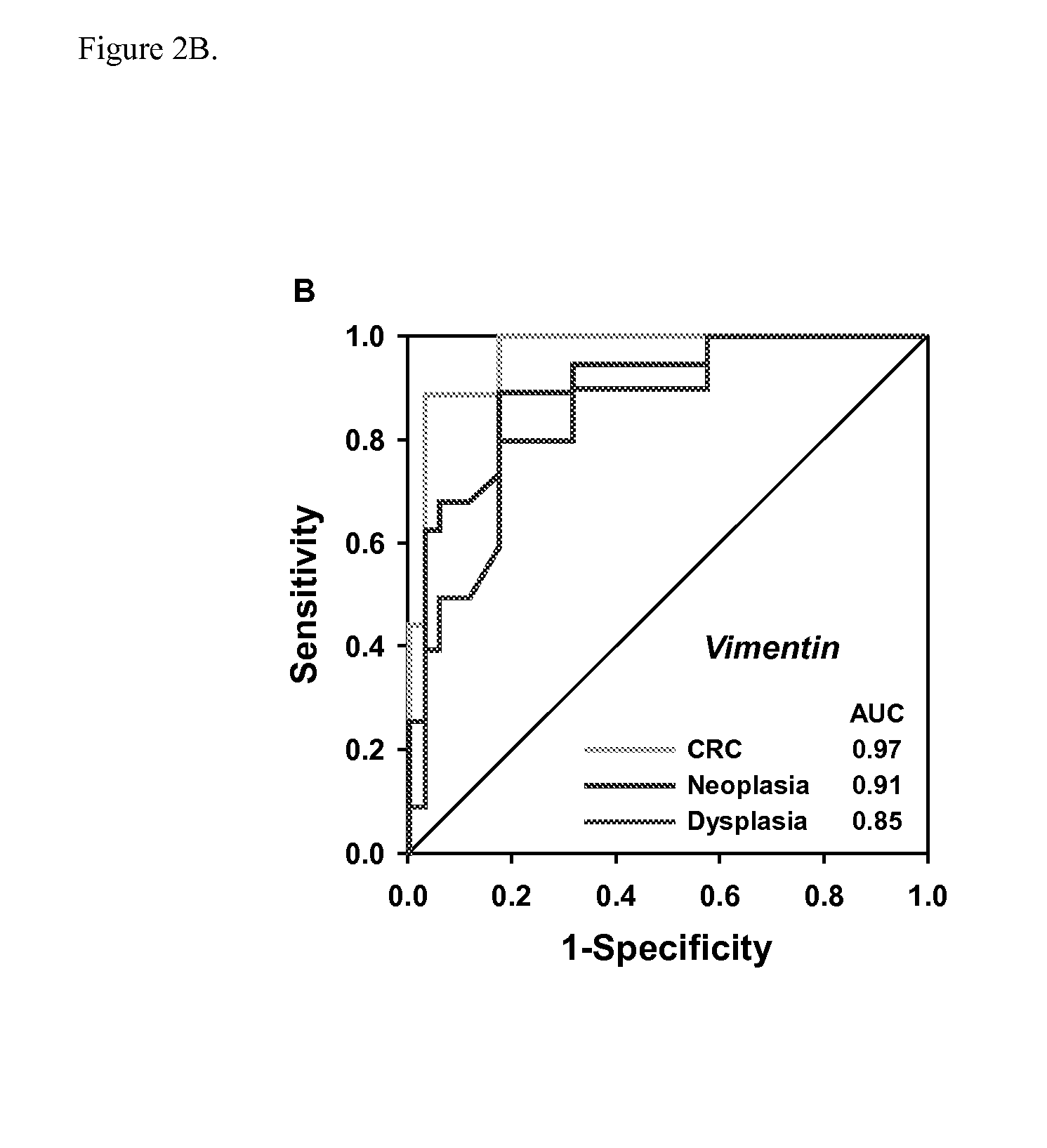
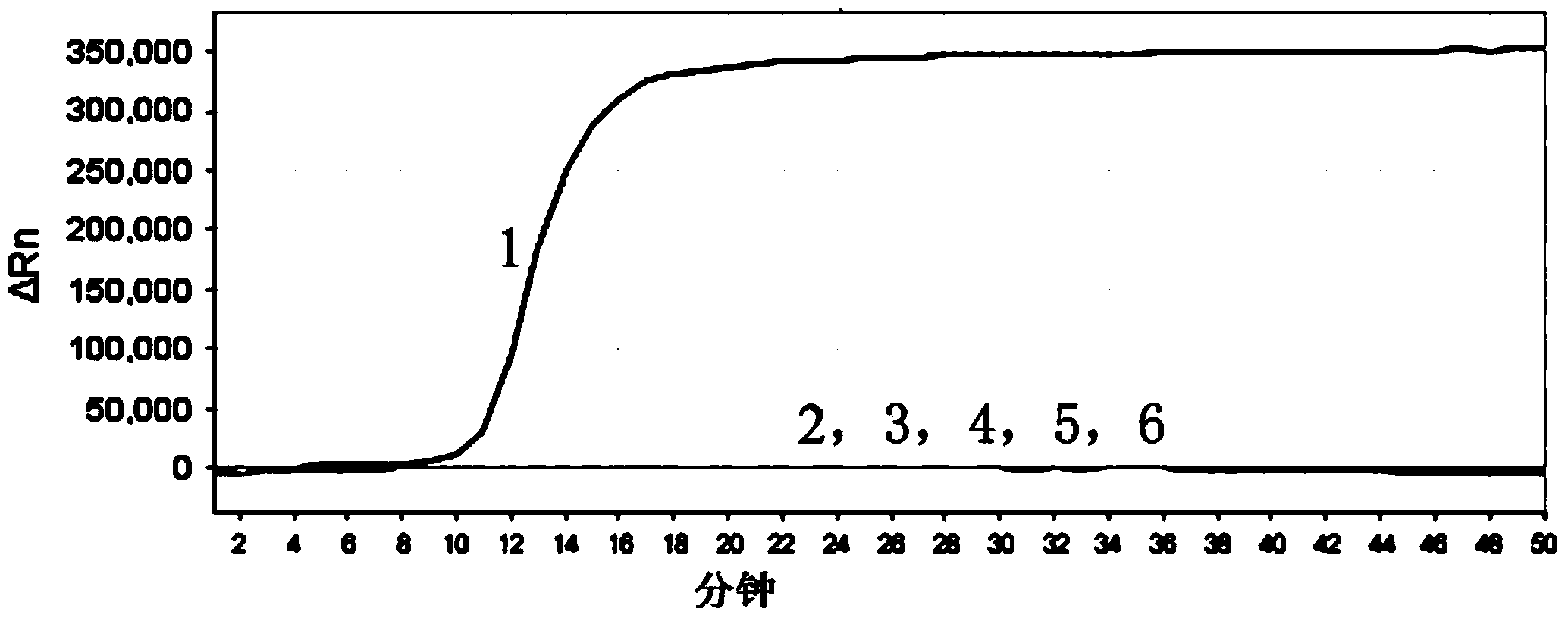
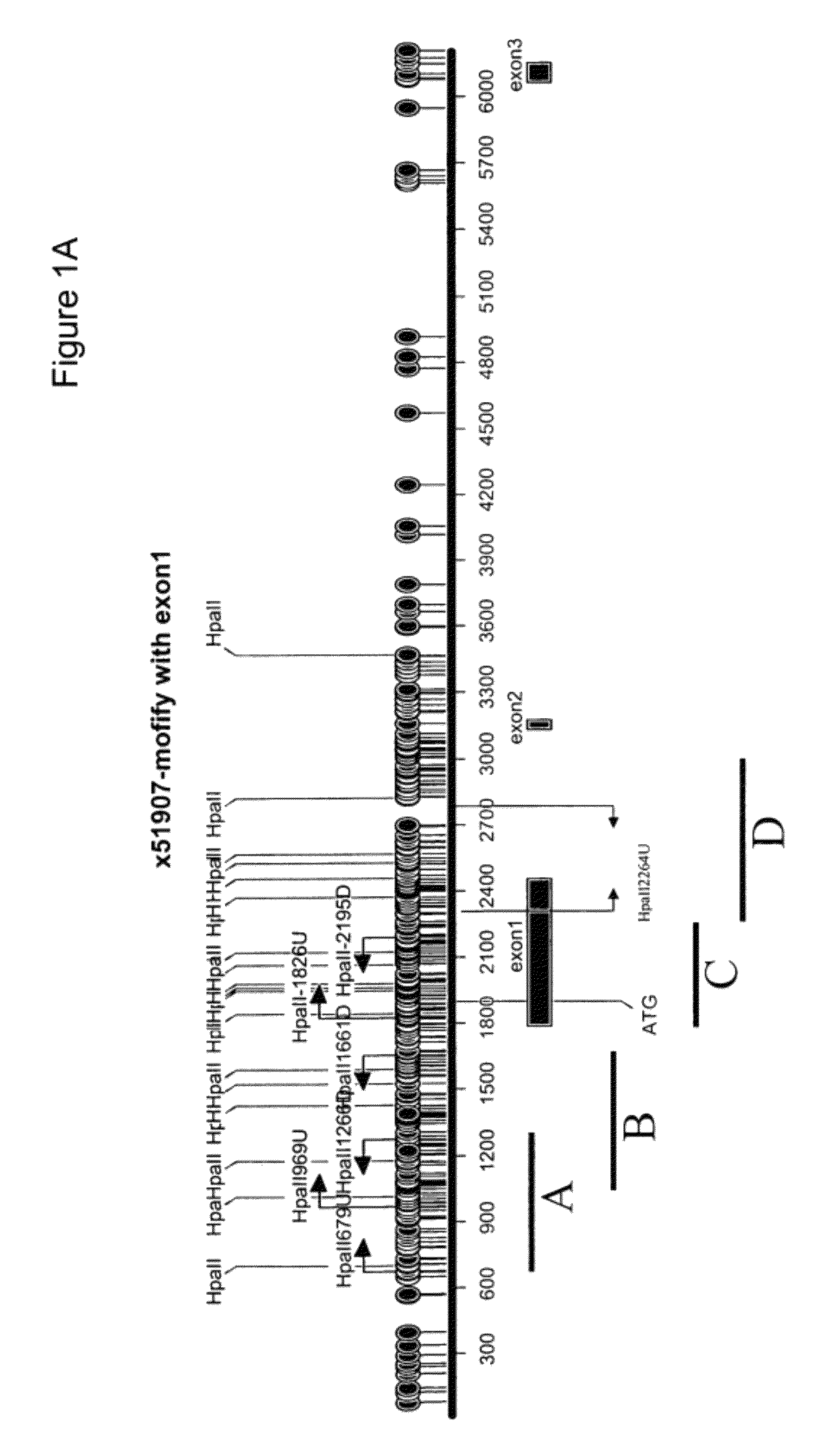
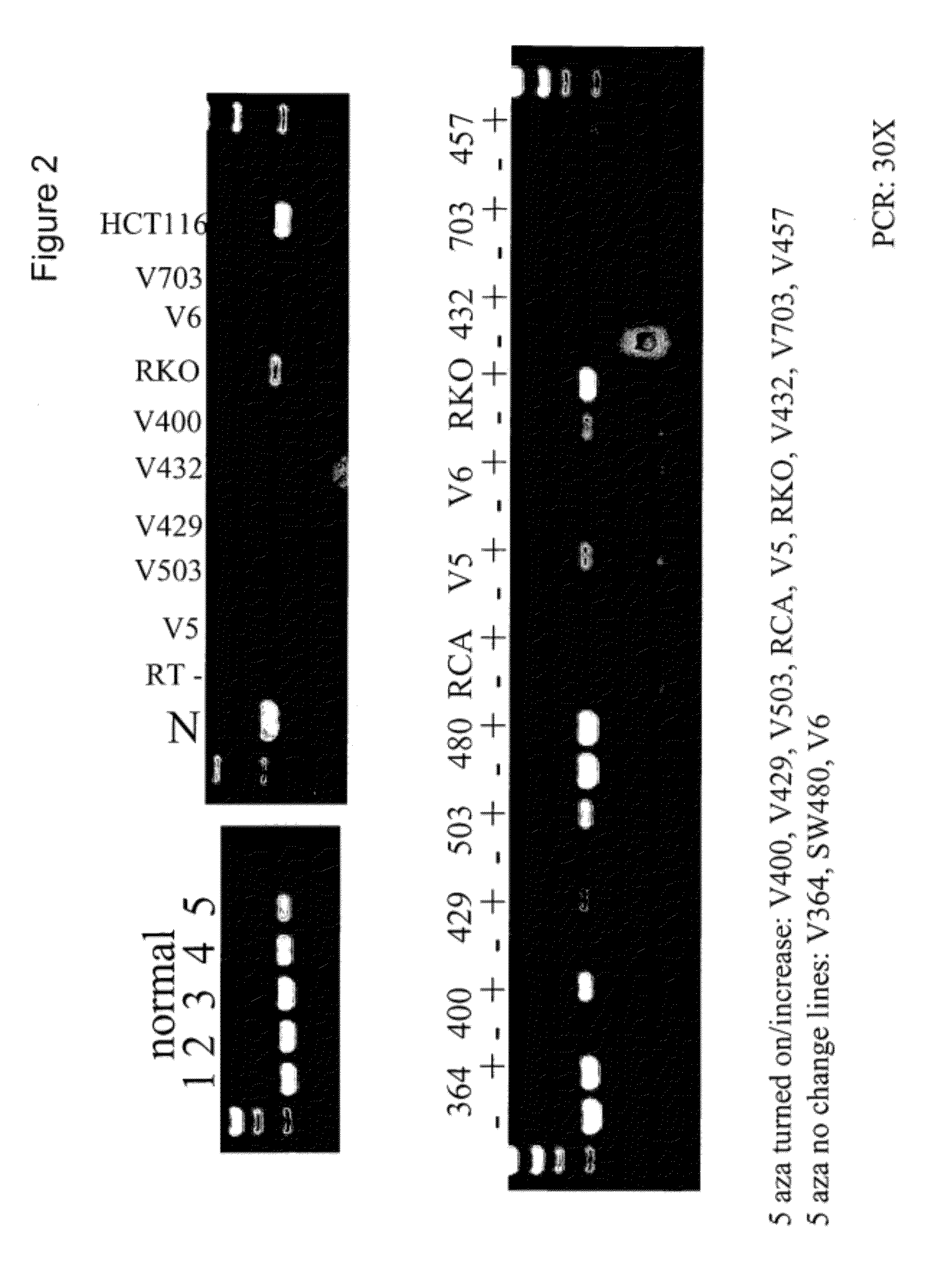
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
110 results about "Vimentin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
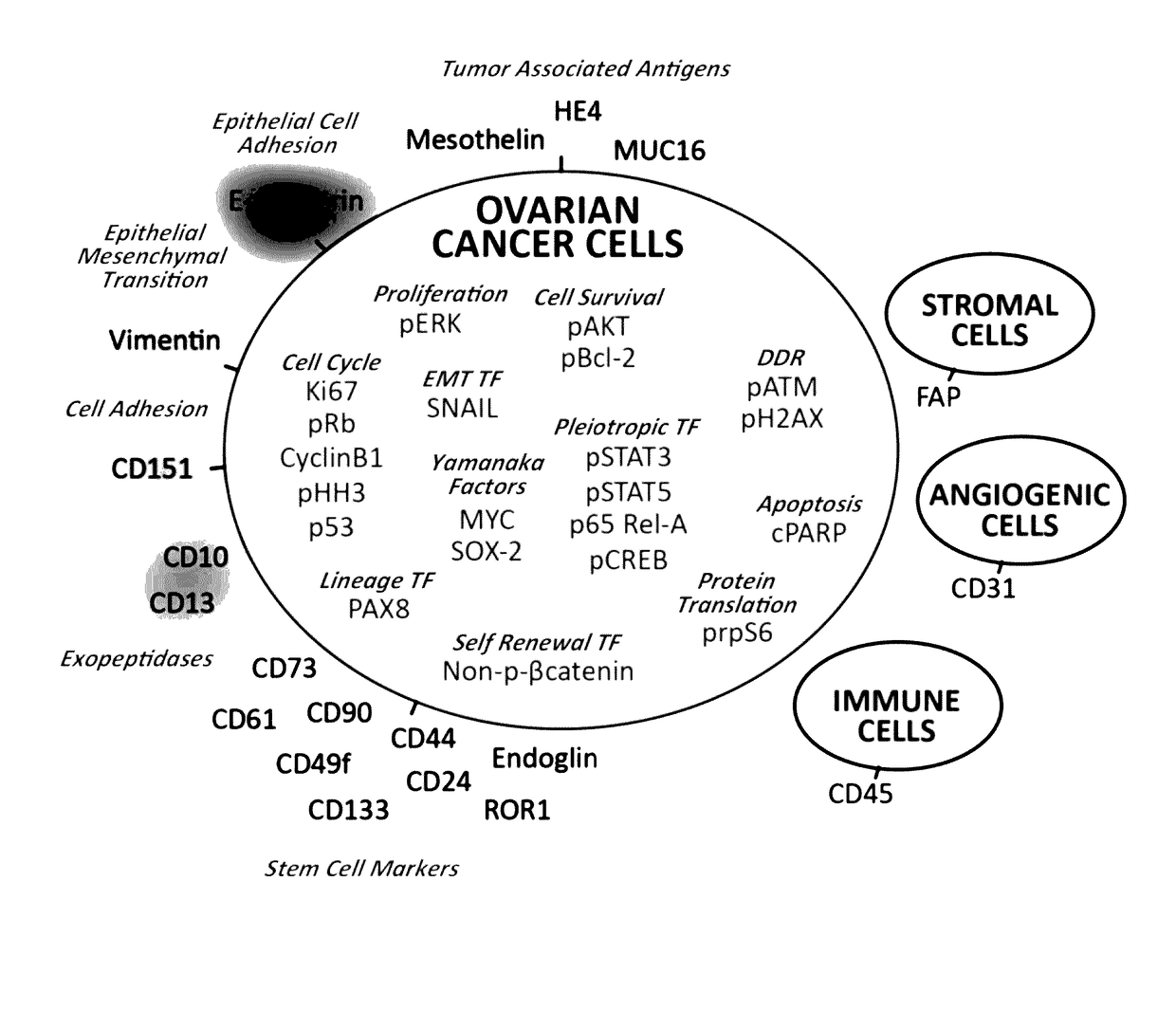
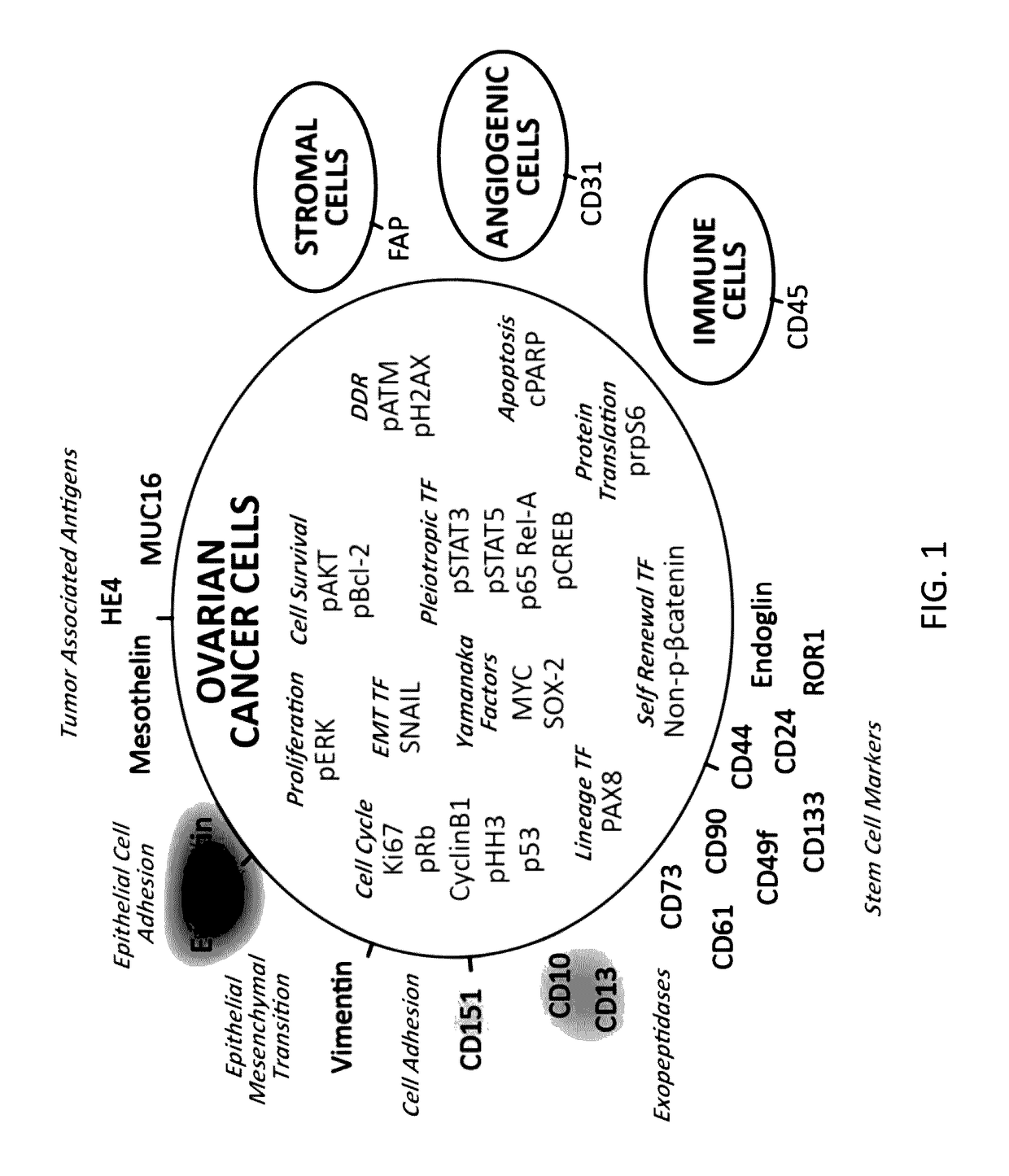
Vimentin is a structural protein that in humans is encoded by the VIM gene. Its name comes from the Latin vimentum which refers to an array of flexible rods. Vimentin is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein that is expressed in mesenchymal cells. IF proteins are found in all animal cells as well as bacteria. IF, along with tubulin-based microtubules and actin-based microfilaments, comprises the cytoskeleton. All IF proteins are expressed in a highly developmentally-regulated fashion; vimentin is the major cytoskeletal component of mesenchymal cells. Because of this, vimentin is often used as a marker of mesenchymally-derived cells or cells undergoing an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during both normal development and metastatic progression.
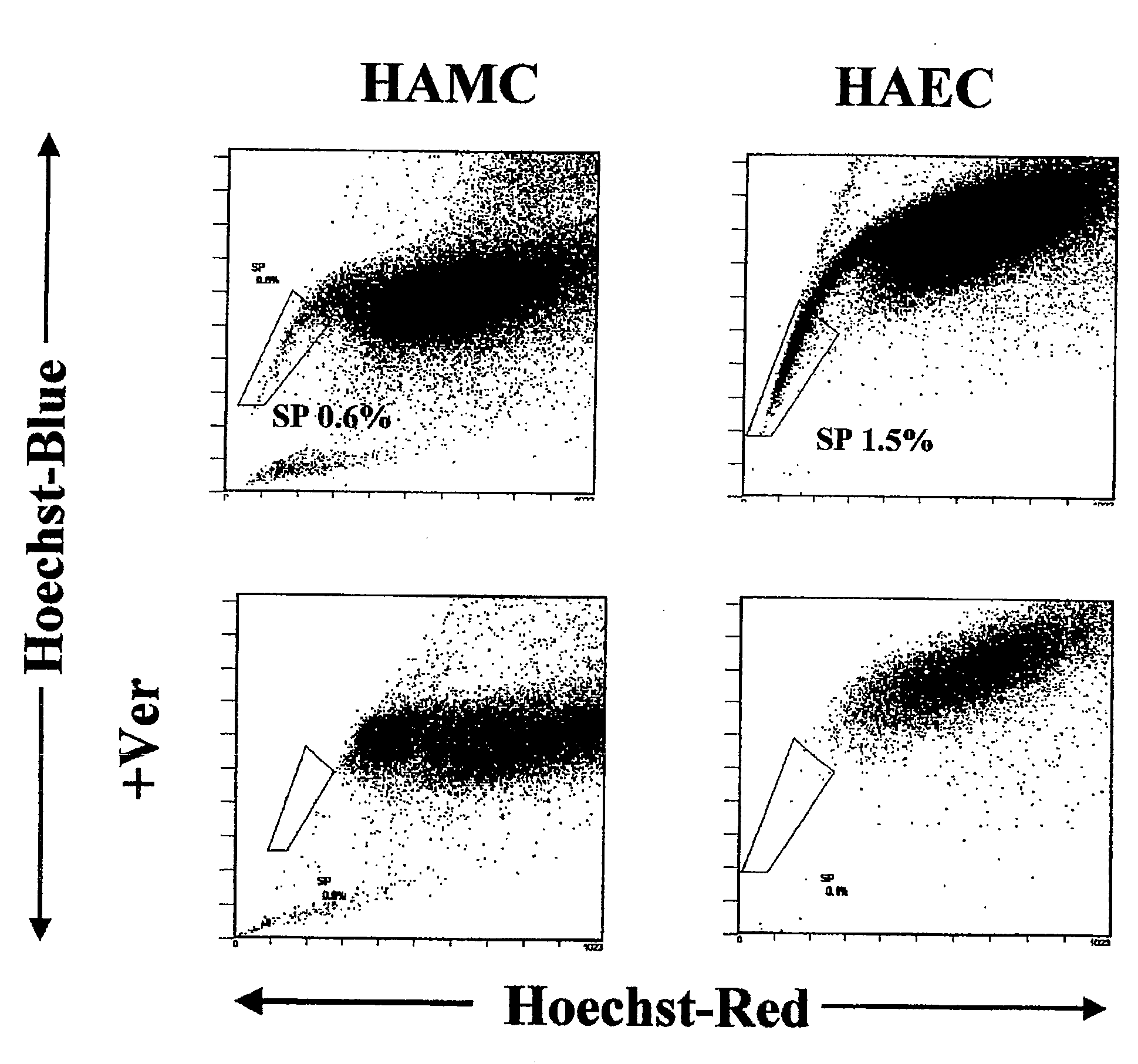
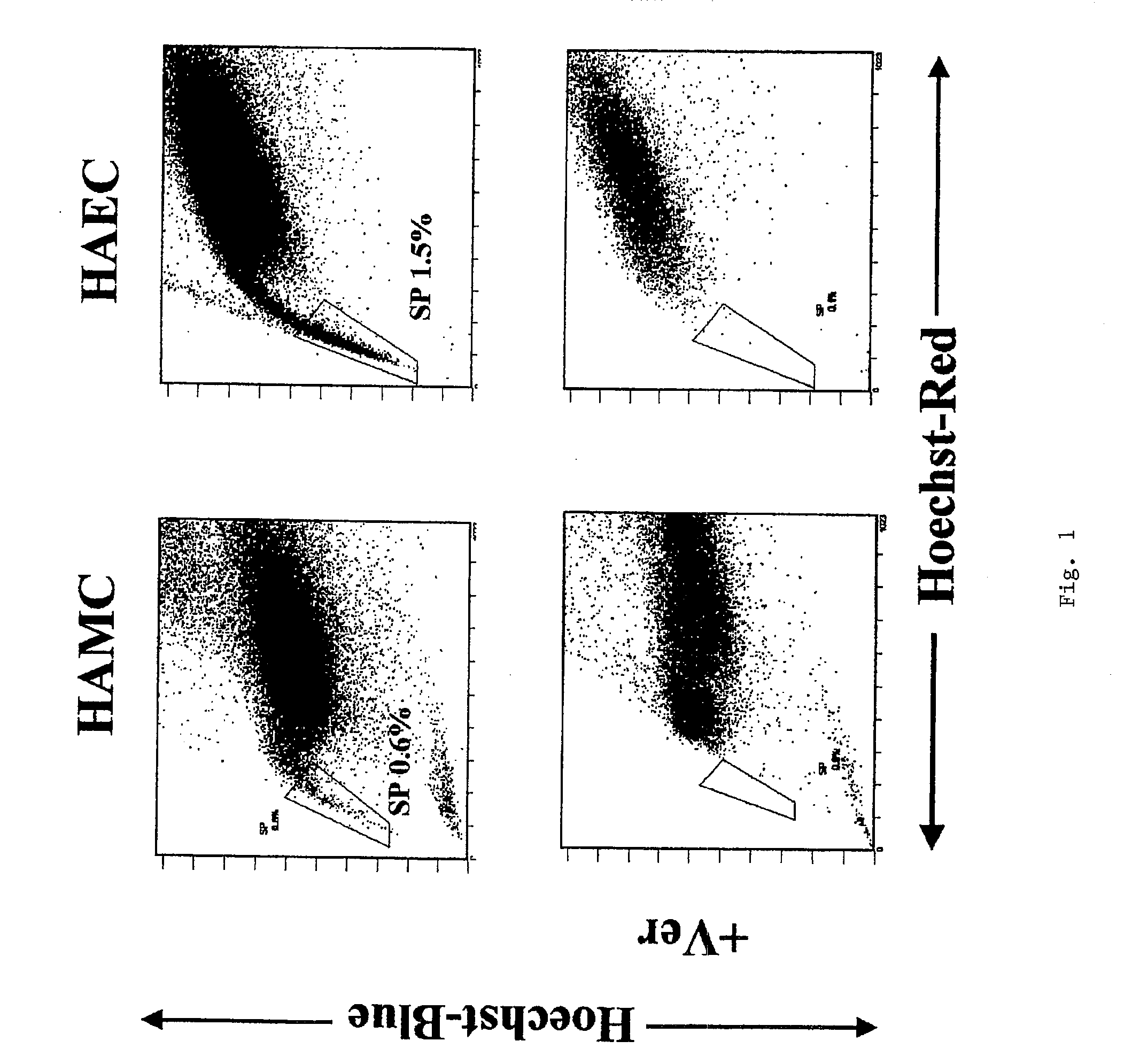
Human stem cells originating from human amniotic mesenchymal cell layer
InactiveUS20060281178A1Stable supplyEffective drug deliveryNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsCell layerOsteocyte
Owner:SAKURAGAWA NORIO +1
Methods and compositions for detecting colon cancers
ActiveUS7485420B2Significant positive effectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotide sequencingDifferential Methylation
