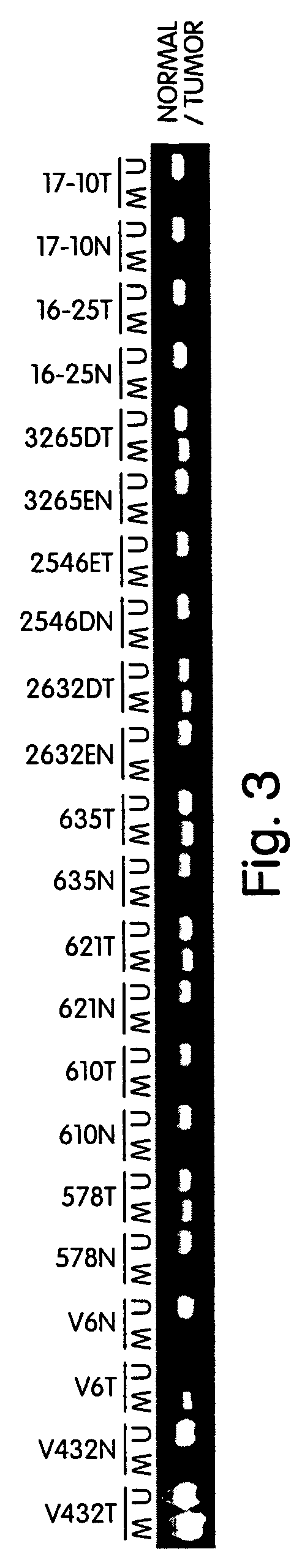
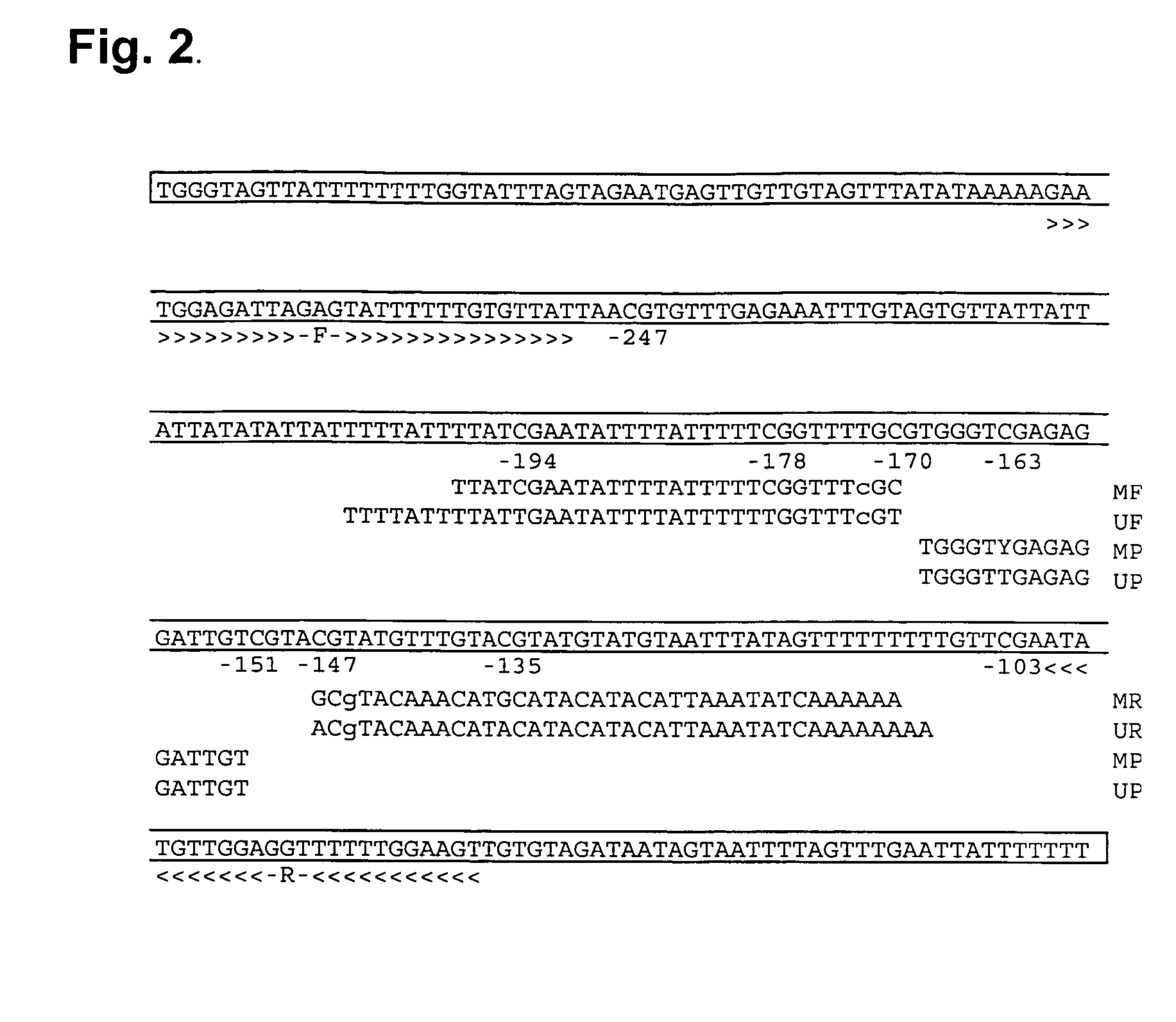
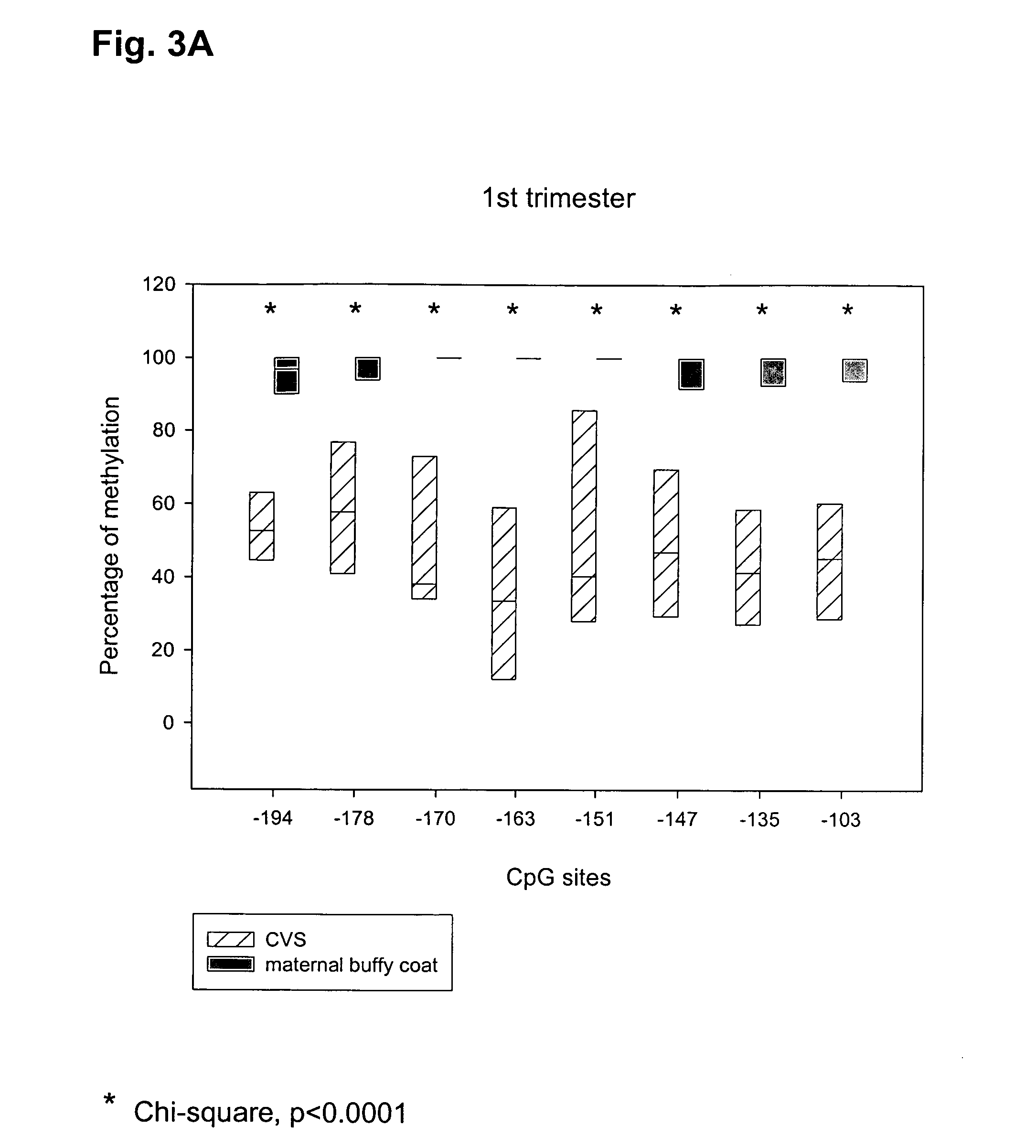
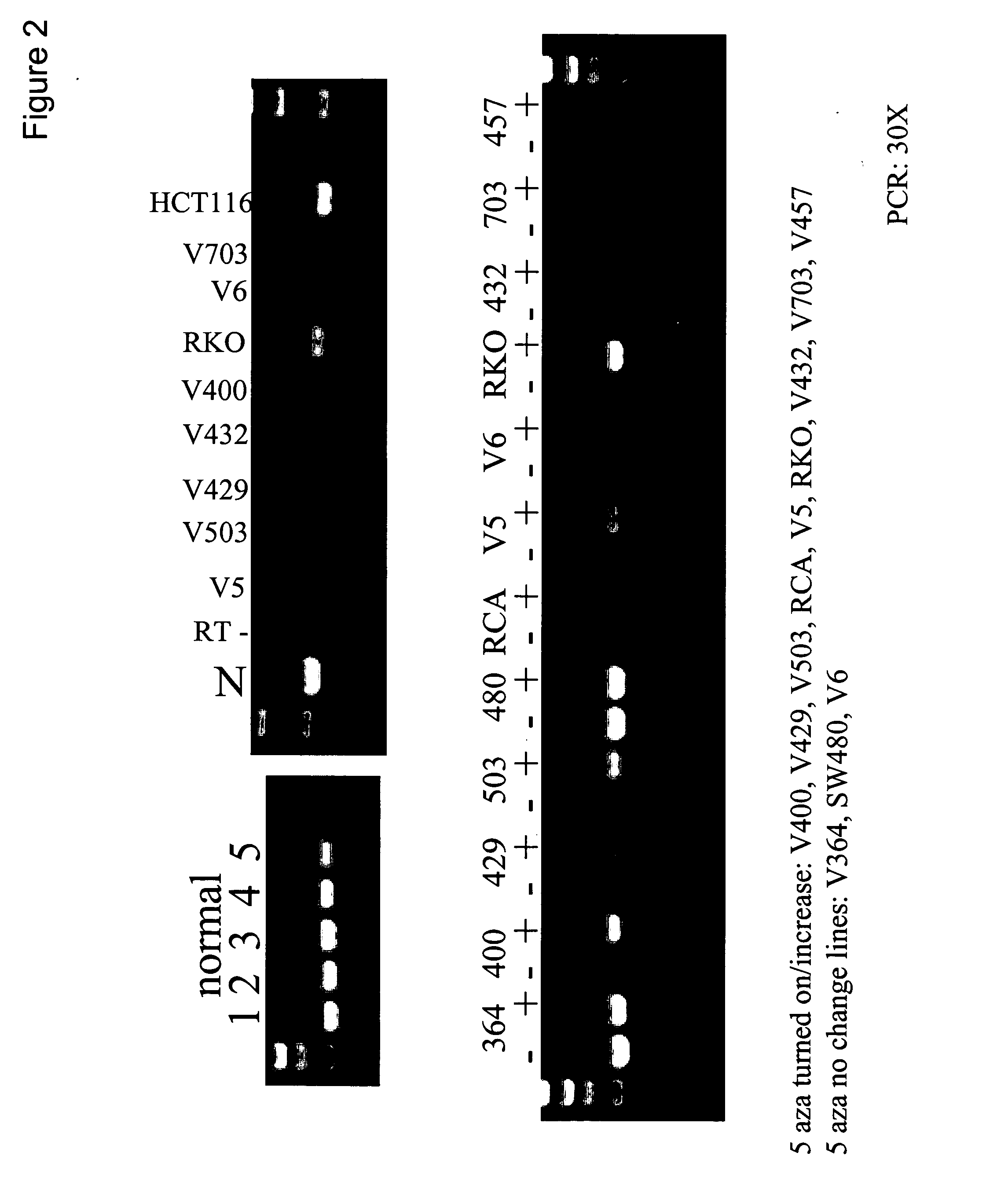
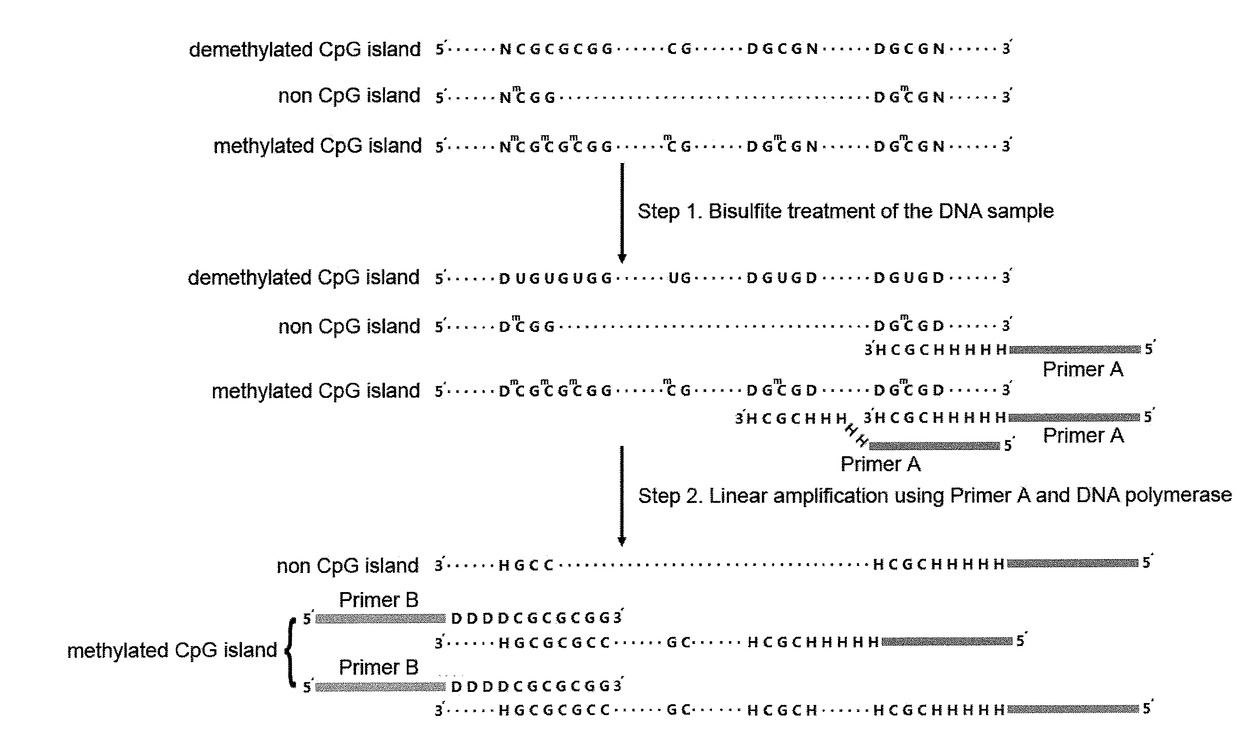
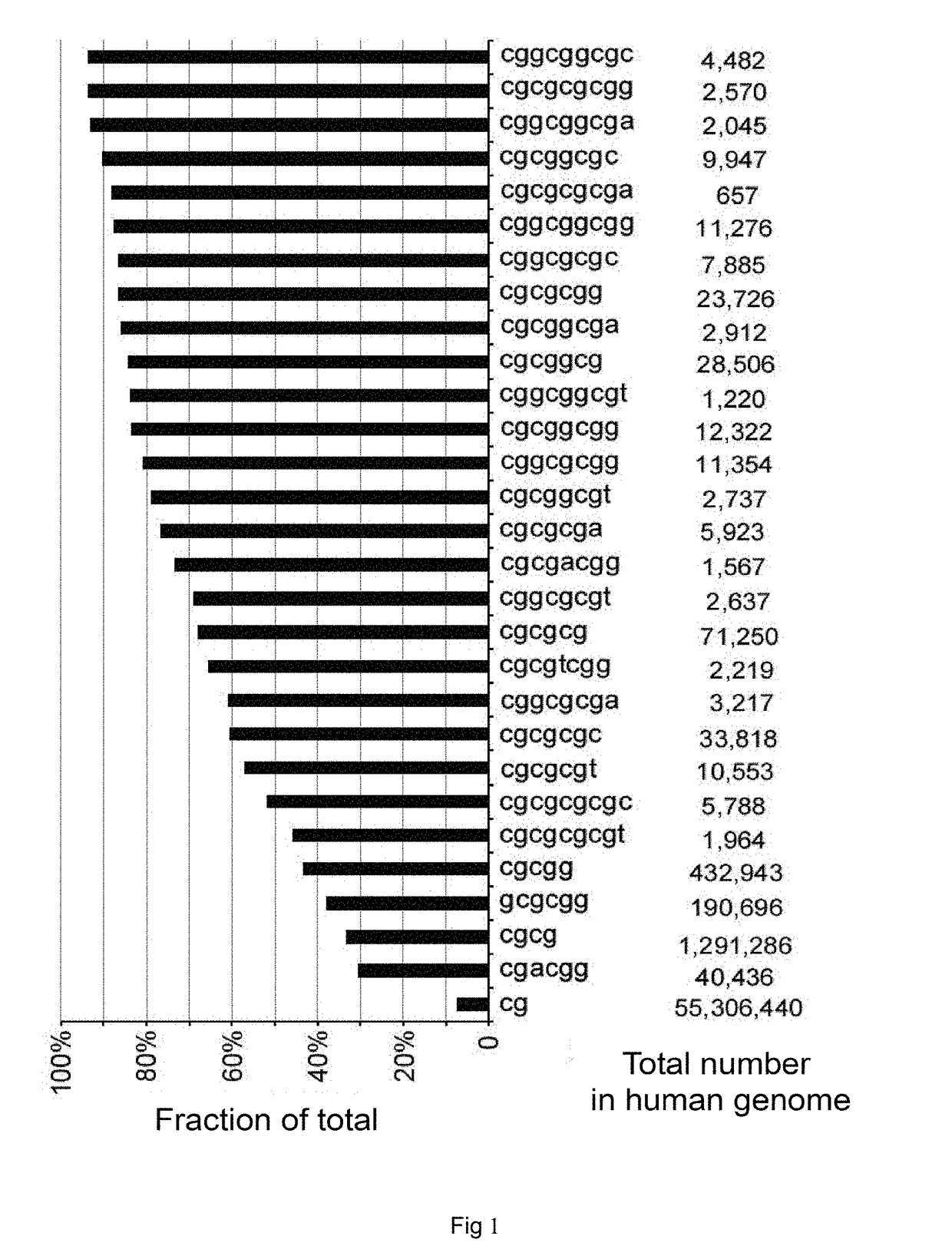
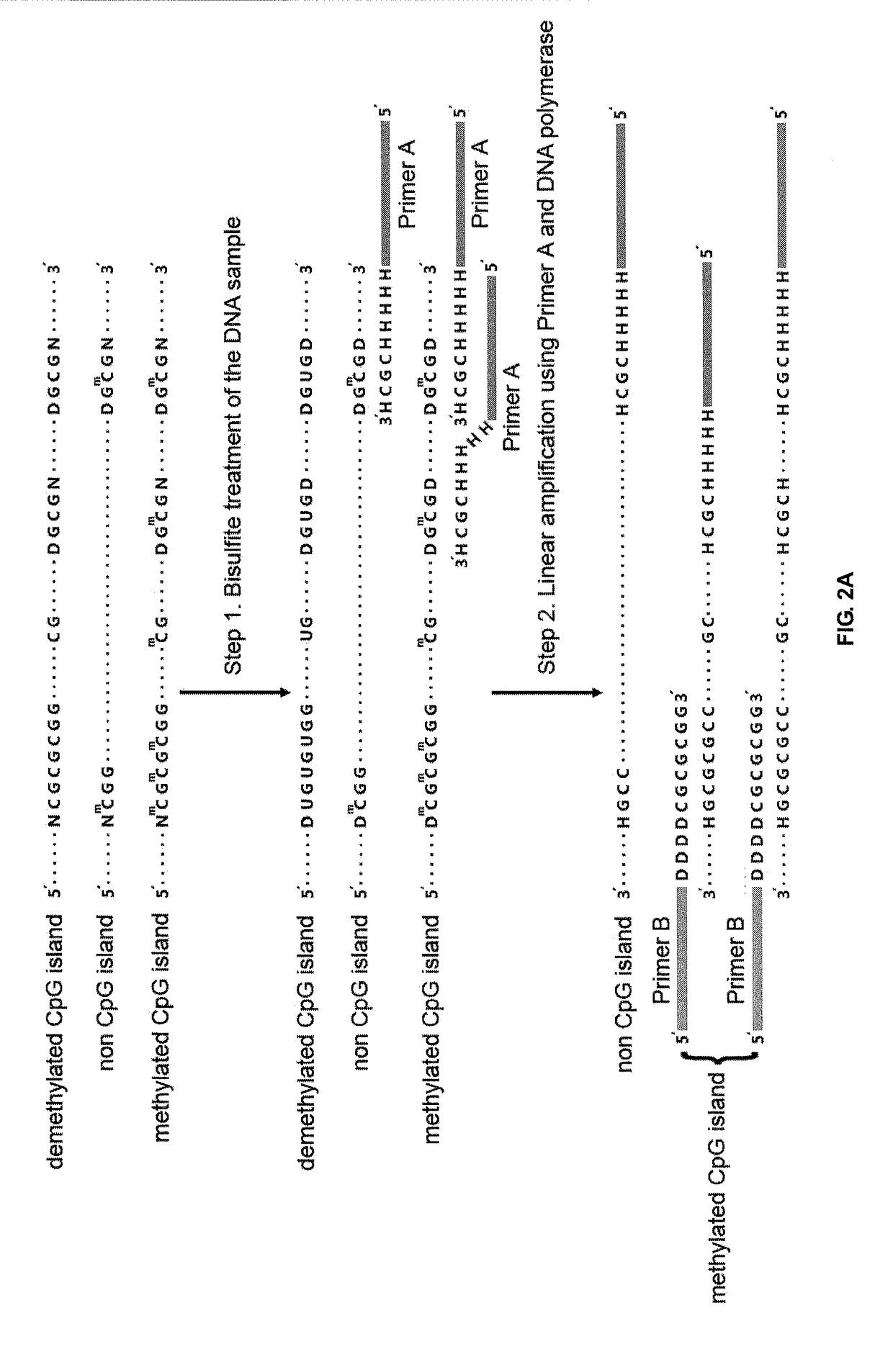
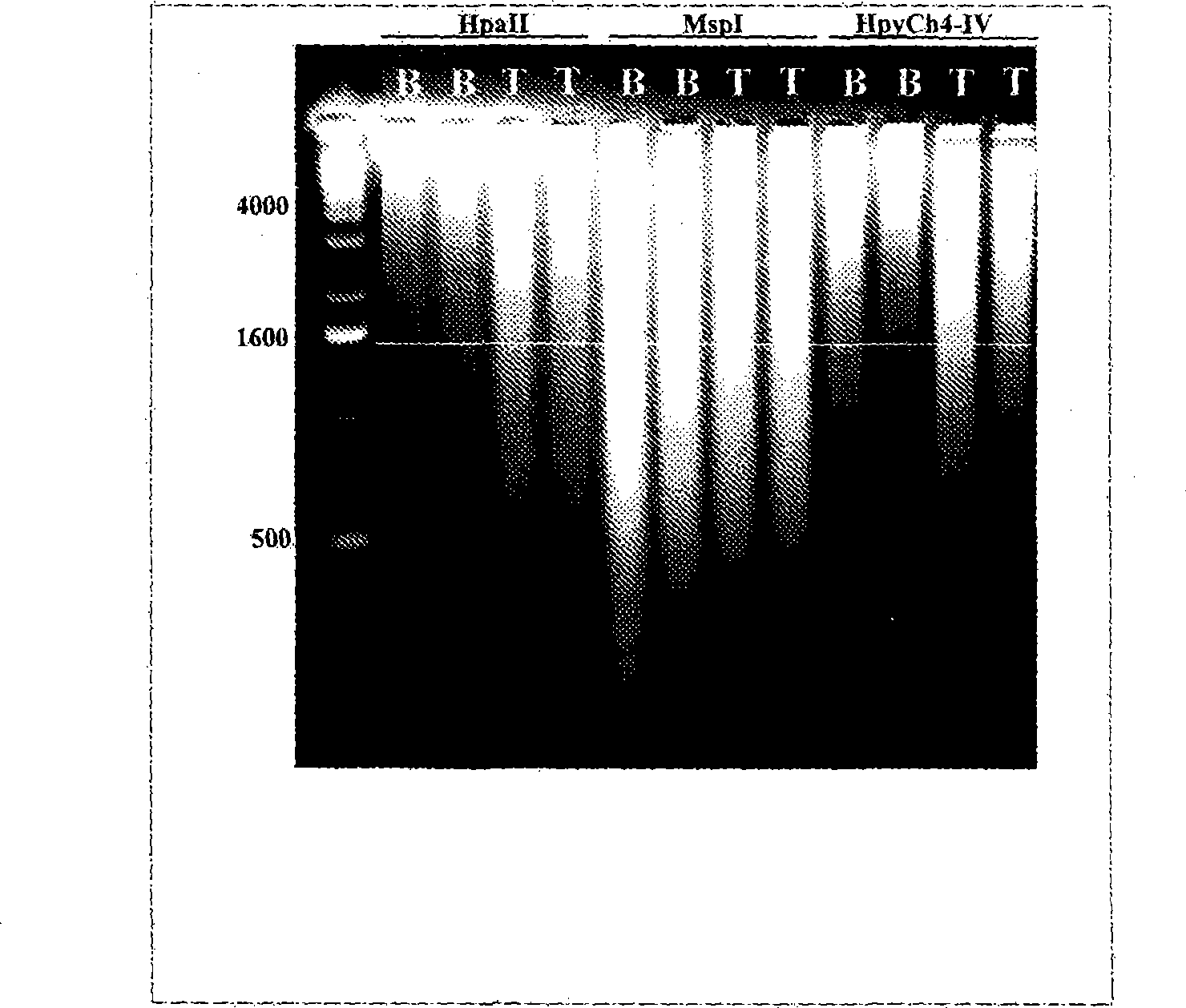
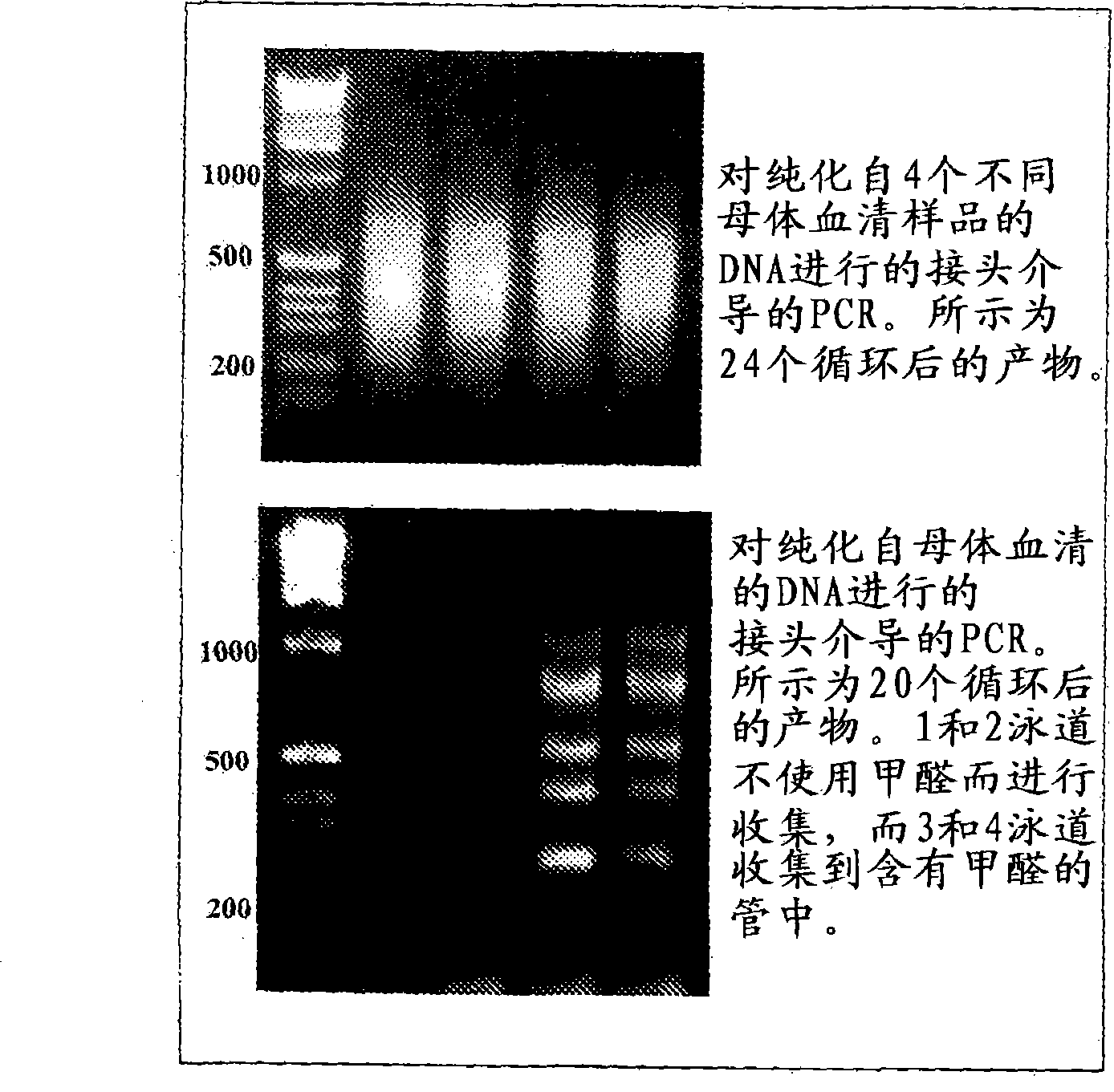
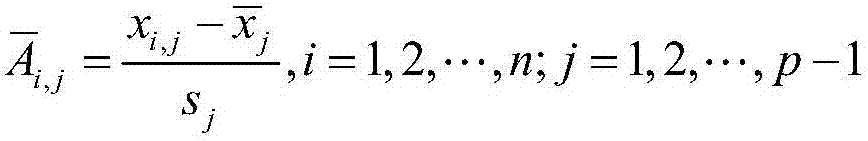Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
84 results about "Differential Methylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
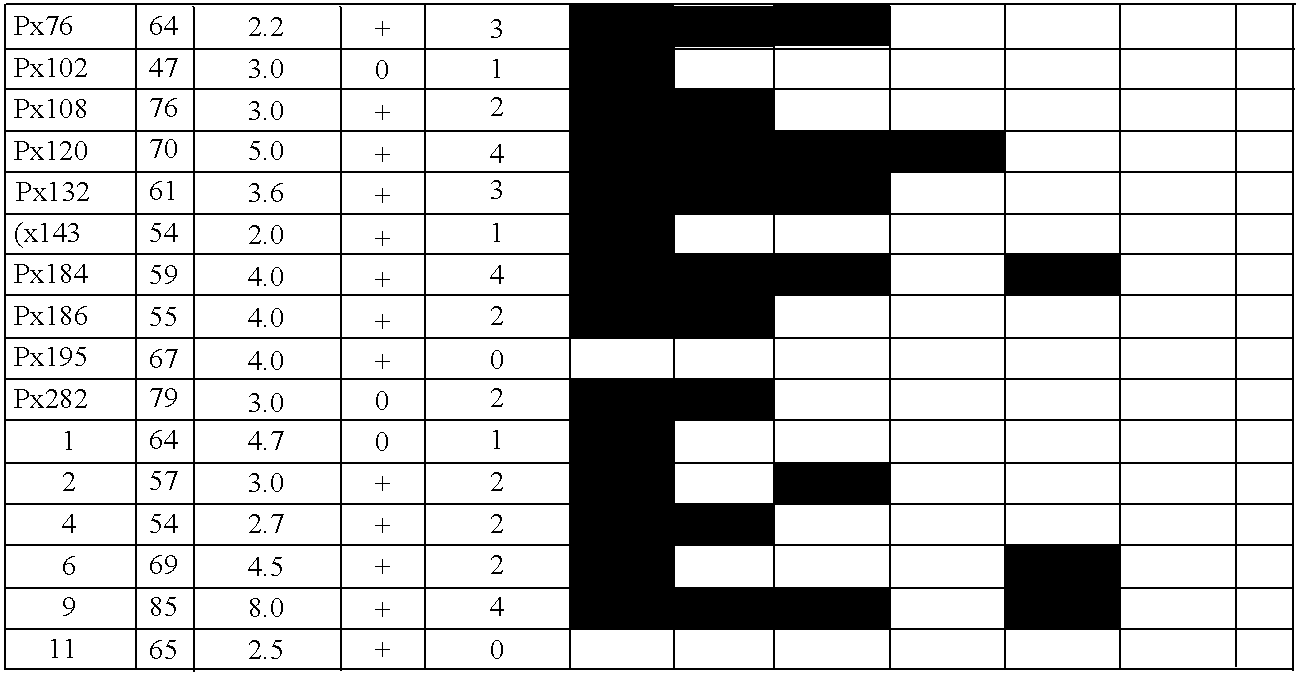
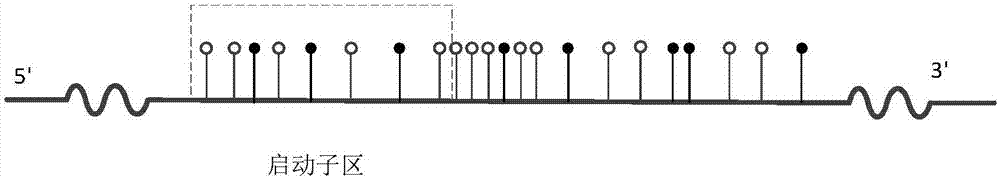
Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) are genomic regions with different DNA methylation status across different biological samples and regarded as possible functional regions involved in gene transcriptional regulation.
Marker for prenatal diagnosis and monitoring
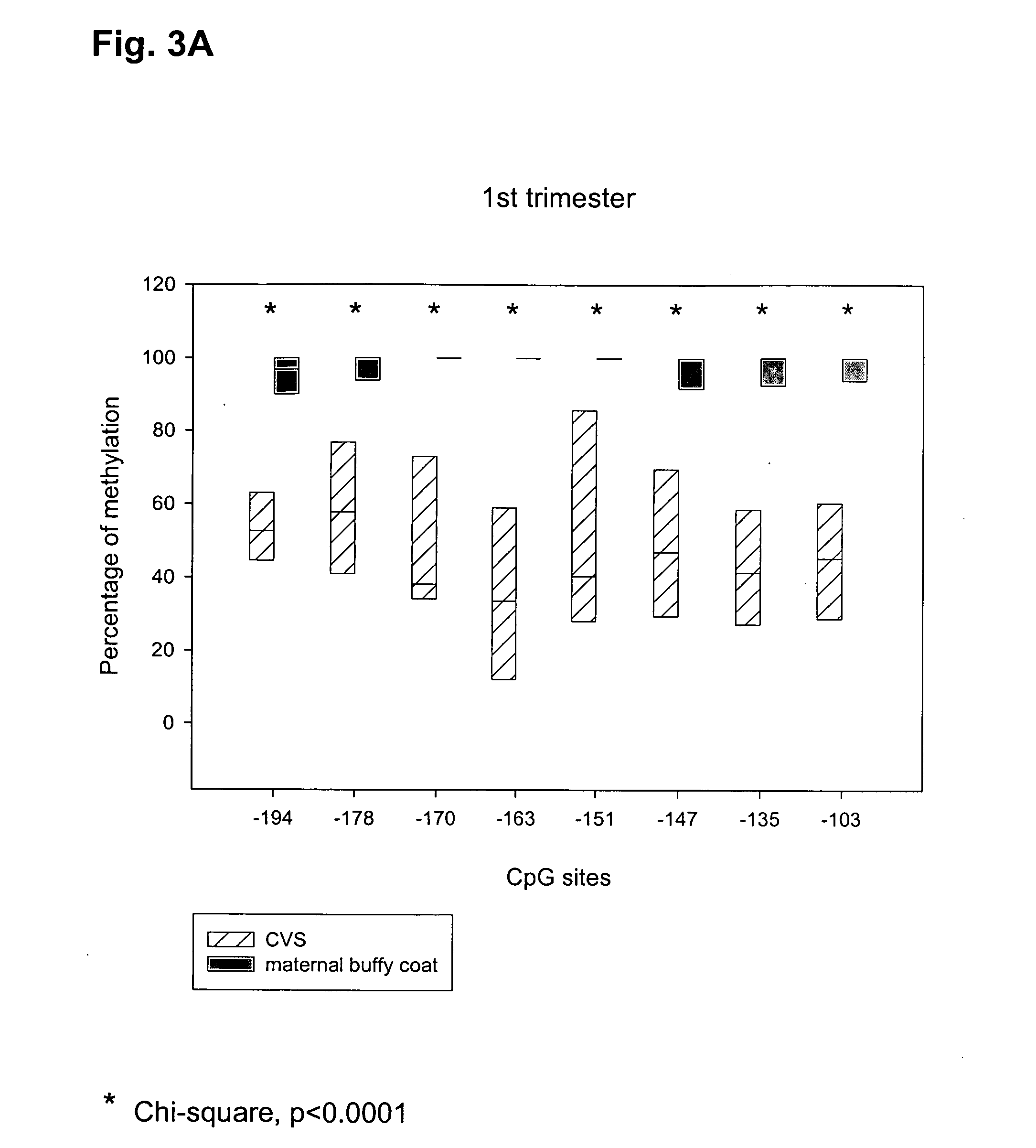
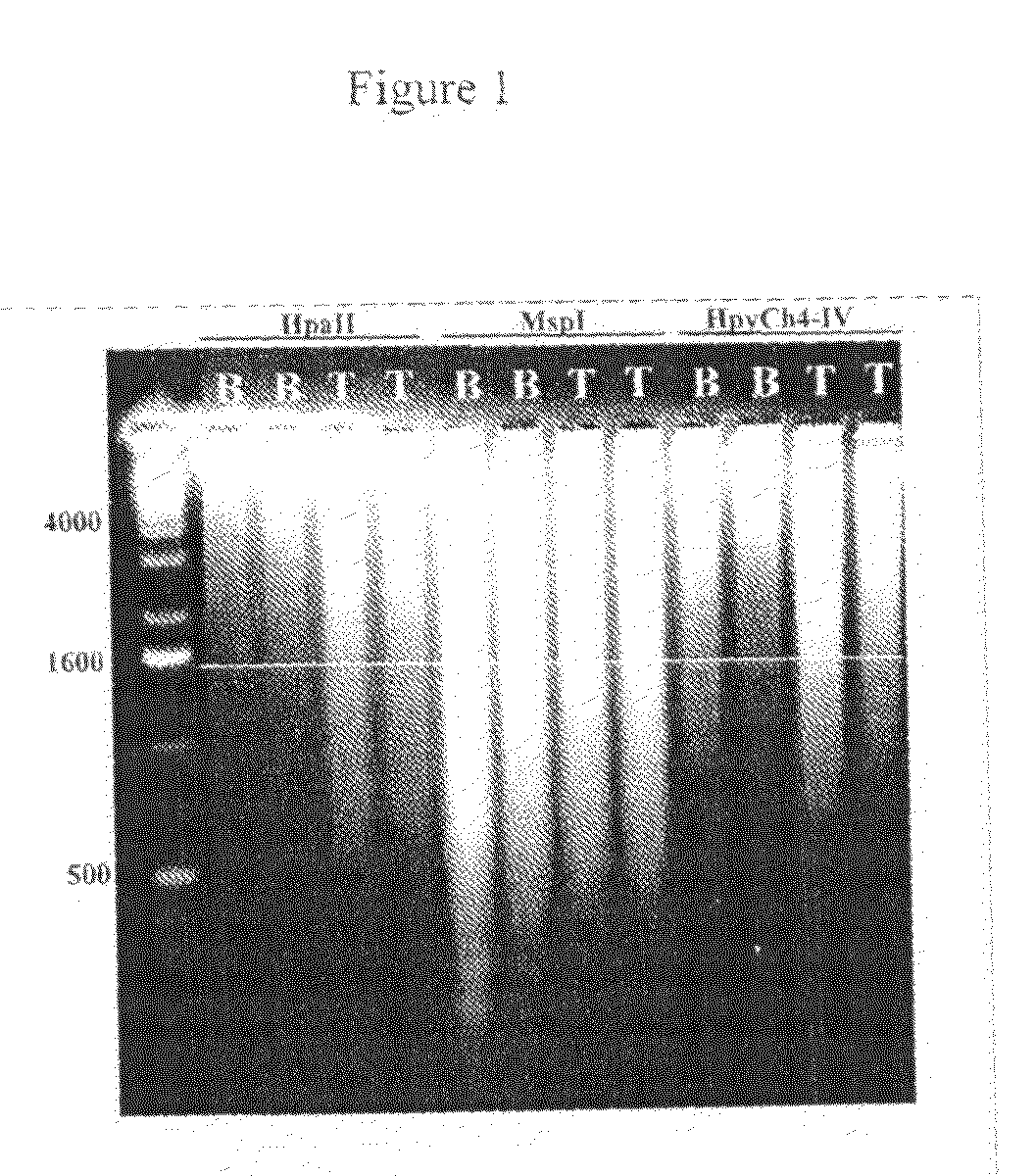
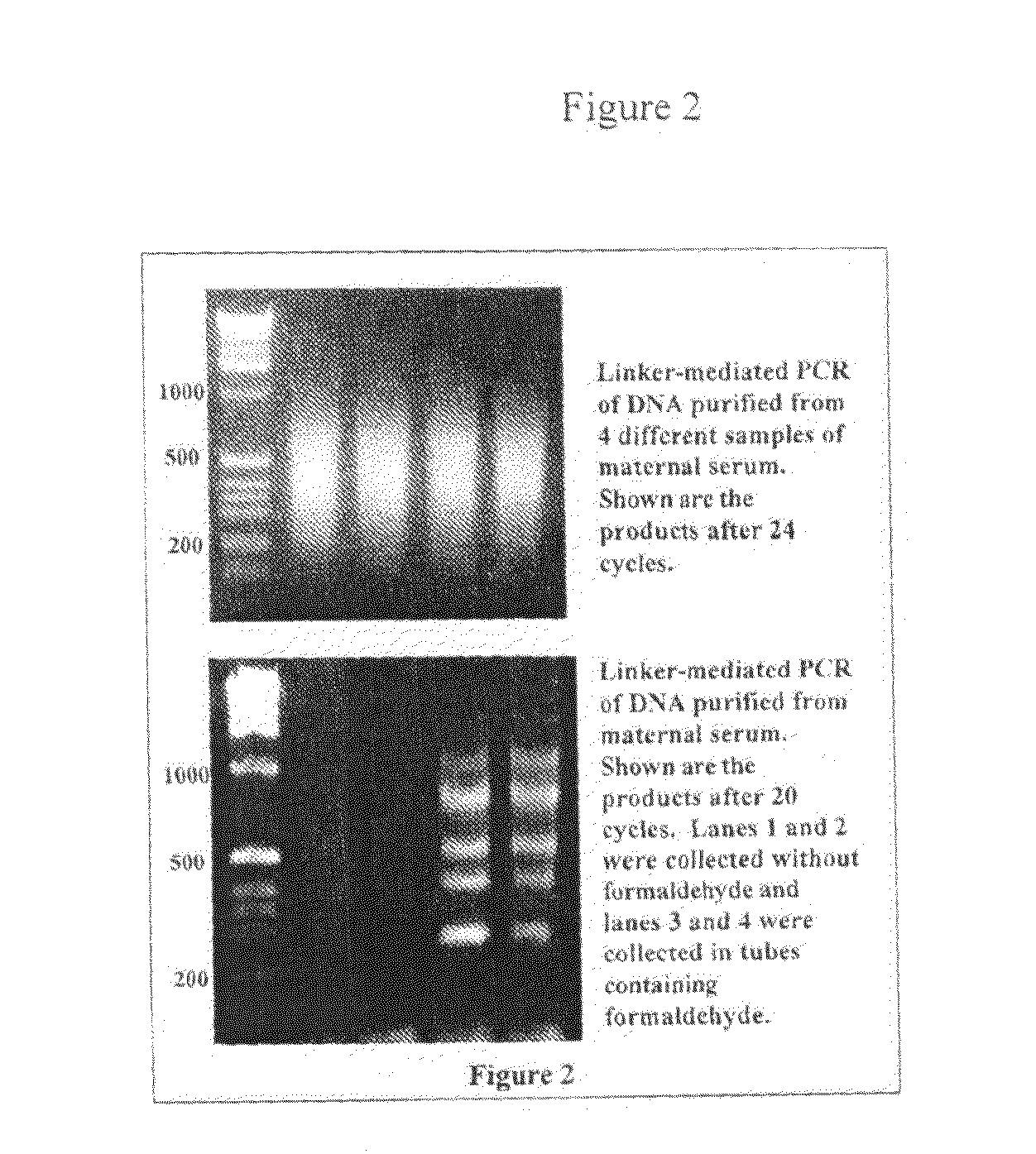
The present invention relates to new methods for diagnosing a pregnancy-associated disorder by analyzing fetal DNA present in the mother's blood. More specifically, this invention relies on the discovery that the maspin gene is differentially methylated in fetal DNA and in maternal DNA and provides these new diagnostic methods, which distinguish fetal DNA from maternal DNA and detect prenatal disorders based on abnormalities in fetal DNA level and methylation status.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
High-throughput methods for detecting DNA methylation
InactiveUS6605432B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNA methylationHybridization probe
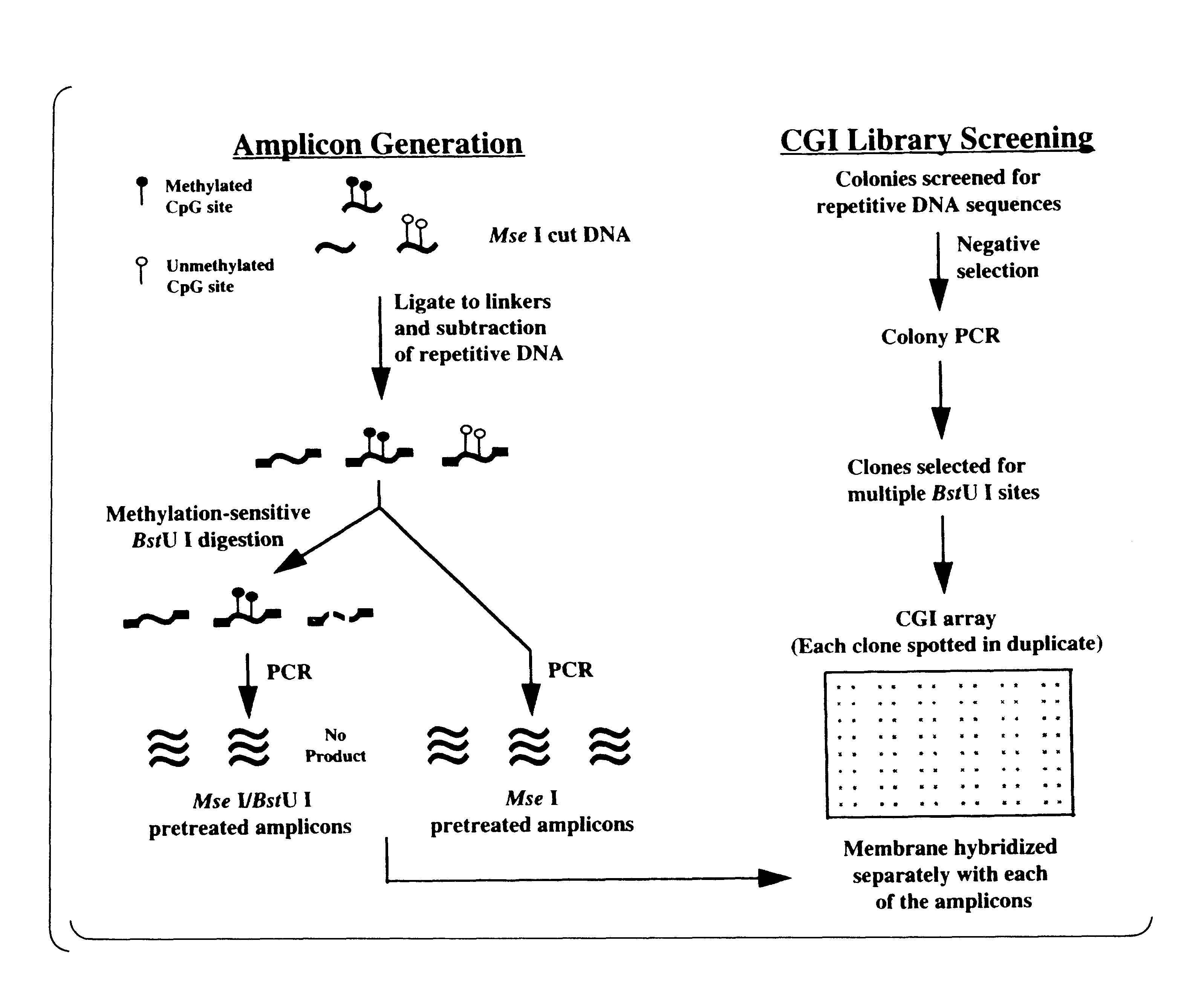
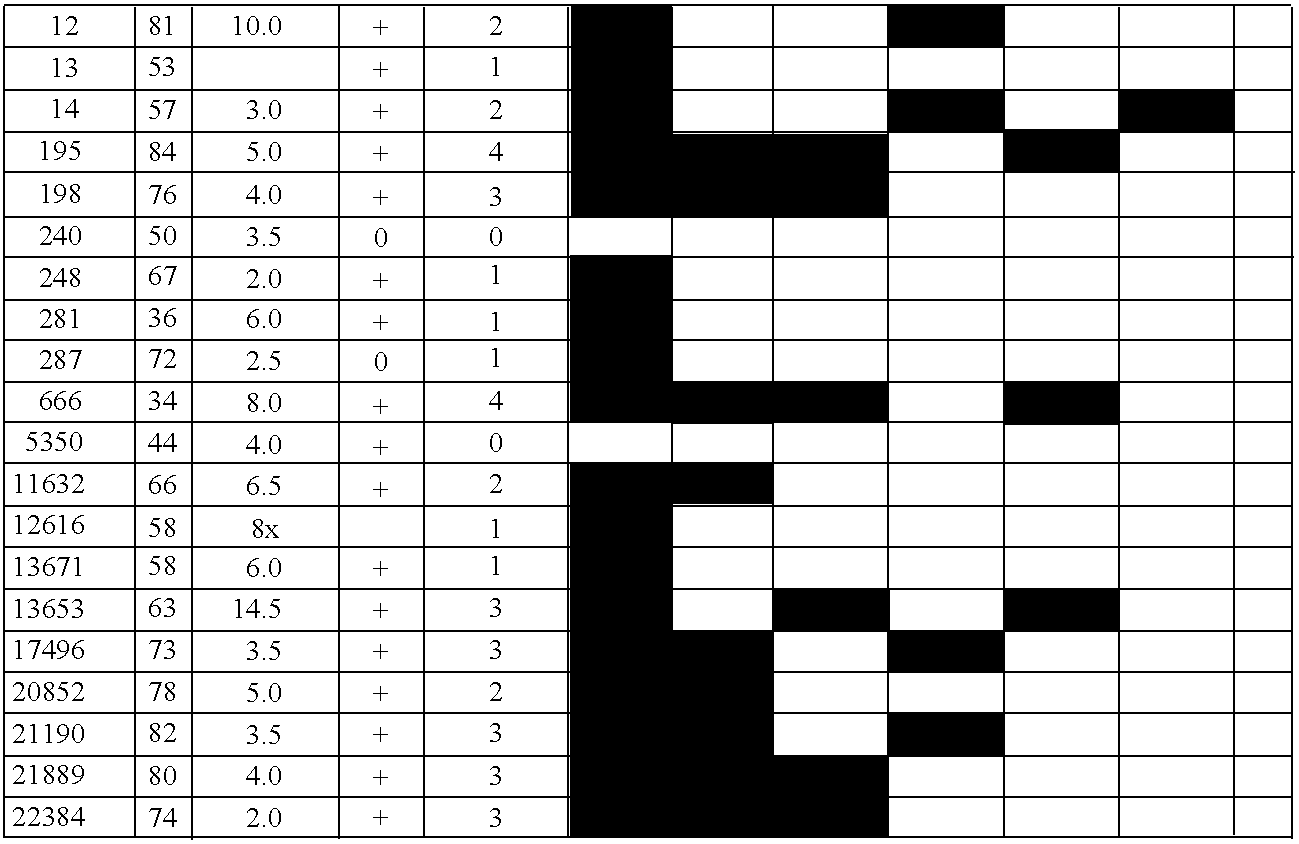
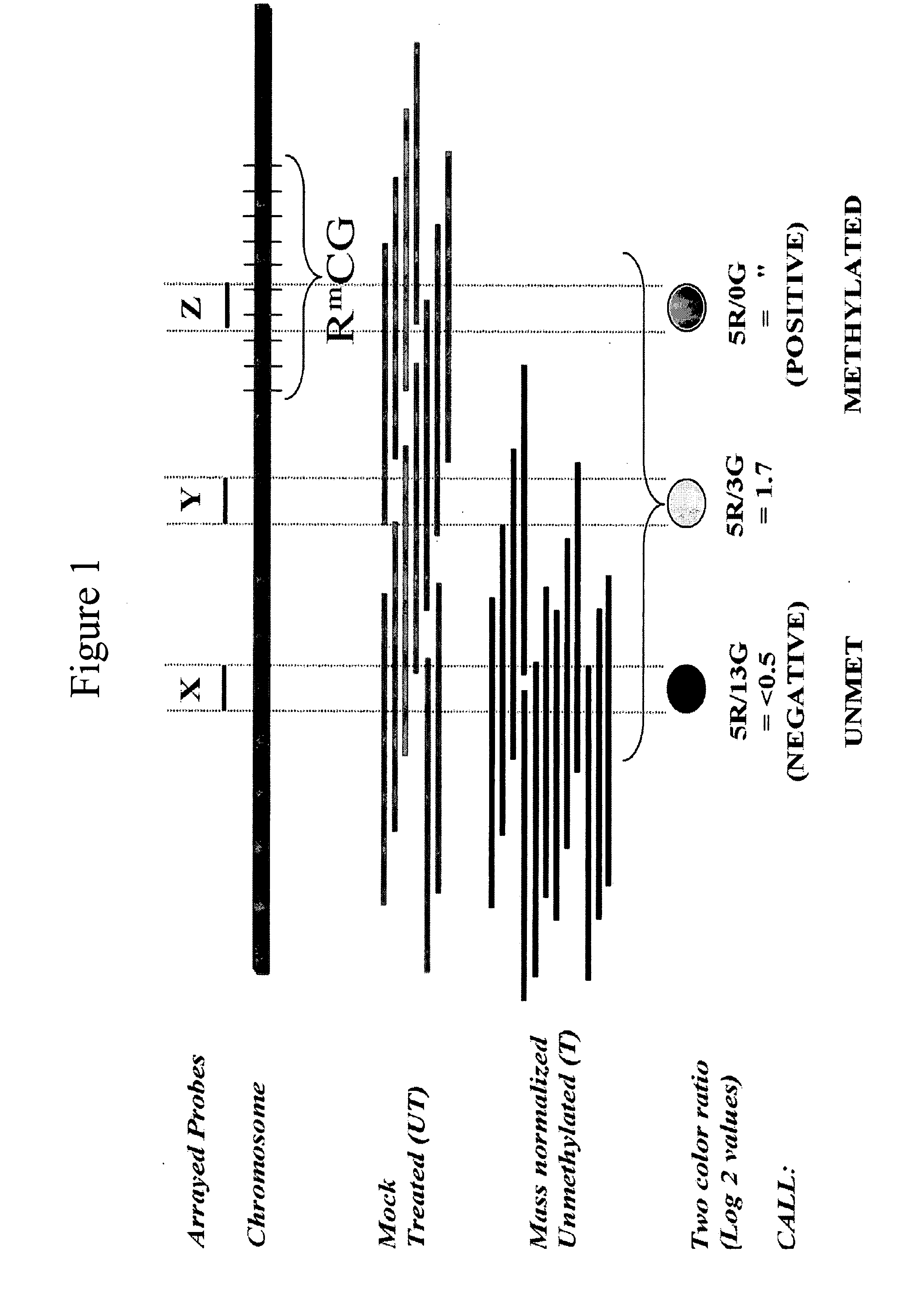
The present invention provides a method of hybridization, differential methylation hybridization (DMH) for high throughput methylation analysis of multiple CpG island loci. DMH utilizes nucleic acid probes prepared from a cell sample to screen numerous CpG dinucleotide rich fragments affixed on a screening array. Positive hybridization signals indicate the presence of methylated sites. Methods of preparing the hybridization probes and screening array are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
High-throughput methods for detecting DNA methylation
InactiveUS20030129602A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNA methylationHybridization probe
