Specific amplification of fetal DNA sequences from a mixed, fetal-maternal source
A specific, DNA probe technology, applied in the field of selective amplification of fetal DNA sequences, can solve the problems of maternal DNA contamination, large-scale or systematic research that has not been reported
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
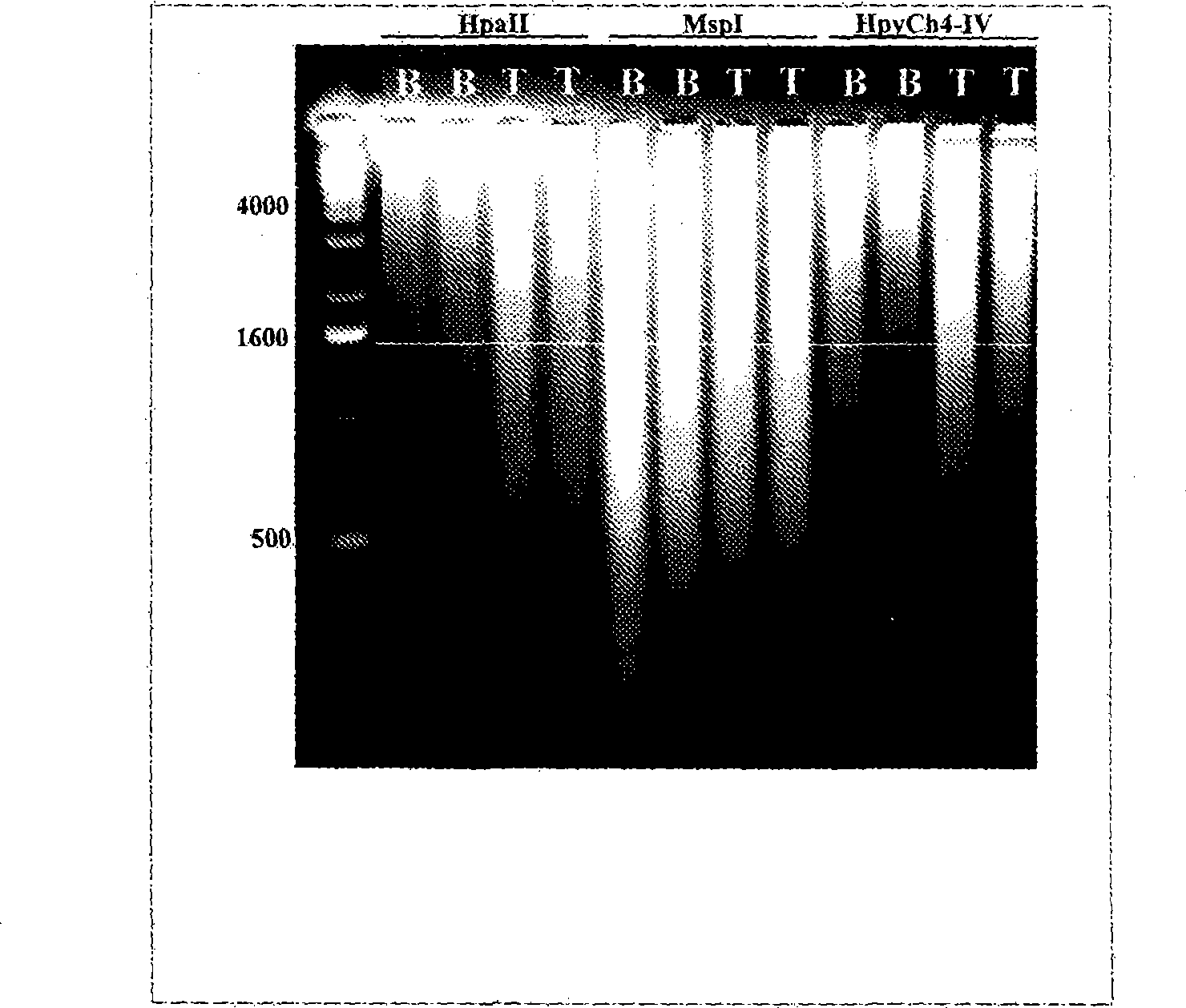
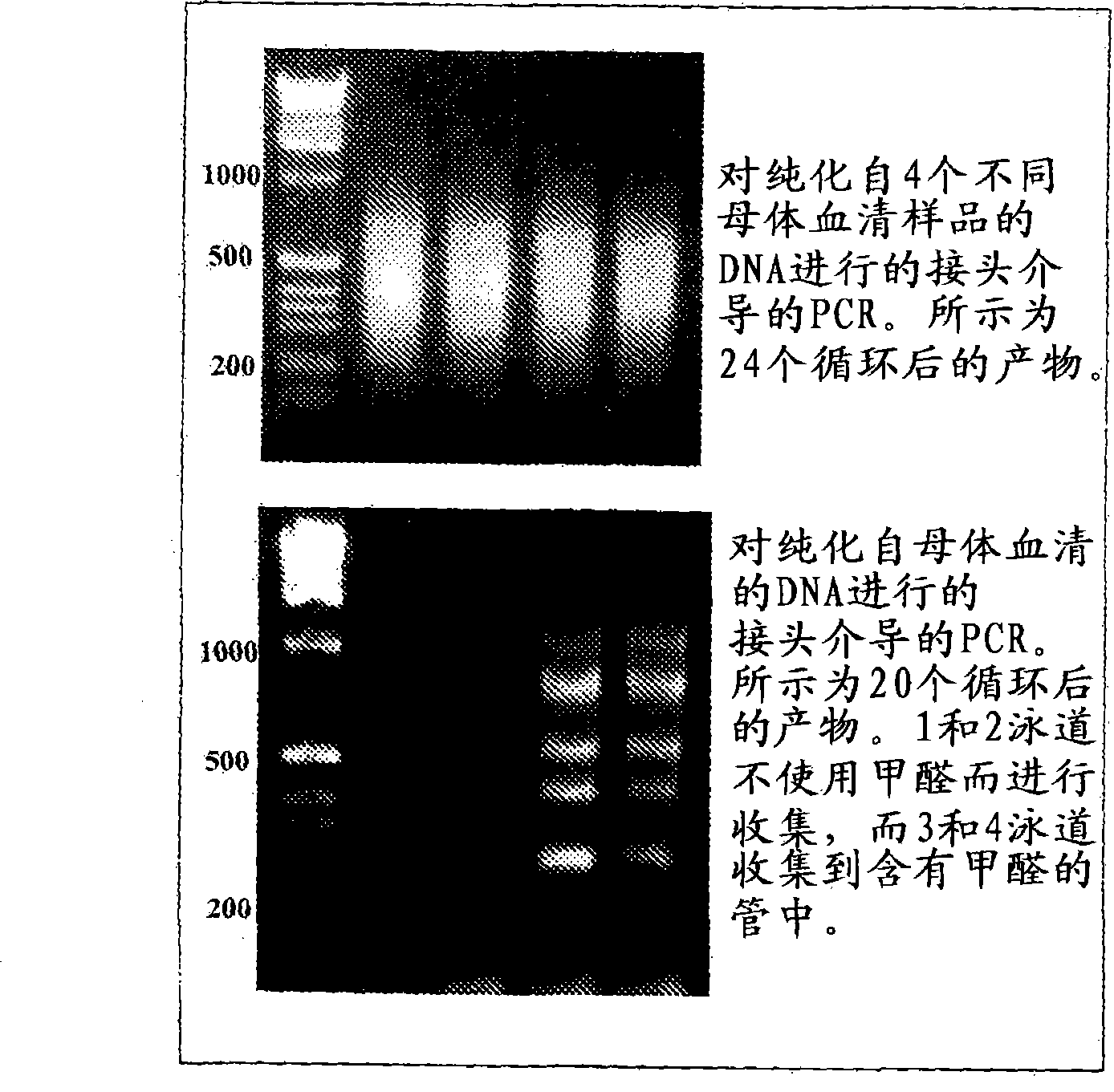
[0041] Example 1 demonstrates the successful use of adapter-mediated amplification on DNA isolated from maternal plasma. Purified DNA was digested with the CpG methylation-sensitive enzyme HpyCh4-IV prior to amplification. After digestion, the adapters were annealed and ligated to the digested DNA, and finally the top strand of the adapter pair was used for PCR according to published protocols. See Example 1 and Guillaud-Bataille, M., et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 32:e112 (2004). Notably, it has been determined that no formaldehyde should be involved in maternal blood collection methods.
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 demonstrates successful adapter-mediated methylation-specific amplification of trophoblast / fetal DNA. Trophoblast / fetal DNA and DNA samples from whole blood were digested with the CpG methylation sensitive enzyme Acll. Similar to Example 1, after enzyme digestion, the adapters were annealed and ligated to the digested DNA, and finally the upper strand of the adapter pair was used for PCR according to the same PCR protocol as described in Example 1. Notably, trophoblast / fetal DNA consistently yielded more and apparently different PCR products than whole blood. However, it has been determined that despite the fact that CpG methylation sensitive enzymes are used, non-trophoblast / fetal DNA (ie DNA from whole blood) is still amplified. Therefore, the inventors determined that adapter-mediated PCR amplification alone is not sufficient for specific amplification of trophoblast / fetal DNA.
[0043] Thus, in the adapter-mediated PCR step of the present invention, a mi...
Embodiment 4
[0060] The invention also provides methods of identifying fetal-specific amplicons. See embodiment 5 for details. The method comprises separately preparing methylation-sensitive representatives from fetal DNA and whole blood DNA using the method for selectively amplifying fetal DNA described above. Fetal-specific amplicons refer to amplicons that will be amplified from trophoblast / fetal DNA but not other DNA using the methods described herein. Trophoblast / fetal DNA is hypomethylated DNA compared to adult DNA. Methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes will cleave hypomethylated fetal loci but not methylated maternal loci.
[0061] labeling a methylation-sensitive representative from fetal DNA with a first fluorochrome, and labeling whole blood DNA with a second fluorochrome different from the first fluorochrome to generate a labeled fetal DNA probe and a labeled whole blood DNA probe . Labeled probes are hybridized to an array of oligonucleotides corresponding to predicted ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com