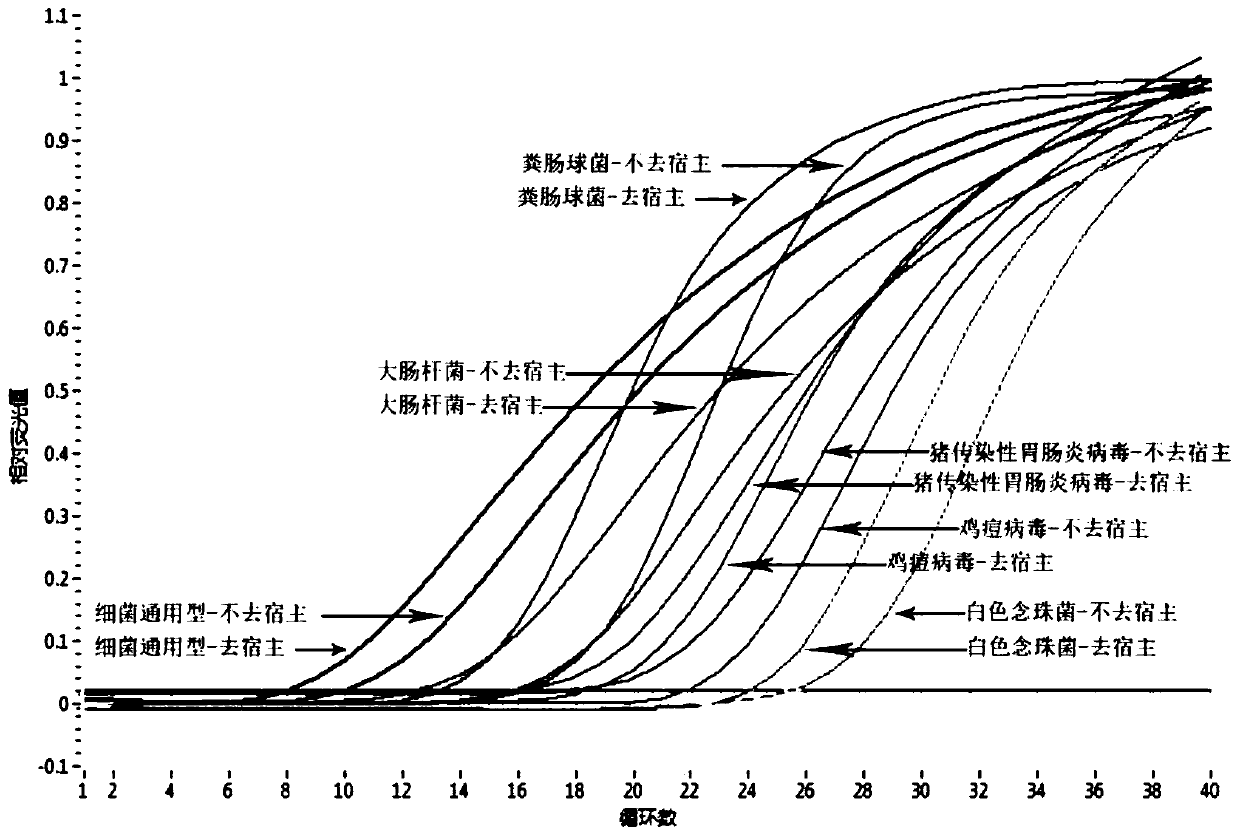
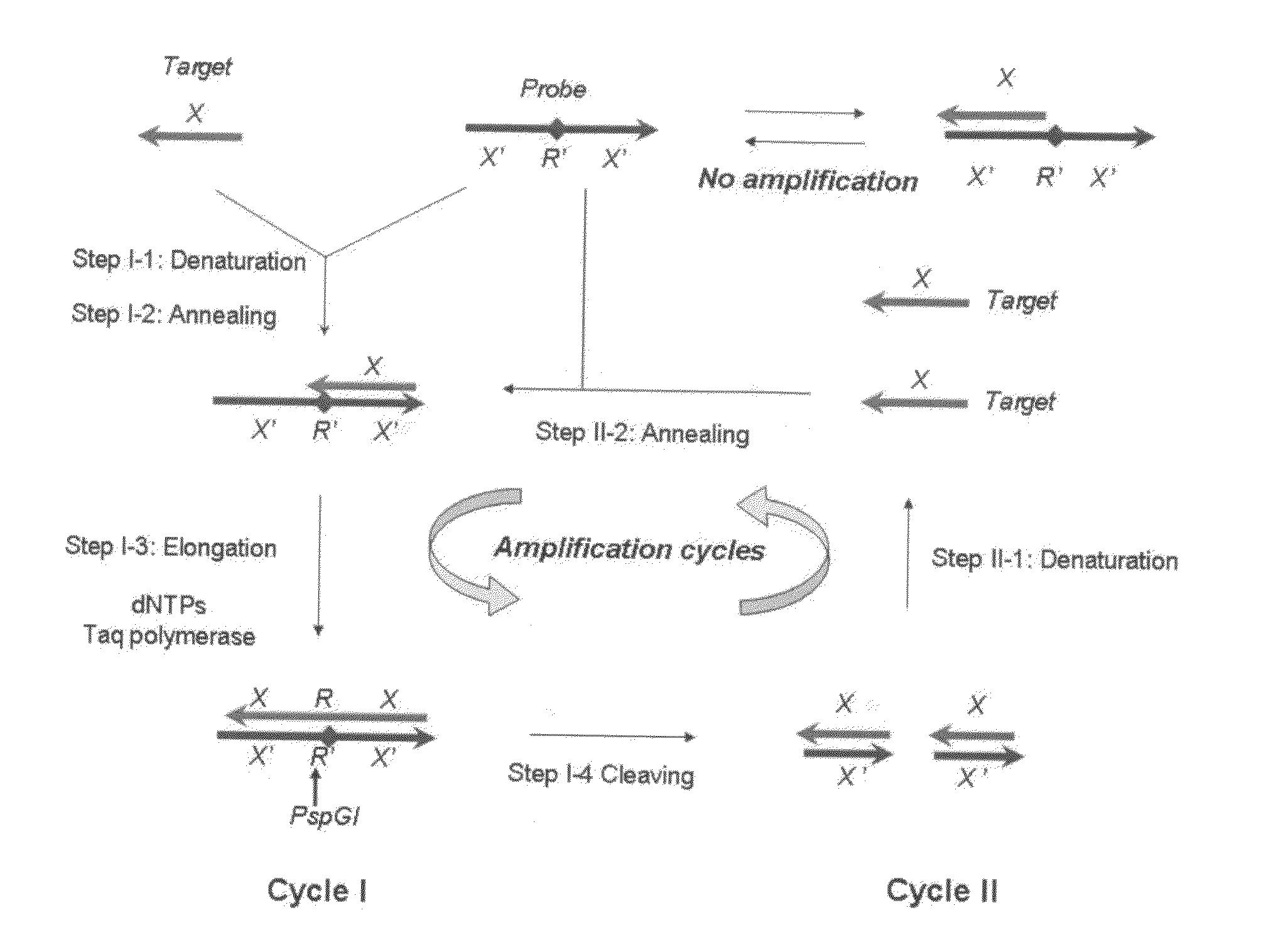
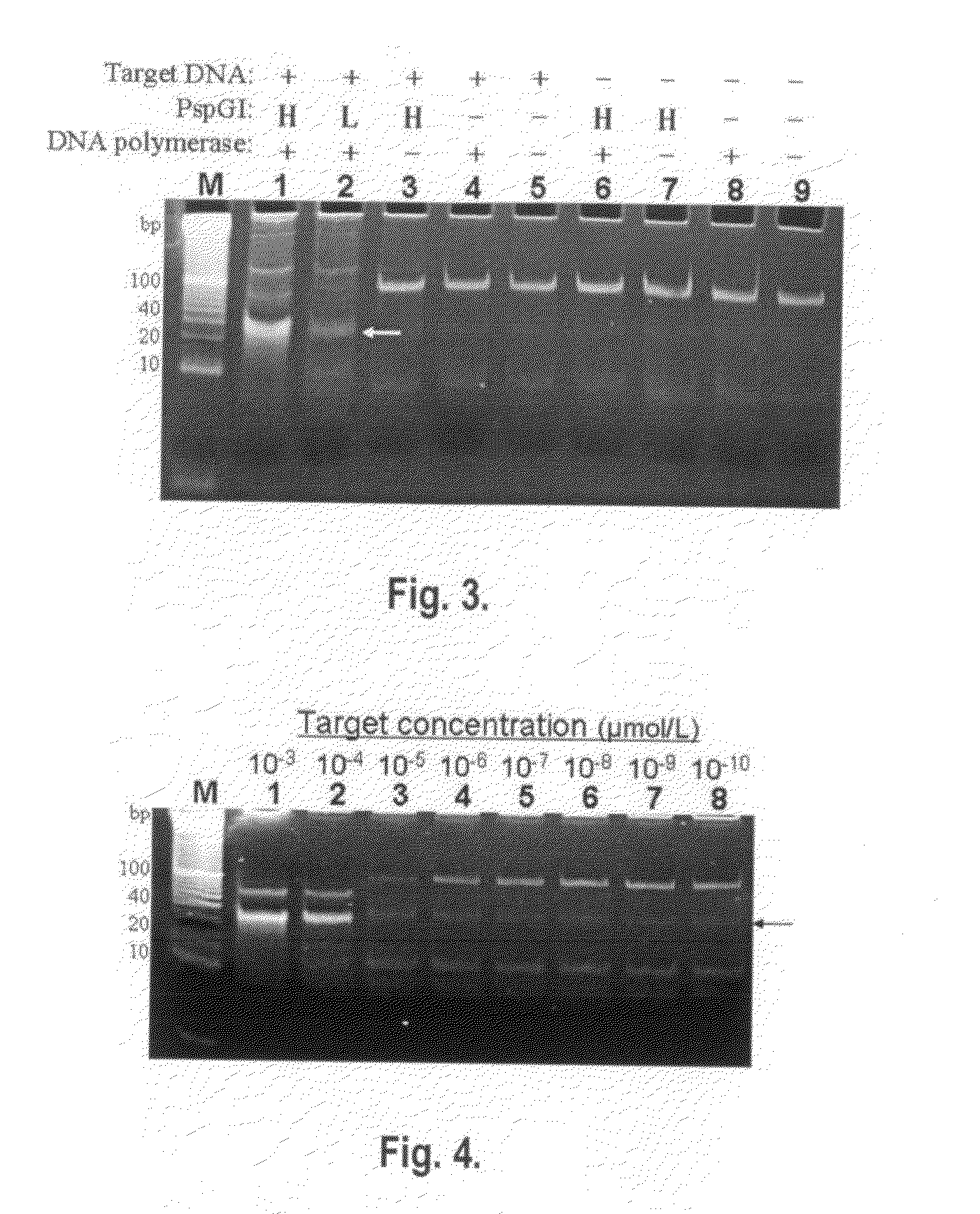
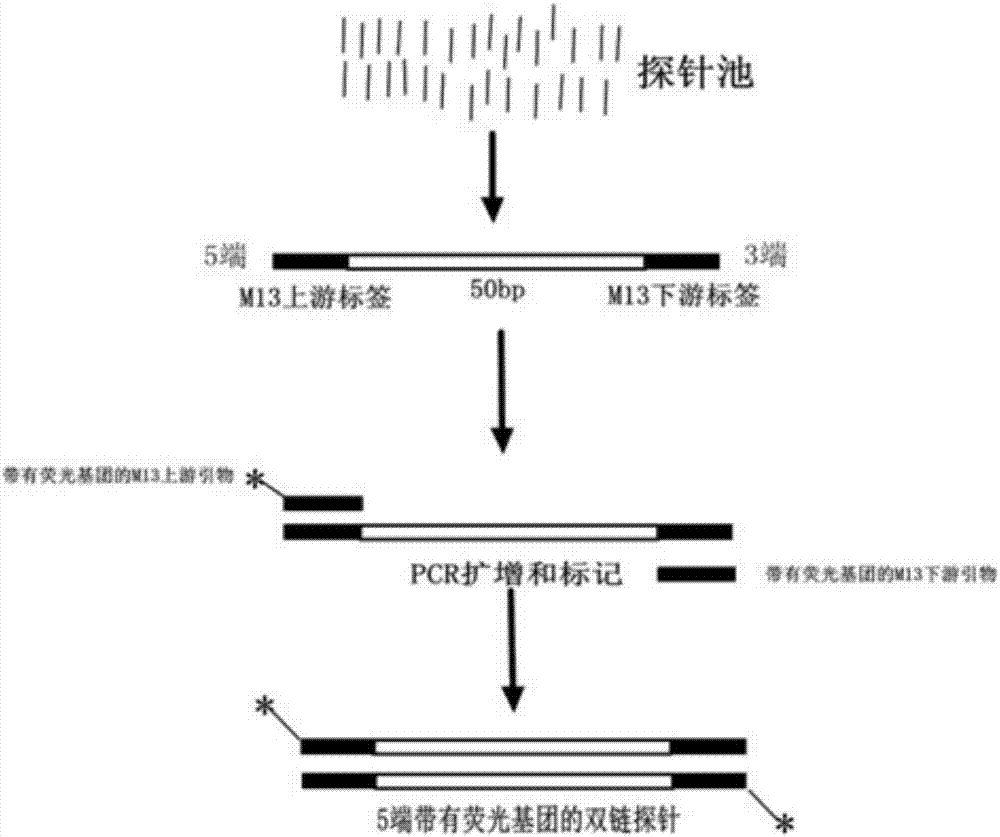
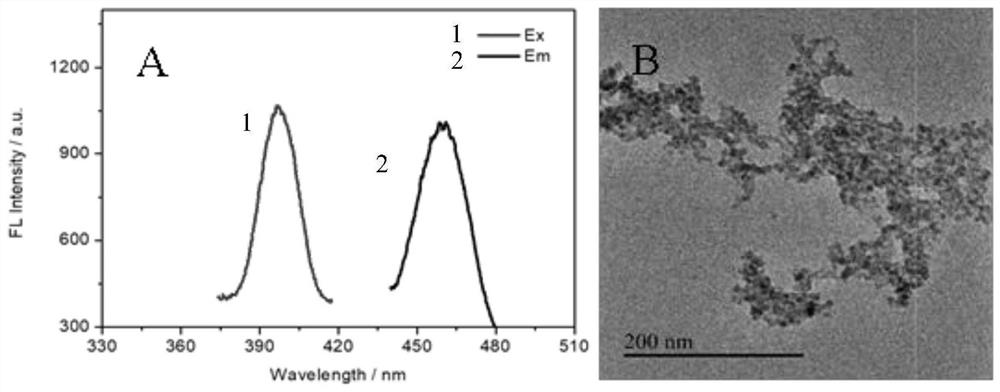
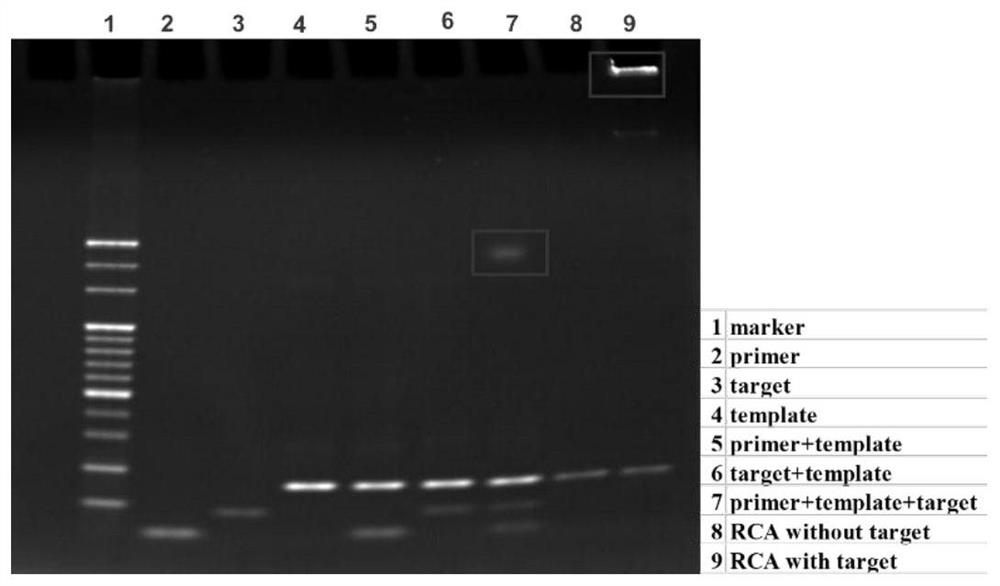
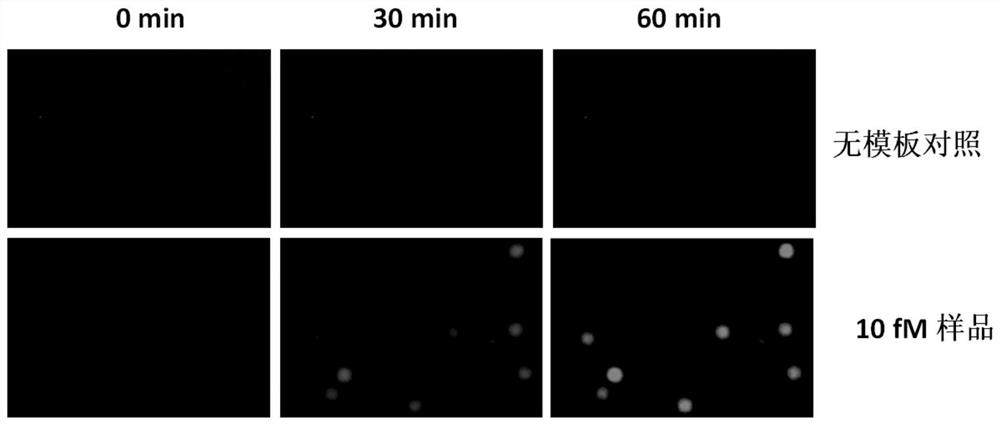
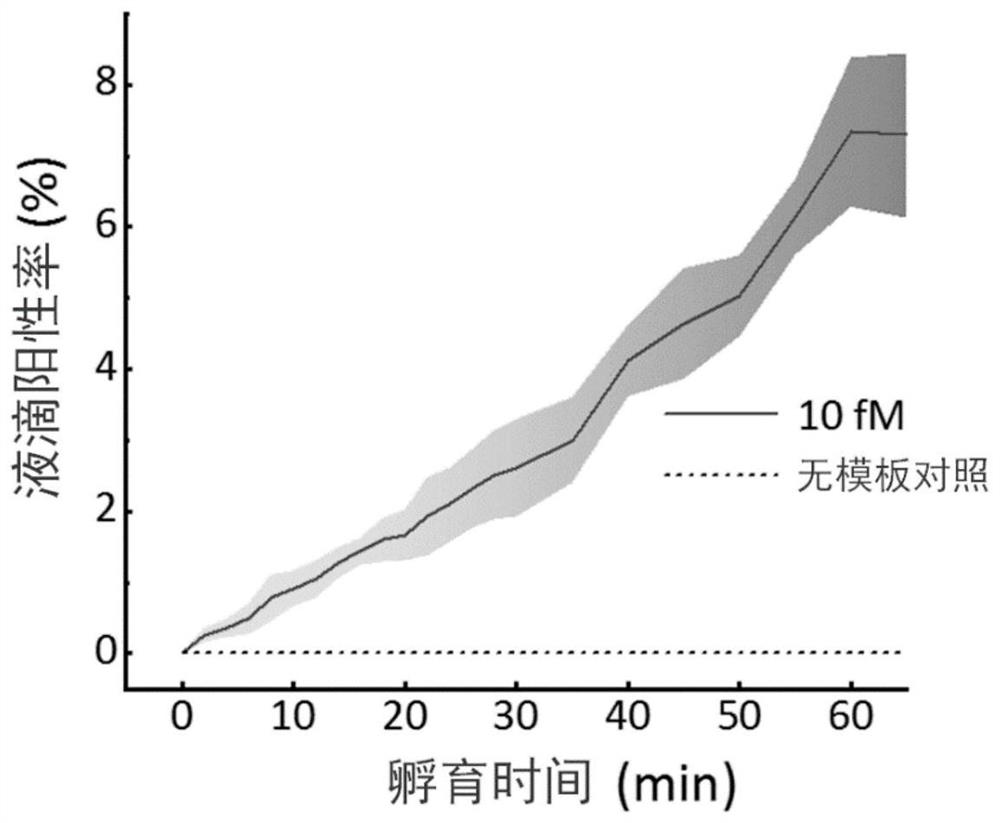
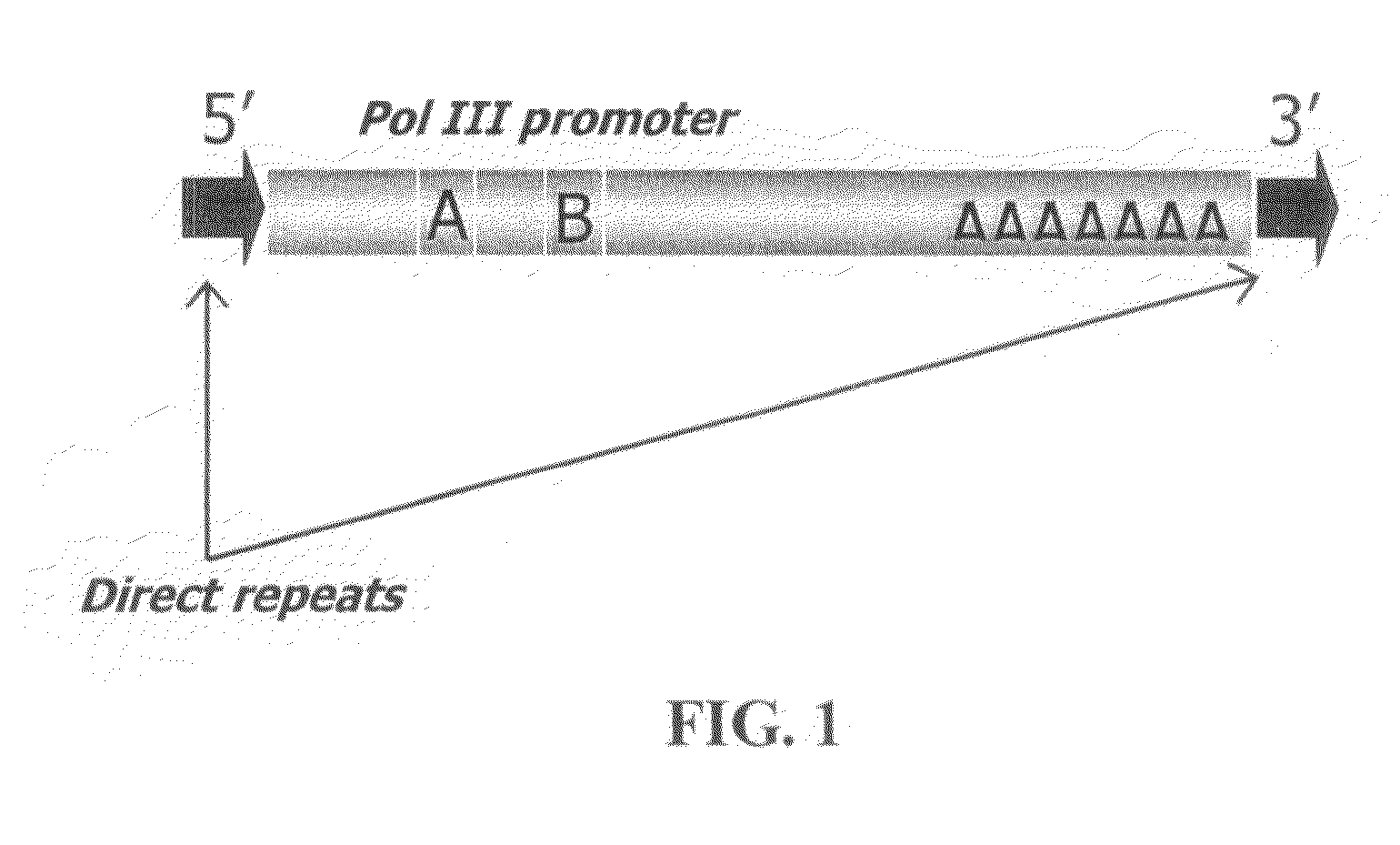
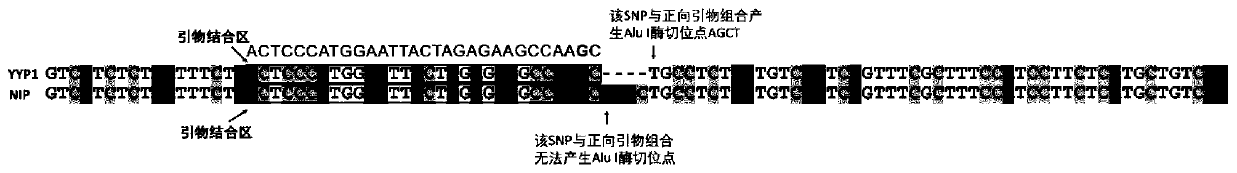
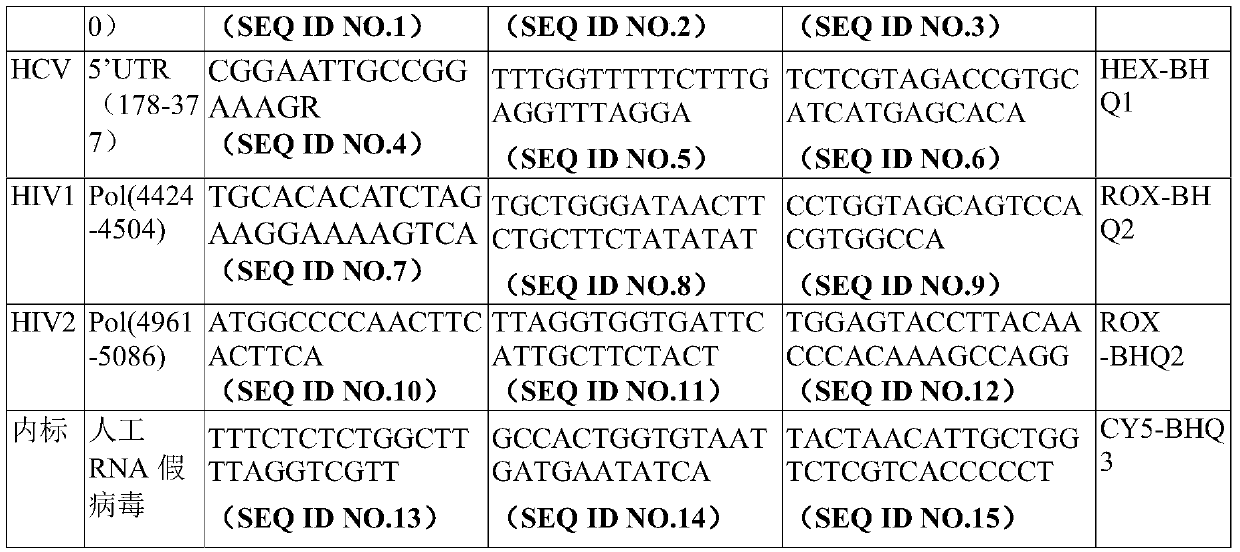
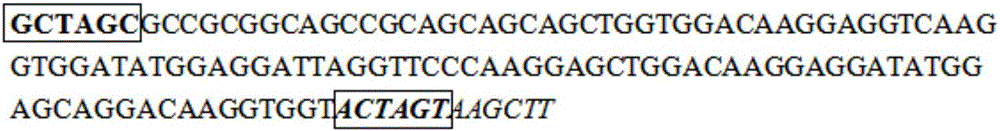Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97 results about "Repeated sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
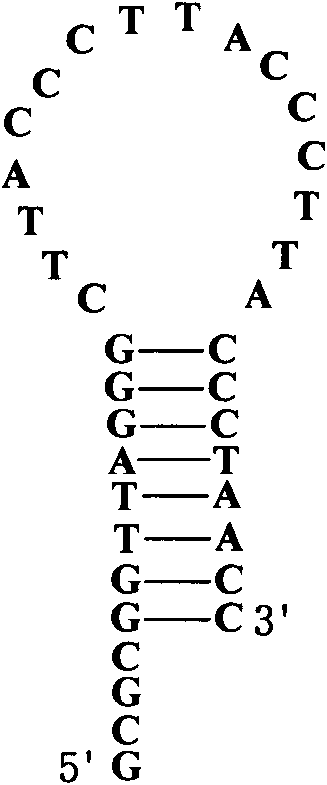
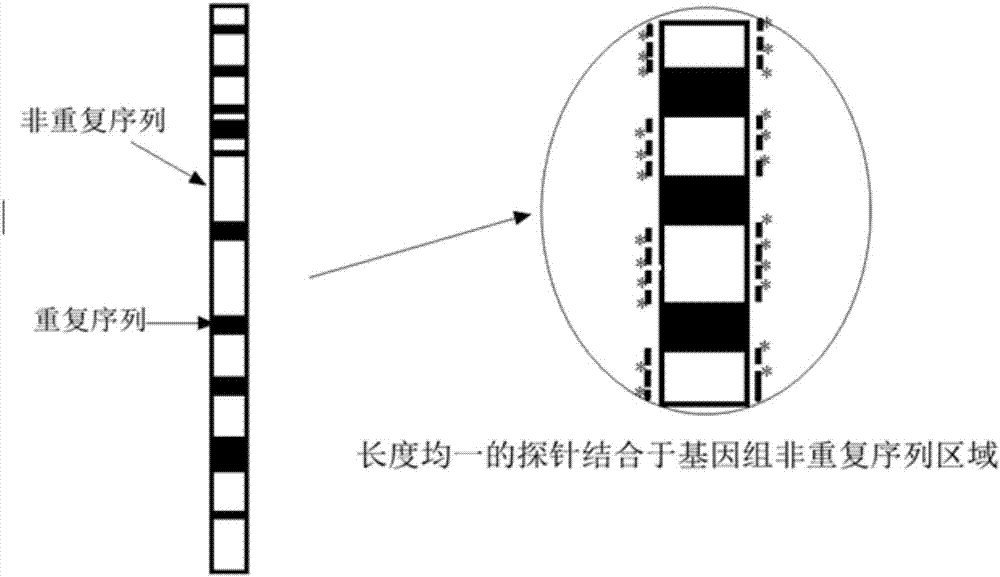
Repeated sequences (also known as repetitive elements,repeating units or repeats) are patterns of nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) that occur in multiple copies throughout the genome. Repetitive DNA was first detected because of its rapid re-association kinetics. In many organisms, a significant fraction of the genomic DNA is highly repetitive, with over two-thirds of the sequence consisting of repetitive elements in humans.
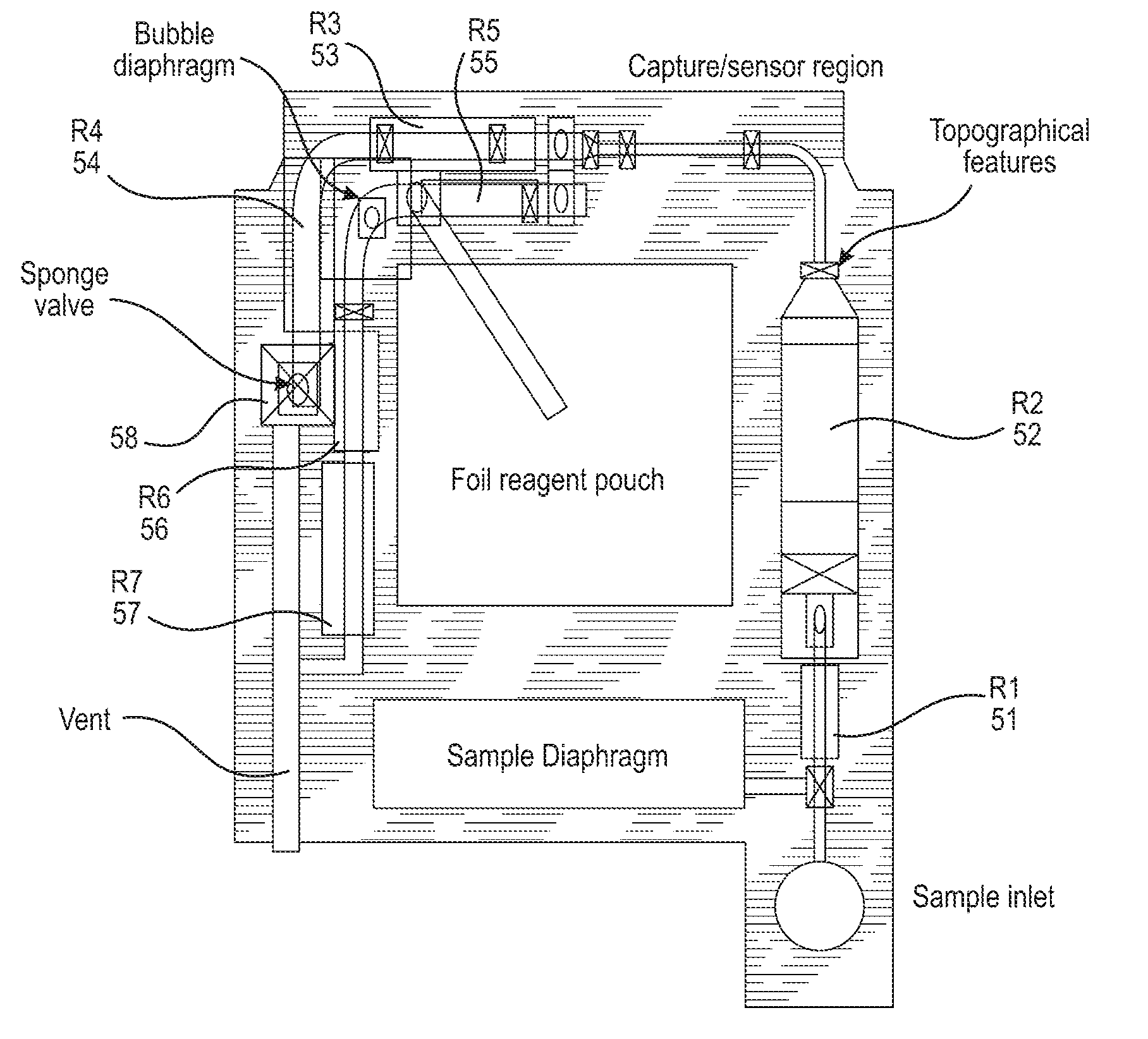
Method and device for immunoassay using nucleotide conjugates
ActiveUS20100167301A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceNucleotide
A composition of matter for use in an immunoassay devices and method comprising a signal antibody, e.g., FAB fragment, covalently linked to a first nucleotide; and one or more signal elements, e.g., signal enzymes such as ALP or fluorescent dyes, each covalently linked to a second nucleotide, wherein the first nucleotide has one or more repeated sequences, and the second nucleotide is bound to one of the one or more repeated sequences on said first nucleotide, and wherein the ratio of the signal antibody to the signal element is controlled by the number of repeated sequences.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Methods and kits comprising AFLP primers, and ramp primers with a part complementary to a compound microsatellite repeat and an anchor part complementary to nucleotides adjacent to the repeat
InactiveUS7217516B2Quick identificationReliable and powerfulMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisNucleotide
The present invention discloses methods for identifying and analysing microsatellite-associated polymorphisms between different DNA samples. Different DNA samples, e.g. from different individuals, are analysed using a PCR based on the combination of a RAMP-primer and an AFLP-primer and polymorphisms between the different DNA samples are identified. The polymorphisms thus identified may be isolated and further analysed by e.g. DNA sequence analysis both upstream and downstream from the microsatellite-associated polymorphism. These sequences may subsequently be used to devise and synthesise new means for analysis of the polymorphic locus, such as e.g. PCR-primer pairs or oligonucleotide probes.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
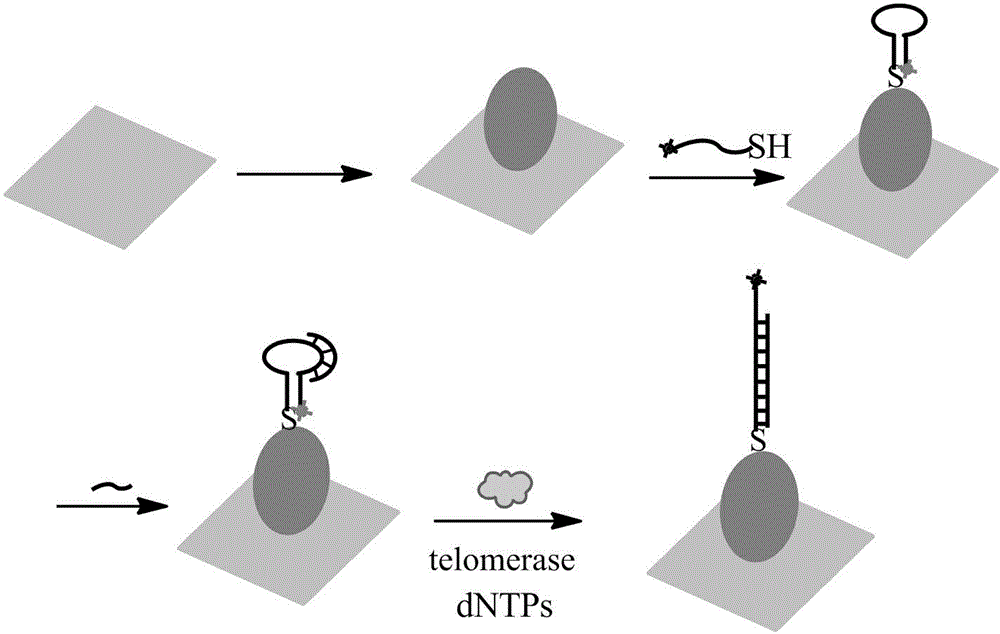
Surface-enhanced Raman technology based on signal-off and used for detecting intracellular telomerase activity
InactiveCN104611416ARealize highly sensitive detectionEnhanced Raman signalMicrobiological testing/measurementTelomeraseSignalling molecules
