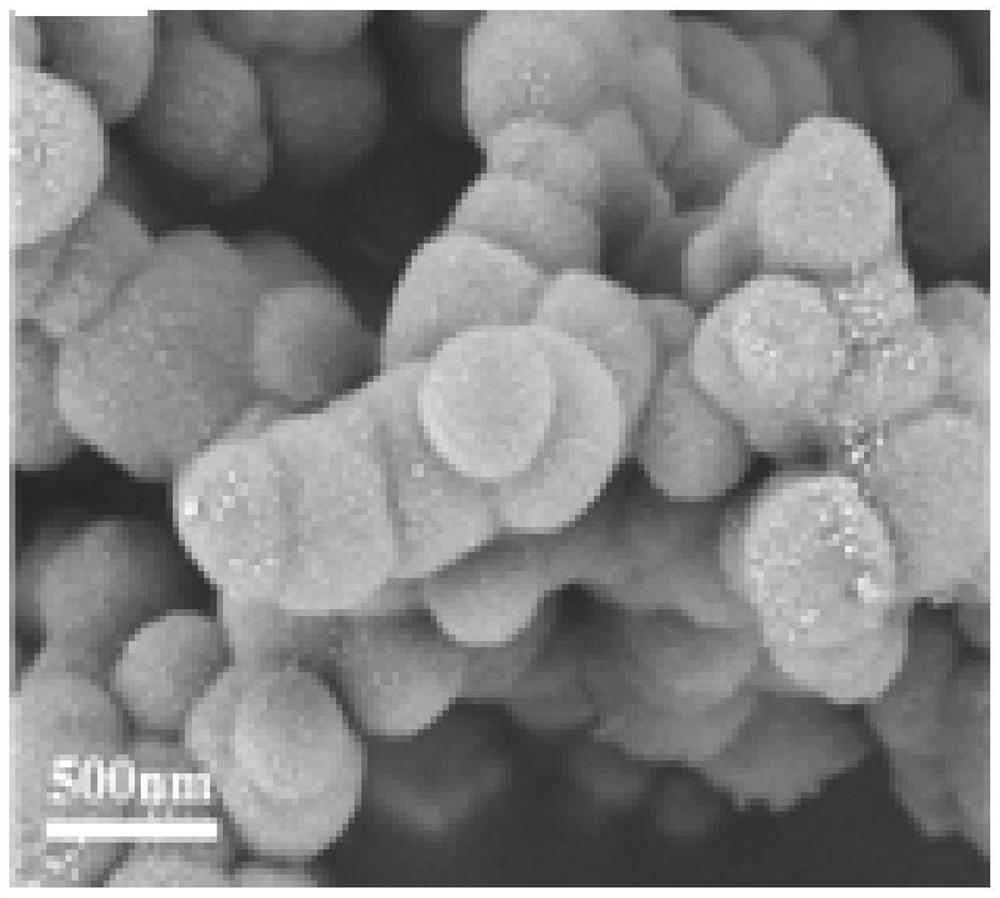
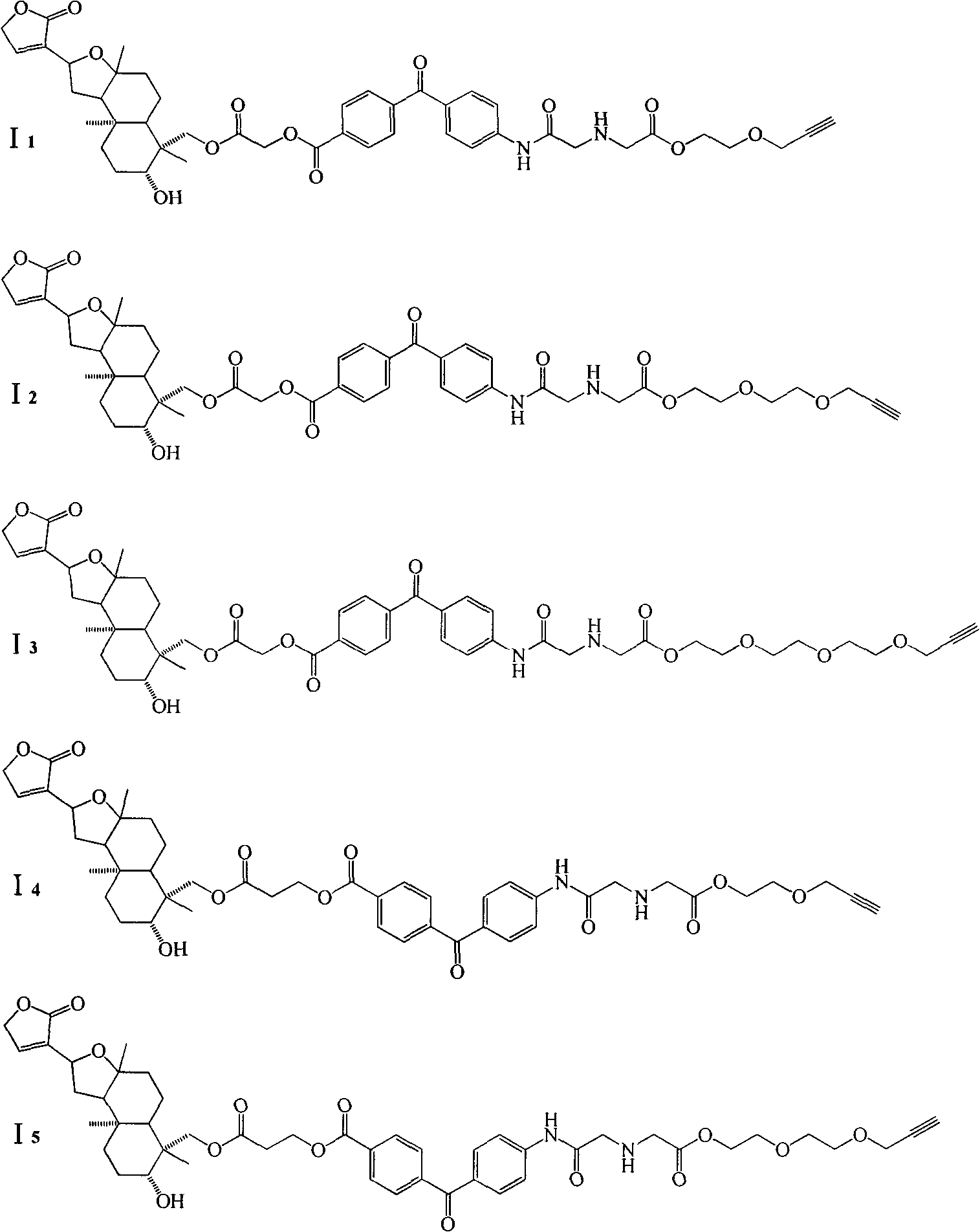
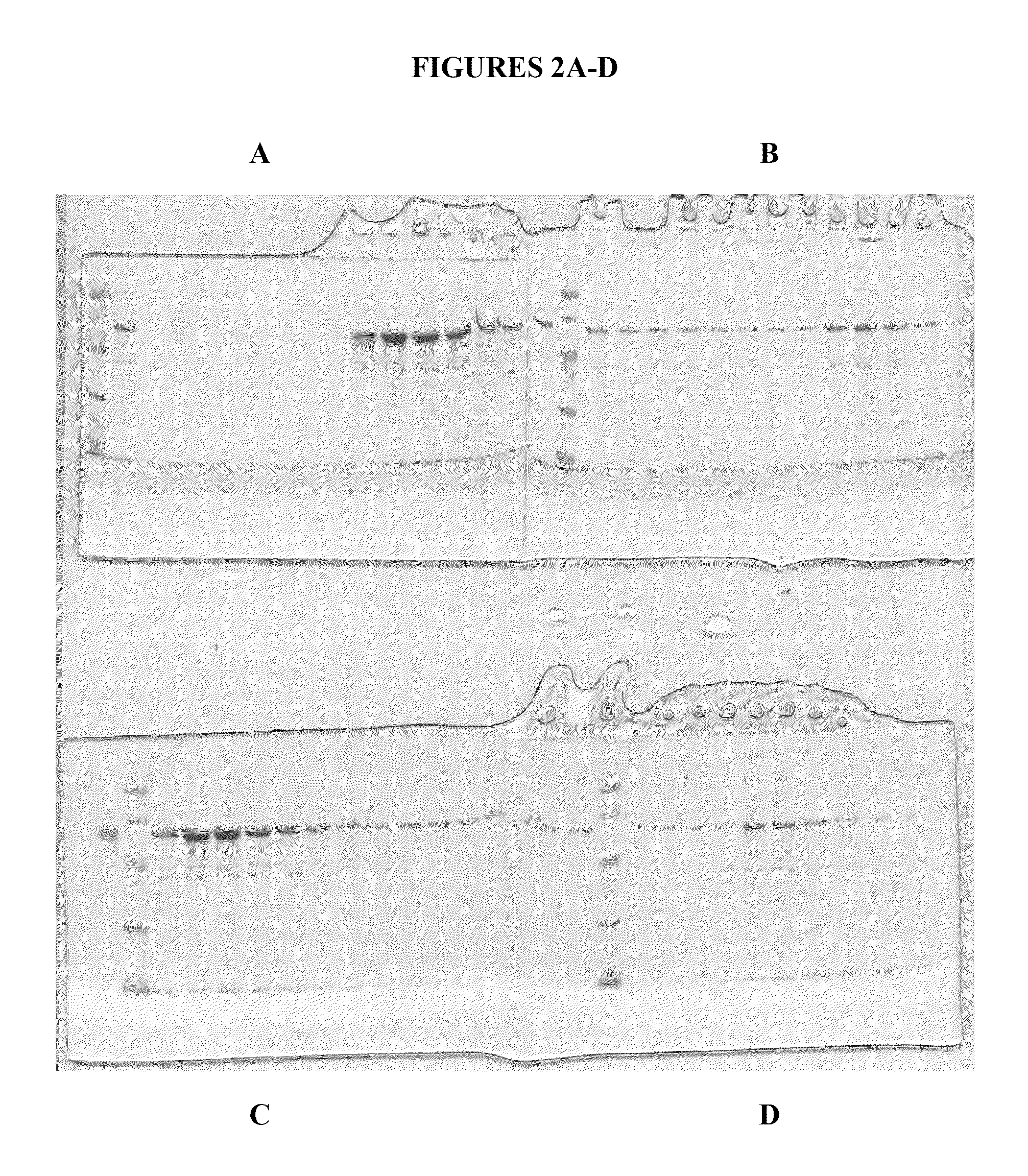
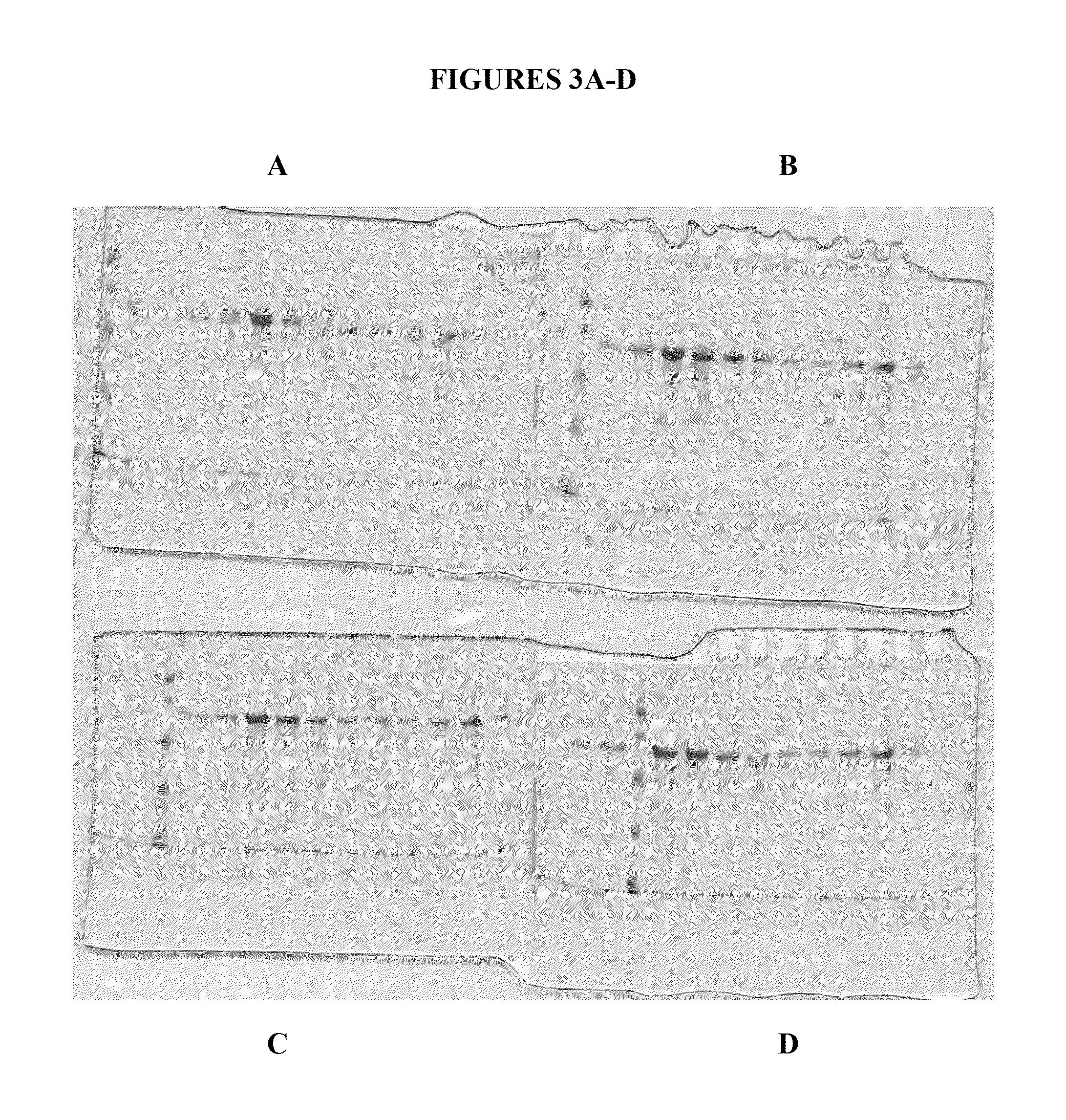
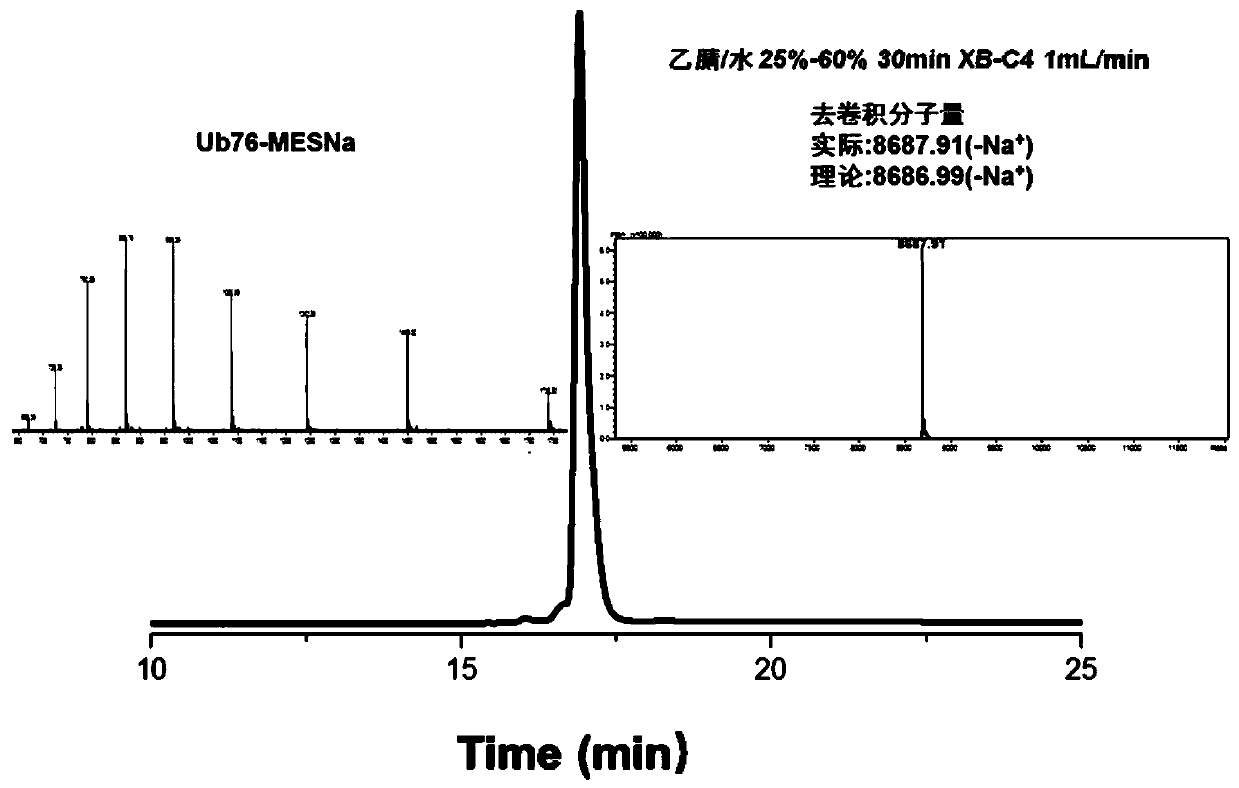
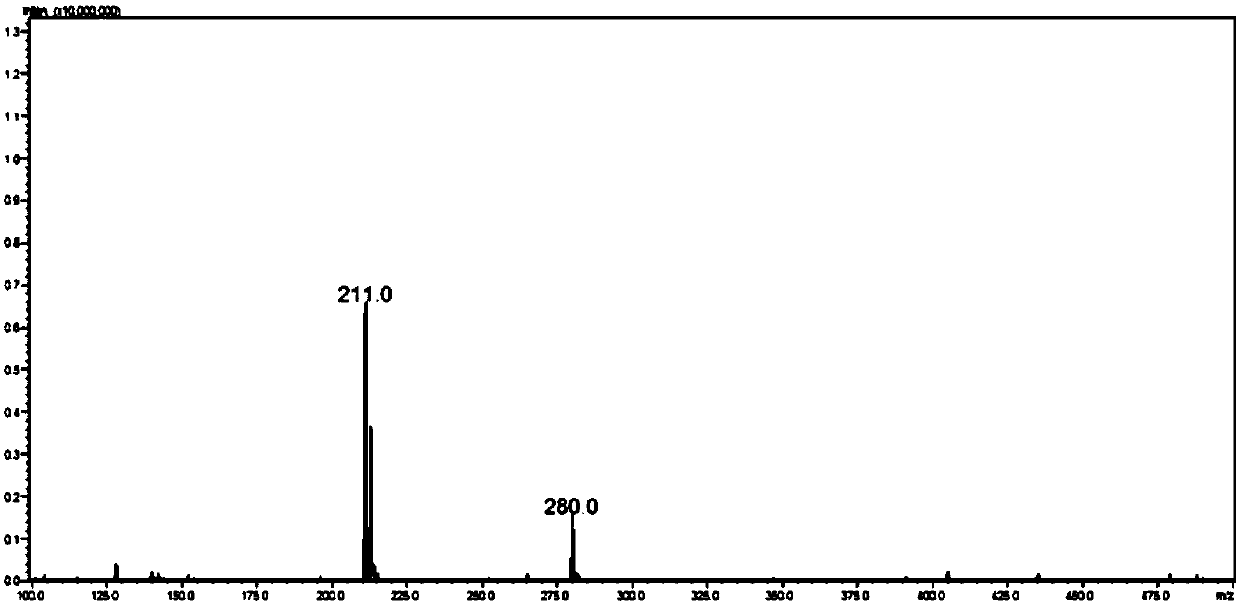
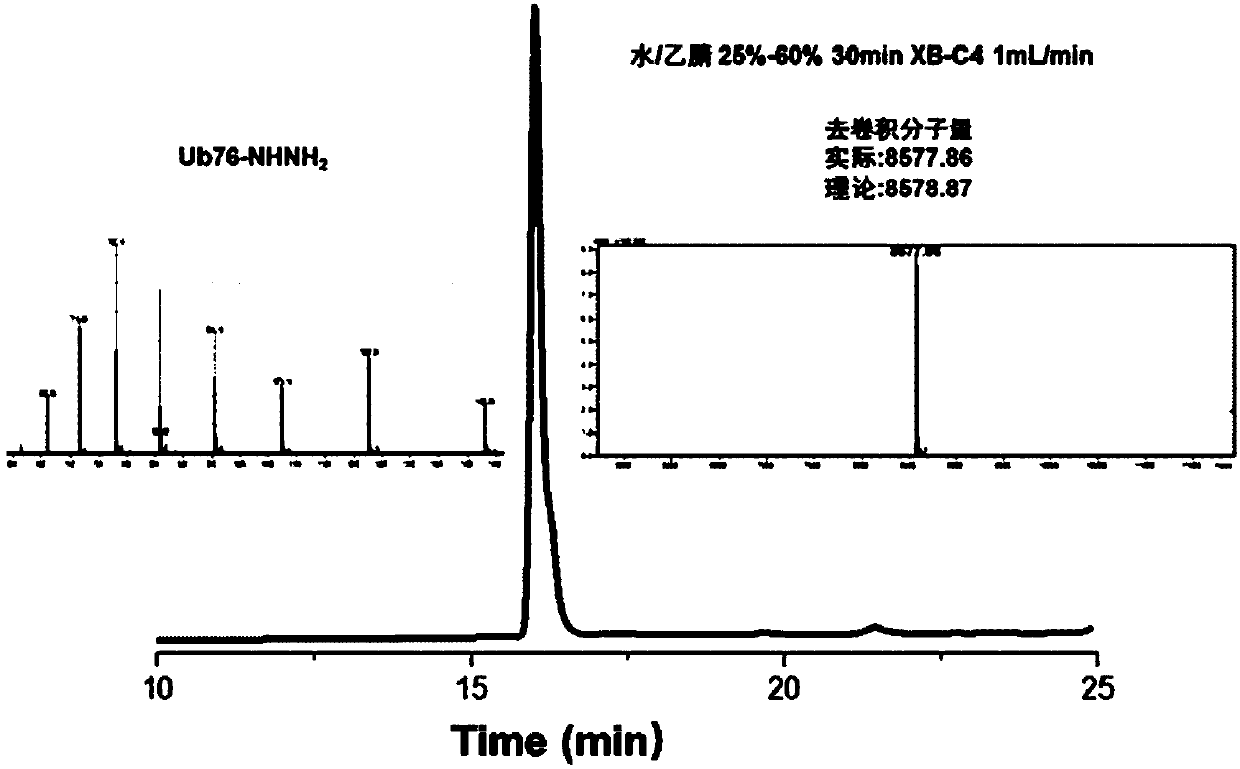
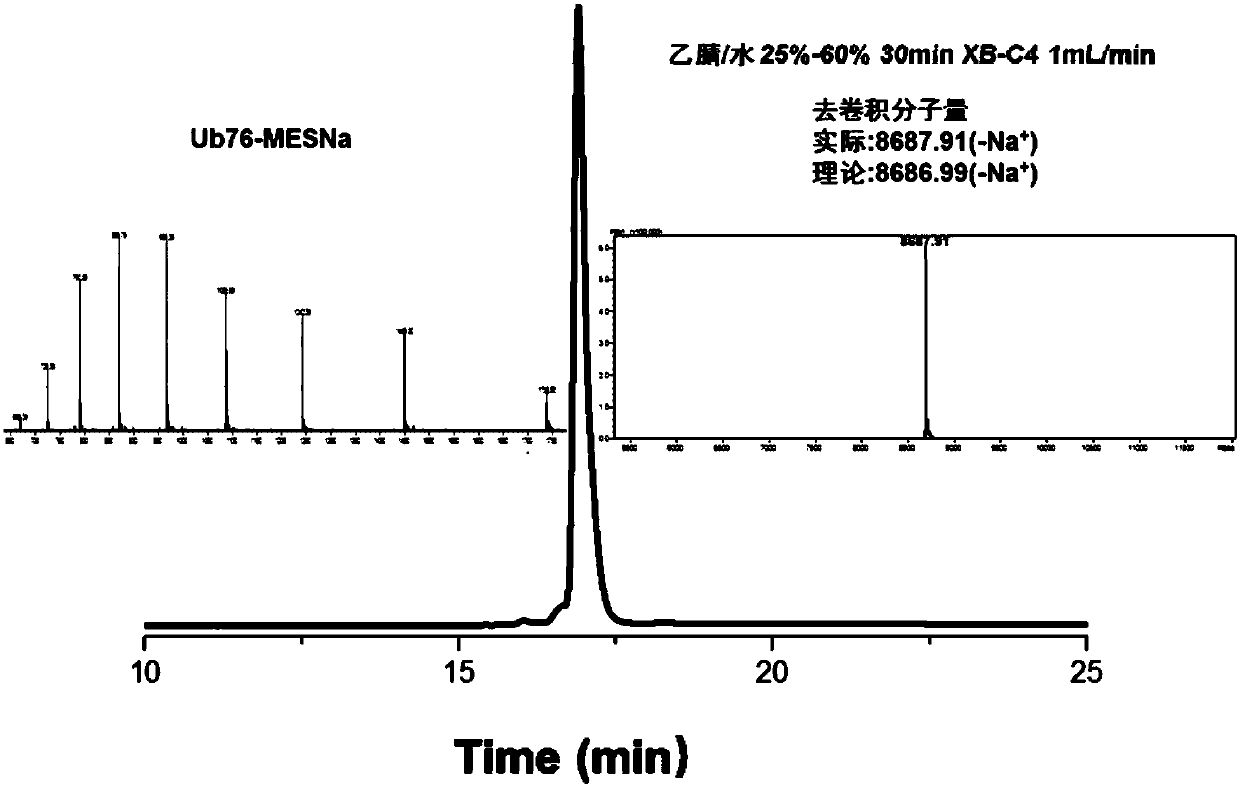
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Affinity label" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Affinity labels are a class of enzyme inhibitors that covalently bind to their target causing its inactivation. The hallmark of an affinity label is the use a targeting moiety to specifically and reversibly deliver a weakly reactive group to the enzyme that irreversibly binds to an amino acid residue. The targeting portion of the label often resembles the enzyme's natural substrate so that a similar mode of noncovalent binding is used prior to the covalent linkage. Their usefulness in medicine can be limited by the specificity of the first noncovalent binding step whereas indiscriminate action can be utilized for purposes such as affinity labeling - a technique for the validation of substrate-specific binding of compounds.
