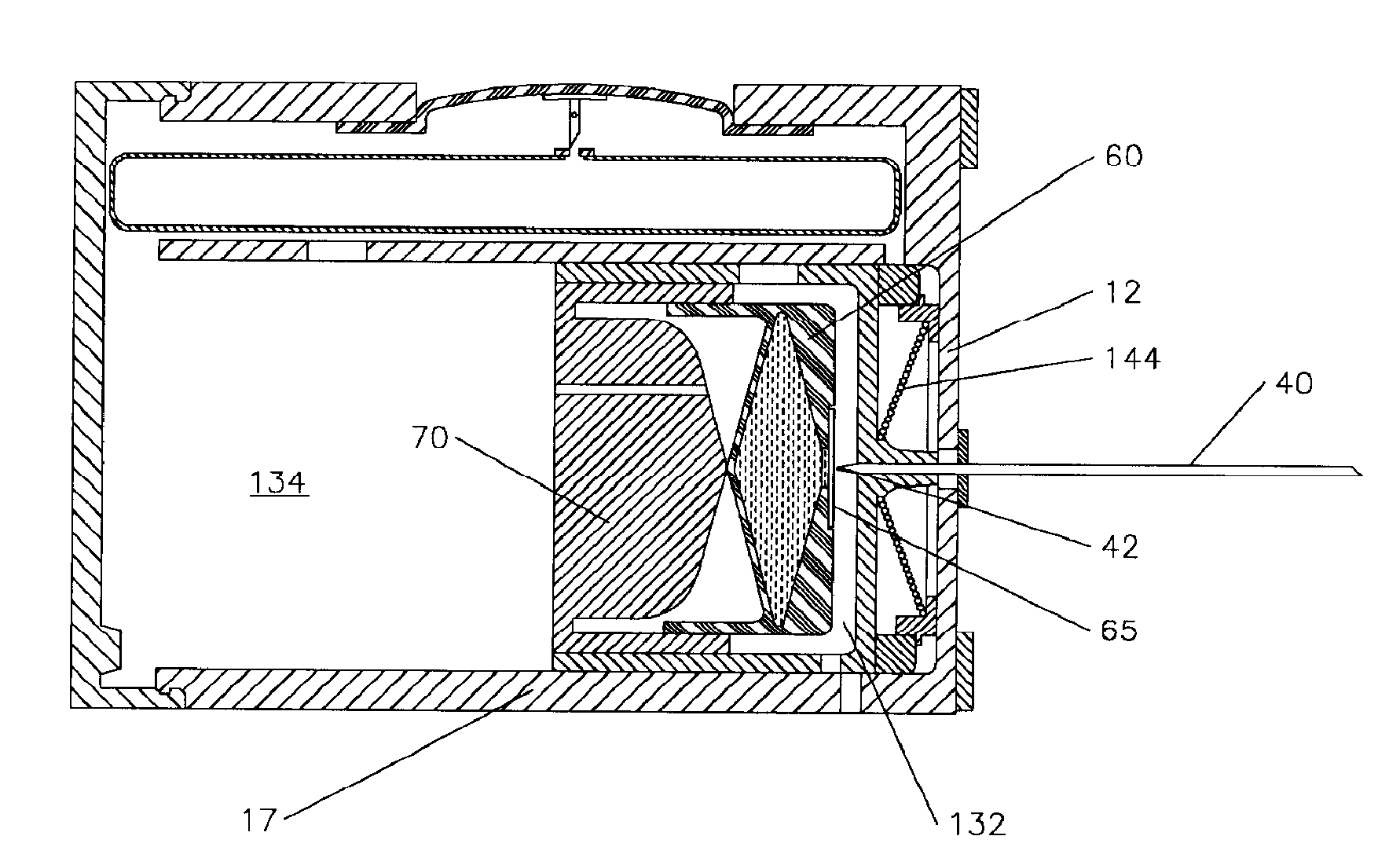
A flow meter obtains the individual flow rates of gas, liquid hydrocarbons, and water in a predominantly gas-containing flowing fluid mixture. The flow meter comprises a water content meter (7) provides a signal representing a measure of the water content of said fluid. It also comprises a double differential pressure generating (3) and measuring (4) structure, denoted a DDP-unit (2), that provides two measurement signals (6A and 6B) representing two independent values of differential pressure (DP) in said fluid (1). In addition to the above, the meter also comprises a signal processing unit (8) having inputs (9A-C) for receiving the measurement signals and the water content signal, and a calculation module (10) which calculates values representing the volumetric flow rates of said gas, liquid hydrocarbons and water in said fluid.
Owner:ROXAR FLOW MEASUREMENT
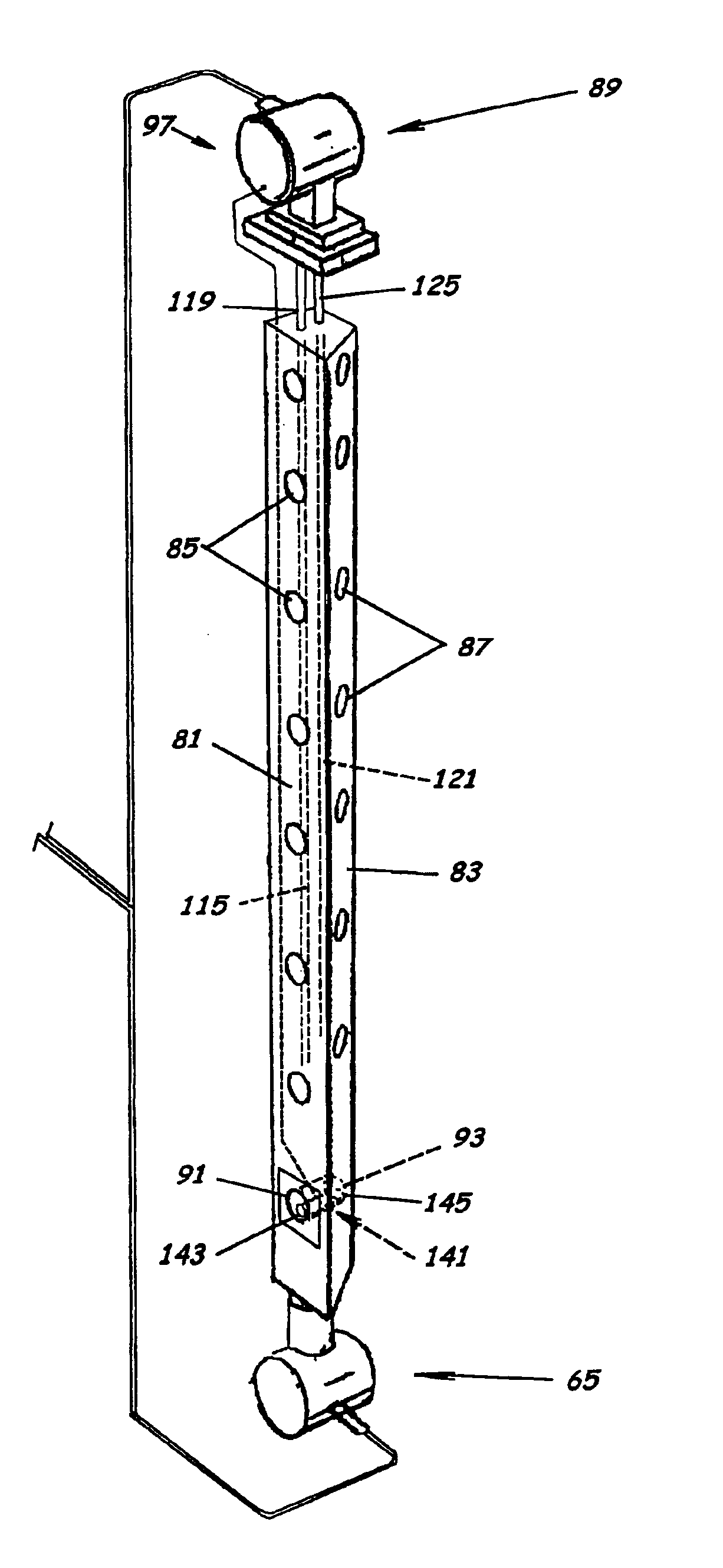
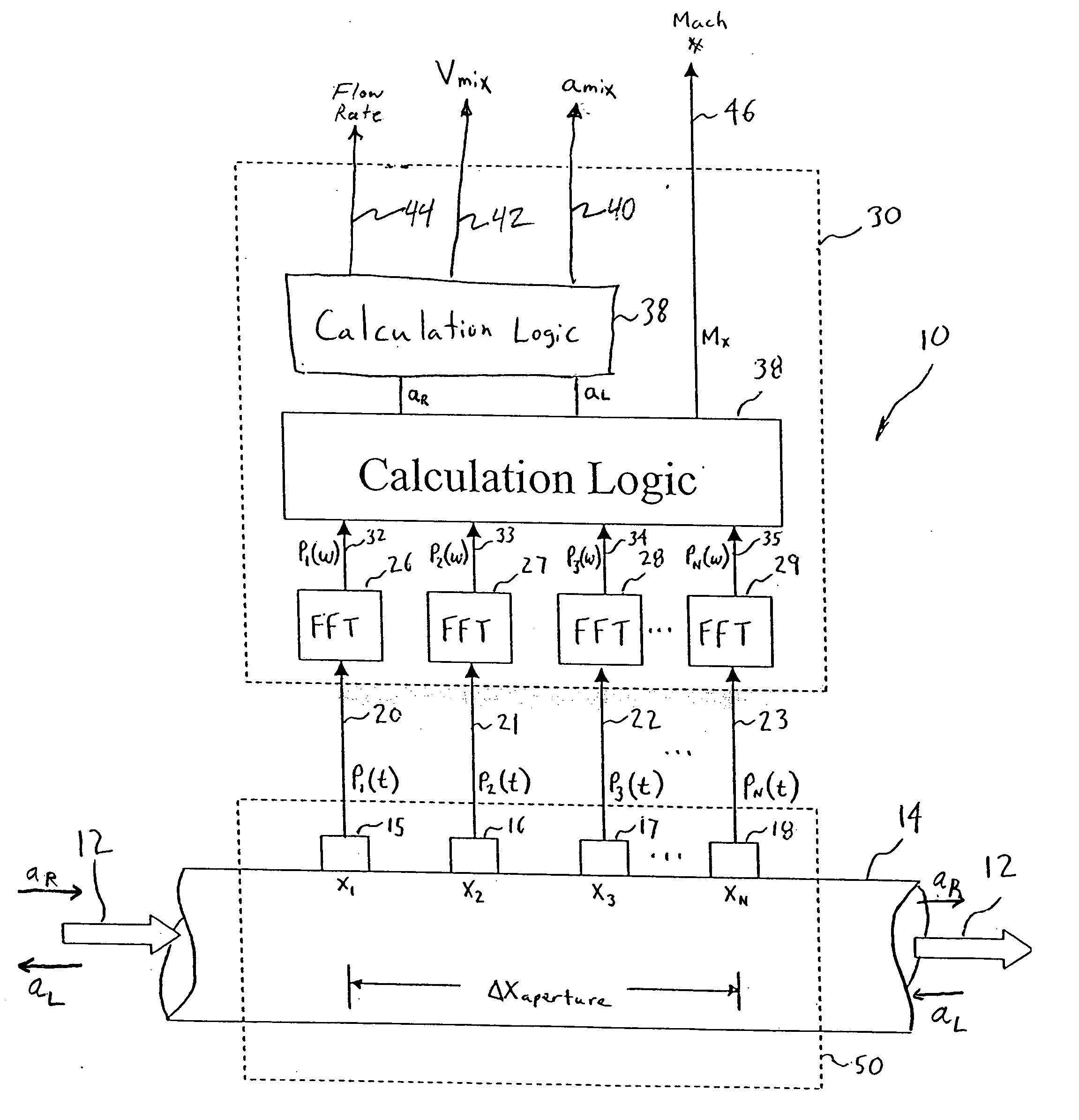
Probe for measuring parameters of a flowing fluid and/or multiphase mixture
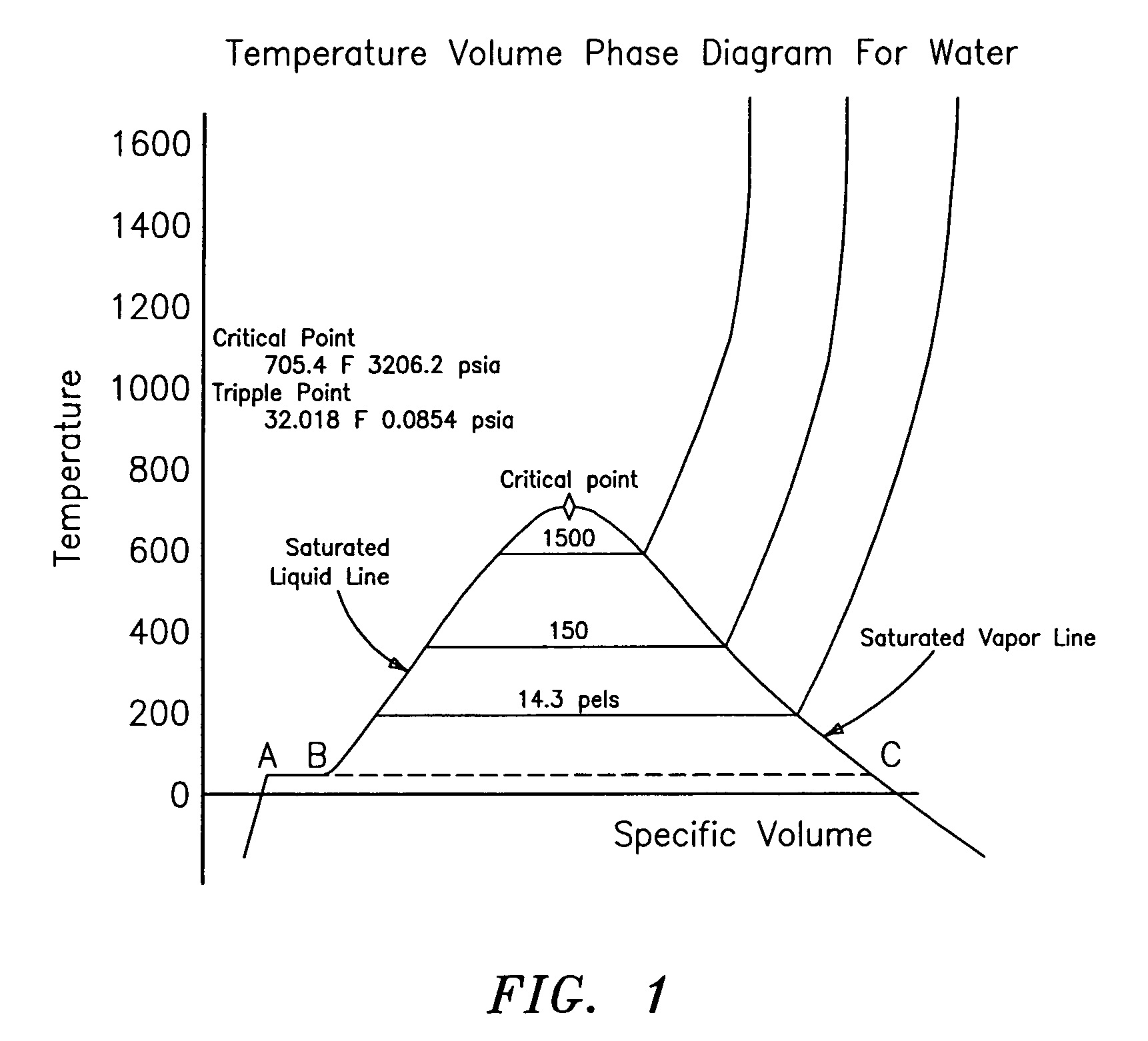
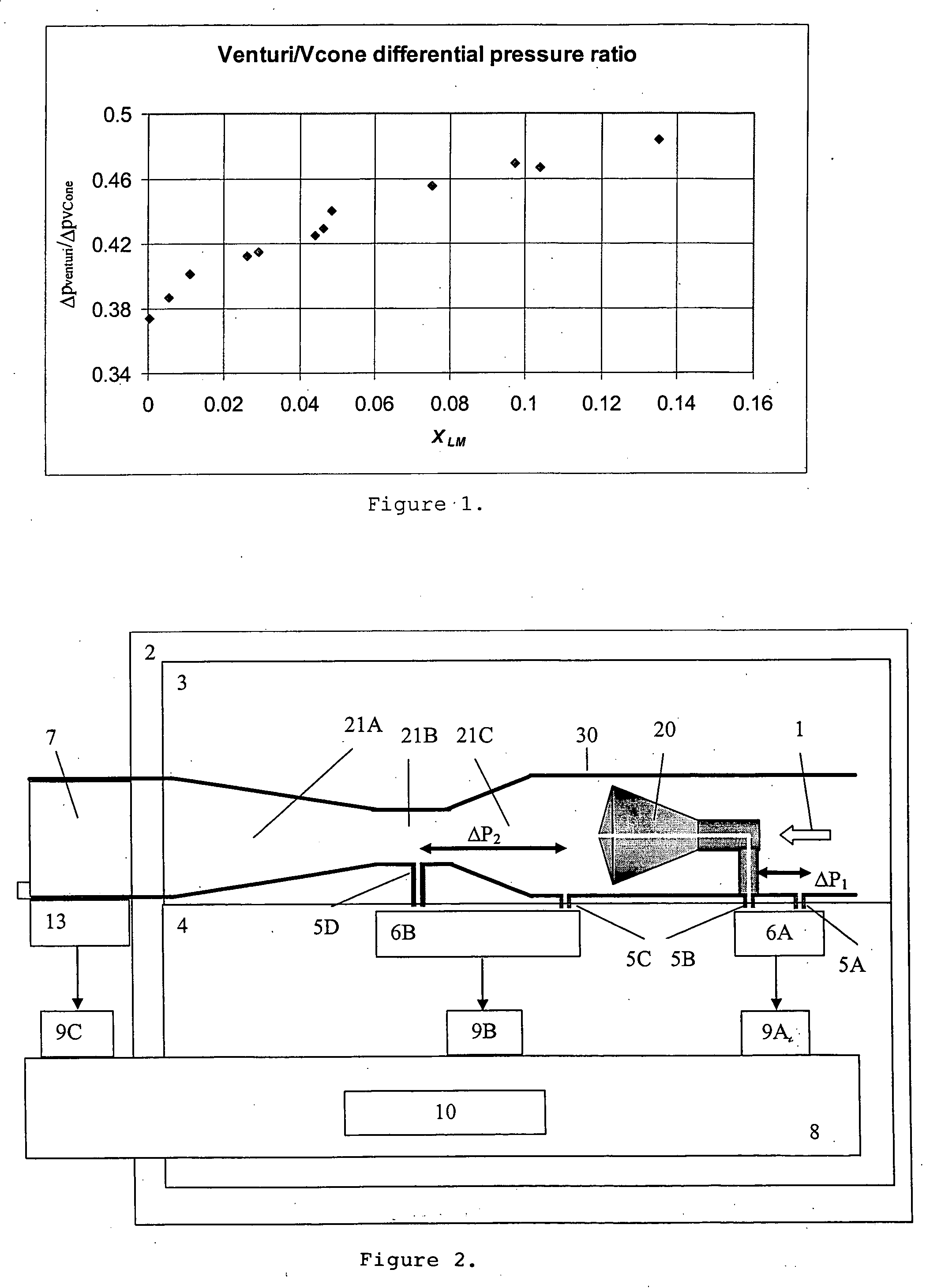
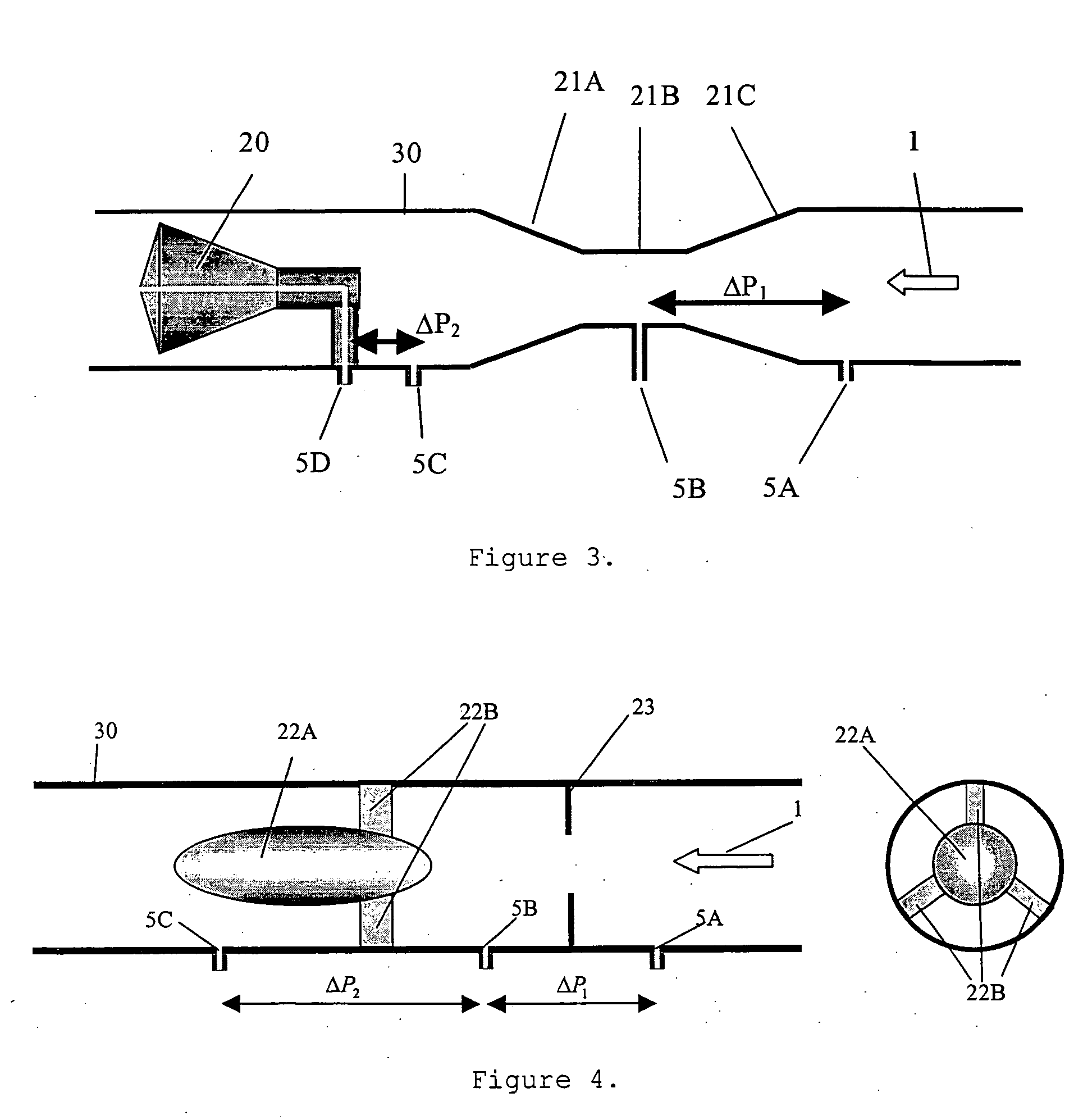
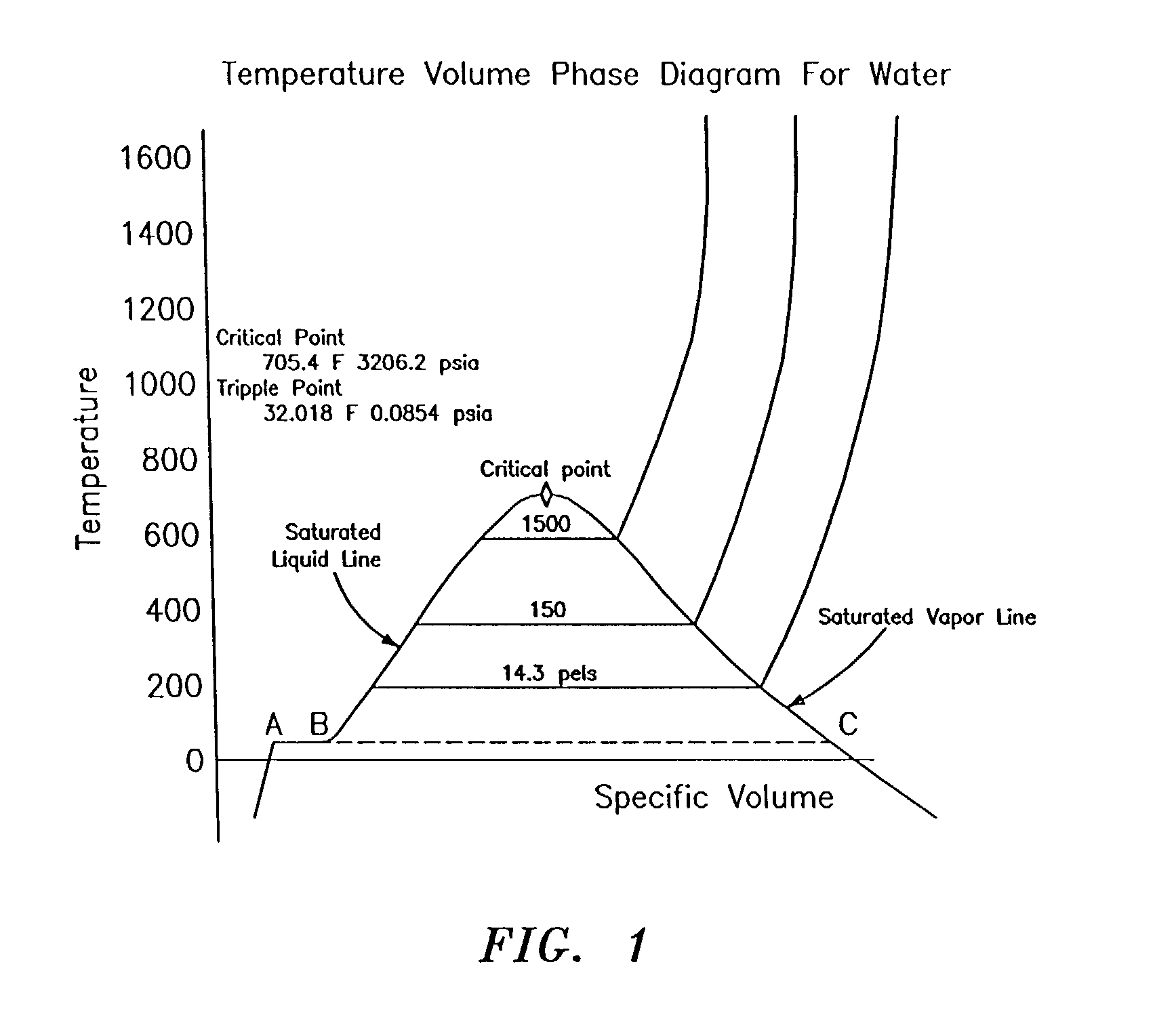
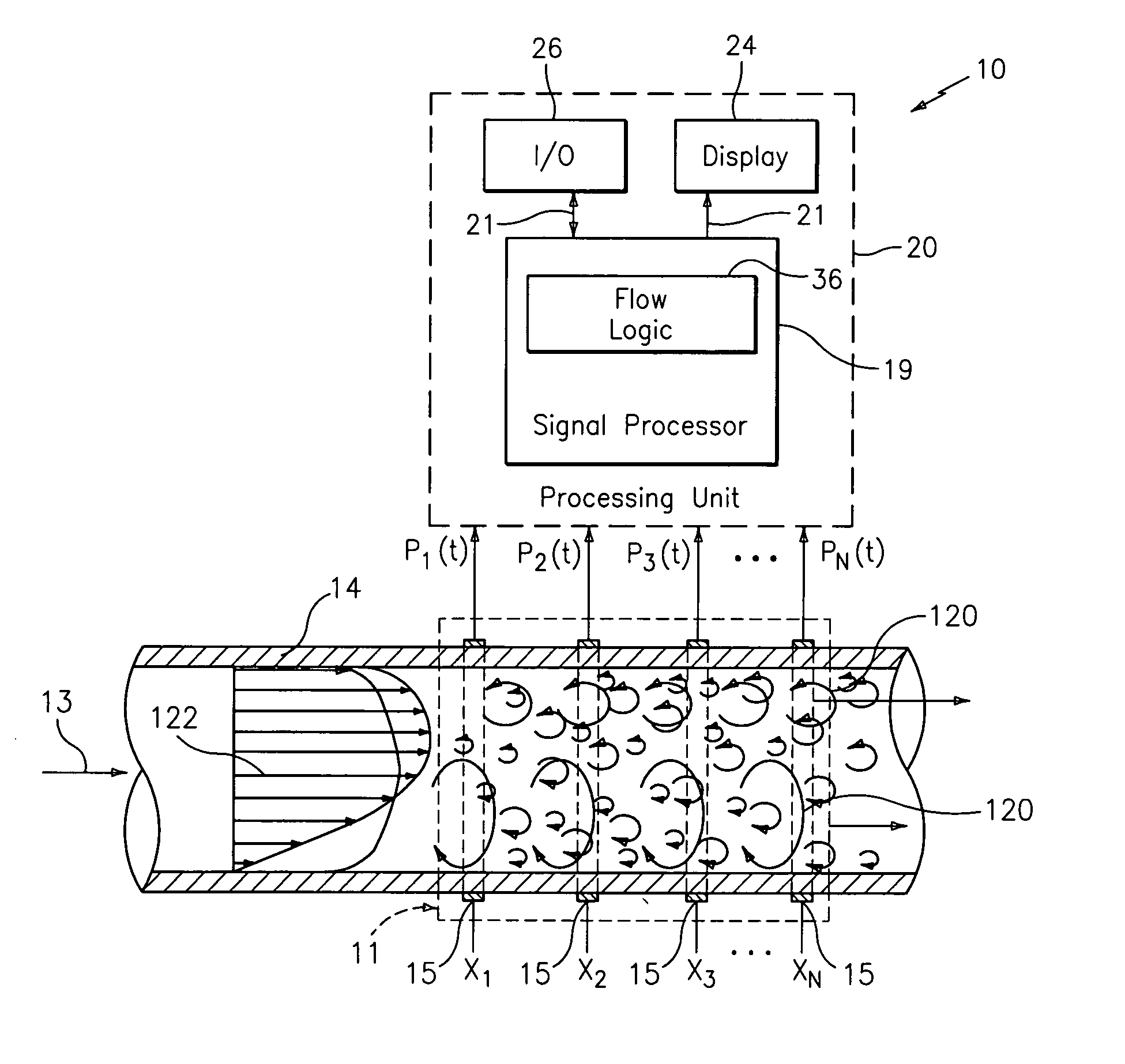
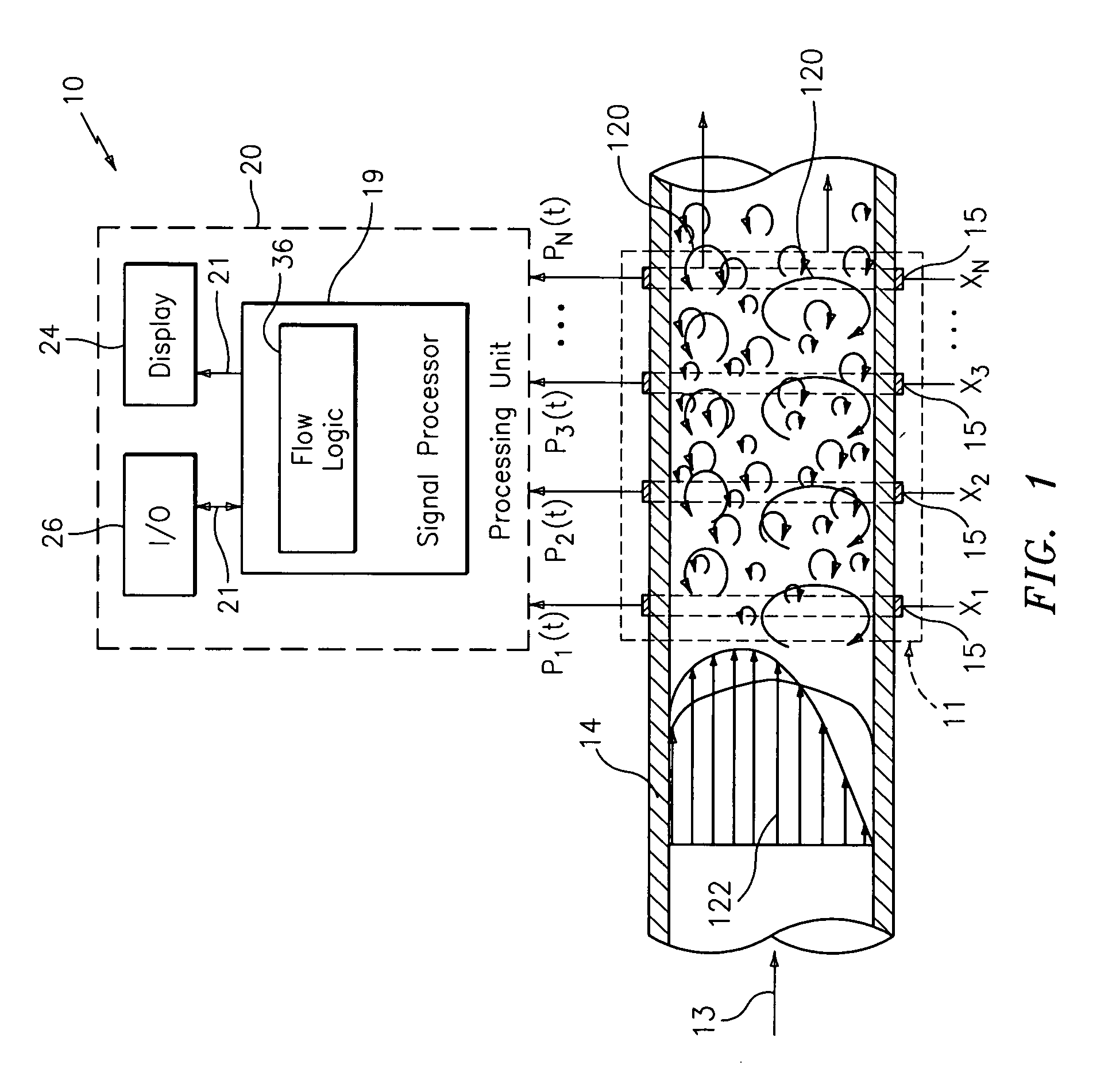
A probe 10,170 is provided that measures the speed of sound and / or vortical disturbances propagating in a single phase fluid flow and / or multiphase mixture to determine parameters, such as mixture quality, particle size, vapor / mass ratio, liquid / vapor ratio, mass flow rate, enthalpy and volumetric flow rate of the flow in a pipe or unconfined space, for example, using acoustic and / or dynamic pressures. The probe includes a spatial array of unsteady pressure sensors 