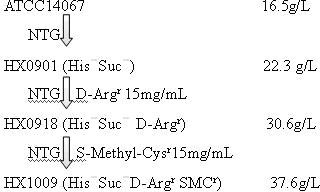Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Brevibacillus borstelensis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Brevibacillus borstelensis is a Gram-positive, aerobic, rod-shaped, endospore-forming bacterium of the genus Brevibacillus. The genome of several B. borstelensis strains have been sequenced. Brevibacillus borstelensis strain 707 is a thermophilic strain capable of degrading and using polyethylene as its sole source of carbon. This strain was shown to reduce the amount of polyethylene by 30% (30 days at 50°C) and demonstrates that nondegradable plastics like polyethylene can be degraded under appropriate conditions.
Heavy metal contaminated soil microbe repairing agent and application thereof
The invention provides a heavy metal contaminated soil microbe repairing agent which comprises the following components: brevibacillus borstelensis, candida tropicalis, nutrients and a carrier. The heavy metal contaminated soil microbe repairing agent is used in the heavy metal contaminated soil repairing microbe, the microbe used in the heavy metal contaminated soil microbe repairing agent can rapidly colonize and grow in soil and form a strong colony, can directly adsorb heavy metal ions into the microbial cell walls or cells for curing and passivation, heavy metal mobility is decreased, and crop heavy metal ion absorption can be reduced. The technology is low in repair cost and convenient in construction, provides a new method for soil microbe repairing, and has good application value.
Owner:SOOCHOW KH BIO SCI & TECH CO LTD KHB
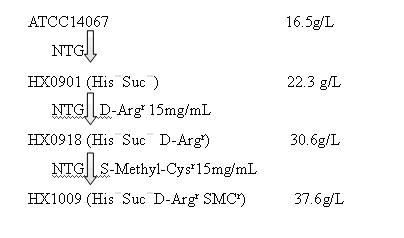
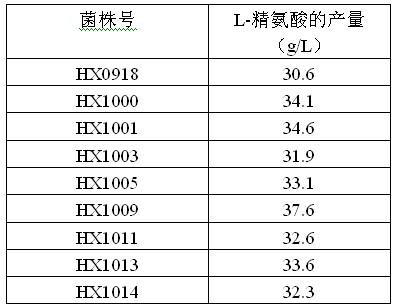
Strain capable of producing L-arginine and method for producing L-arginine by same
The invention relates to a strain capable of producing L-arginine and a method for producing the L-arginine by the strain and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. For the strain, Brevibacterium flavum ATCC 14067 is used as a starting strain; nitrosoguanidine is adopted to carry out mutagenesis step by step; mutant strains with histidine and succinic acid auxotrophic strains are screened out so as to cut off a competitive metabolic pathway; and mutant strains (His-, Suc-, D-Argr, SMCr) with resistances of arginine structural analogs and cysteine structural analogs are screened out. The strain is named as Brevibacterium flavum HX1009, is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center, has the preservation number of CGMCC No.4464 and has the genetic characters of histidine auxotroph His-, succinic acid auxotroph Suc-, D-arginine resistance D-Argr and S-methyl cysteine resistance SMCr for improving the yield of the L-arginine. Under the optimized condition, the L-arginine is produced by fermentation on a fermentation tank with the volume of 5L to 5M3 and the arginine production level achieves 50 to 70g / L.
Owner:FUJIAN GUTIAN PHARMA
Potsdam Bacillus brevis and use thereof
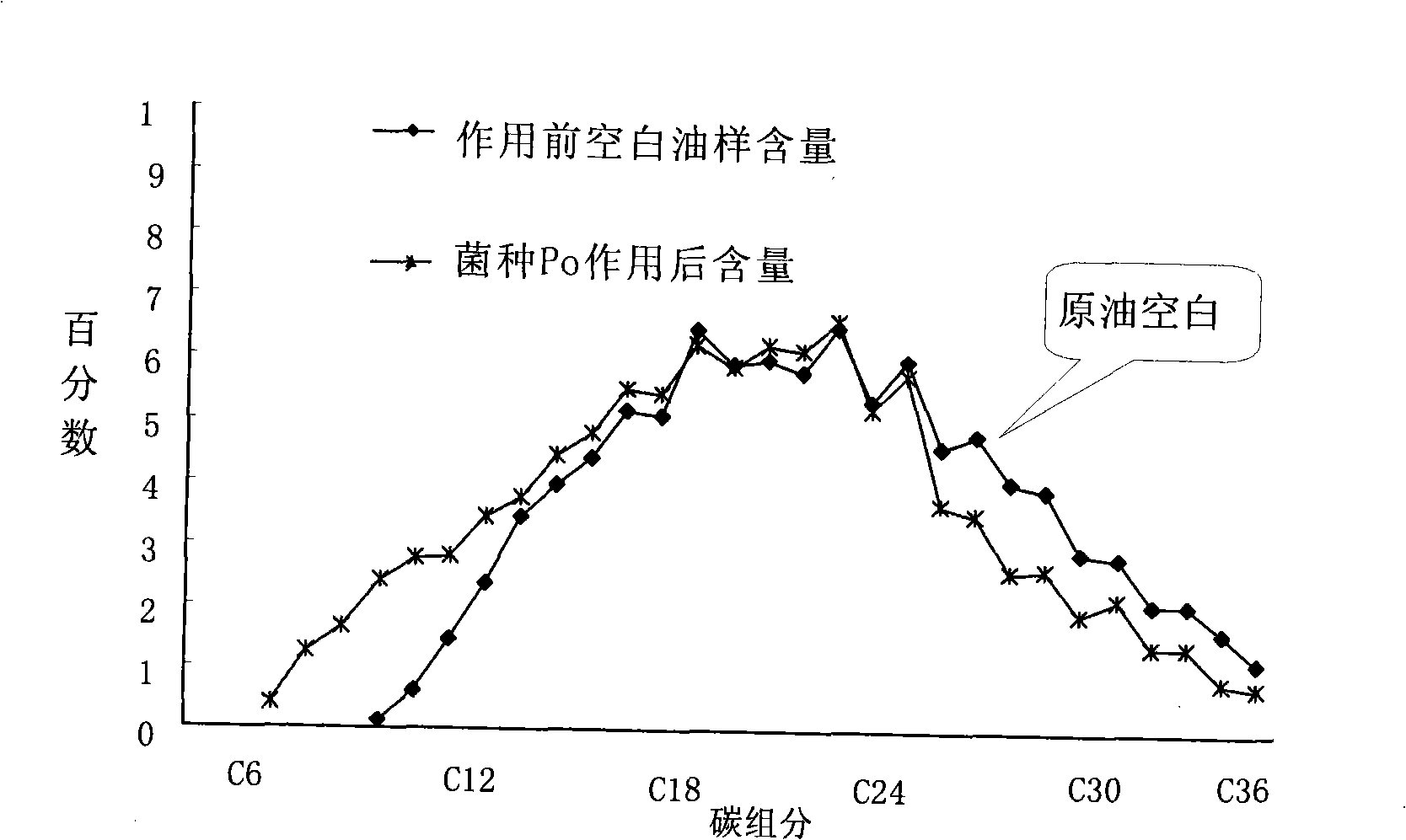
The invention discloses a Brevibacillus borstelensis Po CGMCC No. of 2441 and the application thereof. A microbial inoculum that contains the brevibacillus borstelensis Po CGMCC No. of 2441 also belongs to the extent of protection of the invention. Model oil displacing experiment results indicate that after the oil displacement with polymers, the brevibacillus borstelensis oil displacement can be used for raising the recovery factor by 3 to 5 percent (OOIP), the brevibacillus borstelensis oil displacement combined with a polymer protecting slug can be used for raising the recovery factor by about 7 percent (OOIP), and a brevibacillus borstelensis oil displacing method that is combined with chemical oil displacement can be used for raising the recovery factor by 6 to 13 percent (OOIP). The experiment results indicate that the strain can be widely applied into the field of oil exploiting industries and particularly into the field of enhanced microorganism oil exploiting, and is applicable to large-area popularization and application.
