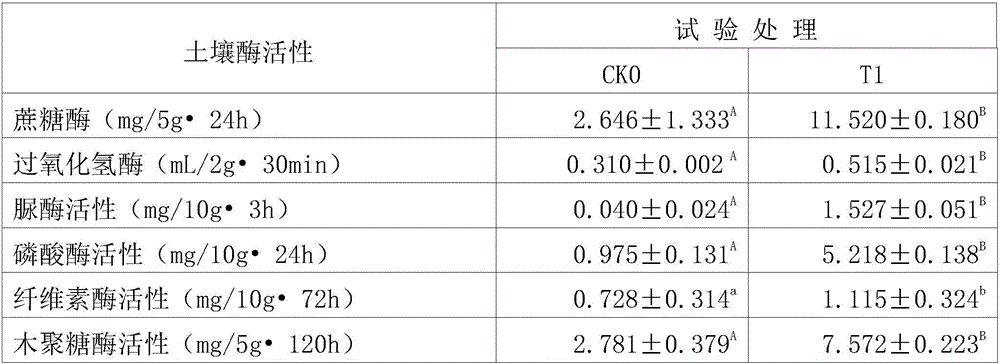
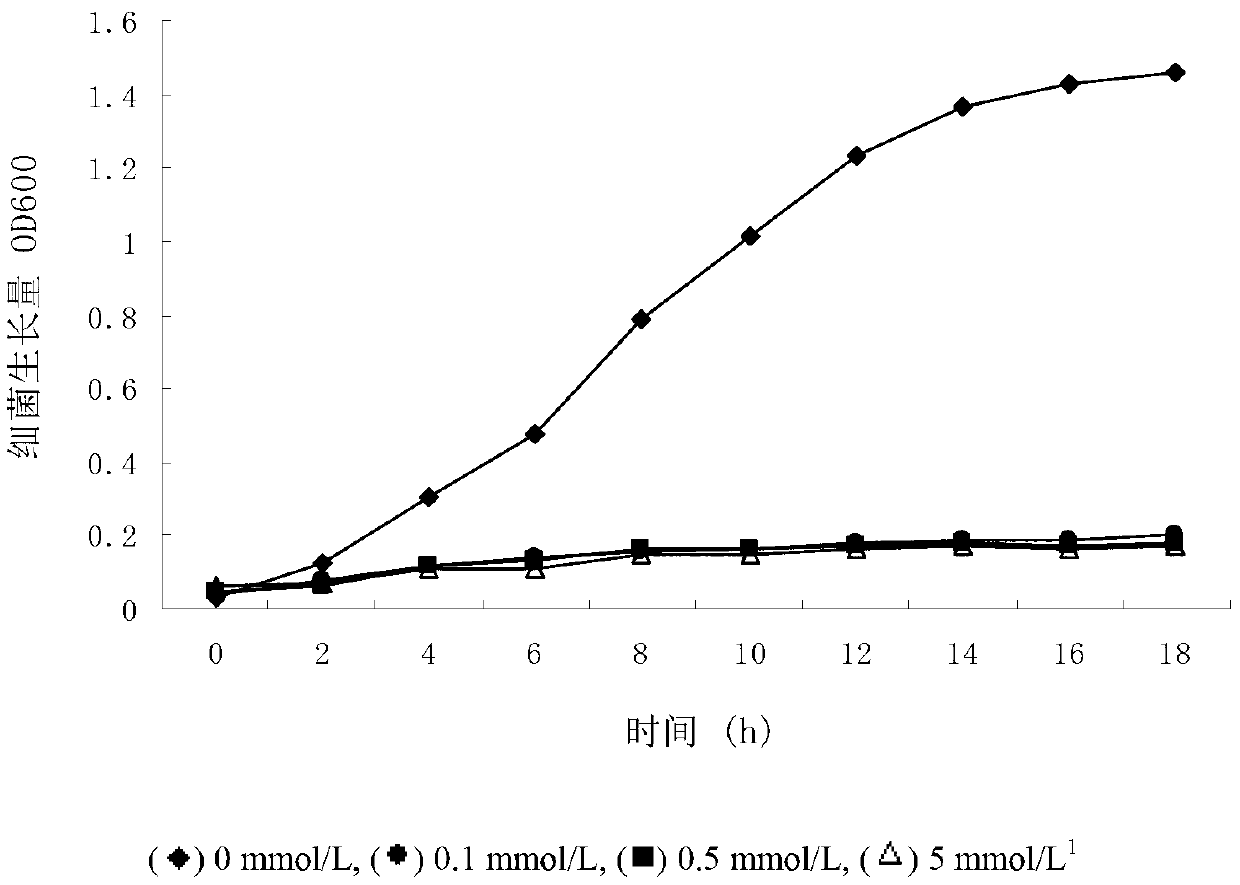
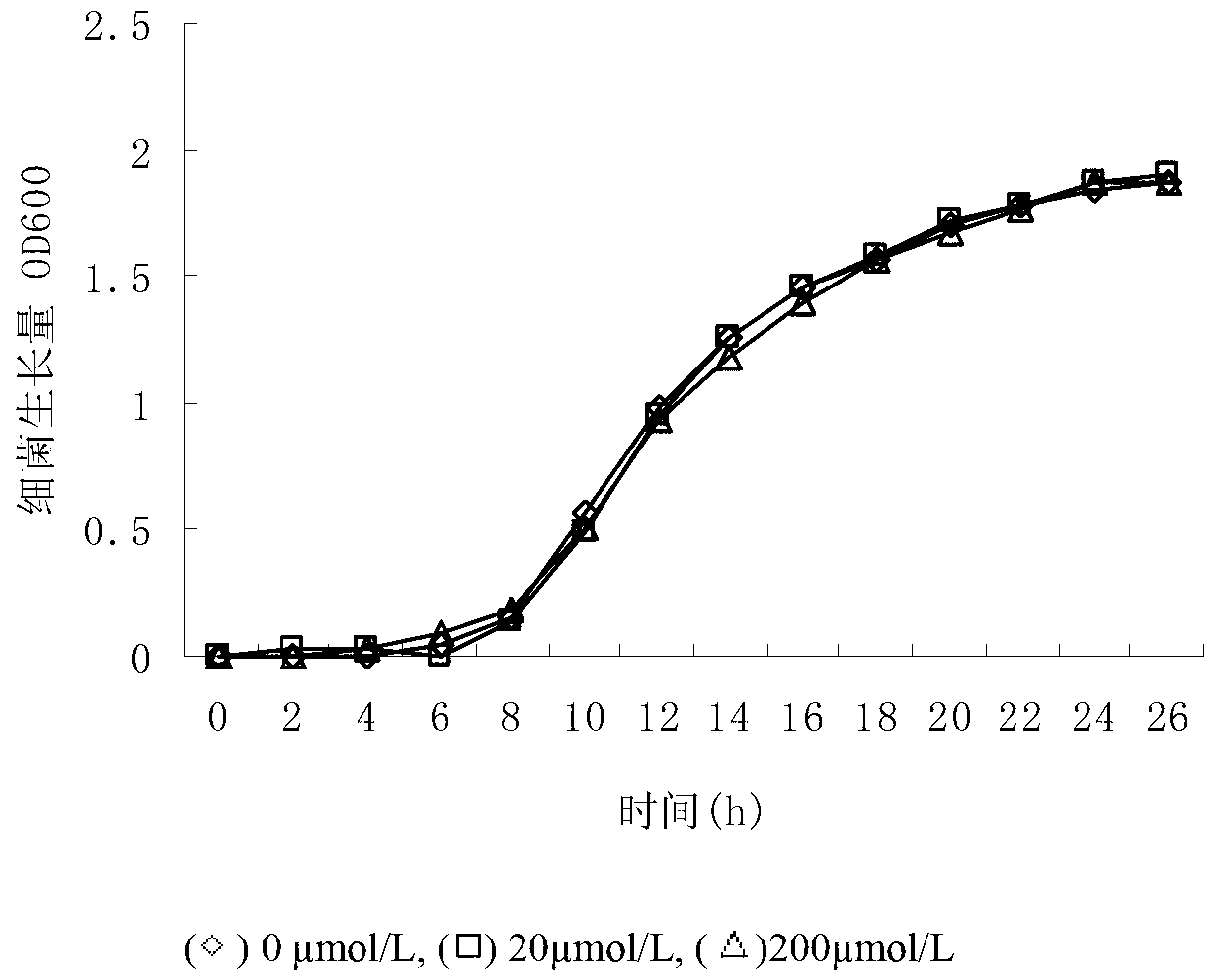
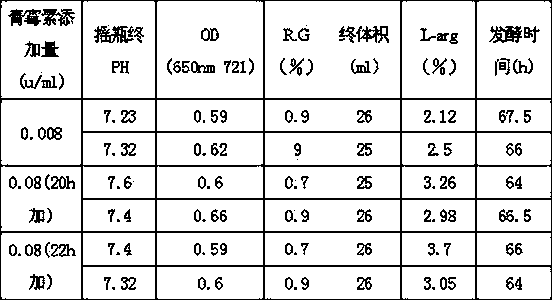
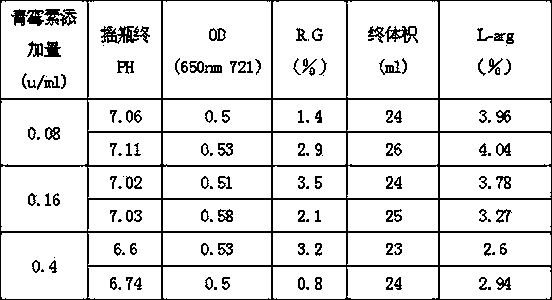
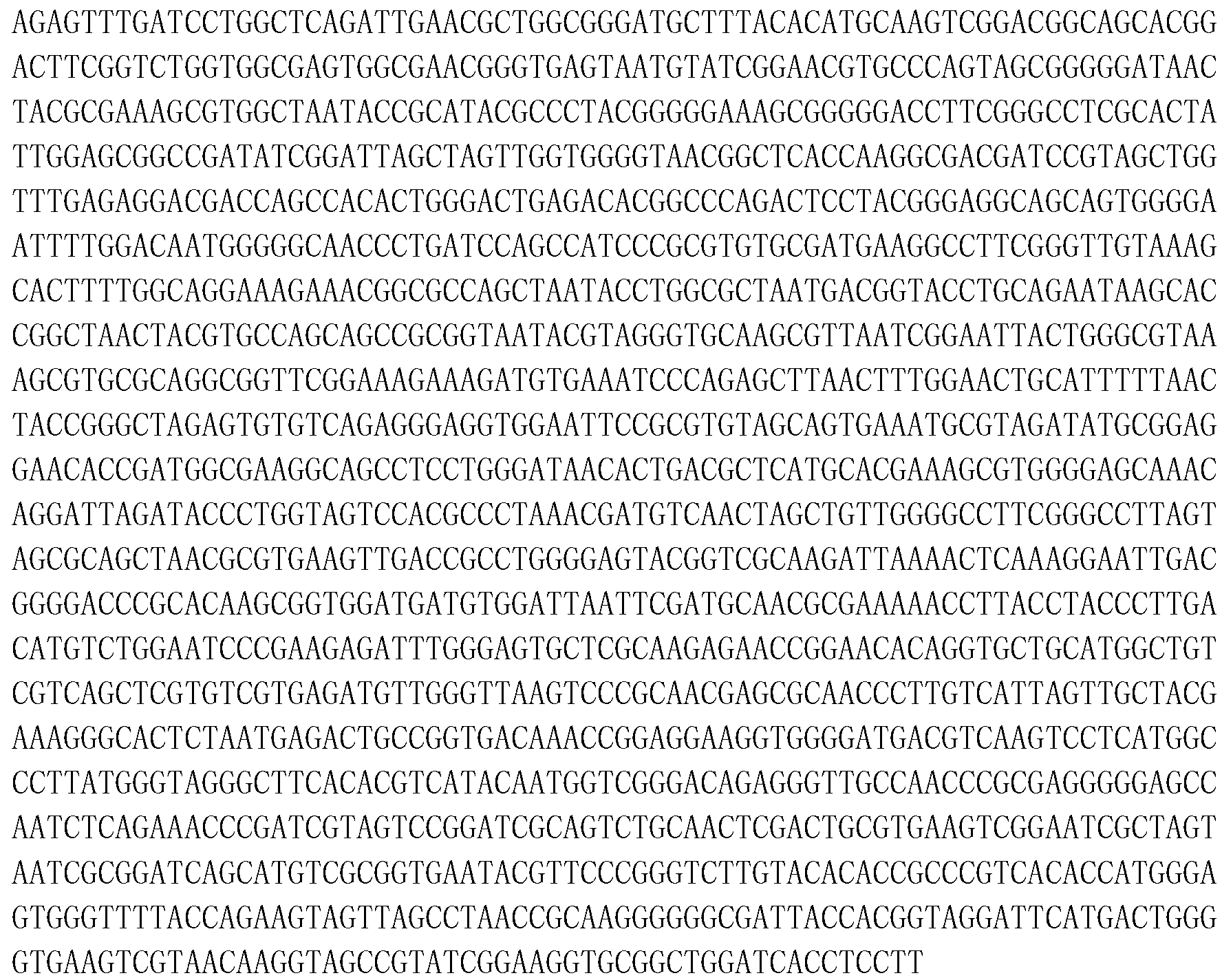Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79 results about "Brevibacterium sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
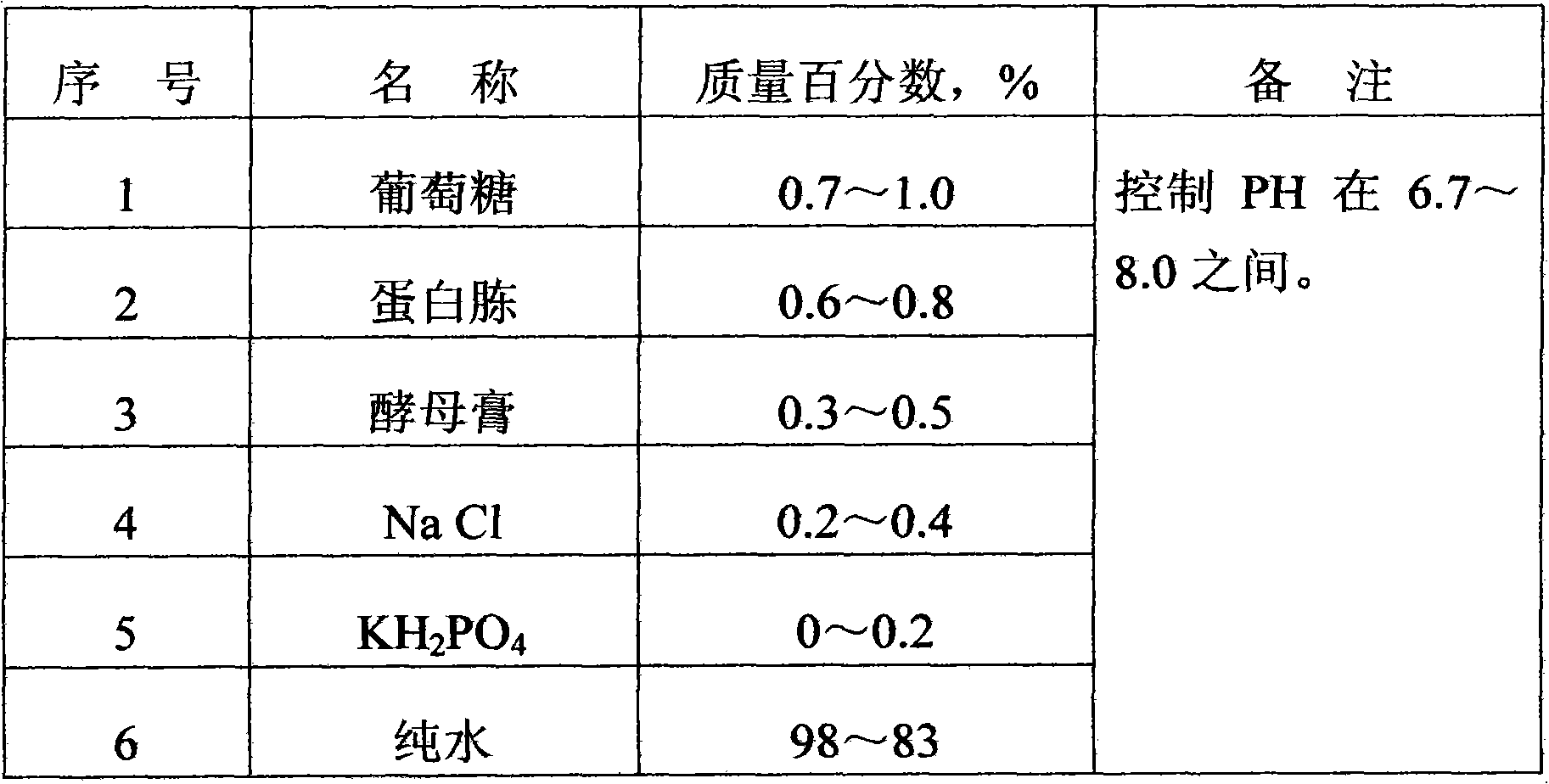
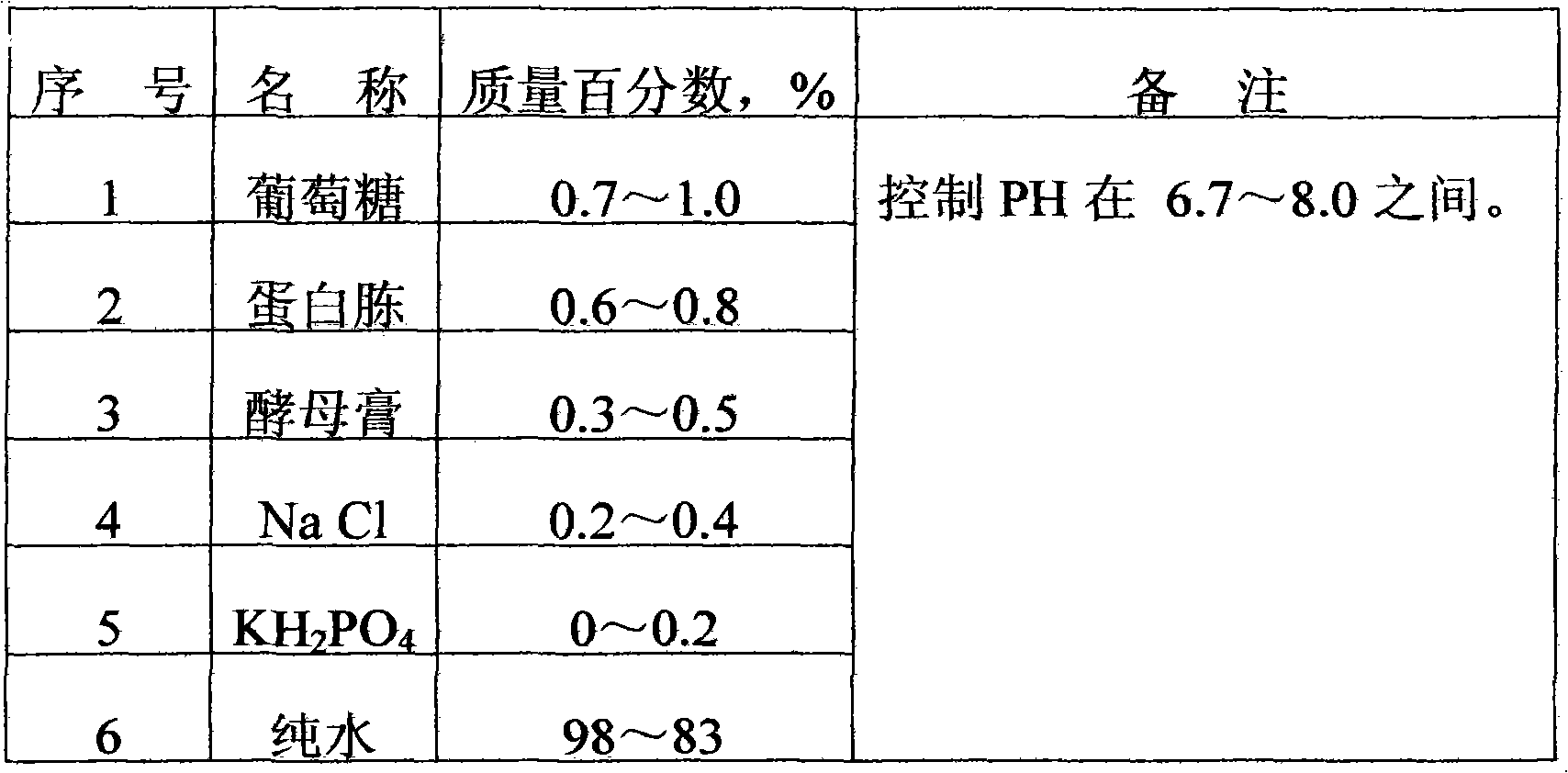
Halophilic bacterial agent and preparation method thereof as well as biological treatment system fixed with bacterial agent and application thereof
ActiveCN102146342AShort processEasy to operateBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyHalomonas salina
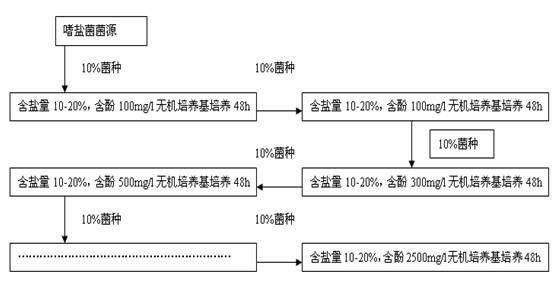
The invention discloses a halophilic bacterial agent and a preparation method thereof as well as a biological treatment system fixed with the bacterial agent and application thereof. In the invention, strains are screened from sewage, sludge and soil to be prepared into a bacterial agent, wherein the bacterial agent comprises four strains including Providenciasp. CJ-4, Oceanobcillussp. CJ-10, Brevibacterium epidermidis CJ-12 and Halomonassp. CJ-13. The invention also provides the biological treatment system fixed with the bacterial agent and a method for treating waste water by using the same. The bacterial agent disclosed by the invention has stronger degradation capability on phenolic wastewater, can adapt to high-salt environments and has very good degradation effects under an environment with the salt content of 2-25% and the phenol concentration of 2500 mg / l; and compared with the traditional active sludge method, the bacterial agent has obvious advantages in the performance of degrading phenolic compounds, and the degradation effect on the phenolic compounds in water can reach more than 99.9%.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIFANG RAINBOW CHEM
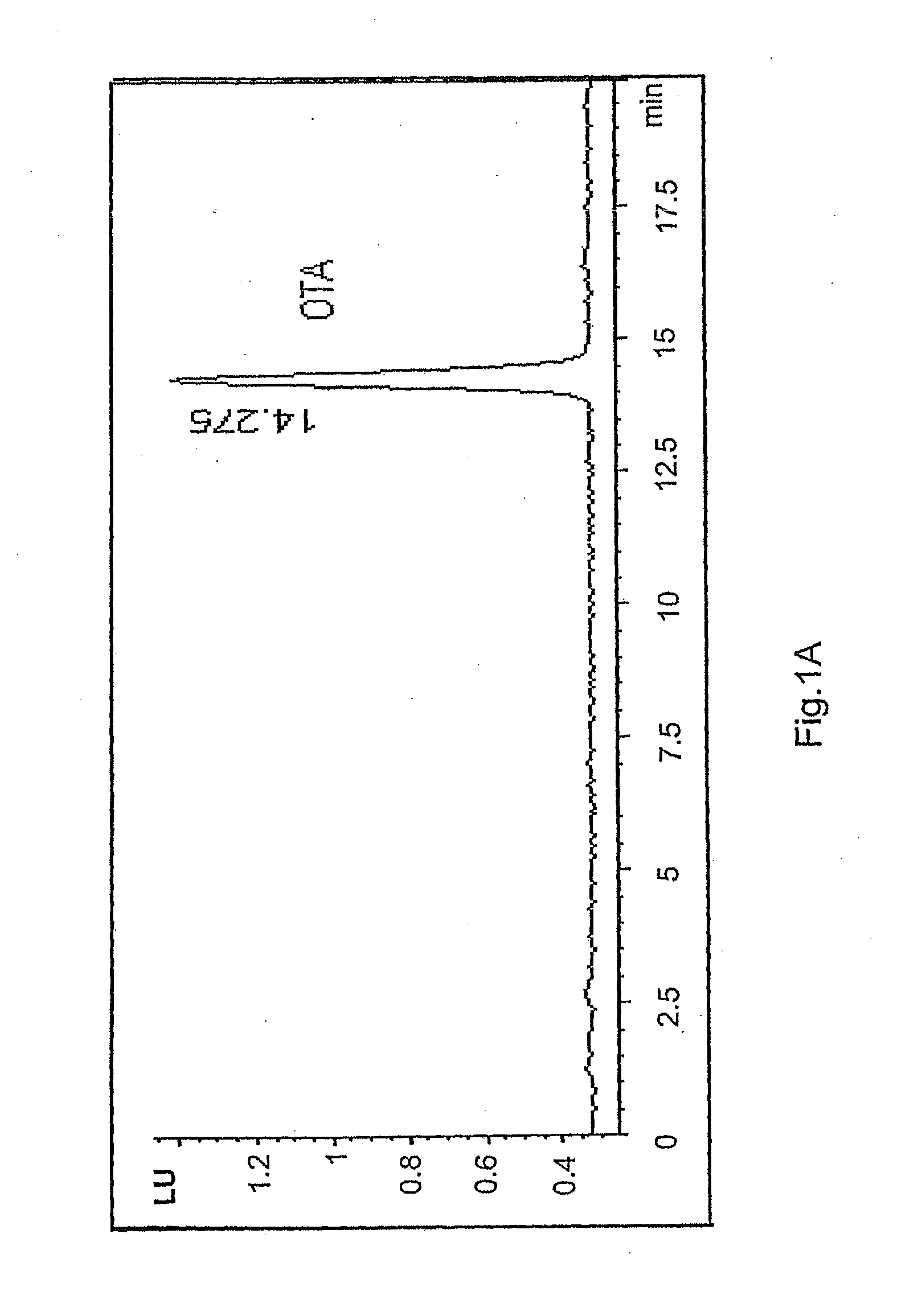
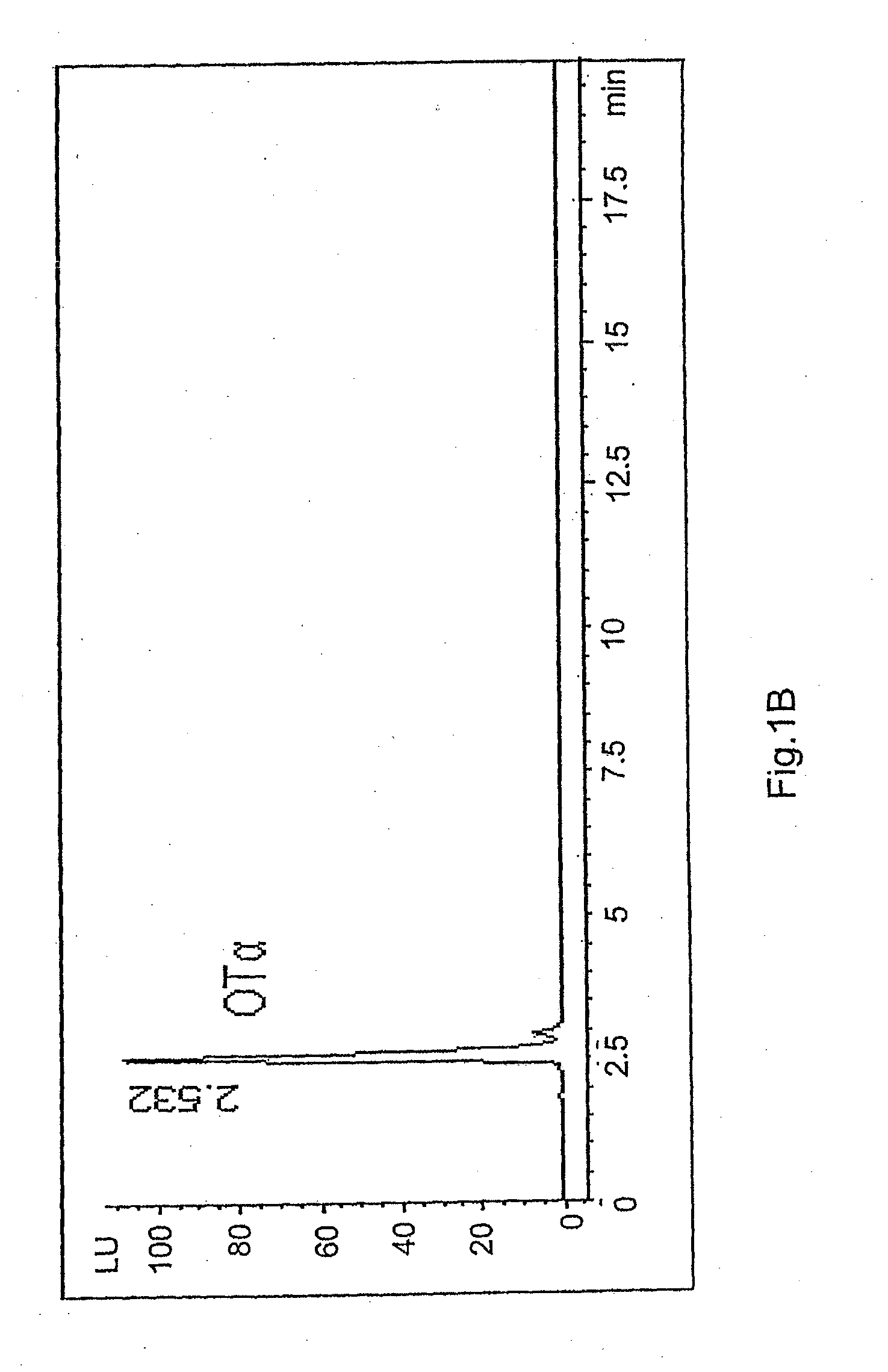
