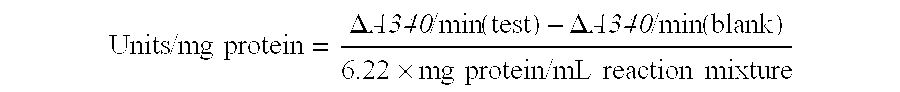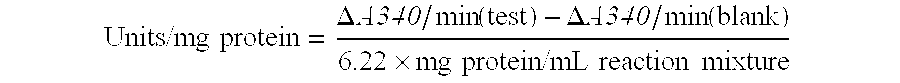Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Low copy number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low Copy Number (LCN) is a DNA profiling technique developed by the UK Forensic Science Service (FSS) which has been in use since 1999. In the United Kingdom use of the technique was suspended between 21 December 2007 and 14 January 2008 while the Crown Prosecution Service conducted a review into its use - this suspension has now been lifted.
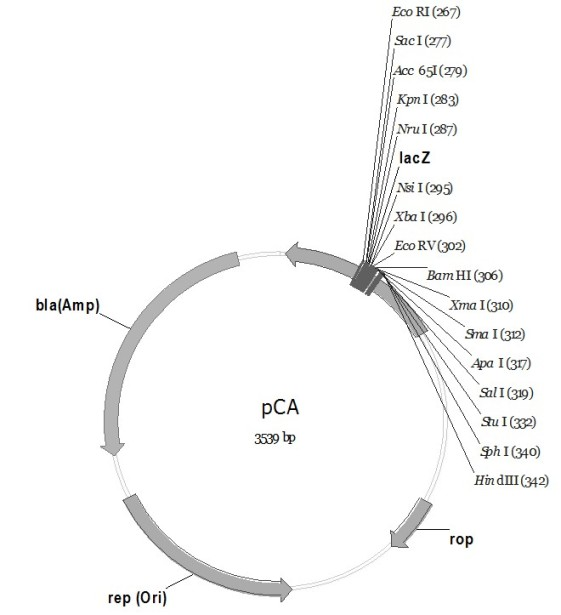
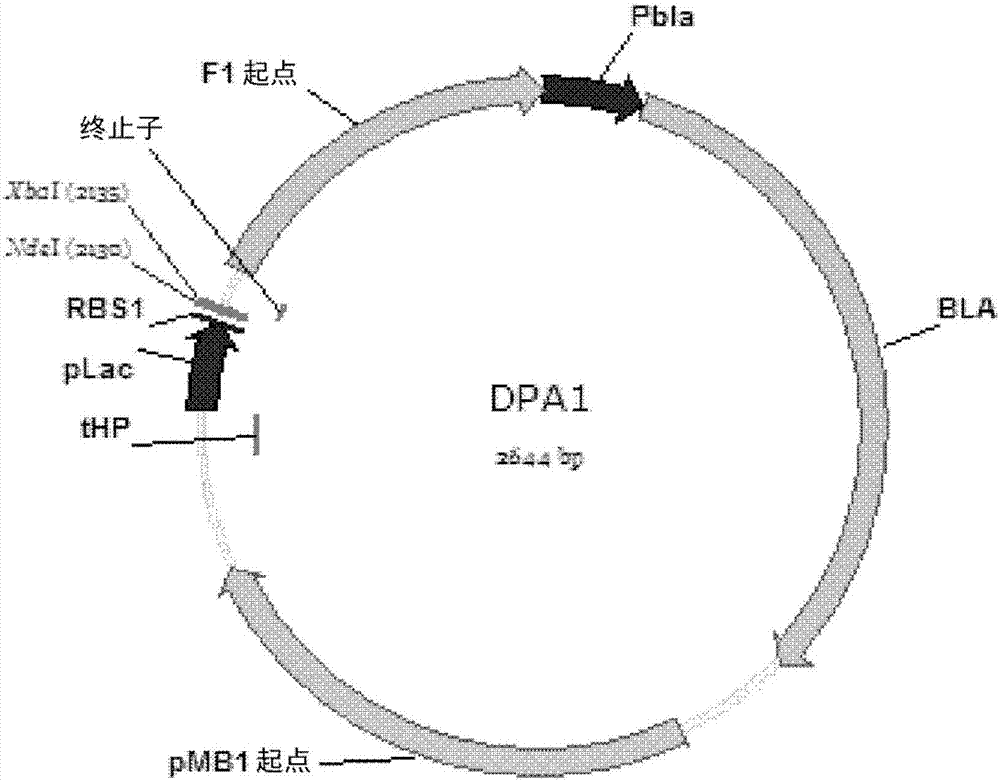
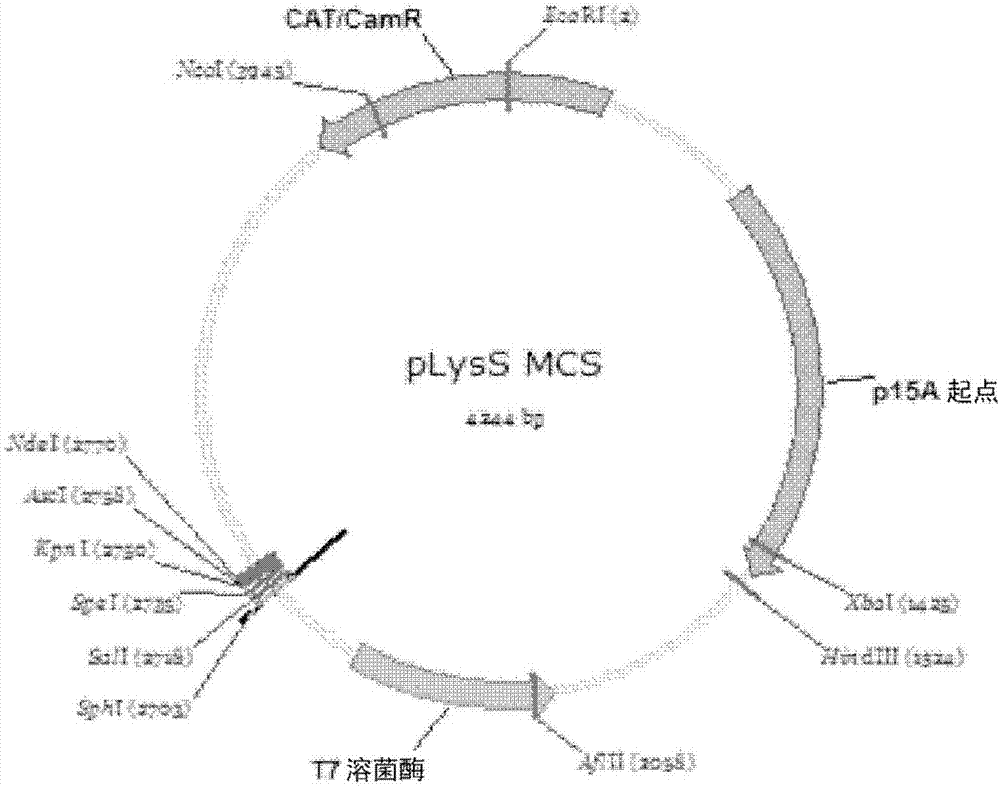
Promoter and plasmid system for genetic engineering
This invention provides a series of low-copy number plasmids comprising restriction endonuclease recognition sites useful for cloning at least three different genes or operons, each flanked by a terminator sequence, the plasmids containing variants of glucose isomerase promoters for varying levels of protein expression. The materials and methods are useful for genetic engineering in microorganisms, especially where multiple genetic insertions are sought.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
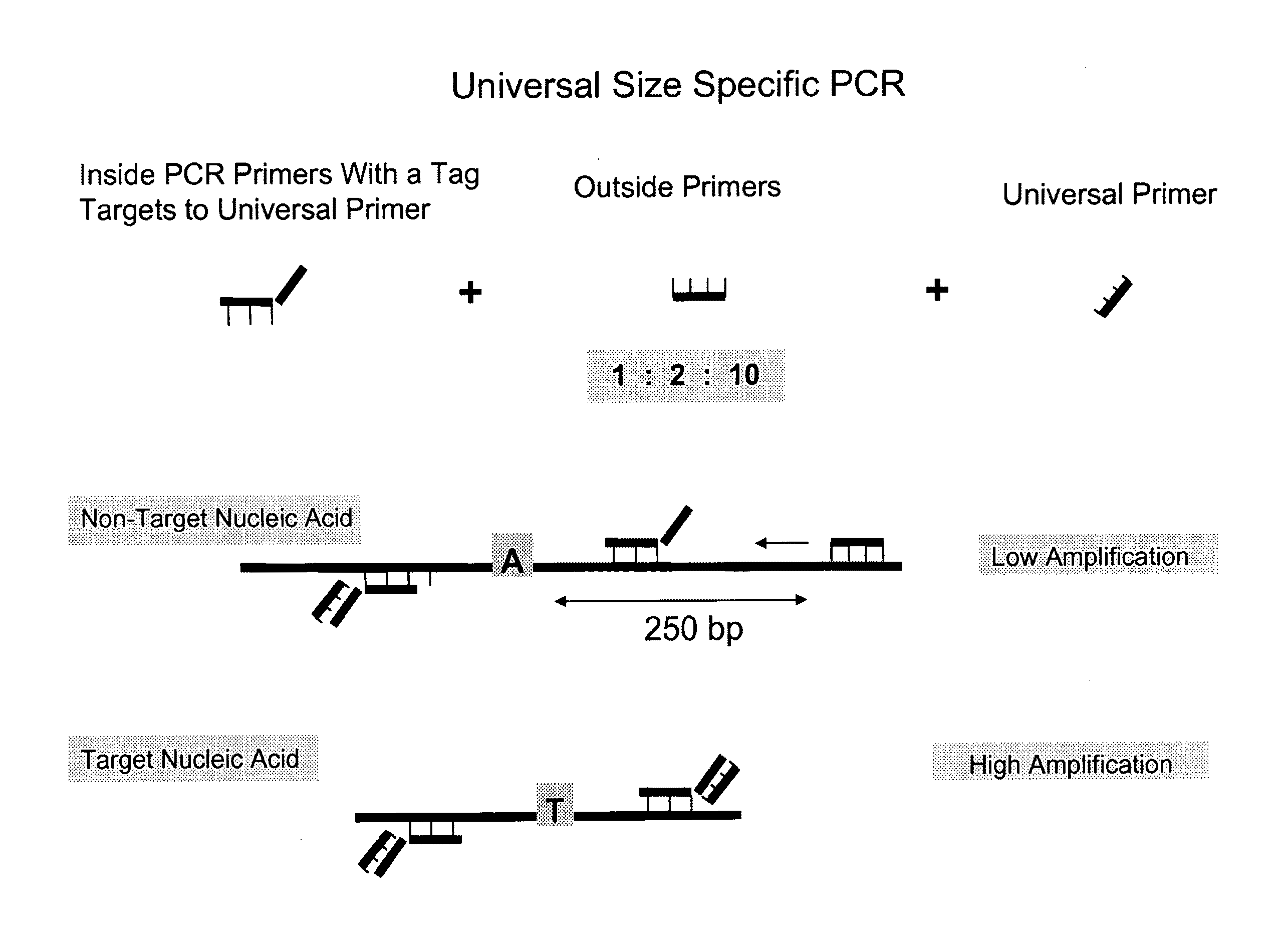
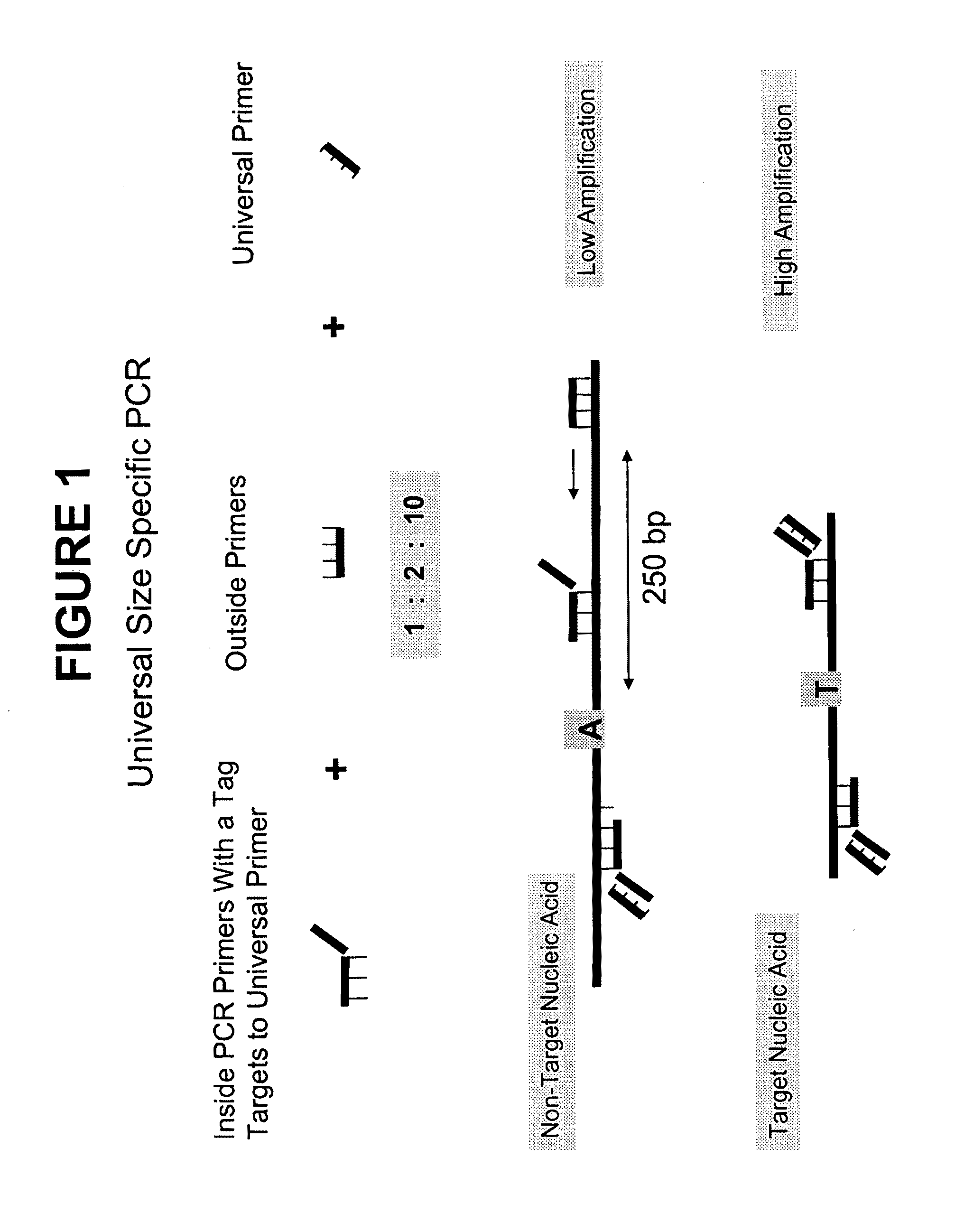
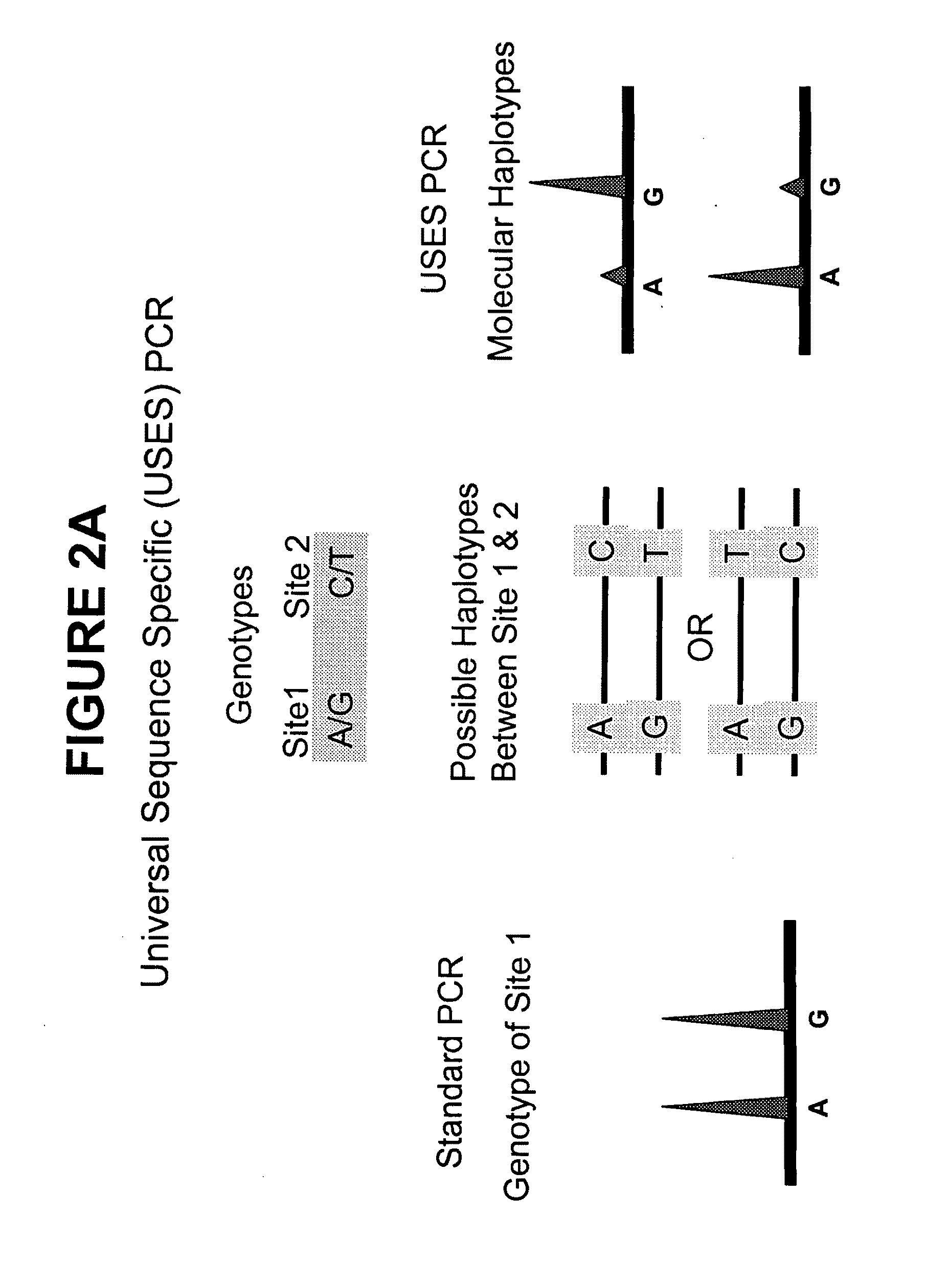
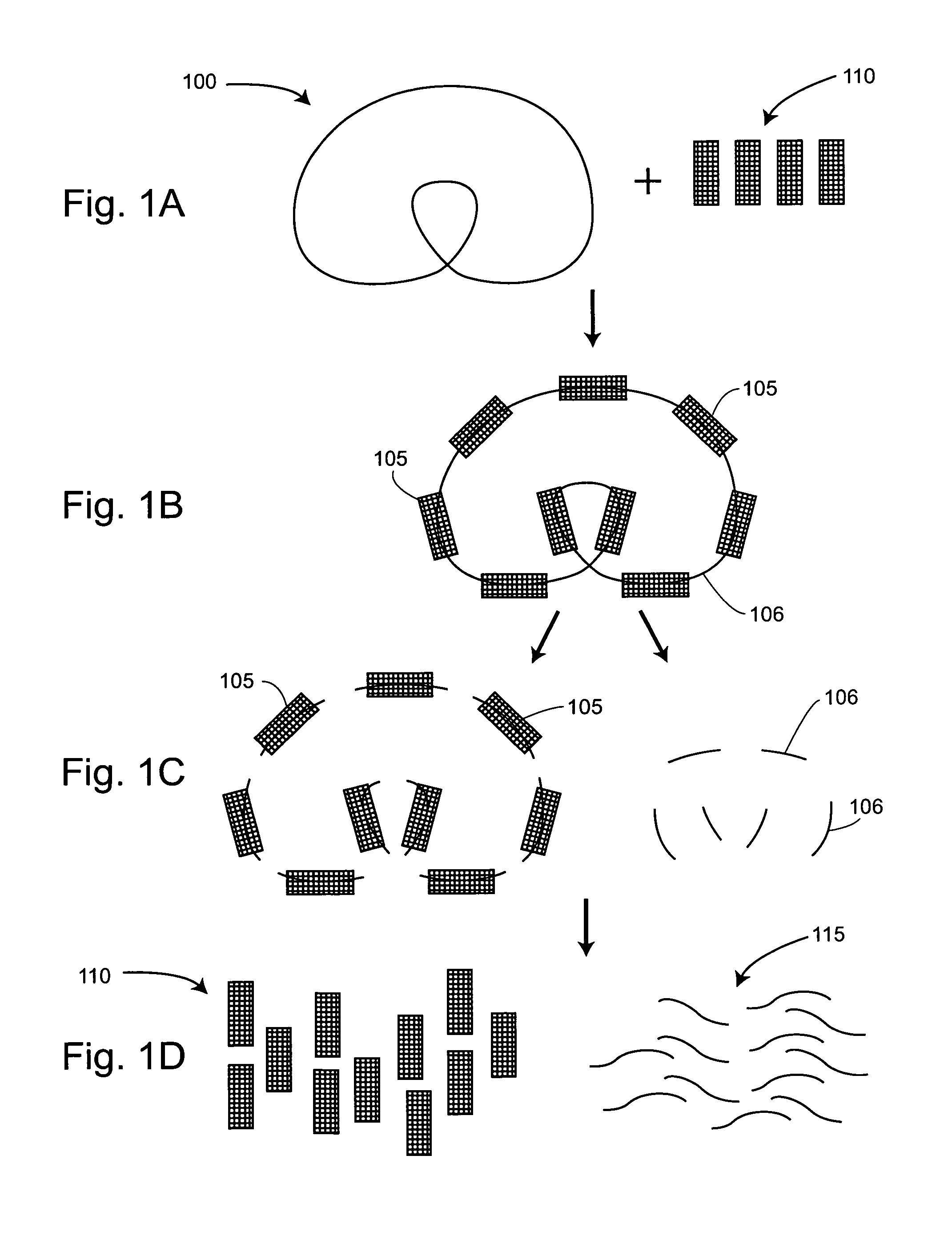
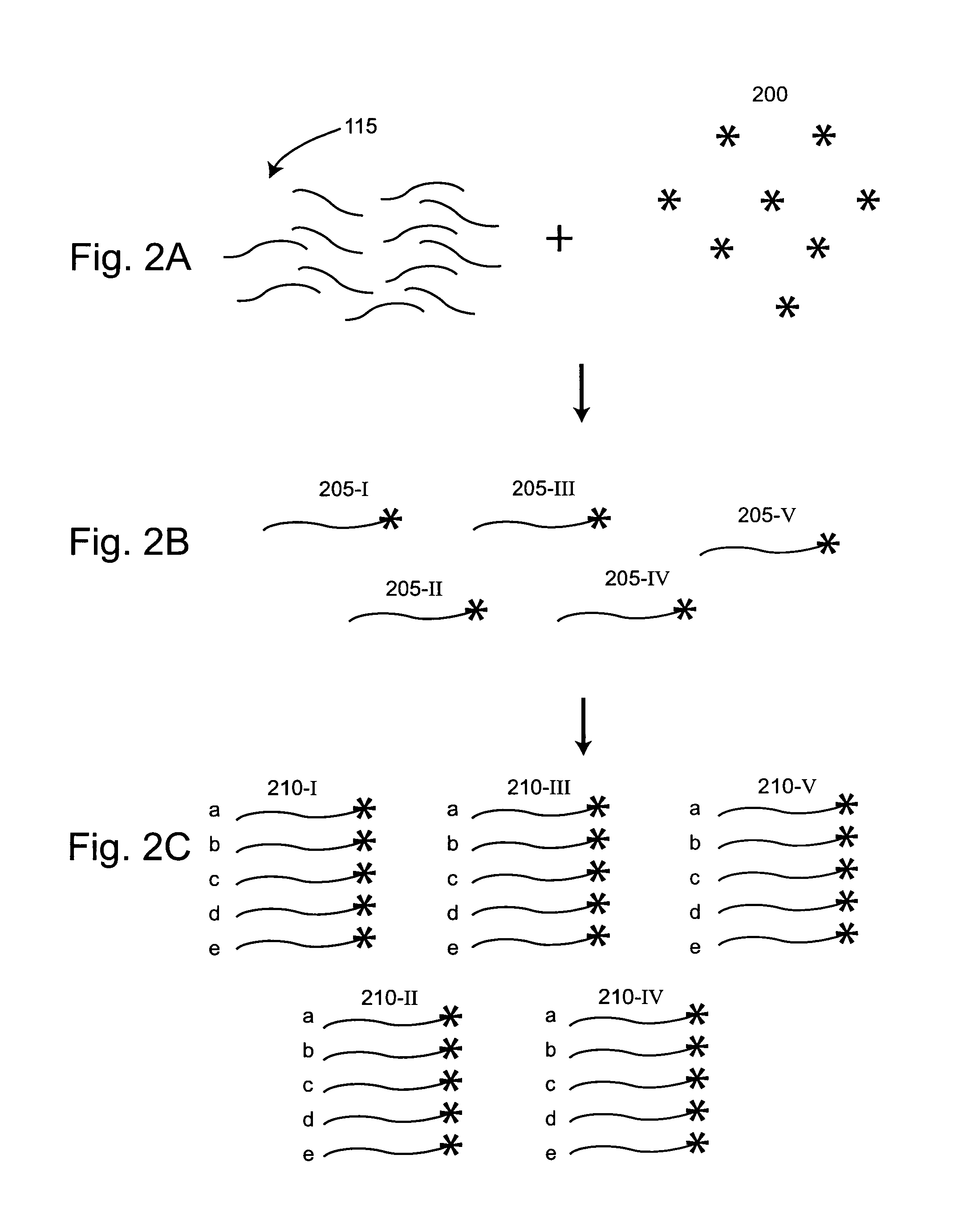
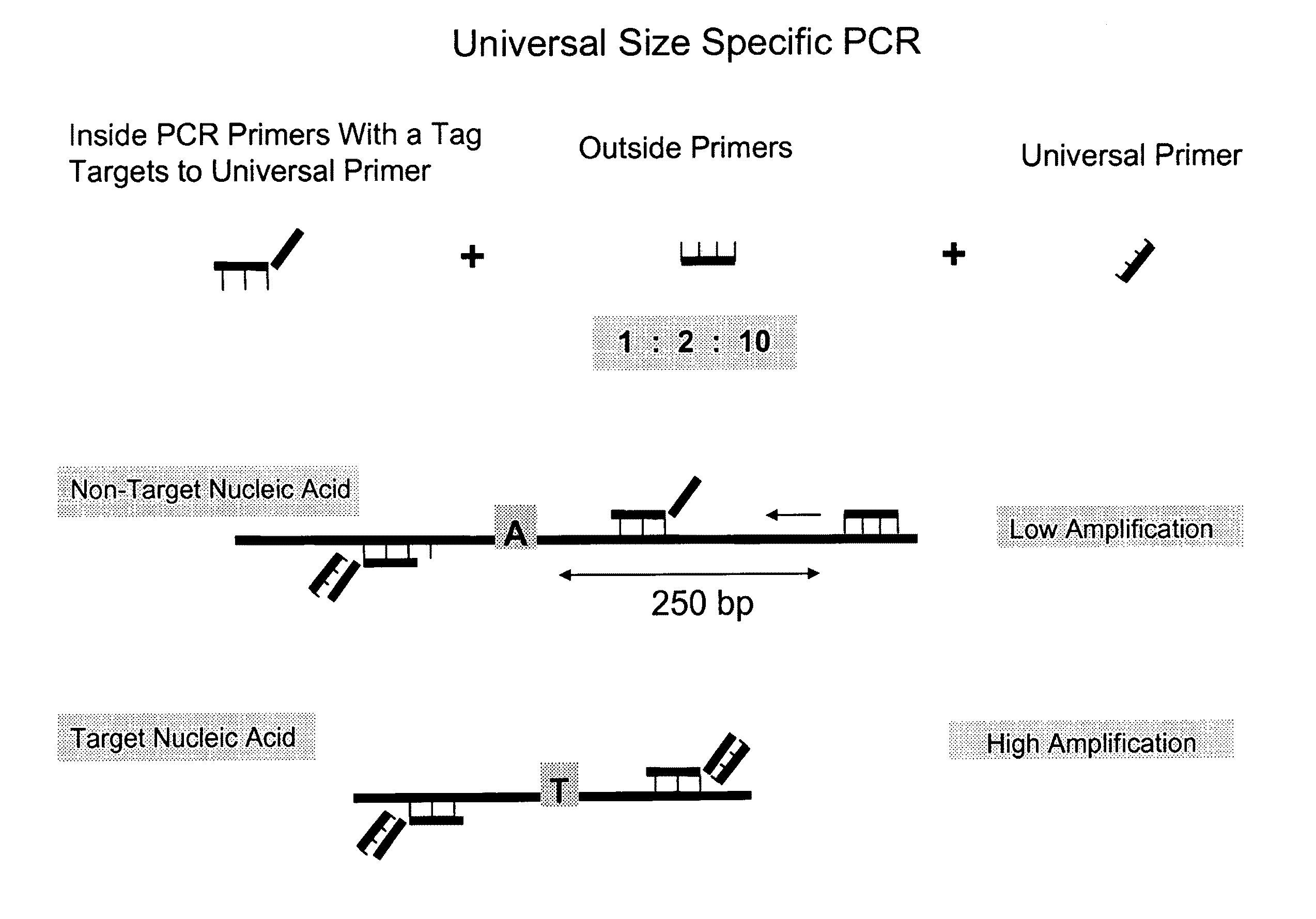
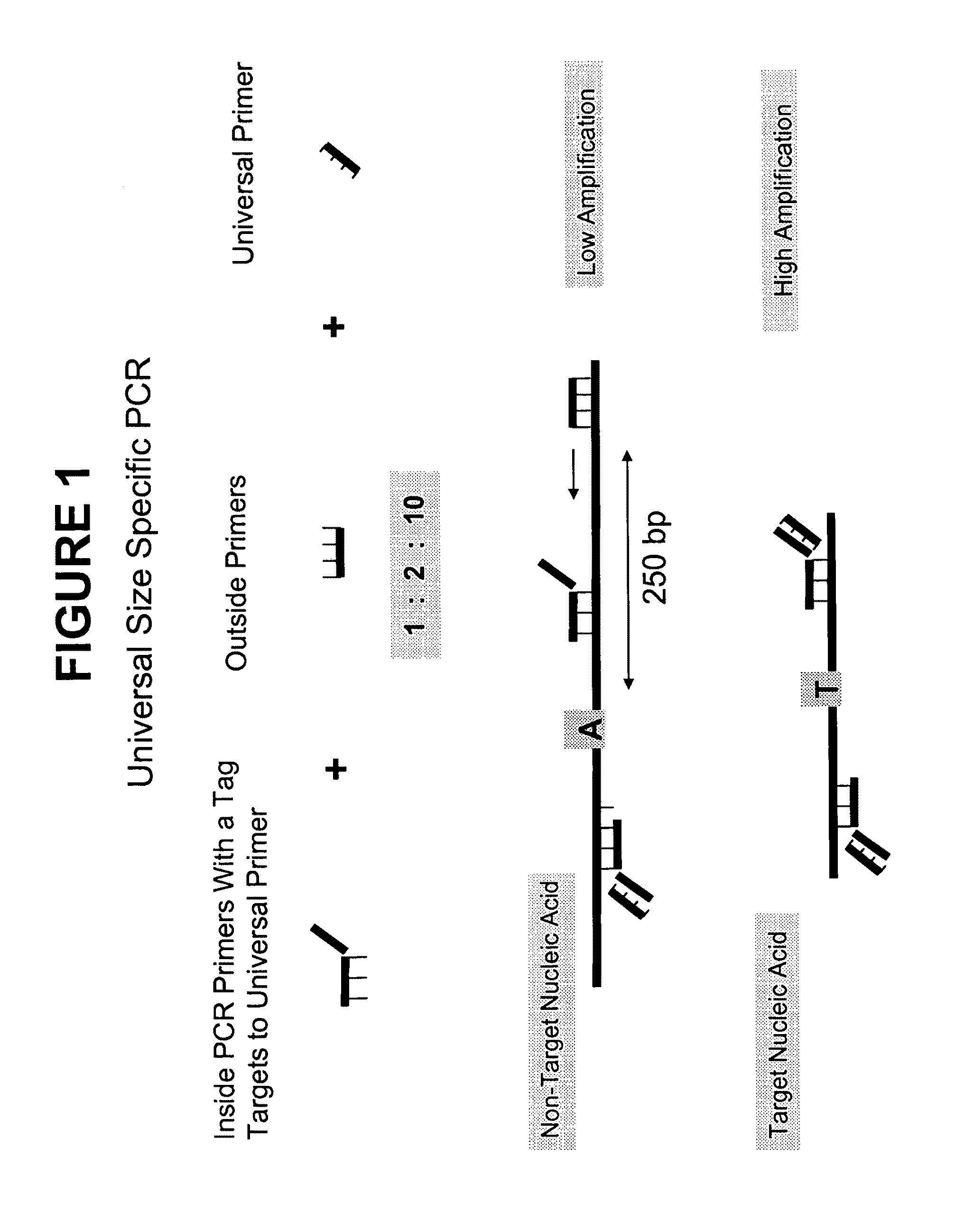
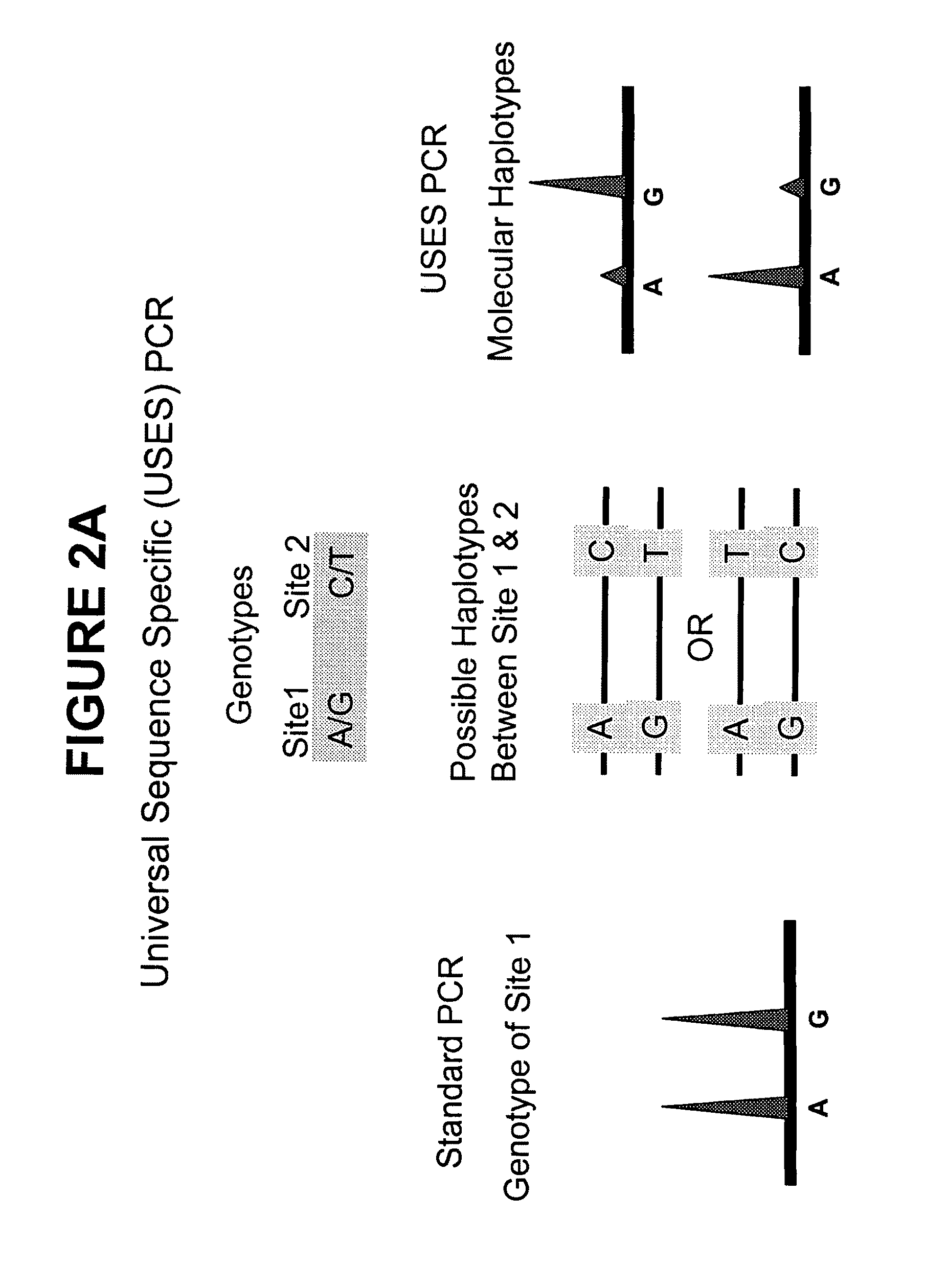
Methods and compositions for universal size-specific PCR
ActiveUS20110294699A1Simple and cost-effectiveSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomeComputational biology