Methods for protein labeling based on acyl carrier protein
InactiveUS7666612B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesCoenzyme A biosynthesisCarrier protein
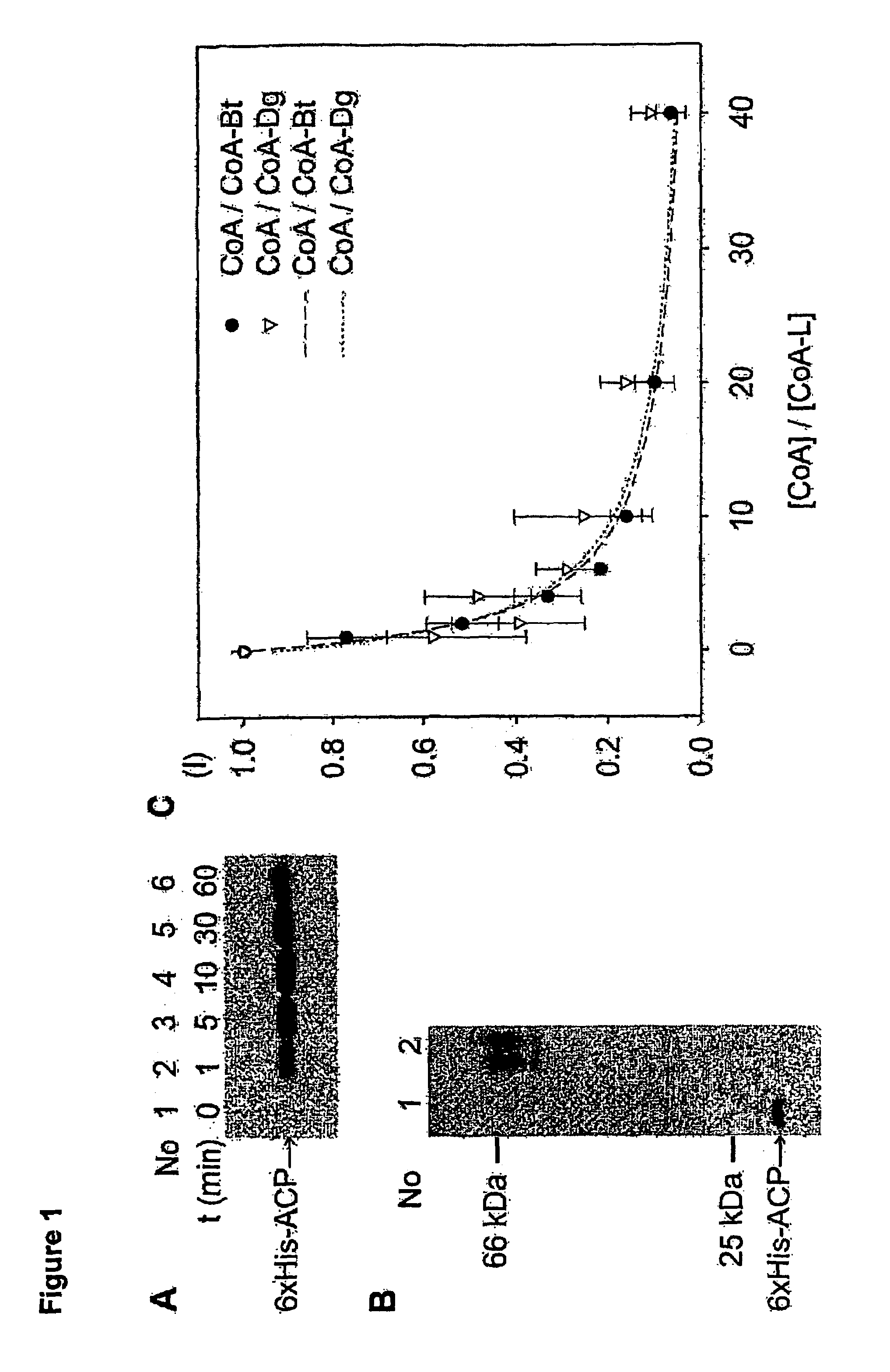
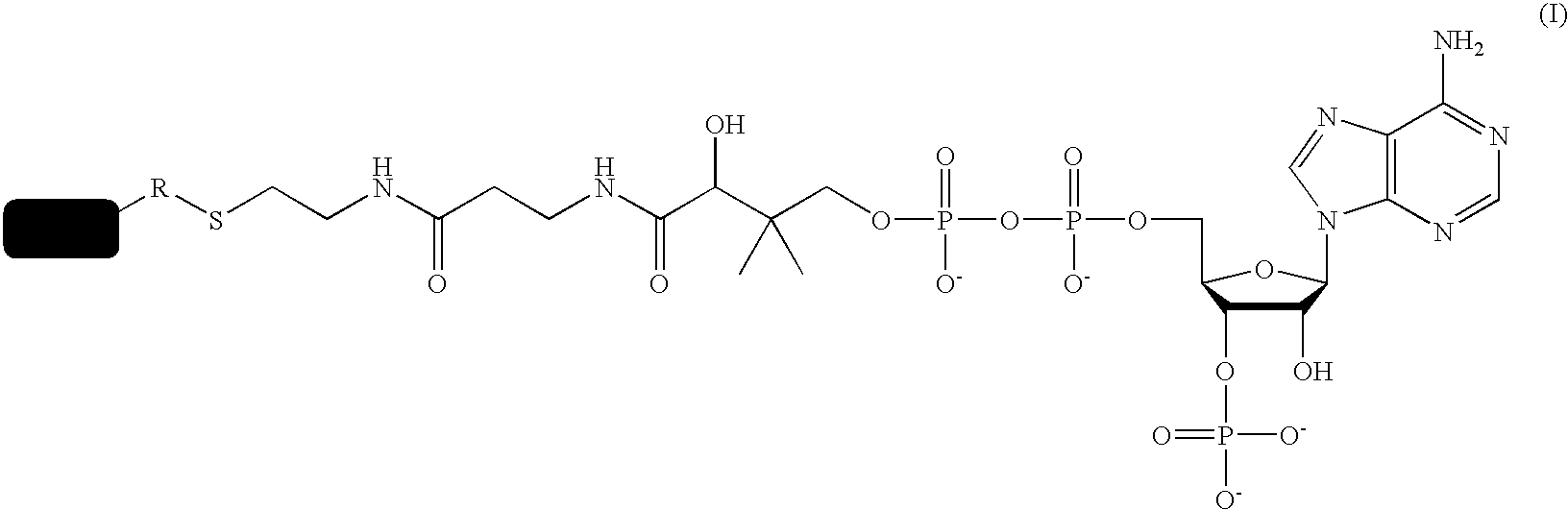
A method for labeling acyl carrier protein (ACP) fusion proteins with a wide variety of different labels is disclosed. The method relies on the transfer of a label from a coenzyme A type substrate to an ACP fusion protein using a holo-acyl carrier protein synthase (ACPS) or a homologue thereof. The method allows detecting and manipulating the fusion protein, both in vitro and in vivo, by attaching molecules to the fusion proteins that introduce a new physical or chemical property to the fusion protein. Examples of such labels are, among others, spectroscopic probes or reporter molecules, affinity tags, molecules generating reactive radicals, cross-linkers, ligands mediating protein-protein interactions or molecules suitable for the immobilization of the fusion protein.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Rapid quantitative analysis of proteins or protein function in complex mixtures
InactiveUS7544518B2Facilitates quantitative determinationFacilitates quantitative determination of the absolute amountsComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIsotopic labelingProtein expression profile
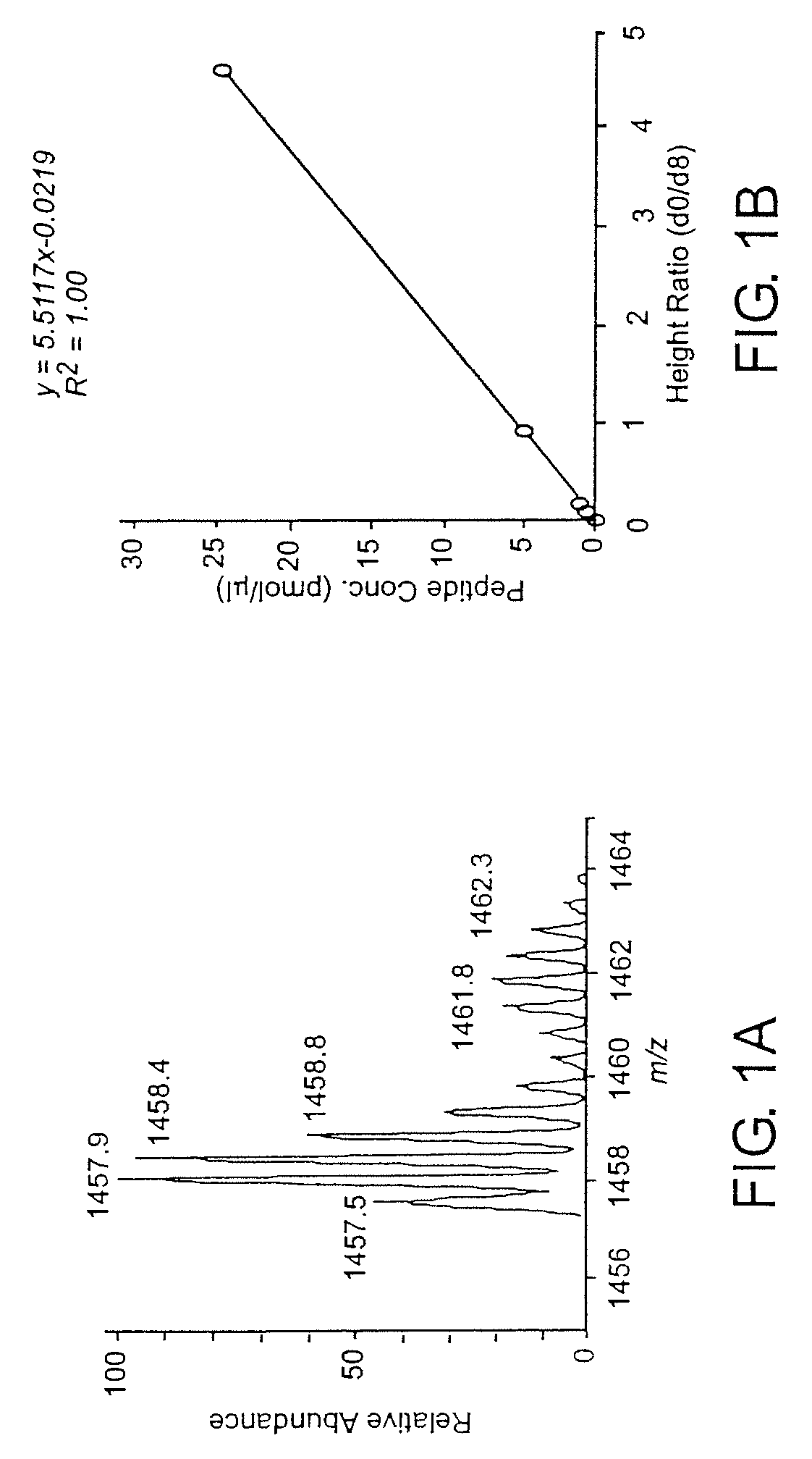
Analytical reagents and mass spectrometry-based methods using these reagents for the rapid, and quantitative analysis of proteins or protein function in mixtures of proteins. The methods employ affinity labeled protein reactive reagents having three portions: an affinity label (A) covalently linked to a protein reactive group (PRG) through a linker group (L). The linker may be differentially isotopically labeled, e.g., by substitution of one or more atoms in the linker with a stable isotope thereof. These reagents allow for the selective isolation of peptide fragments or the products of reaction with a given protein (e.g., products of enzymatic reaction) from complex mixtures. The isolated peptide fragments or reaction products are characteristic of the presence of a protein or the presence of a protein function in those mixtures. Isolated peptides or reaction products are characterized by mass spectrometric (MS) techniques. The reagents also provide for differential isotopic labeling of the isolated peptides or reaction products which facilitates quantitative determination by mass spectrometry of the relative amounts of proteins in different samples. The methods of this invention can be used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of global protein expression profiles in cells and tissues, to screen for and identify proteins whose expression level in cells, tissue or biological fluids is affected by a stimulus or by a change in condition or state of the cell, tissue or organism from which the sample originated.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Methods and compositions for tagging via azido substrates
InactiveUS7070941B2Immobilised enzymesOrganic active ingredientsBiotin-streptavidin complexProtein insertion
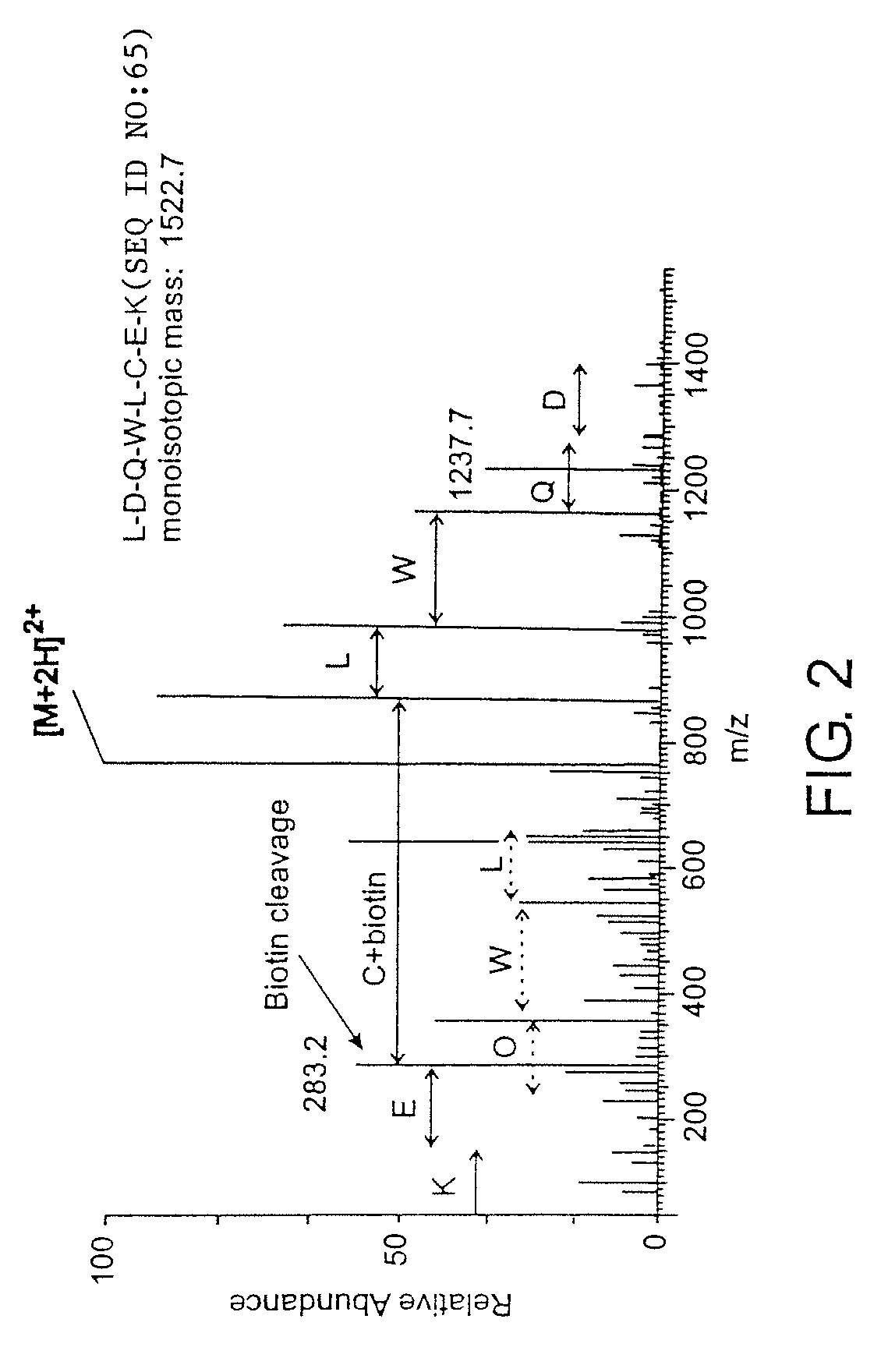
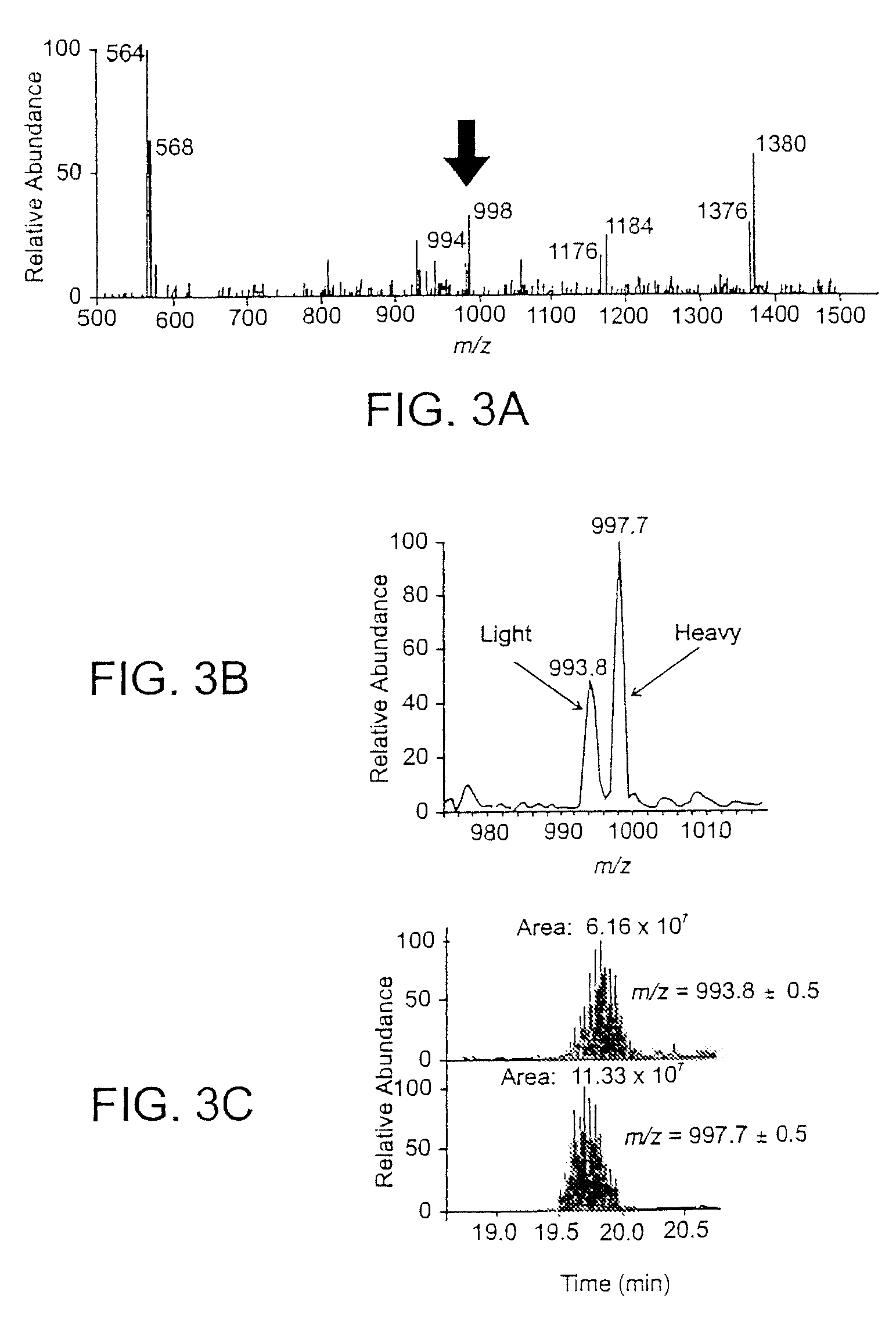
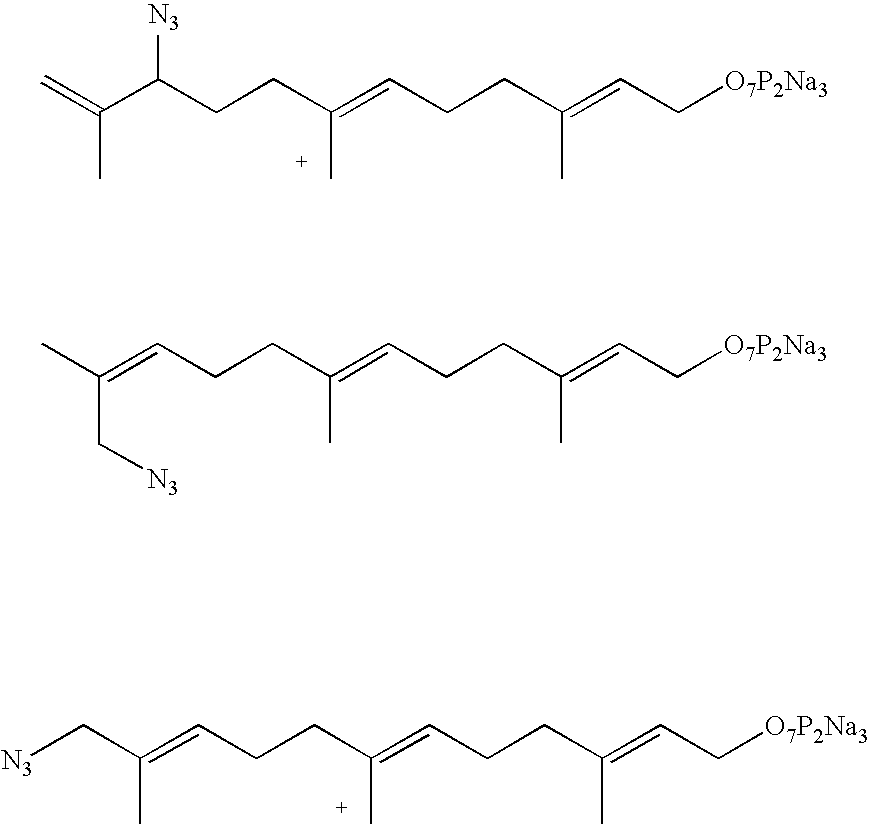
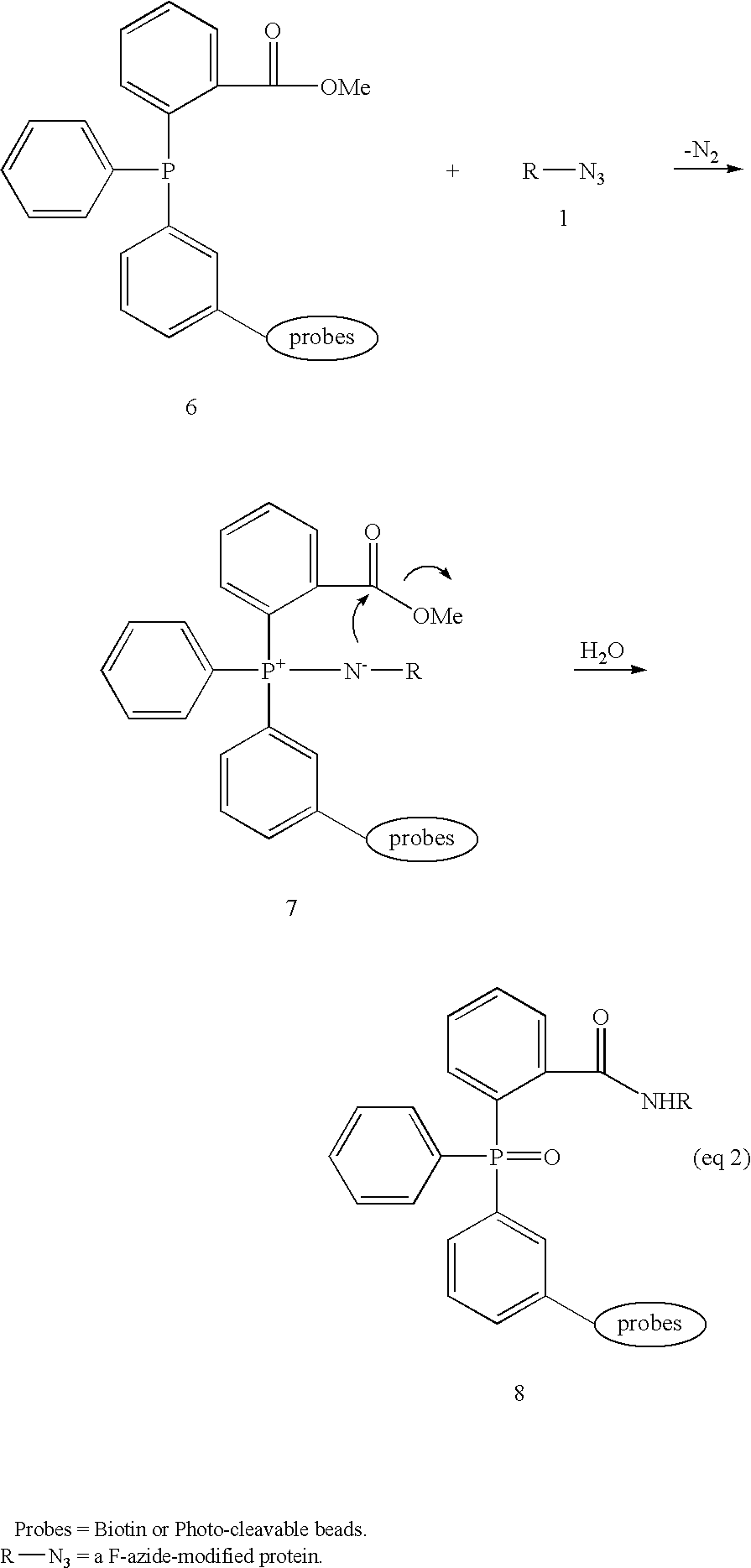
