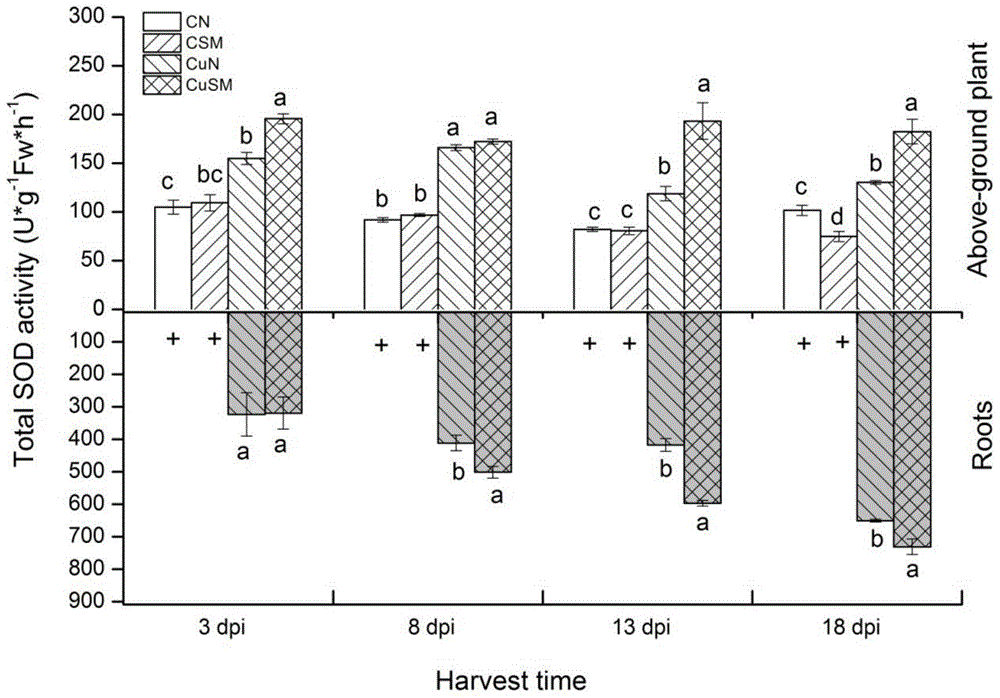
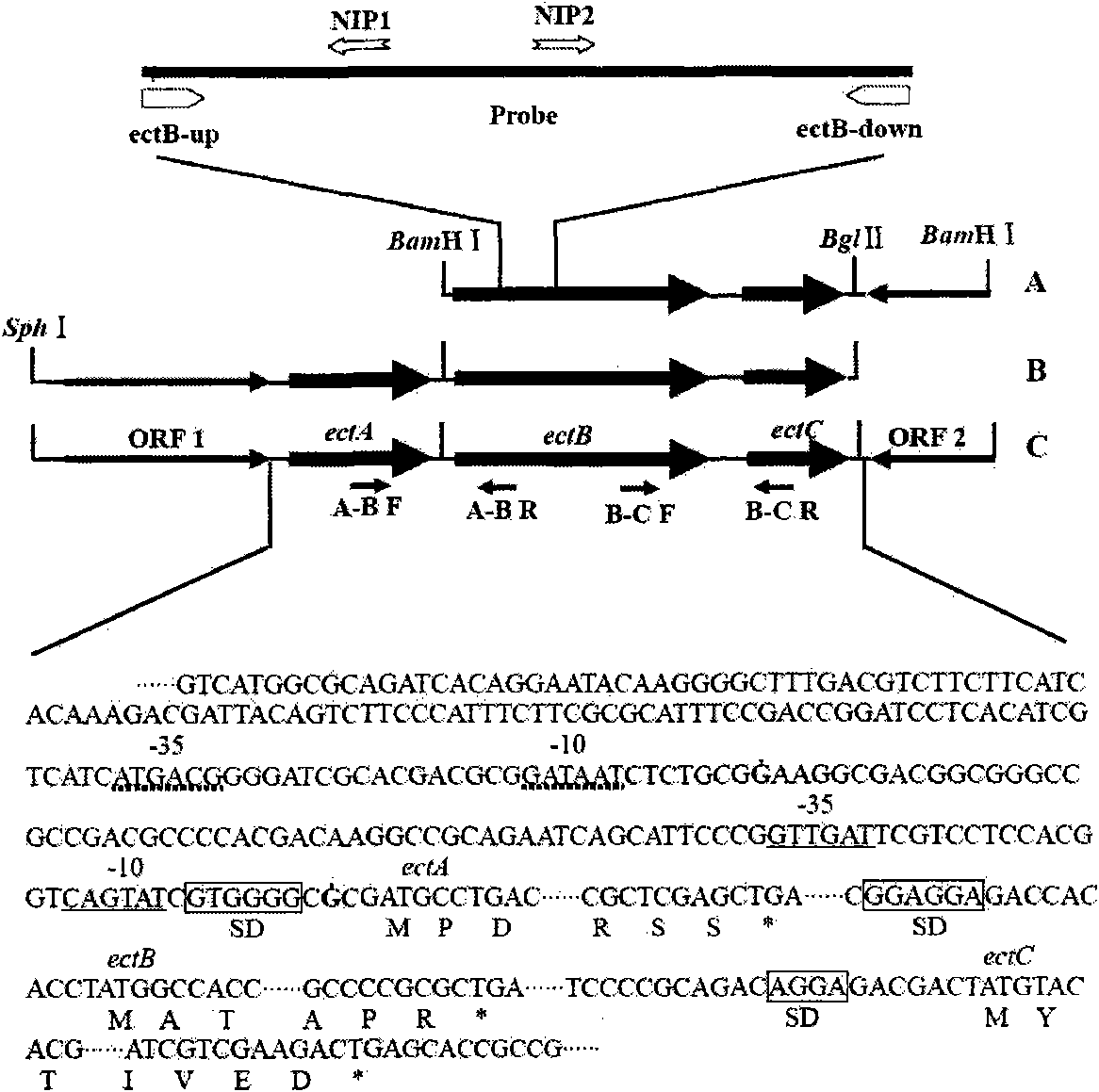
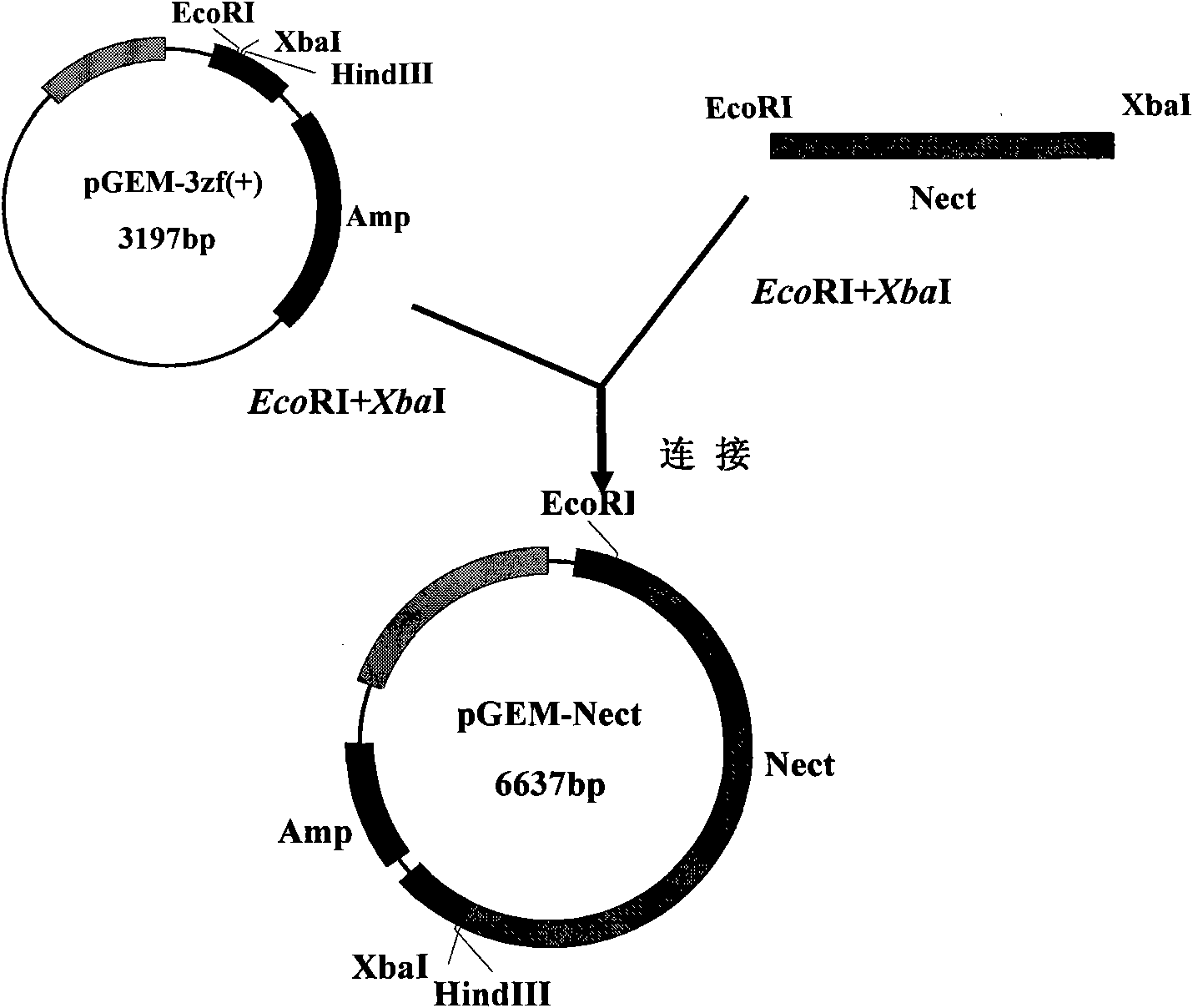
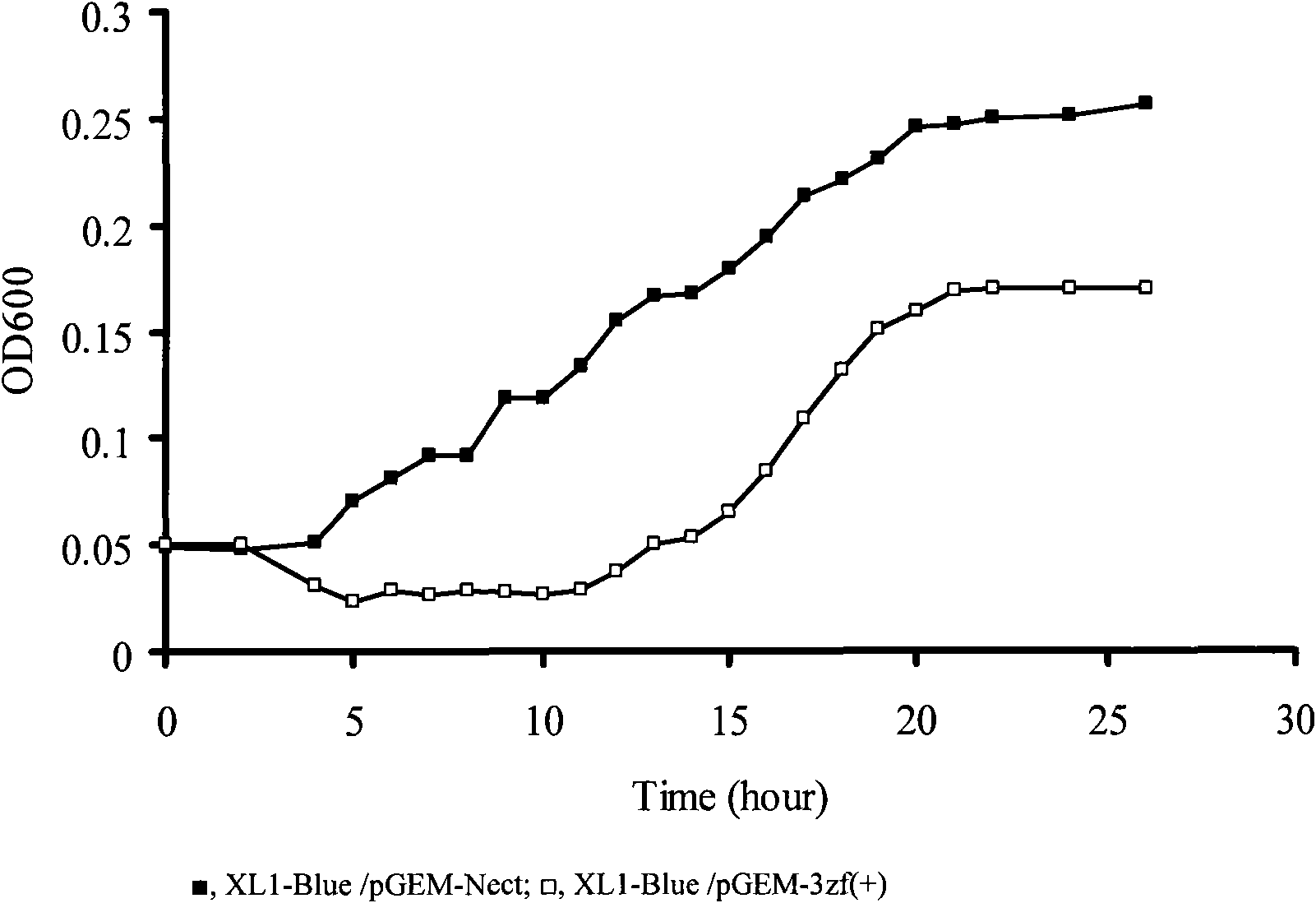
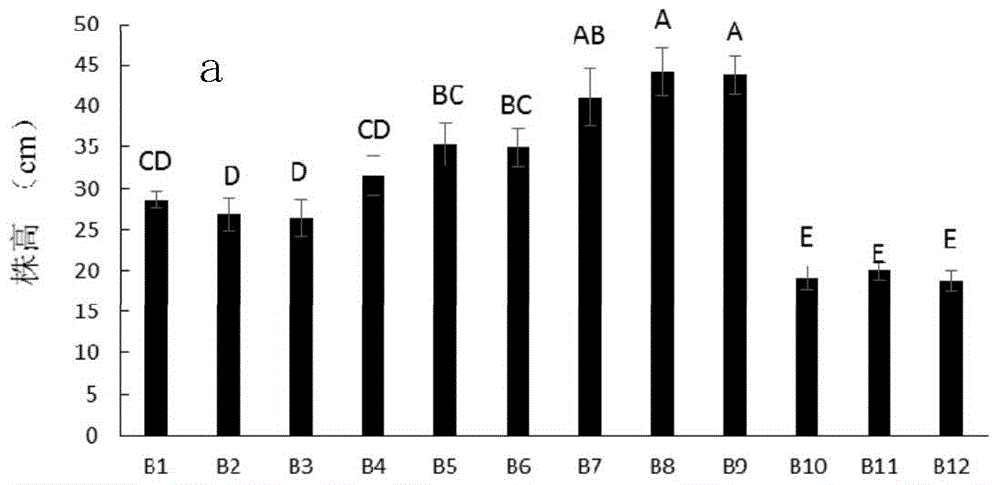
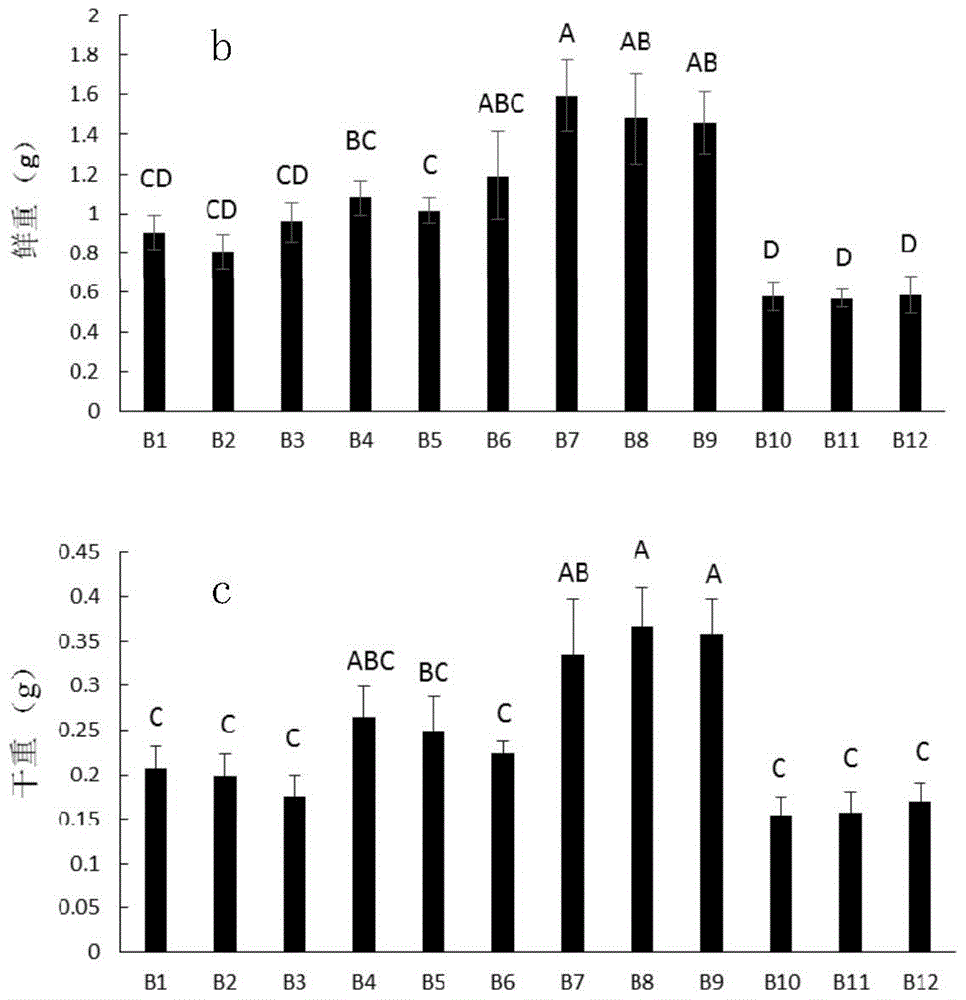
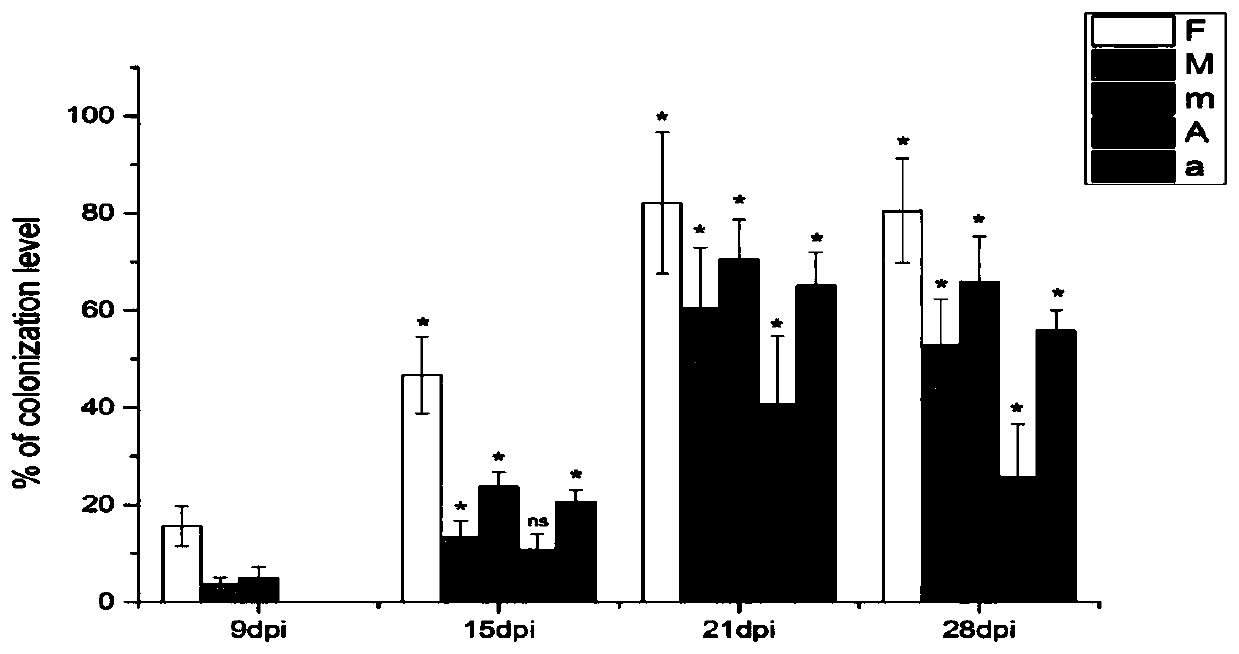
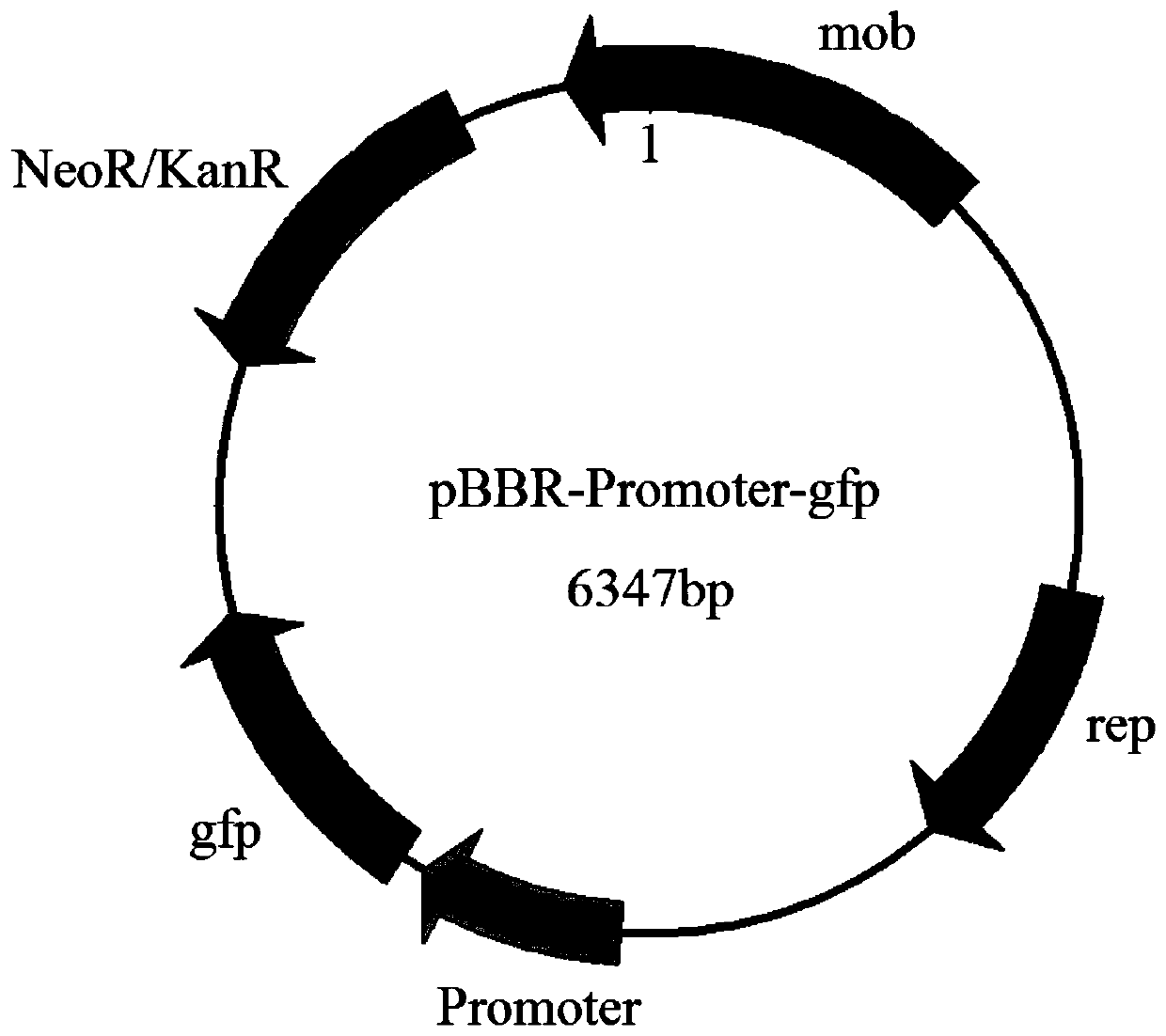
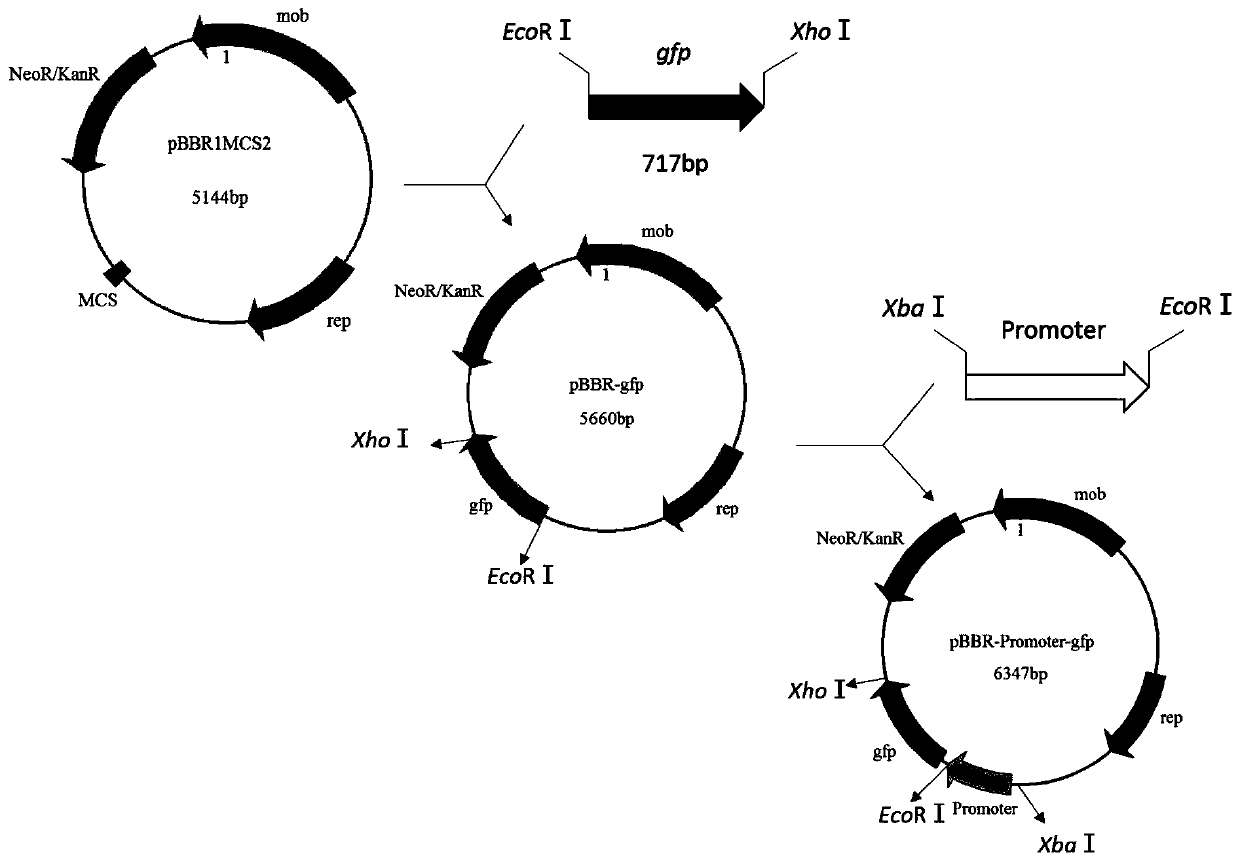
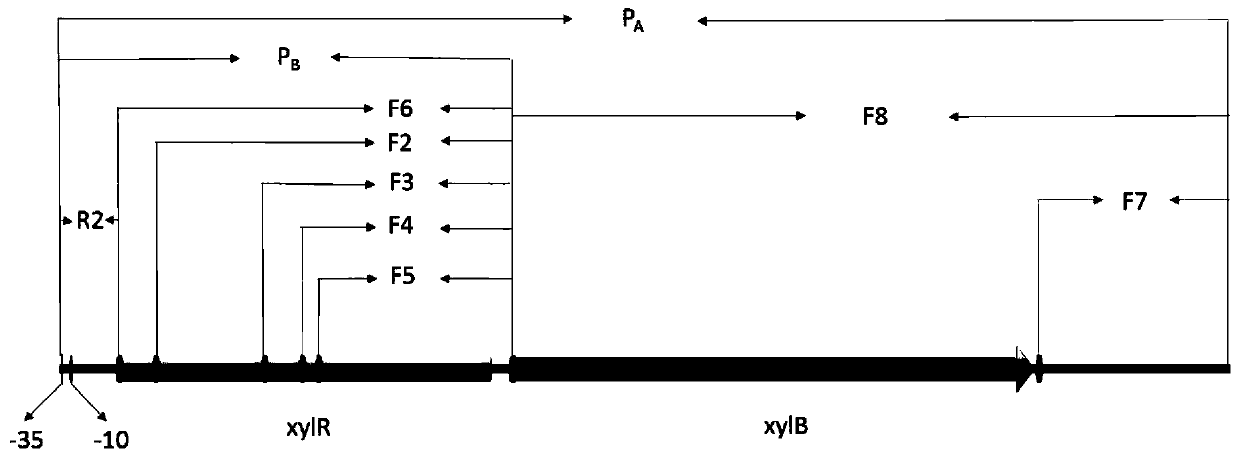
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Sinorhizobium meliloti" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sinorhizobium meliloti is a Gram-negative bacterium which fixes atmospheric nitrogen. It forms a symbiotic relationship with legumes from the genera Medicago, Melilotus and Trigonella, including the model legume Medicago truncatula. This symbiosis results in a new plant organ termed a root nodule and is deemed symbiotic as it leaves excess nitrogen behind for the plant. S. meliloti are mobile and possess a cluster of peritrichous flagella. The S. meliloti genome contains four genes coding for flagellin. These include fliC1C2–fliC3C4. The genome contains three replicons: a chromosome (~3.7 megabases), a chromid (pSymB; ~1.7 megabases), and a plasmid (pSymA; ~1.4 megabases). Individual strains may possess additional, accessory plasmids. Five S. meliloti genomes have been sequenced to date: Rm1021, AK83, BL225C, Rm41, and SM11 with 1021 considered to be the wild type.
Sinorhizobium meliloti strain and composition and application of sinorhizobium meliloti strain
ActiveCN104342390ASimple ingredientsEasy to trainBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySinorhizobium sp.
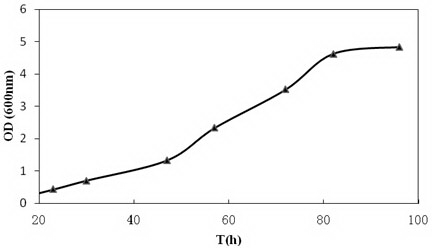
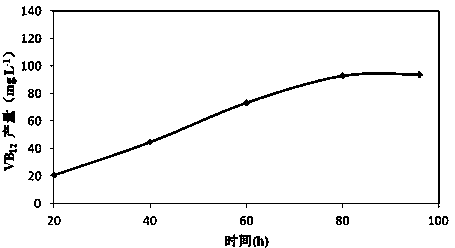
The invention discloses a sinorhizobium meliloti strain capable of being applied to fermentation to generate vitamin B12, wherein the preservation number of the sinorhizobium meliloti strain is CGMCC No.9638. The invention also discloses a production and preparation method of vitamin 12 by the sinorhizobium meliloti strain in a fermentation manner. The method comprises a fermentation culture condition of the strain and an extraction method of the vitamin 12 in fermentation liquor; the method comprises the following steps: inoculating the strain on a solid culture medium into a triangular flask as a seed solution; inoculating the seed solution into a fermentation culture medium at 30 DEG C with 10% of inoculation amount; fermenting and cultivating at 200rpm for 200 hours, and then collecting the fermentation liquor; and adding a transforming agent to transform the fermentation liquor into cyano cobalt amine. The vitamin 12 is widely applied to the industries such as feeds, additives, medicines and cosmetics as a special factor in an adjusting organism growth process; and the requirement of the vitamin 12 rises year by year. The strain fermentation process is easy to control, so that the strain fermentation process is not affected by the factors such as seasons; the requirements on raw materials are simple; and fermentation production is developed into a main production mode.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