Owner:DAQING OILFIELD CO LTD +1
Preparation and application of garden waste compound degrading microbial agent
ActiveCN105567612AEfficient and stable degradation abilityAccelerates the composting processBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaCelluloseStreptomyces thermocarboxydus
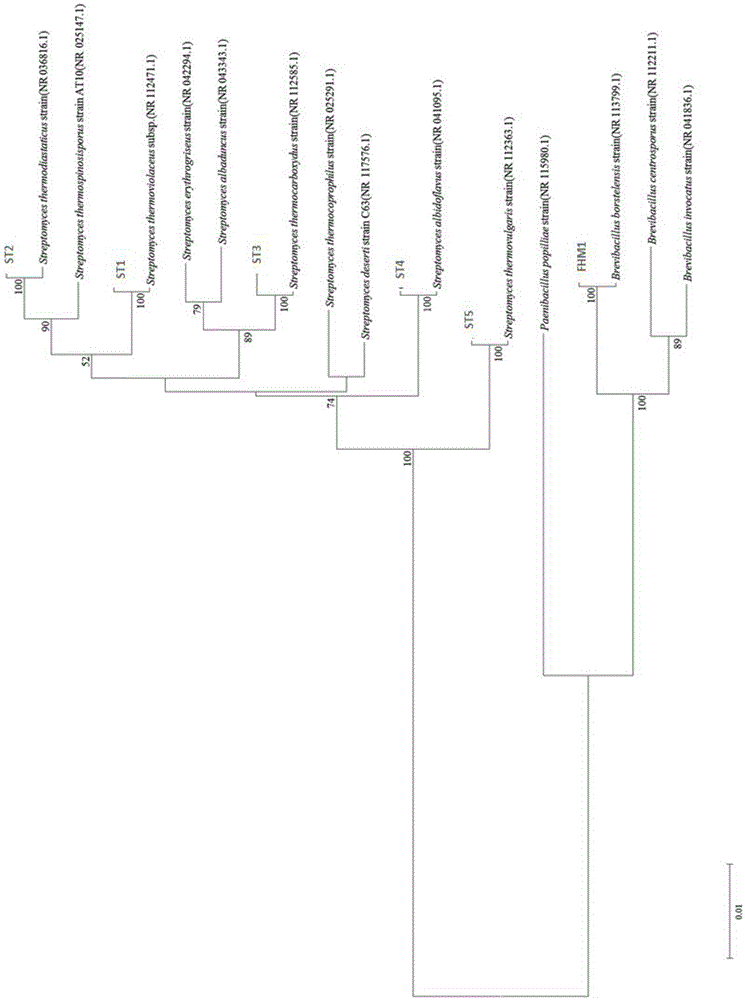
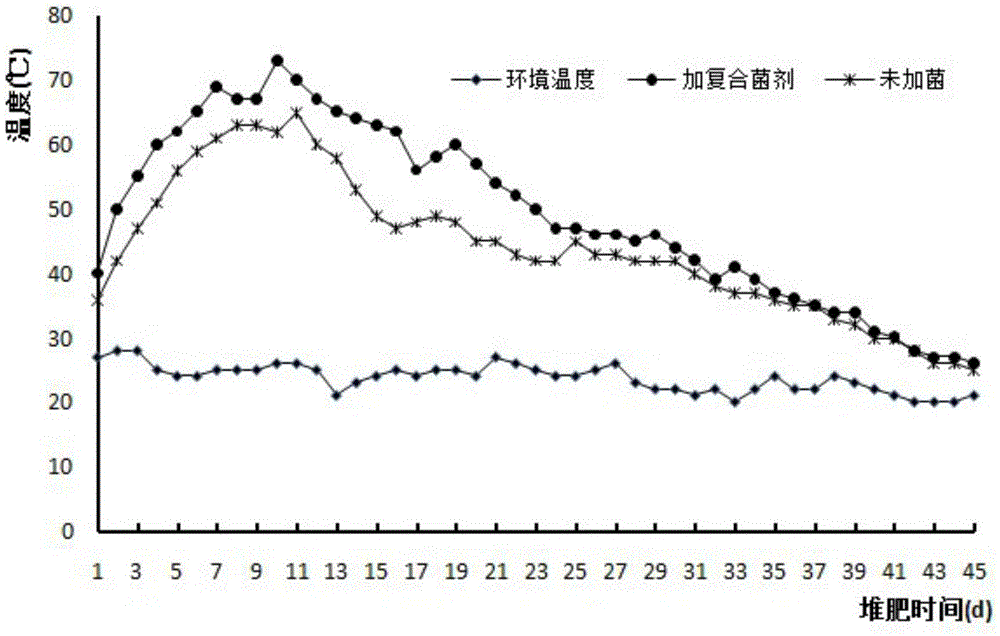
The invention discloses a compound microbial agent with a function of effectively degrading cellulose at high temperature. The compound microbial agent contains five actinomycetes: Streptomyces thermoviolaceus, Streptomyces thermodiastaticus, Streptomyces thermocarboxydus, Streptomyces albidoflavus and Streptomyces thermovulgaris, and one bacteria: Brevibacillus borstelensis. The compound microbial agent solves the problem of slow composting and long cycle of garden waste due to the limitation in cellulose degradation difficulty, accelerates cellulose degradation in the composting process, shortens the fermentation period, and improves the conversion efficiency, thereby having a broad application prospect in the aspects such as the application of composting treatment and resource utilization of garden waste, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Small brevibacterium strain capable of carrying out biological denitrification under high-salt condition and application of small brevibacterium strain to wastewater treatment
ActiveCN102703349ATo achieve the purpose of denitrificationStrong toleranceTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaBrevibacillus borstelensisTotal nitrogen
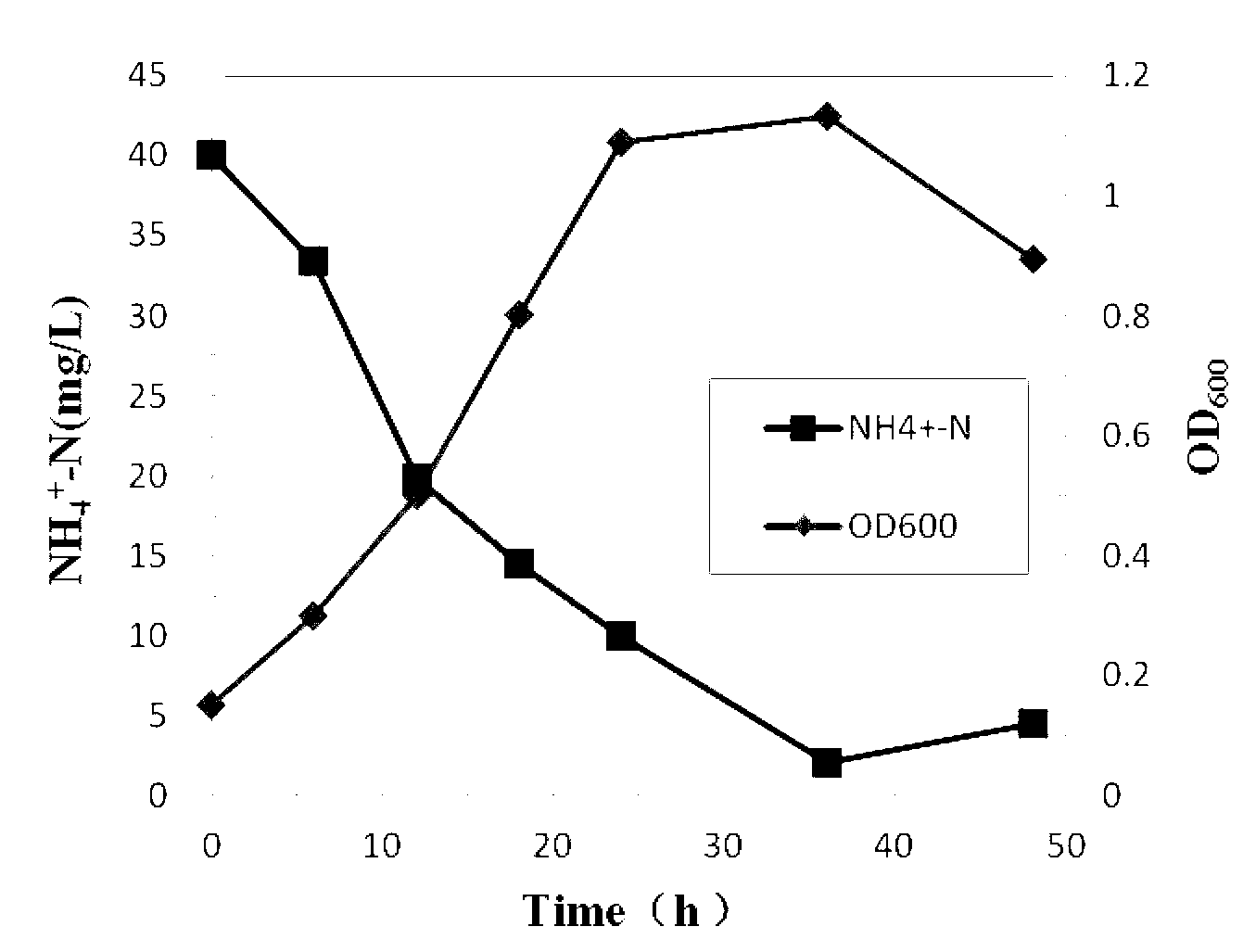
The invention discloses a small brevibacterium strain capable of carrying out biological denitrification under the high-salt condition and application of the small brevibacterium strain. The small brevibacterium strain provided by the invention is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC for short) on March 29th, 2012, with the preservation number of CGMCC No.5947. At the salinity (counted by NaCl) is 3-10 percent, the strain is added into nitrogen-containing wastewater with dissolved oxygen of 2-6mg / L for biological denitrification. The strain has strong resistant ability for high salinity and heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification capabilities and can better grow under the high-salinity condition. Under the high-salinity and aerobic conditions, the strain can be used for synchronous nitrification and denitrification and efficiently and thoroughly removing total nitrogen in sewage, and thus the major problem that biological denitrification is difficult to carry out under the high-salinity condition is effectively solved and a favorable application prospect is obtained.
Owner:北京大学科技开发有限公司
Cadmium contaminated soil microbe repairing agent and application thereof
InactiveCN104531551AReduced mobilityReduce absorptionFungiBacteriaBrevibacillus borstelensisCandida tropicalis
The invention provides a cadmium contaminated soil microbe repairing agent which comprises the following components: brevibacillus borstelensis, candida tropicalis, nutrients and a carrier. The microbe used in the cadmium contaminated soil microbe repairing agent can rapidly colonize and grow in soil and form a strong colony, can directly adsorb cadmium ions into the microbial cell walls or cells for curing and passivation, cadmium mobility is decreased, crop cadmium ion absorption can be reduced. The technology is low in repair cost and convenient in construction, provides a new method for soil microbe repairing, and has good application value.
Owner:SOOCHOW KH BIO SCI & TECH CO LTD KHB
Method for preparing lysine-rich fermented soybean meal
