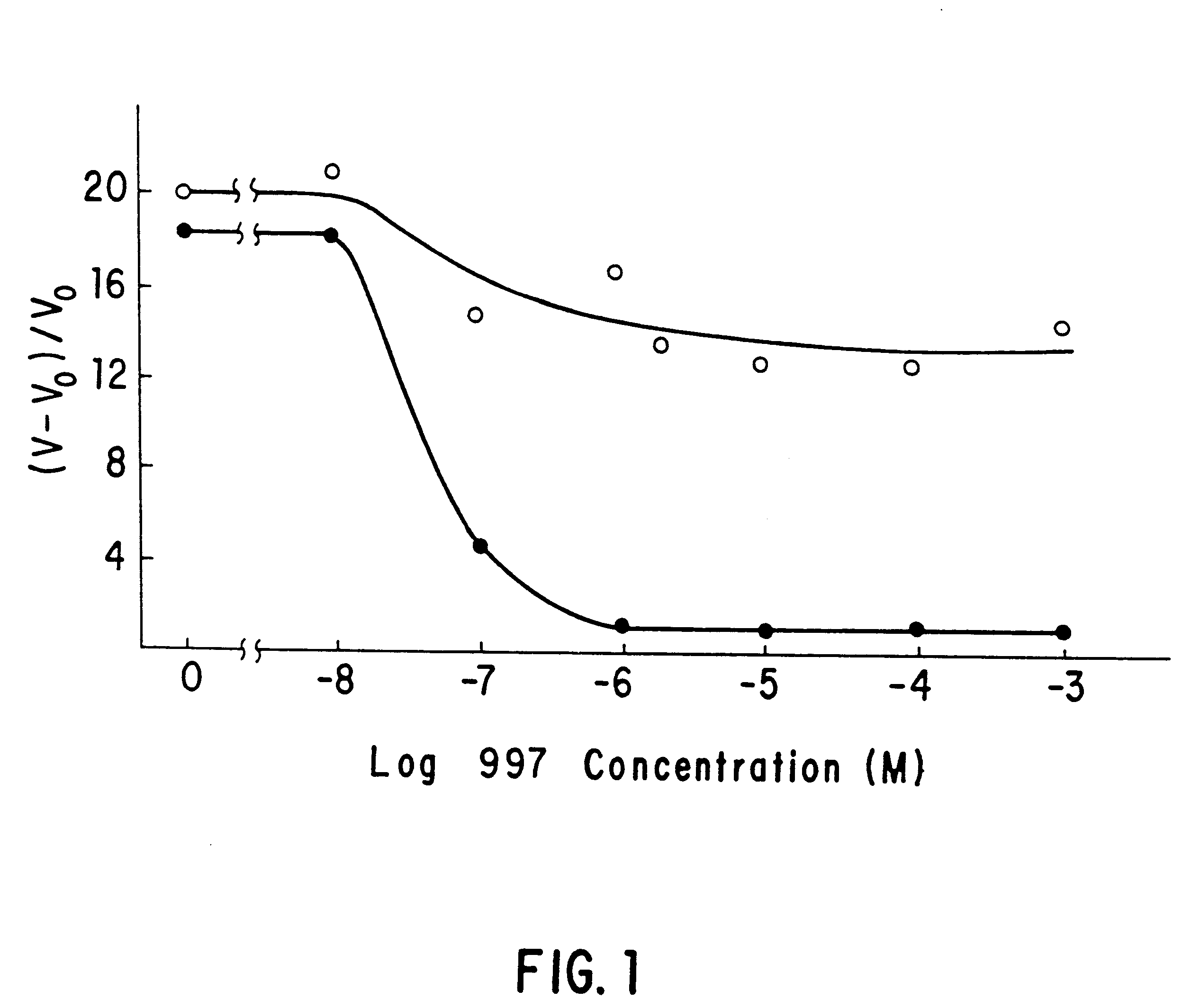
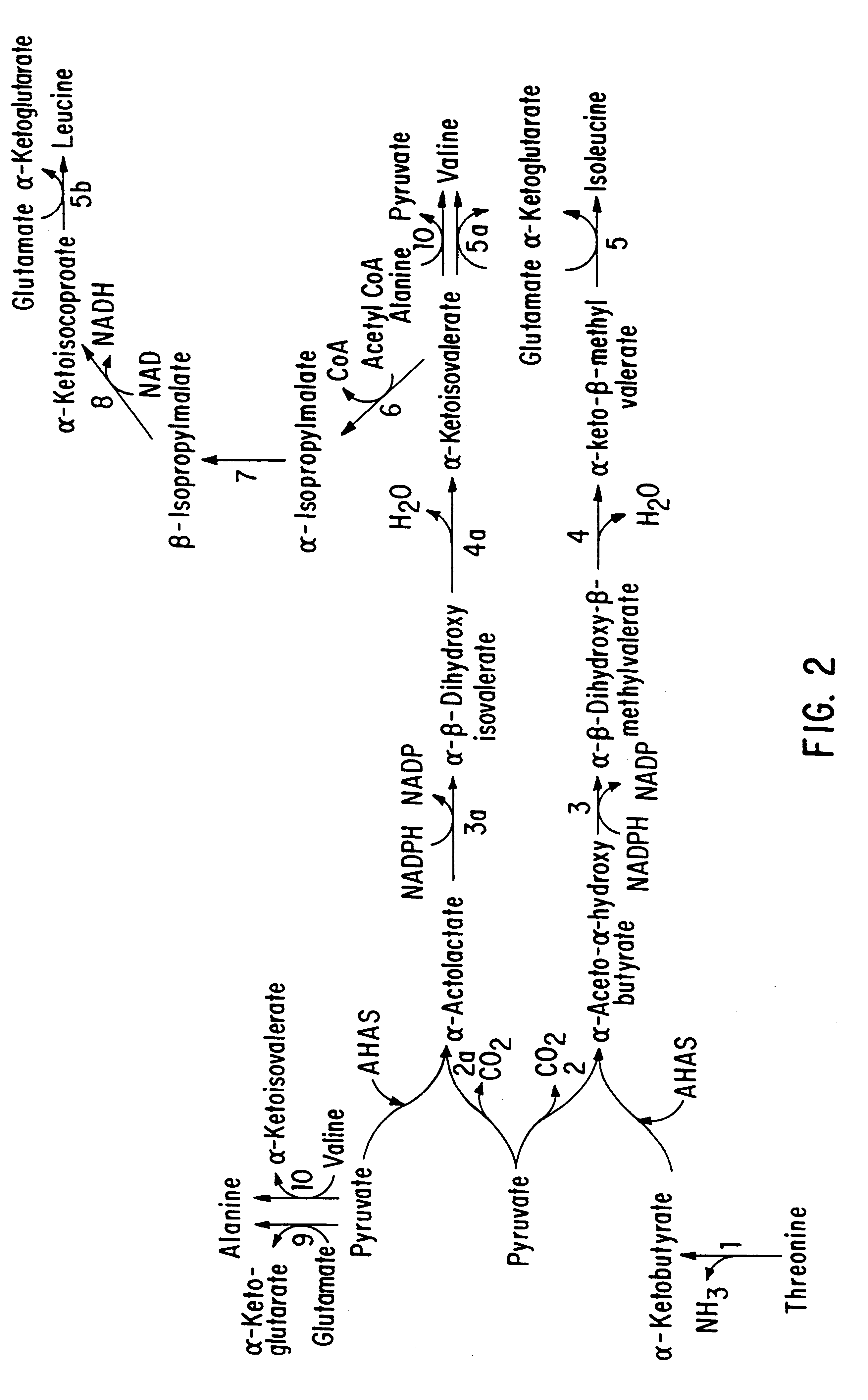
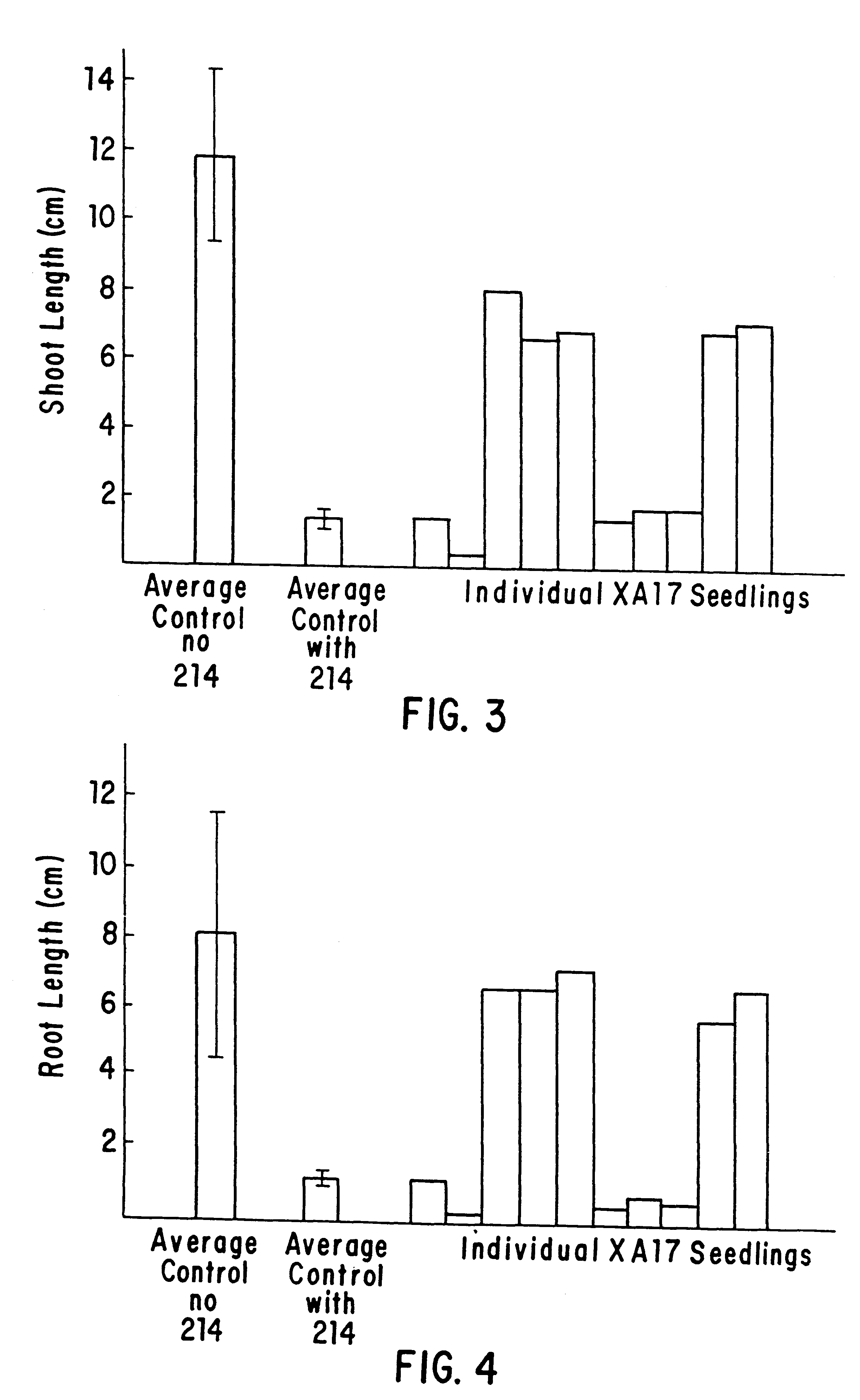
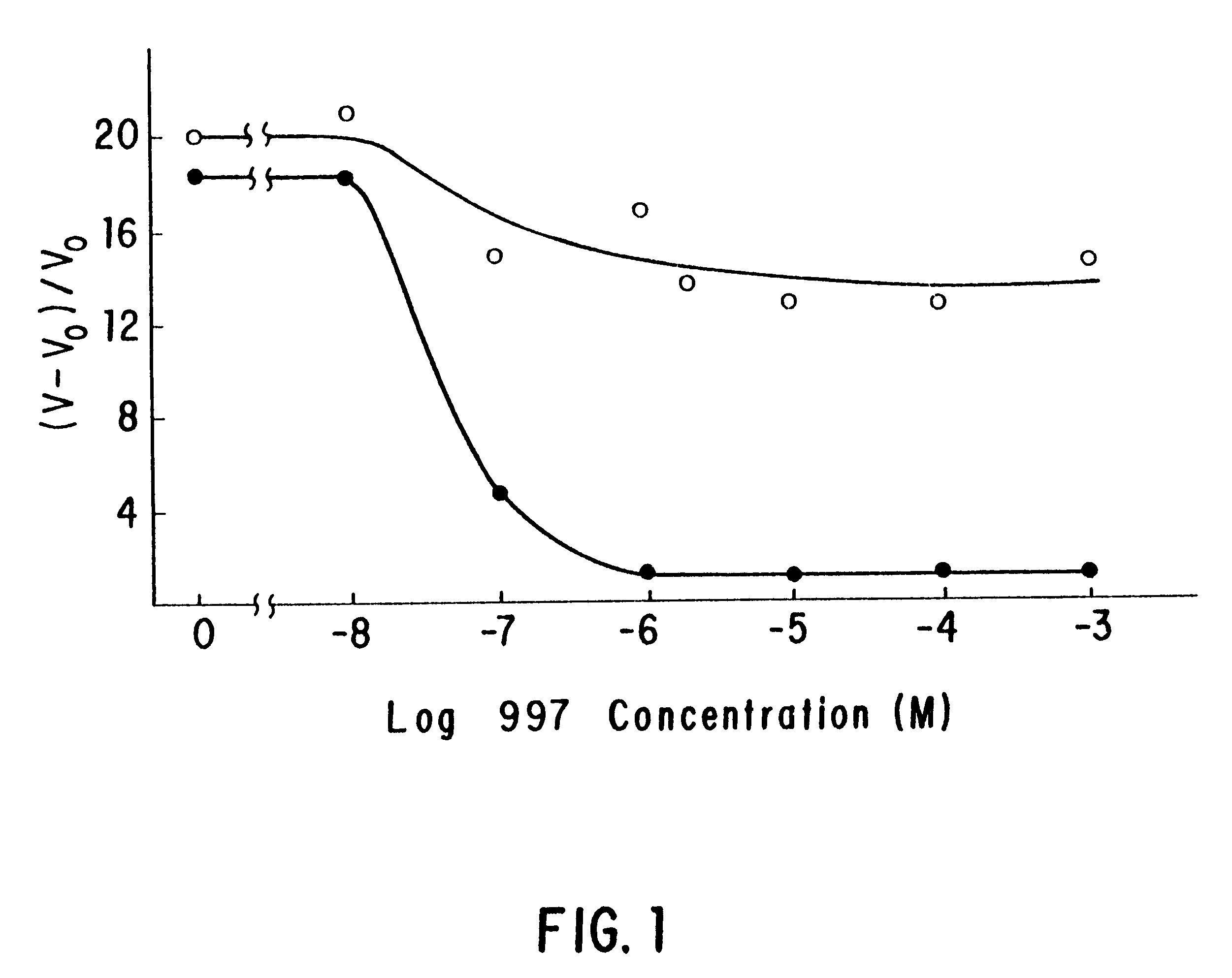
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Acetohydroxyacid synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6222100B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemBiocideSeed and root treatmentPlant tissueNovel gene
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6211438B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemMutant preparationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant tissueNovel gene
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6211439B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemLyasesPlant genotype modificationPlant tissuePlanting seed
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
Herbicide resistant rice
InactiveUS6274796B1Growth inhibitionGood flexibilityBiocideMutant preparationRice plantsAcetohydroxy Acid Synthetase
Rice plants are disclosed with two separate, but synergistic mechanisms for resistance to herbicides that normally inhibit a plant's acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) enzyme. The herbicide resistance of plants with both resistance mechanisms is substantially greater than one would expect from a simple combination of the two types of resistance. The first of the two resistance mechanisms is a metabolic pathway that is not fully understood, but