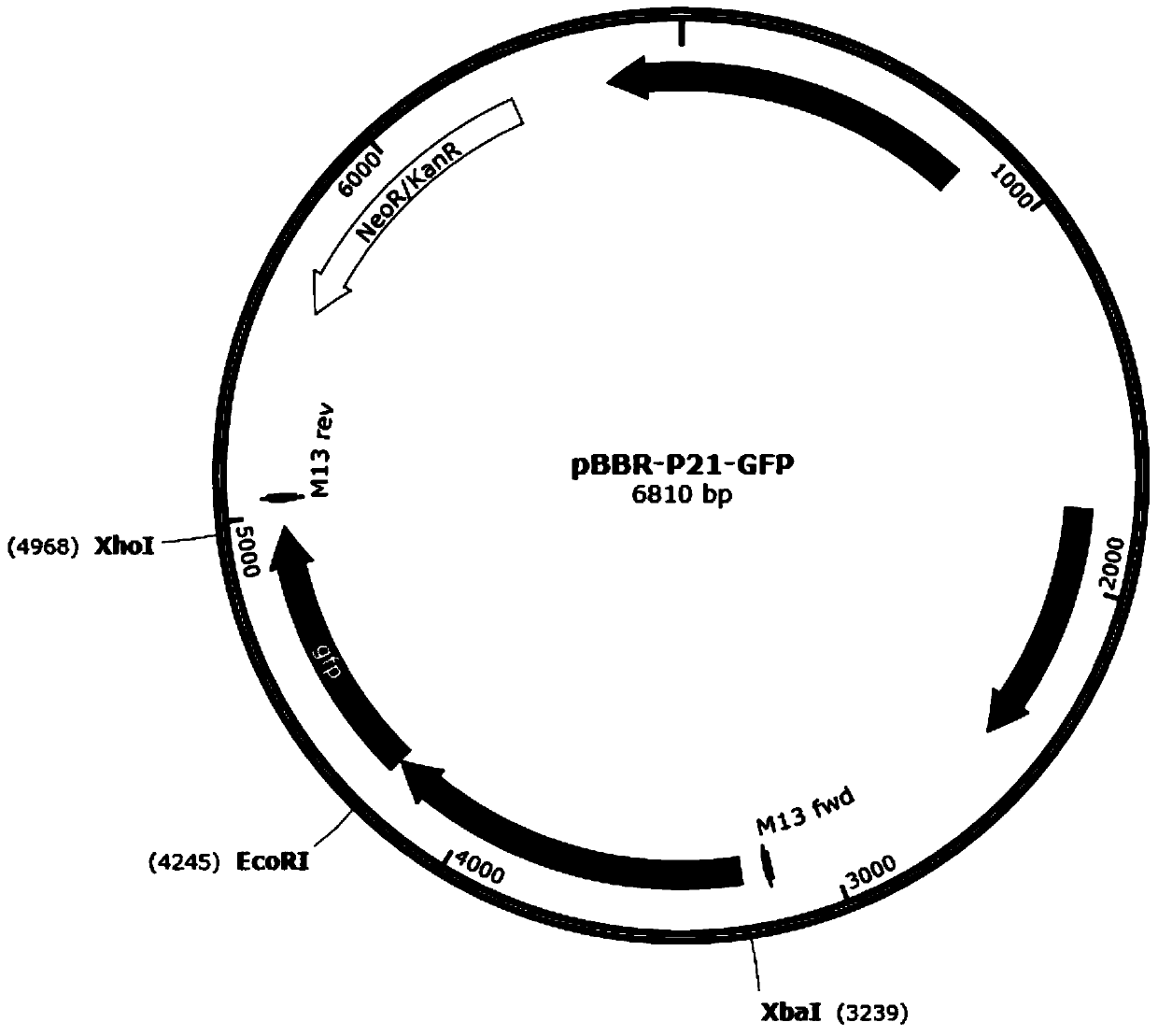
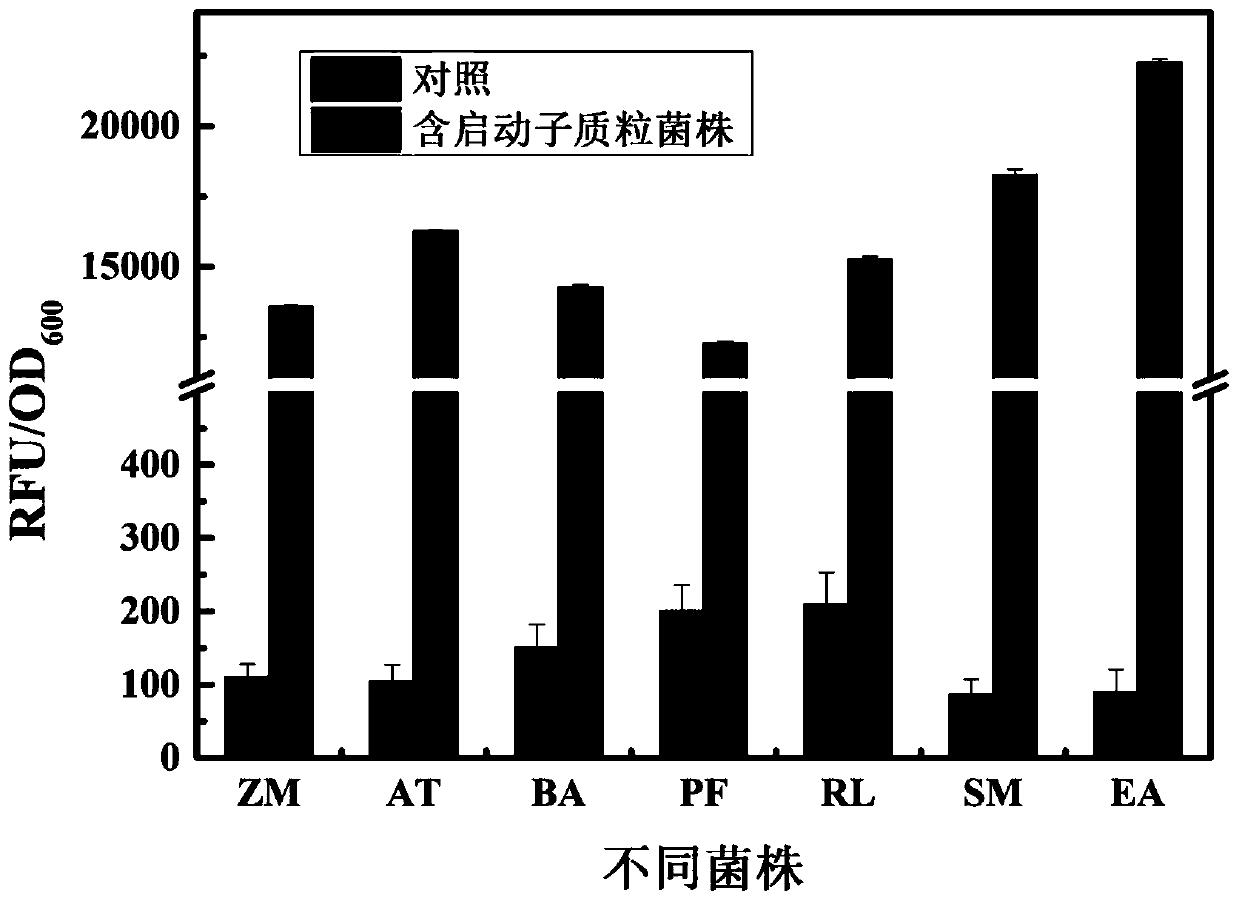
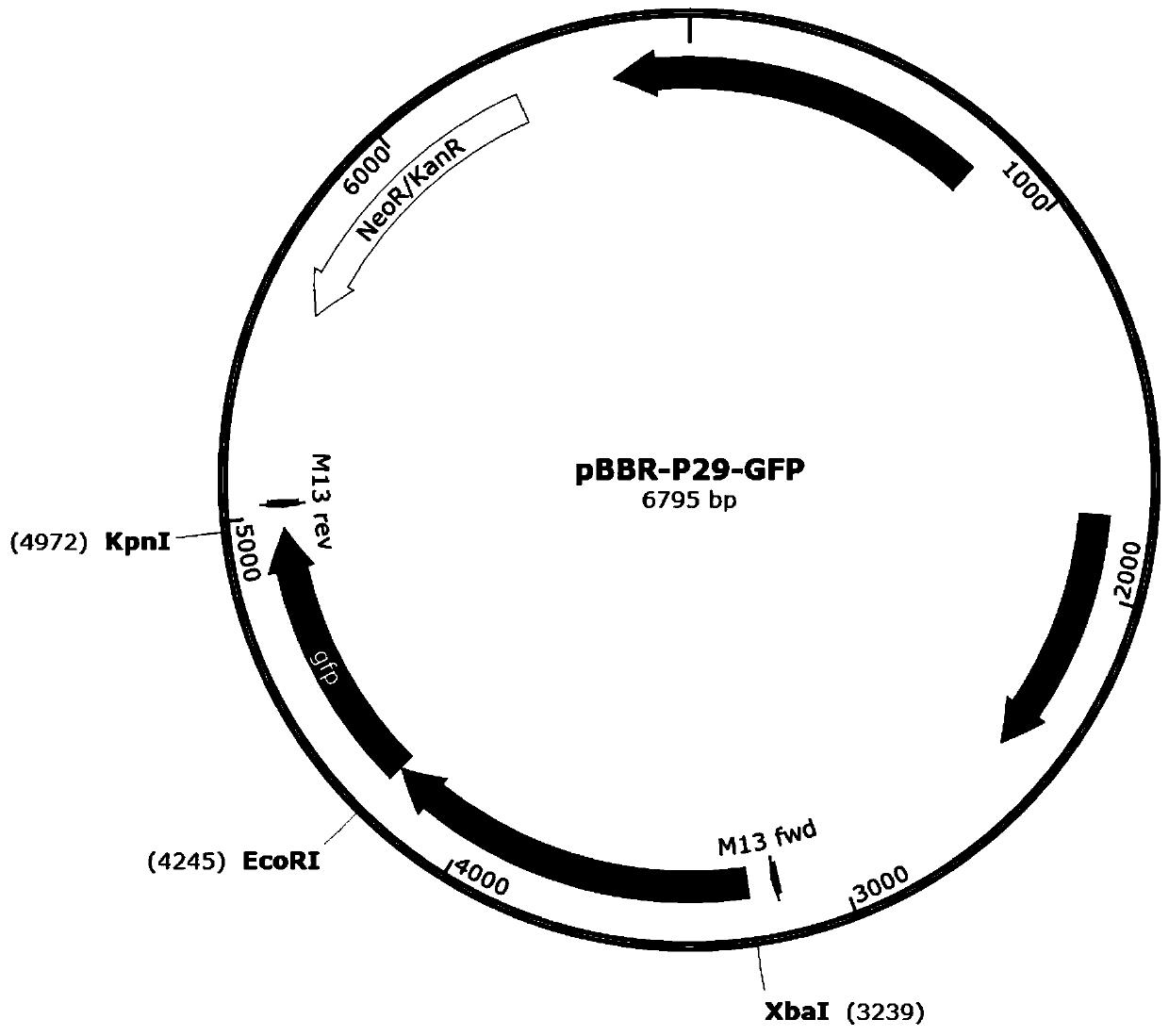
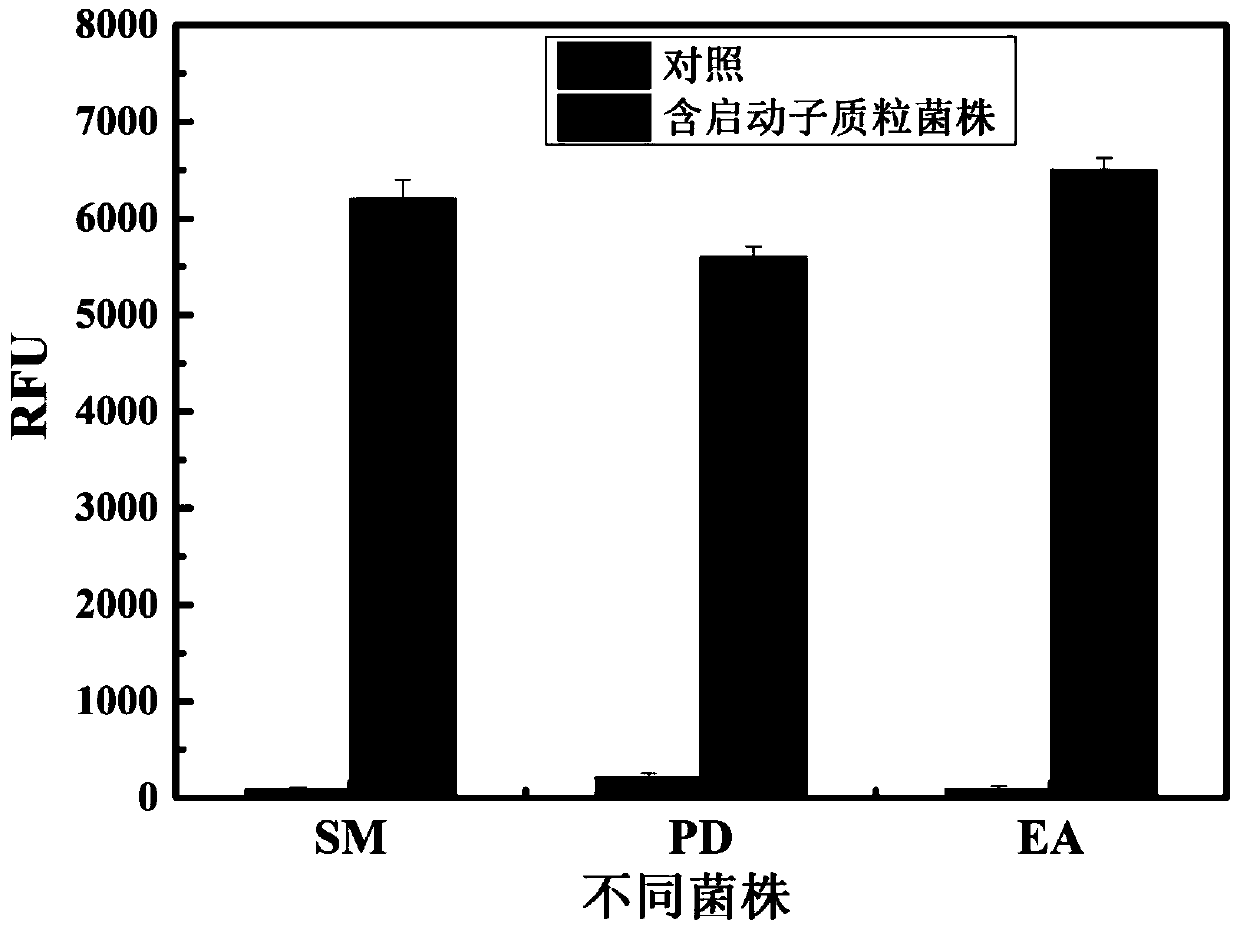
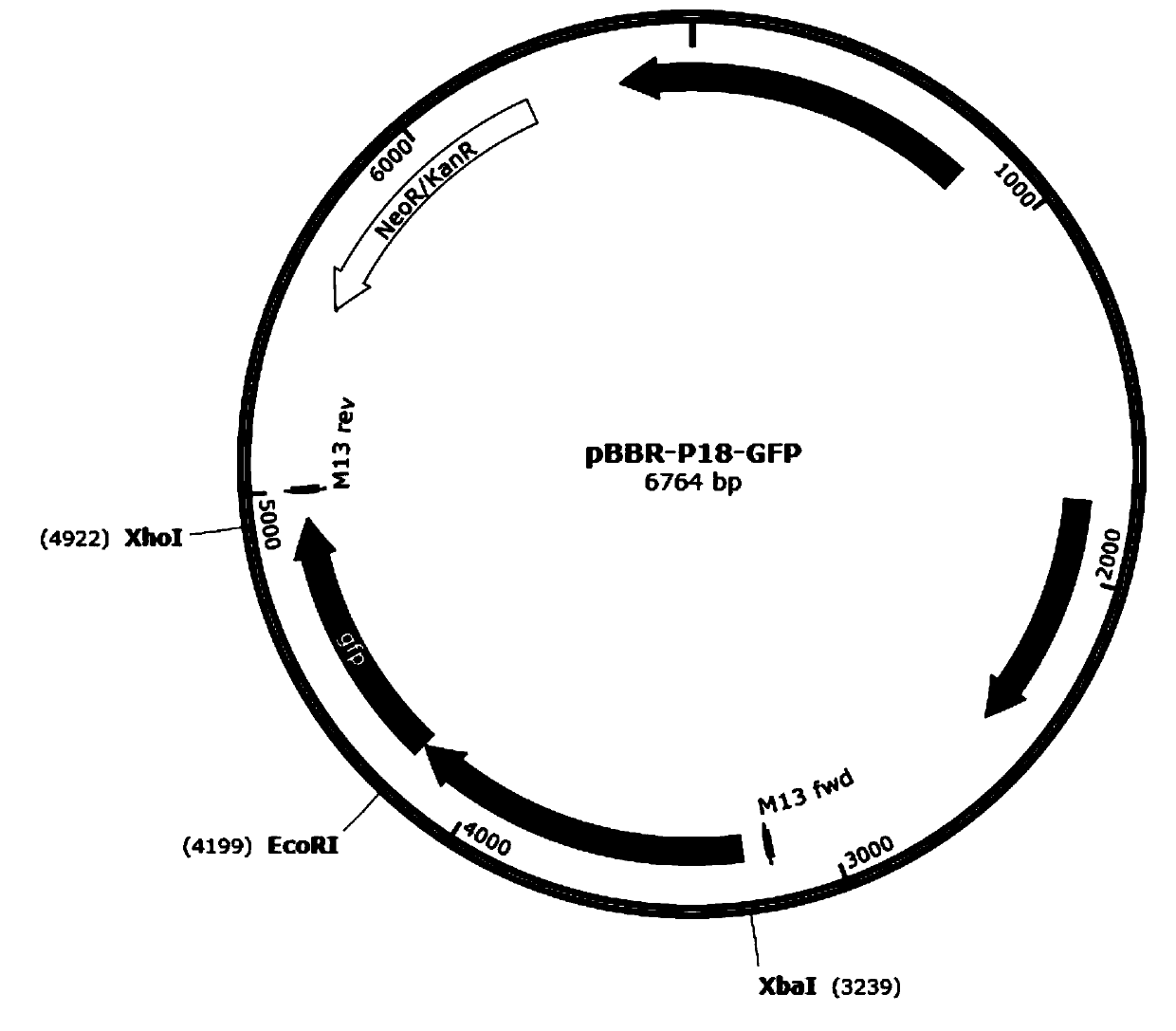
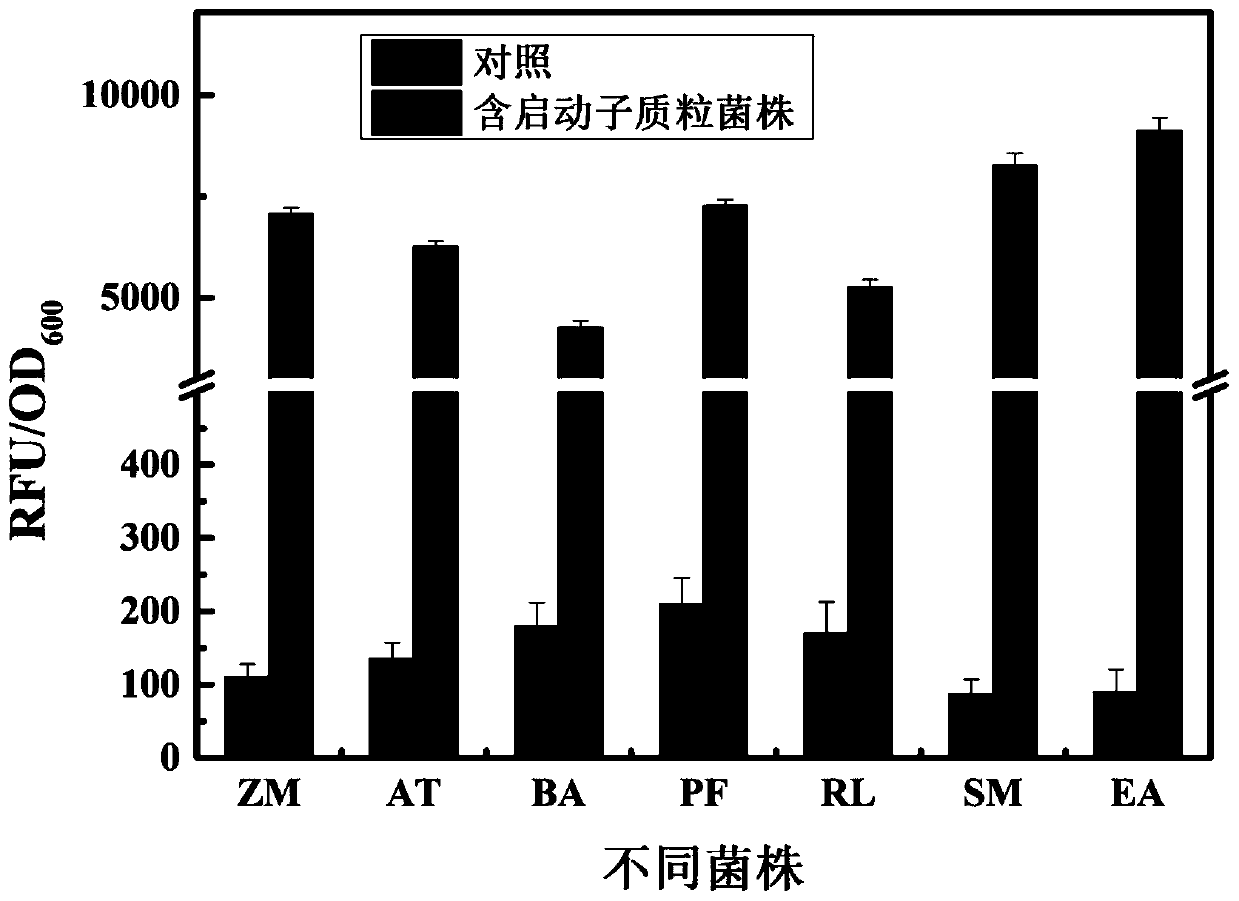
Strong promoter and plasmid vector containing strong promoter and application of strong promoter and plasmid vector
According to the invention, through amplifying a strong promoter in Ensifer adhaerens and carrying out bioinformatics analysis and functional verification, a strong promoter is obtained, and the strong promoter can be widely used for gene expression, genetic manipulation and strain improvement in Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosarum, Ensifer adhaerens and other alpha-proteobacteria and has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a genetic engineering strain by using the strong promoter, and an application of the corresponding strain and ahost cell in starting expression of a target gene.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
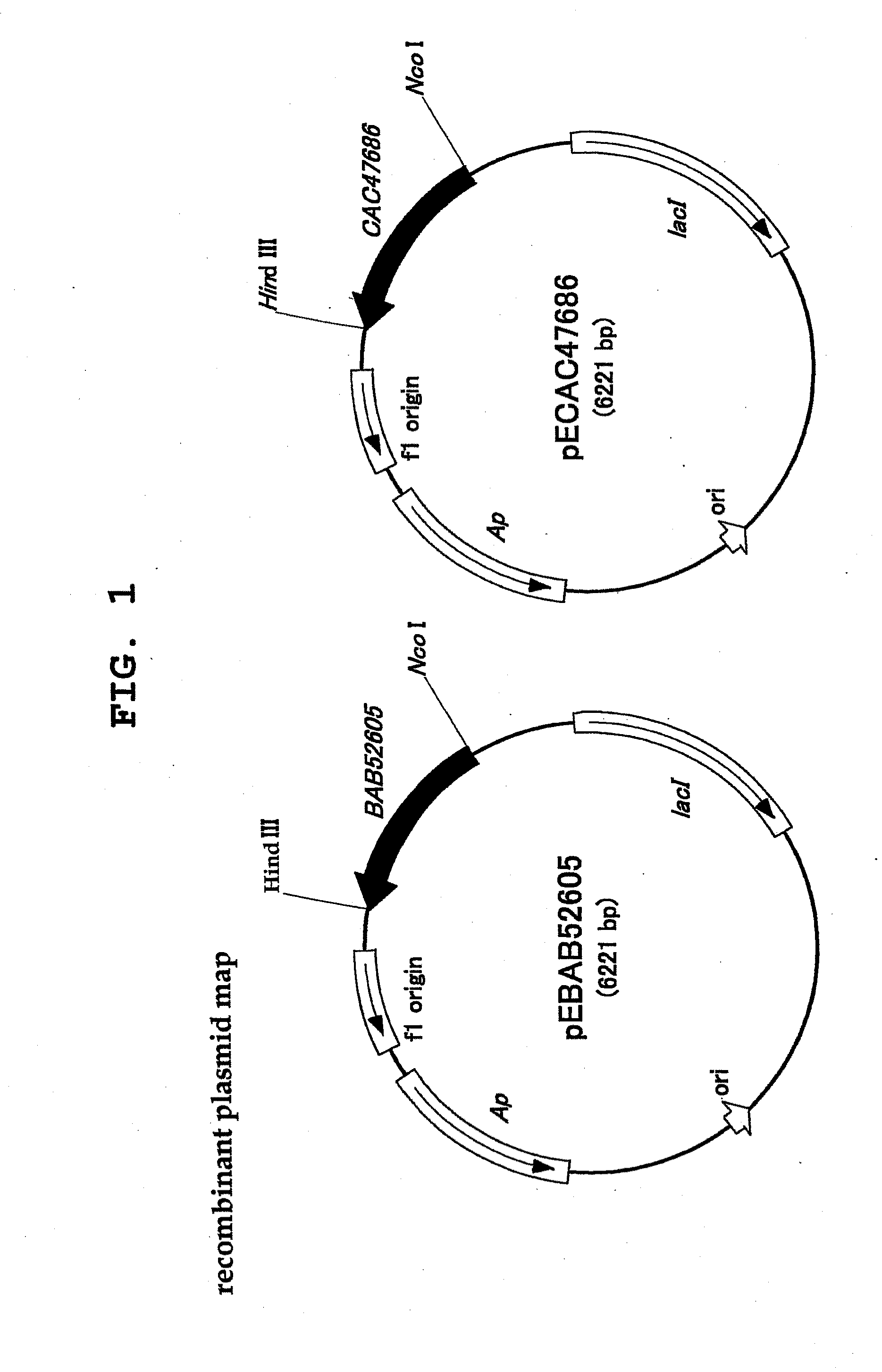
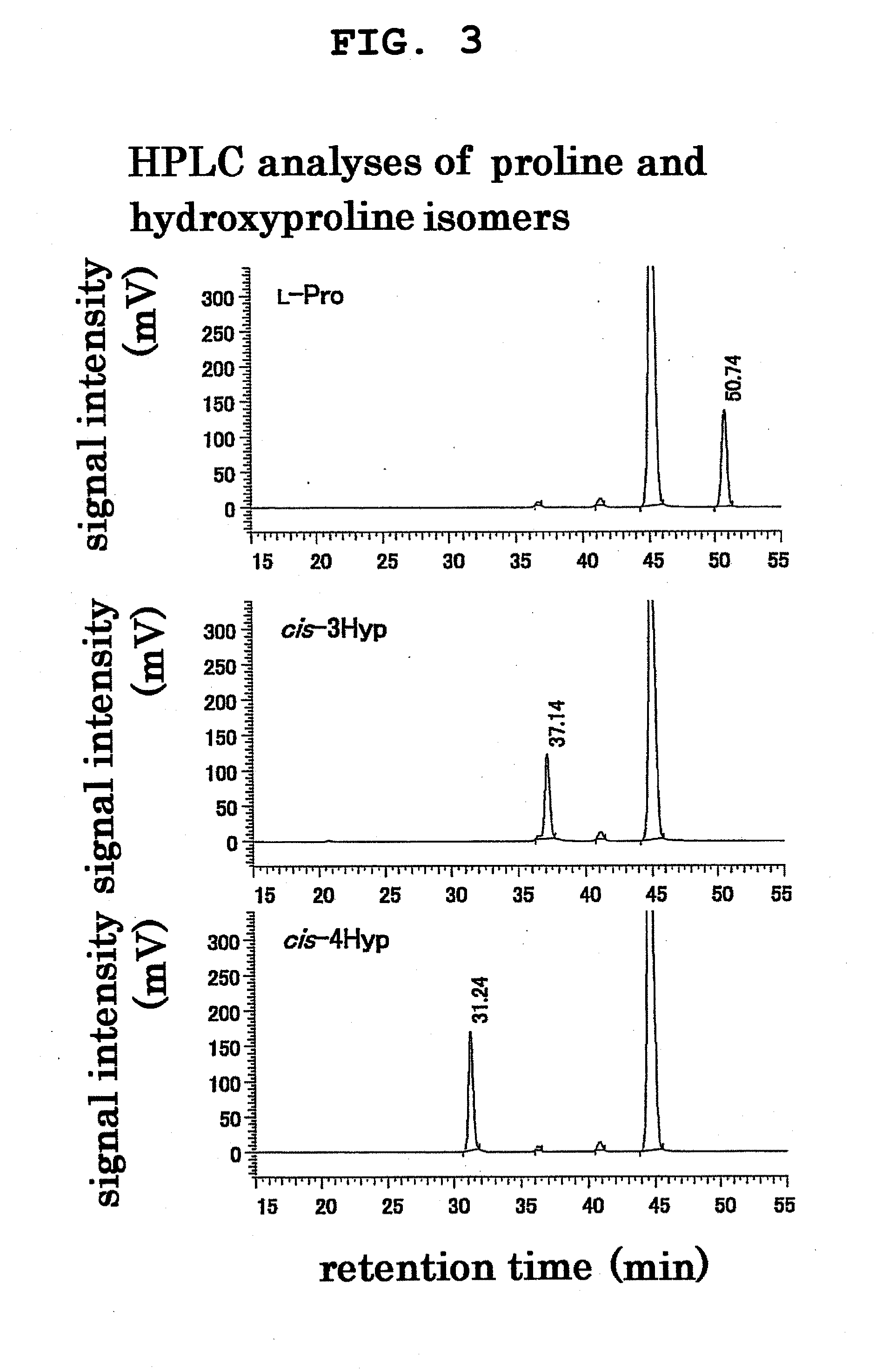
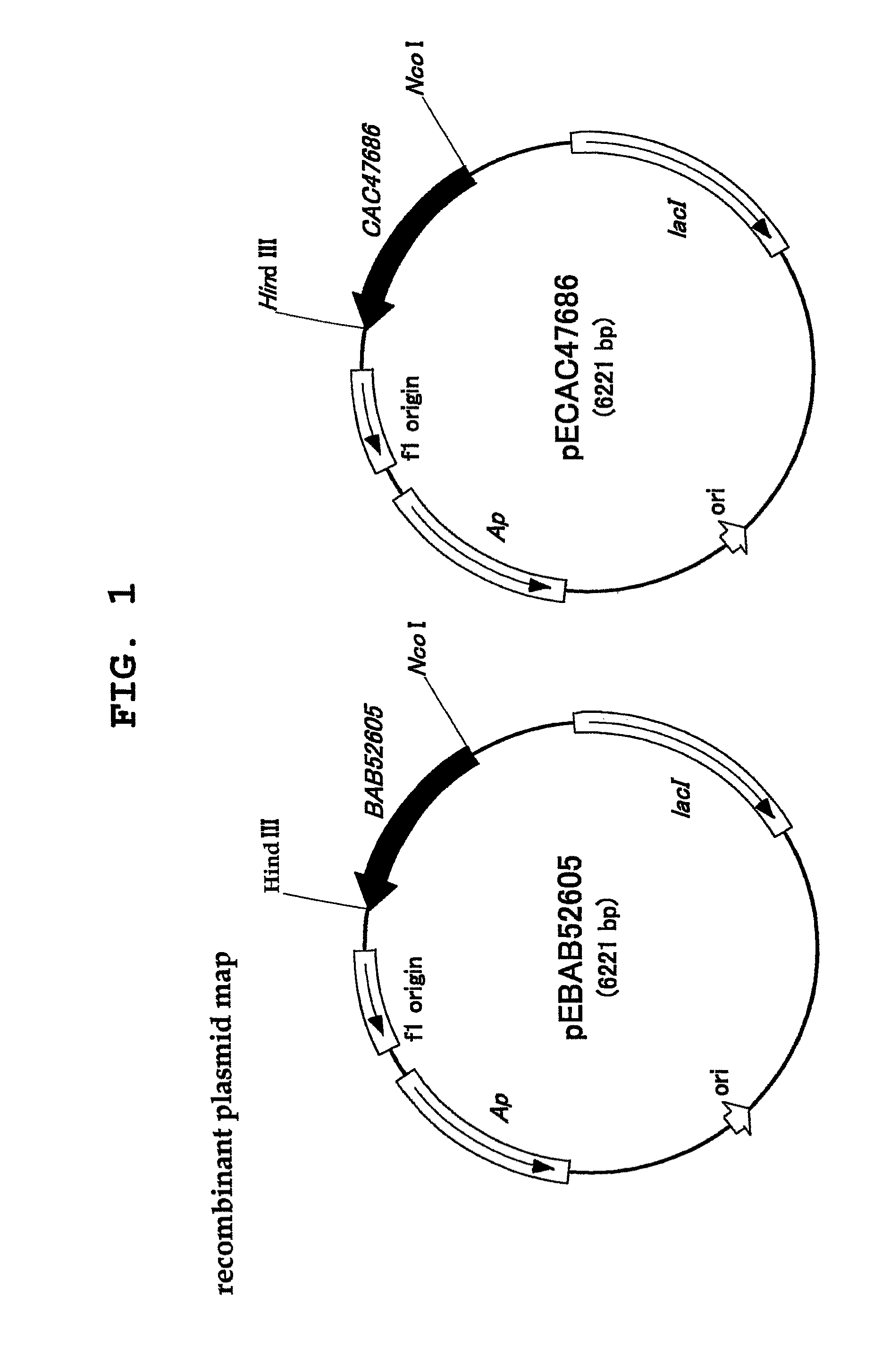
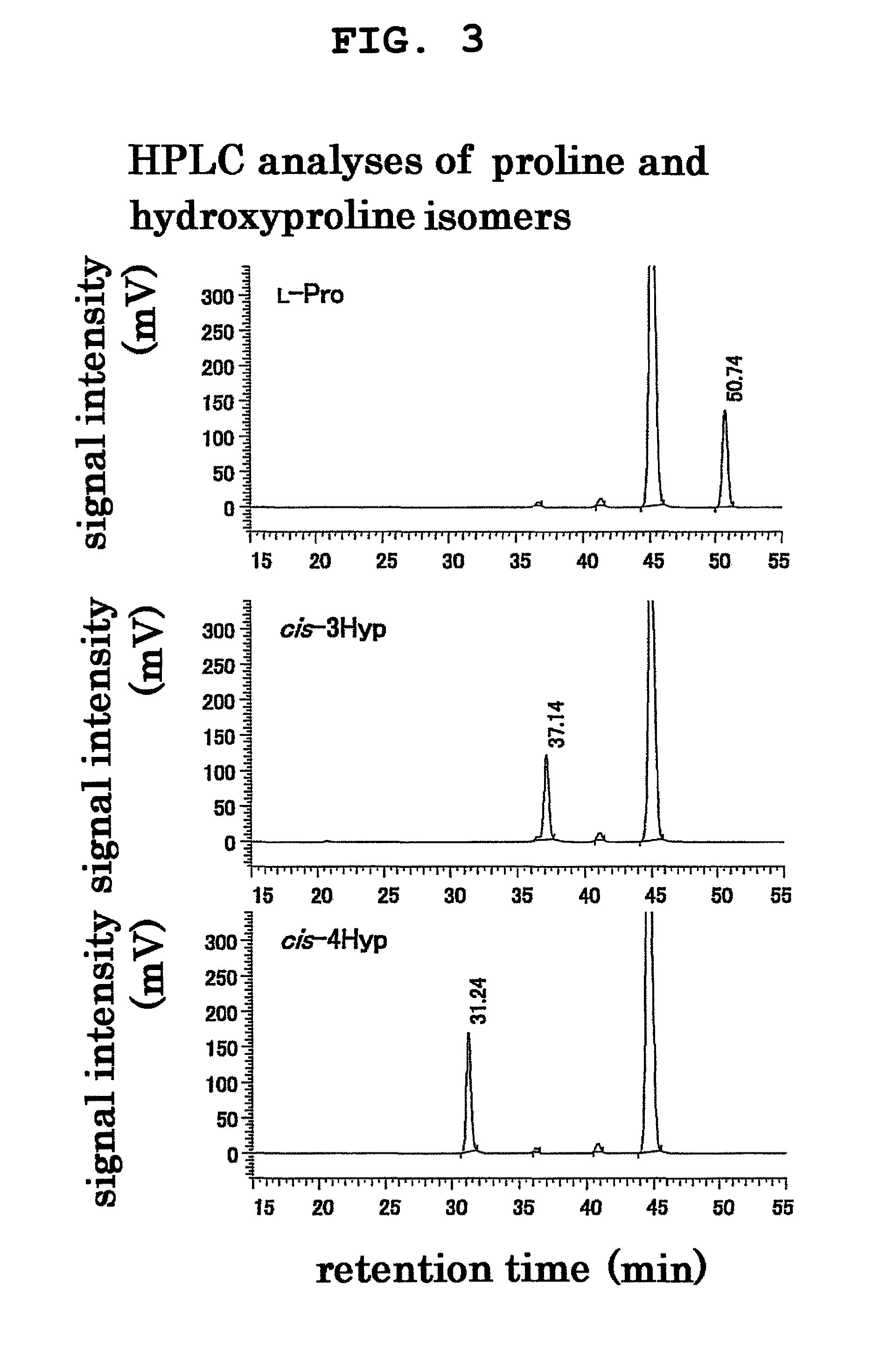
Process for production of cis-4-hydroxy-l-proline
Development of a method of economically and efficiently producing cis-4-hydroxy-L-proline. The present invention provides L-proline cis-4-hydroxylase. This enzyme may be derived from Lotus corniculatus rhizobia, Mesorhizobium loti or Medicago sativa rhizobia, Sinorhizobium meliloti. The present invention provides a method of producing cis-4-hydroxy-L-proline from L-proline by using this enzyme. The present invention provides a recombinant vector containing a polynucleotide encoding the enzyme and a transformant containing the vector.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO BIO CO LTD
Application of Sinorhizobium meliloti CCNWSX0020
ActiveCN104542714AIncrease biomassIncrease plant heightPlant growth regulatorsBiocideStress conditionsEnzyme system
The invention relates to application of Sinorhizobium meliloti CCNWSX0020, and particularly relates to application of Sinorhizobium meliloti CCNWSX0020 to improving response of antioxidant enzyme systems in plants to heavy metal. Under the excessive heavy metal stress condition, the Sinorhizobium meliloti CCNWSX0020 can be used for improving the biomass, plant height, total N content and heavy metal absorptive amount of plants to different extents. Meanwhile, the inventor finds that the Sinorhizobium meliloti CCNWSX0020 can be used for remarkably promoting the response of the antioxidant enzyme systems in plants under excessive heavy metal stress condition. A symbiotic nitrogen fixation system formed by the Sinorhizobium meliloti CCNWSX0020 and the host plant medicago lupulina has a certain application potential in the bioremediation of heavy metal polluted soil.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Sinorhizobium meliloti and method for applying same for fermenting to produce manganese peroxidase
