Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
81 results about "Prokaryote organisms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Prokaryote, also spelled procaryote, any organism that lacks a distinct nucleus and other organelles due to the absence of internal membranes. Bacteria are among the best-known prokaryotic organisms.
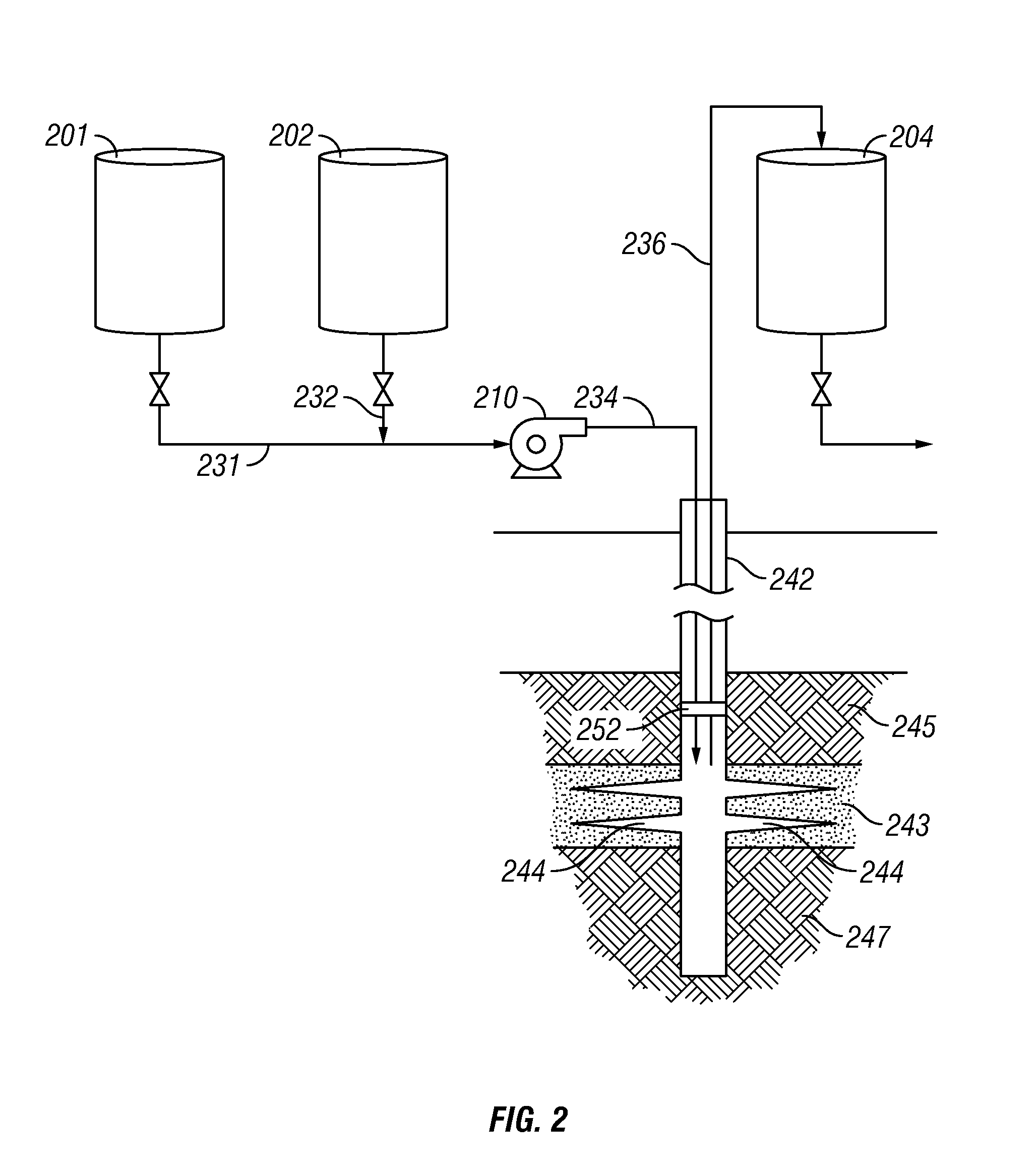
Use of prokaryote viruses to remediate bio-fouling
InactiveUS8252576B2Extended service lifeLower cost of capitalBacteriaArchaeabacteria virusesProkaryote organismsSulphate reduction
This invention provides a process for control in oil and gas wells and related facilities of prokaryote caused souring, fouling and corrosion by reduction of problematic prokaryotes with naturally occurring lysing organisms, particularly sulfate-reducing prokaryotes by proliferating suitable virulent lysing organisms under conditions in which problematic prokaryotes thrive, including in a gas production wellbore. The process provides in situ proliferation of virulent lysing organism in a wellbore by providing both virulent lysing organisms and their host prokaryotes to selectively grow an effective control amount and concentrations of lysing organisms in a well formation.
Owner:PHAGE BIOCONTROL RES
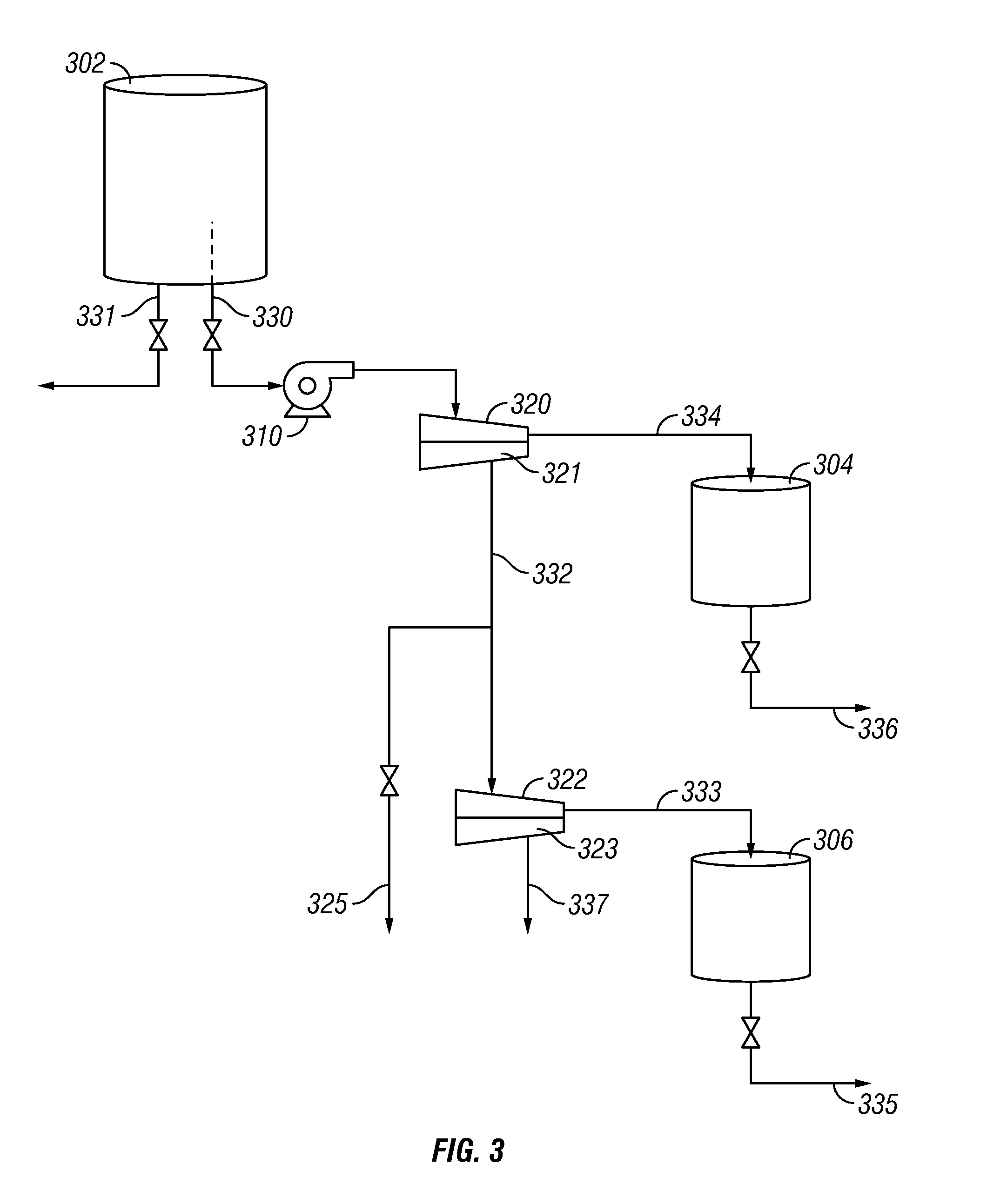
System and method for the production of recombinant proteins
InactiveUS20040265954A1Promote growthEasy to handleCosmetic preparationsBacteriaBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
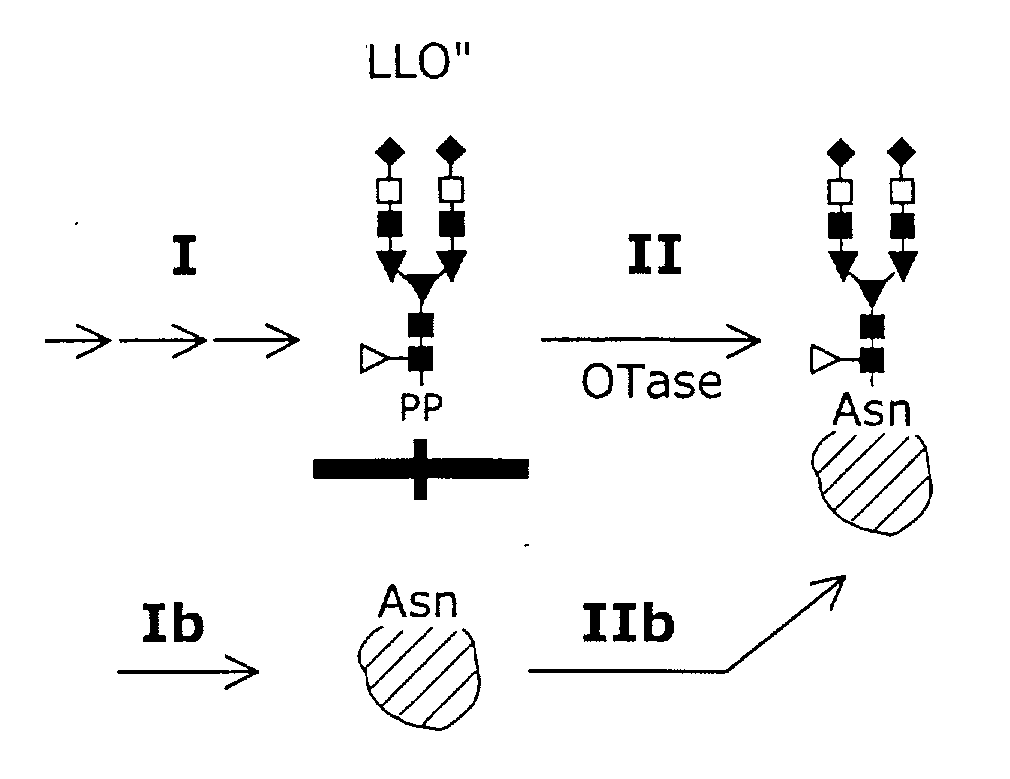
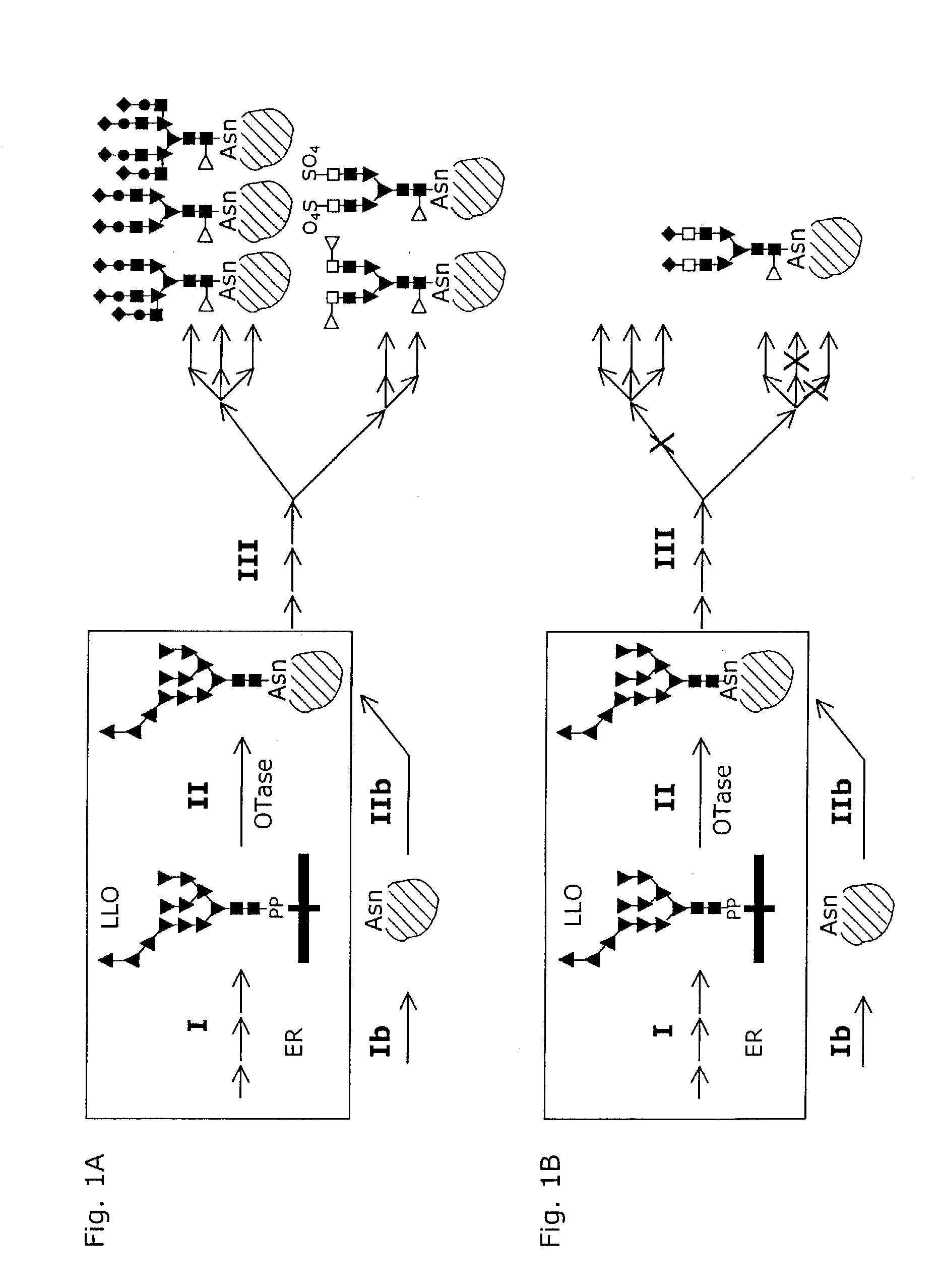
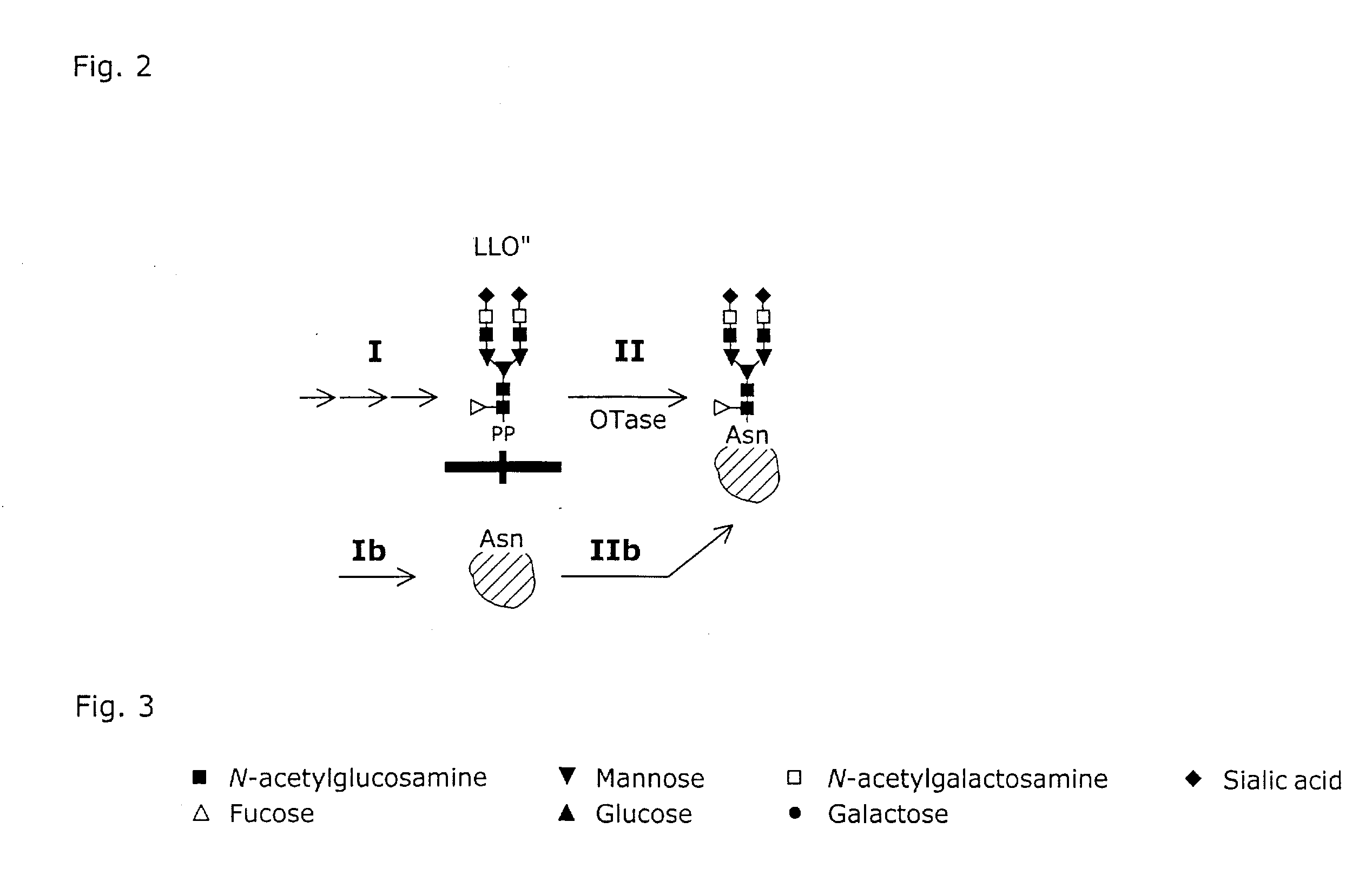
