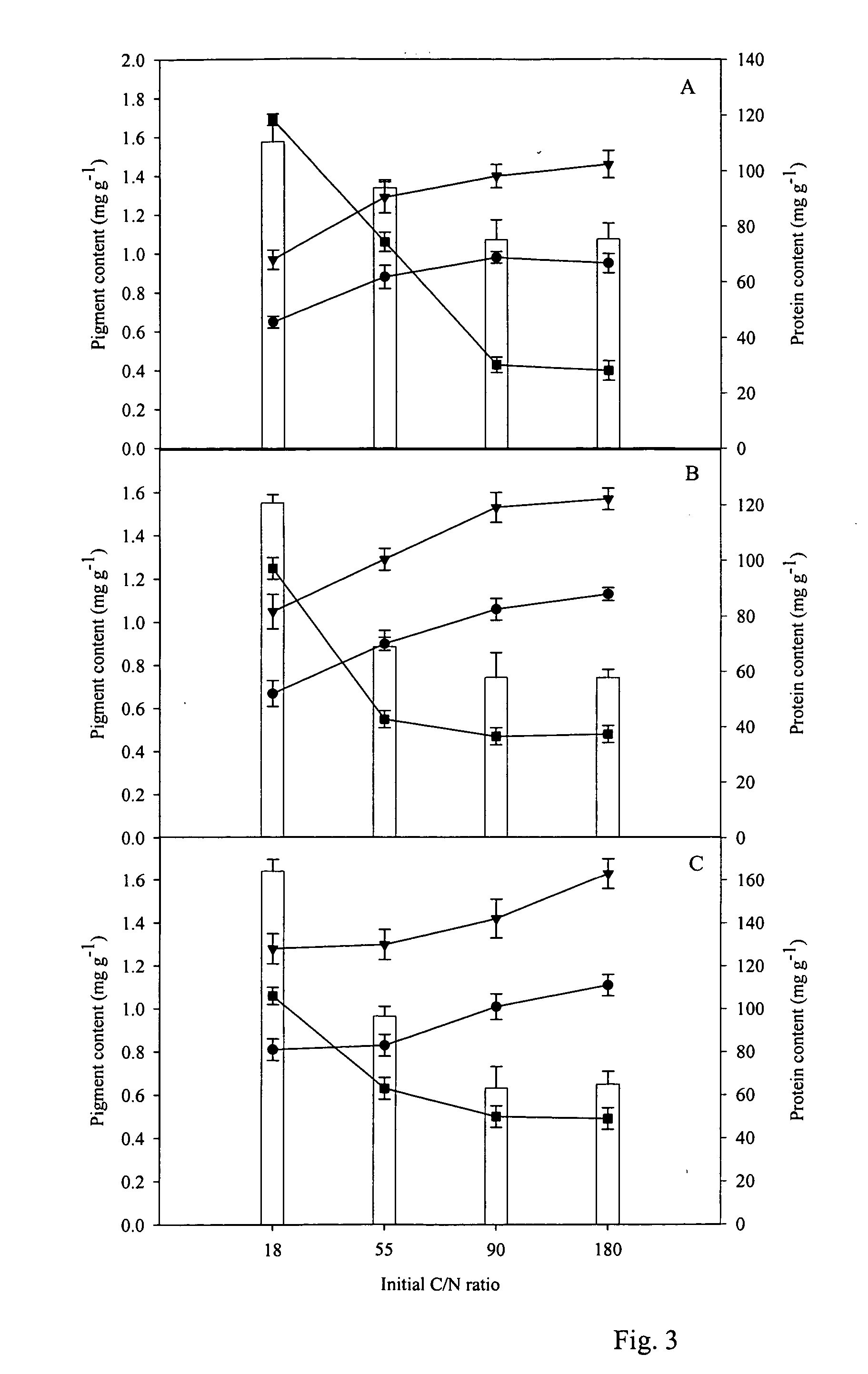
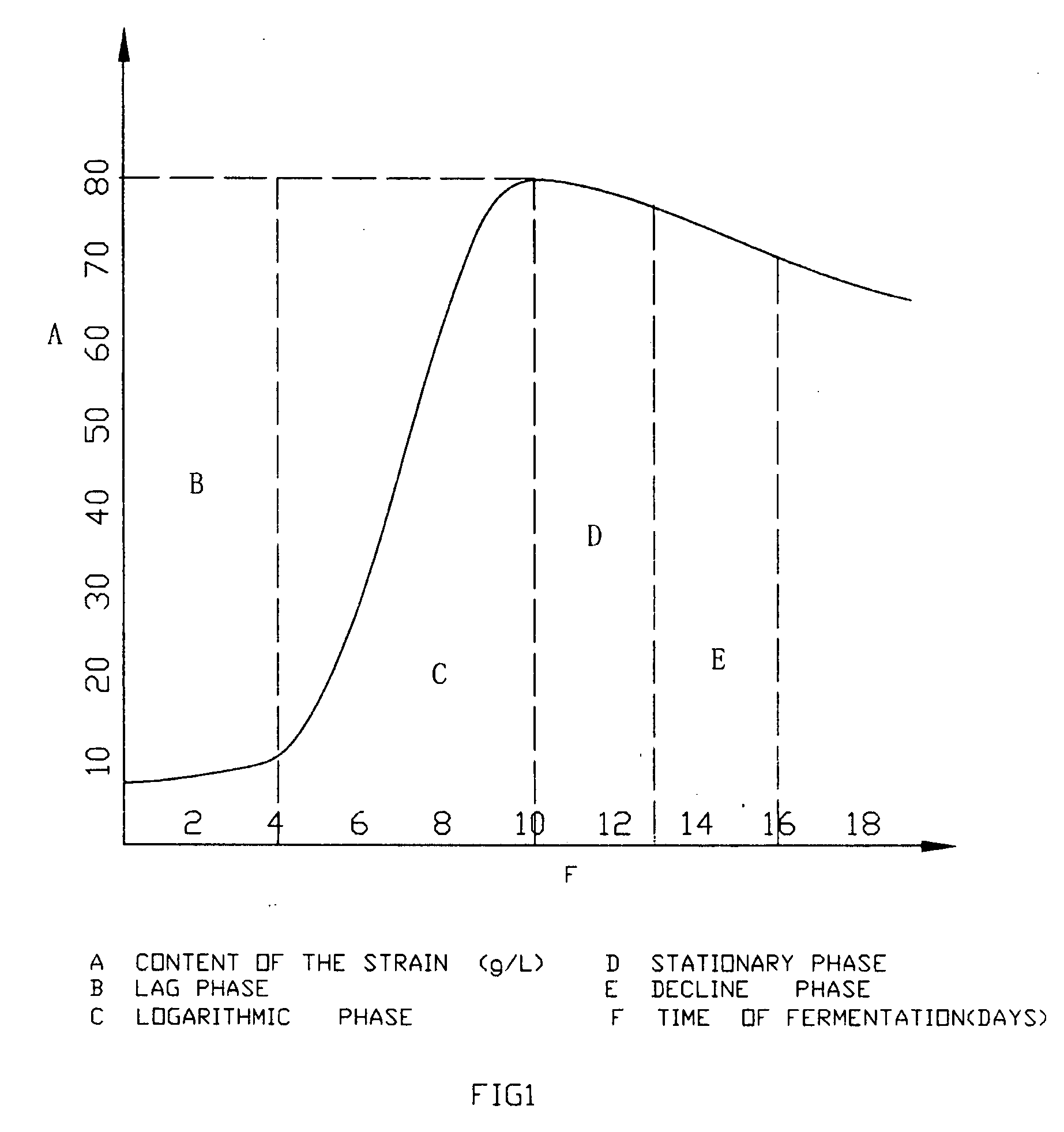
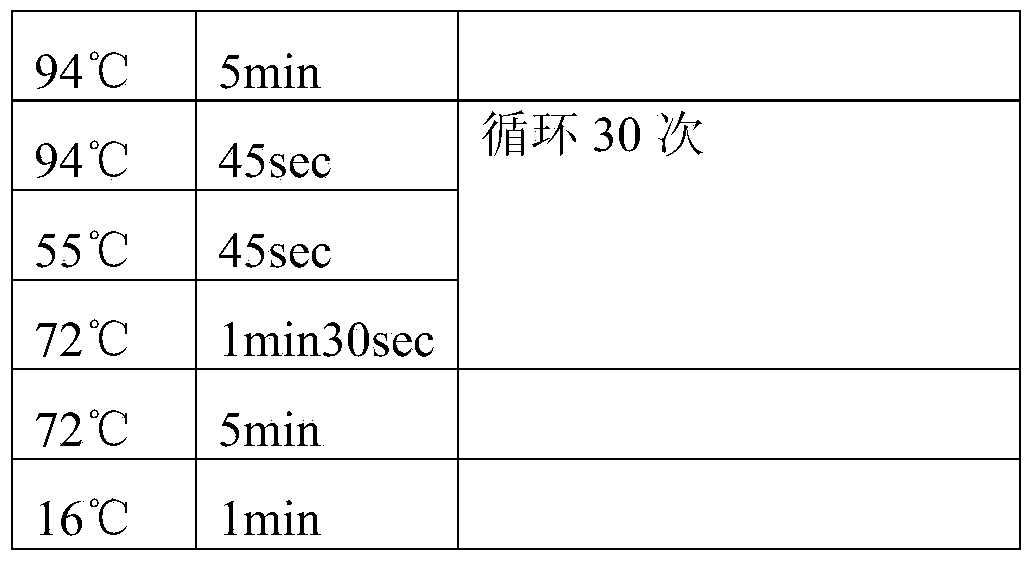
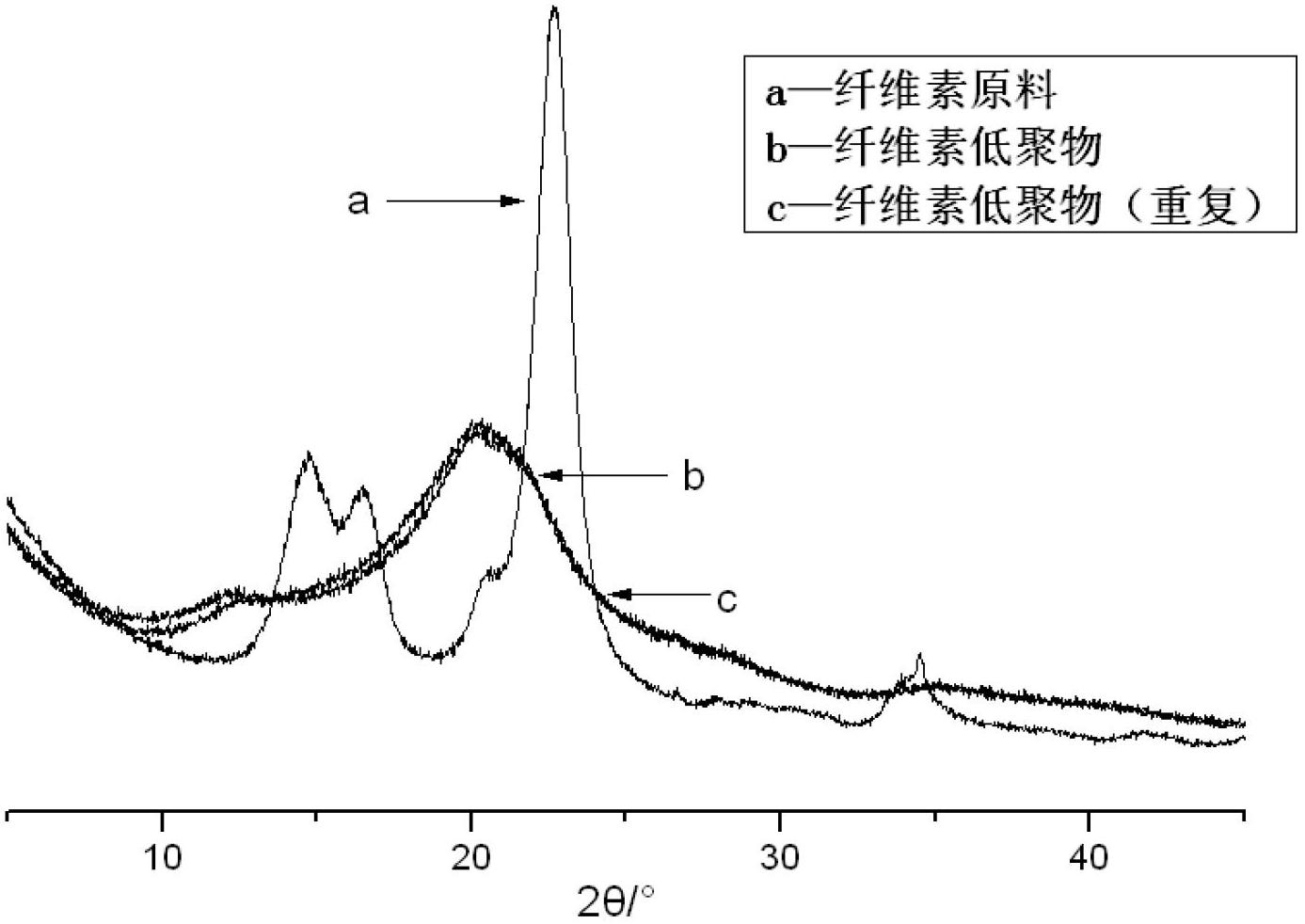
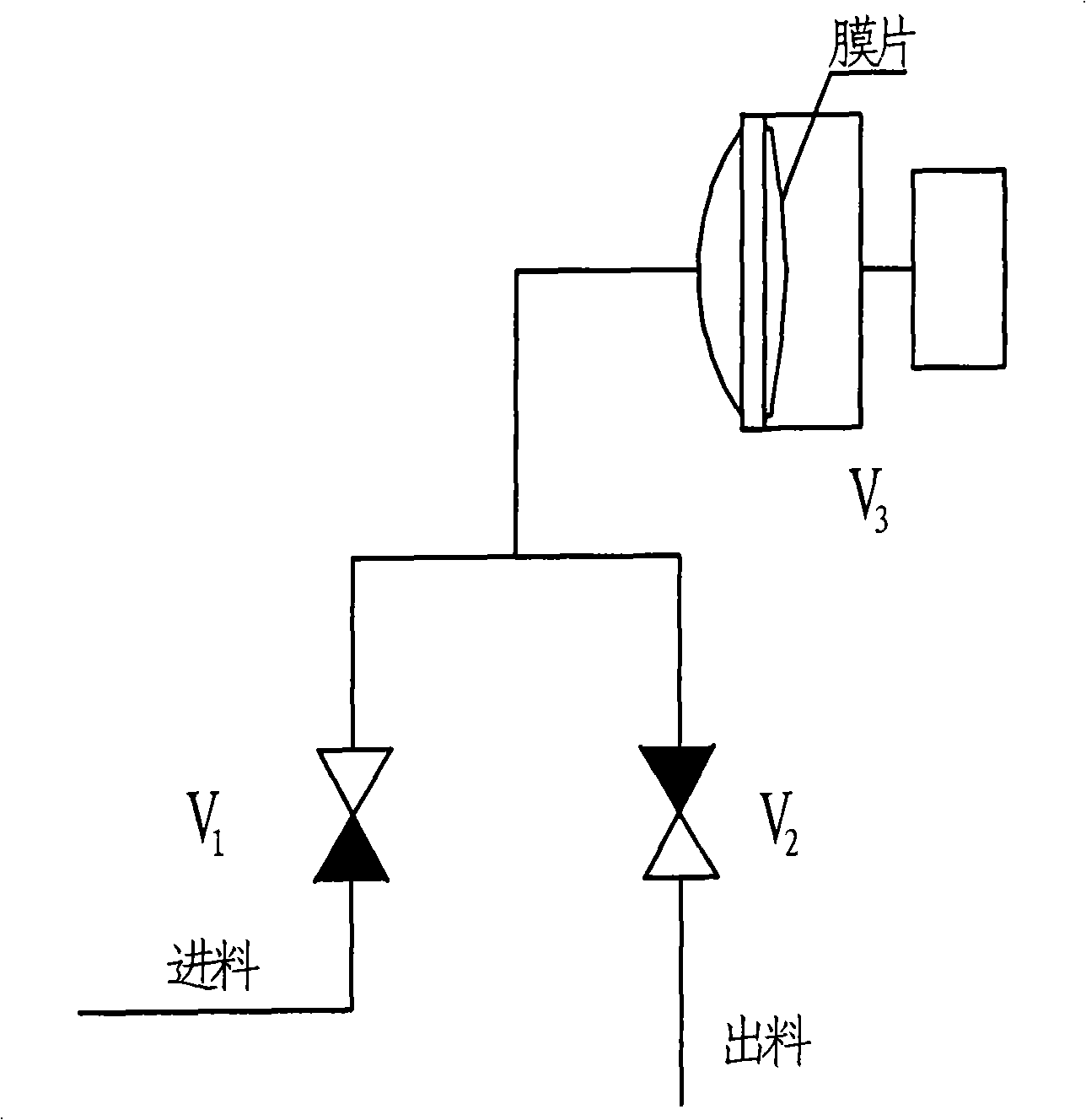
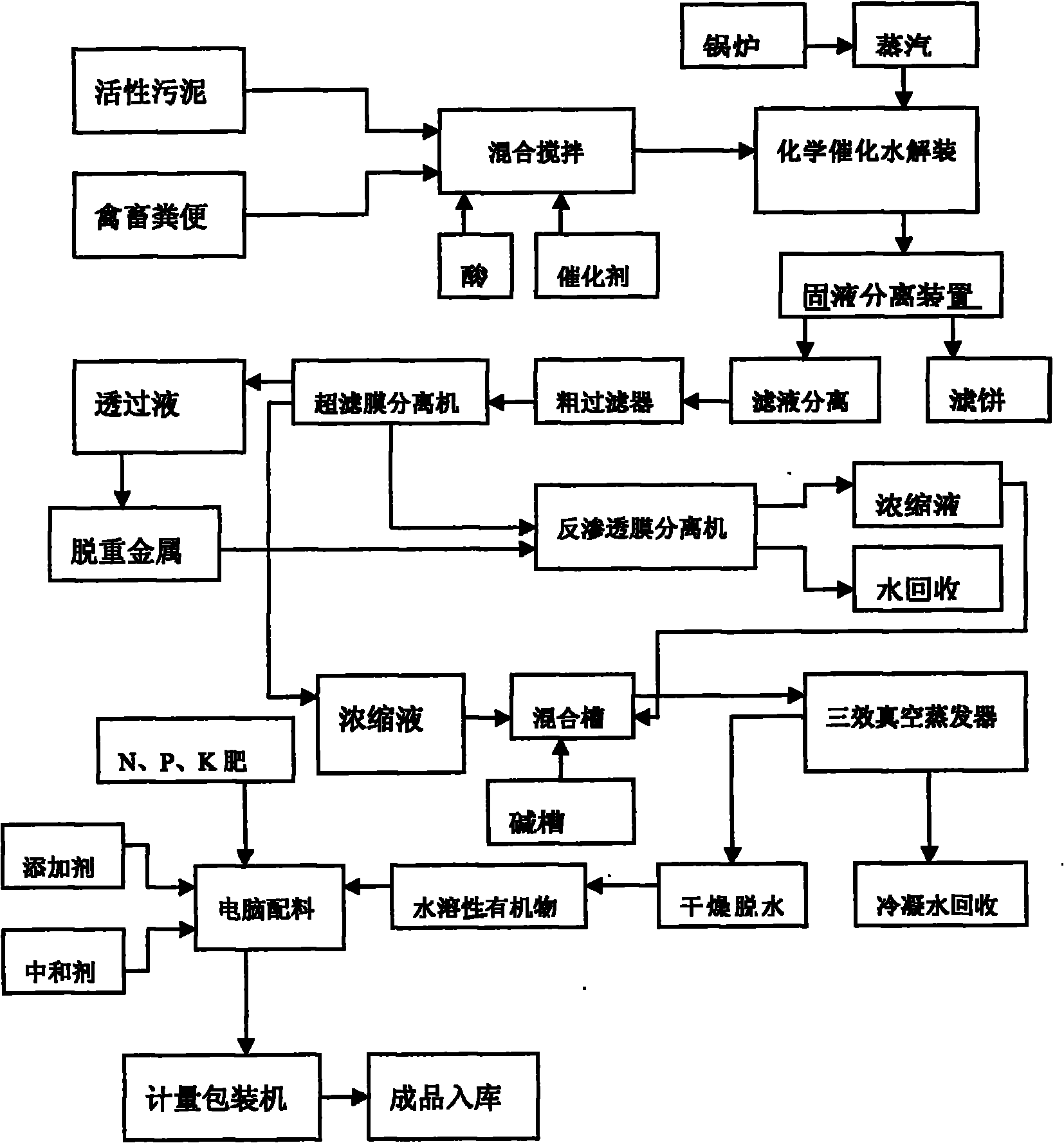
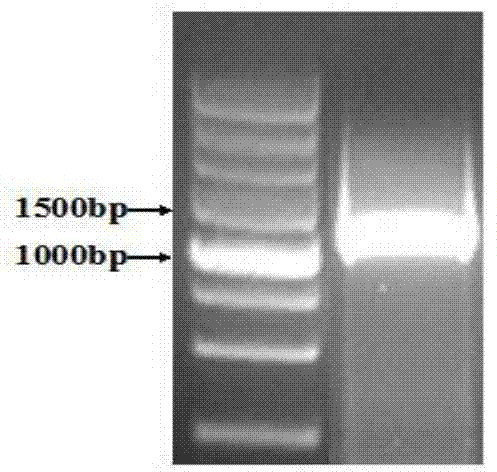
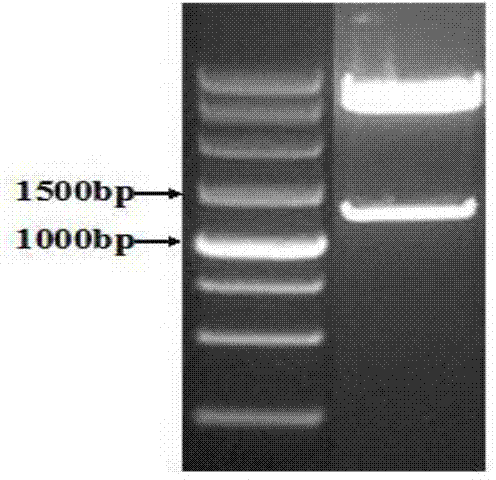
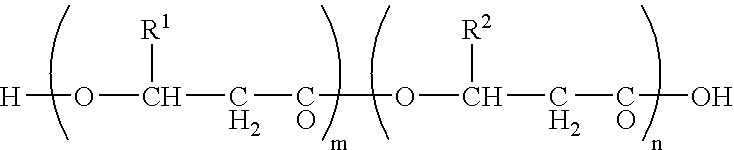Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
382 results about "Industrial fermentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Industrial fermentation is the intentional use of fermentation by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi as well as eukaryotic cells like CHO cells and insect cells, to make products useful to humans. Fermented products have applications as food as well as in general industry. Some commodity chemicals, such as acetic acid, citric acid, and ethanol are made by fermentation. The rate of fermentation depends on the concentration of microorganisms, cells, cellular components, and enzymes as well as temperature, pH and for aerobic fermentation oxygen. Product recovery frequently involves the concentration of the dilute solution. Nearly all commercially produced enzymes, such as lipase, invertase and rennet, are made by fermentation with genetically modified microbes. In some cases, production of biomass itself is the objective, as in the case of baker's yeast and lactic acid bacteria starter cultures for cheesemaking. In general, fermentations can be divided into four types...
Gene-substituted microorganisms, and production method of polyesters using the same