Provided herein are products and processes for the amplification, detection and sequencing of short-stranded nucleic acid in the presence of a high background of long-stranded genomic material (e.g., host or maternal nucleic acids). The methods rely on the use of inside and outside primers introduced at varying concentrations, as well as universal amplification reactions that preferentially amplify short, low copy number nucleic acid.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
Error-free amplification of DNA for clonal sequencing
ActiveUS20090105094A1Reduce probabilitySequencing errorMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCloning sequencingDNA
Methods of preparing nucleic acid templates and providing the nucleic acid templates to low copy number reaction volumes are provided. Related compositions of nucleic acid templates are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Error-free amplification of DNA for clonal sequencing
ActiveUS8003330B2Reduce probabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCloning sequencingDNA
Provided are methods of producing low copy number circularized nucleic acid variants that can be distributed to reaction volumes. The methods include providing a template nucleic acid; producing a population of clonal nucleic acids from the template nucleic acid; generating a set of partially overlapping nucleic acid fragments from the population of clonal nucleic acids; circularizing the partially overlapping nucleic acid fragments to produce circularized nucleic acid variants; and aliquotting the circularized nucleic acid variants into reaction volumes. Related compositions of nucleic acid templates are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods and compositions for universal size-specific PCR
ActiveUS9404150B2Simple and cost-effectiveSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomeComputational biology
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
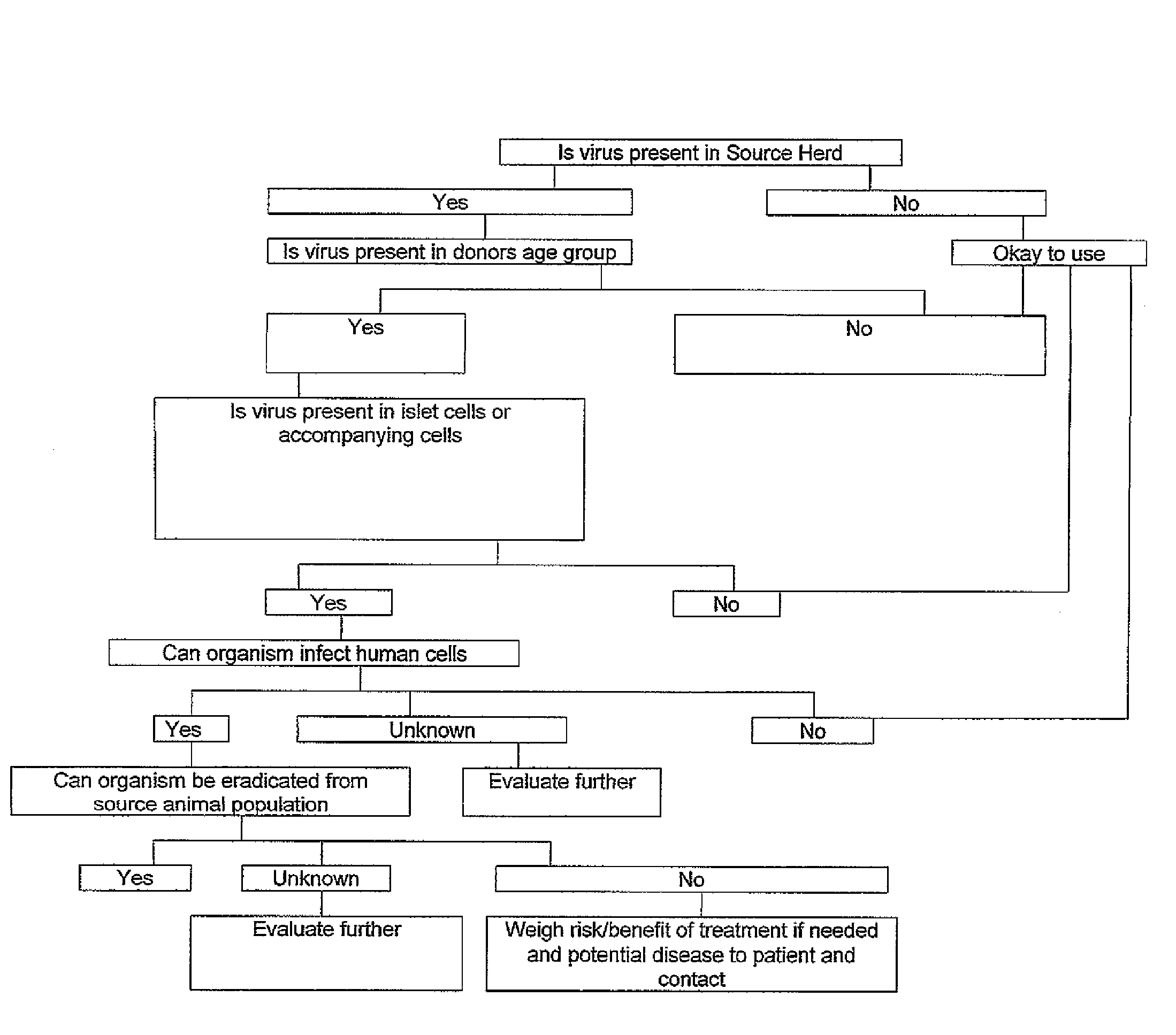
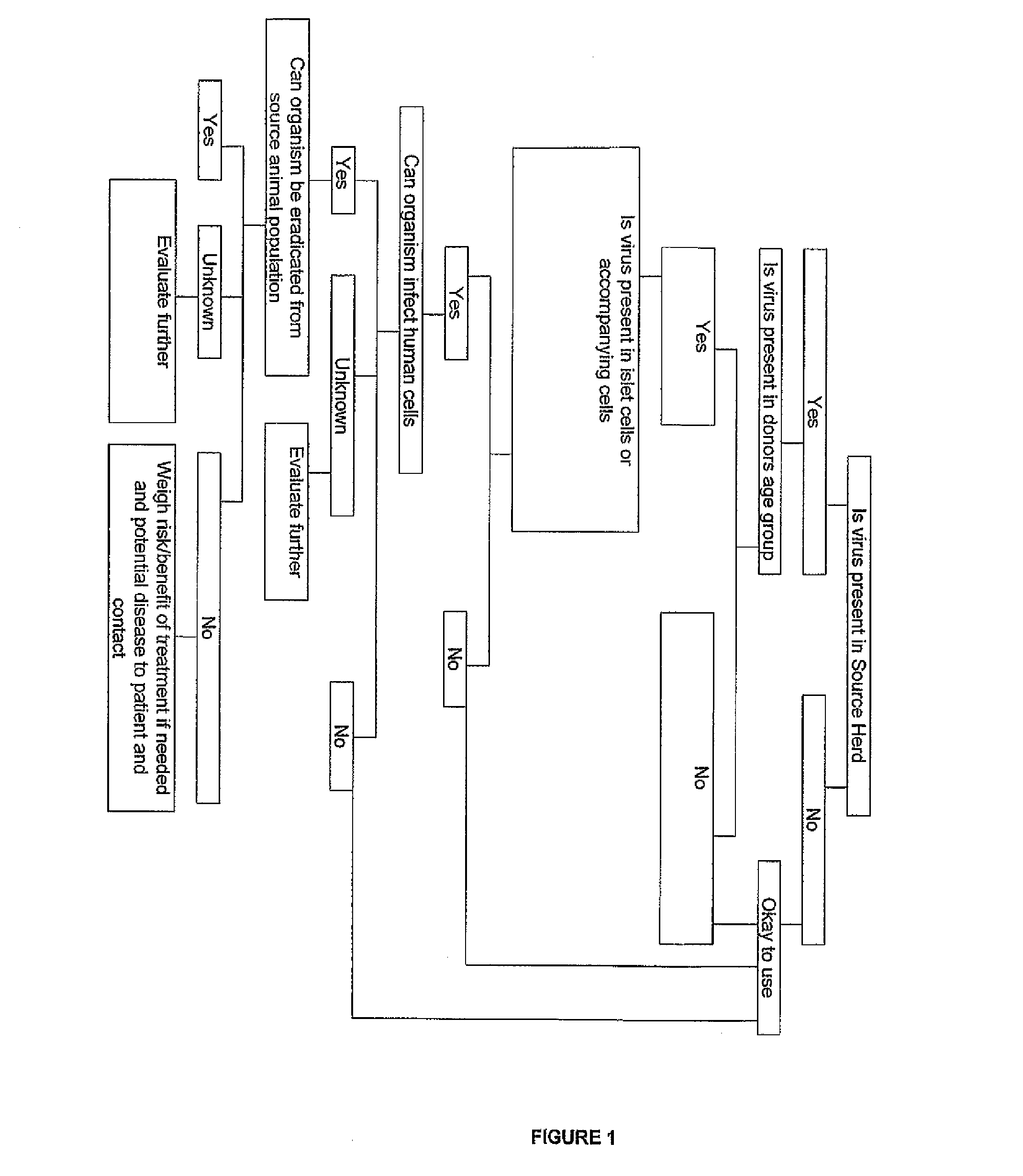
Swine population having low levels of porcine endogenous retrovirus and uses thereof