ActiveCN102417890AWith industrial productionHigh biological nitrogen fixation activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyManganese peroxidase
The invention relates to sinorhizobium meliloti and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of microbial fermentation. The sinorhizobium meliloti J09 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with the number of CCTCC NO: M 2011318. A method for applying the strain for producing manganese peroxidase through liquid fermentation comprises the following steps of: (1) slant culture; (2) seed culture; and (3) liquid fermentation culture: inoculating the cultured seed into a fermentation medium with the inoculation rate of 1 percent to 2 percent, and culturing at 32-36 DEG C for 96-136 hours with the rotating speed of a table concentrator of 150rpm. The sinorhizobium meliloti provided by the invention has the advantages that: the CCTCC NO: M 2011318 has the capability of producing the manganese peroxidase and higher biological nitrogen fixation activity. Since the strain is used for producing manganese peroxidase through liquid fermentation, the advantages that the production period is short, the production cost is low, the growth conditions are easy to control, and the like are achieved, and the method has potential for industrialization production. At the same time, the high-efficient biological nitrogen fixation activity shows that the strain has the capabilities of improving soil fertility and promoting high yield of crops.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Salt-tolerant sinorhizobium meliloti NSM18 and special gene cluster thereof
InactiveCN101875940AExcellent nodulation nitrogen fixation abilityImprove salt toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGene clusterMicrobiology
The invention discloses salt-tolerant sinorhizobium meliloti NSM18 and a special gene cluster thereof. The gene cluster is expressed as a sequence 1 in a sequence table. The gene cluster is transferred to sinorhizobium meliloti to construct an engineering strain NSM18. Salt-tolerant experiments show that the engineering strain can tolerate the salt concentration conditions of 1.4mol / L NaCl, 1.5mol / L KCl and 0.6mol / L LiCl; and the engineering strain can be grown at the temperature of 42 DEG C, while a contrast cannot be grown, and the engineering strain shows high-temperature resistance. Moreover, apart from the advantages, the engineering strain NSM18 still keeps good nodulation and nitrogen fixation capabilities.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Microorganism soil conditioner for saline-alkali soil and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108410470ANo antagonistic effectImprove fertilityAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesHalobacterium jilantaienseAlkali soil