The invention relates to a surface-enhanced Raman technology based on signal-off and used for detecting intracellular telomerase activity. According to the technology, graphene, carbon nitride, MoS2, SiO2 and the like are taken as carriers, nano-gole or nano-silver with controllable dimension and morphology or a composite magnetic nano-particle with a core-shell structure is supported by the carriers, and then a hairpin probe containing a telomerase primer and a Raman molecule beacon is fixedly disposed on the nano=particle surface, so that the high-sensitivity high-selectivity SERS detection method based on signal-off is established. When a target exists, the primer extends and generates a DNA chain with a repeat sequence under the effect of telomerase, and the DNA chain is hybridized with the probe molecule, then the DNA hairpin structure is opened, a Raman signal molecule with the single-chain labeled end is far away from a Raman substrate, the Raman signal is reduced, and high-sensitivity detection on telomerase is realized. The probe prepared by taking Hela cervical carcinoma cell as a model realizes intracellular telomerase activity detection and dynamic detection on intracellular telomerase activity variation under effect of a telomerase inhibiting medicament. By using multiple cells for imaging, the probe is confirmed to be capable of distinguishing tumor cells and normal cells.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
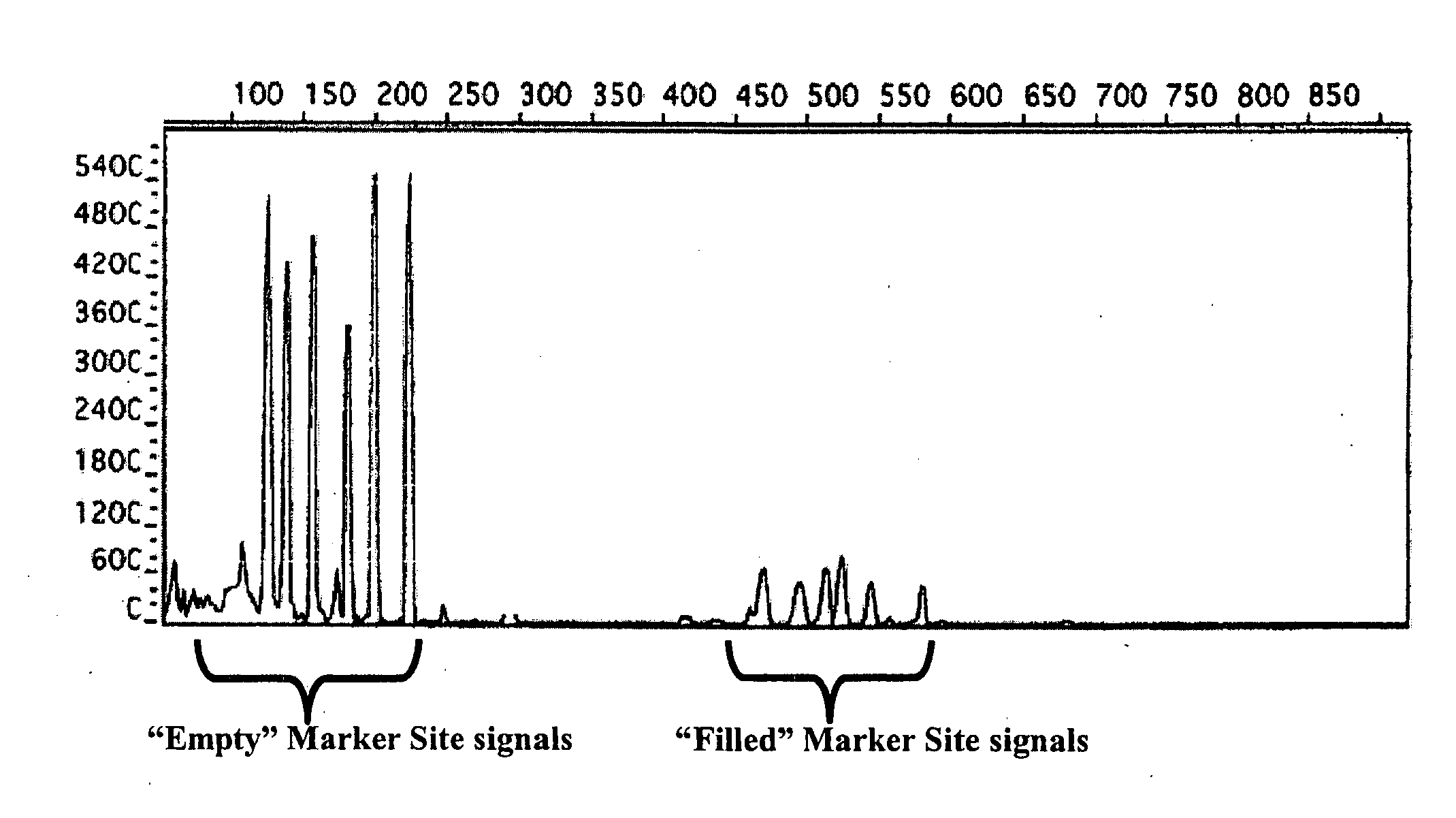
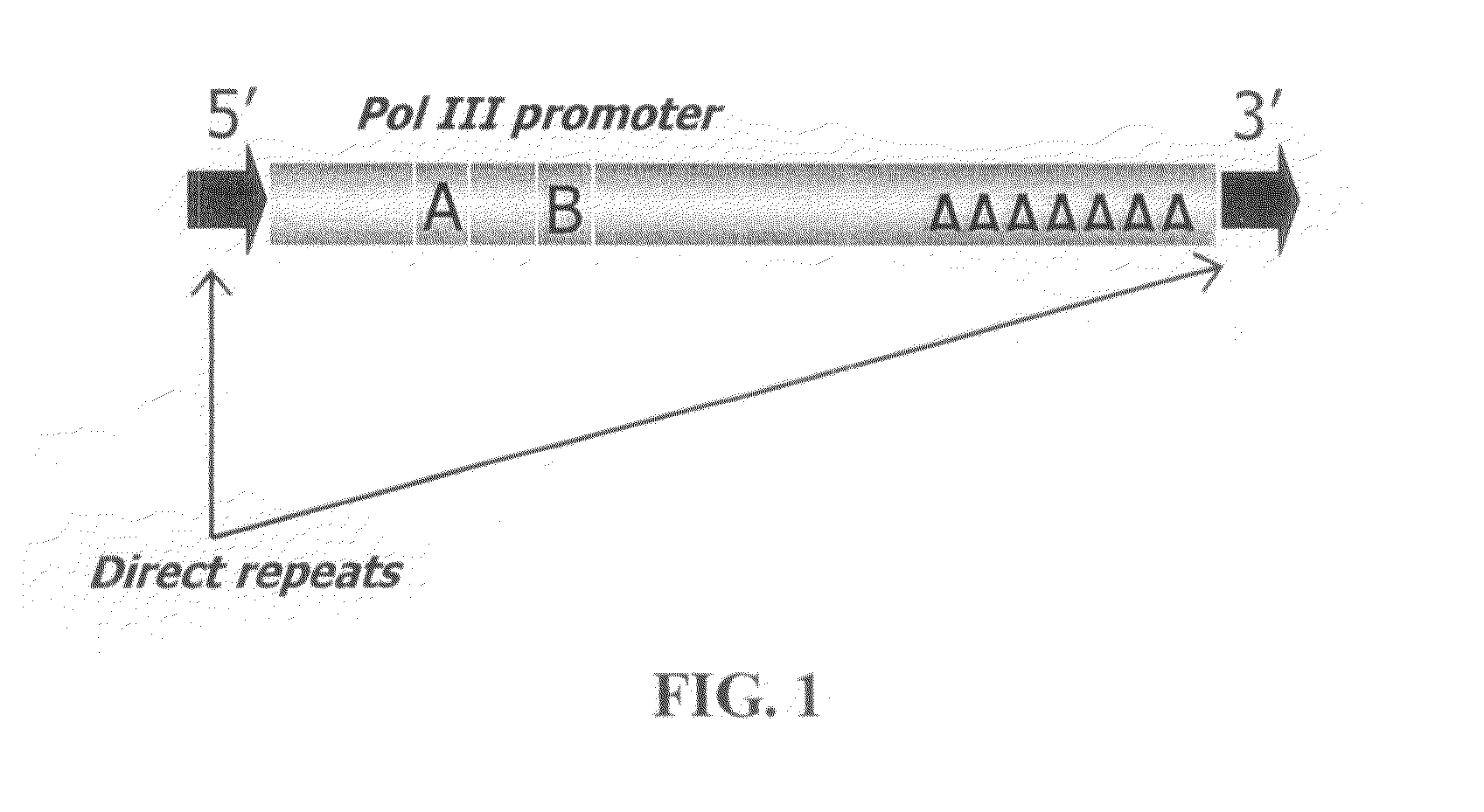
Method for genetic detection using interspersed genetic elements
ActiveUS20080206755A1Easy to testSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenetic element
The way to design a “filled” site (which contains an interspersed element) primer set to target a particular locus is to design one of the two primers such that it encompasses that unique information (e.g., interspersed element+flanking genomic sequence+direct repeat). The way to design an “empty” site primer is to design one of the two primers such that the entire direct repeat sequence in addition to flanking genomic sequence is included on both sides. To improve efficiency, the “empty” site primer designed around the direct repeat should not be too long. This primer design of the present invention allows for the ability to test any type of interspersed genetic element containing characteristic direct repeat sequences (direct repeats). This gives the option of many new polymorphic marker sites because Alu elements are not the only interspersed genetic elements having direct repeats flanking their core sequence.
Owner:RELIAGENE TECH INC A CORP CHARTERED IN & EXISTING UNDER THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF LOUISIANA +1
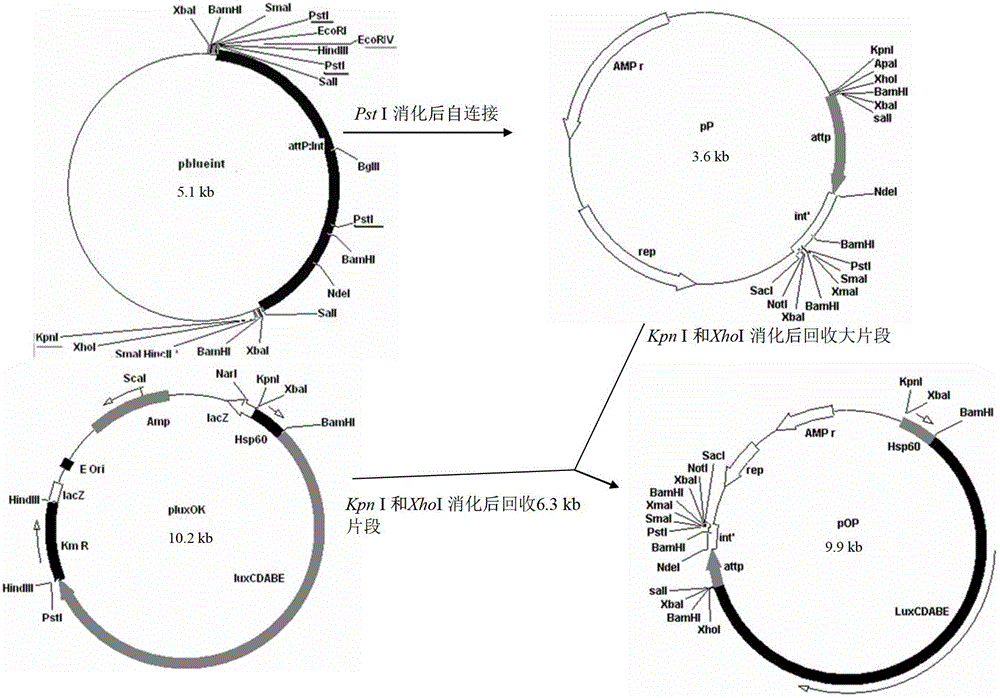
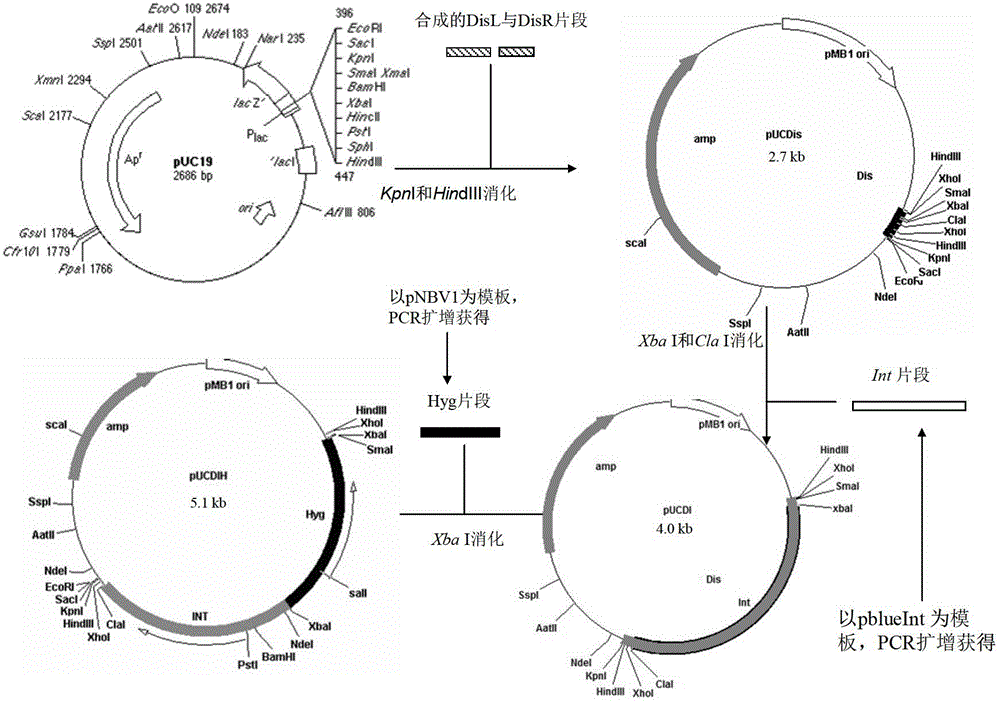
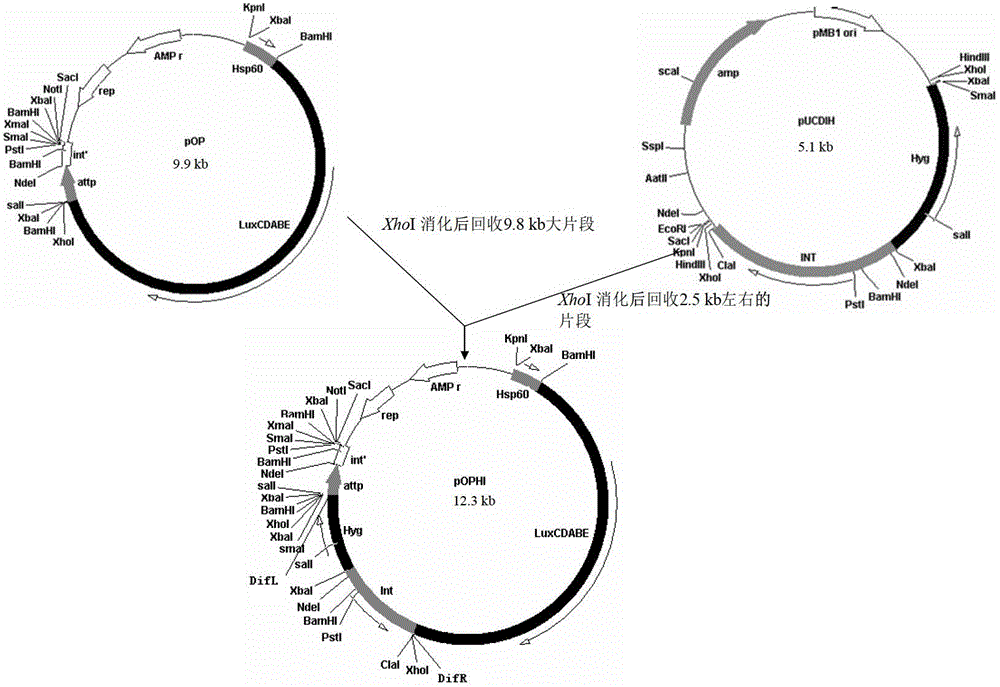
Integrative plasmid pOPHI and resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium
ActiveCN102719471AExperimental data is credibleHigh sensitivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneDirect repeat
The invention discloses an integrative plasmid pOPHI and a resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium. The integrative plasmid pOPHI comprises a promoter, an enzyme gene (LuxCDABE) needed for luminescence, a fusion gene of an integrase gene (Int) and a resistance screening gene, direct repeat sequences DifR and DifL positioned on two ends of the fusion gene, a phage integration site (attP) and a replicon. After the integrative plasmid pOPHI is transferred into the mycobacteria, a photobacterium of which the resistance gene and the integrase gene are lost is screened out by subculturing, and the photobacterium is the resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium. Whether the resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium obtained by construction is dead or not is judged according to whether the bacterium is luminescent or not, the mycobacterium can be used for a plurality of detections of experiments, and credible experimental data can be quickly obtained.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