The invention provides methods and compositions for azide tagging of biomolecules. In one embodiment of the invention, proteins are tagged by metabolic incorporation of prenylated azido-analog substrates. Examples of such analogs are azido farnesyl diphosphate and azido farnesyl alcohol. The azido moiety in the resulting modified proteins provides an affinity tag, which can be chemoselectively captured by an azide-specific conjugation reaction, such as the Staudinger reaction, using a phosphine capture reagent. When the capture agent is biotinylated, the resulting conjugates can be detected and affinity-purified by streptavidin-linked- HRP and streptavidin-conjugated agarose beads, respectively. The invention allows detection and isolation of proteins with high yield, high specificity, and low contamination without harsh treatment of proteins.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Selective labeling and isolation of phosphopeptides and applications to proteome analysis
InactiveUS7052915B2Easy to separateImprove isolationComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhosphatePhosphoric acid
A method for selective labeling of phosphate groups in natural and synthetic oligomers and polymers in the presence of chemically related groups such as carboxylic acid groups. The method is specifically applicable to biological oligomers and polymers, including phosphopeptides, phosphoproteins and phospholipids. In a specific embodiment, selective labeling of phosphate groups in proteins and peptides, for example, facilitates separation, isolation and detection of phosphoproteins and phosphopeptides in complex mixtures of proteins. Selective labeling can be employed to selectively introduce phosphate labels at phosphate groups in an oligomer or polymer, e.g., in a peptide or protein. Detection of the presence of the label, is used to detect the presence of the phosphate group in the oligomer or polymer. The method is useful for the detection of phosphoproteins or phosphopeptides. The phosphate label can be a colorimetric label, a radiolabel, a fluorescent or phosphorescent label, an affinity label or a linker group carrying a reactive group (or latent reactive group) that allows selective attachment of the oligomer or polymer (protein or peptide) to a phosphate label, to an affinity label or to a solid support. The method can be combined with well-known methods of mass spectrometry to detect and identify phosphopeptides and phosphoproteins.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Mass spectrometry-based methods for detection and differentiation of botulinum neurotoxins
InactiveUS20060024763A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSpectroscopyMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention is directed to a method for detecting the presence of clostridial neurotoxins in a sample by mixing a sample with a peptide that can serve as a substrate for proteolytic activity of a clostridial neurotoxin; and measuring for proteolytic activity of a clostridial neurotoxin by a mass spectroscopy technique. In one embodiment, the peptide can have an affinity tag attached at two or more sites.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY +1
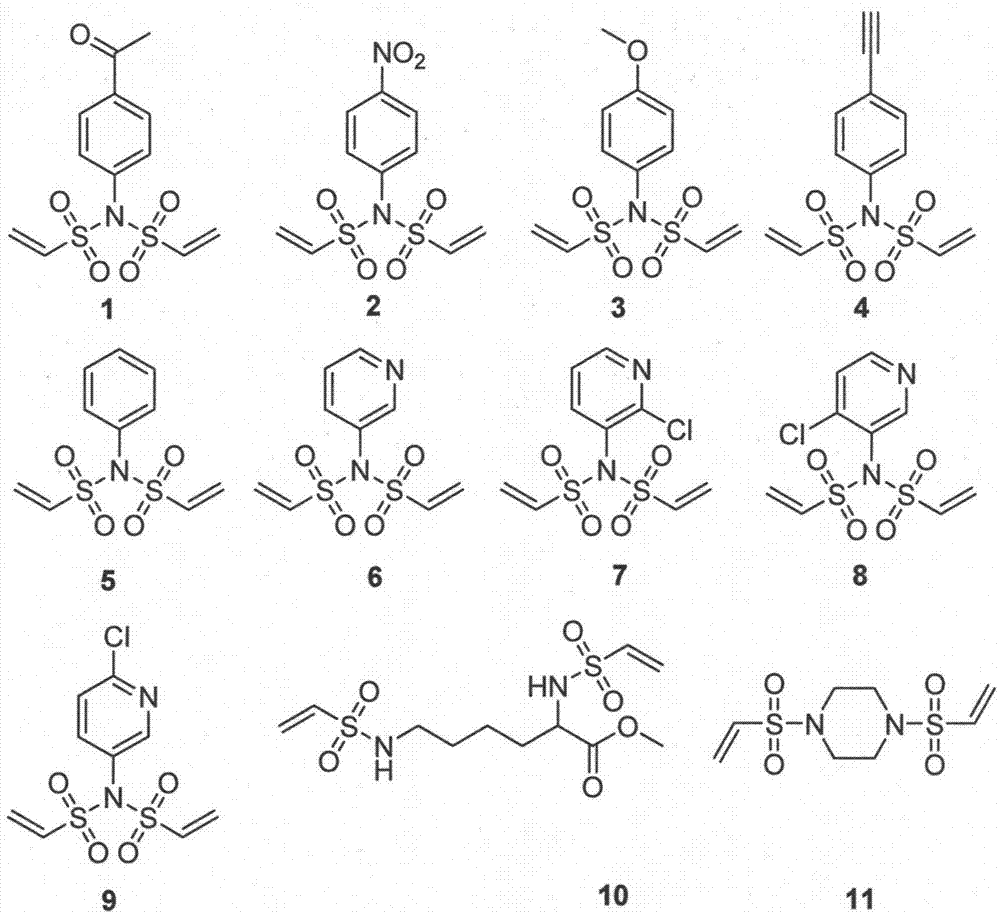
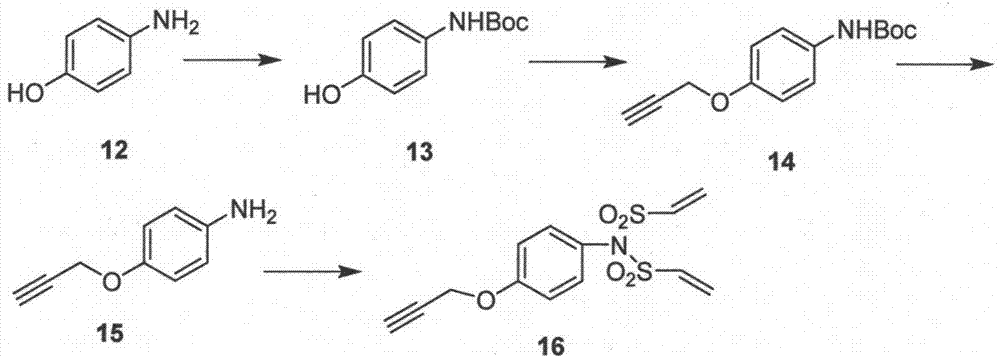
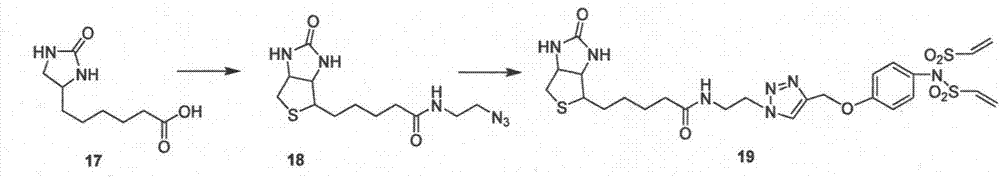
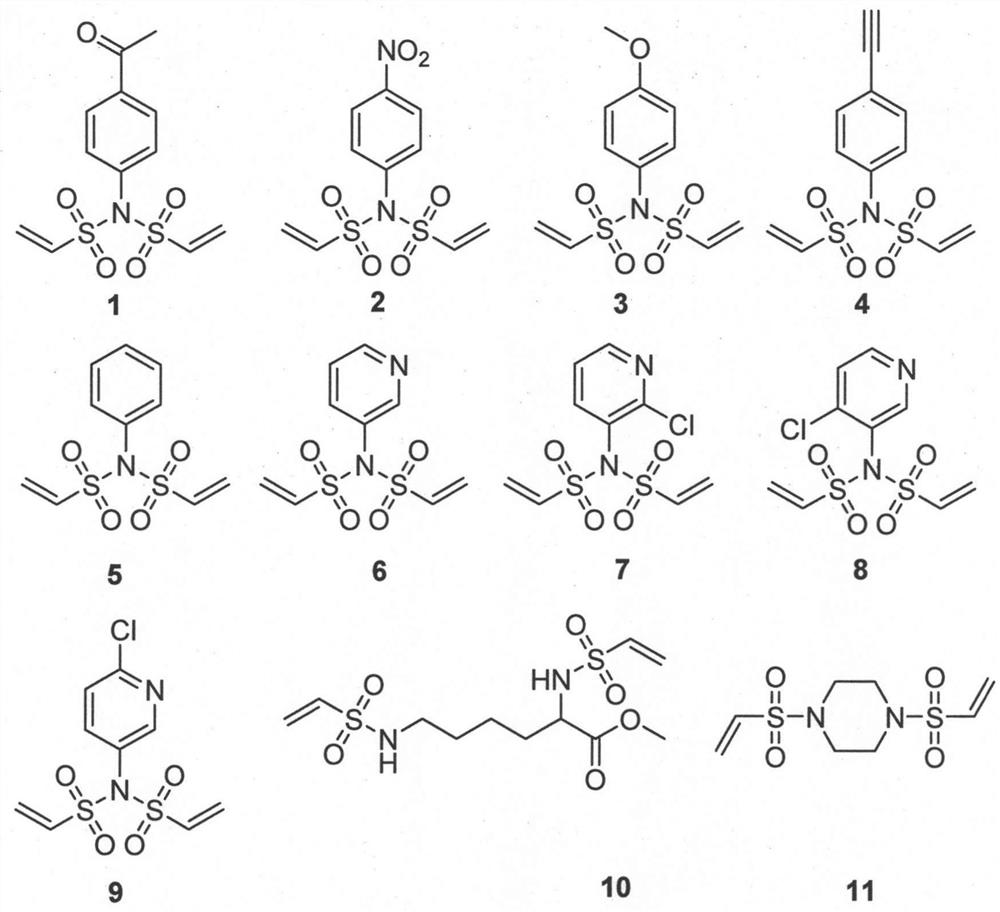
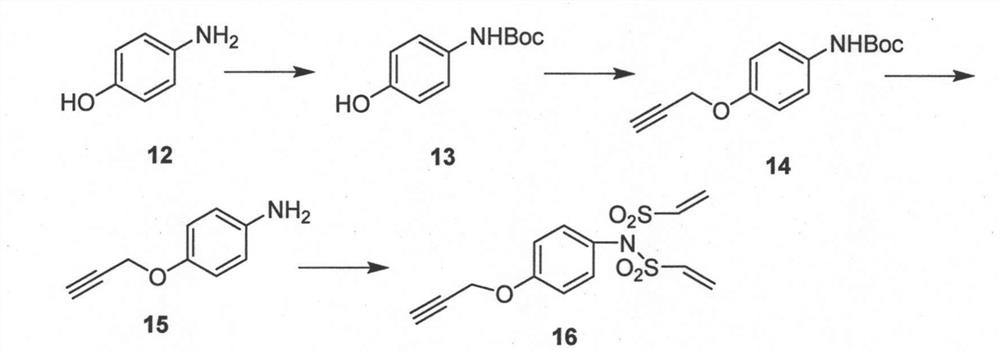
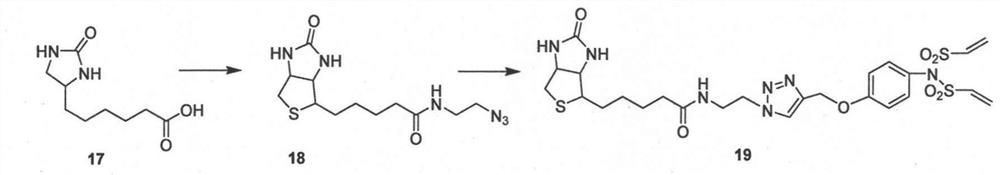
Divinyl sulfamide linker as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN107400072AEasy to makeEfficient preparationPeptide preparation methodsSulfonic acid amide preparationStructural formulaStereochemistry