ActiveUS8088969B2Avoid damageReduce rejectionBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsPorcine endogenous retrovirusBiology
The invention relates to methods of selecting and maintaining a population of pigs having a low copy number of porcine endogenous retrovirus, and the use of such pigs as a source of cells, tissue and / or organs suitable for xenotransplantation. The invention further relates to methods for selecting cells, tissue and / or organs from such pigs for suitability for use in xenotransplantation.
Owner:DIATRANZ OTSUKA
Preparation method of glyphosate resistant transgenic rice
InactiveCN104004781AReduce the number of copiesShort processPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMolecular identificationGenetically modified rice
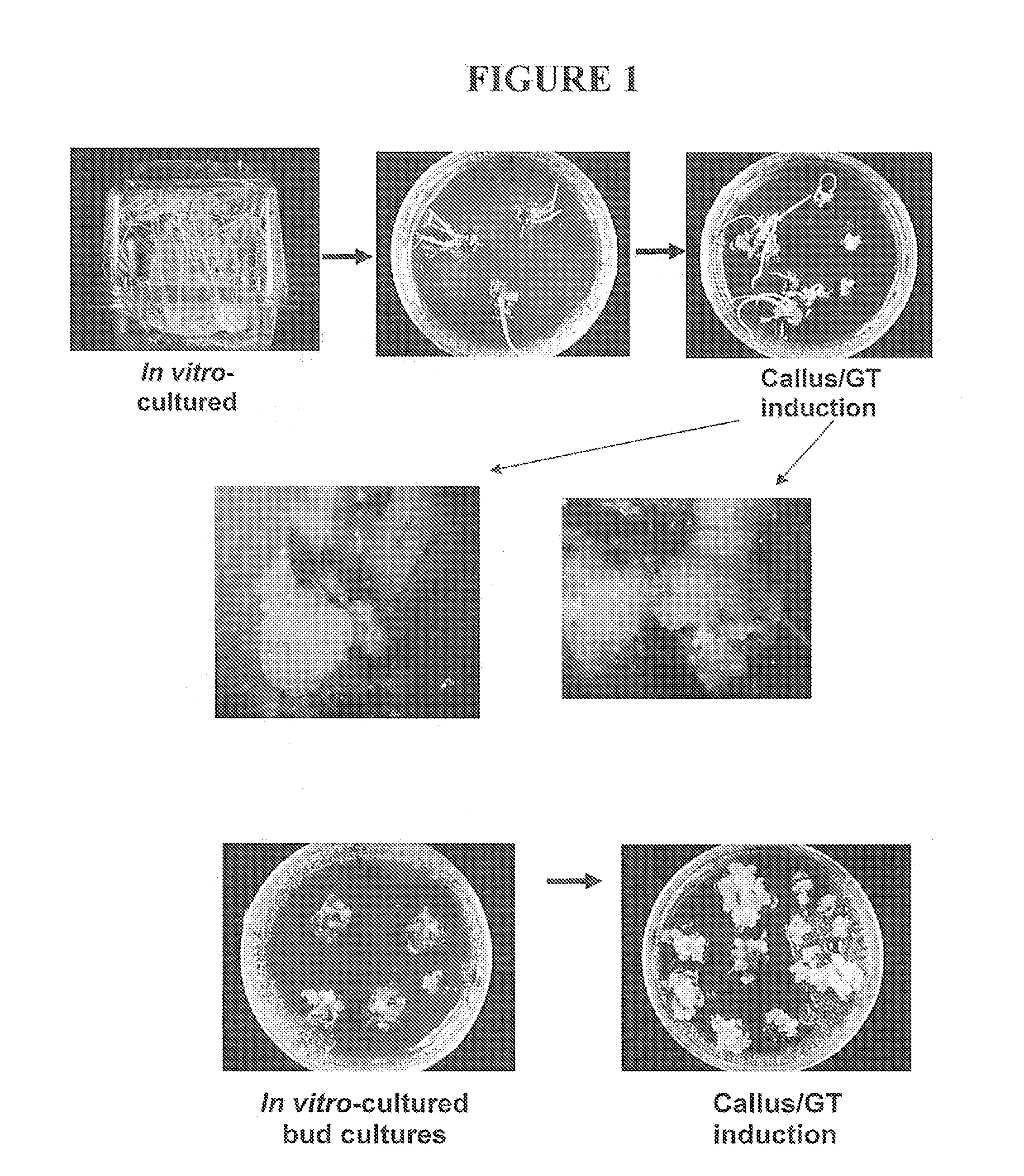
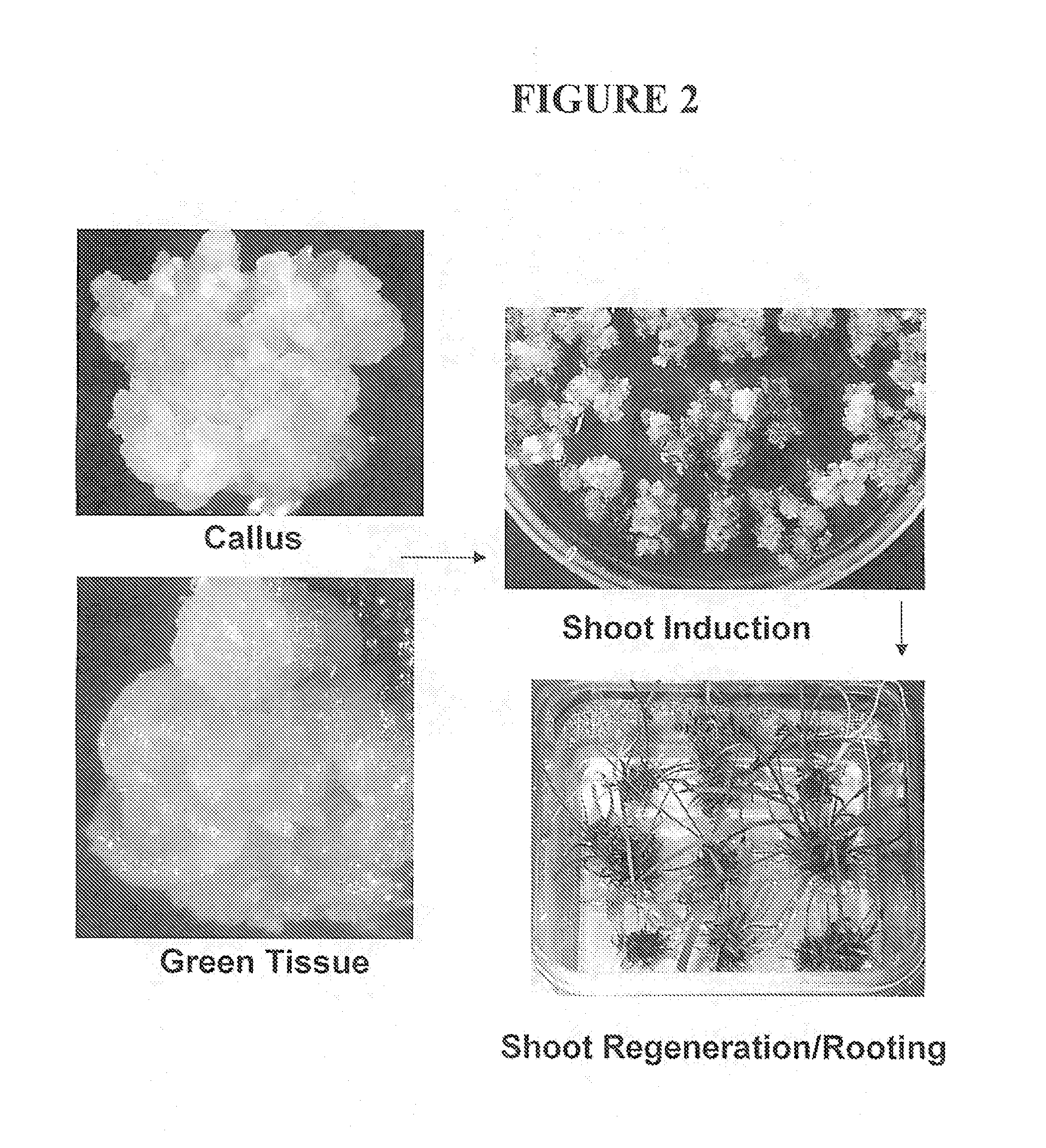
The invention provides a preparation method of glyphosate resistant transgenic rice. The method comprises the following steps: converting an expression vector containing glyphosate resistant gene into Agrobacterium tumefaciens, invading rice calluses by the Agrobacterium tumefaciens, transferring the calluses to a selective aluminum containing glyphosate for screening, choosing resistant calluses, differentiating, rooting, hardening-seedling, and transplanting to obtain glyphosate resistant transgenic rice. A molecular identification result shows that an exogenous gene is stably expressed. The obtained glyphosate resistant transgenic rice contains glyphosate herbicide resistant gene, contains no other screening marker genes, and can be used as a commercial herbicide resistant rice kind to reduce the reduce the later process and accelerate the breeding pace. The method has the advantages of simple operation, low copy number of transgenic plants, stable heredity properties, and good market application prospect.