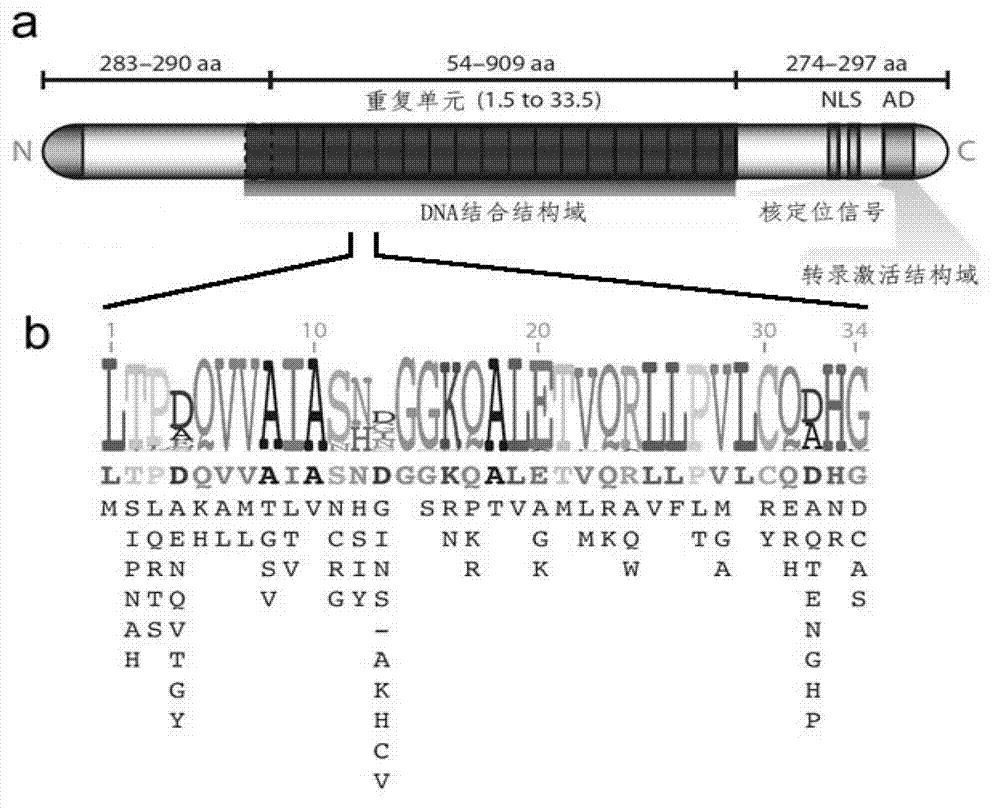
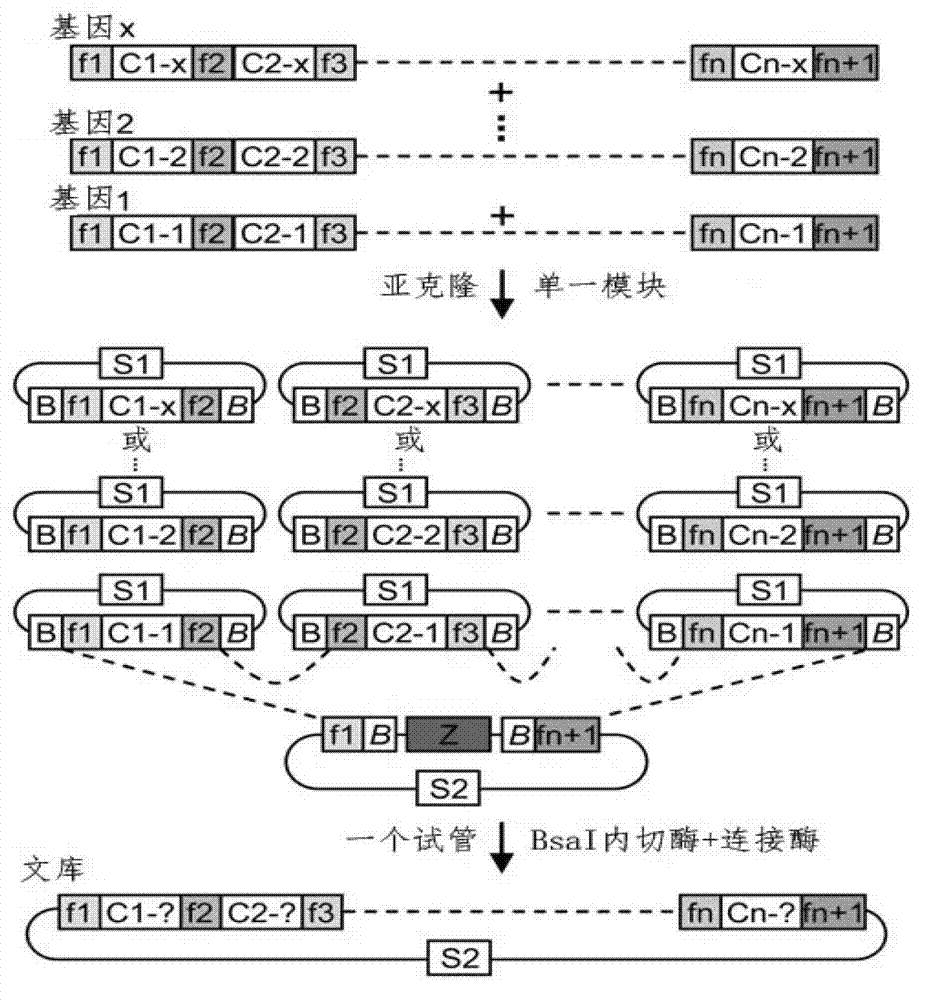
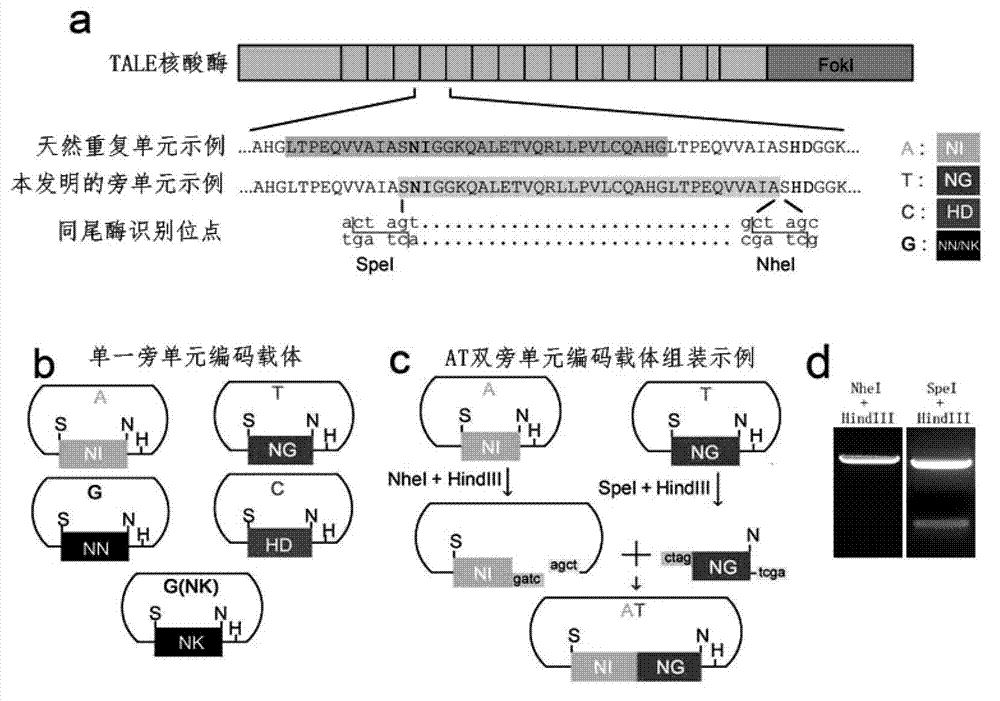
Method for building TALE (transcription activator-like effector) repeated sequences
ActiveCN102787125AHas a cumulative effectShorten the timeMicroorganism based processesFermentationNucleotideTAL effector
The invention discloses a side unit used for building TALE (transcription activator-like effector) repeated sequences. The side unit is a repeated unit DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segment containing isocaudarner or different flat terminase identification sites at two ends, and the preated unit DNA segment codes repeated units of RVD (repeated variable di-residue) containing NI, NG, HD, NK or NN or variants of the repeated units, wherein in the 5'end isocaudarner or flat terminase identification sites, the 3' end of the identification sites at least has one nucleotide participating in the amino acid coding the N end of the side unit; and in the 3' end isocaudarner or flat terminase identification sites, the 5' end of the identification sites at least has one nucleotide participating in the amino acid coding the C end of the side unit. The side unit has the advantages that the TALE repeated sequences containing any repeated unit number and any ranging sequences, plasmid vectors containing TALE repeated sequences, coding TALE protein DNA combined structural domains and various derived fusion protein plasmid vectors can be conveniently built.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Electrochemical sensor for detecting telomerase activity and detection method thereof
ActiveCN110243905AAvoid steric hindranceIncrease contactMaterial electrochemical variablesTelomeraseMagnetic bead
The invention provides an electrochemical sensor for detecting telomerase activity and a detection method thereof which are constructed based on functionalized nanometer magnetic beads and an exonuclease III-assisted amplification strategy, and the detection of the telomerase activity of the tumor cells is realized. In the invention, complementary probes can be hybridized with an extended telomerase primer repeated sequence, a hybrid is separated by the magnetic beads, a telomerase primer repeated sequence chain is identified and degraded by exonuclease III, a plurality of methylene blue marked hairpin DNA probes can be hybridized and opened by the released complementary probes, after the secondary degradation of the exonuclease III, the complementary probes can enter the next cycle of hybridization with an MB-marked hairpin-like structure, and the MB-marked probe is combined with a capture probe on the surface of a gold electrode, so that a peak current value which is in direct proportion to the telomerase activity is generated. According to the electrochemical sensor and the detection method thereof, the telomerase activity can be detected at a single-cell level.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF NANJING +1
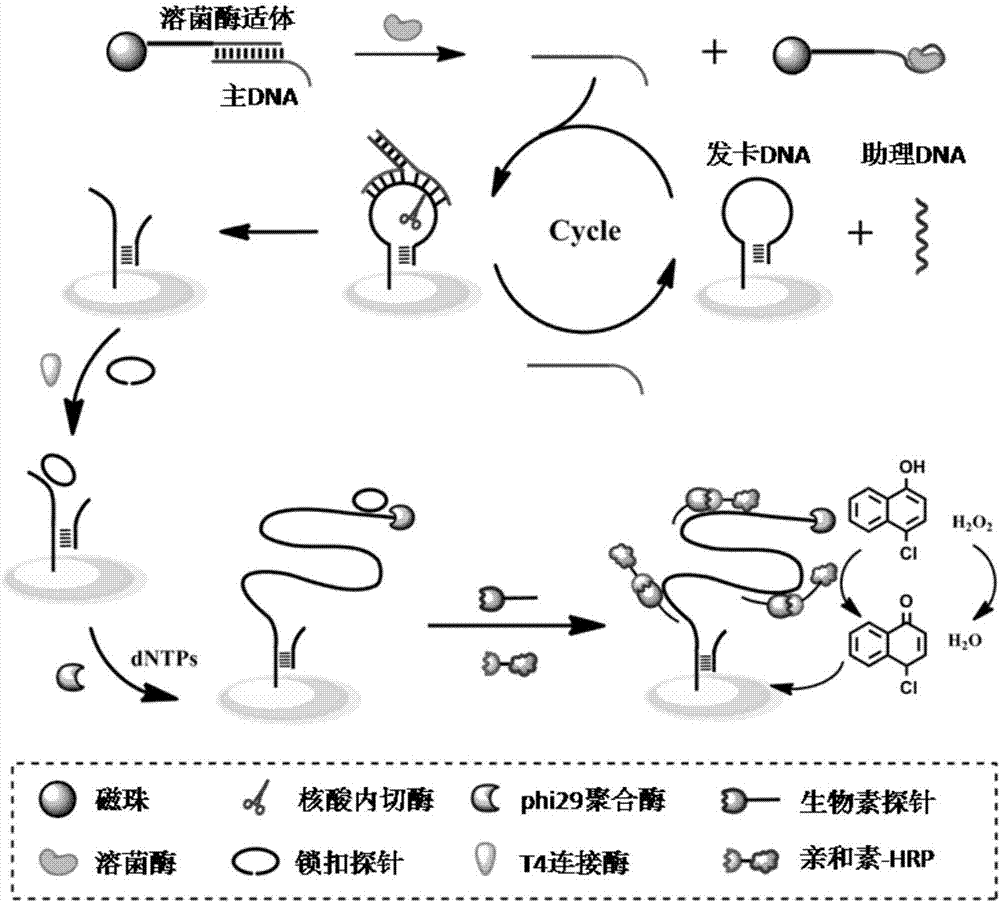
QCM detection method for detecting lysozyme based on multiple signal amplification technologies and application
