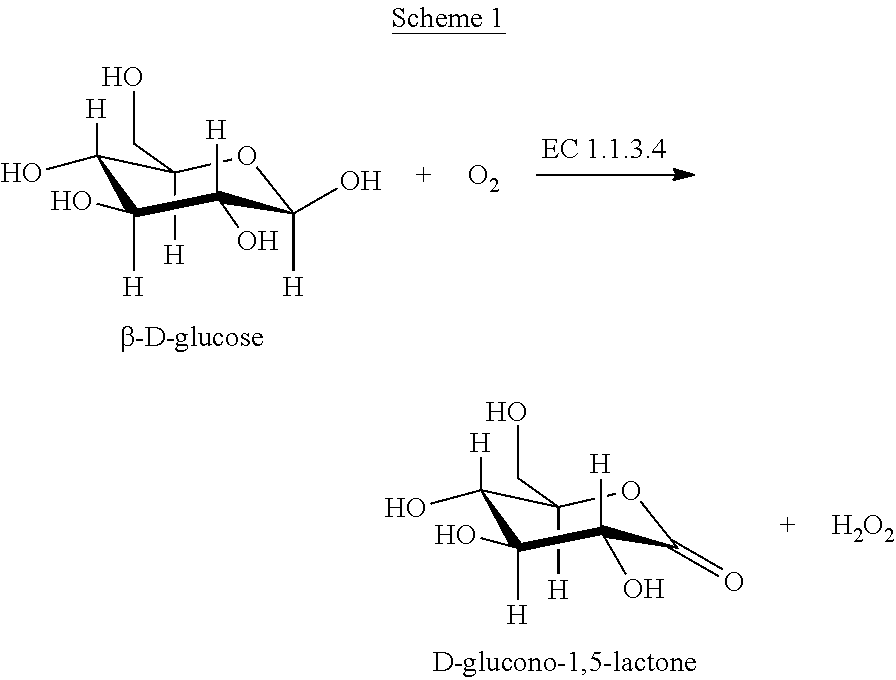
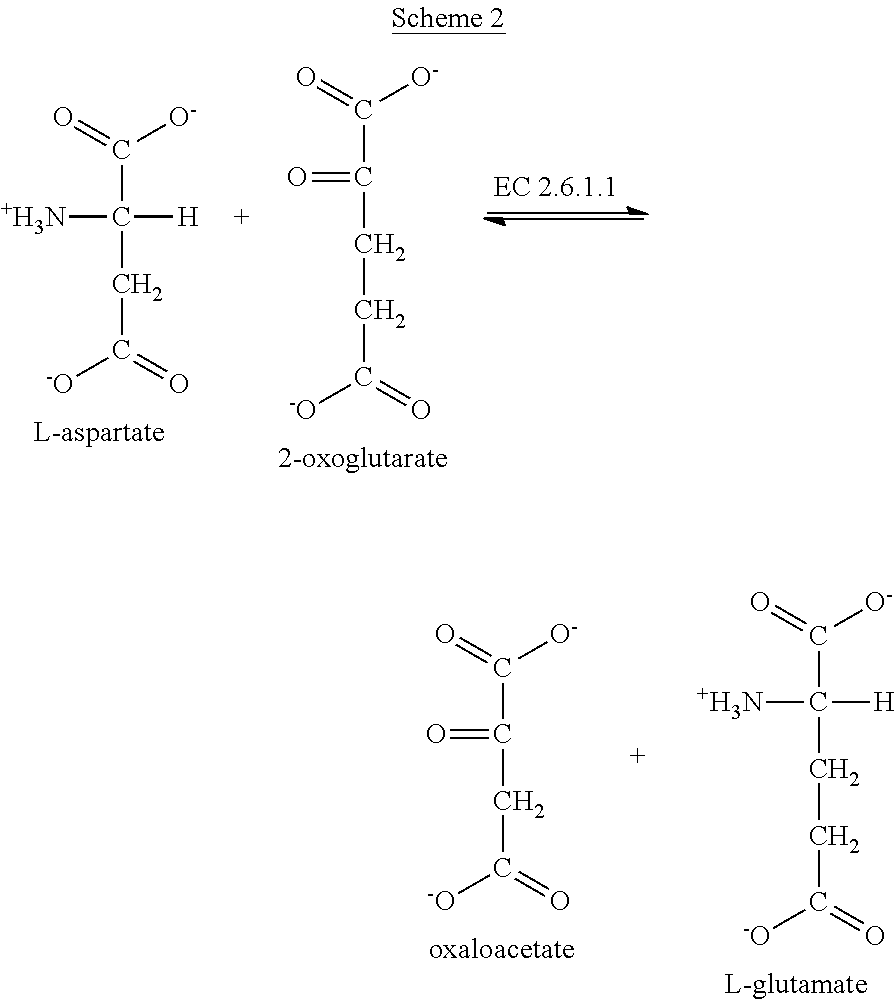
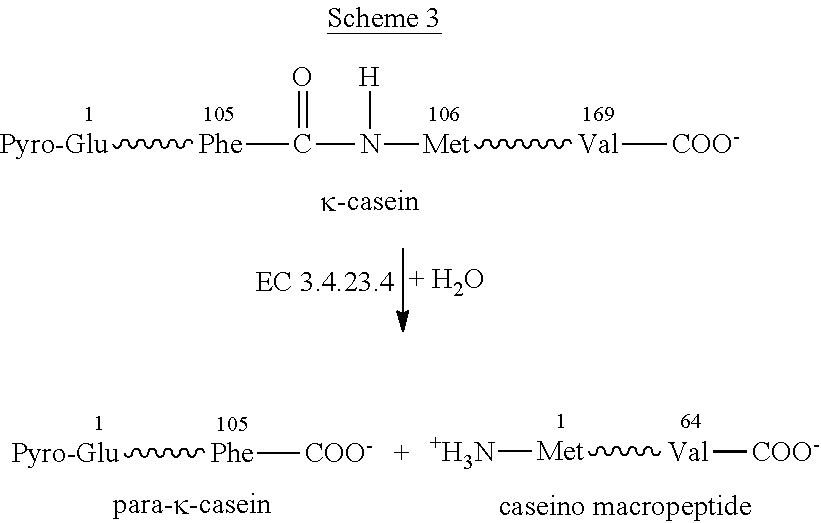
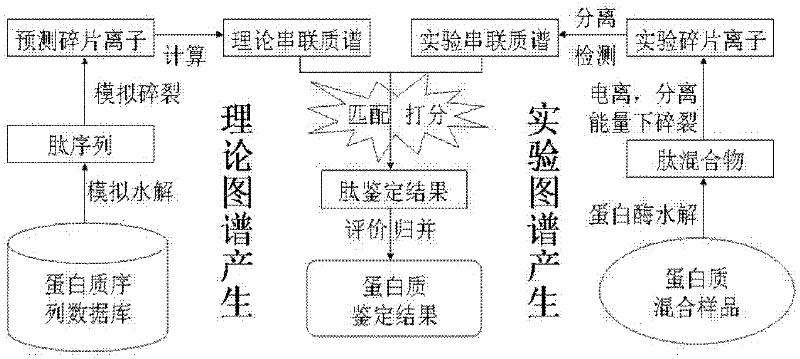
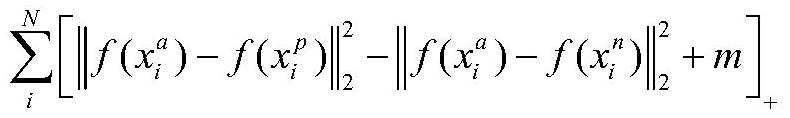Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "Protein Databases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein structure database. In biology, a protein structure database is a database that is modeled around the various experimentally determined protein structures. The aim of most protein structure databases is to organize and annotate the protein structures, providing the biological community access to the experimental data in a useful way.
Classification of Protein Sequences and Uses of Classified Proteins
A searchable protein database is disclosed. The protein database comprises a plurality of entries, each entry having a sufficiently short predicting sequence and a protein classifier corresponding to the predicting sequence. An unclassified protein sequence can be classifiable by the database via searching therein for a motif of amino acids matching a predicting sequence of the database, thereby attributing to the unclassified protein a protein classifier.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
System and method for identifying complex patterns of amino acids
A method and system are disclosed for identifying and / or locating complex patterns in an amino acid sequence stored in a computer file or database. According to an aspect of the present invention, techniques are provided to facilitate queries of protein databases. For protein descriptions received in response to the queries, embodiments of the present invention may scan the received protein descriptions to identify and locate Replikin patterns. A Replikin pattern is defined to be a sequence of 7 to about 50 amino acids that include the following three (3) characteristics, each of which may be recognized by an embodiment of the present invention: (1) the sequence has at least one lysine residue located six to ten amino acid residues from a second lysine residue; (2) the sequence has at least one histidine residue; and (3) at least 6% of the amino acids in the sequence are lysine residues.
Owner:BOGOCH SAMUEL +3
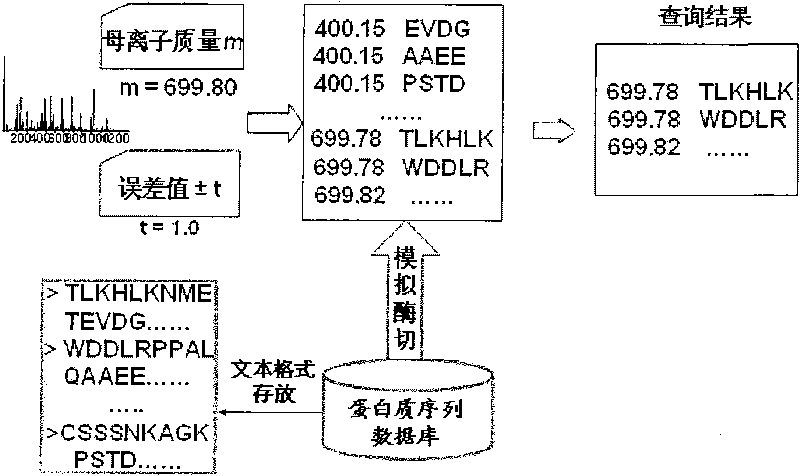
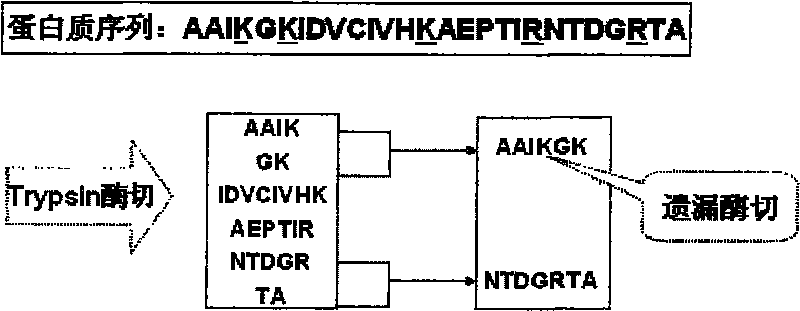
Protein secondary mass spectrometric identification method based on probability statistic model
InactiveCN102495127AMore identificationThe result of the identification method is excellentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein DatabasesMass number
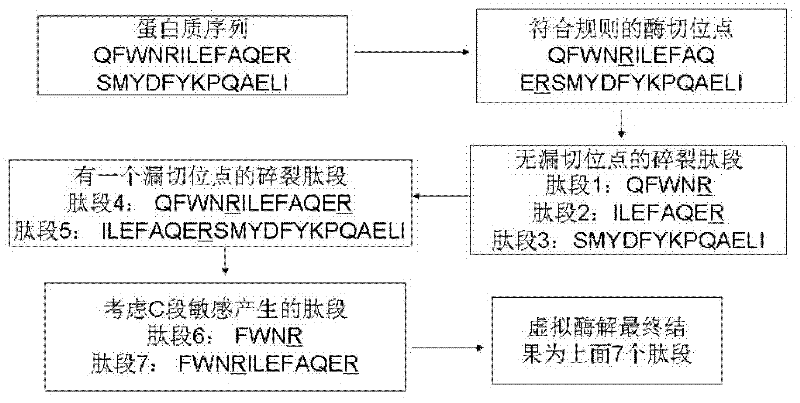
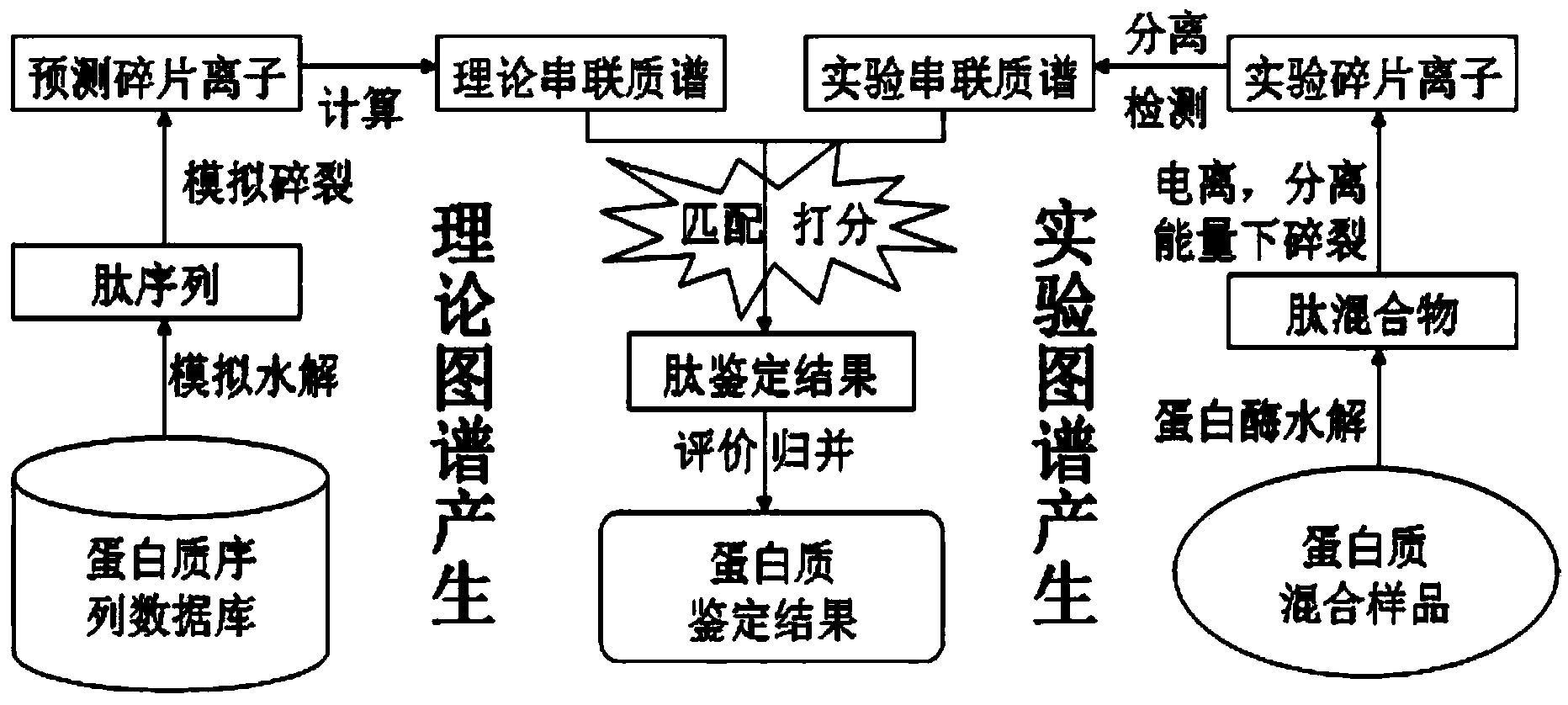
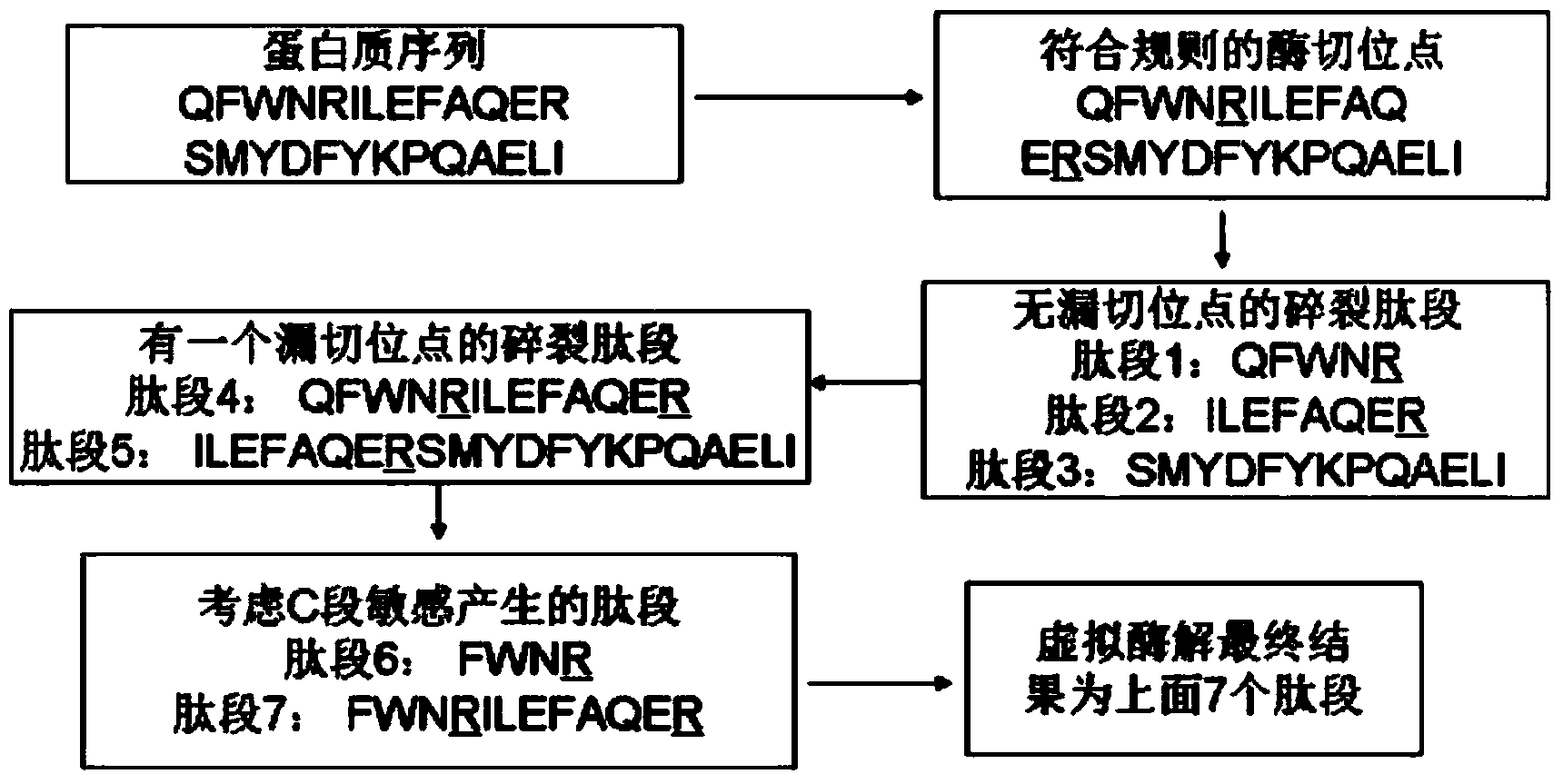
The invention discloses a protein secondary mass spectrometric identification method based on a probability statistic model. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, virtualizing an enzymolysis protein database array, and establishing a peptide section database and a peptide section database index for peptide sections processed by the enzymolysis according to the mass number of the peptide sections; secondly, finding out standby peptide sections meeting the requirements from the peptide section database according to a nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio of parent ions in an experiment map to be analyzed, and generating a theoretical map meeting the requirements by all the standby peptide sections; thirdly, removing isotopes and noises from the experiment map to be analyzed; matching the processed experiment map to be analyzed and the theoretical map of each standby peptide section and grading, and selecting the standby peptide section with the highest score as an identification result of the experiment map; and finally, carrying out whole false positive control according to all the experiment map identification results. According to the invention, the quantity of effective massspectrums and the quantity of the protein peptide sections are higher than those of an existing algorithm; and the method has the advantages of capability of dynamically selecting peaks and fast operation speed.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
