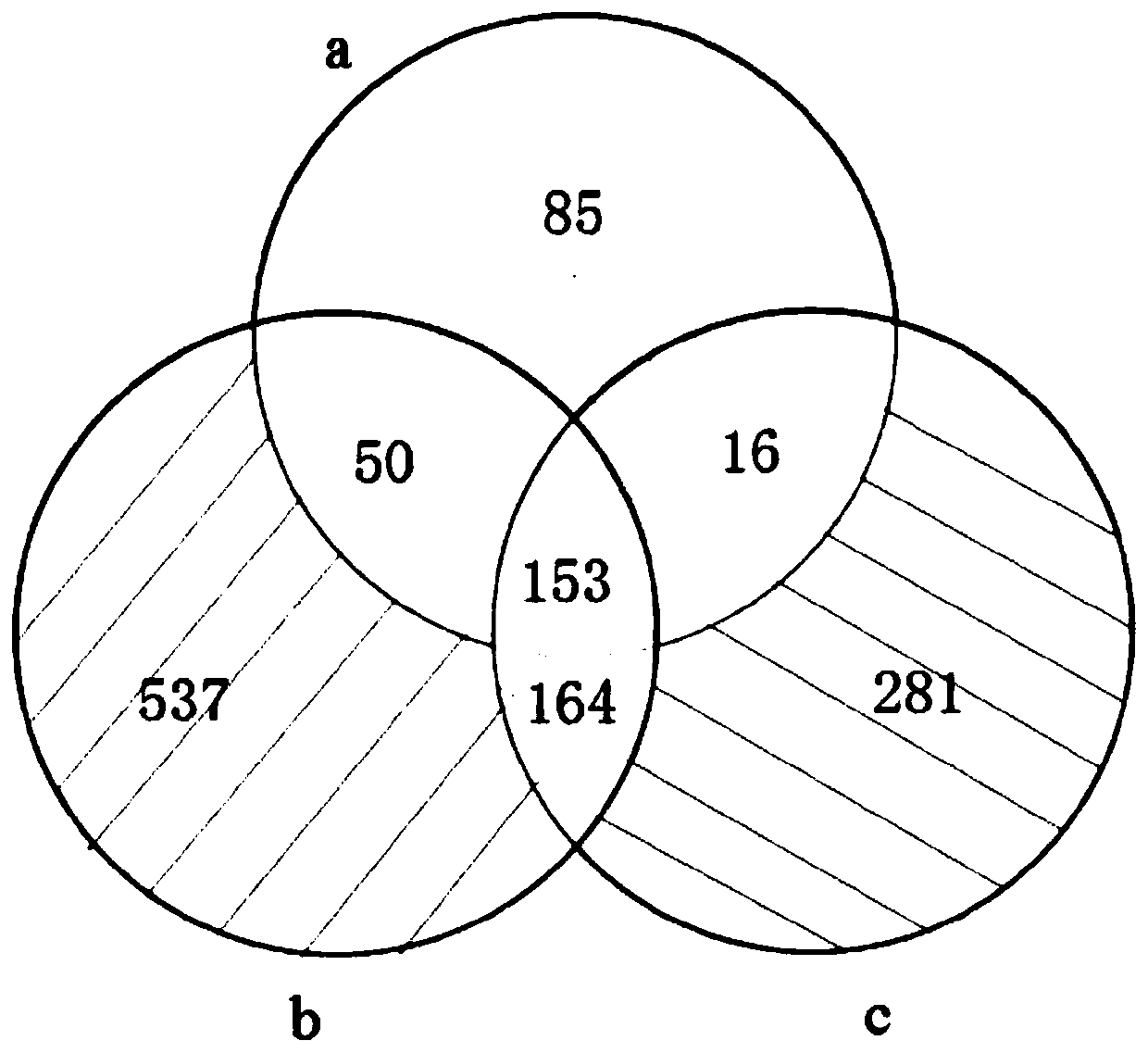
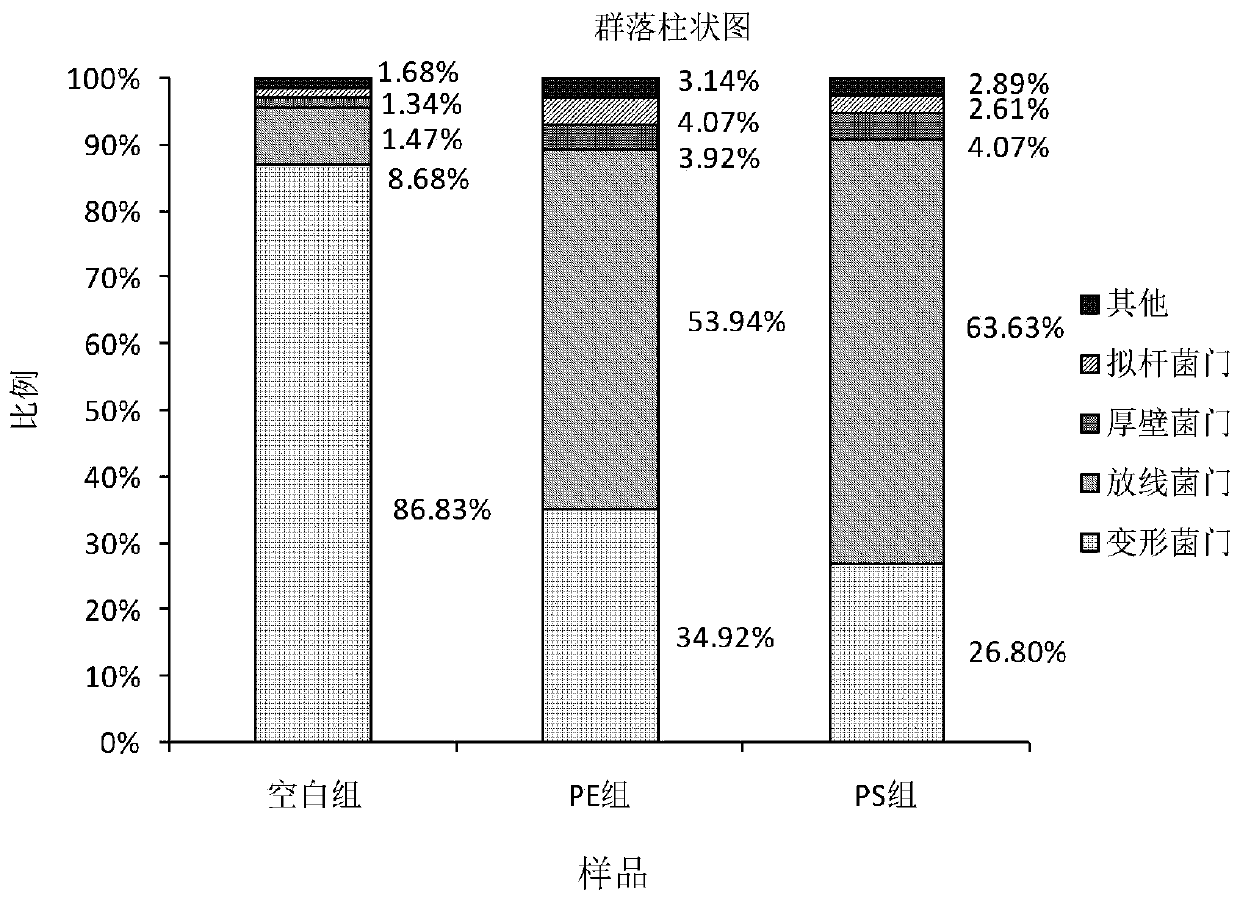
Method for evaluating ecotoxicological impact of microplastics
A technology of toxicology and microplastics, applied in the field of high-throughput sequencing, can solve problems such as the analysis of the intestinal flora of artemia that has not been applied, and achieve the effect of short experimental period, simple operation and rapid detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] A method for evaluating the ecotoxicological impact of microplastics, comprising the following steps:
[0033] (1) Artemia exposure experiment:
[0034] Absorb mature Artemia and put it into artificial seawater as the blank group, put into the suspension of polyethylene microspheres with a concentration of 0.13g / L as the experimental group 1 (PE group), put into the polystyrene microspheres with a concentration of 0.13g / L The suspension is the experimental group 2 (PS group), and each group is equipped with 6 parallel sample beakers, and each beaker draws 50 mature artemia individuals, feeds 30ml of chlorella every other day, and cultivates them under the conditions of 28°C and light intensity of 1500lx 9 days;
[0035] The solvent of the plastic microsphere suspension is artificial sea water;
[0036] (2) Collect intestines:
[0037] Draw Artemia in the blank group and the experimental group, dissect the Artemia in the ultra-clean bench, and collect the Artemia inte...
Embodiment 2
[0060] (1) Artemia exposure experiment:
[0061] Absorb mature Artemia and put it into artificial seawater as the blank group, put it into the polyethylene microsphere suspension with a concentration of 0.1g / L as the experimental group 1, and put it into the polystyrene microsphere suspension with a concentration of 0.1g / L as the experimental group. Group 2, set up 6 parallel sample beakers in each group, absorb 50 mature artemia individuals in each beaker, feed 30ml chlorella every other day, and cultivate for 10 days under the condition of 25°C and light intensity of 2000lx;
[0062] The solvent of the plastic microsphere suspension is artificial sea water;
[0063] (2) Collect intestines:
[0064] Draw Artemia in the blank group and the experimental group, dissect the Artemia in the ultra-clean bench, and collect the Artemia intestinal tract;
[0065] (3) DNA extraction and PCR amplification:
[0066] according to Soil Kit Instructions Extract the total intestinal DNA ...
Embodiment 3
[0081] (1) Artemia exposure experiment:
[0082] Absorb mature Artemia and put it into artificial seawater as the blank group, put it into the polyethylene microsphere suspension with a concentration of 0.15g / L as the experimental group 1, and put it into the polystyrene microsphere suspension with a concentration of 0.15g / L as the experimental group. Group 2, set up 6 parallel sample beakers in each group, absorb 50 mature artemia individuals in each beaker, feed 30ml of chlorella every other day, and cultivate for 8 days under the condition of 30°C and light intensity of 1500lx;
[0083] The solvent of the plastic microsphere suspension is artificial seawater;
[0084] (2) Collect intestines:
[0085] Absorb the Artemia in the blank group and the experimental group, dissect the Artemia in the ultra-clean bench, and collect the Artemia intestine;
[0086] (3) DNA extraction and PCR amplification:
[0087] according to Soil Kit Instructions Extract the total intestinal DN...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com