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Circulating tumor cell identification kit and circulating tumor cell identification method
ActiveCN104031993AComprehensive detectionAvoid false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeFluorescence
The invention discloses a circulating tumor cell identification kit and a circulating tumor cell identification method. The circulating tumor cell identification kit comprises a detection probe for detecting mRNA of an epithelial cell marking gene and / or mRNA of a mesenchymal cell marking gene, wherein the epithelial cell marking gene is selected from one or more of CDH2, VIMENTIN, FN1 and AKT2. Multiple RNA probes are adopted in the identification method, specific genes of a plurality of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) can be marked at the same time and are divided into genes I (epithelial genes), genes II (epithelial-mesenchymal genes) and genes III (mesenchymal genes), and false positive results caused by lack of part of the specific genes of the CTCs in a process that the CTCs enter peripheral blood for circulation are reduced; the method can be finished within eight hours, and a single copied mRNA hybridization probe is combined with a corresponding fluorescent probe by virtue of a signal amplification system, so that the detection sensitivity of in-situ RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) hybridization is remarkably improved.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
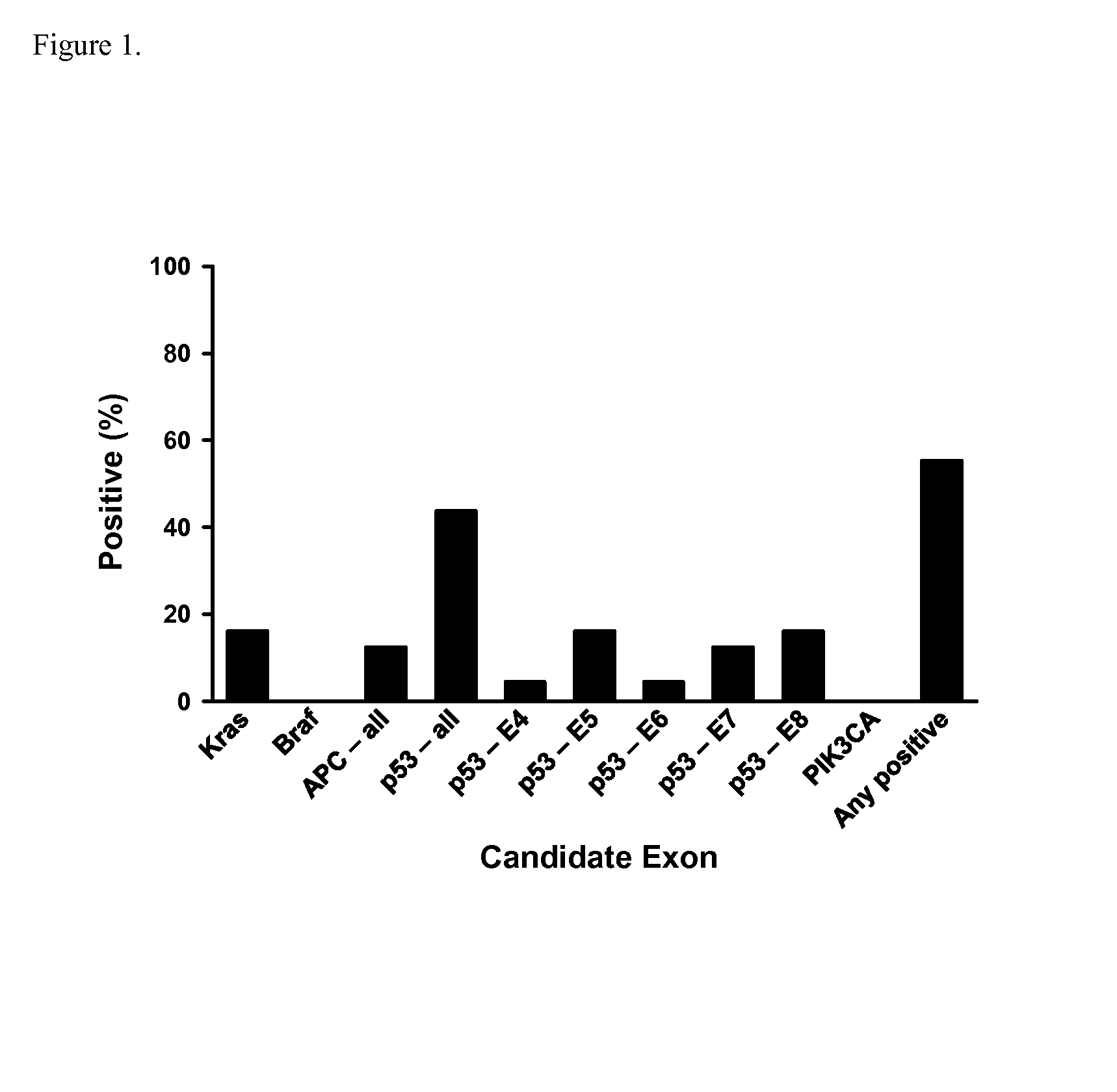
Methods and materials for detecting colorectal cancer and adenoma