ActiveCN102763769AAddress nutrient contentSolve two key problems to make up for the lack of lysine in fermented soybean mealFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBrevibacillus borstelensisSaccharomyces
The invention discloses a method for preparing lysine-rich fermented soybean meal, which is simple and can effectively improve the content of nutrients of the soybean meal. The method is technically characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) preparing strains: a, inoculating the brevibacterium flavum into the brevibacterium flavum liquid culture medium, and vibrating and culturing at 28-37 DEG C to obtain the first-level brevibacterium flavum strain when the OD590 value of the brevibacterium flavum liquid is 0.25-0.30; b, the inoculating the saccharomycetes into the saccharomycetes liquid culture medium, and vibrating and culturing at 28-37 DEG C to obtain the first-level saccharomycetes strain when the OD590 value of the saccharomycetes liquid is 0.25-0.30; and c, inoculating the lactobacillus into the lactobacillus liquid culture medium, and vibrating and culturing at 30-37 DEG C to obtain the first-level lactobacillus strain when the OD590 value of the lactobacillus liquid is 0.25-0.30; (2) preparing a fermentation substrate; and (3) inoculating the fermentation substrate. The method for preparing the lysine-rich fermented soybean meal belongs to the technical field of feed preparation.
Owner:广东希普生物科技股份有限公司
Blocking remover and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111019621AReduce oil-water interfacial tensionUnblockDrilling compositionActive agentBrevibacillus borstelensis
The invention discloses a blocking remover and a preparation method thereof. The blocking remover comprises following raw materials: Brevibacillus borstelensis biosurfactant fermentation liquid and hydrophobic nano silicon dioxide, and an emulsifier, an anti-scaling agent, an anti-swelling agent and a cosolvent can also be contained. The preparation method of the blocking remover comprises the following steps: firstly, adding the biosurfactant fermentation liquid, the emulsifier and the cosolvent into a reaction container, heating, and uniformly stirring; secondly, adding the anti-scaling agent and the anti-swelling agent into the solution obtained in the former step, and stirring for dissolving; and finally, continuously heating a prepared solution, adding hydrophobic inorganic nanoparticles into the reaction container, and uniformly stirring. The blocking remover has low oil-water interfacial tension, can effectively strip and emulsify residual oil and colloidal asphaltene deposits in a medium-low permeable layer to form a low-viscosity emulsion, remove organic blocking, resist hypersalinity, can be completely degraded by microorganisms, and is green and environment-friendly.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Brevibacterium frigoritolerans as well as microbial inoculant and application of brevibacterium frigoritolerans and microbial inoculant
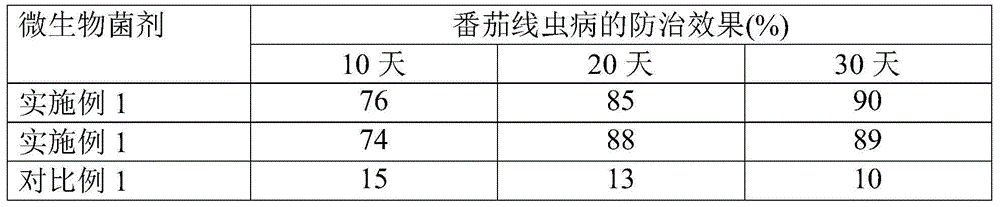
The invention provides brevibacterium frigoritolerans of which the collection number is CGMCC NO.8837. The invention also provides a microbial inoculant containing thalli and a culture medium, wherein the thalli comprises brevibacterium frigoritolerans of which the collection number is CGMCC NO.8837. The invention also provides applications of brevibacterium frigoritolerans and the microbial inoculant in preventing and treating crop diseases. By adopting the technical scheme, brevibacterium frigoritolerans and the microbial inoculant disclosed by the invention can be used for preventing and treating nematode diseases of crops more effectively.