System and method for identifying complex patterns of amino acids
InactiveUS7774144B2SsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsProtein DatabasesHistidine residue
A method and system are disclosed for identifying and / or locating complex patterns in an amino acid sequence stored in a computer file or database. According to an aspect of the present invention, techniques are provided to facilitate queries of protein databases. For protein descriptions received in response to the queries, embodiments of the present invention may scan the received protein descriptions to identify and locate Replikin patterns. A Replikin pattern is defined to be a sequence of 7 to about 50 amino acids that include the following three (3) characteristics, each of which may be recognized by an embodiment of the present invention: (1) the sequence has at least one lysine residue located six to ten amino acid residues from a second lysine residue; (2) the sequence has at least one histidine residue; and (3) at least 6% of the amino acids in the sequence are lysine residues.
Owner:BOGOCH SAMUEL +3
Protein second-level mass spectrum identification method based on peak intensity recognition capability
ActiveCN104076115AThe result of the identification method is excellentImprove identification efficiencyComponent separationSpecial data processing applicationsProtein DatabasesMass number
The invention discloses a protein second-level mass spectrum identification method based on peak intensity recognition capability. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, virtualizing enzymatically hydrolyzed protein database sequence, establishing a peptide fragment database and a peptide fragment database index for peptide fragments subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis according to the mass number of the peptide fragments; then, finding out candidate peptide fragments conforming to the requirement from the established peptide fragment database according to the mass number of parent ions without charges in a to-be-analyzed experiment spectrum; then removing an isotopic peak and selecting an effective peak from the to-be-analyzed experiment spectrum so as to generate a theory spectrum of the candidate peptide fragments conforming to the requirement, counting peak intensity information of different ions, calculating the peak intensity recognition capability of different types of ions at different intervals, marking each candidate peptide fragment based on the peak intensity recognition capability, and selecting the peptide fragment with the highest mark as the authentication result of the experiment spectrum; and finally, performing quality control on the authentication result. The number of valid mass spectra and the number of valid protein peptide fragments, which are authenticated by the method, are both higher than those obtained by an existing algorithm; peaks can be selected dynamically; the running speed is high.
Owner:广州辉骏生物科技股份有限公司
Methods for comparing functional sites in proteins
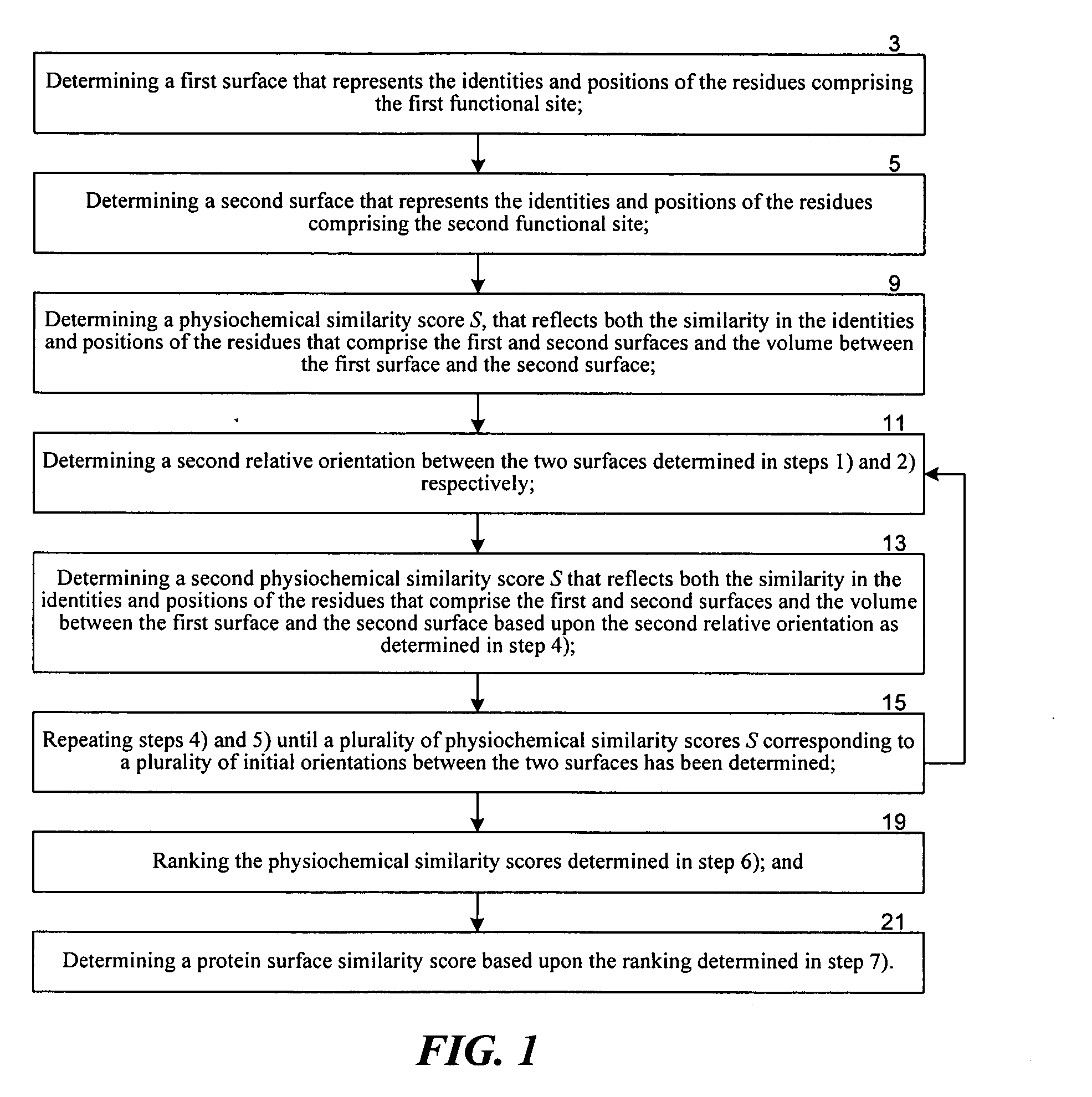
InactiveUS20050192758A1Effective calculationComputationally efficientProteomicsGenomicsTARP ProteinProtein surface
The present invention relates to methods and systems for representing and scoring the similarity of two protein by iteratively rotating and translating one protein surface representation relative to the other protein surface representation in order to maximize (or minimize) a score that represents both the volume between the two surface representations and the similarity in the identities and positions of the residues comprising the two protein surfaces. In another aspect of the invention, such methods and systems are used to compare and annotate a protein comprising a putative functional site of unknown function with a database of reference proteins of known function.