A system and a method for the production of recombinant N-glycosylated target proteins. The system comprises a prokaryotic organism (e.g. Escherichia coli) into which is introduced a genetic information encoding for a metabolic apparatus capable of carrying out the requested N-glycosylation of the target protein. Said prokaryotic organism also contains the genetic information required for the expression of one or more recombinant target proteins. The metabolic apparatus preferably comprises specific glycosyltransferases for the assembly of the oligosaccharide on a lipid carrier and an OTase that covalently links this oligosaccharide to specific residues of the desired protein.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Recombinant DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment containing roundup ready gene and application thereof
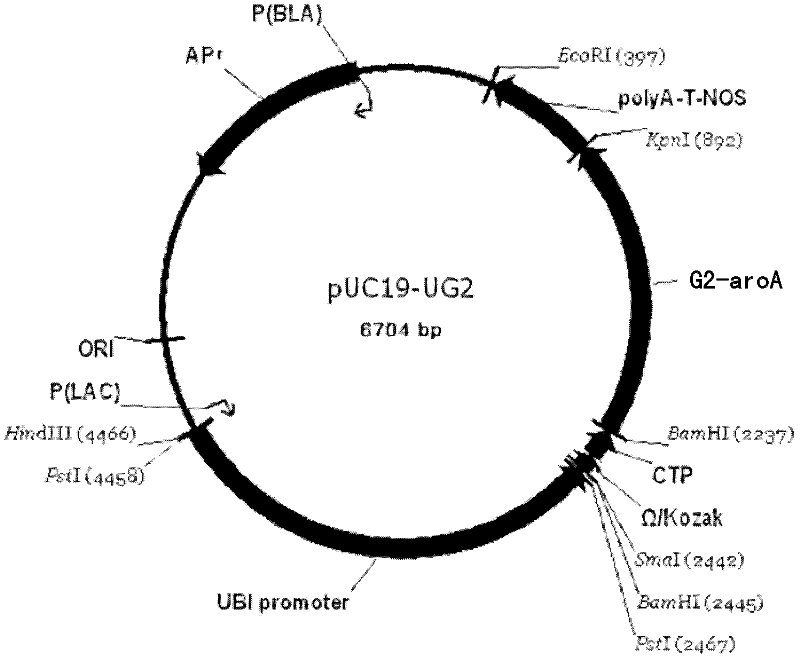
The invention discloses a recombinant DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment containing a roundup ready gene and application thereof. The recombinant DNA fragment provided by the invention comprises the following components from 1) to 3): 1) a promoter; 2) the roundup ready gene which is promoted by the promoter to be transcribed, the nucleotide sequence of the roundup ready gene is a) or b), wherein a) represents a sequence 2 in a sequence table, and b) represents a protein which has at least 98% of identity with the sequence 2 in the sequence table and is shown by a coding sequence 9; and 3) tanscription termination sequence. Compared with the transgenic corn which contains the recombinant DNA fragment in which prokaryote roundup ready gene G2-aroA is transplanted, the transgenic corn which is transplanted with the recombinant DNA fragment provided by the invention is obviously higher in the expression quantity of G2-aroA protein; and the transgenic corn is also obviously higher in the glyphosate tolerance.