15-18 placed at predetermined axial locations x1-xN disposed axially along a tube 14. For measuring at least one parameter of a saturated vapor / liquid mixture 12, such as steam, flowing in the tube 14. The pressure sensors 15-18 provide acoustic pressure signals P1(t)-PN(t) to a signal processing unit 30 which determines the speed of sound amix propagating through of the saturated vapor / liquid mixture 12 in the tube 14 using acoustic spatial array signal processing techniques. Frequency based sound speed is determined utilizing a dispersion model to determine the parameters of interest.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
System to measure density, specific gravity, and flow rate of fluids, meter, and related methods
ActiveUS6957586B2Little maintenanceMinimization needsVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsSpecific gravity using flow propertiesDifferential pressureDisplay device
A system to measure fluid flow characteristics in a pipeline, meter, and methods includes a pipeline having a passageway to transport flowing fluid therethrough, a process density meter including at least portions thereof positioned within the pipeline to provide flowing fluid characteristics including volumetric flow rate, fluid density, and mass flow rate of the flowing fluid, and a fluid characteristic display to display the fluid characteristics. The process density meter includes a vortex-shedding body positioned within the pipeline to form vortices and a vortex meter having a vortex frequency sensor to measure the frequency of the vortices and to determine the volumetric flow rate. The process density meter further includes a differential pressure meter positioned adjacent the vortex-shedding body to produce a differential pressure meter flow rate