The invention discloses a microorganism soil conditioner for saline-alkali soil. The microorganism soil conditioner is formed by the following raw materials according to the parts by weight: 20-30 parts of ectothiorhodospirasp fermented liquid, 5-10 parts of halobacterium jilantaiense fermented liquid, 10-20 parts of lactobacillus plantarum fermented liquid, 10-15 parts of trichoderma viride fermented liquid, 5-10 parts of pseudomonas fluorescens fermented liquid, 5-10 parts of sinorhizobium meliloti fermented liquid, 20-30 parts of an organic fertilizer, 0.5-1 part of humic acid, and 0.5-1 part of Grondverbeteraar. In addition, the invention further provides a preparation method of the microorganism soil conditioner for the saline-alkali soil. The soil conditioner is capable of improvingthe soil physical and chemical properties of the saline-alkali soil, and creating a soil environment suitable for the crop growth, and improving the soil fertility and the overground part biomass thereof. In addition, the soil conditioner uses the pure biological raw materials, is green and environmental, and has no hazard to the soil and the environment.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABLE DEV IN AGRI CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Cultivation medium containing microbial growth promoting agents and application of cultivation medium in seedling raising of fruits and vegetables
PendingCN109258398AImprove resistance to pests and diseasesQuality improvementGrowth substratesCulture mediaPlant rootsGrowth promoting
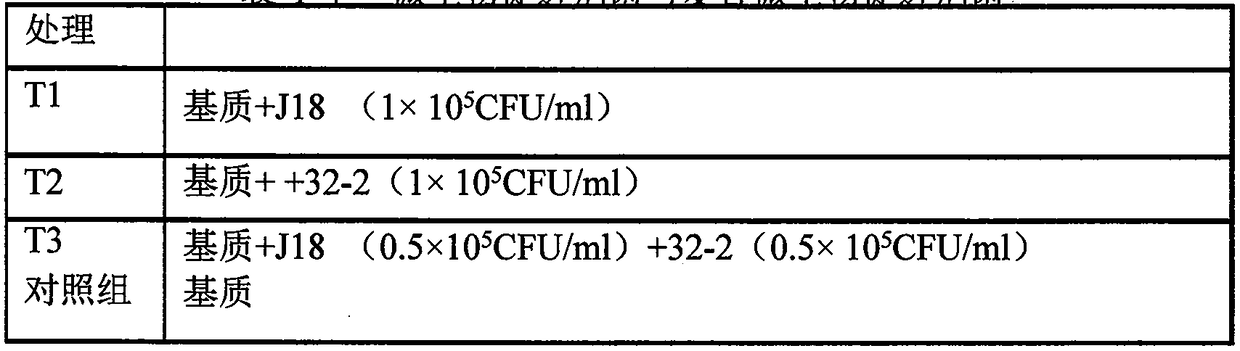
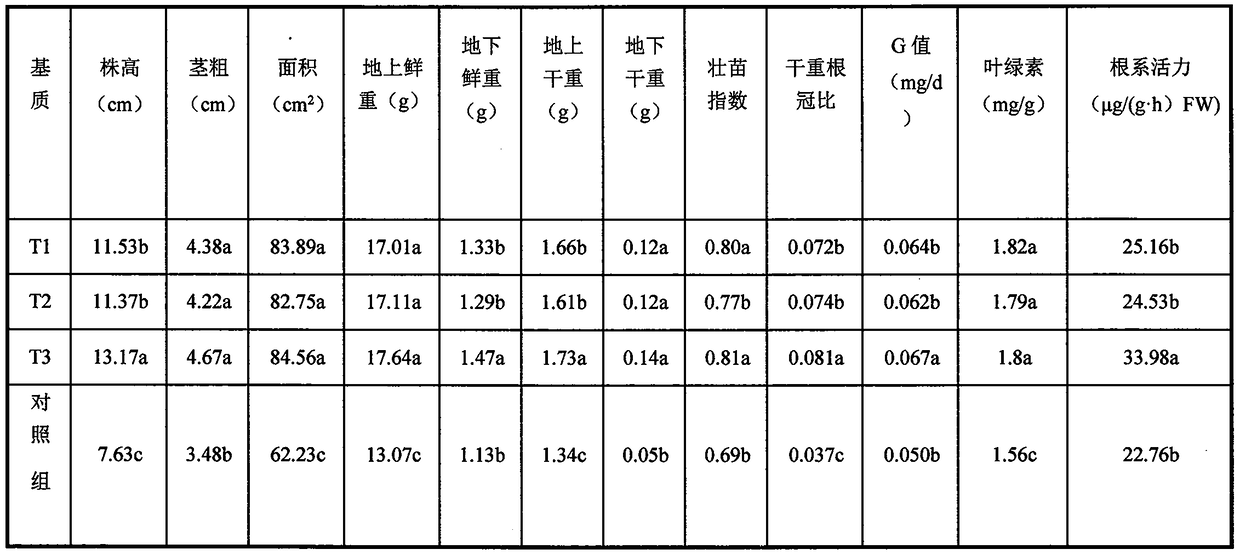
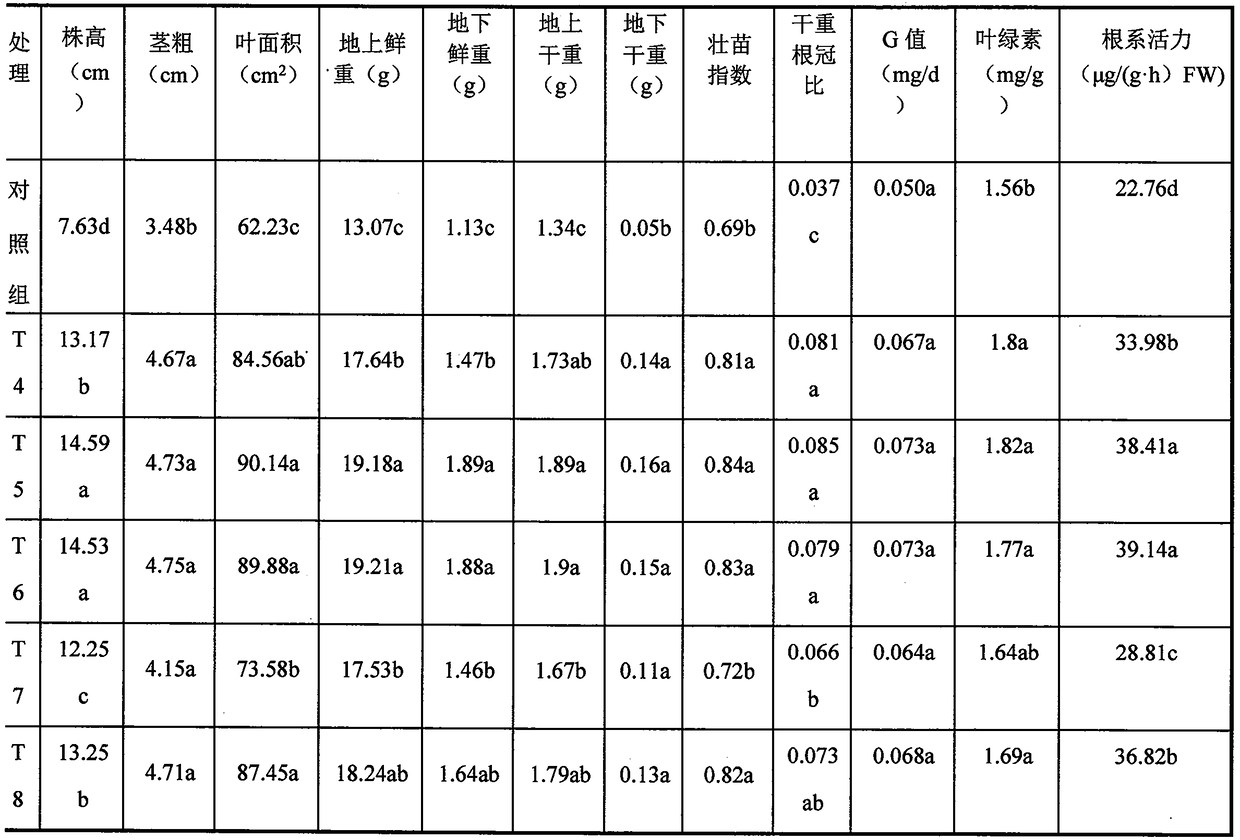
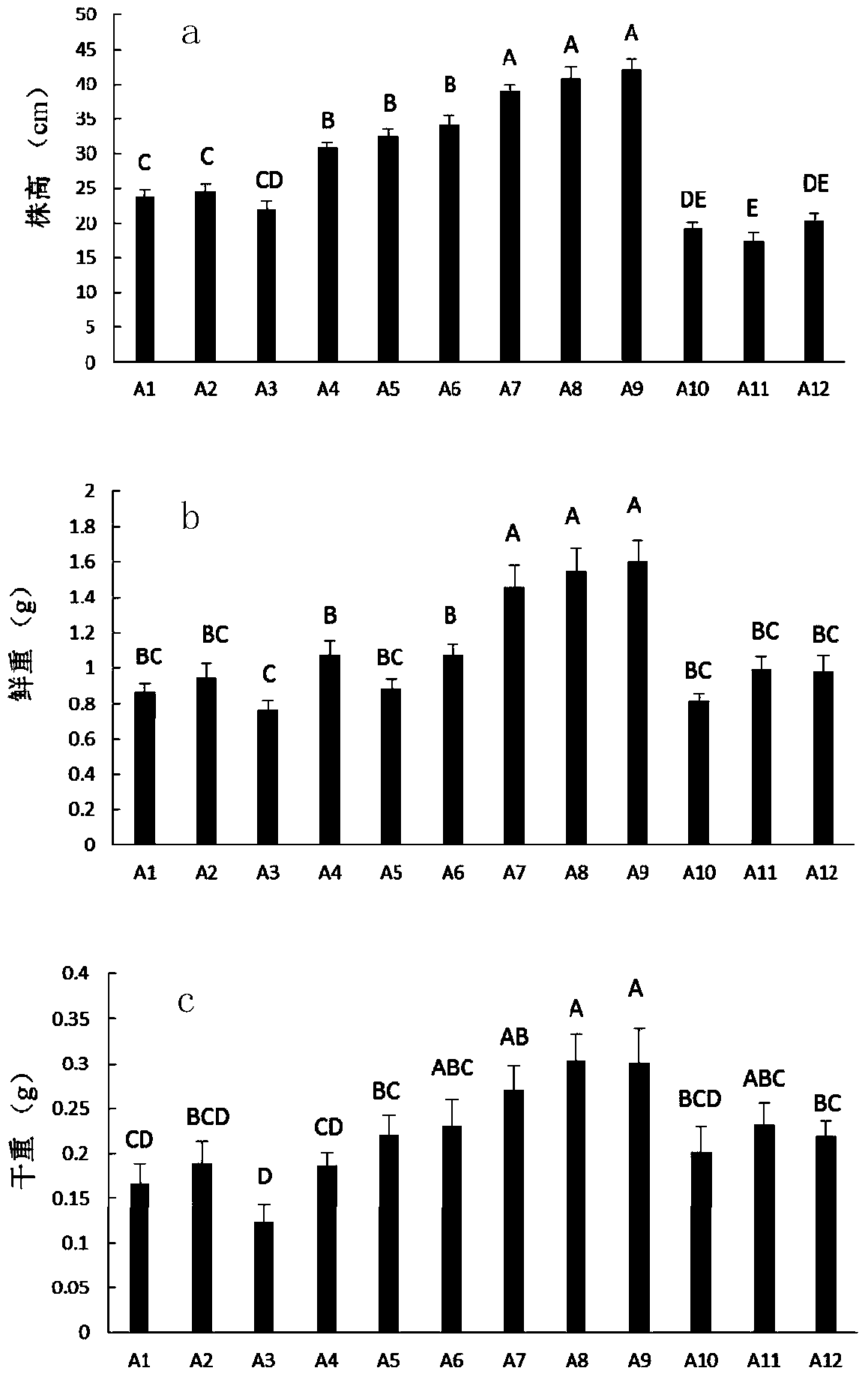
The invention discloses a cultivation medium containing microbial growth promoting agents and application of the cultivation medium in seedling raising of fruits and vegetables and belongs to the technical field of seedling cultivation. Bacillus subtilis J18 and Sinorhizobium meliloti 32-2 serving as the microbial growth promoting agents are added into the medium for seedling raising, the microbial growth promoting agents can quickly permeate into the medium and plant roots, not only can the capability of seedlings to resist pests and diseases be improved, but also the growth of seedling plants can be promoted, the quality of the seedlings can be improved, and meanwhile, application of the microbial growth promoting agents can reduce the use of chemical fertilizer.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF SCI
Alfalfa seed rhizobia seed coating agent and applications thereof
InactiveCN104387150AWide variety of sourcesSimple production processSuperphosphatesCalcareous fertilisersAdhesiveMass content
The present invention discloses an alfalfa seed rhizobia seed coating agent and a preparation method thereof. The alfalfa seed rhizobia seed coating agent of the present invention is prepared from raw materials containing a rhizobia agent, an adhesive and a substrate, wherein the rhizobia agent is formed by uniformly mixing a rhizobia liquid and a rhizobia adsorbent, the active ingredient of the rhizobia liquid is the Sinorhizobium meliloti, the mass content of ammonium molybdate in the rhizobia agent is 0.1-0.2%, and the ammonium molybdate content in 100 g of the rhizobia agent is (0.1-0.2) g and the Sinorhizobium meliloti content in 100 g of the rhizobia agent is