Owner:EIDOGEN SERTANTY INC
Index acceleration method and corresponding system in scale protein identification
InactiveCN101714187AReduce space consumptionEasy to storeSpecial data processing applicationsProtein DatabasesEnzyme digestion
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cysteine-containing peptides having antioxidant properties
InactiveUS7217785B2Novel antioxidant activityIncrease capacityApolipeptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein DatabasesTARP Protein
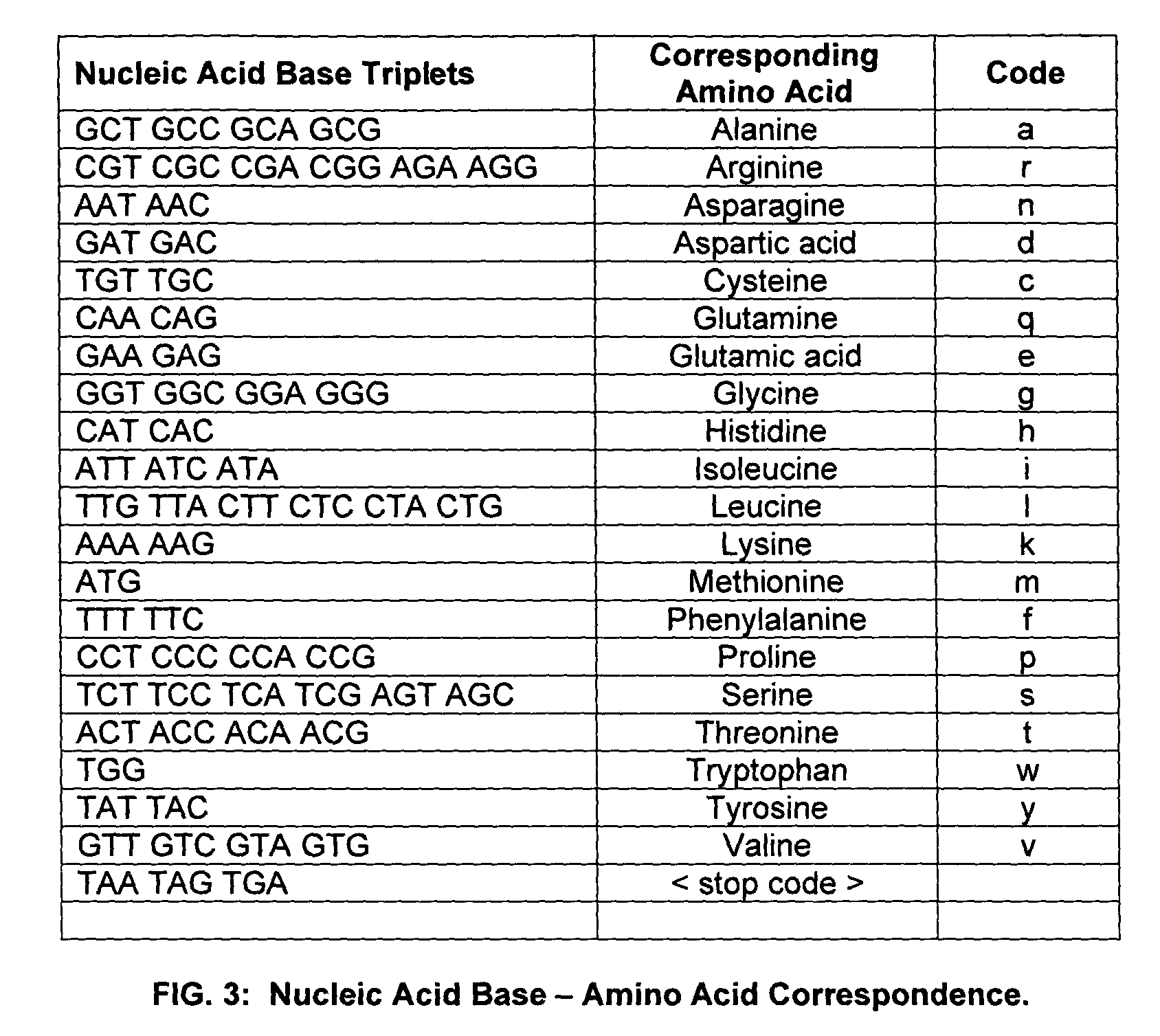
The term “homology” or “homologous” means an amino acid similarity measured by the program, BLAST (Altschul et al (1997), “Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs”, Nucleic Acids Res. 25:33 89–3402), and expressed as —(% identity n / n). In measuring homology between a peptide and a protein of greater size, homology is measured only in the corresponding region; that is, the protein is regarded as only having the same general length as the peptide, allowing for gaps and insertions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and system for predicting functions of compound
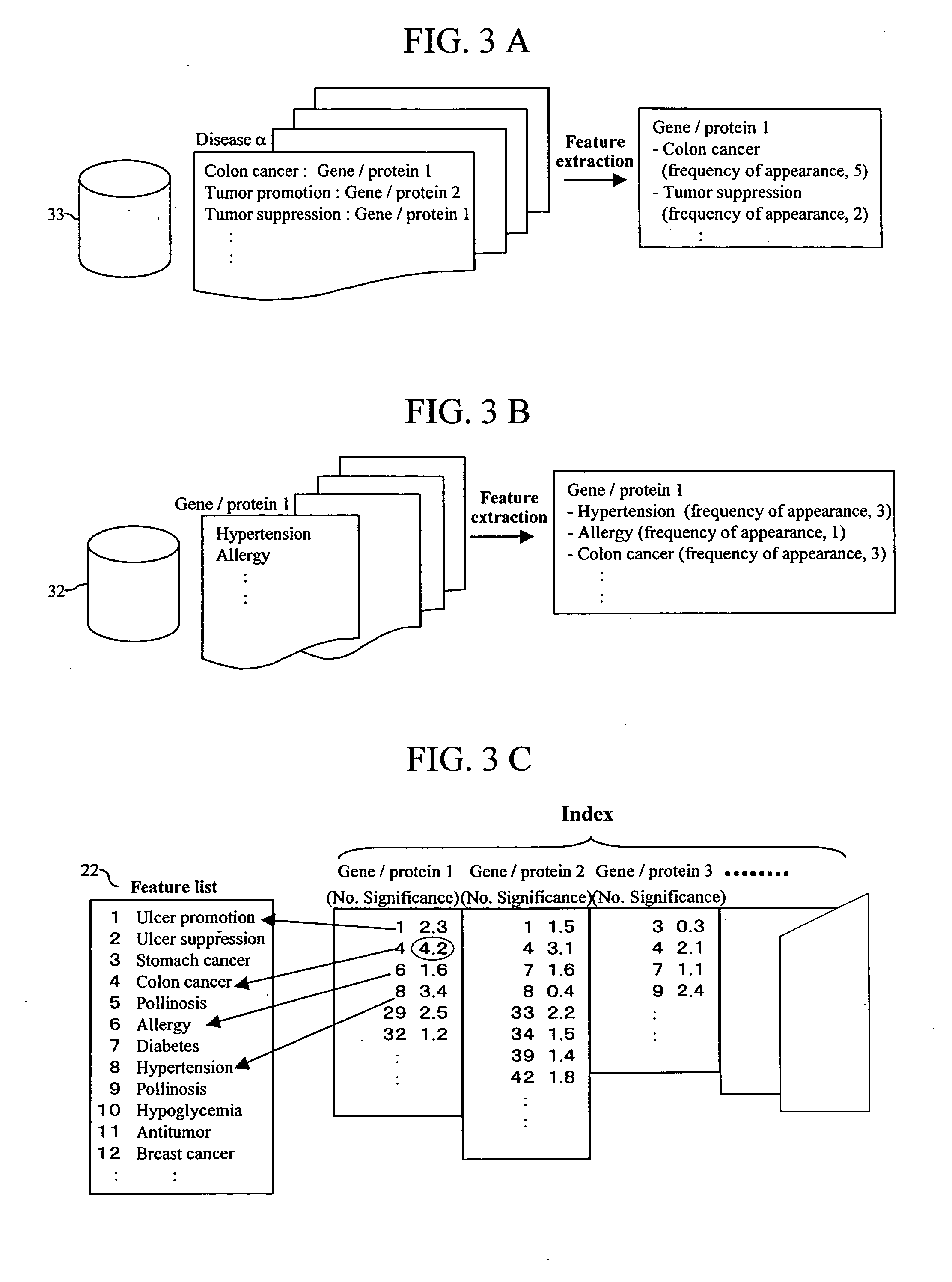
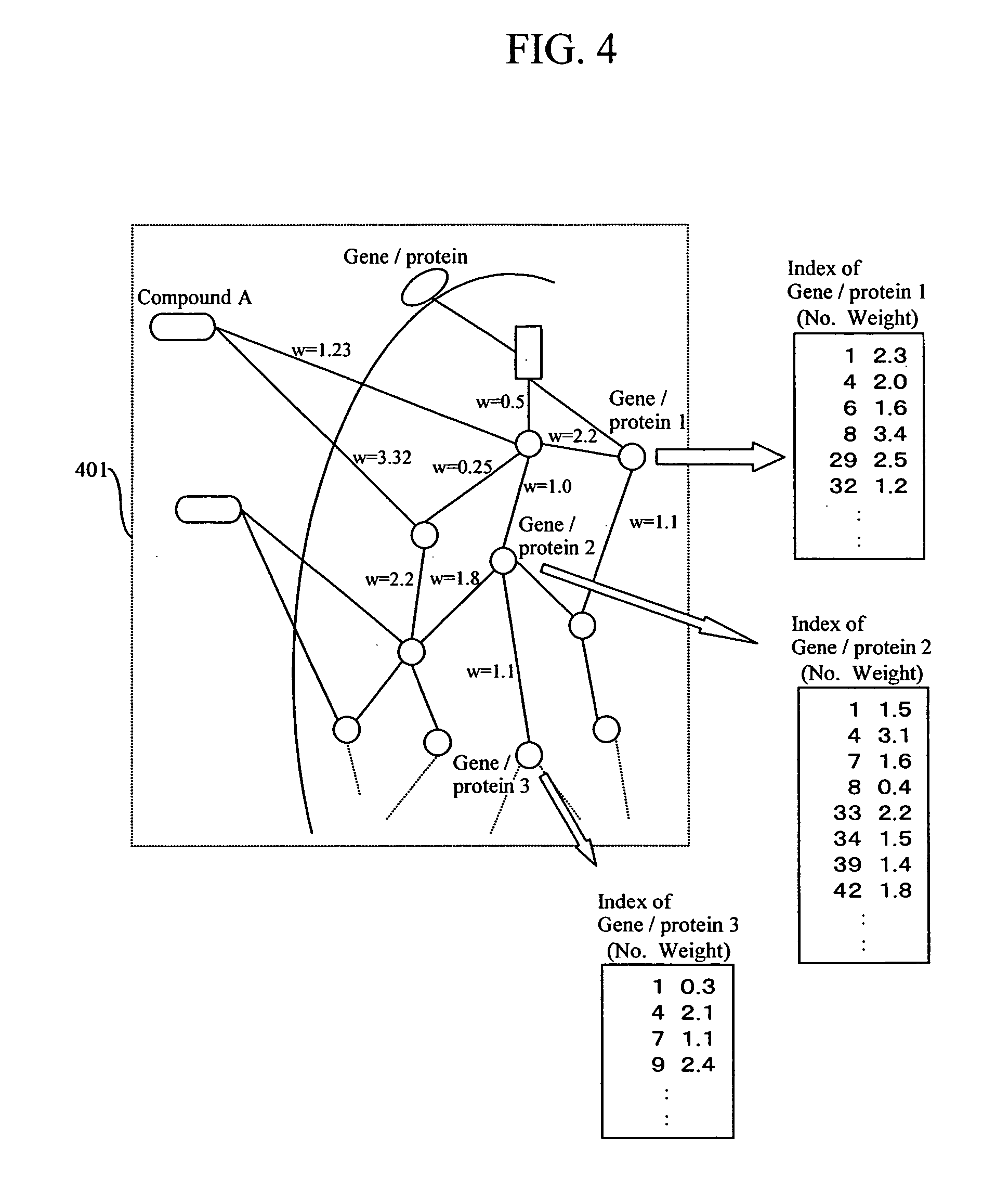
InactiveUS20060106544A1Improve efficiencyShorten the development cycleChemical property predictionMolecular designProtein DatabasesBibliographic database
Feature of a compound is predicted by using information on interactions between substances. A database of interactions between compounds and genes / proteins is constructed on the base of information collected from bibliographic databases, gene / protein databases, and disease databases, and an interaction network is prepared by mapping the collected information to thereby enable prediction of the features of a compound.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
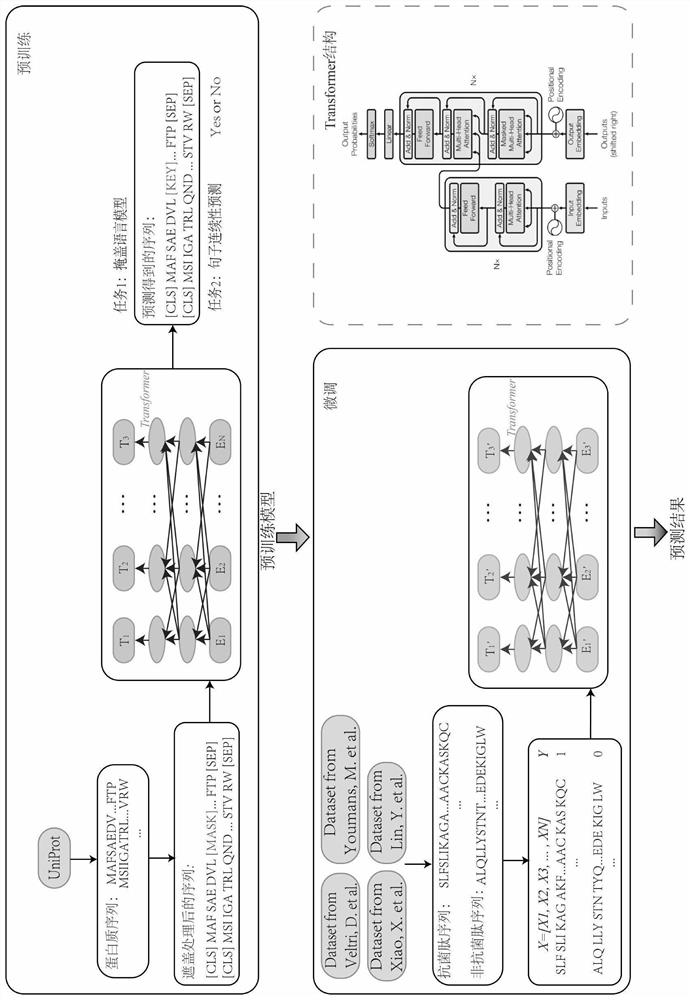
Antibacterial peptide prediction method and device based on protein pre-training representation learning
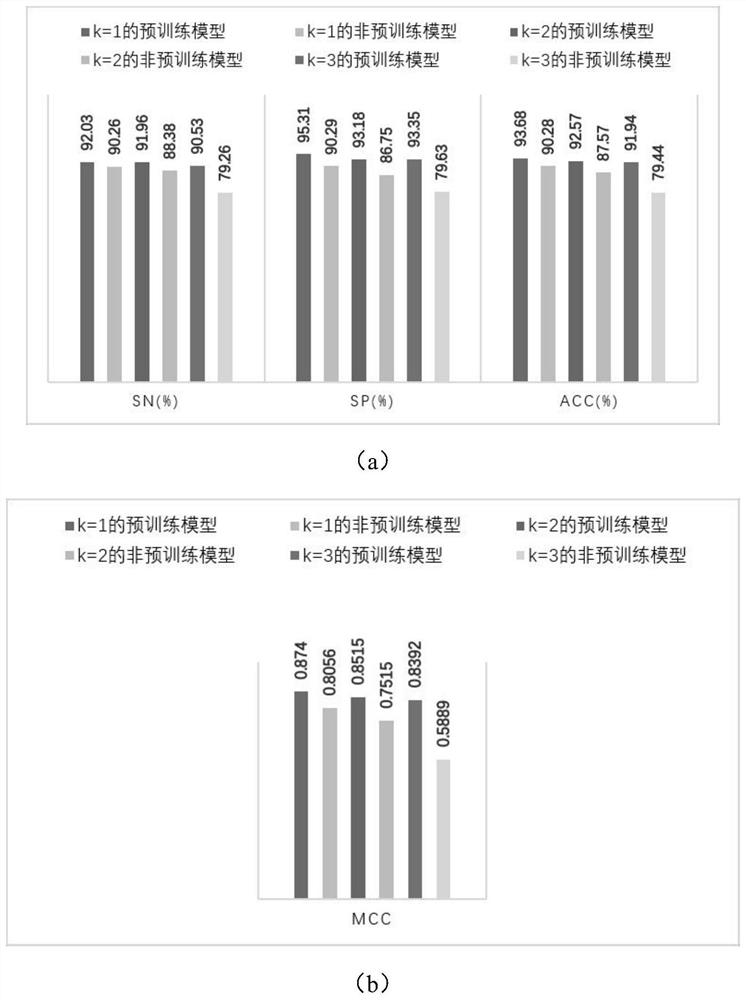
The invention discloses an antibacterial peptide prediction method and device based on protein pre-training representation learning; the method comprises the following steps: S1, employing a pre-training strategy to carry out the word segmentation and covering of a label-free protein sequence from a protein database, and obtaining a pre-training representation learning model, carrying out pre-training of two tasks of covering a language model and sentence continuity prediction, capturing expressions of a word level and a sentence level, and helping the model to learn general structural features of a protein sequence; S2, for the antibacterial peptide pre-recognition and prediction task, changing an output layer of a pre-training model, and performing fine adjustment on the model by using an antibacterial peptide data set with a label to generate an antibacterial peptide prediction model; and S3, according to the antibacterial peptide pre-identification and prediction task, adopting an antibacterial peptide prediction model for identification, and outputting a prediction result. Pre-training is applied to the field of antibacterial peptide recognition and prediction, and an efficient antibacterial peptide prediction model is established based on a known antibacterial peptide sequence with small data volume and unbalanced distribution.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
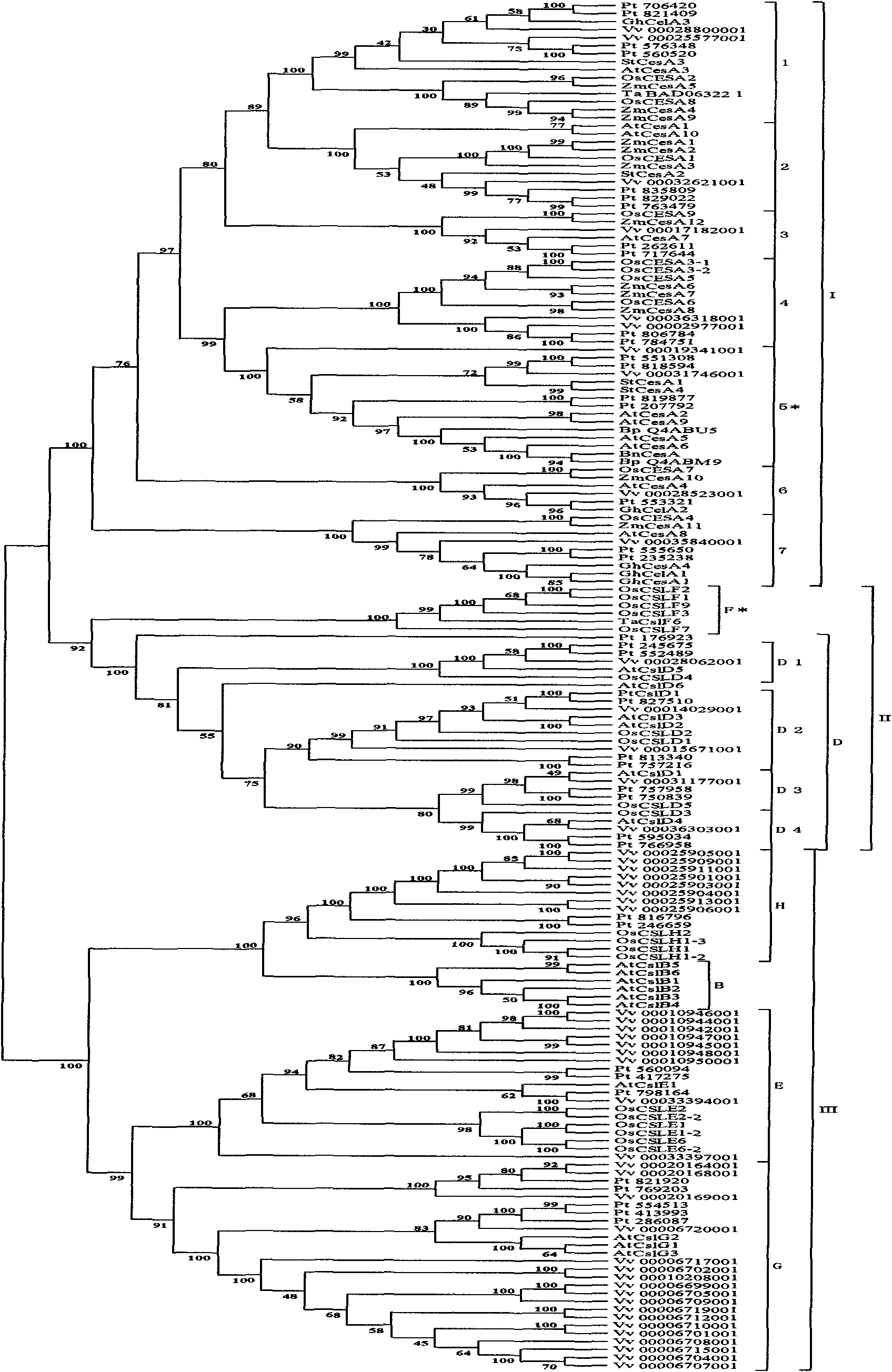
Method for establishing phylogenetic tree aiming at target gene of target organism
InactiveCN101962671AMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsProtein DatabasesOrganism
The invention relates to a method for establishing a phylogenetic tree aiming at a target gene of a target organism. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) acquiring data; 2) comparing and analyzing sequences; and 3) establishing the phylogenetic tree, wherein the step 1) is finished by downloading a structure domain of a protein of the target gene, acquiring a sequence which contains the structure domain by searching a biological protein database of which genomes and proteomes are sequenced, and searching a protein sequence of a kindred plant by using the target gene of an organism of which the genomes and the proteomes are sequenced. Because the method of the invention comprises the steps and in particular combines the phylogenetic relationships of species with the database of which the genomes and the proteomes are sequenced, a more accurate phylogenetic tree can be established.
