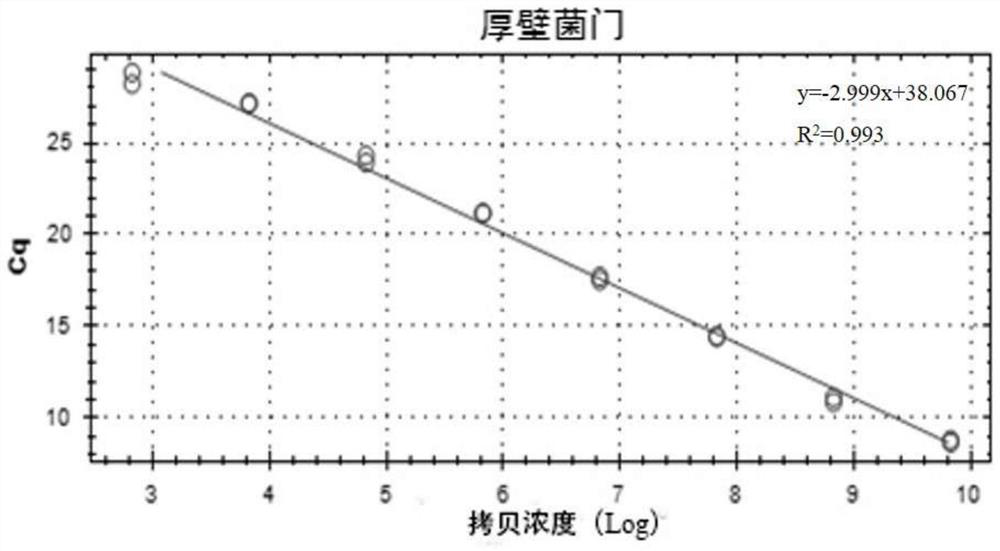
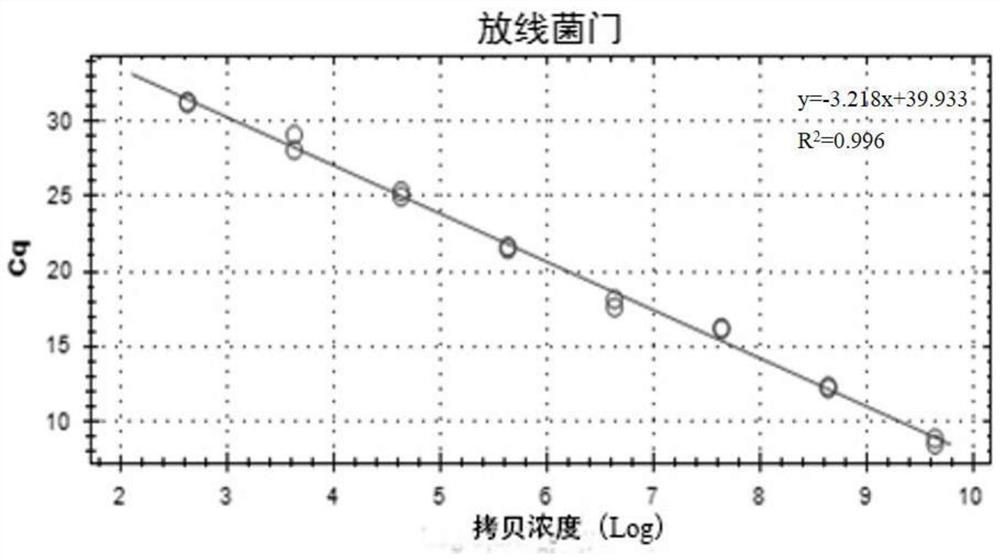
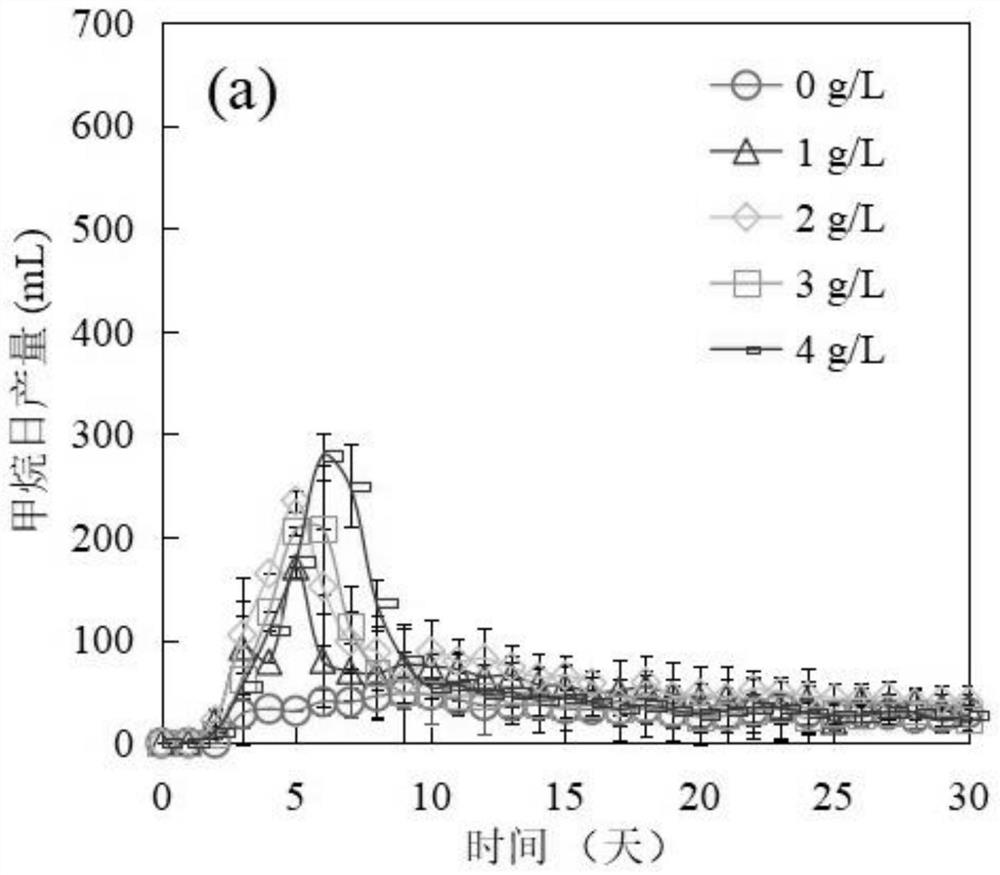
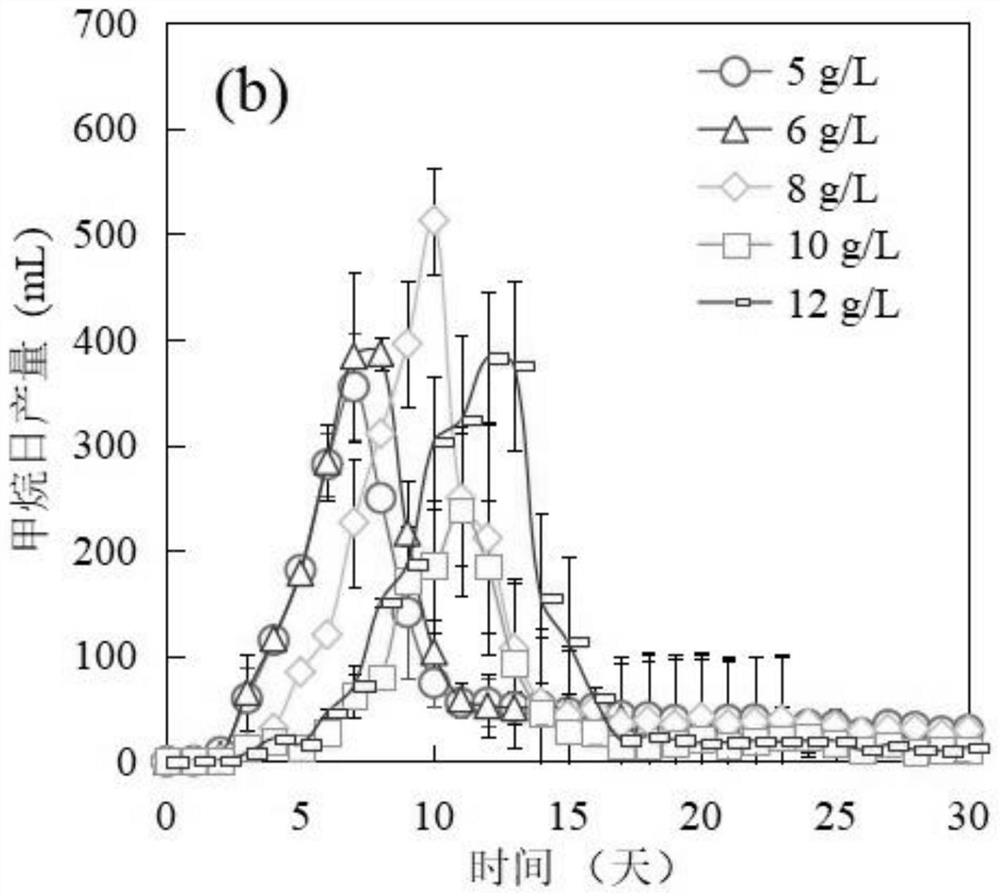
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Proteobacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Proteobacteria is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. They include a wide variety of pathogenic genera, such as Escherichia, Salmonella, Vibrio, Helicobacter, Yersinia, Legionellales, and many others. Others are free-living (nonparasitic) and include many of the bacteria responsible for nitrogen fixation.
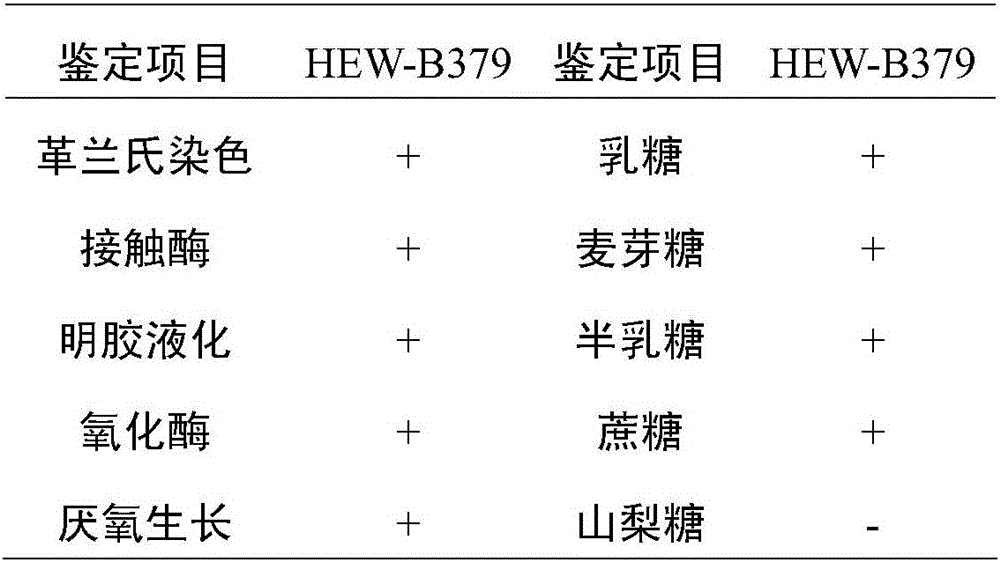
Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 with probiotic effect, and application thereof
ActiveCN106011036AStrong heat resistanceStrong fermentation abilityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliFeed conversion ratio
The invention provides a Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 with a probiotic effect. The above strain is named as HEW-B379, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.12553. The Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 has a substantial probiotic property, and can effectively inhibit growth breeding of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhi, salmonella, Shigella, Proteus species, Shewanella putrefaciens and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The Bacillus coagulans HEW-B379 has strong stress resistance, can resist high temperature and simulated gastric juice and simulate bile salt environment, can keep the survival rate of 99-100%, and can effectively adjust microbial balance of animal intestinal tracts, inhibit growth of harmful microbes, promote nutrition absorption of animals, improve the conversion rate of a feed and improve the productivity of the animals.
Owner:BEIJING HESWOF BIOTECH CO LTD
Terephthalic acid producing proteobacteria
This invention relates to a biocatalytic process to produce terephthalic acid and isophthalic acid from p-xylene and m-xylene, respectively. Terephthalic acid has been prepared by oxidizing p-xylene with bacteria belonging to the genus Burkholderia. Conversion of p-xylene into terephthalic acid is accomplished by a single bacterial strain that produces all of the requisite enzymes. In addition, this invention relates to the preparation of isophthalic acid from a mixture of m- and p-xylene.
Owner:BRAMUCCI MICHAEL G +3
Microbial inoculant and application thereof in livestock breeding
InactiveCN109468249AGrow fastShorten breeding timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacillus licheniformis
The invention specifically discloses a microbial inoculant, in particular to a microbial inoculant prepared from swine borne bacillus licheniformis YHSH-02 and the application thereof in livestock breeding. The culture is preserved in CGMCC, 3#, Yard #1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, with the preservation number of CGMCC NO. 15454 and the preservation date of 15th, March, 2018. The bacillus licheniformis YHSH-02 is separated from a swine intestinal tract, can generate rich lipopeptides bacilli, antifungal proteins and the like, and can inhibit escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterococcus faecalis, enterobacter cloacae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, proteusbacillus vulgaris, staphylococcus aureus, salmonella and clostridium. The bacillus licheniformis YHSH-02 obtained from the swine intestinal tract is a biological control potential culture which is high in preventing and treating efficiency and wide in preventing and treating range and can promote growth obviously,and has a good application and development prospect in non-resistant breeding.