Biological degradation of ochratoxin a into ochratoxin alpha
The invention relates to the use of a microorganism of the genus Brevibacterium for the biological degradation of ochratoxin A, in which the microorganism is preferably Brevibacterium casei, Brevibacterium linens, Brevibacterium iodinum or Brevibacterium epidermidis. In addition, the invention relates to a method for the production of ochratoxin α using said microorganism.
Owner:CENT DI RICERCA PER LENOLOGIA CRA ENO
Genes and enzymes for the production of adipic acid intermediates
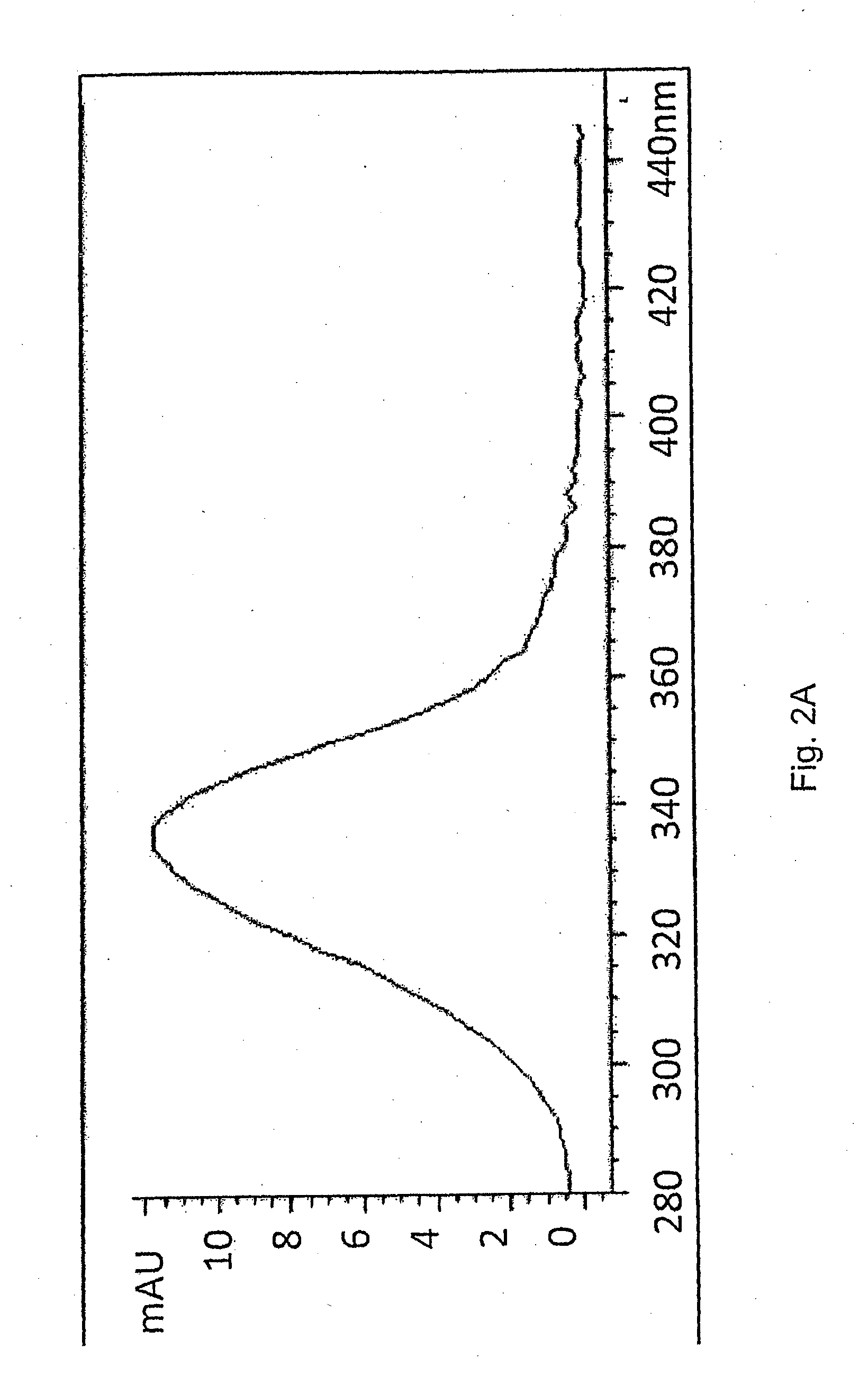
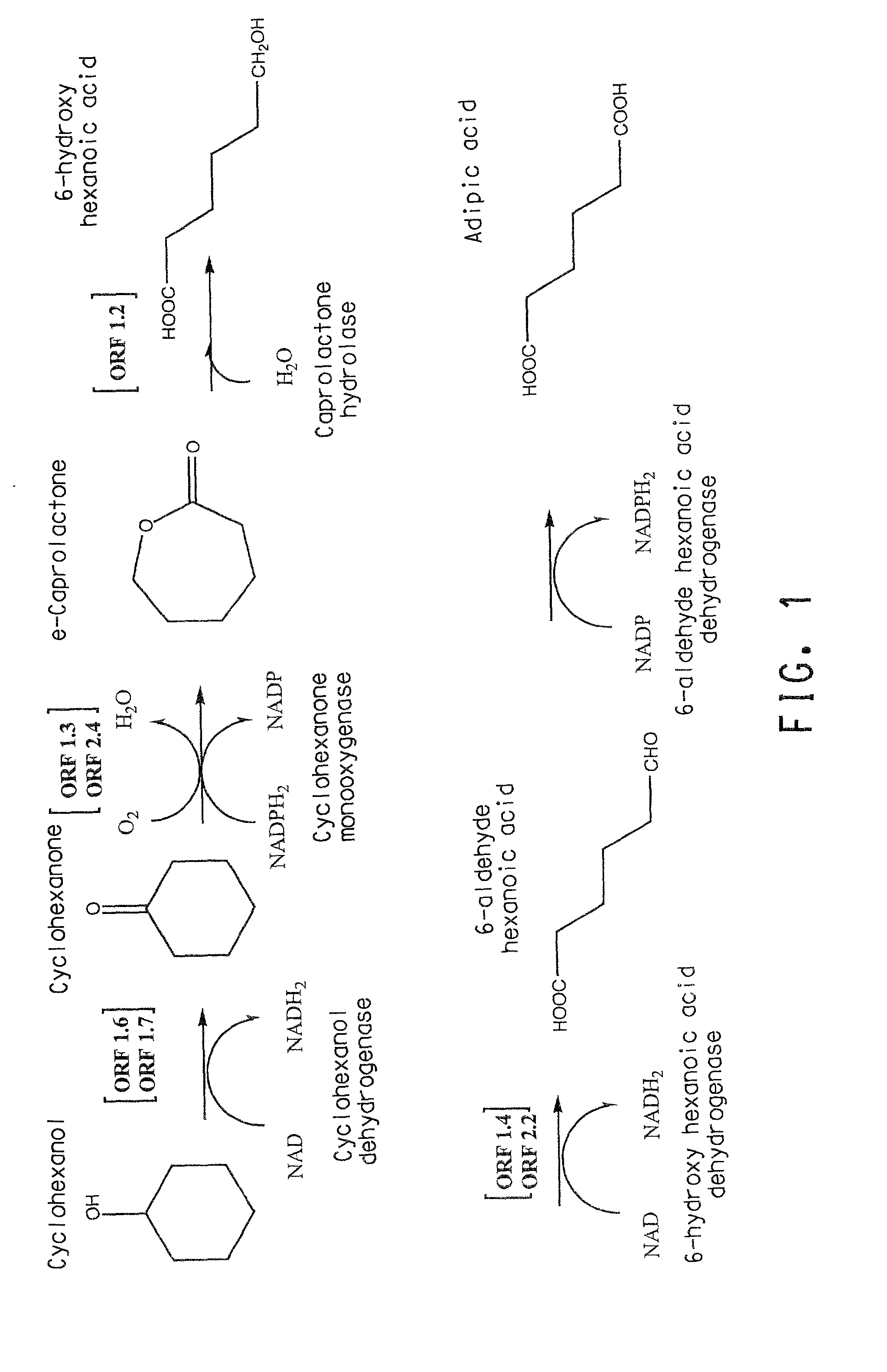
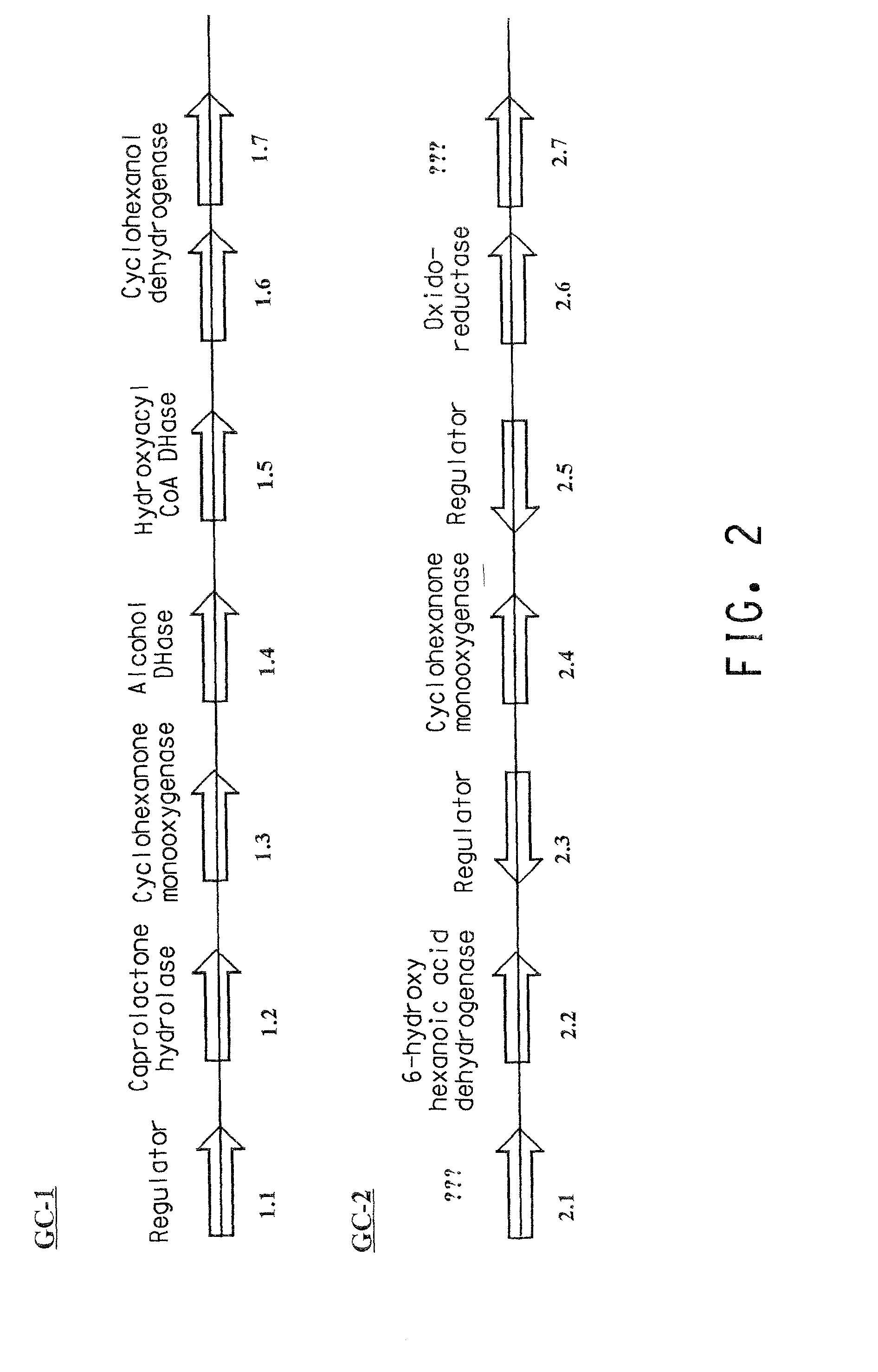
Two gene clusters have been isolated from an Brevibacterium sp HCU that encode the enzymes expected to convert cyclohexanol to adipic acid. Individual open reading frames (ORF's) on each gene cluster are useful for the production of intermediates in the adipic acid biosynthetic pathway or of related molecules. All the ORF's have been sequenced. Identification of gene function has been made on the basis of sequence comparison and biochemical analysis.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Brevibacterium halotolerans and application thereof in ecological restoration of soils
ActiveCN106434496AIncrease nitrogenase activityImprove fertilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAzotobacter chroococcumMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a brevibacterium halotolerans with relatively high azotase activity and application thereof in ecological restoration. The brevibacterium halotolerans GDSD21 is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the collection number of CGMCC No.12402. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are separated from rhizosphere soils of field-crop roots, further strains with relatively high azotase activity are screened, and finally the efficient nitrogen-fixing bacterium brevibacterium halotolerans GDSD21 is screened. The azotase activity of the brevibacterium halotolerans