The present invention provides a method of hybridization, differential methylation hybridization (DMH) for high throughput methylation analysis of multiple CpG island loci. DMH utilizes nucleic acid probes prepared from a cell sample to screen numerous CpG dinucleotide rich fragments affixed on a screening array. Positive hybridization signals indicate the presence of methylated sites. Methods of preparing the hybridization probes and screening array are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Methods and compositions for detecting colon cancers
ActiveUS7485420B2Significant positive effectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotide sequencingDifferential Methylation
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Methods and compositions for detecting colon cancers
InactiveUS7432050B2Significant positive effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHLTFNucleotide sequencing
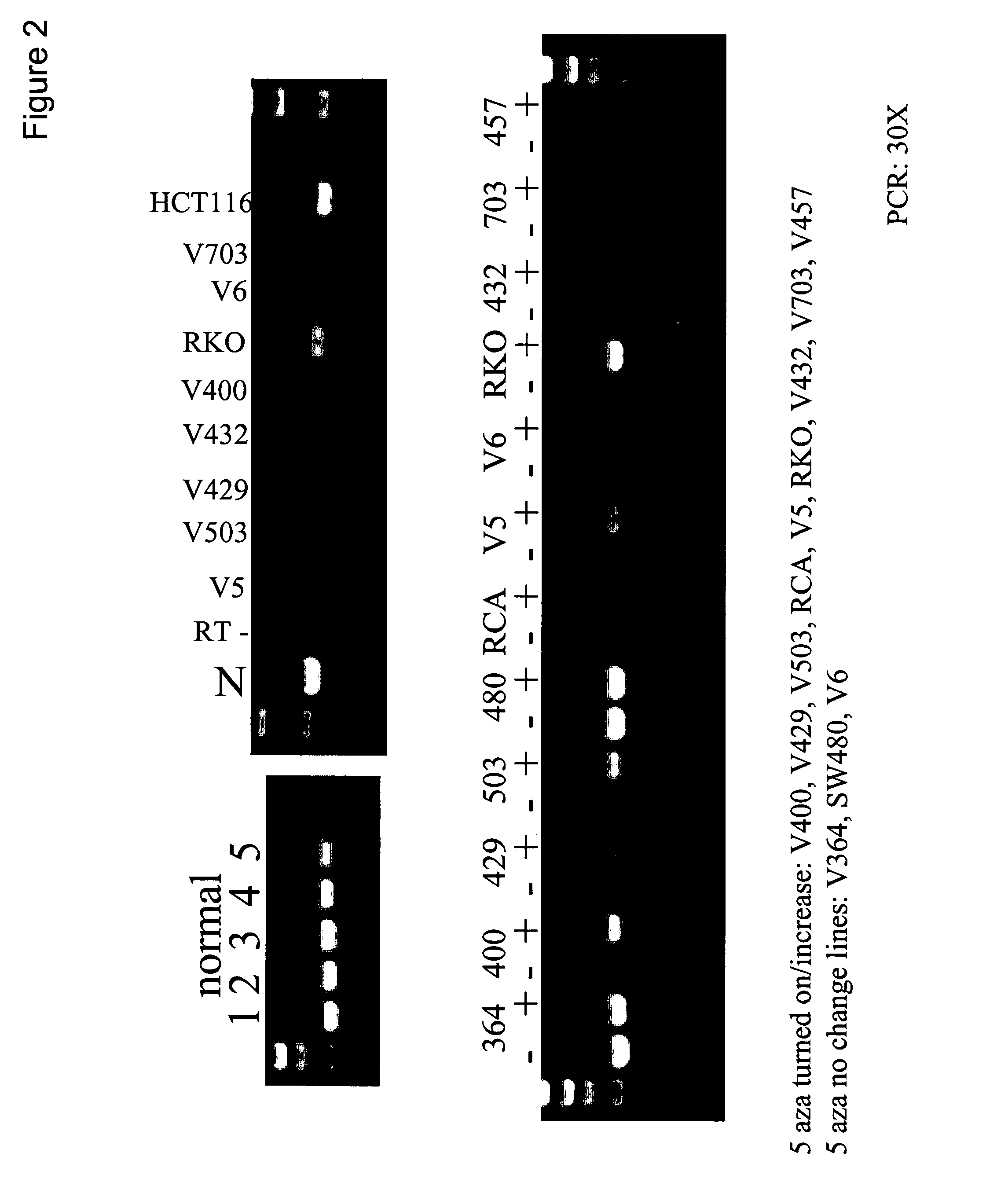
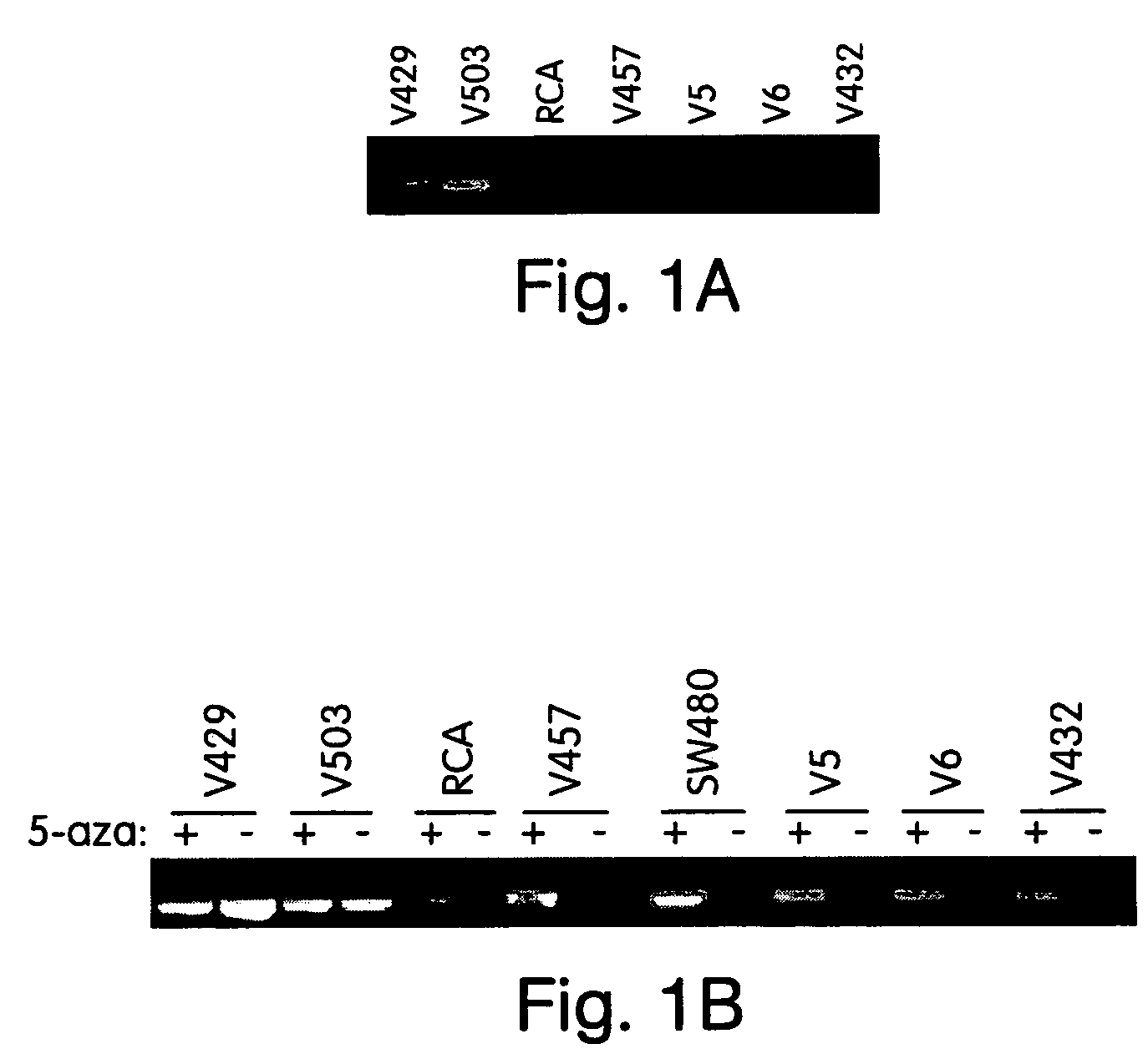
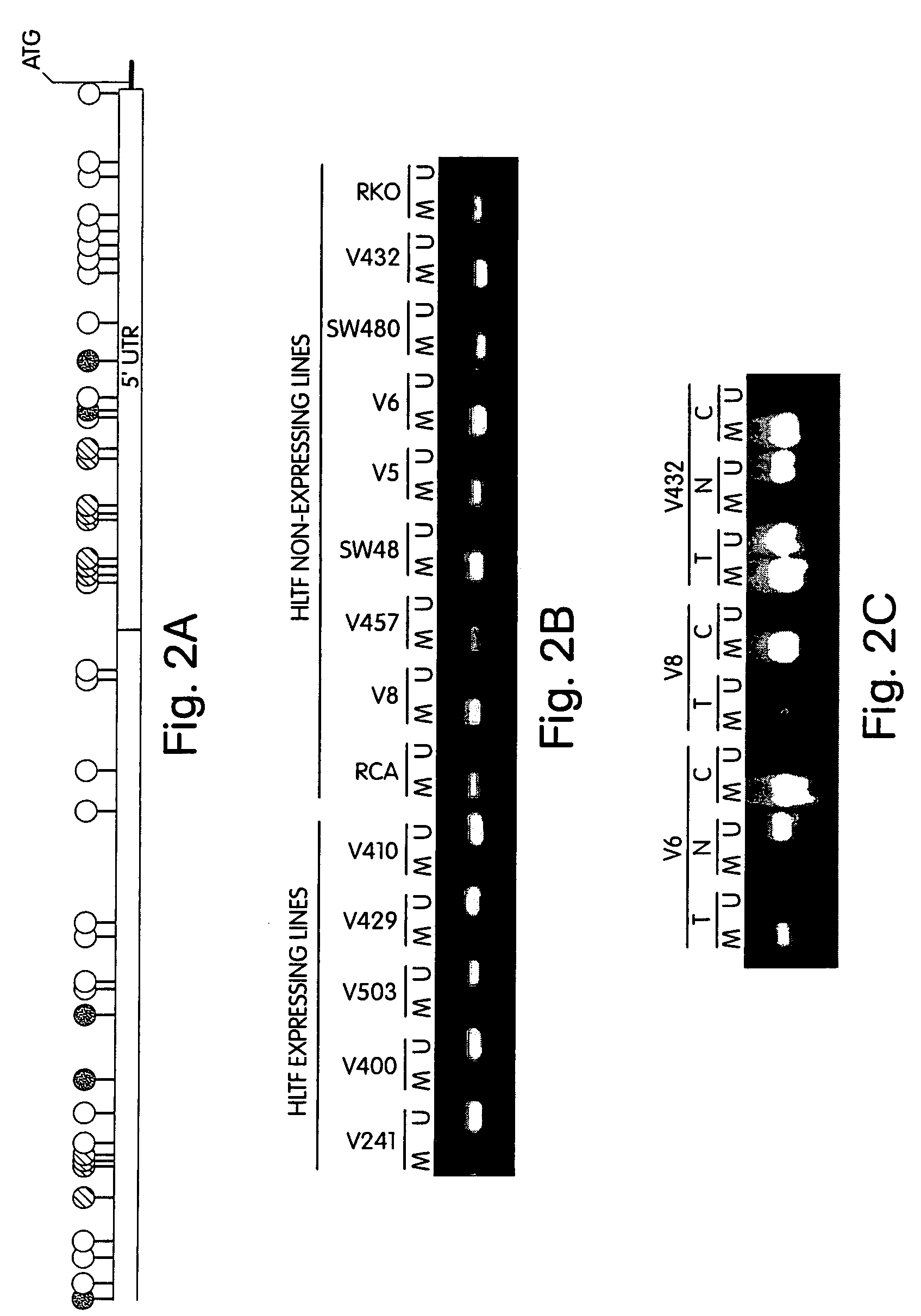
This application describes methods and compositions for detecting and treating HLTF-associated neoplasia. Differential methylation of the HLTF nucleotide sequences has been observed in HLTF-associated neoplasia such as colon neoplasia.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Marker for prenatal diagnosis and monitoring
The present invention relates to new methods for diagnosing a pregnancy-associated disorder by analyzing fetal DNA present in the mother's blood. More specifically, this invention relies on the discovery that the maspin gene is differentially methylated in fetal DNA and in maternal DNA and provides these new diagnostic methods, which distinguish fetal DNA from maternal DNA and detect prenatal disorders based on abnormalities in fetal DNA level and methylation status.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
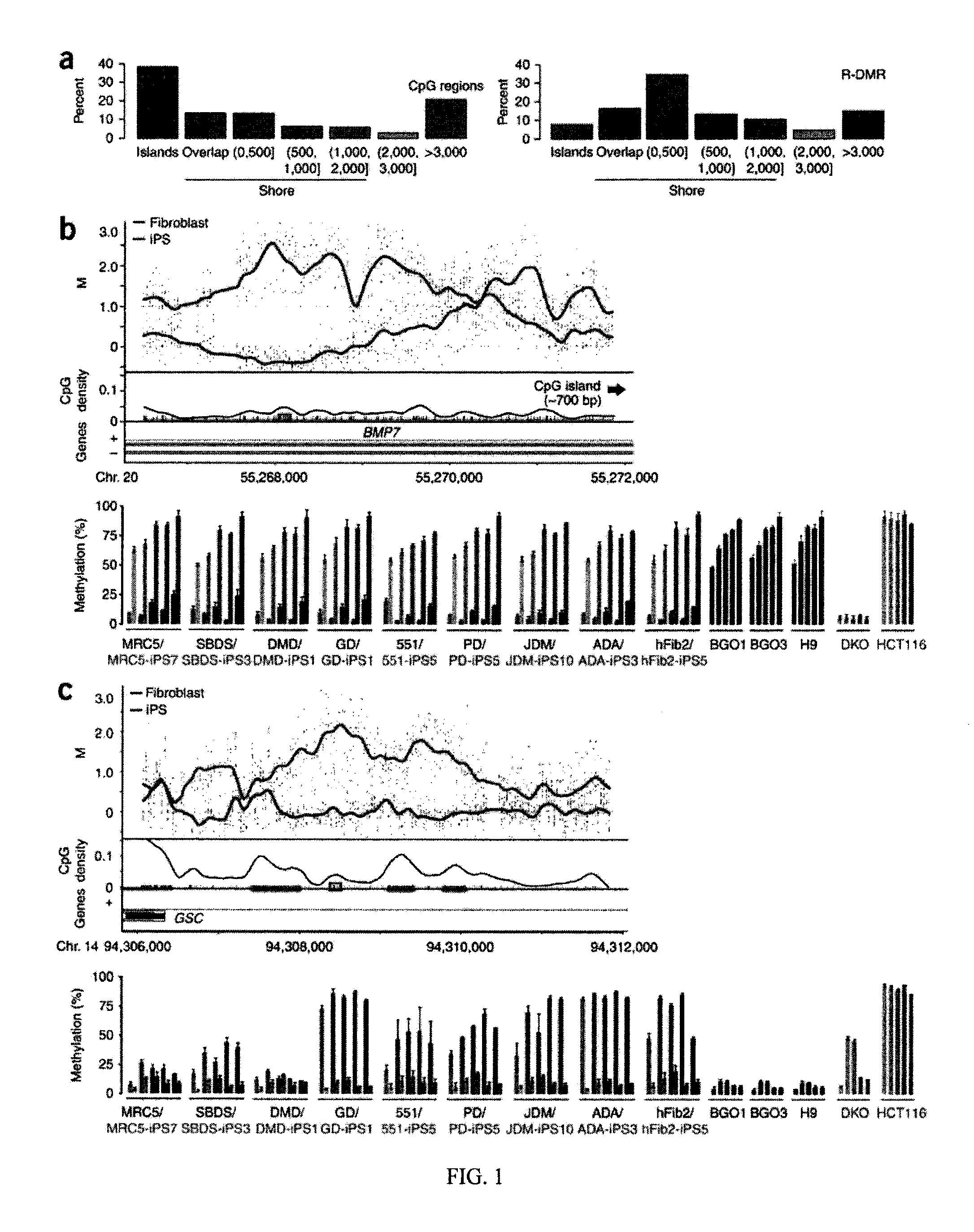
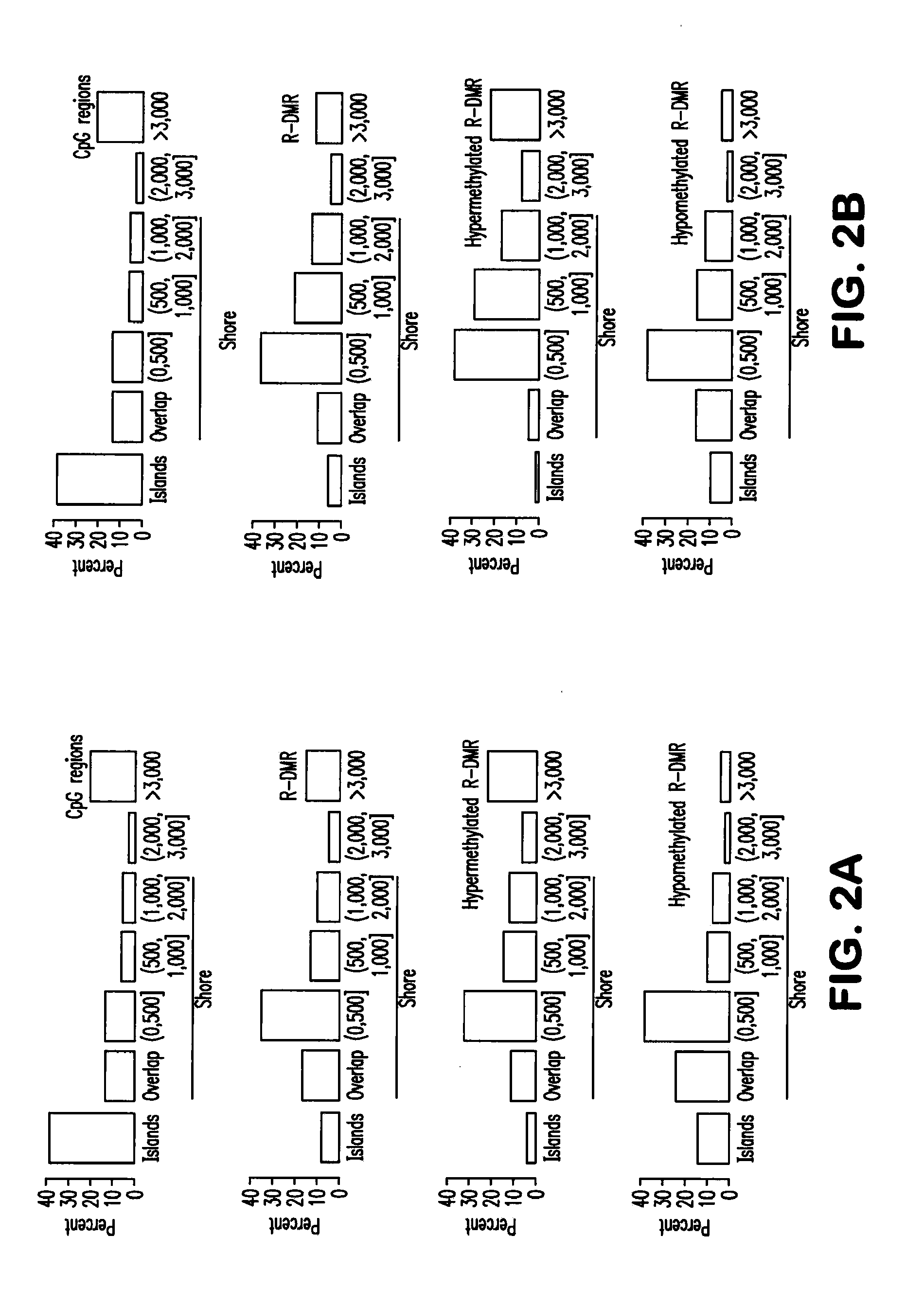
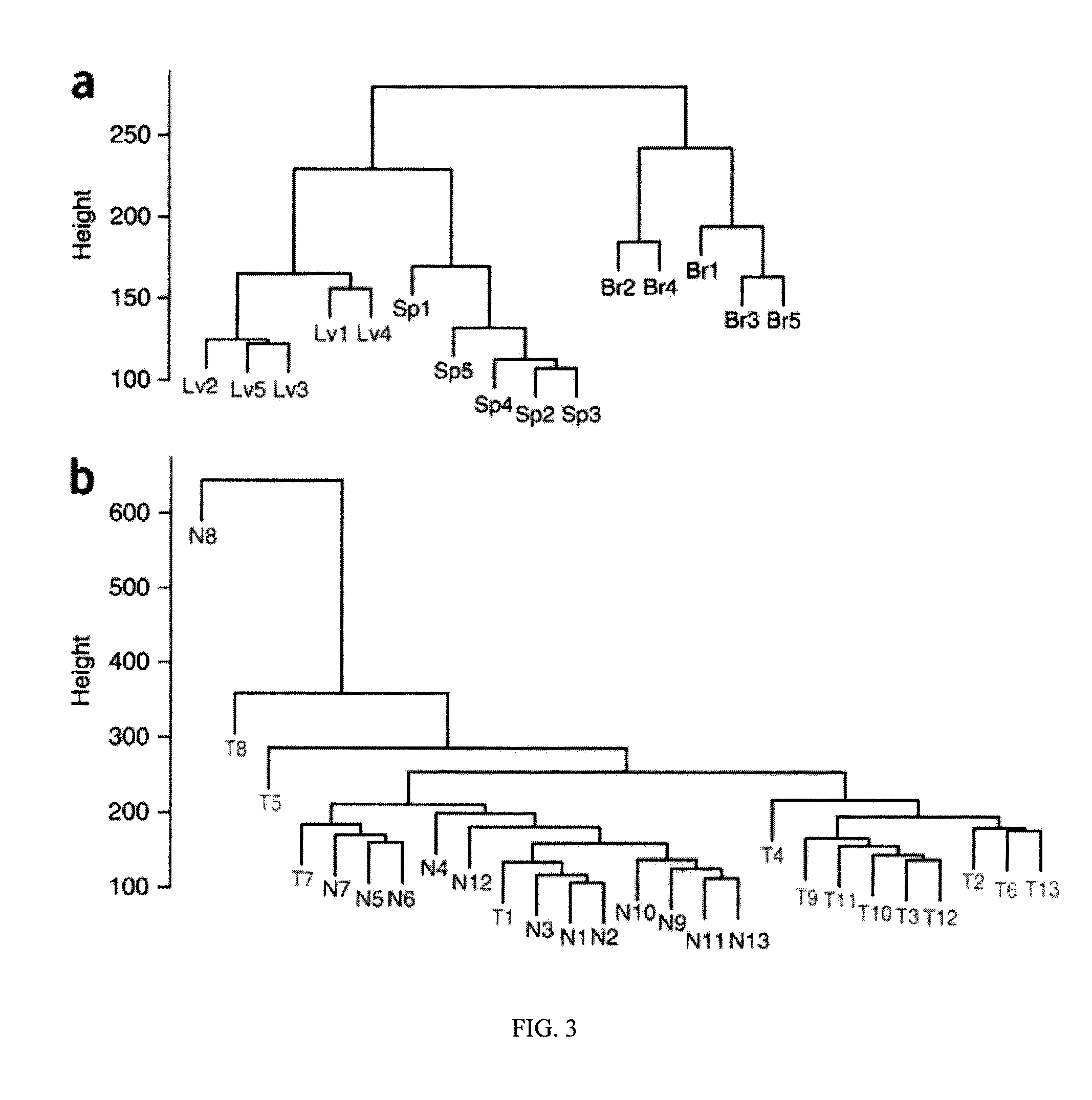
Differentially methylated regions of reprogrammed induced pluripotent stem cells, method and compositions thereof
InactiveUS20120164110A1Differentiation potentialReducing epigenetic memoryBiocideNucleotide librariesDifferentially methylated regionsDifferential Methylation
Provided herein are differentially methylated regions (DMRs) of reprogrammed iPS cells (R-DMRs) and methods of use thereof. The invention provides methods for detecting and analyzing alterations in the methylation status of DMRs in iPS cells, somatic cells and embryonic stem (ES) cells as well as methods for reprogramming somatic cells to generate an iPS cell.
Owner:FEINBERG ANDREW P +1
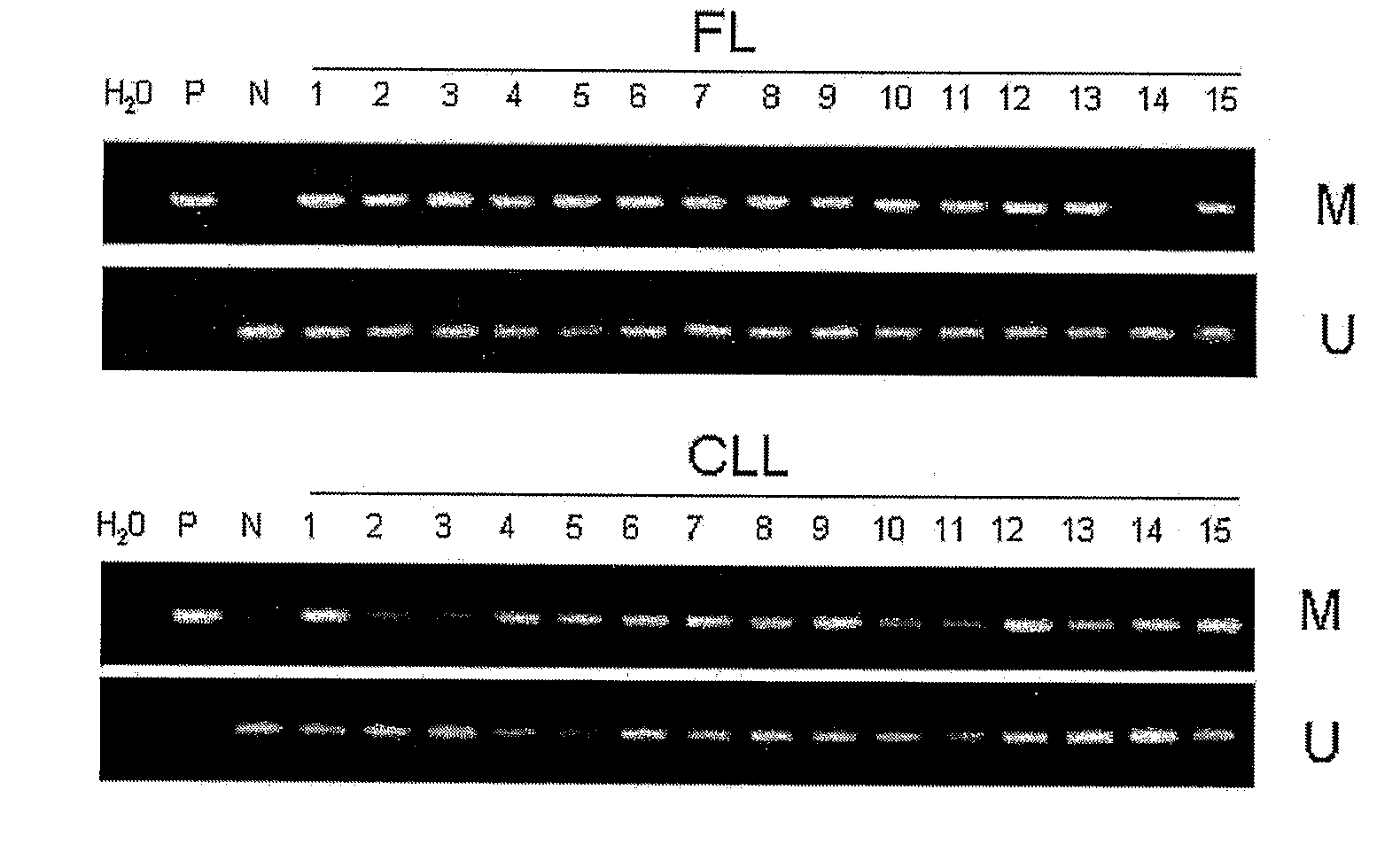
DNA methylation biomarkers in lymphoid and hematopoietic malignancies