The present invention provides a recombinant microbial strain capable of stably producing a polyhydroxyalkanoic acid (PHA) at a high production rate in an industrial fermentation process. The present invention also relates to a recombinant microbial strain prepared by substituting an exogenous polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthase gene for a polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthase gene on the chromosome of the microorganism.
Owner:DANIMER IPCO LLC +1
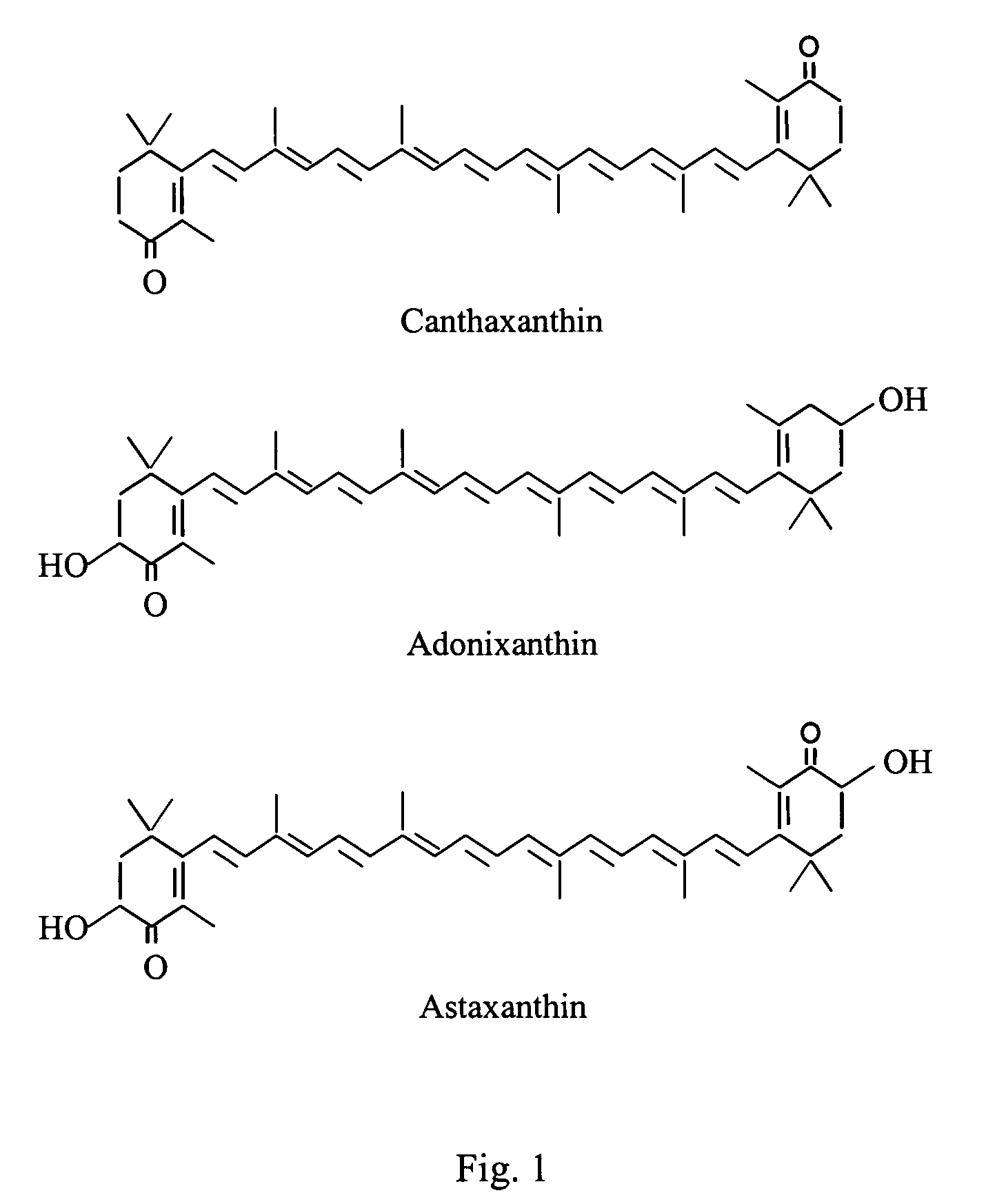
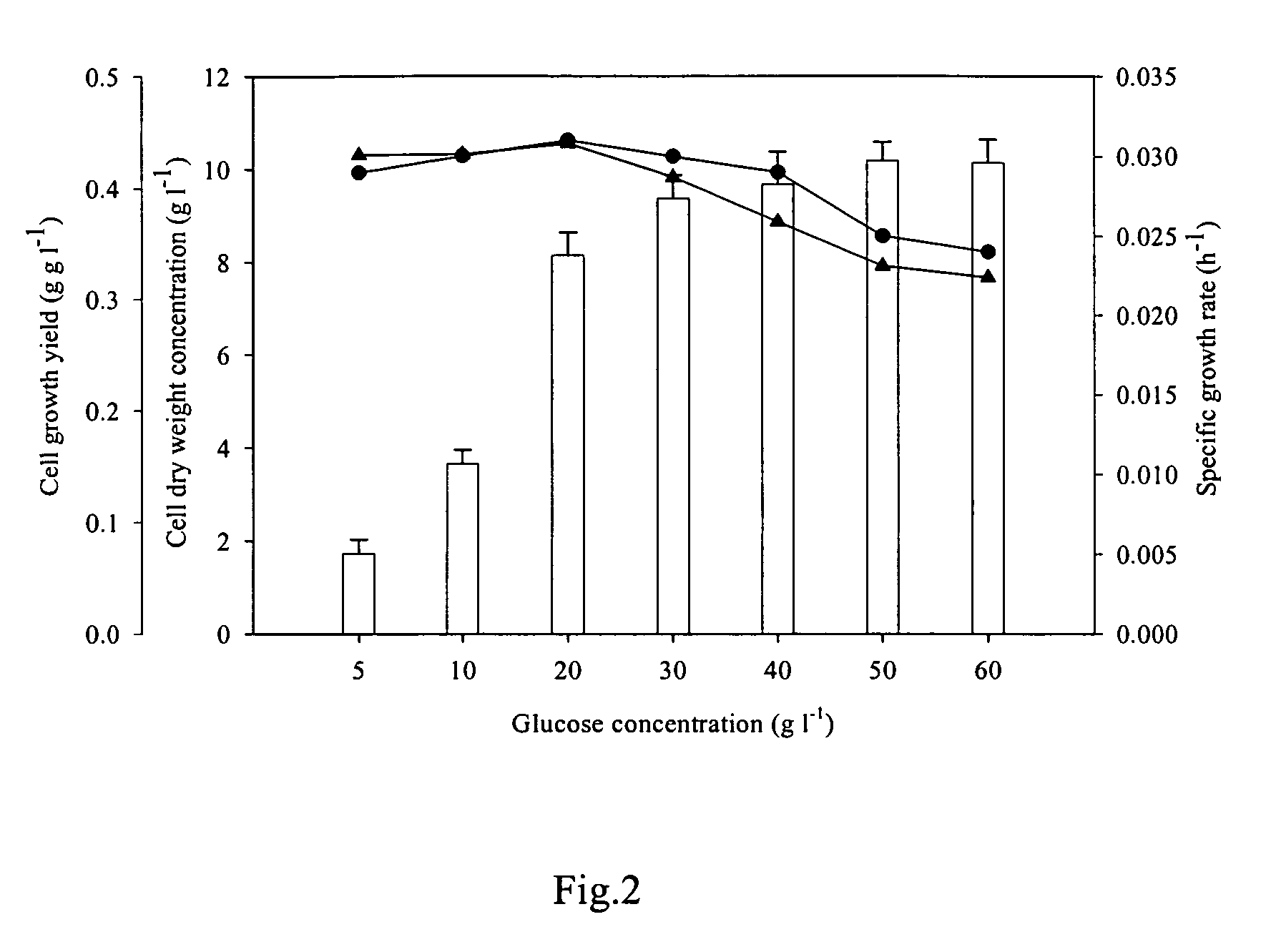
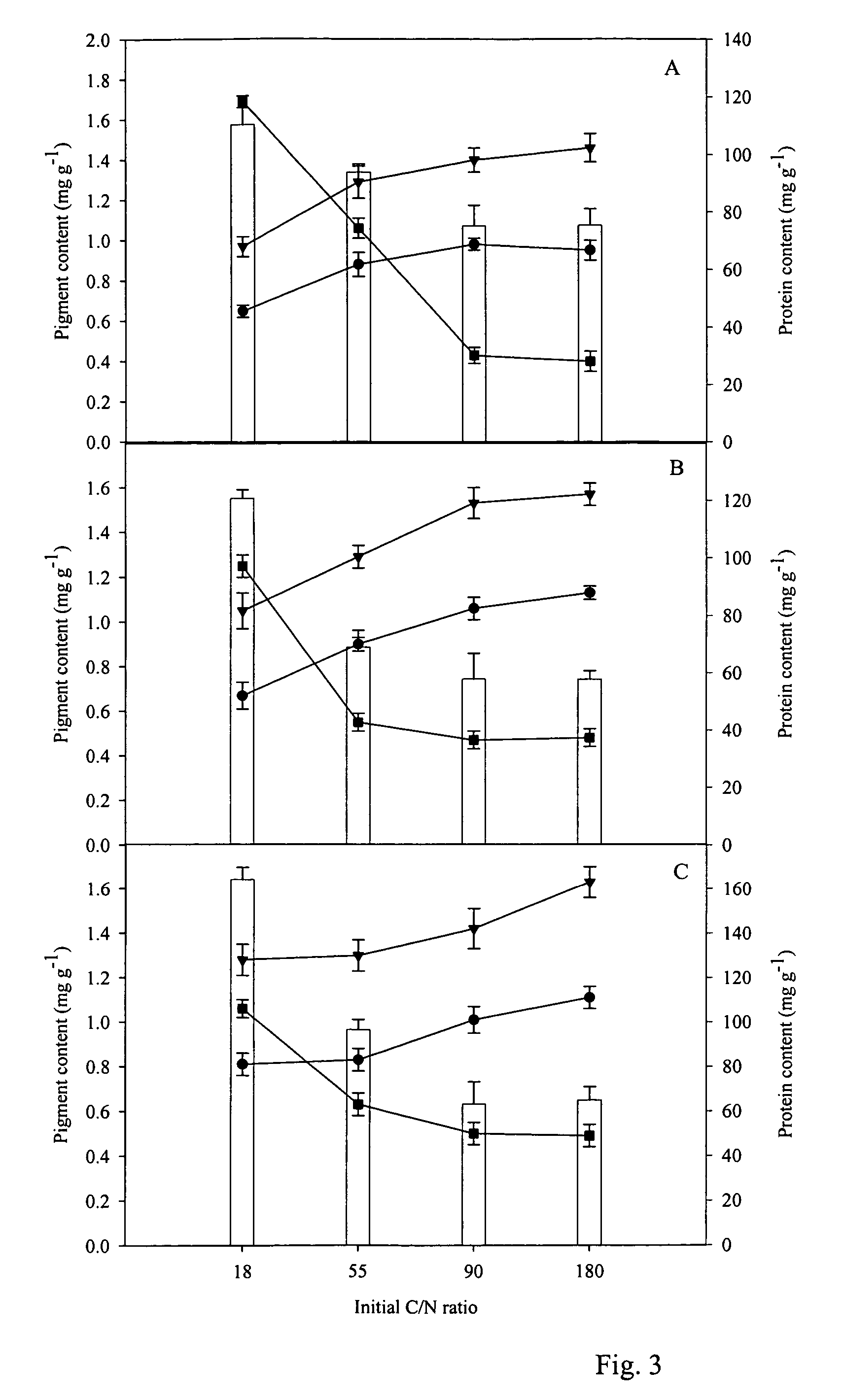
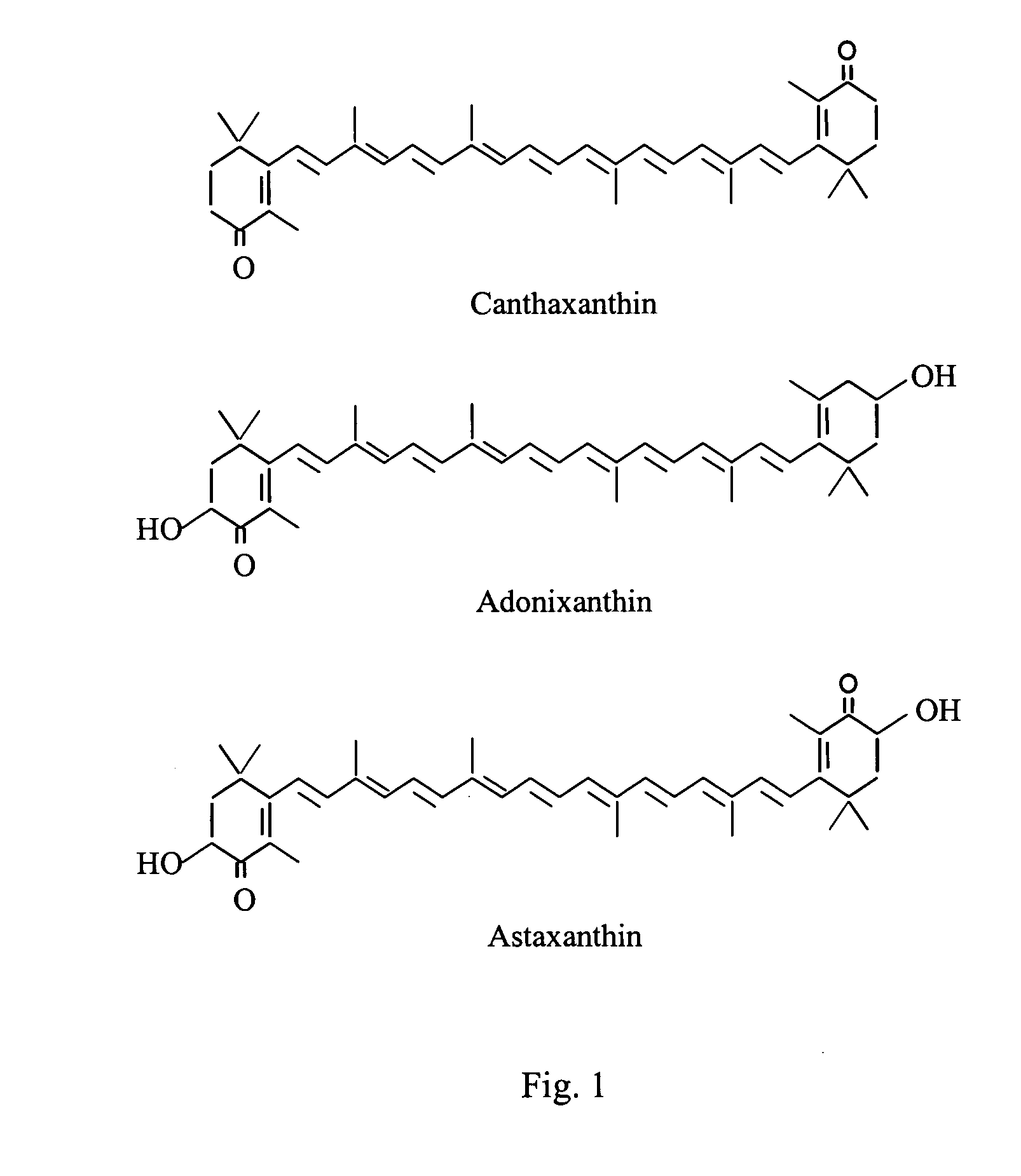
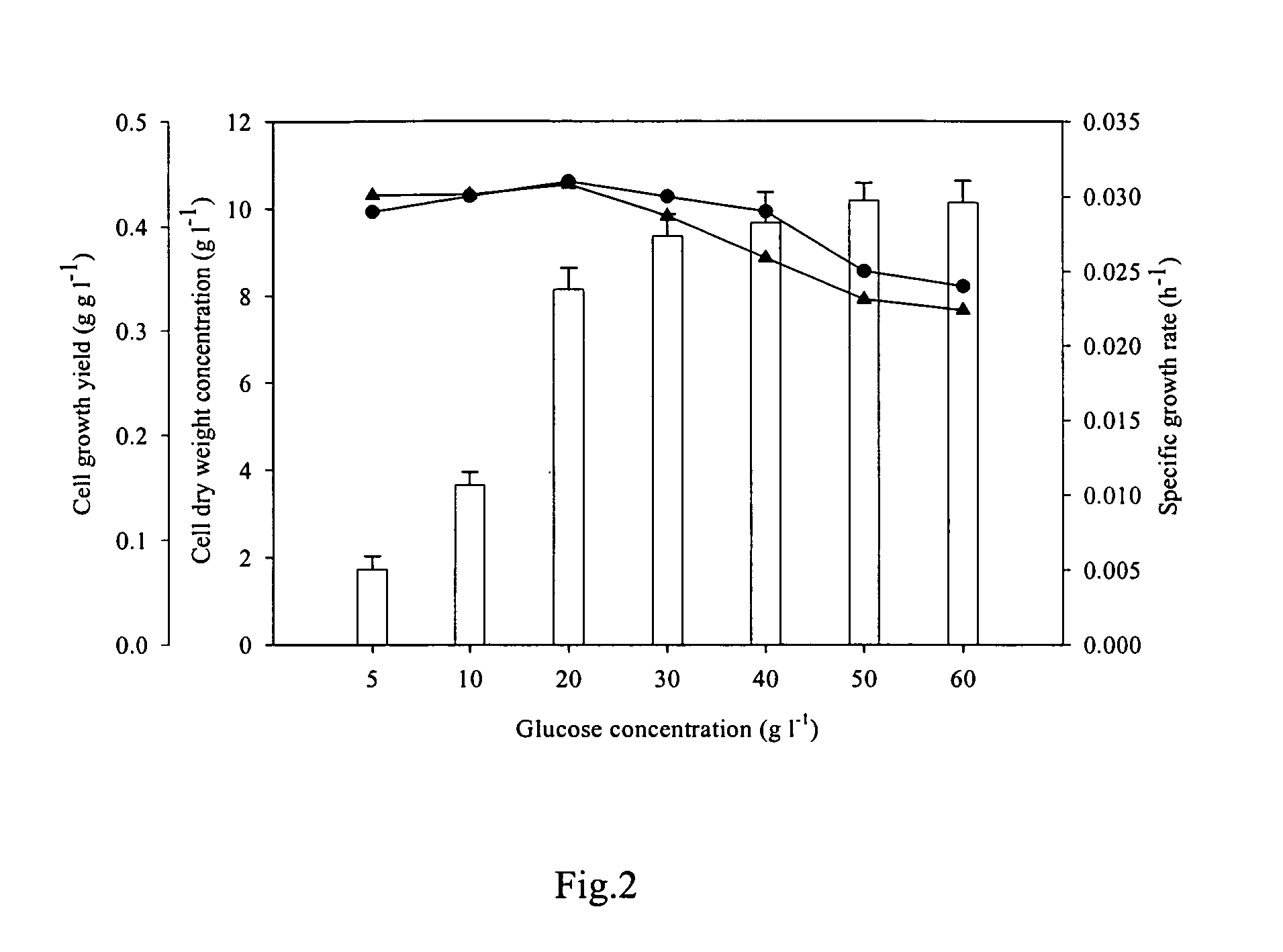
Methods for production of astaxanthin from the green microalgae Chlorella in dark-heterotrophic cultures
A method for producing the high-value ketocarotenoid astaxanthin by the green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis in dark-heterotrophic cultures shows excellent growth and high-yield astaxanthin production on glucose-supplemented media in the dark. The specific growth rate and astaxanthin yield can be as high as 0.031 h−1, and 10.3 mg l−1, respectively, which are the highest so far reported in heterotrophic algal cultures. The light-independent astaxanthin-producing ability of Chlorella zofingiensis can be employed for commercial production of astaxanthin using industrial fermenters.
Owner:HONG KONG UNIV OF
Microorganism cleaning bactericide capable of removing multiple poisonous and harmful substances
ActiveCN101791421AEfficient removalHigh removal rateDispersed particle separationDeodrantsAlkaneDecomposition