InactiveUS20130012410A1High detectionHigh level of sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFOXE1Mammal
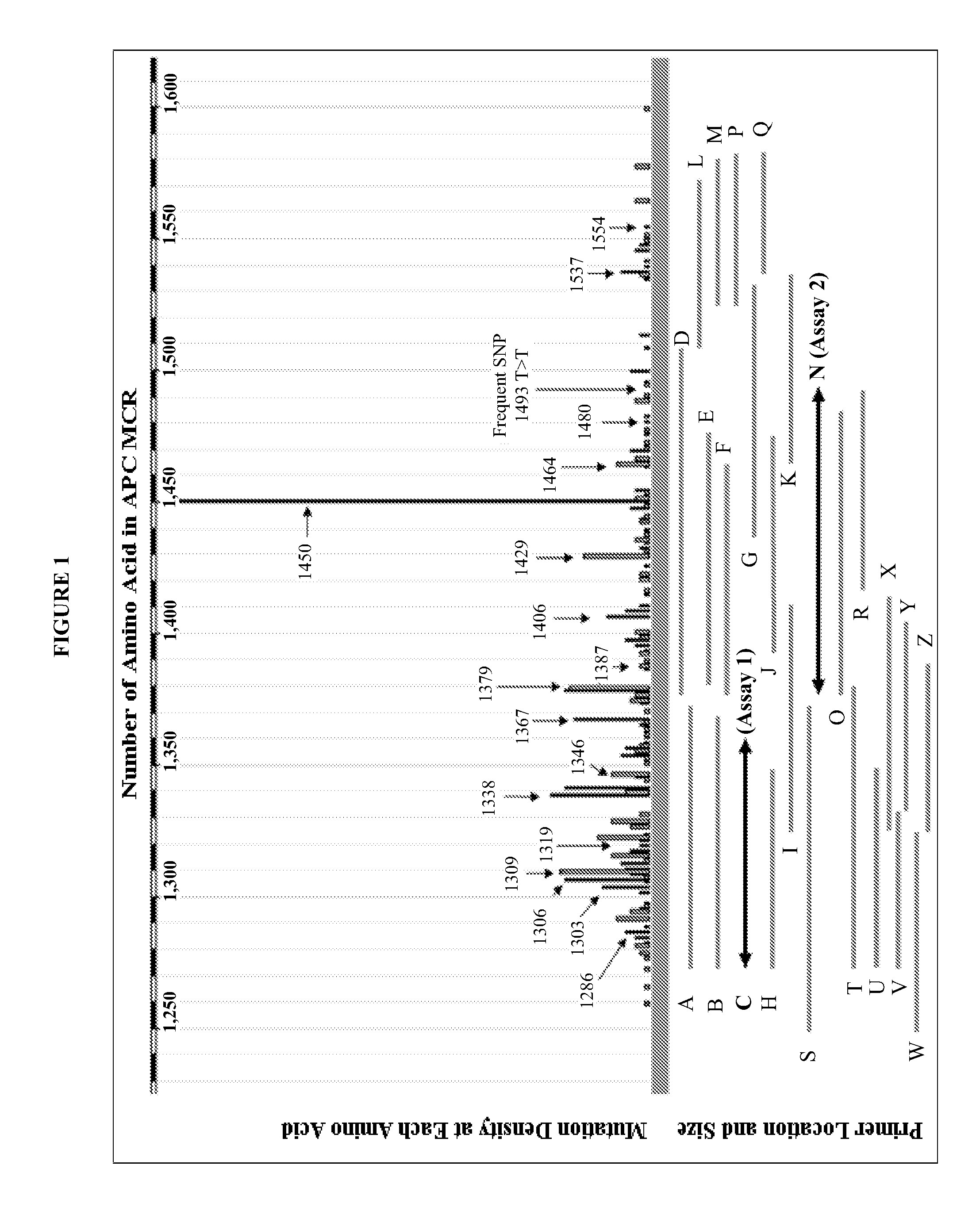
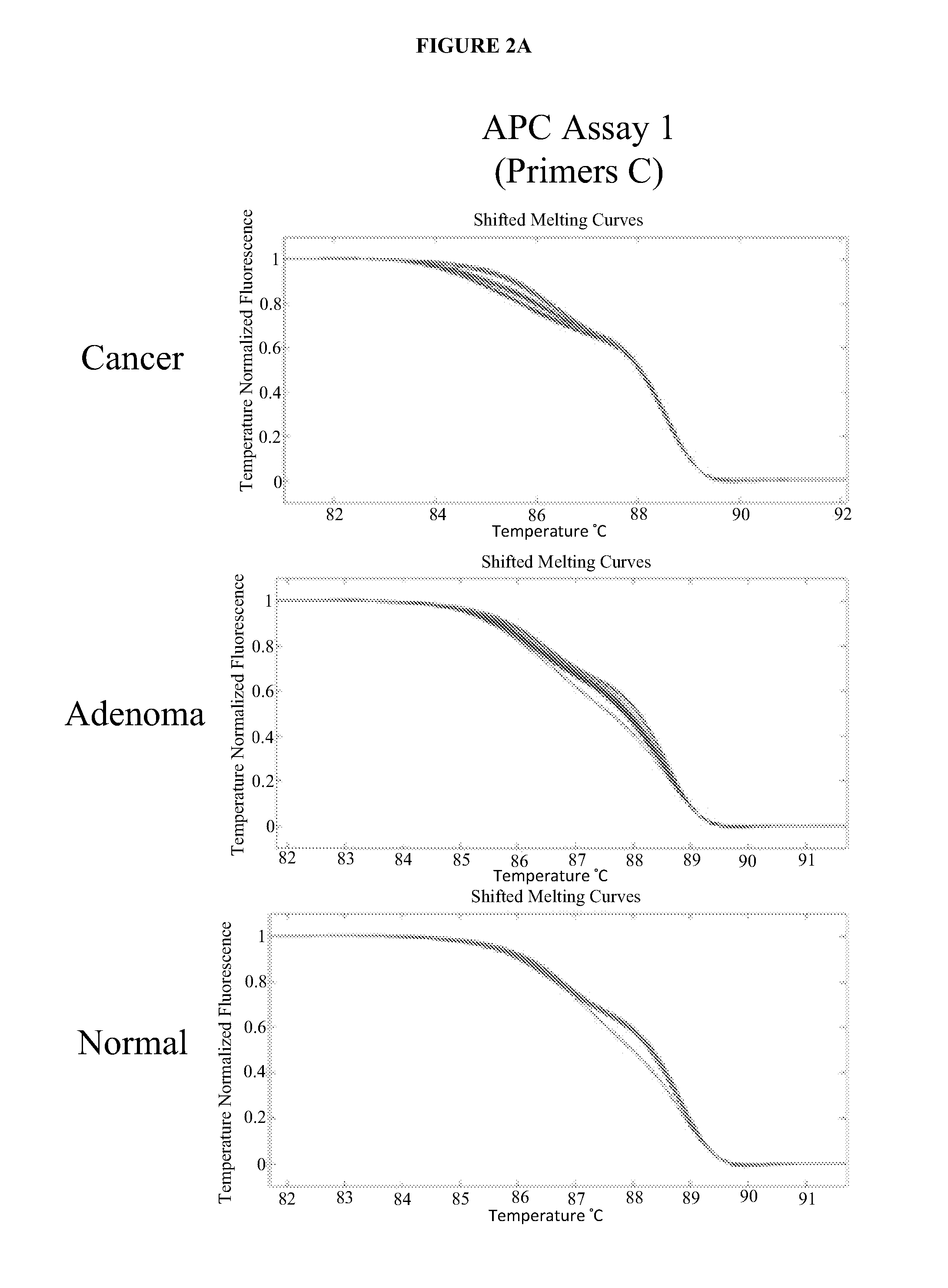
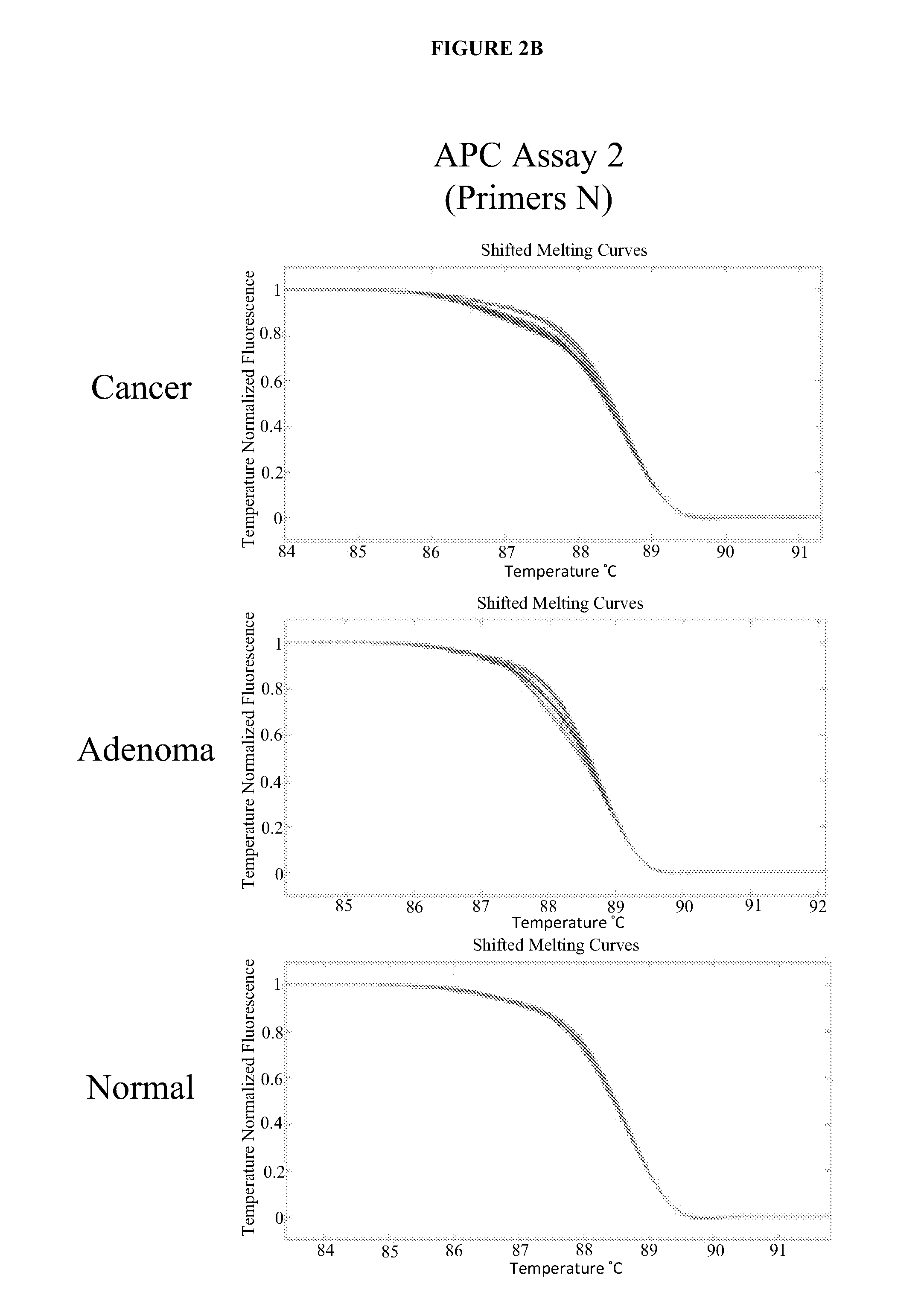
The present invention provides methods and materials related to the detection of colorectal neoplasm-specific markers (e.g., markers associated with colorectal cancer, markers associated with adenoma) in or associated with a subject's stool sample. In particular, the present invention provides methods and materials for identifying mammals (e.g., humans) having a colorectal neoplasm by detecting the presence and level of indicators of colorectal neoplasia such as, for example, long DNA (e.g., quantified by Alu PCR) and the presence and level of tumor-associated gene alterations (e.g., mutations in KRAS, APC, melanoma antigen gene, p53, BRAF, BAT26, PIK3CA) or epigenetic alterations (e.g., DNA methylation) (e.g., CpG methylation) (e.g., CpG methylation in coding or regulatory regions of bmp-3, bmp-4, SFRP2, vimentin, septin9, ALX4, EYA4, TFPI2, NDRG4, FOXE1) in DNA from a stool sample obtained from the mammal.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Side population cells originated from human amnion and their uses
InactiveUS20100015712A1Stable supplyUseful in therapyBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseSide population
Cells which may be differentiated at least into nerve cells, which are useful for therapies of brain metabolic diseases, are disclosed. The cells are side population cell separated from human amniotic mesenchymal cell layer, in which expressions of Oct-4 gene, Sox-2 gene and Rex-1 gene are observed by RT-PCR, and which are vimentin-positive and CK19-positive in immunocytostaining.