Owner:CHINA NAT SEED GRP
Methods for tissue culture and transformation of sugarcane
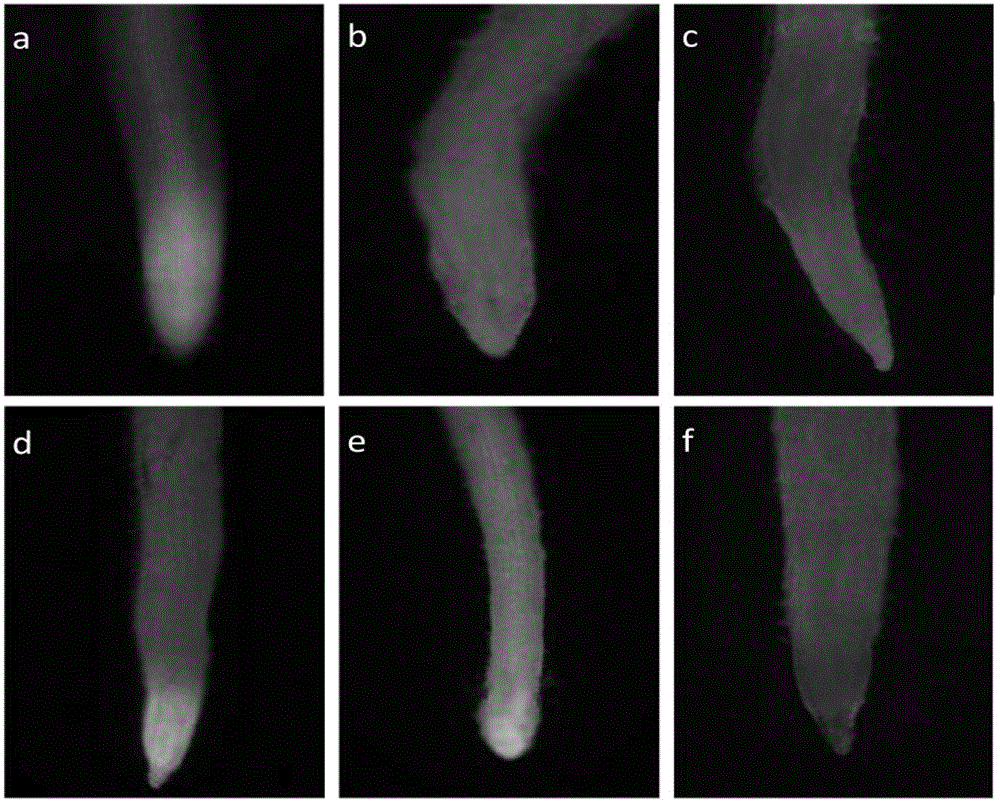
InactiveUS20130055472A1Efficient regenerationLong-term regenerabilityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationTransformation efficiencyGMO Plants
Compositions and methods for the efficient transformation and regeneration of monocot plants are provided. The methods of transformation involve infection with Agrobacterium. In this manner, any gene of interest can be introduced into the monocot plant with high transformation efficiency and in low copy number. Transformed and regenerated monocot cells, tissues, plants, and seed are also provided. The invention encompasses regenerating transformed plants, transgenic seeds produced therefrom, and transgenic plants and transgenic seeds from subsequent generations.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Promoter and plasmid system for genetic engineering
This invention provides a series of low-copy number plasmids comprising restriction endonuclease recognition sites useful for cloning at least three different genes or operons, each flanked by a terminator sequence, the plasmids containing variants of glucose isomerase promoters for varying levels of protein expression. The materials and methods are useful for genetic engineering in microorganisms, especially where multiple genetic insertions are sought.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Assay for detecting and quantifying HIV-1
InactiveUS20060068380A1Easy to separateMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeOligonucleotide
Compositions, methods and kits for detecting HIV-1 nucleic acids using nucleic acid amplification. Particularly described are oligonucleotides that are useful as hybridization probes and amplification primers for detecting very low levels of HIV-1 nucleic acids by real-time monitoring of amplicon production. The invented assays are characterized by high levels of precision in the quantitation of HIV-1 targets at low copy numbers, and by accurate detection of different HIV-1 subtypes, including M group and O group variants.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Internal standard gene suitable to exogenous gene detection such as transgene cotton and application thereof
InactiveCN1557966ABreed fastMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetically modified riceCopy number analysis
The present invention is internal standard gene suitable for quantitative and qualitative PCR detection of foreign gene of transgenic cotton, tomato, rice and rape and copy number analysis and its application. Based on the intraspecific non-specificity, interspecific specificity, monocopy or low copy number, and through bioinformatical analysis and biological experiment, four internal standard genes, including cotton SADI, tomato LAT52, rice SPS and rape HMGI / Y gene are found out separately in cotton, tomato, rice and rape. The detection sensitivity and precision of these internal standard genes are experiment proved in PCR method. At the same time, the quantitative and qualitative PCR detection systems for foreign gene of transgenic cotton, tomato, rice and rape are established separately based on these internal standard genes, and corresponding PCR detection and analysis platforms are established.
Owner:上海市农业科学院生物技术研究中心
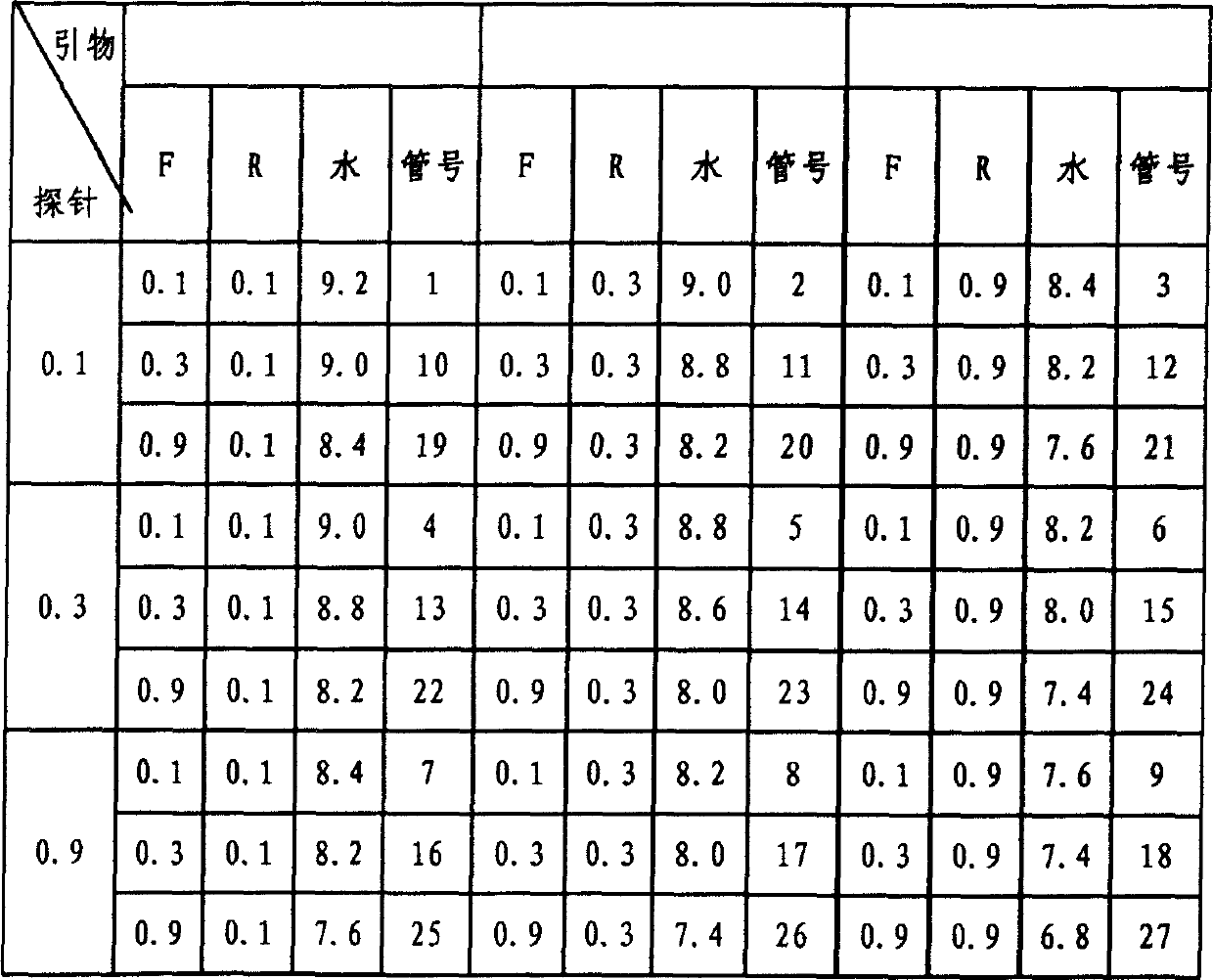
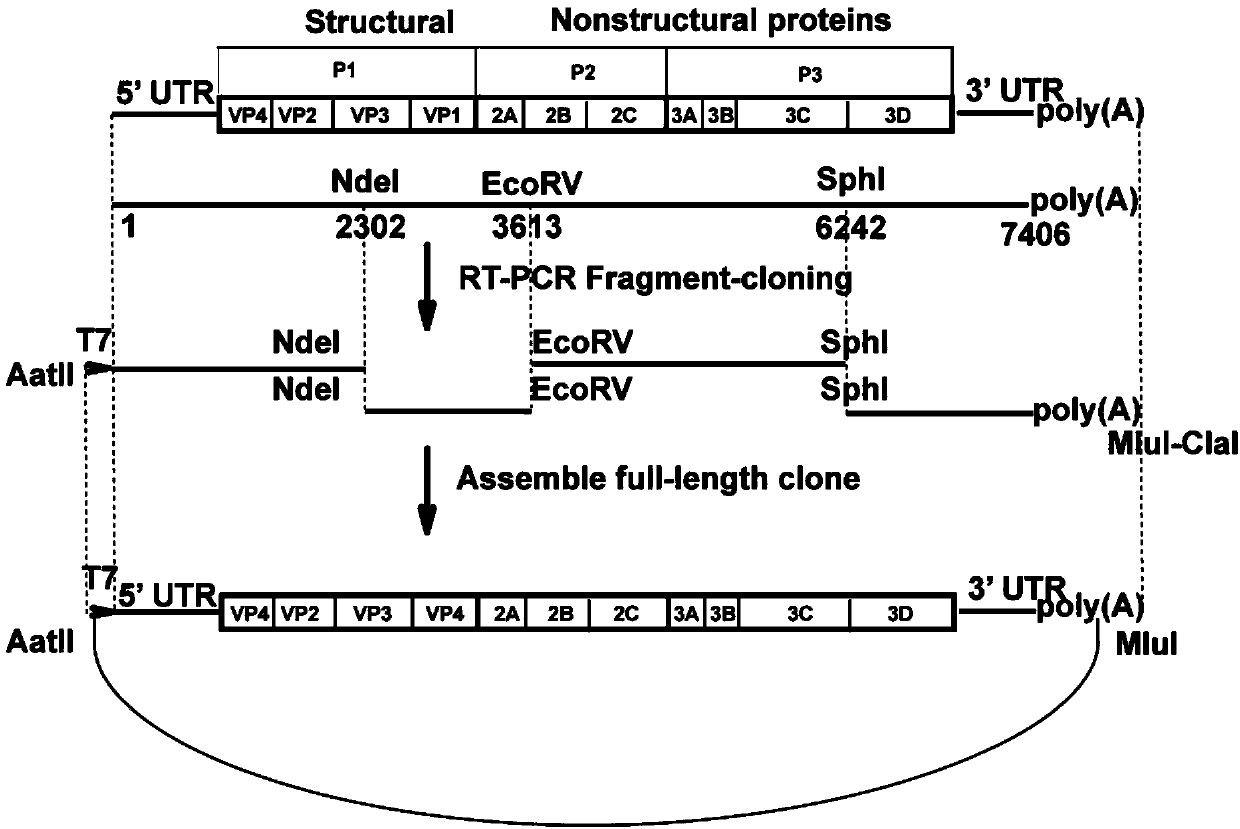
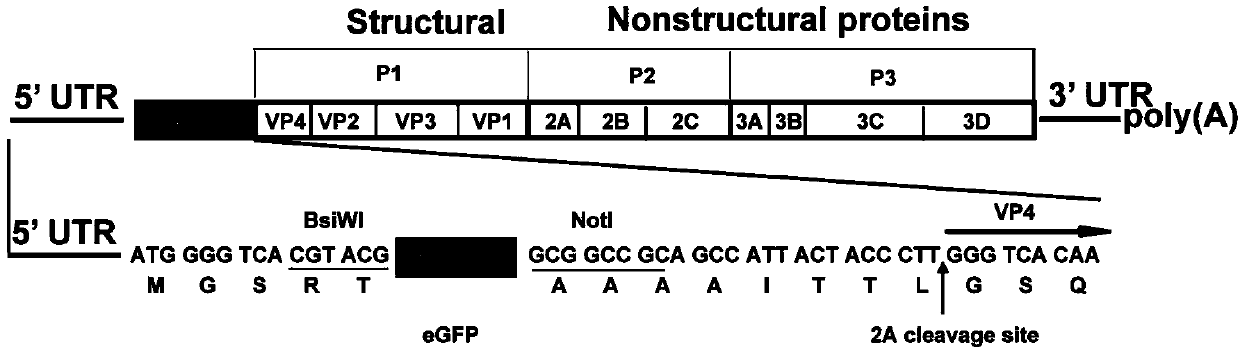
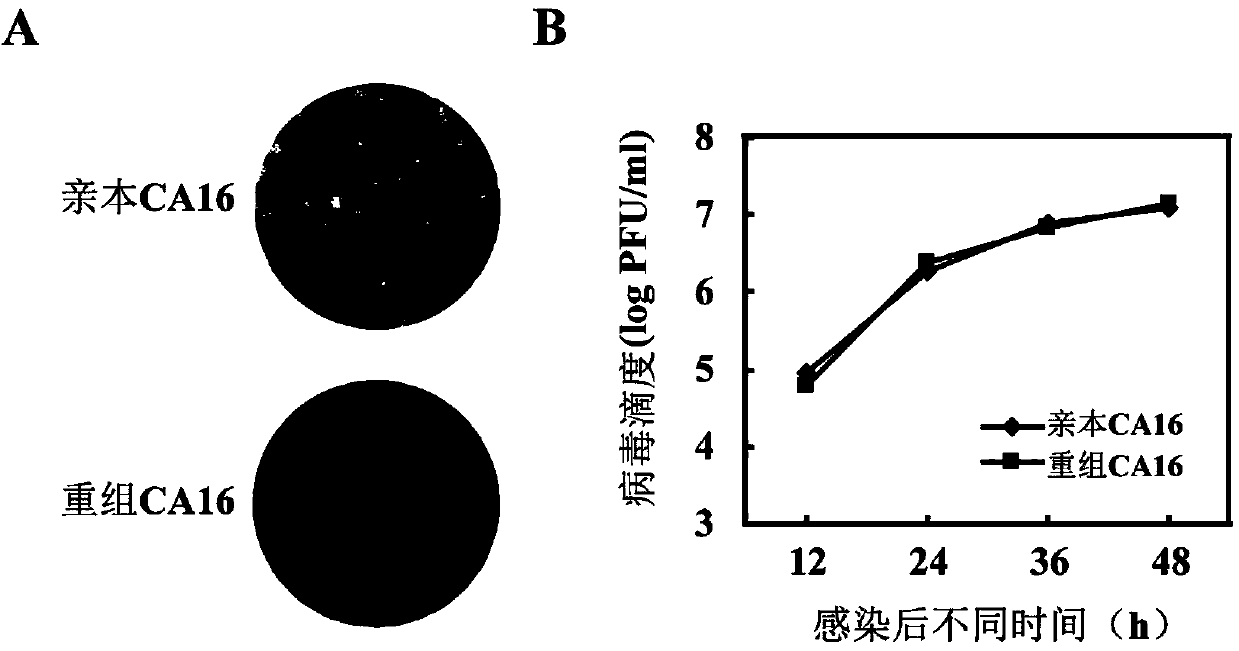
CA16 infectious clone with green fluorescent protein gene as well as construction method and application of CA16 infectious clone