GDSD21 is obviously higher than that of common production strain azotobacter chroococcum ACCC11103 for microbial fertilizers, and the brevibacterium halotolerans GDSD21 has extensive application prospects in soil improvement, increasing of the soil fertility, ecological restoration of a virgin land, and production of industrialized seedling-rearing inoculation agents, nitrogen-fixing microbial agents and bio-organic fertilizers for vegetables.
Owner:北京复天科技有限公司 +1
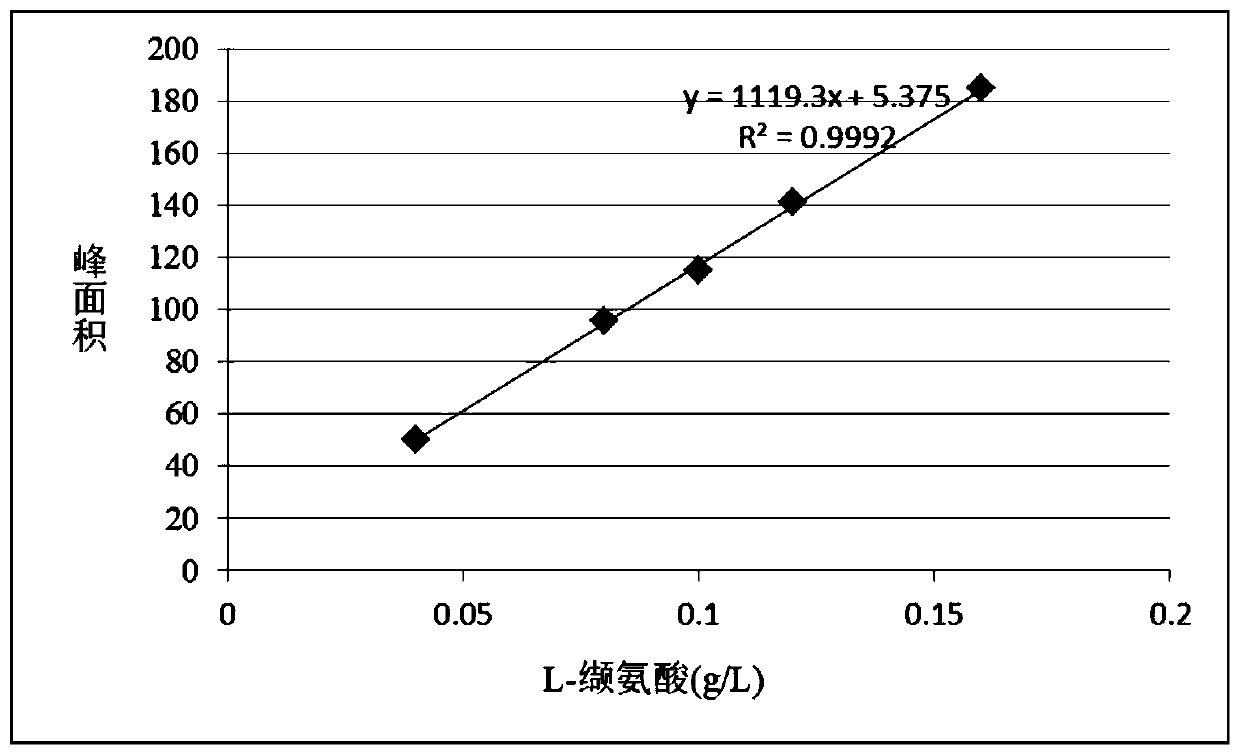
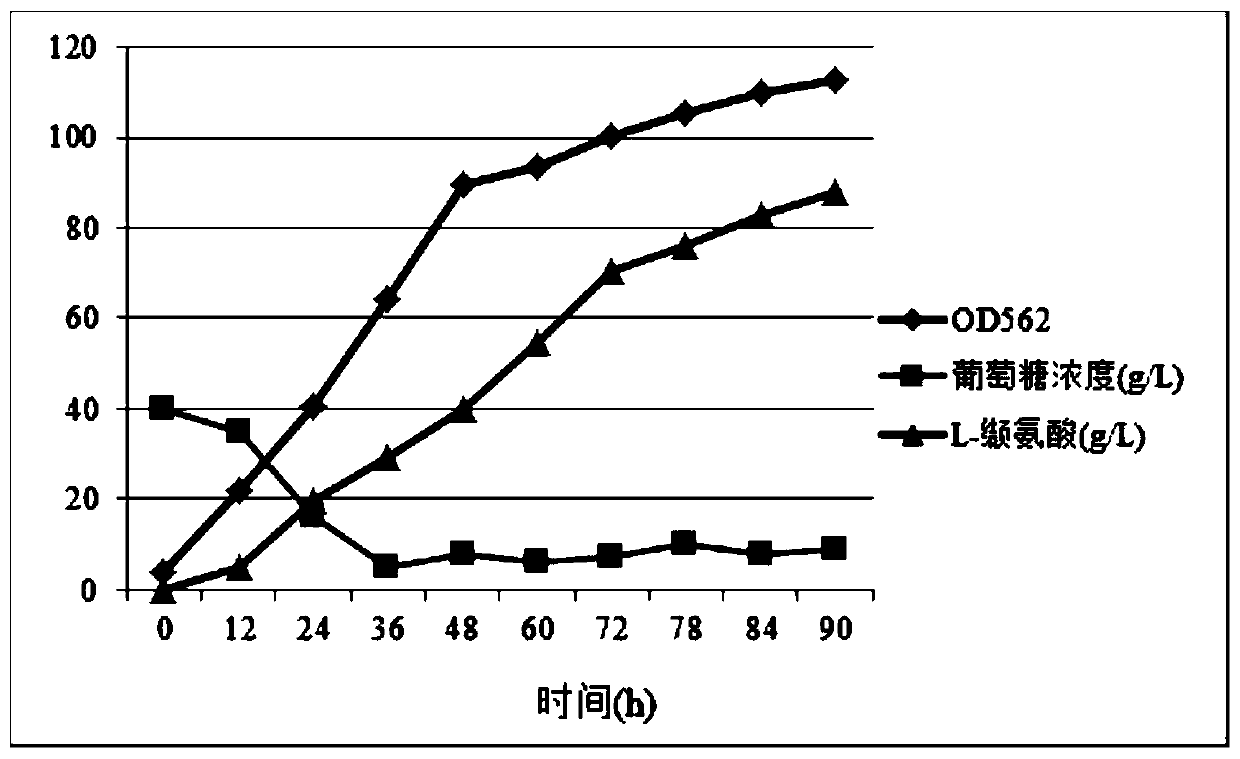
L-valine-producing brevibacterium flavum and method for producing L-valine by using brevibacterium flavum
ActiveCN110643547APromote reproductionReduce consumptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The present invention belongs to the field of bioengineering technology and particularly relates to L-valine-producing brevibacterium flavum. The brevibacterium flavum is preserved in China Center forType Culture Collection on July 01, 2019, a preservation number is CCTCC M2019496 and a preservation address is Luojia Hill, Bayi Road, Wuchang District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province. The present invention also relates to a method for producing L-valine by using the brevibacterium flavum, the brevibacterium flavum strain is subjected to activation culture and seed liquid culture, and obtained seedliquid is inoculated into a fermentation culture medium for fermentation culture, and the fermentation culture process is firstly aerobic fermentation and then anaerobic fermentation. L-valine production is carried out by using the preserved strain and the production method, yield is high, sugar-acid conversion rate is high, besides, fermentation process takes a short time, and production efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:BAYANNUR HUAHENG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Process for producing arginine by microbial fermentation
InactiveCN103695487AQuality improvementHigh yieldOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Owner:滨州市生物技术研究院有限责任公司