Owner:SAKURAGAWA NORIO +1
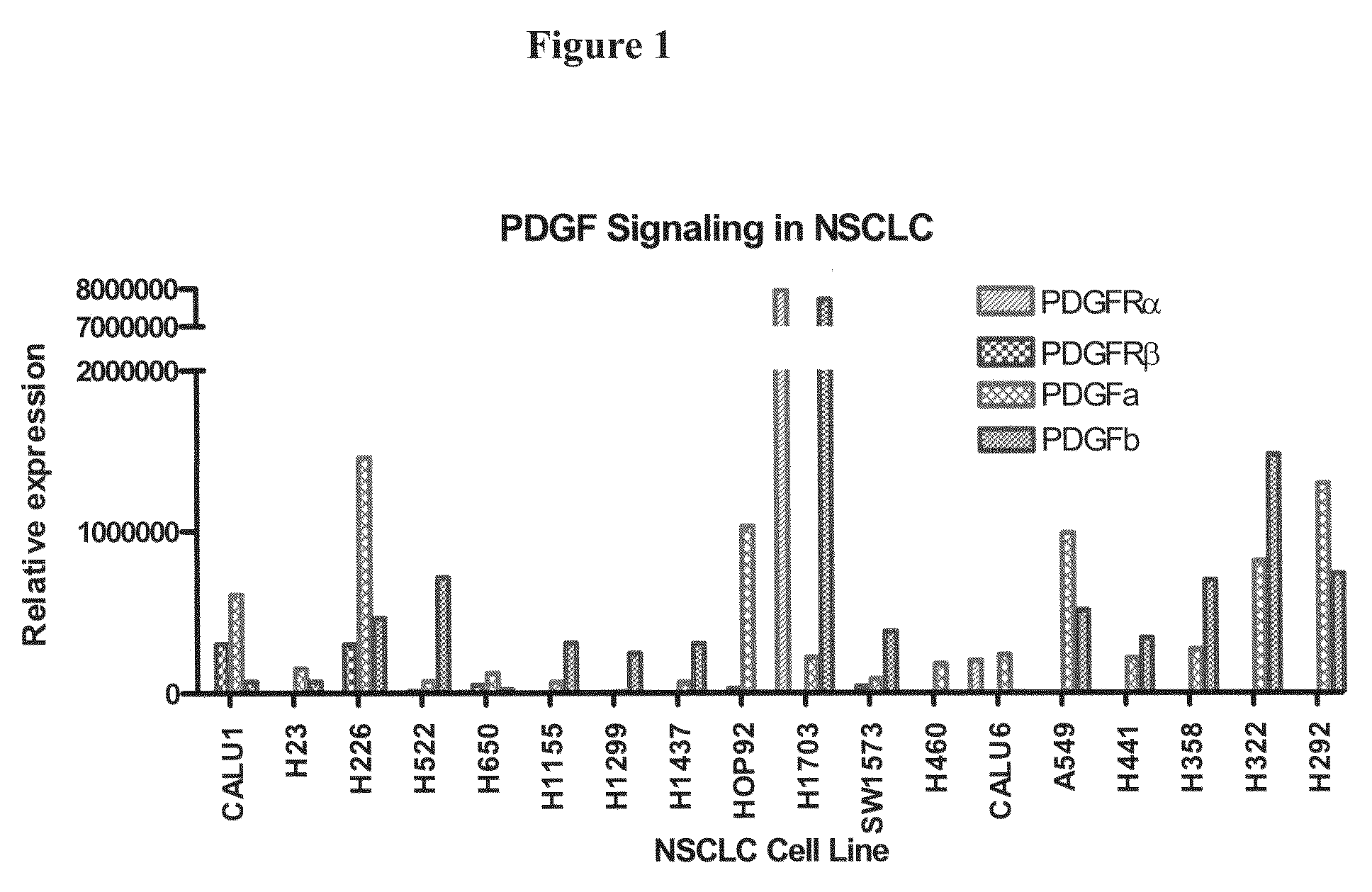
Biological markers predictive of anti-cancer response to kinase inhibitors
InactiveUS20080312260A1Reduce sensitivityHigh sensitivityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsReceptor Protein-Tyrosine KinasesRaf Kinase Inhibitor
The present invention provides diagnostic and prognostic methods for predicting the effectiveness of treatment of a cancer patient with inhibitors of EGFR kinase, PDGFR kinase, or FGFR kinase. Based on the surprising discovery that tumors cells after having undergone an EMT, while being mesenchymal-like, still express characteristics of both epithelial and mesenchymal cells, and that such cells have altered sensitivity to inhibition by receptor protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors, in that they have become relatively insensitive to EGFR kinase inhibitors, but have frequently acquired sensitivity to inhibitors of other receptor protein-tyrosine kinases such as PDGFR or FGFR, methods have been devised for determining levels of specific epithelial and mesenchymal biomarkers that identify such “hybrid” tumor cells (e.g. determination of co-expression of vimentin and epithelial keratins), and thus predict the tumor's likely sensitivity to inhibitors of EGFR kinase, PDGFR kinase, or FGFR kinase. Improved methods for treating cancer patients with EGFR, PDGFR or FGFR kinase inhibitors that incorporate such methodology are also provided.