signal indicative of the density of fluid when flowing through the pipeline. The process density meter also includes a thermal flow meter positioned adjacent the vortex-shedding body to produce a mass flow rate signal indicative of the mass flow rate of fluid when flowing through the pipeline. The process density meter produces an output of a volumetric flow rate, a flowing fluid density, and a mass flow rate to be displayed by the fluid characteristic display.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
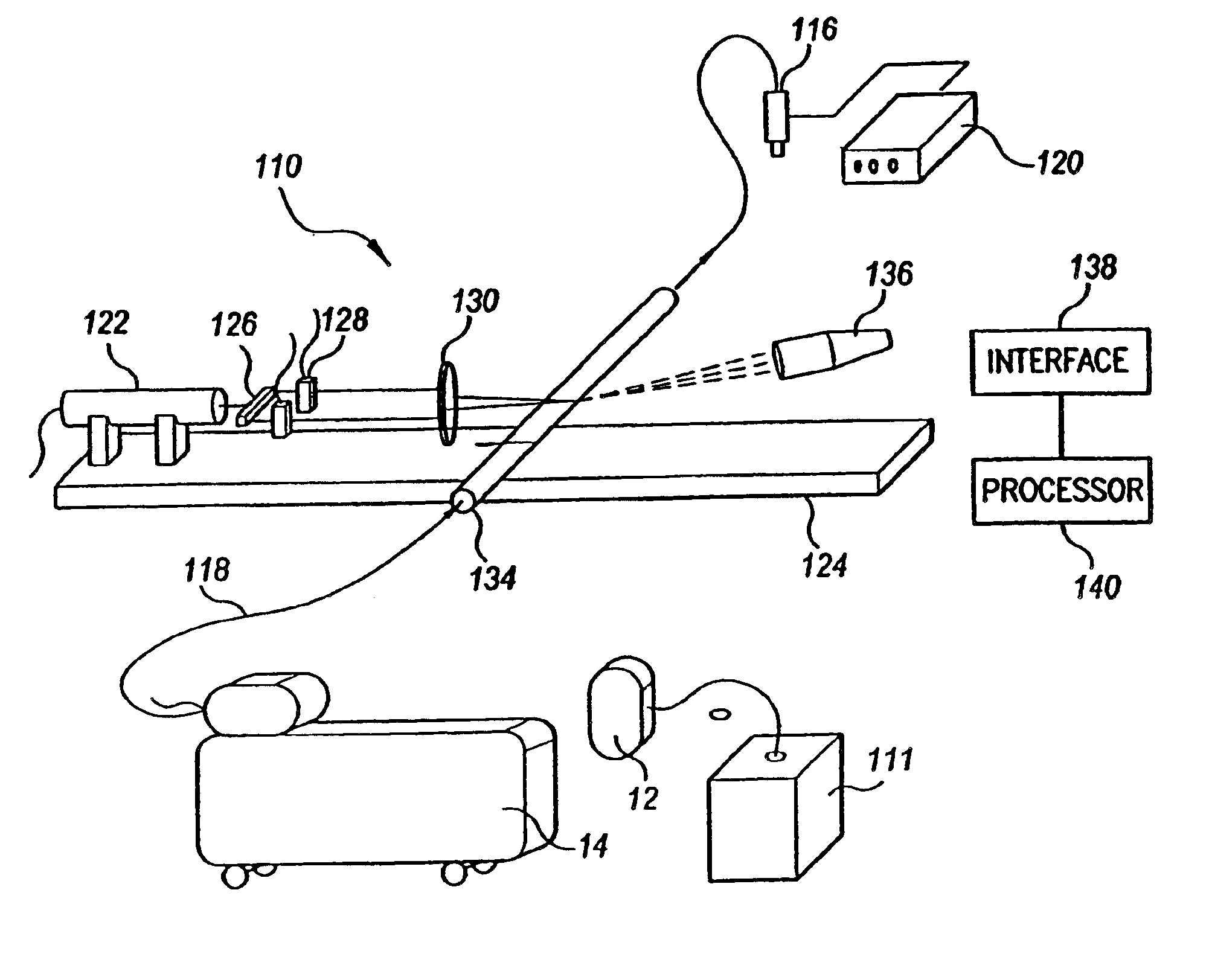
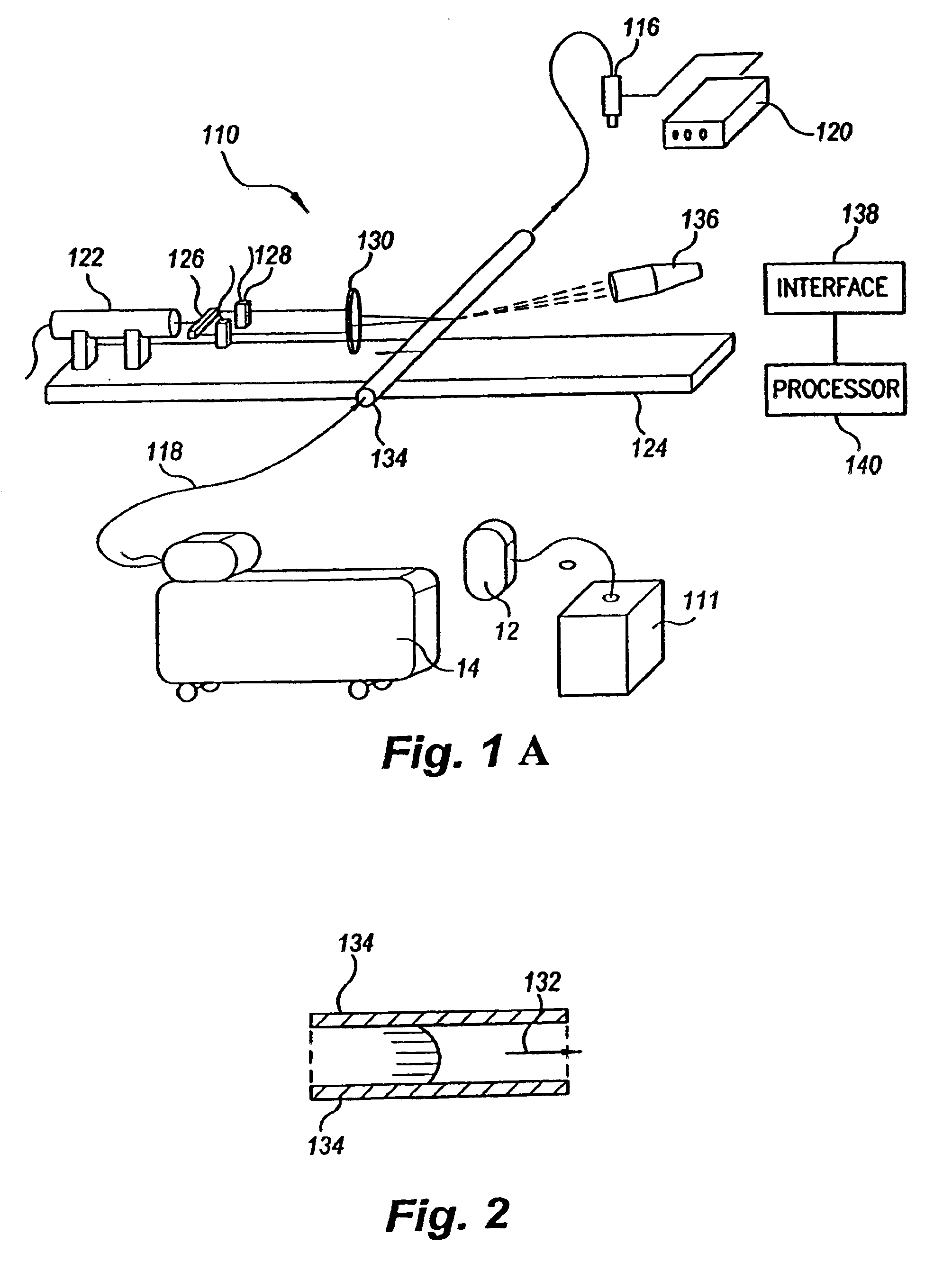
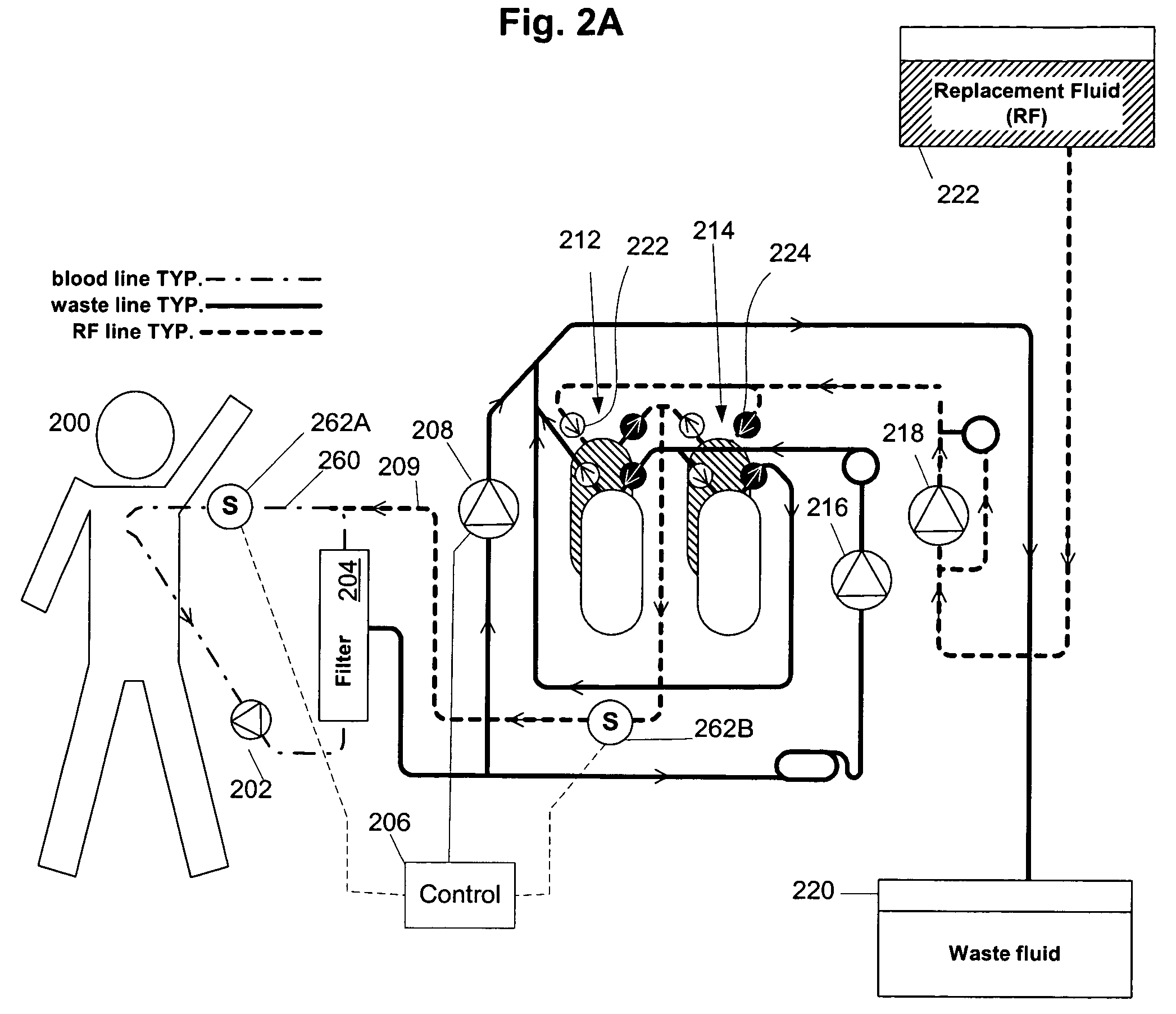
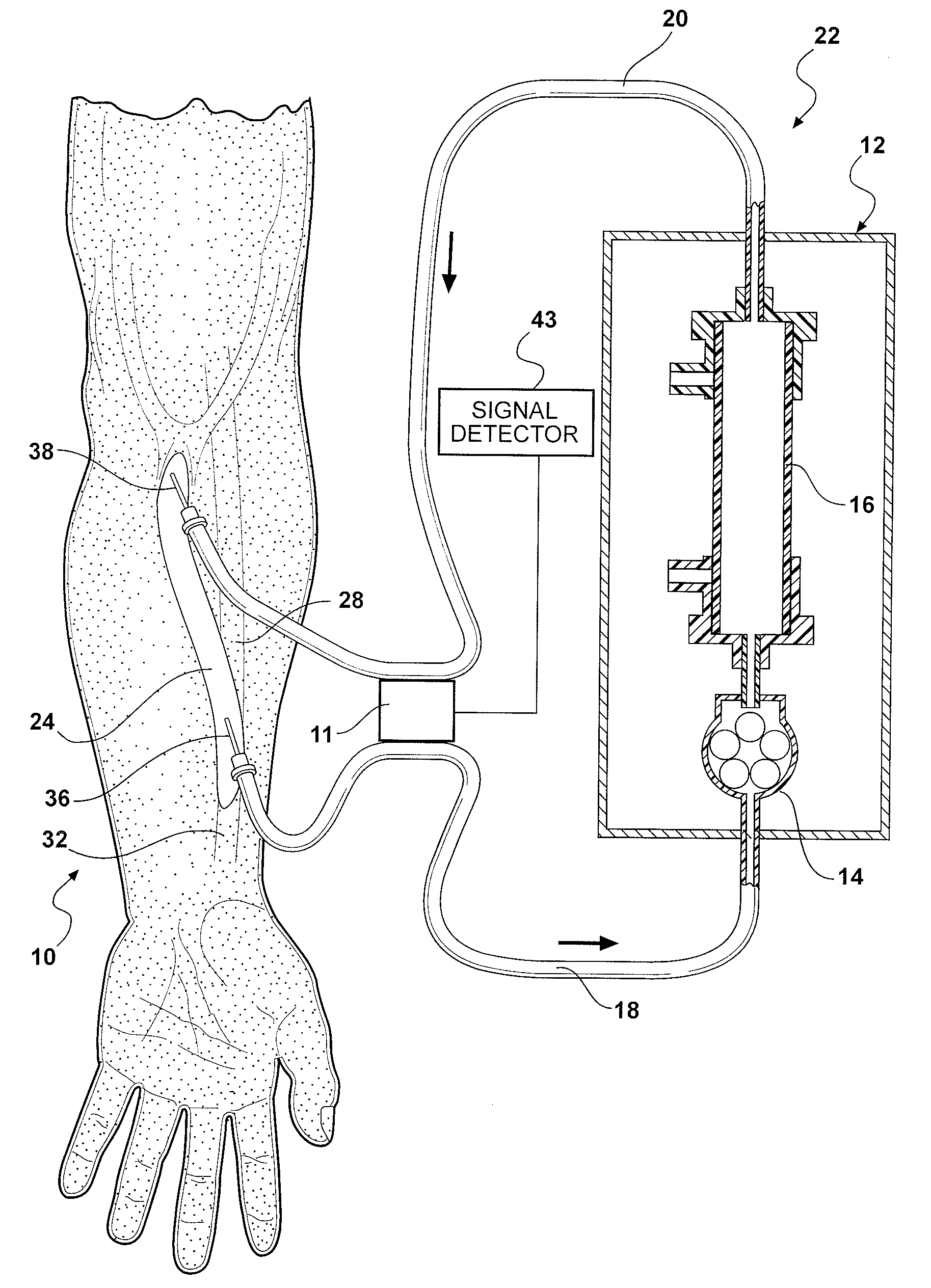
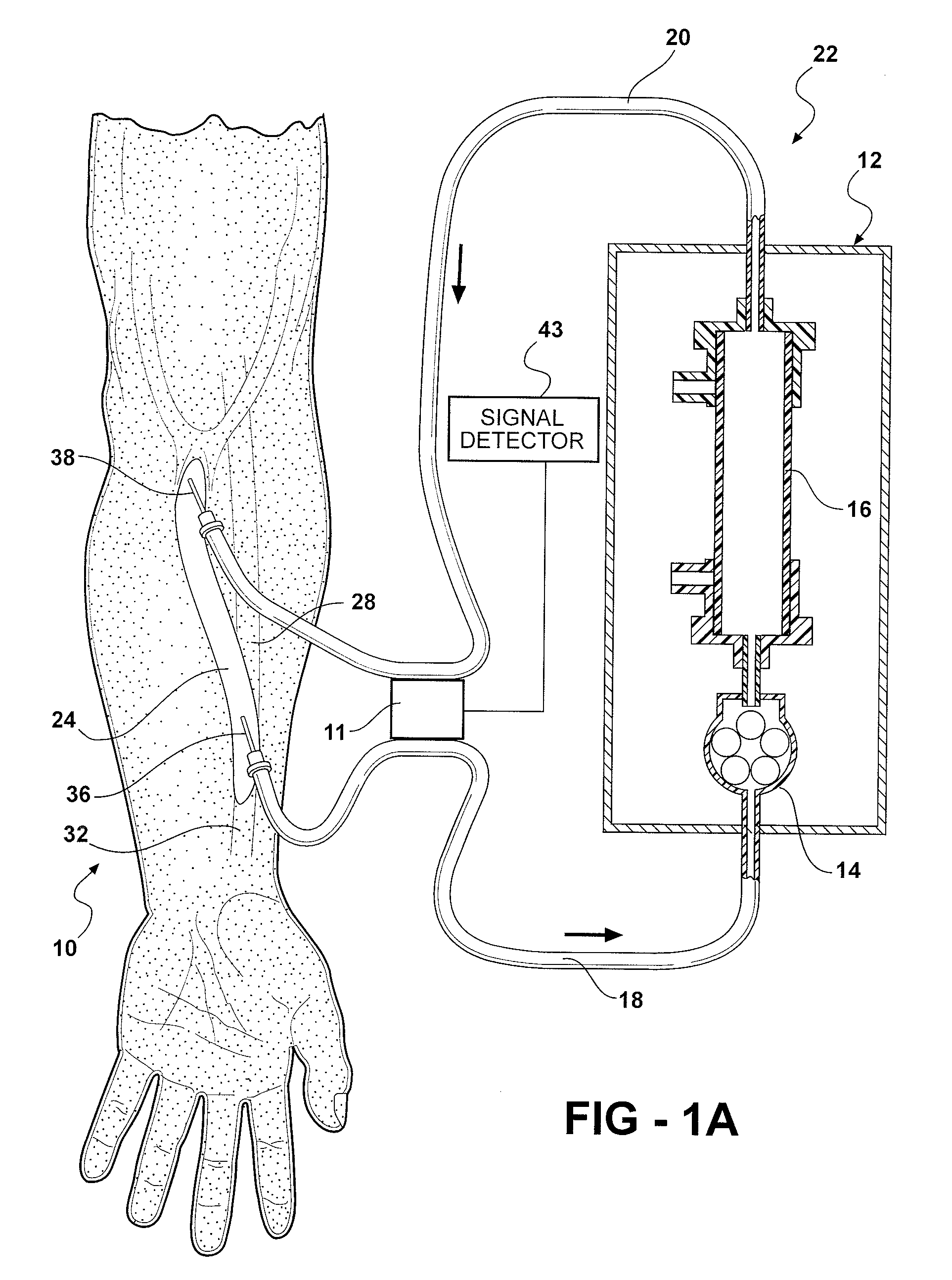
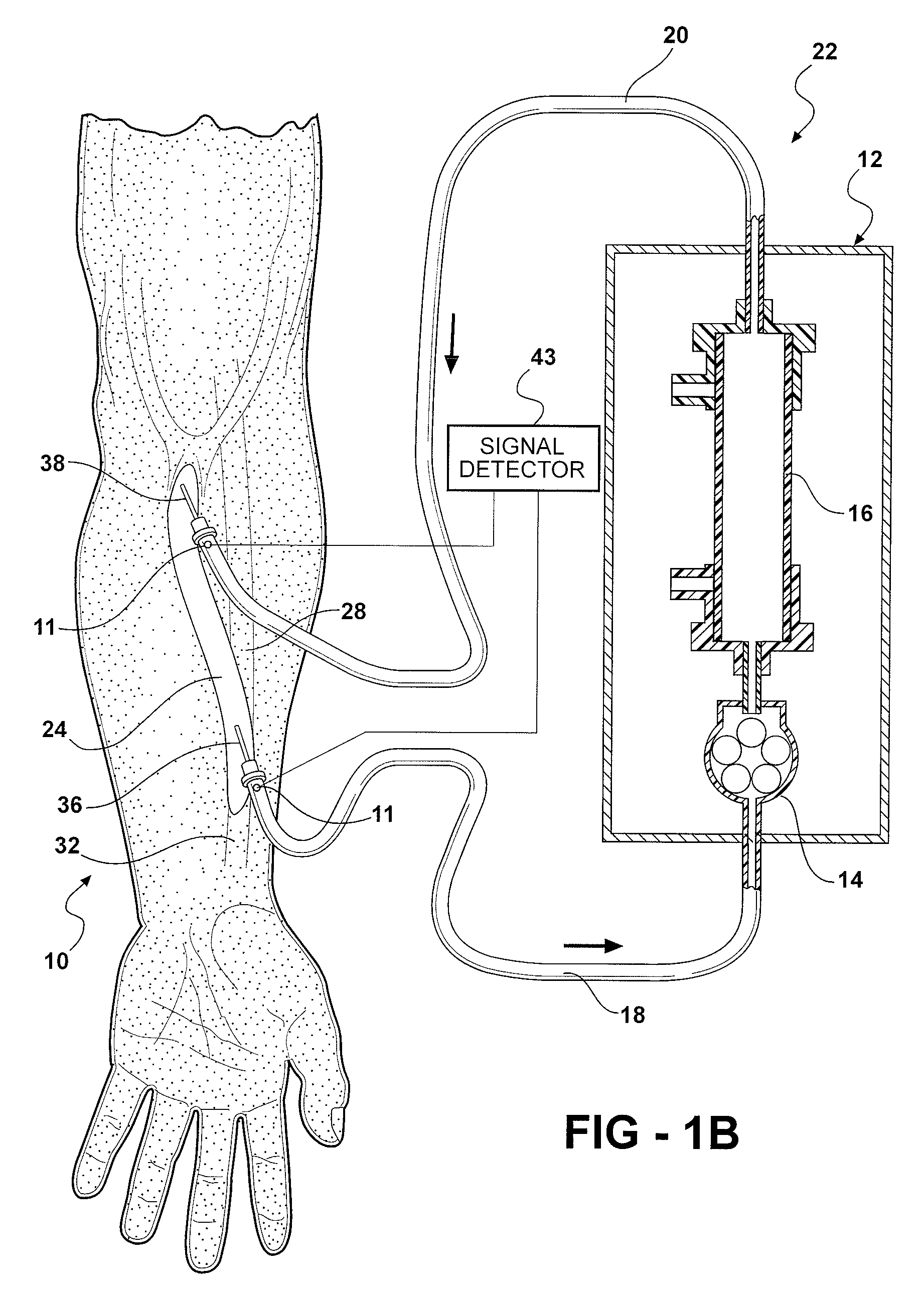
Methods and Systems for Determining Volume Flow in a Blood or Fluid Conduit, Motion, and Mechanical Properties of Structures Within the Body
The present invention provides a system for determining blood flow rate in a vessel which communicates blood between two locations of a patient, the system comprising: a conduit in fluid communication with the vessel; at least one sensor in communication with the vessel for determining differential blood pressure (? P) between two or more locations within the vessel; and a processor operably connected to the at least one sensor for processing the ? P to obtain blood flow rate within the vessel.A method for determining blood flow rate in a vessel which communicates blood between two locations of a patient, the method comprising: diverting blood from the vessel at a diversion point to obtain a flow of diverted blood in a conduit; determining differential blood pressure (? P) of the diverted blood through the conduit; and processing the ? P to obtain blood flow rate within the vessel.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Flow meter for measuring fluid mixtures