Owner:王颖
High-throughput retrieval method for drug targets
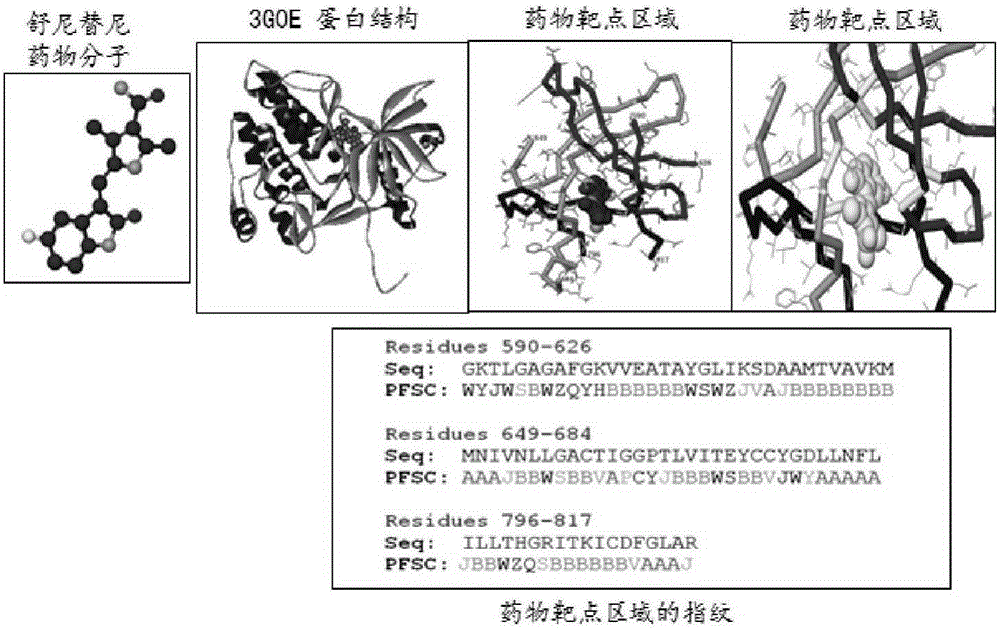
ActiveCN105205351ASolve the problem of different parameters and different processing methods for different peopleUniversally applicableSpecial data processing applicationsProtein DatabasesProtein target
The invention relates to a high-throughput retrieval method for drug targets, and belongs to the field of bioinformatics. The high-throughput retrieval method includes the steps that a drug and target complex serves as reference, a drug combining bag is defined, all fragments in the combining bag are represented with protein structural fingerprints, and the protein structural fingerprints include amino acid sequences, protein folding shape codes, physicochemical properties and vector coupling; the digital drug combining bag is input, a global known protein structure database is retrieved to perform fingerprint comparison and quantitative evaluation, and protein structures are arrayed in the sequence of fingerprint similarity from high to low; structural protein is selected as possible target spot regions, wherein similarity scores of the protein folding codes and similarity scores of the amino acid physicochemical properties reach top two thousand at the same time, and possible target protein of drugs is analyzed and predicted. The high-throughput retrieval method can be applied to secondary development and research of the drugs, and new effects of the approved clinic drugs are developed by finding the new targets.
Owner:MICRO PHARMATECH
Protein drug binding site prediction method based on deep learning
PendingCN111435608AAccurate predictionGuaranteed accuracyProteomicsGenomicsProtein DatabasesBinding site
The invention provides a protein drug binding site prediction method based on deep learning, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, selecting a plurality of proteins in a protein database toform a training set, a plurality of proteins to form a verification set, and a plurality of proteins to form a test set, wherein the training set being used for training a training model; step 2, carrying out feature extraction and label extraction on the protein database through the trained training model to obtain data, finishing training of a neural network and obtaining a prediction model; and 3, inputting the new protein into the prediction model, and positioning and predicting the position of the binding site. The method has the advantages that the forming factors of the binding site are comprehensively considered, and the binding site is positioned and predicted based on deep learning.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA +1
Peptide identification method based on subset error rate estimation
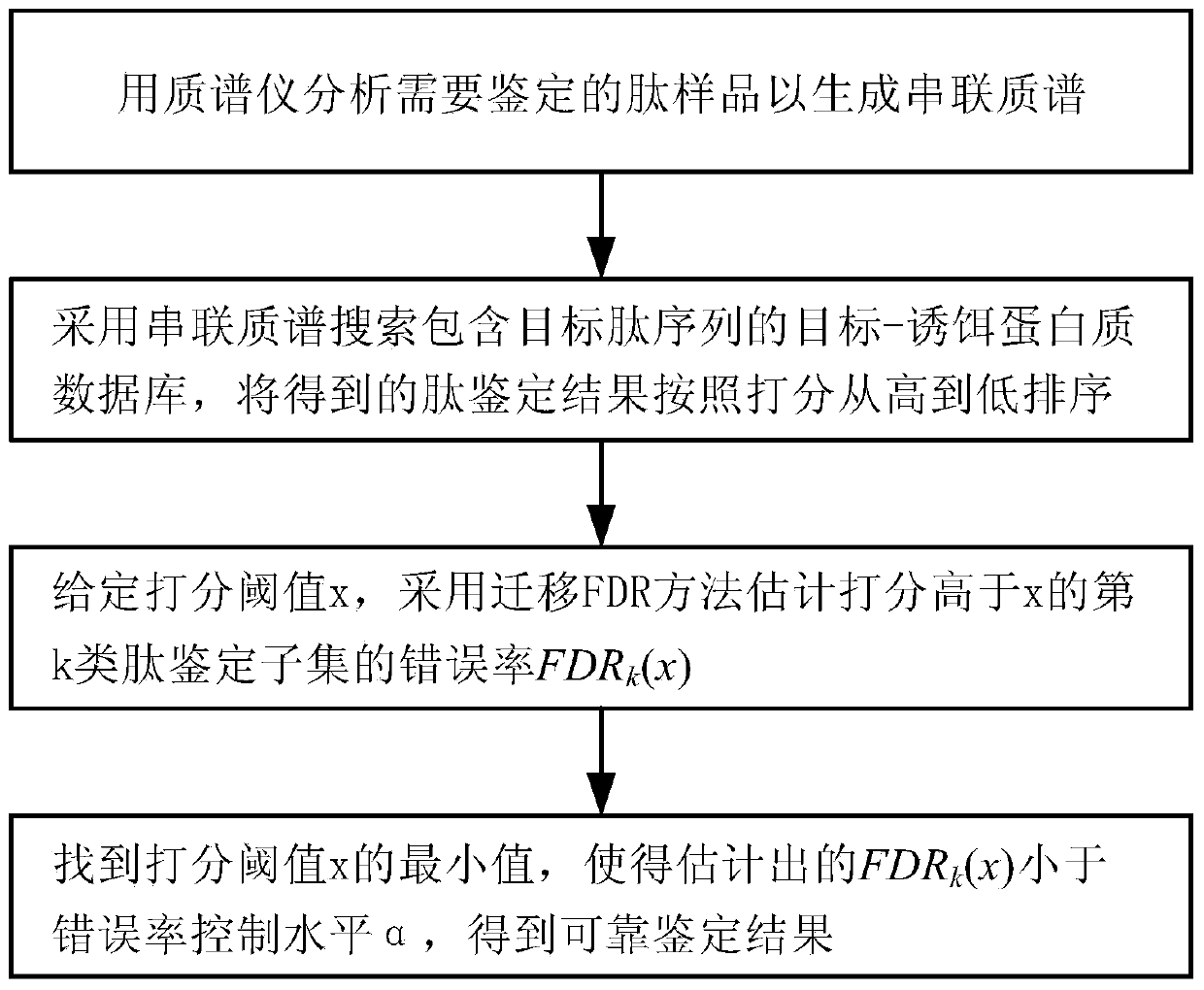
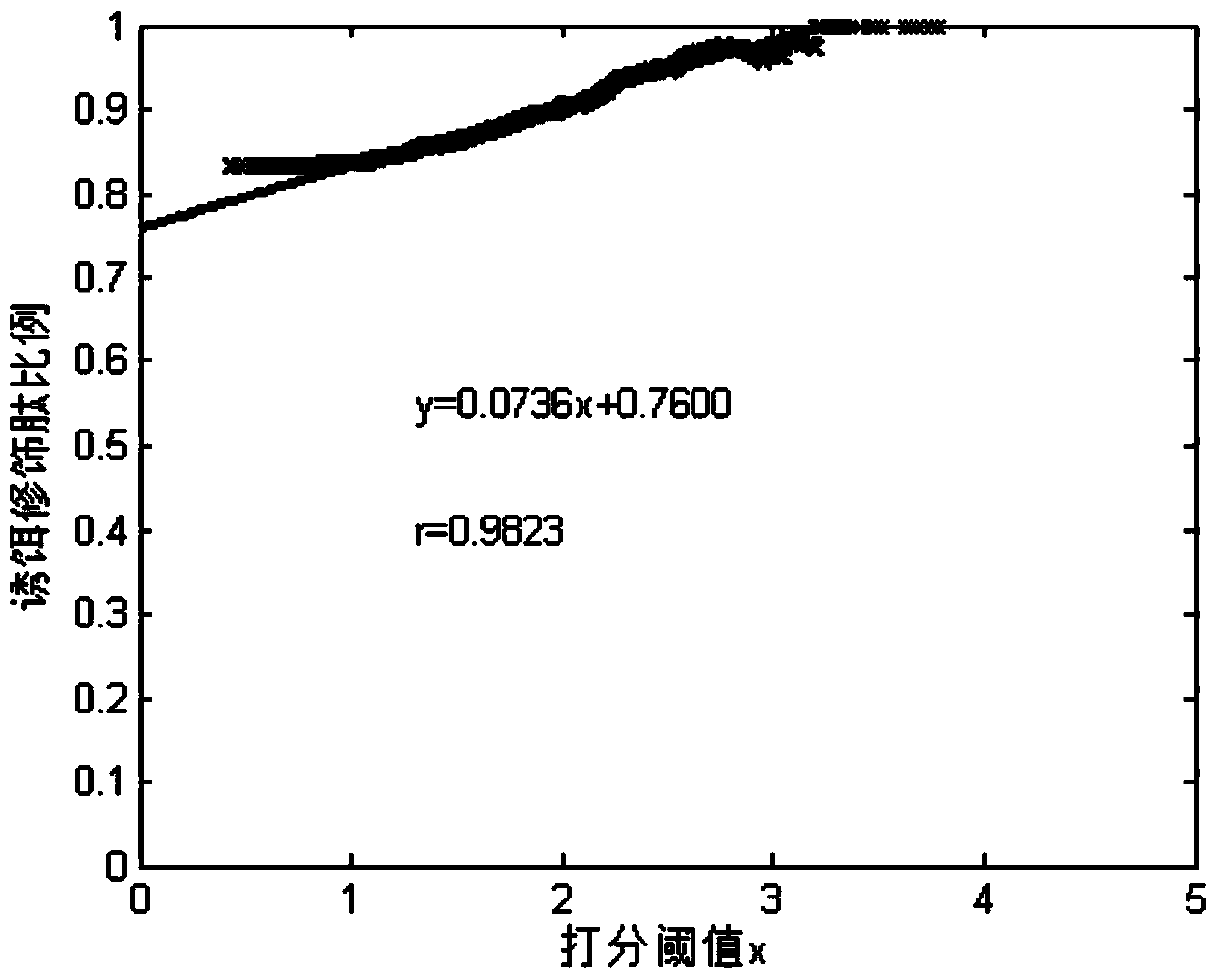
ActiveCN103439441AAccurate and reliable identification resultsImprove accuracyComponent separationProtein DatabasesTarget peptide
The invention relates to a peptide identification method based on subset error rate estimation. The peptide identification method comprises the following steps: 1, analyzing a peptide sample to be identified by a mass spectrometer to generate a tandem mass spectrum; 2, searching a target-bait protein database containing a target peptide sequence in the tandem mass spectrum, and sorting obtained peptide identification results according to scores from high to low; 3, setting a score threshold value x, and estimating the error rate FDRk(x) of a type k peptide identification subset, the score of which is higher than x, by a transferring FDR (False Discovery Rate) method; 4, finding the minimum value of x by adjusting the score threshold value x to enable the estimated FDRk(x) to be less than a given error rate control level alpha, so that the obtained type k peptide identification result with the score higher than x serves as an acceptable reliable identification result. The peptide identification method provided by the invention estimates the subset error rate through the transferring FDR method and obtains the reliable peptide identification result through the subset error rate, thus having high identification accuracy.