that does not itself involve a mutant AHAS enzyme. The second resistance mechanism is a mutant AHAS enzyme, an enzyme that shows direct resistance to levels of herbicide that normally inhibit the enzyme, in both in vivo and in vitro assays. Besides controlling red rice, many AHAS-inhibiting herbicides also effectively control other weeds that are common in rice fields. Several of these herbicides have residual activity, so that a treatment controls both existing weeds as well as weeds that sprout later. No herbicide currently available for use on rice has residual activity against a broad spectrum of weeds including red rice. With effective residual activity against red rice and other weeds, rice producers now have a weed control system superior to those currently used.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Resistance to acetohydroxyacid synthase-inhibiting herbicides
InactiveUS20050198705A1High success rateImprove efficiencyBiocideOther foreign material introduction processesRice plantsPyrithiobac sodium
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Herbicide resistant rice
InactiveUS7019196B1Seed and root treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementRice plantsResidual activity
Rice plants are disclosed with multiple sources of resistance to herbicides that normally inhibit a plant's acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) enzyme. Besides controlling red rice, many AHAS-inhibiting herbicides also effectively control other weeds that are common in rice fields. Several of these herbicides have residual activity, so that one treatment can control both existing weeds and weeds that sprout later. With effective residual activity against red rice and other weeds, rice producers now have a weed control system superior to those that are currently available commercially.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Rice Cultivar CL171-AR
A rice cultivar designated CL171-AR is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of rice cultivar CL171-AR, to the plants of rice CL171-AR, to methods for producing a rice plant produced by crossing the cultivar CL171-AR with itself or another rice variety, and to methods for controlling weeds in the vicinity of plants of rice cultivar CL171-AR, which comprises increased resistance to acetohydroxyacid synthase-inhibiting herbicides. The invention further relates to hybrid rice seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar CL171-AR with another rice cultivar.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Rice cultivar CL171-AR
ActiveUS7642434B2Improve nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationRice plantsCultivar