ActiveUS7293471B2Specific gravity by measuring pressure differencesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDifferential pressureLiquid hydrocarbons
Owner:ROXAR FLOW MEASUREMENT
Method and device for painless injection of medication
InactiveUS20100076400A1Simple and inexpensive to performSimple and inexpensive to and operateAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesMedication injectionAnesthetic
A method for providing a substantially painless injection of medication into a patient, including inserting an injection needle having an outside diameter greater than 0.20 mm and less than about 0.38 mm, and injecting a medicament through the needle and into the patient at a substantially constant volumetric flow rate of about 0.05 μL / s to about 50 μL / s that provides a painless injection. The method does not require the use of an anesthetic or that the medical personnel to spend a substantial amount of time performing the injection procedure, is relatively simple and inexpensive to perform and operate, and provides a relatively high degree of safety for both the medical personnel and for the patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
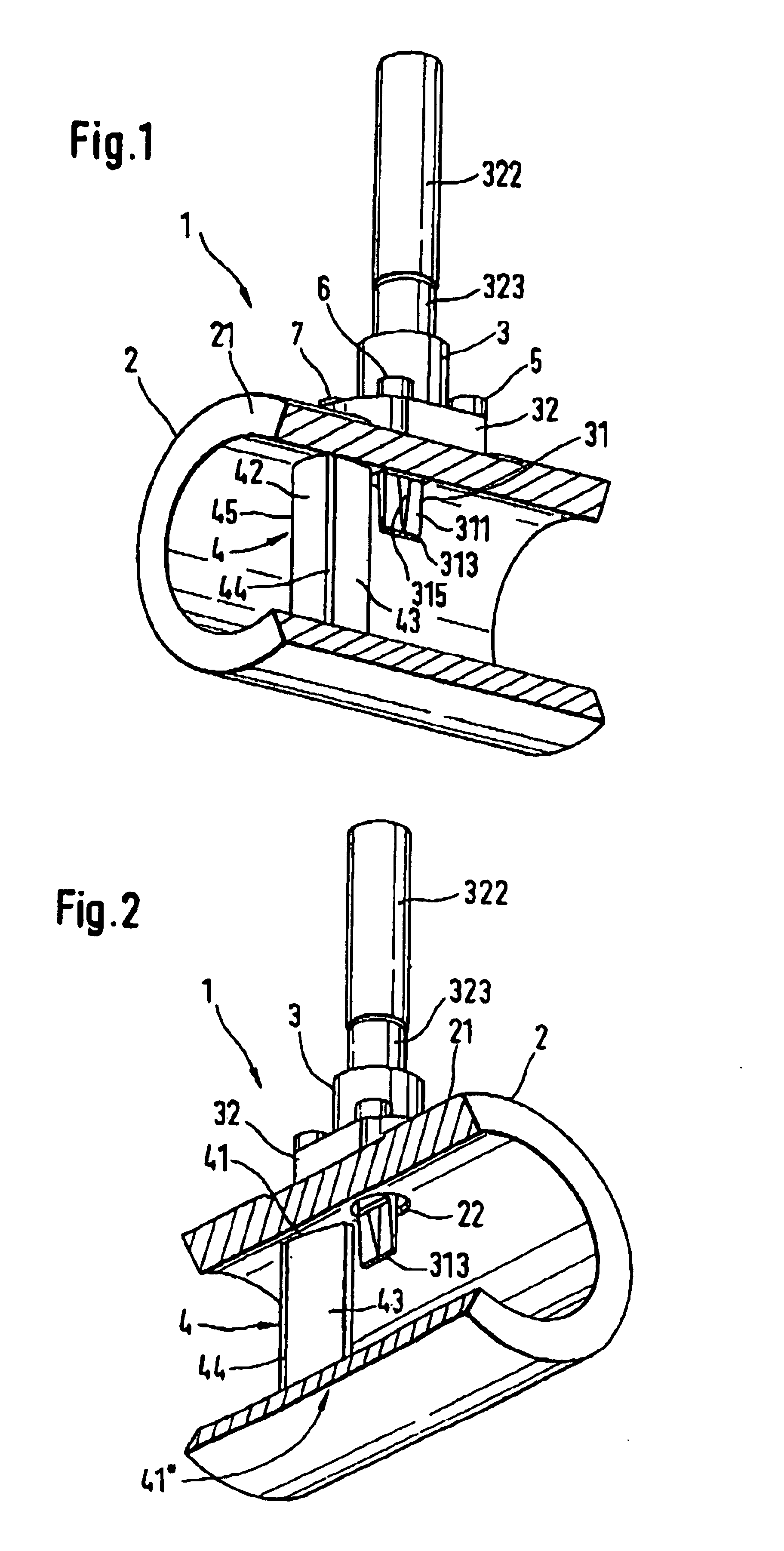
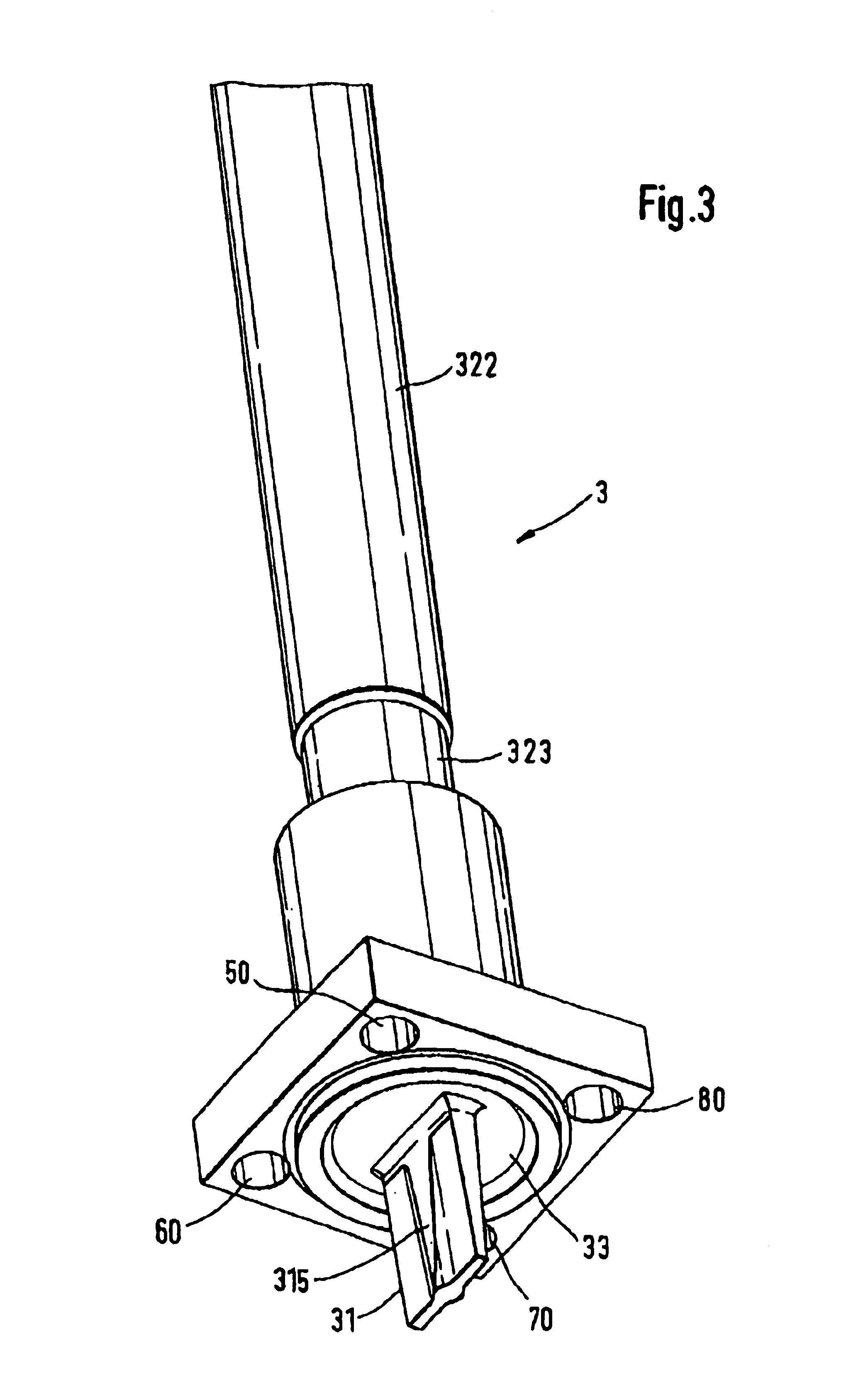
Device and method for controlling/balancing flow fluid flow-volume rate in flow channels
InactiveUS6899095B2Minimize quasi-steady flow effectEasy to cleanDomestic stoves or rangesDispersed particle filtrationControl flowControl system