more than or equal to 5*10<11> cfu according to the ratio of the ammonium molybdate in the rhizobia agent to the Sinorhizobium meliloti. According to the invention, the alfalfa rhizobia and the molybdenum with the optimal concentration are matched, and the skimmed milk is added to the adhesive as the protection agent, such that the prepared alfalfa seed pill coating agent has characteristics of rhizobia activity prolonging, plant nodulation and nitrogen-fixation promoting, substantial alfalfa yield increasing and alfalfa quality improving.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Rhizobium capable of degrading polychlorinated biphenyl and application thereof
ActiveCN103382446APromote degradationImprove degradation rateBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPolychlorinated biphenylPollution
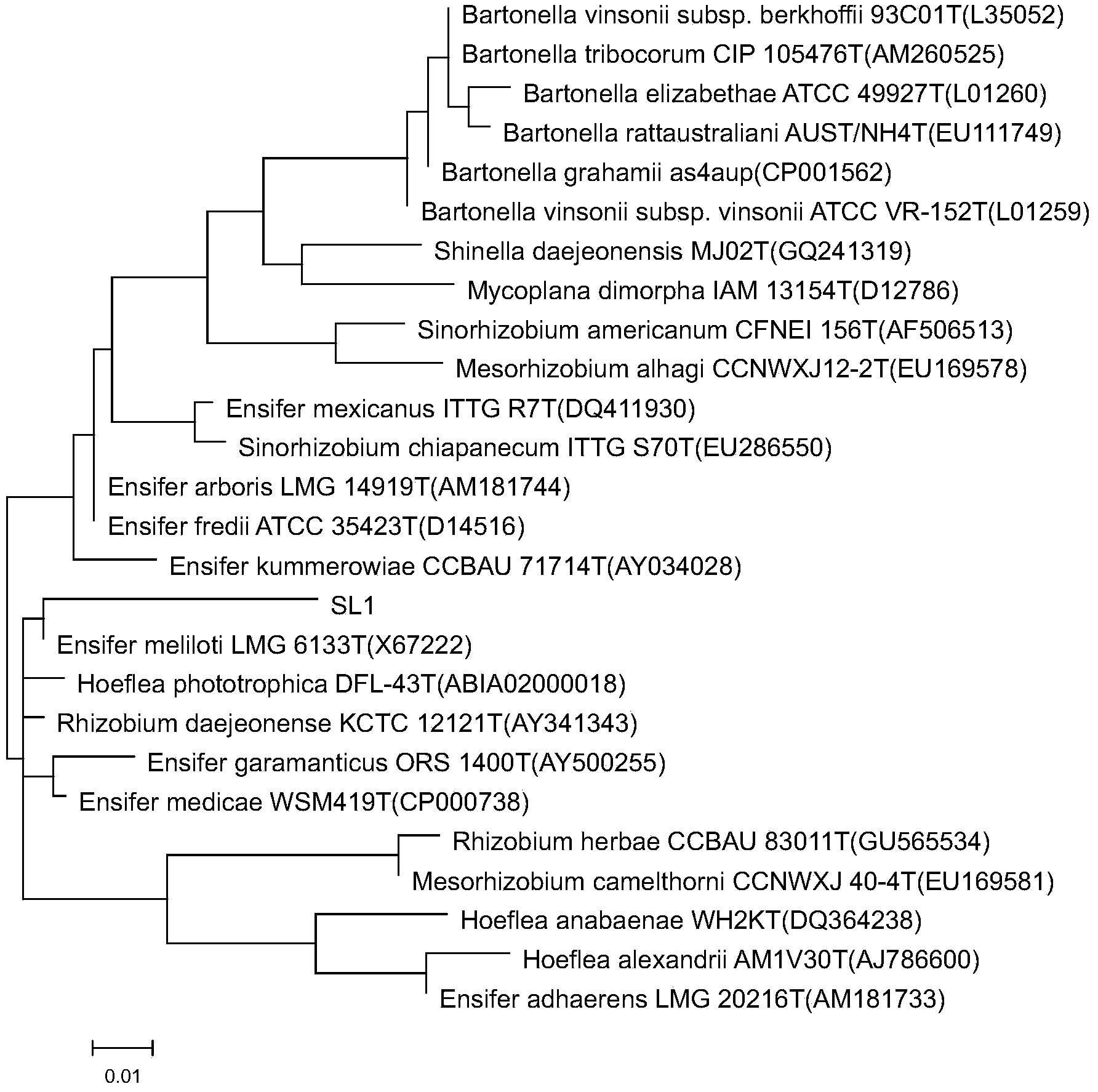
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism and relates to rhizobium capable of degrading polychlorinated biphenyl and an application thereof. Sinorhizobium melilon SL1 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, CGMCC on December, 10th, 2012. The collection number is CGMCC No.6962. The strain can grow by the utilization of polychlorinated biphenyl as the sole carbon source and energy, and has good capability of degrading both 2,4,4'-TCB and 3,3',4,4'-PCB under the condition of a shake flask in a laboratory. Degradation conditions are optimized, and the polychlorinated biphenyl degrading effect of the strain is further raised. The strain provides foundations for biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyl and water body pollution restoration.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
L-proline cis-4-hydroxylase and use thereof to produce cis-4-hydroxy-L-proline
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO BIO CO LTD
Sinorhizobium meliloti and application thereof
InactiveCN105543135ANodulation rate is highIncrease nodulation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobial agent
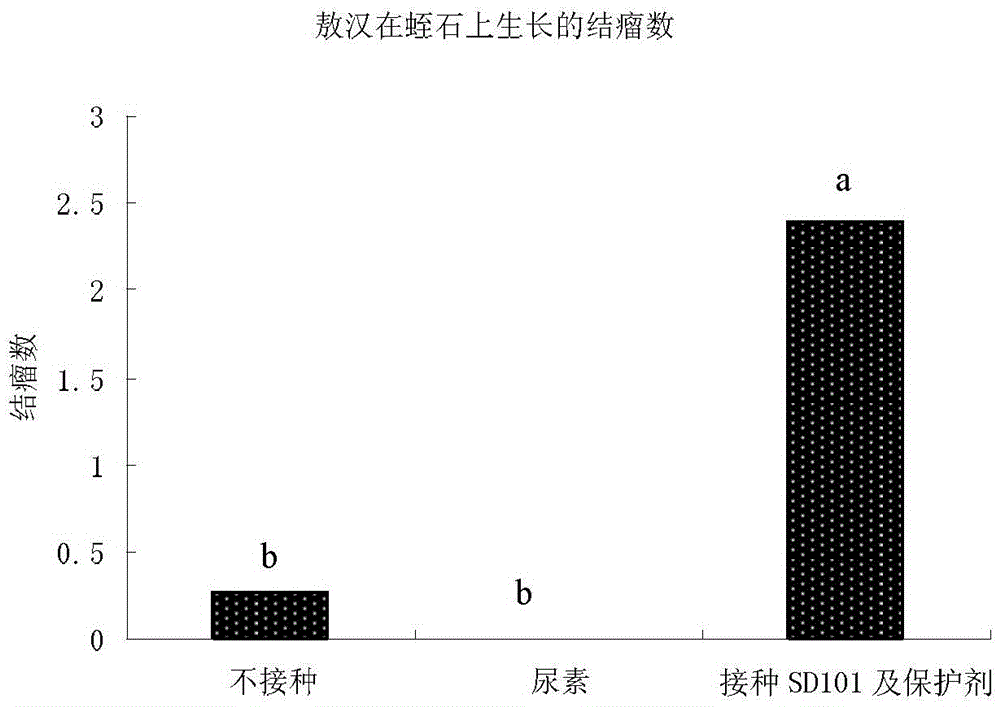
The invention discloses sinorhizobium meliloti and application thereof and belongs to the field of agricultural microorganism application. The sinorhizobium meliloti is preserved in the Common Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, the preservation number is CGMCC No. 11589, the preservation date is 25, November, 2015, and the preservation address is No. 3, courtyard 1, Beichen Rd, Chaoyang District, Beijing City. Through combined use of a sinorhizobium meliloti microbial agent and a protective agent, the nodulation rate and yield of domestic medicago sativa can be remarkably raised, and in particular, the nodulation rate of the domestic medicago sativa at the seedling stage is remarkably raised. Raising of the nodulation rate at the seedling stage shows that the sinorhizobium meliloti can enhance nodulation fixation rate and competitiveness of the inoculation microbial agent. Meanwhile, as the nodulation rate is raised, nitrogen fixation efficiency is also improved, and the plant height and yield are remarkably increased.