The invention relates to a microorganism cleaning bactericide capable of removing multiple poisonous and harmful substances and a preparation method thereof. The microorganism cleaning bactericide comprises the mixture of compound balsamic extract liquor and the fermentation product of compound microbial bacterium system protospecies liquid in an industrial fermentation culture solution. The invention utilizes the high-efficiency adsorption, assimilation and metabolism of the microbial bacterium system to purify and treat aldehydes, benzenes, alcohols, esters, phenols, amines, alkanes, sulfur-containing substances, TVOC, putrefying bacteria secreta, obnoxious gases of pathogenic bacteria, pathogenic bacteria secreta and the like, or the harmful substances of the solution thereof by the degradation and decomposition processes; harmful substances, such as formaldehyde, benzene, volatile organic compounds and the like in environment, which are released by housing decoration, office furniture and new car decoration, are converted into nontoxic, harmless and scentless substances; and meanwhile, the invention also performs the functions of sterilization to the pathogenic bacteria and the secreta thereof and realizes the targets of thoroughly improving air quality and protecting the health of people.
Owner:上海市大盛魁生物技术有限公司
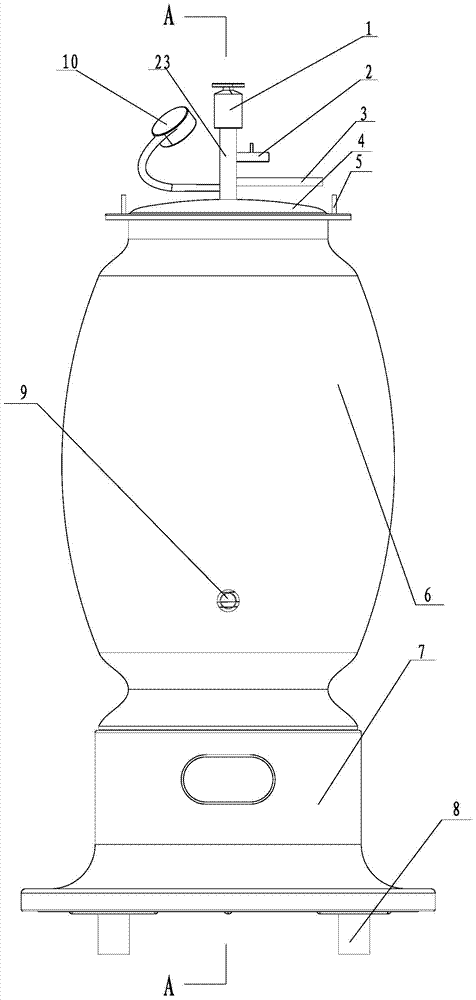
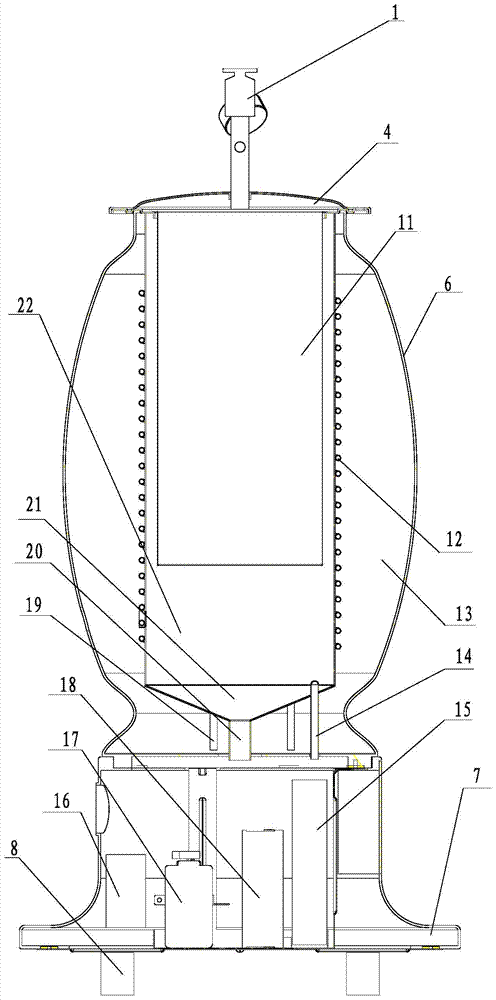
Household wine brewing machine and method for brewing wine by using household wine brewing machine
ActiveCN104498246ARealize integrated productionRich choiceWine preparationHops treatmentFruit wineIndustrial fermentation