Owner:OSI PHARMA LLC
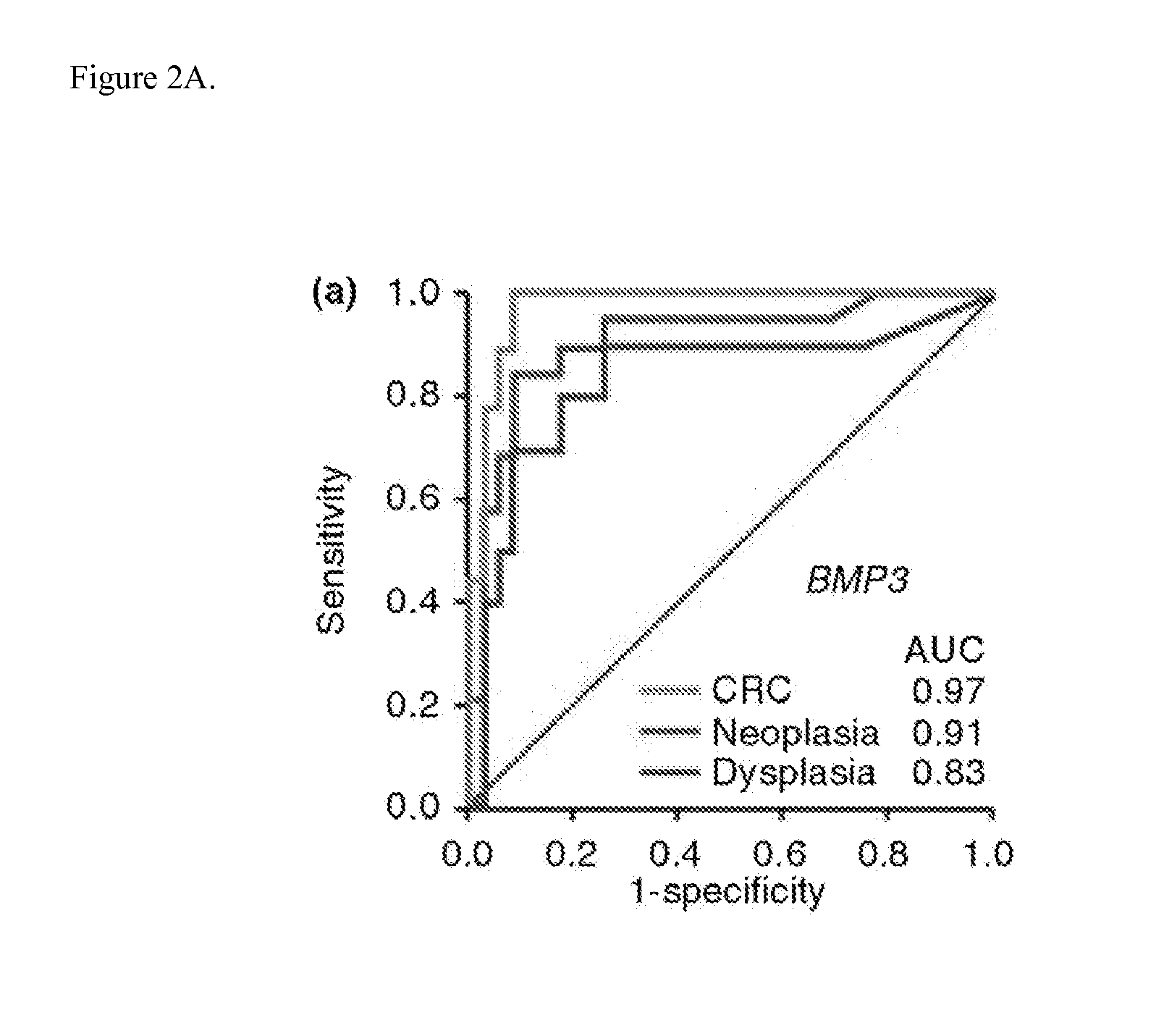
Methods and materials for noninvasive detection of colorectal neoplasia associated with inflammatory bowel disease
InactiveUS20130244235A1Improve discriminationSensitive highMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationMammal
The present invention provides methods and materials related to the detection of colorectal neoplasia (CRN) associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The present invention provides markers specific for colorectal neoplasia associated with inflammatory bowel disease in or associated with a subject's stool sample. In particular, the present invention provides methods and materials for identifying mammals (e.g., humans) having colorectal neoplasia associated with inflammatory bowel disease by detecting the presence and level of indicators of colorectal neoplasia such as, for example, epigenetic alterations (e.g., DNA methylation) (e.g., CpG methylation) (e.g., CpG methylation in coding or regulatory regions of BMP3, NDRG4, vimentin, EYA4) in DNA from a stool sample obtained from the mammal.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) primers, kit and detection method for detecting common carbapenemase genes of gram negative bacilli
ActiveCN103614465APrecise screeningSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesNucleotideEnterobacteriaceae bacterium
The invention discloses loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) primers, a kit and a detection method for detecting common carbapenemase genes of gram negative bacilli. In the LAMP primers disclosed by the invention, klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) and new delhi metallo-b-lactamase (NDM) primer groups can detect all subtypes except for NDM-10; hypoxanthine nucleotide (IMP) and vimentin (VIM) primer groups can detect common subtypes at home and abroad. The LAMP kit built by the invention is applied to joint detection of KPC, NDM, IMP and VIM genes, can cover the common carbapenemase genes of non-fermentative bacteria and enterobacteriaceae, can accurately and quickly screen the common carbapenemase genes, and has great clinical significance for timely detecting and further controlling fulminant epidemic caused by propagation of the carbapenemase genes in enterobacteriaceae. The kit disclosed by the invention is high in detection sensitivity and the minimum detection limits of the KPC, NDM, IMP and VIM genes can reach 100 CFU / reaction.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Human stem cells originating from human amniotic mesenchymal cell layer
InactiveUS20100330672A1Stable supplyEfficient deliveryNervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell layerOsteocyte
Neural stem cells which can be provided stably and which are free from the problem of compatibility in transplantation are disclosed. The stem cells are separated from human amniotic mesenchymal cell layer and express vimentin, nestin and BrdU which are markers of neural stem cells. The stem cells can also be differentiated to cells expressing alkaline phosphatase, that is, osteocytes, and to cells expressing collagen type II, that is, chondrocytes.
Owner:SAKURAGAWA NORIO +1
Biological markers predictive of Anti-cancer response to epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors
InactiveUS20120142028A1Long survival progression free survivalEffectiveness of treatmentDisease diagnosisAntineoplastic agentsEpidermal Growth Factor Receptor KinaseErlotinib
The present invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting the effectiveness of treatment of a cancer patient with an EGFR kinase inhibitor. These methods are based on the surprising discovery that the effectiveness of treatment with an EGFR kinase inhibitor is predicted by whether a patient's tumor cells express a high or a low level of the biomarkers vimentin and E-cadherin, such that patients whose tumors express a high level of at least one of the biomarkers vimentin and E-cadherin have a longer overall survival and progression free survival than patients whose tumors express a low level of both vimentin and E-cadherin. The present invention further provides a method for treating tumors or tumor metastases in a patient, comprising the steps of diagnosing a patient's likely responsiveness to an EGFR kinase inhibitor by assessing whether tumor cells express a high level of at least one of the biomarkers vimentin and E-cadherin, and administering to said patient a therapeutically effective amount of an EGFR kinase inhibitor (e.g. erlotinib), particularly when effectiveness of the inhibitor is predicted.
Owner:OSI PHARMA LLC
Separation, purification and identification methods of human amnion mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN102559586AMeet the treatment needsAccurate identification methodIndividual particle analysisEmbryonic cellsLow glucoseStaining
The invention discloses separation, purification and identification methods of human amnion mesenchymal stem cells. The separation method of hAMSCs (human amnion mesenchymal stem cells) comprises the following steps: fragmentating human amnion; and carrying out two-step rotating digestion with trypsin of EDTA (ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid) and collagenase of DNaseI, filtering with a steel mesh and collecting cell filtrate namely separated original hAMSCs. The purification method of hAMSCs comprises the following steps: incubating original hAMSCs with an LG (low glucose)-DMEM (dulbecco modified eagle medium) culture medium in a CO2 incubator; removing amnion epithelial cells which do not perform complete adherence growth under an inverted microscope; replacing a new culture medium on the third day; digesting with a trypsin-EDTA solution after cell converge degree reaches 80-90%; and collecting cells so as to obtain high-purity hAMSCs. The identification method of hAMSCs comprises the following steps: identifying hAMSCs and the amnion epithelial cells by adopting immunocytochemical staining vimentin and CK19; and detecting expressions of CD29, CD44, CD166, CD34 and CD45 by adopting a flow cytometry. The separation and purification methods disclosed by the invention have the advantages of high yield, high activity and high purity of hAMSCs; and the identification method is simple, convenient and precise.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZUNYI MEDICAL COLLEGE
Methods and compositions for detecting gastrointestinal and other cancers
ActiveUS8415100B2Significant positive effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLower Gastrointestinal TractNucleotide
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis urine protein marker, and application of same to diagnosis and prognosis
The invention relates to an idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis urine protein marker, and application of the same to diagnosis and prognosis. Specifically, the invention relates to application of a urine protein marker obtained by using an idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis model and mass spectrometry to early-stage diagnosis, pathogenesis monitoring and curative effect assessment of human pulmonary fibrosis. The urine protein marker comprises collagen alpha-1(I) chain, vimentin, protein RUFY3, keratin type-II skeleton 8, a sodium-hydrogen exchange regulation factor NHE-RF2, a threonine synthase sample 2, zinc-actin binding repeat protein 2, low-density lipoprotein receptor-associated protein 4, alpha-11 of a guanine nucleotide binding protein subunit, an alpha-1 chain of tropomyosin, mitochondrial stress-70 protein, NSFL1 cofactor P47, ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1, etc.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
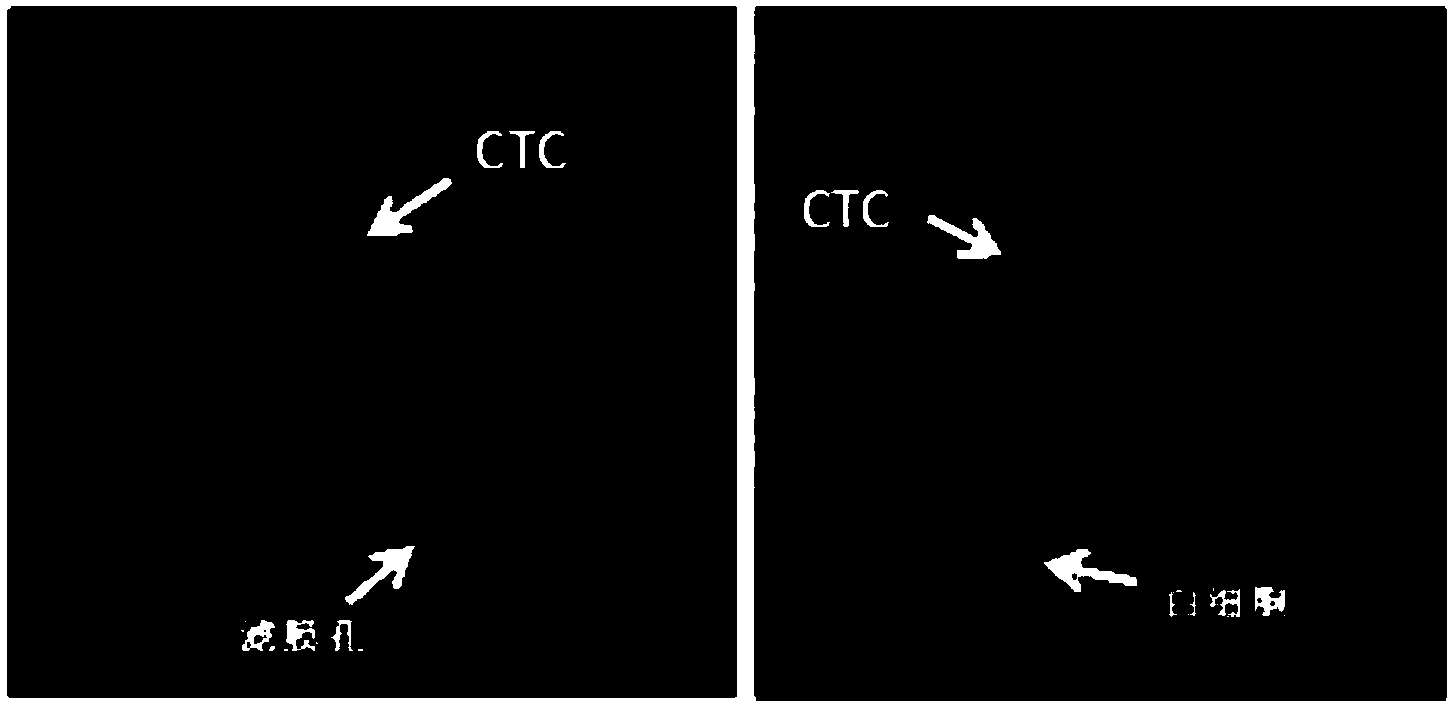
Specific detection tool for mesenchymal and epithelial-mesenchymal transformed circulating tumor cells
ActiveUS20160009812A1Animal cellsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSpecific detectionCirculating cancer cell
The present invention includes the discovery of cell-surface vimentin as a novel biomarker to detect and isolate mesenchymal and epithelial-mesenchymal transformed circulating tumor cells from blood of cancer patients. In addition, an antibody specific for the detection of cell-surface vimentin on circulating tumor cells and the use the antibody to detect, enumerate, and isolate CTC are provided.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Vimentin directed diagnostics and therapeutics for multidrug resistant neoplastic disease
InactiveUS20040259112A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisNormal cellNeoplastic cell
Disclosed are methods for detecting multidrug resistance in neoplastic or damaged cells or multidrug resistant (MDR) neoplastic or damaged cells by detecting an increase in the cell surface expression of vimentin protein in such cells as compared to the level of cell surface expression of vimentin protein in a normal cell or a non-MDR neoplastic cell.