Owner:FOSHAN YANHUI BIOTECH CO LTD
Preparation method for dichloro substituted II-type halogenated polyketone compound and antibacterial activity application
ActiveCN107937453AImprove reproductive performanceTo promote metabolismAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCandida famata
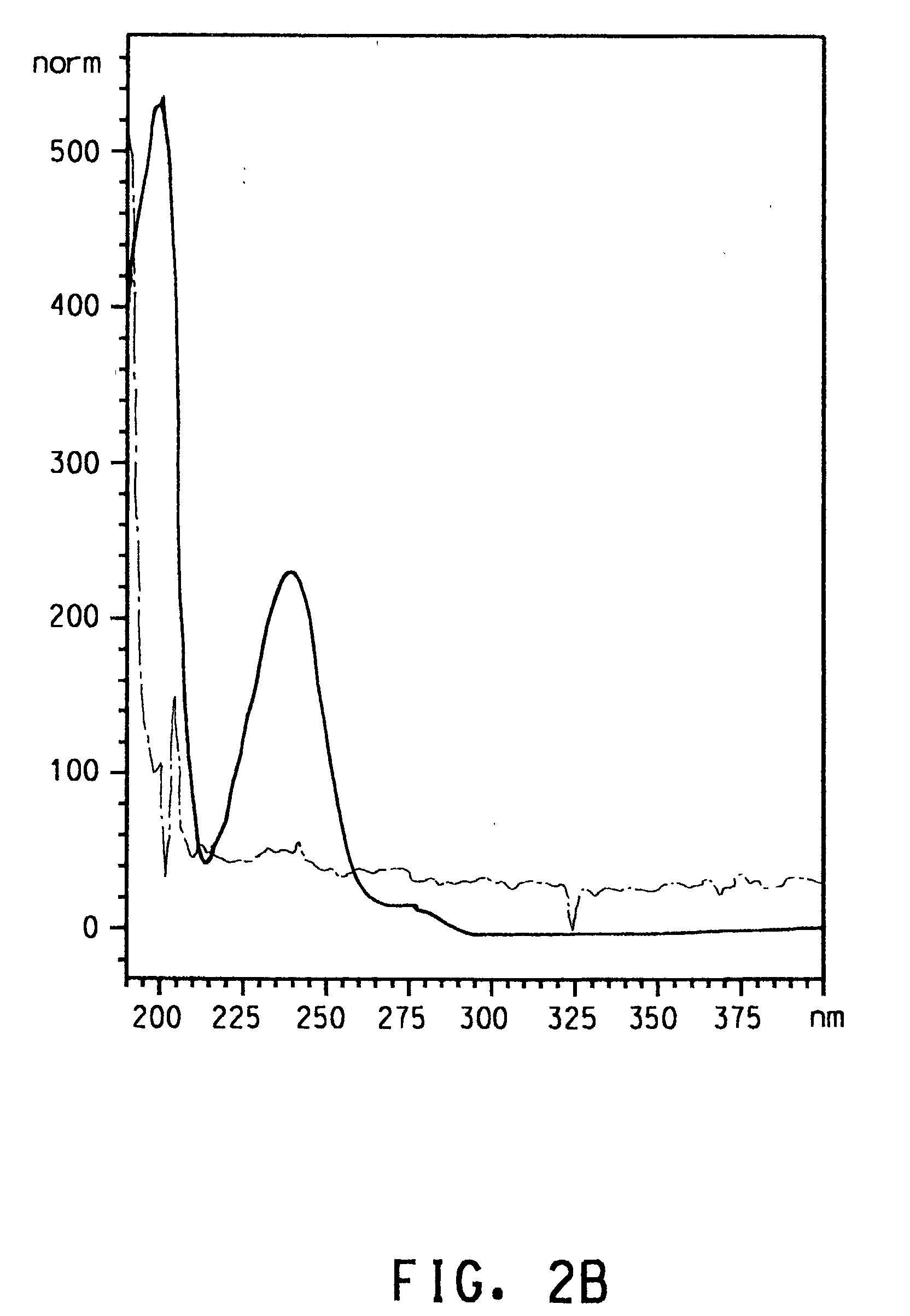
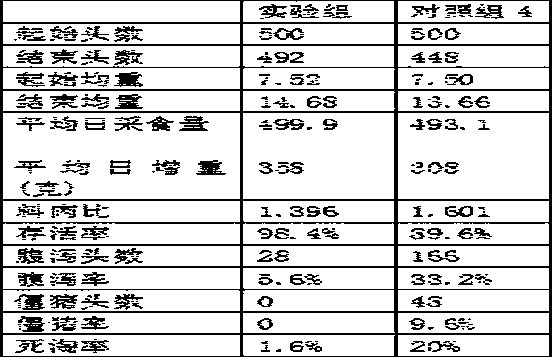
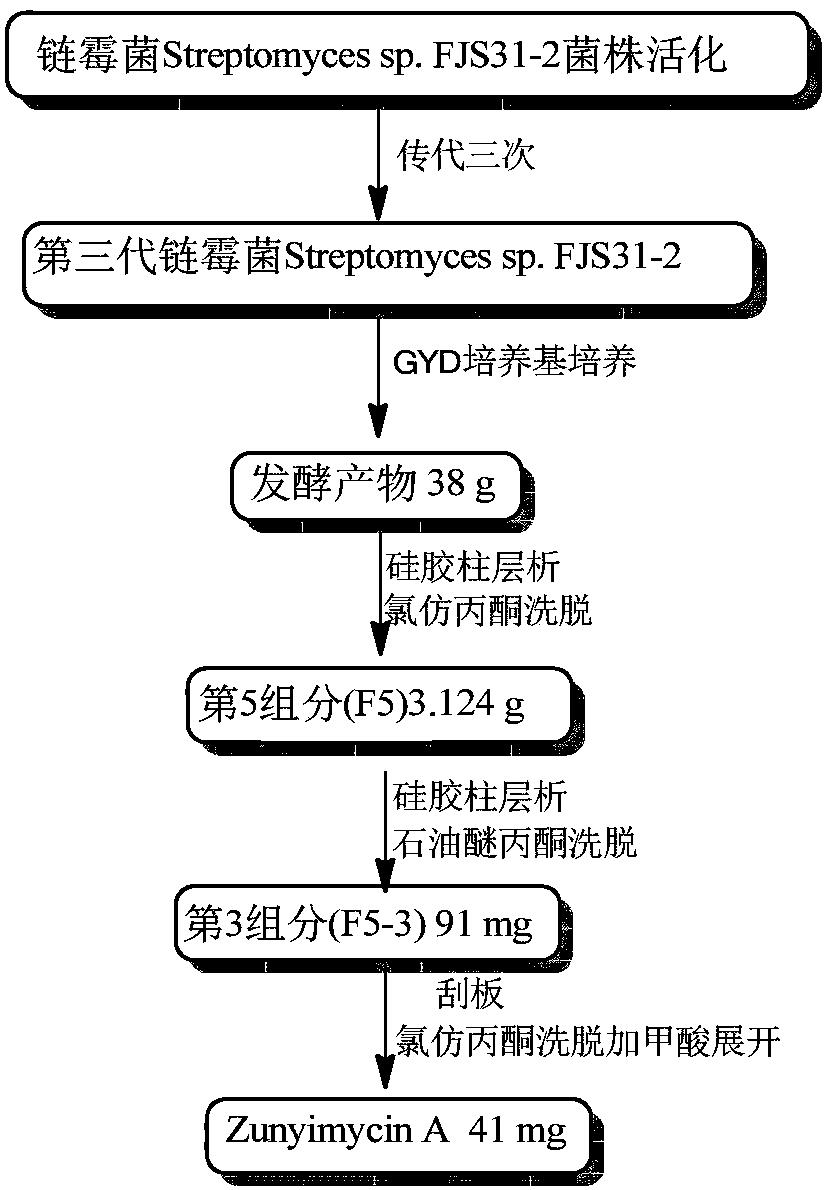
The invention discloses a preparation method for a dichloro substituted II-type halogenated polyketone compound zunyimycin A, wherein the compound is derived from a secondary metabolite of a streptomyces sp.FJS31-2 strain (with the strain preservation number of CGMCC4.7321), and finally, a structure is identified and determined after strain activation, expansion culture and isolation. The compoundcan be used in treatment of diseases infected by gram-positive bacteria such as staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and drug-resistant bacteria thereof, staphylococcus epidermidis, bacillus subtilis and thelike, is used in treatment of diseases infected by gram-negative bacteria such as super-spectrum beta-lactamase escherichia coli (ESBL), proteusbacillus vulgaris, bacterium burgeri and the like, andis used for treatment of diseases infected by fungi, such as candida albicans.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
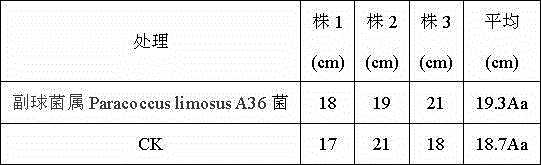
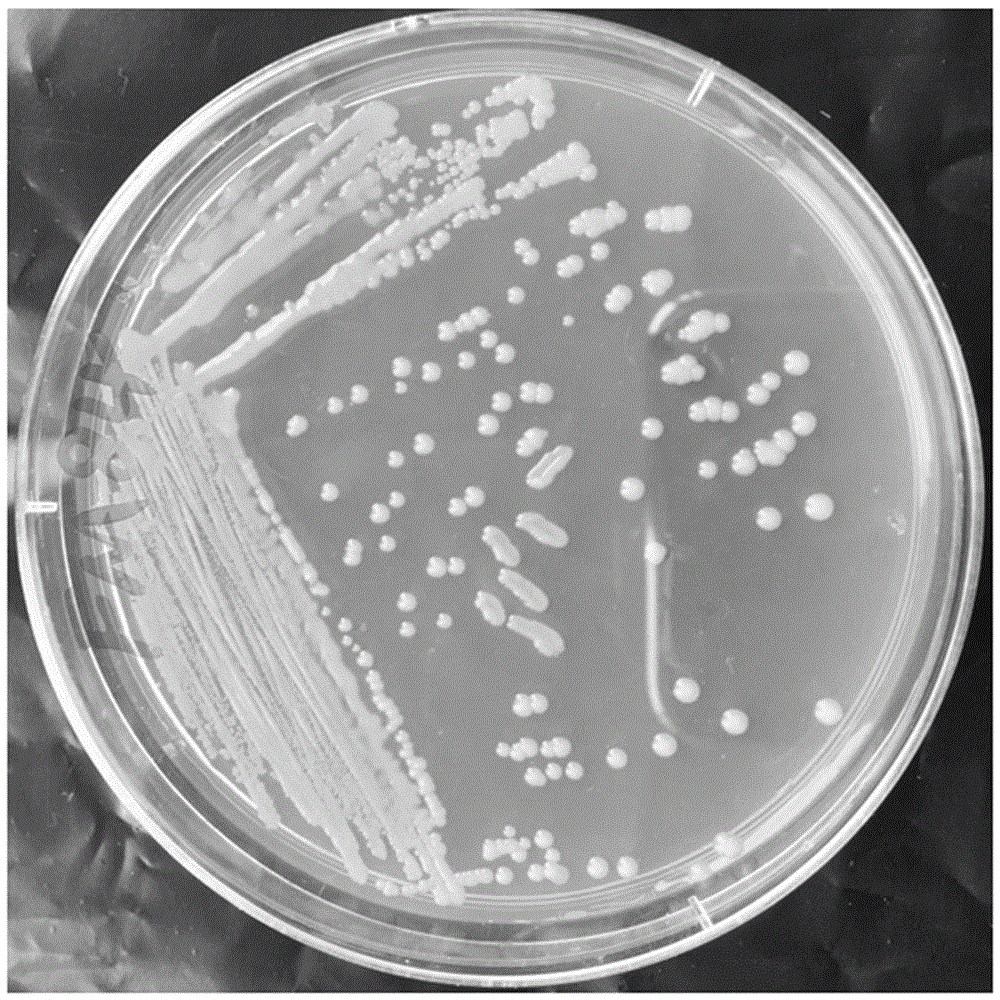
Paracoccus limosus, bacterium thereof, method for preparing bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN104877916AReduce applicationsIncrease contentFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyRhodobacterales
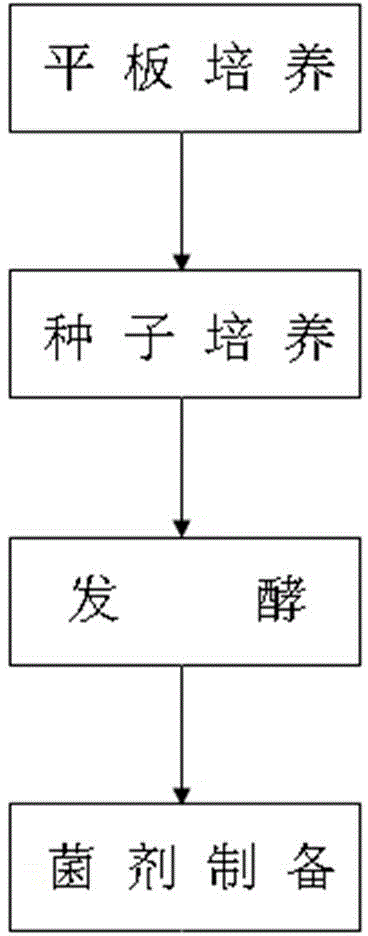
The invention discloses paracoccus limosus, a bacterium thereof, a method for preparing the bacterium and application thereof. The paracoccus limosus is paracoccus limosus A36, is preserved in preservation authority which is the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on November 21st, 2014, and the preservation number of the paracoccus limosus is CGMCC No.10032; the paracoccus limosus belongs to paracoccus versutus of rhodobacteraceae of rhodobacterales of alpha-proteobacteria of proteobacteria of bacteria. The radial paracoccus limosus is cultivated on a plate, and seeds are cultivated and fermented to obtain the bacterium with the paracoccus limosus which is an active ingredient. The method for preparing the bacterium with bacillus which is an active ingredient includes steps of cultivating the paracoccus limosus on the plate; cultivating the seeds; fermenting the seeds; preparing the bacterium. The bacterium can be applied to preparing basic fertilizers with functions of dissolving phosphorus and potassium and increasing quick-acting nitrogen in soil.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI +1
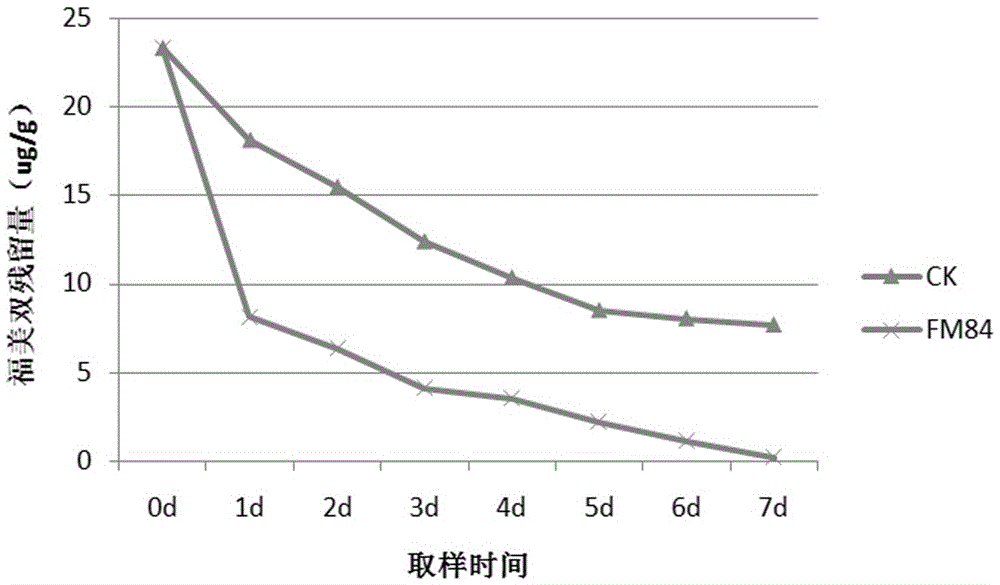
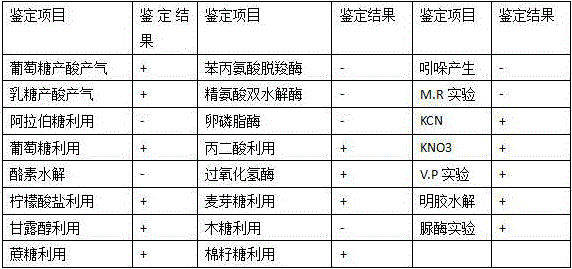
Klebsiella pneumoniae, bacterium agent of klebsiella pneumoniae and preparation method and application
InactiveCN106754497AReduce manufacturing costLow production costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGamma proteobacteriaBacteroides dorei
The invention discloses Klebsiella pneumoniae, a bacterium agent of the Klebsiella pneumoniae and a preparation method and application. The Klebsiella pneumoniae FM84 is a thiram degradation bacterium; the preservation unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC); the preservation date is December 15, 2015; the preservation number is CGMCC N0. 11663; the Klebsiella pneumoniae belongs to bacteria, proteobacteria, gamma-proteobacteria, enterobacteriales, enterobacteriaceae and Klebsiella. The bacterium agent with the Klebsiella pneumoniae as an active ingredient is a bacterium agent prepared by activating the Klebsiella pneumoniae FM84 through strains, culturing seeds, producing and culturing and preparing with a preparation. The preparation method comprises an activation culture step and a fermentation culture step; the invention provides application of the bacterium agent to preparation of agricultural plants capable of degrading thiram. The bacterium agent comprising the strains has a simple preparation process, is low in cost and convenient to use, and has very good application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
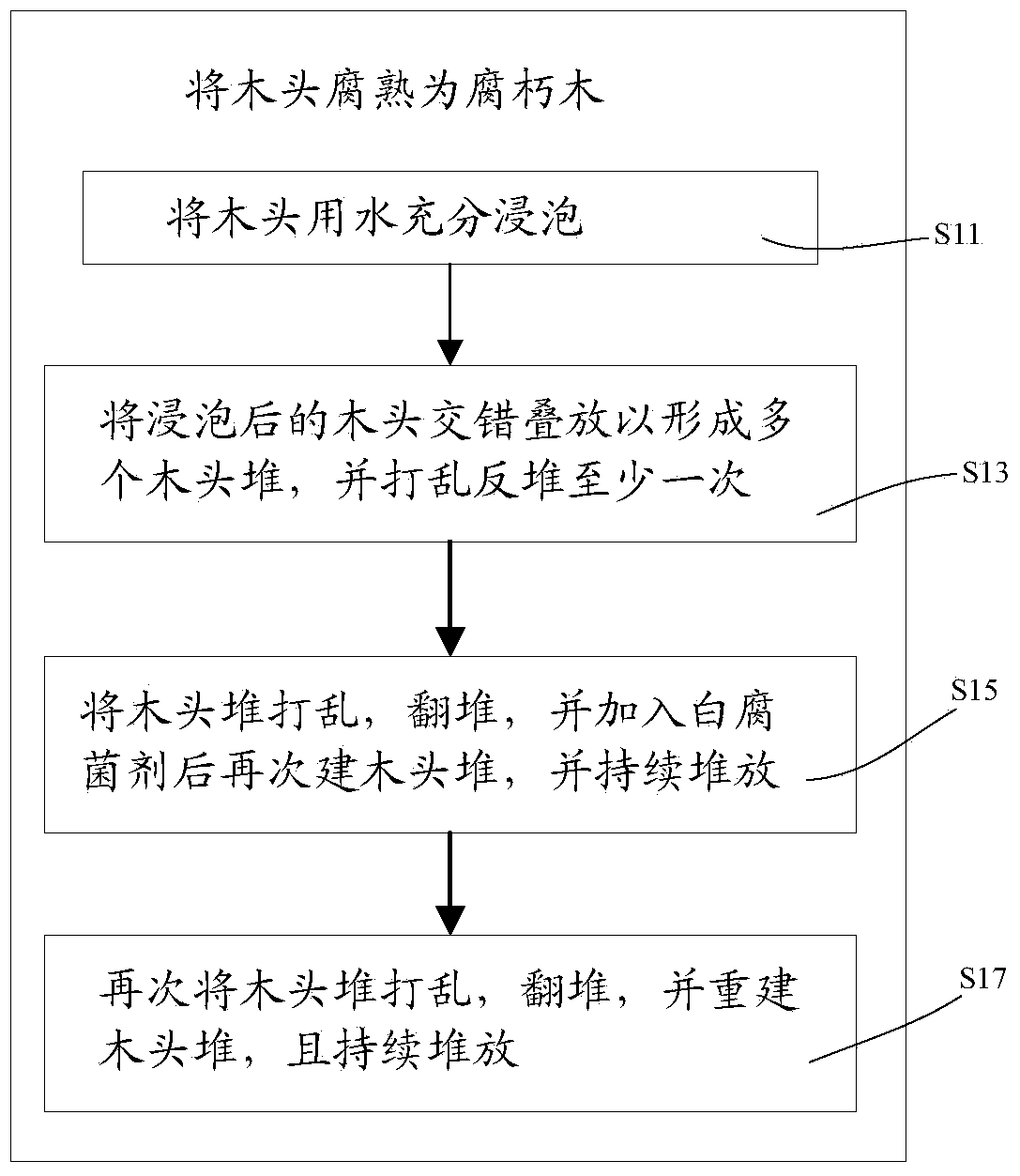
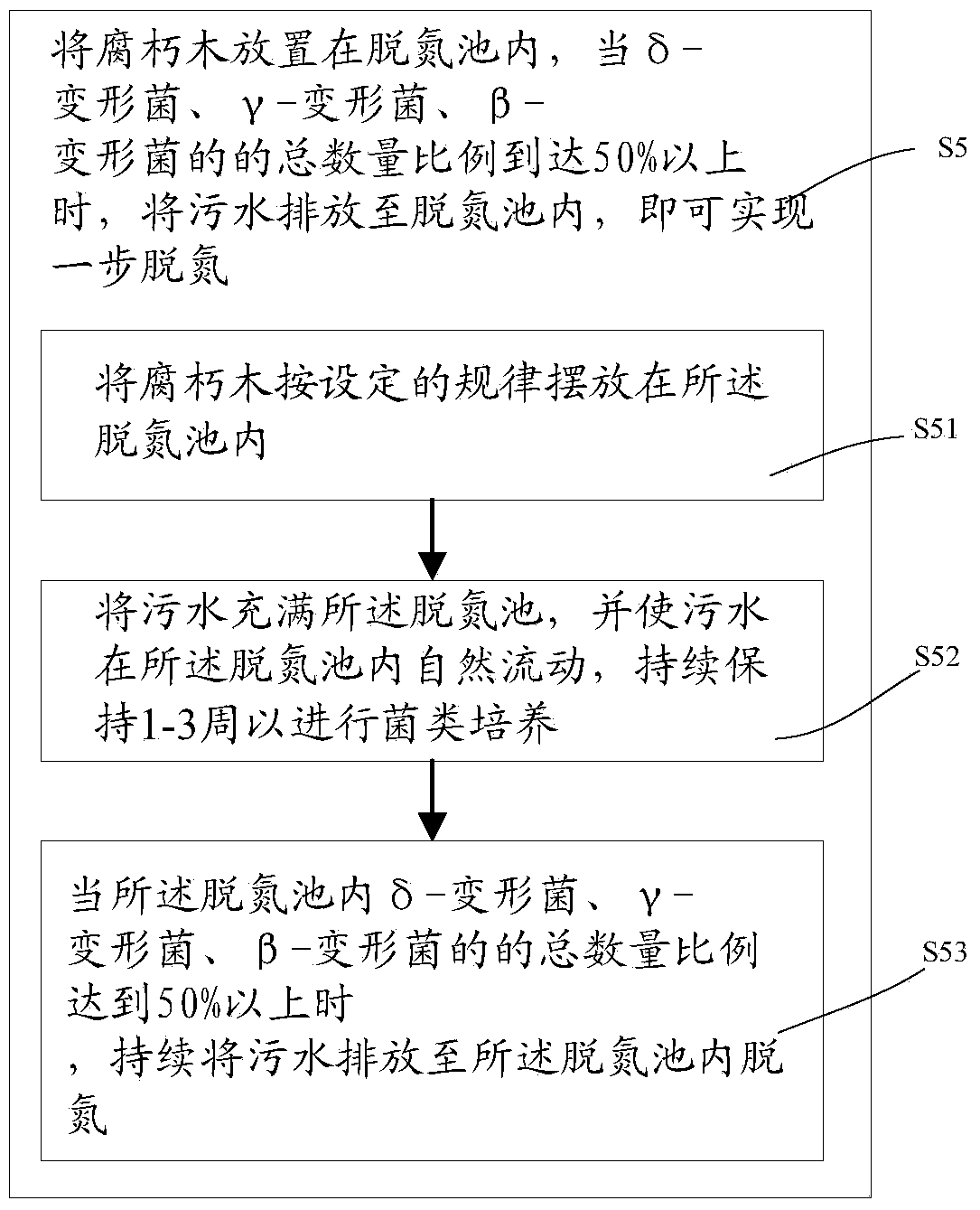
Method for one-step denitrification by utilizing wood and decayed wood for enrichment of denitrification environment microbial communities