A rice cultivar designated CL171-AR is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of rice cultivar CL171-AR, to the plants of rice CL171-AR, to methods for producing a rice plant produced by crossing the cultivar CL171-AR with itself or another rice variety, and to methods for controlling weeds in the vicinity of plants of rice cultivar CL171-AR, which comprises increased resistance to acetohydroxyacid synthase-inhibiting herbicides. The invention further relates to hybrid rice seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar CL171-AR with another rice cultivar.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Ahas inhibiting herbicide resistant wheat and method for selection thereof
InactiveUS7034208B1Reduce application rateReduce water pollutionMutant preparationFermentationTriticeaeScreening method
This invention is directed to a screening method for the selection of mutations which confer acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) inhibiting herbicide resistance to wheat. After mutagenesis of wheat seeds, the seeds are soaked in an AHAS inhibiting herbicide-containing solution containing a particular class of AHAS inhibiting herbicide. After planting, the soil containing the seeds is sprayed with an AHAS inhibiting herbicide of the same class as that used in the seed soak step prior to the emergence of the seedlings from the soil. Those wheat seedlings which emerge and are normal in appearance demonstrate resistance to the class of AHAS inhibiting herbicides used in the seed soak and spraying steps. This invention is also directed to the wheat selections and seeds identified by the screening method.