Owner:AURELIUM BIOPHARMA
Methods and compositions for detecting colon cancers
ActiveUS20050106593A1Significant positive effectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotide sequencingDifferential Methylation
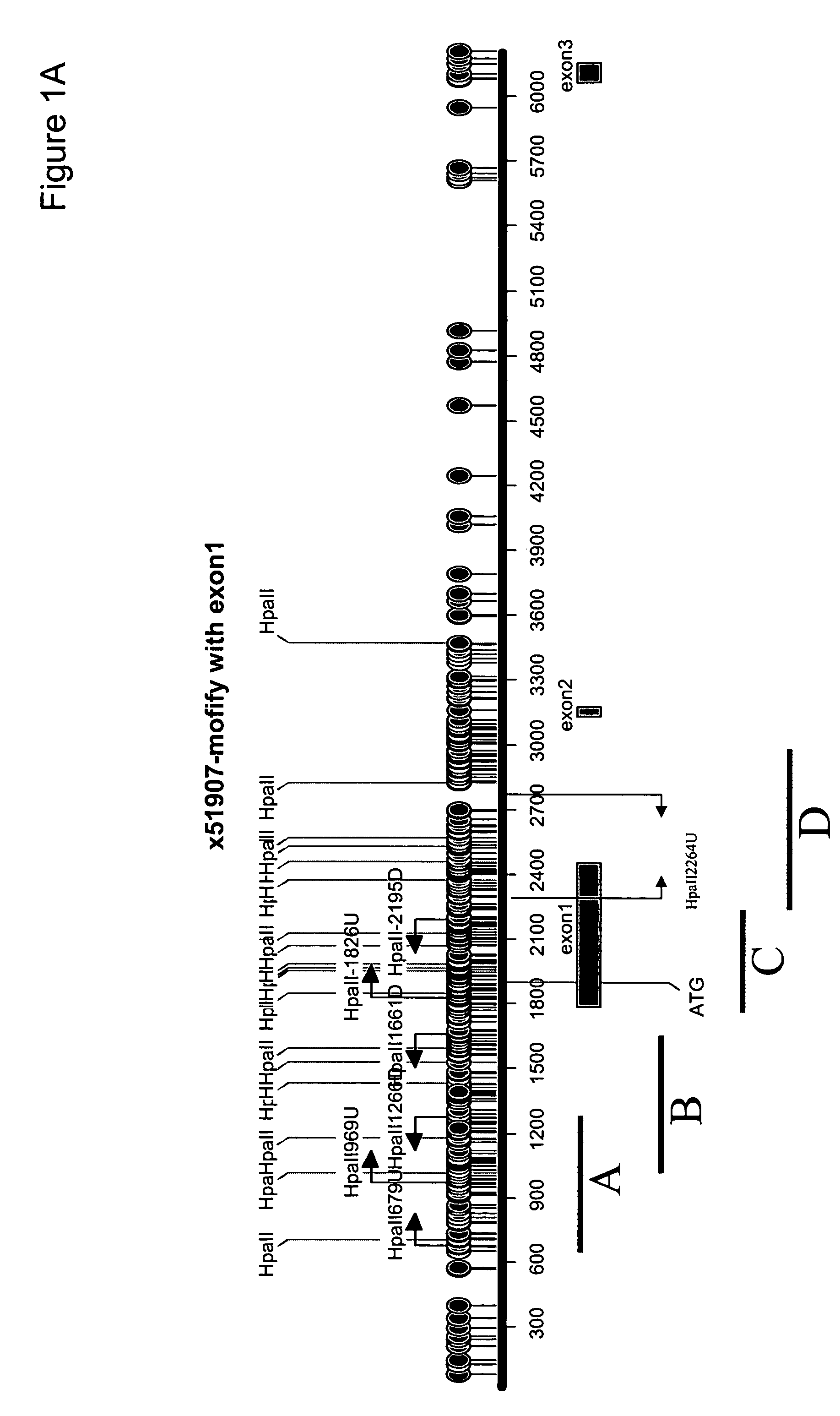
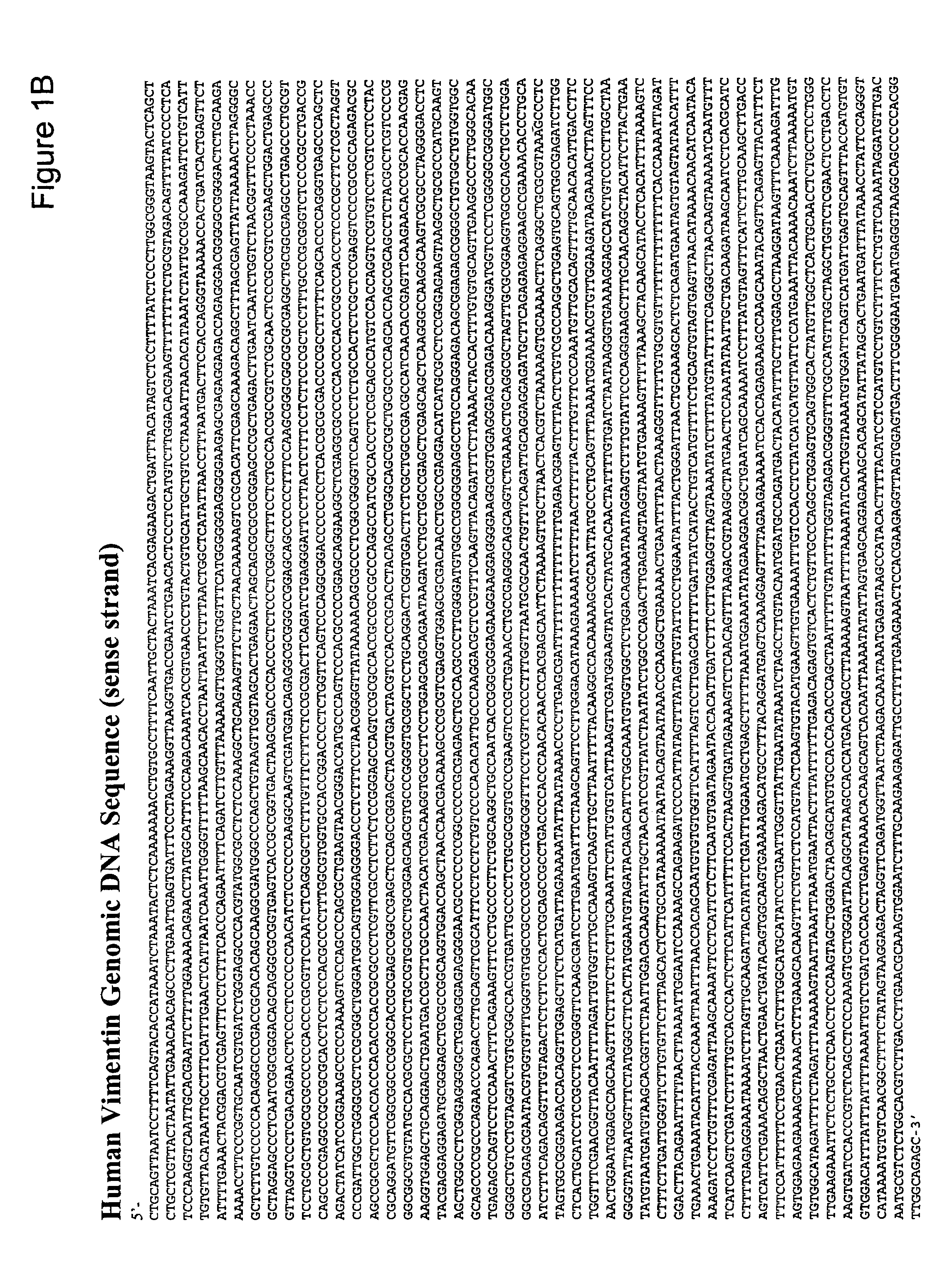
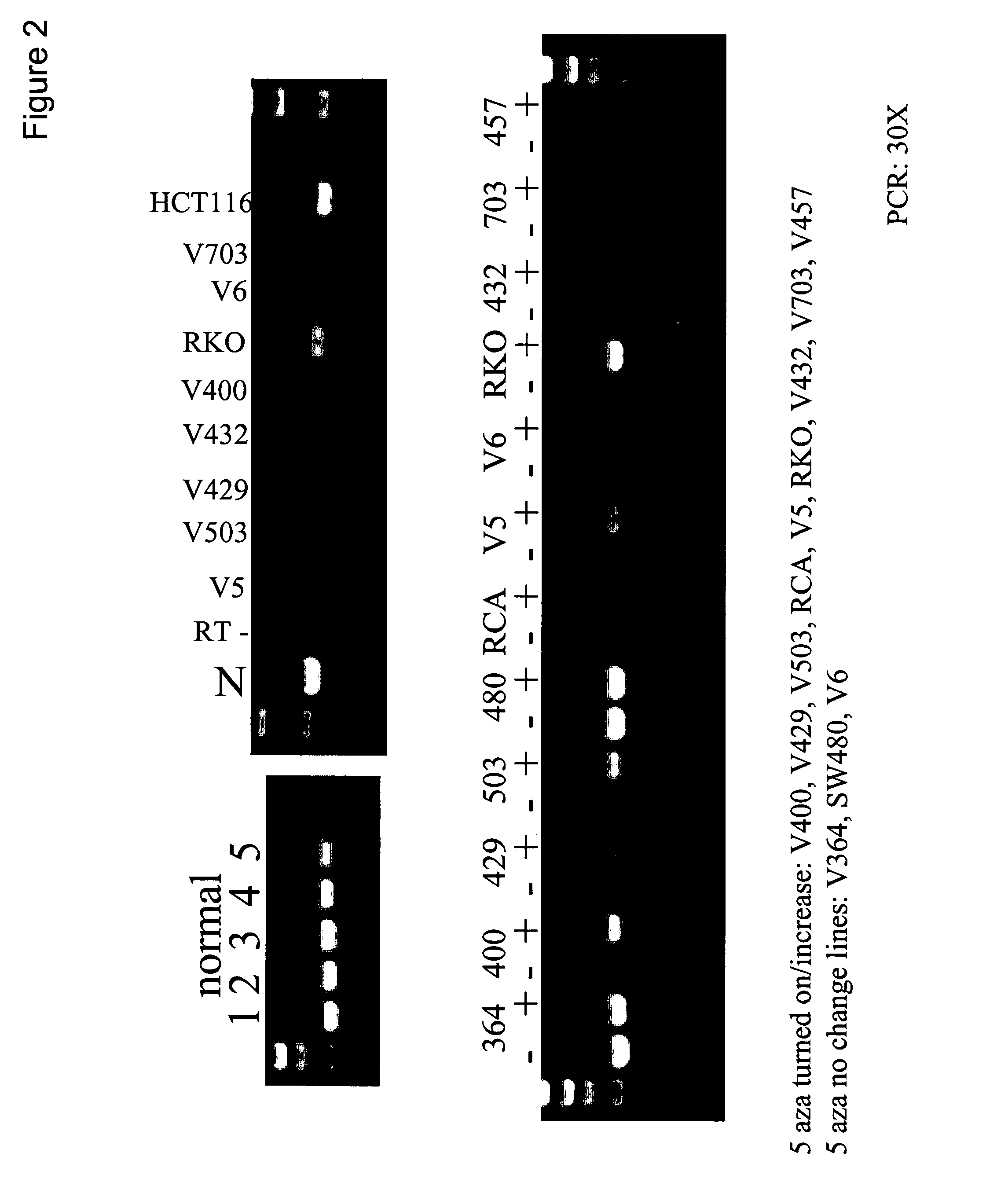
This application describes methods and compositions for detecting and treating vimentin-associated neoplasia. Differential methylation of the vimentin nucleotide sequences has been observed in vimentin-associated neoplasia such as colon neoplasia.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Methods of prognosis and diagnosis of ovarian cancer
Cellular markers indicating a poor prognosis for ovarian cancer patients are disclosed. In particular, the invention relates to methods utilizing the frequency of a subset of cells in ovarian tumor tissue expressing vimentin, cMyc, or HE4, or any combination thereof, to predict an ovarian cancer patient will relapse.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Immunofluorescent staining and interpretation method for circulating tumor cell
InactiveCN107402296AAvoid missing detectionImprove recognition efficiencyFluorescence/phosphorescenceStainingImmunofluorescent stain
The invention discloses an immunofluorescent staining and interpretation method for circulating tumor cells. The method comprises the following steps: S10, performing centrifugal treatment on a blood sample diluted with a phosphoric acid buffer solution, and removing erythrocyte and leukocyte in the blood sample; S20, moistening the treated blood sample with the phosphoric acid buffer solution, adding a stationary liquid for immobilizing cells in the blood sample, adding a permeabilization liquid for permeabilization, and further adding a confining liquid for sufficient confining; and S30, dripping dye liquids of anti-pan-CK-FITC, anti-CD45-AF59 and anti-Vimentin-FITC into the treated blood sample at a dark place, performing light shielded incubation, removing the dye liquids, adding a nucleic acid fluorescent dye to continue incubation. The interpretation method comprises steps of scanning observation and result interpretation. Compared with the prior art, the dyeing method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being simple and convenient to operate, easy to popularize and the like, and the interpretation method has the advantages of being accurate interpretation and the like.
Owner:亚能生物技术(深圳)有限公司
Prognostic markers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Methods and compositions for detecting a form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in a subject are described which allow for distinguishing more aggressive forms of the disease from less aggressive forms. Particularly described methods include assaying a sample obtained from the subject having or suspected of having chronic lymphocytic leukemia for a marker selected from a vimentin cleavage product, annexin 5 and 6-phosphogluconolactonase. A combination of any of these markers may be assayed in particular embodiments of a method according to the present invention. In particular embodiments, detection of an intermediate weight vimentin cleavage product is indicative of a less aggressive form of CLL associated with good prognosis.
Owner:GEERAERTS BEN +4
Biological markers predictive of anti-cancer response to kinase inhibitors
The present invention provides diagnostic and prognostic methods for predicting the effectiveness of treatment of a cancer patient with inhibitors of EGFR kinase, PDGFR kinase, or FGFR kinase. Based on the surprising discovery that tumors cells after having undergone an EMT, while being mesenchymal-like, still express characteristics of both epithelial and mesenchymal cells, and that such cells have altered sensitivity to inhibition by receptor protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors, in that they have become relatively insensitive to EGFR kinase inhibitors, but have frequently acquired sensitivity to inhibitors of other receptor protein-tyrosine kinases such as PDGFR or FGFR, methods have been devised for determining levels of specific epithelial and mesenchymal biomarkers that identify such “hybrid” tumor cells (e.g. determination of co-expression of vimentin and epithelial keratins), and thus predict the tumor's likely sensitivity to inhibitors of EGFR kinase, PDGFR kinase, or FGFR kinase. Improved methods for treating cancer patients with EGFR, PDGFR or FGFR kinase inhibitors that incorporate such methodology are also provided.