InactiveUS20090264306A1Guaranteed maximum utilizationImprove the detection rateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA methylationLymphocytic cell
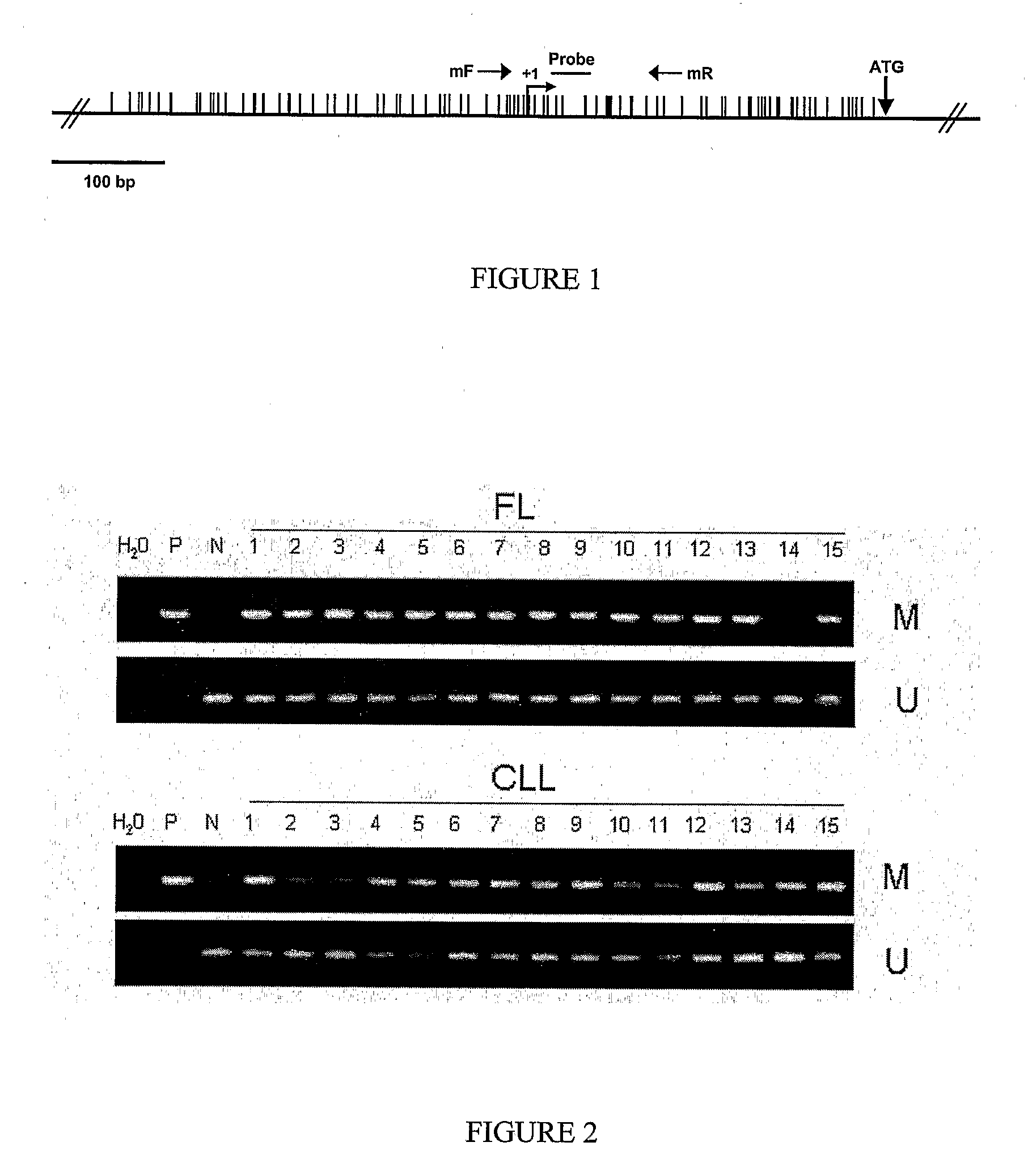
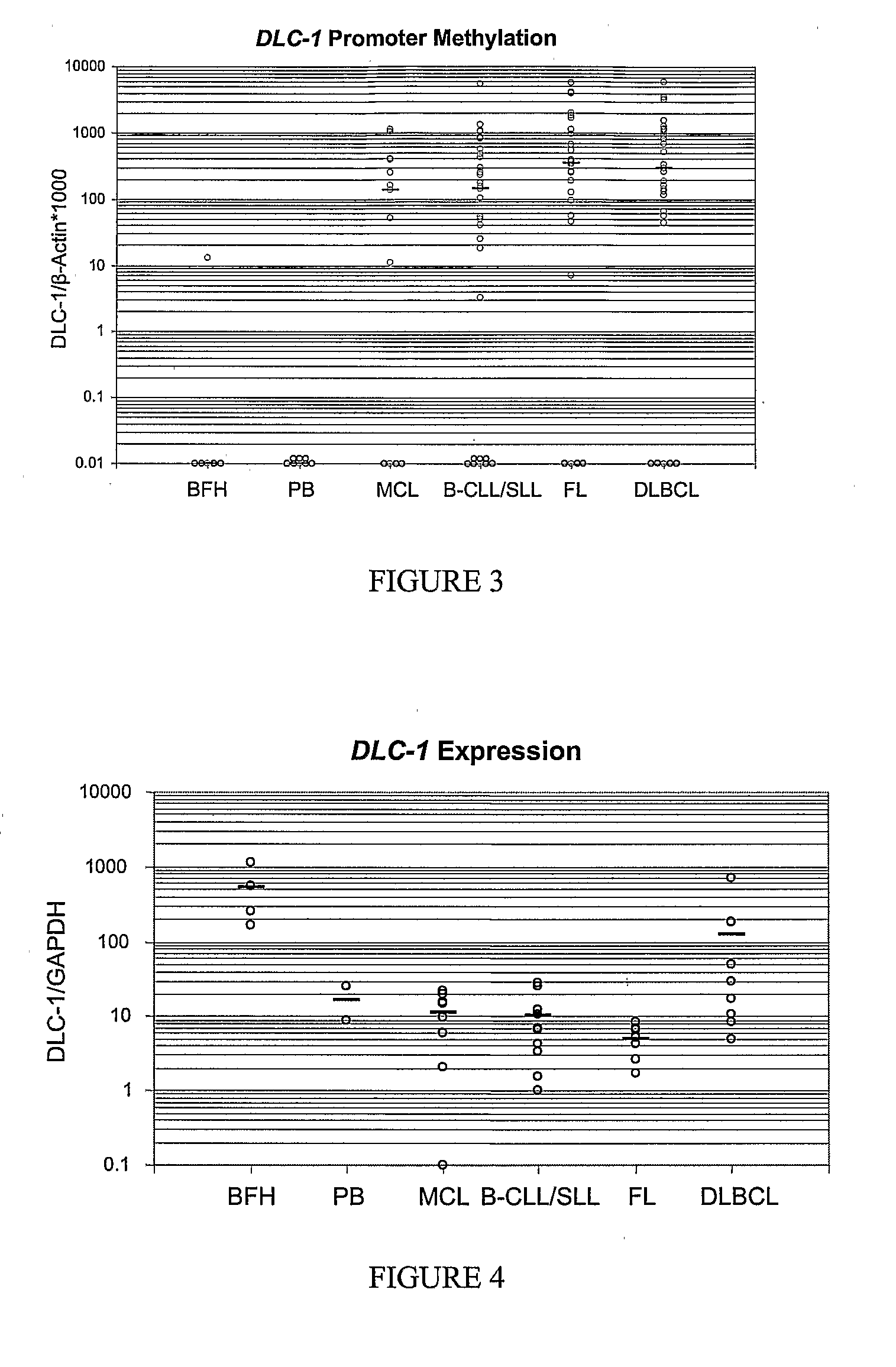
Differential Methylation Hybridization (DMH) was used to identify novel methylation markers and methylation profiles for hematopoieetic malignancies, leukemia, lymphomas, etc. (e.g., non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (NHL), small B-cell lymphomas (SBCL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma (FL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia / small lymphocytic lymphoma (B-CLL / SLL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), multiple myeloma (MM), acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), etc.). Particular aspects provide novel biomarkers for NHL and subtypes thereof (e.g., MCL, B-CLL / SLL, FL, DLBCL, etc.), AML, ALL and MM, and further provide non-invasive tests (e.g. blood tests) for lymphomas and leukemias. Additional aspects provide markers for diagnosis, prognosis, monitoring responses to therapies, relapse, etc., and further provide targets and methods for therapeutic demethylating treatments. Further aspects provide cancer staging markers, and expression assays and approaches comprising idealized methylation and / or patterns” (IMP and / or IEP) and fusion of gene rankings.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Methods and compositions for diagnosing conditions associated with specific DNA methylation patterns
InactiveUS20050026183A1Improve the level ofMany applicationsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationGenomic DNA
The present invention provides a method for identification of differentially methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences associated with cancer in an individual by obtaining a biological sample comprising genomic DNA from the individual measuring the level or pattern of methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences for two or more of the genomic targets in the sample, and comparing the level of methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences in the sample to a reference level of methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences, wherein a difference in the level or pattern of methylation of the genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences in the sample compared to the reference level identifies differentially methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences associated with cancer. As disclosed herein, the methods of the invention have numerous diagnostic and prognostic