InactiveCN104129847AHigh activityIncrease reproduction speedTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesInorganic saltsMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for one-step denitrification by utilizing wood and decayed wood for enrichment of denitrification environment microbial communities. The method includes: S1, soaking the decayed wood by a hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 9-10% for 20-30h continuously, then getting the decayed wood out and washing it clean; S3, soaking the decayed wood in a basic inorganic salt solution for 28-32d; and S5, placing the decayed wood in a denitrification pool in an anaerobic ammonia oxidation environment to perform bacteria culture, and keeping the temperature inside the pool at 20-30DEG C, introducing sewage into the pool, letting microbial communities grow on the decayed wood gradually, and making the Delta-proteobacteria composition proportion reaches over 50%, thereby realizing one-step denitrification. The decayed wood is employed to provide a parasitic environment for anaerobic bacteria, and increases the survival property and reproduction speed. The denitrification process has no need for chemical or organic matters, and aeration. The dominant environment microbial communities for denitrification are formed on the surface of the carrier, bacteria are cultured to swallow nitrogen-containing substances in flowing sewage so as to reach decontamination, thus saving raw materials, manpower and material resources, and reducing the cost.
Owner:WUHAN FENGLIN ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH
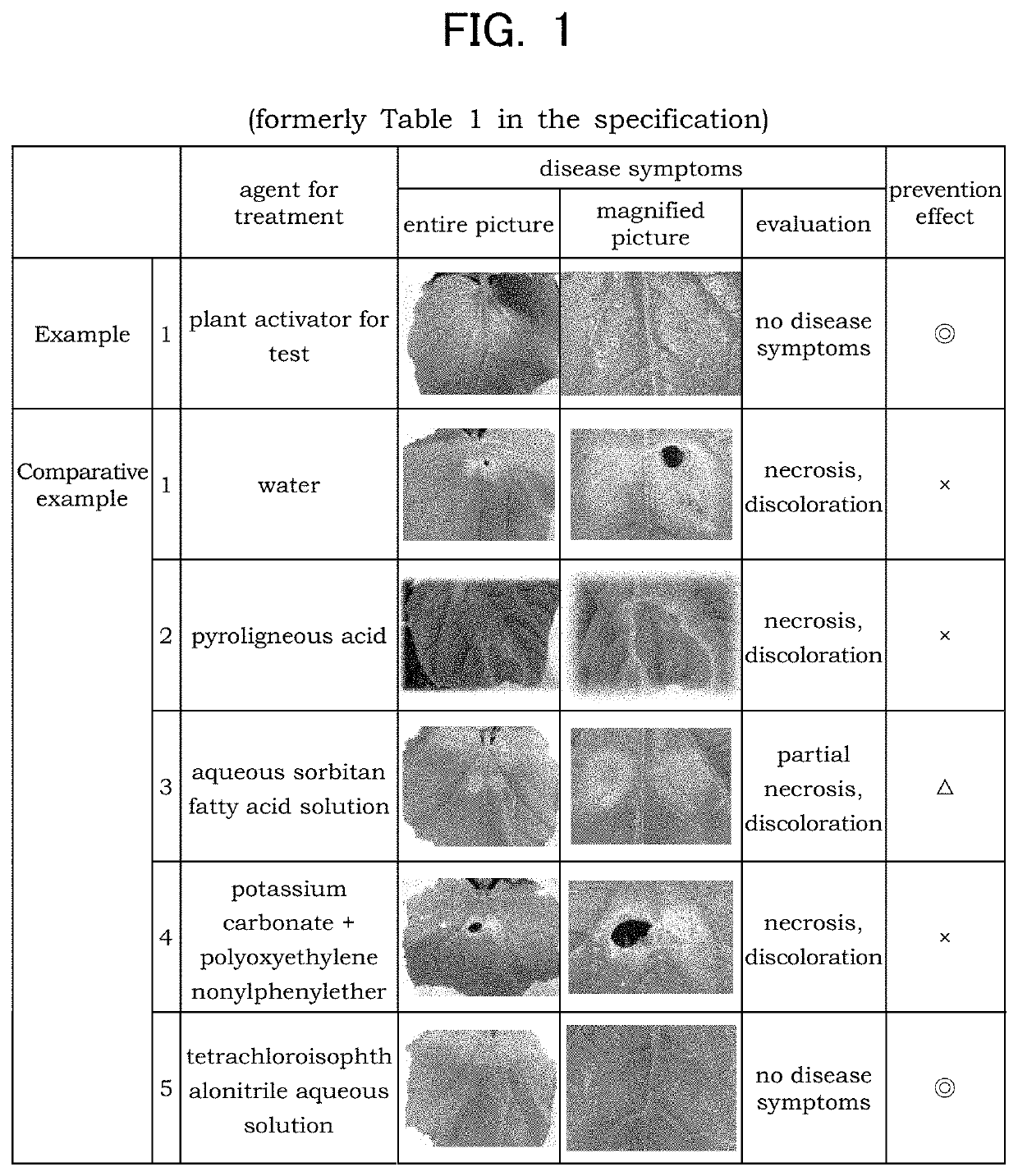
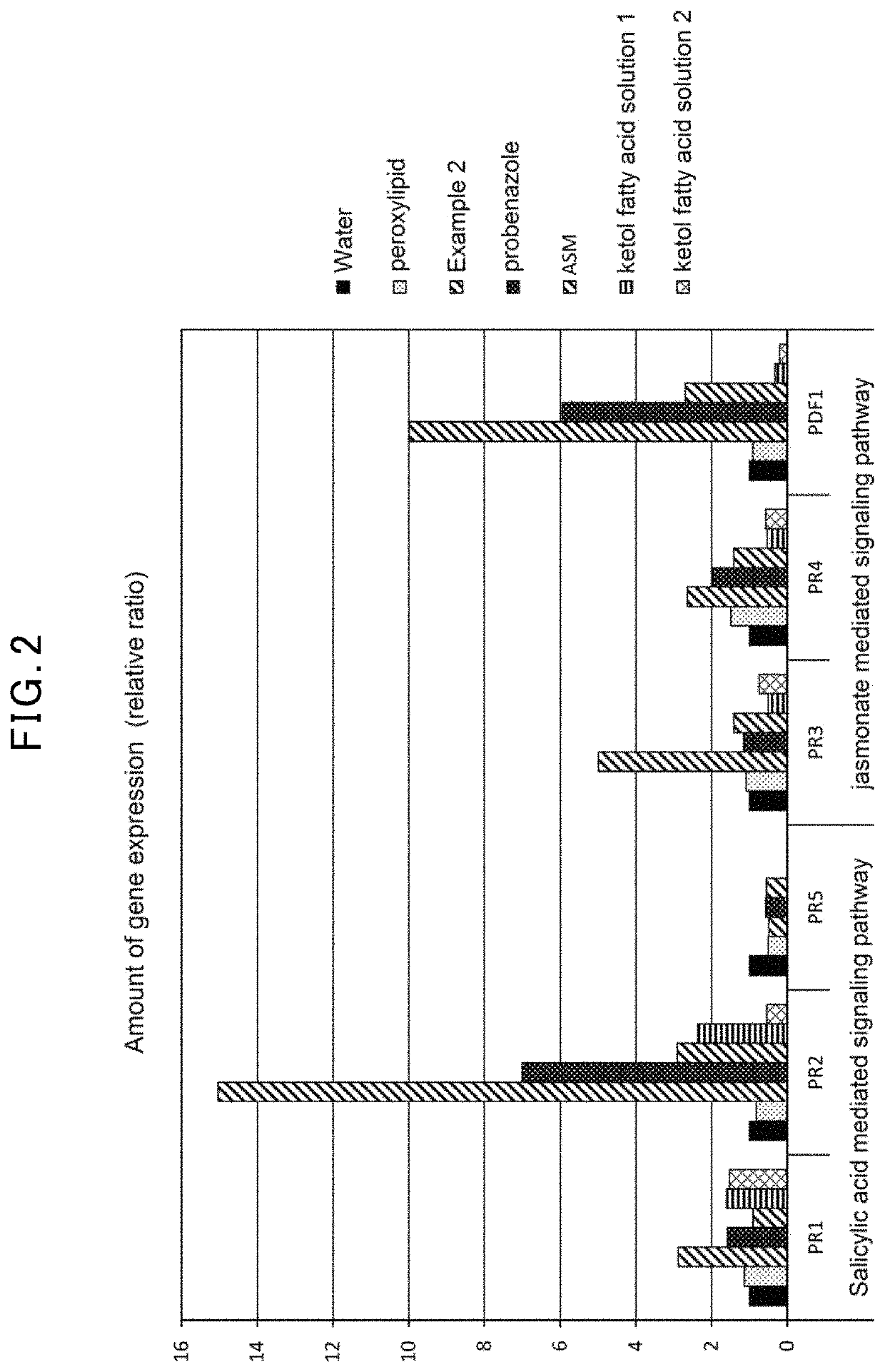
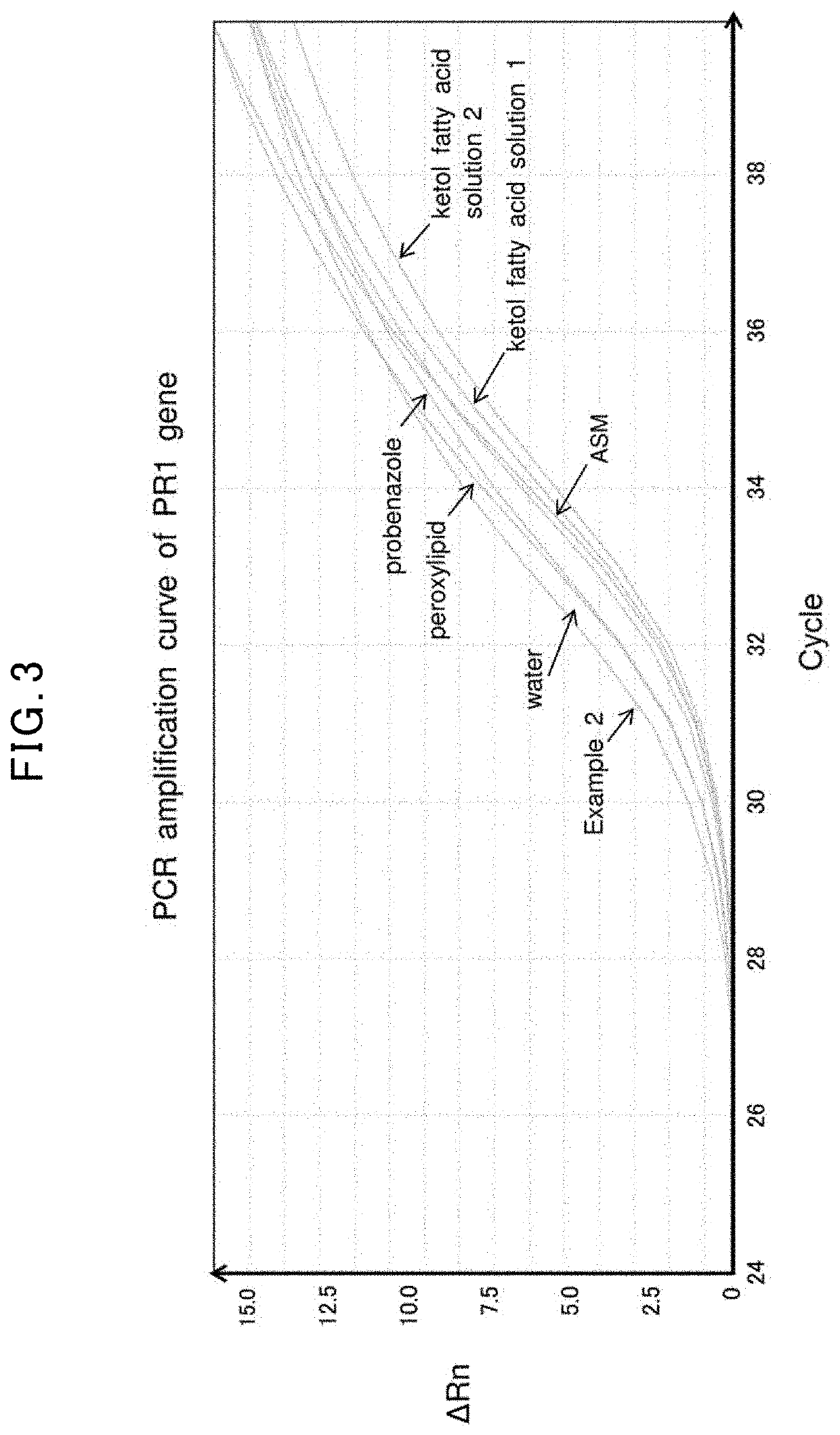
Plant activator and a method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS11382281B2Superior resistance-inducing activityLow toxicityBiocideAnimal repellantsMetabolitePollution soil
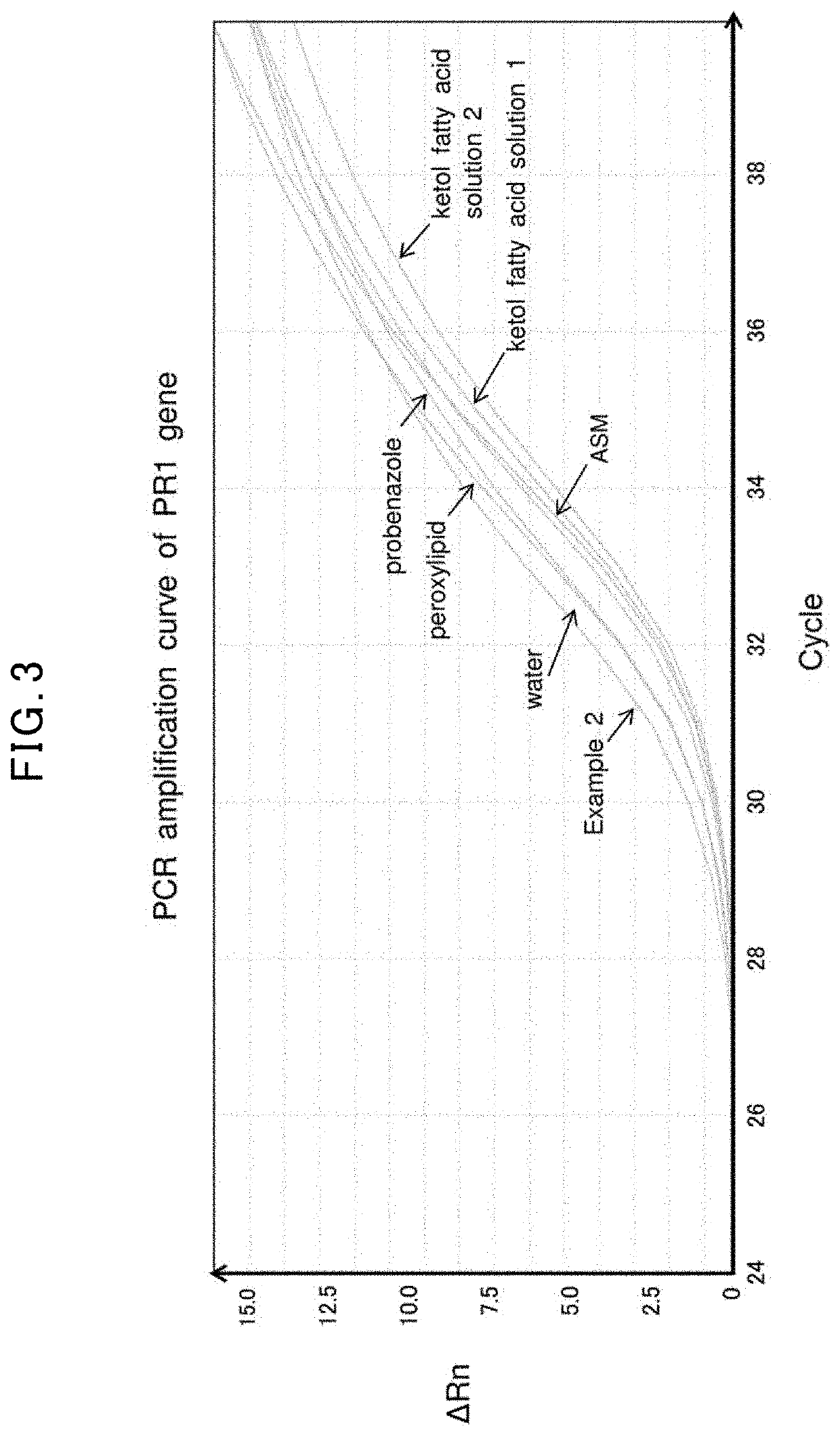
The objective of the invention is to provide a plant activator with superior resistance-inducing activity and growth promoting activity and low toxicity and soil contamination. A plant activator comprising a fatty acid metabolite obtainable by a metabolism of a fatty acid with 4 to 30 carbon atoms by a proteobacteria under a dissolved oxygen concentration of 0.1-8 mg / L, and a method for manufacturing a plant activator comprising a fatty acid metabolite, comprising a step for fatty acid metabolism wherein a fatty acid with 4 to 30 carbon atoms is subjected to a proteobacterial metabolization under a dissolved oxygen concentration of 0.1-8 mg / L. A method for manufacturing a plant activator comprising a fatty acid metabolite, comprising a step for fatty acid metabolism wherein a fatty acid with 4 to 30 carbon atoms is subjected to a proteobacterial metabolization under a dissolved oxygen concentration of 0.1-8 mg / L.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Broad bean rhizobium with drought tolerance and application thereof
PendingCN114381408AImprove drought resistanceIncrease productionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsRhizobiaceaePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses broad bean rhizobium with drought tolerance and application of the broad bean rhizobium. The separated broad bean rhizobium strain with drought tolerance is obtained from a broad bean host, the strain is subjected to shape, physical and chemical property and whole genome analysis and identification, the strain belongs to a new strain in the bacteria field, proteobacteria, alpha-proteobacteria, rhizobium, rhizobiaceae and rhizobium, and the microbial preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.24092. According to the broad bean rhizobium provided by the invention, PEG (Polyethylene Glycol) is used for simulating drought stress, a broad bean artificial water control potted plant drought test and a rain-fed agricultural area field inoculation verification test prove that the broad bean rhizobium provided by the invention has the characteristics of drought tolerance, efficient nodulation, strong nitrogen fixation capability and the like; and the broad bean biomass and yield are increased, and the broad bean has application prospects in the aspects of improving the stress resistance of leguminous crops, promoting growth, improving the yield and the like.
Owner:QINGHAI UNIVERSITY
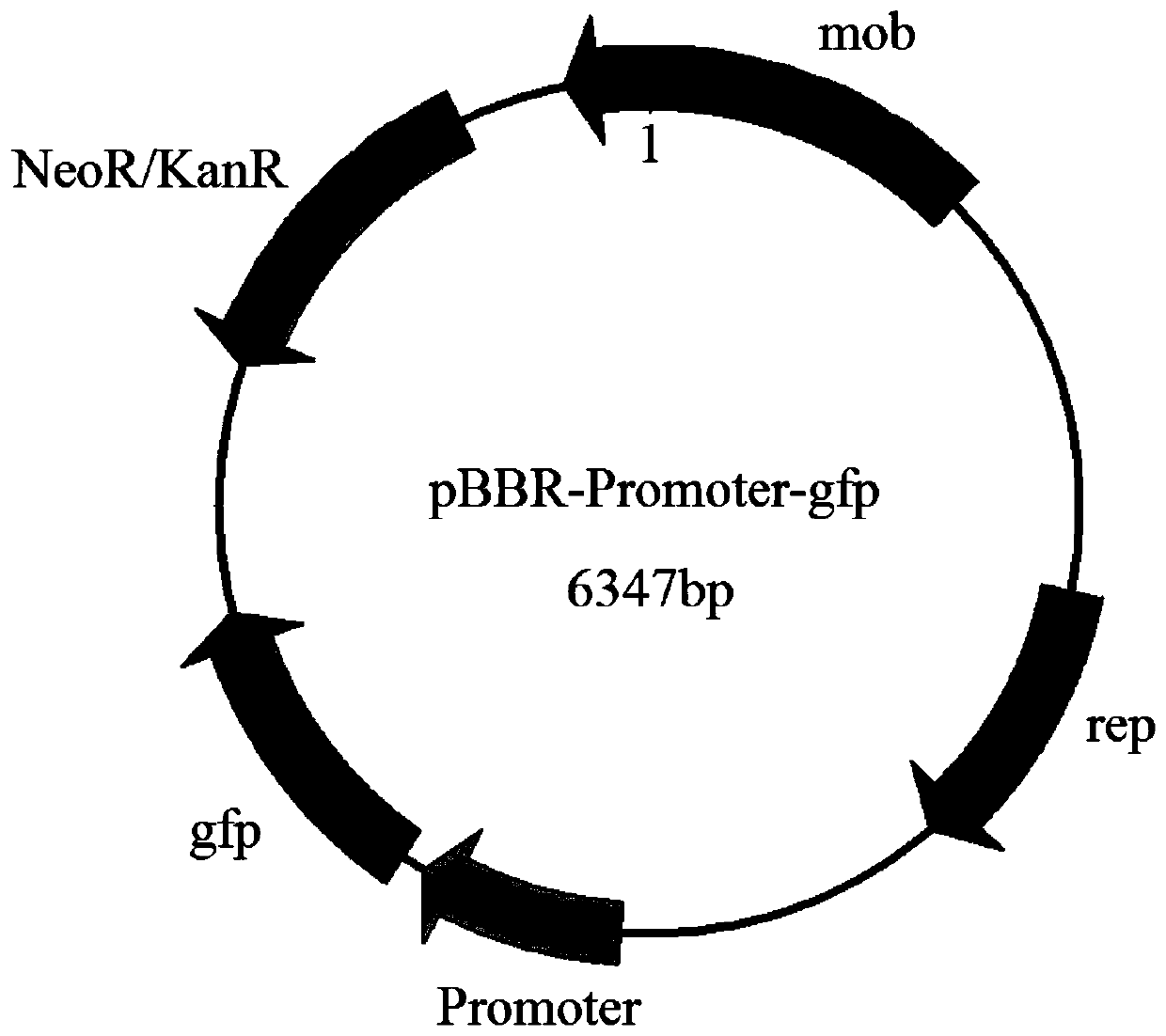
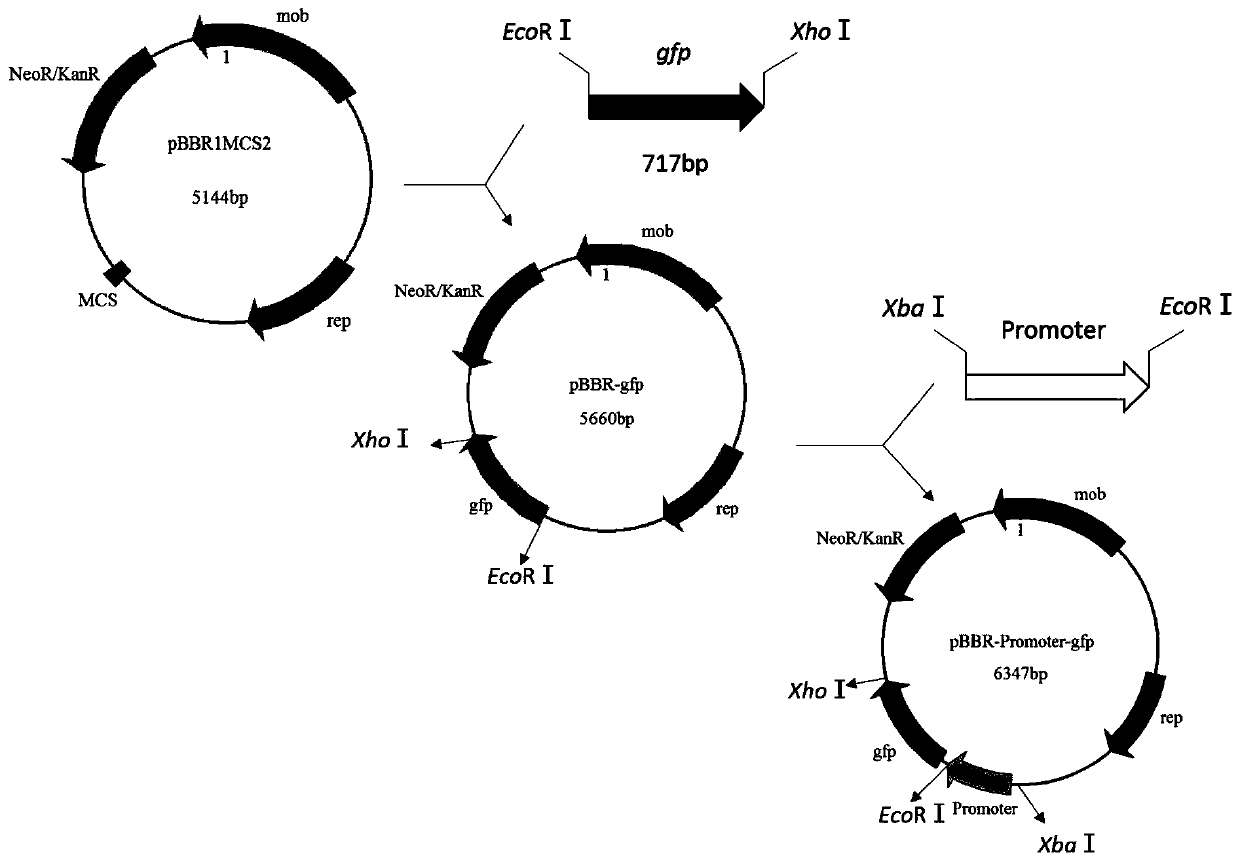
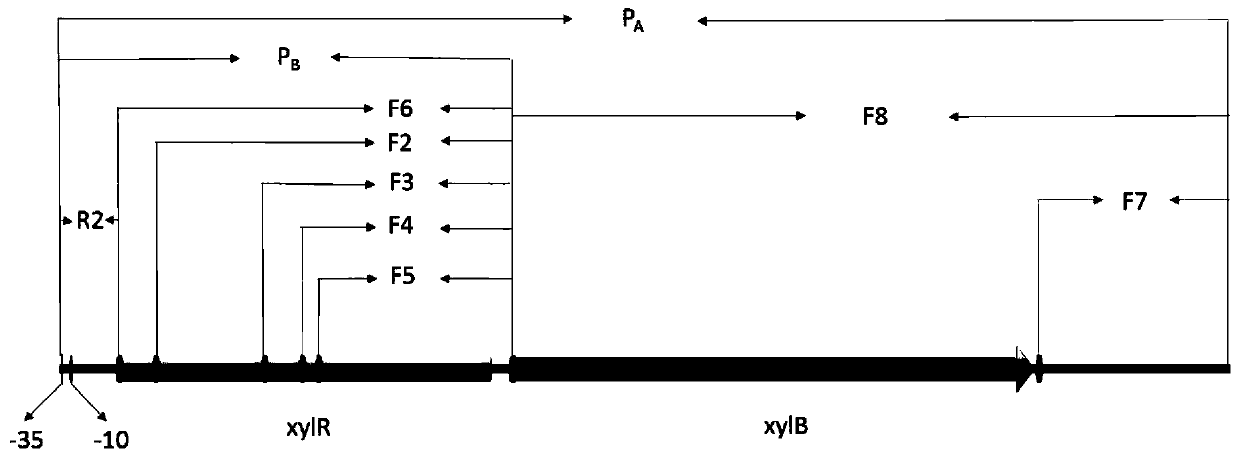
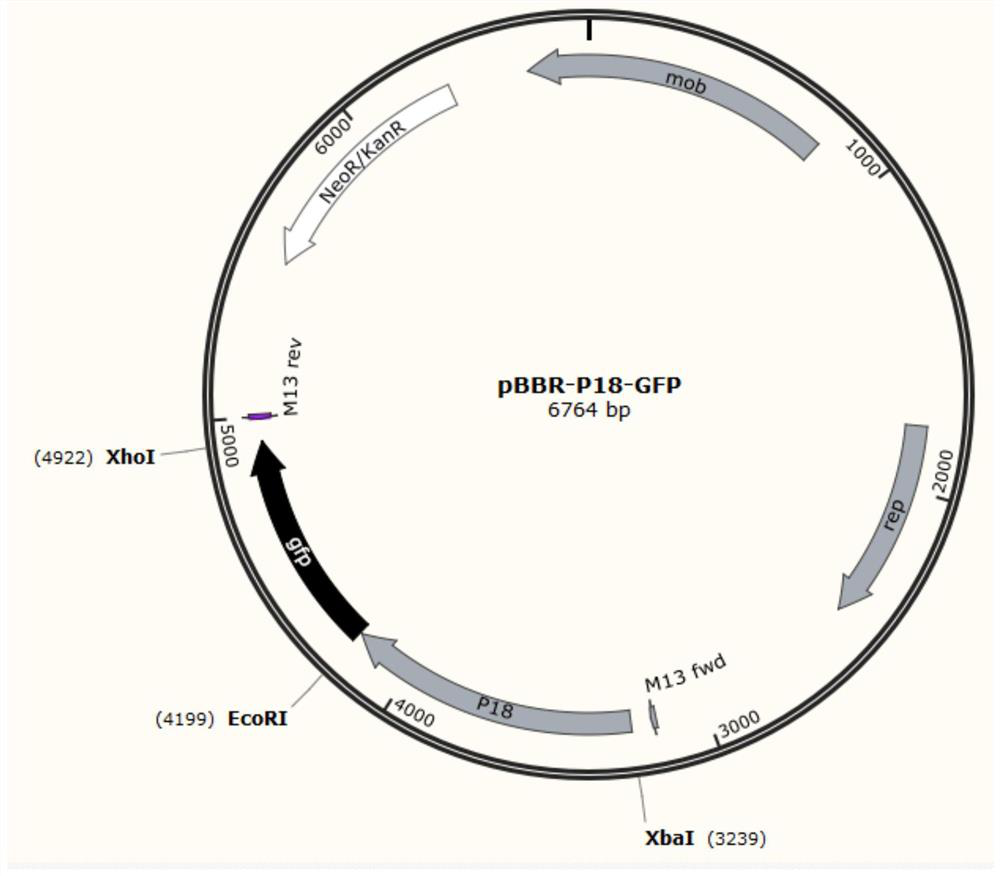
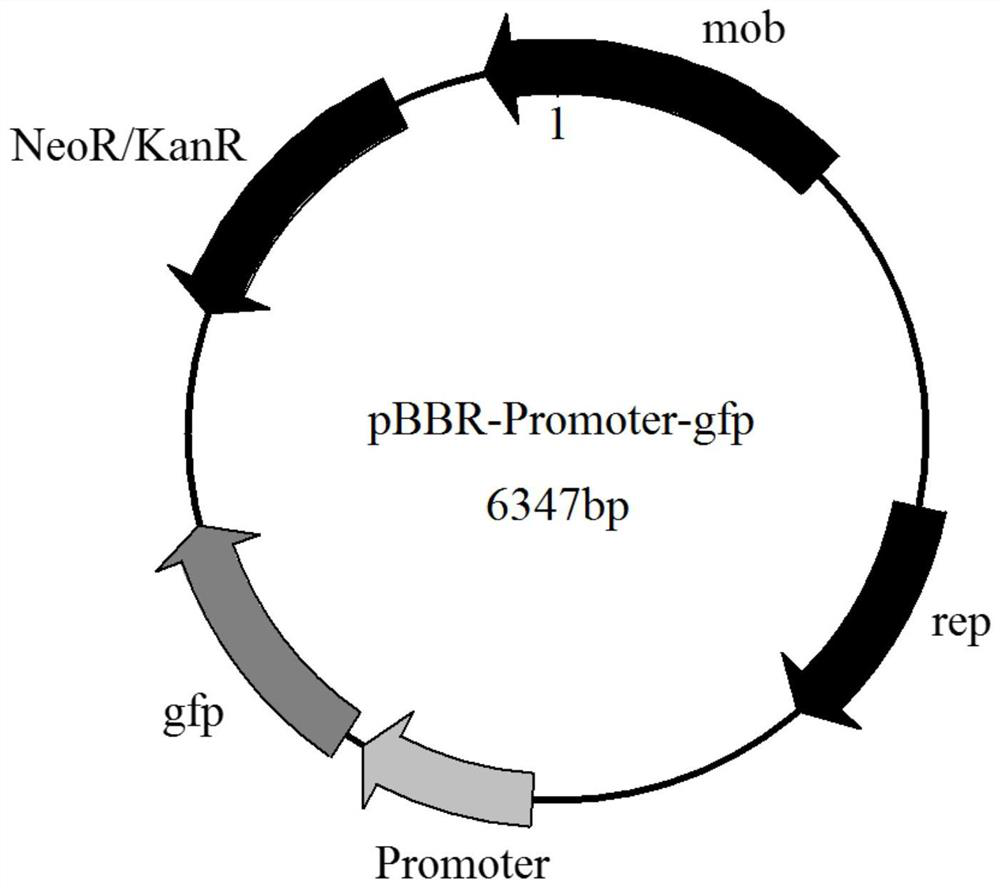
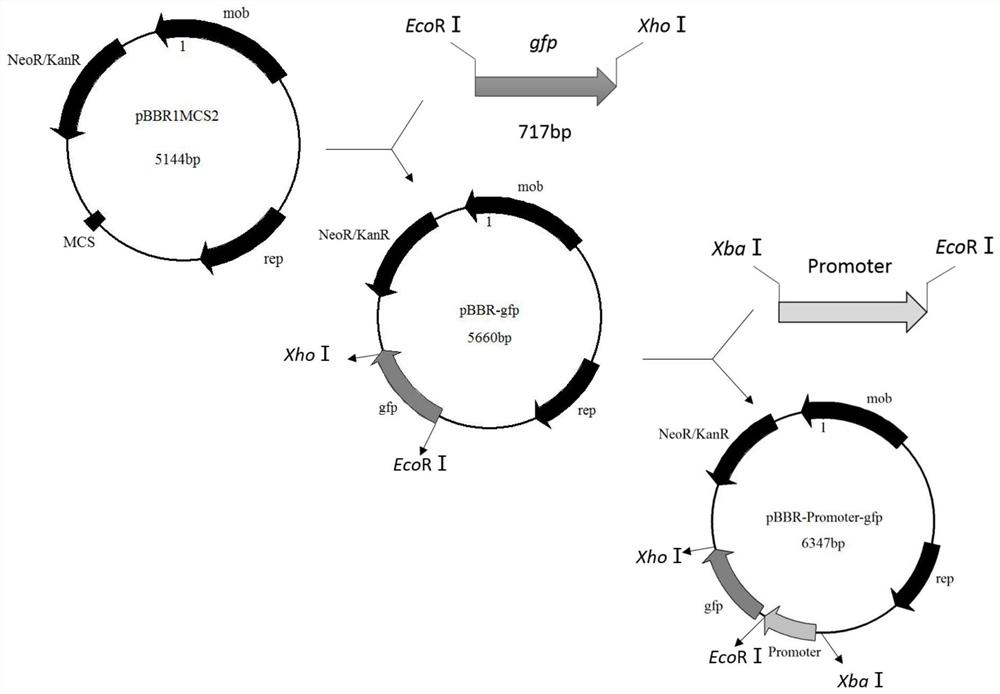
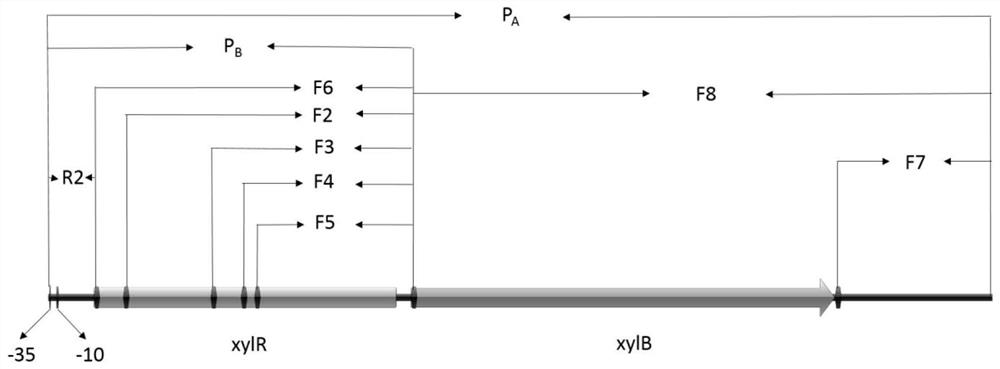
Xylose-induced promoter and plasmid vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a xylose-induced promoter. By amplifying a xylose-induced promoter in sinorhizobium meliloti, bioinformatics analysis and function verification are carried out, the xylose-induced promoter which can be widely applied to gene expression, genetic gene operation and strain improvement in alpha-proteobacteria such as Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosarum and Sinorhizobium adhaerens is obtained, and the nucleotide sequence of the promoter is SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the xylose-induced promoter, a method for constructing a genetic engineering strain by using thepromoter, a corresponding strain, and application of a host cell to induction and starting of expression of a target gene under xylose inducible conditions.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for further denitrogenation by using wood and rotten wood