Owner:YANTAI DIYUAN BIOTECH
Microbe composite bacterial liquid and application thereof in preparing organic fertilizer
ActiveCN102492621AReduce usageConducive to ecological protectionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBrevibacillus borstelensisPotassium
The invention relates to a microbe composite bacterial liquid comprising live bacteria of clostridium thermopalmarium, clostridium thermosuccinogenes, brevibacillus borstelensis, paenibacillus barengoltzii, bacillus subtilis, pseudomonas mendocina, and providencia rettgeri. The invention also provides a bacterial preparation prepared by using the composite bacterial liquid. The bacterial preparation is used for preparing an organic fertilizer. According to the invention, with the composite microbe bacterial liquid, during a composite fertilizer utilization process, the dosage of inorganic composite fertilizer can be reduced, such that production cost can be reduced. Also, with a synergetic effect provided by the microbe bacterial preparation, when dosages of nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium in organic-inorganic composite fertilizers are low, agricultural and forestry waste stalks with low prices and rich organic substances such as nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium and calcium are converted into micro-molecular substances such as monosaccharide and oligosaccharide which can be utilized by plants. Therefore, a relatively high crop yield is obtained, and a substantial yield increasing effect is provided. Agriculture in our nation has a severe dependence on chemical fertilizers. With the composite bacterial liquid provided by the invention, the situation can be changed, and agricultural ecological protection can be enhanced.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
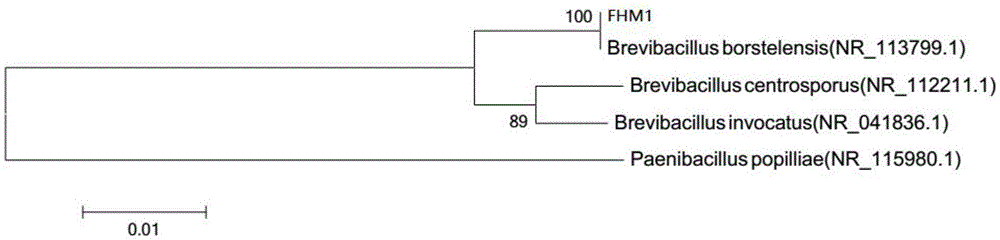
High-temperature-resistant garden waste decomposition bacterium FHM1 and application thereof
ActiveCN105647832AExtension of timeSpeed up the ripening processBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaCelluloseDecomposition
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant cellulose decomposition bacterium Brevibacillus borstelensis, collected under CGMCC No. 12138. This bacterium can produce massive enzymes at a high temperature of 40-70 DEG C, has high cellulose activity, features high temperature resistance and efficient cellulose degradation, can be used as a microbial agent for application in high-temperature composting systems and is applicable to garden waste composting.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing L-tyrosine from fermentation broth of Chinese prickly ash endogenous brevibacterium frigoritolerans
InactiveCN104805146AMicroorganism based processesFermentationBrevibacterium frigoritoleransWater baths