Brevibacterium strain and method for in-situ remediation of heavy metal polluted farmland using same
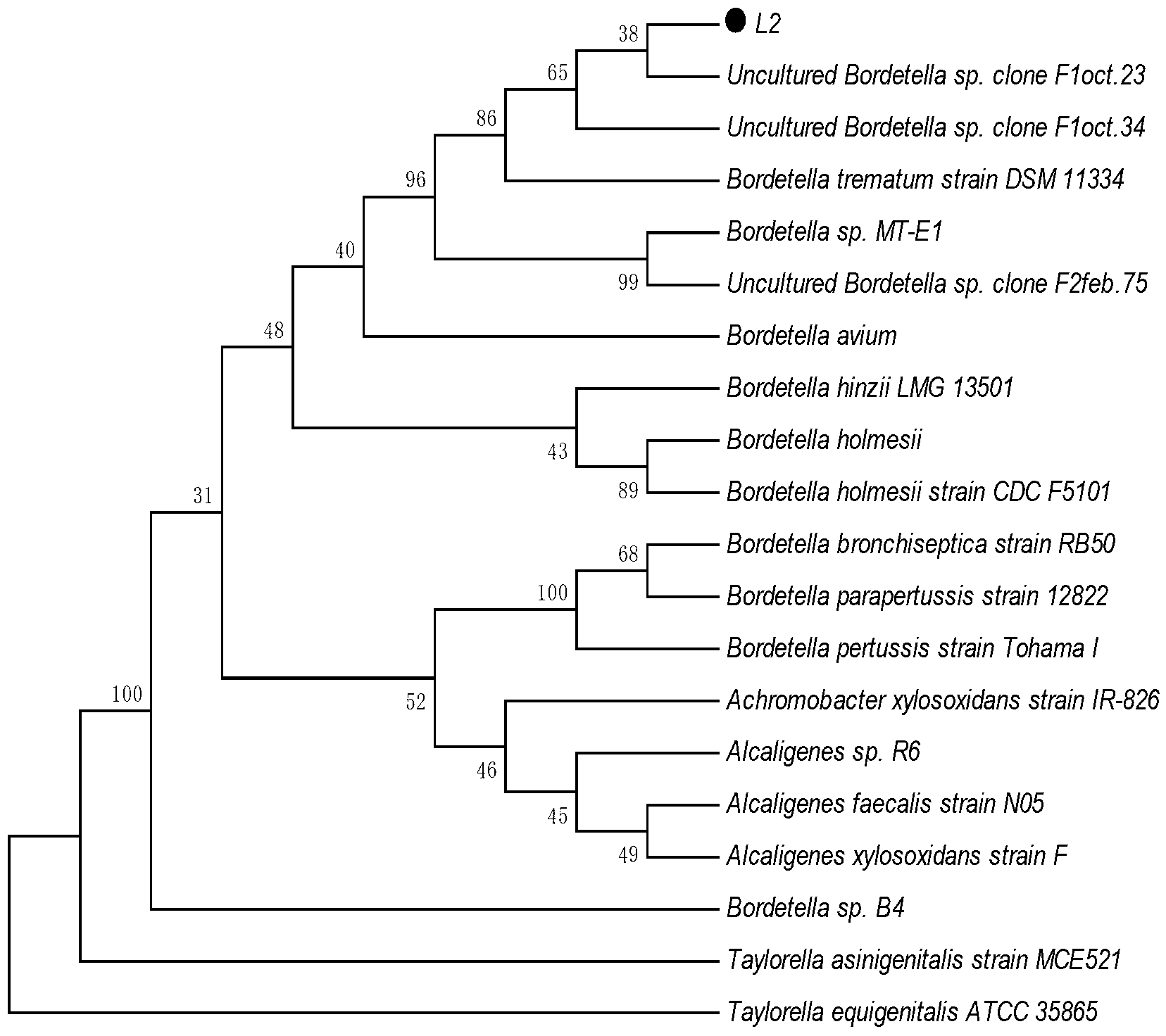
The invention provides a brevibacterium strain and a method for in-situ remediation of heavy metal polluted farmland by using the same. The class name of the brevibacterium is named: Brevibacterium spGRINM L2; and the brevibacterium is collected by the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 3#, No.1 Courtyard, West BeichenRoad, Chaoyang District, Beijing, on September 29, 2016 and with a collection number: CGMCC No.13064. In the presence of high-concentration heavy metal ions, the bacteria can efficiently convert insoluble phosphate into soluble phosphate and can be applied to the remediation of heavy metal polluted farmland.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Construction method and applications of genetic engineering bacterium for producing L-arginine
InactiveCN103966151AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyColiform bacilli
The invention relates to a construction method and applications of a genetic engineering bacterium for producing L-arginine. The invention discloses a novel genetic engineering bacterium strain for producing L-arginine. Recombinant plasmid pXMJ19-argH can be orderly converted and introduced into colibacillus and auxotroph brevibacterium flavum AN78 by the genetic engineering bacterium strain, and then the argininosuccinase in the AN78 containing recombinant plasmids is over-expressed and fermented to produce L-arginine. The invention further discloses a construction method and applications of the genetic engineering bacterium. The genetic engineering bacterium can increase the L-arginine production output and reduce the production cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI KING SHINE BIOLOGY TECH
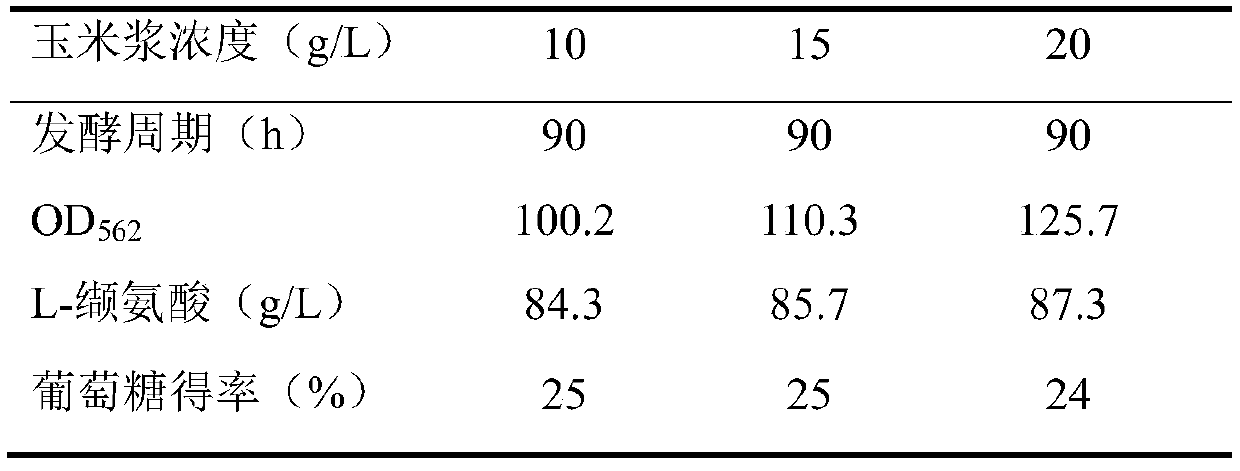
Strain of brevibacterium flavum producing L-valine and application of brevibacterium flavum