InactiveCN103663723AHigh activityIncrease reproduction speedTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSurvivabilityAnaerobic bacteria
The present invention discloses a method for further denitrogenation by using wood and rotten wood. The method comprises: S1, continuously soaking rotten wood for 20-30 h by using a hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 9-10%, taking the rotten wood out, and rinsing; S3, placing the rotten wood into an anaerobic ammonium oxidation base inorganic salt solution to soak for 28-32 days; and S5, placing the rotten wood in a denitrogenation tank to carry out bacterial culture, maintaining the temperature in the denitrogenation tank at 20-30 DEG C, maintaining the oxygen concentration and the like of 5-8 mg / L, discharging sewage into the denitrogenation tank, and gradually growing the microbial flora on the rotten wood, wherein one-step denitrogenation can be achieved when the proportion of delta-Proteobacteria achieves more than 50%. According to the present invention, the rotten wood is adopted to create the nature parasitism environment for the anaerobic bacteria, and the survivability and the propagation speed of the bacteria are improved; and any chemical or organic substances are not required to be added during the denitrogenation process, aeration is not required, and the bacteria in the sewage are directly utilized to carry out back-bite decontamination, such that raw material consumption is reduced, and manpower and resources are saved so as to reduce cost.
Owner:WUHAN BIHU ENVIRONMENTAL ENG DESIGN
Plant activator and a method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20200060100A1Superior resistance-inducing activityLow toxicityBiocideAnimal repellantsMetabolitePollution soil
The objective of the invention is to provide a plant activator with superior resistance-inducing activity and growth promoting activity and low toxicity and soil contamination. A plant activator comprising a fatty acid metabolite obtainable by a metabolism of a fatty acid with 4 to 30 carbon atoms by a proteobacteria under a dissolved oxygen concentration of 0.1-8 mg / L, and a method for manufacturing a plant activator comprising a fatty acid metabolite, comprising a step for fatty acid metabolism wherein a fatty acid with 4 to 30 carbon atoms is subjected to a proteobacterial metabolization under a dissolved oxygen concentration of 0.1-8 mg / L. A method for manufacturing a plant activator comprising a fatty acid metabolite, comprising a step for fatty acid metabolism wherein a fatty acid with 4 to 30 carbon atoms is subjected to a proteobacterial metabolization under a dissolved oxygen concentration of 0.1-8 mg / L.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
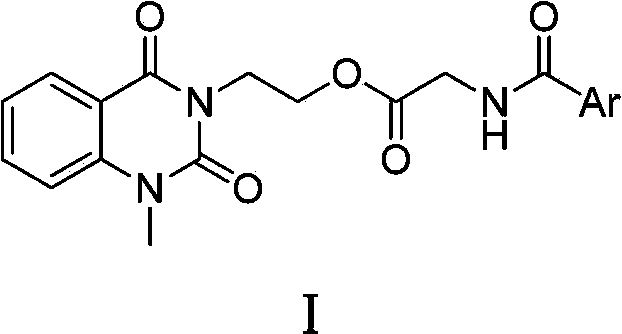
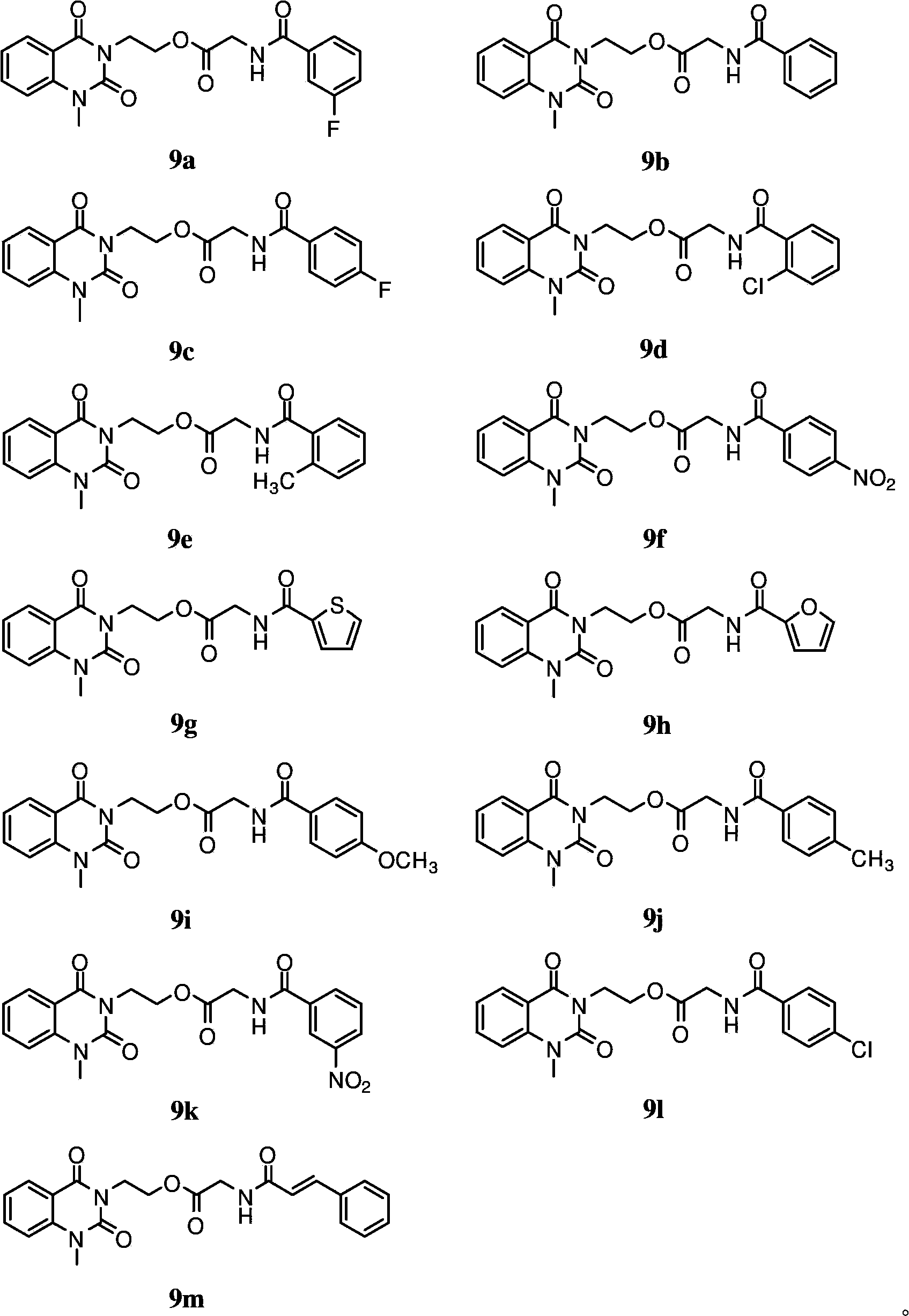
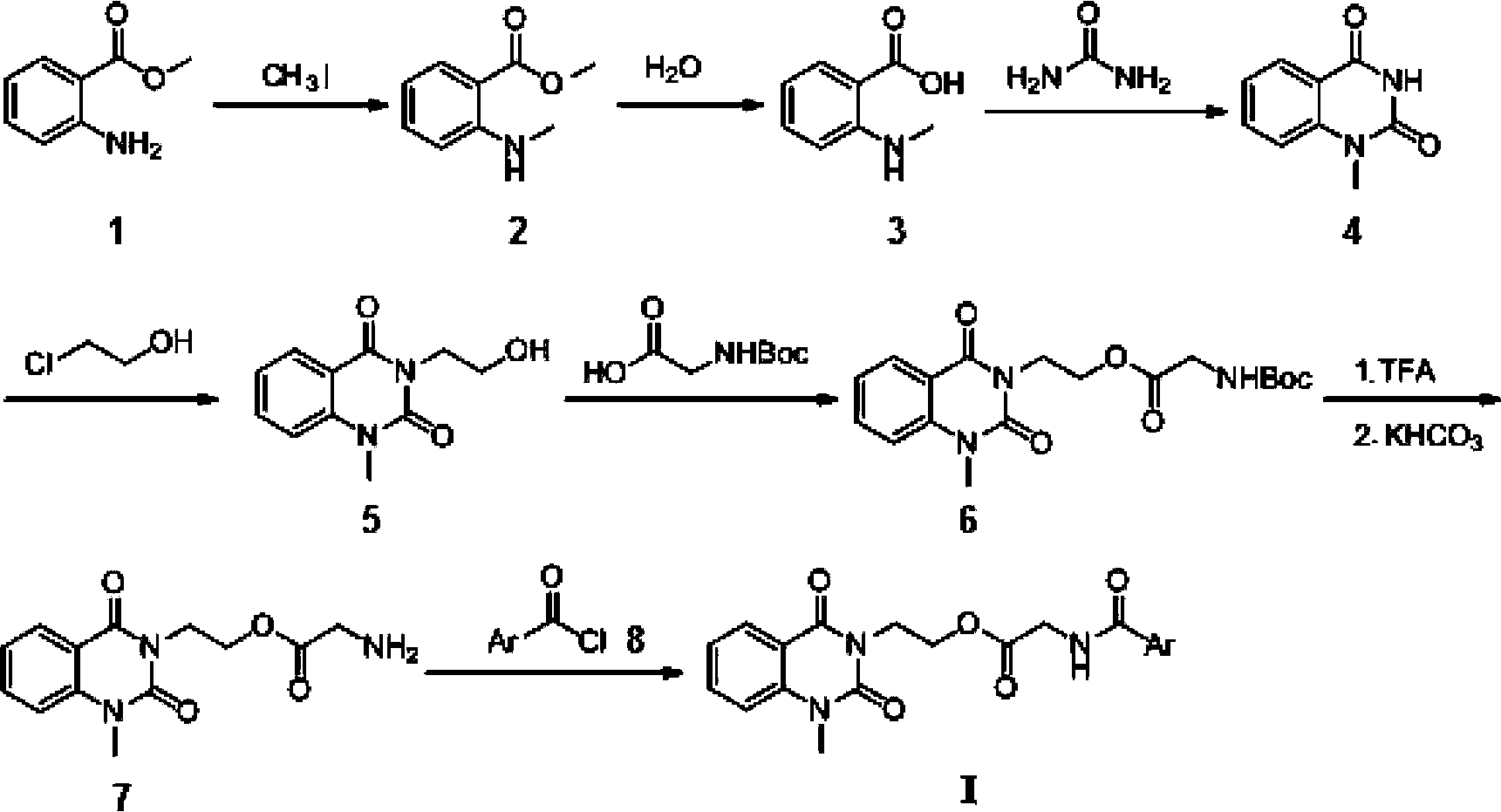
3-substituted-1-methyl-quinazoline-2,4-dione compounds, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102675226BEasy to prepareRaw materials are easy to getAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliAntifungal
The invention discloses 3-substituted-1-methyl-quinazoline-2,4-dione compounds shown in formula 1, a preparation method and application of the 3-substituted-1-methyl-quinazoline-2,4-dione compounds. Through in-vitro anti-microbial activity test, it is found that these compounds have certain inhibitory activity on gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis), gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, proteusbacillus vulgaris, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and fungus (Nostoc, Candida Albicans). Inhibitory activities of partial compounds on partial tested strains are approximate to or even superior to those of existing drugs such as streptomycin sulfate and polyoxin D. The compounds are especially sensitive to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, can be prepared into antibacterial and / or anti-fungal drugs, and have the advantages of simple preparation method, easily-accessible materials and low cost.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
New immunogenic compositions
PendingUS20220218810A1Reduce transmissionEfficient use ofBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyImmunity response
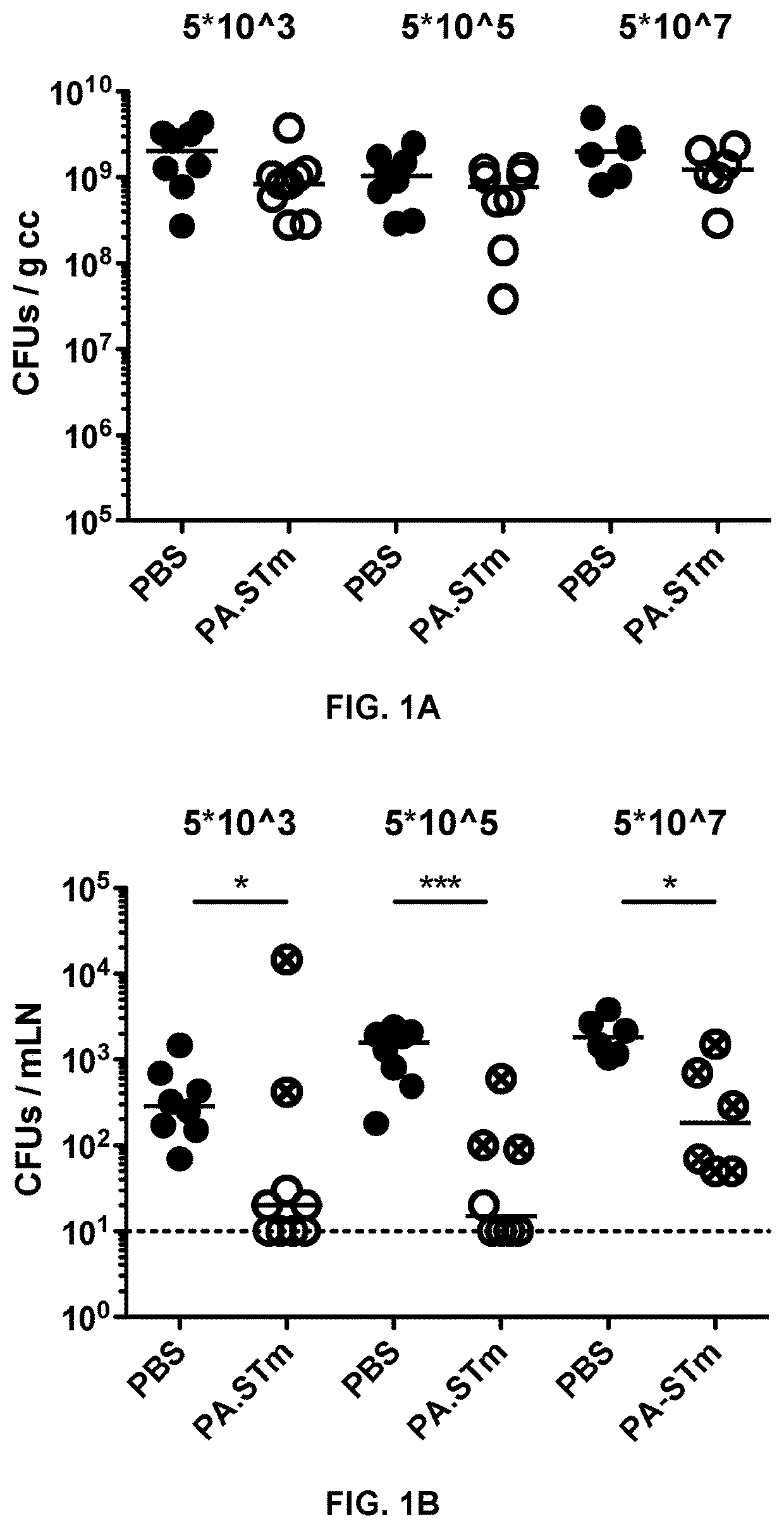
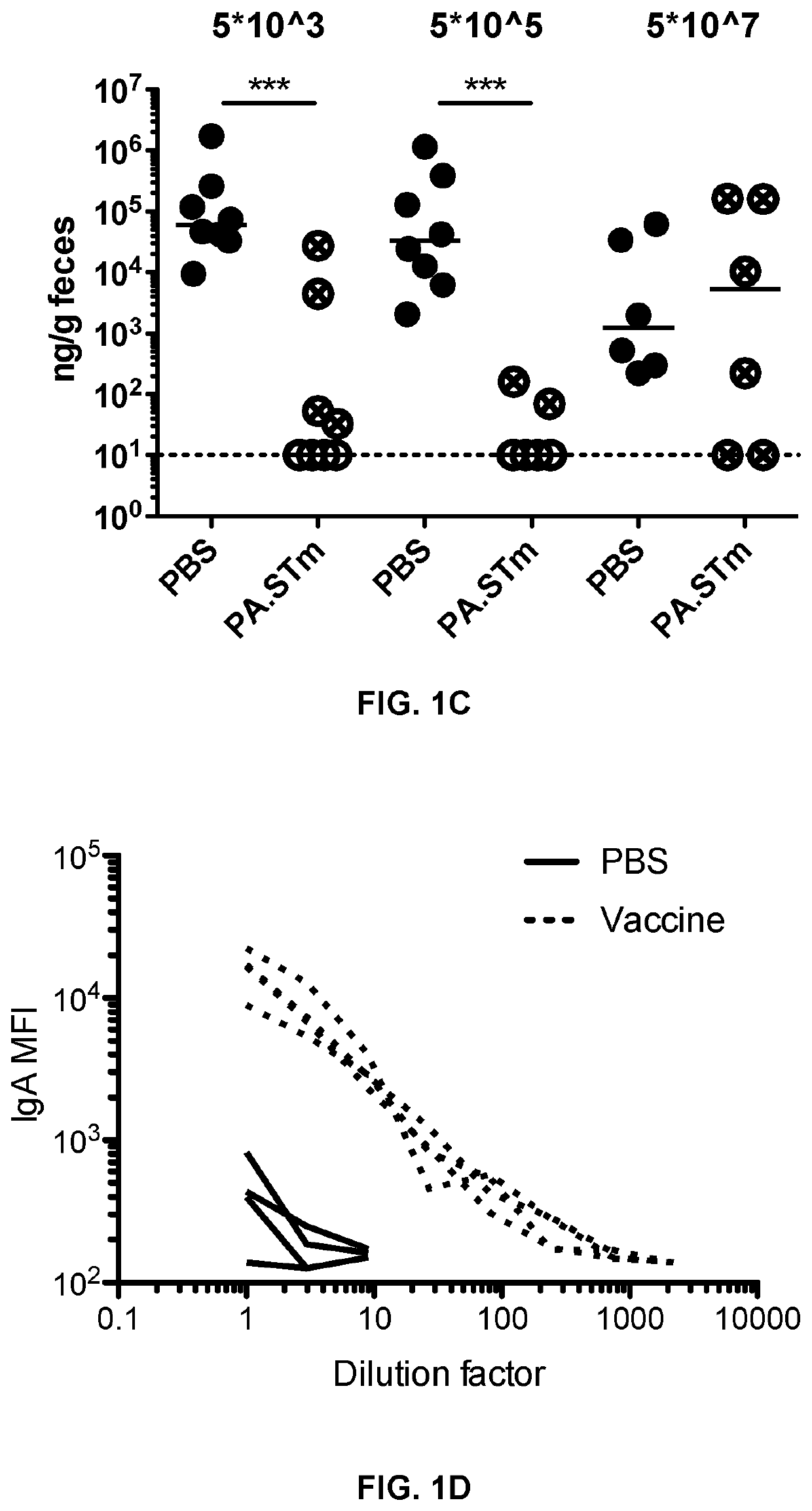
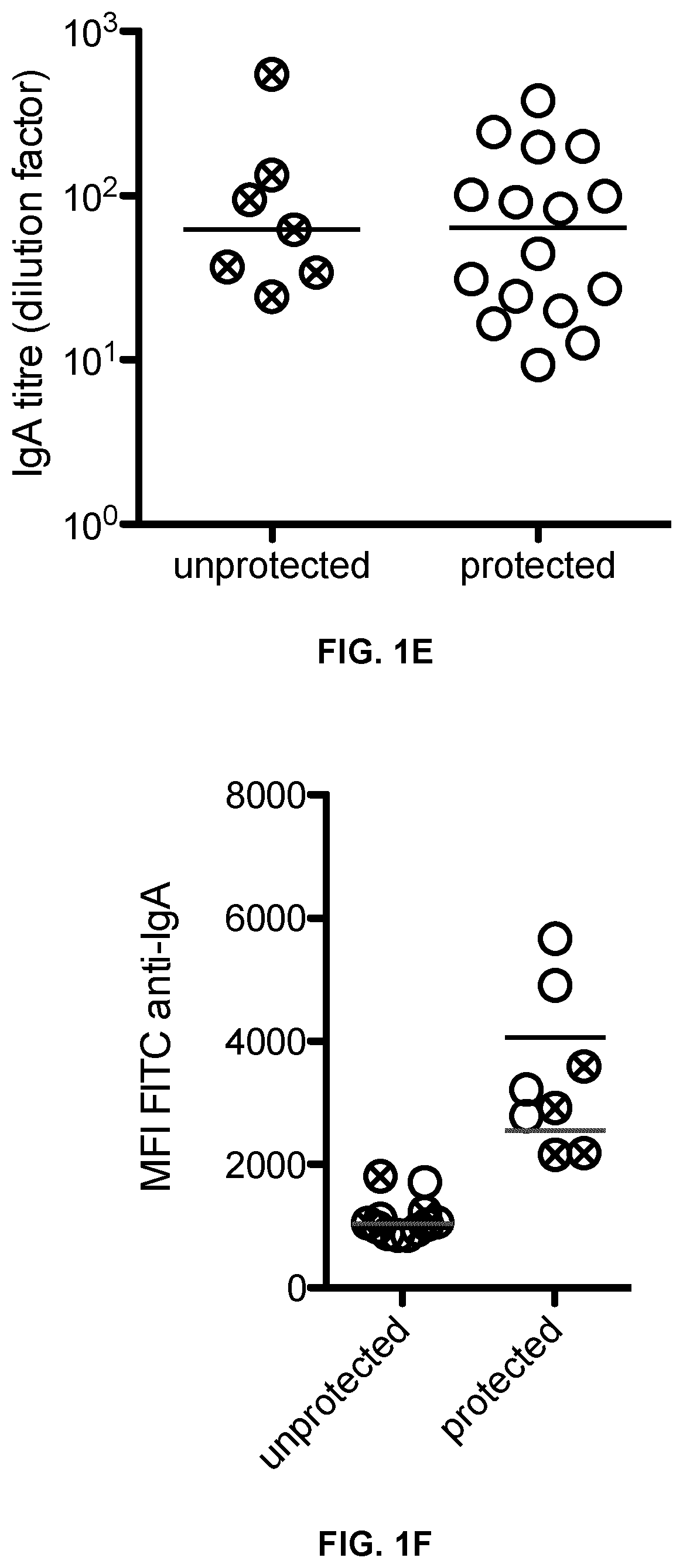