Owner:BASF AG
Construction and application of high-yield L-valine engineering bacteria
ActiveCN104561074AHigh yieldReduce the rate of contaminationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetohydroxy Acid SynthetaseDihydroxyacid dehydratase
The invention discloses construction and an application of high-yield L-valine engineering bacteria and provides a method for preparing recombinant bacteria. The method comprises steps as follows: an acetohydroxyacid synthase mutant coding DNA module, an acetohydroxyacid isomerism reductase coding DNA module, a branched chain amino acid aminotransferase coding DNA module and a dihydroxy acid dehydrase DNA molecule are introduced into target bacteria and then the recombination bacteria are obtained. An experiment proves that when Brevibacterium flavum MDV-07 is used for fermenting and producing L-valine, the yield of L-valine and a conversion rate can be greatly increased, and great production application value is realized.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV +1
Ahas mutants
ActiveCN101668419AIncreased herbicide resistanceBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolynucleotide
The invention provides nucleic acids encoding mutants of the acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) large subunit comprising at least two mutations, for example double and triple mutants, which are useful for producing transgenic or non-transgenic plants with improved levels of tolerance to AHAS-inhibiting herbicides. The invention also provides expression vectors, cells, plants comprising the polynucleotides encoding the AHAS large subunit double and triple mutants, plants comprising two or more AHAS large subunit single mutant polypeptides, and methods for making and using the same.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Herbicide-resistant rice plants, polynucleotides encoding herbicide-resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase large subunit proteins, and methods of use
Herbicide-resistant rice plants, isolated polynucleotides that encode herbicide resistant and wild-type acetohydroxy-acid synthase large subunit 1 (AHASL1) polypeptides, and the amino acid sequences of these polypeptides, are described. Expression cassettes and transformation vectors comprising the polynucleotides of the invention, as well as plants and host cells transformed with the polynucleotides, are described. Methods of using the polynucleotides to enhance the resistance of plants to imidazolinone herbicides, and methods for controlling weeds in the vicinity of herbicide-resistant plants are also described.
Owner:INST NACIONAL DE TECNOLOGIA AGROPECUARIA
Herbicide-resistant sunflower plants, polynucleotides encoding herbicide=resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase large subunit proteins, andmethods of use
Herbicide-resistant sunflower plants, isolated polynucleotides that encode herbicide-resistant and wild-type acetohydroxyacid synthase large subunit (AHASL) polypeptides, and the amino acid sequences of these polypeptides, are described. Expression cassettes and transformation vectors comprising the polynucleotides of the invention, as well as plants and host cells transformed with the polynucleotides, are described. Methods of using the polynucleotides to enhance the resistance of plants to herbicides, and methods for controlling weeds in the vicinity of herbicide-resistant plants are also described.
Owner:BASF AG +1
AHAS mutants
InactiveCN104017816AIncreased herbicide resistanceBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolynucleotide
The invention provides nucleic acids encoding mutants of the acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) large subunit comprising at least two mutations, for example double and triple mutants, which are useful for producing transgenic or non-transgenic plants with improved levels of tolerance to AHAS-inhibiting herbicides. The invention also provides expression vectors, cells, plants comprising the polynucleotides encoding the AHAS large subunit double and triple mutants, plants comprising two or more AHAS large subunit single mutant polypeptides, and methods for making and using the same.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Rice cultivar taggart
ActiveUS8134058B2Improve nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationRice plantsCultivar
A rice cultivar designated Taggart is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of rice cultivar Taggart, to the plants of rice Taggart, to methods for producing a rice plant produced by crossing the cultivar Taggart with itself or another rice variety, and to methods for controlling weeds in the vicinity of plants of rice cultivar Taggart, which comprises increased resistance to acetohydroxyacid synthase-inhibiting herbicides. The invention further relates to hybrid rice seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar Taggart with another rice cultivar.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing alpha-ketobutyric acid and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN103865869AGrow fastShort fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing alpha-ketobutyric acid as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium, belonging to the technical field of biology. The strain is relatively high in production efficiency when used for producing alpha-ketobutyric acid through fermentation. The genetically engineered bacterium is obtained through carrying out genetic engineering modification on Escherichia coli MG1655; the genetic engineering modification is realized by knocking out a large-subunit encoding gene ilvB of acetohydroxyacid synthase I, a large-subunit encoding gene ilvI of acetohydroxyacid synthase III and a threonine operon leading peptide encoding gene thrL in an over-expressive threonine dehydratase encoding gene ilvA. When the bacterium is used for producing alpha-ketobutyric acid by using a fermentation method, defects such as complex reaction conditions, high energy consumption, serious pollution or high production cost, serious pollution and the like existing in a chemical synthesis method, an enzyme method or a microbial conversion method can be overcome; after the bacterium is fermented for 20-24h, the yield of alpha-ketobutyric acid is up to 8.5-15.7g / L; aerobic fermentation is adopted in a fermentation process; the bacterium is rapid in growth, short in fermentation period and high in acid production rate; any reports for producing alpha-ketobutyric acid by using a direct fermentation method are not found at present.