Owner:BEIJING ORIGIN SEED TECH
Rapid and comprehensive identification of prokaryotic organisms
ActiveUS20080261222A1Accurate identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismProkaryote organisms
An improved method for rapid identification of microorganisms is disclosed, along with sequences of PCR primers optimized for this purpose. The primers are designed based on information analysis of sequences from a large number of organism to amplify certain segments of genomic DNA whose sequences are unique among different organisms. The PCR products are compared with a DNA sequence database to obtain the identity of the microorganisms. This approach provides an accurate and fast identification and taxonomic assignment of microbial species.
Owner:ROGAN PETER K
Inducible Gene Expression Composition for Using Eukaryotic Pol-2 Promoter-Driven Transcription in Prokaryotes and the Applications Thereof
InactiveUS20130210120A1Adapt quicklyBacteriaOrganic compound preparationMessenger RNAADAMTS Proteins
Eukaryotic protein-coding messenger RNAs and non-coding microRNAs are naturally transcribed by type II RNA polymerases (pol-2) but not prokaryotic RNA polymerases. As a result, current eukaryotic RNA and protein production is performed either using eukaryotic pol-2 promoters in hybridomas or mammalian cells or using prokaryotic promoters in bacterial cells. However, because prokaryotic RNA transcription tends to be error-prone, frequent mutation is a big problem. Also, growing hybridomas or mammalian cells is relatively laborious and costly. To overcome these problems, the present invention provides a novel inducible composition and method for producing eukaryotic RNAs and / or their related peptides / proteins directly using eukaryotic pol-2 promoter-driven gene expression in fast growing bacteria, without the need of changing to prokaryotic promoters or growing hybridomas / mammalian cells. The RNAs and peptides / proteins so obtained can be used to develop drugs, cure diseases, treat tumors / cancers, produce pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, enhance wound healing, and make foods.
Owner:MELLO BIOTECH
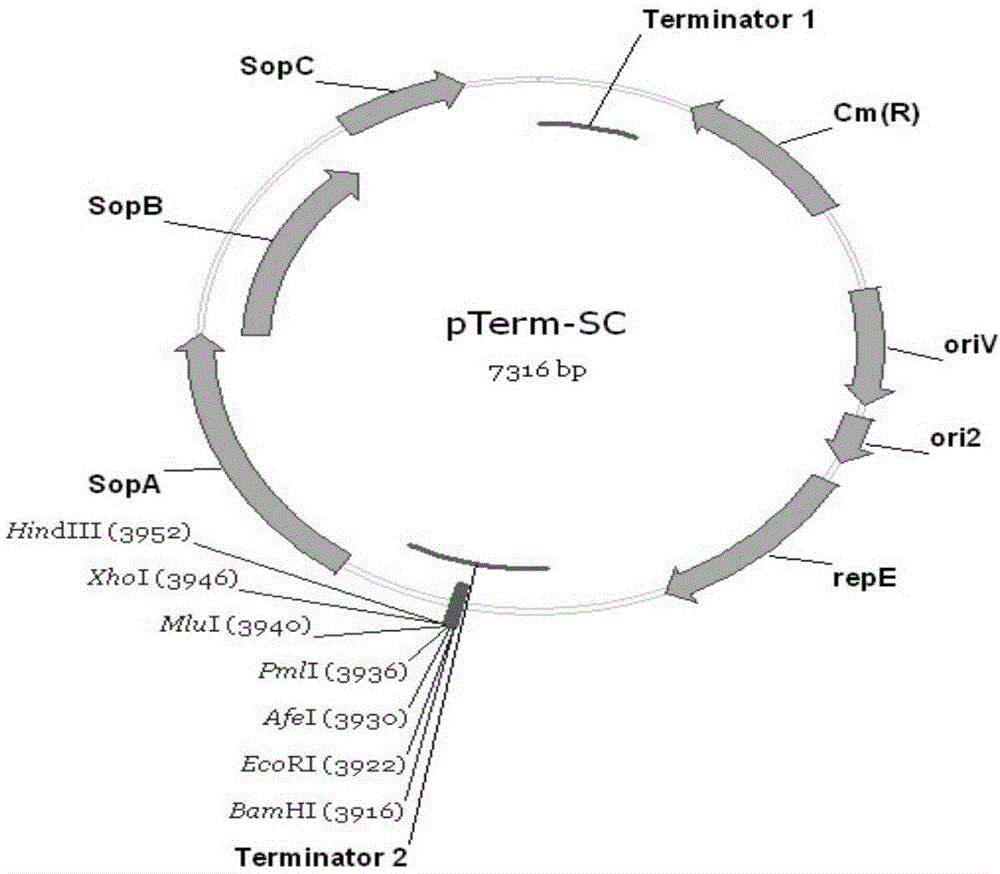
PTerm-SC plasmid as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN104480130AEasy extractionTranscriptional repressionMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAntibiotic YGene engineering
The invention relates to a pTerm-SC plasmid as well as a construction method and application thereof. The pTerm-SC plasmid comprises a repE gene, a sopA gene, a sopB gene, a sopC gene, an ori2 replicon, an oriV replicon, prokaryote transcription terminators and antibiotics resistance genes. The pTerm-SC plasmid has the characteristics of very low copy number, high volume and stability and the like, can be applied to gene engineering fields such as the cloning, the screening, sequencing and the genome construction of complex-structure genes including repetitive-sequence genes, instable genes and long-fragment genes and has important role in the high-efficiency and high-quality synthesis of genes.
Owner:GENEWIZ INC SZ
Prokaryote-derived argonaute protein and application thereof
ActiveCN112538470AShort synthesis cycleLow priceHydrolasesFermentationProkaryote organismsGene Modification
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and discloses prokaryote-derived argonaute protein and application thereof. The prokaryote-derived argonaute protein is derived frommedium-temperature prokaryote kurthia masiliensis, and the prokaryote-derived argonaute protein is named as KmAgo. According to the protein and the application, polypeptide, nucleic acid, an expression vector, a composition, a kit and a method can perform site-specific modification on intracellular and extracellular genetic substances so that the protein can be effectively applied to many fields of biotechnology, such as nucleic acid detection, gene editing and gene modification, and a new tool is provided for gene editing, modification and molecular detection of the prokaryote-derived Argonaute polypeptide.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Detoxication engineering bacteria, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101935669ADegradation Spectrum BroadeningSolve pollutionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsWater sourceMalathion
The invention discloses detoxication engineering bacteria, and a preparation method and application thereof. The invention provides a recombinant plasmid which is obtained by introducing coded genes of detoxication esterase and coded genes of hydrolase into an enzyme cutting site in plasmid pETDuet-1. The engineering bacteria of the invention can be obtained by introducing the recombinant plasmidinto host bacteria. The engineering bacteria comprise the coded genes of the detoxication esterase and the hydrolase and can realize inducible expression of the detoxication esterase and the hydrolase. Crude enzyme solution obtained by fermentation of the engineering bacteria can also be protected. The engineering bacteria and the crude enzyme solution thereof can simultaneously degrade organic acid esters such as malathion, parathion, high-efficiency cypermethrin, acetofenate and the like and organophosphorus pesticides, and can be used for detoxication of organophosphorus poisoned warm-blooded animals. The invention provides a new way for biological pollution treatment of toxic and harmful compounds such as pesticides remained in water sources, soil and the like by using natural resources of eukaryote and prokaryote.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compositions of prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyase variants and methods of using compositions thereof
Provided herein are phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) variants produced by prokaryotes, wherein such prokaryotic PAL variant has a greater phenylalanine-converting activity and / or a reduced immunogenicity as compared to a wild-type PAL. Further provided are compositions of prokaryotic PAL and biologically active fragments, mutants, variants or analogs thereof, as well as methods for the production, purification, formulation, and use of such compositions for industrial and therapeutic purposes, [e.g., treating hyperphenylalaninemia, (including phenylketonuria)], and other disorders (including cancer).