applications. The methods of the invention can be combined with a miniaturized array platform that allows for a high level of assay multiplexing and scalable automation for sample handling and data processing. Also provided by the invention are genomic targets and corresponding nucleic acid probes that are useful in the methods of the invention as they enable detection of differentially methylated genomic CpG dinucleotide sequences associated with cancer, for example, adenocarcenomas and sqamous cell carcinomas of the lung.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods and compositions for detecting gastrointestinal and other cancers
ActiveUS8415100B2Significant positive effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLower Gastrointestinal TractNucleotide
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Specific amplification of tumor specific DNA sequences
InactiveUS20100240549A1Useful in detectionNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer detectionTumor specific
The present invention provides methods for cancer detection and diagnosis. The present invention provides a method of selectively amplifying hypomethylated tumor DNA sequences derived from a subject for detection of cancer. This method utilizes differential methylation to allow for the selective amplification of tumor specific sequences from DNA mixtures that contain a high proportion of normal host DNA. The invention also provides methods of using the amplified tumor DNA sequences for evaluation of methylation.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods and compositions for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidies
ActiveUS20120282613A1Accurate predictionDiagnosing fetal aneuploidiesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMethylated DNA immunoprecipitationAdult female
The invention provides methods and compositions for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidies. A large panel of differentially methylated regions (DMRs) have been identified. Certain of these DMRs are hypomethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypermethylated in fetal DNA, whereas others are hypermethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypomethylated in fetal DNA. Moreover, DMRs that are hypomethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypermethylated in fetal DNA have been shown to accurately predict a fetal aneuploidy in fetal DNA present in a maternal blood sample during pregnancy. In the methods of the invention, hypermethylated DNA is physically separated from hypomethylated DNA, preferably by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation.