The invention provides a divinyl sulfamide linker as well as preparation and an application thereof. The divinyl sulfamide linker has the structural formula shown in the formula I or the formula II. One end of the novel divinyl sulfamide linker can be coupled with a polypeptide or protein, and the other end can be connected with an affinity tag or a tracing fluorescent substance or an active drug.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
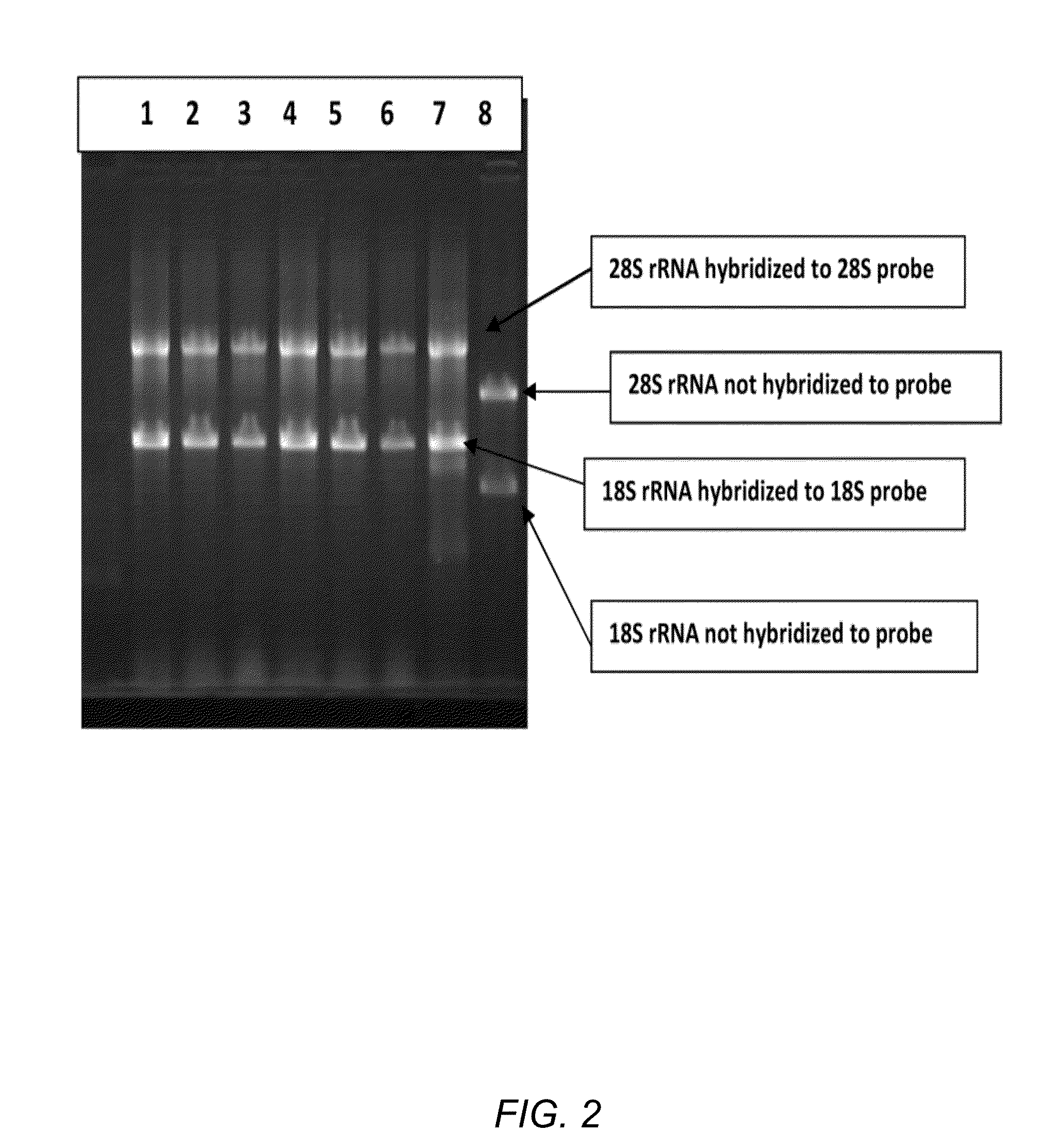
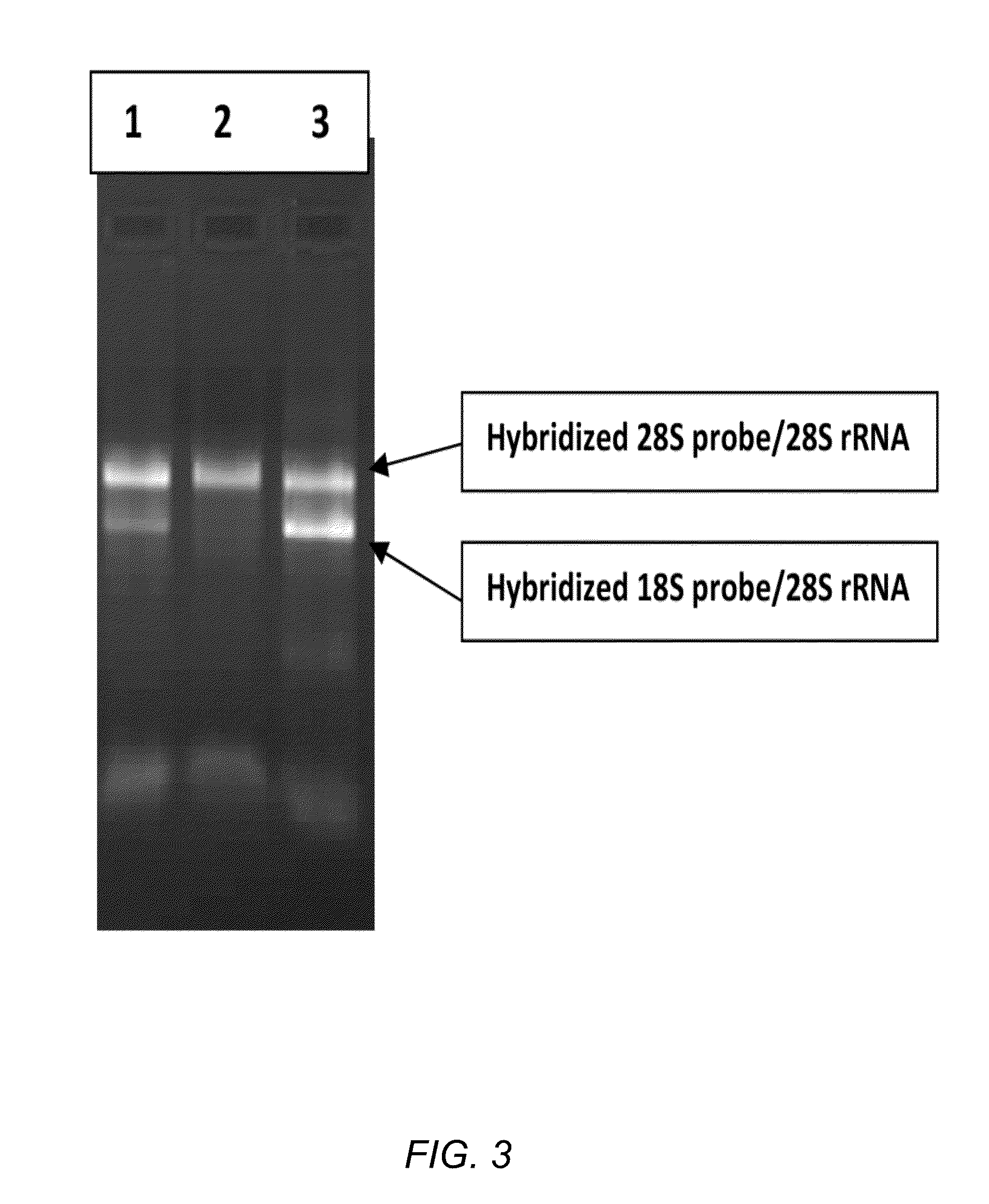
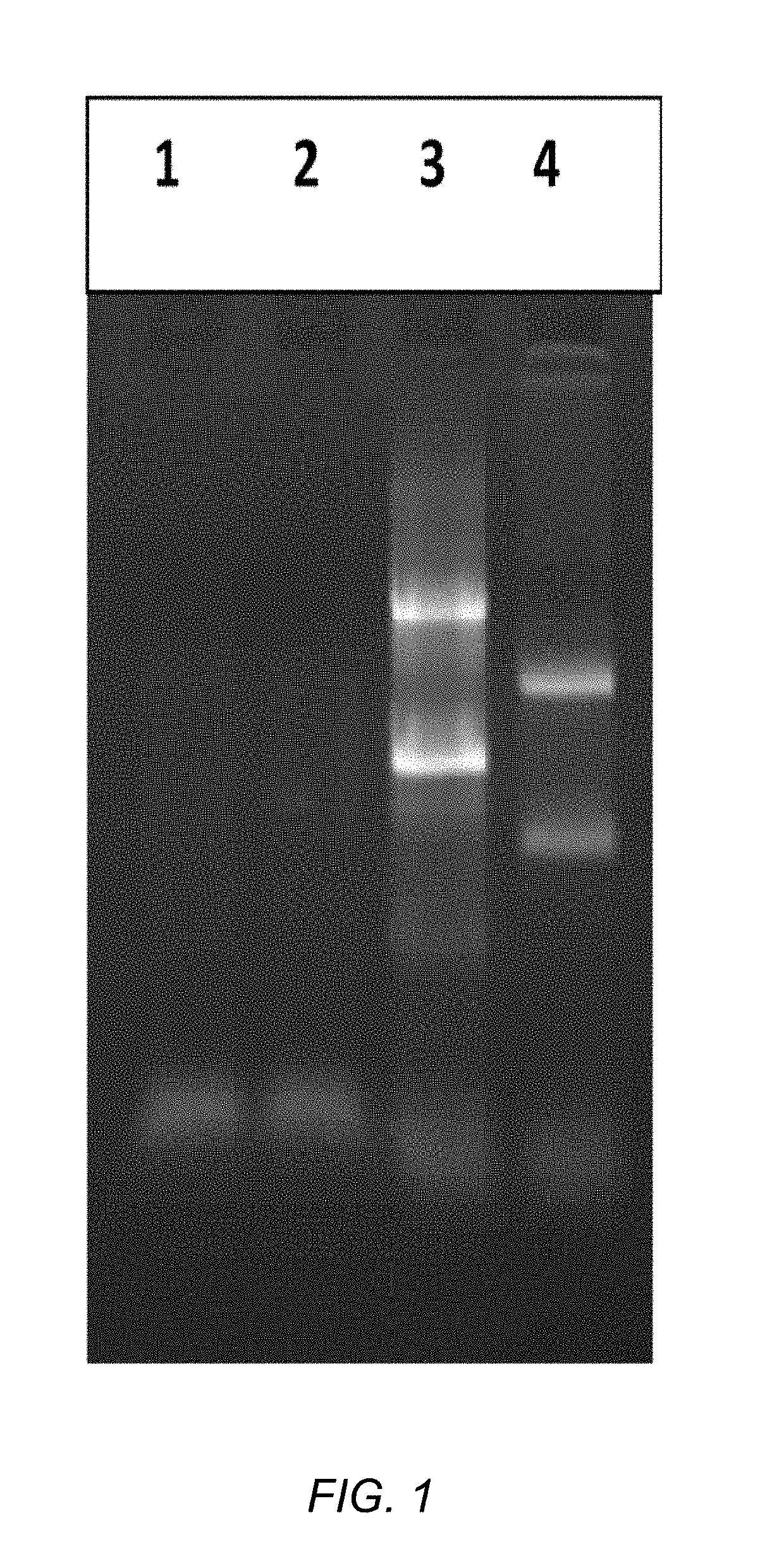
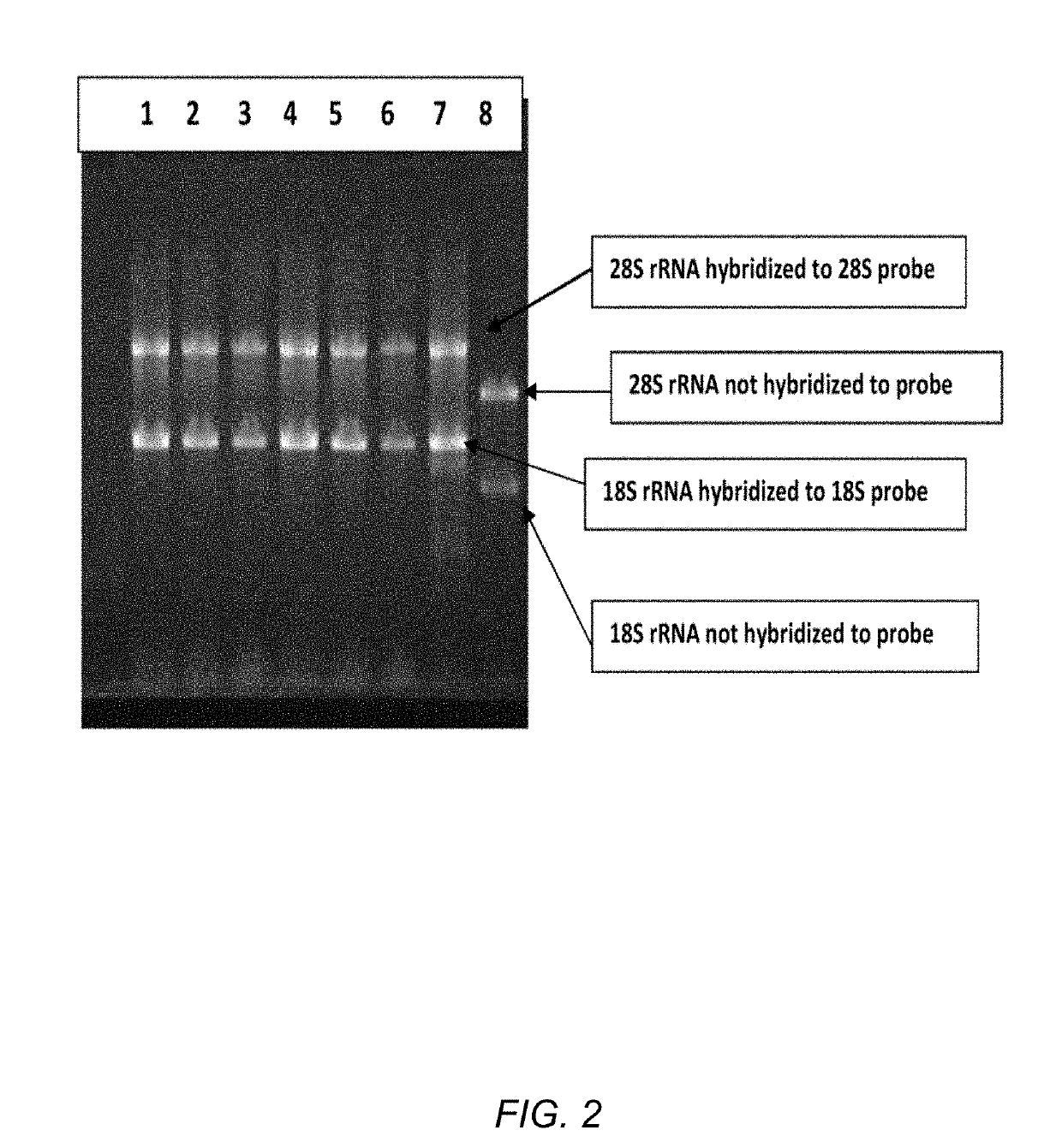
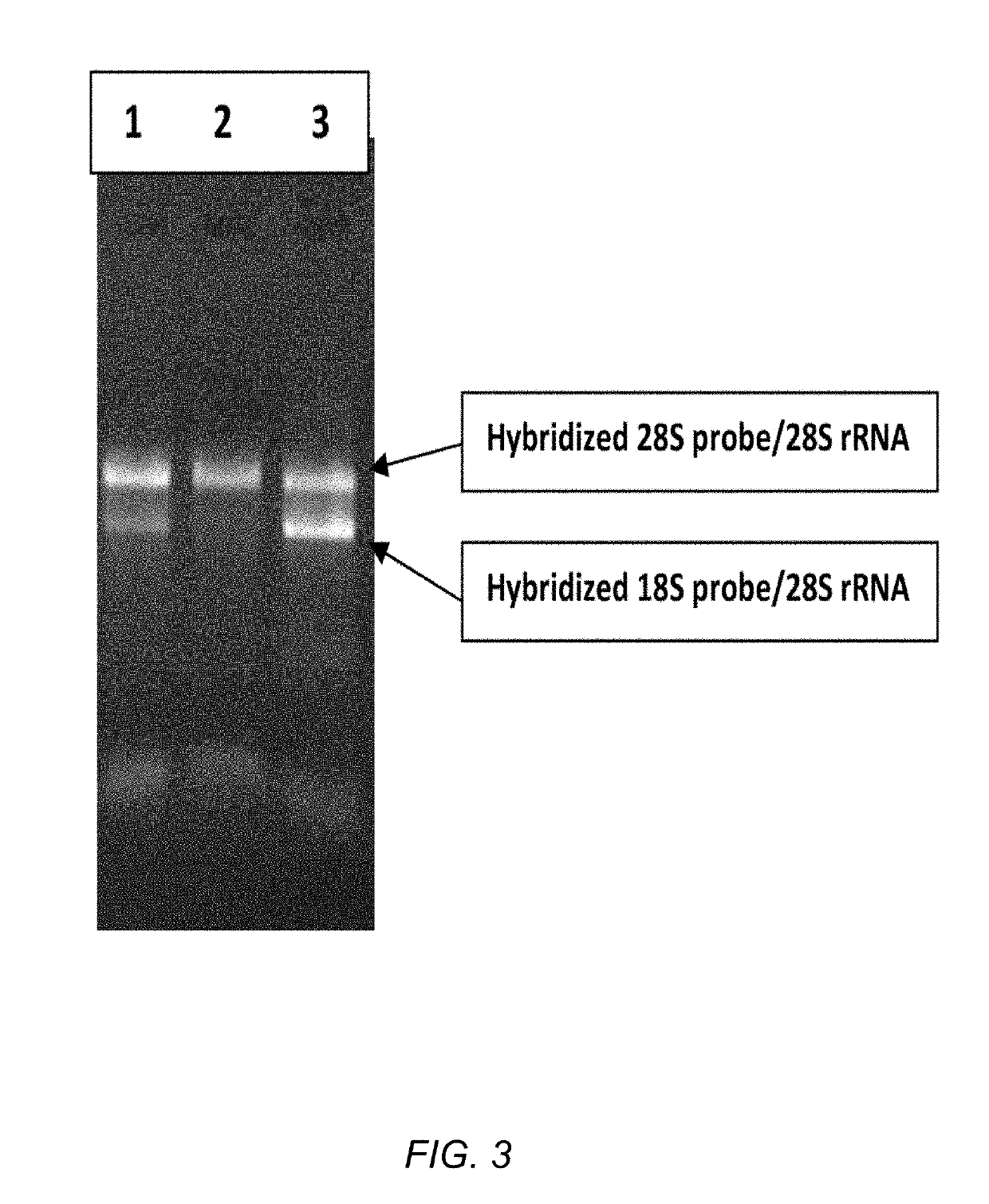
Methods and compositions for improving removal of ribosomal RNA from biological samples
The invention generally relates to compositions for maximizing capture of affinity-labeled molecules on solid supports. The disclosed methods and compositions were developed to maximize depletion of ribosomal RNA from total RNA samples, which is useful to improve the quality of RNA preparations used for applications such as massively parallel sequencing. The RNA depletion method is based on using long affinity-labeled RNA molecules that are complementary to all or part of the target ribosomal RNAs, as subtractive hybridization probes.
Owner:BICO SCI CORP
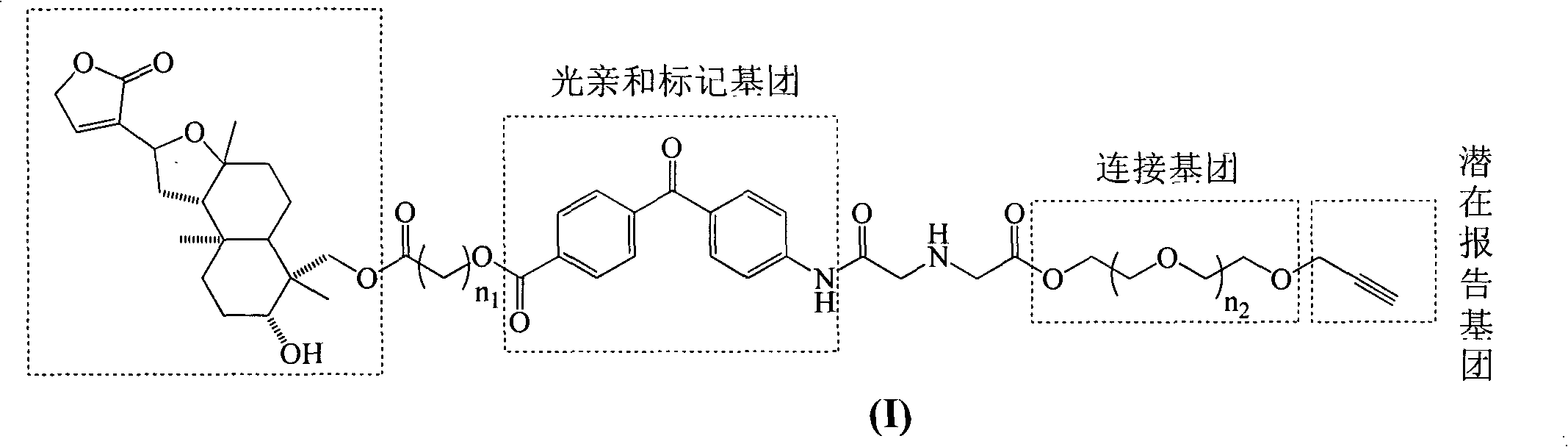
Isoandrographolide photoaffinity labeling molecular probe, preparation method and pharmaceutical composition of molecular probe
The invention discloses an isoandrographolide photoaffinity labeling molecular probe. The structure of the molecular probe is represented in a formula (I), wherein n1 ranges from 1 to 5 and n2 ranges from 0 to 2. Furthermore, the invention discloses a preparation and a pharmaceutical composition of the isoandrographolide photoaffinity labeling molecular probe. The compound, which is excellent in TNF-alpha inhibitory activity, can be used for researching and discovering target protein of isoandrographolide having an action of regulating macrophage function, and the compound, as a tool medicine, can be used for medicine development of a diagnostic reagent of the target protein as well as a regulator thereof.
Owner:XIAMEN JSY PHARMA TECH CO LTD
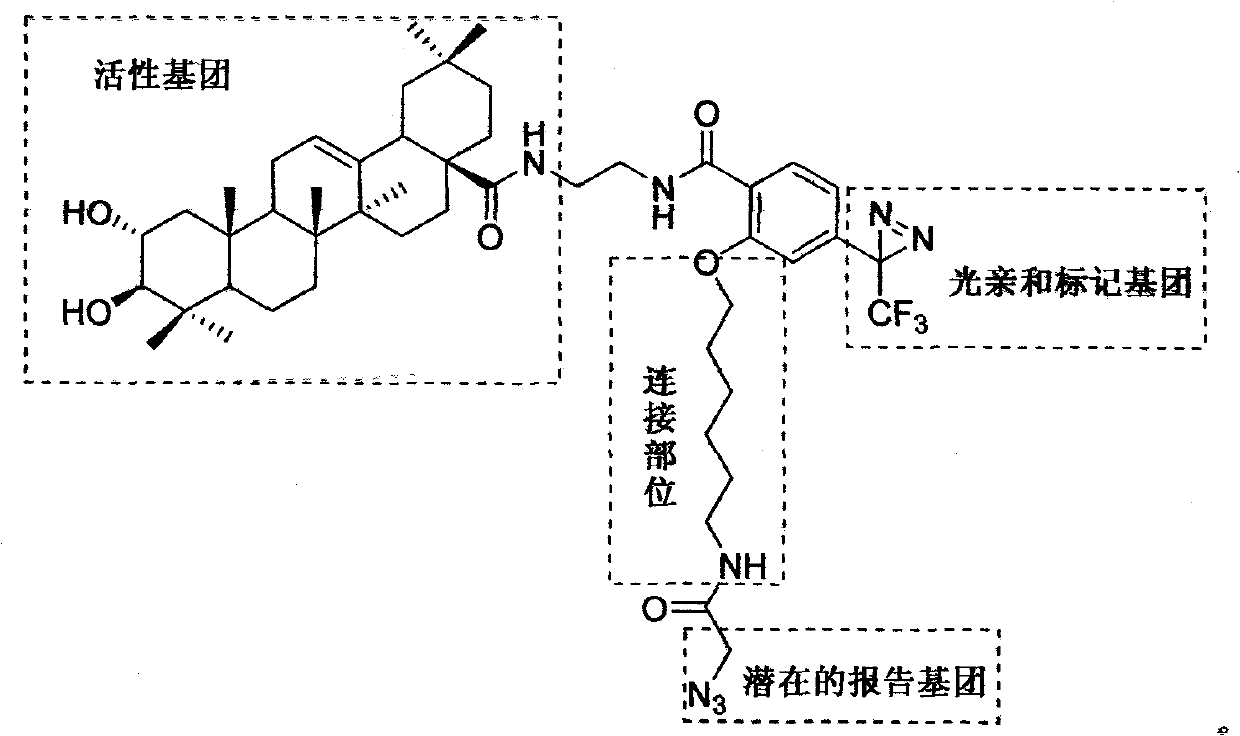
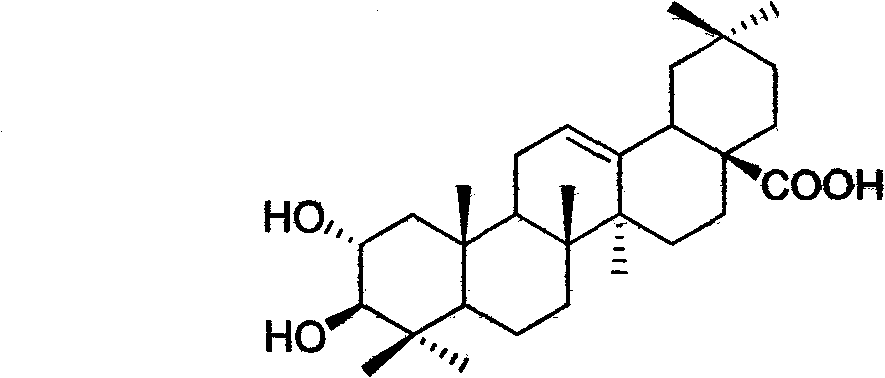
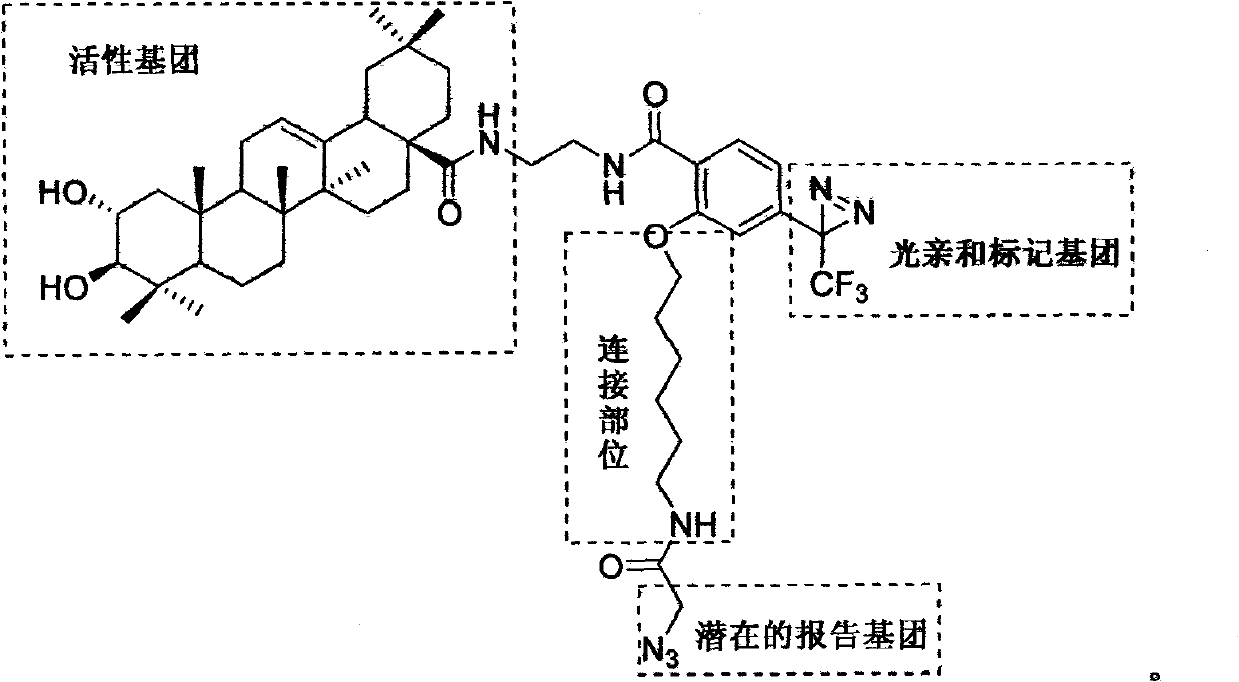
Light affinity labelling small molecular probe based on maslinic acid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101792478APromote research and developmentSteroidsBulk chemical productionEthylenediamineLabelling
The invention relates to a light affinity labelling small molecular probe based on maslinic acid and preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of organic compound and preparation thereof. Natural product maslinic acid is taken as initial raw material, compound I is obtained under the protection of acetyl, the compound I reacts with oxalyl chloride to obtain compound II, the compound II reacts with ethane diamine under single protection of Boc to obtain compound III, the compound III firstly strips Boc protecting group in HCl ethyl acetate solution and then reacts with segment IV with light affinity labelling group to obtain compound V, the compound V strips acetyl protecting group by hydrolysis with presence of alkali, so as to obtain light affinity labelling small molecular probe VI. The probe molecule can be used for researching and discovering active compound maslinic acid in vivo action target, action mode of target spot and structural information of active site and provides important information for research and development of related medicine.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Method for production and purification of macromolecular complexes