Owner:DAQING BRANCH OF HEILONGJIANG ACAD OF SCI
Alfalfa seed coating agent suitable for saline and alkaline land as well as preparation method thereof
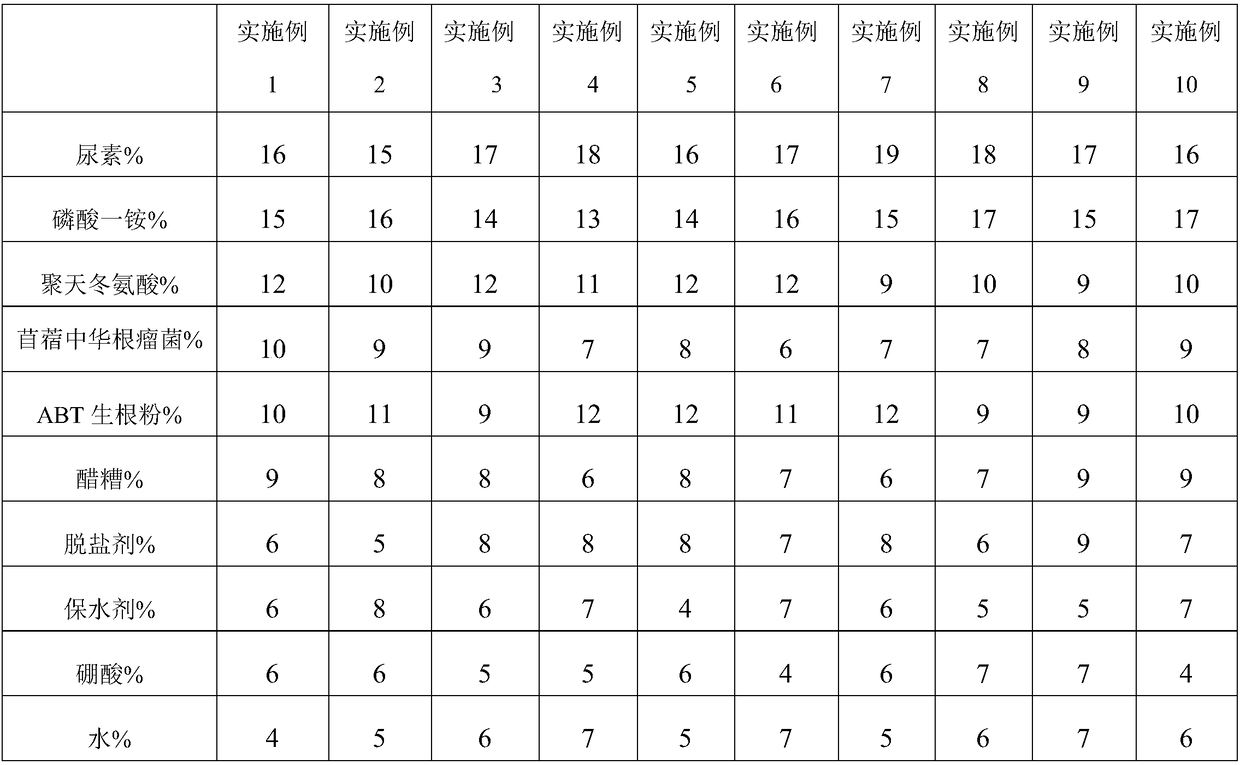
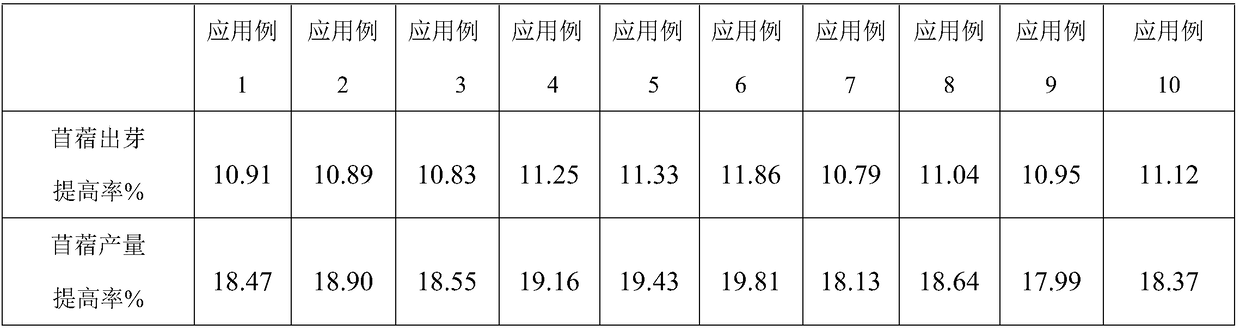
InactiveCN108129188AImprove germination rateIncrease productionAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersPhosphateBoric acid
The invention is suitable for the technical field of plant planting in saline and alkaline land, and provides an alfalfa seed coating agent suitable for the saline and alkaline land as well as a preparation method thereof. The coating agent comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 15 to 19 percent of urea, 13 to 17 percent of monoammonium phosphate, 9 to 12 percent of polyaspartic acid, 6 to 10 percent of sinorhizobium meliloti, 9 to 12 percent of ABT rooting powder, 6 to 9 percent of vinegar residues, 5 to 9 percent of a desalting agent, 4 to 8 percent of a water-retainingagent, 4 to 7 percent of boric acid, 4 to 7 percent of water, 2 to 4 percent of argil powder and 2 to 4 percent of talcum powder. Therefore, the invention provides the alfalfa seed coating agent for the saline and alkaline land, which can increase the germination rate of the alfalfa seeds and increase the yield of the alfalfa in the saline and alkaline land.
Owner:SHANDONG SHENGJING TOURISM DEV CO LTD
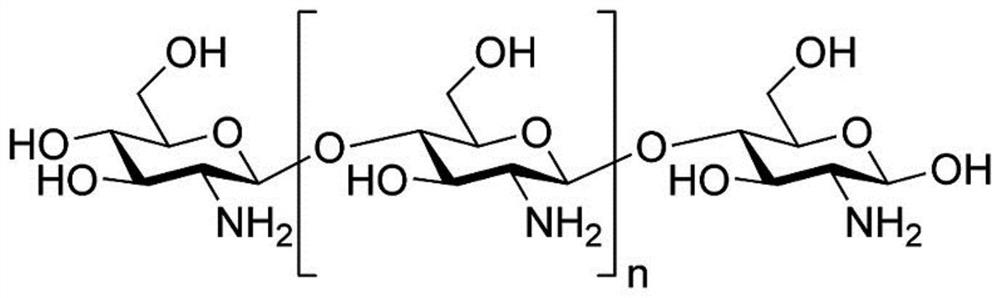
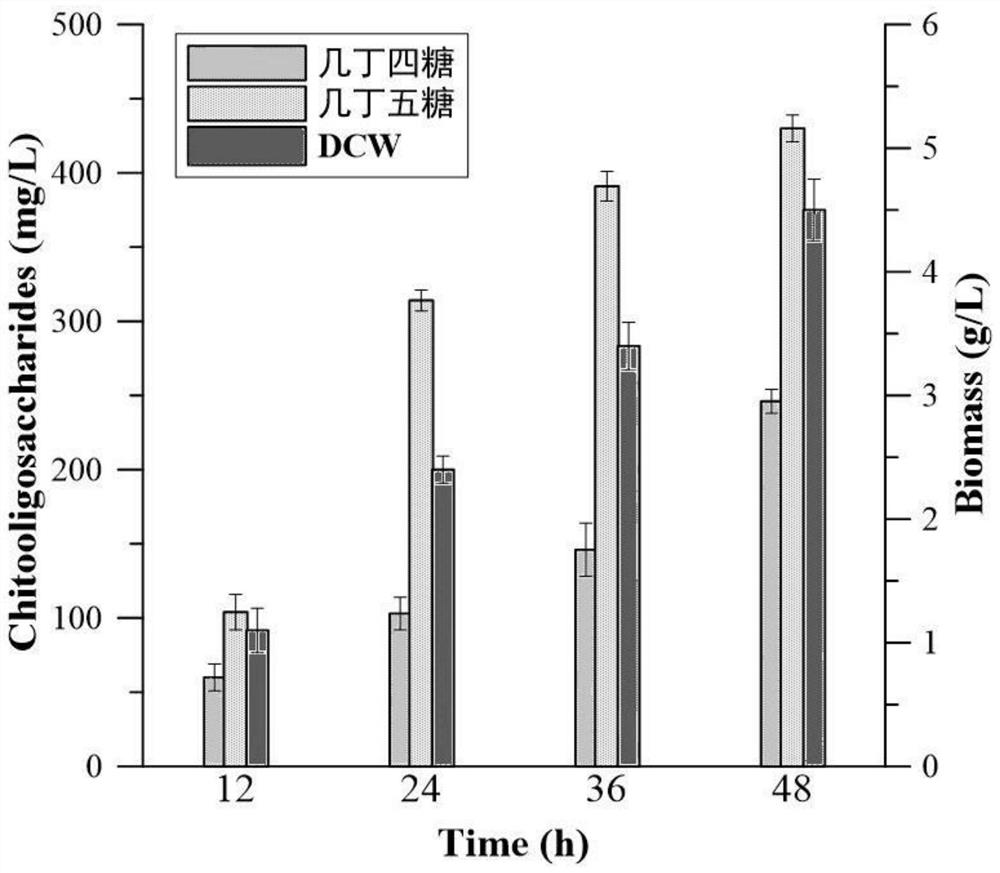
Codon-optimized N-acetylglucosamine transferase gene and application thereof
ActiveCN113528553AImprove the level ofBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideEngineered genetic
The invention discloses a codon-optimized N-acetylglucosamine transferase gene and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the invention, a Nodc gene from Sinorhizobium meliloti is taken as a starting sequence, the N-acetylglucosamine transferase is subjected to codon optimization according to codon preference of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and then is subjected to whole-gene synthesis, and a nucleotide sequence of the N-acetylglucosamine transferase is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. A recombinant vector is constructed aby using the codon-optimized N-acetylglucosamine transferase, and the recombinant vector is transferred into host bacillus amyloliquefaciens to obtain the genetically engineered bacterium capable of producing the chitosan oligosaccharide by fermentation. The concentration of the chitooligosaccharide in extracellular fermentation liquor of the genetically engineered bacterium reaches 676mg / L, and the contents of the chitotetraose and the chitopentaose are 246mg / L and 430mg / L respectively, so that a new fermentation process for extracellular synthesis of the chitooligosaccharide such as the chitotetraose and the chitopentaose can be realized by utilizing the recombinant strain.
Owner:YANGZHOU RIXING BIO TECH
Sinorhizobium meliloti with potassium-releasing function and application of sinorhizobium meliloti
ActiveCN104480048AShorten the production cycleLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPotassiumMicrobiology
The invention discloses sinorhizobium meliloti with a potassium-releasing function and an application of sinorhizobium meliloti. The sinorhizobium meliloti is a strain with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.8343 or is a direct passage culture of the strain. According to the strain, potassium-rich shale of the area can be dissociated into rapidly available potassium capable of being absorbed and utilized by plants, the production period of the strain can be greatly shortened, a large quantity of cost is saved, and the application prospect is very broad.
Owner:河北绿茵生化科技有限公司
Method for regenerating ATP using rationally designed enzyme
ActiveCN105624238ALow costComply with temperature requirementsTransferasesFermentationPhosphoric acidTetra
The invention relates to a method for regenerating ATP using a rationally designed enzyme. Through rational design after sequence alignment, polyphosphate kinase from sinorhizobium meliloti is mutated and heterologously expressed; and under the catalysis of the polyphosphate kinase, the regeneration of ATP is realized by adopting polyphosphate with low polymerization degree as a phosphoric acid donor. Compared with existing ATP regeneration method, the polyphosphate kinase used in the invention is a normal-temperature enzyme which can react for coupling with multiple enzymes; the enzyme can take tetra-polyphosphate as a phosphoric acid donor; compared with phosphoric acid with high polymerization rate, the tetra-polyphosphoric acid is more common and easily available; and the feasibility of ATP regeneration is increased on the basis of simplifying the ATP regeneration process, and the cost of ATP regeneration is reduced. The activity of PPK enzyme is not inhibited by the polyphosphate concentration, and industrial large-scale production is possible.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Virulence-Associated Adhesins
InactiveUS20070274994A1Inhibition of attachmentLower Level RequirementsAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntigenVirulent characteristics
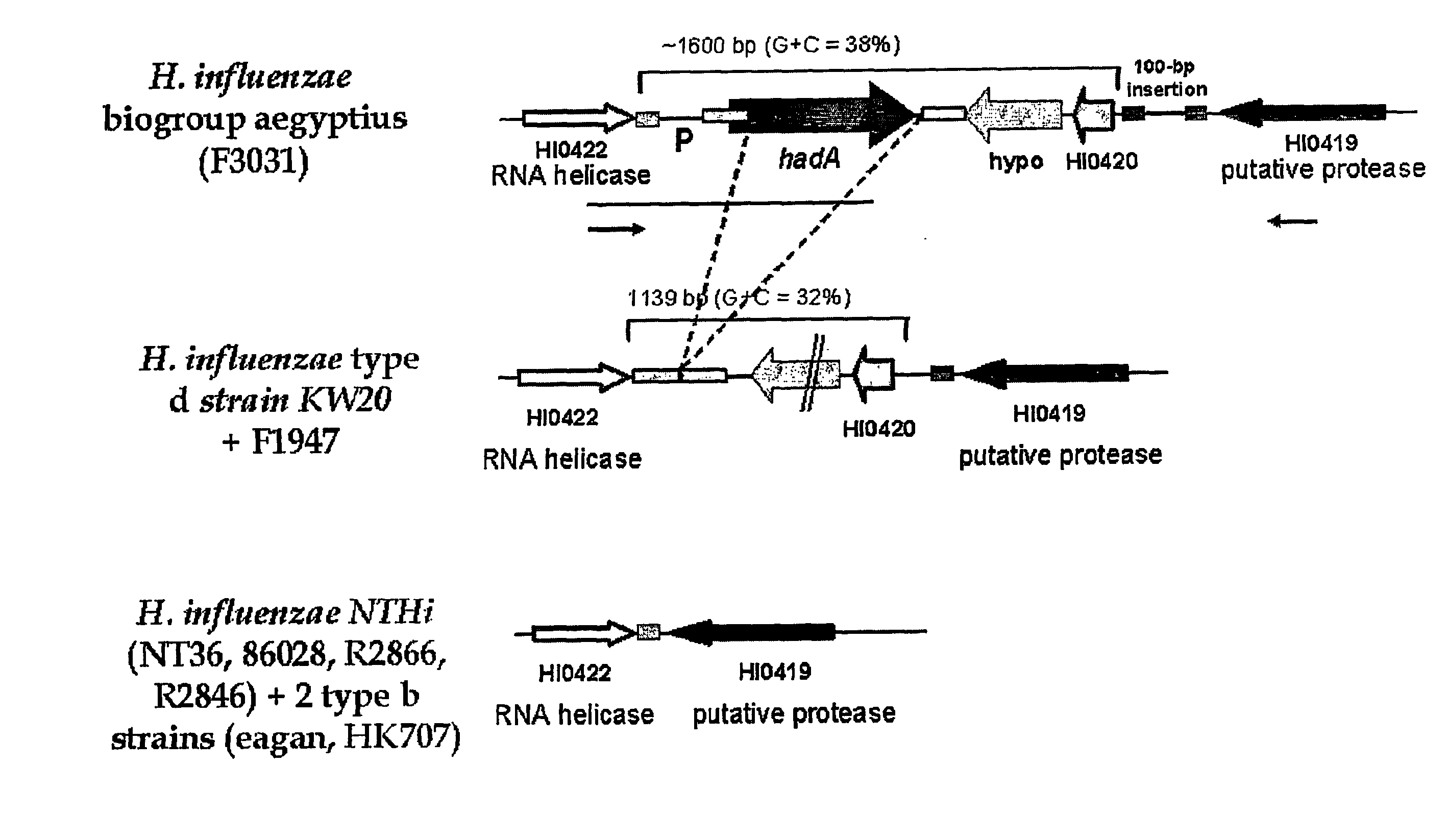
Virulence-associated antigens involved in adhesin have been identified in several organisms: Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius; Escherichia coli K1; EHEC E.coli; Actinobacillus actinomycetencomitans; Haemophilus somnus; Haemophilus ducreyi; EPEC E.coli; EA EC E.coli; uropathogenic E.coli; Shigella flexneri; Brucella melitensis; Brucella suis; Ralstonia solanacearum; Sinorhizobium meliloti; Bradorhizobium japonicum; and Burkholderia fungorum. Although the degree of sequence identity between the adhesins is low, they share a common arrangement of domains from N-terminus to C-terminus, namely: a leader peptide; a globular head; a coiled-coil region; and a transmembrane anchor region.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Strong promoter and application thereof in vitamin B<12>-producing strains
The invention provides a strong promoter and application thereof in vitamin B<12>-producing strains. According to the invention, a strong promoter in Ensifer adhaerens is amplified; bioinformatics analysis and functional verification are carried out to obtain the strong promoter which can be widely applied to the vitamin B<12>-producing strains such as Sinorhizobium meliloti, Pseudomonas denitrificans and Ensifer adhaerens for gene expression, genetic gene operation and strain improvement, and the nucleotide sequence of the obtained strong promoter is SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a gene engineering strain by using the promoter and a corresponding strain thereof, and application of a host cell in promoting expression of a target gene.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
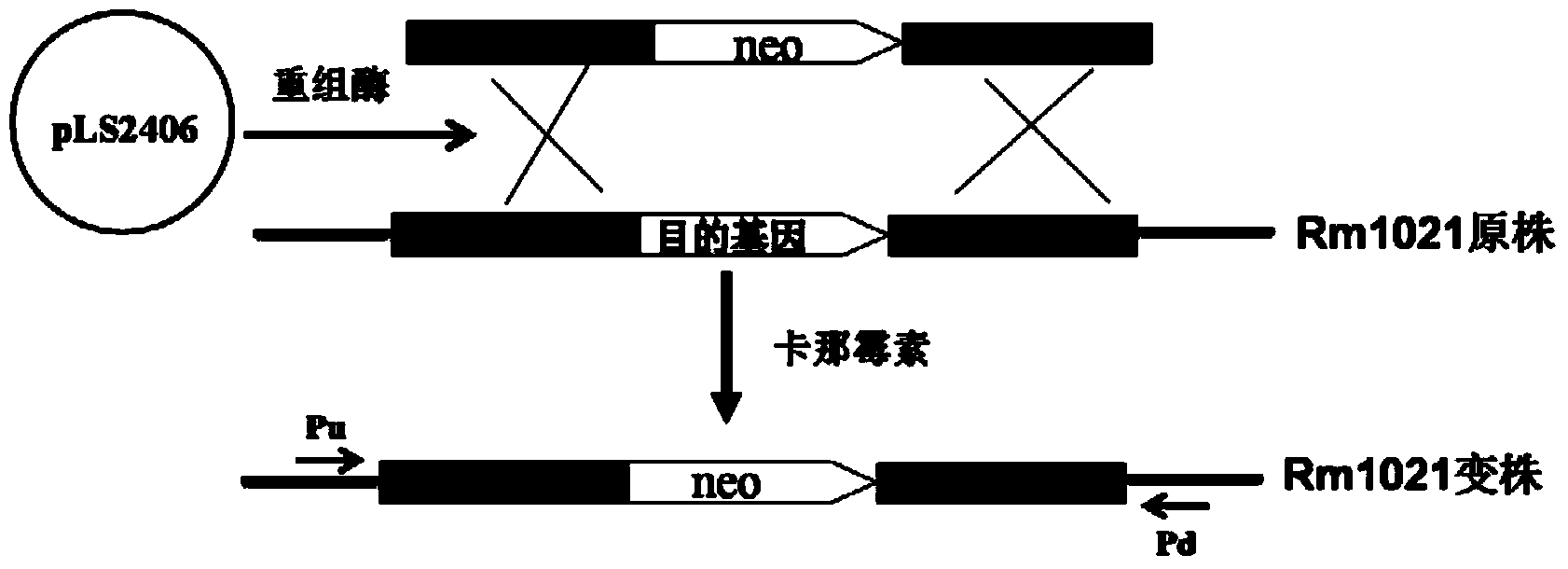
Re-engineering mediated sinorhizobium meliloti Rm1021 gene knockout method
