Method for rapidly identifying strain-level pathogenic bacteria in food through double adsorption
A pathogenic bacteria and double-adsorption technology, which is applied in the field of detection and identification of pathogenic bacteria at the strain level in liquid food, can solve the problems of multiple detection steps and time-consuming and labor-intensive detection of pathogenic bacteria at the strain level, and overcome the time-consuming and labor-intensive problems. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
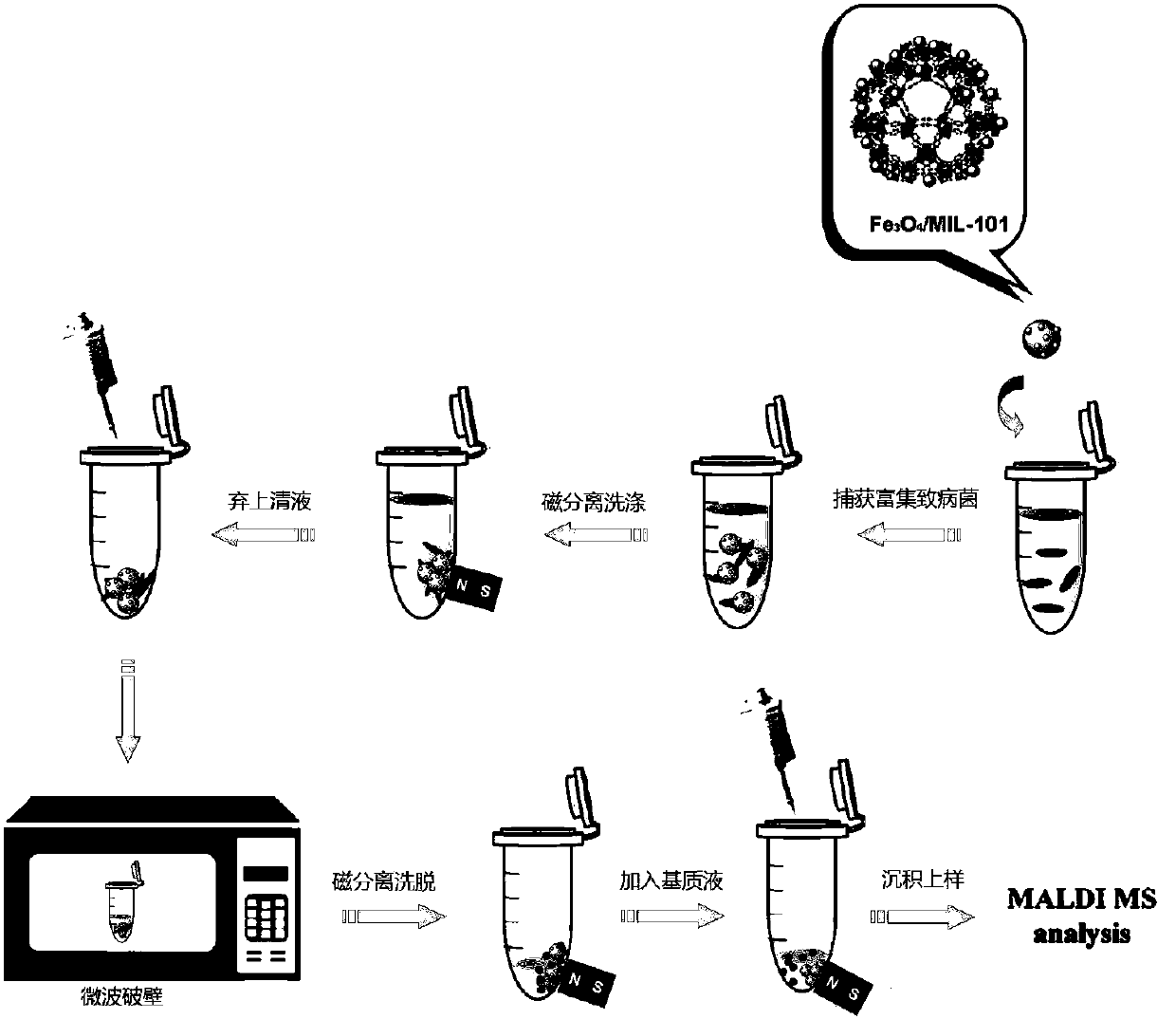
[0037] At 37°C, Escherichia coli O157:H7 was inoculated in 25 mL of sterilized TSB medium, and the shaker was 120 r min -1 After culturing for 16 h, 1 mL of bacterial suspension was centrifuged (12000 r min -1 ) for 5 min, pour out the supernatant, and wash twice with PBS buffer solution, then, dilute Escherichia coli with different concentrations, and count them by counting viable bacteria. At the same time, MIL-101 magnetic particles (Fe 3 o 4 -COOH@MIL-101) can be synthesized independently or purchased from the market ( figure 2 is the transmission electron microscope image of MIL-101 magnetic particles).