Owner:江苏澳创生物科技有限公司
Novel mutation involved in increased tolerance to imidazolinone herbicides in plants
The present invention is directed to nucleic acids encoding polypeptides that confer upon a plant tolerance to an imidazolinone and / or other acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) inhibiting herbicide when expressed in the plant. The present invention also provides plants having increased tolerance to an imidazolinone and / or other AHAS-inhibiting herbicide. More particularly, the present invention includes plants containing at least one IMI nucleic acid. The present invention also includes seeds produced by these plants and methods of controlling weeds in the vicinity of these wheat plants.
Owner:BASF AGROCHEMICAL PROD BV +1
Compositions and methods for modulating the sensitivity of cell to AHAS inhibitors
Methods and materials useful for modulating the sensitivity of cells to an inhibitor of acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) are disclosed. For example, nucleic acid molecules encoding AHAS large subunits are disclosed as well as methods for using such nucleic acid molecules to transform microbial cells and plant cells, and to confer modulated sensitivity to AHAS-inhibiting compounds onto such cells. Further provided are materials and methods useful for modulating growth, development, activity, and characteristics of host cells and organisms.
Owner:SYNTHETIC GENOMICS INC
Acetohydroxyacid synthase and application thereof
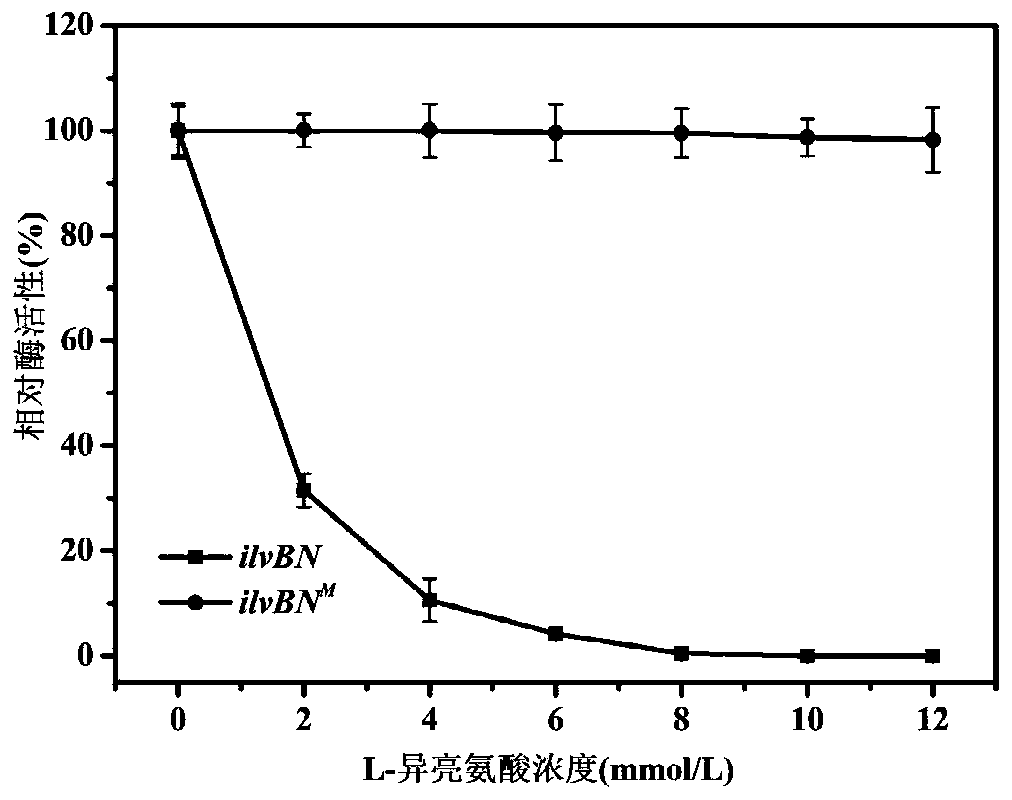
The present invention relates to an acetohydroxyacid synthase capable of relieving L-isoleucine feedback inhibition, and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. Theacetohydroxyacid synthase encoded by an ilvBN<M> gene has the following characteristics: the enzyme relieves the feedback inhibition of L-isoleucine, an ilvBN<M> enzyme activity is free of obvious changes under a condition of a concentration of the L-isoleucine at 0-12 mmol / L, an activity of the acetohydroxyacid synthase is not obviously lowered compared with wild-type ilvBN-encoded acetohydroxyacid synthase, and the acetohydroxyacid synthase can be applied in production of the L-isoleucine.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Herbicide-resistant sunflower plants with multiple herbicide resistant alleles of AHASL1 and methods of use
Owner:BASF AGROCHEMICAL PROD BV +1
Herbicid resistant rice
Rice plants are disclosed with multiple sources of resistance to herbicides that normally inhibit a plant's acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) enzyme. Besides controlling red rice, many AHAS-inhibiting herbicides also effectively control other weeds that are common in rice fields. Several of these herbicides have residual activity, so that one treatment can control both existing weeds and weeds that sprout later. With effective residual activity against red rice and other weeds, rice producers now have a weed control system superior to those that are currently available commercially.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Preparation and preservation method for colon bacillus acetohydroxyacid synthase