InactiveCN103805634AGuaranteed fidelityAvoid difficult operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesTerra firmaAntiviral drug
The invention discloses a CA16 infectious clone with a green fluorescent protein gene as well as a construction method and an application of the CA16 infectious clone. The method comprises the steps of firstly, inserting full-length cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) of a CA16 / GD09 / 24 virus strain by taking a low copy number plasmid pACYC177 as a carrier; then, inserting an eGFP (enhanced green fluorescent protein) reporter gene and adding a 2A protease cleavage site (AITTL) between 5'UTR and VP4 by taking the full-length infectious clone as a skeleton so as to obtain a full-length infectious clone of the CA16 with the eGFP reporter gene. The CA16 infectious clone with the green fluorescent protein gene, constructed by the method, disclosed by the invention, can be used for saving an eGFP-CA16 reporter virus of which the growth tendency is similar to that of a recombinant CA16 virus and a parent CA16, and can also be used for screening antiviral drugs, thereby providing a convenient platform for deepening virus replication and pathogenesis researches and laying a solid foundation for screening and developing novel vaccines in future.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
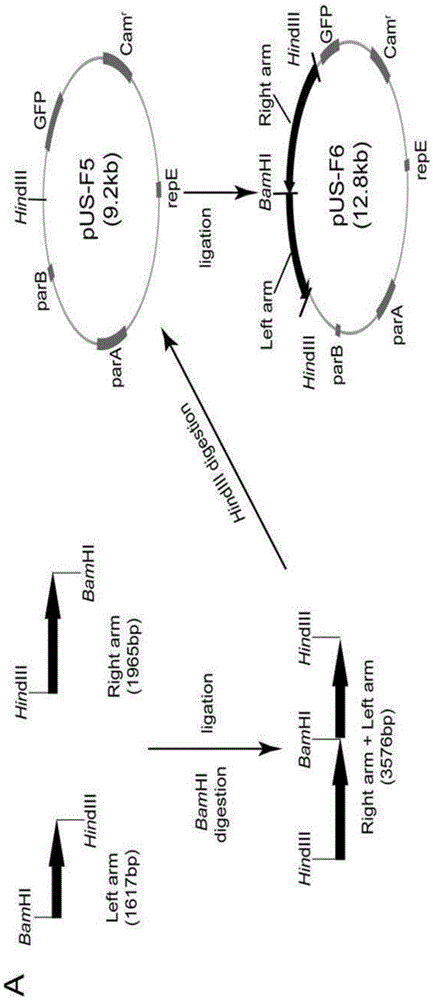
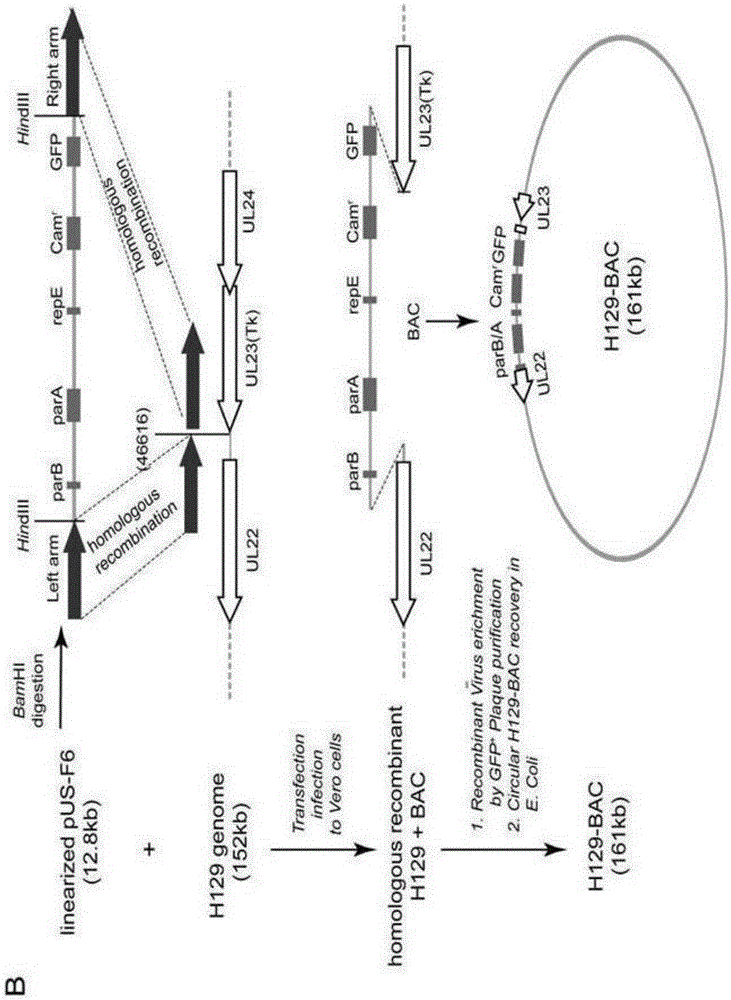
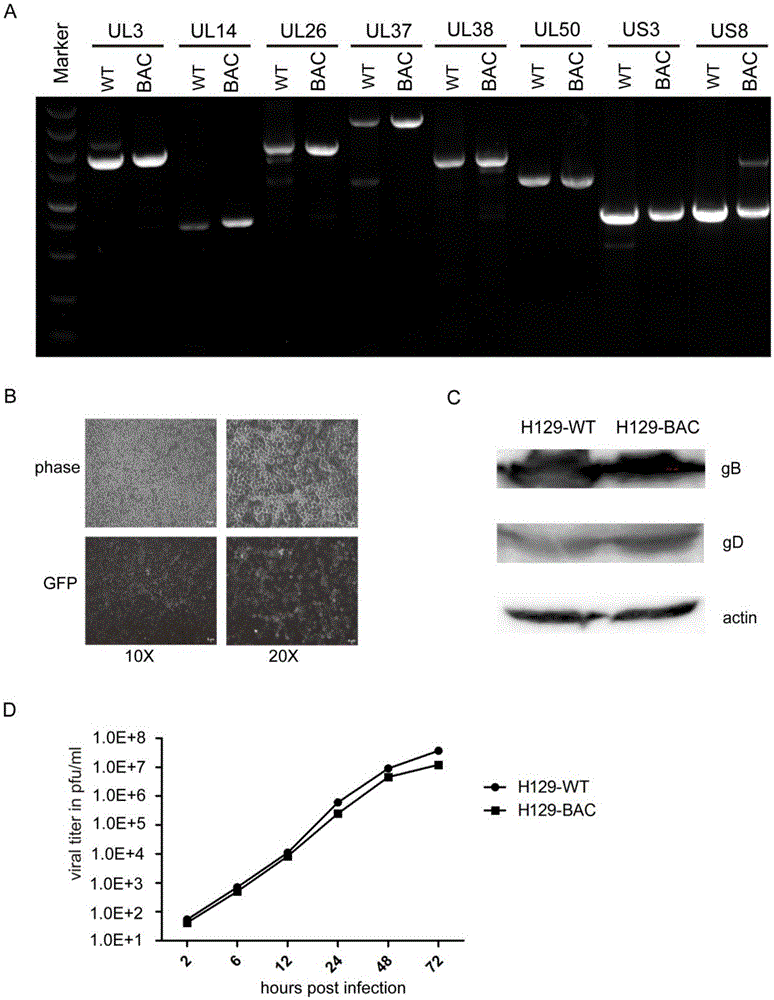
Construction method and application of HSV1-H129-BAC and mutant thereof
ActiveCN105567618ASmall molecular weightDoes not affect structure and functionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHerpes simplex virus DNAMutant
The invention relates to the biotechnical field, and concretely relates to an HSV1-H129-BAC and a mutant thereof. The above virus and the mutant thereof carry a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), can keep low-copy number self-replication in specific bacteria, and solve the disadvantages of unable long-term preservation, unable self-replication and inconvenient molecular biologic mutation reconstruction due to too large herpes virus genomes. The virus and the mutant thereof also carry a GFP reporter gene, and substantially develop the application prospect of the herpes virus as a tool virus. The invention also provides a construction method of the H129-BAC and the mutant thereof. The method allows H129 to be reconstructed in order to obtain H129-BAC and endows the H129-BAC with more mutant types; and the construction method, the H129 and the mutant thereof form a genetic modification platform with high application possibility.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
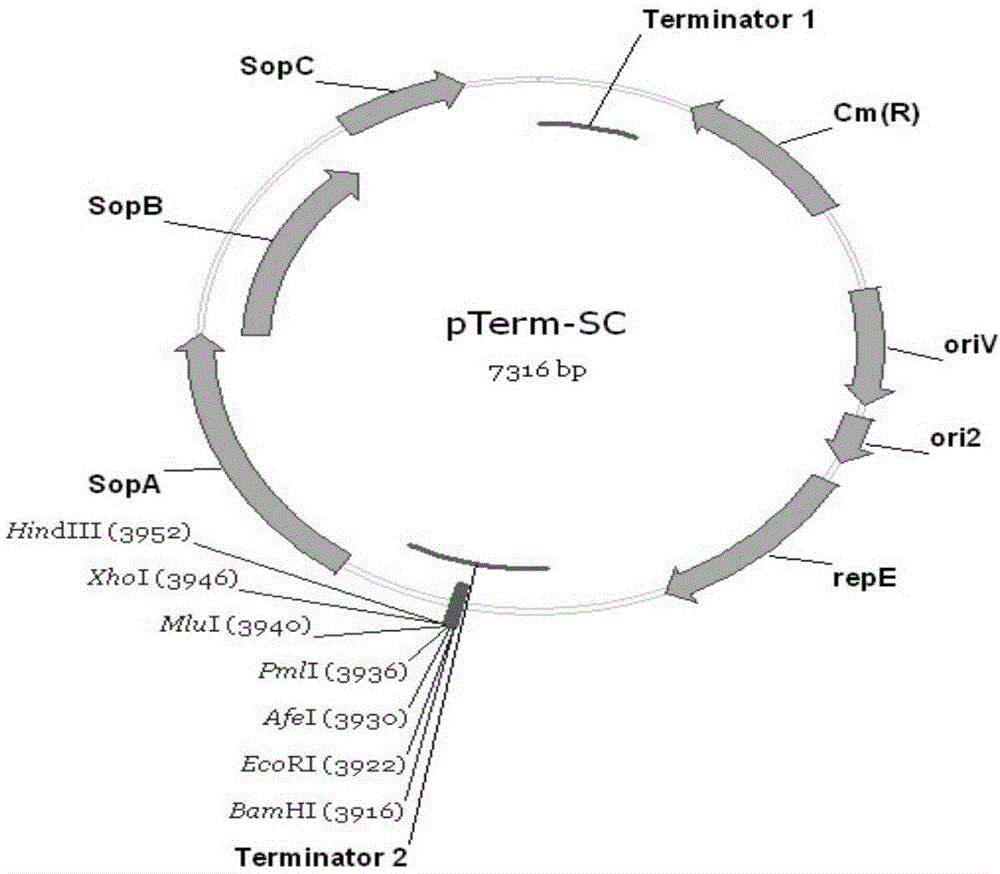
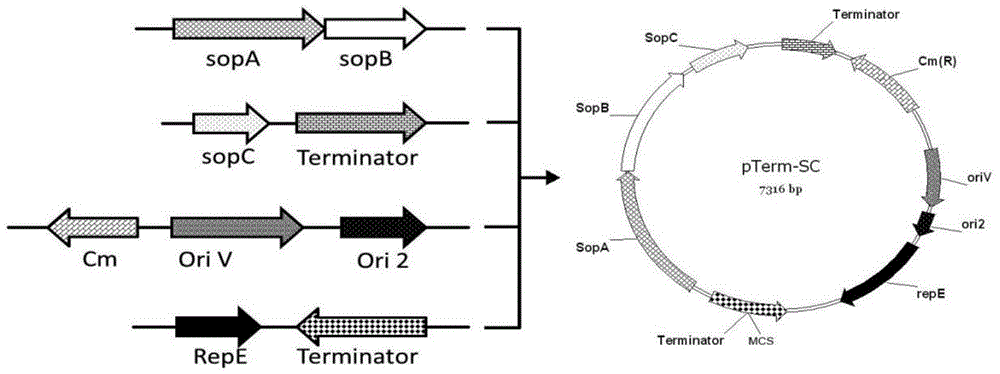
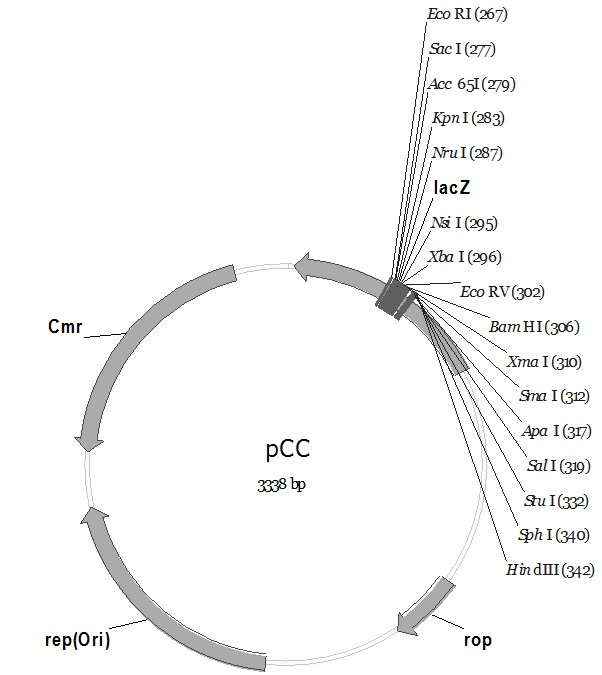
PTerm-SC plasmid as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN104480130AEasy extractionTranscriptional repressionMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAntibiotic YGene engineering
The invention relates to a pTerm-SC plasmid as well as a construction method and application thereof. The pTerm-SC plasmid comprises a repE gene, a sopA gene, a sopB gene, a sopC gene, an ori2 replicon, an oriV replicon, prokaryote transcription terminators and antibiotics resistance genes. The pTerm-SC plasmid has the characteristics of very low copy number, high volume and stability and the like, can be applied to gene engineering fields such as the cloning, the screening, sequencing and the genome construction of complex-structure genes including repetitive-sequence genes, instable genes and long-fragment genes and has important role in the high-efficiency and high-quality synthesis of genes.