Owner:NIPD GENETICS PUBLIC CO LTD
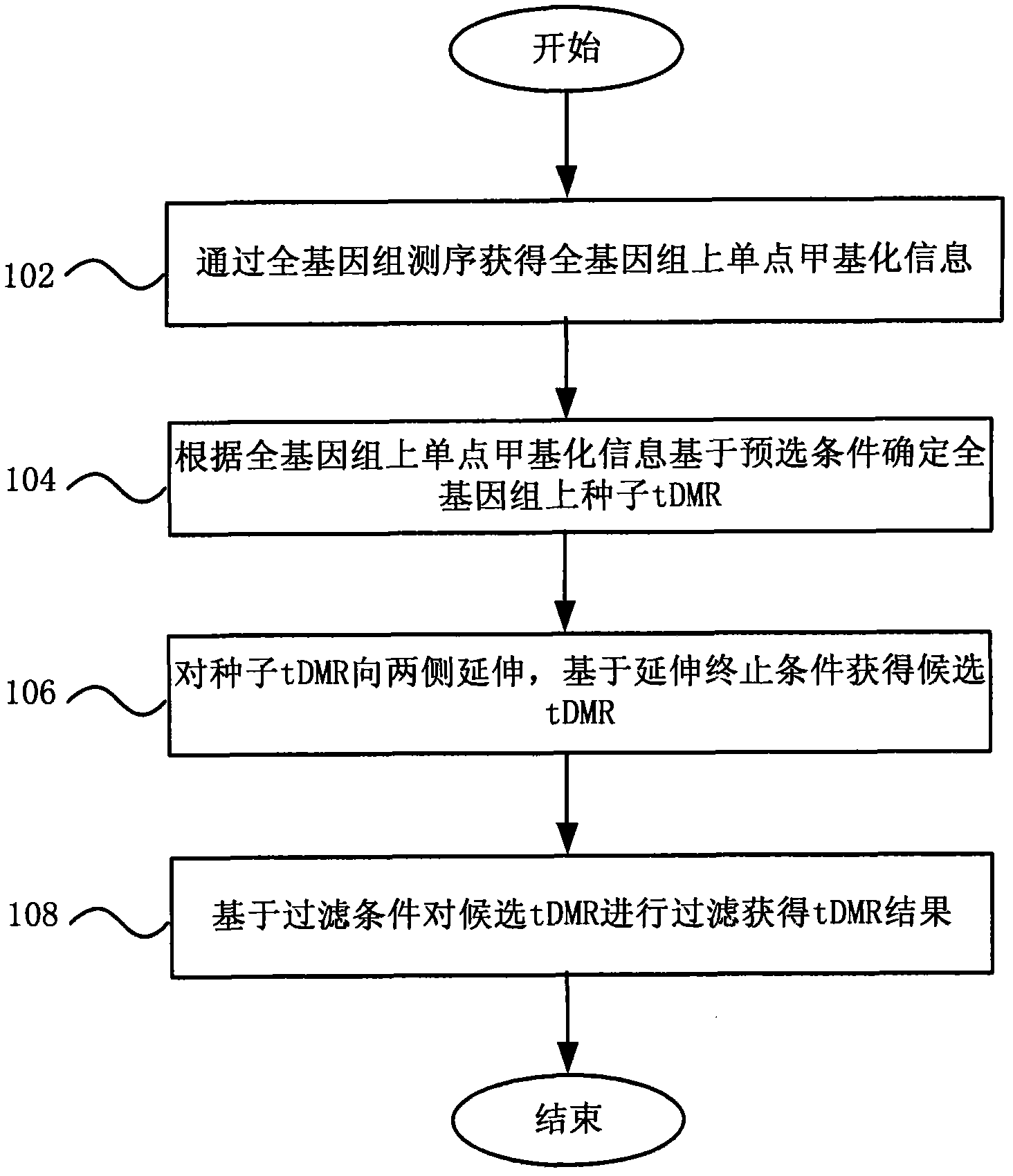
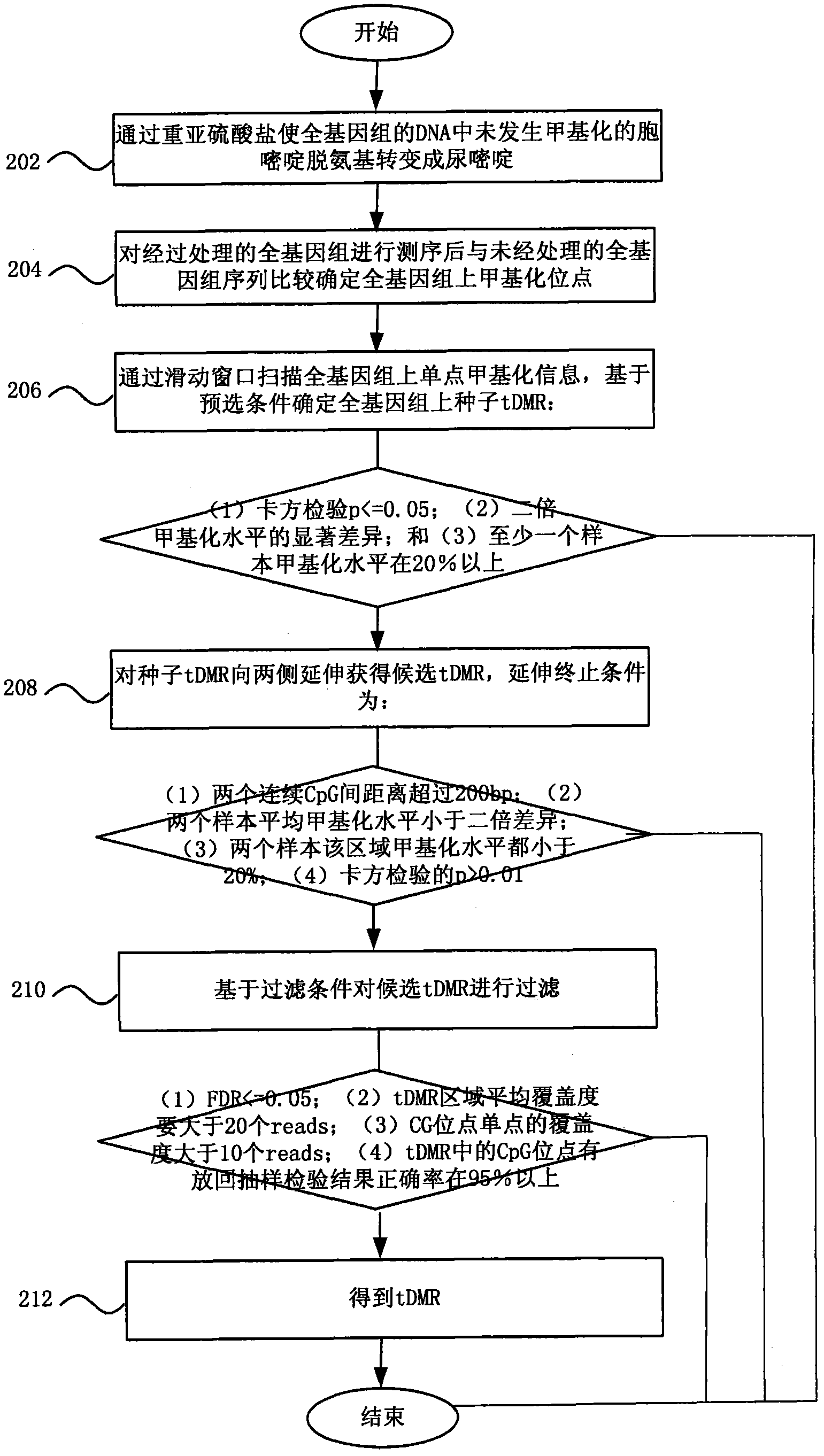
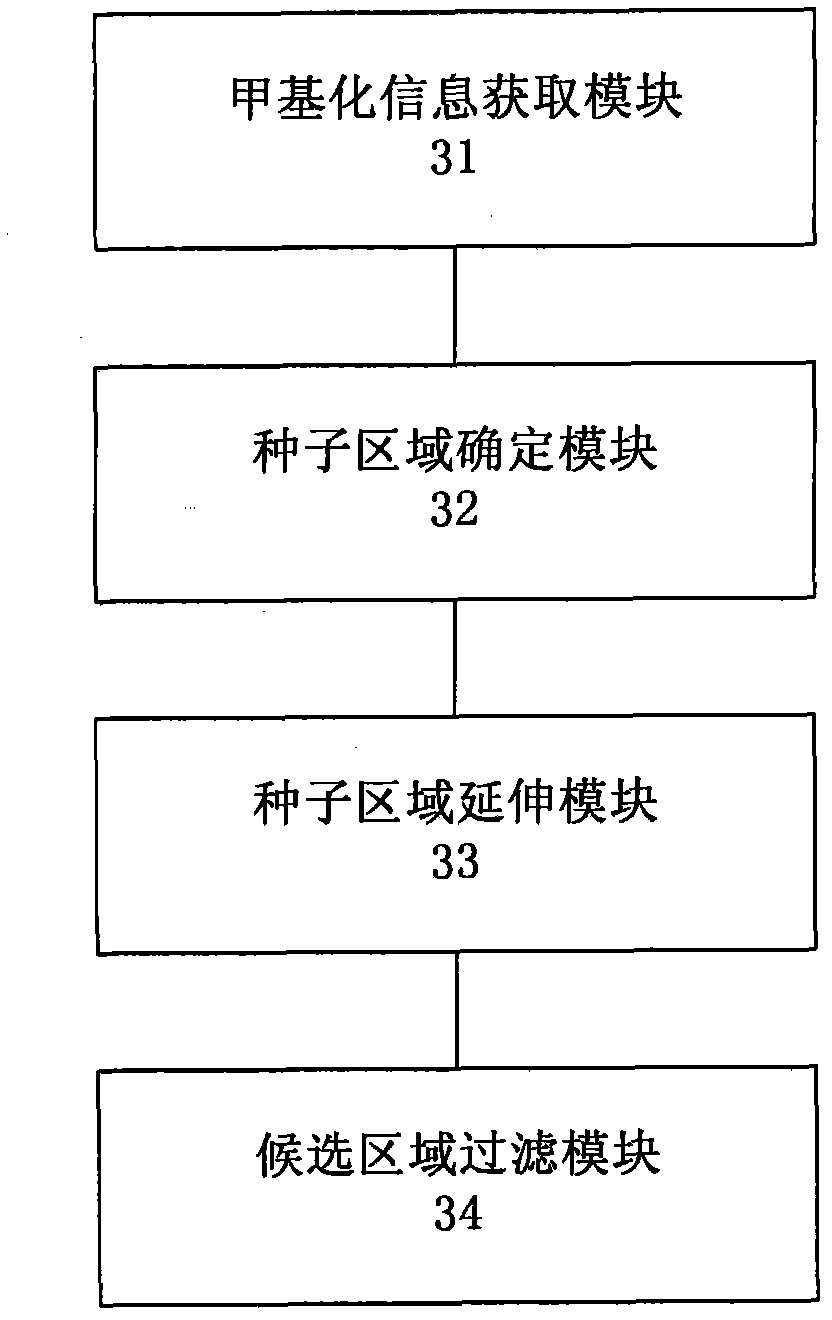
Method and system for detecting tissue-specific differentially methylated region (tDMR)
The invention discloses a method and a system for detecting a tissue-specific differentially methylated region (tDMR). The method comprises the following steps: obtaining single-point methylation information on a complete genome by genome-wide sequencing; determining a seed tDMR on the complete genome under a pre-selection condition according to the single-point methylation information on the complete genome; extending the seed tDMR along two sides, and obtaining candidate tDMRs based on an extension terminal condition; and filtering the candidate tDMRs based on a filtering condition to obtain the tDMR result. By means of the method and the system provided by the invention, the methylation state of each site on the complete genome can be defined so as to determine the tDMR within the range of the complete genome, thus greatly improving the detection efficiency and lowering the cost. Subsequent validation shows that the found tDMR has high accuracy rate up to 85%; and validation in a plurality of species (not only limited to mammals) shows that the method has higher accuracy and higher sensitivity compared with other methods such as vardhman Rakyan and the like.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Method for mining methylation pattern by whole genome data
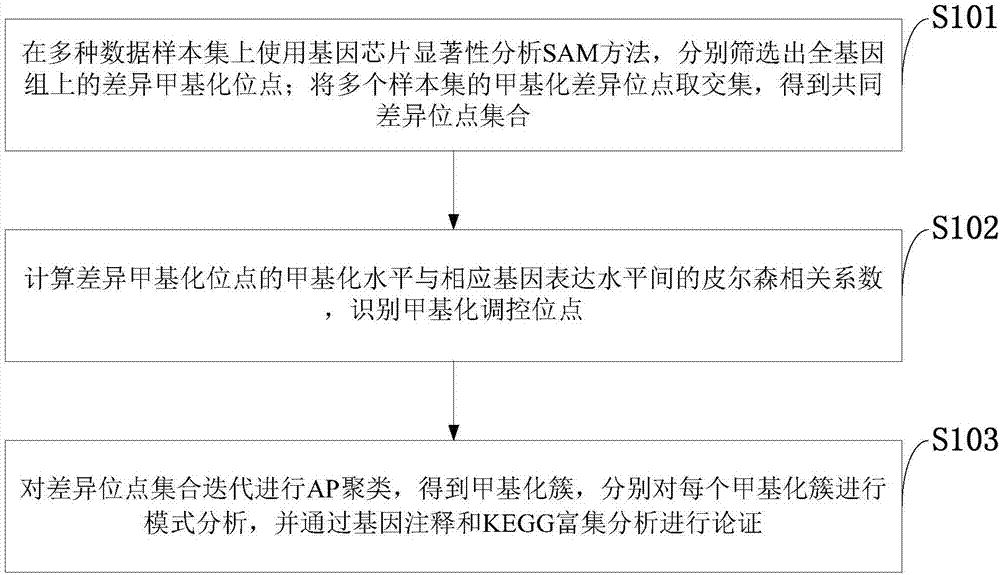
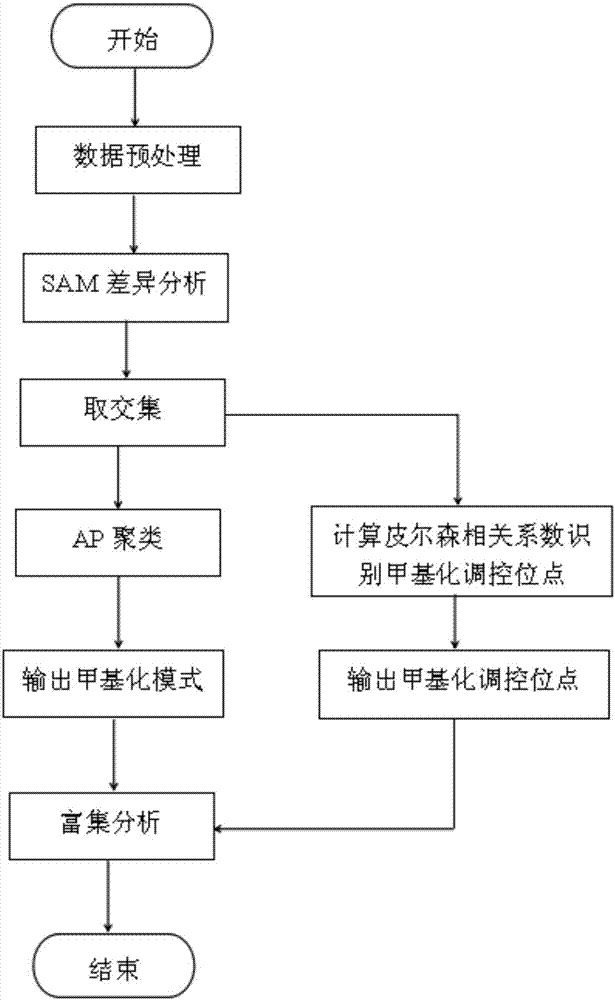
InactiveCN107301330AAddress distribution requirementsProof of validityBiostatisticsHybridisationDifferential MethylationMethylation Site
The invention belongs to the technical field of data processing of bioinformatics, and discloses a method for mining the methylation pattern by whole genome data. The method comprises the following steps that: using a SAM (Significance Analysis of Microarrays) method in various data sample sets to independently screen differential methylation sites on a whole genome; taking an intersection from the differential methylation sites of a plurality of sample sets to obtain a common difference site set; calculating a Pearson correlation coefficient between the methylation levels of the differential methylation sites and a corresponding gene expression level, and identifying a methylation regulation and control site; and carrying out AP (Affinity Propagation) clustering on the differential methylation site set to obtain a methylation cluster, independently carrying out pattern analysis on each methylation cluster, and carrying out demonstration through gene annotation and KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) enrichment analysis. By use of the method, references can be provided by aiming at a demethylation medicine, different types of diseases have generality on a methylation pattern, and the method has a practical and clinic meaning for researching a relationship between the methylation pattern and the disease from a perspective of the whole genome.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Methods and compositions for detecting colon cancers
ActiveUS20050106593A1Significant positive effectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotide sequencingDifferential Methylation
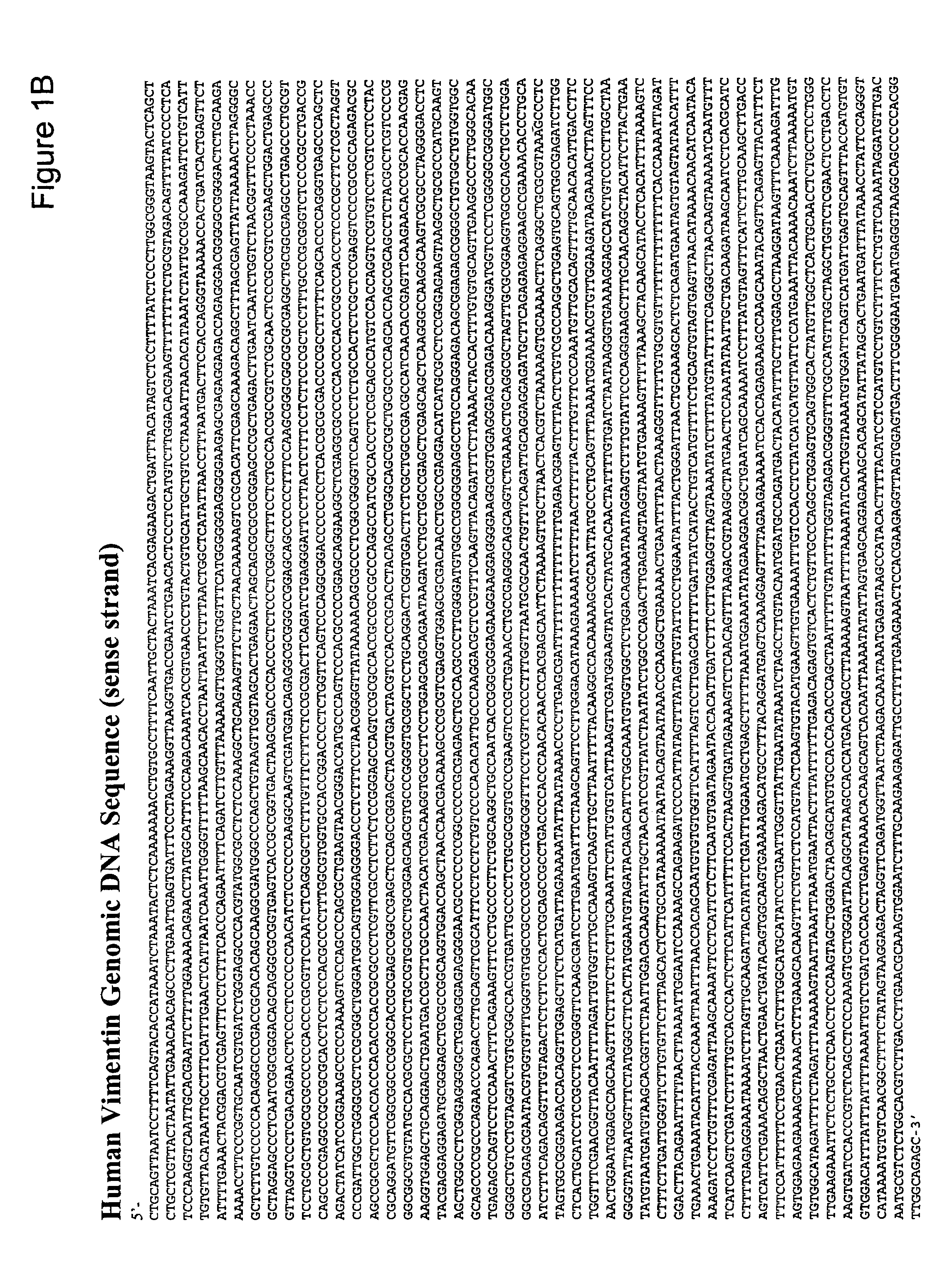
This application describes methods and compositions for detecting and treating vimentin-associated neoplasia. Differential methylation of the vimentin nucleotide sequences has been observed in vimentin-associated neoplasia such as colon neoplasia.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Method for detecting differentially methylated cpg islands associated with abnormal state of human body
InactiveUS20180143198A1Reduce tearingReduce wearNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman bodyHepatocellular carcinoma