The invention relates to a re-engineering mediated sinorhizobium meliloti Rm1021 gene knockout method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out amplification via chain reactions of overlapping-extending polymerases so as to obtain homologous fragments which have about 500bp and aim at genes to be knocked out at two sides and a combined DNA fragment of kanamycin resistance genes at the middle; secondly, electrically converting the DNA fragment into a cell Rm1021 expressed by recombinase induced by isopropyl-Beta-D-sulfo-galactoside; replacing target genes with the kanamycin resistance genes under the kanamycin resistance screening so as to obtain a gene knockout mutation strain; and finally, culturing the strain in a solid culture medium containing 0.4% of saccharose so as to eliminate plasmids containing recombinase genes. The adopted ecombinase genes are derived from Lambda phages and cloned on plasmids pLS2406. Meanwhile, the plasmids pLS2406 contain negative-screening marked sacB genes.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
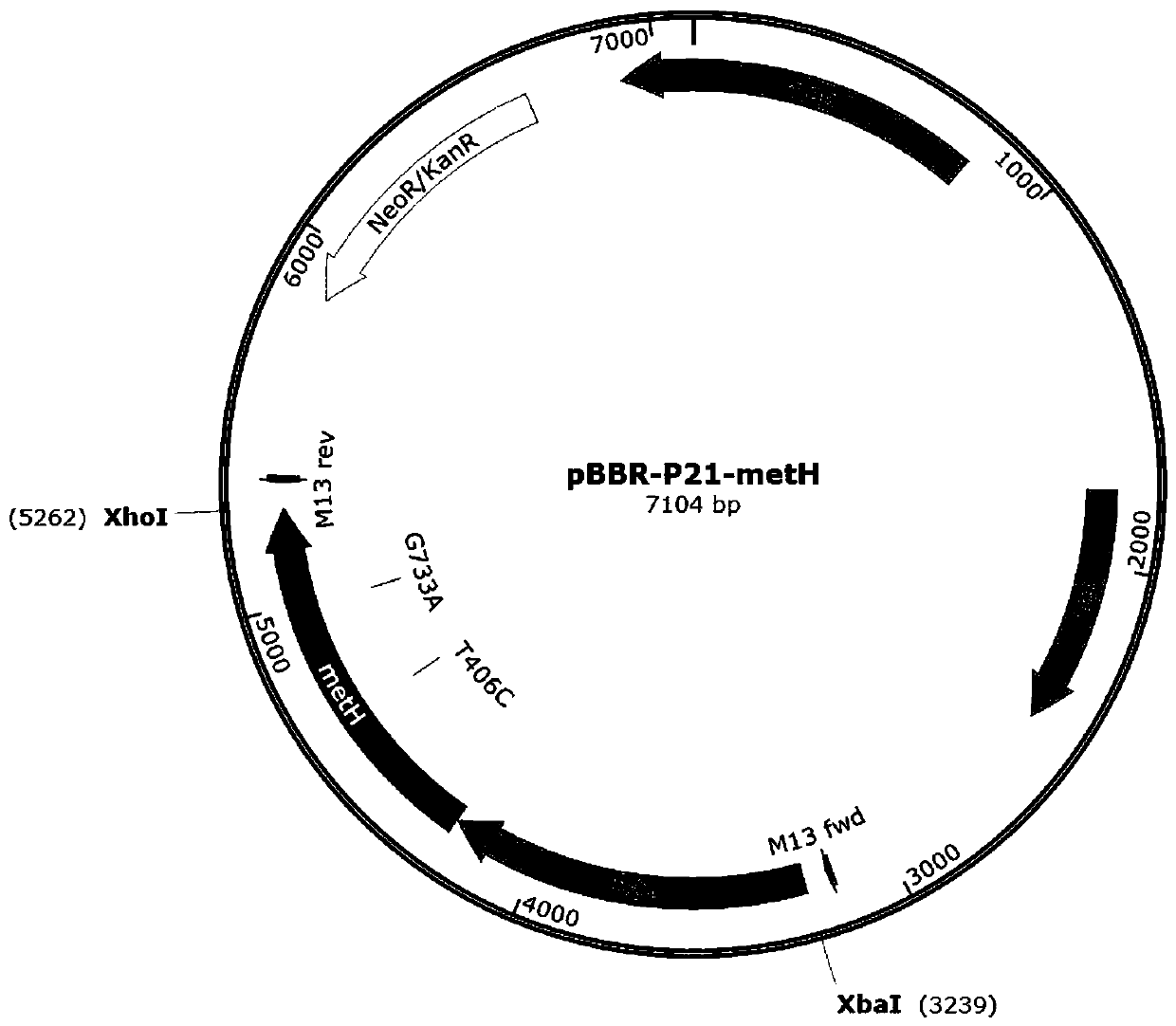
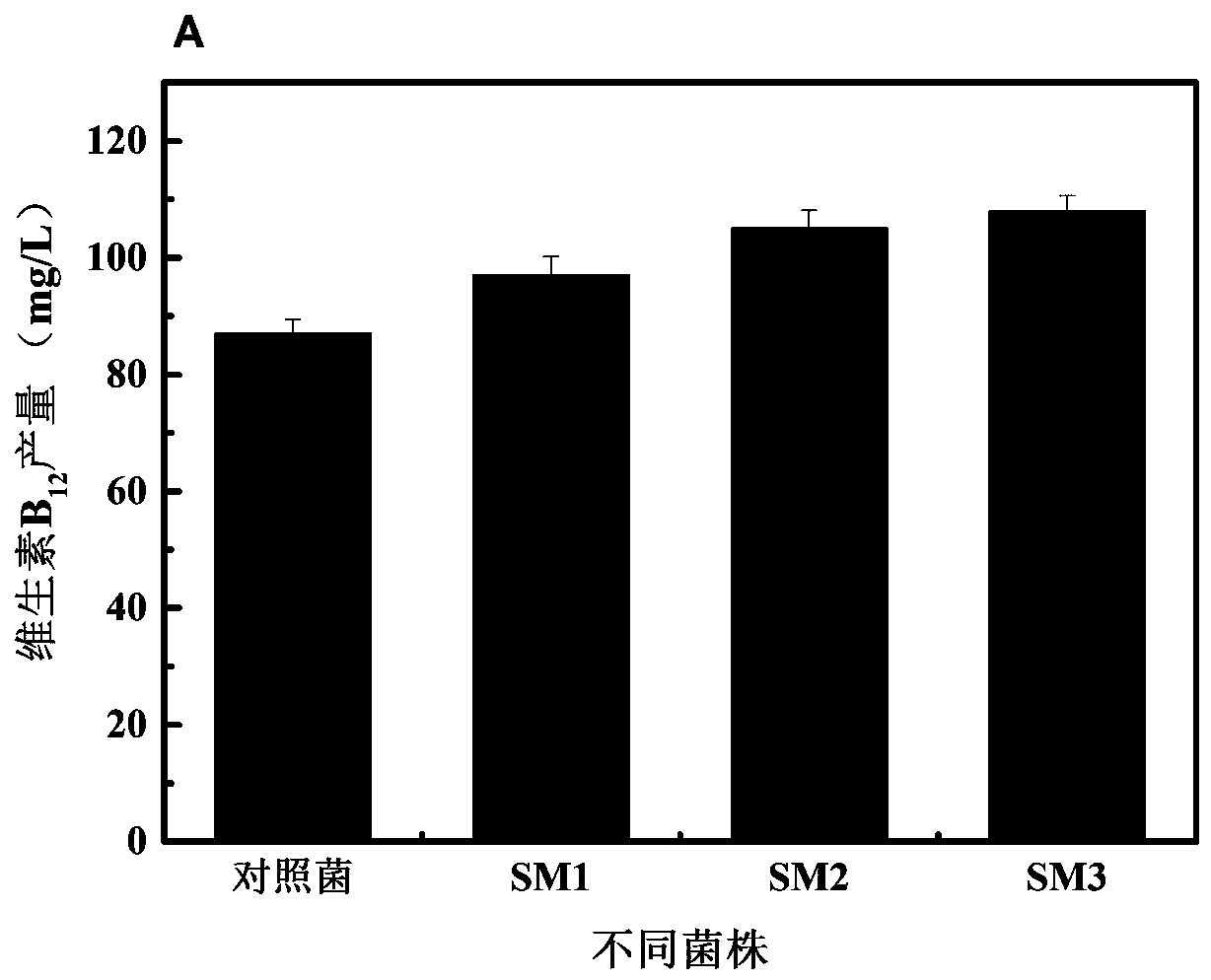
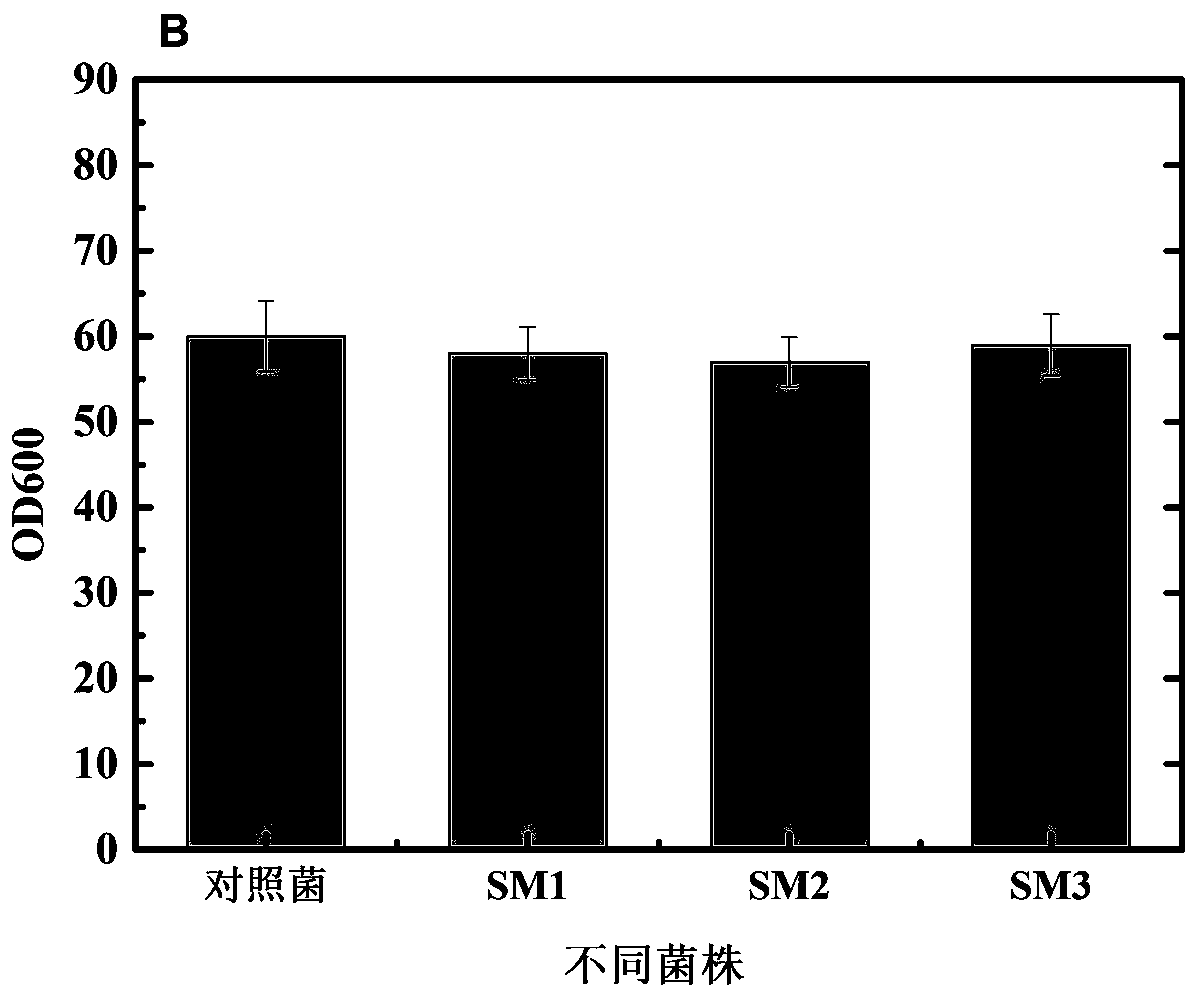
Methionine synthetase mutant, mutant gene and application of methionine synthetase mutant and mutant gene in preparation of vitamin B12
The invention discloses a methionine synthetase mutant, a mutant gene and an application of the methionine synthetase mutant and the mutant gene in preparation of vitamin B12. Overexpressed genetic engineering strains of a methionine synthetase gene and a mutant gene in Sinorhizobium meliloti have greatly-improved vitamin B12 producing capability, scarcely have influence on biomass during fermentation culture and have relatively high application and popularization values.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Alfalfa Seed Rhizobium Seed Coating Agent and Its Application
InactiveCN104387150BWide variety of sourcesSimple production processCalcareous fertilisersSuperphosphatesAdhesiveBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention discloses an alfalfa seed rhizobia seed coating agent and a preparation method thereof. The alfalfa seed rhizobia seed coating agent of the present invention is prepared from raw materials containing a rhizobia agent, an adhesive and a substrate, wherein the rhizobia agent is formed by uniformly mixing a rhizobia liquid and a rhizobia adsorbent, the active ingredient of the rhizobia liquid is the Sinorhizobium meliloti, the mass content of ammonium molybdate in the rhizobia agent is 0.1-0.2%, and the ammonium molybdate content in 100 g of the rhizobia agent is (0.1-0.2) g and the Sinorhizobium meliloti content in 100 g of the rhizobia agent is more than or equal to 5*10<11> cfu according to the ratio of the ammonium molybdate in the rhizobia agent to the Sinorhizobium meliloti. According to the invention, the alfalfa rhizobia and the molybdenum with the optimal concentration are matched, and the skimmed milk is added to the adhesive as the protection agent, such that the prepared alfalfa seed pill coating agent has characteristics of rhizobia activity prolonging, plant nodulation and nitrogen-fixation promoting, substantial alfalfa yield increasing and alfalfa quality improving.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Promoter report gene for detecting superoxide radical ions in nodules and application thereof
InactiveCN109136223AIntuitive detection distributionIntuitive detectionOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionRoot noduleSinorhizobium meliloti
The invention relates to a promoter reporter gene for detecting superoxide radical ions in nodules and an application thereof. The promoter reporter gene is a base sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1. A sodB promoter and a reporter gene uidA fusion plasmid are constructed for the first time, and can be directly transferred into the sinorhizobium meliloti strain to directly detect the distribution and the intensity condition of the superoxide ions in the nodule.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Strong promoter from ensifer adhaerens as well as plasmid vector and application of strong promoter
The invention discloses a strong promoter from ensifer adhaerens as well as a plasmid vector and an application of the strong promoter. Function verification is performed by amplifying one strong promoter in ensifer adhaerens, and the strong promoter which can be widely applied to gene expression, gene operation and strain improvement of alpha-proteobacteria such as sinorhizobium meliloti, zymomonas mobilis, caulobacter crescentus, pseudomonas denitrificans, agrobacterium tumefaciens, brucella abortus, pseudomonas fluorescens, rhizobium leguminosarum and ensifer adhaerens is obtained and has the nucleotide sequence being SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also relates to the plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a gene engineering strain by use of the promoter, the corresponding strain and an application of a host cell in starting target gene expression.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
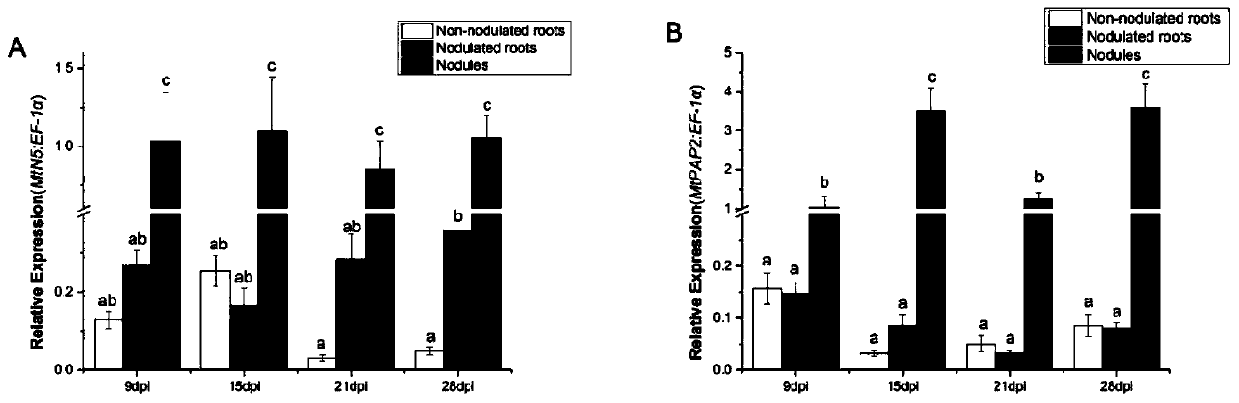
Study method of functions of acid phosphatase in symbiosis of alfalfa root nodules and alfalfa mycorrhiza
ActiveCN111066593AHigh expressionHigh infection ratePlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsBiotechnologyArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
The invention discloses a study method of functions of acid phosphatase in symbiosis of alfalfa root nodules and alfalfa mycorrhiza, and belongs to the field of studies on legumes. The study method ofthe functions of the acid phosphatase in the symbiosis of the alfalfa root nodules and the alfalfa mycorrhiza comprises the following steps: 1) selecting medicago truncatula seeds, and carrying out surface sterilizing, forced germinating and sprouting; 2) respectively inoculating the sprouted medicago truncatula with sinorhizobium meliloti and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, and carrying out separate pot experiments at different phosphorus concentrations; 3) detecting tissue-specific expression of MtPAP2 in the alfalfa root nodules, tissue-specific expression of MtPAP2 in the alfalfa mycorrhiza, influence of the phosphorus on MtPAP2 gene expression, influence of the phosphorus on the alfalfa root nodules and influence of the phosphorus on the alfalfa mycorrhiza; and 4) studying the roles ofthe sinorhizobium meliloti and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the symbiosis with the alfalfa by utilizing spatiotemporal expression, promoter localization, overexpression and silencing means. Thus, direct experimental evidence is obtained to provide new insights on molecular mechanisms of plant response to low phosphorus stress and coordination of phosphorus homeostasis in the plants by themselves.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Xylose-induced promoter and plasmid vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a xylose-induced promoter. By amplifying a xylose-induced promoter in sinorhizobium meliloti, bioinformatics analysis and function verification are carried out, the xylose-induced promoter which can be widely applied to gene expression, genetic gene operation and strain improvement in alpha-proteobacteria such as Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosarum and Sinorhizobium adhaerens is obtained, and the nucleotide sequence of the promoter is SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the xylose-induced promoter, a method for constructing a genetic engineering strain by using thepromoter, a corresponding strain, and application of a host cell to induction and starting of expression of a target gene under xylose inducible conditions.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