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-tyrosine from a fermentation broth of Chinese prickly ash endogenous brevibacterium frigoritolerans. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out constant temperature incubation on Chinese prickly ash endogenous brevibacterium frigoritolerans at the temperature of 30 DEG C for 24h, inoculating the strain to a fermentation medium, and carrying out constant temperature shaking fermentation culture by water bath at 28-37 DEG C and at 120-180 r / min; centrifuging the fermentation broth at normal temperature and at the speed of 4000-6000 r / min for 15 min to remove thalli so as to obtain a supernatant, and carrying out freeze-drying on the supernatant; processing the fermentation broth through a Sephadex LH-20 chromatographic column under the condition that mass ratio of the sample to Sephadex LH-20 is 1:20-50 and loading quantity of sample is 20% of the column volume, carrying out isocratic elution with 100 mL of pure water, and equally collecting eluants F1-F5 according to the collection amount of 20 mL for each eluant; and carrying out separation and purification on the component F3 by a preparative liquid chromatograph, and carrying out freeze-drying to obtain L-tyrosine with the yield being 8-15 mg / L.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Tylosin degrading bacteria and application thereof
The invention discloses tylosin degrading bacteria and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microorganism degrading antibiotics residues. The tylosin degrading bacteria TYL2 is brevibacillus borstelensis TYL2 and is preserved in the common microorganism center of the China microorganism culture preservation management council, wherein the preservation date is 29 / 12 / 2018, thepreservation serial number is CGMCC No.17051, and the preservation address is No.3 microorganism research laboratory of Chinese Academy of Sciences in No.1 yard at the Beichen west road of Chaoyang district of Beijing. With drug residues being primary raw materials for sieving, an obtained strain and a prepared fungicide can be directly used for treating waste of a tylosin enterprise, and can be also used for repairing surrounding soil and a water body environment which are polluted by tylosin.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
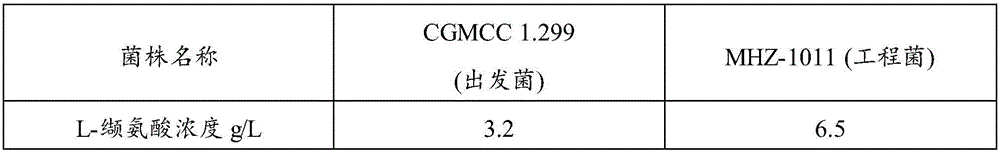
Recombinant strain as well as construction method and application thereof
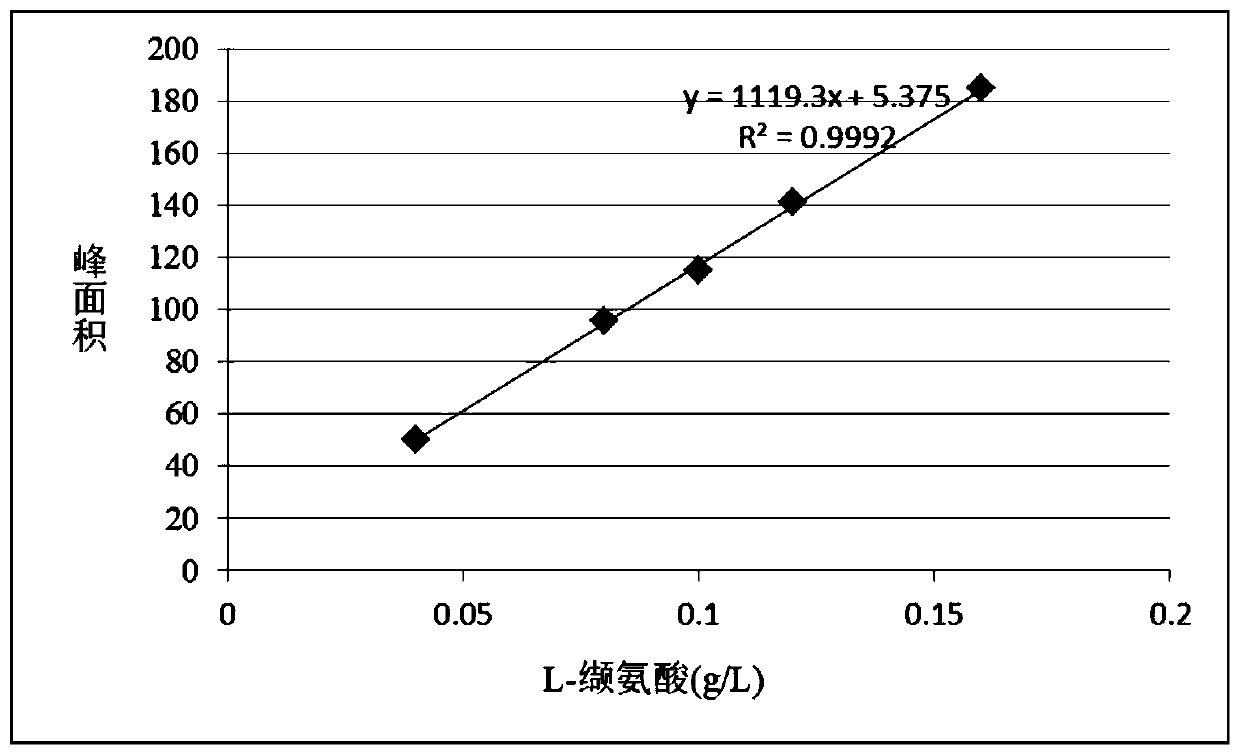
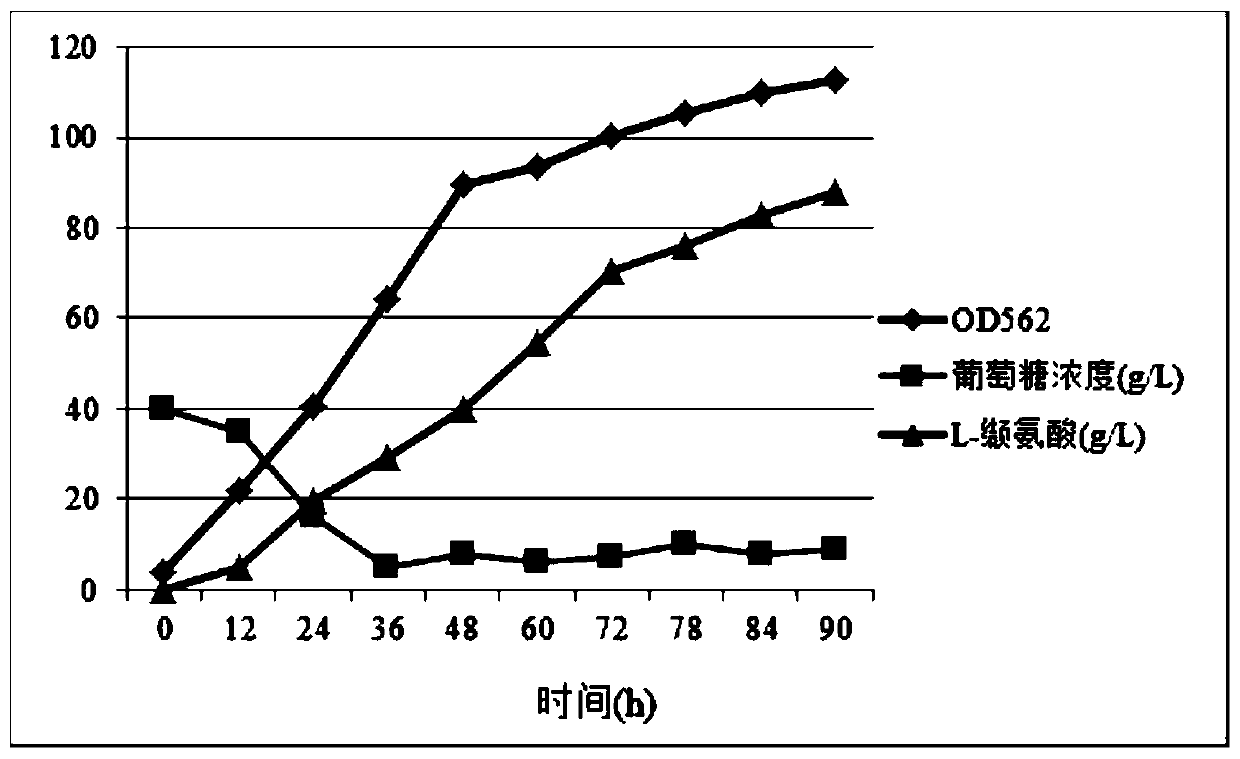
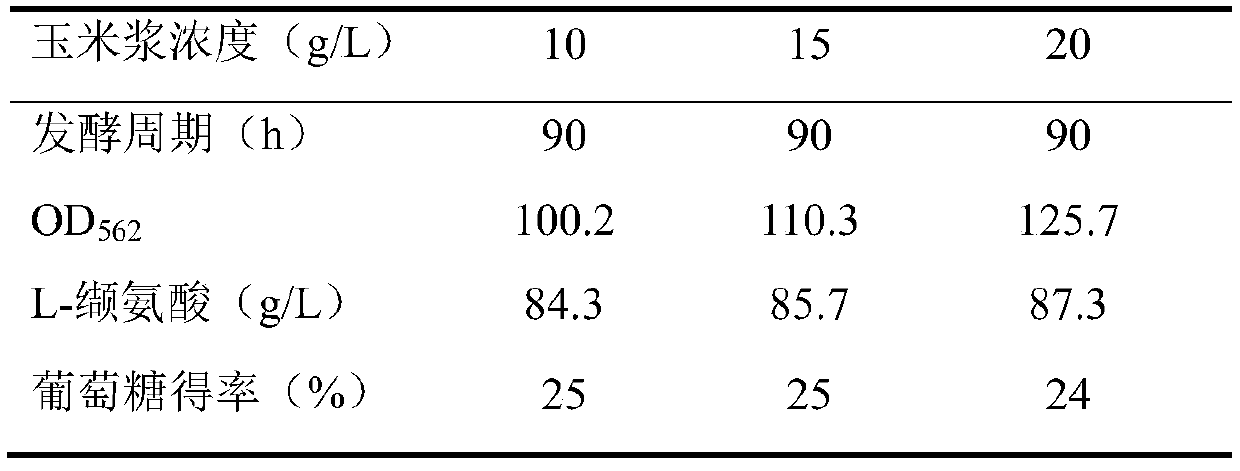
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to recombinant strains, construction methods and applications thereof. The invention protects the engineered strain obtained by introducing the target gene into Corynebacterium or Brevibacterium by means of recombinant plasmid or insertion into chromosome. The result of the experiment of producing L-valine by shaking flask fermentation showed that the L-valine yield of the starting strain CGMCC 1.299 was 3.2g / L, while the L-valine yield of the engineering strain MHZ-1011 of the present invention was 6.5g / L. L, the yield was 103% higher than that of the starting strain, with a very significant difference (P<0.01). The experimental results of L-valine production by 50L tank fermentation show that: the L-valine yield of the starting strain CGMCC1.299 is 7.3g / L, while the L-valine yield of the engineering bacterium MHZ-1011 of the present invention is 18.4g / L, the yield was 152% higher than that of the starting strain, with a very significant difference (P<0.01).