A system and method for controlling flow in filtering systems and for balancing the flow through fluid systems employs flow control devices that minimize suspended matter precipitation. Several embodiments are included. In a first embodiment, a smooth-walled flow control device (410) with no abrupt transitions is provided in a flow conduit section. In a second embodiment, a filter (305) acts as a flow control device. A variation of the latter locates a flow control device (300) immediately adjacent to the filter (305) and upstream of it. In other embodiments, a control system (950) detects the real time status of the load to provide on the fly critical balancing.
Owner:HALTON GROUP LTD
Hydrogen peroxide vaporizer
ActiveUS20070253859A1Modifies flowModifies temperatureLavatory sanitoryDeodrantsLiquid hydrogenEngineering
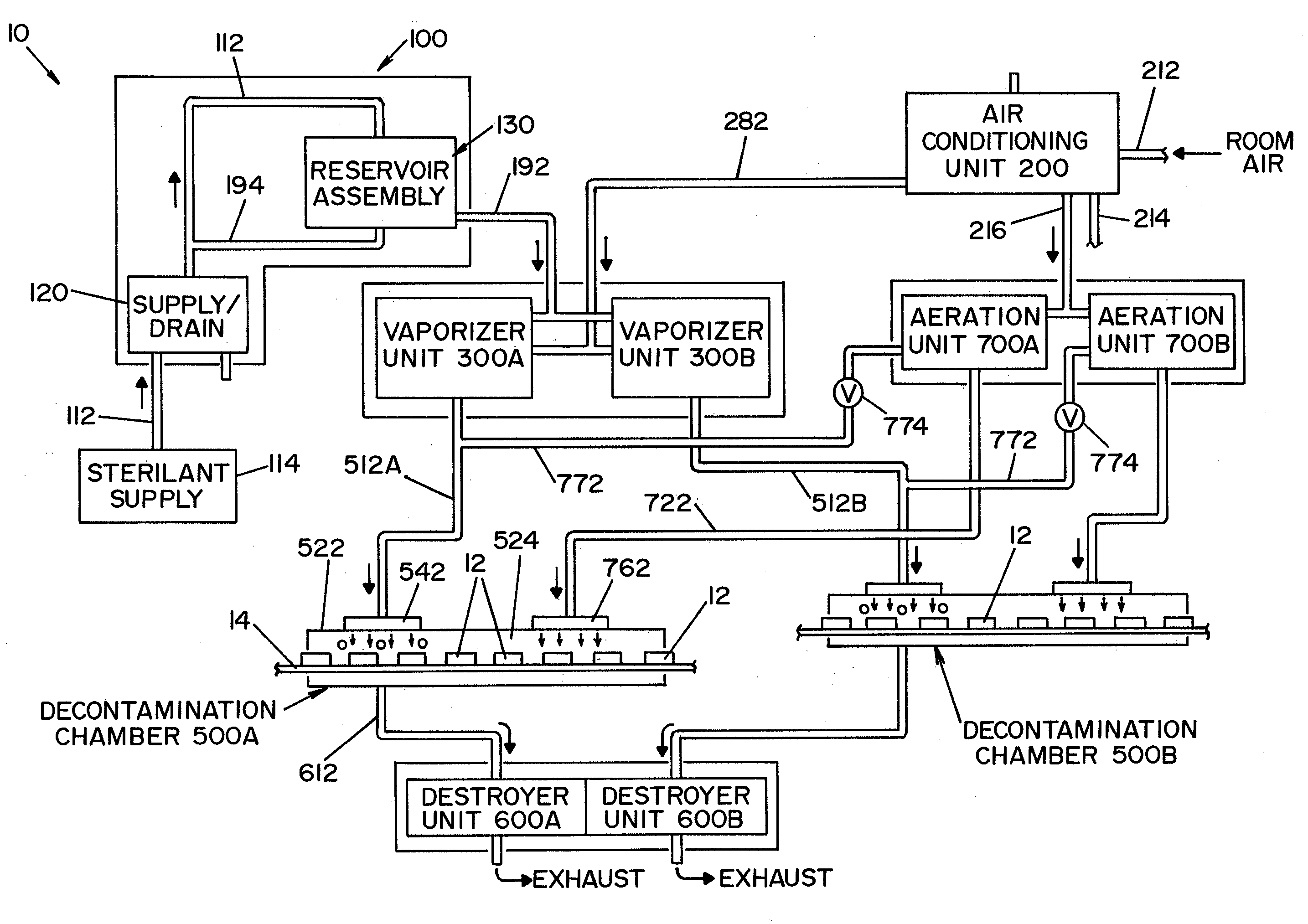
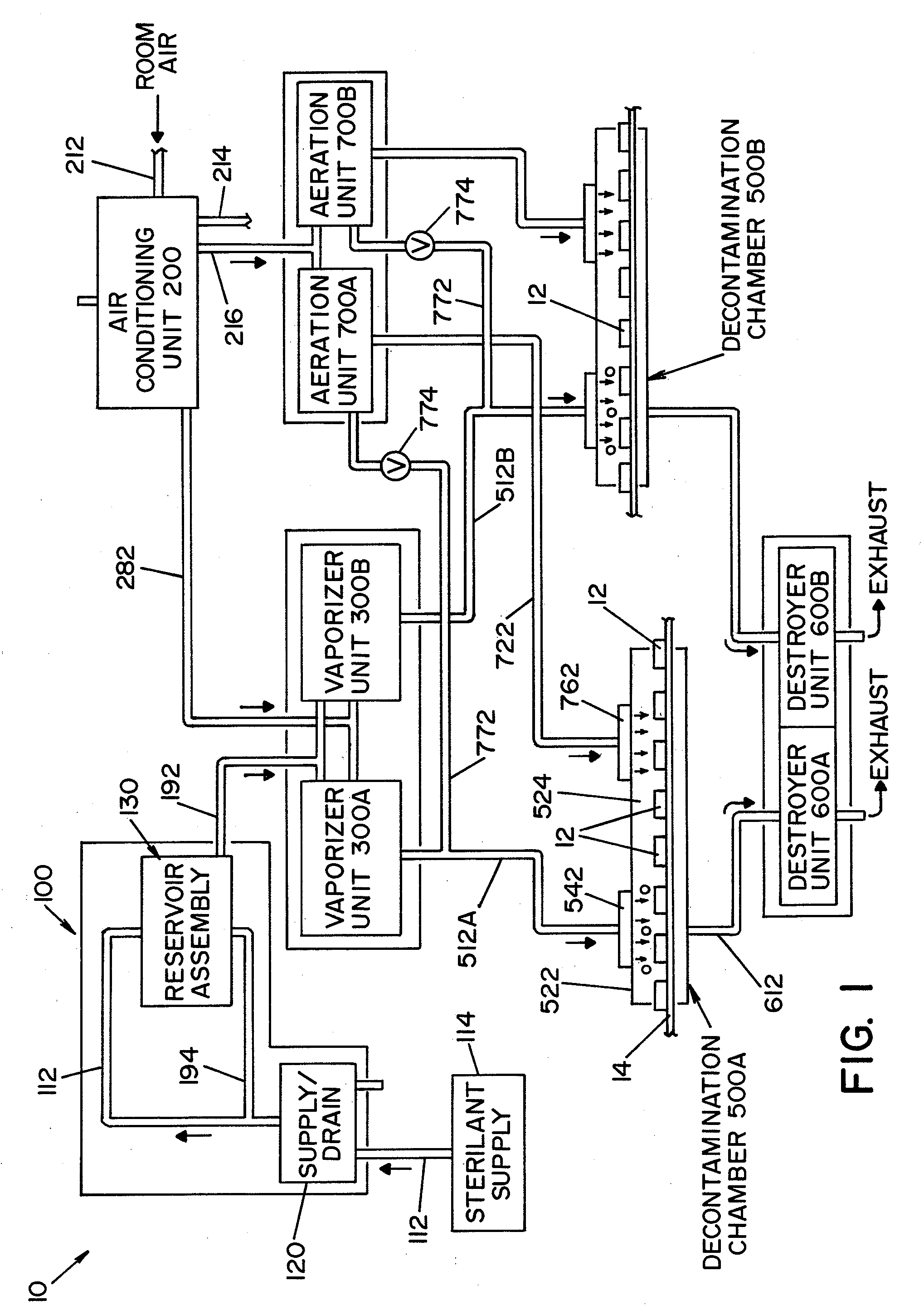
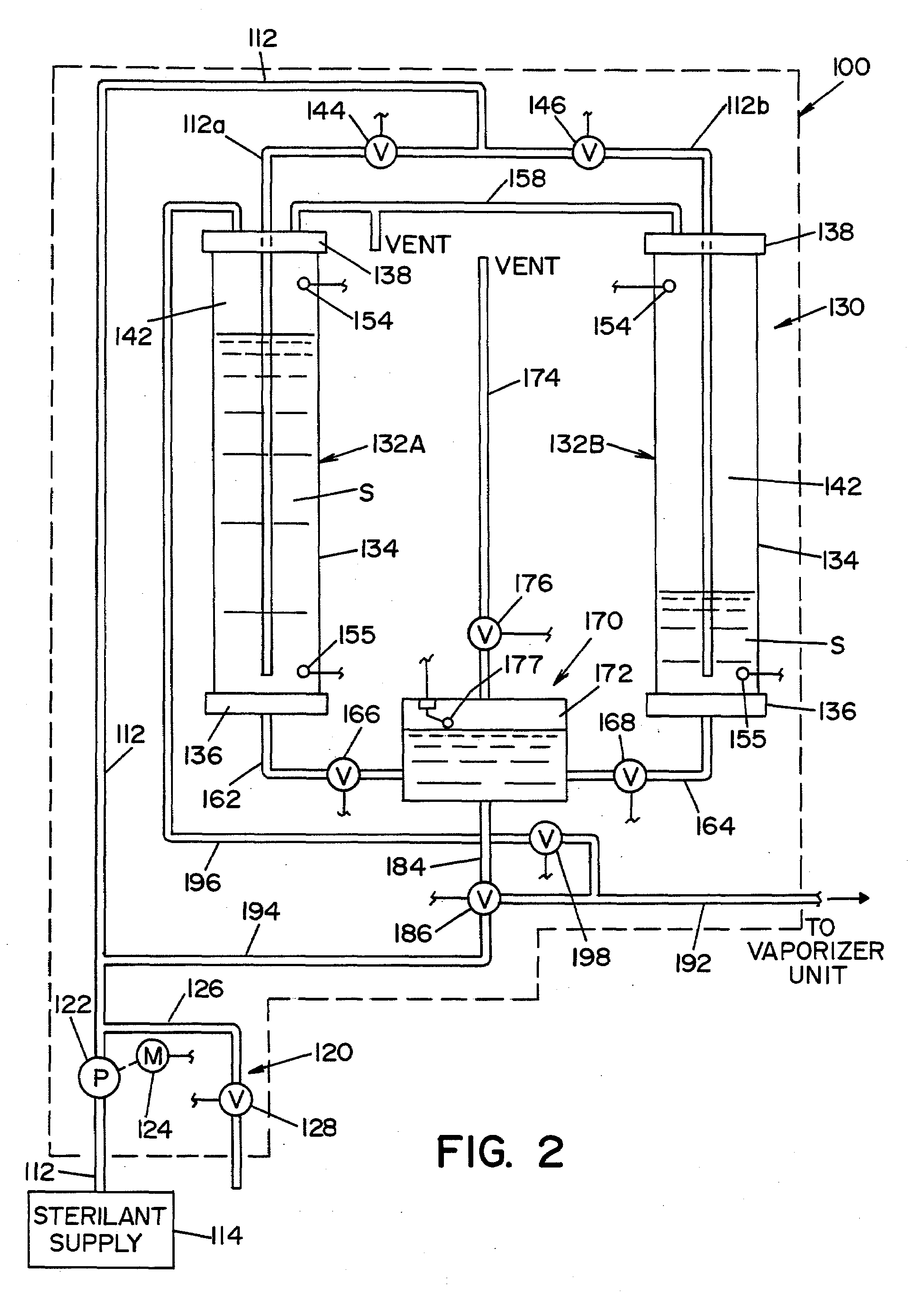
A method of decontaminating articles, comprising the steps of:(a) moving a plurality of articles having a known temperature along a first path;(b) conveying a carrier gas along a second path that includes an elongated plenum, the second path intersecting the first path downstream from the plenum;(c) heating the carrier gas to a temperature of at least about 105° C. at a location upstream of the plenum;(d) introducing into the carrier gas in the plenum an atomized mist of a liquid hydrogen peroxide of known concentration; and(e) controlling the following:(1) the volumetric flow of carrier gas along the second path;(2) the volume of hydrogen peroxide introduced into the carrier gas; and(3) the temperature of the carrier gas introduced into the plenum, such that the concentration of the vaporized hydrogen peroxide in the carrier gas where the first path intersects the second path has a dew point temperature below the known temperature of the articles.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