Owner:GENEWIZ INC SZ
One-step droplet digital PCR method for quantitatively detecting GII type norovirus in fruits and vegetables
ActiveCN107338328ASensitive detection methodThe detection method is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr methodQuarantine
The invention discloses a one-step droplet digital PCR method for quantitatively detecting the GII type norovirus in fruits and vegetables. According to the method, RT-ddPCR is utilized, a primer and a probe for RT-qPCR detection of the GII type norovirus are combined for use, reaction is carried out, and then the high-sensitivity rapid detection for the GII type norovirus is realized. The method is high in sensitivity and can achieve about 2copies / [mu] L, but the sensitivity of the conventional RT-qPCR is usually 10 copies / [mu] L; the amplification efficiency is high, the amplification efficiency is 95.4%, R2 is equal to 0.9973. Under low copy number, compared with RT-qPCR, the method provided by the invention can more effectively avoid the influences of inhibitors in fruits and vegetables, and the false negative generation is reduced. Therefore, the detection method provided by the invention is sensitive, accurate and visual, a novel detection method is provided for the government departments including the agriculture department and the inspection and quarantine bureau, and related detection mechanisms and enterprises, and guiding significance is also achieved.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for quantitatively detecting white spot syndrome virus through TaqMan probe
InactiveCN108342512AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular DiseaseWhite spot syndrome
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively detecting white spot syndrome virus through a TaqMan probe. The method comprises the steps: firstly, extracting genome DNA of a sample to be detected; then designing a primer and the TaqMan probe; finally, performing fluorogenic quantitative PCR detection on the genome DNA of the sample to be detected through the designed primer and the designedTaqMan probe. The detection method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high detection flexibility and good specificity, short used time, no false positive situation generation, application to molecular disease detection and early warning of prawn farming in China and good application prospect; furthermore, the lowest copy number which can be detected by the detection method is 7.8.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
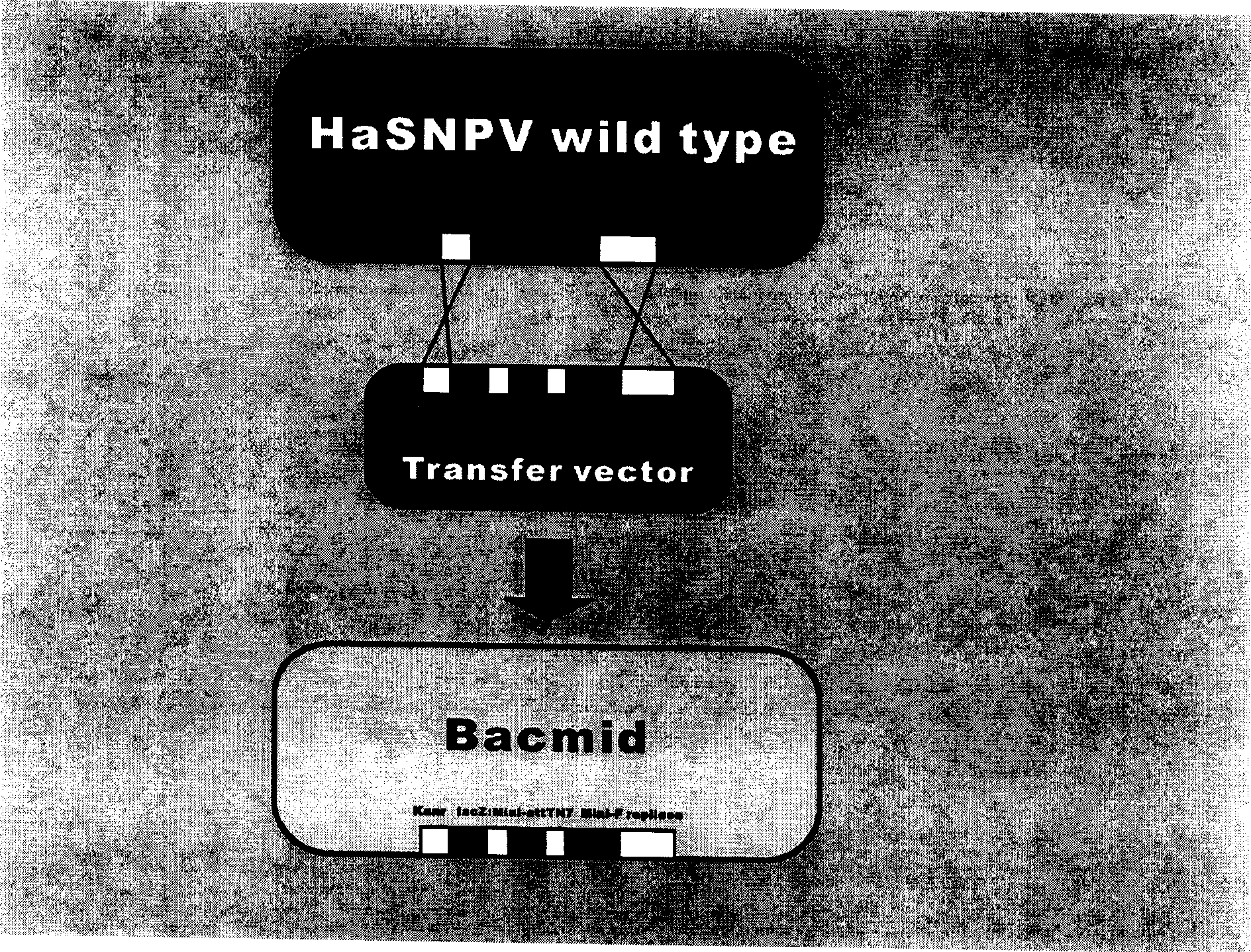
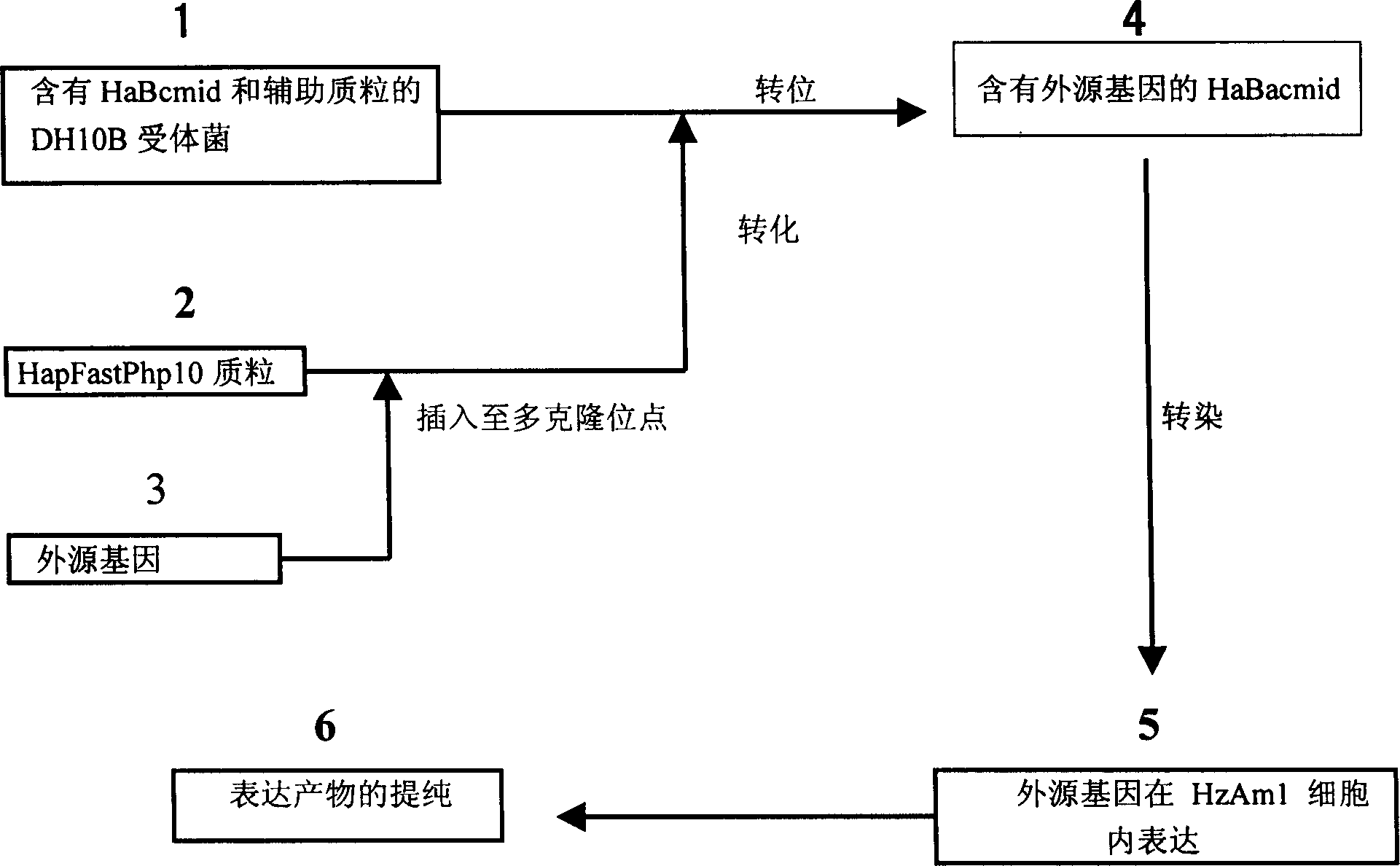
Cotton bollworm single particle embedded nuclear polyhedrosis virus shuttle expression carrier and preparation method
A single embedded polyhedronvirus shuttle expression carrier of bollworm is configured through inserting the low-copy bacterium F replicon, kanamycine resistant gene and beta galactosidase gene to the polyhedrom gene site of the virus genom. The doner plasmid is used to transfer the exogenous gene to the insetion site of transposon in the said shuttle expression carrier. After bollworm cell is transfected by said DNA, the infections recombinant virus particles are formed to express exogenous gene under control of polyhedron promoter and P10 promoter.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Construction and use of catalogued nucleic acid libraries that contain advantageously adjusted representations of defined components
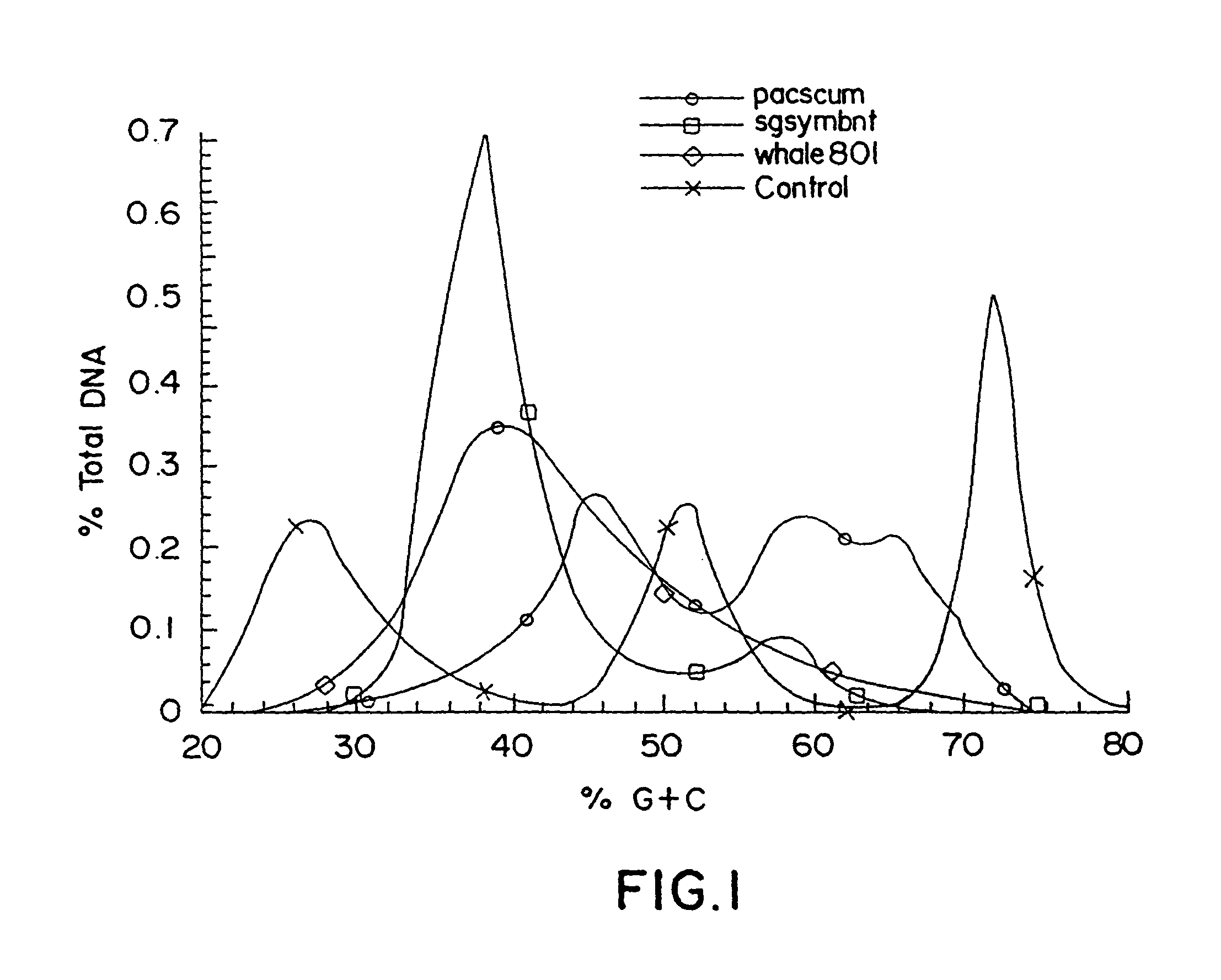
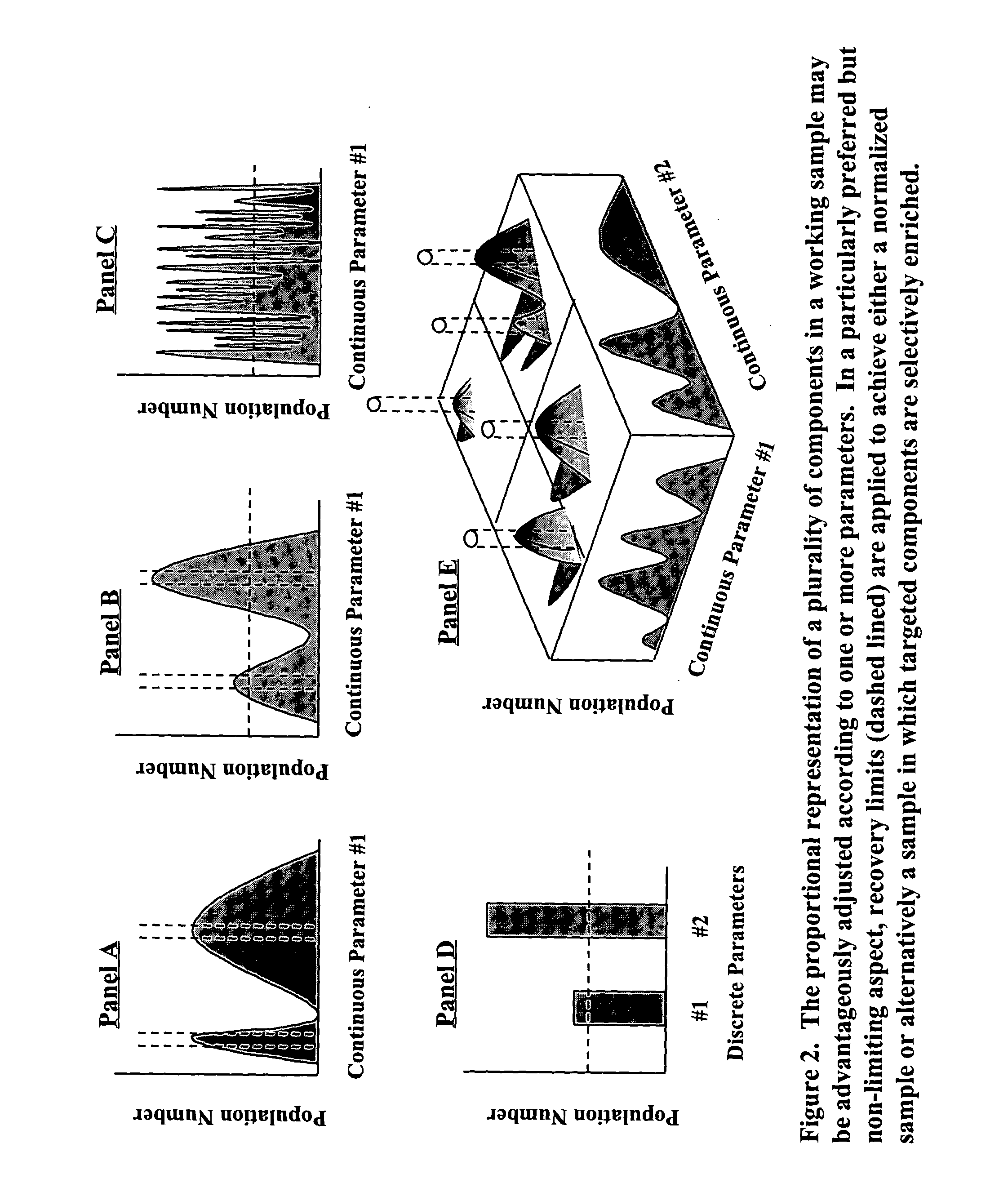
InactiveUS8476011B1Reduce redundancyIncreases proportional representationSugar derivativesOrganic chemistry methodsBiological bodyGene product
A process for constructing a catalogued nucleic acid library in which the proportional representation of the constituents is adjusted to advantage through the use of disclosed technologies for positive and negative selection. The resultant benefit is that significantly fewer library constituents will need to be screened in order to identify a potentially desired constituent. Moreover, library constituents that previously would have been essentially “lost” are now recoverable. Preferred embodiments of this invention include the cataloguing, normalization, and enrichment of library constituents. By way of example, but not limitation, this technology is serviceable for constructing a library that contains an adequate representation of desirable constituents that (1) are initially found in low-copy numbers within a sample source or (2) originate from an organism that is problematic to culture. Applicable uses of this invention include any library-screening endeavor previously hindered by logistical impediments.By expanding previous logistical frontiers this invention allows for a novel generation of previously unattainable molecules—particularly molecules that are “unclonable” from conventional, unadjusted libraries—to now be detected, cloned, manipulated, expressed, studied, and used. By disclosing the construction and screening of high yielding nucleic acid libraries from mixed and uncultivated organisms, the instant technology eclipses former boundaries in the area of biological discovery and enables the full breadth of biological diversity to be accessed in the search for previously undiscovered genes and gene products. The benefits of the present invention are seen to extend to areas of diagnosis, medicine, agriculture, manufacturing, and academia.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
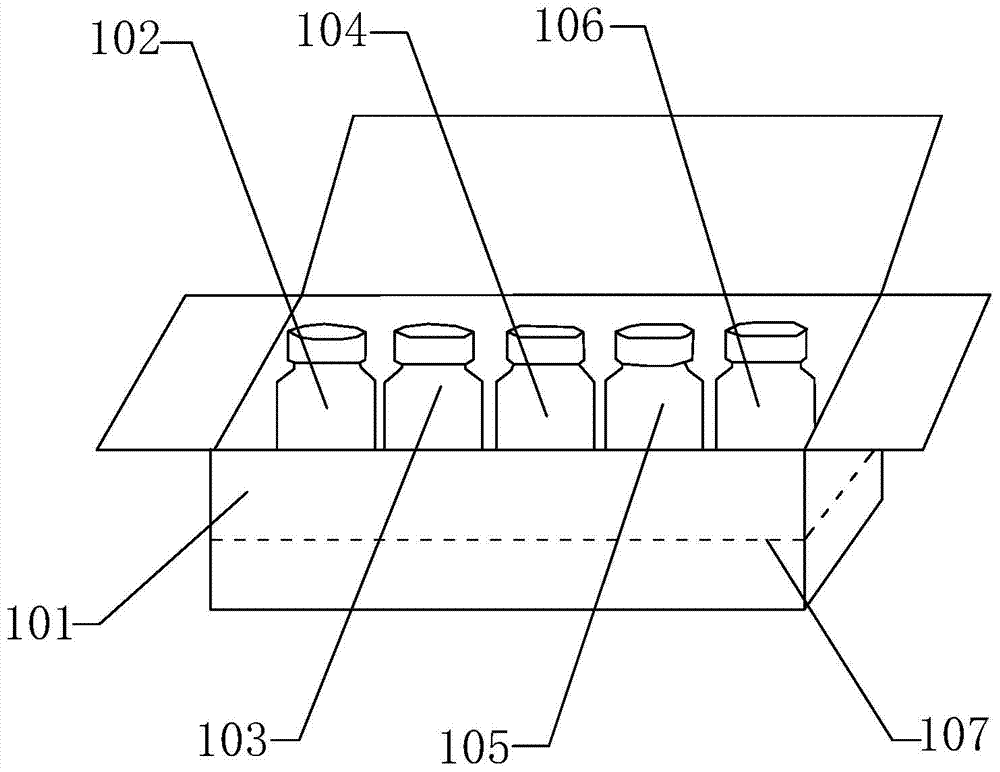
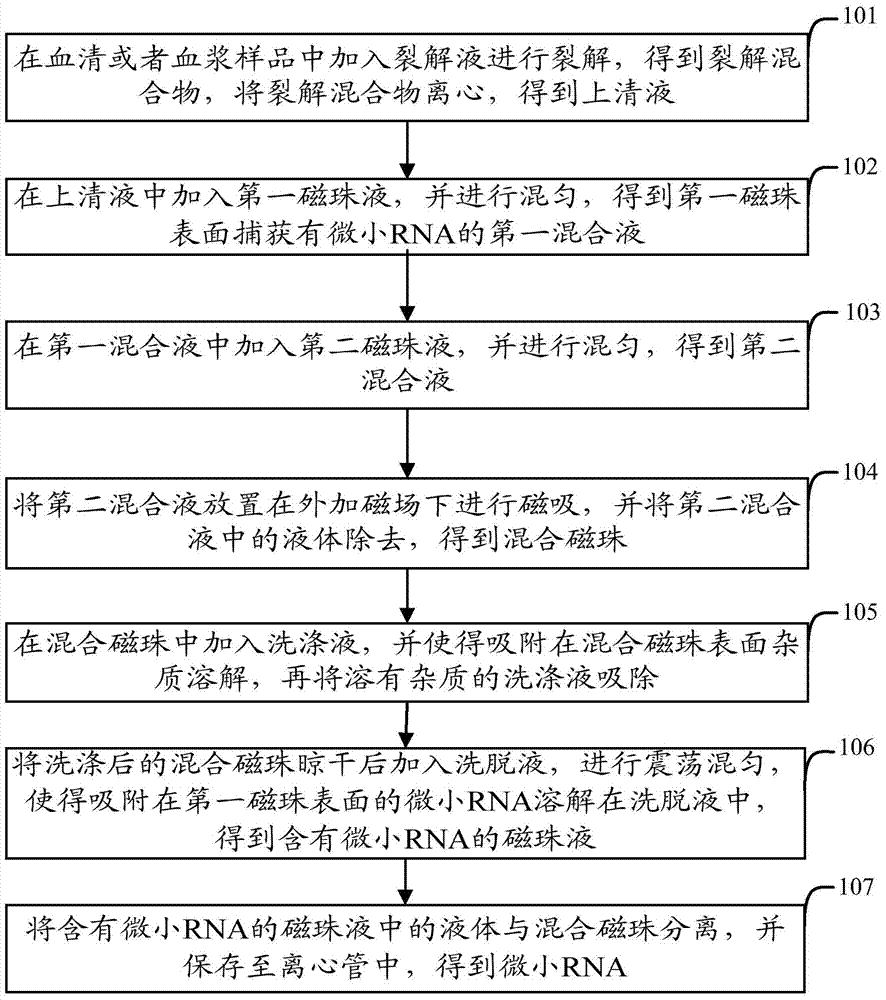
Kit and extraction method for extracting micro ribonucleic acid (RNA)