InactiveUS20100273240A1Quick and simple purificationHigh yieldBacteriaStable introduction of DNAPurification methodsNucleotide
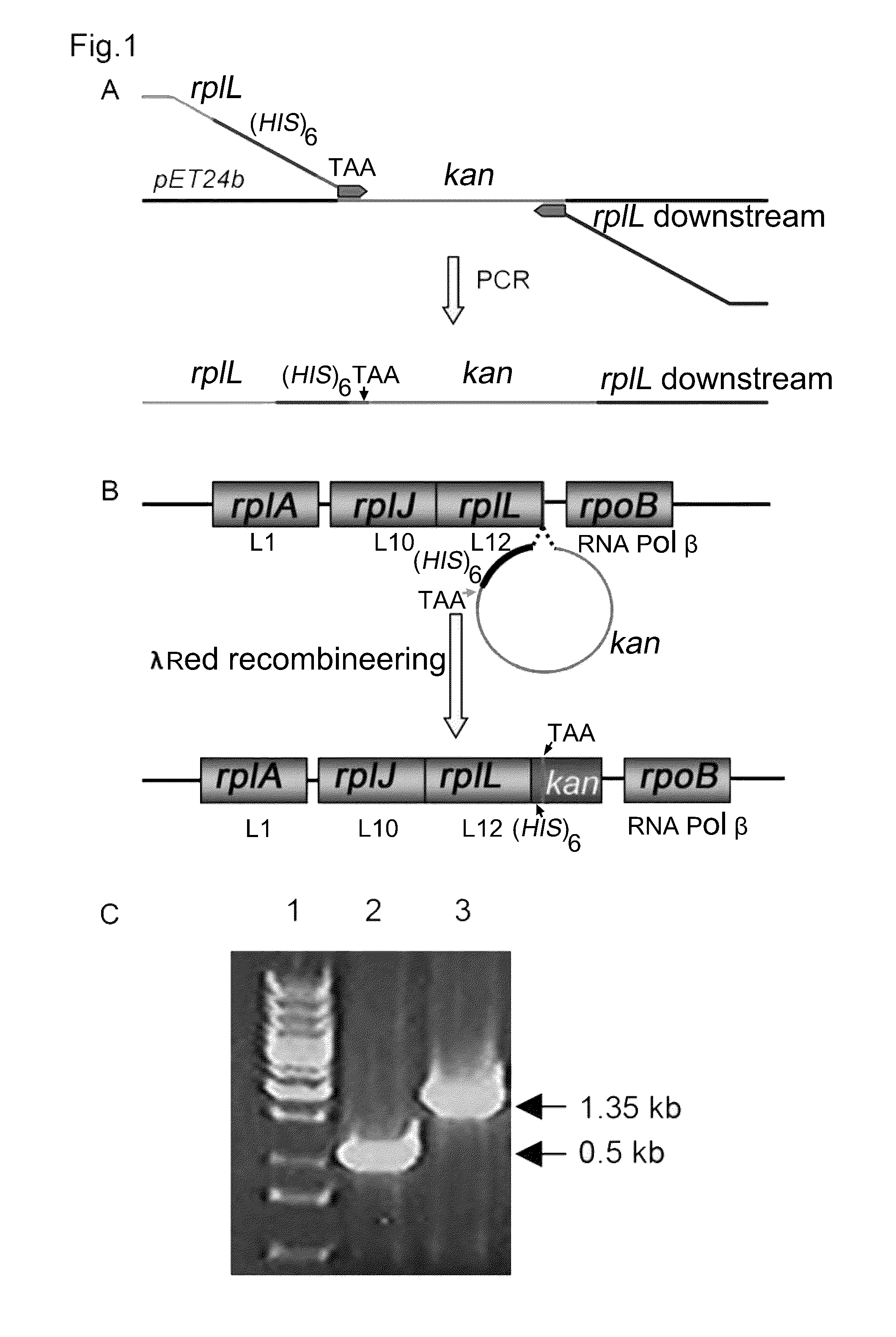
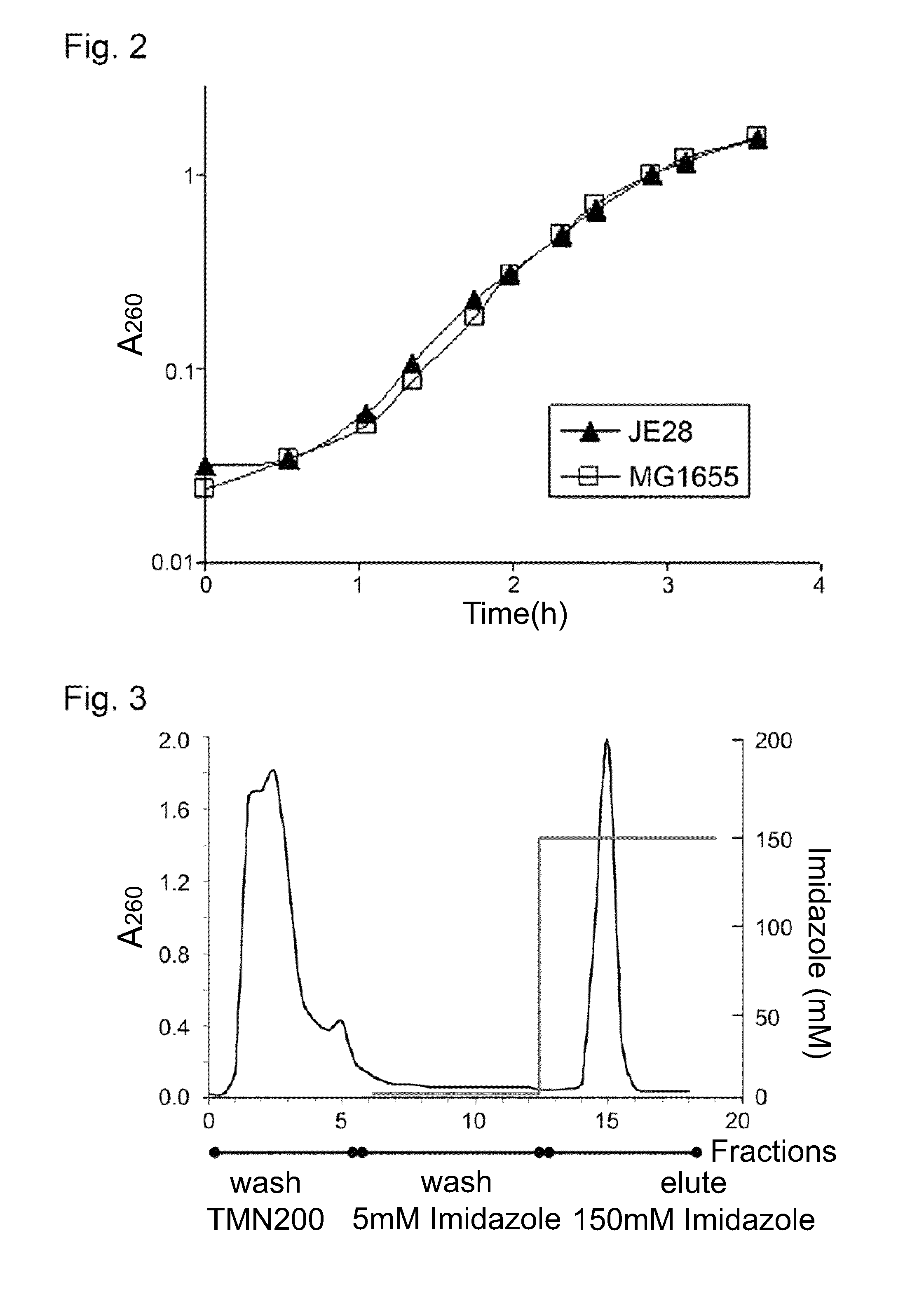
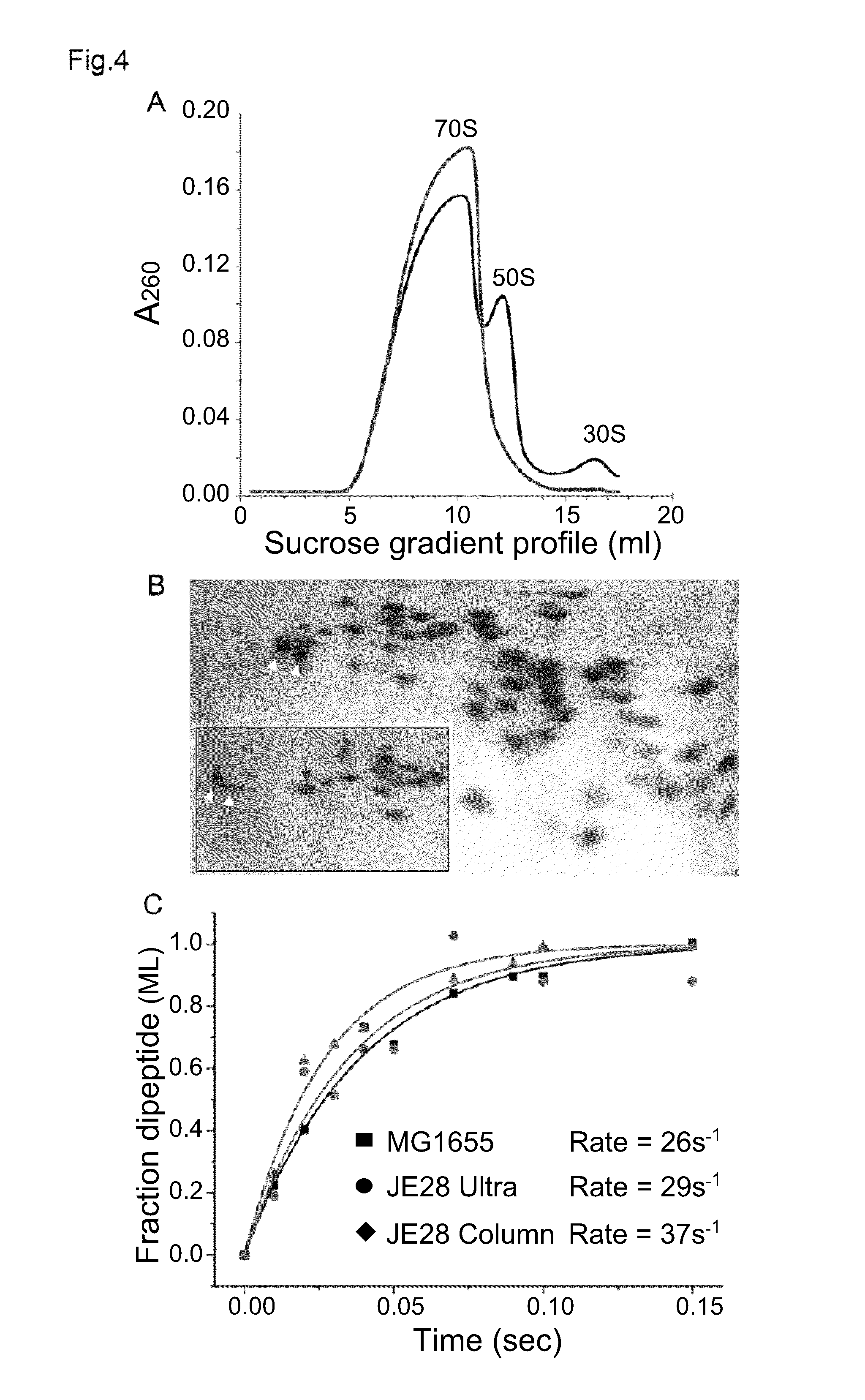
The present invention relates to a method for production and purification of affinity tagged macromolecular complexes, such as ribosomes. More closely, the method comprises in-frame fusion of a nucleotide sequence specific for an affinity tag and a selection marker, wherein the fusion is at the chromosomal site of a gene encoding a multicopy protein, and wherein the macromolecular complex is expressed with multiple copies of said affinity tag. The invention also relates to affinity tagged ribosomes, to cells comprising such affinity tagged ribosomes, and to various uses thereof.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
PROCESS FOR PREPARATION OF SECRETORY IgA AND SECRETORY IgM
ActiveUS20170058018A2Antibacterial agentsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifEpitopeSecretory IgM
A process for synthesizing and separating secretory IgA from a mixture of IgA monmer and IgA dimer is provided. The process includes covalently binding affinity tagged or epitope tagged recombinant secretory component to the IgA dimer in the mixture and binding the affinity tagged or an epitope tagged secretory IgA to immobilized moieties on the solid phase support resin to which the affinity tag or epitope tag binds and then eluting the affinity tagged or an epitope tagged secretory IgA with release buffer. A process for synthesizing and separating secretory IgM from a mixture of IgM and other plasma proteins is also provided. The process includes covalently binding affinity tagged or an epitope tagged recombinant secretory component to the IgM in the mixture and binding the affinity tagged or an epitope tagged secretory IgM to immobilized moieties on the solid phase support resin and then eluting the peptide tagged secretory IgM with a release buffer.
Owner:BROWN STEPHEN C +1
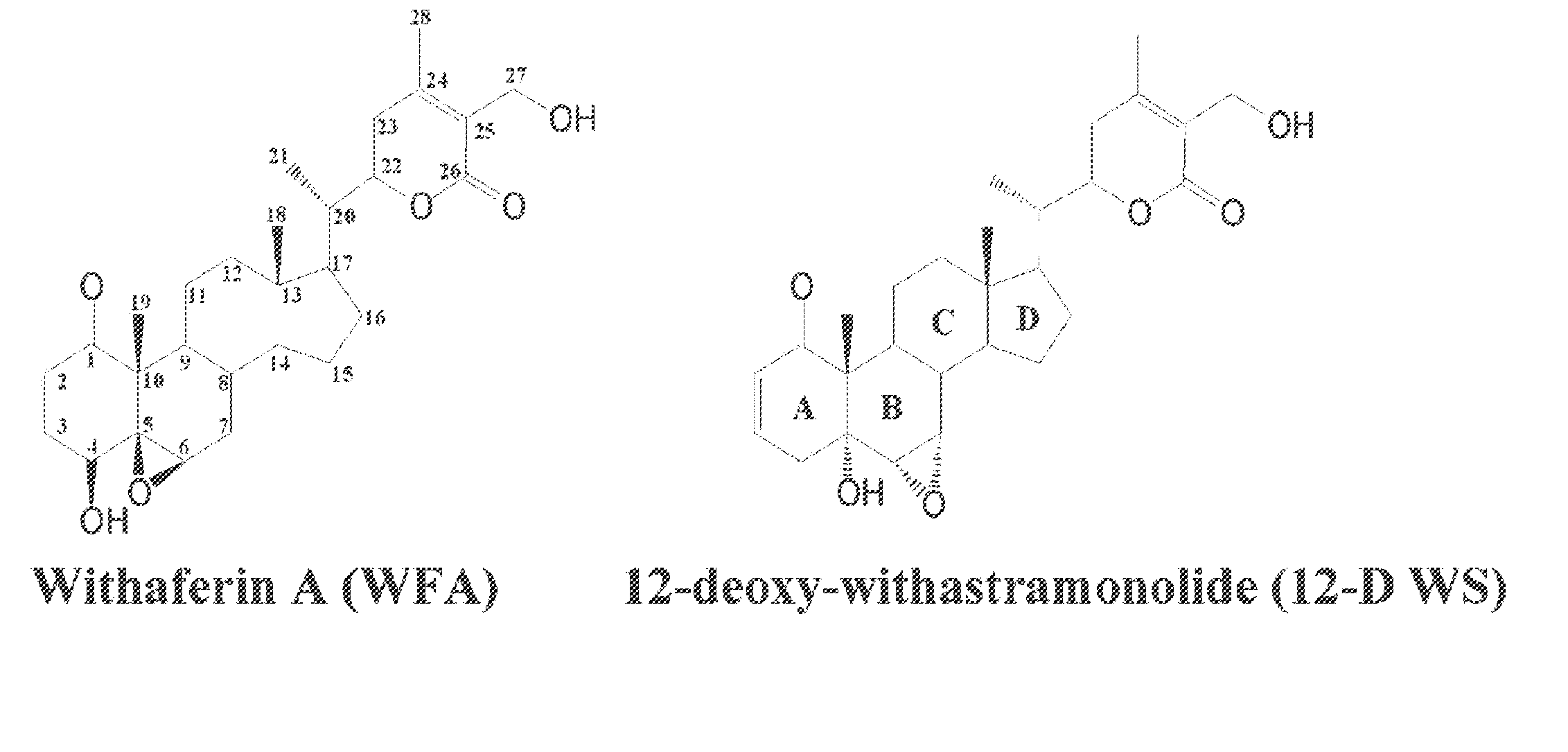
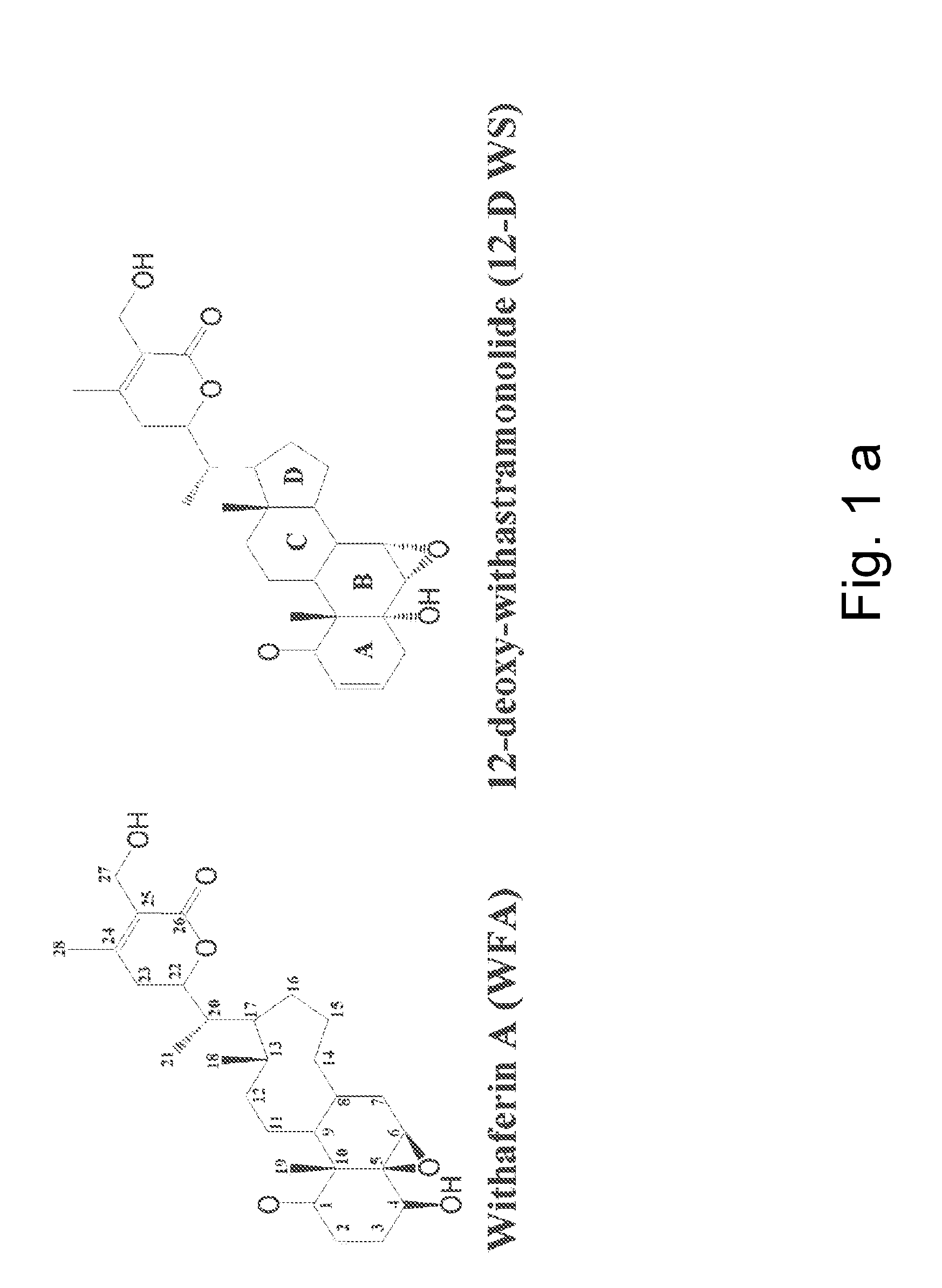
Withanolides, probes and binding targets and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080207574A1Long separationOrganic active ingredientsContaminated soil reclamationDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
Novel withanolide chemical genetic probes identify the in vivo binding target of withaferin A, which is the intermediate filament type III protein vimentin. In addition, a withanolide-based small molecule screening method screens drug candidates that target intermediate filament type III proteins. The method includes introducing a tagged linker covalently bonded to the withanolide molecule to form a withanolide probe. Better or alternative small molecule compounds as potential drug candidates can be generated based on their likely affinity for the determined binding site in vimentin. The affinity labeled withanolide can also be used to find intermediate filament-associated proteins using chemical proteomics by extracting proteins from cells that were exposed to withanolide-biotin analog. The withanolide probes can be used to monitor expression of vimentin, in tumor samples or other diseased tissues. Withaferin analogs can be used as a treatment for diverse vimentin-associated disorders, such as cancers, angiofibrotic diseases, and chronic inflammation.