InactiveCN107419005AEnhanced signalEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementAptamerBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention discloses a QCM detection method for detecting lysozyme based on multiple signal amplification technologies and application. The QCM detection method comprises the following steps that DNA hybridizes with lysozyme aptamer partially in a complementary mode, and through the specific binding reaction of the lysozyme and the lysozyme aptamer, the DNA is released; a Y-shaped structure is formed by complementary hybrid of the released DNA with hairpin DNA and assistant DNA modified on a gold leaf, and under the action of restriction enzyme, the hairpin DNA is cut and opened through specific identification sites; under the action of DNA ligase and DNA polymerase, using locking-ring-shaped DNA as a template chain, polymerization growing along the opened hairpin DNA is carried out, and a single chain with a large number of repeated sequences is formed; a signal probe marked with biotin hybridizes with the generated repeated sequences in a complementary mode, and after binding with streptavidin marked by HRP, hydrogen peroxide is catalyzed to oxidize 4-chloro naphthol, and precipitation reaction is generated; and accordingly the chip surface quality is increased, and the high-sensitivity detection of the QCM to the lysozyme is realized.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Dual temperature rapid cycling fluorescence quota PCR method for detecting telomerase activity and kit
The invention relates to a dual temperature rapid cycling fluorescence quota PCR method for detecting telomerase activity and a kit. The method provided by the invention comprises steps of: combining primers, which are the anchored hairpin primers (AHP), with a duplex scorpion primers (DS) to form a DS / AHP-TRAP system; detecting the activity of telomerase in immortalized cell protein extracts under the condition of dual temperature rapid cycling PCR; taking a telomerase extension product R6 containing 6 telomere repeat sequences as a quantitative standard substance, and drafting a quantitative curve of the extension product of the detected telomerase; comparing the quantitative standard curve of the immortalized cell sample and that of R6 to obtain an anastomosis graph of the detected telomerase activity quantitative curve and the telomerase extension product quantitative curve; supposing that a TPG value is a telomerase extension product generated by an immortalized cell and determining the number of R6 represented by the TPG value. The kit provided by the invention can be used to accomplish a real-time detection of telomerase activity in large quantities on the fluorescence quota PCR instrument in a simpler and faster manner, and has a wide prospect in the early diagnosis of malignant tumor and the screening of anticancer drugs.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Tools and Methods for the Quantification of Dna Repeats
The invention relates to an assay method allowing the quantification of the copy number of a repeated nucleic acid sequence in a genetic sample. Typically such sample comprises the genome of a microbial, plan, animal or human subject. Furthermore, the invention provides a particular example wherein the assay is used to determine the susceptibility to disease of a subject. Such information can be used in selecting the optimal treatment for a particular diseased subject.