InactiveCN103710328AHigh purityHigh activityTransferasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention provides a method for preparing AHAS (Acetohydroxyacid Synthase) which has good purity and high activity and can exist stably. The method comprises the following steps: upstream and downstream primers are designed according to a gene sequence of a colon bacillus AHAS catalytic subunit, wherein the designed upstream primer carries an Xho I enzyme digestion site and the downstream primer carries a BamHI enzyme digestion site; a colon bacillus BL21 strain genomic DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is used as a template and a target segment ahas is obtained by a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification technology; the target segment ahas is connected onto an expression carrier PGEX-AT-1 to obtain a recombinant plasmid PGEX-4T-1-ahas; inducible expression is realized in a prokaryotic expression system; an expressed enzyme is purified by agarose gel resin modified by glutathione sulfur transferase (GST) so as to obtain the acetohydroxyacid synthase with good activity.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Brevibacterium flavum recombinant strain producing L-isoleucine and construction method thereof
InactiveCN109554324AIncrease productionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaHeterologousBrevibacillus borstelensis
The present invention discloses a brevibacterium flavum recombinant strain producing L-isoleucine and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The genetic engineering means is utilized to strengthen acetohydroxyacid synthase, dihydroxy acid reductoisomerase and branched chain amino acid aminotransferase in the brevibacterium flavum, and heterologously expresses catabolic threonine dehydratase encoded by tdcB, and thus constructs a L-isoleucine high-yield strain B. flavum I12 / pEC-XK99E-ilvBNCE-tdcB. The yield of the accumulated isoleucine is increased to 22.65 g / L in the recombinant strain and is 25.48% higher than that of an original strain, and the maximum biomass reaches 20.95 g DCW / L. The strain can turn lysine pathway carbon source to the L-isoleucine and a brand-new idea for constructing the L-isoleucine high-yield strain is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Herbicide resistant rice
InactiveUS20020019313A1Effective controlEffective activityBiocideSeed and root treatmentBiotechnologyPaddy field
Rice plants are disclosed with multiple sources of resistance to herbicides that normally inhibit a plant's acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) enzyme. Besides controlling red rice, many AHAS-inhibiting herbicides also effectively control other weeds that are common in rice fields. Several of these herbicides have residual activity, so that one treatment can control both existing weeds and weeds that sprout later. With effective residual activity against red rice and other weeds, rice producers now have a weed control system superior to those that are currently available commercially.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Methods for making and using wheat plants with increased grain protein content
InactiveUS20090300783A1High in proteinOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationAcetohydroxyacid synthaseProtein content
The present invention provides novel methods for making wheat plants with increased grain protein content. The methods involve introducing a gene encoding herbicide-resistant, wheat acetohydroxyacid synthase large subunit (AHASL) protein. The invention further provides wheat plants that produce high protein grain and human and animal food products derived thereof.