Owner:KENTUCKY RES FOUND
N-terminal and C-terminal markers in nascent proteins
This invention relates to non-radioactive markers that facilitate the detection and analysis of nascent proteins translated within cellular or cell-free translation systems. Nascent proteins containing these markers can be rapidly and efficiently detected, isolated and analyzed without the handling and disposal problems associated with radioactive reagents. Methods are described for incorporating N-terminal, C-terminal and (optionally) affinity markers into a nascent protein
Owner:AMBERGEN INC
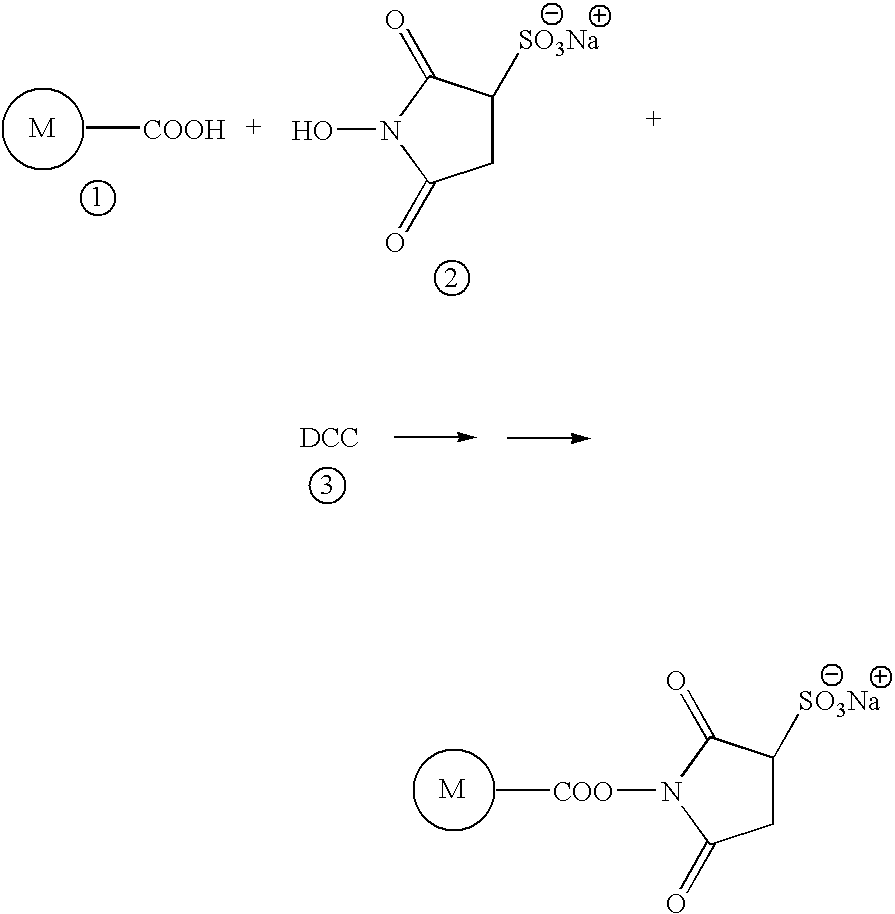
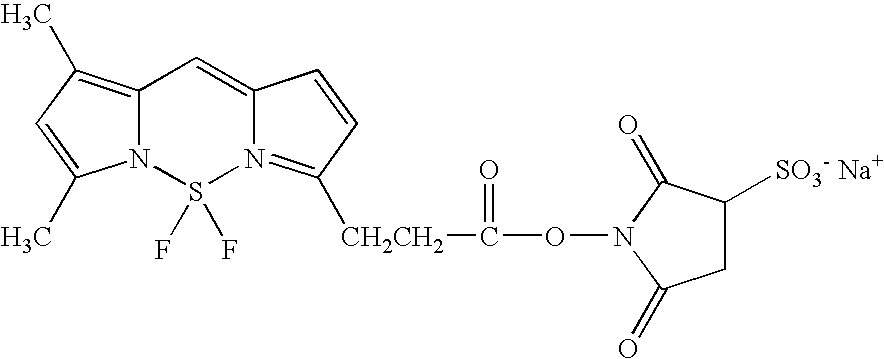
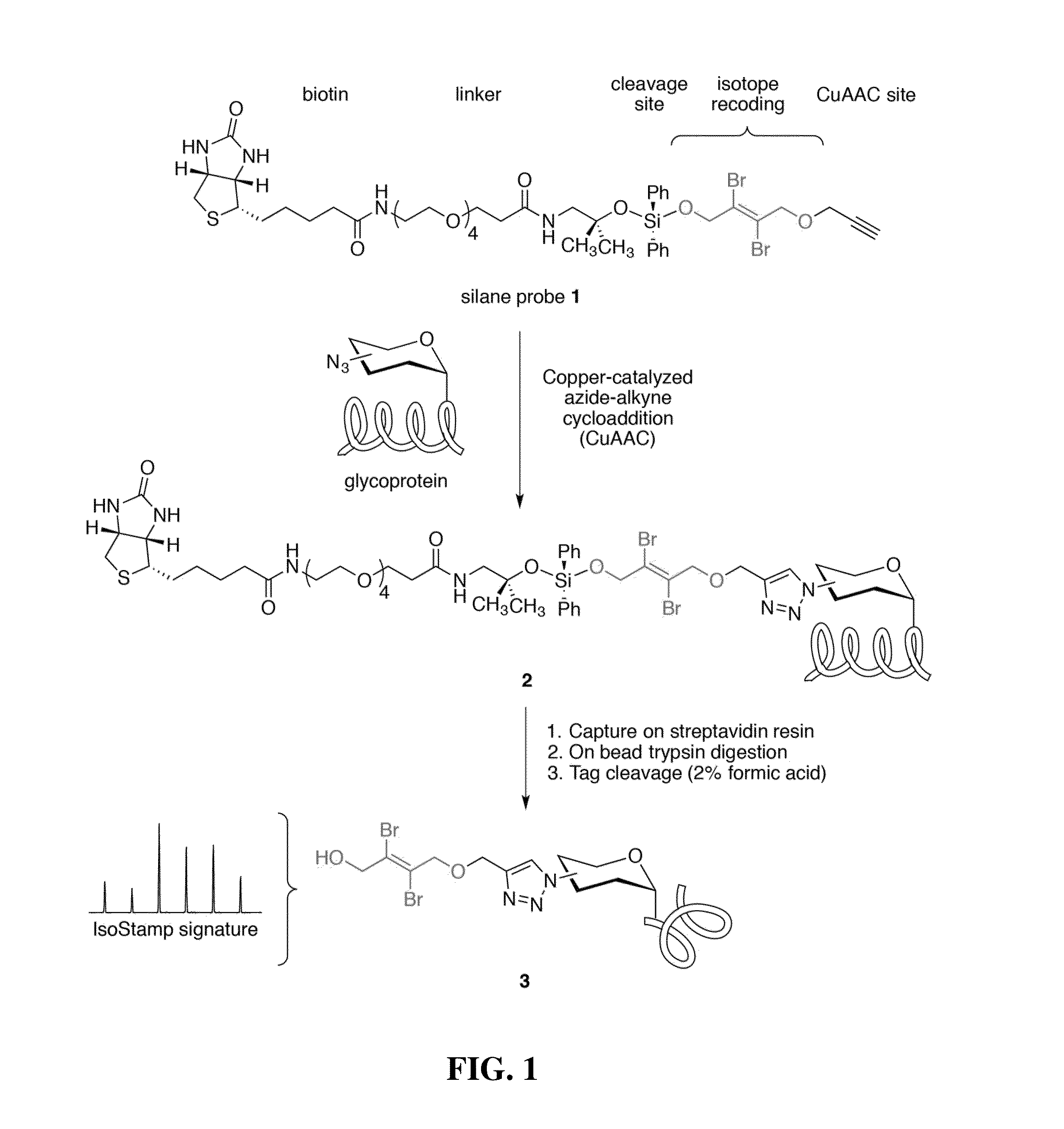
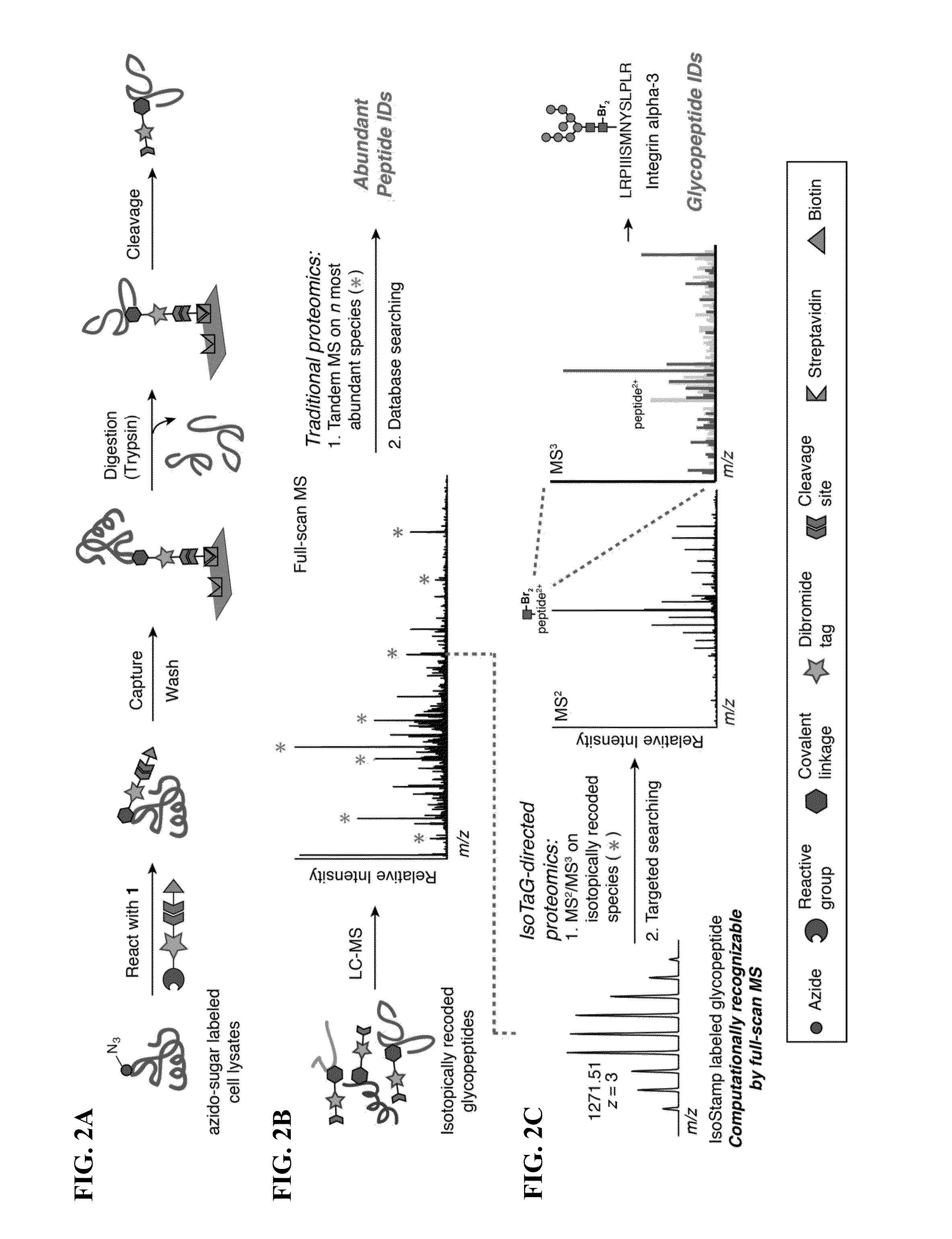
Cleavable probes for isotope targeted glycoproteomics and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20160187350A1Produce lotReduce detectionSilicon organic compoundsMicrobiological testing/measurementCross-linkMass spectrometric
Methods for producing isotopically-labelled peptides are provided. Aspects of the method include: contacting a sample including a metabolically tagged protein with a cleavable probe to produce a probe-protein conjugate; separating the probe-protein conjugate from the sample; digesting the probe-protein conjugate to produce a probe-peptide conjugate; and cleaving a cleavable linker to release an isotopically labelled peptide. The method may further include: identifying a predetermined isotopic pattern in a mass spectrum; determining an amino acid sequence of the isotopically labelled peptide; and identifying the site of protein glycosylation based on the determined amino acid sequence. Also provided are cleavable probes for practicing the subject methods, described by the Formula: A-L-(M-Z) where A is an affinity tag, L is a cleavable linker, M is an isotopic label and Z is a chemoselective tag capable of cross-linking a metabolically tagged protein. Compositions and kits for practicing the subject methods are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Novel Rotaxane-Type Probe For Molecular Imaging
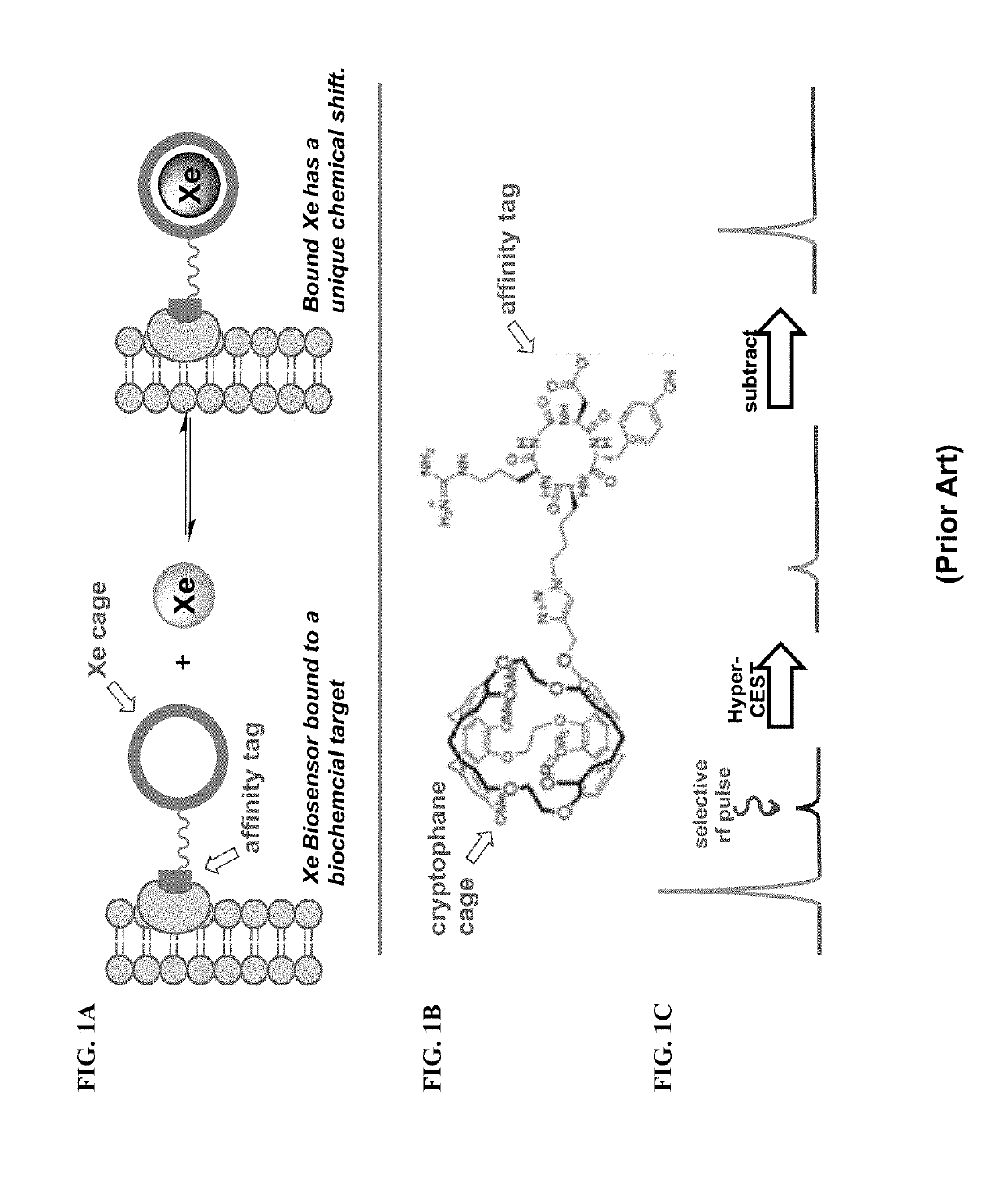
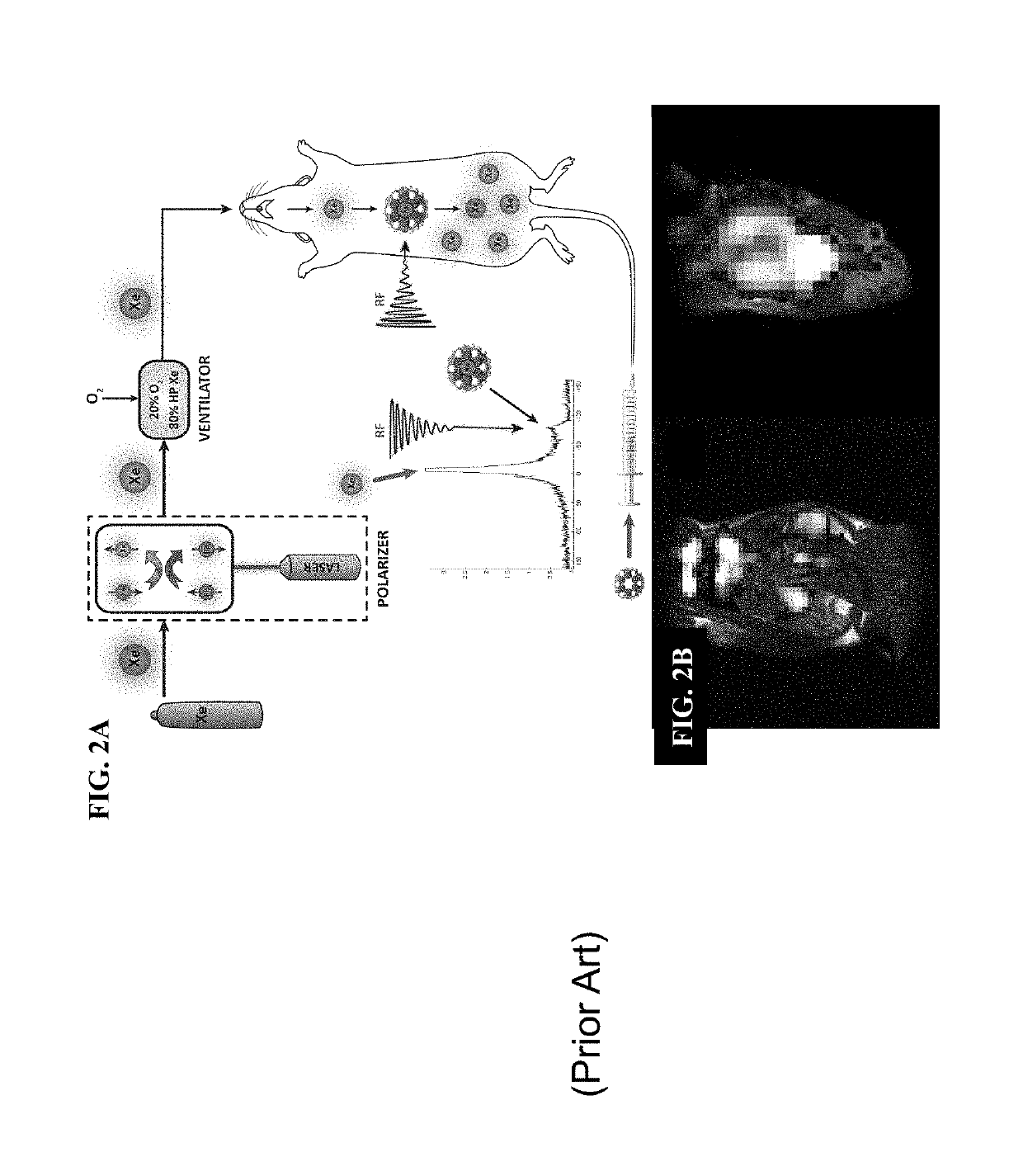
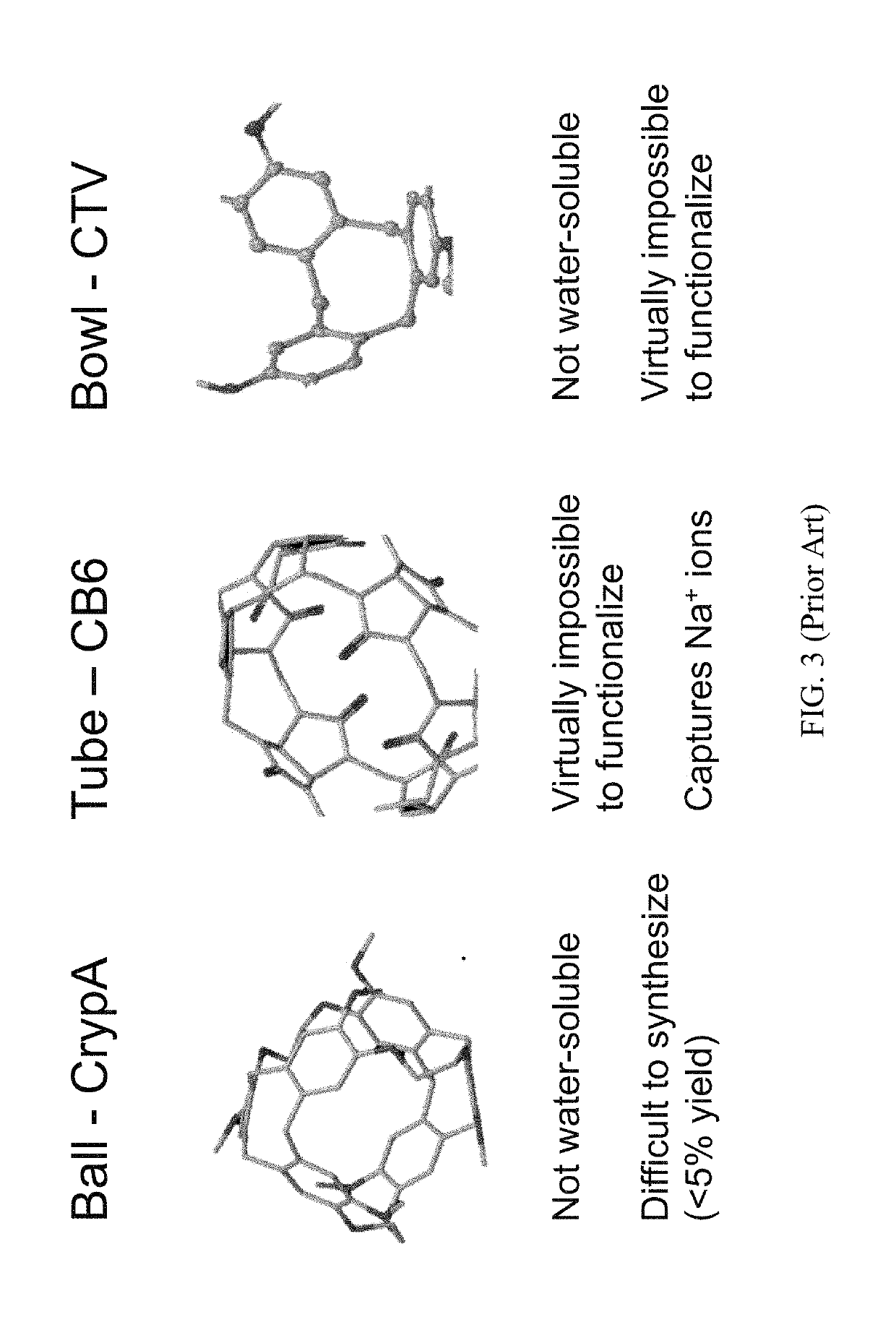
The invention provides a novel method for synthesizing hyperpolarized xenon-129 (HP Xe) biosensors by using pseudo-rotaxane structures of gamma-cyclodextrin. These supramolecular complexes form novel ternary structures in the presence of HP Xe which can be detected via 129Xe MR spectroscopy and imaging techniques. The rotaxane-type complex can be tagged with an affinity label for detecting a target in a biological subject.