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Biosynthetic system that produces immunogenic polysaccharides in prokaryotic cells
ActiveUS8846342B2Efficient productionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsProkaryote organismsIsomerase
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Production and extraction of MicroRNA precursor as drug for cancer therapy
ActiveUS9399773B2Reduce the number of copiesStrong specificitySugar derivativesBacteriaProkaryote organismsReprogramming
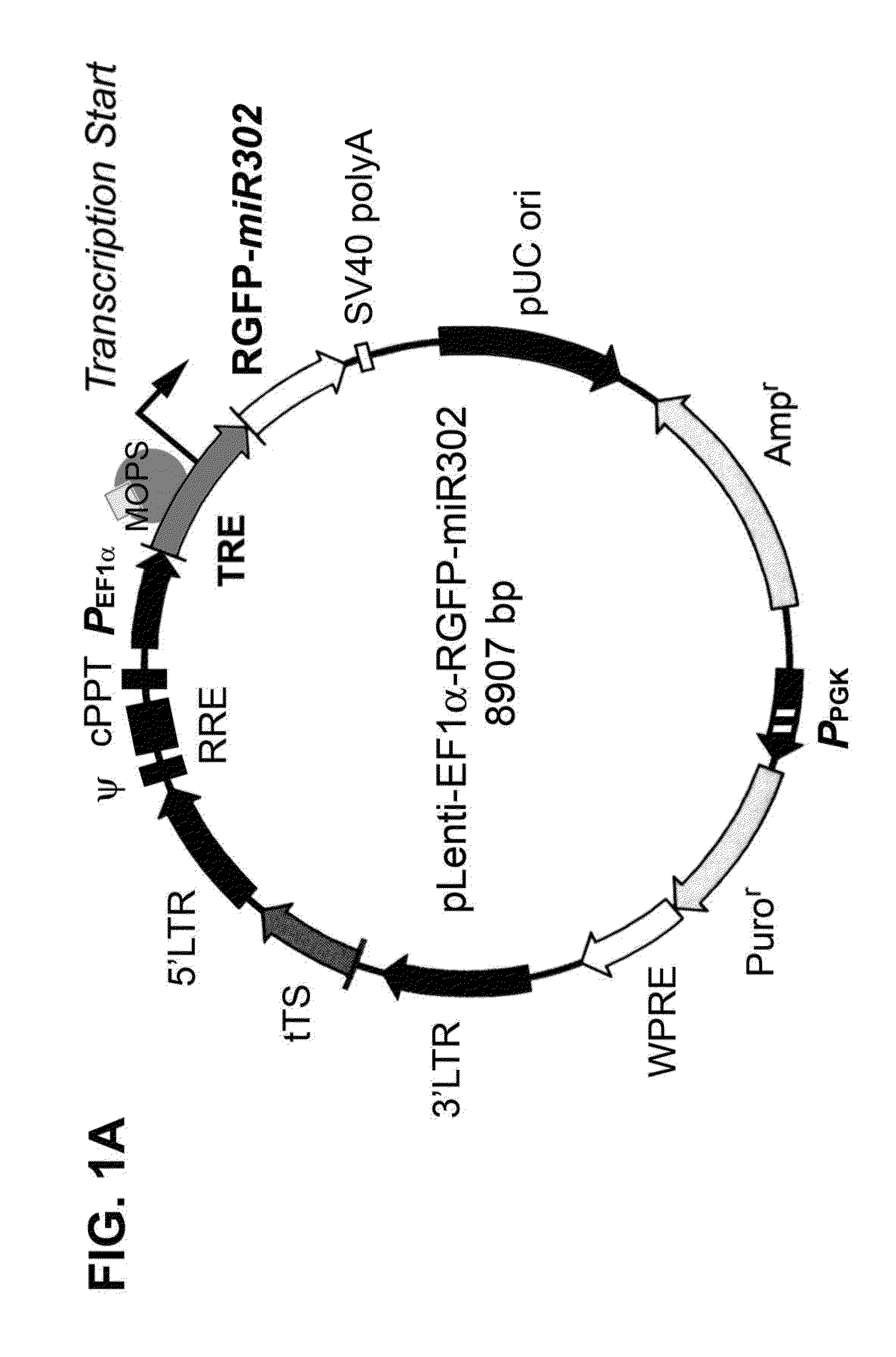
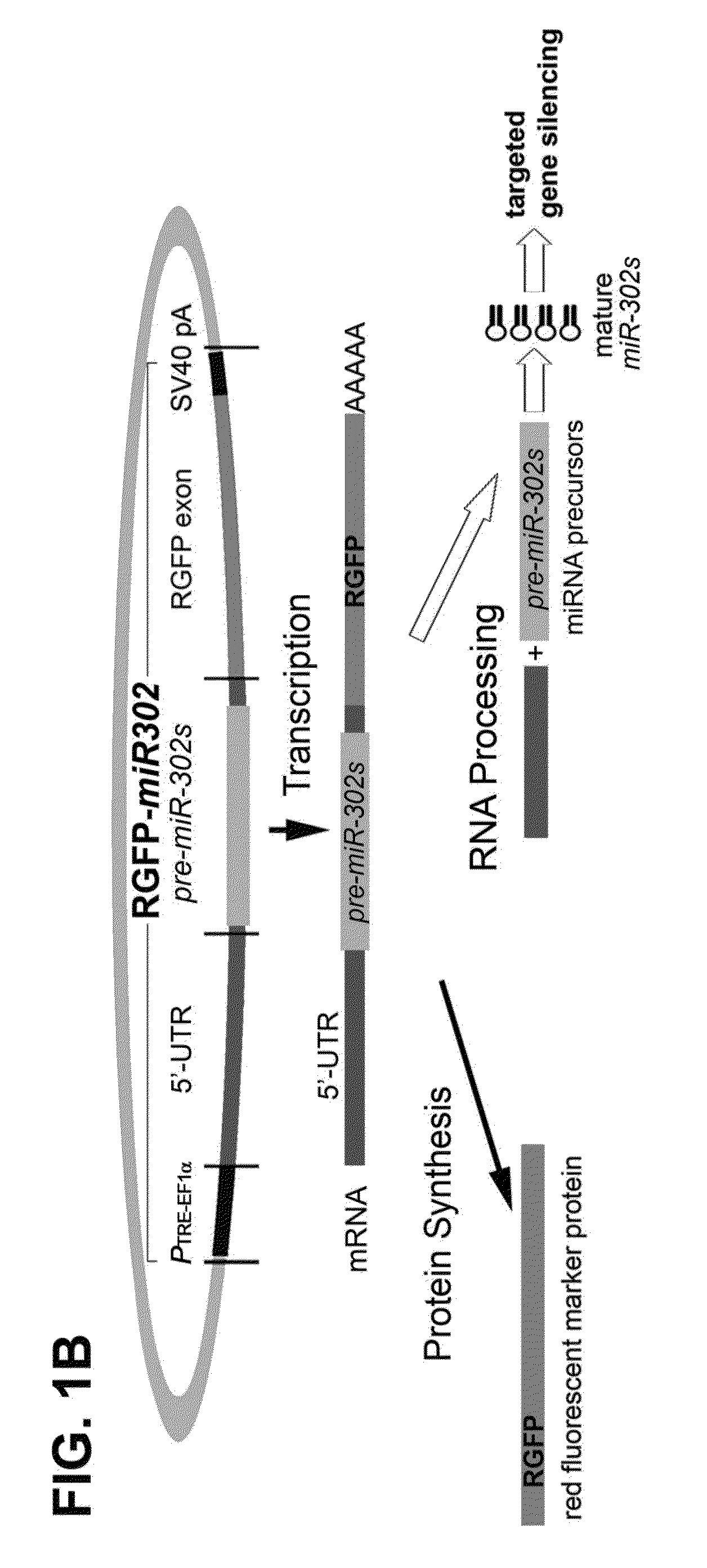
This invention generally relates to a composition for developing novel anti-cancer drugs and / or vaccines and producing microRNA precursor (pre-miRNA) and / or its shRNA homologs / mimics / derivatives, and a method thereof. The present invention also relates to a use of a composition in producing novel prokaryote-produced microRNA precursor (pro-miRNA) capable of being delivered into human cells and processed by the cells into microRNA-like effectors to elicit specific silencing effects on certain targeted oncogenes, subsequently leading to a therapeutic result of tumor suppression and cancer therapy. Specifically, the method of the present invention includes inducing an expression of the pre-miRNA / pro-miRNAs, particularly human pre-miR-302, in prokaryotes through pol-2 or pol-2-like RNA promoter. Most importantly, the composition of the present invention is further a novel pre-miRNA-based drug that is capable of reprogramming the malignant properties of high-grade human liver cancers into a low-grade benign or even relatively normal stage—a mechanism called “Cancer Reversion”.
Owner:MELLO BIOTECH +1
Therapeutic gene for anaerobic tissue targeting delivery and selectivity stabilization expression method and its application
InactiveCN102477440AReduce potential in vivo toxicitySolve puzzlesGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseNitroso
The invention belongs to biology technical field, concretely relates to a method for realizing a therapeutic gene on anaerobic tissue targeting delivery and selectivity stabilization expression. According to the invention, a prokaryotic bacteria nitroso reductase promoter PnirB induced by prokaryotes anaerobe is taken as composition of a therapeutic gene promoter, anaerobic targeting bacteria, low copy plasmid and the like, so that therapeutic gene enables an specific expression under low oxygen or hypoxia environment in vivo and in vitro. The method for realizing the therapeutic gene on the anaerobic tissue targeting delivery and selectivity stabilization expression is effectively treating the anaerobic tissue diseases containing tumor, or treating the anaerobic tissue diseases comprising tumor by combining other chemical medicaments and traditional Chinese medicines, and can be used for preparing antitumor drugs.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
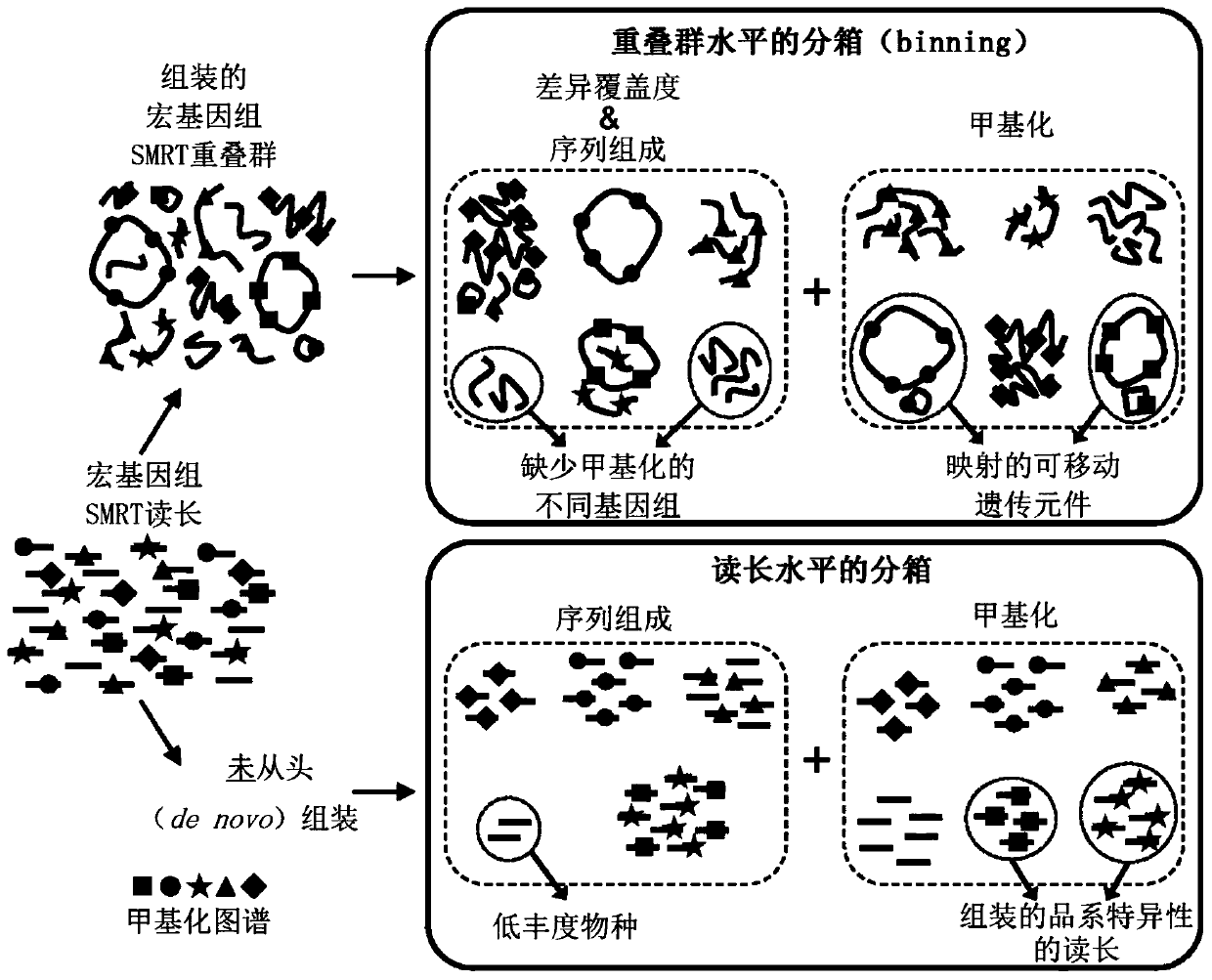
Methods for high-resolution microbiome analysis
Methods are presented for binning metagenomic sequences that leverage long reads from a single-molecule long-read sequencing technology and utilize DNA methvlation signatures inferred from these readsto resolve individual reads and assembled contigs into species- and strain-level clusters. Methods for deconvolving prokaryotic organisms in a microbiome sample are presented. Methods for mapping mobile genetic elements to their host organisms in a microbiome sample are also presented.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
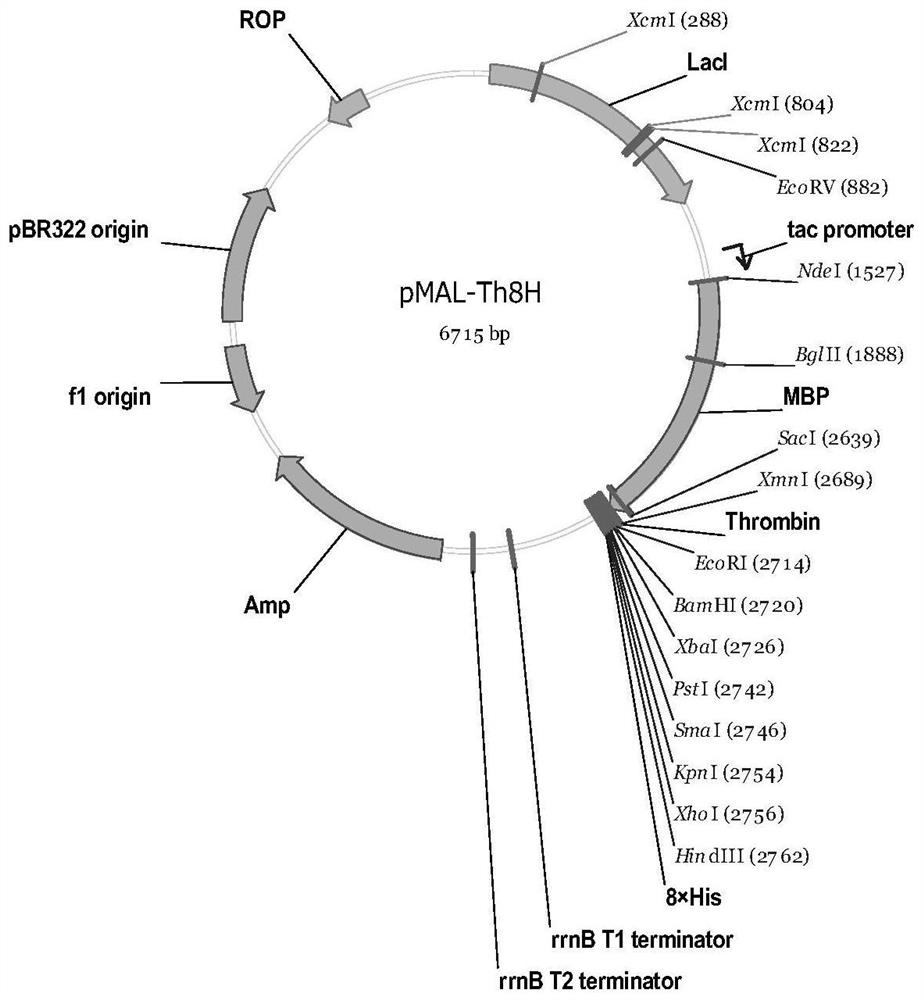
Expression vector and method for detecting membrane protein interaction in bacteria
ActiveCN112063643AEfficient purificationGood water solubilityPeptide preparation methodsBiological testingProkaryote organismsMembrane protein interactions