The invention relates to a household wine brewing machine and a method for brewing wine by using the household wine brewing machine. The household wine brewing machine can be used for overcoming the defects that the existing industrial fermentation equipment is oversized and cannot achieve miniaturization and domestication. The household wine brewing machine is divided into four parts, namely a sealing cover, a fermentation tank, a control part and a power part, wherein the fermentation tank adopts a brand-new design. The household wine brewing machine not only can be used for producing grape wine, but also can be used for producing various fruit wines and beers, so that the integrated production of various wines is realized to provide more choices for consumers, the equipment cost is lowered and the product quality is guaranteed.
Owner:山东九道生物科技有限公司
Industrial fermentation ramee rapid extraction technique for Erwinia
ActiveCN101235357AReduce technical difficultyImprove activation process parametersBacteriaMutant preparationAnimal ForagingHigh pressure
The invention discloses a technique for rapidly extracting ramie hemp erwinia bacterium factory production fermentation, the technique comprises preprocessing material, immersing or sprinkling and inoculating, immersing or fermenting, deactivating with hot water, and the procedure of circulation washing, water dressing and fiber finish, erwinia bacterium which has broad-spectrum and high effective to degumming, pulping and saccharifying of herb fiber material, and bacterial agent preparation and activated technical parameter. The erwinia bacterium addicts the mannose, the