Owner:OSI PHARMA LLC
Methods of secretory vimentin detection and modulation
InactiveUS20040121419A1Enhanced anti-microbial responseScreening and modulating bioavailabilityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAntiendomysial antibodiesDrug target
The present invention relates to methods for screening and modulating the bioavailability of extracellular secretory vimentin. In particular, the present invention provides inhibitors and activators of secretory vimentin including antibodies, small interfering RNAs, and antisense oligonucleotides. The present invention thus provides novel drug targets for enhanced anti-microbial response, and methods of using such modulators to beneficially alter the pathophysiologic effects of secretory vimentin.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Marker panel for detecting cancer
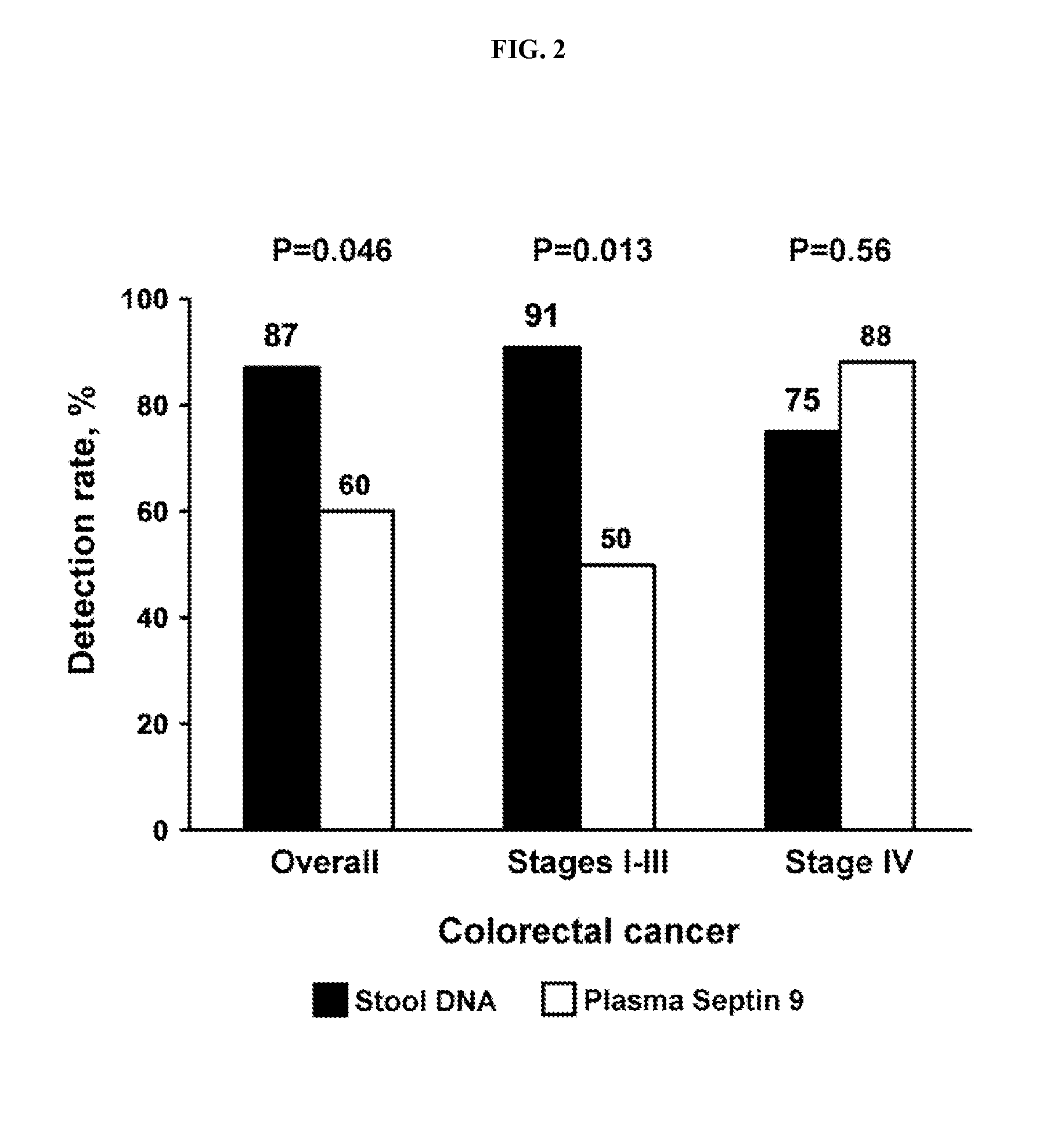
InactiveUS20150072866A1More sensitiveAdvanced technologyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningStool dnaBlood plasma
Provided herein is technology relating to detecting cancer and particularly, but not exclusively, to methods for detecting colorectal cancer by evaluating multiple markers in paired plasma and stool samples. In particular, the technology relates to CRC screening by assaying plasma for methylated Septin 9 and assaying stool DNA for methylated vimentin, NDRG4, BMP3, and / or TFPI2.
Owner:EXACT SCI CORP +1
Tumor angiogenesis associated genes and a method for their identification
InactiveUS20090035312A1Inhibit angiogenesisReduced microvessel densityOrganic active ingredientsFungiAbnormal tissue growthMouse tumor
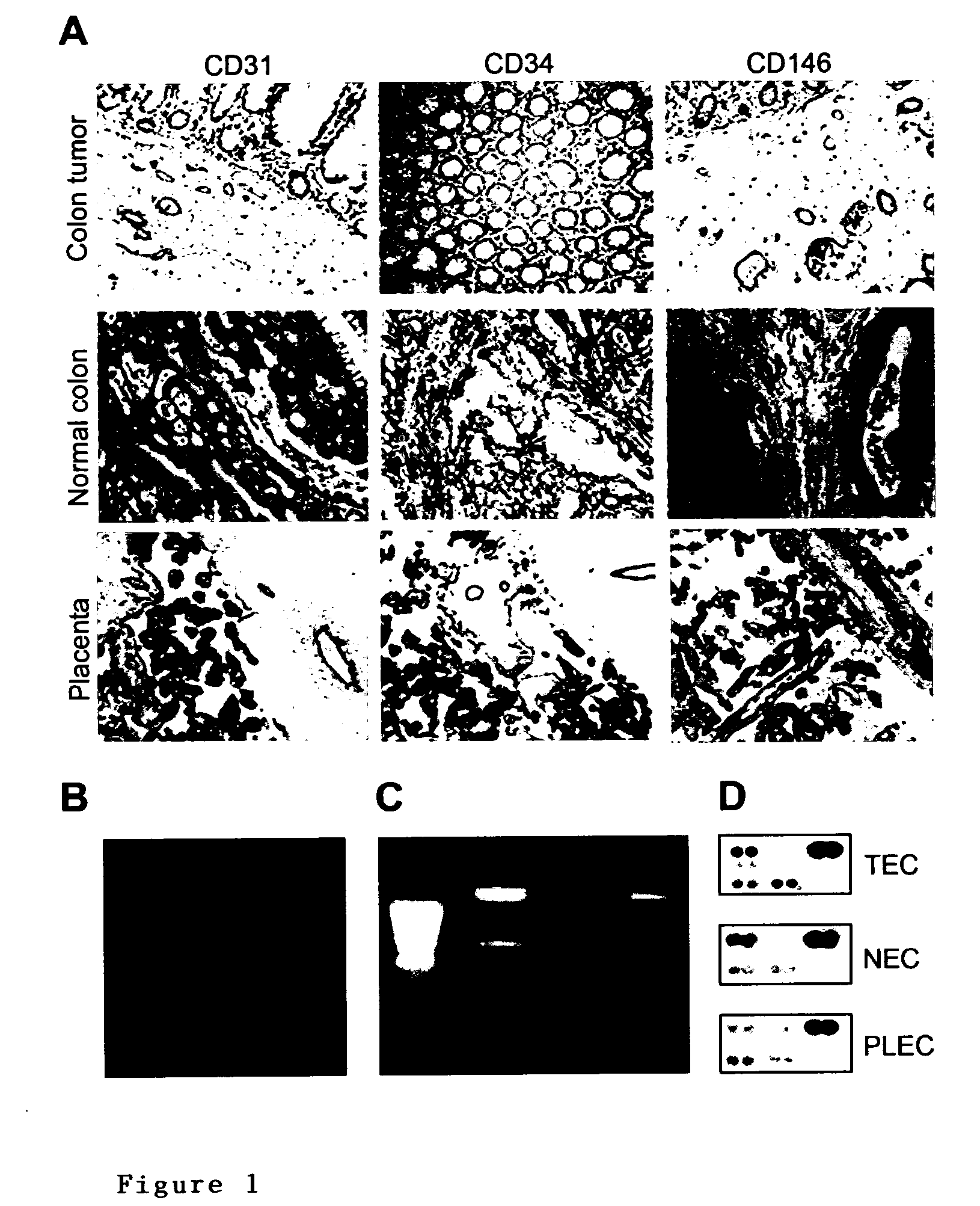
Methods of identifying specific target molecules for design of anti-angiogenic and vascular targeting approaches are disclosed. Transcriptional profiles of tumor endothelial cells were compared with that of normal resting endothelial cells, normal but angiogenically activated placental endothelial cells, and cultured endothelial cells. Although the majority of transcripts were classified as general angiogenesis markers, 17 genes were identified that show specific overexpression in tumor endothelium. Antibody targeting of four cell-surface expressed or secreted products (vimentin, CD59, HMGB1 and IGFBP7) inhibited angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Finally, targeting endothelial vimentin in a mouse tumor model significantly inhibited tumor growth and reduced microvessel density. The results demonstrate the utility of the identification and subsequent targeting of specific tumor endothelial markers for anticancer therapy.
Owner:MAASTRICHT UNIVERSITY
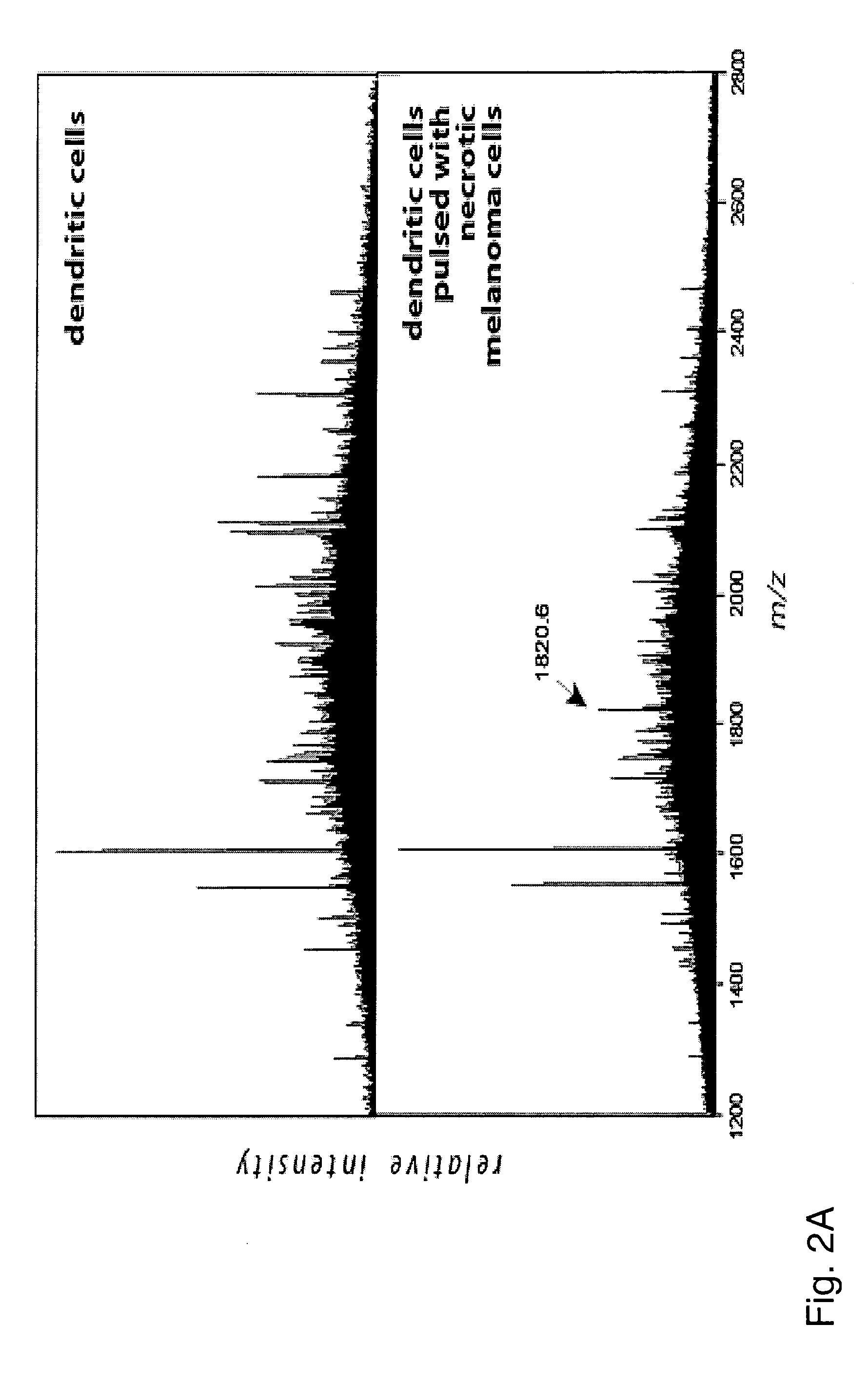
Classifying Skin Lesions Using Mass Spectrometry Proteomic Approach
The present invention provides for a mass spectrometry proteomic approach to distinguishing Spitz nevi from Spitzoid malignant melanoma. Histology directed mass spectral profiling allows for targeted analysis of sites of melanocytic lesion within formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded excisional biopsies. The classification system identified 5 peptide peaks, of which two have been identified as originating from vimentin and actin. A sensitivity and specificity for Spitz nevi of 97% and 90%, respectively, were achieved.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Carcinoma Homing Peptide (CHP), Its Analogs, and Methods of Using
ActiveUS20120208770A1Inhibit tumor growthImprove survivalOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSquamous CarcinomasWild type
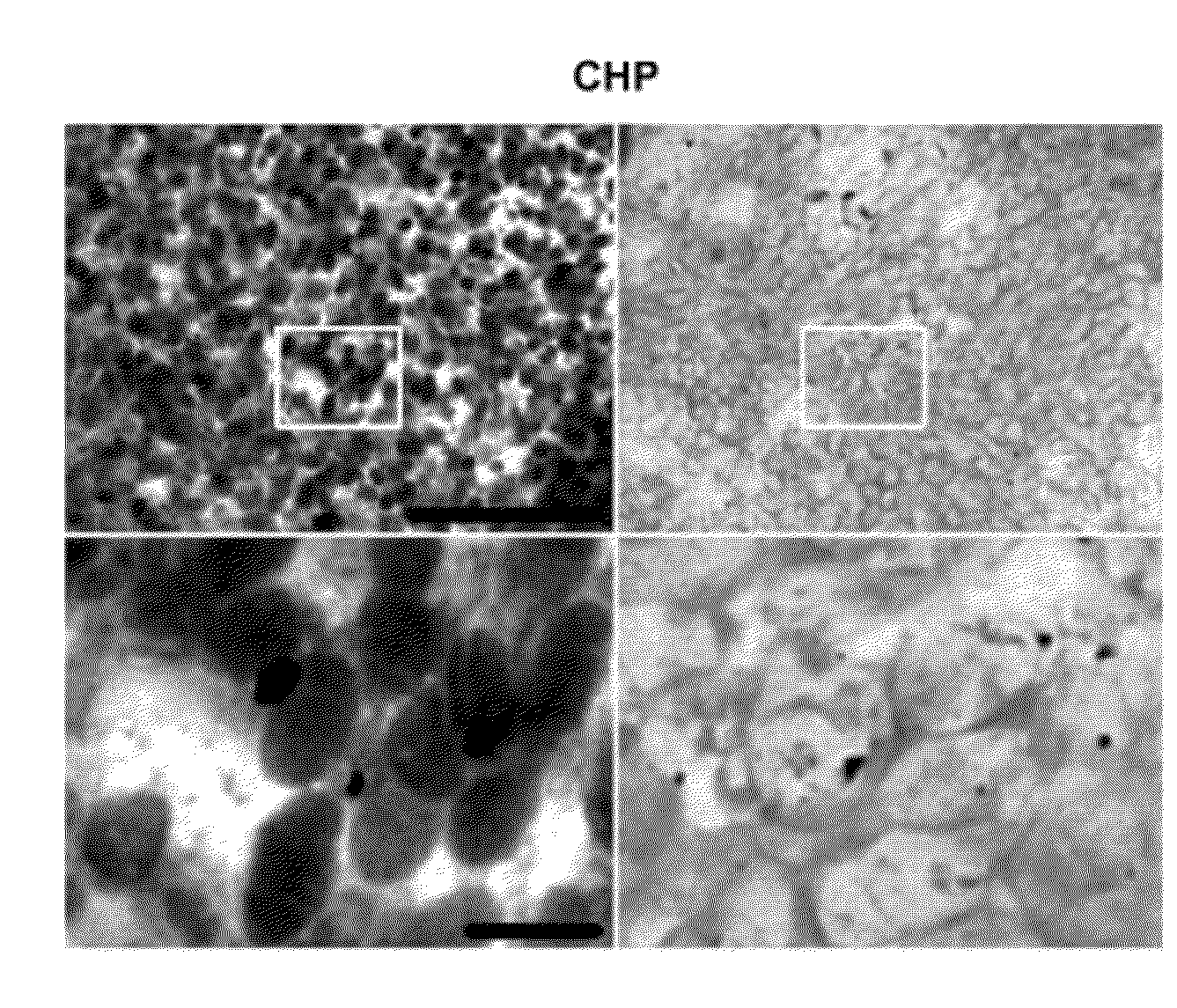
A mini-peptide and its analogs have been found to target gene products to tumors. The peptide, named Carcinoma Homing Peptide (CHP), increased the tumor accumulation of the reporter gene products in five independent tumor models, including one human xenogeneic model. A CHP-IL-12 fusion gene was also developed using CHP and the p40 subunit of IL-12. The product from CHP-IL-12 fusion gene therapy increased accumulation of IL-12 in the tumor environment. In three tumor models, CHP-IL-12 gene therapy inhibited distal tumor growth. In a spontaneous lung metastasis model, inhibition of metastatic tumor growth was improved compared to wild-type IL-12 gene therapy, and in a squamous cell carcinoma model, toxic liver lesions were reduced. The receptor for CHP was identified as vimentin. CHP can be used to improve the efficacy and safety of targeted cancer treatments.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Method for screening donor cell line based on blastocyst gene expression level