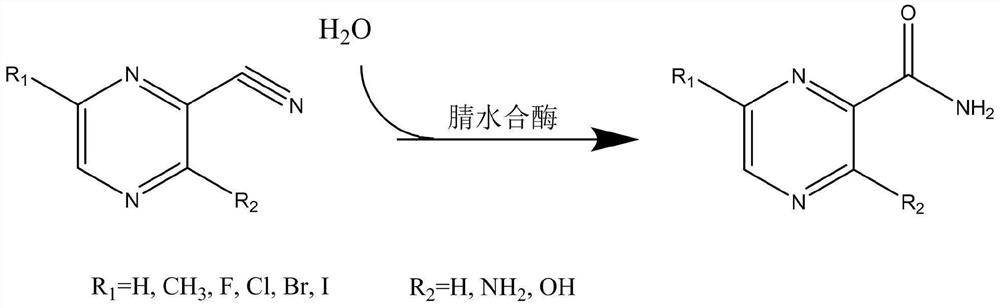
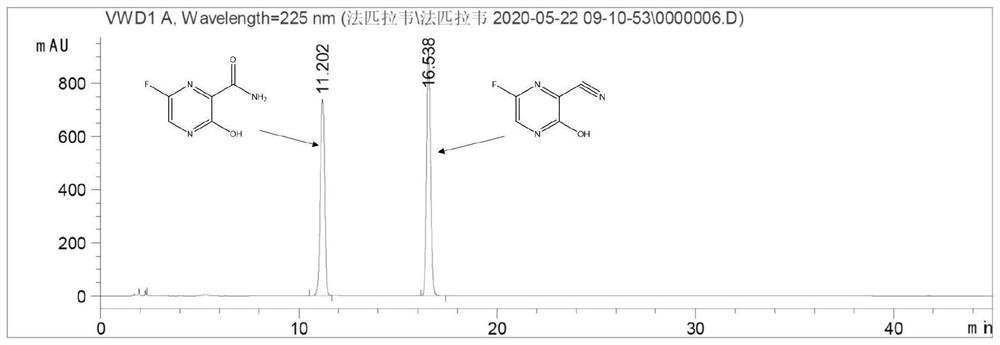
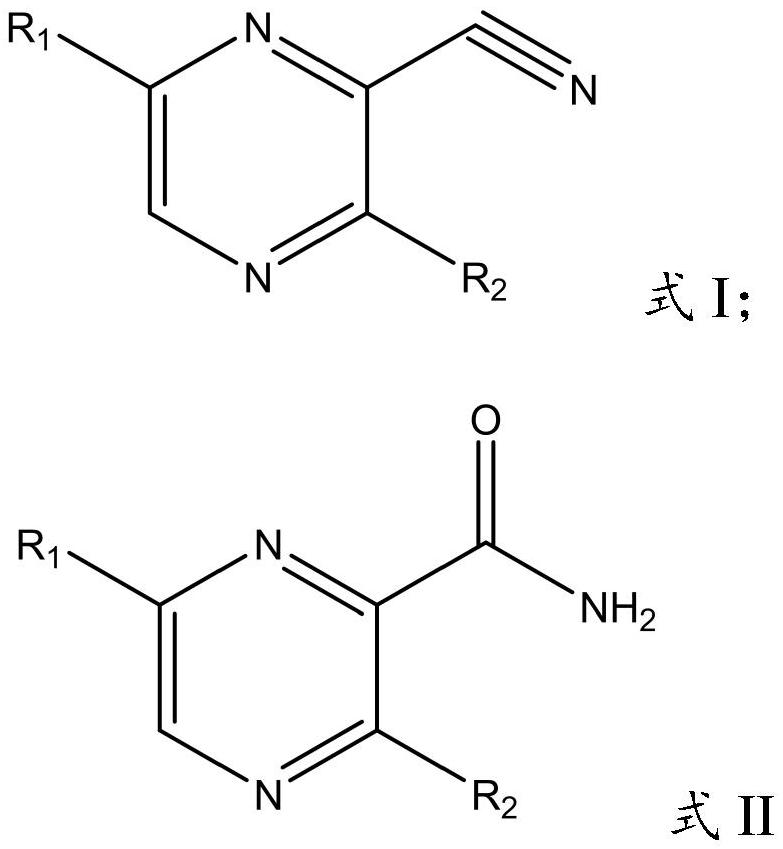
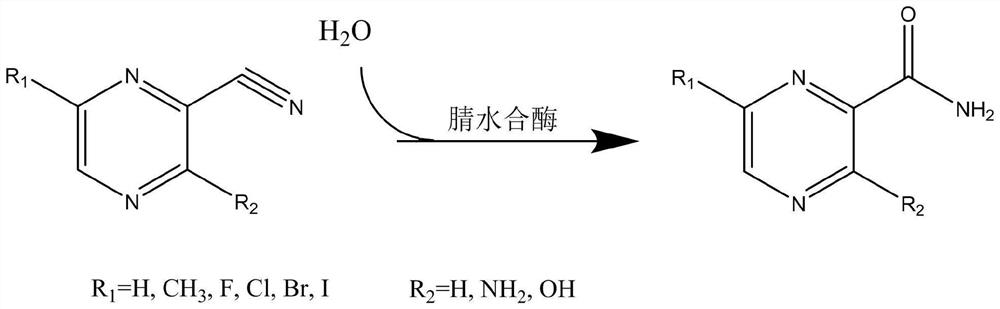
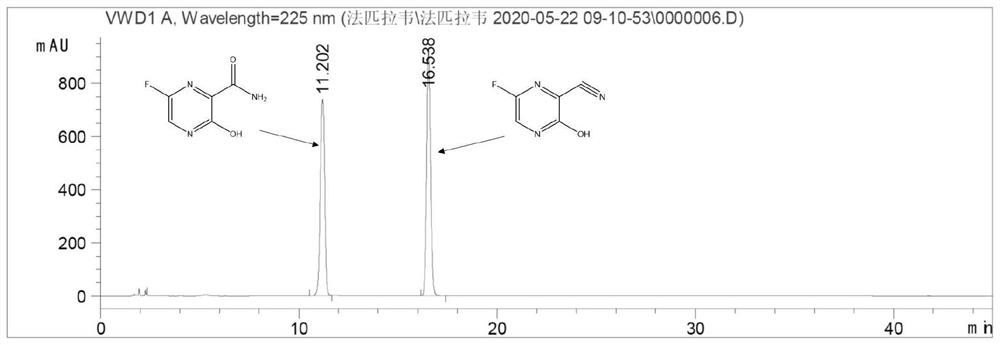
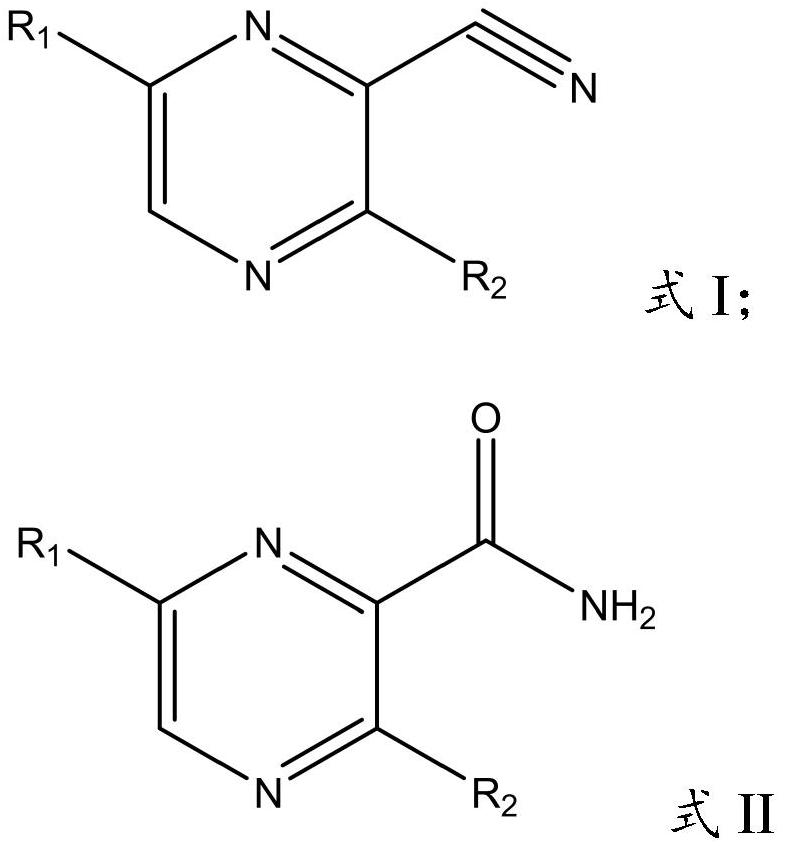
Application of nitrile hydratase in catalyzing hydration reaction of cyanopyrazine compound to generate amide pyrazine compound
ActiveCN111662938AImprove conversion rateHigh purityFermentationCarbon-oxygen lyasesHydration reactionPtru catalyst
The invention provides an application of nitrile hydratase in catalyzing a hydration reaction of a cyanopyrazine compound to generate an amide pyrazine compound, and belongs to the technical field ofbiochemical engineering. The nitrile hydratase is derived from Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Stappia aggregata IAM 12614 or Sinorhizobium meliloti. The cyanopyrazine compound is used as a substrate, in-vitro nitrile hydratase or a cell expressing the nitrile hydratase is used as a catalyst, the hydration reaction is carried out, and the amide pyrazine compound can be obtained. The applied raw material is high in conversion rate and free of side reaction, and the product is easy to separate and purify and is relatively high in purity; and compared with a traditional chemical catalysis process, theprocess is environmentally friendly and easy and convenient to operate, and the yield exceeds 99%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SANMEN HYGECON PHARMA CO LTD
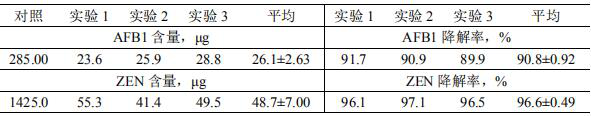
Compound fermentation inoculant for fermenting mycotoxin polluted feed and application of compound fermentation inoculant
The invention provides a compound fermentation inoculant for fermenting polluted feed and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The compound fermentation bacterial agent provided by the invention is prepared from lysine bacillus HQ08 and sinorhizobium meliloti, the preservation number of the lysine bacillus HQ08 is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.24221, and the preservation number of the sinorhizobium meliloti CM77 is CGMCC No.24222. The compound fermentation bacterial agent provided by the invention has the advantages that the compound fermentation bacterial agent can be used for preparing a compound fermentation bacterial agent; the compound fermentation inoculant provided by the invention can effectively reduce zearalenone toxin and aflatoxin B1 in the feed at the same time, and has excellent effects.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
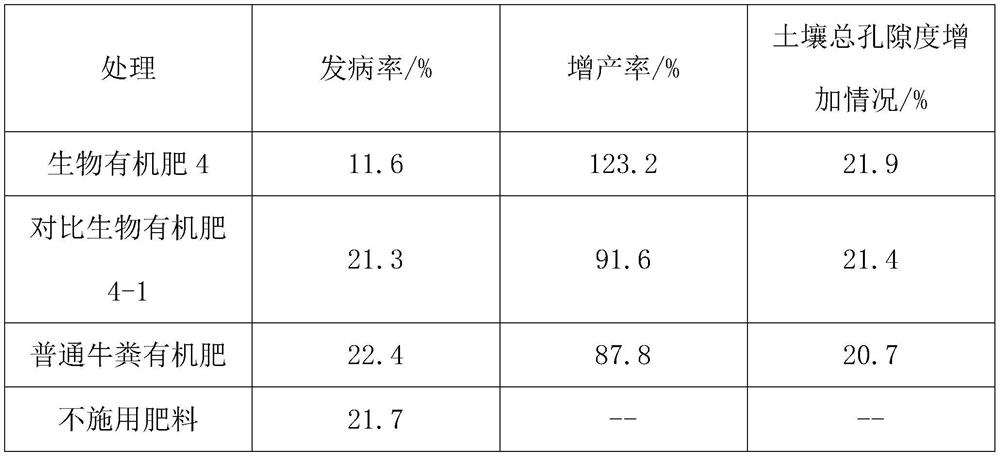
Bio-organic fertilizer for enhancing disease resistance and stress resistance of crops and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112939690AAvoid pollutionReduce growth impactBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersSinorhizobium sp.Poultry manure
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural soil bio-fertilizers, and particularly discloses a bio-organic fertilizer for enhancing disease resistance and stress resistance of crops and a preparation method thereof. The bio-organic fertilizer is prepared by inoculating raw materials of livestock and poultry manure, medicine residues, straws and bagasse with a compound bacteria solution composed of lactobacillus kitanensis, sinorhizobium meliloti and saccharomycetes, and then fermenting the raw materials of the livestock and poultry manure, the medicine residues, the straws and the bagasse. The fertilizer can be used for enhancing disease resistance and stress resistance of crops, and is beneficial to promoting improvement of planting soil and increasing crop yield.
Owner:广西沃瑞德生物科技有限公司
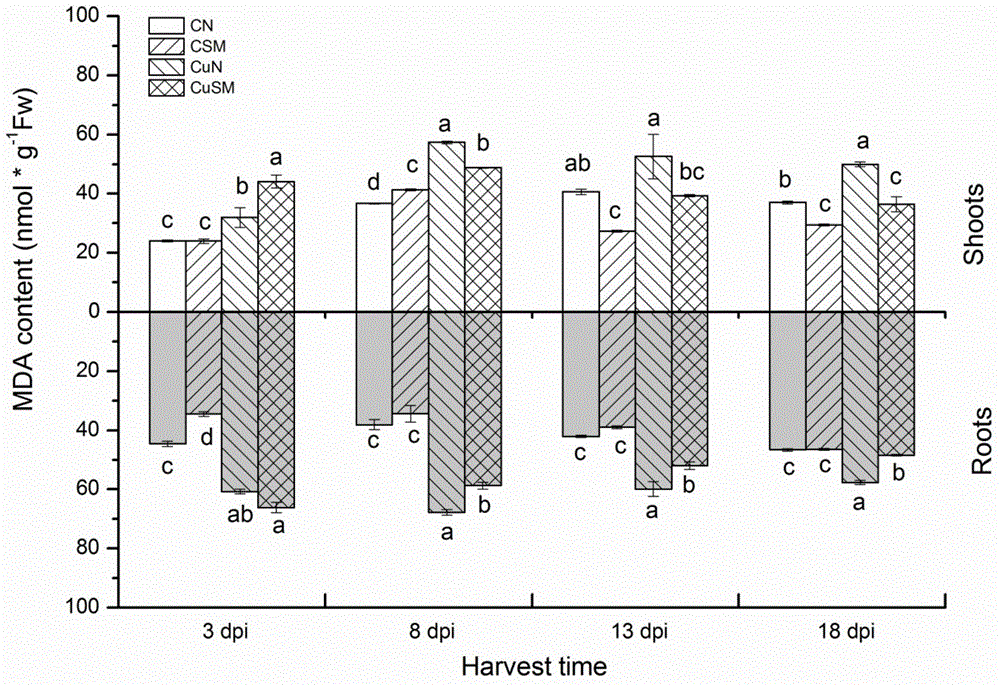
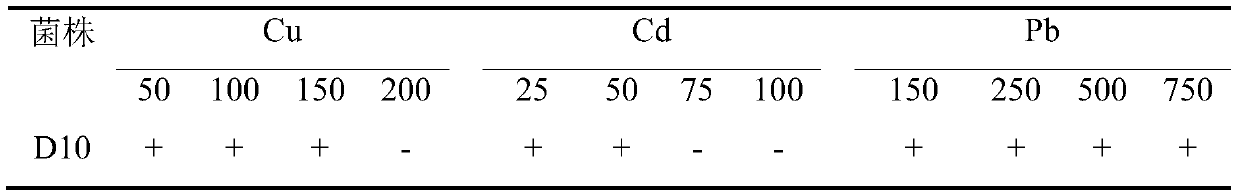
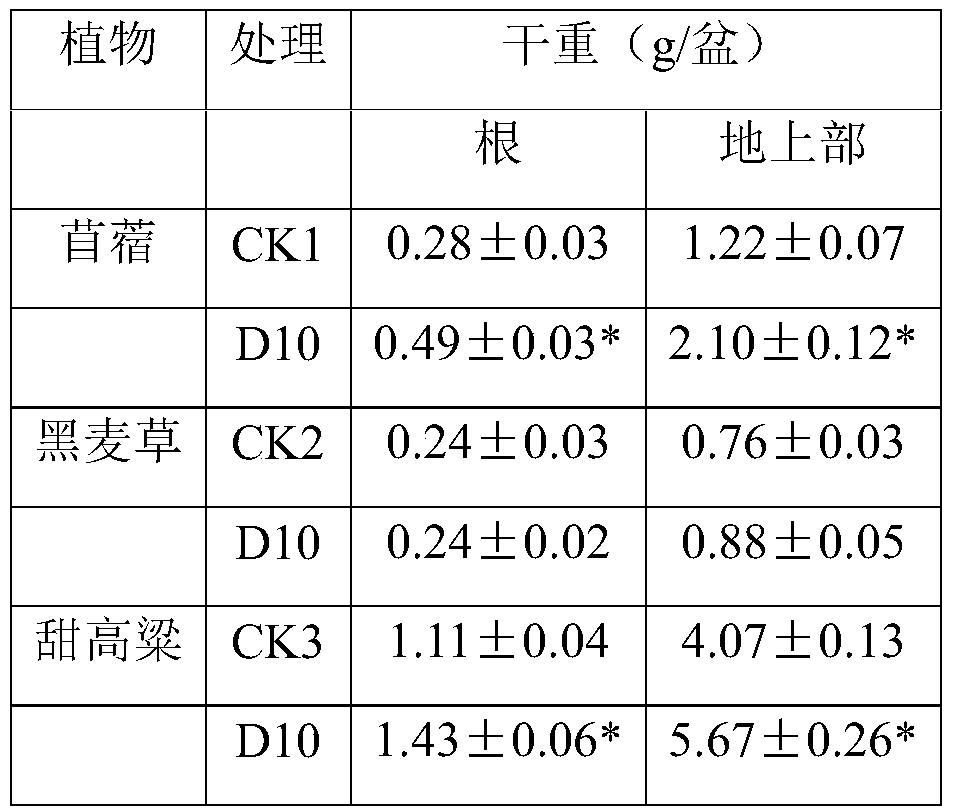
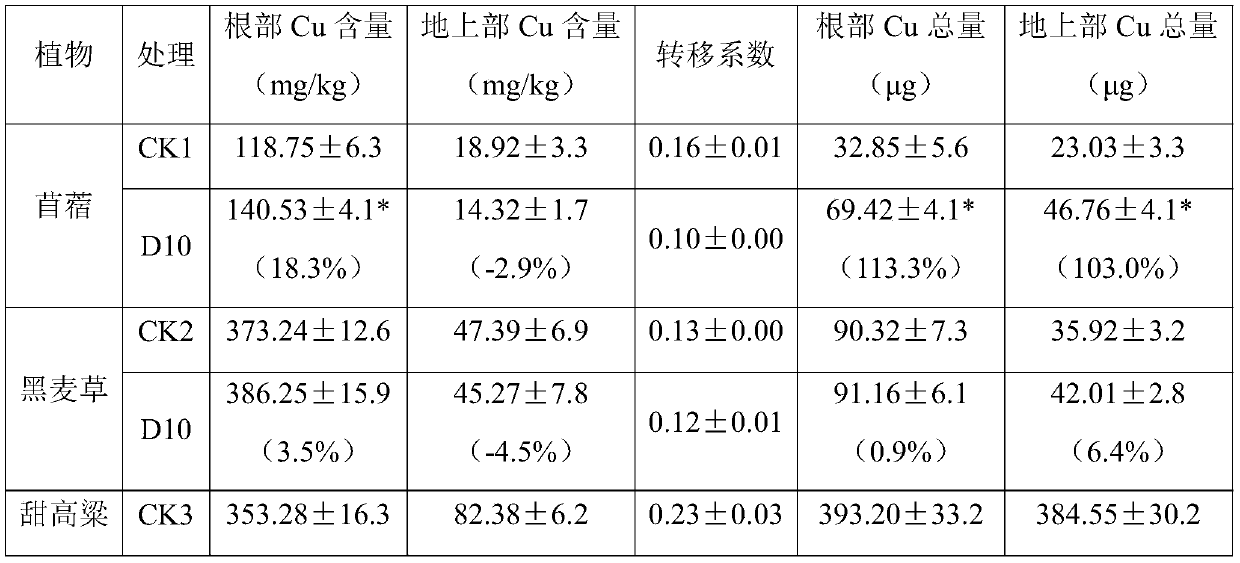
Bacteria d10 for improving the effectiveness of heavy metals and its application
ActiveCN107937302BPromote growthPromote absorptionBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBiotechnologyPlant roots
The invention discloses a bacterium D10 for improving the effectiveness of heavy metals and an application thereof. A bacterium D10 that improves the effectiveness of heavy metals, named Sinorhizobium meliloti D10, is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the strain preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2016554. The D10 strain was used as the raw material, and the bacterial suspension was prepared after being activated by the culture medium. In heavy metal polluted soil in mining areas, inoculation of D10 bacterial suspension can increase the growth of energy plants, increase the extractable copper content in plant rhizosphere soil, and increase the copper content and total copper absorption in plant roots. Alfalfa and ryegrass inoculated with D10 can be used for fixed remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil, and sweet sorghum inoculated with D10 can be used for both fixed and extractive remediation. And after the D10 bacterial suspension was inoculated, the IAA content of the plant rhizosphere microorganisms increased, and the soil fertility increased.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of nitrile hydratase from Sinorhizobium meliloti in preparation of amide pyrazine compound
ActiveCN113025671AImprove conversion rateHigh purityFermentationCarbon-oxygen lyasesHydration reactionPyrazine
The invention provides an application of nitrile hydratase from Sinorhizobium meliloti in preparation of an amide pyrazine compound and belongs to the technical field of biochemical engineering. The nitrile hydratase catalyzes a hydration reaction of a cyanopyrazine compound to generate an amide pyrazine compound; The nitrile hydratase is derived from the Sinorhizobium meliloti (Singorhizobium meliloti). The cyanopyrazine compound is taken as a substrate, in-vitro nitrile hydratase or cells for expressing the nitrile hydratase are taken as a catalyst, a hydration reaction is carried out, and the amide pyrazine compound can be obtained. The raw material conversion rate is high, no side reaction exists, and the product is easy to separate and purify and high in purity; Compared with the traditional chemical catalysis process, the process is green and environment-friendly, the operation is simple and convenient, and the yield exceeds 99%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SANMEN HYGECON PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com