Owner:UNIV OF RHODE ISLAND BOARD OF TRUSTEES
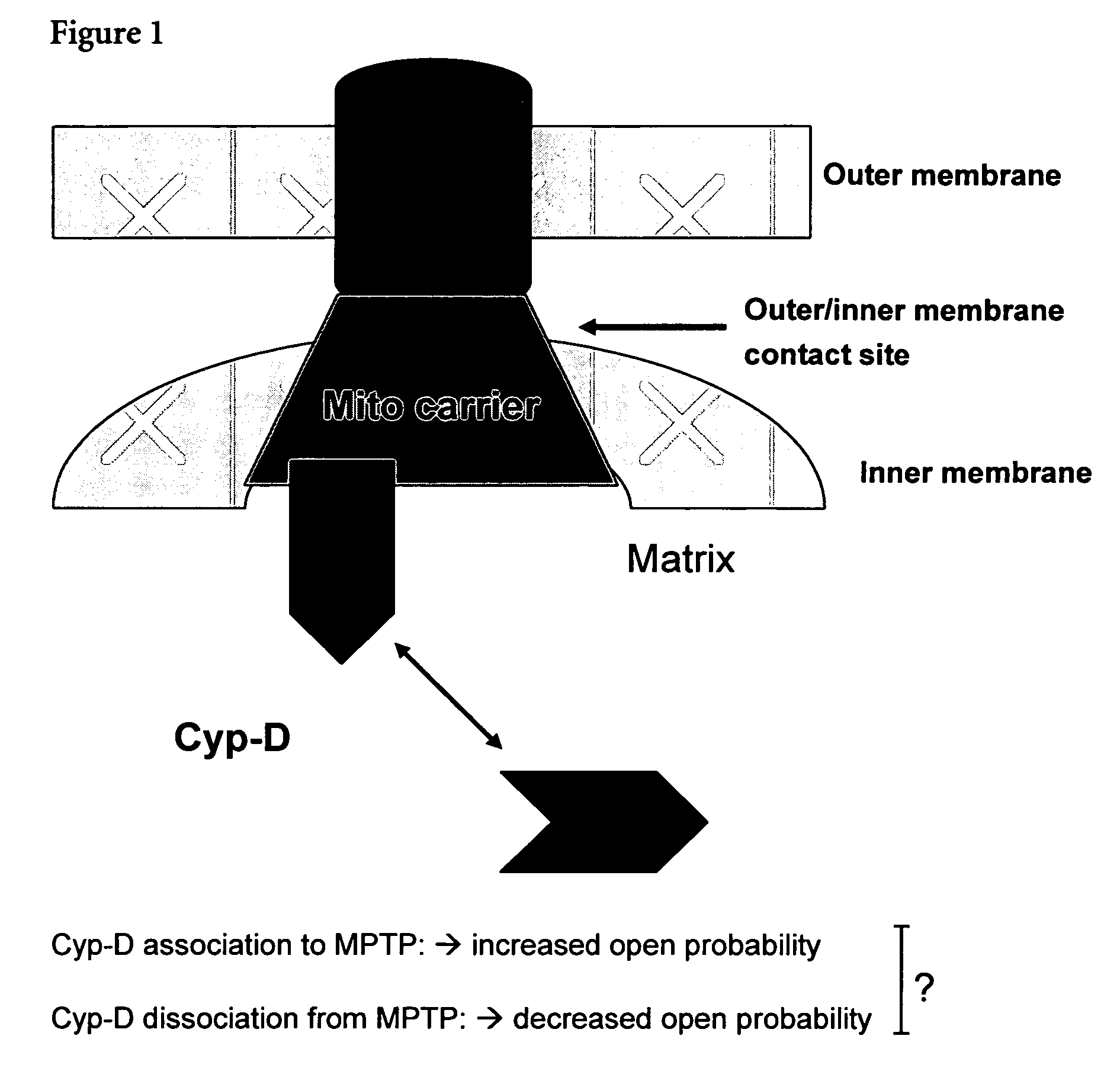
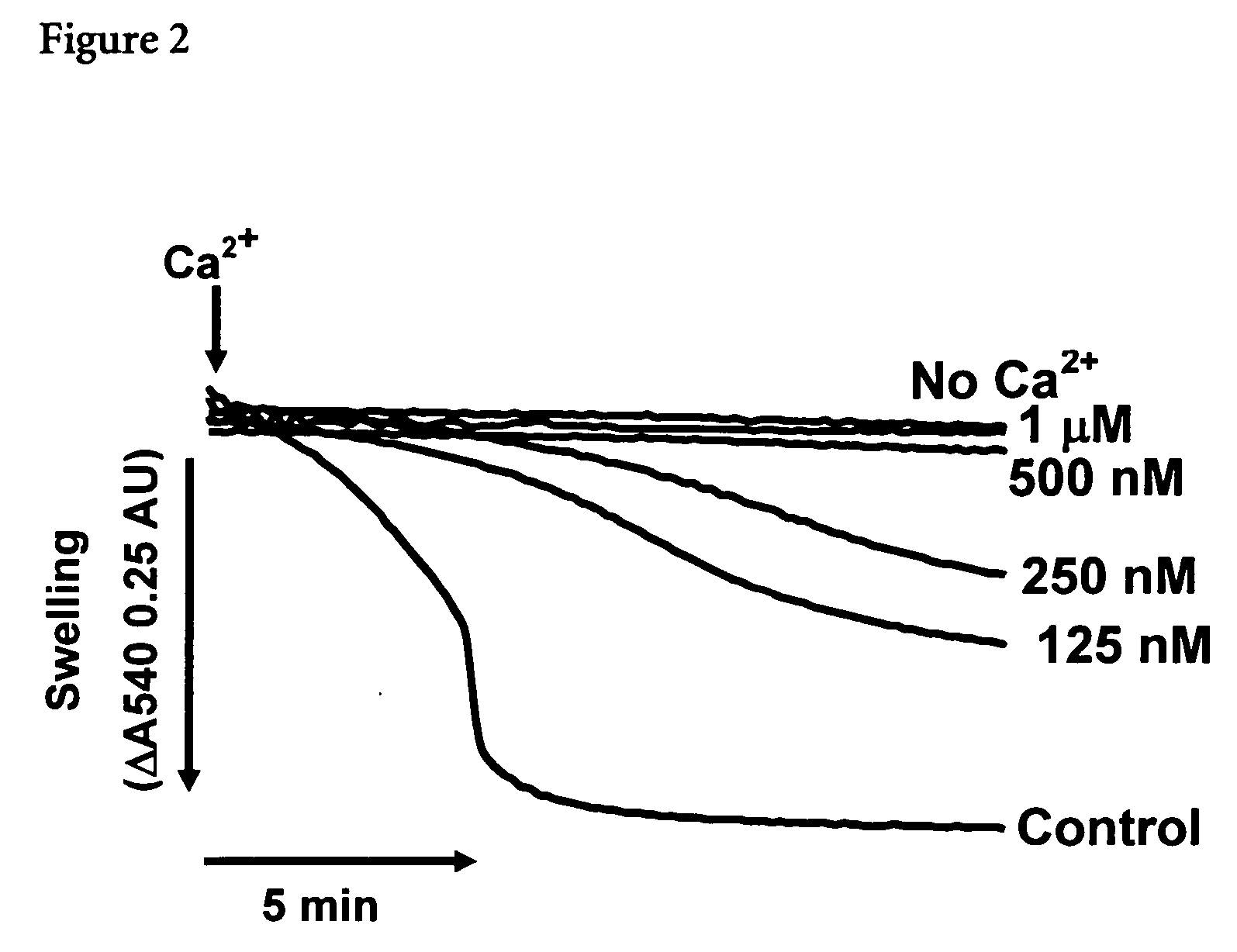
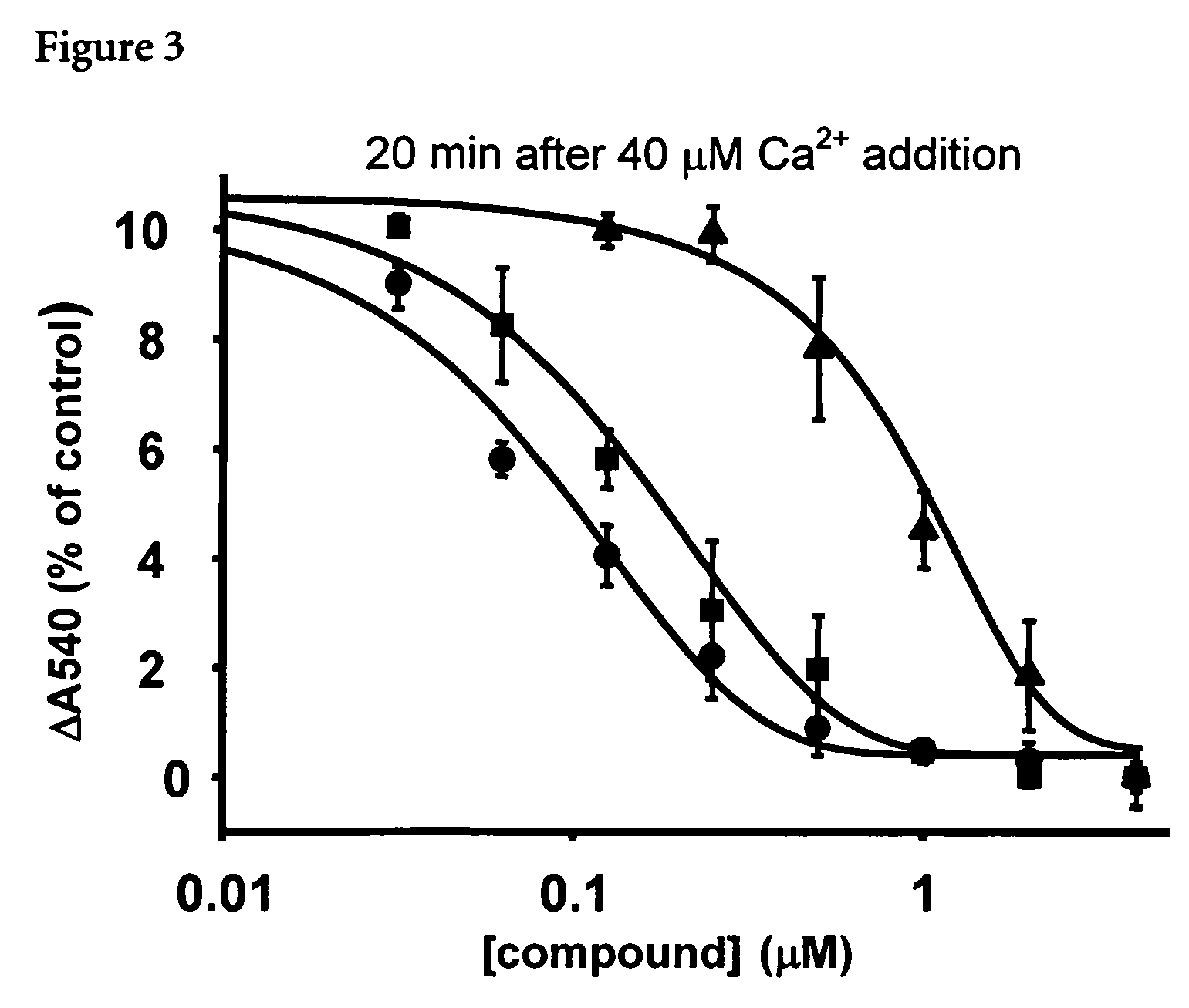
Mitochrondrial permeability transition pore affinity labels and modulators
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
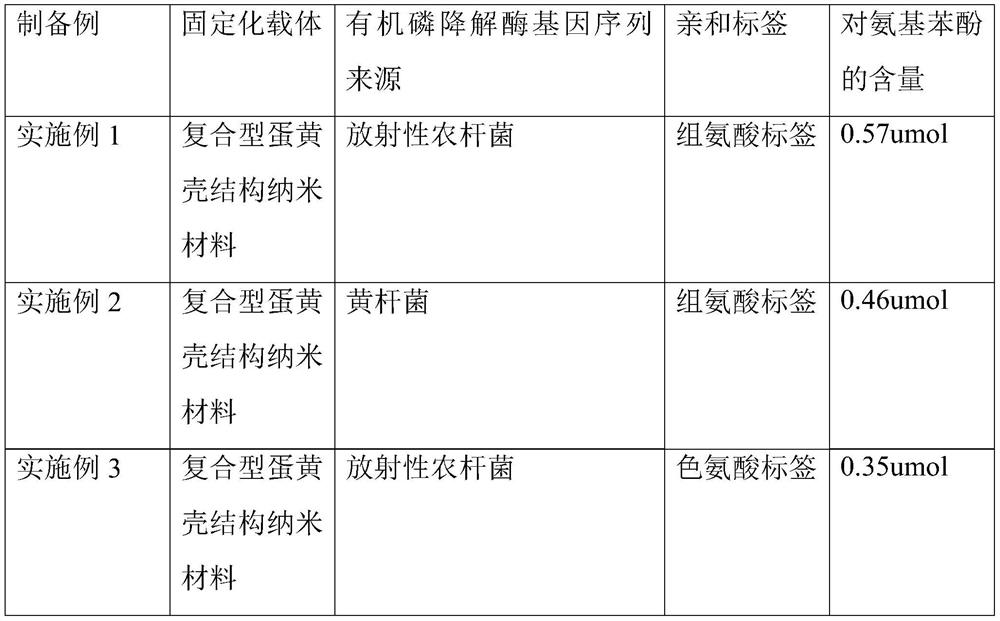
Preparation method of organophosphorus degrading enzyme-based multifunctional catalyst, organophosphorus degrading enzyme-based multifunctional catalyst and application of organophosphorus degrading enzyme-based multifunctional catalyst
ActiveCN111690637ALow purity requirementFix stability issuesHydrolasesOrganic compound preparationBiotechnologyPtru catalyst
The invention provides a preparation method of an organophosphorus degrading enzyme-based multifunctional catalyst, the organophosphorus degrading enzyme-based multifunctional catalyst and applicationof the organophosphorus degrading enzyme-based multifunctional catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a composite yolk shell structure nano material is directly added into crude enzyme liquid of organophosphorus degrading enzyme with an affinity label, mixed and separated, and then the organophosphorus degrading enzyme-based multifunctional catalyst is obtained. The preparation method of the organophosphorus degrading enzyme-based multifunctional catalyst is easy to operate, the requirement for the enzyme purity is low, the carrier can be directionally combined with the enzyme, the prepared organophosphorus degrading enzyme-based multifunctional catalyst is low in cost, an organophosphorus pesticide can be detected, the organophosphorus pesticide can be further degraded in a cascade mode, and a final product, namely p-aminophenol has important application value.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
A kind of bisethylene sulfonamide linker and its preparation and application
ActiveCN107400072BEasy to makeEfficient preparationPeptide preparation methodsSulfonic acid amide preparationSulfamidePharmaceutical drug
The invention provides a divinyl sulfamide linker as well as preparation and an application thereof. The divinyl sulfamide linker has the structural formula shown in the formula I or the formula II. One end of the novel divinyl sulfamide linker can be coupled with a polypeptide or protein, and the other end can be connected with an affinity tag or a tracing fluorescent substance or an active drug.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
Compositions and methods for purifying calreticulin
The present invention relates to compositions, methods for expressing, and related methods for purifying calreticulin that is free of an affinity label or tag (i.e., non-tagged calreticulin). The invention provides useful methods for commercial production of human calreticulin in a bacterial expression system such as Escherichia coli.
Owner:CALRETEX
Target region enrichment method based on multiplex pcr, and reagent
ActiveUS20180163251A1Low costImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationEnrichment methodsSingle strand
Provided are a target region enrichment method based on multiplex PCR, and a reagent, the method comprising: connecting a first linker and a second linker respectively at two ends of a nucleic acid segment containing target regions to be enriched so as to obtain a linker-connected product; performing a PCR amplification on the linker-connected product using a first primer specifically bound to the first linker and a second primer specifically bound to the second linker to obtain an amplified product, the first primer or the second primer having a first affinity label; capturing a single strand having the first affinity label in the amplified product using a solid phase carrier; performing single primer linear amplification using a third primer with the captured single strand as a template; performing exponential amplification using the third primer and the first primer, with the linearly amplified product as the template, to obtain a product containing the target regions.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
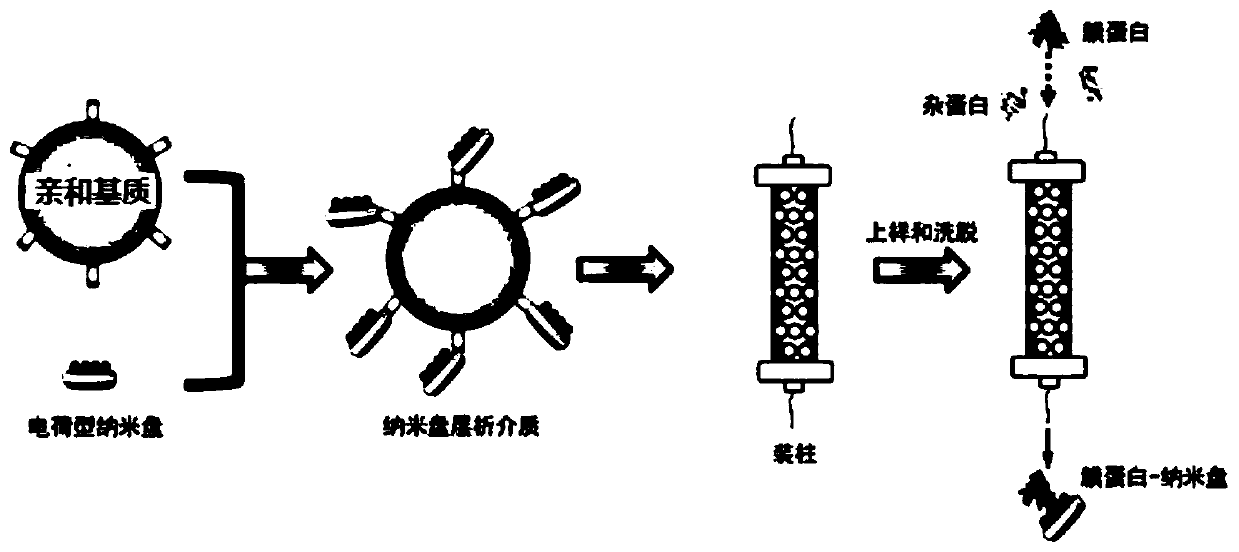
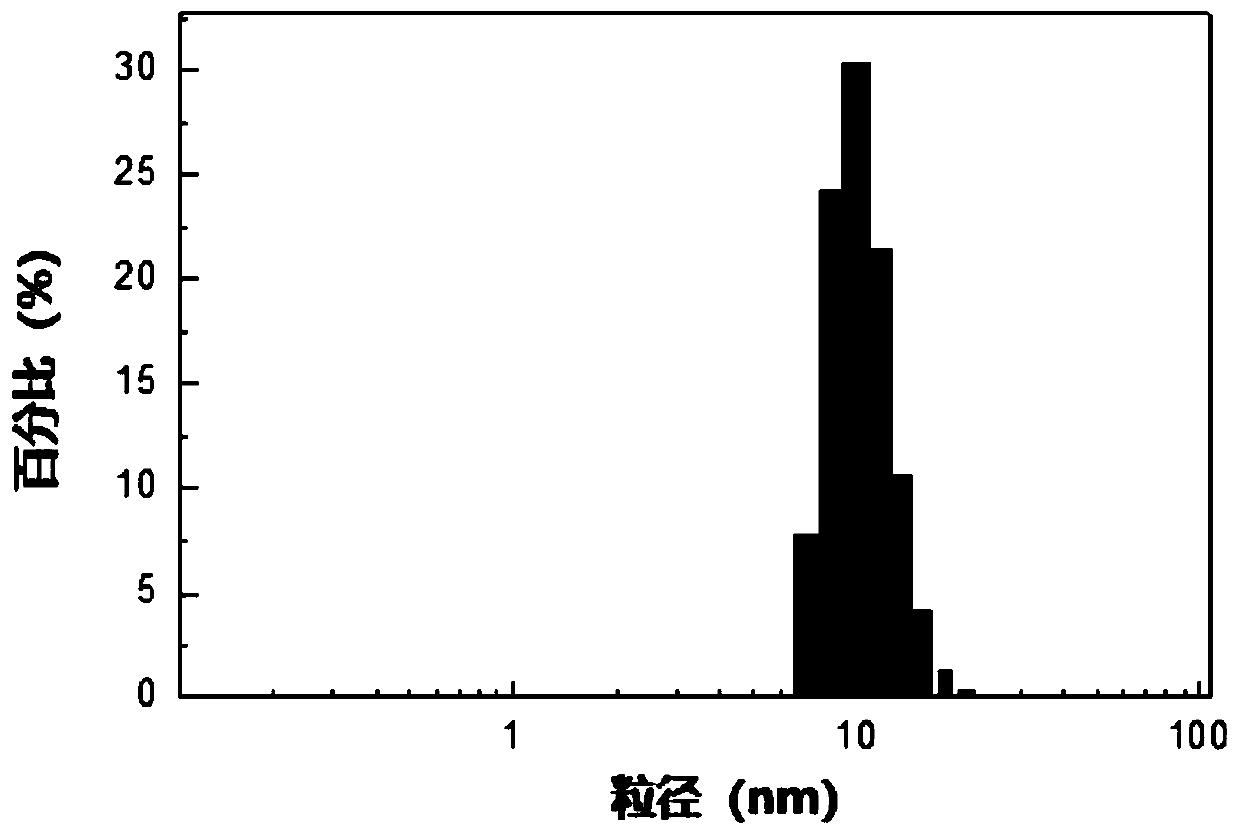
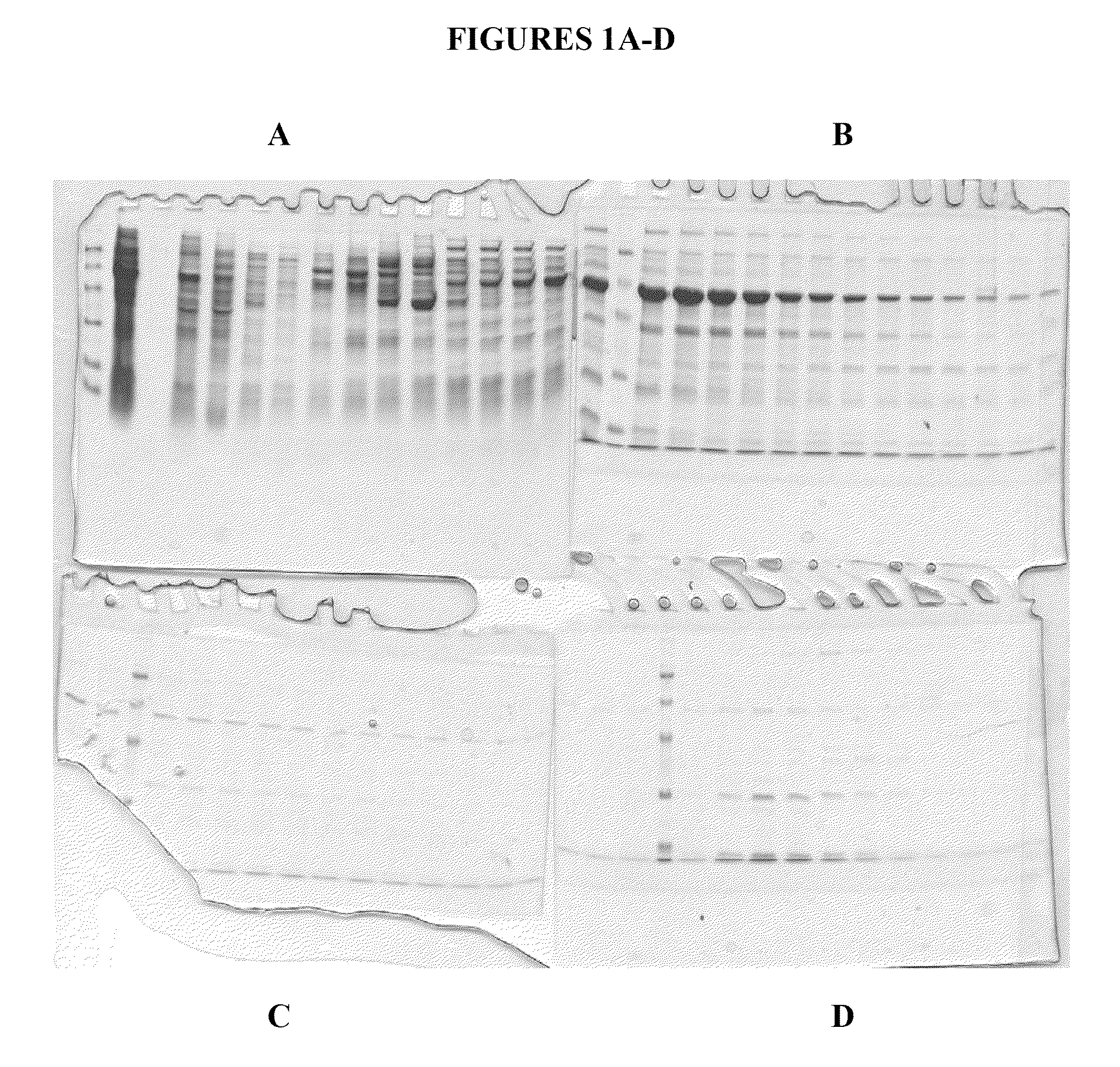
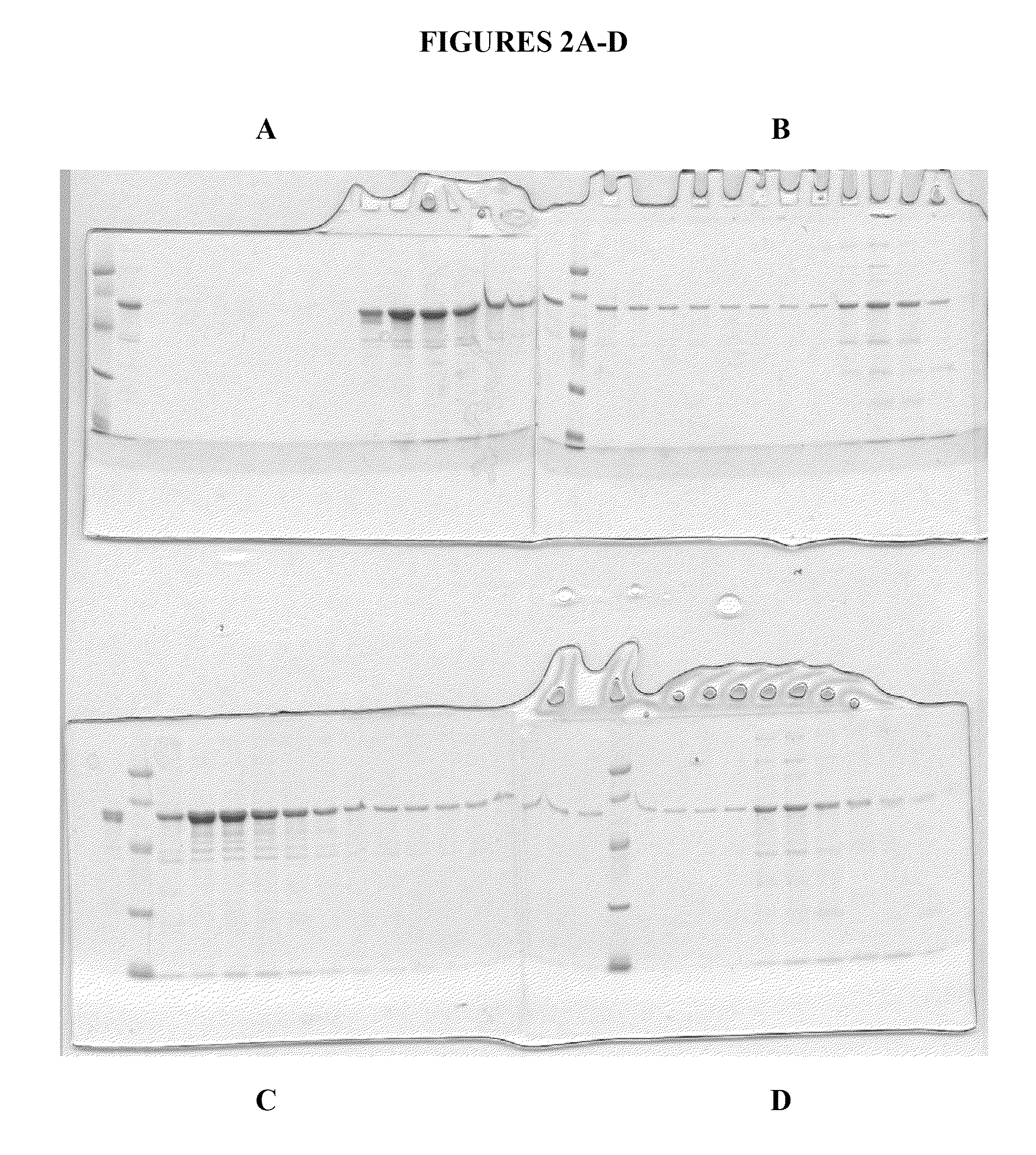
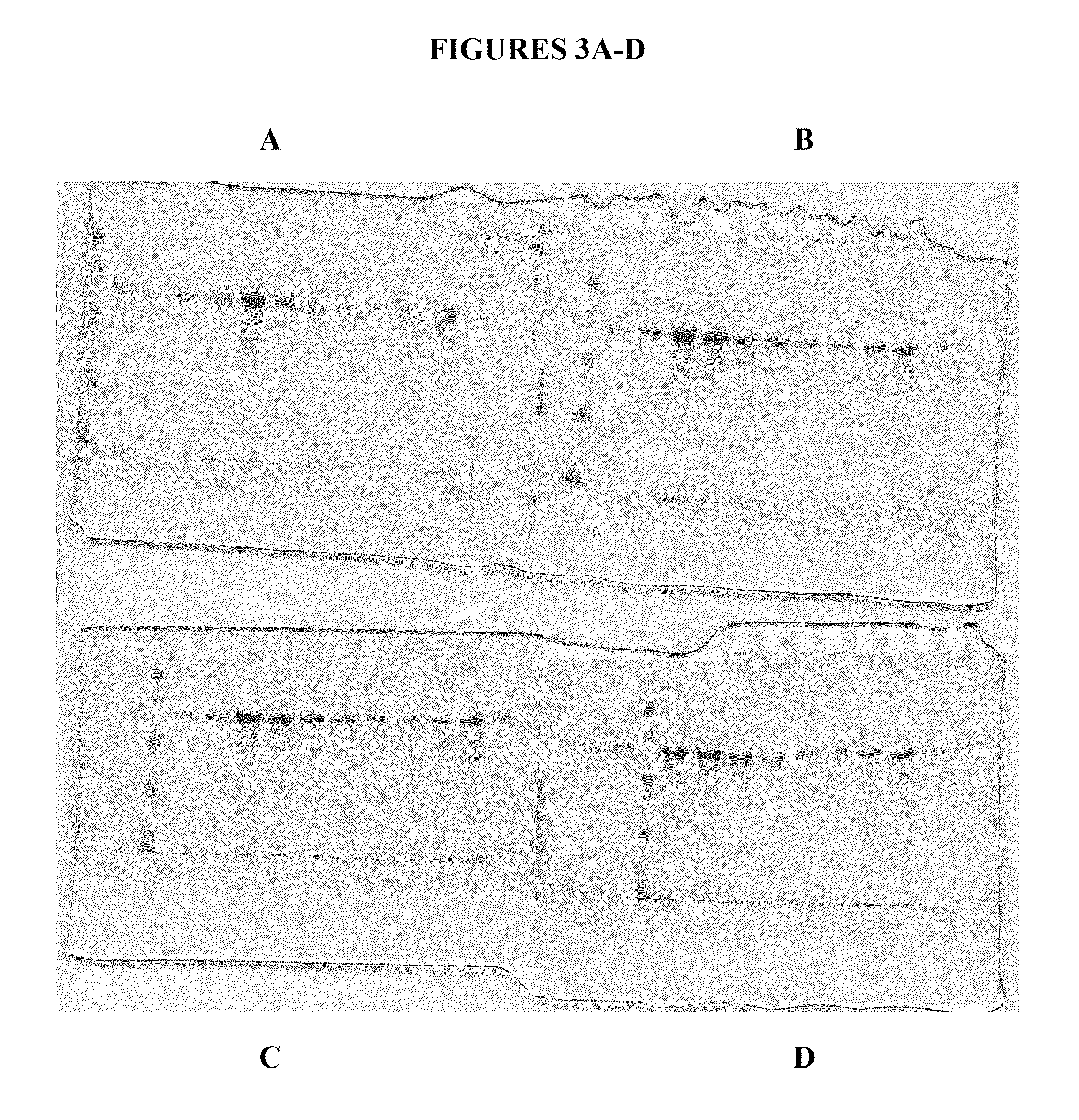
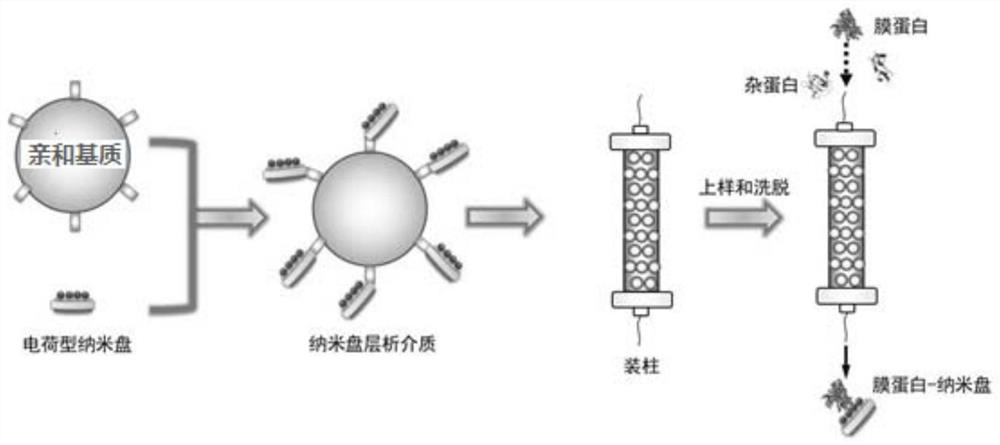
Phospholipid nano-disk chromatography medium and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110292916AGuaranteed protection functionFunction to purify proteinOther chemical processesDepsipeptidesPhospholipidProtein activity
The invention relates to a phospholipid nano-disk chromatography medium and a preparation method and application thereof. The phospholipid nano-disk chromatography medium comprises a charged phospholipid nano disk and an affinity matrix; the charged phospholipid nano disk comprises phospholipid and a film scaffold protein with an affinity label; the charged phospholipid nano disk is connected withan affinity matrix through the affinity label. The phospholipid nano-disk chromatography medium has both binding capacity and protection capacity to film proteins, so that the actual system containing the film proteins can be purified and reconstructed on a chromatography column in one step; and the phospholipid nano-disk chromatography medium has reversibility and regeneration performance; the phospholipid nano-disk chromatography medium solves the problems of serious protein activity loss, long and complicated steps and time-consuming and labor-consuming operation in the traditional film protein research technology, is simple and efficient to operate, improves the film protein activity recovery rate by more than 20 times, and shortens the treatment time by more than 95%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Expression-linked gene discovery
InactiveUS9695469B2High frequencyObtain dataNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentGenomic DNA
Owner:STICHTING GENETWISTER IP
Methods and compositions for improving removal of ribosomal RNA from biological samples
The invention generally relates to compositions for maximizing capture of affinity-labeled molecules on solid supports. The disclosed methods and compositions were developed to maximize depletion of ribosomal RNA from total RNA samples, which is useful to improve the quality of RNA preparations used for applications such as massively parallel sequencing. The RNA depletion method is based on using long affinity-labeled RNA molecules that are complementary to all or part of the target ribosomal RNAs, as subtractive hybridization probes.