peak for secreting non-cellulose to degrade key enzyme (pectic enzyme, beta-mannase and xylanase) can be achieved through purely culturing for 7h to 9h. Bacterial agent is inoculated on herb fiber material such as ramie and the like for activating the bacterial agent for 5h-6h, fermentation forage fodder turns to blue after fermenting for 5h-6h, pectine, hemicellulose and partial lignin which are partially degraded and associated in fiber cell are stripped, non-cellulose residues which are absorbed on fiber can be removed by means of the flushing of high-pressure flushing, and the purpose of extracting net fiber can be reached.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for separating and purifying N-acetylneuraminic acid produced by microbiological fermentation
ActiveCN104628794AEasy to separatePromote flocculationEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention provides a method for separating and purifying N-acetylneuraminic acid produced by microbiological fermentation. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: by taking fermentation liquid in fermenting production of N-acetylneuraminic acid by escherichia coli as a raw material, sterilizing; removing proteins; decoloring; desalting; crystallizing and the like to obtain a high purity N-acetylneuraminic acid product. Through tests, the product purity is at least 98%, and the requirements in the fields of foods, healthcare, medicines, cosmetics and the like can be satisfied. Moreover, the method is simple and easy to operate and is particularly suitable for industrial fermentation production of N-acetylneuraminic acid.