The invention discloses an expression vector and a method for detecting membrane protein interaction in bacteria. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, constructing a double-label protein expression vector with a maltose binding protein label (MBP) and a histidine label (8*His), and expressing and purifying insoluble membrane protein by using the vector to increase the solubility ofthe membrane protein; and then, detecting the interaction between the membrane protein and other proteins by utilizing a pull down technology. Meanwhile, the method can also be used for screening proteins interacting with the membrane protein in bacterial whole-cell proteins. The method for detecting the interaction of the membrane proteins in the bacteria breaks through the technical difficultyof insolubility of the membrane proteins in prokaryotes, provides an experimental means for researching the functions of the bacterial membrane proteins, and has important application value.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Operon, carrier thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN109097362AHigh expression activityEfficient expressionPeptidesVector-based foreign material introductionOperonMicrobiology
The invention discloses an operon, a carrier thereof and application thereof. The sequence of the operon at least comprises any basic group of 201-257 bp, whose 3' ends are located in the upstream place of a corynebacterium glutamicum SEQ ID NO: 6 gene coding sequence ATG, and any basic group of 308-345 bp, whose 5' ends are located in the upstream place of the corynebacterium glutamicum SEQ ID NO: 6 gene coding sequence ATG. After the operon disclosed by the invention is induced by an inducing agent, the protein expression activity of the operon is obviously higher than the induced expressionactivity of a traditional Ptac; and the operon is an ultra-efficient operon. The operon disclosed by the invention can be used for efficient expression of procaryotic organism endogenous proteins orheterologous proteins.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombination expression of cynoglossus semilaevis antibacterial peptide hepcidin and application thereof
InactiveCN102242138ALow costSolve the problem of cumulative excessAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologySynthesis methods
The invention relates to recombination expression of cynoglossus semilaevis antibacterial peptide hepcidin and application thereof. A nucleic acid fragment used for recombining and expressing the cynoglossus semilaevis antibacterial peptide hepcidin with the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 is inserted into an expression vector, recombinant protein of the cynoglossus semilaevis antibacterial peptide hepcidin is expressed in host bacteria, a simple and effective method for purifying the recombinant protein is found out, and the protein expressed by the recombinant protein is applied to antibacterial products. In the invention, the vector and the host bacteria capable of carrying out antibacterial peptide recombination expression are constructed and sifted, the fusion expression and the simple and effective purification of the cynoglossus semilaevis antibacterial peptide in prokaryote are realized; compared with the traditional polypeptide synthesis method and the method for extracting polypeptide from natural resources, the preparation method provided by the invention makes large scale production in low cost possible and can be applied to feedstuff additives of marine cultivation fish, cultivation livestock and control of bacterial diseases.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Polysialic acid, blood group antigens and glycoprotein expression
The invention described herein generally relates to glycoengineering host cells for the production of glycoproteins for therapeutic use. Host cells are modified to express biosynthetic glycosylation pathways. Novel prokaryotic host cells are engineered to produce N-linked glycoproteins wherein the glycoproteins comprise polysialic acid or blood group antigens.