The present invention relates to an immunogenic composition for Proteobacteria protection and reduced transmission. We have identified Proteobacteria serovar variant combinations that generate an immune response capable of robustly driving bacterial enteropathogens into an evolutionary dead end and reducing the transmission of the bacterium. These inactivated immunogenic positions and typically oral vaccines are easy to apply, cheap to produce, and can be stored long-term without cold-chain requirements making them ideal for application in livestock, or in resource-poor areas. They are believed to be the only immunogenic compositions and vaccine formulations capable of breaking the chain of transmission for these types of pathogen.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
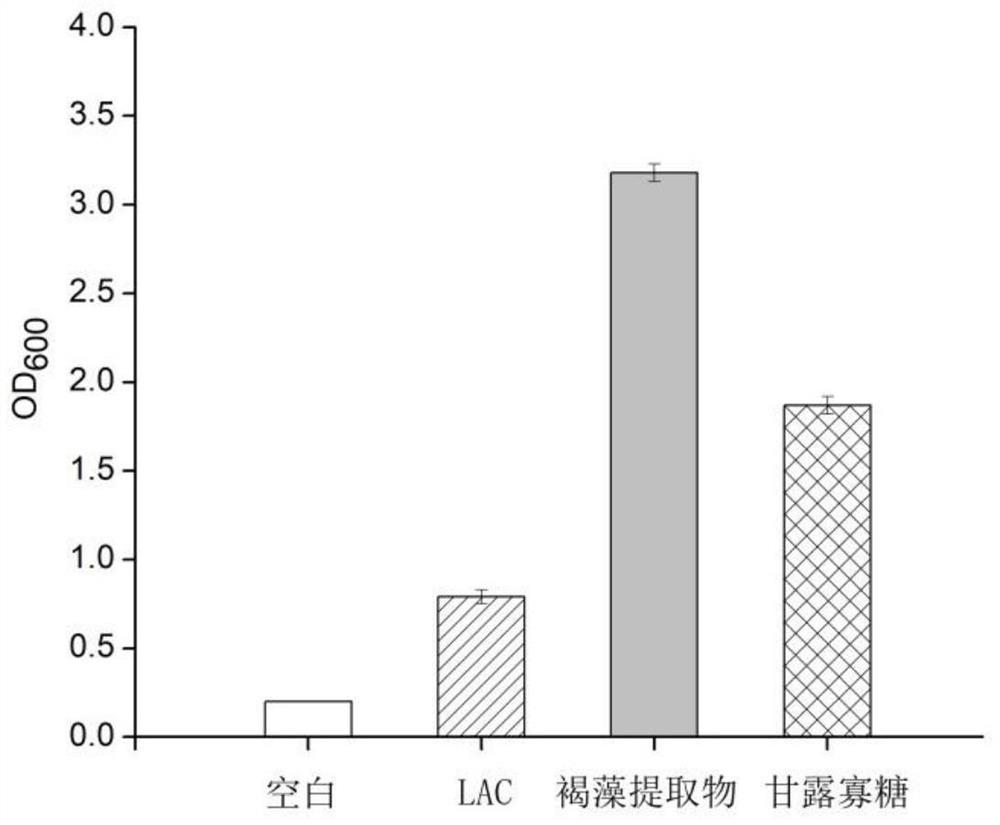
Composition based on brown algae extract and lactobacillus reuteri and application of composition
ActiveCN113209141APromote growthImprove the ability to produce short-chain fatty acidsMetabolism disorderDigestive systemBiotechnologyFasting glucose
The invention discloses a composition based on brown algae extract and lactobacillus reuteri and application of the composition. The composition disclosed by the invention is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 30 to 97 parts of brown algae extract and 3 to 70 parts of lactobacillus reuteri. The combination of the brown algae extract and the lactobacillus reuteri can promote field planting of the lactobacillus reuteri in intestinal tracts, and the field planting rate is remarkably increased. The combination of the brown algae extract and the lactobacillus reuteri can significantly reduce the fasting blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin concentration of type 2 diabetes model mice, improve the insulin secretion amount, significantly improve the abundance of beneficial bacteria such as bifidobacterium and lactobacillus in intestines, reduce the abundance of conditioned pathogenic bacteria such as enterococcus and proteobacteria. Good application prospects are realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of flavonoid glycosides of blancia in improving intestinal barrier function
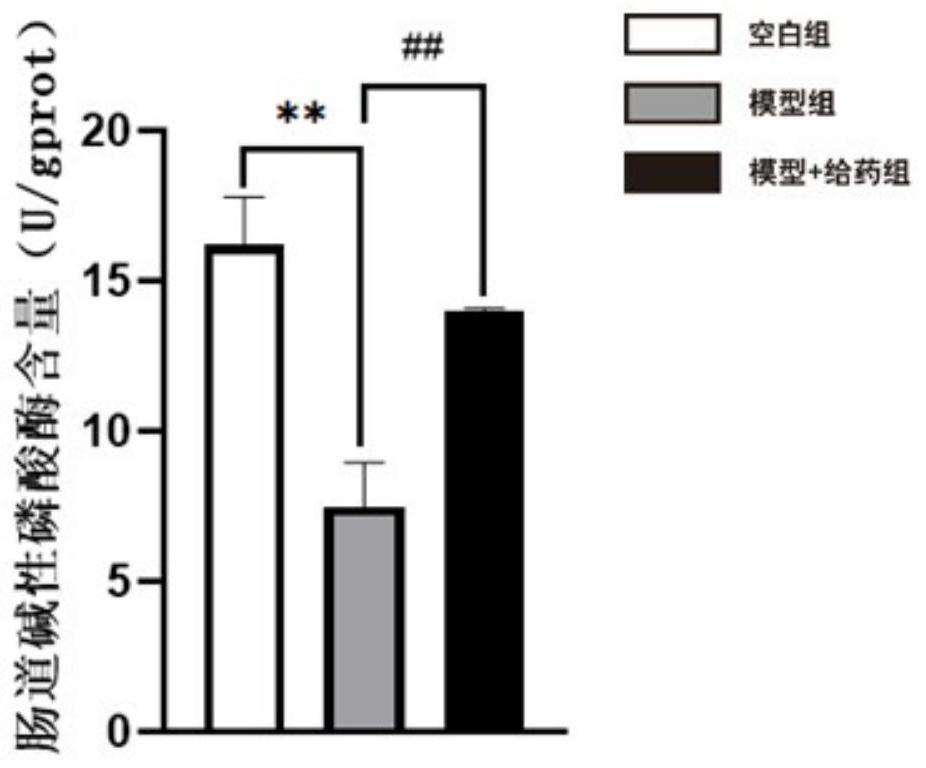
ActiveCN112791091BReduced serum endotoxin levelsIncrease abundanceOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemPropanoic acidIntestinal alkaline phosphatase
The invention discloses the application of flavonoid glycosides of varicoseline in improving intestinal barrier function, and belongs to the technical field of drug development. In the present invention, the main active ingredient of blalicius seeds - the flavonoid glycosides of blalicius, is applied to improve intestinal barrier function. This natural substance can significantly improve the intestinal barrier function of animals, reduce the serum endotoxin content of mice with impaired barrier function, increase the intestinal alkaline phosphatase level and tight junction protein expression, and short-chain fatty acids in feces Propionic acid and butyric acid content, and can adjust the balance of intestinal flora, reduce the relative abundance of Firmicutes, and increase the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of improving Fenton oxidation method combined with solid microbial agents to remediate organic matter-contaminated soil
ActiveCN110125169BShort repair timePH requires no additional adjustmentContaminated soil reclamationIron sulfateMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a method for improving Fenton's oxidation combined with solid microbial agents to restore organic-contaminated soil, adding sodium pyrophosphate or malic acid to the sieved soil, adding ferric sulfate solution, and then adding hydrogen peroxide; Proteobacteria, β‑proteobacteria, yeasts, Pseudopora cyanicola, Pleurotus pellagra, Trametesmetamorphus, Bacillus subtilis, photosynthetic bacteria and lactic acid bacteria are cultured in liquid medium; then inoculated with straw, peanuts The microbial strain carrier composed of shell, bran and sawdust is cultivated and dried to obtain a solid bacterial agent; the solid bacterial agent is added to the soil to maintain soil moisture for restoration. The method of the present invention adopts the method of improving the Fenton reaction combined with microorganisms, the degradation rate is very high, up to 85-98.5%, and the repair time is short; the reaction can be carried out under the neutral pH condition of the soil, without additional adjustment of the soil pH; Use Fe3+ instead of Fe2+ to avoid the instability of hydrogen peroxide during Fe2+ reaction.
Owner:重庆桂溪生态环境科技有限公司
a no 3 - Method for reducing hexavalent chromium in methane matrix biofilm
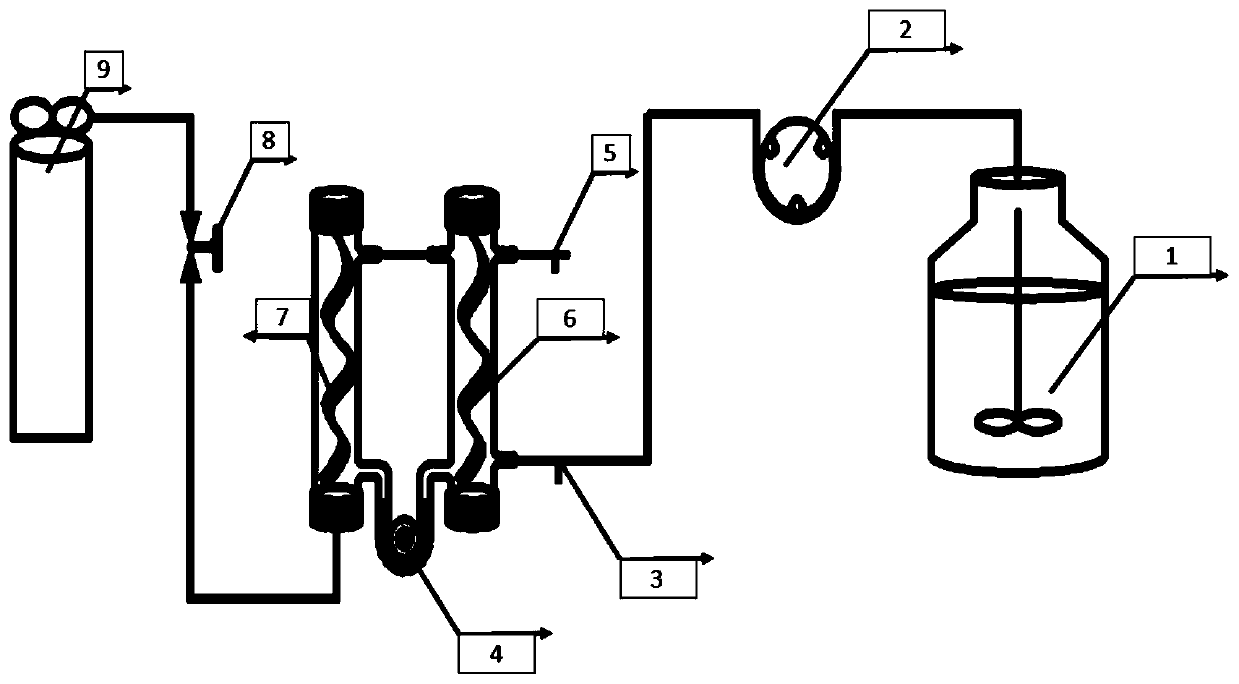
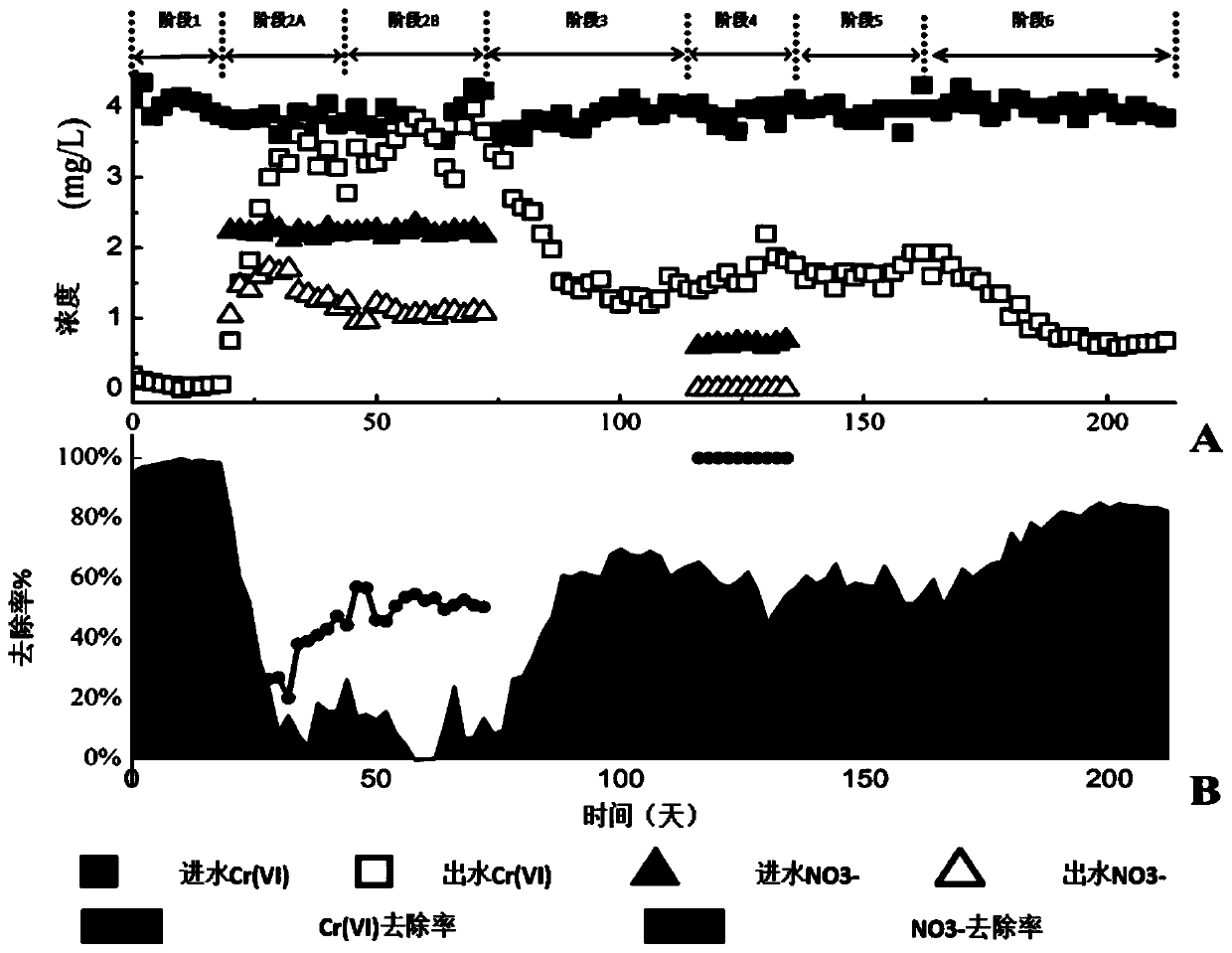
ActiveCN108675445BEnhanced inhibitory effectIrreversible inhibitionBiological treatment regulationWater contaminantsActivated sludgeBiofilm