Owner:武汉中科光谷绿色生物技术有限公司
Bacillus subtilis lipo-peptide biological pesticide and use
The present invention relates to biological bacillus lipopeptide pesticide and its application, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The lipopeptide pesticide is prepared through fermentation culture in culture medium of glucose, cane sugar or corn slurry at temperature of 30-37 deg.c, rotation speed of 300-1000 rpm and dissolved oxygen of 30% for 30-36 hr; centrifugation to collect supernatant, adding HCl to regulate pH to 2.0-2.5, centrifugal extraction to collect supernatant, methanol or ethanol extraction, merging extracted liquid, and vacuum drying. The present invention is used in the green prevention and control of pests and diseases of field.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes and application of flora
InactiveCN105859339AImprove the current situation of serious hardeningHigh nutritional valueFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisBacillus thuringiensis
The invention is suitable for the technical field of recycling organic wastes, and discloses a flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes. The flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes is efficiently compounded from a variety of bacteria such as bacillus subtilis, aspergillus niger, saccharomycete and soil flora, wherein the soil flora is extracted from the natural world and comprises three or more of bacillus megatherium, bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus thuringiensis, bacillus laterosporus, bacillus mucilaginosus, streptomyces jingyangensis, mycorrhiza fungi, azotobacter vinelandii, photosynthetic bacteria, bacillus coagulans, aspergillus oryzae, and paecilomyces lilacinus. According to the flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes, disclosed by the invention, by virtue of mutual promotion, mutual coordination and combined action of a variety of beneficial microorganisms, the organic wastes are recycled, environmental pollution is reduced, and wastes are changed into valuables; and the flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes can be used for producing industrial fermentation products and improving the health and growth conditions of animals, and can also improve the current situation of serious soil hardening at present and improve soil quality, thereby promoting the rapid development of agricultural economics.
Owner:王云飞
Eosinophil beta-mannanase MAN5A and gene and application thereof
ActiveCN101457207AWide pH range of actionImprove heat resistanceFungiBacteriaNucleotideGenetic engineering
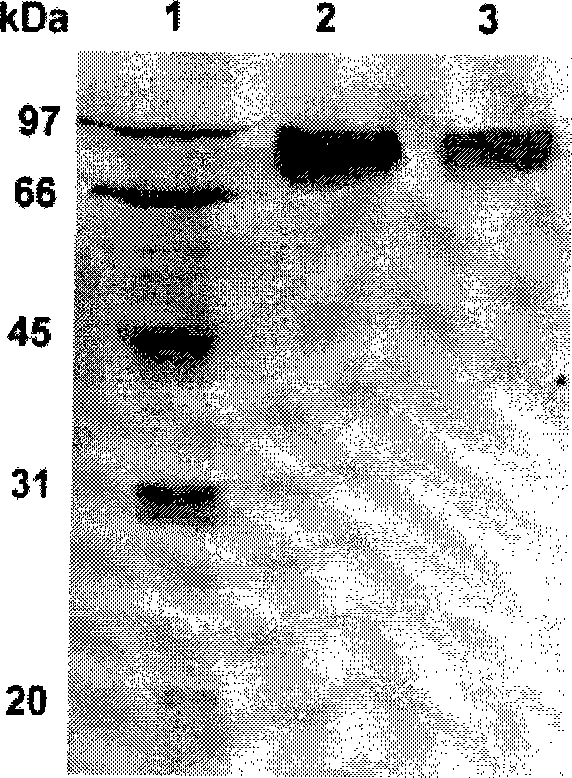
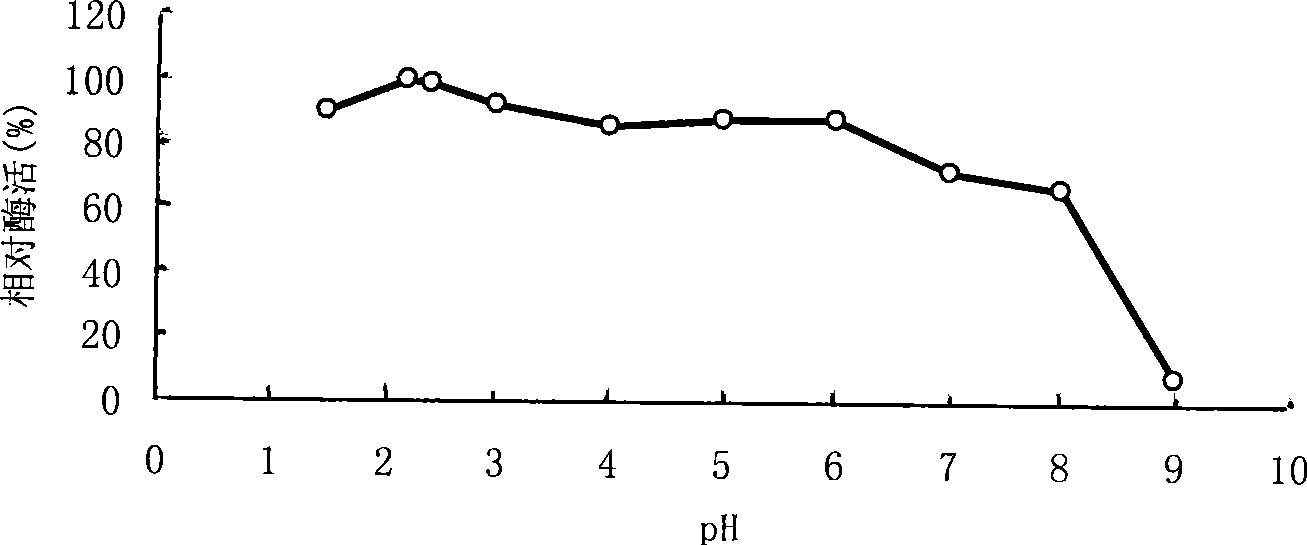
The invention relates to the genetic engineering field, especially to a strain Bispora sp.MEY-1 which produces an acidophilic beta-mannanase and the acidophilic beta-mannanase MAN5A got from the strain having an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or 2, a gene man5A for coding said beta-mannanase having a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or 2, and a recombinant vector containing said gene and applications. The beta-mannanase of the invention has the following advantages: the optimum pH 1.0-1.5, the optimum temperature 65 DEG C, good pH stability and thermostability, high specific activity, good protease resistance and easy for industrial fermentation production. The product of the invention can be widely used for the animal feeding-stuffs, the food, the medicament, the brewing and the energy industry as a novel enzyme preparation.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High-protein straw feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101816371AHigh protein contentPromote absorptionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyProtein structure
The invention discloses a high-protein straw feed, which comprises crop straw powder, actinomycetes, nocardia, lactobacillus acidophilusis and bacillus subtilis, the weight ratio of the strains is 0.8-1.2:1.6-2.4:0.8-1.2:1.8-1.2, and the weight ratio of the total strain amount to the crop straw powder is 1:1,000-1,200. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: respectively screening, separating, purifying, rejuvenating and culturing various strains, transplanting the strains into an industrial fermentation tank for fermentation, mixing in a ratio, and adsorbing by using an adsorptive support; and inoculating the obtained composite viable bacteria powder into crop straw powder or a mixture of the crop straw powder, staking and fermenting at the temperature of between 60 and 70 DEG C, uniformly turning once every two days, and obtaining the high-protein straw feed after 30 to 35 days. The high-protein straw feed has the advantages of improving protein content, optimizing protein structure, improving the absorption and nutrient conversion rate of the straw feed, and improving the immunity of livestock.
Owner:苏州荣基生态生物科技有限公司
Methods for production of astaxanthin from the green microalgae Chlorella in dark-heterotrophic cultures
ActiveUS20050214897A1Increased formationUnicellular algaeFermentationIndustrial fermentationGlucose polymers
A method for producing the high-value ketocarotenoid astaxanthin by the green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis in dark-heterotrophic cultures shows excellent growth and high-yield astaxanthin production on glucose-supplemented media in the dark. The specific growth rate and astaxanthin yield can be as high as 0.031 h−1, and 10.3 mg l−1, respectively, which are the highest so far reported in heterotrophic algal cultures. The light-independent astaxanthin-producing ability of Chlorella zofingiensis can be employed for commercial production of astaxanthin using industrial fermenters.
Owner:HONG KONG UNIV OF
Method for preparing industrial fermentation pickled vegetable
ActiveCN101697751AAdd beneficial ingredientsGood antibacterial effectFruits/vegetable preservation using acidsSaline waterIndustrial fermentation
A method for preparing industrial fermentation pickled vegetable relates to a method for preparing fermentation pickled vegetable, solving the problems that pickled vegetable produced by the current large-scale factory is still prepared by traditional technique depending on natural fermentation and the cabbage in the fermentation jar can be easily damaged by other bacteria and be easily rotten and goes bad. The method comprises the following steps: 1, palletizing cabbages; 2, adding pickled vegetable fermentation engineering bacteria; 3, fully injecting brine to the fermentation jar; 4, carrying out fermentation to obtain the product of pickled vegetable. The method uses controllable industrial technique to ferment the pickled vegetable; the added components are known and controllable; thus, the method avoids the pollution of the cabbage by other bacteria, rot and metamorphism.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Industrial fermenting production process of Hirsutella hepiali Chen & Shen of anamorphic fungi related to Chinese Cordyceps Sinensis
InactiveUS20070004022A1Wide market prospectYield of the hyphae has been upgradedFungiImmunological disordersBiotechnologyIndustrial fermentation
The present invention discloses a fermenting production process of Hirsutella hepiali Chen & Shen for industrial purpose. It contains steps: a. Isolating new stain from original source; b. identifying whether the stain can grow stroma or not; c. culturing the strain in solid medium for rejuvenescence purpose; d. Secondly culturing the strain in liquid culture medium; e. fermenting. Said method provides a fermenting production process, which can continually identify whether the anamorphic fungi related to Chinese Cordyceps sinensis change or not, whether it retains the property of original strain or not. It also can be modified continually. According to these processes, the quality of the obtained product will be stable and the property will be retained stable for quite a long time. Therefore this method overcome the problems exist in the art that change of the strain, instability of quality of the product and so on.