Owner:BICO SCI CORP
Application of ubiquitin-binding domain fusion protein in detection and separation of ubiquitination protein
InactiveCN103059141ALow detectabilityReduce sensitivityTransferasesBiological testingEscherichia coliADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to a method for utilizing ubiquitin-binding domain (UBD) fusion protein to separate and detect ubiquitination protein. The principle is that a fusion protein is constructed by using an affinity label and a ubiquitin-binding domain. The fusion protein can be expressed in colon bacillus, purified and fixed on a gel particle through the ligand of the affinity label. Mixed culture is carried out on the gel particle with the ubiquitin-binding domain fusion protein and lysate of cell or tissue, and the ubiquitination protein in the lysate can be separated out through precipitation. On the aspect of the detection of ubiquitination protein, the method disclosed by the invention is higher in efficiency, detection capacity and flexibility compared with the current antibody immune precipitation detection method. Moreover, on the aspect of economic benefit, the cost of detecting ubiquitination protein in the invention is extremely lower than that of expensive antibody immune precipitation method; and the method can be applied to fundamental research of protein ubiquitination and the detection of ubiquitination protein in medical diagnosis test.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Compositions and methods for purifying calreticulin
ActiveUS8399631B2Organic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationBacteriaEscherichia coliCalreticulin
The present invention relates to compositions, methods for expressing, and related methods for purifying calreticulin that is free of an affinity label or tag (i.e., non-tagged calreticulin). The invention provides useful methods for commercial production of human calreticulin in a bacterial expression system such as Escherichia coli.
Owner:CALRETEX
A kind of phospholipid nano disc chromatography medium and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110292916BGuaranteed protection functionFunction to purify proteinOther chemical processesDepsipeptidesNanodiscPhospholipid
The invention relates to a phospholipid nano-disk chromatography medium and a preparation method and application thereof. The phospholipid nano-disk chromatography medium comprises a charged phospholipid nano disk and an affinity matrix; the charged phospholipid nano disk comprises phospholipid and a film scaffold protein with an affinity label; the charged phospholipid nano disk is connected withan affinity matrix through the affinity label. The phospholipid nano-disk chromatography medium has both binding capacity and protection capacity to film proteins, so that the actual system containing the film proteins can be purified and reconstructed on a chromatography column in one step; and the phospholipid nano-disk chromatography medium has reversibility and regeneration performance; the phospholipid nano-disk chromatography medium solves the problems of serious protein activity loss, long and complicated steps and time-consuming and labor-consuming operation in the traditional film protein research technology, is simple and efficient to operate, improves the film protein activity recovery rate by more than 20 times, and shortens the treatment time by more than 95%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Compounds and their preparation methods and applications
Provided is a compound. According to the embodiment of the invention, the invention relates to the compound represented by the formula (I), or stereoisomers, tautomers, nitrogen oxides, solvates, metabolites, pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs of the compound represented by the formula (I). The compound can effectively obtain two or three or more ubiquitin chains and ubiquitin modifiedsubstrates; moreover, the compound can be used for modifying polypeptide or protein side chains with affinity labels, fluorescent groups, PEG or fatty hydrocarbons and the like; and the compound can play an important role in design of polypeptide drugs, biochemical testing, functional optimization and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Compound and preparation method and application thereof
Provided is a compound. According to the embodiment of the invention, the invention relates to the compound represented by the formula (I), or stereoisomers, tautomers, nitrogen oxides, solvates, metabolites, pharmaceutically acceptable salts or prodrugs of the compound represented by the formula (I). The compound can effectively obtain two or three or more ubiquitin chains and ubiquitin modifiedsubstrates; moreover, the compound can be used for modifying polypeptide or protein side chains with affinity labels, fluorescent groups, PEG or fatty hydrocarbons and the like; and the compound can play an important role in design of polypeptide drugs, biochemical testing, functional optimization and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Solubility and Affinity Tag for Recombinant Protein Expression and Purification
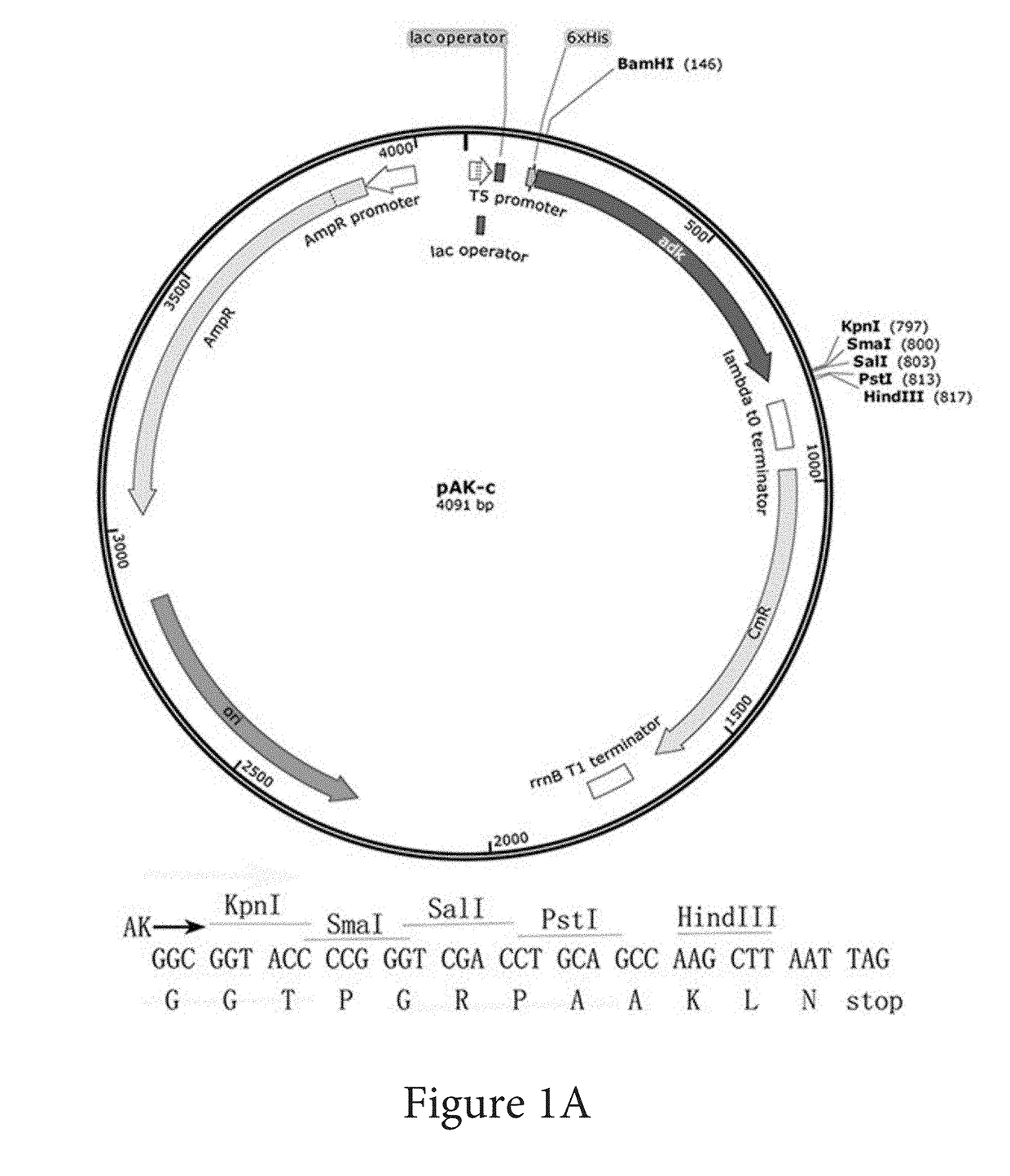
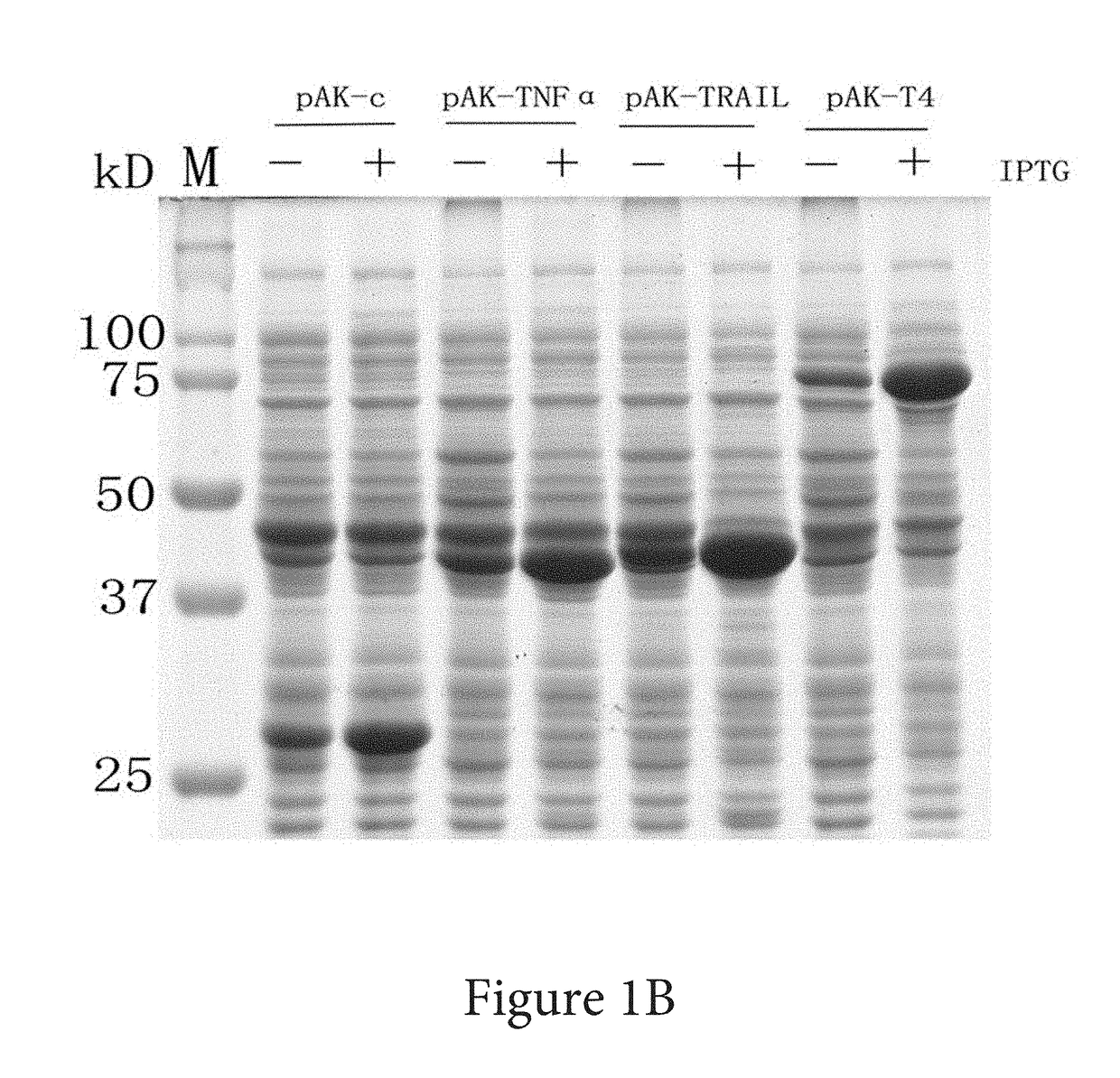
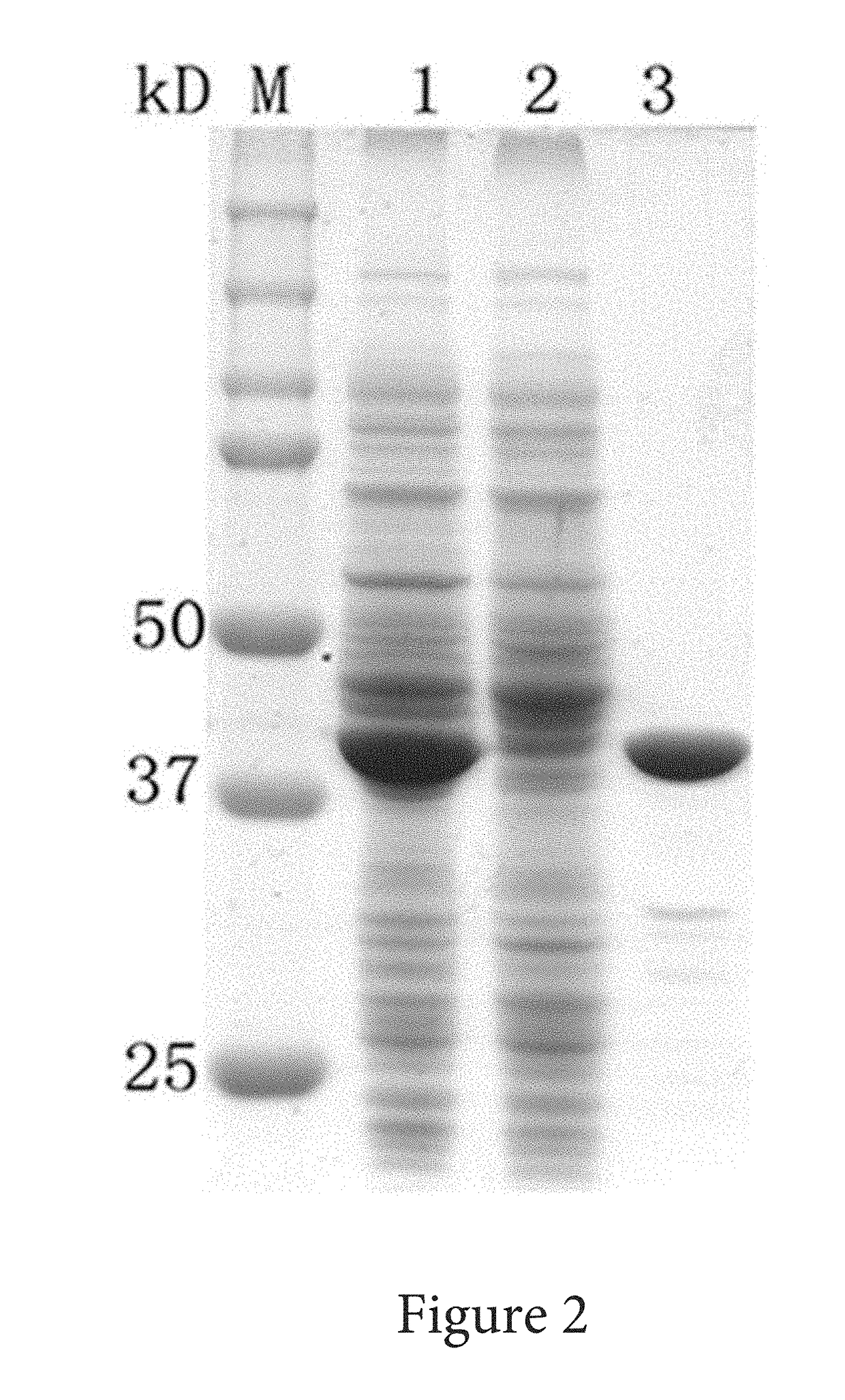
InactiveUS20170226489A1Convenient verificationHigh purityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTumor necrosis factorSolubilityAdenylate kinase
Systems and methods of coding for and isolating a fusion protein are provided. The fusion protein may be expressed by a DNA sequence and comprise an adenylate kinase linked by its carboxy-terminus to a biologically active polypeptide or protein. Later processing steps include isolating the biologically active polypeptide or protein via affinity elution of the fusion proteins with substrate analog of adenylate kinase.
Owner:GENHUNTER
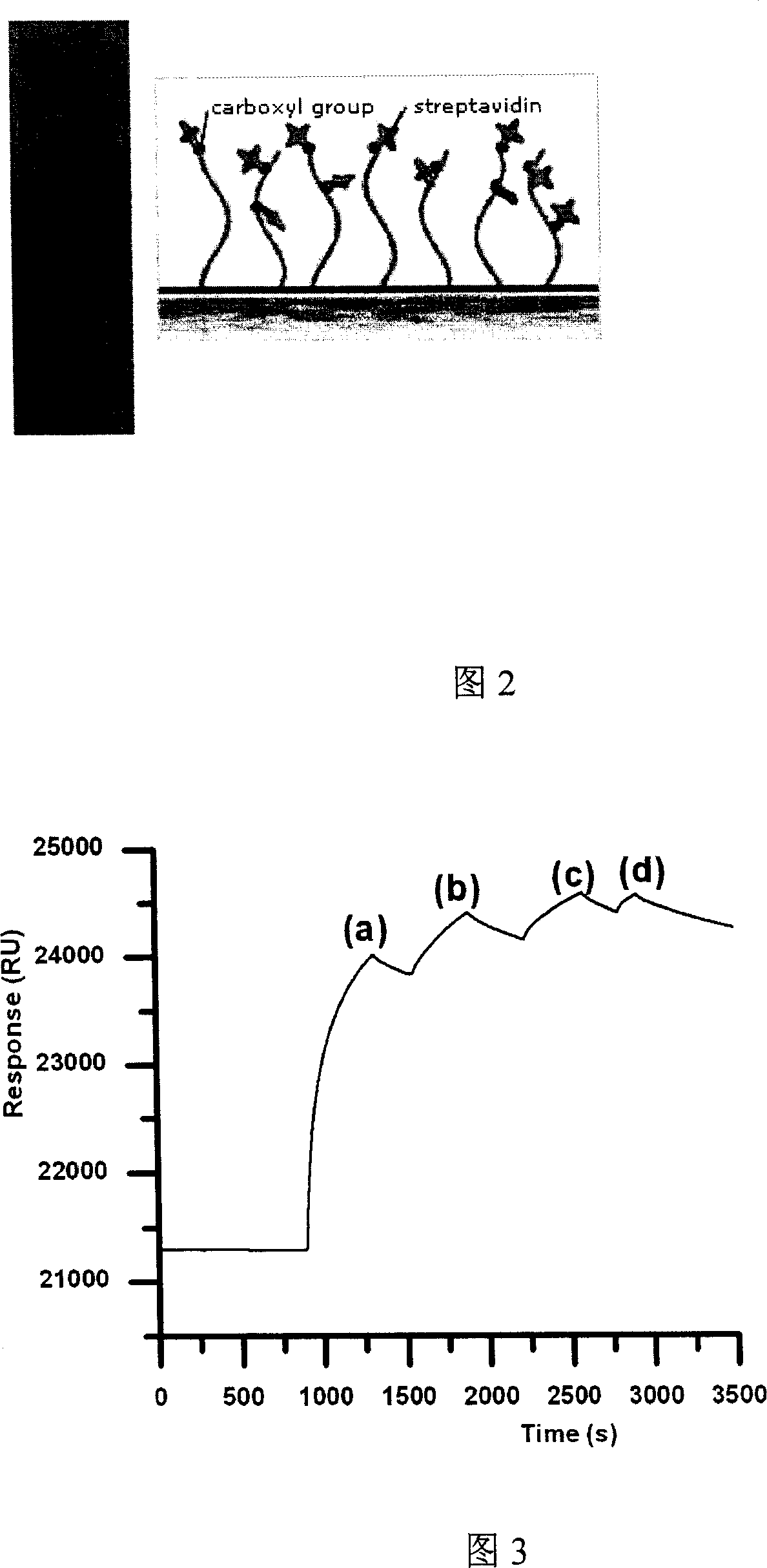
Reversible fixture for aglucon of streptavidin envelope chip surface
InactiveCN100999760ADoes not interfere with biological activityAchieving directional fixationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBiotin-streptavidin complexMedicine
The present invention discloses one kind of ligand fixing mode for the streptavidin coated chip (SA-chip) surface in BIAcore biosensor. In traditional SA-chip, the ligand is fixed by means of the specific mutual action between biotin and streptavidin, and the very powerful mutual action makes the SA-chip become disposable commodity. Instead, the present invention fuses the affinity label and the target ligand by means of the mutual action between streptavidin and affinity label to realize the directional fixing of target ligand. Under mild controllable condition, the chip surface may be regenerated for reuse of the SA-chip. The new ligand fixing process results in greatly lowered experiment cost and possesses high application value.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com