Owner:ACAD OF MATHEMATICS & SYSTEMS SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for rapidly identifying strain-level pathogenic bacteria in food through double adsorption
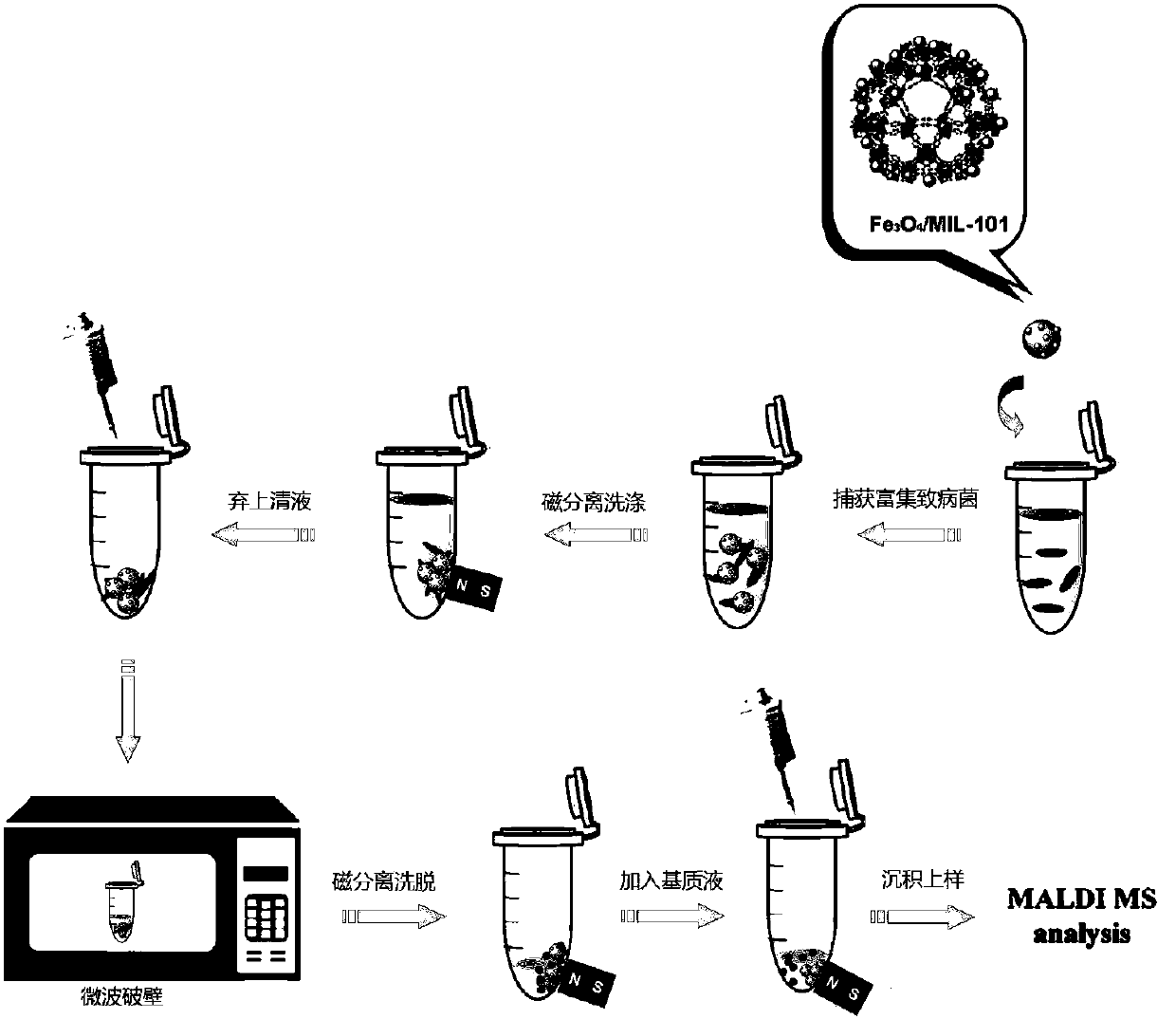
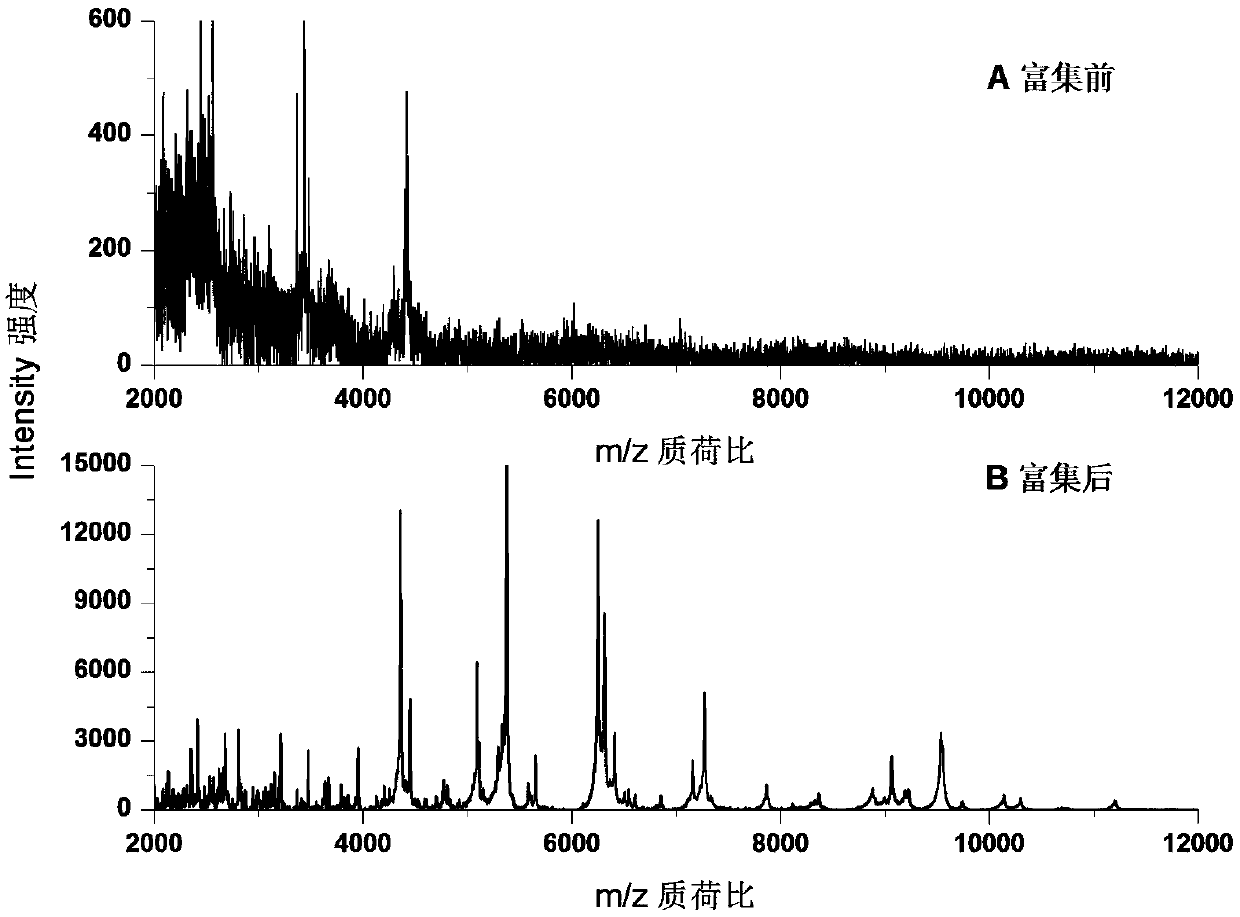
InactiveCN108020674AHigh-resolutionStrengthen the effect of microwave wall breakingBiological testingProtein DatabasesRibosomal protein E-L30
The invention discloses a method for rapidly identifying strain-level pathogenic bacteria in food through double adsorption. The method comprises main steps as follows: a) strain-level pathogenic bacteria in liquid food are adsorbed by MIL-101 magnetic particles, and wall breaking is performed under microwave assistance; after wall breaking, to-be-identified pathogenic bacterium protein is rapidlyenriched through the MIL-101 magnetic particles; b) a mass spectrum graph of the pathogenic bacterium protein is collected through MALDI / TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization / time of flight mass spectrometry); c) a Tagident search tool is used for performing protein database searching on mass spectrum peak, and ribosomal protein is selected; d) a rapid microorganism identification database is sought by use of ribosomal protein obtained through searching, and the attributes of the strain-level pathogenic bacteria are determined. The method has the advantages of simplicity and rapidness. Enrichment of pathogenic bacteria, wall breaking and mycoprotein enrichment are integrated, finally, a ribosomal protein database is used for rapidly identifying the pathogenic bacteria, and the strain level of pathogenic bacteria in the liquid food is rapidly identified.