ActiveCN103789197AIncrease acquisition rateEnhanced magnetic fieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCrystallographySerum samples
The invention relates to the technical field of organisms, and particularly relates to a kit and an extraction method for extracting micro ribonucleic acid (RNA). The kit comprises a box body, a reagent bottle containing first magnetic bead liquid, a reagent bottle containing second magnetic bead liquid, a reagent bottle containing lysate, a reagent bottle containing an eluent, and a reagent bottle containing a scrubbing solution, wherein a foam pad is arranged on the inner bottom wall of the box body; the edge of the foam pad is attached to the inner lateral wall of the box body; five grooves are arranged on the foam pad; one reagent bottle is respectively arranged inside each groove; the first magnetic bead liquid contains a plurality of first magnetic beads, and a targeting sequence or a random sequence capable of being paired with the micro RNA is modified on the surface of each magnetic bead; the second magnetic bead liquid contains a plurality of second magnetic beads, and a hydrophilic high-molecular polymer with negative charge is modified on the surface of each magnetic bead. By adopting the kit disclosed by the invention, the micro RNA in plasma or serum can be more efficiently extracted, and the kit is especially applicable to extraction of the micro RNA with low content or low copy number in a plasma or serum sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIDA BIOTECH
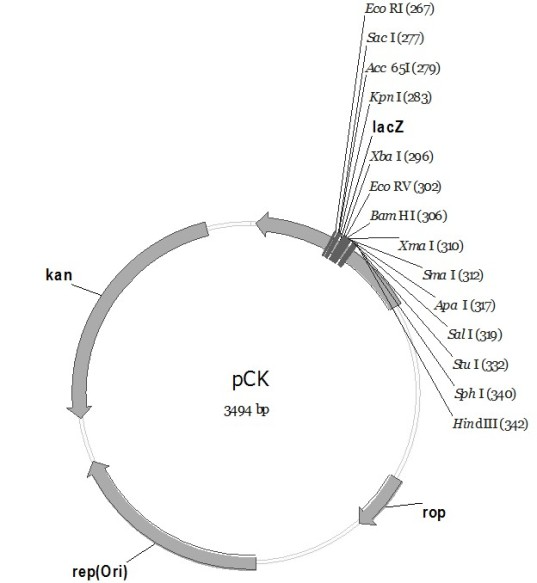
PC series plasmid as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN102352371BLarge capacitySmooth extractionVector-based foreign material introductionAntibiotic YGene engineering
Owner:GENEWIZ INC SZ
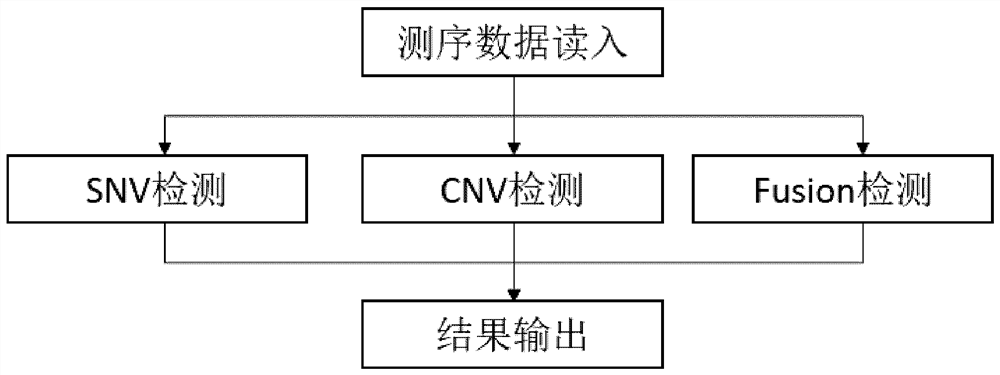
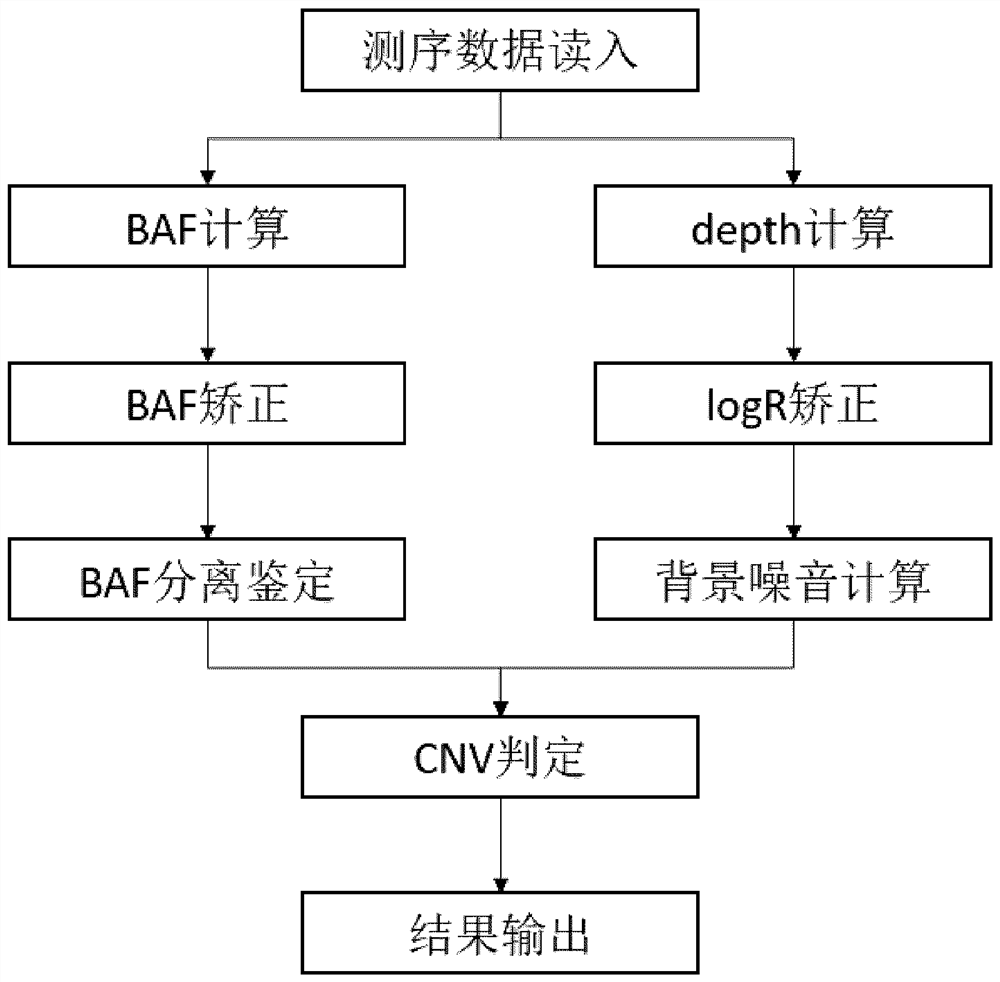
Method and device for jointly detecting SNV, CNV and FUSEON variations
The invention relates to a method and device for jointly detecting SNV, CNV and FUSEON variations. More specifically, the device comprises a sequencing data reading module, an SNV detection module, a CNV detection module, a FUSEON variation detection module and a result output module, wherein the CNV detection module comprises a BAF calculation module, a BAF correction module, a BAF separation and identification module, a sequencing depth calculation module, a logR correction module, a logR background noise calculation module and a CNV judgment module. The method and device, based on BAF+logR information, detect the SNV, CNV and FUSEON variations in a sample with an extremely low ctDNA proportion, especially the CNV variation with low copy number amplification, with high sensitivity and high specificity.
Owner:上海思路迪医学检验所有限公司
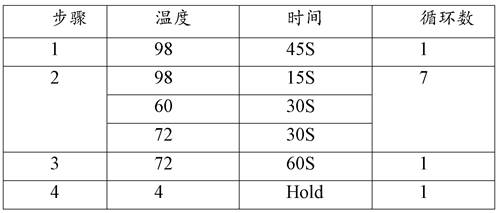
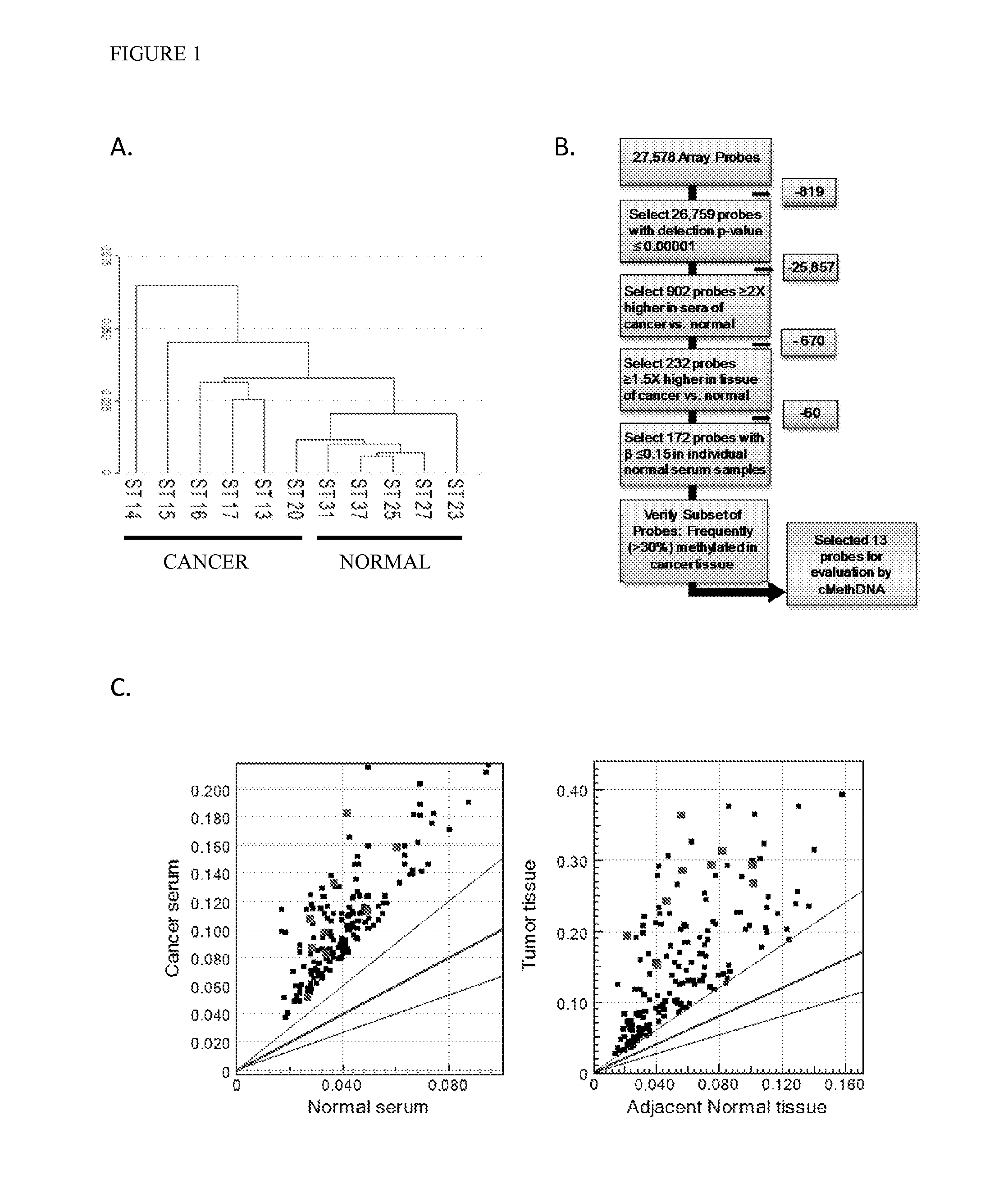
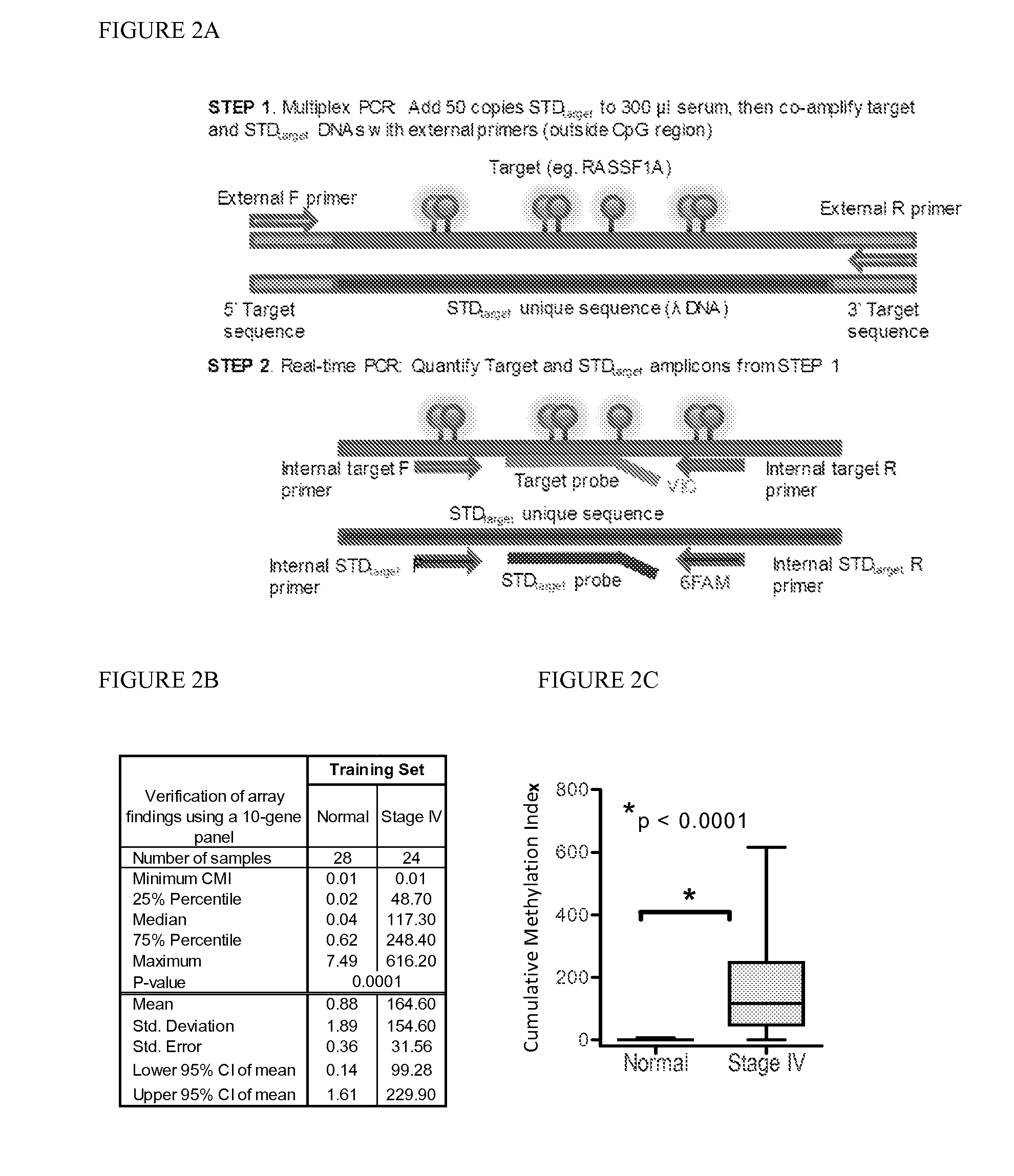
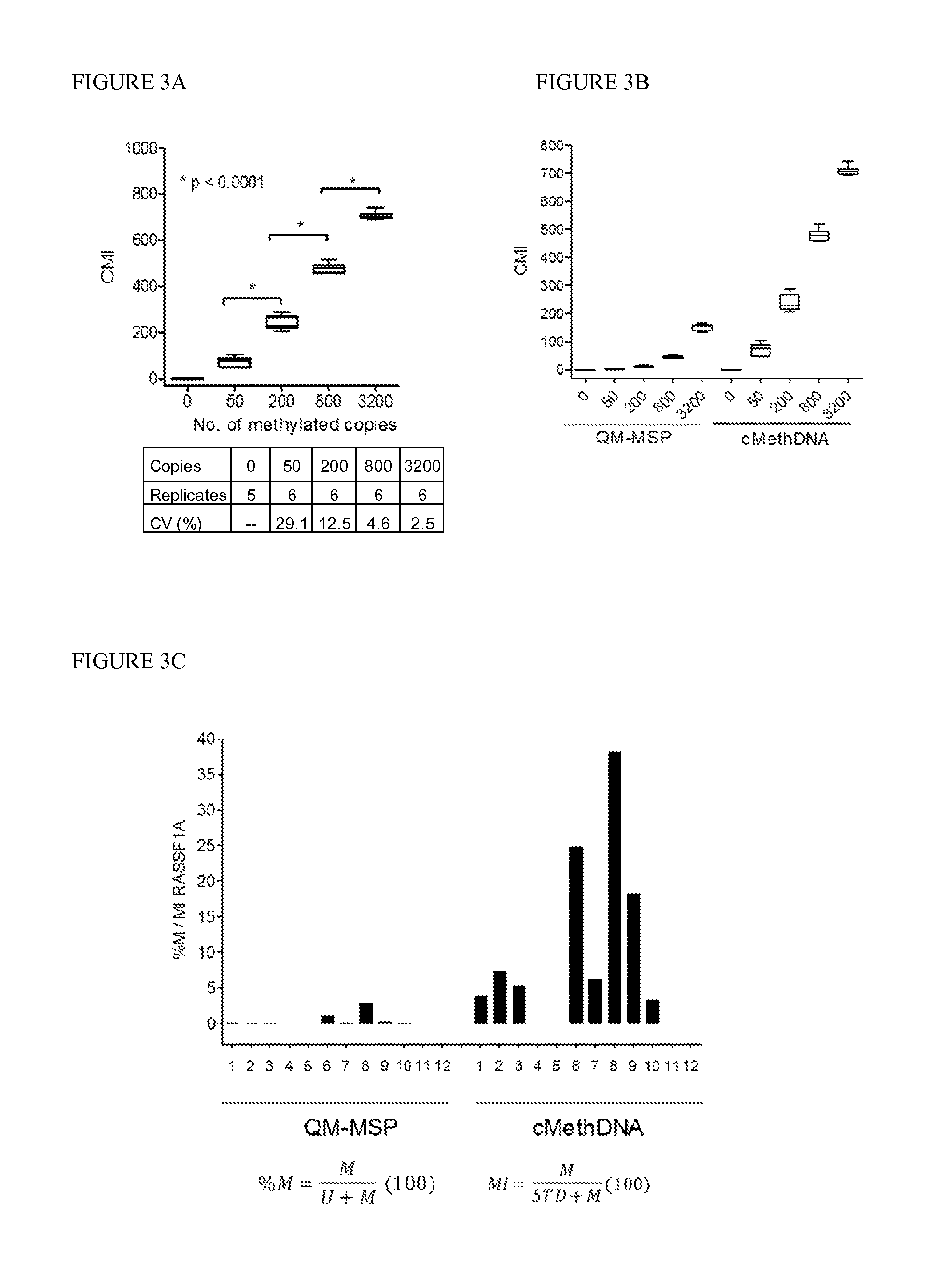
QUANTITATIVE MULTIPLEX METHYLATION SPECIFIC PCR METHOD- cMethDNA, REAGENTS, AND ITS USE
ActiveUS20150094222A1Evaluate responsePotential to evaluate response to treatmentSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesBlood plasmaPolynucleotide
The cMethDNA method of the present invention is a novel modification of the QM-MSP method (U.S. Pat. No. 8,062,849), specifically intended to quantitatively detect tumor DNA (or other circulating DNAs) in fluids such as serum or plasma at the lowest copy number yet reported. Unique compared to any other PCR-based assay, a small number of copies of a synthetic polynucleotide standard (STDgene) is added to an aliquot of patient serum. In a standard procedure, a cocktail of standards for a plurality of genes of interest (TARGETgene) is added to a sample of serum. Once total DNA is purified and processed, a PCR (multiplex step) is performed wherein the STDgene and the TARGETgene are co-amplified with the same external primer set. In the N second nested PCR step, amplicons present in a dilution of the first PCR reaction are subjected to real time PCR, and quantified for each gene in one well by two-color real-time PCR. Products are calculated by absolute quantitation with internal primer sets specific for the methylated TARGETgene and associated STDgene. Methods of making the STDgene standards and the use of the cMethDNA methods and kits containing the same are disclosed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
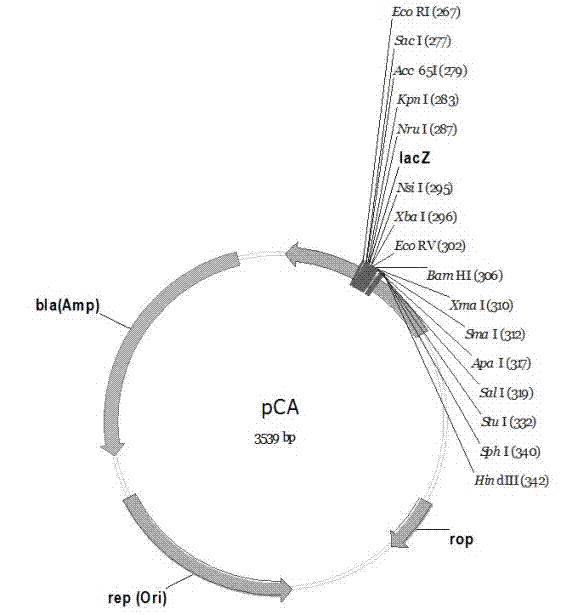
PC series plasmid as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN102352371ALarge capacitySmooth extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAntibiotic YGene engineering
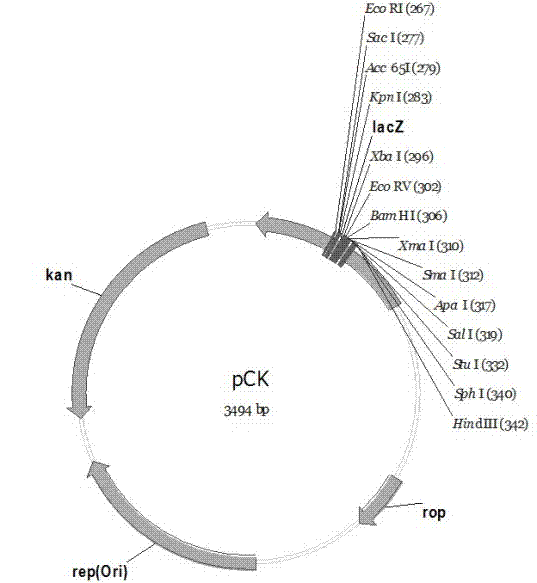
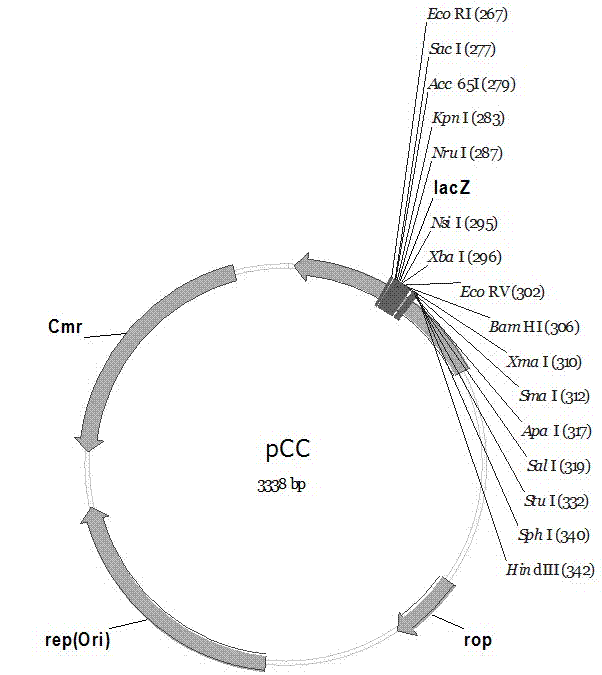
The invention discloses a pC series plasmid as well as a construction method and application thereof, wherein the pC series plasmid comprises a rep gene, a rop gene, a lacZ gene and an antibiotics resistance gene which are sequentially connected with one another end to end. The pC series plasmid has the characteristics of small molecular weight, large capacity, low copy number, high stability andthe like, can be used for instable genes with complicated structures and repeated sequence, cloning, screening and sequencing long section of genes, genome construction and other gene engineering fields.
Owner:GENEWIZ INC SZ
Primer composition used for detecting genome target zone and application thereof
InactiveCN107365867AImprove efficiencyImprove overall utilizationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBlood plasmaLung cancer
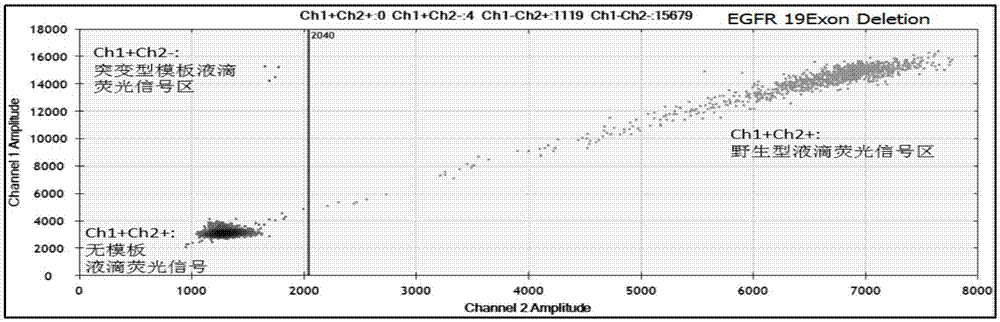
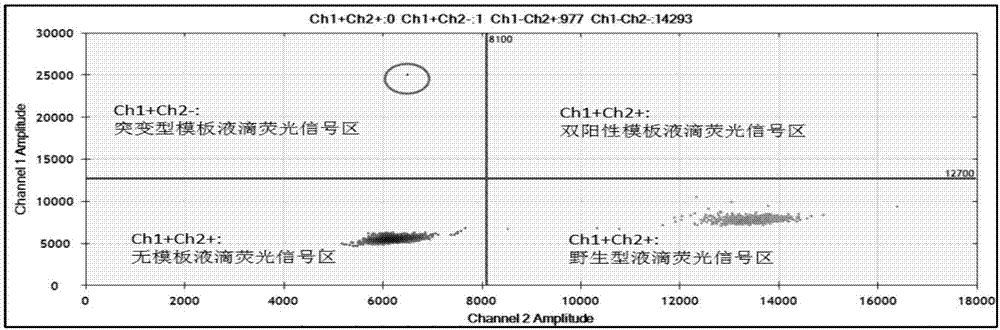