Disclosed is a method for detecting differentially methylated CpG islands associated with an abnormal state of a human body, characterized by detecting very minute amounts of methylated CpG short tandem nucleic acid sequences in highly fragmented DNA samples with genome scale, identifying differentially methylated CpG islands associated with abnormal state of human body and determining the corresponding abnormal state of human body. Sequencing libraries are constructed by using CpG short tandem sequences as primers to perform three steps of PCR reactions on DNAs which are conversed by nodifiers, and detections of very minute amounts of methylated CpG short tandem nucleic acid sequences are implemented with high throughput sequencing technology. A group of genome sequences and methylation patterns of differentially methylated CpG islands which are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma are also disclosed; they may be used for distinguishing between hepatacellular carcinoma and non-cancerous state.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Mesenchymal stem cells as a vehicle for ion channel transfer in syncytial structures
InactiveUS20090203002A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationMesenchymal stem cellDifferential Methylation
The present invention provides a method of selectively amplifying fetal DNA sequences from a mixed, fetal-maternal source. This method utilizes differential methylation to allow for the selective amplification of trophoblast / fetal specific sequences from DNA mixtures that contain a high proportion of non-trophoblast / fetal DNA. The invention also provides methods of using the amplified fetal DNA sequences for aneuploidy detection.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Differential methylation site identification method
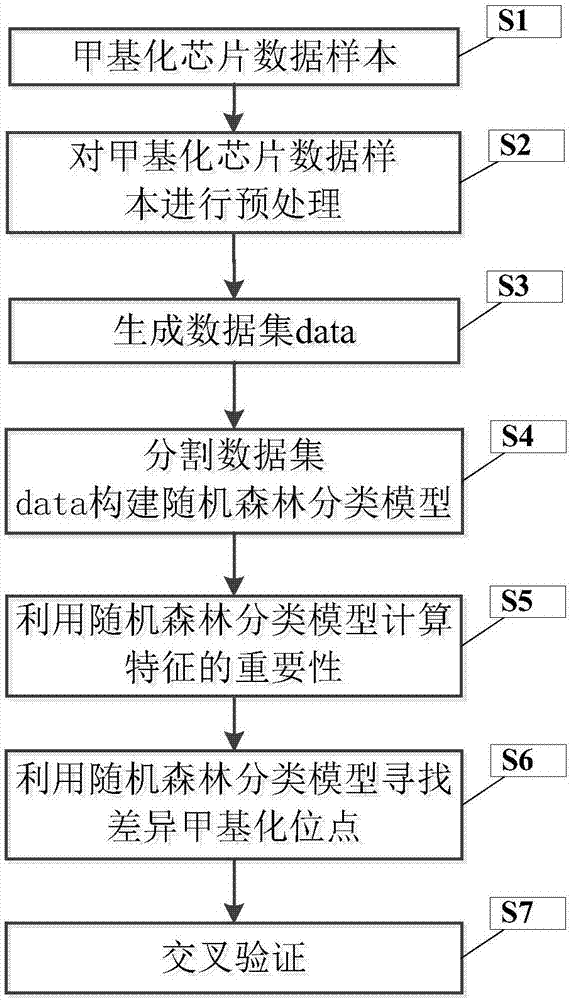
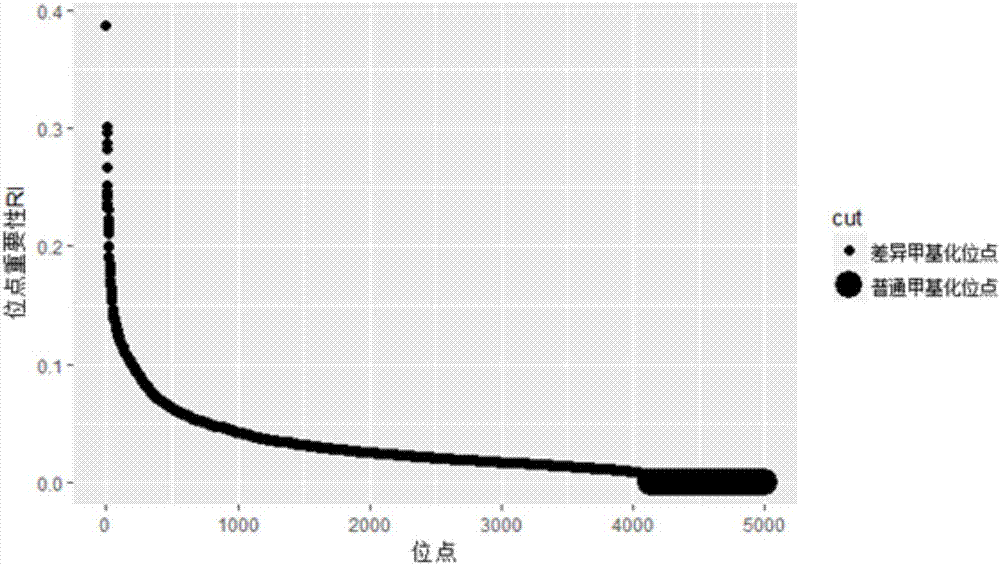
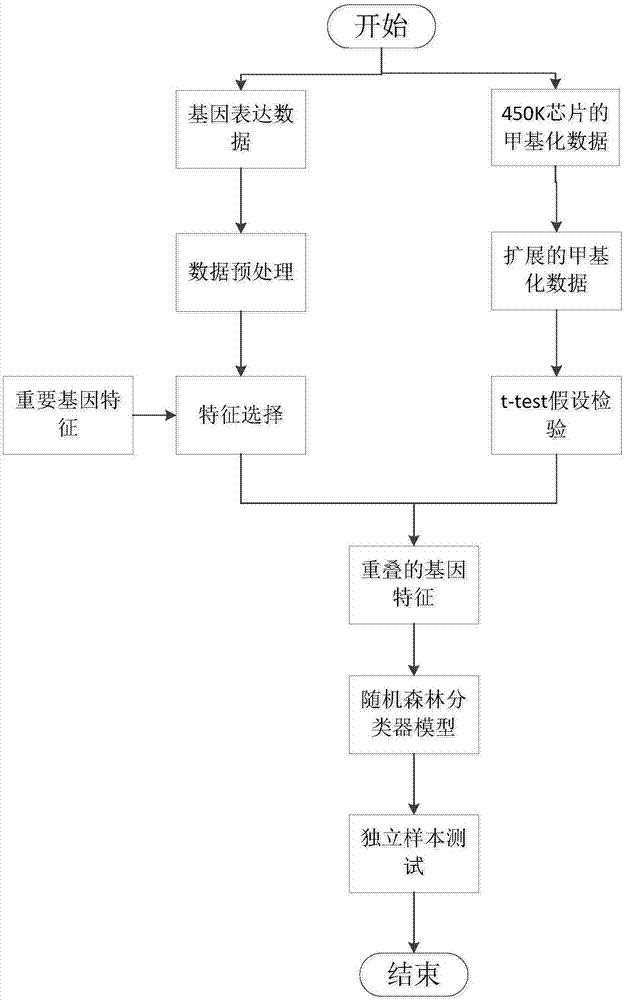
ActiveCN107247873AIncrease reflectionEasy to handleBiostatisticsProteomicsCancers diagnosisData pre-processing
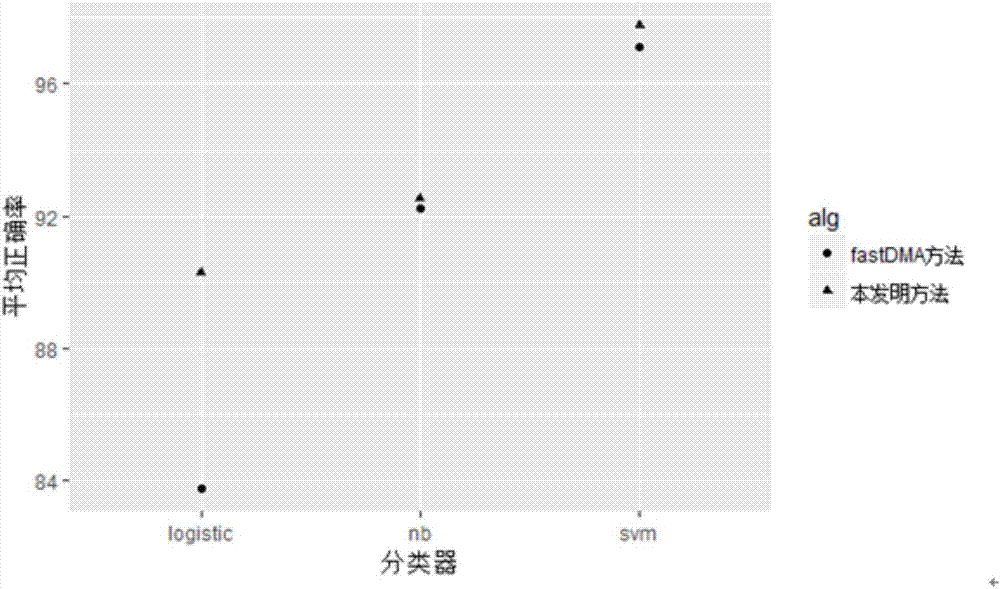
The invention discloses a differential methylation site identification method. According to a thought of classification, identification for differential methylation sites is converted to searching of sites having important contributions to classification by a feature selection approach, and the sites having important contributions to classification are differential methylation sites. Specifically the differential methylation site identification method includes: firstly preprocessing 450K methylation chip data acquired from a public data standardizing the 450K methylation chip data to eliminate within-block errors, eliminating batch effects to eliminate inter-group errors and eliminating the sites small in variances; secondarily, constructing a random forest model to obtain contribution values of every site to classification; finally, determining the site as the differential methylation site if the contribution value of the site is larger than 0. The differential methylation site identification method has the advantages that the obtained differential methylation sites have better class judging performances and can provide more accurate results for cancer diagnosis.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Methylation detection
InactiveUS20090176655A1Reduce the possibilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEpigenetic ProfileDifferential Methylation
A method of identifying nucleic acid molecules differentially methylated in a disease comprises steps of incubating fragmented DNA, from a disease cell, with a reagent which specifically binds to methylated DNA to thus concentrate methylated DNA fragments, incubating fragmented DNA, from a disease cell related to the disease cell utilised in step (a) in which DNA methyltransferase expression and / or activity has been inhibited, with a reagent which specifically binds to methylated DNA to thus concentrate methylated DNA fragments and comparing the methylated DNA fragments obtained in steps (a) and (b) to identify nucleic acid molecules differentially methylated in the disease. A method of detecting a predisposition to, or the incidence of, colorectal cancer in a sample comprises detecting an epigenetic change in at least one gene selected from RASGRF2, SCNN1B, HOXD1, PLK2 and BHLHB9 wherein detection of the epigenetic change is indicative of a predisposition to, or the incidence of, colorectal cancer.
Owner:ONCOMETHLOME SCI
Differentially methylated sequences in pancreatic cancer
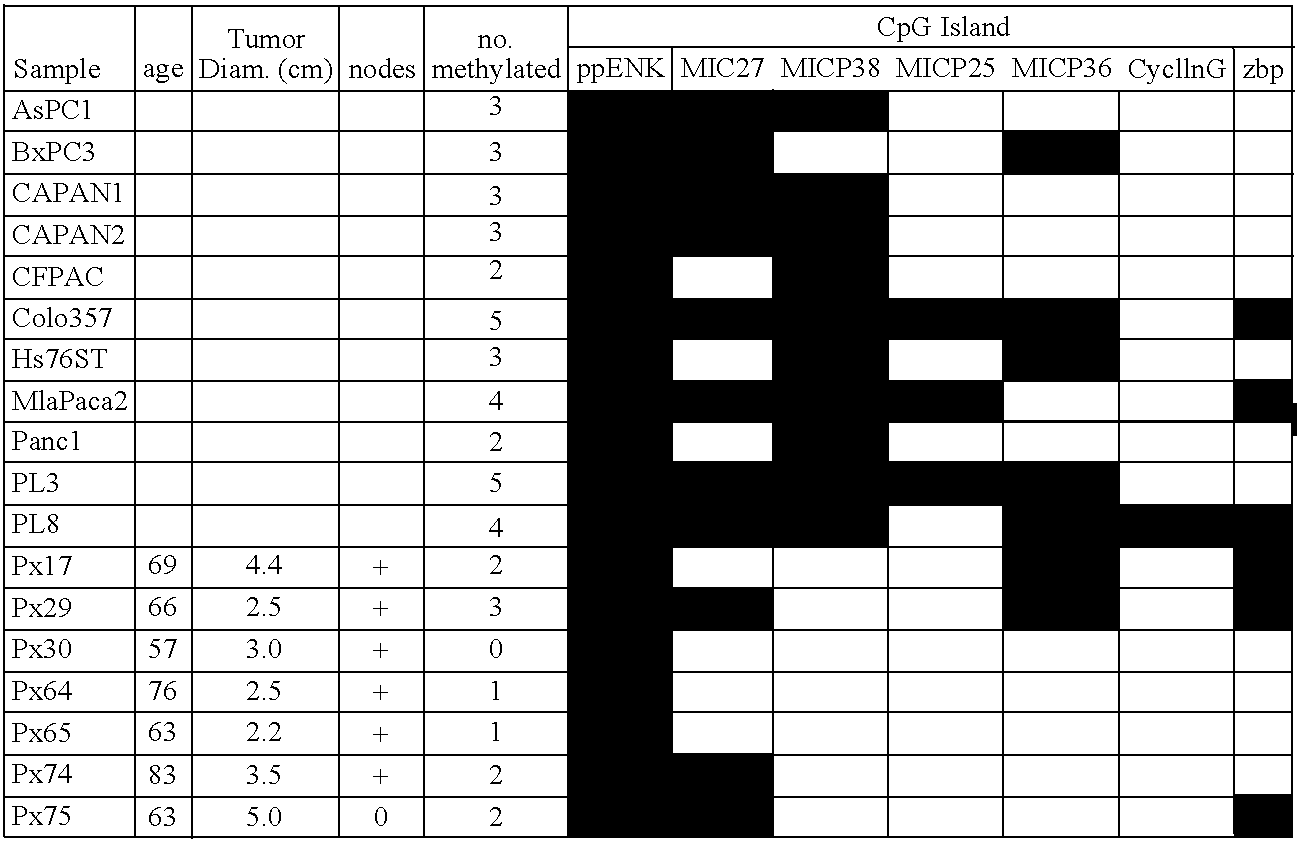
InactiveUS7153653B2Raise the possibilityHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesDifferential MethylationCancer research