Owner:TIANJIN MODERN VOCATIONAL TECH COLLEGE
Method of anticipating interaction between proteins
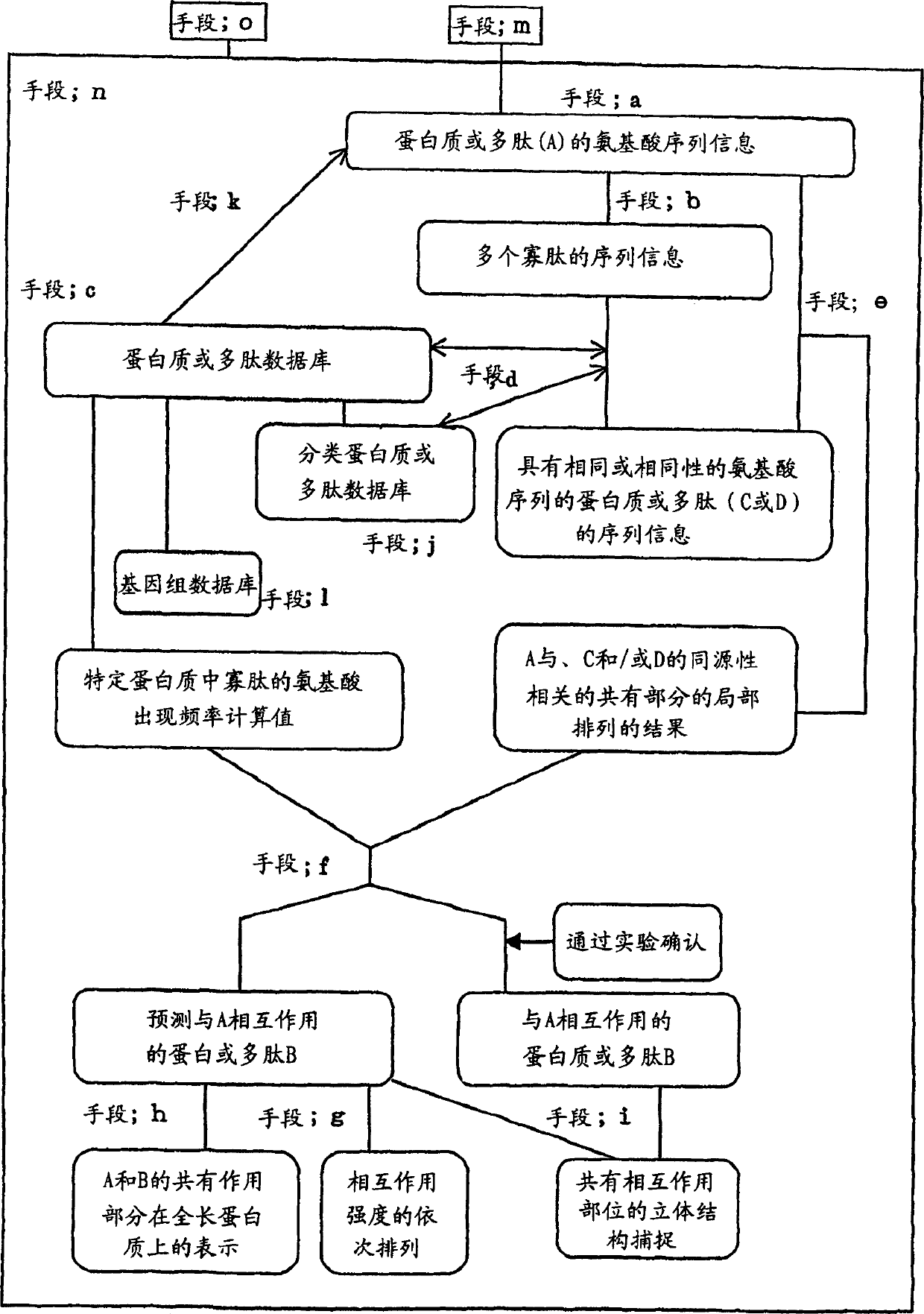
InactiveCN1416549ALibrary screeningPeptide preparation methodsProtein DatabasesAmino acid sequence alignment
The present invention relates a method for predicting a protein or polypeptide (B) that interacts with a specific protein or polypeptide (A), wherein the method is characterized by comprising: 1) decomposing the amino acid sequence of protein or polypeptide (A) into a series of oligopeptides having a pre-determined length as sequence information; 2) searching, within a database of protein or polypeptide amino acid sequences, for a protein or polypeptide (C) comprising an amino acid sequence for each member of the series or for a protein or polypeptide (D) comprising an amino acid sequence homologous to an amino acid sequence for each member of the series; 3) carrying out local amino acid sequence alignment between said protein or polypeptide (A) and the detected protein or polypeptide (C) or detected protein or polypeptide (D); and 4) predicting whether the detected protein or polypeptide (C) and / or protein or polypeptide (D) is a protein or polypeptide (B) that interacts with the protein or polypeptide (A) based on the results of the local amino acid sequence alignment and a value calculated from a frequency of amino acids and / or a frequency of said oligopeptides in said amino acid sequence database; and to a recording medium for carrying out the above method, a device comprising the recording medium, and proteins obtained thereby.
Owner:DAIICHI SEIYAKU CO LTD +1
System and method for creating lead compounds, and compositions thereof
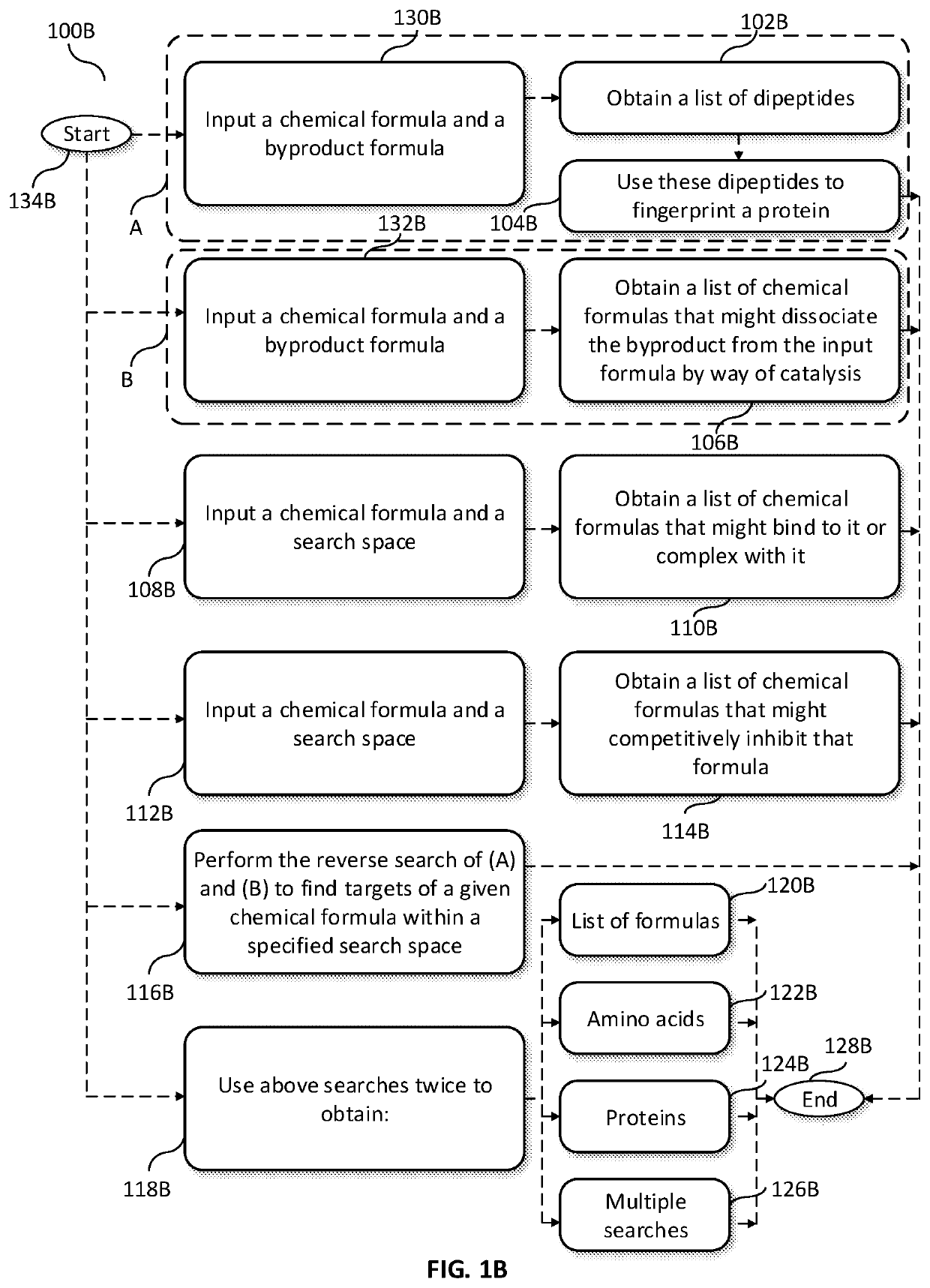
A method is provided to create lead compound(s) by discovering a general chemical structure, moieties, formula(s) to explore suitable compositions by computer simulation and / or robotic biological or biochemical experiments at least partially based upon employing said lead compound(s) discover method, which includes steps for inputting at least one chemical formula and at least one byproduct formula, steps for creating a list of dipeptides that might dissociate the byproduct from the input formula by way of catalysis, steps for using these dipeptides to fingerprint a protein from its peptide sequence, and searching a protein database or use experimental methods to search for such proteins. A composition creating means is provide by way of computer simulation and / or robotic biological or biochemical experiments at least partially based upon employing, as lead compound(s), the final chemical structure, moieties, formula(s) generated and communicated the above method.
Owner:BHAVNAGRI BURZIN
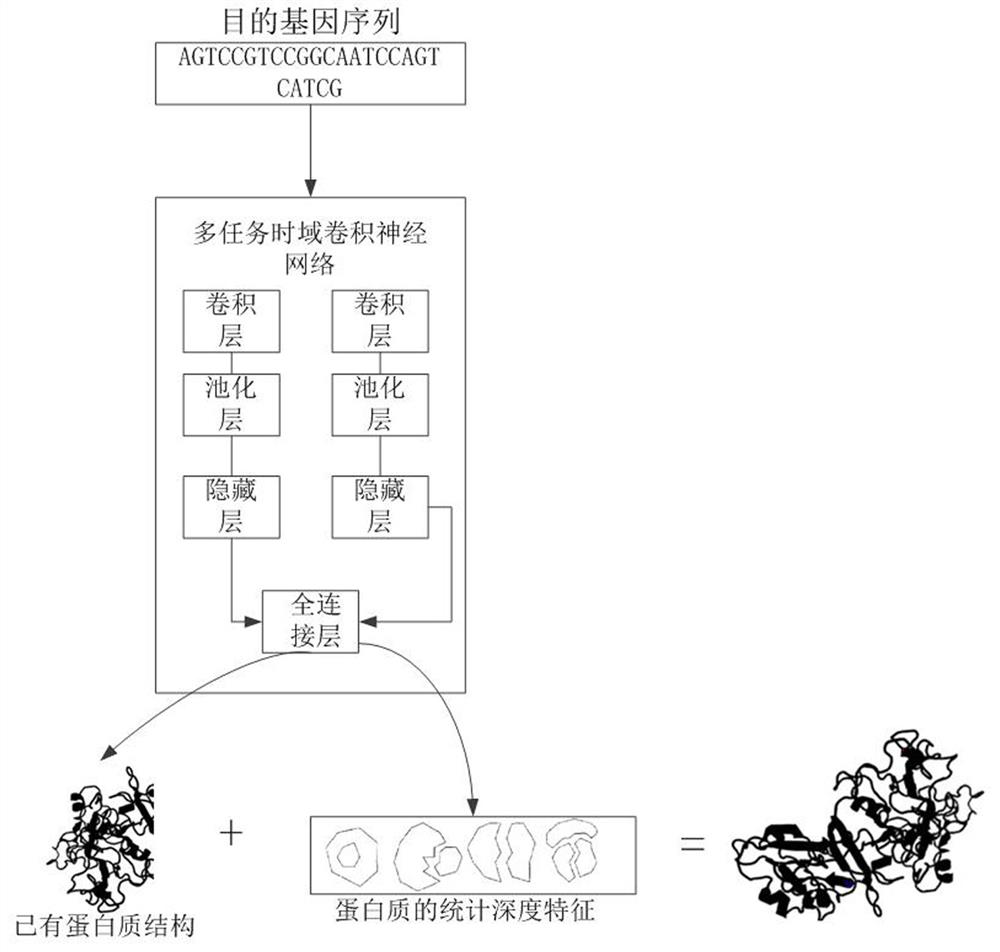
Protein structure prediction method and device based on multi-task time domain convolutional neural network
ActiveCN112289370AReduce dimensionalityReduce complexityBiostatisticsNeural architecturesProtein DatabasesA-DNA
The invention relates to a protein structure prediction method and device based on a multi-task time domain convolutional neural network. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining a target gene sequence and a protein database; establishing a DNA RNAamino acid ternary sequence data set corresponding to each protein according to the genetic code table and a protein database; establishing a multiple regression equation according to the residue depth and physicochemical properties of amino acids in the protein database to obtain statistical depth characteristics of each protein; clustering theternary sequence data set and mapping the ternary sequence data set into a multi-dimensional feature vector; taking the multi-dimensional feature vector and the statistical depth feature of the protein as the input of a multi-task time domain convolutional neural network, and training the multi-task time domain convolutional neural network; and predicting the protein structure by utilizing the statistical depth characteristics of the protein. According to the invention, the statistical depth characteristics of the protein are combined with the multi-task time domain convolutional neural network, so that the complexity of the model is reduced, and the generalization and the fitting degree are improved.
Owner:WUHAN GENECREATE BIOLOGICAL ENG CO LTD
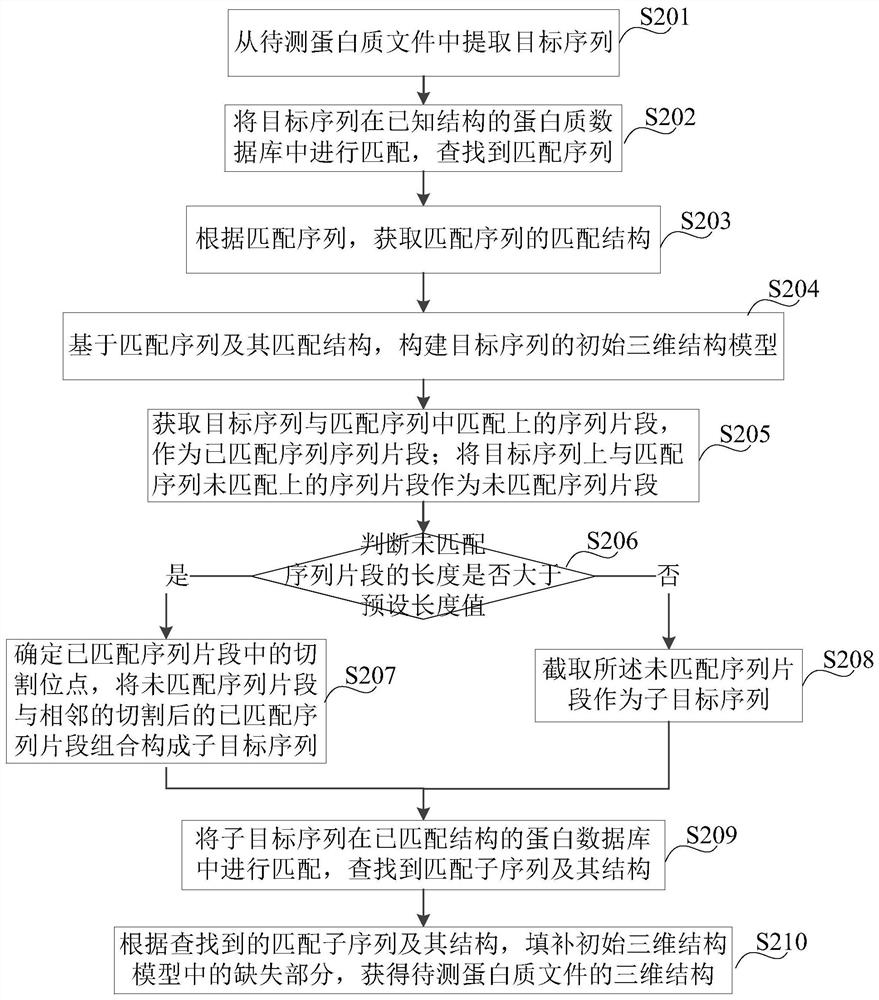
Protein structure prediction method and device, platform and storage medium
PendingCN112530517APrediction is accurateImprove forecast accuracyData visualisationSequence analysisProtein DatabasesAlgorithm
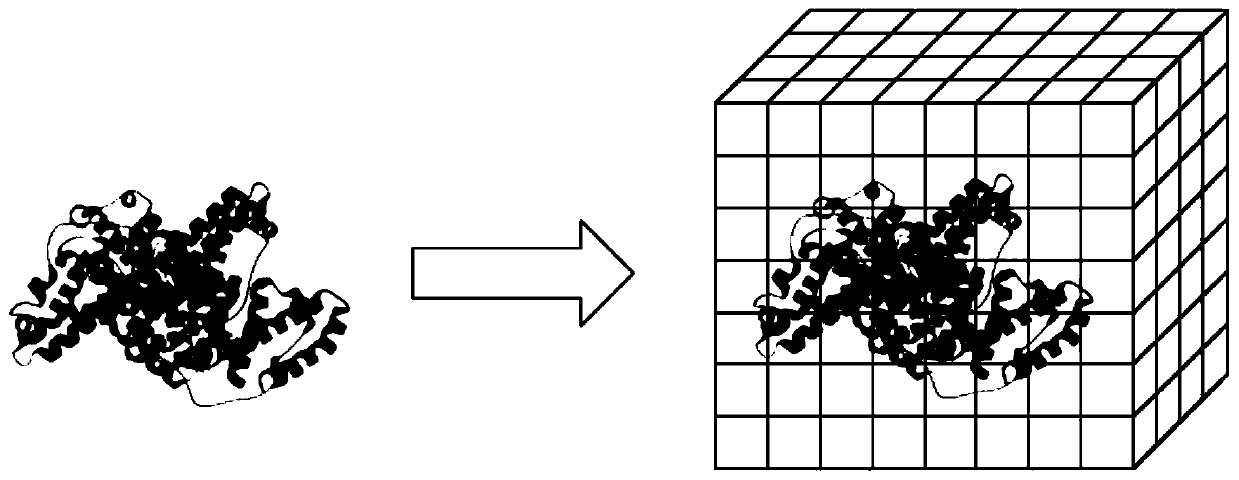
The invention discloses a protein structure prediction method. The method comprises the following steps: extracting a target sequence from a to-be-detected protein file; matching the target sequence in a protein database with a known structure to find a matching sequence; obtaining a matching structure of the matching sequence according to the matching sequence; constructing an initial three-dimensional structure model of the target sequence based on the matching sequence and the matching structure thereof; combining the unmatched sequence segment of the target sequence with one part of the adjacent matched sequence segment to form a sub-target sequence; searching a matching subsequence and a structure of the matching subsequence of the sub-target sequence in a protein database with a known structure; and filling the missing part in the initial three-dimensional structure model according to the searched matching subsequence and the structure thereof to obtain the three-dimensional structure of the to-be-detected protein file. By adopting the protein structure prediction method provided by the invention, the structure of the protein can be more accurately predicted.