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV
Chromosome copy number variation detection device based on low-depth high-throughput genome sequencing
The invention relates to the technical field of bioinformatics, and particularly discloses a chromosome copy number variation detection device based on low-depth high-flux genome sequencing. The device comprises a detection module, a data quality control module, a data preprocessing module, a data correction and processing module and a judgment module. The data correction and processing module is used for correcting deviations caused by different chromosome baselines by a weighted linear regression model through repeated sequence and group CNV elimination, renormalization, sex chromosome diploidy processing, GC correction and mappability correction, PCA noise reduction, CBS algorithm noise reduction, maternal pollution elimination and the like, and other processing modules are combined to provide the chromosome copy number variation detection device with higher detection accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING USCI MEDICAL LAB CO LTD
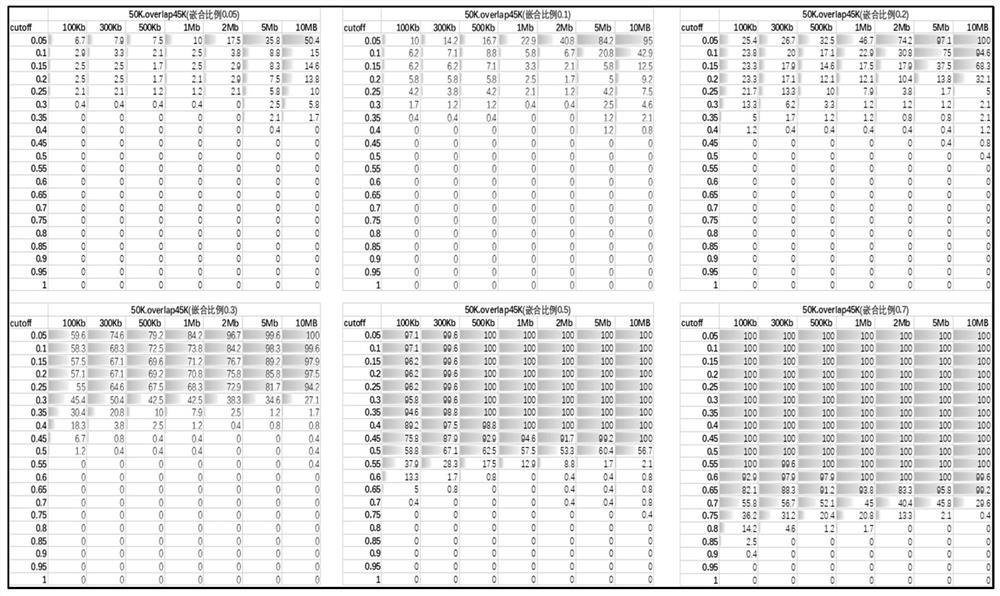
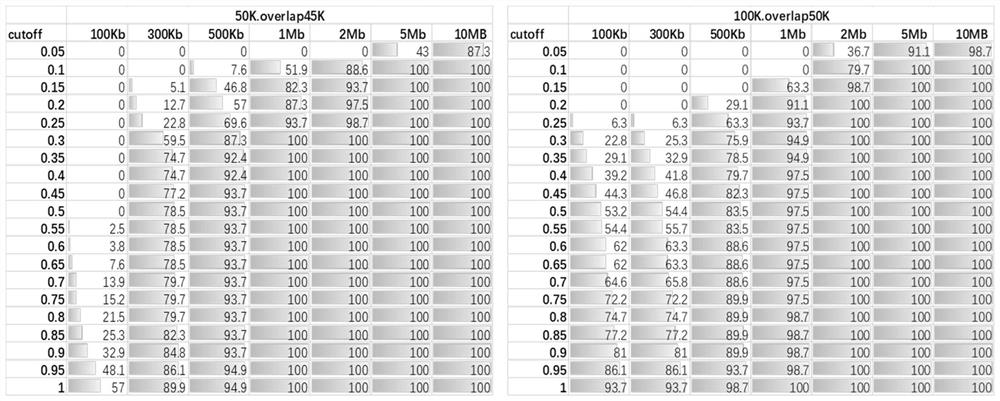
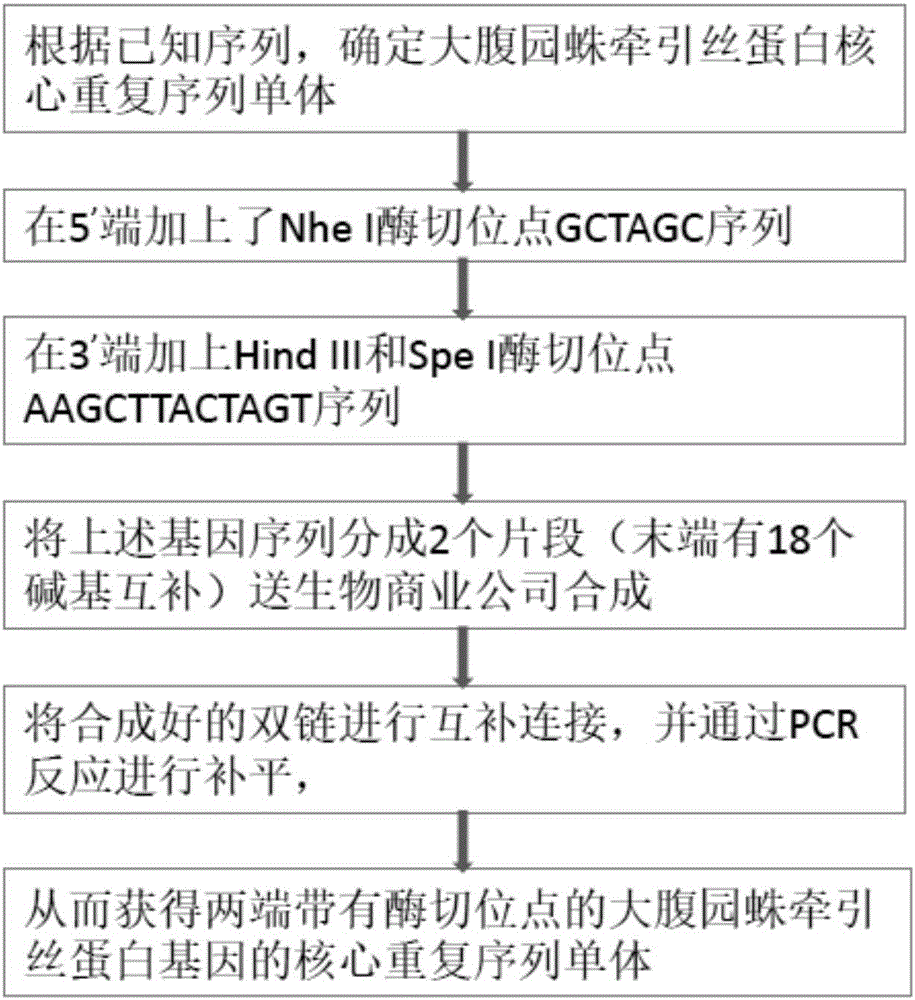
Artificially constructed araneus ventricosus dragline silk protein gene and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106754946ASimple and efficient processLow costFermentationAnimals/human peptidesEscherichia coliRestriction Enzyme Cut Site
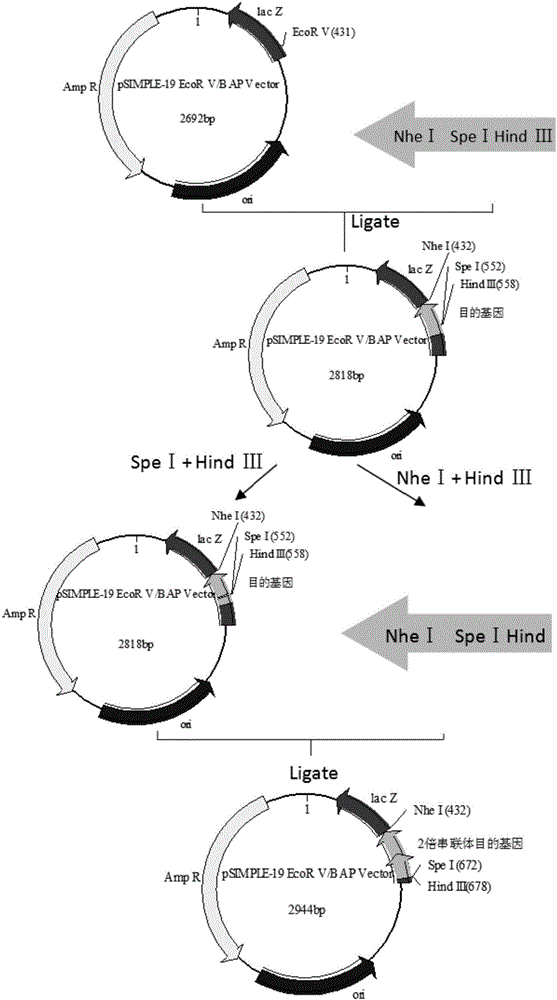
The invention discloses an artificially constructed araneus ventricosus dragline silk protein gene and a construction method thereof. The sequence of the araneus ventricosus dragline silk protein gene is shown as SEQIDNO.6. According to part of cDNA sequence of araneus ventricosus dragline silk protein, first, most-representative core repeat 108BP is selected, and artificially synthesized, both ends of the core repeat sequence are additionally added restriction enzyme cutting sites, then the core repeat sequence is connected with a pSIMPLE-19EcoRV / BAP vector, and transformed into Escherichia coli to obtain monomer recombinant plasmid, by an isocaudarner recursive directional ligation method, gene monomers are polymerized into a 16-time concatemer, 1836bp araneus pseudoventricosus dragline silk protein gene can be successfully obtained, the 1836bp araneus pseudoventricosus dragline silk protein gene can be successfully expressed for production of the araneus ventricosus dragline silk protein, and the whole process is simple and efficient, saves the cost, improves the work efficiency, and has good application prospects.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Single copy genomic hybridization probes and method of generating same
InactiveUS20050064449A1Eliminates spurious hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentHybridization probe