The invention relates to a biological reduction technology for composite pollutants, and aims to provide a method for reducing hexavalent chromium in a methane matrix biomembrane by NO<3><->. The method includes the following steps: adding Na2CrO4 and NaNO3 to an inorganic medium, and allowing the obtained medium, for later use, to stand under a micro-aerobic condition; introducing simulated wastewater into a methane matrix membrane bioreactor, adding CrO<4><2-> and activated sludge, and carrying out self-circulation to obtain the a bacterial solution; introducing the simulated wastewater andCH4 into the reactor in a continuous flow manner, and controlling the concentration of NO<3><-> in inlet water in stages; and ensuring that the concentrations of the CrO<4><2-> and NO<3><-> in outletwater reach a steady state for at least 10 days in every running stage. Compared with the prior art, the method has the following advantages: the high load of NO<3><-> has a significant irreversible inhibition effect on the reduction of Cr(VI); the introduction of the NO<3><-> deceases Meiothermus originally involved in the reduction of Cr(VI) and makes alpha-proteobacteria enriched; and when theNO<3><-> is removed, beta-proteobacteria become important, so the beta-proteobacteria play a potential role in Cr(VI) reduction.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
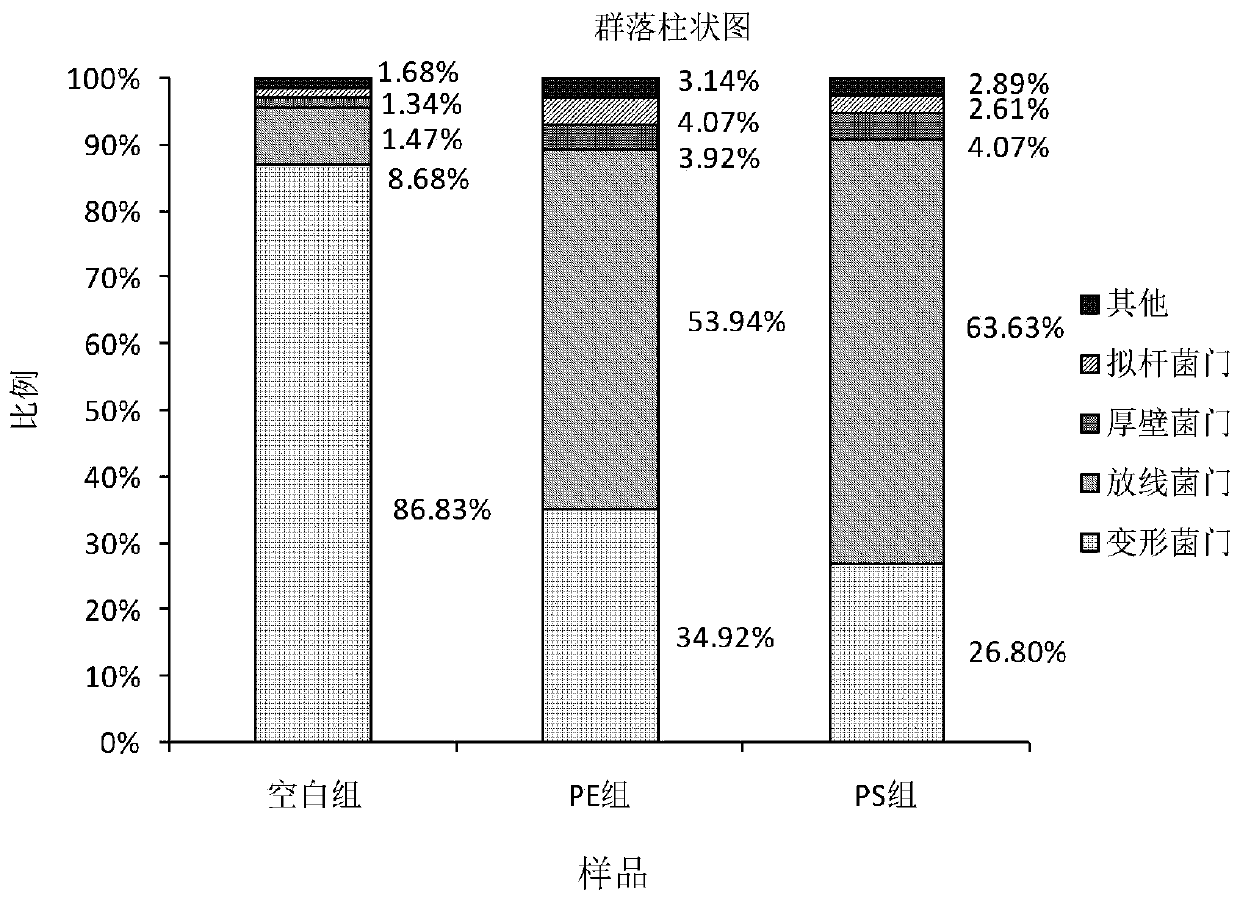
Method for evaluating ecotoxicological impact of microplastics
PendingCN110747265AQuick checkQuick evaluationMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryIntestinal microorganismsOrganism
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the ecotoxicological impact of microplastics. The method includes the following steps that (1) artemia exposure experiment is performed; (2) intestinaltract collecting is performed; (3) DNA extraction and PCR amplification are performed; (4) Illumina Miseq sequencing is performed; (5) data processing is performed; (6) data analysis is performed, specifically, cluster analysis of the processed data finds that the main phylums in each group at the phylum level are Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria; and (7) ecotoxicology evaluation is performed, specifically, the microplastics have a certain toxic effect on organisms. The method is simple in operation, high in accuracy and short in experimental period, and can rapidly detect intestinal microorganisms. The method can quickly and accurately evaluate the ecotoxicological impact of the microplastics.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for detecting intestinal flora to assist in analysis of bronchial asthma by using 16srDNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequencing technology
PendingCN114717340AIatrogenic injuryEffective judgmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesFeces
The invention discloses a method for detecting intestinal flora to assist in analysis of bronchial asthma by using a 16SrDNA sequencing technology, which comprises the following steps: S1, taking fecal tissues of a plurality of healthy people, carrying out quantitative detection and sequencing on bacteria in the fecal tissues, and carrying out door-to-door statistics on proportion data of bacteroides, firmicobacteria, proteobacteria and deferribacteria; s2, fecal tissues of a patient are taken, bacteria of the fecal tissues are subjected to quantitative detection and sequencing, and proportion data of bacteroides, firmicobacteria, proteobacteria and deferribacteria are subjected to door-to-door statistics; and S3, comparing the patient data obtained in the step S2 with the healthy population data obtained in the step S1 to obtain a detection result. According to the method, the 16SrDNA sequencing technology is adopted, the intestinal flora is detected, the detection result is compared with the intestinal flora detection result of a normal healthy patient, the asthma and asthma types are judged in an auxiliary mode, the accuracy rate is high, and the great auxiliary diagnosis reference value is achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Feed for inhibiting intestinal proteobacteria of triploid rainbow trout
InactiveCN111109438APromote proliferationAffect developmentFood processingClimate change adaptationCelluloseAnimal science
The invention discloses a feed for inhibiting intestinal proteobacteria of triploid rainbow trout, belongs to the technical field of aquatic feeds, and relates to a feed for improving intestinal floraof the triploid rainbow trout. The feed provided by the invention is to solve the technical problem that of the intestinal proteobacterium diseases of the triploid rainbow trout are epidemic with enlargement of a culture scale and reinforcement of a culture density and continuous increase of environmental stress. The feed is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 200 parts of wheat middling, 398 parts of fish meal, 290 parts of soybean meal, 60 parts of fish oil, 20 parts of phospholipid oil, 10 parts of monocalcium phosphate, 3 parts of a vitamin premix, 2 parts of a traceelement premix, 2 parts of choline chloride, 5-10 parts of xylooligosaccharide and 0-5 parts of cellulose. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple and scientific steps, reasonable formula and the like. The feed disclosed by the invention can inhibit the intestinal proteobacteria of the triploid rainbow trout, so intestinal health is improved, and rapid growth is promoted.According to the feed disclosed by the invention, in breeding practice, the feed coefficient is reduced by 0.08, and the growth speed is increased by 0.7%-9%.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