ActiveCN103305551AImprove cloning efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSOX2Gene expression level
The invention discloses a method for screening a donor cell line based on blastocyst gene expression level. The method comprises the steps of: detecting expression levels of TCF7, DGCR8, SENP7, DNMT3B, Vimentin, IFI6, EFNA2, F5, IRAK1, PRICKLE1, TNFRSF1A, ARG2, NEK6, OCT4, NANOG, SOX2, CDX2, XIST and IGF2R at a blastula stage after carrying out nuclear transferring on the donor cell lines from different individuals; and selecting the donor cell line which is not significant in difference of all expression levels of these genes on cloned blastocysts and the expression level of normally growing in vitro fertilization blastocyst as a nuclear donor cell. The cloning efficiency of bovine somatic cells can be significantly improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV +1
Multiplex immunoassay for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases
Rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases are diagnosed by multiplex assays for antibodies to a panel of antigens that includes cyclic citrullinated peptide and at least five members of a list that includes BRAF1 506-525, BRAF2 656-675, Vimentin (protein) citrullinated, Vimentin 415-433 cit cyclic, Vimentin 58-77 cit3 cyclic, Clusterin 231-250 cit sm1 cyclic, Fibrinogen A 556-575 cit sm cyclic, Fibrinogen A 616-635 cit sm cyclic, Histones2A H2A / a 1-20 cit sm2 cyclic, Filaggrin 48-65 cit2v1 cyclic, BRAF (catalytic domain from v raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homologue B1, amino acids 416-766).
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Method for Inhibiting HIV Replication in Mammal and Human Cells
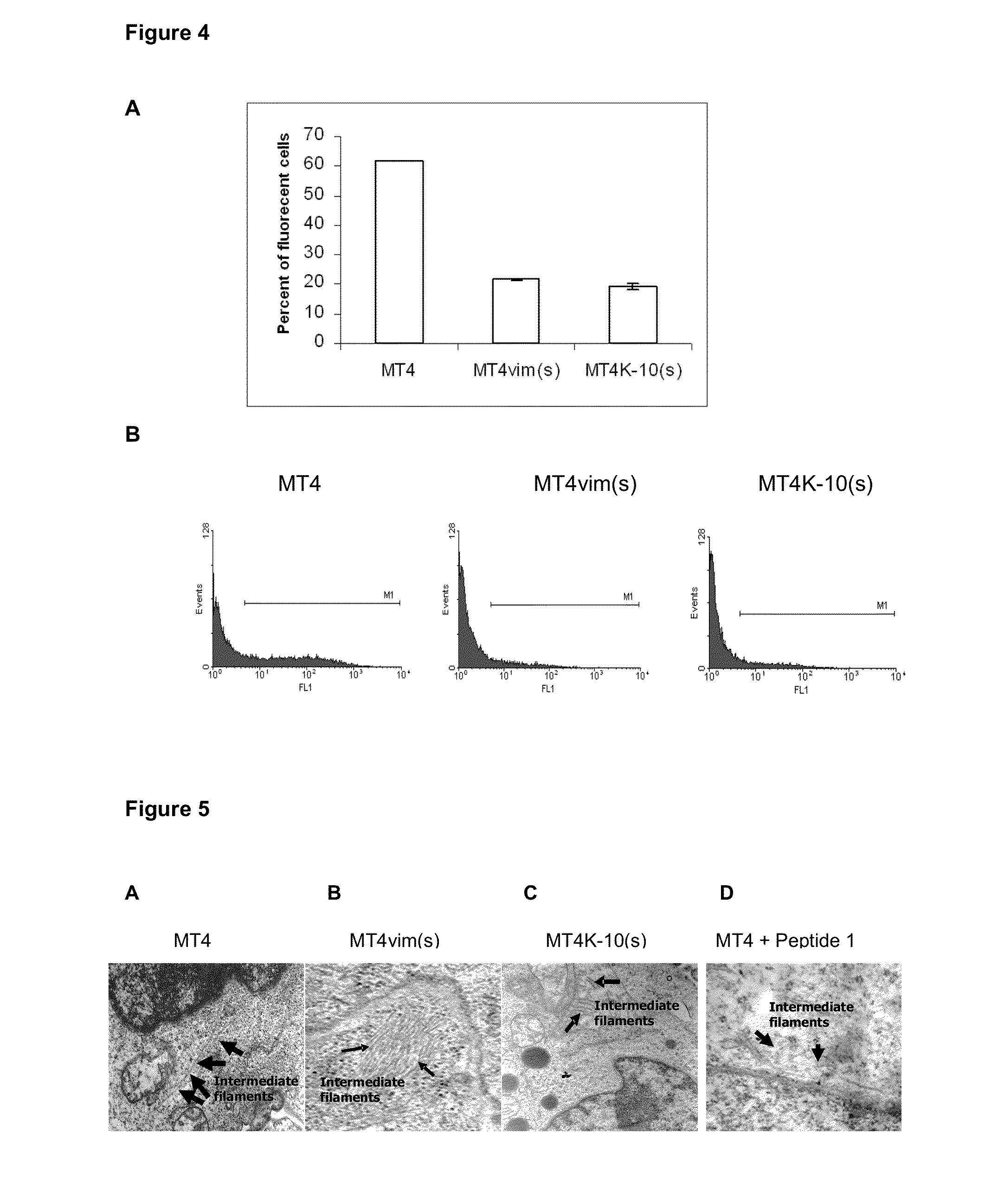
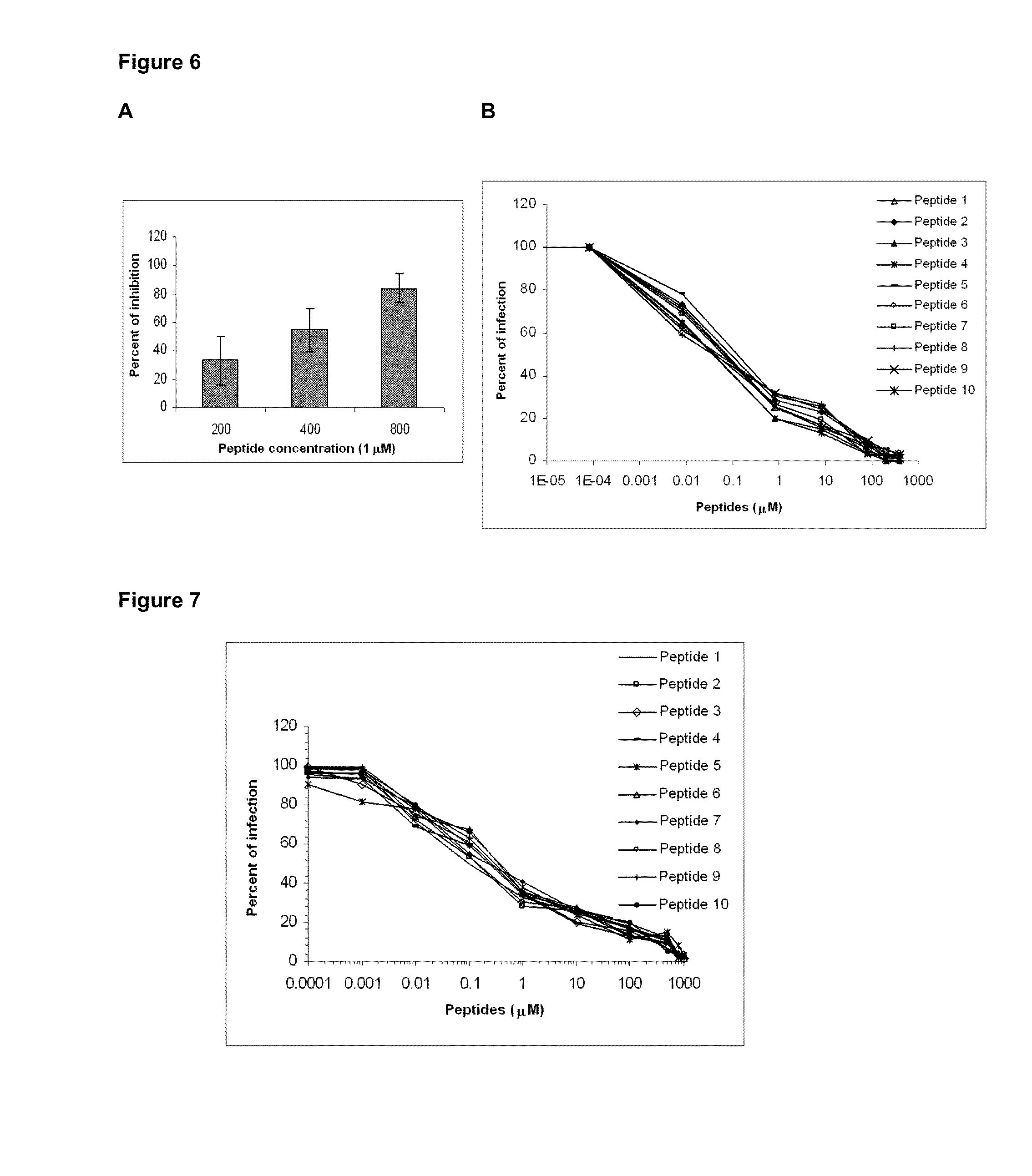
ActiveUS20130130971A1Avoids viral resistanceReduce probabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunodeficiency virusADAMTS Proteins
The present invention describes a method to inhibit replication of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) by negatively modulating or altering the cytoskeleton, more precisely the proteins forming the intermediate cytoskeletal filaments, wherein the said proteins are vimentin and / or keratin-10. The replication of the virus is inhibited in human cells by intervening in the structure of these proteins. The present invention is also related to the use of agents, which comprise peptides and / or interfering RNA and / or lipidic compounds, said agents producing a negative modulation or alteration of the cytoskeleton to prevent or to treat the HIV infection. The invention provides means and methods for altering the cytoskeleton / filament structure of cells, as a result of which the infection of human cells by HIV is disturbed and can even be completely inhibited. The cytoskeleton is altered by reducing the amount of vimentin and / or keratin (e.g. by transcriptional control using interfering RNA) or by using peptides that disrupt the cytoskeleton.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
Novel MHC II associated peptides
InactiveUS20050202009A1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthMHC class II
The present invention provides novel naturally-processed antigenic peptides which are candidate tumor antigens in melanoma and other tumors. These antigenic peptides are presented by human MHC class II HLA-DR molecules. They originate from the translation factor eIF-4A, the IFN-gamma-inducible protein p78, the cytoskeletal protein vimentin and the iron-binding surface protein melanotransferrin. The antigenic peptides of the present invention can be used as markers in diagnosis of the respective tumors and in therapy as anti-tumor vaccines.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com