Nucleic acid (e.g., DNA) hybridization probes are described which comprise a labeled, single copy nucleic acid which hybridizes to a deduced single copy sequence interval in target nucleic acid of known sequence. The probes, which are essentially free of repetitive sequences, can be used in hybridization analyses without adding repetitive sequence-blocking nucleic acids. This allows rapid and accurate detection of chromosomal abnormalities. The probes are preferably designed by first determining the sequence of at least one single copy interval in a target nucleic acid sequence, and developing corresponding hybridization probes which hybridize to at least a part of the deduced single copy sequence. In practice, the sequences of the target and of known genomic repetitive sequence representatives are compared in order to deduce locations of the single copy sequence intervals. The single copy probes can be developed by any variety of methods, such as PCR amplification, restriction or exonuclease digestion of purified genomic fragments, or direct synthesis of DNA sequences. This is followed by labeling of the probes and hybridization to a target sequence.
Owner:KNOLL JOAN +1
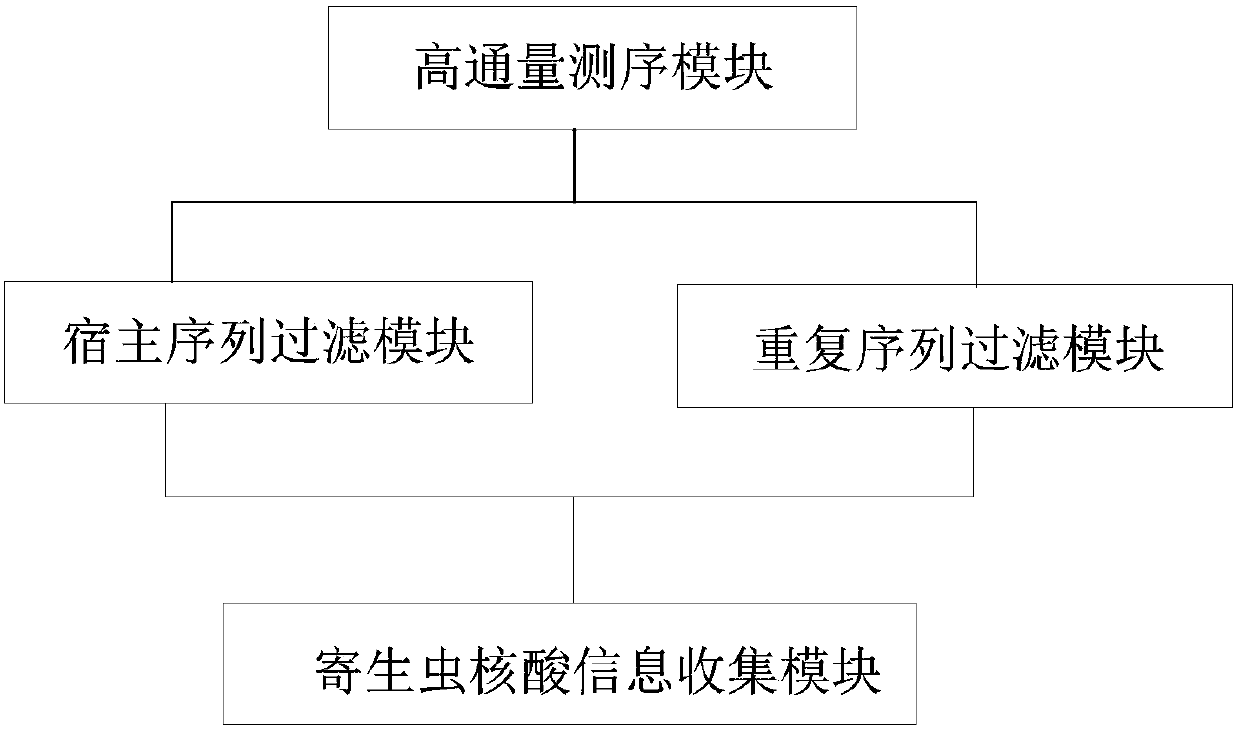
Methods and systems for acquiring nucleic acid information of parasites and classifying parasites by sequencing
PendingCN110272984ATo achieveRealize classification and identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingFree dna
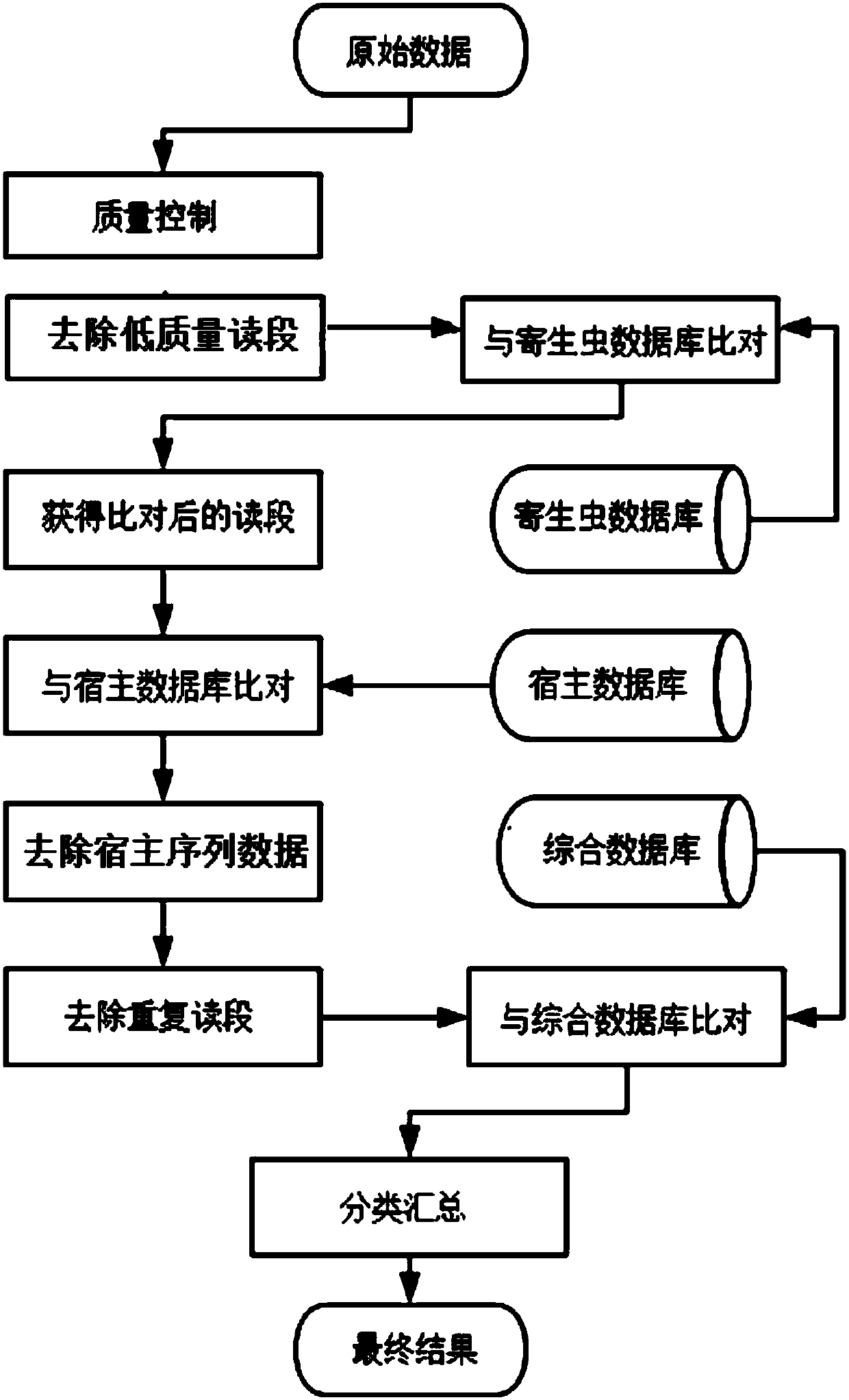
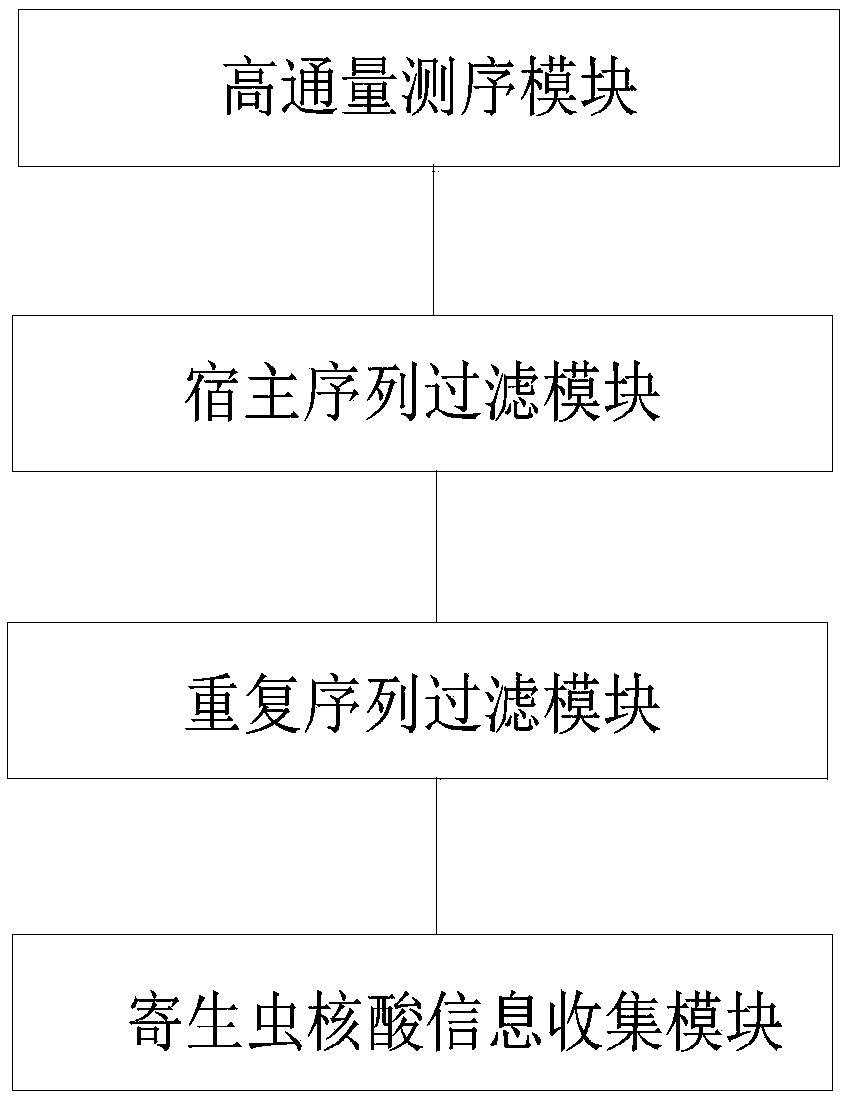
The invention relates to the field of high-throughput sequencing and particularly relates to methods and systems for acquiring nucleic acid information of parasites on a host and classifying parasites by high-throughput sequencing. The method for acquiring nucleic acid information of parasites comprises the following steps: acquiring sequence data of free DNA in host blood based on high-throughput sequencing; filtering off host nucleic acid data in the sequence data of free DNA in the host blood by taking the nucleic acid sequence of the host as a reference; filtering off repeated sequence data in the sequence data of free DNA in the host blood; and acquiring the nucleic acid data of parasites to acquire the nucleic acid information of parasites on the host. Based on the method, the invention further provides the system for acquiring the nucleic acid information of parasites, and a method and system for identifying the species of a parasite on a host. The methods and systems are not limited to prior knowledge, can improve the universality of detection methods, have high sensitivity and are rapid.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
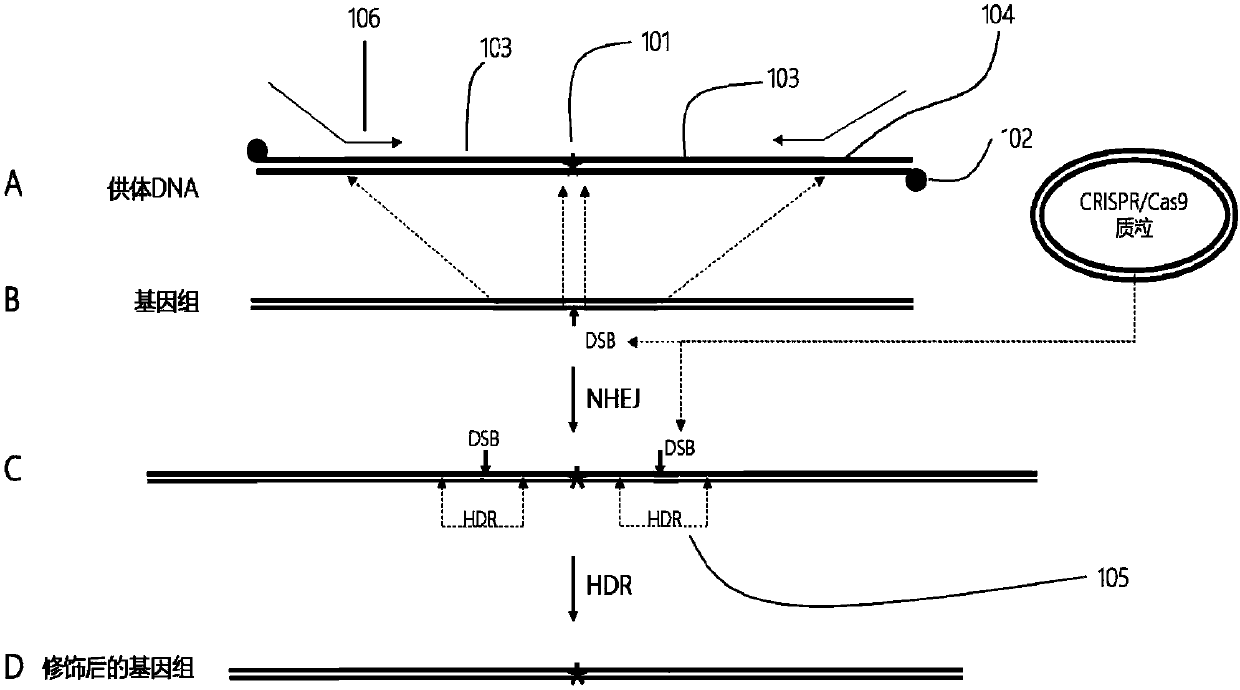
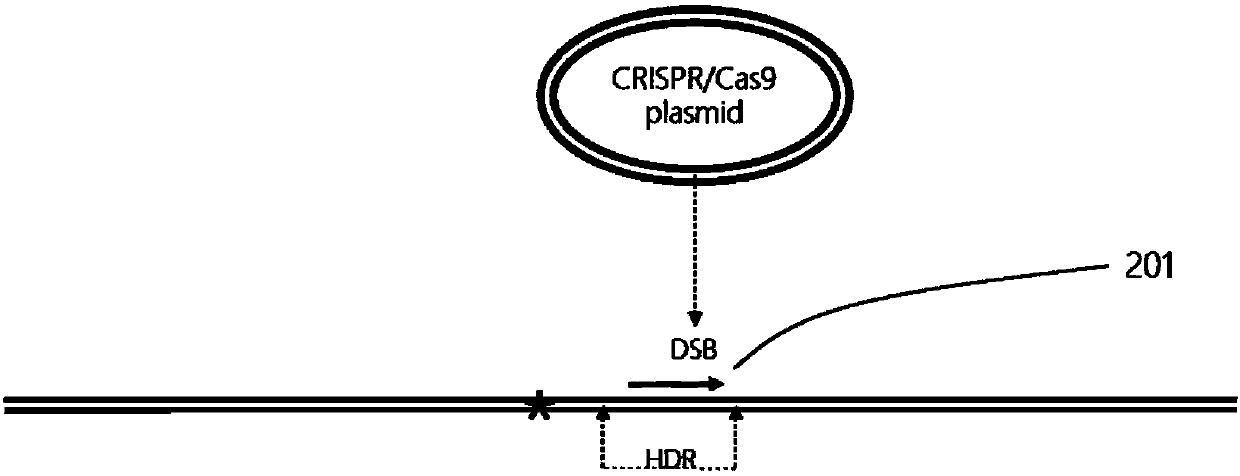
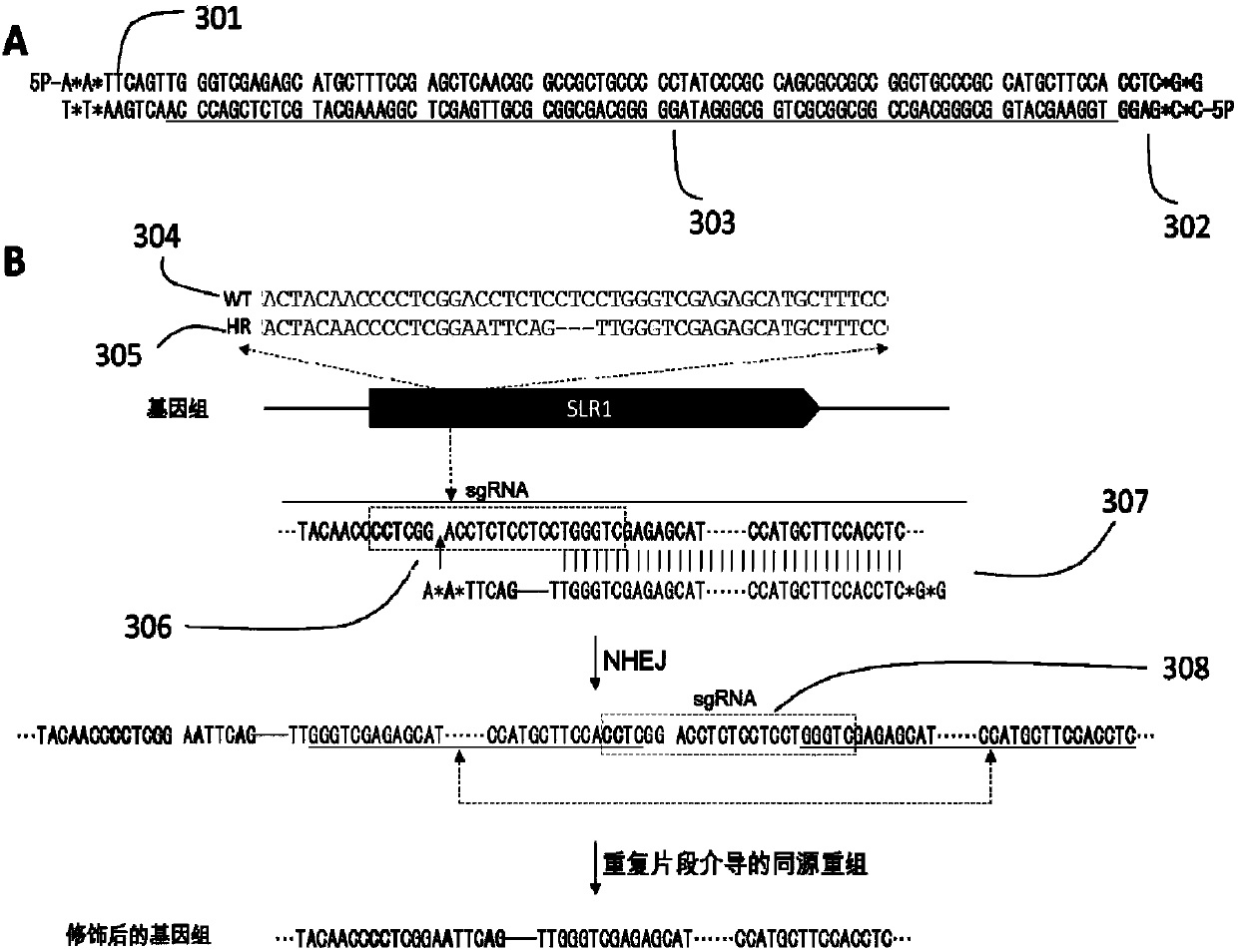
Plant site-directed recombination method mediated by repeated fragments
The invention provides a plant site-directed recombination method mediated by repeated fragments. Specifically, the present invention provides a donor DNA with a specific repeat sequence, and a reagent combination for gene editing. According to the invention, the donor DNA with a specific structure is adopted, and a specific site of a target gene is cut by means of a site-directed cutting nuclease, so that the donor DNA fragment is efficiently integrated into a cutting site.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
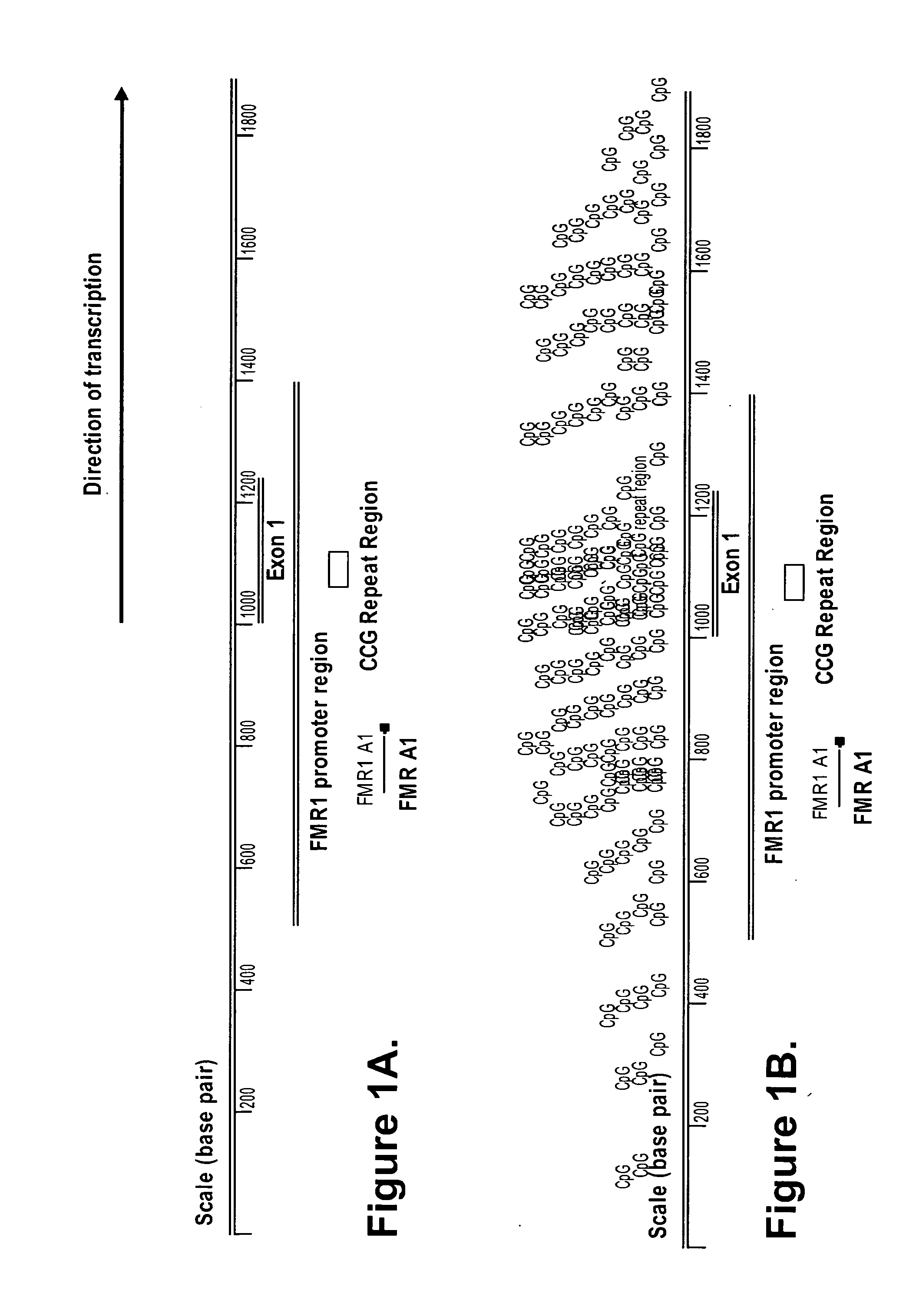
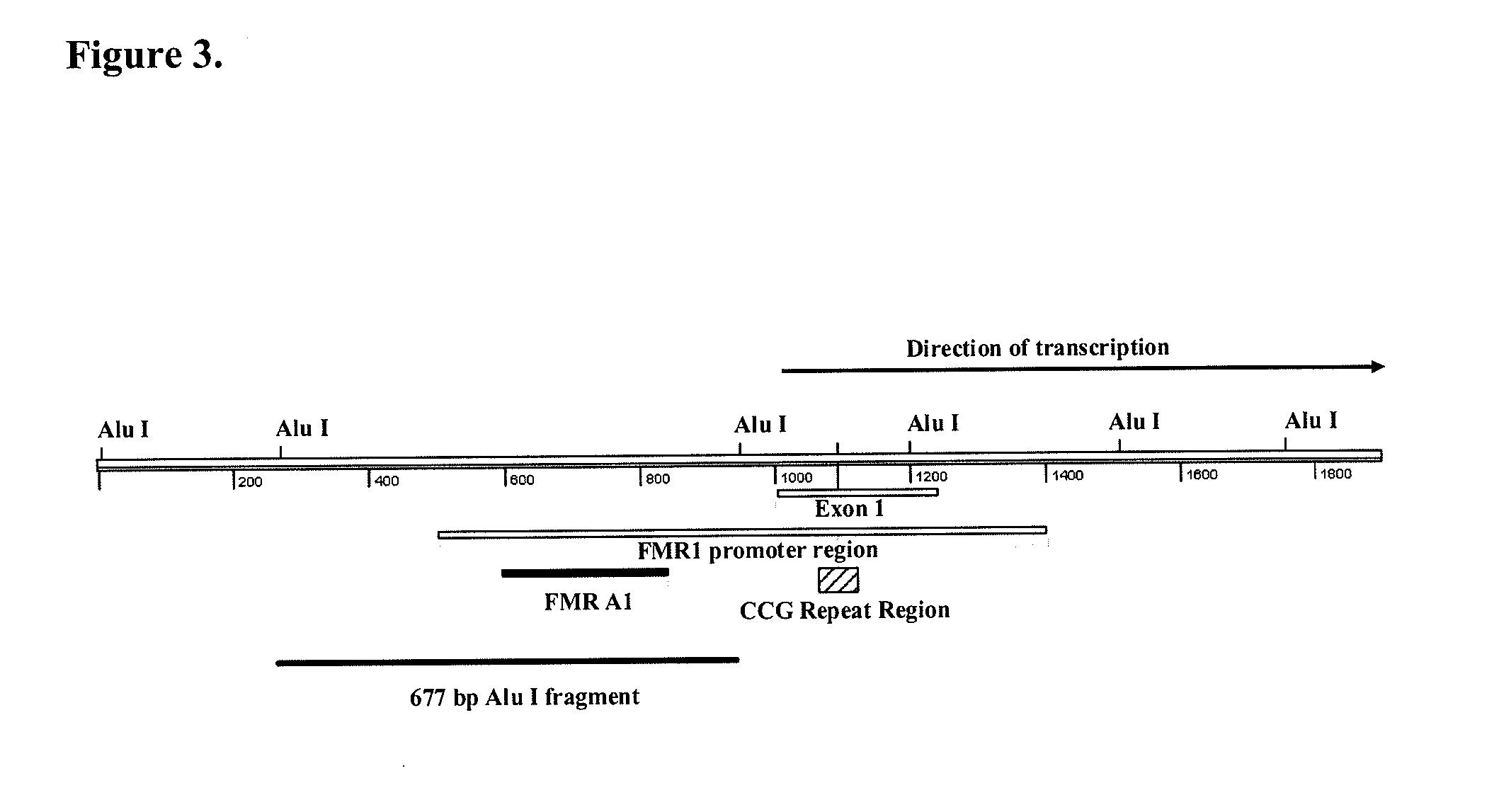
Detection of nucleic acid sequences adjacent to repeated sequences
The present invention provides methods of quantifying a target locus adjacent to an extended repeat sequence in genomic DNA. The present invention further provides methods and kits for detecting methylation at a target locus adjacent to an extended repeat sequence in genomic DNA.