The present invention provides a method for detecting a cellular proliferative disorder in a subject. The method includes contacting a nucleic acid-containing specimen from the subject with an agent that provides a determination of the methylation state of at least one gene or associated regulatory region of the gene and identifying aberrant methylation of regions of the gene or regulatory region, wherein aberrant methylation is identified as being different when compared to the same regions of the gene or associated regulatory region in a subject not having said cellular proliferative, thereby detecting a cellular proliferative disorder in the subject.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Comprehensive DNA methylation profiling in a human cancer genome identifies novel epigenetic targets
InactiveUS20070224626A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingHuman cancerEpigenetic Profile
The present invention provides DNA marker sequences that are differentially methylated in samples from normal individuals and individuals with brain cancer. The invention further provides methods of identifying differentially methylated DNA marker sequences and their use the detection and diagnosis of gliomas.
Owner:ORION GENOMICS
Method for identifying cancer biomarkers
ActiveCN107025387AReduce biasMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsDNA methylationFeature extraction
The invention discloses a method for identifying cancer biomarkers. Genetic expression data and DNA methylation data of cancer are acquired from a public database; the genetic expression data are subjected to pre-processing and feature extraction, and feature genes are obtained; the DNA methylation data are subjected to extension and t-test hypothesis testing, and a differential methylation locus is obtained; finally, comparison with existing genes is performed by means of the differential methylation locus, the intersection of successfully compared existing genes and the feature genes is solved, overlapping genes are obtained and the overlapping genes are identified potential cancer biomarkers.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
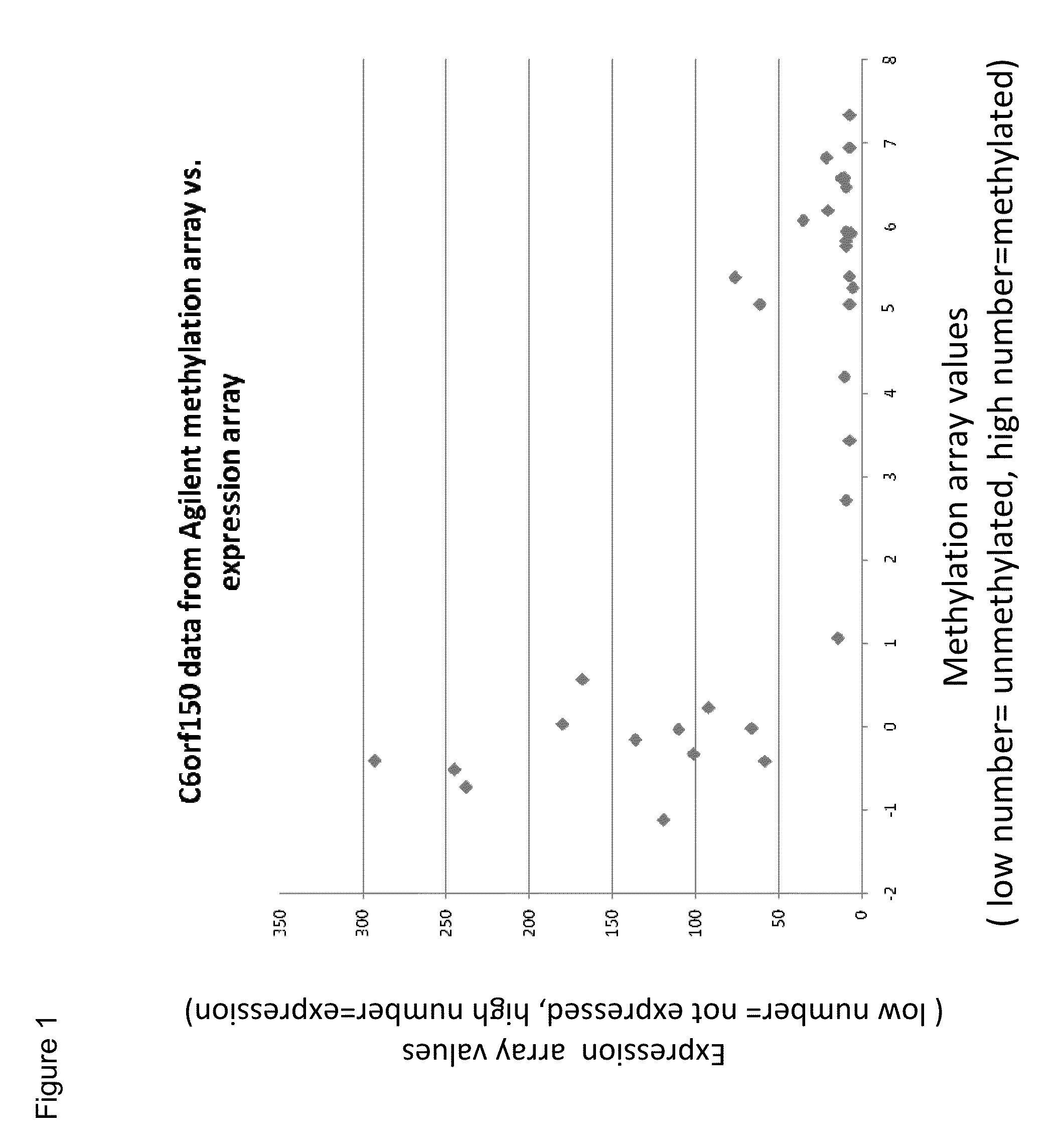
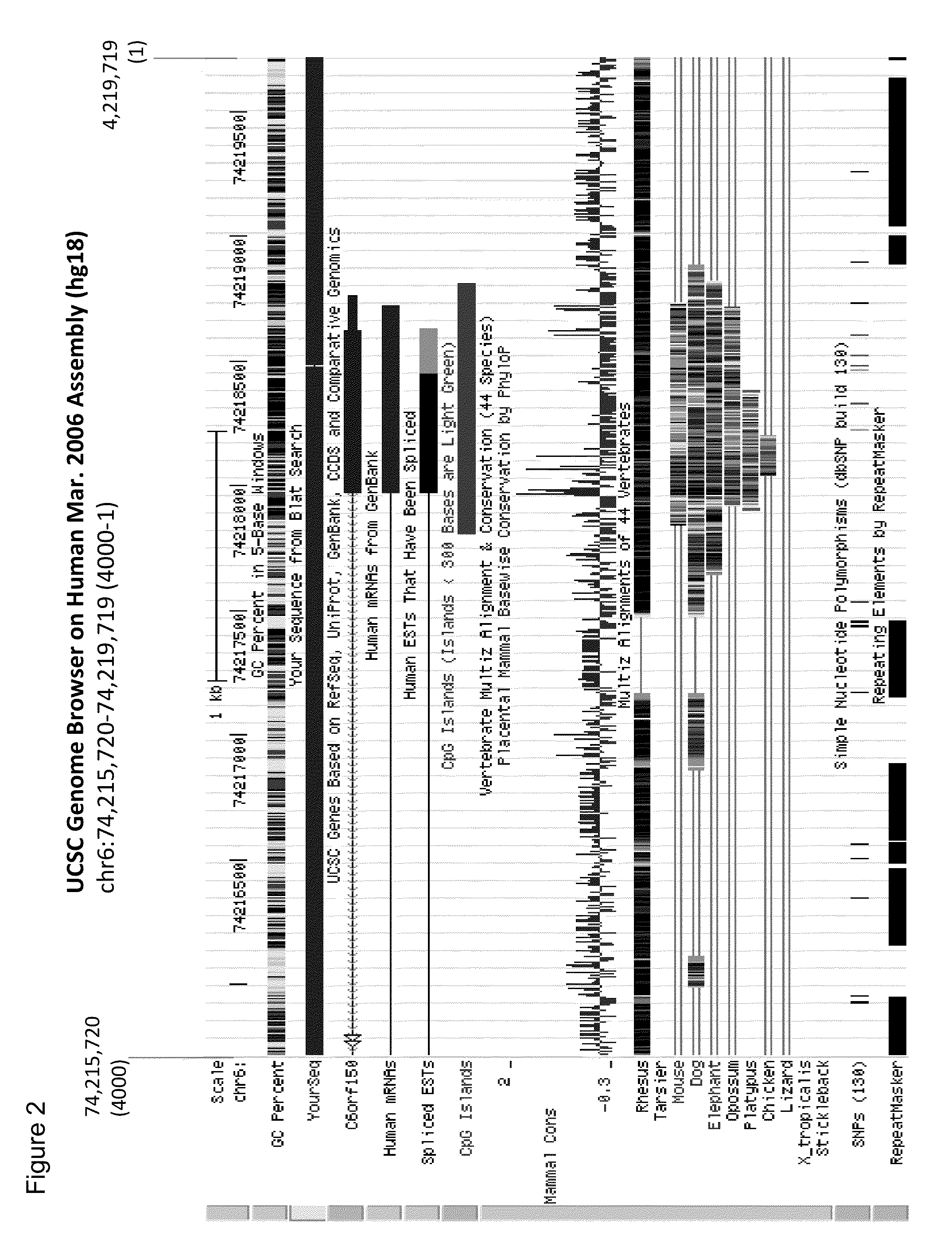
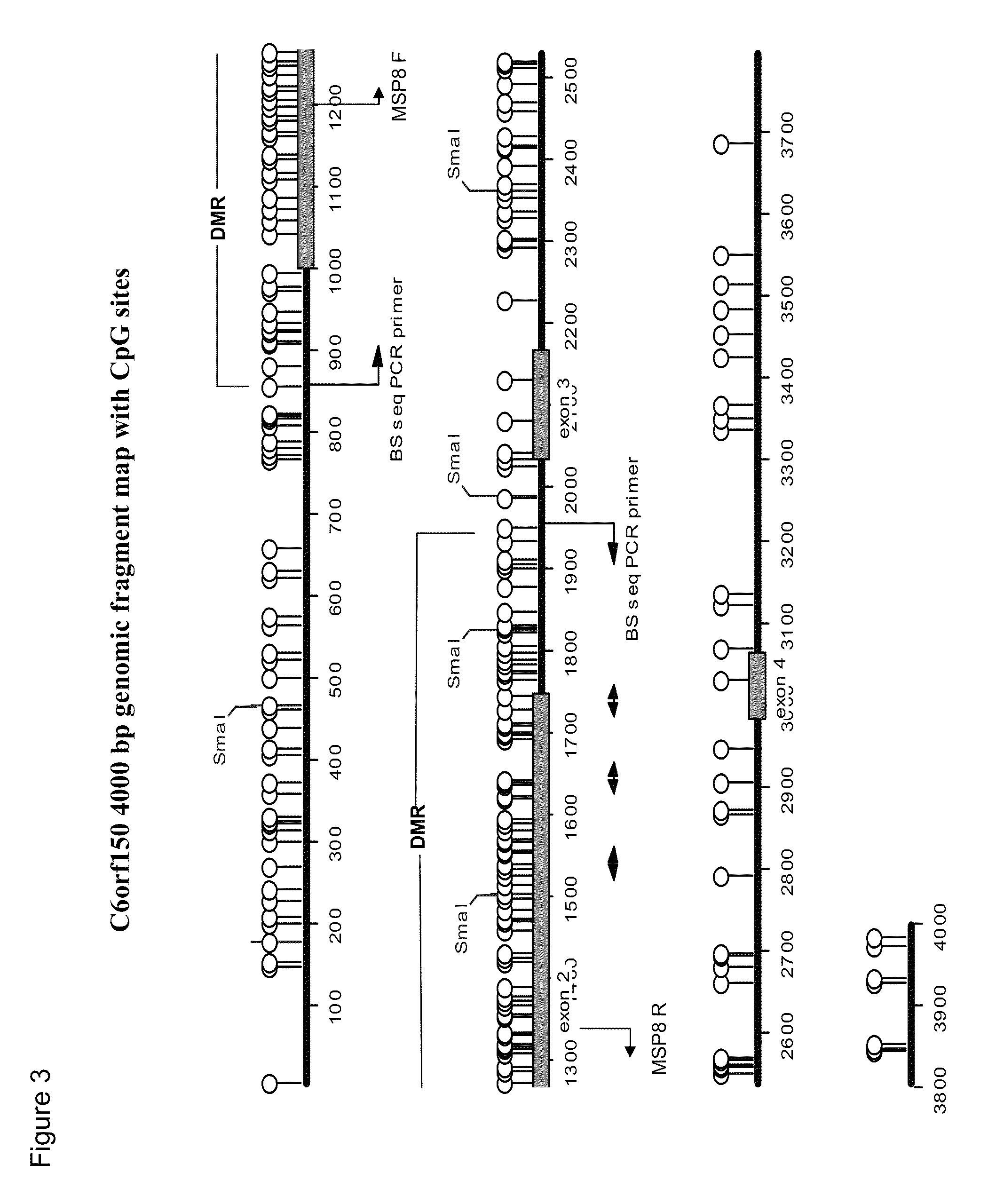
Aberrant methylation of C6Orf150 DNA sequences in human colorectal cancer
InactiveUS8642271B2Compound screeningApoptosis detectionNucleotide sequencingDifferential Methylation
This application describes methods and compositions for detecting and treating C6Orf150-associated neoplasia. Differential methylation of the C6Orf150 nucleotide sequences has been observed in C6Orf150-associated neoplasia such as colon neoplasia.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
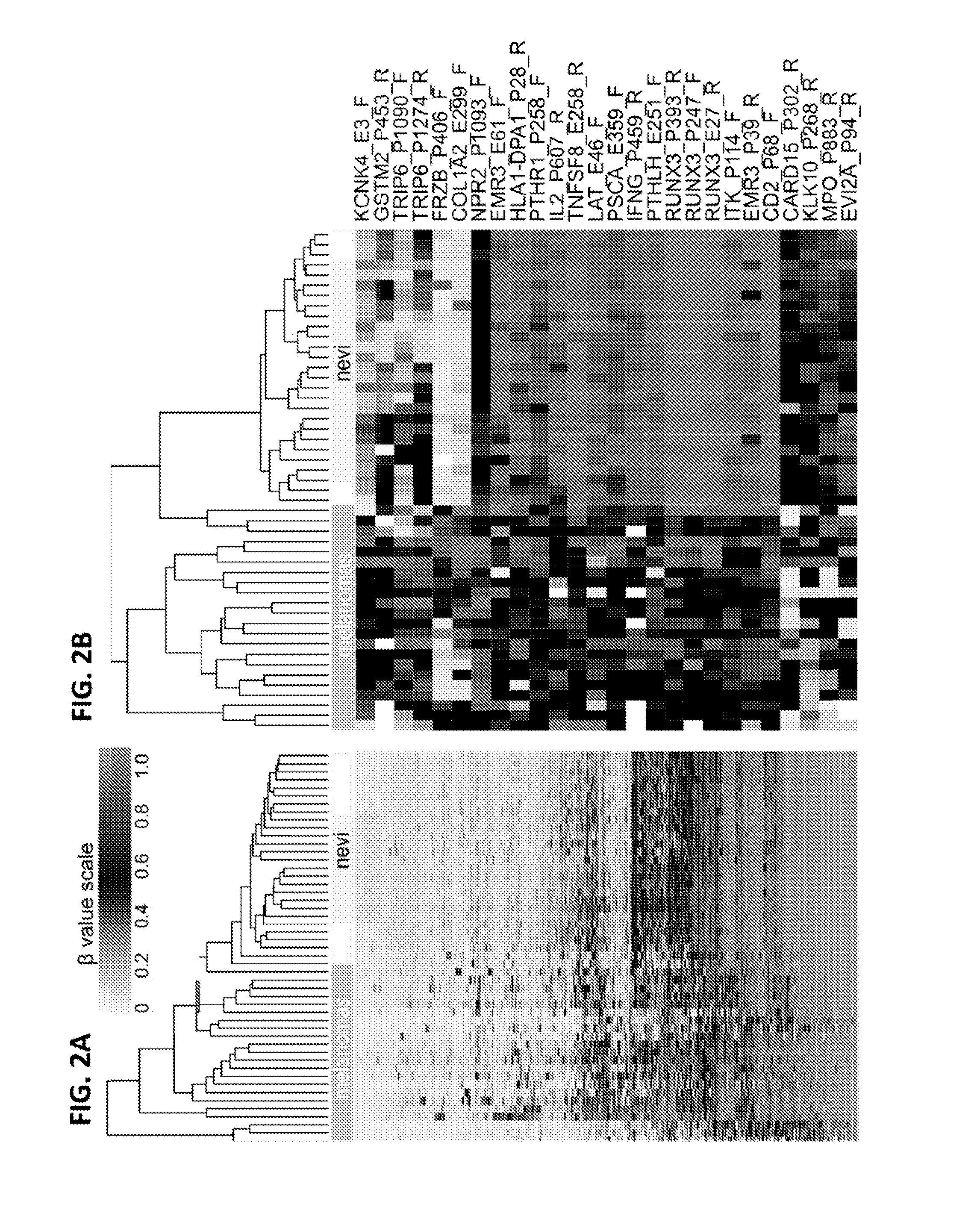
Methods and kits for detecting melanoma
InactiveUS20150376717A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue sampleDifferential Methylation
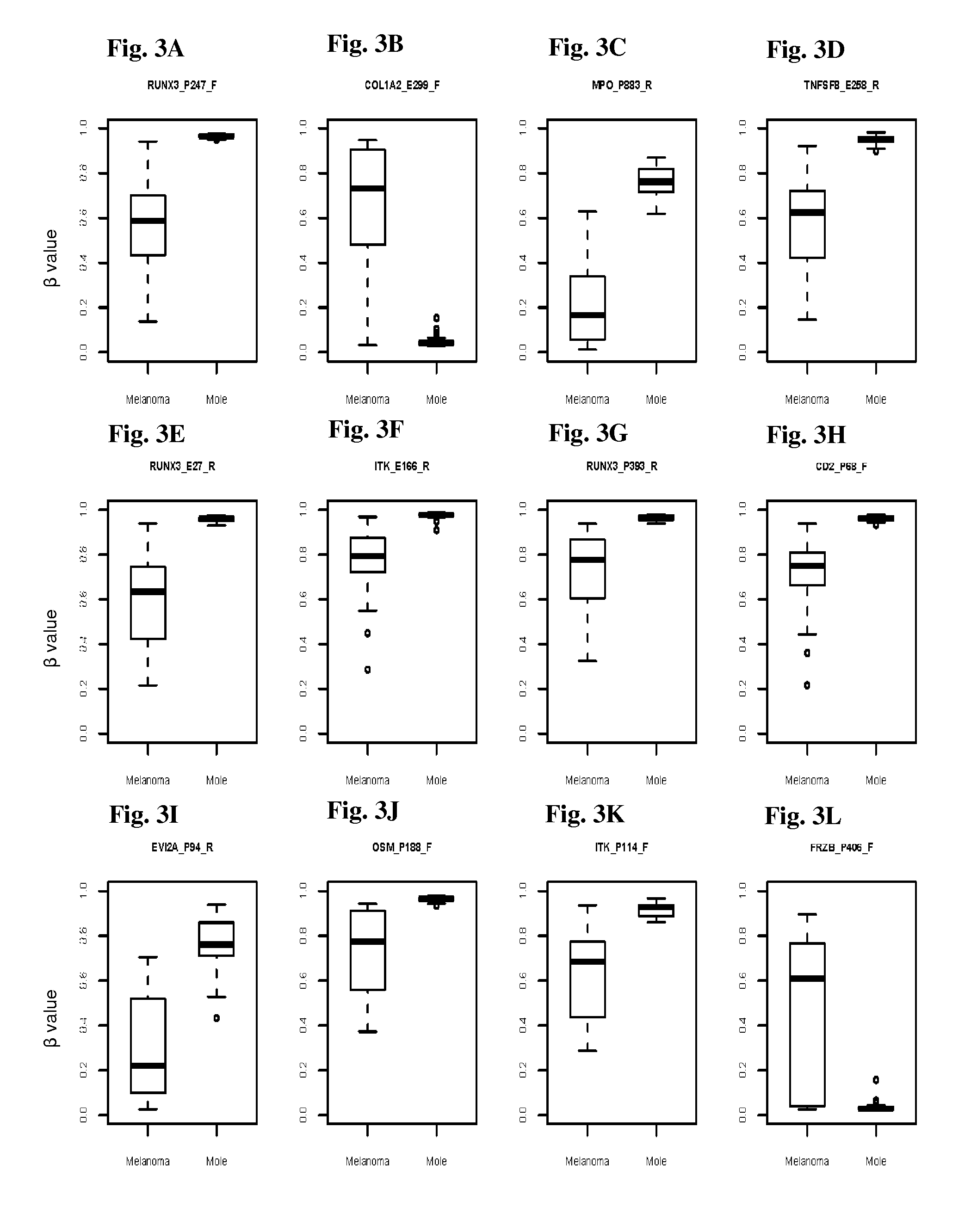
This invention is directed to a method for detecting melanoma in a tissue sample by measuring a level of methylation of one or more regulatory elements differentially methylated in melanoma and benign nevi. The invention provides methods for detecting melanoma, related kits, and methods of screening for compounds to prevent or treat melanoma.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Combined diagnosis model and system for early breast cancer
ActiveCN111863250AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityMedical data miningMicrobiological testing/measurementEarly breast cancerOncology
The invention discloses a combined diagnosis model and system for early breast cancer. The combined diagnosis model comprises a parameter cfDNA differential methylation area marker, ultrasonic examination and molybdenum target X-ray examination. The combined diagnosis model is constructed by adopting an LASSO method, and a breast cancer patient can be effectively judged.
Owner:WENZHOU INST UNIV OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +3
Specific amplification of tumor specific DNA sequences
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
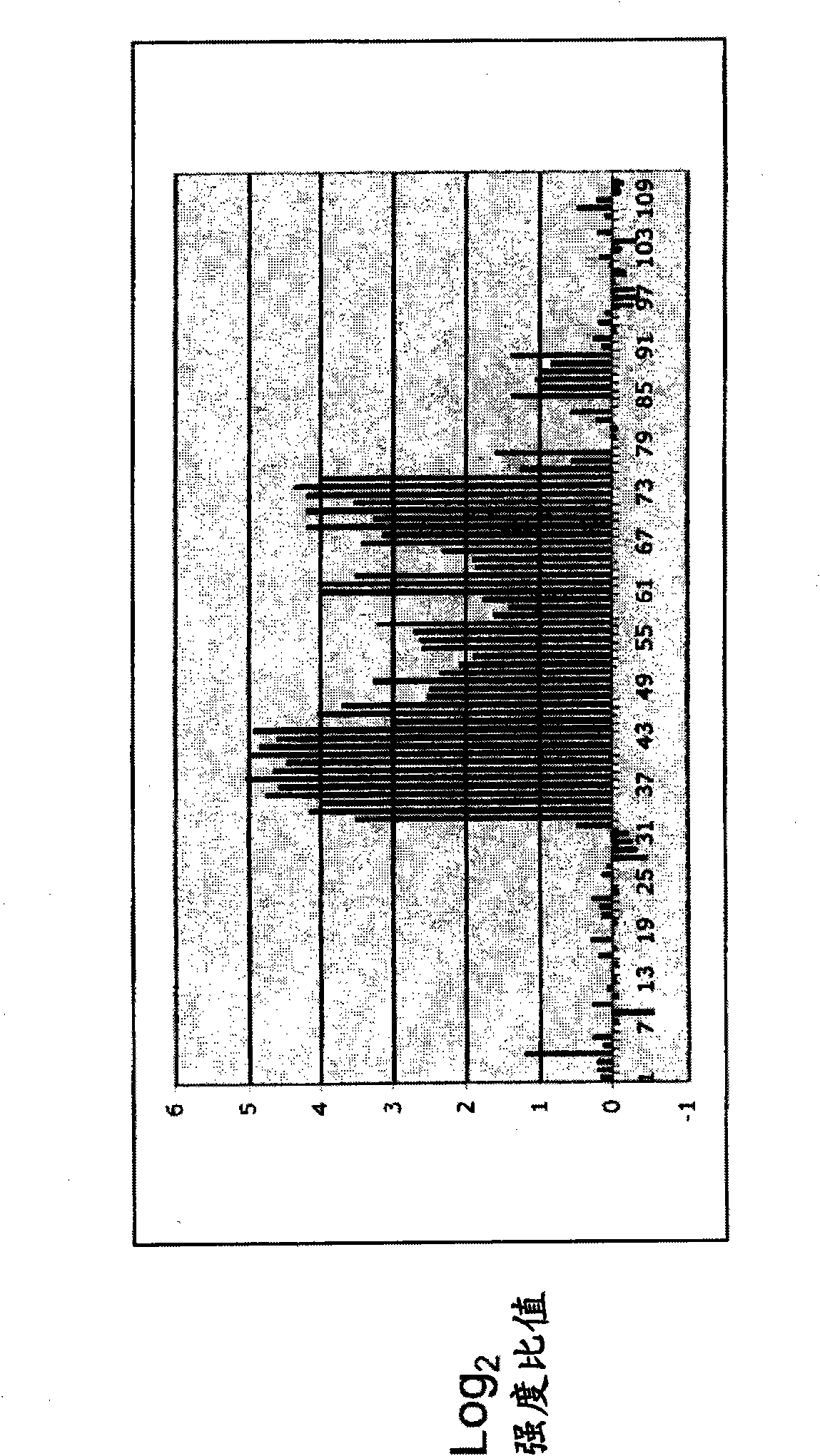
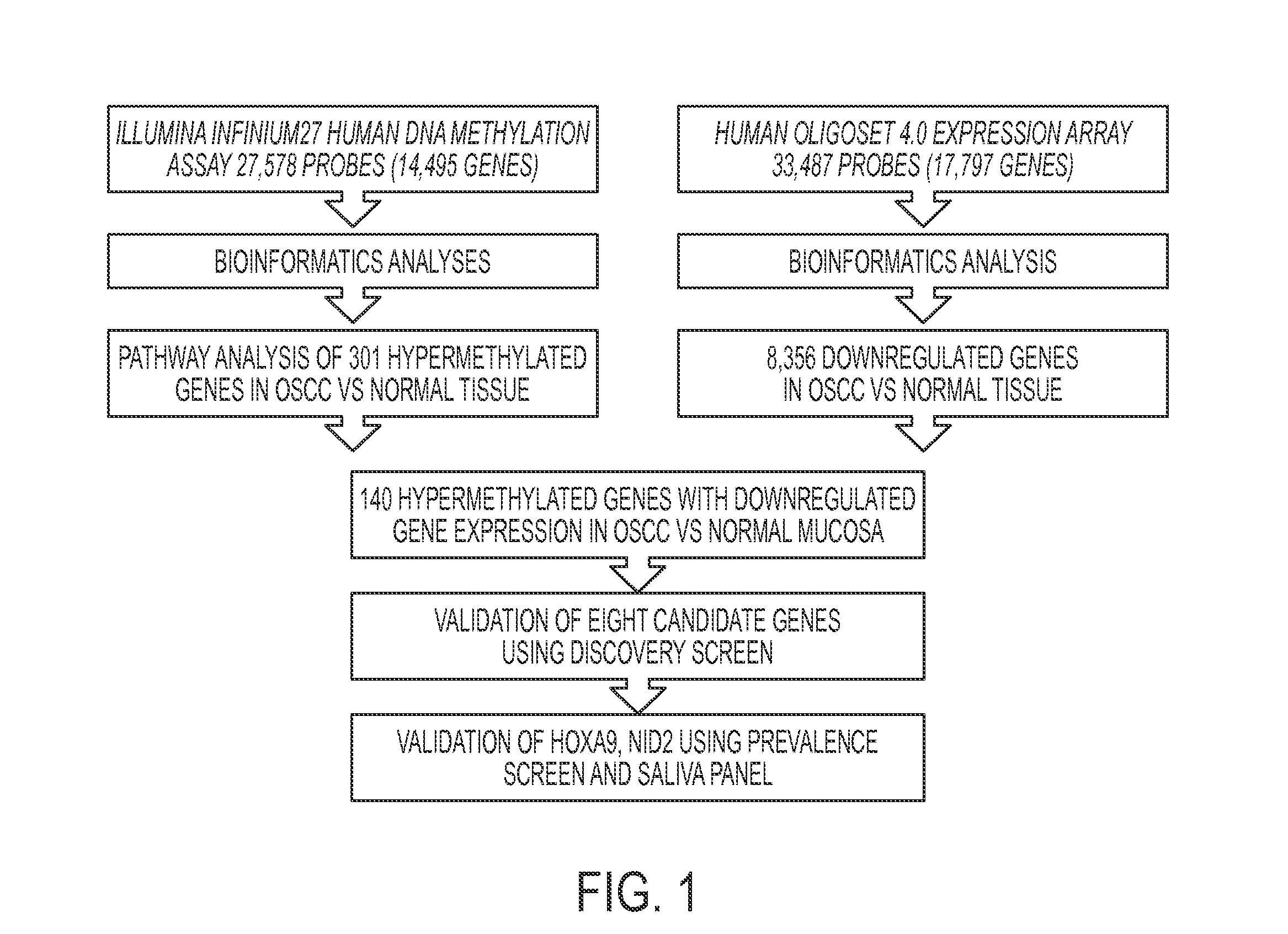
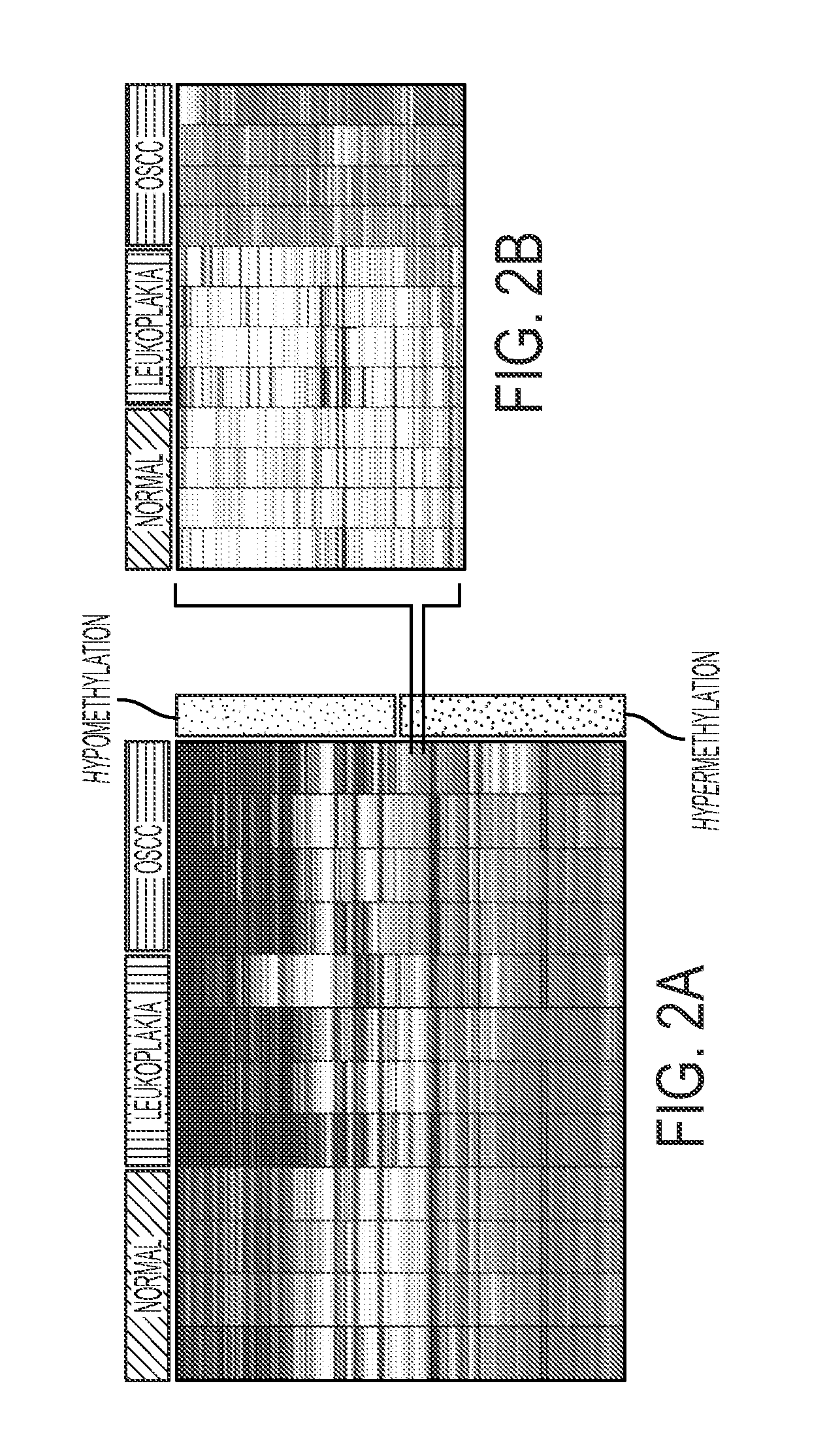