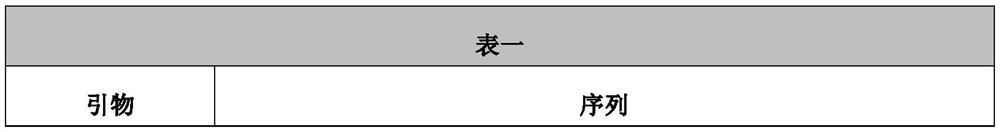
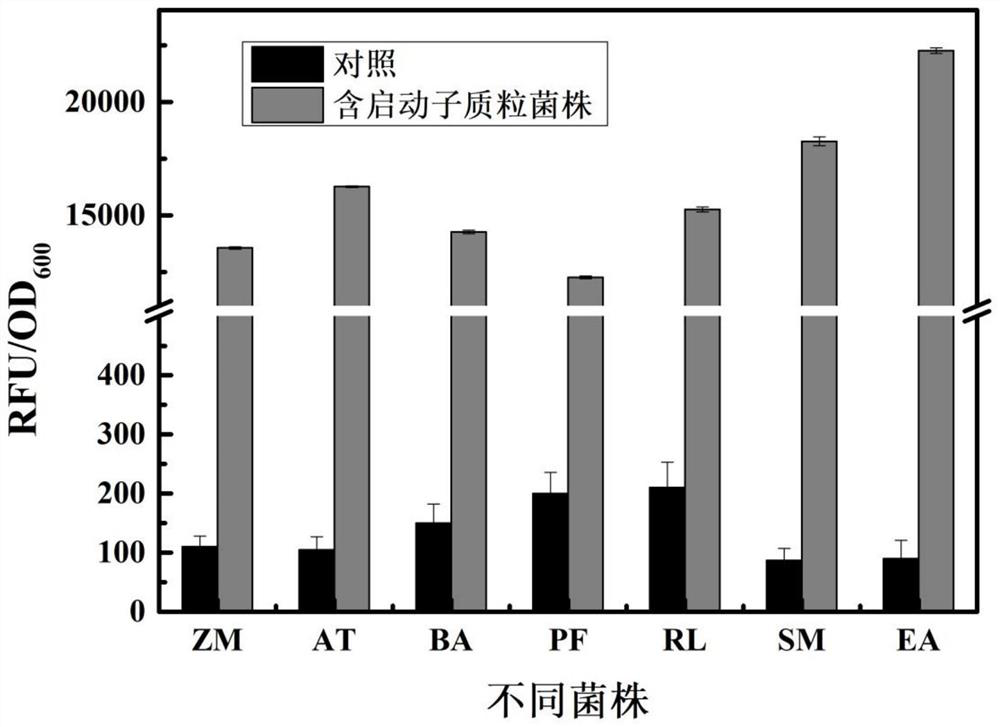
The strong promoter derived from the cohesin bacteria and its plasmid vector and application
The invention discloses a strong promoter derived from the cohesin bacterium and its plasmid carrier and application. In the present invention, by amplifying a strong promoter in S. cohescens and performing functional verification, the obtained promoter can be widely used in Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrification, tumorigenic A strong promoter for gene expression, genetic manipulation and strain improvement in α-proteobacteria such as Agrobacterium abortus, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosae and Sword bacteria adherent, its nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO: 1. The present invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a genetically engineered bacterial strain using the promoter, a corresponding bacterial strain, and the application of host cells in promoting the expression of an objective gene.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A kind of strong promoter and its plasmid carrier and application
In the present invention, by amplifying a strong promoter in S. cohescens, bioinformatics analysis and functional verification are carried out to obtain a promoter that can be widely used in Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, and Pseudomonas denitrification. Strong promoters for gene expression, genetic manipulation and strain improvement in α-Proteobacteria such as A. The nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO:1. The present invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a genetically engineered bacterial strain using the promoter, a corresponding bacterial strain, and the application of host cells in promoting the expression of an objective gene.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A biomarker, kit, detection method and application thereof for detecting or assisting in detecting proton ray radiation
ActiveCN113957143BTimely accident rescueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicroorganismFlora
The invention relates to a biomarker for detecting or assisting in detecting proton ray radiation, a kit, a detection method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The present invention provides a microbial flora biomarker for detecting or assisting detection of proton ray radiation, said microbial flora including Cyanophyta Cyanobacteria , ε Proteus Epsilonbacteraeota , Anaerovorax , Helicobacter Helicobacter at least one of the In the present invention, by detecting the expression amount or relative expression amount of the microbial flora DNA, it is determined whether the object to be tested has been exposed to proton ray radiation, and timely accident rescue, wounded treatment and clinical application are of great significance to radiation treatment.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit and method for predicting sepsis infection
ActiveCN108486228BReliable Evidence of InfectionReduce the likelihood of infectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerIntestino-intestinal
The invention discloses a fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit and a method thereof for predicting sepsis infection. The kit includes: Bacteroidetes forward primer and reverse primer, Firmicutes forward primer and reverse primer, Proteobacteria forward primer and reverse primer, Actinobacteria forward primer and reverse primer Primers, PCR master mixes and reagents for fluorescent quantitative PCR detection methods. The invention provides reliable evidence of infection and the etiological type of infection for the diagnosis of sepsis by detecting the classification level structure of human intestinal flora, can be used for auxiliary diagnosis of clinical sepsis, and provides relevant antibiotic treatment for patients. Effective basis, good prospects for clinical application.
Owner:FLASHDX SHENZHEN INC
Method for improving gas production rate by adding sodium propionate to domesticate microbial community of anaerobic fermentation system and application of method
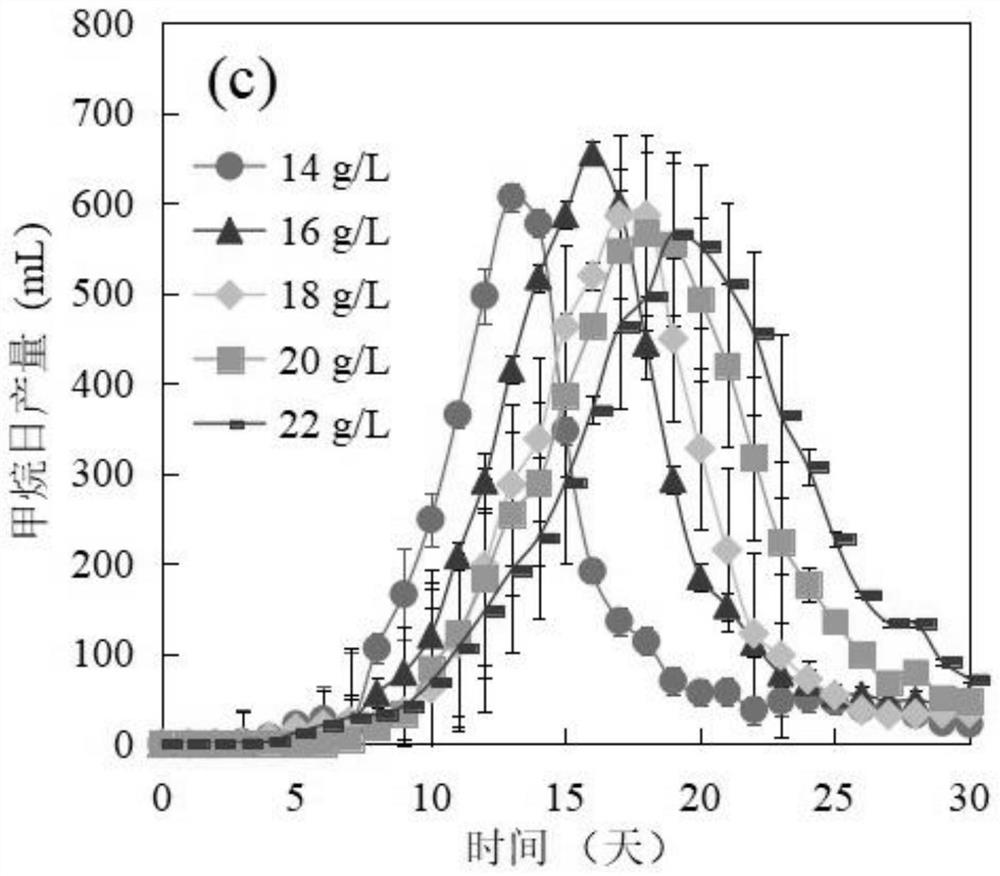
PendingCN114854793AIncrease productionHigh cumulative yieldBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaPropanoic acidMethane yield