Owner:ORION GENOMICS
Methods and systems of molecular recording by crispr-cas system
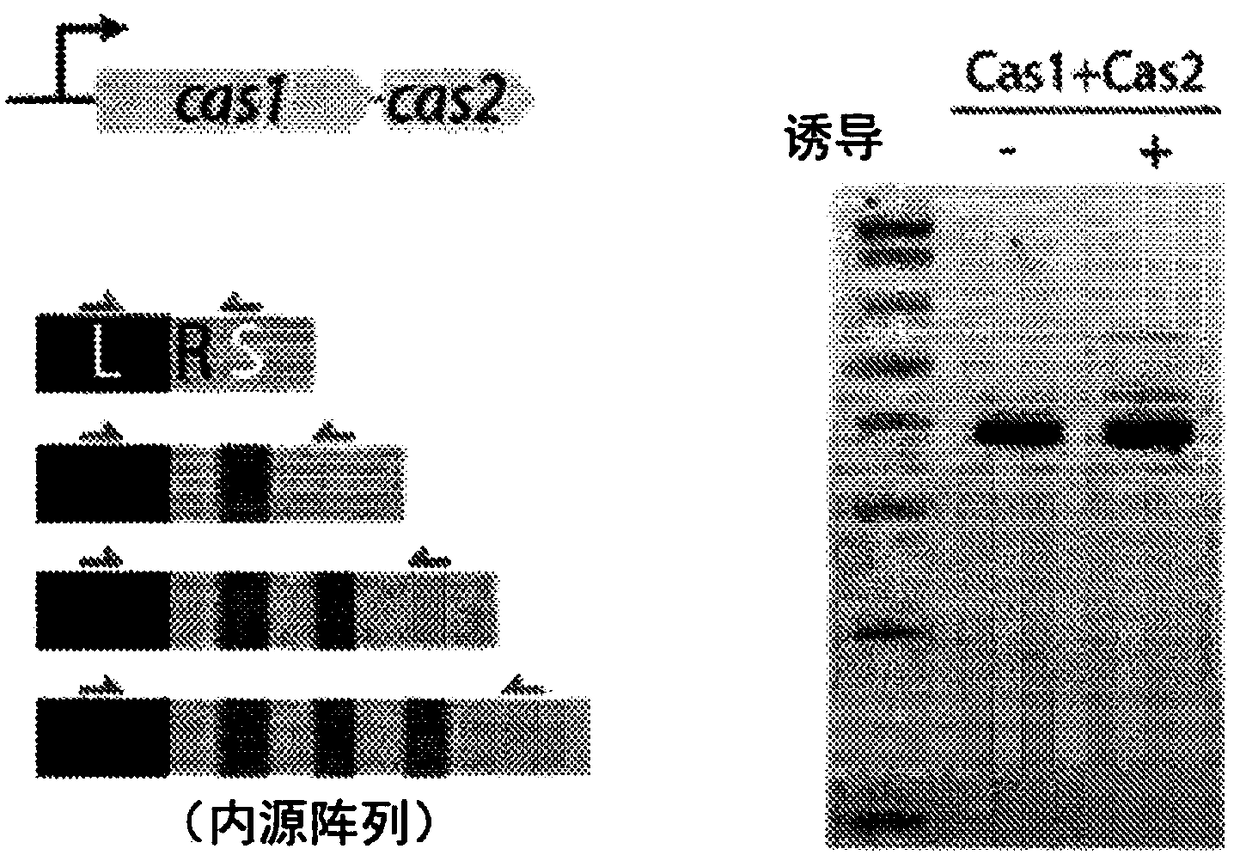
This invention provides methods of altering a cell including providing the cell with a nucleic acid sequence encoding a Cas1 protein and / or a Cas2 protein of a CRISPR adaptation system, providing thecell with a CRISPR array nucleic acid sequence including a leader sequence and at least one repeat sequence, wherein the cell expresses the Cas1 protein and / or the Cas2 protein and wherein the CRISPRarray nucleic acid sequence is within genomic DNA of the cell or on a plasmid. Also provided are methods and systems for nucleic acid storage and in vivo molecular recordings of events into a cell.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for storing audio or video file based on DNA sequence and storage medium
ActiveCN111368132AEasy to editImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsVideo data indexingComputer graphics (images)Transcoding
The invention discloses a method for storing an audio or video file based on a DNA sequence and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: encoding a to-be-processed file into a binary file, further converting the binary file into a base sequence, and converting the to-be-processed file into an oscillogram; enabling the base sequences to correspond to the coordinates of the oscillogram in sequence to obtain a corresponding relation graph of the bases and the oscillogram coordinates. The method comprises the following steps: transcoding binary characters to eliminate repeated character strings in the binary characters, recoding the converted character strings to obtain an optimized base sequence, and carrying out base balance on the repeated sequence by adopting a label positioning replacement method to obtain a coded base sequence. According to the invention, DNA sequence-based information storage can be carried out on audios and videos, and the video and audio encoding and decoding accuracy is improved.
Owner:GENEIS TECH BEIJING CO LTD
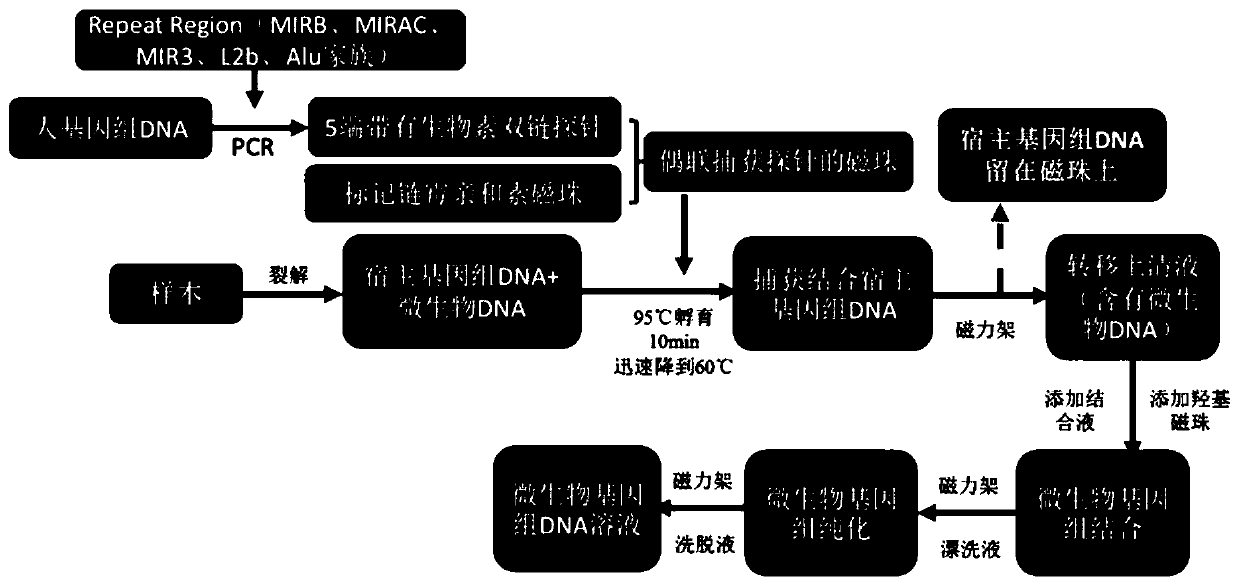
Microbial nucleic acid extraction method with host genome DNA removal function and kit
PendingCN111057747AIncrease concentrationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrobial GenomesMicroorganism
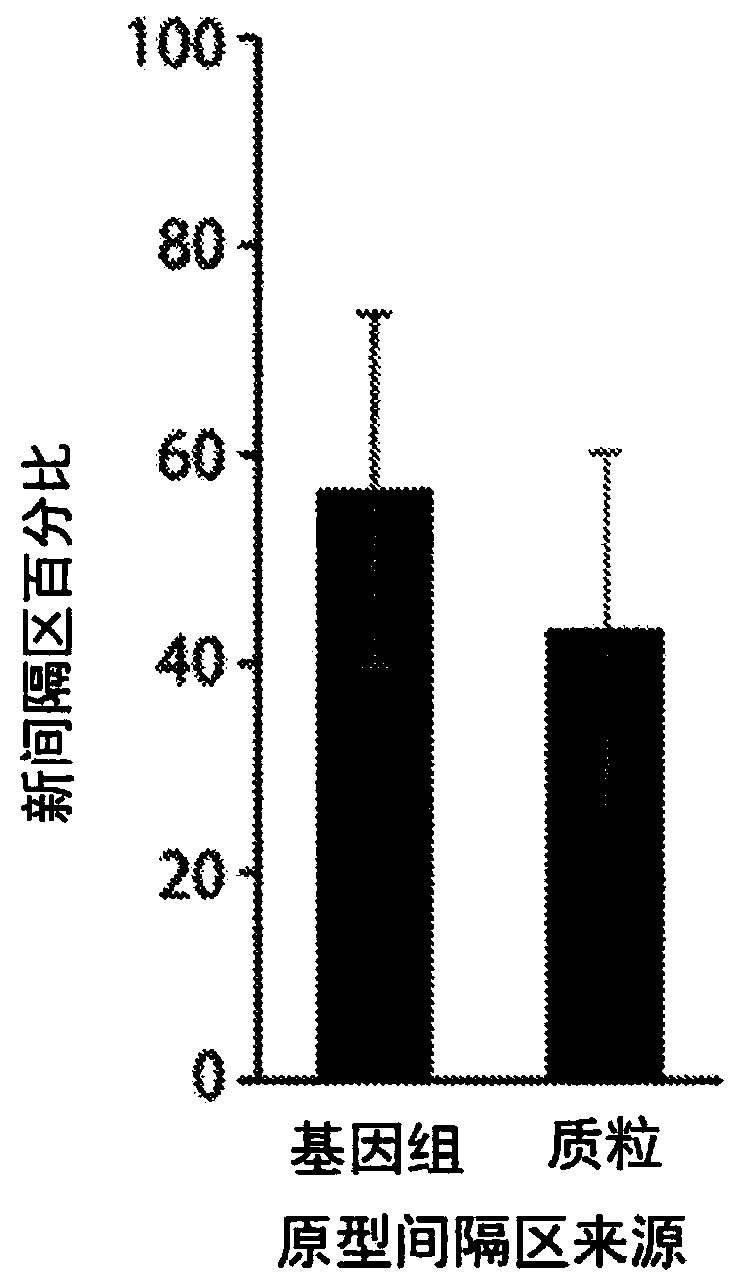
The invention discloses a microbial nucleic acid extraction method with a host genome DNA removal function and a kit. The invention provides a complete set of primer pairs, including one or more primer pairs. Each primer pair correspondingly amplifies one highly repetitive sequence in host genome DNA, wherein the highly repetitive sequence is selected from at least one gene in the following gene family: the gene family includes an MIR family gene and / or an ALu family gene. The microbial DNA extraction method with the host genome DNA removal function has the advantage that the microbial genomeDNA enrichment effect is stronger. According to the method, the host genome DNA is removed after the nucleic acid is released through lysis, then the microbial genome DNA is enriched for purificationand recovery, and meanwhile, viral nucleic acid in host cells can be enriched without changing the metagenome flora structure.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Method for amplifying oligonucleotide and small RNA by using polymerase-endonuclease chain reaction
InactiveUS20120028253A1Simple and stable and efficientStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiological studiesSingle strand
A method for amplifying oligonucleotide in vitro by polymerase-endonuclease chain reaction (PECR) which utilizes a single-stranded DNA probe containing repeat sequences, extends a target oligonucleotide by a thermostable DNA polymerase, cleaves extended products with a thermostable endonuclease, and amplifies target oligonucleotide by thermocycling. In PECR, a specific oligonucleotide is exponentially amplified using one single probe instead of a pair of primers, and the reaction is precisely controlled by thermal cycles whose parameters are flexibly adjustable according to length, sequence, melting temperature and initial amount of the target oligonucleotide. Amplification speed depends totally on initial amount of target oligonucleotide present in the reaction system. The method can be used to amplify specific small nucleic acids, such as oligonucleotides and microRNAs, and further conduct quantitative analysis. PECR is easy to conduct with high efficiency, specificity and stability, and thus can be widely used in molecular biology studies.
Owner:WANG XIAOLONG
PML/RARA (promyelocytic leukemia/retinoic acid receptor alpha) fusion gene quick detection probe with low cost and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106929576AReduce manufacturing costHigh labeling rateMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationFluorescenceRetinoic acid receptor beta
The invention belongs to the field of molecule biology, and particularly relates to a PML / RARA (promyelocytic leukemia / retinoic acid receptor alpha) fusion gene quick detection probe with low cost and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of downloading non-repeated sequences of g genomeene groups in the area covered by PML and RARA gene probes from USCS Genome Browser, and importing the segmented sequences into OligoArray software by batches to design the probes; adding a tag sequence onto the designed probe, and directly synthesizing; using a tag primer with a fluorophorefluorescent gene to amplify and mark the probe, so as to obtain the PML / RARA fusion gene quick detection probe. The prepared PML / RARA fusion gene quick detection probe has the advantages that the hybridizing time is short, the hybridizing experiment can be completed within 15 to 30min, the hybridizing signal is bright, the signal to noise ratio is high, the preparation cost is low, and the like.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHCHART BIOLOGICAL TECH
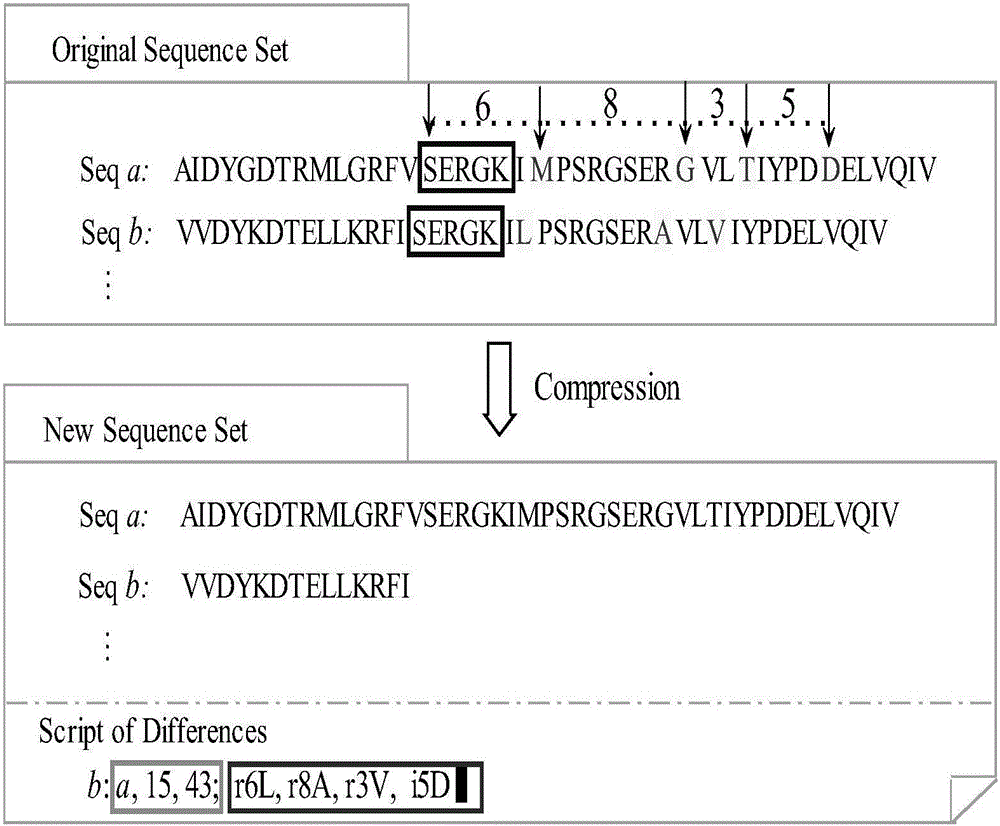
Compression and clustering-based batch protein homology search method
ActiveCN106022000AShorten the timeBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsProtein DatabasesSequence clustering
The invention discloses a compression and clustering-based batch protein homology search method and belongs to the cross field of computer application technologies and bio-technologies. The method comprises the steps of firstly performing compression operation on a query sequence and a protein database through redundancy analysis and redundancy removal processes by fully utilizing sequence similar information existent in a protein database sequence and the query sequence; secondly performing similar sub-sequence clustering on the compressed protein database; thirdly performing a search by utilizing a mapping principle based on the clustered database to discover potential results, and establishing an executable database according to the found potential result set; and finally performing a homology search in the executable database to obtain a final homology sequence. According to the method, the homology search is performed in the established executable database, so that the time for repeated sequence comparison and gapless expansion is greatly shortened.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
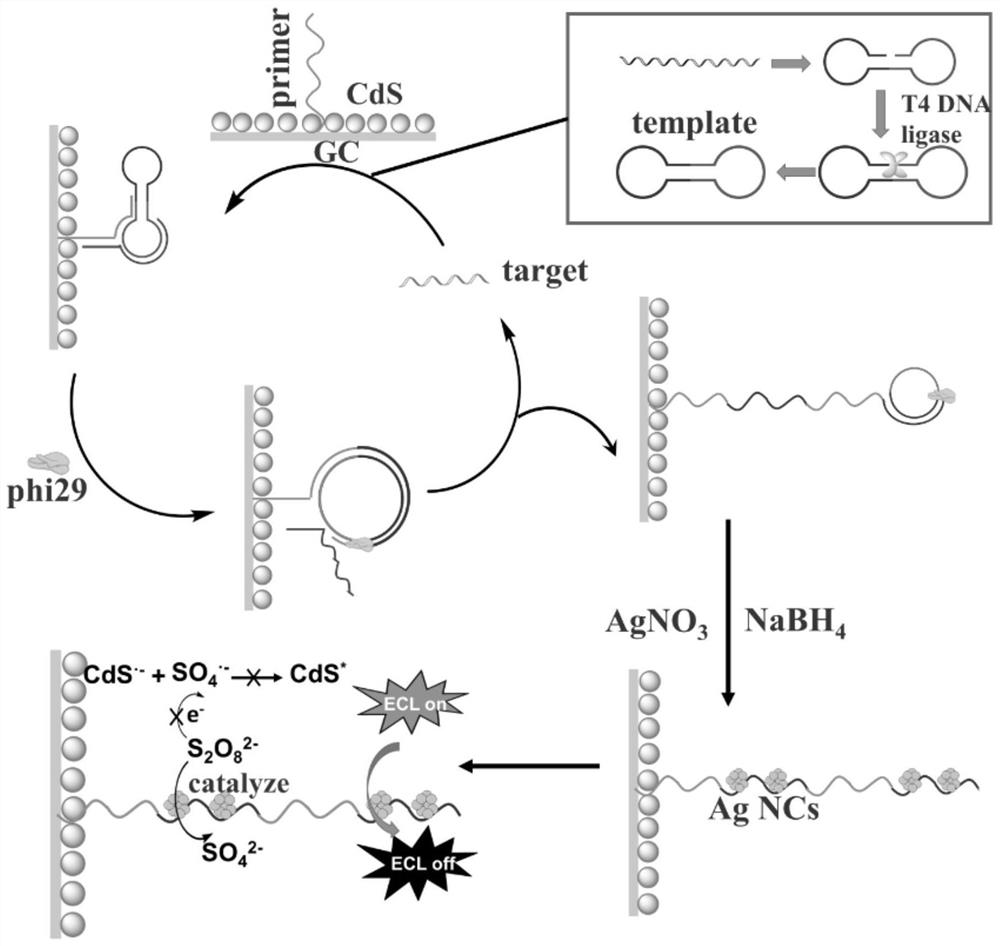
Helicobator pylori nucleic acid sensor, detection method and application
ActiveCN111733264AEnables ultra-sensitive detectionLow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCytosineHelicobacter
The invention discloses a helicobator pylori nucleic acid sensor, a detection method and application. The sensor comprises a glassy carbon electrode, a primer sequence, a template sequence, a DNA ligase, a DNA polymerase, a water-soluble silver salt and a reducing agent; the primer sequence and CdS quantum dots are connected with the surface of the glassy carbon electrode; the template sequence can form a dumbbell-shaped structure, and the dumbbell-shaped structure can be connected with the DNA ligase to be closed by the DNA ligase; and the template sequence, the primer sequence and a helicobator pylori nucleic acid sequence can form a trimer structure, the trimer structure can make the primer sequence subjected to rolling circle amplification under the action of the DNA polymerase, and anamplified DNA long chain has repetitive sequences rich in cytosine bases. By means of the helicobator pylori nucleic acid sensor, the detection method and application, ultra-sensitive detection of helicobator pylori nucleic acid can be achieved.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Amplification-free RNA quantitative detection method
PendingCN112813143AEasy to operateImprove detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JFunctional modification
The invention discloses an amplification-free RNA quantitative detection method. The method comprises the following steps: designing a crRNA sequence which is complementarily paired with a target RNA base and has a 5 '-terminal repetitive sequence stem-loop structure; preparing a Cas13 reaction system; mixing an object to be detected with the Cas13 reaction system, dispersing the mixed system into a large number of micro-reaction units which are uniform in size and do not exceed nano-flow, and providing proper temperature conditions to incubate the micro-reaction units; and reading signals of the micro-reaction units after the incubation reaction is completed, and calculating the content of the target RNA in the sample to be detected. According to the amplification-free RNA quantitative detection method disclosed by the invention, RNA quantitative detection at the single molecule level can be realized, internal reference correction and standard curve establishment are not needed, steps of reverse transcription and nucleic acid replication are not needed, marking and functional modification are not needed, thermal circulation is not needed in thermostatic reaction, the operation steps are simple, and the detection precision is high.