Owner:SHEN NANYING
Novel holomonas and method for producing tetrahydropyrimidine by novel holomonas
ActiveCN103451137ALow synthetic capacityReduce corrosionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIndustrial fermentationNitrogen source
The invention discloses novel halomonas sp. HS-2255 which can be used for producing tetrahydropyrimidine, and a mutant strain thereof. The preservation number of the novel halomonas sp. HS-2255 is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 6248. The invention further discloses a culture method of the strain and a method for producing the tetrahydropyrimidine by fermentation. The strain has a higher tetrahydropyrimidine yield in a culture medium with a carbon source and a nitrogen source which are assimilable, and lower NaCl content, and the content of a byproduct hydroxyl tetrahydropyrimidine is lower, and therefore, the novel halomonas sp. HS-2255 can be used for industrial fermentation production of tetrahydropyrimidine, and has good application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Two-step hydrolysis method for preparing reducing sugars with cellulose
ActiveCN102690897AEffective separation and reuseReduce dosageGlucose productionCelluloseIndustrial fermentation
The invention discloses a two-step hydrolysis method for preparing reducing sugars with cellulose, comprising the following steps: step (1) of dissolving the cellulose into a solvent to obtain a cellulose solution; in the cellulose solution, enabling the cellulose to contact water by the action of a first catalyst to perform a first-step hydrolysis and obtain hydrolysate; adding a precipitator into the hydrolysate, and separating after precipitating to obtain precipitate; step (2) of adding a second catalyst in the precipitate obtained in the step (1) by utilizing water as a medium to perform a second-step hydrolysis and obtain the reducing sugars, wherein productivity of the reducing sugars reaches 40-85%. The invention further discloses application of the two-step hydrolysis method for preparing reducing sugars with cellulose in fermentation and preparation for compounds such as ethanol, lactic acid and so on in the carbohydrate industry. Cellulose solvent, catalyst and precipitator utilized by the invention can effectively separated and used repeatedly; hydrolysis condition is relatively mild; dosage of acid catalysts is less; and the method is featured with simple operation, low energy consumption, fast reaction and high productivity.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Supplementary food weighing and metering control device
ActiveCN101514918AHigh feeding accuracyHigh feed accuracyWeighing apparatus with automatic feed/dischargeIndustrial fermentationMonitoring system
The invention discloses a fluid supplementary food weighing and metering control device, which comprises a supplementary food cup, a valve system, a fermentation tank and a supplementary food tank, and is characterized by also comprising a weighing system and an electronic monitoring system, wherein the weighing system comprises a weighting sensor, a suspension arm, a fixed bracket and a weighing cup, the supplementary food cup is connected with the weighting sensor to weigh the supplementary food in the supplementary food cup, the electronic monitoring system comprises an A / D conversion module, an alarming and display module, a keyboard, a mouse, a touch screen, a comparator, a setter, a CPU and a food supplementation speed controller. As the supplementary food is metered by the weighing device, the device has the advantages of up to 0.5 percent high food supplementation accuracy and providing a reliable guarantee for the optimization and amplification of an industrial fermentation process.
Owner:SHANGHAI GUOQIANG BIOCHEMICAL ENG EQUIP CO LTD
Preparation method of wild pawpaw fruit wine
InactiveCN101928657ARetain nutritional valueShorten the production cycleAlcoholic beverage preparationMicroorganism based processesFruit wineIndustrial fermentation
This invention discloses a preparation method of a wild pawpaw fruit wine. The method comprises the following steps of: after treating rice pulp with a liquefying enzyme and a saccharifying enzyme, mixing the treated rice pulp and wild pawpaw juice according to a proportion of 1:1-1.5(W / W) and fermenting the mixture to obtain the wild pawpaw fruit wine. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method of the invention simplifies the production process, shortens the production period, reduces the production cost, improves the economic benefit and contributes to the industrial fermentation mass production of the wild pawpaw fruit wine. The wild pawpaw fruit wine prepared by the method is mellow, has the faint scent of wild pawpaw, is amber and transparent in colour, offers a pure mouthfeel and long lingering aftertaste, better retains the nutritional value and special flavor of the wild pawpaw and also has better nutritional and healthy functions of fruit wines.
Owner:贵阳南瓜蔬蔬科技有限公司
Method for preparing culture medium for industrial fermentation by using agricultural raw materials subjected to steam explosion treatment
InactiveCN103881945AConducive to subsequent processing and utilizationImprove solubilityBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention discloses a method for processing agricultural raw materials and producing a culture medium for industrial fermentation by utilizing a steam explosion technology aiming at the problems that the raw material utilization rate is low, the crushing power consumption is high, the amount of hydrolysis acids and alkalis is large and the like when the agricultural raw materials are used for an industrial fermentation culture medium. By utilizing the steam explosion technology, starch, proteins, lipids, celluloses, hemicelluloses, lignins and other components in the agricultural raw materials are degraded or modified, macromolecular substances are degraded into small molecular substances, and fermentation promoted substances are generated. According to the method, the energy consumption in the process of further processing the agricultural raw materials is reduced, the product performance of the agricultural raw materials serving as the industrial fermentation culture medium is improved, the raw material utilization rate in the fermentation process is improved, and growth and metabolism of microbes and the conversion rate of the fermented product are promoted by a fermentation accelerant generated in the steam explosion treatment process. The agricultural raw materials subjected to the steam explosion treatment can serve as a culture medium for solid state fermentation and also can be used for a culture medium for liquid state fermentation.
Owner:北京中科百瑞能工程技术有限责任公司
Method for preparing water soluble quick-acting organic fertilizer from activated sludge
InactiveCN101863688AShorten the production cycleNo pollution in the processClimate change adaptationSewage/sludge fertilisersActivated sludgeSlag
The invention relates to a method for preparing a water soluble quick-acting organic fertilizer from activated sludge. In the method, the activated sludge is used as a main material, livestock and poultry excrement and sorted organic domestic garbage or furfural slag, xylitol slag, industrial fermentation waste residue or crop straws are used as auxiliary materials, and the main material and the auxiliary materials are subjected to chemical catalytic degradation, ammonia-fixing treatment, solid-liquid separation, membrane concentration to remove heavy metal, vacuum evaporation and concentration, and dehydration to form a closed cycle without three wastes; the prepared water soluble quick-acting organic fertilizer with high additional value can be used as a base fertilizer and an additional fertilizer. The method has the advantages of greatly reducing the using amount of the fertilizer, greatly improving nutrient utilization rate, greatly reducing pollution due to wastage of the fertilizer, improving the quality of agricultural products, optimizing soil structure, and quickly increasing soil fertility.
Owner:SHANGHAI MULIANG IND CO LTD
Engineering bacteria based on beta-glucosidase and implementation method thereof
The invention provides engineering bacteria based on beta-glucosidase in the technical field of bioengineering and an implementation method thereof. A beta-glucosidase gene is cloned from Streptomyces griseorubens (Streptomyces griseorubens) JSD-1, and then is connected to an expression vector to obtain a recombinant expression vector, and the recombinant expression vector is further introduced into escherichia coli and is induced to synthesize beta-glucosidase. The engineering bacteria provided by the invention overcomes the defects that the beta-glucosidase in the prior art is generally endoenzyme and the expression quantity is very low, and the like, the beta-glucosidase gene of the invention is expressed by genetically engineered bacteria to prepare beta-glucosidase, and a new method is provided for producing beta-glucosidase by industrial fermentation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Antrodia cinnamomea growth medium and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an antrodia cinnamomea growth medium and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the field of bioengineering technology. The antrodia cinnamomea growth medium consists of the following raw materials: 100-250ml of 2% boiled liquid of cinnamomum camphora leaves, 150-250g of potato, 12-18g of glucose, 1-5g of sodium chloride, 0.005-0.03g of cinnamomum camphora oil and water with the rest volume of 1,000ml; the pH is 6.5-7.0. Compared with the prior art, the antrodia cinnamomea growth medium disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that (1) the medium is simple to prepare and convenient to store, the adopted technology is mature, and the medium contains all nutritional ingredients required for the antrodia cinnamomea growth and is suitable for the culture and large-scale industrial fermentation production of antrodia cinnamomea; (2) the cultured antrodia cinnamomea mycelia have high biomass and high intracellular triterpene output, wherein the biomass of mycelia reaches 12.1-14.2g / 1,000ml, and the intracellular triterpene output reaches 33.32-46.54mg / g.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Industrial fermentation method of riboflavin
ActiveCN102154426AIncreased industrial fermentation unitsImproving the process conditions of fed-batch fermentationFermentationGLUCOSE LIQUIDCulture mediums
The invention discloses an industrial fermentation method of riboflavin, which comprises the following steps of: filling a seed culture medium into a 10m<3> seed tank, and performing oxic cultivation; and filling a fermentation medium into a 200m<3> fermentation tank for fermentation, mechanically stirring, adding sterilization starch glucose liquid, stopping fermenting till that the glucose is completely consumed or the dissolved oxygen is raised to be 60%, and extracting the riboflavin from the fermentation liquid. After the industrial fermentation method is used, the conventional riboflavin material-supplementing fermentation technology is changed, the low-concentration raw material cultivating bacteria is adopted, the material is quantificationally supplemented according to the changeof the dissolved oxygen of the fermentation solution, the excessive multiplication of the thallus can be effectively controlled, the deviation of the optimum control temperature caused by the excessive supersession can be avoided, the defects of the insufficient ventilation and oxygen supply can be remitted, and the thallus vigor can be kept, so that the indusial fermentation unit of the riboflavin is improved by more than 18g / L, and the yield is increased by 20% compared with the common fermentation.