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Brevibacterium flavum recombinant strain producing L-isoleucine and construction method thereof
InactiveCN109554324AIncrease productionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaHeterologousBrevibacillus borstelensis
The present invention discloses a brevibacterium flavum recombinant strain producing L-isoleucine and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The genetic engineering means is utilized to strengthen acetohydroxyacid synthase, dihydroxy acid reductoisomerase and branched chain amino acid aminotransferase in the brevibacterium flavum, and heterologously expresses catabolic threonine dehydratase encoded by tdcB, and thus constructs a L-isoleucine high-yield strain B. flavum I12 / pEC-XK99E-ilvBNCE-tdcB. The yield of the accumulated isoleucine is increased to 22.65 g / L in the recombinant strain and is 25.48% higher than that of an original strain, and the maximum biomass reaches 20.95 g DCW / L. The strain can turn lysine pathway carbon source to the L-isoleucine and a brand-new idea for constructing the L-isoleucine high-yield strain is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
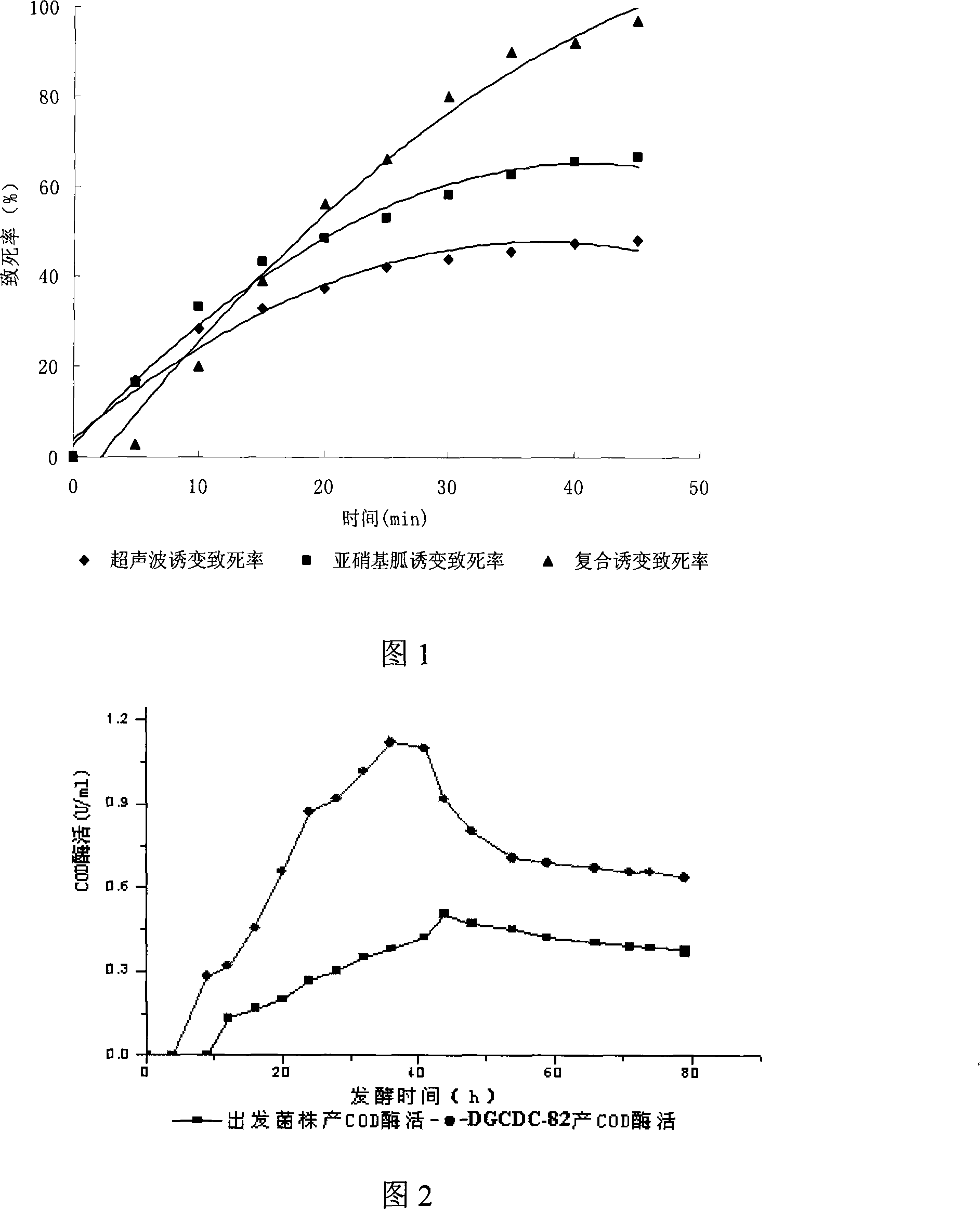
Red steroid brevibacterium for highly yielding cholesterol oxidase
InactiveCN101186897AHigh fermentation enzyme activityBacteriaMutant preparationMicroorganismBrevibacillus borstelensis
Provided is red brevibacterium sp of high-yield cholesterol oxidase, which belongs to the technical field of microorganism bacterial strain. The bacterial strain of the invention is classified and named as brevibacterium sp. DGCDC-82 (choB), and is preserved in the Preservation Center of Chinese Typical Culture, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M207182. The bacterial strain of the invention is mutagenized and achieved by the process of combining nitrosoguanidine with ultrasonic on the basis of white brevibacterium sp. The fermentation study finds that the vitality for producing cholesterol oxidase of the red brevibacterium achieves 1.21U per milliliter, which is increased by 140%. The relation of the bacterial strain enzyme production and haematochrome is studied with the process of reverse mutation, finding that the content of the bacterial strain enzyme production has positive correlation with the content of haematochrome, the darker the red color of the bacteria is, the higher the vitality of fermentation and enzyme production is.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Strain of brevibacterium flavum producing L-valine and application of brevibacterium flavum
ActiveCN109943511AHigh yieldHas industrial practical valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBrevibacillus borstelensisMicrobiology
The invention discloses a strain of brevibacterium flavum producing L-valine and application of the brevibacterium flavum, and belons to the technical field of bioengineering. The brevibacterium flavum is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on January 17, 2019 under the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2019053, and the preservation address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.The brevibacterium flavum FMME447 exhibits the ability to accumulate high-level L-valine, and it is verified that the valine tolerance of the brevibacterium flavum reaches 100 g / L. The yield of the L-valine through the fermentation of the brevibacterium flavum reaches 80-90 g / L, the yield of glucose reaches up to about 25-30%, and the brevibacterium flavum has industrial practical value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method for producing edible mushroom nutrient solution by fermentation method
The invention discloses a method for producing an edible mushroom nutrient solution by a fermentation method, which relates to the technical field of an organic fertilizer. The method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing brevibacterium flavum, namely inoculating the brevibacterium flavum, which is taken as an original strain, to a shake flask culture medium for culturing so as to obtain a brevibacterium flavum solution; (2) carrying out submerged fermentation, namely inoculating the brevibacterium flavum solution into a fermentation tank culture medium to carry out the submerged fermentation so as to obtain a fermentation solution; and (3) treating the fermentation solution, namely separating and concentrating the fermentation solution to obtain the edible mushroom nutrient solution. The edible mushroom nutrient solution obtained by the method disclosed by the invention is rich in various nutrition elements including crude proteins, short-chain peptides, amino acids, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin C and the like and is easy to absorb and high in utilization rate; the mushroom growing period can be prolonged and the biotransformation efficiency is improved; the quality and the yield of edible mushrooms are improved obviously.