The invention provides a method for improving gas yield by adding sodium propionate to domesticate microbial communities of an anaerobic fermentation system and application of the method, and belongs to the technical field of environmental protection. According to the method, sodium propionate with different concentrations is added into biogas residues subjected to anaerobic fermentation, and then culture is performed through a culture medium, so that the conclusion that the yield of methane is obviously and regularly changed and the diversity and richness of microbial communities are respectively improved along with the increase of the concentration of sodium propionate is obtained; meanwhile, the optimal sodium propionate concentration, the optimal fermentation time and the like are determined when the methane daily yield and the methane cumulative yield are the highest, and the relative abundance of the firmicobacteria bacteria, the proteobacteria bacteria, the methanosarcina archaea and the methanomycorrhiza archaea is the maximum; therefore, the purposes of accurately controlling and remarkably increasing the methane yield and improving the microbial community composition are achieved.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Application of cinnamic acid derivative in preparation of medicine for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
PendingCN113648295ARestrict growthRelieve stressOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemBacteroidesPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses application of a cinnamic acid derivative in preparation of a medicine for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. Experiments prove that the cinnamic acid derivative can be used for regulating intestinal flora, increasing the number of Bacteroides bacteria and inhibiting abundance of alpha-proteobacteria; the medicine has a good effect on treating the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by restoring intestinal micro-ecological balance, wherein the application is disclosed for the first time and has outstanding substantive features. The derivative is applied to preparation of medicines for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases and has a good market application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN OPEN UNIV
High-efficacy crispri system and strong synthetic promoters for alphaproteobacteria and gammaproteobacteria
Described herein are synthetic inducible promoters including 5′-(UP element)-(−35 element)-(spacer element)-(−10 element)-(discriminator element)-3′. Also included are vectors, α-Proteobacteria strains and γ-Proteobacteria strains including the synthetic inducible promoters. A Mobile-CRISPRi plasmid and methods of partially or fully knocking-down expression of a gene in α-Proteobacteria or γ-Proteobacteria are also described. Further included are methods of making an α-Proteobacteria or γ-Proteobacteria strain.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Xylose Inducible Promoter and Its Plasmid Vector and Application
The present invention amplifies the xylose-inducible promoter in Sinorhizobium meliloti, conducts bioinformatics analysis and functional verification, and obtains a gene that can be widely used in Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, and denitrification pseudomonas. Xylose for Gene Expression, Genetic Genetic Manipulation, and Strain Improvement in α-Proteobacteria, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosae, and Sinorhizobium sativaceae Inducible promoter, its nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ ID NO:2. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing a xylose-inducible promoter, a method for constructing a genetically engineered bacterial strain by using the promoter, a corresponding bacterial strain, and an application of host cells to induce and start expression of a target gene under xylose-inducing conditions.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Luterial and method for isolating and culturing the same
The present invention relates to blood-derived luterial and a method for isolating and culturing the same. The luterial according to the present invention is a cell or cell-like structure having the following characteristics: (1) it is present in body fluids, including blood, sperm, intestinal juices, saliva, and cellular fluids; (2) it shows a positive staining with Janus green B, Acridine Orange and Rhodamine 123 in an immunofluorescence test; (3) in an optimal environment (pH 7.2-7.4), it has the property of expressing the genes homologous to beta-proteobacteria and gamma-proteobacteria, and has a size of 30-800 nm; (4) in an acidic environment, it has the property of expressing not only the genes homologous to beta-proteobacteria and gamma-proteobacteria, but also eukaryote-derived genes (particularly Streptophyta gene), and grows to a size ranging from 400 nm or more to 2000 nm or more; (5) it is involved in ATP production under normal conditions; and (6) it differs from mitochondria, completely differs from exosomes, and has fusion characteristics corresponding to those of an intermediary between a prokaryote and an eukaryote.
Owner:LUTERION CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com