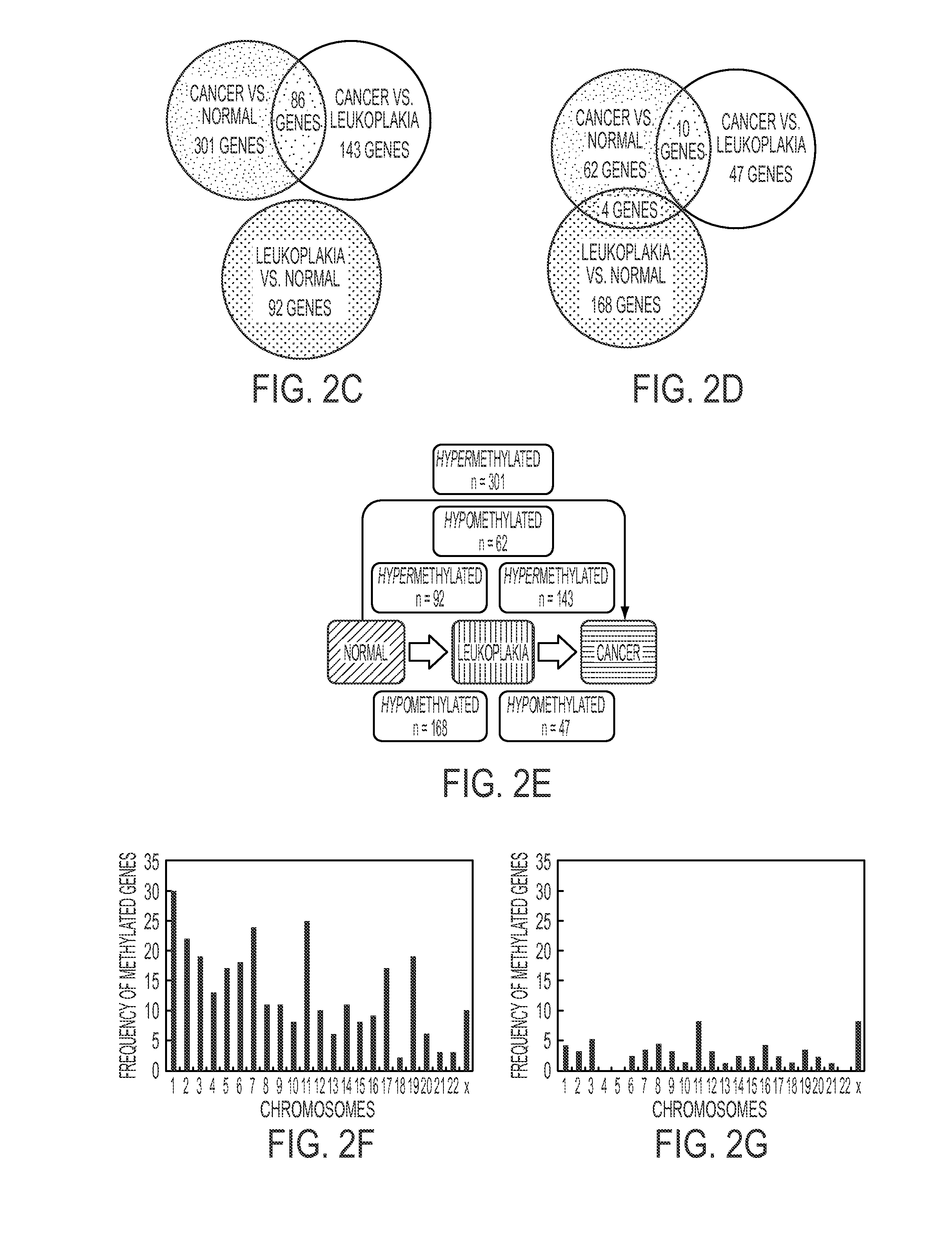
Hypermethylation Biomarkers for Detection of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer
Differentially methylated oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) biomarkers, identified in-vitro and validated in well-characterized surgical specimens, have shown poor clinical correlation in cohorts with different risk profiles. To overcome this lack of relevance we used the HumanMethylation27 BeadChip, publicly available methylation and expression array data, and Quantitative Methylation Specific PCR to uncover differential methylation in OSCC clinical samples with heterogeneous risk profiles. A two stage-design consisting of Discovery and Prevalence screens was used to identify differential promoter methylation and deregulated pathways in patients diagnosed with OSCC and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. This Phase I Biomarker Development Trial identified a panel of differentially methylated genes in normal and OSCC clinical samples from patients with heterogeneous risk profiles. This panel may be useful for early detection and cancer prevention studies.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Specific amplification of fetal DNA sequences from a mixed, fetal-maternal source
InactiveCN101421410AMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesDifferential MethylationDNA
The present invention provides a method of selectively amplifying fetal DNA sequences from a mixed, fetal-maternal source. This method utilizes differential methylation to allow for the selective amplification of trophoblast / fetal specific sequences from DNA mixtures that contain a high proportion of non- trophoblast / fetal DNA. The invention also provides methods of using the amplified fetal DNA sequences for aneuploidy detection.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods for identifying cancer risk
InactiveUS7611870B2Increased riskSubject is at riskSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAIncreased risk
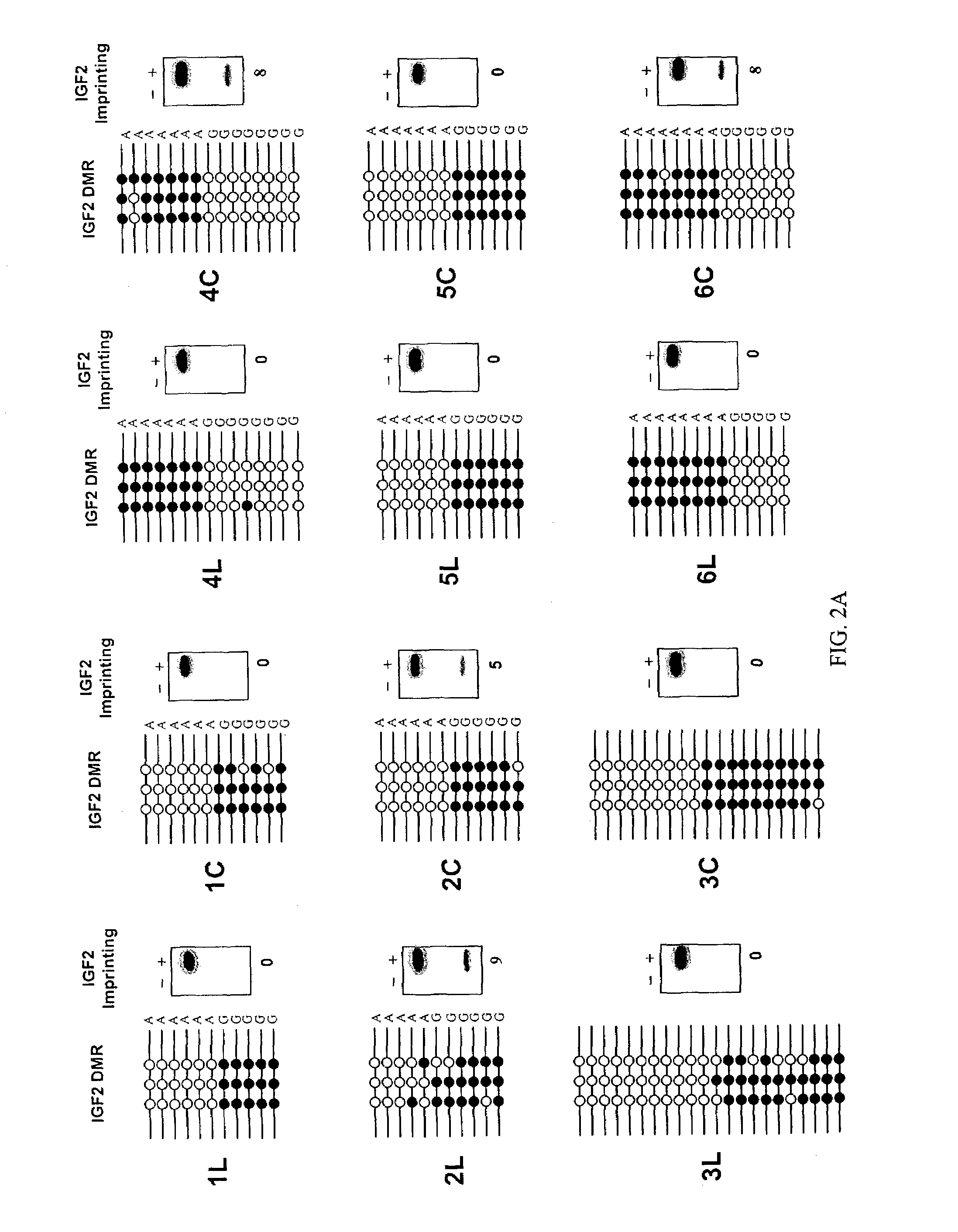
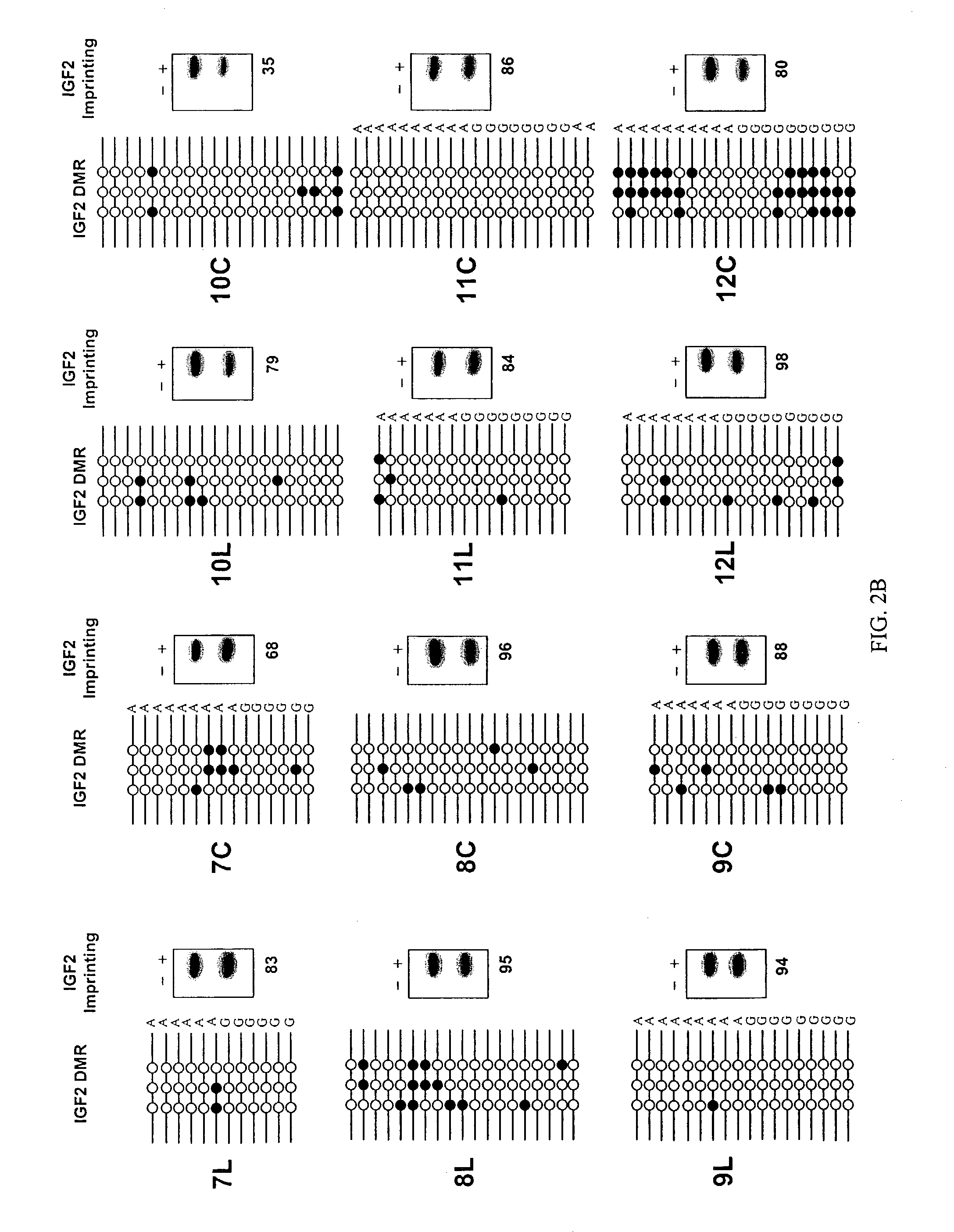
The present invention provides methods and kits for identifying an increased risk of developing cancer in a subject. The methods include analyzing a first biological sample, such as a blood sample, from the subject for loss of imprinting of the IGF2 gene. According to the methods a loss of imprinting is indicative of an increased risk of developing cancer. The method can include analyzing genomic DNA from the sample for altered methylation of the IGF2 gene. The altered methylation for example includes hypomethylation of a differentially methylated region of IGF2, corresponding to SEQ ID NO:1 or a polymorphism thereof. The method can be performed on a subject having no apparent or suspected hyperproliferative disorder such as cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Kit, method and primers for analyzing methylation status of MLH1 promoter in DNA sample
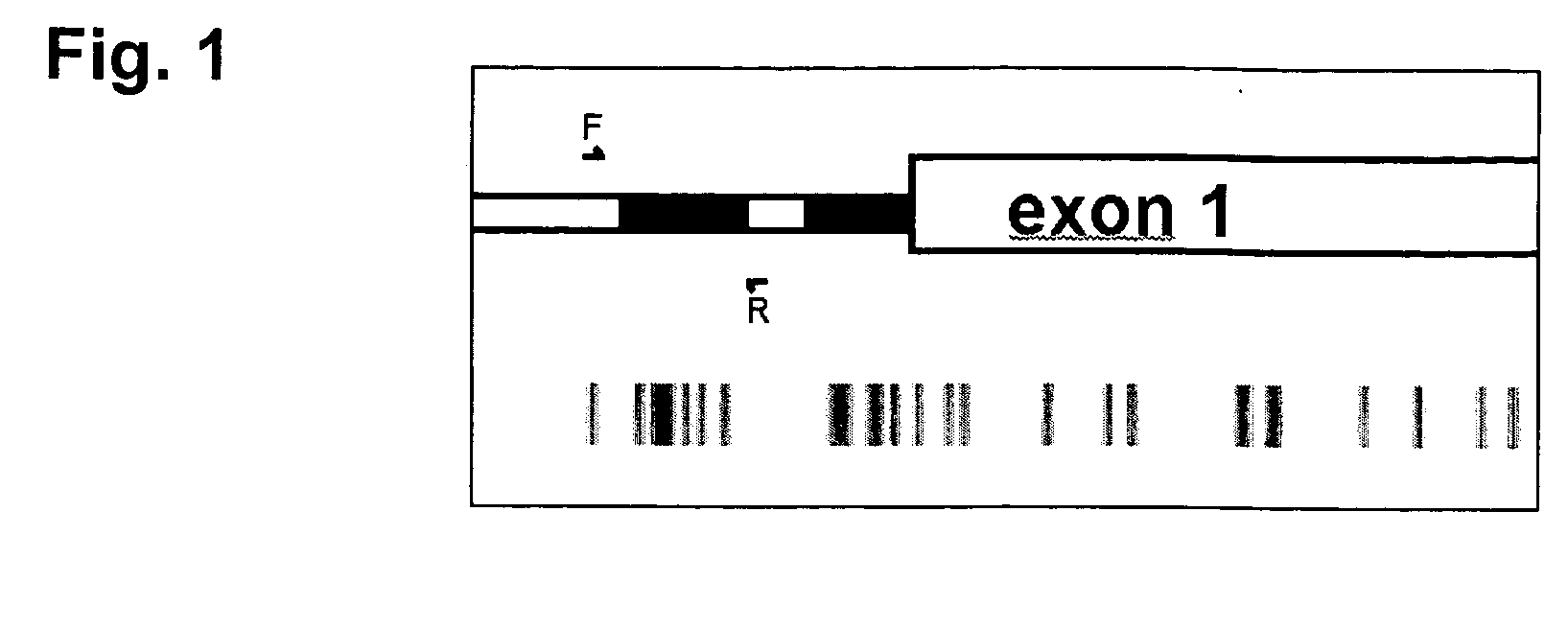
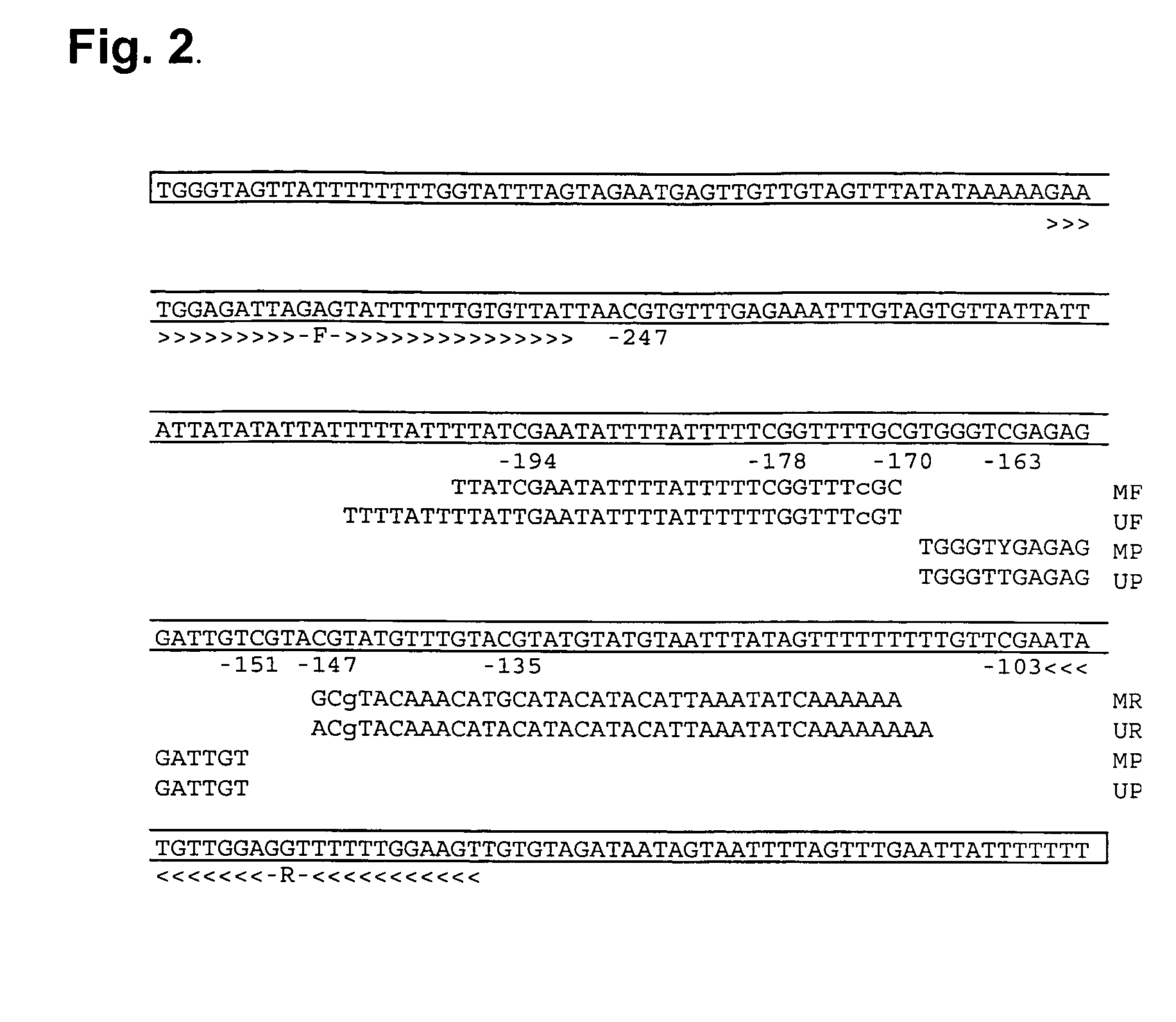
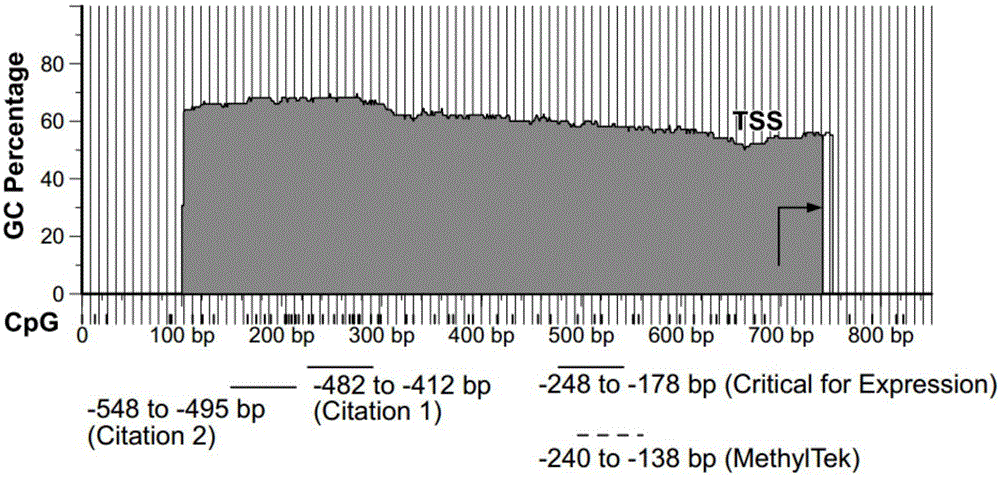
InactiveCN105018476AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAnalysis dnaOligonucleotide primers
The present invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a kit, a method and primers for analyzing methylation status of an MLH1 promoter in a DNA sample. The invention provides a kit for analyzing the methylation status of a neoplastic disease associated MLH1 promoter in a DNA sample. The kit comprises oligonucleotide primers, the oligonucleotide primers are complementary with at least part of the sequence of the MLH1 promoter in a zone from -248bp to -178bp relative to a transcription start site and overlap with the methylation sites in the zone. The present invention discloses accurate and sensitive test, composition and method for detection of differential methylation of genomic MLH1 promoter DNA in clinical sample. The test, composition and method can be used in allow diagnosis and symptom method; and the applicable characteristic is that the presenting level of methylation genomic MLH1 promoter DNA in the absence of a specific disorder is distinguished from illness of methylation genomic MLH1 promoter DNA level.
Owner:常州杰傲病理诊断技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com