Owner:JING JING PHARMA
Method for efficiently producing L-isoleucine
ActiveCN108841884AImprove acid production performanceMeet the needs of industrial productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismBrevibacillus borstelensis
The invention discloses a method for efficiently producing L-isoleucine, and belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation. In the method provided by the invention, brevibacterium lactofermentation is taken as a production strain of L-isoleucine, and the brevibacterium lactofermentation and corynebacterium pekinense are co-cultured, so that the acid production capacity of the brevibacterium lactofermentation is significantly improved from 13g / L to 21g / L, which can meet the needs of industrial production.
Owner:WUXI JINGHAI AMINO ACID
Brevibacterium frigoritolerans strain capable of denitrification and efficient flocculation and application thereof
ActiveCN109706096ANo secondary pollutionImprove flocculation abilityBacteriaWater contaminantsBrevibacterium frigoritoleransNitrogen removal
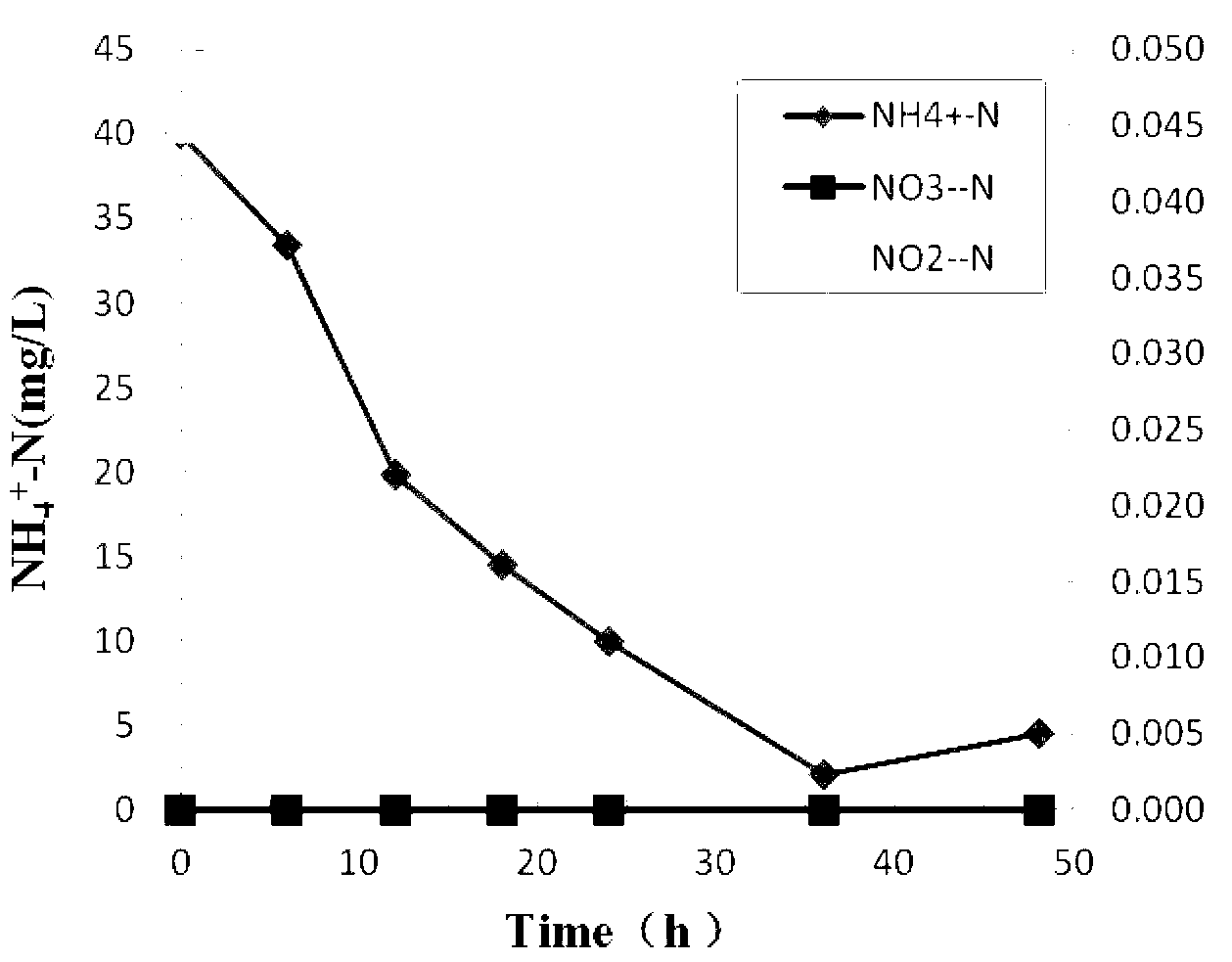
A Brevibacterium frigoritolerans strain capable of denitrification and efficient flocculation and application thereof are disclosed. The strain is named as Brevibacterium frigoritolerans ZQ 1-1 with an accession number of GDMCC No:60520. The stain has efficient flocculation capability and high ammonia nitrogen removing capability, wherein the flocculation rate of the strain for a kaolin suspensionhaving a concentration of 5 g / L in 10 min reaches 90% or above; in a medium the initial ammonia nitrogen concentration of which is 150 mg / L, the NH<+><4> nitrogen removal rate of the strain is 87% orabove; in pig manure slurry the initial ammonia nitrogen concentration of which is as high as 600 mg / L, the ammonia nitrogen removing rate of the strain is 60% or above, and nitrite nitrogen is not accumulated during ammonia nitrogen removing, thus avoiding secondary pollution. The strain can be used for water denitrification.
Owner:GUANGDONG BOWOTE BIOTECH CO LTD
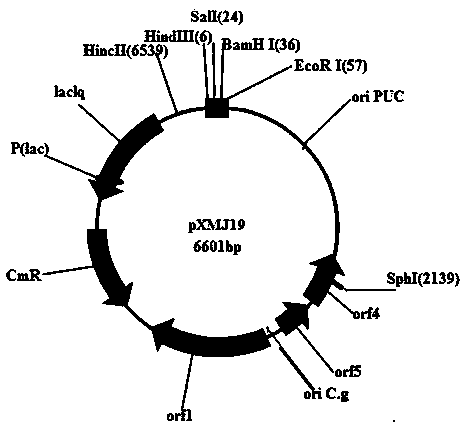
Conversion method for introducing shuttle plasmids into brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum)
InactiveCN103966251AClear thinkingSimple and fast operationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a rapid and effective method for converting recombinant plasmids that can perform shuttle expression in escherichia coli and brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum) into corynebacterium glutamicum and auxotroph brevibacterium flavum. The method comprises two steps namely competent cell preparation and high-temperature culture and conversion: (1) inoculating auxotroph brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum) into a specially-prepared culture medium to enable the auxotroph brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum) to carry out rapid proliferation, and then transforming the auxotroph brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum) to a culture medium with inefficient nutrients to prepare competent cells; (2) evenly mixing plasmids to be converted and the prepared competent cells, placing the mixture into an ice bath, culturing under a constant temperature, and finally introducing the plasmids into brevibacterium flavum (or corynebacterium glutamicum) to be converted. The method provided by the invention can reduce the restrictive enzyme digestion effect of brevibacterium flavum on shuttle plasmids, the shuttle plasmids can be stably copied and transmitted, and thus the method has the advantages of good conversion effect and convenient operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI KING SHINE BIOLOGY TECH +1
Brevibacterium and method for separating and purifying fumarase from Brevibacterium fermentation broth
InactiveCN105647834ASimple processHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFumaraseInorganic salts
The invention relates to Brevibacterium and a method for separating and purifying fumarase from Brevibacterium fermentation broth. Latin name of this bacterium is Brevibacterium sp., reference is made to a microorganism: NJWGY2133, and Brevibacterium sp. is collected on 26th May, 2008 under CGMCC No. 2520. The method for separating and purifying fumarase comprises the specific steps: preparing crude enzyme liquid through Brevibacterium sp. fermentation broth culturing and ultrasonic crushing, and preparing a polyethylene glycol-inorganic salt two aqueous phase extraction system; carrying out two aqueous phase extraction; preparing fumarase through dialytic desalting and freeze drying. The process of the invention is simple, production cycle is short, operation conditions are mild, cost is low, high-purity enzymes may be acquired from microorganisms, and enzyme activity yield is higher than 90%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Potsdam Bacillus brevis and use thereof
The invention discloses a Brevibacillus borstelensis Po CGMCC No. of 2441 and the application thereof. A microbial inoculum that contains the brevibacillus borstelensis Po CGMCC No. of 2441 also belongs to the extent of protection of the invention. Model oil displacing experiment results indicate that after the oil displacement with polymers, the brevibacillus borstelensis oil displacement can beused for raising the recovery factor by 3 to 5 percent (OOIP), the brevibacillus borstelensis oil displacement combined with a polymer protecting slug can be used for raising the recovery factor by about 7 percent (OOIP), and a brevibacillus borstelensis oil displacing method that is combined with chemical oil displacement can be used for raising the recovery factor by 6 to 13 percent (OOIP). Theexperiment results indicate that the strain can be widely applied into the field of oil exploiting industries and particularly into the field of enhanced microorganism oil exploiting, and is applicable to large-area popularization and application.