ActiveCN109943511AHigh yieldHas industrial practical valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBrevibacillus borstelensisMicrobiology
The invention discloses a strain of brevibacterium flavum producing L-valine and application of the brevibacterium flavum, and belons to the technical field of bioengineering. The brevibacterium flavum is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on January 17, 2019 under the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2019053, and the preservation address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.The brevibacterium flavum FMME447 exhibits the ability to accumulate high-level L-valine, and it is verified that the valine tolerance of the brevibacterium flavum reaches 100 g / L. The yield of the L-valine through the fermentation of the brevibacterium flavum reaches 80-90 g / L, the yield of glucose reaches up to about 25-30%, and the brevibacterium flavum has industrial practical value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
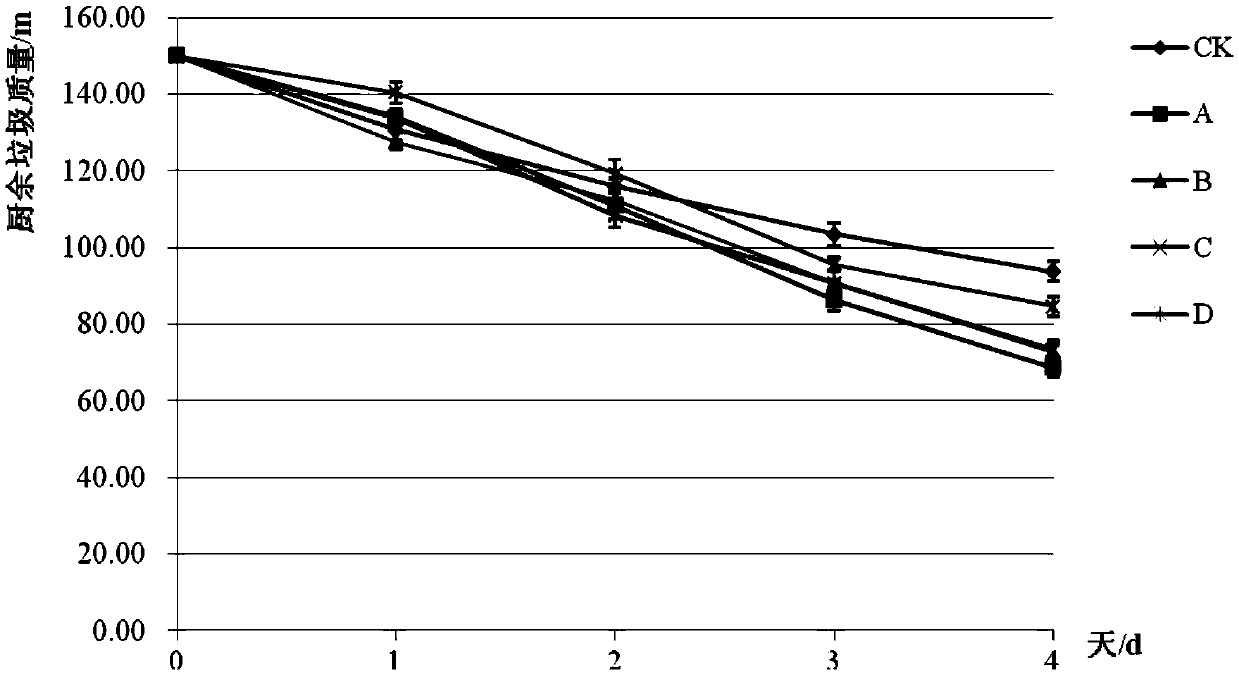
Complex microbial inoculant, method for preparing same and application of complex microbial inoculant
InactiveCN105368741AGood composting effectImprove germination rateFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention relates to a complex microbial inoculant. The complex microbial inoculant comprises eleven types of complex inoculants and accessories. The complex inoculants comprise seven types of bacteria such as saccharomyces cerevisiae, pseudomonas veronii and brevibacterium epidermidis and are added to the accessories, and the complex inoculants and the accessories are subjected to solid fermentation to obtain the complex microbial inoculant. The complex microbial inoculant has the advantages that kitchen waste can be effectively reduced by the complex microbial inoculant as compared with other commercially available inoculants, odor generated by the kitchen waste in compost maturity procedures can be effectively reduced, and the compost maturity level can be upgraded.