Owner:GLYCOBIA +4
System and method for the production of recombinant glycosylated proteins in a prokaryotic host
A system and a method for the production of recombinant N-glycosylated target proteins. The system comprises a prokaryotic organism (e.g. Escherichia coli) into which is introduced a genetic information encoding for a metabolic apparatus capable of carrying out the requested N-glycosylation of the target protein. Said prokaryotic organism also contains the genetic information required for the expression of one or more recombinant target proteins. The metabolic apparatus preferably comprises specific glycosyltransferases for the assembly of the oligosaccharide on a lipid carrier and an OTase that covalently links this oligosaccharide to specific residues of the desired protein.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Prokaryote-derived Mbp_Argonaute protein and application thereof
ActiveCN113373129AHave binding activityHas nuclease activityHydrolasesFermentationProkaryote organismsPlant cell
The invention discloses a prokaryote-derived Mbp_Argonaute protein and application thereof. The Mbp_Argonaute protein has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or as shown in a sequence which has at least 50% or at least 80% of homology with SEQ ID NO: 1. According to the invention, an Argonaute protein gene derived from a cold-resistant prokaryotic organism Mucilaginibacter paaluis is synthesized, the protein is named as MbpAgo, and researches find that the MbpAgo has binding activity to single-stranded guide DNA and has nuclease activity to target RNA and / or target DNA complementarily paired with the single-stranded guide DNA, therefore, the MbpAgo can be used for targeted RNA editing in vivo and in vitro, and then specific site modification of genetic material. The MbpAgo not only can modify RNA with a high-grade structure, but also does not influence an endogenous RNAi pathway of animal and plant cells, provides a brand new powerful tool for RNA editing, and is high in cutting activity and good in specificity.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
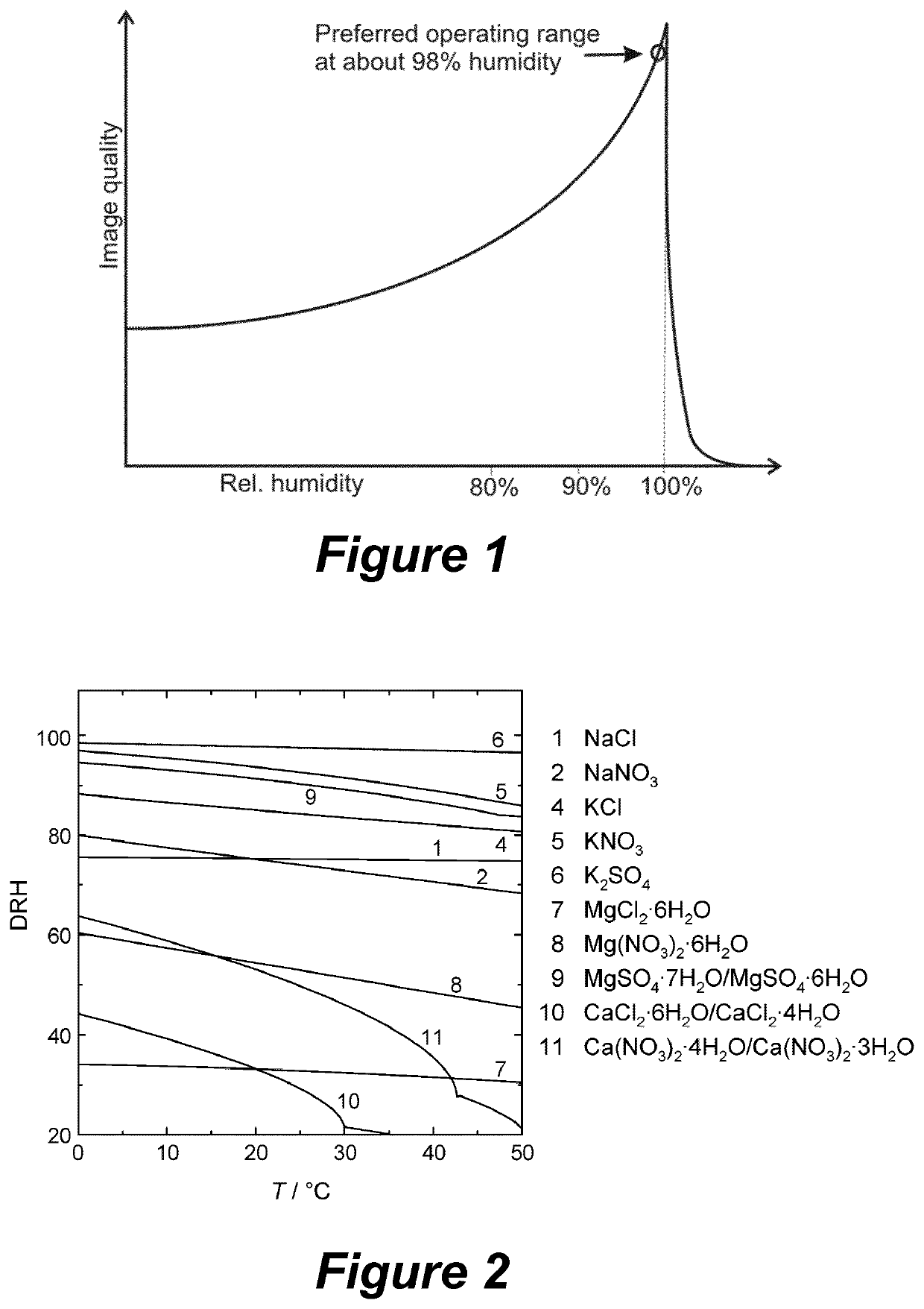
Humidity stabilization during the preparation of biological samples for spectrometry
ActiveUS20210404916A1Samples introduction/extractionPreparing sample for investigationProkaryote organismsSuccinic acid
The invention proposes preparing biological samples for spectrometry which contain cell structures and / or whole cells of human or animal origin (e.g. thin human and animal tissue sections) or prokaryotes (e.g. microorganisms), and which require constant relative humidity, in a temperature-controlled gas volume whose humidity is determined by a saturated substance solution, for example a suitable salt solution. The invention exploits a physico-chemical phenomenon called “deliquescence”, which manifests itself by keeping the relative humidity above the saturated substance solution constant with a high degree of precision when a specified temperature is maintained. Pure succinic acid exhibits deliquescence at approx. 99% relative humidity, for example. Since an enormous variety of deliquescent salts and other suitable substances are available, it is possible to find the suitable substance for almost any desired relative humidity, with adjustment of the temperature, where necessary.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Recombinant microorganisms and uses thereof
The present invention provides live recombinant microorganisms such as prokaryote organisms, particularly enterobacteria, preferably Salmonella enterica, containing SEQ. ID. no. 1 and SEQ. ID. no. 2 capable of expressing VapG and / or VapA / VapG lipoproteins (SEQ. ID. no. 3 and SEQ. ID. no. 4), optionally in combination with other active ingredients, methods for preparing vaccine strains, antigens (SEQ. ID. no. 3 and SEQ. ID. no. 4) and vaccine compositions, preferably vectored vaccines. Additionally, the present patent application relates to the use of the vaccine vectors in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions, particularly vaccines indicated for the prevention and / or treatment of infections by Rhodococcus equi, its antibodies and / or antisera, diagnostic kits and methods for the prophylaxis and / or treatment of infections by R. equi.
Owner:UNIV DE SAO PAULO +1
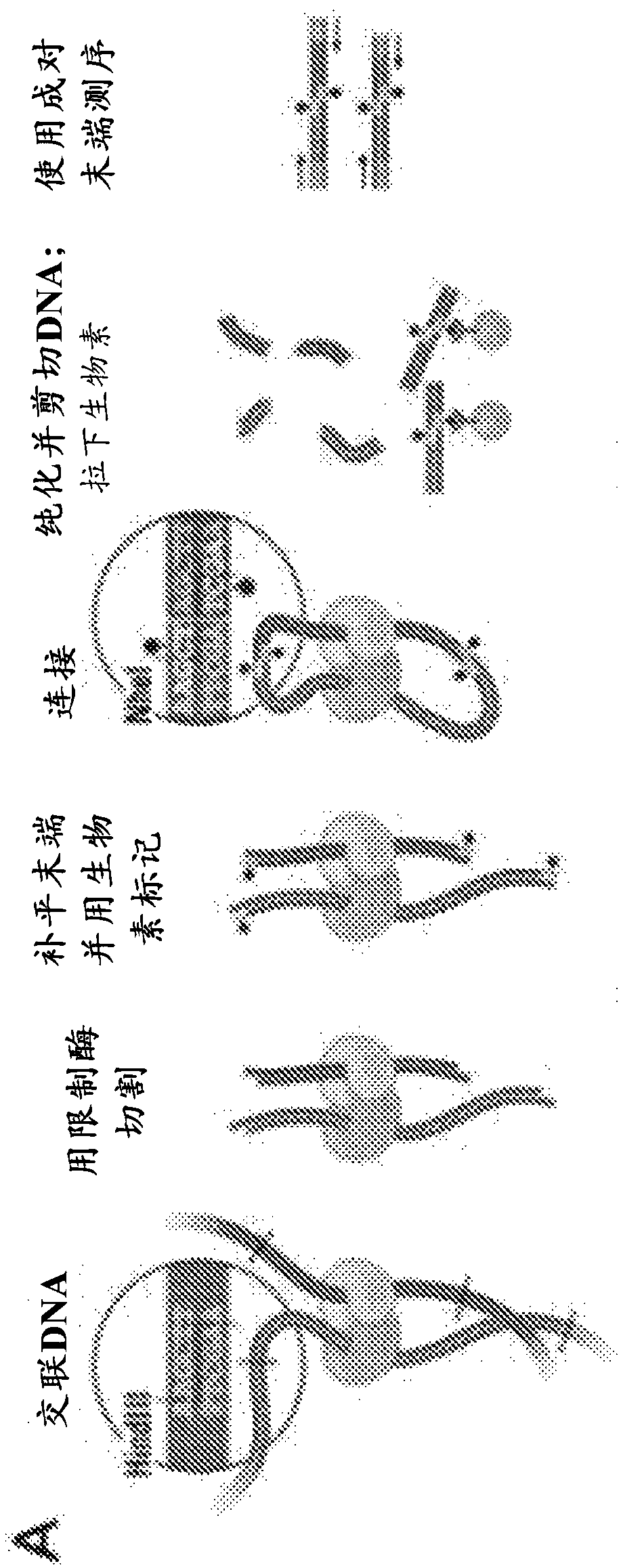
Methods for genome assembly, haplotype phasing, and target independent nucleic acid detection
ActiveCN108368542AMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisGenomicsNucleic acid detection
The disclosure provides methods to assemble genomes of eukaryotic or prokaryotic organisms. The disclosure provides methods for haplotype phasing and meta-genomics assemblies. The disclosure providesa streamlined method for accomplishing these tasks, such that intermediates need not be labeled by an affinity label to facilitate binding to a solid surface. The disclosure also provides methods andcompositions for the de novo generation of scaffold information, linkage information, and genome information for unknown organisms in heterogeneous metagenomic samples or samples obtained from multiple individuals. Practice of the methods can allow de novo sequencing of entire genomes of uncultured or unidentified organisms in heterogeneous samples, or the determination of linkage information fornucleic acid molecules in samples comprising nucleic acids obtained from multiple individuals.