Owner:康码芯(上海)智能科技有限公司
Method for obtaining tumor urine protein marker and obtained stray urine protein library related to tumor
ActiveCN108334747AEliminate distractionsComponent separationProteomicsProtein DatabasesReference range
The invention provides a method for obtaining a tumor urine protein marker and an obtained stray urine protein library related to a tumor. The method comprises the steps that based on a built quantitative reference range of human urine protein in a healthy human urine protein database, a mode of hypergeometric distribution detection is used for screening stray protein as the tumor urine protein marker from a urine proteome dataset of a tumor patient, and the stray urine protein library related to the tumor is established. The method for obtaining the tumor urine protein marker and the obtainedstray urine protein library related to the tumor can better eliminate the interference of physiological fluctuation and inter-individual differential protein in the process of finding a urine proteinbiomarker.
Owner:北京松果天目健康管理有限公司
Compression and clustering-based batch protein homology search method
ActiveCN106022000AShorten the timeBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsProtein DatabasesSequence clustering
The invention discloses a compression and clustering-based batch protein homology search method and belongs to the cross field of computer application technologies and bio-technologies. The method comprises the steps of firstly performing compression operation on a query sequence and a protein database through redundancy analysis and redundancy removal processes by fully utilizing sequence similar information existent in a protein database sequence and the query sequence; secondly performing similar sub-sequence clustering on the compressed protein database; thirdly performing a search by utilizing a mapping principle based on the clustered database to discover potential results, and establishing an executable database according to the found potential result set; and finally performing a homology search in the executable database to obtain a final homology sequence. According to the method, the homology search is performed in the established executable database, so that the time for repeated sequence comparison and gapless expansion is greatly shortened.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
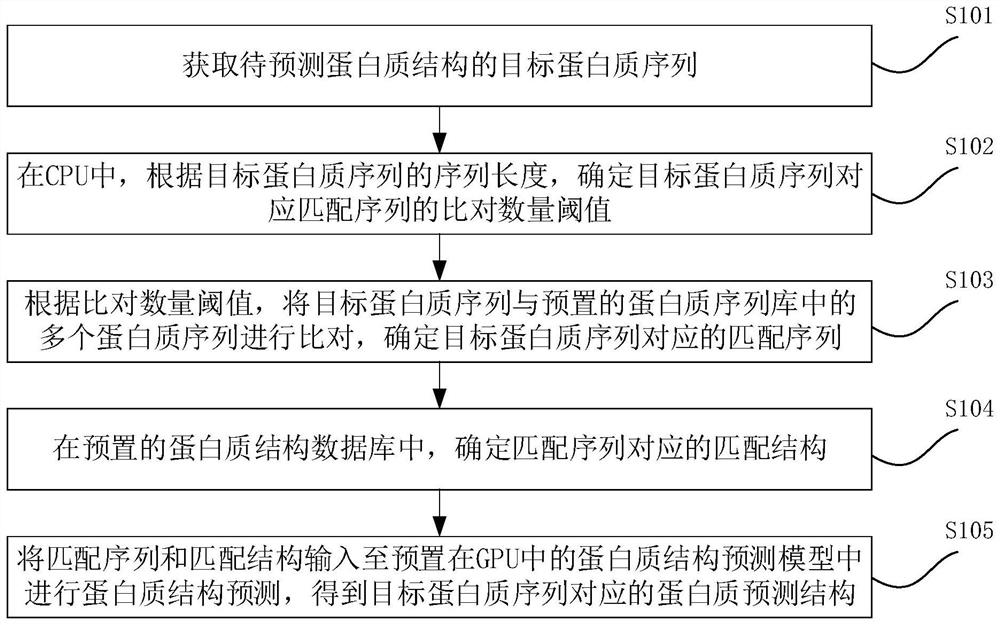
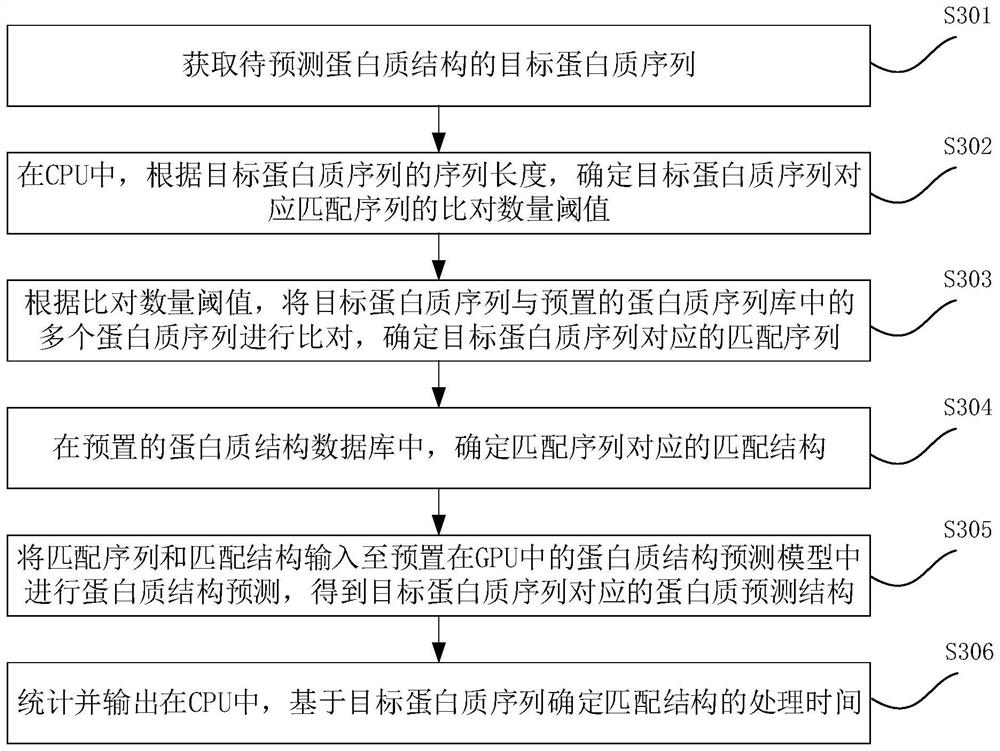
Protein structure prediction method, protein structure prediction device and medium
The invention provides a protein structure prediction method, a protein structure prediction device and a medium. The protein structure prediction method is applied to the computer equipment, the computer equipment comprises a CPU and at least one GPU, and the method comprises the following steps: obtaining a target protein sequence of a to-be-predicted protein structure. And in the CPU, according to the sequence length of the target protein sequence, determining an alignment quantity threshold value of a matching sequence corresponding to the target protein sequence. And comparing the target protein sequence with a plurality of protein sequences in a preset protein sequence library according to the comparison quantity threshold, and determining a matching sequence corresponding to the target protein sequence. And determining a matching structure corresponding to the matching sequence in a preset protein structure database. And inputting the matching sequence and the matching structure into a protein structure prediction model preset in a GPU for protein structure prediction, and obtaining a protein prediction structure corresponding to the target protein sequence. The memory occupation of the GPU can be reduced, the operation speed of the GPU is improved, and the prediction rate is accelerated.
Owner:SUZHOU LANGCHAO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
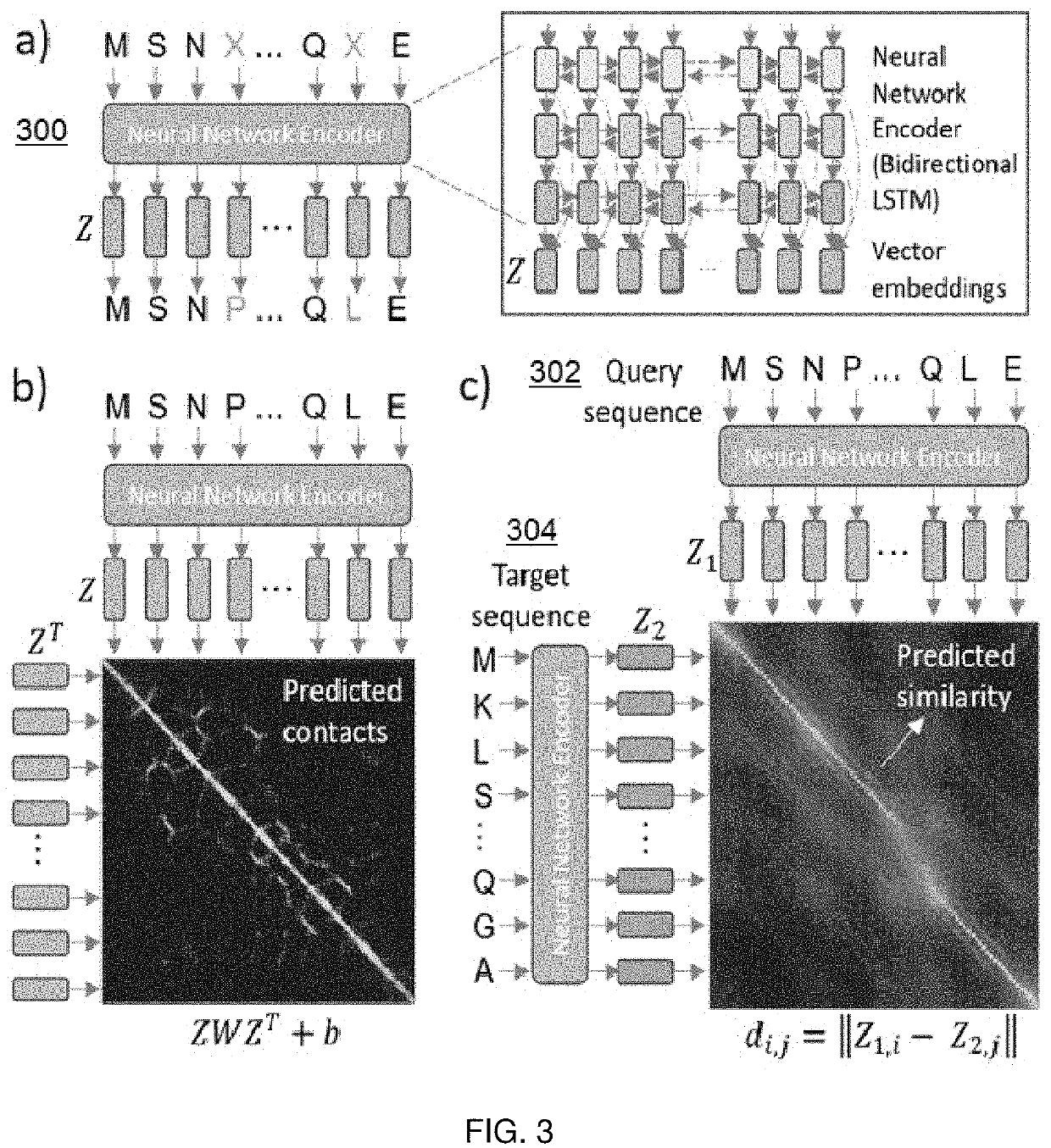
Protein database search using learned representations
ActiveUS20220165356A1Rapid and accurate searchEfficient searchBiostatisticsNeural architecturesProtein DatabasesSequence database
A method for efficient search of protein sequence databases for proteins that have sequence, structural, and / or functional homology with respect to information derived from a search query. The method involves transforming the protein sequences into vector representations and searching in a vector space. Given a database of protein sequences and a learned embedding model, the embedding model is applied to each amino acid sequence to transform it into a sequence of vector representations. A query sequence is also transformed into a sequence of vector representations, preferably using the same learned embedding model. Once the query has been embedded in this manner, proteins are retrieved from the database based on distance between the query embedding and the protein embeddings contained within the database. Rapid and accurate search of the vector space is carried out using exact search using metric data structures, or approximate search using locality sensitive hashing.