Owner:YANGZHOU KEHUI ECOLOGICAL ENG TECH CO LTD
6-aminopenicillanic acid degrading bacterium and screening method thereof
ActiveCN103184177AImprove the ability to hydrolyze 6-aminopenicillanic acidBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismScreening method
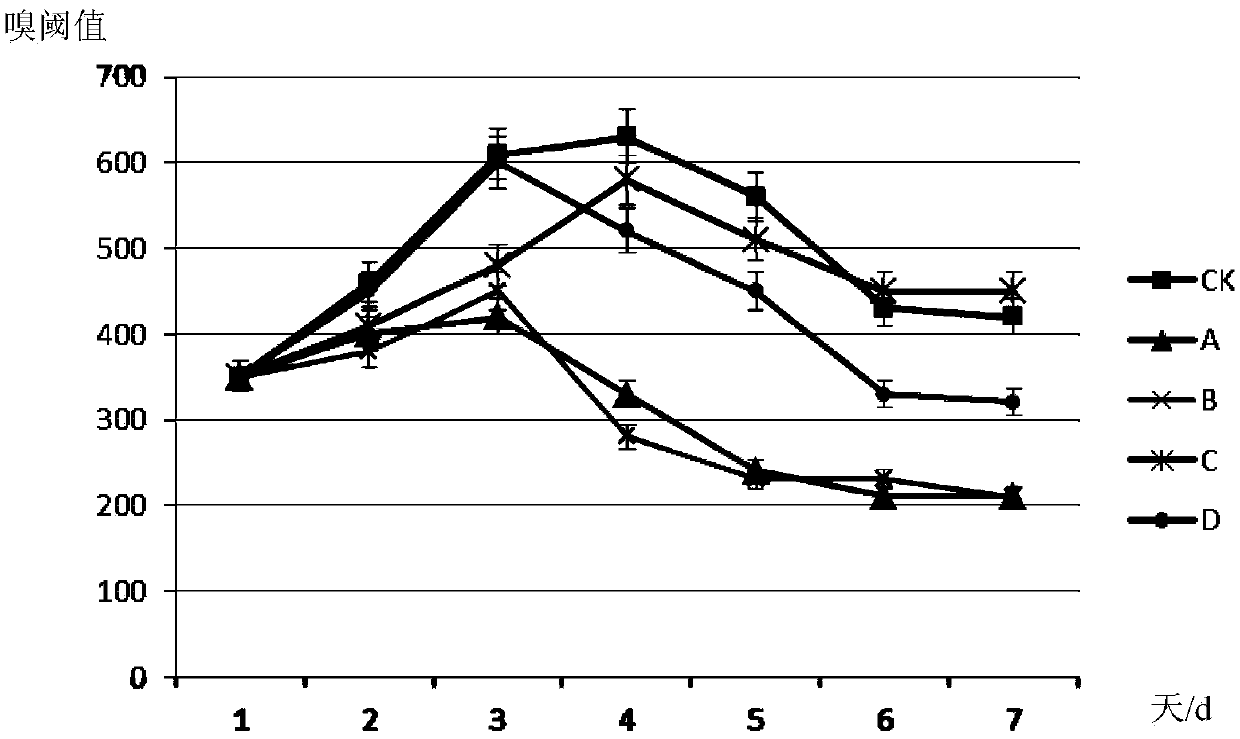
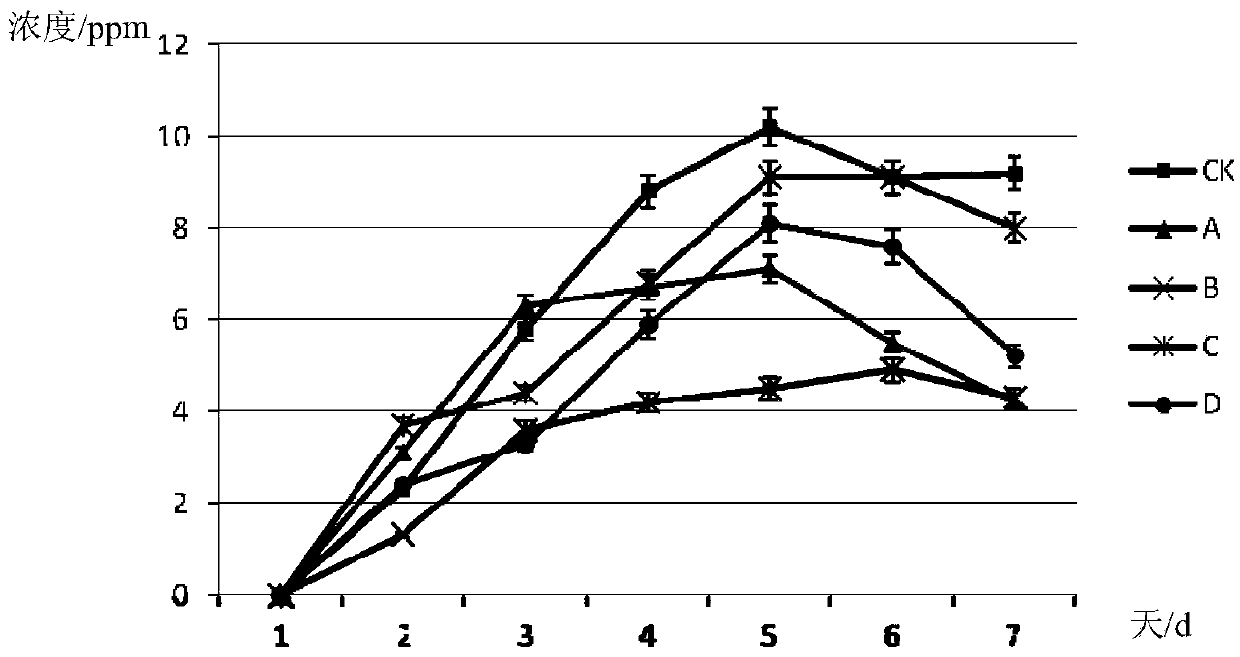
The invention relates to a 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) degrading bacterium and a screening method thereof. Particularly, the invention relates to a strain of 6-APA degrading bacterium Bordetella sp.L2, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on October 18, 2012, with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 6691; and the GenBank registration number of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of the 6-APA degrading bacterium Bordetella sp.L2 is HQ840720. The 6-APA degrading bacterium Bordetella sp.L2 is an aerobic bacillus brevis; and when the pH value is 8.0, the 6-APA degradation rate of the 6-APA degrading bacterium Bordetella sp.L2 is 28%. The strain achieves higher 6-APA degradation capability and has a practical significance and an important engineering application value for treatment of waste water containing 6-APA cephalosporin.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES CORPORATION
Desertification region plant growth improving microbial preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109730088APromote growthImprove germination rateBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicrobial agentPlant growth
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial preparations and relates to a desertification region plant growth improving microbial preparation and a preparation method thereof. The desertification region plant growth improving microbial preparation is composed of, by weight part, 40-60 parts of starch, 10-20 parts of charcoal, 2-5 parts of humic acid, 8-10 parts of microbial agent and15-30 parts of algal polysaccharides, wherein the microbial agent is Brevibacterium Sp. TS22 domesticated at low altitudes and normal temperature with a preservation number of CGMCC 16576; the microbial agent also comprises 0-20% of phosphate solubilizing bacteria by weight. The preparation method of the desertification region plant growth improving microbial agent comprises by weight part mixingthe raw materials of the desertification region plant growth improving microbial agent inside a mixer for reaction to obtain the desertification region plant growth improving microbial agent. The desertification region plant growth improving microbial agent can be applied separately or by being compounded with agricultural and forestry organic fertilizers. The desertification region plant growthimproving microbial agent is simple in operation and low in production cost and improve the emergence rate of desertification region plants by more than 50%.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Bacterial strain used for arsenic polluted soil remediation and application method thereof
ActiveCN104004691AHarmfulHarm reductionBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationArsenic pollutionVirulent characteristics
The invention discloses a bacterial strain Brevibacterium sp.YZ-1 used for arsenic polluted soil remediation and an application method of the bacterial strain used for arsenic polluted soil remediation Brevibacterium sp.YZ-1. The collection number of the strain is CGMCC No.8329. The toleration for As (III) reaches above 1000 mg / L, and an As (III) solution with the concentricity of 100 mg / L can be oxidized by over 75%. Through the strain, water-soluble As (III) of arsenic polluted soil can be reduced by 82.6%, and the effective state As (III) can be reduced by 84.1%. The arsenic virulence in the environment is greatly reduced. The research shows that the strain has good application prospects in the aspect of environment arsenic pollution control.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Phosphoserine phosphatase gene of coryneform bacteria
The present invention provides a DNA coding for a protein defined in the following (A) or (B) is obtained from Brevibacterium flavum chromosomal DNA library by cloning a DNA fragment that complicates serB deficiency of Escherichia coli as a open reading frame in the DNA fragment.(A) A protein which comprises an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID: 2 in Sequence Listing; or(B) A protein which comprises an amino acid sequence including substitution, deletion, insertion, addition or inversion of one or several amino acids in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 in Sequence Listing, and which has phosphoserine phosphatase activity.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
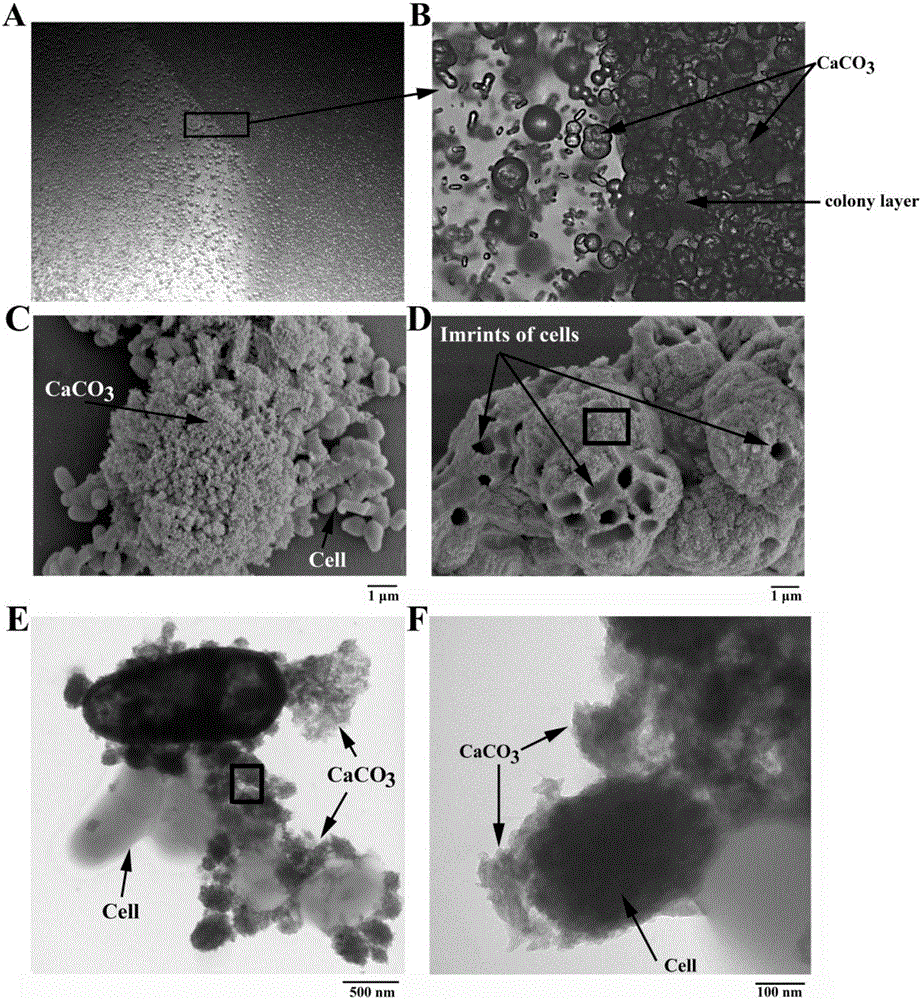
Calcium carbonate producing actinomycetes and application thereof
InactiveCN106635882AAchieve biomineralizationTo achieve the purpose of heavy metal repairBacteriaWater contaminantsIonMicro environment
The invention belongs to the technical field of functional microbiological screening and application, and particularly relates to calcium carbonate producing actinomycetes and application thereof. The calcium carbonate producing actinomycetes is brevibacterium linens BS258, a strain is preserved in the Common Microorganism Center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms in Number 3 (the Institute of Microbiology) of the Number 1 courtyard on the West Beichen Road in the Chaoyang District of Beijing on September 26th, 2016, a preservation number of the strain is CGMCC 1.15904, and a taxonomy name of the strain is brevibacterium linens BS258. The calcium carbonate producing actinomycetes and the application have the advantages that calcium carbonate precipitates can be induced by the actinomycetes, and the strain can tolerate high-calcium-ion environments and can resist diversified heavy metal ions; calcium ions in the environments can be induced under the effect of carbonic anhydrase by the aid of alkaline micro-environments generated in urea decomposition procedures to form the calcium carbonate precipitates, the heavy metal ions can be co-precipitated in calcium carbonate forming procedures, accordingly, the purposes of biological mineralization and heavy metal restoration can be achieved, and the shortcomings in the prior art can be overcome.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing fermentation strains of microbial organic fertilizer
InactiveCN102031233AIncrease productionHigh outputBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention provides fermentation strains Brevibacterium sp D1 (with the perservation number of CCTCC No: M 2010250) and bacillus amyloliquefaciens S4 ( with the preservation number of CCTCC No: M 2010249) of a microbial organic fertilizer of tobacco straws; the fermentation strains Brevibacterium sp D1 and the bacillus amyloliquefaciens S4 are separated and screened from the tobacco straws under a high-temperature and heavy-nicotine condition, and can exist in the presence of the nicotine; and after being cultivated and proliferated, the ermentation strains Brevibacterium sp D1 and the bacillus amyloliquefaciens S4 are added into a waste tobacco straw mixture, and are subjected to solid fermentation under a natural condition to convert the tobacco straw wastes into the tobacco straw microbial organic fertilizer. The tobacco straw microbial organic fertilizer can replace other fertilizers to produce the tobacco, and has the advantages of increasing yield of the tobacco leaves, increasing production values of the tobacco leaves, improving smoking quality of the tobacco leaves, and simultaneously removing pollution to the environment by the tobacco straw wastes.