Owner:DAQING OILFIELD CO LTD +1
Nucleoside phosphorylase, encoding gene and high-producing strain and application of nucleoside phosphorylase
ActiveCN105670979AEasy to purifyLower conversion rateBacteriaTransferasesAdditive ingredientBrevibacillus borstelensis
The invention provides nucleoside phosphorylase, an encoding gene and a high-producing strain and application of the nucleoside phosphorylase and relates to the technical field of biological pharmacy.The high-producing strain of the nucleoside phosphorylase is classified and named Potsdam brevibacillus borstelensis LK01, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2015685.The nucleoside phosphorylase generated by the strain and the encoding gene of the nucleoside phosphorylase are further provided.The invention further provides a gene containing recombinant expression vector or recombinant bacteria and application thereof.The nucleoside phosphorylase is used for preparing nucleoside medicine, the reaction conditions are mild, the product ingredient is single, no by-product is generated, the substrate conversion rate is high, the product is easy to purify, the problems existing in existing chemical method galactosylated modification of nucleoside medicine are solved, and good application potential is achieved.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Brevibacillus borstelensis strain having capability of degrading thioanisole and application thereof
ActiveCN103013877BHas the ability to degrade sulfide anisoleEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismBrevibacillus borstelensis
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and discloses a Brevibacillus borstelensis strain having a capability of degrading thioanisole and application thereof. The Brevibacillus borstelensis strain having a capability of degrading thioanisole is named as Brevibacillus borstelensis GIGAN1 and was collected at China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University in Wuhan, Hubei province, China on November 8, 2012; and the collection number is CCTCC NO:M 2012451. The capability of the strain, of degrading thioanisole in the environment, can be up to 96.2%; and the strain can be used for degrading thioanisole in the environment, thereby achieving the purpose of environment renovation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Marine microbial strain YS0810 capable of yielding alkaline catalase
The invention relates to a marine microbial strain YS0810 capable of highly yielding alkaline catalase. The strain is a wild strain capable of highly yielding alkaline catalase, which is screened from a Qingdao sea-area bottom sludge sample, belongs to Acinetobacter sp. Gram-negative bacilli and has no spores, a milky colony of 2-3mm is formed through carrying out plate culture for 24h, has a smooth surface and regular edges, is sticky and is easy to pick up, the strain is brevibacterium, the size of the strain is relatively small, the length is about 1 micron, and the width is about 0.5 micron. The length of the gene sequence of 16S rDNA of the strain YS0810 is 1443bp. The strain has a short fermentation cycle, relatively high enzyme activity and excellent enzyme performance, can highly yield catalase, and can be applied to clinical analysis, food processing, spinning, paper making, medical appliance disinfection, medicaments and the like.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Small brevibacterium strain capable of carrying out biological denitrification under high-salt condition and application of small brevibacterium strain in wastewater treatment
ActiveCN102703349BStrong toleranceQuick removalBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesBrevibacillus borstelensisTotal nitrogen
Owner:北京大学科技开发有限公司
Fermentation method for increasing yield of L-isoleucine
ActiveCN109652475AIncrease productionImprove effective utilizationMicroorganism based processesFermentationSaccharic acidLactobacillus rhamnosus
The invention provides a fermentation method for increasing the yield of L-isoleucine. The method comprises the following steps that (1) brevibacterium lactofermentum (Brevibacterium lactofermentum) is inoculated into a seed culture medium for expansion culture to obtain a seed solution 1; (2) lactobacillus rhamnosus (Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG) inoculated into the seed culture medium for expansion culture to obtain a seed solution 2; (3) firstly, the seed solution 2 is inoculated into a fermentation culture medium, then the seed solution 1 continues to be inoculated, and fermentation cultureis carried out to obtain a fermentation liquid. The fermentation method for increasing the yield of the L-isoleucine has the advantages that through the combined use of the brevibacterium lactofermentum seed solution and the lactobacillus rhamnosus seed solution, the conversion rate of saccharic acid and the yield of the L-isoleucine are significantly increased; through the further control of theuse amount ratio of the brevibacterium lactofermentum to the lactobacillus rhamnosus in the fermentation process, the conversion rate of the saccharic acid and the yield of the L-isoleucine are increased again.
Owner:内蒙古拜克生物有限公司
Method for producing recombinant proteins using recombinant brevibacillus
ActiveUS10435732B2Increase probabilityHigh protein yieldPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesBrevibacillus borstelensis
The present invention provides a method for producing a recombinant protein, which can increase the cell growth rate in culture while stably maintaining plasmids in the cells, thereby improving the recombinant protein yield. The present invention provides a method for producing a recombinant protein, including a high-temperature culture step of culturing at 32° C. or higher a Brevibacillus bacterium that contains a gene encoding a recombinant protein, and a low-temperature culture step of culturing the Brevibacillus bacterium at a temperature lower than 32° C. after the high-temperature culture step.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Preparation and application of a compound microbial agent for degrading garden waste
ActiveCN105567612BEfficient and stable degradation abilityAccelerates the composting processBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaStreptomyces thermocarboxydusCellulose
The invention discloses a compound microbial agent with a function of effectively degrading cellulose at high temperature. The compound microbial agent contains five actinomycetes: Streptomyces thermoviolaceus, Streptomyces thermodiastaticus, Streptomyces thermocarboxydus, Streptomyces albidoflavus and Streptomyces thermovulgaris, and one bacteria: Brevibacillus borstelensis. The compound microbial agent solves the problem of slow composting and long cycle of garden waste due to the limitation in cellulose degradation difficulty, accelerates cellulose degradation in the composting process, shortens the fermentation period, and improves the conversion efficiency, thereby having a broad application prospect in the aspects such as the application of composting treatment and resource utilization of garden waste, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com