Owner:HOWIE WILLIAM J +4
Rice cultivar CL 181-AR
ActiveUS8440892B2Improve nutritional qualityBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesRice plantsCultivar
A rice cultivar designated CL 181-AR is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of rice cultivar CL 181-AR, to the plants of rice CL 181-AR, to methods for producing a rice plant produced by crossing the cultivar CL 181-AR with itself or another rice variety, and to methods for controlling weeds in the vicinity of plants of rice cultivar CL 181-AR, which comprises increased resistance to acetohydroxyacid synthase-inhibiting herbicides. The invention further relates to hybrid rice seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar CL 181-AR with another rice cultivar.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Polynucleotides encoding mature AHASL proteins for creating imidazolinone-tolerant plants
Isolated polynucleotide molecules that encode mature, wild-type and imidazolinone-tolerant acetohydroxyacid synthase large subunit (AHASL) polypeptides, and the amino acid sequences encoding these polypeptides, are described. Expression cassettes and transformation vectors comprising the polynucleotide molecules of the invention, as well as plants and host cells transformed with the polynucleotide molecules, expression cassettes, and transformation vectors, are described. Methods of using the polynucleotide molecules to enhance the resistance of plants to herbicides, and methods for controlling weeds in the vicinity of such plants are also described.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Rice cultivar CL172
A rice cultivar designated CL172 is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of rice cultivar CL172, to the plants of rice CL172, to methods for producing a rice plant produced by crossing the cultivar CL172 with itself or another rice variety, and to methods for controlling weeds in the vicinity of plants of rice cultivar CL172, which comprises increased resistance to acetohydroxyacid synthase-inhibiting herbicides. The invention further relates to hybrid rice seeds and plants produced by crossing the cultivar CL172 with another rice cultivar.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
AHAS mutants
ActiveCN104017817AIncreased herbicide resistanceBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPolynucleotideTransgene
The invention provides nucleic acids encoding mutants of the acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) large subunit comprising at least two mutations, for example double and triple mutants, which are useful for producing transgenic or non-transgenic plants with improved levels of tolerance to AHAS-inhibiting herbicides. The invention also provides expression vectors, cells, plants comprising the polynucleotides encoding the AHAS large subunit double and triple mutants, plants comprising two or more AHAS large subunit single mutant polypeptides, and methods for making and using the same.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Herbicide-resistant sunflower plants with multiple herbicide resistant alleles of AHASL1 and methods of use
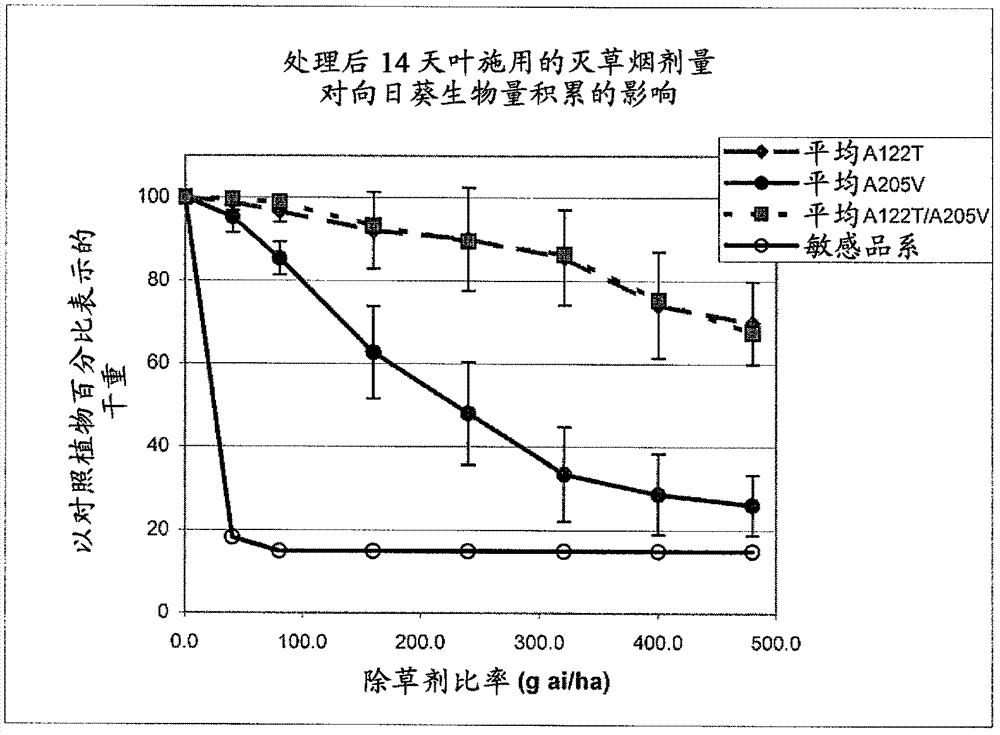
Herbicide resistant sunflower plants comprising two different herbicide-resistant alleles of the sunflower acetohydroxyacid synthase large subunit 1 (AHASL1) gene are described. Methods for making these sunflower plants and methods for controlling weeds or other undesired vegetation growing in the vicinity of these sunflower plants are disclosed. Such methods involve the use of acetohydroxyacid synthase-inhibiting herbicides. Methods for controlling parasitic weeds growing on sunflower plants are also described. Additionally provided are methods for determining the genotype of sunflower plants for AHASL1 gene.
Owner:BASF AGROCHEMICAL PROD BV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com