Owner:中国烟草总公司湖北省公司
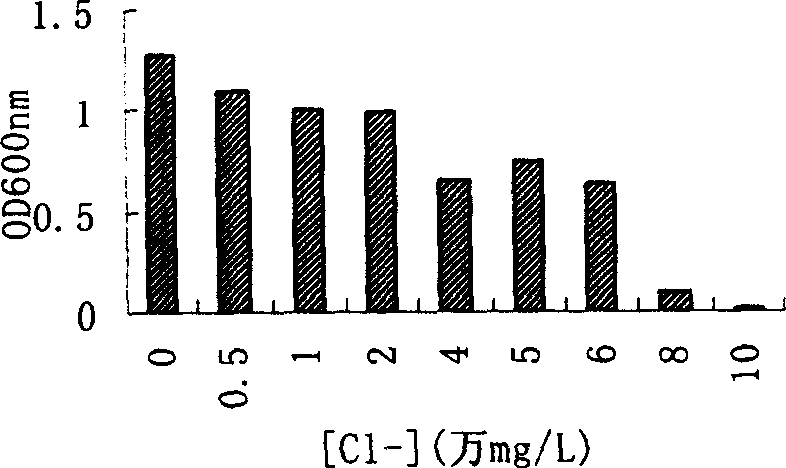
Chlorine resisting strain No.1 and screening process thereof
InactiveCN1793326AImprove growth performanceEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationArginine
The invention relates to chlorine proof microorganism. It is chlorine proof strain No.1. Its features are as follows: it is brevibacterium linens B723-1 CCTCC NO.M205122; its colonial morphologies are creamy white, rule circular, un-transparent, smooth, stiff, and pink after 5M KOH processing; physiological characteristics that young bacterial is irregular baculiform, 0.6-1.2um*1.5-6.0um, single or pairs arrangement, common V shape; old is irregular globular, and gram positive; its main biological and chemical features are concurrently character anaerobic, chemoheterotrophic bacteria, contacting enzyme positive, oxidase negative, producing arginine double hydrolase, lysine decarboxylase, ornithine decarboxylase, and urease, and producing acid from glucose, no moving, no spore; its optimum temperature is 25-37 centigrade degree. It can live in high concentration chloride ion condition, and high effectively degrade high concentration organic pollutant.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
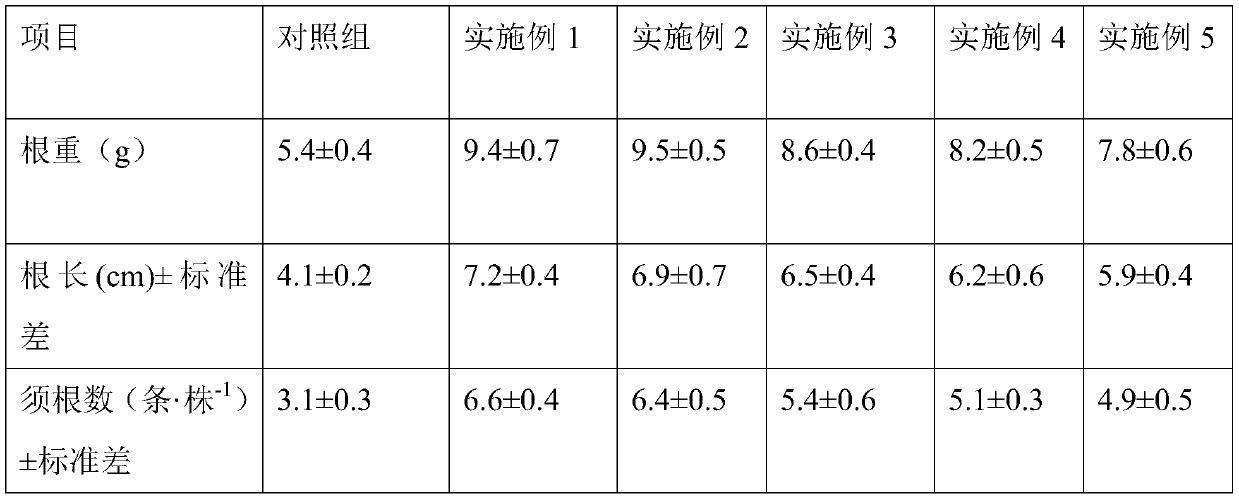
Microbial preparation for promoting plant root system growth and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109730089APromote growthIncrease the number of fibrous rootsBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAmyrisPlant roots
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial preparations, and relates to a microbial preparation for promoting plant root system growth and a preparation method thereof. The microbial preparation comprises 60-70 parts of starch, 8-10 parts of a special microbial agent, and 20-32 parts of algal polysaccharide, wherein the microbial agent is low-altitude and normal-temperature domesticated Brevibacterium sp. TS22, and a preservation number is CGMCC 16576; and the microbial agent further comprises a mixed bactericide of a phosphate solubilizing bacterial strain and a soil rooting agrobacterium, and a weight is 0-20% of the microbial agent. The preparation method for the microbial preparation comprises the following steps: putting raw material components of the microbial preparation in parts by weight into a stirrer, stirring and reacting, to obtain the microbial preparation for promoting the plant root system growth. The microbial preparation is independently used or compounded with an agriculture and forestry organic fertilizer for using. The microbial preparation is simple and convenient in operation, low in production cost, and capable of remarkably improving the rootsystem growth of a plant.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Microbial preparation for facilitating saline and alkaline land plant growth and preparation method of microbial preparation
InactiveCN109734484APromote growthIncreased root lengthOrganic fertilisersPlant rootsMicrobial agent
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial preparations, and relates to a microbial preparation for facilitating saline and alkaline land plant growth and a preparation method of the microbial preparation. The microbial preparation comprises, by weight, 60-70 parts of starch, 8-10 parts of microbial agents and 20-32 parts of algal polysaccharides. The microbial agent is Brevibacterium sp.TS22 which is domesticated at low altitude and at the normal temperature, and the collection number is CGMCC 16576. The microbial agents include mixed agents of halophilic bacteria and bacilli,and the mixed agents account for 0-20% of the weight of the microbial agents. The preparation method of the microbial preparation includes the steps: feeding raw materials of the microbial preparationinto a stirrer; performing reaction in a stirred manner to obtain the microbial preparation for facilitating growth of plant root systems. The microbial preparation is separately used or compounded with agriculture and forestry organic fertilizers to be used. The microbial preparation is simple to operate and low in production cost and can effectively facilitate growth of saline and alkaline landplants.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Process for producing protein a-like protein with use of brevibacillus genus bacterium
The present invention relates to an efficient and economical process for producing a protein A-like protein. Hosts such as Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis have been used in the production of a protein A-like protein using a genetic recombination technique and however, their low productivity has been a big cause of high cost. Thus, it has been desired strongly to immediately establish a technique enabling the inexpensive, large-scale production of a protein A-like protein using recombinant DNA techniques other than Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. The present invention provides a process for producing a protein A-like protein in large amounts, for example, a process comprising allowing a recombinant Brevibacillus genus bacterium to express and secrete the protein in large amounts into a culture solution and separating and collecting the accumulated protein A-like protein from the culture solution.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Se-dopy ZM bacillus brevis and its uses in preparing biological red selenium
ActiveCN1995328ATime Proven Safe and EffectiveNo toxic side effectsBacteriaFermentationDiseaseSporocytophaga
The invention discloses an application of ZM brevibacterium to make biological umangite with reserving name as Sporocytophaga sp. and reserving data in the Apr. 21th 2006 and reserving number at CGMCC1694, which comprises the following steps: (A) inoculating ZM bacterium in the culture medium; (B) 1) adding bacterium liquid and sodium selenite in the culture medium; displaying the ferment liquid from light yellow into red to slide through microscope under visible red light; 2) condensing to obtain the product.
Owner:张敏
Complex microbial inoculant for petroleum hydrocarbon and benzene series treatment as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology and environmental protection, in particular to a microbial inoculant, and particularly relates to a complex microbial inoculant for petroleum hydrocarbon and benzene series treatment as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The active ingredients of the complex microbial inoculant comprise aspergillus oryzae, streptomyces, pseudomonas putida, pseudomonas alcaligenes, brevibacterium epidermidis and Erwinia; and the complex microbial inoculant is especially suitable for treating soil polluted by petroleum hydrocarbon and benzeneseries. After the complex microbial inoculant disclosed by the invention is added into the soil polluted by the petroleum hydrocarbon and benzene series, indigenous degrading flora can be rapidly propagated, and the remediation process can be rapidly started; in the repairing process, the indigenous degrading bacteria are always in the dominant flora status, and high degradation efficiency is kept for a long time through the synergistic cooperation of the flora in the complex microbial inoculant; and finally, the polluted soil is completely repaired, the degradation rate of petroleum hydrocarbon and benzene series is high, and the removal rate of BTEX and TPH can reach 98% or above.