Owner:广州市第一人民医院 +1
Method for genetic detection using interspersed genetic elements
ActiveUS7794983B2Easy to testSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenetic element
Owner:RELIAGENE TECH INC A CORP CHARTERED IN & EXISTING UNDER THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF LOUISIANA +1
Primers for identifying types of rice GS5 gene and GLW7 gene and application of primers for identifying types of rice GS5 gene and GLW7 gene
PendingCN110894542AAccurate identificationGood amplification effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenotype Analysis
The invention discloses primers for identifying types of a GS5 gene and a GLW7 gene and application of the primers for identifying the types of the GS5 gene and the GLW7 gene, and belongs to the technical field of rice variety identification. According to the primers for identifying the types of the GS5 gene and the GLW7 gene and application of the primers for identifying the types of the GS5 geneand the GLW7 gene, by turning simply-repeated sequences of the rice GS5 gene and the rice GLW7 gene into digestion molecule markers, the types of the GS5 gene and the GLW7 gene are identified, and nucleotide sequences of the primers for identifying the types of the GS5 gene and the GLW7 gene are shown in SEQ ID NO.: 1-6 as shown in the description. By means of the molecule markers of the primersfor identifying the types of the GS5 gene and the GLW7 gene, the favorable variation types of the GS5 gene and the GLW7 gene can be accurately identified, the breeding screening efficiency can be improved, and a breeding screening process can be sped up; and the designed digestion molecule markers have good amplification effects, and selected enzymes are common enzymes which are low in price so that the identification cost can be greatly reduced, and the primers for identifying the types of the GS5 gene and the GLW7 gene are suitable for genotype analysis of a large number of varieties.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Digital PCR-based primers, probes and kit for blood source screening
PendingCN110923361AShorten the windowHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAbsolute quantificationVirology
The invention provides a digital PCR-based primer combination, probe combination and kit including the above primer combination and probe combination for blood source screening, and a detection methodfor blood source screening by using the kit. According to the kit provided by the invention, the amplification primers and the taqman probes are designed based on the gene sequences of HBV, HCV, HIVand TP to specifically detect target genes, and the main criteria for screening detection loci are sequence conservation and no repeated sequences. The kit provided by the invention can realize absolute quantification without the need of a standard curve, the sensitivity to the detection of the HBV, the HCV, the HIV and the TP is improved by 10 times or more compared with that of fluorescence PCR,and the window phase of pathogen detection is further shortened.
Owner:湖南圣洲生物科技有限公司
Microsatellite loci for detecting msi, screening method and application thereof
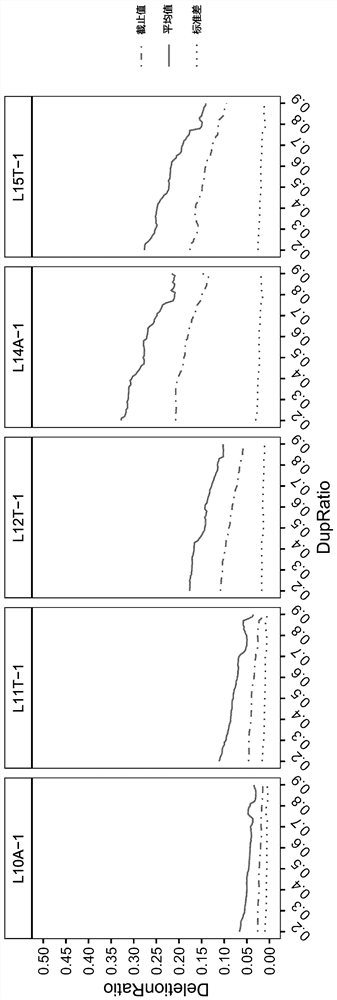
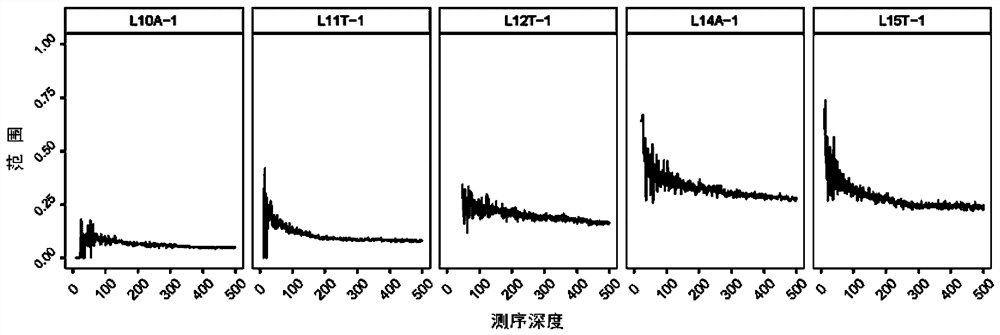
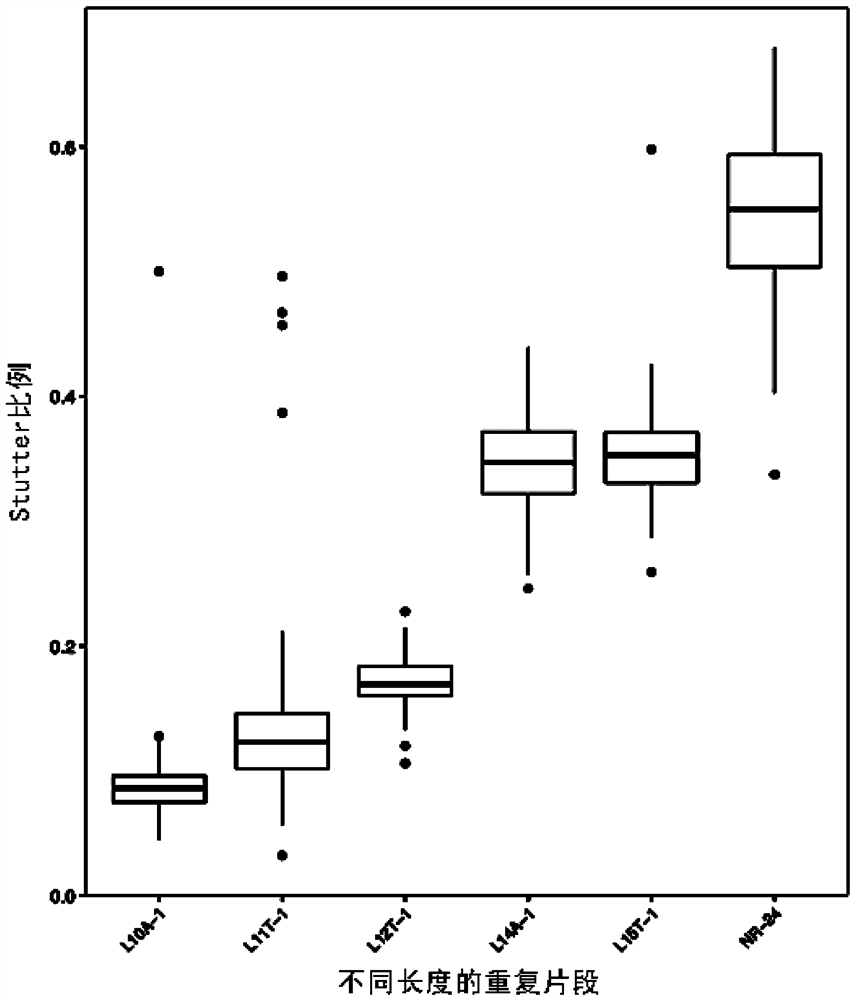
The invention provides a microsatellite site for detecting MSI, its screening method and application. The screening method includes: selecting microsatellite loci with A or T single-base repeat sequences of ≤15 bp and whose flanking sequence similarity value is lower than the similarity threshold, and recording them as the first locus set; obtaining sequencing data of multiple MSS samples and Screen and count the type of repeating unit and the frequency of each repeating unit in the first locus set; select the locus that satisfies the second condition as the second locus set, and the second condition includes: 1) the highest frequency The type of repeating unit is consistent with the reference sequence; 2) The capture efficiency in the process of library construction and sequencing is higher than the capture threshold; 3) The polymorphism in the population is less than 5%; count and retain every Sites where there is a significant difference in the deletion ratio between the negative sample group and the positive sample group. The screened sites can improve the sensitivity and specificity of detection.
Owner:臻和(北京)生物科技有限公司 +1
Method of analyzing DNA using contiguous repeats
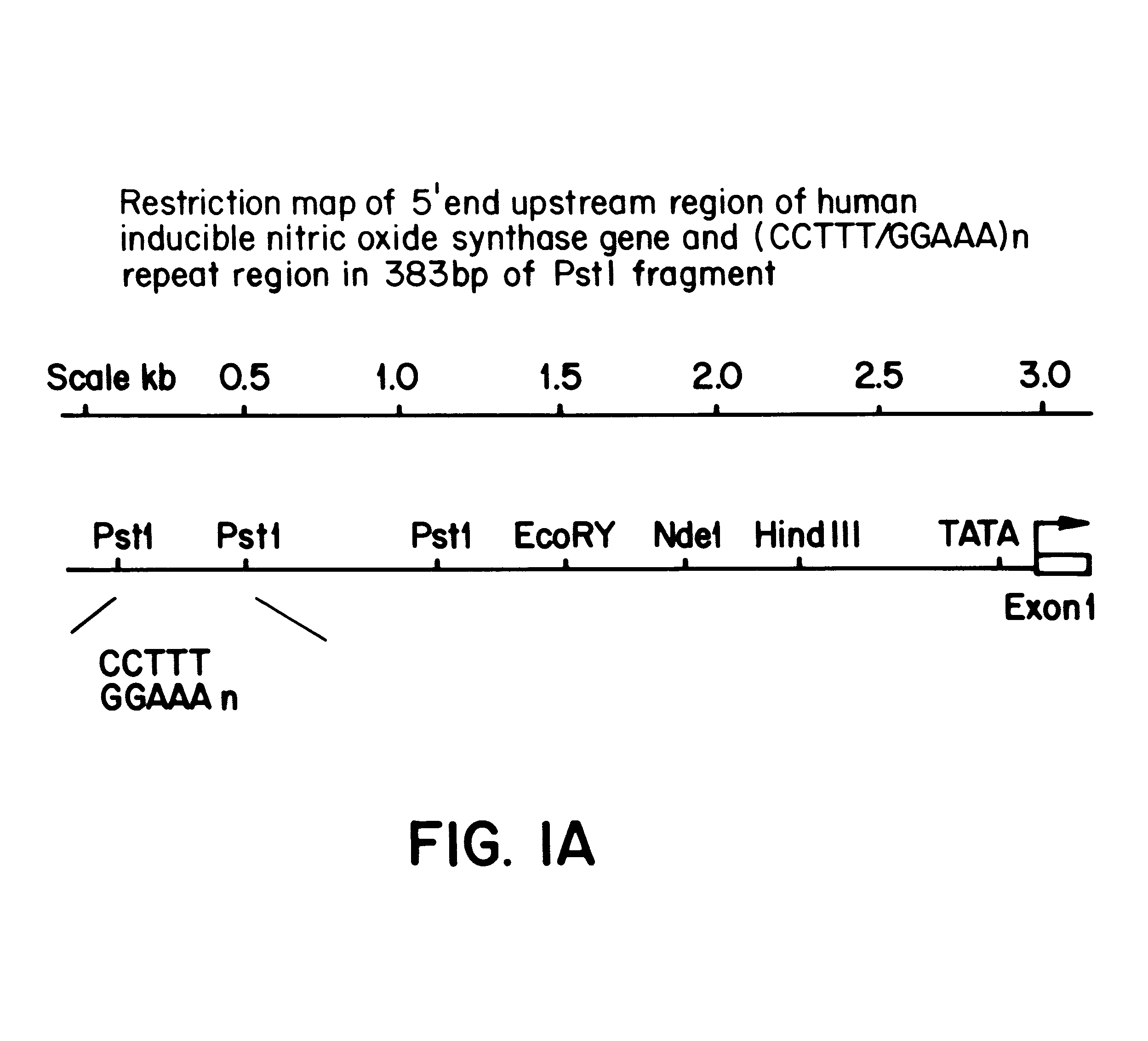
InactiveUS6197509B1Easy to distinguishHighly polymorphicSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseAllele
A novel, highly polymorphic DNA marker based on the pentanucleotide repeat (CCTTT / GGAAA)n has been identified in the human inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) gene. Twelve different alleles, having between 7 and 18 repeats, have been identified. The repeat is highly polymorphic in the human population and so lends itself to use as a microsatellite marker with uses in, for example, forensic medicine, population studies, family linkage studies and disease diagnosis.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Two black mustard repeated DNA sequences and application thereof
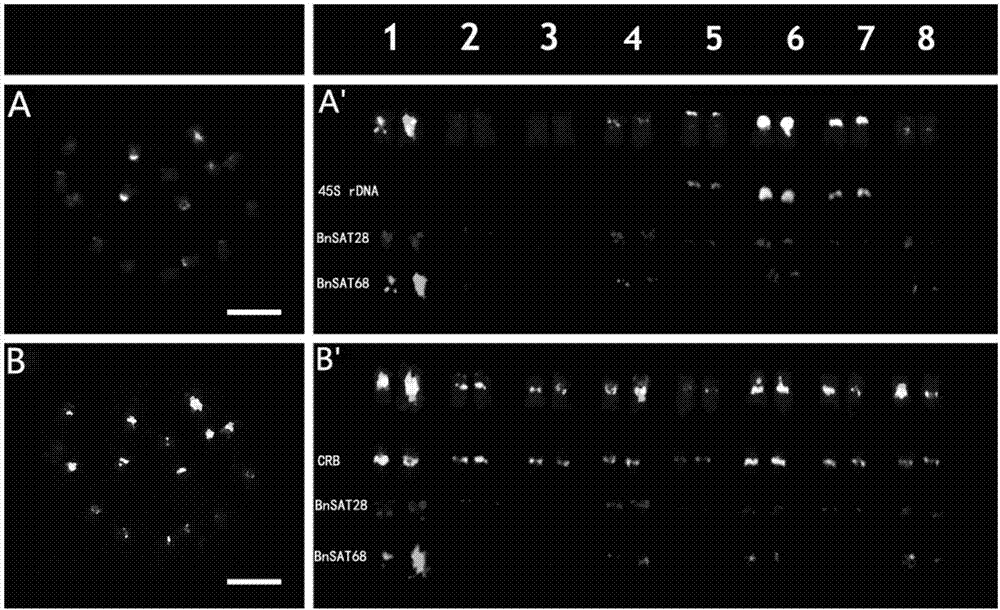
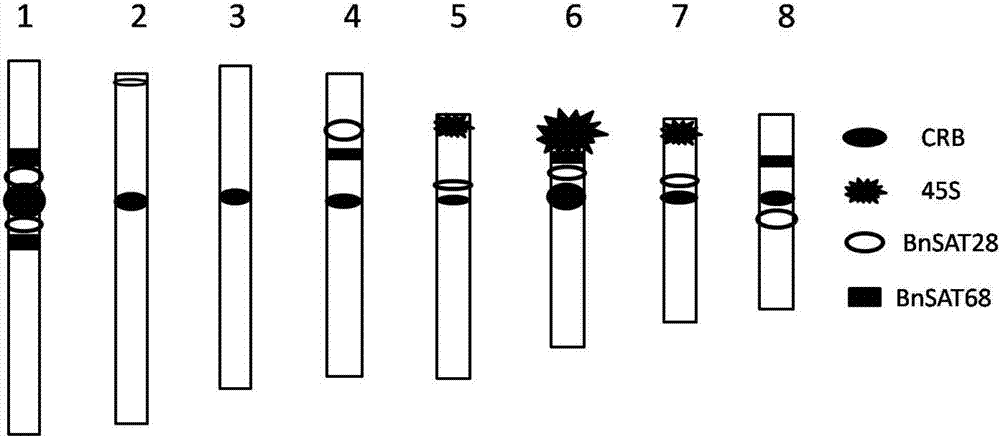
ActiveCN106916895AEasy to identifyAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionA-DNASingle strand dna
The invention discloses two black mustard genome DNA sequences and application thereof, and provides a DNA molecule set used for identifying a B genome of brassica plants. The DNA molecule set is composed of a single stranded DNA molecule as shown in sequence 1 in a sequence table and a single stranded DNA molecule as shown in sequence 2 in the sequence table. Experiments prove that by obtaining BNSAT28 and BNSAT68, chromosomes of brassica plants can be identified more easily and more accurately, and the problem that no ideal probe is available for identification of chromosomes of brassica plants is solved.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com