Vortex flow sensor for measuring fluid flow through a flow tube
InactiveUS6910387B2Improve thermal conductivityEasy to measureVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectIndirect mass flowmetersTwo temperatureEngineering
The vortex flow sensor is designed to measure the mass flow rate, the volumetric flow rate, or the flow velocity of a fluid flowing in a flow tube having a tube wall, and has two temperature sensors arranged in such a way that the vortex flow sensor may also be used with fluids which would corrode the temperature sensors. A bluff body in the flow tube sheds vortices and thus causes pressure fluctuations. A vortex sensor device responsive thereto is fitted downstream of the bluff body in a hole provided in the wall of the flow tube. The vortex sensor device comprises a sensor vane extending into the fluid. The temperature sensors are disposed in a blind hole of the sensor vane. Alternatively, the temperature sensor may be disposed in blind hole of the bluff body.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Apparatus for measuring velocity and flow rate of a fluid having a non-negligible axial mach number using an array of sensors
ActiveUS20050005712A1Volume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectMaterial analysisSensor arrayEngineering
Owner:EXPRO METERS
Method and apparatus for measuring parameters of a stratified flow
InactiveUS20050246111A1Volume flow measuring devicesVolume/mass flow by differential pressureSensor arrayEngineering
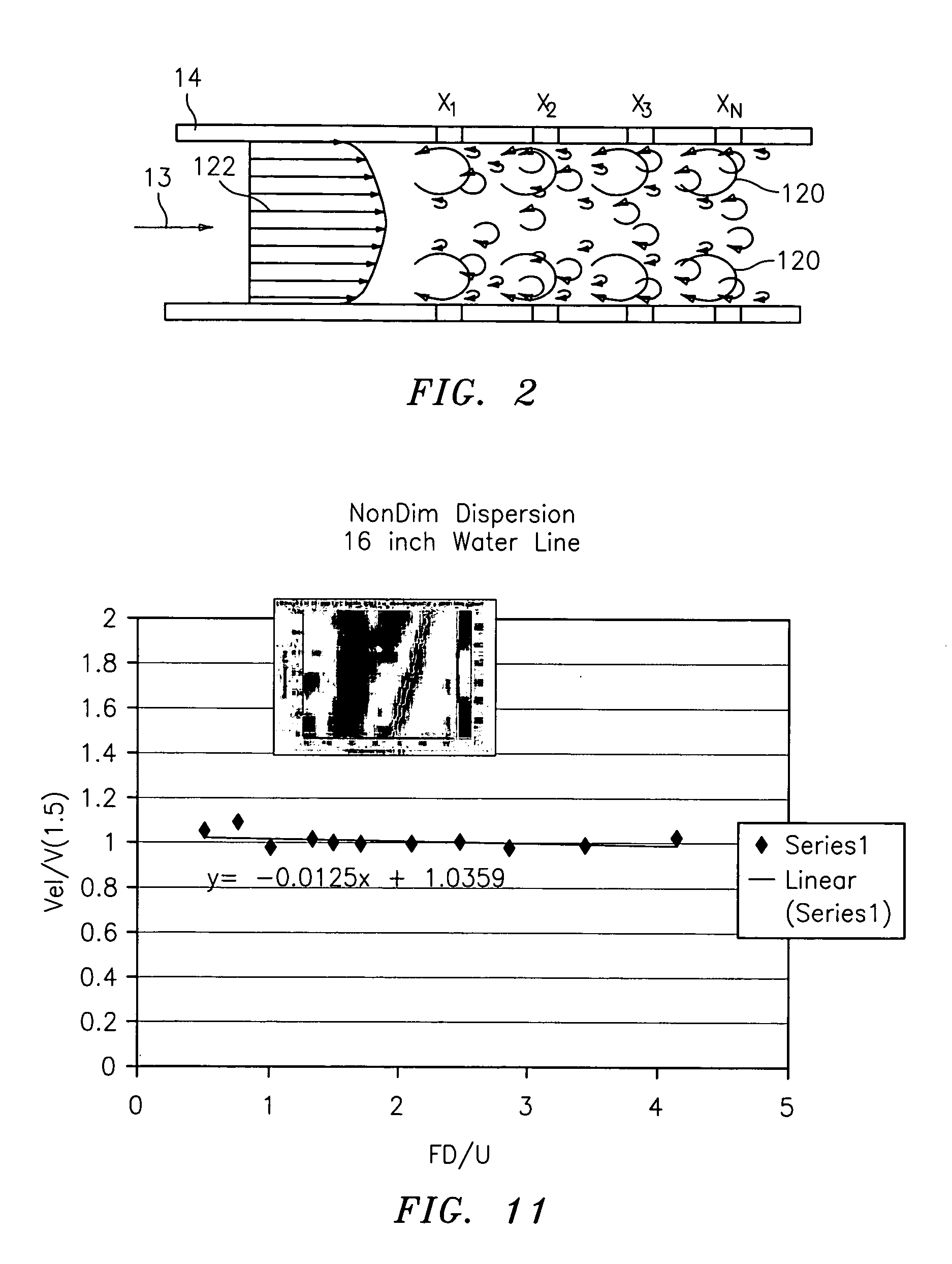