Owner:GUANGJI PHARMA MENGZHOU
Method for producing DHA by Crypthecodinium cohnii industrial fermentation
ActiveCN101538592AReduce fermentation costsQuality improvementMicroorganism based processesFermentationProduction rateInorganic salts
The invention discloses a method for producing grease containing triglyceride type DHA by Crypthecodinium cohnii industrial fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: taking the Crypthecodinium cohnii as a strain, employing a culture medium comprising a carbon source, a nitrogen source and inorganic salts, and obtaining the DHA grease by fermentation; the nitrogen source contains hydrolytic liquor of slow-release bean pulp powder as nitrogen source. The grease produced by the fermentation contains more than 50% of DHA, among which EPA content is below 1%, and the DHA productivity reaches 4.6g / L per day. The DHA has high output, high purity, safe and reliable quality, low production cost, stable production, and little or no EPA; The method can produce environment-friendly and safe high DHA content triglyceride type DHA grease in quantity with low cost.
Owner:湖北福星生物科技有限公司
Bacillus subtilis and use thereof in bio-control preparation for preventing and controlling powdery mildew
InactiveCN102250814APromote healingEase of industrial productionBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis and use thereof in bio-control preparation for preventing and controlling powdery mildew and belongs to the field of microbial pesticides. The strain is (bacillus subtilis)FBR1 with a collection number of CGMCC No.4915. The industrial fermentation culture medium for the bacillus subtilis is prepared from 0.8 percent of corn flour, 1.5 percent of soybean flour, 0.1 percent of yeast powder, 0.5 percent of peptone, 0.8 percent of monopotassium phosphate, 0.15 percent of calcium carbonate, 0.02 percent of magnesium sulfate and 0.001 percent of defoamer, and by the steps of adjusting the pH value to 7.0, fixing volume by using water, and fermenting for 24 to 36 hours under conditions of a fermentation temperature of 28 to 35 DEG C, a ventilation volumeof 0.2 to 0.4 v / v / min and a stirring speed of 100 to 150r / min. The invention also discloses a bio-control preparation which contains bacillus subtilis and can be used for preventing and controlling powdery mildew in economic crops such as melons, vegetables, tobacco and strawberry in place of spray chemical medicines without polluting the environment.
Owner:滨州国虹生物科技有限公司
A genetically engineered bacteria, its constructing method and use thereof
The present invention relates to one kind of genetic engineering bacteria, one kind of soybean disease causing variety of clove pseudomonads with preservation number of CGMCC 1276, and its construction process and use. The genetic engineering bacteria is obtained through inserting Tn5 transposon S17-1 into the genome of the initial strain to deactivate its temperature controlling gene. The strain may be used in industrial fermentation production of crown bacterin at 26-28 deg.c, in the yield near the initial bacteria and up to 35-40 mg / L.
Owner:CHENGDU NEWSUN CROPSCI
Purification compound bacterium and purification compound probiotic preparation as well as preparation method of compound probiotic preparation
InactiveCN103881929AImprove processing efficiencyNo secondary pollutionFungiBacteriaYeastIndustrial fermentation
The invention relates to a purification compound bacterium. The compound bacterium consists of 10-30% of beer yeast, 10-30% of plant lactic bacillus, 10-30% of lactobacillus acidophilus, 10-30% of bacillus subtilis, 5-15% of bacillus cereus and 5-15% of rhizobium radiobacter. Furthermore, the invention relates to a purification compound probiotic preparation and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of inoculating the purification compound bacterium on a comprehensive liquid culture medium, and implementing multi-strain compound fermentation within a temperature range of 28-35 DEG C. By combining various aerobic, facultative and anaerobic strains, the purification compound probiotic preparation is prepared through an advanced industrial fermentation technology. The compound probiotic preparation has such advantages as being wide in application scope, high in treatment efficiency, free from secondary pollution, simple in equipment required, convenient for operation, low in operation cost, low in environmental load, and simple and convenient maintenance and management.
Owner:ZHANJIANG DEYUE BIOENG CO LTD
Method of producing mixed feedstuff of straw and trester by using bio-fermentation method
InactiveCN101061830AWide variety of sourcesLow priceAnimal feeding stuffIndustrial fermentationAmmonia
The invention relates to a method for preparing mixed fodder of stalk and trester through biofermentation, which comprises mixing stalk 40-50 parts, trester 30-50 parts, bran 10-20 parts, ammonia sulfate 2-4 parts, ultramide 2-4 parts and EM dilution homogeneously, charging into an industrial fermentation tank, evacuating air to obtain anaerobic state, controlling the temperature within the range of 28-30 deg C. , fermenting five days.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABLE DEV IN AGRI CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Luteimonas sp., and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103865820ALow viscosityHigh viscosityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIndustrial fermentationNutrient solution
The invention relates to a Luteimonas sp. and its application. The Luteimonas sp. HB-2CGMCC No.6457 has been preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center since August 17, 2012. The Luteimonas sp. is used for oil reservoir flooding. The above strain is fermented in a 12m<3> industrial fermentation tank at 45DEG C for 48h, a bacterial solution with the mass concentration of 1% obtained after the fermentation and a nutritional liquid with the mass concentration of 1% are injected into the oil reservoir from a water injection well, and the injection amount is 0.07PV, so the viscosity of crude oil decreases by 53%, the recovery efficiency increases by above 5.0%, and the input-output ratio is 1:6.4.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Acidic xylanase XYL10A and gene and application thereof
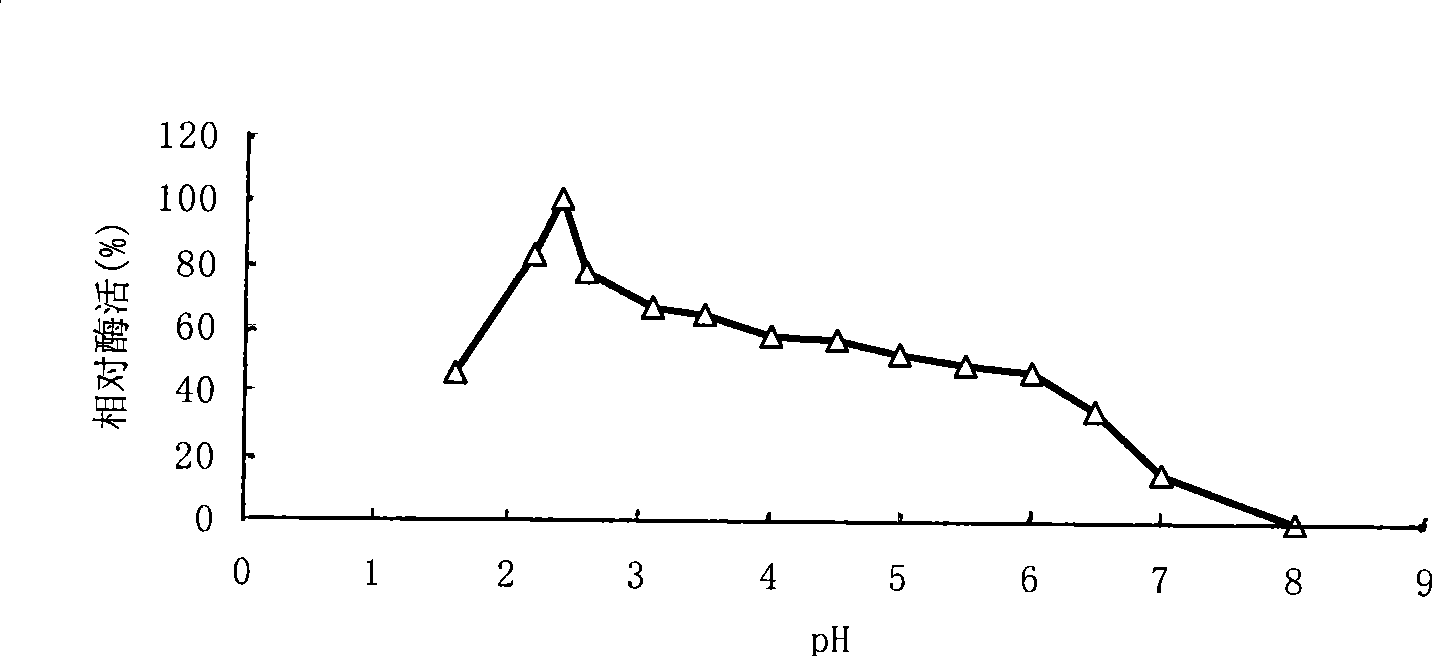
The invention relates to the genetic engineering field, especially to a strain Bispora sp.MEY-1 which produces an acidic xylanase and the acidic xylanase XYL10A got from the strain having an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or 2, a gene for coding said xylanase having a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or 2, and application of a recombinant vector, a recombinant strain and a recombinant enzyme containing said gene. The xylanase of the invention has the following advantages: the optimum pH 2.4, the optimum temperature 80 DEG C, good pH stability and thermostability, specific activity 5437 U / mg, good protease resistance and easy for industrial fermentation production. The product of the invention can be widely used for the animal feeding-stuffs, the food, the medicament, the brewing and the energy industry as a novel enzyme preparation.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for producing poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid by microbial fermentation and purification method thereof
InactiveCN103361283AReduce manufacturing costHigh degree of polymerizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPurification methods
The invention provides a method for producing poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid by fermentation of escherichia coli CGMCC NO.5585 and a purification method of the poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid. The high-purity poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid without endotoxins is further obtained and can meet the production requirements of foods, cosmetics and medicaments. According to the methods provided by the invention, the fermentation raw material uses cheap glucose to replace more expensive sorbitol, the yield of 5-6g / L can be still obtained during the fermentation stage, and the methods are particularly suitable for industrial fermentation production of PSA (polysialic acid); and finally, through the follow-up purification step, the high-purity PSA with the polymerization degree of at least above 70000Da, the purity of at least more than 95% (HPLC(high performance liquid chromatography)) and the yield of 4-4.5g / L can be obtained.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com