Owner:DOVETAIL GENOMICS
Plant acyl-CoA synthetases
InactiveUS7105722B2Inhibit expressionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
The present invention relates to genes encoding plant acyl-CoA synthetases and methods of their use. In particular, the present invention is related to plant acyl-coenzyme A synthetases. The present invention encompasses both native and recombinant wild-type forms of the enzymes, as well as mutant and variant forms, some of which possess altered characteristics relative to the wild-type enzyme. The present invention also relates to methods of using acyl-CoA synthetases, including altered expression in transgenic plants and expression in prokaryotes and cell culture systems.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
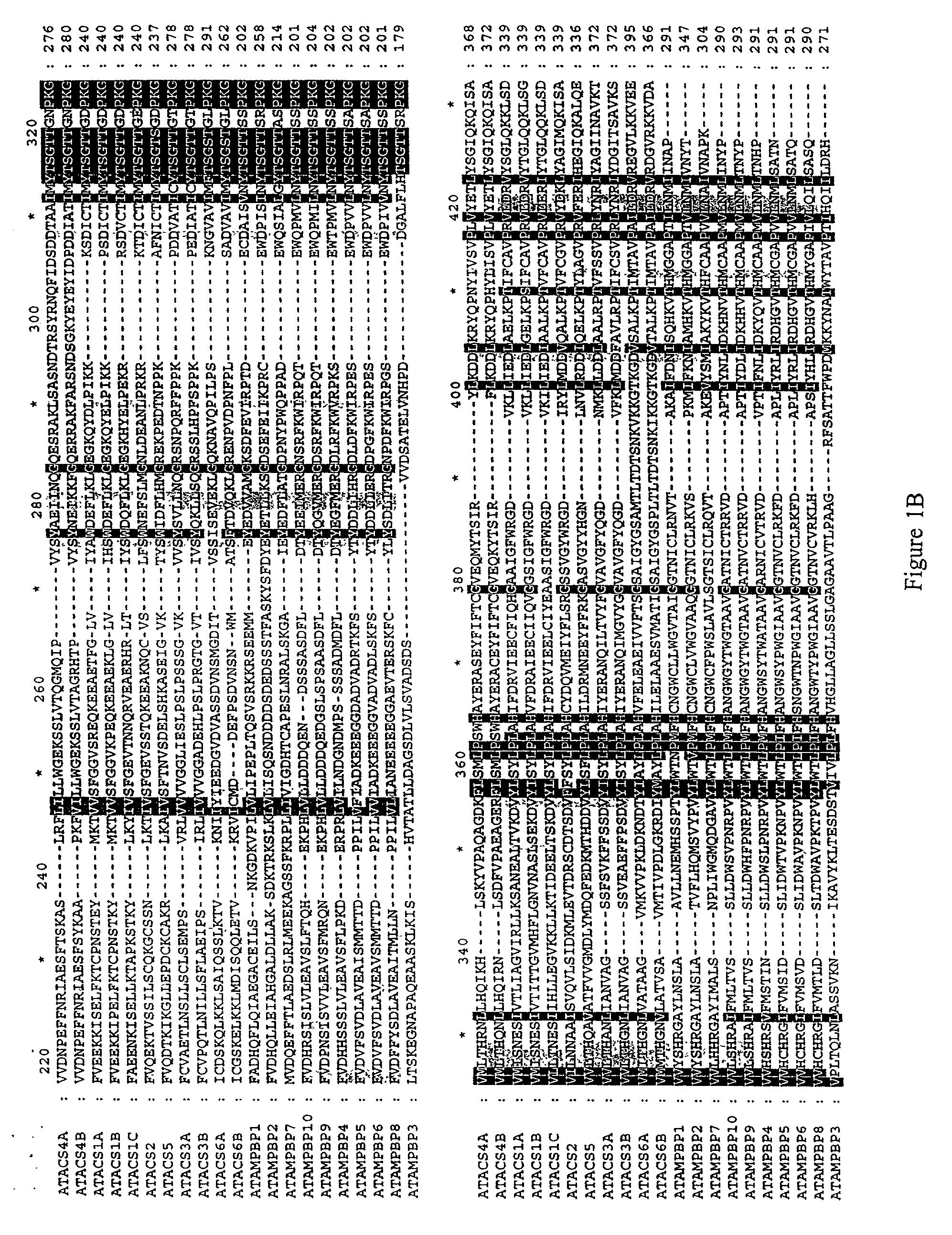
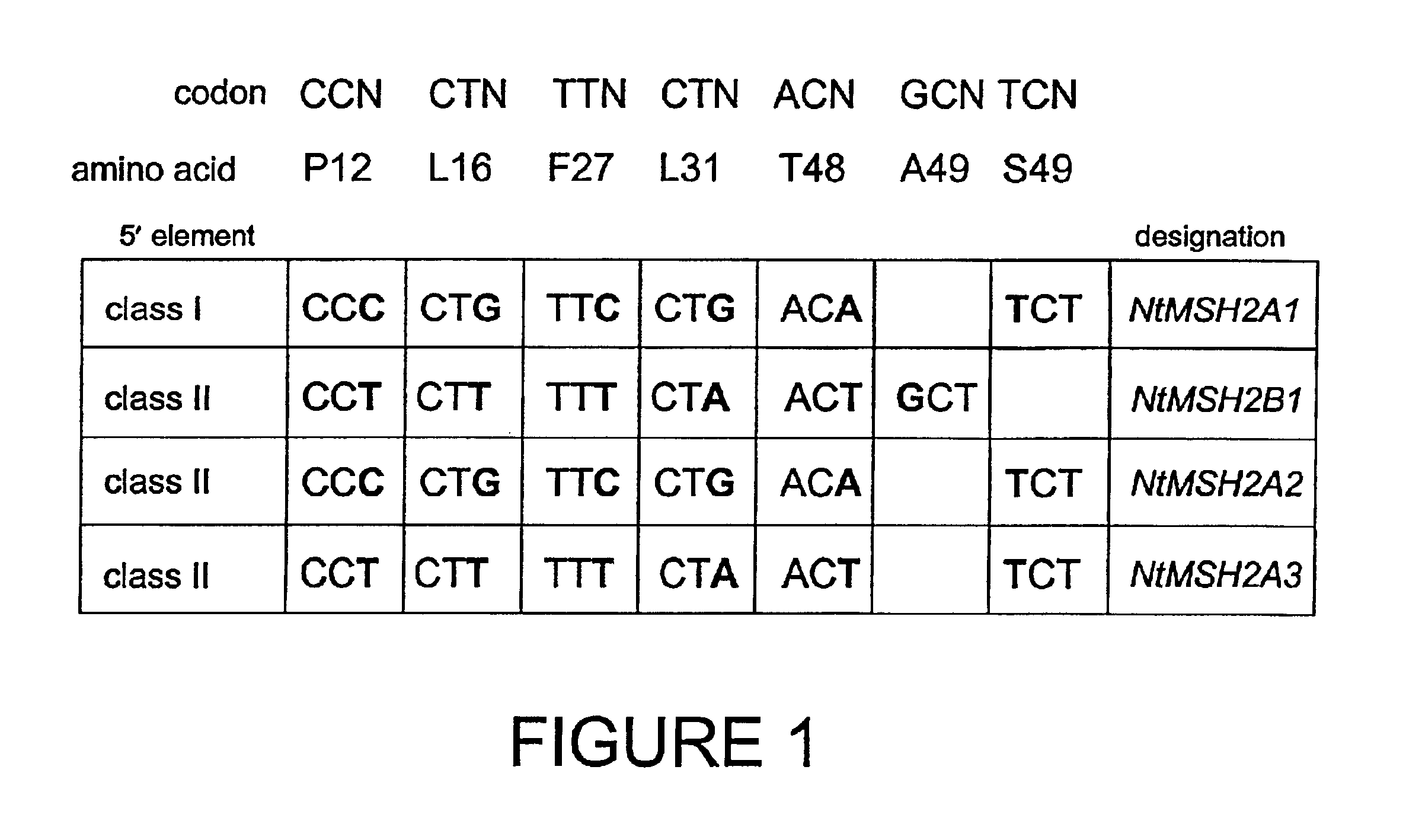
Plant MSH2 sequences and methods of use
InactiveUS6906243B2Improve efficiencyReduce expressionImmunoglobulinsFermentationBiological bodyMSH2
The invention relates to isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding MutS homologues (MSHs). Such MSH proteins are involved in DNA mismatch-repair processes in organisms. The invention provides isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising MSH2 nucleotide sequences which encode MSH2 proteins and MSH2 nucleotide sequences which encode dominant-negative MSH2 variants. Such MSH2 nucleotide sequences find use in altering mismatch repair, mutation rates and recombination frequencies in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms. The invention also provides isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising MSH2 promoter nucleotide sequences. Such MSH2 promoter nucleotide sequences find use in regulating the expression of genes of interest in plants. Additionally provided are isolated proteins, transformed host cells, and transformed plants, tissues, cells and seeds thereof.
Owner:BOYCE THOMPSON INST FOR PLANT RES +1
Kit for rapidly detecting shigellae in food
InactiveCN105821130AAchieving Specific DetectionImprove the level of security detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyConserved sequence
The invention provides a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) kit with internal amplification control and for detecting shigellae in food, relating to the technical field of biology. A method is convenient to use, has the advantages of good reliability, short detection period, high sensitivity, strong specificity, low cost and simple operating steps, is suitable for high throughput operation and standardized operation, can avoid misjudgment caused by false negative results obtained because DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase inhibitors exist in samples, and can be used for detecting shigellae in various food. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) utilizing a pair of specific primers ipaHF / ipaHR which are designed by primer premier 6.0 software and aim at shigellae, then adding primers 27F / 1492R amplifying a prokaryote 16S rDNA conserved sequence as the internal amplification control and carrying out amplification by the two pairs of primers jointly; (2) carrying out enrichment culture on a sample to be detected for 6-8 hours and extracting genomic DNA from enrichment fluid obtained after culture as a template by adopting a boiling and freeze-thaw method to carry out amplification; and (3) preparing 25mu l of reaction system with PCR reaction premix of the kit to carry out amplification and observing the detection results under an ultraviolet lamp after agarose gel electrophoresis.