Various methods are described for measuring parameters of a stratified flow using at least one spatial array of sensors disposed at different axial locations along the pipe. Each of the sensors provides a signal indicative of unsteady pressure created by coherent structures convecting with the flow. In one aspect, a signal processor determines, from the signals, convection velocities of coherent structures having different length scales. The signal processor then compares the convection velocities to determine a level of stratification of the flow. The level of stratification may be used as part of a calibration procedure to determine the volumetric flow rate of the flow. In another aspect, the level of stratification of the flow is determined by comparing locally measured velocities at the top and bottom of the pipe. The ratio of the velocities near the top and bottom of the pipe correlates to the level of stratification of the flow. Additional sensor arrays may provide a velocity profile for the flow. In another aspect, each of the sensors in the array includes a pair of sensor half-portions disposed on opposing lateral surfaces of the pipe, and the signal processor determines a nominal velocity of the flow within the pipe using the signals.
Owner:CIDRA
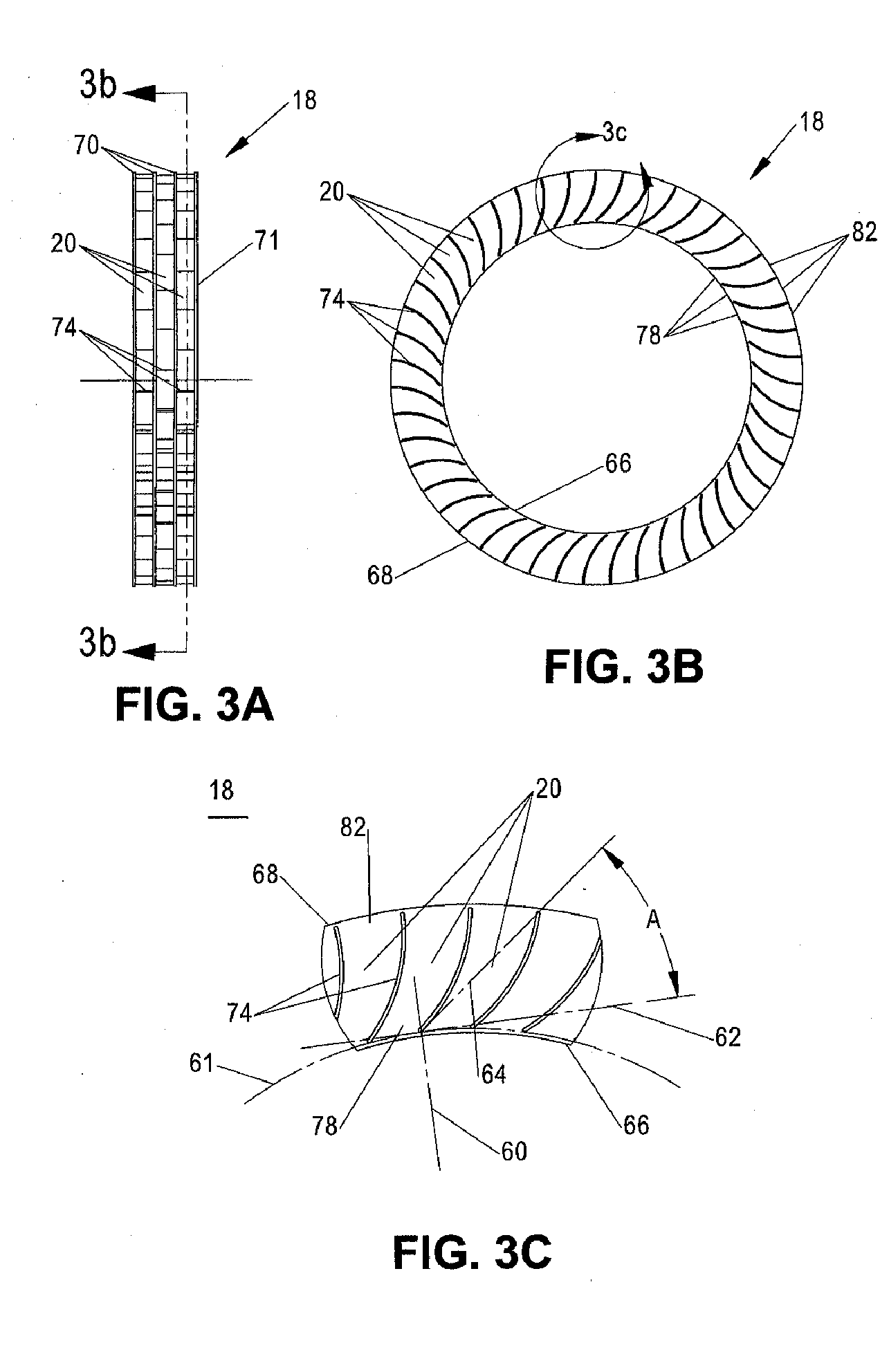
High efficiency fluid mover
A fluid mover includes a rotor to transfer momentum with a fluid when operated at a given volumetric flow rate through the rotor. The rotor includes a plurality of enclosed passages to transfer momentum in or out of the fluid as the fluid passes through the enclosed passages in response to rotation of the rotor. The passages are formed with a cross sectional shape and cross sectional dimensions along their entire length sufficient to establish and maintain laminar flow of the fluid along the entire length of the enclosed passages when the fluid is passing through the rotor at the given volumetric flow rate. The fluid mover also includes a housing having at least one inlet and at least one outlet for the fluid.