Owner:NE47 BIO INC
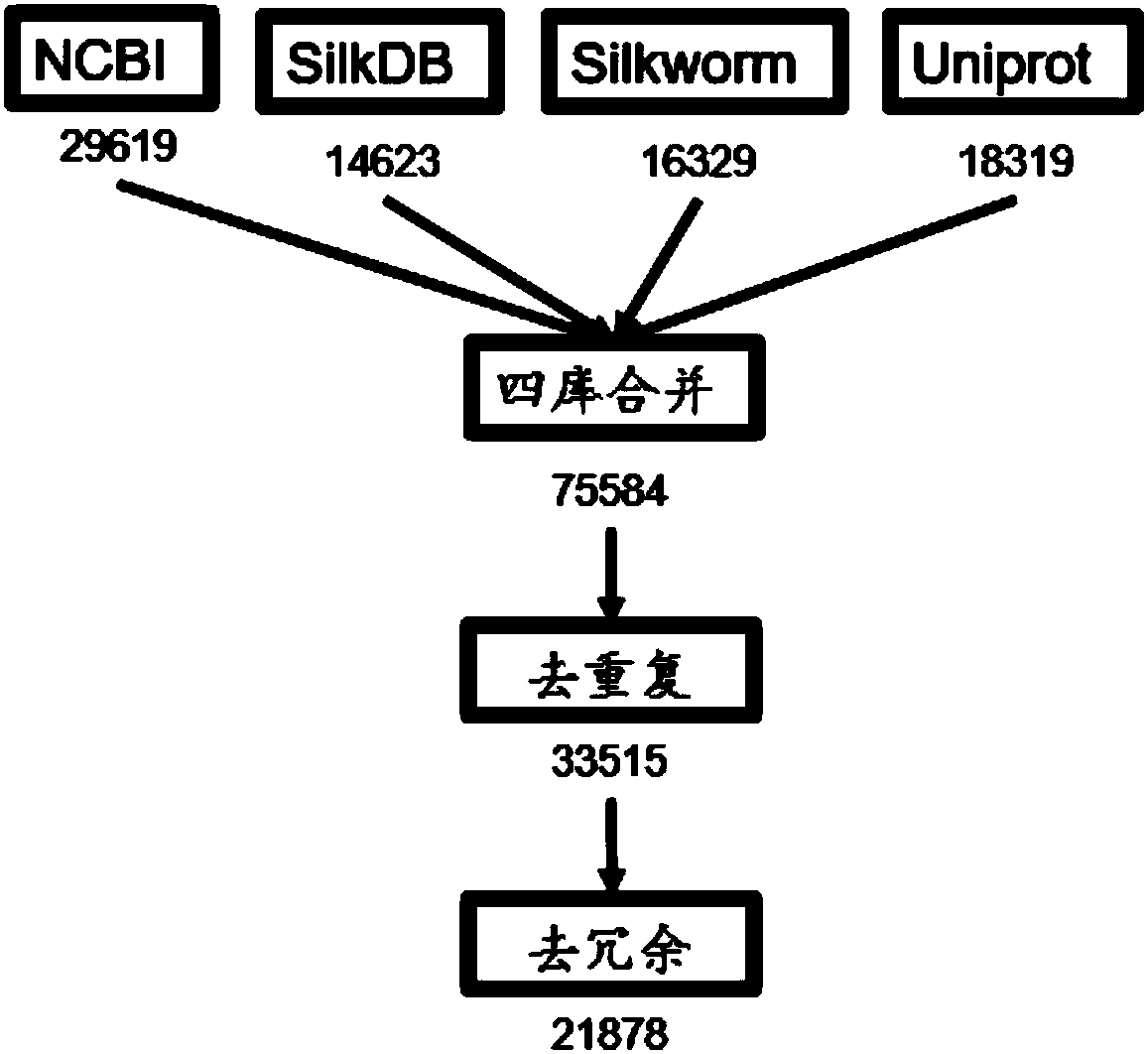
Method for carrying out large-scale proteomics identification based on silkworm tissue sample
ActiveCN108572214AExtract comprehensiveAvoid blockageMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein DatabasesHydrogen
The invention relates to a method for carrying out large-scale proteomics identification based on a silkworm tissue sample. The method comprises the following steps: pre-treating a domestic silkworm proteomics sample, carrying out graded peptide fragment mass spectrum online detection and constructing a silkworm protein database. By optimizing a protein extraction method, a peptide fragment is divided into 8 grades by adopting a high pH (Potential of Hydrogen) grading method and silkworm fat body samples can be extracted as many as possible, so that the protein identification quantity is improved; a condition that a sample spraying needle is blocked, caused by the fact that a feeding amount is too great, is prevented through optimizing a sample feeding amount and chromatography gradient time; the detection time is shortened through optimizing the chromatography gradient time; a Streamline database containing 21,878 protein sequences is established; the database can be used for identifying more protein quantity and redundant sequences are removed by the database; later-period proteomics data analysis is facilitated. According to the method provided by the invention, a stable and efficient domestic silkworm proteomics identification platform is established and the method has important meaning on silkworm proteomics large-scale identification.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Disulfide bond link mode detection method based on PCA dimensionality reduction technology
InactiveCN101477113AReduce redundancyIncrease the relative effective data volumeCharacter and pattern recognitionBiological testingFeature vectorProtein Databases
The invention relates to a detection method of disulfide bond connection mode based on PCA dimension reduction technology in the technical field of biological information. The detection method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting multiple sequence eigenvector from a protein database and secondary structure eigenvector detected by PSIPRED to obtain a 623-dimensional vector; secondly, adopting dimension reduction technology of a principle component analytical method to reduce the 623-dimensional eigenvector to 300 dimensions; and finally, inputting the 300-dimensional vector into an SVR classifier to carry out detection and obtain detection result. The detection method increases the relatively effective characteristic quantity of protein eigenvector input in the SVR, and can be used to increase the detection precision of disulfide bond connection mode.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Index acceleration method and corresponding system in scale protein identification
InactiveCN101714187BReduce space consumptionEasy to storeSpecial data processing applicationsProtein DatabasesEnzyme digestion
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
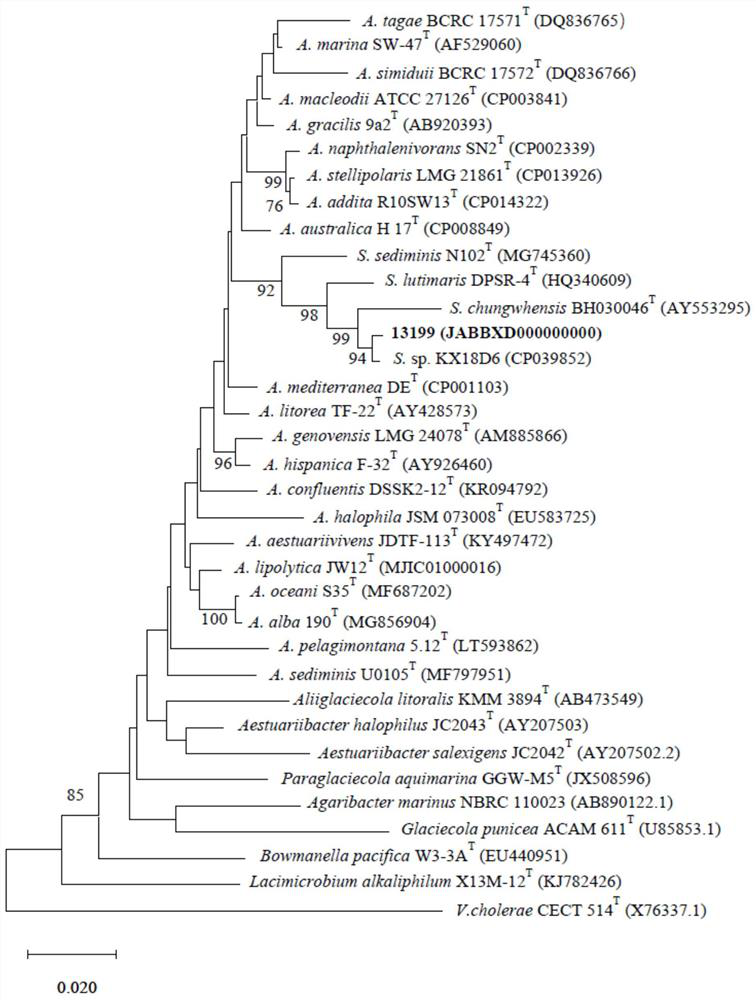
Salinimonas profundi 13199 as well as CRISPR-Cas system and application thereof
The invention discloses salinimonas profundi 13199. The salinimonas profundi has the preservation number being CGMCC1.17396 and a classification name being Salinimonas profundi. The strain is a new bacterial species derived from deep sea, and contains a special CRISPR-Cas system and a large number of heavy metal resistance genes. The sequence homologies of the Cas protein and a protein which is included in a high-quality protein database UniProtKB / Switch-Prot subjected to a certain degree of functional researches are lower than 65%, and possibly have different activities and characteristics. The strain Salinimonas prodi 13199 and the CRISPR-Cas system thereof are novel materials for developing and utilizing the CRISPR-Cas system and performing related researches, and furthermore, the strain has a certain application prospect in the aspects of heavy metal polluted environmental modification preparations.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
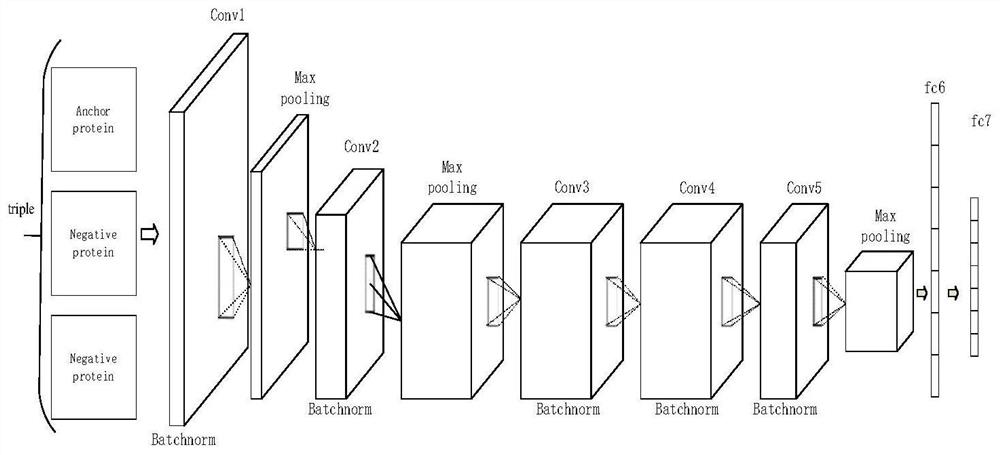
Protein folding identification method based on triple loss
ActiveCN112116949AStrong structural featuresImprove recognition accuracyNeural architecturesMolecular structuresProtein DatabasesData mining
The invention discloses a protein folding identification method based on triple loss, which comprises the following steps of encoding protein by using one-hot encoding, inputting the encoded protein into an SSA program to obtain a contact graph between protein residues, and using the contact graph as input data. inputting the input data into a pre-trained deep learning framework, wherein the output of the network is the characteristic that the protein is specific to folding identification, comparing characteristics of the query protein with template proteins of known protein folding categoriesin a protein database, and assigning the folding category of the template protein closest to the query protein to the query protein. According to the method, the training thought of triple loss is used for reference, so that protein structures of the same class are closer, protein structures of different classes are farther, feature expression of protein has higher discriminability, and the recognition efficiency is higher.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Salt-resistant gene in wheat
The invention obtains the specific expression protein of wheat salt tolerant mutant, and finds by mass spectrum identification, Web protein database search and bio-information technique that the protein has high homology with one assumed protein on the 4th rice chromosome. Accordingly, it designs primer, amplifies by PCR to obtain the corresponding wheat salt tolerance gene with 153 amino acids and 462bp length; clones the gene to construct pronucleus expression vector to express out a specific protein with molecular weight as 16.8KD and improve the salt tolerance of escherichia coli obviously. This invention settles foundation for wheat salt tolerance mechanism.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
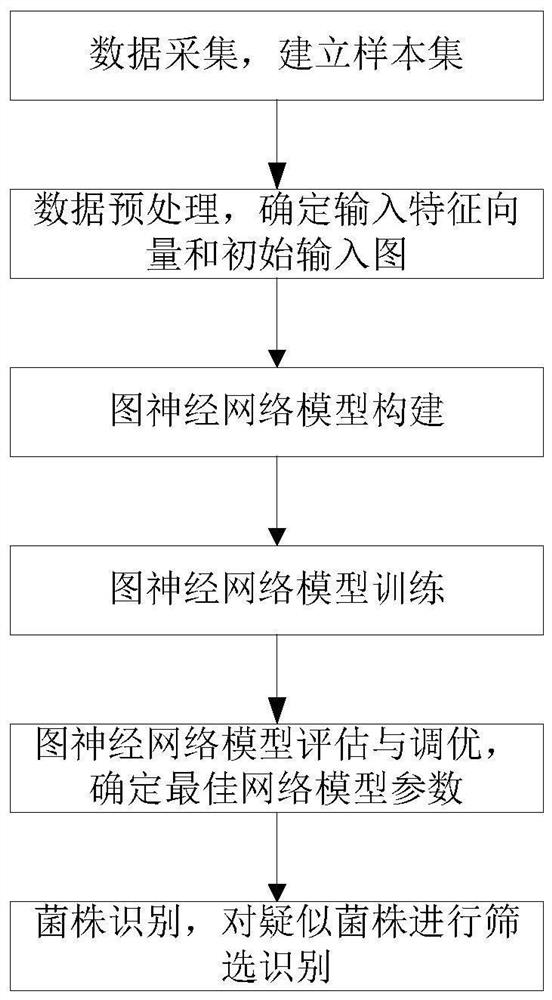
Method for predicting antibacterial peptides of lactic acid bacteria based on graph neural network
ActiveCN113571133AAccurate classificationRealize batch recognitionBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionProtein DatabasesAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses a method for predicting antibacterial peptides of lactic acid bacteria based on a graph neural network. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a positive sample by searching known antibacterial peptides of lactic acid bacteria, establishing a negative sample by collecting sequences with the length of 5 to 255 from a protein database, and removing redundant sequences and similarities; performing feature extraction according to the positive and negative samples to obtain a feature vector and an initial input graph, and establishing a graph neural network model on the basis; through training, evaluation and loop optimization of the graph neural network model, determining parameters such as the optimal layer number, the optimal training round number and the learning rate of the graph neural network; and finally, predicting data of strains suspected to have antibacterial activity according to the graph neural network model. By adopting the method for predicting the antibacterial peptides of the lactic acid bacteria, wet experiment screening in a laboratory is replaced by computer model prediction, the judgment time of the protein sequence of the antibacterial peptides of the lactic acid bacteria is shortened, accurate and efficient batch identification is realized, and an effective alternative method is provided for screening lactic acid bacteria strains with antibacterial characteristics.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com