Owner:BOHAI UNIV
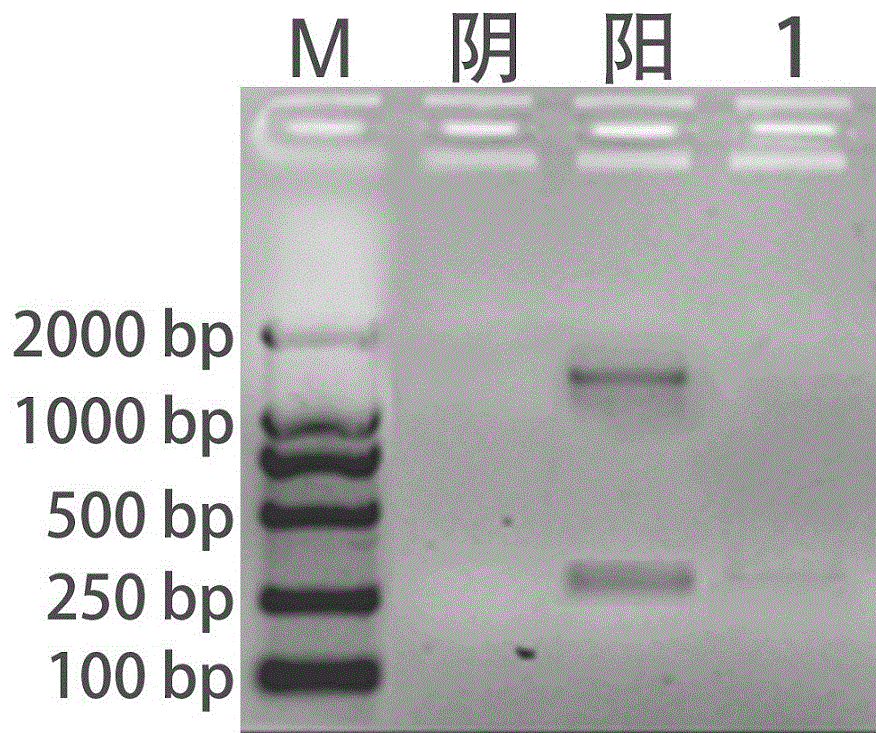
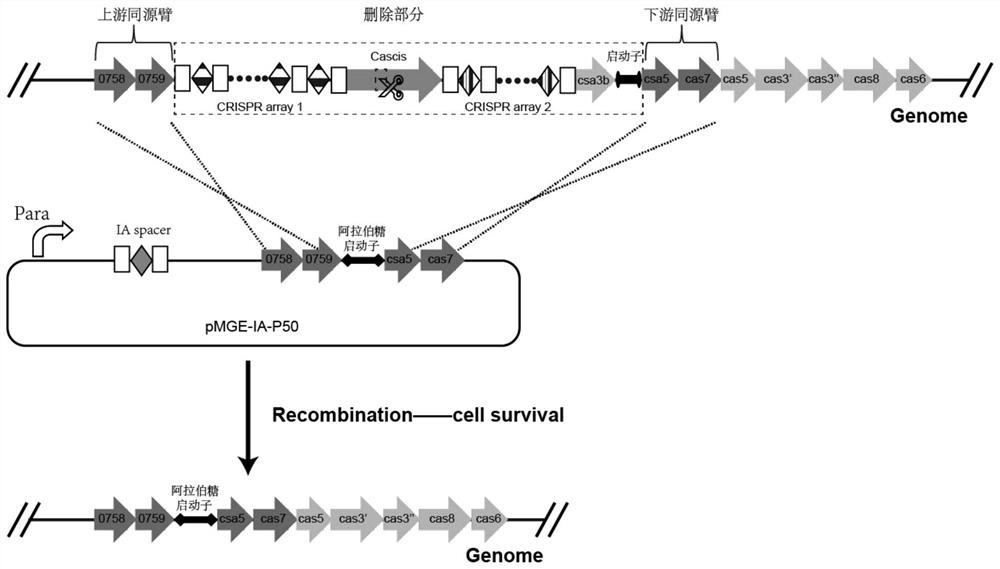
Construction method of inducible endogenous CRISPR-Cas system and application of inducible endogenous CRISPR-Cas system in simultaneous editing of multiple genes
ActiveCN112746075AImprove editing efficiencyShorten the timeHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAGenomicsProkaryote organisms
The invention provides a construction method of an inducible endogenous CRISPR-Cas system and application of the inducible endogenous CRISPR-Cas system in simultaneous editing of multiple genes, and belongs to the technical field of genomics, genetic engineering and biology. According to the inducible endogenous CRISPR-Cas system disclosed by the invention, only one plasmid containing a CRISPR cluster containing a plurality of spacers and a plurality of donor DNA fragments and a strain with the inducible endogenous CRISPR-Cas system need to be constructed. A large number of CRISPR-Cas effect compounds generated during induction are utilized to complete simultaneous targeted cutting of a plurality of genes and homologous recombination repair of DNA of a plurality of donors, so that simultaneous editing of the plurality of genes is realized. According to the method, the gene editing efficiency is high, the multi-gene editing of the prokaryote can be completed at one time or by fewer times, the required time, energy and cost are greatly saved, and the applicable host range is wide, so that the method has good practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
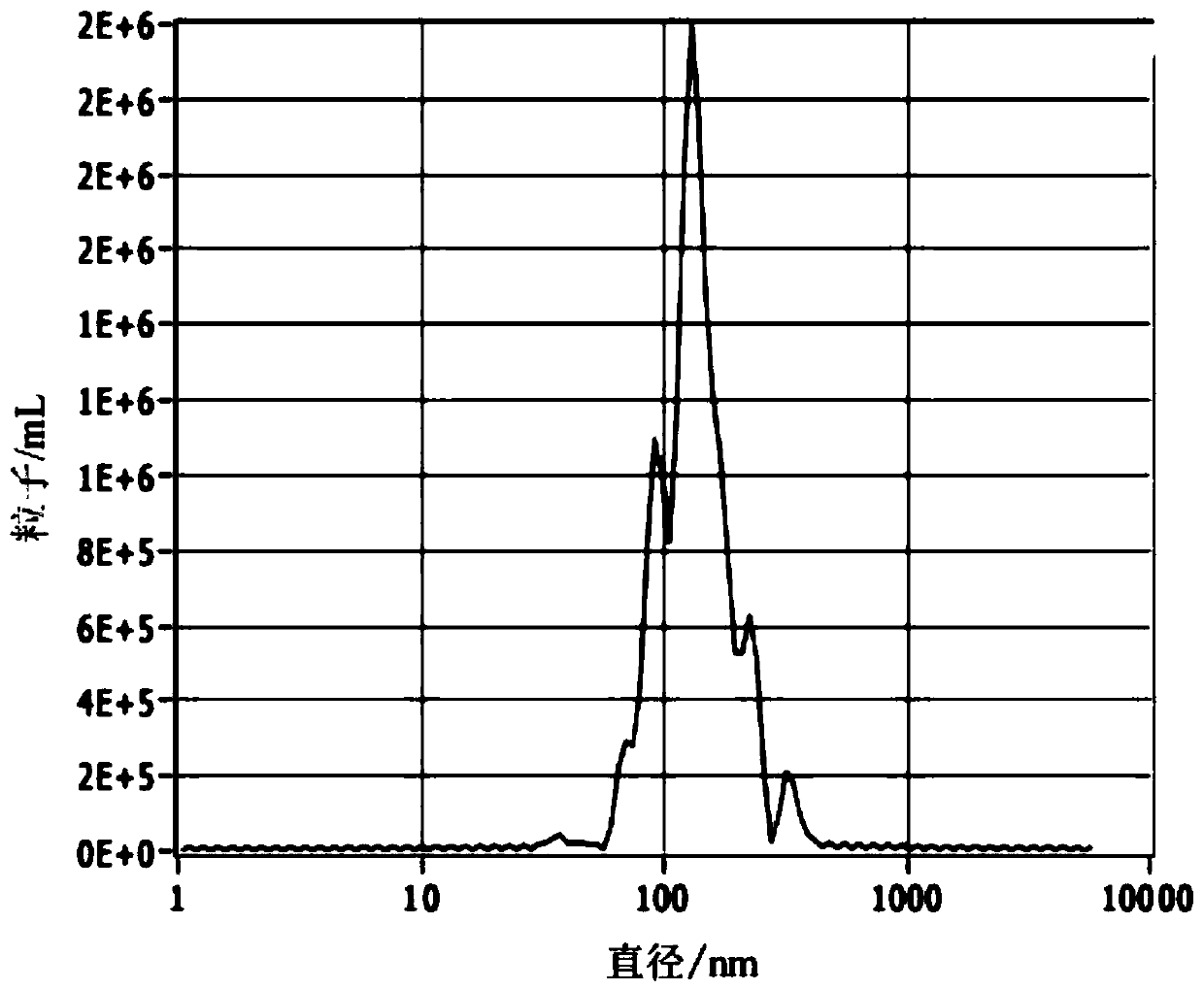
Prokaryotic exosome and extraction and separation method and application thereof
PendingCN110885770AEfficient extractionMeet the testing standardsBacteriaMicroorganism separationLipidomeProkaryote organisms
The invention discloses a prokaryotic exosome and an extraction and separation method and application thereof, which belongs to the technical field of exosome extraction methods. The method comprisesthe steps of carrying out fermentation culture on prokaryotes, and centrifuging to acquire fermentation liquor; and carrying out multiple times of ultracentrifugation on the fermentation liquor to finally acquire the prokaryote exosome. The characteristics of the prokaryote exosome are identified through particle size analysis and nano transmission electron microscope analysis. According to the invention, the particle size of the prokaryotic exosome extracted and separated by the method integrally meets the standard, and the particle concentration can reach E + 9 or above; a clear vesicular structure can be seen in the field of view of an electron microscope, and the particle size of vesicles meets the detection standard of the exosome; the prokaryotic exosome extracted and separated by the method can be applied to transcriptomics, proteomics and lipidomics correlation analysis and preparation of an exosome drug loading system.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Use of Prokaryote Viruses to Remediate Bio-Fouling
InactiveUS20120040439A1Extended service lifeLower cost of capitalBacteriaArchaeabacteria virusesProkaryote organismsSulphate reduction
This invention provides a process for control in oil and gas wells and related facilities of prokaryote caused souring, fouling and corrosion by reduction of problematic prokaryotes with naturally occurring lysing organisms, particularly sulfate-reducing prokaryotes by proliferating suitable virulent lysing organisms under conditions in which problematic prokaryotes thrive, including in a gas production wellbore. The process provides in situ proliferation of virulent lysing organism in a wellbore by providing both virulent lysing organisms and their host prokaryotes to selectively grow an effective control amount and concentrations of lysing organisms in a well formation.
Owner:PHAGE BIOCONTROL RES
Prokaryote-based cell-free system for the synthesis of glycoproteins
The present invention is directed to a cell-free system for producing a glycosylated protein. This system comprises an isolated oligosaccharyltransferase capable of transferring a glycan from a lipid carrier molecule to a glycoprotein target, one or more isolated glycans, where each glycan is linked to a lipid carrier molecule, and a glycoprotein target comprising one or more glycan acceptor amino acid residues or a nucleic acid molecule encoding said glycoprotein target. The present invention further relates to kits and methods for producing a glycosylated protein in this cell-free system.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
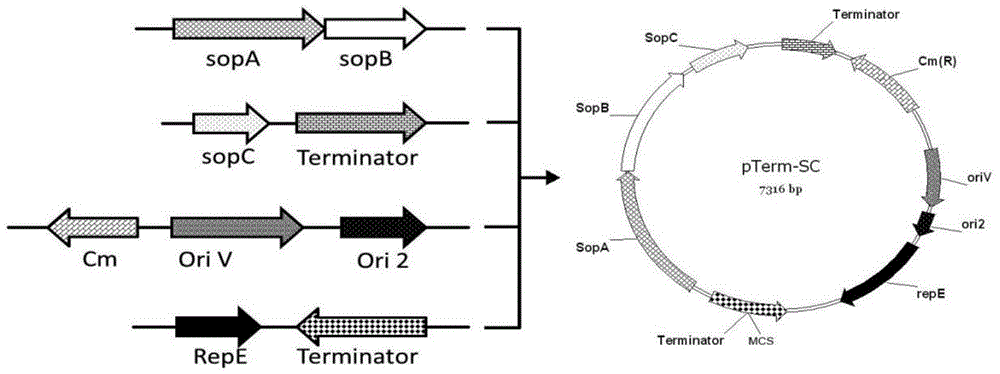
A kind of low copy pterm plasmid and its construction method and application
ActiveCN104404069BTranscriptional repressionInhibition of translationVector-based foreign material introductionInstabilityGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a low-copy pTerm plasmid and its construction method and application. The low-copy pTerm series plasmids include rop gene, rep gene, prokaryote transcription terminator and antibiotic resistance gene. A low-copy pTerm series plasmid of the present invention has the characteristics of low copy number, large capacity, and high stability, and can be used for cloning, screening, sequencing, and genome construction of genes with complex structures, including repetitive sequences, unstable genes, and long-segment genes In the field of genetic engineering, it plays an important role in the high-efficiency and high-quality synthesis of genes.
Owner:GENEWIZ INC SZ
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com