Owner:INTEL CORP
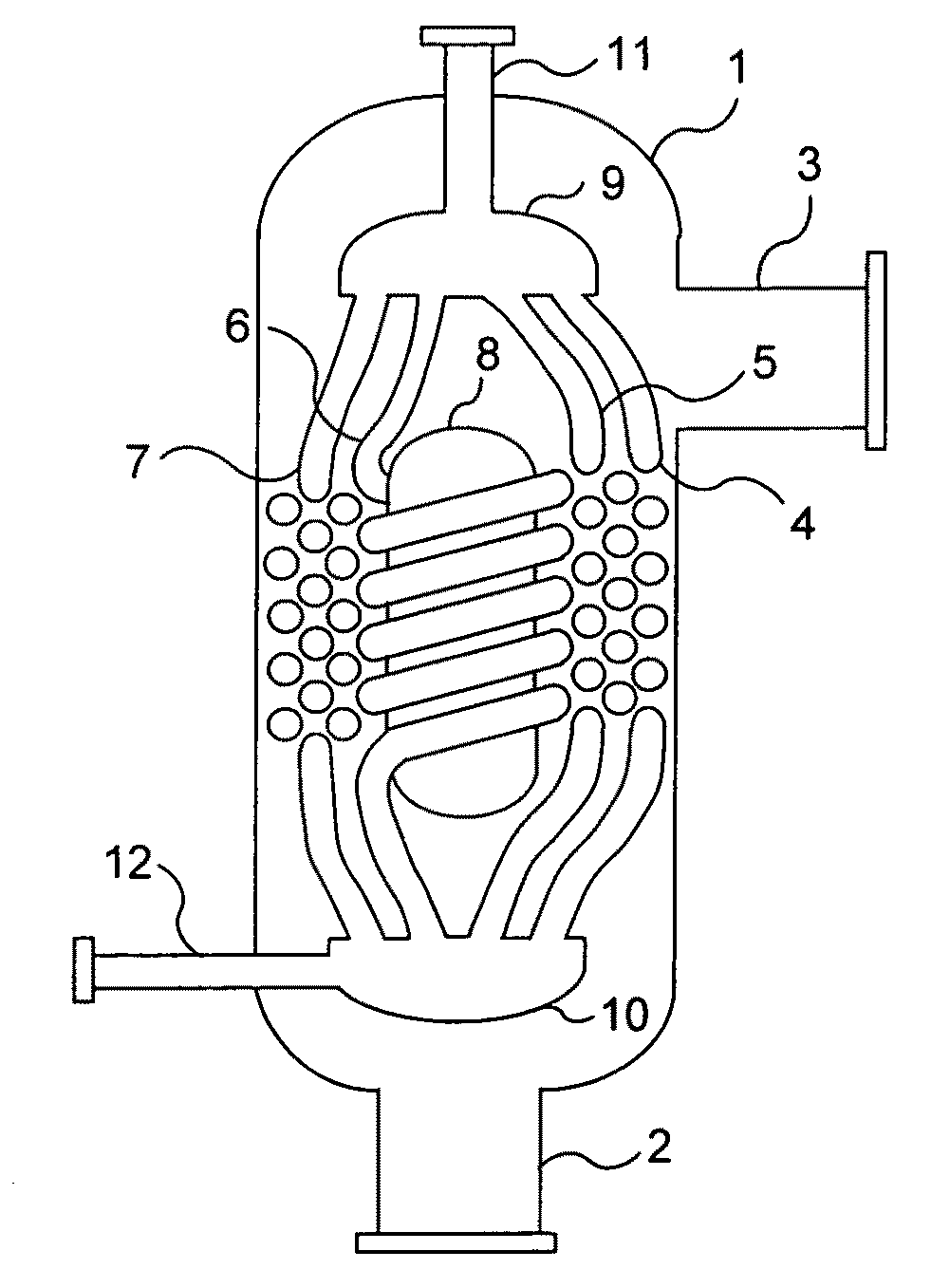
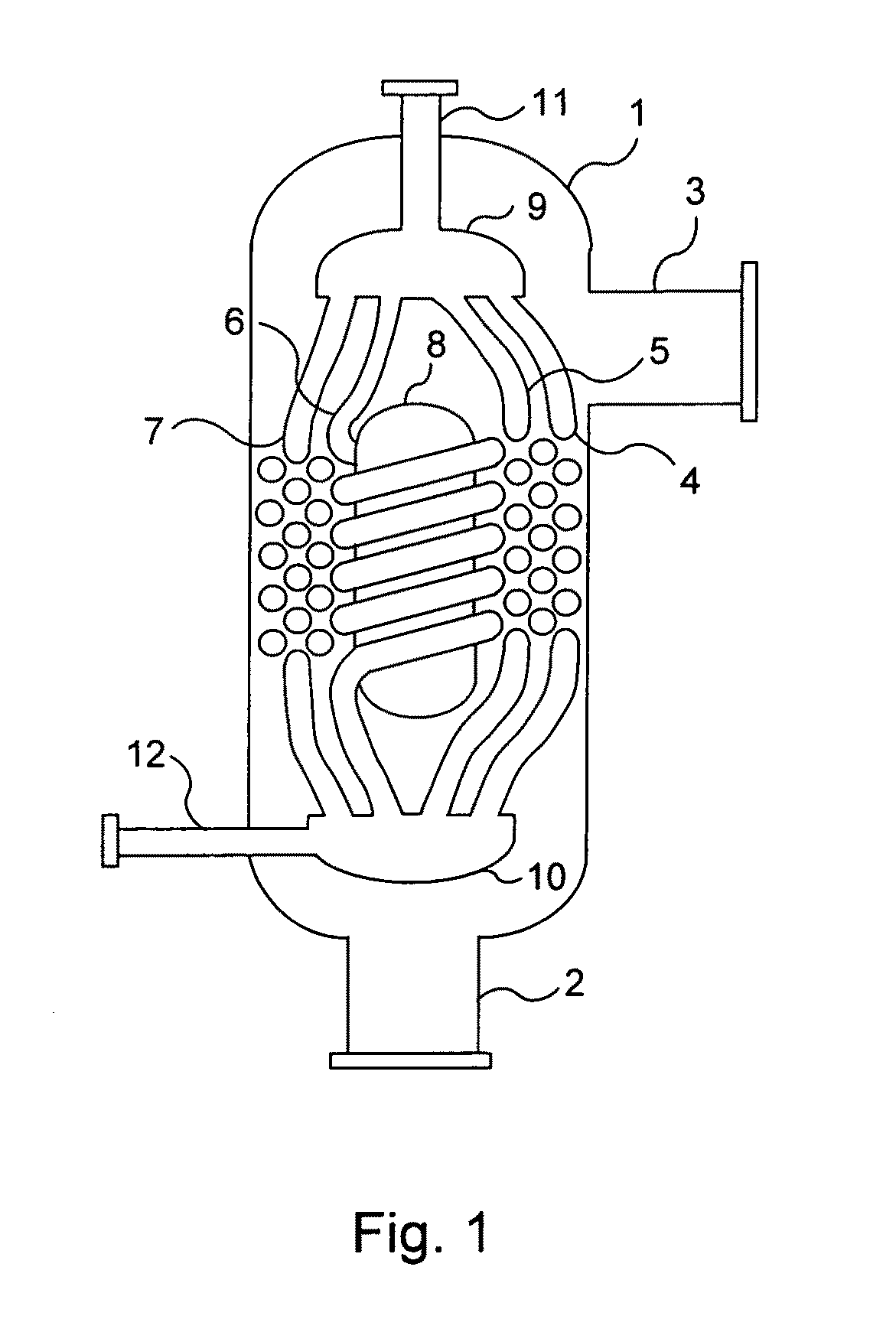
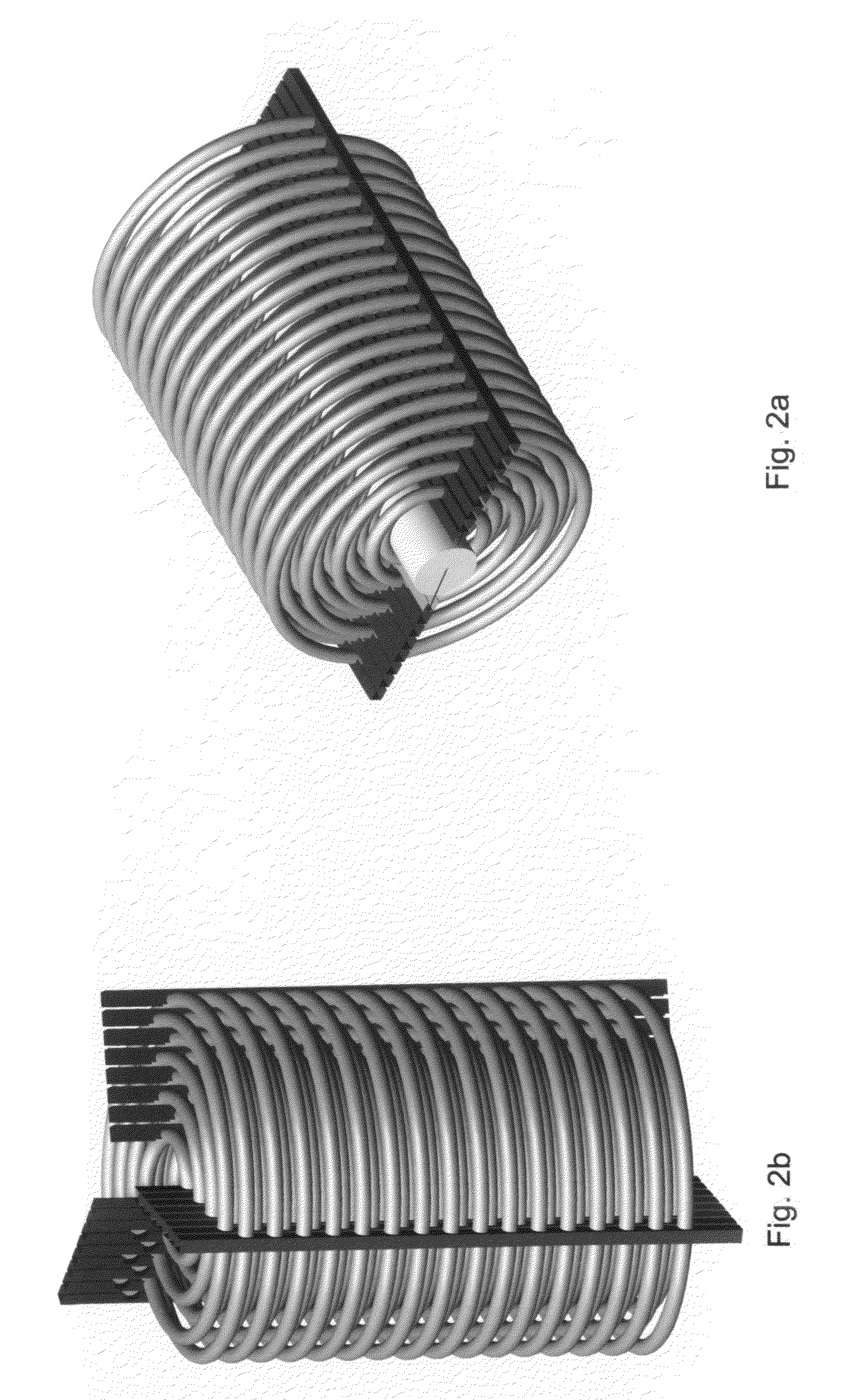
Multiple concentric cylindrical co-coiled heat exchanger
A compact shell and coil heat exchanger is disclosed that accommodates widely differing volumetric flowrates between the two fluids undergoing heat exchange. Multiple co-coiled helical coils of tubing are concentrically arranged, and coil spacers are provided which maintain the tubes in overall staggered alignment, as illustrated in FIG. 1. Uniformly high transfer coefficients are maintained throughout the bundle of coils via means for ensuring that the tube-side flow through the tubes of each coil, and the shell-side flow across each coil, are kept proportional to the tube surface area of each coil.
Owner:ERICKSON DONALD CHARLES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com