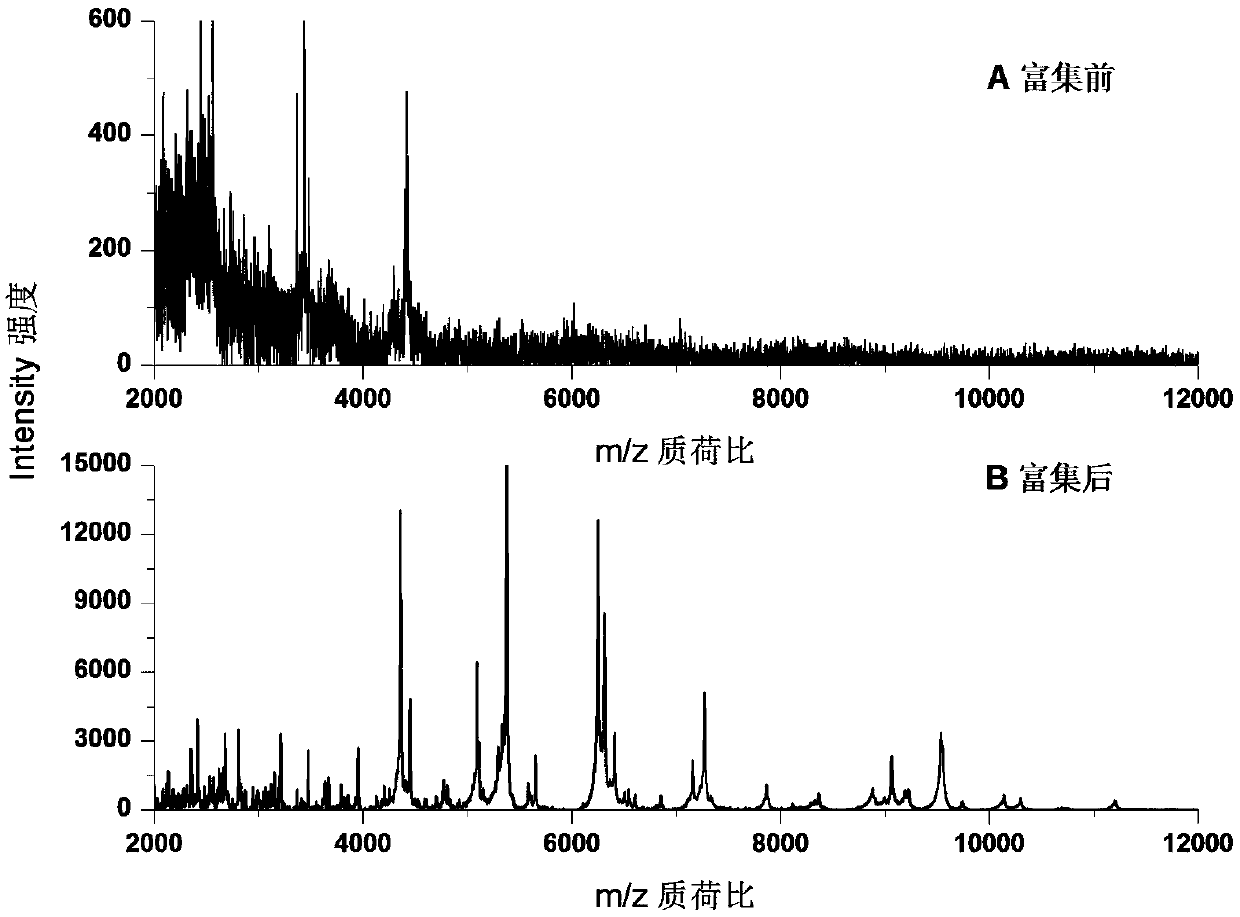
[0038] Using carbonated beverages, add different concentrations (5 × 10 5 cfu mL -1 ) of Escherichia coli O157:H7 bacterial suspension, and then utilize Fe 3 o 4 - COOH@MIL-101 enrichment and microwave-assisted wall breaking, MALDI / TOF MS detection, and ribosomal protein database for strain level identification. image 3 Escherichia coli Fe in carbonated beverag...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Using carbonated beverages, add different concentrations (5 × 10 3 cfu mL -1 ) of Escherichia coli O157:H7 bacteria suspension, after Fe 3 o 4 - COOH@MIL-101 enrichment and microwave-assisted wall breaking, MALDI / TOF MS detection, and ribosomal protein database for strain level identification. There are 9 ribosomal proteins searched by Tagident (see Table 1), and Escherichia coli O157:H7 can be identified through the ribosomal protein database (Rapid Microorganism Identification Database; http: / / rmidb.org), Figure 5 Escherichia coli O157:H7 (bacterial concentration is 5×10 3 cfu mL -1 ) ribosomal protein database identification results.
[0041] Table 1 Escherichia coli O157:H7 protein ribosomal protein search results in Swiss-Prot / TrEMBL database a
[0042]
[0043] a The protein database search matching error is ±3Da.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com