The invention relates to a primer composition used for detecting a genome target zone and application thereof and in particular relates to a primer composition for detecting EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) mutation sites of lung cancer by virtue of free plasma DNA and digital PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), as well as a detection kit and application thereof. The primer composition disclosed by the invention corresponds to the same template zone, the effect is achieved in the same amplified reaction, the amplification efficiency can be improved on premise of ensuring the specific amplification, and the primer composition is applicable to amplification of short fragment templates with low copy number. Moreover, the primer composition has high sensitivity, is capable of detecting 23 hotspot low frequency mutations of EGFR genes, has low sample amount, is applicable to plasma and other liquid samples, and is excellent in detection result and capable of taking complete genes into account.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL LAB BGI +2
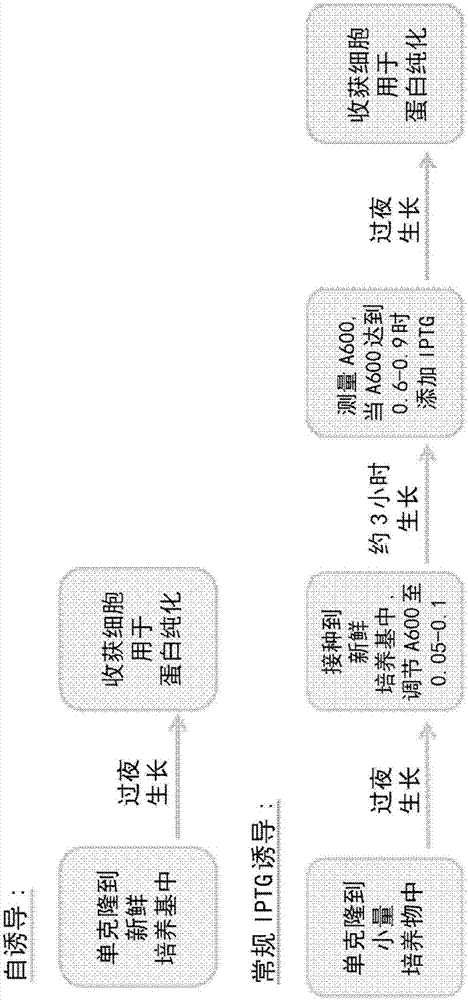
Methods and systems for autoinduction of protein expression
ActiveCN107532178ASerum immunoglobulinsVector-based foreign material introductionFusion Protein ExpressionBiological activation
Methods and systems for autoinduction of gene expression, without the need to add exogenous inducers. A dual genetic element system, which includes a first, high copy number genetic element comprisinga first gene of interest that is under the control of an inducible promoter, and a second, low copy number genetic element comprising a gene encoding a transcriptional factor which, upon expression,regulates transcription from the inducible promoter, wherein activation of transcription from the inducible promoter does not require addition of an exogenous inducer.
Owner:ADAGENE INC
BCR diversity detection kit and application thereof
InactiveCN106834472AGain preferenceGain genetic preferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGeneticsNucleotide sequencing
The invention provides a kit for detection BCR diversity. The kit comprises a set of multiple PCR primers. The multiple PCR primer contains upstream primers and downstream primers. The upstream primers are composed of a group of sequences which have a one-to-one correspondence with nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO:1- SEQ ID NO: 13. Sequences in the upstream primer have 0-3 more or less nucleotides than the corresponding sequences in the SEQ ID NO:1- SEQ ID NO:13. The downstream primers are composed of a group of sequences which have a one-to-one correspondence with nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO:14- SEQ ID NO:17. Sequences in the downstream primer have 0-3 more or less nucleotides than the corresponding sequences in the SEQ ID NO:14- SEQ ID NO:17. By the use of the kit, BCR sequences of human can be efficiently obtained, human specific BCR CDR3 sequences are obtained, and detection rate of low-copy-number B cell clones can be raised.
Owner:GENEMIND BIOSCIENCES CO LTD
Swine Population Having Low Levels of Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20080152625A1Avoid damageReduce rejectionBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsPorcine endogenous retrovirusBiology
The invention relates to methods of selecting and maintaining a population of pigs having a low copy number of porcine endogenous retrovirus, and the use of such pigs as a source of cells, tissue and / or organs suitable for xenotransplantation. The invention further relates to methods for selecting cells, tissue and / or organs from such pigs for suitability for use in xenotransplantation.
Owner:DIATRANZ OTSUKA
Methods for generating transgenic plants
ActiveUS10443063B2Reduced survival rateIncrease percentageVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotidePlant cell
This invention provides a method for generating transgenic plants with a low copy number. Plant cells are transformed with polynucleotides containing transcriptional cassettes designed to trigger silencing of a gene which is essential for the plant cell to survive the transformation and regeneration process. The present invention enables the recovery of an increased number of transgenic plants which have only one copy of each desired transcriptional cassette.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Recombinant gene expression
ActiveUS9273324B2High expressionTissue cultureFermentationCulture cellBacterial artificial chromosome
Genes are expressed by culturing cells comprising a host chromosome comprising an integrated artificial chromosome comprising recombinant genes, under conditions whereby each recombinant gene is expressed copy number dependently and position independently. Deletions increase expression from recombinant gene(s) inserted into the artificial chromosome.
Owner:BELMONT ANDREW S
Methods for generating transgenic plants
ActiveUS20140366223A1Reduced survival rateIncrease percentageOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationNucleotidePlant cell
This invention provides a method for generating transgenic plants with a low copy number. Plant cells are transformed with polynucleotides containing transcriptional cassettes designed to trigger silencing of a gene which is essential for the plant cell to survive the transformation and regeneration process. The present invention enables the recovery of an increased number of transgenic plants which have only one copy of each desired transcriptional cassette.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com