Owner:BEIJING GUOHUAN TSINGHUA ENVIRONMENT ENG DESIGN & RES INST CO LTD BEIJING CHINA
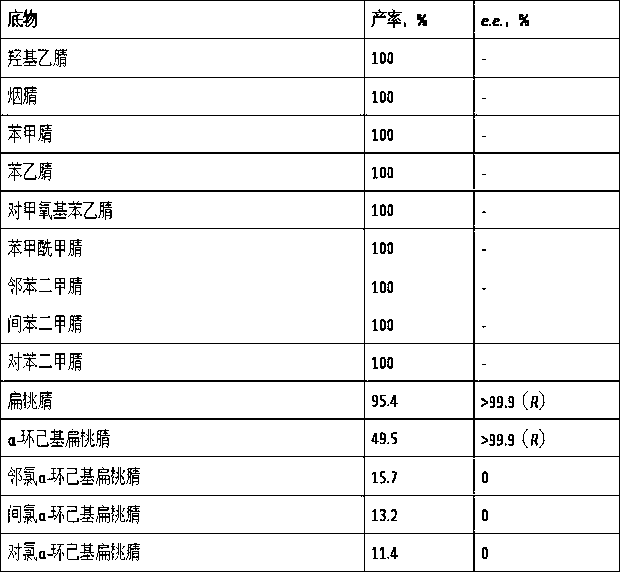
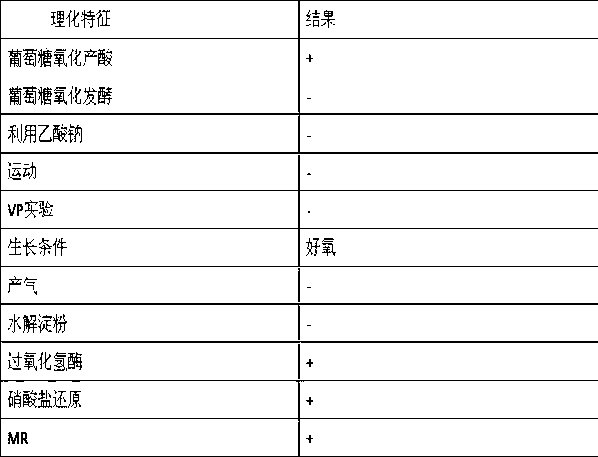
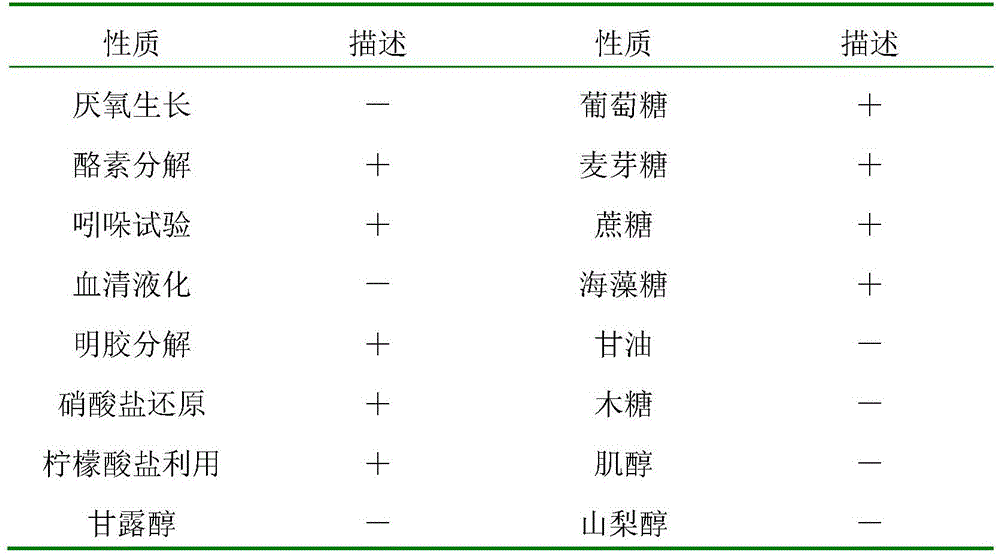
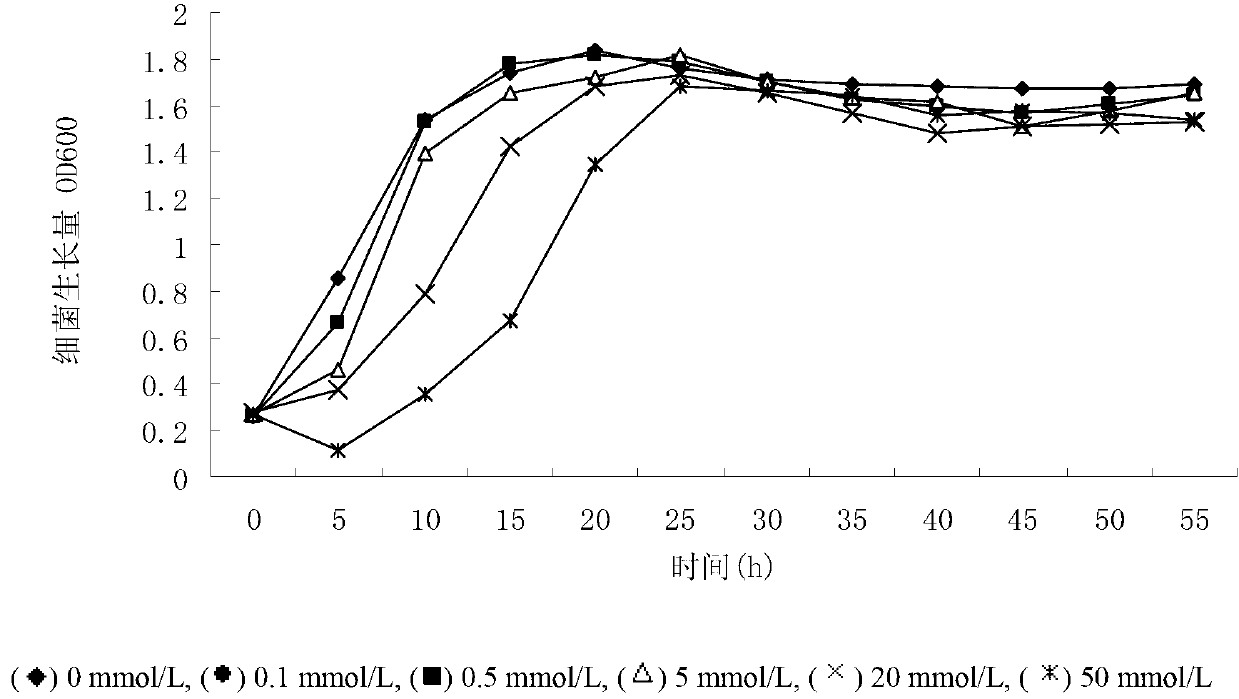
Brevibacterium and hydrolytic synthesis method of alpha-cyclo hexyl mandelic acid through nitrile and derivative
ActiveCN103103156ASimple process routeMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMandelonitrileMandelic acid
The invention discloses brevibacterium and a hydrolytic synthesis method of alpha-cyclo hexyl mandelic acid through nitrile and a derivative, which belongs to microbe technical field. A preservation number of brevibacterium sp.CCZU12-1 is CGMCCNo. 7042, and the brevibacterium is suggested to be classified and named brevibacterium sp.. alpha-cyclohexyl mandelonitrile and its derivative are taken as an initial raw material, a brevibacterium sp.CCZU12-1 resting cell is taken as a biocatalyst, and then the biosynthesis of alpha-cyclo hexyl mandelic acid and its derivative can be carried out under certain condition. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple technical route, mild reaction condition and no pollution.
Owner:江苏溢坤医疗科技有限公司
Compound microbial agent and method for soil fertility enhancement and ecological improvement by using compound microbial agent
ActiveCN111378590ANo ecological riskSimple structureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention provides a compound microbial agent which is prepared by mixing the following microorganisms in equal proportion: Bacillus megaterium GRINML5, Azotobacter salinestris strain GRINML6, Pseudomonas sp GRINML7, Bacillus licheniformis GRINML8, Stenotrophomonas sp. GRINML9 and Brevibacterium sp GRINM L2. The invention also provides a method for soil fertility enhancement and ecological improvement by using the compound microbial agent. A plurality of strains of microorganisms beneficial to plant growth are separated from an environment and are artificially compounded to form microbialfertilizer. A microbial ecological system for promoting solidification, release and conversion of vegetation nutrients is built by artificially supplementing the microbial fertilizer into soil to promote plant growth, the virtuous cycle that microorganisms promote plant growth, plants promote microorganism growth and plants and microorganisms promote each other is gradually formed, and the soil ecology is fundamentally improved.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Preparation method of bionic immobilized 3-cyanopyridine nitrile hydratase
InactiveCN104894092AAdvantages of catalytic hydrolysis performanceImprove repeated use stabilityOn/in organic carrierHydrolysisNitrile hydratase
The invention discloses an indium oxide nanosphere coating brevibacterium flavum nitrile hydratase, a preparation method and application. The multilayered structure of cells is simulated by referring to the existence form of the hydratase in a living body, and the indium oxide nanosphere is prepared through bionic design of components, functions and processes and used for embedding of the brevibacterium flavum nitrile hydratase. The characteristics that the immobilized nitrile hydratase is high in stability, high in activity, easy to recycle and the like are used for catalyzing 3-cyanopyridine to be transformed into nicotinamide in an efficient hydrolysis mode. The preparation method of the bionic immobilized hydratase can provide reference significance for preparation of a microcyst immobilized carrier, and provide a novel research idea for biotransformation of the 3-cyanopyridine.
Owner:ANHUI COSTAR BIOCHEM CO LTD
Brevibacterium and method for separating and purifying fumarase from Brevibacterium fermentation broth
InactiveCN105647834ASimple processHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFumaraseInorganic salts
The invention relates to Brevibacterium and a method for separating and purifying fumarase from Brevibacterium fermentation broth. Latin name of this bacterium is Brevibacterium sp., reference is made to a microorganism: NJWGY2133, and Brevibacterium sp. is collected on 26th May, 2008 under CGMCC No. 2520. The method for separating and purifying fumarase comprises the specific steps: preparing crude enzyme liquid through Brevibacterium sp. fermentation broth culturing and ultrasonic crushing, and preparing a polyethylene glycol-inorganic salt two aqueous phase extraction system; carrying out two aqueous phase extraction; preparing fumarase through dialytic desalting and freeze drying. The process of the invention is simple, production cycle is short, operation conditions are mild, cost is low, high-purity enzymes may be acquired from microorganisms, and enzyme activity yield is higher than 90%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
A kind of microbial fermentation process to produce arginine
InactiveCN103695487BQuality improvementHigh yieldOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a process for producing arginine by microbial fermentation. Brevibacterium flavum MQA121 is adopted. The method comprises the following steps: preparing fermentation liquid, namely performing slant culture, performing shake-flask culture, performing primary seed culture, performing secondary seed culture, and continuing to ferment; extracting and refining a fermented product, namely preprocessing the fermentation liquid, performing secondary crystallization, performing color and impurity removal, performing membrane concentration and separation, drying, and packaging to obtain arginine as a finished product. The method has the benefits that organic and inorganic matters and bacteria in subsequent extracting and refining liquid of arginine can be remarkably reduced and the arginine yield can be increased; in addition, the product quality is improved and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:滨州市生物技术研究院有限责任公司
Pseudomonasnitroreducens with paraquat resistance
The invention relates to a pseudomonasnitroreducens with resistance to paraquat (PQ). The strain number is S3. Pseudomonasnitroreducens is separated from PQ contaminated soil, belongs to Gram-negative brevibacterium, grows on a culture medium containing strong oxidant PQ or sodium nitroprusside (SNP), has nitrification reduction property and denitrification reduction property, shows positive in a catalase experiment and shows negative in an indole experiment. Pseudomonasnitroreducens is beneficial to the research of oxidation resistance, nitrification reduction and denitrification mechanism of bacteria and also plays an important role in the control of weeds and the research of other agricultural chemical industries. In the invention, the PnPQR gene is cloned from S3, and the gene codes a member of an atypical major facilitator superfamily (MFS). PnPQR is expressed in the escherichia coli BL21 strain and can increase resistance to paraquat. A transgenic tobacco plant with PnPQR excessively expressed has paraquat resistance.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Biological agent for shortening withering period of lawn and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109730090ADecrease in the number of days of withering and yellowing periodImprove the immunityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicrobial agentGibberellin
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial preparations and relates to a biological agent for shortening a withering period of a lawn and a preparation method thereof. The biological agent comprises 60-70 parts of starch, 8-10 parts of special microbial agent, 19.5-31.5 parts of algal polysaccharides and 0.5 part of gibberellin; the microbial agent is Brevibacterium sp.TS22 domesticated under the conditions of low altitude and normal temperature, and the preservation number is CGMCC 16576; the microbial agent further includes phosphate solubilizing bacteria, the weight of whichis 0-20% of the weight of microbial agent. The microbial agent is prepared according to the following steps: putting the raw materials of the microbial agent into a blender in parts by weight, stirring and reacting, thereby acquiring the biological agent for shortening the withering period of the lawn. The biological agent disclosed by the invention can be singly used or used together with agricultural organic fertilizers, is simple and convenient in operation, is low in production cost, is capable of effectively shortening the withering period of the lawn and is beneficial to overwintering oflawn.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Fermentation process for increasing yield of L-arginine
The invention aims at providing a fermentation process for increasing the yield of L-arginine. The adopted technical scheme is as follows: brevibacterium flavum ATCC21493 (SD<R>) is adopted as a starting bacterium, a strain TA189 is obtained through NTG (Nitrosoguanidine) treatment and mutagenesis and can directly synthesize arginine by using glucose, the arginine production capacity is strong, the strain production capacity and the fermentation process are controlled to reach indexes, and the comprehensive level of the process reaches the leading domestic level. According to the fermentation process provided by the invention, the characteristics of the fermentation processes of amino acid and antibiotics are combined, the vitality of starting and ending thalli is strictly controlled by adopting trend control and a midway feed and glucose supplementing process, and a relatively high arginine production level is obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG MINQIANG BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com